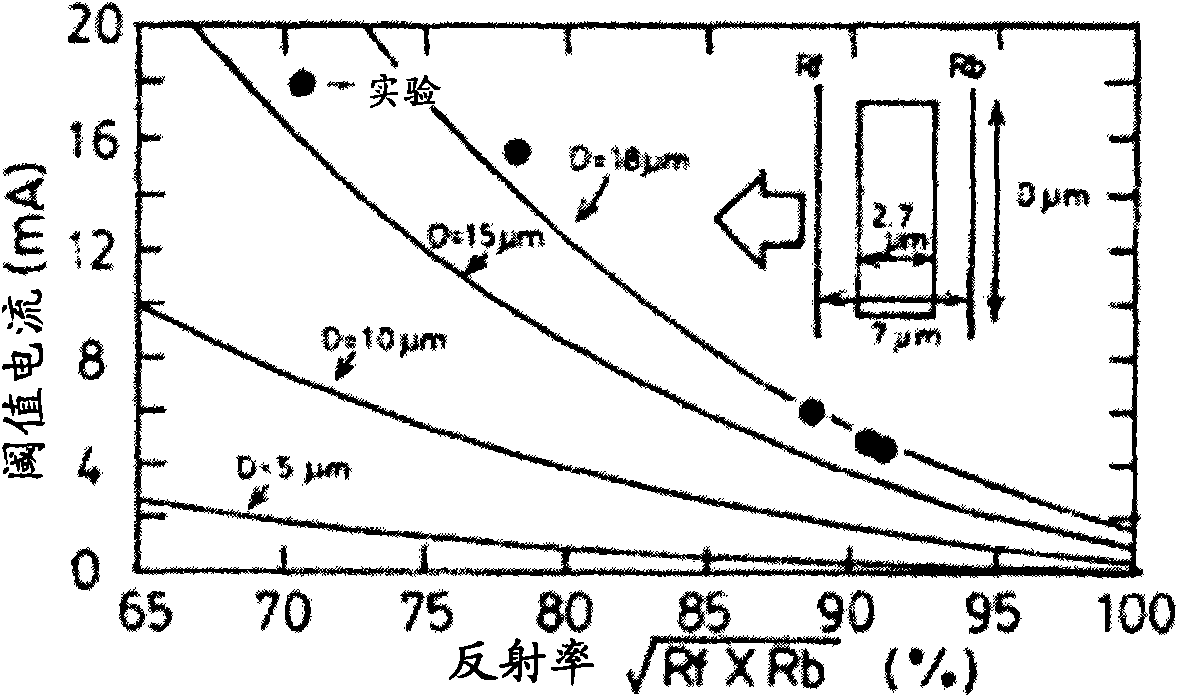
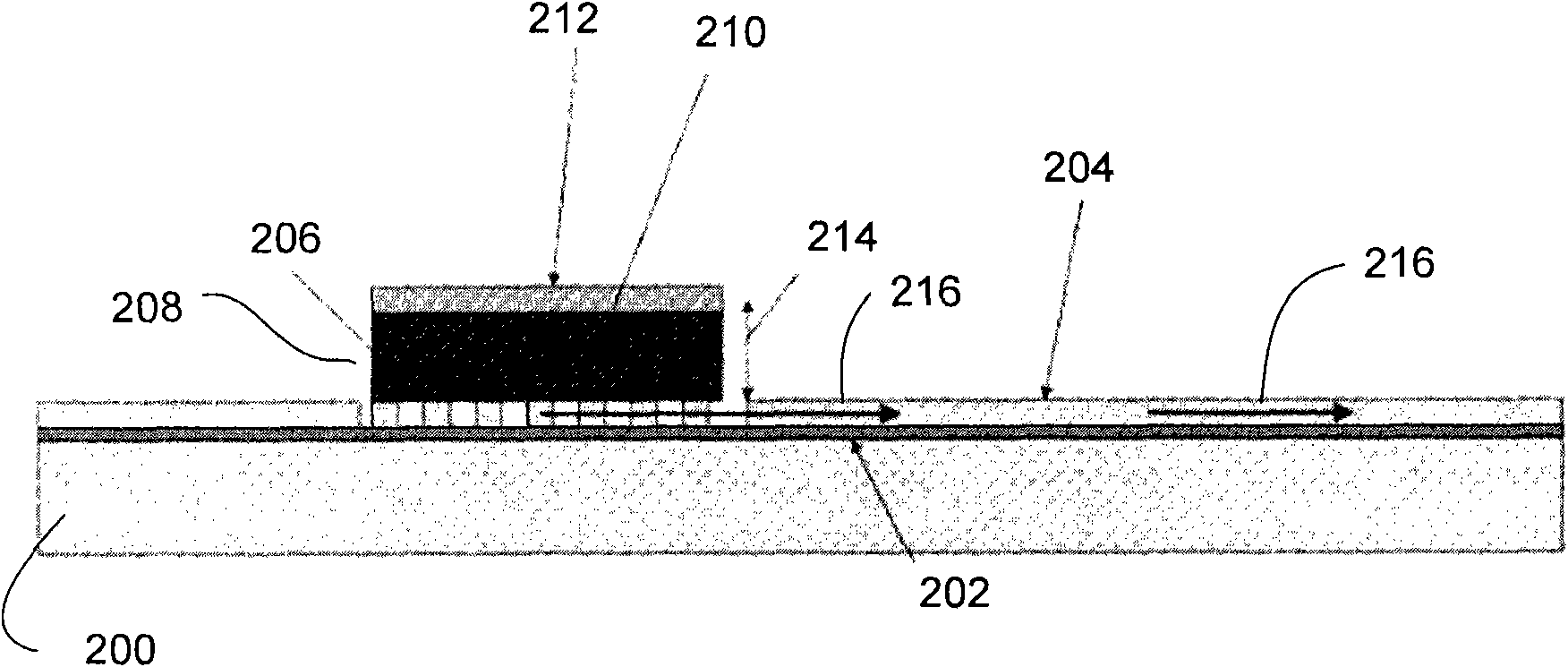
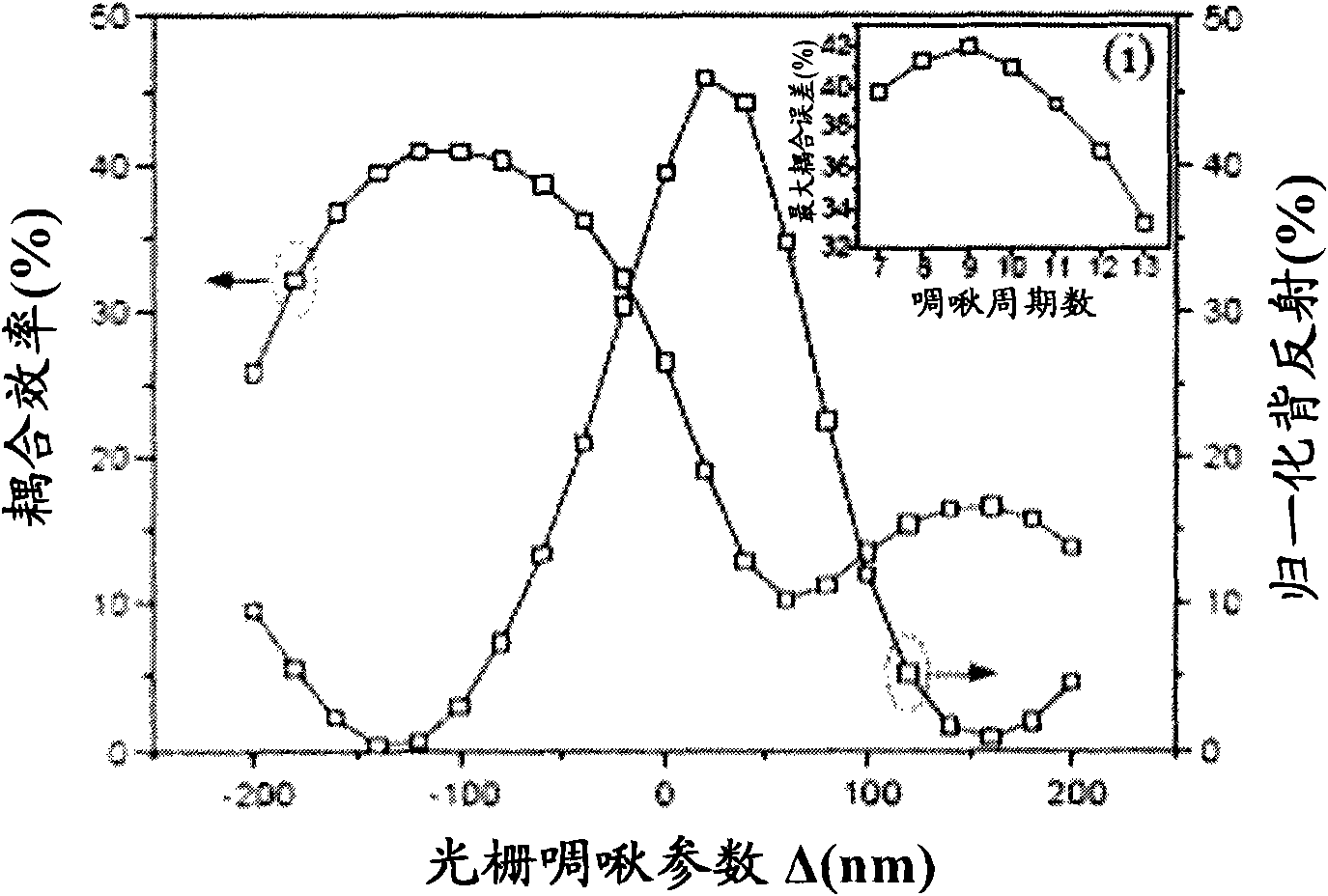
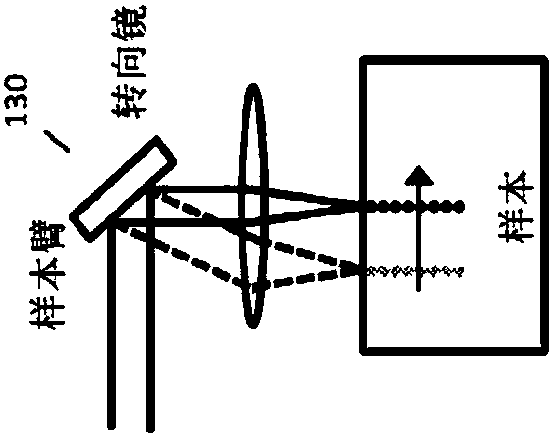
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Vertical cavity lasers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
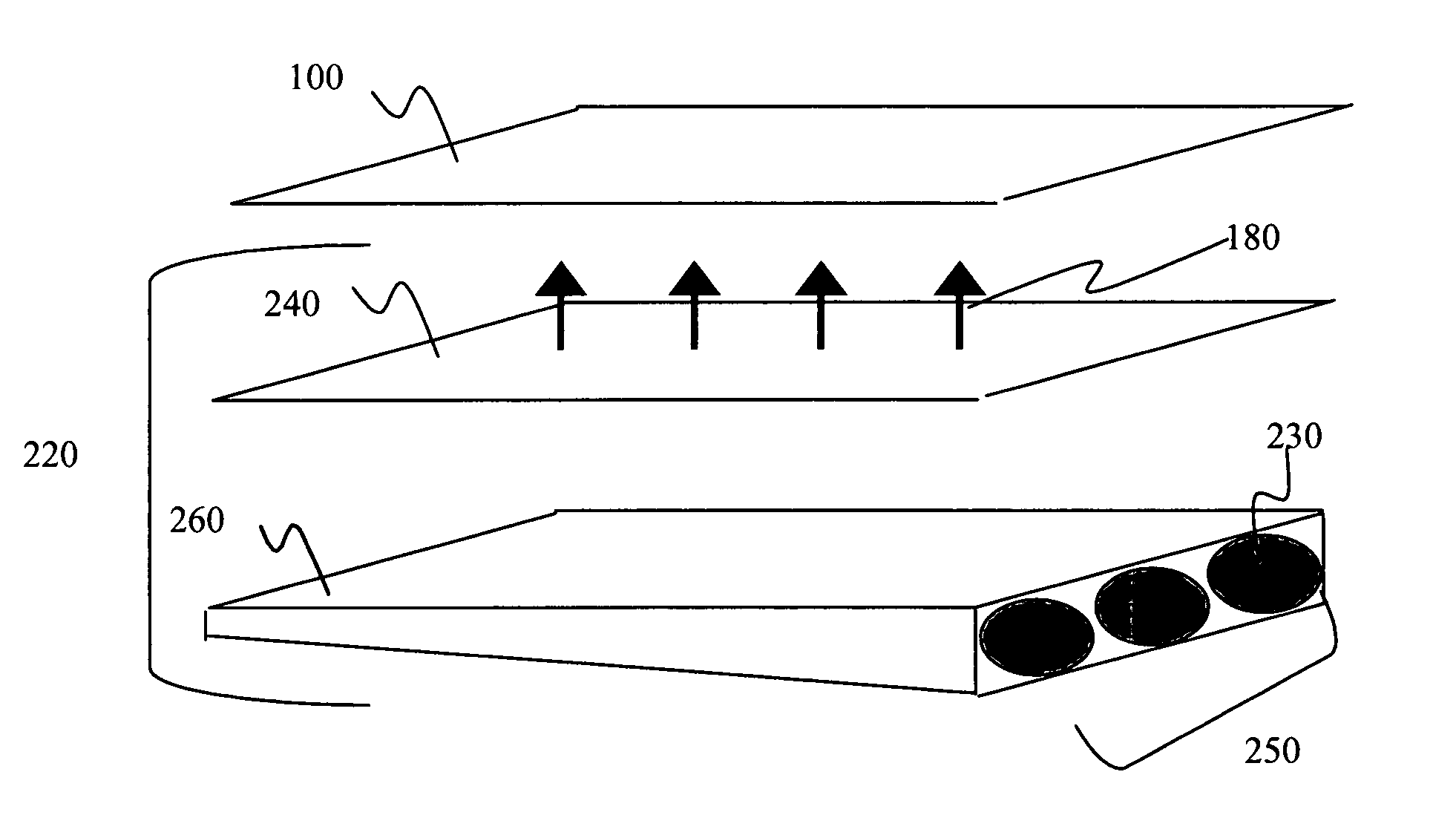
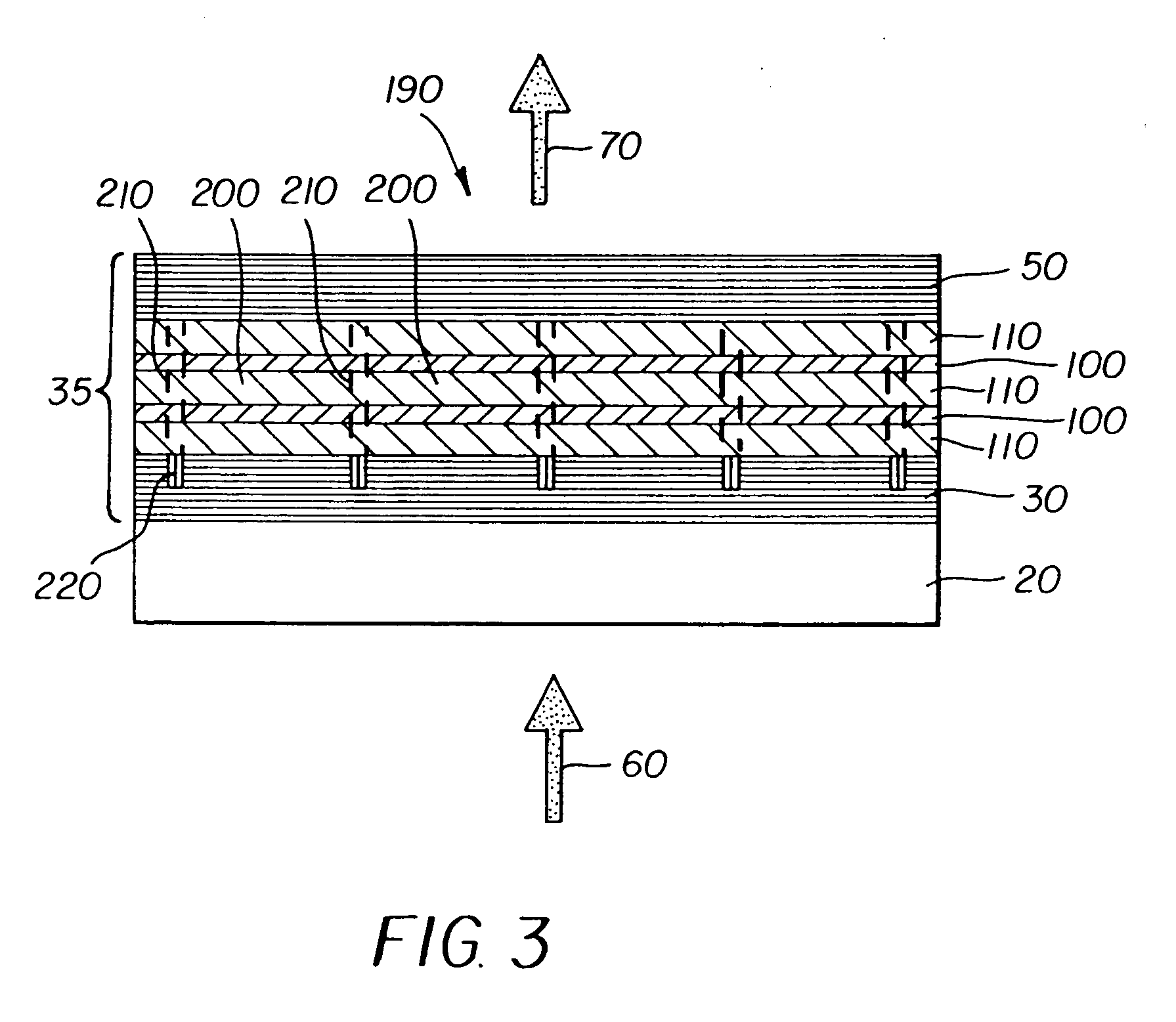
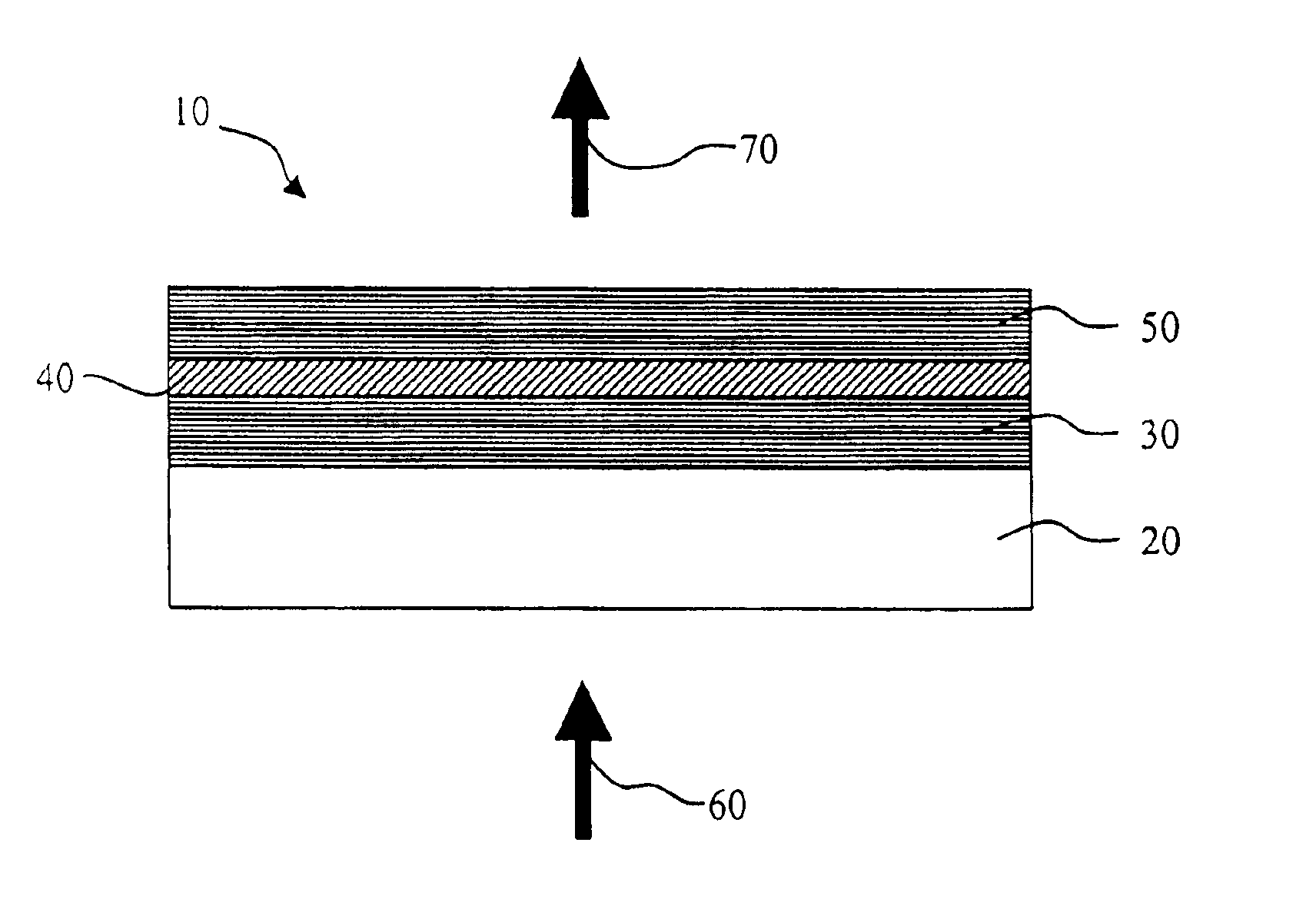
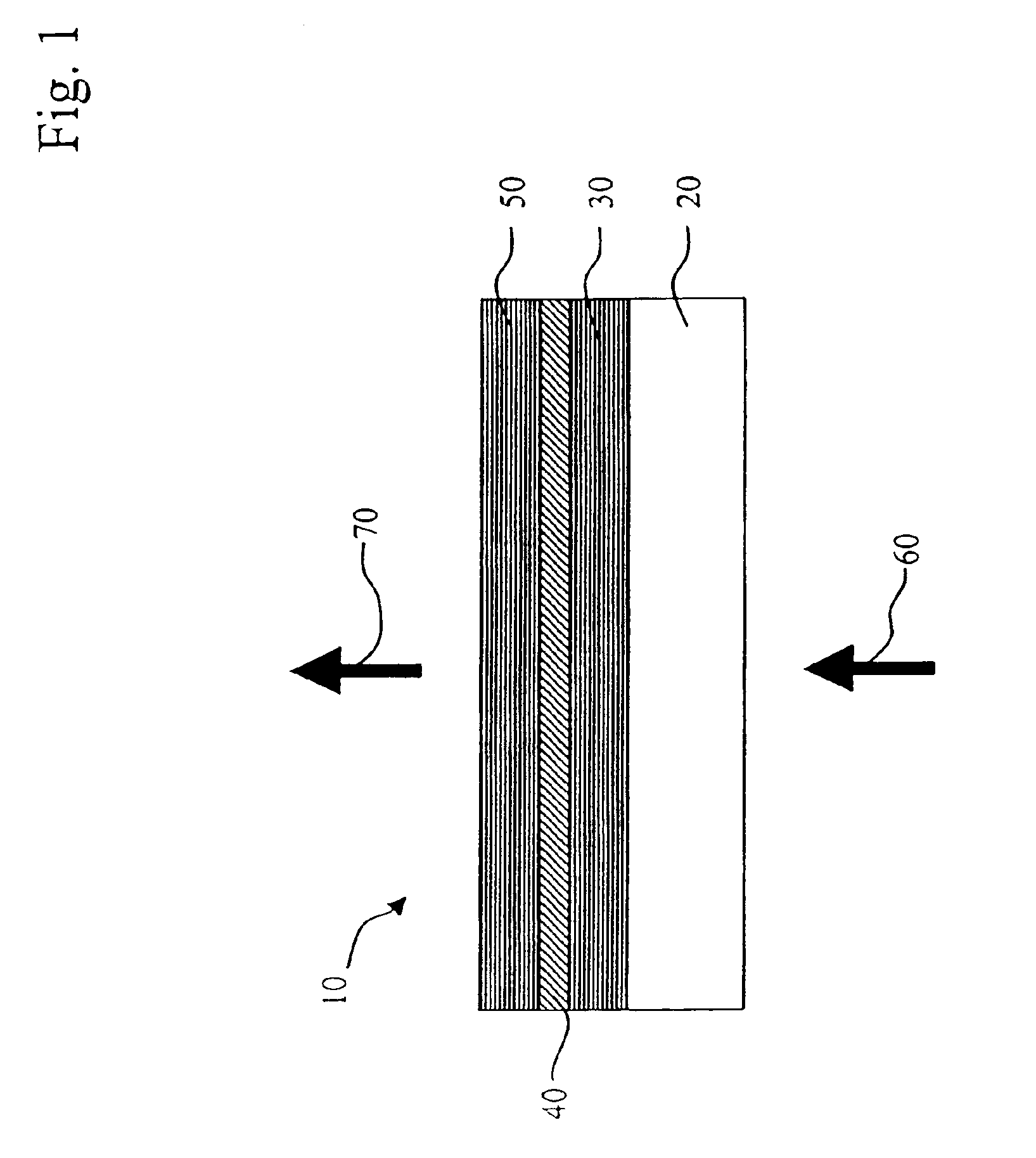
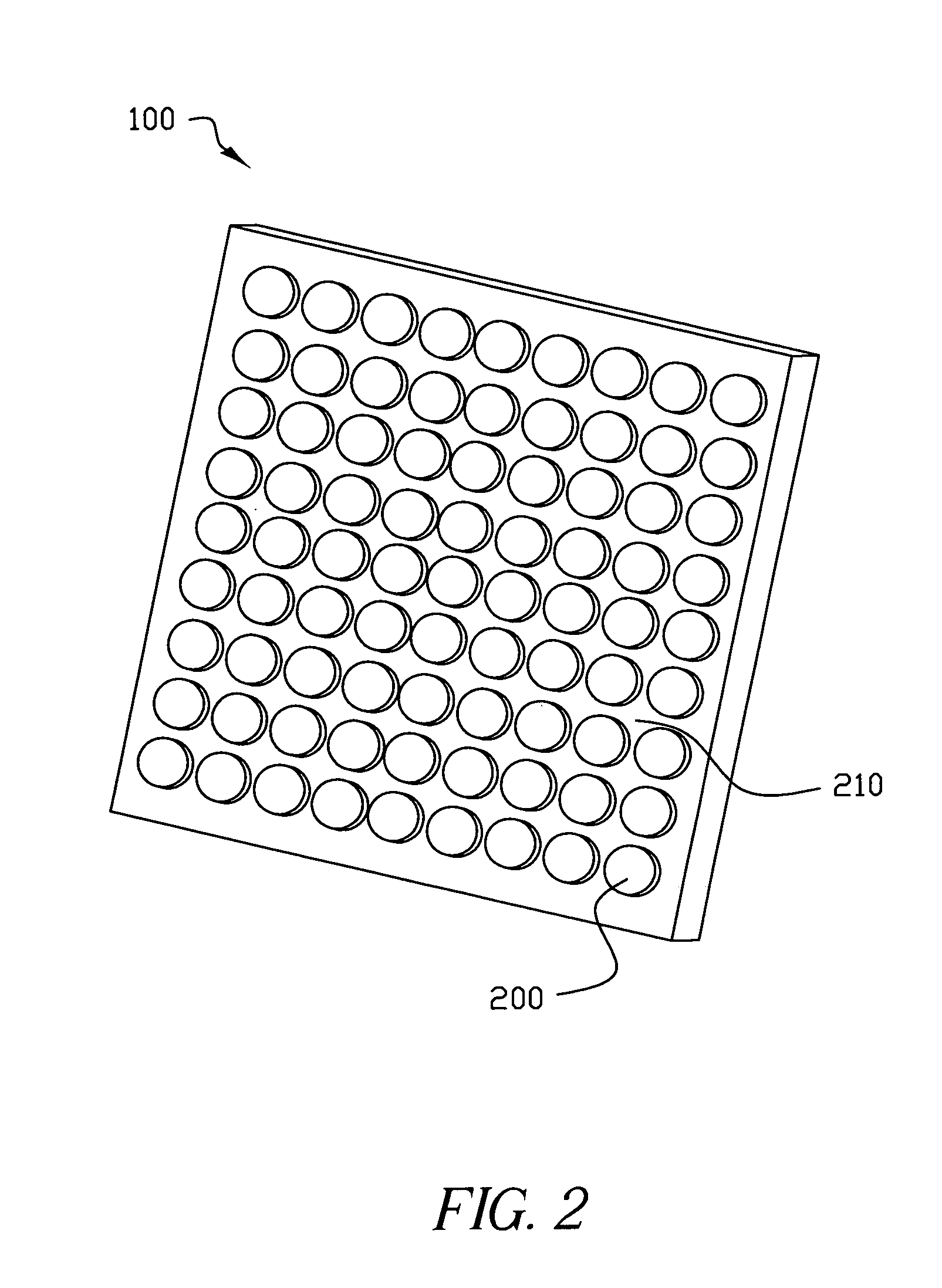
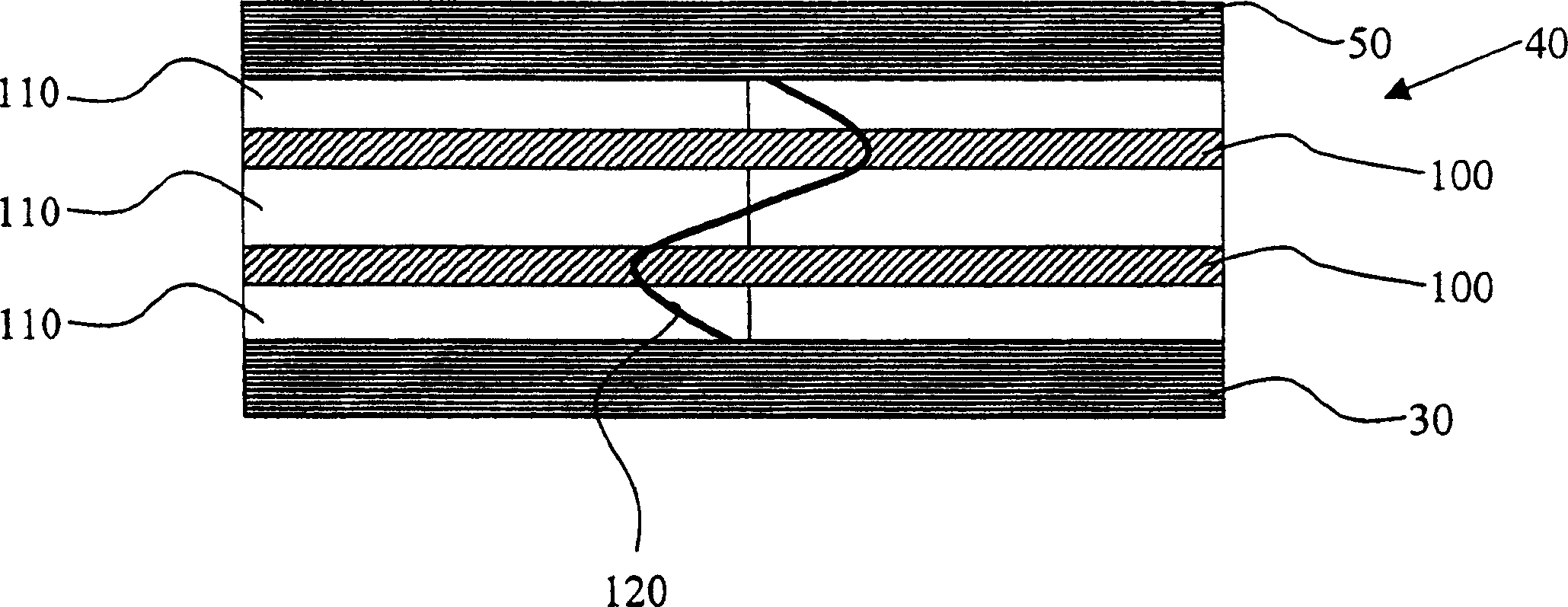
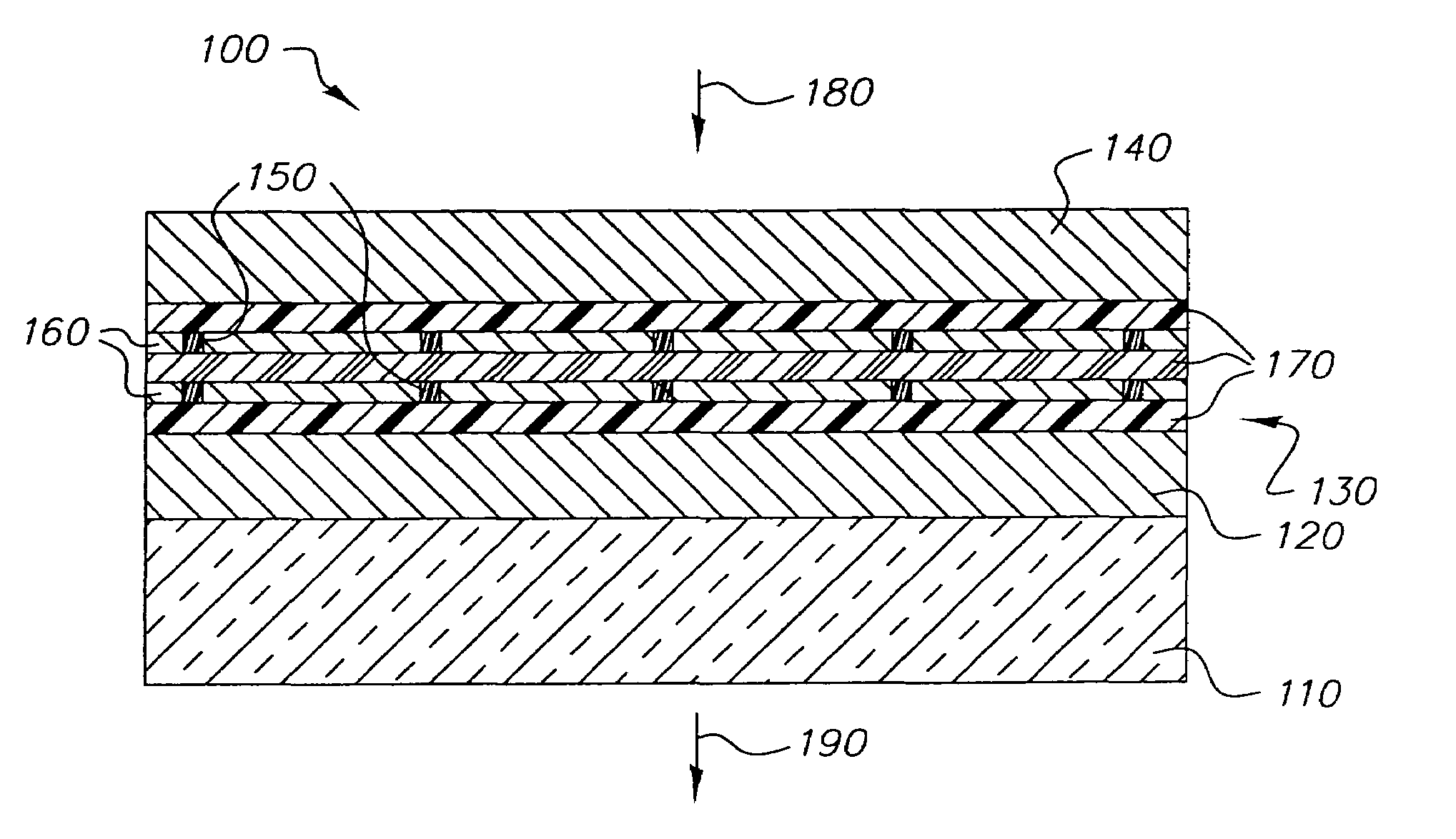
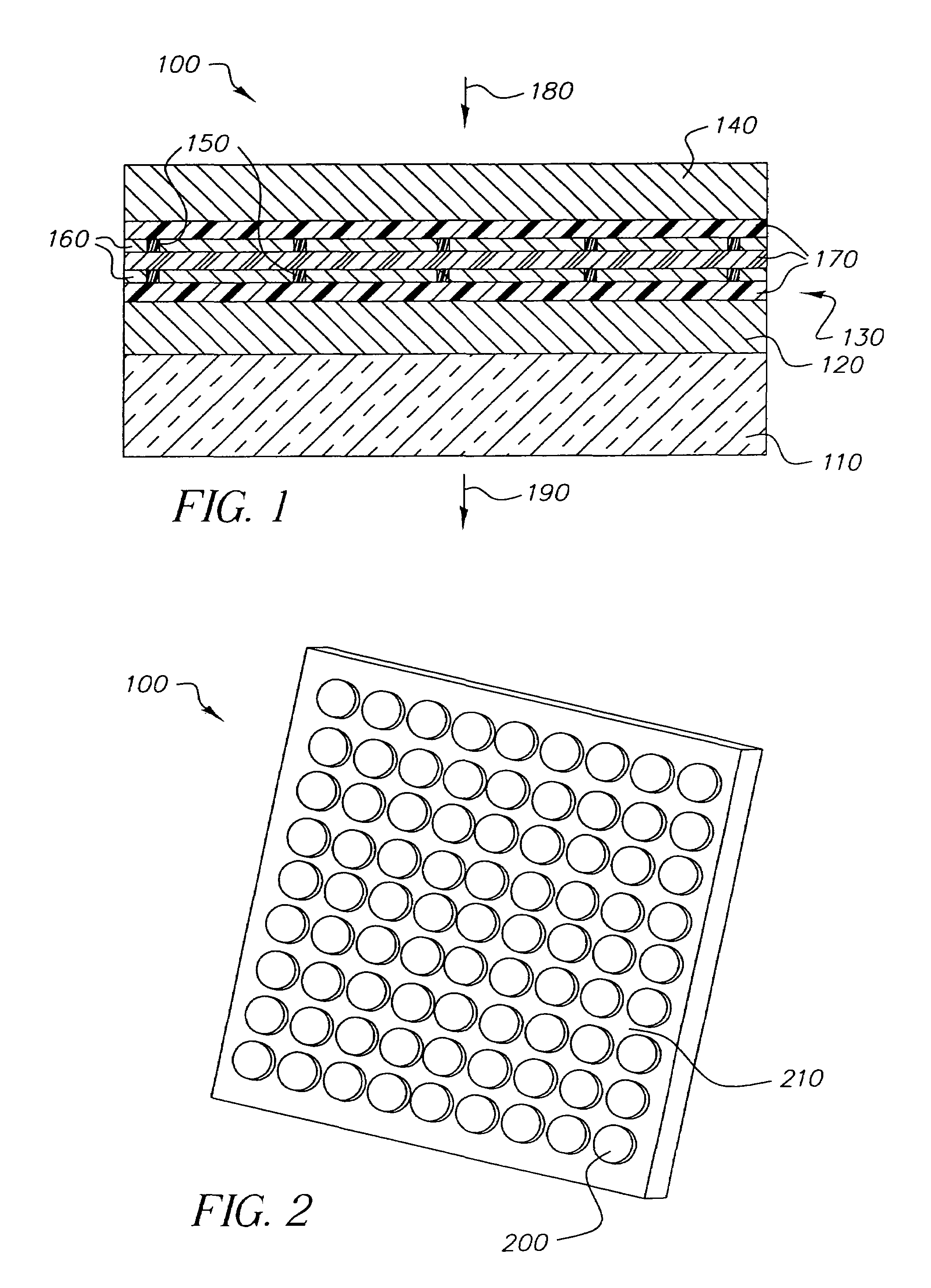
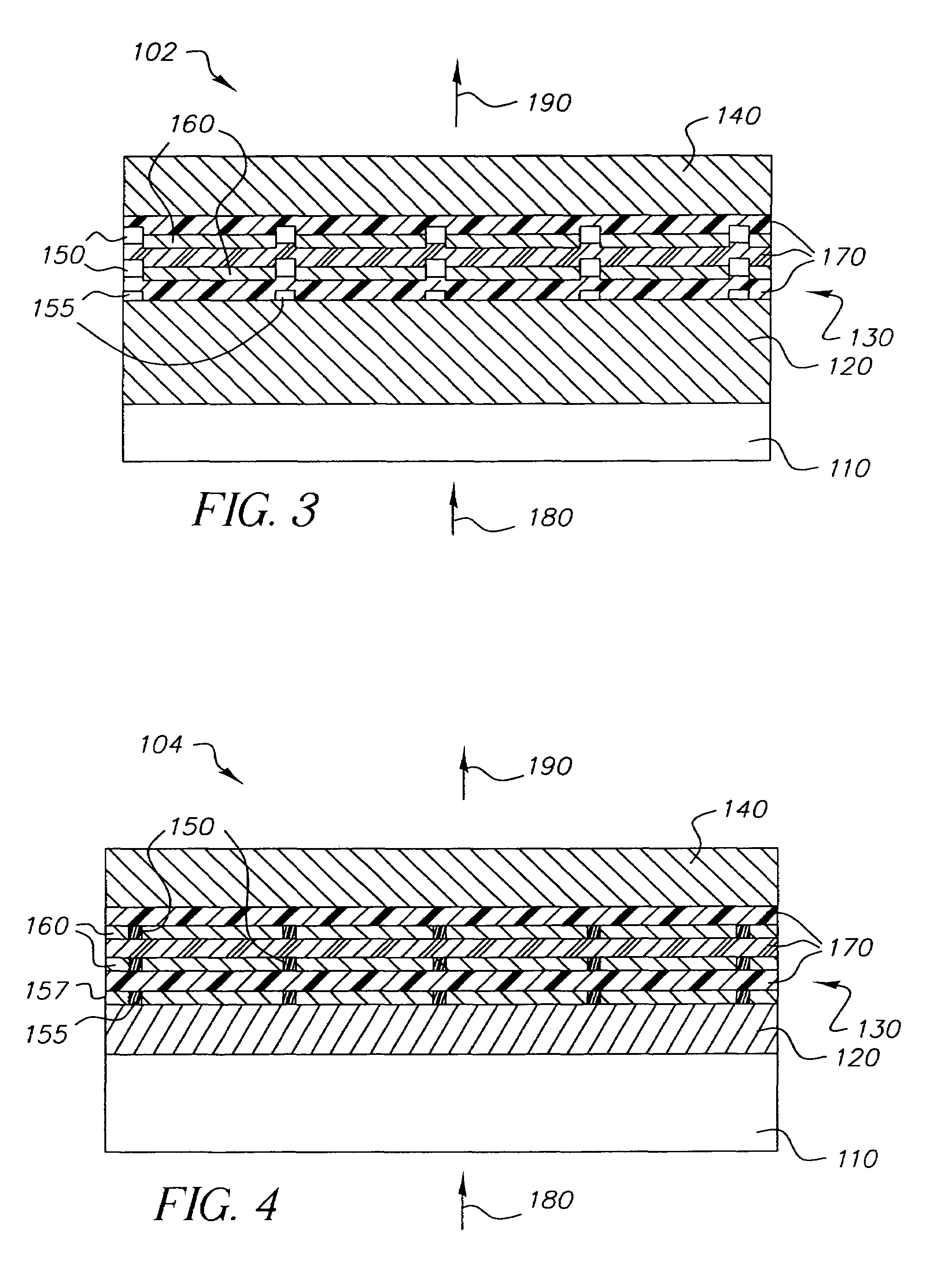
Display device using vertical cavity laser arrays
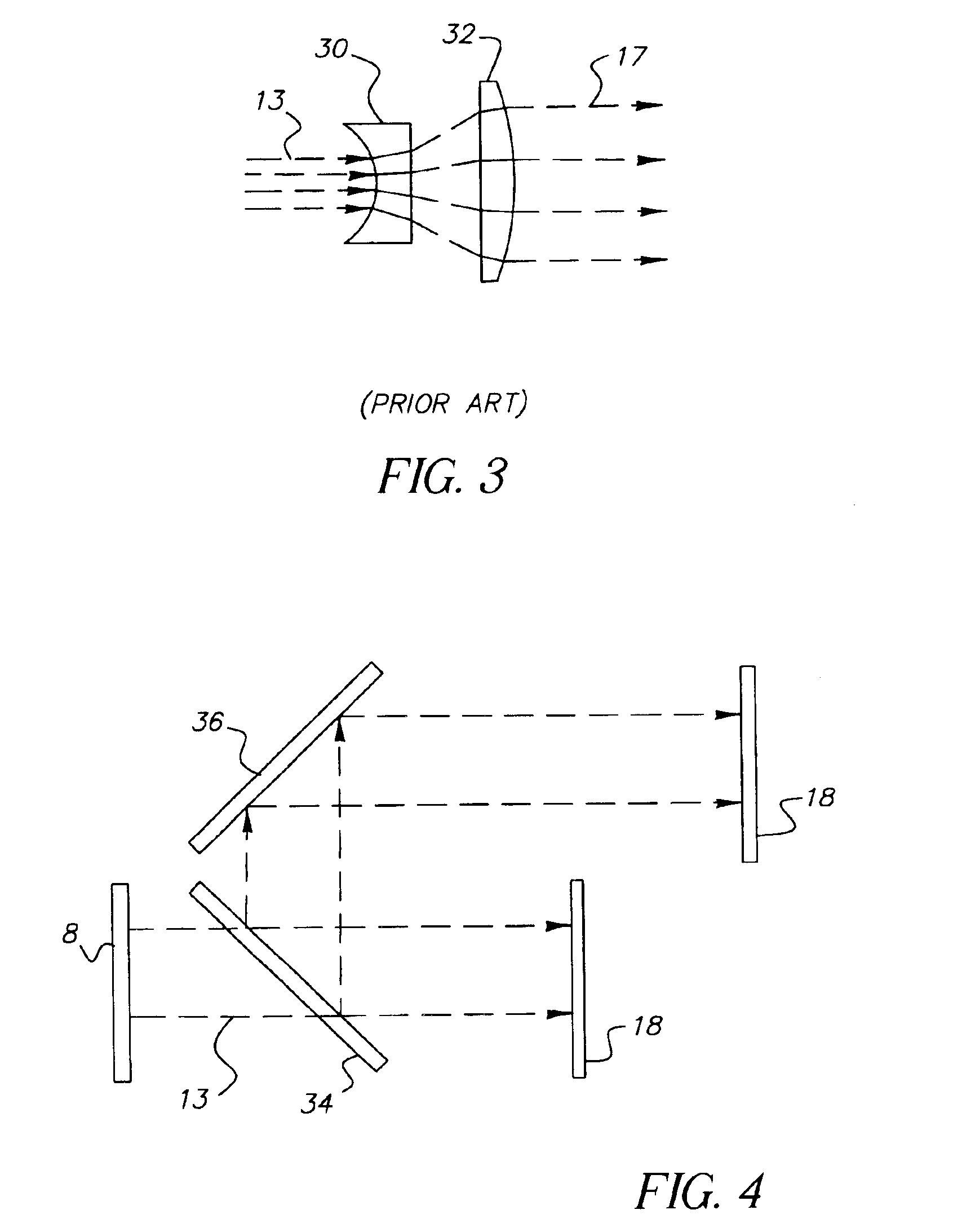
InactiveUS20050275615A1Reduced divergence angleProcess controlStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDielectricBeam expander
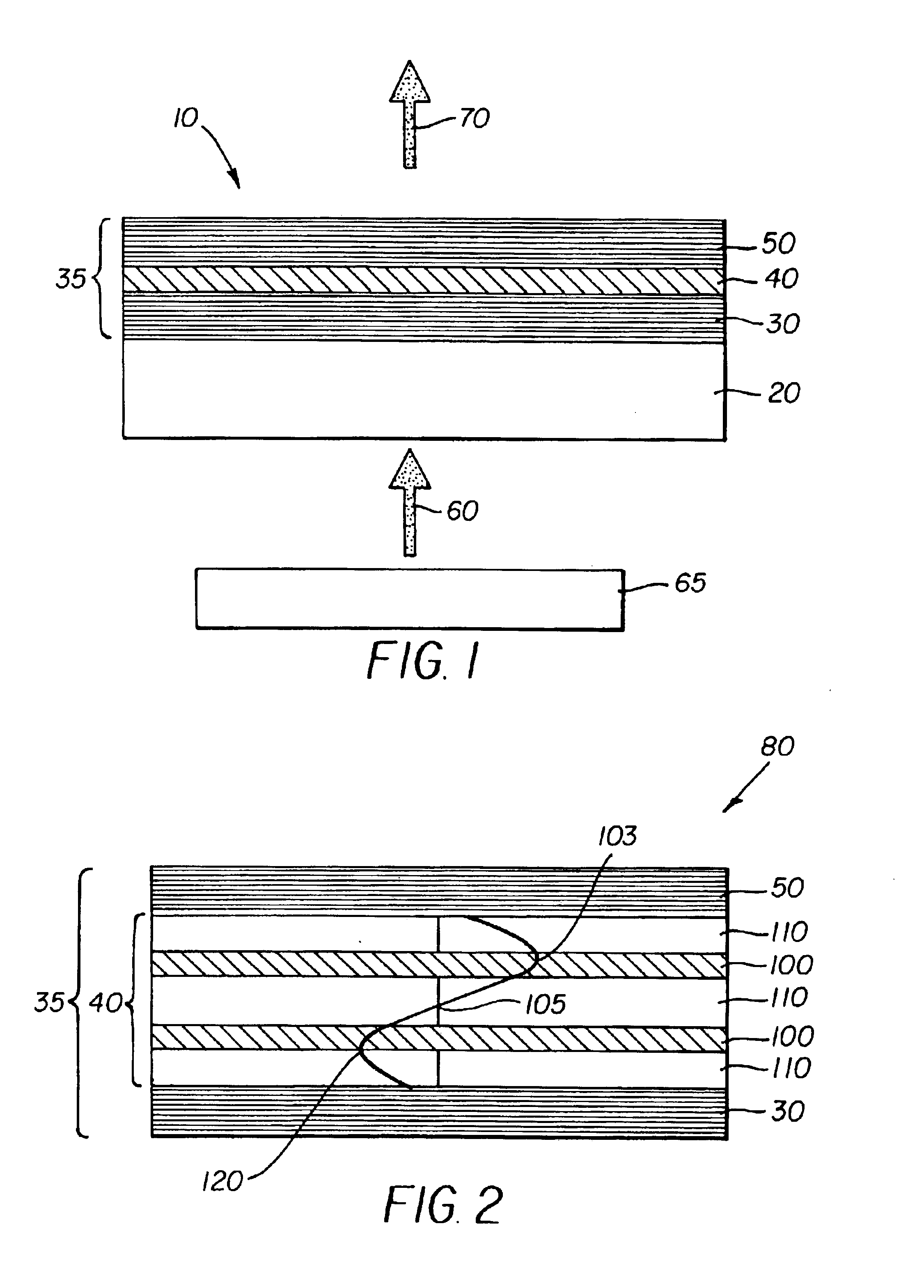
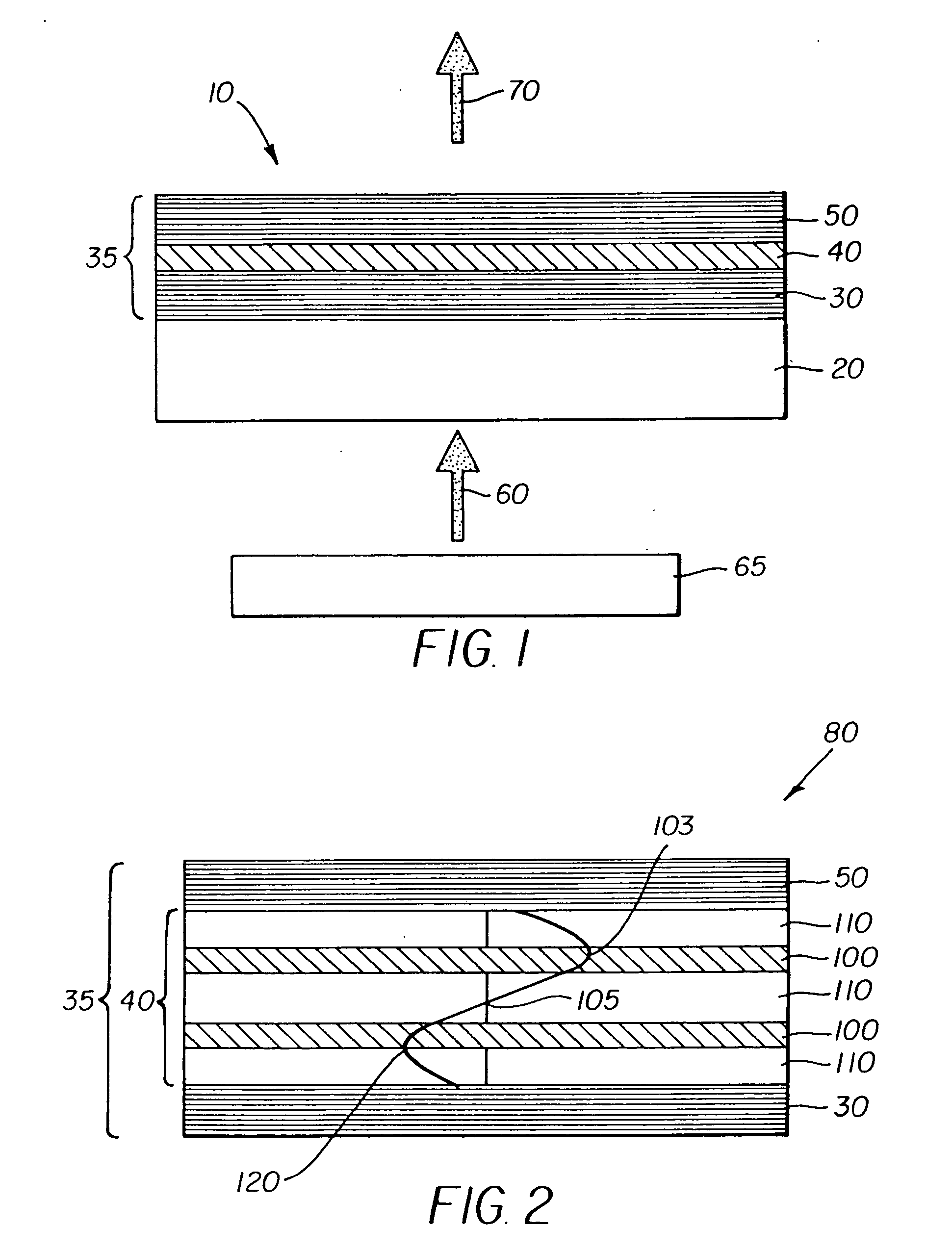
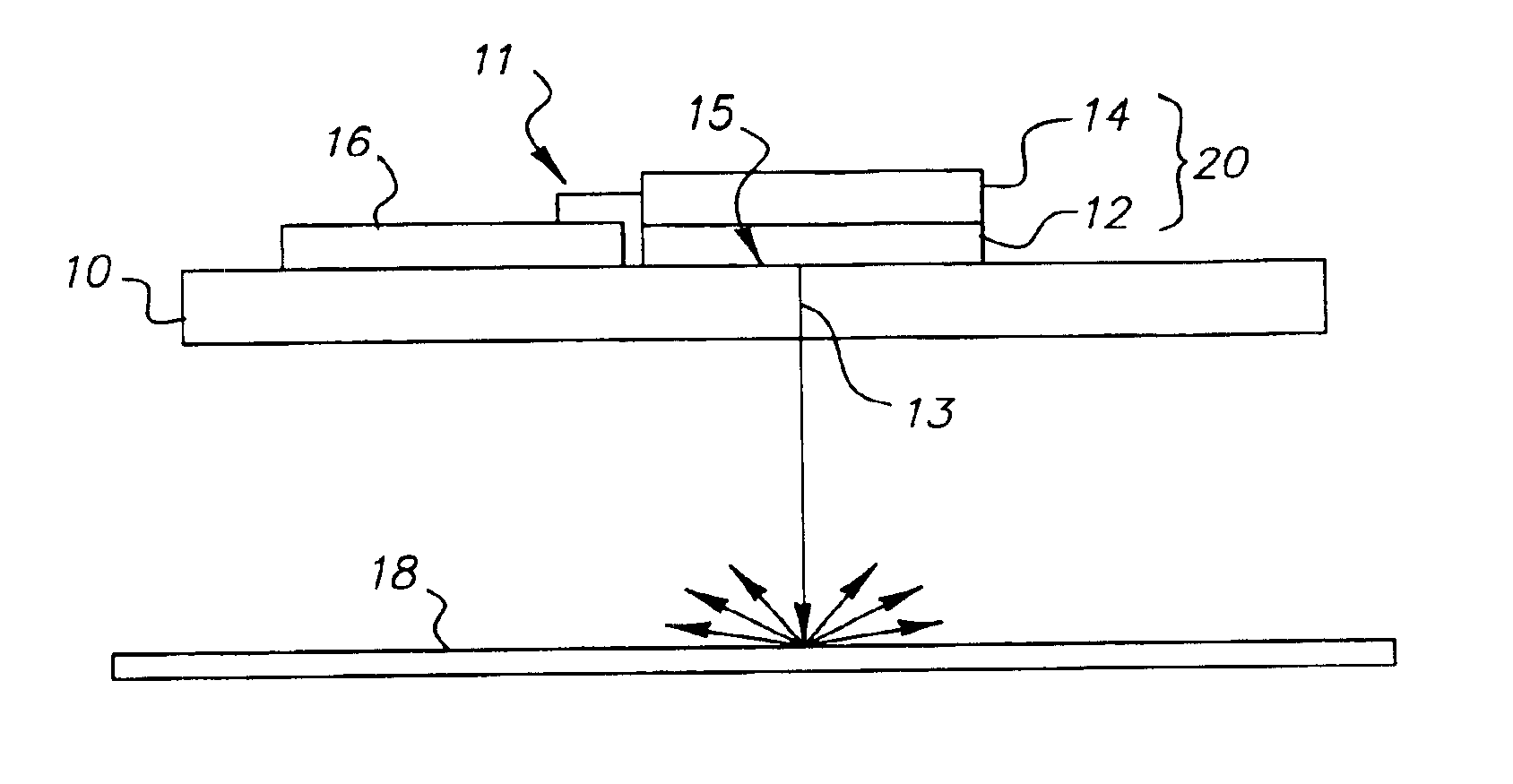
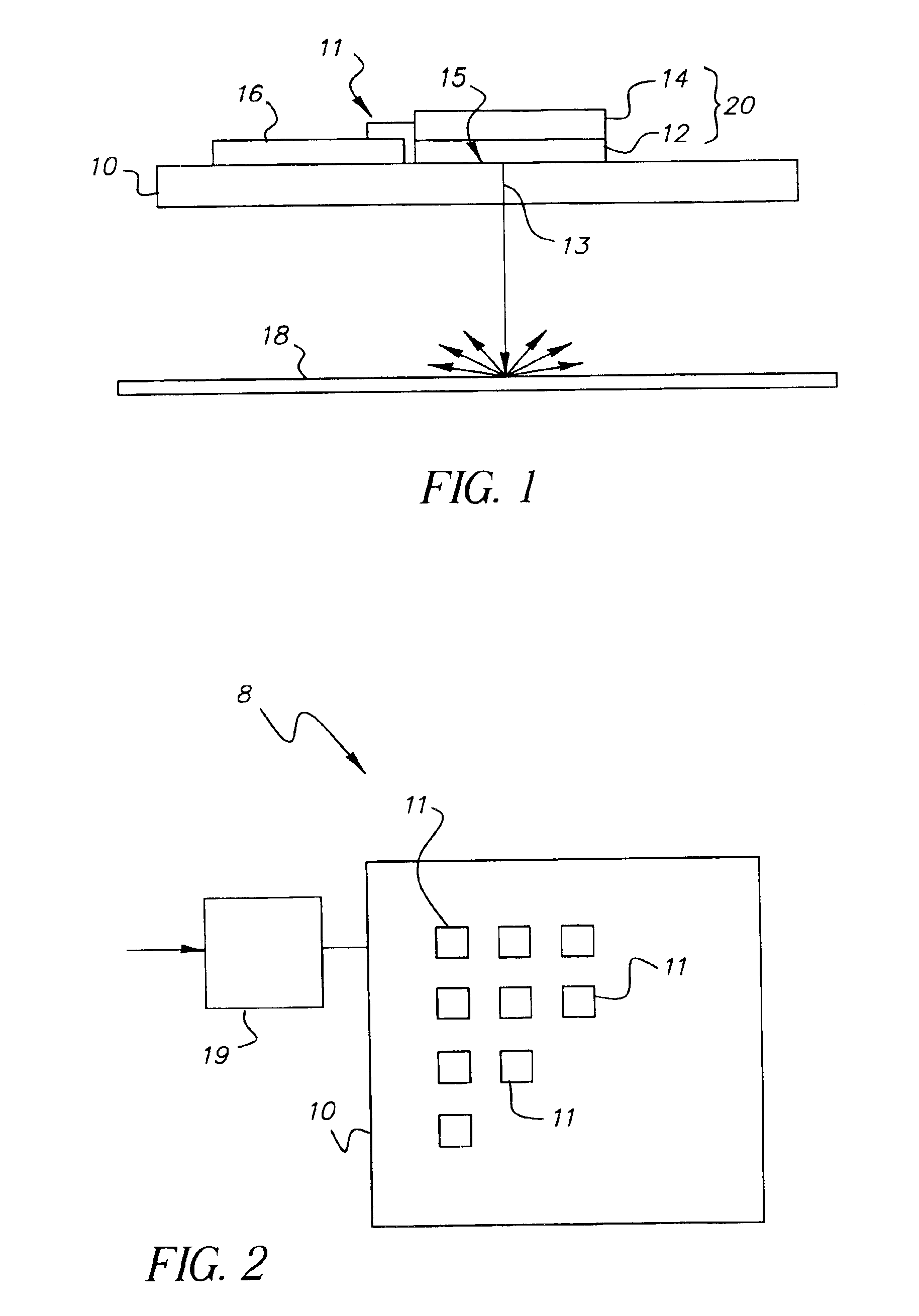
A display apparatus for producing colored pixelated light includes a backlight unit for providing a pump-beam light. The apparatus also includes a microcavity light-producing array responsive to pump-beam light and having pixels wherein each pixel including a transparent substrate, a bottom dielectric stack reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths, an active region responsive to pump-beam light for producing display light, and a top dielectric stack spaced from the bottom dielectric stack and reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. The apparatus further includes a light shutter for permitting selected display light from the microcavity light-producing array to pass therethrough, a polarizing layer disposed between the microcavity light-producing array and the light shutter, and a beam expander disposed over the light shutter for increasing the angular cone of view of the display light.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Organic vertical cavity laser and imaging system
