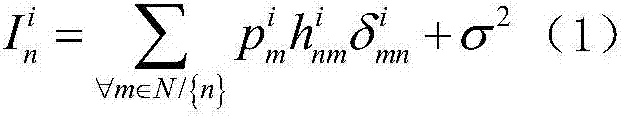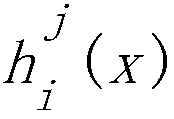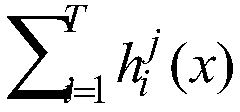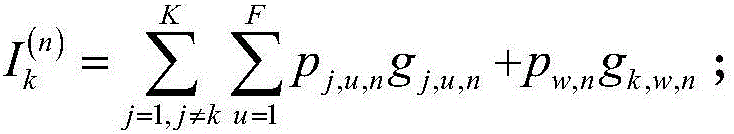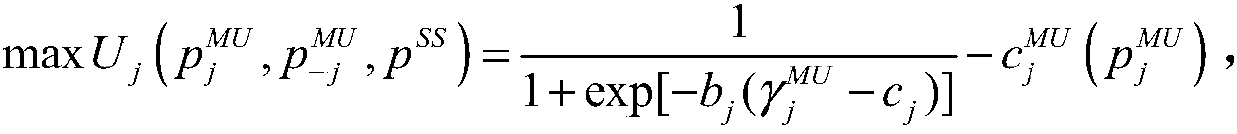Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
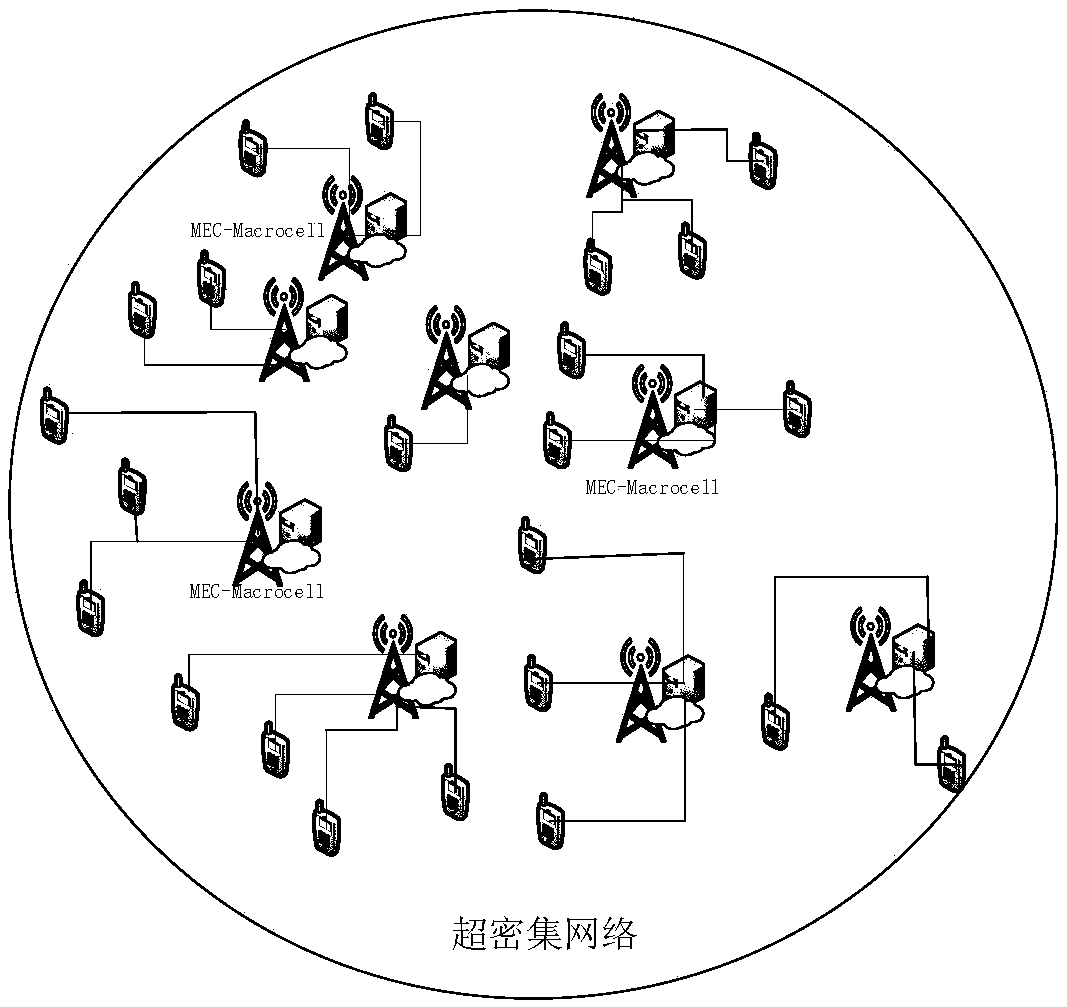
242 results about "Ultra dense network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
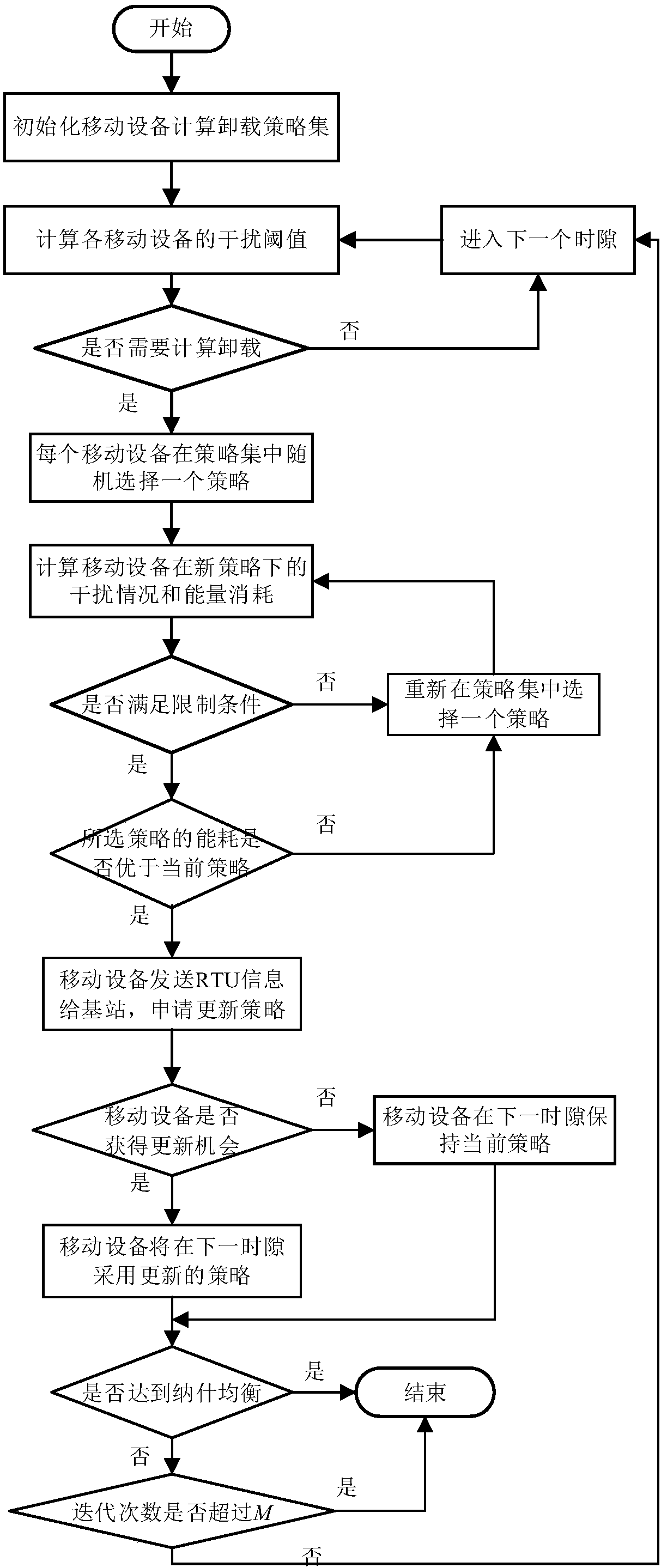
Distributed mobile edge computing unloading method in ultra-dense network architecture
ActiveCN107819840AReduce overheadMinimize Energy ExpenditureWireless commuication servicesTransmissionNetwork architectureMobile edge computing
The invention discloses a distributed mobile edge computing unloading method in an ultra-dense network architecture, belonging to the technical field of wireless communication network and cloud computing. The method includes the following steps: calculating the interference of mobile equipment, and if unloading is needed, carrying out computing unloading by selecting a strategy that meets the loadlimitation, interference limitation and delay limitation; further, when the energy overhead of the selected strategy is superior to a current computing unloading strategy, sending update request information to a currently-selected base station to request to update the own computing unloading strategy; after the mobile equipment acquires the information that the base station allows to update the computing strategy, notifying other mobile equipment that the current update opportunity has been acquired, and adopting the updated strategy in the next time slot; and if the mobile equipment does notacquire the update opportunity, maintaining the existing strategy in the next time slot. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the energy consumption in a computing unloading process can be effectively reduced under the premise of guaranteeing a certain delay limitation, the purpose of saving the energy consumption can be effectively achieved, and the good leading effect and applicability can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
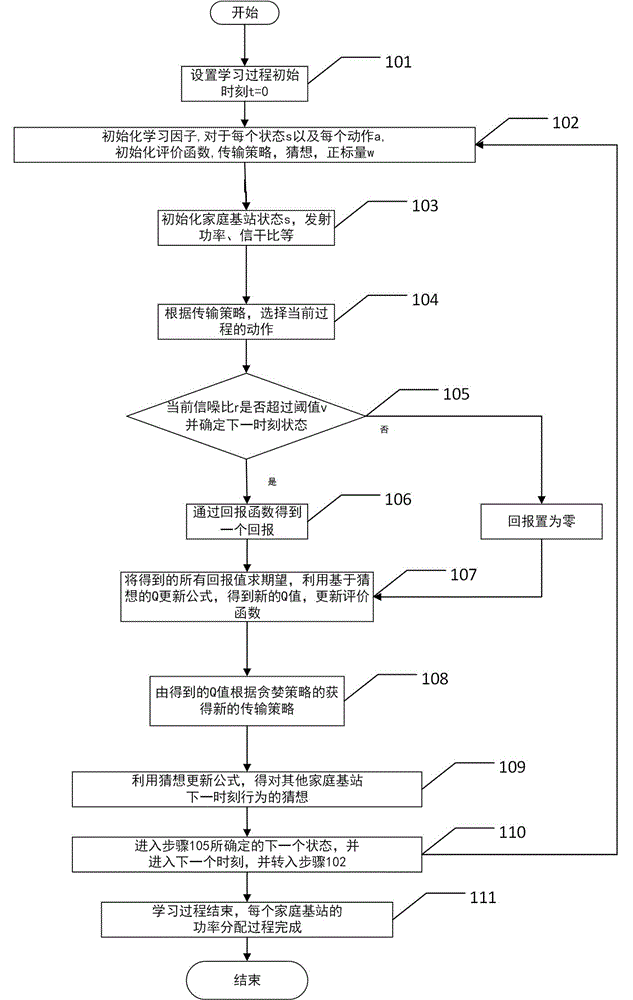
Resource allocation method for reinforcement learning in ultra-dense network
InactiveCN106358308AImprove performancePower managementNetwork topologiesSystem capacityTransmitted power
A resource allocation method for reinforcement learning in an ultra-dense network is provided. The invention relates to the field of ultra-dense networks in 5G (fifth generation) mobile communications and provides a method for allocating resources between a home node B and a macro node B, between a home node B and another home node B and between a home node B and a mobile user in a dense deployment network; the method is implemented through power control, each femotcell is considered as an intelligent body to jointly adjust transmitting powers of home node Bs, the densely deployed home node Bs are avoided causing severe jamming to a macro node B and an adjacent B when transmitting at maximum powder, and system throughput is maximized; user delay QoS is considered, and traditional 'Shannon capacity' is replaced with 'available capacity' that may ensure user delay; a supermodular game model is utilized such that whole network power distribution gains Nash equilibrium; the reinforcement learning method Q-learning is utilized such that the home node B has learning function, and optimal power distribution can be achieved; by using the resource allocation method, it is possible to effectively improve the system capacity of an ultra-dense network at the premise of satisfying user delay.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Resource allocation method based on non-cooperative gambling in super dense network
ActiveCN105636057AAvoid interferenceNetwork planningHigh level techniquesFrequency spectrumSystem capacity
The invention provides a resource allocation method based on non-cooperative gambling in a super dense network. A double-layer network in the super dense network is analyzed to propose a shared and orthogonal hybrid spectrum allocation method based on perception; a multi-dimensional resource allocation model of base station connection, a user channel and power allocation is obtained by describing the base station connection, a channel model and system capacity; the resource allocation method based on the non-cooperative gambling is proposed to solve the multi-dimensional resource allocation problem, the algorithm describes a non-cooperative gambling model, an allowed domain is introduced to solve optimal power allocation, the 0-1 discrete variable of the base station connection is relaxed to a variable of a (0,1) section, an allocation channel is judged by normative punishment, and an algorithm for mutual iteration of the base station connection, the user channel and the power allocation is formed. The cross-layer and co-layer interference and the multi-dimensional radio resource allocation problem between a macro cell and a micro cell are solved, and the resource allocation method has certain superiority of inhibiting the interference and improving the throughput of the entire system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for reducing switch failures in ultra-dense wireless network
InactiveCN104486784ARealize adaptive adjustment of switching parametersThe way of grouping is preciseWireless communicationFailure rateSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a method for reducing switch failures in an ultra-dense wireless network and belongs to the mobility optimization technique in wireless communication. The method comprises the following steps: configuring different initial switching parameters for UE at different speeds, and then automatically adjusting the switching parameters according to the switching history; calculating the failure times and the success times of switching within the given time window length, and thus providing a new method for dynamically adjusting switch parameters. In the ultra-dense network, under the condition that Picocells are densely deployed in the area, the method can realize self-adaptative adjustment for the switch parameters, effectively reduces the switch failure rates when the UE passes through the area with the densely-deployed Picocells, and can realize the balance of reducing the switch failure rates and reducing small ping-pong ball rate.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
