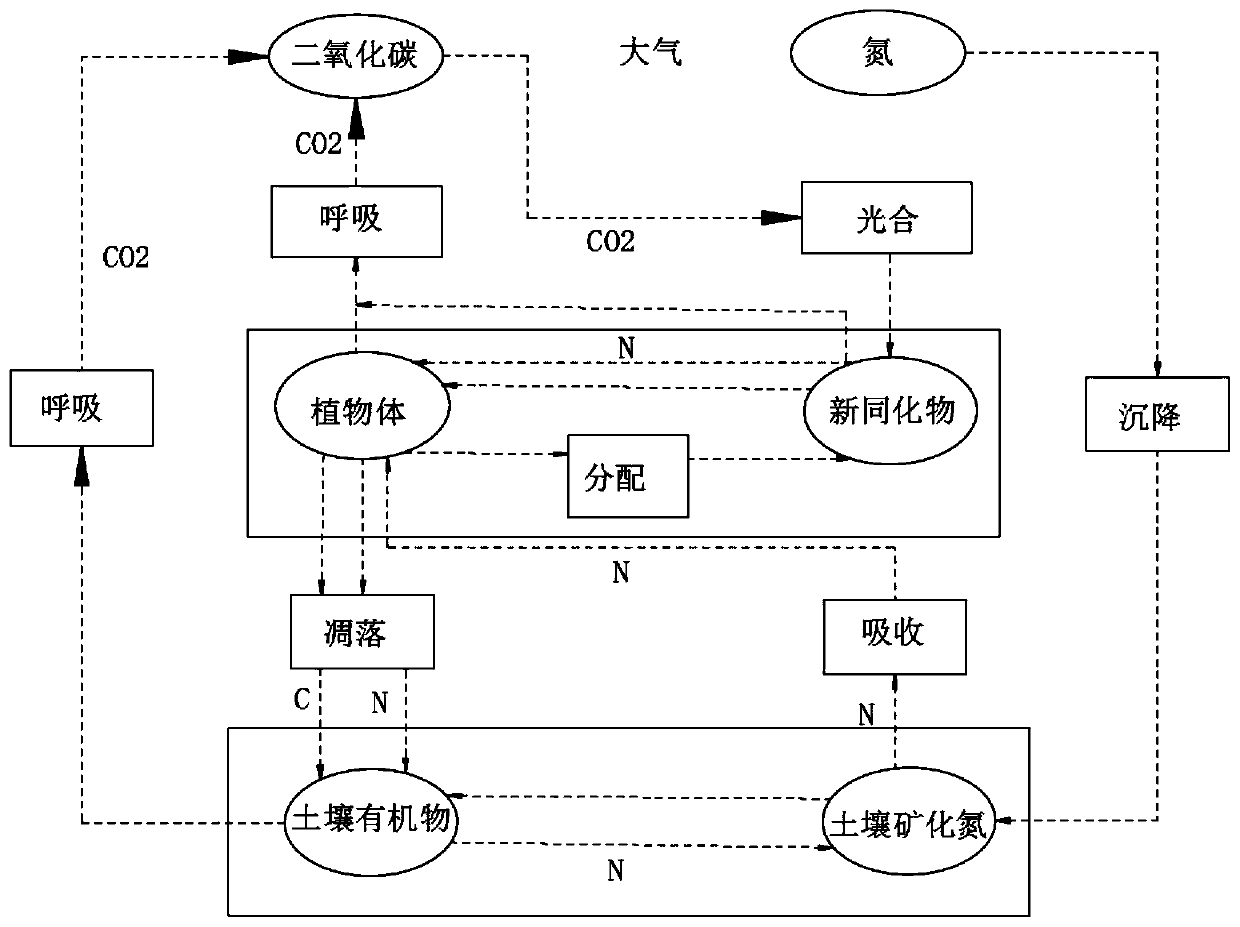
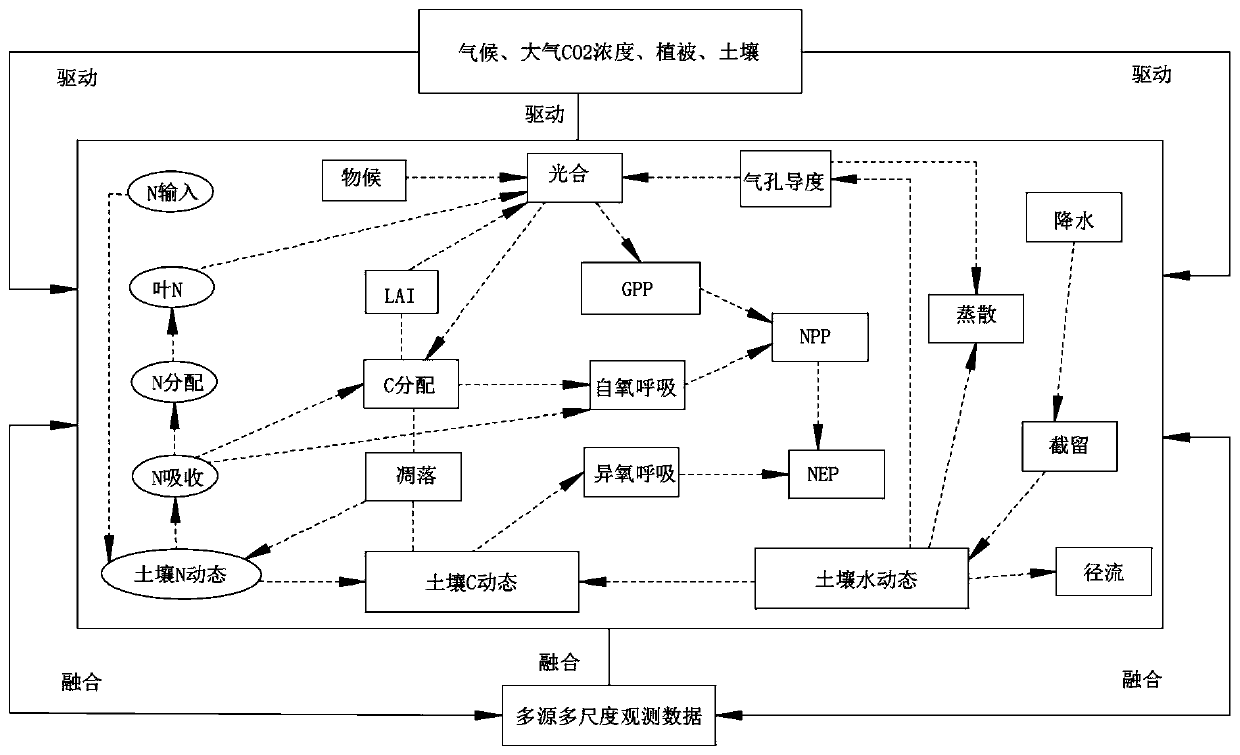
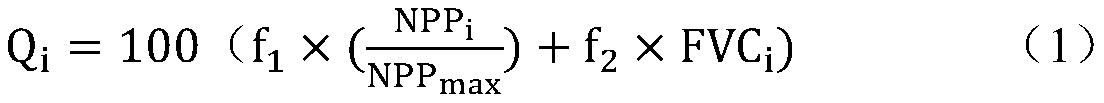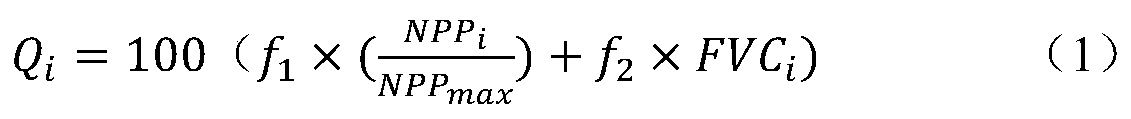Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Terrestrial ecosystem" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
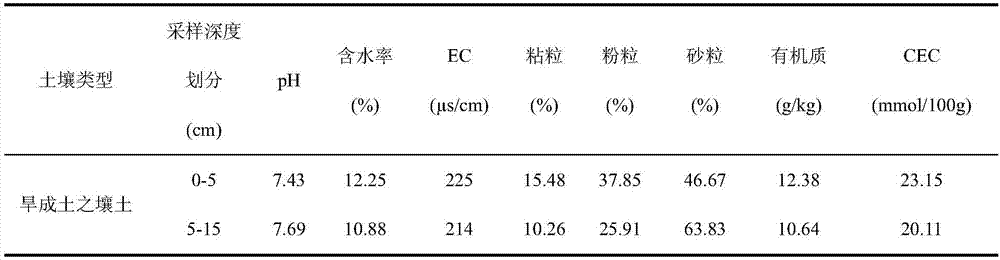
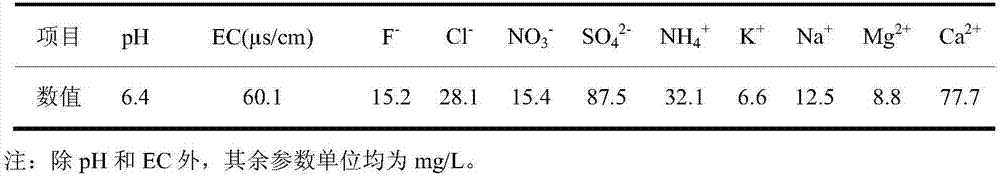
A terrestrial ecosystem is a type of ecosystem found only on landforms. Seven primary terrestrial ecosystems exist: tundra, tuforest, tropical rain forest, grassland, deserts. A community of organisms and their environment that occurs on the land masses of continents and islands, terrestrial ecosystems are distinguished from aquatic ecosystems by the lower availability of water and the consequent importance of water as a limiting factor. Terrestrial ecosystems are characterized by greater temperature fluctuations on both a diurnal and seasonal basis that occur in aquatic ecosystems in similar climates. The availability of light is greater in terrestrial ecosystems than in aquatic ecosystems because the atmosphere is more transparent inland than in water. Gases are more available in terrestrial ecosystems than in aquatic ecosystems. Those gases include carbon dioxide that serves as a substrate for photosynthesis, oxygen that serves as a substrate in aerobic respiration, and nitrogen that serves as a substrate for nitrogen fixation. Terrestrial environments are segmented into a subterranean portion from which most water and ions are obtained, and an atmospheric portion from which gases are obtained and where the physical energy of light is transformed into the organic energy of carbon-carbon bonds through the process of photosynthesis.
Ecotype prefabricated building bock bank revetment
InactiveCN102322040APromote growthPromote reproductionBreakwatersQuaysAquatic ecosystemWater quality
The invention discloses an ecotype prefabricated building bock bank revetment. The upper part is built by dryly laying plant type cavity building blocks, and the lower part is built by dryly laying fish nest type cavity building blocks; the plant type cavity building blocks are built into a stepped bank revetment and are provided with top-to-bottom cavities; the cavities of the plant type cavity building blocks are filled with an earth material in which plants are planted; the fish nest type cavity building blocks are provided with run-through cavities in water flow direction and are provided with holes on the water side; the fish nest type cavity building blocks and the plant type cavity building blocks are made of water-permeable concrete or water-impermeable concrete; and when the cavity building blocks are made of the water-impermeable concrete, the back side is provided with water-permeable holes. The bank revetment has a certain structural strength, is resistant against scour and has a protection effect on the revetment; the cavity structure of the building block meets an ecological design principle and contributes to plant growth and small organism propagation; and the building blocks are water-permeable, are used for communicating an aquatic ecosystem with a land ecosystem and have a certain natural purification effect on water pollution.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Regional terrestrial ecosystem respiratory monitoring method based on remote sensing
InactiveCN103513290AHigh precisionSolve the problem of lack of expressivenessOptical detectionGrowing seasonTime dynamics
The invention provides a regional terrestrial ecosystem respiratory monitoring method based on remote sensing. The monitoring method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining time series satellite remote sensing data within a region; S2, performing remote sensing retrieval to key parameters; S3, quantifying key physiological and ecological parameters of different vegetation forms based on land cover or land utilization data; S4, obtaining meteorological interpolation data of time series; S5, carrying out cloud removal to obtain vegetation growing season curve without noise impact; S6, determining the annual respiratory capacity of the regional terrestrial ecosystem. The method is based on the time series remote sensing data, considers spatial difference of the vegetation form, determines the ecosystem respiratory algorithm within the region, solves the problem that the regional terrestrial ecosystem respiratory monitoring only relies on meteorological data but is insufficient to express heterogeneous information of the land cover within large scale, improves the precision of regional scale ecosystem respiratory estimation, and accurately and quantitatively describes temporal dynamics of the respiration in different ecosystems.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Online monitoring equipment for soil carbon flux
PendingCN109212167AEasy to controlImprove efficiencyEarth material testingThe InternetData acquisition
The invention relates to online monitoring equipment for soil carbon flux. The online monitoring equipment comprises a terminal monitoring device and a monitor, wherein the terminal monitoring devicecomprises a base with a monitoring hole, an opaque cover body, a first driving mechanism, a transparent cover body and a second driving mechanism; the opaque cover body and the transparent cover bodyare provided with monitoring sensor interfaces respectively; the monitor comprises a data acquisition module, a data processing unit and a wireless communication module; the monitoring sensor of the data acquisition module is connected to the interface of the monitoring sensor; the data processing unit is connected with the data acquisition module, the wireless communication module and the first and second driving mechanisms respectively; and the wireless communication module communicates with the Internet. The online monitoring equipment for soil carbon flux can be used for monitoring soil respiration under illumination and no illumination, which is beneficial to further study the relationship between illumination and soil respiration, and has important significance for promoting the study of carbon flux of a terrestrial ecosystem. Through adoption of the online monitoring equipment, remote online monitoring can be realized; manpower is saved; and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
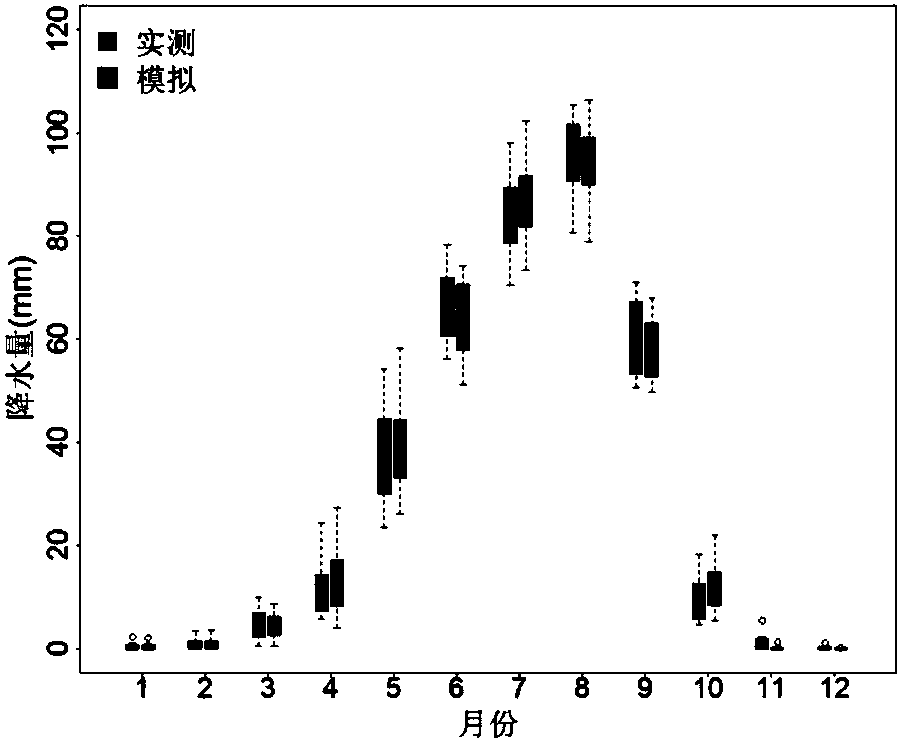
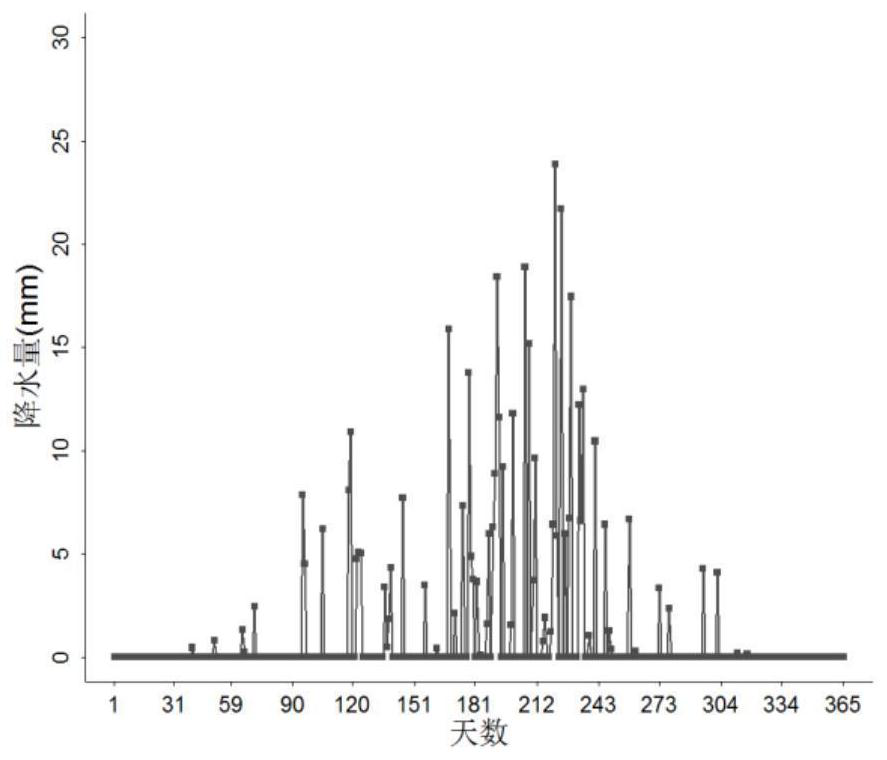
Day time scale-based rainfall generator
ActiveCN108595814ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHydrometryAtmospheric sciences