InactiveUS6947459B2Semiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureLaser transmitterLaser light
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Multi-spectral laser array and optical system
InactiveUS20050147135A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureLaser transmitterLaser array
An organic vertical cavity laser light producing device (10) comprises a substrate (20). A plurality of laser emitters (200) emits laser light in a direction orthogonal to the substrate. Each laser emitter within the plurality of laser emitters has a first lateral mode structure in a first axis orthogonal to the laser light direction and has a second lateral mode structure in a second axis orthogonal to both the laser light direction and the first axis. Each laser emitter comprises a first mirror provided on a top surface of the substrate (20) and is reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. An organic active region (40) produces laser light (350). A second mirror is provided above the organic active region and is reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. A pumping means excites the plurality of laser emitters.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
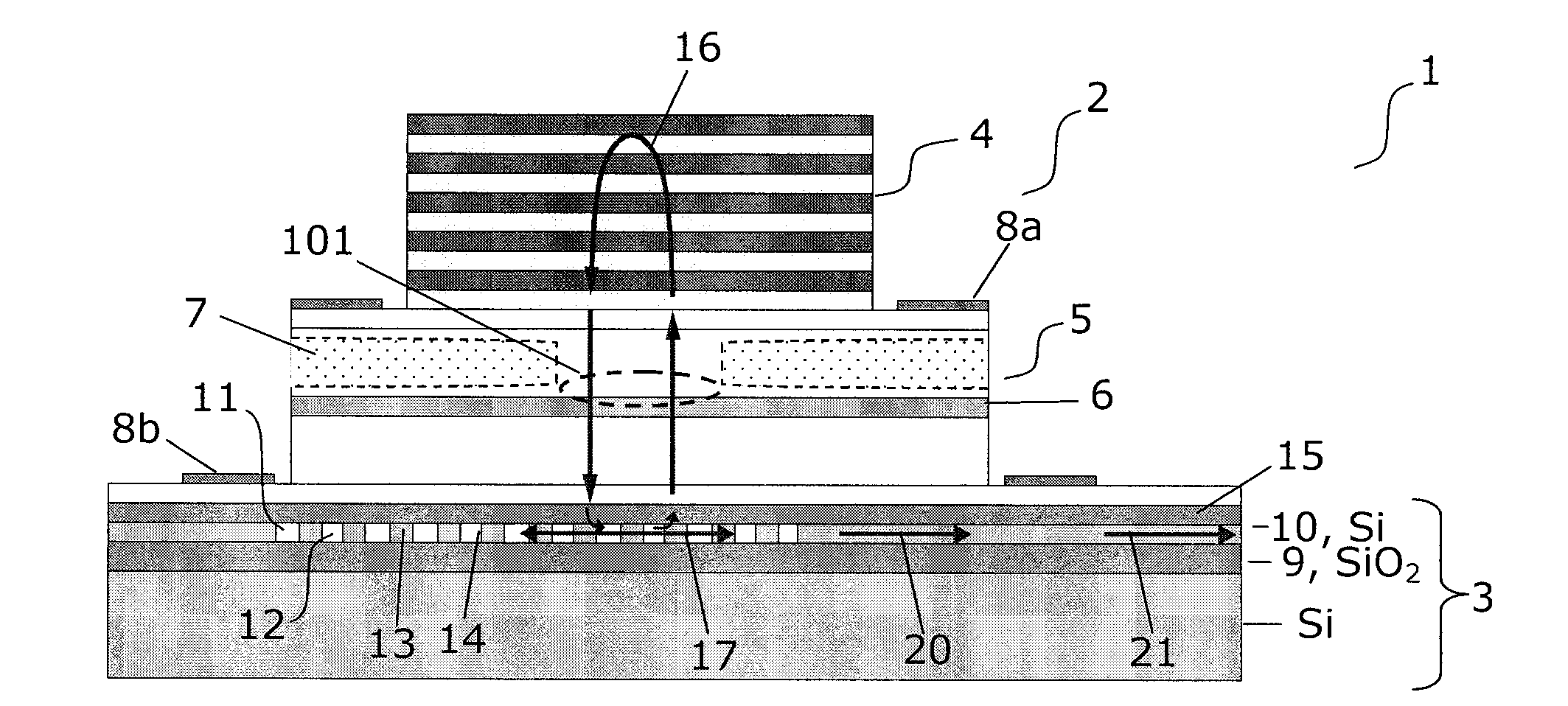
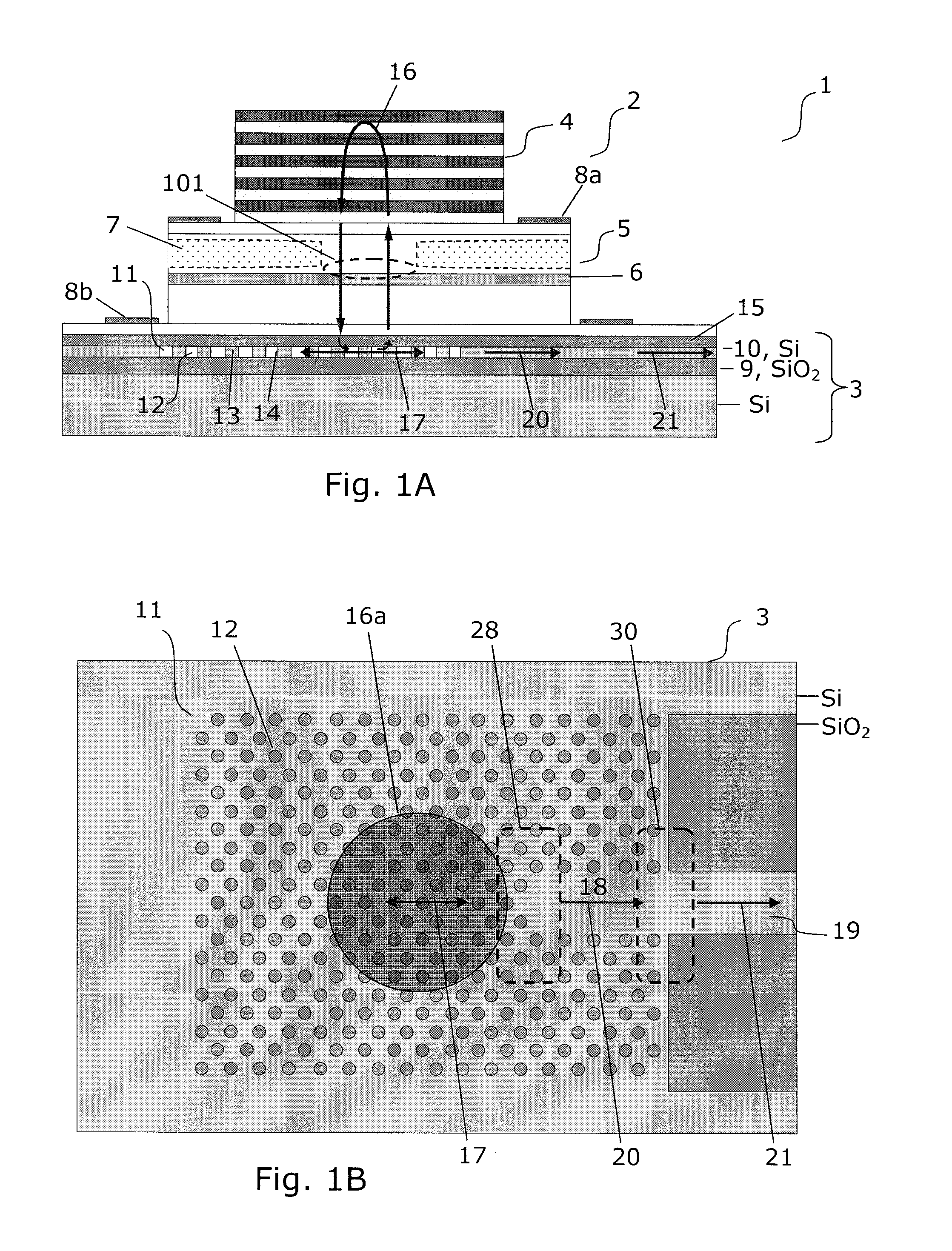
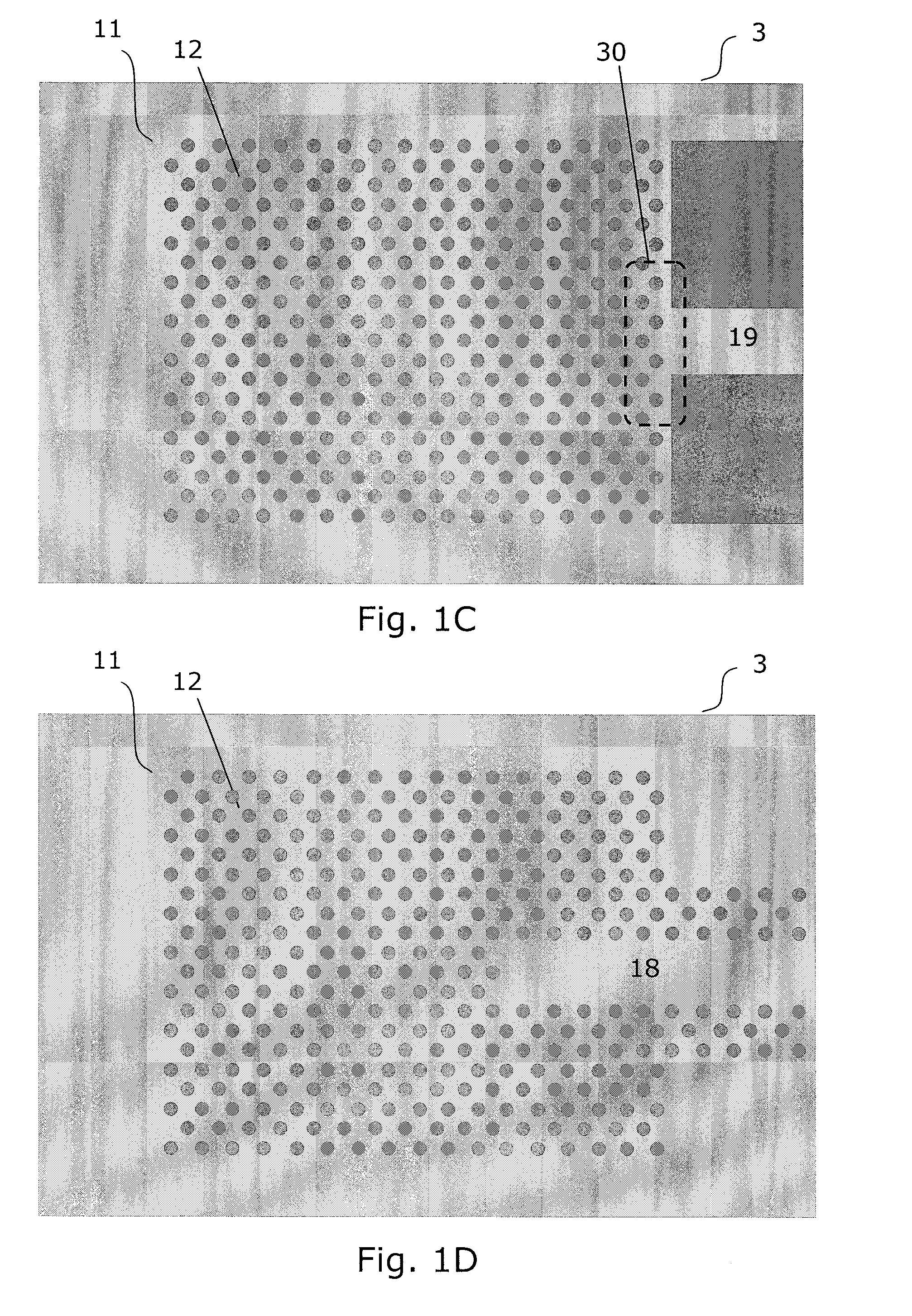
Hybrid vertical-cavity laser
InactiveUS20120008658A1Decrease unwanted scattering lossImprove routing efficiencyLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionIn planeCMOS
The present invention provides a light source (2) for light circuits on a silicon platform (3). A vertical laser cavity is formed by a gain region (101) arranged between a top mirror (4) and a bottom grating-mirror (12) in a grating region (11) in a silicon layer (10) on a substrate. A waveguide (18, 19) for receiving light from the grating region (11) is formed within or to be connected to the grating region, and functions as an 5 output coupler for the VCL. Thereby, vertical lasing modes (16) are coupled to lateral in-plane modes (17, 20) of the in-plane waveguide formed in the silicon layer, and light can be provided to e.g. photonic circuits on a SOI or CMOS substrate in the silicon.