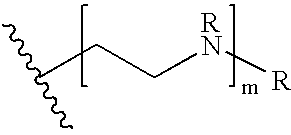
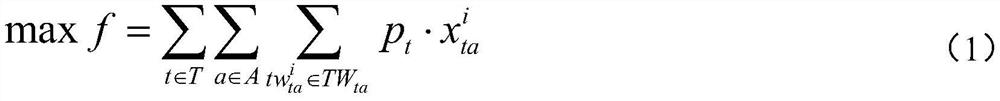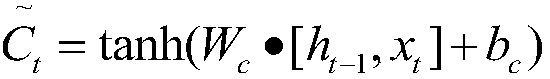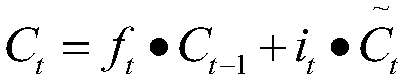Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Sequence dependence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods and compositions for therapeutic use of RNA interference
InactiveUS20030157030A1Effective amountImprove angiogenesisOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryGene expressionSmall interfering RNA
Abstract of Disclosure The present invention provides methods and compositions for attenuating expression of a target gene in vivo. In general, the method includes administering RNAi constructs (such as small-interfering RNAs (i.e., siRNAs) that are targeted to particular mRNA sequences, or nucleic acid material that can produce siRNAs in a cell), in an amount sufficient to attenuate expression of a target gene by an RNA interference mechanism, e.g., in a sequence-dependent, PKR-independent manner. In particular, the subject method can be used to alter the growth, survival or differentiation of cells for therapeutic and cosmetic purposes.
Owner:INSERT THERAPEUTICS INC
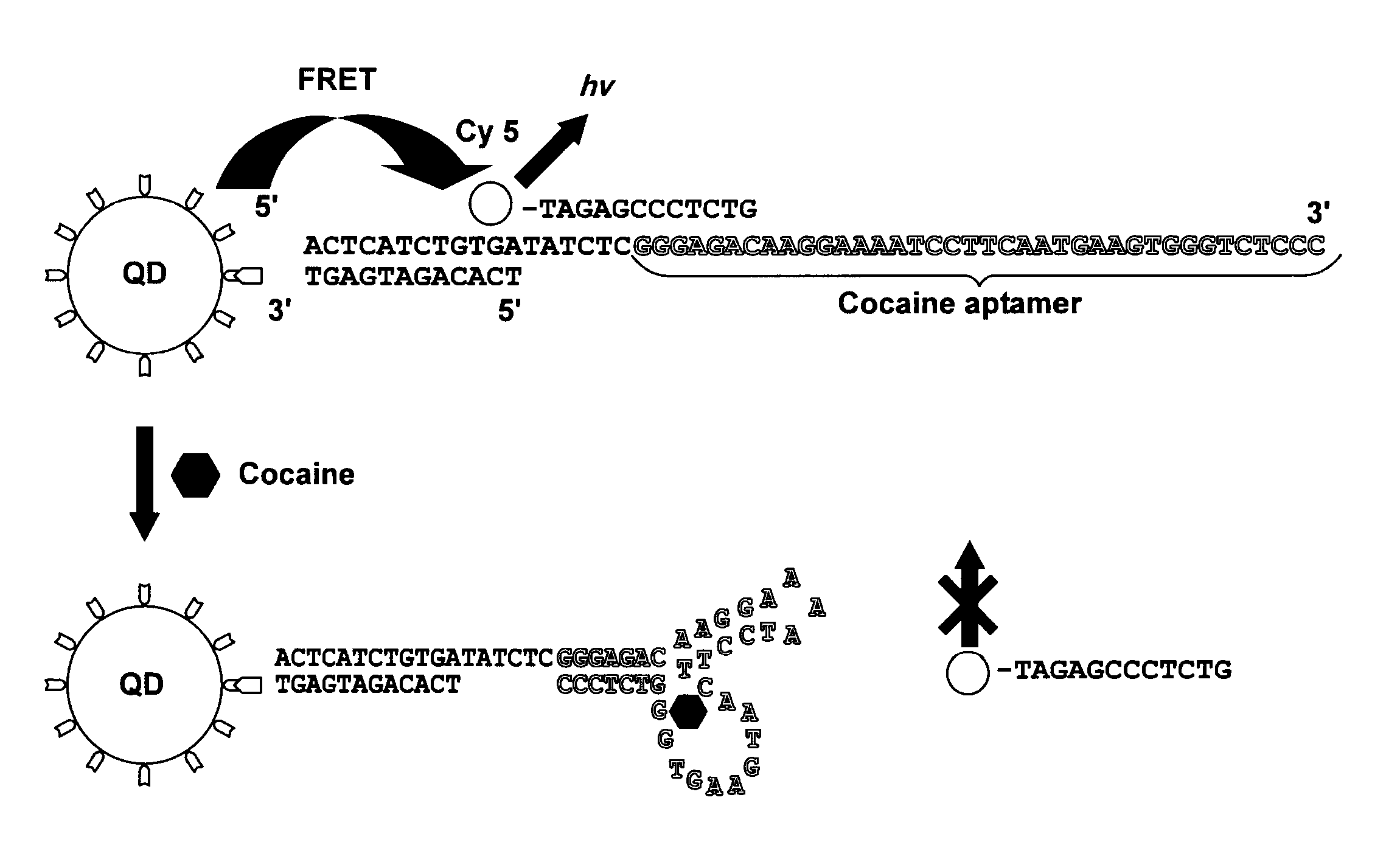
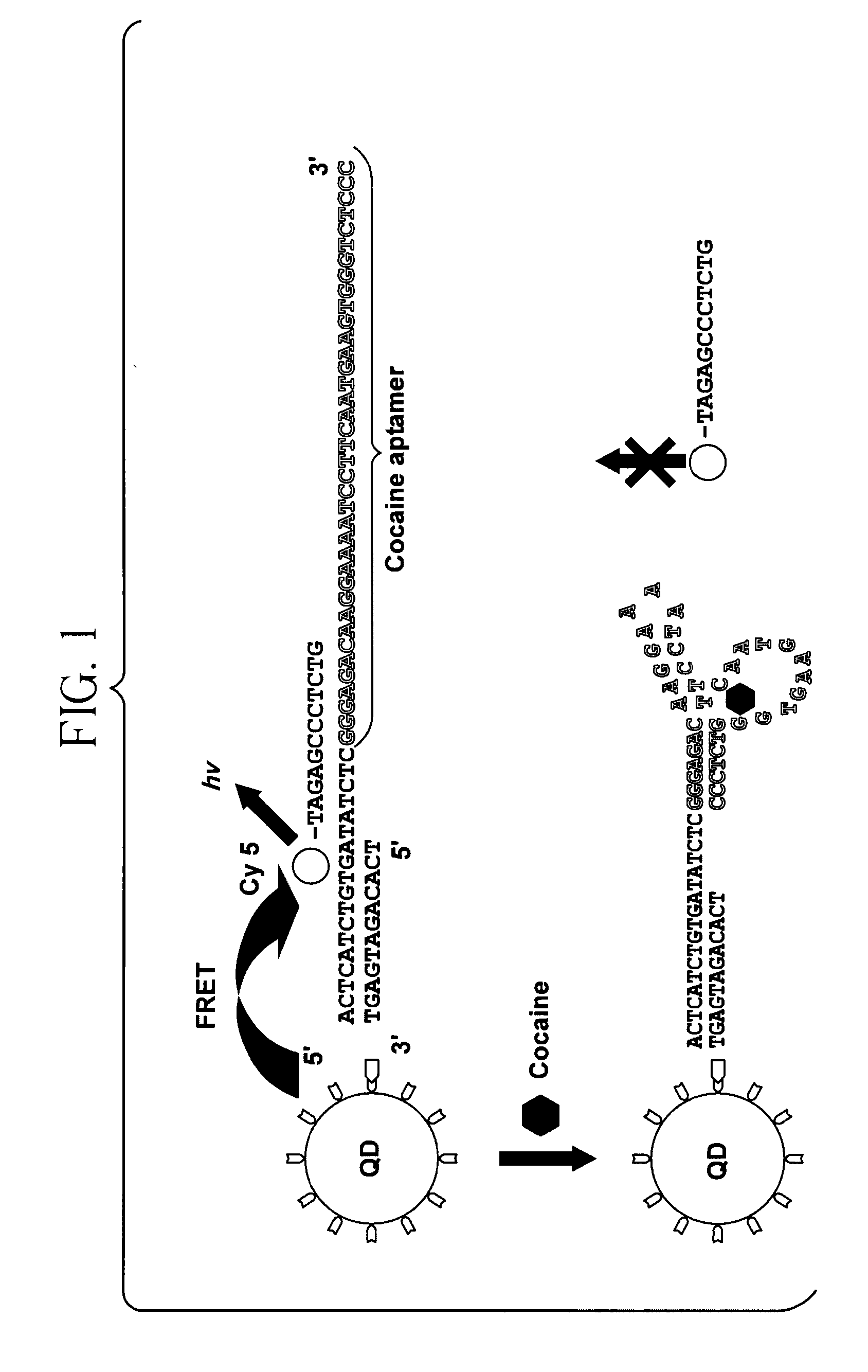
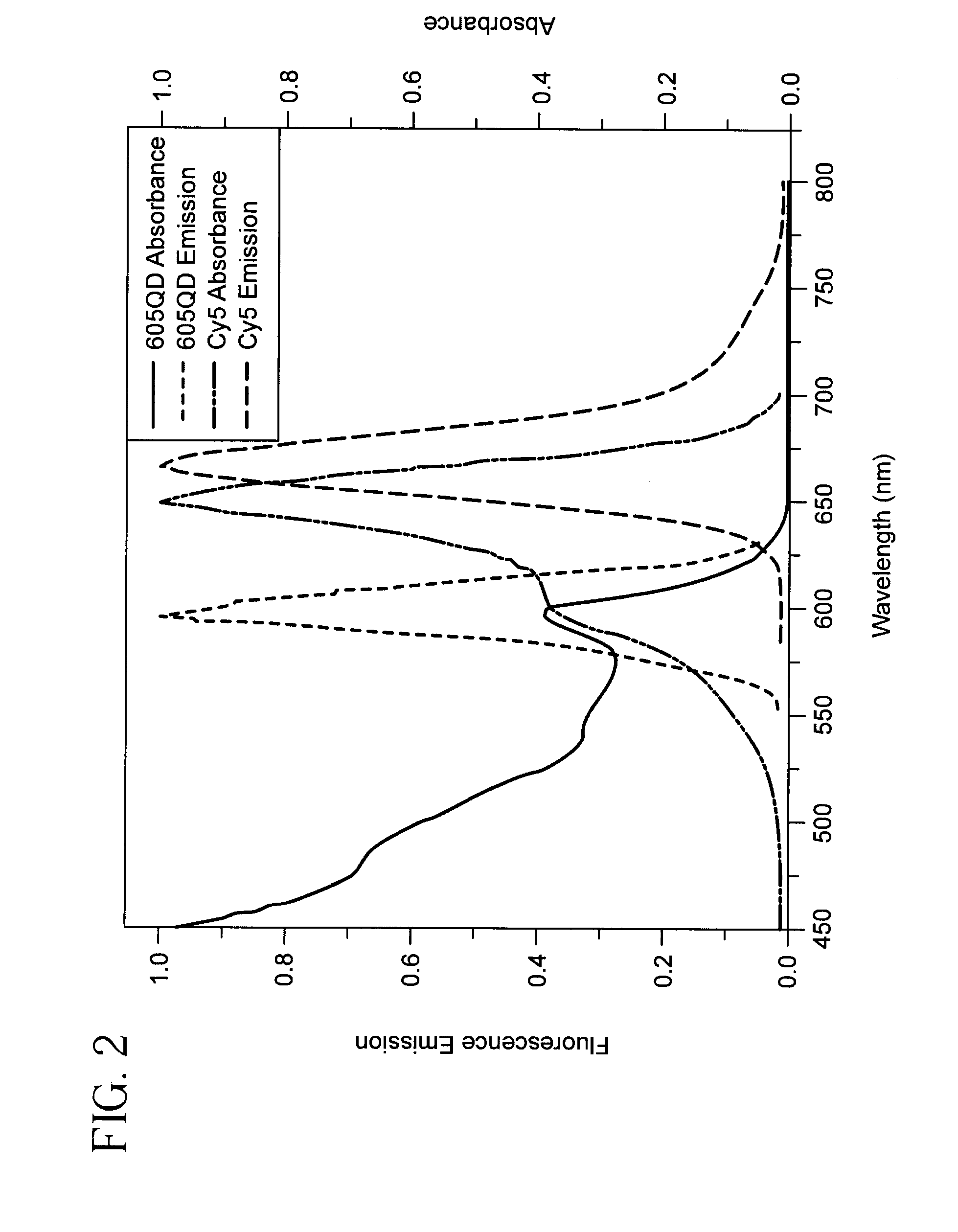
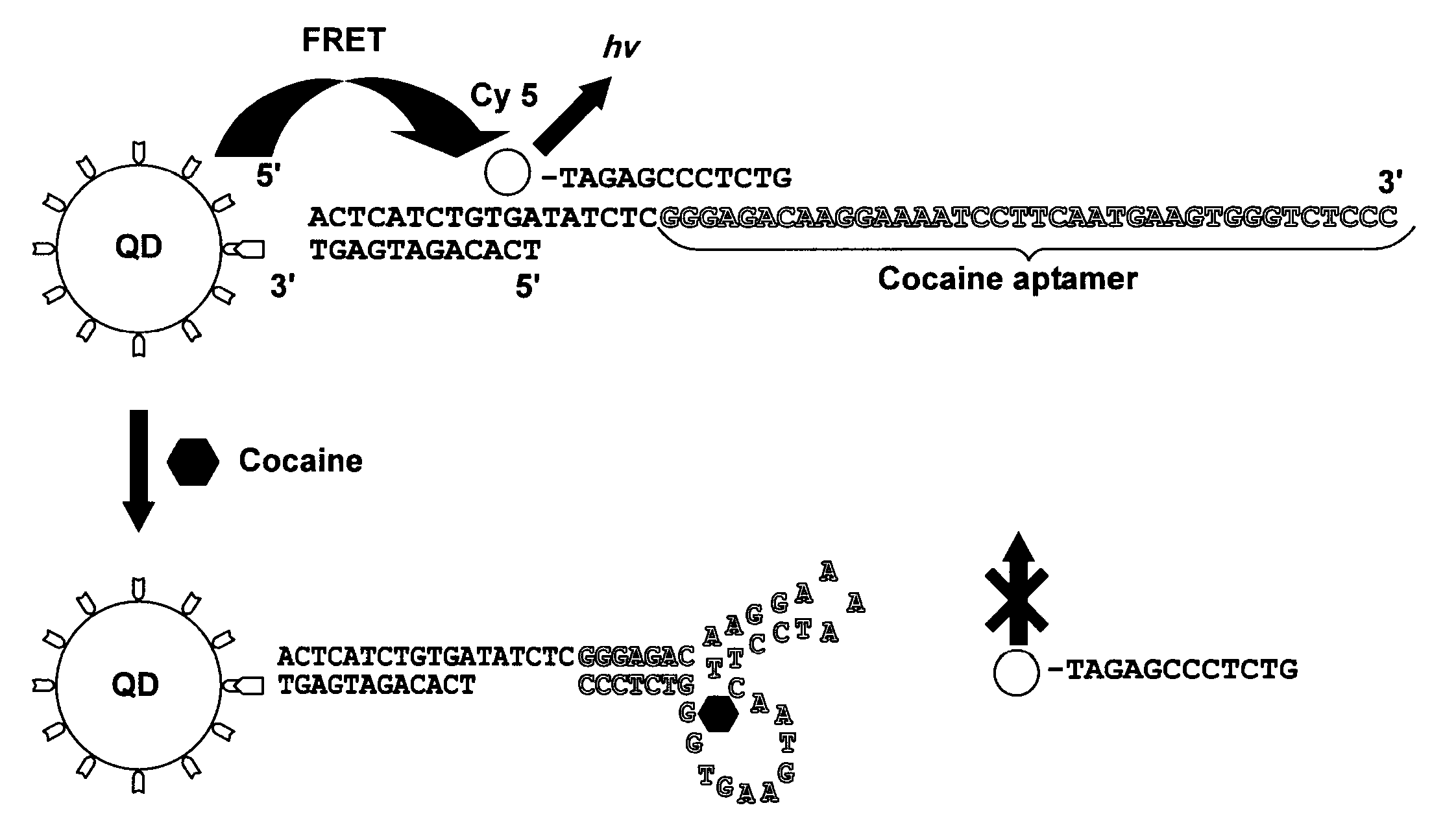
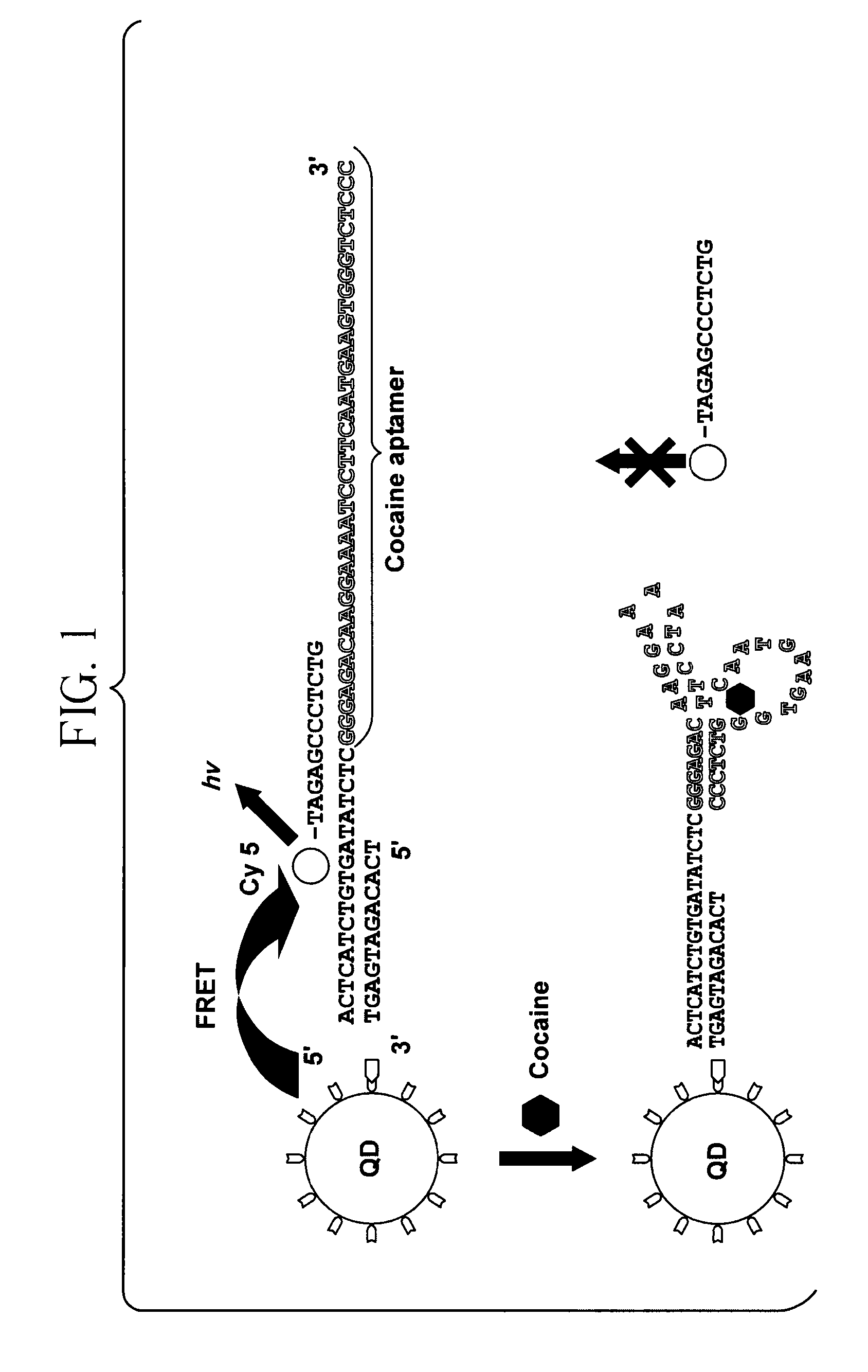
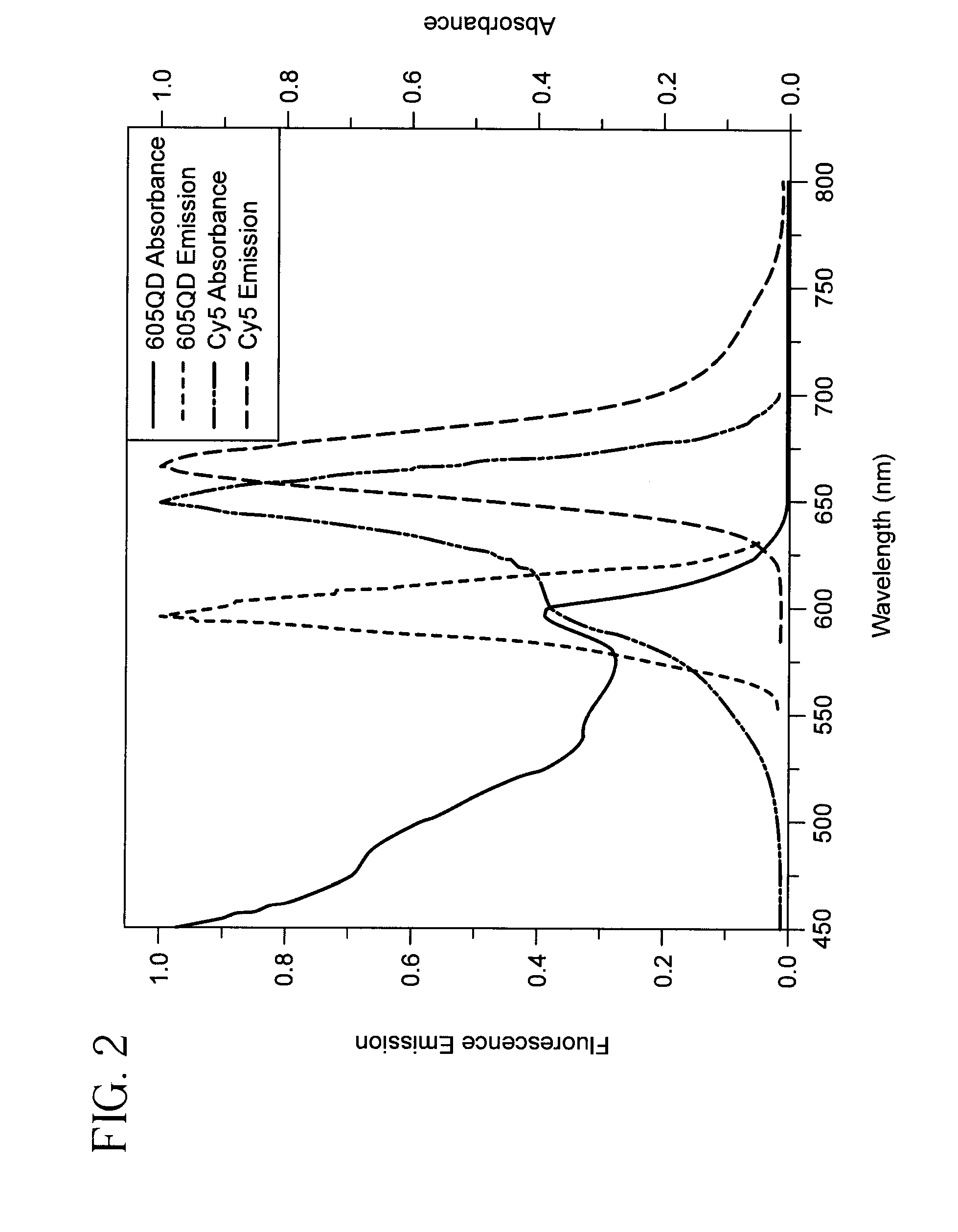
Single quantum-dot based aptameric nanosensors
ActiveUS20110287557A1Simple sample preparationHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAptamerQuantum dot
A signal-off-quantum-dot-based sensor for detecting the presence of a target molecule comprising: an aptamer probe having a nucleotide sequence which specifically interacts with the target molecule by sequence-dependent interaction, wherein the aptamer probe is sandwiched between (a) an oligonucleotide which is immobilized on the surface of a quantum dot (QD), and (b) a fluorophore-labeled oligonucleotide, wherein when the sensor is excited by an energy source: (i) in the absence of specific interaction between the target molecule and the aptamer probe, a baseline signal is emitted, and (ii) in the presence of specific interaction between the target molecule and the aptamer probe, a detection signal is emitted, wherein the baseline signal is greater than the detection signal, whereby the presence of the target molecule is detected.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
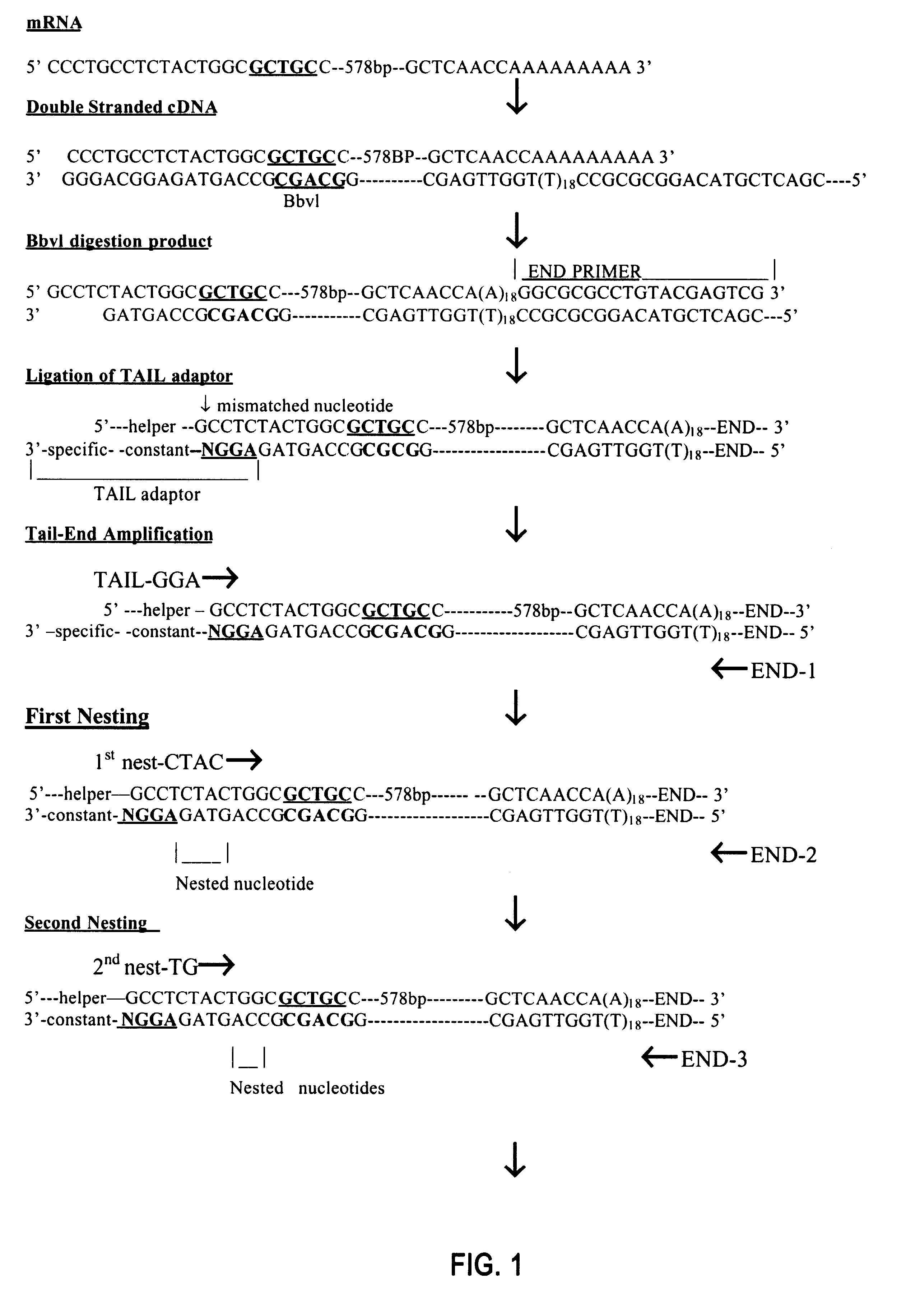
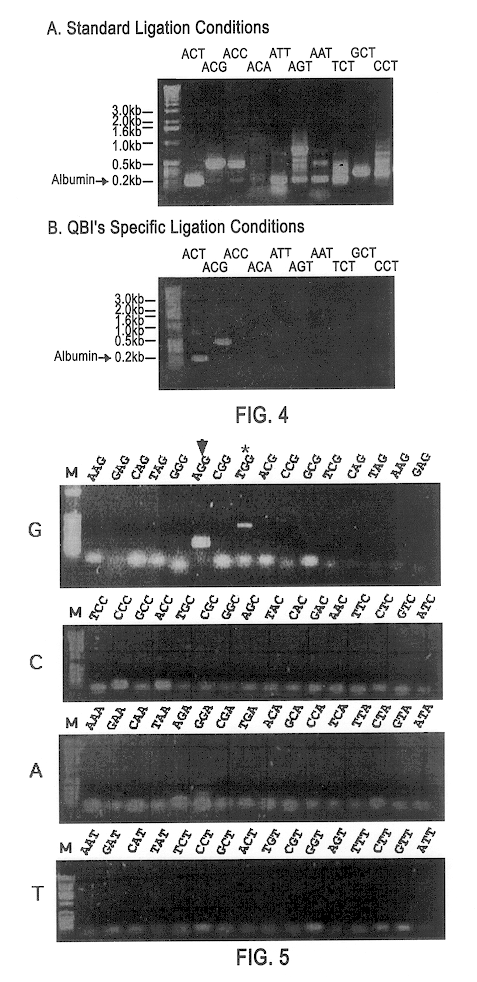
Sequence-dependent gene sorting techniques
InactiveUS6468749B1Without redundancySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneComputational biology
This invention provides a method of sorting genes comprising: (1) preparing ds cDNA molecules from mRNA molecules (2) digesting the ds cDNA molecules (3) ligating to the digested cDNA molecules a set of dsDNA oligonucleotide adaptors; (4) amplifying the ligated cDNA molecules; and (5) sorting the amplified cDNA molecules into nonoverlapping groups. This invention also provides two additional methods of sorting genes. This invention further provides a method of making sub-libraries of ligation sets.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Inversion probes
Unitary hybridization probes having stem-and-loop structures, wherein the stem portion of the structure comprises a pair of interactive arms that are substantially prevented from interacting with target polynucleotides. One arm of the invented parallel-stem hybridization probe has a backbone polarity opposite that of the target-complementary loop sequence of the probe. Rather than interacting in an antiparallel fashion, the arms of parallel-stem hybridization probes interact in a parallel fashion. The arms of the invented dual inversion probes interact in a conventional antiparallel fashion, but have backbone polarities opposite that of the target-complementary loop portion of the probe. Arm portions of the inversion probes do not substantially contribute to sequence-dependent stabilization of probe:target hybrids. Incorporating inversion linkages into the structures of these probes dramatically simplifies the process of designing stem-and-loop hybridization probes.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
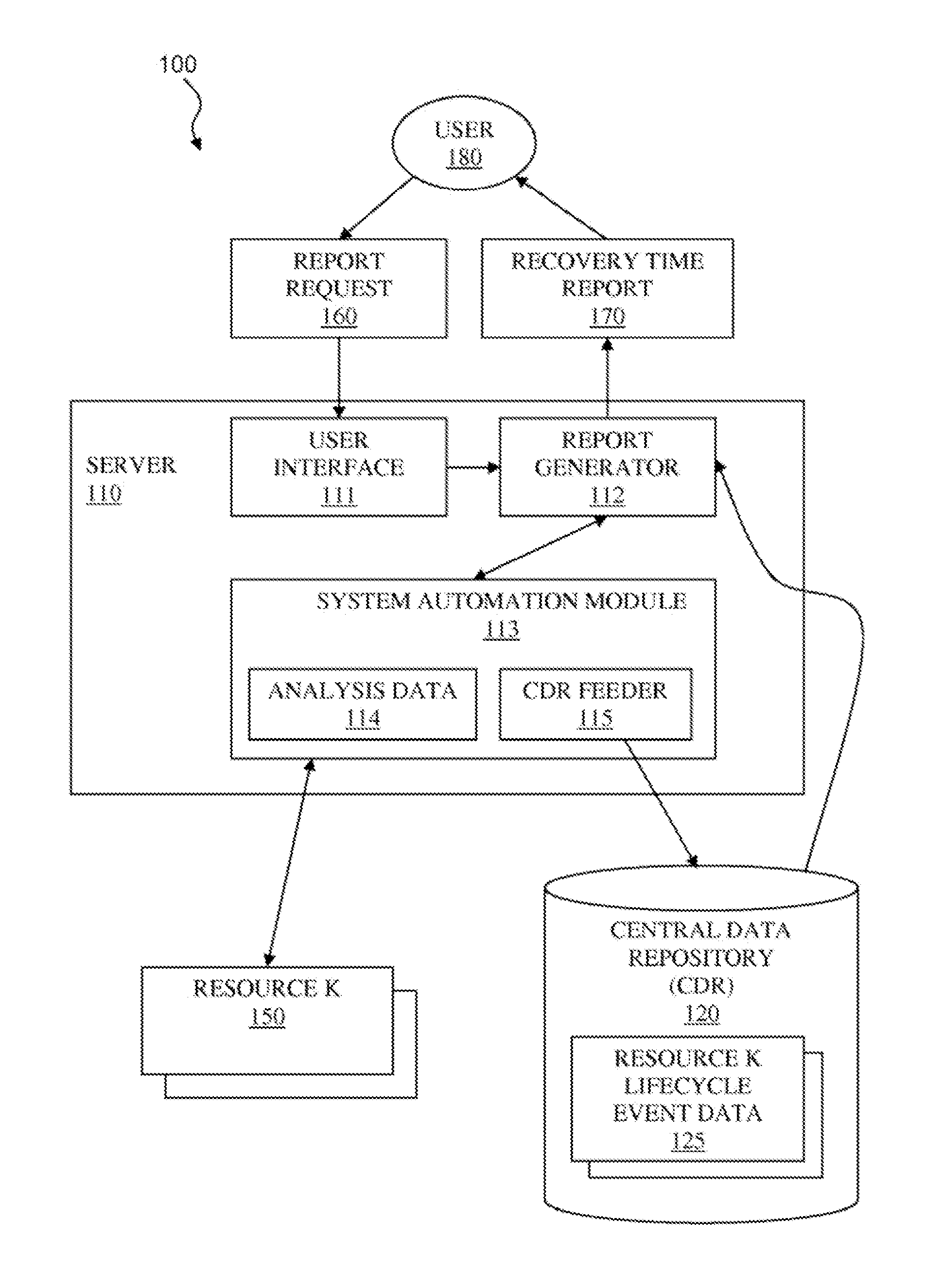
System and method for determining recovery time for interdependent resources in heterogeneous computing environment
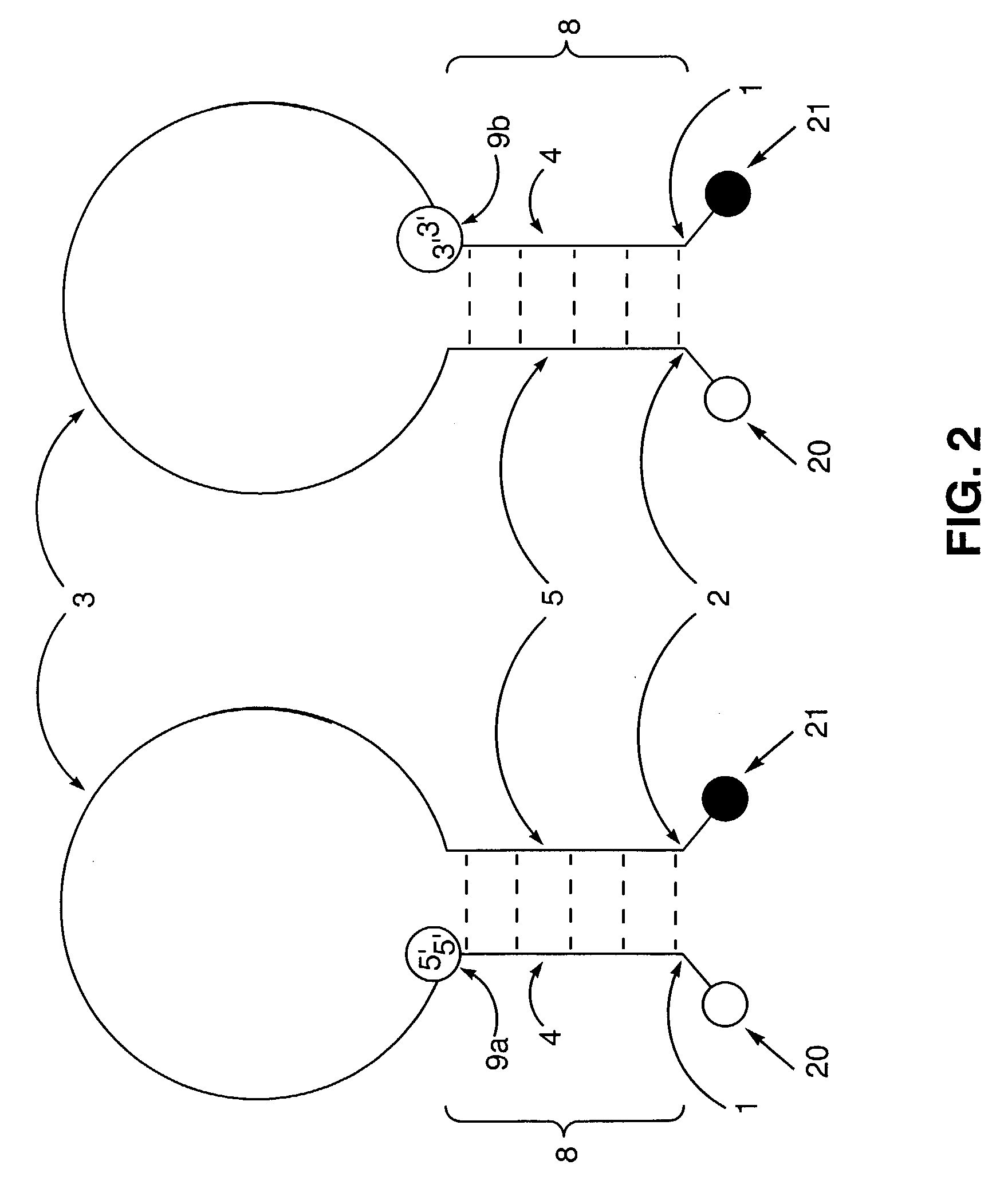
