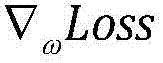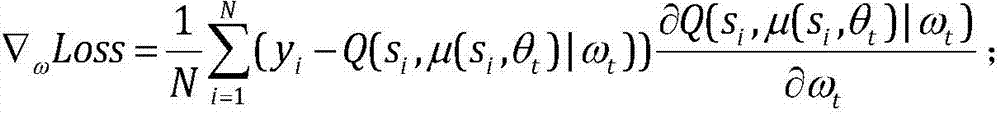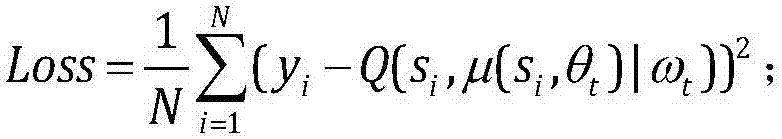Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3172 results about "Underwater robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
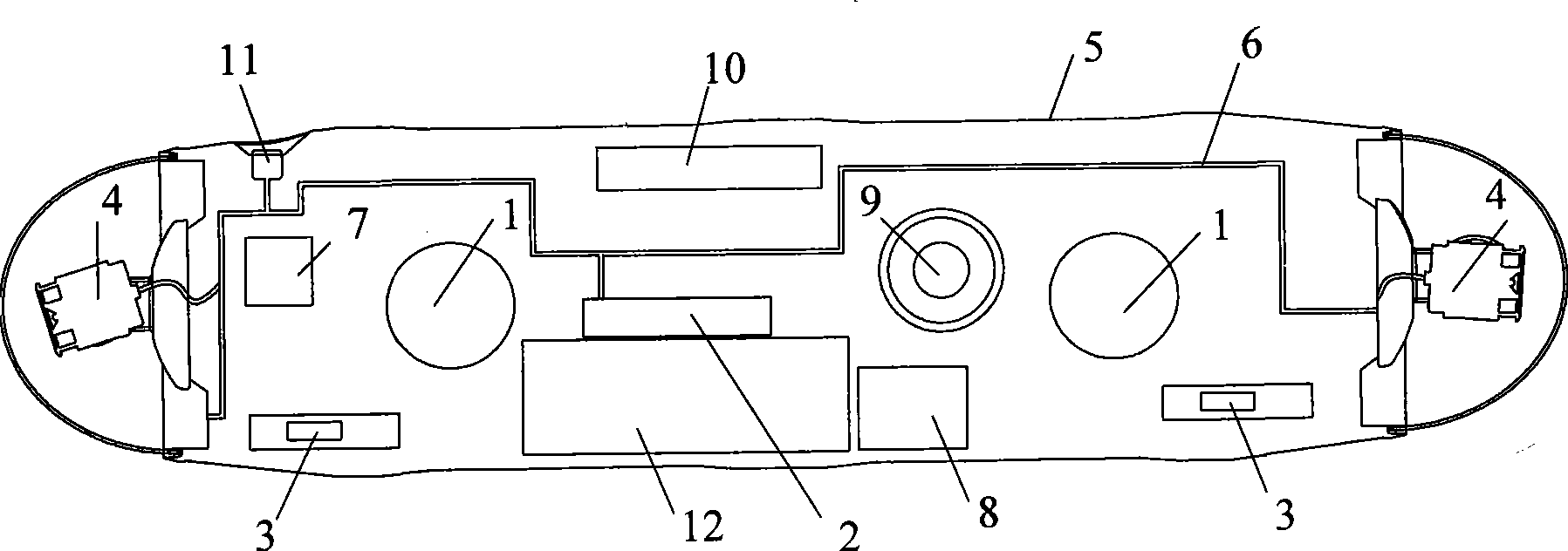
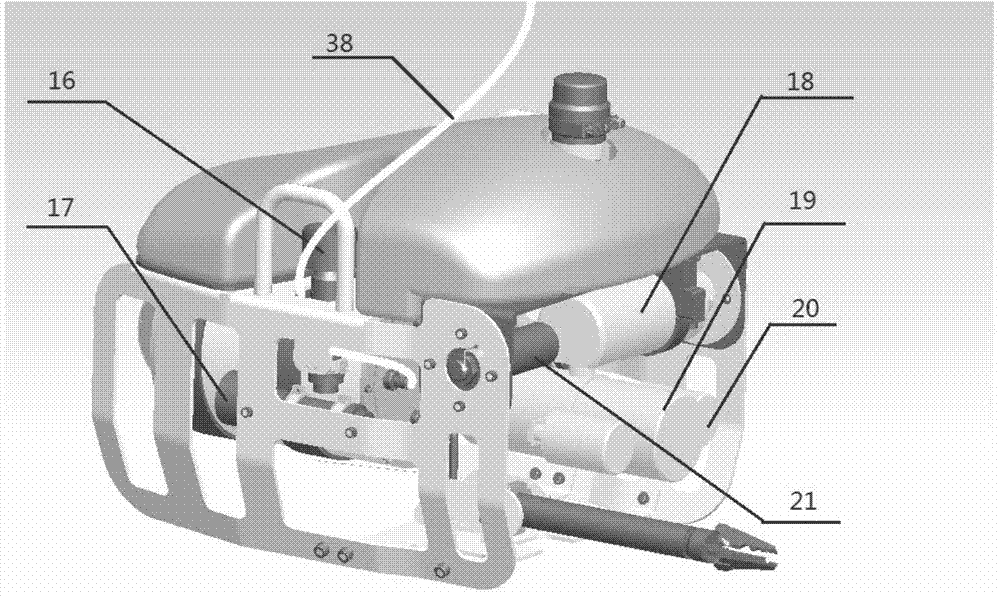
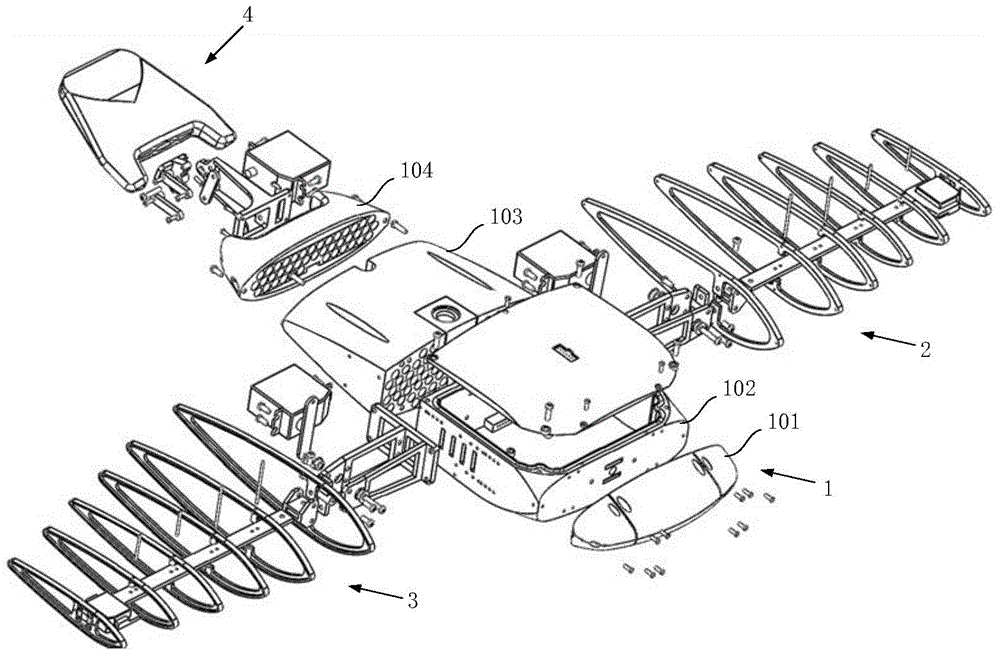
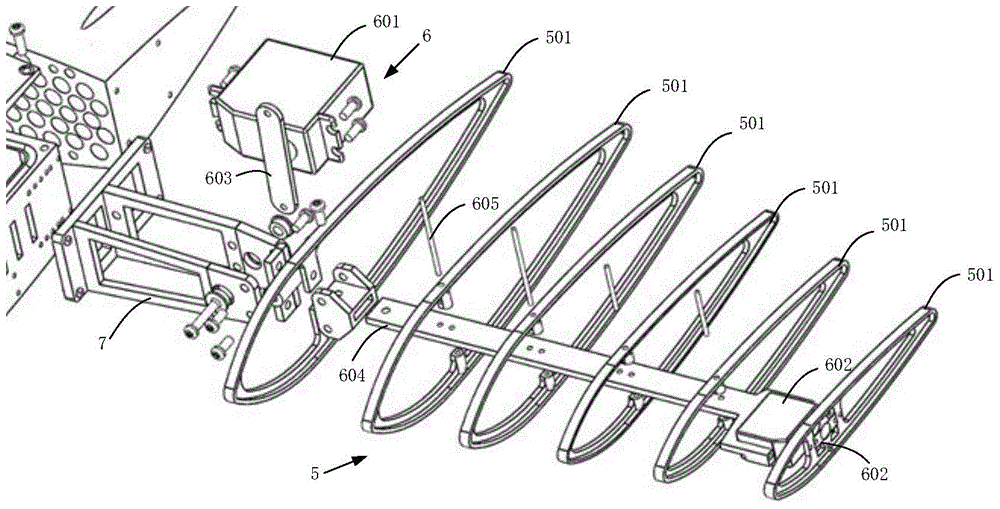
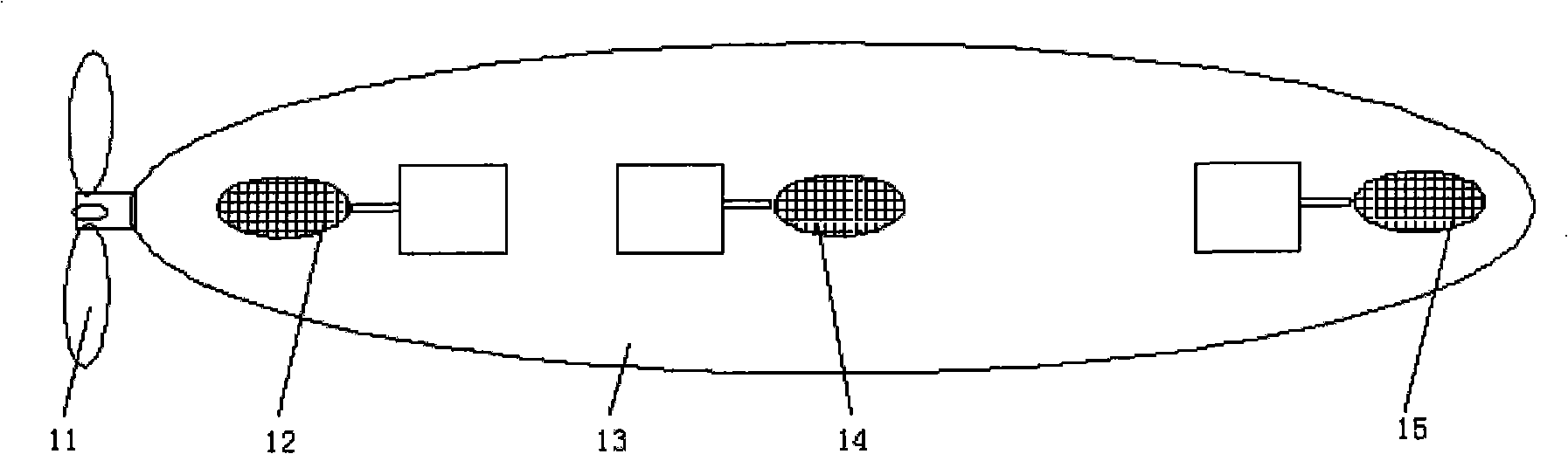
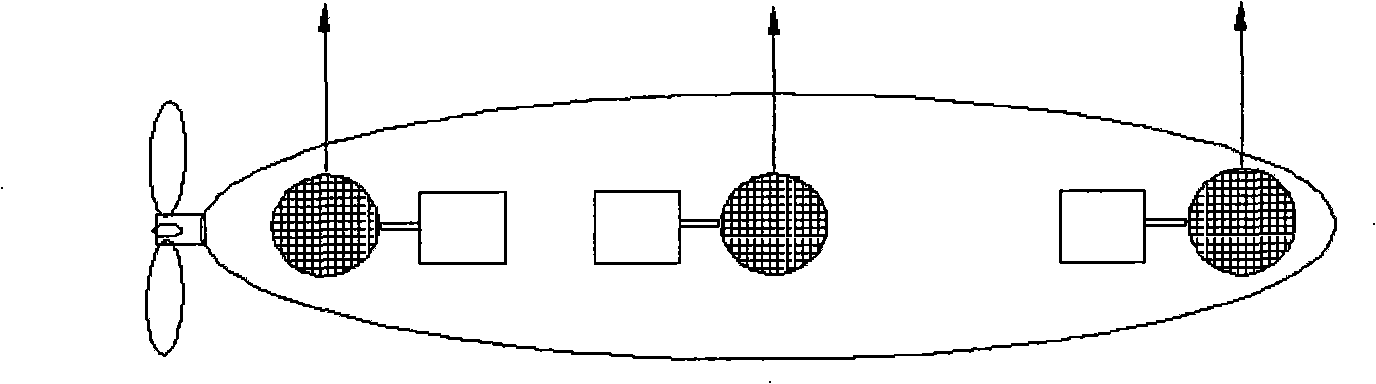
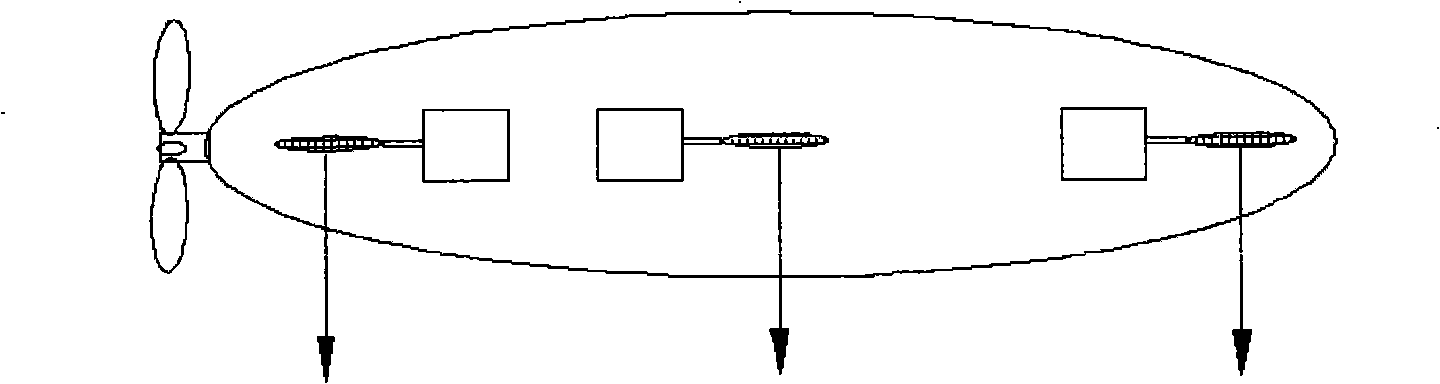
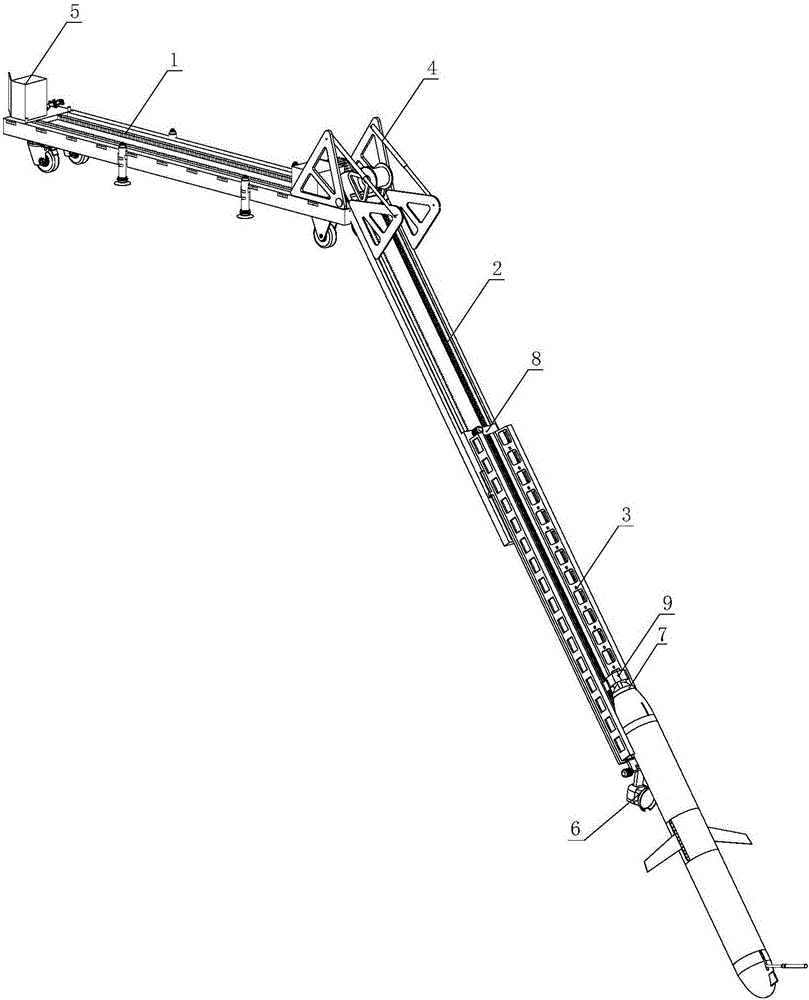
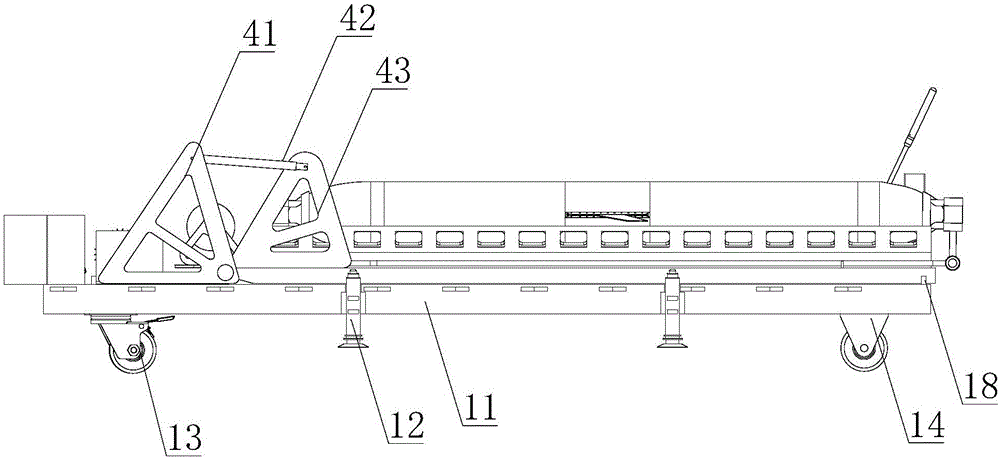
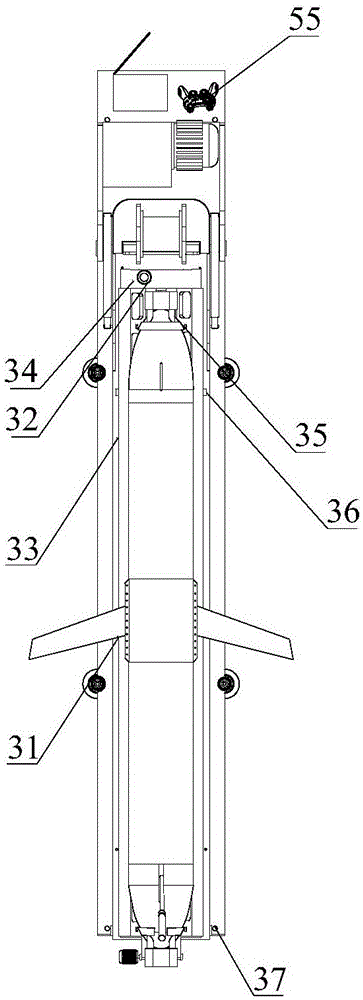
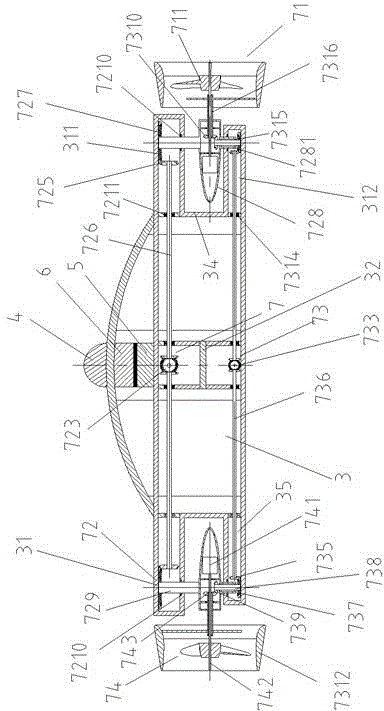
Submarine cable detection underwater robot and operating method
InactiveCN108045530AUpload in real timeHas the function of reliefUnderwater vesselsUnderwater equipmentOcean bottomUsability inspection
The invention discloses a submarine cable detection underwater robot and an operating method. Mutual switching of a ROV mode and an AUV mode can be achieved by means of a cable security interface, thecapabilities of autonomous navigation, long-distance control and accurate detection are achieved, and the submarine cable detection underwater robot is used for construction exploration, daily routing inspection and failure detection of a submarine cable project. Construction exploration can be conducted on landform of a submarine cable route before the submarine cable project starts, daily inspection is conducted on burying and operation conditions of submarine cables which are put into operation already, and on-site close observation is conducted on the submarine cables being subjected to breaking down or cracking accidents.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +2
Underwater robot recovery system and recovery method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of underwater robots, and specifically relates to an underwater robot recovery system and a recovery method thereof. The system includes a mother ship, an underwater robot, an automatic line throwing device and a lifting seat arranged on the underwater robot, a butting lifting device and a draw gear. After the underwater robot completes the mission, a haulage rope is thrown out from the ship bow. The staff on the mother ship picks up the haulage rope through a rope picking device, and then the rope is traversed through the draw gear. The underwater robot is driven by the mother ship for navigation to overcome the effects of waves in the sea. A guidance rope is thrown by a remote control command. The butting lifting device is driven by a hoist installed on the mother ship, and falls down along the guidance rope to abut with the underwater robot and clamp. The whole recycling process is realized. The underwater robot recovery system of the present invention has the characteristics of compact structure, convenient operation, safety and reliability, small influence by the sea state, no transform to the hoist, and small requirement to the mother ship, and can achieve the laying and recovering by the same system for the underwater robot under four grade sea conditions.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
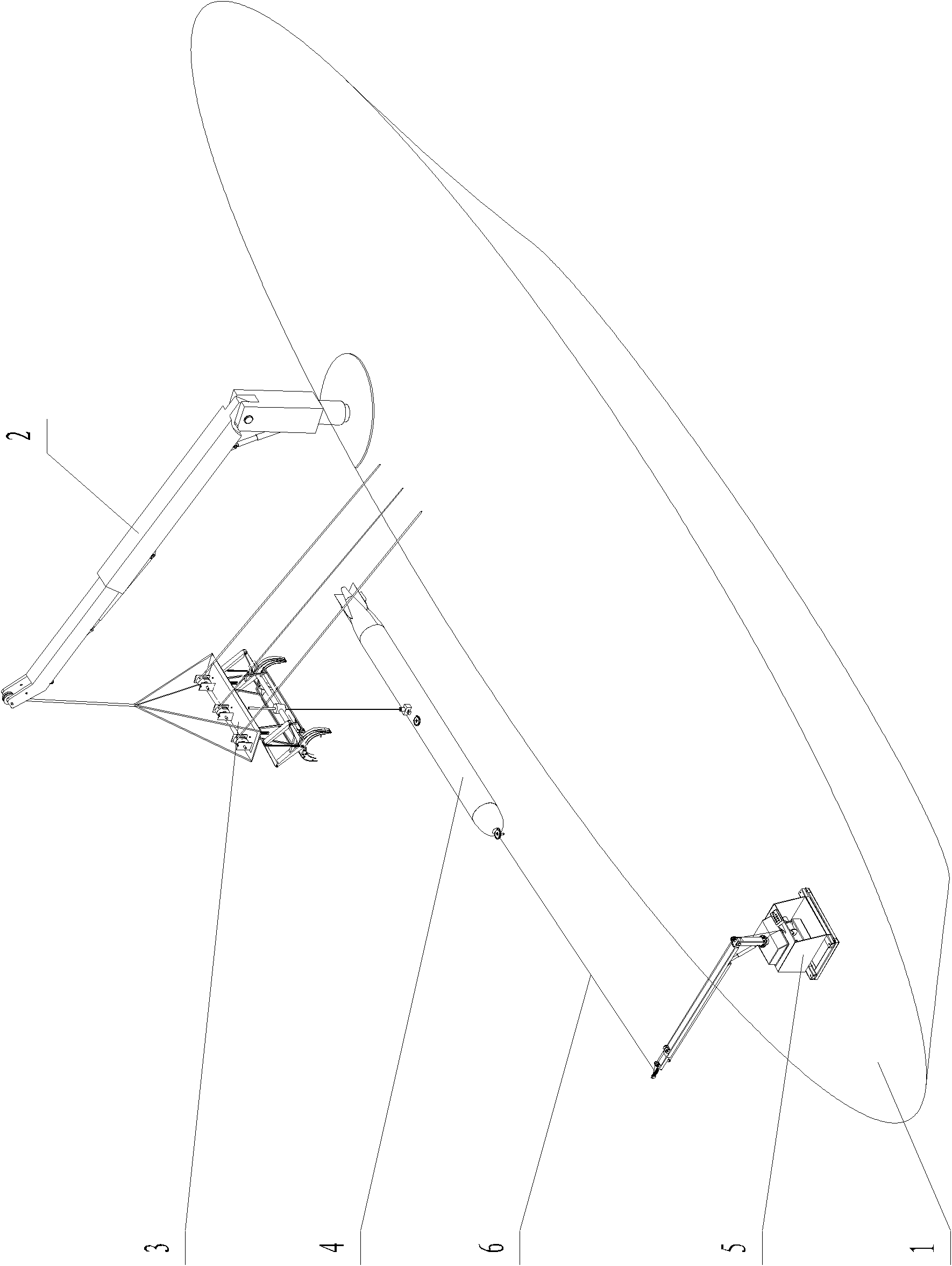
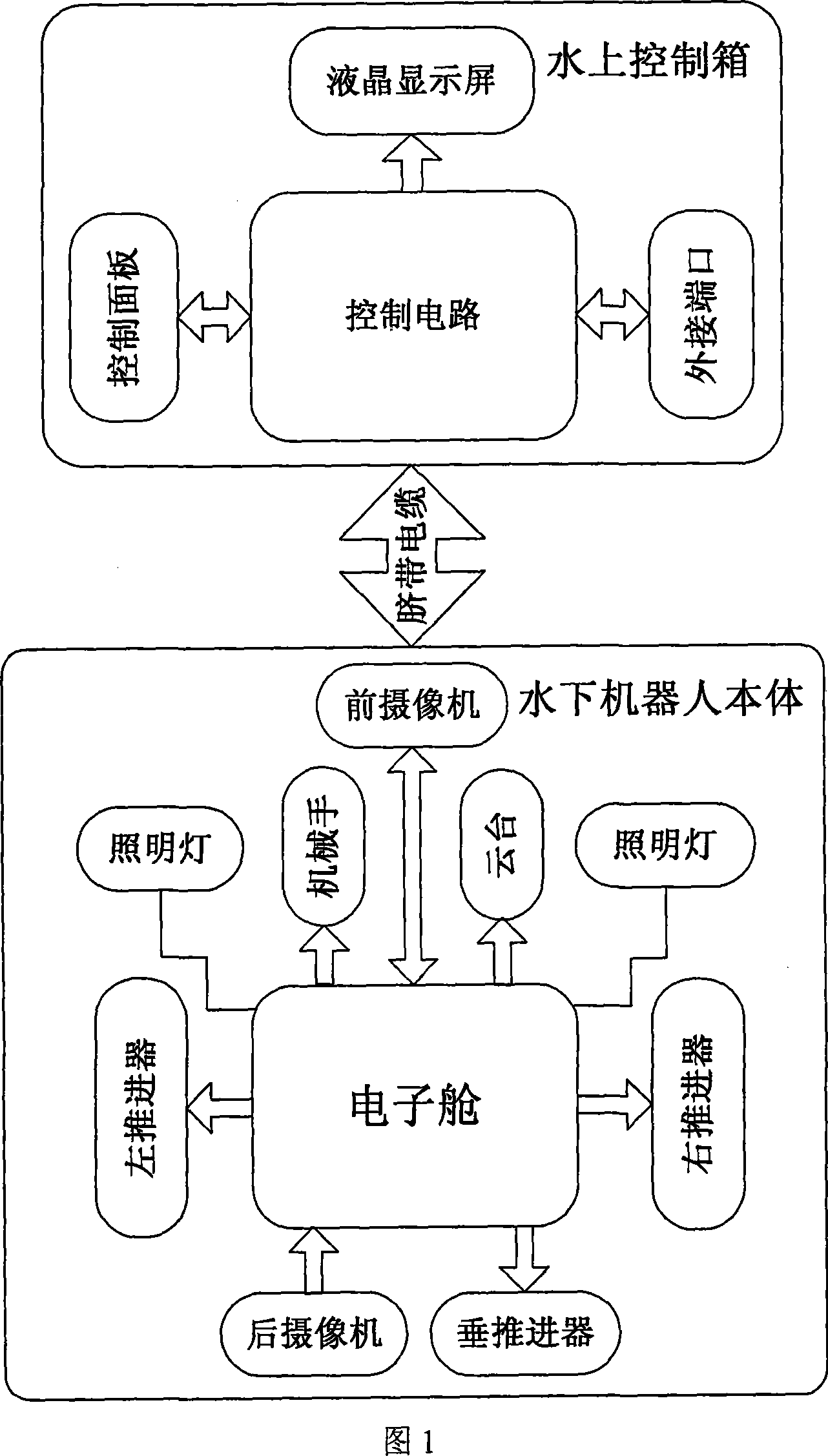
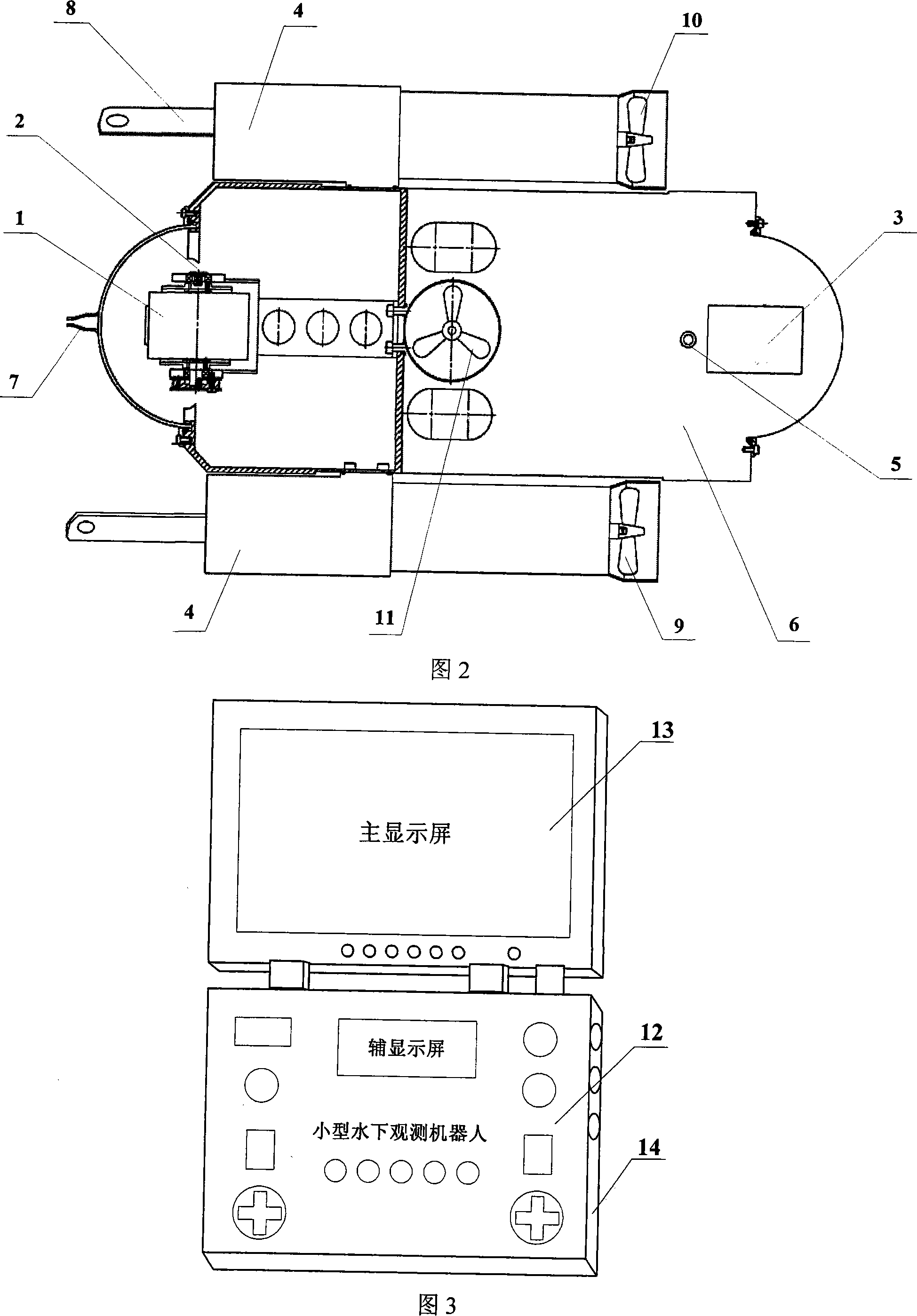
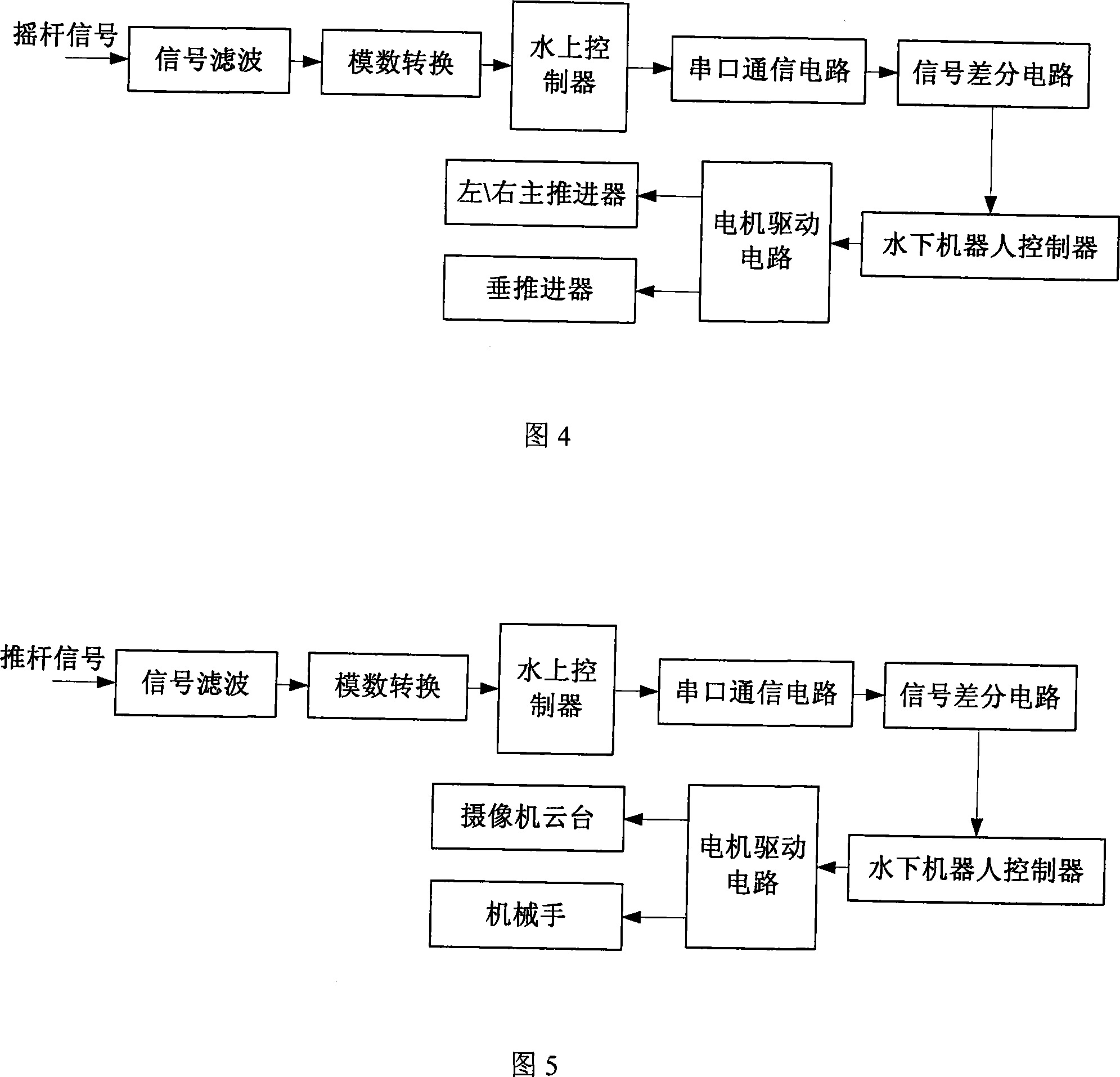
Small-sized underwater observation robot
InactiveCN101234665AReduce the number of coresReduce volumeClosed circuit television systemsUnderwater vesselsShielded cableEngineering
The invention relates to a mini-size underwater observing robot, which comprises an underwater robot body and an above-water control box, wherein, two sides of an electronic cabin on the underwater robot body are horizontally provided with a left propeller, a right propeller and a lamp; a middle part on the electronic cabin is vertically provided with a vertical propeller; a bracket and a manipulator are arranged together with a lower part of the electronic cabin, the interior of which is provided with a compass, a temperature gauge, a depth gauge and a control circuit board; a front part on the electronic cabin is provided with a camera with variable focus, a camera pan and tilt and a lamp; a back part on the electronic cabin is provided with a camera with fixed focus; video images are transferred to a display on the above-water control box through shielded cable; the above-water control box consists of a control panel, a control circuit, a liquid crystal display and a chassis body. The invention transfers the shapes and the movement state of observed objects under water to the above-water control box through a video sensor, so the repair personnel can analyze the images; besides, the arranged manipulator can carry out grabbing work with light weight.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Underwater robot
InactiveCN101475055AMeet the needs of different occasionsIncrease underwater speedUnderwater vesselsUnderwater equipmentProgram instructionMotor drive
The invention discloses an underwater robot, which comprises a robot body with a closed cabin, an under water camera arranged inside the robot body and a control system for wirelessly receiving and importing program instructions, wherein the control system has a motor driving circuit, the robot body is movably connected with a plurality of power push units for outputting power and rotating the robot body at an angle. The robot can realize dynamic hovering in water under certain flow speed and keeps certain up and down inclination angles so as to cooperate to meet the requirements for detection work, scientific exploration, unmanned investigation and the like. The robot can complete water temperature, depth and acoustic susceptance detection, water imaging and other works and has the advantages of light weight, flexibility, reliable work and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI XPARTNER ROBOTICS
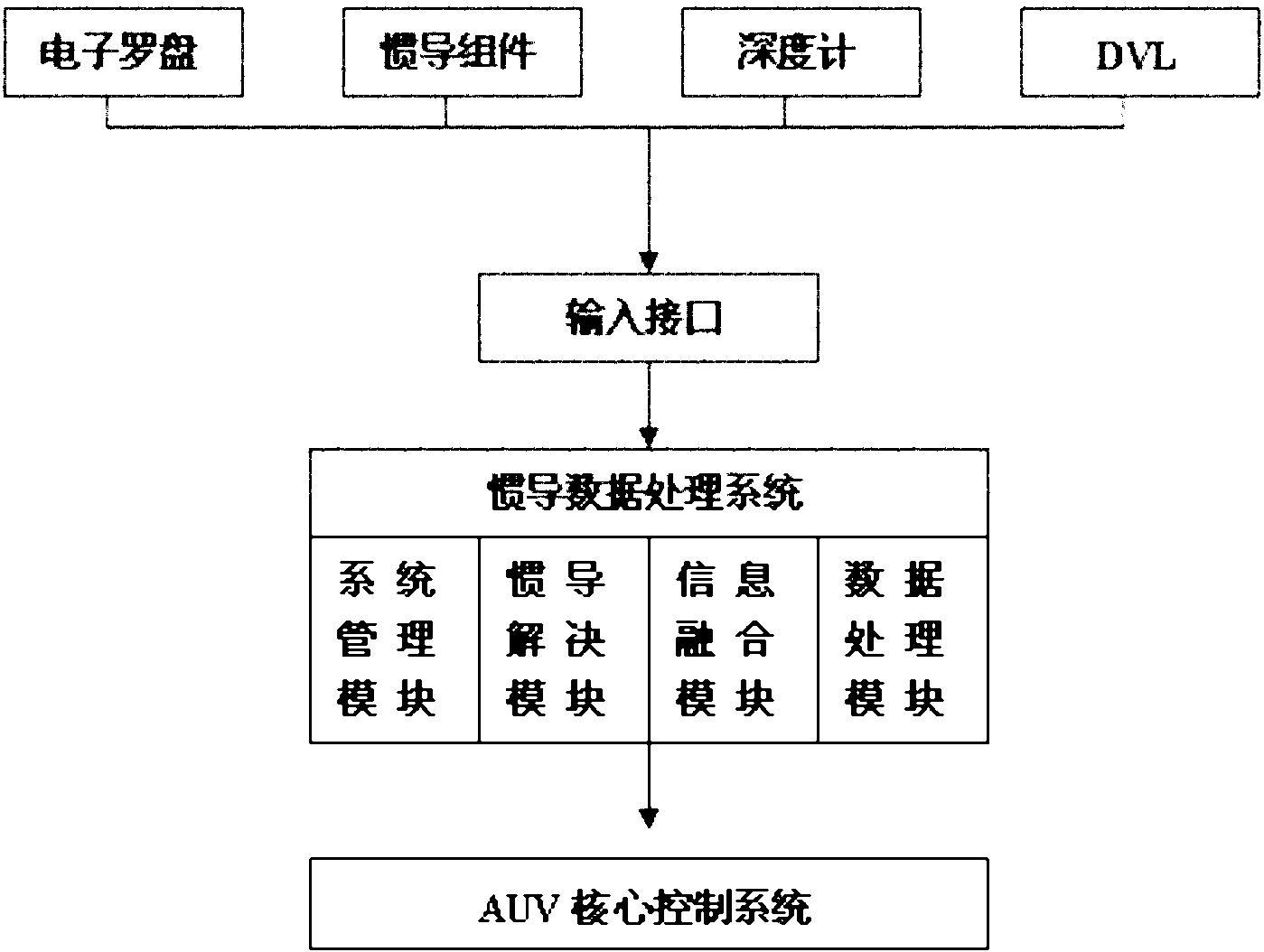
Autonomous underwater vehicle combined navigation system
ActiveCN102042835ARealize autonomous navigationPrecise NavigationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation systemVisual perception