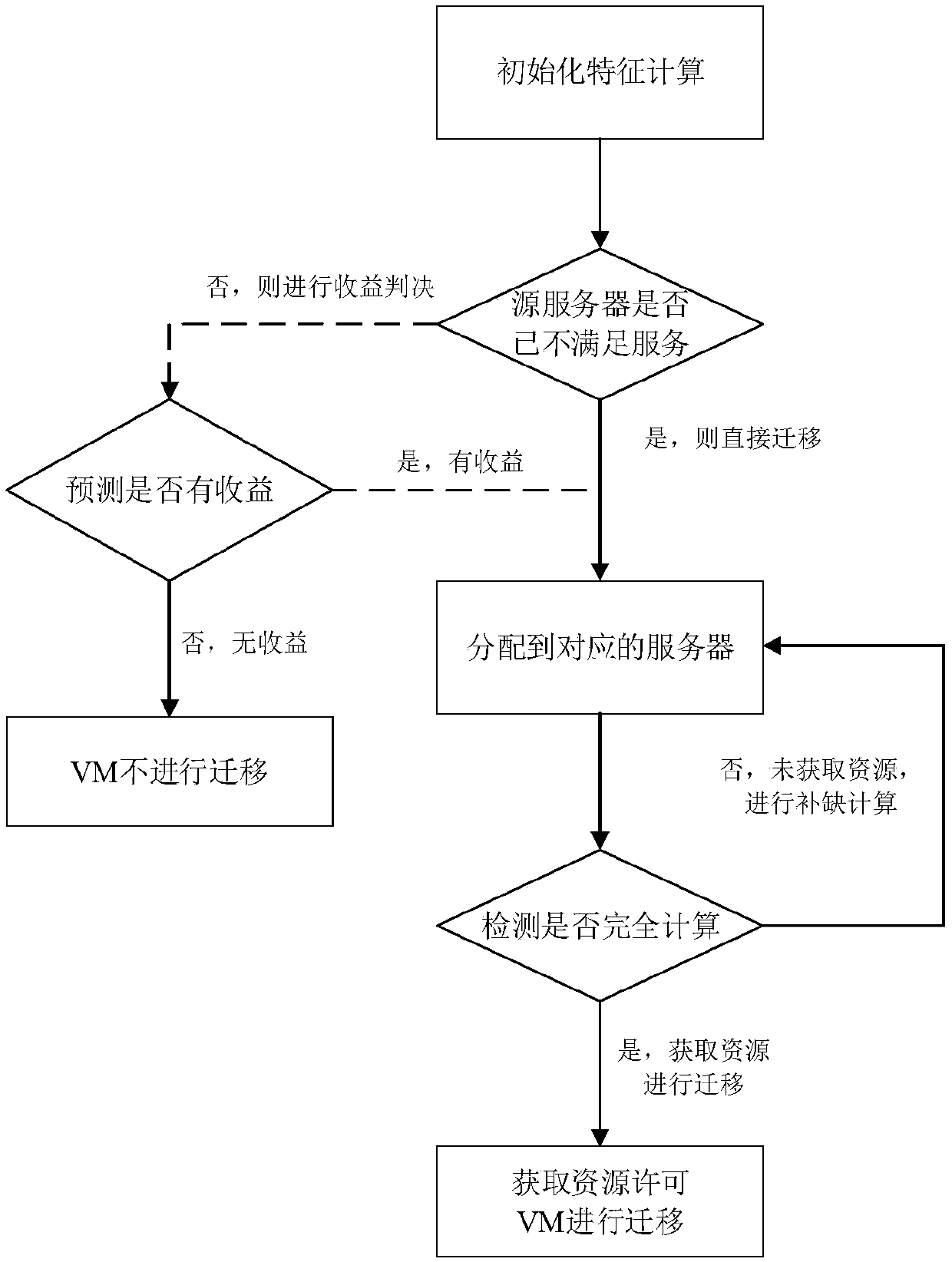
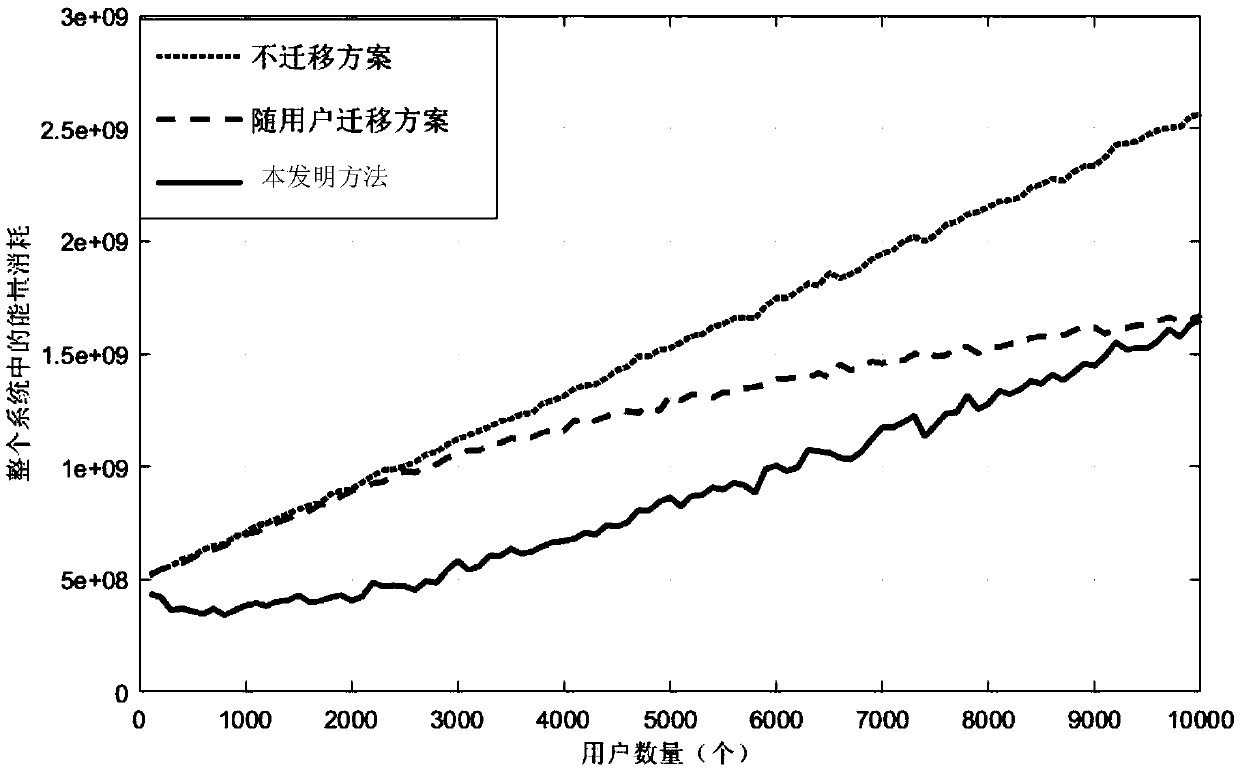
Method for optimizing VM migration between MEC nodes in ultra-dense network
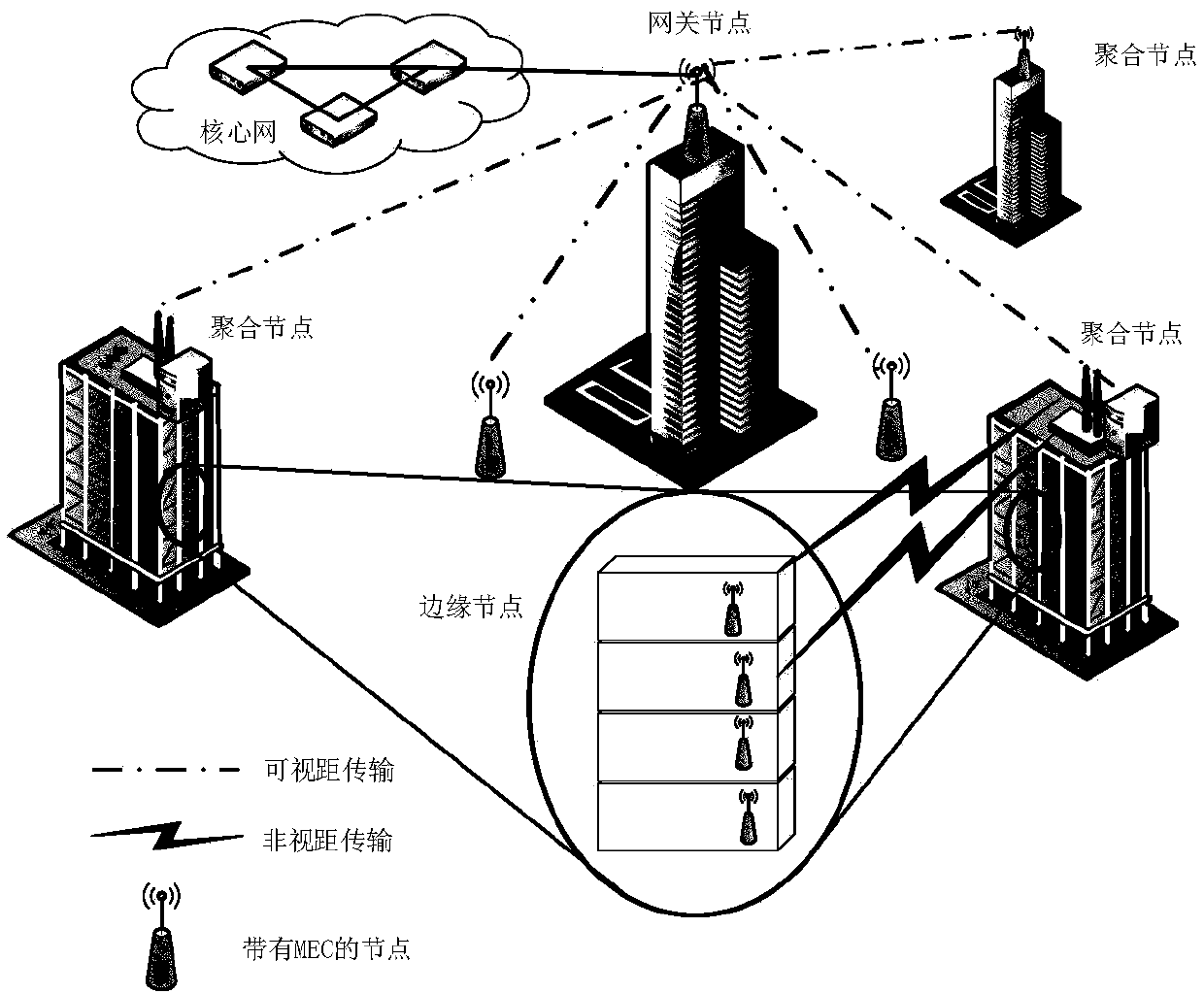
ActiveCN107919986ARealize flexible migration functionReduce energy consumptionData switching networksSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEdge nodeMobile edge computing
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communication, and particularly relates to a method for optimizing VM migration between mobile edge computing (MEC) nodes in an ultra-dense network. The applied ultra-dense network includes gateway nodes, aggregation nodes and edge nodes. The method includes the following steps: when a VM of the MEC nodes needs to be migrated, firstly calculating initialization characteristics, and calculating the energy consumption generated by the interaction with the VM when a user moves in the same gateway node range according to the predicted migration time of the user, wherein the energy consumption includes the energy consumption Wmig generated by transmitting data to a destination node, the energy consumption Wpre generated by transmitting the data to a source node, and the energy consumption Wafter generated by performing connection with the VM to carry out data transmission in three categories of node coverage areas when the location ofthe user changes; secondly, establishing an optimal return model; and finally, solving the optimal return model to select an optimal VM migration strategy. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a flexible migration function of the VM in a special scene can be realized, the energy consumption of the system can be effectively reduced, and the migration efficiency can be improved; andreasonable resource matching can be achieved, and service requirements of the user can be met.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Allocation method for wireless resources of ultra dense network based on dynamic clustering
ActiveCN107172682AReduce complexityEfficient allocationWireless communicationResource blockUltra dense network
The invention discloses an allocation method for wireless resources of an ultra dense network based on dynamic clustering. The allocation method comprises a base station dynamic clustering process and a resource block allocating process, and is characterized in that in the base station dynamic clustering process, dynamic clustering is performed on base stations randomly distributed in the network, a lot of base stations in the network are clustered according to an improved K-mean clustering method, and an effective allocation space is provided for inter-cluster resource block allocation of different modes of users; and in the resource block allocating process, joint processing is performed on single base station resource allocation of center users and inter-cluster CoMP resource allocation of edge users according to a clustering result in the step one, resource blocks with an excellent channel state of the base stations are allocated preferentially in clusters where the users are located according a provided proportional fairness based resource block allocation method, the received interference is reduced at the same time, the proportional fairness among the different modes of users is ensured, and an optimal resource block allocation result is acquired. The method disclosed by the invention can effectively improve the sum rate of the system users and achieves an ultimate objective of overall network resource optimization.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGXIN TECH CO LTD
Switching method based on adjustable prediction threshold hysteresis margin in super-dense network
ActiveCN105208615AReduce signaling volumeSimplify and speed up the transfer processWireless communicationHysteresisFailure rate
In a fifth generation (5G) mobile system, large-scale MIMO antennas and super-dense deployment networks are two modes for realizing high throughout. In allusion to a problem of frequent switching of super-dense networks, the invention provides a switching management method for hysteresis margin automatic adjustment according to movement conditions of terminal equipment based on an idea of super-dense network clustering. According to the invention, clustering management is carried out on small base stations, switching of user equipment between cells is divided into a pre-switching stage and a formal switching stage, and the switching threshold hysteresis margin is adjusted correspondingly according to the speed of the equipment, thereby completing a switching process of the equipment between the cells. The method provided by the invention can effectively reduce the switching time delay and the switching failure rate of the equipment.
Owner:CERTUS NETWORK TECHNANJING
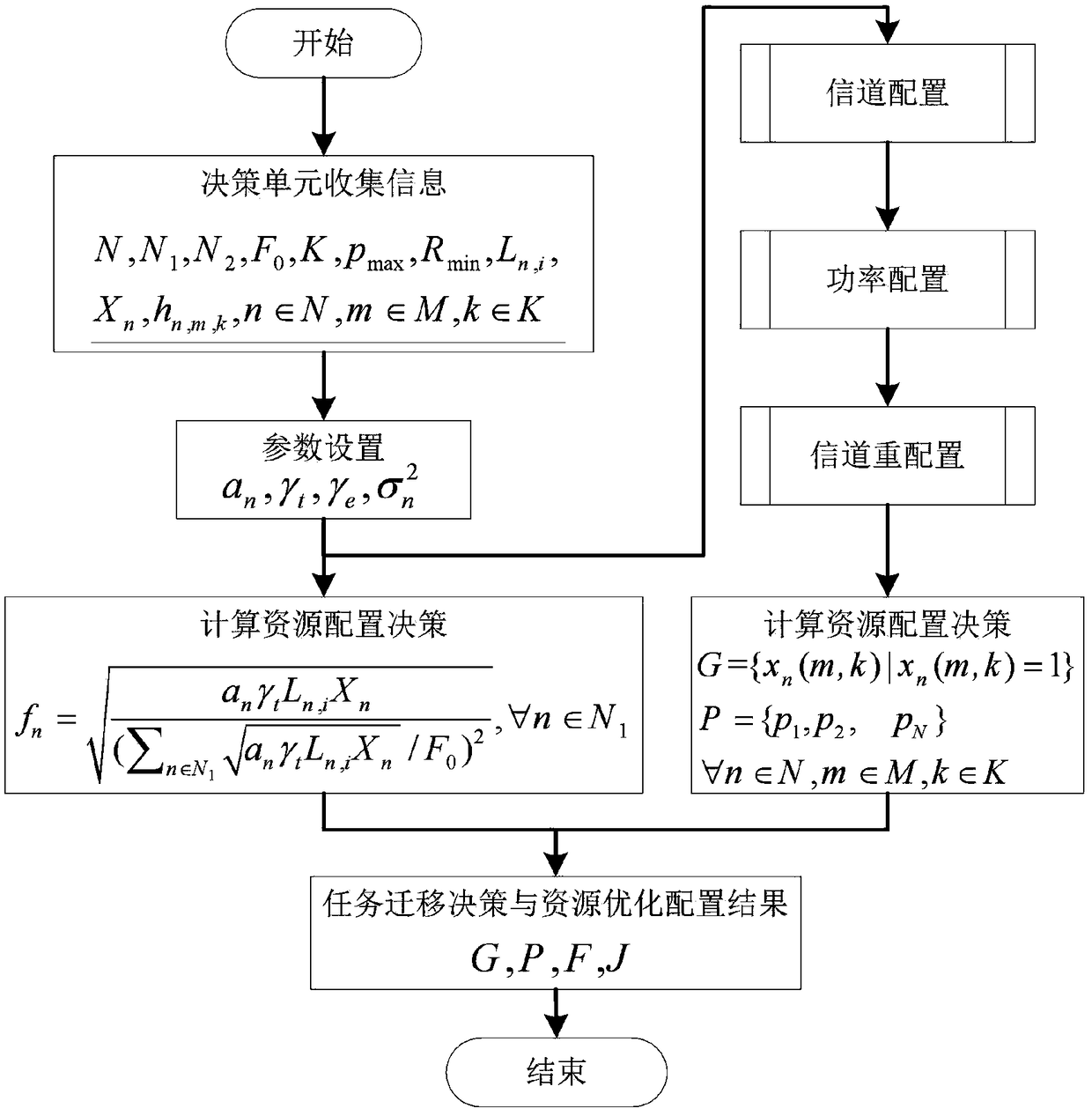
Migration decision and resource optimization distribution method for mobile edge computing ultra-dense network
ActiveCN109151864AStrong targetingReduce performance lossPower managementTransmissionMobile edge computingUltra dense network
The invention discloses a migration decision and resource optimization distribution method for a mobile edge computing ultra-dense network, and belongs to the field of wireless communication. For theapplication scene that a computing terminal and a communication terminal simultaneously initiate task request in the mobile edge computing ultra-dense network, a computing request terminal task migration decision and resource optimization configuration method capable of guaranteeing the minimum communication rate requirement of a communication request terminal is disclosed. The method takes the weighted sum of the task migration processing time delay and the energy consumption of each computing request terminal as the task migration cost, and an optimization model is established by taking thetask migration cost sum of all the computing request terminals as the target, the optimization model is decomposed into a calculation resource optimization configuration model and a joint channel configuration and power configuration optimization model, a KKT condition is adopted to obtain a calculation resource optimization configuration decision; an alternative iteration is adopted to obtain a channel and power suboptimum configuration decision.
