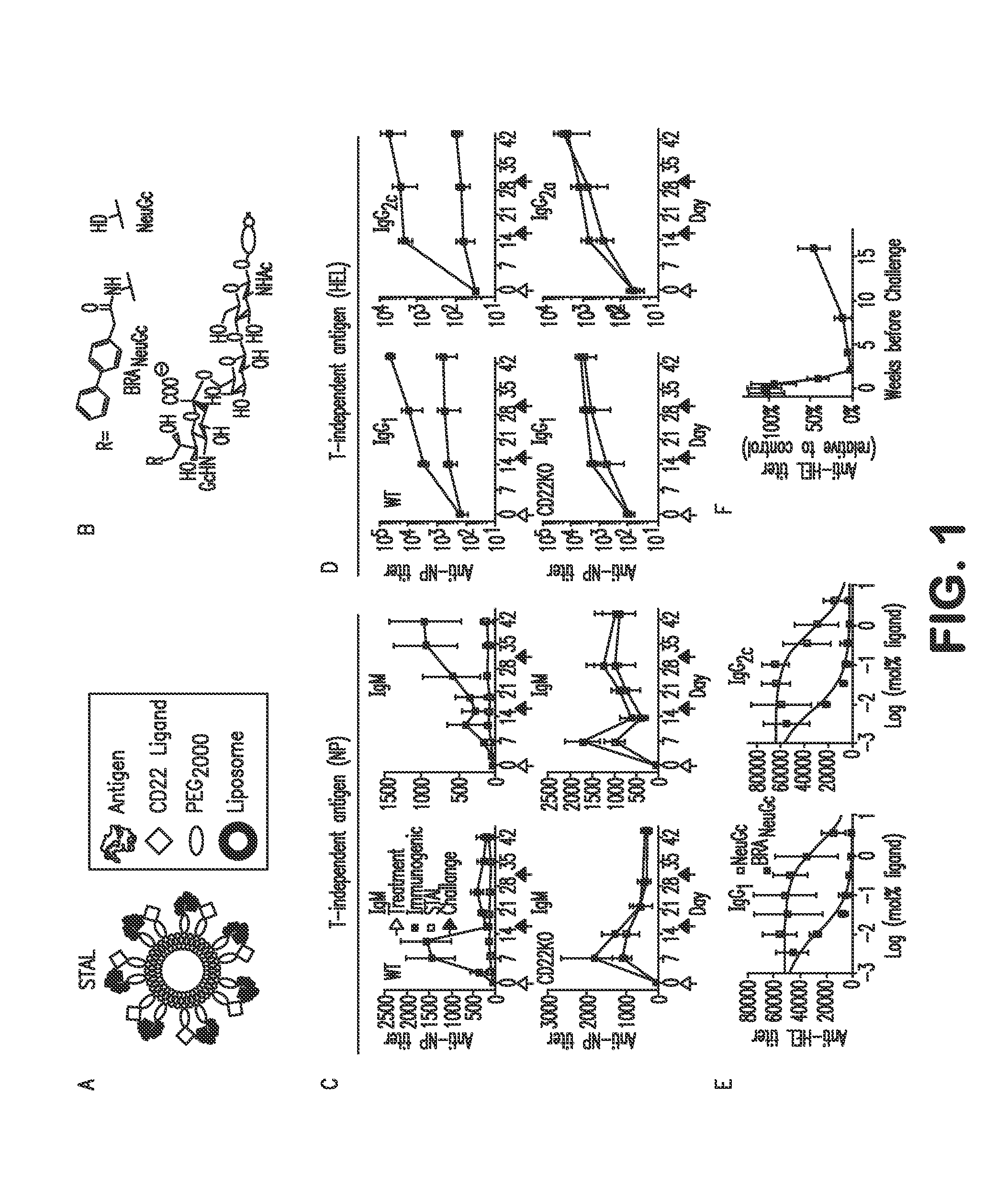
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Sialic acid binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with sialic acid, any of a variety of N- or O- substituted derivatives of neuraminic acid, a nine carbon monosaccharide. Sialic acids often occur in polysaccharides, glycoproteins, and glycolipids in animals and bacteria. [CHEBI:26667, GOC:add, http://www.biology-online.org, ISBN:0721601465]
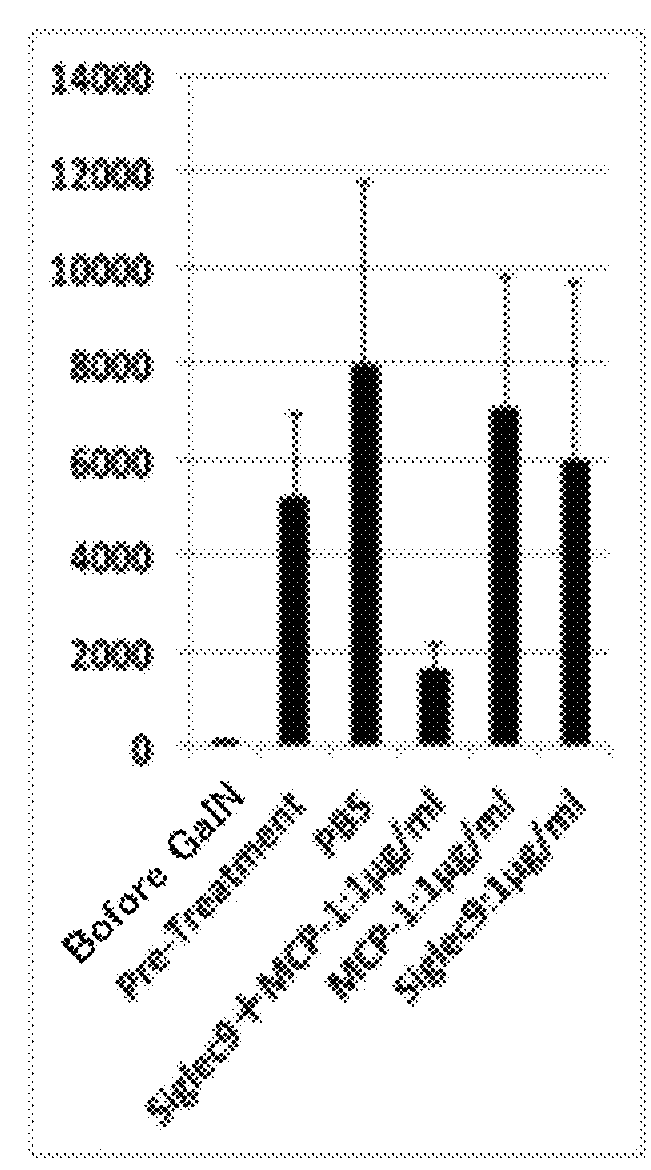
Method for purification of viral vectors having proteins which bind sialic acid
ActiveUS7319002B2Method be rapidMethod is fastBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBinding siteViral vector
A method for isolating, from a mixture, a virus having a surface protein with a binding site for sialic acid is provided. The method involves contacting the mixture with mucin which has been linked to a solid support and washing the solid support to remove material from the mixture is non-specifically bound to the mucin-linked support. Thereafter, the specifically bound virus (e.g., AAV4 or AAV5) may be removed in a further washing step utilizing a concentrated slat or solution with low pH. Also described are pharmaceutical kits containing solid supports linked to mucin for use in isolating virus having a surface protein with a binding site for sialic acid, or detecting the presence of the virus in a biological sample.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Methods and Compositions for Treating Bleeding Disorders
InactiveUS20160060324A1Induce immune toleranceFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsImmune toleranceB cell
The present invention provides immune conjugates for inducing antigen specific immune tolerance to coagulation Factor VIII. The immune conjugates contain a FVIII protein or antigenic fragment that is conjugated to a binding moiety for a sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin (Siglec) expressed on B cells. The