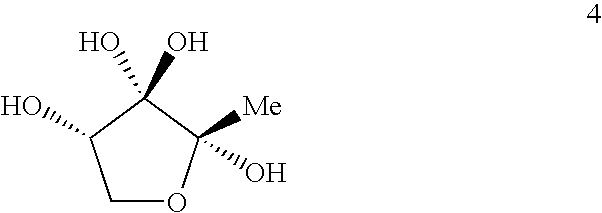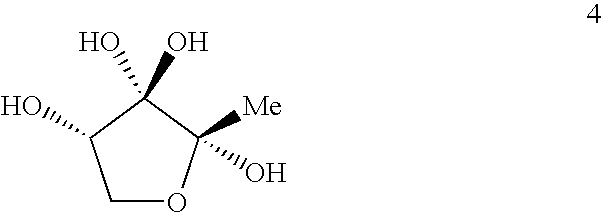Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66 results about "X-ray crystallography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
X-ray crystallography (XRC) is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information.
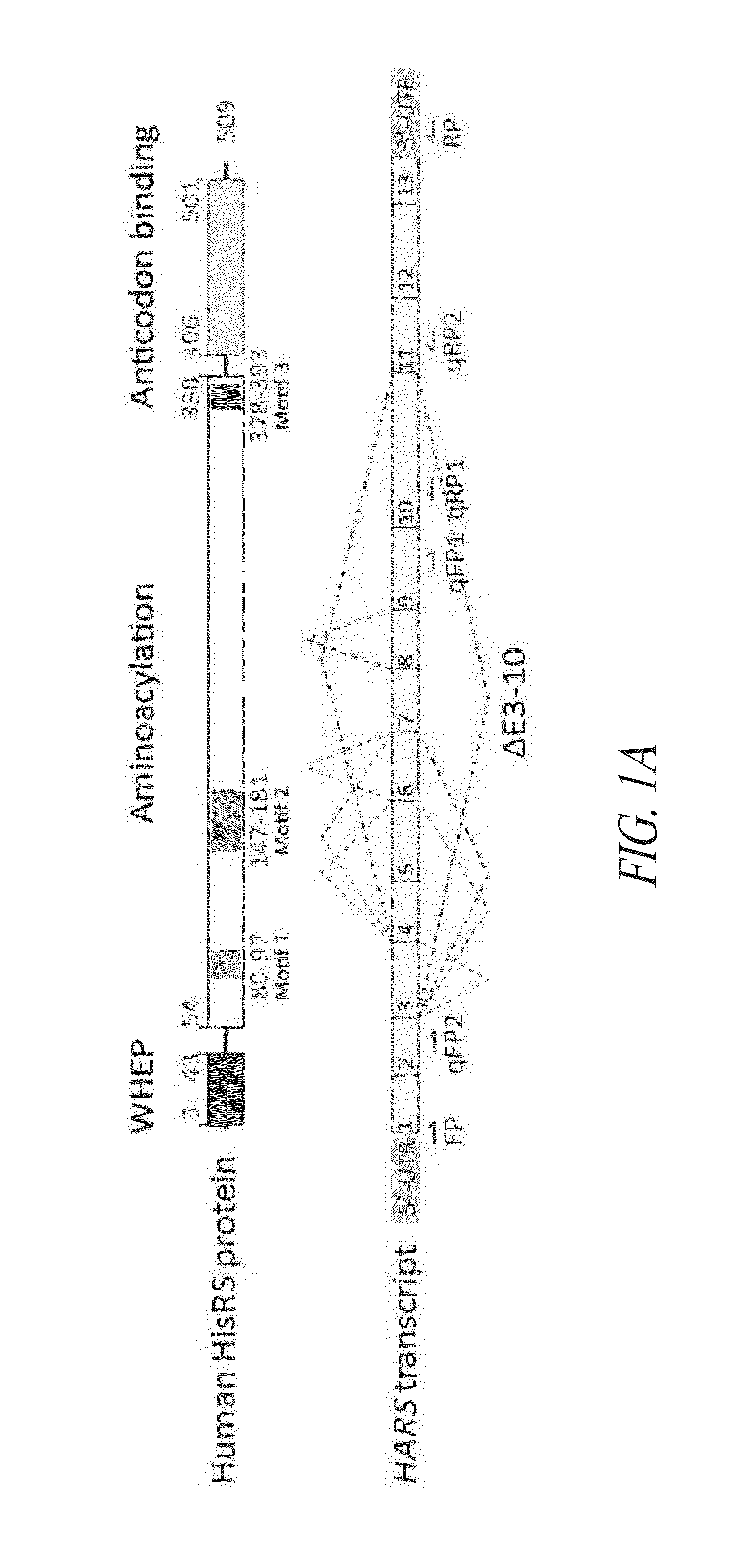
Structures of human histidyl-trna synthetase and methods of use
InactiveUS20140066321A1Improve homogeneityLibrary screeningAnalogue computers for chemical processesMedicineX-ray
Provided are histidyl-tRNA synthetase variant polypeptides, X-ray crystallographic and NMR spectroscopy structures of HRS polypeptides, and related compositions and methods for therapy and drug discovery.
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC +1
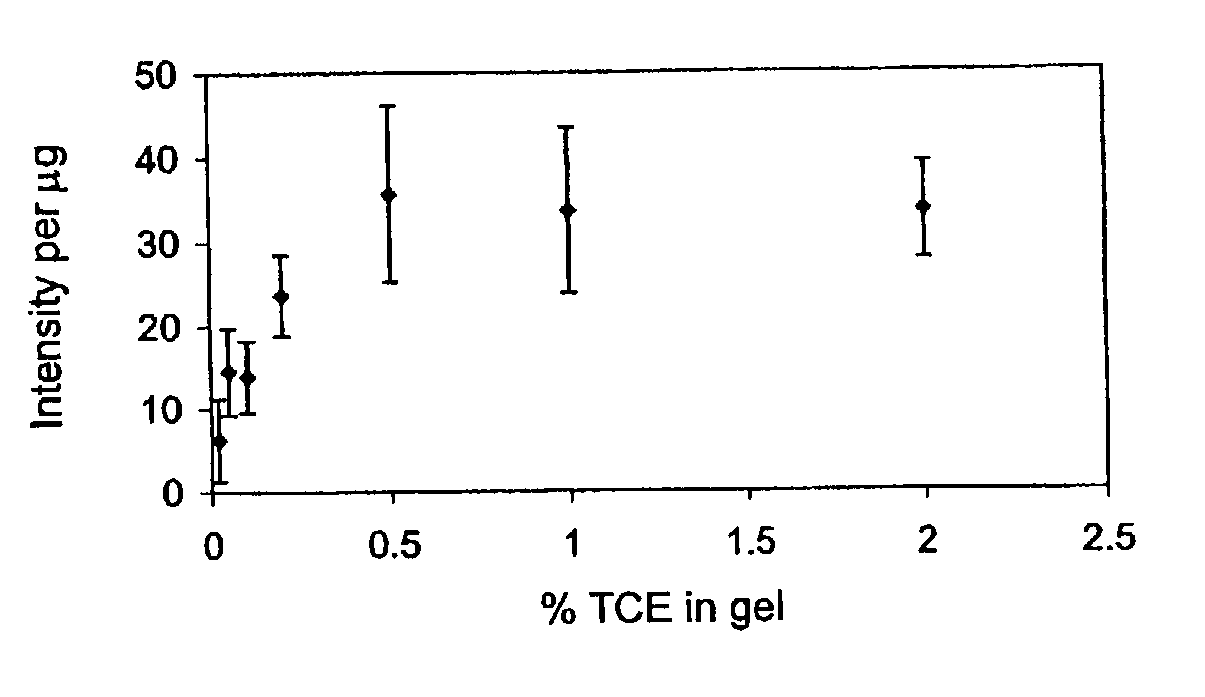
Fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels
ActiveUS7569130B2Laborious labelingLaborious staining stepElectrolysis componentsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSpectroscopyTryptophan
The mechanism of the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and chloroform, and the structure of the modified tryptophan and polypeptides including such modified tryptophan residues. The excited indole moiety, which is formed upon UV light irradiation, emits a solvated electron which initiates a series of events that yield fluorescent derivatives that have CHO group covalently bound to the indole moiety. These derivatives are herein referred to as formyltryptophan, and are relatively stable. Similar reactions are observed when 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-fluorotryptophan, or N-methylindolacetate are used in place of tryptophan, or when other haloalkanes, such as trichloracetic acid, trichlorethanol, trichlorethane, bromoform, and iodoactetate are used in place of chloroform. The derivatives can be used in a variety of applications in fluorescence spectroscopy, and for nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray crystallography, infra-red spectroscopy, circular dicroism and mass spectroscopy. Additionally, the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and haloalkanes can be used to prepare derivatives of tryptophan for chemical cross-linking studies of proteins and peptides.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
Fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels
InactiveUS20100089753A1Without laborious labeling and staining stepElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementSpectroscopyTryptophan
The mechanism of the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and chloroform, and the structure of the modified tryptophan and polypeptides including such modified tryptophan residues. The excited indole moiety, which is formed upon UV light irradiation, emits a solvated electron which initiates a series of events that yield fluorescent derivatives that have CHO group covalently bound to the indole moiety. These derivatives are herein referred to as formyltryptophan, and are relatively stable. Similar reactions are observed when 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-fluorotryptophan, or N-methylindolacetate are used in place of tryptophan, or when other haloalkanes, such as trichloracetic acid, trichlorethanol, trichlorethane, bromoform, and iodoactetate are used in place of chloroform. The derivatives can be used in a variety of applications in fluorescence spectroscopy, and for nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray crystallography, infra-red spectroscopy, circular dicroism and mass spectroscopy. Additionally, the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and haloalkanes can be used to prepare derivatives of tryptophan for chemical cross-linking studies of proteins and peptides.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
Computer Controllable LED Light Source for Device for Inspecting Microscopic Objects
InactiveUS20090080611A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationSupporting apparatusCamera lensLed array