Owner:GUIZHOU POWER GRID CO LTD
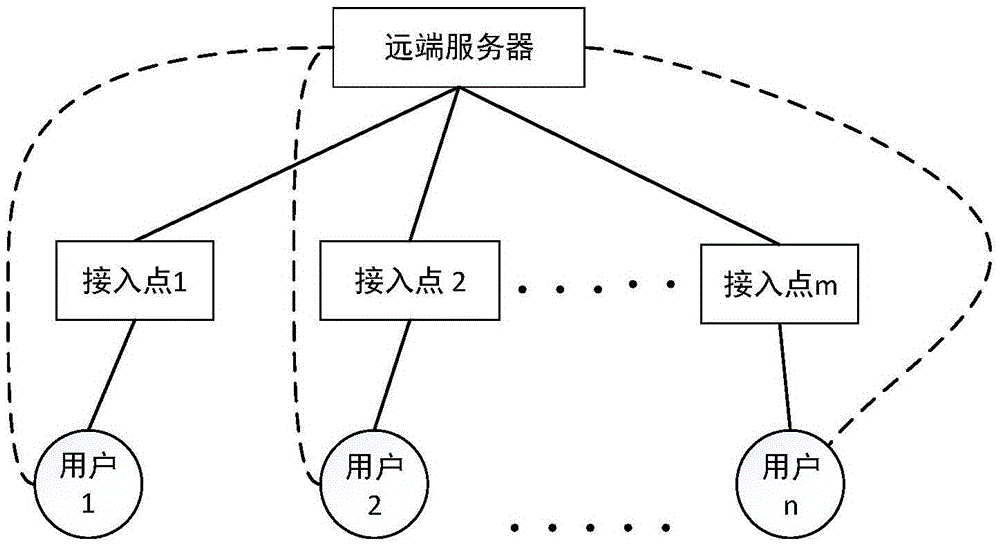
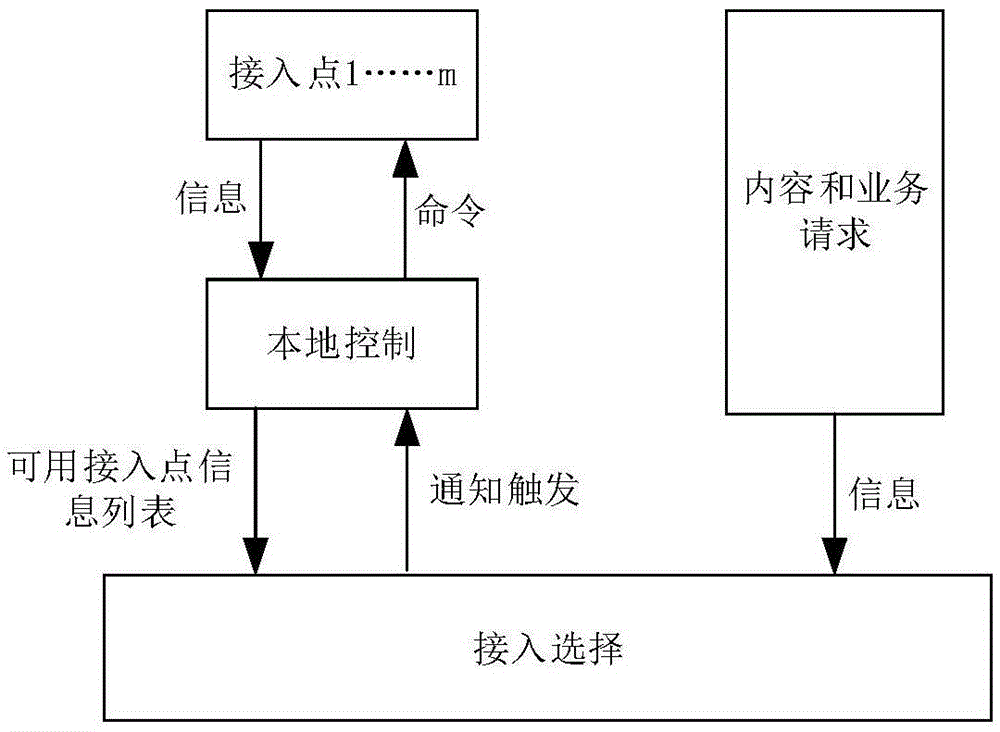
Method for combining dynamic access and subcarrier allocation under cache-based ultra-dense network
ActiveCN105611574AImprove Spectrum Utilization EfficiencyImprove Resource Management EfficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionComputer networkFrequency spectrum
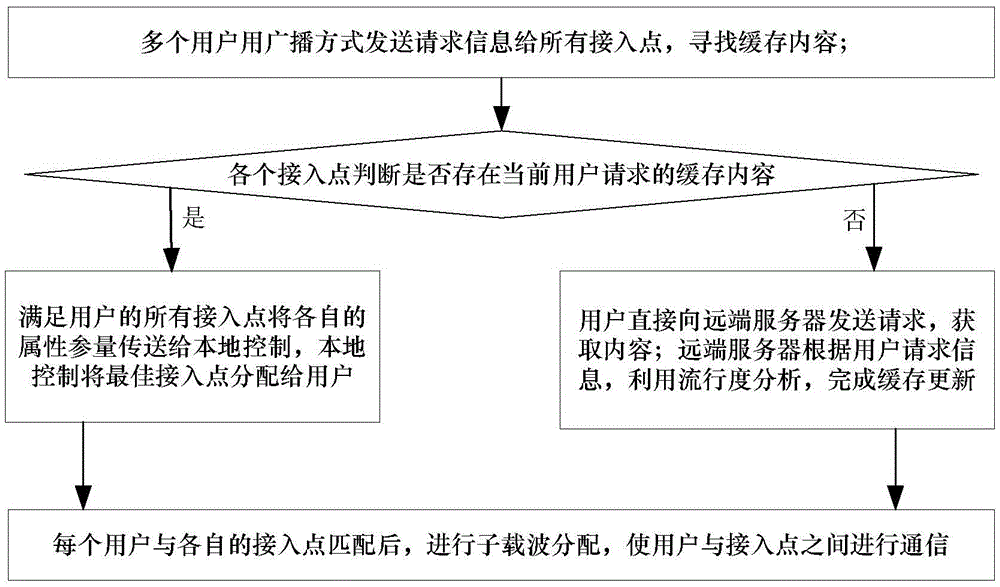
The invention discloses a method for combining dynamic access and subcarrier allocation under a cache-based ultra-dense network. The method comprises the following specific steps that firstly, multiple users simultaneously send request information to all access points to search a caching content; secondly, each access point judges whether a caching content requested by the current user K exists, all access points meeting the user K transmit respective property parameters to local control, and the local control allocates the optimal access point to the user K, otherwise the user K directly sends a request to a remote server to obtain the content; thirdly, the remote server utilizes popularity analysis to complete cache updating according to the user request information; and lastly, after each user is matched with the respective access point, subcarrier allocation is carried out, so that each user is communicated with the respective access point. The method has the following advantages that multiple factors are synthesized to complete access selection, and promotion of the resource management efficiency and dynamic allocation of the subcarrier are realized, so that the spectral efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Collaborative edge caching algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning in ultra-dense network
PendingCN111970733AReduce download delayImprove spectrum resource utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmissionUser deviceAlgorithm
The invention discloses a collaborative edge caching algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning in an ultra-dense network. The collaborative edge caching algorithm comprises the following specificsteps: 1, setting each parameter of a system model; and 2, making an optimal cache decision for each SBS by adopting a Double DQN algorithm so as to maximize the total content cache hit rate of all the SBSs. According to the algorithm, a DQN algorithm and a Double Q-learning algorithm are combined, so that the over-estimation problem of the DQN algorithm on a Q value is effectively solved. In addition, the algorithm adopts a priority experience playback technology, so that the learning speed is increased. The method further comprises a step 3, making an optimal bandwidth resource allocation decision for each SBS by adopting an improved branch and bound method so as to minimize the total content downloading delay of all user equipment. According to the method, the content downloading delayof all users in the ultra-dense network can be effectively reduced, the content cache hit rate and the spectrum resource utilization rate are improved, and the method has good robustness and expandability and is suitable for the large-scale user-intensive ultra-dense network.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Seamless handover method based on collaborative base station clustering in ultra-dense network
The invention relates to a seamless handover method based on collaborative base station clustering in an ultra-dense network. The method comprises the steps of firstly, collaboratively clustering small base stations deployed in an ultra-dense manner; implementing overlapped clustering to acquire an overlapped cluster node; when a user moves in a cluster, adopting a dynamically self-updating method for a service base station group to meet the intra-cluster handover requirement of the user; and when the user moves across the clusters, adopting a handover pre-warning mechanism to perform pretreatment early for handover, thus reducing preparation time for handover, then executing a handover process, and finally completing seamless handover. According to the method, the collaborative base station clustering and handover pre-warning serve as entry points, according to the moving conditions of the mobile user such as moving in the cluster, and moving across the clusters, the different handover strategies are used for performing efficient cell handover, the handover delay is reduced, the handover failure rate is lowered, and the seamless handover experience of the user is enhanced.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
Edge computing resource allocation method and system for ultra-dense network
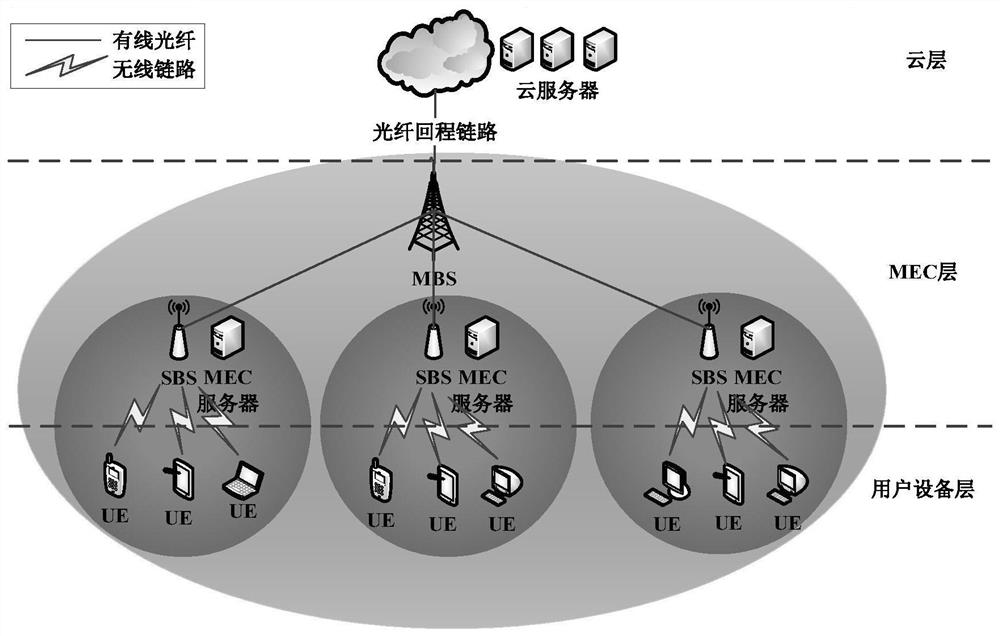
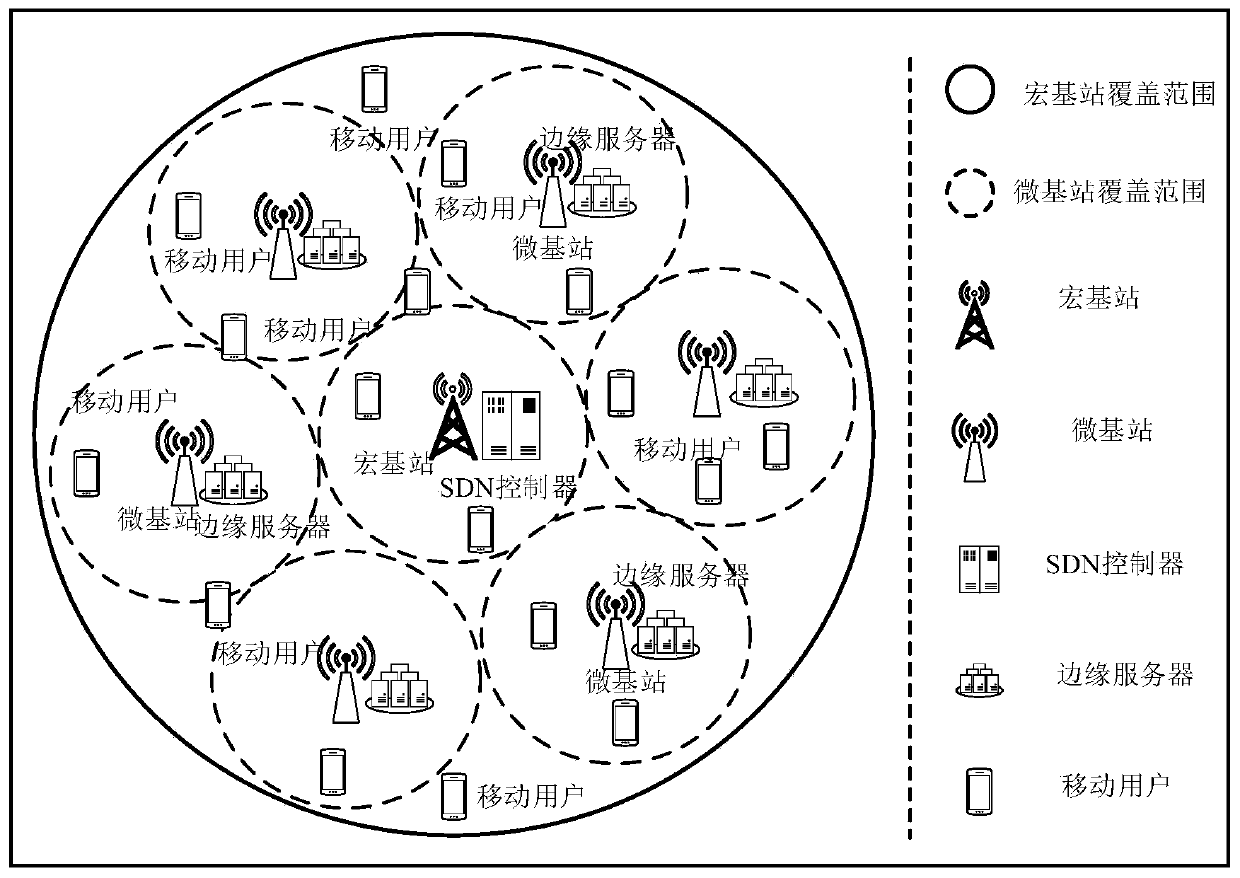
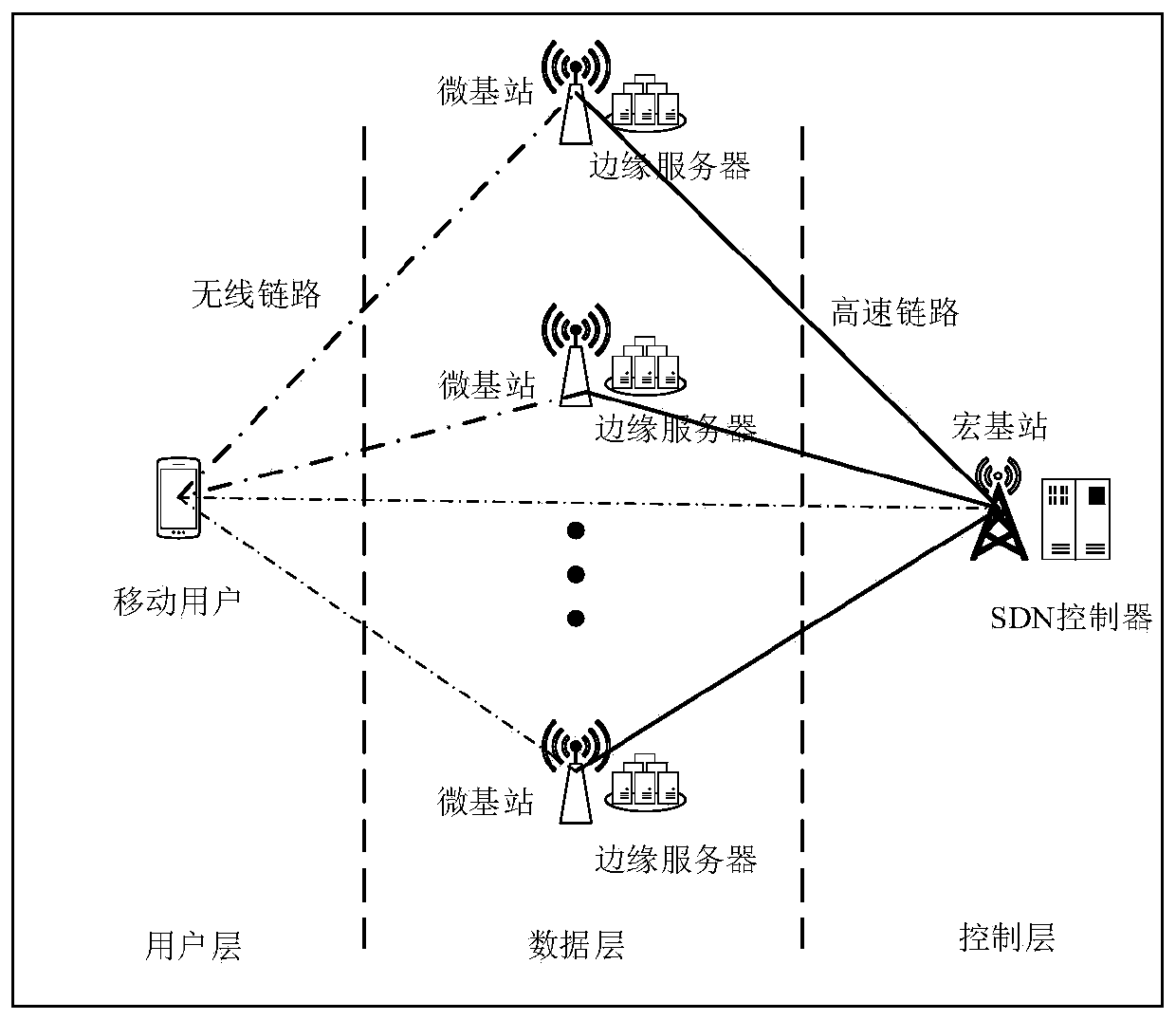
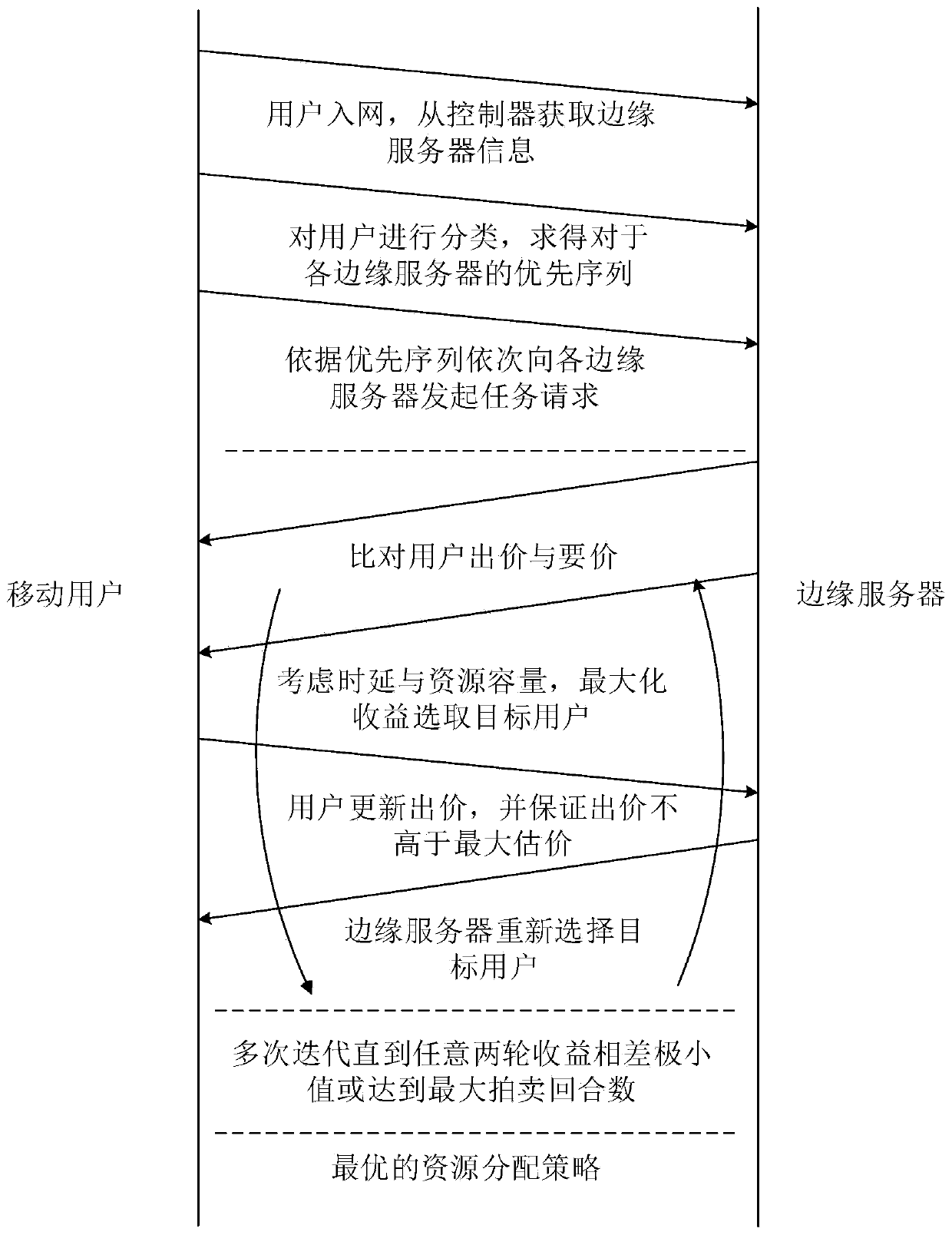
ActiveCN110012508ABalance network loadTotal revenue maximizationNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmissionQuality of serviceEdge server
The invention discloses an edge computing resource allocation method and system for an ultra-dense network, and the method comprises the steps: collecting task requests of all terminal devices and resource states of all edge servers from a global perspective, and carrying out the reasonable allocation of computing resources of all the edge servers through employing an SDN controller as a decisionbody; the system comprises a macro base station, a micro base station and an edge server, and the macro base station is connected with each micro base station through a high-speed optical fiber link,and is in wireless connection with a mobile user. And the macro base station manages the resource condition of the whole network from the overall perspective and collects the information of each mobile user. According to the invention, the effectiveness of edge server computing resources, the resource total quantity of each server and performance difference are fully considered; a bidirectional multi-round auction mechanism is introduced into the multi-server computing resource distribution process in the ultra-dense network, the total income of the servers is maximized on the premise that theuser service quality is guaranteed, and the loads of all the servers are balanced.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
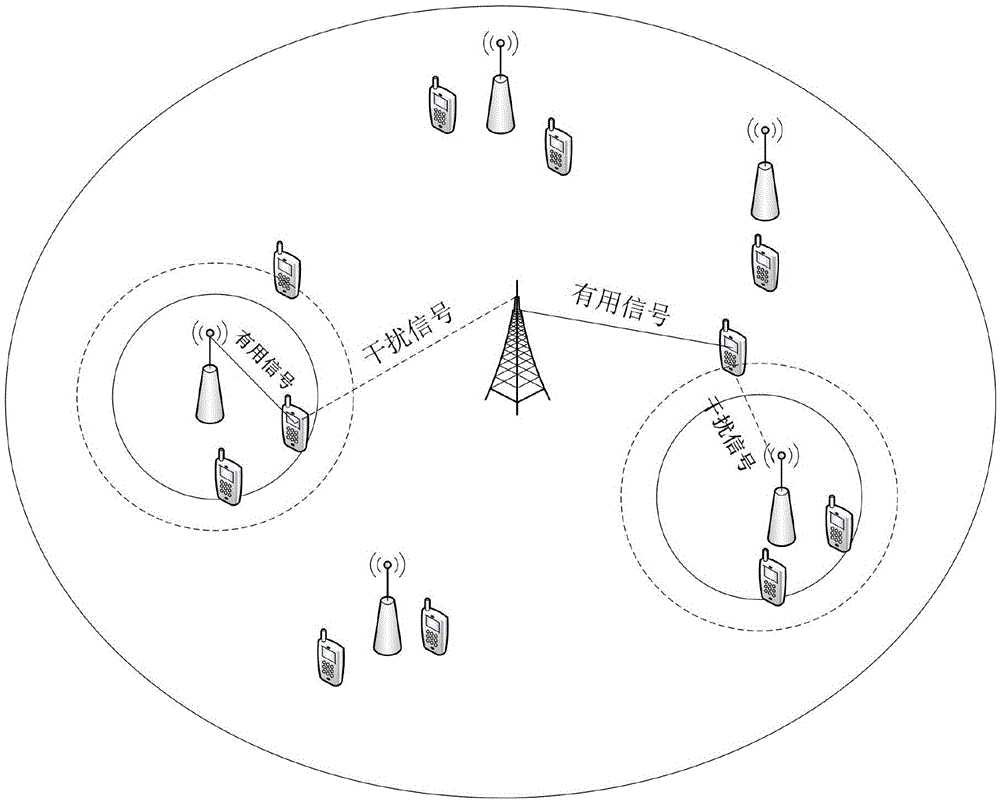
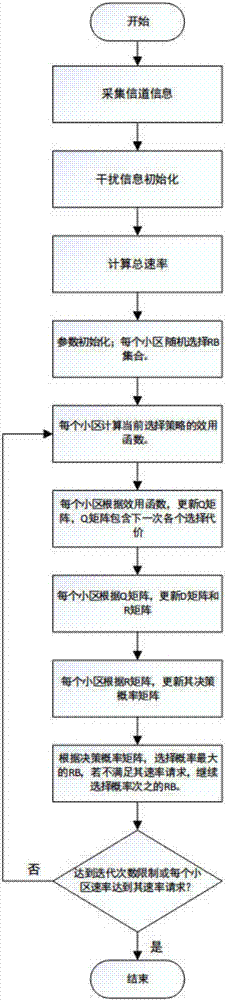
Distributed ultra-dense heterogeneous network interference coordination method based on non-cooperative game
ActiveCN107094060AReduce distractionsIncrease capacityOrthogonal multiplexFrequency spectrumSpectral efficiency
The invention discloses a distributed ultra-dense heterogeneous network interference coordination method based on a non-cooperative game. A network interference problem is modeled as a non-cooperative game problem by analyzing a dynamic feature of an ultra-dense network, cells in the network are used as game participants, and autointerference is minimized to be a utility function. In order to deduce existence of a Nash equilibrium solution, building of a game model is deduced into a potential game problem, and a feedback method based on random learning is provided accordingly to solve the Nash equilibrium solution. According to the method, a probability matrix is built according to the utility function of each cell for each time of iteration, and the final Nash equilibrium solution is acquired by continuously updating the probability matrix. According to the method provided by the invention, the closed-form solution can achieved by convergence without information exchange between the cells, so that at last the whole network interference is minimal, when all the cells are converged to the Nash equilibrium solution, network capacity is improved, and the requirement of dynamic variation of user speed is met, and the difficulty among network densification, network capacity and spectrum efficiency is effectively solved with relatively low complexity.
Owner:上海瀚芯实业发展合伙企业(有限合伙)
A switching algorithm based on machine learning in a UDN
ActiveCN109447275AReduce unnecessary switchingReduce latencyMachine learningWireless communicationMacro base stationsAlgorithm