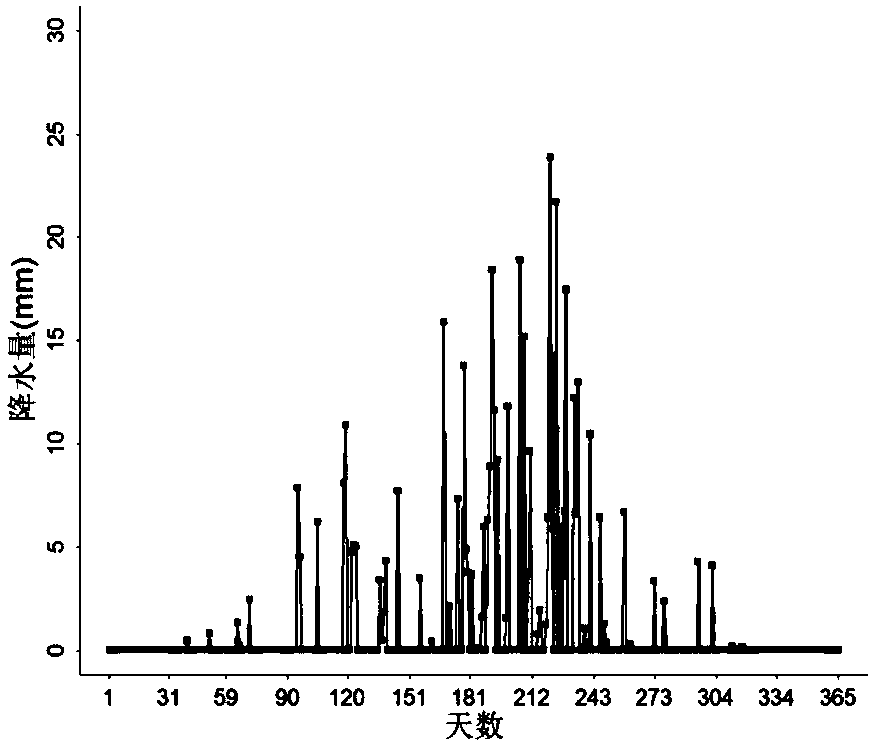
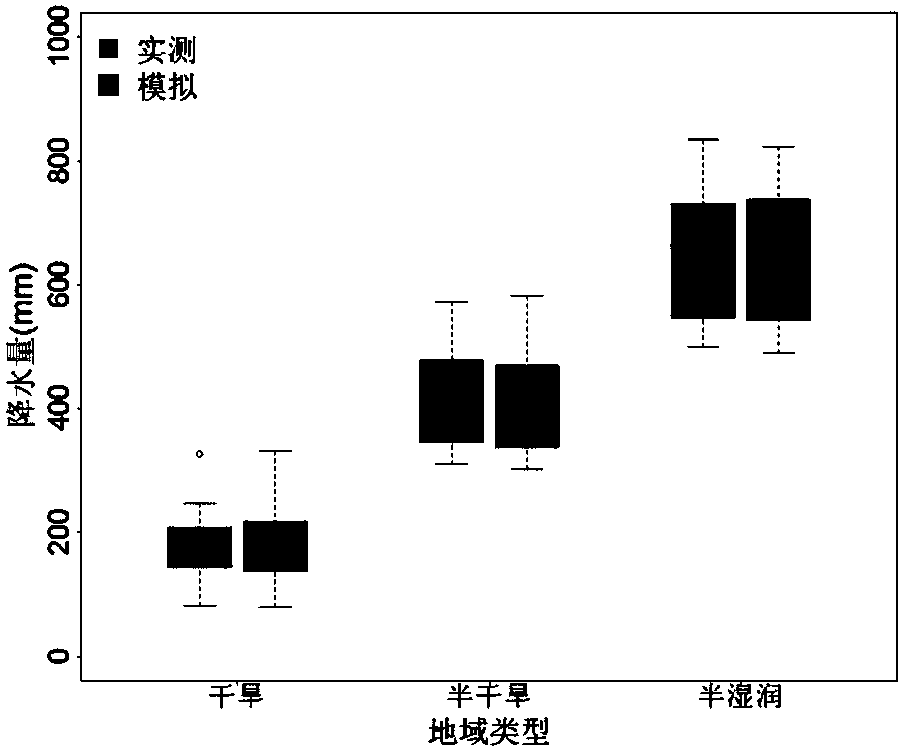
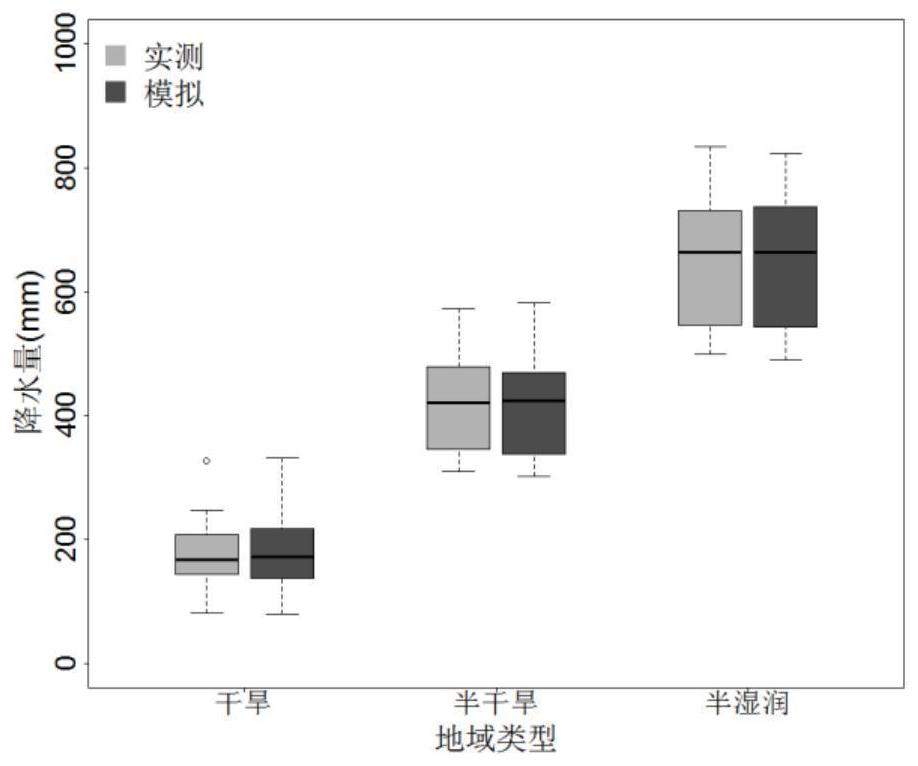
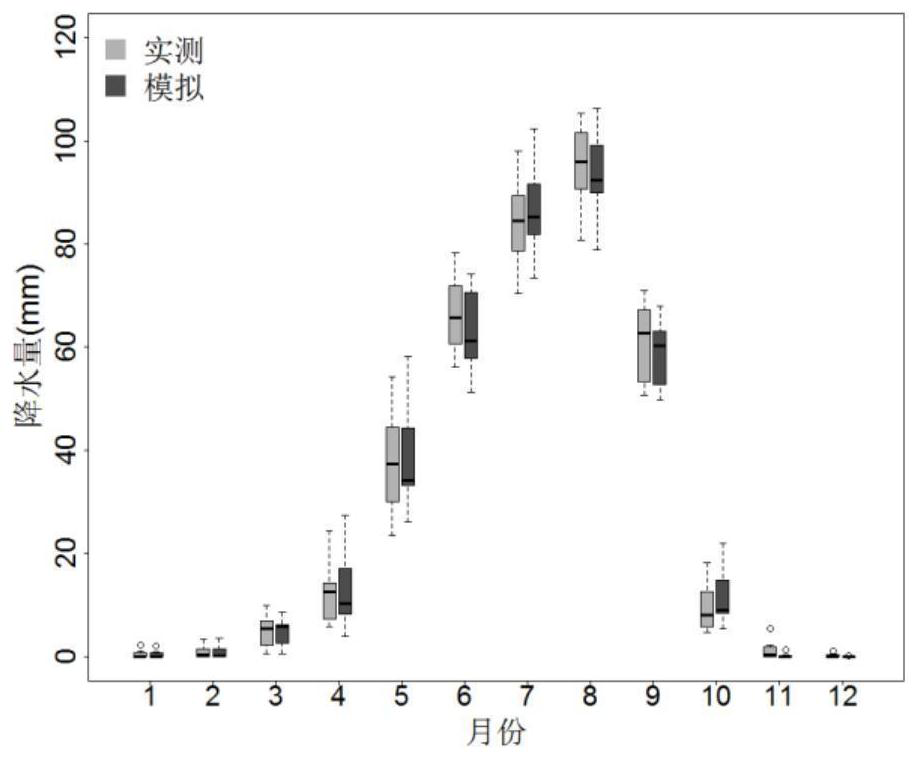
Aiming at the problems that terrestrial ecosystems are relatively short in historical period rainfall record data of partial regions and large in data loss of a plurality of years, the invention discloses a rainfall generator taking days as time scales. The generator inputs rainfall data, measured on the basis of a target region, of each year, each month and each day in a long term. At first, a frequency distribution of a rainfall precipitation of each month, average rainfall precipitations of each month and each day, maximum rainfall precipitations of each month and each day and an annual number of rainfall days is determined; feature parameters of distribution curves are extracted; an index equation is constructed to simulate and generate daily rainfall precipitations; and the daily rainfall precipitations are accumulated to obtain monthly rainfall precipitations and annual rainfall precipitations. Simulated time sequence data is compared and verified with measured data on the time scales of year and month. After the verification, the rainfall generator considers the distribution of extreme rainfall events, so that the rainfall generator can better reflect the laws of rainfall distributions under natural conditions. The rainfall generator is beneficial for assessing the influences, on hydrologic cycle of the terrestrial ecosystems, of rainfalls and predicting the ecological effects of climate changes.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
In-situ monitoring method for litter decomposing soluble nutrient release amount
InactiveCN101477091AEasy to operateAccurate measurementComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationSample plotLitter
The invention discloses an in situ monitoring method of the release amount of dissoluble nutrients in decomposed litters. The in situ monitoring method comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting resin granules or resin membranes as ion exchange resin, and making resin granules or resin membranes into a resin bag; then, burying the resin bag under the litters on the surface of a sample plot and taking the resin bag after a period of time to measure adsorbed nutrient amount; and finally, according to the area, adsorbed nutrient amount and field burying time of the resin bag, calculating the content of dissoluble nutrients released by decomposed litters inside sample plot per unit area within the period of time. The in situ monitoring method has simple operation and can realize actual, accurate and dynamic monitoring of the release amount of dissoluble nutrients in decomposed litters on ground surface under natural conditions; moreover, the method is suitable for measuring the content of nutrient elements existing in any terrestrial ecosystem in the form of anion and cation and released into soil by decomposed litters on ground surface.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Monitoring device for researching relation between illumination and soil carbon flux
The invention relates to a monitoring device for researching a relation between illumination and a soil carbon flux. The monitoring device comprises a base; a monitoring hole is formed in the middle part of the base; a lighttight cover body and a light-transmitting cover body are respectively hinged to positions, located on two sides of the monitoring hole, on the base; the lighttight cover body is driven by a first driving mechanism to do turning motion, so as to close or open the monitoring hole; the light-transmitting cover body is driven by a second driving mechanism to do turning motion,so as to close or open the monitoring hole; and interfaces for mounting monitoring sensors are respectively formed in the lighttight cover body and the light-transmitting cover body. The monitoring device disclosed by the invention can be used for monitoring soil respiration related parameters under a natural environment and can be also used for monitoring soil respiration related parameters undera dark environment; two groups of comparative data are acquired, so as to further research the relation between the illumination and the soil respiration favorably; and the monitoring device has an important significance for pushing the research on the carbon flux of a terrestrial ecosystem.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
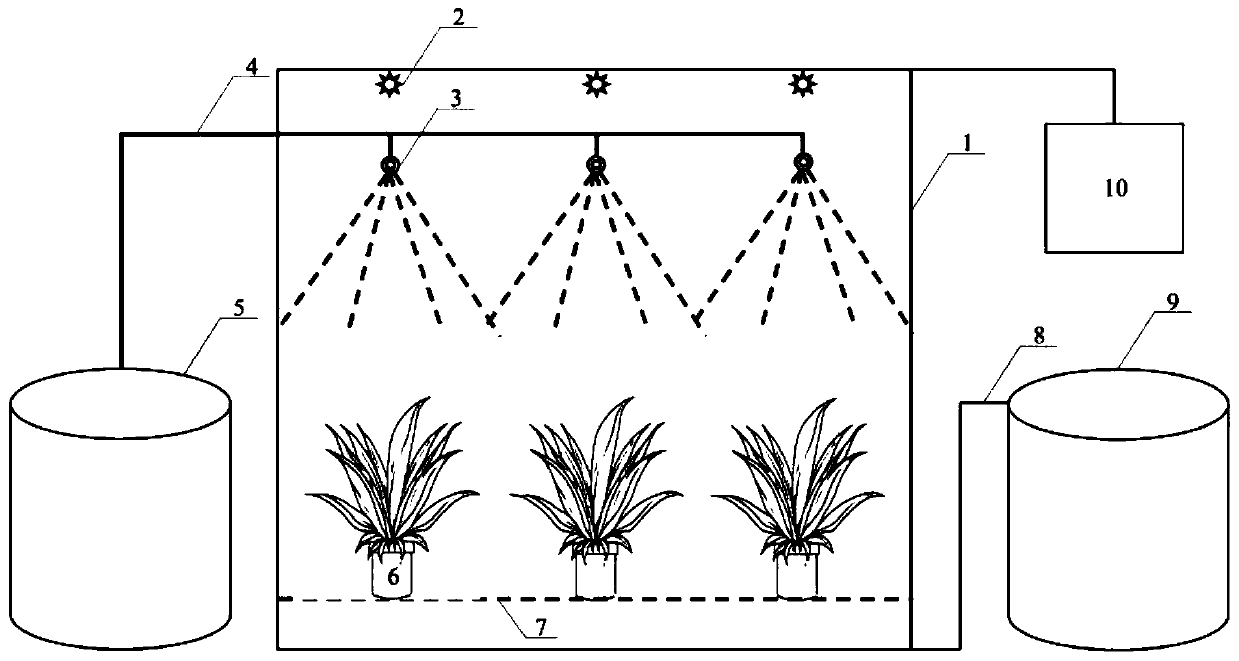
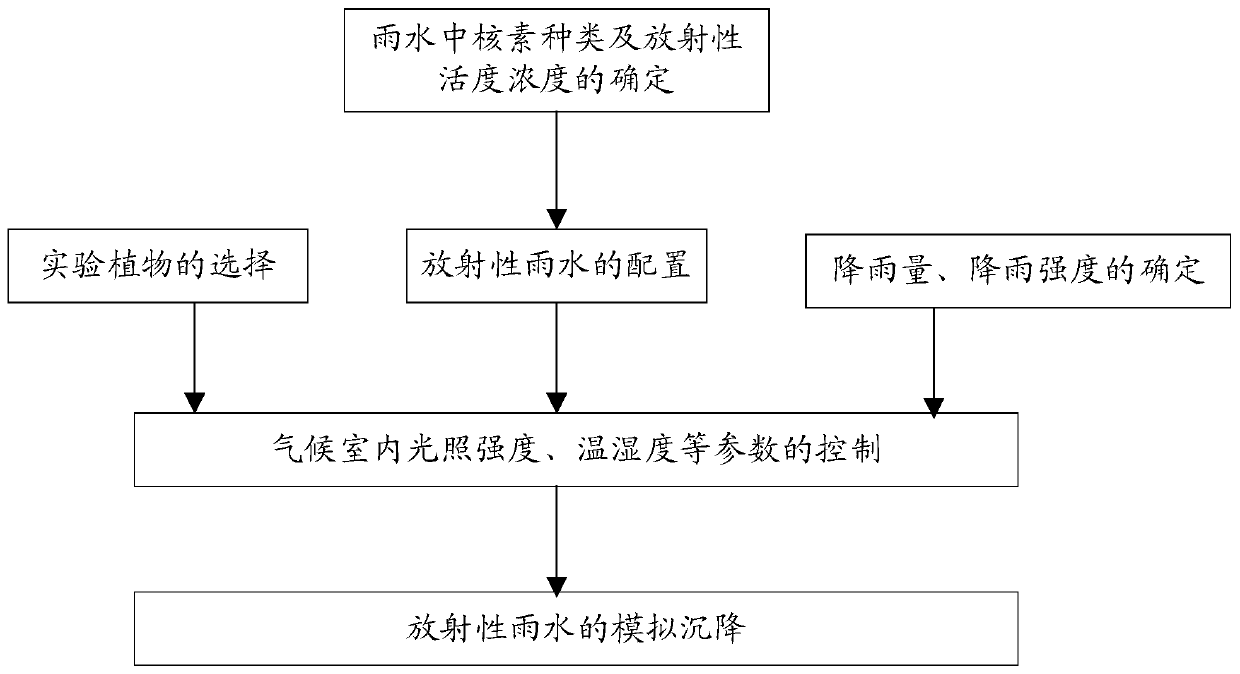
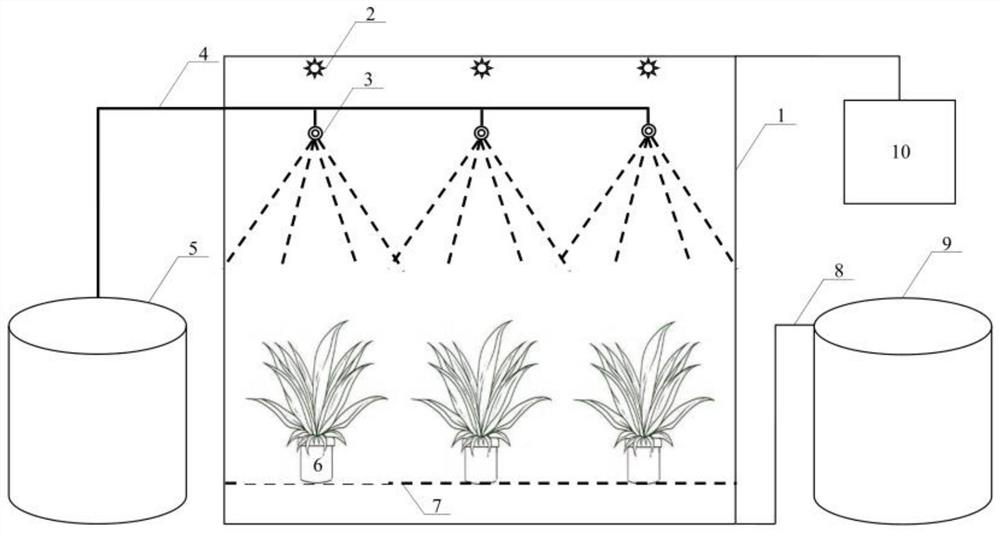
Device for simulating radionuclide wet deposition
The invention provides a device for simulating the radionuclide wet deposition. The device comprises a rainfall artificial climate chamber, a contaminated water tank connected with the rainfall artificial climate chamber through a water distribution pipeline of a rainfall system, and an automatic control and monitoring system electrically connected with the rainfall artificial climate chamber; therainfall artificial climate chamber comprises a rainfall system, a temperature and humidity regulating system, a fresh air system, a light source system and a CO2 concentration regulating system, anda seedbed and experimental plants are placed at the bottom of the rainfall artificial climate chamber. The device simulates and studies the influence process of changes of meteorological factors including temperature, humidity, CO2, light and the like and the complex climatic conditions of plant sites for migration of nuclides in a terrestrial ecosystem.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Vegetation ecological quality index construction method based on vegetation NPP and coverage
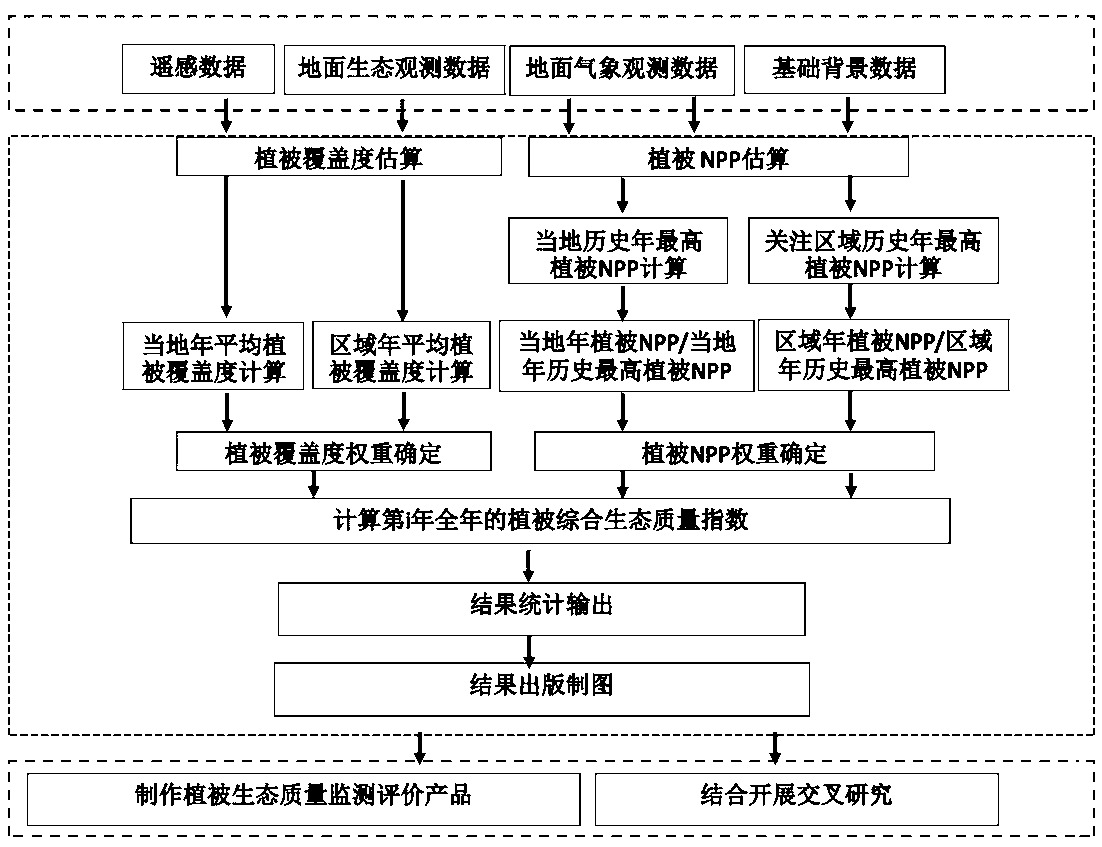
PendingCN110135767AResolved not being able to pass vegetation NPPSolve quality problemsResourcesVegetationEnvironmental resource management