A device for inspecting microscopic objects. A plurality of LEDS is arranged in an array underneath a lens. Some of the LEDS are lighted and some of the LEDS are unlighted. A computer is in control of the LED array. The computer turns on selected LEDS from the array to form the lighted LEDS. Also, the computer turns off selected LEDS from the array to form the unlighted LEDS. The lighted LEDS form a pattern of lighted LEDS underneath the lens. In a preferred embodiment, the lens is connected to a computer controlled camera and the microscopic objects are microscopic crystals. In another preferred embodiment UV LEDS are utilized and illuminate crystals from above. In another preferred embodiment UV LEDS are utilized to illuminate a loop of a Hampton pin to locate a crystal in the loop of a Hampton pin for the purpose of x-ray crystallography.
Owner:RIGAKU AUTOMATION
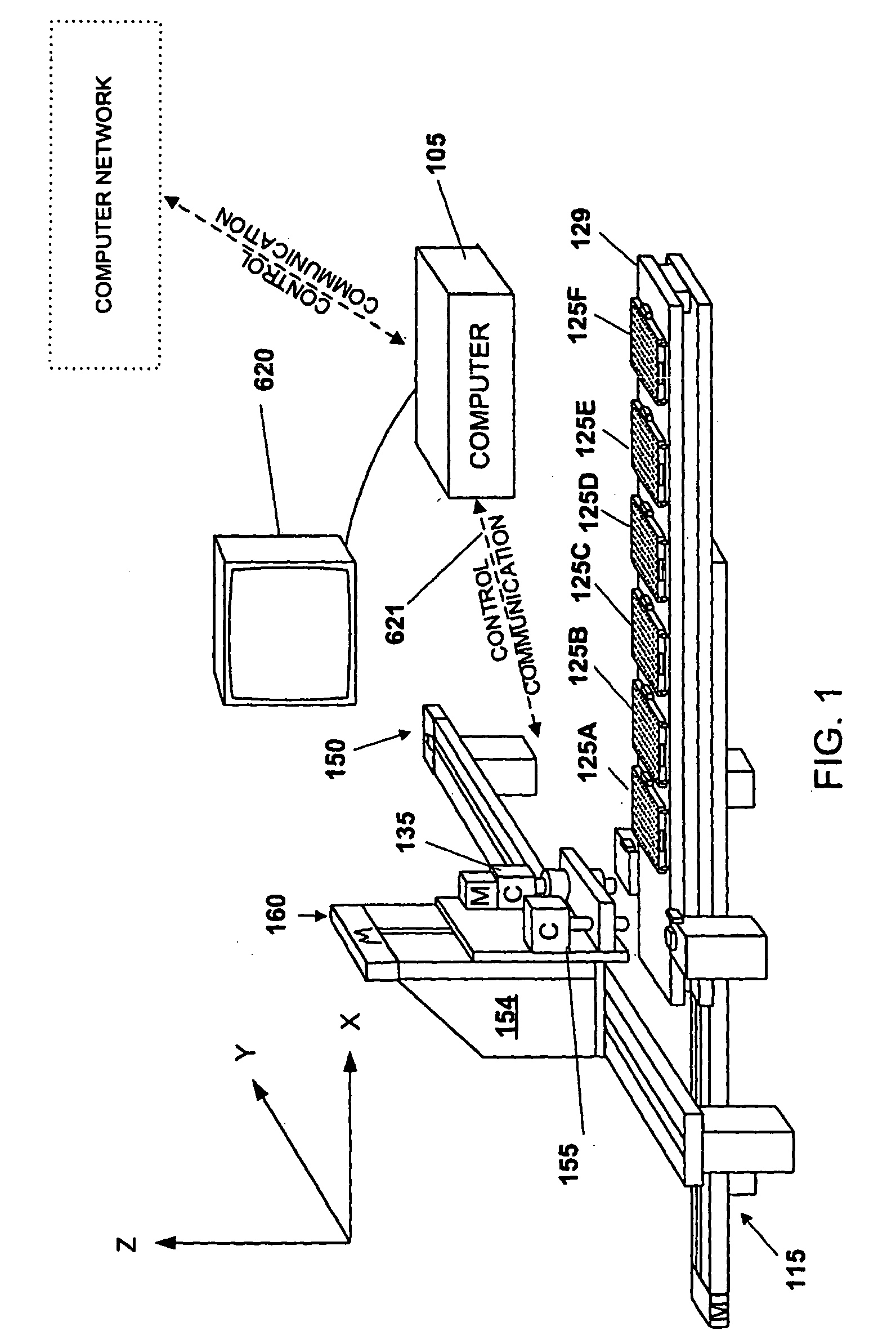
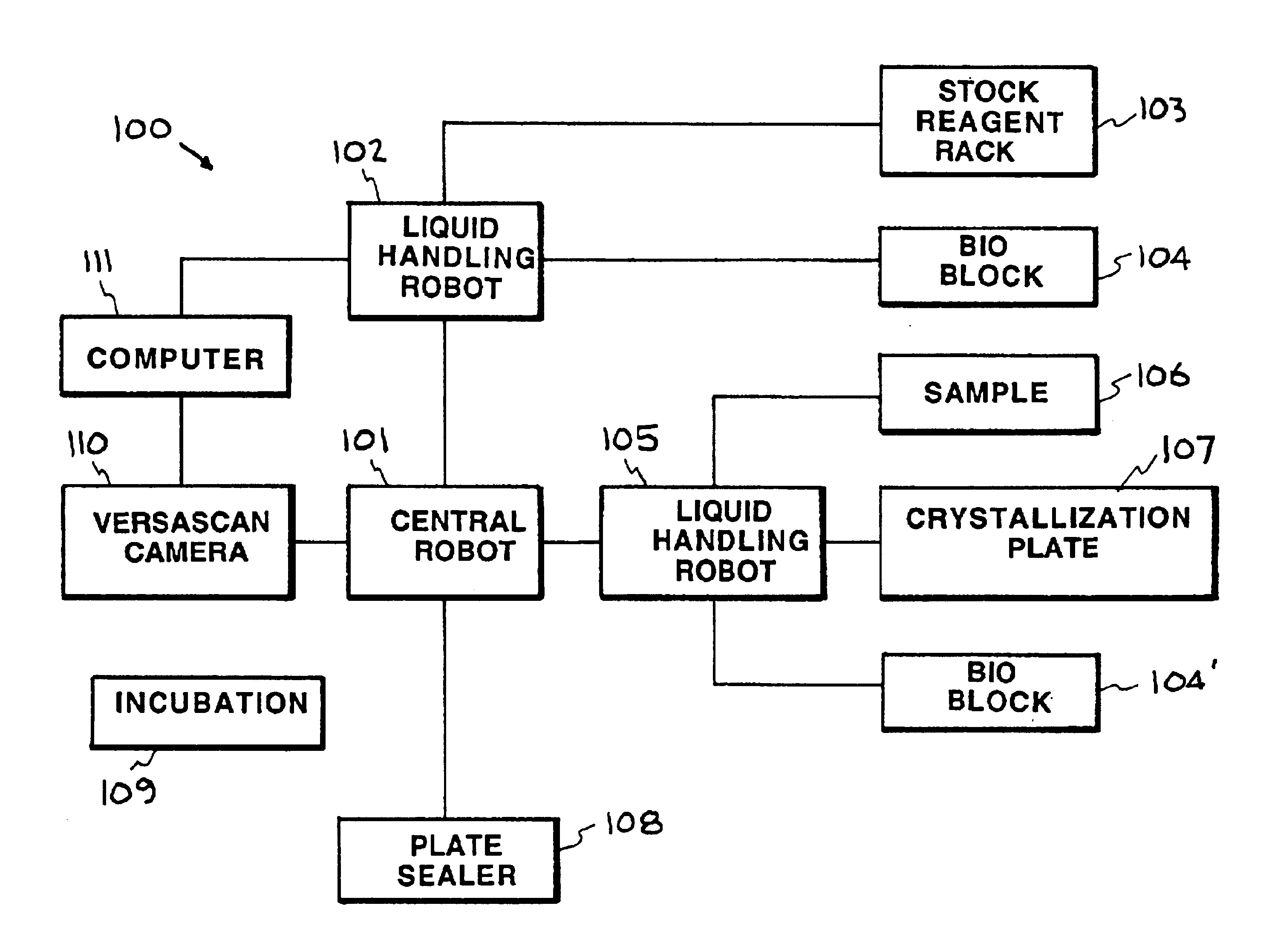
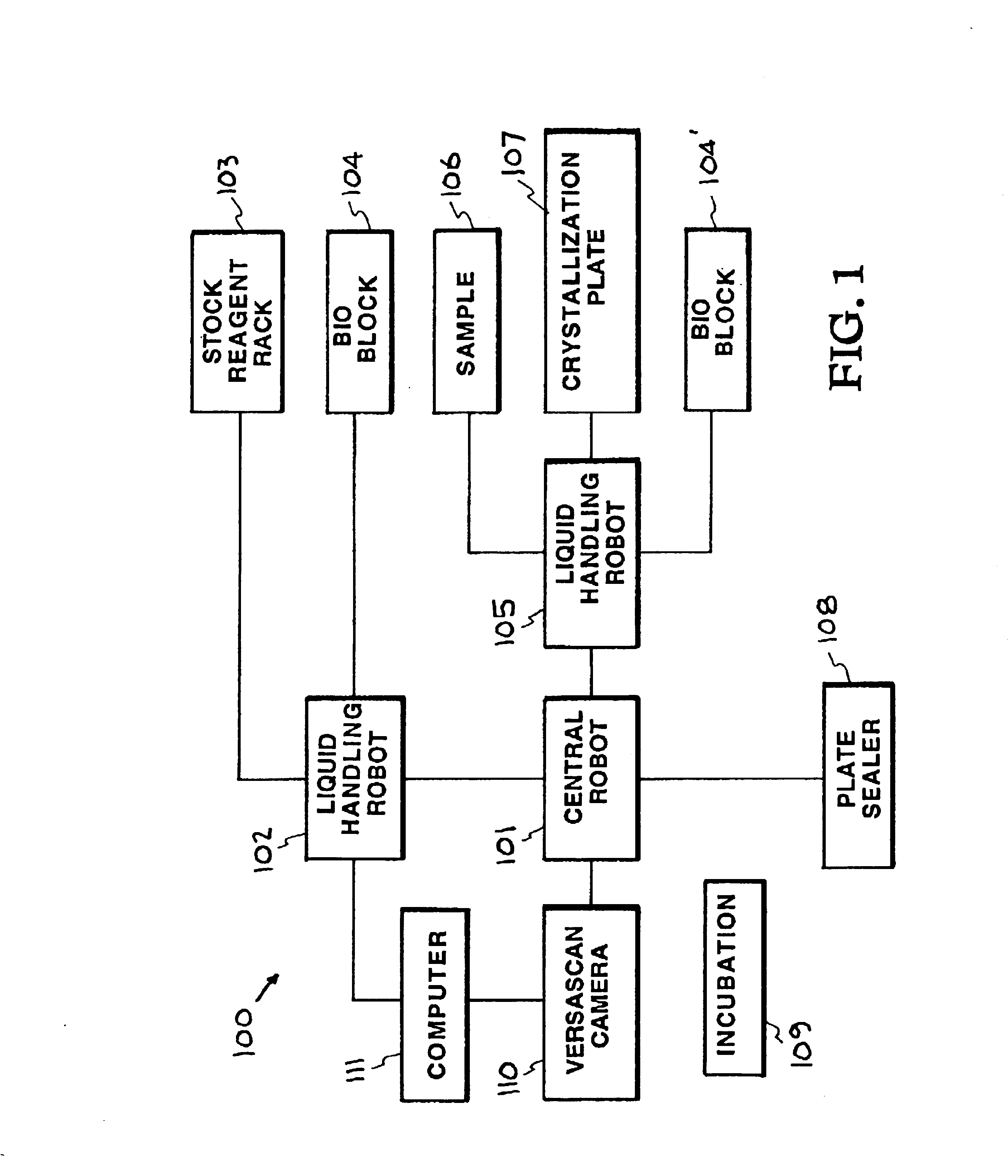
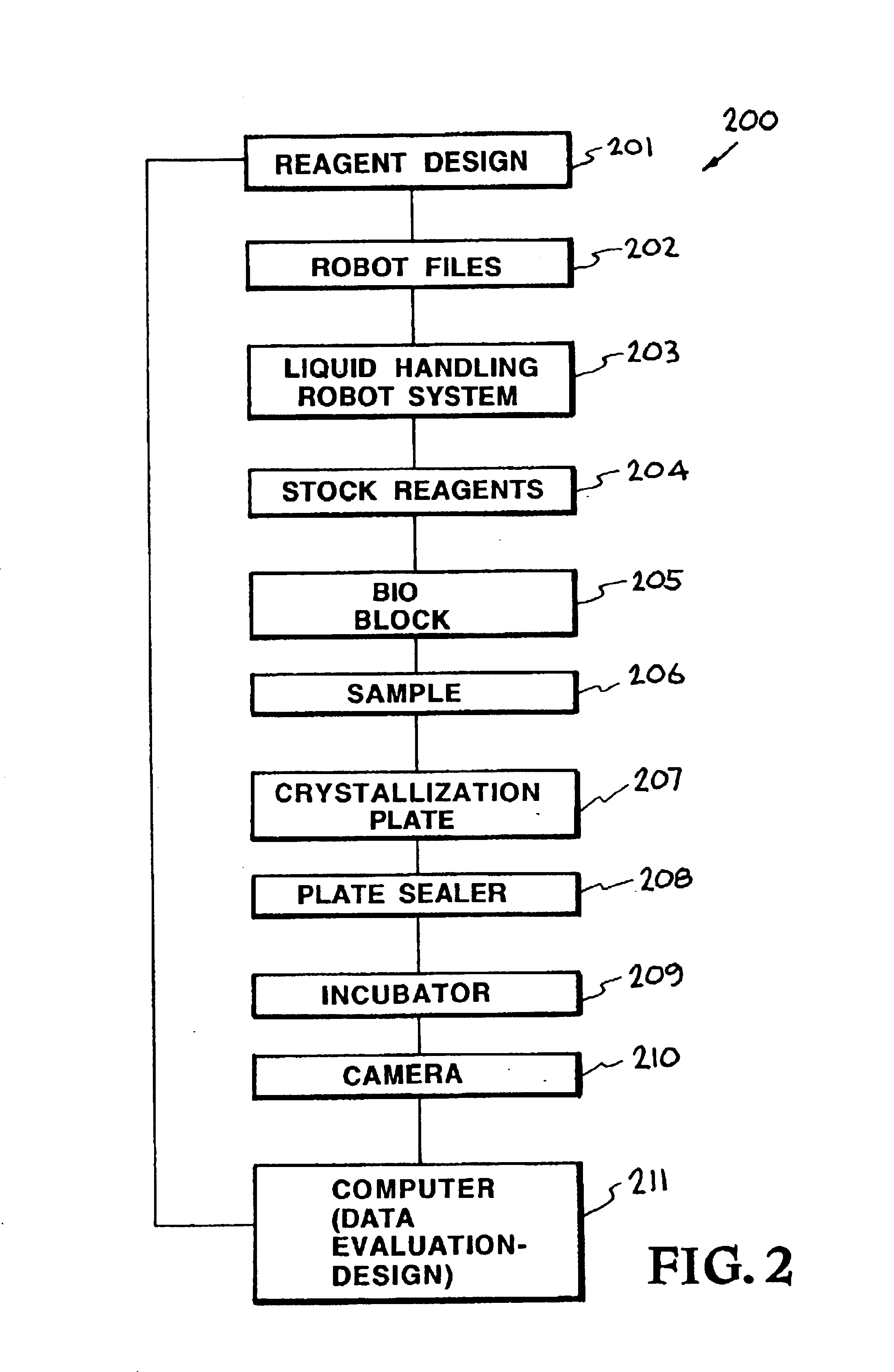
Automated macromolecular crystallization screening
An automated macromolecular crystallization screening system wherein a multiplicity of reagent mixes are produced. A multiplicity of analysis plates is produced utilizing the reagent mixes combined with a sample. The analysis plates are incubated to promote growth of crystals. Images of the crystals are made. The images are analyzed with regard to suitability of the crystals for analysis by x-ray crystallography. A design of reagent mixes is produced based upon the expected suitability of the crystals for analysis by x-ray crystallography. A second multiplicity of mixes of the reagent components is produced utilizing the design and a second multiplicity of reagent mixes is used for a second round of automated macromolecular crystallization screening. In one embodiment the multiplicity of reagent mixes are produced by a random selection of reagent components.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
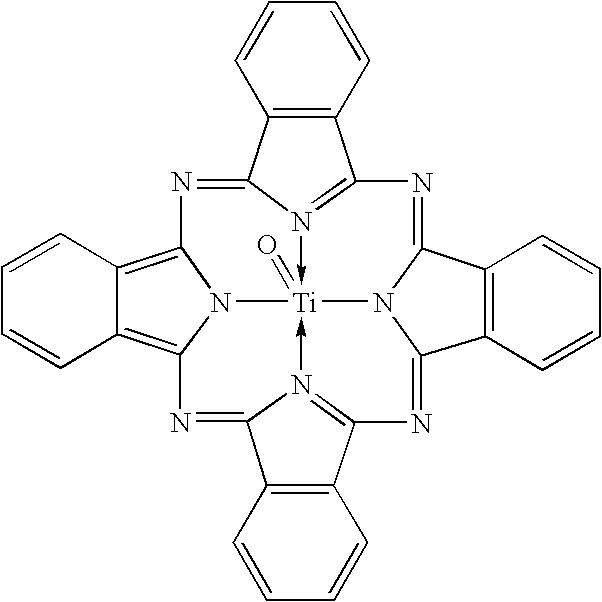
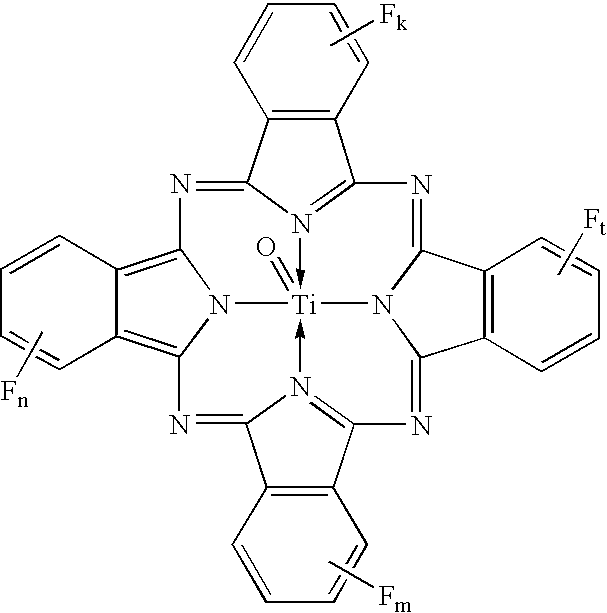
Coating solution containing cocrystals and or crystals of a charge-generation pigment or a mixture of charge-generation pigments
A method for preparing a coating solution containing a cocrystallized titanyl phthalocyanine-titanyl fluorophthalocyanine, the method comprising: dry milling a charge-generation pigment or mixtures of charge-generation pigments; increasing the amorphousness of the pigment mixture as determined by X-ray crystallography using X-radiation characteristic of Cu Kα at a wavelength of 1.541 Å of the Bragg angle 2θ to provide an amorphous pigment mixture; contacting the amorphous pigment mixture with a first organic solvent having a gammac hydrogen bonding parameter of less than 9, with or without the presence of a dispersant material, to produce a crystalline pigment of the charge-generation pigment prior to contacting the pigment with a second organic solvent having a gammac hydrogen bonding parameter greater than 9; mixing at least one of a second organic solvent, a dispersant and a binder with the crystalline pigment / first solvent mixture without isolating the crystalline pigment to produce a mixture; and, adjusting the concentrations of the first organic solvent, crystalline pigment, binder, dispersants and second organic solvent as required to produce the coating solution of a selected composition.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
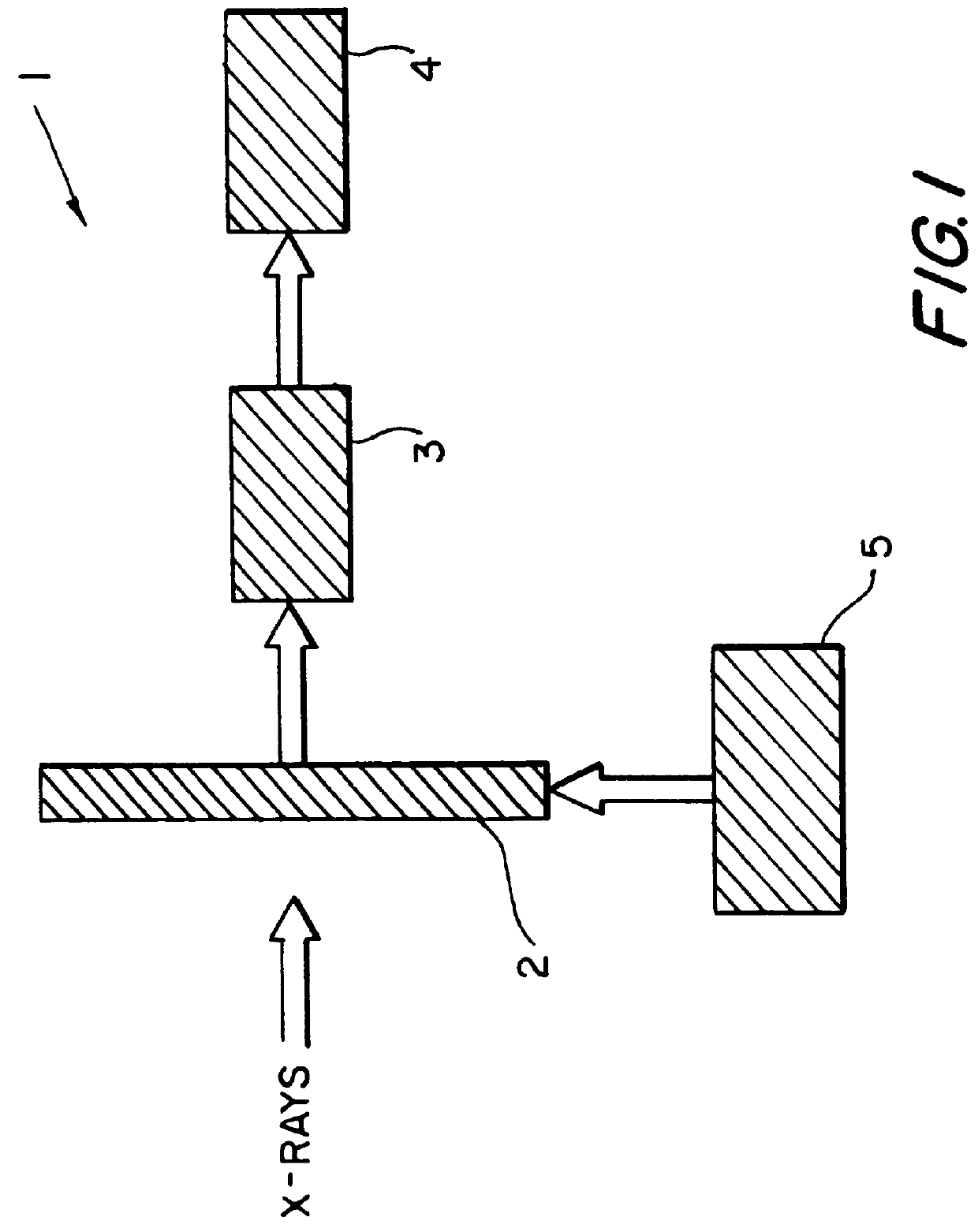
High speed crystallography detector
InactiveUS6057552AReduce signal to noise ratioSlow readoutSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansX-rayDetector array
A device for the collection, digitization and analysis of synchrotron x-ray crystallographic data using an area detector which detects x-ray photons directly on arrays of solid state detectors and stores the information on capacitors located on readout unit cell array chips. The device consists of a two dimensional area detector, for amplification, collection and conversion of the diffracted x-rays to electrical signals, drive electronics for providing the timing pulses and biases to the area sensor, output electronics for converting the x-ray signals to digital signals and storing the signals, and a data processor to analyze the digital signal form the output electronics. The solid-state detector array is made up of a variable-area three-dimensional array of detector array chips where each chip is in turn made up of an array of solid-state detectors. Each detector on the detector array chip is electrically connected to a readout unit cell on a readout array chip directly beneath the detector array chip. The readout unit cell contains the circuitry for storage, switching and readout of the x-ray signals.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