The invention discloses a switching algorithm based on machine learning in a UDN, and the algorithm comprises the following steps of A when a mobile device needs to be switched to a new micro cell each time, firstly reporting a feature information report of the position where the mobile device is located to a macro base station, and discretizing the feature information by the macro base station; Brespectively training the discretized feature information data by adopting four learners of machine learning decision tree prediction, neural network prediction, SVM prediction and random forest prediction to obtain each training model; C making a decision on each prediction result by using a majority voting method to obtain a decision result; and D when the decision result is that the mobile device needs to be switched and a pre-switching condition is met, using the macro base station to send a pre-switching request to a pre-switched target micro cell, and using the target micro cell to start to prepare resources for the mobile device and implement switching. According to the present invention, the unnecessary switching is reduced, and the average time delay of the system in the ultra-dense network is reduced.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
High energy efficiency power control method which takes energy harvest into consideration in ultra-dense network
ActiveCN105898851AImprove energy efficiencyGuaranteed reliabilityPower managementMacro base stationsHigh energy
The invention discloses a high energy efficiency power control method which takes energy harvest into consideration in an ultra-dense network. The method comprises following steps of 1, setting a double-layer heterogeneous network scene; 2, distributing subchannels; 3, carrying out initial power distribution on each subchannel of a macro base station and each home base station; 4, judging whether the power distribution of all home base stations is converged or not, or whether the number of iterations exceeds an upper limit or not; 5, solving the optimum transmitting power distribution of the home base stations; 6, stopping iteration of this time; finishing distribution of wireless resources of each home base station; and waiting for scheduling of next time. According to the method, the QoS demands of the users of the home base stations are taken into consideration, and moreover, the energy efficiency of the heterogeneous network is improved greatly by using an energy harvest technique.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Heterogeneous network segmentation method and system for 5G
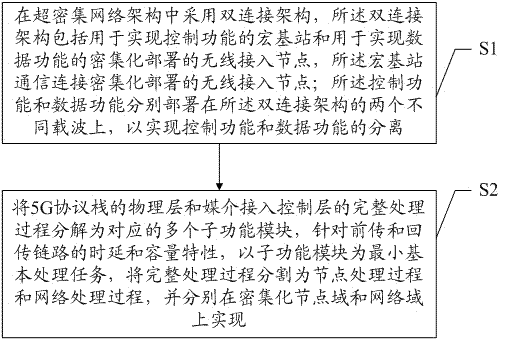
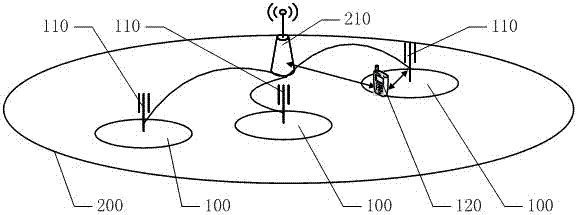
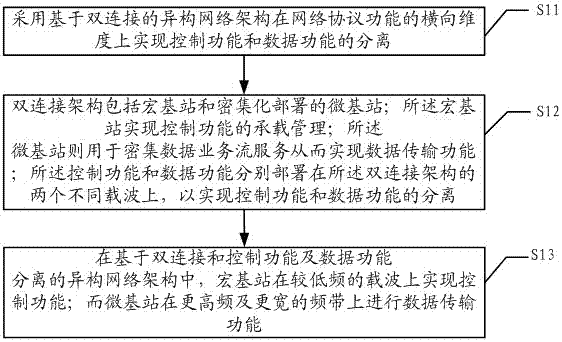
ActiveCN106993339ASeparate control functionLow costSignal allocationConnection managementMacro base stationsCarrier signal
The invention discloses a heterogeneous network segmentation method and system for 5G. The method comprises the following steps: adopting a dual connection architecture in an ultra-dense network architecture, wherein the dual connection architecture comprises a macro base station for realizing a control function and densely-deployed wireless access nodes for realizing a data function, the macro base station is in communication connection with the densely-deployed wireless access nodes, and the control function and the data function are separately deployed on two different carriers of the dual connection architecture to achieve the separation between the control function and the data function; and decomposing the whole processing procedure of a physical layer and a medium access control layer of a 5G protocol stack into multiple corresponding sub-function modules, segmenting the whole processing procedure into a node processing procedure and a network processing procedure by taking the sub-function modules as minimum basic processing tasks aiming at the delay and capacity characteristics of forward and return links, and separately performing the processing procedures in dense node domains and network domains. The ultra-dense network with low cost, easy deployment and light maintenance can be achieved.
Owner:HUIZHOU TCL MOBILE COMM CO LTD
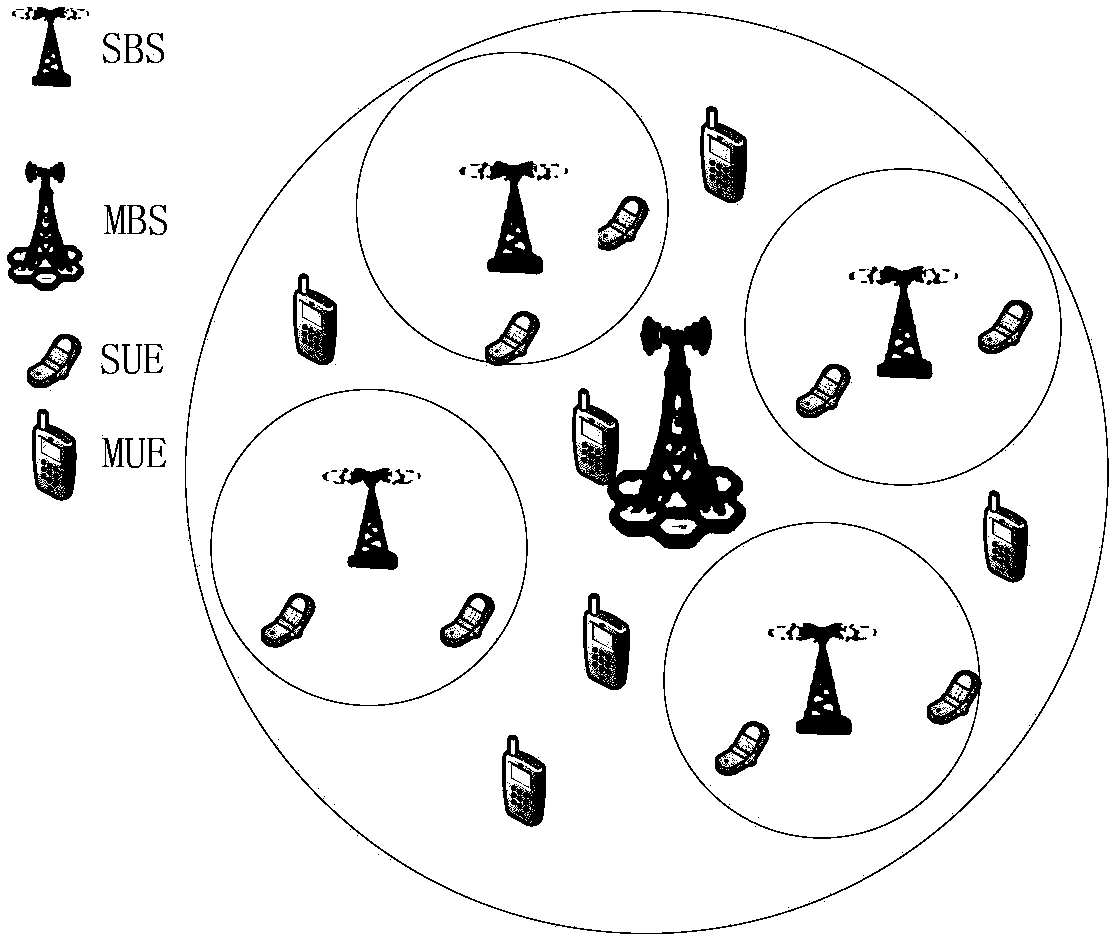
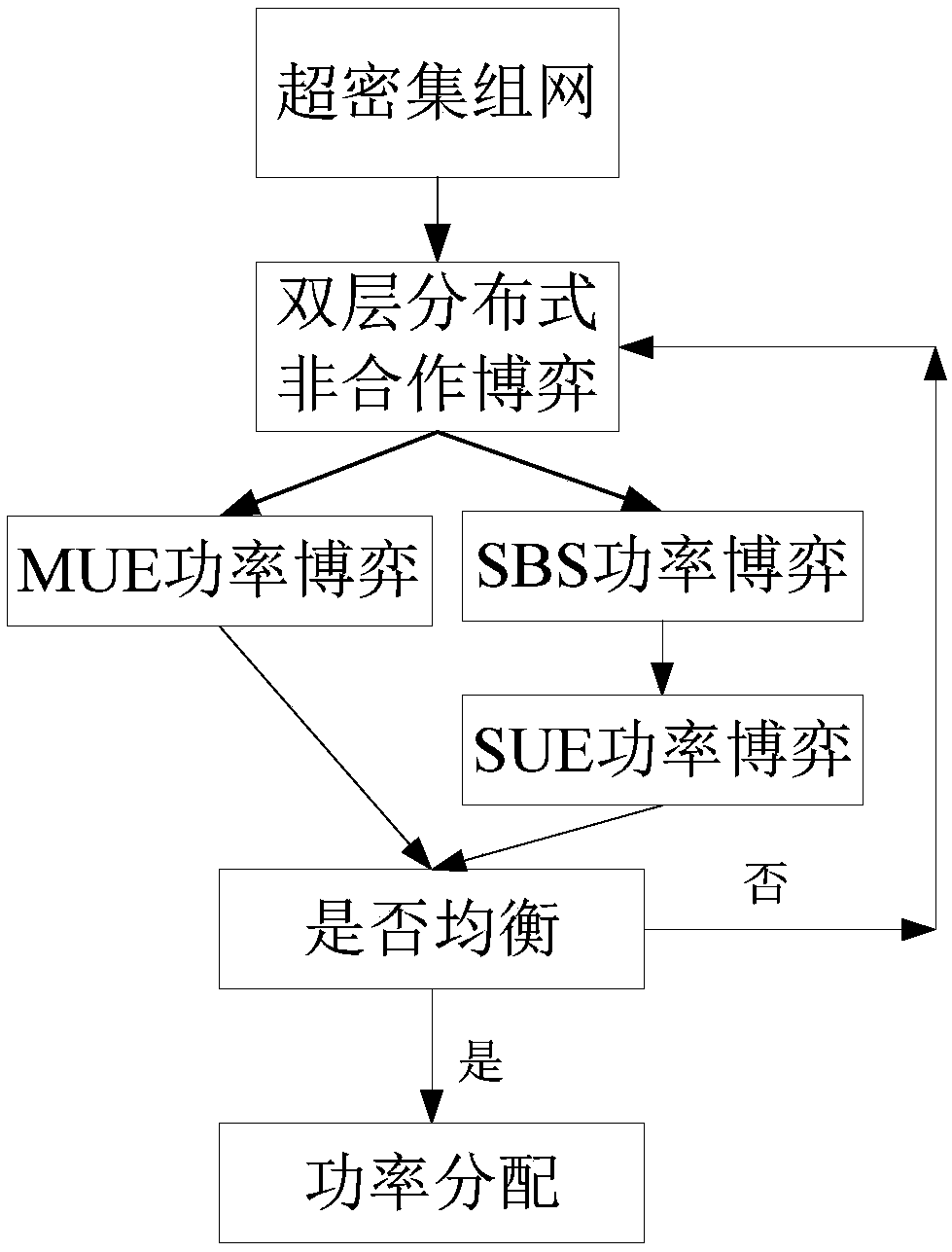
Power allocation method based on double-layer non-cooperative game theory in ultra dense network and wireless network power allocation modeling method in ultra dense network
ActiveCN108322938ACoordinated Power AllocationControl interferenceHigh level techniquesWireless communicationUltra dense networkComputer science
The invention discloses a power allocation method based on a double-layer non-cooperative game theory in an ultra dense network. The method comprises the following steps of setting power initial allocation values of SBSs and MUE; carrying out game according to preset pricing factors and respective game revenue functions; selecting respective game policies, namely, power allocation policies until equilibrium values arrive; setting the power initial allocation values of SUE; and carrying out power game according to the set pricing factors and the game revenue functions until the equilibrium values arrive after the SBSs obtain respective equilibrium values of the game. According to the method, the power allocation among networks can be coordinated, the interference of each layer is controlled, and moreover, the optimum power allocation set is solved effectively through the game.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Cluster-based cache configuration method and device in ultra-dense network
ActiveCN108667653AImprove performanceData switching networksComputation complexitySpectral clustering algorithm
The invention provides a cluster-based cache configuration method and device in an ultra-dense network, aiming to solve a problem that the existing small base station caching method cannot consider both calculation complexity and cache hit rate in an ultra-dense scene. The method comprises the steps of first, creating a cache configuration policy optimization problem with a goal of maximizing users served by a small base station; then clustering users by using a spectral clustering algorithm based on user preference and user position, and grouping small base stations according to a clusteringresult, wherein the grouped small base station serves users of small base stations of the same group only but does not serve users of small base stations of other groups; then breaking the original optimization problem into subproblems according to the clustering result, wherein the optimization goal of the subproblem is to maximize users served by the small base stations of the same group; and finally, resolving each subproblem independently by using a greedy caching algorithm, so as to obtain a cache configuration policy of small base stations of the same group. Compared with the prior art,the method considers both calculation complexity and cache hit rate.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Small base station switch control method based on deep neural network
ActiveCN108134979AReduce power consumptionOptimize resource allocationPower managementLocation information based serviceMathematical modelNetwork model
The invention provides a small base station switch control method based on a deep neural network. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring user information in a base station; integratingall user data into a path data sample set capable of being trained by a model; establishing a neural network model; inputting data and training the model; collecting to-be-predicted user data, and predicting a position of a user at the next moment; and computing the number of future service users of the base station, and controlling switch of the base station. According to the method, by predicting the number of people to be serviced in the base station, the switch of the small base station in an ultra-dense network is controlled, so that the purposes of reducing the power consumption of the base station, reducing the interference between the base stations and optimizing resource distribution in the ultra-dense network are achieved; the method combines data mining and machine learning in aprocess of establishing a mathematical model, so that the prediction accuracy and the system practicability are improved.