The invention relates to an underwater vehicle navigation system, in particular to an autonomous underwater vehicle combined navigation system. The system comprises an inertia basis navigation device and an external sensor navigation device, wherein the inertia basis navigation device comprises a Doppler velocimeter, an optical fiber gyro, a pressure sensor, an electronic compass and a depthometer; and the external sensor navigation device comprises a sonar. The combined navigation system also comprises an underwater structure optical sensor and an underwater binocular vision platform, wherein the underwater structural optical sensor comprises a forward-vision structure optical sensor positioned on the front of an outer frame of an autonomous underwater vehicle, and a downward-vision structure optical sensor positioned at the bottom of the outer frame; the underwater binocular vision platform comprises a forward-vision binocular vision platform positioned on the front of the outer frame, and a downward-vision binocular vision platform positioned at the bottom of the outer frame; the forward-vision structure optical sensor and the forward-vision binocular vision platform form a forward-vision structure optical and visual system module positioned on the front of the outer frame; and the downward-vision structure optical sensor and the downward-vision binocular vision platform form a downward-vision structure optical and visual system module positioned at the bottom of the outer frame.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
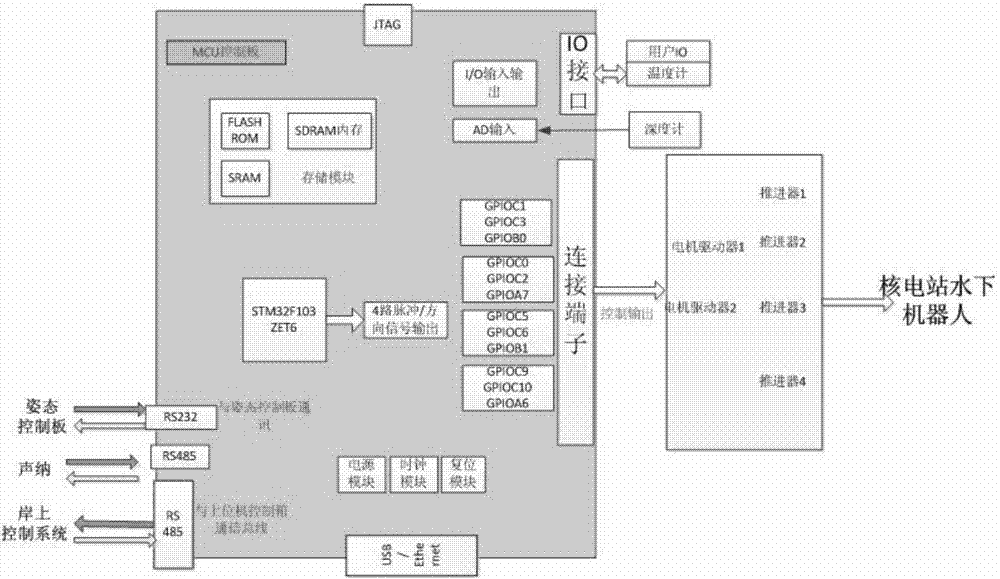
Microminiature operation underwater robot of nuclear power plant
The invention relates to a microminiature operation underwater robot of a nuclear power plant, and the robot comprises an underwater robot body and an onshore control system, wherein two propellers are respectively arranged in the horizontal and vertical directions of the robot body, a depth gauge is arranged on the right side of the front part of the robot body, a manipulator is arranged at the bottom in front of the robot body, and a sonar is arranged on the top of the robot body; a control cabin is arranged in the middle rear part of the robot body; an outer cabin is sealed by a transparent glass cover, and is provided with a rearview camera and an auxiliary lighting light-emitting diode (LED) lamp; a front-view camera system is arranged at the front part of the robot body, and comprises a zooming radiation resistant camera tube, a tripod head and a lighting lamp; a video image and control signal is transmitted to the onshore control system through a shield cable; and the control system comprises a movement control rod, a manipulator control button, a keyboard, a main display screen and a speed governing knob. The microminiature operation underwater robot of the nuclear power plant is used for the monitoring and the simple foreign body fishing of a core pool, a spent fuel pool and a component pool of the nuclear power plant.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
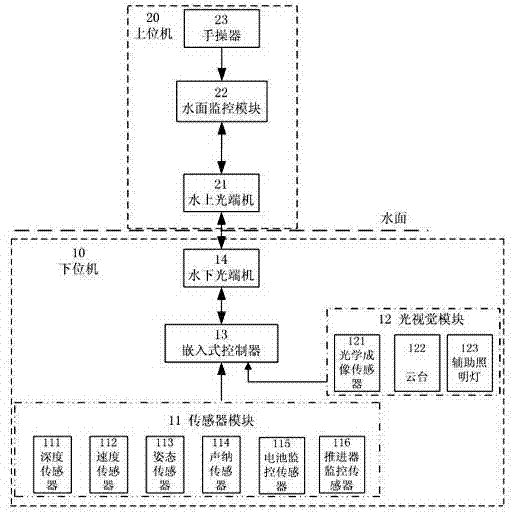
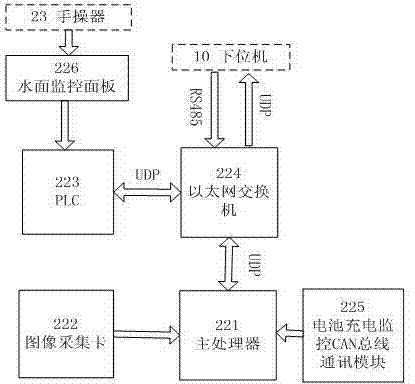
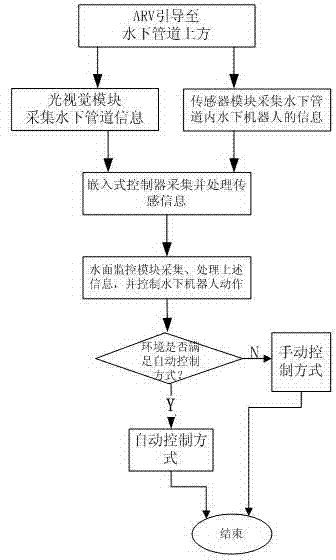
Underwater pipeline detection tracking system and detection method of automatic remote control underwater robot
InactiveCN103488175AAvoid draggingImproved underwater mobilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsTransceiverOptical Module
The invention discloses an underwater pipeline detection and tracking system and detection method of an automatic remote control underwater robot. The underwater pipeline detection and tracking system comprises a lower computer and an upper computer. The lower computer is arranged underwater, and the upper computer is arranged on a water surface mother ship. The lower computer comprises a sensor module, an optical visual module, an embedded controller and an underwater optical transceiver. The sensor module and the optical visual module are connected with the signal input end of the embedded controller respectively. The signal output end of the embedded controller is connected with the signal input end of the underwater optical transceiver. The upper computer comprises an overwater optical transceiver, a water surface monitoring module and a manual operator. The manual operator is in circuit connection with the water surface monitoring module which is in circuit connection with the overwater optical transceiver. The underwater optical transceiver is connected with the overwater optical transceiver through optical fibers. The automatic remote control underwater robot can transmit images in real time, the water surface mother ship can monitor the underwater environment in real time, safety of the complex underwater operation condition is guaranteed, and detection and tracking tasks of an underwater pipeline are finished.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
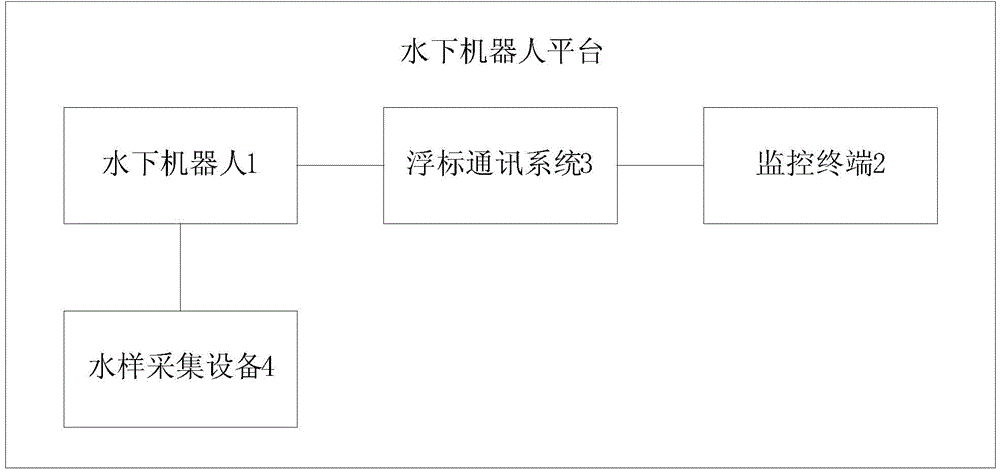
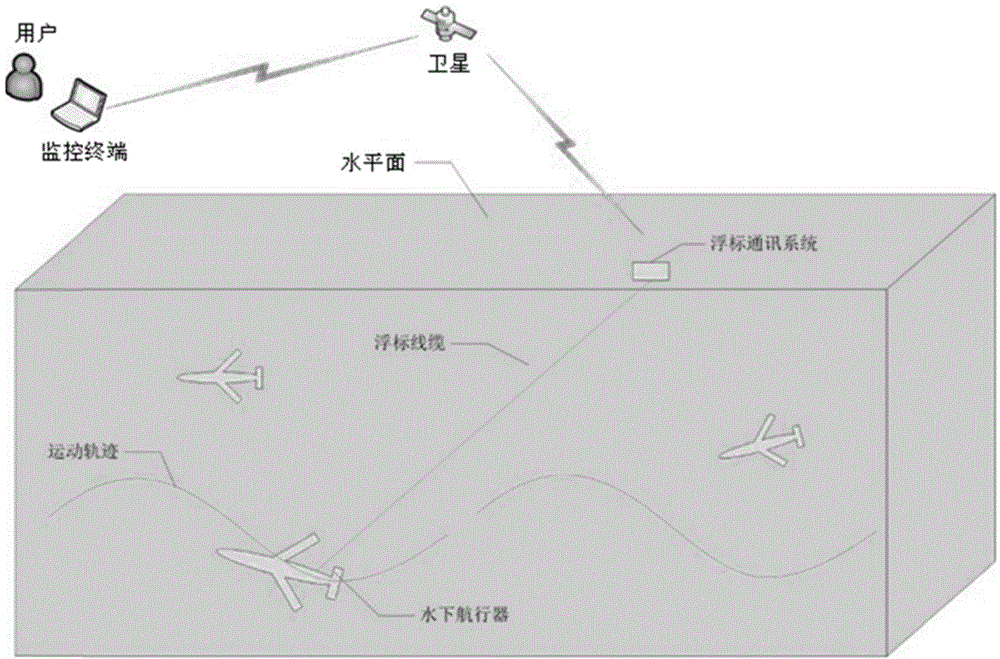
Underwater robot platform
InactiveCN104142688AEnable collaborative movementLow costPosition/course control in three dimensionsCommunications systemBuoy
The invention provides an underwater robot platform. The underwater robot platform comprises at least one underwater robot, a monitor terminal, a buoy communication system and a water sampling device. The monitor terminal is used for sending motion and task instructions to all underwater robots; the buoy communication system is connected with the underwater robots through CAN cables to receive the motion and task instructions through the CAN cables, and the buoy communication system moves under dragging of the underwater robots and obtains positioning information and communication information of the underwater robots; the water sampling device communicates with the underwater robots through standardized interfaces and is used for collecting and recording water sample information; the underwater robots are used for completing corresponding motion and tasks according to the received motion and task instructions. The propulsion mode combining CPG bionic propulsion and gliding propulsion is adopted, the multiple underwater robots are cooperatively controlled through a wireless sensor network technology, and the underwater robot platform is high in real-time performance, movability and efficiency and has the long-time cruising ability.
Owner:SHENZHEN LEZHI ROBOT
Novel modular bionic underwater robot based on full-flexible pectoral fins
InactiveCN104943839AImprove mobilityImprove concealmentPropulsive elements of non-rotary typePhase differenceBionics