invention also provides methods of using the FVIII immune conjugates to induce immune tolerance to FVIII in a subject. Additionally provided in the invention are methods for treating bleeding disorders such as hemophilia A via the use of the FVIII immune conjugates and an unconjugated FVIII with coagulating activity.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
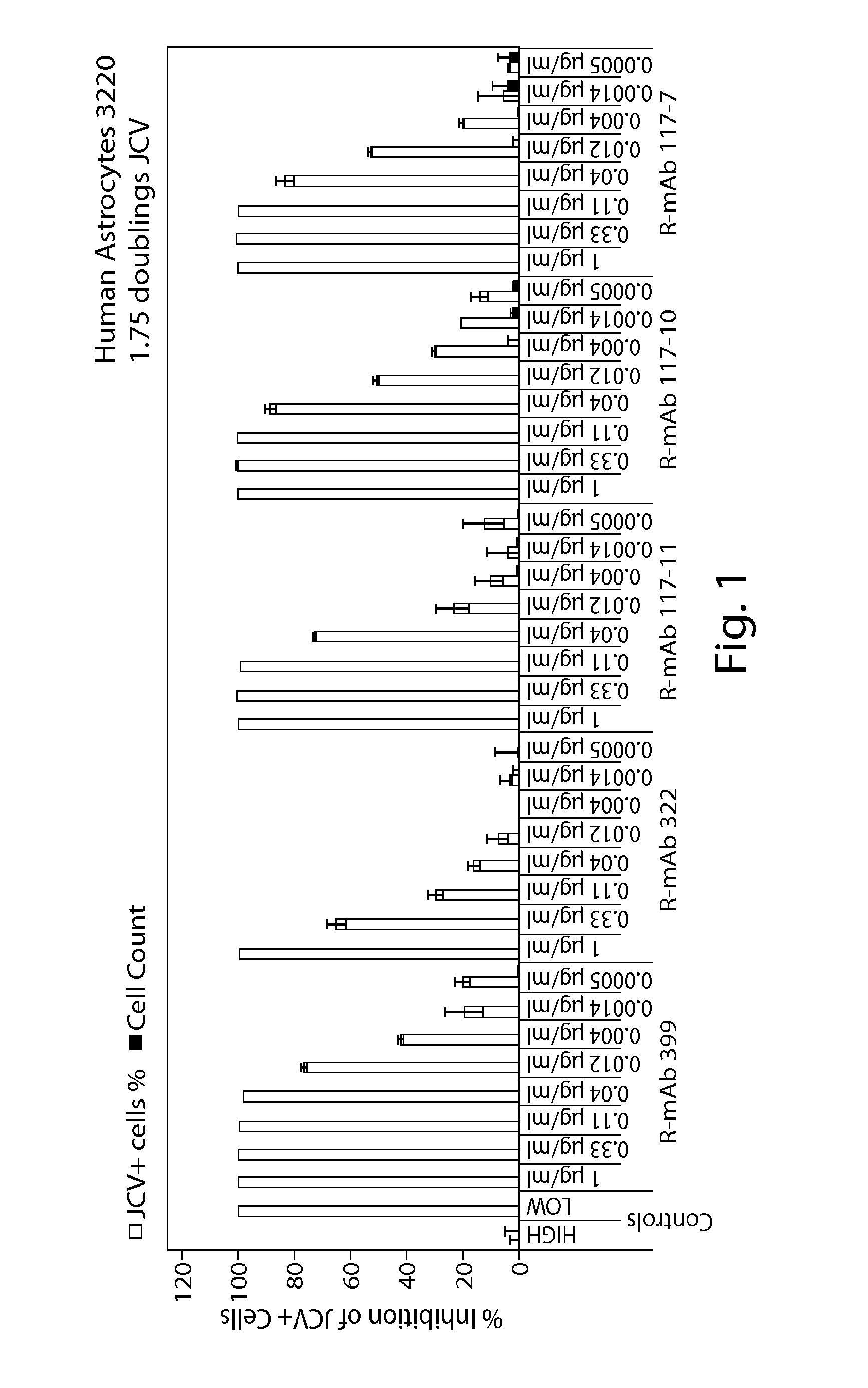
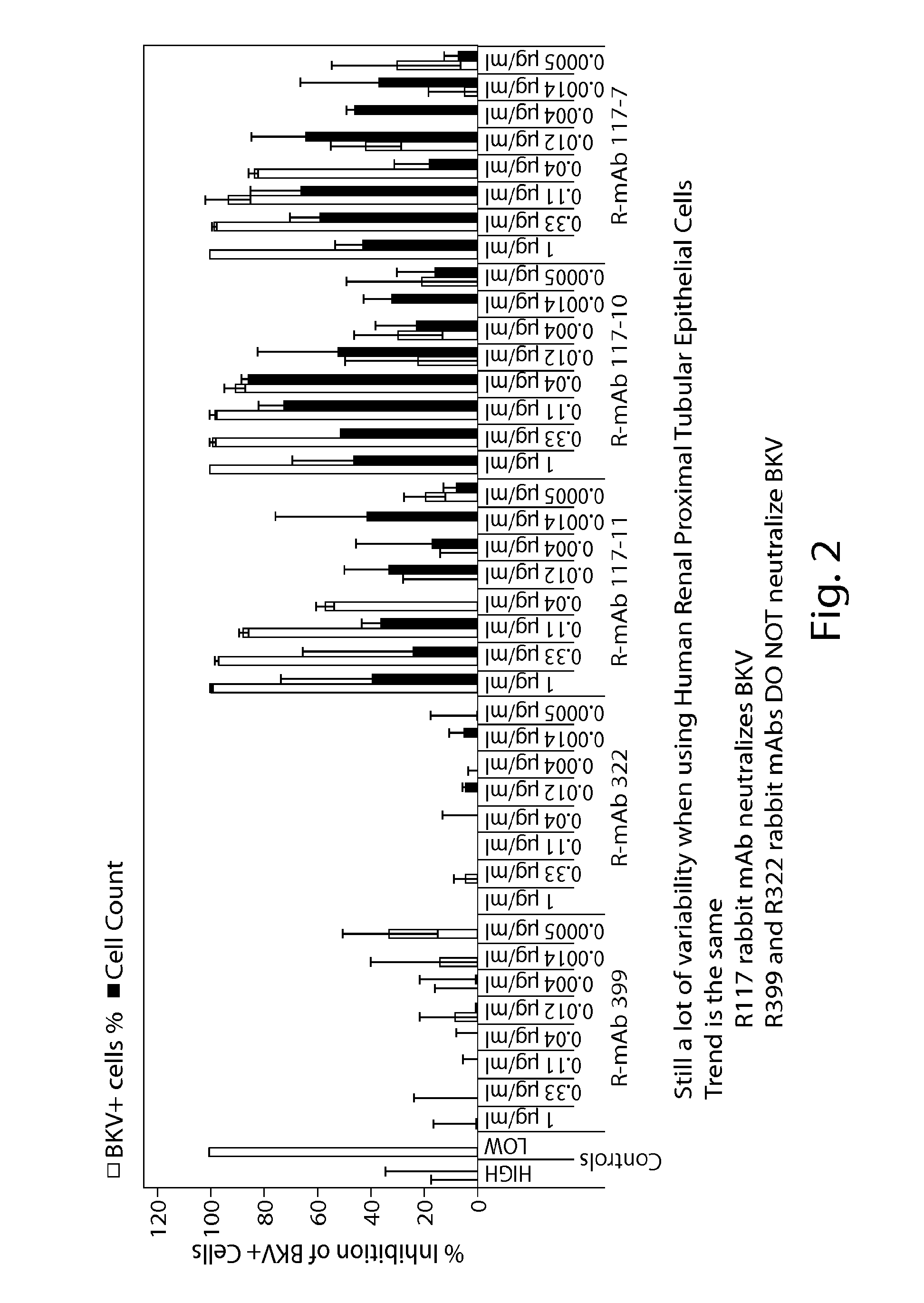
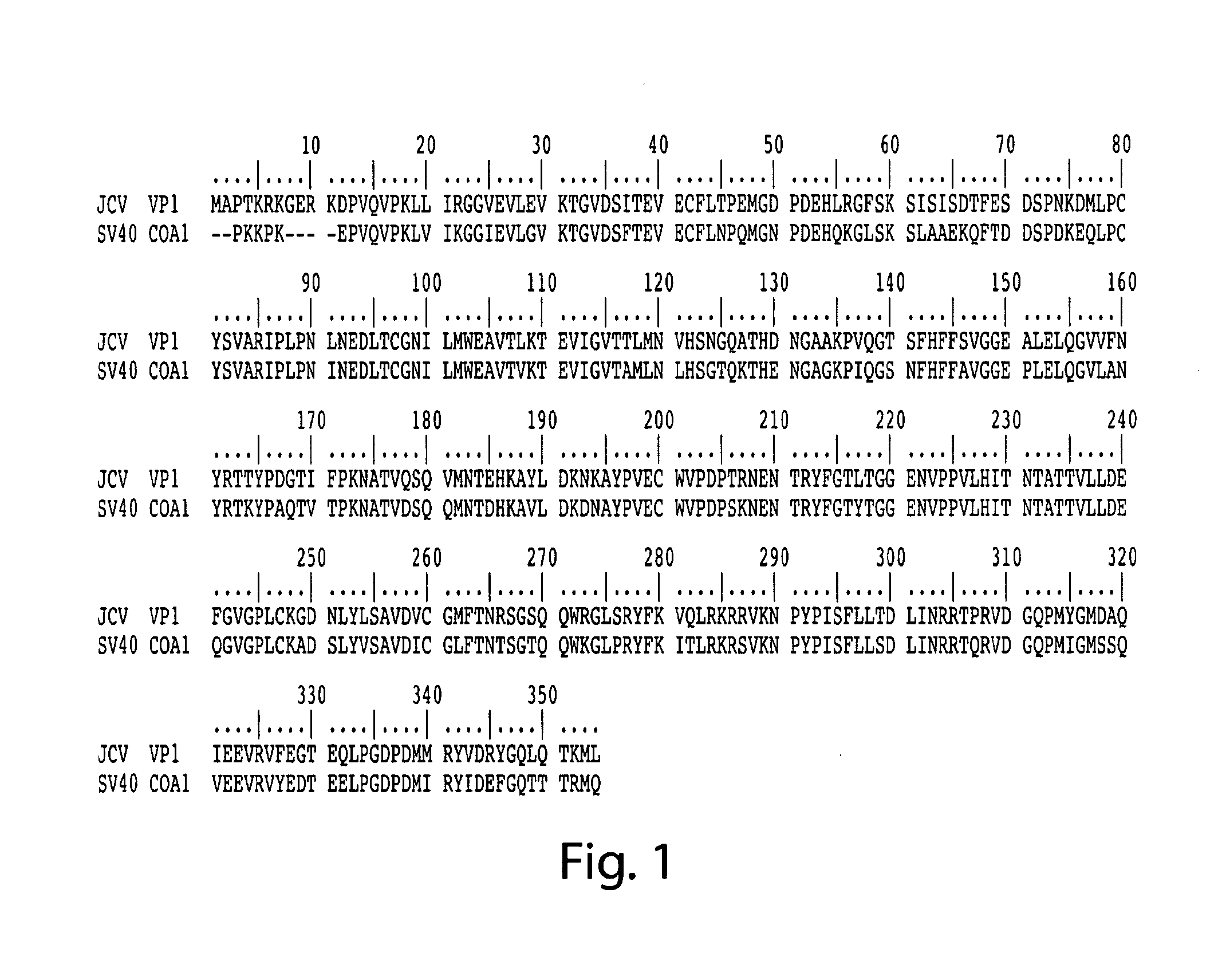
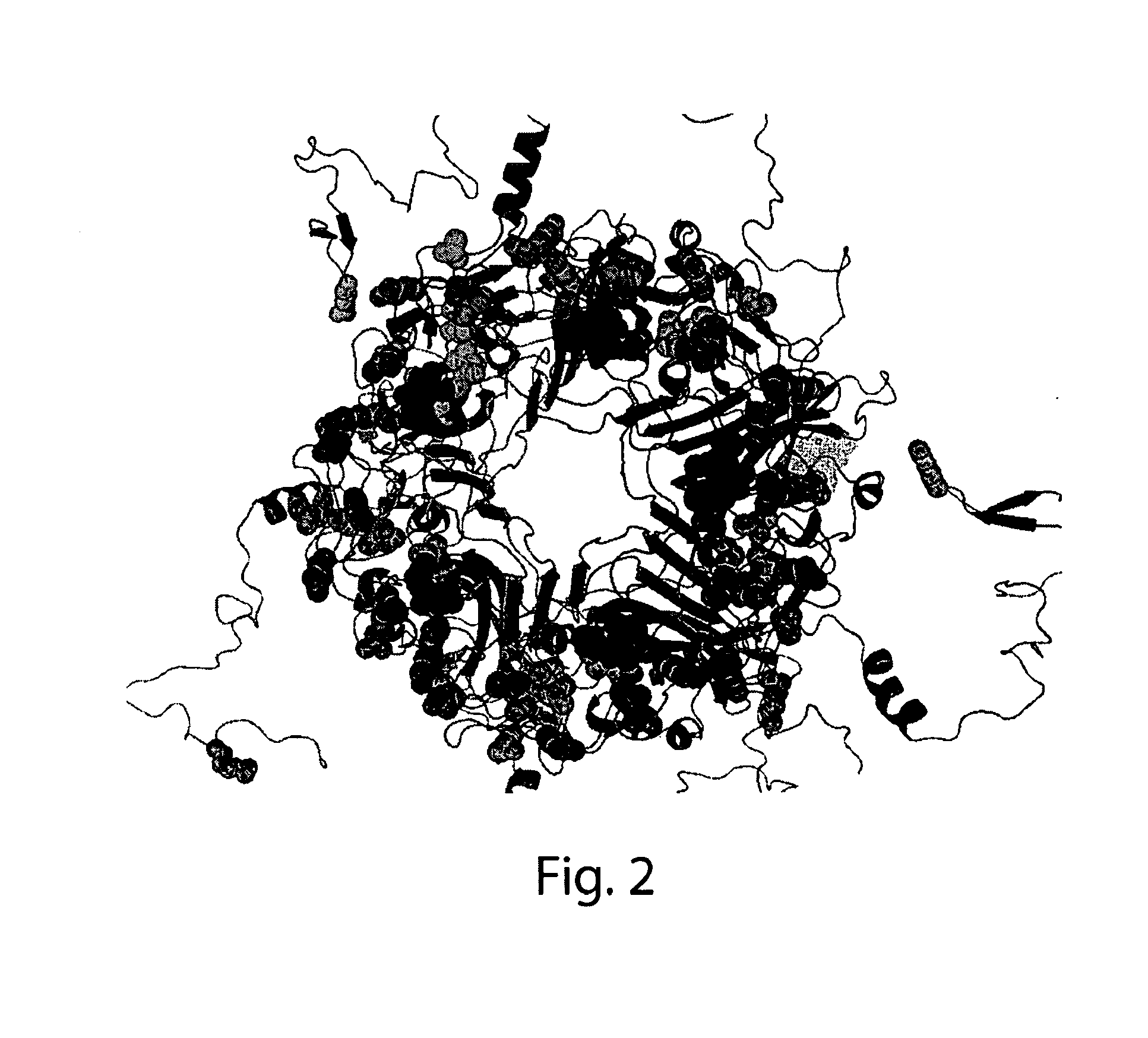
Jcv neutralizing antibodies
ActiveUS20150056188A1Reduce viral loadIncrease awarenessImmunoglobulins against virusesAntibody ingredientsAntibody SuppressionAntiendomysial antibodies
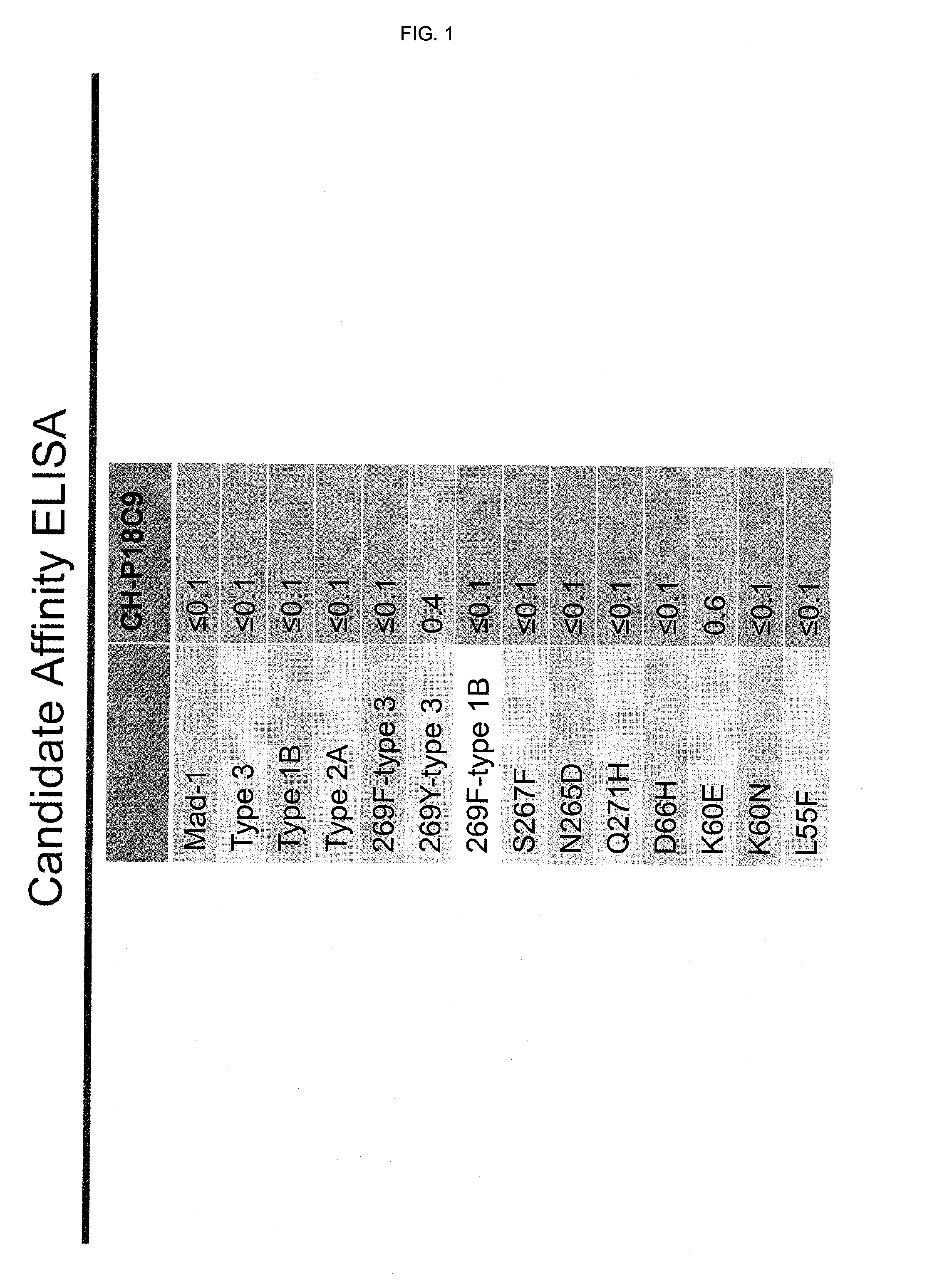
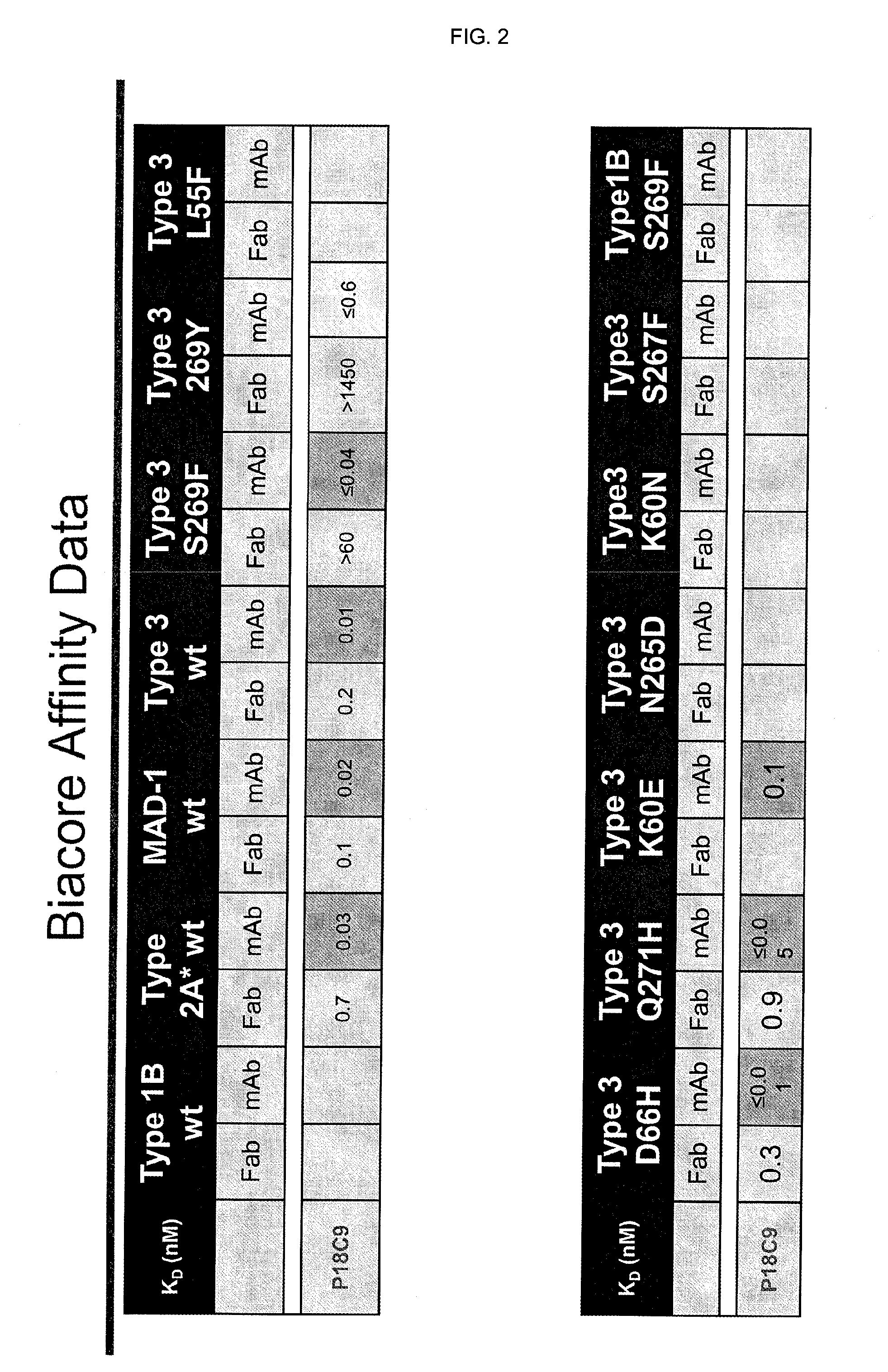
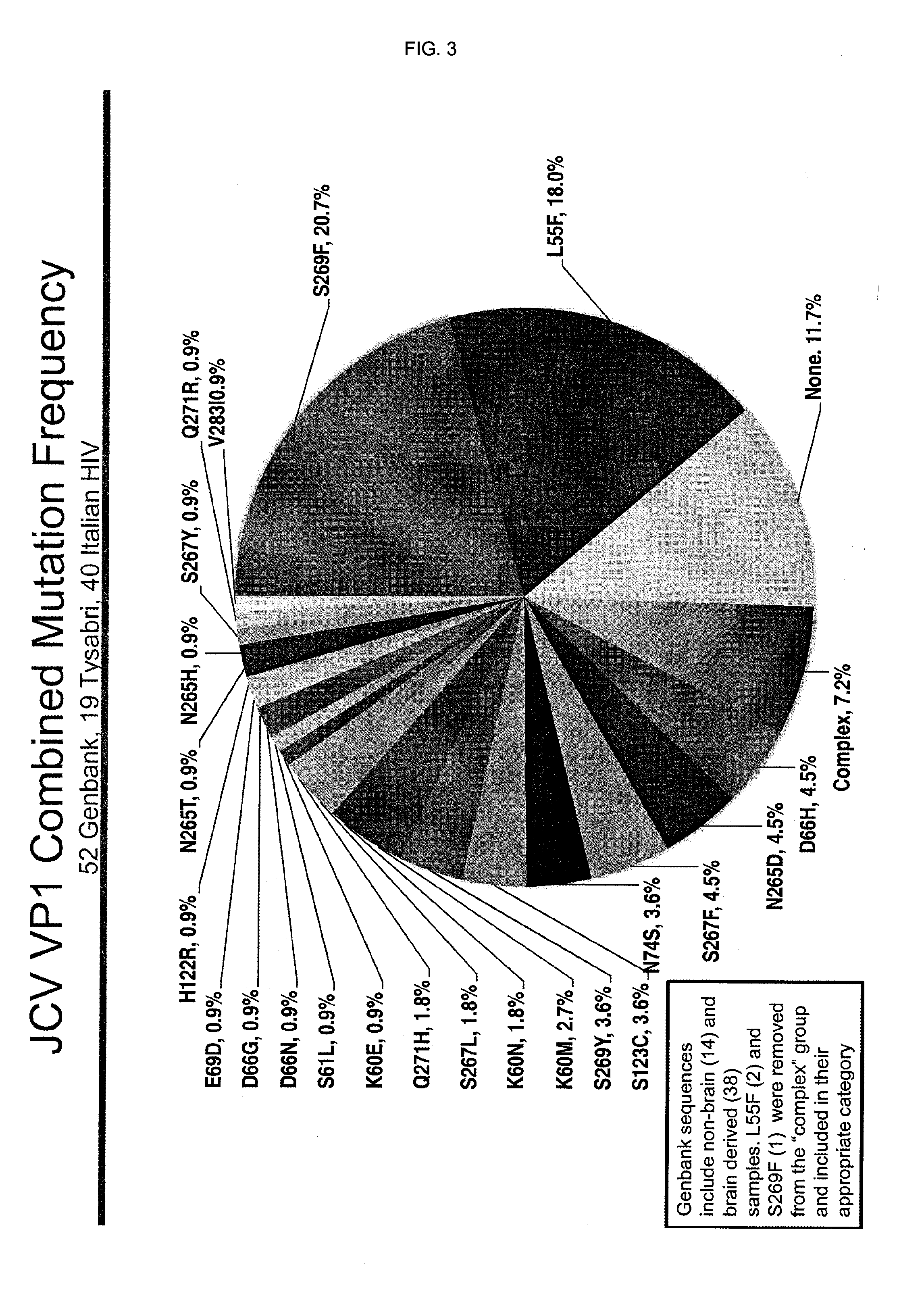
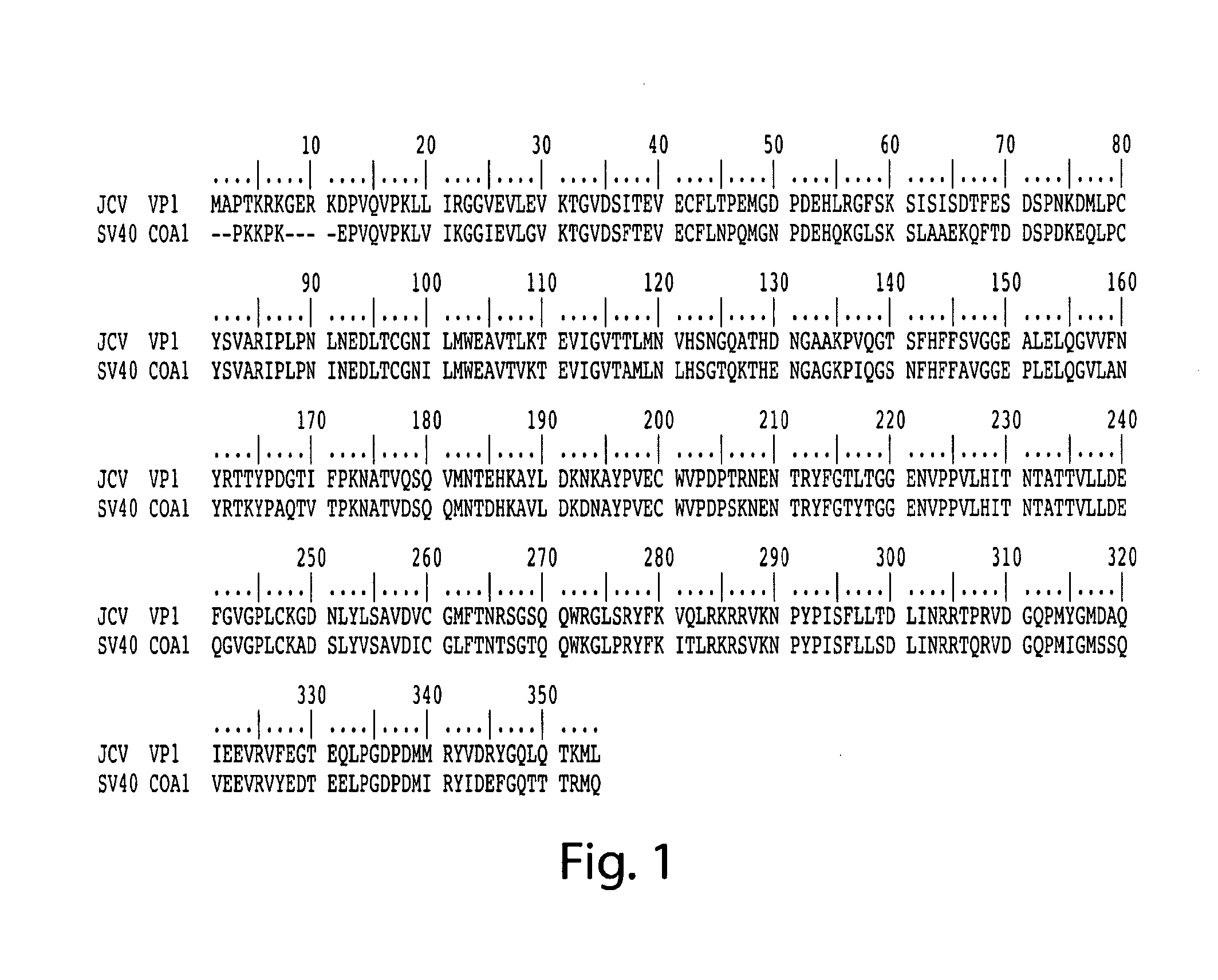
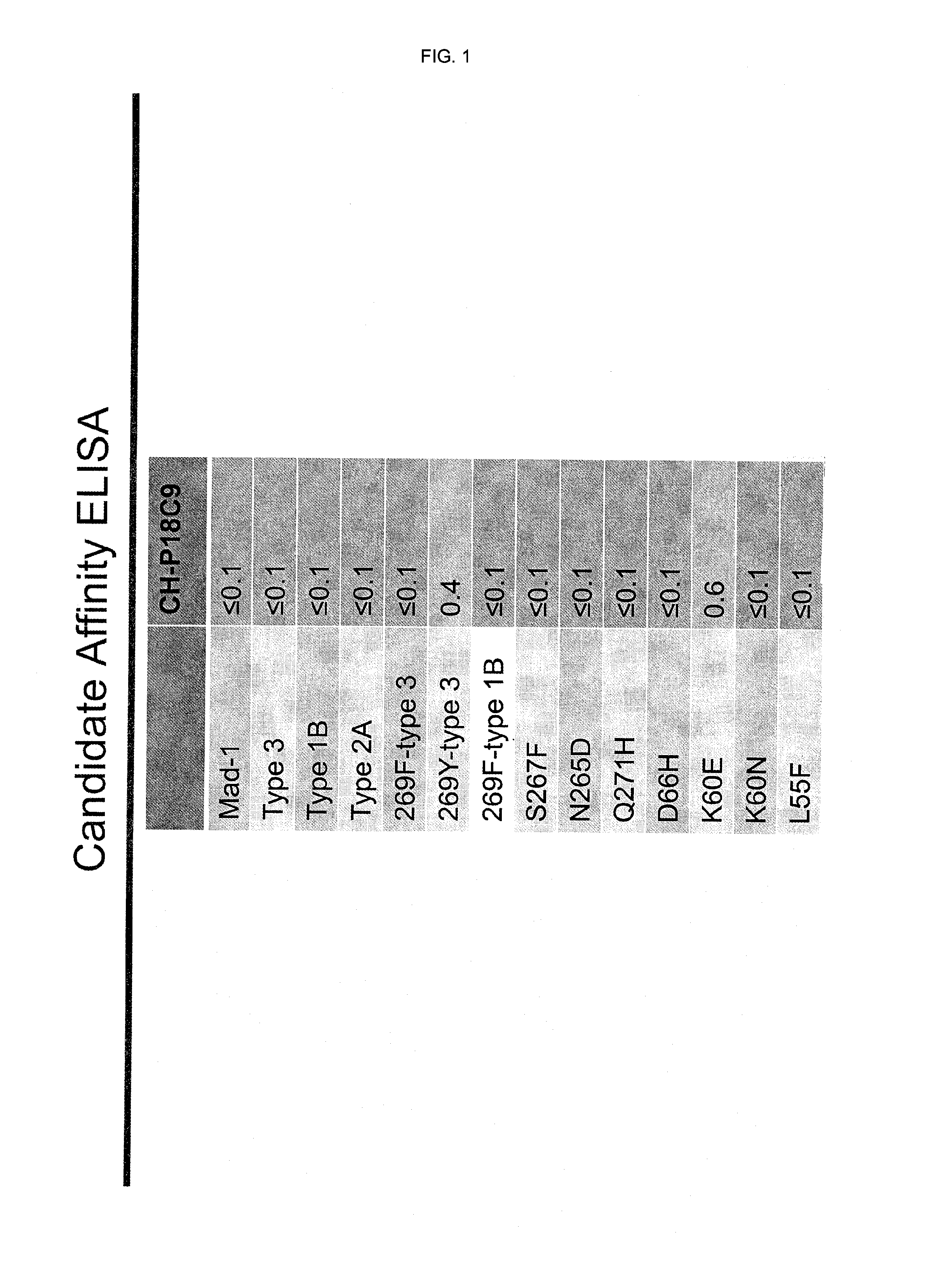
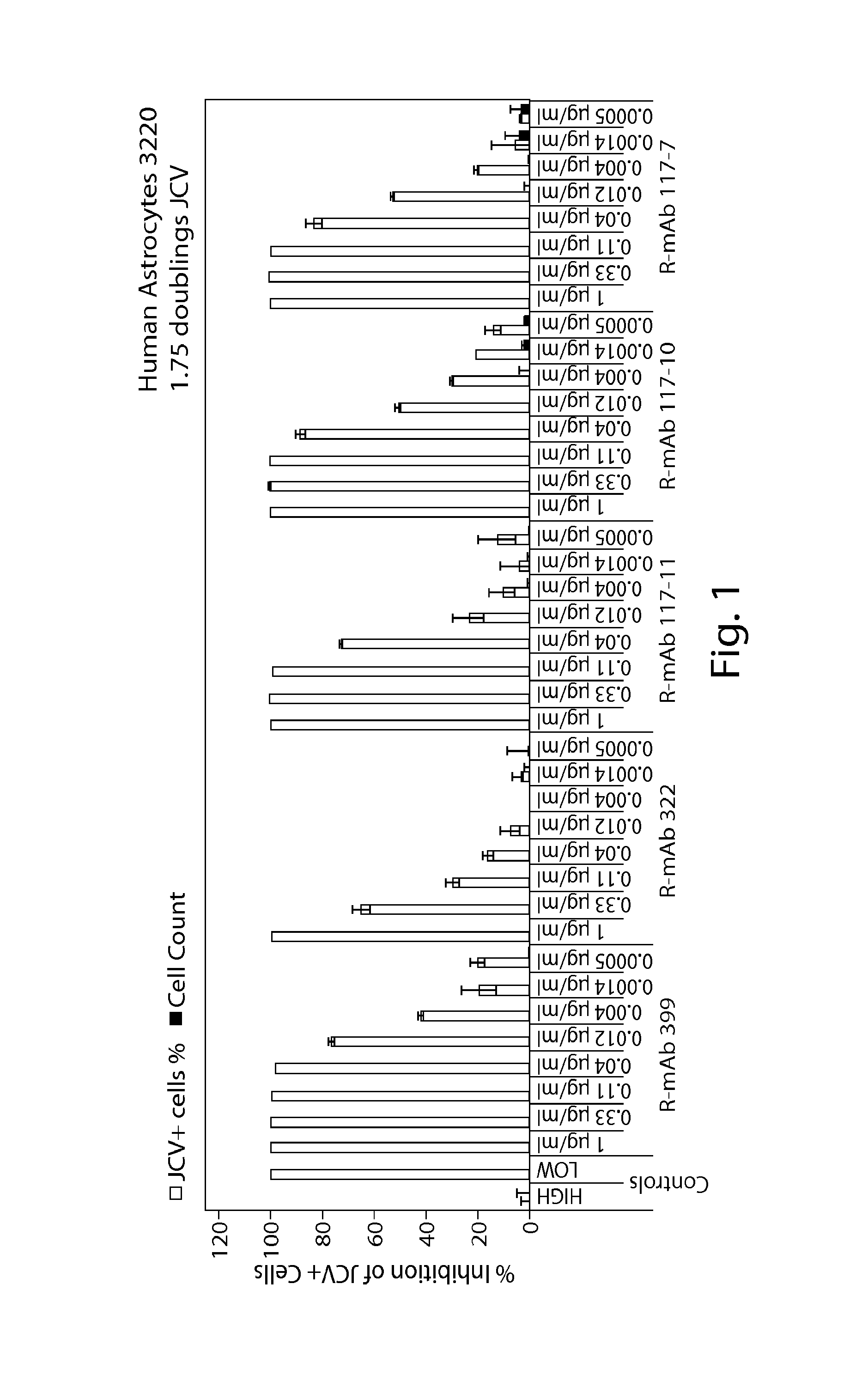
In one aspect, the disclosure provides neutralizing antibodies against JCV and methods for the treatment of PML. In some embodiments, aspects of the invention relate to an isolated JC-virus neutralizing monoclonal antibody against JCV capsid protein VPI (JCV-VP1). In some embodiments, the antibody suppresses infectivity of the JC-virus. In some embodiments, the antibody binds the sialic acid binding pocket of JCV-VPI. In some embodiments, the antibody binds JCV-VP 1 comprising one or more of the following mutations: S269F, S269Y, S267F, N265D, Q271 H, D66H, K60E, K60N and L55F.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Compositions for- detecting of influenza viruses and kits and methods using same
InactiveUS20090220941A1Quick checkOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding domainSialic acid binding
An isolated composition-of-matter comprising a sialic acid bound to a sialic acid binding domain of a polypeptide is provided. Uses thereof and kits comprising same are also provided.