Owner:白盒子(上海)微电子科技有限公司
Frequency domain resource distribution method based on graph coloring in ultra-dense network
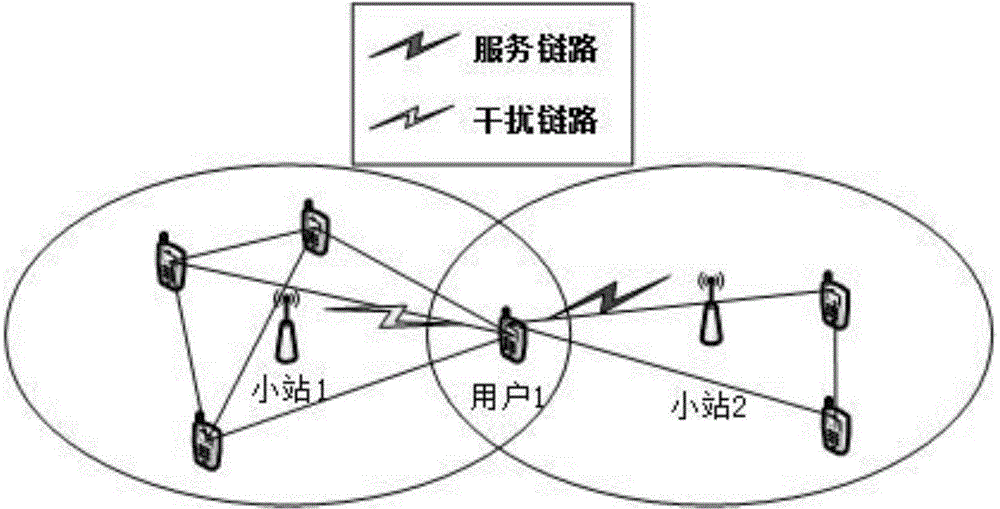
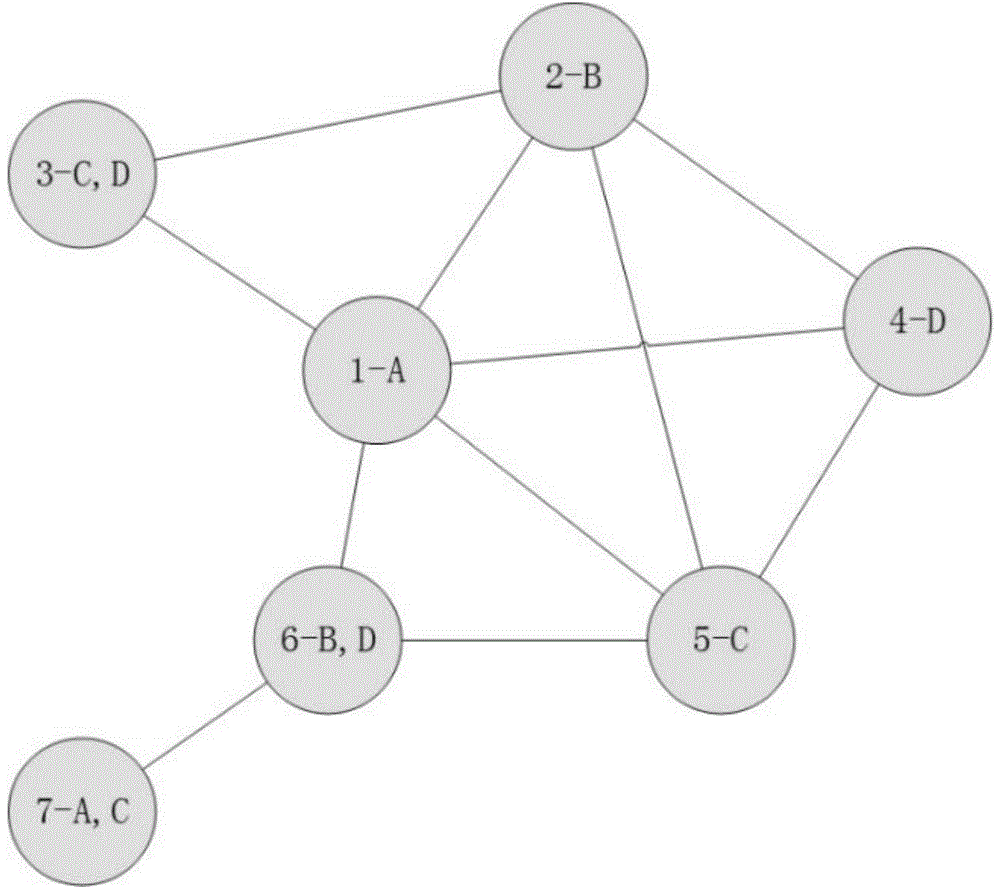
The invention discloses a frequency domain resource distribution method based on graph coloring in an ultra-dense network. The frequency domain resource distribution method comprises the following steps: reflecting a disturbed condition between small stations by utilizing a disturbance relationship graph; and coloring the disturbance relationship graph by utilizing a multiplexing algorithm based on a conventional graph coloring Brelaz algorithm, and distributing sub-band for each user according to the coloring results, thereby achieving a purpose of reducing the disturbance between the small stations. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for remarkably reducing the disturbance between the small stations, so that the total throughput and edge throughput of the system are increased.
Owner:上海瀚芯实业发展合伙企业(有限合伙)
Cache method based on small base station self-organization cooperation in super-dense network
ActiveCN109194763AReduce download latencyImprove cache hit ratioTransmissionWireless communicationCache hit rateLoad capacity
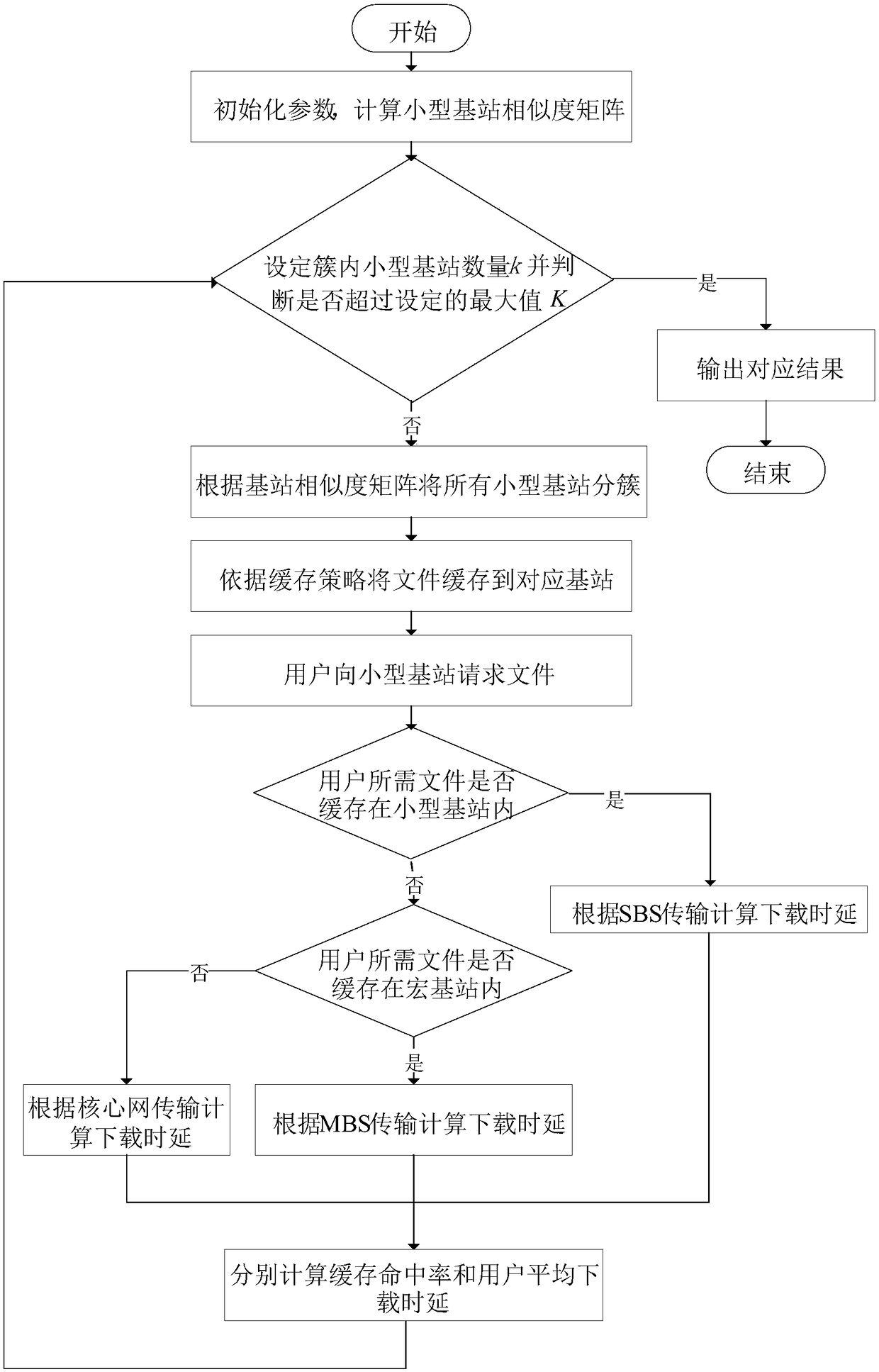
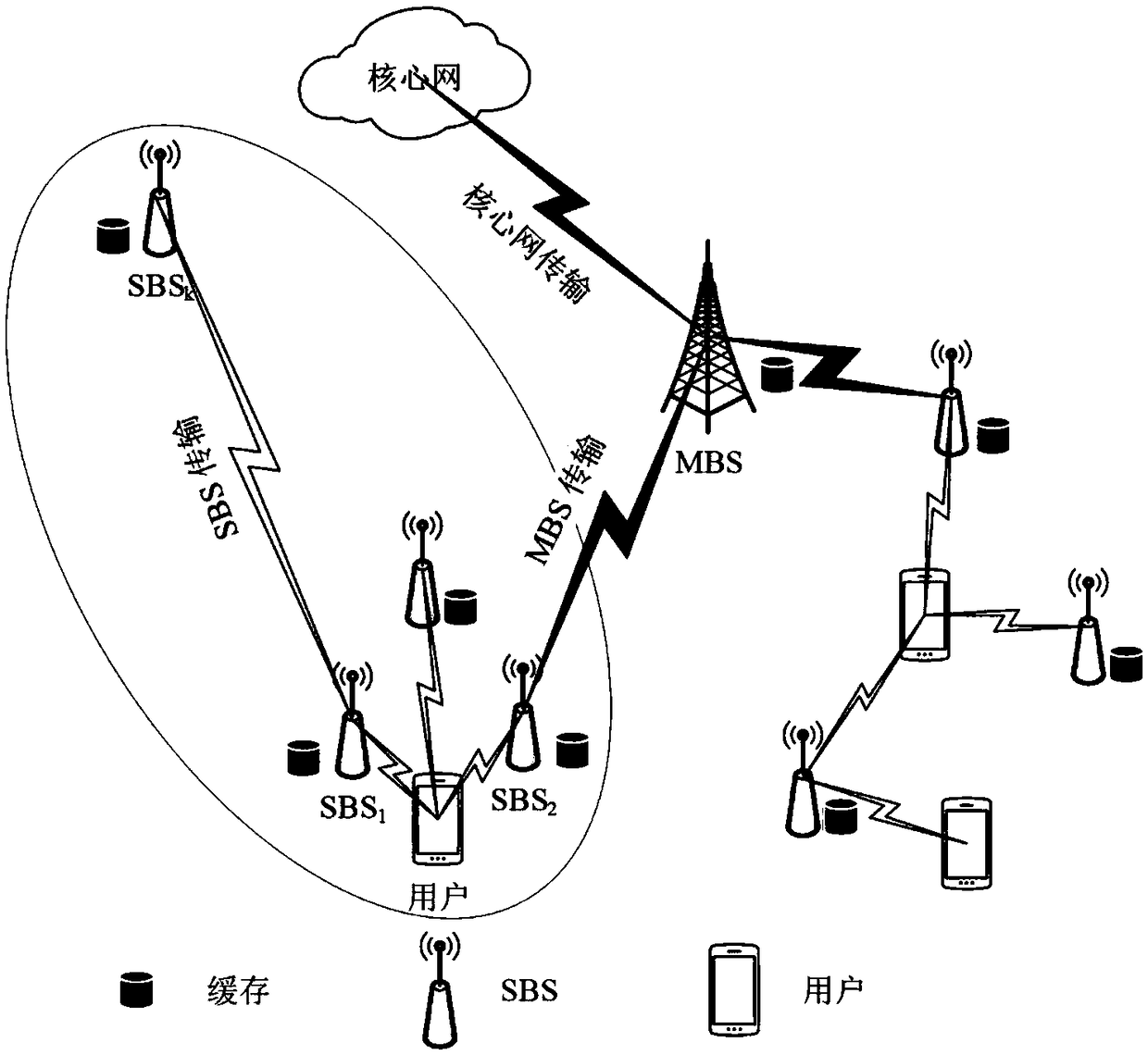
The present invention provides a cache method based on small base station self-organization cooperation in a super-dense network, belonging to the technical field of wireless communication. The methodcomprises the steps of: according to the load capacities and the positions of small base stations in a super-dense network, obtaining a similarity matrix of the small base station; according to the similarity matrix and the quantity k of the small base stations in each cluster, performing clustering, and selecting a small base stations with the best load capacity as a cluster head; according to afile cache strategy, caching the file into the small base station and a macro station; after users access the base stations, requesting to obtain a file; and finally, determining the value of the k exceeds the maximum value k set in the cluster or not, if yes, outputting a k value with the minimum average download delay of the user; or else, continuously updating the k value, and continuously performing re-clustering. Through the self-organization thought, the resources in the cluster are distributed, and the mutual cooperation and self organization between the small base stations are employed to reduce the user download delay while effectively improving the cache hit ratio and meet the business demands.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Cooperative edge caching algorithm for delay optimization in ultra-dense network
PendingCN111565419AReduce download delayImprove spectrum resource utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementMachine learningAlgorithmReinforcement learning algorithm
The invention discloses a collaborative edge caching algorithm for delay optimization in an ultra-dense network. The collaborative edge caching algorithm comprises the following specific steps: 1, setting each parameter of a system model; 2, making an optimal cache decision for each SBS by adopting a multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithm based on the game theory so as to maximize the content cache hit rate of each SBS; 3, making an optimal bandwidth resource allocation decision for each SBS by adopting an improved branch and bound method so as to minimize the total content downloading delay of all user equipment. According to the method, the content downloading delay of all users in the ultra-dense network can be effectively reduced, the content cache hit rate and the spectrum resource utilization rate are improved, and the algorithm has good robustness and expandability and is suitable for the large-scale user-intensive ultra-dense network.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