The invention discloses a novel modular bionic underwater robot based on full-flexible pectoral fins. A hydrodynamic module of eagle ray pectoral fins is analyzed, and motion of the pectoral fins is decomposed into vertical bending flapping in the vertical body longitudinal axis direction and twisting motion taking the vertical body longitudinal axis direction as the axis. The whole robot comprises a sectioned main body, a left flexible pectoral fin module, a right flexible pectoral fin module and a tail fin module, and a group module is formed by connecting fin connecting parts; the left and right flexible pectoral fin modules are identical in structure and are in mirror symmetry; a pectoral fin framework adopts a structure similar to that of a plane rib, a symmetrical airfoil is taken as the basic shape, and the pectoral fin modules with streamline sections are spliced through serial connection of straight pectoral fin trunk bones and steel wires. A large steering engine and a small steering engine are arranged at the root and the tip of each pectoral fin to control vertical flapping and twisting motion of each pectoral fin. Through adjustment of motion amplitude, motion frequency and phase difference of the two steering engines of each pectoral fin, different pectoral fin motion postures can be realized, and fish body motion can be finished better.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
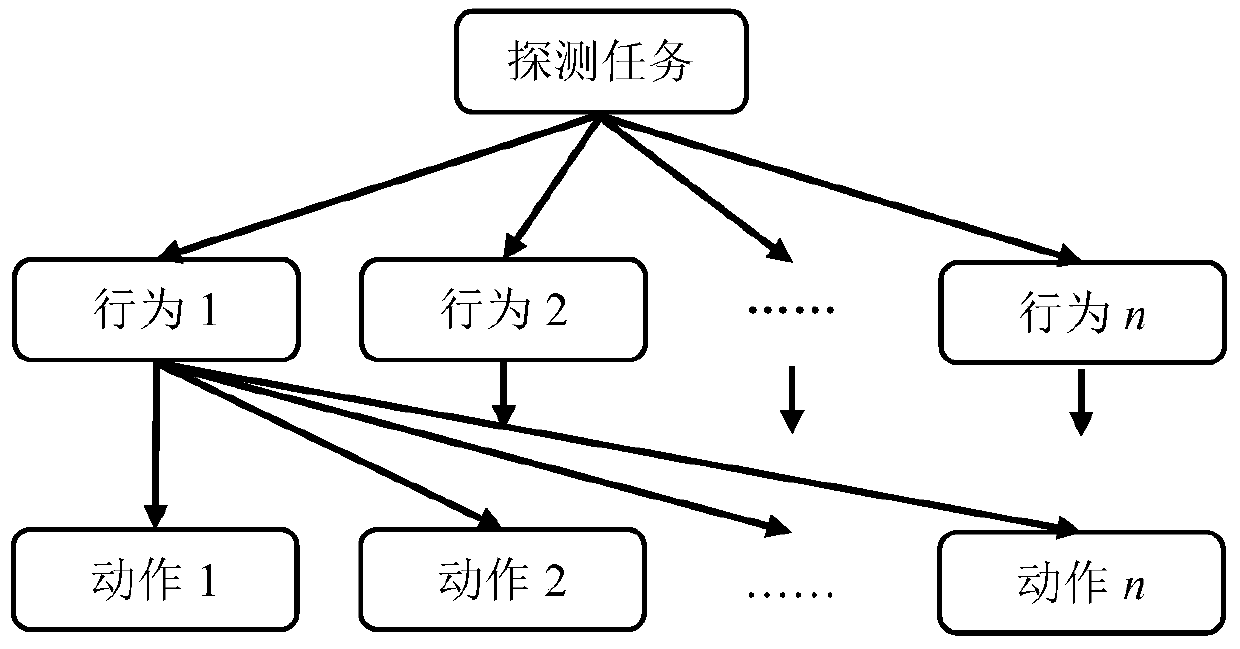
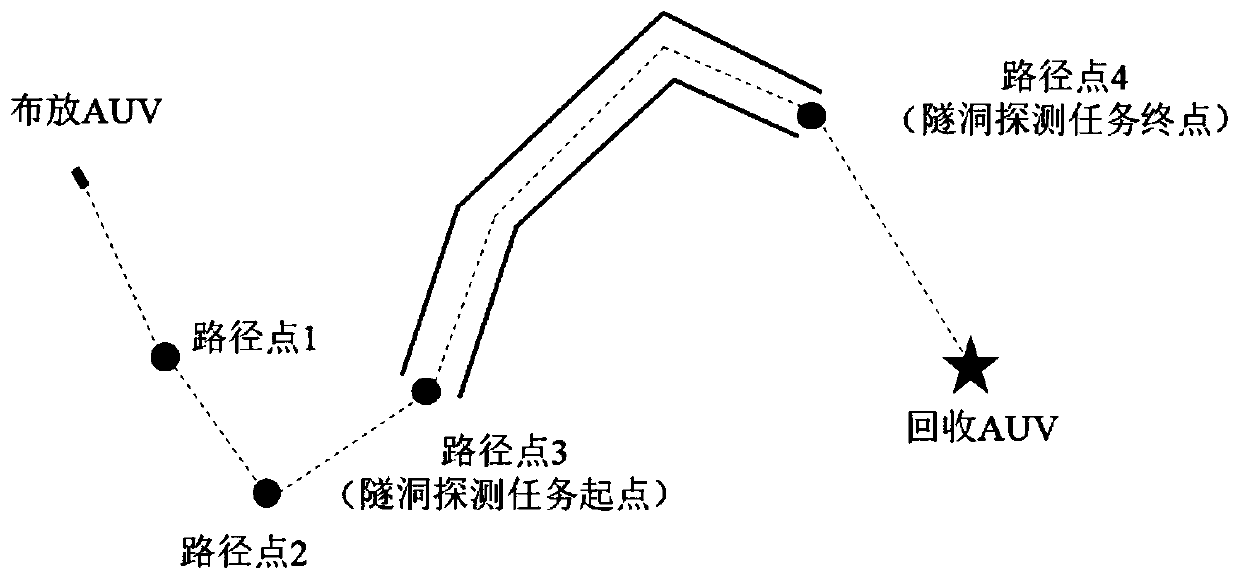
Reinforcement learning-based AUV behavior planning and motion control method
ActiveCN110333739ASolve the "curse of dimensionality" problemEasy to controlNeural architecturesPosition/course control in three dimensionsTask completionObstacle avoidance
The invention discloses a reinforcement learning-based AUV behavior planning and motion control method, which belongs to the technical field of underwater robots and aims at solving the problems of limited training experience and difficult application in a real environment as complex task planning by the AUV depends much on manual experience and a control method designed based on an intelligent algorithm needs an accurate environment mode. AUV tunnel detection is defined as a general task; behaviors corresponding to task completion comprise target trending, wall tracking and obstacle avoidance; a control instruction generated by the robot under water to complete the planned behavior is defined as an action; and when the AUV executes a tunnel detection task, a deep reinforcement learning DQN algorithm is used for real-time behavior planning, a corresponding deep learning behavior network is constructed, and planning of the tunnel detection task is completed. The AUV action network is trained by the DDPG method, the AUV is regarded as an environment model, and force-to-state mapping is obtained, thereby realizing the action control of the AUV.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Long-term fixed-point vertical-section observation-type underwater robot
ActiveCN105644742AImprove abilitiesImprove the level ofUnderwater vesselsUnderwater equipmentSection planeMarine engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of underwater robots, in particular to a long-term fixed-point vertical-section observation-type underwater robot. The long-term fixed-point vertical-section observation-type underwater robot comprises a propulsion section, a stern buoyancy adjusting section, a battery cabin section, an electronic cabin section, a bow buoyancy adjusting section and an observation load section, wherein the propulsion section and the observation load section use open frame structures; the observation load section carries an oceanographic hydrological data observation sensing equipment; the upper part of the propulsion section is provided with a satellite antenna; the stern buoyancy adjusting section, the battery cabin section, the electronic cabin section and the bow buoyancy adjusting section are arranged in a full-sealed pressure resistant cabin; and through double-way buoyancy adjusting of the stern buoyancy adjusting section and the bow buoyancy adjusting section, the motion posture of the underwater robot is adjusted and the underwater robot can hover at a fixed point. The underwater robot realizes a high-accuracy repeatable double-way buoyancy adjusting function and can realize autonomous balancing and fixed-point hovering.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
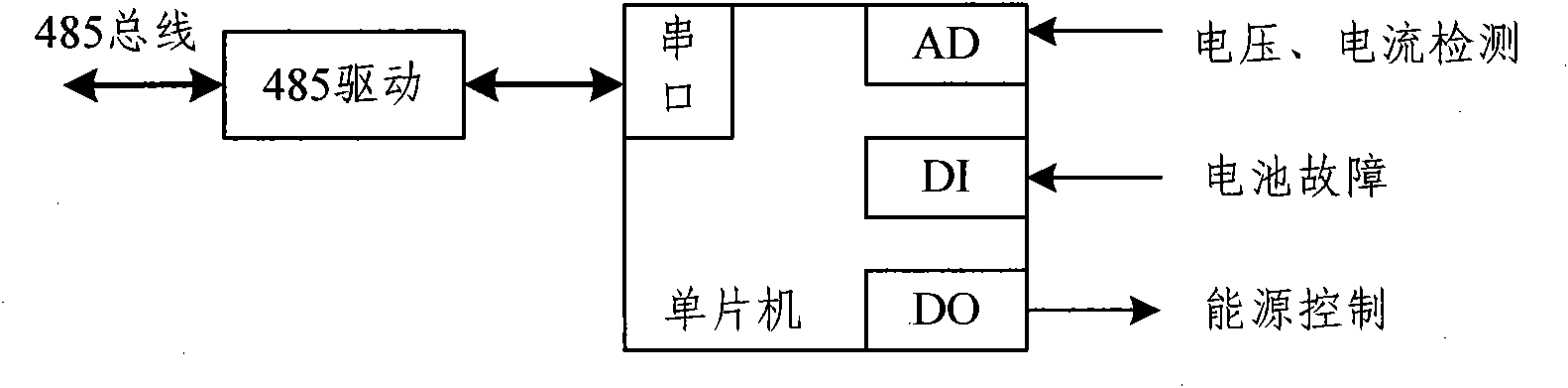
Underwater robot adjusted by three oil-bags and depth-setting control method thereof
ActiveCN101337578AImplement static latencyRealize regulationUnderwater vesselsUnderwater equipmentGravitational forceExercise state
The invention provides an underwater robot adjusted through three oil pockets, and a depth-setting control method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: information, such as depth, longitudinal velocity and attitude angle, etc., is obtained through corresponding sensors; the static submergence or dynamic submergence is determined according to a host computer instruction; if the instruction indicates the static submergence, a bow, a midship and a stern respectively pump oil from the oil pockets at the same time, therefore, the displacement volumes of the oil pockets are reduced, the buoyancy force of the underwater robot is smaller than the gravity force in general, and the underwater robot sinks; if the instruction indicates the dynamic submergence, an axial main thruster is started, and enters a constant speed motion state with acceleration, an oil storage tank at the bow part sucks oil from the bow oil pocket, and therefore, the displacement volumes of the bow oil pocket is reduced; since the oil is discharged to the stern oil pocket from an oil storage tank at the stern part, the displacement volume of the bow oil pocket is increased; the underwater robot is changed into a state of trim by head from zero pitch, and bow trim occurs; the bow trim motion is coupled by the axial motion at the moment, and longitudinal trim submergence is realized; and the oil suction action and the oil discharge action are opposite when the static floating or dynamic floating occurs. The method has significance for the long-distance voyage underwater robot regarding to energy conservation.
