Dynamic access method based on energy efficiency and spectral efficiency under ultra-dense network
An ultra-dense network and energy-efficient technology, applied in the field of dynamic access based on energy efficiency and spectrum efficiency, can solve problems such as the inability to meet the surge in user traffic
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] The ACS in Embodiment 1 selects 5 APs, including: 1 relay type, 1 pico base station type and 3 home base station types; the ACS in embodiment 2 selects 5 APs that are all home base station types.
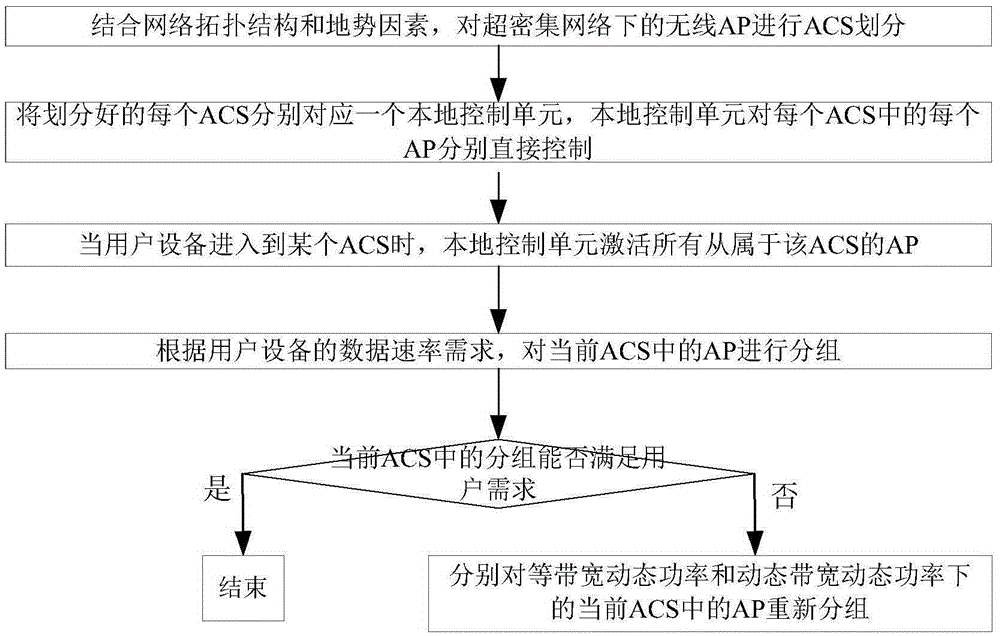
[0063] Step 2, each divided ACS corresponds to a local control unit, and the local control unit directly controls each AP in each ACS;
[0064] The local control unit selects relay stations, each relay station corresponds to an ACS, and directly controls each AP in the ACS.
[0065] Step 3: When the user equipment enters a certain ACS, the local control unit activates all APs subordinate to the ACS. The ACS entered by the user equipment is set as the current ACS;
[0066] Step 4: Group the APs in the current ACS according to the data rate requirement of the user equipment.
[0067] Grouping must be able to provide services that meet user needs, rather than guaranteeing user needs as much as possible. If the AP does not provide services in the current ACS, the local control...
Embodiment 2
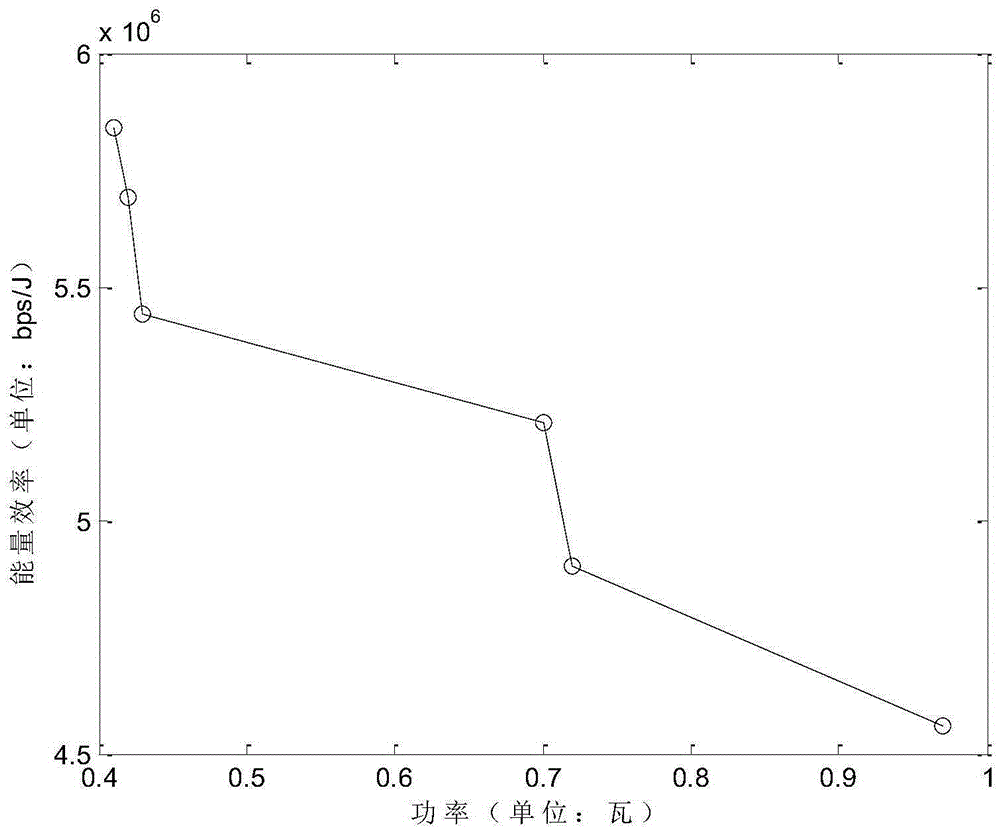
[0119] Energy efficiency at constant bandwidth dynamic power:
[0120] One of the three unified AP types, all of which are home base station types. AP cooperation provides users with a rate that meets their business needs, and the maximum transmission power is limited to 0.1 watts. The grouping results including power allocation and AP selection are shown in the following formula:
[0121] x 21 ={1,1,1,1,1,0.07,0.08,0.05,0.02,0.08}
[0122] x 22 ={1,0,1,1,1,0.08,0.09,0.03,0.05,0.03}
[0123] x 23 ={1,1,1,1,1,0.002,0.07,0.08,0.01,0.05}
[0124] x 24 ={1,1,1,1,0,0.03,0.05,0.03,0.05,0.06}
[0125] x 25 ={1,1,1,1,1,0.01,0.003,0.02,0.07,0.002}
[0126] x 26 ={0,1,1,1,1,0.08,0.07,0.073,0.05,0.03}
[0127] According to the results, the energy efficiency diagram drawn as Figure 4 As shown, it can be concluded from the results that under the same simulation parameters, the active group rate C provided to users in this scenario is almost the same as that of the above-mentio...
Embodiment 3
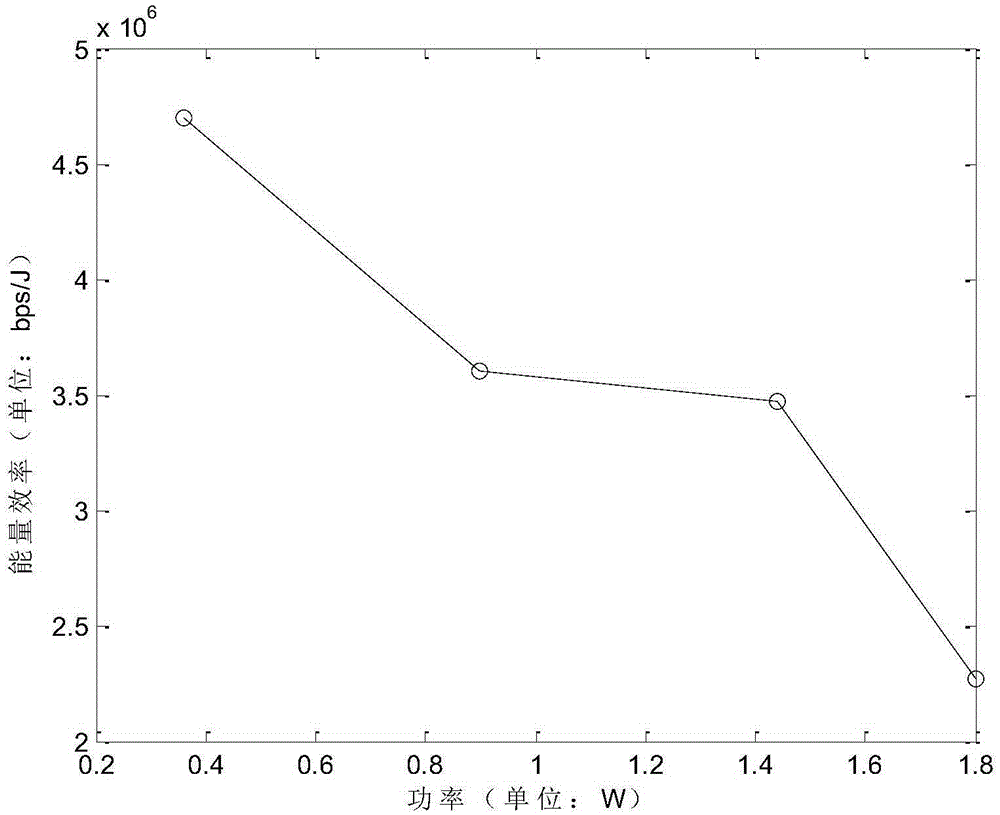
[0136] 5 APs are selected for mixed networking. The AP types are 1 relay type, 1 pico base station type and 3 home base station types. The 3 types of APs provide services for users in a cooperative manner; realize the power and bandwidth of APs joint resource allocation; the service data rate requirement is R=5×10 8 bps
[0137] The dynamic power and dynamic bandwidth allocation under mixed AP types are shown in Table 4:
[0138] Table 4
[0139] AP status
1
1
1
1
1
AP power (W)
0.06
0.3
0.04
0.07
0.03
AP Bandwidth (MHz)
28.2
15.1
29.5
29.7
18.2
[0140] AP status
1
1
1
1
1
AP power (W)
0.5
0.16
0.02
0.02
0.08
AP Bandwidth (MHz)
6.01
28.1
33.3
15.3
27.2
AP status
1
1
1
1
1
AP power (W)
0.36
0.46
0.06
0.09
0.03
AP Bandwidth (MHz)
20.9
27....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com