Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97 results about "Venous pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
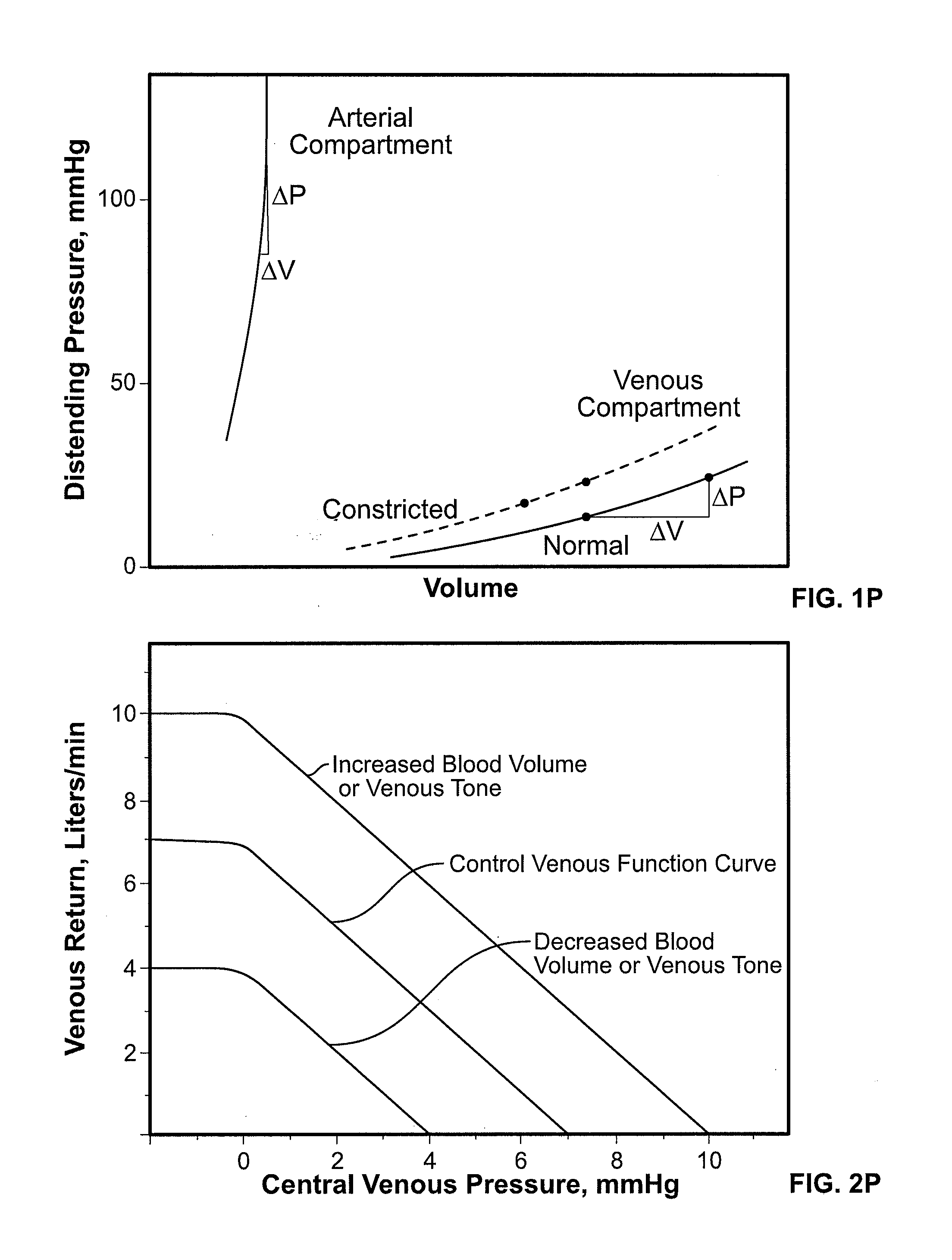
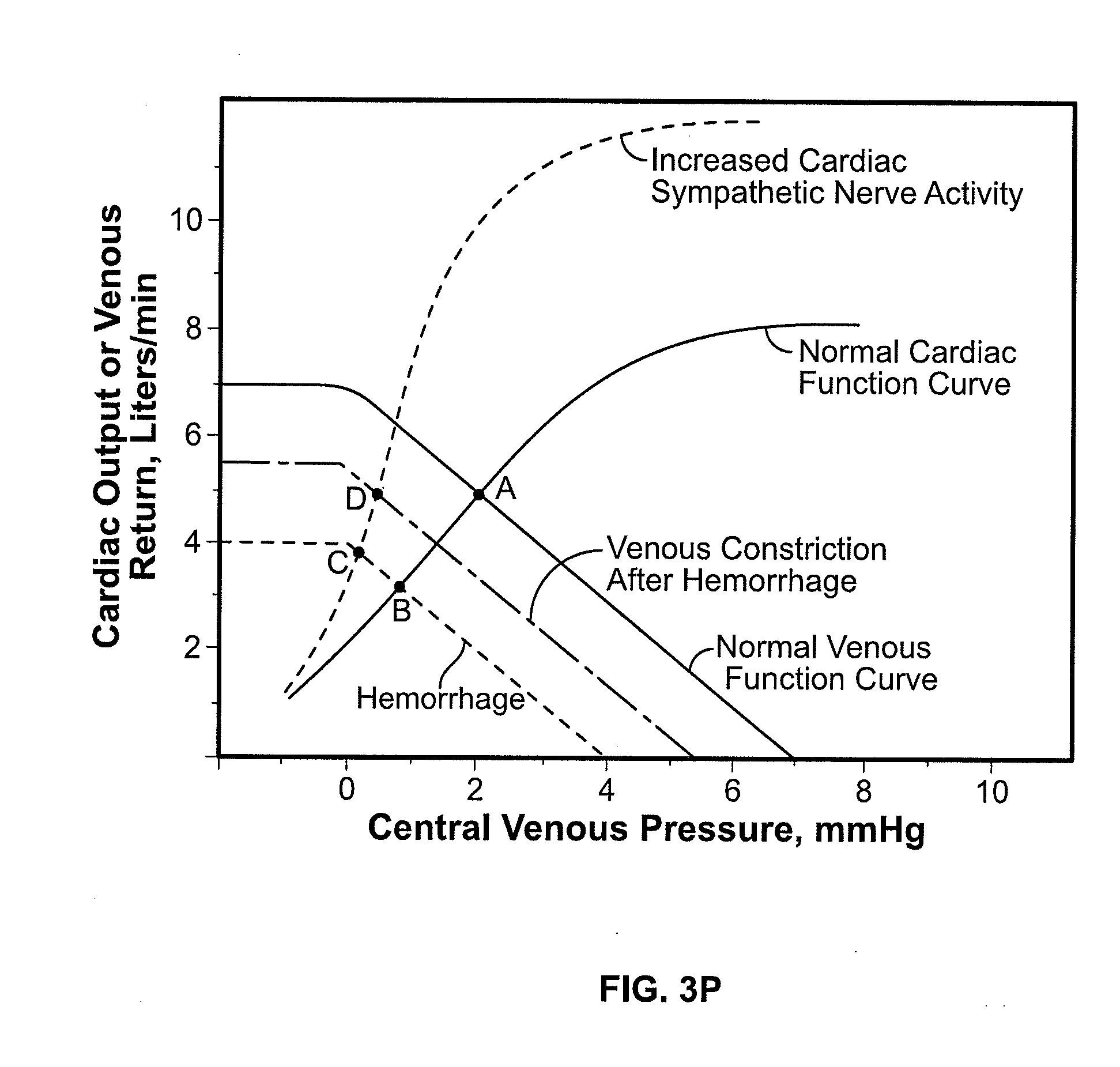
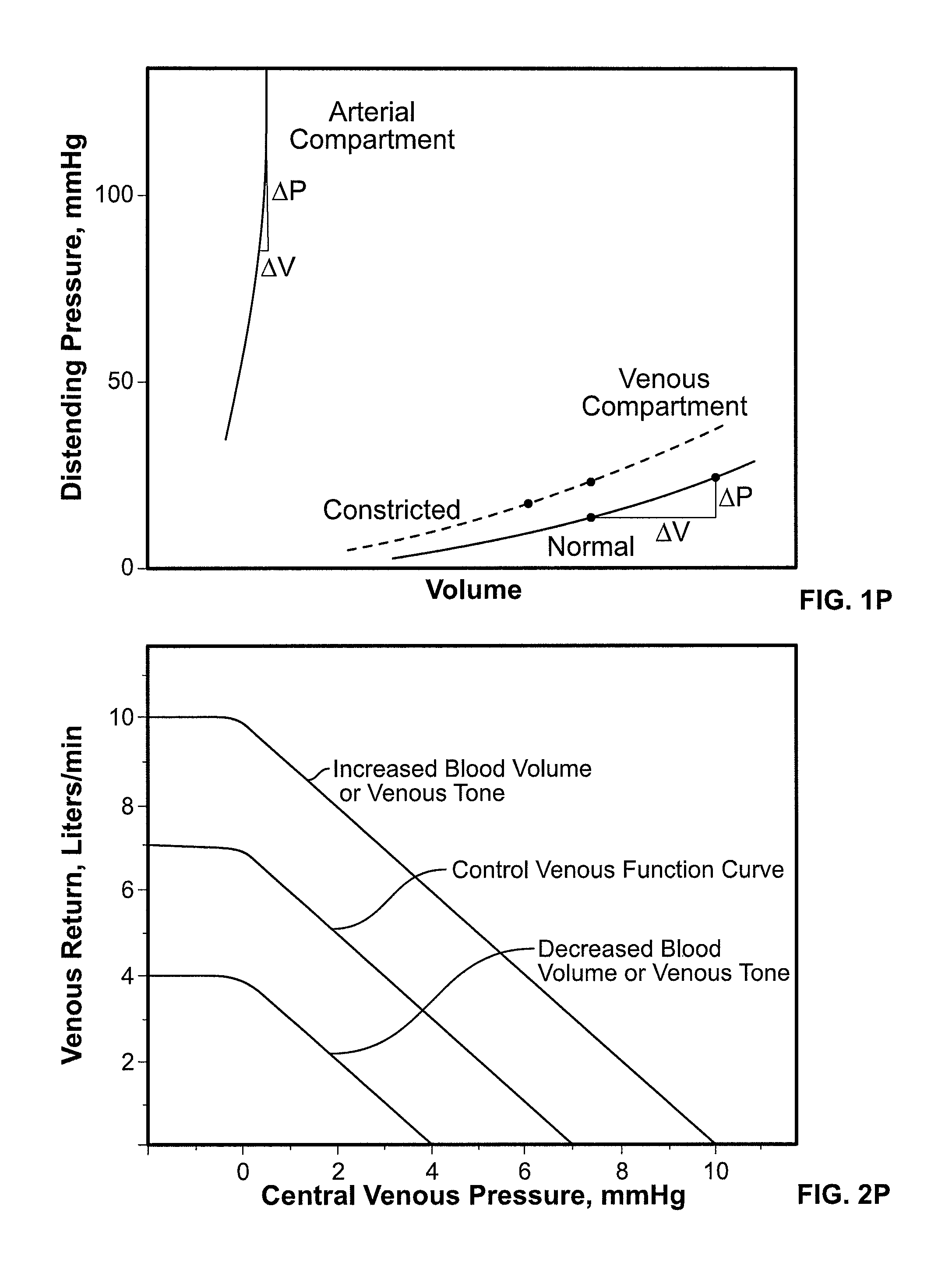
Venous pressure is a term that represents the average blood pressure within the venous compartment. The term " central venous pressure " (CVP) describes the pressure in the thoracic vena cava near the right atrium (therefore CVP and right atrial pressure are essentially the same).