Owner:哈尔滨哈船特装科技发展有限公司
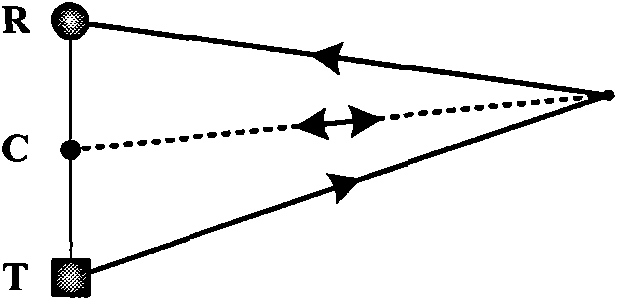
Underwater target positioning method
The invention relates to an underwater target positioning method. The underwater target positioning method includes that (1) a recognition system is provided and comprises a buoy subsystem, a sonar subsystem, a target recognition subsystem and a control subsystem, the buoy subsystem floats on a water surface above an underwater robot, the target recognition subsystem, the sonar subsystem and the control subsystem are disposed on the underwater robot, the buoy subsystem is used for determining global positioning system (GPS) position of a buoy, the sonar subsystem is used for determining a buoy relative position between the buoy and the underwater robot, the target recognition subsystem is used for determining the type of an underwater target and for determining a target relative distance between the underwater target and the underwater robot, and the control subsystem determines the GPS position of the underwater robot and the GPS position of the underwater target according to the buoy GPS position, the buoy relative position and the target relative distance; (2) positioning is performed by means of the recognition system. By means of the underwater target positioning method, GPS positions of the underwater robot and the underwater target can be accurately determined, and meanwhile, the type of the underwater target can be recognized.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAHONG INDAL GROUP
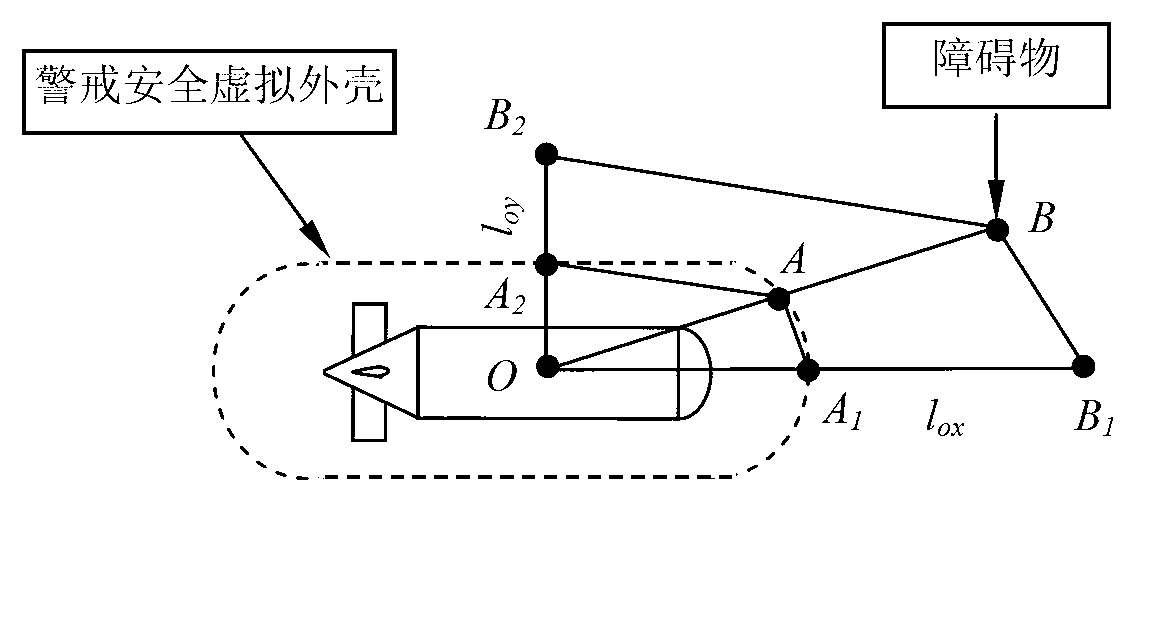
Automatic obstacle avoidance method for intelligent underwater robots
ActiveCN102999050AImprove survivabilityAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsTask completionSurvivability
The invention relates to an automatic obstacle avoidance method for intelligent underwater robots, in particular to a method for considering underwater robot moving objects and obstacles and underwater robot control performances integrally to achieve obstacle avoidance. The method comprises performing global path planning according to job tasks and chart database information; reading underwater robot motion sensor information and obstacle avoidance sonar information; calculating underwater robot safety alerting distances, and establishing a safe virtual outer casing of an underwater robot; determining whether obstacle avoidance is needed; and determining whether an object is reached, and the task is completed if the object is reached. According to the automatic obstacle avoidance method, effects of speed information of underwater robots are introduced in robot obstacle avoidance strategies, local obstacle avoidance planning and control and hydrodynamic performances of underwater robots are combined, established obstacle avoidance strategies can reflect dynamic obstacle avoidance capacities of underwater robots, and underwater robot survival capabilities are improved.
Owner:哈尔滨哈船特装科技发展有限公司
Water environment mobile robots
A water environment robotic system that includes a control station, an underwater robotic vehicle, and a water-surface robotic vehicle. The underwater robotic vehicle is in communication with the water-surface robotic vehicle and the water-surface robotic vehicle is in communication with the control station. Accordingly, the water-surface robotic vehicle can act as a relay between the control station and the underwater robotic vehicle. The water-surface robotic vehicle is further capable of detecting the position of the underwater vehicle and automatically adjusting the position of the underwater vehicle in order to maintain general vertical alignment between the two vehicles.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
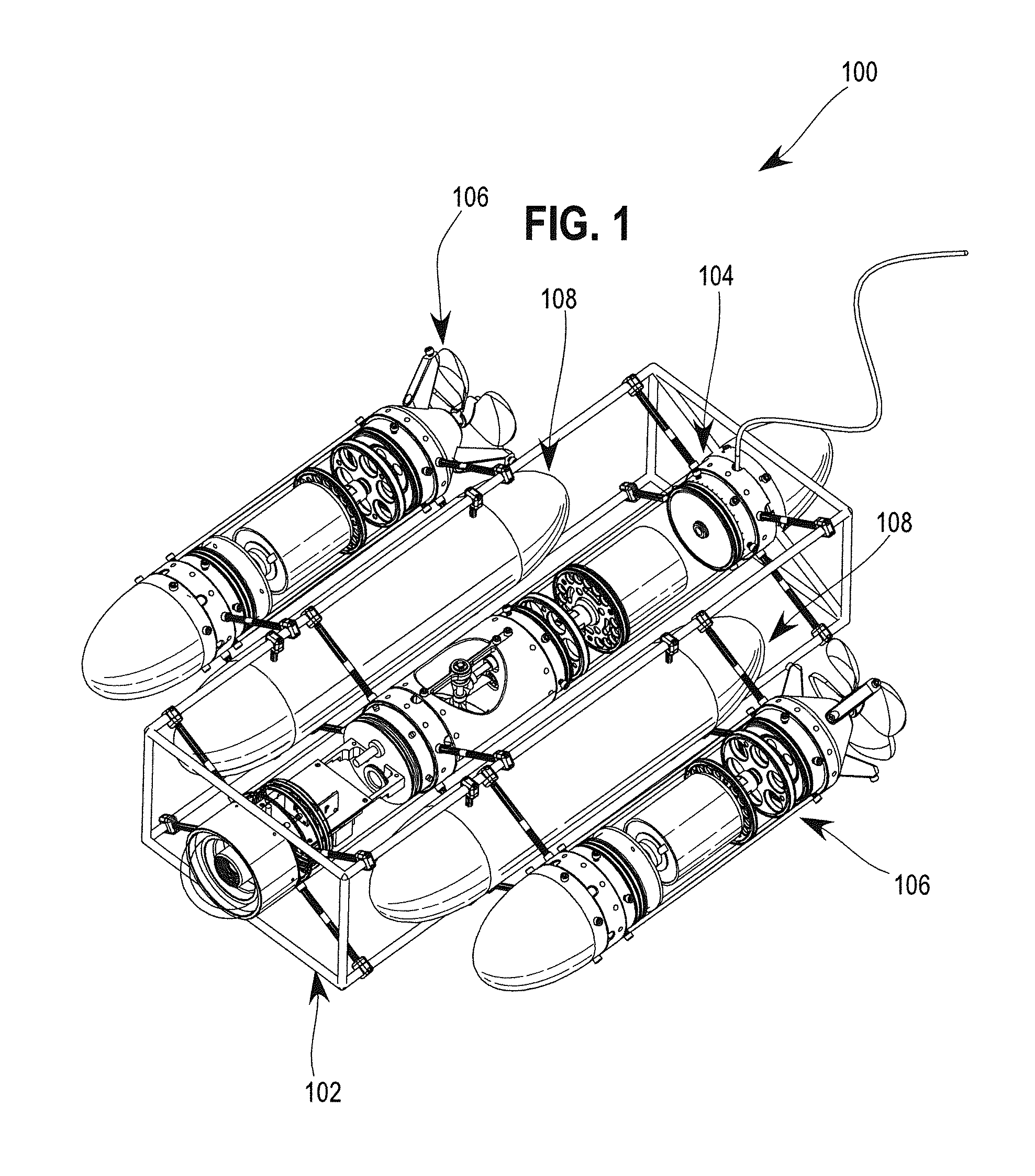
Modular rapid development system for building underwater robots and robotic vehicles
A modular system for building underwater robotic vehicles (URVs), including a pressure vessel system, modular chassis elements, a propulsion system and compatible buoyancy modules. The pressure vessel system uses standardized, interchangeable modules to allow for ease of modification of the URV and accommodation of different internal and external components such as sensors and computer systems. The system also includes standard, reconfigurable connections of the pressure vessel to the modular chassis system. A standardized, modular propulsion system includes a magnetic clutch, and a magnetic sleeve used to power the URV on or off.
Owner:WILLIAMS EDDIE HUGH
Cooperation control system for underwater multi-robot
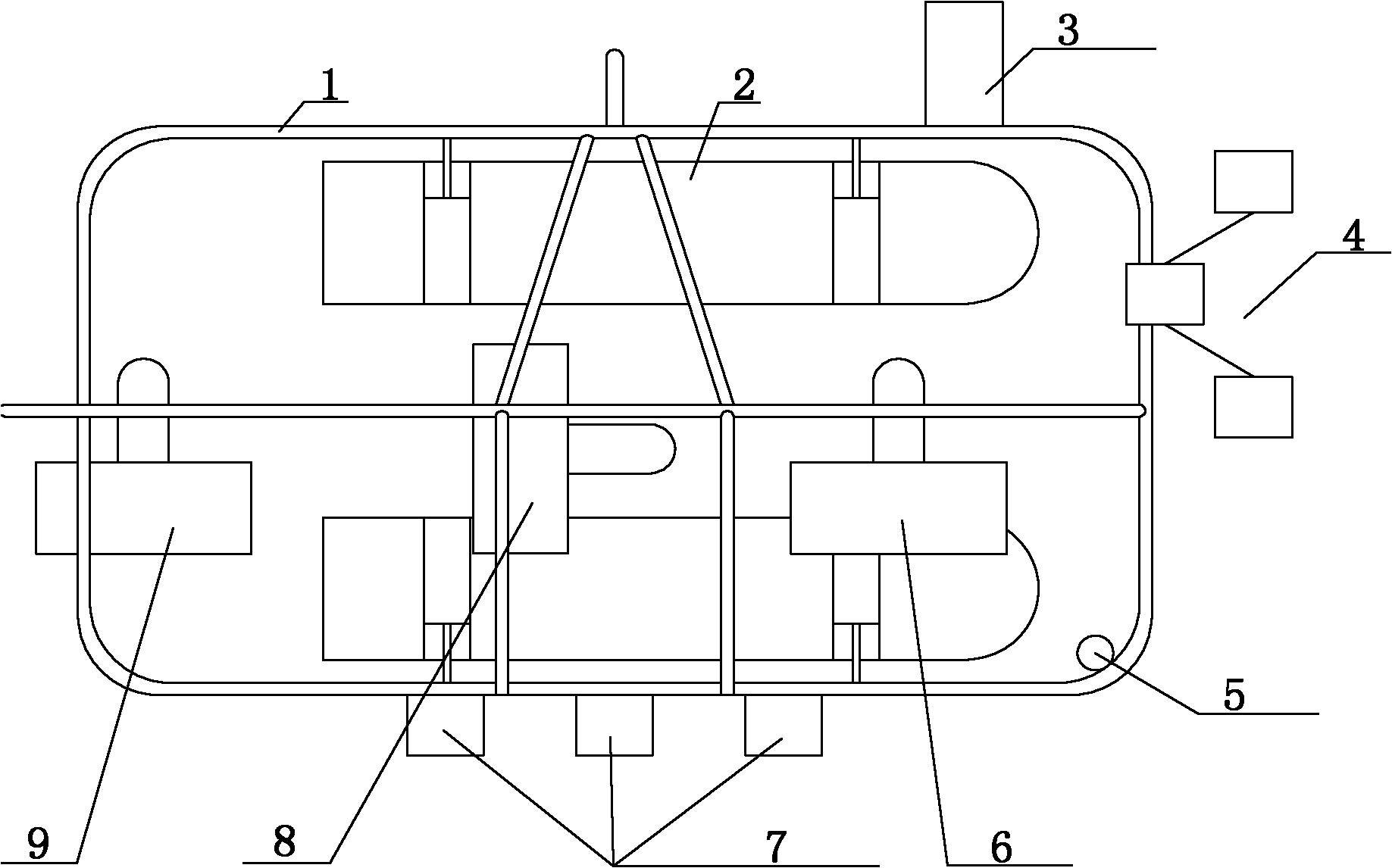
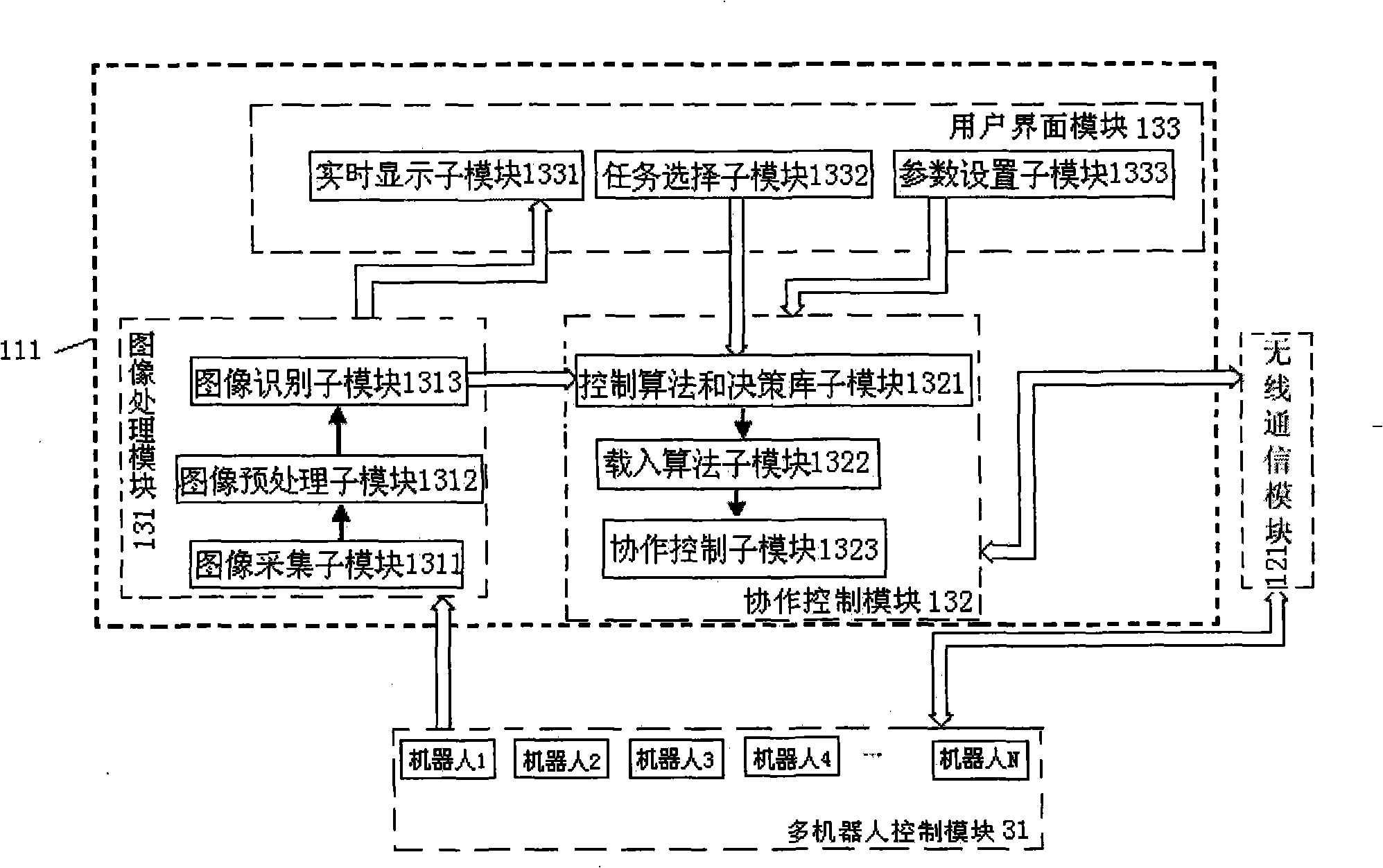