Owner:MND DIAGNOSTICS LTD
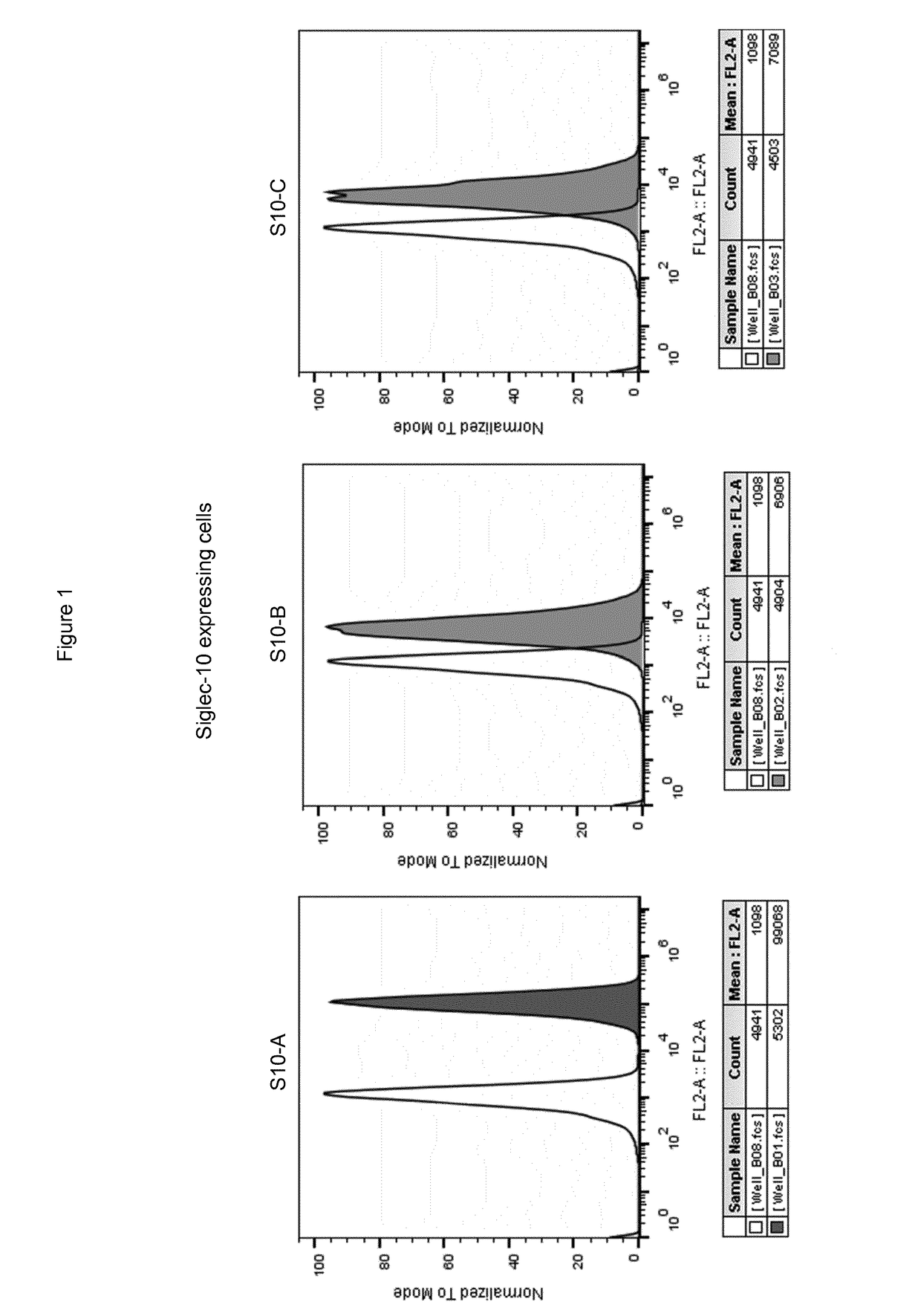
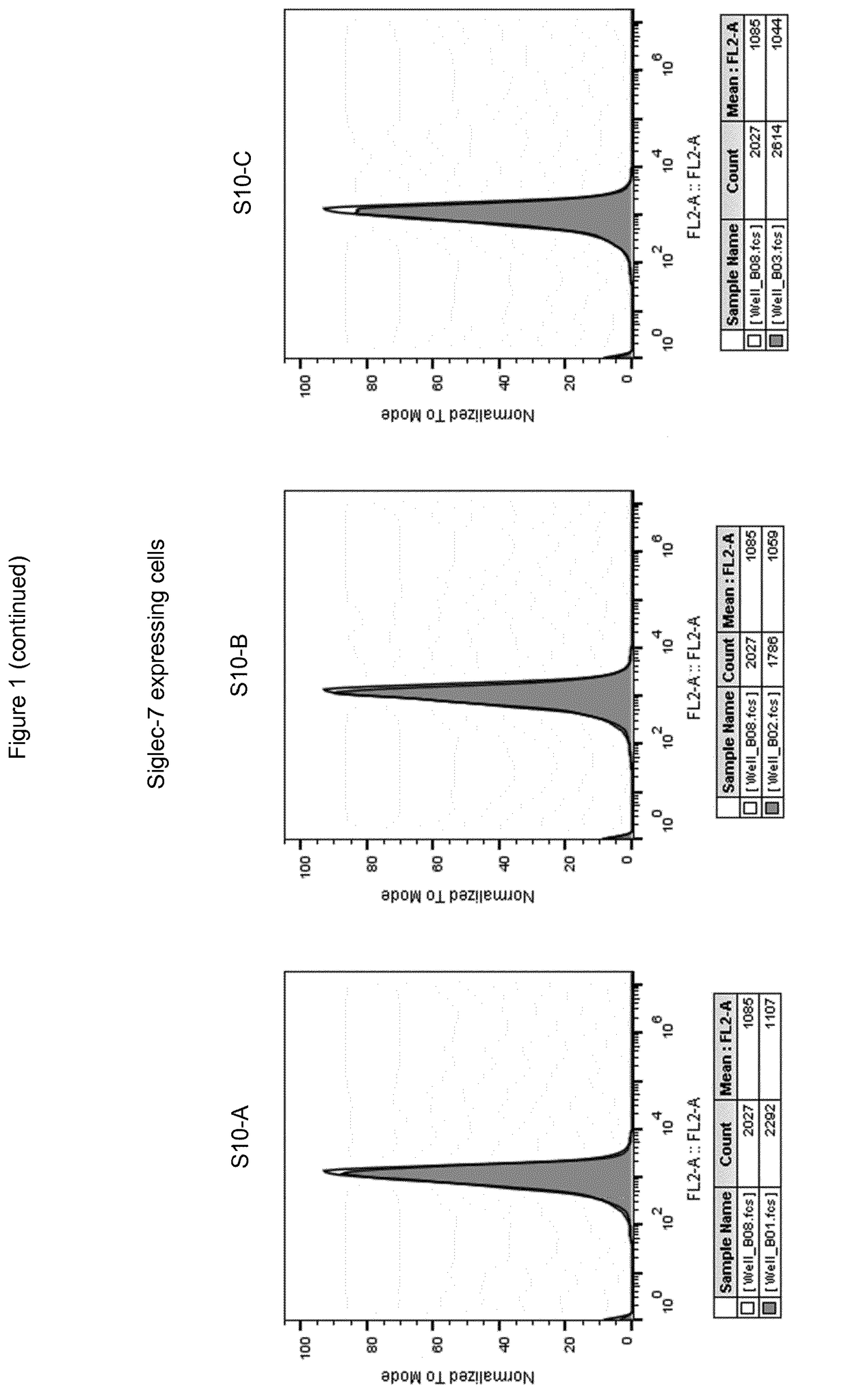
Siglec-10 antibodies
ActiveUS20180344829A1Improve abilitiesInhibit bindingCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLymphocyteWilms' tumor
This disclosure relates to agents that bind and neutralize the inhibitory activity of Siglec-10 in lymphocytes, notably by inhibiting the binding of Siglec-10 to its sialic acid ligands on target cells, notably tumor cells. Such agents can be used for the treatment of cancers.
Owner:INNATE PHARMA SA
Methods for the detection of jc polyoma virus
InactiveUS20120258443A1Improved profileHigh profileMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisSequence variationSialic acid binding
Methods and compositions for determining whether a subject is at risk for PML, including subjects being treated with immunosuppressants, by determining whether the subject harbors a JCV variant with reduced binding for sialic acid relative to a normal JCV, are presented. Furthermore, combinations of JCV-VP1 sequence variations that are associated with PML and that can be used as a basis of an assay for identifying subjects susceptible to PML, subjects with PML (e.g., early stage PML), or subjects at risk of developing PML in response to an immunosuppressive treatment are provided.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Binding domains from Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte binding proteins
The present invention provides isolated polypeptides useful in the treatment and prevention of malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum or P. vivax. In particular, the polypeptides are derived from the binding domains of the proteins in the EBL family as well as the sialic acid binding protein (SABP) on P. falciparum merozoites. The polypeptides may also be derived from the Duffy antigen binding protein (DABP) on P. vivax merozoites.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Novel epitope and mechanism of antigen-antibody interaction in an influenza virus
InactiveUS20140086927A1Molecular designMicrobiological testing/measurementHemagglutininNeutralizing antibody
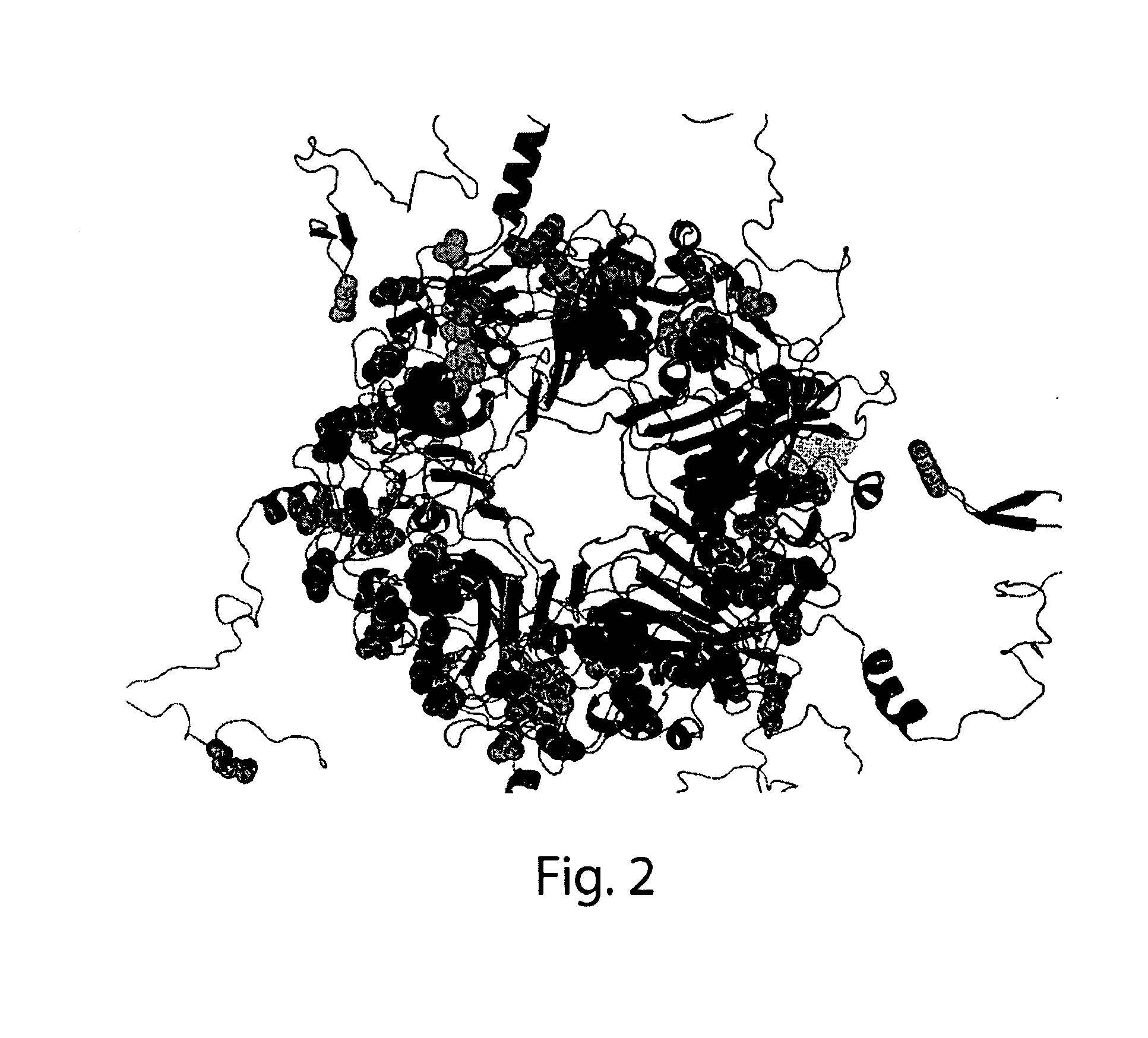
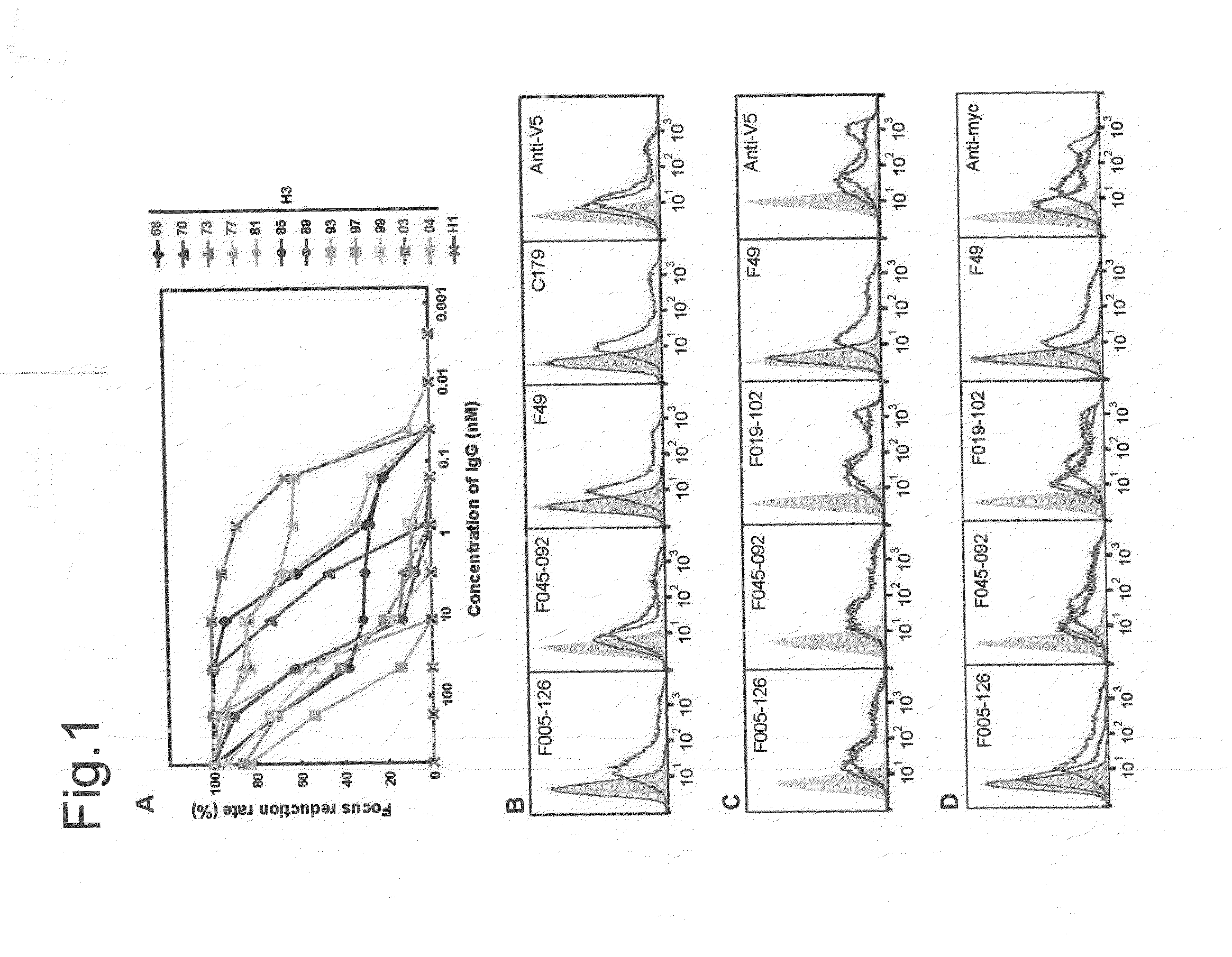
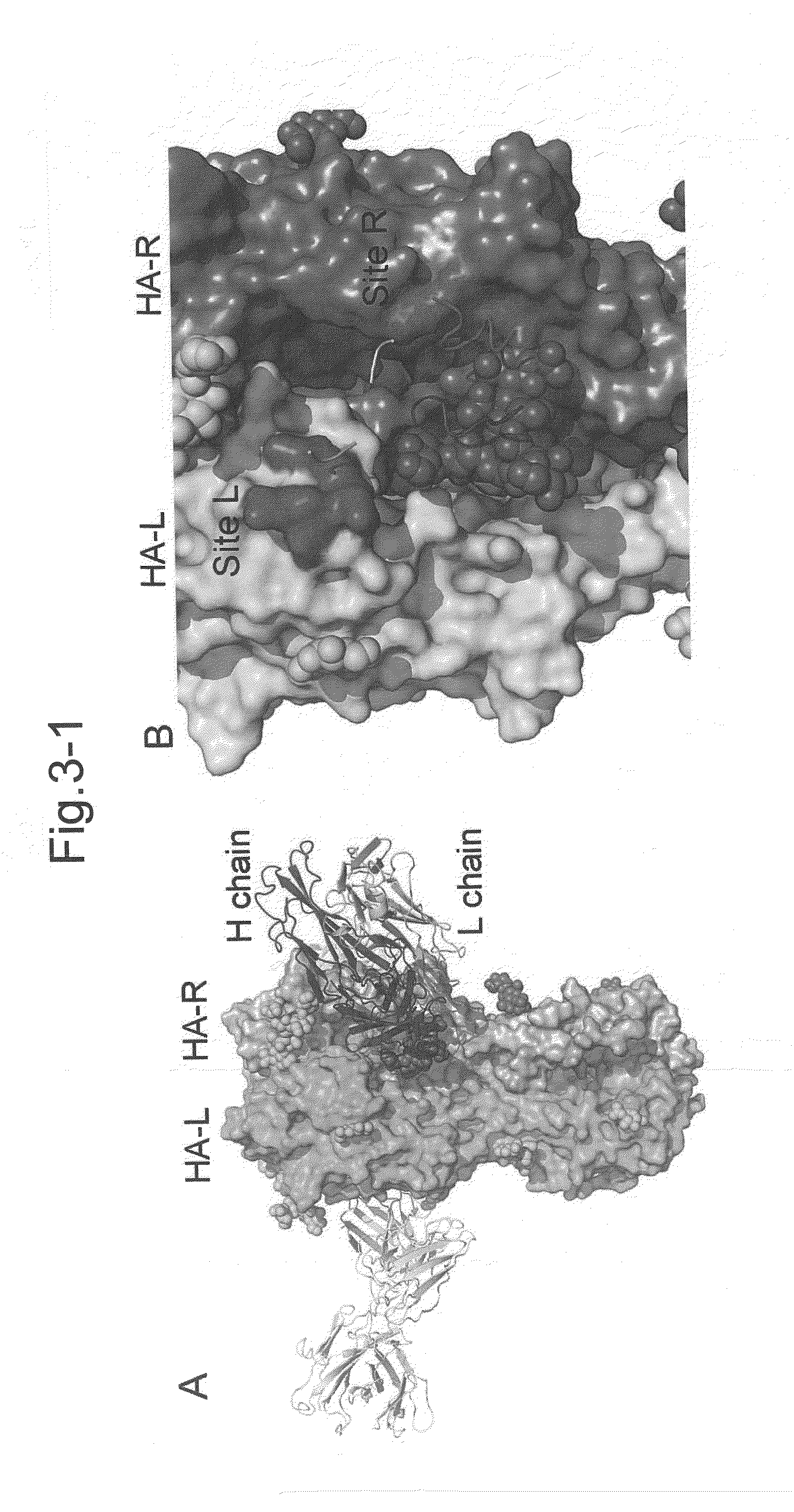
Antibodies (Abs) play roles in protection against influenza. Neutralizing Abs either inhibit the binding of hemagglutinin (HA) to cellular receptors or prevent the conformational change of HA induced by low pH. The former Ab binds to the regions near the sialic acid-binding pocket on the globular head formed by HA1 and generally shows narrow strain specificity. The latter Ab binds to the stem region formed mainly by HA2 and shows broad strain specificity. We isolated a broadly neutralizing Ab against H3N2 viruses. X-ray analysis of the HA / Ab complex indicated that the Ab binds to the valley formed by two neighboring HA monomers at the side of the globular head. The Ab shows neutralizing activity by preventing the conformational change of HA induced at low pH.