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Hybrid silicon vertical cavity laser with in-plane coupling
A silicon vertical cavity laser with in-plane coupling comprises wafer bonding an active III-V semiconductor material above a grating coupler made on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) wafer. This bonding does not require any alignment, since all silicon processing can be done before bonding, and all III-V processing can be done after bonding. The grating coupler acts to couple the vertically emitted light from the hybrid vertical cavity into a silicon waveguide formed on an SOI wafer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Tunable laser array system
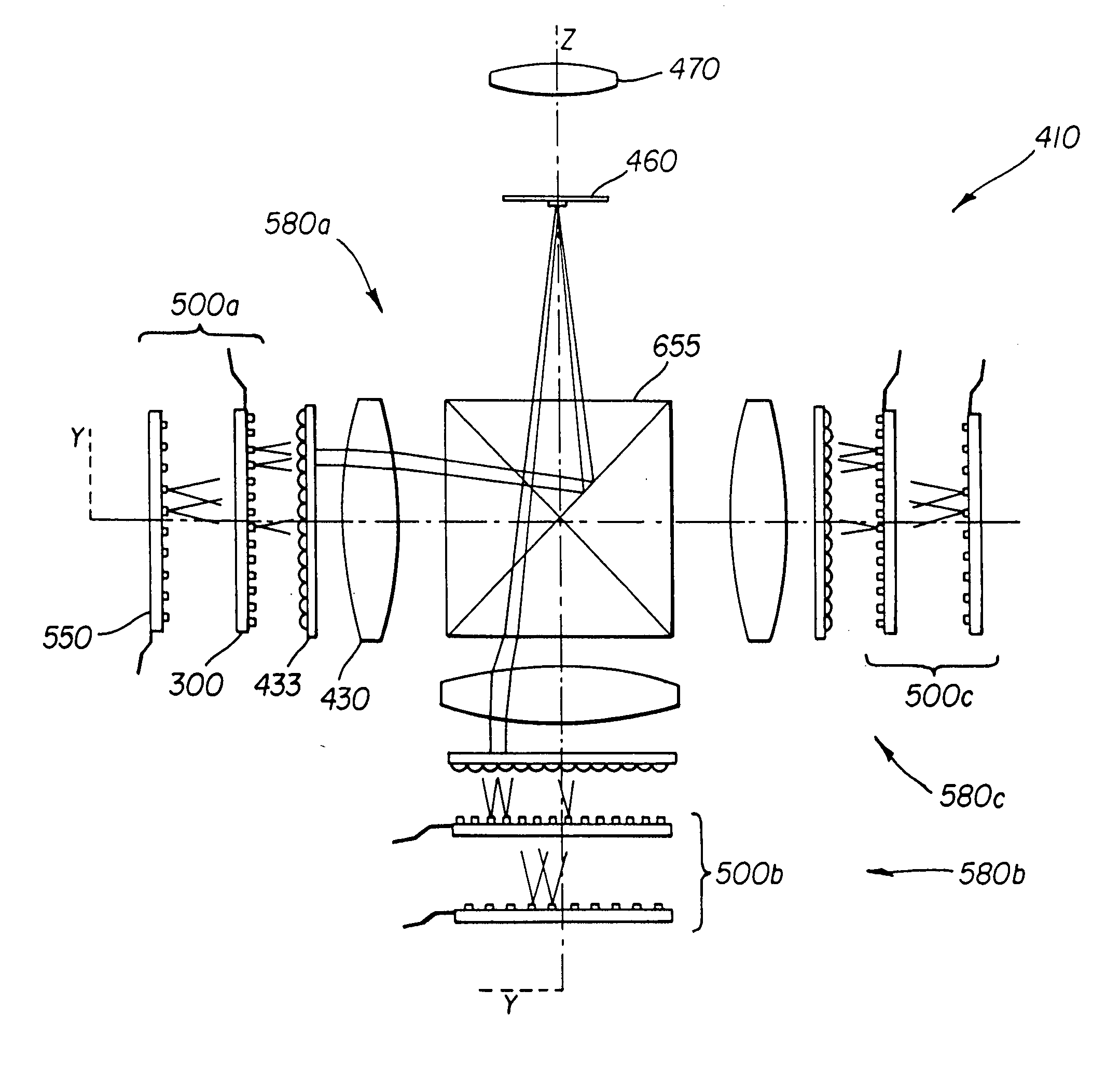
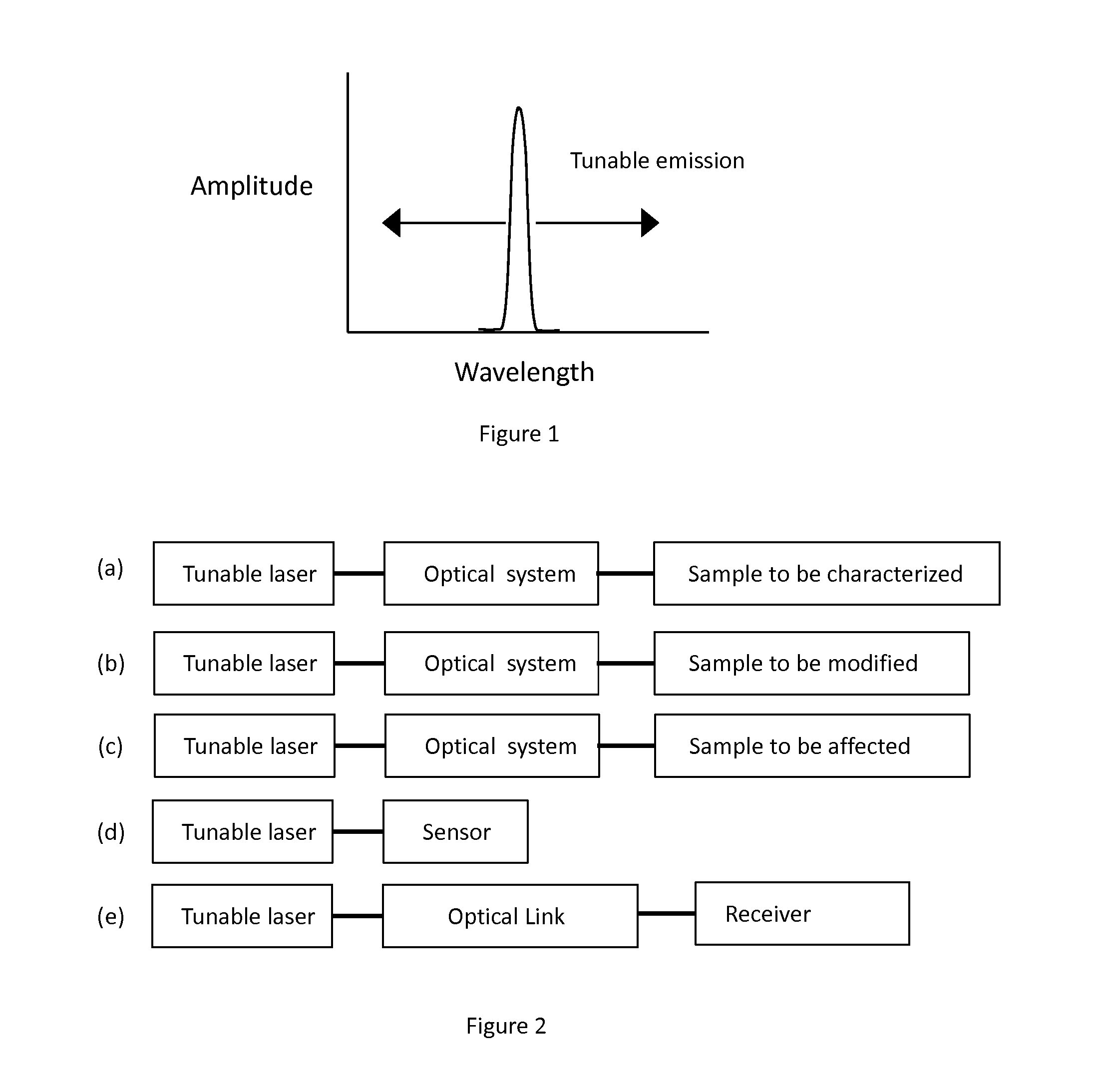
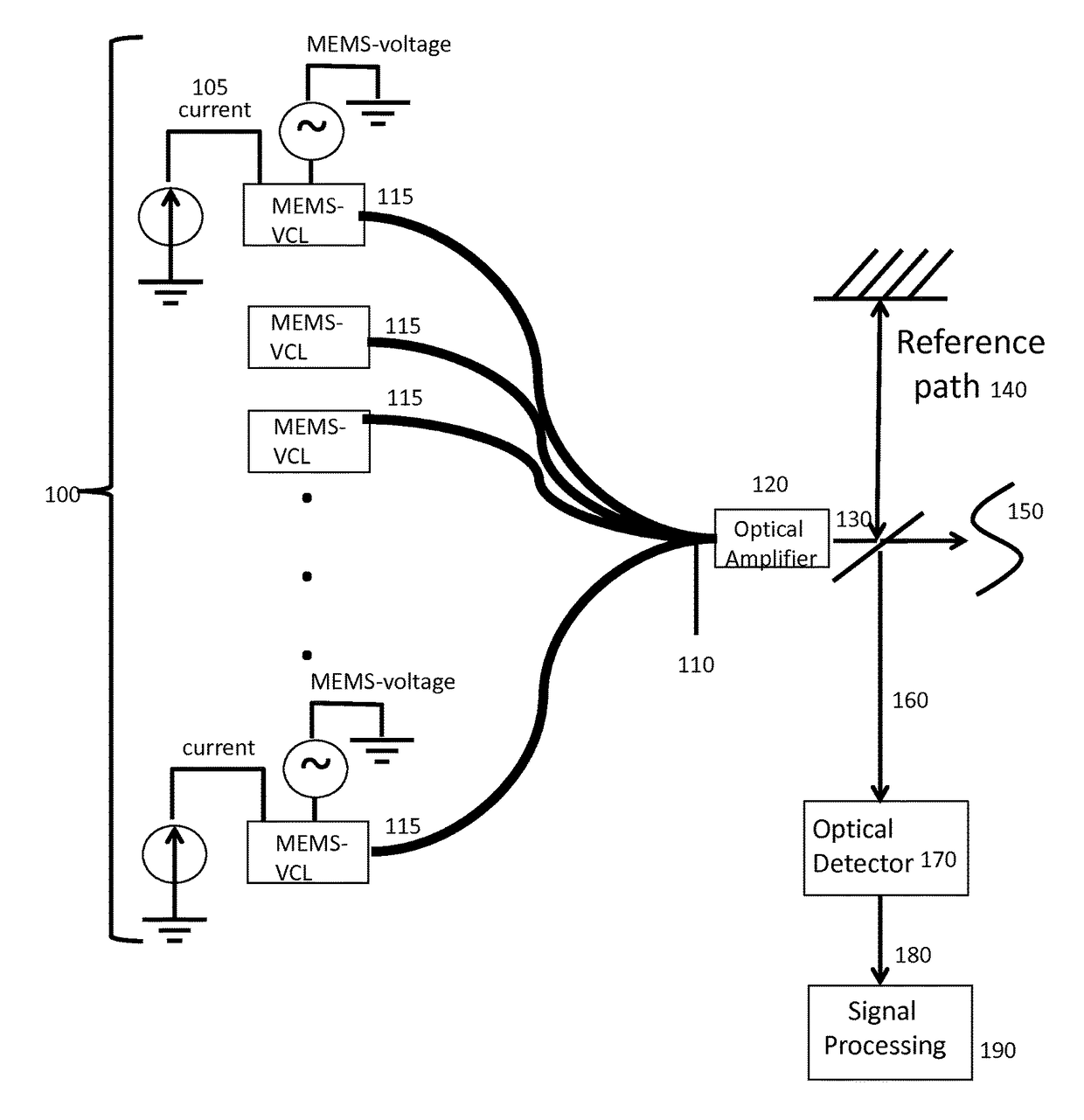
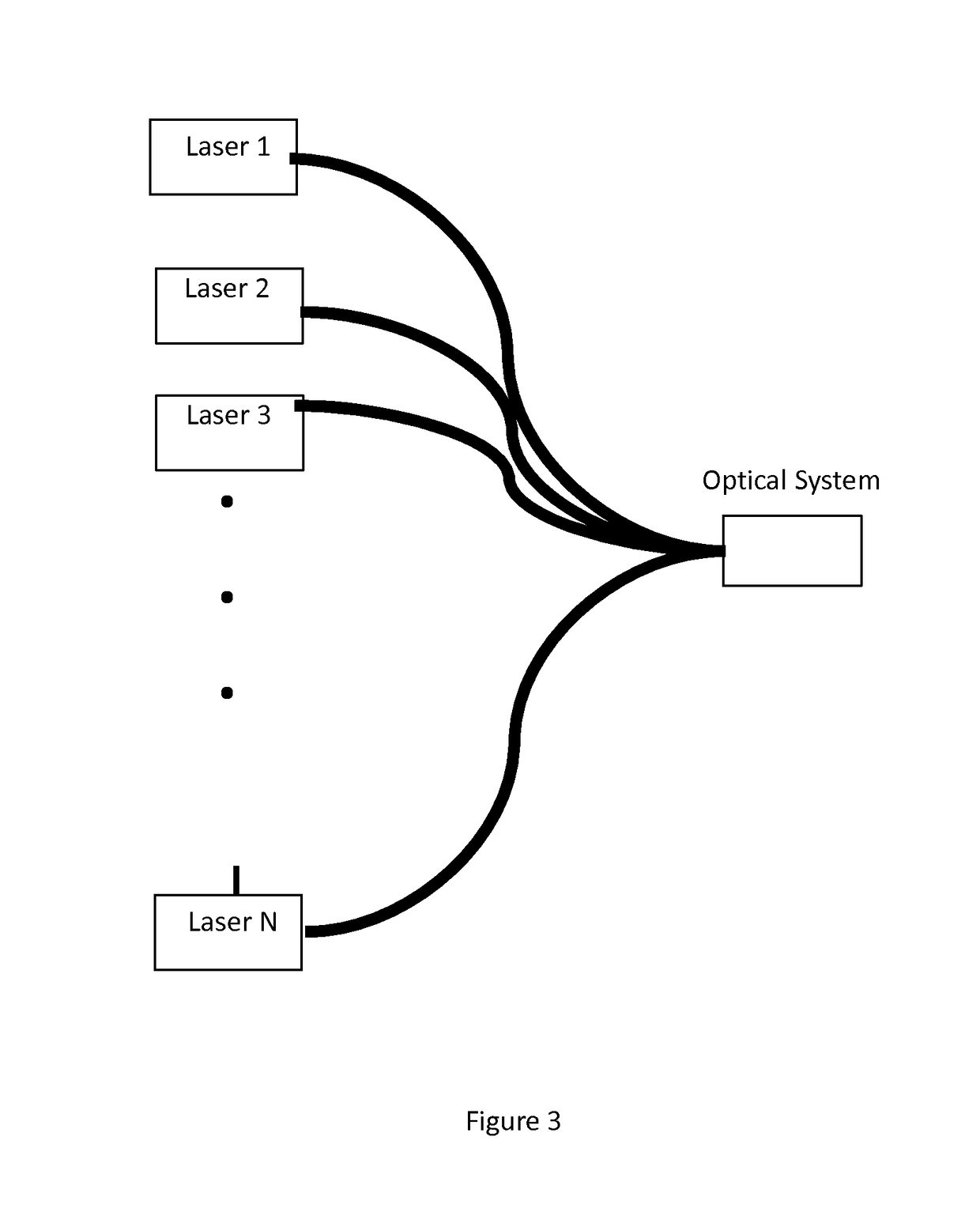
A system for swept source optical coherence tomography, the system including a light source emitting multiplexed wavelength-swept radiation over a total wavelength range, the light source including N wavelength-swept vertical cavity lasers (VCL) emitting N tunable VCL outputs having N wavelength trajectories, a combiner for combining the N tunable VCL optical outputs into a common optical path to create the multiplexed wavelength-swept radiation, a splitter for splitting the multiplexed wavelength-swept radiation to a sample and a reference path, an optical detector for detecting an interference signal created by an optical interference between a reflection from the sample and light traversing the reference path, and a signal processing system which uses the interference signal to construct an image of the sample, wherein at least one of the N wavelength trajectories differs from another of the N wavelength trajectories with respect to at least one parameter.