InactiveCN101359225ATest effectivenessDetection versatilityCharacter and pattern recognitionProgramme total factory controlGraphical user interfaceImaging processing
The invention relates to a multi-underwater-robot collaborative control system, comprising a control system, an image acquisition equipment, a plurality of underwater robots and a power supply; the control system comprises a master control device and a wireless communication equipment; the master control device comprises a computer, a real-time display equipment and an operating equipment; the master control device keeps communication with each underwater robot through the wireless communication equipment; an image processing module, a collaborative control module and a user interface module are arranged in the computer; a robot control module is arranged in each underwater robot; each robot control module receives an instruction from the computer and sends the instruction to the corresponding underwater robot, and feedbacks the internal state information of the underwater robot to the computer at the same time. The multi-underwater-robot collaborative control system is provided with strong universality and scalability and has a graphical user interface; and the system also can simulate the dynamic process and has the recording and playback functions.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
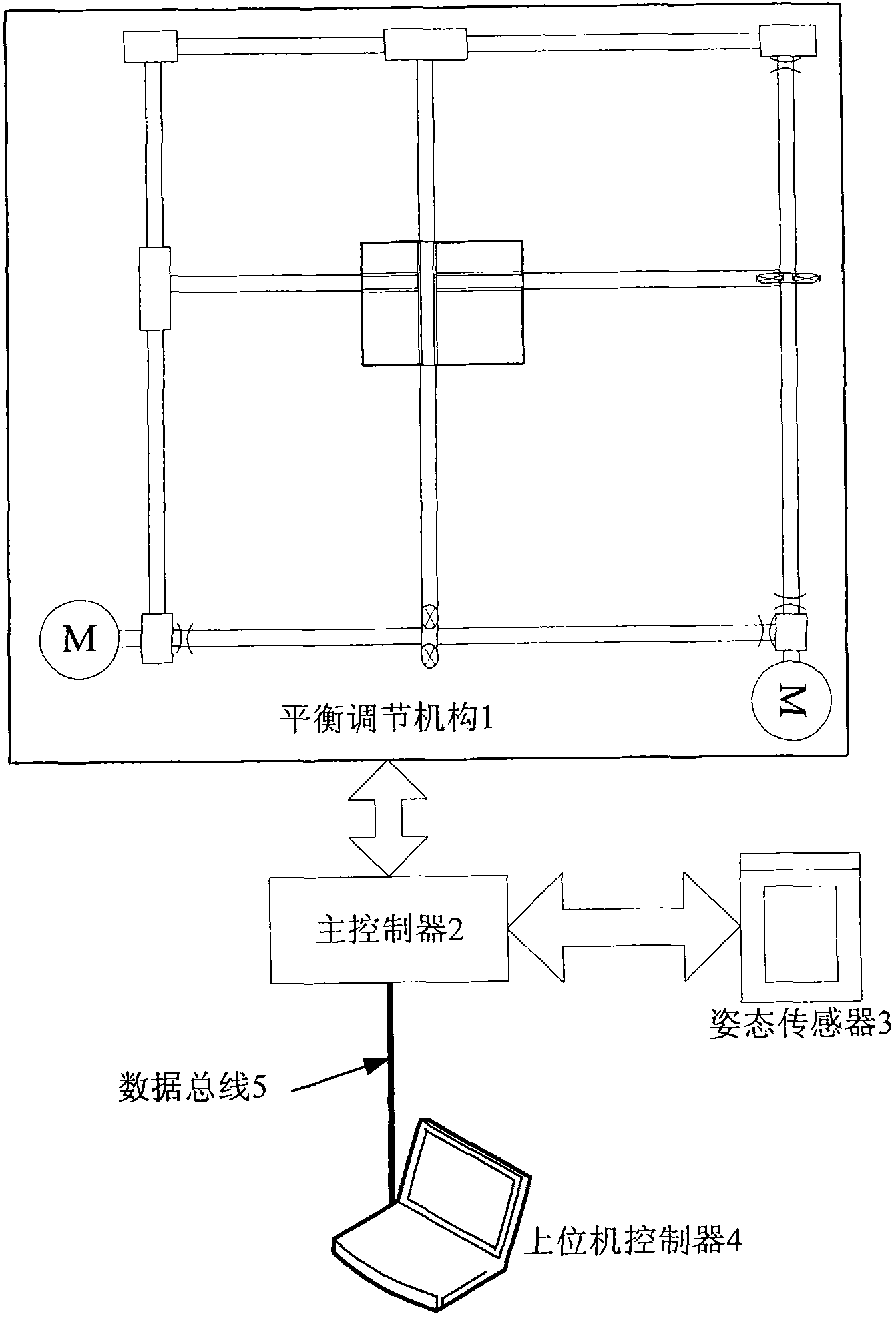
Inner system for controlling gestures of underwater robot
InactiveCN102012704AControl postureAttitude control is widely applicableAttitude controlUnderwater equipmentControl systemEngineering
The invention discloses an inner system for controlling the gestures of an underwater robot, comprising a main controller connected with an adjustment mechanism, a gesture sensor, and an upper computer controller, wherein the adjustment mechanism is a balance adjustment mechanism arranged inside the underwater robot, and comprises a gravity slider, a double-shaft drive motor, a worm, a guiderail, a slide bar, a limit switch and a mechanism platform; the double-shaft drive motor is connected with the worm to drive the worm to rotate bidirectionally; the worm drives the slide bar to perform planar movement through the transmission of a lead screw; one end of the slide bar is connected with the lead screw of the worm and penetrates the gravity slider, while the other end thereof is connected with the guiderail by a slider and drives the gravity slider to move in a plane so as to realize the gravity adjustment of the underwater robot and control the transverse swing and longitudinal incline gestures of the underwater robot. The control system for gestures can be widely applied to the gesture control of the underwater robot.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
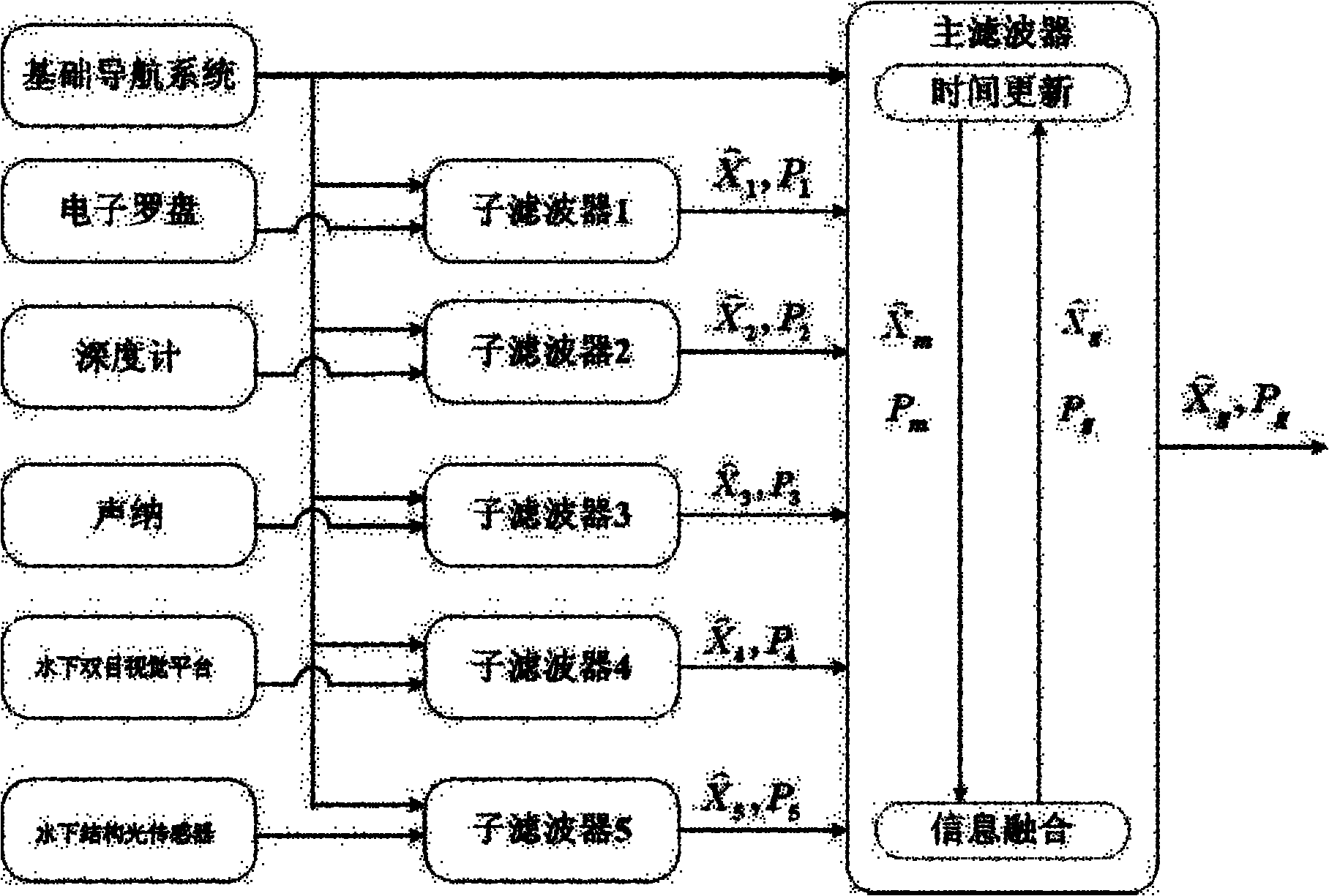
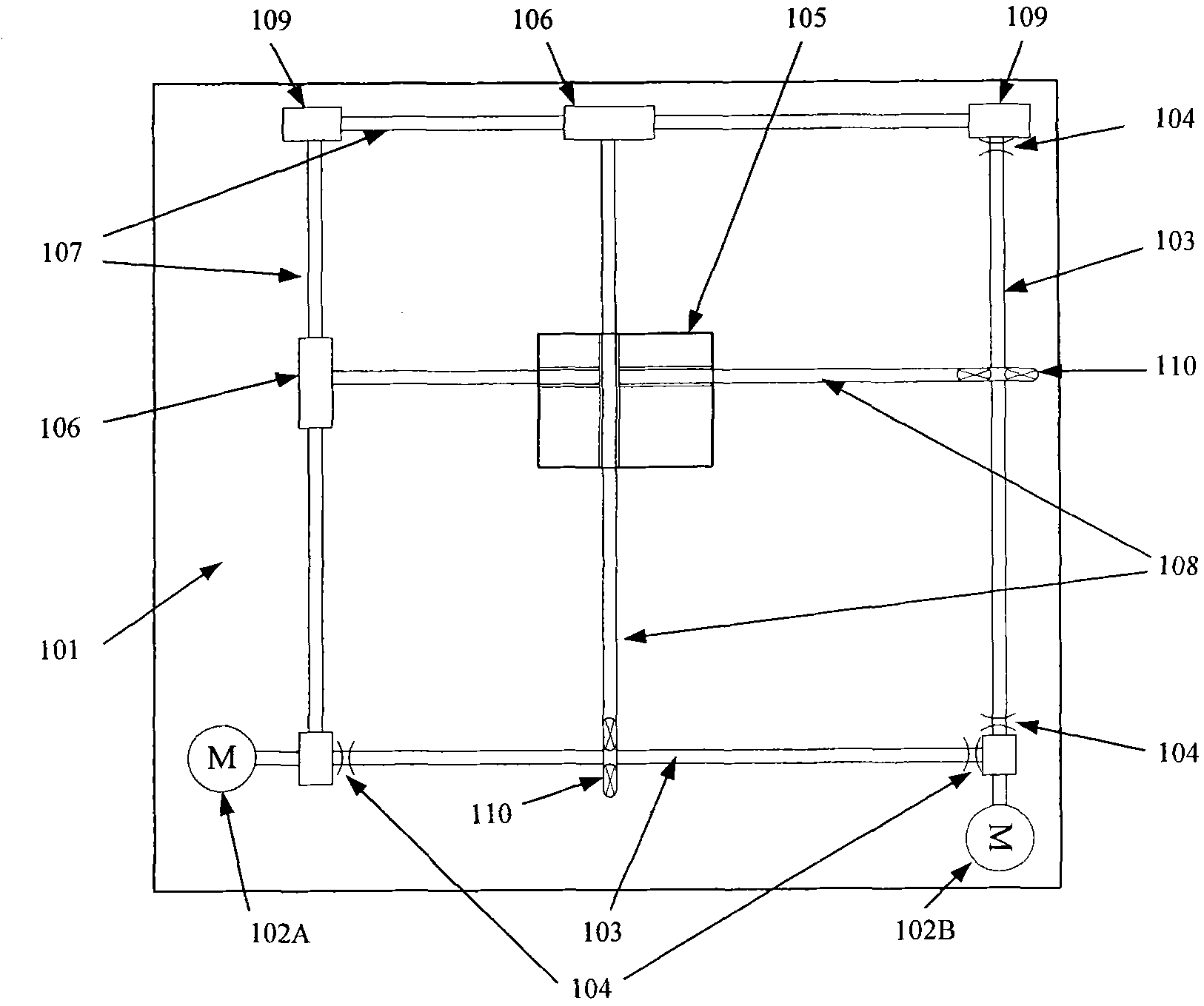
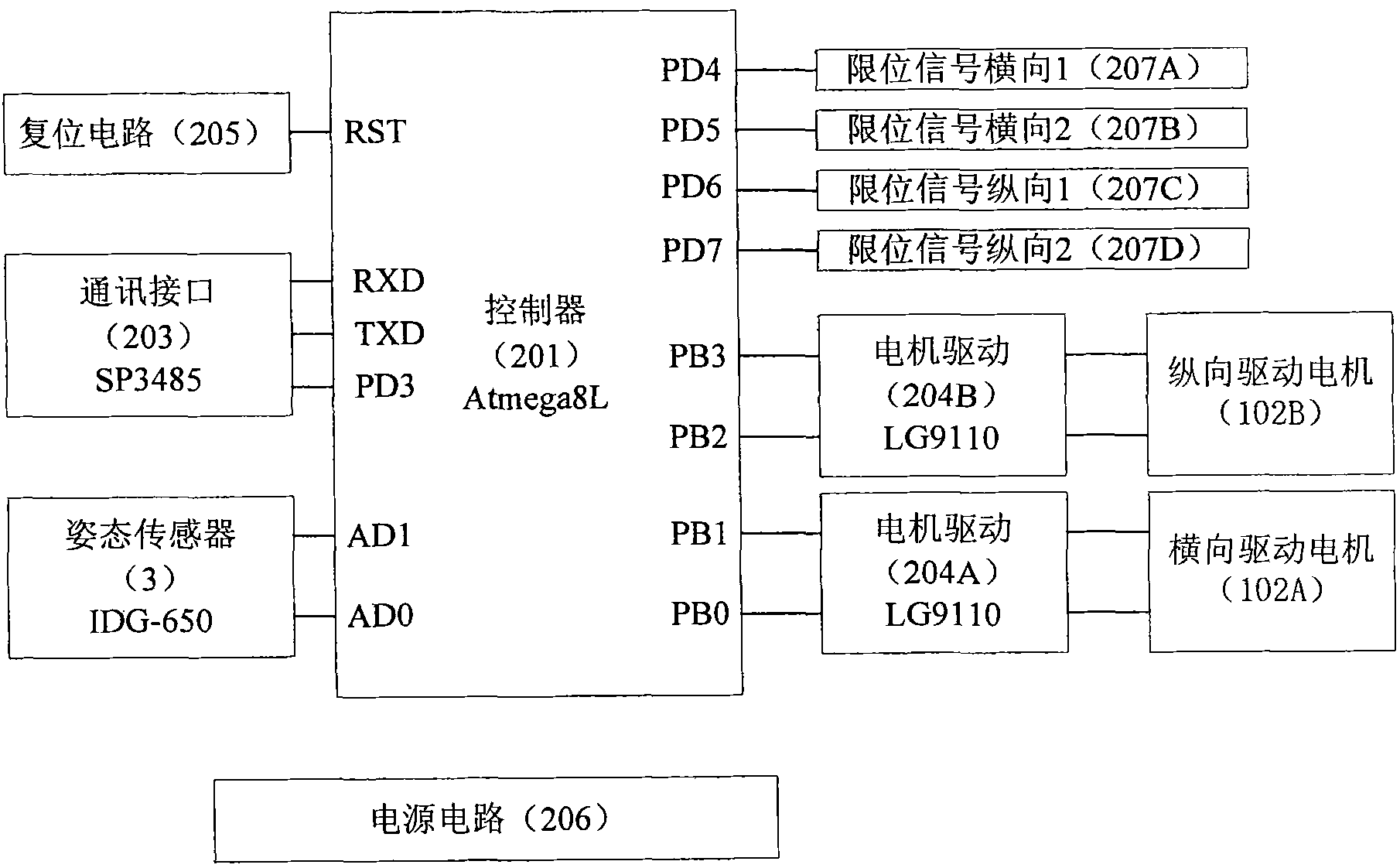
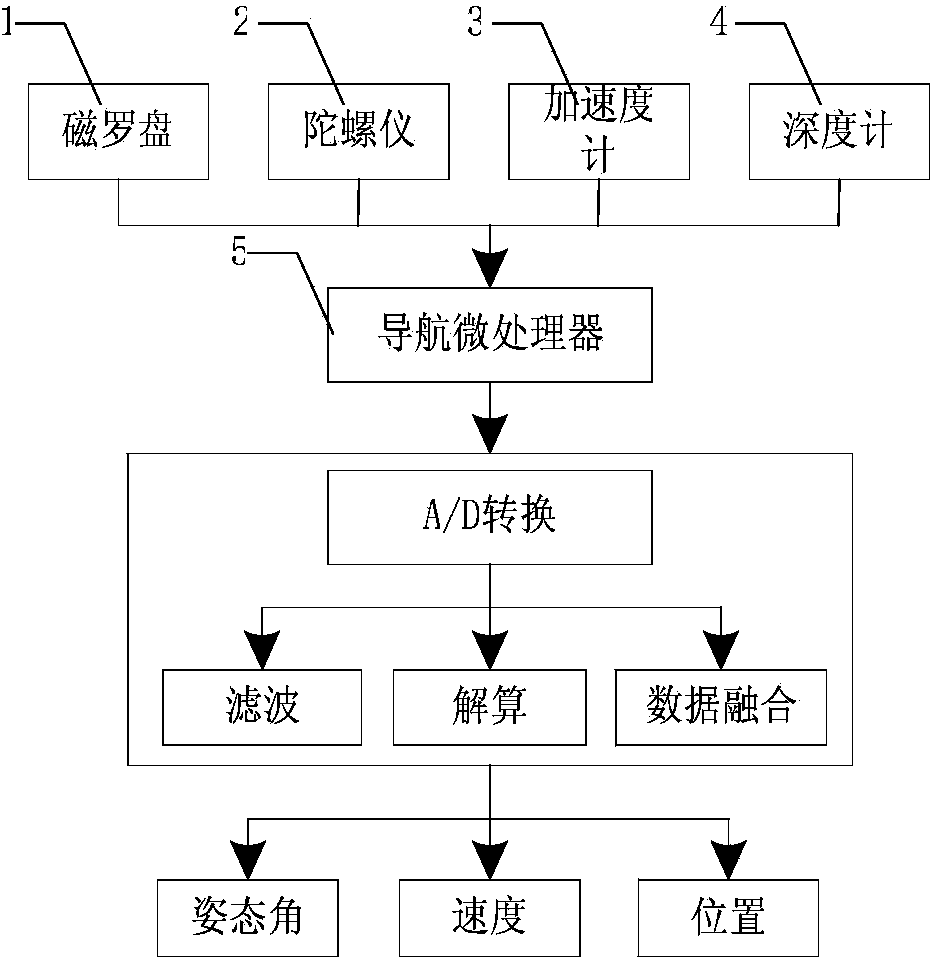
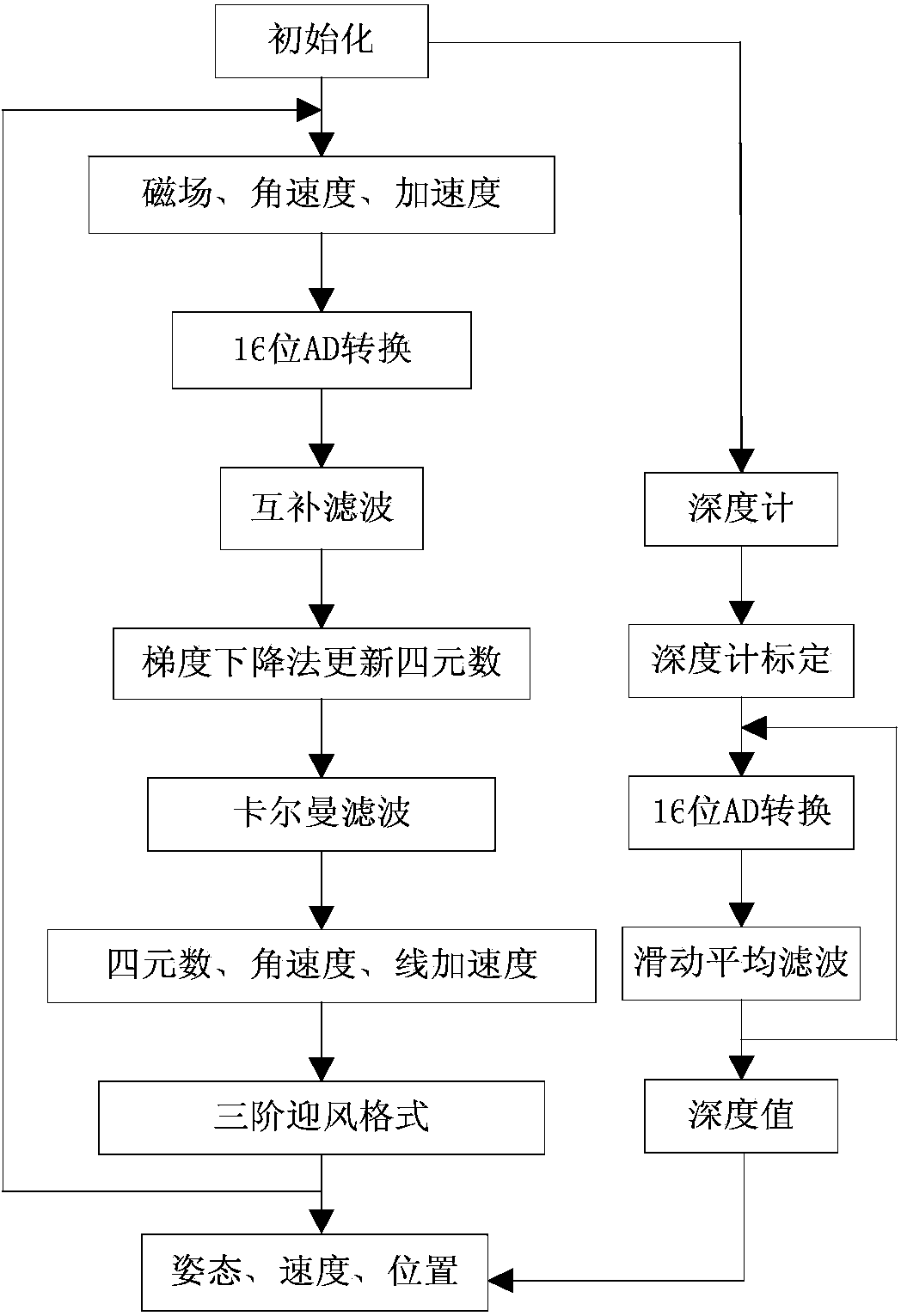
Real-time navigation system and real-time navigation method for underwater structure detection robot
ActiveCN104197927AAvoid divergenceReduce Attitude DriftNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMoving averageAccelerometer
The invention discloses a real-time navigation system and a real-time navigation method for an underwater structure detection robot. The navigation system comprises a magnetic compass, a gyroscope, an accelerometer, a depth meter and a navigation microprocessor, wherein the magnetic compass, the gyroscope, the accelerometer and the depth meter are used for respectively collecting magnetic field intensity, an angular speed, a linear speed and submerged depth data and transmitting the magnetic field intensity, the angular speed, the linear speed and the submerged depth data to the navigation microprocessor; the navigation microprocessor is used for calculating attitude and position of the underwater robot according to the collected data. The navigation method comprises an attitude algorithm, a speed algorithm and a depth algorithm; according to the attitude algorithm, a complementary filtering method, a quaternion gradient descent method and a Kalman algorithm are combined for obtaining an attitude matrix and an attitude angle; the speed algorithm is used for calculating the speed and the position of the robot by using a three-order upwind scheme with rotary compensation; the depth algorithm is used for processing the data of the depth meter by using a moving average filter algorithm so as to obtain the submerged depth. By virtue of the real-time navigation system for the underwater structure detection robot and the method thereof, the navigation cost is reduced and a relatively good navigation precision is achieved.