The invention discloses a vegetation ecological quality index construction method based on vegetation NPP and coverage. The method includes: according to the climate adaptability principle of vegetation growth and the importance of ecological service functions, on the basis of calculating vegetation NPP and coverage, calculating an annual vegetation comprehensive ecological quality index of a local or concerned area by weighting the weight; calculating the ratio of the current-year vegetation NPP to the historical highest value; determining the weight of the vegetation NPP and the coverage inthe comprehensive ecological quality index; converting the current-year vegetation NPP is converted from gram carbon / square meter * year to a ratio of relative historical highest values, wherein the value is between 0 and 1; and matching the vegetation coverage with the numerical value of 0-1. The problem of comprehensively and quantitatively calculating the vegetation ecological quality is solved, the method is more objective and comprehensive compared with single use of vegetation NPP or coverage quantitative expression vegetation ecological conditions, the method is suitable for estimationof the vegetation ecological quality of the whole land ecological system, and important technical support is provided for monitoring and evaluating the vegetation ecological quality and developing ecological meteorological services.
Owner:NATIONAL METEOROLOGICAL CENTRE
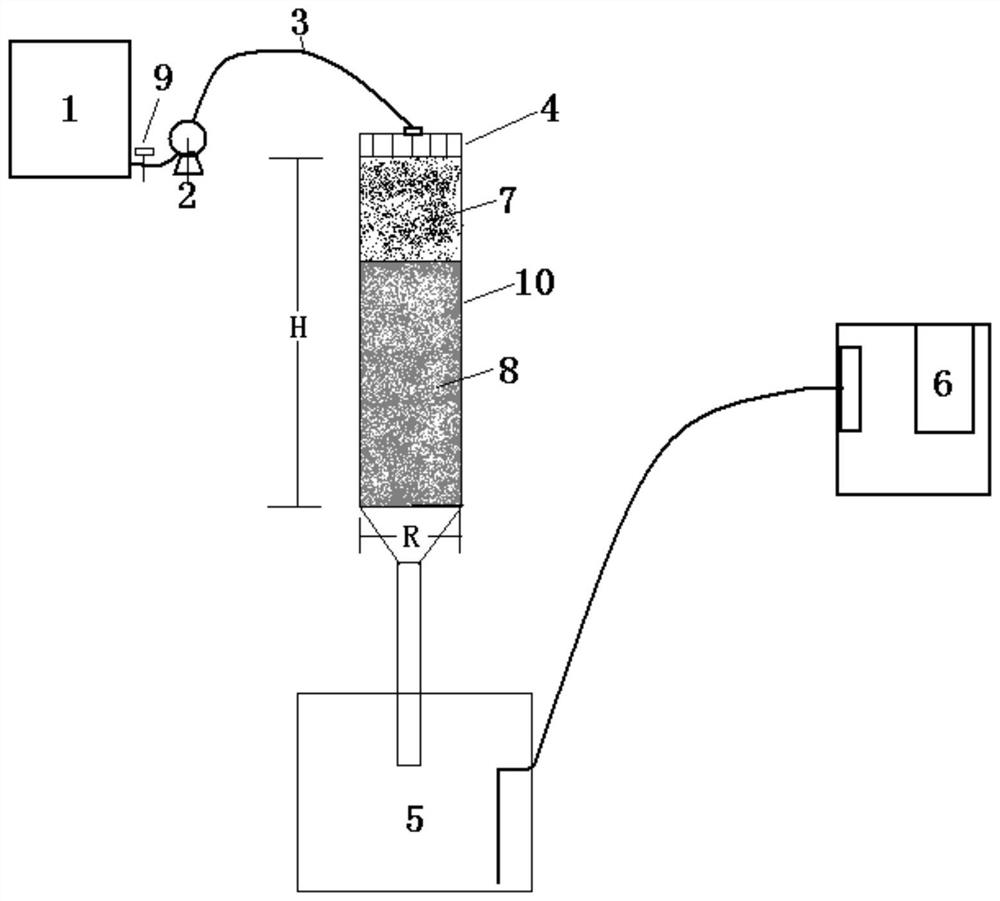
Overground and underground synchronous carbon flux measuring experimental device
ActiveCN110095589AImprove the protective effectGood weather resistanceEarth material testingAgriculture gas emission reductionNutrient solutionCarbon flux
The invention relates to an overground and underground synchronous carbon flux measuring experimental device comprising a monitoring device for studying the soil carbon flux and a transparent cylindrical body for cultivating plants. A partition plate is arranged at the middle part of the transparent cylindrical body and is used for separating a ground portion and a soil portion of the plant in twoseparate chambers. A liquid supply interface for providing a nutrient solution for the plant is further disposed on the side wall of the chamber for accommodating the soil portion of the plant. Through holes through which plants pass are formed in the partition plate. The two ends of the transparent cylindrical body are connected to monitoring holes of the monitoring device respectively. According to the invention, the overground and underground synchronous carbon flux measuring experimental device is used for monitoring parameters related to soil respiration below the surface as well as thecarbon flux variation parameters above the ground to obtain two groups of overground and underground monitoring data, thereby analyzing the soil respiration relationship. The overground and underground synchronous carbon flux measuring experimental device has the great significance in prompting the study on the carbon flux in the terrestrial ecosystem.
Owner:福建师范大学地理研究所
Method for determining dinitrogen monoxide discharging quantity of plants
The invention belongs to the global change- terrestrial ecosystem-greenhouse gas change field, in particular to a method of measuring the amount of nitrous oxide (N2O) discharged by plants. The particular measuring process is that: fresh plant branches and leaves are taken, washed, fragmented and put in a homogenate cup; right-amounted precooling homogenate buffer solution is put in the cup and homogenated. The homogenated solution is put in a non-light tight container and the container is sealed and put under light to be cultured. GC-ECD is used for measuring the volume concentration of the nitrous oxide (N2O). According to the increase of the quality of the nitrous oxide (N2O) in the container gas phase, the volume of the gas phase in the container and the dry weight of plants during the time of culturing, the discharge flux of the nitrous oxide (N2O) of the plants is calculated. The invention solves the problems that the prior enclosed box method is time-consuming, easy to injure plants and can not be used to measure the plants with big size or small discharge amount. The invention is a method of measuring the amount of nitrous oxide(N2O) discharged by plants, is applicable to the plants with different sizes and different discharge amounts and is of simple operation and low cost.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
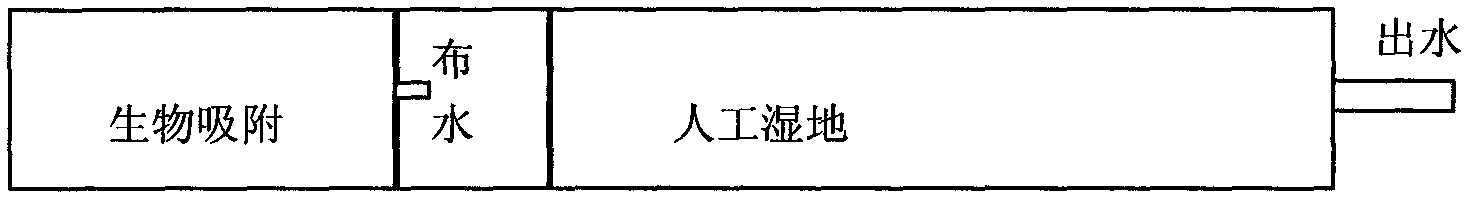
Artificial wetland-biological regeneration integration enhancement denitrogenation and phosphorus removal treatment process
InactiveCN103011487AStrengthen the rapid purification abilityImprove purification effectMultistage water/sewage treatmentConstructed wetlandNitrogen
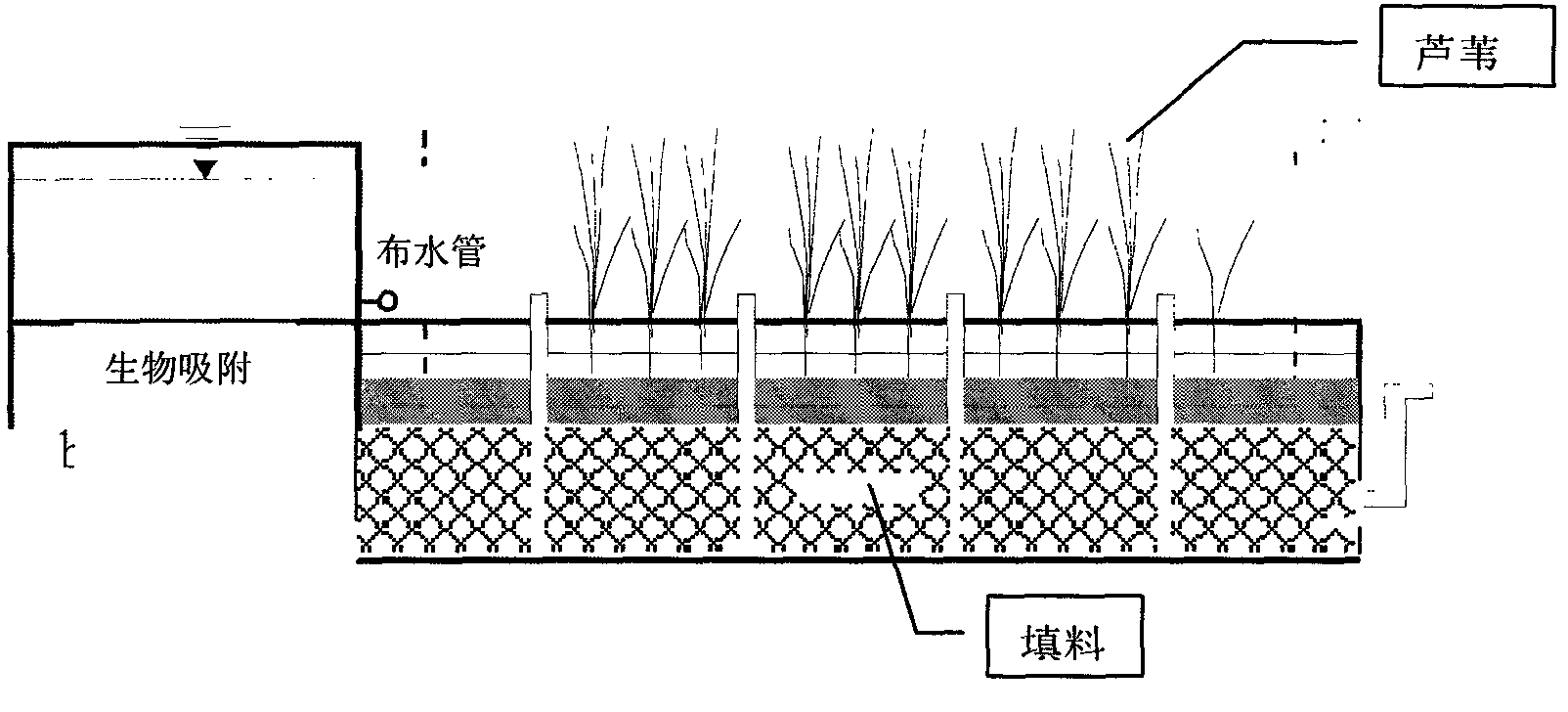
The present invention relates to an artificial wetland-biological regeneration integration enhancement denitrogenation and phosphorus removal treatment process. According to an ecology technology series connection process, plants are introduced into a sewage treatment system, and a multi-layer matrix is introduced to configure a biological adsorption layer to form a microorganism-plant-materialization effect integrated land ecosystem, wherein the system has a self-regulation mechanism and a comprehensive pollutant purification function, harmonization of rapid denitrogenation and phosphorus removal, and ecological purification is achieved, cost is low, and an eco-friendly characteristic is provided.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Research method of biomass distribution characteristics of emblic leafflower fruit bushwood ecosystem
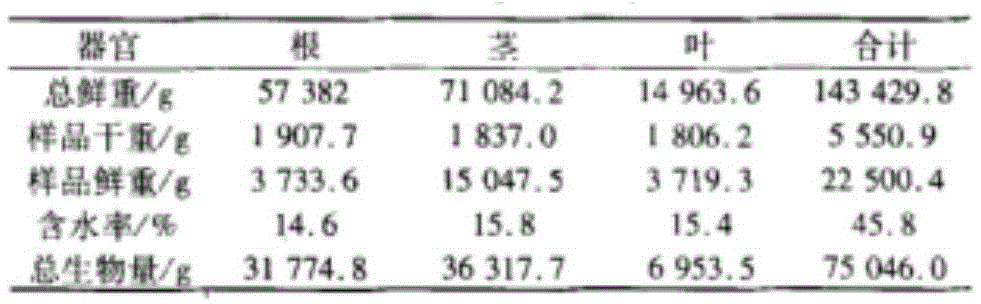
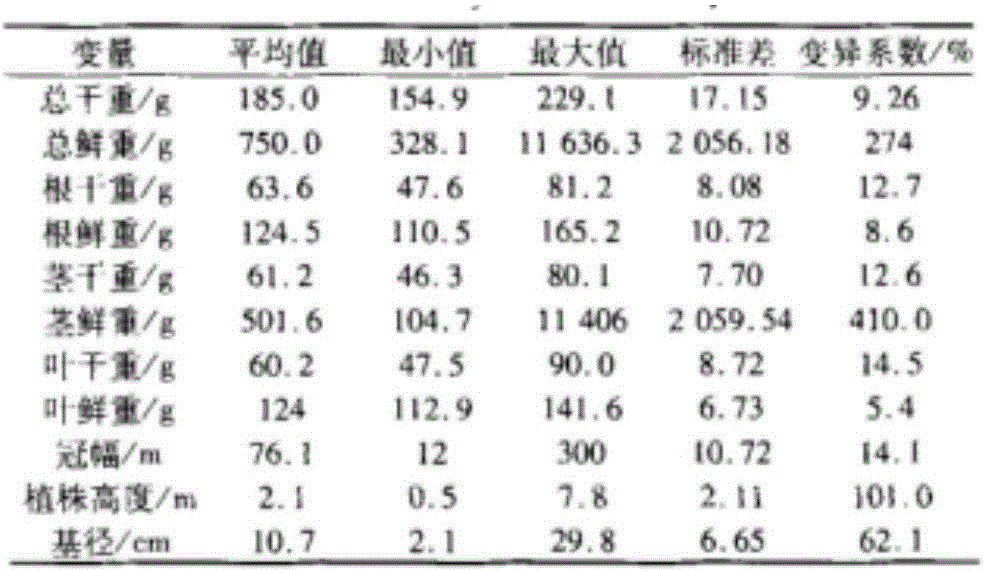
The invention discloses a research method of the biomass distribution characteristics of an emblic leafflower fruit bushwood ecosystem, and relates to the technical field of the biomass distribution research of the ecosystem. The research method comprises the following specific research steps: (1) selecting a proper research area; (2) setting sample plots; (3) processing samples indoor; (4) carrying out data analysis and modeling; (5) obtaining a result, and carrying out analysis on (a) the biomass distribution characteristics of emblic leafflower fruits, (b) different growth parameter characteristics of the emblic leafflower fruits, (c) the biomass distribution characteristics of the emblic leafflower fruits of different branch diameters, (d) the biomass distribution characteristics of the emblic leafflower fruits of different plant heights and (e) the biomass distribution characteristics of the emblic leafflower fruits of different crown breadth areas; and (6) obtaining a conclusion. The research method is of great significance for the understanding of emblic leafflower fruit bushwood in the aspects of the fixation, the consumption, the distribution, the accumulation and the conversion of the substances and the energy of a terrestrial ecosystem and nutrition accumulation of the system and also has a great value in accurately estimating a terrestrial ecosystem carbon pool and carbon exchange.