Owner:PRAEVIUM RES +1
Laser image projector
InactiveUS6939012B2Static indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesLaser lightLight-emitting diode
A laser image projector includes a substrate; and a two dimensional array of individually addressable laser pixels formed on the substrate for emitting an imagewise beam of laser light perpendicular to the substrate, each of the laser pixels including an addressable organic light emitting diode (OLED) and an organic vertical cavity laser that is arranged to be pumped by the OLED.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Display device using vertical cavity laser arrays
InactiveUS7122843B2Process controlImprove color gamutSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive medium materialBeam expanderLight beam
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
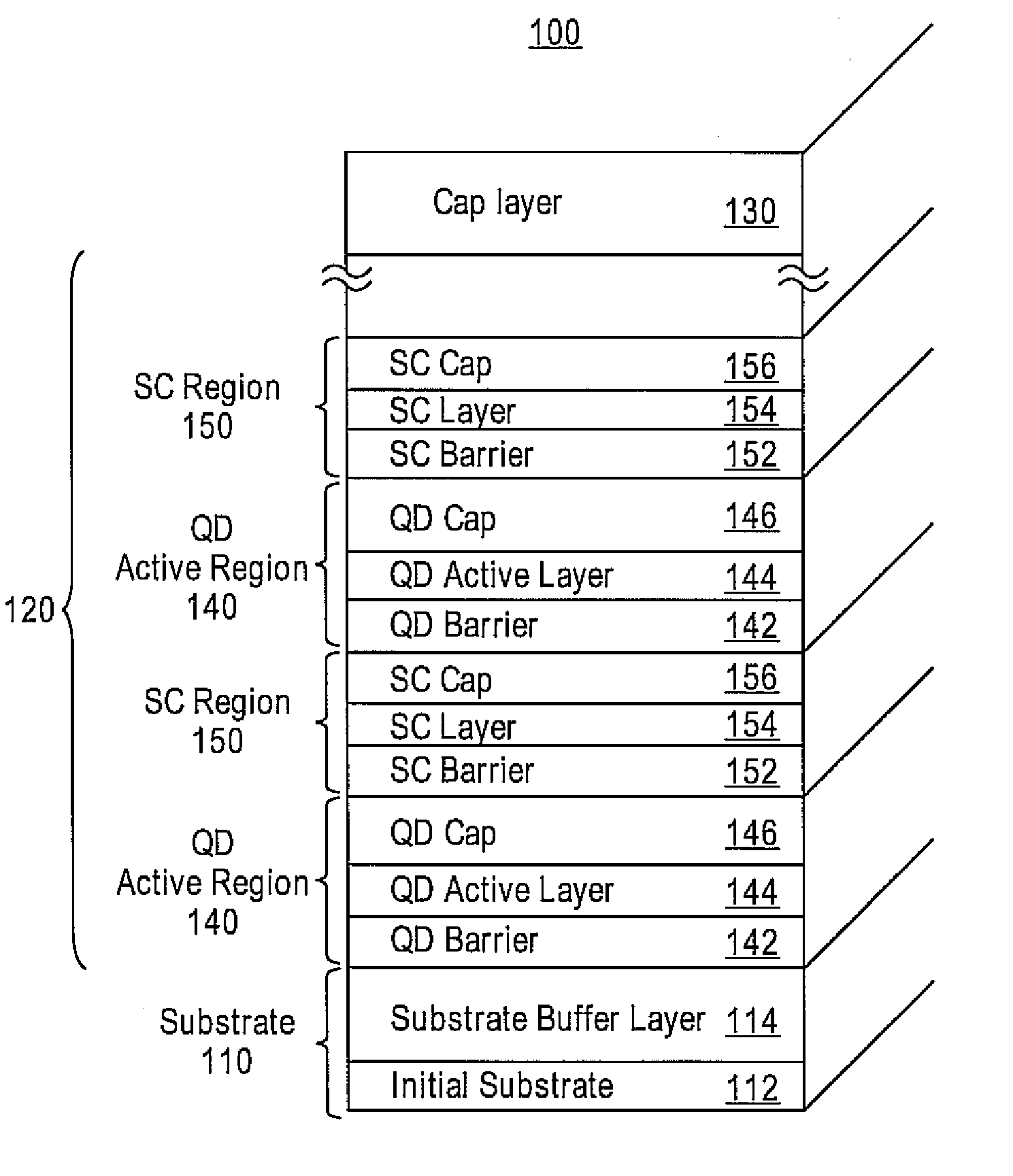
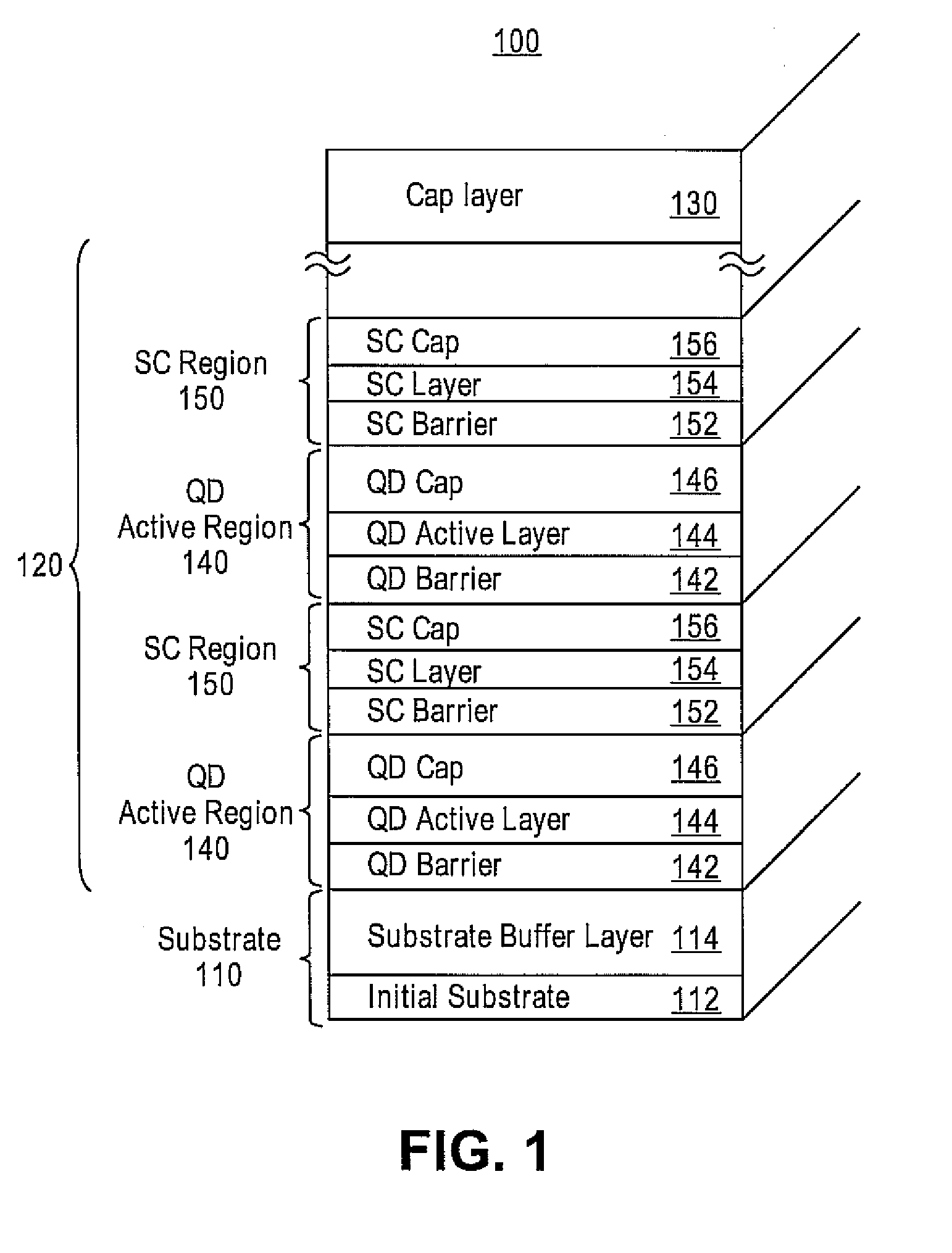
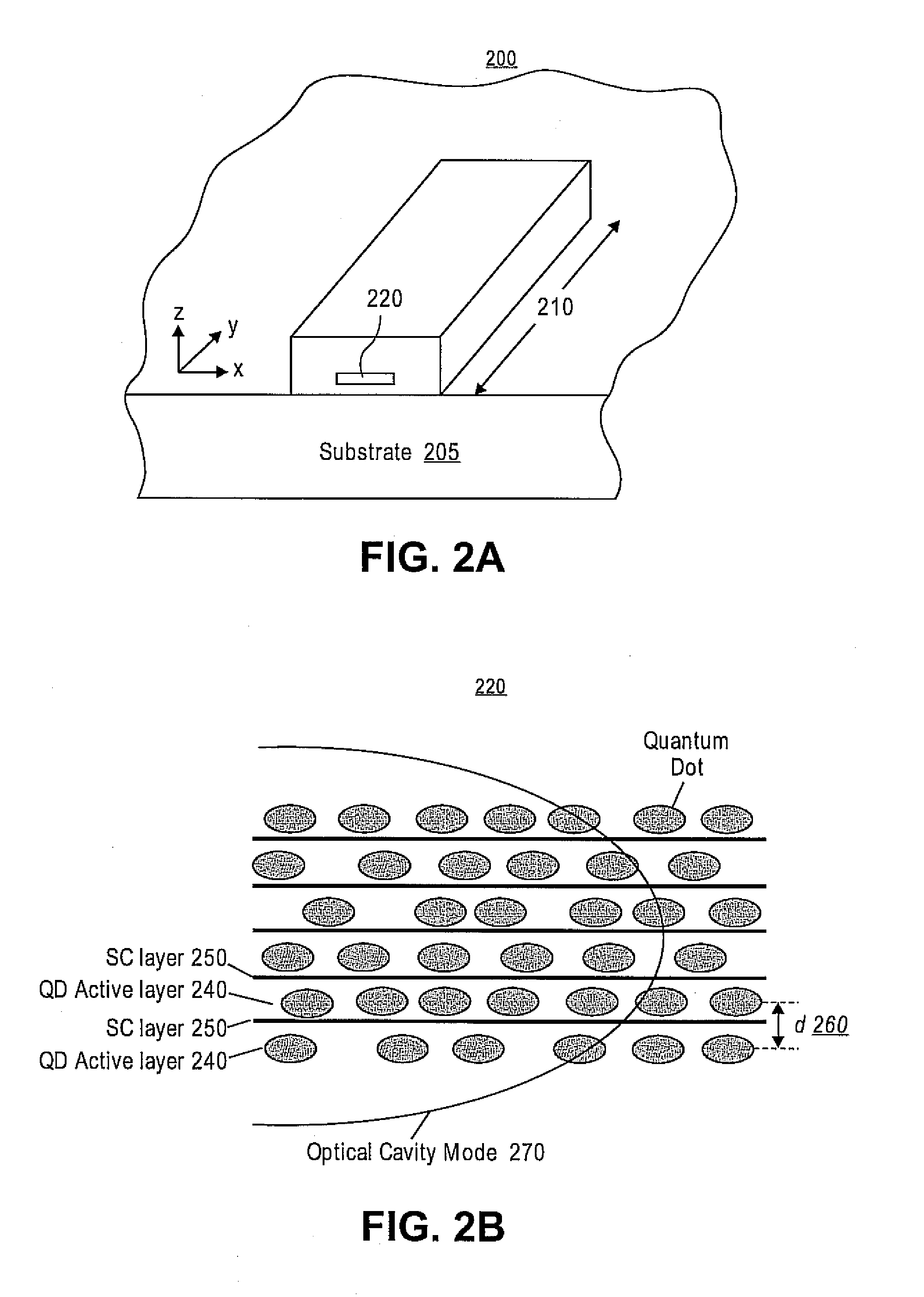
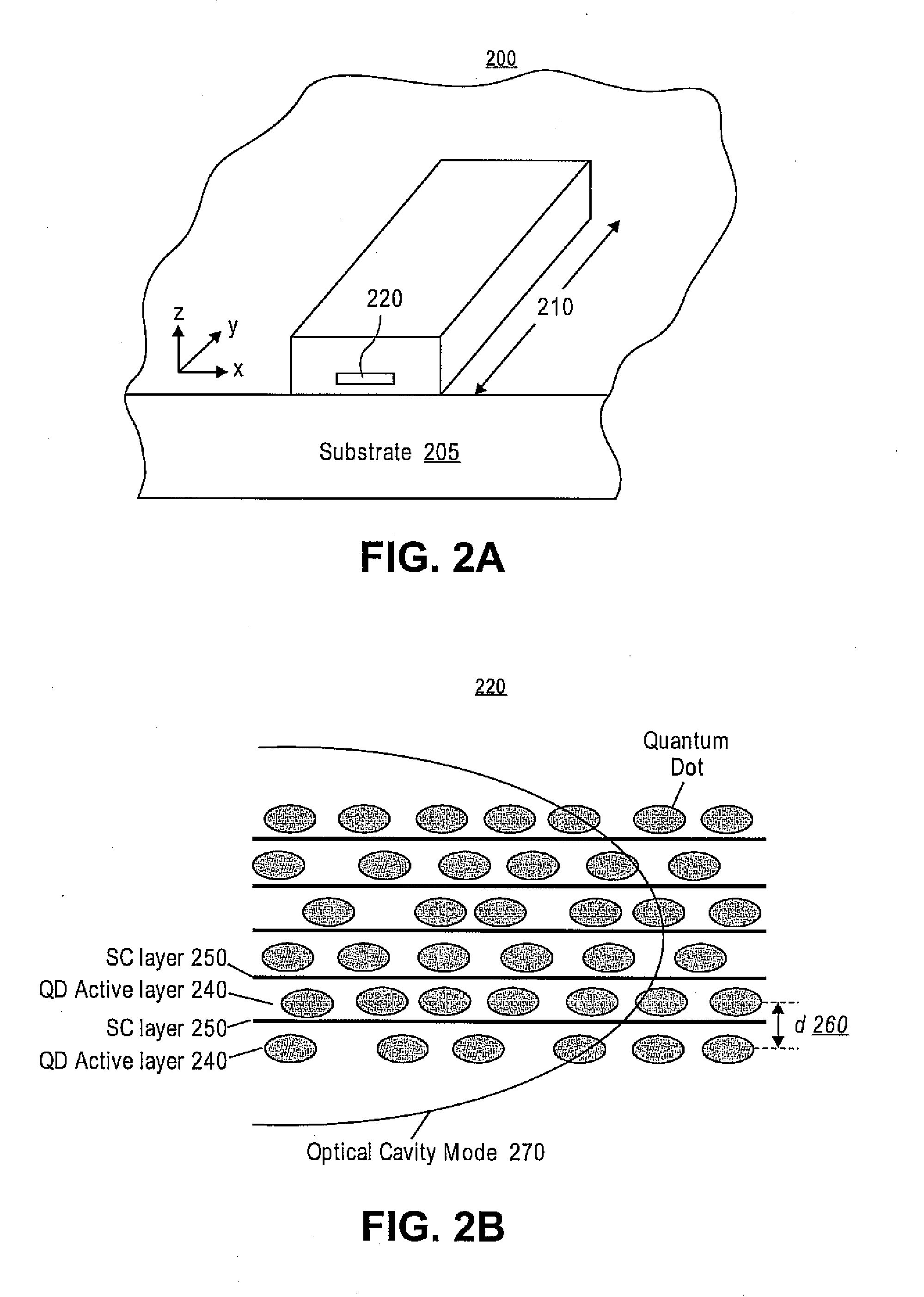
Densely stacked and strain-compensated quantum dot active regions
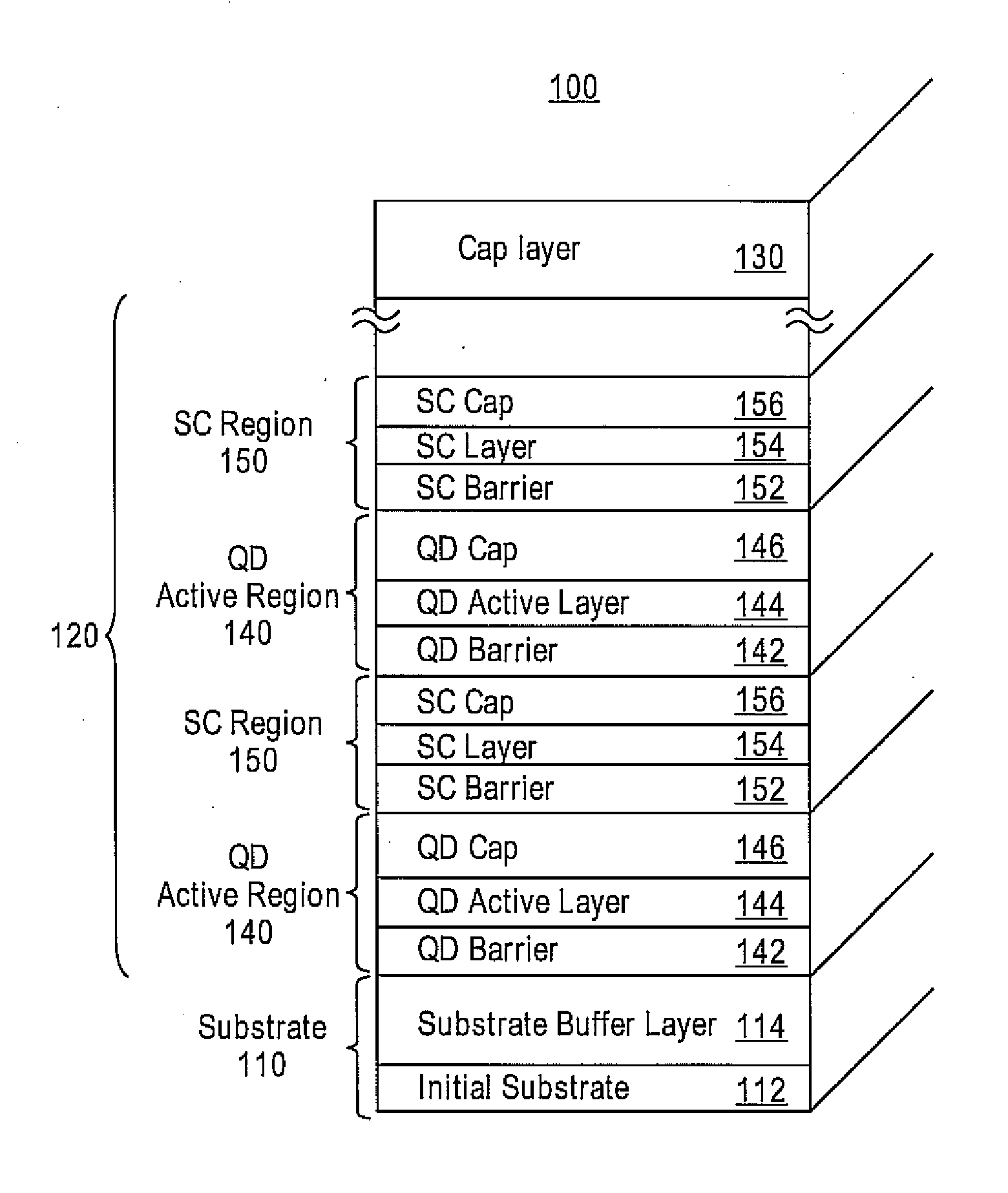
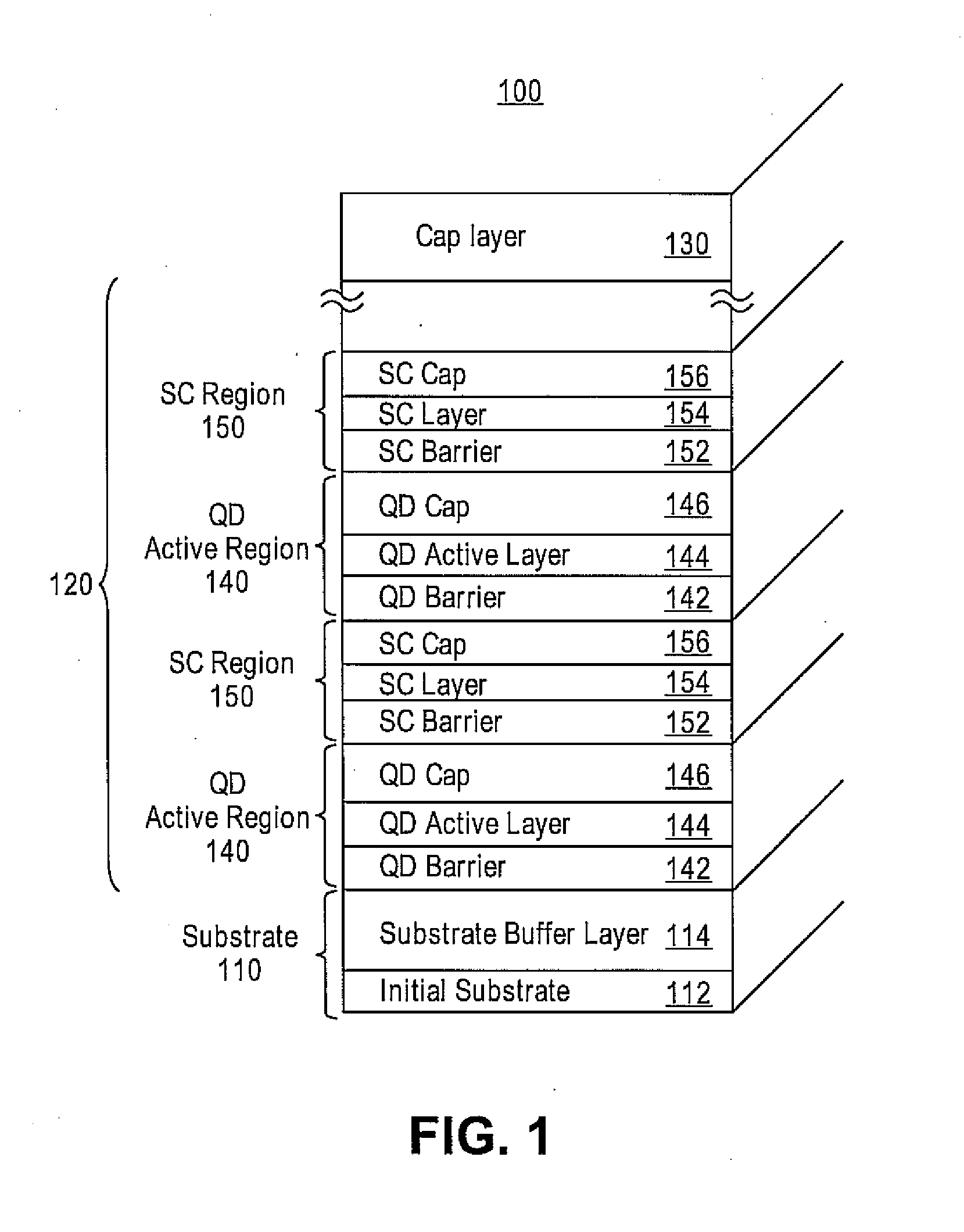
Embodiments provide a quantum dot active structure and a methodology for its fabrication. The quantum dot active structure includes a substrate, a plurality of alternating regions of a quantum dot active region and a strain-compensation region, and a cap layer. The strain-compensation region is formed to eliminate the compressive strain of an adjacent quantum dot active region, thus allowing quantum dot active regions to be densely-stacked. The densely-stacked quantum dot active region provides increased optical modal gain for semiconductor light emitting devices such as edge emitting lasers, vertical cavity lasers, detectors, micro-cavity emitters, optical amplifiers or modulators.
Owner:STC UNM
Hybrid vertical cavity laser for photonic integrated circuit
ActiveUS20140098833A1Coupling efficiency is improvedOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsGratingRefractive index
According to example embodiments, a hybrid vertical cavity laser for a photonic integrated circuit (PIC) includes: a grating mirror between first and second low refractive index layers, an optical waveguide optically coupled to one side of the grating mirror, a III-V semiconductor layer including an active layer on an upper one of the first and second low refractive index layers, and a top mirror on the III-V semiconductor layer. The grating mirror includes a plurality of bar-shaped low refractive index material portions arranged parallel to each other. The low refractive index material portions include a plurality of first portions having a first width and a plurality of second portions having second width in a width direction. The first and second widths are different.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Temperature insensitive VCSEL
Owner:OPTICAL COMM PRODS
Densely stacked and strain-compensated quantum dot active regions
Embodiments provide a quantum dot active structure and a methodology for its fabrication. The quantum dot active structure includes a substrate, a plurality of alternating regions of a quantum dot active region and a strain-compensation region, and a cap layer. The strain-compensation region is formed to eliminate the compressive strain of an adjacent quantum dot active region, thus allowing quantum dot active regions to be densely-stacked. The densely-stacked quantum dot active region provides increased optical modal gain for semiconductor light emitting devices such as edge emitting lasers, vertical cavity lasers, detectors, micro-cavity emitters, optical amplifiers or modulators.