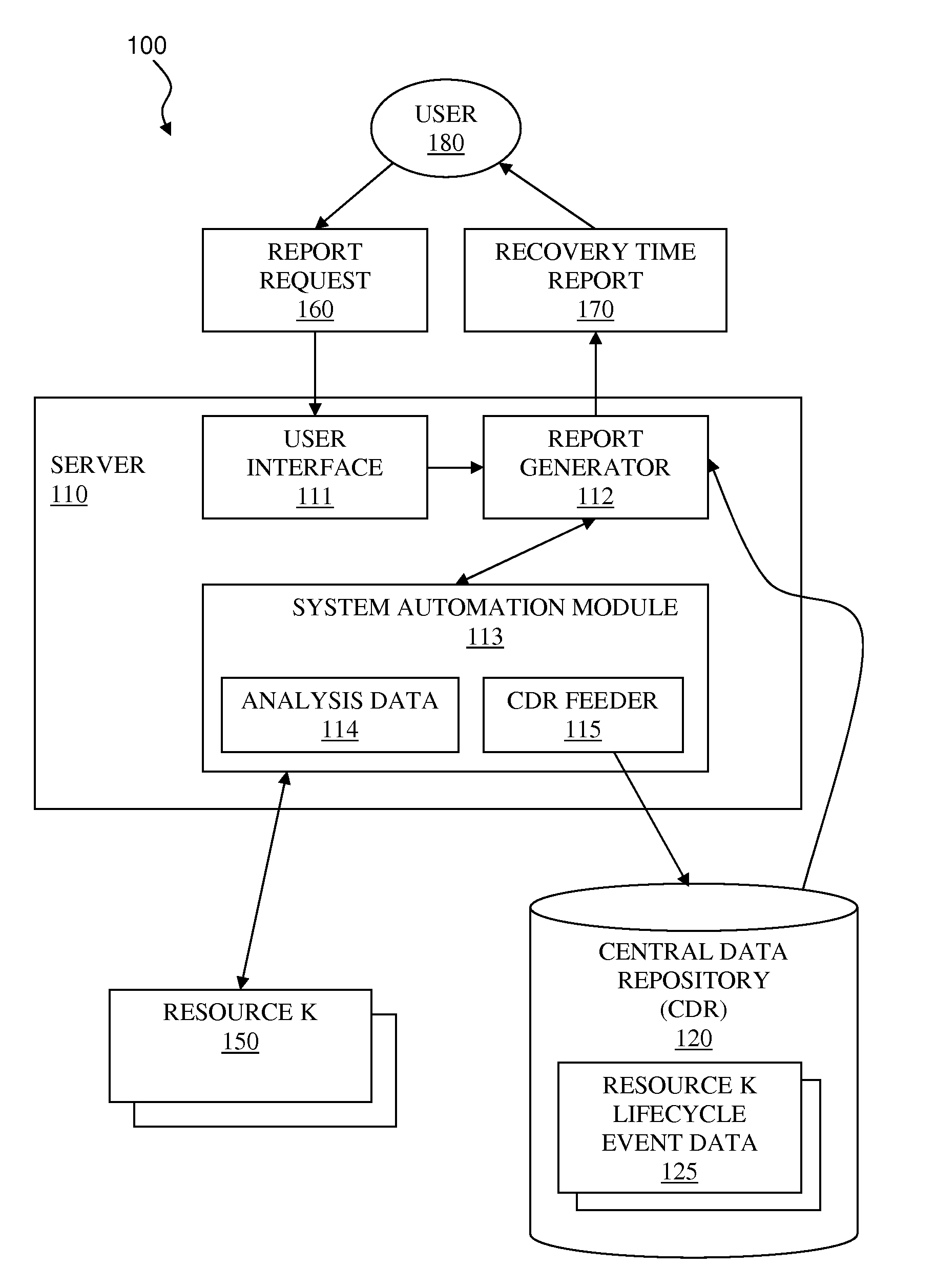
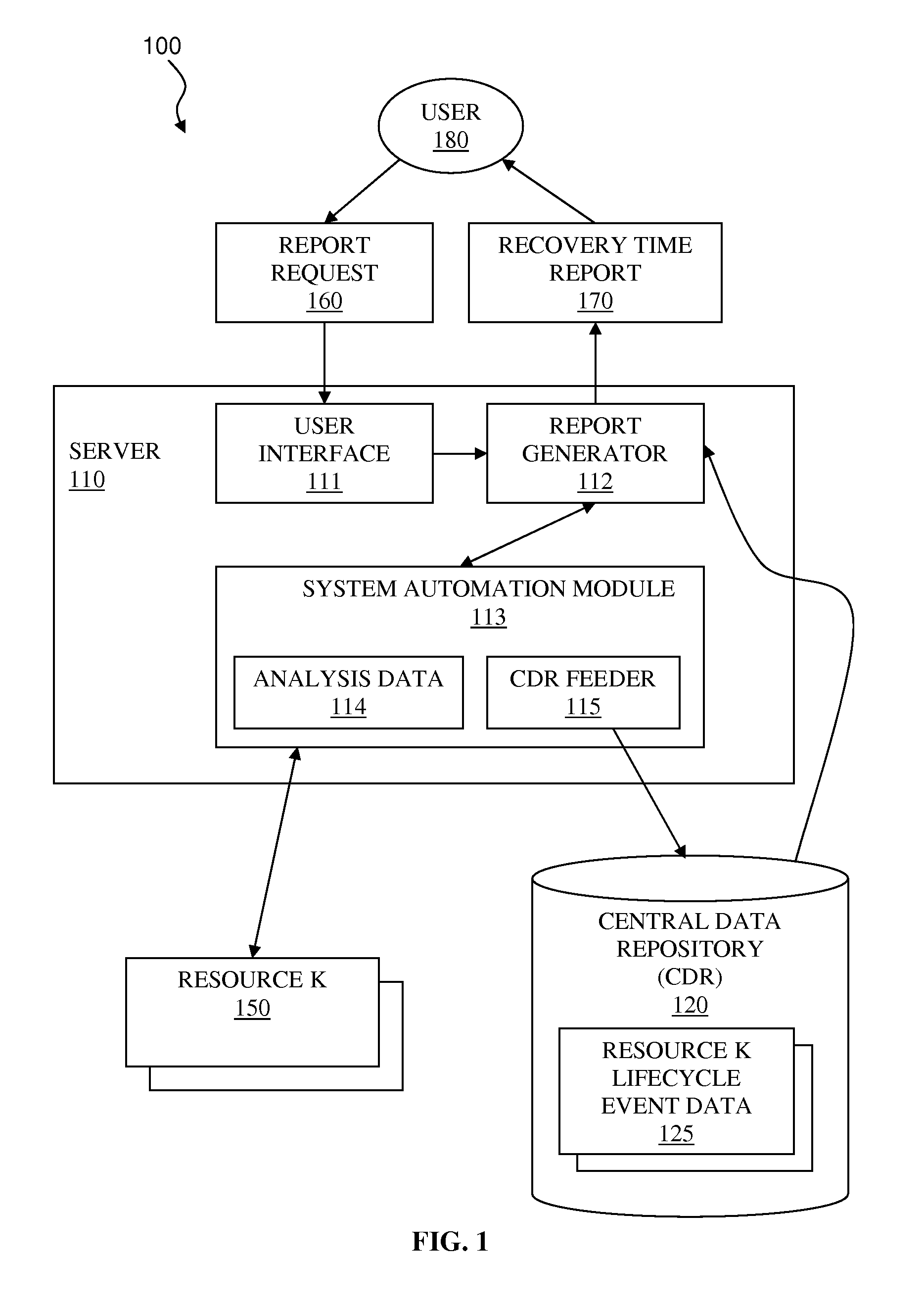
InactiveUS20100169720A1Overcome disadvantagesDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringSymmetric multiprocessor systemLaunch Time
A system and associated method for determining a recovery time for a resource in a heterogeneous computing environment comprising interdependent resources. A graph for the resource representing all sequence dependencies and all group relations are created. The recovery time may be a cumulative startup time or a cumulative shutdown time of the resource considering interdependencies of the resource to other resources. The recovery time for all support resources having sequence dependencies with the resource is calculated and each node representing the support resources are removed from the graph. Then the recovery time for all member resources left in the graph that have group relations with the resource is calculated per a group type of the resource. The recovery time for the resource is a sum of the recovery time of all support resources, the recovery time of all member resources, and a unit recovery time of the resource.
Owner:IBM CORP
Polynucleotide detection method employing self-reporting dual inversion probes
InactiveUS20060246500A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeElectrical polarity
Method of detecting a target polynucleotide based on the use of dual inversion hybridization probes having stem-and-loop structures, wherein the stem portion of the structure comprises a pair of interactive arms that are substantially prevented from interacting with target polynucleotides. The arms of the dual inversion hybridization probes interact in a conventional antiparallel fashion, but have backbone polarities opposite that of the target-complementary loop portion of the probe. Arm portions of the dual inversion probes do not substantially contribute to sequence-dependent stabilization of probe:target hybrids. Incorporating inversion linkages into the structures of these probes dramatically simplifies the process of designing stem-and-loop hybridization probes.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Method for acquiring accurate latest deadline in multi-core realtime fault-tolerant system
The invention provides a method for acquiring an accurate latest deadline in a multi-core realtime fault-tolerant system. The method includes the following steps: according to given task scheduling and on the basis that original data dependence is maintained, increasing scheduling sequence dependence for adjacent tasks scheduled on a same core; increasing two virtual task nodes with execution time to be zero, and enabling one of the virtual task nodes to be executed before all other tasks and the other virtual task node to be executed after all other tasks; supposing that at most X soft errors appear in the process of task execution and on the basis of original scheduling, realizing fault tolerance by immediately re-executing erroneous tasks on the same core, determining key tasks of a task set, and acquiring the accurate latest deadline of the task set. By the method, if N tasks is contained in the task set and at most X soft errors appear in the process of execution, the accurate latest deadline of the task set can be determined within O(n^2) to guarantee fault tolerance, and high efficiency and quickness are realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Methods and systems for estimating the melting temperature (TM) for polynucleotide molecules
ActiveUS6889143B2Reliably estimating melting temperatureComputationally tractableMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to methods and systems for predicting or estimating the melting temperature of duplex nucleic acids, particularly duplexes of oligonucleotides which may be used, for example, as primers or probes in PCR and / or hybridization assays. The invention also relates to methods and systems for designing and selecting oligonucleotide probes and primers having a predicted melting temperature which is optimized for such assays. To this end, algorithms and methods are provided for predicting the melting temperature of a nucleic acid having a predetermined sequence. These methods and algorithms estimate the melting temperature of a nucleic acid duplex under particular salt conditions. The methods and algorithms use novel formulas, having terms and coefficients that are functions of the particular nucleotide sequence, to estimate the effect of particular salt conditions on the melting temperature. As such, the methods and systems of the invention provide superior result compared to existing methods, which do not consider sequence dependent effects of changing salt conditions.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
