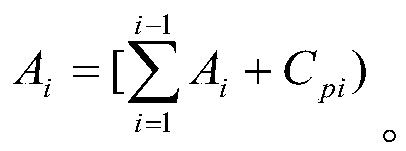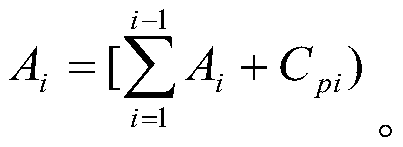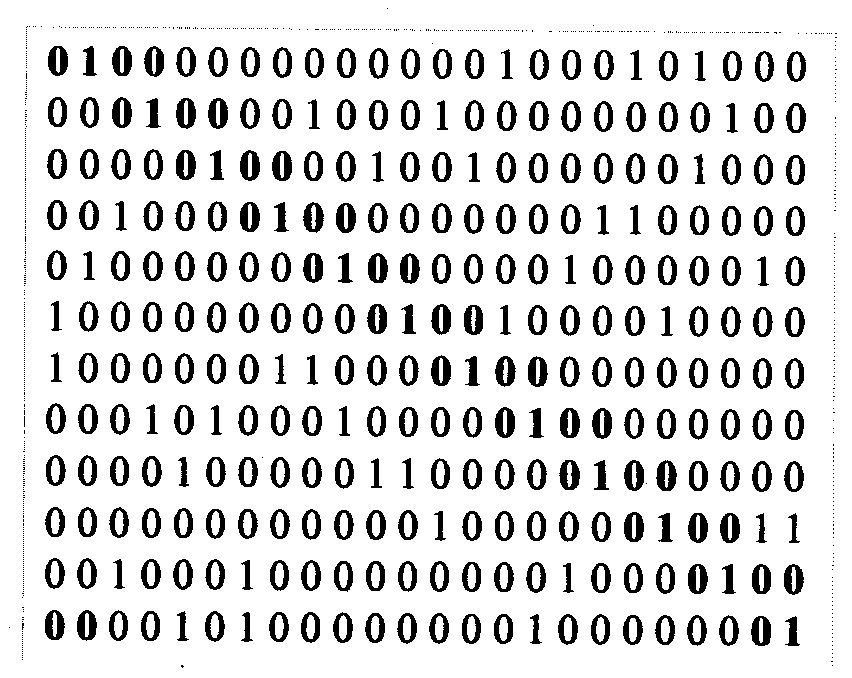Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Quasi random" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quasi Random. A form of random vibration energy with a frequency spectrum very similar, but not mathematically identical to, white noise derived random vibration energy.
Systems and methods for authenticating and protecting the integrity of data streams and other data
InactiveUS6959384B1Authentication is convenientDetecting errorUser identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionError checkFault tolerance
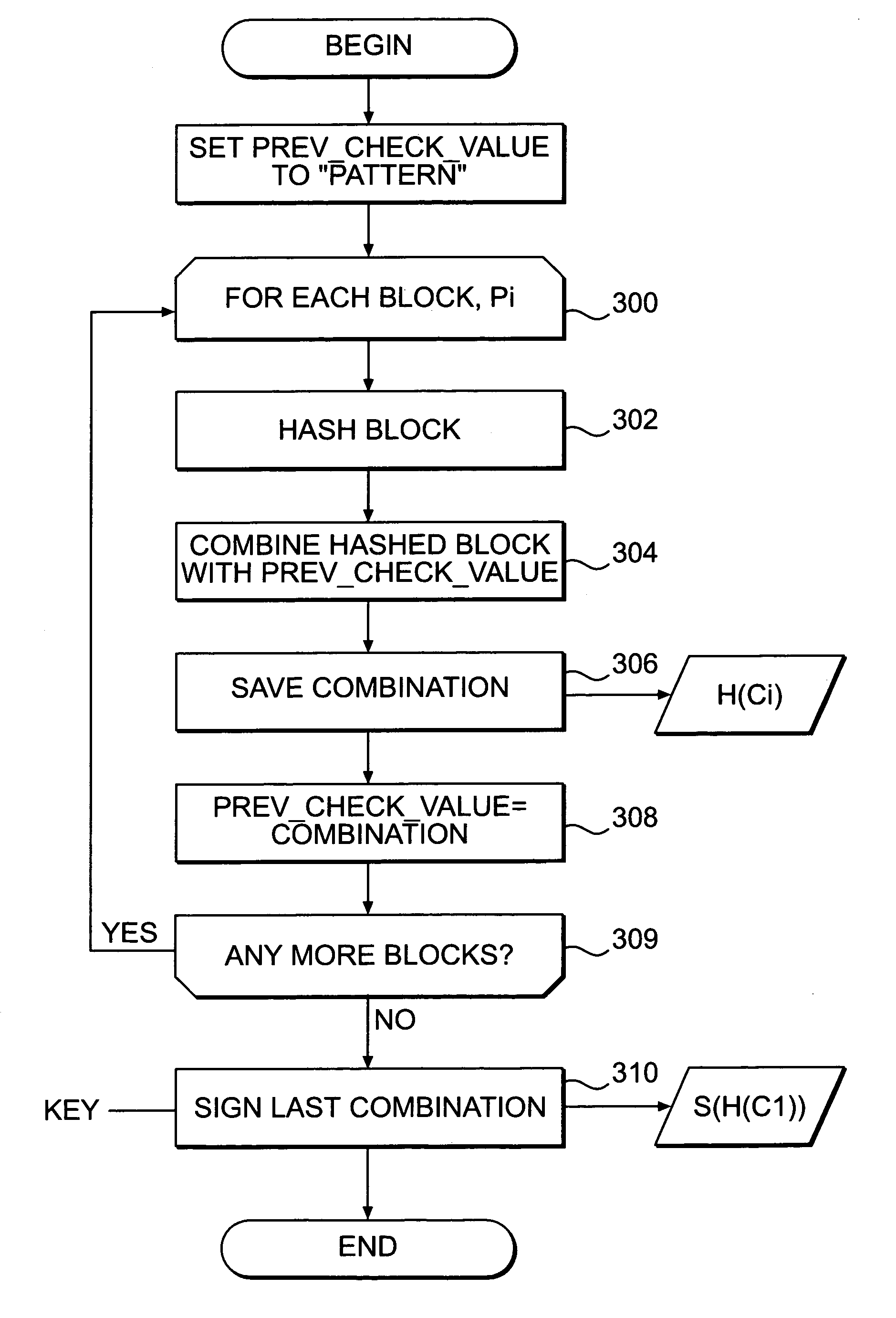
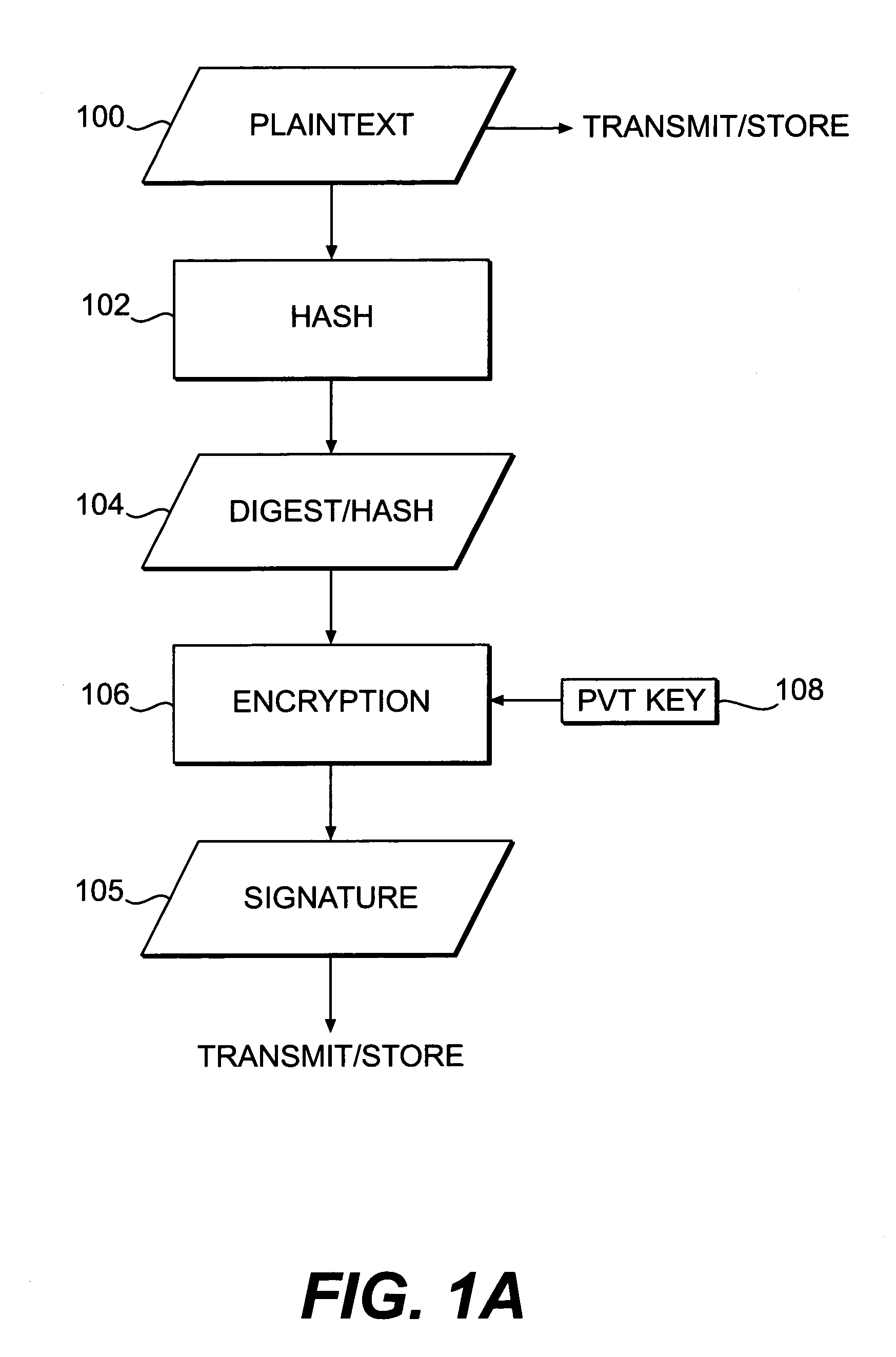
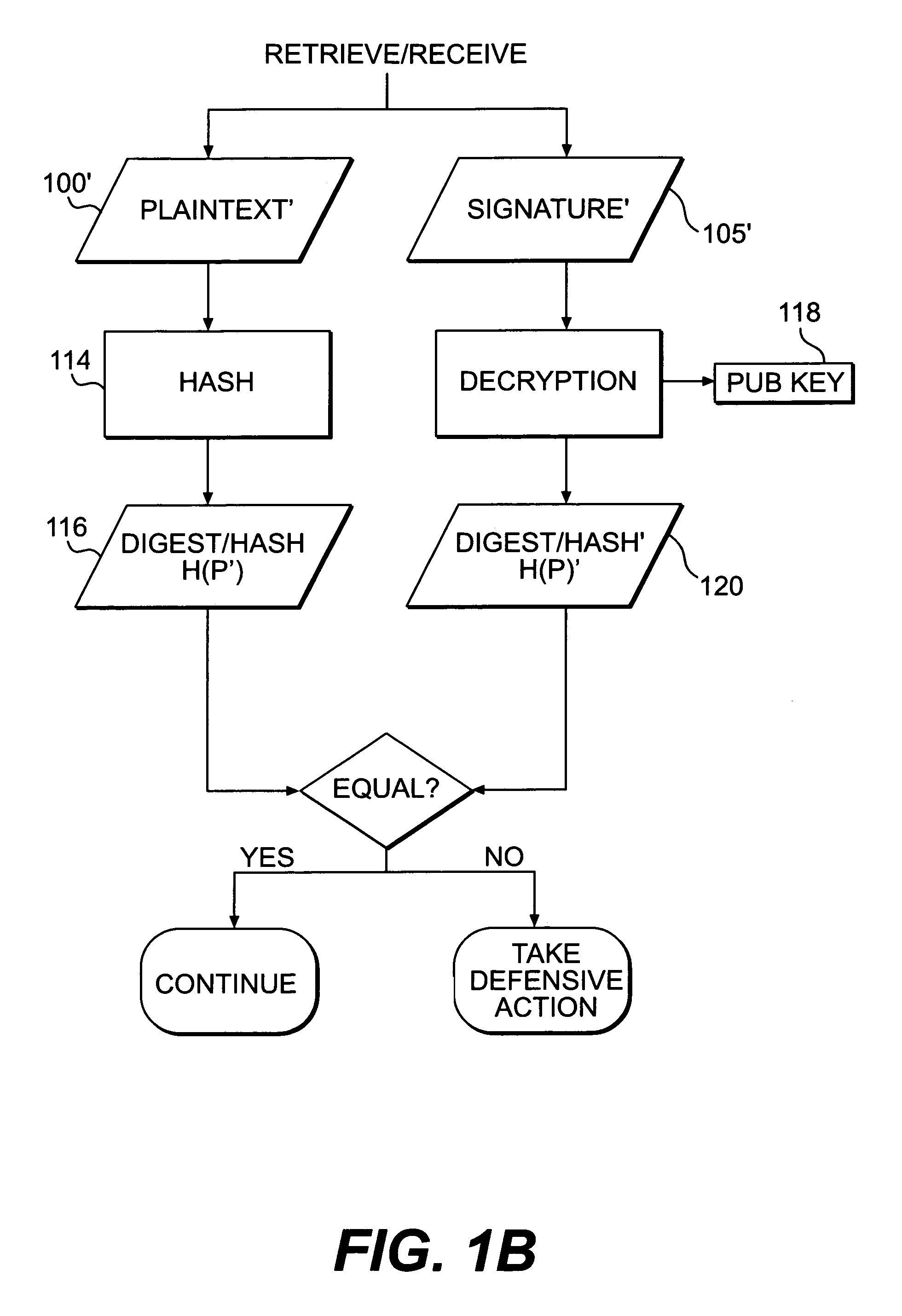
Systems and methods are disclosed for enabling a recipient of a cryptographically-signed electronic communication to verify the authenticity of the communication on-the-fly using a signed chain of check values, the chain being constructed from the original content of the communication, and each check value in the chain being at least partially dependent on the signed root of the chain and a portion of the communication. Fault tolerance can be provided by including error-check values in the communication that enable a decoding device to maintain the chain's security in the face of communication errors. In one embodiment, systems and methods are provided for enabling secure quasi-random access to a content file by constructing a hierarchy of hash values from the file, the hierarchy deriving its security in a manner similar to that used by the above-described chain. The hierarchy culminates with a signed hash that can be used to verify the integrity of other hash values in the hierarchy, and these other hash values can, in turn, be used to efficiently verify the authenticity of arbitrary portions of the content file.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
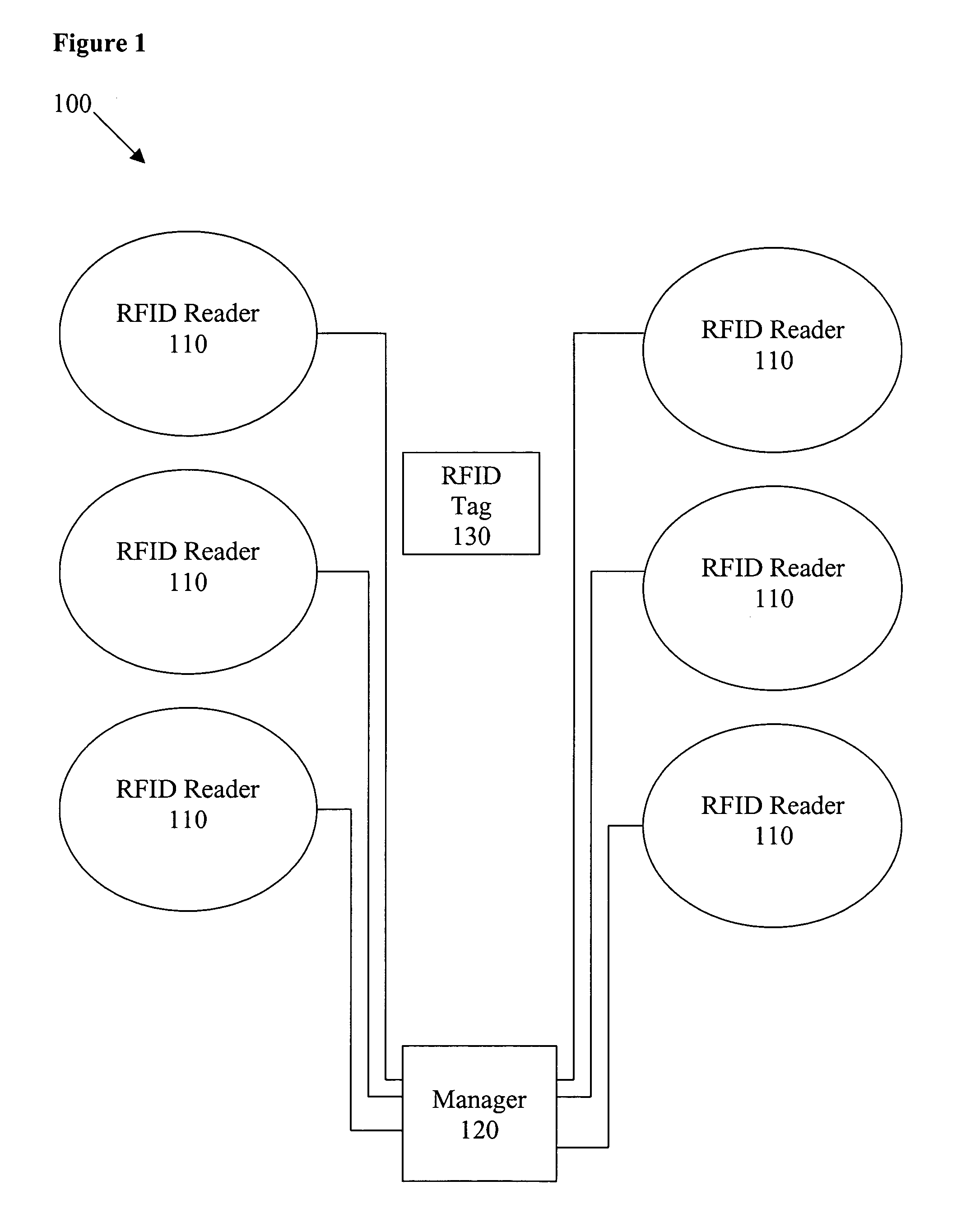
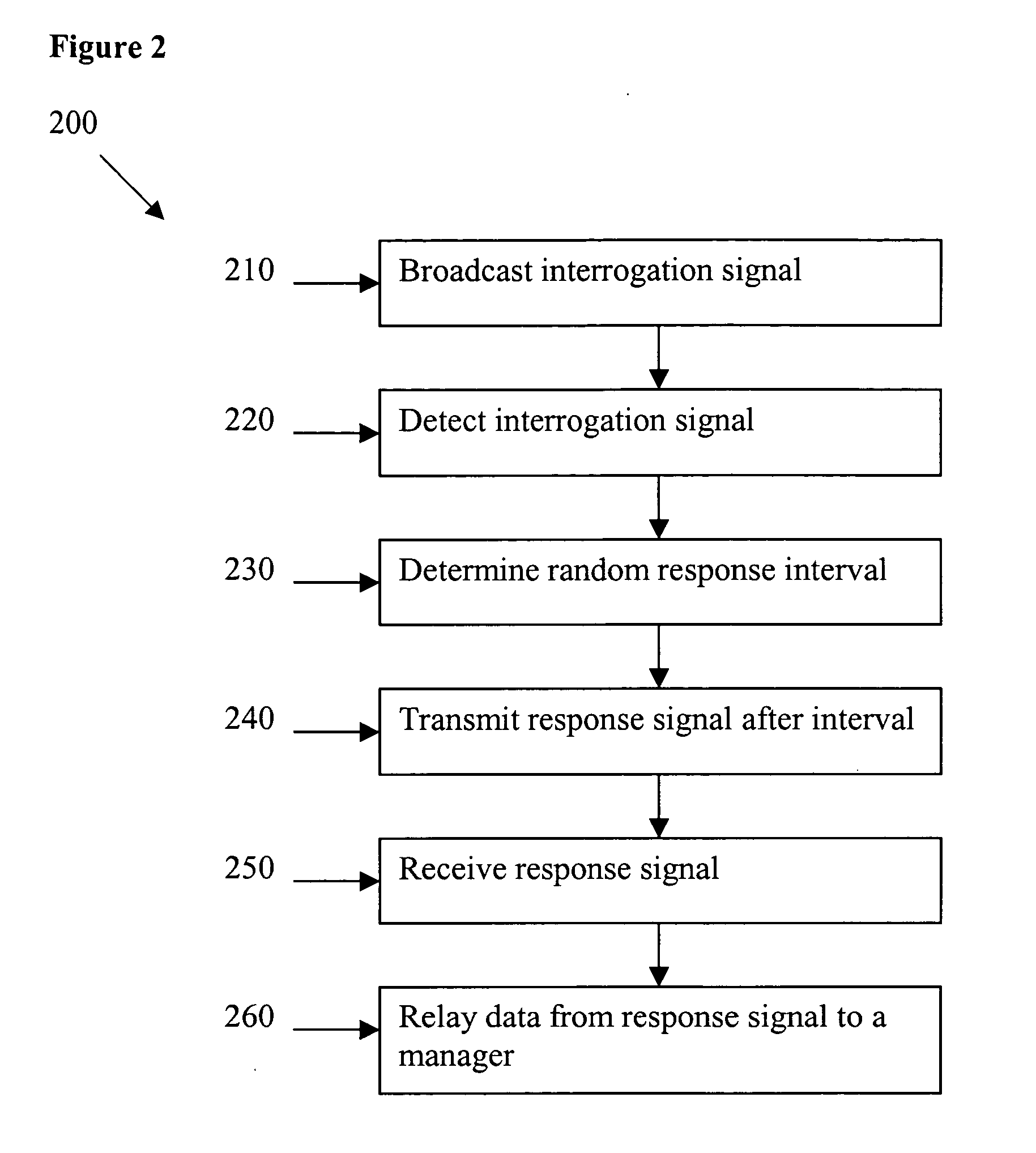
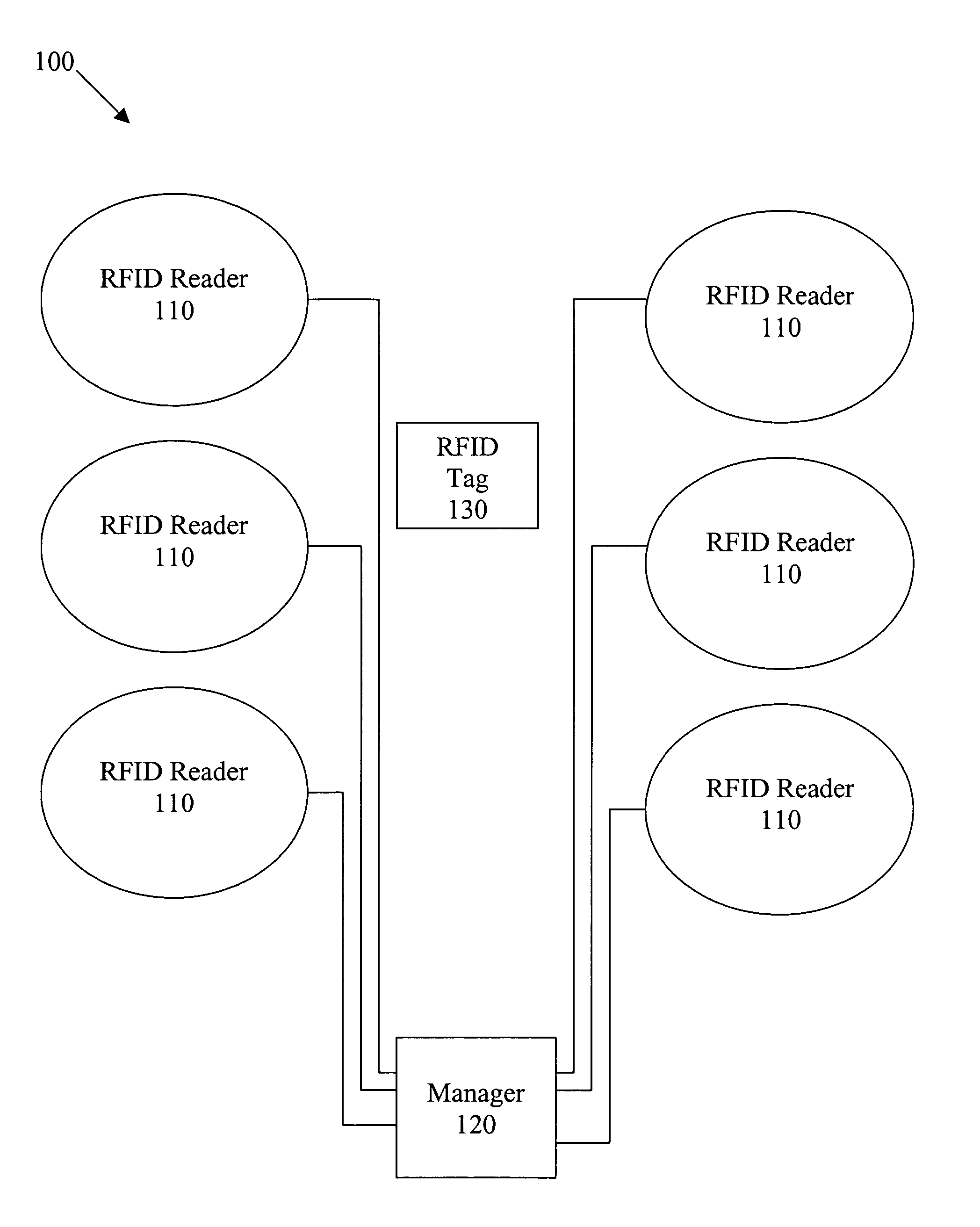
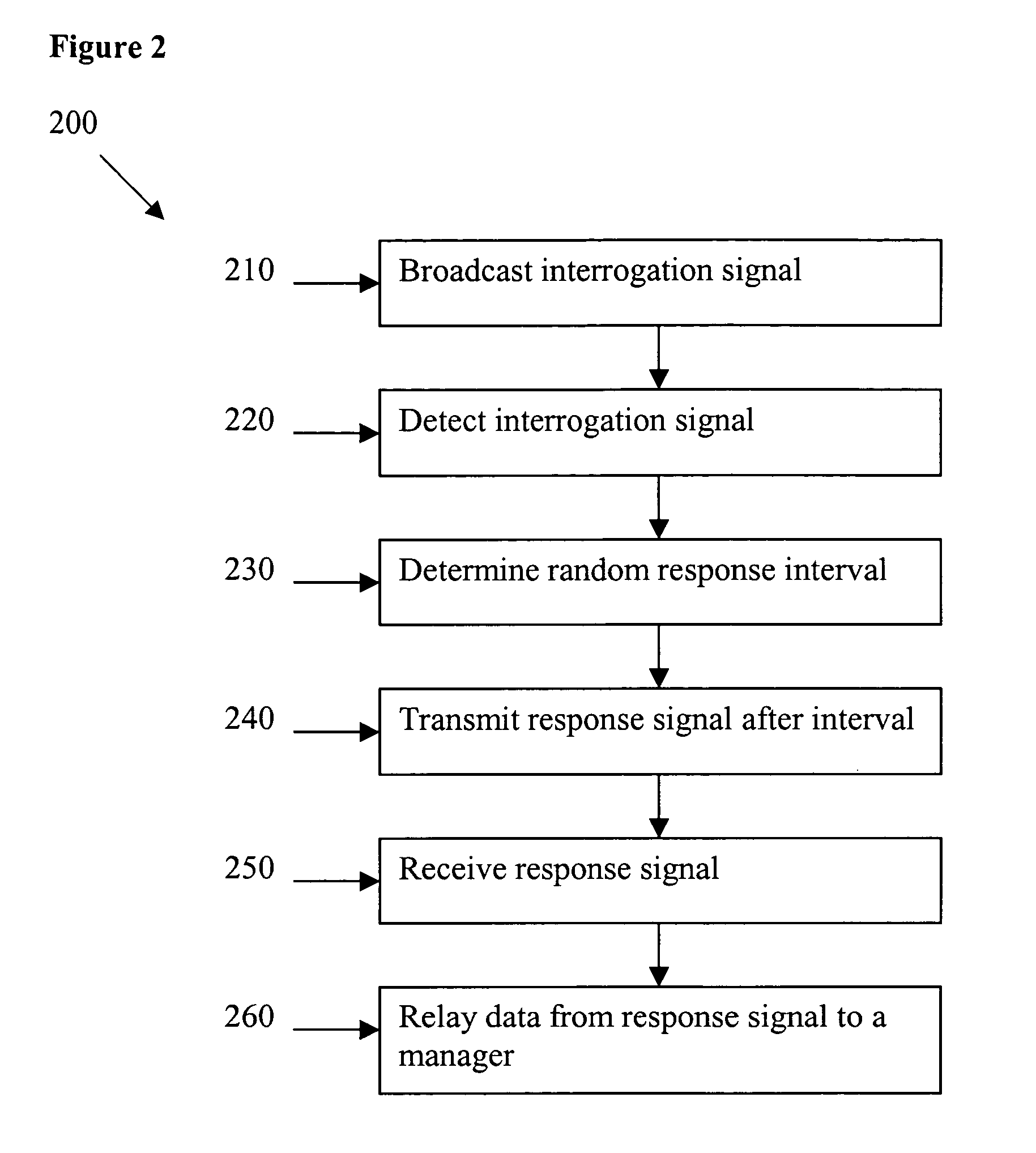
Method and apparatus for synchronization of proximate RFID readers in a gaming environment
ActiveUS20060076401A1Easy to trackMemory record carrier reading problemsElectric testing/monitoringProximateComputer science
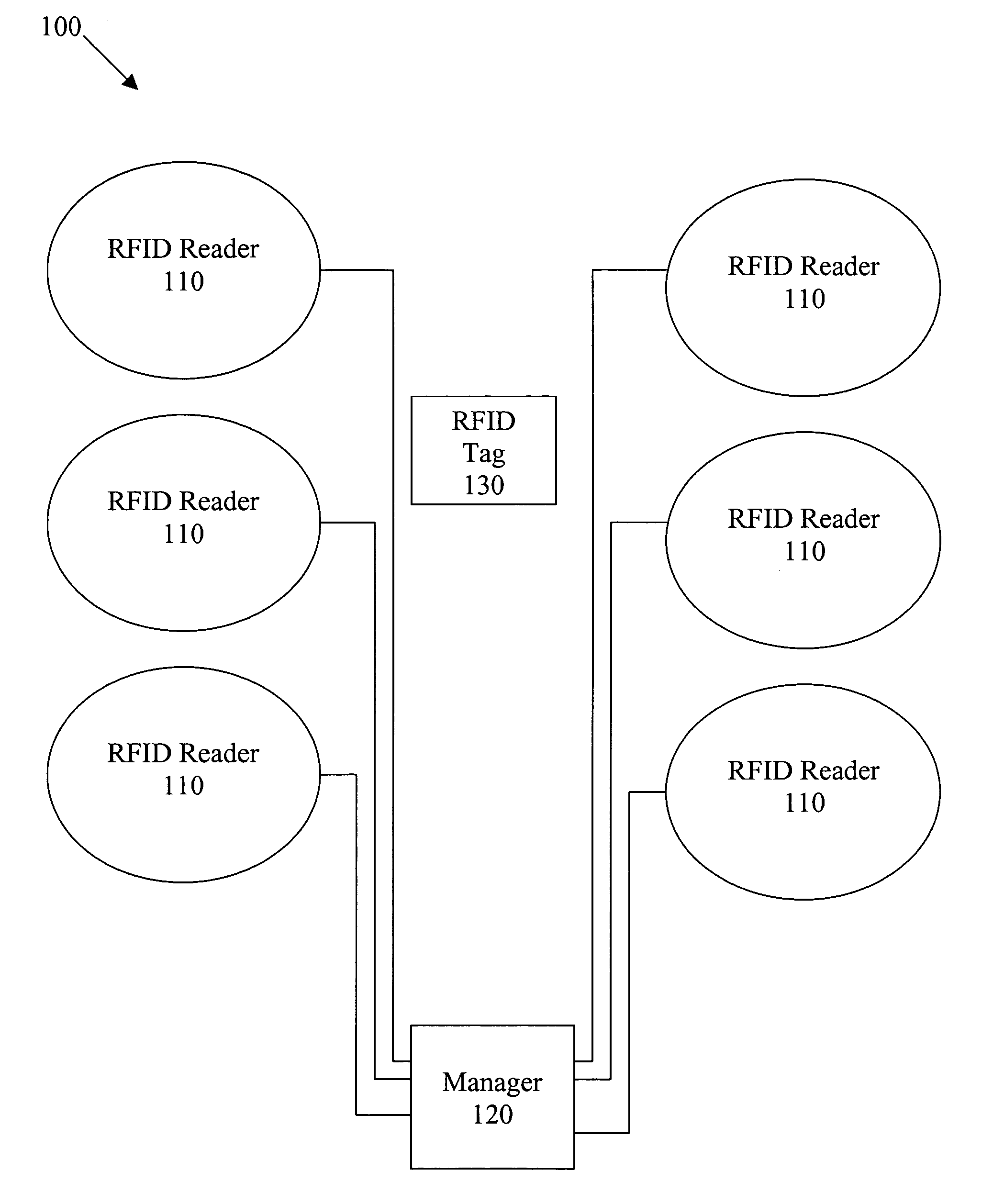