Owner:STC UNM
Display device using vertical cavity laser arrays
InactiveUS7262758B2Reduce divergenceColor limitedStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesBeam expanderDielectric
A display apparatus for producing colored pixelated light includes a backlight unit for providing a pump-beam light. The apparatus also includes a microcavity light-producing array responsive to pump-beam light and having pixels wherein each pixel including a transparent substrate, a bottom dielectric stack reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths, an active region responsive to pump-beam light for producing display light, and a top dielectric stack spaced from the bottom dielectric stack and reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. The apparatus further includes a light shutter for permitting selected display light from the microcavity light-producing array to pass therethrough, a polarizing layer disposed between the microcavity light-producing array and the light shutter, and a beam expander disposed over the light shutter for increasing the angular cone of view of the display light.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Hybrid silicon vertical cavity laser with in-plane coupling
InactiveUS8257990B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersIn planeGrating
A silicon vertical cavity laser with in-plane coupling comprises wafer bonding an active III-V semiconductor material above a grating coupler made on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) wafer. This bonding does not require any alignment, since all silicon processing can be done before bonding, and all III-V processing can be done after bonding. The grating coupler acts to couple the vertically emitted light from the hybrid vertical cavity into a silicon waveguide formed on an SOI wafer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Vertical cavity laser producing different color light
InactiveUS7045825B2Excitation process/apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamColored light
A display apparatus for producing colored pixelated light includes a backlight unit for producing pump-beam light and a vertical cavity laser array device including a structure for modulating the properties of the device at spaced locations so as to provide an array of spaced laser pixels which have higher net gain than the interpixel regions, and an active region which produces blue light in response to the pump-beam light. The apparatus also includes a light shutter and a color conversion layer including different portions, where selected different portions in response to blue light produce a different colored light and being adapted to increase the angular cone of view of the selected colored light.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
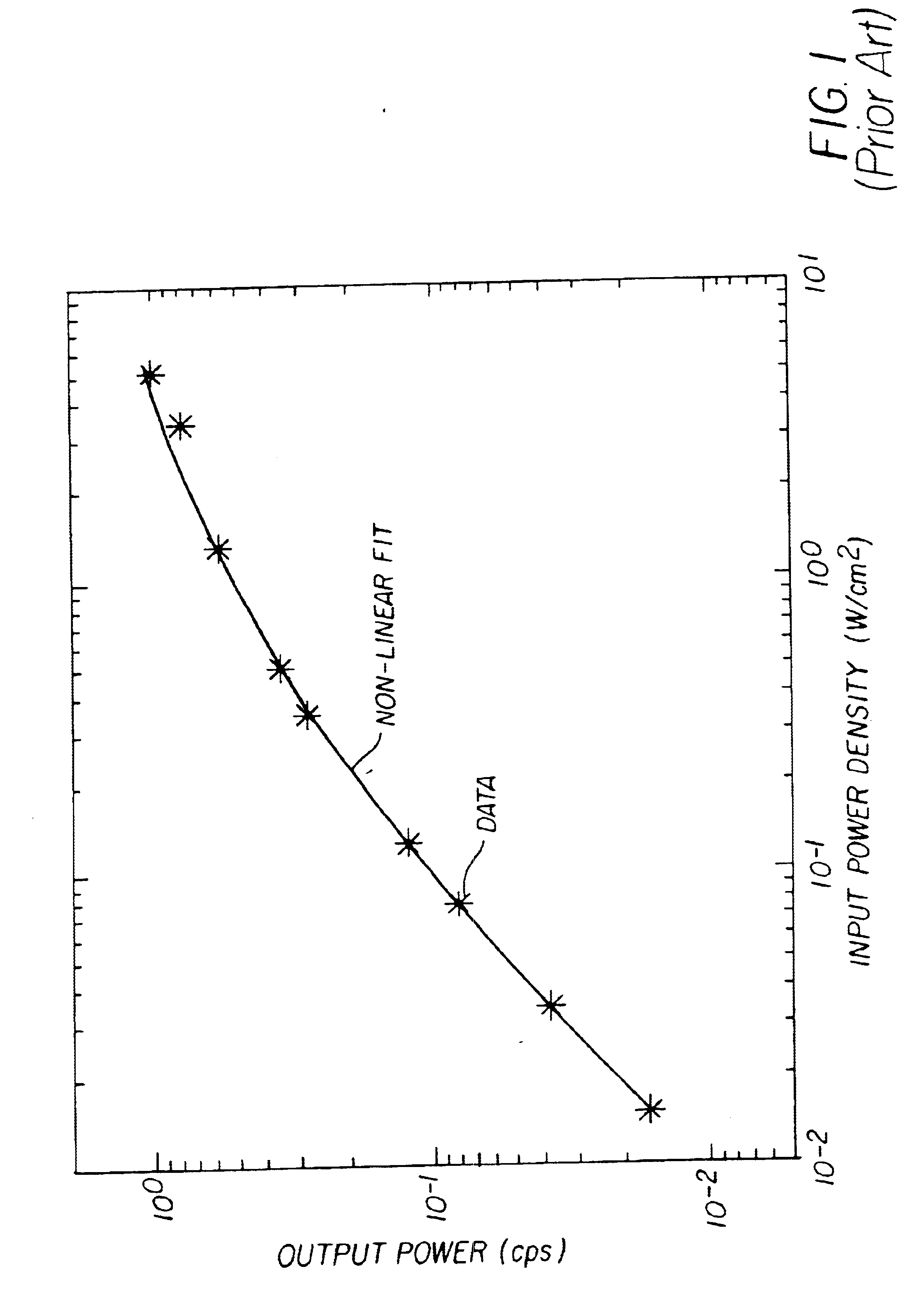
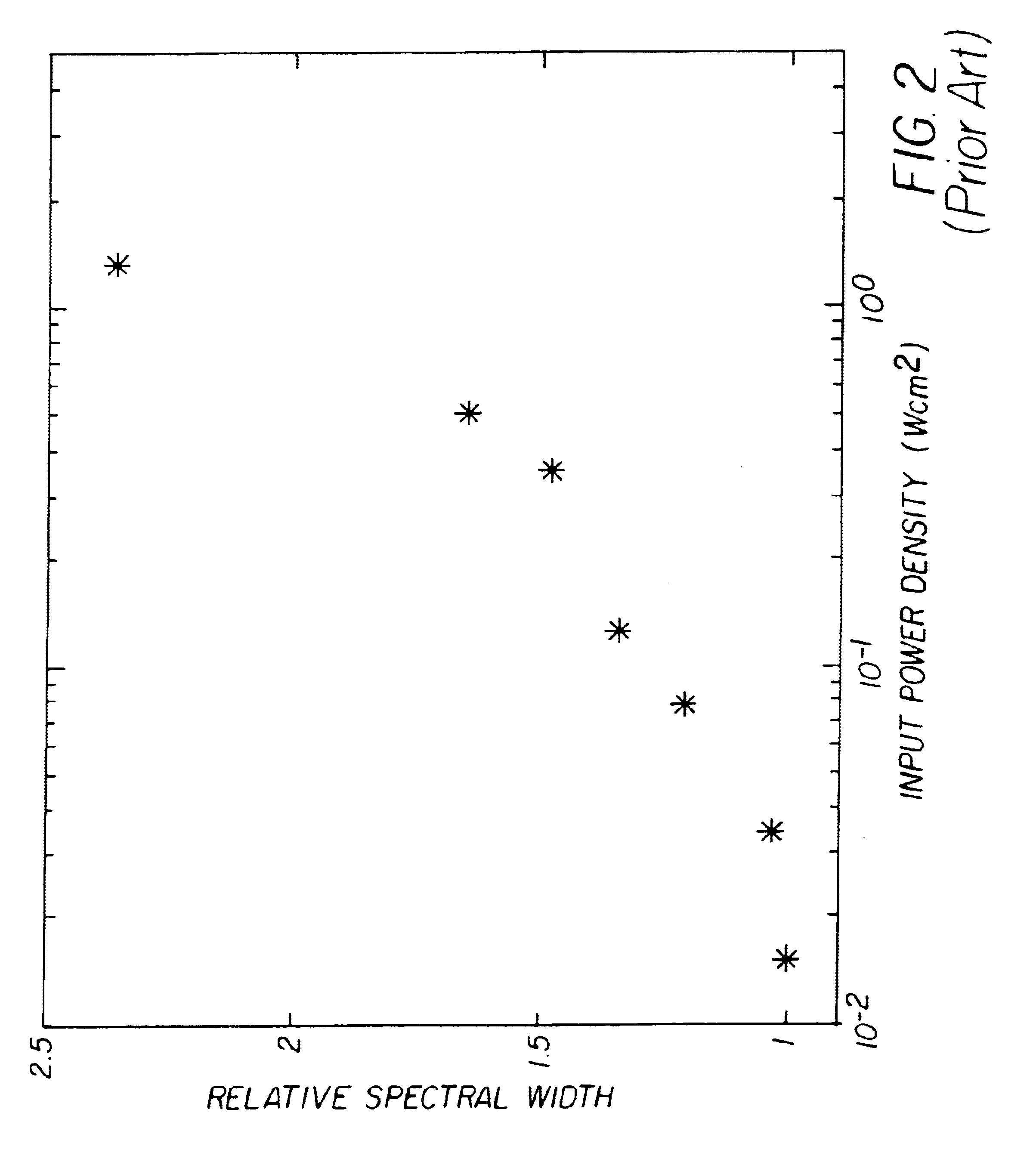
Organic laser having improved linearity
InactiveUS6870868B2Reducing the spectral linewidth broadeningLaser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusLight reflexDielectric
An organic vertical cavity laser device includes a substrate; a bottom dielectric stack reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths and being disposed over the substrate, and an organic active region for producing laser light. The device also includes a top dielectric stack spaced from the bottom dielectric stack and reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths, and a thermally conductive transparent layer disposed between the bottom dielectric stack and the organic active region or between the top dielectric stack and the organic active region or both.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Tunable laser array system
A system for swept source optical coherence tomography, the system including a light source emitting multiplexed wavelength-swept radiation over a total wavelength range, the light source including N wavelength-swept vertical cavity lasers (VCL) emitting N tunable VCL outputs having N wavelength trajectories, a combiner for combining the N tunable VCL optical outputs into a common optical path to create the multiplexed wavelength-swept radiation, a splitter for splitting the multiplexed wavelength-swept radiation to a sample and a reference path, an optical detector for detecting an interference signal created by an optical interference between a reflection from the sample and light traversing the reference path, and a signal processing system which uses the interference signal to construct an image of the sample, wherein at least one of the N wavelength trajectories differs from another of the N wavelength trajectories with respect to at least one parameter.
Owner:PRAEVIUM RES +1
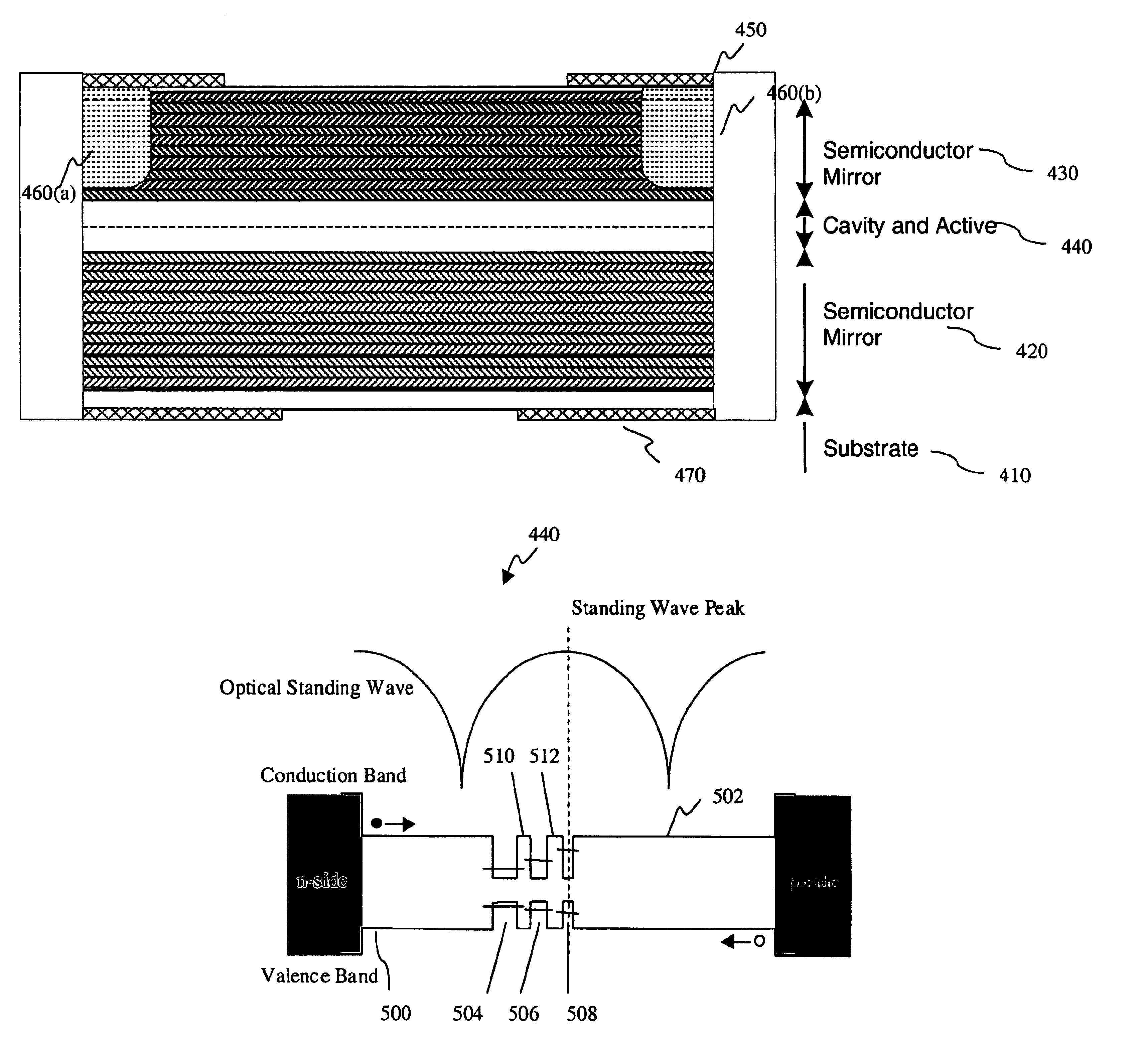
Grating coupled vertical cavity optoelectronic devices
InactiveUSRE38682E1Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionStimulated emissionWaveguide