Method for analyzing reliability of standby redundant system on basis of fault tree
ActiveCN108388740ATrue failure pathAccurate quantitative evaluationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSystem failureAccurate estimation
The invention discloses a method for analyzing reliability of a standby redundant system on the basis of a fault tree. The method comprises: establishing a fault tree model of the standby redundant system; carrying out qualitative analysis on the established fault tree; on the basis of a qualitative analysis result, carrying out quantitative analysis on the fault tree. When the fault tree model ofthe standby redundant system is established, according to a system-subsystem-equipment-equipment failure mode sequence, a system-redundant row model, a sequence failure group and a model of a sequence dependence relationship among redundant rows, equipment and equipment failure modes are sequentially established, and each equipment failure mode is completely analyzed and used as a lowermost layerevent. According to the fault tree modeling and analysis method disclosed by the invention, a more real system failure path is described, a system failure probability is subjected to more accurate quantitative evaluation, the unnecessary conservative property possibly introduced in an original fault tree method is eliminated, and more accurate estimation on the reliability level of the system isimplemented.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
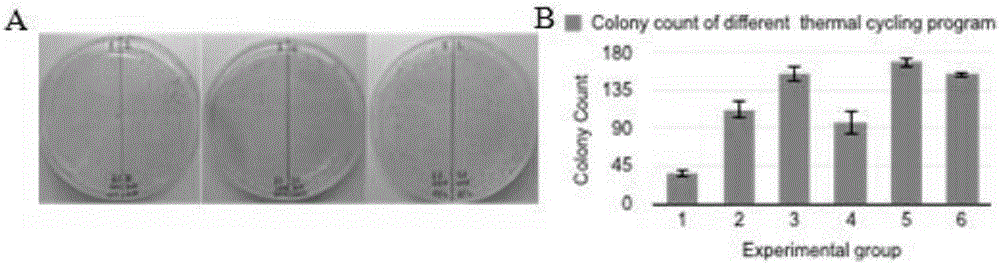
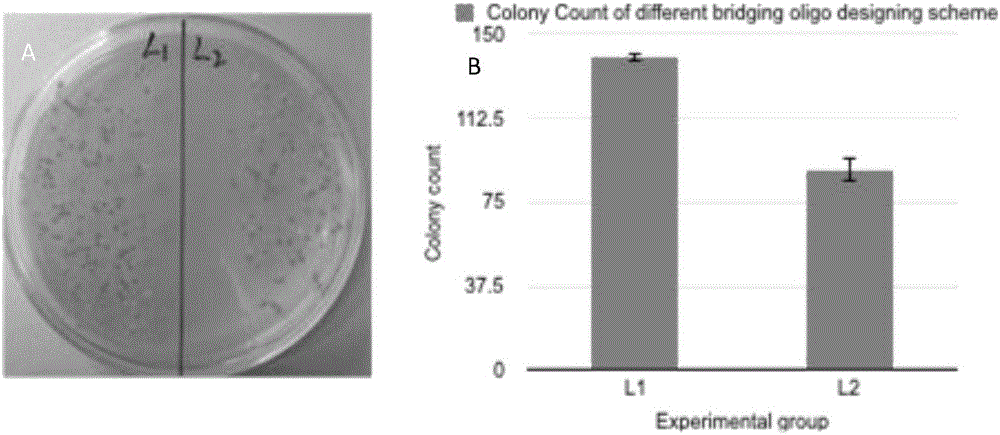
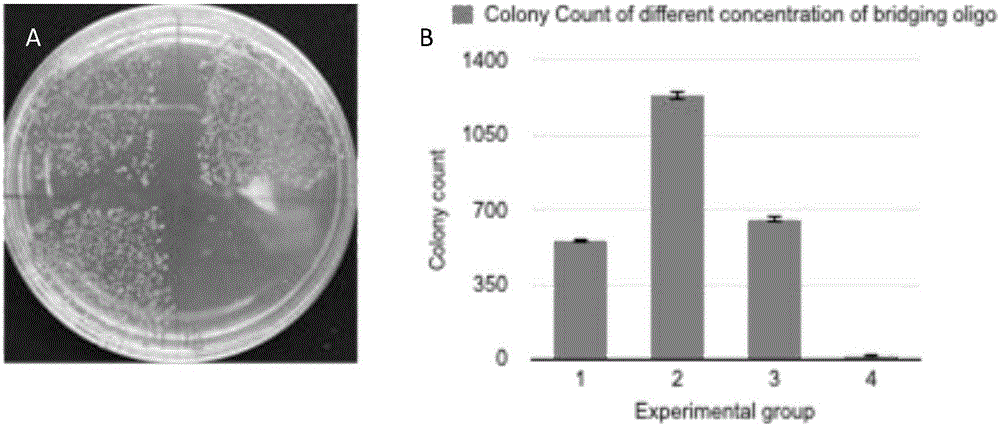
One-tube reaction type DNA molecule clone splicing method
ActiveCN106591294AImprove ligation reaction efficiencyLow costFermentationDNA preparationEnzyme digestionPhosphorylation
The invention provides a one-tube reaction type DNA molecule clone splicing or reconstructing method. A reaction system is formed by mixing a target DNA fragment, a bridging primer, polynucleotide kinase, a heat stability ligase and a reaction buffer solution, the buffer solution contains ATP, NAD<+> and Mg<2+>, the pH value is 6-10, and the method is completed through a heat cycle process. The method realizes one-shot completion of a linking reaction in one tube, greatly improves the linking connection efficiency, and also has the following advantages: 1, phosphorylation and splicing steps of the DNA fragment are completed in one tube through one step to realize the linking reaction, so high cost caused by use of a phosphorylation primer is avoided; 2, the DNA fragment is seamlessly linked, so no superfluous nucleotides are introduced; 3, DNA sequence dependence is avoided; 4, not other nucleotides are introduced to the tail end of the spliced DNA fragment, and the DNA fragment can be reused for other construction works; and 5, the price is low, and is lower than that of routine enzyme digestion linking methods.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
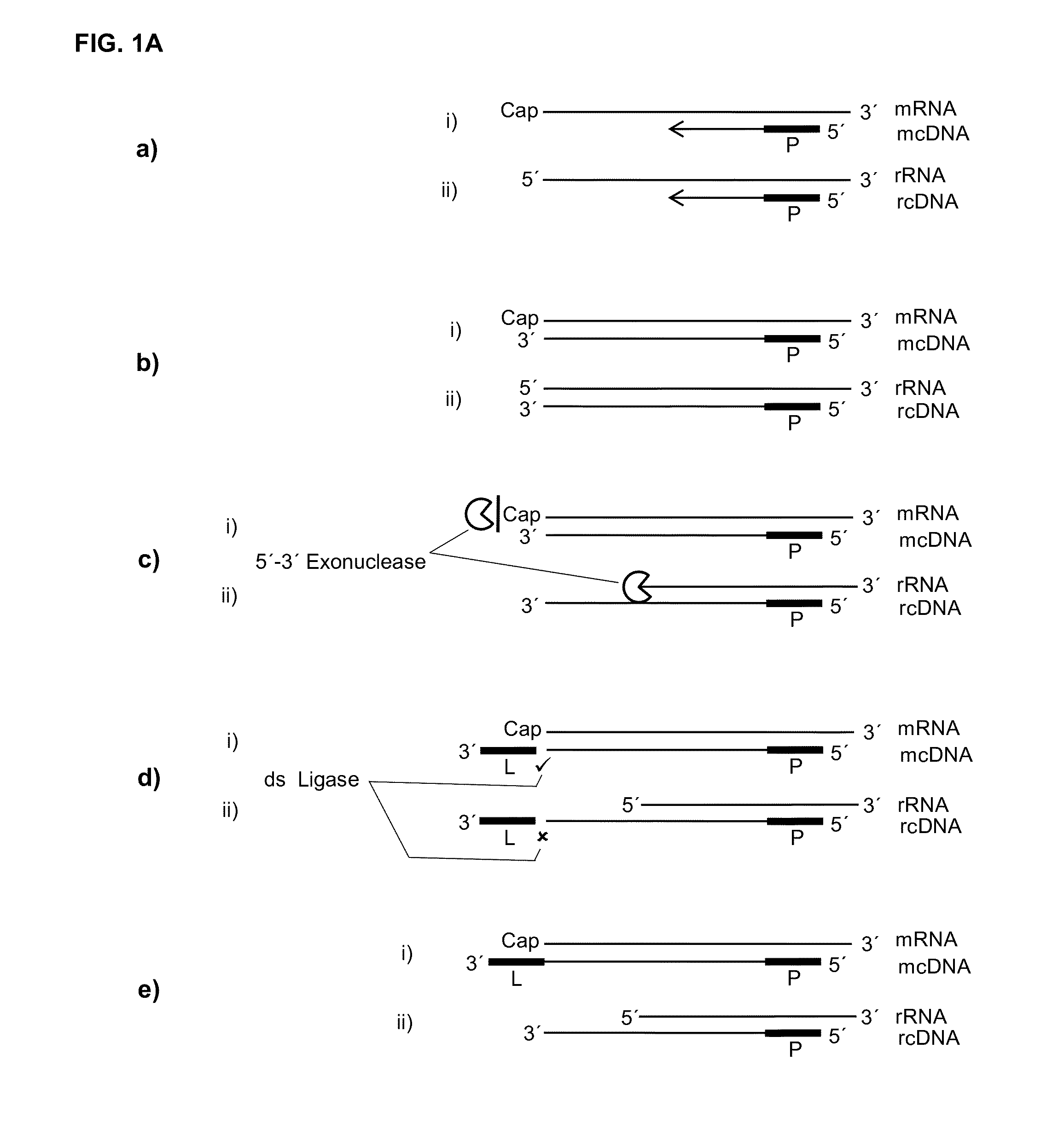
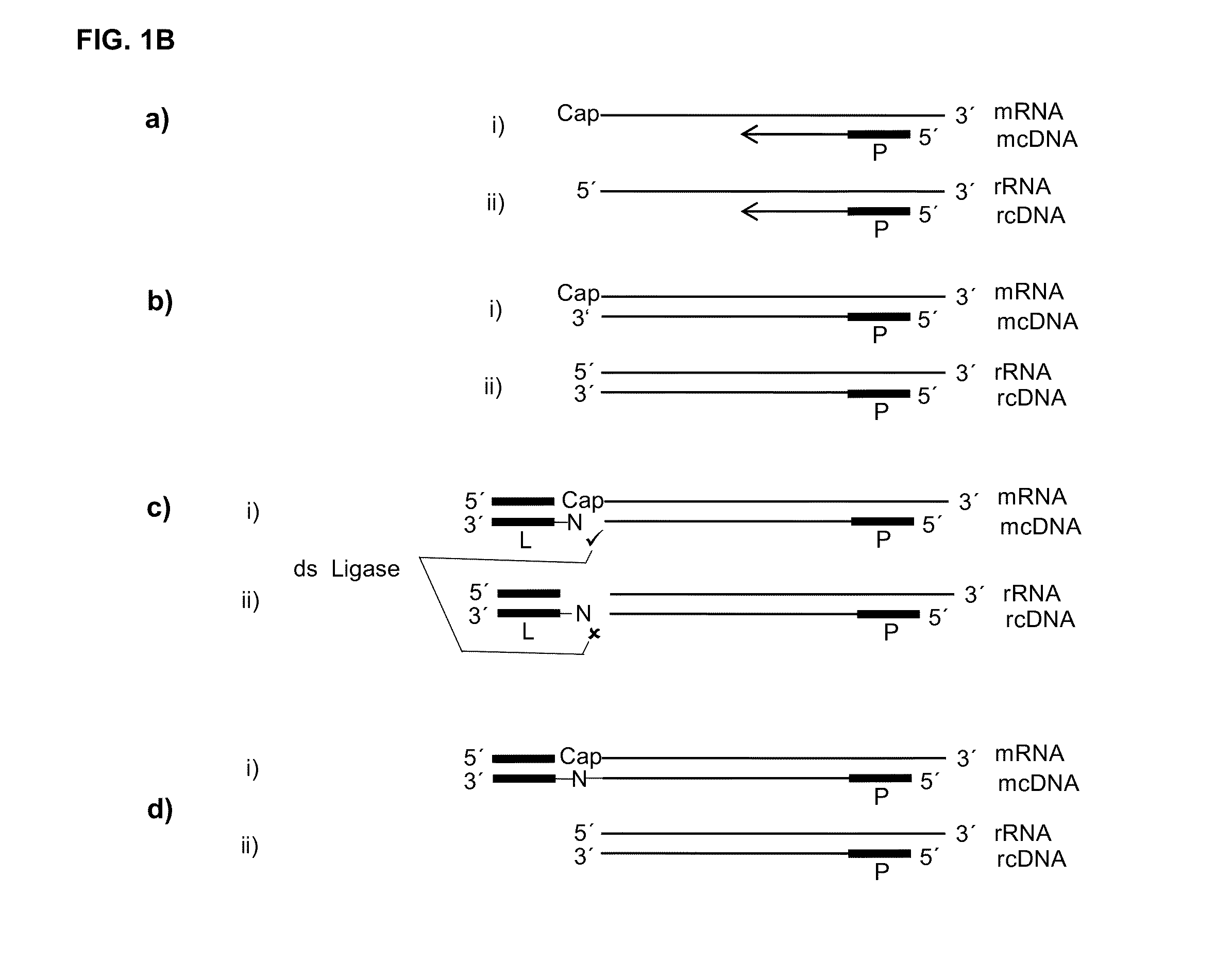
5' protection dependent amplification
ActiveUS20150147785A1High activityInhibit and reduce degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOligonucleotide PrimerDouble stranded
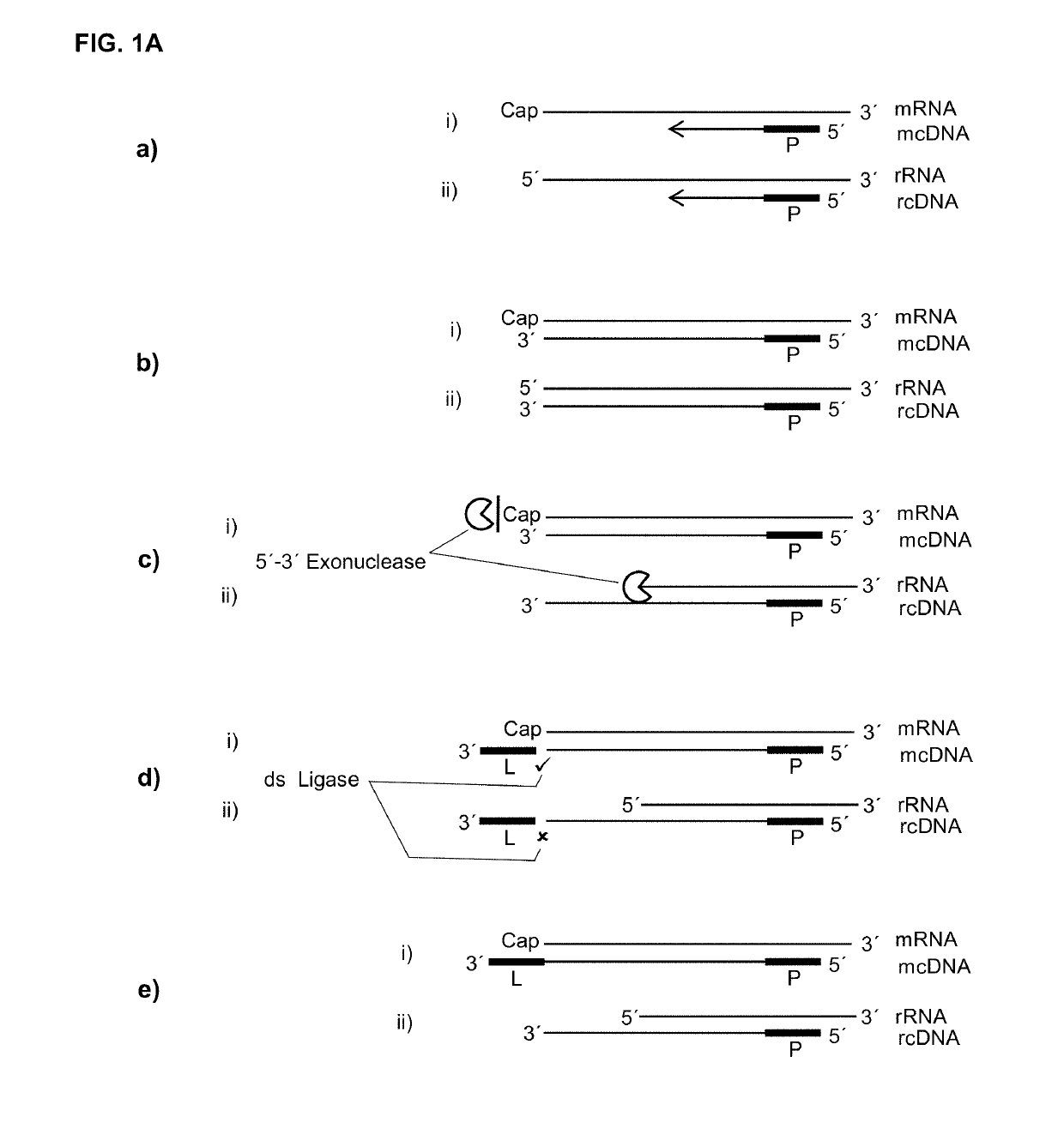
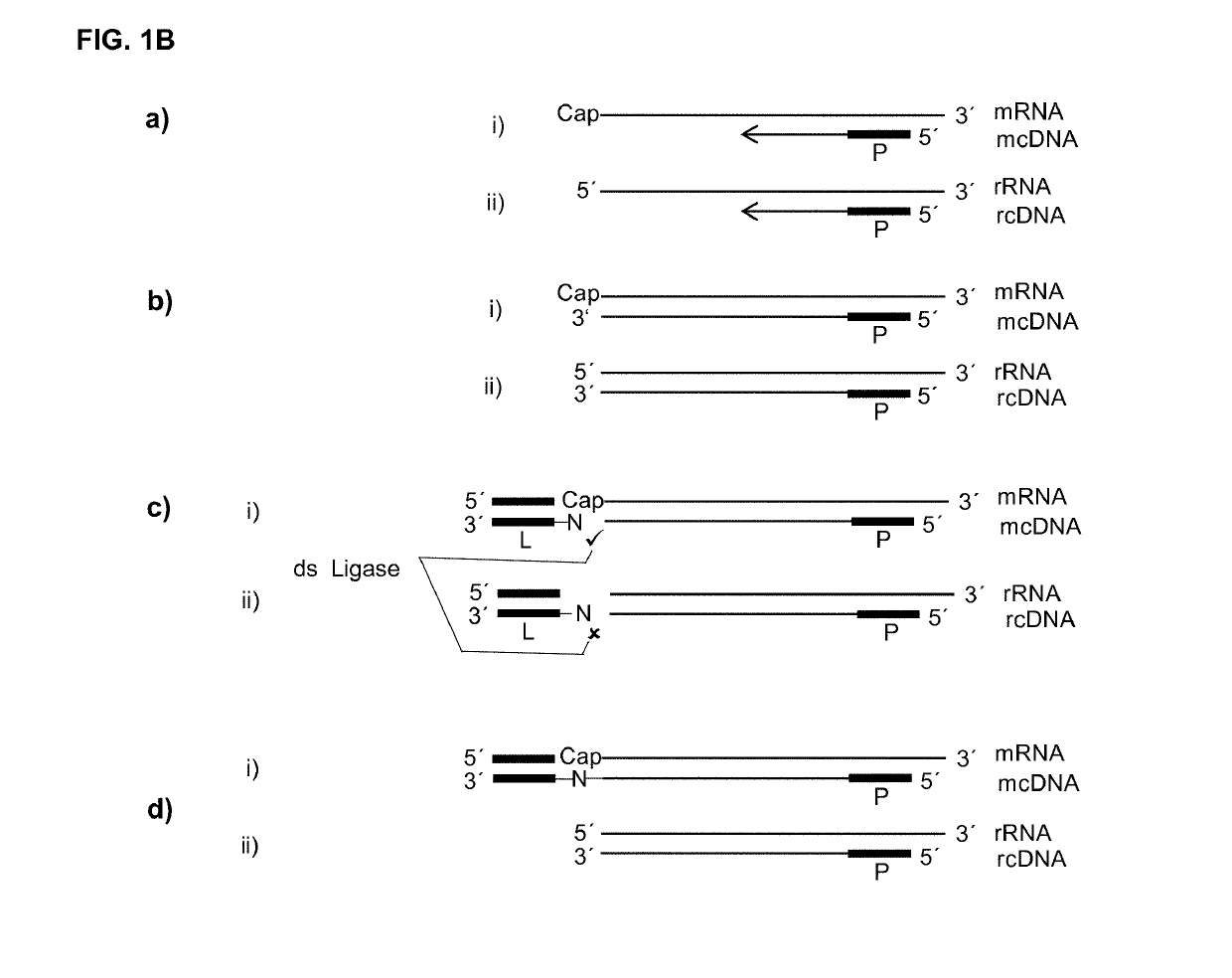
The present invention relates to methods for generating a labelled nucleic acid from an RNA comprising a 5′ protecting group, said method comprises the steps of obtaining a mixture of template strands of nucleic acids, said mixture comprising said RNA and further potentially other nucleic acids without a 5′ protecting group, annealing at least one oligonucleotide primer to the template strand of said RNA and potentially other nucleic acids, and template sequence dependent extending said primer, thereby obtaining a complementary nucleic acid strand annealed to its template strand, or providing the RNA in duplex with a complementary nucleic acid strand annealed to its template strand, andoptionally modifying the extension product of said nucleic acids without 5′ protecting group either on the 5′ end of the template strand or on the 3′ end of the complementary strand, or both, and labelling a complementary nucleic acid of a double stranded nucleic acid not modified, wherein therefore the labelled nucleic acid did have a 5′ protecting group on the RNA template strand, said 5′ protecting group being optionally removed after modification, and / or labelling a complementary nucleic acid of a double strand dependent on the presence of the 5′ protecting group on the complementary nucleic acids template RNA strand by double strand dependent ligation, thereby specifically generating a labelled nucleic acid complementary to an RNA at least originally comprising a 5′ protecting group.