The present invention provides a system and method for an improved player tracking in a gaming environment. Certain embodiments include a plurality of radio frequency identification (RFID) readers for detecting a response signal from an RFID tag, an RFID tag generating a response signal including identification data in response to an interrogation signal transmitted by one of the plurality of RFID readers, and a location manager controlling transmission by the plurality of RFID readers according to at least one collision-avoidance scheme. The collision-avoidance scheme may include one or more of the following schemes: localized RFID reader managers coordinating electrical operation of the plurality of RFID readers, an active RFID reader transmitting the interrogation signal and a plurality of passive RFID readers listening for the response signal, an RFID reader multiplexed through a plurality of antennas, TDMA, CDMA, and / or quasi-random synchronization for the RFID readers, for example.
Owner:ARISTOCRAT TECH INC
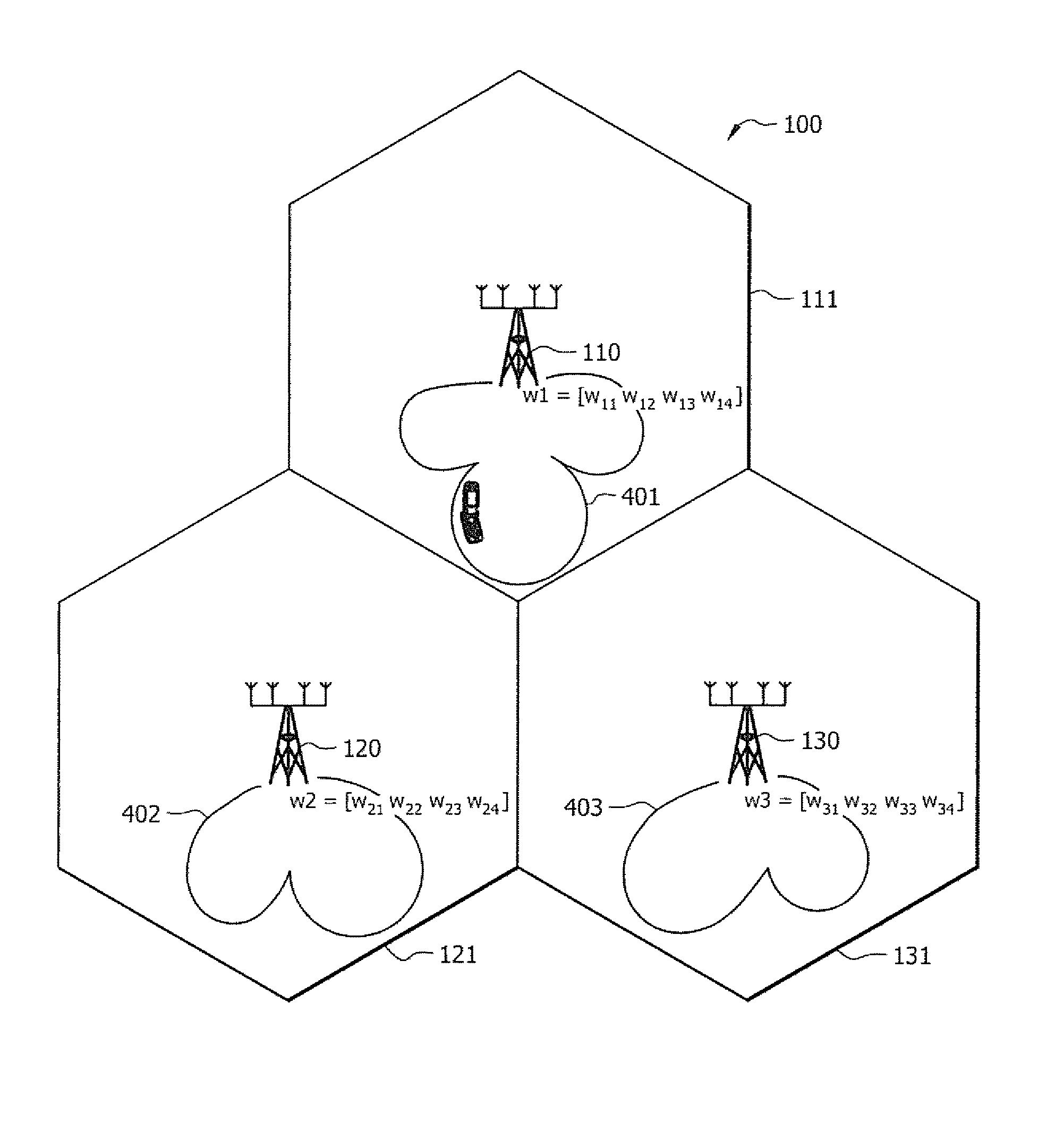
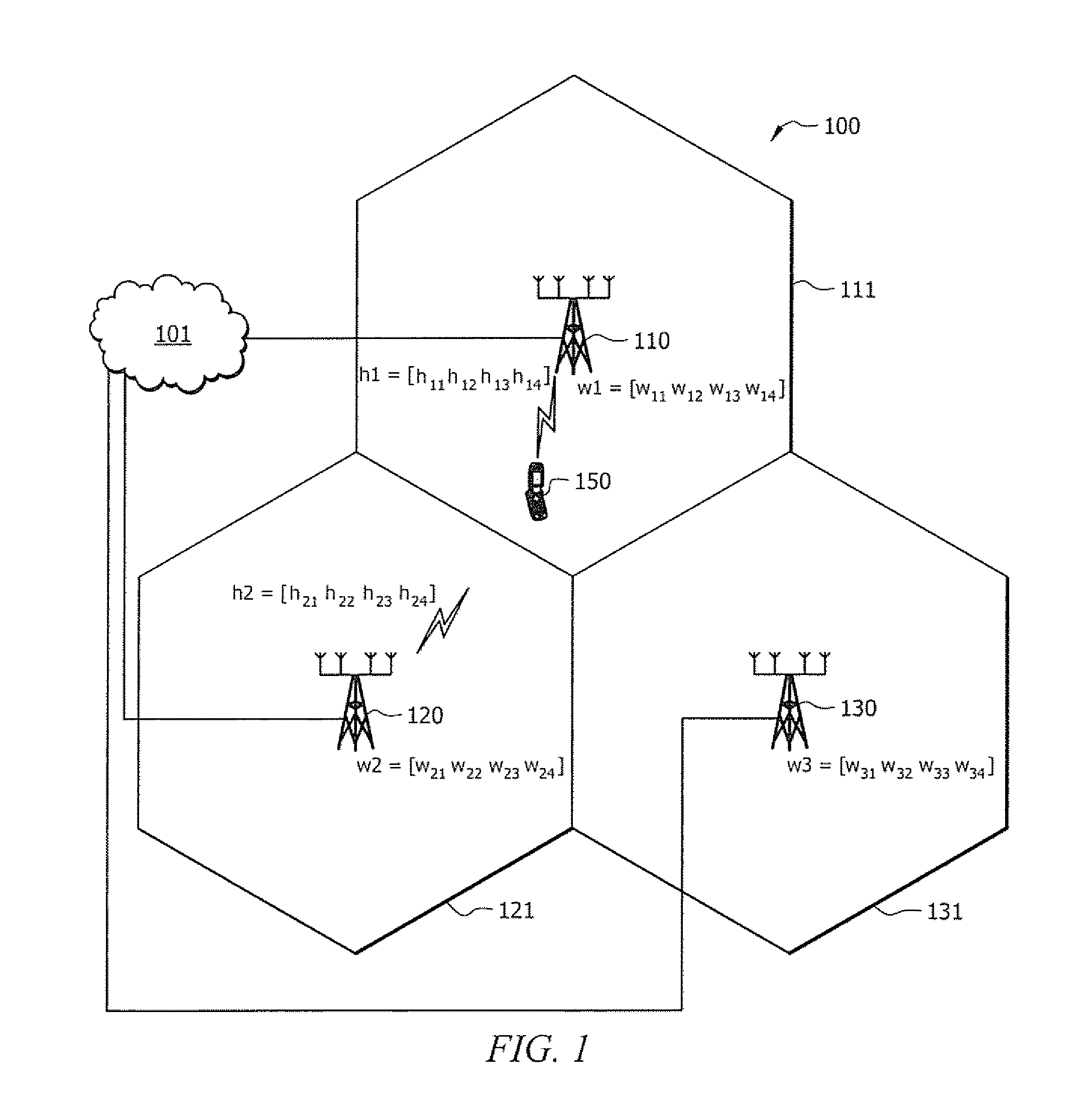
Reducing multi-cell interference using cooperative random beam forming
InactiveUS8280444B1Reduce communication interruptionsAggressive frequency reuseSite diversitySubstation equipmentCarrier signalSubcarrier
Systems and methods which implement cooperative random or quasi-random beam forming as between a plurality of base stations in a wireless network to reduce multi-cell interference are shown. For example, a plurality of base stations in a wireless network cooperate to provide frequency resources, such as channels, subchannels, subcarriers, etc., in a plurality of randomesque beams. In operation, subscriber stations preferably analyze signals as received on a plurality of the randomesque beams to determine one or more “best” beams for use in communication between the subscriber station and base station. Assuming an identified beam is available for use by the subscriber station, payload communications may be provided using one or more beams identified by the subscriber station as a “best” beam. The base stations of the wireless network preferably cooperate to periodically reform the randomesque beams.
Owner:ADAPTIX
Moire reducing optical substrates with irregular prism structures
An optical substrate having a structured surface that enhances brightness and reduces moiré effect. The optical substrate has a three-dimensionally varying, structured light output surface that comprises an irregular prismatic structure. The irregular prismatic structure may be viewed as comprising longitudinal prism blocks or rows thereof, arranged laterally defining peaks and valleys. Adjacent peaks, adjacent valleys, and / or adjacent peak and valley may be parallel or non-parallel, in an orderly, semi-orderly, random, or quasi-random manner. The lateral adjacent peaks, adjacent valleys, and / or adjacent peak and valley are not parallel. The adjacent irregular prism blocks may be irregular longitudinal sections having the same length, or random or quasi-random irregular sections having different lengths. The facets of each prism block may be flat, or curved (convexly and / or concavely).
