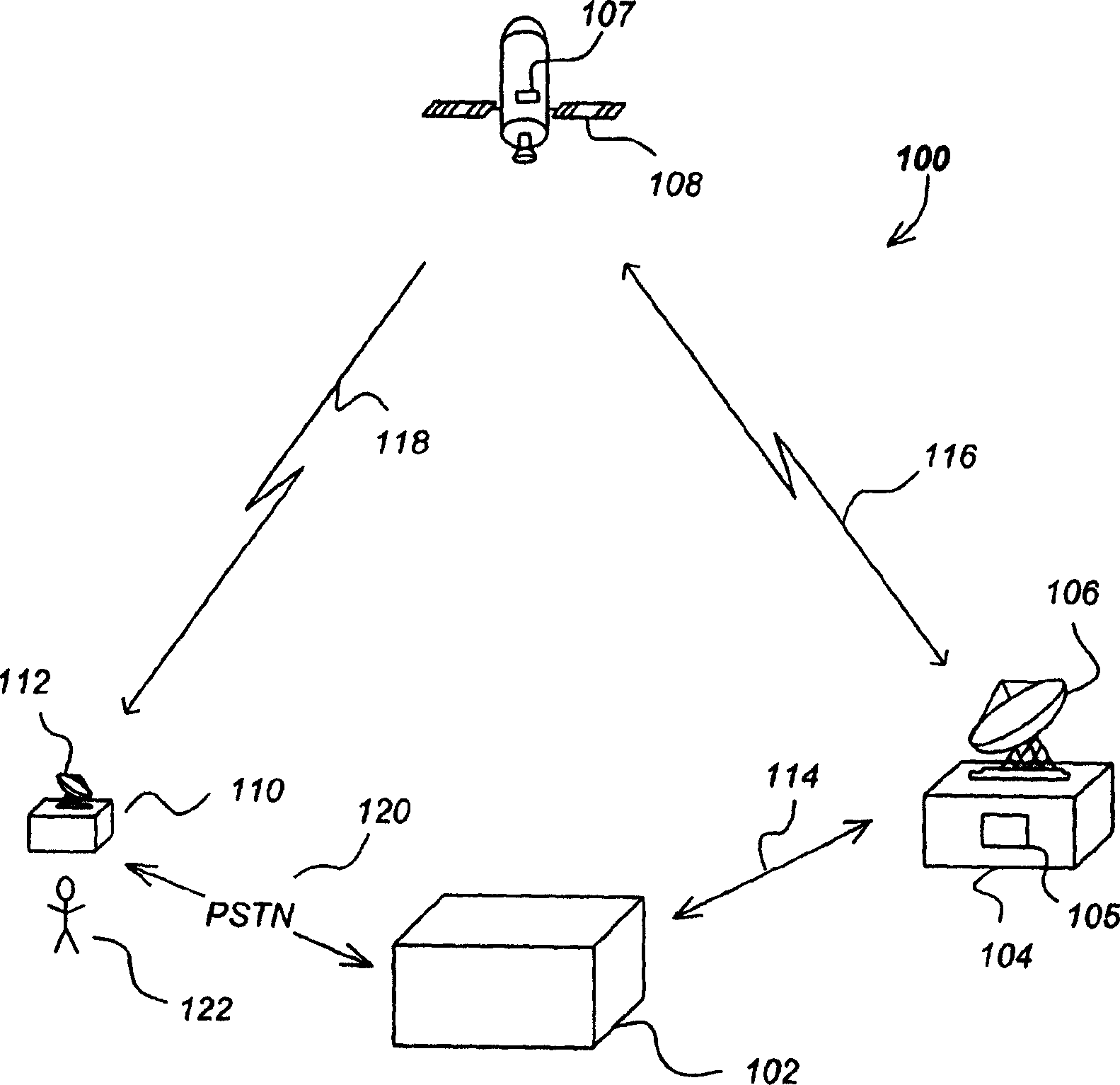
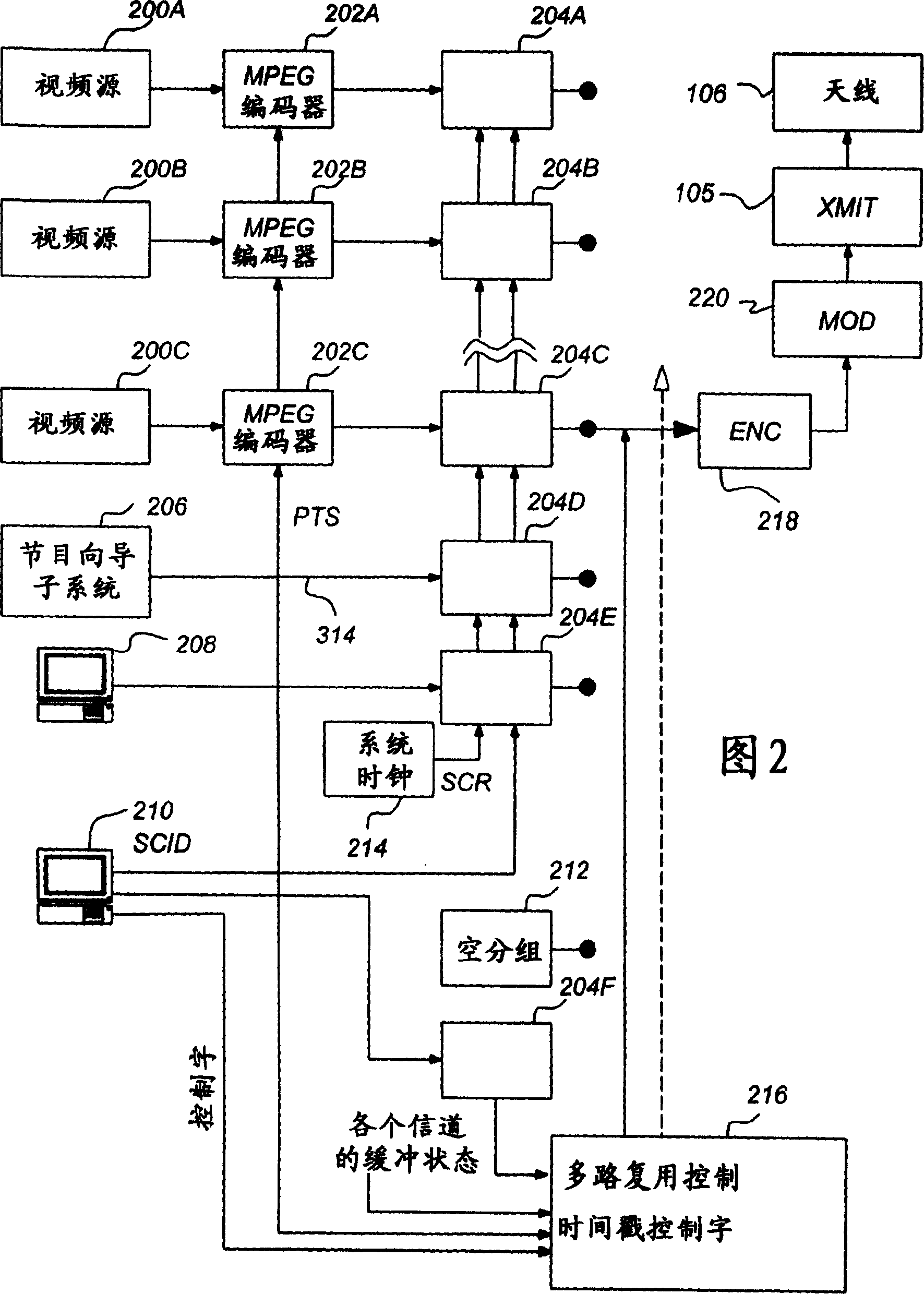
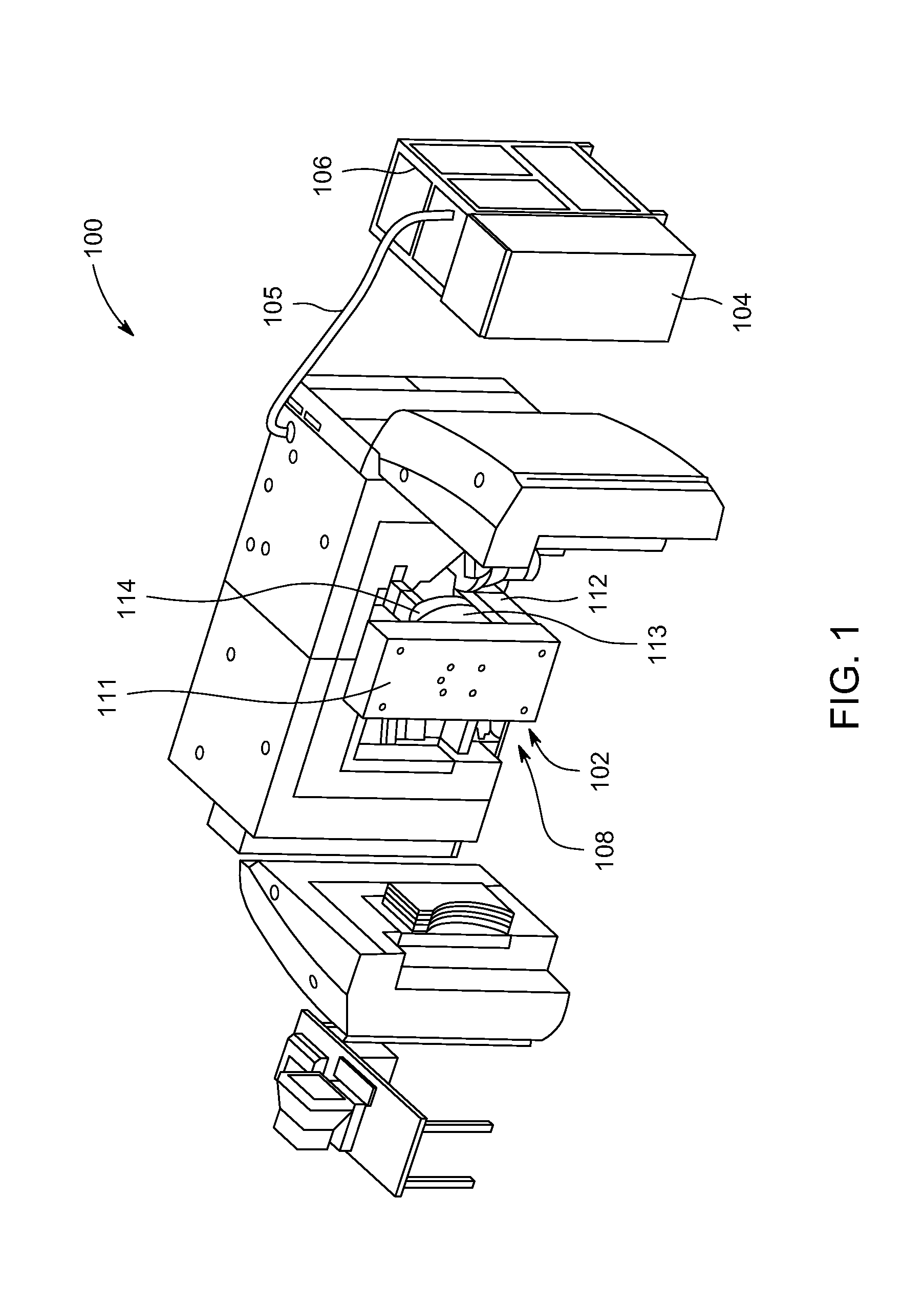
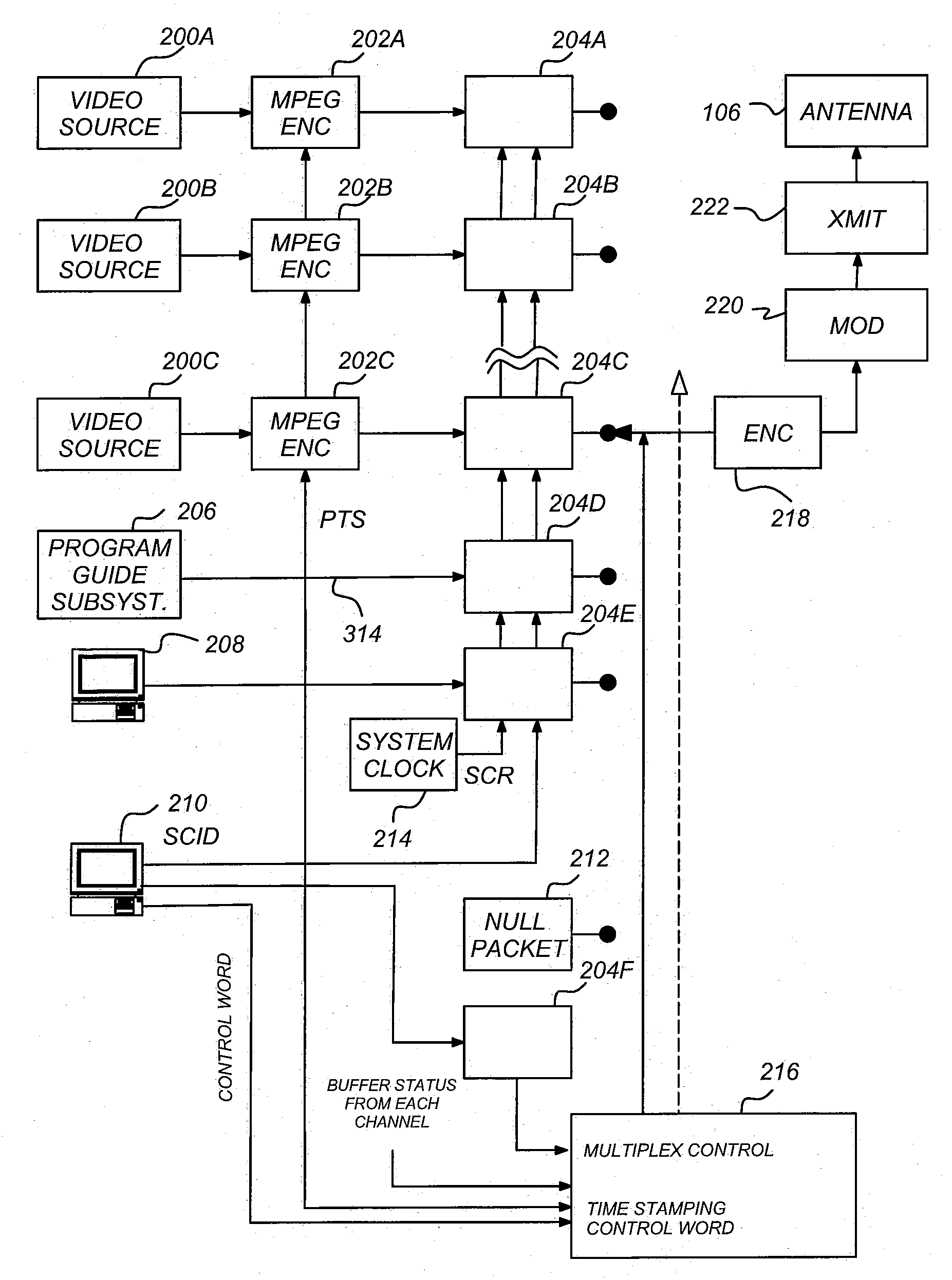
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
132results about "Amplifiers with transit-time effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
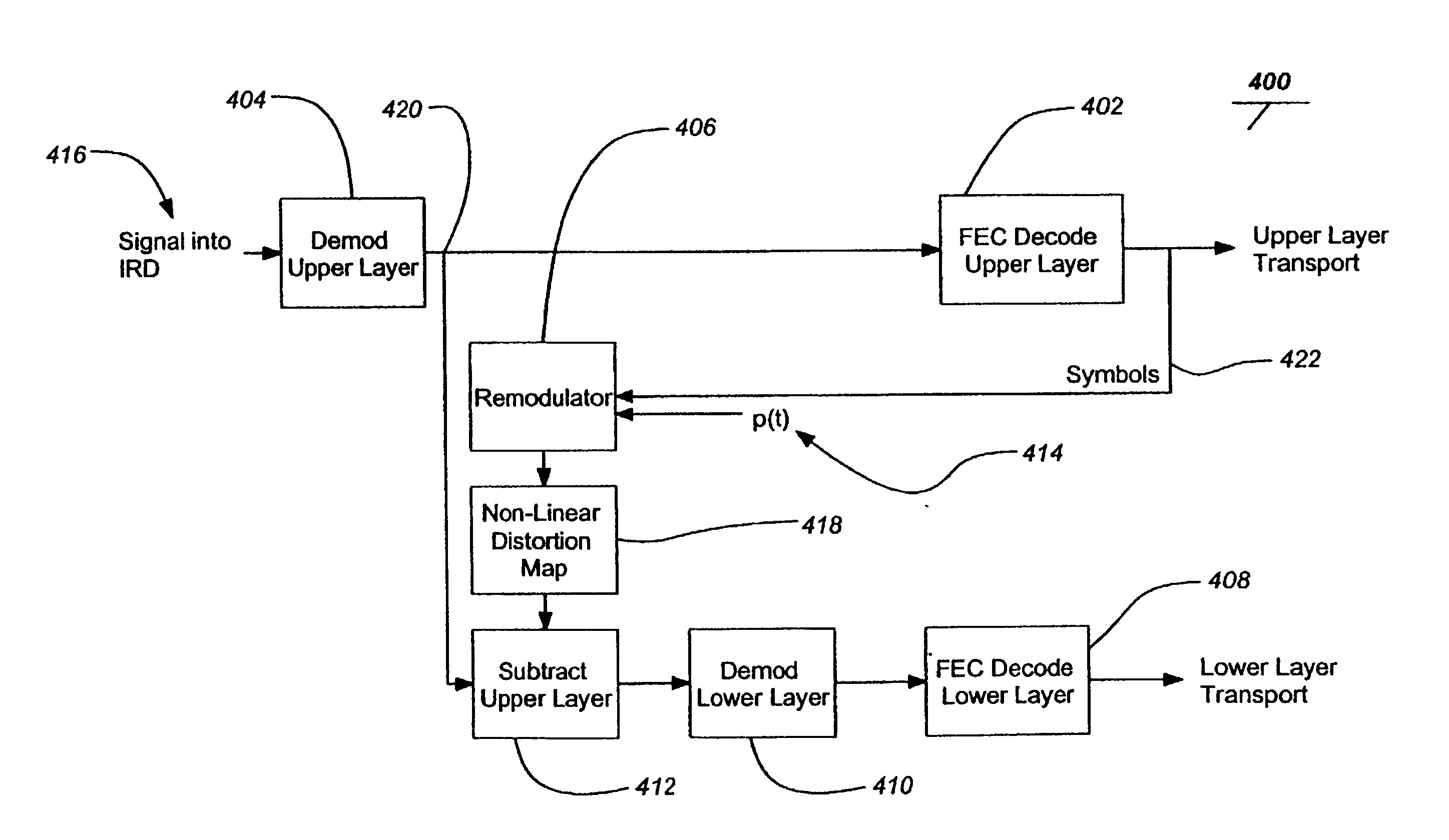
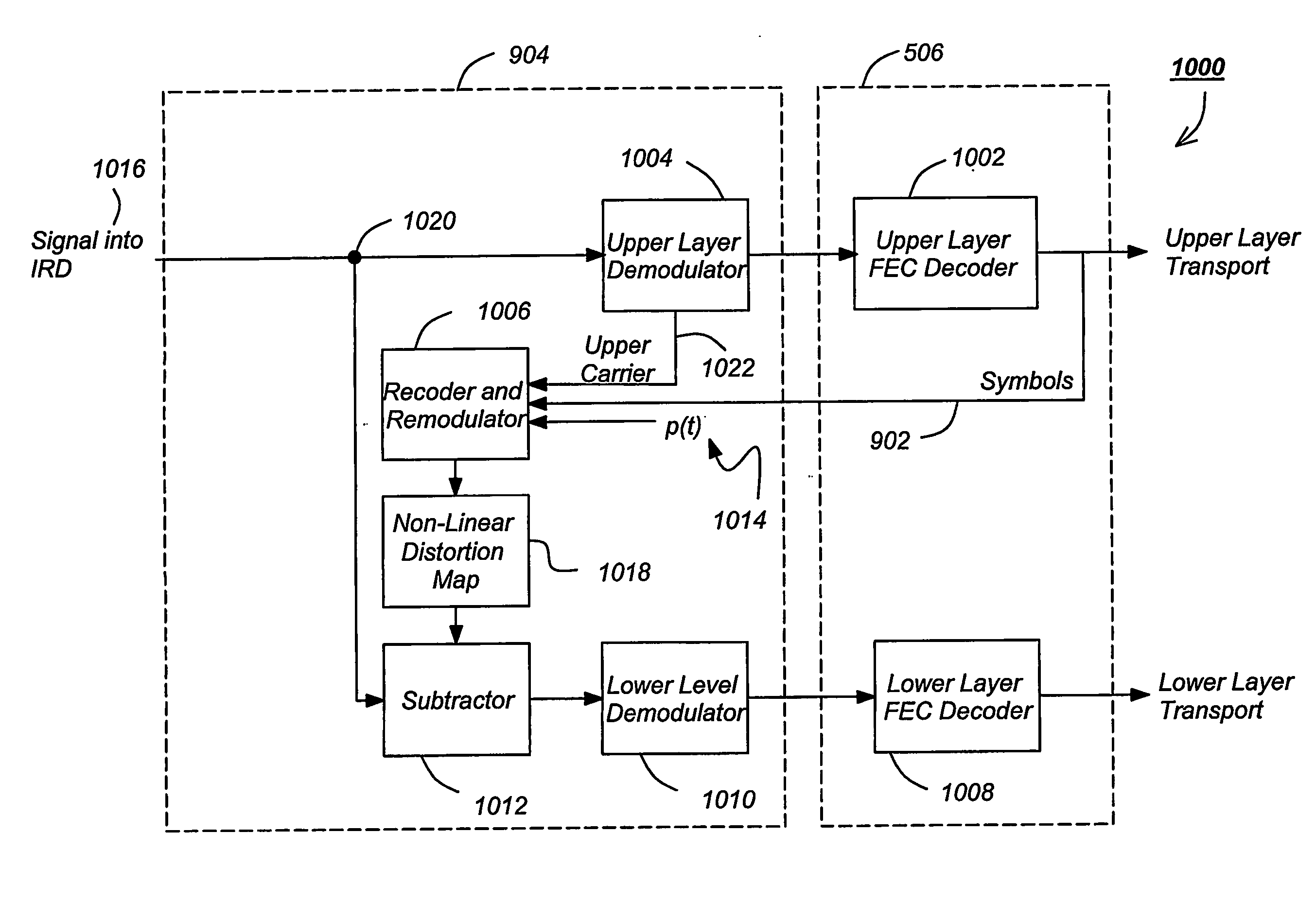
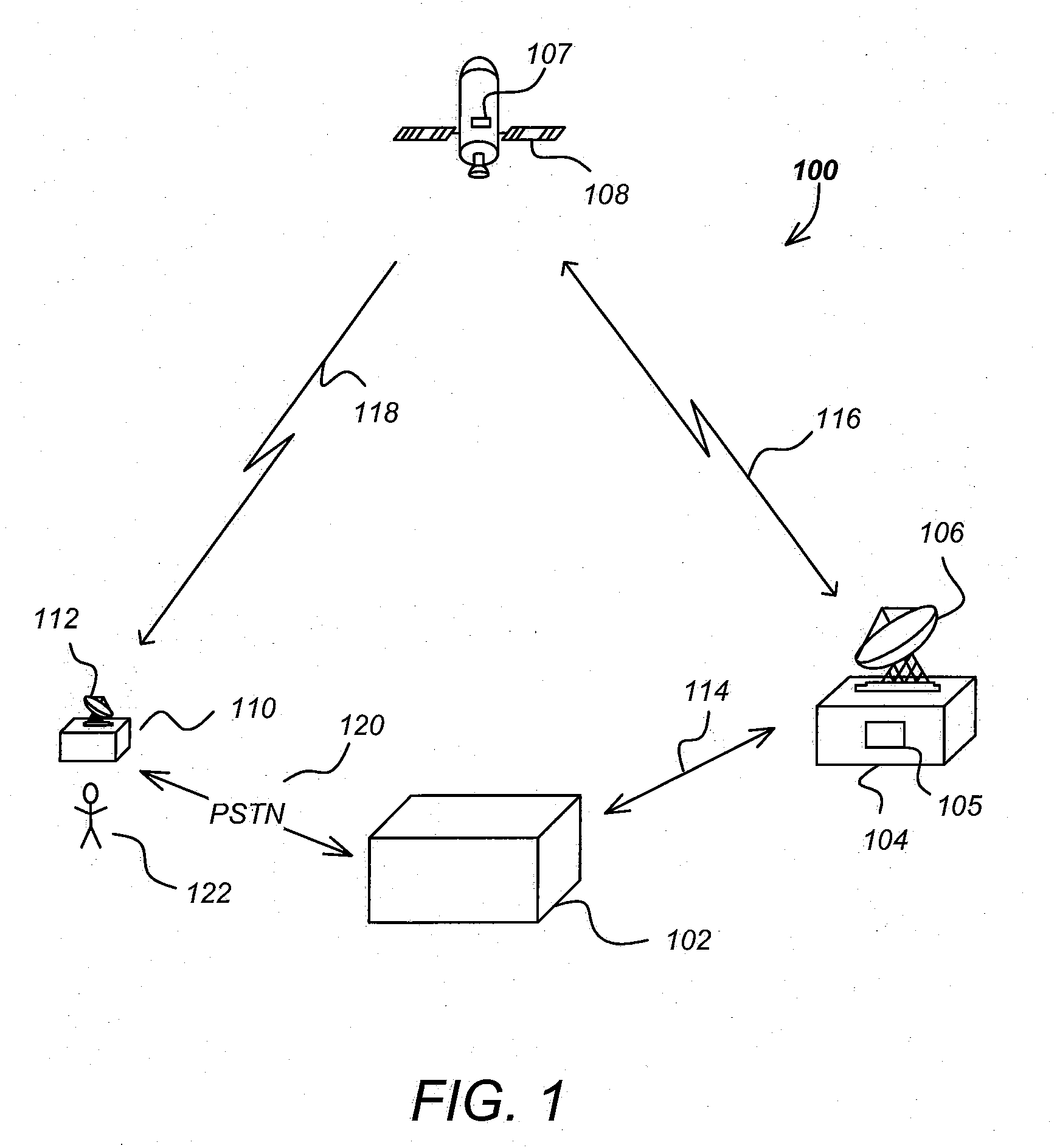
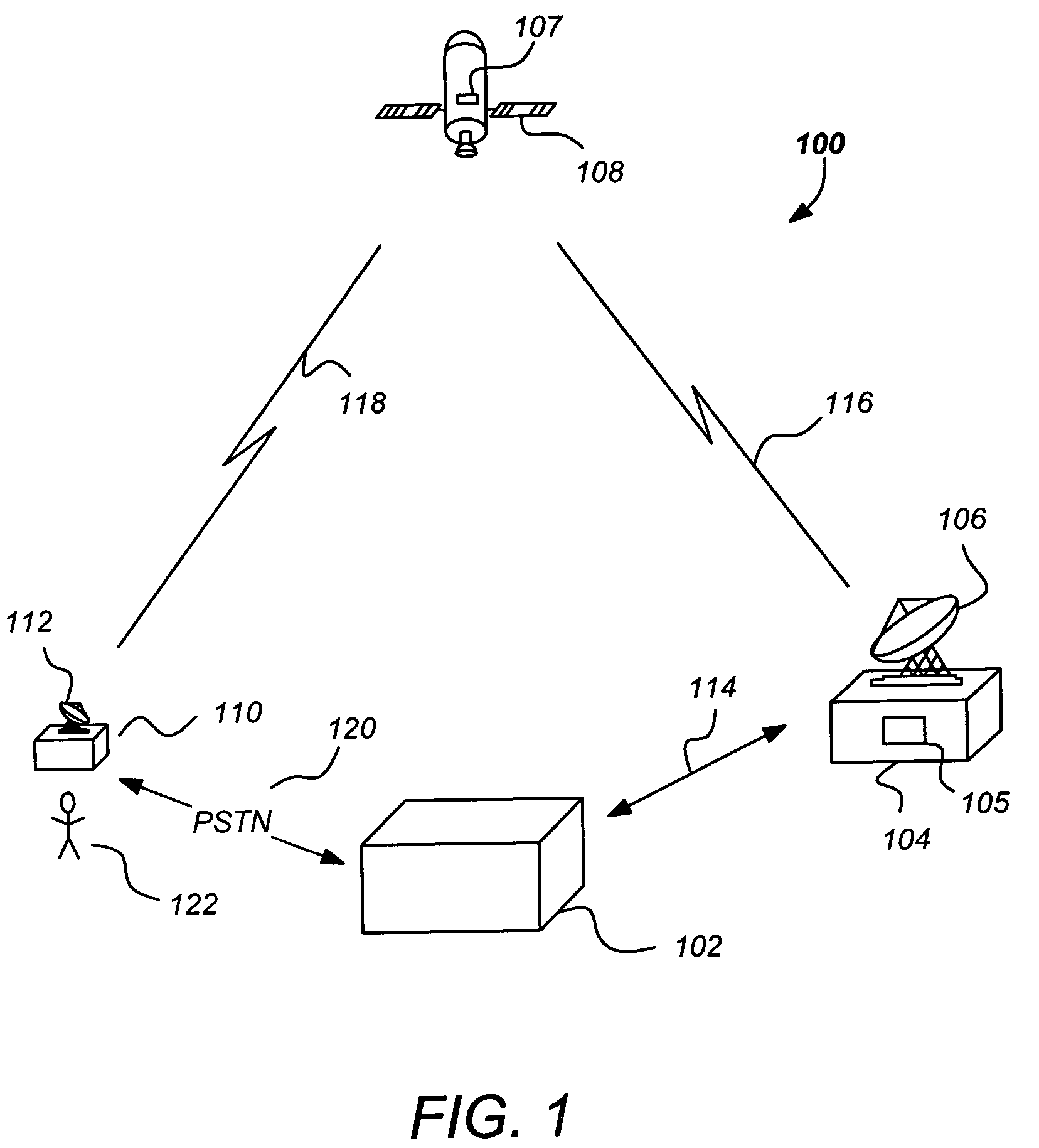
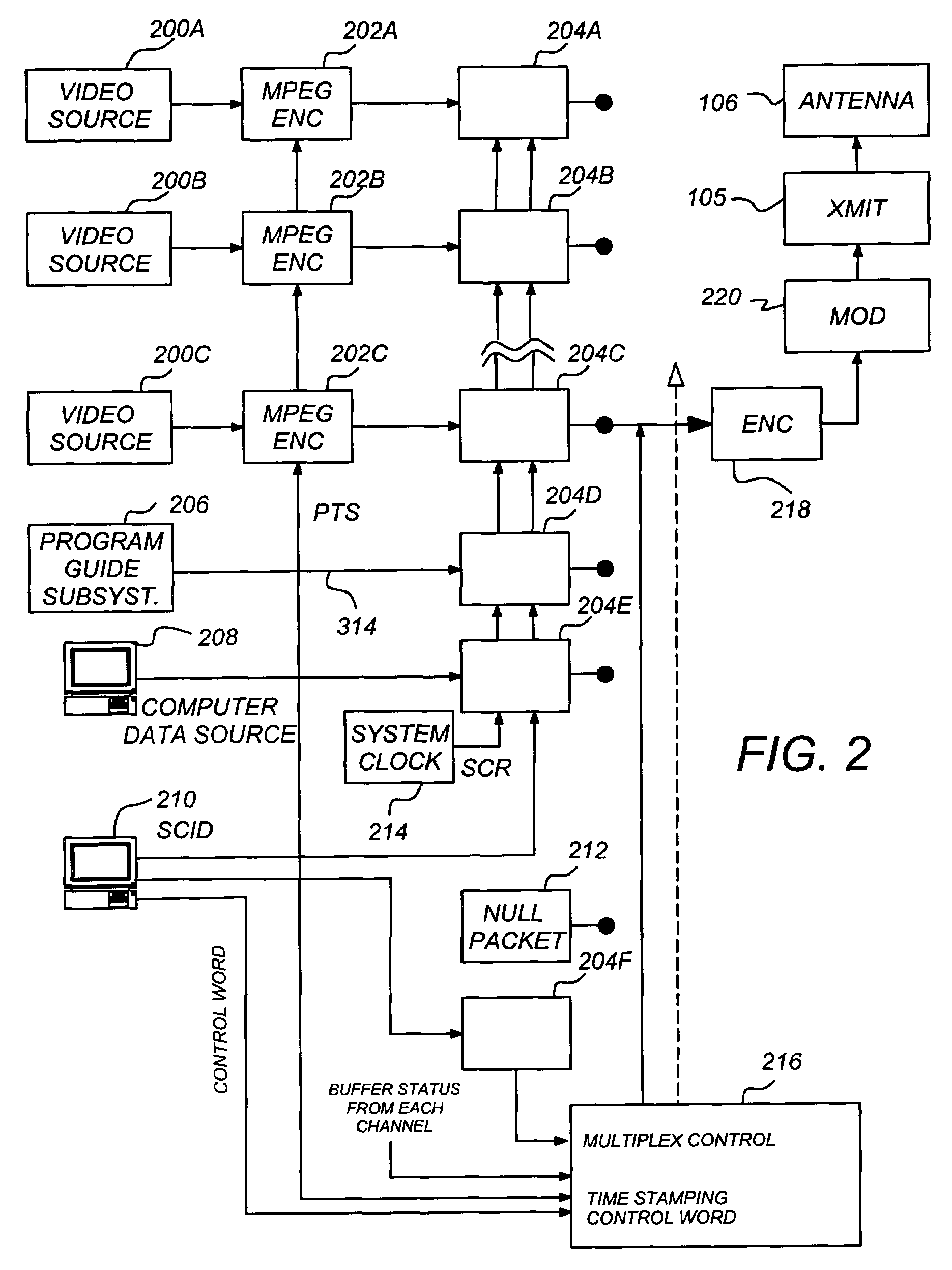
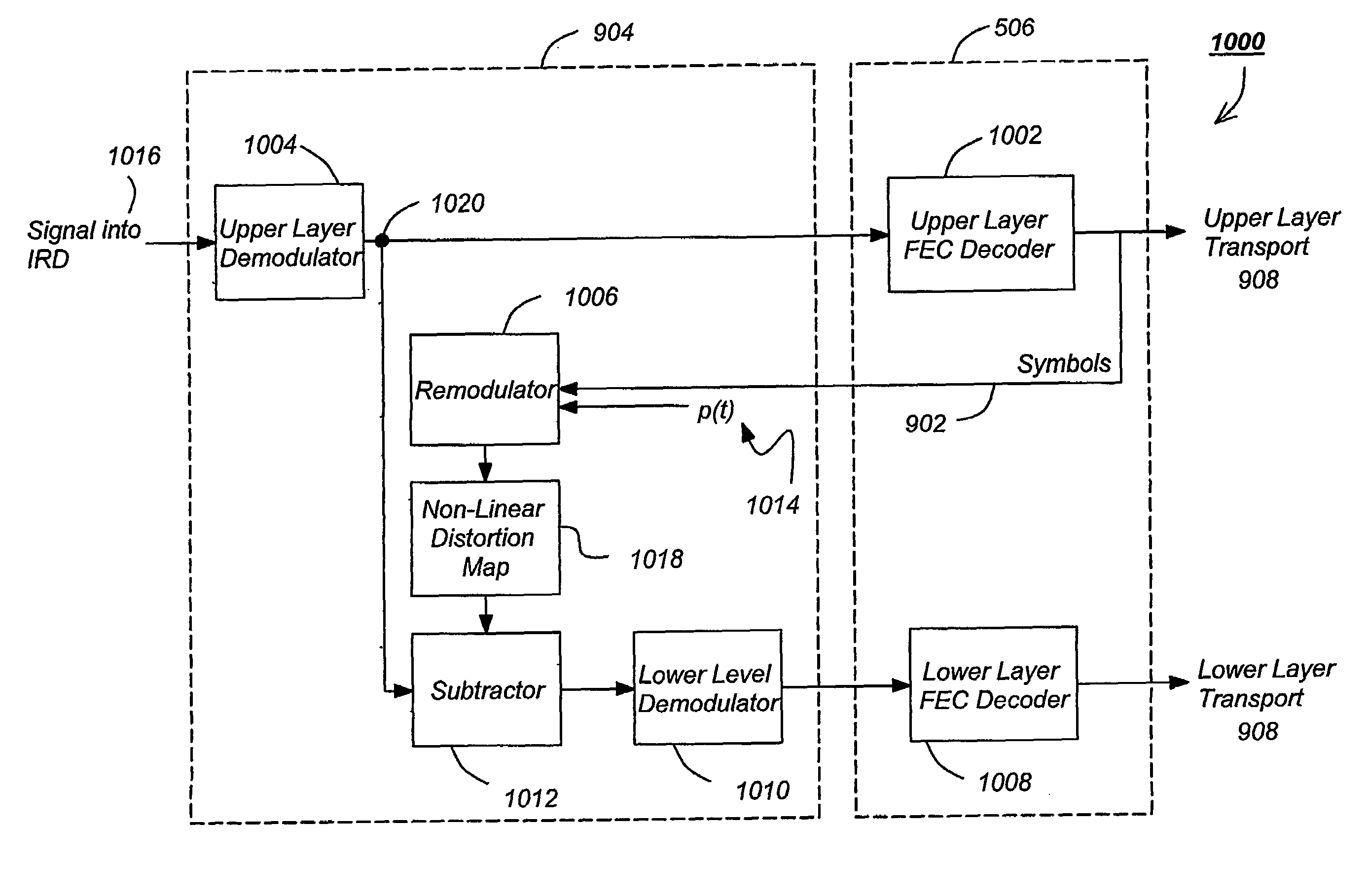
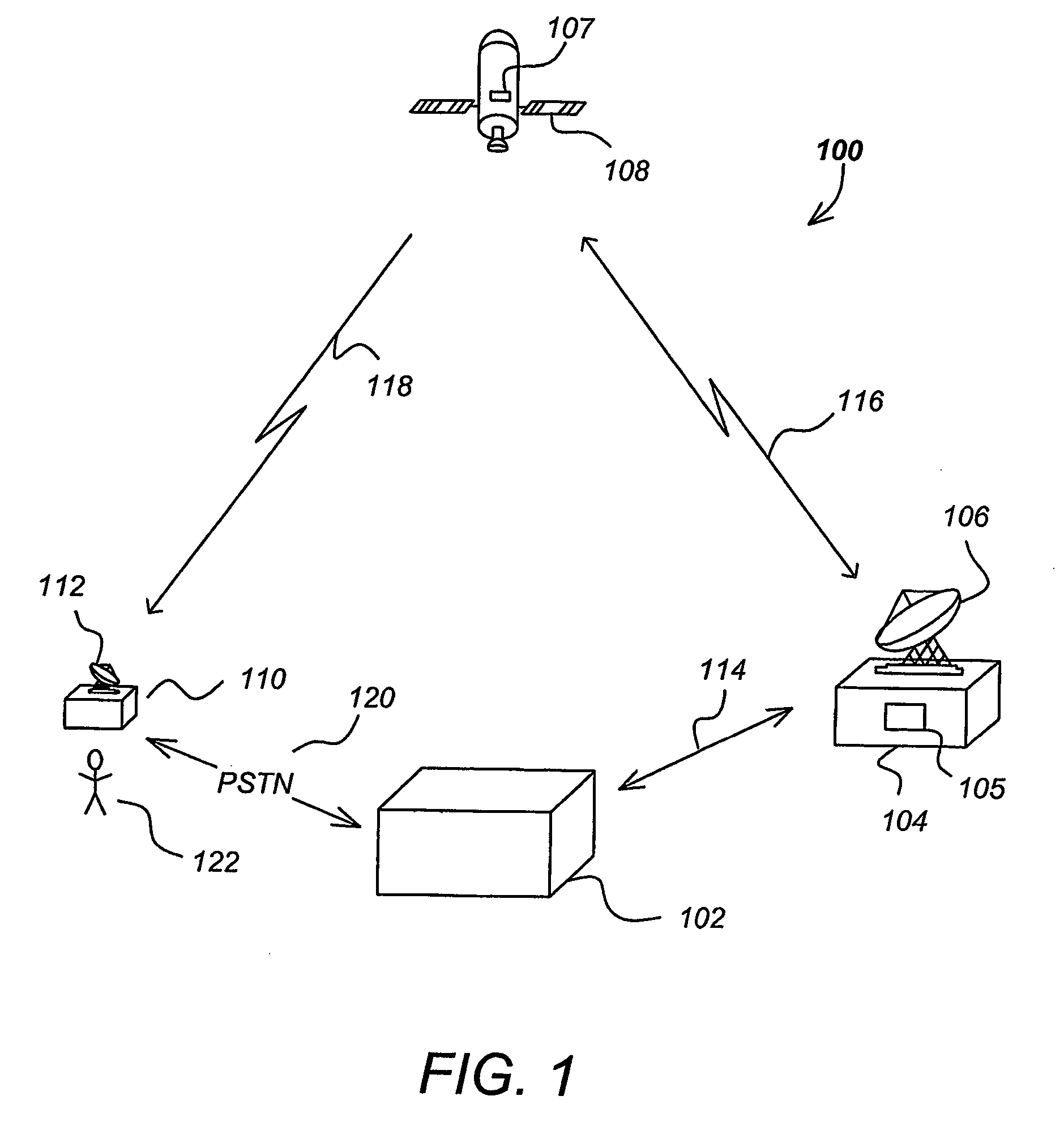
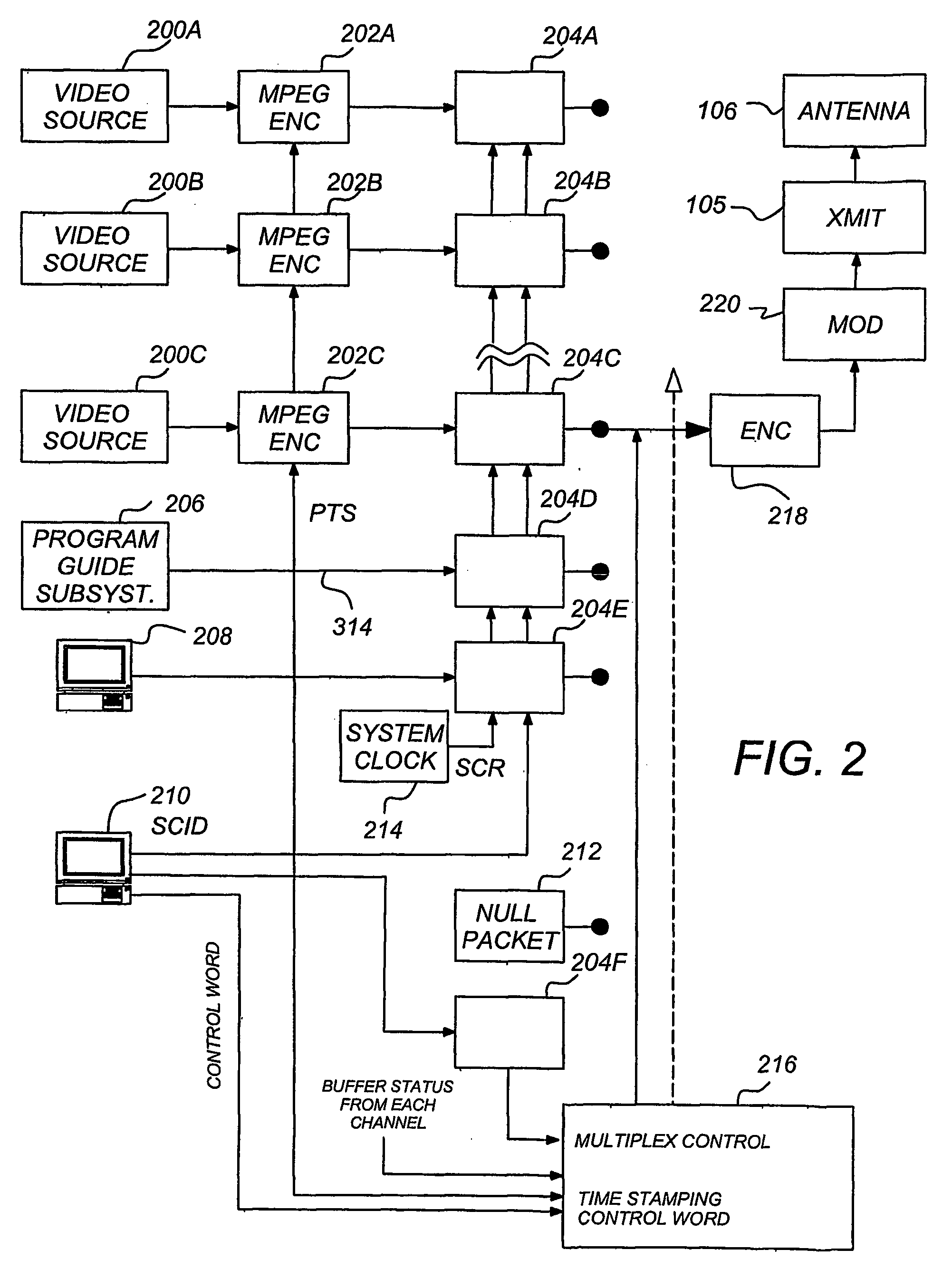
Layered modulation for digital signals
InactiveUS7209524B2Increase capacityGood serviceError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorResource management arrangementsCarrier signalDigital signal
Signals, systems and methods for transmitting and receiving layered modulation for digital signals are presented. A layered signal for transmitting data, comprises a first signal layer including a first carrier and first signal symbols for a first digital signal transmission and a second signal layer including a second carrier and second signal symbols for a second signal, transmission disposed on the first signal layer, wherein the layered signal has the first carrier demodulated and first layer decoded to produce the first signal symbols for a first layer transport, the first signal symbols are remodulated and subtracted from the layered signal to produce the second signal layer, and the second signal layer has the second carrier demodulated and decoded to produce the second signal symbols for a second layer transport.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GROUP
Carrier to noise ratio estimations from a received signal
InactiveUS20050008100A1Good signal cancellationTelevision system detailsReceivers monitoringA d converterEngineering
Techniques for measuring the carrier to noise ratio (CNR) in a received digital signal are disclosed. The methods can operate on a received digital signal, such as a layered modulation signal used in a satellite television system. The CNR measurement can be made at the output of a carrier recovery loop or a timing recovery loop in a demodulator. Alternately, the CNR measurement can be made when the received signal is digitized in an analog to digital (A / D) converter at base-band by the demodulator.