Methods for reduction of pressure effects of cardiac tricuspid valve regurgitation
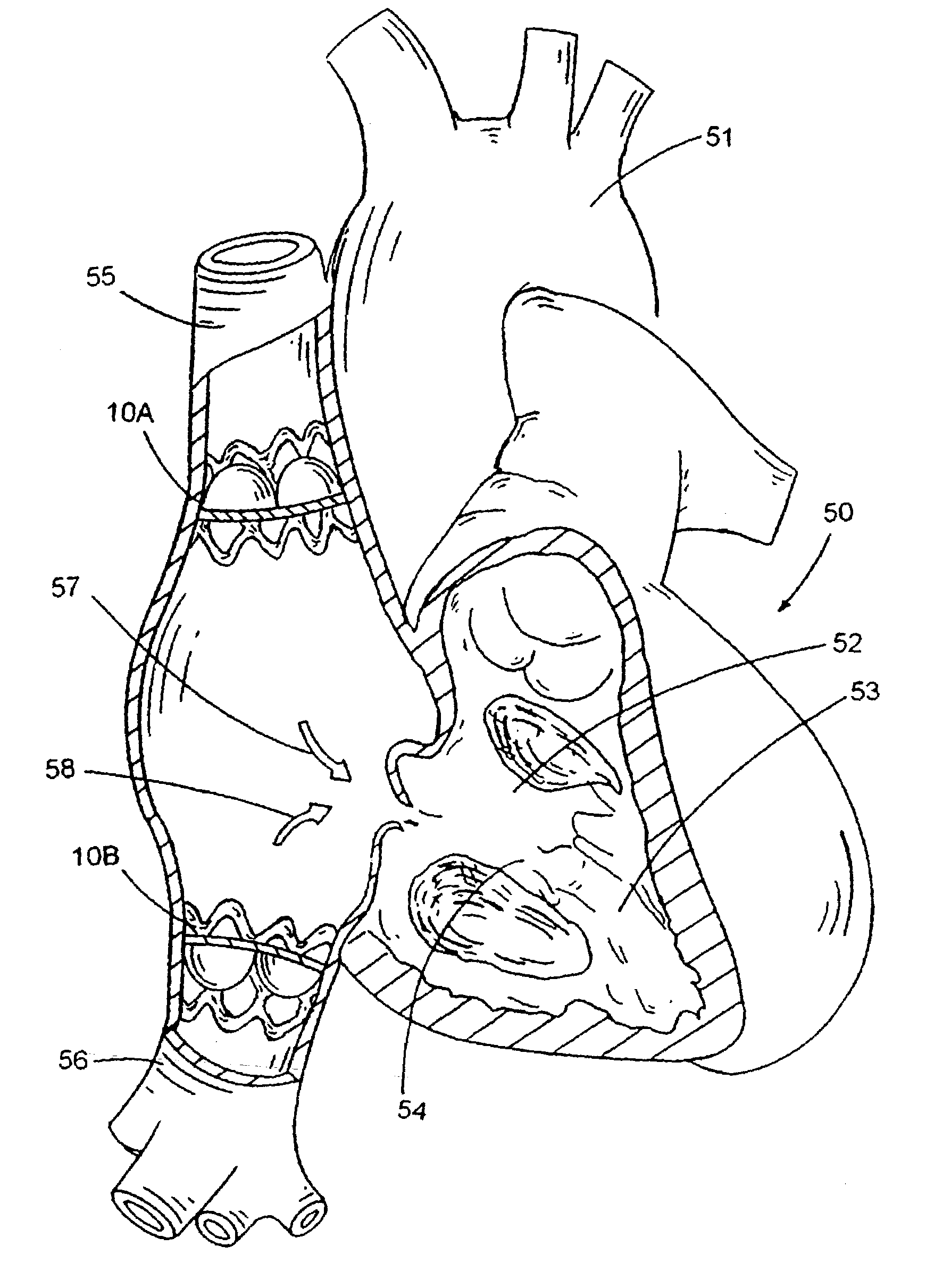
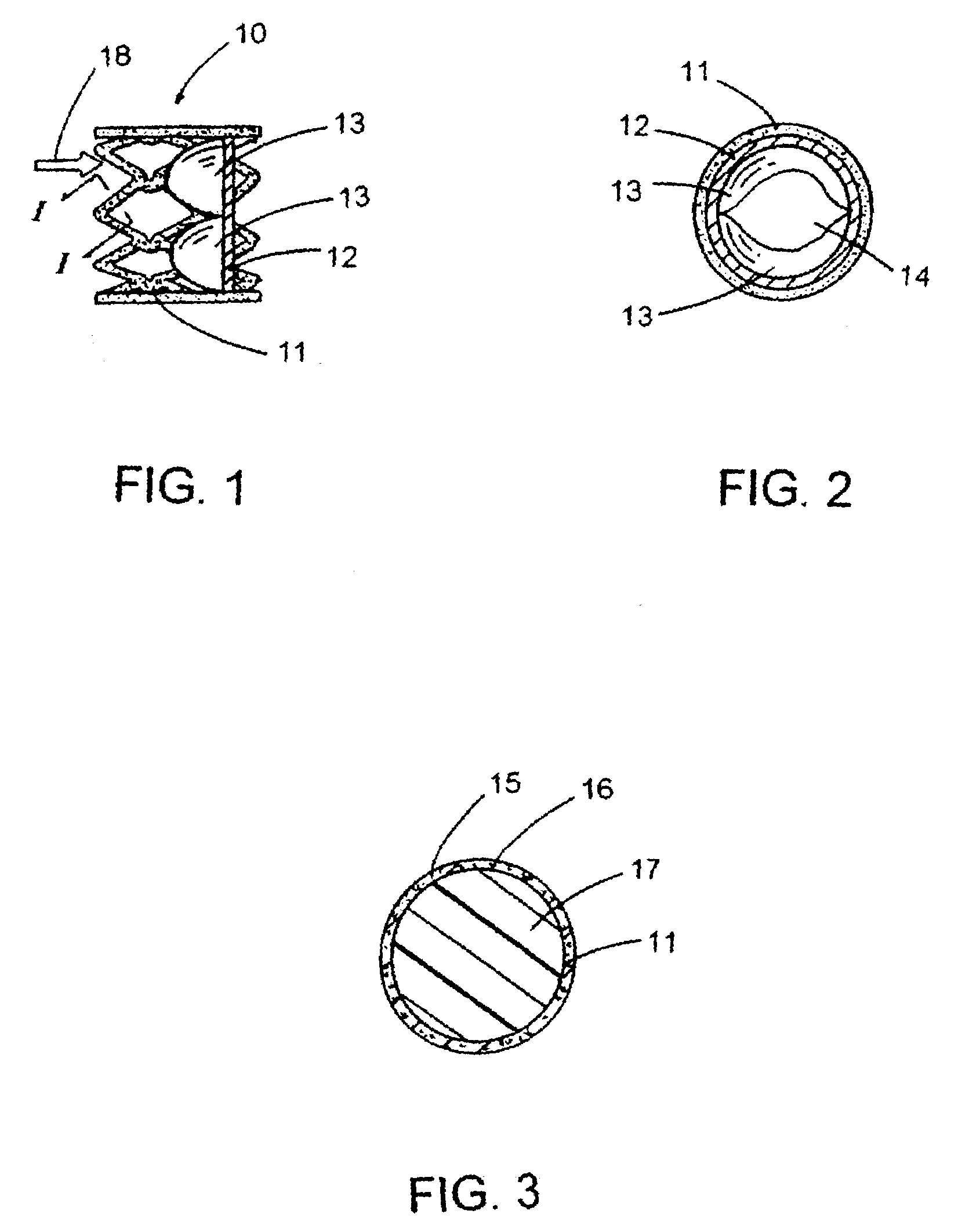
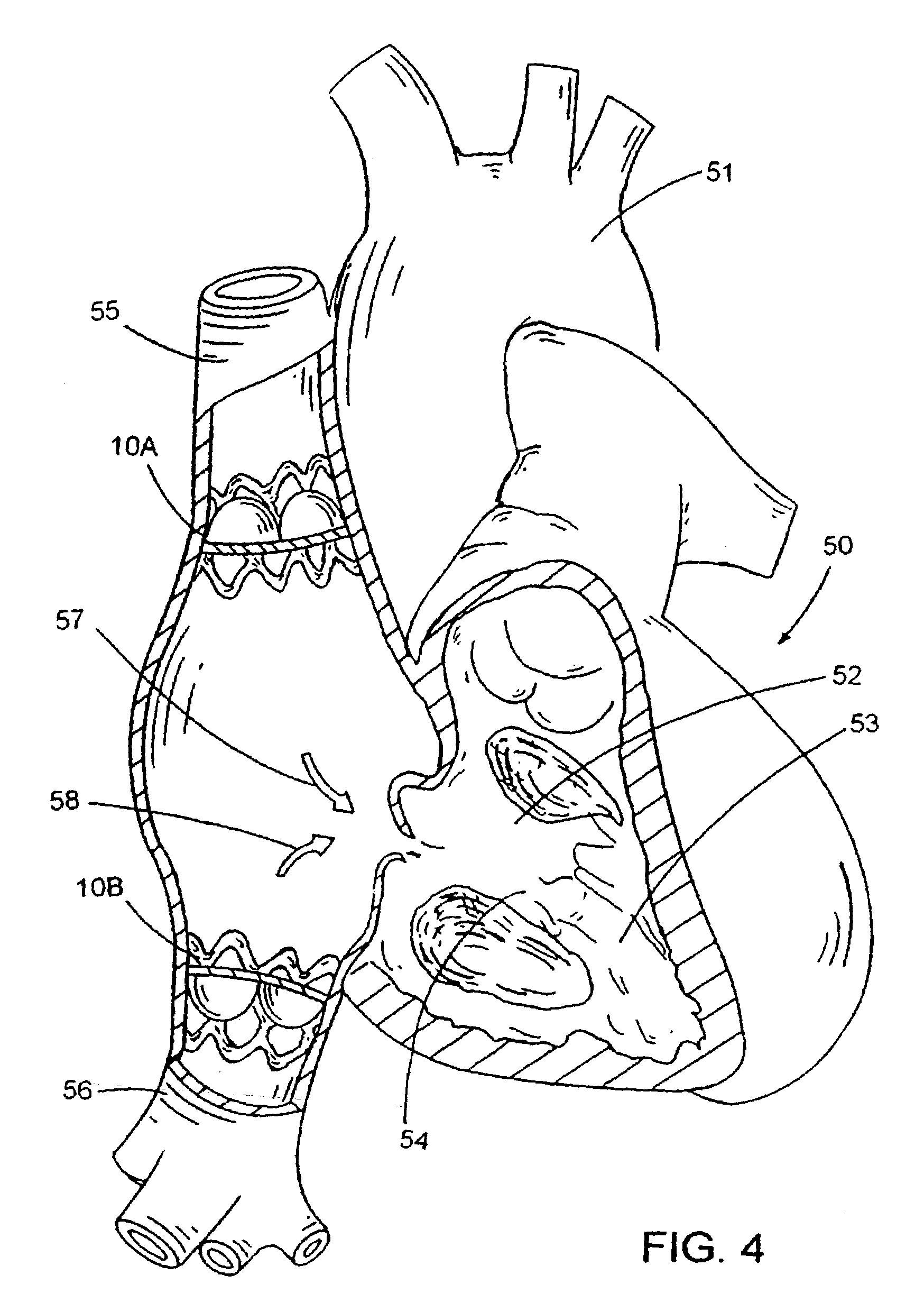
A method of protecting an upper body and a lower body of a patient from high venous pressures comprising implanting a first stented valve at the superior vena cava and a second stented valve at the inferior vena cava, wherein the first and second valves are configured to permit blood flow towards a right atrium of the patient and prevent blood flow in an opposite direction.
Owner:3F THERAPEUTICS
Method and apparatus for surgical training
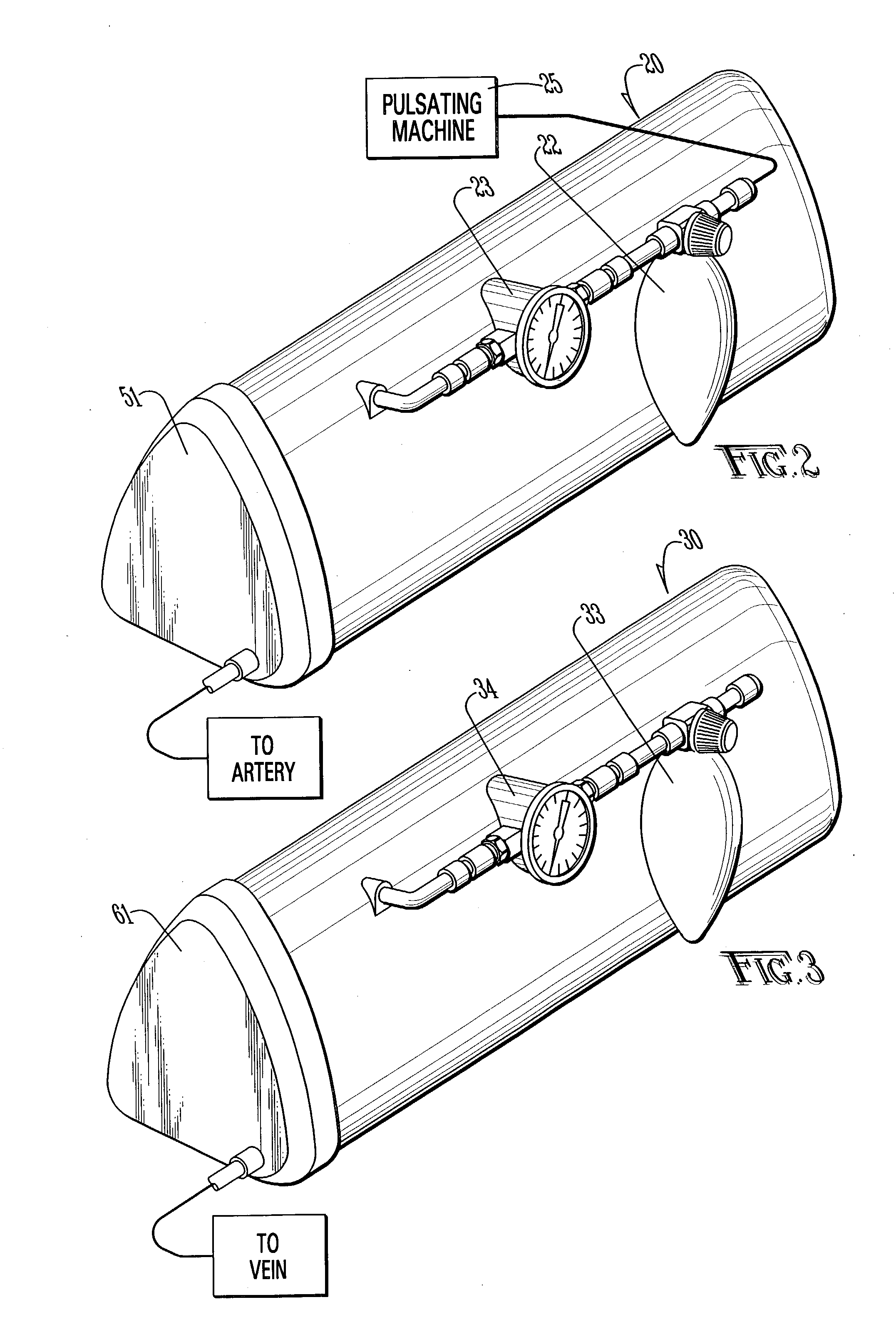
An apparatus and method for microsurgical training using cadaveric anatomy with filling of the vascular system by fluids under pressure to simulate the appearance and function of live surgery. One or more arteries on the specimen of cadaveric anatomy are cannulated and connected to an arterial reservoir having a flexible container holding an arterial fluid simulating the appearance of blood circulating in the arteries of the living organism from which the cadaveric anatomy is derived. Suitable static pressure simulating the arterial pressure appropriate to that of the living organism is applied to the air in an air-tight space surrounding the flexible container in the arterial reservoir. A pulsating machine provides air pulsations to the space surrounding the flexible fluid container to simulate the normal pulsations of the arterial system. One or more veins on the specimen are also cannulated and connected to a venous reservoir having a flexible container holding a venous fluid simulating the appearance of blood circulating in the veins of the living organism. Suitable static pressure simulating the venous pressure appropriate to that of the living organism is applied to the air in an air-tight space surrounding the flexible container in the venous reservoir. Optionally, if the specimen includes at least a portion of spinal canal, a clear fluid reservoir can be connected to the specimen through the spinal canal to simulate cerebrospinal fluid.