Owner:UBRIGHT OPTRONICS CORP
Method for encryption or decryption using finite group operations
InactiveUS6314187B1Decryption is difficultLow costSecret communicationAnalogue-digital convertersComputer hardwareGroup operation
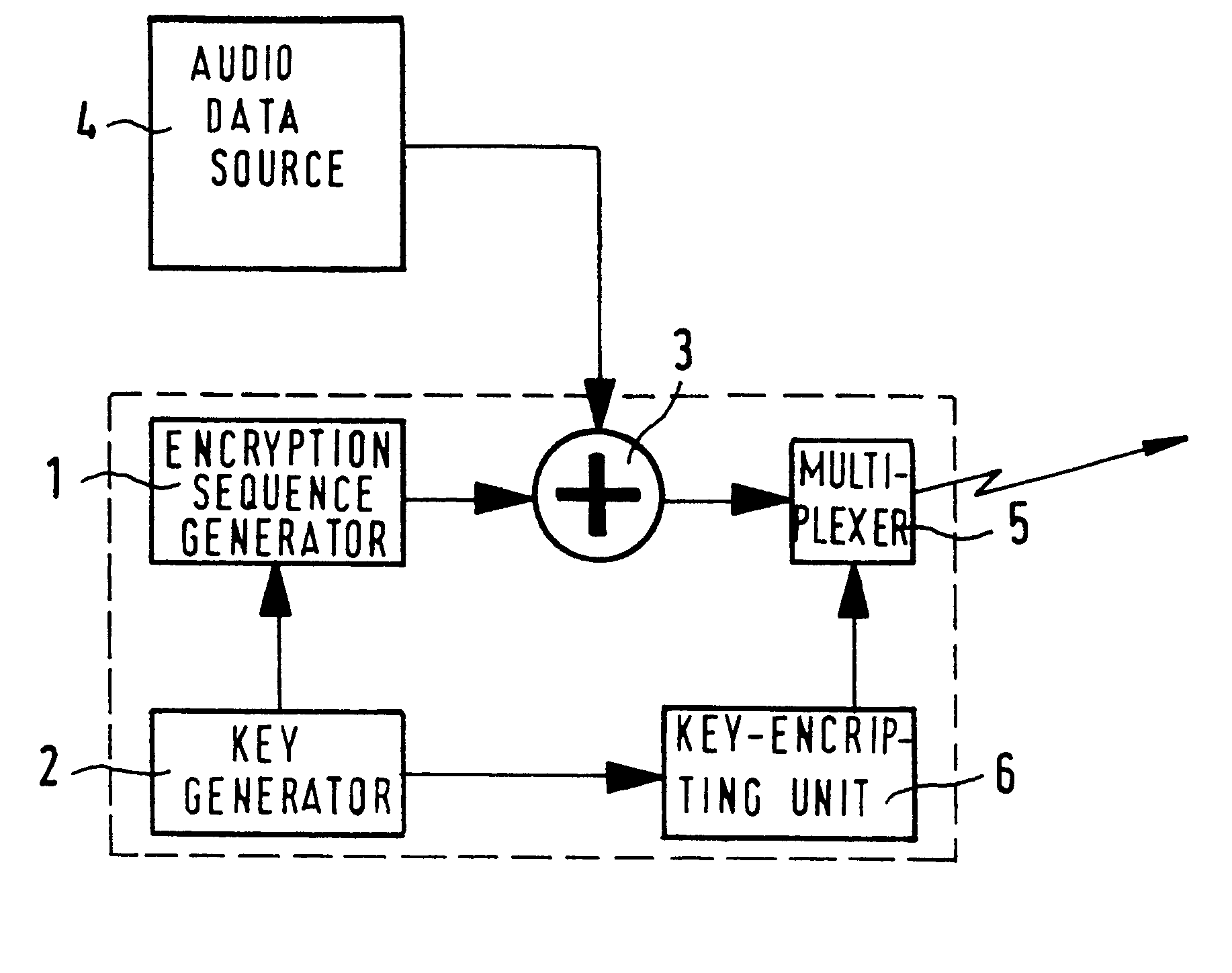
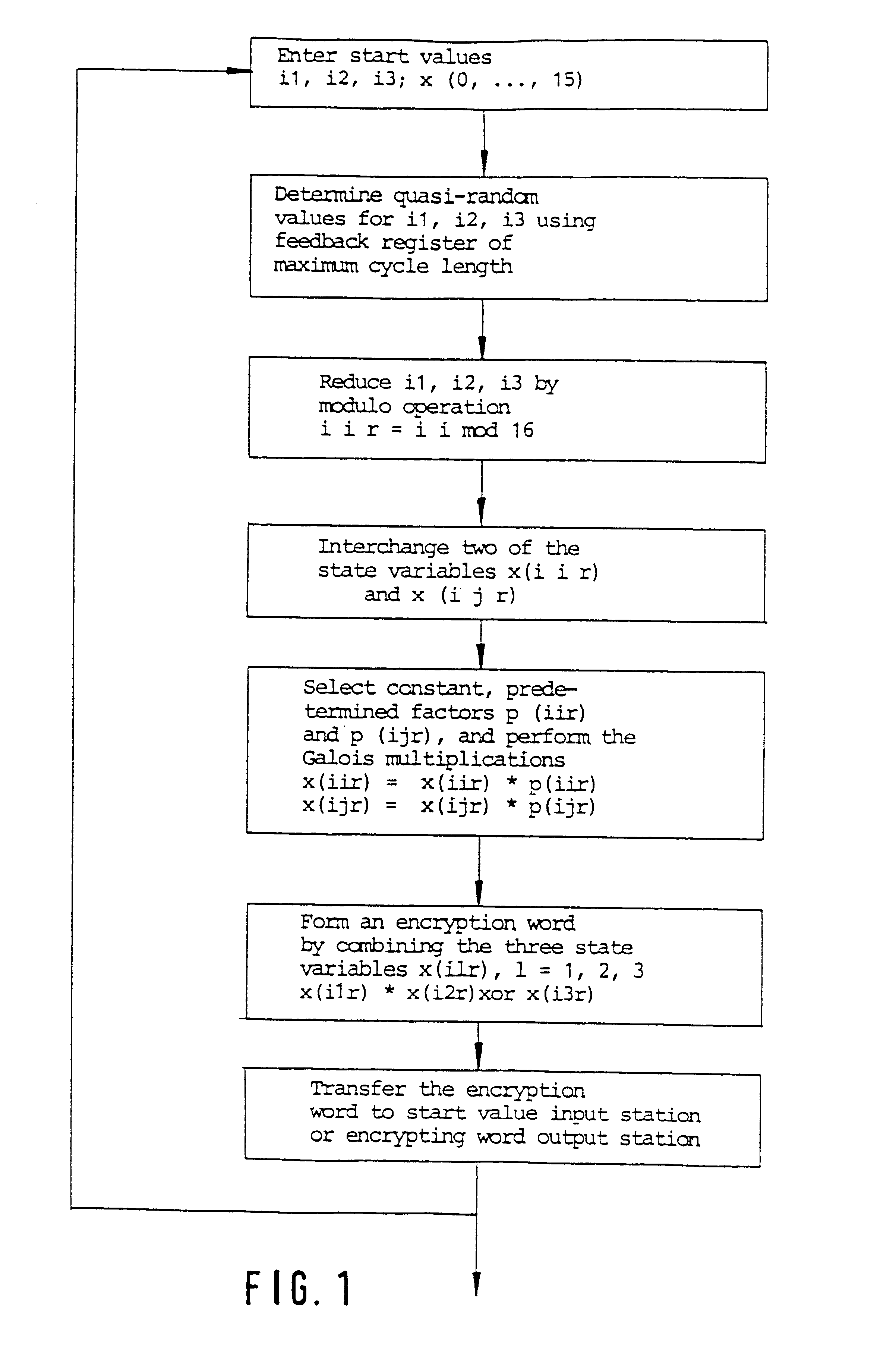
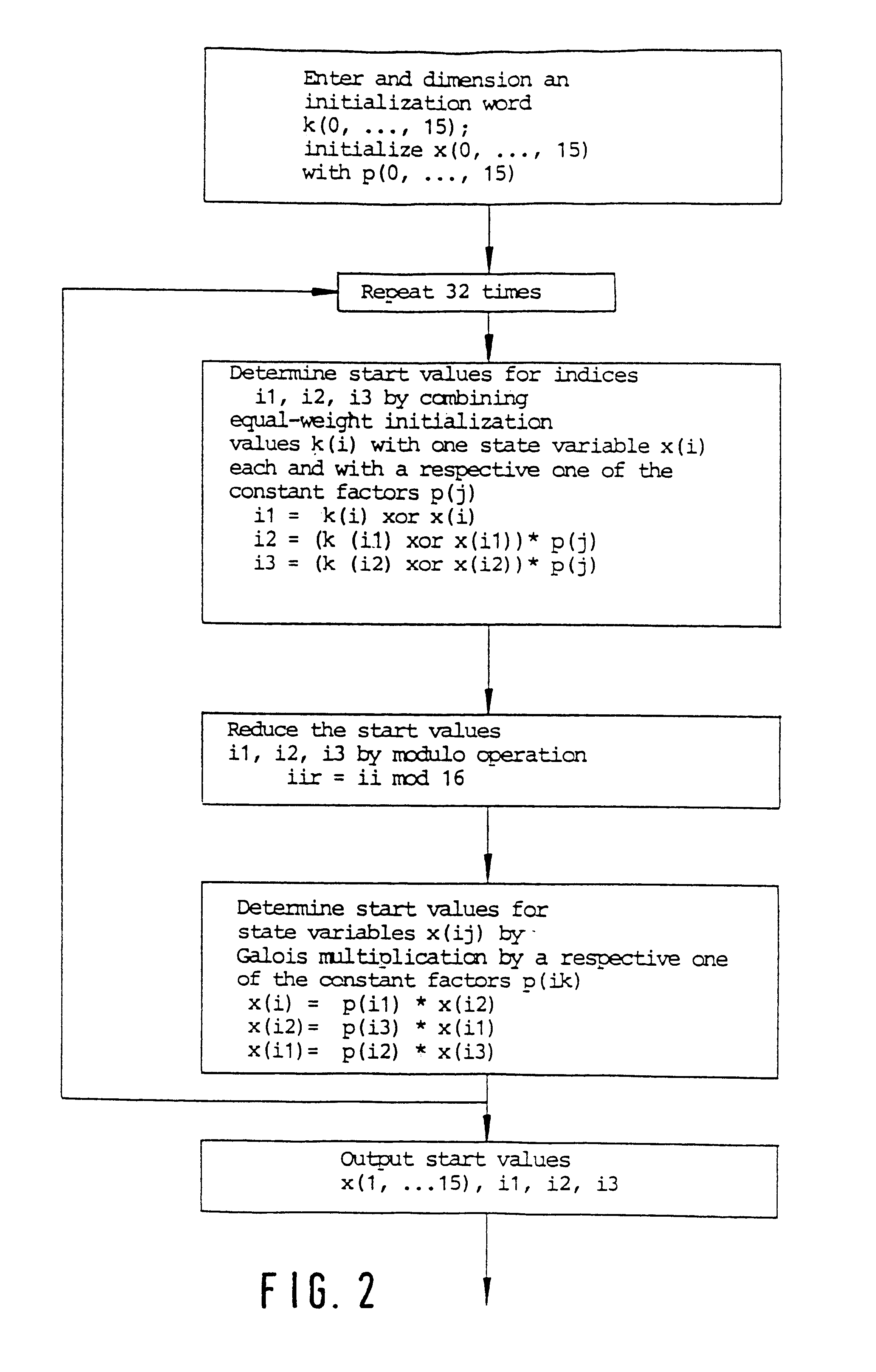
The invention relates to a method for encrypting or decrypting a sequence of successive data words in a data communications device, the method comprising executing an algorithm in which a sequence of quasi-random encryption words is generated from predetermined start values by performing operations in a finite group, and in which a respective one of the encryption words is combined with a respective one of the data words.
Owner:MICRONAS INTERMETTAL GMBH
Method and apparatus for training an automated software test
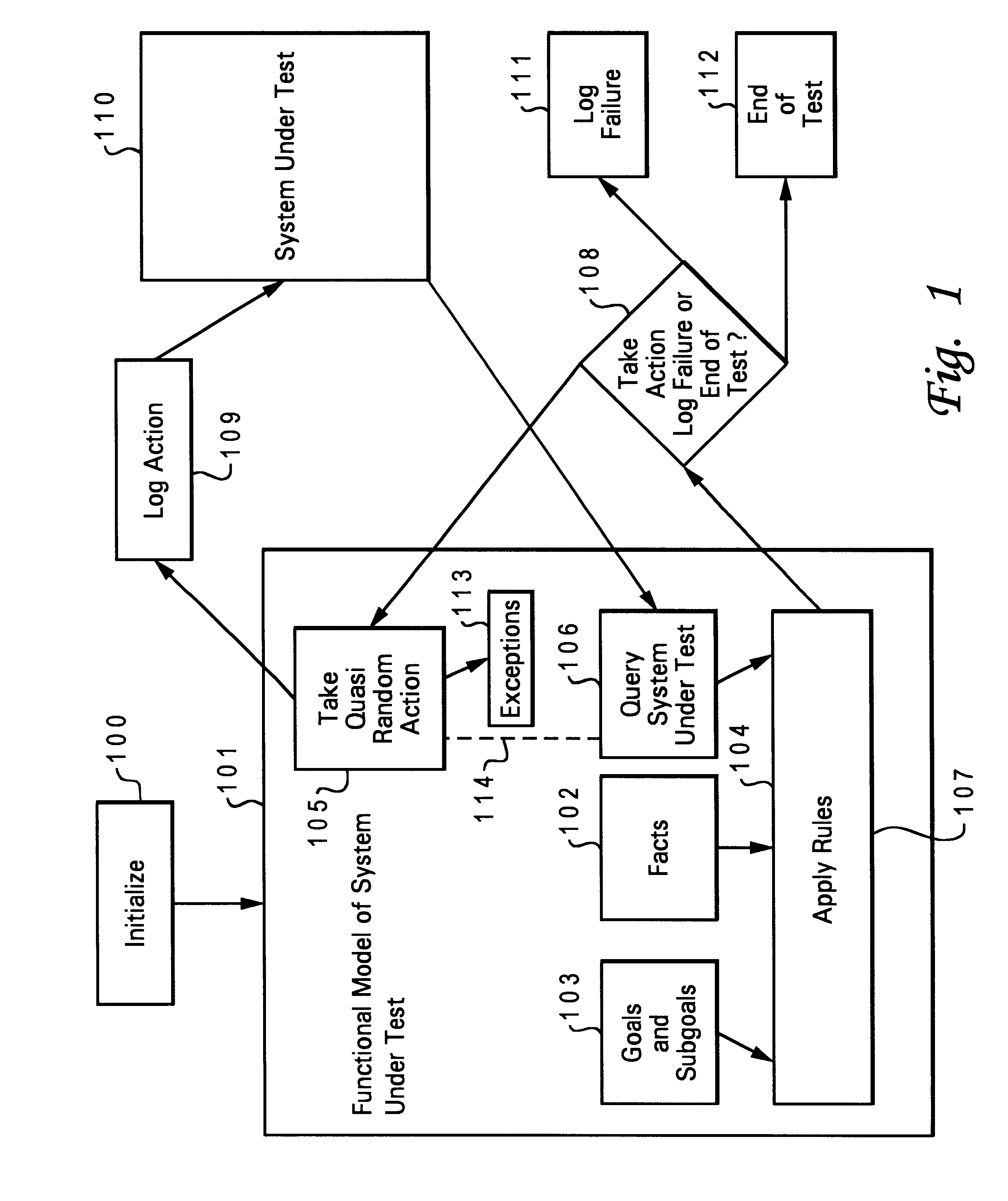
InactiveUS6349393B1Efficient testingSoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsSystem under testFeature model
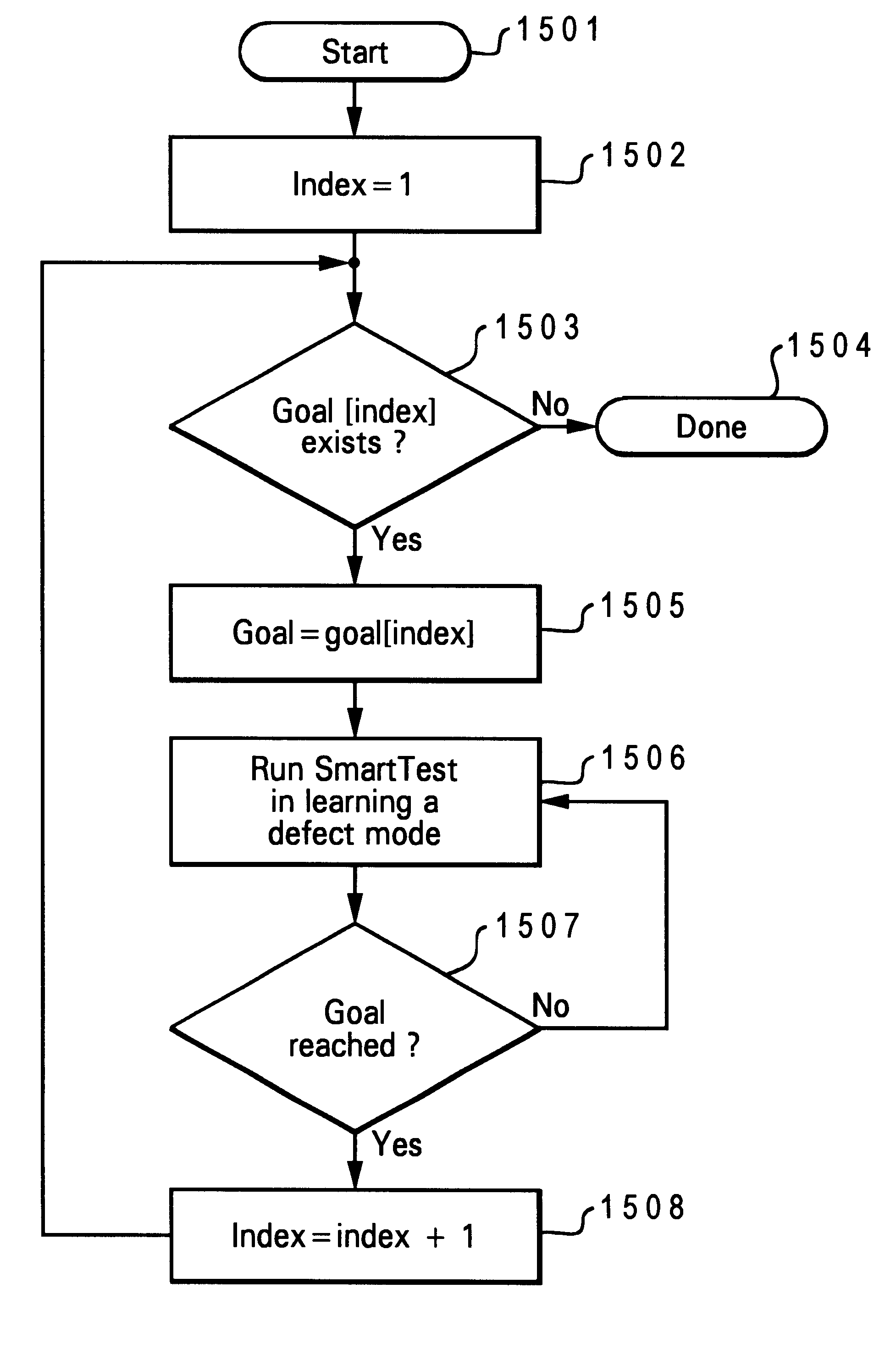
An automated software test is provided which includes a functional model of a system to be tested. The automated software test is utilized to operate a system under test in accordance with specified facts, goals and rules. Quasi-random actions are taken within the system in accordance with specified rules and facts until a defined goal has been accomplished. Training the automated software test is accomplished by specifying a particular goal, i.e. identifying a particularly known defect, and thereafter running the test in a quasi-random fashion until the particular goal has been achieved. The number and nature of actions required to achieve that goal are logged and the process is then repeated until the shortest path required to achieve that goal has been determined. The log of actions which eventually reach a particularly defect may also be utilized a probable cause tree structure for future analysis.