Owner:LEXOGEN GMBH
Satellite measurement and control scheduling method and system based on clustering
PendingCN114781508AResolve dependenciesQuality improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionResourcesCluster algorithmLocal search (optimization)
The invention provides a satellite measurement and control scheduling method and system based on clustering, tasks are divided into K classes according to task characteristics, the close relation between the tasks is evaluated, similar tasks are close as far as possible, different tasks are far as far as possible, and when a genetic algorithm based on clustering is used for crossover and variation of populations, the clustering algorithm is used for clustering, so that the clustering efficiency is improved. Two different types of individuals are subjected to crossover variation, so that the balance of global search and local search is realized, a solution with higher quality can be obtained, and the problem of sequence dependence is well solved. Experiments show that the same optimization effect can be achieved in about one third of the time of a knowledge-based genetic algorithm by using the method disclosed by the invention.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
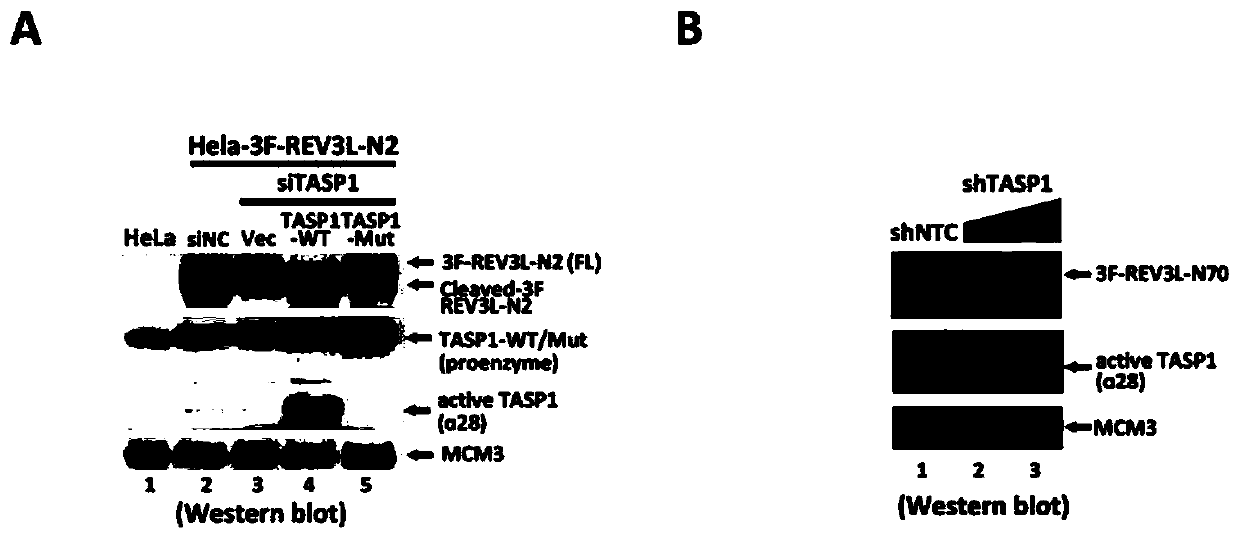
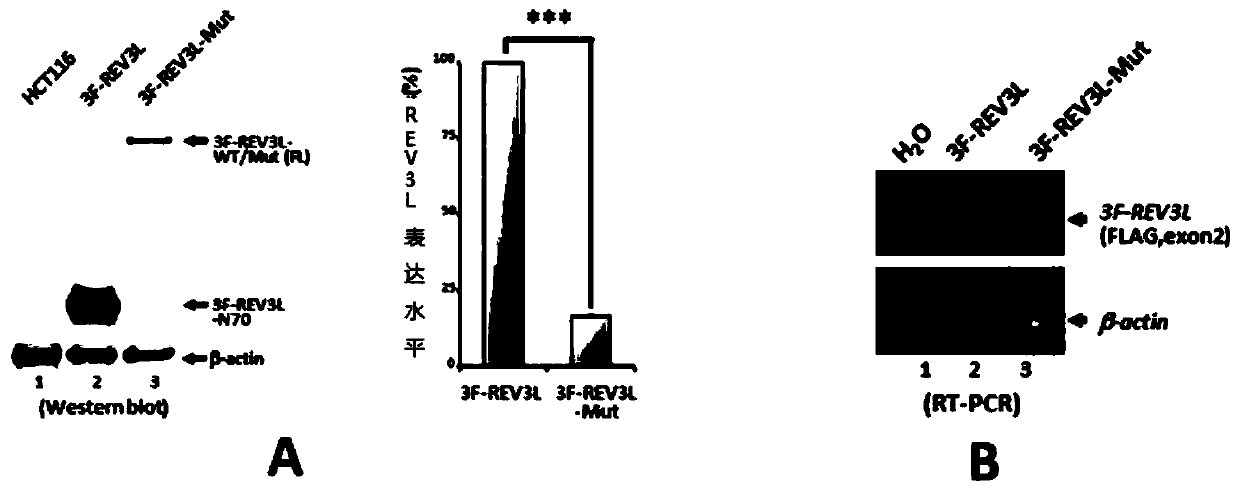
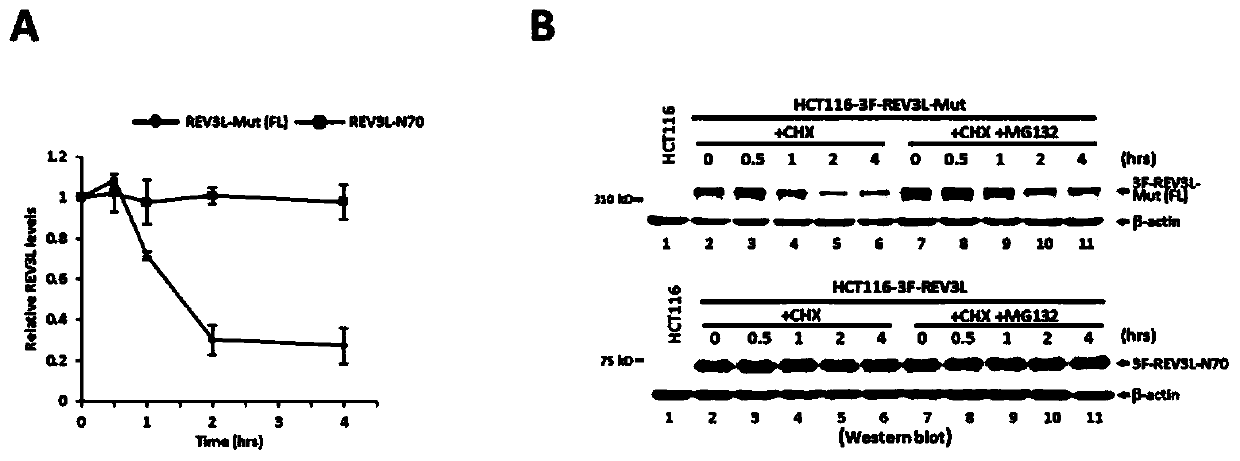
Human REV3L protein cleavage inhibitor and application thereof
InactiveCN111467493AIncreased sensitivityDelay drug resistanceHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseDrug target
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicine, and particularly relates to a human REV3L protein cleavage inhibitor and application thereof. The invention discloses a drug for improvingsensitivity of tumor cells to DNA damage and controlling drug resistance of tumor cells. The action target of the drug is obtained by a protease TASP1 mediated human REV3L protein position specific cleavage event. The inventor finds that the human REV3L protein has a TASP1 mediated sequence dependent protein cleavage event; polyubiquitination modification of REV3L protein and proteasome mediated degradation can be effectively promoted by interfering the REV3L protein cleavage event, so that low-fidelity cross-damage DNA synthesis activity in tumor cells is further reduced, DNA mutation inducedby DNA damage is reduced, sensitivity of tumor cells to DNA damage is remarkably improved, and therefore, a new potential drug target is provided for enhancing the radiotherapy and chemotherapy effects of tumors and other diseases taking induction of DNA damage as a molecular basis and controlling generation of drug resistance.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A system and method for analyzing public opinion
InactiveCN109086393AGuaranteed purityReduce mistakesNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsNetwork structureNetwork model
The invention discloses an analysis method of public opinion, which comprises the following steps: preprocessing public opinion information; word segmentation; according to the result of word segmentation, the word index being created and the word frequency being counted. dividing the data to be processed into a training set and a test set; defining the network structure; training the network model to save the eigenvalues; combined with the network model and eigenvalues, determining whether the new public opinion information is positive or negative public opinion, to achieve public opinion information judgment. According to the characteristics of the LSTM model, when the information enters the control unit, the control unit will judge the information, leave the information conforming to the rule and forget the information not conforming to the rule, so as to solve the problem of long sequence dependence in the neural network.