Owner:ABOUD GHAITH +1
Method and devices for decreasing elevated pulmonary venous pressure
Owner:SHAKNOVICH ALEXANDER
Chronic access system for extracorporeal treatment of blood including a continously wearable hemodialyzer
ActiveUS8109893B2More convenientEliminates the need for time-consuming, sedentary, hospital or clinic dialysisSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionIntravenous cannulaHaemodialysis machine
Owner:LANDE ARNOLD J
Volume Status Monitor: Peripheral Venous Pressure, Hypervolemia and Coherence Analysis
ActiveUS20100191128A1Reduce blood volumeEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterFluid replacementCoherence analysis
Systems and methods are provided for monitoring changes in blood volume using waveforms in the peripheral vasculature. In particular, the systems and methods relate to detecting ventilation-induced variation (VIV) of waveforms in the peripheral vasculature. Advantageously, the systems and methods may relate to analyzing VIV in peripheral venous pressure (PVP). Thus, the VIV of PVP may be measured, wherein decreased VIV is indicative of decreased blood volume In exemplary embodiments, such as involving spontaneous breathing, it may be necessary to account for changes in respiratory signal strength. Thus systems and methods are also provided for assessing coherence between ventilation and VIV for a flow or pressure waveform. Specifically, coherence is evaluated by comparing the waveform to a detected respiratory signal. Finally, systems and method are provided for distinguishing the impact of respiration on the PG signal during hypervolemia as compared to hypovolemia. Such systems and methods may advantageously be utilized to monitor fluid status during fluid replacement.
Owner:SHELLEY KIRK H +2
Method and device for detecting the detachment of the venous needle from a patient during dialysis
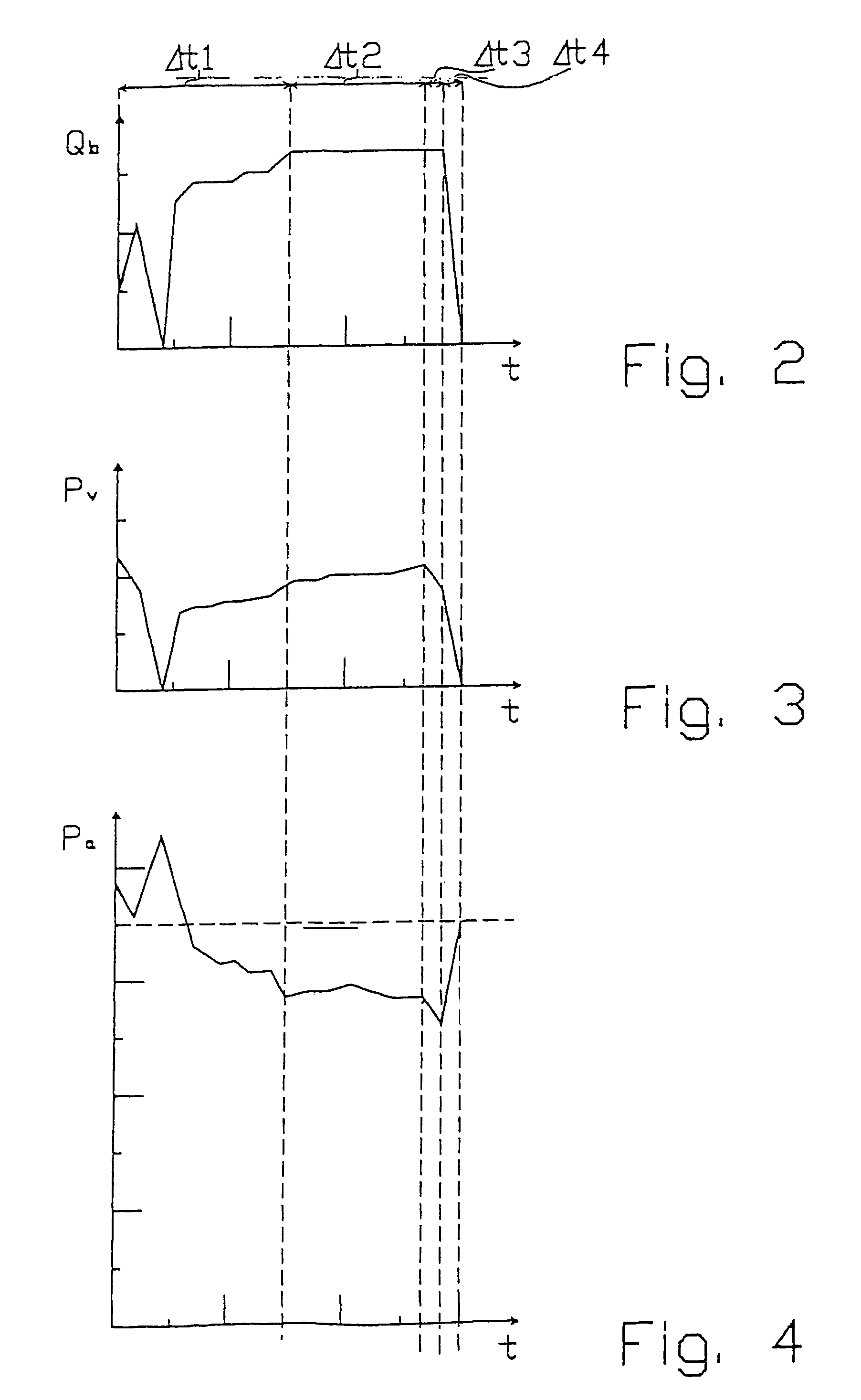
A method of detecting the detachment of the venous needle from a patient during an extracorporeal blood treatment in a dialysis machine having an extracorporeal blood circuit provided with an arterial branch and a venous branch. The arterial pressure (Pa) is measured in the arterial branch and the venous pressure (Pv) is measured in the venous branch, and the determination is made of whether or not decreases of the arterial pressures (Pa) and venous pressures (Pv) are occurring during the dialysis treatment in normal conditions.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
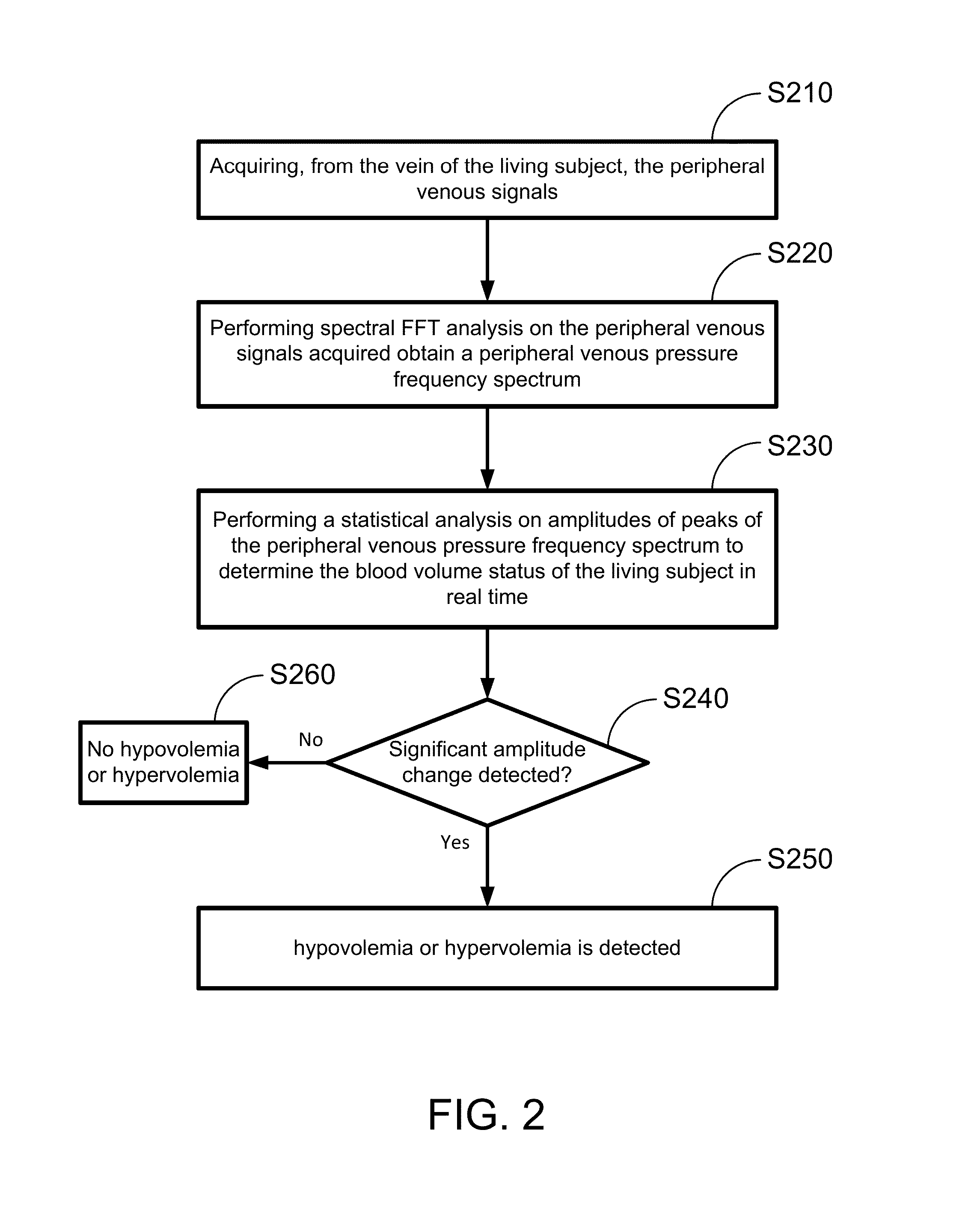
Hypovolemia/hypervolemia detection using peripheral intravenous waveform analysis (PIVA) and applications of same
Aspects of the invention relates to systems and methods for hypovolemia and / or hypervolemia detection of a living subject using peripheral intravenous waveform analysis. In one embodiment, the method includes: acquiring, from a vein of the living subject, peripheral venous signals; performing a spectral analysis on the acquired peripheral venous signals to obtain a peripheral venous pressure frequency spectrum; and performing a statistical analysis on amplitudes of peaks of the peripheral venous pressure frequency spectrum to determine the blood volume status of the living subject in real time. Specifically, at least two peaks, respectively corresponding to a first frequency and a second frequency, are obtained on the peripheral venous pressure frequency spectrum. Amplitude change of the second peak is used to determine the blood volume status of the living subject. Hemorrhage may be detected when a significant amplitude decrease is detected from the second baseline peak to the second peak.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
System for management and prevention of venous pooling
A monitoring system comprises sensors adapted to be worn by a user, and, a processor linked with the sensor. The processor receives sensor data and processes this data to determine user posture data including data indicative of vertical distance between level of the user's heart and ankle. Based on the posture data together with a value for degree of user chronic venous insufficiency and / or blood density, generate an estimate of user static venous pressure while the user is static, without calf muscle pump activity. The processor also processes the sensor data to determine if there is calf muscle pump activity, and generates an estimate of user active venous pressure according to the static venous pressure estimate, rate of calf muscle activity, and a value for degree of user chronic venous insufficiency. The processor may generate the venous pressure estimate in real time, and may control an NMES device accordingly.