Owner:IBM CORP
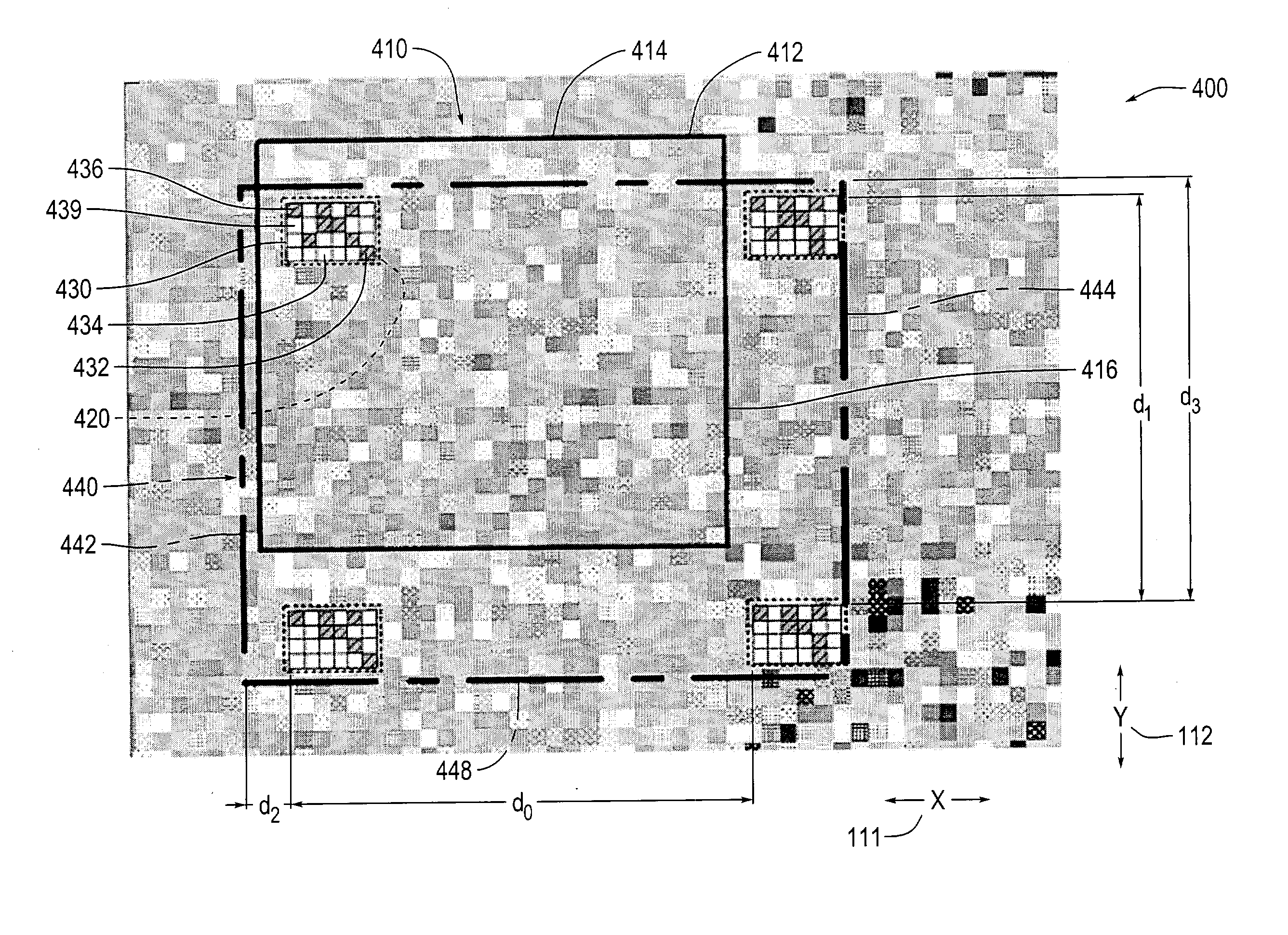
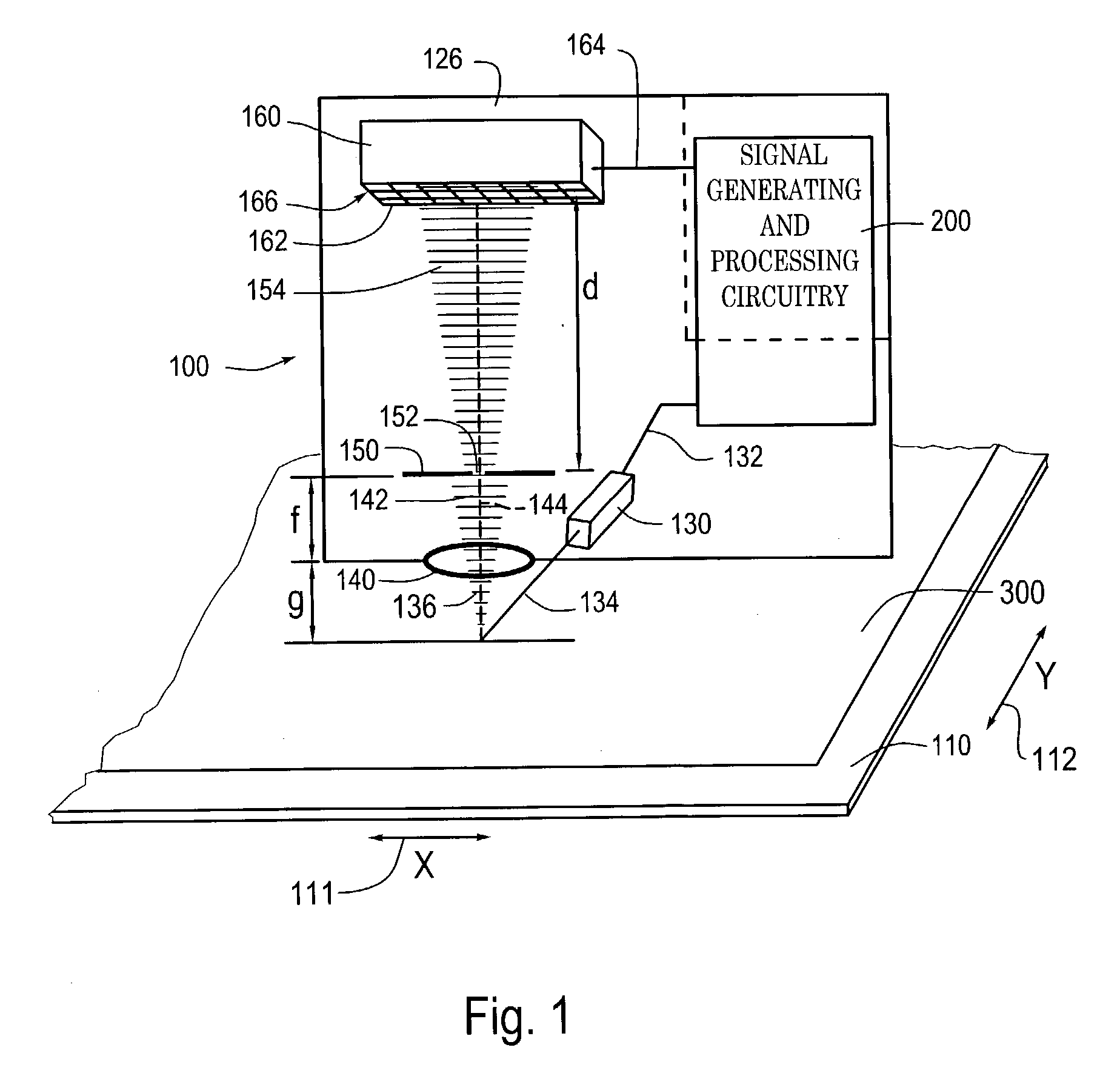
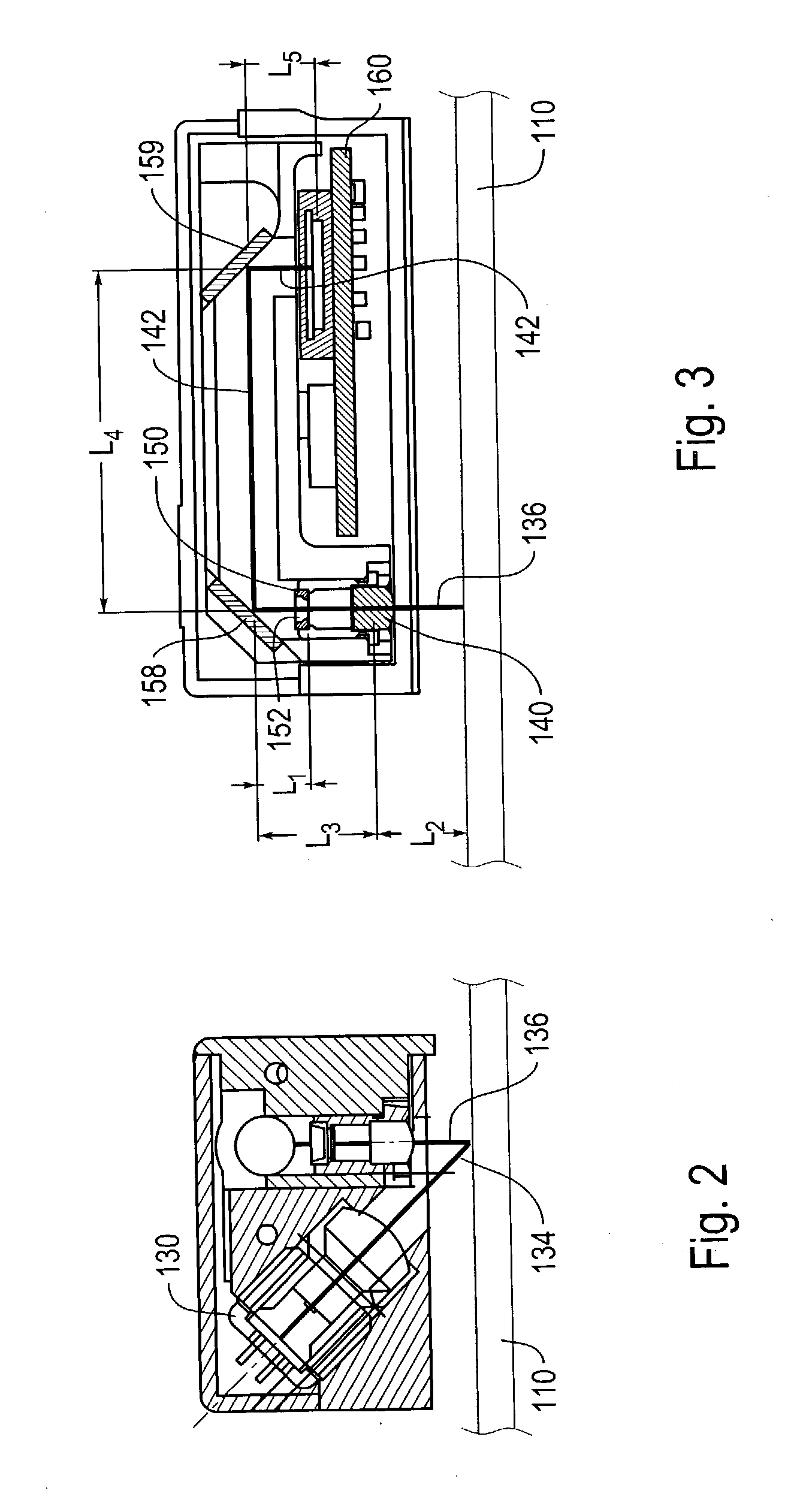
Systems and methods for absolute positioning using repeated quasi-random pattern
ActiveUS6937349B2Reduce the amount requiredHigh resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImage resolution
An absolute 2D position-sensing device is usable to measure the position of a first element with respect to a second element. A 2D absolute scale includes an integrated 2D absolute scale pattern extending over the 2D scale area along each measuring axis of the scale. The integrated 2D absolute scale pattern includes a predetermined quasi-random pattern repeatedly interleaved with a plurality of code portions along each axis. Each code portion includes a plurality of code elements indicative of an absolute measurement value. The offset of the quasi-random pattern relative to a readhead of the device is combined with the absolute measurement value to determine an absolute position to a very high resolution over a relatively large 2D range.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Method and apparatus for synchronization of proximate RFID readers in a gaming environment
ActiveUS7357299B2Memory record carrier reading problemsElectric testing/monitoringProximateRadio frequency
Owner:ARISTOCRAT TECH INC
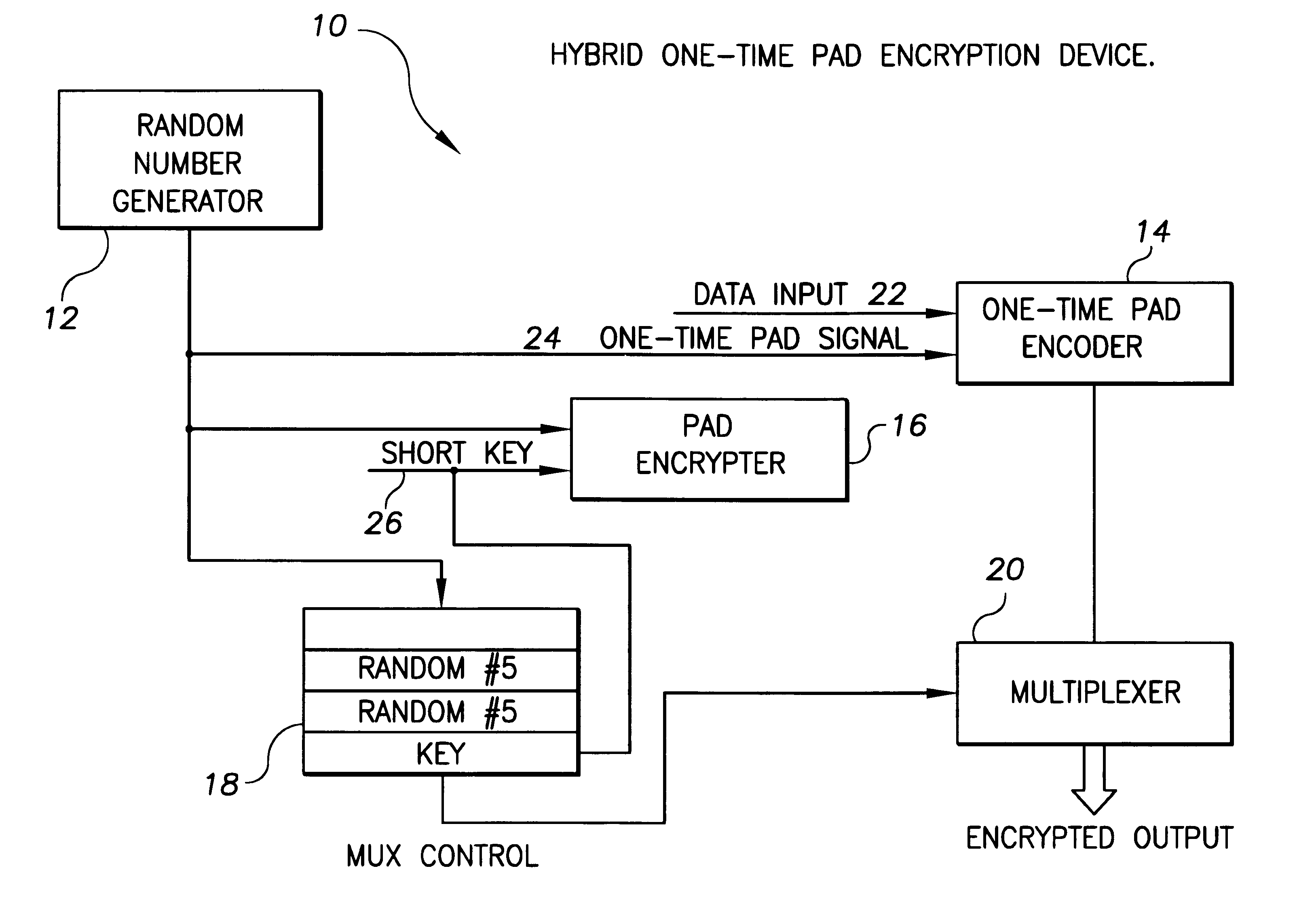
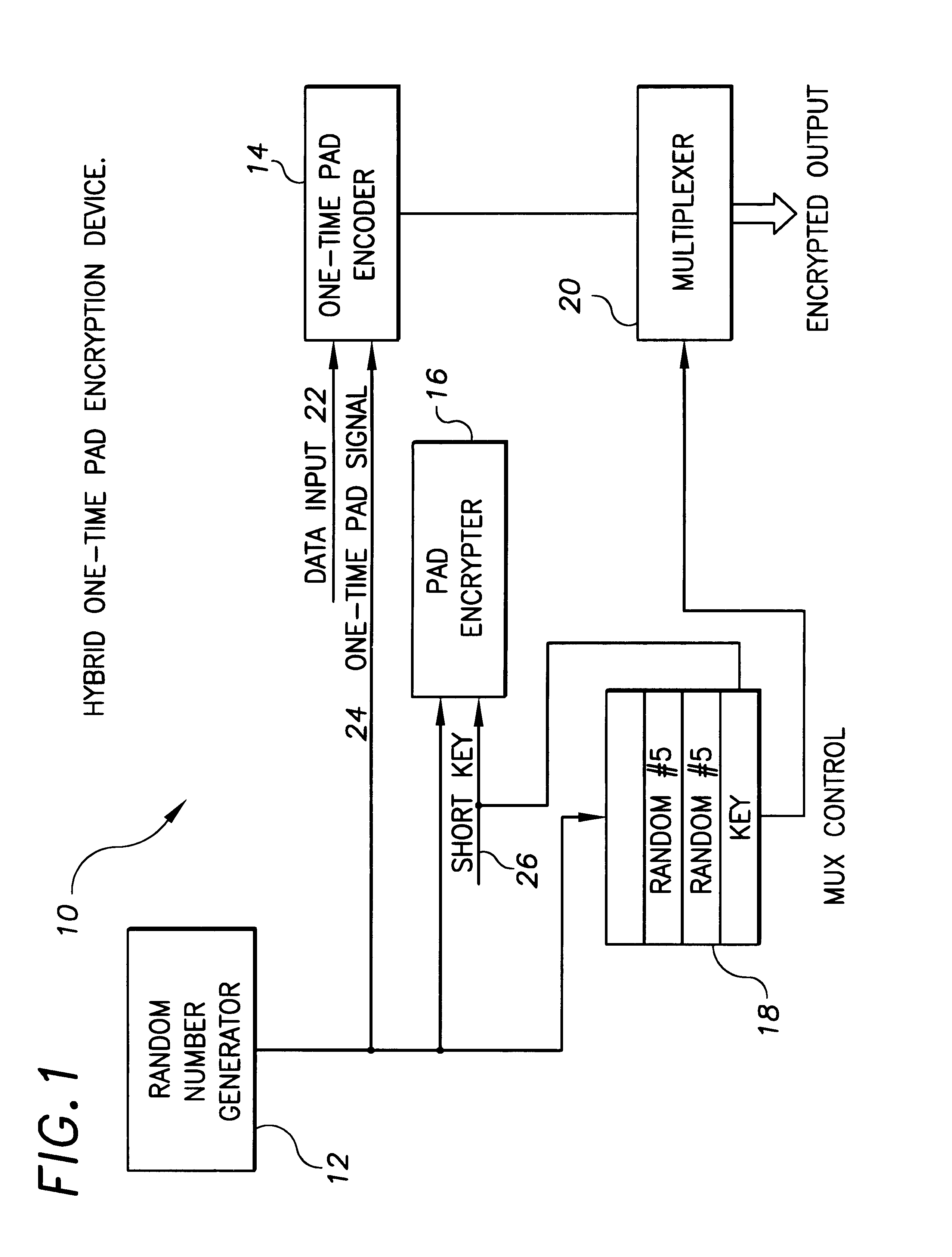
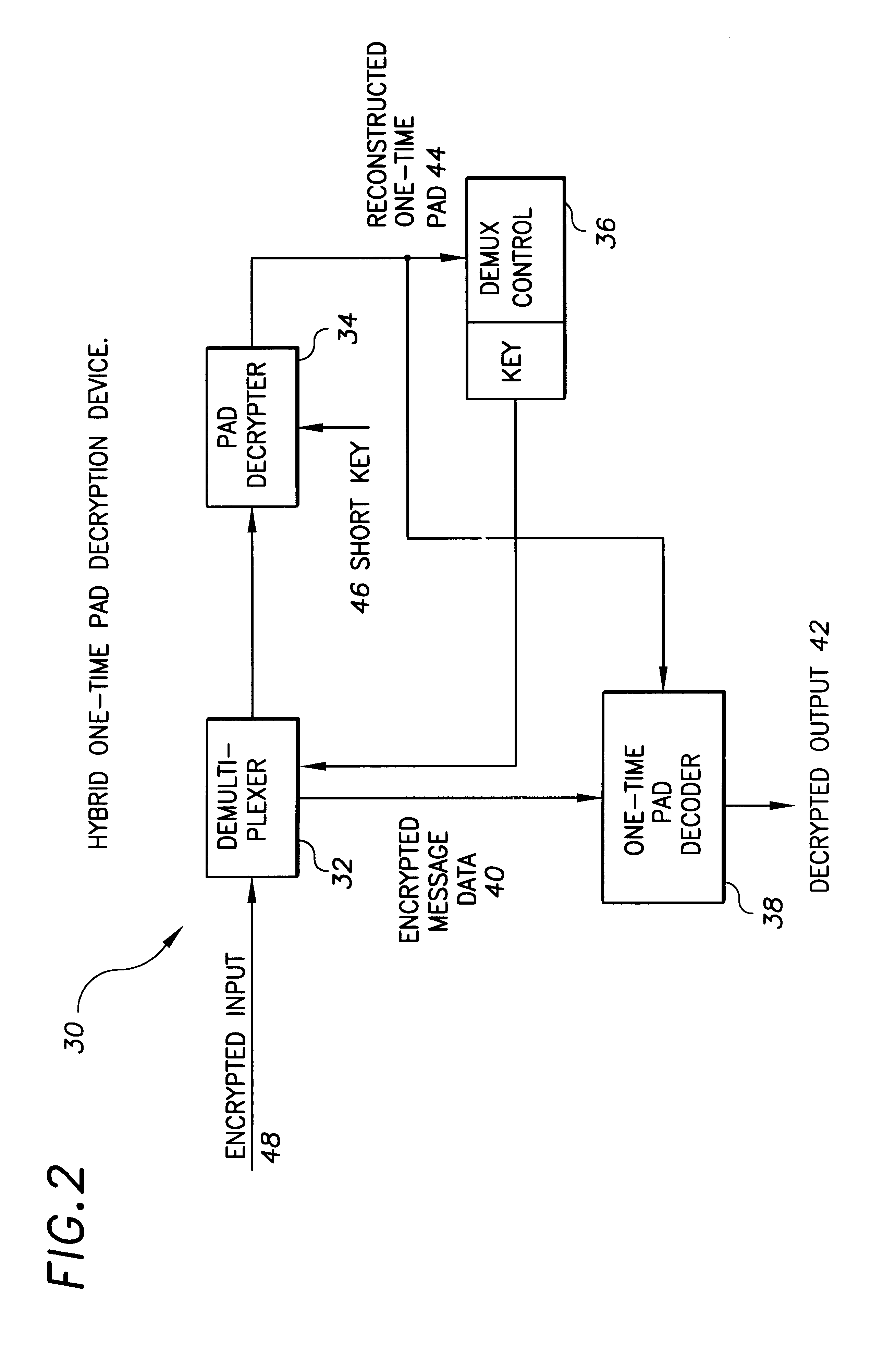
Hybrid one time pad encryption and decryption apparatus with methods for encrypting and decrypting data
InactiveUS6363152B1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareOne-time pad
A hybrid one time pad encryption and decryption apparatus with methods for encrypting and decrypting data wherein a one time random number pad provides high security encryption. The random number sequence is encrypted using DES, RSA or other technique and embedded in the message as a function of the random pad itself. This generates an encryption message that is impervious to attempts to directly decode the message text as the message is randomly dispersed throughout a message and the message contains as much quasi-random data as text. The message is also relatively impervious to attempts to decode the cipher, as the cipher is randomly interrupted by the encrypted data.