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
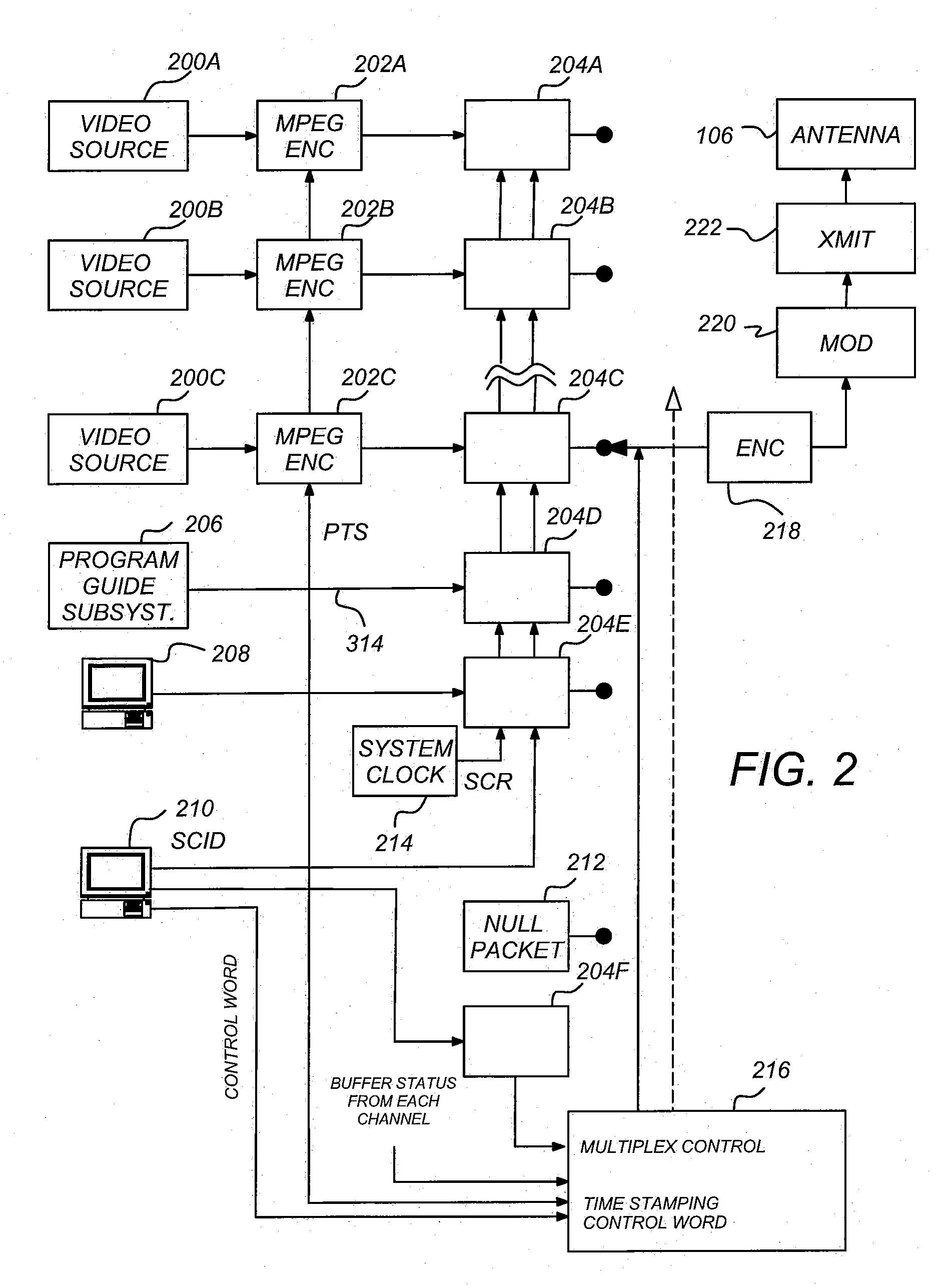
Lower complexity layered modulation signal processor
InactiveUS20060153315A1Television system detailsAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionComputer scienceLow complexity
A method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving a coded signal having an upper layer signal and a lower layer signal is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of combining the upper layer signal and the lower layer signal, encoding the combined upper layer signal and lower layer signal, delaying the upper layer signal, modulating the delayed upper layer signal, modulating the lower layer signal, transmitting the delayed upper layer signal and transmitting the lower layer signal. The apparatus comprises an encoder, for encoding a combined upper layer signal and lower layer signal, a delay, communicatively coupled to the encoder, for delaying the upper layer signal, a first modulator, for modulating the delayed upper layer signal, a second modulator, for modulating the lower layer signal, a transmitter, communicatively coupled to the first modulator, for transmitting the delayed upper layer signal, and a second transmitter, communicatively coupled to the second modulator.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GRP INC
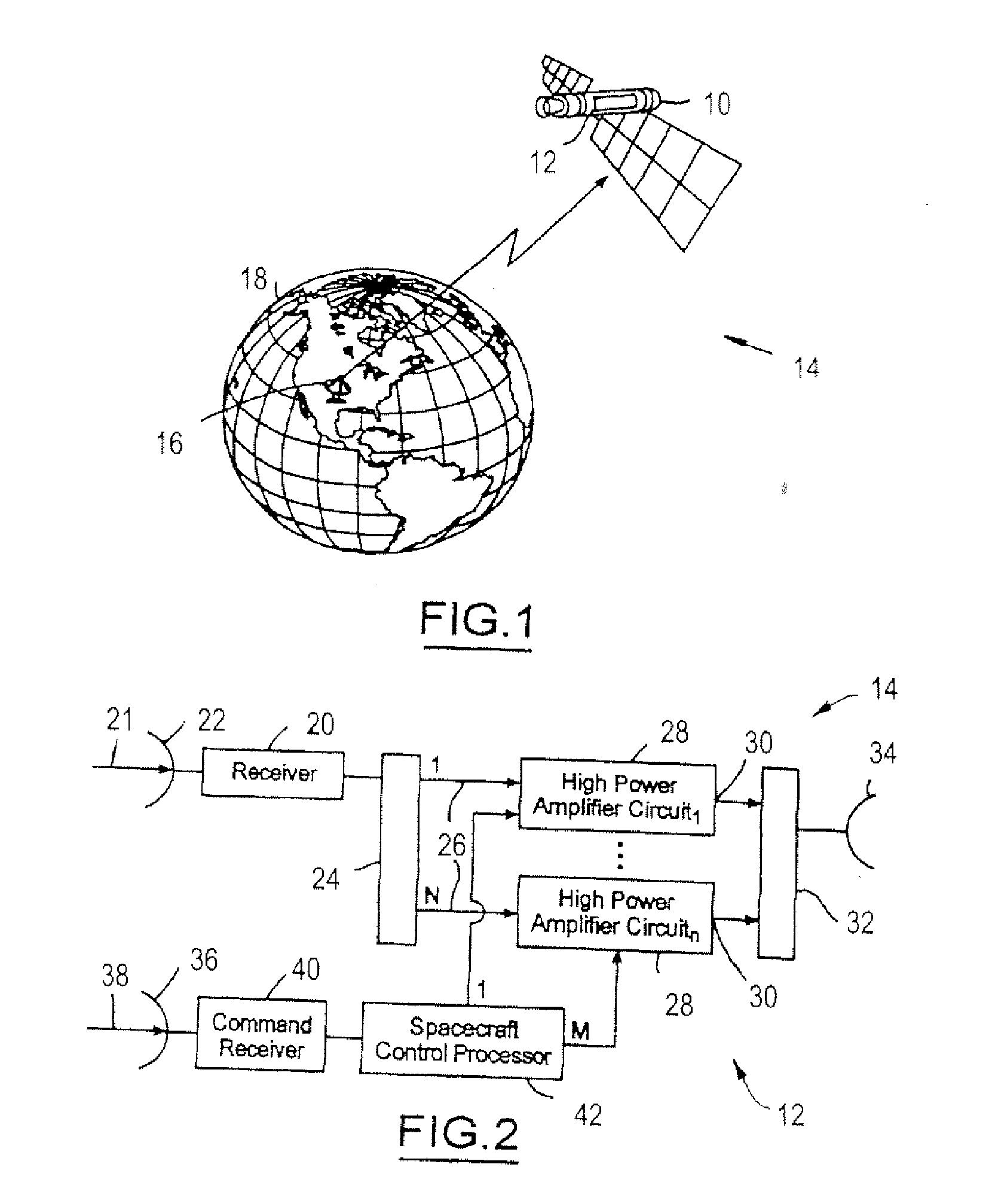
High-power microwave system employing a phase-locked array of inexpensive commercial magnetrons
InactiveUS20060208672A1Facilitates coherent combinationEfficient and inexpensiveTravelling-wave tubesRF amplifierMicrowave applicationsAs Directed
A high-power microwave generator employing a plurality of inexpensive commercial magnetron tubes cross-coupled by means of a secondary coupling path between each magnetron output pair, whereby a portion of the output energy from a first magnetron tube is injected into a second magnetron tube and a portion of the output energy from the second magnetron tube is similarly injected into the first magnetron tube. The resulting cross-injection of microwave energies brings the respective magnetron tube pair into a phase-lock sufficiently stable to permit coherent combination of their outputs for many high-power microwave applications, such as directed energy weapon systems. The magnetron phase-locking system requires no external components other than the secondary coupling paths of this invention.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
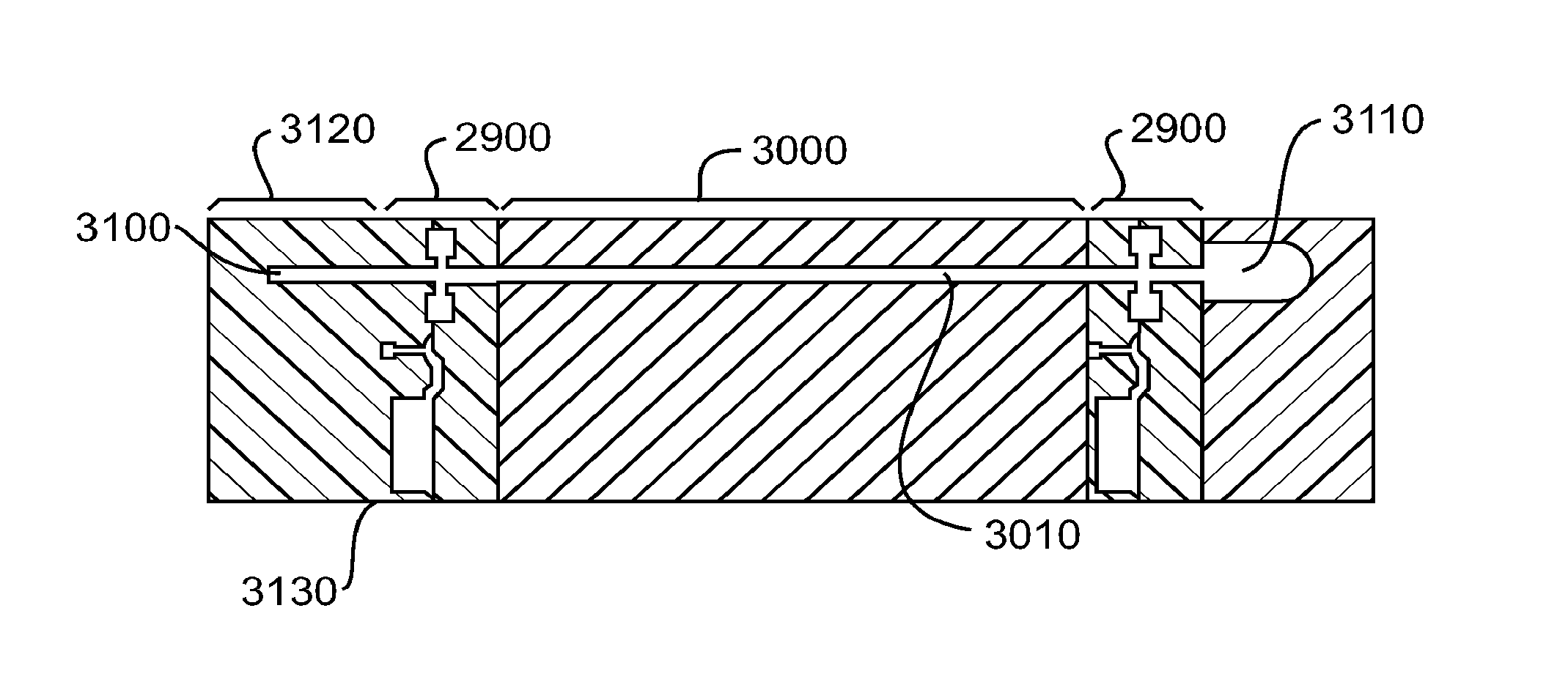
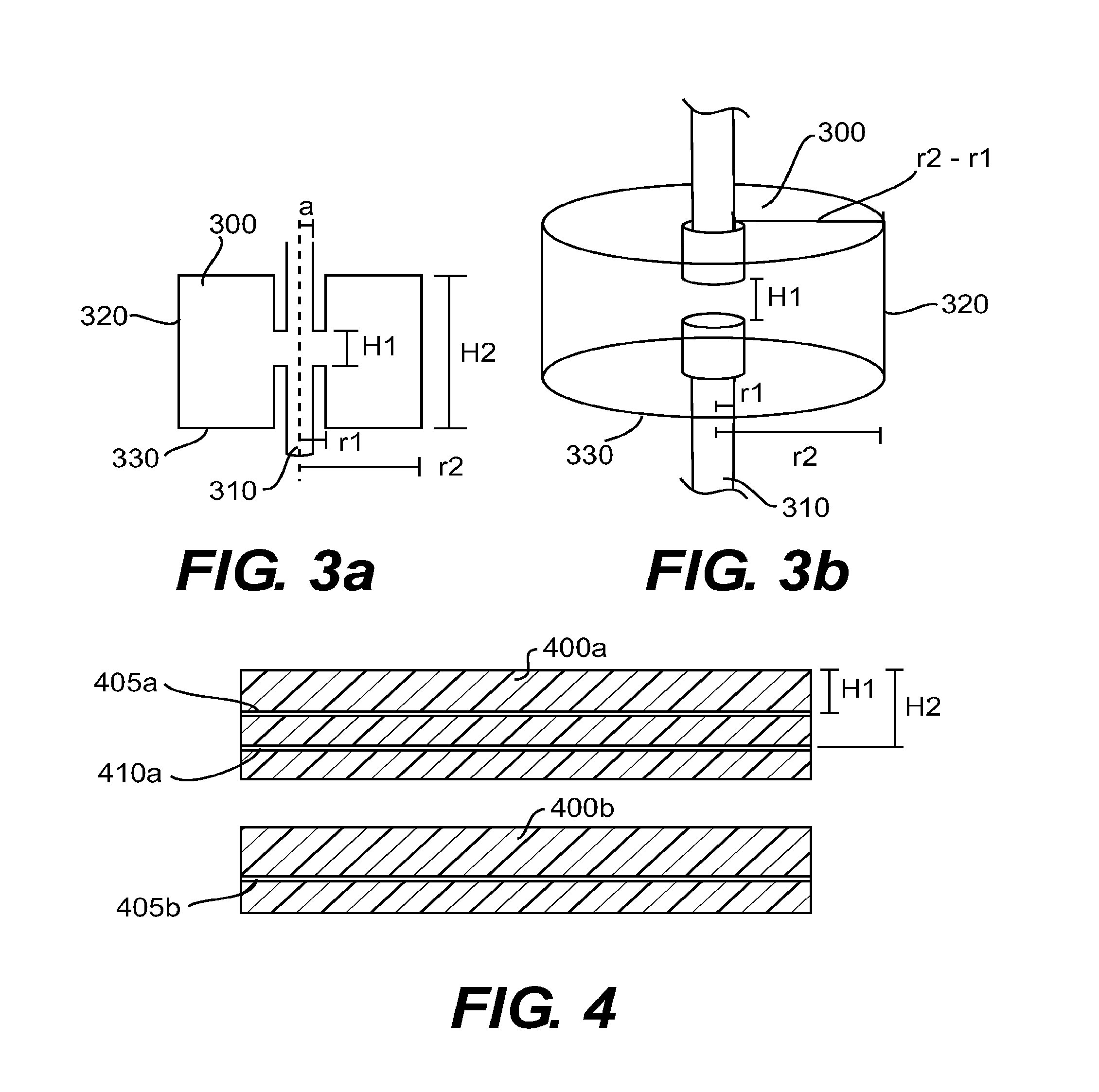
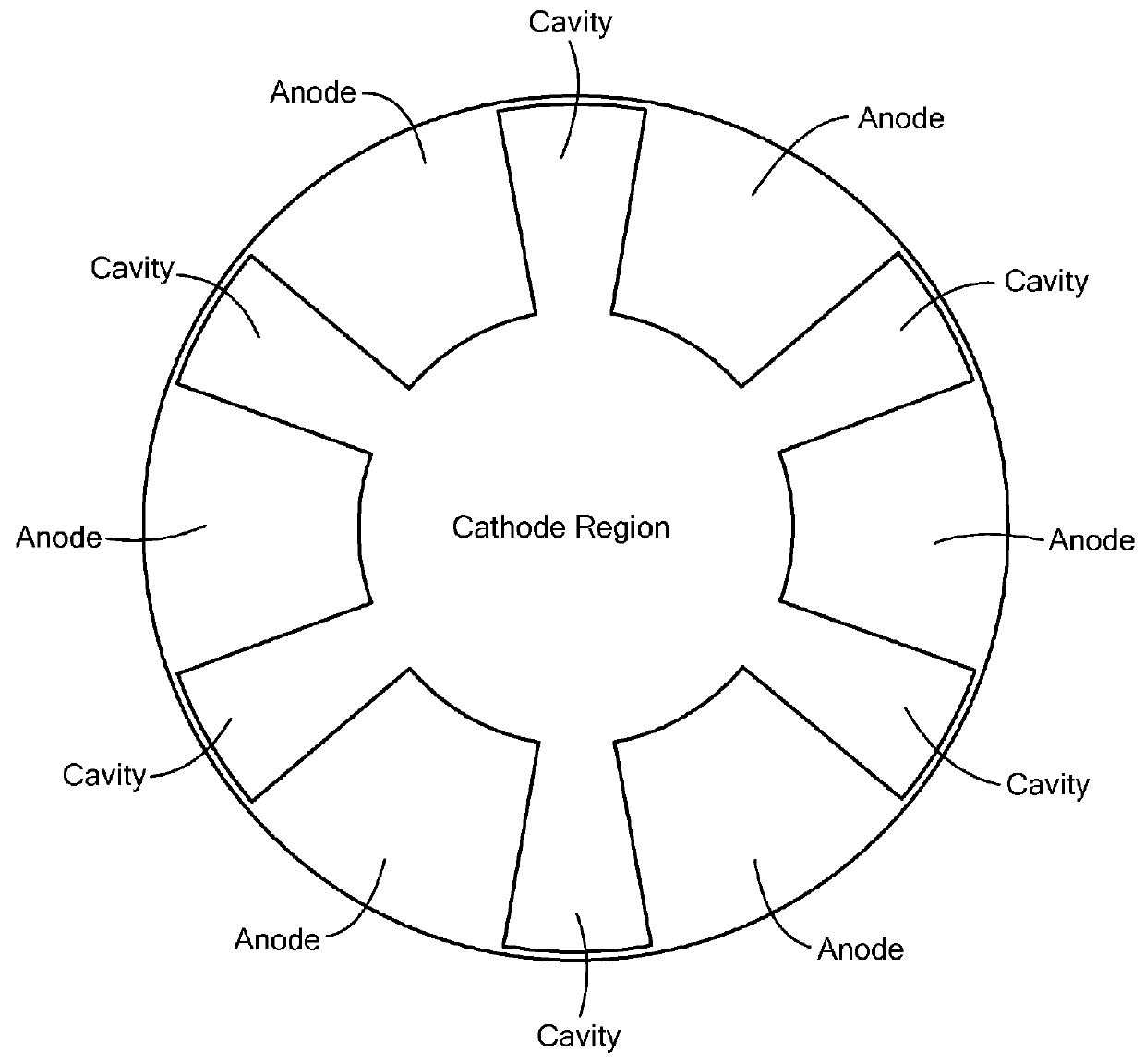
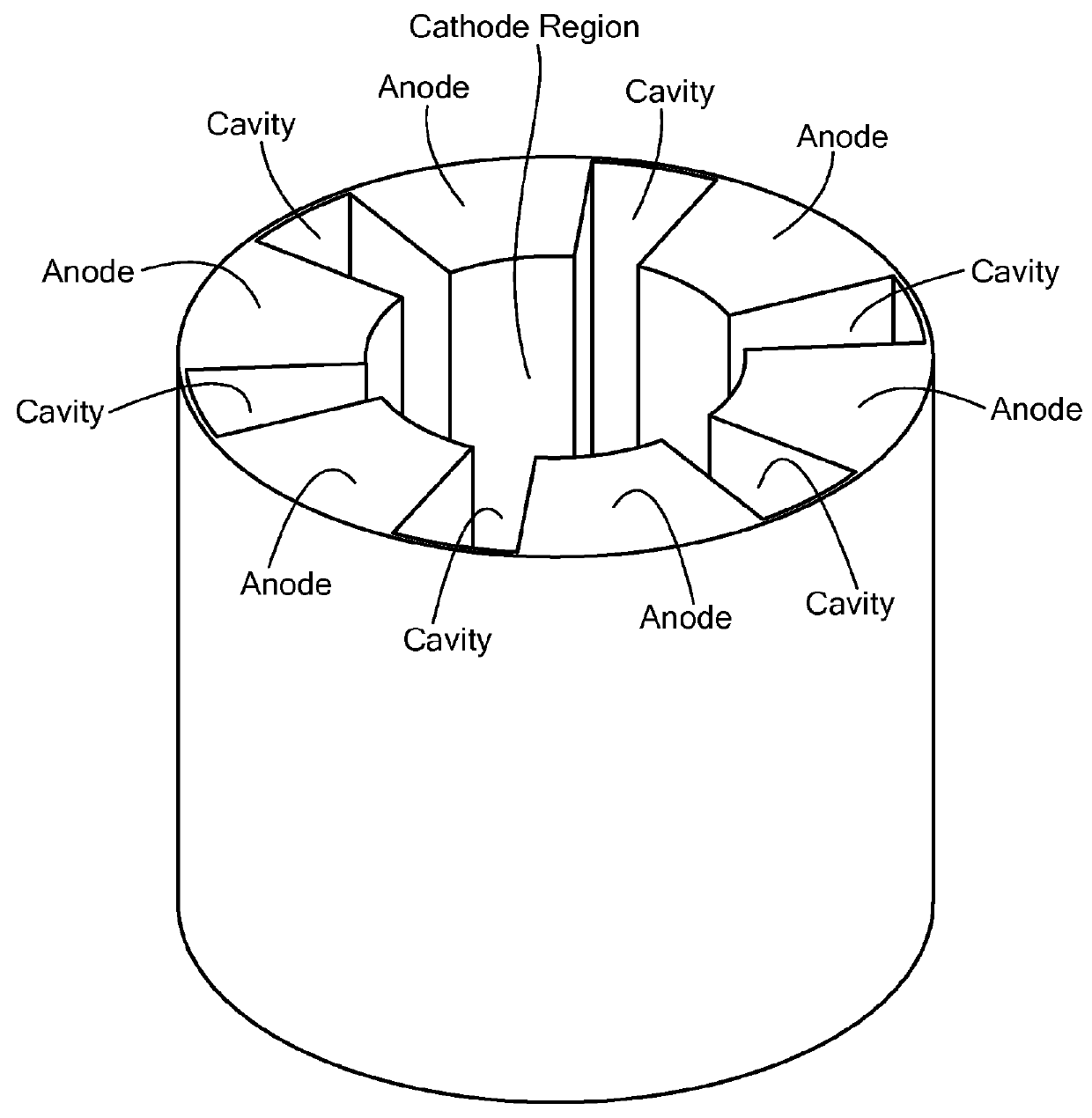
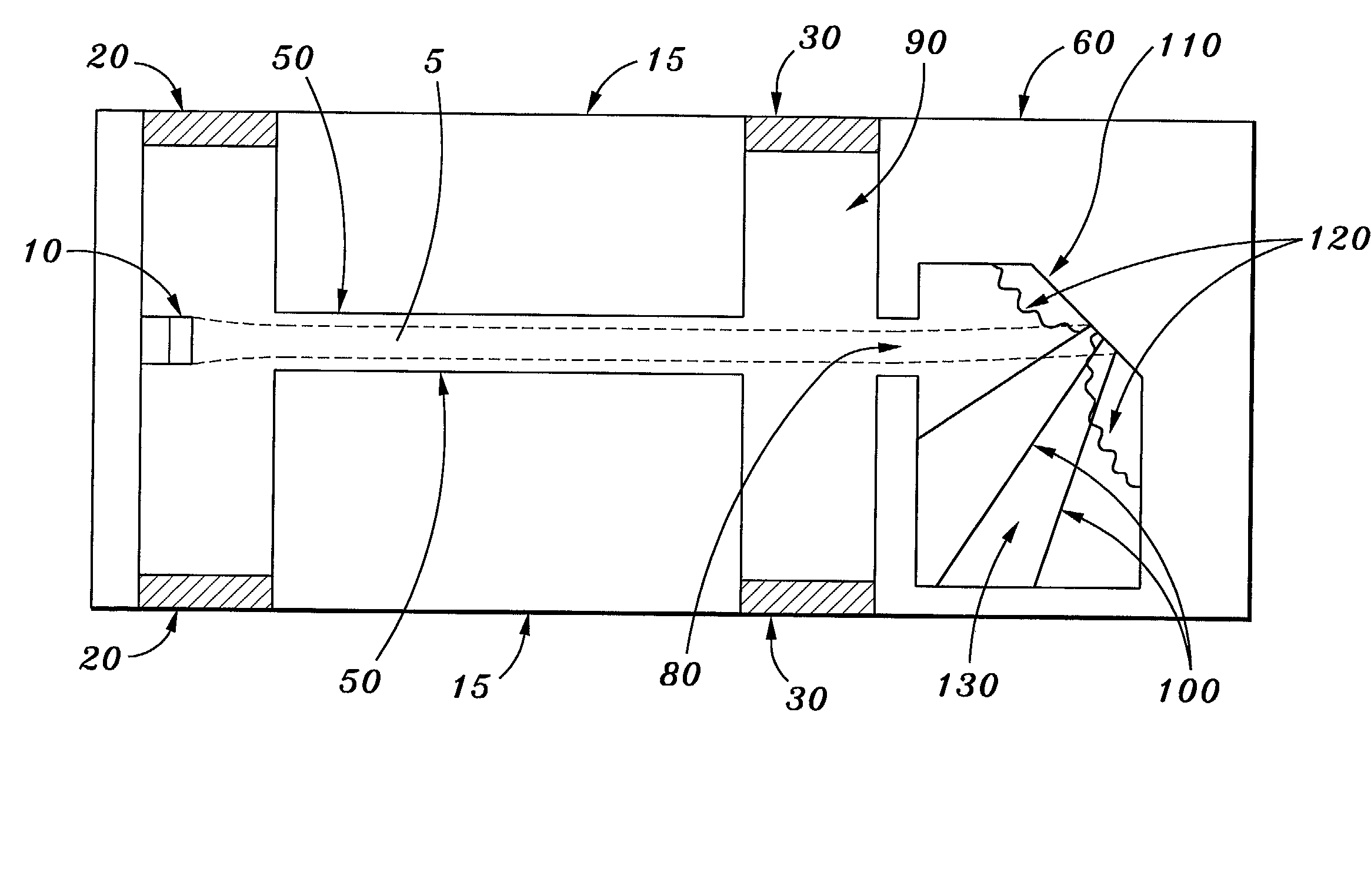
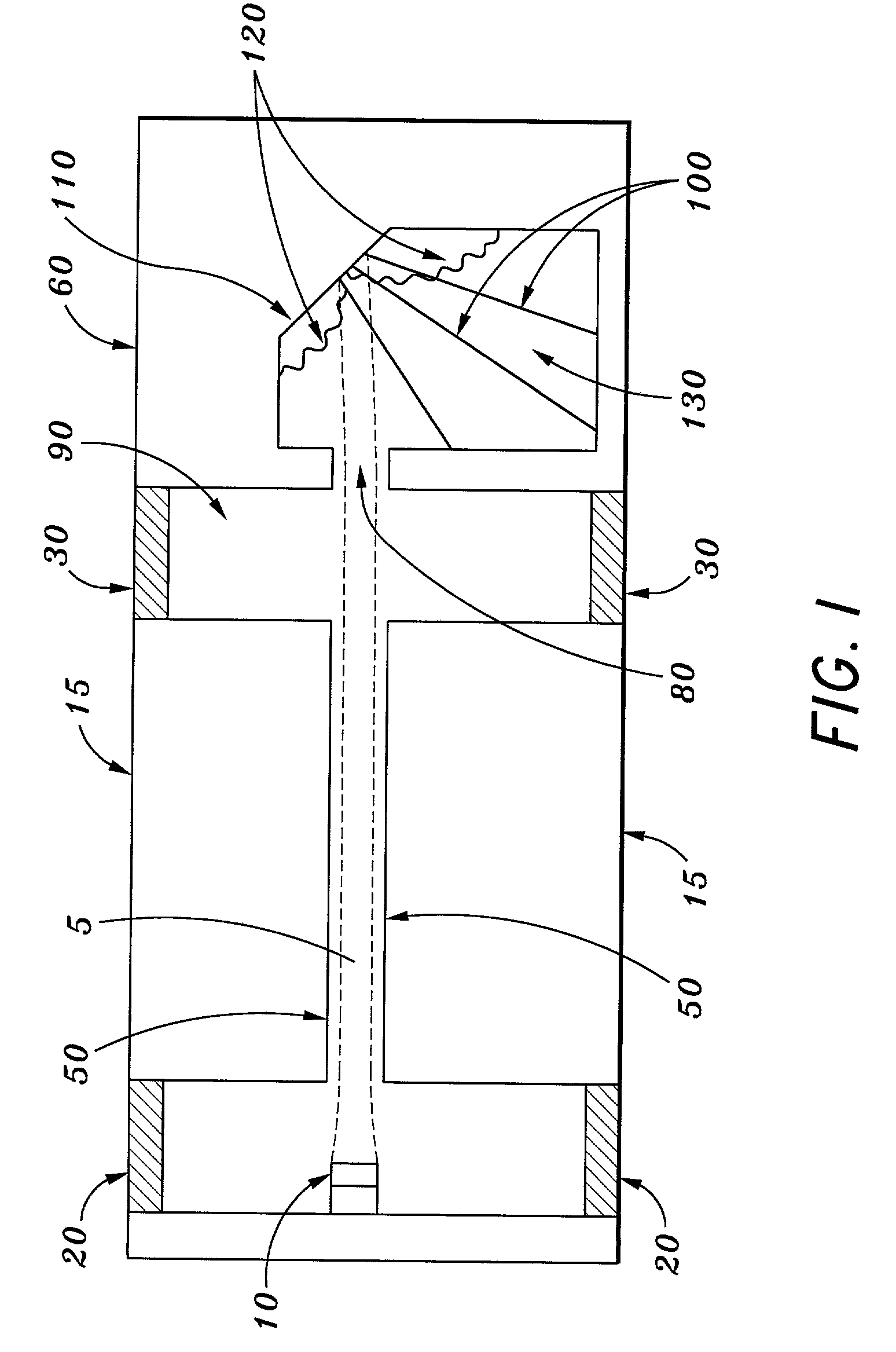
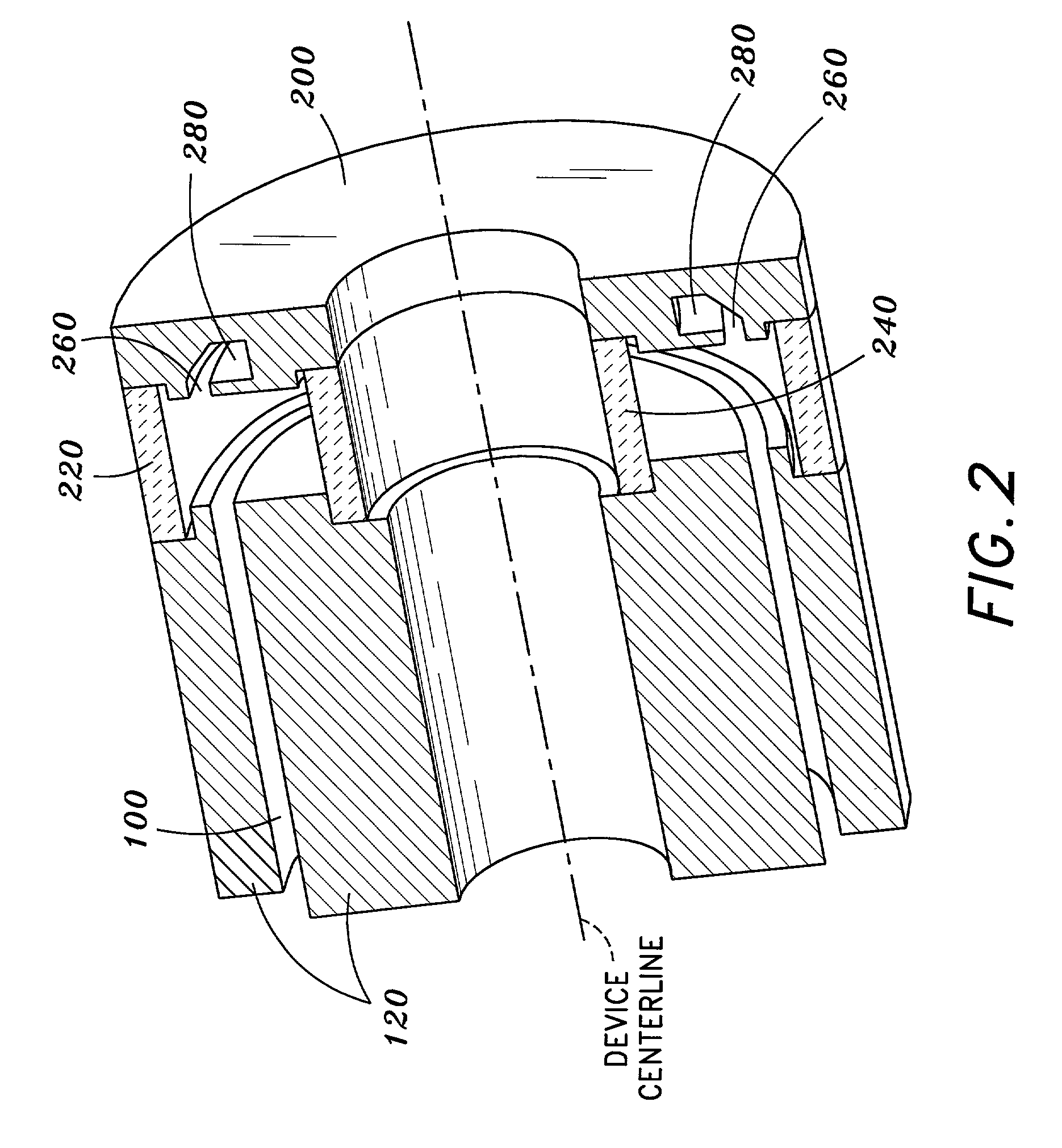
Vacuum Electronic Devices and Cavities and Fabrication Methods Therefor
The present invention relates to the formation of a vacuum electronics circuit by the fusion bonding of multiple substrate wafers, e.g., silicon, copper, or other suitable conductive material, each etched using DRIE, cut using EDM, or machined by other suitable means. Other aspects of the invention relate to the alignment of a cathode with tube by fusion bonding the cathode wafer to a tube built using the fabrication methods described herein. Yet other aspects involve the alignment of dies or wafers during the fabrication of a vacuum electronics device using the “lego” technique outlined herein. In yet other aspects, fabrication methods are described.