Owner:THE NAT UNIV OF IRELAND GALWAY +1
Portable blood purifying system
InactiveCN102389594AEfficient removal capacityImprove purification efficiencyDialysis systemsExtracorporeal circulationLiquid waste
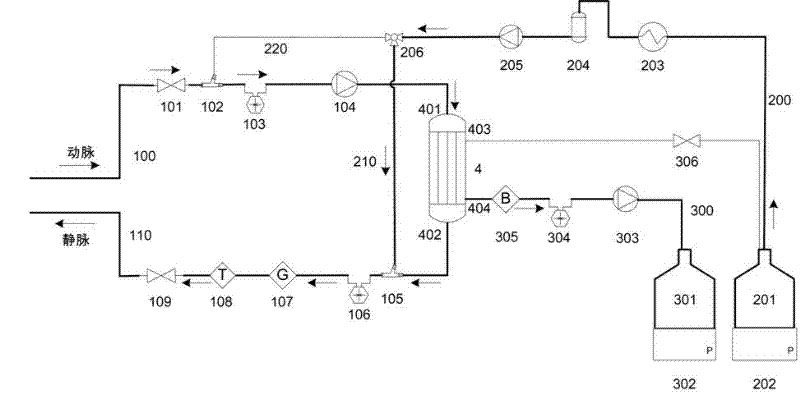
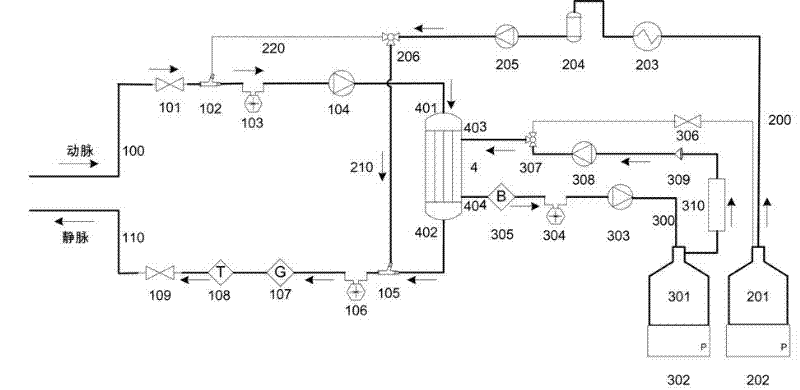
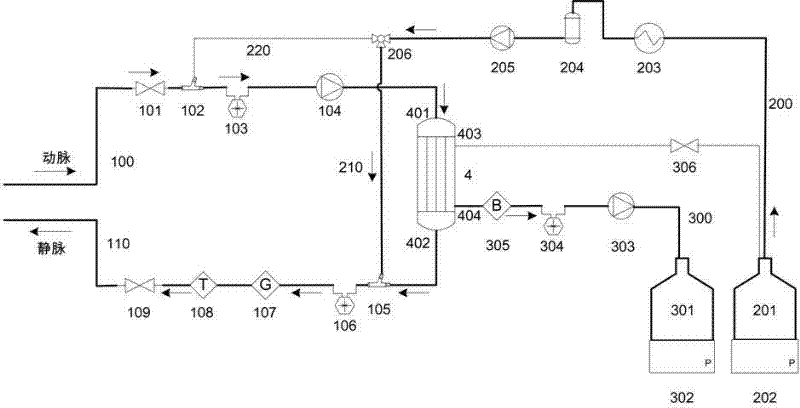
The invention relates to a portable blood purifying system, which comprises a high throughput dialyzer with an arterial duct, a venous duct, a washing liquid tube and a transfusion tube; the arterial duct is in turn connected in series with an arterial valve, an arterial pressure sensor and a blood pump; the venous duct is in turn connected in series with a venous valve, a venous temperature sensor, a venous bubble detector and a venous pressure sensor, so that an external circulation unit is formed; the washing liquid tube is connected in series with a pre-charging valve and is communicated with a washing liquid container; the transfusion tube is in turn connected in series with a temperature controller, a transfusion tube bubble collector and a transfusion pump, and is communicated with a waste liquid container, so that a waste liquid processing unit is formed; and the system also comprises a transfusion pump, a temperature control device, a transfusion tube, a gating valve and a first transfusion branch and a second transfusion tube branch, so that a transfusion unit is formed. The system is simplified in structure and convenient to carry; and the system is suitable for patients to do short-time dialysis for several times or night dialysis treatment at home as household treatment equipment, so that toxin tolerance of dialysis patients during dialysis period is relieved while medical cost is reduced.
Owner:黄昱
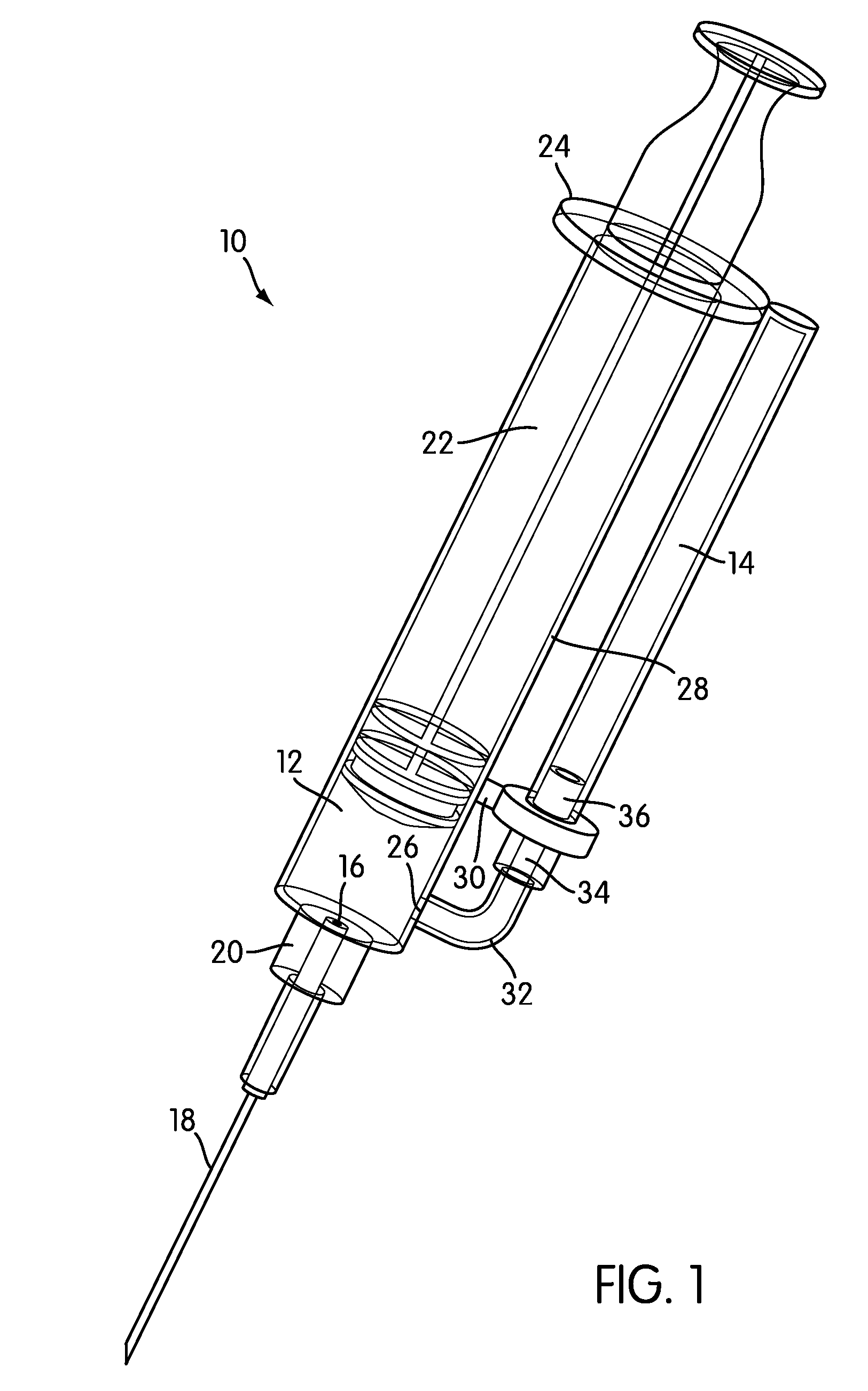
Devices for collecting blood and administering medical fluids
InactiveUS20050027233A1Preventing vacuum-induced collapseFacilitating active flow of bloodSamplingInfusion syringesBLOOD FILLEDBlood collection
Novel devices which can be used to both collect blood samples from and administer medical fluids to a patient on a repeated and continual basis using one rather than multiple needle insertions. The devices are capable of removing blood from one of the patient's veins using the intrinsic venous pressure of the blood and capillary action of the device, thereby preventing vacuum-induced collapse of the vein. The device typically includes a main tubing segment confluently connected to a cannula for insertion in the patient's vein. A syringe port and a volumeter for collecting blood branch separately from the main tubing segment. The device is used to collect blood by attaching an empty blood collection syringe to the syringe port, inserting the cannula in the patient's vein, allowing passive flow of blood from the main tubing segment into the volumeter under intrinsic venous blood pressure and capillary action, and then facilitating active flow of blood from the volumeter into the blood collection syringe by extending the syringe plunger. The blood-filled syringe may be replaced by additional empty blood collection syringes and the procedure repeated, as needed, depending on the quantity of blood to be obtained. The device may be used to administer medical fluids to the patient by first removing the residual blood from the main tubing segment and volumeter, flushing the main tubing segment with sterile normal saline and administering the fluids to the patient through the main tubing segment from a medical fluid syringe or catheter attached to the syringe port.
Owner:ONE STICK LLC
Venous-arterial detector and pressure indicator
Owner:DEVICE EVOLUTIONS
Hemodialysis apparatus
Provided is a hemodialyzer for preventing beforehand any medical accident such as air inclusion or blood loss during a medical treatment by detecting even a minute connection failure, if any. The hemodialyzer includes a hemodialyzer (D), a dialysate supply line (L1), a dialysate discharge line (L2), an artery side blood line (L3), a vein side blood line (L4), first fluid feeding means (P1), second fluid feeding means (P2), third fluid feeding means (P3), a blood pump (P4), a vein side chamber (CV), an overflow line (L5), a venous pressure monitor line (L6), dialysate pressure measuring means (MT), venous pressure measuring means (MV), clamps (CLL4, CLL5), control means (G1) that closes the clamp (CLL5) when a predetermined given period of time has elapsed from the start of priming, and operates the third fluid feeding means (P3) in a reverse filtration direction or in a fluid removal direction, and then opens the clamp (CLL5) when a predetermined given period of time has elapsed, and judging means (J1) that compares a pressure variation amount in the dialysate pressure or the venous pressure for a period of time when the clamp (CLL5) is closed with a predetermined reference value to judge normality of a circuit connection.
Owner:JMS CO LTD
Blood return prevention infusion connector
ActiveCN104888310APrevent backflowAvoid bleedingIntravenous devicesTube connectorsVeinElastic Barrier
The invention provides a blood return prevention infusion connector which comprises an outer connector, an inner connecting seat and an elastic barrier piece. The outer connector is hermetically connected with the inner connecting seat, the elastic barrier piece is arranged between a liquid inlet of outer connector and a liquid outlet of the inner connecting seat, the periphery of the elastic barrier piece is connected with the inner wall of the liquid inlet, the elastic barrier piece is provided with a closed portion and a liquid though port, and the closed portion covers a liquid outlet of the inner connecting seat. By the aid of the blood return prevention infusion connector, the elastic barrier piece is fixed for the first time, one-way flow of liquid medicine is realized by only depending on deformation of the elastic barrier piece, the blood return can be prevented by the infusion connector even if liquid pressure is equal to human venous pressure or the pressure difference between the liquid pressure and the human venous pressure are smaller, the connector effectively solves the problem that a blood return prevention infusion connector cannot really function in preventing blood return in prior art, so that blood return is avoided even if an infusion person optionally walks or lifts an arm in the infusion process, and clinical application is more facilitated.
Owner:LUOHE SHUGUANG HUIZHIKANG BIOTECH
Decellularized anti-calcification heart patch and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104998299ASuitable degradation cycleSlightly altered collagen structureProsthesisActive agentHeart chamber
The invention relates to a preparation method of a decellularized anti-calcification heart patch. The method mainly comprises the steps that raw material pericardial tissue is degreased through an organic reagent and processed by a mixed solution of a high salt, a surface active agent and alkali, and finally sterilization treatment is performed to obtain the decellularized anti-calcification heart patch. According to the obtained heart patch, due to the special decellularized anti-calcification technology, the collagenous fiber three-dimensional pore structure of the raw materials is reserved, meanwhile, cells contained in the materials are effectively removed, and the immunogenicity is lowered; the materials can guide cells to grow in the materials, scar tissue generation is reduced, and the good anti-calcification ability is achieved; the excellent mechanical property is achieved, arterio-venous pressure difference between heart chambers can be resisted, and the repair effect is ensured. The preparation method is applicable to atrial septal defects, ventricular septal defects, aortic stenosis and the like caused by the congenital heart disease.