Owner:VLSI TECHNOLOGY
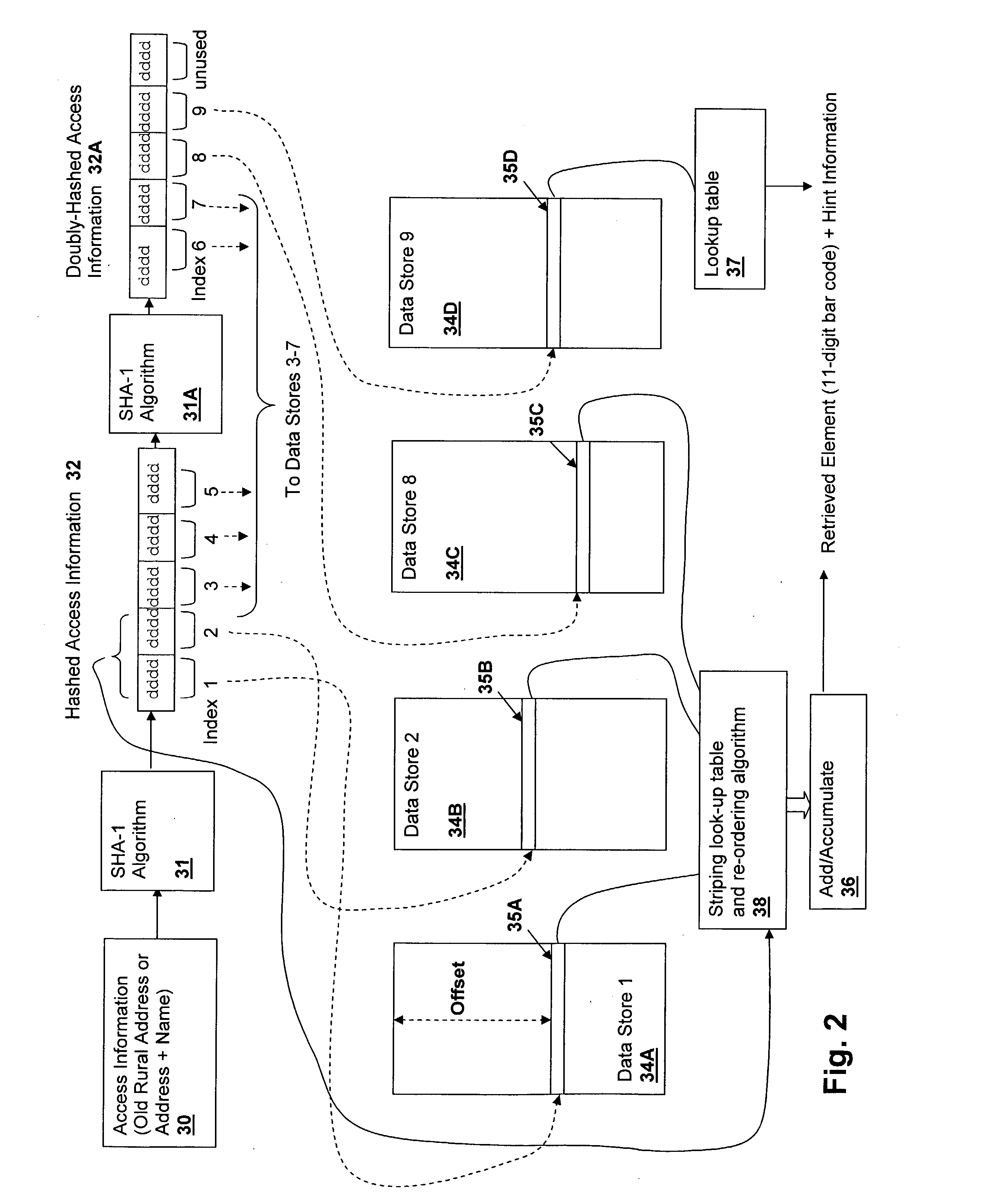
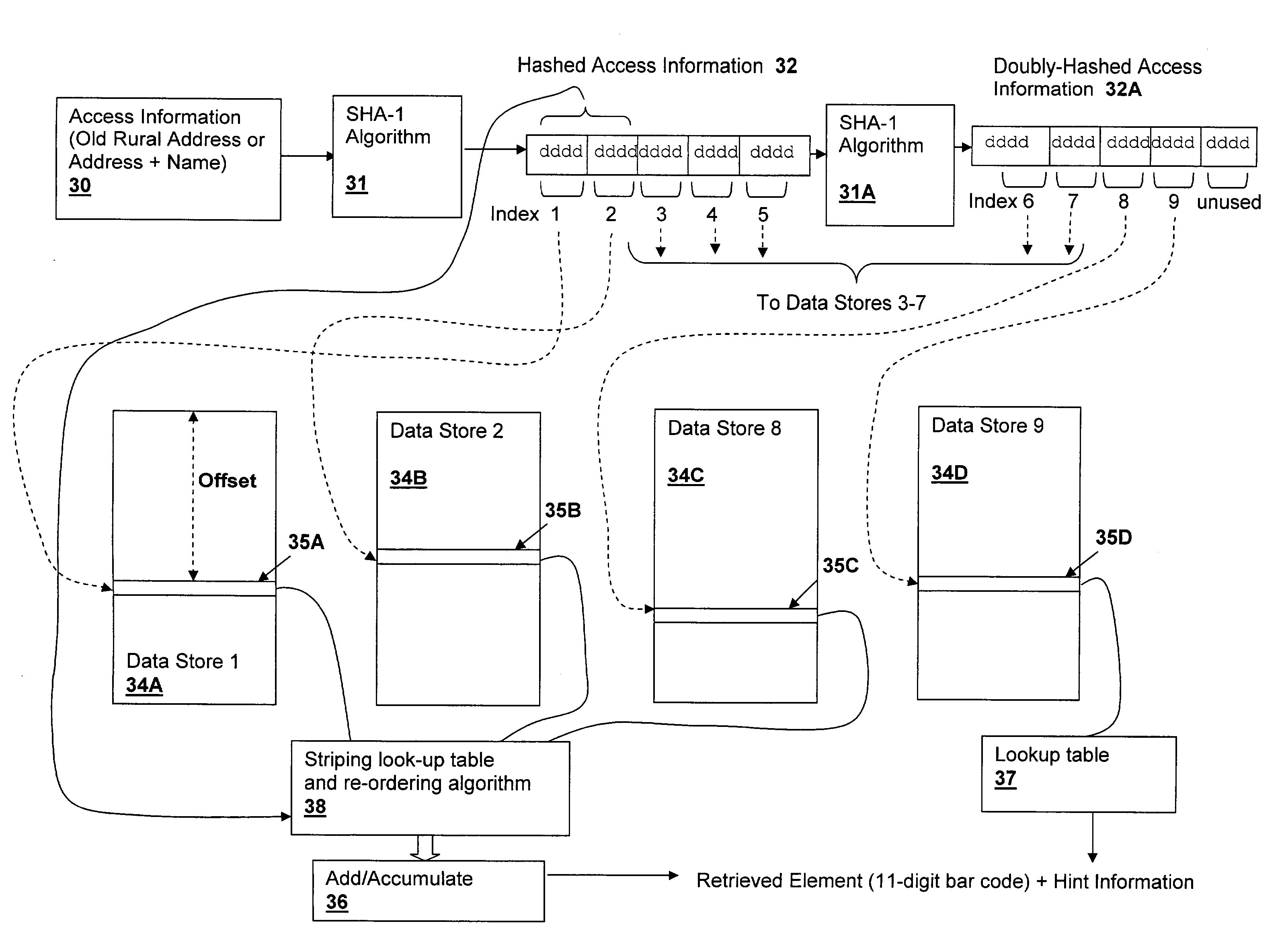
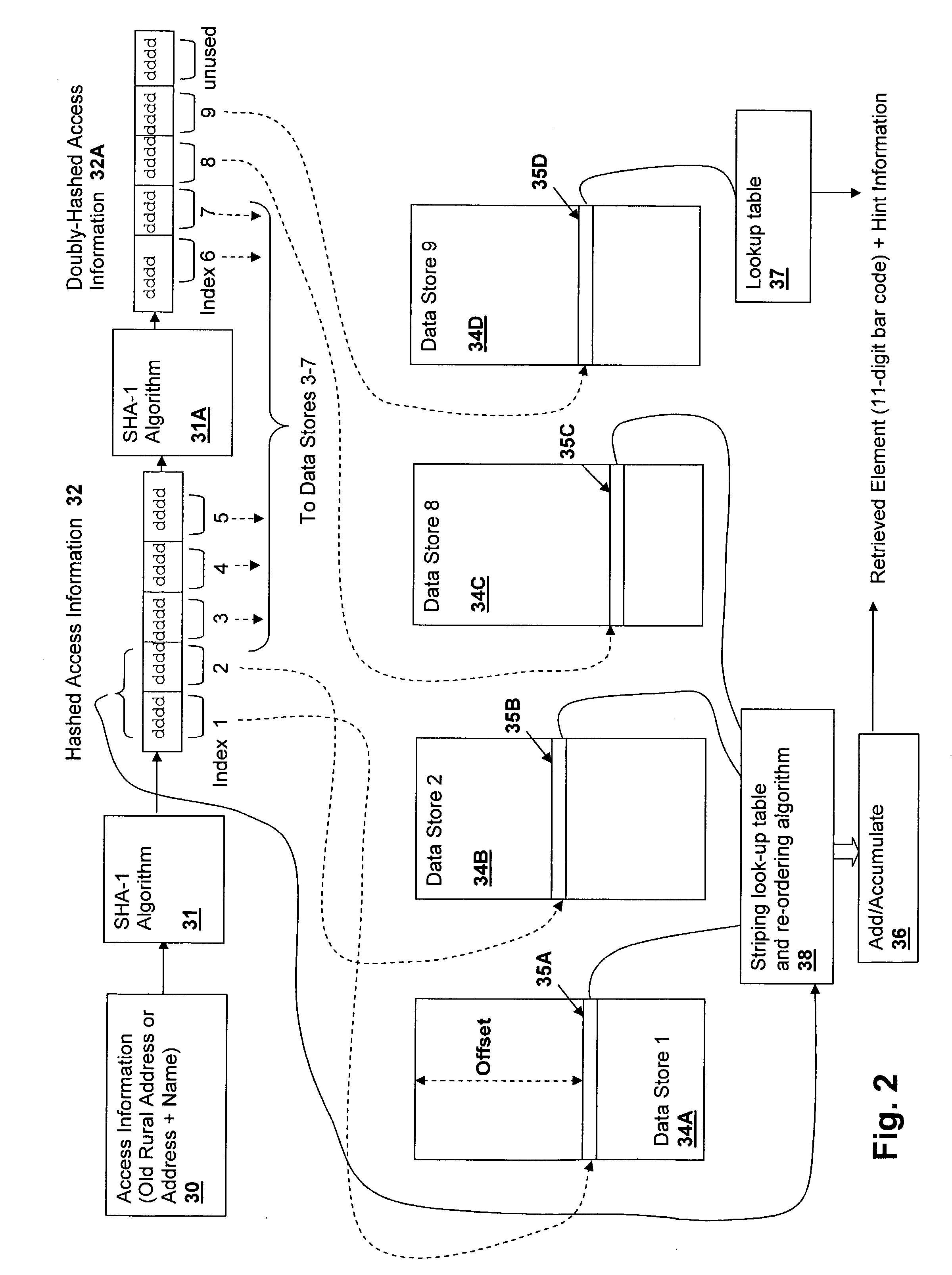
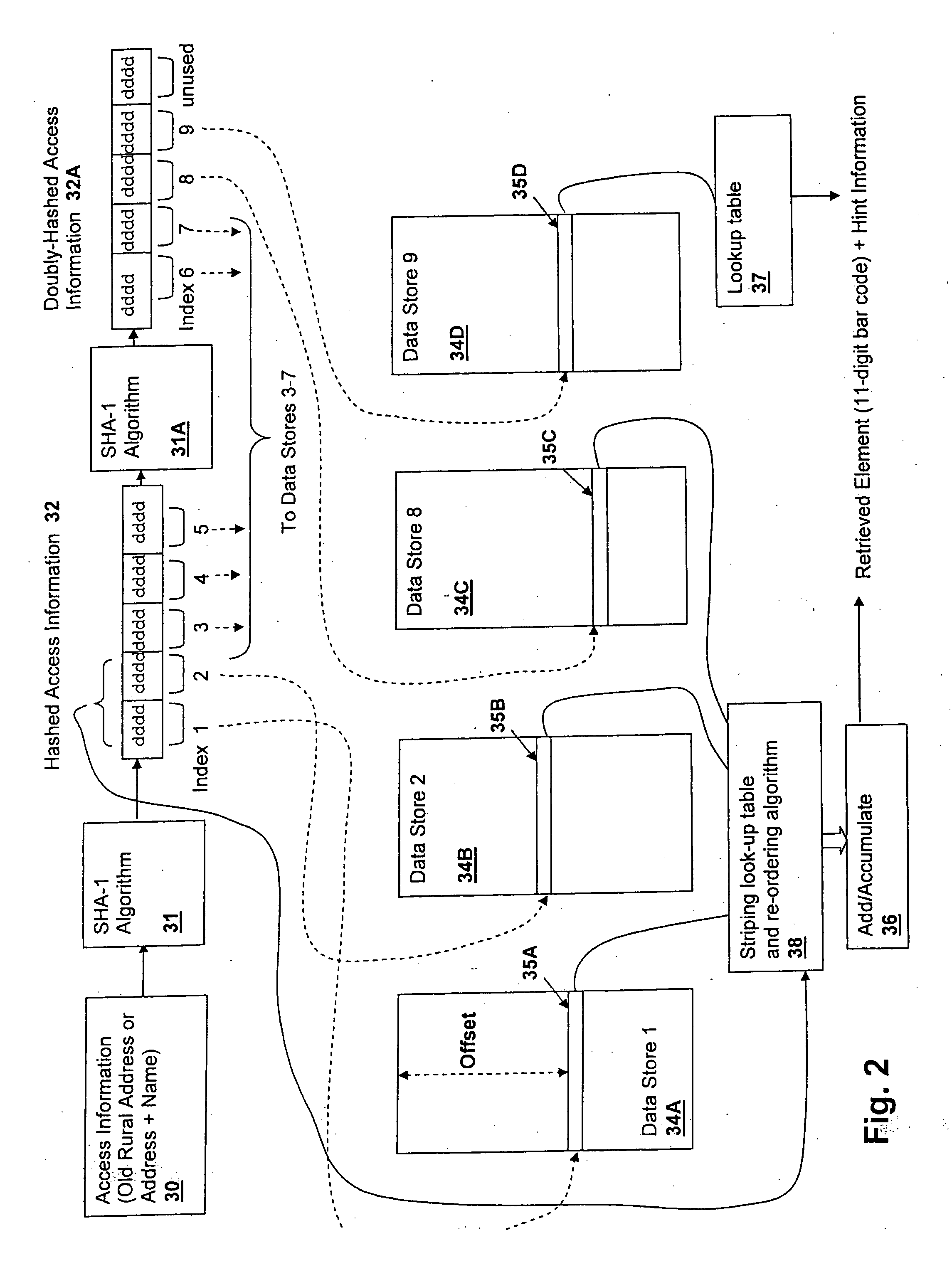
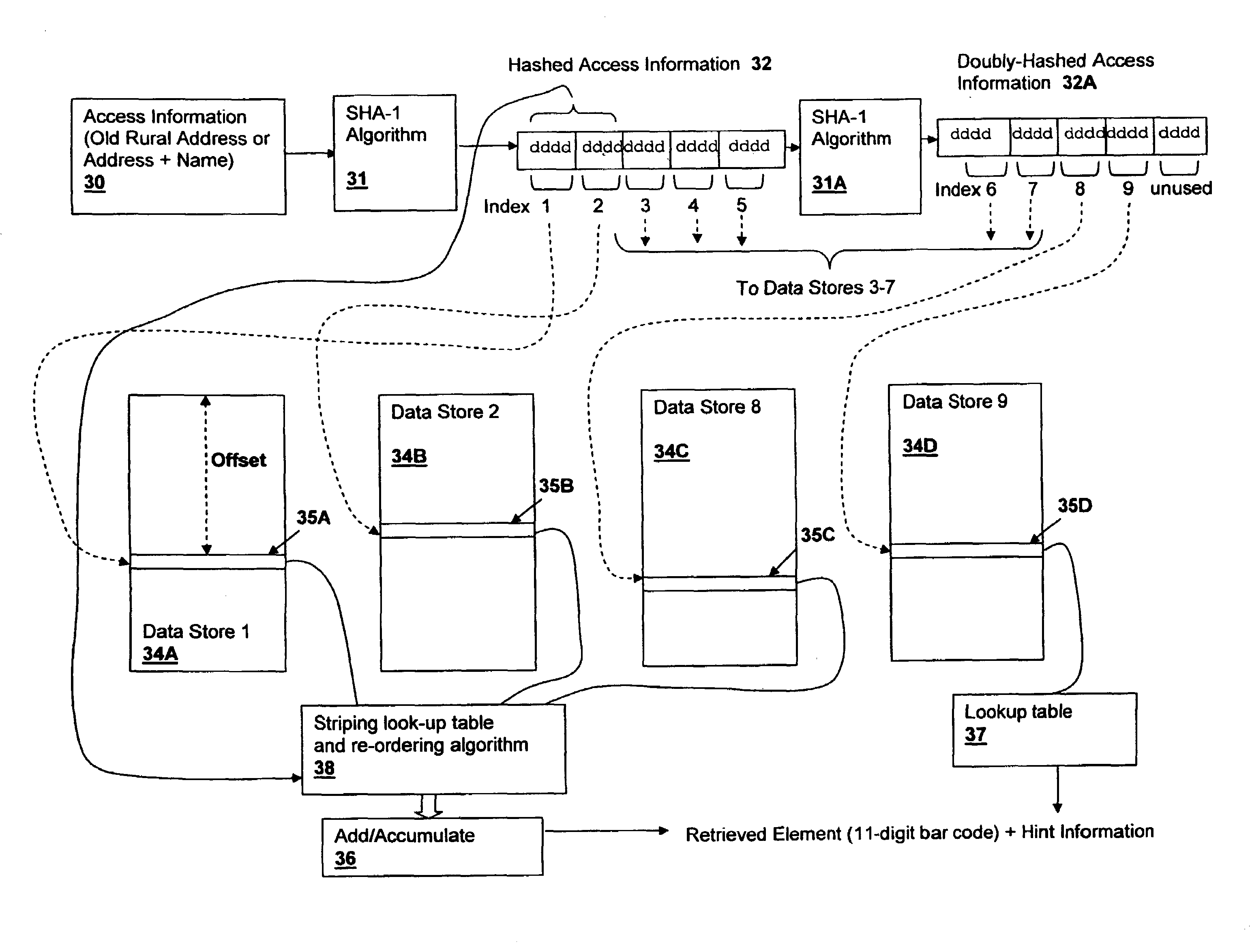
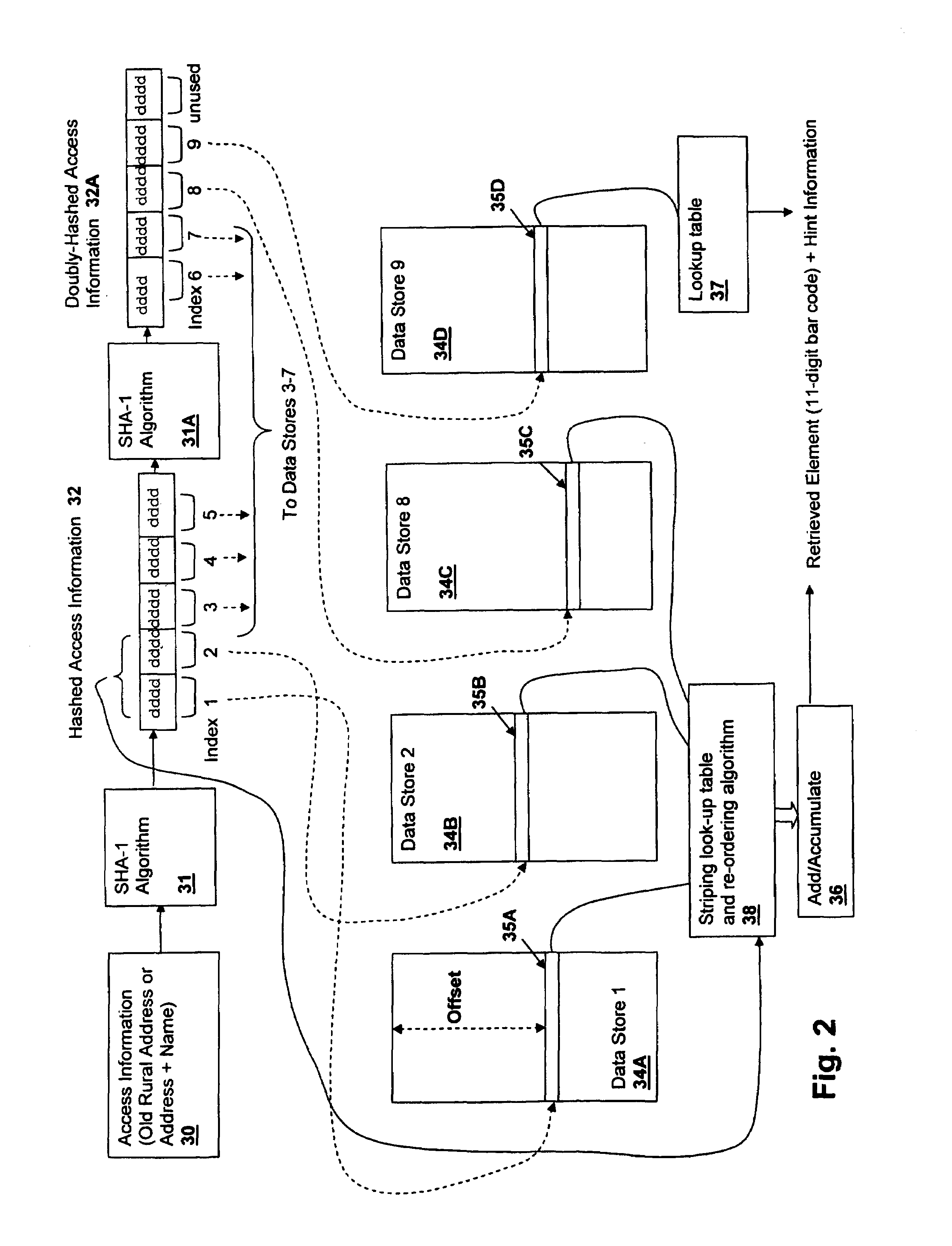
Method and system for storing and retrieving data using hash-accessed multiple data stores
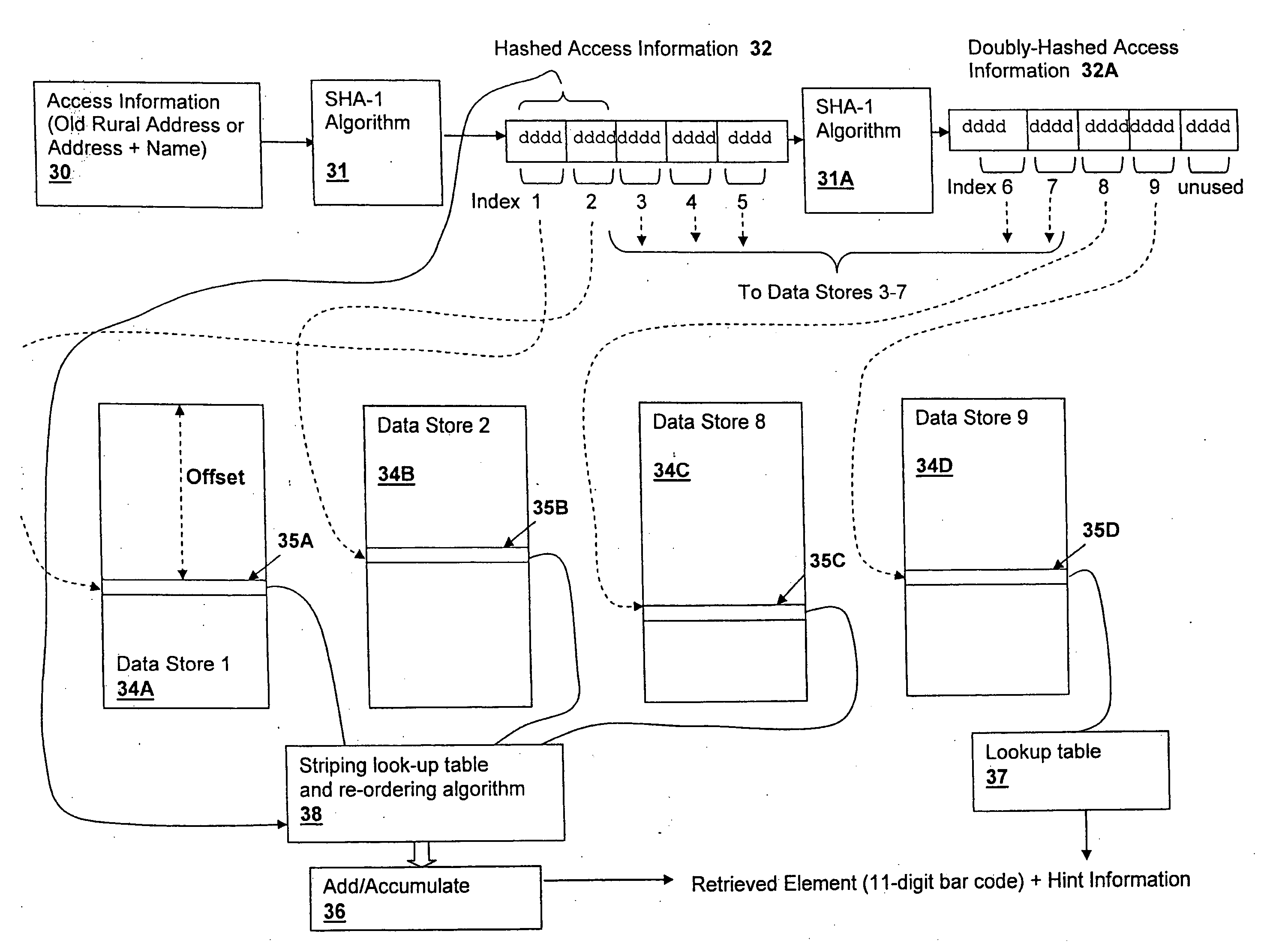
A method and system for storing and retrieving data using hash-accessed multiple data stores, provides data protection while requiring low computational overhead and further provides storage and retrieval access based on only a single piece of access information, which is generally public. The algorithms provide high security against data-mining and other examination of the data stores. The access information is hashed and is split into offset fields used as indices into a plurality of data stores, generating a quasi-random relationship between the access information and the location of portions of a stored data element. Further protection may be provided by striping the data across the data stores in conformity with a striping order selected by a field of the hashed access information.