Crystalline ingenol mebutate
The present invention relates to a novel crystalline form of ingenol mebutate, methods of preparation thereof, and to its use. More specifically, the invention relates to the conversion of amorphous ingenol mebutate (ingenol-3-angelate, PEP005) to a crystalline form, which was characterized by single crystal X-Ray crystallography (XRC), attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared (FTIR-ATR) spectroscopy and Differential Scanning calorimetry (DSC).
Owner:LEO LAB
Modification of pertussis toxin
InactiveUS6018022ABeneficially modifyingBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaBiological propertyPertussis toxin
The three-dimensional structure of crystalline pertussis holotoxin (PT) has been determined by X-ray crystallography. Crystal structures have also been determined for complexes of pertussis toxin with molecules relevant to the biological activity of PT. These three-dimensional structures were analyzed to identify functional amino acids appropriate for modification to alter the biological properties of PT. Similar procedures may be used to predict amino acids which contribute to the toxicity of the holotoxin, to produce immunoprotective, genetically-detoxified analogs of pertussis toxin.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB +1
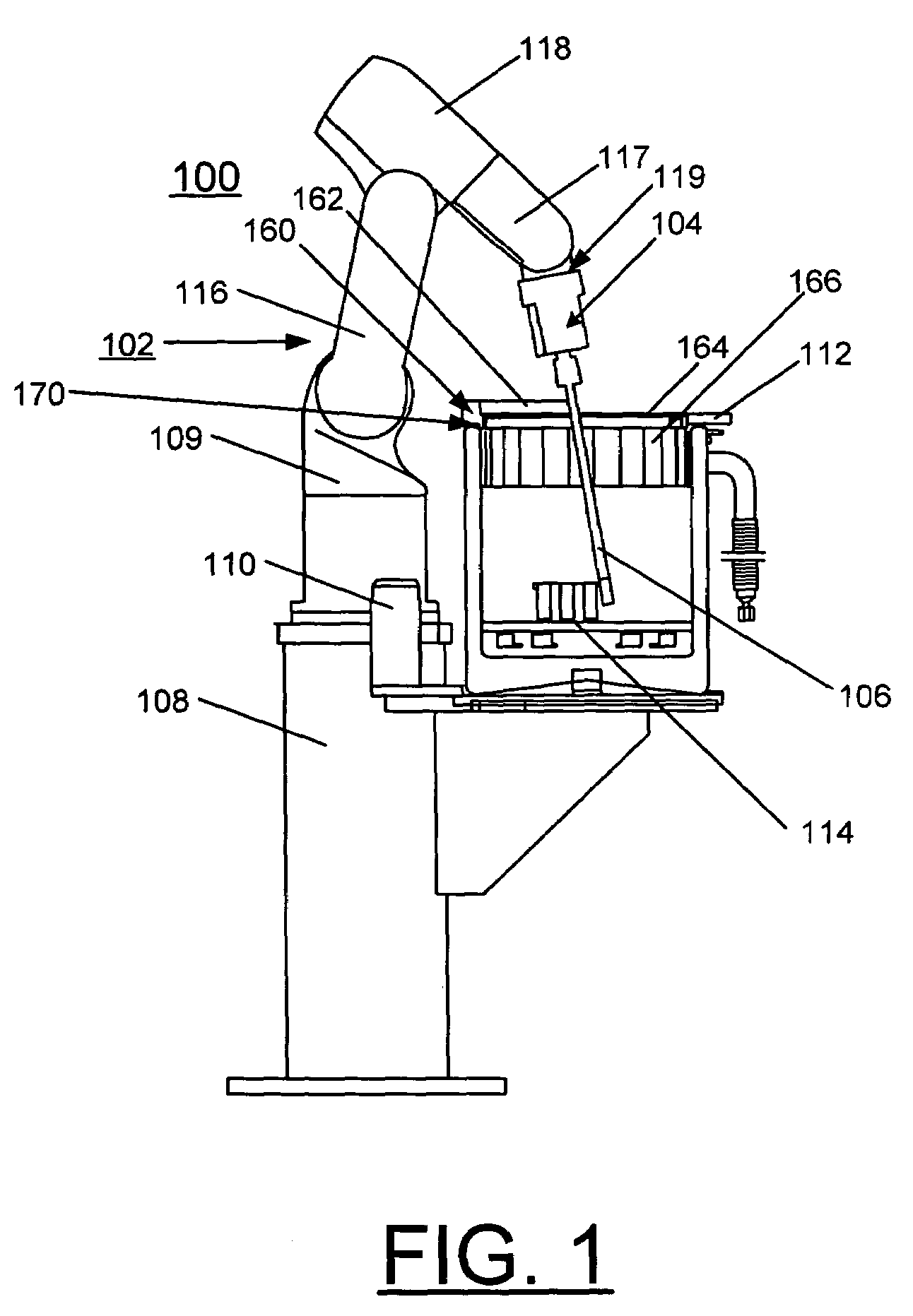
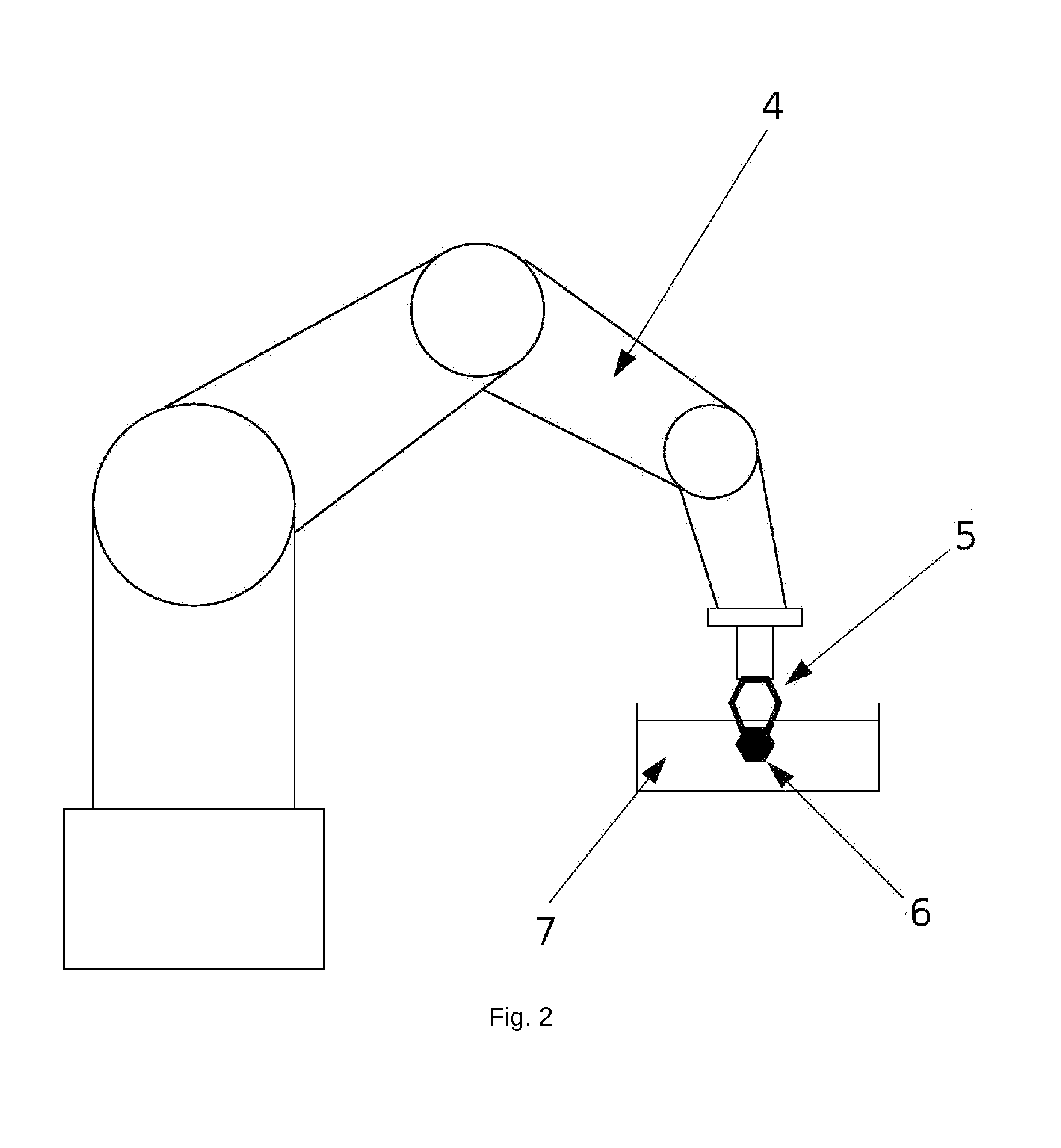
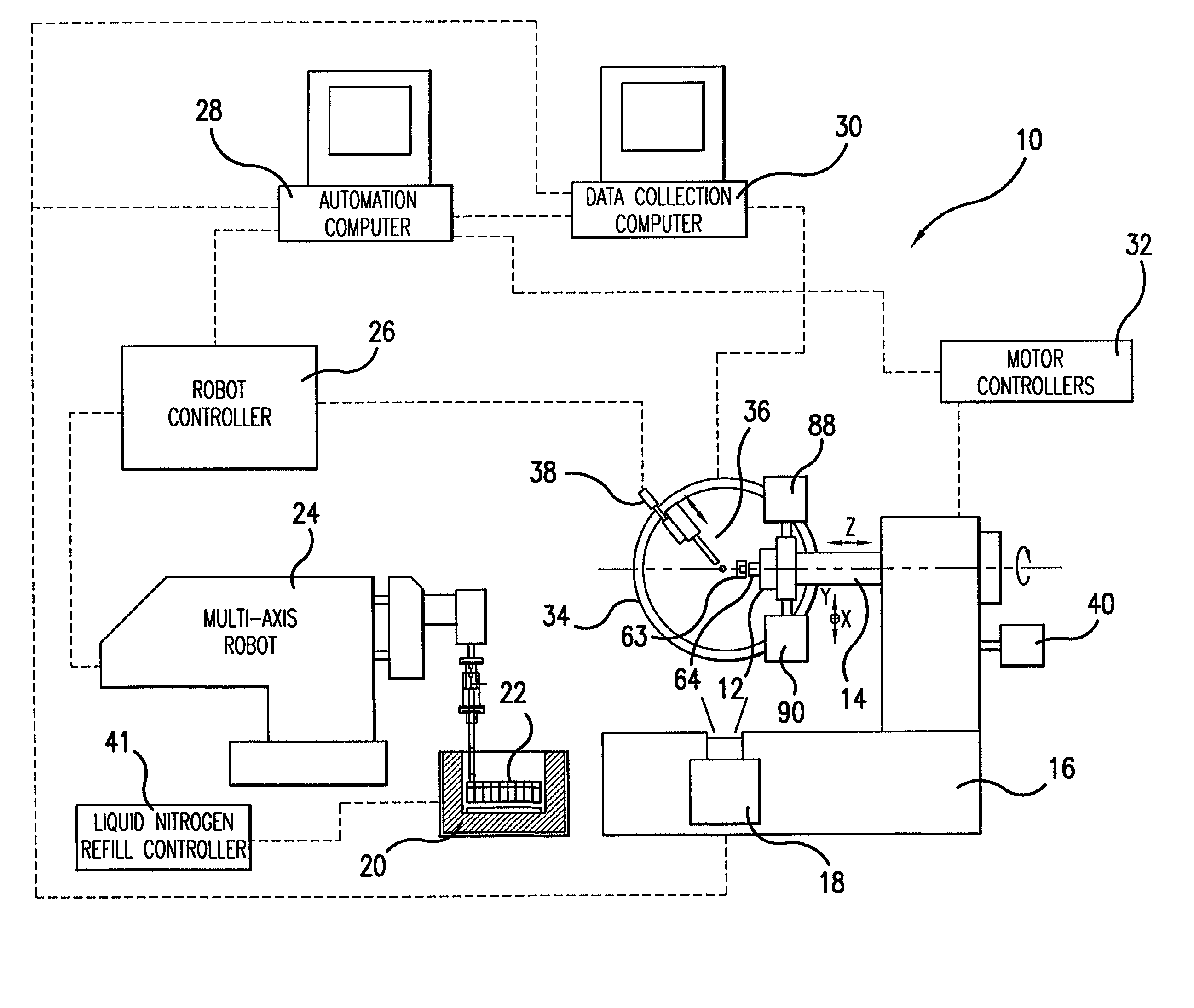
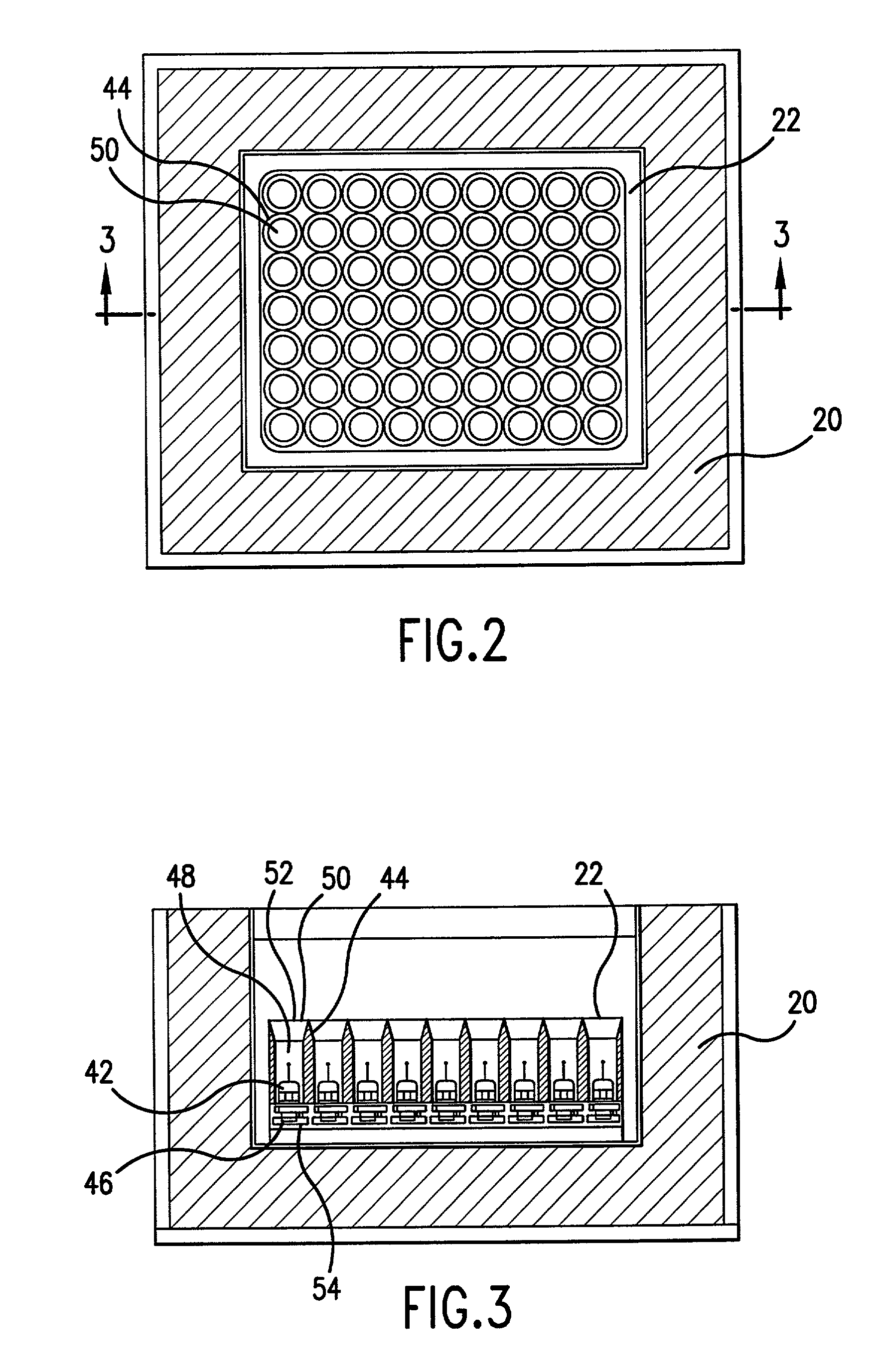
Robot-based automation system for cryogenic crystal sample mounting
InactiveUS7162888B2Avoid lostMaximized Dewar space usageMachines using refrigerant evaporationX-ray apparatusX-rayContact force
A method and robot-based automation system are provided for cryogenic crystal sample mounting, for example, for use for cryogenic crystal sample mounting in the x-ray crystallography station at an x-ray source. The system includes a robot arm carrying a handset. The handset includes a pair of elongated fingers for sample mounting, and each finger carrying a set of strain gauge arrays for providing force sensing. A slim finger design allows a sample mounting process with no interference with the beam stop, cryostreem and x-ray detectors. The handset can detect the contact force intensity and direction; provide a precise gripping action; and feel the results of the gripping. The finger design incorporates a mechanism to maintain the sample temperature well below the cryogenic safety margin for the crystal viability. A Dewar container is provided with an ice control system and liquid nitrogen flow control. A triangular sample magazine maximizes the Dewar space usage. A miniature kinematical mounting sample holder provides near micron positioning repeatability. These capabilities make the robot-arm more powerful, flexible, and reliable.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
Goniometer base apparatus and method
ActiveUS20110211674A1Small gripping surface areaSmall surface areaMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionGoniometerEngineering
A goniometer base for X-ray crystallography comprises a magnetic steel part with a cylindrical hole, a compliant cylindrical part that is inserted into this hole, and a cylindrical tube that is press-fit into the hole and holds the compliant part in place, such that when a crystal mounting tool is inserted through the concentric holes in each part, it is positively gripped and held in place at both T=300 K and T=100 K.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Modification of pertussis toxin
InactiveUS6168928B1Beneficially modifyingHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological propertyPertussis toxin