Owner:SOUTHWEST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Device and method for simulating influence of fire disturbance of surface land ecological system to underground water
ActiveCN107462692AHigh precisionSimple and fast operationEarth material testingContinuous flowEngineering
The invention provides a device and a method for simulating influence of fire disturbance of a surface land ecological system to underground water. The method comprises the following steps of collecting a plurality of soil samples of aridisol by a soil drilling method, and separating obtained undisturbed soil columns into surface layer soil and middle layer soil; after the fire disturbance on the surface layer soil is simulated by a laboratory, sequentially loading the surface layer soil and the middle layer soil into a leaching column according to the order of the undisturbed soil column; using prepared simulated rainwater as a leaching solution, leaching by a continuous flow falling type water intake method, and qualitatively and quantitatively surveying the fine components of the soil leaching water sample. The method has the advantages that the influence of the fire disturbance of the surface land ecological system to the underground water, especially submersible water, can be simulated by a miniature leaching device of the laboratory; the accuracy is higher, the operation is simple and convenient, the cost is low, the controllability is good, the risk to environment is low, the application range is wide, the pertinency is strong, and the method is favorable for evaluating the comprehensive ecological effect of the underground water after the fire disturbance in a fully new view.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Rocky hydro-fluctuation belt floating plate elegant greening method
InactiveCN105706829ASolve the difficult greening problemRich species diversityCultivating equipmentsMarine site engineeringAquatic ecosystemPlankton
The invention relates to a rocky hydro-fluctuation belt floating plate elegant greening method which is used for greening a rocky hydro-fluctuation belt which is periodically exposed out of peripheral submerged land due to seasonal water level fluctuating. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: digging a planting furrow above a high water level line of the rocky hydro-fluctuation belt, arranging an anchor rod, paving chain-type connected floating plates on the rocky surfaces of the rocky hydro-fluctuation belt to a low water level line, and planting large wooden vine plants in the planting furrow; pulling the growth direction of vines of the vine plants to the floating plates by virtue of a manual pulling method, and extending the vines towards the floating plates on the rocky hydro-fluctuation belt so as to ensure that the vines float and grow on the floating plates by depending on the floating plates and the floating plates move up and down constantly along with water level fluctuating of the hydro-fluctuation belt. The exposed rocky hydro-fluctuation belt is greened, favorable biological conjunction of an aquatic ecosystem and a terrestrial ecosystem is realized, inhabiting and proliferation environments for animals and plants such as snails, plankton and amphibians are provided, and the diversity of species in the rocky hydro-fluctuation belt is enriched.
Owner:ZHEJIANG PROVINCE LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE DESIGN CO LTD +2
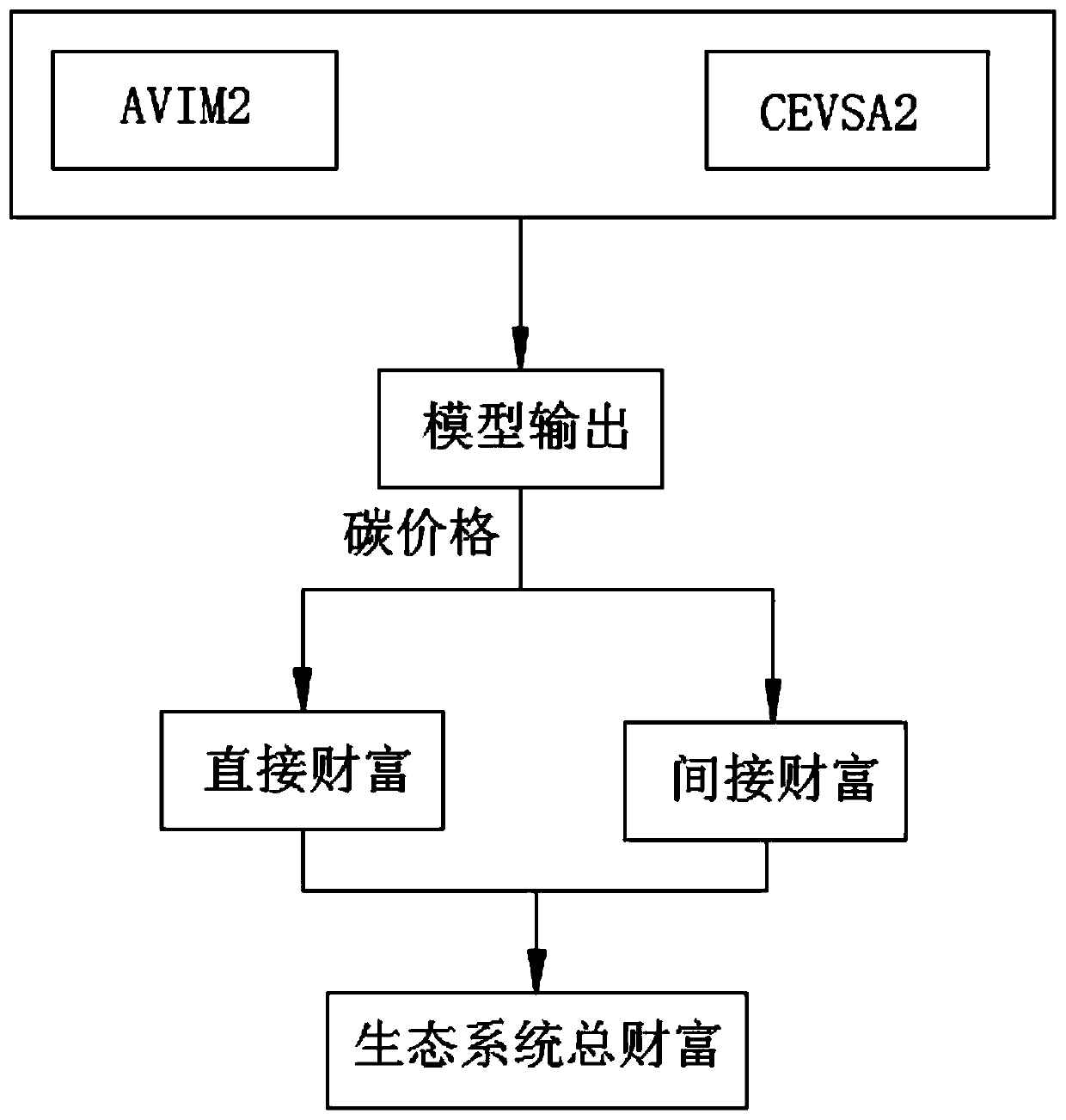
Algorithm for evaluating land ecological wealth
The invention discloses an algorithm for evaluating land ecological wealth. The algorithm comprises the following steps: 1) direct ecological wealth EWDi is calculated, wherein the direct ecological wealth EWDi calculates a product provided by a land ecological system; 2) indirect ecological wealth EWIi is calculated, wherein indirect ecological wealth EWIi is an economic value provided by supportservice, regulation service and culture service of an ecological system; and 3) the land ecological wealth calculates benefits directly and indirectly obtained from the ecosystem function by human beings, and the indirect ecological wealth EWIi and the direct ecological wealth EWDi are added to obtain the total wealth EWi of the ecosystem. The invention provides a quantifiable evaluation index ofthe service value of the land ecosystem, and provides an important tool for ecological benefit evaluation of natural resource and ecological environment auditing, ecological restoration, ecological engineering and major decisions.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS +1
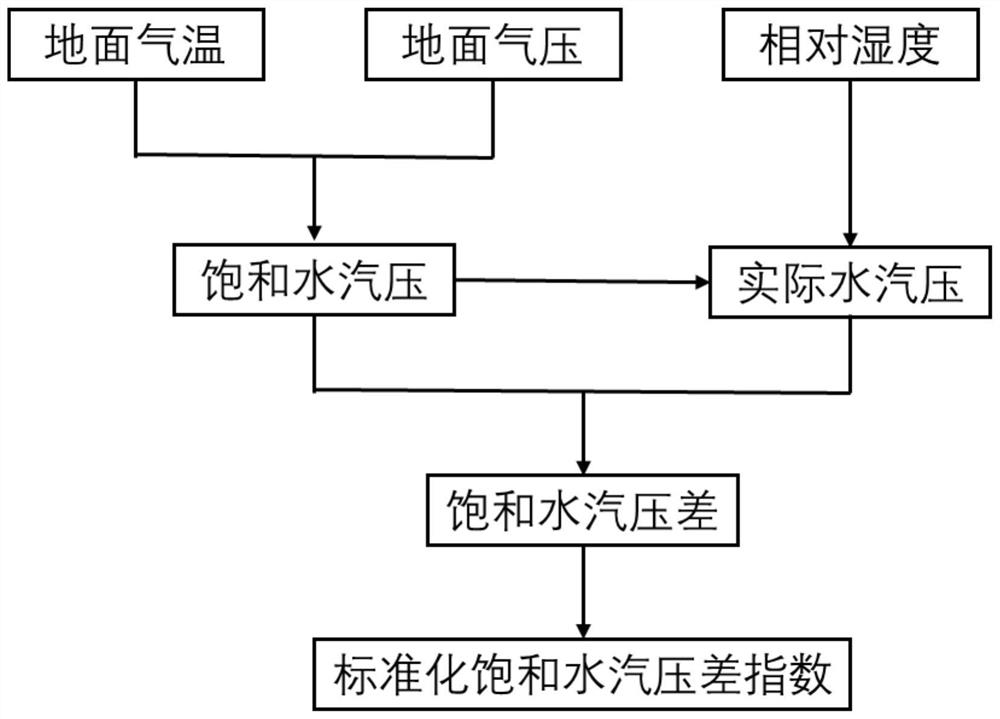
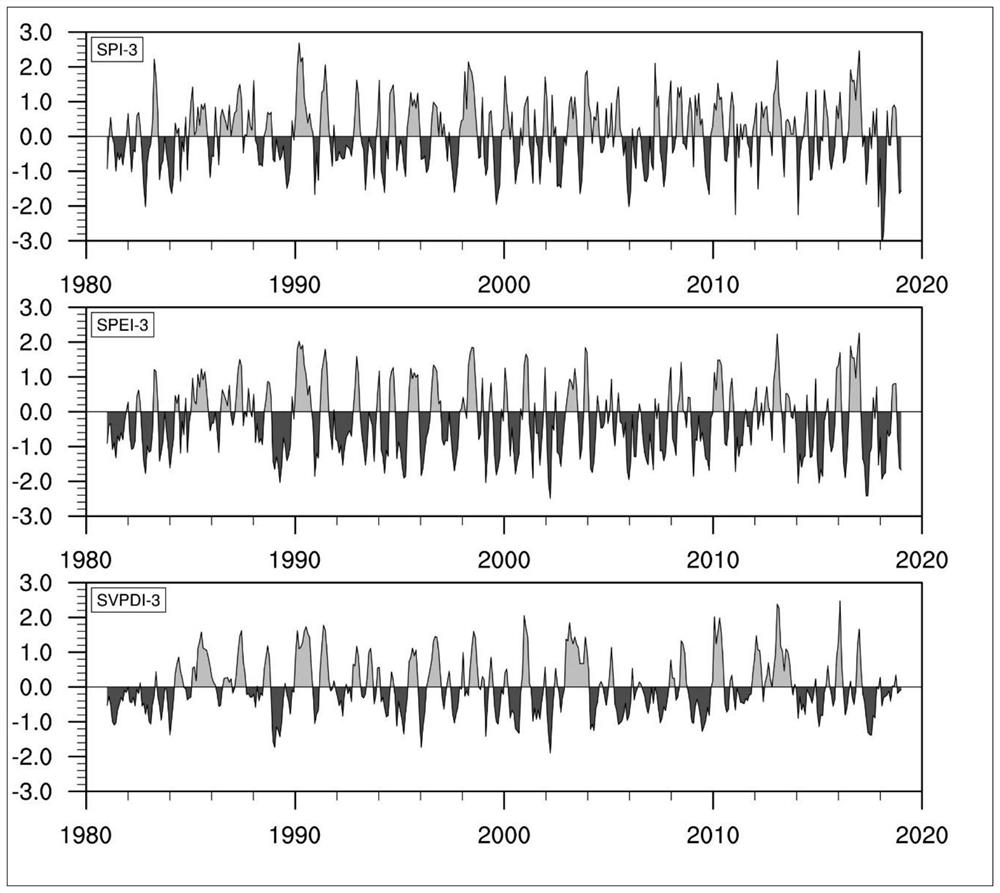
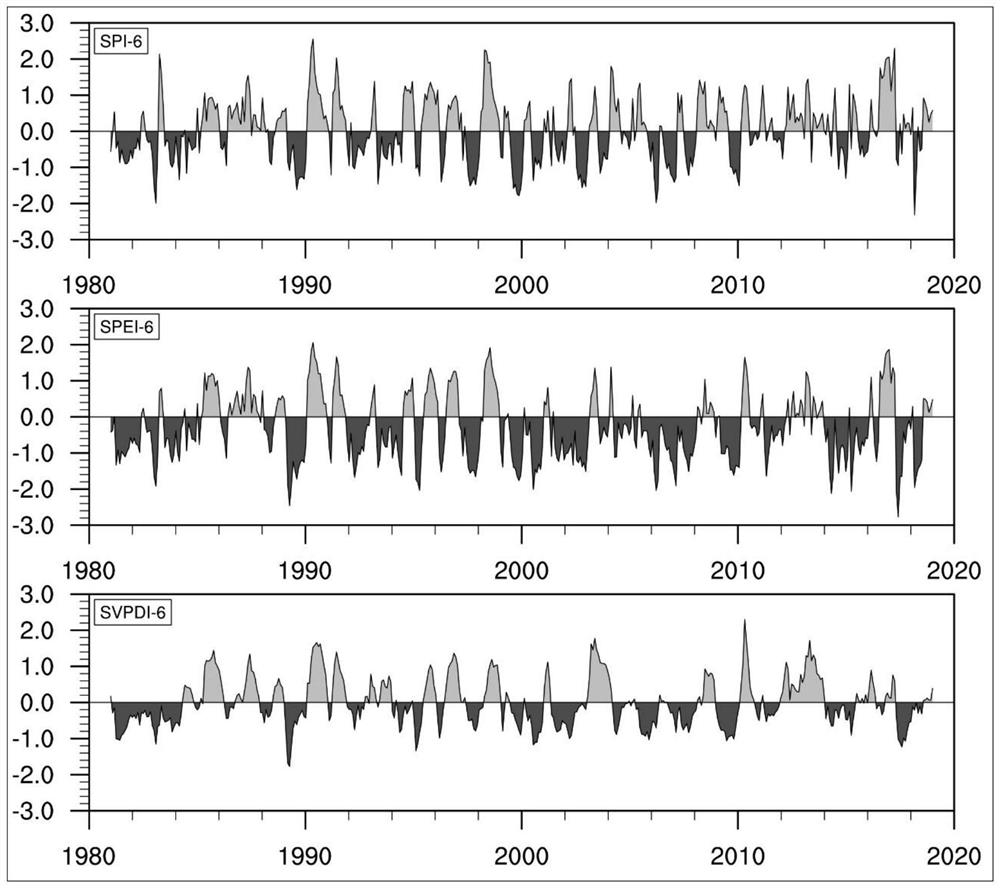
Drought index calculation method based on saturated water vapor pressure difference
ActiveCN112734244ANo maintenance costsCalculation method is simpleResourcesSaturated water vaporGrassland