Owner:US POSTAL SERVICE
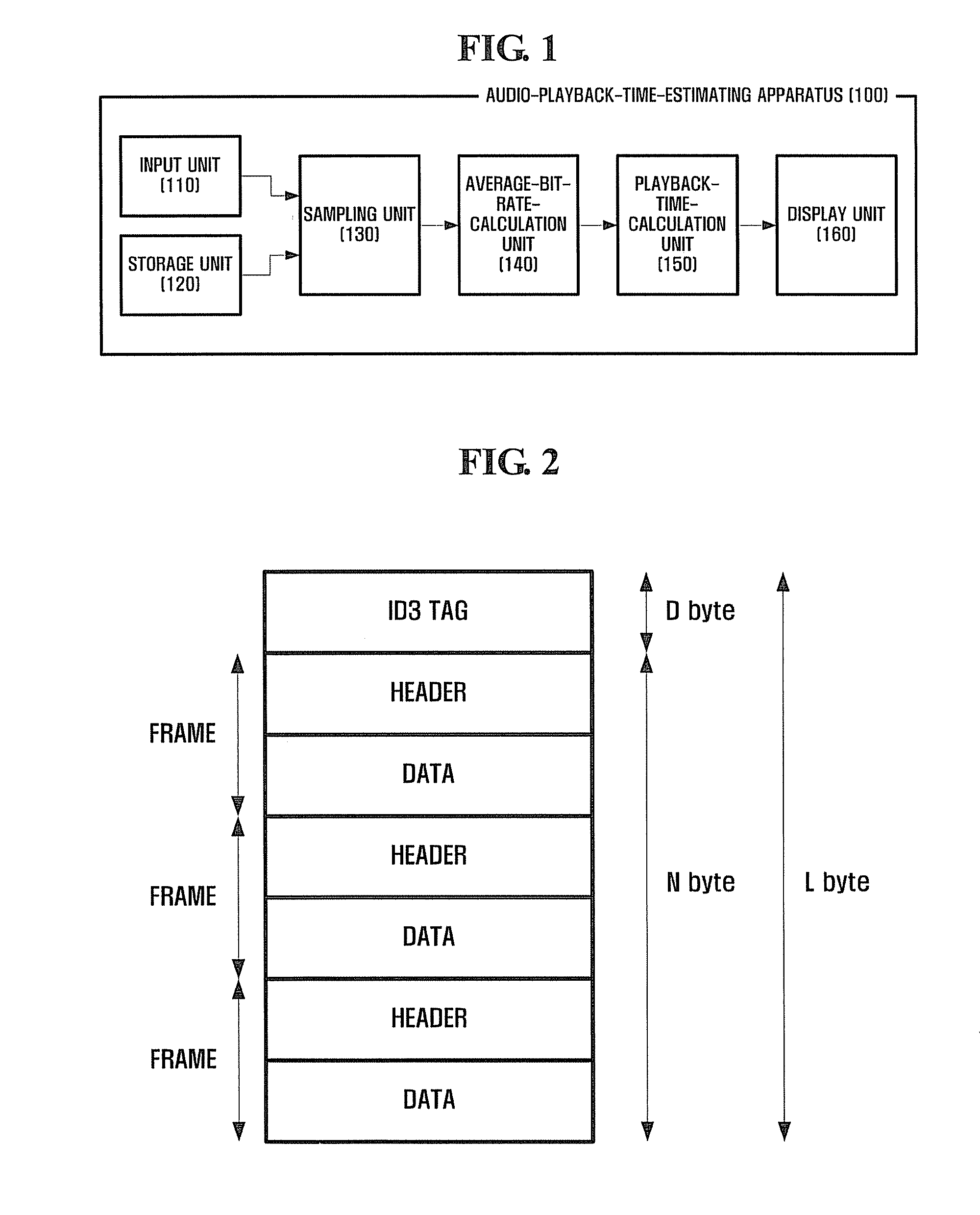
Audio playback time estimating apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080172140A1Effective estimateRandom number generatorsRecord information storageID3Computer science
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods for absolute positioning using repeated quasi-random pattern
ActiveUS20040218181A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImage resolution
An absolute 2D position-sensing device is usable to measure the position of a first element with respect to a second element. A 2D absolute scale includes an integrated 2D absolute scale pattern extending over the 2D scale area along each measuring axis of the scale. The integrated 2D absolute scale pattern includes a predetermined quasi-random pattern repeatedly interleaved with a plurality of code portions along each axis. Each code portion includes a plurality of code elements indicative of an absolute measurement value. The offset of the quasi-random pattern relative to a readhead of the device is combined with the absolute measurement value to determine an absolute position to a very high resolution over a relatively large 2D range.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Method and system for storing and retrieving data using hash-accessed multiple data stores
A method and system for storing and retrieving data using hash-accessed multiple data stores, provides data protection while requiring low computational overhead and further provides storage and retrieval access based on only a single piece of access information, which is generally public. The algorithms provide high security against data-mining and other examination of the data stores. The access information is hashed and is split into offset fields used as indices into a plurality of data stores, generating a quasi-random relationship between the access information and the location of portions of a stored data element. Further protection may be provided by striping the data across the data stores in conformity with a striping order selected by a field of the hashed access information.
Owner:US POSTAL SERVICE
Automatic tuning of motion controllers using search techniques
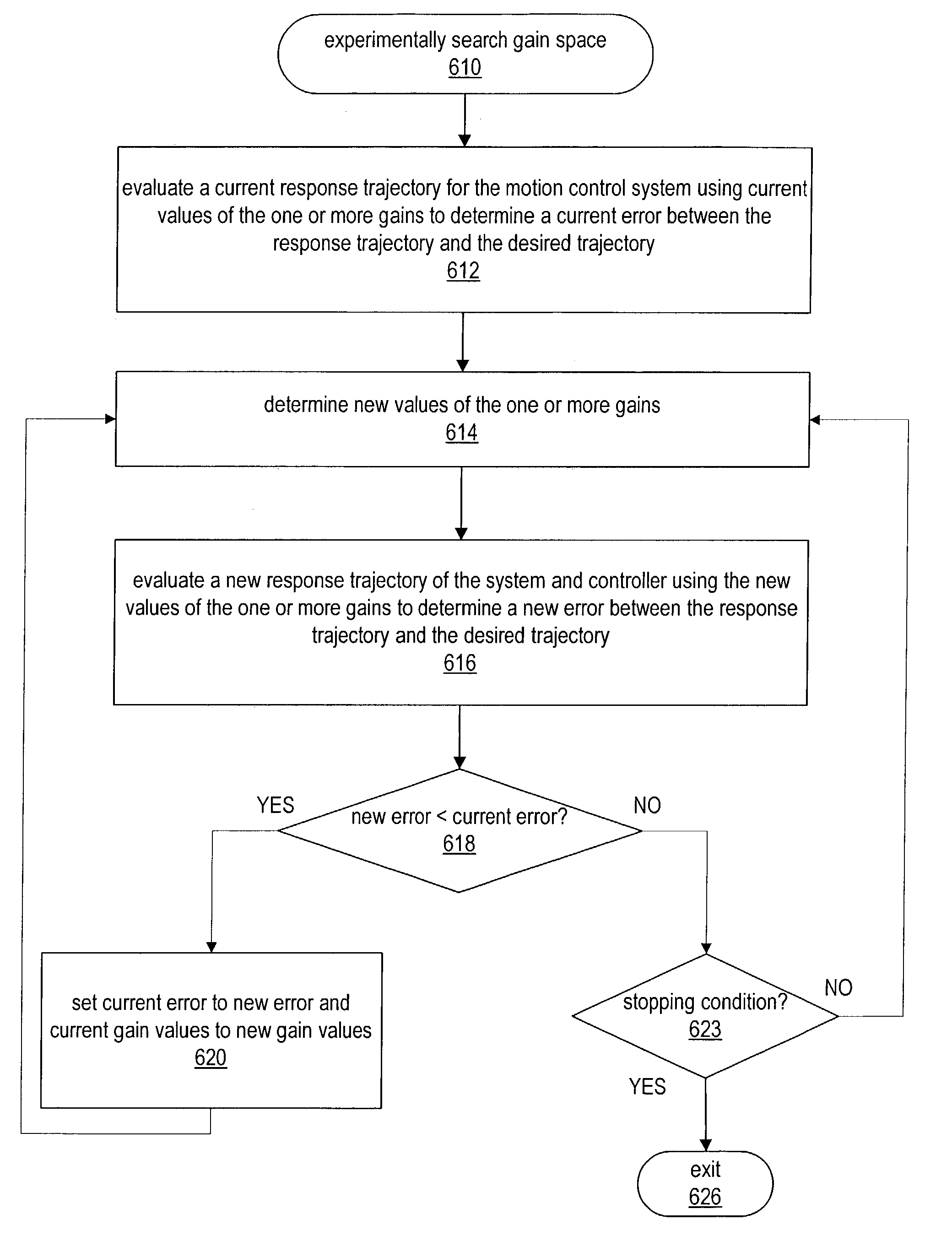
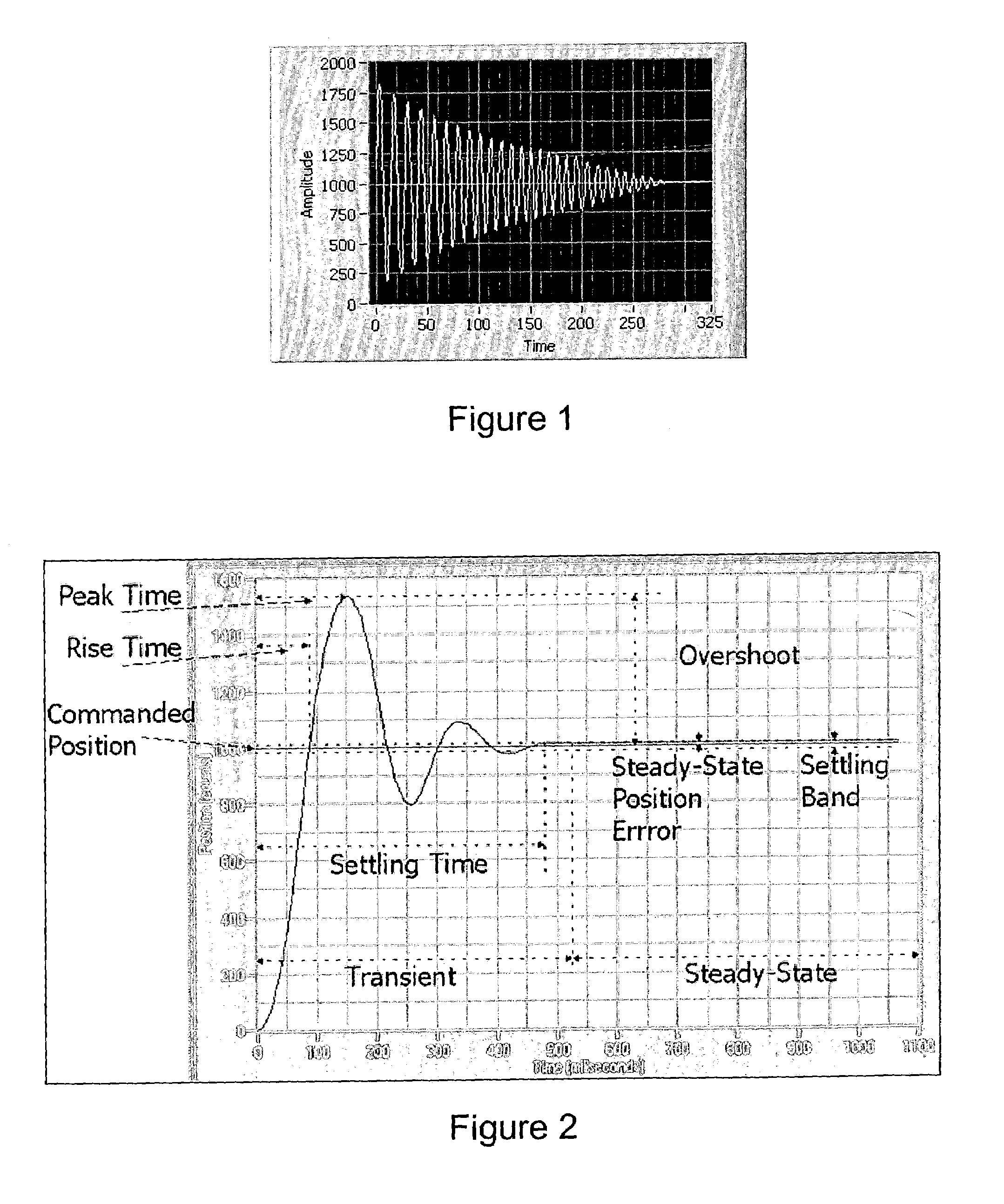
ActiveUS7035694B2Improve performanceGradient is effectivelyComputer controlSimulator controlDeterministic methodControl system
System and method for user configuration of an autotuning algorithm for a controller in a motion control system. A desired trajectory in one or more dimensions for the motion control system is received. Values of one or more gains for a controller are initialized. A response trajectory of the controller and motion control system in response to the desired trajectory is received, and an error determined between the response trajectory and the desired trajectory. A gain space is then experimentally searched to determine final values of the one or more gains for the controller that minimize the error (e.g., Euclidean norm) between the response trajectory and the desired trajectory, e.g., via simulated annealing, or other stochastic, quasi-random, and / or deterministic approaches. After experimentally searching, the controller is operable to control the motion control system substantially in accordance with the desired trajectory using the determined values of the one or more gains.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Field Effect Mode Electro-Optical Device Having a Quasi-Random Photospacer Arrangement
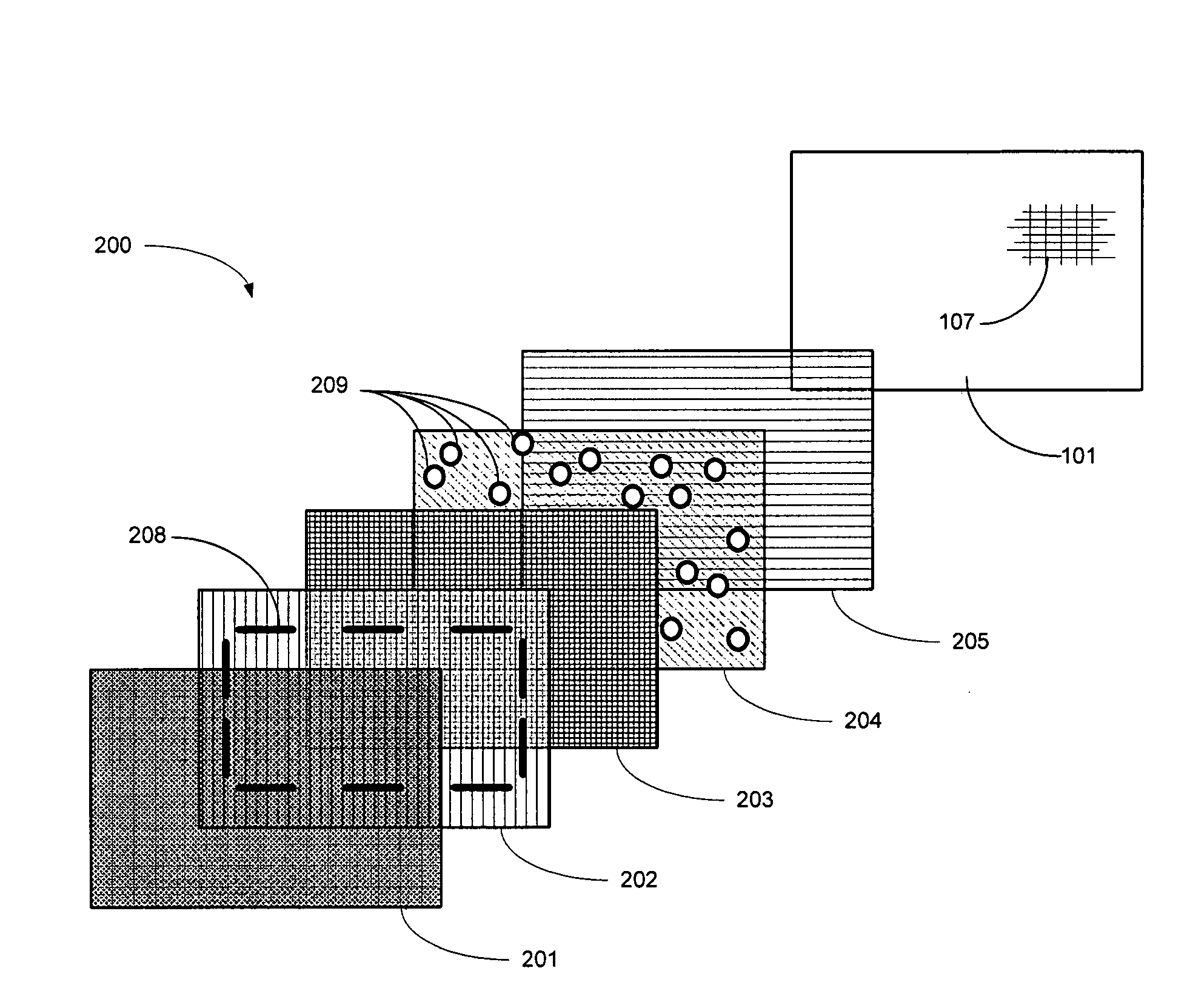
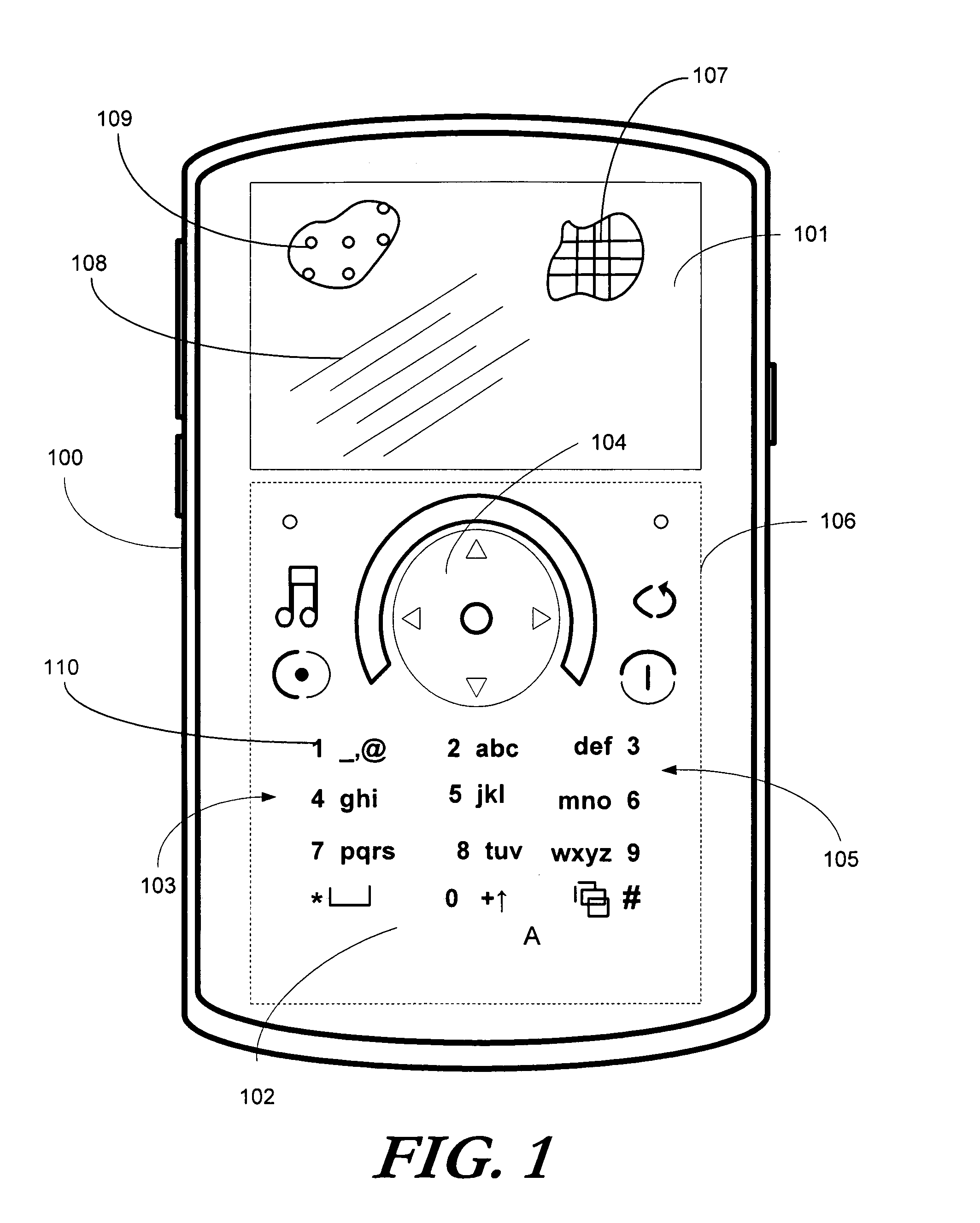
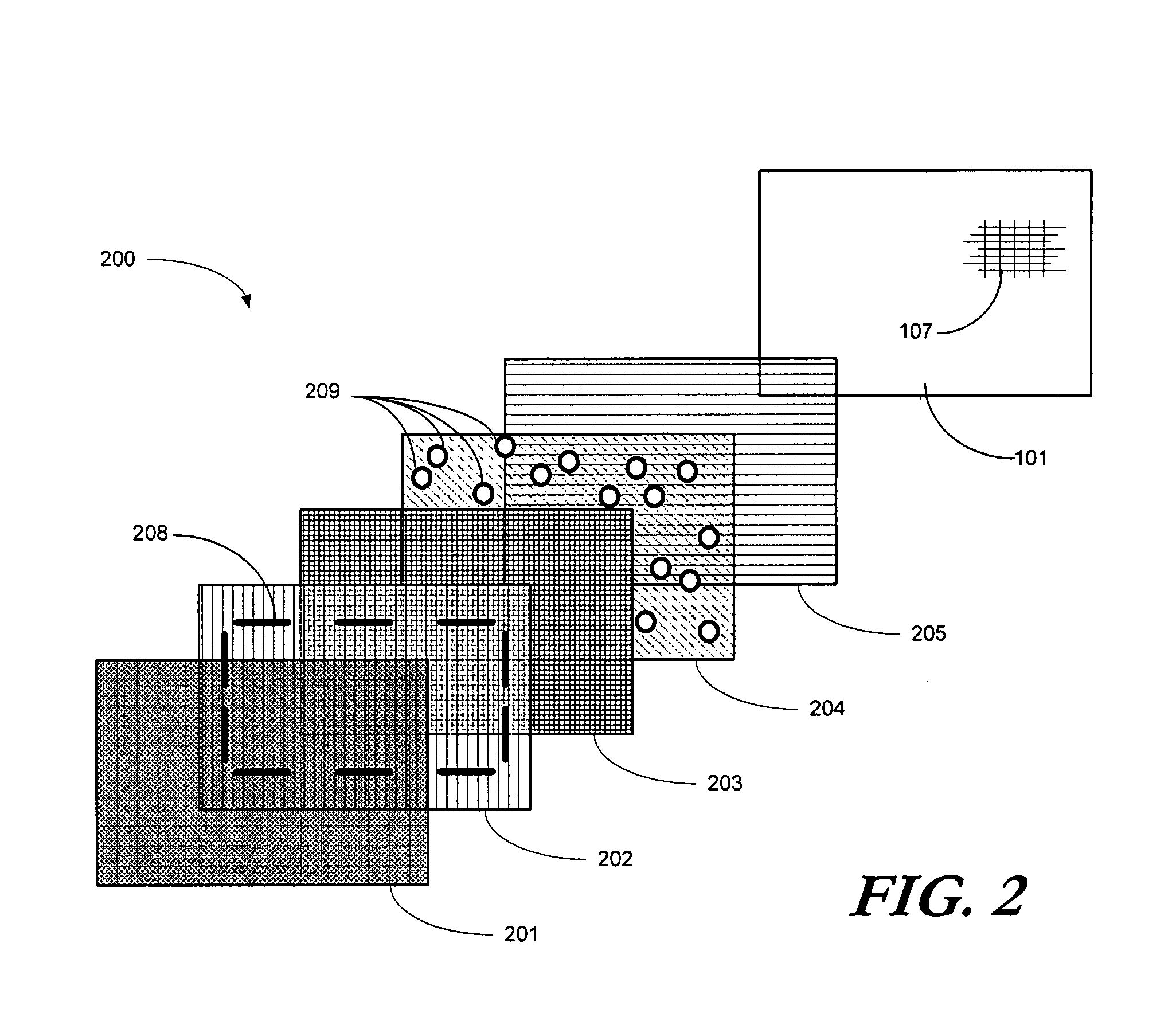
ActiveUS20090161059A1Digital data processing detailsNon-linear opticsCorrelation functionDisplay device
A segmented optical shutter (200) is used with a high-resolution display (101) to provide a dynamic user interface (400) for a portable electronic device (100). To reduce optical interference corresponding to a correlation function for transmitted light occurring between the photospacers (209) in the segmented optical shutter (200) and the black matrix (107), the photospacers (209) are disposed along a light transmitting substrate (204) of the segmented optical shutter (200) in a quasi-random arrangement. The quasi-random arrangement, which may include varying the horizontal and vertical placement of the photospacers (209), repeating asymmetrical subsections of photospacer configurations, varying the size or shape of the photospacers (209), or combinations thereof, misaligns the photospacers (209) relative to the black matrix (107) or other elements to reduce optical interference and moiré patterns that may otherwise be perceptible to a user.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Quantum lattice diffracting rasters