The three-dimensional structure of crystalline pertussis holotoxin (PT) has been determined by X-ray crystallography. Crystal structures have also been determined for complexes of pertussis toxin with molecules relevant to the biological activity of PT. These three-dimensional structures were analyzed to identify functional amino acids appropriate for modification to alter the biological properties of PT. Similar procedures may be used to predict amino acids which contribute to the toxicity of the holotoxin, to produce immunoprotective, genetically-detoxified analogs of pertussis toxin.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
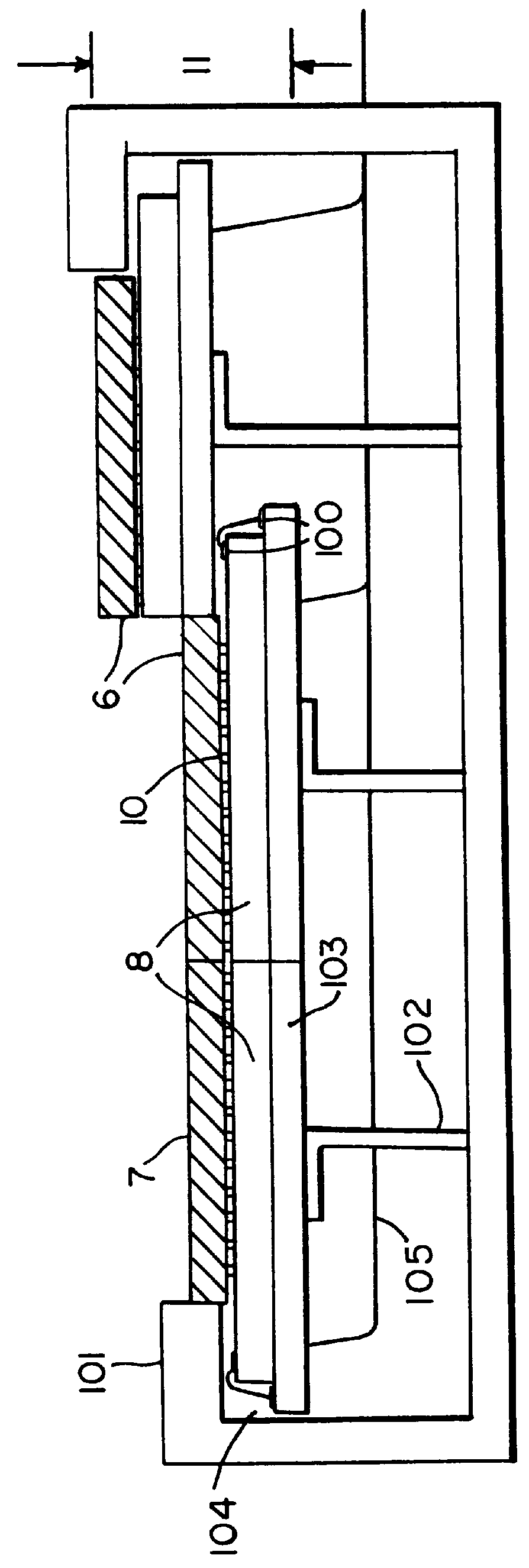
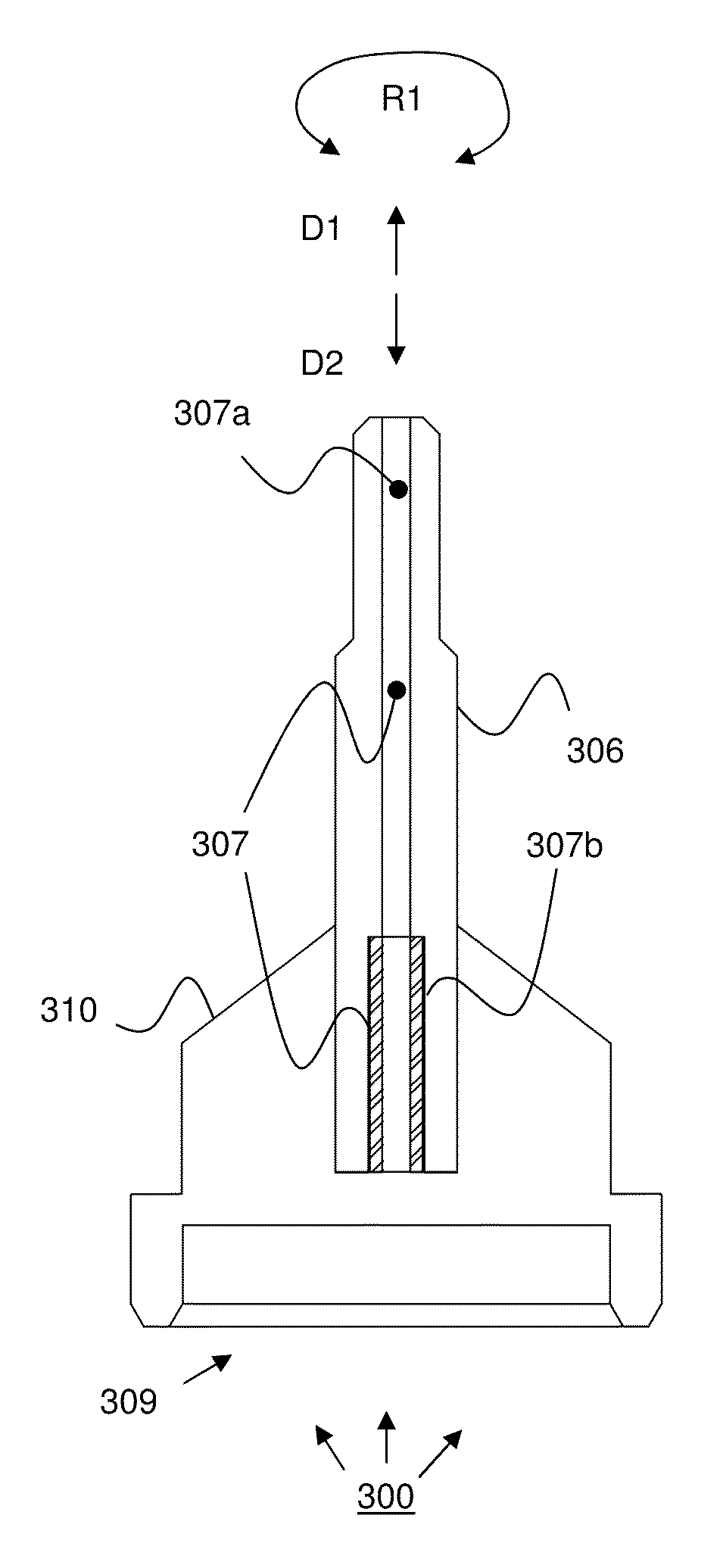
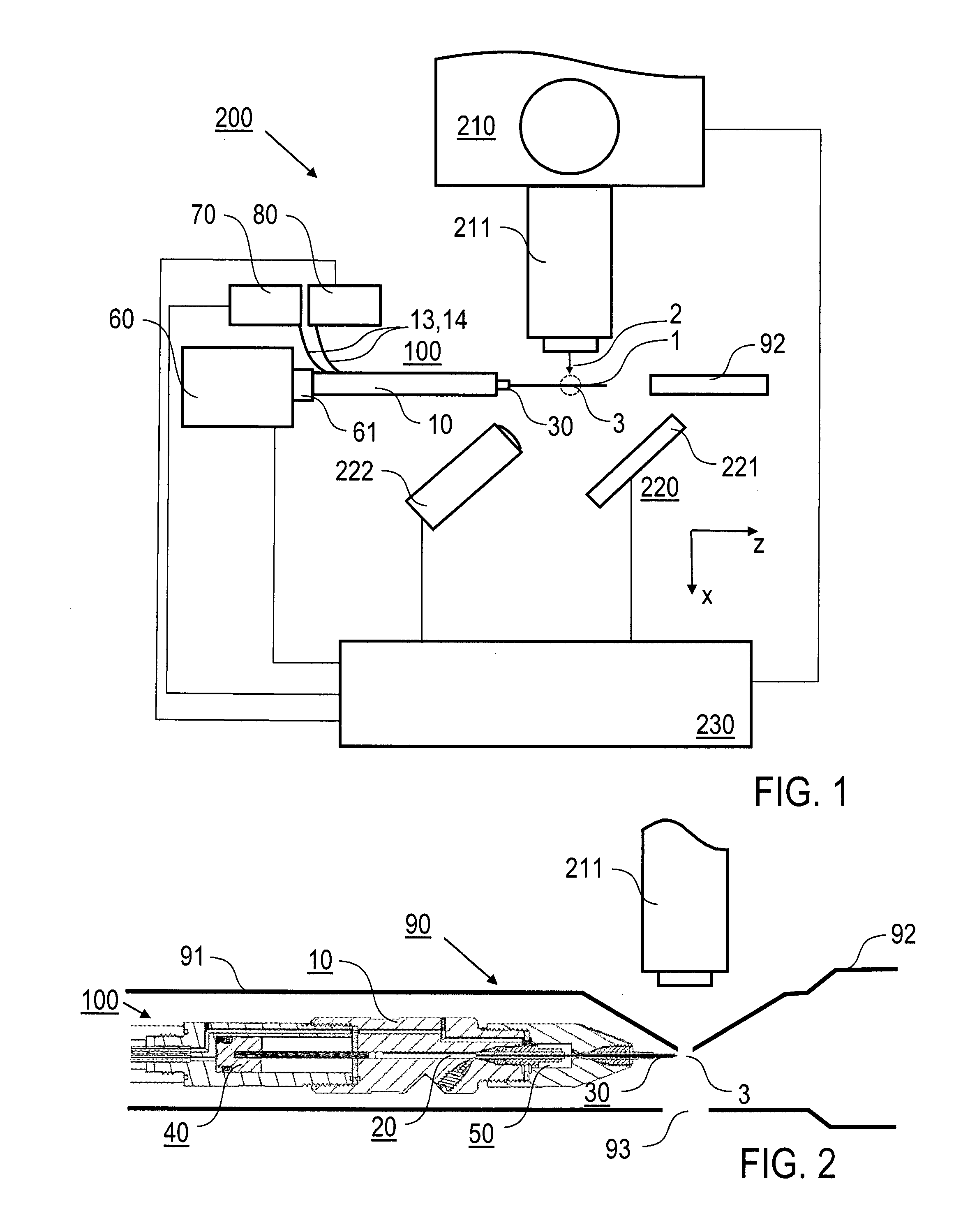
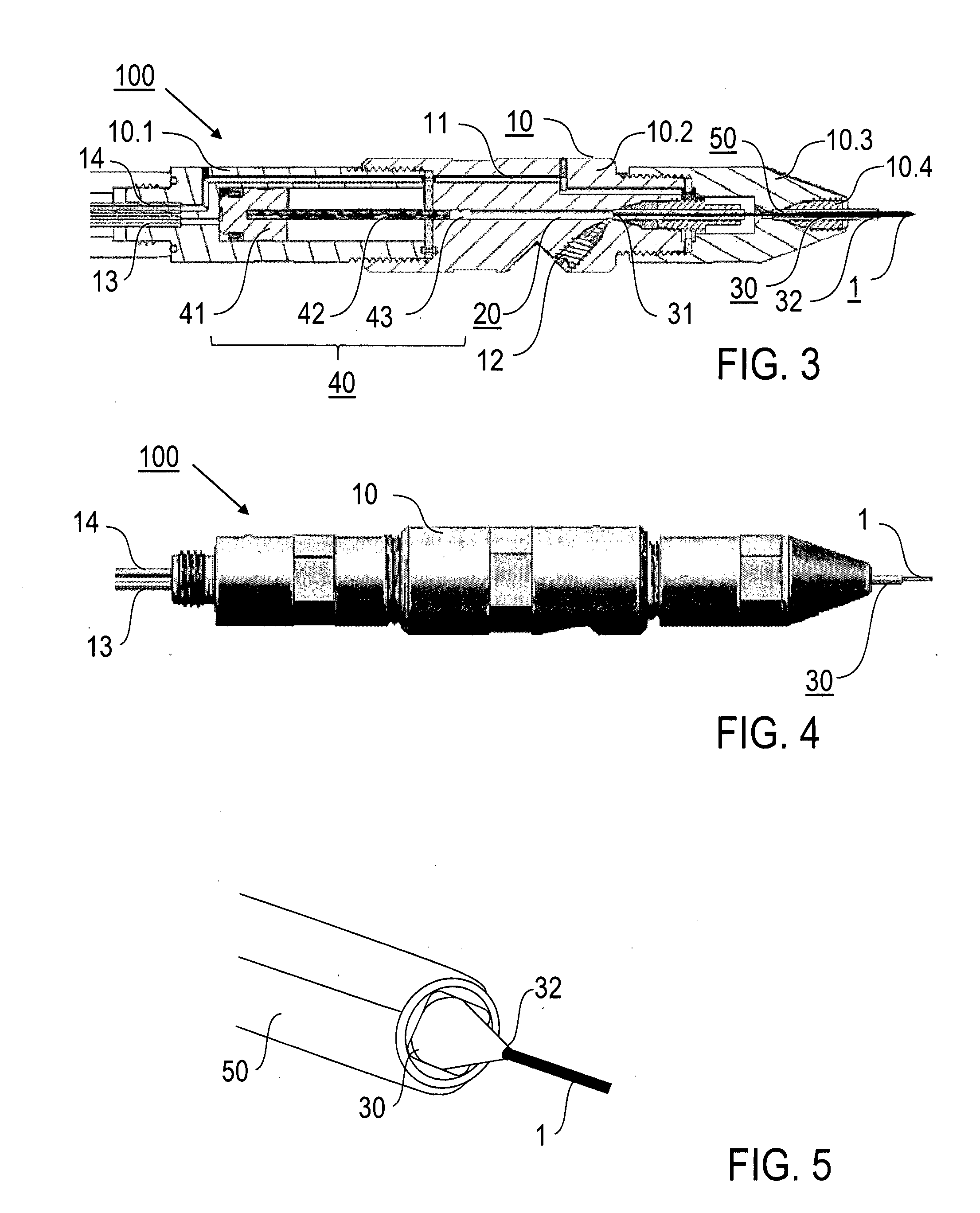
Method and Devices for X-Ray Crystallography, in Particular with Microcrystals of Biological Macromolecules
InactiveUS20160341675A1Shorten speedHigh molecular weightMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionViscous liquidInjector nozzle
A method of X-ray crystallography for investigating microscopic crystals, in particular microscopic crystals of biological macromolecules, comprises the steps of extruding a sample stream (1) with an injector nozzle device (100), wherein the sample stream (1) comprises a viscous liquid with microscopic crystals embedded therein, providing an X-ray beam (2) with a synchrotron source device (210) and irradiating the sample stream (1) with the X-ray beam (2), and collecting diffraction image data created by diffraction of the X-ray beam (2) by the microscopic crystals with a series of X-ray exposures of the sample stream (1). Furthermore, an injector nozzle device (100) and an X-ray crystallography apparatus (200) for X-ray crystallography investigations of microscopic crystals are described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +1
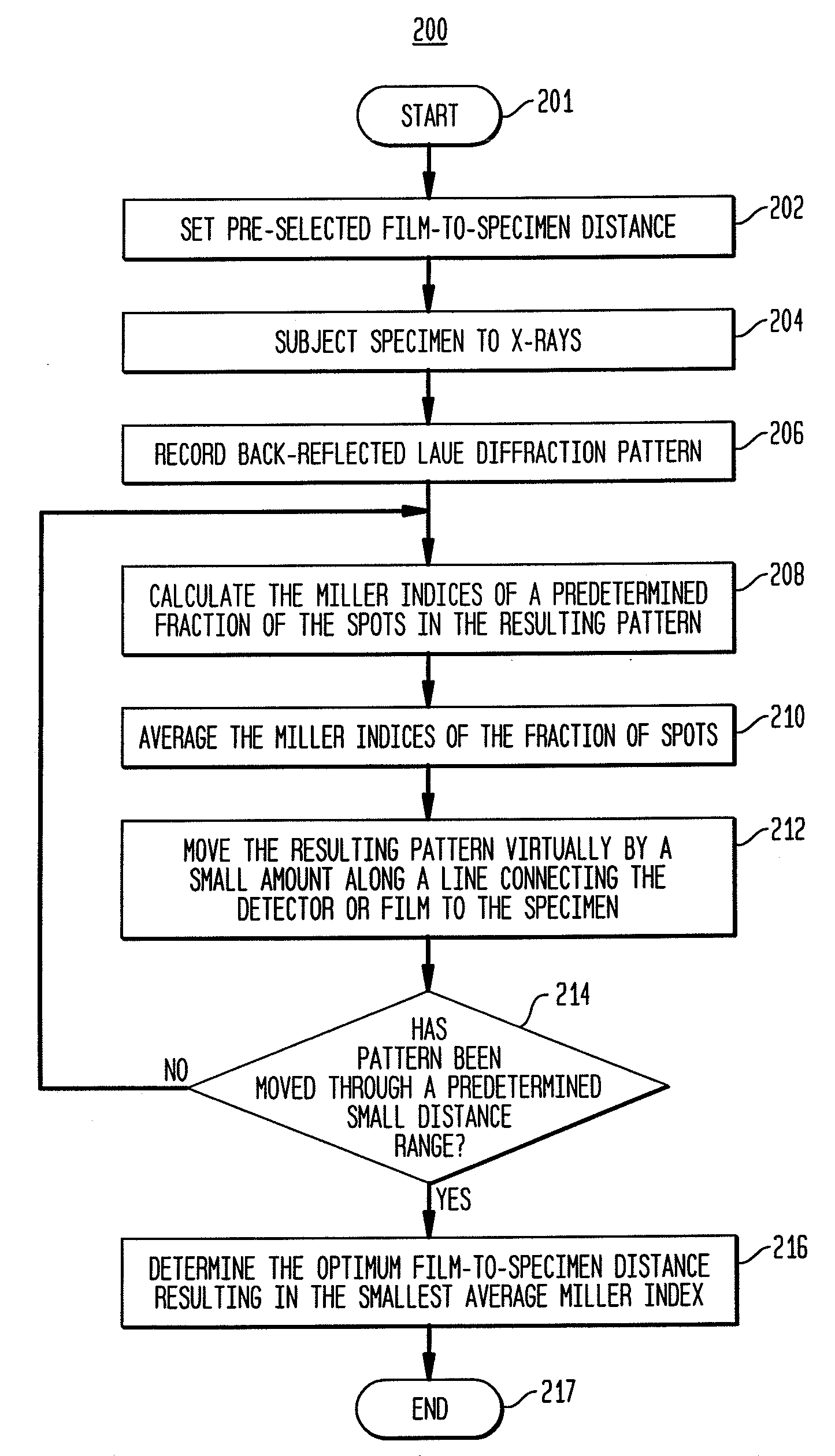
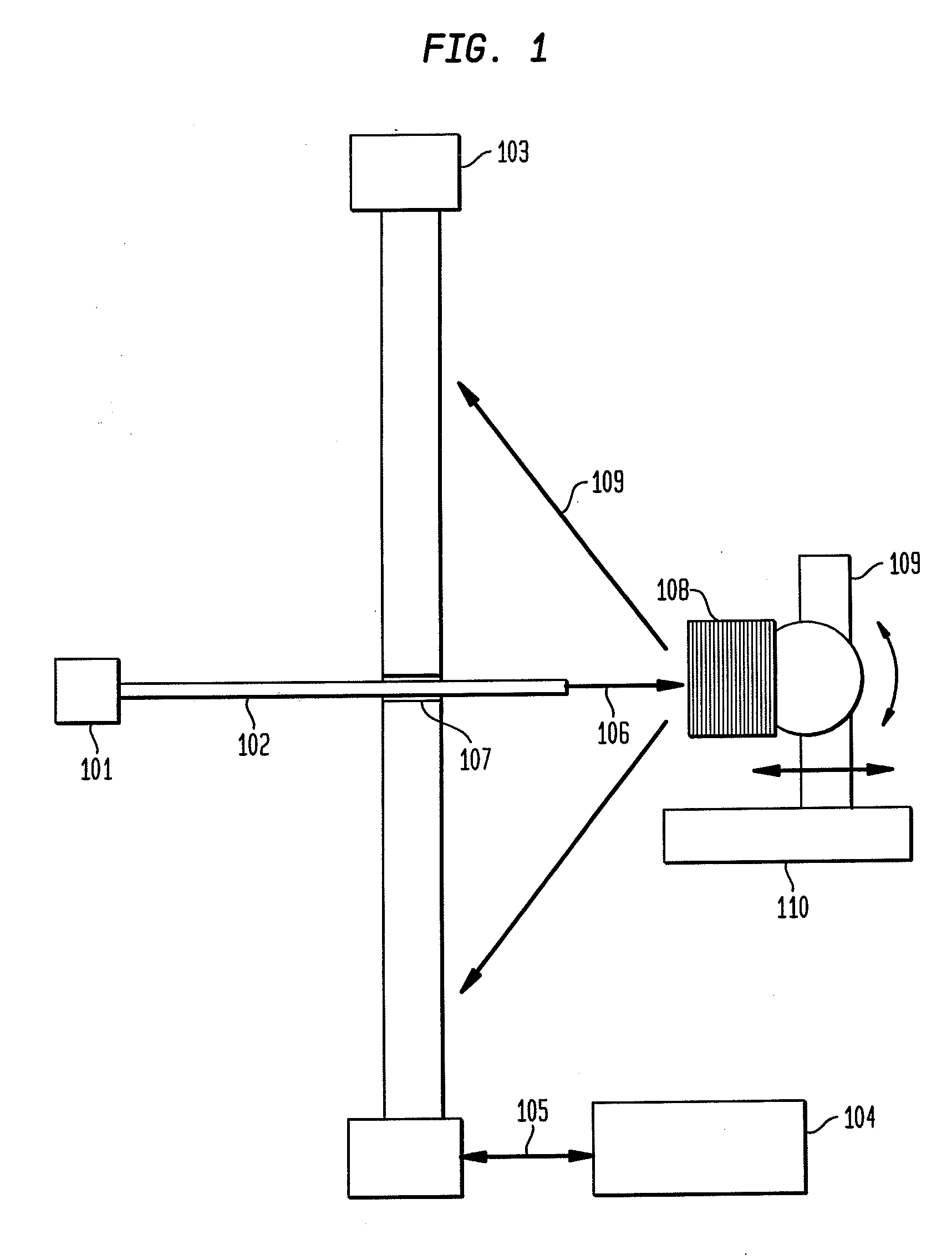
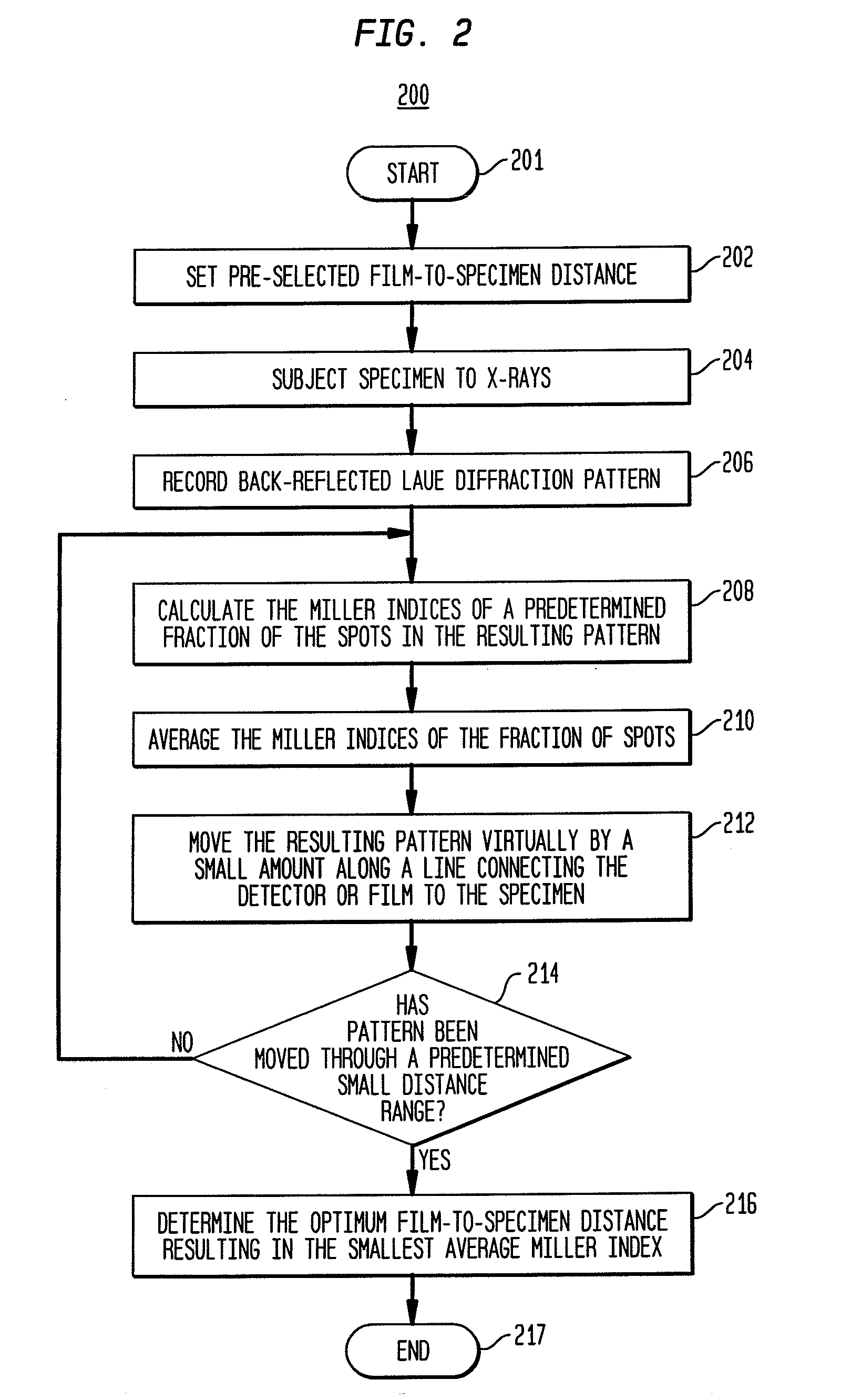
Back-reflection x-ray crystallography method and system
Provided is a method and system for back-reflection X-ray diffraction of a specimen that yields the orientation of a crystalline sample in a quick and an automated way. The method includes setting an approximate pre-selected X-ray detector to specimen distance, subjecting the specimen to X-rays, recording the Laue diffraction pattern, calculating the Miller indices of a fraction of the spots in the resulting pattern, averaging the Miller indices, moving a virtual representation of the specimen by a small amount along a line connecting the film to the specimen, changing the film-to-specimen distance, repeating the calculation, averaging and moving in small angular steps until the virtual representation of the specimen has been moved through a small distance range and best fits to the observed data, and determining the optimum film-to-specimen distance resulting in the smallest average Miller index.
Owner:MULTIWIRE LAB
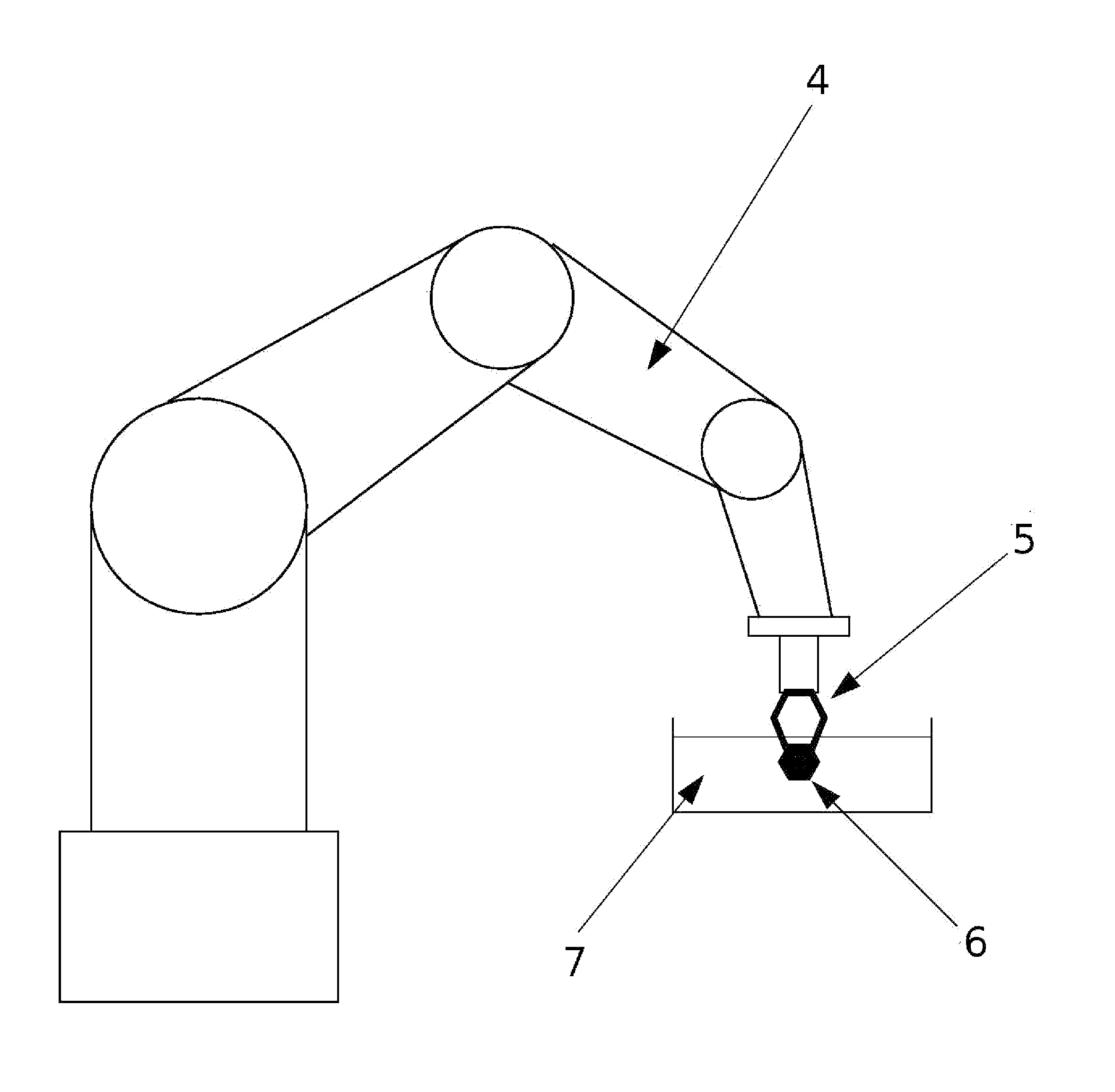
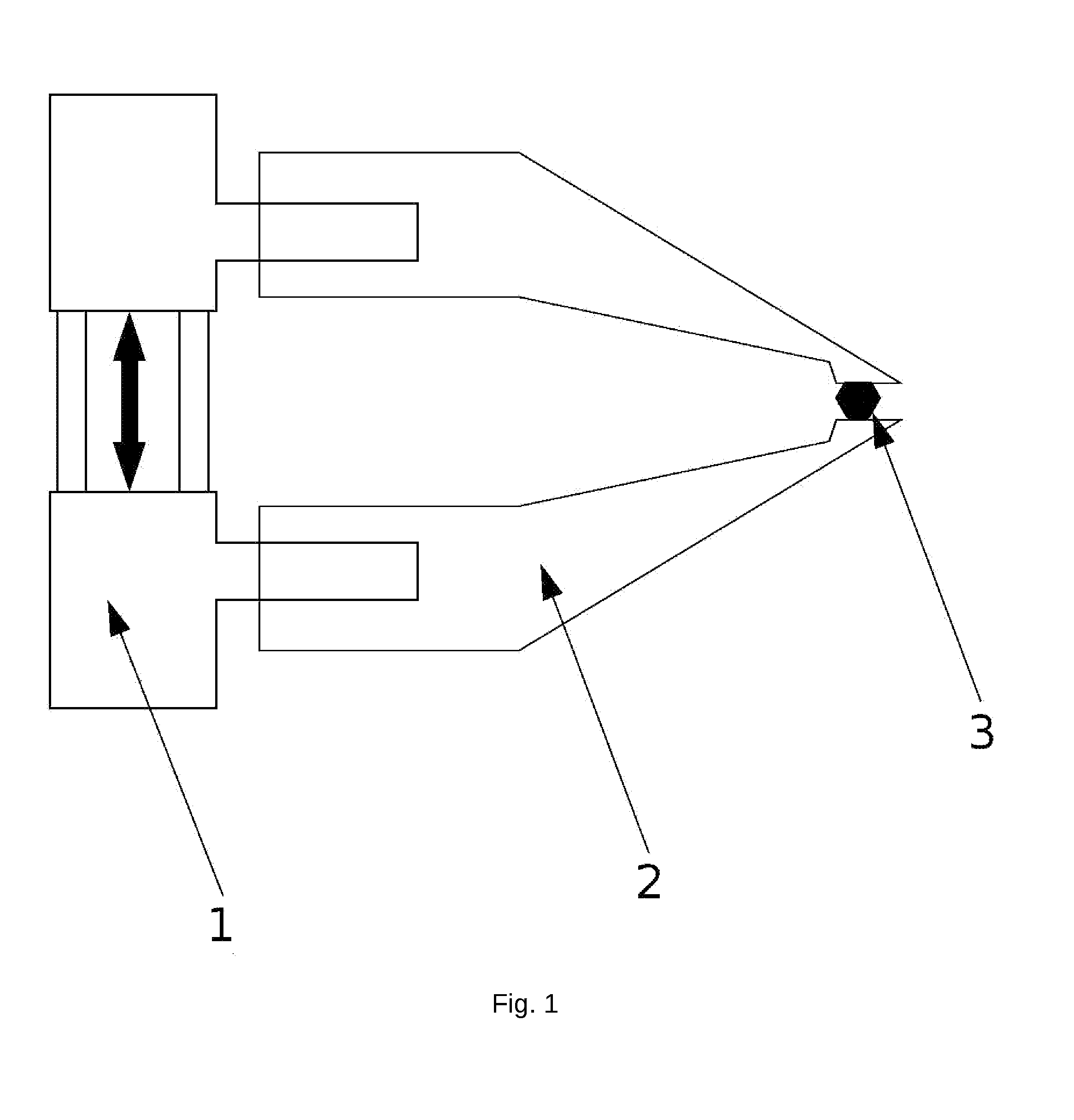
Micro-gripper for Automated Sample Harvesting and Analysis
InactiveUS20140044237A1Easy to dismountProgramme-controlled manipulatorMicromanipulatorRobotic armBiology
The present invention relates to a micro-gripper comprising tweezers, designed to be used for the harvesting of fragile sub-millimeter samples from their production or storage medium. The tweezers may be equipped with removable soft ending elements to prevent the deterioration of the sample. When coupled to a robotic arm, this micro-gripper allows automated flow of operations in a continuous and automated process, from harvesting to sample preparation and analysis. The present invention is particularly used in X-ray crystallography.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
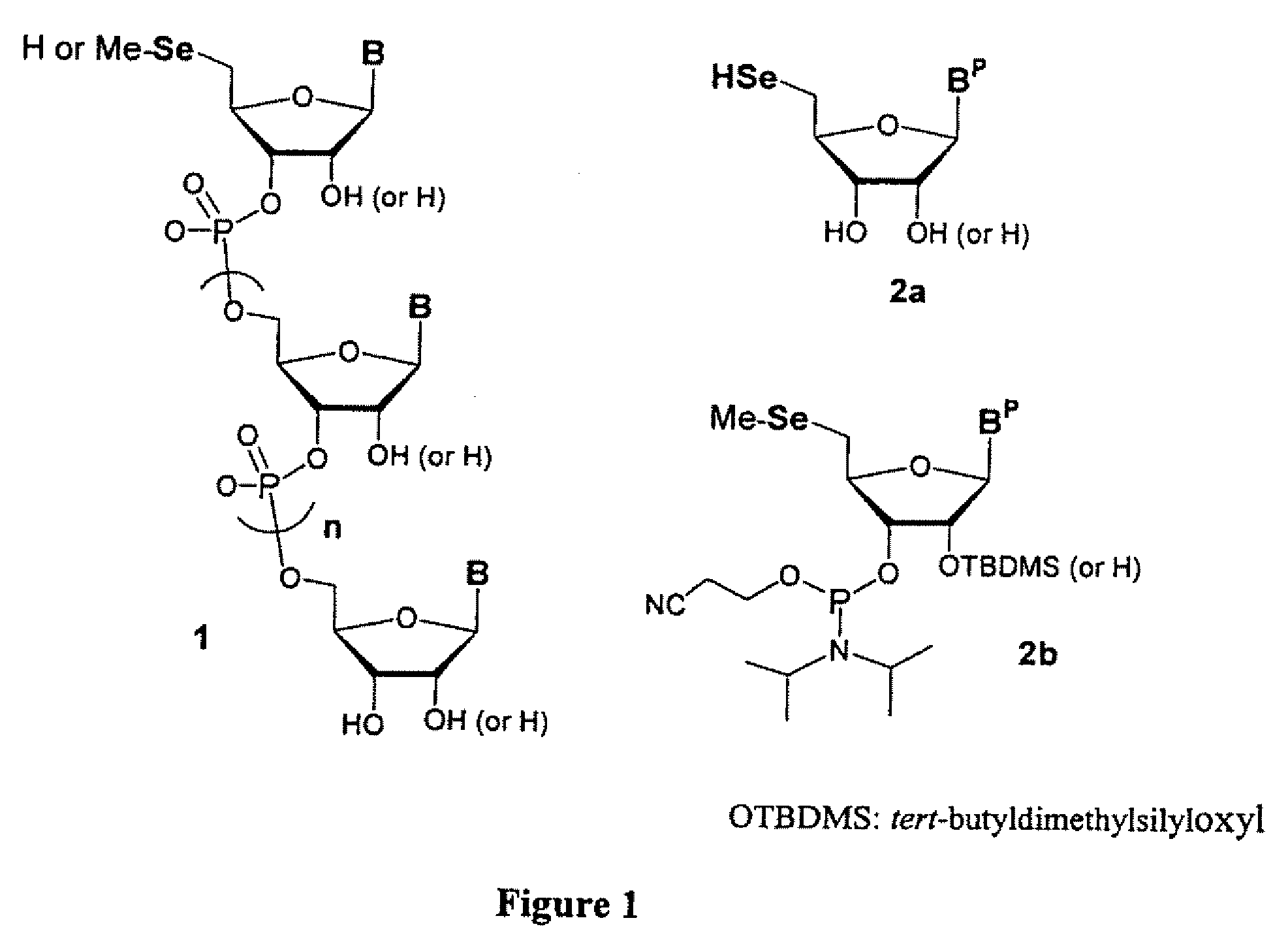
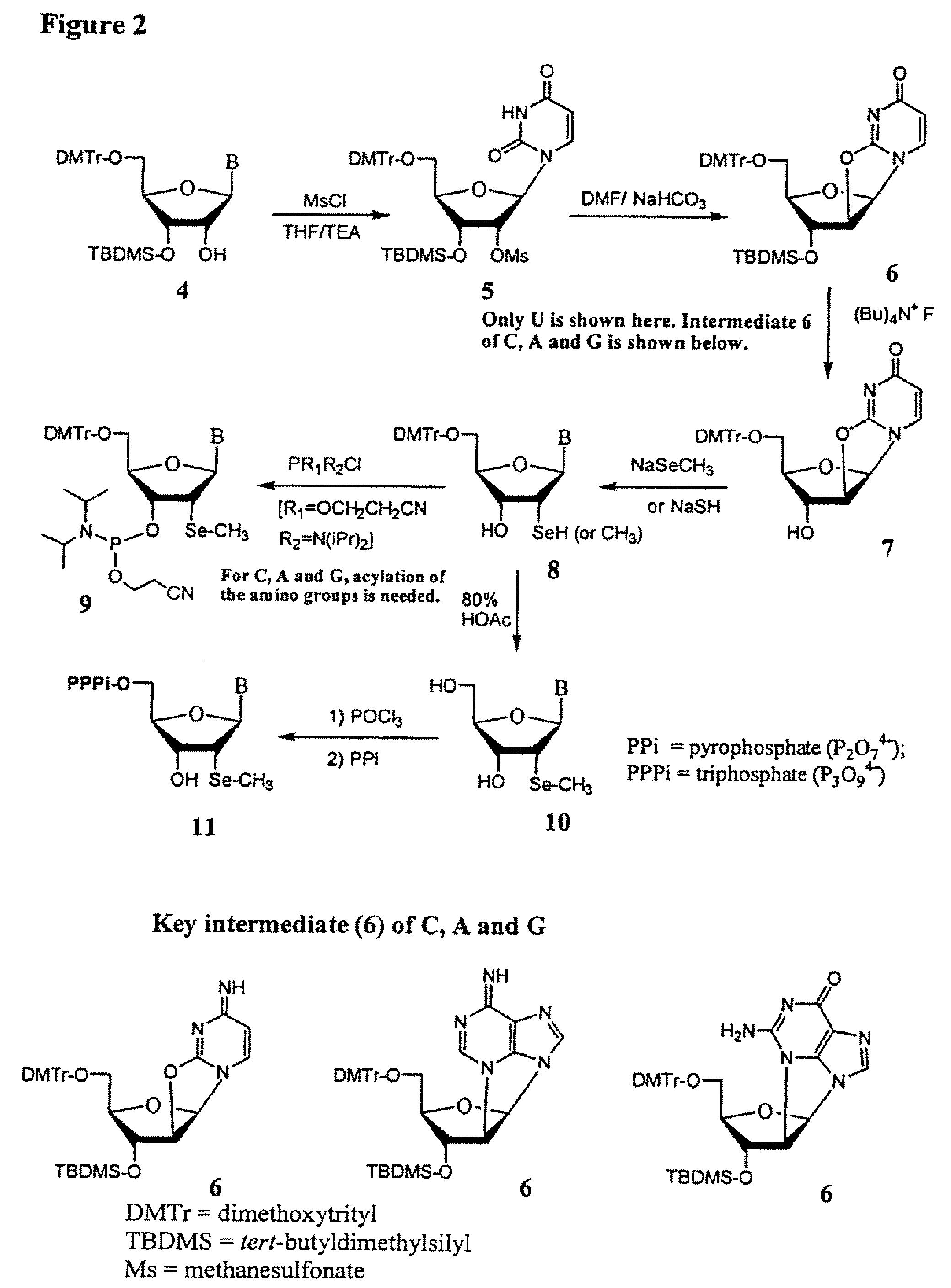
Synthesis of selenium-derivatized nucleosides, nucleotides, phosphoramidites, triphosphates and nucleic acids
The present invention provides selenium derivatives of nucleosides, nucleoside phosphoramidites, nucleotides, nucleotide triphosphates, oligonucleotides, polynucleotides, and larger nucleic acids and methods for their synthesis. Selenium derivatives of both ribonucleic acids and deoxyribonulcleic acids, as well as methods for their synthesis, crystallization and uses in structural determinations, particularly by X-ray crystallographic techniques are disclosed. The selenium derivatives of the present invention are also useful as food supplements.