The invention discloses a drought index calculation method based on saturated water vapor pressure difference, and the method comprises the steps: defining a standardized saturated water vapor pressure difference index as a drought index, representing the drought condition, and monitoring the drought condition of a land ecosystem; the standardized saturated water vapor pressure difference index calculation method comprises the following steps: acquiring meteorological data of ground temperature, ground air pressure and relative humidity of a meteorological station or a field observation station; calculating saturated water vapor pressure and actual water vapor pressure according to meteorological data; and calculating a standardized saturated water vapor pressure difference index according to the saturated water vapor pressure difference. The new drought index provided by the invention is applied to drought monitoring of agricultural or ecological systems, can reflect drought conditions except atmospheric precipitation supply shortage, is simple in calculation method and accurate and stable in result, and observation data participating in calculation is easy to obtain and does not depend on additional observation instruments, so that the installation and maintenance cost of the additional instruments can be avoided, time and space continuity is achieved, and drought occurring in land ecosystems such as farmlands, forests and grassland can be described more accurately.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
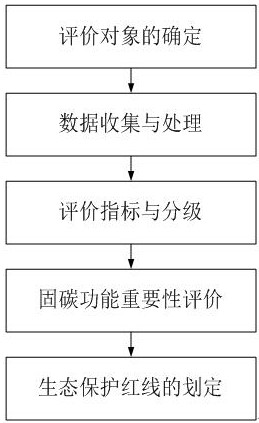
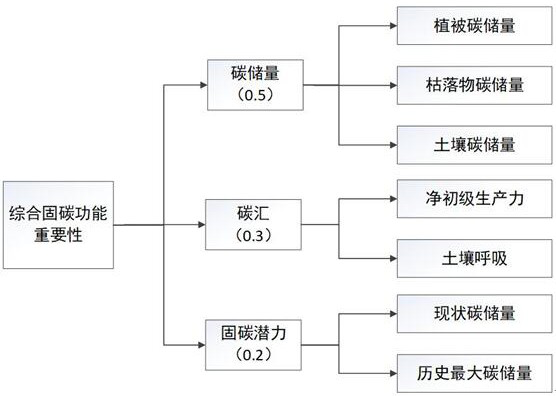
Ecological protection red line delimiting method for carbon sequestration function of terrestrial ecosystem
InactiveCN113837673ASolve the problem of accurate delineationActively respond to global climate changeResourcesCarbon sinkZoology
The invention discloses an ecological protection red line delimiting method for a carbon sequestration function of a terrestrial ecosystem, and the method comprises the steps: selecting a typical terrestrial ecosystem as an evaluation object in a land area range of a research area; collecting data of the evaluation object related to the carbon sequestration function; constructing a land ecosystem carbon sequestration function importance evaluation index from three dimensions of carbon reserve, carbon sink and carbon sequestration potential, determining an index grading assignment standard, and dividing the evaluation index into a plurality of grades; evaluating the importance of carbon reserves, carbon sequestration and carbon sequestration potential of the terrestrial ecosystem, and respectively extracting pattern spots with the highest importance levels of the three; performing spatial superposition and combination to generate extremely important pattern spots with a comprehensive carbon sequestration function; and carrying out aggregation and converting into a vector range of the ecological protection red line. According to the method, the problem that the protection red line of the carbon sequestration function of the terrestrial ecosystem cannot be accurately delimited can be solved, and scientific and technological support is provided for expanding ecological protection red line delimitation, positively coping with global climate changes and achieving a carbon neutralization target.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
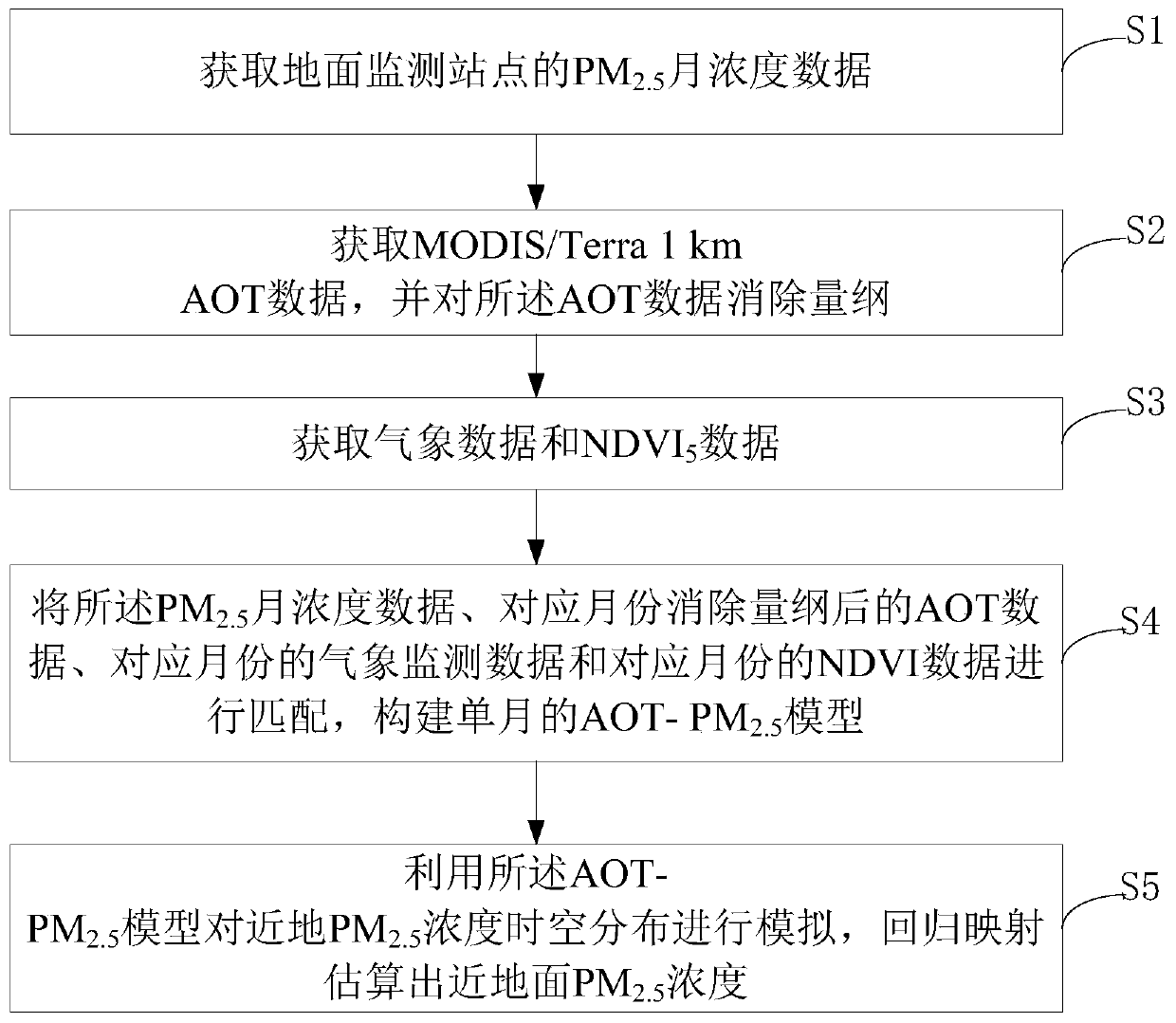
Near-surface atmospheric fine particulate matter concentration estimation method based on space-time weighted regression model
ActiveCN111125937ADesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingFine particulateAtmospheric sciences
The invention relates to a near-surface atmospheric fine particulate matter concentration estimation method based on a space-time weighted regression model. The method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring PM2.5 monthly concentration data of a ground monitoring station; S2, obtaining MODIS / Terra 1km AOT data, and eliminating dimensions of the AOT data; S3, obtaining meteorological data andNDVI data, S4, matching the PM2.5 monthly concentration data, the AOT data after dimension elimination of the corresponding month, the meteorological monitoring data of the corresponding month and theNDVI data of the corresponding month, and constructing a monthly AOT-PM2.5 model. The spatial-temporal change characteristics of the atmospheric fine particulate matter concentration can be accurately indicated, the defects of few ground monitoring stations and non-uniform distribution are overcome, and the data provides a scientific basis for atmospheric fine particulate matter exposure health evaluation and influence evaluation of atmospheric fine particulate matters on a land ecosystem.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
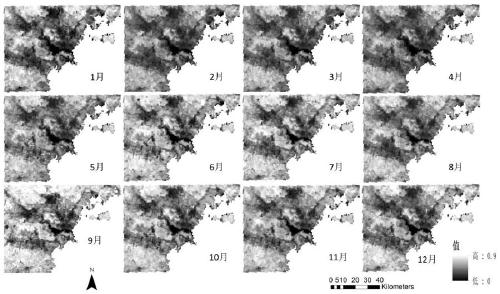