A diffraction grating of quantum dot array is prepared by arranging large amount of quantum dots in quasi-random way on grating base, placing dots on one dimensional space of surface is random distribution and on another dimensional space in sine distribution for obtaining quantum dot array grating. The senior diffraction of the grating is so low as to be ignored.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
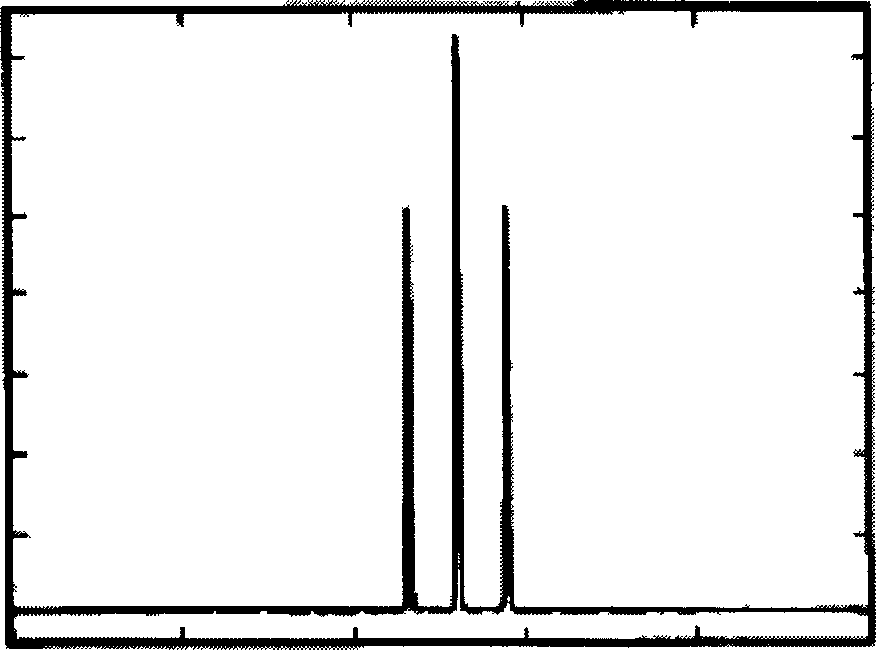
Random number generation method based on multivariate non-normal distribution, parameter estimation method thereof, and application to simulation of financial field and semiconductor ion implantation
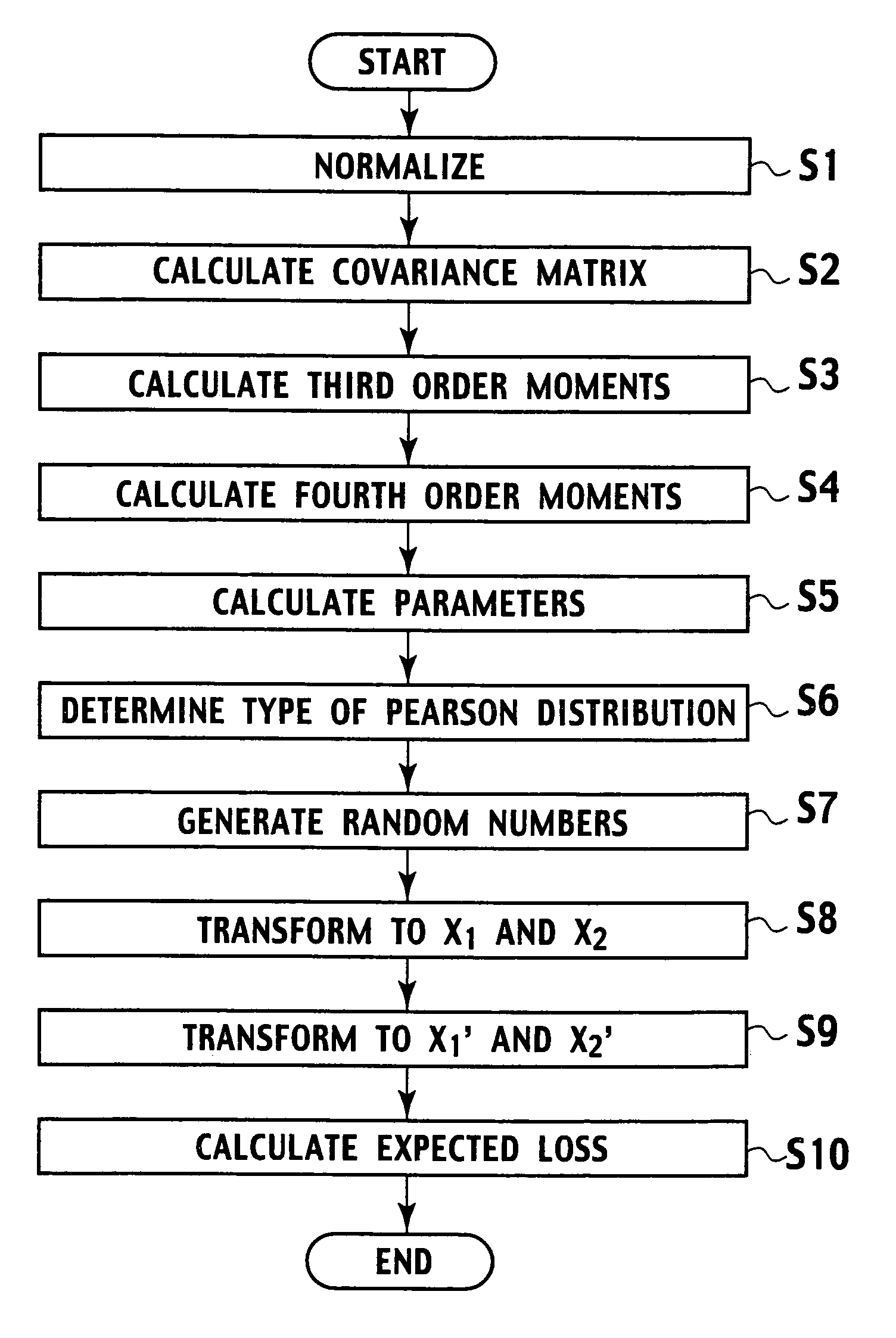
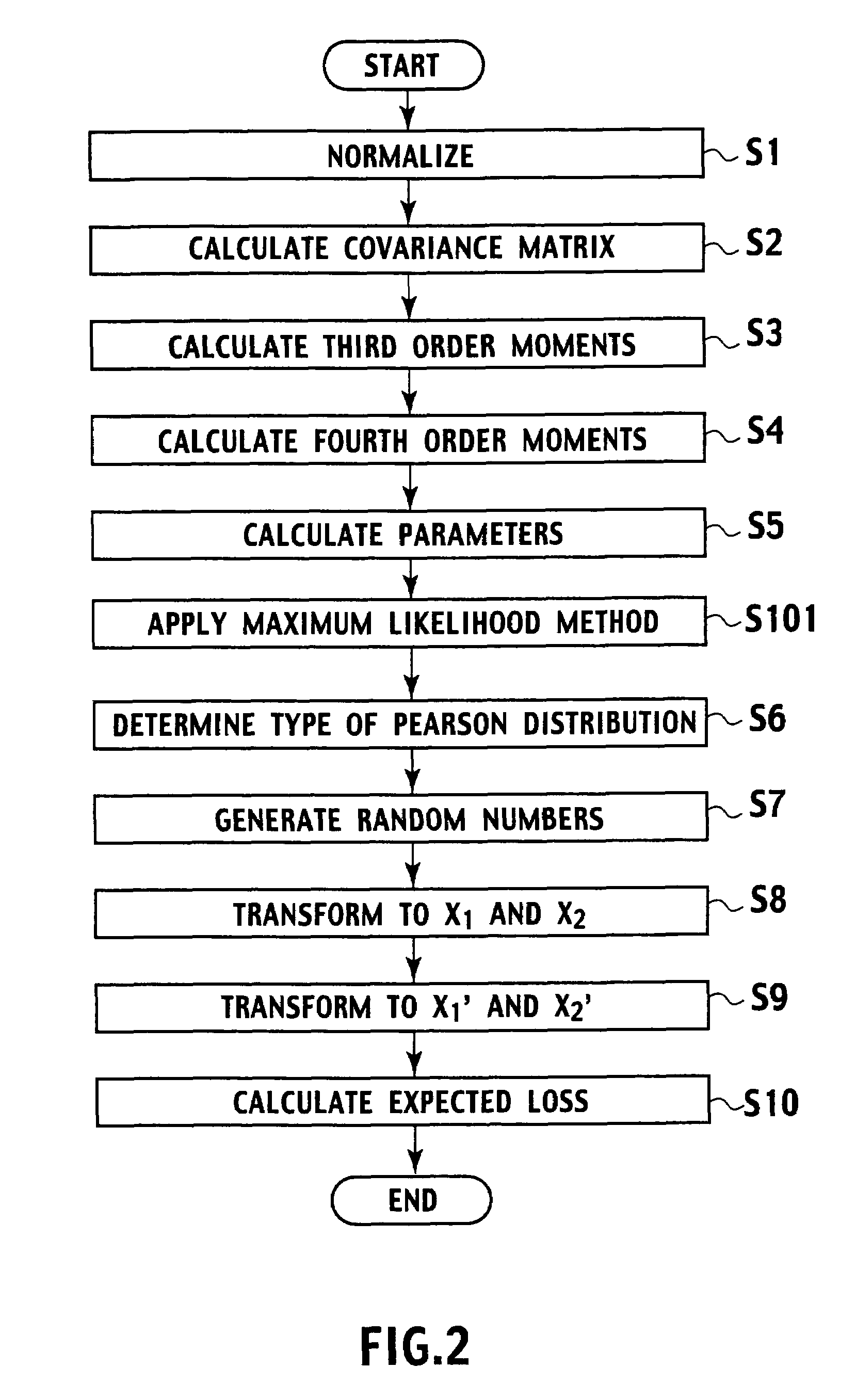
Random number generating method for generating random numbers in accordance with multivariate non-normal distributions based on the Yuan and Bentler method I on computer. The method includes application steps for applying n-dimensional multivariate non-normal distributions to n-dimensional experience distribution by using computer and steps for generating random numbers including pseudo-random numbers, quasi-random numbers, low discrepancy sequences, and physical random numbers by methods including additive generator method, M-sequence, generalized feedback shift-register method, and Mersenne Twister, and excluding congruential method, by using computer. The application steps use predetermined relationship equations for the third and fourth order moments to perform application associated with the third and fourth order moments of the empirical distributions. Moreover, by using random numbers generation method, parameters are estimated by maximum likelihood method. Furthermore, the random number generation method and the parameters estimation method are applied to simulation of financial field, semiconductor ion implantation, and the like.
Owner:NAGAHARA YUICHI
Transmission method based on quasi-random back-off strategy in wireless distributed network
InactiveCN104703288AReduce sending conflictsReduce transmission delayData switching networksWireless communicationNetwork packetArrival time
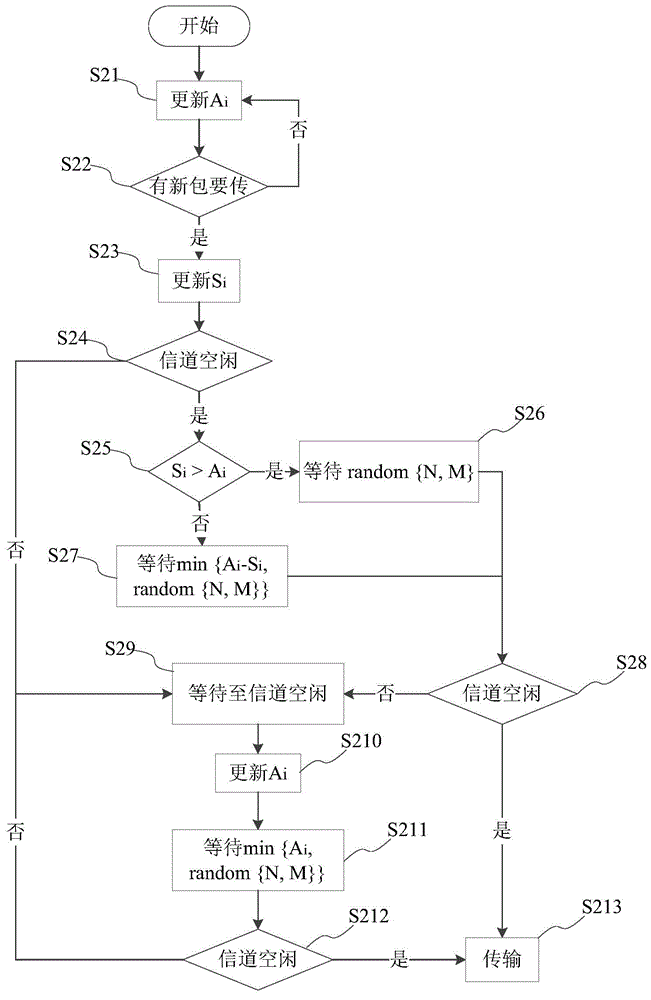
The invention provides a transmission method based on a quasi-random back-off strategy in a wireless distributed network. The transmission method comprises the following steps: counting the number Ai of data packets successfully transmitted by other sites except a transmission site i; counting an interval Si between the last busy end time slot of a channel to the transmission site arrival time slot of new data packets; determining first waiting time based on a time slot threshold value N on which certain back-off is turned into random back-off and a maximum back-off window length M in a quasi-random back-off process according to Ai and Si when the channel is judged to be idle for the first time, and transmitting the new data packets when the channel is judged to be idle for the second time; when a second judgment result indicates that the channel is busy, waiting till the channel is idle; if the channel is busy, waiting till the channel is idle; updating Ai; determining second waiting time according to Ai, N and M; judging whether or not the channel is idle for the third time, and returning to wait till the channel is idle if a third judgment result indicates that the channel is busy; and if the third judgment result indicates that the channel is idle, transmitting the new data packets.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM +1
Method and system for securing interface access via visual array paths in combination with hidden operators
InactiveUS20060047969A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationUser inputTheoretical computer science
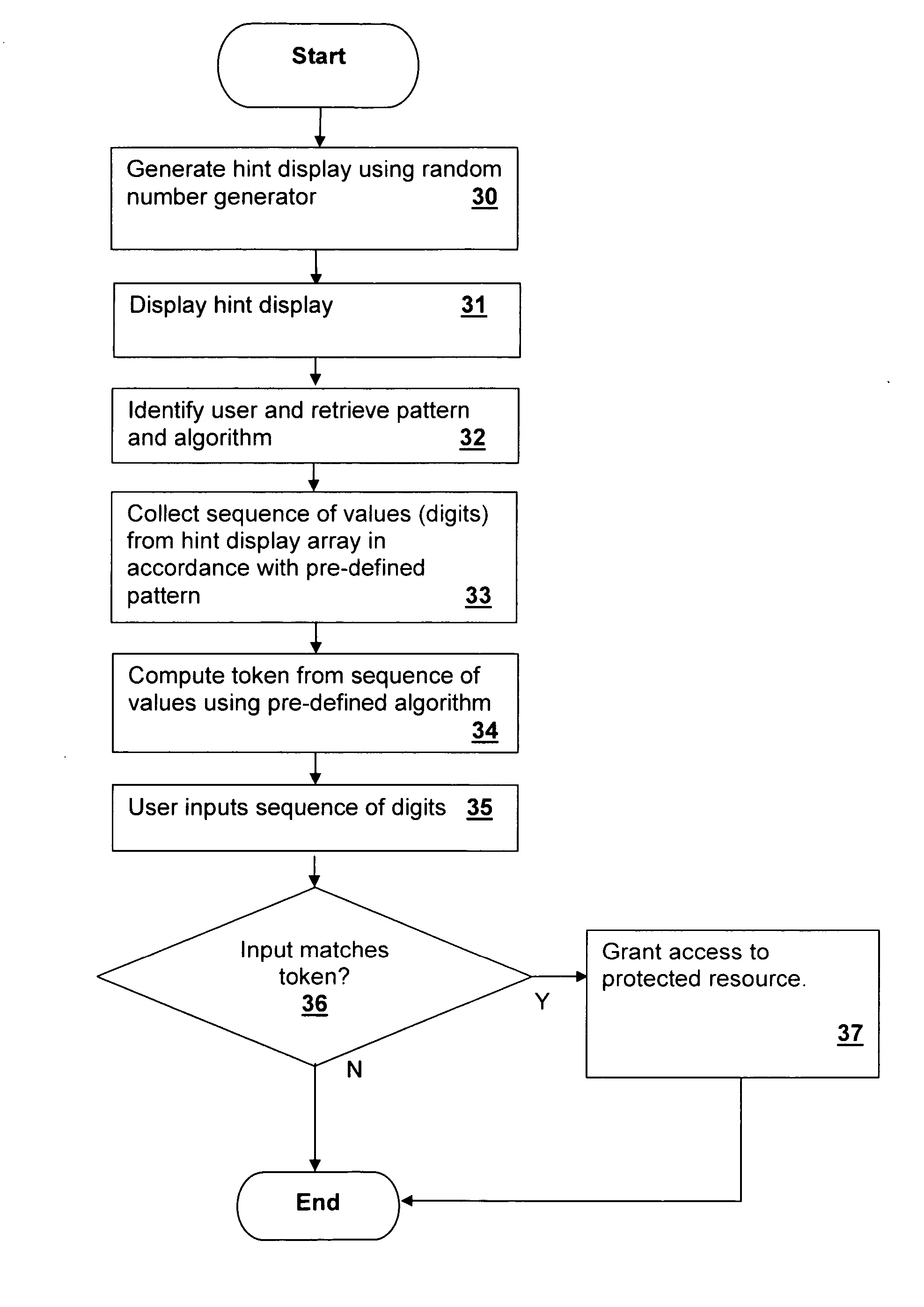
A method and system for securing interface access via visual array patterns in combination with hidden operations improves the security of computer systems and dedicated terminals. A hint display is generated in at least a quasi-random fashion that may be an array of numerical digit values. A user input is received that represents selection of a pattern of elements chosen from the hint display and combined in an algorithm using one or more mathematical, relational and / or logical operations. A pre-defined pattern and algorithm are used to generate a token from the hint display that is compared with the user input to verify that the user knows the pattern and algorithm. Further ease of use can be provided by dividing a hint display array into sub-arrays while providing a clue such as color to indicate each sub-array to the user.