A edge emitting waveguide laser is obtained that derives its optical power from a vertical cavity laser structure. The vertical cavity laser with top and bottom Distributed Bragg Reflectors produces stimulated emission by resonance in the vertical direction but the optical power so generated is diffracted by a second order grating into an optical mode propagating in the optical waveguide formed by the upper and lower mirrors as cladding layers. The efficiency of the diffraction grating and the reflectivity of the mirrors are maximized so that essentially all of the light is coupled into the guide and the loss through the mirrors can be neglected. The same structure can be utilized as a detector, a modulator or an amplifier. The designated laser structure to achieve this form of operation is the inversion channel laser which is a laterally injected laser having both contacts on the top side of the device. Then the anode and cathode of the laser are essentially coplanar electrodes and the device is implemented in the form of a traveling wave laser, detector, modulator or amplifier which forms the basis for very high frequency performance.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Hybrid silicon vertical cavity laser with in-plane coupling
A silicon vertical cavity laser with in-plane coupling comprises wafer bonding an active III-V semiconductor material above a grating coupler made on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) wafer. This bonding does not require any alignment, since all silicon processing can be done before bonding, and all III-V processing can be done after bonding. The grating coupler acts to couple the vertically emitted light from the hybrid vertical cavity into a silicon waveguide formed on an SOI wafer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus and methods for one or more wavelength swept lasers and the detection of signals thereof
An optical instrument including at least a first and second wavelength swept vertical cavity laser (VCL) sources. The wavelength sweeping ranges spanned by the first and second VCL sources may differwith a region of spectral overlap. The first and second VCL sources may be operable under different modes of operation, wherein the modes of operation differ in at least one of: sweep repetition rate,sweep wavelength range, sweep center wavelength, and sweep trajectory. A VCL source may also exhibit sweep-to-sweep variation. Apparatus and methods are described for aligning sample signal data fromthe first VCL and sample signal data from the second VCL to generate output digital data. The output digital data is aligned with respect to at least one of: wavelength, wavenumber, and interferometric phase. The apparatus and methods can also be used to phase stabilize successive sweeps from the same VCL source or wavelength swept source.
Owner:THORLABS INC +1
Organic vertical cavity lasing device having organic active region
InactiveUS6876684B2Easy to operateImprove conversion efficiencyResistance electrode holdersExcitation process/apparatusDielectricLaser light
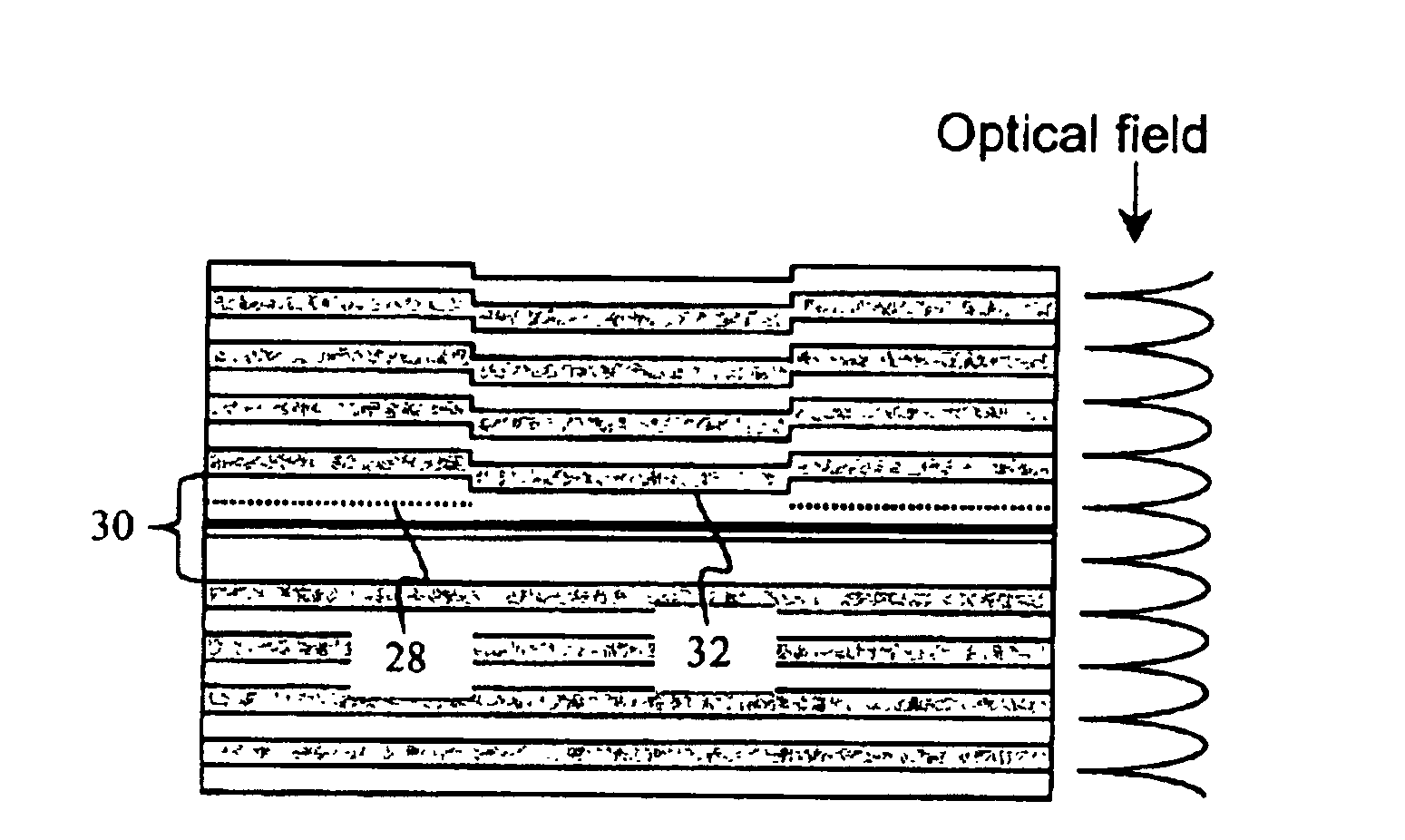
An organic vertical cavity laser light producing device includes a bottom dielectric stack reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths; an organic active region for producing laser light, and having an organic active region including emissive material; and a top dielectric stack spaced from the bottom dielectric stack and reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. Pump-beam light is transmitted and introduced into the organic active region through at least one of the dielectric stacks. The organic active region includes one or more periodic gain region(s) and organic spacer layers disposed on either side of the periodic gain region(s) and arranged so that the periodic gain region(s) is aligned with the antinodes of the device's standing wave electromagnetic field, and wherein the spacer layers are substantially transparent to the laser light.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
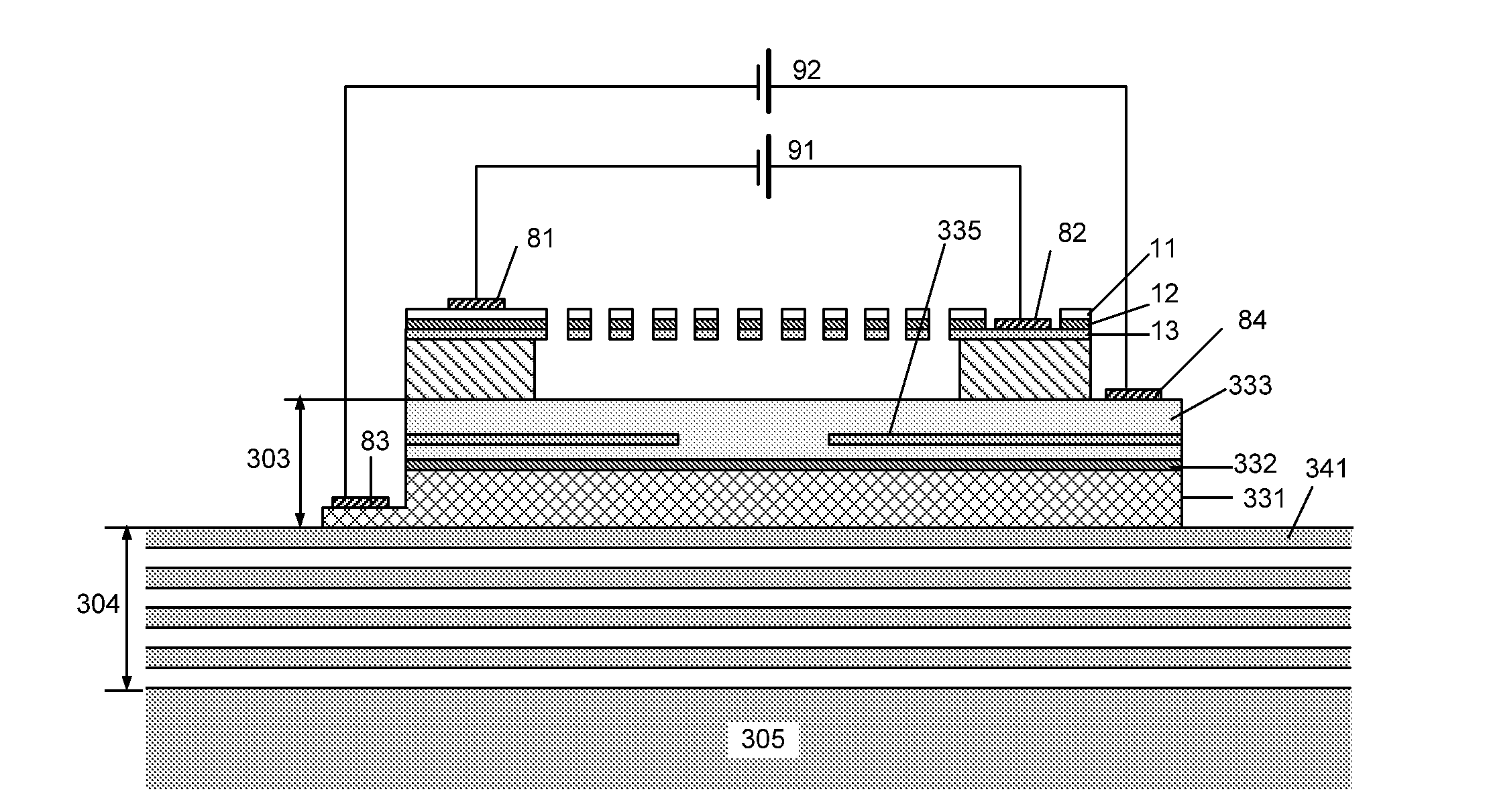
Reflectivity-modulated grating mirror
InactiveUS20140219301A1Higher obtainable data rateReduce energy consumptionLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingCoupling
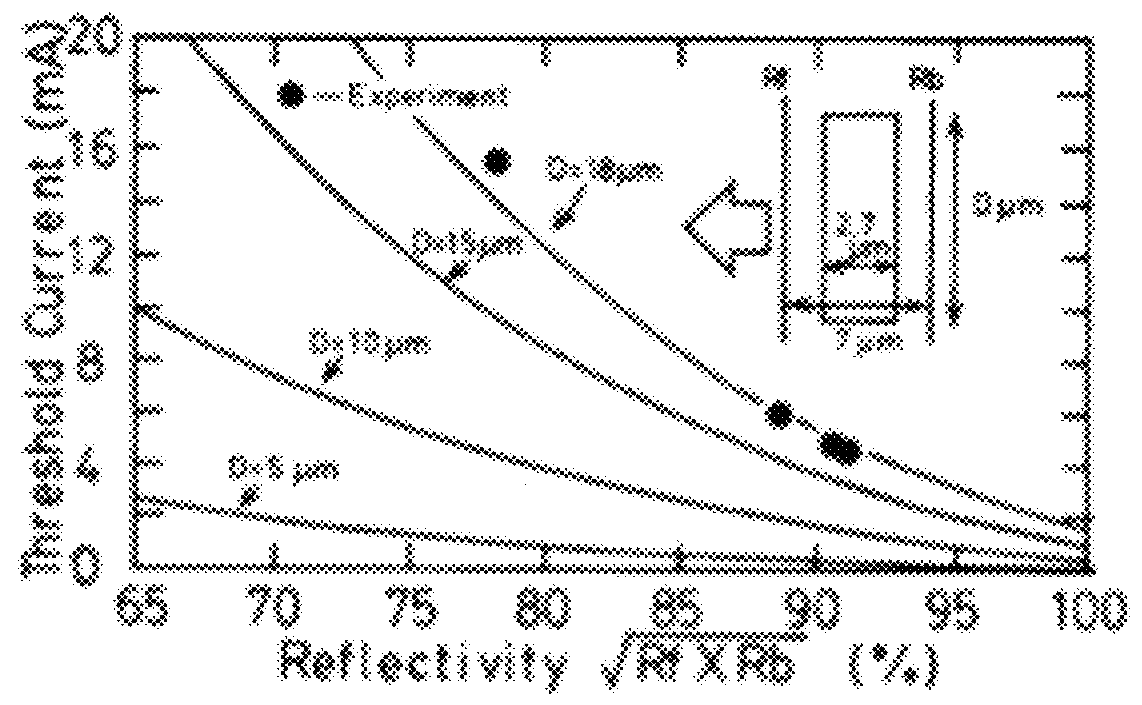
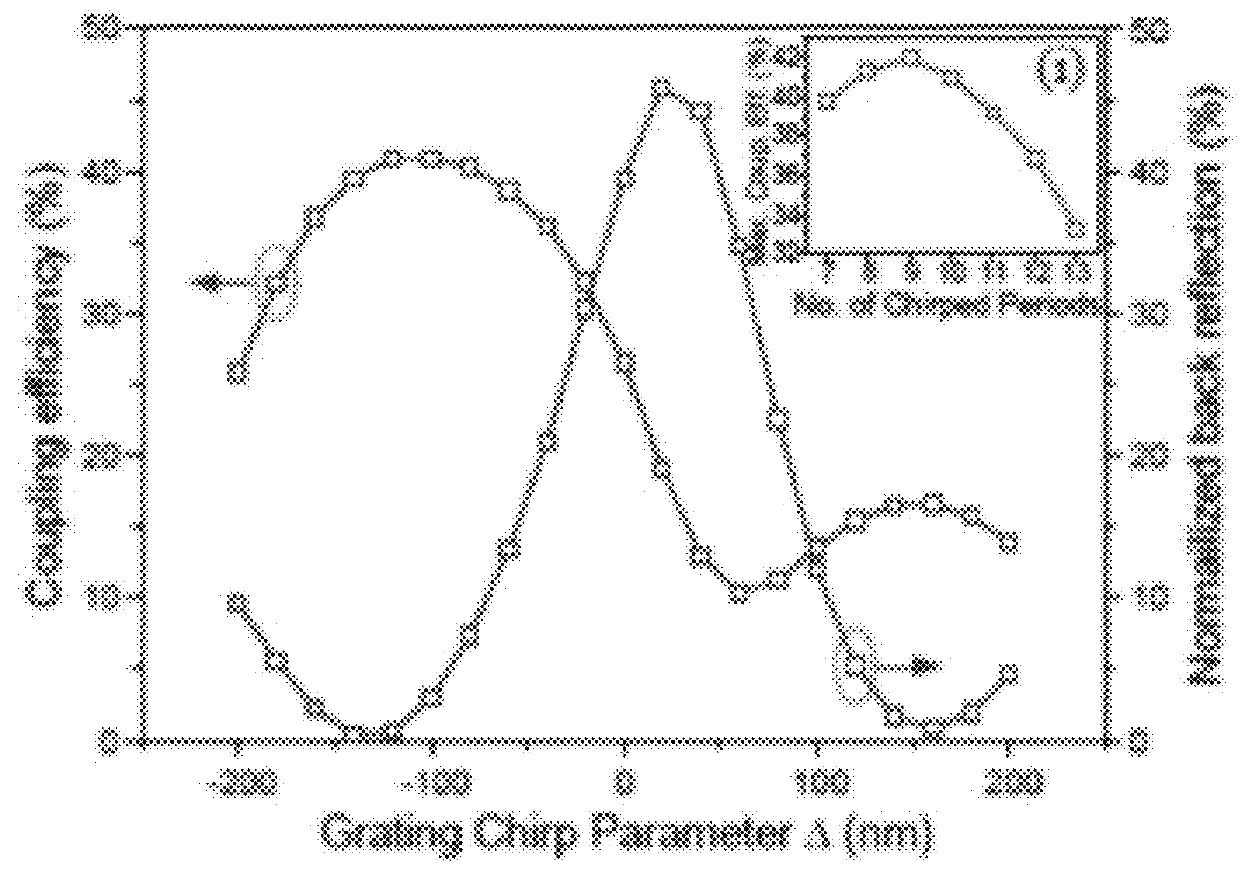
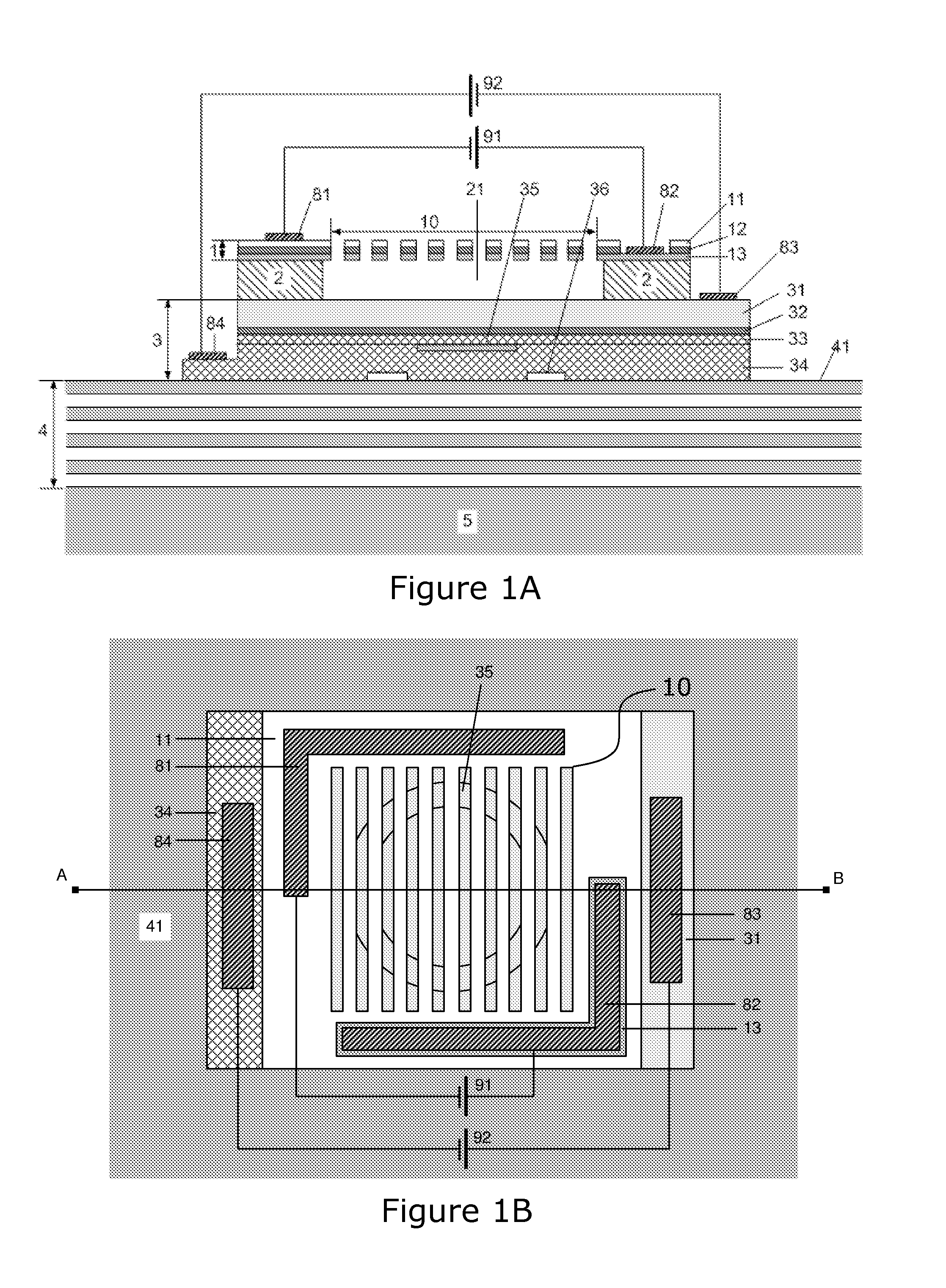
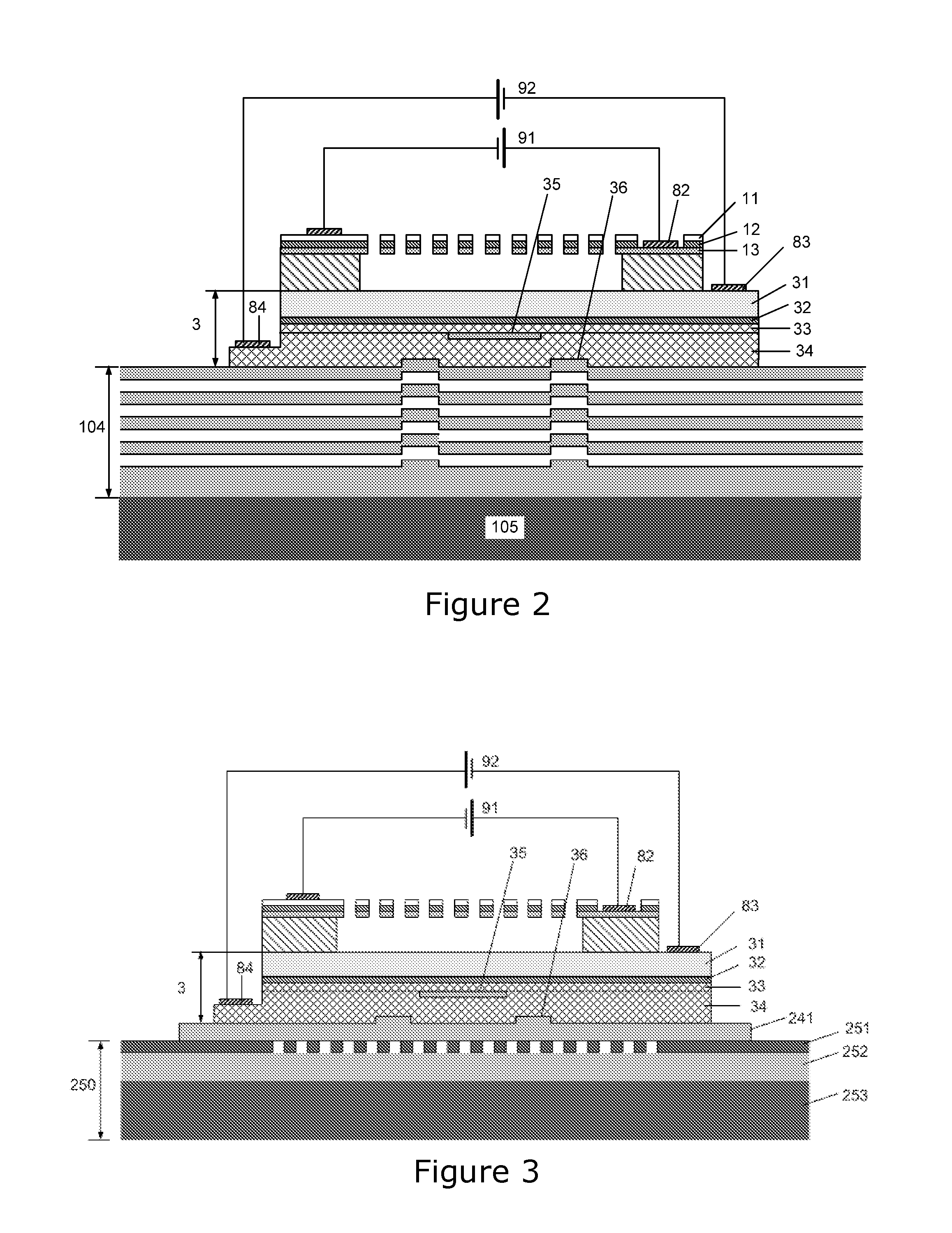
The invention relates to vertical cavity lasers (VCL) incorporating a reflectivity-modulated grating mirror (1) for modulating the laser output. A cavity is formed by a bottom mirror (4), an active region (3), and an outcoupling top grating mirror (1) formed by a periodic refractive index grating region in a layer structure comprising a p- and a n-doped semiconductor layer with an electrooptic material layer (12) arranged there between. The grating region comprises a grating structure formed by periodic perforations to change the refractive index periodically in directions normal to the oscillation axis. A modulated voltage (91) is applied in reverse bias between the n- and p-doped layers to modulate the refractive index of the electrooptic material layer (12) and thereby the reflectivity spectrum of the grating mirror (1). The reflectivity of the grating mirror (1) can be modulated between a reflectivity with little or no out coupling and a reflectivity with normal out coupling, wherein lasing in the VCL is supported at both the first and the second reflectivity. As the out coupling mirror modulates the output, the lasing does not need to be modulated, and the invention provides the advantage of lower power consumption at high modulation speeds.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