Owner:GEORGIA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
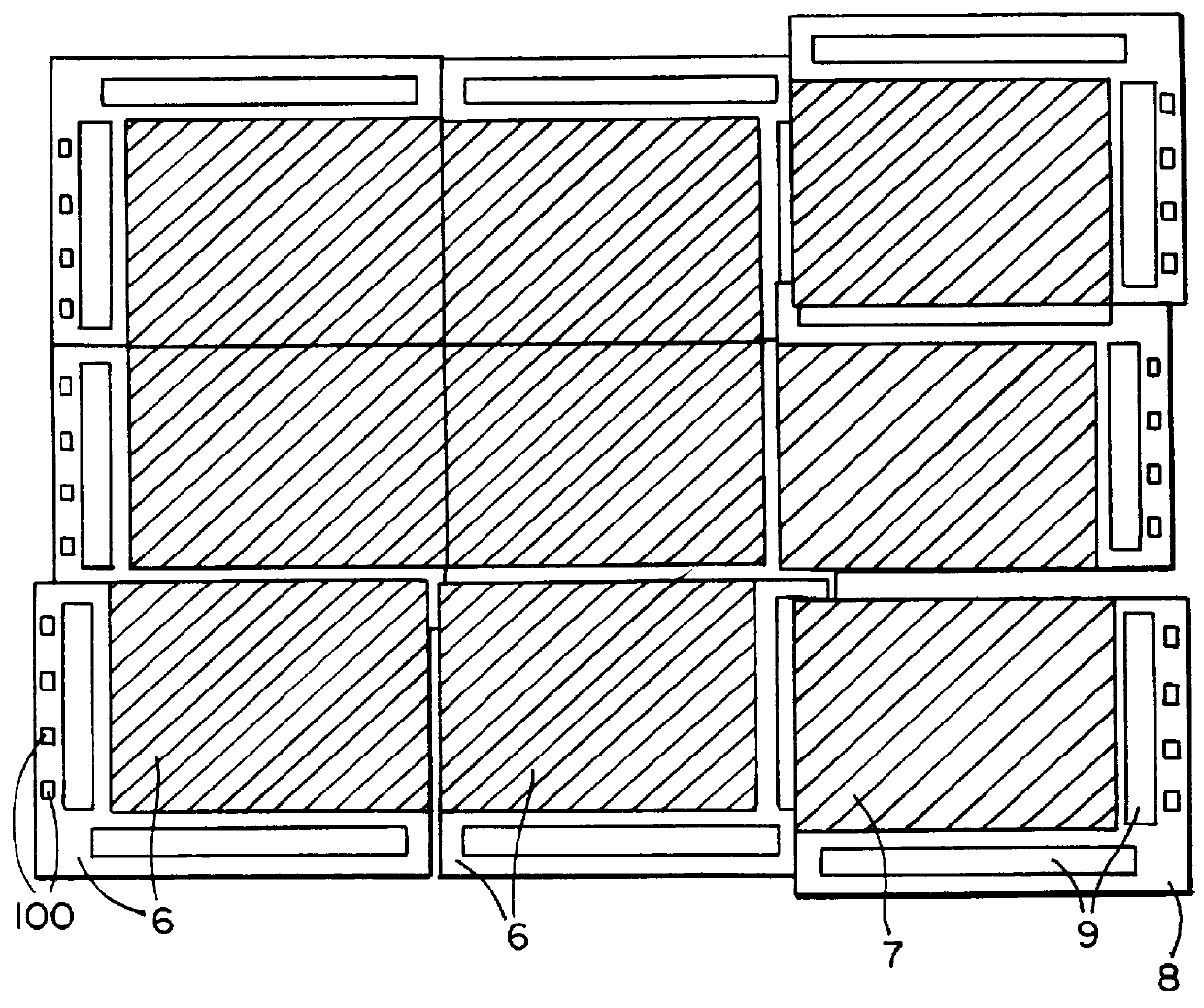
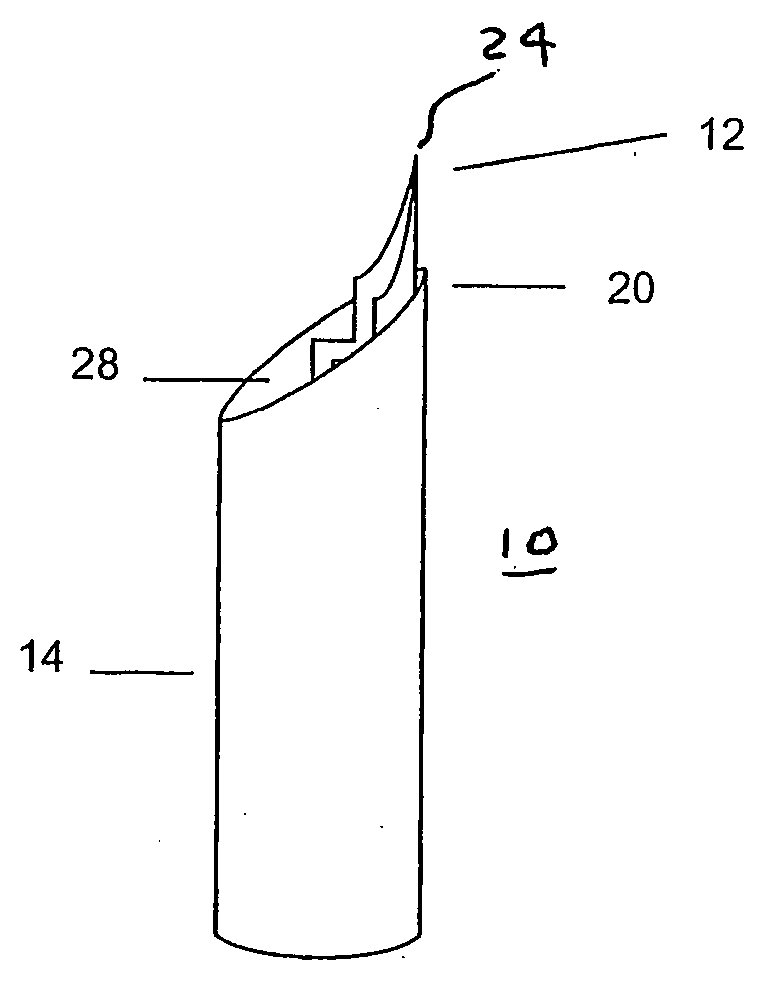
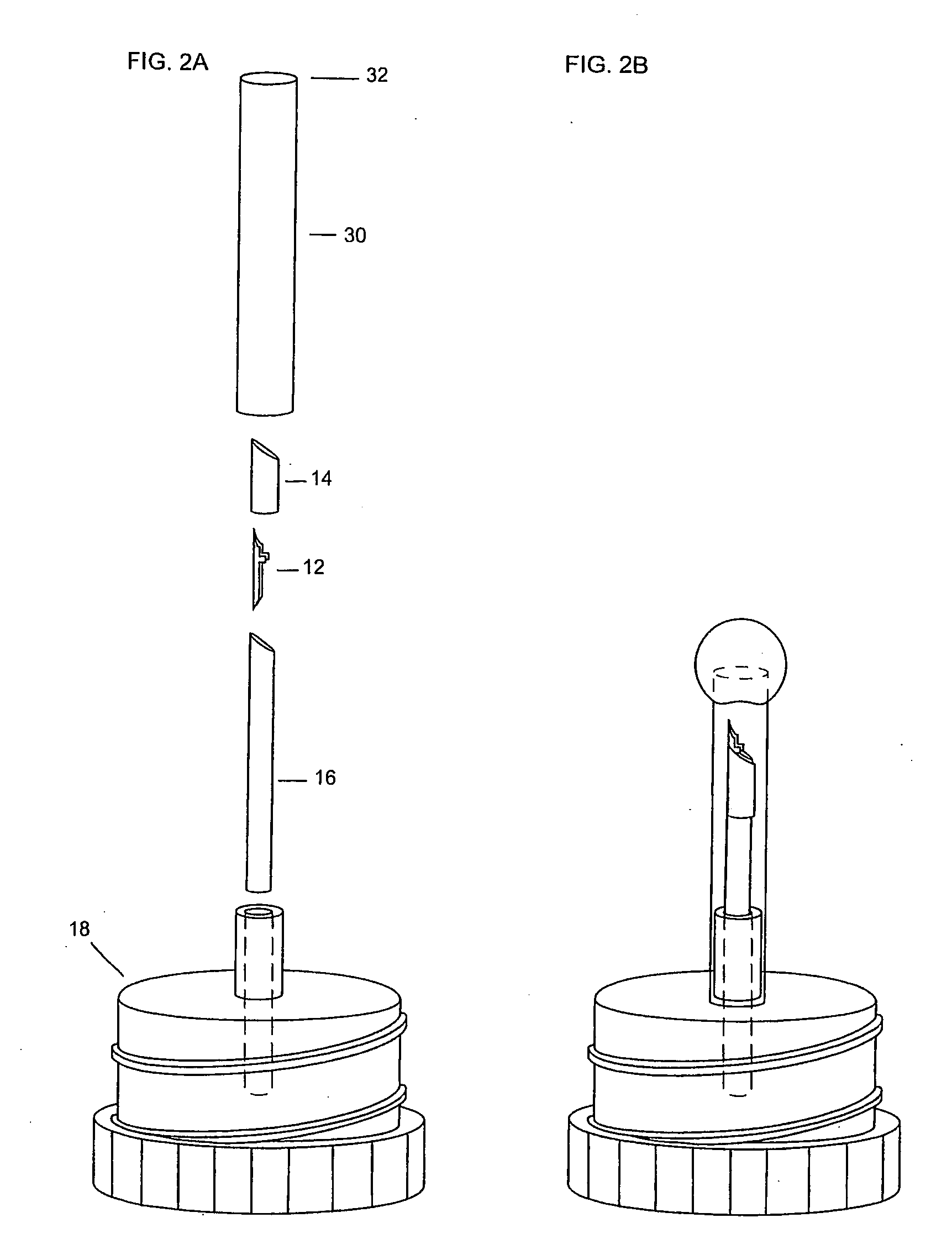
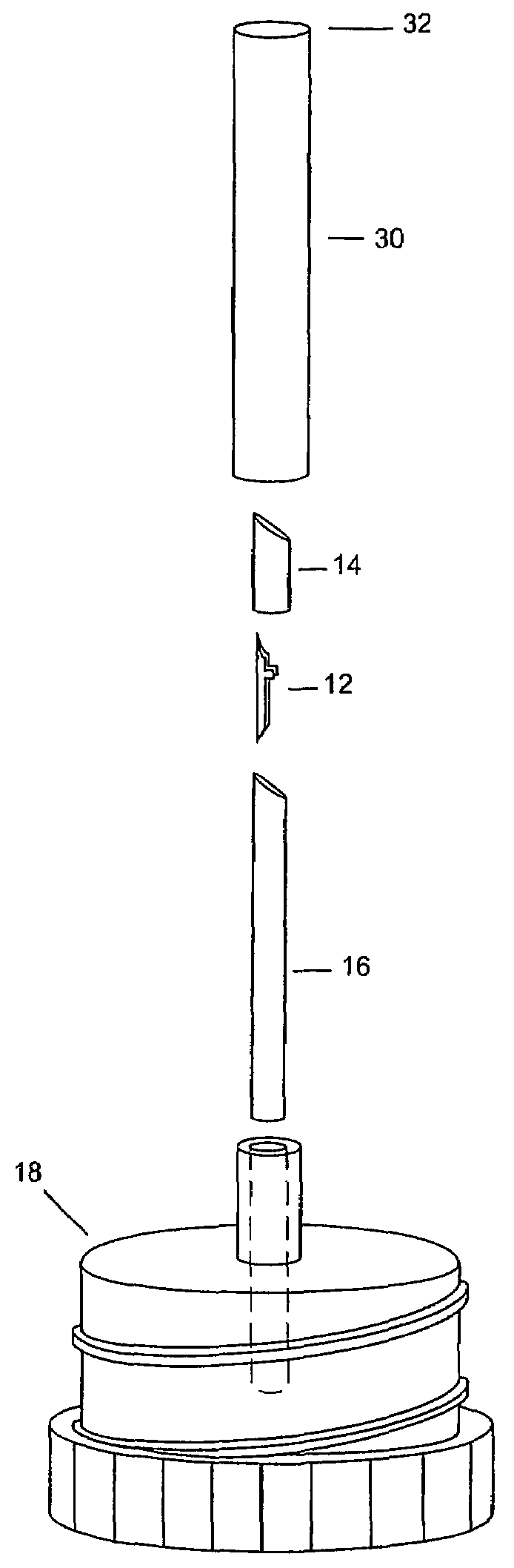
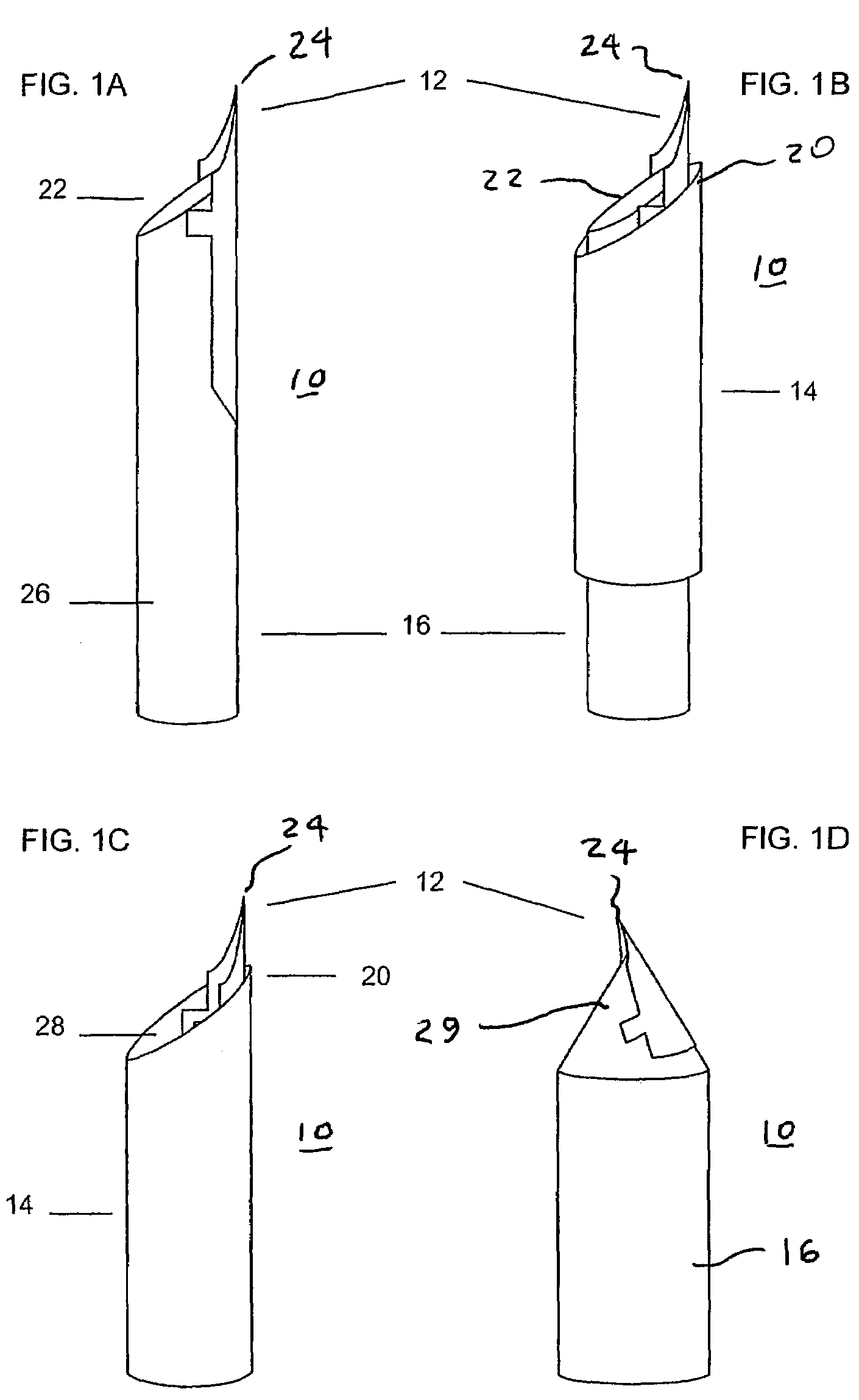
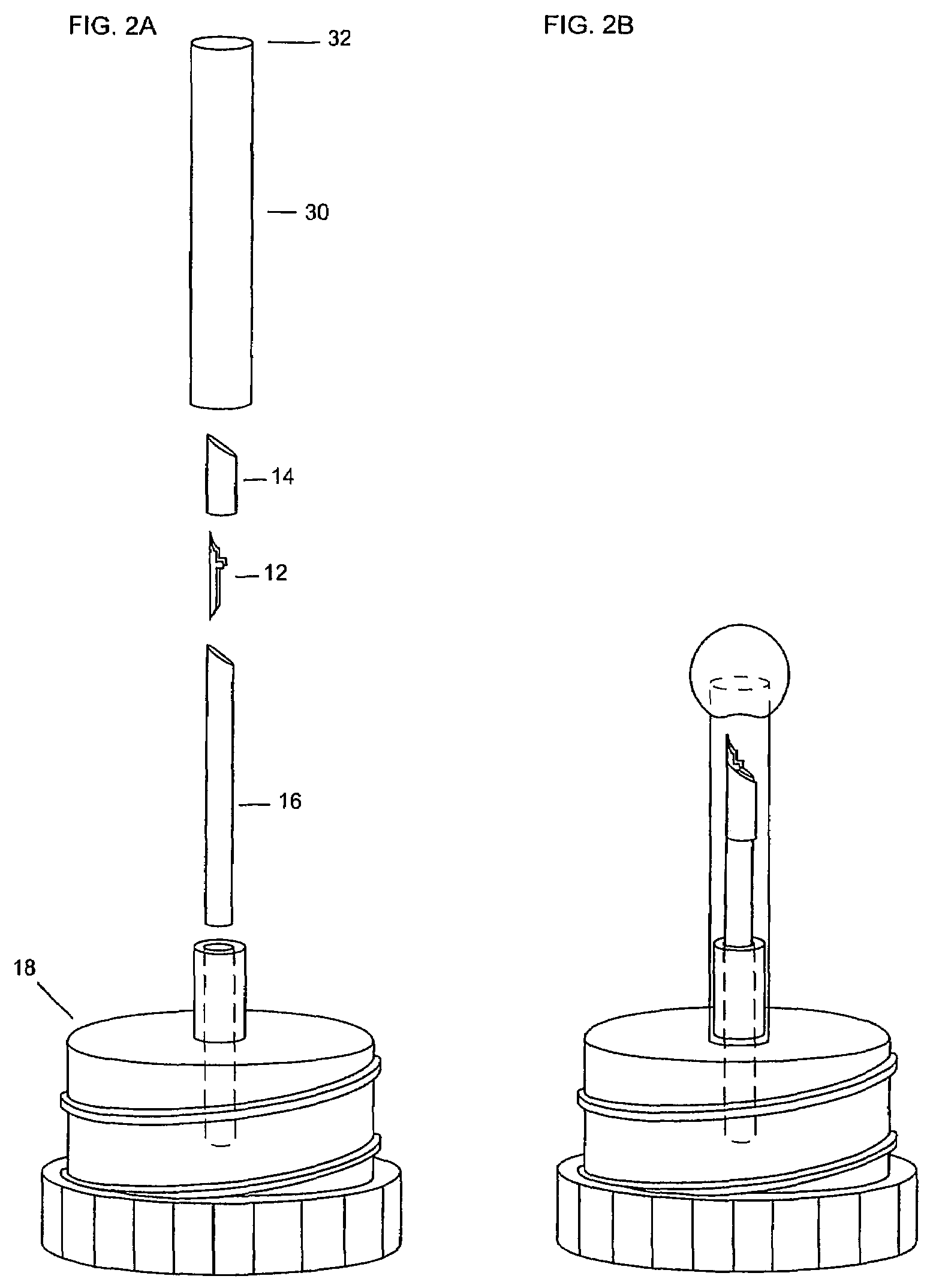
Sample mounts for microcrystal crystallography
ActiveUS20060086315A1Reduces background scattering of X-raysImprove structural rigidityOptical radiation measurementBy pulling from meltSmall sampleEngineering
Sample mounts (10) for mounting microcrystals of biological macromolecules for X-ray crystallography are prepared by using patterned thin polyimide films (12) that have curvature imparted thereto, for example, by being attached to a curved outer surface of a small metal rod (16). The patterned film (12) preferably includes a tapered tip end (24) for holding a crystal. Preferably, a small sample aperture is disposed in the film for reception of the crystal. A second, larger aperture can also be provided that is connected to the sample aperture by a drainage channel, allowing removal of excess liquid and easier manipulation in viscous solutions. The curvature imparted to the film (12) increases the film's rigidity and allows a convenient scoop-like action for retrieving crystals. The polyimide contributes minimally to background and absorption, and can be treated to obtain desired hydrophobicity or hydrophilicity.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Automated sample handling for X-ray crystallography
InactiveUS20020126802A1Reduce in quantityIncrease speedX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayPhysics
Method and apparatus for mounting a sample comprising a crystal for X-ray crystallographic analysis, a method for aligning a sample comprising a crystal for X-ray crystallographic analysis, which sample is mounted on a positioning device, and a method for determining the structure of a sample containing a crystal by means of X-ray crystallography.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Crystallization cassette for the growth and analysis of macromolecular crystals and an associated method
InactiveUS7118626B2Increase opportunitiesPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsDiffusion methodsX-ray
The invention is a crystallization cassette and associated method for growing and analyzing macromolecular crystals in situ by X-ray crystallography. The cassette allows proteins (as well as other macromolecules) to be crystallized by the counter-diffusion method in a restricted geometry. Using this procedure, crystals can be adequately prepared for direct X-ray data analysis such that the protein's three-dimesional structure can be solved without crystal manipulation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Sample mounts for microcrystal crystallography
ActiveUS7263162B2Reduces background scattering of X-raysImprove structural rigidityOptical radiation measurementLevel indicatorsSmall sampleEngineering