Owner:CETC NINGBO MARINE ELECTRONICS RES INST
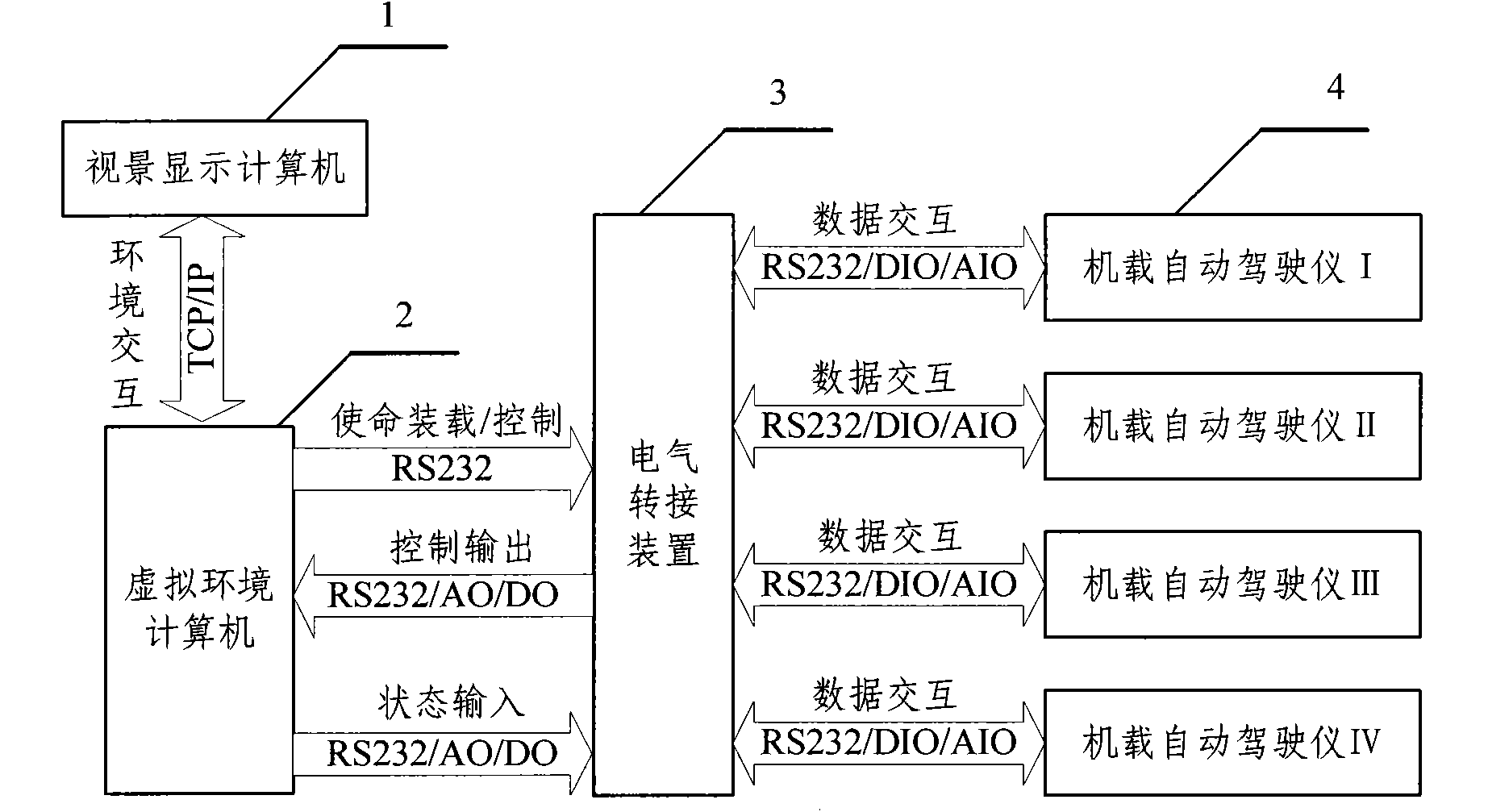
Multi-underwater robot semi-physical simulation system and control method thereof
ActiveCN102117071AImprove scalabilityImprove portabilityVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlDynamic modelsClosed loop
The invention relates to a multi-underwater robot semi-physical simulation system and a control method thereof. The system comprises a visual scene display computer, a virtual environment computer, an electric switching device and an airborne autopilot. The visual scene display computer is in network communication connection with the virtual environment computer; kinematics models and dynamics models of each robot are stored in the virtual environment computer, and various kinds of virtual sensor device information is generated through model computation; the electric switching device switchesa standard cable interface of an expansion card of the virtual environment computer to be an interface capable of conveniently connecting the multi-underwater robot airborne autopilot; the airborne autopilot is a real underwater robot soft hardware control system, and is used for generating the executor control quantity according to own motion planning and closed loop, transmitting the executor control quantity to the virtual environment computer through the electric switching device and transmitting cooperation information to other robots through the virtual environment computer according tomission requirements. The multi-underwater robot semi-physical simulation system and the control method thereof are convenient to expand sensors and device nodes, and the system is excellent in expandability, high in transportability and convenient to configure various kinds of underwater robots.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Launching and recycling system and corresponding method of shipborne underwater glider
ActiveCN106240772ARealize the tightening functionAchieve precise positioningCargo handling apparatusPassenger handling apparatusRecovery methodMarine engineering
The invention relates to launching and recycling technologies for underwater gliders or other underwater or water surface vehicles, in particular to an intelligent underwater robot shipborne launching and offshore recycling mechanism and corresponding method. The recycling mechanism comprises a shipborne body, a main recycling slide way, an auxiliary recycling slide way, an electric turning mechanism, an electric control cabinet, a tensioning mechanism, a multi-sensor fusion positioning system, a dragging unit and a hook system. The recycling mechanism is simple, reasonable, reliable in structure, and easy and convenient to operate, the underwater gliders, autonomous underwater vehicles (AUV), other underwater robots and the like can be launched and recycled quickly and efficiently, the workload of sailors and related staff on a ship are greatly relieved, the dangerous factors in the launching and recycling processes of the underwater robots are avoided, and the problem that the launching and recycling processes waste time and labor is solved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Underwater gliding detector
The invention relates to an underwater glide detector, which comprises a glide frame, a variable buoyancy system, an attitude adjusting system and a communication navigation system, wherein when working, the driving device of attitude adjusting system can make the internal battery move along the axis of glide frame, to change the position of gravity center; the micro electromagnetic valve and micro pump of variable buoyancy system will cooperate to change the discharge volume of external oil vesicle, to change the buoyancy; therefore, the invention can realize saw-shaped motion in sea. Compared with present underwater robot, the invention has small volume, low cost and low energy consumption. And it can avoid screw and propeller, that powered by battery to operate in months.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
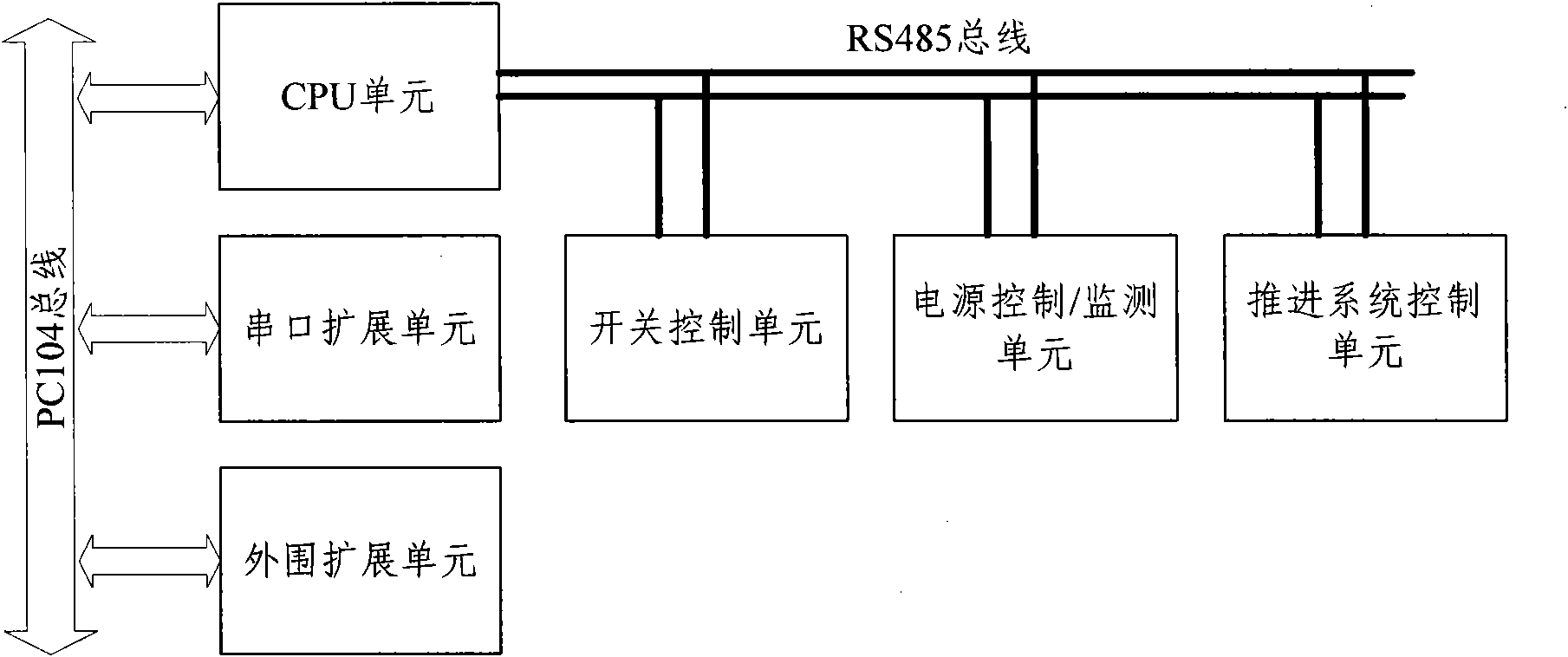
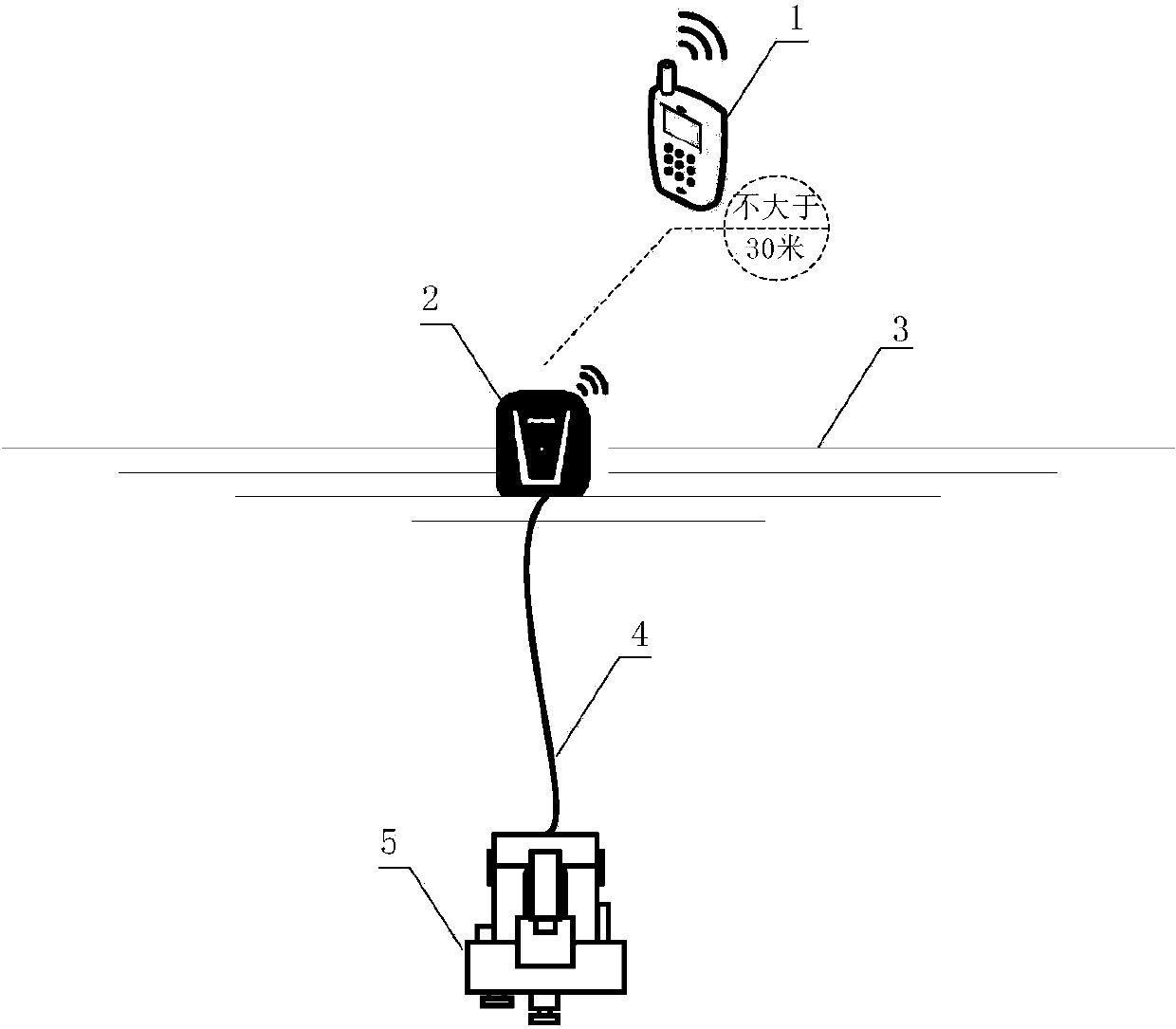
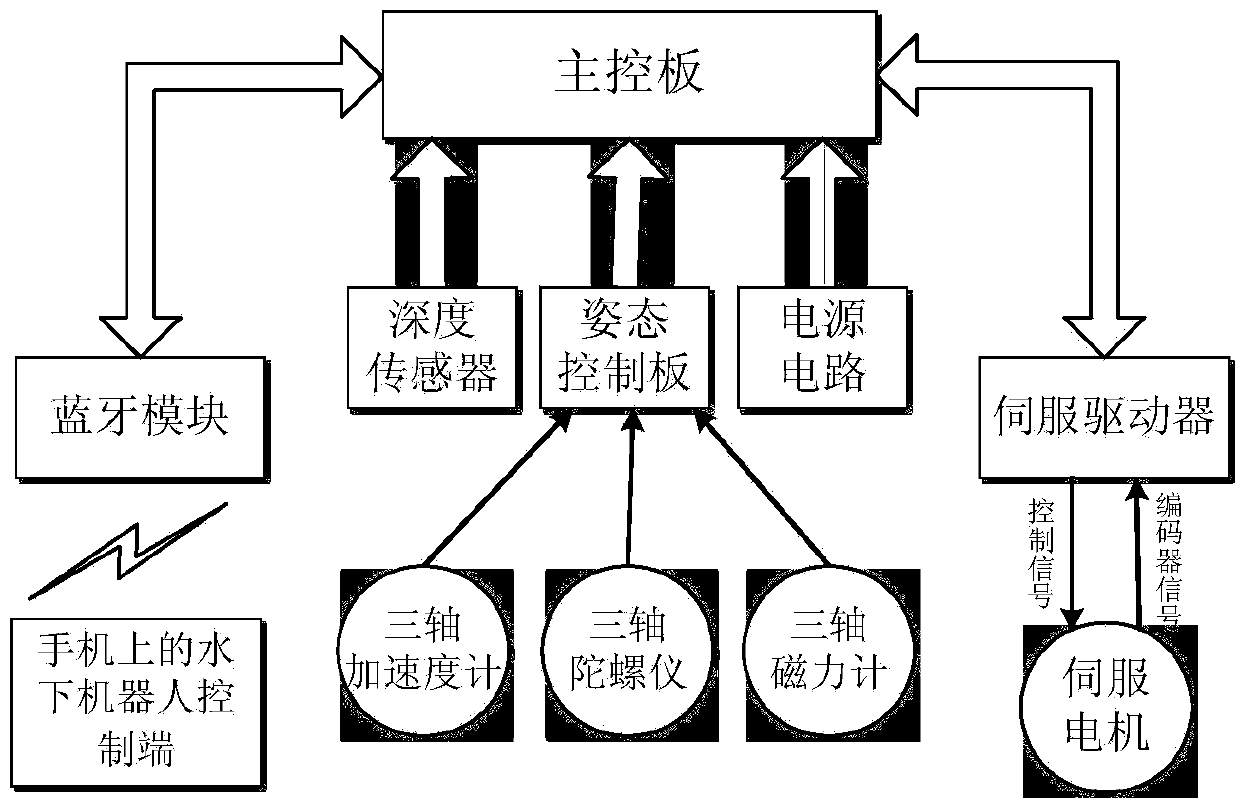
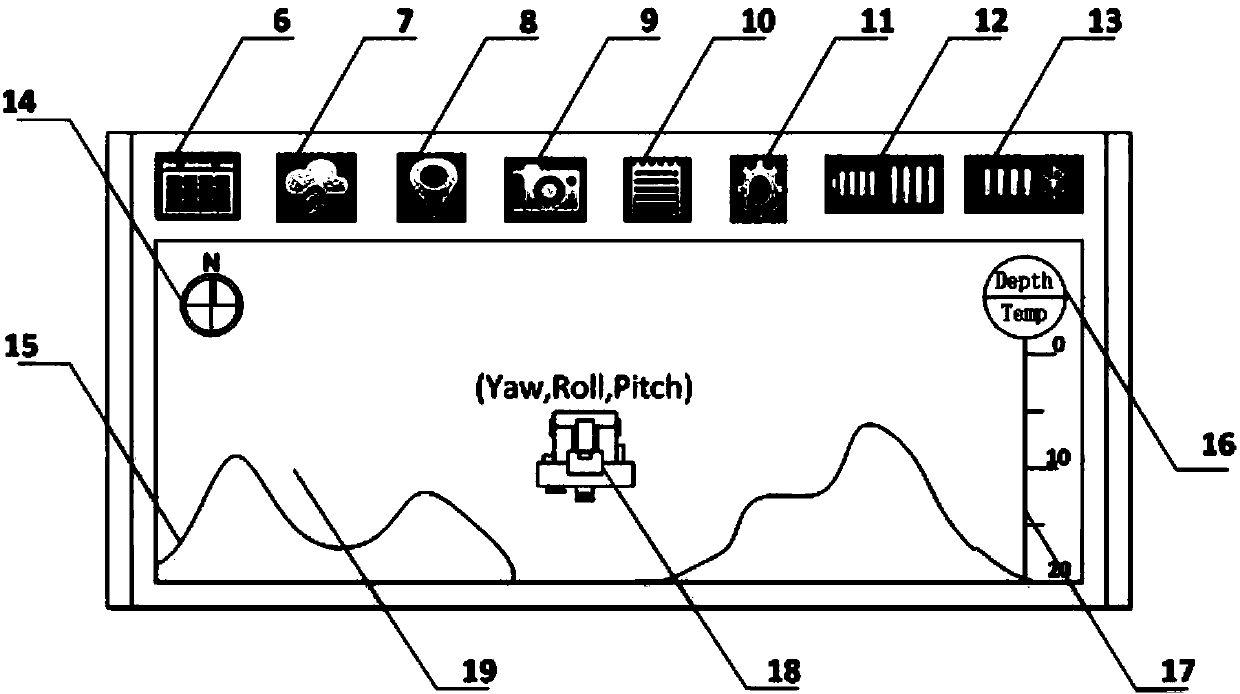
Underwater robot control system based on mobile phone Bluetooth technology
InactiveCN104199459AGuaranteed flexible movementImprove motor flexibilityPosition/course control in three dimensionsAttitude controlControl system
The invention discloses an underwater robot control system based on a mobile phone Bluetooth technology. The system comprises a processing system arranged in an underwater robot carrier, a Bluetooth device packaged in a buoy and an underwater robot control end on a mobile phone, wherein the underwater robot control end is communicated with an underwater robot through the Bluetooth device, the buoy is connected with the underwater robot through a zero-buoyancy cable to conduct data transmission, and a main control board of the processing system controls the rotating speed and the rotating direction of a propeller through the actual depth of the underwater robot and acquired through a depth sensor and the actual gesture acquired through a gesture control board to finally achieve functions of underwater suspension, depth keeping and the like. The system can well overcome the shortcoming that the underwater robot is insufficient in real time performance under the autonomy mode and poor in flexibility in the cable mode, meets the requirement for real-time communication and provides well hardware support for flexible movement of portable acquisition of underwater robot information and flexible movement of the underwater robot.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