Owner:贵州中科恒运软件科技有限公司
5′ protection dependent amplification
ActiveUS10538795B2High activityInhibit and reduce degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOligonucleotide PrimerLigation
The present invention relates to methods for generating a labelled nucleic acid from an RNA comprising a 5′ protecting group, said method comprises the steps of obtaining a mixture of template strands of nucleic acids, said mixture comprising said RNA and further potentially other nucleic acids without a 5′ protecting group, annealing at least one oligonucleotide primer to the template strand of said RNA and potentially other nucleic acids, and template sequence dependent extending said primer, thereby obtaining a complementary nucleic acid strand annealed to its template strand, or providing the RNA in duplex with a complementary nucleic acid strand annealed to its template strand, andoptionally modifying the extension product of said nucleic acids without 5′ protecting group either on the 5′ end of the template strand or on the 3′ end of the complementary strand, or both, and labelling a complementary nucleic acid of a double stranded nucleic acid not modified, wherein therefore the labelled nucleic acid did have a 5′ protecting group on the RNA template strand, said 5′ protecting group being optionally removed after modification, and / or labelling a complementary nucleic acid of a double strand dependent on the presence of the 5′ protecting group on the complementary nucleic acids template RNA strand by double strand dependent ligation, thereby specifically generating a labelled nucleic acid complementary to an RNA at least originally comprising a 5′ protecting group.
Owner:LEXOGEN GMBH
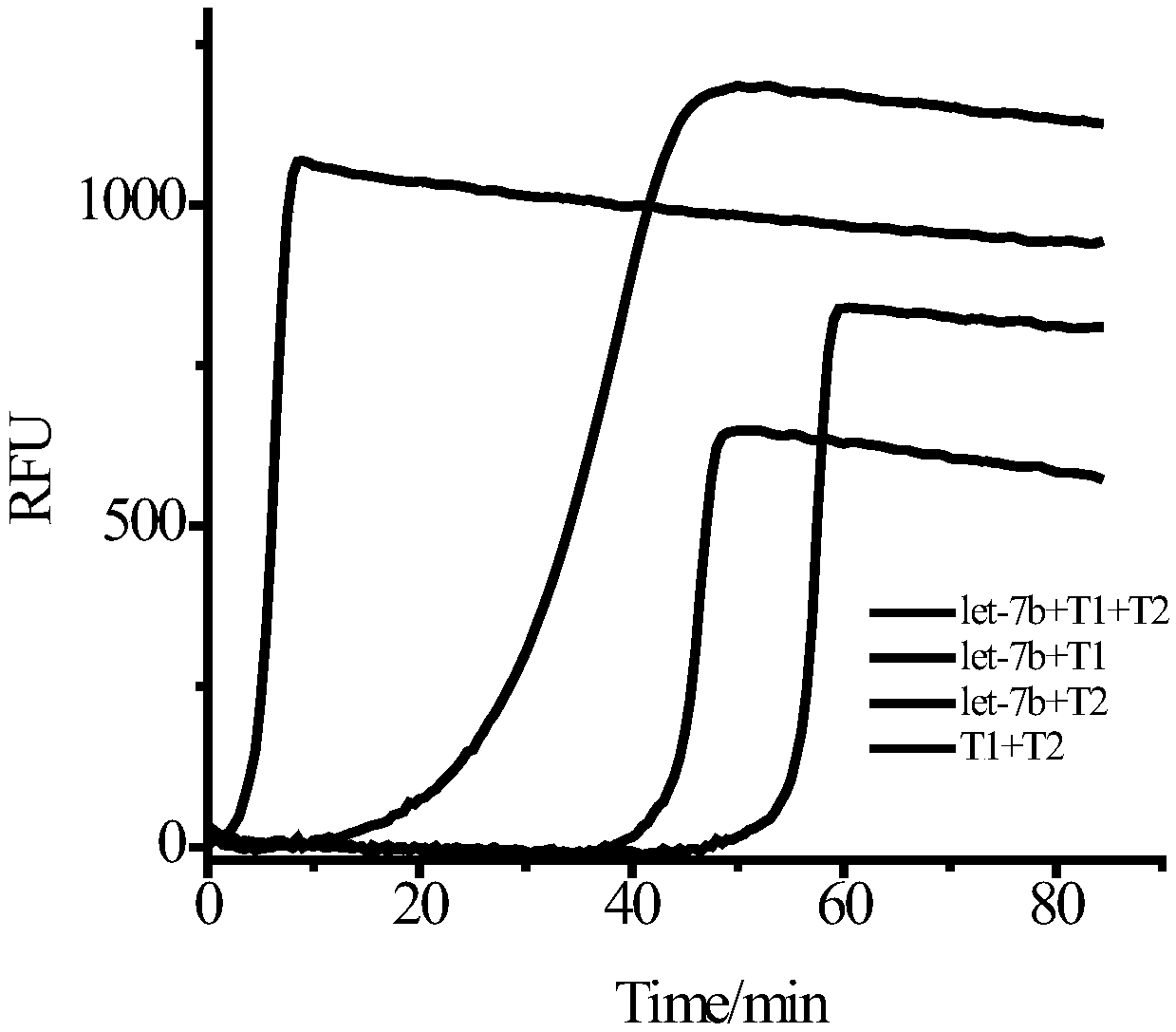
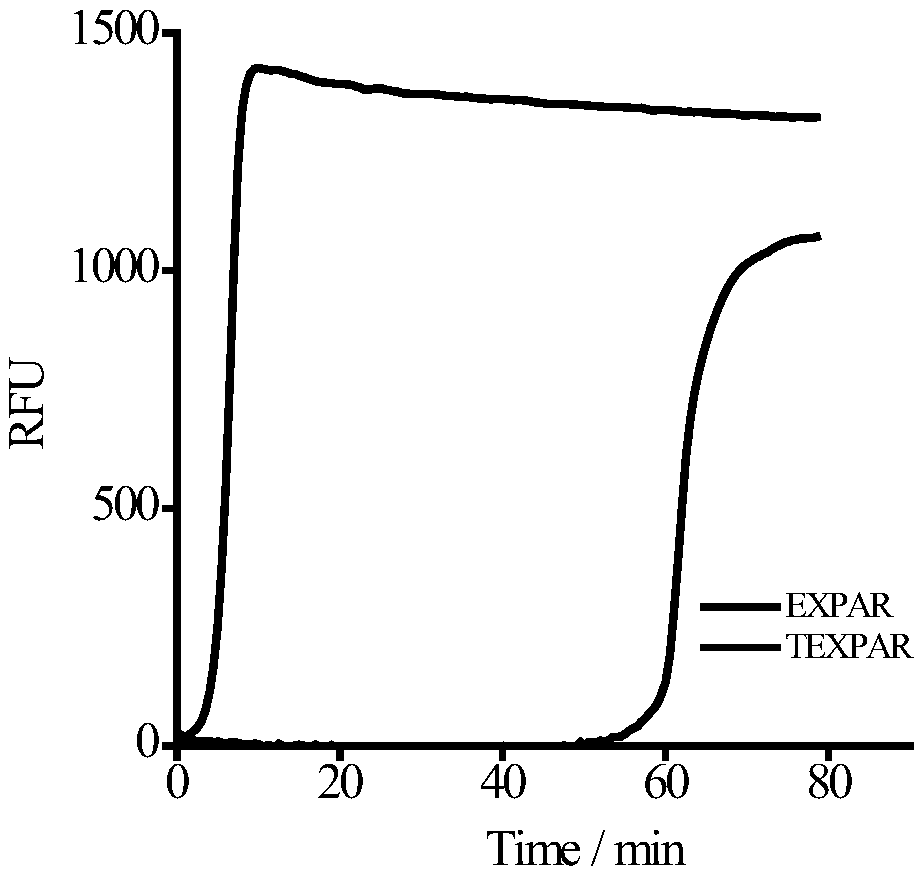
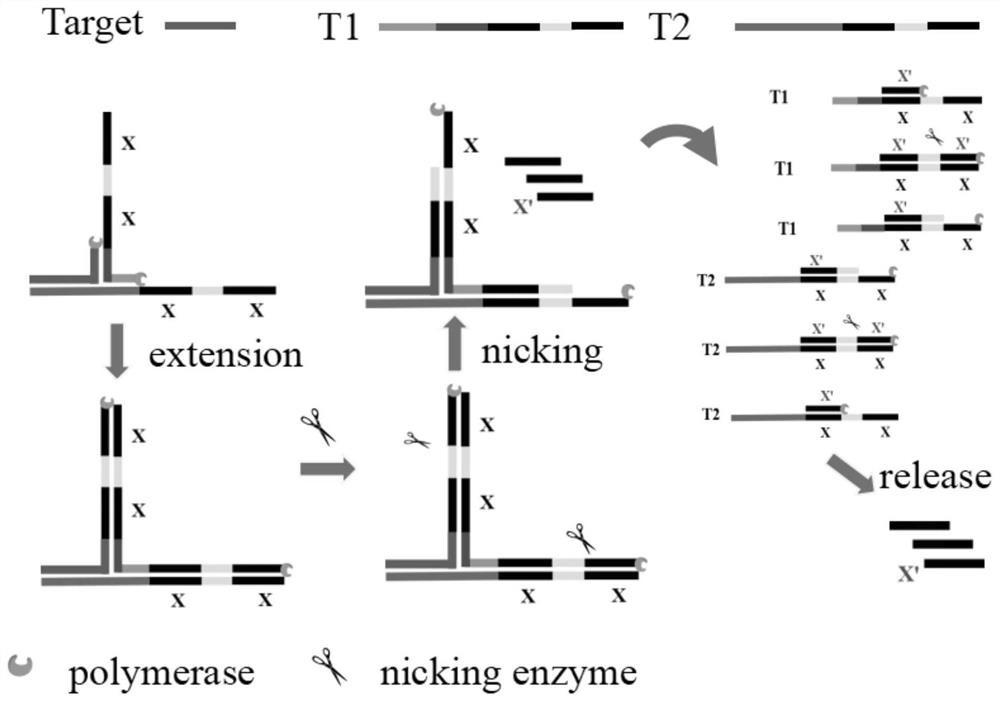
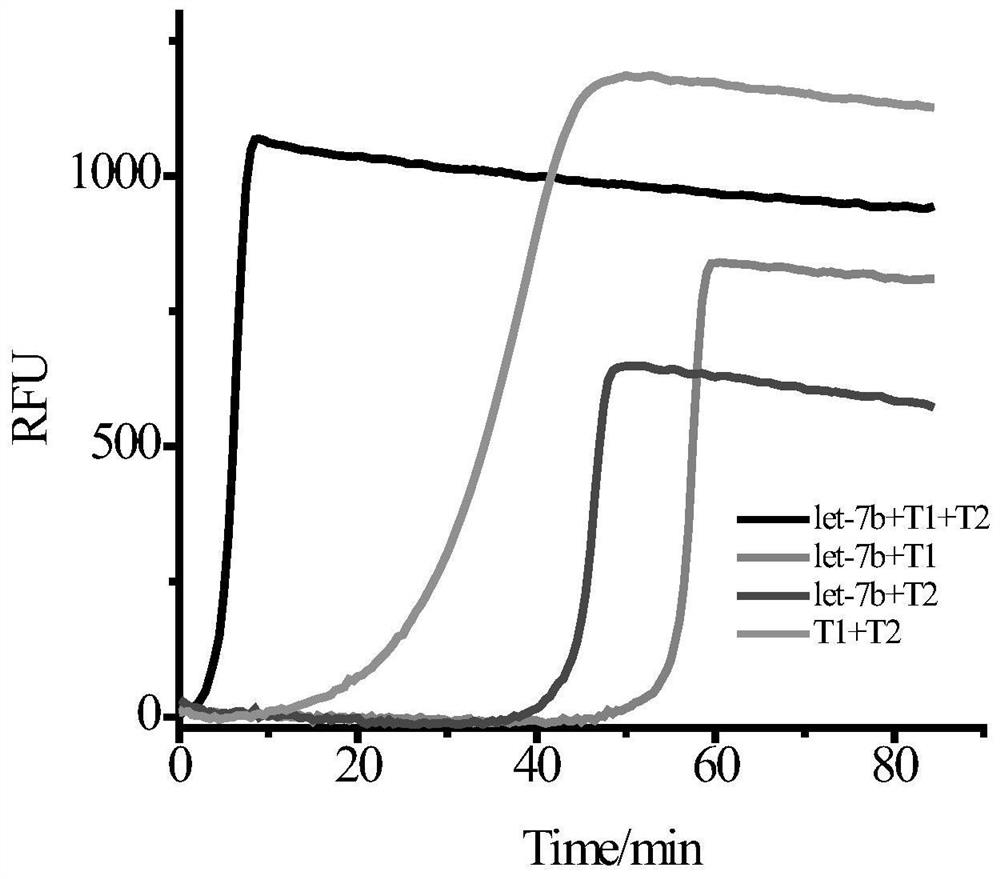
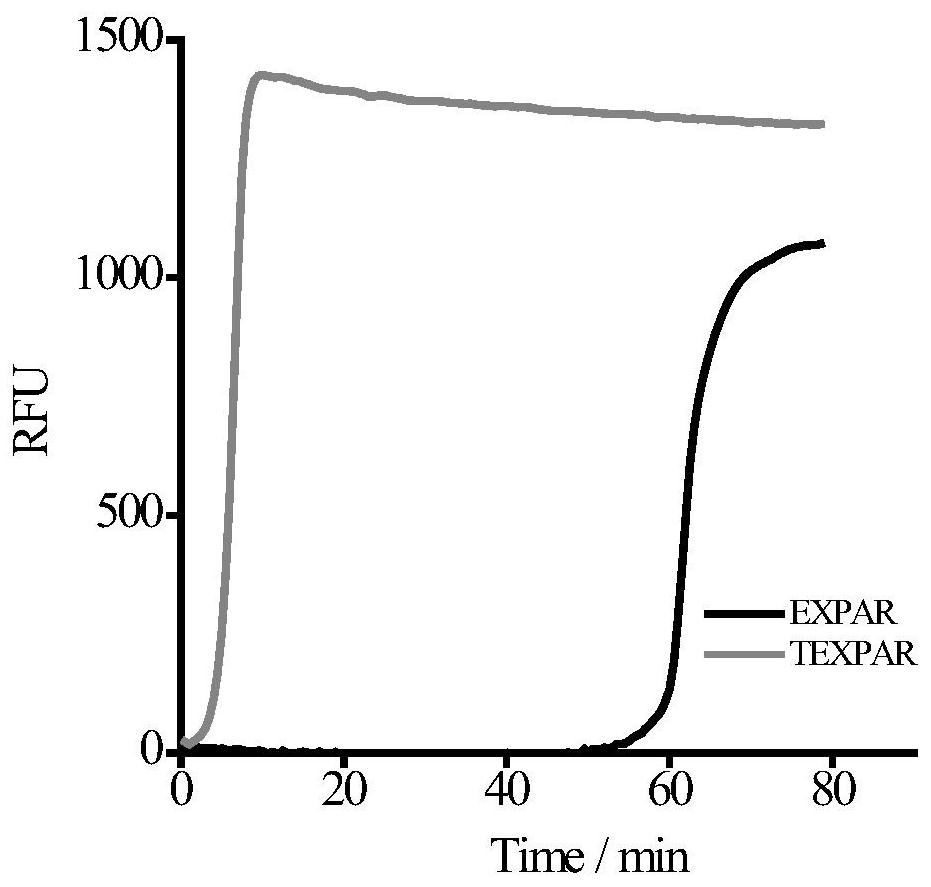
Method for low-sequence-dependence and high-order constant-temperature-index amplification testing of microRNA
ActiveCN109136353AHigh amplification efficiencyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroRNAEnzyme
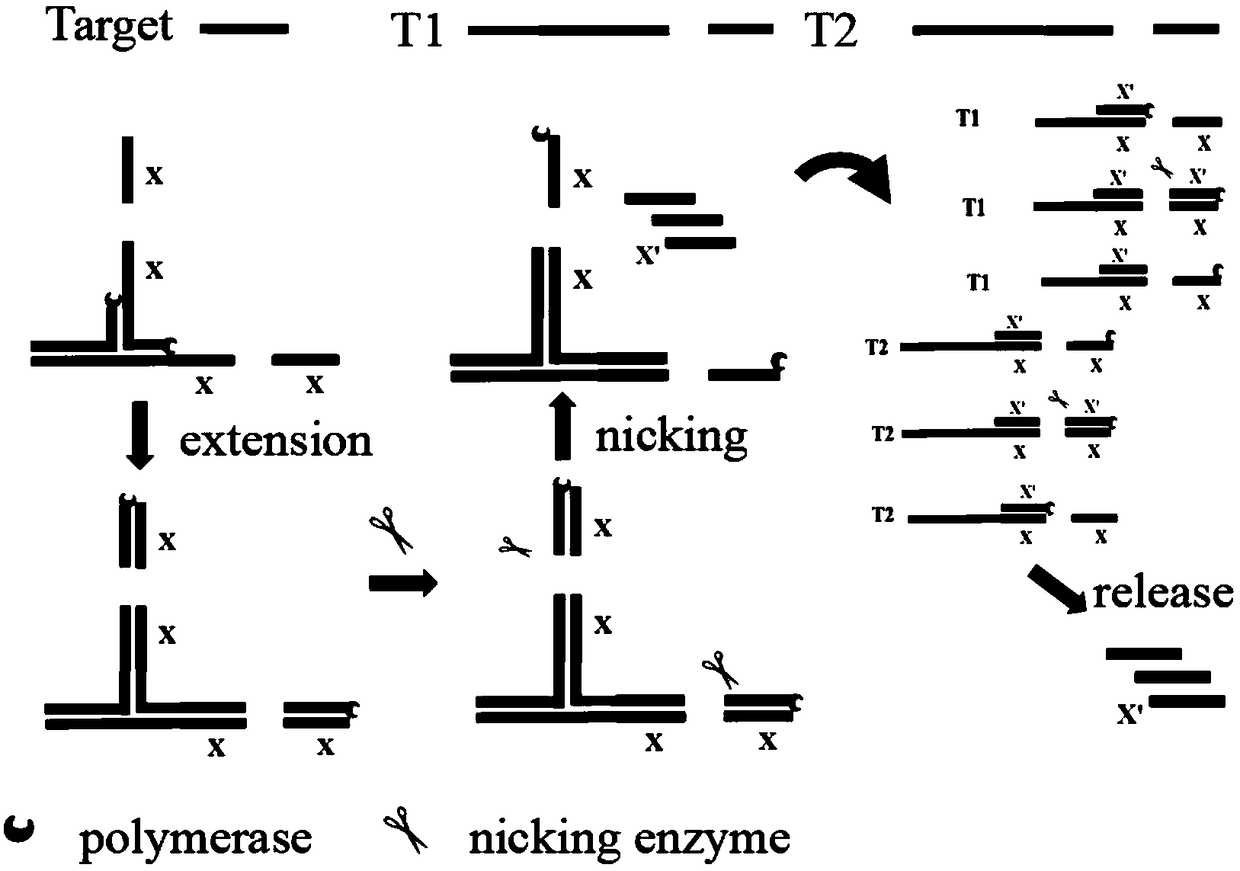
The invention discloses a method for low-sequence-dependence and high-order constant-temperature-index amplification testing of microRNA. The method comprises the steps of designing specific templatesT1 and T2 which can detect target microRNA; mixing the templates T1 and T2, DNA polymerase, incising incision enzyme and dNTP; reacting at a temperature of 35-50 DEG C; detecting an amplification curve; and judging whether a sample contains the target microRNA according to the amplification curve and the standard curve. By the method, the specific content of the target microRNA in the sample canbe calculated further. The method is high in amplification efficiency and high in sensitivity, and the analyzing time is shortened; the method has low sequence dependence on the target microRNA, and the universality is high; a detection linear range is wide, and the specificity is good; and an amplification system is simple, can be developed into a kit and is popularized to markets.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Single quantum-dot based aptameric nanosensors
ActiveUS8642260B2Simple sample preparationHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAptamerNucleotide
A signal-off-quantum-dot-based sensor for detecting the presence of a target molecule comprising: an aptamer probe having a nucleotide sequence which specifically interacts with the target molecule by sequence-dependent interaction, wherein the aptamer probe is sandwiched between (a) an oligonucleotide which is immobilized on the surface of a quantum dot (QD), and (b) a fluorophore-labeled oligonucleotide, wherein when the sensor is excited by an energy source: (i) in the absence of specific interaction between the target molecule and the aptamer probe, a baseline signal is emitted, and (ii) in the presence of specific interaction between the target molecule and the aptamer probe, a detection signal is emitted, wherein the baseline signal is greater than the detection signal, whereby the presence of the target molecule is detected.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