Sample mounts (10) for mounting microcrystals of biological macromolecules for X-ray crystallography are prepared by using patterned thin polyimide films (12) that have curvature imparted thereto, for example, by being attached to a curved outer surface of a small metal rod (16). The patterned film (12) preferably includes a tapered tip end (24) for holding a crystal. Preferably, a small sample aperture is disposed in the film for reception of the crystal. A second, larger aperture can also be provided that is connected to the sample aperture by a drainage channel, allowing removal of excess liquid and easier manipulation in viscous solutions. The curvature imparted to the film (12) increases the film's rigidity and allows a convenient scoop-like action for retrieving crystals. The polyimide contributes minimally to background and absorption, and can be treated to obtain desired hydrophobicity or hydrophilicity.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Phase detection method based on only amplitude detection
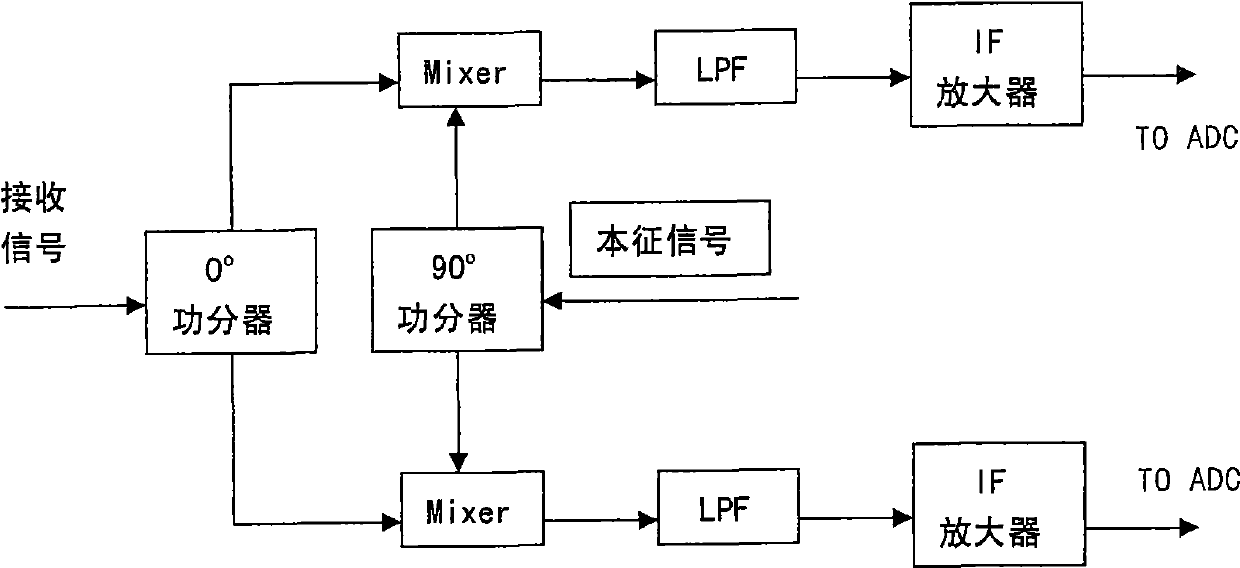
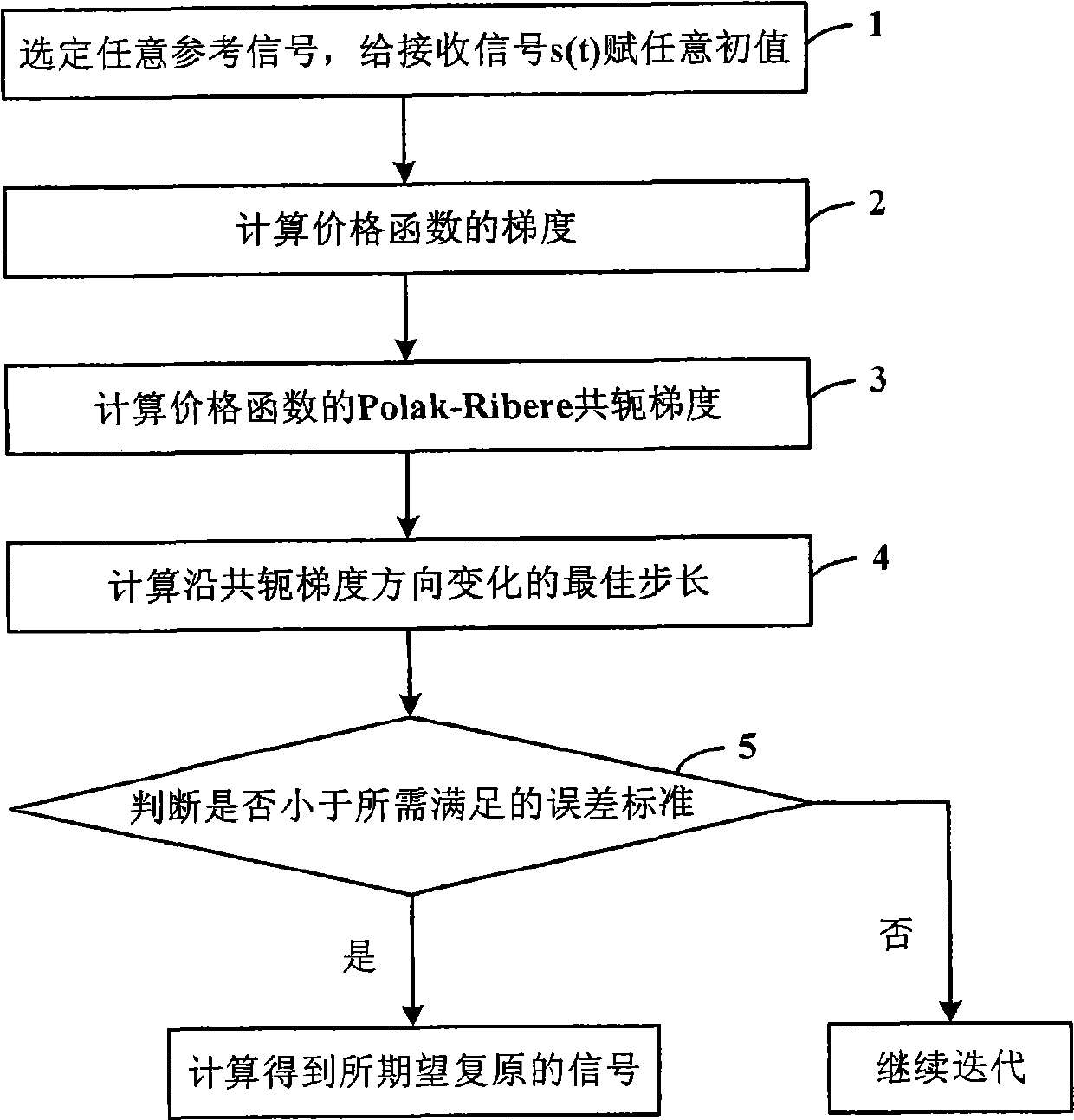
InactiveCN101545929APhase detection implementationSolving difficult problems that require prior informationVoltage-current phase angleMultiple carrier systemsAstronomical image processingMicrowave
The invention discloses a phase detection method based on only amplitude detection. The method comprises the following steps: an arbitrary reference signal s0(t) is selected, and a receiving signal s(t) to be reconstructed is endued with an arbitrary initial value; the gradient of a cost function phi is calculated; the Polak-Ribere conjugate gradient of the cost function phi is calculated; the optimum step length gamma of variation along the direction of the conjugate gradient is calculated; whether the phi is less than the error standard required to be met or not is judged, and if the phi is less than the error standard, the signal expected to be released is calculated by using a formula that s(tk) is equal to Sigma (Xin+jgamman)e<-j2Pi(kn / (2N+1))>, then the loop exits; and otherwise, if the phi is equal to or more than the error standard, the iteration continues. By using the method, the invention realizes the phase detection based on the only amplitude detection, solves the difficult problem that the phase retrieval method needs apriori information in various fields of X-ray crystallography, optics, astronomical image processing, and the like, and lays the foundation of the phaseless detection imaging principle, therefore, the hardware cost of the microwave, the terahertz and the optic imaging system can be greatly reduced.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Protein structure
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
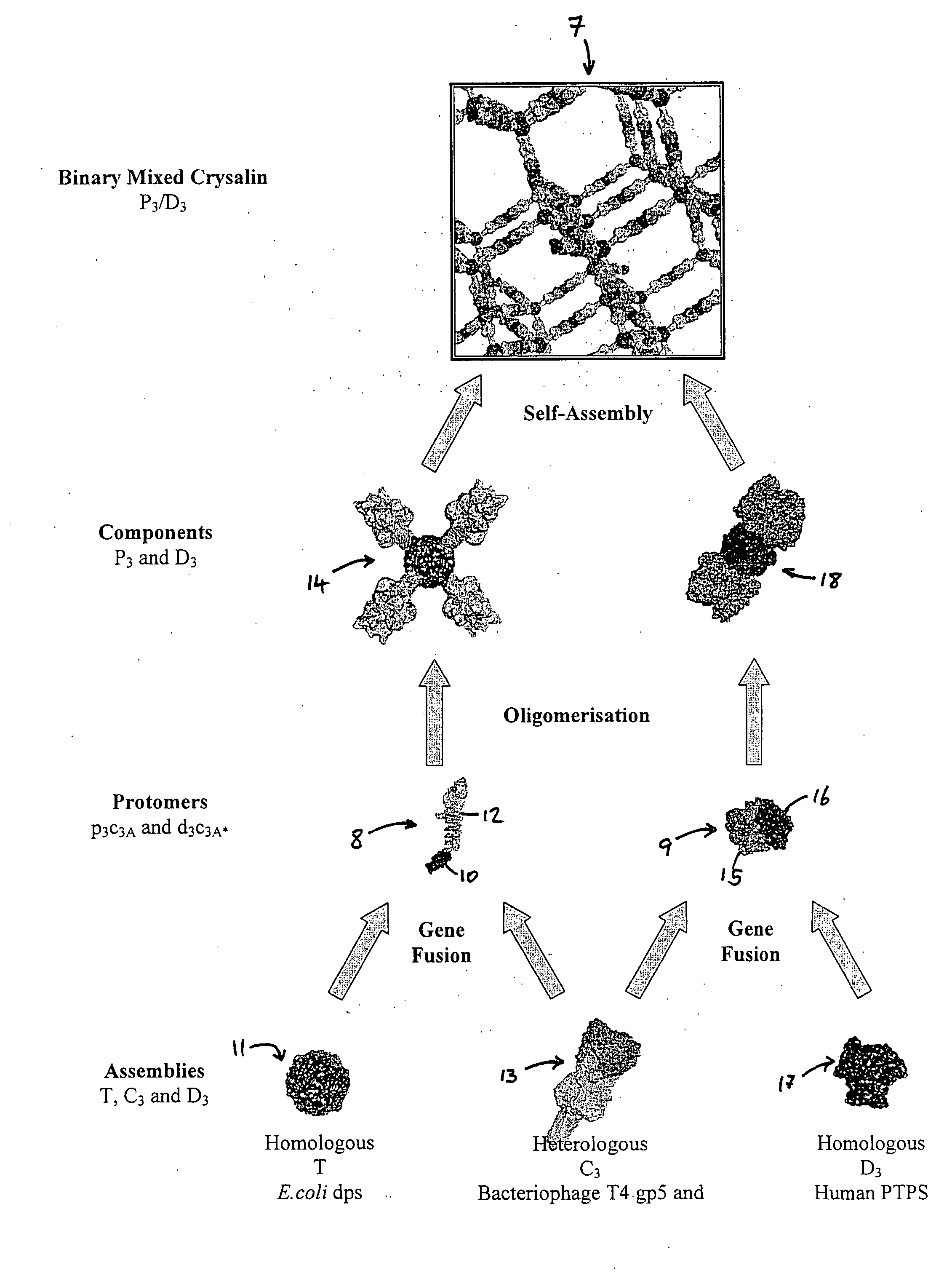
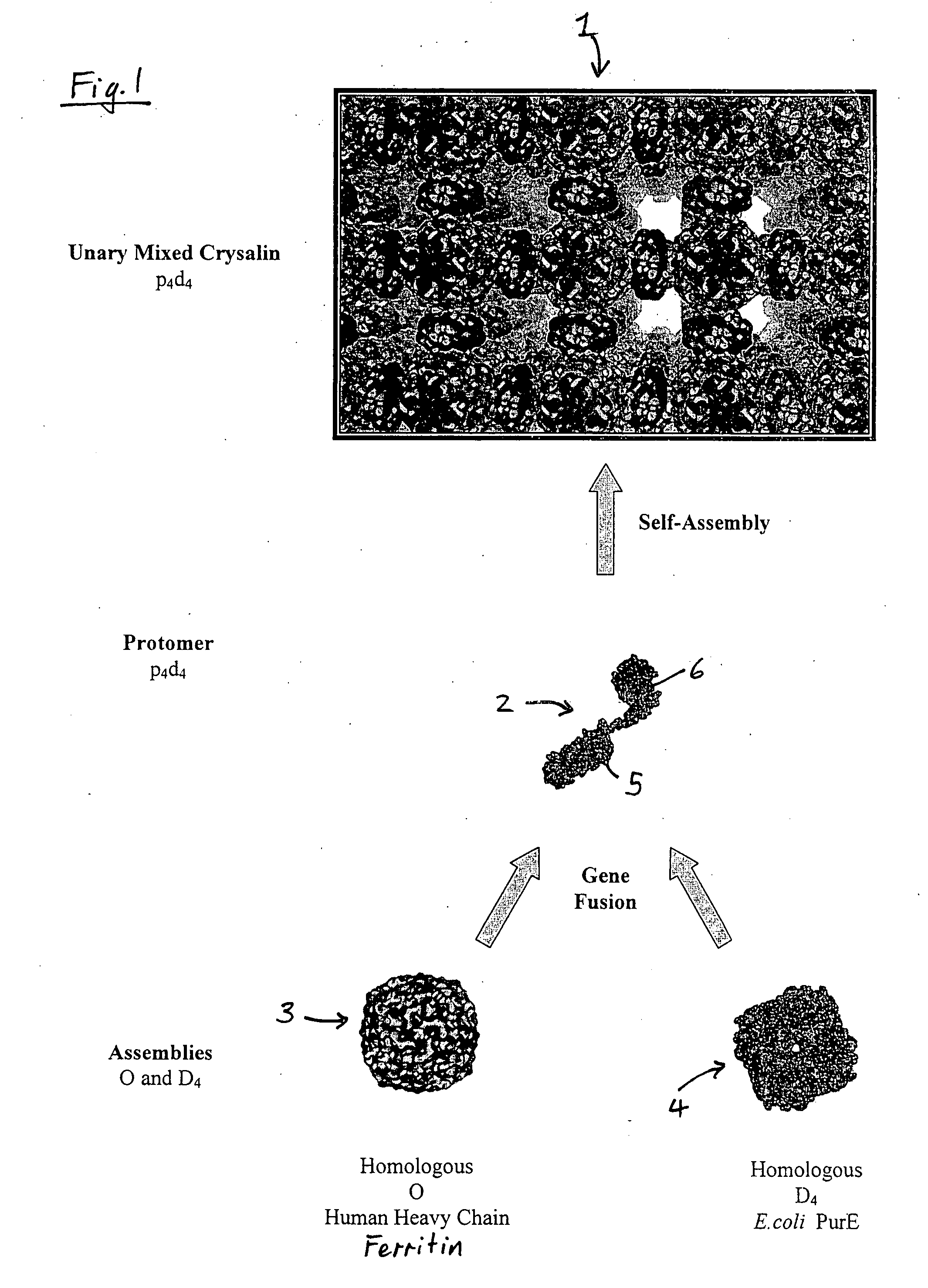