Owner:FUJITA HEALTH UNIVERSITY
Process for producing virus vector containing membrane protein having sialic acid-binding in envelope with the use of gram-positive bacterium origin nueraminidase
InactiveUS20060128019A1Reduce riskWider range of infectivitySsRNA viruses negative-senseFermentationHematopoietic cellMucous cell
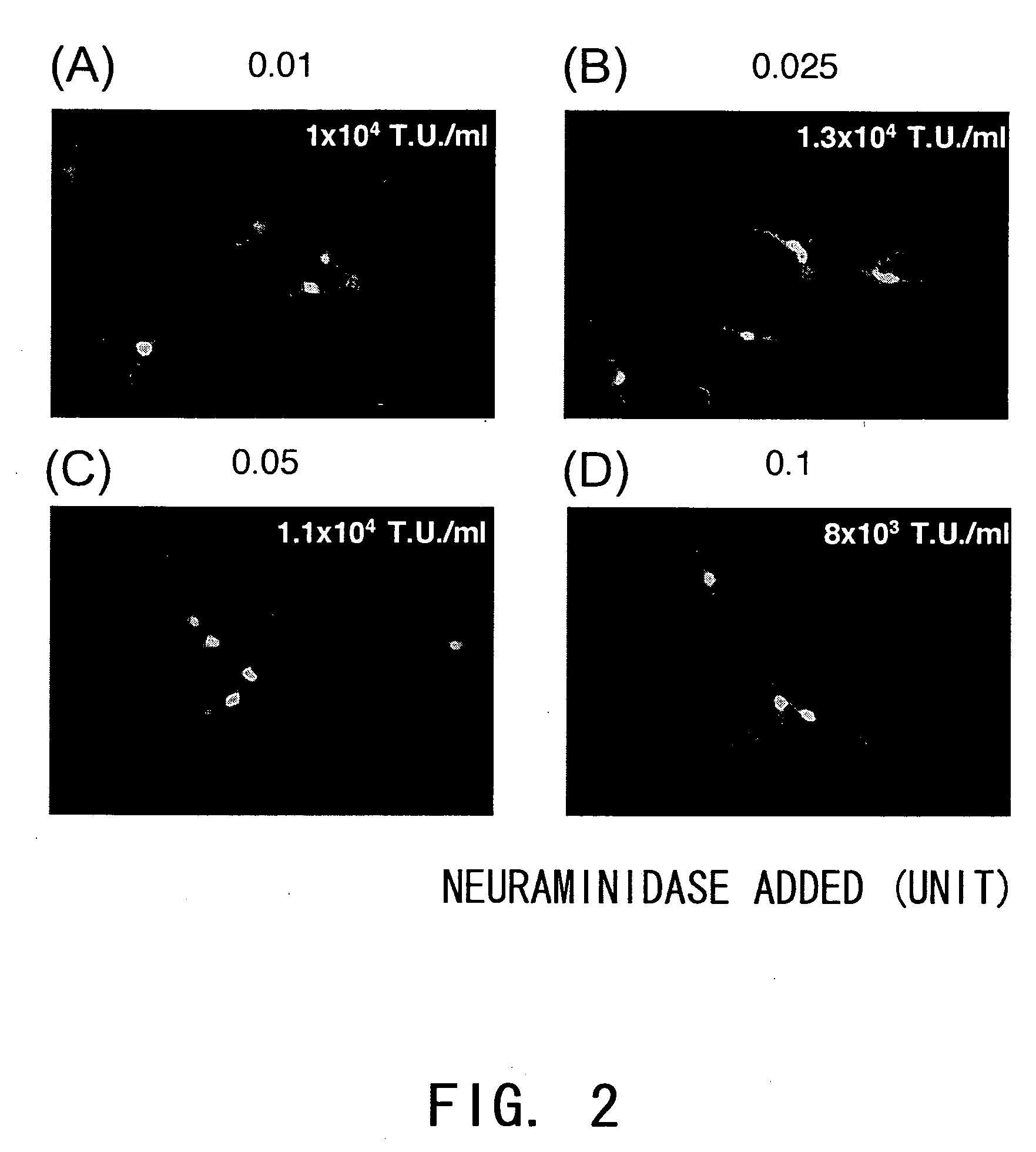
The present invention provides methods for producing a viral vector comprising a membrane protein that binds to sialic acid as a component of the envelope, using neuraminidase (NA) derived from Gram-positive bacteria. The methods comprise the steps of culturing cells producing a viral vector in the presence of an NA from Gram-positive bacteria, and recovering the produced virus. The methods of this invention enable the production of high titer virus at high cost performance. Such a viral vector is capable of transferring genes at high efficiency into cells such as blood cells and hematopoietic cells, including hematopoietic stem cells, and mucous cells including mucoepithelial cells, those not amenable to gene transfer by conventional methods, and therefore should be useful as a vector for gene therapy.
Owner:DNAVEC RES
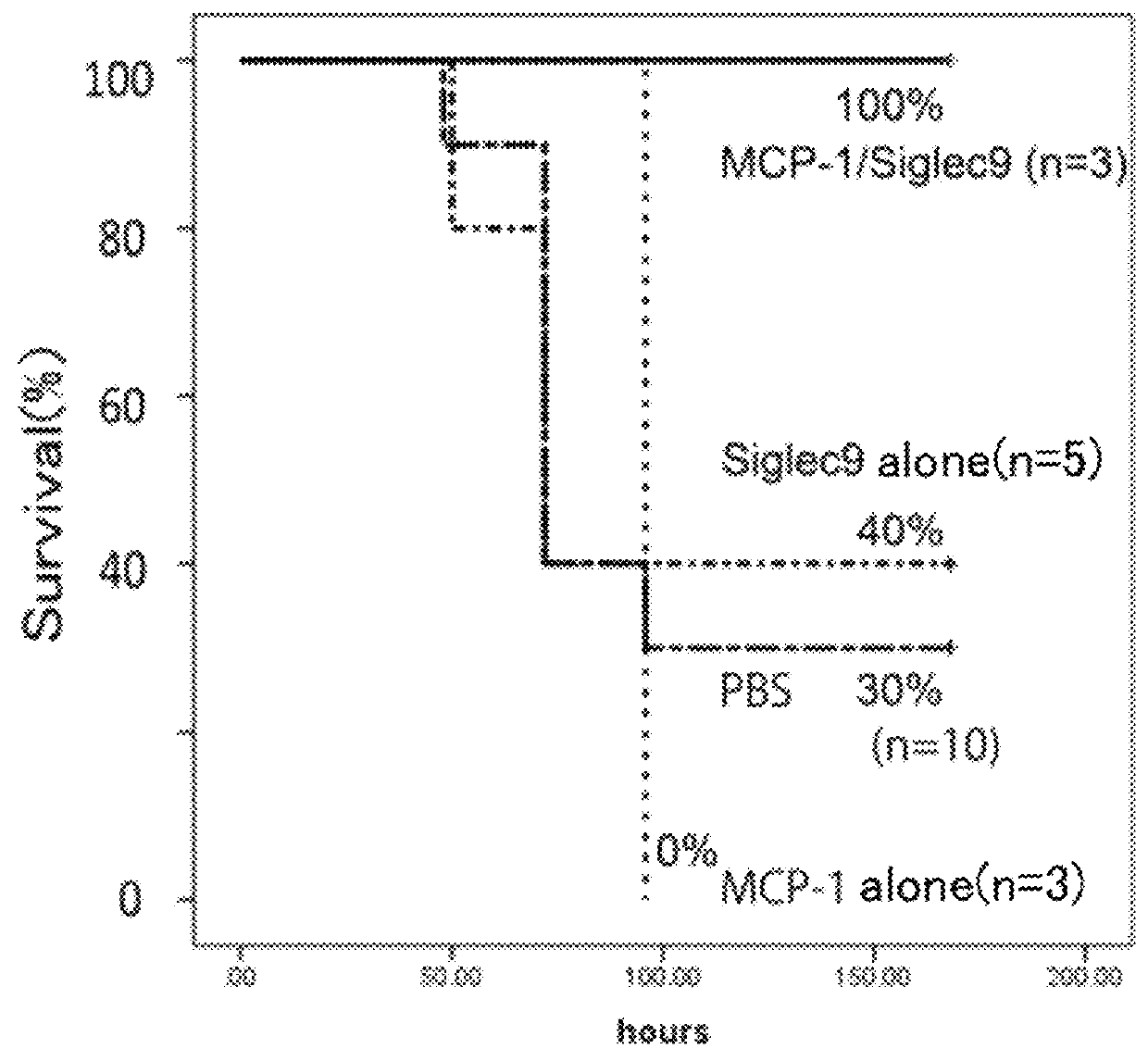
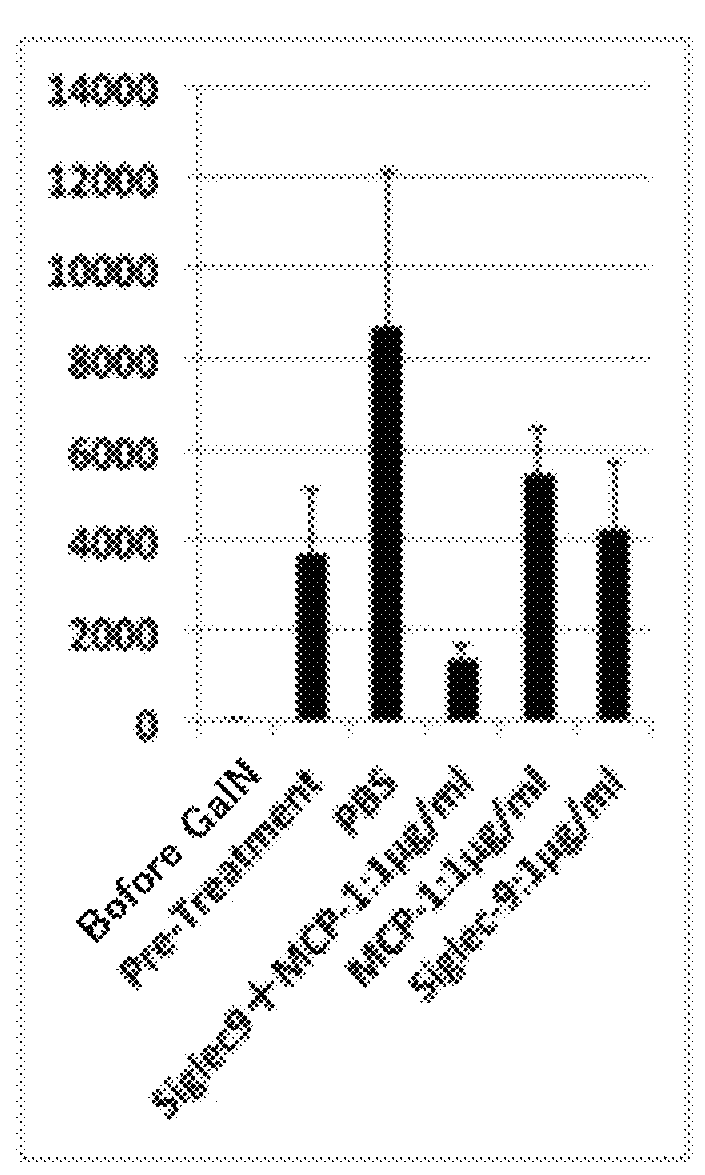
Composition having tissue-repairing activity, and use therefor
ActiveUS20180311313A1Promote productionIncrease in anti-inflammatory cytokinesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderTissue repairChondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycans
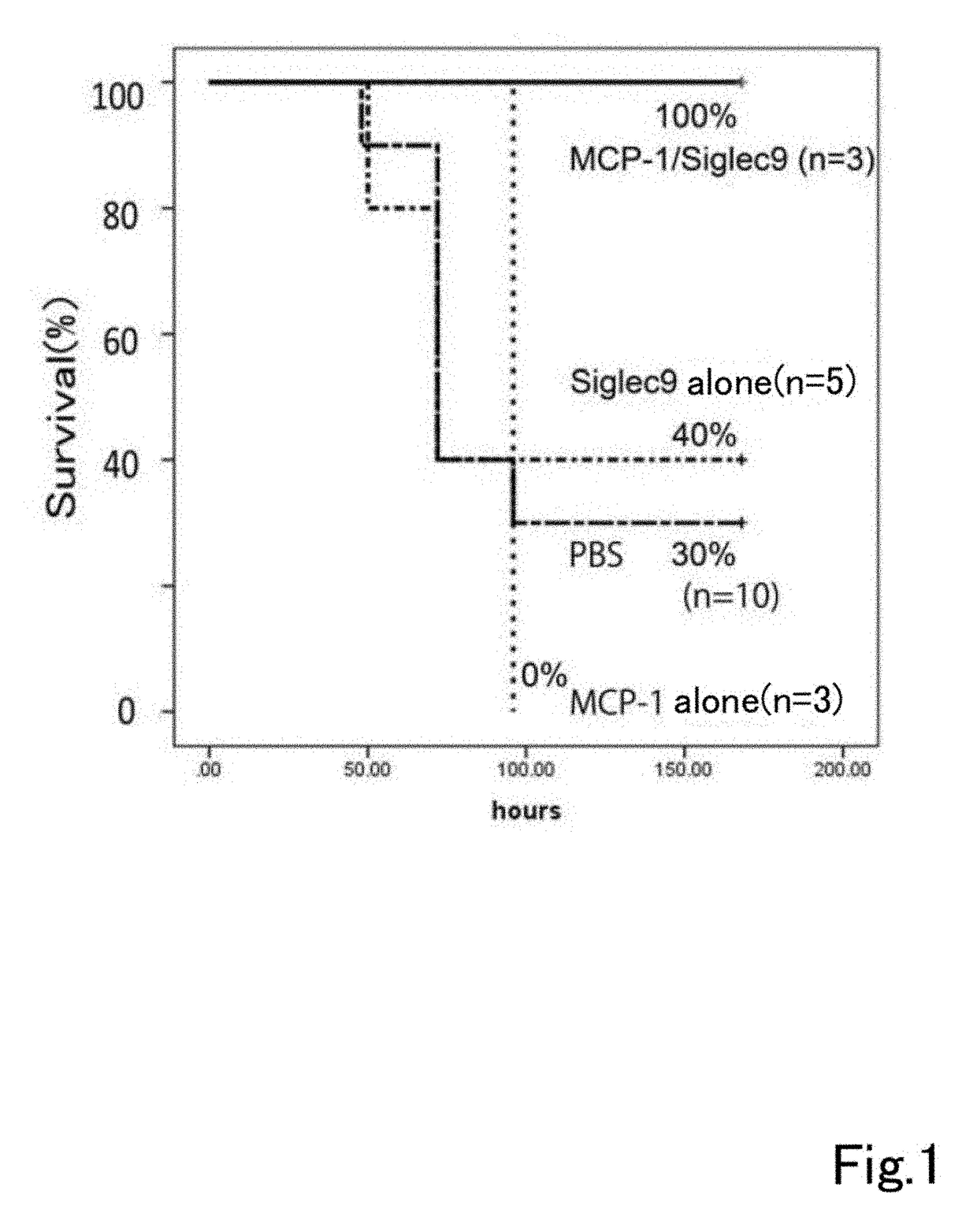
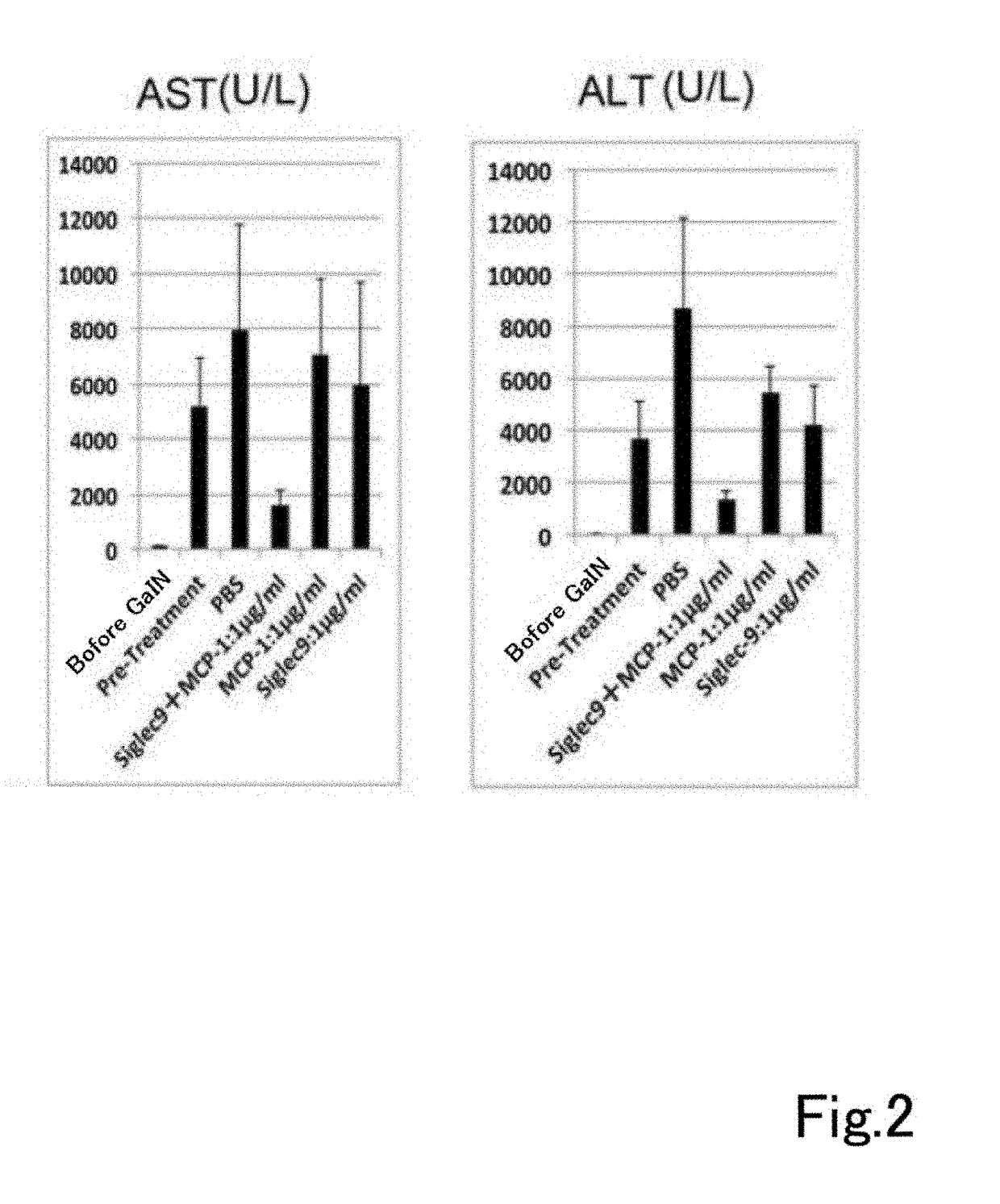
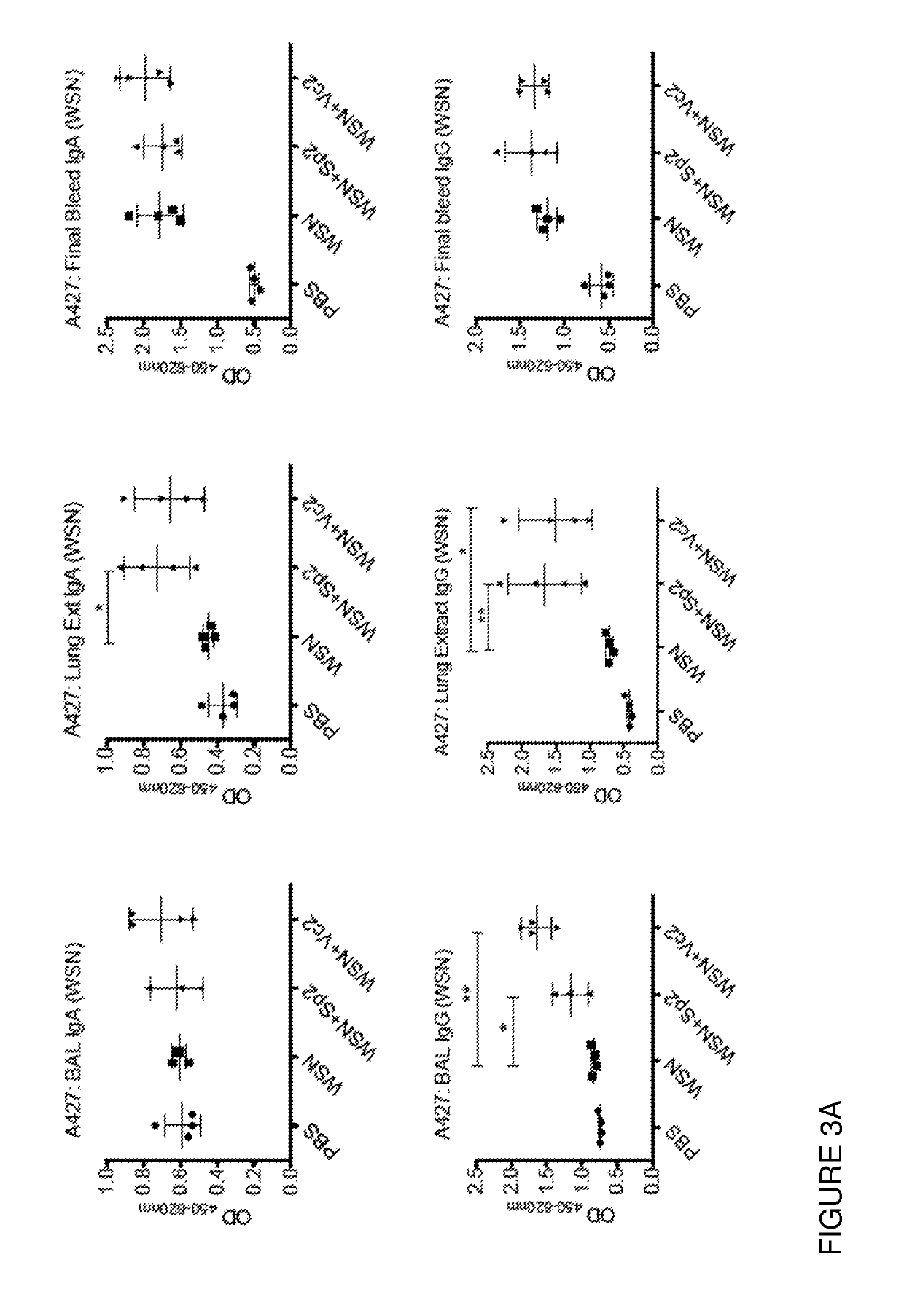
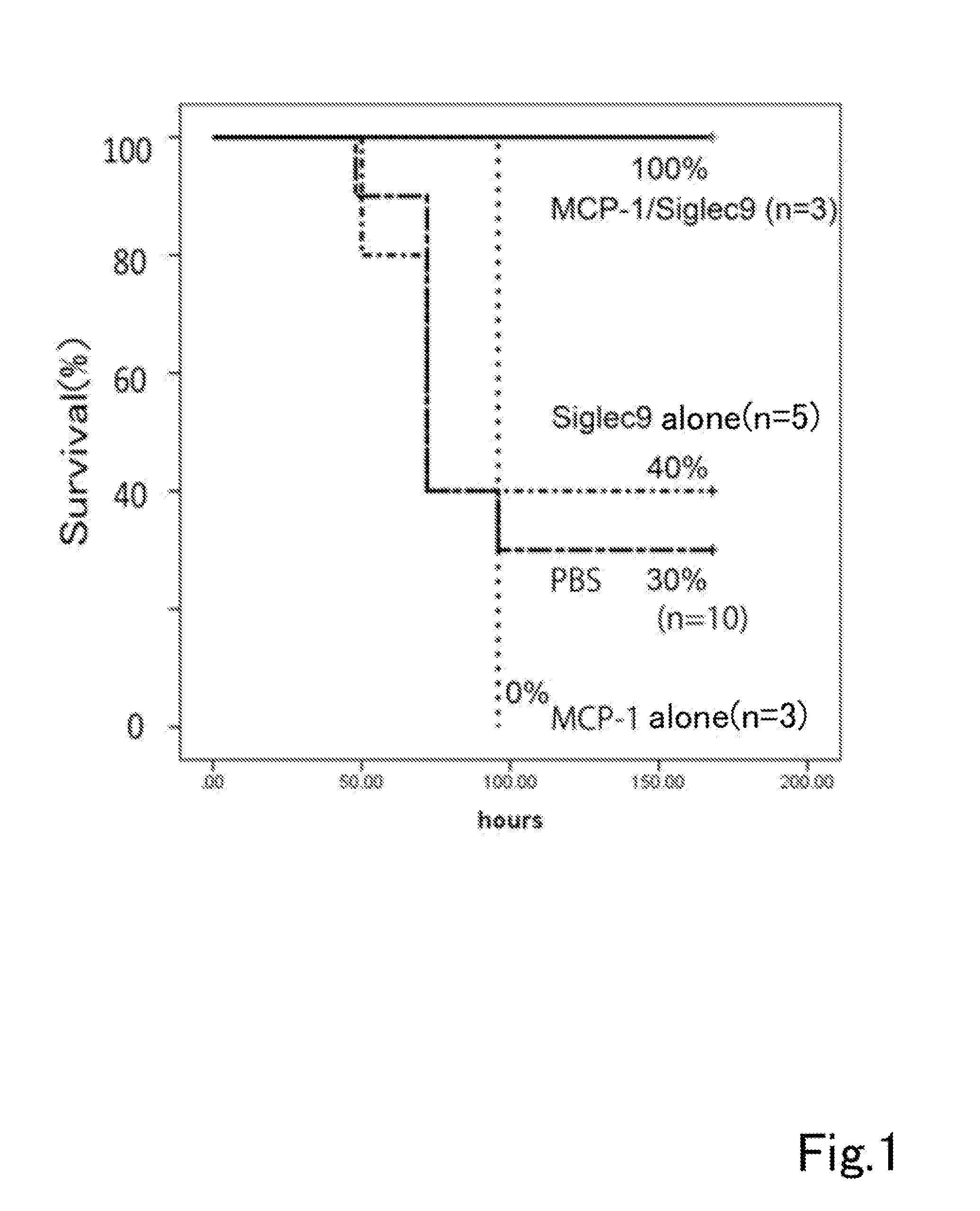
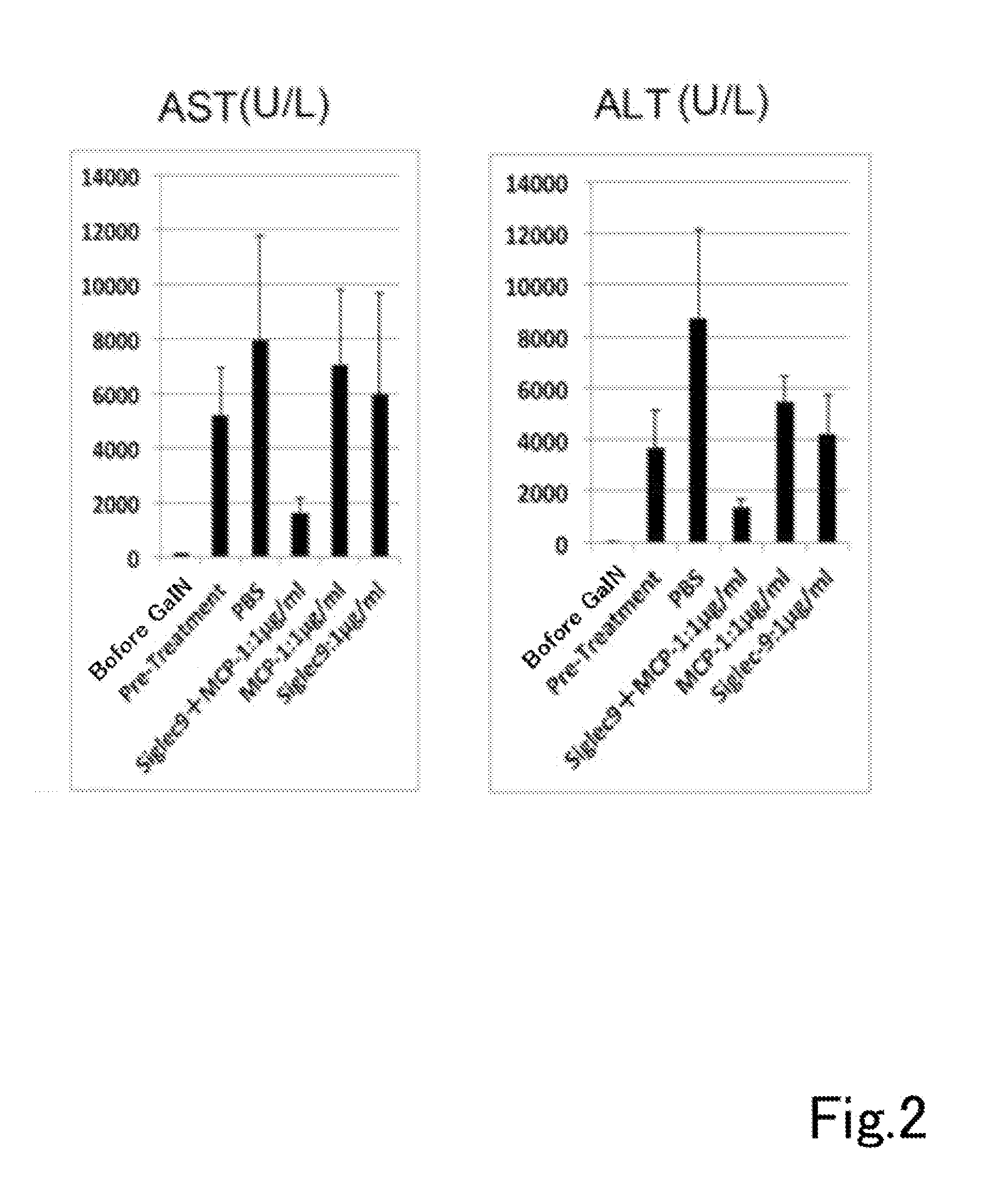
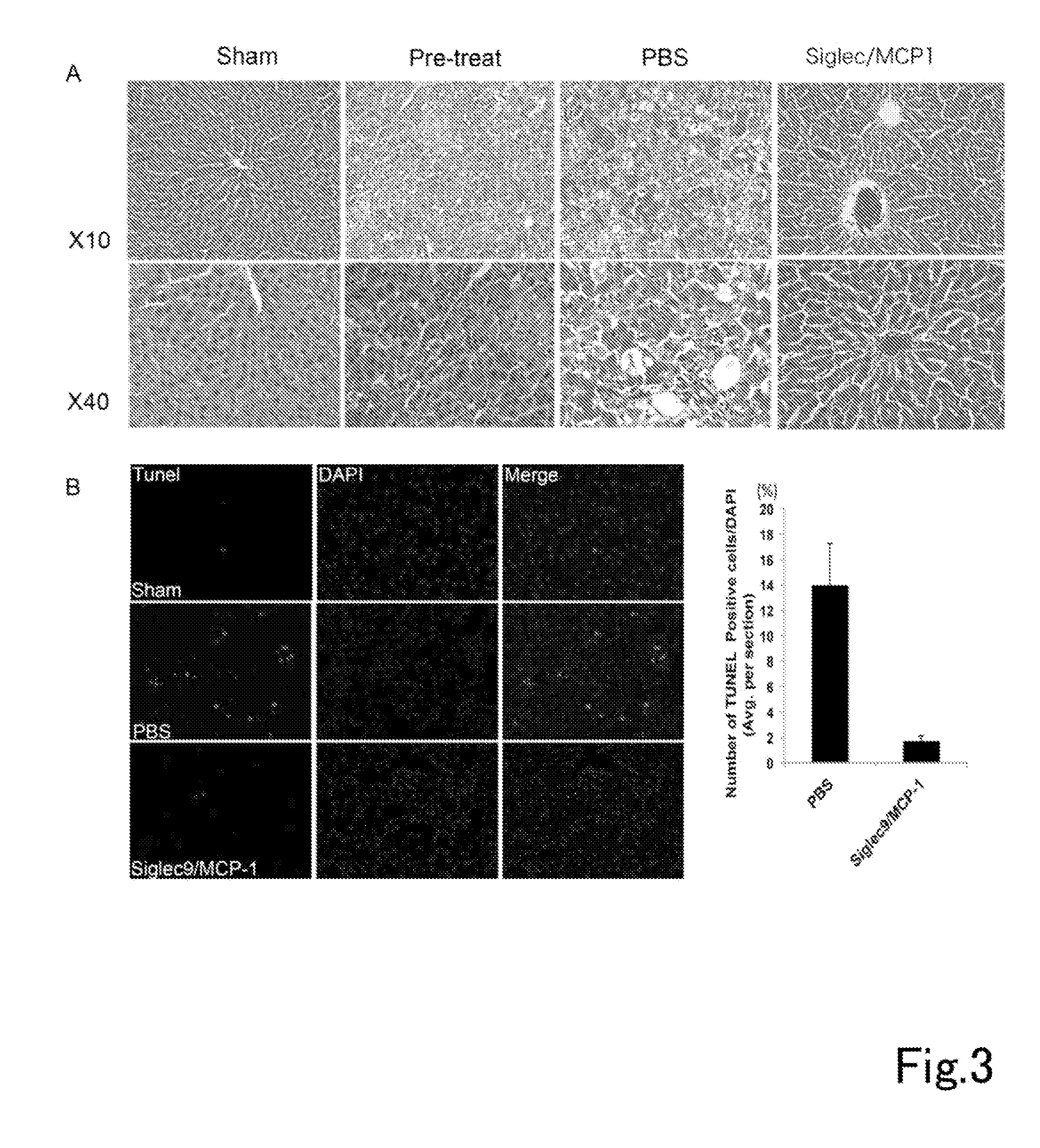
A composition having tissue repair activity, which is capable of promoting reactions associated with tissue repair, contains at least one selected from the group consisting of a first component that is a protein having a monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) activity, a second component that is a protein having the extracellular domain activity of sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectin-9 (Siglec-9), and a third component that is at least one of chondroitin sulfate and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOKUSHIMA
Immunomodulatory compounds
ActiveUS20170007692A1Avoid infectionFacilitate pathogen loadSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsDiseaseSialic acid binding
The present invention is based on the finding that in addition to interfering with or blocking, preventing and / or inhibiting the interaction between a pathogen and, for example, a sialic acid containing cell surface receptor, certain sialic acid binding molecules have immunomodulatory properties. The invention provides methods and uses which exploit sialic acid binding molecules in the treatment and / or prevention of disease by modulation and / or priming of the host immune response.