Owner:LOGOS TECH HOLDCO INC
Gallium nitride traveling wave structures
InactiveUS7936210B2Solid-state devicesAmplifiers with transit-time effectAudio power amplifierCascode
A traveling wave device employs an active Gallium Nitride FET. The Gallium Nitride FET has a plurality of gate feeding fingers connecting to an input gate transmission line. The FET has a drain electrode connected to an output drain transmission line with the source electrode connected to a point of reference potential. The input and output transmission lines are terminated with terminating impedances which are not matched to the gate and drain transmission lines. The use of Gallium Nitride enables the terminating impedance to be at much higher levels than in the prior art. The use of Gallium Nitride permits multiple devices to be employed, thus resulting in higher gain amplifiers with higher voltage operation and higher frequency operation. A cascode traveling wave amplifier employing GaN FETs is also described having high gain and bandwidth.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP +1
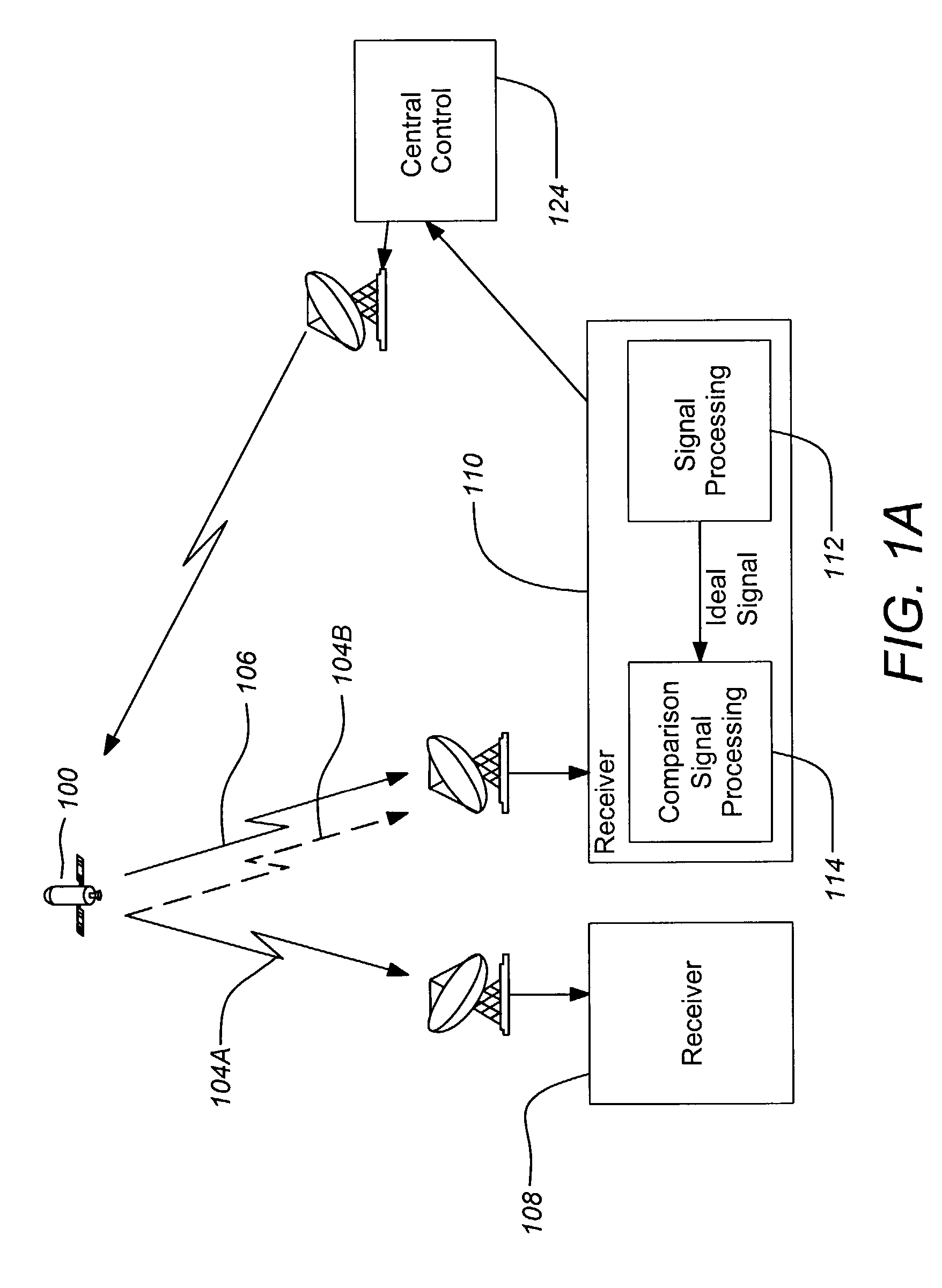
Coherent averaging for measuring traveling wave tube amplifier nonlinearity
InactiveUS20050078778A1Convenient and accurateAccurate extractionTelevision system detailsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorAudio power amplifierEngineering
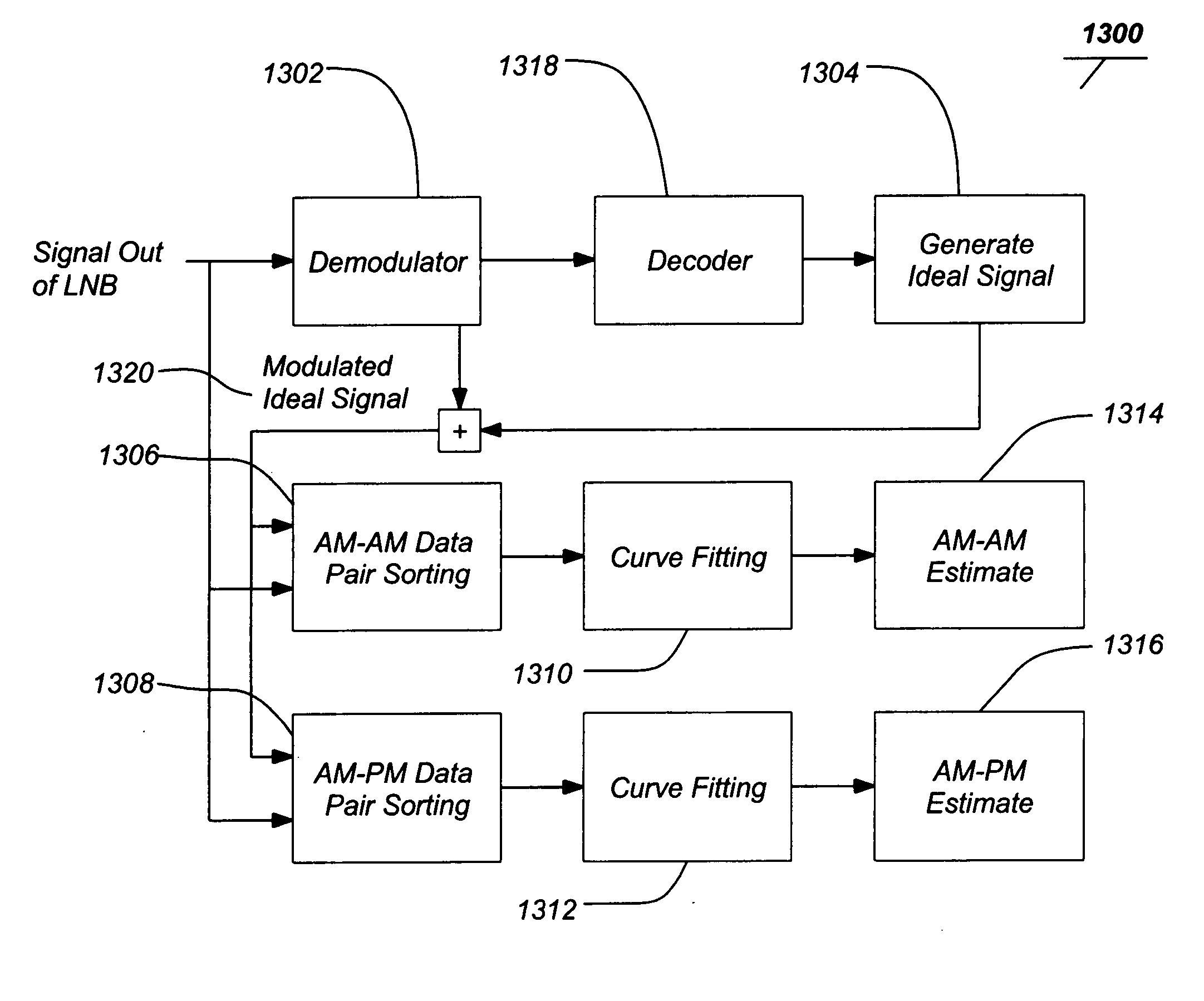
A method and system provide the ability to measure a transmission performance characteristic. A signal is received and demodulated. An ideal signal is generated from the demodulated signal. The received signal is coherently averaged to reduce noise. The performance characteristic is the estimated TWTA nonlinearity from a difference between the coherently averaged ideal signal and received signal.
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
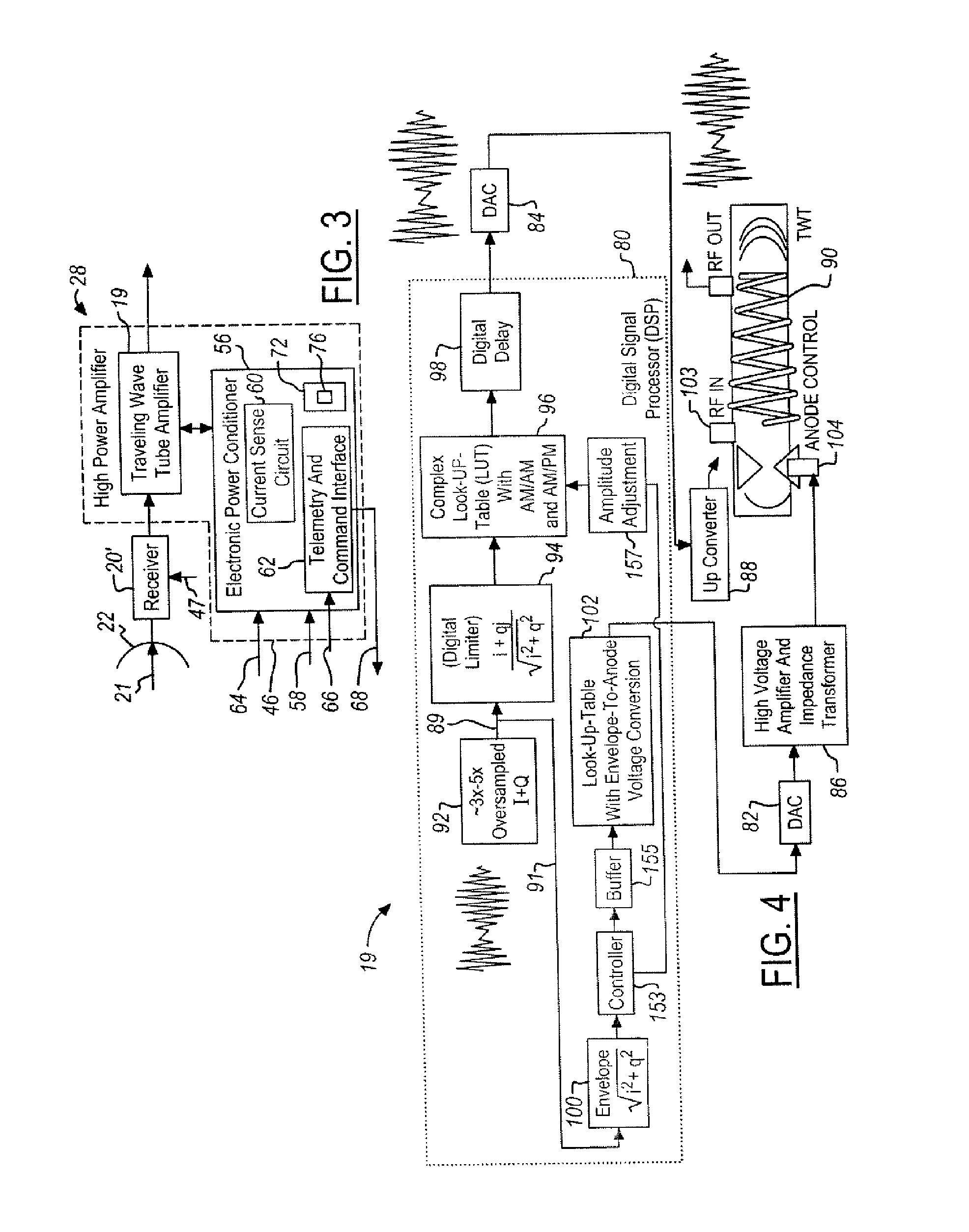
System and Method for Envelope Modulation
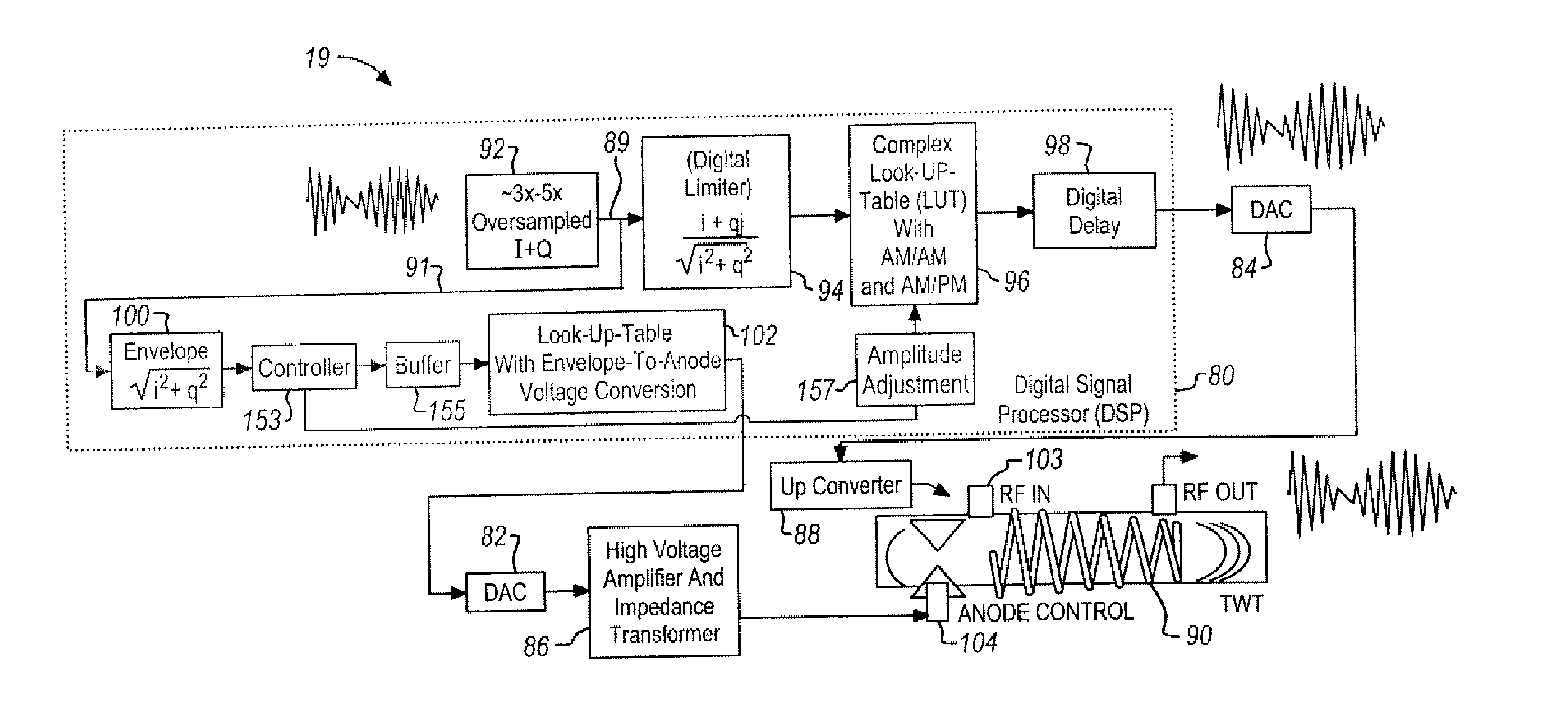
ActiveUS20060103460A1Maintain gainMaintain efficiencyTravelling-wave tubesAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyPower control systemWave shape
A power control system for a satellite receiving radio-frequency signals includes a digital processor and a traveling wave tube amplifier system and corresponding traveling wave tube. An anode voltage of the traveling wave tube amplifier system is used to modulate or saturate the current of the electron beam of the traveling wave tube so that the output power of the traveling wave tube amplifier system, from the saturated electron beam, is proportional to a waveform envelope of the radio-frequency signals. The digital processor controls anode and RF input signal amplitudes to the traveling wave tube and predicts necessary corrections.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