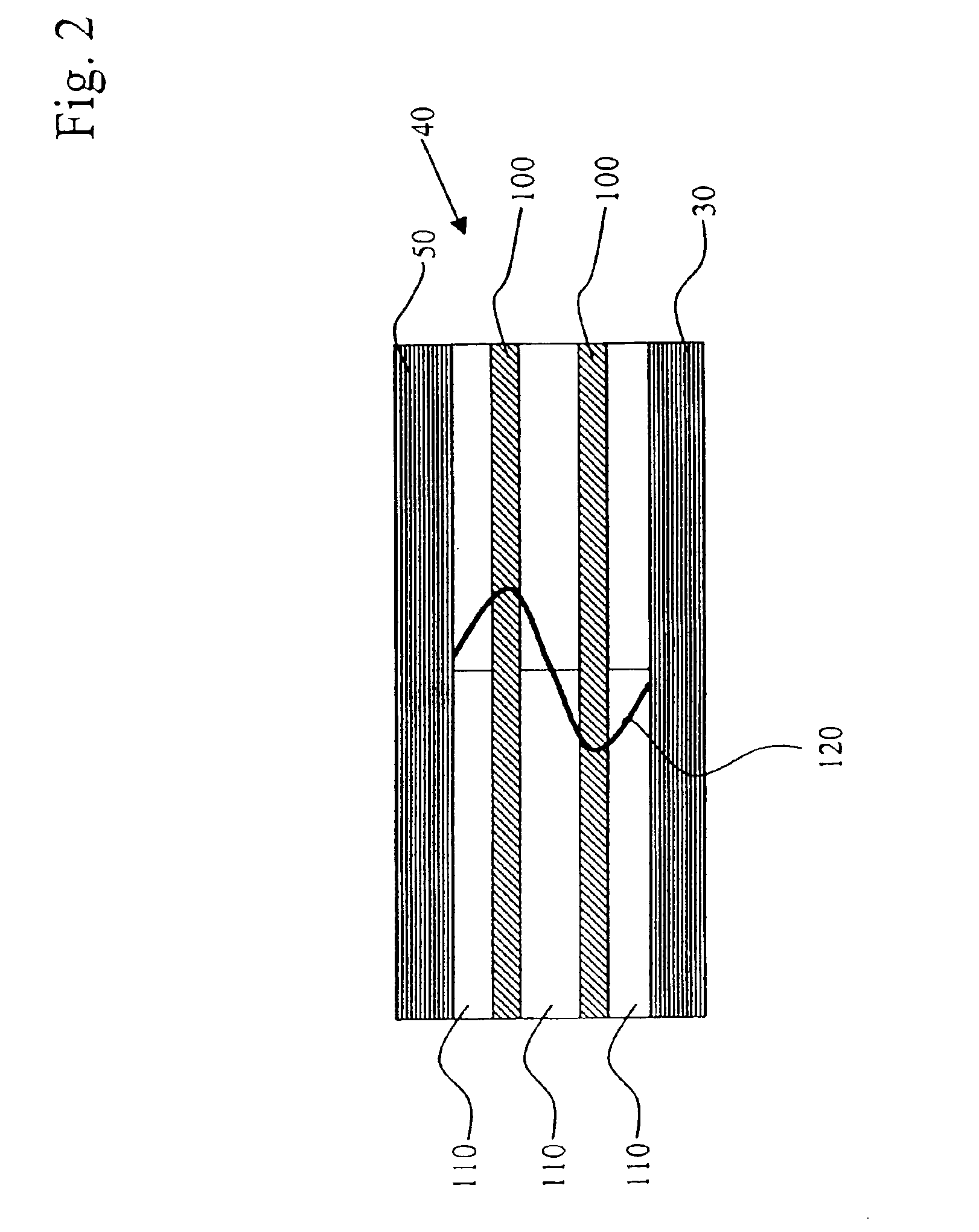
Providing an improved organic vertical cavity laser array device
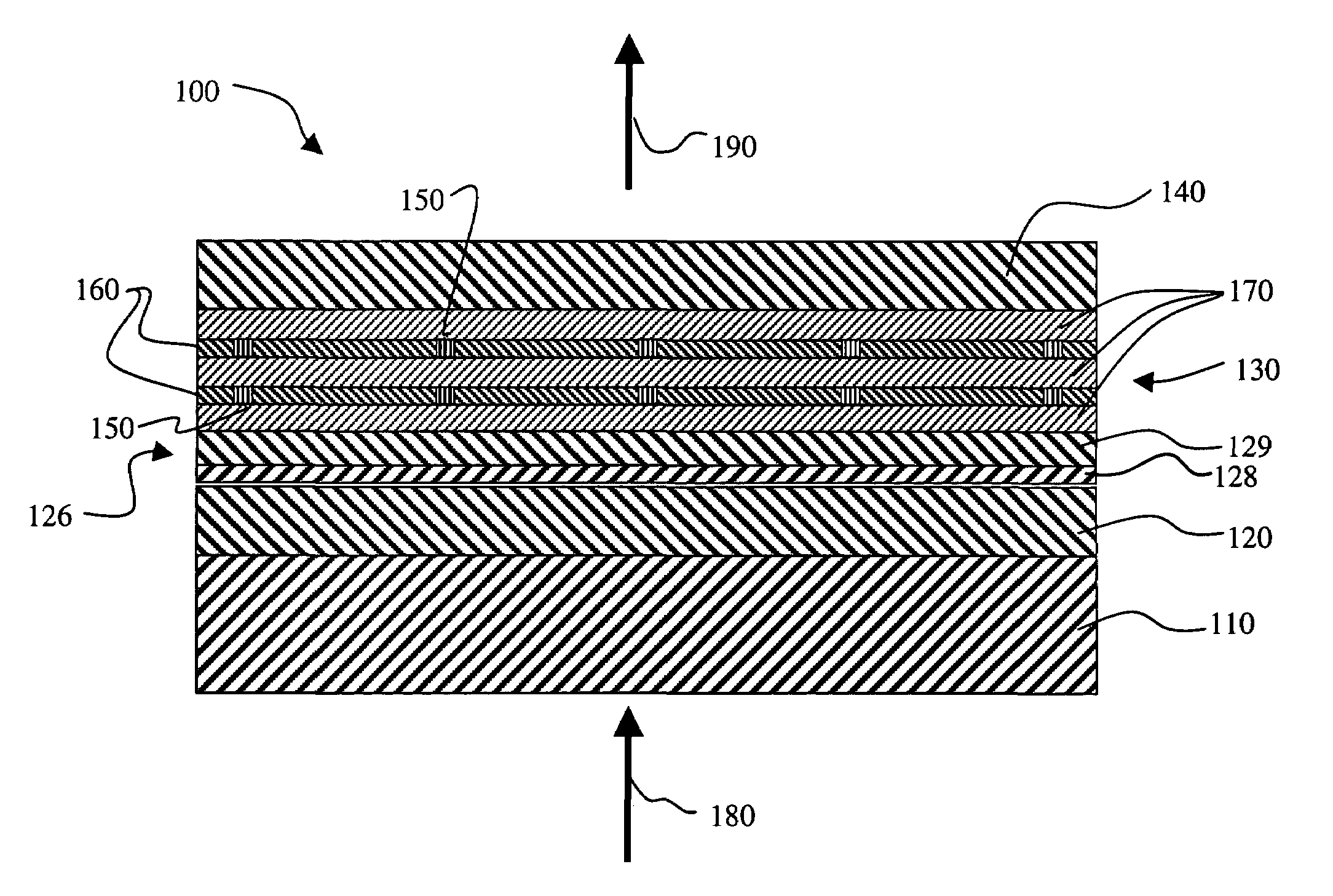
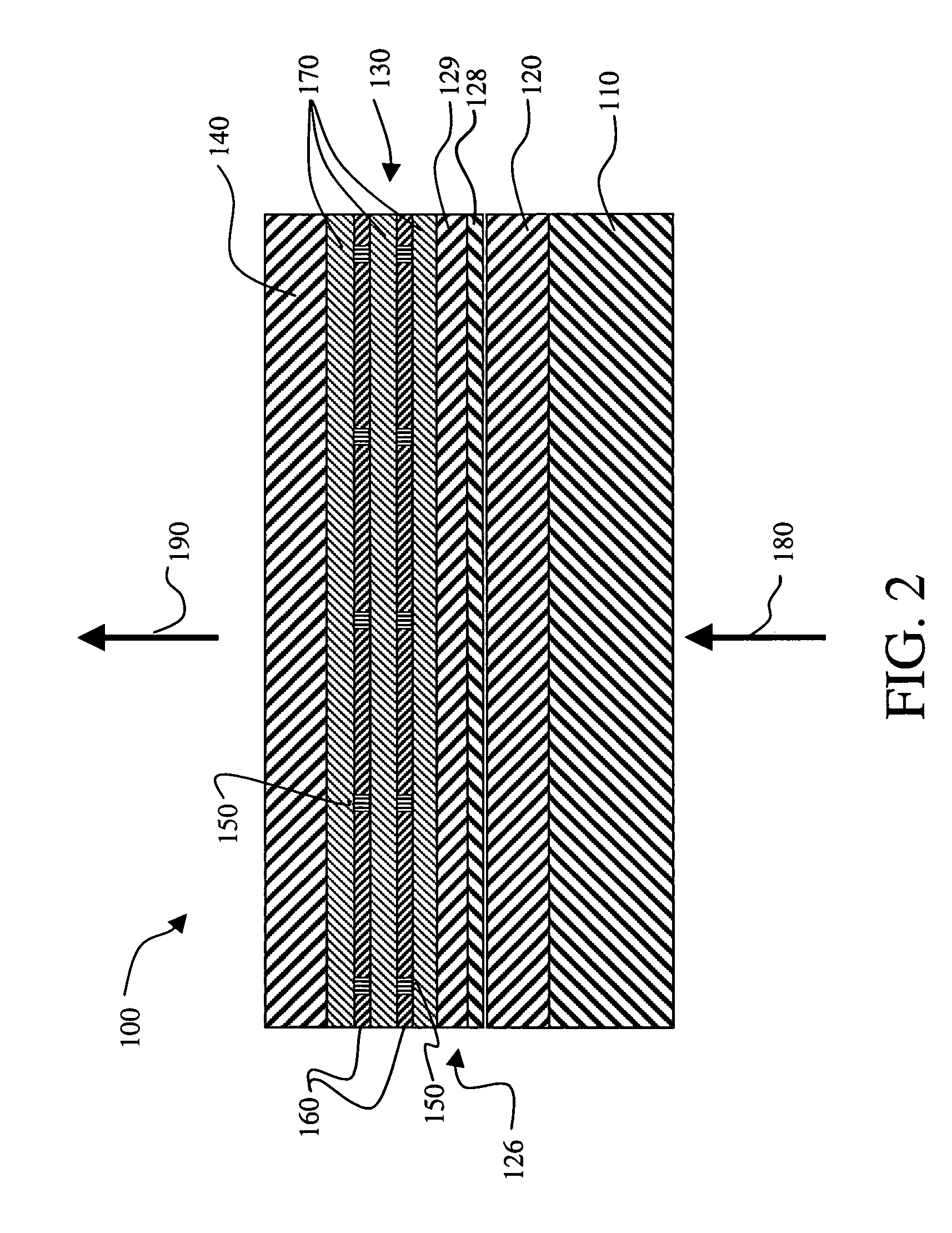
InactiveUS6996146B1Reduced scattering lossImprove power conversion efficiencyLaser active region structureOptical resonator shape and constructionDielectricLaser light
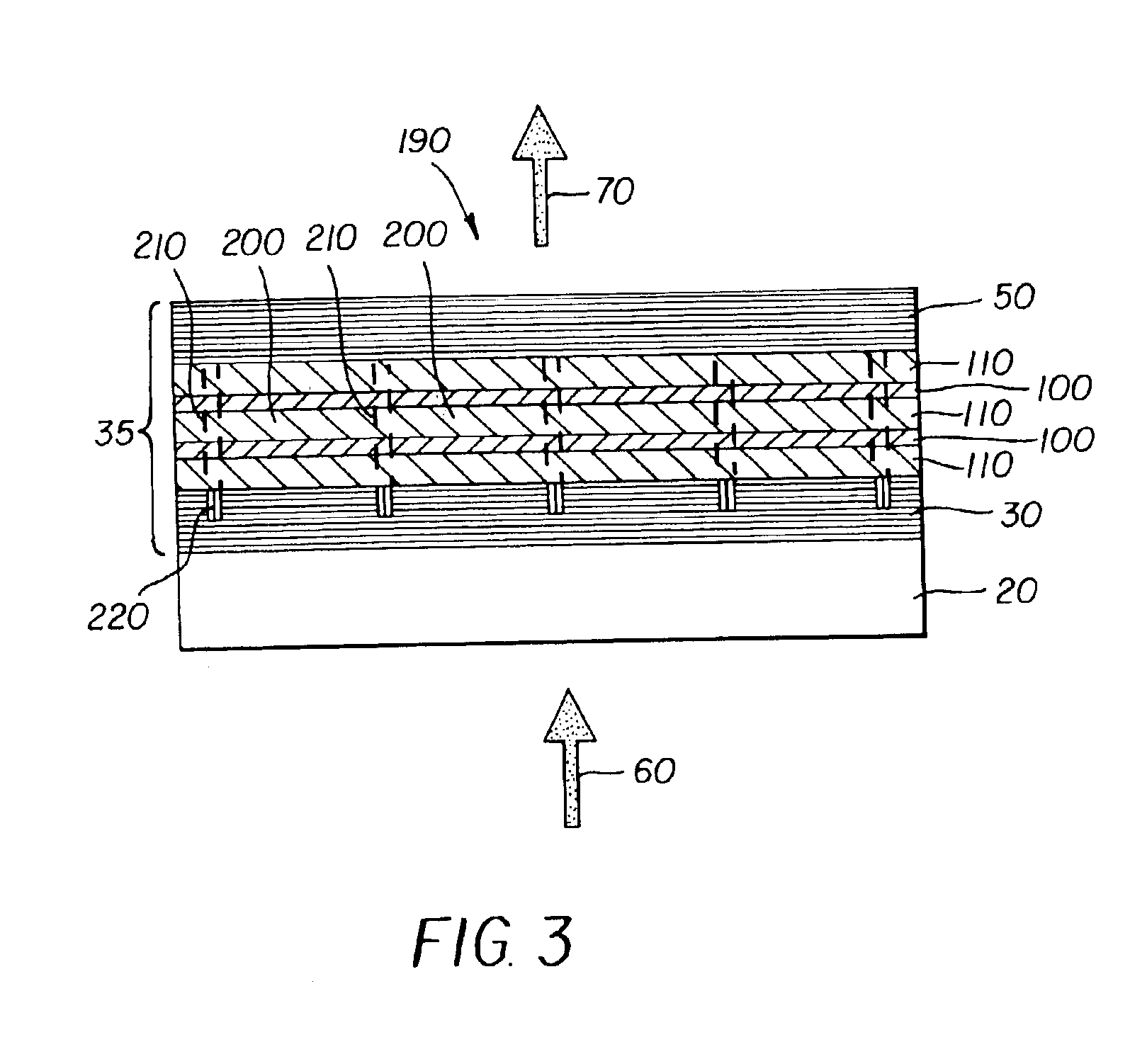
A method of making an organic vertical cavity laser array device includes providing a substrate and a bottom dielectric stack reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths and being disposed over the substrate; forming an etched region in the top surface of the bottom dielectric stack to define an array of spaced laser pixels which have higher reflectance than the interpixel regions so that the array emits laser light; and forming a planarization layer over the etched bottom dielectric stack. The method also includes forming an active region over the planarization layer for producing laser light; and forming a top dielectric stack spaced from the bottom dielectric stack and reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Organic vertical cavity laser element with organic active region
InactiveCN1497812AEasy to operateHigh power conversion rateLaser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusDielectricLaser transmitter
An organic vertical cavity laser light producing device includes a bottom dielectric stack reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths; an organic active region for producing laser light, and having an organic active region including emissive material; and a top dielectric stack spaced from the bottom dielectric stack and reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. Pump-beam light is transmitted and introduced into the organic active region through at least one of the dielectric stacks. The organic active region includes one or more periodic gain region(s) and organic spacer layers disposed on either side of the periodic gain region(s) and arranged so that the periodic gain region(s) is aligned with the antinodes of the device's standing wave electromagnetic field, and wherein the spacer layers are substantially transparent to the laser light.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Modulating the properties of the gain region at spaced locations in an organic vertical cavity laser array device
InactiveUS7012942B2Improve launch performanceLaser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusOptoelectronicsLaser light
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
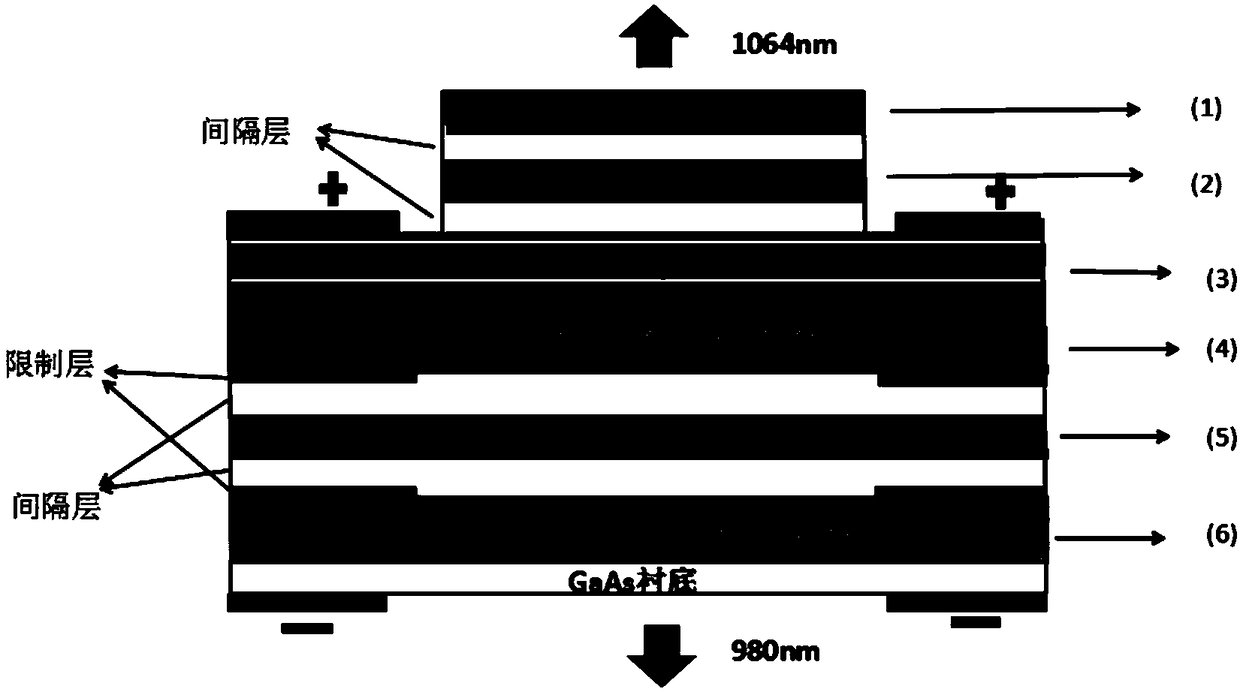
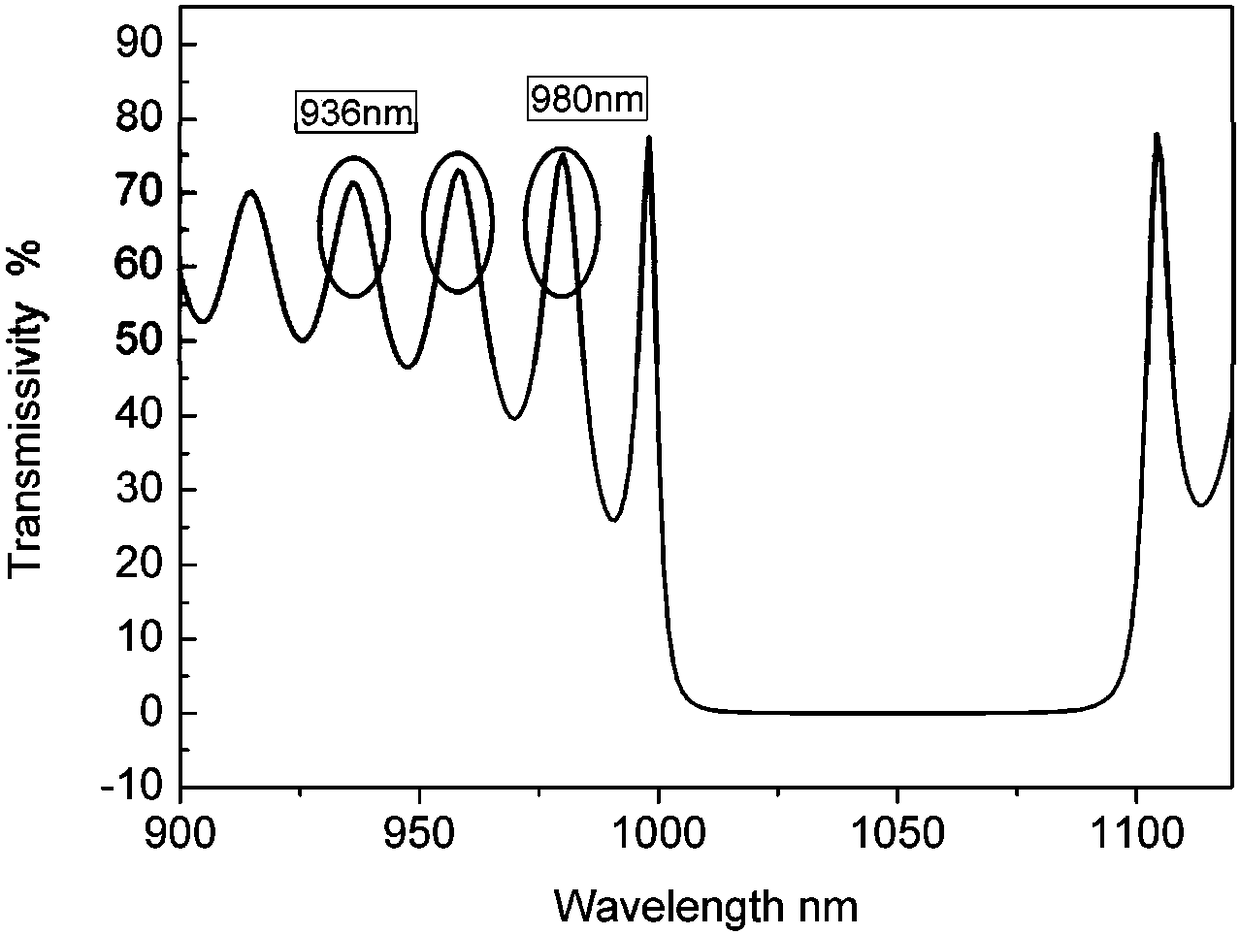
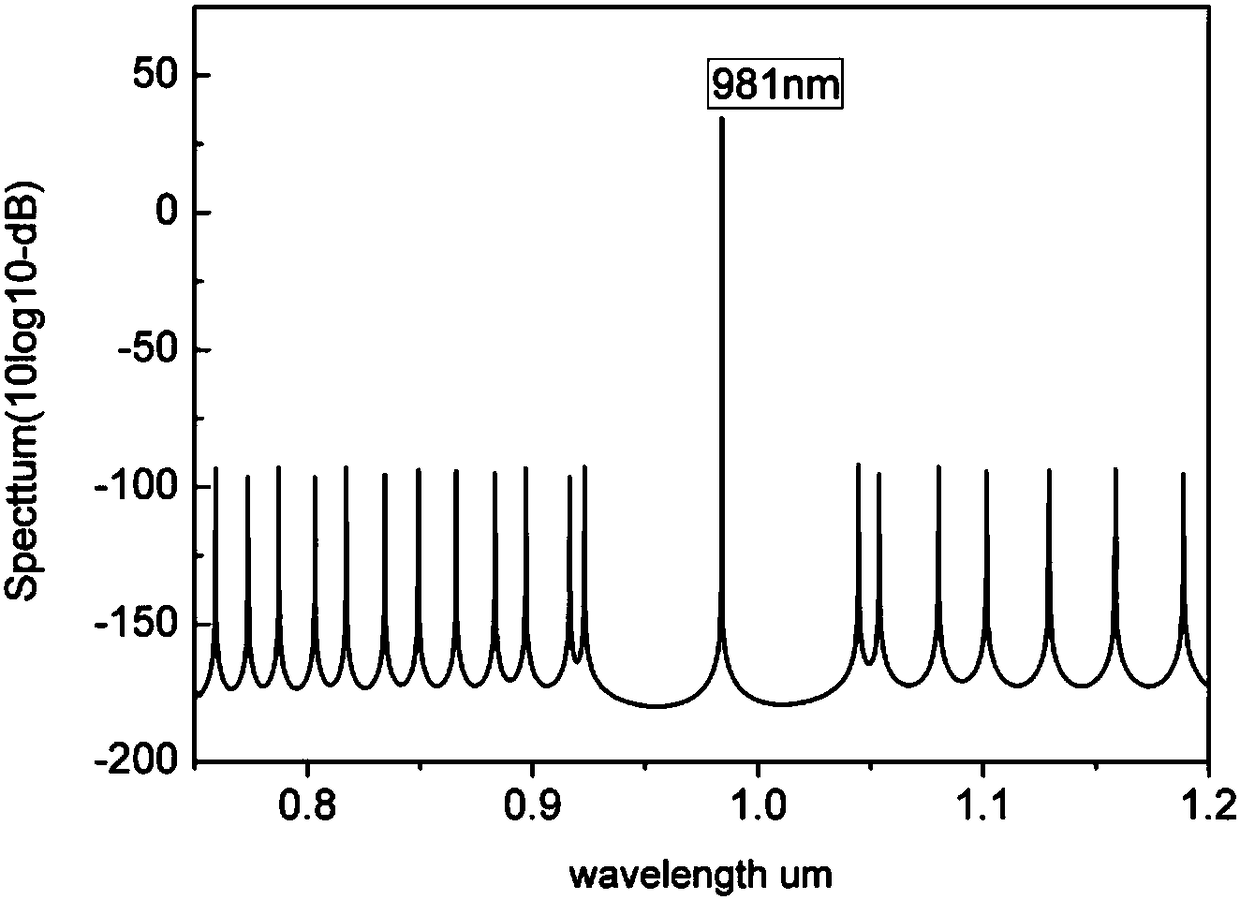
Primary epitaxial growth dual-wavelength semiconductor laser device
InactiveCN108155561AUpper and lower light output power controllableLight output power controllableLaser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusOptical powerLaser light
The invention discloses a primary epitaxial growth dual-wavelength semiconductor laser device which comprises a pump light vertical cavity, an excited vertical cavity and a GaAs substrate. Laser lightwith adjustable output optical power can be simultaneously generated by the pump light vertical cavity in the up-down directions, emergent laser light in the upper direction is used as pump light tobe transmitted into the excited vertical cavity, lasing of laser devices of the excited vertical cavity can be pumped by the light, accordingly, dual-wavelength lasing of integrated vertical cavitiescan be implemented, dual-wavelength laser light can be subjected to emergence from the integrated vertical cavities in the upper direction and the lower direction, and the pump light vertical cavity and the excited vertical cavity are formed by means of primary epitaxial growth.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mid-infrared vertical cavity laser
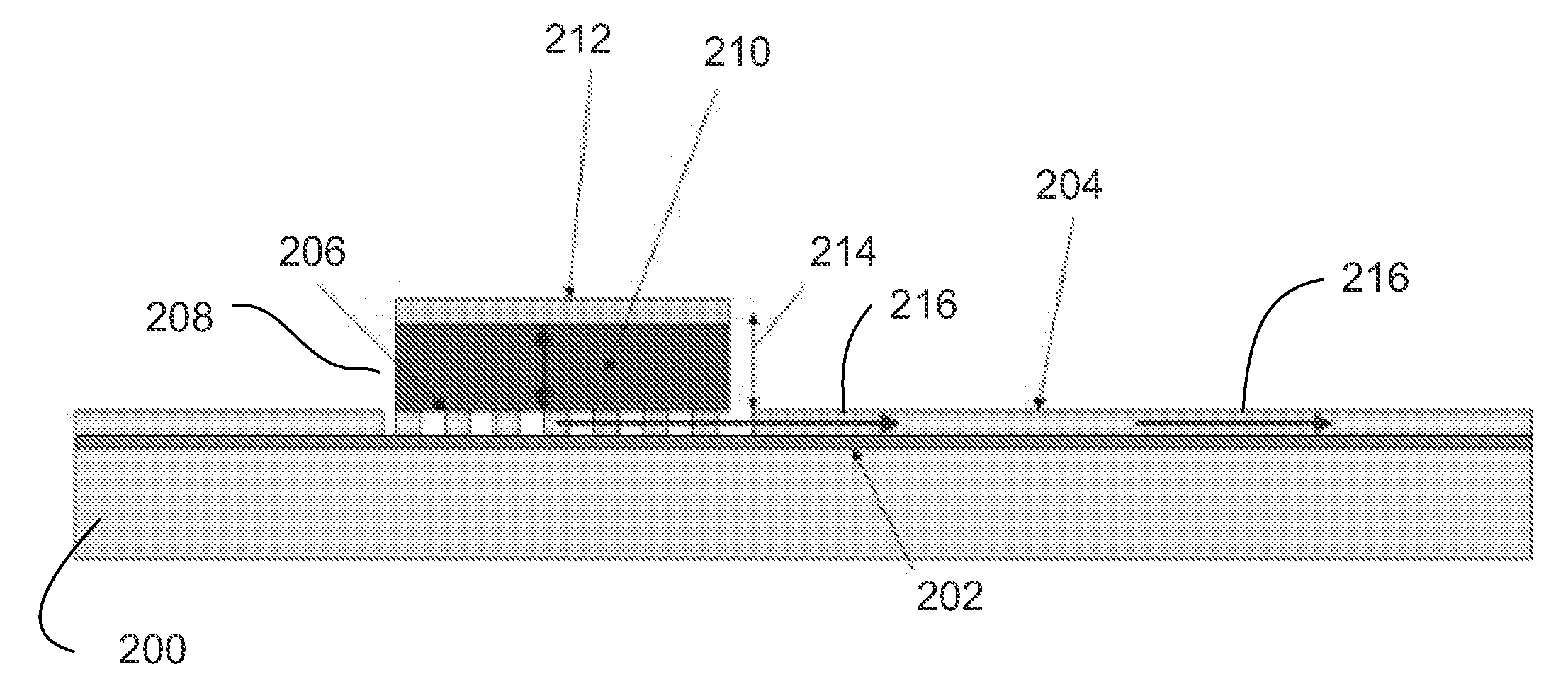
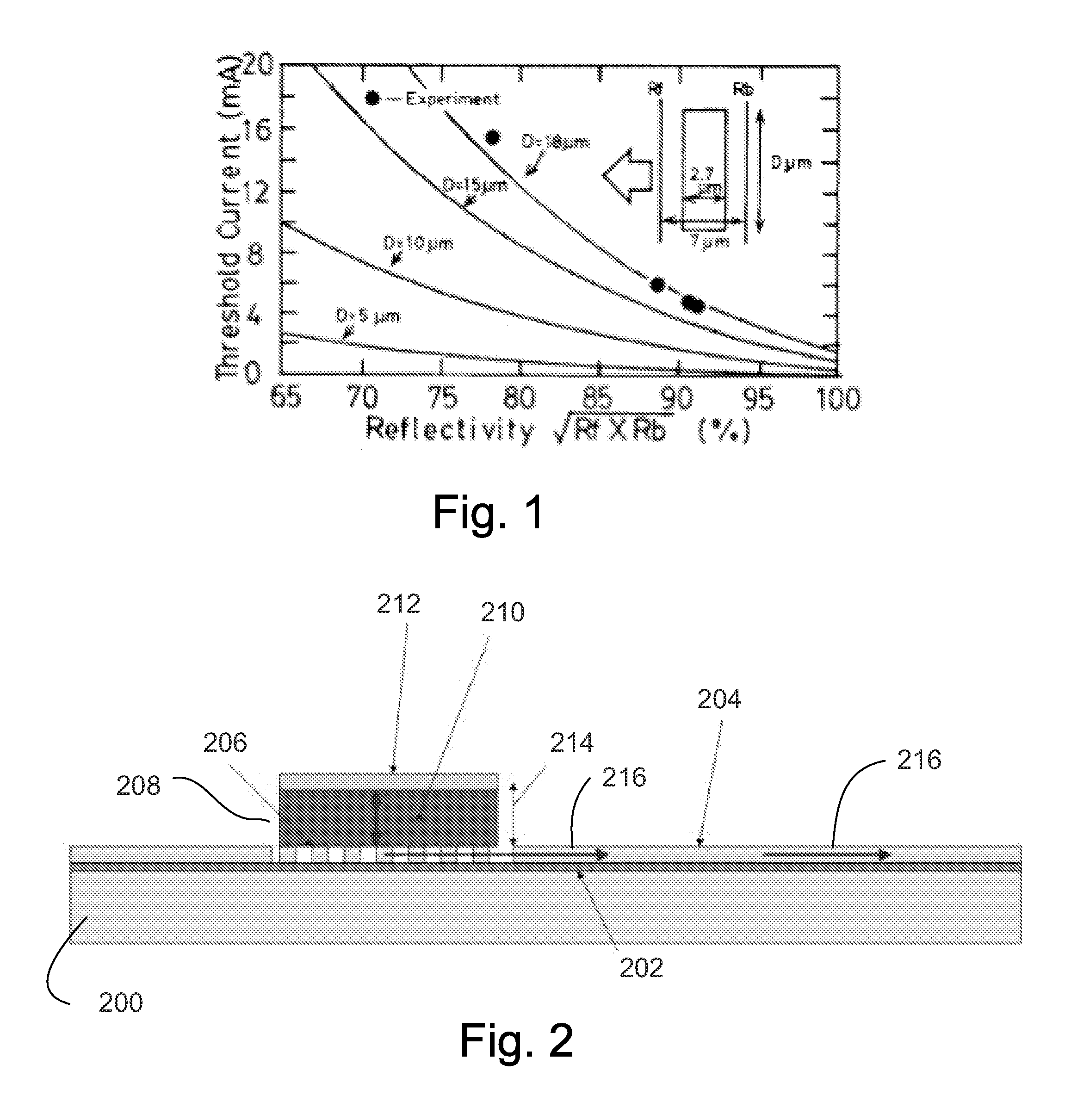
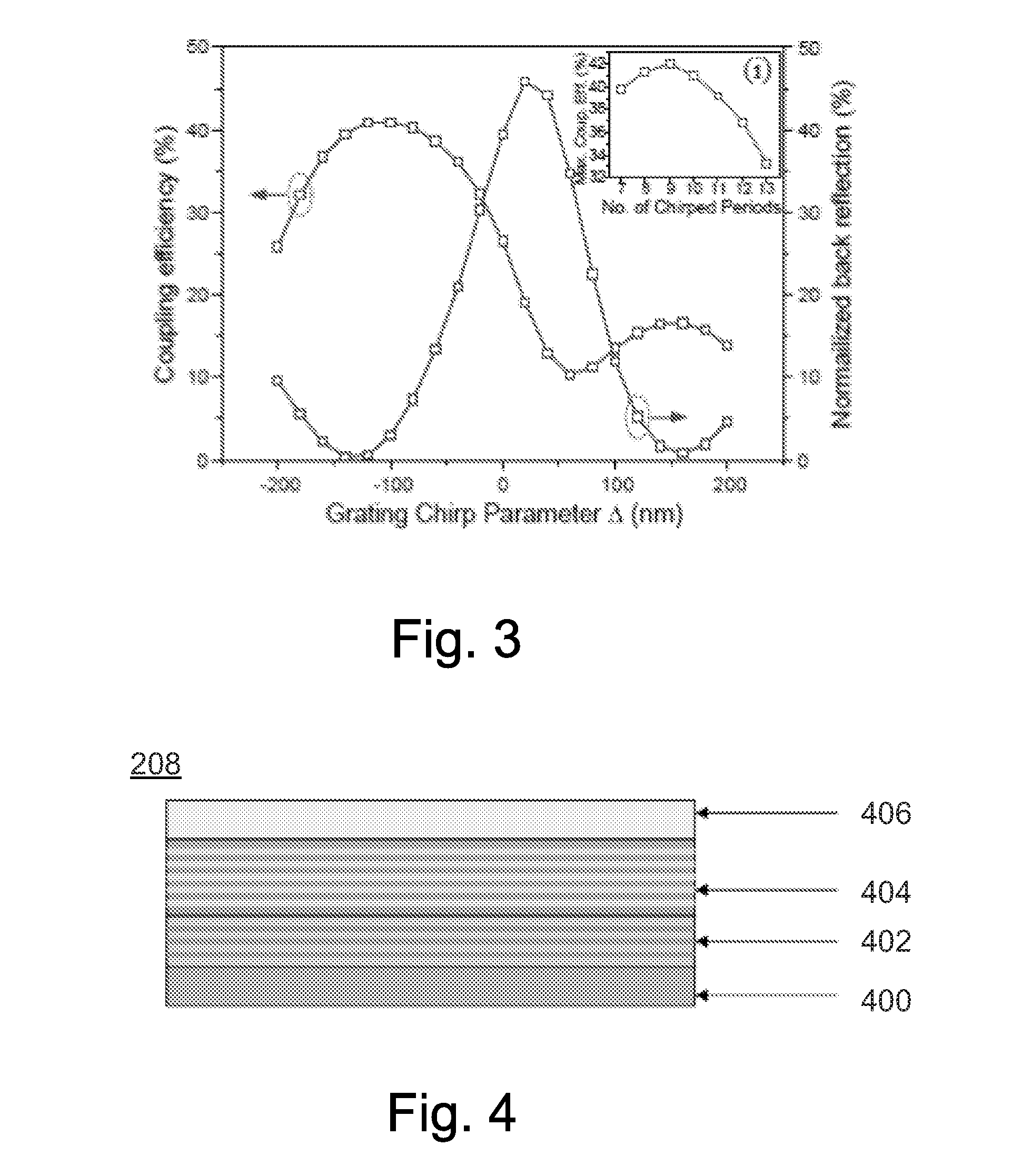
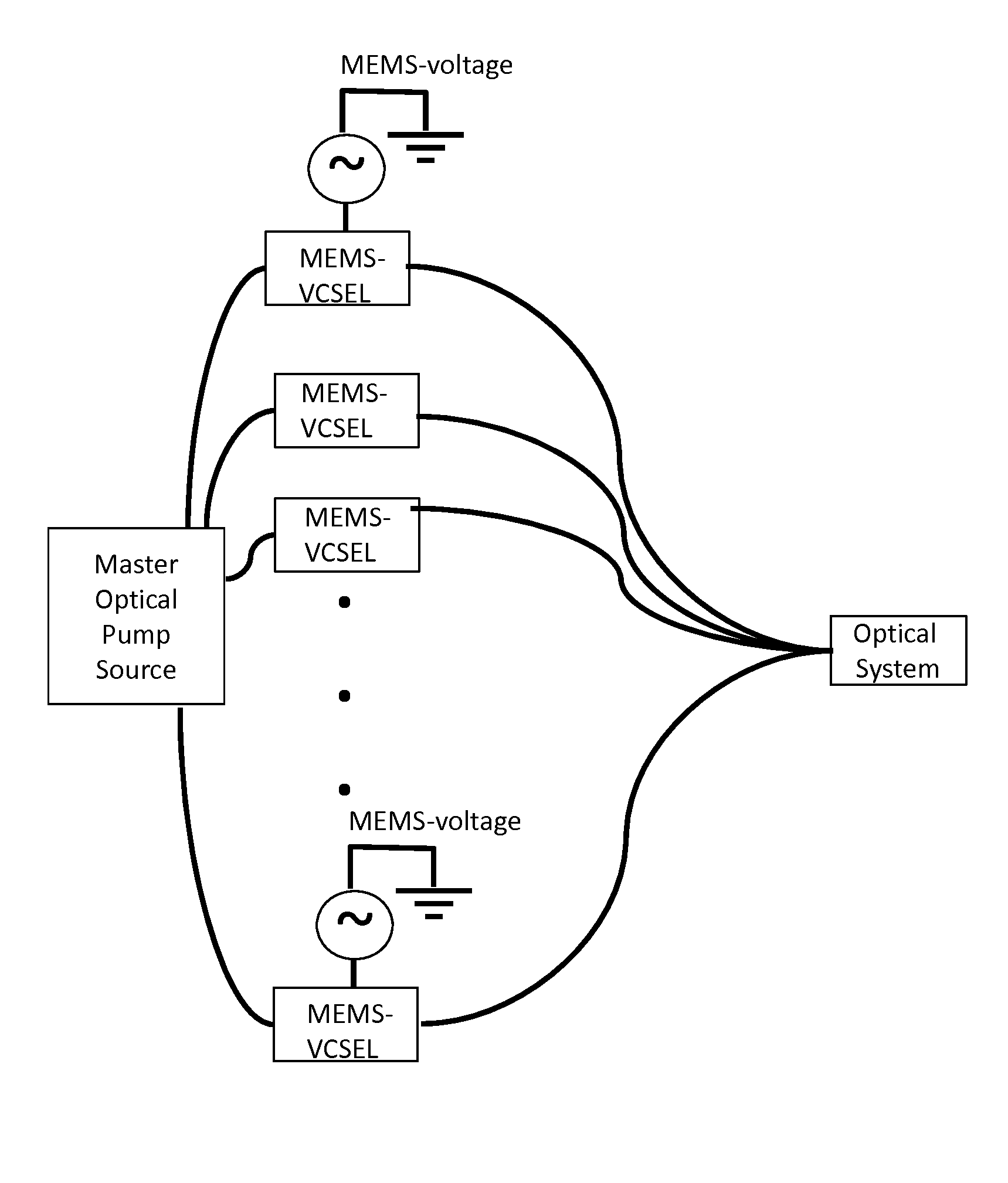
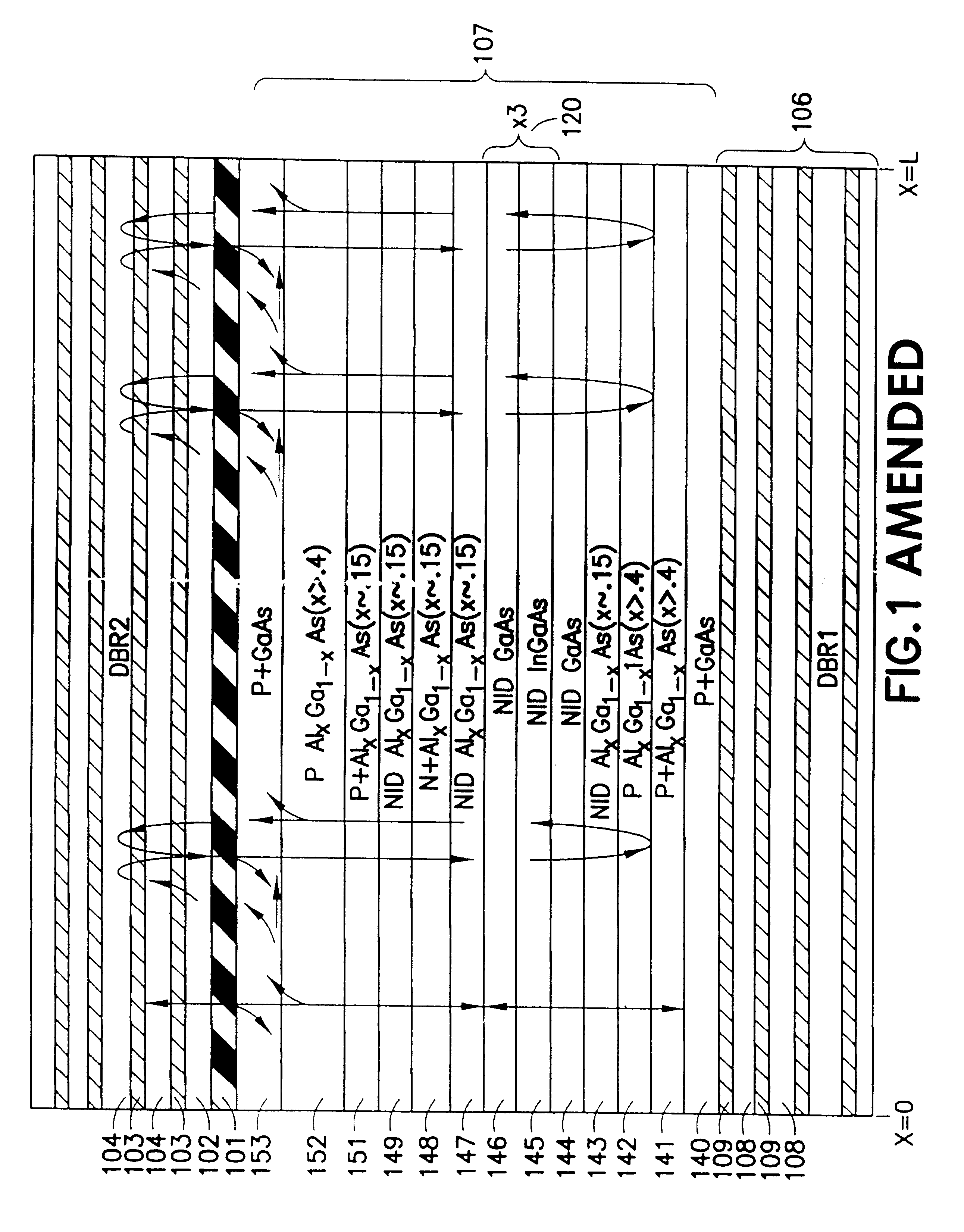
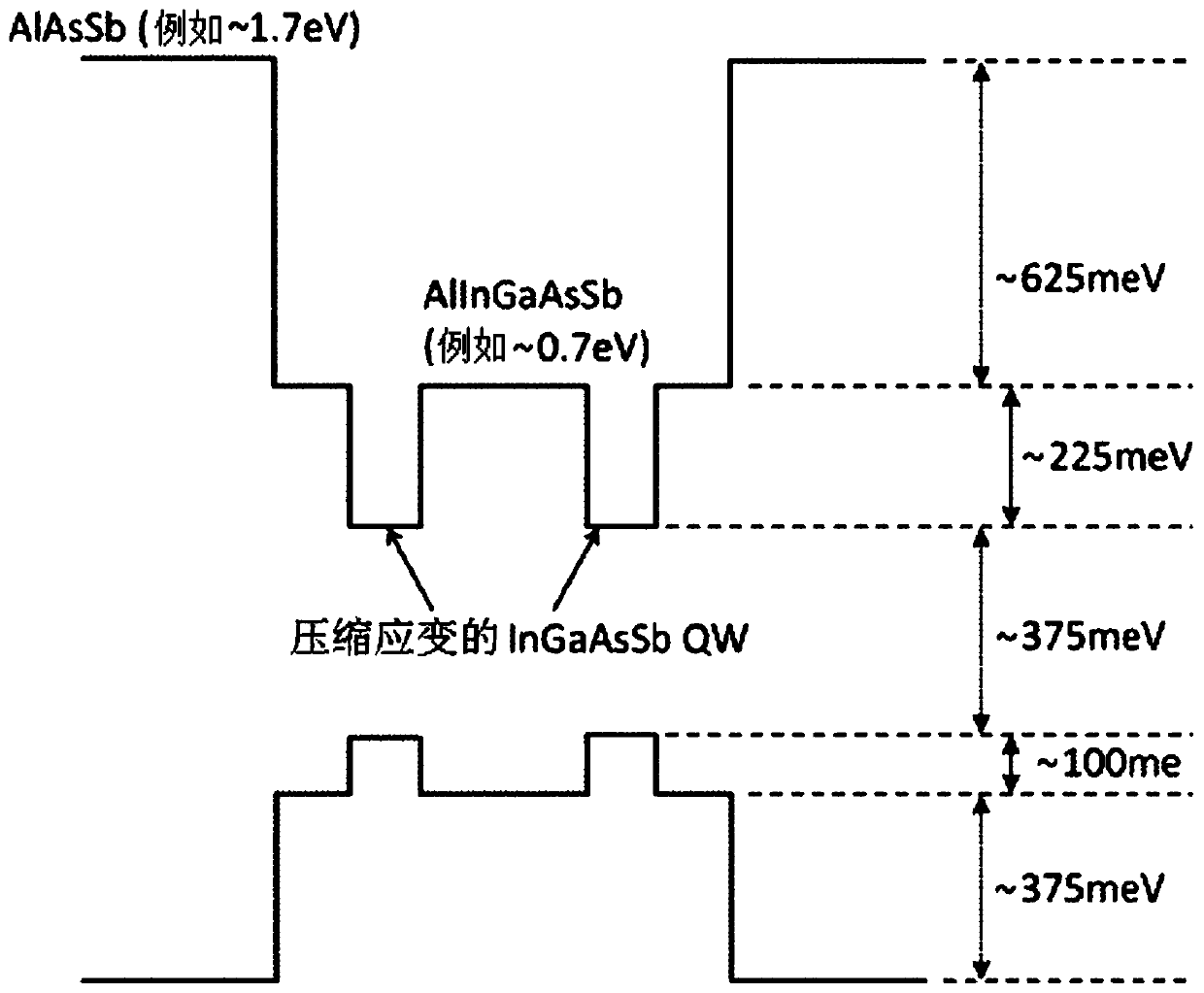
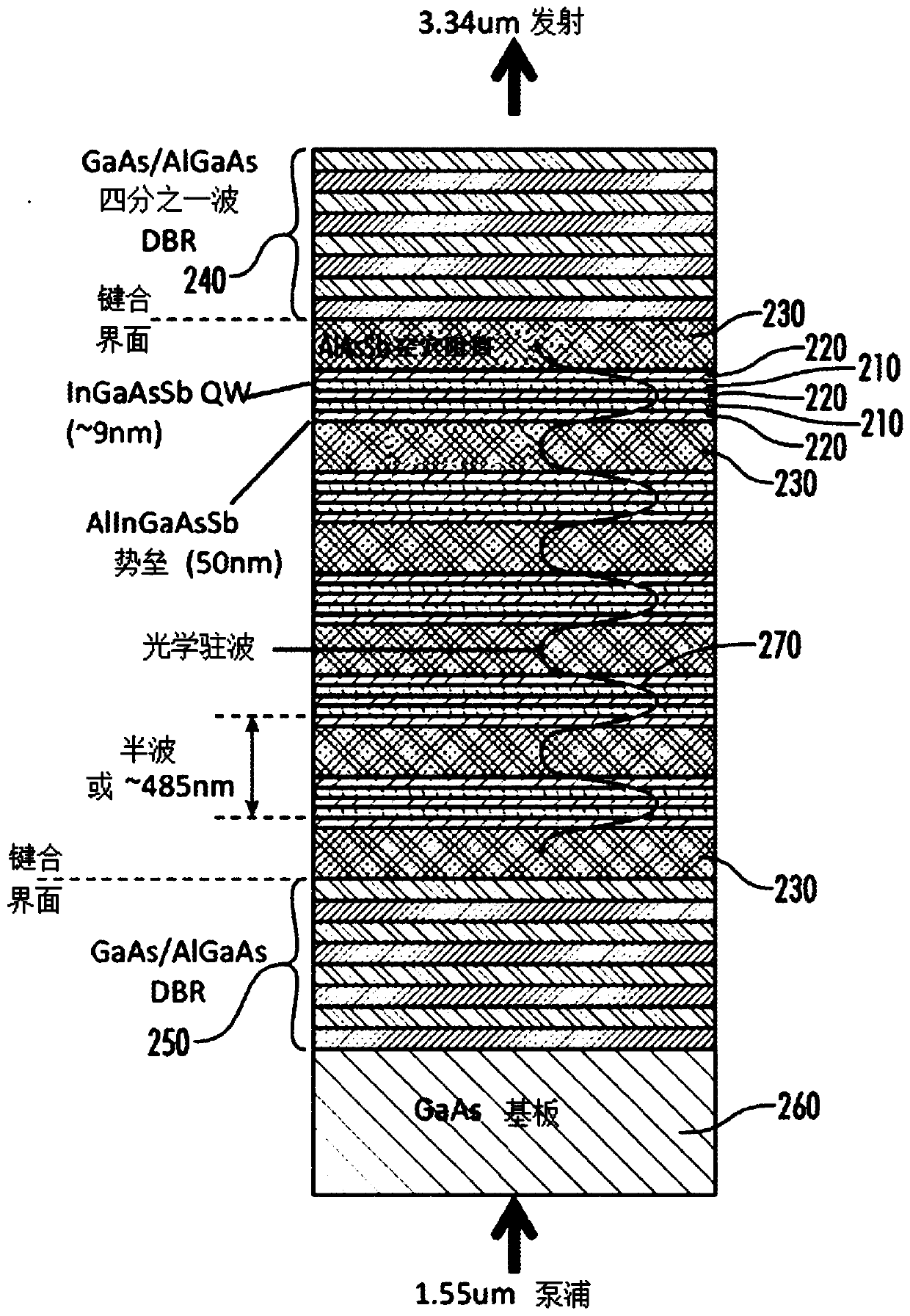
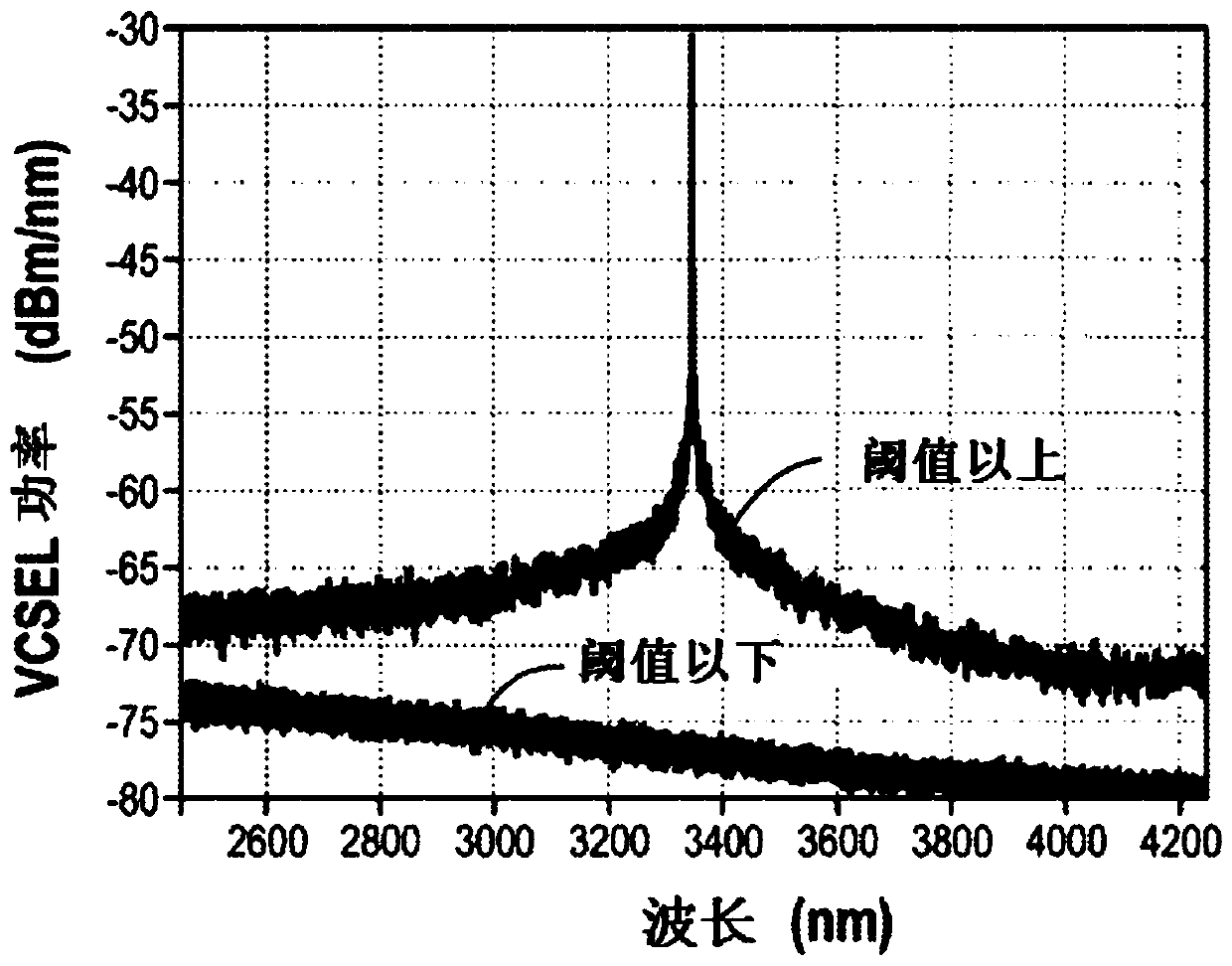
Disclosed is an optically pumped vertical cavity laser structure operating in the mid-infrared region, which has demonstrated room-temperature continuous wave operation. This structure uses a periodicgain active region with type I quantum wells comprised of InGaAsSb, and barrier / cladding regions which provide strong hole confinement and substantial pump absorption. A preferred embodiment includesat least one wafer bonded GaAs-based mirror. Several preferred embodiments also include means for wavelength tuning of mid-IR VCLs as disclosed, including a MEMS-tuning element. This document also includes systems for optical spectroscopy using the VCL as disclosed, including systems for detection concentrations of industrial and environmentally important gases.