Owner:PNEUMAGEN LTD
Jcv neutralizing antibodies
ActiveUS20150050271A1Reduce viral loadIncrease awarenessImmunoglobulins against virusesAntibody ingredientsMonoclonal antibodyNeutralizing antibody
In one aspect, the disclosure provides neutralizing antibodies against JCV and methods for the treatment of PML. In some embodiments, aspects of the invention relate to an isolated JC-vims neutralizing monoclonal antibody against JCV capsid protein VPI (JCV-VP1). In some embodiments, the antibody suppresses infectivity of the JC-vims. In some embodiments, the antibody binds the sialic acid binding pocket of JCV-VP1.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Composition having tissue-repairing activity, and use therefor
ActiveUS9962428B2Promote productionIncrease in anti-inflammatory cytokinesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderTissue repairChondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycans
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOKUSHIMA
Methods for the detection of jc polyoma virus
InactiveUS20130101985A9Improved profileHigh profileMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisSequence variationSialic acid binding
Methods and compositions for determining whether a subject is at risk for PML, including subjects being treated with immunosuppressants, by determining whether the subject harbors a JCV variant with reduced binding for sialic acid relative to a normal JCV, are presented. Furthermore, combinations of JCV-VP1 sequence variations that are associated with PML and that can be used as a basis of an assay for identifying subjects susceptible to PML, subjects with PML (e.g., early stage PML), or subjects at risk of developing PML in response to an immunosuppressive treatment are provided.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
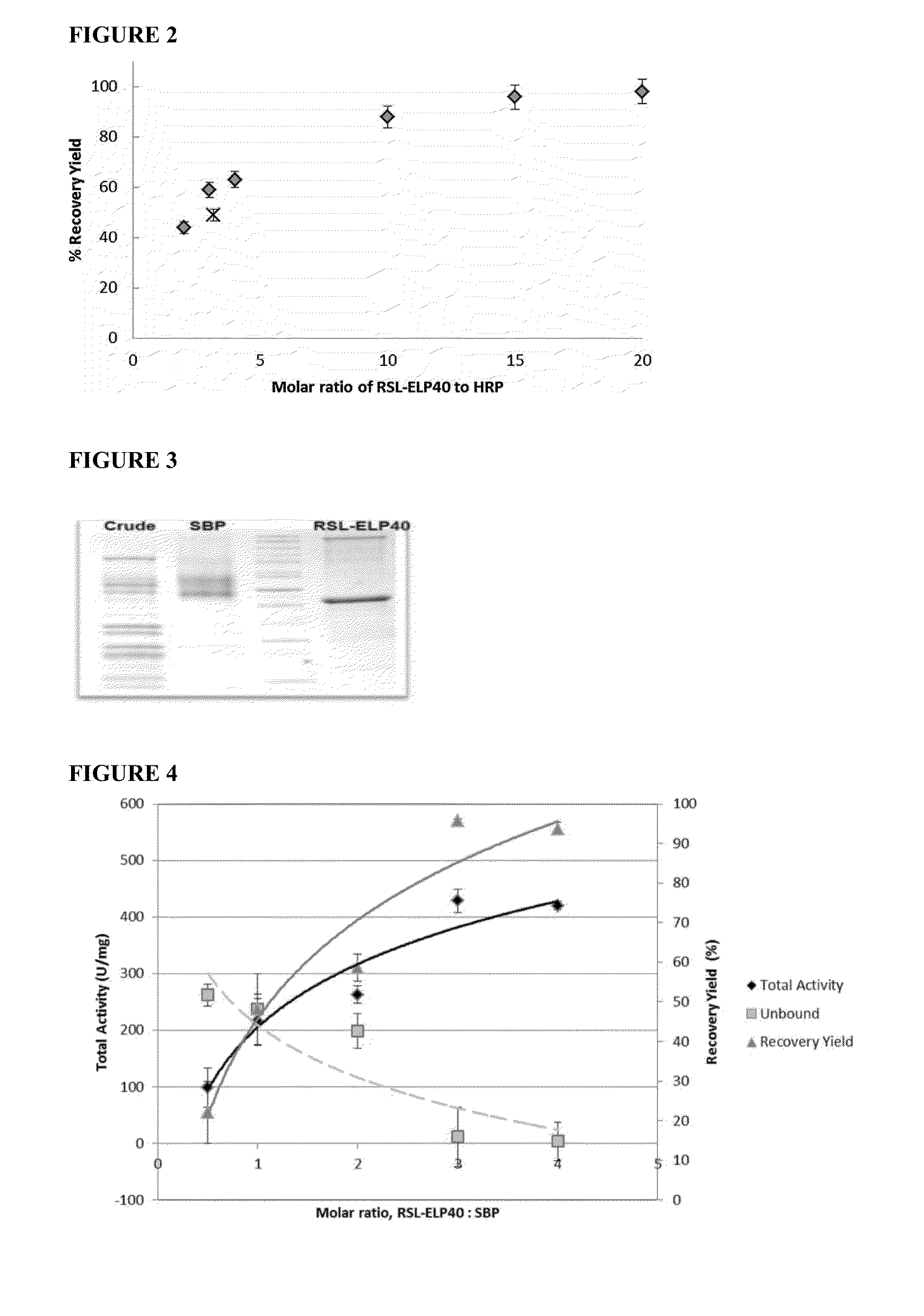
Thermo-responsive lectin-elp fusion binding ligands for glycoprotein purification by affinity precipitation
InactiveUS20150307546A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsElastin like polypeptidesNeuraminidase
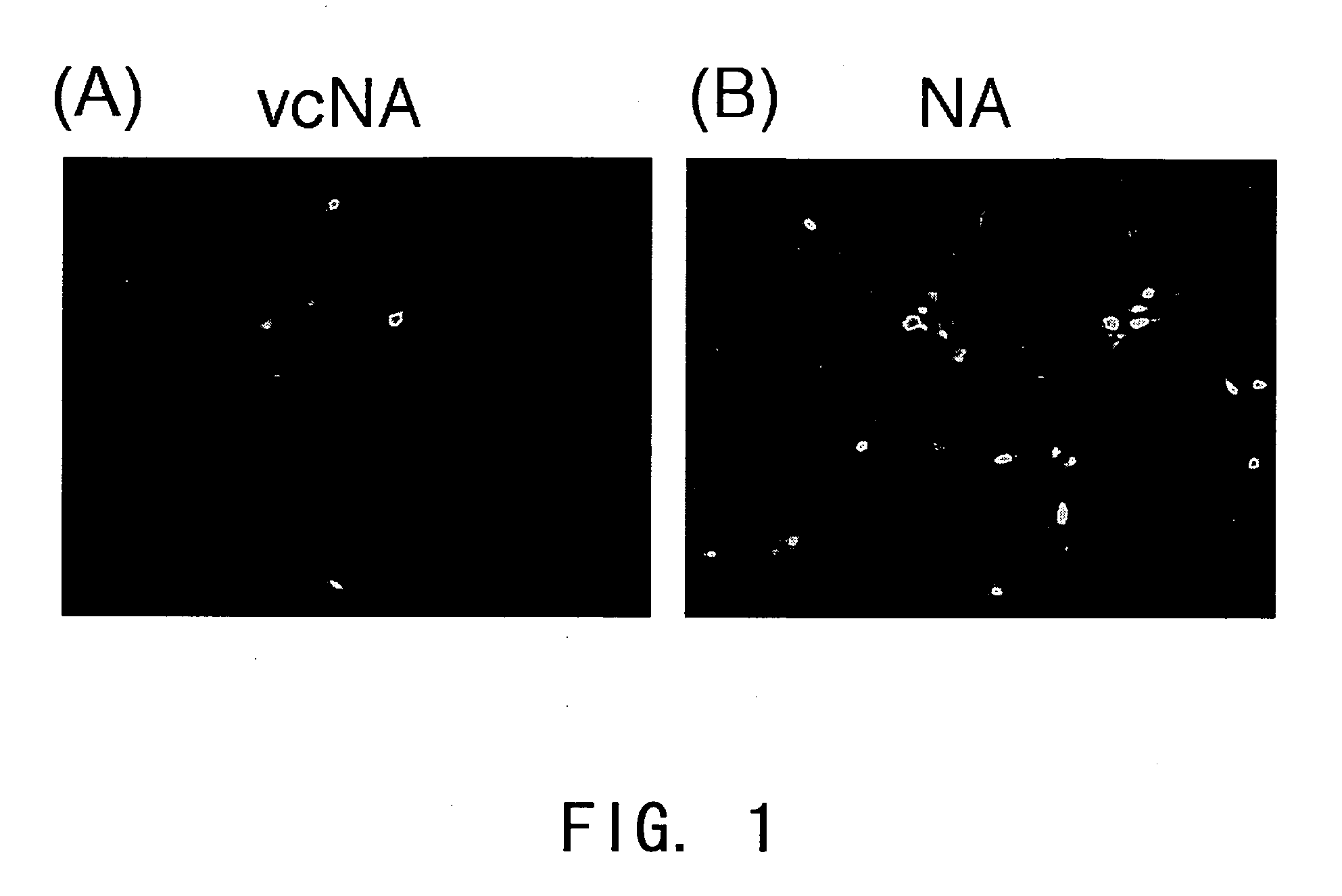
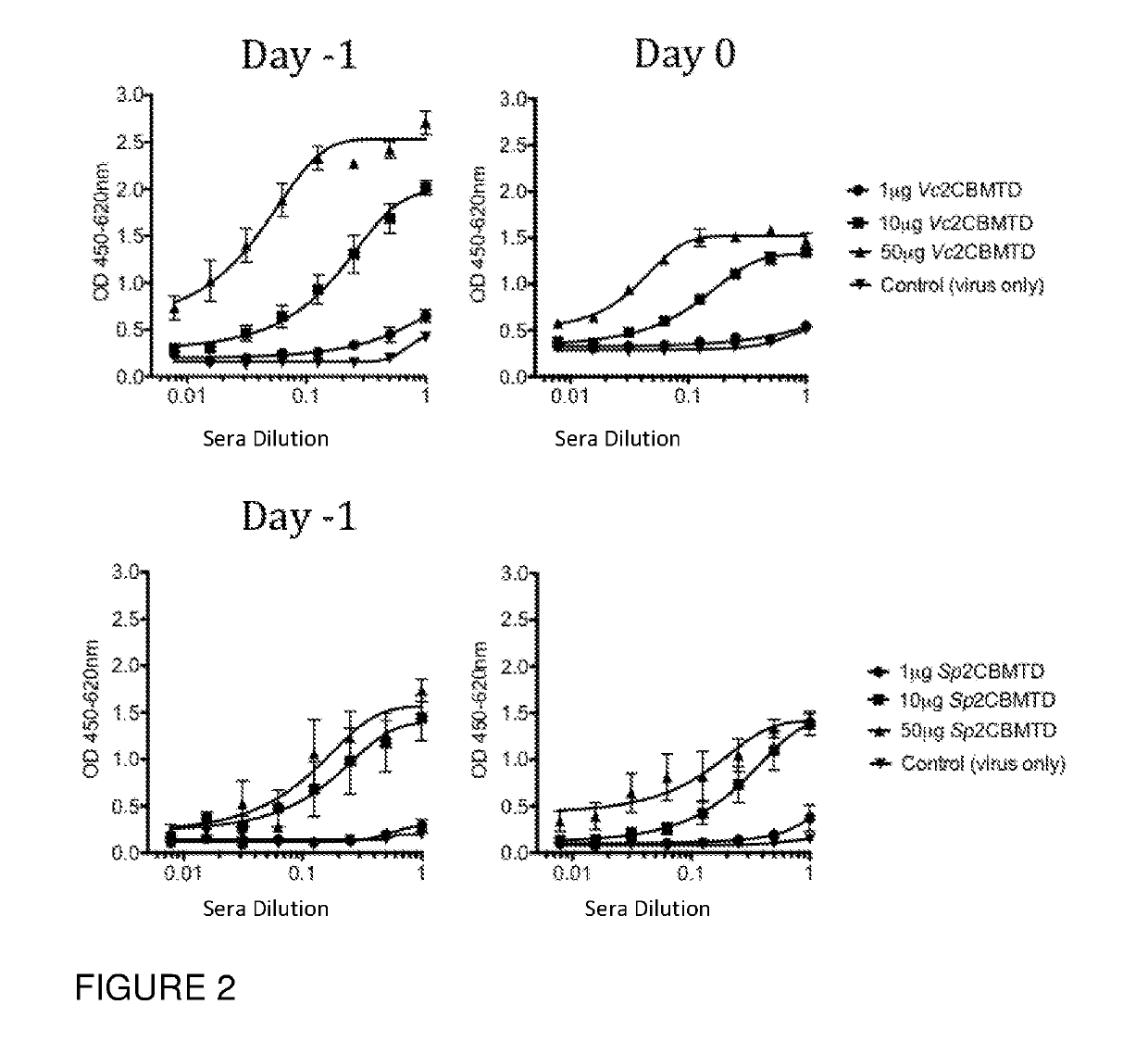
The invention provides novel affinity fusion ligands, and method of use thereof, for glycoprotein purification by affinity precipitation. The affinity fusion ligand of the invention comprises a bacterial lectin, e.g., from Ralstonia solanacearum (RSL) that binds to fucose, and / or from the Vibrio cholera neuraminidase (VCNA) that binds to saialic acid, fused with a thermo-responsive polypeptide, e.g., an elastin-like polypeptides (ELP) repeats. Methods of using the lectin-ELP fusion ligand for purifying a glycoprotein via affinity precipitation are also provided herewith.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
JCV neutralizing antibodies
ActiveUS9567391B2Immunoglobulins against virusesAntibody ingredientsPolyomavirus JCMonoclonal antibody
In one aspect, the disclosure provides neutralizing antibodies against JCV and methods for the treatment of PML. In some embodiments, aspects of the invention relate to an isolated JC-virus neutralizing monoclonal antibody against JCV capsid protein VPI (JCV-VP1). In some embodiments, the antibody suppresses infectivity of the JC-virus. In some embodiments, the antibody binds the sialic acid binding pocket of JCV-VPI. In some embodiments, the antibody binds JCV-VP 1 comprising one or more of the following mutations: S269F, S269Y, S267F, N265D, Q271 H, D66H, K60E, K60N and L55F.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
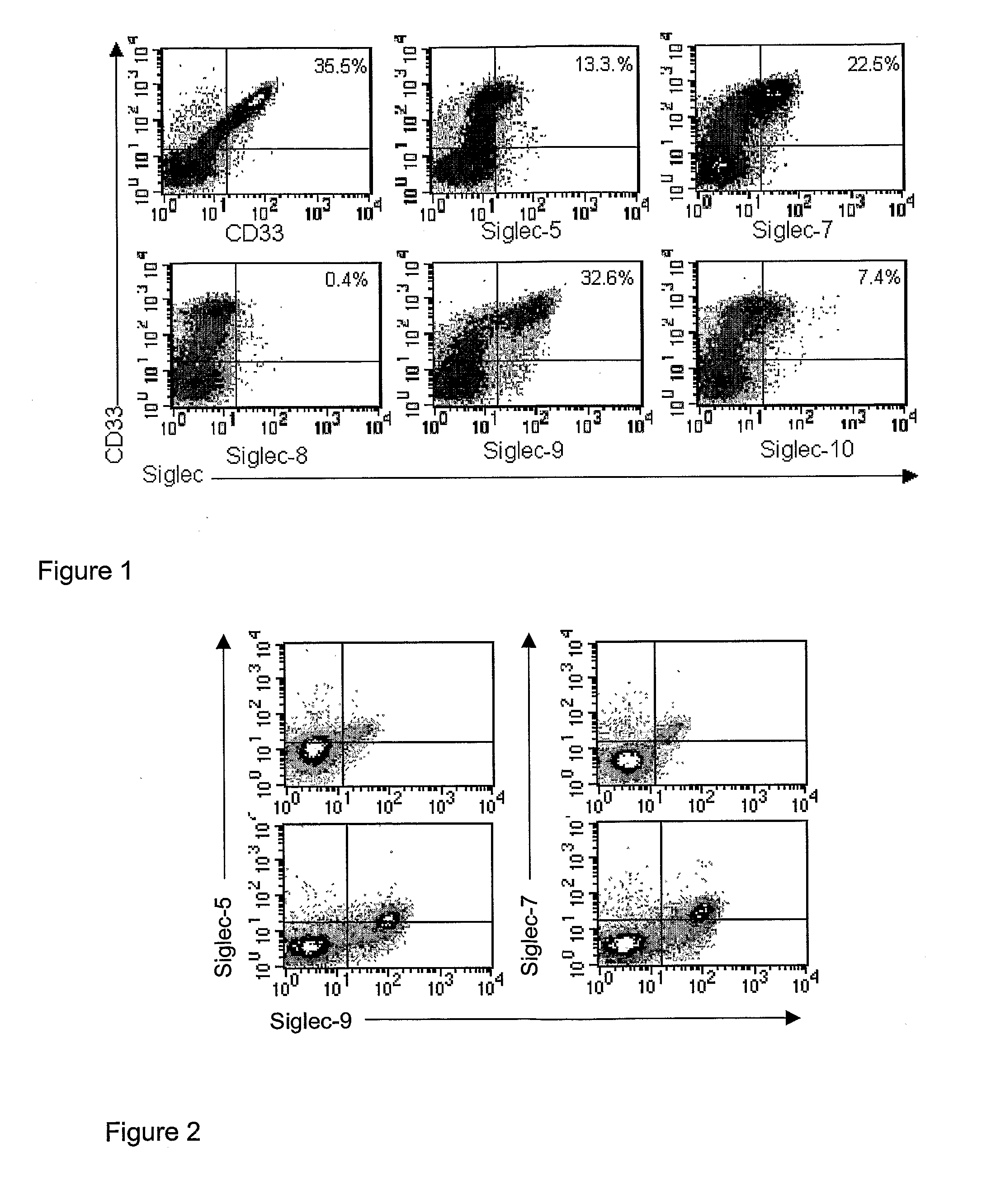
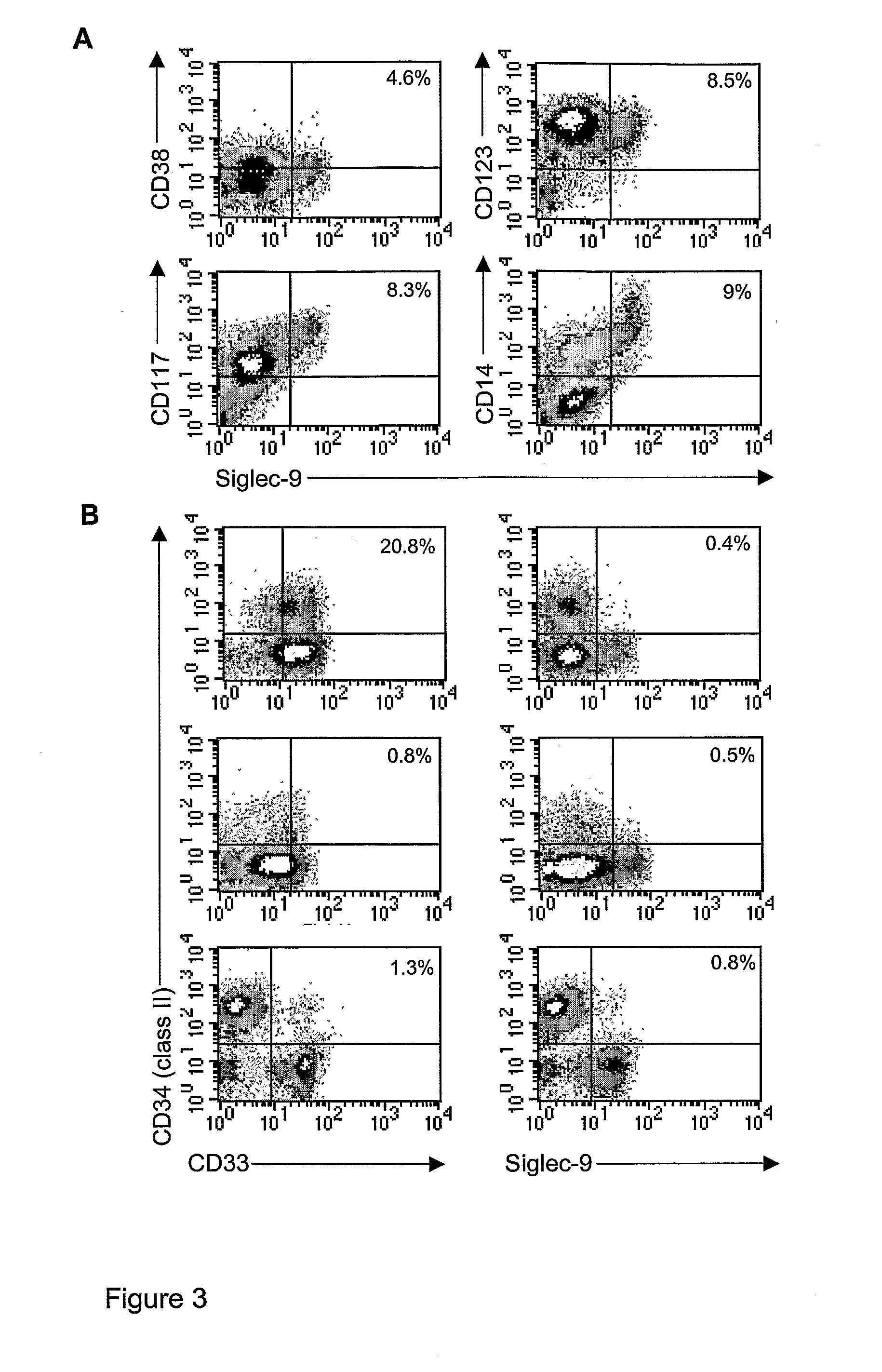
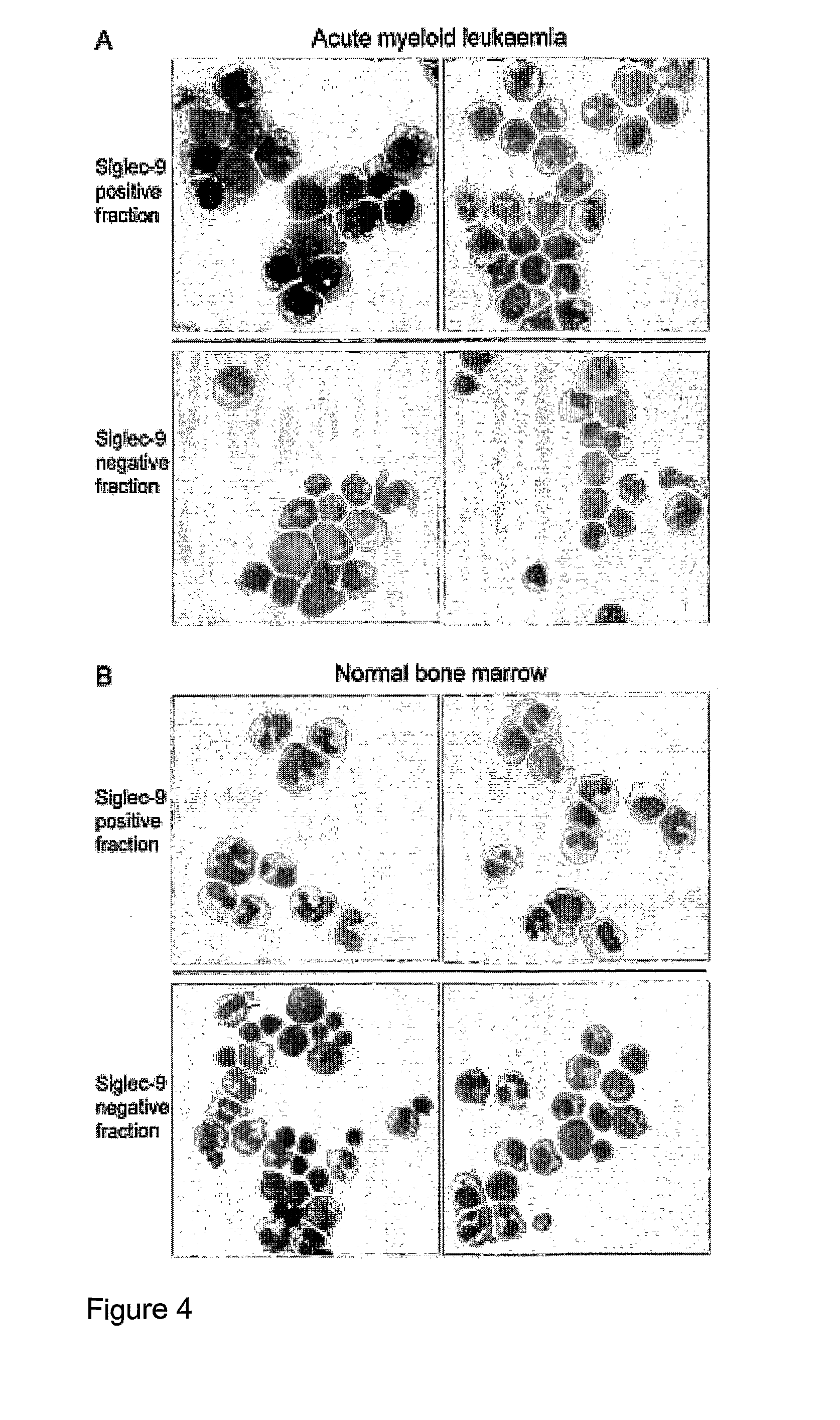
Singlec-9 binding agents
InactiveUS20090220509A1Strong specificityStructuredPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseSialic Acid Binding Immunoglobulin-like Lectins
The present invention relates to agents capable of binding sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-9 (Siglec-9) and their use in the treatment of cell proliferation and differentiation disorders. Furthermore, the present invention provides associated pharmaceutical formulations and methods.