Owner:SHAANXI BOYU REGENERATIVE MEDICINE CO LTD
Nerve cuff stimulation electrode, control device for a vagus nerve stimulation system, and vagus nerve stimulation system
ActiveUS20150374296A1Improves state-of-the-artImprove complianceSpinal electrodesCatheterNerve cuffSEMI-RECUMBENT
A nerve cuff stimulation electrode for cervical VNS is provided and configured to be arranged so as to at least partially surround or enclose one of the vagus nerves. The cuff stimulation electrode has at least two contacts configured to deliver electric stimulation pulses to a vagus nerve. The cuff stimulation electrode further has or may be attached or connected to a tilt sensor, a kinematic sensor, and / or a pulsation sensor configured to generate a signal representative of arterial and venous pressures. The implantable tilt sensor is configured to output a posture signal indicating a patient's posture, thus allowing discrimination between supine and semi-recumbent or erect postures.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
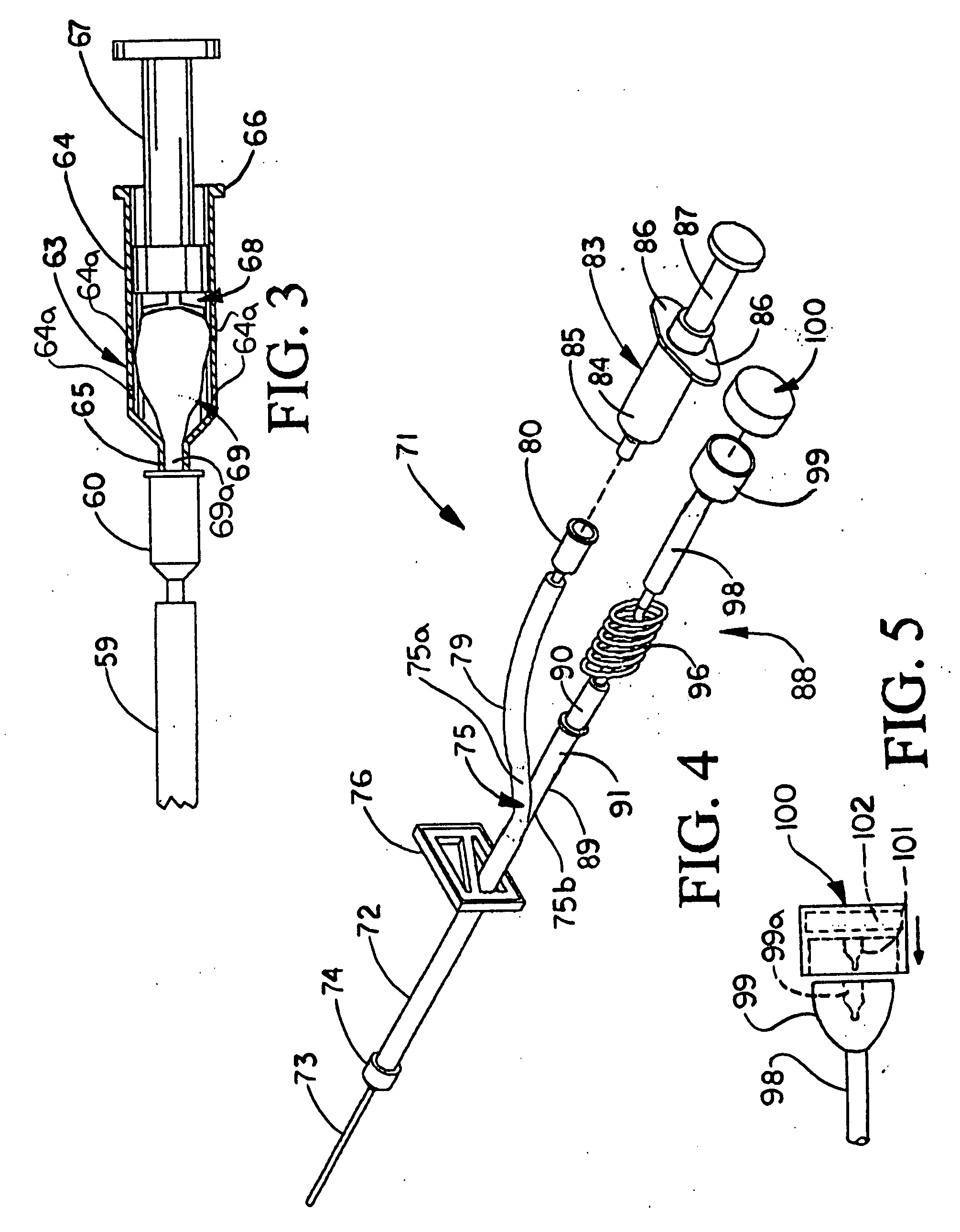
Venous-Arterial Detector and Pressure Indicator
A venous-arterial detector is disclosed. The detector includes a first chamber in fluid communication with a needle, and an indicator chamber in selective fluid communication with the first chamber through a valve. The indicator chamber is pre-pressurized to a defined pressure that preferably exceeds typical venous pressure, and the valve retains that pressure within the indicator chamber. When the needle is inserted into a vessel, if the pressure in the vessel is greater than the defined pressure in the indicator chamber, blood will flow into the indicator chamber, indicating that the vessel is most likely to be an artery.
Owner:DEVICE EVOLUTIONS
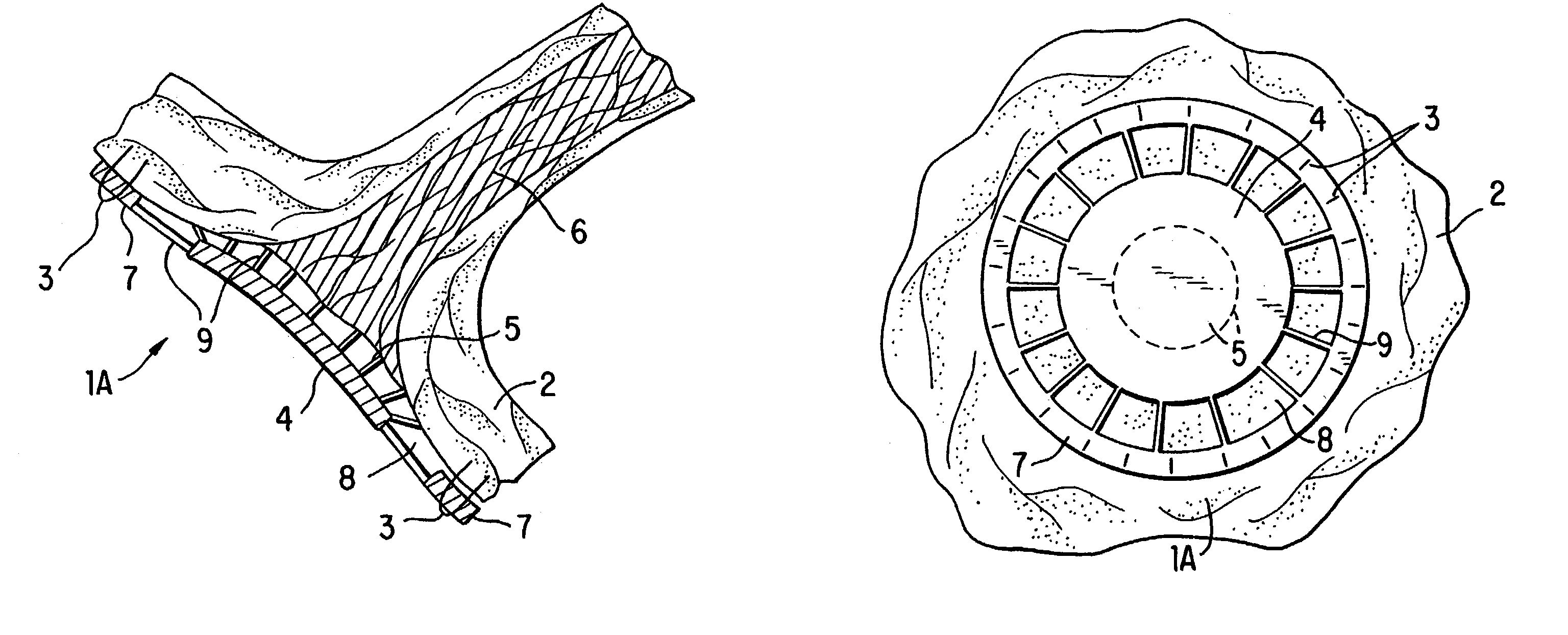
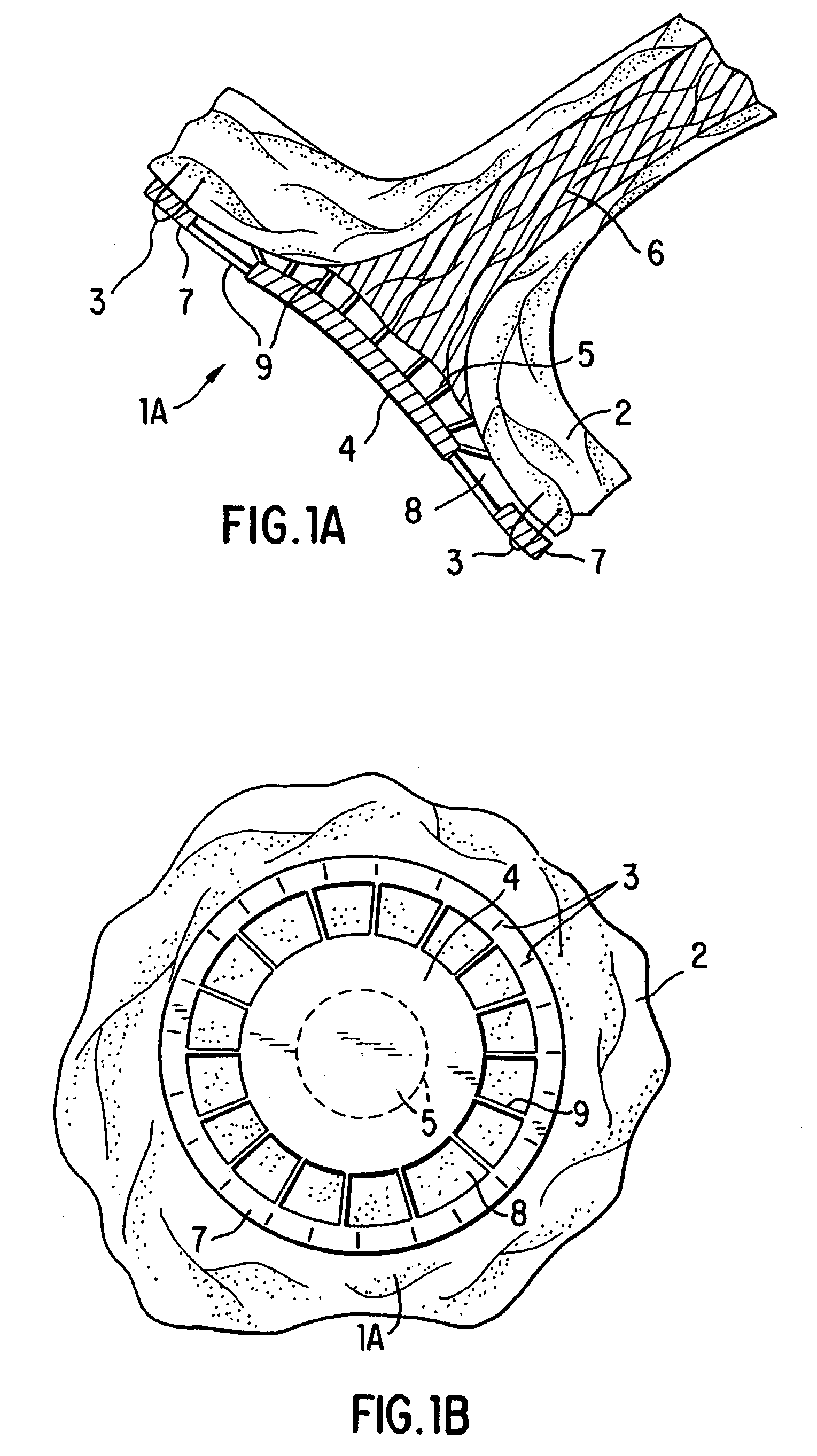
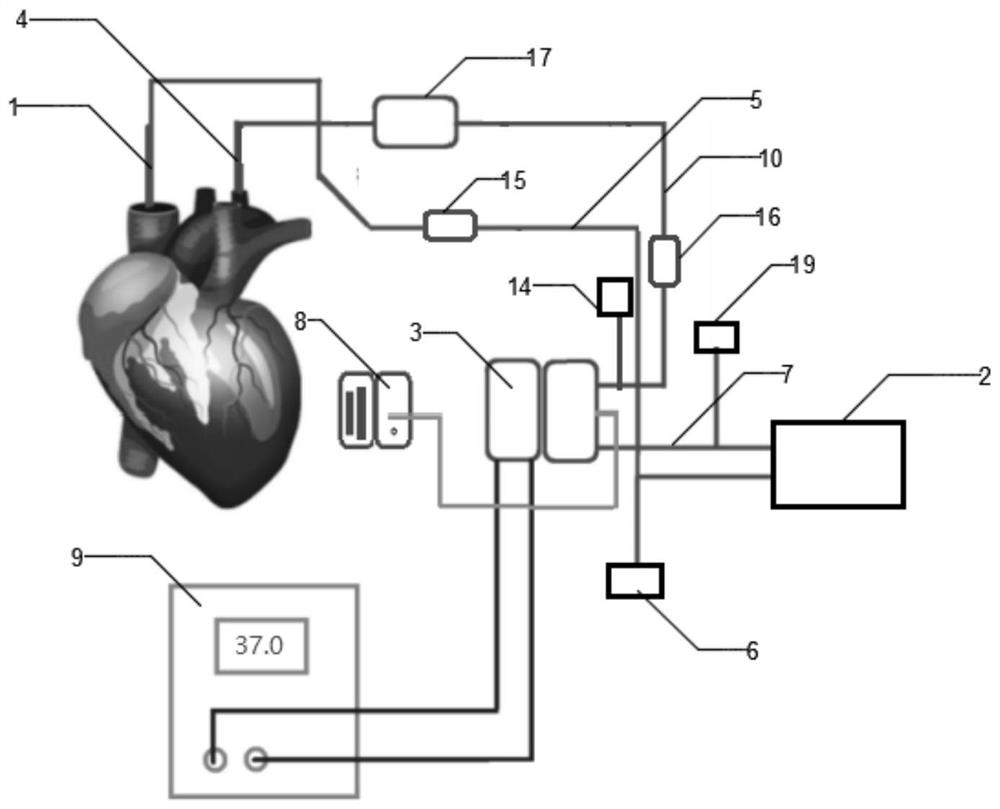
Venous pressure measuring probe as well as mounting method and use method thereof
The invention discloses a venous pressure measuring probe as well as a mounting method and a use method thereof. The venous pressure measuring probe comprises a flexible liner, a rigid shell and a stress transfer medium, wherein the liner is filled with the stress transfer medium; the liner is mounted on the shell; the liner comprises a bracket, an optical fiber pressure sensor, an optical fiber lead and a cylindrical film cylinder; the film cylinder is sleeved on the bracket; a sealing cavity is formed by the film cylinder and the bracket; the optical fiber pressure sensor is in optical hot-melting connection with the optical fiber lead; the optical fiber pressure sensor is accommodated in the sealing cavity; and the optical fiber lead passes through the liner and extends out of the bracket. The venous pressure measuring probe has the advantages that the venous pressure measuring probe is small in size, so that a pressure measuring operation can be performed by inserting the venous pressure measuring probe into a detected part in human body by virtue of a medical endoscope and a biopsy tool channel; the venous pressure measuring probe can serve as a key part of a non-invasive venous pressure measuring device; and the venous pressure measuring probe is suitable for an effective non-invasive detecting device for measuring venous pressure in human body.