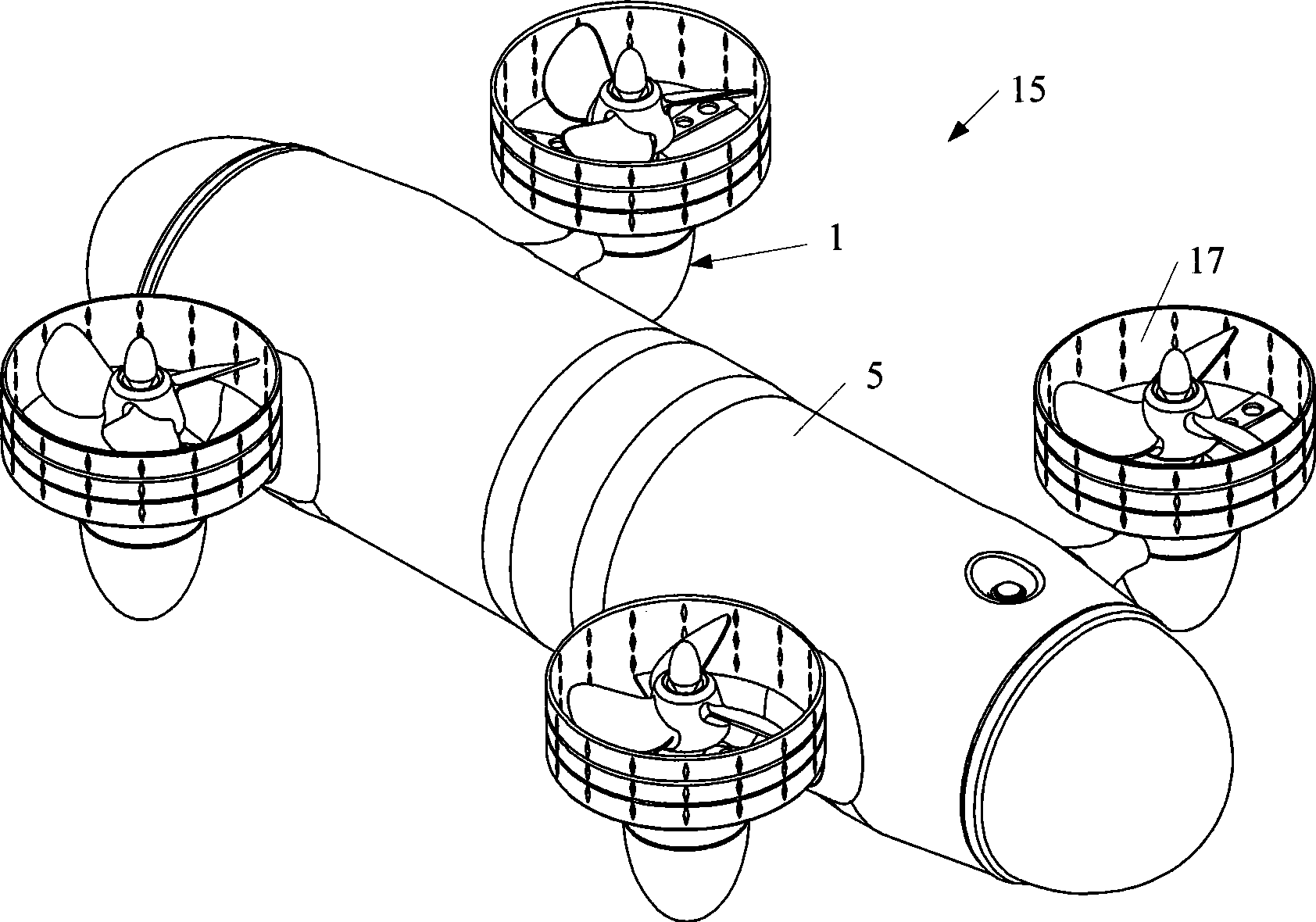
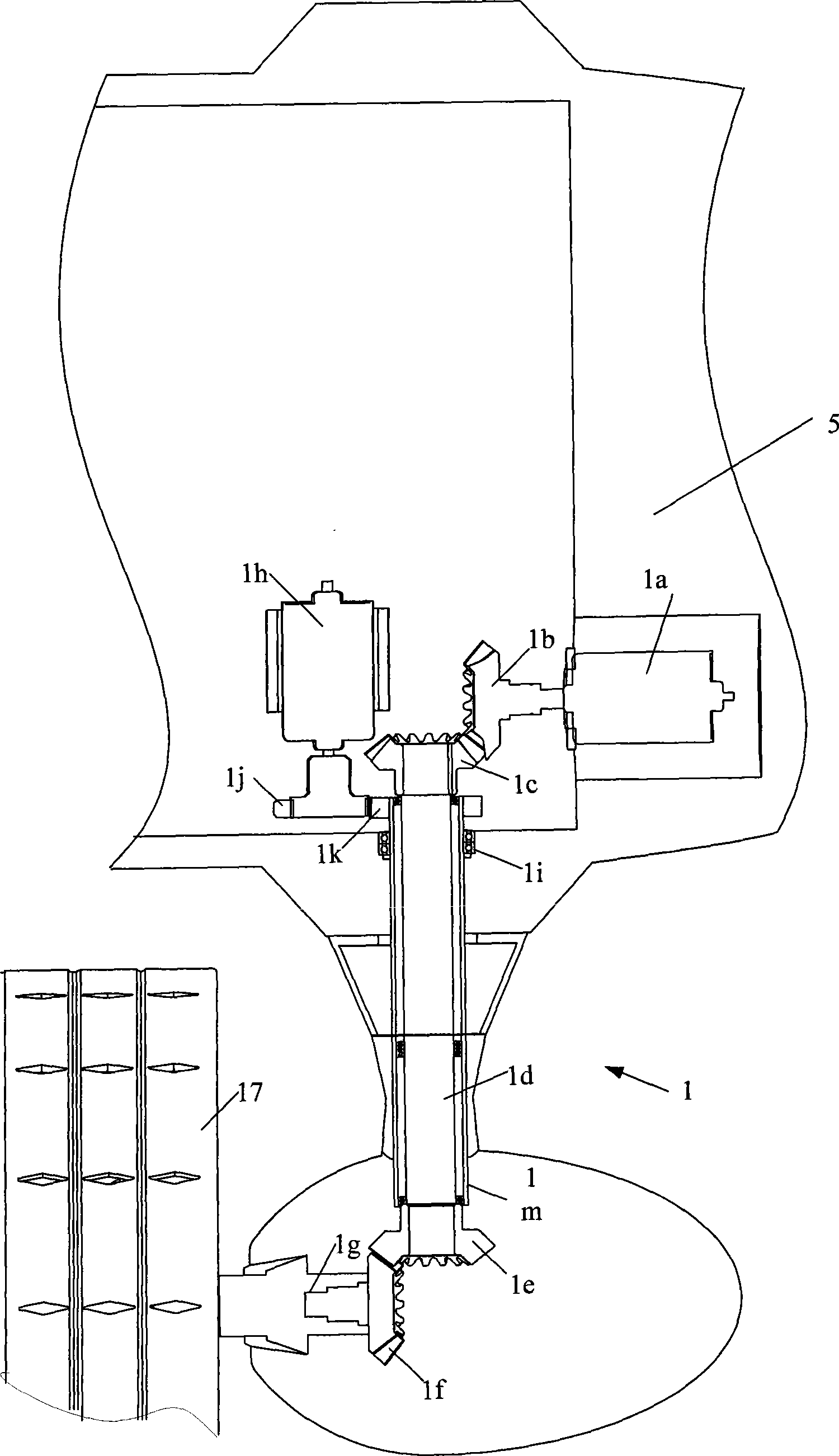
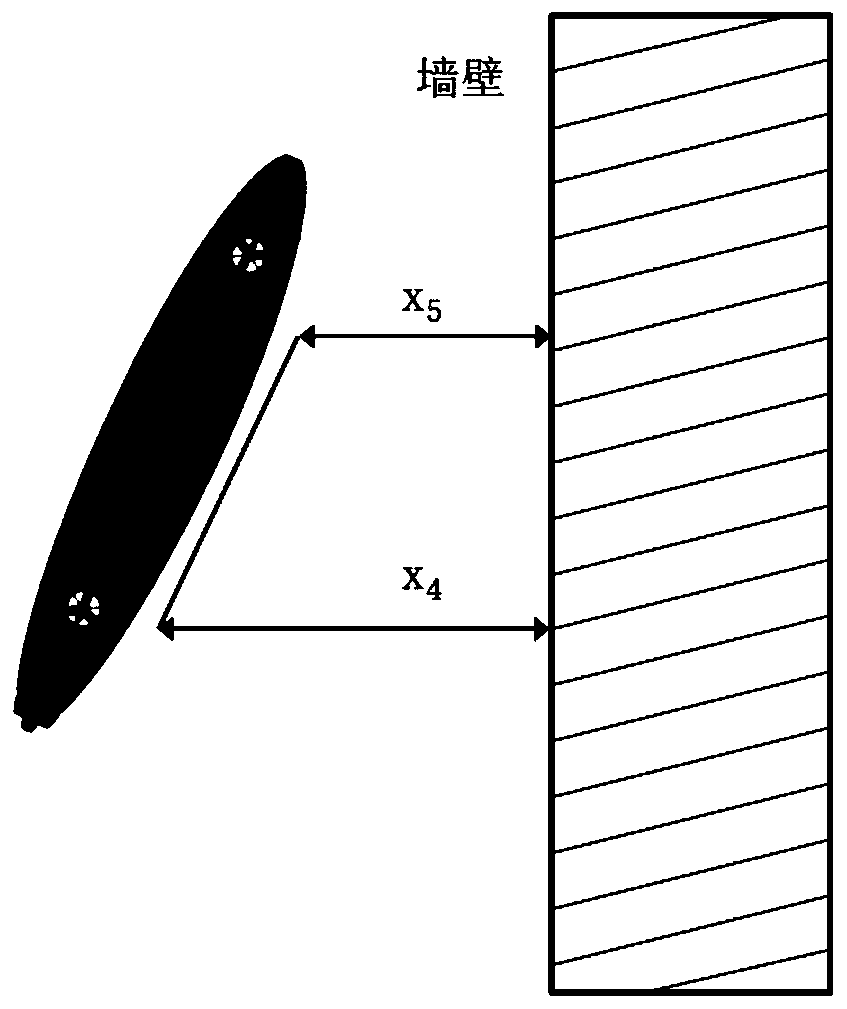
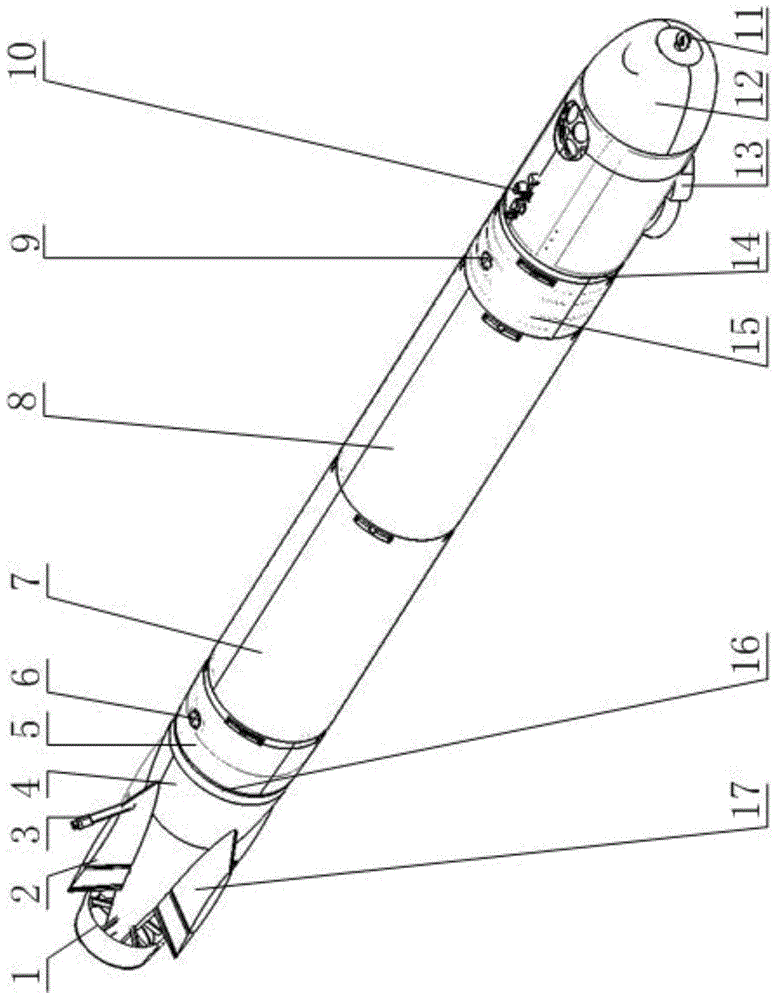
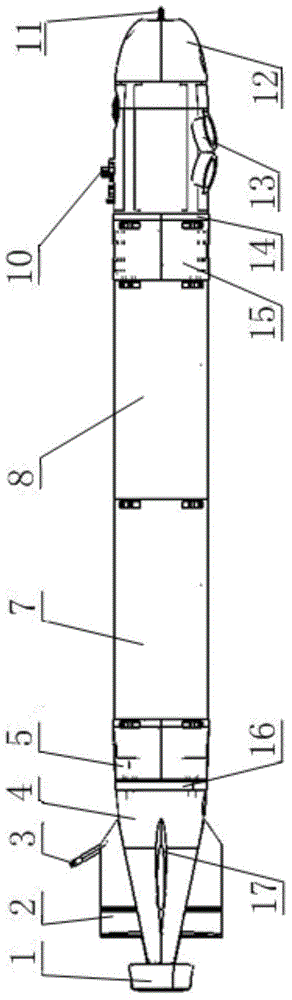
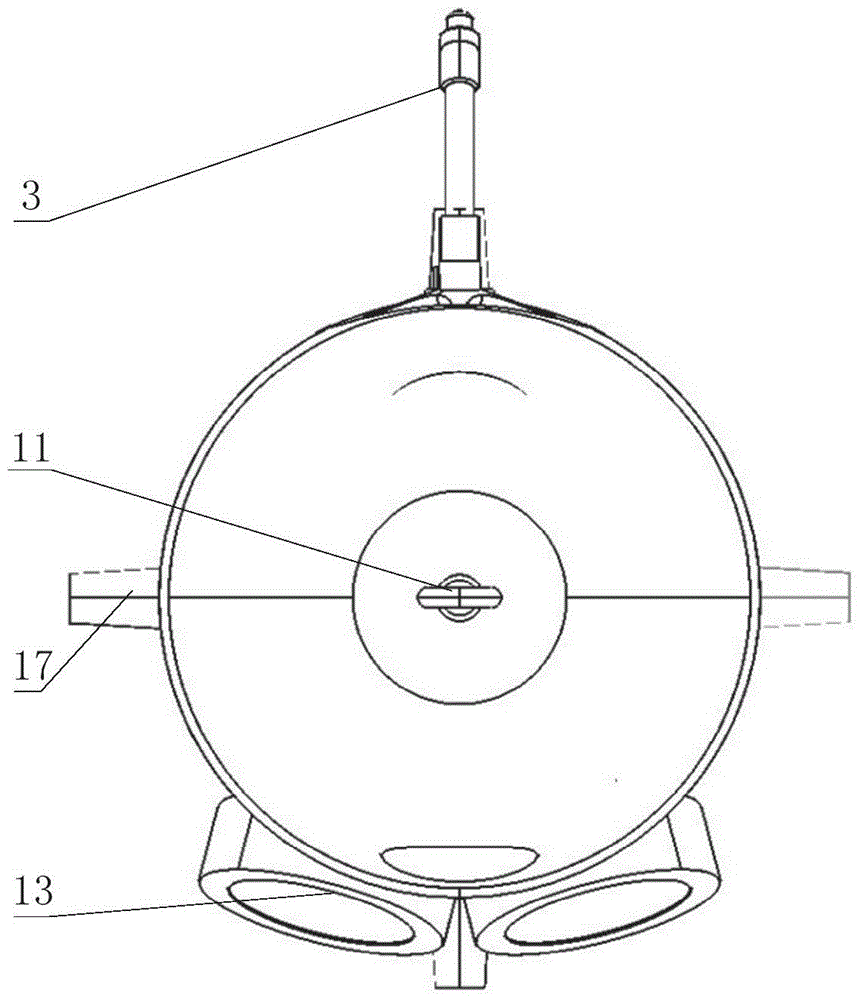
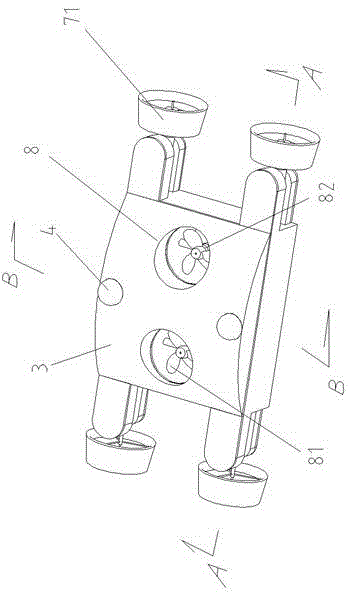
Omni-directional floating and wall-climbing underwater robot
The invention discloses an omni-directional floating and wall-climbing underwater robot. The omni-directional floating and wall-climbing underwater robot comprises a sealed cabin, an underwater high-definition camera, a main control module, underwater sensing equipment, an omni-directional power system and a vertical power system, wherein the underwater sensing equipment is arranged inside and outside the cabin; the omni-directional power system and the vertical power system are arranged inside and outside the cabin; the omni-directional power system comprises four shrouded propellers, shrouded propeller steering devices, climbing devices and floating devices; the floating devices are arranged in the cabin; one end of each floating device is connected with the corresponding shrouded propeller; the shrouded propeller steering devices and the climbing devices are divided into upper and lower layers, are respectively arranged in the cabin and are connected with each other through respective transmission devices; the vertical power system is vertically arranged inside the cabin. The omni-directional floating and wall-climbing underwater robot has functions of floating, adsorption, wall-climbing and underwater monitoring, is flexible to move, high in practicality, high in maneuverability and wide in application range, can be used for omni-directional floating operation or omni-directional wall-climbing operation, is suitable for working in a narrow water area, and is compact in structure and convenient and easy to operate; the manufacturing cost is reduced; the accuracy of floating movement is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
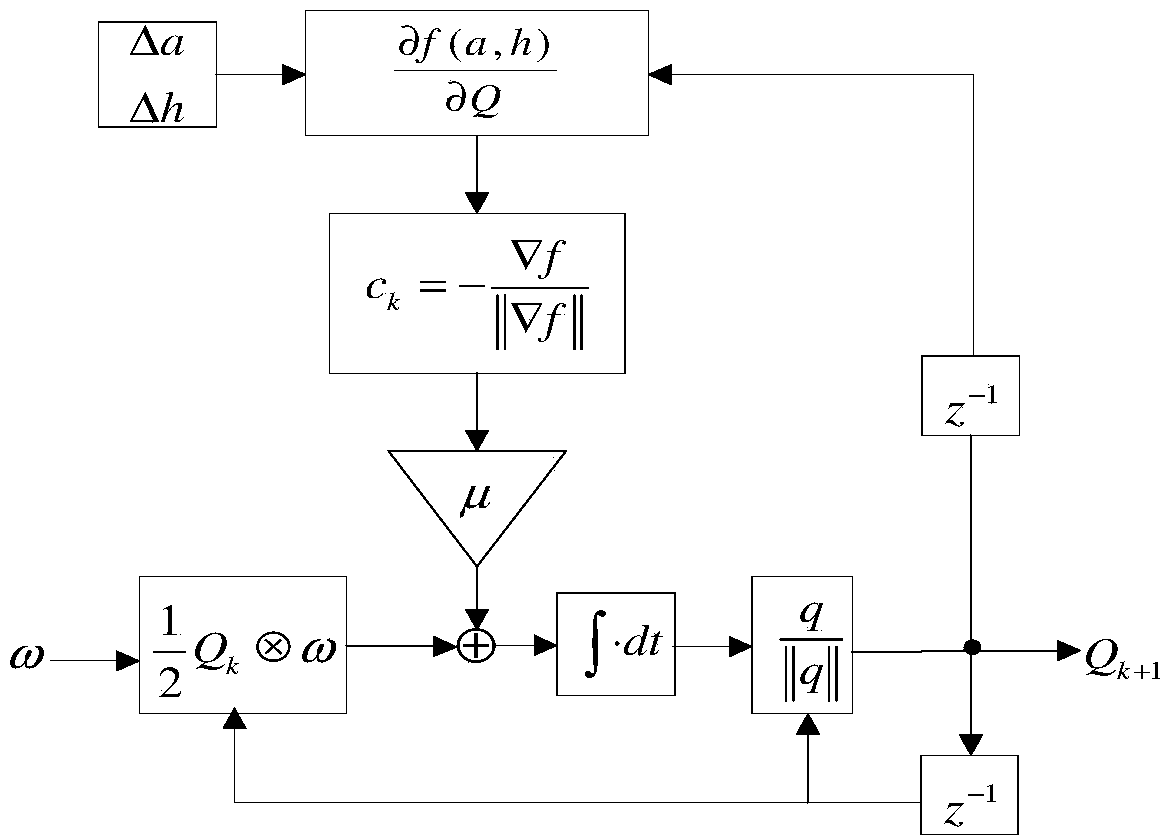
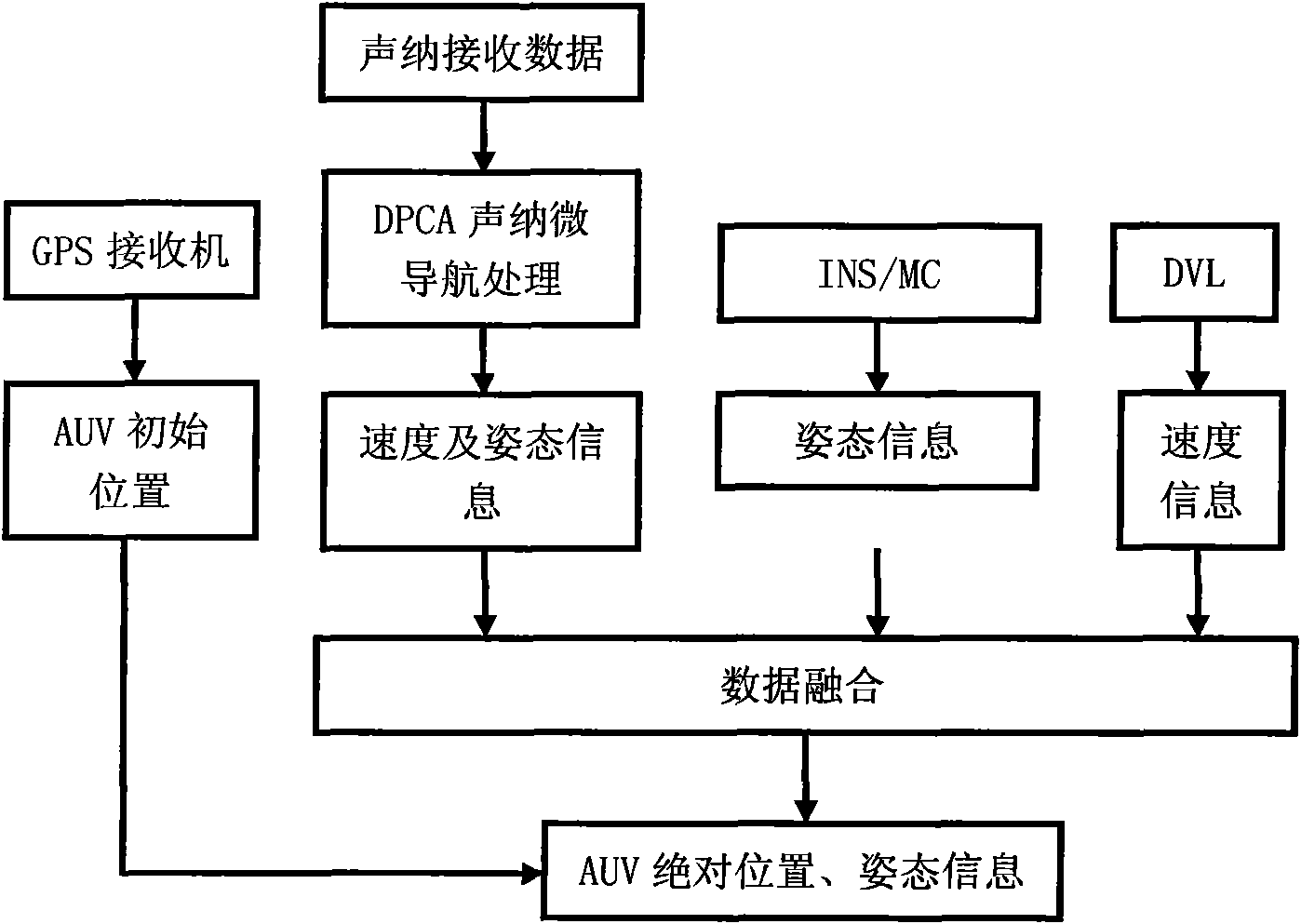
Combined navigation method of integrated sonar micro navigation autonomous underwater robot
InactiveCN101900558AImprove navigation accuracyNavigation instrumentsAcoustic wave reradiationMarine engineeringComputer vision
The invention discloses a combined navigation method of an integrated sonar micro navigation autonomous underwater robot, mainly comprising the following steps of: (1) acquiring initial absolute position information of the autonomous underwater robot by using a global positioning system, acquiring speed information and posture information of the autonomous underwater robot by using a sensor and estimating the speed information and / or posture information of the autonomous underwater robot by using a sonar system; and (2) fusing the speed information and the posture information which are acquired by the sensor and the speed information and / or posture information estimated by the sonar system by using a data fuse method and acquiring absolute position information and posture information of the autonomous underwater robot by combing the initial absolute position information of the autonomous underwater robot. The invention has the advantages that the absolute position of an AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) can be estimated and the navigation precision of the AUV can be improved by fusing the speed and / or posture information estimated by AUV-boarded sonar and the speed and posture information acquired by the sensor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
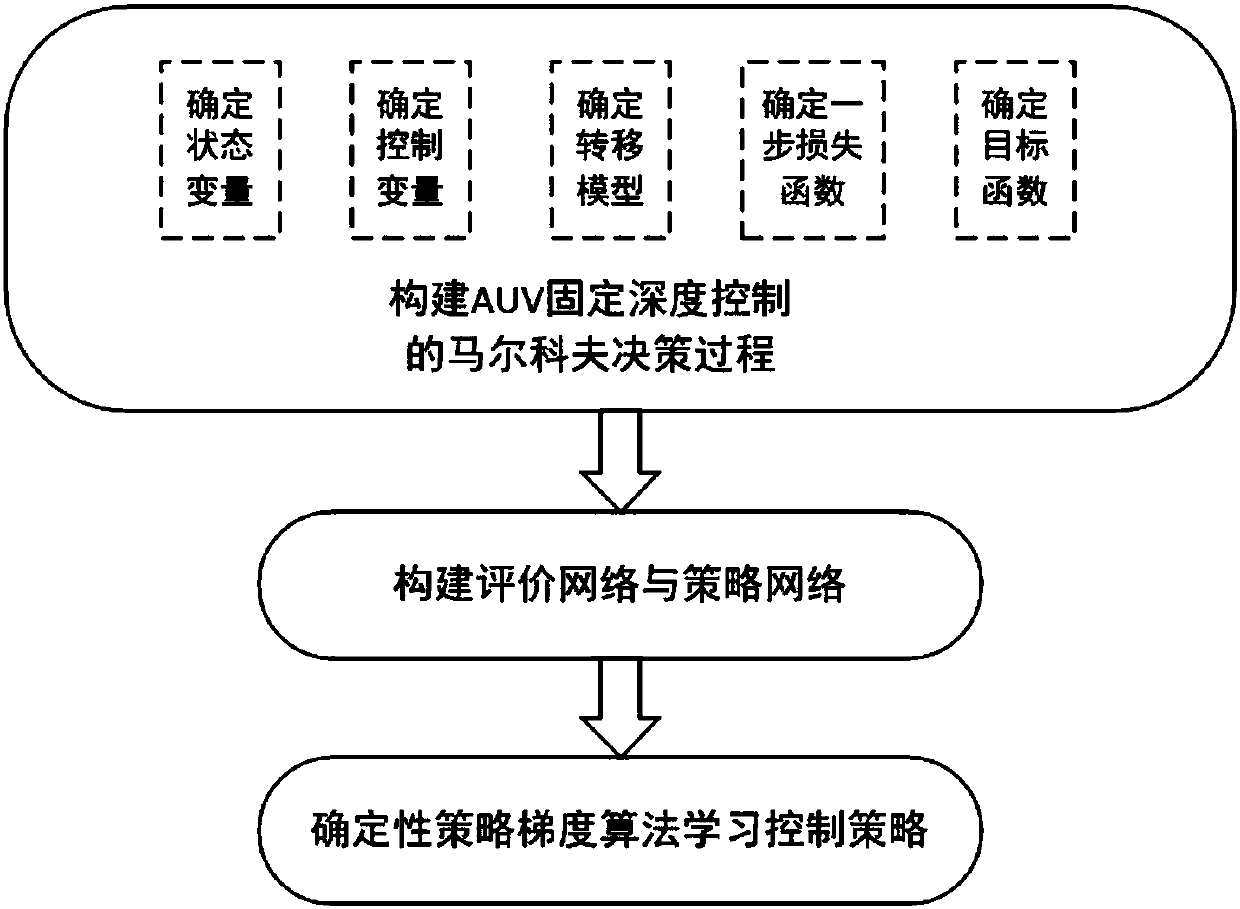
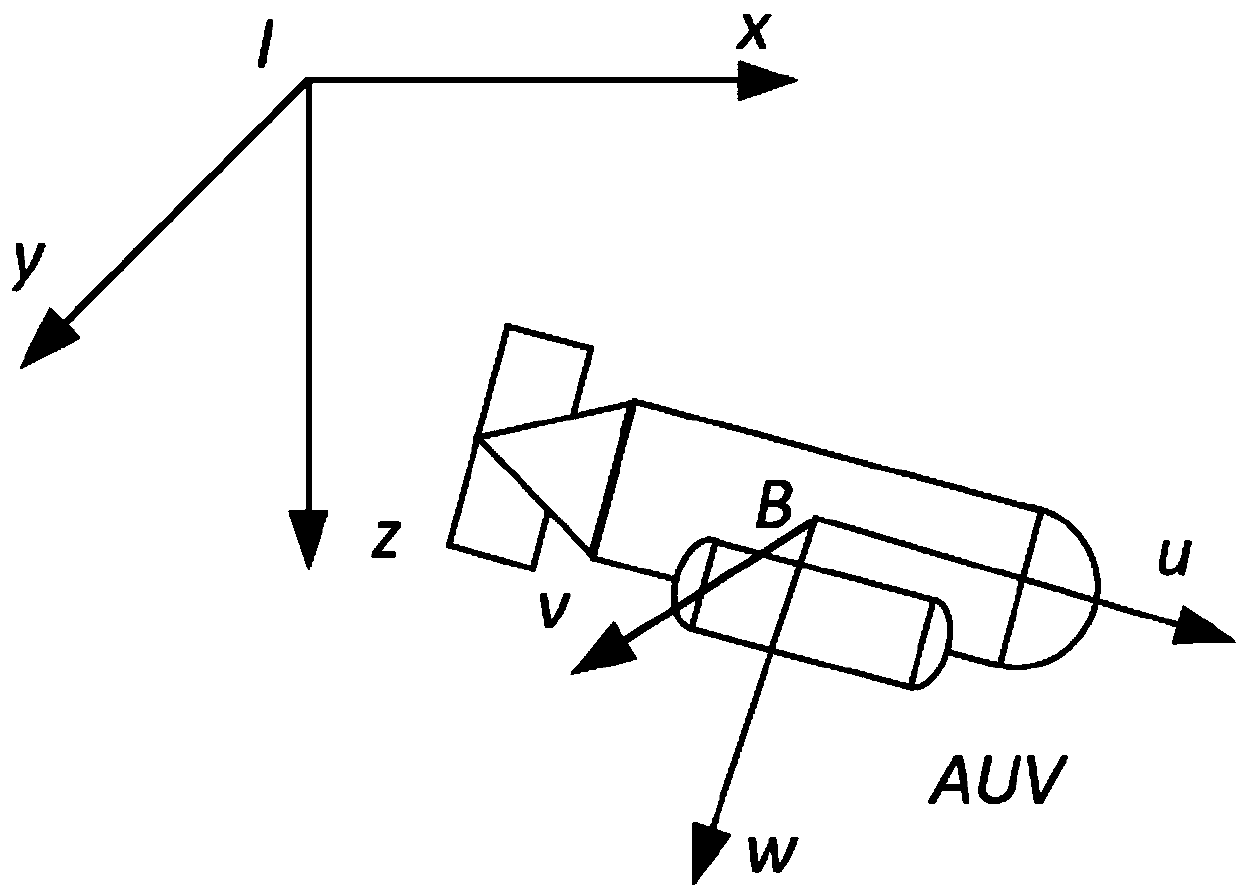
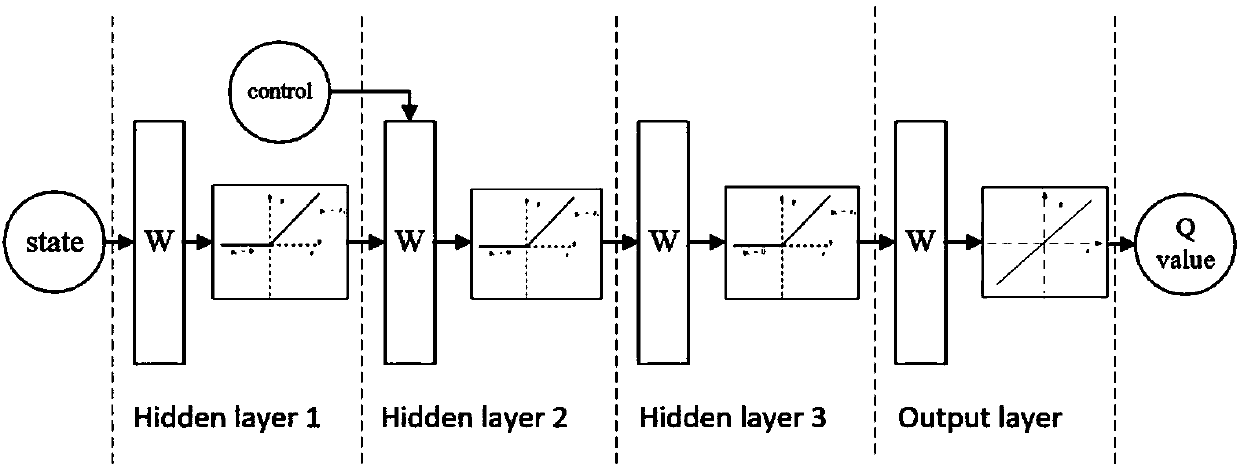
Underwater autonomous robot fixed depth control method based on reinforcement learning
ActiveCN107748566AEnhance expressive abilityIdeal control strategyAdaptive controlAltitude or depth controlTransfer modelDynamic models
The invention provides an underwater autonomous robot fixed depth control method based on reinforcement learning and belongs to the underwater robot control field. The method comprises steps that firstly, a Markoff decision process model for underwater autonomous robot fixed depth control is constructed, and expressions of a state variable, a control variable, a transfer model and a one-step lossfunction for underwater autonomous robot fixed depth control are respectively acquired; the decision network and the evaluation network are respectively established; through reinforcement learning, the decision network and the evaluation network can be continuously updated whenever an underwater autonomous robot moves forwards for each step during fixed depth control training till convergence; thefinal decision network for fixed depth control is acquired. The method is advantaged in that fixed depth control on the underwater autonomous robot under the condition of a completely-unknown underwater autonomous robot dynamic model is realized, and the practical value is high.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
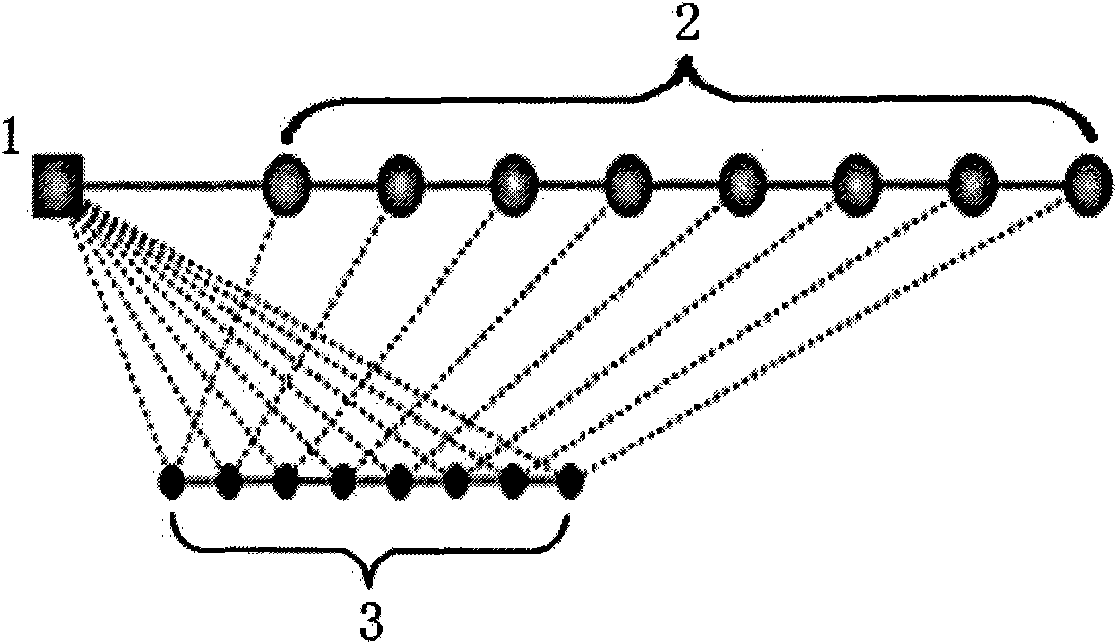
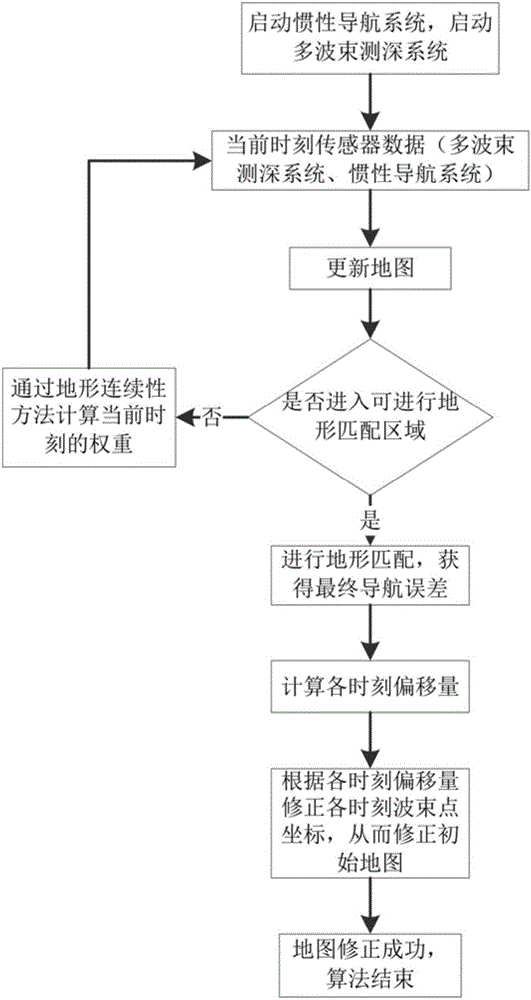
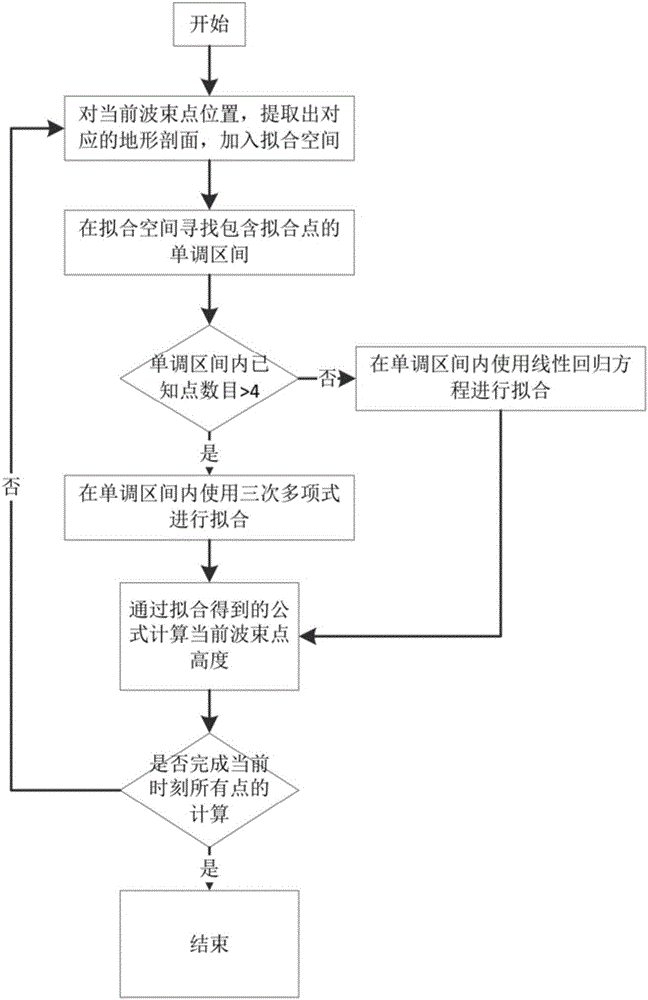
Underwater topographic mapping and correcting method adopting AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle) equipped with multi-beam sonar