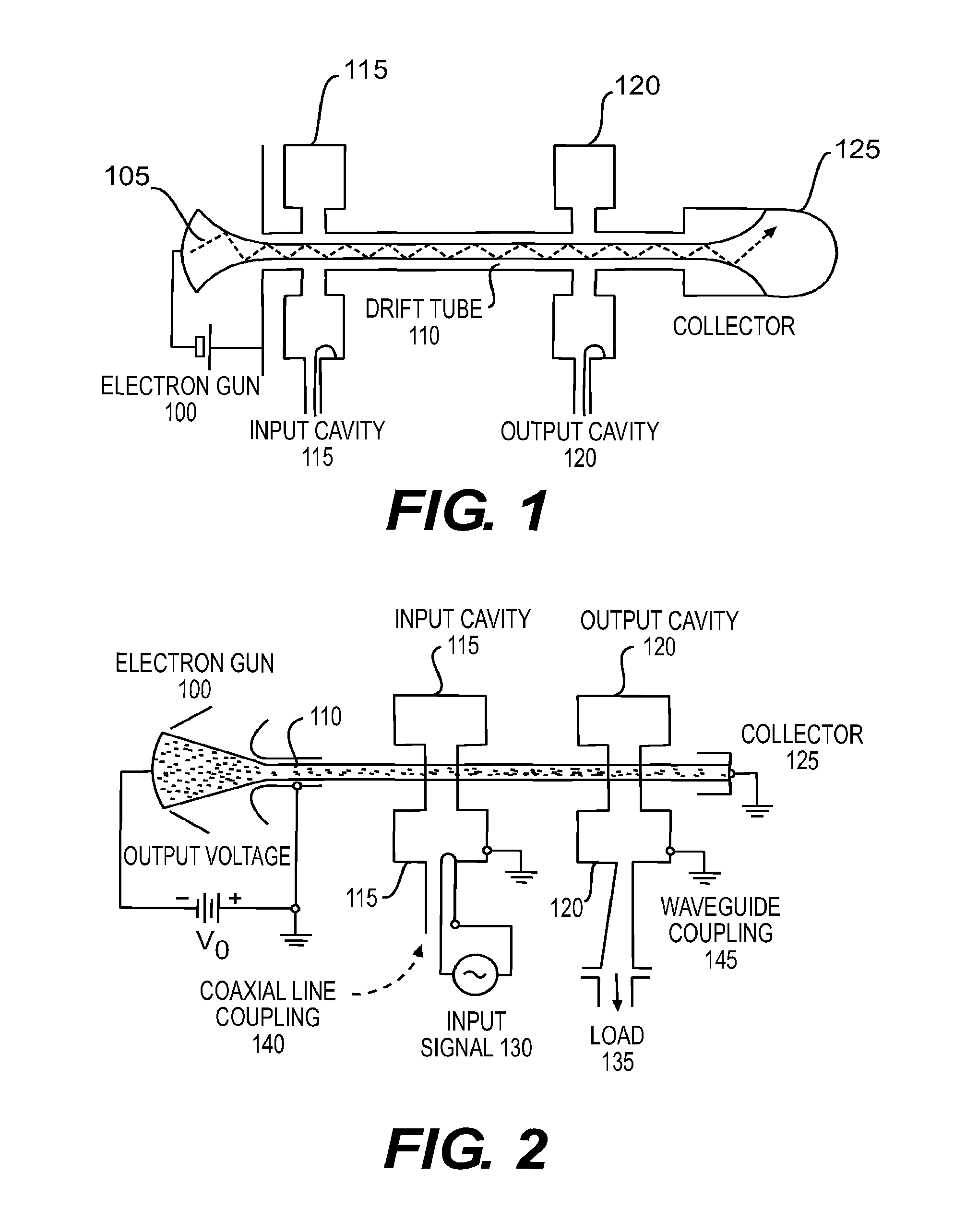
Inductive output tube having a broadband impedance circuit
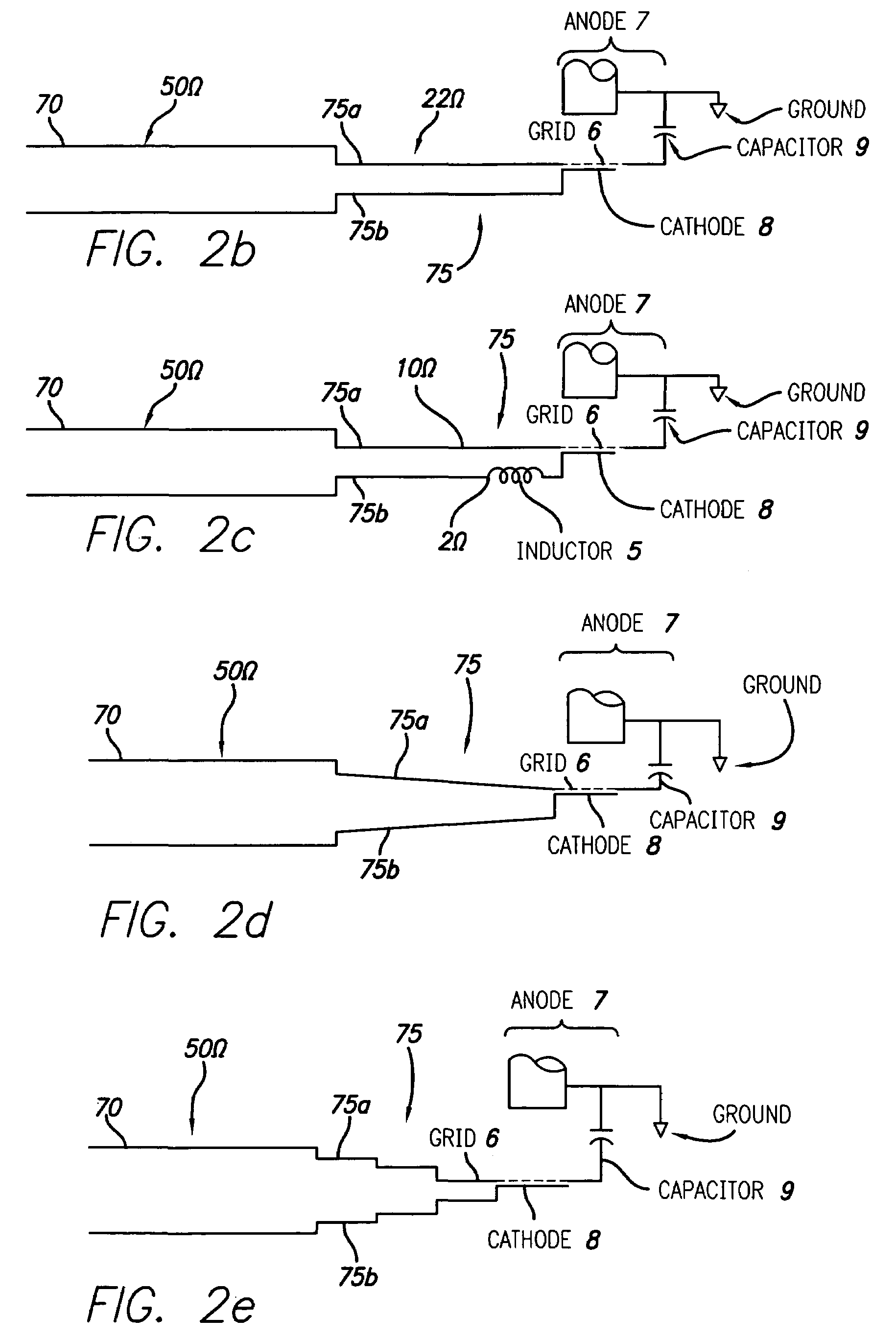
An inductive output tube (IOT) provides improved efficiency and larger bandwidth. In one embodiment, an IOT is provided with an electron gun that generates an electron beam, a tube body, a collector for collecting the electron beam, and an extended-interaction output circuit. The electron beam travels through the tube body and the extended-interaction output circuit. The extended-interaction output circuit is located within the tube body. The extended-interaction output circuit comprises a short-circuited resonant structure. The extended-interaction output circuit is used for reducing undesired components of a radio frequency (RF) wave, increasing desired components of the RF wave, and slowing down the propagation of the RF wave. (That is the circuit increases the integral of the electric field along the path of the beam electrons while decreasing the stored energy associated with those fields.) The extended-interaction output circuit also provides the IOT with larger bandwidth operation. The collector may be a multi-stage depressed collector having voltages on the collector to result in a constant efficiency characteristic. The radio-frequency drive power to the tube is connected by means of a broadband impedance matching transformer, and the grid to cathode capacitance may be reduced by depressions in the surface of the cathode directly underneath the grid structure.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
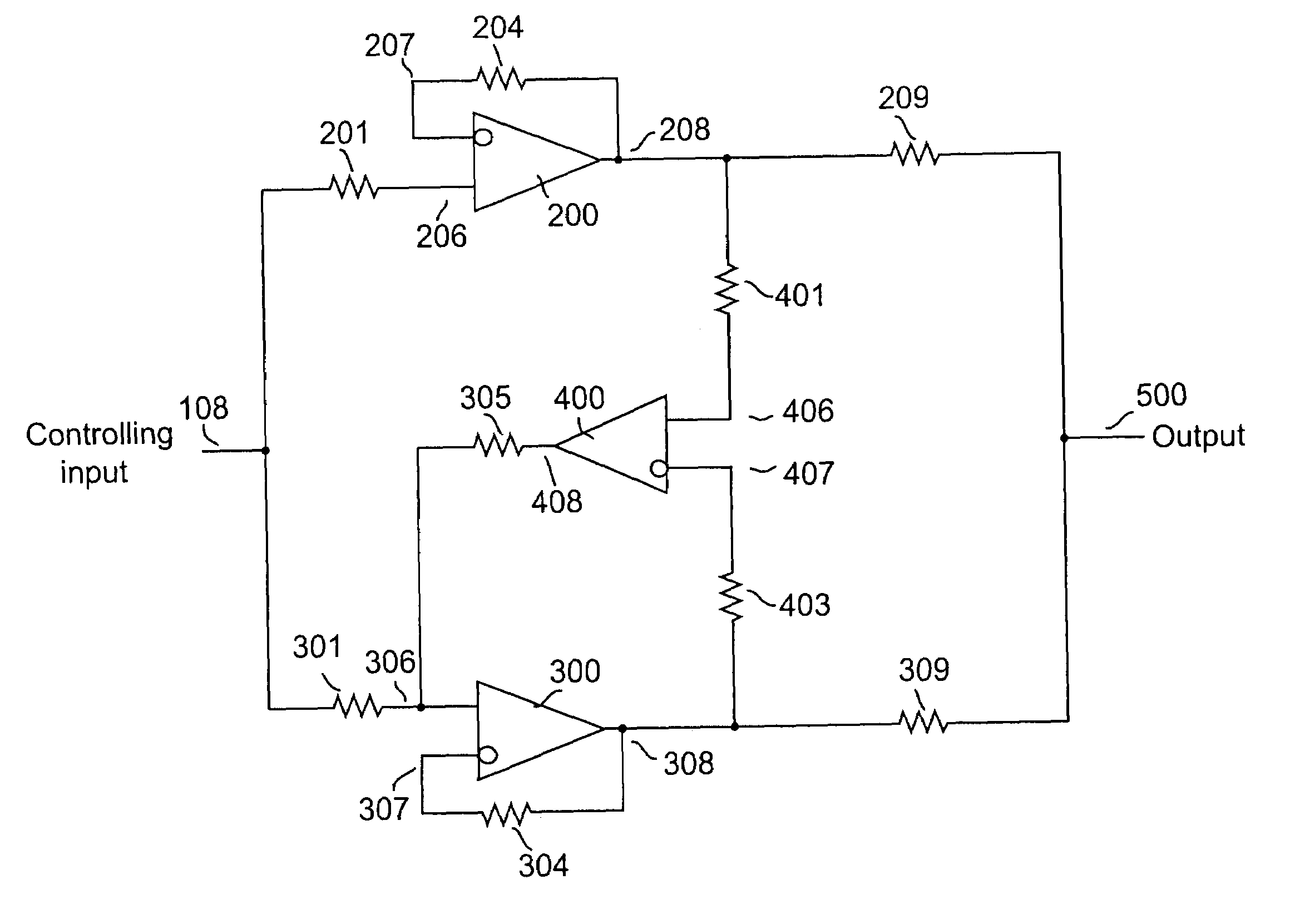
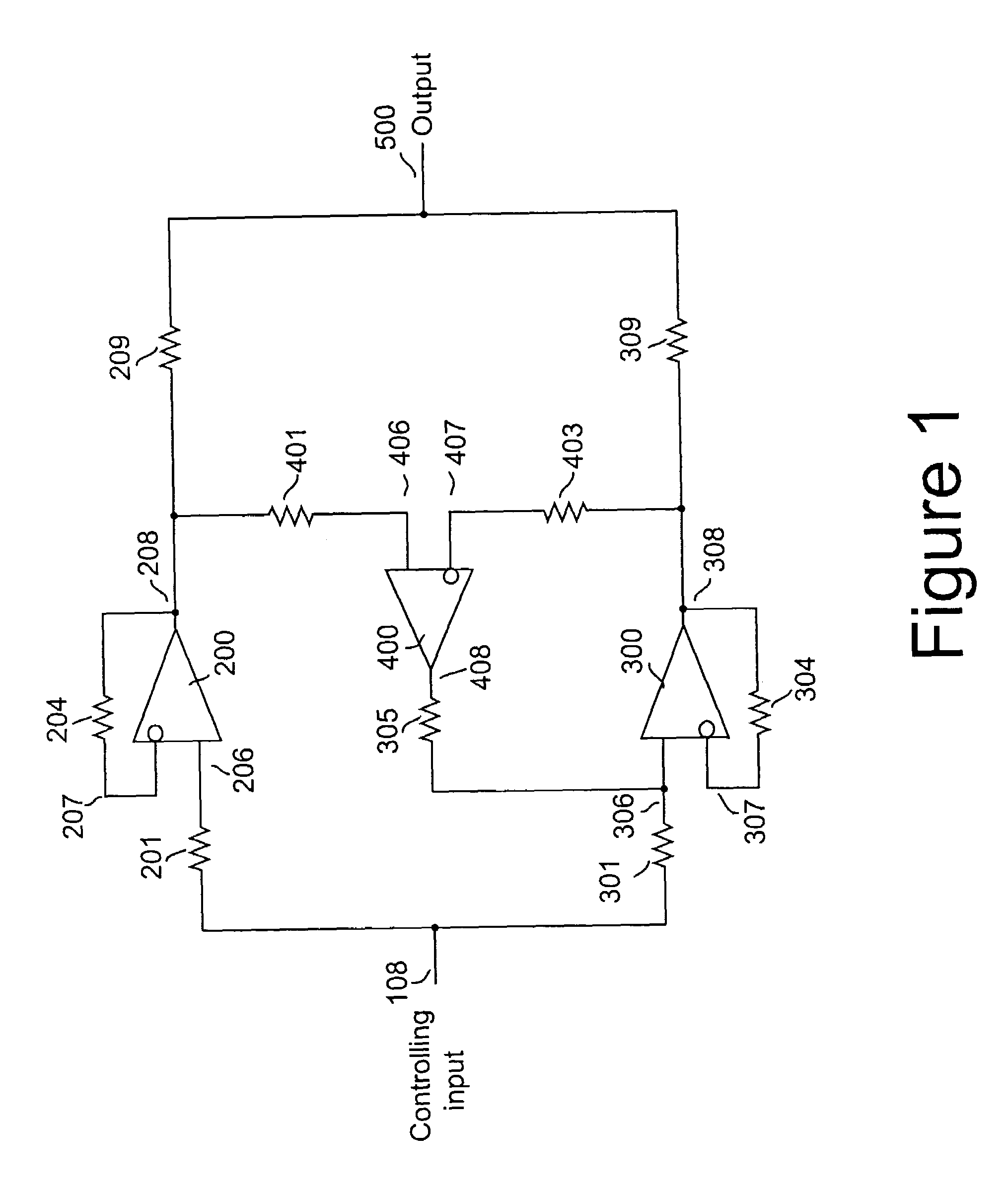
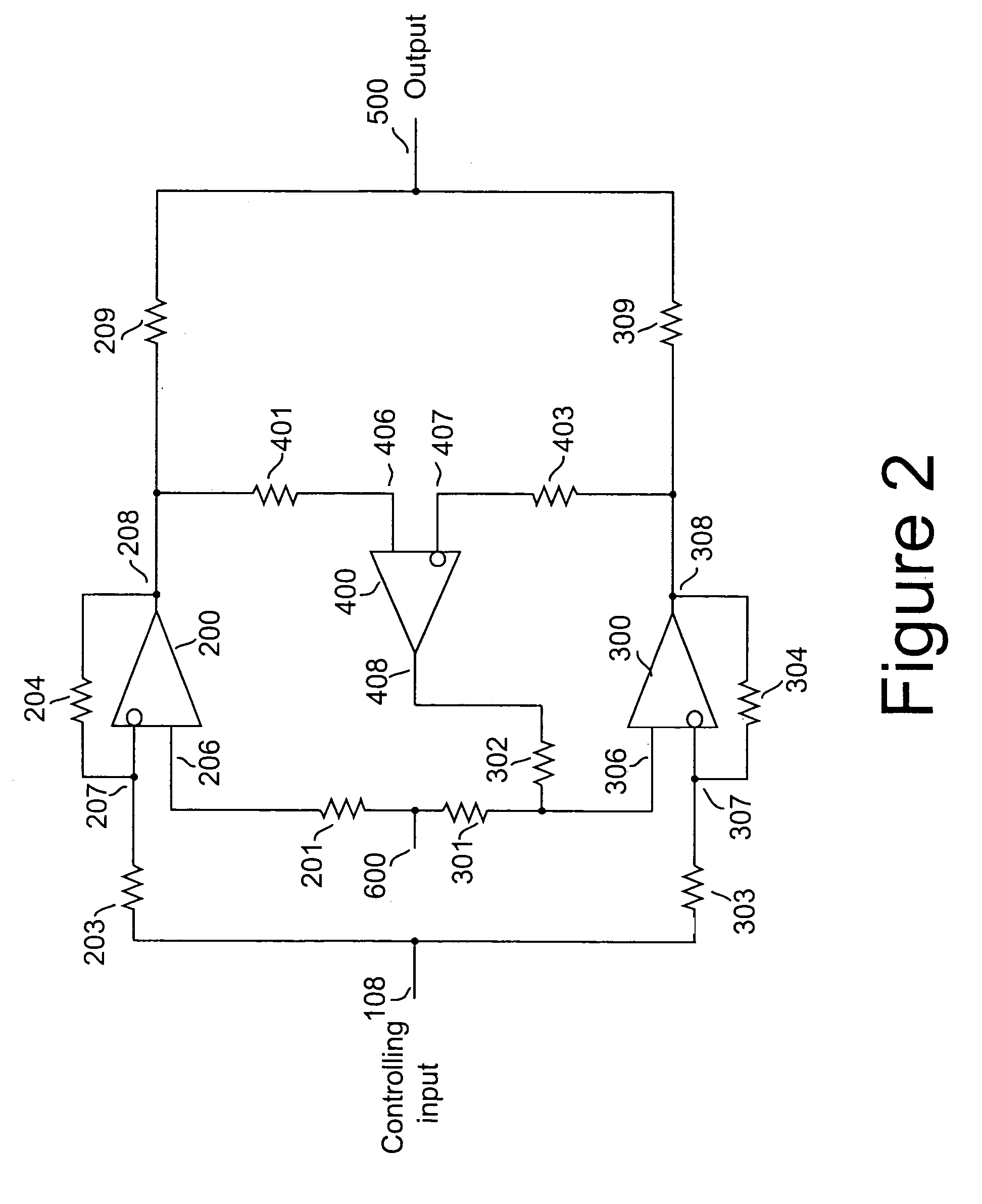
Servo balancing among driver devices
InactiveUS20050237109A1Improve tracking accuracyReduce imbalanceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
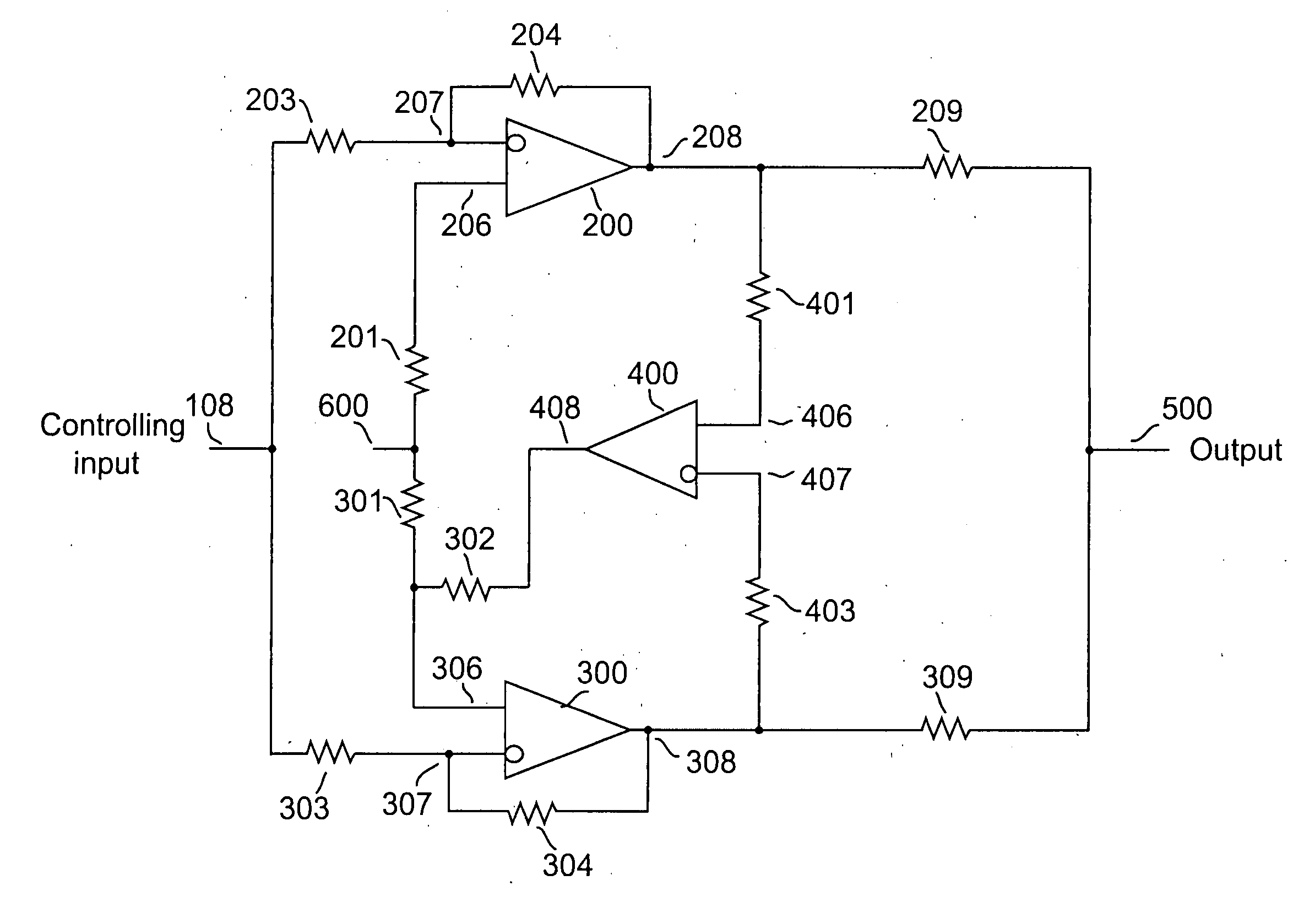
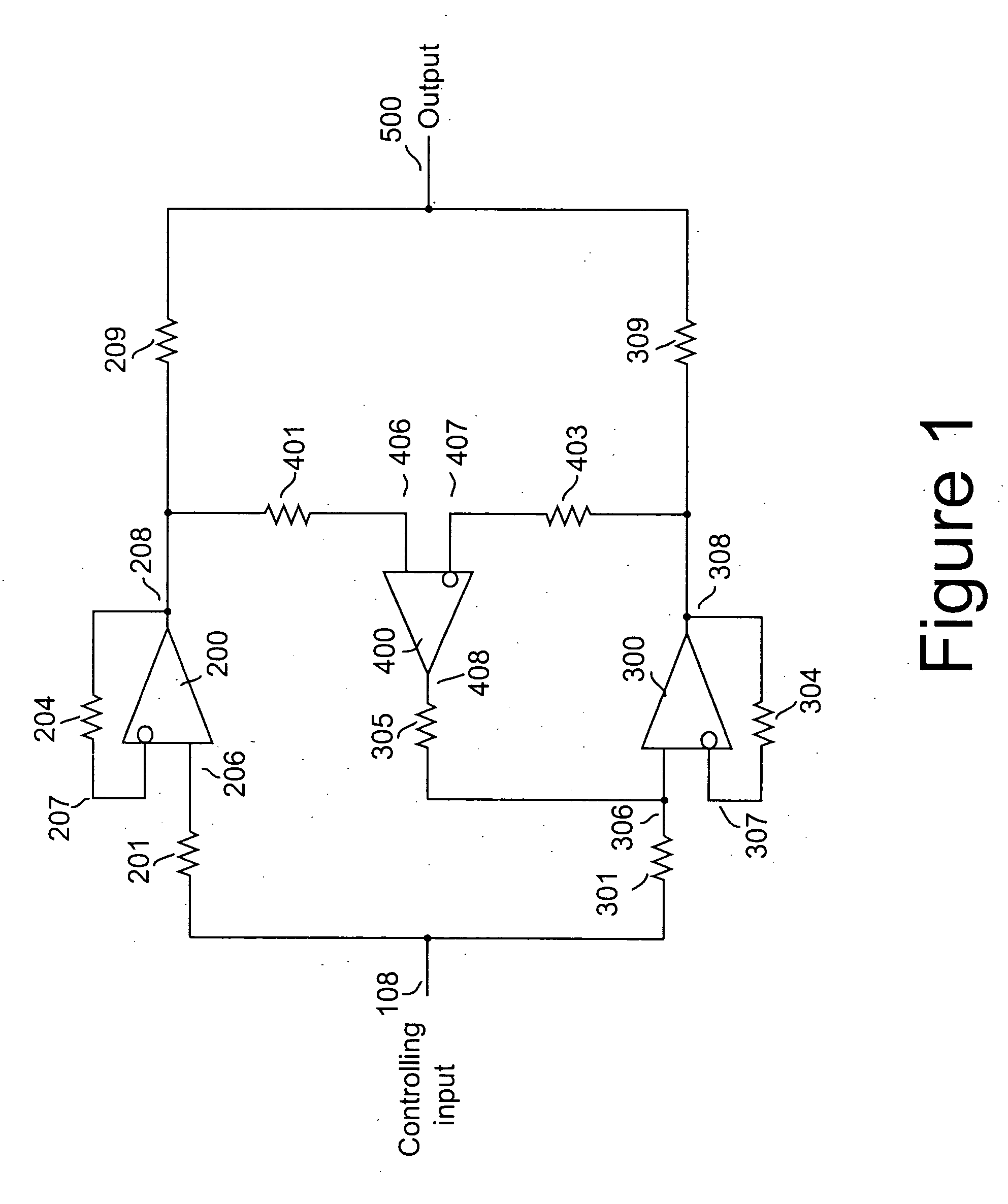
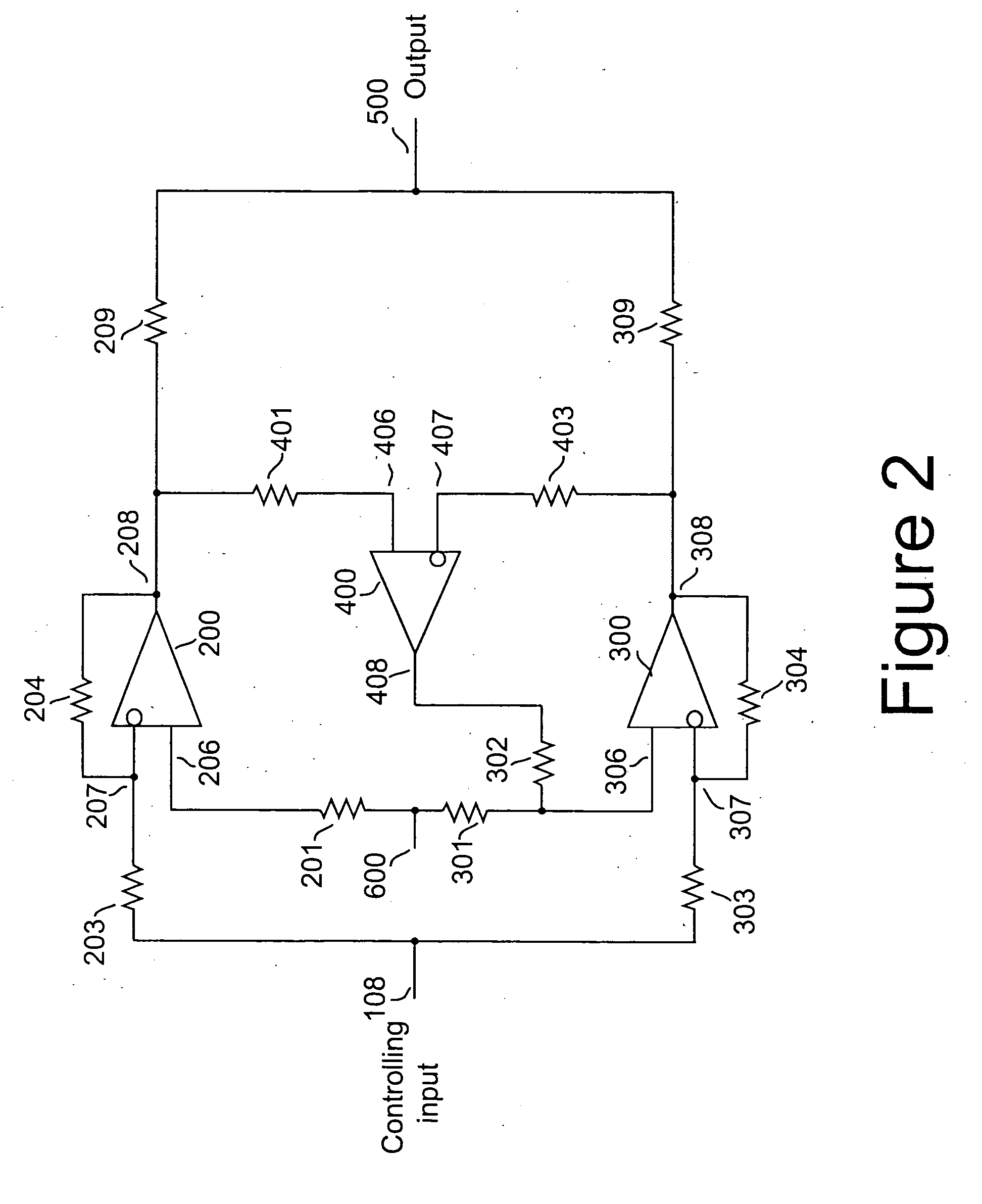
A method and apparatus for reducing imbalances among the outputs of a plurality of driver devices connected in a parallel configuration to drive a common load. One driver is designated as the master, and suitable servo circuitry is provided to each of the other slave drivers, each servo being operative to force the output of its associated slave driver to accurately track the output of the designated master driver. The servo circuitry may be disposed to equalize either the output voltages or output currents of the several drivers to ensure load balancing among the drivers, to reduce cross-conduction currents and attendant power wastage and improve dynamic performance. The plurality of drivers may either operate in an open-loop configuration, or be enclosed within an overall negative feedback loop under the control of a separate controller that itself may be an amplifier.