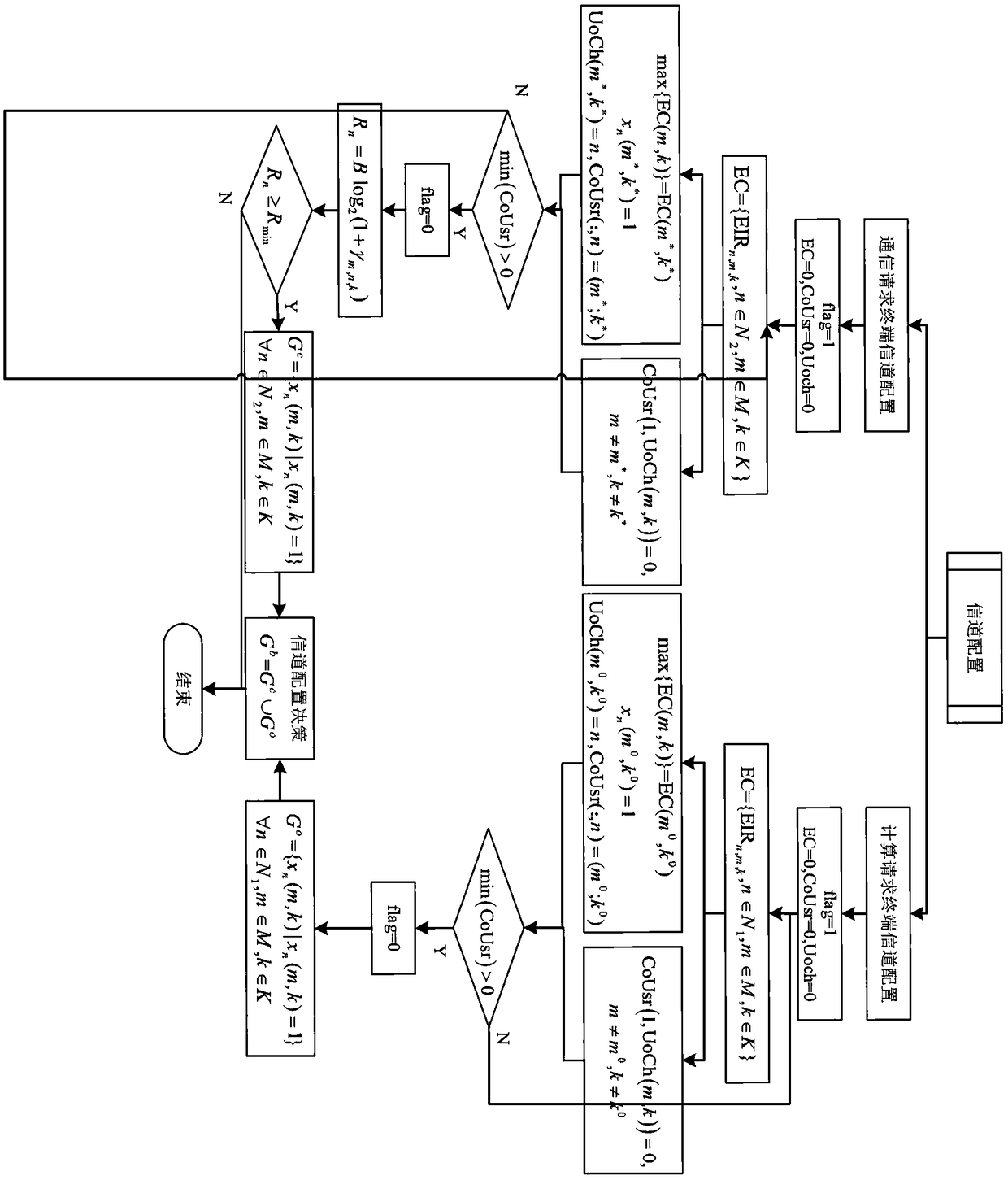
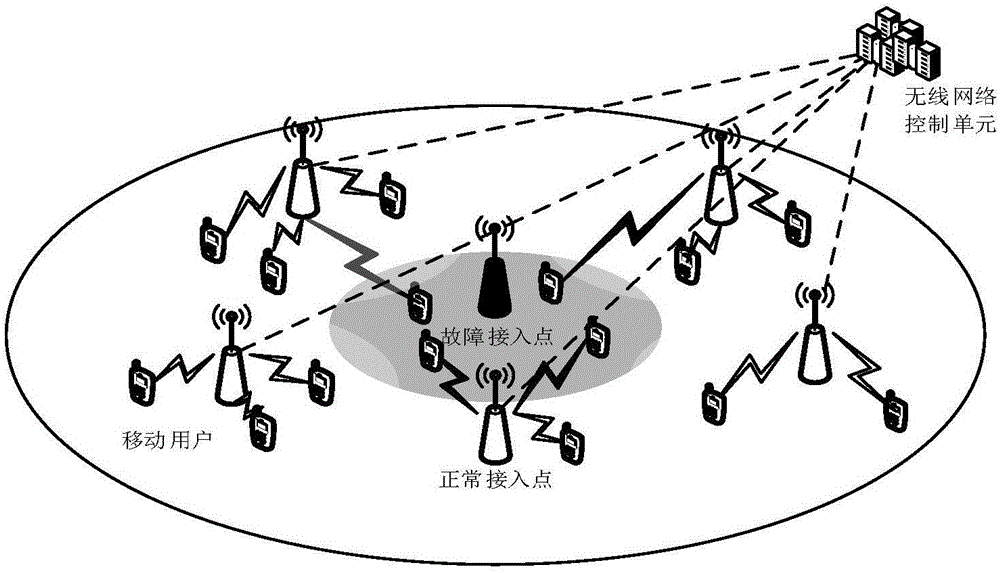
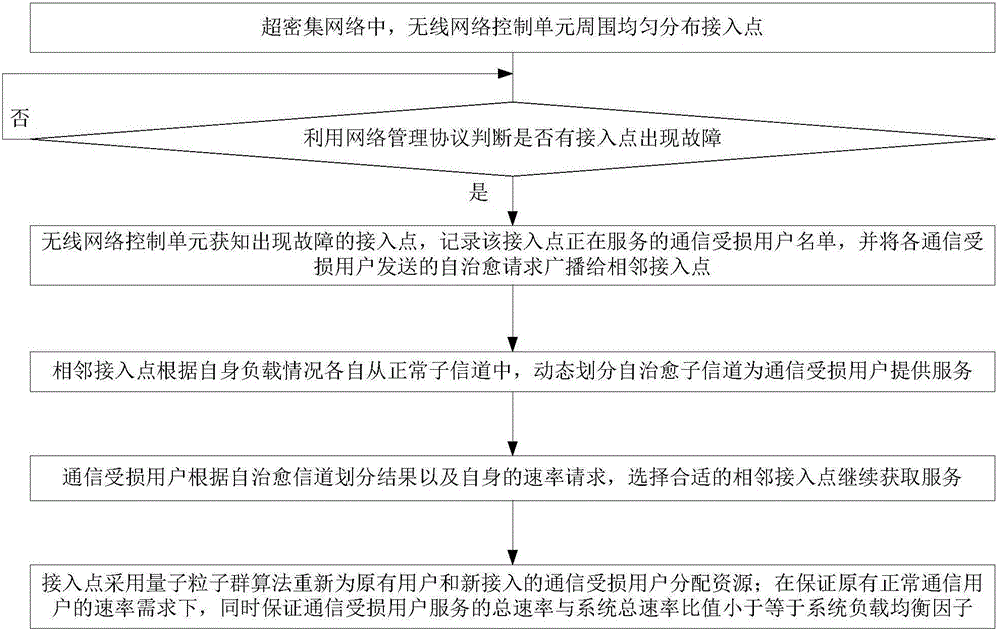
Access point selection and resource distribution combined self-healing method in ultra-dense network
ActiveCN105898807ARealize self-healing functionWarranty Service RequirementsNetwork topologiesHigh level techniquesSelf-healingOperational costs
The invention discloses an access point selection and resource distribution combined self-healing method in an ultra-dense network, and belongs to the field of the ultra-dense network. The method comprises following steps that firstly, a WNCU judges whether faults appear in access points or not; the WNCU records a name list of communication damaged users served by the access points and broadcasts the name list to adjacent access points if the faults appear in the access points; the adjacent access points divide self-healing subchannels from own normal subchannels dynamically; then, the communication damaged users select suitable adjacent access points so as to obtain service continuously according to self-healing channel dividing results and own speed requests; and finally the access points distribute resources to original users and newly accessing communication damaged users again by using a quantum particle swarm optimization algorithm. The method has the advantages that the self-healing function in the ultra-dense network is realized; when the faults appear in the access points, the service demands of the communication damaged users can be effectively ensured; the system energy efficiency is improved; and the operation cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
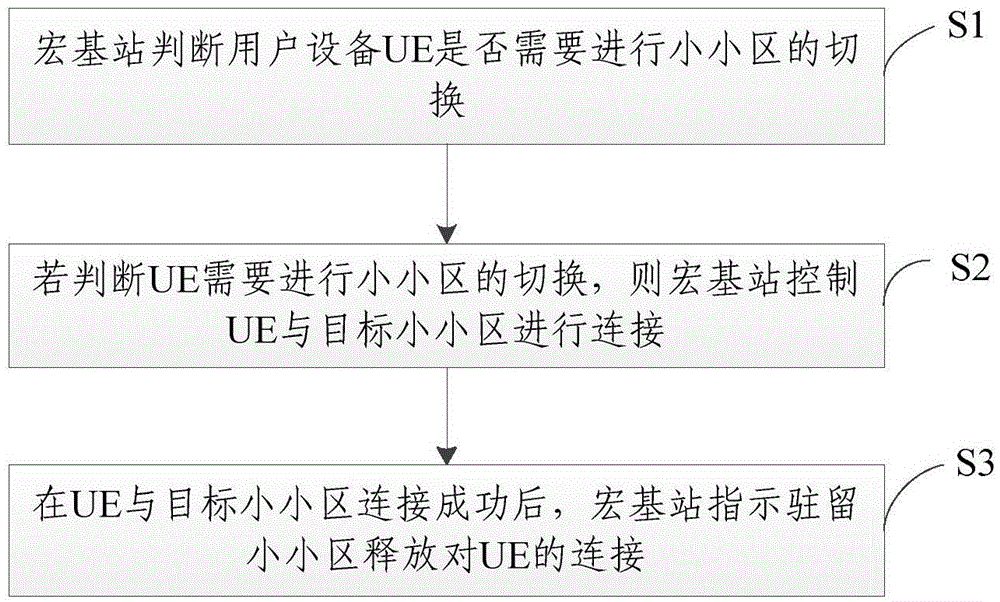
Small cell switching method and system
InactiveCN106817735ARealize seamless soft handoverGuaranteed continuityWireless communicationSoft switchingMacro base stations
The invention relates to the communication technology field and particularly relates to a small cell switching method and system. The method comprises steps that whether user equipment needs small cell switching is determined by a macro base station; if the UE is determined to need small cell switching, the UE is controlled by the macro base station to connect with a target small cell; after the UE is successfully connected with the target small cell, a resident small cell is indicated by the macro base station to release connection with the UE. Through the method, seamless soft switching of the UE from the resident small cell to the target small cell can be realized, continuity of user surface data transmission in a switching process is guaranteed, and user mobility demands in the super dense network are satisfied, and user experience is improved.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH
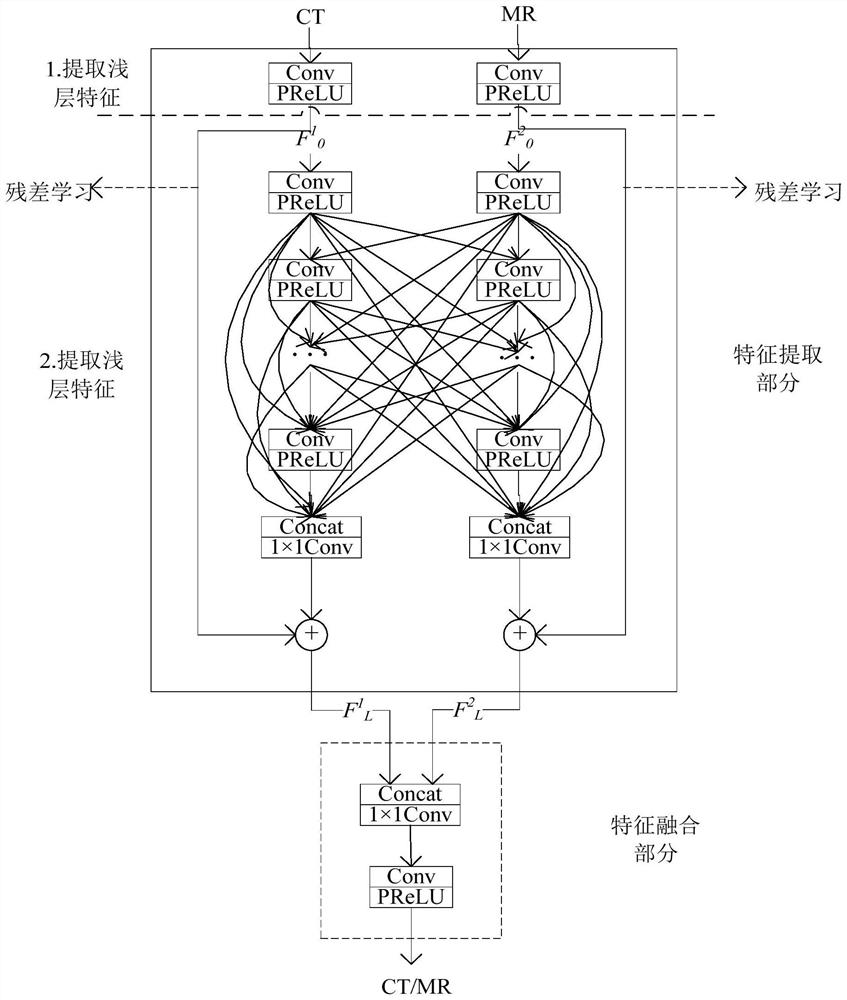
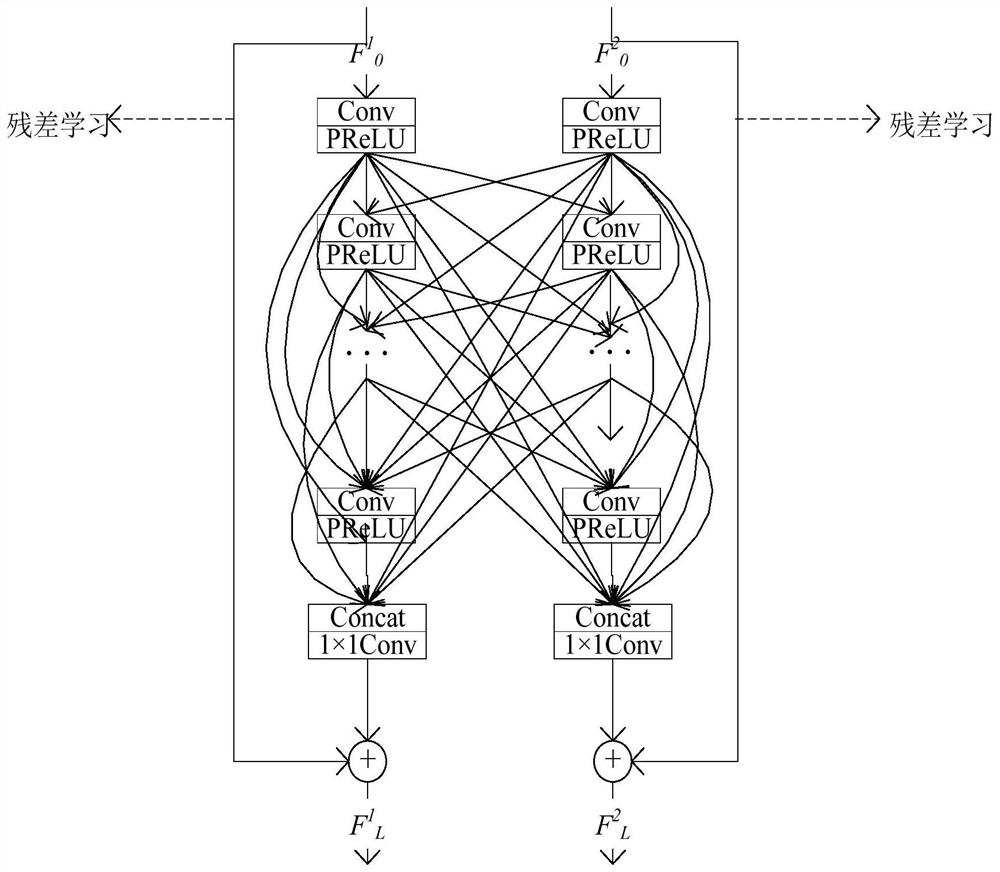
Multi-modal medical image fusion method based on double-residual ultra-dense network
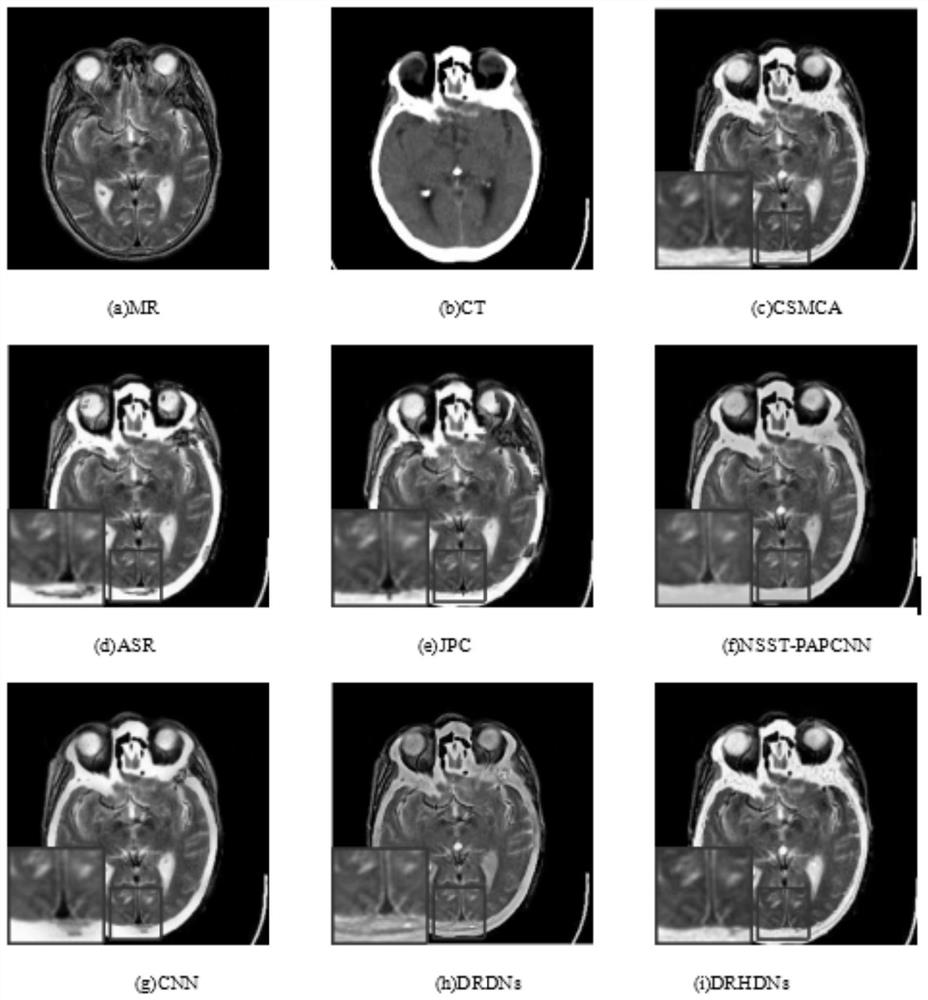
ActiveCN111882514AReduce lossSimplify goalsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionInformation transmission
The invention discloses a multi-modal medical image fusion method based on a double-residual ultra-dense network, and the method comprises the steps: extracting the shallow features of a first modal medical image and a second modal medical image through the convolution of a first Conv layer and the activation of a PReLU layer in the double-residual ultra-dense network; extracting deep features through residual learning and ultra-dense connection; and sequentially performing Concat layer channel dimension splicing in the double-residual ultra-dense network on the deep features, and finally performing Conv layer convolution and PReLU layer