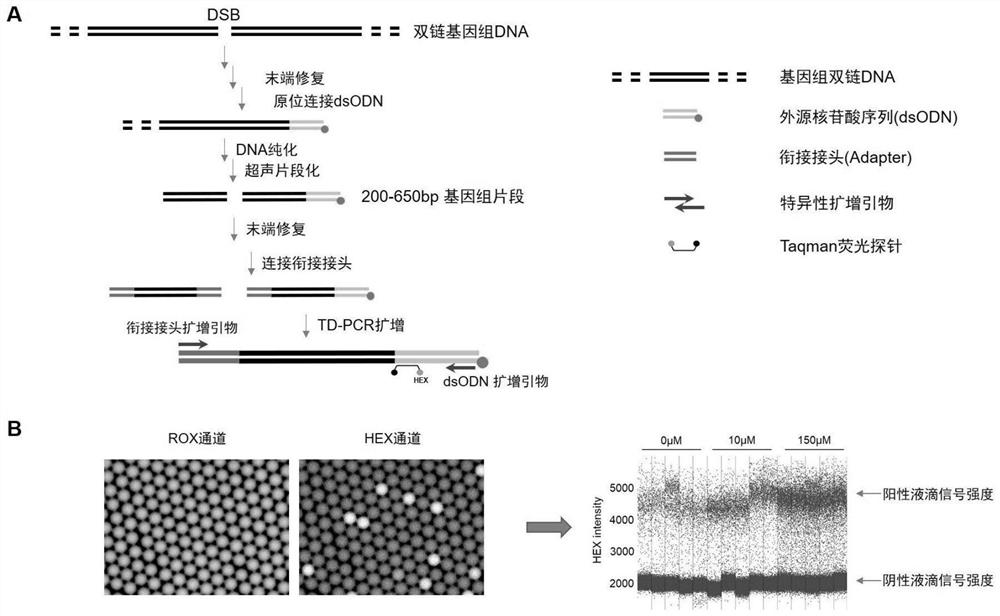
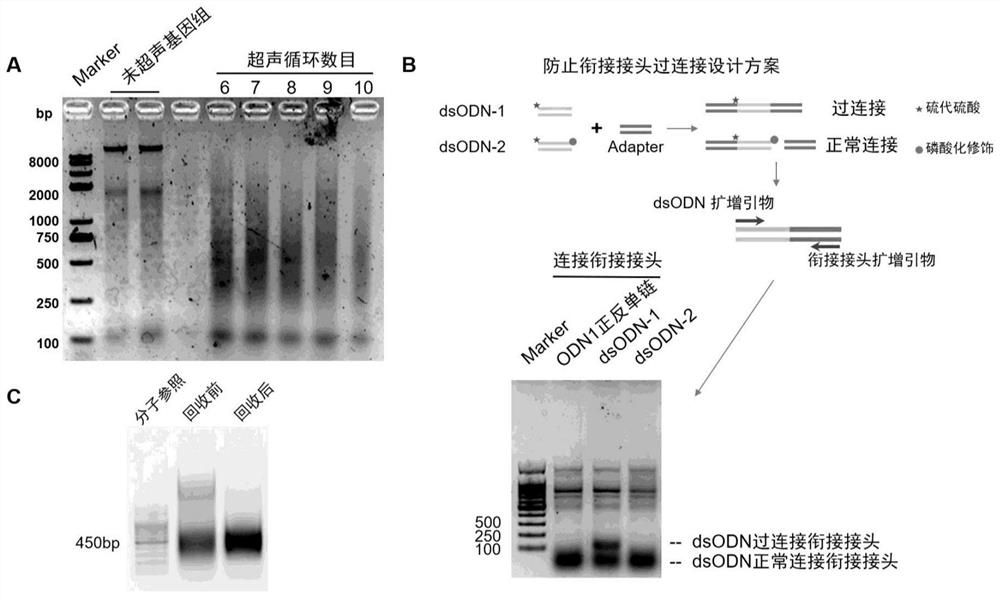
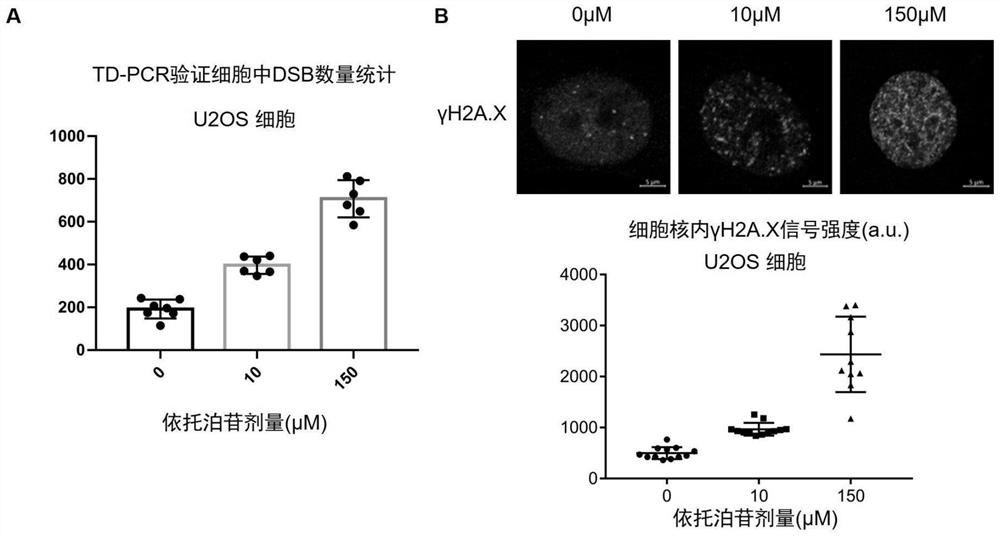
Method for absolutely quantifying number of DNA double-strand fractures in cells and application
A double-strand break, absolute quantitative technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to detect the number of DSBs, the restriction of the detection efficiency of DSBs, and the inability to get rid of the sequence dependence of the detection site, etc. Achieve high sensitivity and cost-effective, low cost, low time cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1. TD-PCR Absolute Quantification of DNA Double-Strand Breaks Produced by the Chemical Drug Etoposide
[0037] (1) Materials
[0038] 1. Cell line: human myeloma cell line U2OS
[0039] 2. Exogenous nucleotide fragments: The nucleotide fragments used in the present invention are designed by the inventor, the forward strand and the reverse complementary strand are chemically synthesized by Qingke Company, and the inventors prepare them by annealing into double strands. Its detailed sequence information is as follows:
[0040] Sense strand sequence:
[0041] 5'-PHO-GCTCGCGTTTAATTGAGTTGTCATATGTTAATAACGGTATACGCGA-PHO-3' (SEQ ID No: 1, wherein "PHO" represents a phosphorylation modification);
[0042] Reverse Complementary Sequence:
[0043] 5'-TCGCGTATACCGTTATTAACATATGACAACTCAATTAAACGCGAGC*T-3' (SEQ ID No: 2, where "*" represents a phosphorothioate bond).
[0044] 3. Adapter: the adapter used in the present invention was designed by the inventor, the forward st...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Example 2. TD-PCR Absolute Quantification of Off-target Efficiency of Gene Editing Nuclease Cas9 and Its Variants
[0081] In the process of gene editing, nuclease Cas9 and its variants rely on it to cut DNA double strands to generate gaps, and rely on intracellular NHEJ and HR repair pathways to repair DNA double strand breaks, thereby editing the genome. During this process, the off-target effect of Cas9 nuclease will non-specifically cut genomic DNA, resulting in DNA double-strand breaks with unknown sequence information. Therefore, we quantify the off-target efficiency of different Cas9 nuclease variants through the sequence independence of TD-PCR.
[0082] (1) Materials
[0083] 1. Cell line: human kidney epithelial cell 293T
[0084] 2. Plasmids containing sequences of different Cas9 nuclease variants
[0085] The carrier is pX330 vector, the nuclease Cas9, espCas9, XCas9 are provided by the laboratory, the target gene locus is EMX1 (NC_000002.12), the sgRNA seq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com