Owner:BIOURJA ENERGY SYST LLC
Coherent averaging for measuring traveling wave tube amplifier nonlinearity
ActiveCN1627741APulse modulation television signal transmissionTransmission monitoringAudio power amplifierEngineering
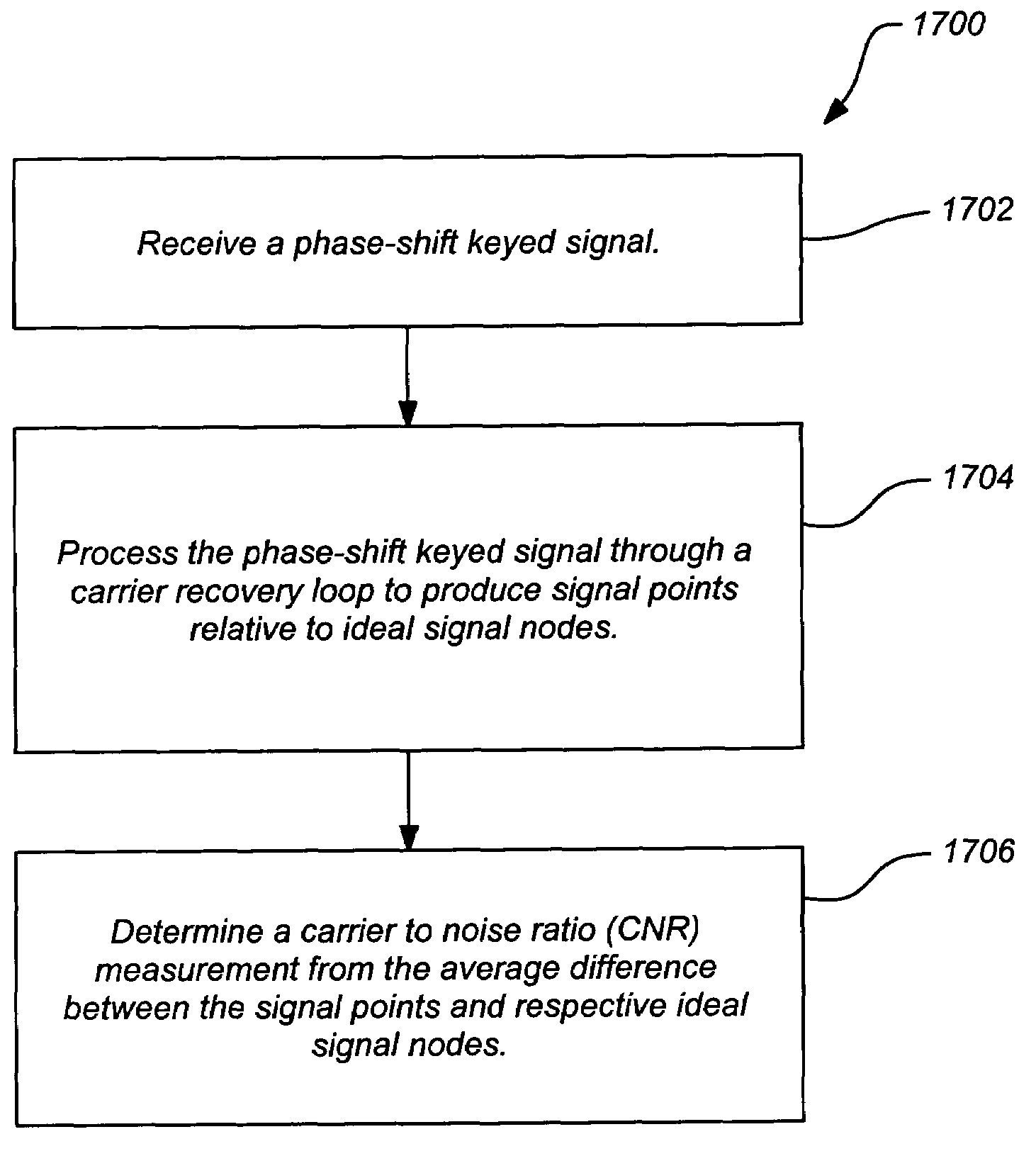
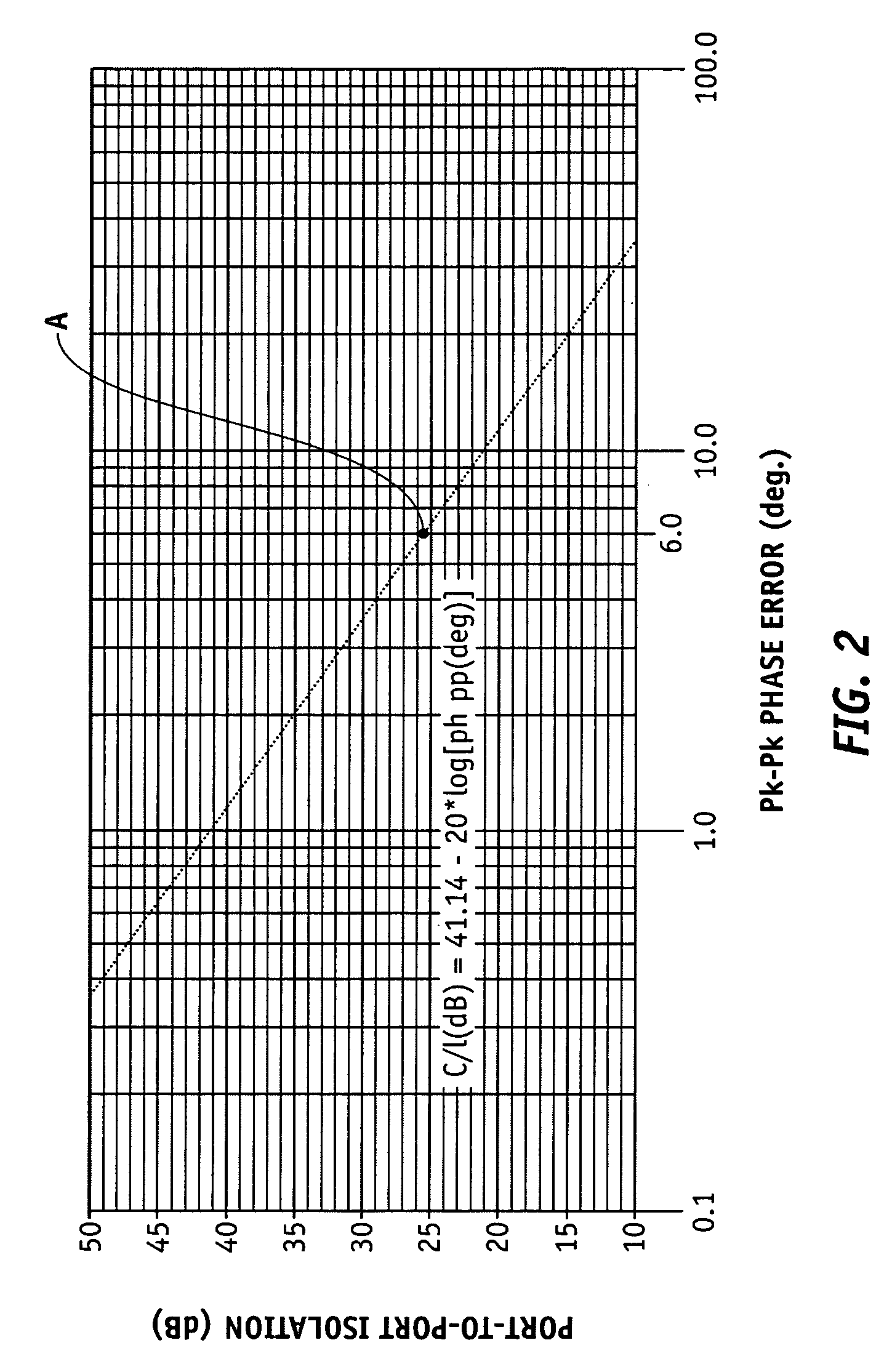
A method and system provide the ability to measure a transmission performance characteristic. A signal is received and demodulated 1302. An ideal signal 1320 is generated 1304 from the demodulated signal. The received signal is coherently averaged 1324 / 1326 to reduce noise. The performance characteristic is the estimated TWTA nonlinearity from a difference between the coherently averaged ideal signal and received signal. <IMAGE>
Owner:THE DIRECTV GROUP
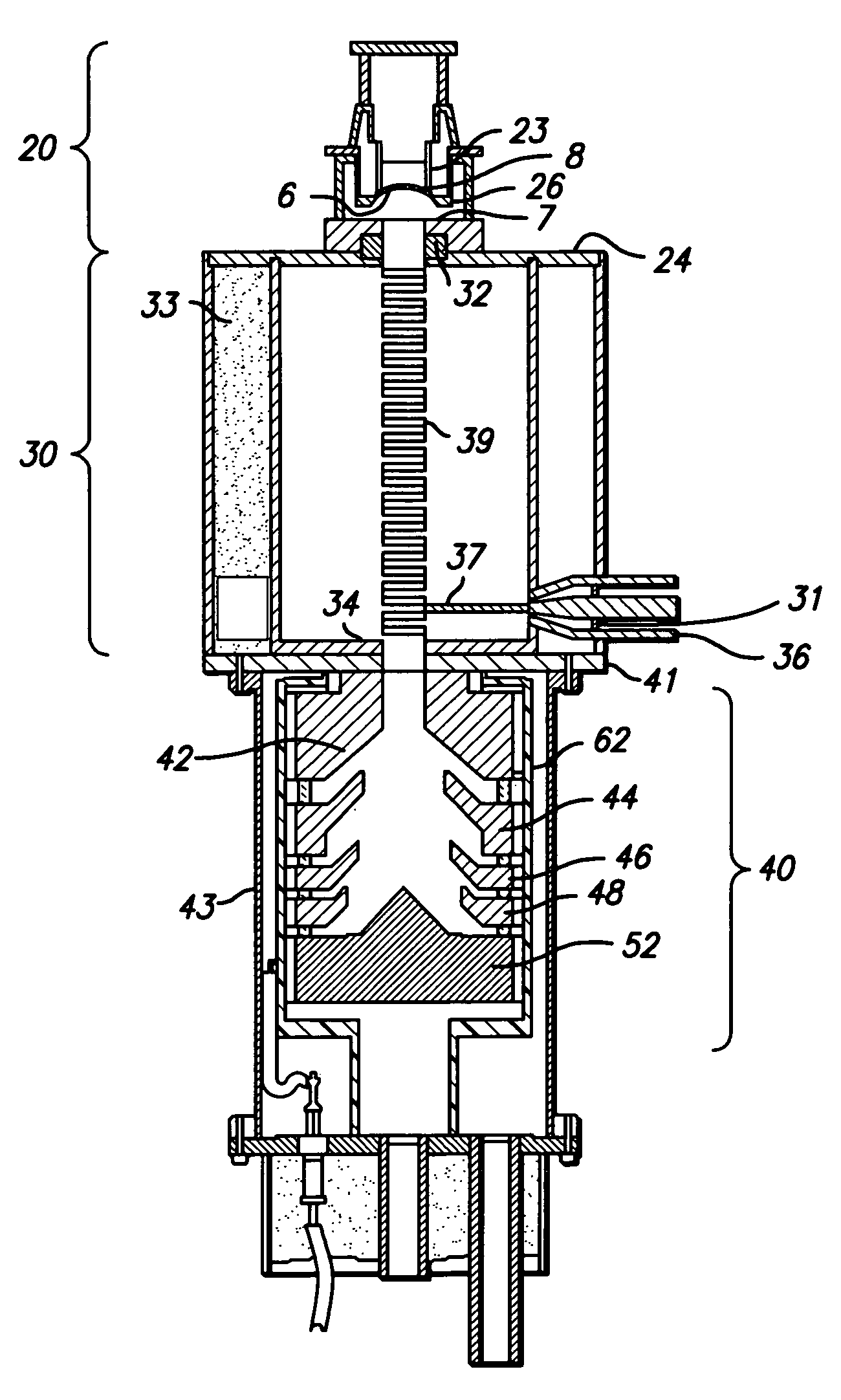
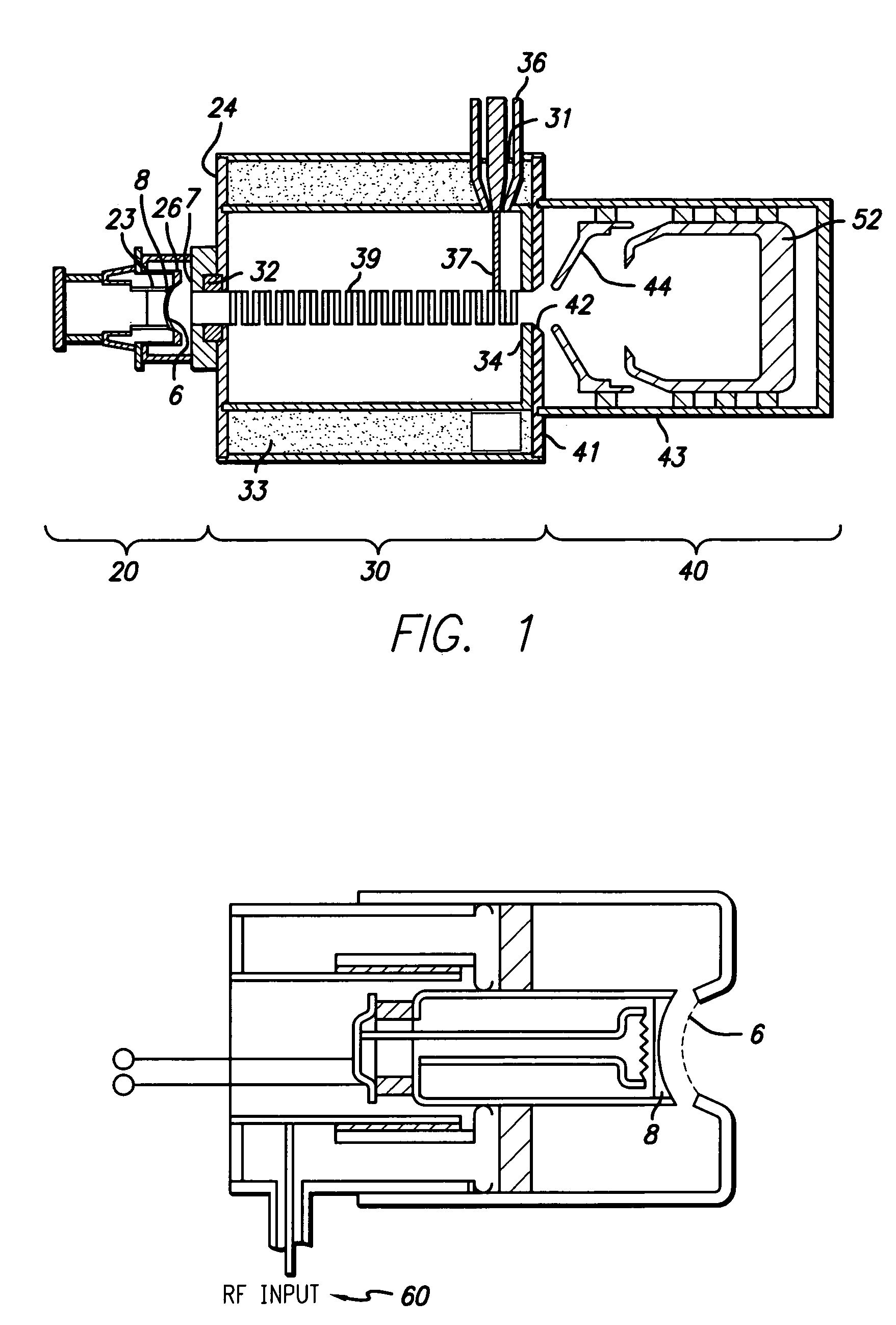
Tube amplifier assembly having a power tube and a capacitor assembly
Tube amplifier assembly including a power tube that is configured to be coupled to a grounding deck and positioned within an opening of the grounding deck. The tube amplifier assembly also includes a tube adapter that is configured to be coupled to the grounding deck. The tube adapter has a capacitive plate that extends parallel to the grounding deck and an adapter wall that is coupled to the capacitive plate. The tube adapter has an adapter opening that is aligned with the deck opening to form a tube passage. The tube adapter includes flexible conductive elements that are electrically coupled to the capacitive plate and surround the tube passage. The flexible conductive elements engage the power tube in the tube passage and electrically couple the power tube to the capacitive plate. The grounding deck and the capacitive plate form a capacitor assembly.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Lower complexity layered modulation signal processor
InactiveUS20090097589A1Television system detailsAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionComputer scienceSignal processing
A method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving a coded signal having an upper layer signal and a lower layer signal is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of combining the upper layer signal and the lower layer signal, encoding the combined upper layer signal and lower layer signal, delaying the upper layer signal, modulating the delayed upper layer signal, modulating the lower layer signal, transmitting the delayed upper layer signal and transmitting the lower layer signal. The apparatus comprises an encoder, for encoding a combined upper layer signal and lower layer signal, a delay, communicatively coupled to the encoder, for delaying the upper layer signal, a first modulator, for modulating the delayed upper layer signal, a second modulator, for modulating the lower layer signal, a transmitter, communicatively coupled to the first modulator, for transmitting the delayed upper layer signal, and a second transmitter, communicatively coupled to the second modulator.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GRP INC
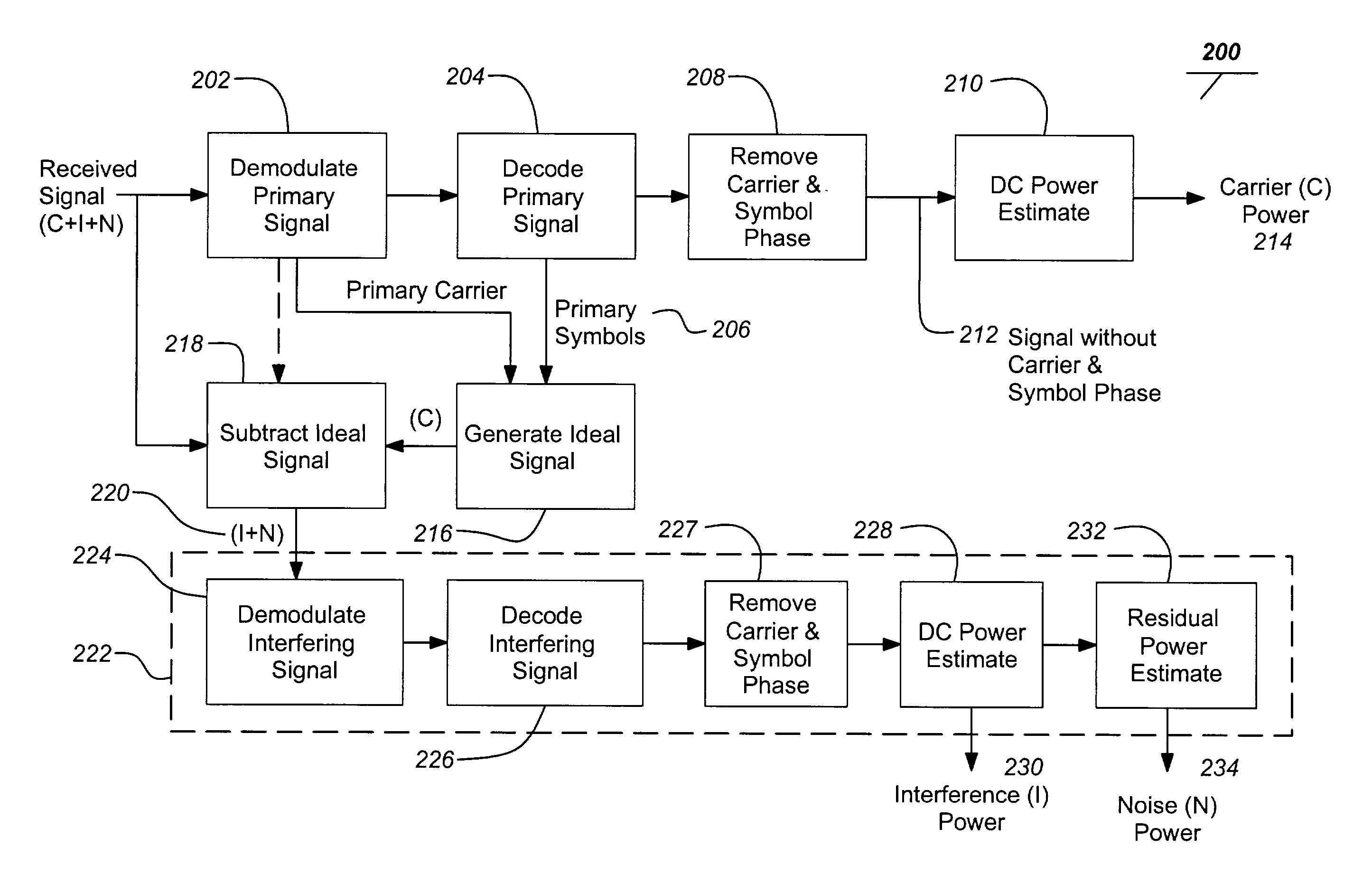
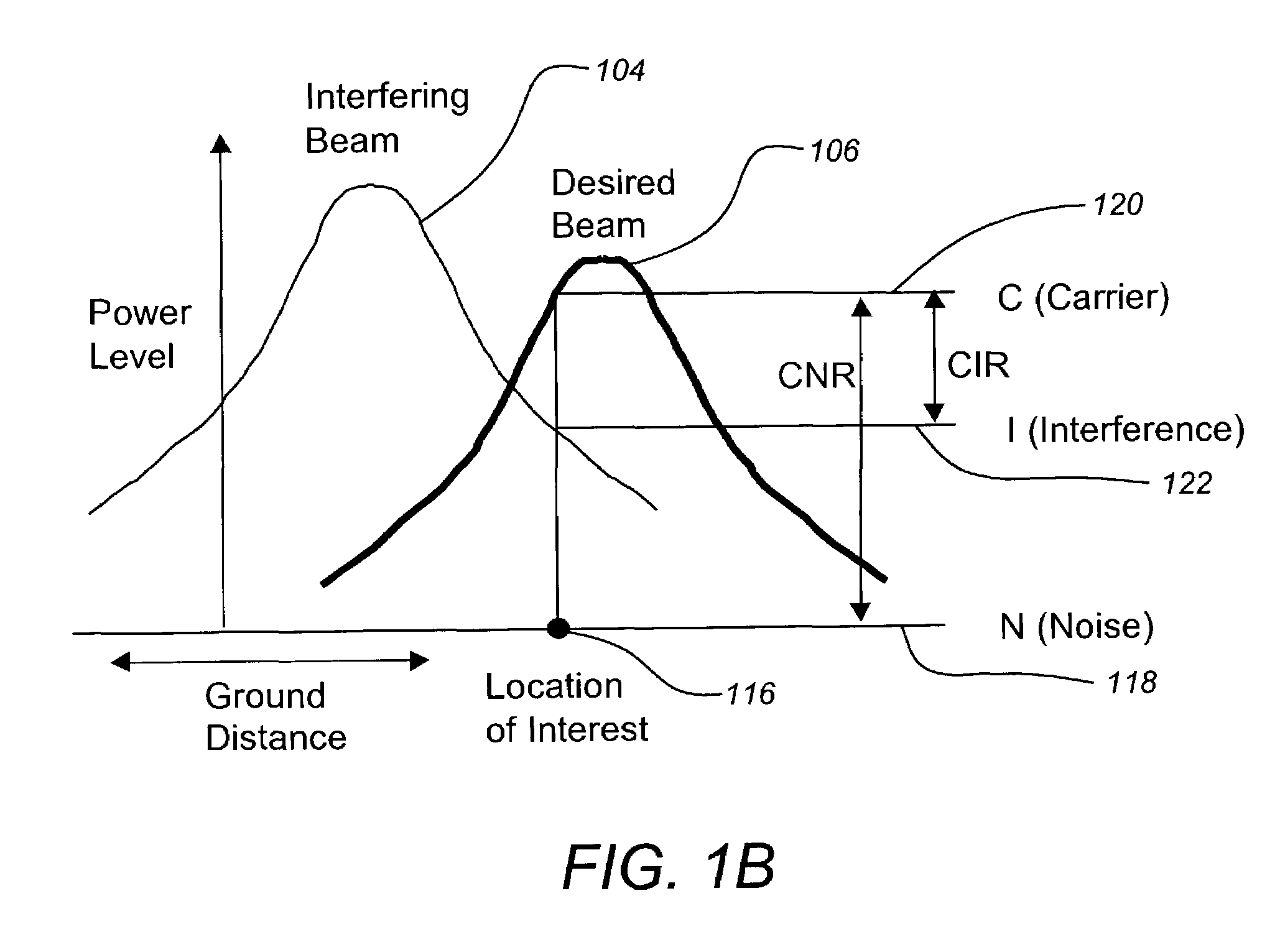
Signal, interference and noise power measurement
ActiveUS7822154B2Consistent and highly accurateError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementEngineeringNoise power
Systems and methods are presented for measuring power levels of primary and interfering signals as well as noise, particularly for satellite transmitted signals. A typical method comprises the steps of receiving a signal comprising a primary signal, an interference signal and noise, demodulating the primary signal to remove a carrier frequency, decoding the primary signal to obtain symbols, estimating a power level of the primary signal based upon the demodulated and decoded primary signal. Additionally, an ideal primary signal can be generated from the carrier power and frequency and the symbols and subtracted from the received signal to produce the noise and interference signal. The noise and interference power is then estimated from the noise and interference signal.
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
Servo balancing among driver devices
InactiveUS7078965B2Reduce imbalanceTotal current dropNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
A method and apparatus for reducing imbalances among the outputs of a plurality of driver devices connected in a parallel configuration to drive a common load. One driver is designated as the master, and suitable servo circuitry is provided to each of the other slave drivers, each servo being operative to force the output of its associated slave driver to accurately track the output of the designated master driver. The servo circuitry may be disposed to equalize either the output voltages or output currents of the several drivers to ensure load balancing among the drivers, to reduce cross-conduction currents and attendant power wastage and improve dynamic performance. The plurality of drivers may either operate in an open-loop configuration, or be enclosed within an overall negative feedback loop under the control of a separate controller that itself may be an amplifier.
Owner:BIOURJA ENERGY SYSTEMS LLC
Traveling-wave valve arrangement
InactiveUS6486604B1Reduce heatLong signal pathTravelling-wave tubesDischarge tube main electrodesActive coolingMechanical engineering
For a traveling-wave valve arrangement with a traveling-wave valve and a linearizing circuit arrangement, it is proposed to design the linearizing circuit arrangement and the traveling-wave valve as one constructional unit and, for the thermal protection of the linearizing circuit arrangement in the simultaneous presence of a high permissible temperature of the valve housing, to maintain the circuit arrangement by means of an active cooling element at a nondamaging temperature lower than the one of the wall of the valve or of a common wall. The cooling element is preferably a Peltier element.