Owner:HEFEI YOUO ELECTRONICS TECH
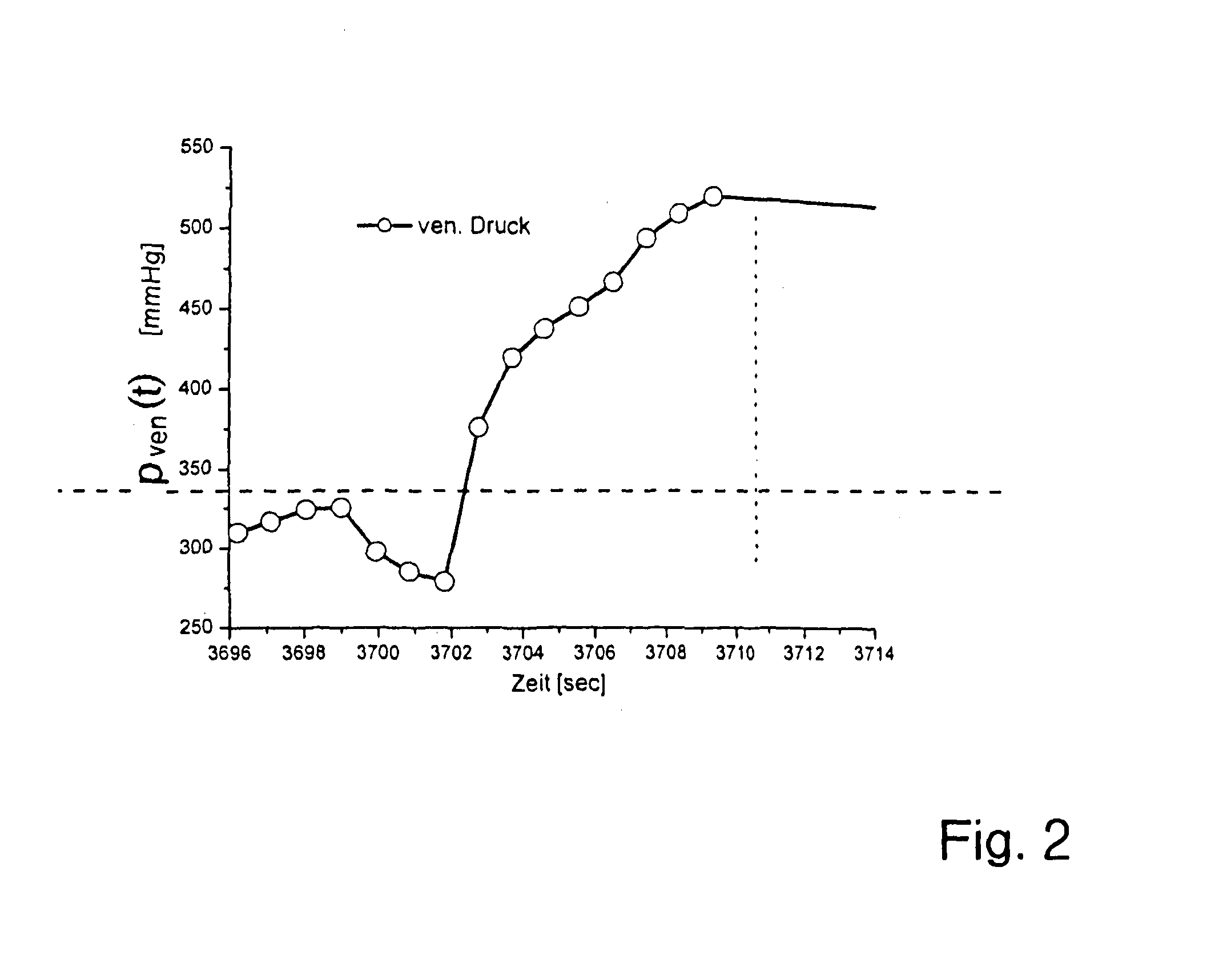
Method and device for monitoring an extracorporeal blood circuit
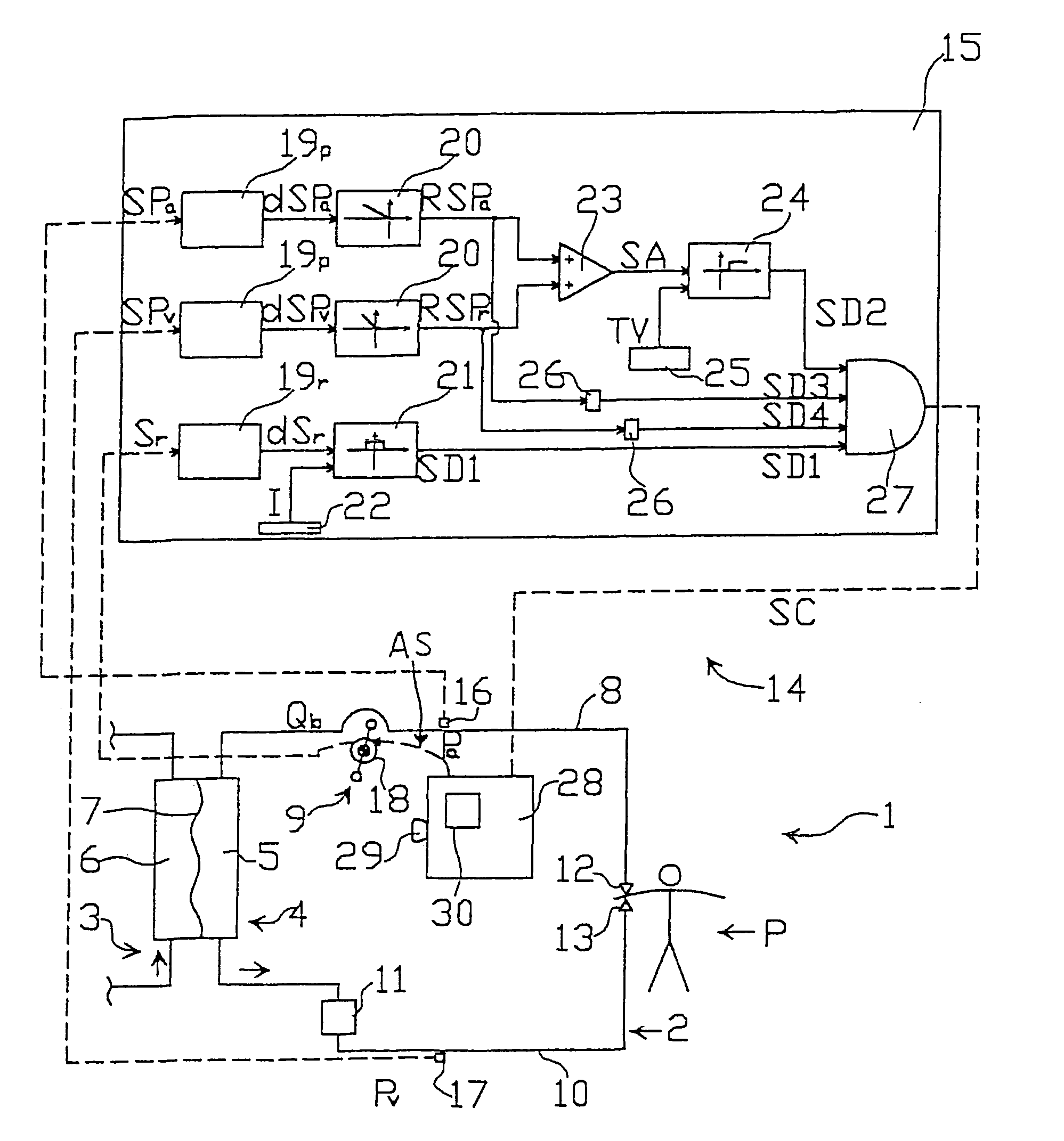
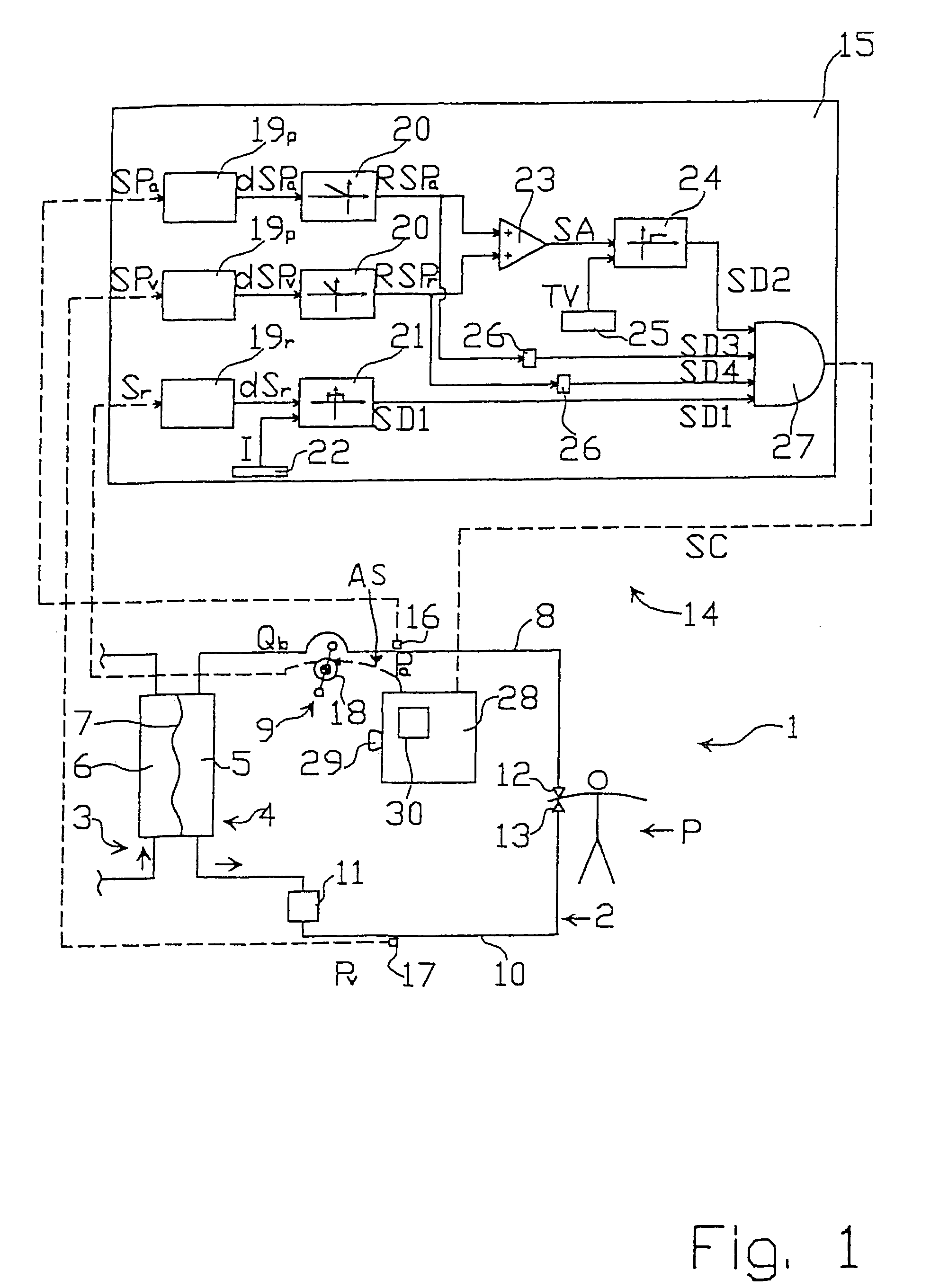
To monitor an extracorporeal blood circuit during an extracorporeal blood treatment, the arterial pressure and venous pressure in the arterial branch and venous branch of the extracorporeal circuit are measured by means of pressure sensors (18, 19), and the sum Ps and the difference deltaP of the arterial pressure and / or venous pressure measured at the same time are formed. A possible error state is indicated when the sum Ps and / or difference deltaP lie outside predetermined limit value windows A and B. To reduce the susceptibility to error, a check is preferably also made to ascertain whether the two above conditions are satisfied for n successive measurements.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
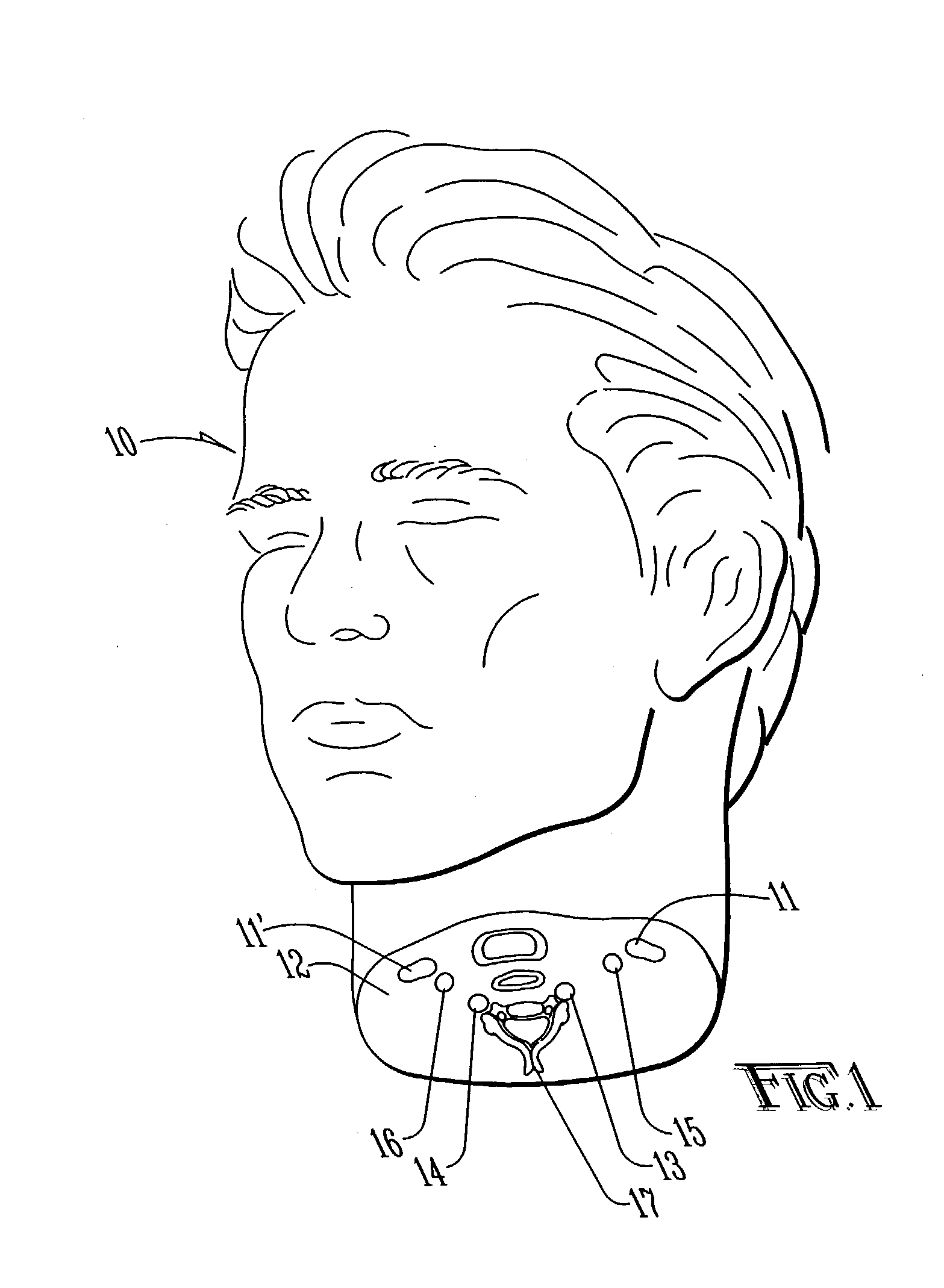
Jugular venous pressure gauge
The present invention is directed to an apparatus for metering the jugular venous pressure of a patient, and a method thereof. The apparatus comprises: a slider which comprises a scale for indicating the venous pressure of a patient; a pointer connected to the sliding member of the slider perpendicularly to the scale, for pointing on the filling level of the jugular venous pressure of the patient. The jugular venous pressure is indicated by positioning the patient at a certain angle, such as 30 to 45 degrees with reference to the floor, placing the tip at the sternal-angle of the patient while the slider is held vertically, sliding the pointer until pointing on the top of the filling level of the jugular vein of the patient.
Owner:KINORI MICHAEL
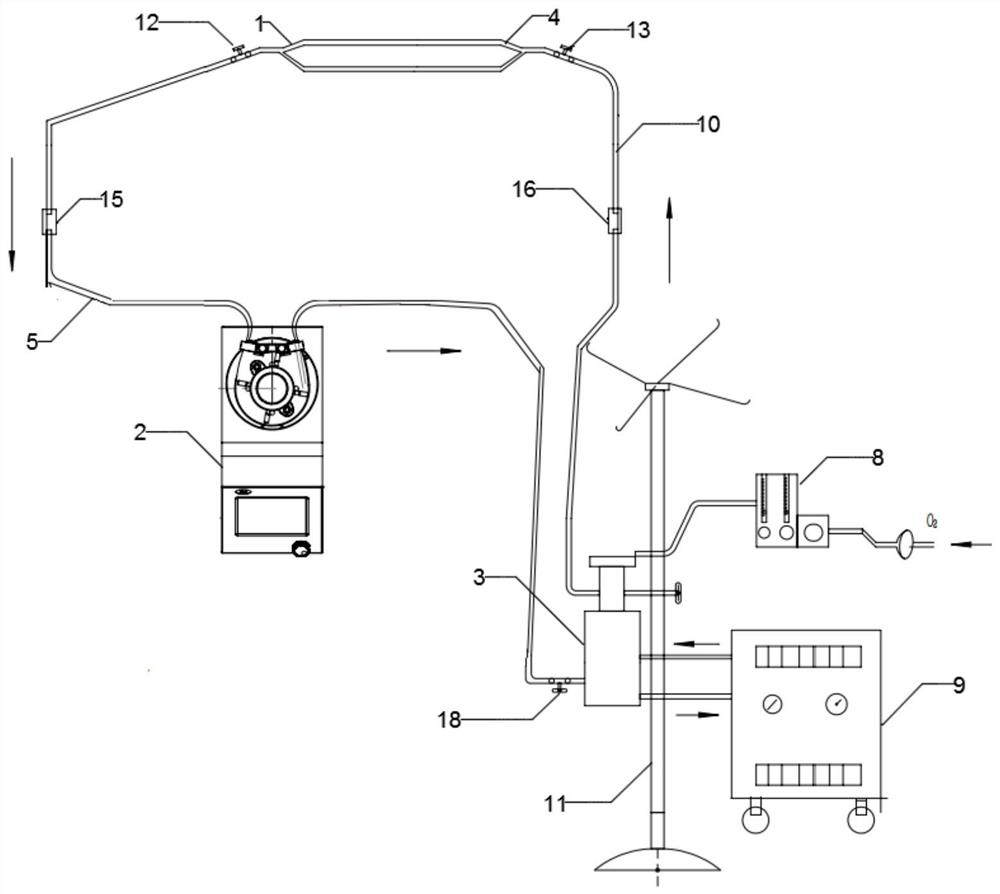
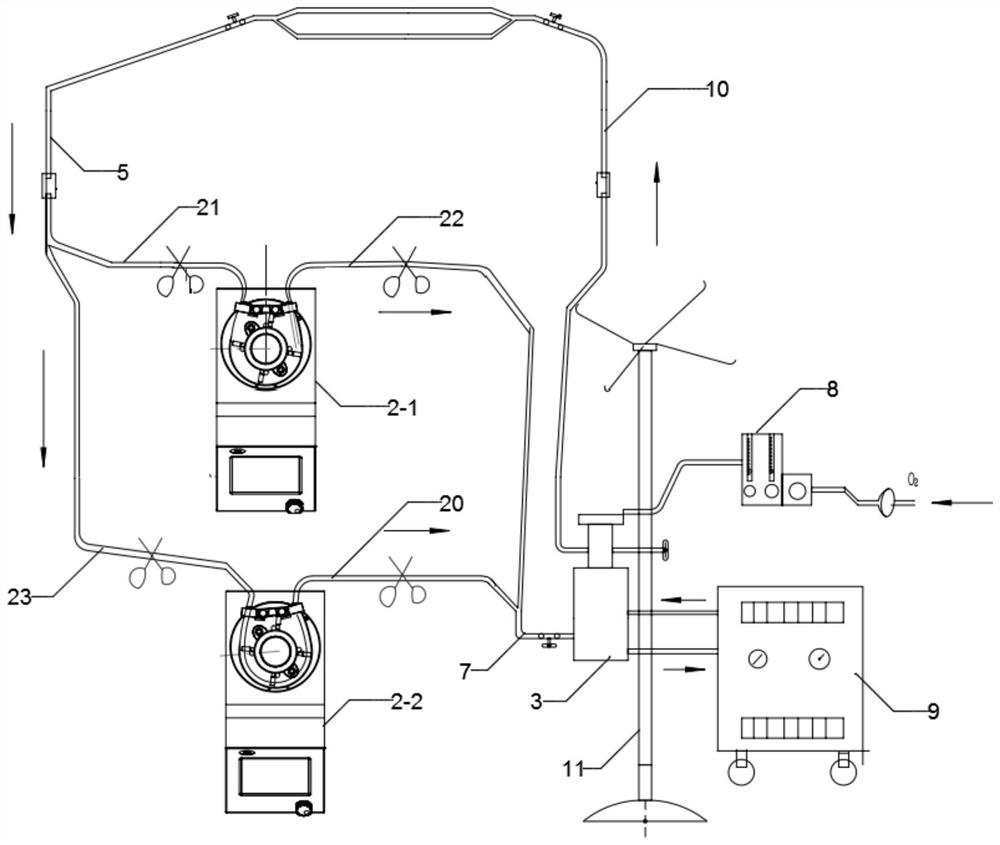
Intelligent ECMO treatment device based on rolling type blood pump and control method of system
PendingCN114470377AAdded pressure monitoring structurePrecise control of perfusion pressureDialysis systemsBlood pumpsVeinArterial catheter
The invention provides an intelligent ECMO treatment device based on a rolling type blood pump and a control method of a system.The intelligent ECMO treatment device comprises a vein cannula, the rolling type blood pump, a membrane lung and an arterial cannula, the vein cannula is connected to an inlet of the rolling type blood pump through a first connecting pipe, and the rolling type blood pump is connected to an outlet of the artery cannula through a second connecting pipe; a venous pressure sensor is arranged on the first connecting pipe; an outlet of the rolling type blood pump is connected to an inlet of the membrane lung through an arteriovenous bridge tube, an artery overpressure sensor is arranged on the arteriovenous bridge tube, the membrane lung is further connected with an air and oxygen mixer and a temperature changing device, an outlet of the membrane lung is connected to the arterial cannula through a second connecting tube, and the arterial cannula is connected with the air and oxygen mixer through a second connecting tube. The venous pressure sensor and the artery overpressure sensor are respectively connected with the rolling type blood pump through the central processing unit. According to the invention, the perfusion pressure can be intelligently and accurately controlled, and finally constant-flow perfusion is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN WELCOME MEDICAL EQUIP