ActiveCN106123850AReduce mistakesRealize topographic mapping tasksNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsProfile tracingOcean bottomStiffness coefficient
The invention provides an underwater topographic mapping and correcting method adopting an AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle) equipped with multi-beam sonar. The method comprises steps as follows: multi-beam sonar and a depth gauge are started to collect data, and each ping is corrected according to sound velocity information collected by a sound velocity section plotter; an accurate relative position between two moments is determined with a topographic matching method, so that a final navigation error of an inertial navigation system is obtained; the inertial navigation system is simplified into a spring model, a relationship between each node error and an actual final navigation error is calculated according to a stiffness coefficient formula of a spring; weight of each time node relative to the final error is determined with a topography continuity method; a final moment error is distributed to each time node. The method is independent of GPS (global position system) information in a submarine topographical map establishing process, the multi-beam sonar can be carried by the AUV for completing submarine topographic mapping of a deeper sea area, the consistency of an established map is better, the time node error is small, and the submarine topographical map can be taken as a priori topography map to be applied to the underwater topographic matching navigation.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
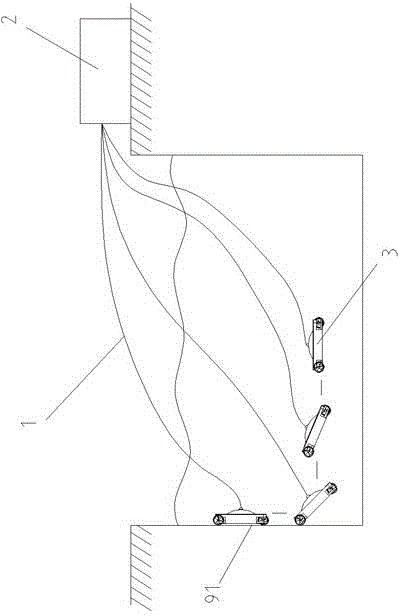
Draft gear for recovering underwater robot
InactiveCN103183111AOvercoming the impact of recyclingReduce difficultyVessel salvagingUnderwater equipmentThree degrees of freedomDegrees of freedom
The invention belongs to the field of recovery of underwater robots, and particularly relates to a draft gear for recovering the underwater robot. The draft gear comprises a hydraulic winch, a box body, a rotary straight girder, a rotating mechanism, a pitching hydraulic cylinder, a stretching hydraulic cylinder and a draft arm with three degrees of freedom, namely a rotating degree of freedom, a pitching degree of freedom and a stretching degree of freedom, wherein the box body is disposed on a mother ship, the hydraulic winch is arranged in the box body, and a traction rope connected with the underwater robot is connected with the hydraulic winch through the draft arm; one end of the rotary straight girder is connected with the rotating mechanism disposed on the box body, the other end of the rotary straight girder is hinged with the draft arm, the stretching hydraulic cylinder is arranged on the draft arm and drives the draft arm to stretch, the pitching hydraulic cylinder is arranged on the rotary straight girder, and an output end of the pitching hydraulic cylinder is hinged with the draft arm; and a hydraulic station is arranged in the box body and is used for supplying power to the hydraulic winch, the rotating mechanism, the pitching hydraulic cylinder and the stretching hydraulic cylinder. The draft gear disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple and reliable structure, complete functions, easiness to operate and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Shape memory alloy wire driven pectoral wave pushing bionic underwater robot
InactiveCN1903656ASimple structureLight in massPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeControl systemShape-memory alloy
The present invention relates to a marmem wire driven pectoral fin wave propulsion bionic underwater robot. It includes self-body and pectoral fin. The described pectoral fin includes at least four pectoral fin wave joints connected with self-body, between every adjacent two pectoral fin wave joints a fin film is connected. The described pectoral fin wave joint is formed from elastic body, marmem wire, skin and matrix. Said invention is simple in structure and is high in working efficiency.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and system for controlling underwater robot locus based on deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN107102644AAvoid control problems with low trajectory tracking accuracyEasy to operateAdaptive controlAltitude or depth controlControl systemSimulation
The present invention discloses a method and system for controlling an underwater robot locus based on deep reinforcement learning. The system comprises a learning phase and an application phase. In the learning phase, a simulator simulates the running process of an underwater robot and collects the data of the simulated running underwater robot, the data comprises the state of each moment and the target state of the next moment corresponding to each moment, and the learning is performed aiming at a decision neural network, an auxiliary decision neural network, an evaluation neural network and an auxiliary evaluation neural network through the data. In the application phase, the state o the underwater robot at the current moment and the target state of the underwater robot at the next moment are obtained and input to the decision neural network obtained through the final learning in the learning phase, and the decision neural network is configured to calculate the propulsive force required by the underwater robot at the current moment. The method and system for controlling underwater robot locus based on the deep reinforcement learning can realize accurate control of the underwater motion track.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com