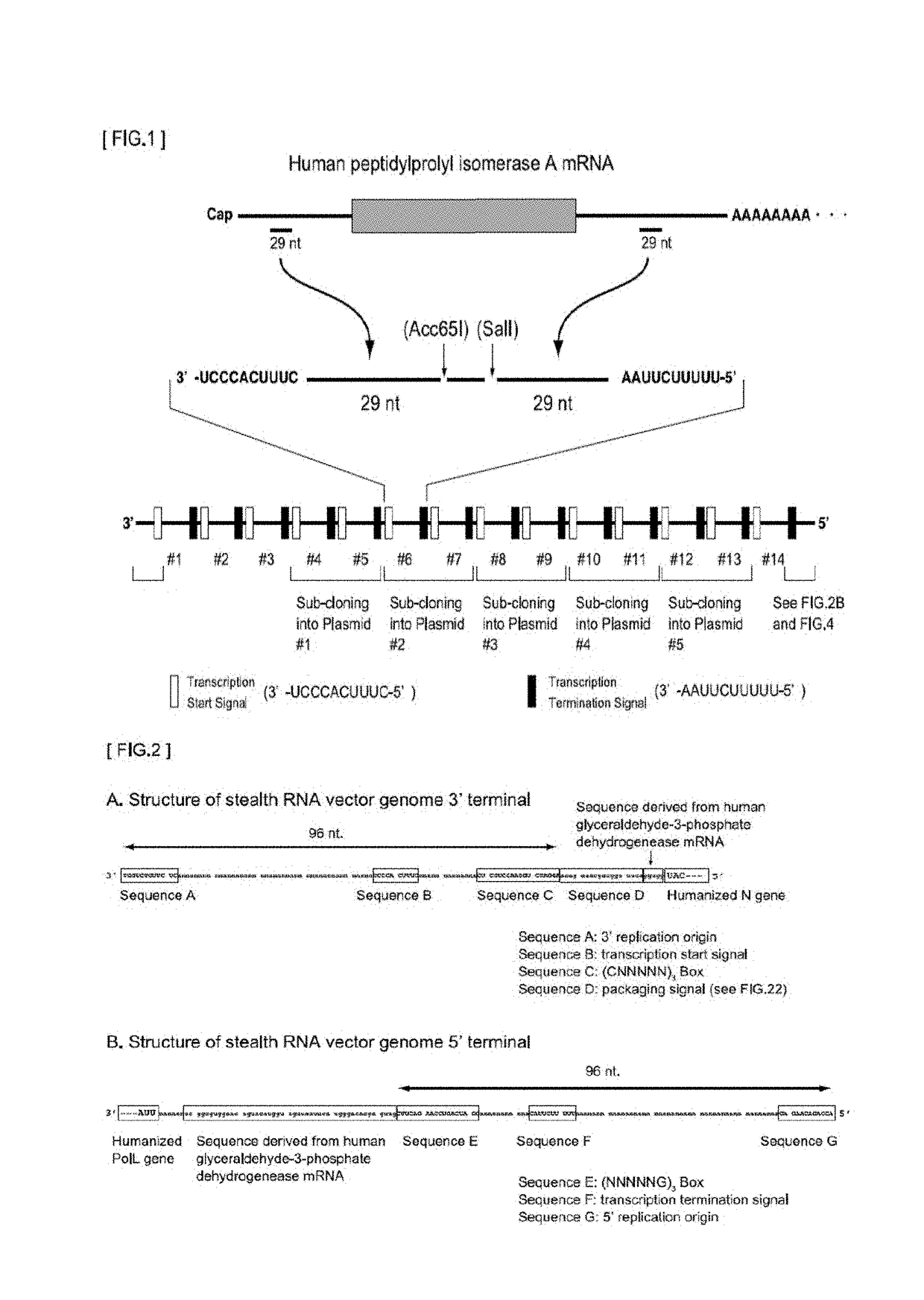
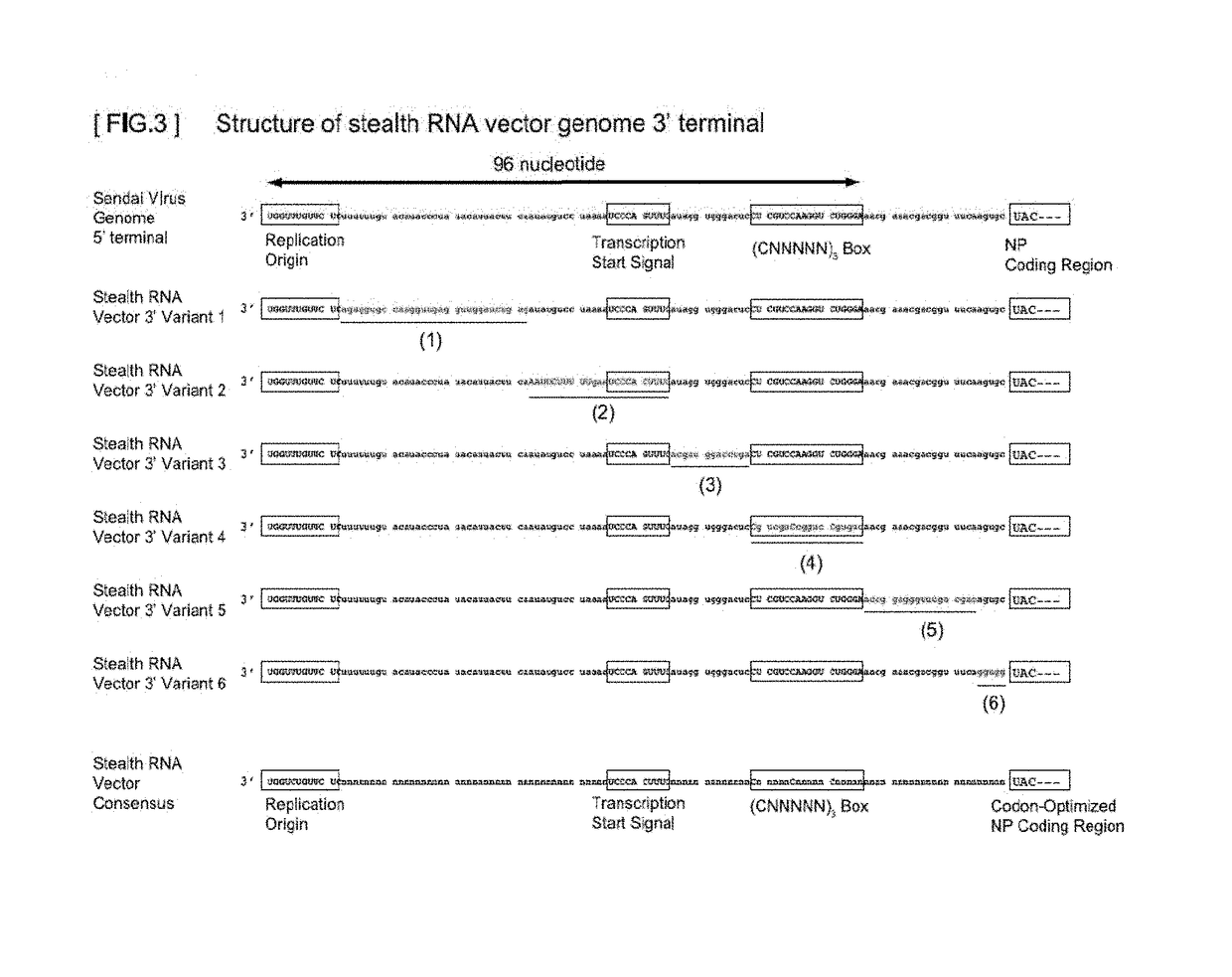
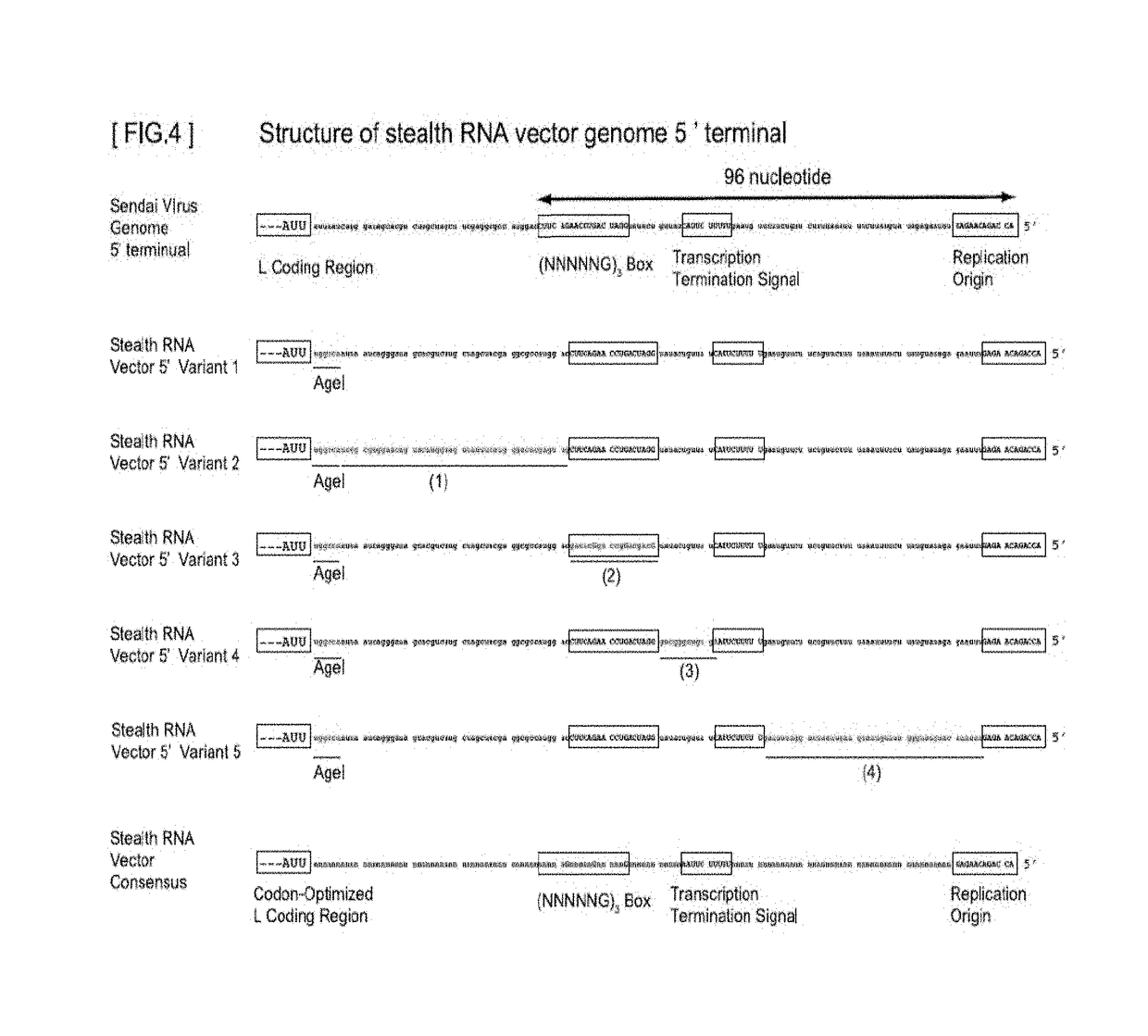
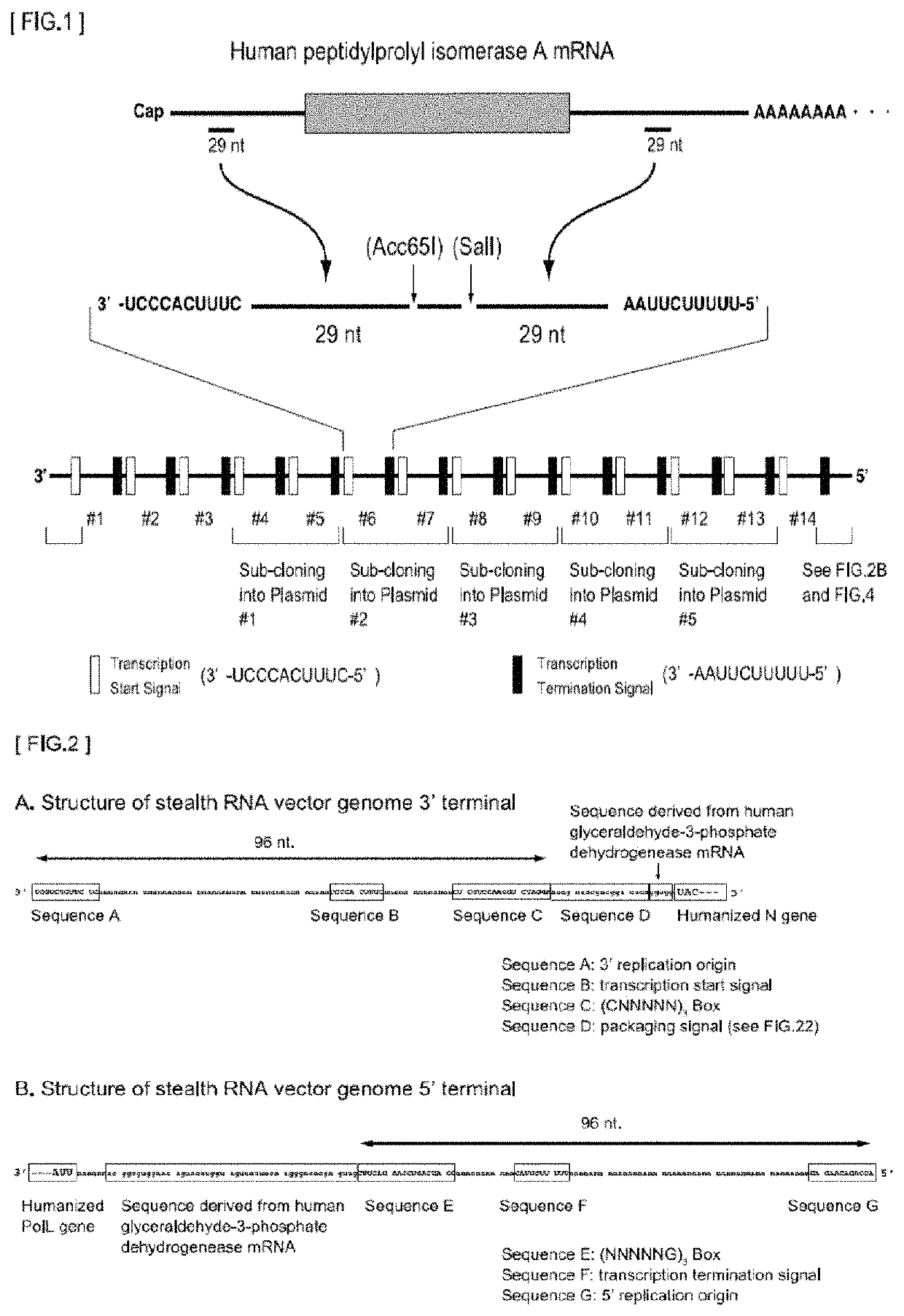
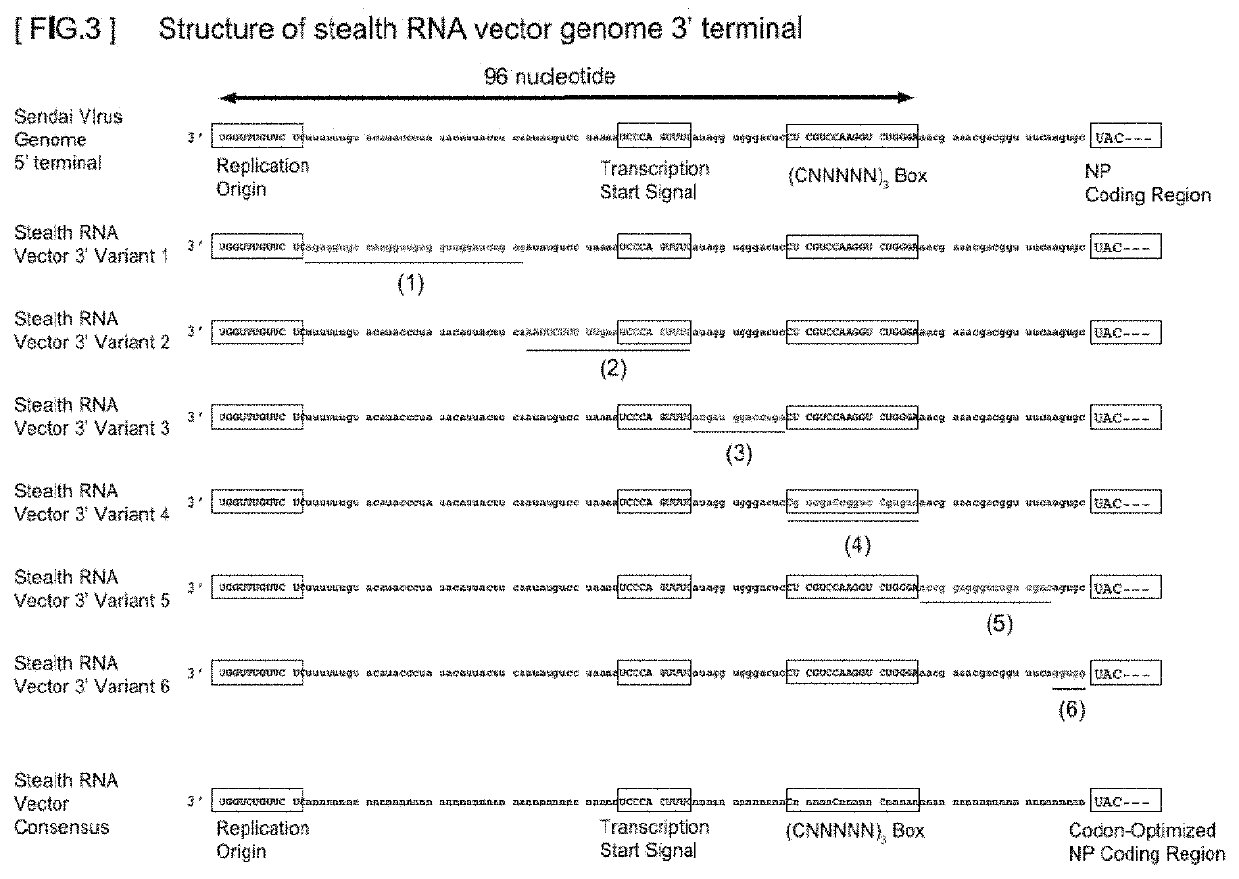
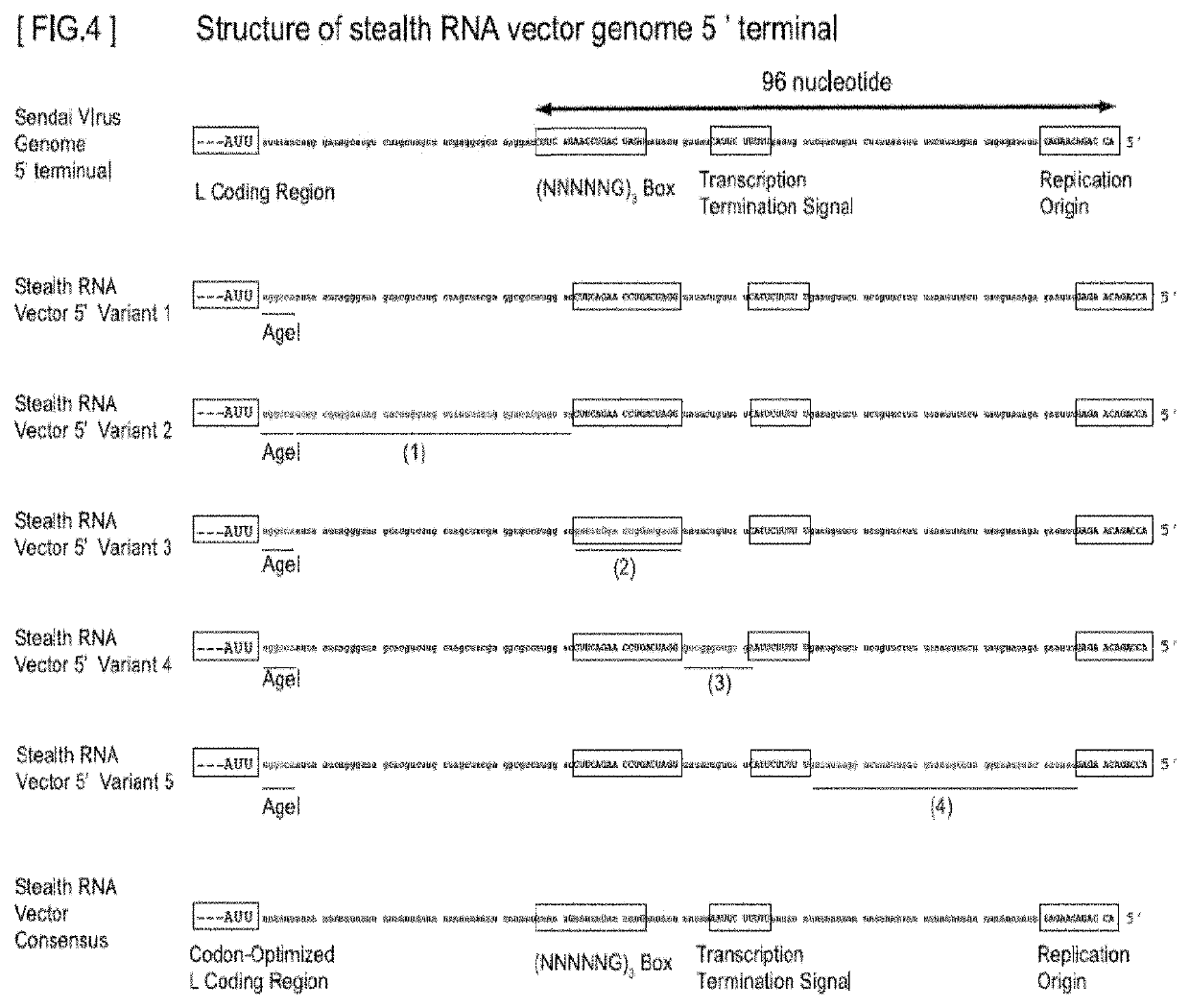
Gene expression system using stealthy RNA, and gene introduction/expression vector including said RNA
ActiveUS20170369903A1Low cytotoxicityDifficult to captureSsRNA viruses negative-senseHybrid immunoglobulinsSingle-Stranded RNAOrigin of replication
Simultaneous expression of a plurality of foreign genes by using a stealthy RNA gene expression system that is a complex that does not activate the innate immune mechanism and is formed from an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, a single-strand RNA binding protein, and negative-sense single-strand RNAs including the following (1) to (8): (1) a target RNA sequence that codes for any protein or functional RNA; (2) an RNA sequence forming a noncoding region and derived from mRNA; (3) a transcription initiation signal sequence recognized by the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; (4) a transcription termination signal sequence recognized by the polymerase; (5) an RNA sequence containing a replication origin recognized by the polymerase; (6) an RNA sequence that codes for the polymerase; (7) an RNA sequence that codes for a protein for regulating the activity of the polymerase; and (8) an RNA sequence that codes for the single-strand RNA binding protein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
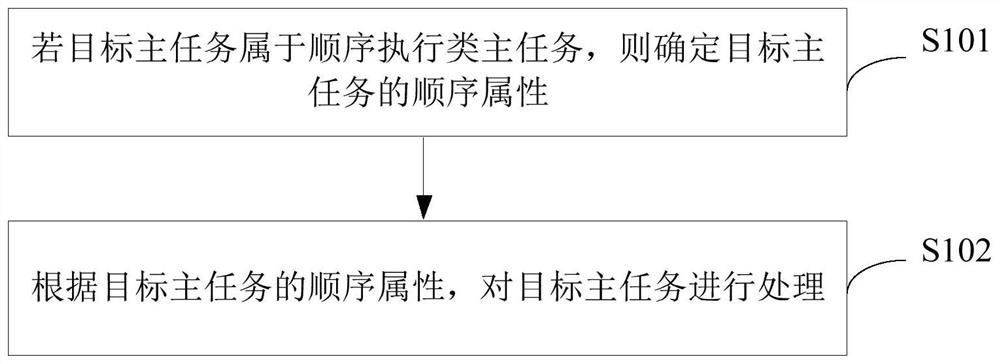
Main task processing method and device, server and storage medium
PendingCN112416552AGuaranteed orderMeet the needs of useProgram initiation/switchingProcessingServer
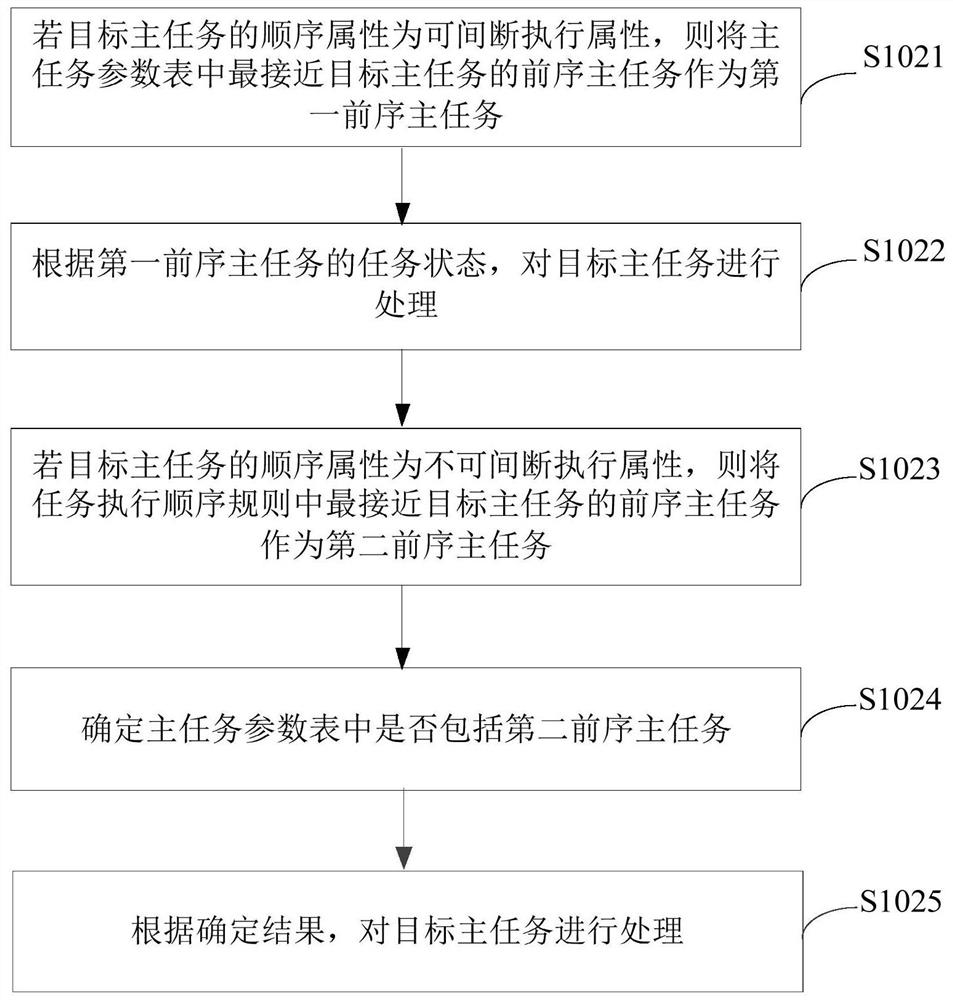
The embodiment of the invention provides a main task processing method and device, a server and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: determining the sequence attribute of a target main task if the target main task belongs to a sequence execution type main task; wherein the sequence attribute is an interruptible execution attribute or an uninterruptible execution attribute; processing the target main task according to the sequence attribute of the target main task, so that the main task with strict sequence dependence is processed, the orderliness of the whole process from preprocessing distribution to final execution completion of the main task is ensured, the use requirements in a special scene can be met, and the application range of a main task processing mechanism is widened.
Owner:CHINA CONSTRUCTION BANK
A low-sequence-dependent high-order isothermal exponential amplification method for the detection of microRNAs
ActiveCN109136353BHigh amplification efficiencyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroRNAEndonuclease
The invention discloses a method for detecting microRNA by low-sequence-dependent high-order constant temperature exponential amplification. The method designs specific templates T1 and T2 capable of detecting target microRNA, and incises the templates T1 and T2, DNA polymerase, and nick endo The enzyme and dNTP are mixed and reacted at 35-50°C, the amplification curve is detected, and whether the sample contains the target microRNA is determined according to the amplification curve and the standard curve. The method of the present invention can further calculate the specific content of the target microRNA in the sample. The method of the present invention has high amplification efficiency and high sensitivity, and shortens the analysis time; the method has little sequence dependence on the target microRNA and has strong versatility; the detection linear range is wide and the specificity is good; the amplification system is simple and can be developed into a kit and promote it to the market.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A Method of Obtaining Accurate Latest Deadline in Multi-core Real-time Fault-tolerant System
The invention provides a method for acquiring an accurate latest deadline in a multi-core realtime fault-tolerant system. The method includes the following steps: according to given task scheduling and on the basis that original data dependence is maintained, increasing scheduling sequence dependence for adjacent tasks scheduled on a same core; increasing two virtual task nodes with execution time to be zero, and enabling one of the virtual task nodes to be executed before all other tasks and the other virtual task node to be executed after all other tasks; supposing that at most X soft errors appear in the process of task execution and on the basis of original scheduling, realizing fault tolerance by immediately re-executing erroneous tasks on the same core, determining key tasks of a task set, and acquiring the accurate latest deadline of the task set. By the method, if N tasks is contained in the task set and at most X soft errors appear in the process of execution, the accurate latest deadline of the task set can be determined within O(n^2) to guarantee fault tolerance, and high efficiency and quickness are realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Gene expression system using stealthy RNA, and gene introduction/expression vector including said RNA
ActiveUS10544431B2Low cytotoxicityEasy to disassembleSsRNA viruses negative-senseHybrid immunoglobulinsOrigin of replicationSingle strand
Simultaneous expression of a plurality of foreign genes by using a stealthy RNA gene expression system that is a complex that does not activate the innate immune mechanism and is formed from an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, a single-strand RNA binding protein, and negative-sense single-strand RNAs including the following (1) to (8): (1) a target RNA sequence that codes for any protein or functional RNA; (2) an RNA sequence forming a noncoding region and derived from mRNA; (3) a transcription initiation signal sequence recognized by the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; (4) a transcription termination signal sequence recognized by the polymerase; (5) an RNA sequence containing a replication origin recognized by the polymerase; (6) an RNA sequence that codes for the polymerase; (7) an RNA sequence that codes for a protein for regulating the activity of the polymerase; and (8) an RNA sequence that codes for the single-strand RNA binding protein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
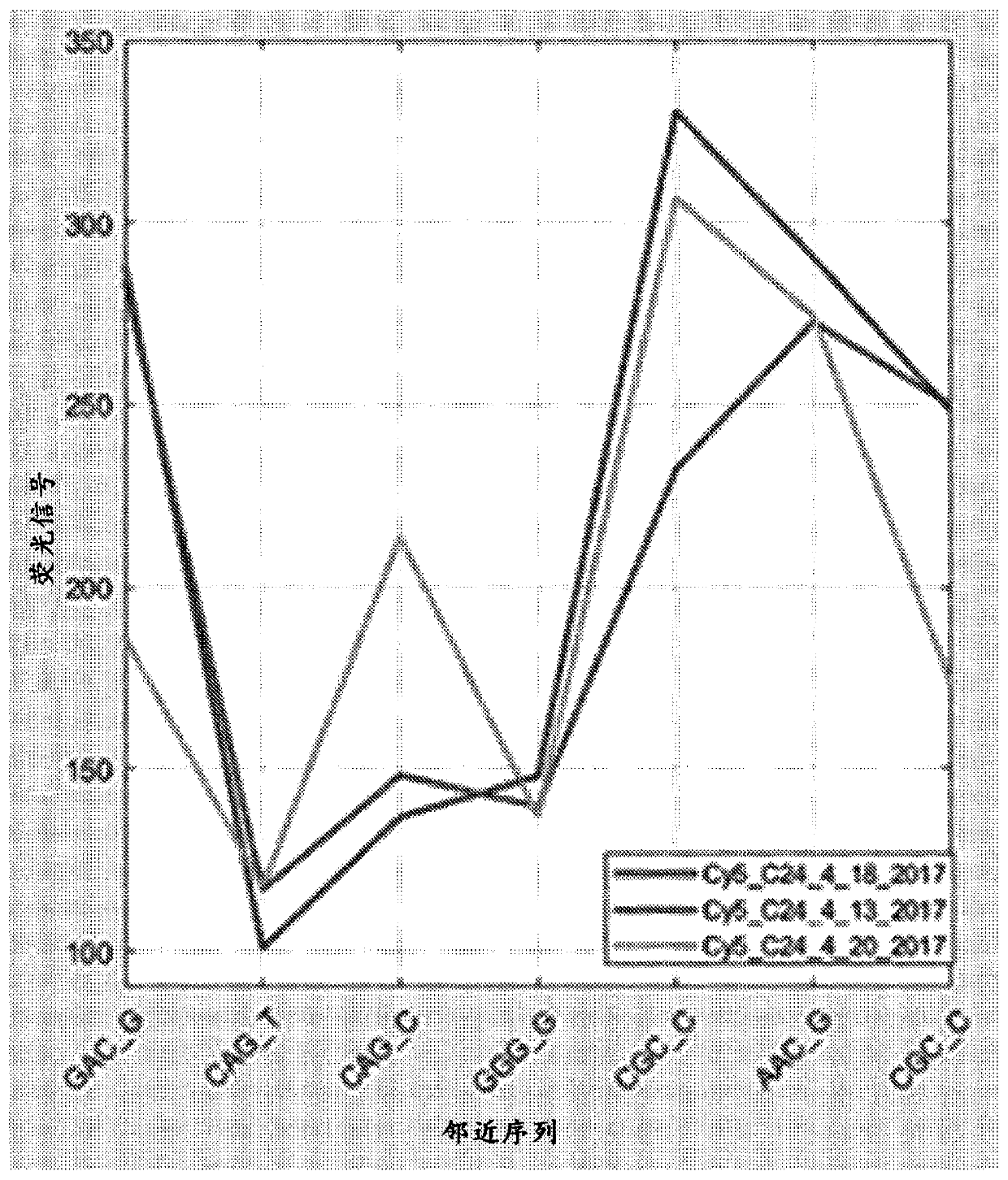
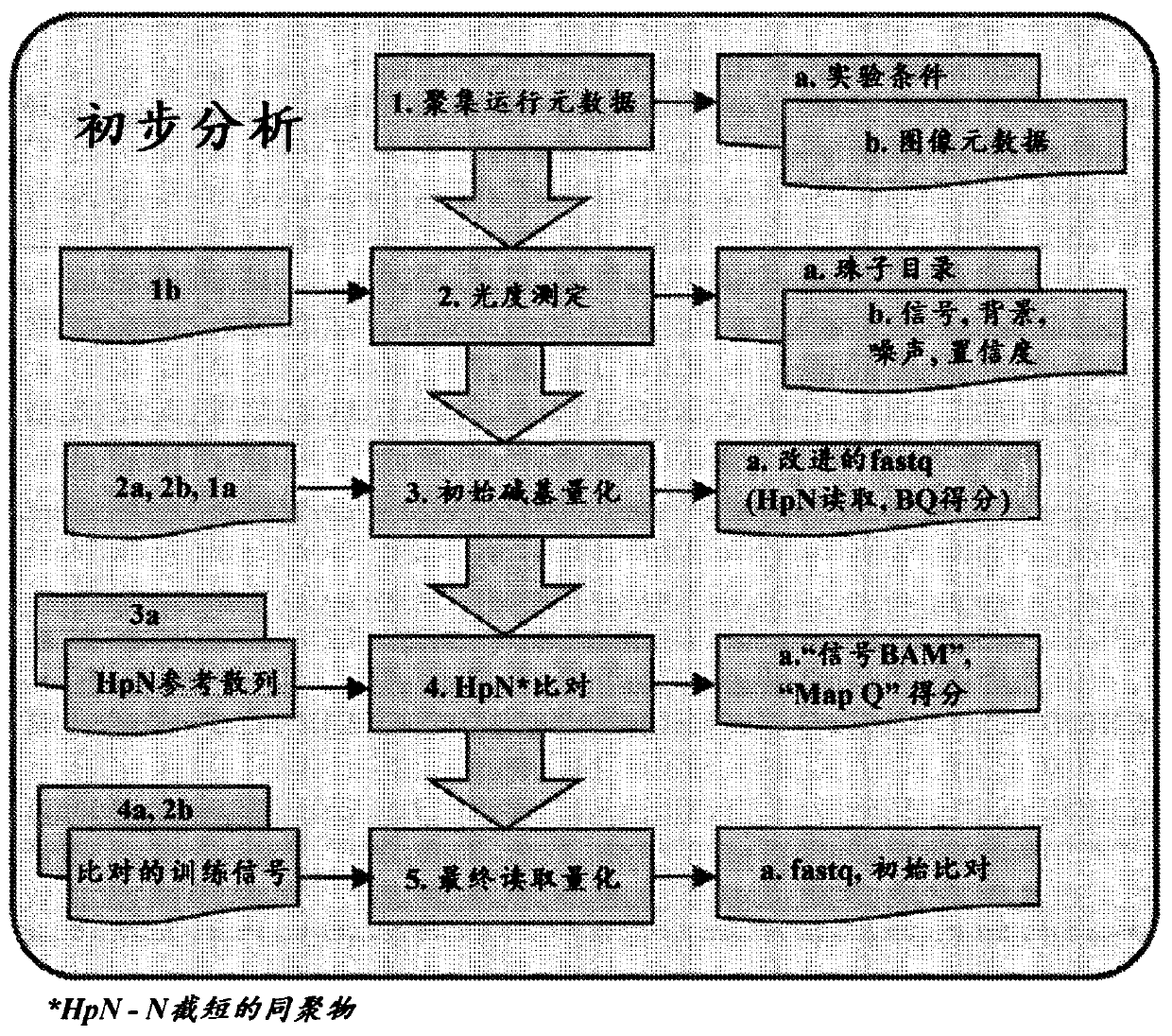
Methods and systems for sequence calling
PendingCN111527044AReduce or remove errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsSequence signalBase calling
The present disclosure provides methods and systems for accurate and efficient context-aware base calling of sequences. In an aspect, disclosed herein is a method for sequencing a nucleic acid molecule, comprising: (a) sequencing the nucleic acid molecule to generate a plurality of sequence signals; and (b) determining base calls of the nucleic acid molecule based at least in part on (i) the plurality of sequence signals and (ii) quantified context dependency for at least a portion of the plurality of sequence signals.