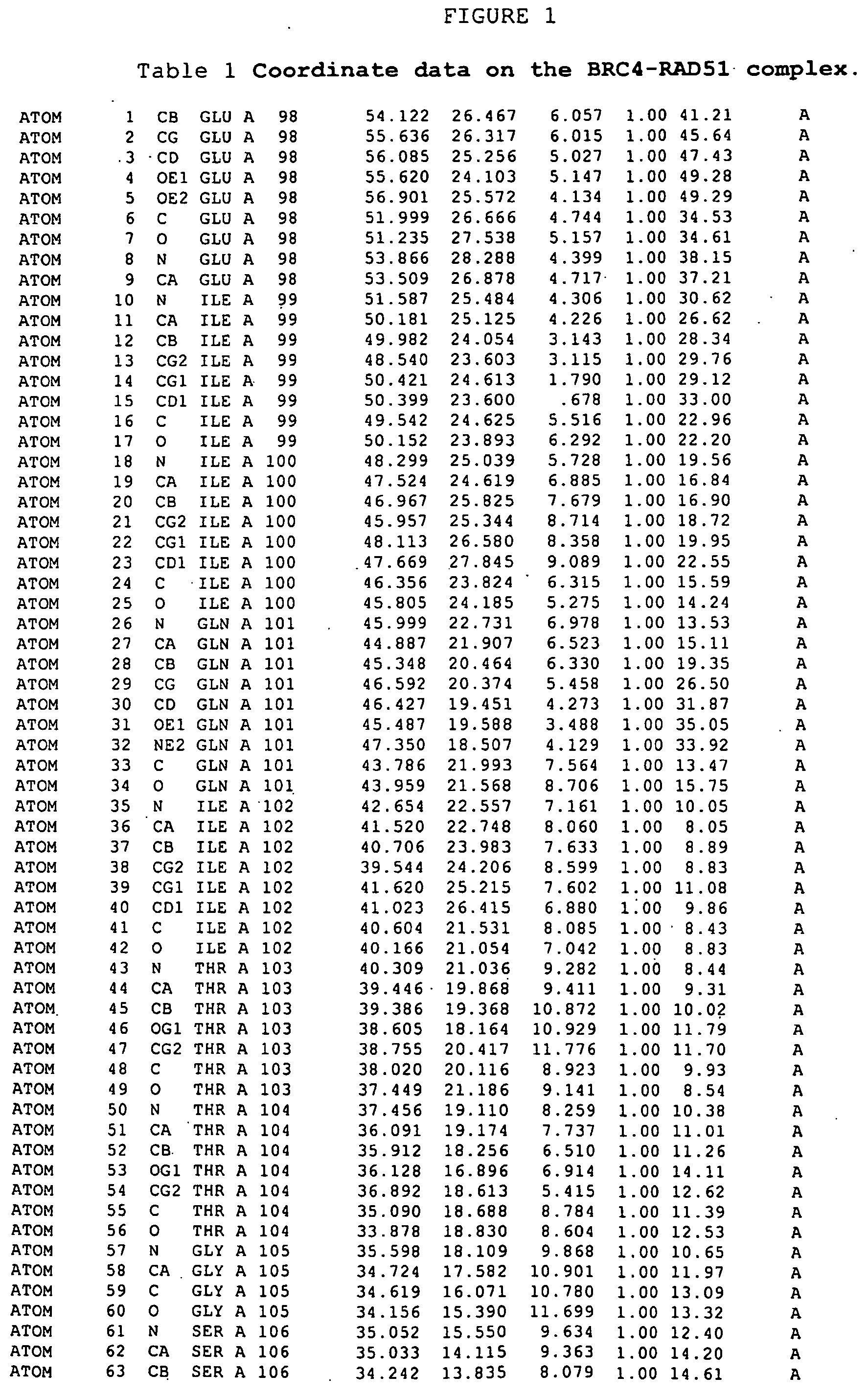
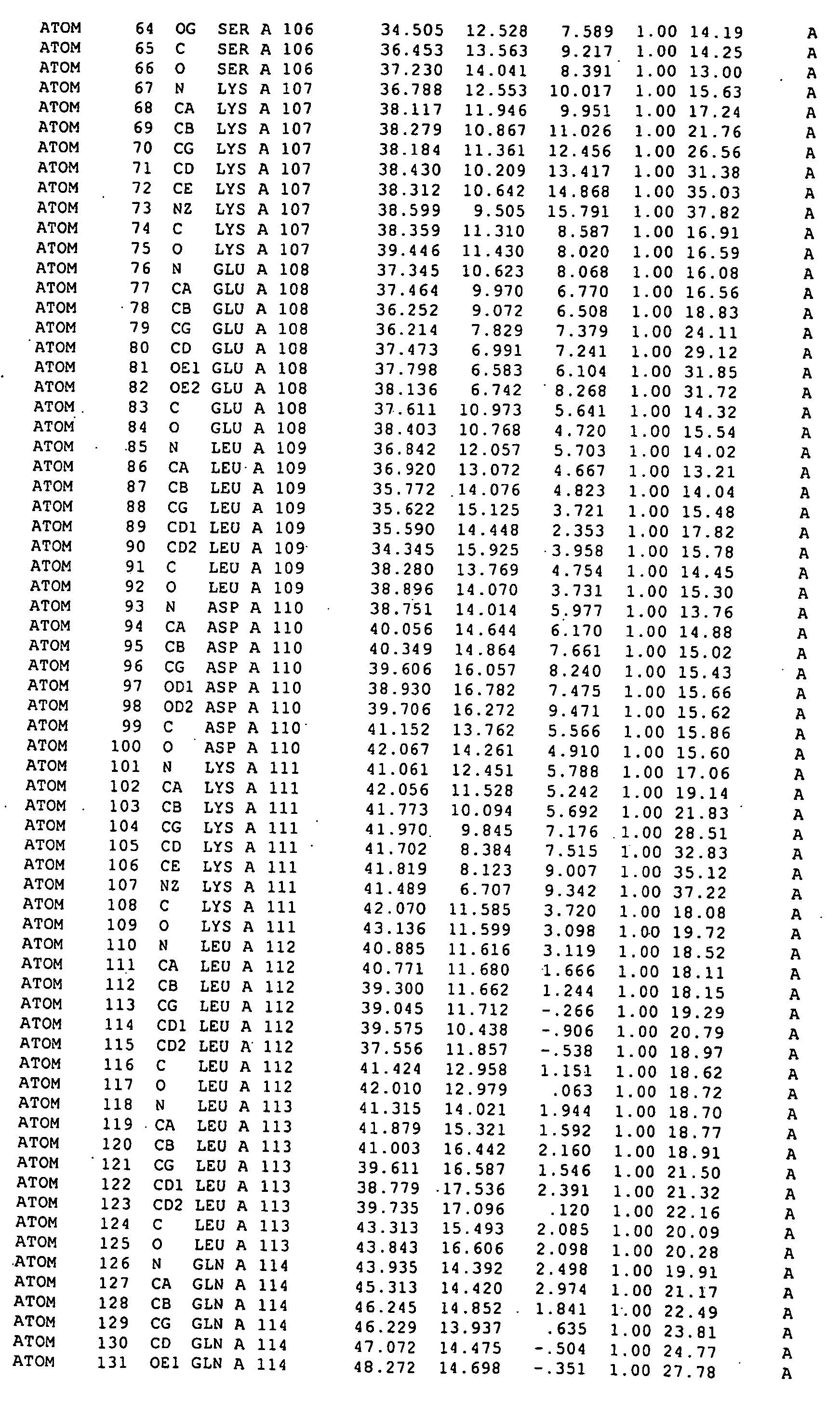
Polypeptide methods and means
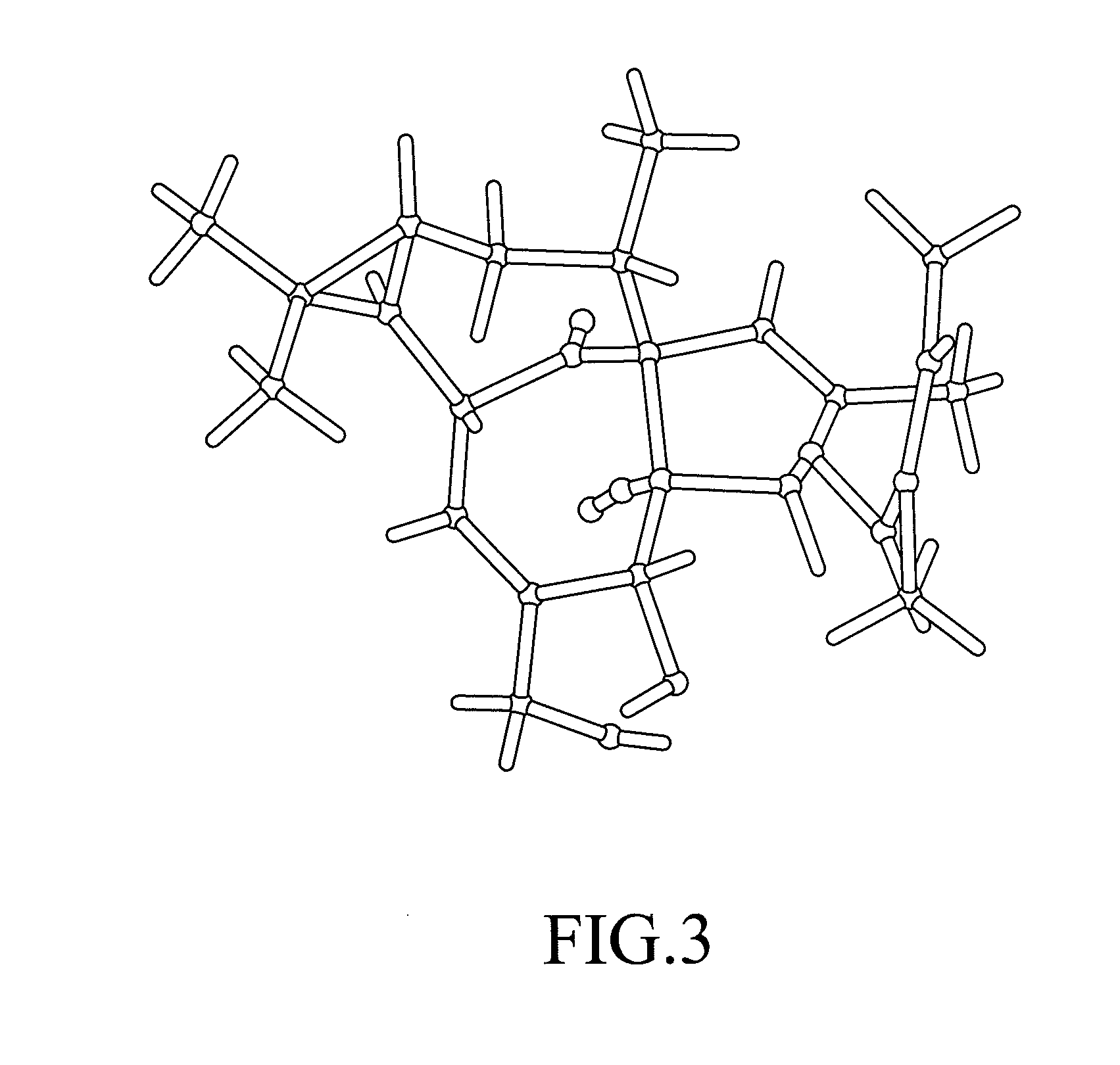
The structure of a RAD51-BRC repeat sequence complex structure is provided. The structure can be used in modelling the interaction of molecular structures such as potential pharmaceutical compounds. Mutant RAD51 and BRCA2 polypeptides and RAD51-BRC repeat sequence chimaera proteins and are also provided. The mutants may be used in assays for finding compounds which interact with or form part of a RAD51 pathway, and the chimaeras can be used to form crystals which may be analysed by X-ray crystallography.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
Methods and compositions relating to anthrax pathogenesis
InactiveUS20080124746A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBacterial exotoxinFactor ii
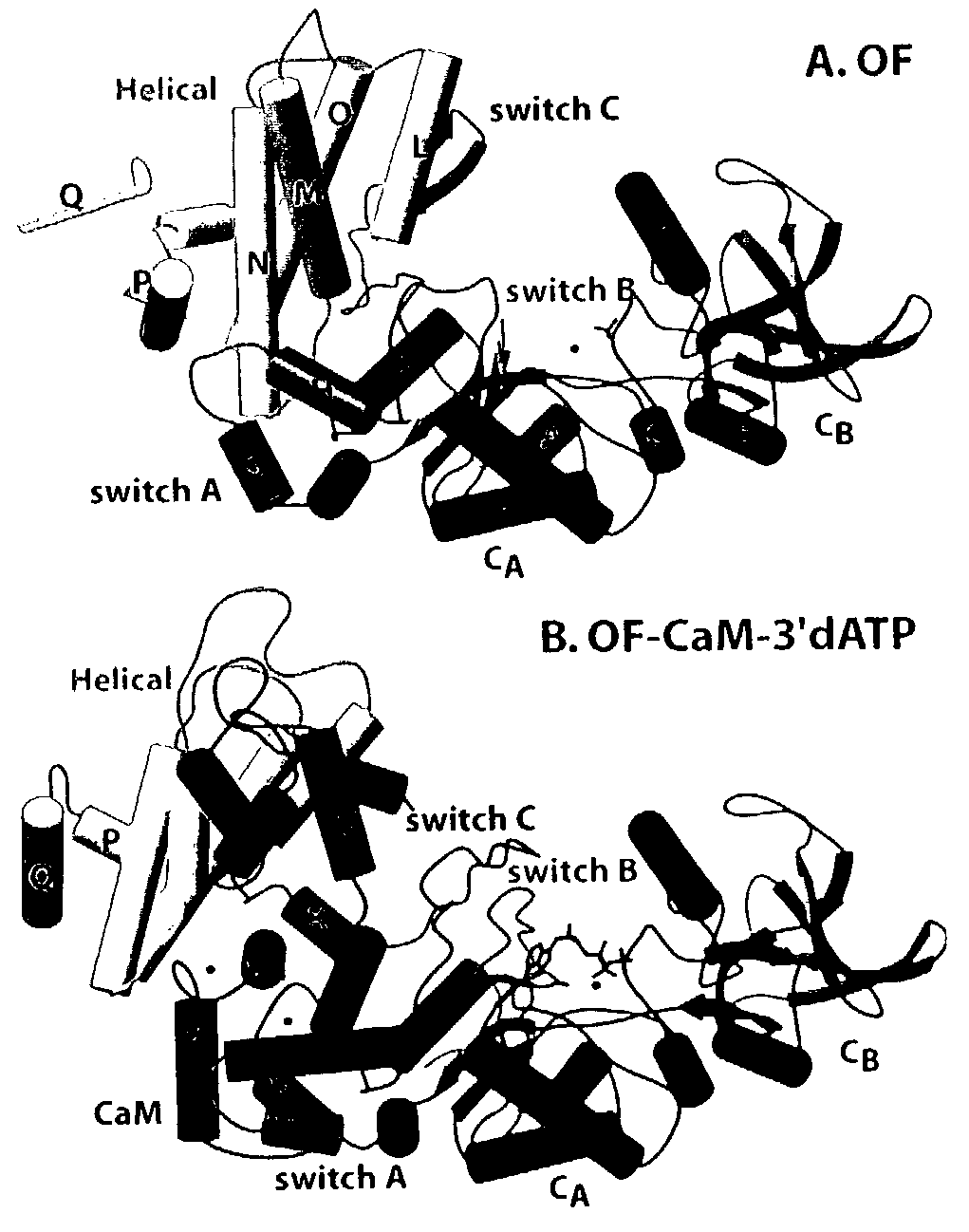
The structures of Edema Factor alone and Edema Factor bound to calmodulin without substrate has been crystallized and its structure determined by x-ray crystallography. Based upon these crystal structures, a method assaying for inhibitors of infection by a bacteria is presented which comprises obtaining a potential inhibitor, obtaining a calmodulin activated adenylyl cyclase exotoxin, obtaining calmodulin, admixing the potential inhibitor, the exotoxin, and the calmodulin, and assaying to determine whether or not the potential inhibitor inhibits production of cAMP by exotoxin.
Owner:BOSTON BIOMEDICAL RES INST +1
Crystalline ingenol mebutate
The present invention relates to a novel crystalline form of ingenol mebutate, methods of preparation thereof, and to its use. More specifically, the invention relates to the conversion of amorphous ingenol mebutate (ingenol-3-angelate, PEP005) to a crystalline form, which was characterized by single crystal X-Ray crystallography (XRC), attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared (FTIR-ATR) spectroscopy and Differential Scanning calorimetry (DSC).
Owner:LEO LAB
Methods and compositions relating to anthrax pathogenesis
InactiveUS7462472B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAdenylyl cyclaseFactor ii
Owner:BOSTON BIOMEDICAL RES INST +1
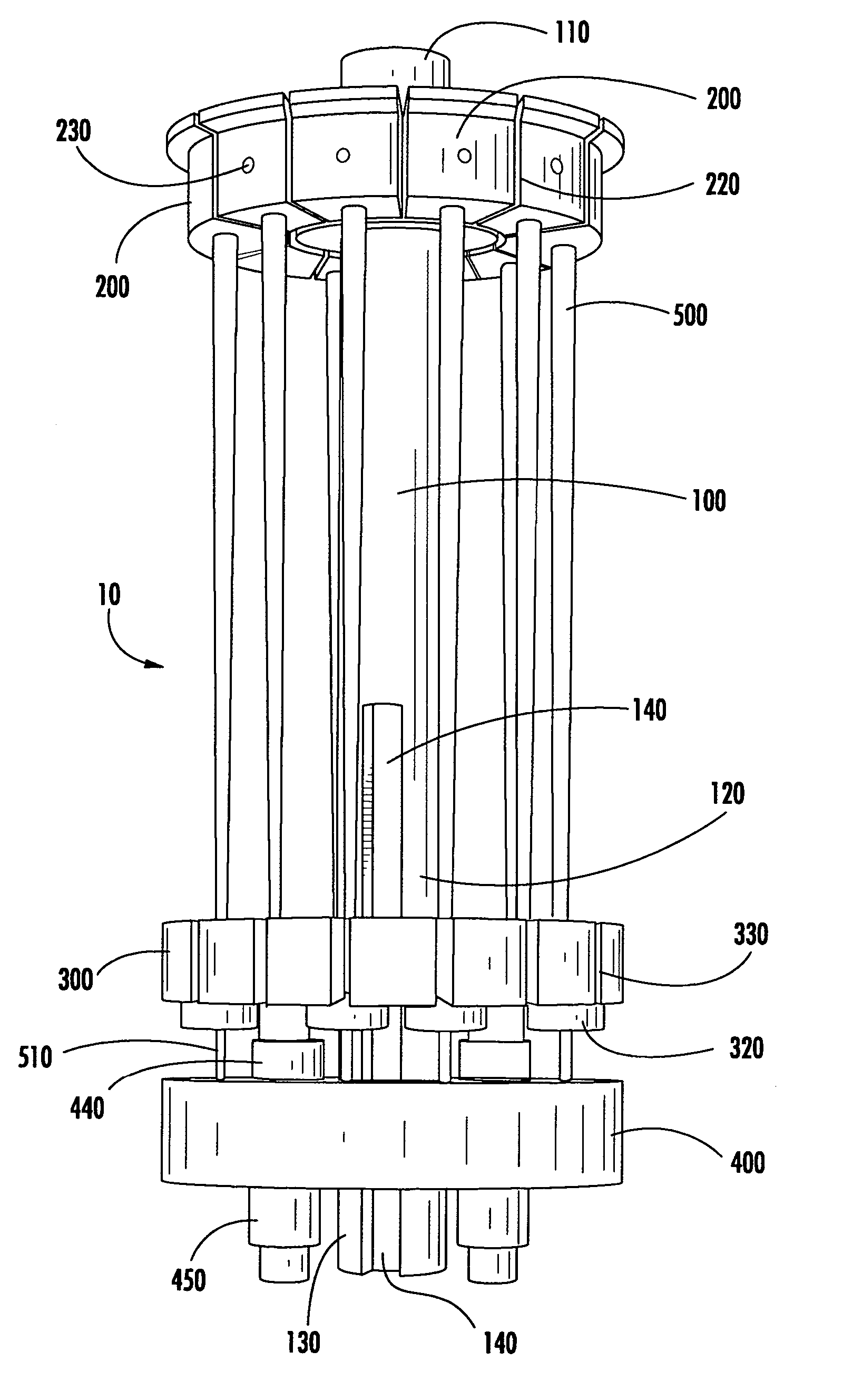
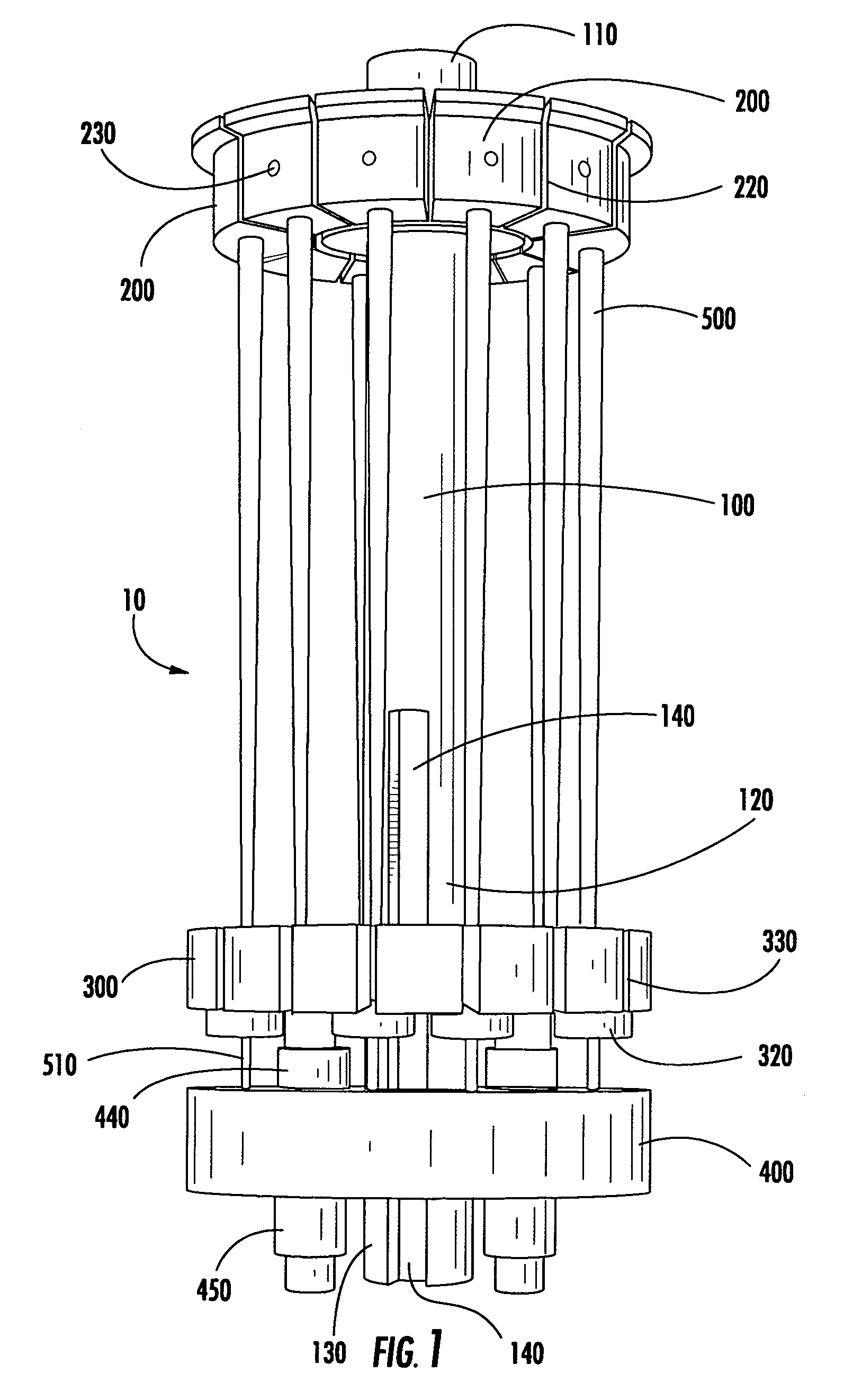
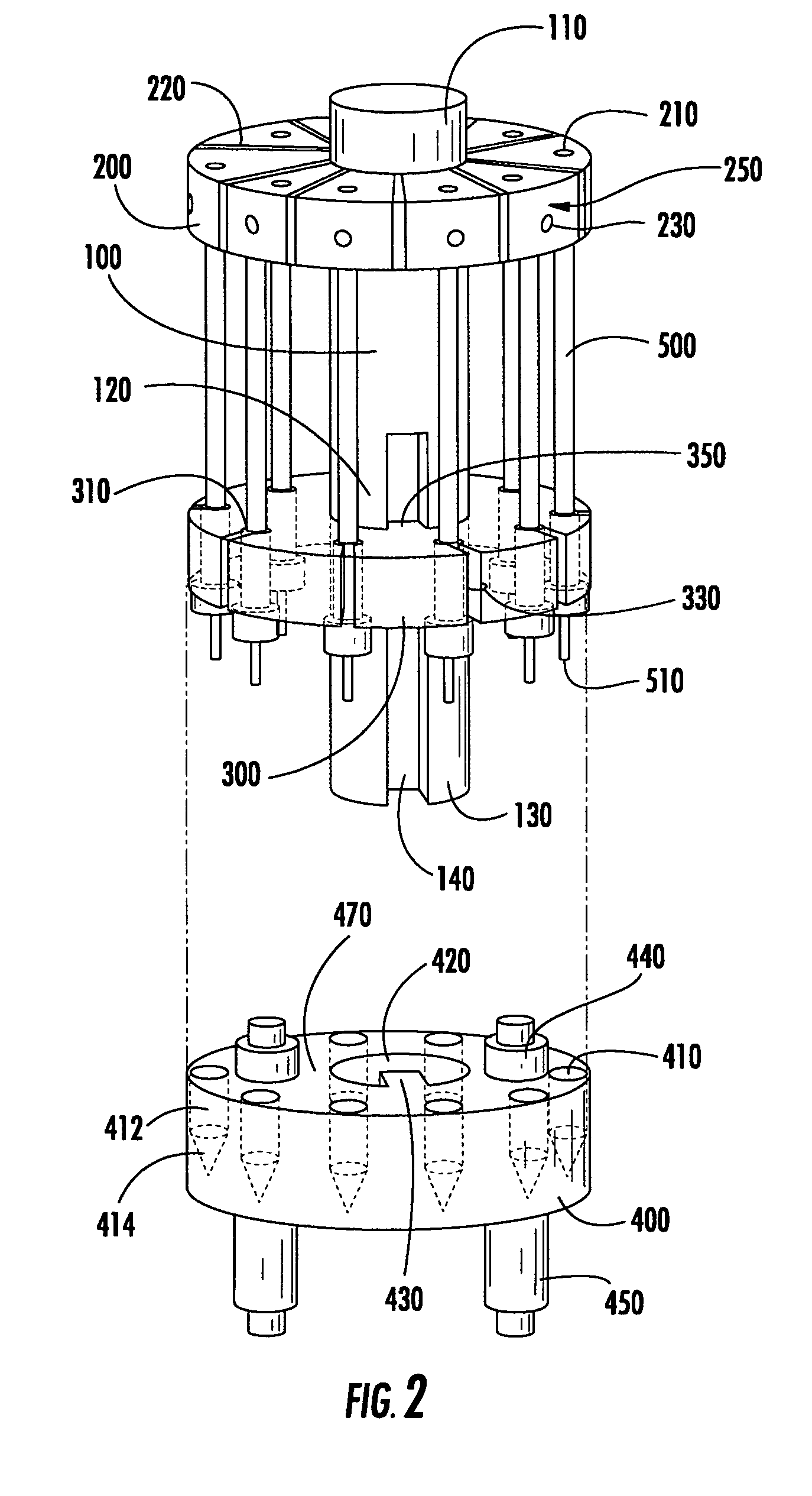
Modular specimen holders for high pressure freezing and x-ray crystallography of a specimen
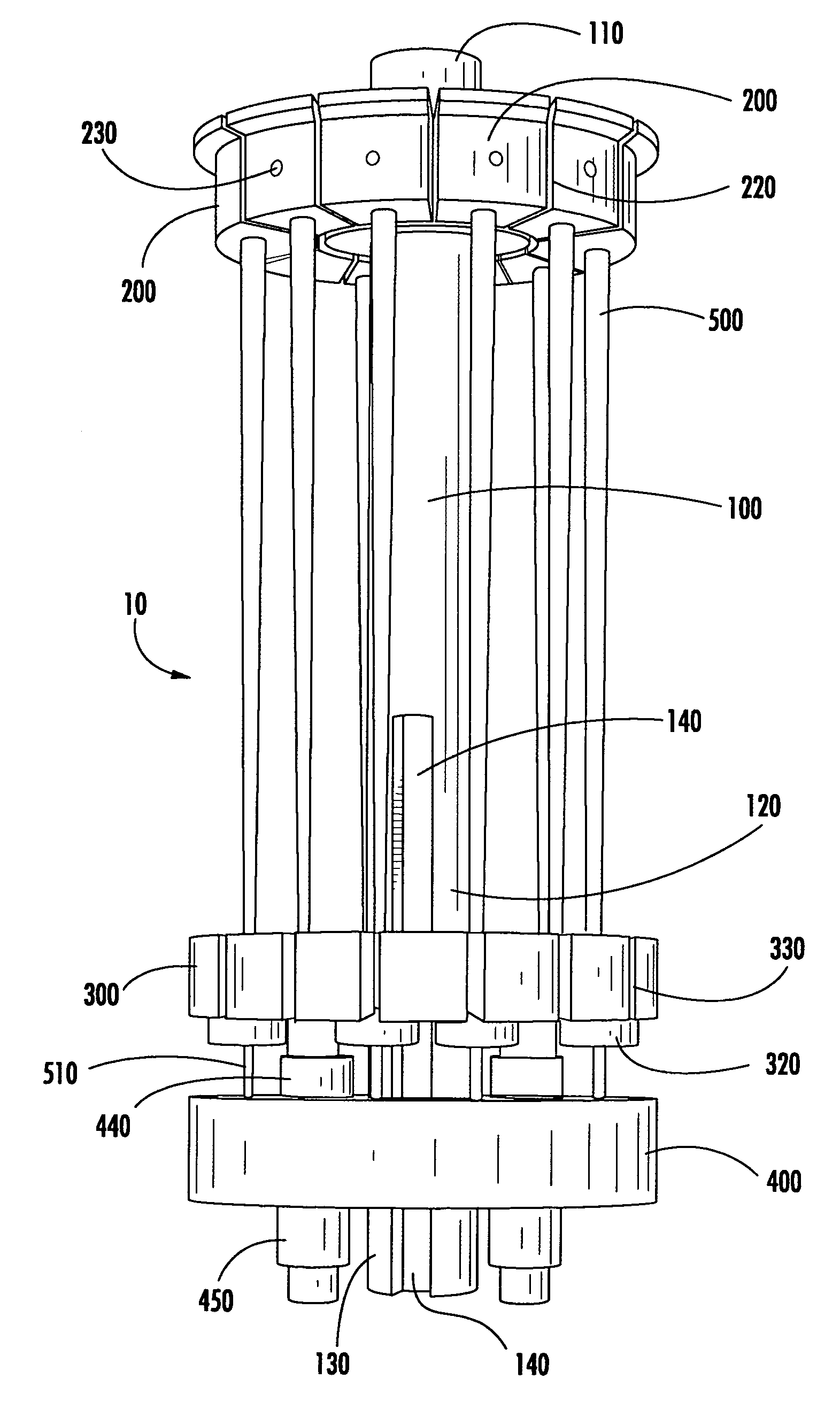
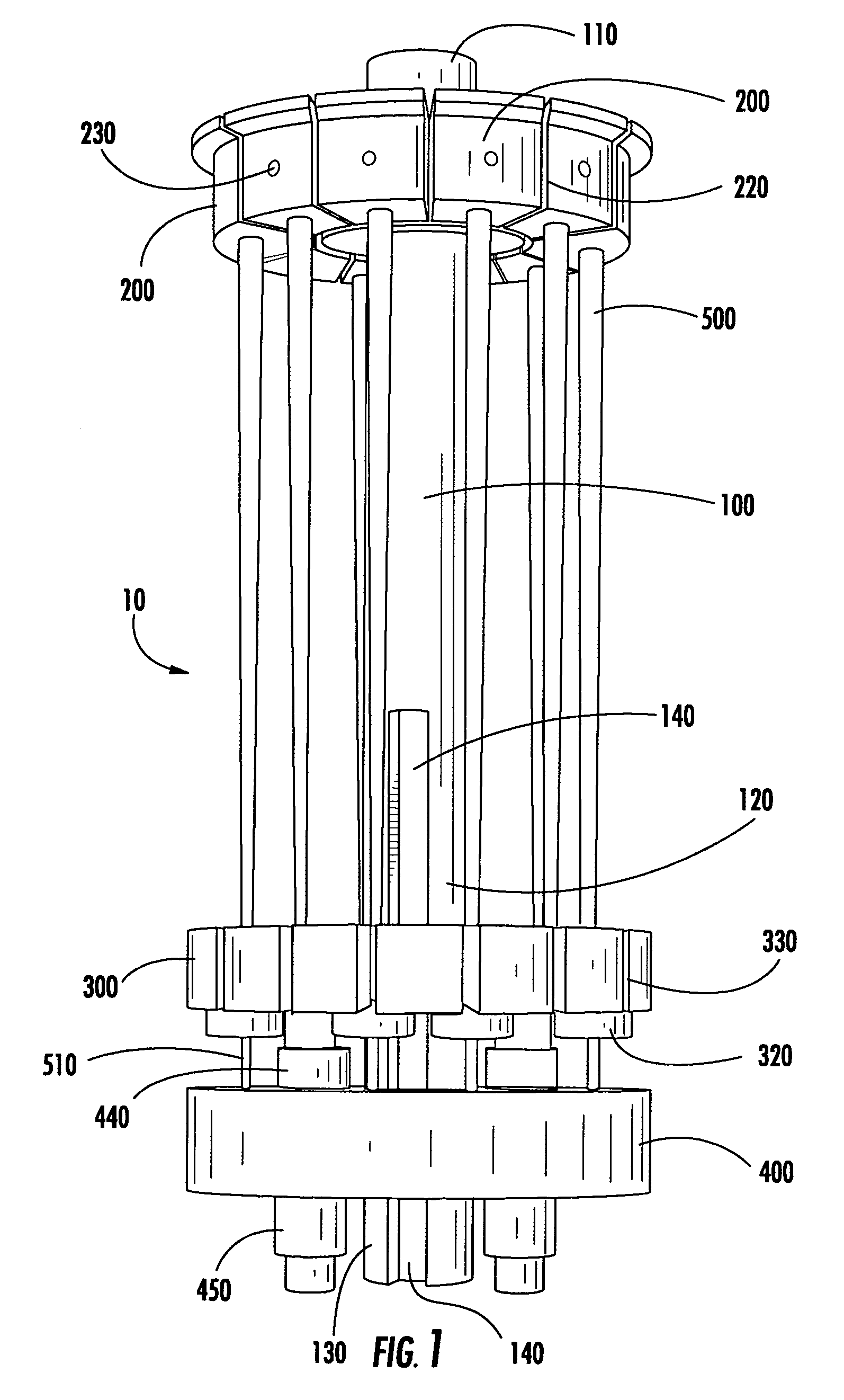
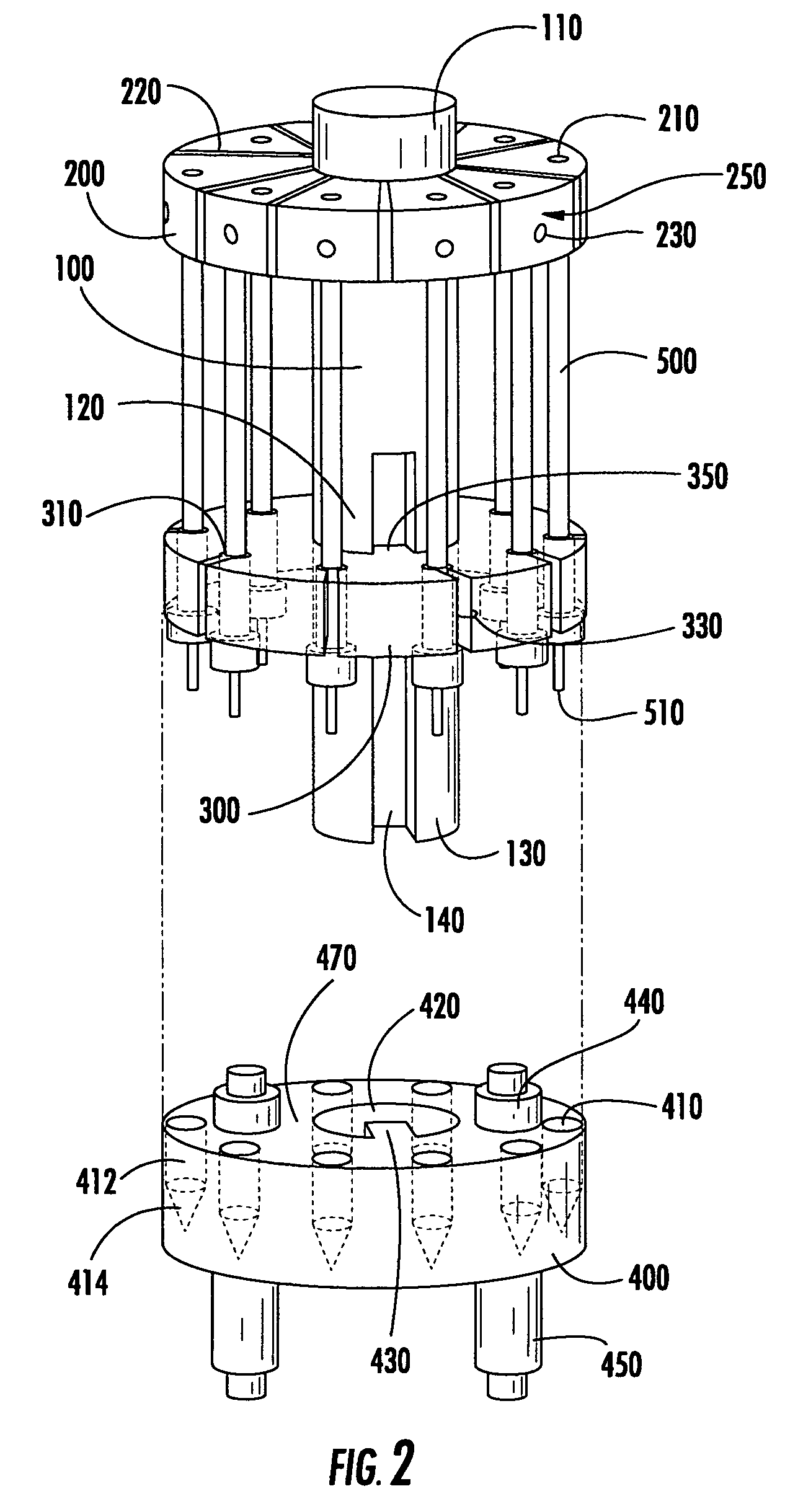
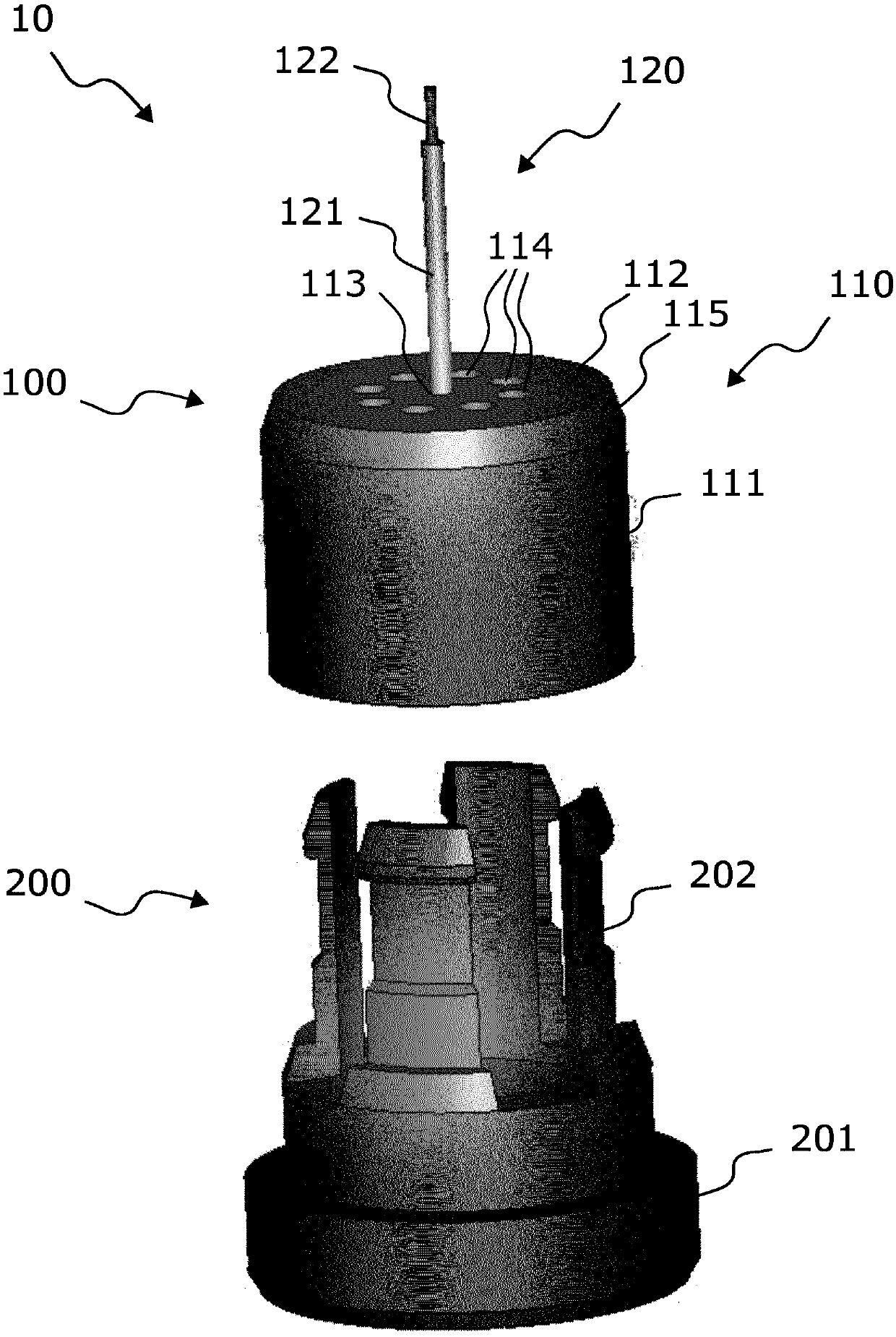
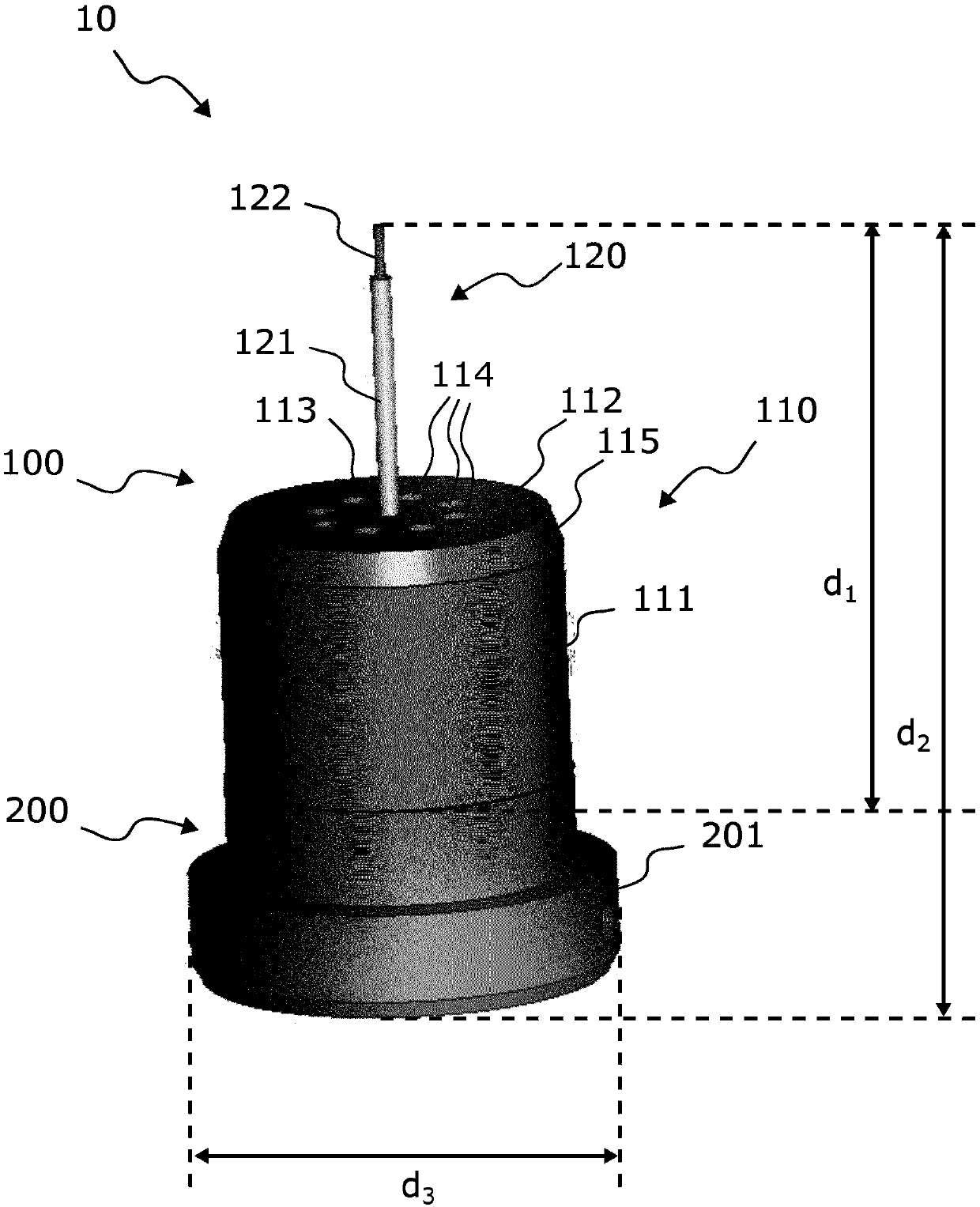
ActiveCN109642880APreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionHigh pressure freezingHigh pressure