Owner:THALES ELECTRON DEVICES
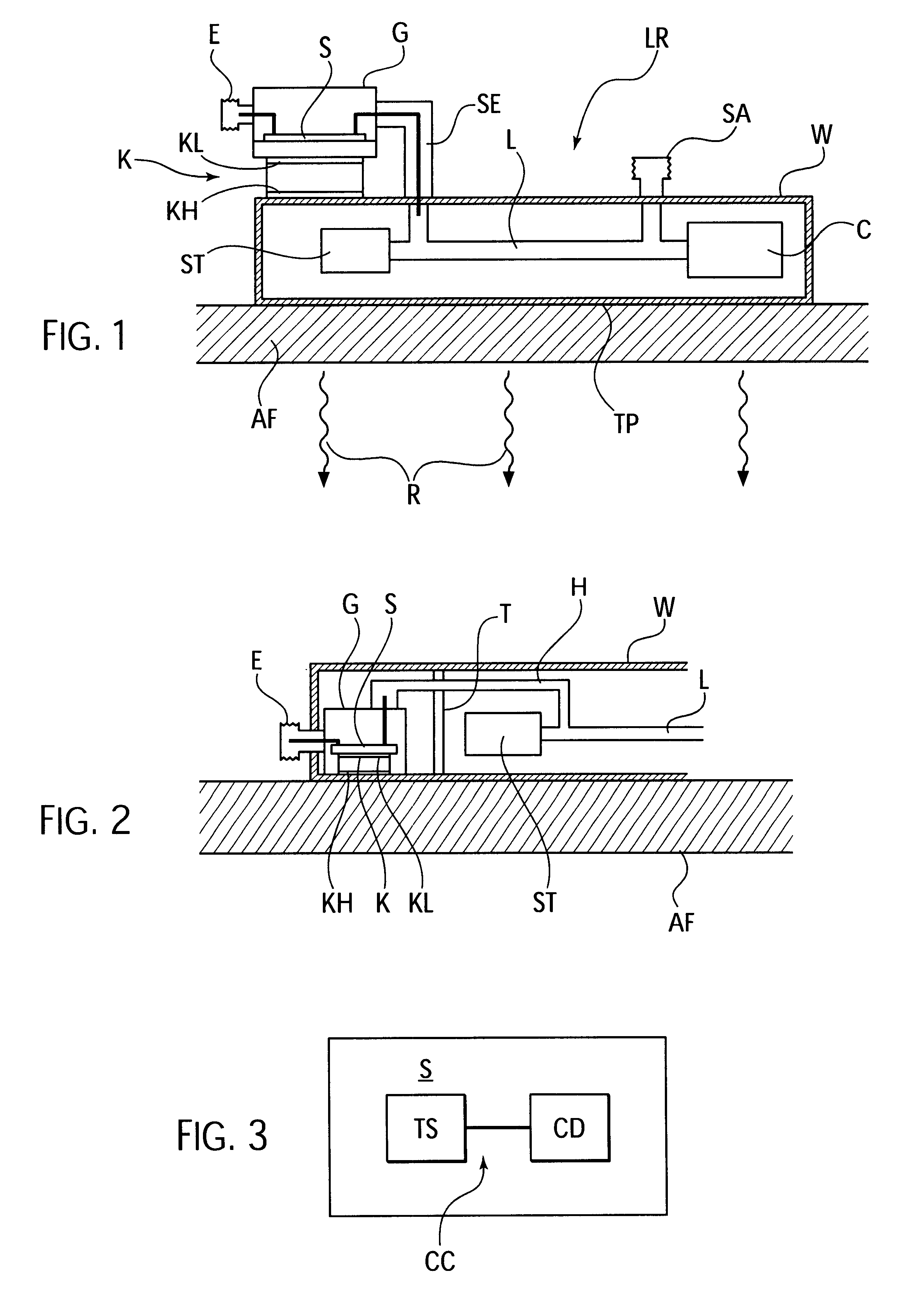
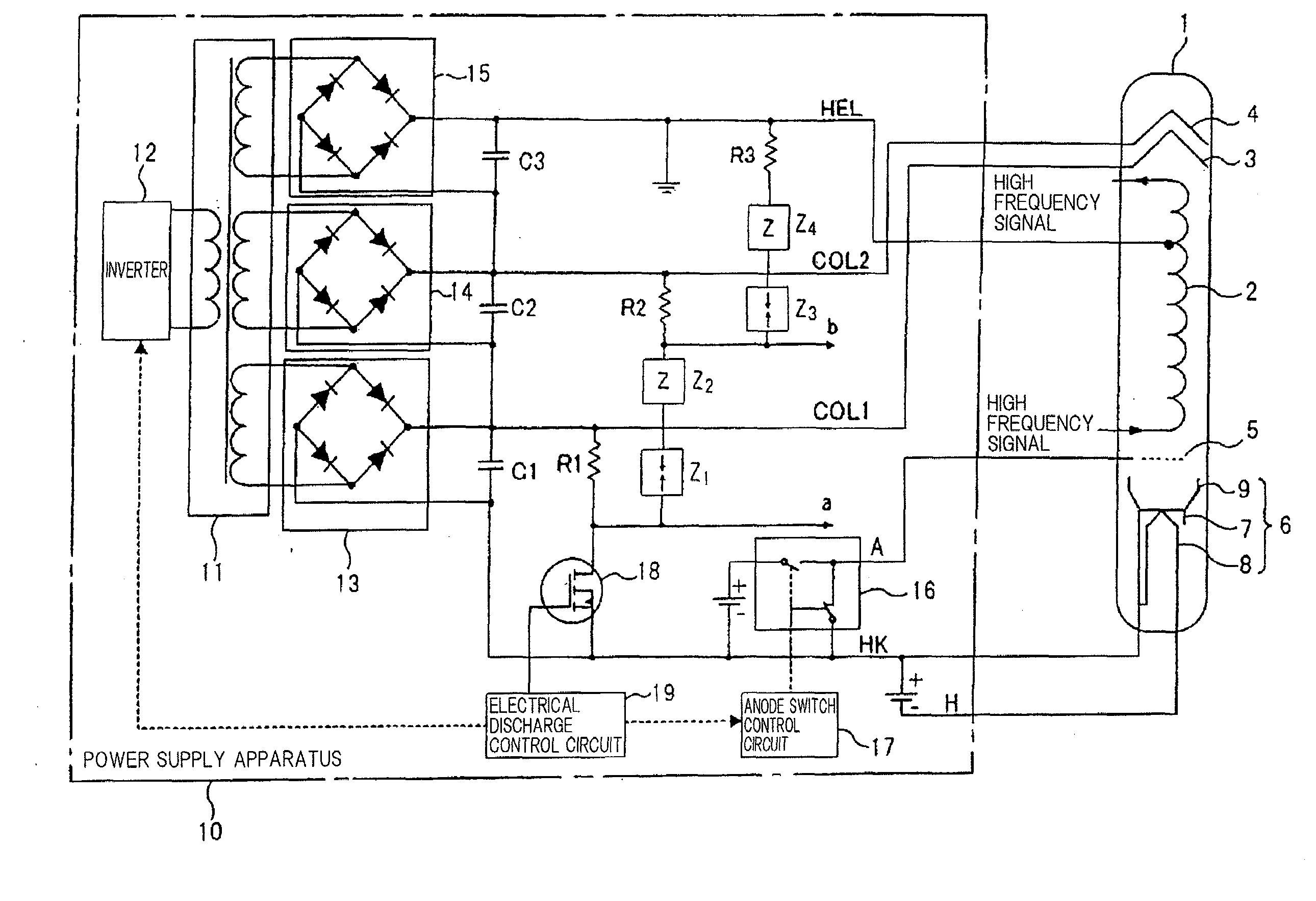
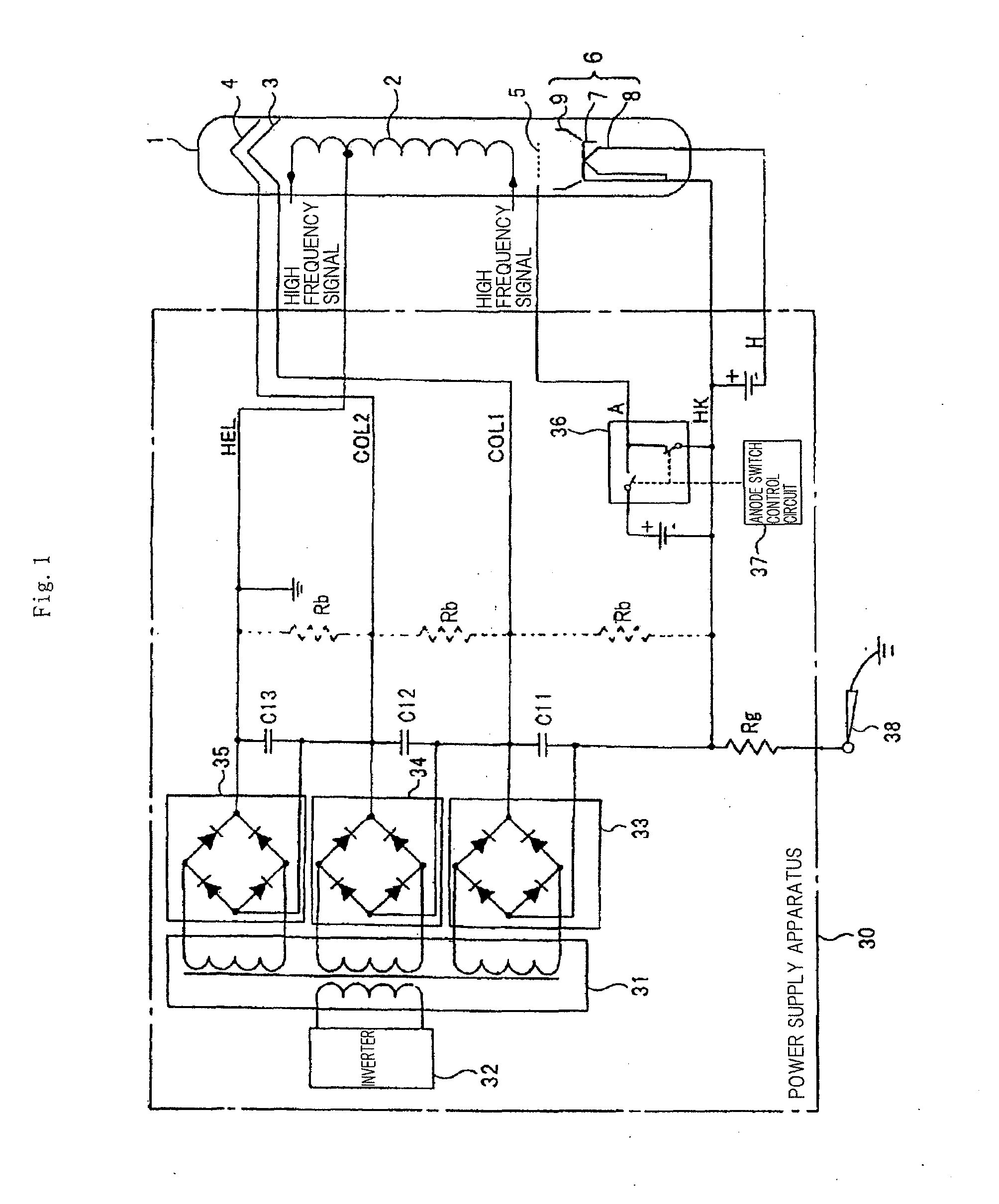
Power supply apparatus and high-frequency circuit system
ActiveUS20090033228A1Low costSimple configurationTravelling-wave tubesAmplifiers with transit-time effectEngineeringControl circuit
A power supply apparatus for a traveling-wave tube includes an electrical discharge switch and a first resistor that are serially connected, and that are connected between a cathode electrode and a first collector electrode; N (N denotes a positive integer) arresters that are serially connected, and that are inserted between a ground potential and a connection node of the electrical discharge switch and the first resistor; N second resistors that are inserted between the N arresters and a second collector electrode to an Nth collector electrode and a ground potential, respectively; and an electrical discharge control circuit that turns off the electrical discharge switch at a time of normal operation of the power supply apparatus and turns on the electrical discharge switch when stopping operation of the power supply apparatus.
Owner:NEC NETWORK & SENSOR SYST
High frequency helical amplifier and oscillator
Disclosed herein is a class of mm and sub mm wavelength amplifiers and oscillators operating with miniature helical slow wave circuits manufactured using micro fabrication technology. The helices are supported by diamond dielectric support rods. Diamond is the best possible thermal conductor, and it can be bonded to the helix. The electron beam is transmitted, not through the center of the helix, but around the outside. In some configurations the RF power produced may be radiated directly from the slow wave circuit. The method of fabrication, which is applicable above 60 GHz, is compatible with mass production.
Owner:TERAPHYSICS CORP
Travelling wave amplifiers
InactiveUS7142052B2Avoid insufficient lengthTravelling-wave tubesAmplifiers wit coupling networksEngineeringInductor
A traveling wave amplifier (TWA) comprising two or more amplification modules, the inputs of adjacent amplification modules being connected together by a first inductance component of a first characteristic impedance, a second inductance component of a second characteristic impedance and a third inductance component of substantially the first characteristic impedance, the first characteristic impedance being greater than the second characteristic impedance. The outputs of adjacent modules may be similarly connected together by first, second and third inductance components. The characteristic impedance of the second inductance components is preferably substantially equal to that of the circuits to which the TWA is connected, e.g. 50Ω. The first and third inductance components have a characteristic of 100Ω. Such a TWA allows balancing of phase velocities between inputs and outputs of the amplification modules, connection of these around via holes, and extends the frequency capability of the TWA.
Owner:FLIR BELGIUM BVBA
Carrier to noise ratio estimations from a received signal
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
Amplifier gain and phase stabilizer
InactiveUS20060116090A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierControl signal
Methods and apparatus are provided for stabilizing the phase and gain of an amplifier in a power pooling arrangement. A pilot signal combining a reference carrier frequency with a reference sideband frequency is passed through the amplifier via an adjustable phase shifter and an adjustable attenuator in the amplifier input line. A portion of the amplified pilot signal is coupled from the output of the amplifier and mixed with the reference frequency. The remaining audio frequency signal is compared to a reference (input) audio signal to determine phase and gain changes during amplification in the amplifier. Phase and gain control signals are developed from this comparison, and are fed back to the adjustable phase shifter and adjustable attenuator, respectively, in order to compensate an incoming signal for phase and gain variations in the amplifier.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Power regulator for intermittent use of traveling wave tube amplifiers in communications satellites
InactiveUS6909235B2Reduces undesired power supply stressImprove reliabilityTravelling-wave tubesGain controlPower conditionerBeam source
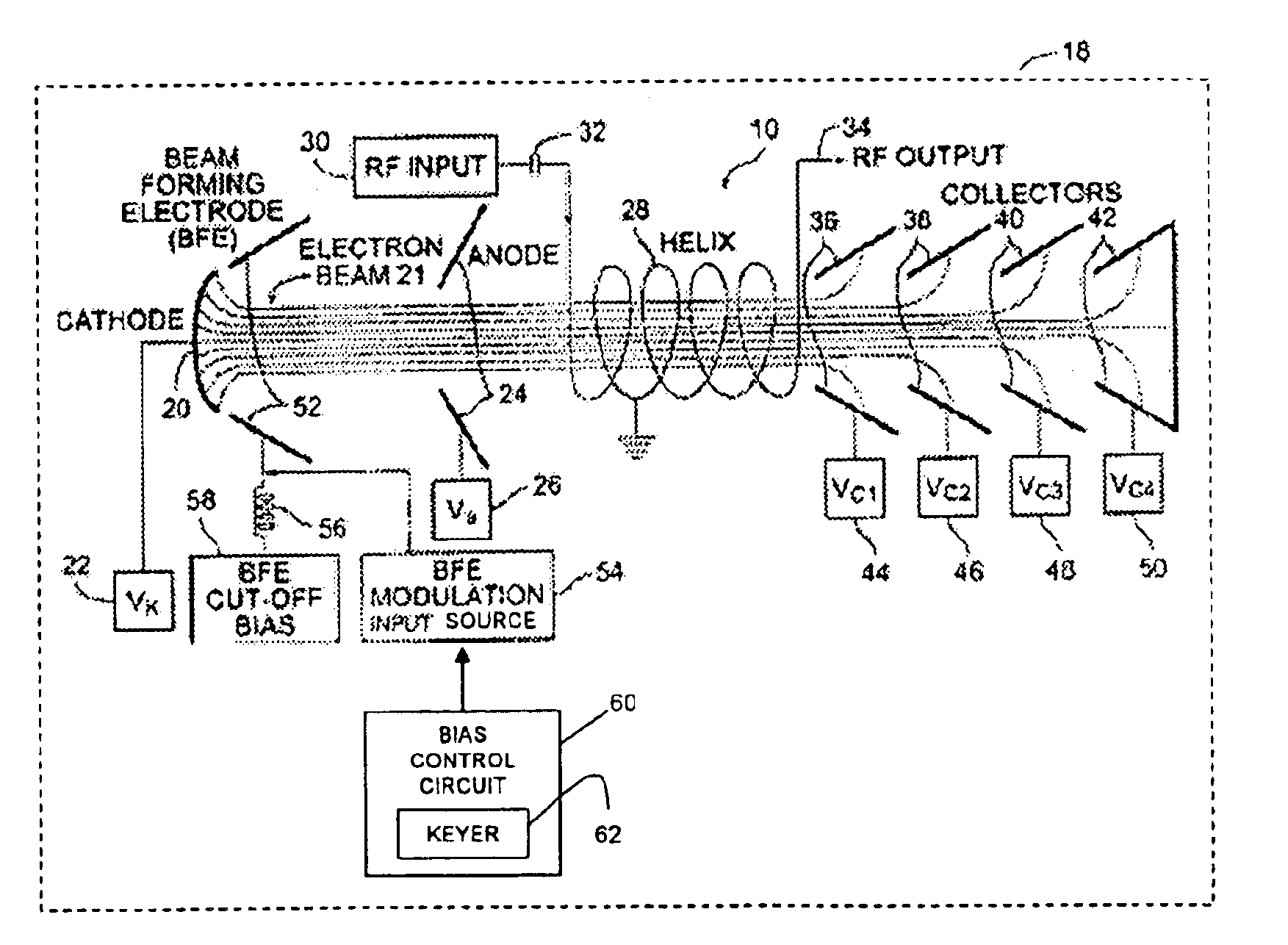
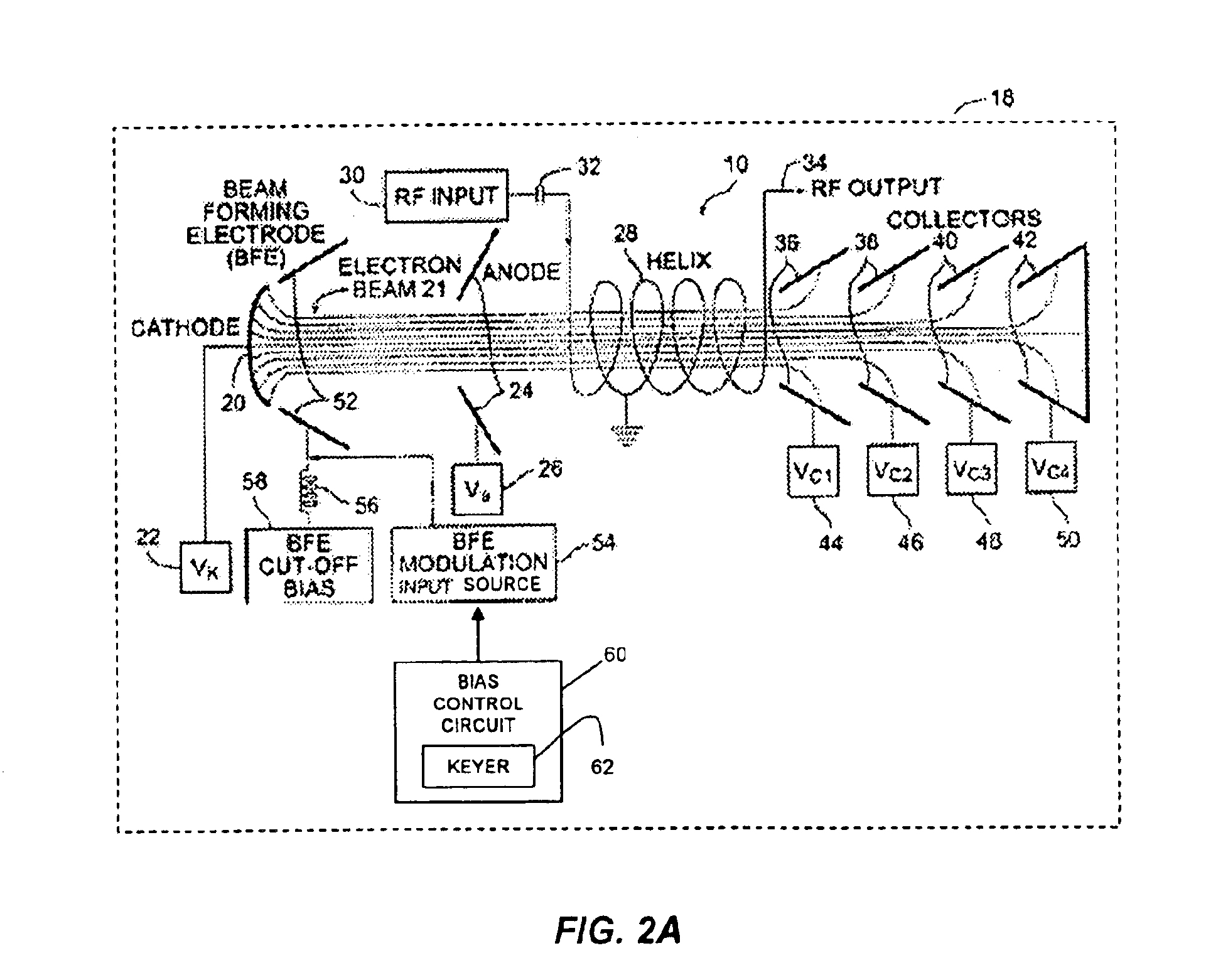
A traveling wave tube (TWT) amplifier includes a beam forming electrode (BFE) and a BFE modulator having a bias-based keyer so that the TWT amplifier signals are keyed off during periods when RF power is not to be amplified. Biasing the beam forming electrode voltage off relative to cathode voltage effectively shuts down the electron beam without shutting down the power supply minimizes power supply stress and significantly improves reliability, so that low-level RF signal input is not amplified, and no significant RF power is output. Likewise, given that no amplification has taken place, no power associated with the TWT amplification function is consumed. Thus, the only power consumed by the TWT amplifier is that associated with the cathode heater and the electronic power conditioner (EPC) used as the electron beam source.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
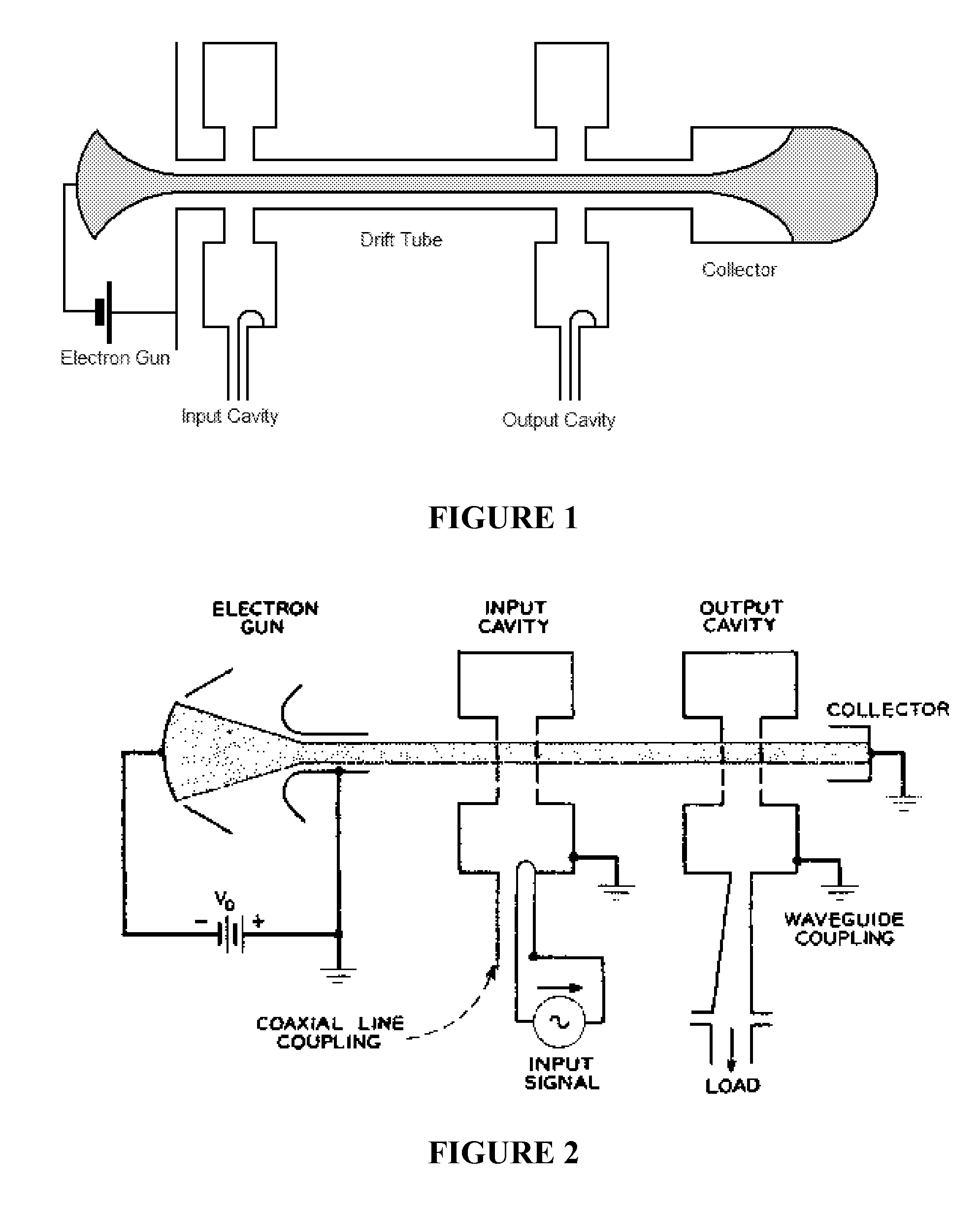
Multi-cavity vacuum electron beam device for operating at terahertz frequencies
The present invention relates to the formation of a vacuum electronics circuit by the fusion bonding of multiple substrate wafers, e.g., silicon, copper, or other suitable conductive material, each etched using DRIE, cut using EDM, or machined by other suitable means. Other aspects of the invention relate to the alignment of a cathode with tube by fusion bonding the cathode wafer to a tube built using the fabrication methods described herein. Yet other aspects involve the alignment of dies or wafers during the fabrication of a vacuum electronics device using the “lego” technique outlined herein. In yet other aspects, fabrication methods are described.