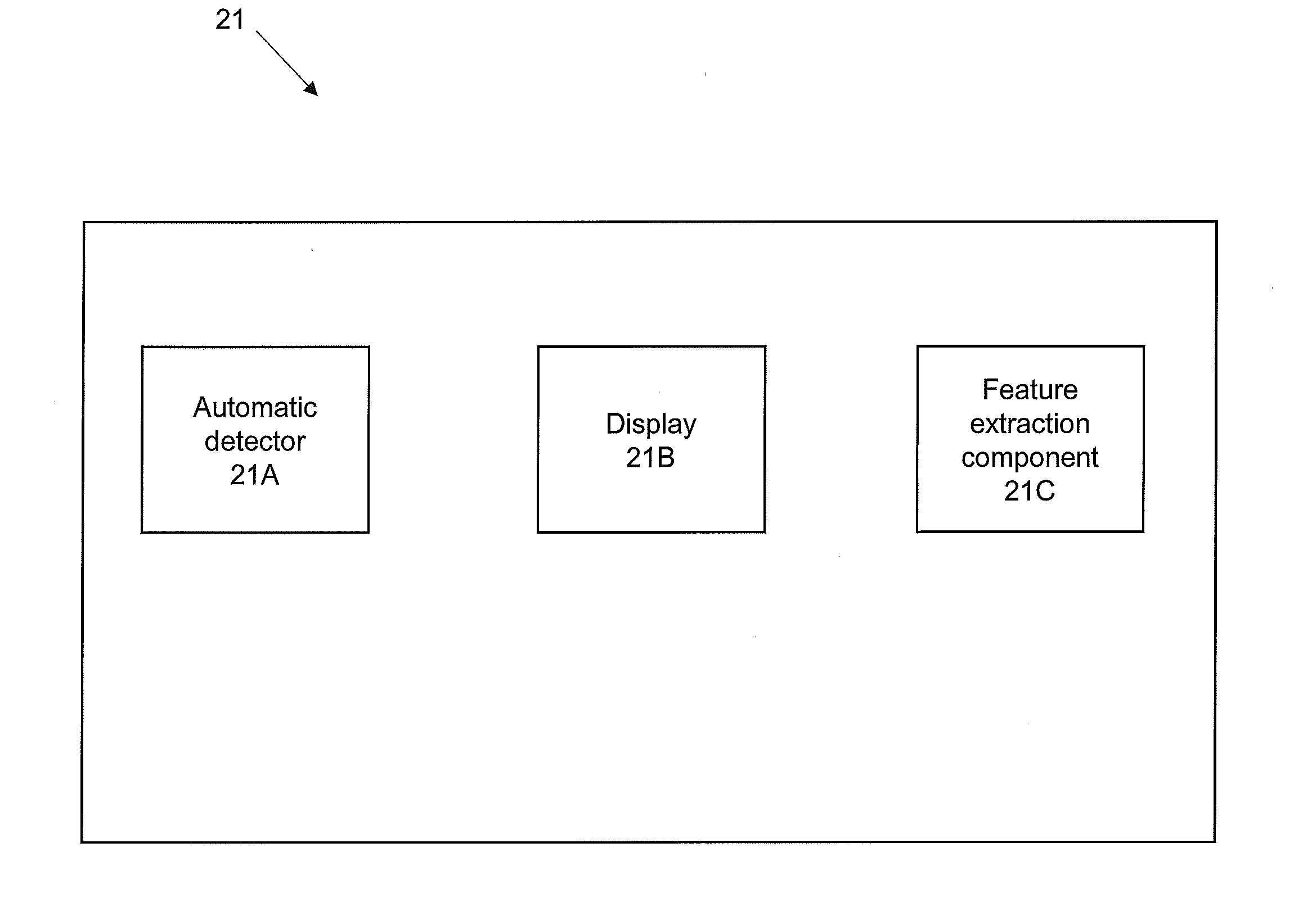
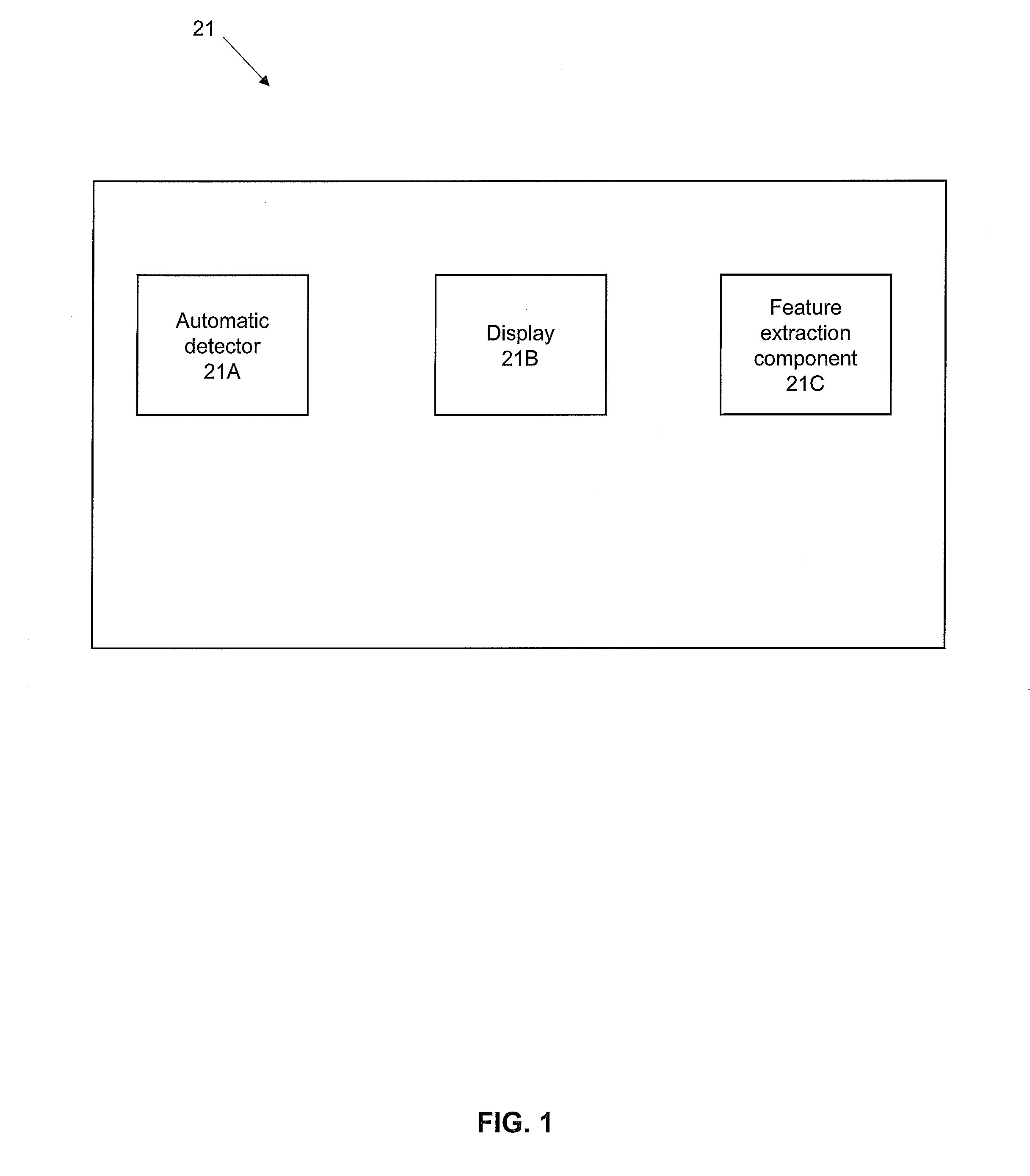
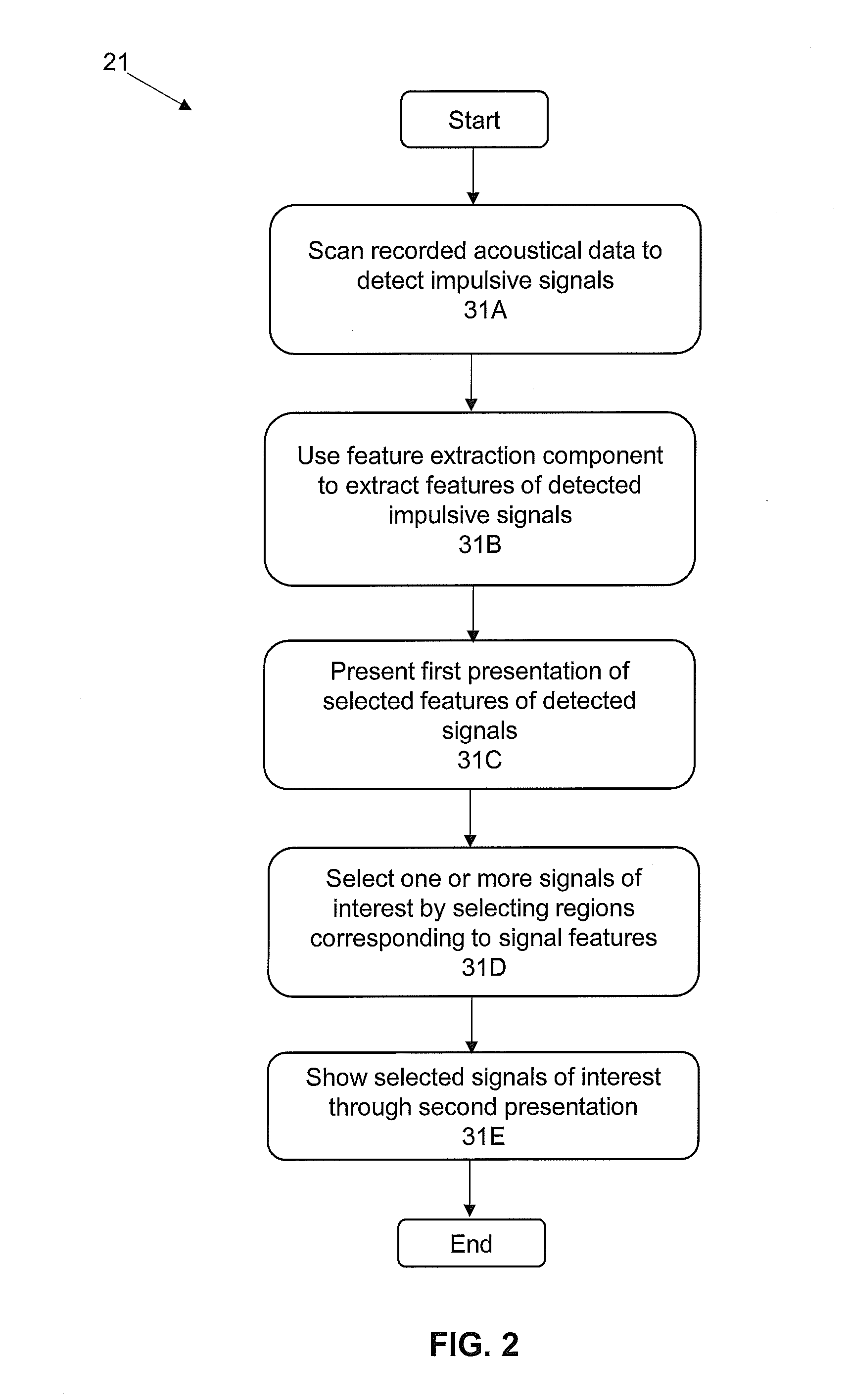
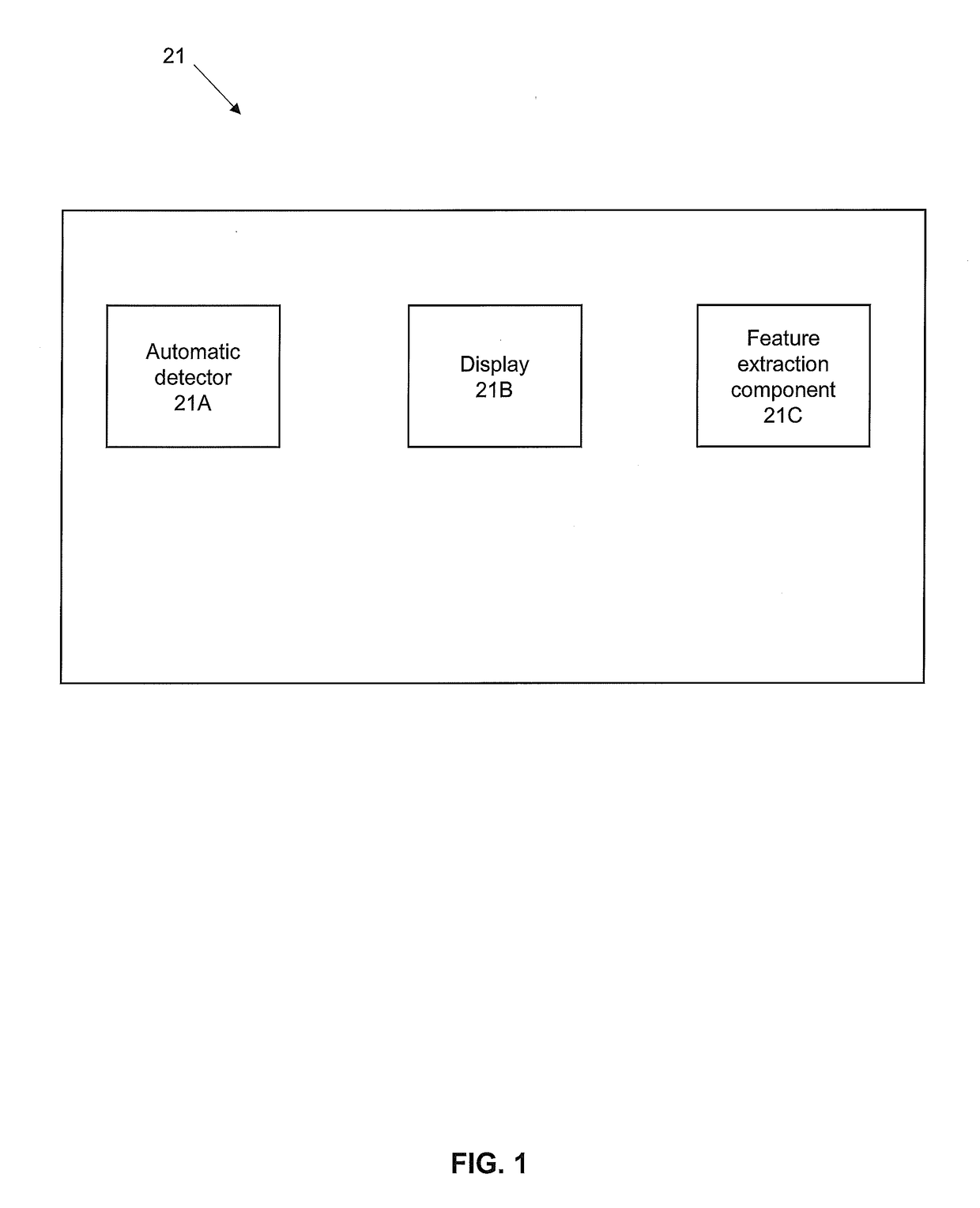
System and methods for processing and the visualization of bioaccoustical information
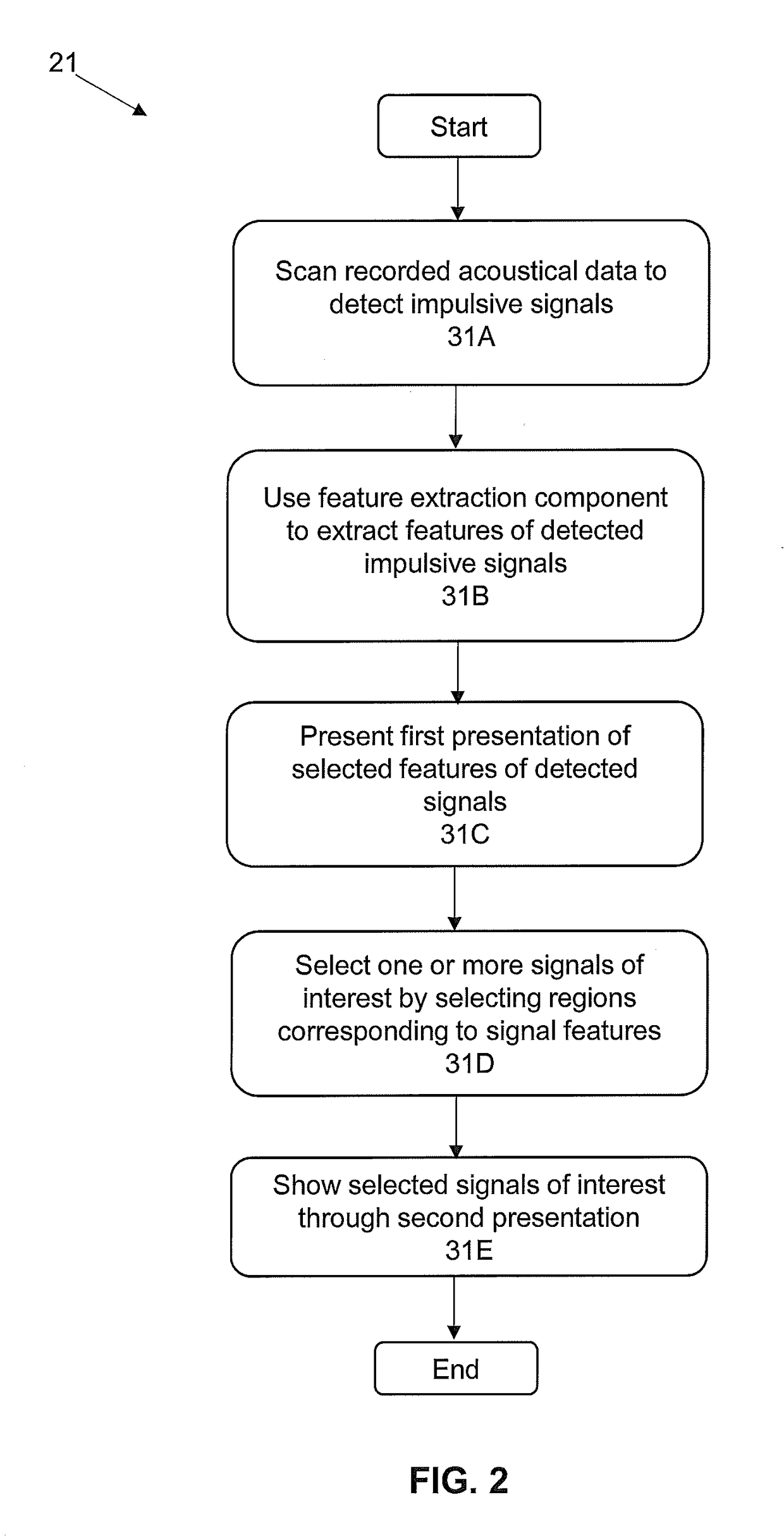
ActiveUS20160252635A1Efficiently determinedQuick analysisAcoustic presence detectionSeismology for water-covered areasVisual presentationSignal of interest
The present invention is directed to acoustics and signal processing. More specifically, the present invention is directed to a system and methods by which whether and the time during which one or more subjects are present within a given area of a marine or terrestrial ecosystem, and other information regarding the subjects can be efficiently determined by the sounds that the subjects produce. Advantageously, certain embodiments of the present invention permit a user to select and rapidly produce one or more visual presentations of the signals of interest (SOI) recorded from the passive acoustic monitoring of a given area of an ecosystem in order to obtain additional information about the subjects.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and method for detecting capability of releasing/mounting COx by land ecosystem
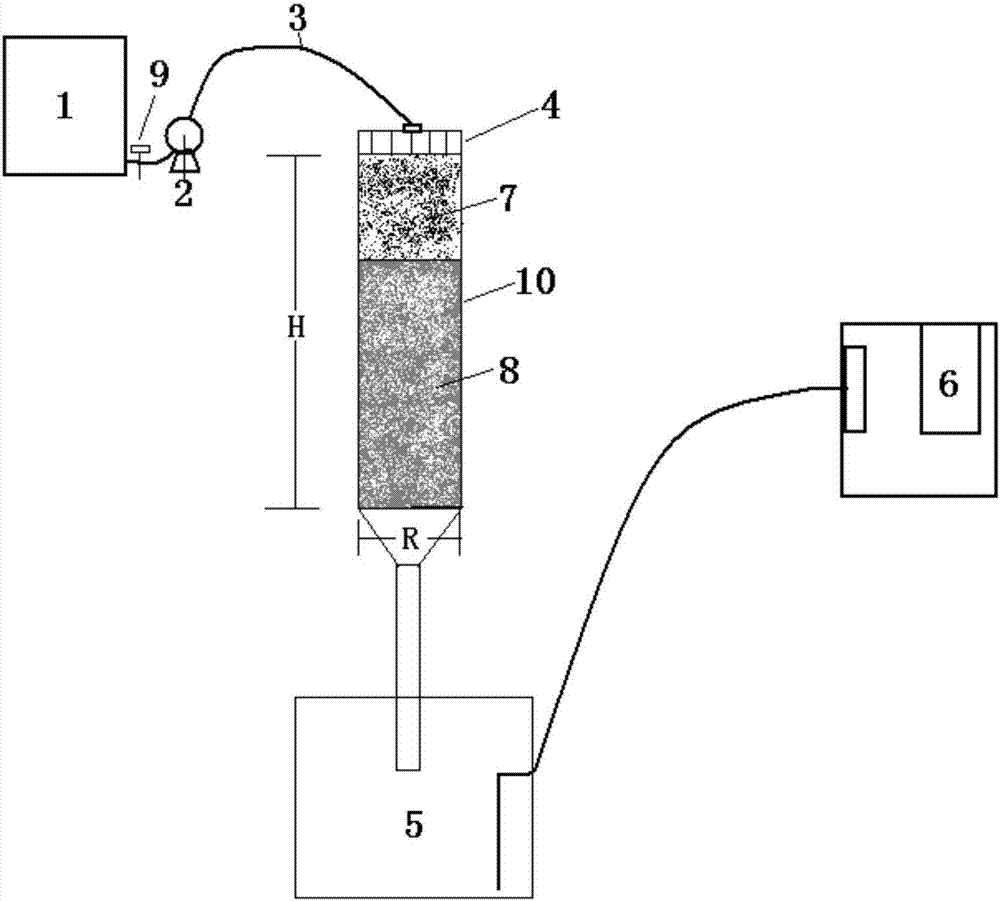
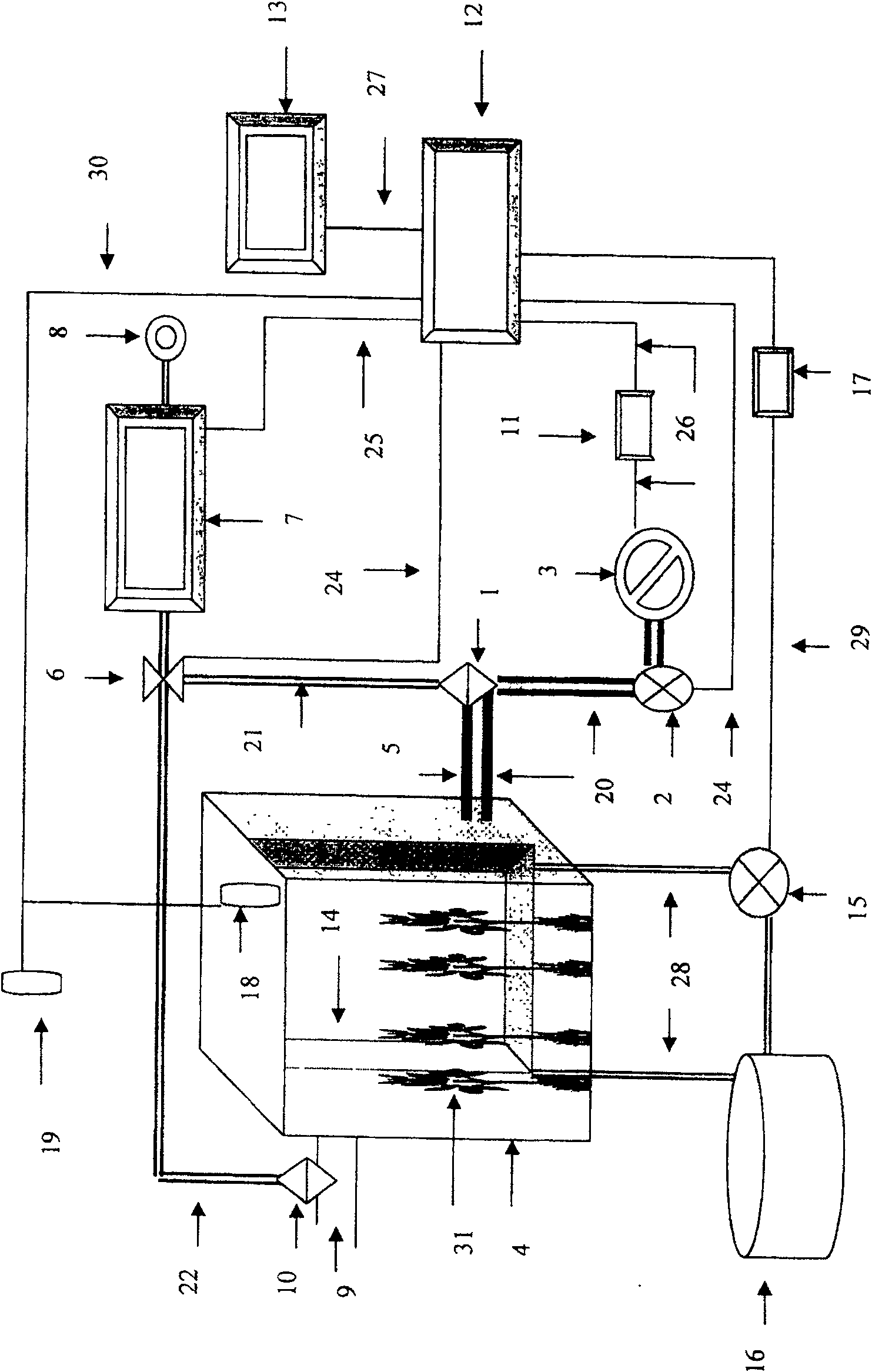
InactiveCN100557441CLittle effect on photosynthesisLow costMaterial analysisContinuous measurementControl system
A device for measuring the ability of terrestrial ecosystems to fix / emit CO2, including: a transparent box, air supply and metering equipment, CO2 concentration measurement equipment, data acquisition and control system, wherein the data acquisition and control system collects and enters from the CO2 concentration measurement equipment and Discharge the CO2 concentration data of the transparent box and calculate the concentration difference, compare the concentration difference with the concentration difference set inside the system, and control the air flow supplied by the air supply and metering equipment to the transparent box according to the comparison result And collect the air flow data, calculate and store the capacity of the terrestrial ecosystem to fix / emit CO2 according to the collected air flow data and concentration difference, so as to realize the automatic dynamic continuous measurement of the ability of the terrestrial ecosystem to fix / emit CO2.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and methods for processing and the visualization of bioaccoustical information
ActiveUS10222493B2Efficiently determinedQuick analysisAcoustic presence detectionSeismology for water-covered areasVisual presentationSignal of interest
The present invention is directed to acoustics and signal processing. More specifically, the present invention is directed to a system and methods by which whether and the time during which one or more subjects are present within a given area of a marine or terrestrial ecosystem, and other information regarding the subjects can be efficiently determined by the sounds that the subjects produce. Advantageously, certain embodiments of the present invention permit a user to select and rapidly produce one or more visual presentations of the signals of interest (SOI) recorded from the passive acoustic monitoring of a given area of an ecosystem in order to obtain additional information about the subjects.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
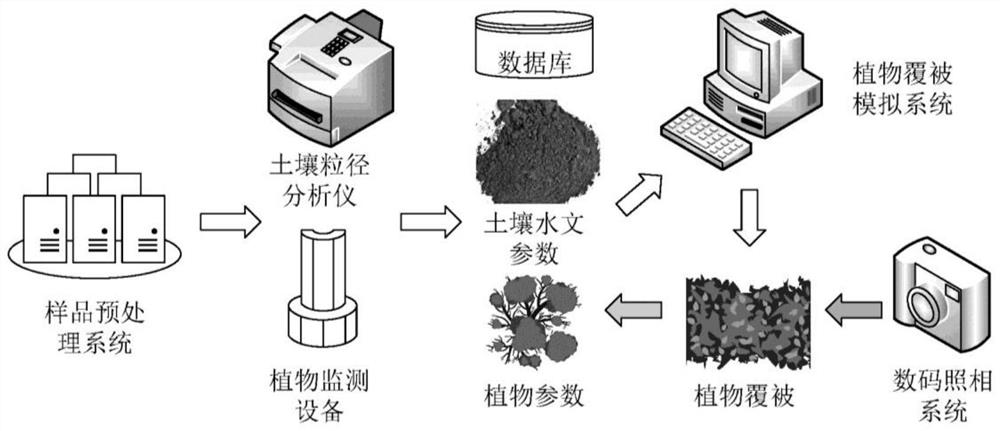
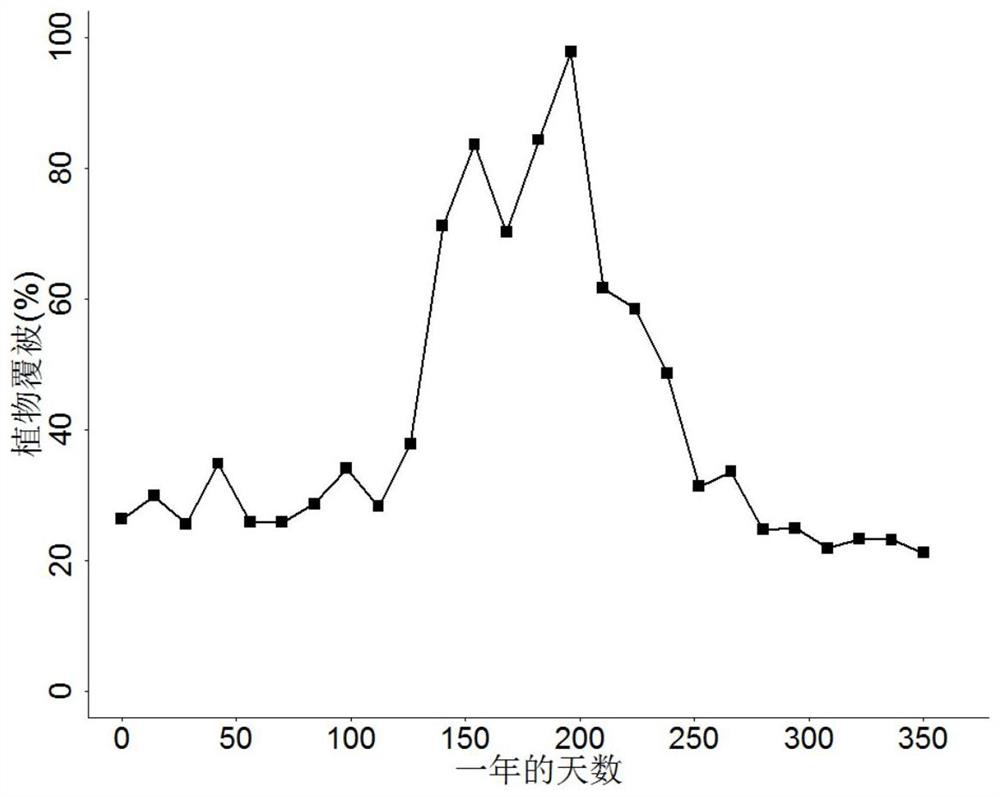
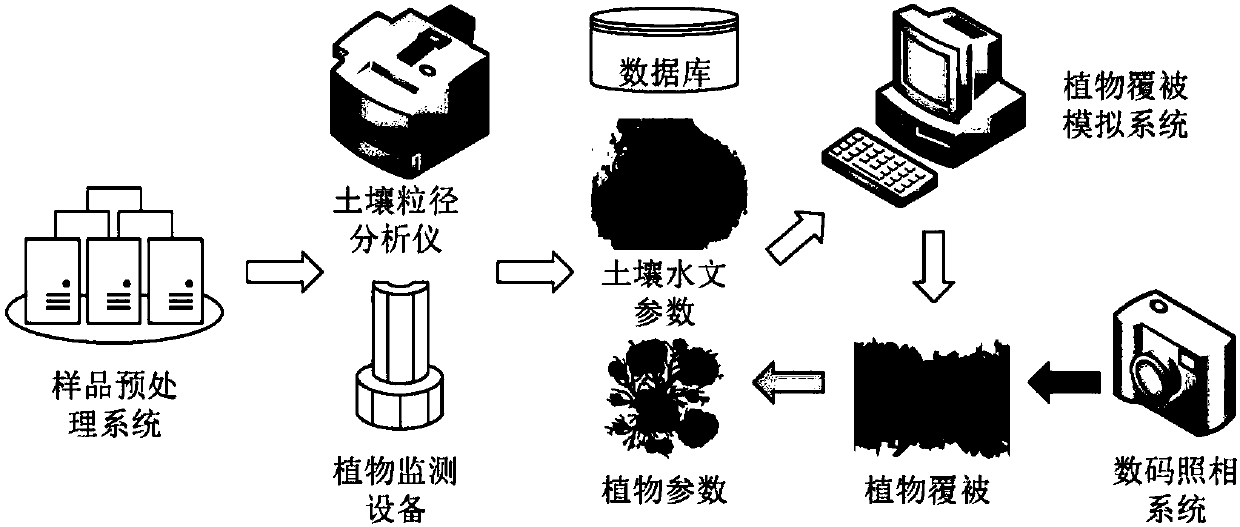
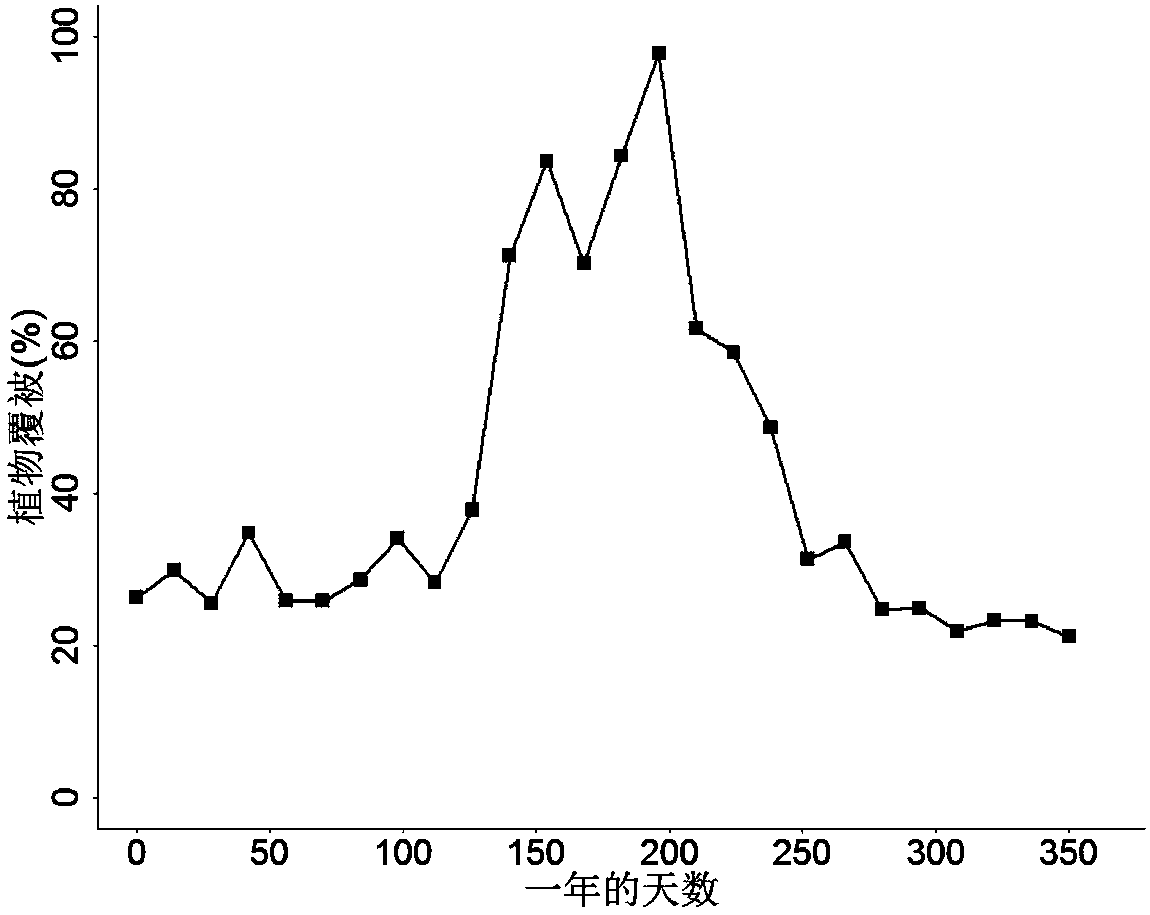
A technology and device for predicting plant community coverage in terrestrial ecosystems
ActiveCN108596379BQuantitative forecast impactMeasurement devicesForecastingSoil sciencePlant community
Aiming at the shortcomings of short observation time, high observation error, large workload and low efficiency of long-term continuous manual observation of plant community coverage in terrestrial ecosystems, the present invention invents a plant that can generate long-term sequences and takes two weeks as the time precision. Coverage technology can be used to quantitatively describe the change of plant community cover under the conditions of climate change and human disturbance. The technology first uses soil analyzers and plant monitoring equipment to obtain soil particle size and plant parameters, and combines soil databases to obtain soil hydrological parameters. Then the dynamic vegetation model is used to simulate the plant community coverage, and the digital camera imaging is used to obtain the measured plant coverage, the simulation results are verified and the soil hydrology and vegetation parameters in the database are corrected. The technology and device have the characteristics of low cost, high prediction accuracy, and wide application range, and have important indicative significance for the study of plant dynamics in terrestrial ecosystems and the protection of biodiversity.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