The present invention relates to modular specimen holder (10') for high pressure freezing and / or X-ray crystallography of a specimen comprising a specimen holding element (100') and an extension element (200') connectable with each other and separable from each other; the specimen holding element (100') comprising a tubule (120') and a base element (110'), wherein the tubule (120') is adapted to hold the specimen, the base element (110') is adapted to hold the tubule (120'), wherein a distance from a bottom of the base element (110') to a top of the tubule (120') is a distance d1; the extension element (200') being adapted to be connected with the base element (110'), wherein, when the extension element (200'} and the base element (110') are connected with each other, a distance from a bottom of the extension element (200') to the top of the tubule (120') is a second distance d2; wherein the second distance d2 is larger than the first distance d1.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS GMBH
Novel methods for high efficiency and rapid getting fine three dimensional structure of target protein composite body and target molecule target molecule
ActiveCN101063682AReduce separation and purification stepsImprove bindingPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionNatural productActive component
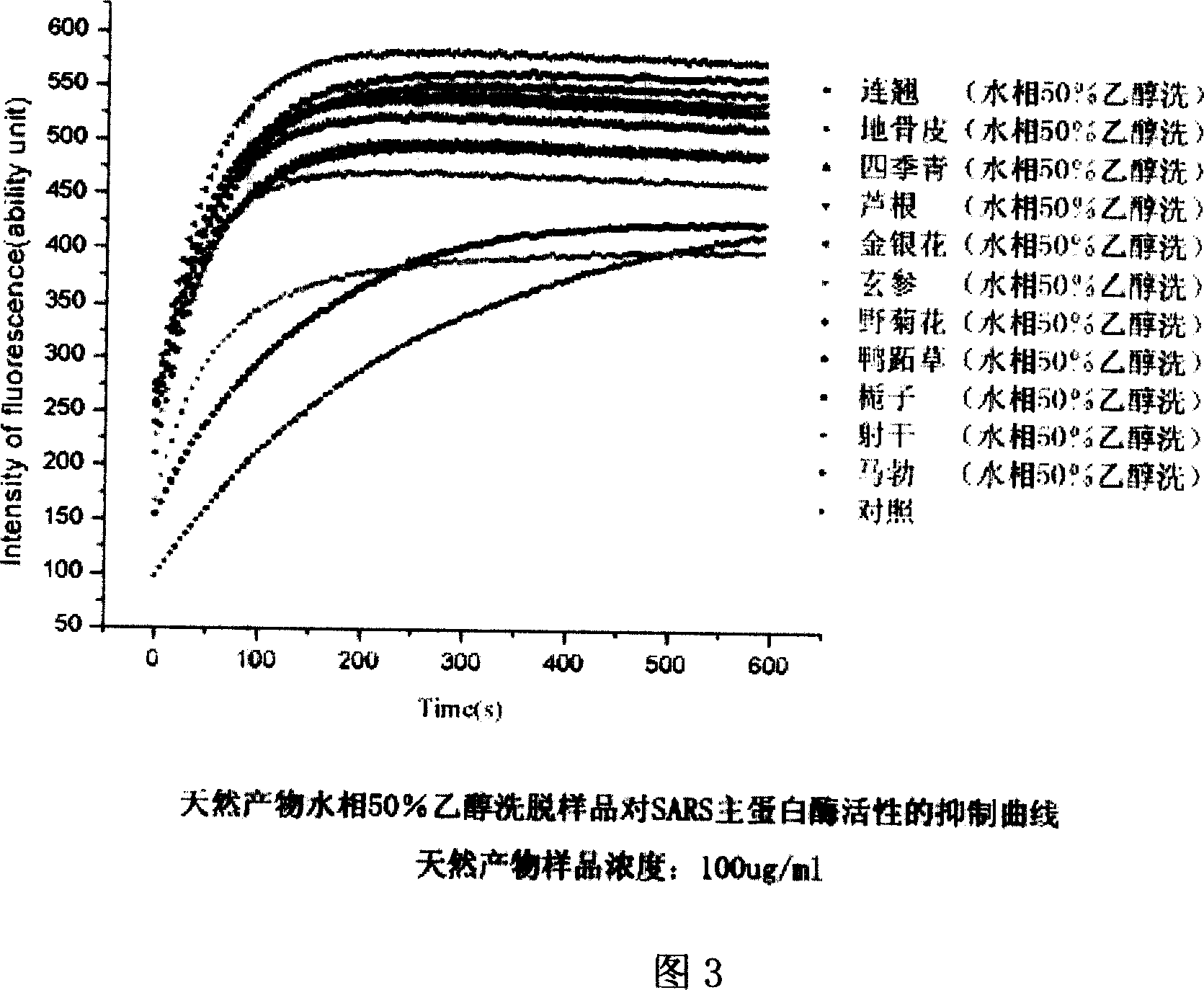
This invention provides one effective and rapid method to extract target molecule and target compound find three dimensional structure from Chinese medicine product, which uses target protein transistor stricture as base and uses X ray transistor means to filter the product for active component and for study from one new respective.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +2
AI-2 compounds and analogs based on Salmonella typhimurium LsrB structure
This invention relates to crystals comprising apo-LsrB and holo-LsrB. The structure of holo-LsrB identifies a tetrahydroxytetrahydrofuran derived from 4,5-dihydroxy-2,3-pentanedione (DPD) as the active autoinducer-2 (AI-2) molecule in Salmonella typhimurium. The X-ray crystallographic data can be used in a drug discovery method. Additionally the invention provides AI-2 analogs based on this discovery as well as pharmaceutical compositions containing those analogs.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Crystallization cassette for the growth and analysis of macromolecular crystals and an associated method
InactiveUS20050045094A1Increase opportunitiesPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsDiffusion methodsX-ray
The invention is a crystallization cassette and associated method for growing and analyzing macromolecular crystals in situ by X-ray crystallography. The cassette allows proteins (as well as other macromolecules) to be crystallized by the counter-diffusion method in a restricted geometry. Using this procedure, crystals can be adequately prepared for direct X-ray data analysis such that the protein's three-dimesional structure can be solved without crystal manipulation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com