Owner:LOGOS TECH HOLDCO INC
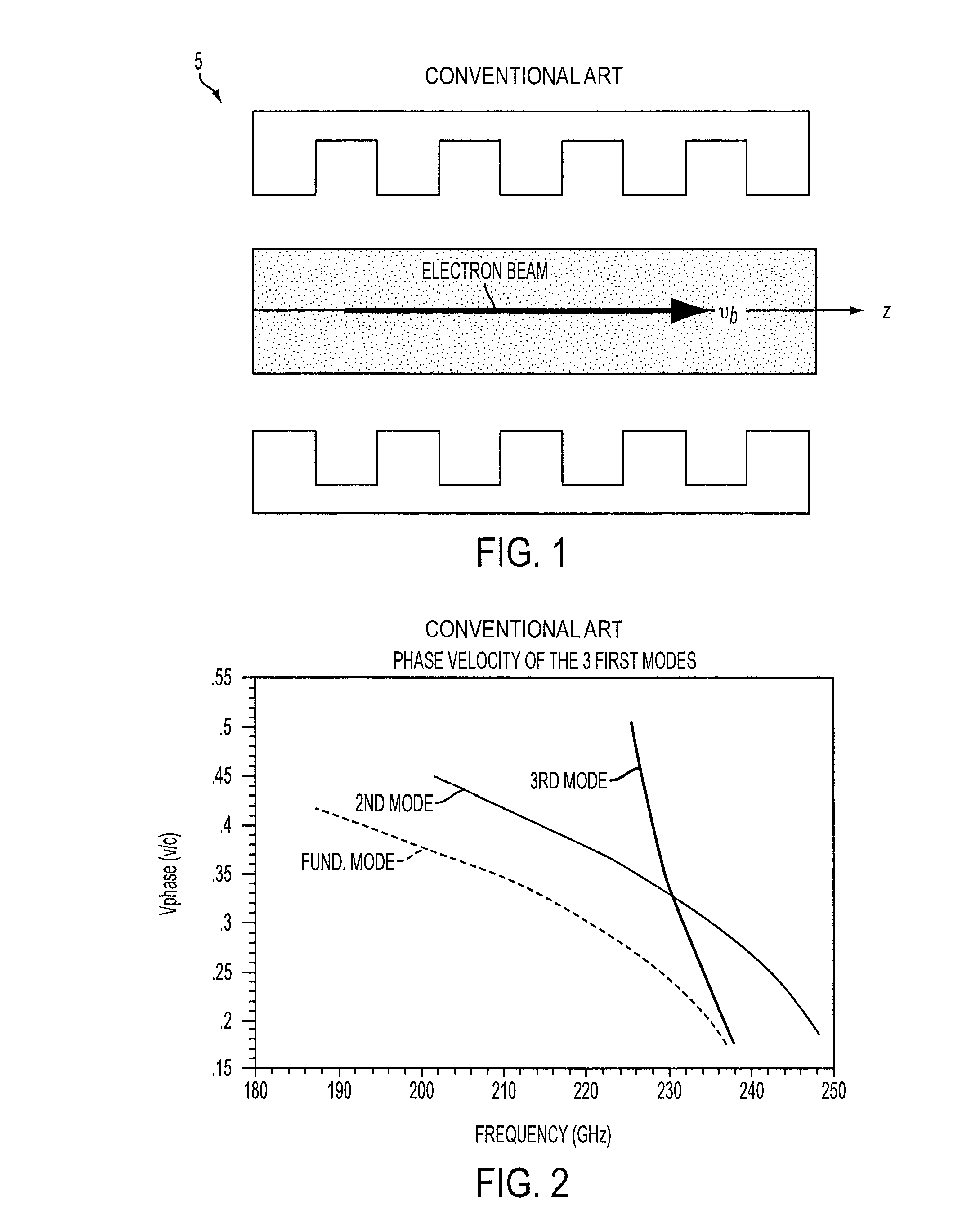
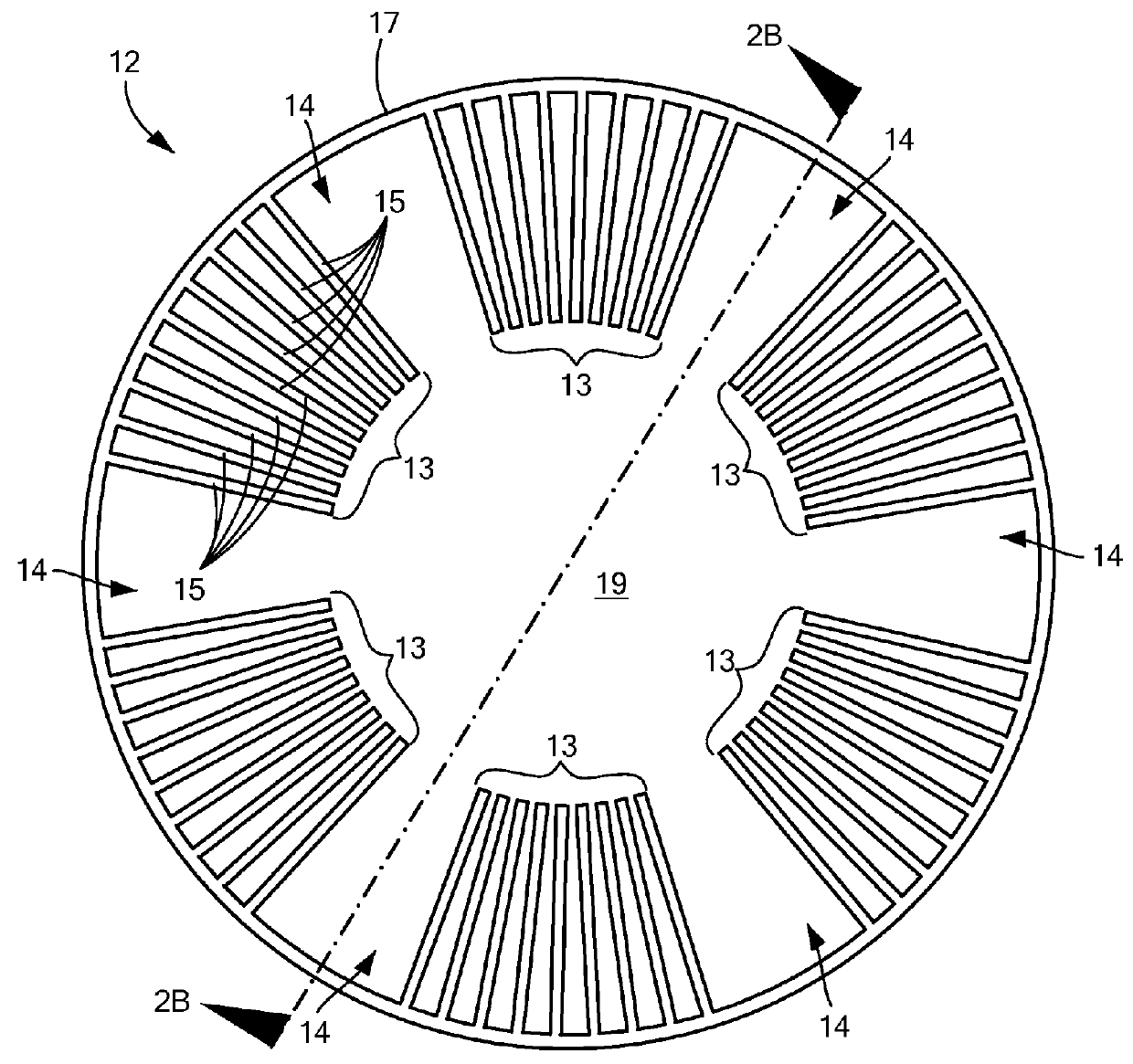
Slow wave structure having offset projections comprised of a metal-dielectric composite stack
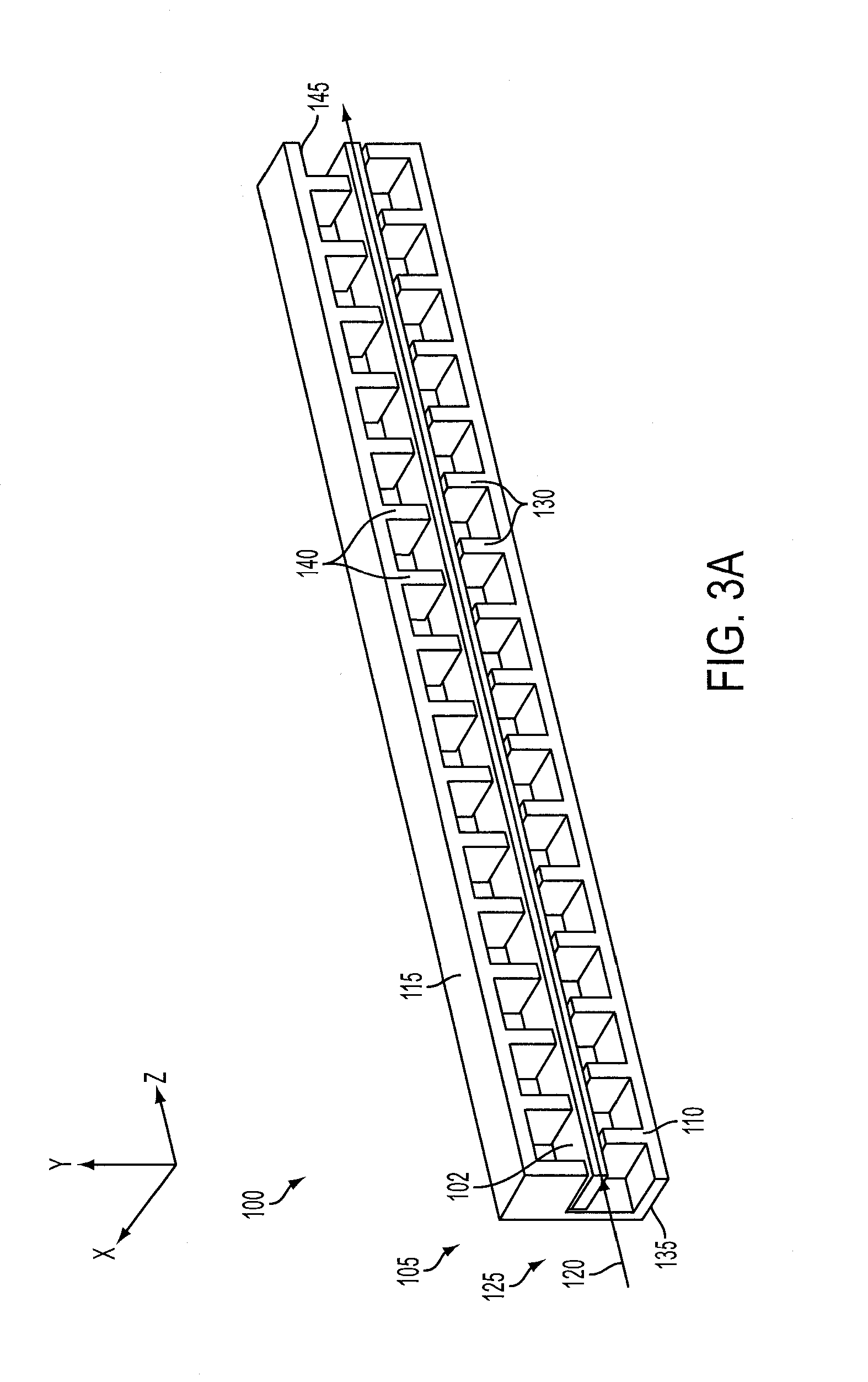
A traveling wave amplifier circuit to receive an RF wave and an electron sheet beam and to effect synchronized interaction therebetween. The circuit includes a wave guide having at least a first wall and a second wall opposite the first wall. The first wall and the second wall are connected to define an axis of propagation and a rectangular wave guide cross-section that is normal to the axis of propagation. The circuit further includes a plurality of first projections located on an interior surface of the first wall of the wave guide, the first projections being pitched in a direction of the axis of propagation. The circuit further includes a plurality of second projections located on an interior surface of the second wall of the wave guide, the second projections being pitched in a direction of the axis of propagation. A number of the second projections are located on the interior surface of the second wall in a staggered configuration in a direction of the axis of propagation relative to a number of corresponding first projections located on the interior surface of the first wall.
Owner:TELEDYNE DEFENSE ELECTRONICS LLC
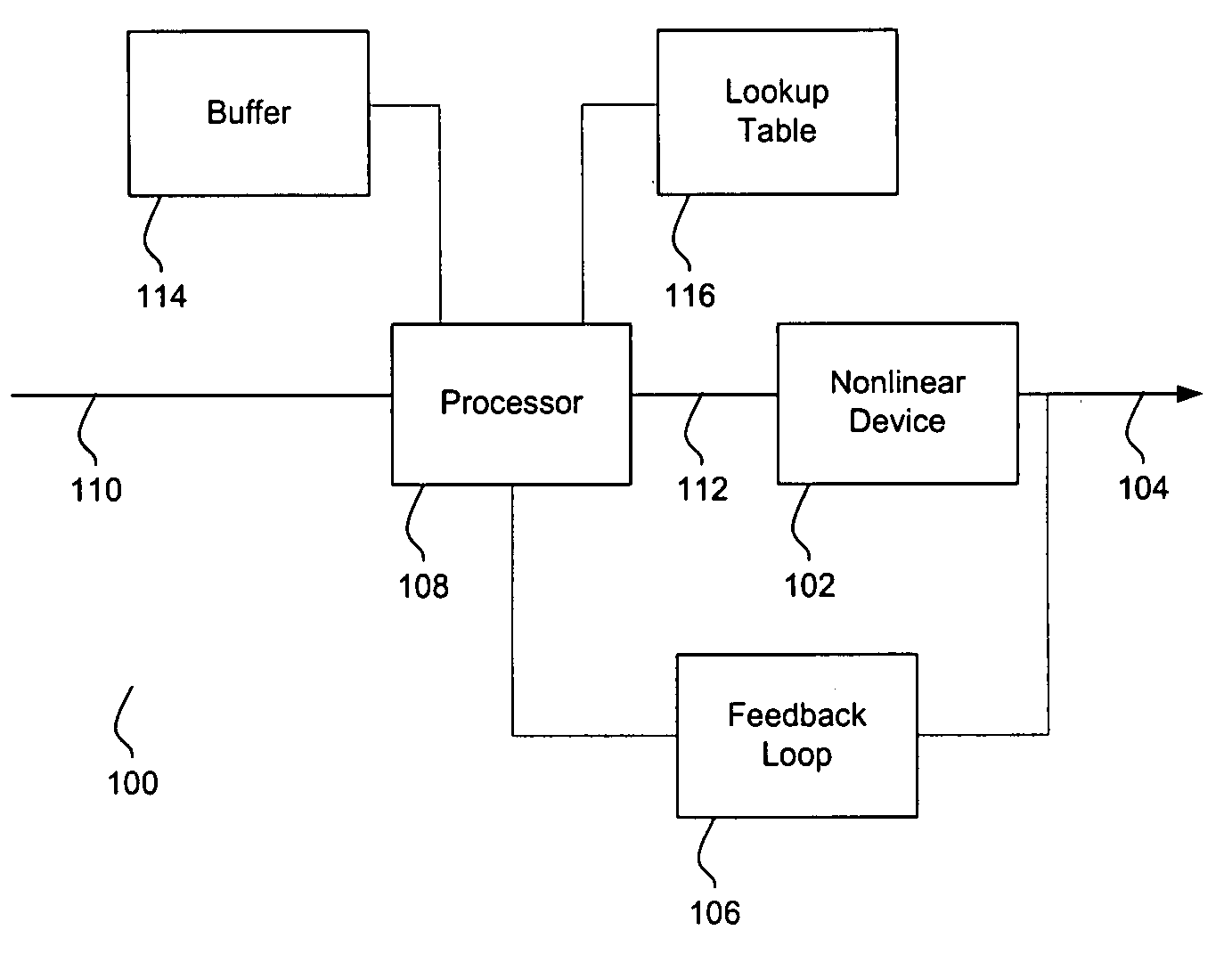
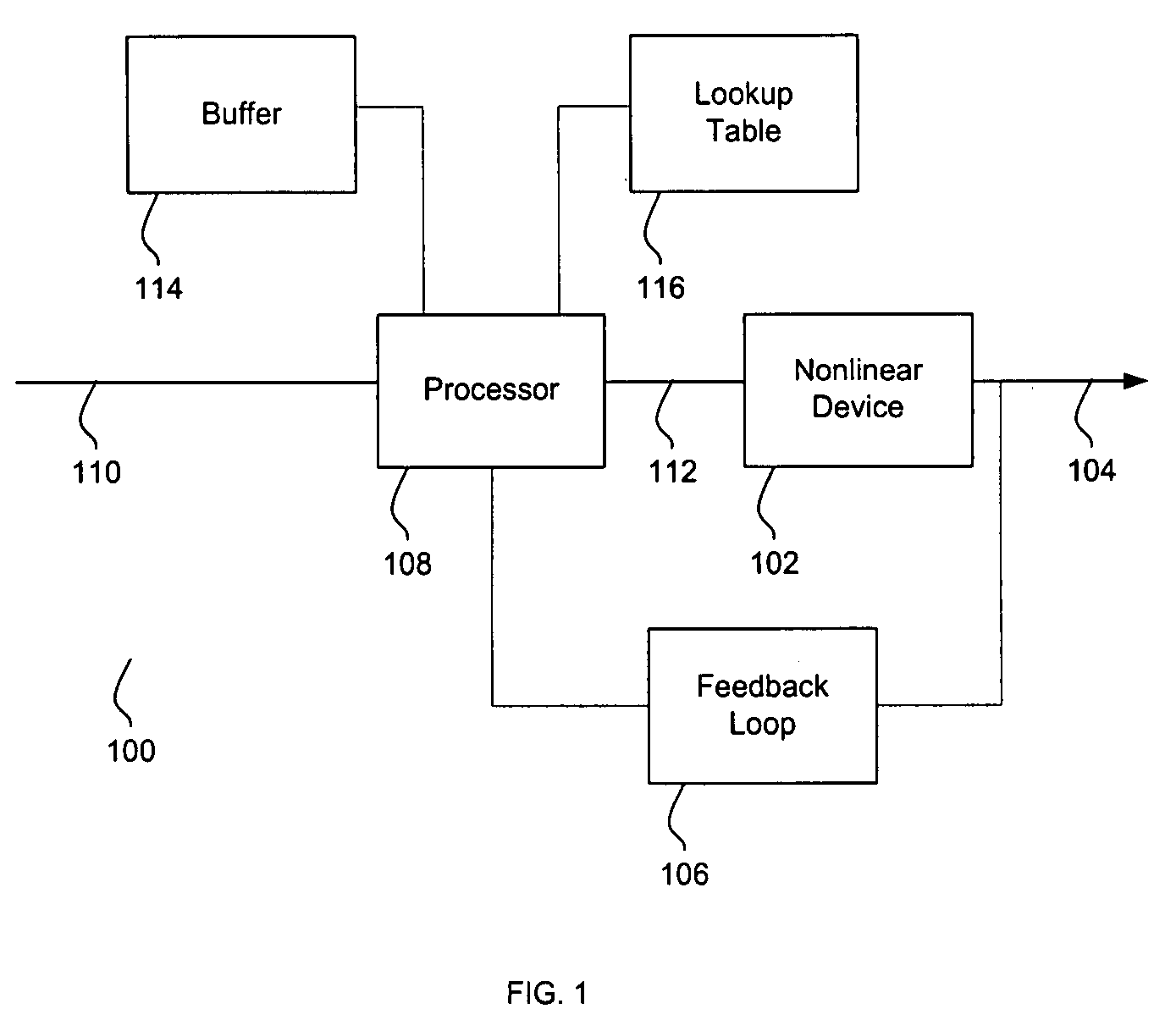
System and method for pre-distorting a device input
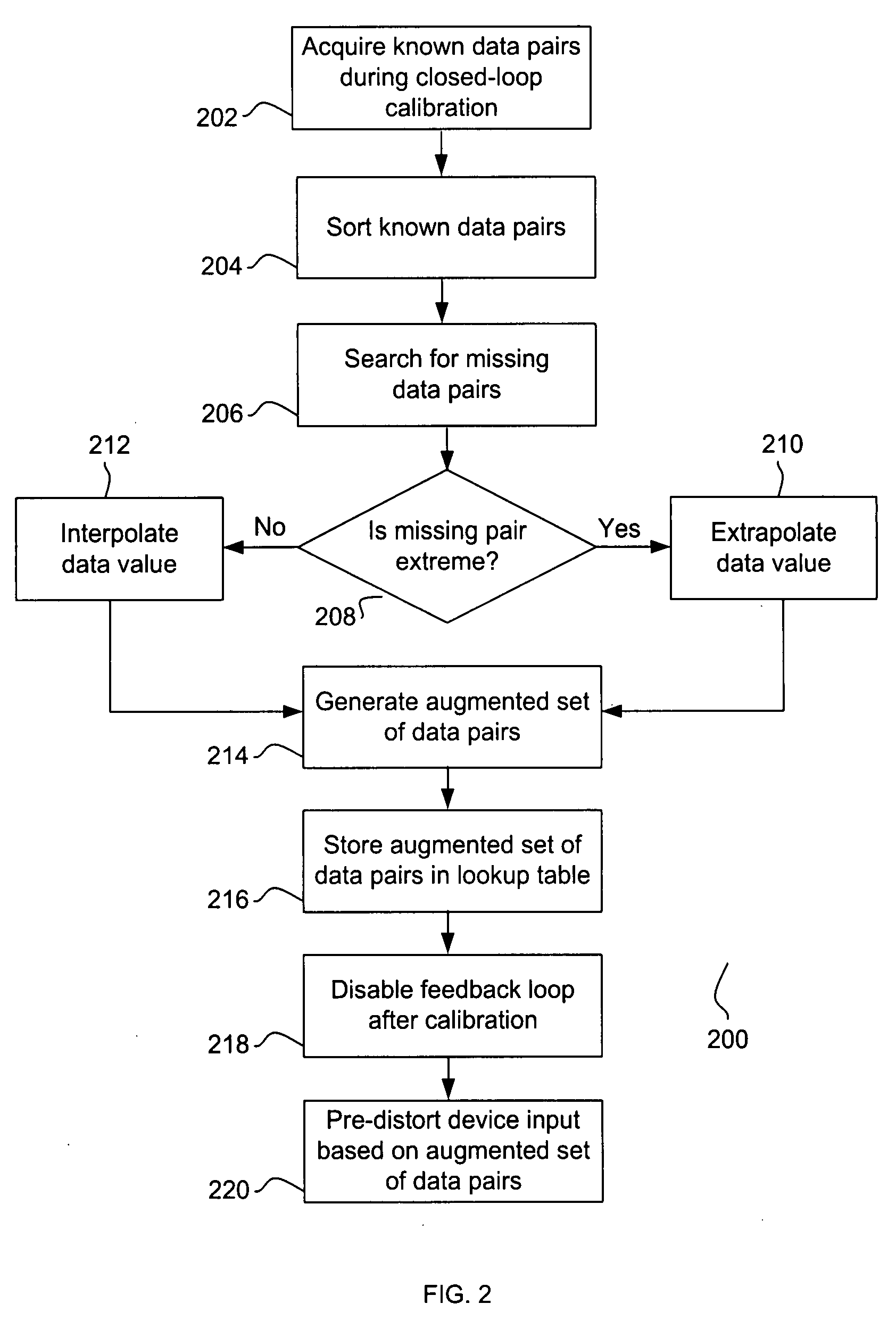
ActiveUS20080228292A1Sampled-variable control systemsAmplifiers with transit-time effectMissing dataClosed loop
A method for pre-distorting an input for a device is provided. A partial set of known data pairs is acquired during a closed-loop device calibration period. The partial set of known data pairs is searched for at least one missing data pair, and at least one data value is interpolated for the missing data pair. An augmented set of data pairs, including the known data pairs and the interpolated data value, is stored in a lookup table. During an open-loop operation period subsequent to the closed-loop device calibration period, the device input is pre-distorted based on the augmented set of data pairs stored in the lookup table.
Owner:EAGLE TECH LLC
High-power microwave system employing a phase-locked array of inexpensive commercial magnetrons
InactiveUS7164234B2Facilitates coherent combinationEfficient and inexpensiveTravelling-wave tubesRF amplifierMicrowave applicationsAs Directed
A high-power microwave generator employing a plurality of inexpensive commercial magnetron tubes cross-coupled by means of a secondary coupling path between each magnetron output pair, whereby a portion of the output energy from a first magnetron tube is injected into a second magnetron tube and a portion of the output energy from the second magnetron tube is similarly injected into the first magnetron tube. The resulting cross-injection of microwave energies brings the respective magnetron tube pair into a phase-lock sufficiently stable to permit coherent combination of their outputs for many high-power microwave applications, such as directed energy weapon systems. The magnetron phase-locking system requires no external components other than the secondary coupling paths of this invention.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Rapid 3D prototyping and fabricating of slow-wave structures, including electromagnetic meta-material structures, for millimeter-wavelength and terahertz-frequency high-power vacuum electronic devices
ActiveUS20160056005A1Fast preparationAdditive manufacturing apparatusTravelling-wave tubesWave structureFrequency spectrum
A method for fabricating slow-wave structures, including electromagnetic meta-material structures, for high-power slow-wave vacuum electronic devices operating in millimeter-wavelength (30 GHz-300 GHz) and terahertz-frequency (300 GHz and beyond) bands of electromagnetic spectrum. The method includes: loading a digital three dimensional model of a slow-wave structure in a memory of a 3D printer, the loaded digital three dimensional model having data therein representative of the slow-wave structure to be fabricated by the 3D printer; loading metal powder material into the 3D printer; and operating the 3D printer to melt the metal powder material in accordance with the loaded three dimensional model of the slow-wave structure and then to solidify the melted layer of the metal powder material to fabricate the slow-wave structure layer by layer.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Estimating the operating point on a non-linear traveling wave tube amplifier
InactiveUS7230480B2Accurate extractionQuantity minimizationElectric devicesCurrent/voltage measurementOperating pointMean square
A method, apparatus, article of manufacture, and a memory structure provide the ability to determine an input operating point and an output operating point on a non-linear traveling wave tube amplifier (TWTA). The non-linearity of the TWTA is measured. An input roots mean-square (RMS) value of an input signal used to measure the non-linearity of the TWTA is computed. The RMS value identifies an input operating point of the measured non-linearity of the TWTA. Lastly, an output operating point is obtained.
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
Real-Time Methods for Magnetic Resonance Spectra Acquisition
ActiveUS20180340997A1Easy maintenanceAffordable constructionOrganic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsFrequency spectrumTime processing
The invention pertains to advances in real-time methods in nuclear magnetic resonance by offering:a new real-time processing method for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrum acquisition without external resonator(s), which remains stable despite magnetic field fluctuations,a new processing method for nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum acquisition, which remains stable despite magnetic field fluctuations and resonator stability,a new method of constructing predetermined magnets from appropriate magnetic material that allows for focusing the magnetic field in a target region,a new dual frequency dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) generator that polarizes the spin of electrons and acts as an NMR transmitter.
Owner:ELEGANT MATHEMATICS LLC
Depressed collector for electron beams
InactiveUS20030122491A1Transit-tube collectorsAmplifiers with transit-time effectBeam energySecondary electrons
A depressed collector for recovery of spent beam energy from electromagnetic sources emitting sheet or large aspect ration annular electron beams operating aver a broad range of beam voltages and currents. The collector incorporates a trap for capturing and preventing the return of reflected and secondary electrons.
Owner:CALABAZAS CREEK RES
Popular searches
Orthogonal multiplex Broadcast information generation Angle demodulation by phase difference detection Amplitude-modulated carrier systems Frequency-modulated carrier systems Radio transmission Phase-modulated carrier systems Multiple carrier systems Transmitter side switching Line-faulsts/interference reduction
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com