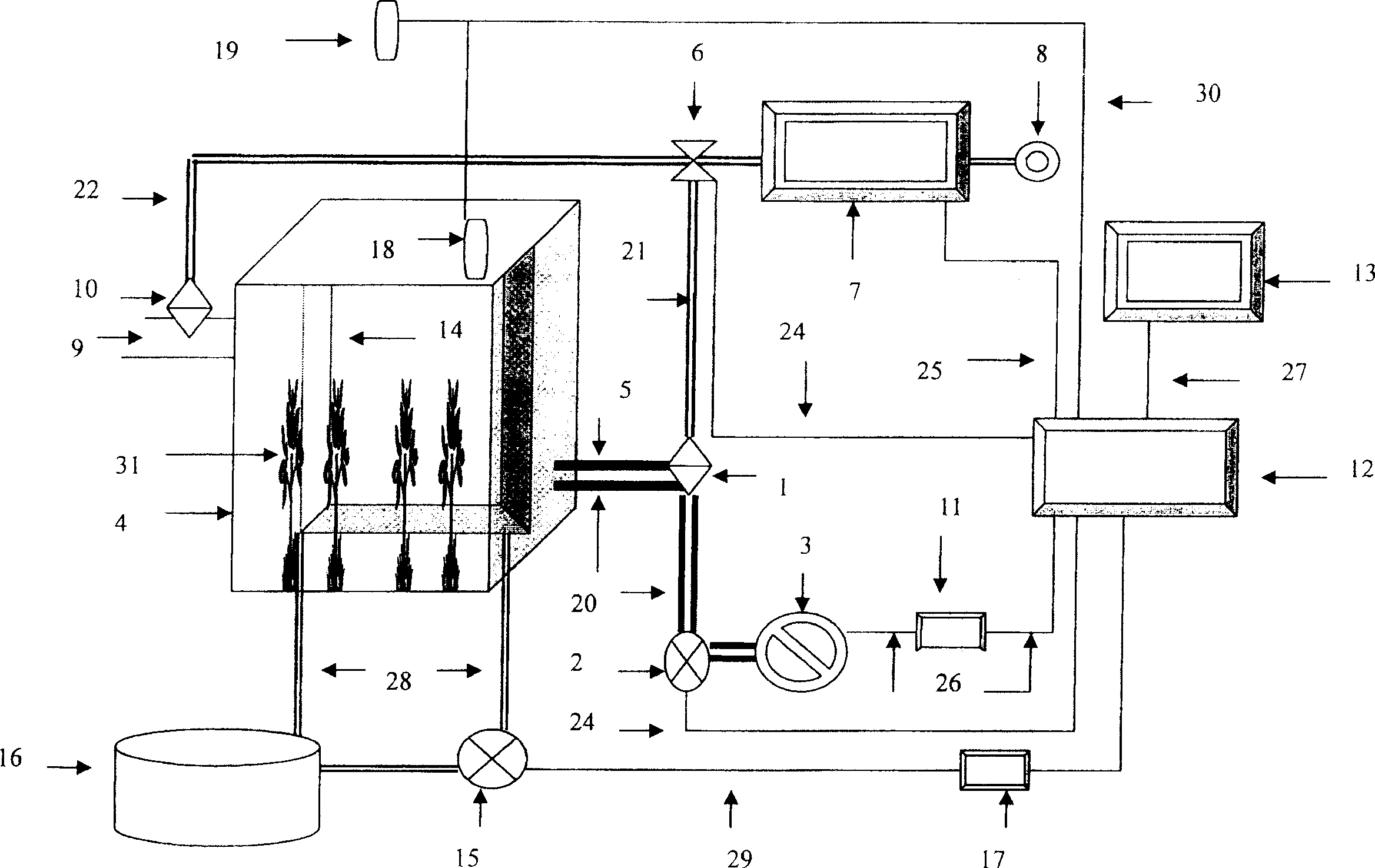
A miniature terrestrial ecosystem experimental device that can operate in a microgravity environment
ActiveCN110077631BEasy to operateEasy maintenanceCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsMicroorganismEnvironmental engineering
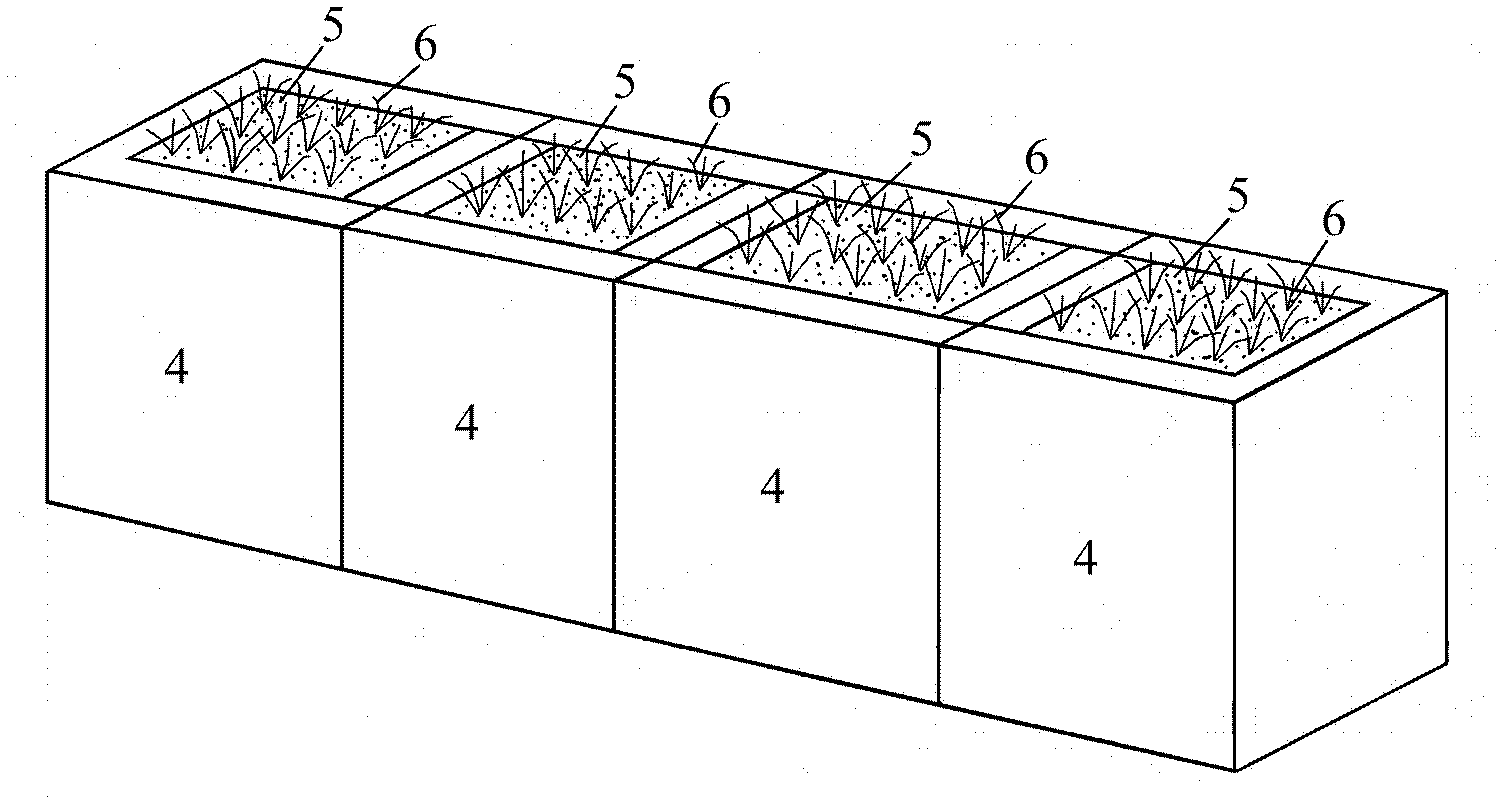
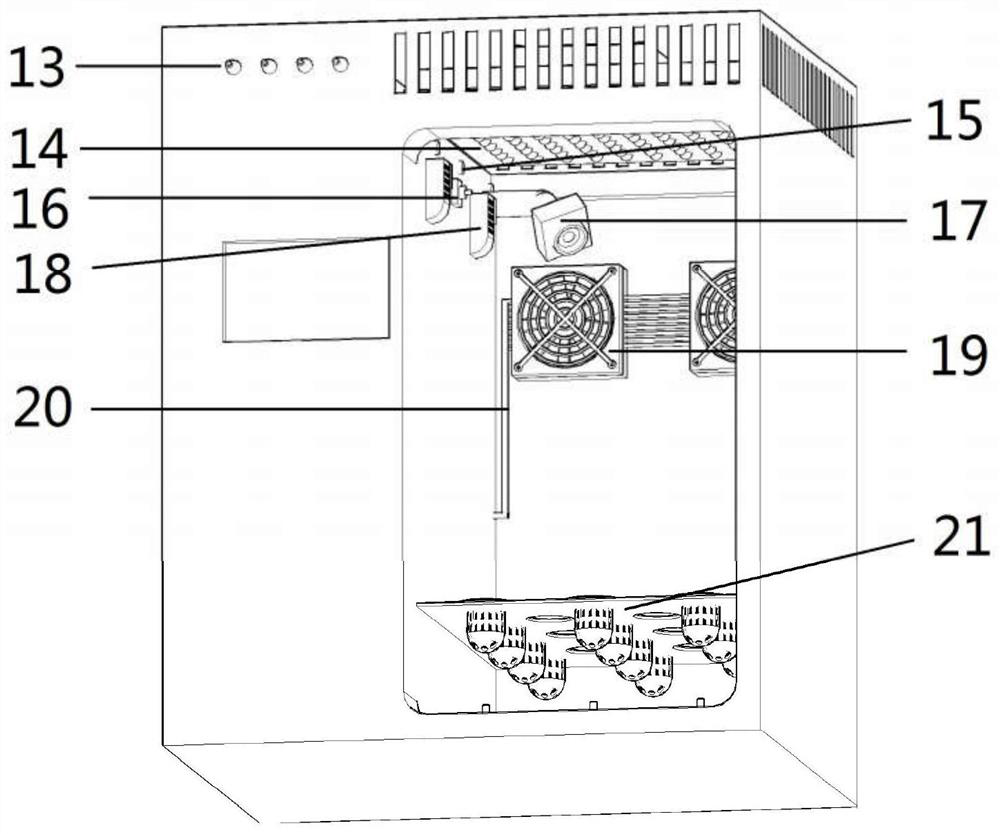
The patent of the invention belongs to the technical field of aerospace life support, and discloses a miniature terrestrial ecosystem that can operate in a microgravity environment, and is mainly used for micro-ecological system operation experiments in a weightless environment. The present invention mainly includes a plant area 1, an animal area 2, a solid waste area 3, a water tank area 4, and an electric control area 5. Plants can be planted in plant area 1 to produce oxygen for biological utilization in animal area 2 and solid waste area 3; animals can be raised in animal area 2, and microorganisms can be inoculated to treat solid waste in solid waste area 3, both of which can produce carbon dioxide for plants Plant utilization in zone 1; water tank zone 4 can provide water for plants and realize system water circulation; electric control zone 5 can monitor and control various physical and chemical indicators and parameters of each zone in the system, and at the same time provide light for plants to ensure normal operation of the device run. The invention has simple structure and high degree of automation, and can be used to study the influence of special conditions of space environment on the whole terrestrial ecological system and each biological chain link.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Technology and device for predicting plant community cover in terrestrial ecosystem
ActiveCN108596379AReduce the cost of observationQuantitative forecast impactMeasurement devicesForecastingApplicability domainPlant community
For the shortcomings of a short observation time, a high observation error, a large long-term continuous manual observation workload and low efficiency of the plant community cover in the terrestrialecosystem, the present invention provides a plant cover technology capable of growing a long-term time sequence and with two weeks as time precision. The technology can be used to quantitatively describe changes in the plant community cover under climate change and human disturbance conditions. The technology comprises: using a soil analyzer and plant monitoring equipment to obtain soil particle sizes and plant parameters, and obtaining soil hydrological parameters by combining soil databases; and using a dynamic vegetation model to simulate the plant community cover, obtaining the measured plant cover through digital camera imaging, verifying simulation results and correcting the soil hydrological and vegetation parameters in the database. The technology and device have the characteristics of a low cost, high prediction accuracy and a wide application range, and have important indication significance for the plant dynamic research and biodiversity conservation of the terrestrial ecosystem.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
A method for simulating daily precipitation based on measured multi-year precipitation data
ActiveCN108595814BDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHydrometryMissing data
The present invention aims at the problem that the time of precipitation record data in some areas of the terrestrial ecosystem is relatively short and the amount of data missing in several years is large, and a precipitation generator capable of generating a day as the time scale is invented. The input to the generator is based on long-term annual, monthly, and daily precipitation data observed in the target area. First determine the frequency distribution of monthly precipitation, monthly average daily precipitation, monthly maximum daily precipitation, and annual precipitation days, extract the characteristic parameters of the distribution curve, construct an exponential equation to simulate the daily precipitation, and accumulate it to obtain the monthly and annual precipitation. The simulated time series data are compared with the measured data on the annual and monthly time scales. The distribution of extreme precipitation events is considered in the verified precipitation generator, so that the precipitation generator can better reflect the law of precipitation distribution under natural conditions. It helps to assess the impact of precipitation on the hydrological cycle of terrestrial ecosystems and predict the ecological effects of climate change.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
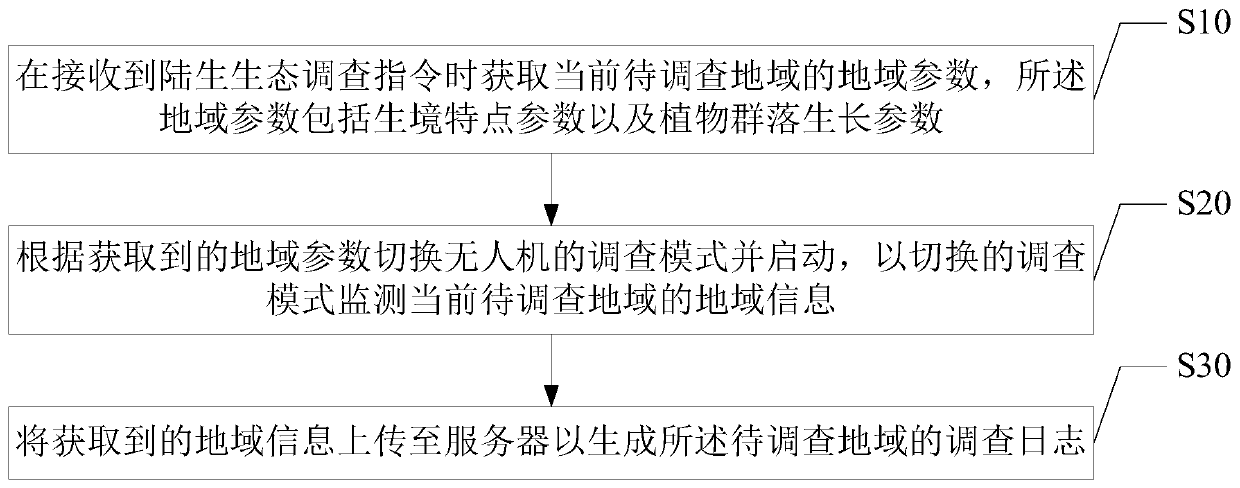