Hemodialysis machine capable of independently adjusting dialysate concentration
ActiveCN104174080AReduce hemodialysis complicationsRealize individualized dialysisDialysis systemsVeinAir monitoring
The invention provides a hemodialysis machine capable of independently adjusting dialysate concentration. The hemodialysis machine comprises a blood monitoring alarm system and a dialysate supply system. The blood monitoring alarm system comprises a blood pump, a heparin pump and an artery and vein pressure monitoring and air monitor, wherein the blood pump, the heparin pump and the artery and vein pressure monitoring and air monitor are sequentially and electrically connected. The dialysate supply system comprises a dialysate distribution system, an air removal system and a blood leakage monitor, the air removal system and the blood leakage monitor are electrically connected, and the dialysate supply system further comprises an independent dialysate adjusting system, wherein the independent dialysate adjusting system is arranged between the dialysate distribution system and the air removal system. The hemodialysis machine is simple in structure, reliable in work, high in efficiency, wide in application range, and capable of independently adjusting dialysate according to requirements of various illness states of patients.
Owner:王卫国
Method and device for recognition of paravasal bleeding
A method and a device for recognition of paravasal bleeding upon a supplying of blood to a vascular access via a line and / or upon the removal of blood from a vascular access via a line is provided. A device for extracorporeal blood treatment comprising a device for recognition of paravasal bleeding is also provided. The method and the device are based on the change of arterial pressure in the arterial branch or the venous pressure in the venous branch of the extra-corporeal circuit being registered during the extracorporeal blood treatment. One aspect of the method and the device is that pressure changes that come from a pressure level exhibiting a large difference from a reference value are more strongly considered than those that come from a pressure level that exhibits only a minor difference from the reference value.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Volume status monitor: peripheral venous pressure, hypervolemia and coherence analysis
Systems and methods are provided for monitoring changes in blood volume using waveforms in the peripheral vasculature. In particular, the systems and methods relate to detecting ventilation-induced variation (VIV) of waveforms in the peripheral vasculature. Advantageously, the systems and methods may relate to analyzing VIV in peripheral venous pressure (PVP). Thus, the VIV of PVP may be measured, wherein decreased VIV is indicative of decreased blood volume In exemplary embodiments, such as involving spontaneous breathing, it may be necessary to account for changes in respiratory signal strength. Thus systems and methods are also provided for assessing coherence between ventilation and VIV for a flow or pressure waveform. Specifically, coherence is evaluated by comparing the waveform to a detected respiratory signal. Finally, systems and method are provided for distinguishing the impact of respiration on the PG signal during hypervolemia as compared to hypovolemia. Such systems and methods may advantageously be utilized to monitor fluid status during fluid replacement.