Owner:THORLABS INC +1
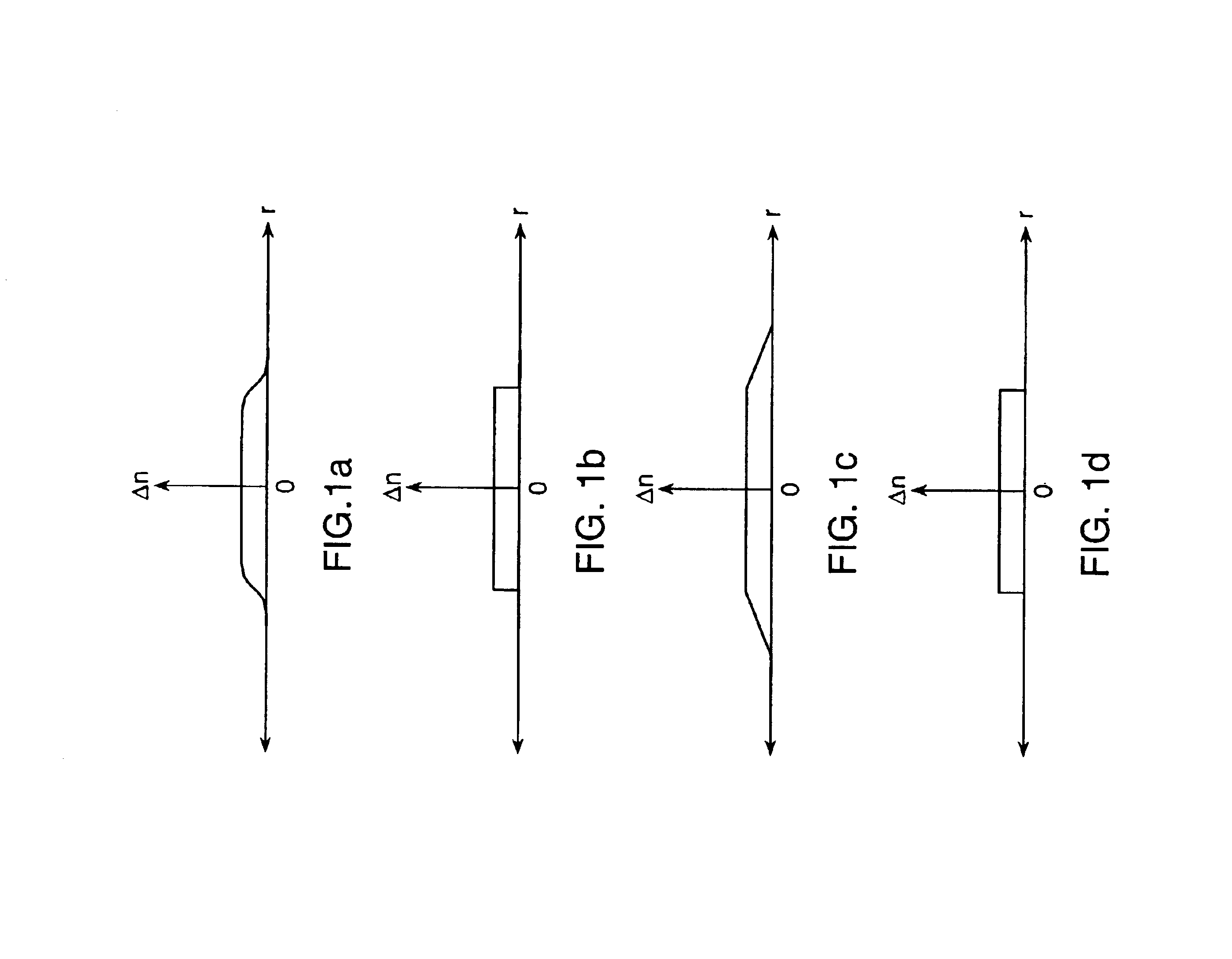
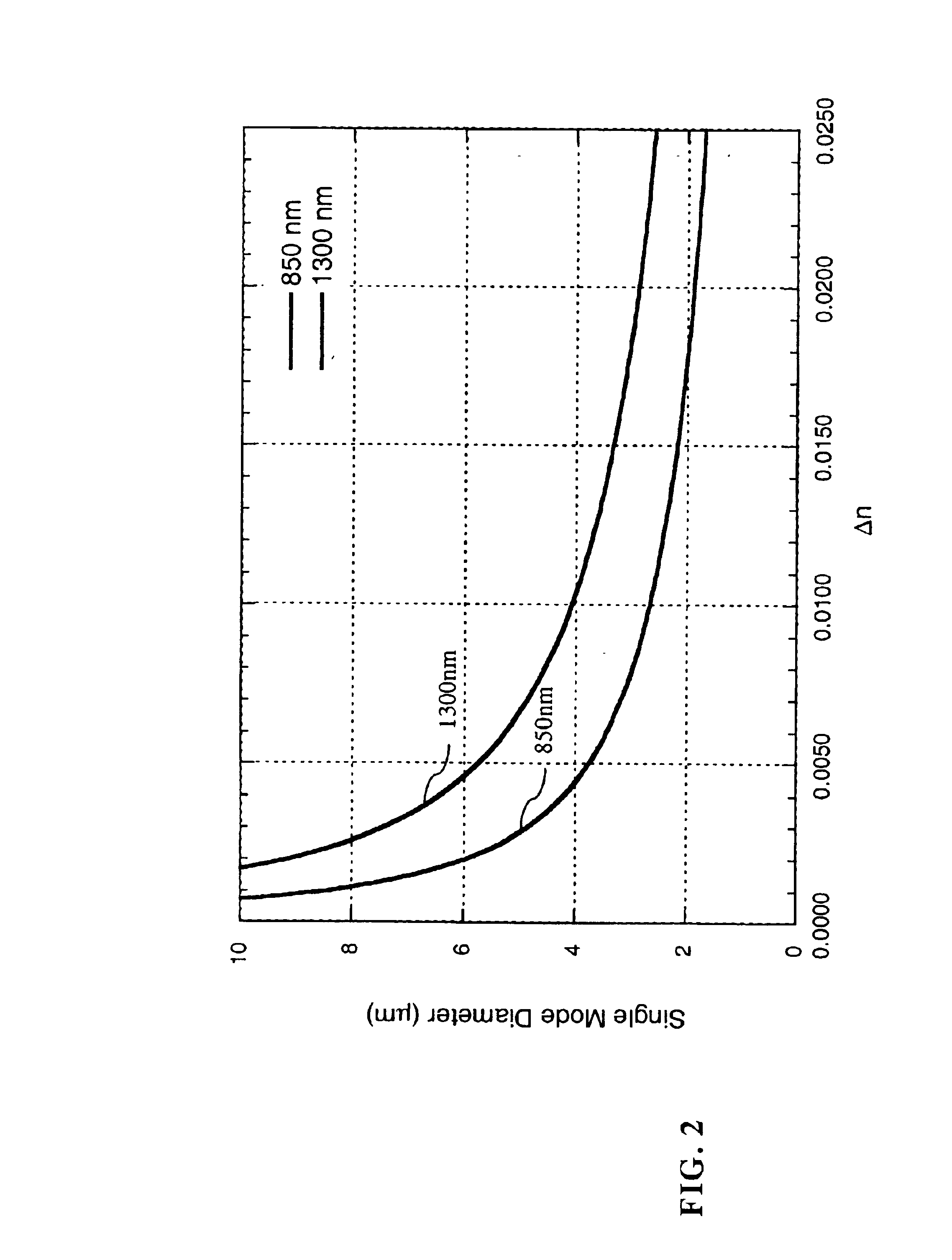
Antiguide single mode vertical cavity laser
InactiveUS6901099B1Large electrical and optical apertureReduce thermal impedance and voltage and resistanceOptical wave guidanceOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical cavityRefractive index
A vertical cavity laser (VCL) including a first mirror formed adjacent a substrate, an optical cavity formed adjacent the first mirror, a second mirror formed adjacent the optical cavity, a first current and / or optical aperture formed within the cavity, within the mirror or at the surface of the mirror, and an antiguide for reducing, balancing, or reversing the index step created by the first current and / or optical aperture. The VCL may further include a second optical aperture for confining the optical mode to provide single mode operation.
Owner:OPTICAL COMM PRODS
Optical modulation device using vertical cavity laser array with electromechanical raster device
InactiveCN1497272AIncrease contrastHigh resolutionLaser detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDiffraction orderGrating
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Hybrid vertical cavity laser and method of manufacturing the same
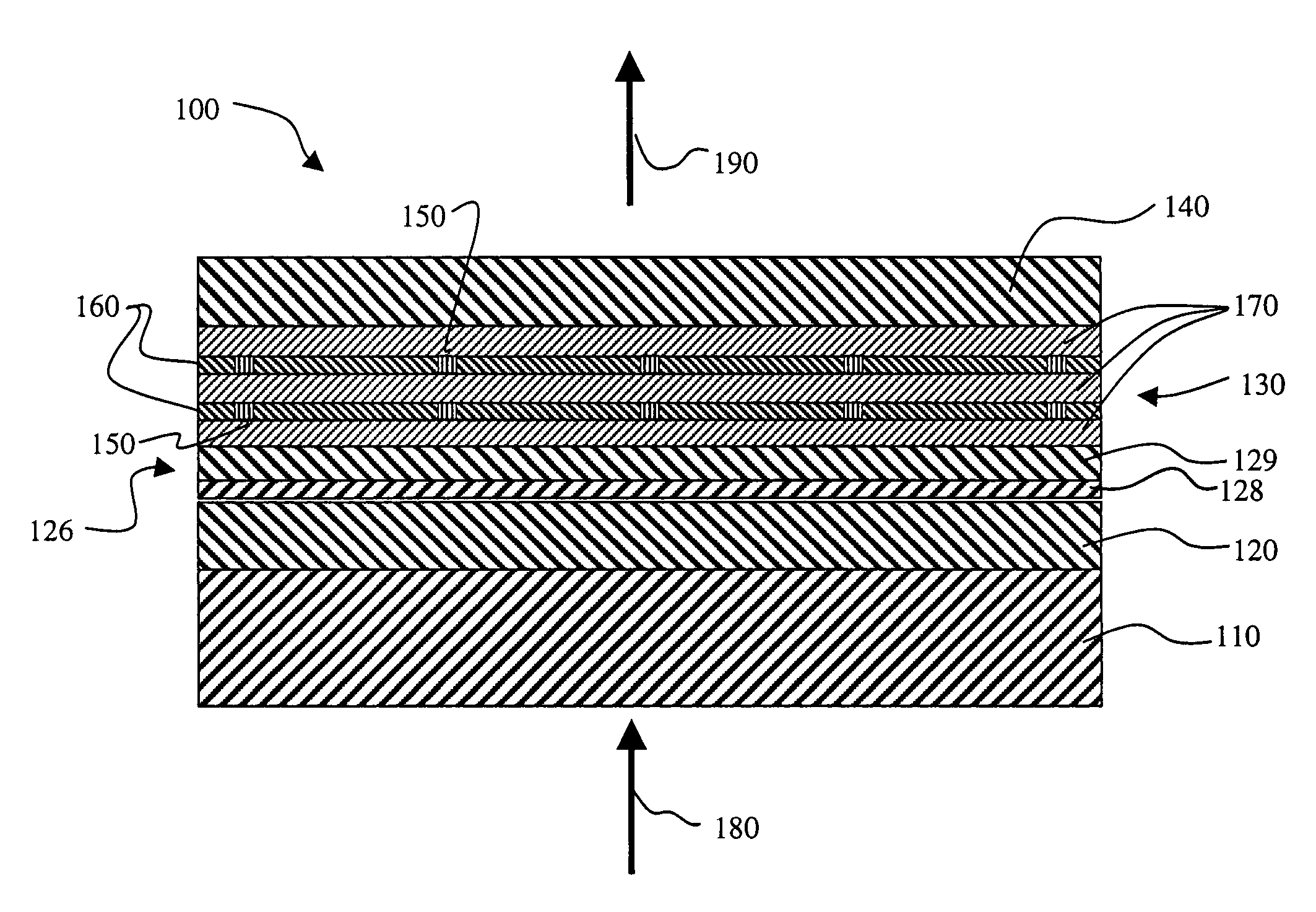
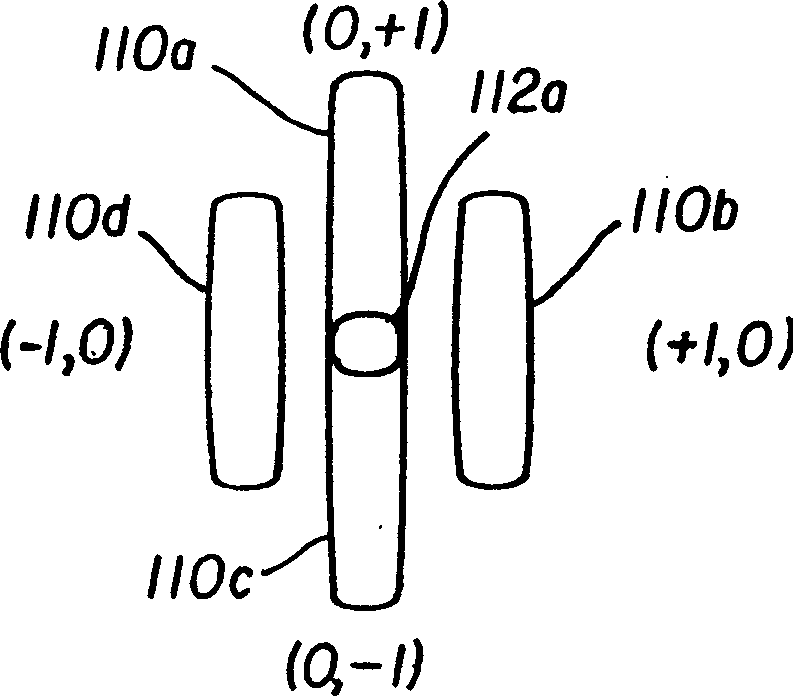
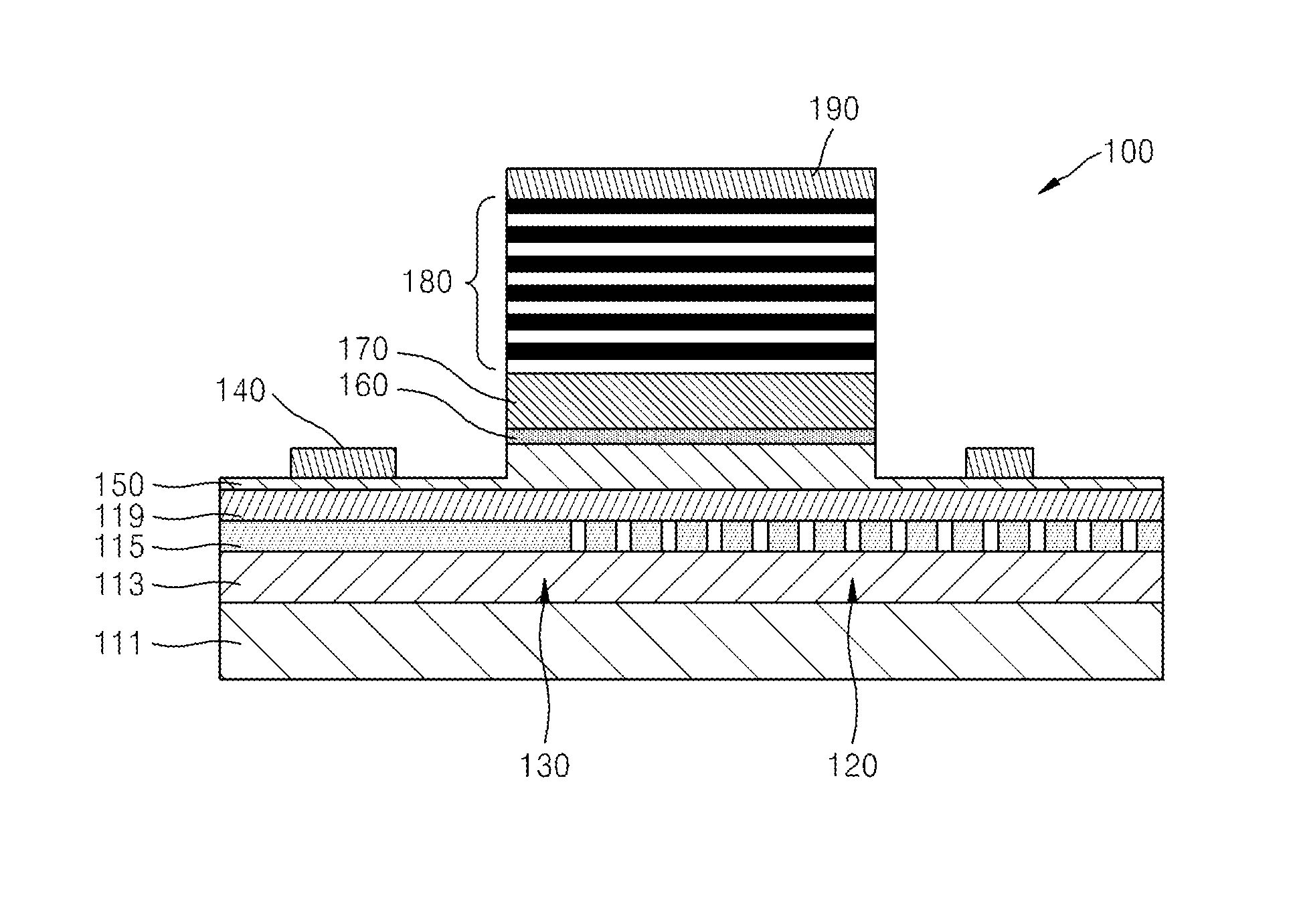
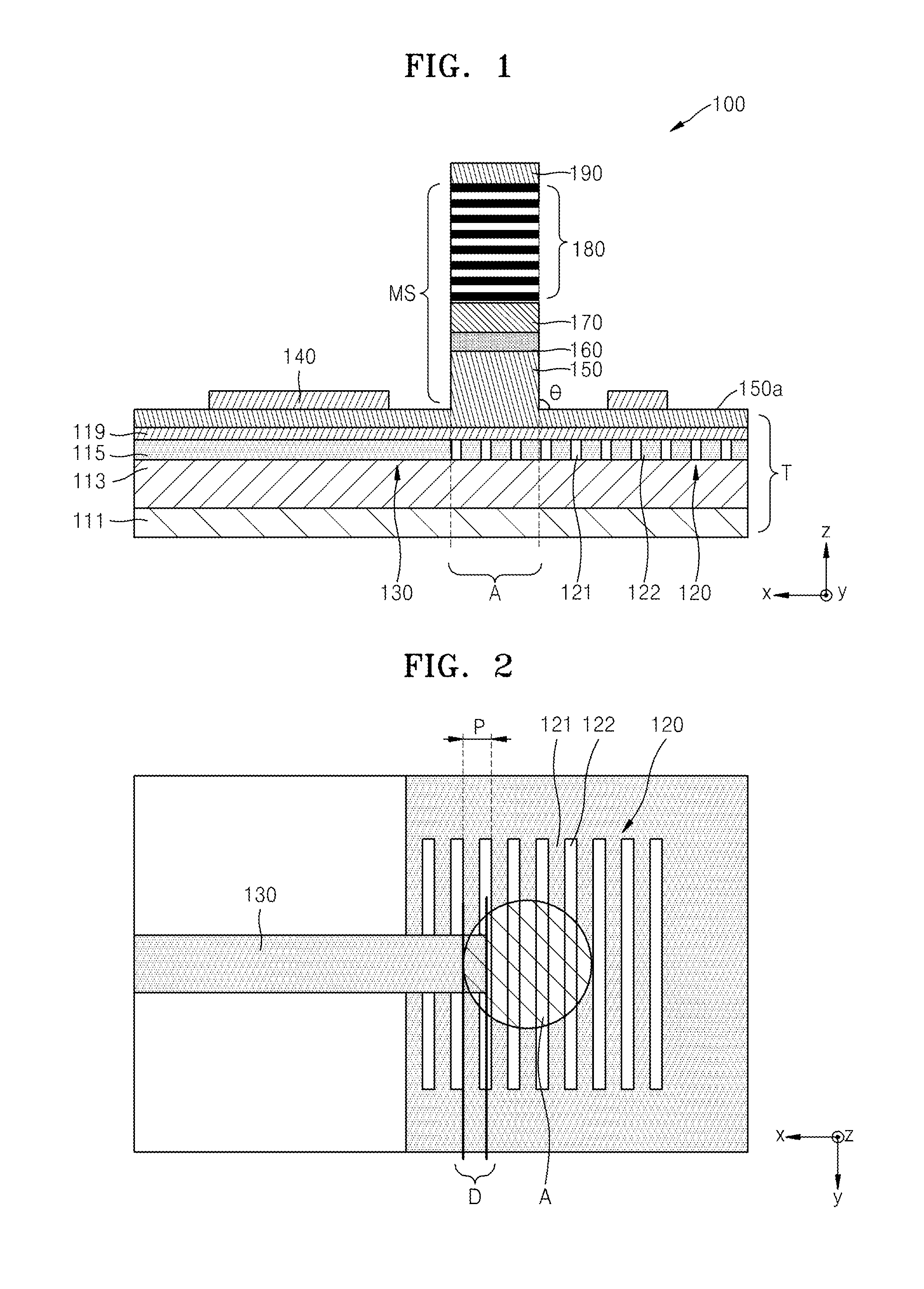
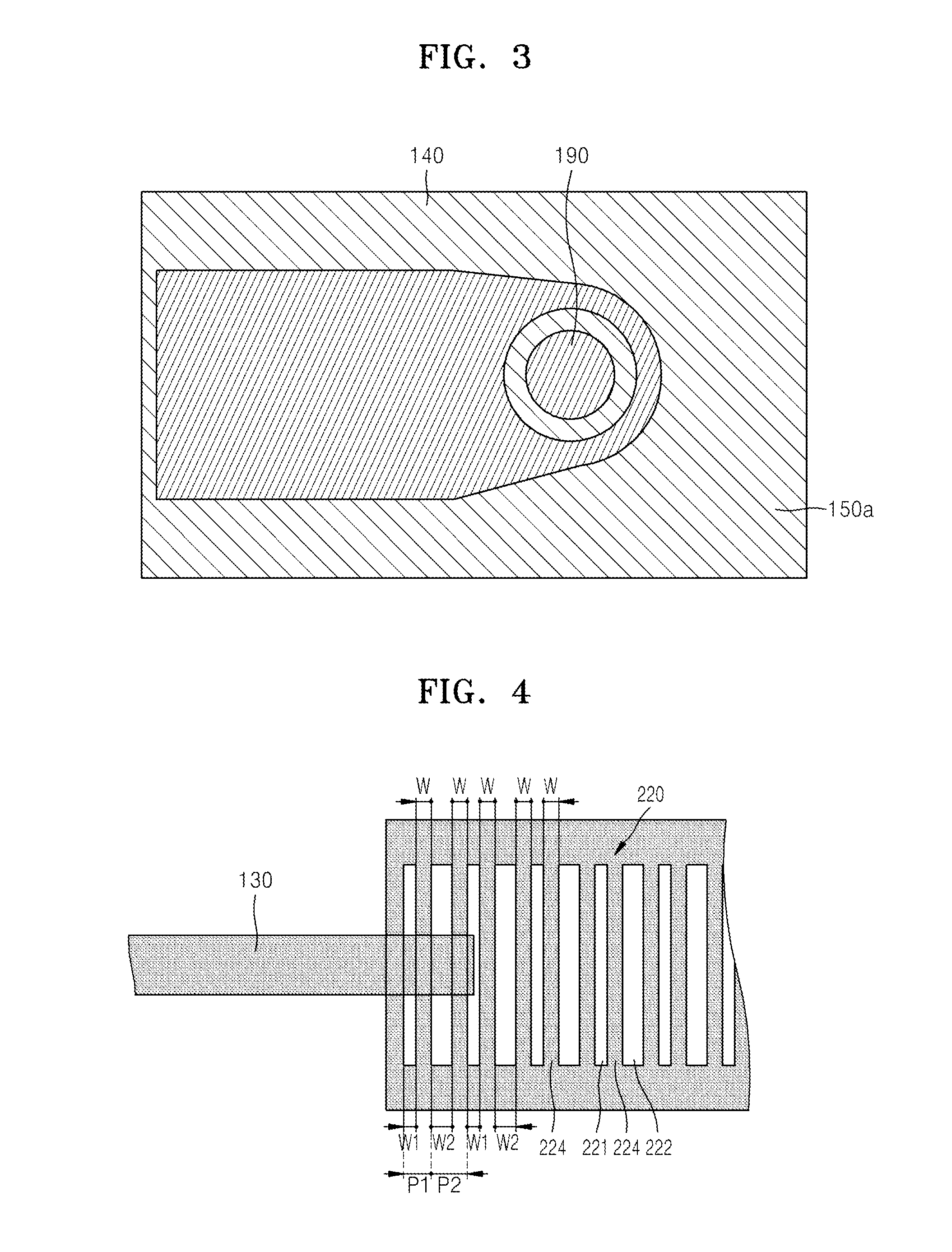
A hybrid vertical cavity laser includes an optical circuit substrate including a grating having refractive index units having a lower refractive index and a higher refractive index with respect to each other that are alternately arranged in a first direction, and a waveguide guiding light in the first direction, a mesa structure on the optical circuit substrate, the mesa structure including a first-type semiconductor layer including an exposed portion, an active layer, a second-type semiconductor layer, and an upper reflective layer sequentially stacked in a second direction perpendicular to the first direction, a first electrode on the exposed portion, and a second electrode on the upper reflective layer. An overlapped length between the waveguide and a mesa aperture forming an opening through which light produced from the active layer enters the grating is D, a pitch of the grating is p, and 0<D<p.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com