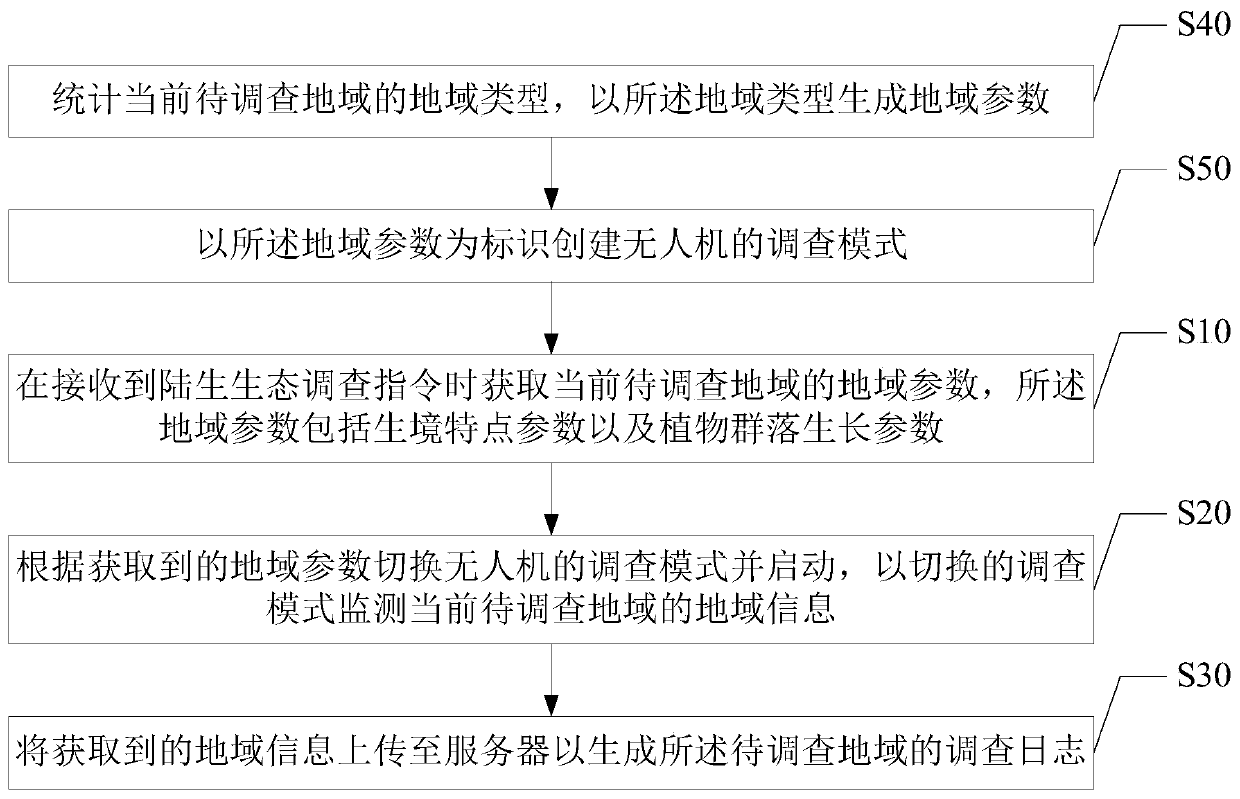
Terrestrial ecological investigation method based on unmanned aerial vehicle, unmanned aerial vehicle and storage medium
ActiveCN111309051ARealize the effect of real-time monitoringPosition/course control in three dimensionsPlant communityUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses a terrestrial ecological investigation method based on an unmanned aerial vehicle. The method comprises the steps: acquiring regional parameters of a current to-be-investigatedregion when a terrestrial ecological investigation instruction is received, and enabling the regional parameters to comprise habitat characteristic parameters and plant community growth parameters; switching an investigation mode of the unmanned aerial vehicle according to the acquired regional parameters and starting an unmanned aerial vehicle, and monitoring regional information of the currentto-be-investigated region according to the switched investigation mode; and uploading the acquired regional information to a server to generate an investigation log of the to-be-investigated region. The invention further discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle and a storage medium. The terrestrial ecosystem is investigated through the unmanned aerial vehicle, different investigation modes are set according to regional types, statistics of regional information is performed according to one or more regional investigation parameters in the investigation modes to generate the regional information, field investigation of related operators is not needed, and the effect of real-time monitoring of the terrestrial ecosystem can be achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN YU CHI TESTING TECH CO LTD
A device and method for simulating the impact of fire disturbance on groundwater in terrestrial ecosystems
ActiveCN107462692BHigh precisionSimple and fast operationEarth material testingEngineeringEarth surface
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A device for simulating wet deposition of radionuclides
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Remote Sensing-Based Monitoring Method of Regional Terrestrial Ecosystem Respiration
InactiveCN103513290BHigh precisionSolve the problem of lack of expressivenessOptical detectionGrowing seasonEcosystem respiration
The invention provides a regional terrestrial ecosystem respiratory monitoring method based on remote sensing. The monitoring method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining time series satellite remote sensing data within a region; S2, performing remote sensing retrieval to key parameters; S3, quantifying key physiological and ecological parameters of different vegetation forms based on land cover or land utilization data; S4, obtaining meteorological interpolation data of time series; S5, carrying out cloud removal to obtain vegetation growing season curve without noise impact; S6, determining the annual respiratory capacity of the regional terrestrial ecosystem. The method is based on the time series remote sensing data, considers spatial difference of the vegetation form, determines the ecosystem respiratory algorithm within the region, solves the problem that the regional terrestrial ecosystem respiratory monitoring only relies on meteorological data but is insufficient to express heterogeneous information of the land cover within large scale, improves the precision of regional scale ecosystem respiratory estimation, and accurately and quantitatively describes temporal dynamics of the respiration in different ecosystems.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Apparatus and method for detecting capability of releasing/mounting COx by land ecosystem
InactiveCN1952657ALittle effect on photosynthesisLow costMaterial analysisContinuous measurementControl system
An apparatus which is measuring the regularize blow-off CO2 capacity of the terrestrial ecosystem is disclosed that comprises: transparent box, air supplying and metering equipment, concentration determination equipment of CO2, data acquisition and control system, the density data of CO2 which is input and output from the transparent box are acquired and calculated to gain the concentration difference via the concentration determination equipment of CO2 by data acquisition and control system, the concentration difference is compared with the concentration difference set in system, the results control the air-flow that the air supplying and metering equipment supplies to the transparent box and acquire the air-flow data, the regularize blow-off CO2 capacity of the terrestrial ecosystem can be calculated and stored based on the air-flow data acquired and the concentration difference, so the full-automatic dynamic continuous measurement of the regularize blow-off CO2 capacity of the terrestrial ecosystem can be realized.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com