Owner:SHELLEY KIRK H +2
Remaining needle
ActiveCN104922759AIncrease the scope of applicationImprove practicalityInfusion needlesValvesVeinElastic compression
A remaining needle comprises a remaining hose, a remaining needle seat, an extension hose seat, an extension hose connected between the remaining needle seat and the extension hose seat and a liquid stopping clamp arranged on the extension hose. The front portions of an upper contact and a lower contact located on a pressing touch portion of the liquid stopping clamp between a clamp piece and a clamp seat of the liquid stopping clamp are provided with at least one elastic compression device which has elasticity and larger clamping area and can form continuous positive pressure on the extension hose. According to the remaining needle, due to the fact that the liquid stopping clamp structure with at least two clamping positions is adopted, not only can the clamp piece of the liquid stopping clamp reliably clamp the extension hose to form liquid stopping, but also the continuous positive pressure compression device is utilized to continuously extrude the extension hose at the remaining needle seat end in a large area to enable the extension hose to generate larger deformation, liquid in an extruding pipe enters the remaining hose to play a continuous positive pressure action, therefore, blood return caused by springback siphon of the extension hose due to the liquid stopping clamp can be effectively avoided, the blood can be effectively prevented from flowing back to the remaining hose due to venous pressure fluctuation in blood vessels, and the purpose of preventing thrombus can be achieved.
Owner:ZHANJIANG JIANLIYUAN MEDICAL PROD
Infiltration detection system
InactiveUS20070112329A1Quick checkAccurate placementMedical devicesIntravenous devicesVeinIV Infusion
An IV infusion system capable of detecting infiltration / extravasation events is described. Flow rate changes due to venous pressure variations are measured; infiltration / extravasation events are detected when these flow rate patterns are altered when infusion is not into a vein.
Owner:SAGE BURTON H JR
Blood purification device
ActiveCN103906538AAccurate detection of blockageDetect congestionDialysis systemsMedical devicesVeinBlood pump
The present invention discloses a blood purification device capable of precisely detecting blockages of an arterial blood circuit in an arterial blood return step. A controlling means (19) detects pressure with a venous pressure sensor (21) while also carrying out a plurality of iterations of arterial blood return steps comprising a pressure accumulation step for forward-driving a blood pump (4) while also closing off a flow path with an electromagnetic valve (V2) to accumulate pressure between the installation position of the blood pump (4) and the installation position of the electromagnetic valve (V2), and a pressure release step for reverse-driving the blood pump (4) while also maintaining the closing off of the flow path by the electromagnetic valve (V2) to return blood from the distal end of an arterial blood circuit (2); and blockages of the flow path in an arterial blood circuit (1) can be detected on the basis of the change in pressure at corresponding predetermined points in time in each of the arterial blood return steps.
Owner:NIKKISO COMPANY
Hepatic venous pressure gradient classification method of CT image as well as computer equipment
ActiveCN110074809ARealize multi-category non-invasive testingThe test result is accurateImage enhancementImage analysisVeinClassification methods
The embodiment of the invention relates to a hepatic venous pressure gradient classification method of a CT image as well as computer equipment. The method comprises the following steps: performing liver image cutting pretreatment on the acquired abdomen CT image of a tester to acquire a plurality of to-be-detected liver image blocks; input the plurality of to-be-detected liver image blocks into aliver predicting submodel which is trained in advance to perform hepatic venous pressure gradient classification test to acquire a plurality of predicting classification of each to-be-detected liverimage block as well as predicting classification probability corresponding to the classification, wherein the hepatic venous pressure gradient of the tester is the same predicting classification within the same preset hepatic venous pressure gradient range; and calculating the average value of the classification probability belonging to the same predicting classification, and determining the maximum value of each average value and the predicting classification corresponding to the maximum value as the hepatic venous pressure gradient classification test result of the tester. According to eachembodiment of the invention, multi-classification noninvasive test of the hepatic venous pressure gradient is realized, the test classification result is high in precision and the generalization ability is higher.
Owner:祁小龙
Remaining needle with elastic contact
ActiveCN104922758APrevent backflowPrevents clamping extension tubes from entering the rear end of the liquidInfusion needlesPositive pressureThree vessels
A remaining needle with an elastic contact comprises a remaining soft pipe, a remaining needle base, an extending pipe base, an extending soft pipe connected between the remaining needle base and the extending pipe base and a liquid stopping clamp arranged on the extending soft pipe. The remaining needle is characterized in that at least one of an upper contact and a lower contact of a pressing-contacting part of the liquid stopping clamp is an elastic contact which can form continuous positive pressure on the extending soft pipe with different liquid stopping clamp hard bodies. The liquid stopping clamp structure with the elastic contact is used, the elastic pressure between the upper contact and the lower contact is larger than human body venous pressure, blood back flowing is effectively prevented, the extending pipe is clamped, and the problem that liquid at the back end enters the remaining soft pipe is avoided. When large external force is applied to the back end of the extending pipe and the external force is larger than the pressure between the elastic contacts of the liquid stopping clamp, the elastic contacts can be slightly stretched so that high-pressure liquid in the back portion of a cavity of the extending pipe can pass, positive pressure is formed in the remaining soft pipe and a front cavity of the extending pipe, and blood flowing back into the remaining soft pipe is forced to flow back to into a blood vessel.
Owner:陈伟权
Measuring blood flow and venous capacitance
Non-invasively measuring a physiological parameter by applying to a subject's body part a venous occlusion plethysmographic device including a first section having a first fluid chamber and at least a second region having a second fluid chamber to engage a first region of the body part and a second region of the body part, proximal of the first region; pressurizing the first chamber to a pressure sufficient to compensate for hydrostatic pressure added to the inherent venous pressure at the maximal vertical lowering level of the body part relative to the subject's heart level; intermittently raising and lowering the pressure in the second fluid chamber to a pressure above or equal to the pressure in the first chamber, but below the arterial blood pressure; measuring changes in volume of the first region of the body part; and utilizing the measured volume changes to provide a measure of the physiological parameter.
Owner:ITAMAR MEDICAL LTD
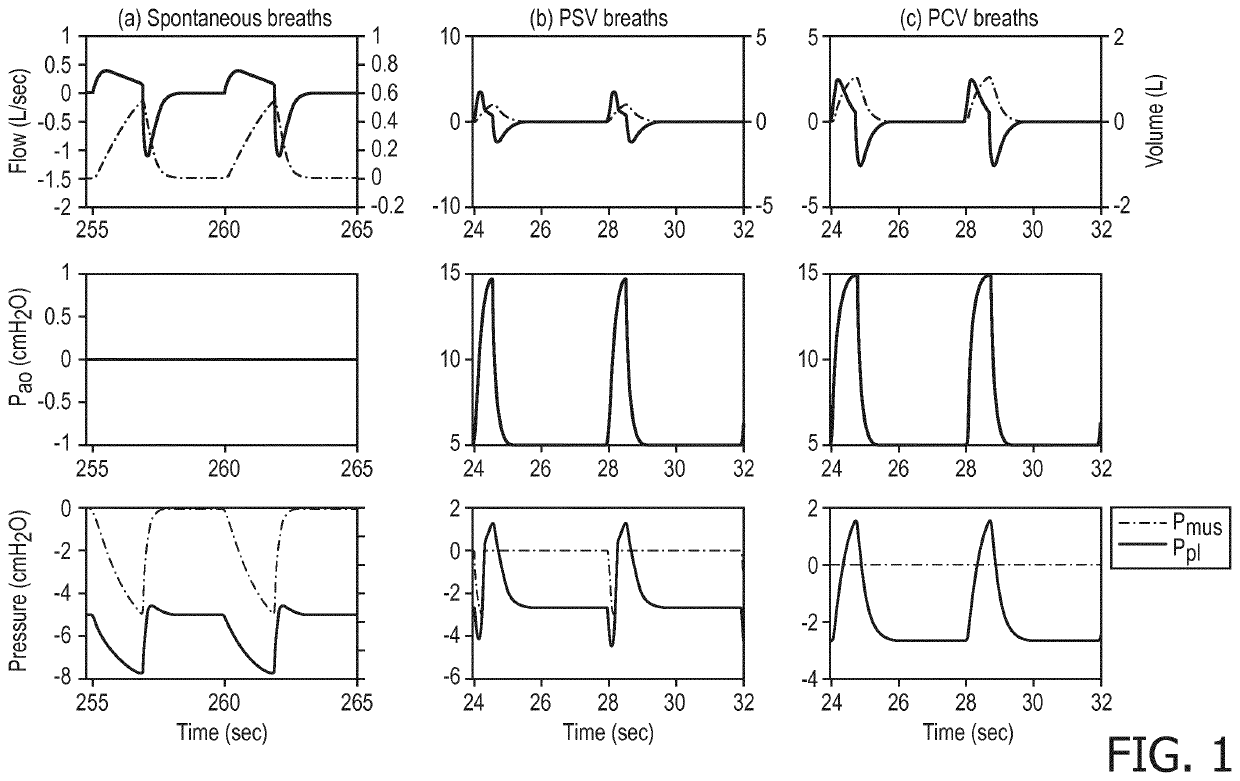
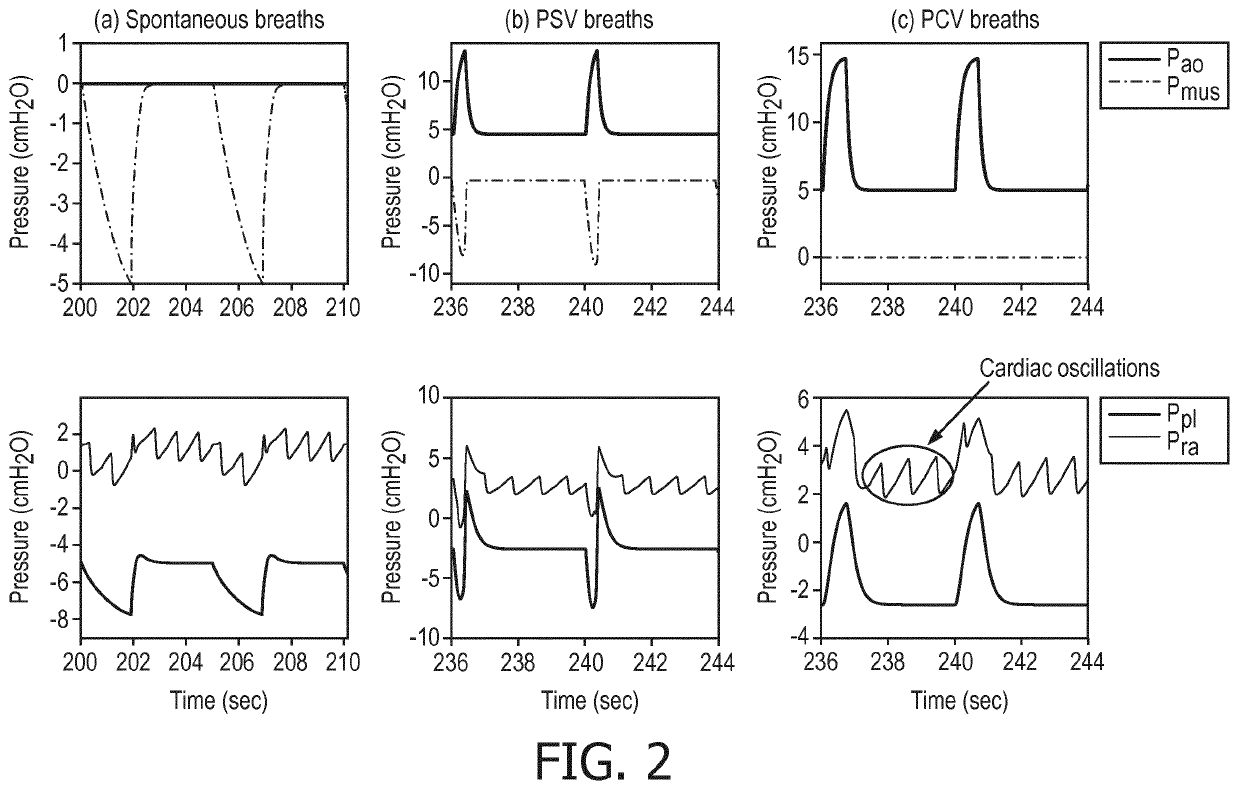
Enhancement of respiratory parameter estimation and asynchrony detection algorithms via the use of centeral venous pressure manometry
ActiveUS20210205558A1Easy to monitorAdjustment of settingRespiratorsElectrocardiographyRespiratory muscleVein
A respiratory monitoring apparatus (10) includes a central venous pressure sensor (24) configured to measure a central venous pressure (CVP) signal of a patient. At least one processor (32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 58) is programmed to process the CVP signal to generate respiratory information for the patient by operations including: segmenting the CVP signal based on detected breath intervals; calculating a surrogate muscle pressure signal from the segmented CVP signal; and filtering the surrogate muscle pressure signal to remove a cardiac activity component a cardiac activity component of the surrogate respiratory muscle pressure signal.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com