activation to obtain a fused image of the first modal medical image and the second modal medical image. The double-residual ultra-dense block provided bycombining the residual dense block and the ultra-dense connection not only applies the dense connection between layers of the same path, but also applies the dense connection between layers crossing different paths, and performs information transmission between two paths for extracting different modal image features, so that the extracted deep features are more detailed and richer, and loss of useful information of the network intermediate layer is reduced.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
5G ultra dense network switching method based on precise point positioning
ActiveCN108737959AHigh precisionImprove estimation accuracyLocation information based serviceMicro cellEngineering
The invention discloses a 5G ultra dense network switching method based on precise point positioning. By means of the precise point positioning technology, the current user location in an ultra densenetwork is measured, the location of the next moment is predicted, decision switching is conducted according to the signal to interference ratio of the current moment and the predicted signal to interference ratio of the next moment, a target micro cell can prepare resources for a possibly-generated access request in advance, the performance of the ultra dense network is improved, the ping-pong effect in the network is reduced, the average delay of the network is shortened, the generality and the validity are considered simultaneously, and the system performance is improved.
Owner:天元瑞信通信技术股份有限公司
Online collaborative caching method based on optimized energy efficiency
ActiveCN110138836AReduce transmission energy consumptionProof of feasibilityPower managementConnection managementMacro base stationsTime distribution
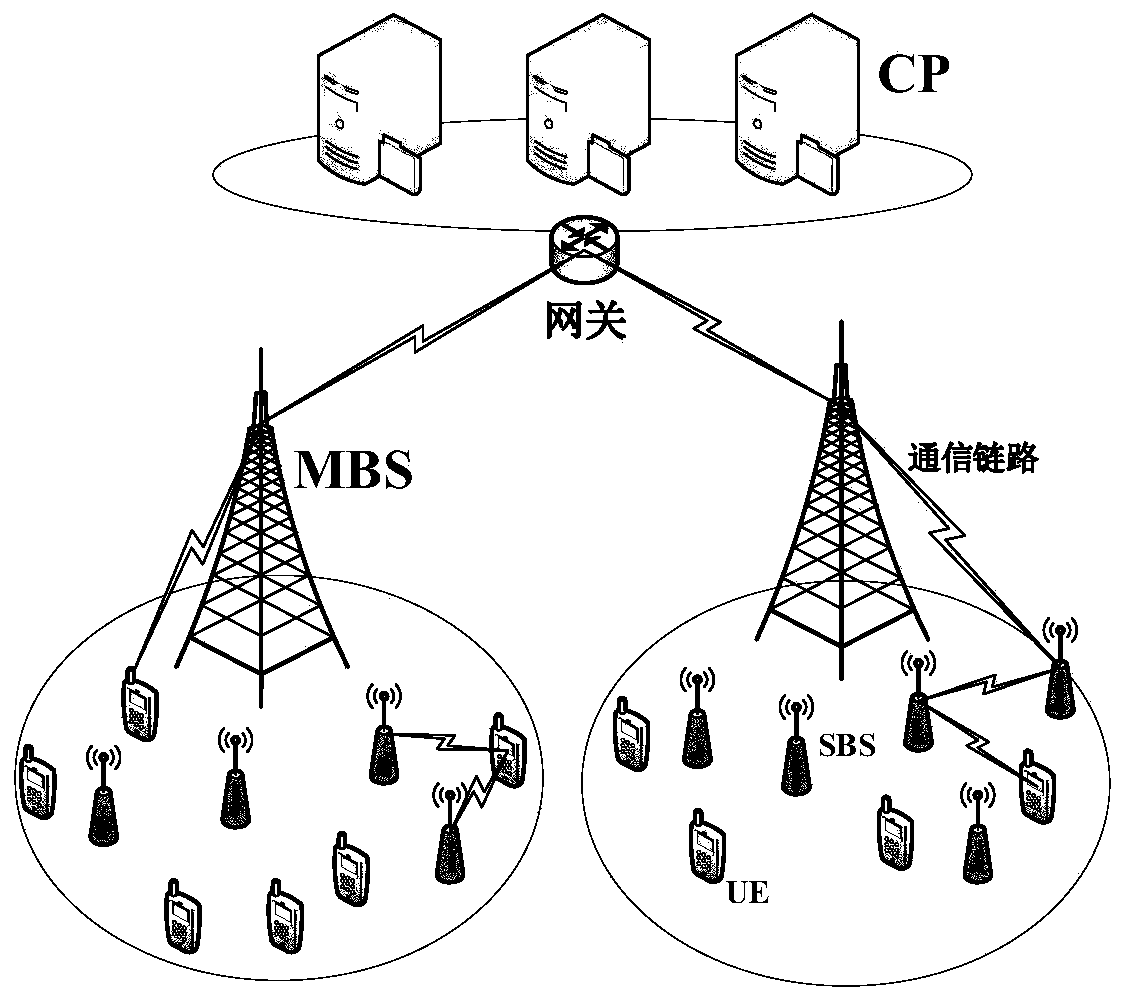
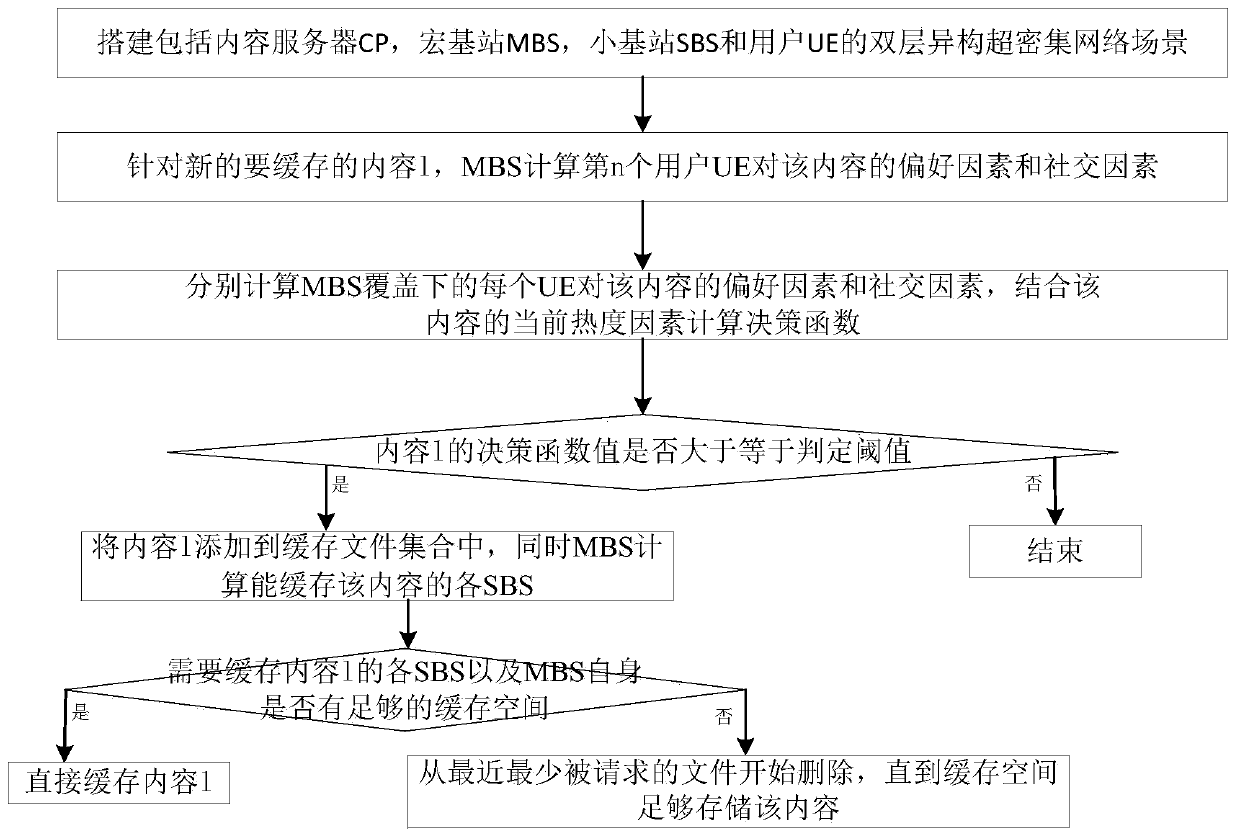
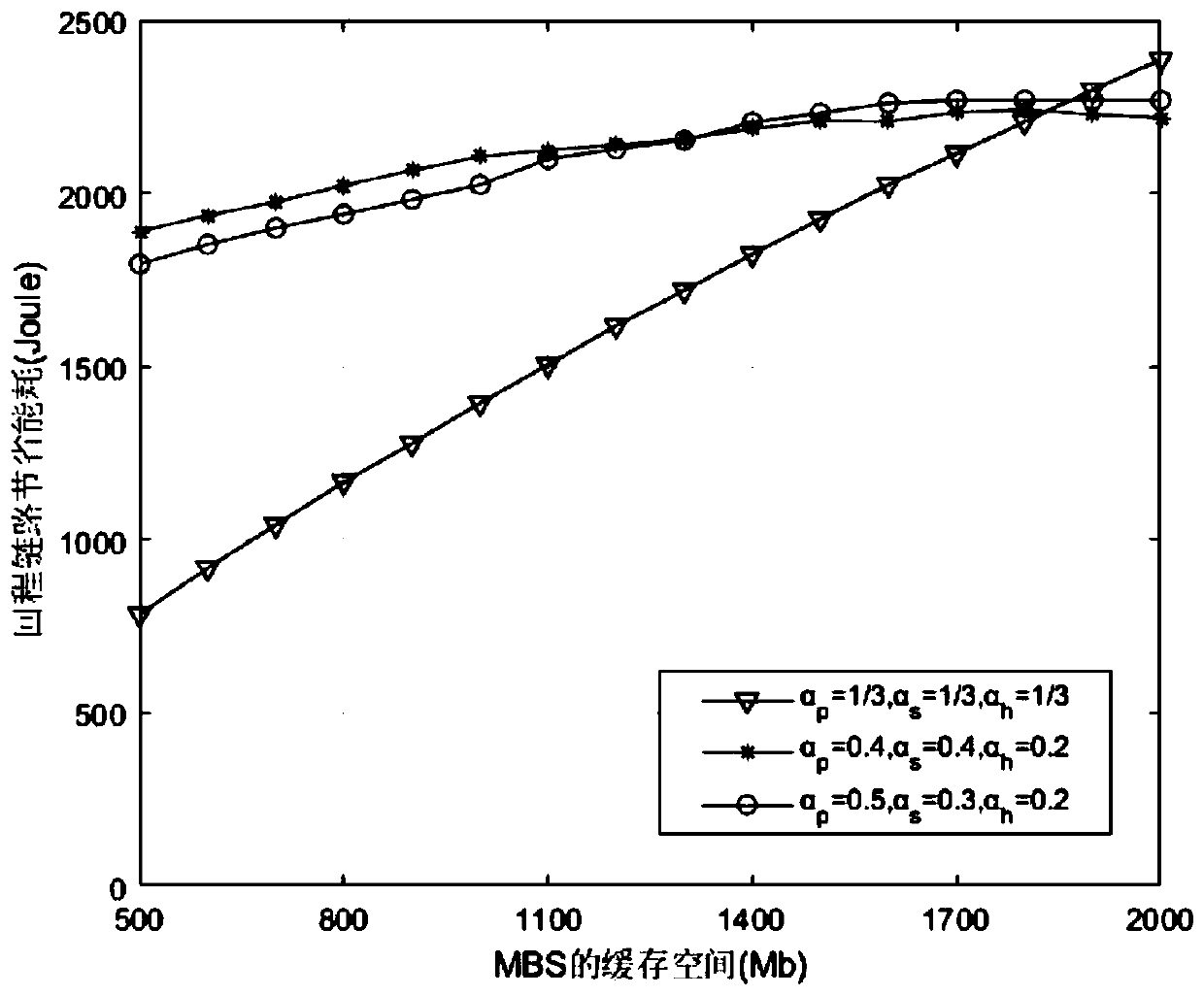
The invention discloses an online collaborative caching method based on optimized energy efficiency, which belongs to the technical field of communication and comprises the following steps of firstly,establishing a double-layer heterogeneous ultra-dense network scene comprising a content server CP, a macro base station MBS, a small base station SBS and user UE; aiming at the new content l to becached, enabling an MBS to calculate a preference factor and a social factor of a certain user UE for the content; further obtaining a preference factor and a social factor of each piece of UE on thecontent, calculating a decision function value by combining the current heat factor of the content l, adding the content l into the cache file set when the decision function value l is greater than orequal to a judgment threshold I0, and meanwhile, calculating each SBS capable of caching the content by MBS; judging whether each SBS needing to cache the content l and the MBS have enough cache space or not, and if so, directly caching the content l; otherwise, deleting from the most recently requested file until the cache space is sufficient to store the content l. According to the invention, the real-time distribution of the cache content can be realized, the energy consumption is saved, and the network cost is saved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Dynamic access method based on energy efficiency and spectral efficiency under ultra-dense network
ActiveCN105357762AImprove spectral efficiencyReduce lossHigh level techniquesWireless communicationScheduling functionFrequency spectrum
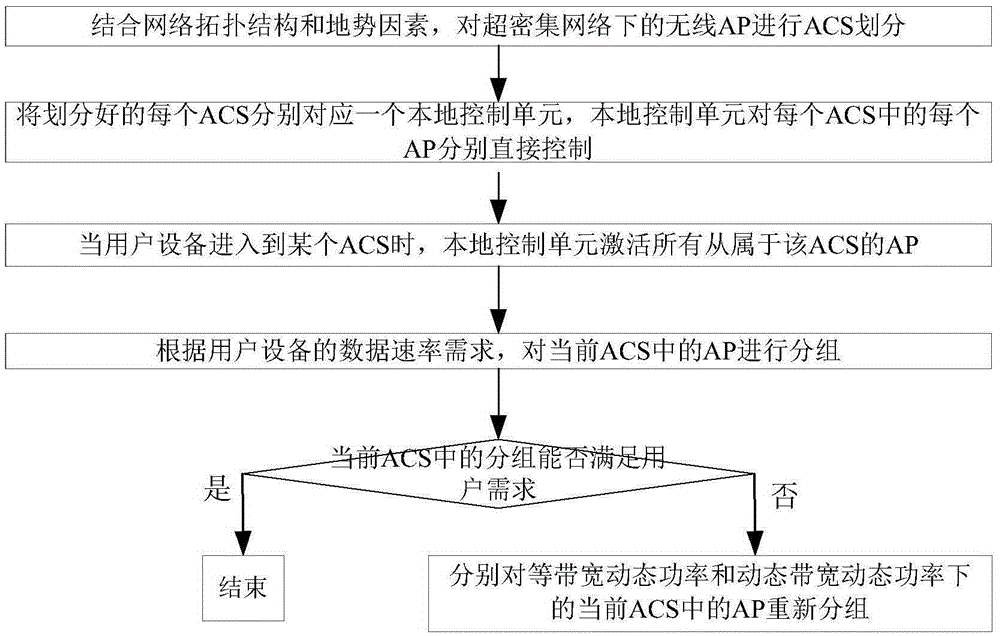