Owner:UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF DUNDEE
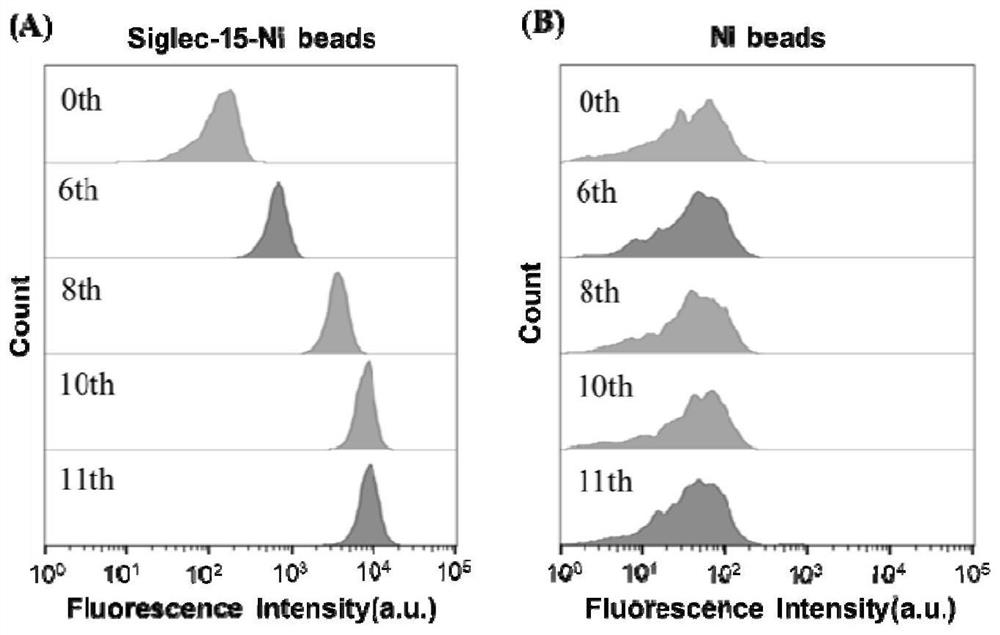
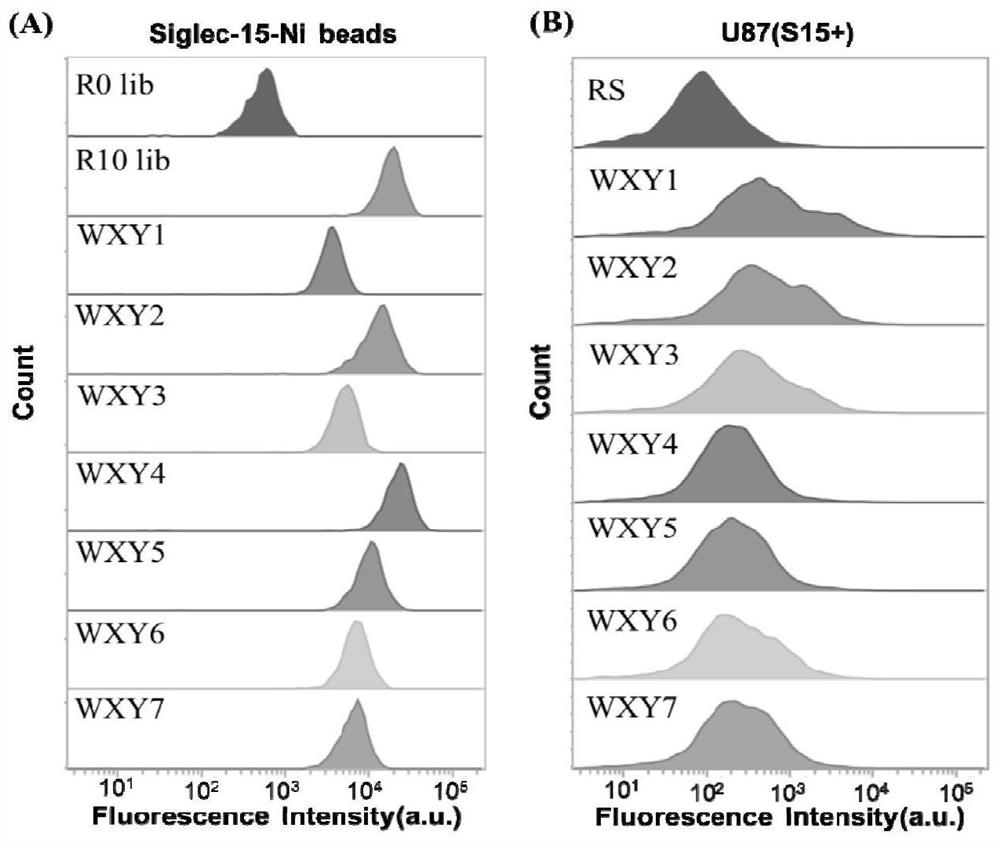
Aptamer of sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-15 protein and application thereof
The invention discloses an aptamer of sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-15 (Siglec-15) protein. The aptamer comprises nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ IDNO: 1- SEQ ID NO: 7. The aptamer provided by the invention can provide rapid and accurate detection on Siglec-15 protein. Meanwhile, The aptamer can block the interaction with T cell surface receptors, and reactivate proliferation of T cells to a certain extent, thereby normalizing immunity in tumor microenvironment without causing serious autoimmune response. The aptamer for Siglec-15 can be used as a medicine for cancers with high Siglec-15 expression in tumor microenvironment, and becomes a potential nucleic acid medicine for tumor immunotherapy. The aptamer of the present invention is possibly effective for patients who have no response to anti-PD-L1 treatment, and further supplements existing tumor diagnosis and immunotherapy systems.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Recombinant MARC-145 cell, and construction method and application thereof
PendingCN112522204APromote rapid proliferationSsRNA viruses positive-senseGenetically modified cellsGene engineeringTGE VACCINE
Owner:LONGYAN UNIV
SingleC-9 Binding Agents
ActiveUS20110104149A1Strong specificityStructuredBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseSialic Acid Binding Immunoglobulin-like Lectins
The present invention relates to agents capable of binding sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-9 (Siglec-9) and their use in the treatment of cell proliferation and differentiation disorders. Furthermore, the present invention provides associated pharmaceutical formulations and methods.
Owner:UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF DUNDEE
Modified protein
ActiveUS20210070814A1Alter half-lifeReduce riskPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCancer preventionAntiendomysial antibodies
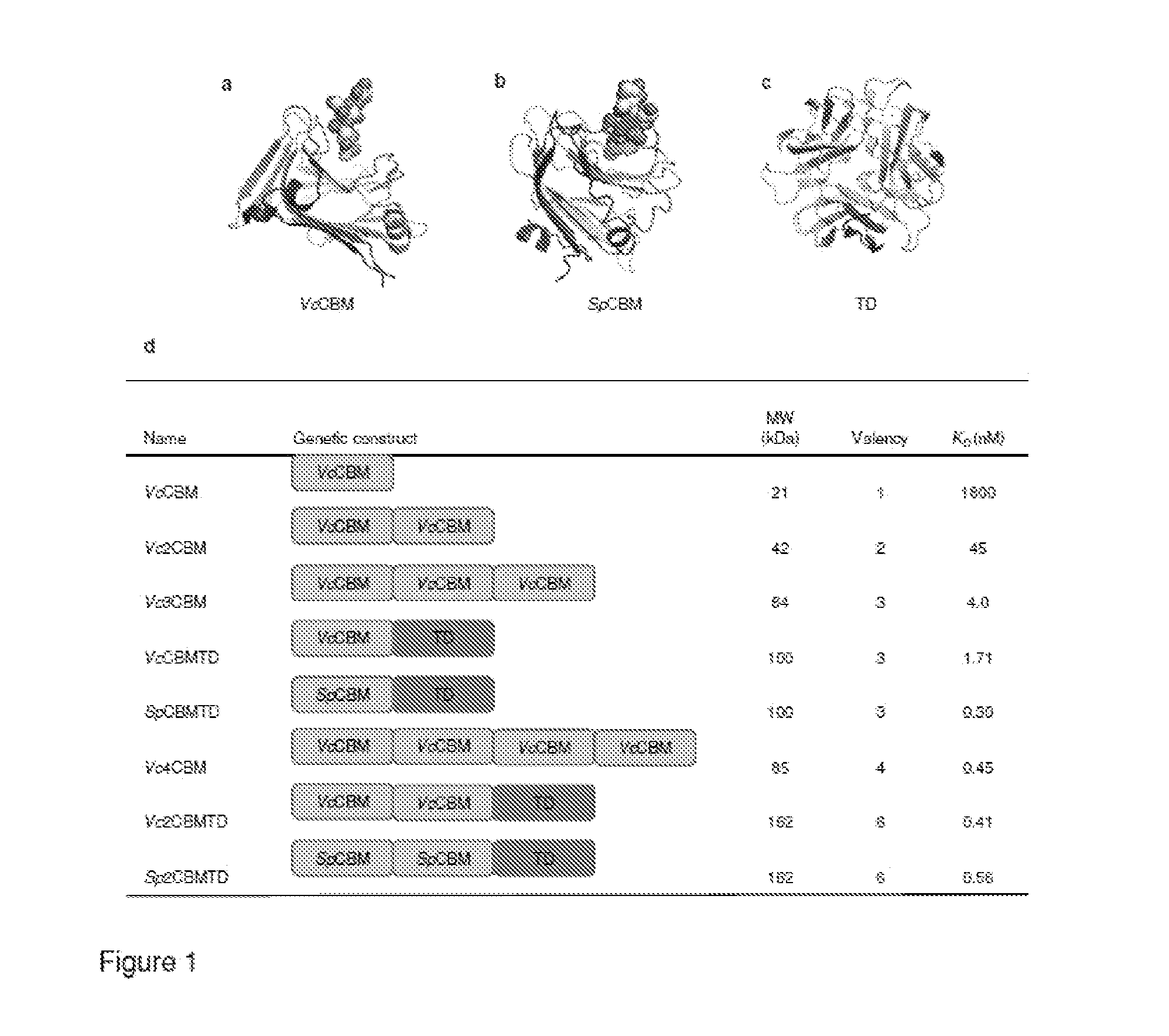
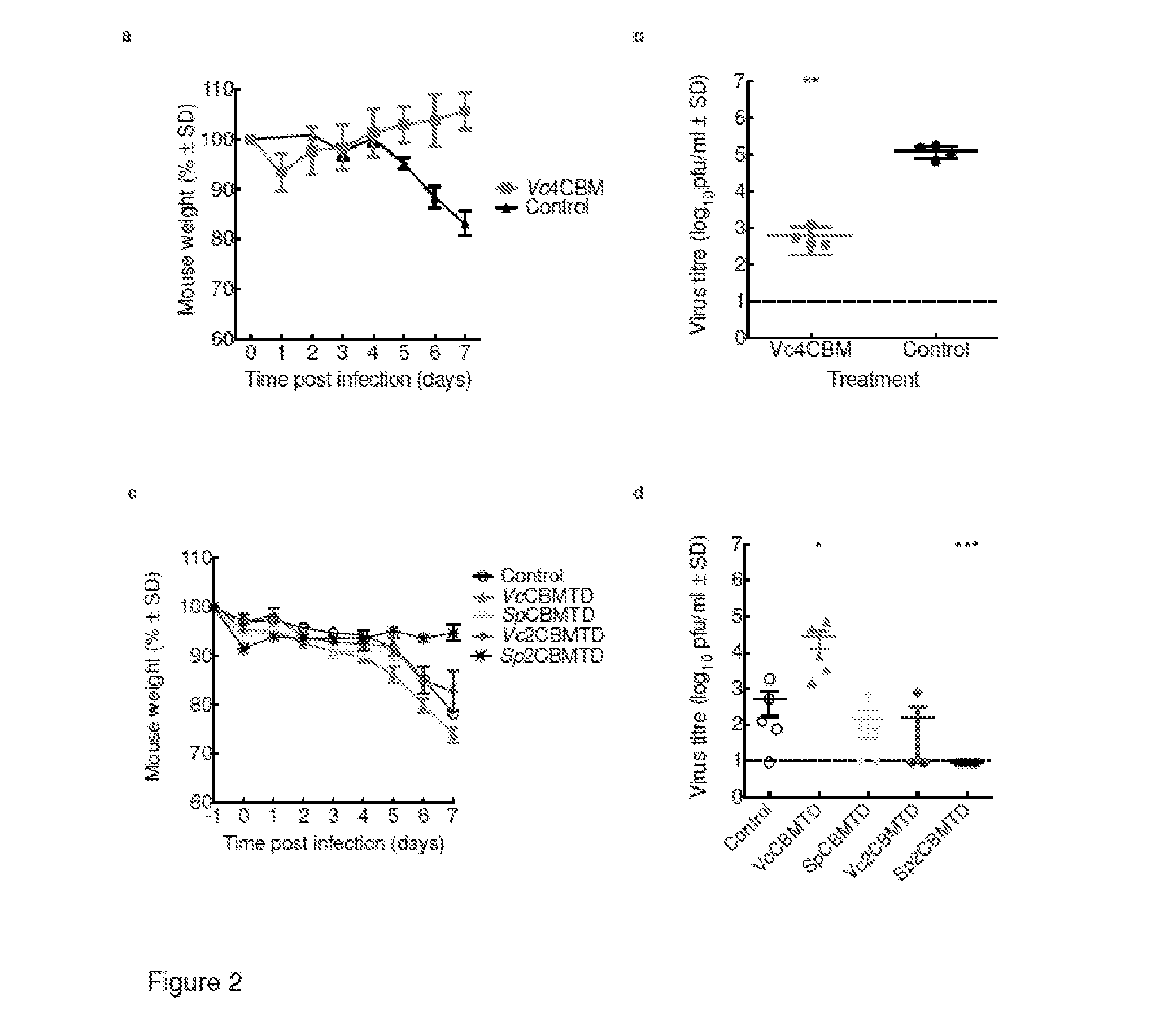
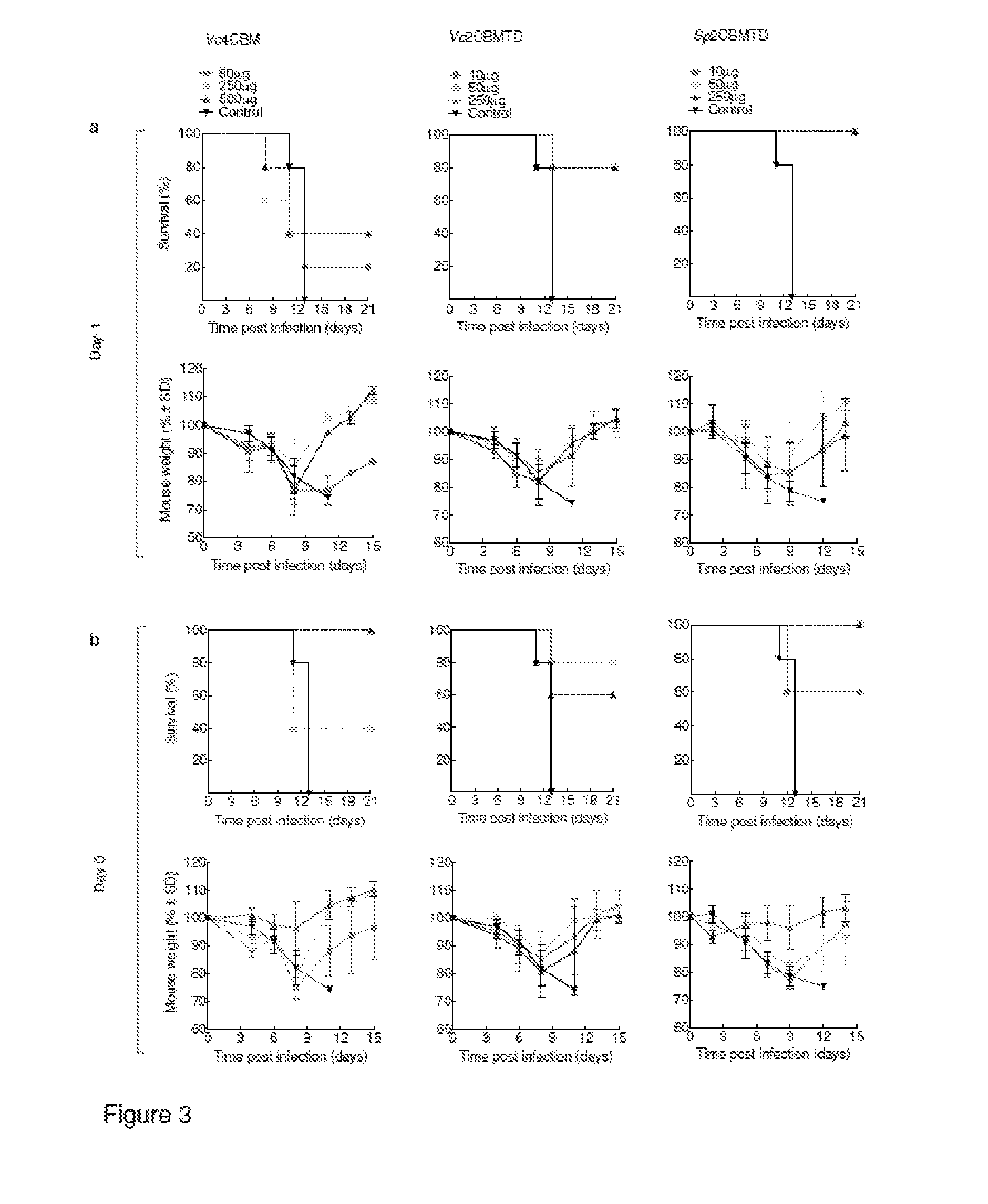
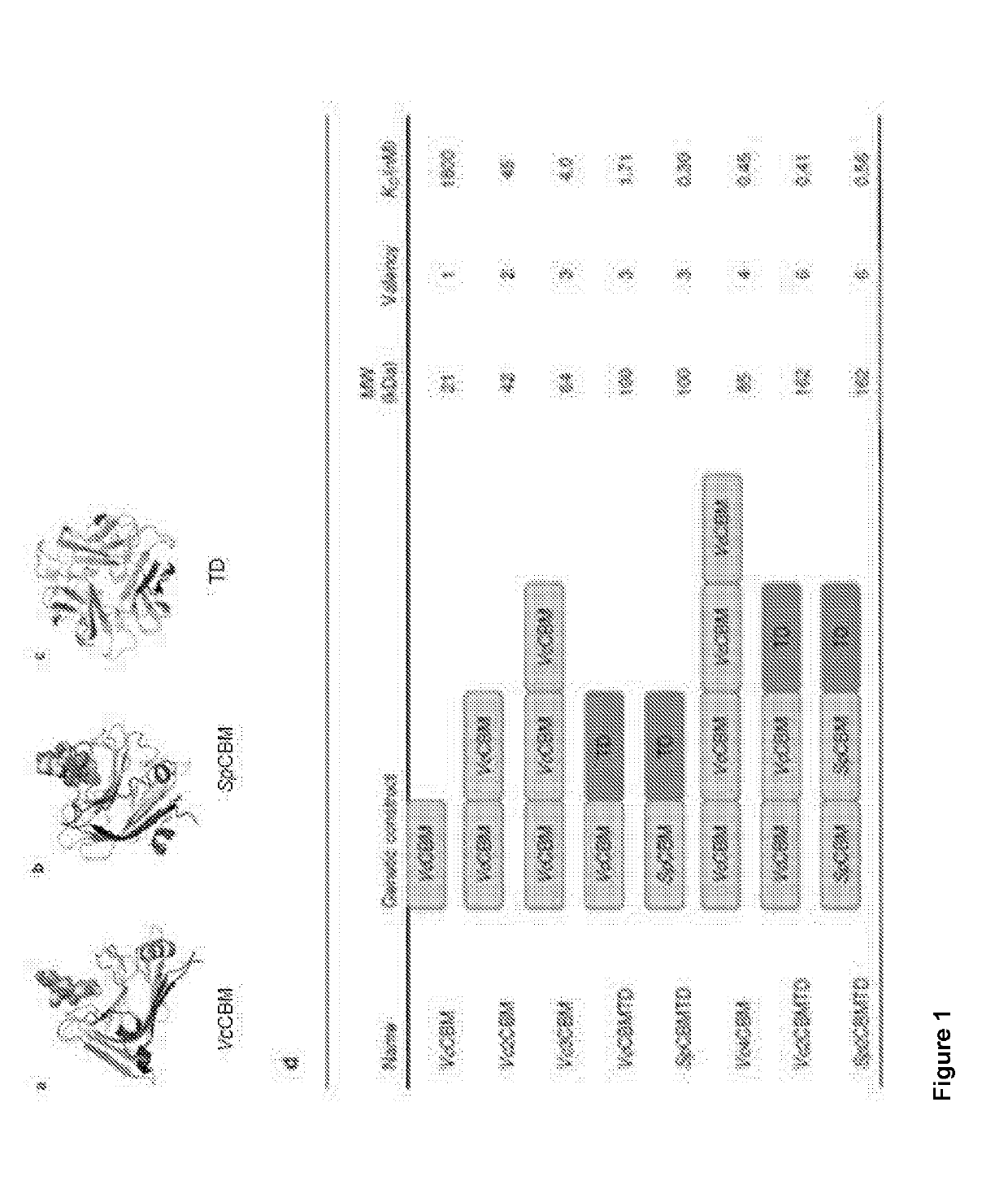
The present disclosure a cohort of sialic acid binding molecules which comprise one or more modified carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs). The modified CBMs reduce the risk of adverse events related to the host immune response and / or the production of anti-drug antibodies (ADAs). The modified CBMs can be used in therapy or as medicaments and find specific application as molecules for the modulation of an immune response and / or cell growth. The modified CBMs may also be used as adjuvants, for example mucosal adjuvants and in the treatment and / or prevention of cancer, sepsis and / or diseases caused or contributed to by a pathogen that binds cell surface sialic acid-containing receptors.