Owner:ULTIMA GENOMICS INC
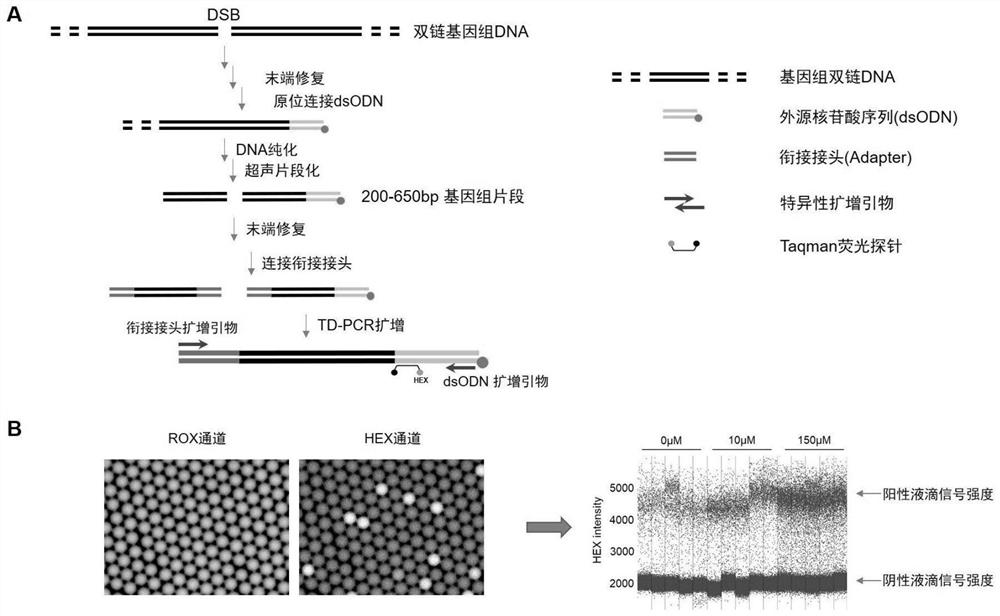
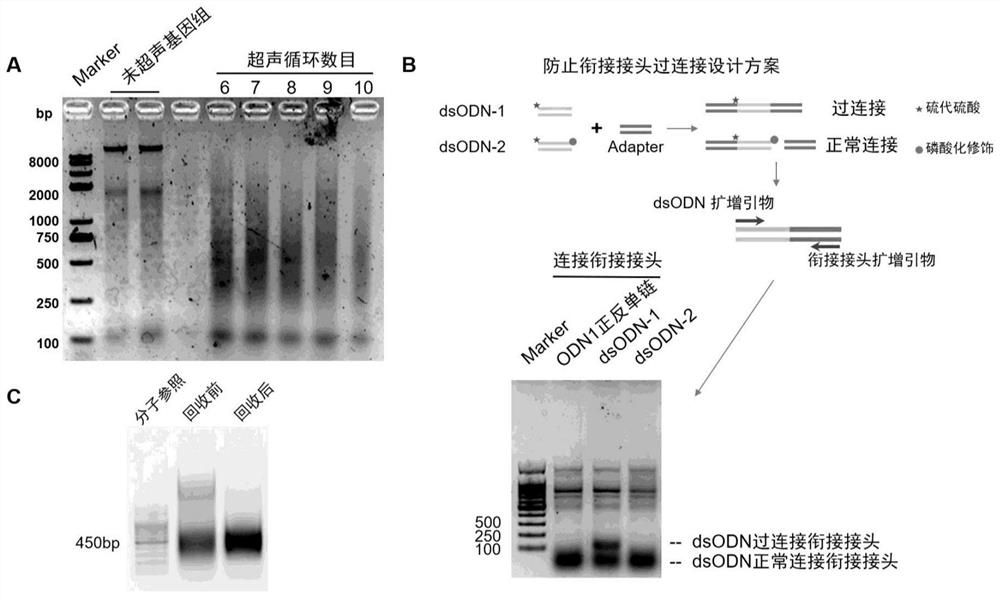
Method for absolutely quantifying number of DNA double-strand fractures in cells and application
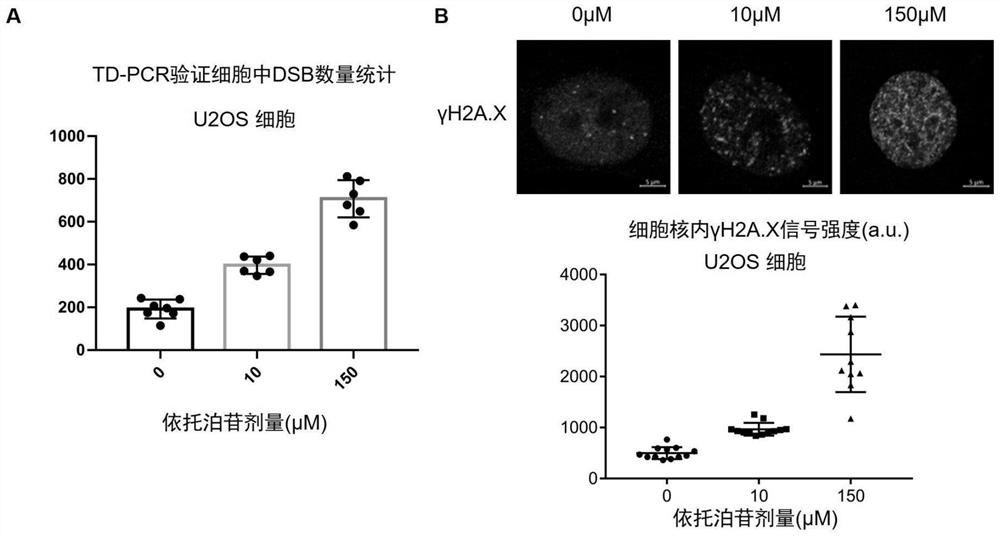
PendingCN114032292ABlock connectionImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseGenomic Segment
The invention discloses a method for absolutely quantifying the number of DNA double-strand fractures in cells and application. The method comprises the following steps: inserting an exogenous nucleotide fragment with terminal modification into a fixed cell genome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) double-chain fracture position, then fragmenting the genome and connecting the genome with an adapter, designing a specific PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer and a specific fluorescent probe aiming at the exogenous nucleotide fragment and the adapter, and constructing a digital droplet PCR system by combining a cell internal reference gene, and quantifying the number of DNA double-strand fractures in the cells. According to the invention, the detection of DNA double-strand fractures gets rid of sequence dependence, the method is widely suitable for absolutely and accurately quantifying the number of DNA double-strand fractures caused by various reasons such as animal and plant endogenous diseases, radiation, drugs or gene editing, and can be used as an effective tool for detecting problems such as ray damage, chemical drug damage, gene editing off-target efficiency and the like; the method has a very wide application prospect in molecular biology and clinical diagnosis.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Sequence Specific Fluorescence for Peptide-Fluorochrome Interactions
InactiveUS20180120325A1Emission reductionAccelerate emissionsBiological material analysisBiological testingPeptideSpecific fluorescence
A method of obtaining fluorochromes that bind to specific sites on proteins is presented. The method consists of synthesizing a peptide bearing a sequence from a parent protein and a second peptide of similar composition but with a scrambled sequence. Each peptide is then added to a test fluorochrome at similar concentrations, and a difference in fluorescence is obtained. A difference in fluorescence indicates a sequence dependent interaction between the peptide and fluorochrome. A large number of fluorochromes can be screened using the two peptides to find one binding in a sequence dependent fashion. This fluorochrome can then be tested for binding to the original full-length protein. The fluorochrome can then serve as scaffold in medicinal chemistry. The fluorochrome / peptide interaction and resulting fluorescence can be inhibited by non-fluorescent test compounds, which are compounds that bind to this peptide. Thus. the peptide / fluorochrome interaction can provide assays screening for therapeutic drugs binding to this site on the protein.
Owner:MEDCHEM IMAGING LLC
Probe and kit for detecting point mutation of DNA and application
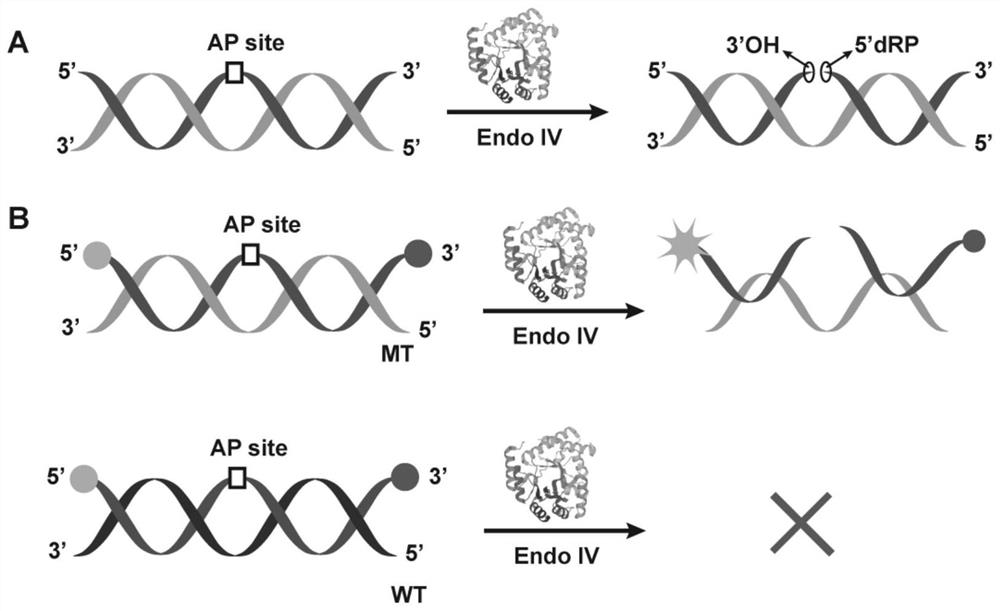
ActiveCN113897418AReduced sequence dependenceReduce design costMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesEnzyme digestionSingle strand
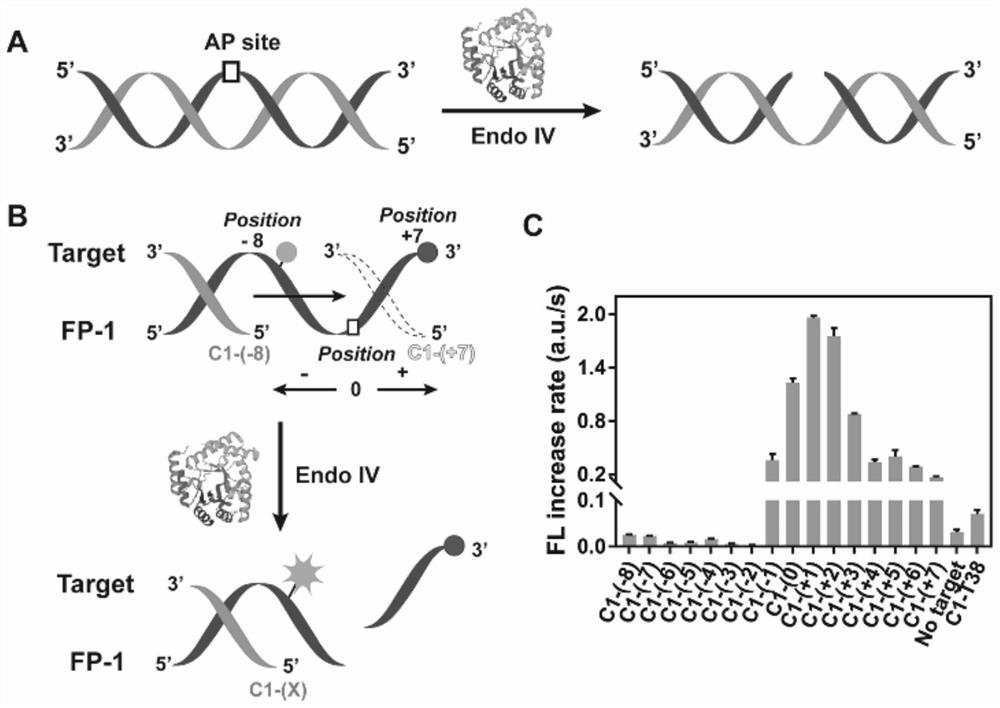
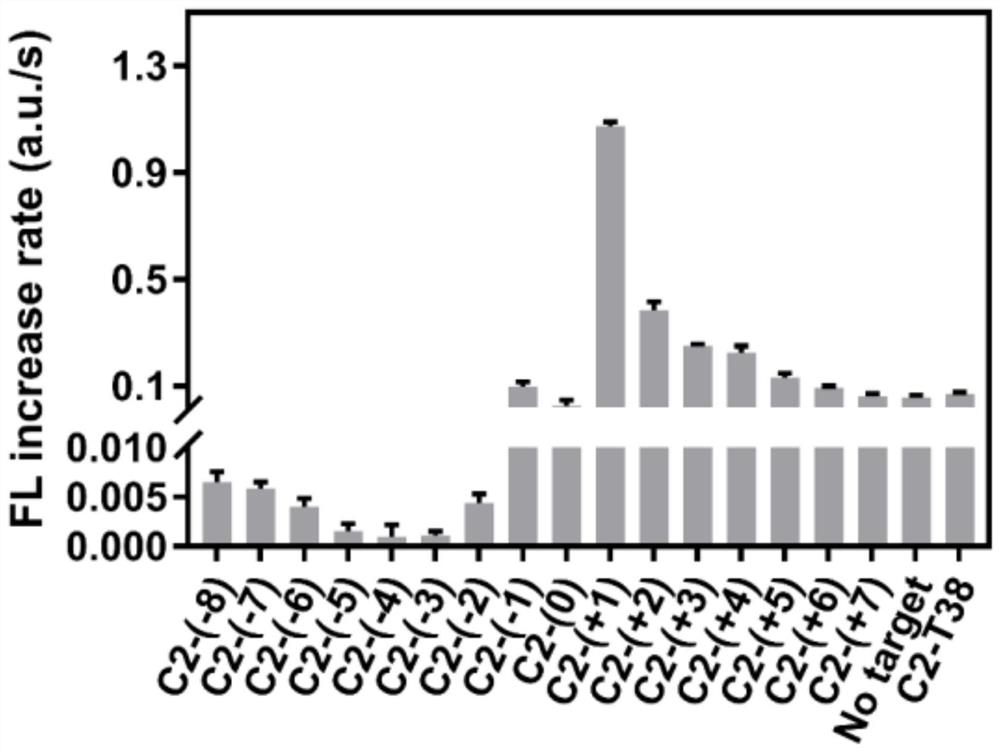
The invention relates to a probe and kit for detecting point mutation of DNA and application. The probe is provided with an AP site used for being digested by endonuclease IV (Endo IV), and the AP site is used for dividing the probe into a first sequence and a second sequence; and the probe can form a first substrate and a second substrate through complementation of partial sequences of the probe with a mutant strand and a wild strand separately, the first substrate and the second substrate separately have first activity and second activity that the first substrate and the second substrate are digested by the endonuclease IV to form a free single strand with a second sequence, and the first activity is higher than the second activity. Due to the fact that the Endo IV has unique enzyme digestion activity on different truncated dsDNA structures such as the first substrate and the second substrate, a unique Endo IV probe is designed, the Endo IV probe and a target chain form the special dsDNA structure, the sequence dependency of the Endo IV is greatly lowered, the detection universality is widened, and the detection cost is reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A one-tube reaction method for DNA molecular cloning and splicing
ActiveCN106591294BImprove ligation reaction efficiencyLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationEnzyme digestionPhosphorylation
The invention provides a one-tube reaction type DNA molecule clone splicing or reconstructing method. A reaction system is formed by mixing a target DNA fragment, a bridging primer, polynucleotide kinase, a heat stability ligase and a reaction buffer solution, the buffer solution contains ATP, NAD<+> and Mg<2+>, the pH value is 6-10, and the method is completed through a heat cycle process. The method realizes one-shot completion of a linking reaction in one tube, greatly improves the linking connection efficiency, and also has the following advantages: 1, phosphorylation and splicing steps of the DNA fragment are completed in one tube through one step to realize the linking reaction, so high cost caused by use of a phosphorylation primer is avoided; 2, the DNA fragment is seamlessly linked, so no superfluous nucleotides are introduced; 3, DNA sequence dependence is avoided; 4, not other nucleotides are introduced to the tail end of the spliced DNA fragment, and the DNA fragment can be reused for other construction works; and 5, the price is low, and is lower than that of routine enzyme digestion linking methods.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Determining recovery time for interdependent resources in heterogeneous computing environment
Provided are techniques for determining a recovery time for a resource in a heterogeneous computing environment comprising interdependent resources. A graph for the resource representing all sequence dependencies and all group relations are created. The recovery time may be a cumulative startup time or a cumulative shutdown time of the resource considering interdependencies of the resource to other resources. The recovery time for all support resources having sequence dependencies with the resource is calculated and each node representing the support resources are removed from the graph. Then the recovery time for all member resources left in the graph that have group relations with the resource is calculated per a group type of the resource. The recovery time for the resource is a sum of the recovery time of all support resources, the recovery time of all member resources, and a unit recovery time of the resource.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
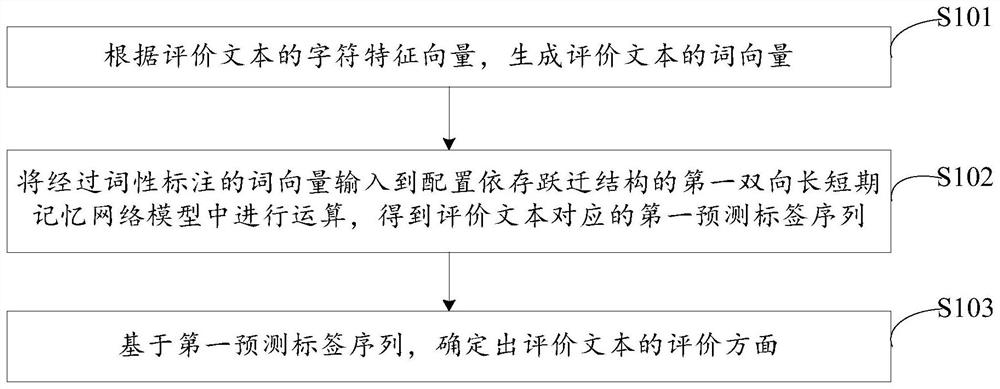
Evaluation aspect determination method and device
ActiveCN111639483AImprove accuracyNatural language data processingNeural architecturesFeature vectorAlgorithm
The invention discloses an evaluation aspect determination method and device, and the method comprises the steps: generating a word vector of an evaluation text according to a character feature vectorof the evaluation text; then, inputting the word vector subjected to part-of-speech tagging into a first bidirectional long-short-term memory network model configured with a dependency transition structure for operation to obtain a first prediction tag sequence corresponding to the evaluation text; and further, based on the first prediction tag sequence, determining an evaluation aspect of the evaluation text. The capability of a bidirectional long-short-term memory network model for learning long-term sequence dependence and syntactic structure priori knowledge provided by dependence transition information are combined, so that the accuracy of determination in the aspect of evaluation is improved, and the technical problems that extra feature engineering is needed and a rule template needs to be manually made in advance are avoided.
Owner:SF TECH
A probe and method for simultaneous detection of multiple microRNAs under constant temperature conditions based on DNA assembly
ActiveCN109055524BSimple designGood precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme functionSingle strand
The invention discloses a probe and method for simultaneously detecting multiple microRNAs under constant temperature conditions based on DNA assembly; the probe of the invention includes 3 probe groups; the 3 probe groups and the target microRNA can self-assemble to form a stable " "I"-shaped structure; combined with the high specificity of restriction endonucleases and the cutting properties of single-stranded DNA, DNA modules with sequence-independent nuclease functions are realized, which are applied to the simultaneous fluorescence detection of multiple miRNAs under constant temperature conditions . Solve the complex problem of the conventional constant temperature amplification method system, and provide a new method for the simultaneous and sensitive detection of multiple miRNAs. This method only needs to add restriction endonucleases and probes with simple design, and can achieve constant temperature signal amplification and detection of nucleic acids without adding dNTPs, and has good accuracy, repeatability and stability, and is suitable for development as a kit and promote it to the market.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com