The invention discloses a dynamic access method based on energy efficiency and spectral efficiency under an ultra-dense network. The method comprises the following steps of (1) carrying out ACS (Access Control System) division on wireless APs (Access Point) under the ultra-dense network; (2) enabling each divided ACS to be respectively corresponding to one local control unit; (3) when user equipment enters one ACS, enabling the local control unit to activate all Aps belonging to the ACS; (4) grouping the APs in the current ACS according to the data rate requirement of the user equipment; and (5) respectively comparing a rate C of an activated group and a rate requirement R of a user, and judging whether the current group meets user requirements; if yes, not changing grouping of the current ACS and finishing an algorithm, otherwise regrouping the Aps in the current ACS. The method has the advantages that a dynamic resource scheduling function is realized, the energy loss is reduced along with increase of the business rate requirement and the energy efficiency is improved; through dynamic allocation of bandwidth, the spectral efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Super dense network clustering method based on density improvement K-Means algorithm
InactiveCN107659973AClustering implementationImprove accuracyWireless communicationLocal optimumDensity based
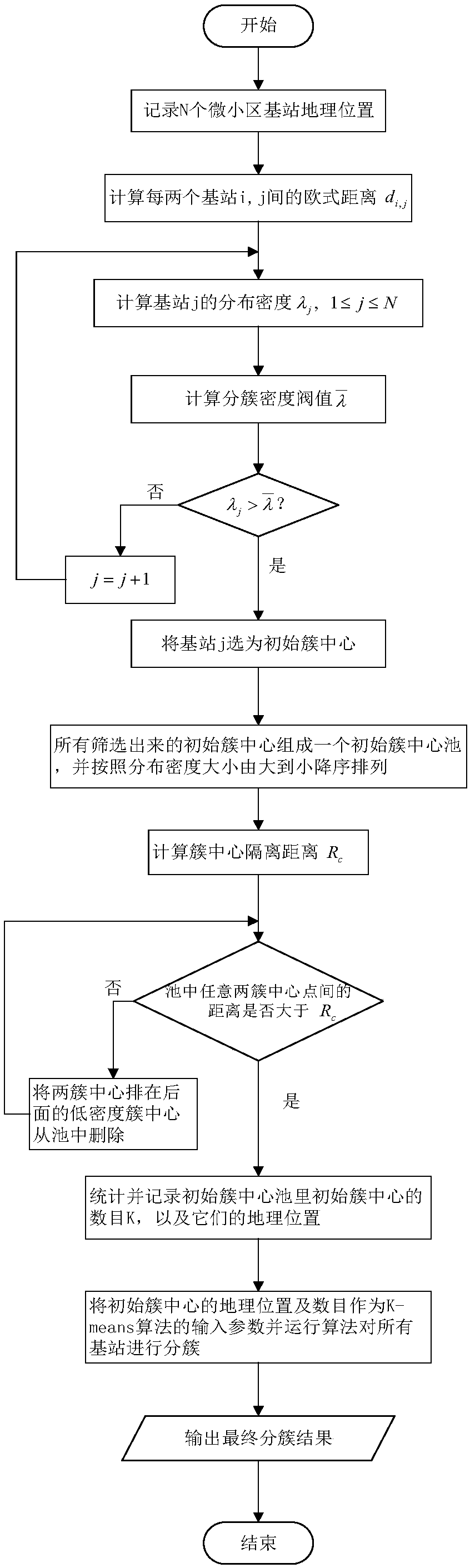
The invention discloses a super dense network clustering method based on a density improvement K-Means algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: firstly calculating distribution density anda clustering density threshold of microcell base stations in a super dense network; selecting the base stations having the distribution density being greater than the clustering density threshold asinitial cluster centers, and forming an initial cluster center pool; screening a final cluster center point by making the distance between any two initial cluster centers in the initial cluster centerpool be greater than a cluster center isolation distance; and using the final cluster center number K and corresponding geographic positions as input parameters of the traditional K-Means, and executing the K-Means algorithm to obtain a clustering result of all base stations in the super dense network. By adoption of the super dense network clustering method, dynamic clustering can be performed according to the change of the network topology, the situation of being caught in a locally optimal solution is avoided by screening the cluster center points, thereby improving the clustering accuracy, meanwhile accelerating the clustering convergence speed, and the super dense network clustering method can be applied to network clustering and base station resource scheduling.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
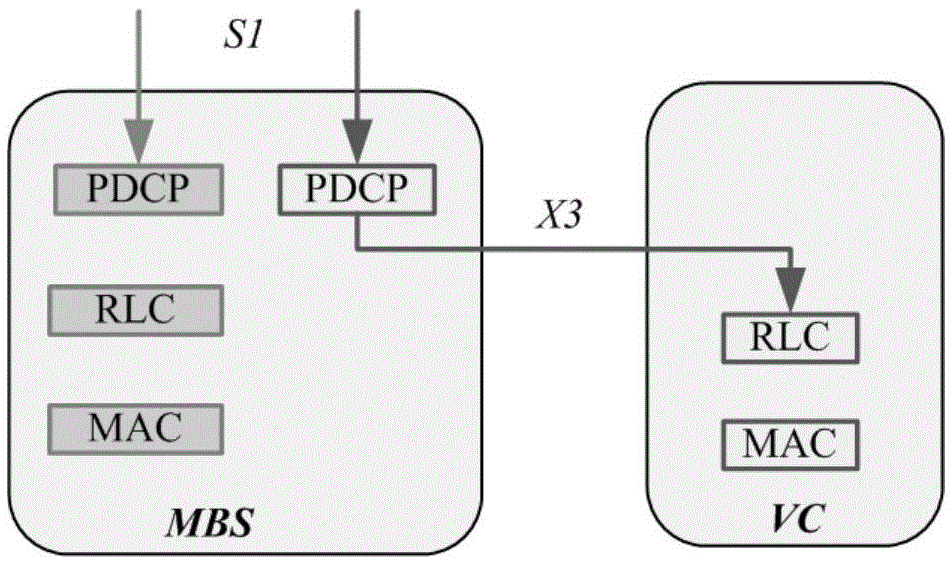
Virtual cell resource allocation method, device and system
ActiveCN105657837AImprove throughputSolve the problem of resource scheduling mechanismSite diversitySignal allocationVirtual cellData transmission
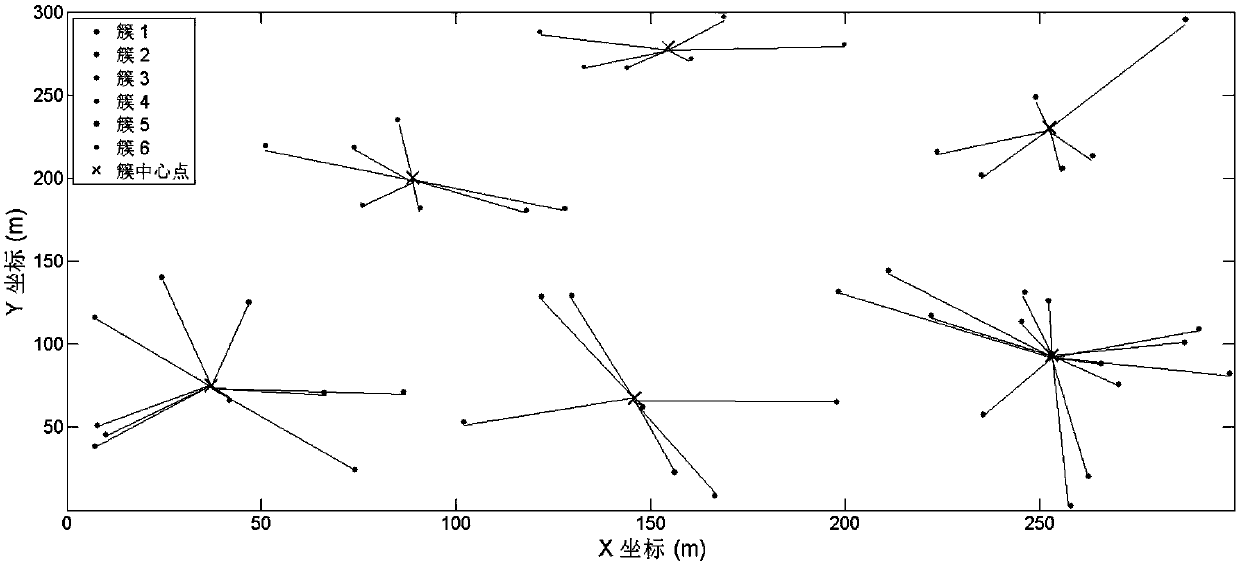
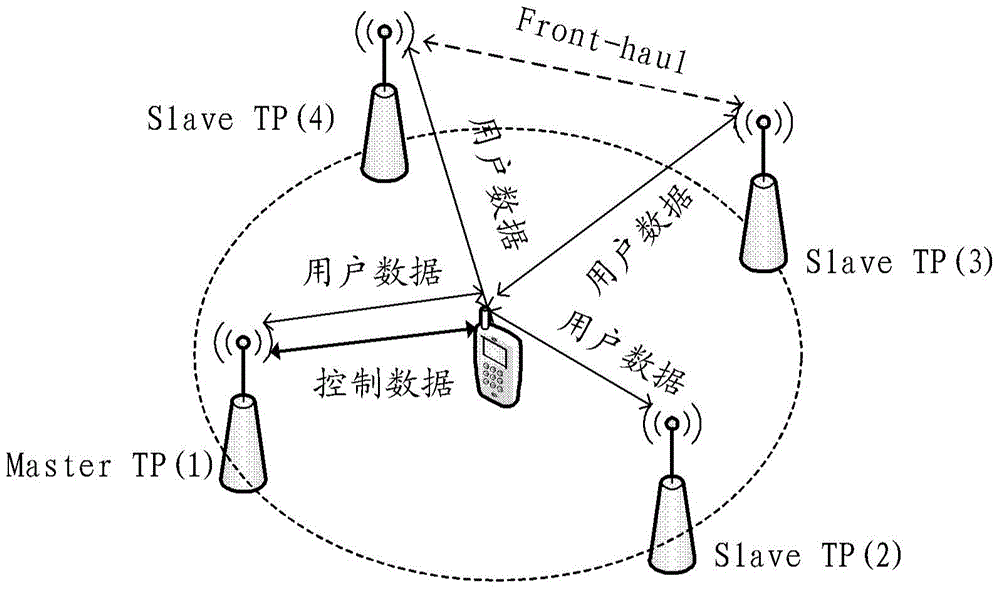
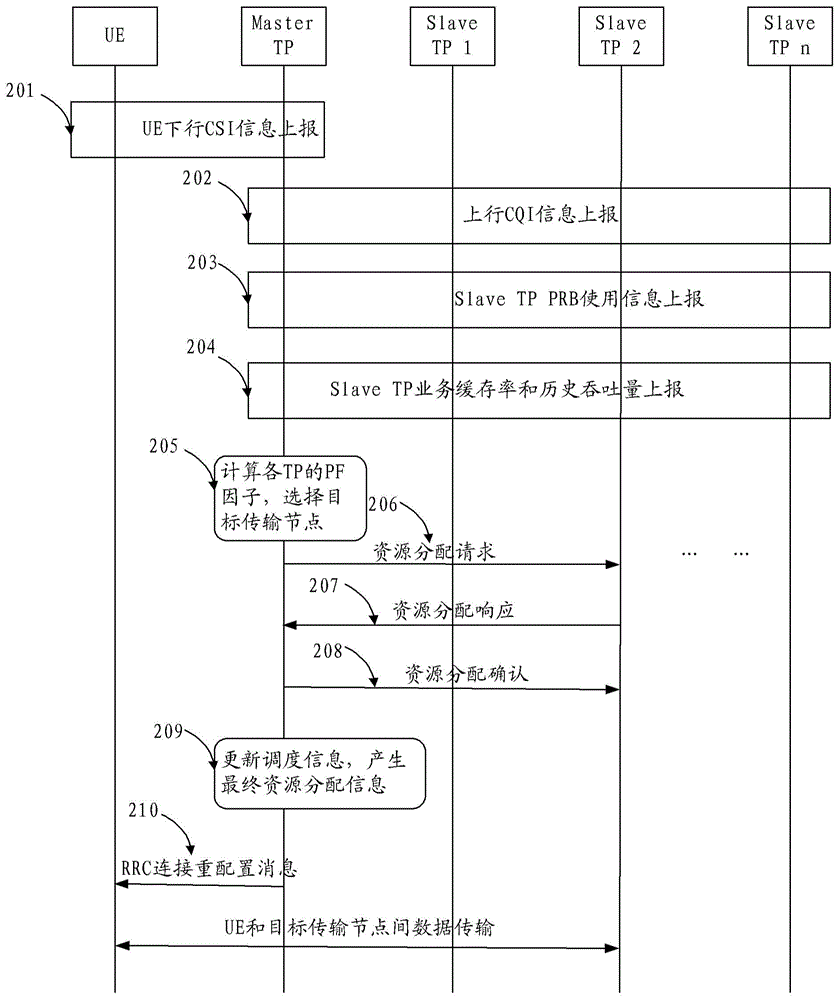
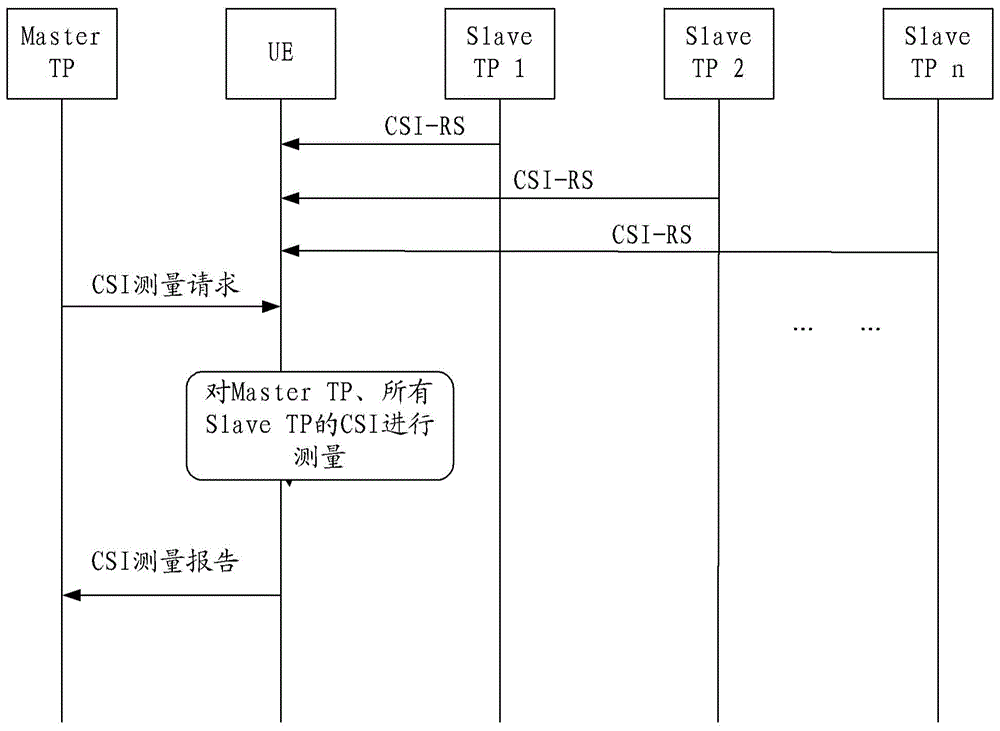
The invention provides a virtual cell resource allocation method, device and system, relates to the field of mobile communication. The method, the device and the system are used for solving the problem of lacking a mechanism for carrying out resource scheduling to the data transmission process in a virtual cell. The method comprises that a master transmission point selects a service transmission point as a target transmission point according to the demands of UE (User Equipment), wherein the master transmission point indicates the UE and the target transmission point to transmit data. The technical solution provided by the invention is applicable to UDN (Ultra-Dense Networks); and the resource negotiation of high user average throughput rate is realized.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com