Owner:PNEUMAGEN LTD
Recombinant protein and porcine epidemic diarrhea vaccine composition
ActiveCN113292659BIncrease productionSimple purification processSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAdjuvantTGE VACCINE
The invention provides a recombinant protein and porcine epidemic diarrhea vaccine composition. The recombinant protein is a fusion protein that is tandemly formed by a truncated fragment from porcine epidemic diarrhea virus S protein (Spike, spike protein) and an Fc fragment of pig IgG. The truncated fragment of S protein is preferably selected from the S1 subunit of S protein. The N-terminal domain (NTD) with sialic acid binding activity in the base, the neutralizing epitope domain (COE) and multiple B cell recognition epitopes in the S2 subunit. The vaccine composition includes recombinant protein and adjuvant. After the recombinant protein of the present invention immunizes mice, it can produce higher levels of IgG antibodies and neutralizing antibody titers, CD 3+ cd 4+ 、CD 3+ cd 8+ The proportion of lymphocytes and the concentration of IFN-γ and IL-4 in lymphocytes showed a significant increase.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
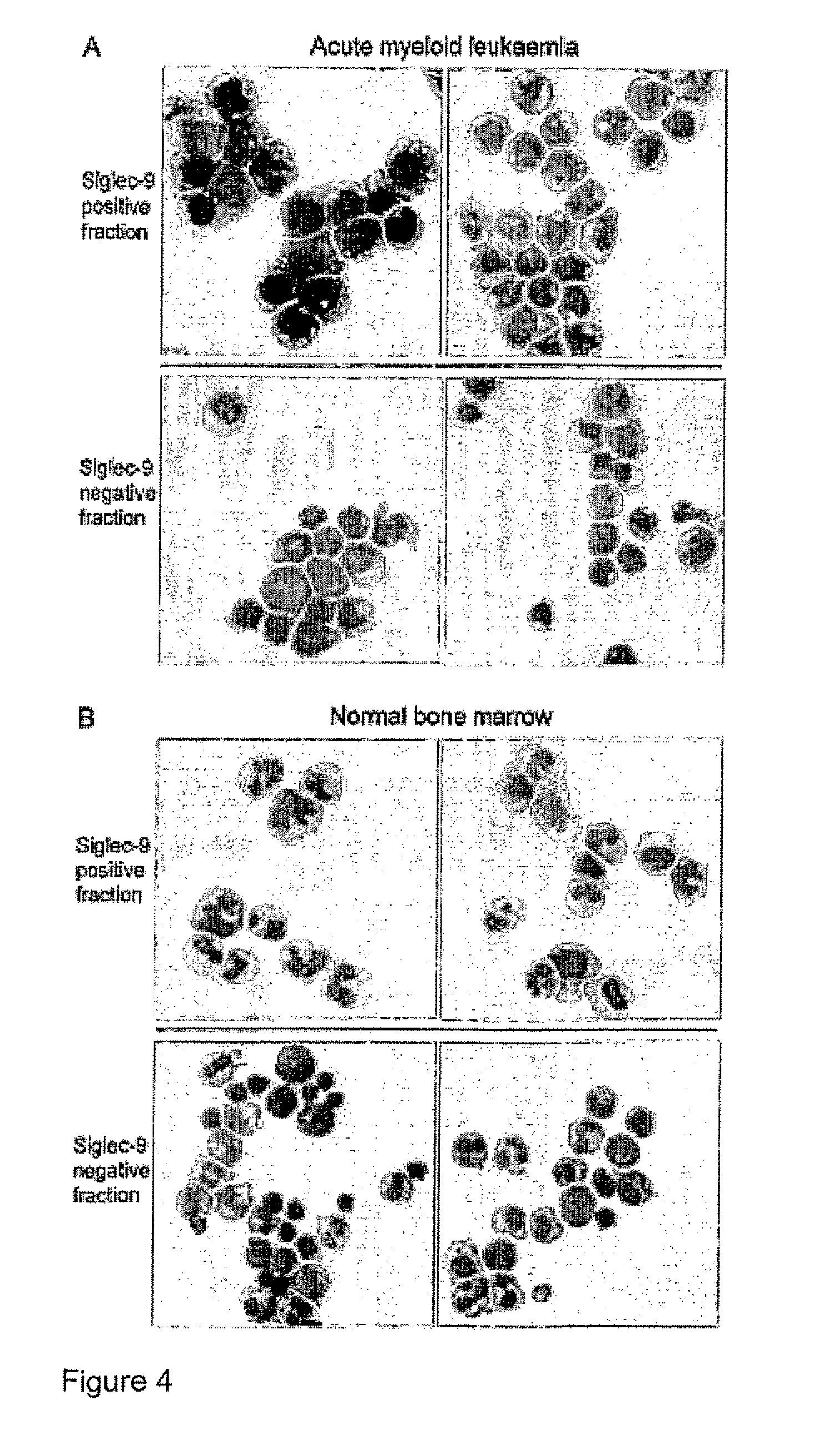
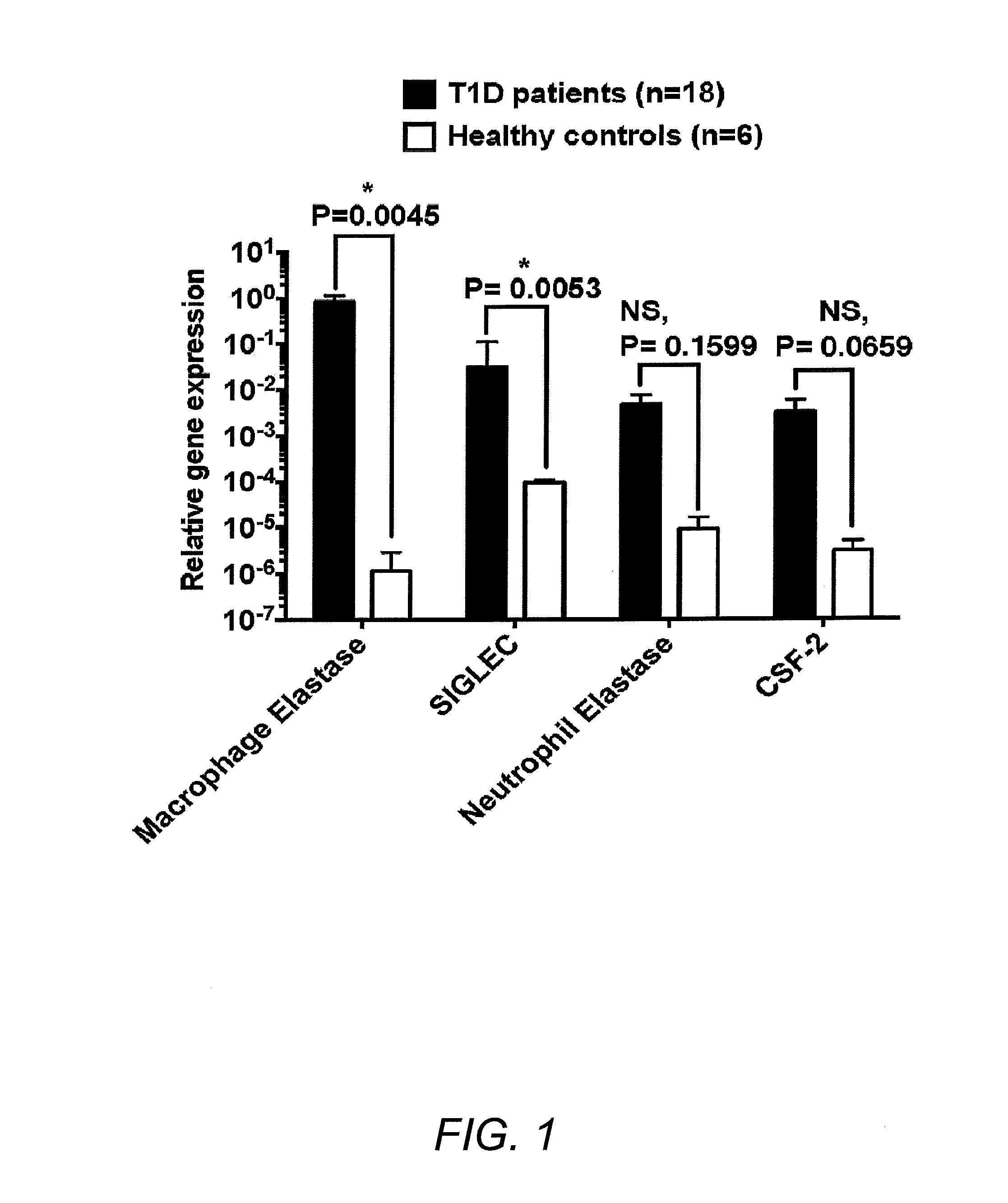
Methods for diagnosing and treating diabetes
ActiveUS20160298191A1Microbiological testing/measurementSialic Acid Binding Immunoglobulin-like LectinsSialic acid binding
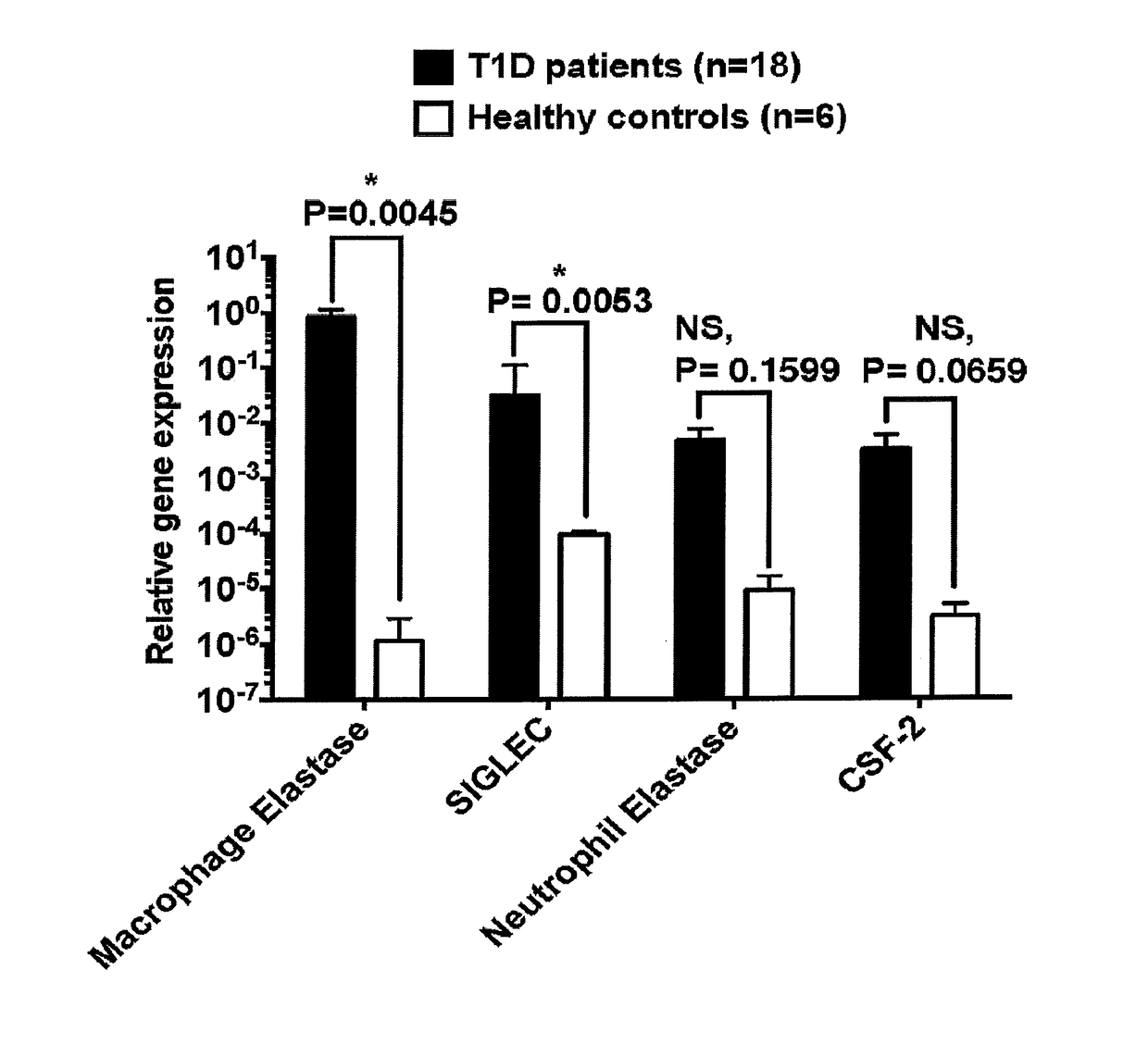
Methods and kits for diagnosing and treating type I diabetes based upon the expression of macrophage-specific Chymotrypsin-Like Elastase Family, Member 3B, either alone or in combination with sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-1, are provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Induction of immunoglobulin class switching by inactivated viral vaccine
InactiveUS6838080B2Short timeImprove stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseNeuraminidase
The present disclosure provides methods and compositions for inducing an immune response to an antigen, especially in an immunogenic composition comprising sialic acid where the antigen comprises sialic acid and wherein the immunogenic composition further comprises a sialic acid binding component, e.g., an inactivated or attenuated paramyxovirus or orthomyxovirus such as an influenza virus comprising a sialic acid binding component, e.g., a neuraminidase. The compositions comprising sialic acid and a sialic acid binding component effectively induce a humoral immune response even in a human or animal which is deficient in CD4+ T cells, due to a disease such as ARC or AIDS, and there is also an immunoglobulin class switching even in the absence of CD4+ T cells.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Compositions for detecting of influenza viruses and kits and methods using same
An isolated composition-of-matter comprising a sialic acid bound to a sialic acid binding domain of a polypeptide is provided. Uses thereof and kits comprising same are also provided.
Owner:MND DIAGNOSTICS LTD
Novel adjuvants
ActiveUS20190224311A1Improve and augment and modify effectStrong and effective and protective mucosal immune responseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAntigenAdjuvant
The present disclosure provides novel adjuvants which may be used in combination with one or more antigens to augment, modulate or enhance a host immune response to the one or more antigens. The adjuvants are based on sialic acid binding molecules and may be combined with any type of antigen. The adjuvants may be formulated for mucosal and / or intranasal administration.
Owner:PNEUMAGEN LTD
Methods for diagnosing and treating diabetes
ActiveUS9850538B2Microbiological testing/measurementSialic Acid Binding Immunoglobulin-like LectinsSialic acid binding
Methods and kits for diagnosing and treating type I diabetes based upon the expression of macrophage-specific Chymotrypsin-Like Elastase Family, Member 3B, either alone or in combination with sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-1, are provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Composition having tissue-repairing activity, and use therefor
ActiveUS20150352187A1Promote productionEffective treatmentSenses disorderNervous disorderTissue repairChondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycans
A composition having tissue repair activity, which is capable of promoting reactions associated with tissue repair, contains at least one selected from the group consisting of a first component that is a protein having a monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) activity, a second component that is a protein having the extracellular domain activity of sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectin-9 (Siglec-9), and a third component that is at least one of chondroitin sulfate and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOKUSHIMA
Modified protein
ActiveUS11466059B2Alter half-lifeReduce riskPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCancer preventionAntiendomysial antibodies
The present disclosure a cohort of sialic acid binding molecules which comprise one or more modified carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs). The modified CBMs reduce the risk of adverse events related to the host immune response and / or the production of anti-drug antibodies (ADAs). The modified CBMs can be used in therapy or as medicaments and find specific application as molecules for the modulation of an immune response and / or cell growth. The modified CBMs may also be used as adjuvants, for example mucosal adjuvants and in the treatment and / or prevention of cancer, sepsis and / or diseases caused or contributed to by a pathogen that binds cell surface sialic acid-containing receptors.
Owner:PNEUMAGEN LTD
JCV neutralizing antibodies
ActiveUS9567392B2Immunoglobulins against virusesAgainst vector-borne diseasesMonoclonal antibodyNeutralizing antibody
In one aspect, the disclosure provides neutralizing antibodies against JCV and methods for the treatment of PML. In some embodiments, aspects of the invention relate to an isolated JC-vims neutralizing monoclonal antibody against JCV capsid protein VPI (JCV-VP1). In some embodiments, the antibody suppresses infectivity of the JC-vims. In some embodiments, the antibody binds the sialic acid binding pocket of JCV-VP1.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com