Owner:PASSRULES CANADIAN SECURITY
Thermoinsulating mat of mineral fibers with random orientation
InactiveUS6851283B2Reducing fiber diameterLow densityGlass making apparatusThermal insulationMicrometerPliability
A mat of mineral fibers has a random or quasi-random fiber orientation. The fibers have diameters which, for the great majority of them, are 2.5 to 4.5 micrometers, and a length of 2 to 15 cm. Its density is less than 40 kg / m3. Its resistance to compression, for a crushing of 10%, is equal to at least 0.5 kN / m2. The fineness of the fibers and their random distribution imparts to the mat an exceptional lightness and an excellent flexibility, making possible the perfect application of the mat on cylindrical surfaces.
Owner:ISOVER SAINT GOBAIN SA
Random number generation method based on multivariate non-normal distribution, parameter estimation method thereof, and application to simulation of financial field and semiconductor ion implantation
Random number generating method for generating random numbers in accordance with multivariate non-normal distributions based on the Yuan and Bentler method I on computer. The method includes application steps for applying n-dimensional multivariate non-normal distributions to n-dimensional experience distribution by using computer and steps for generating random numbers including pseudo-random numbers, quasi-random numbers, low discrepancy sequences, and physical random numbers by methods including additive generator method, M-sequence, generalized feedback shift-register method, and Mersenne Twister, and excluding congruential method, by using computer. The application steps use predetermined relationship equations for the third and fourth order moments to perform application associated with the third and fourth order moments of the empirical distributions. Moreover, by using random numbers generation method, parameters are estimated by maximum likelihood method. Furthermore, the random number generation method and the parameters estimated method are applied to simulation of financial field, semiconductor ion implantation, and the like.
Owner:NAGAHARA YUICHI
Method and system for storing and retrieving data using hash-accessed multiple data stores
ActiveUS20060020575A1Lighten the computational burdenDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData elementData storing
A method and system for storing and retrieving data using hash-accessed multiple data stores, provides data protection while requiring low computational overhead and further provides storage and retrieval access based on only a single piece of access information, which is generally public. The algorithms provide high security against data-mining and other examination of the data stores. The access information is hashed and is split into offset fields used as indices into a plurality of data stores, generating a quasi-random relationship between the access information and the location of portions of a stored data element. Further protection may be provided by striping the data across the data stores in conformity with a striping order selected by a field of the hashed access information.
Owner:US POSTAL SERVICE
Method of Detecting Physical Phenomena
A method is provided for more accurate and reliable sensing of phenomena that are potentially obscured by noise, spoofing or jamming, that is deliberate attempts to obscure the phenomena by false signals or noise in response to the stimuli being provided and / or a detector being activated. The method deploys an array of emitter and detectors that are programmed to interrogate the selected environment at quasi-random intervals
Owner:PHYSICAL LOGIC
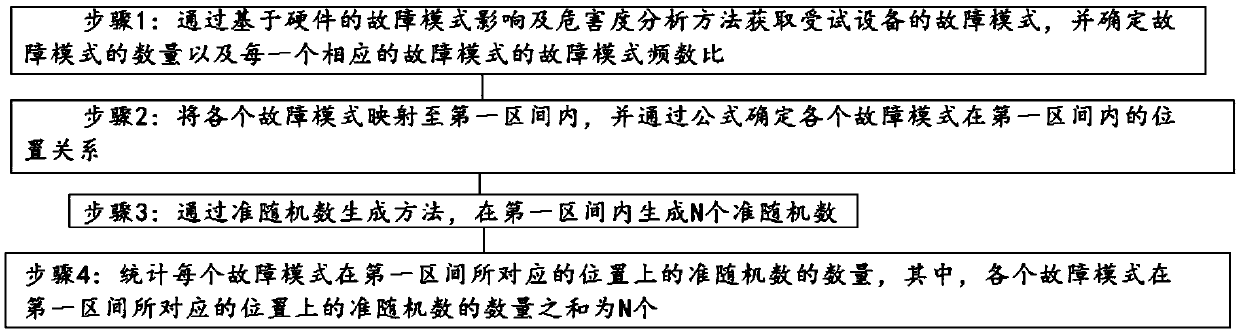
Quasi-random fault sampling method for airborne equipment testability experiments
InactiveCN105512488AGood precisionIncrease coverageSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsDispersityFrequency ratio
The invention discloses a quasi-random fault sampling method for airborne equipment testability experiments. The fault sample size determination method for the airborne equipment testability experiments comprises steps as follows: Step 1: fault modes of tested equipment are acquired with a fault mode effect and hazard degree analyzing method on the basis of hardware, and the number of the fault modes and the fault mode frequency ratio Cp of every corresponding fault mode are determined; Step 2: all the fault modes are mapped to a first interval, and the position relation of all the fault modes in the first interval is determined through a formula; Step 3: with the adoption of a quasi-random number generation method, N quasi-random numbers are generated in the first interval; Step 4: statistics is performed on the number of the quasi-random numbers of each fault mode in the corresponding position in the first interval. The quasi-random fault sampling method for the airborne equipment testability experiments is obviously superior to a pseudo-random sampling method and can significantly improve sampling precision and coverage and reduce dispersity.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Imaging device and methods of manufacturing of the device
InactiveUS20110069391A1High spatial frequencyDecorative surface effectsLayered productsAnodizingRainbow
A method and apparatus for producing low cost miniature images is provided. Modulated layers of materials over silicon substrate provide the shades of gray or colors needed to provide the perception of an image. Reflective characteristics as well as refractive characteristics of materials and modulated layers serve to produce the desired effects. Quasi-random geometries eliminate unwanted rainbow impressions. The resultant image is highly resistant to environmental conditions. Metal anodizing and coloring methods as well as metal anodizing interference thin layers methods are used to add more colors to the images. Relatively high-pitch patterns within the image produce secondary visual effects.
Owner:MELMAN HAIM ZVI
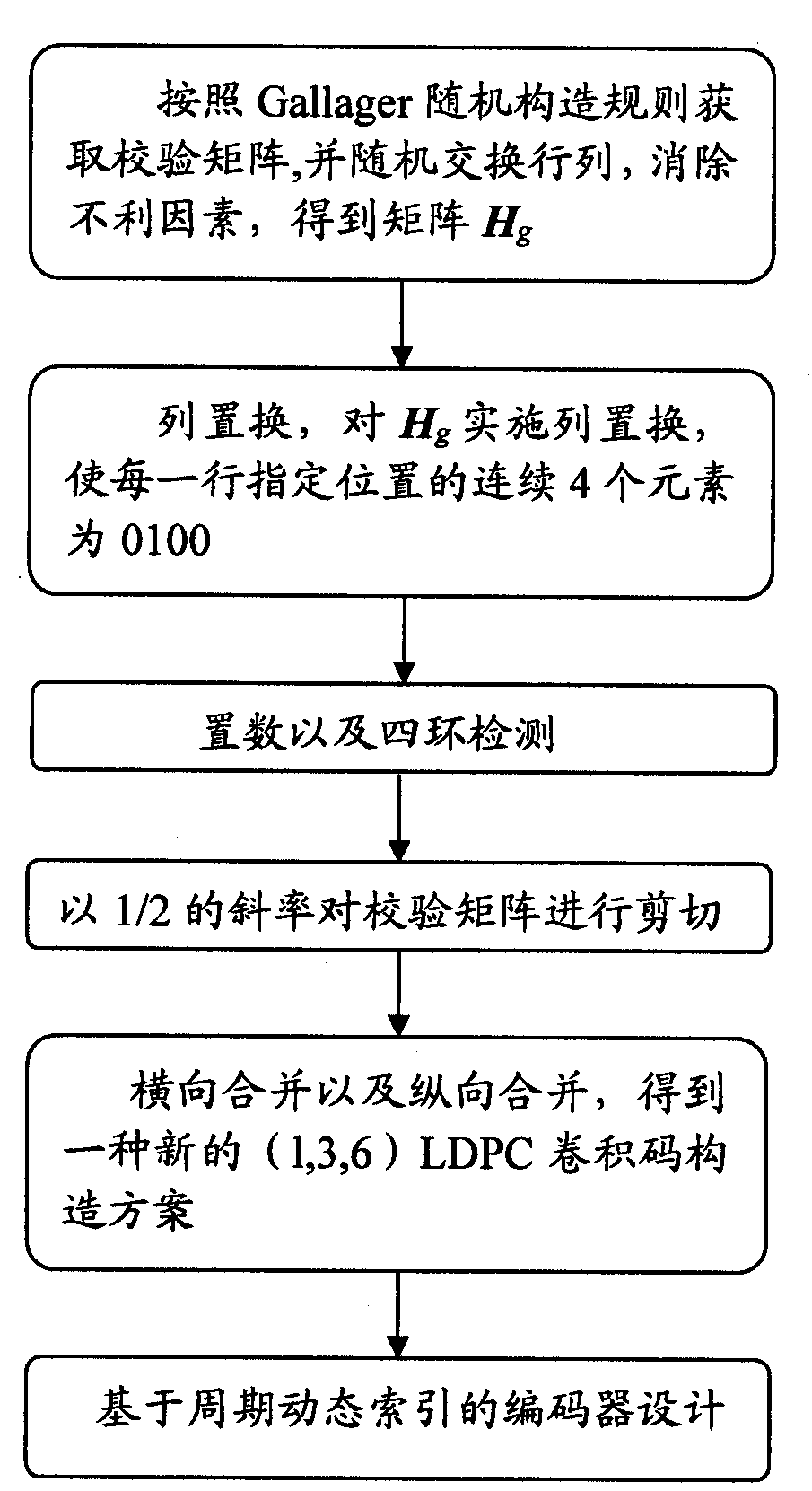
Construction method of quasi-random LDPC (low density parity check) convolutional codes and encoder design
InactiveCN103532570ASimple structureGood error correction performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsBase codeLdpc convolutional codes
The invention provides a construction method of quasi-random LDPC convolutional codes and encoder design. The construction method comprises the steps as follows: obtaining a check matrix of LDPC block codes according to a Gallager random construction rule, performing random exchange of rows and lines to eliminate adverse factors, and obtaining a matrix Hg; successively substituting even number lines and odd number lines from left to right; performing number substitution and four-ring detection; shearing the check matrix with the slope of 1 / 2; performing horizontal and vertical integration to obtain a novel (1, 3, 6) LDPC convolutional code construction scheme; and performing cyclic-dynamic-based coding on the convolutional codes. The construction method of the quasi-random LDPC convolutional codes is concise in process, good error correction performance can be guaranteed, a large number of optional code sources are provided, the construction method has stronger competitiveness power in encoding complexity compared with the LDPC block codes, and the designed encoder based on cyclic dynamic indexes has strong popularity and transportability.
Owner:CHONGQING VOCATIONAL INST OF ENG
Preparation method of ethylene-styrene derivative copolymer
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ethylene-styrene derivative copolymer and belongs to the technical field of high polymer materials. The preparation method of the ethylene-styrene derivative copolymer, provided by the invention, has the benefits that the copolymerization of an ethylene and styrene monomer is catalyzed by utilizing a restricted geometrically-configured rare earthcatalyst composition for the first time, so that the ethylene-styrene derivative quasi-random copolymer is prepared. The copolymer only can be prepared by a restricted geometrically-configured titanium catalyst system previously. Therefore, the preparation method of the ethylene-styrene derivative quasi-random copolymer is very innovative, and a new technical route for the preparation of the ethylene-styrene derivative quasi-random copolymer is developed.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for storing and retrieving data using hash-accessed multiple data stores
ActiveUS7664731B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData elementData storing
A method and system for storing and retrieving data using hash-accessed multiple data stores, provides data protection while requiring low computational overhead and further provides storage and retrieval access based on only a single piece of access information, which is generally public. The algorithms provide high security against data-mining and other examination of the data stores. The access information is hashed and is split into offset fields used as indices into a plurality of data stores, generating a quasi-random relationship between the access information and the location of portions of a stored data element. Further protection may be provided by striping the data across the data stores in conformity with a striping order selected by a field of the hashed access information.
Owner:US POSTAL SERVICE
High efficiency illumination
InactiveUS20120075596A1Electrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesHuman–computer interactionPulse duration
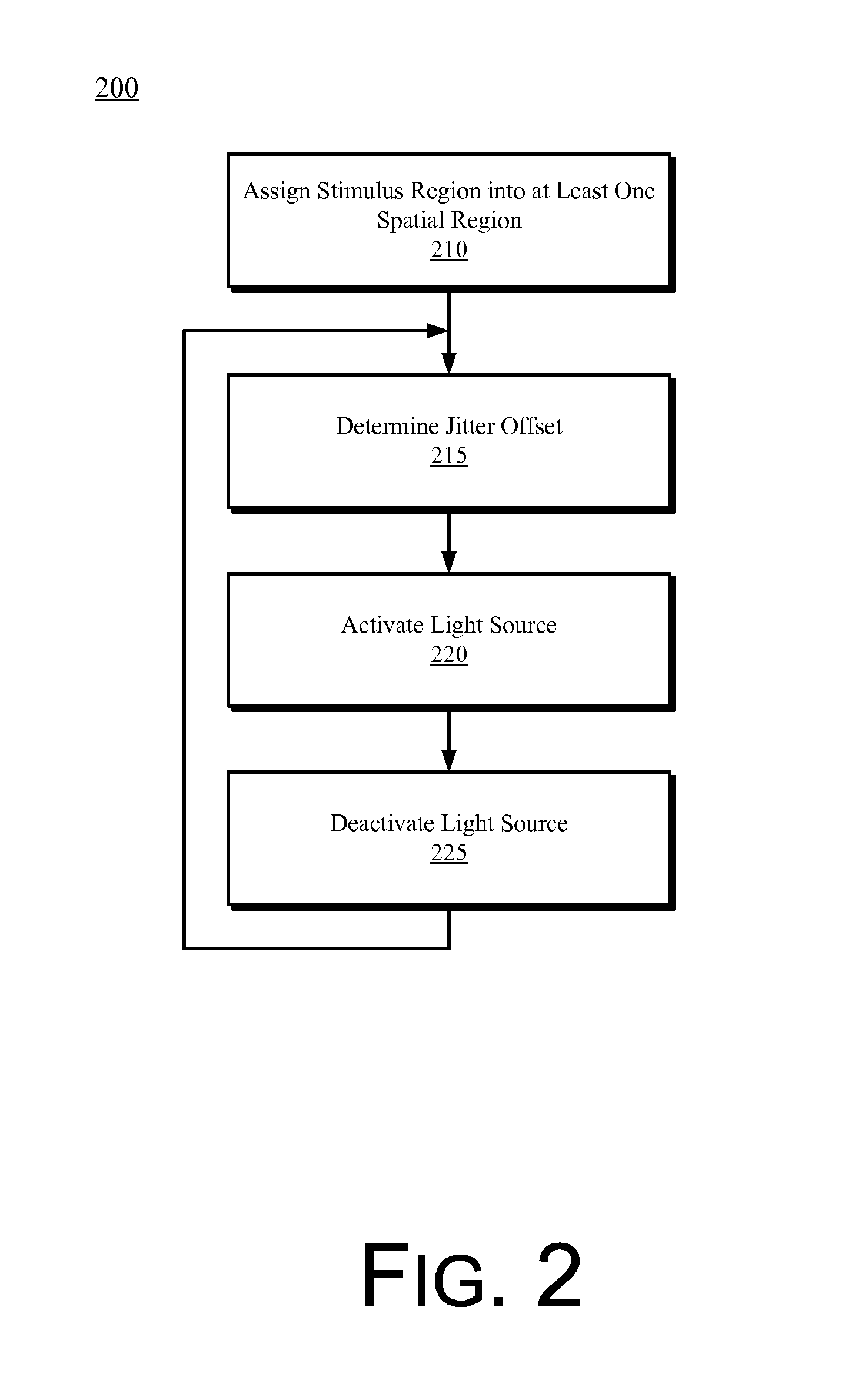
An electronic device comprises a processor, a light source, and a controller coupled to the light source. The controller comprises logic to cycle the light source between an active state and an inactivate state at with a pulse duration that measures between 30 milliseconds and 100 milliseconds and jitter a time onset of the active state by a quasi-random time that measures between 0 and 30 milliseconds for one or more cycles. Other embodiments may be described.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method for making insertional mutations
InactiveCN1319135AIncreased transpositionEasy to manufactureHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementTn5 transposaseNucleotide
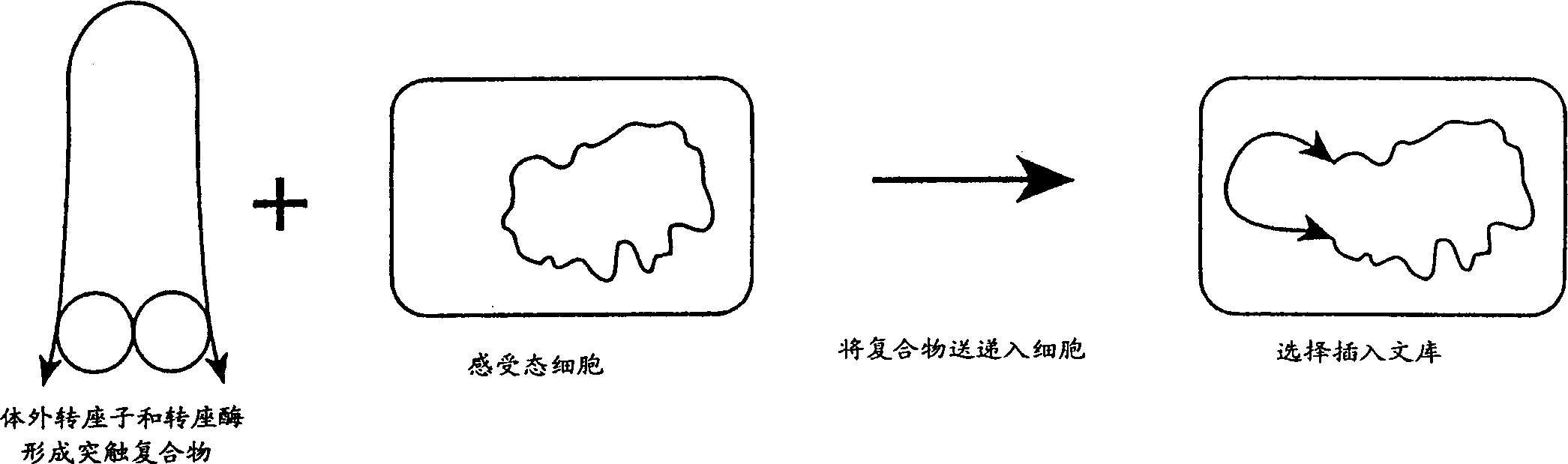
A method for making insertional mutations at random or quasi-random locations in the chromosomal or extra-chromosomal nucleic acid of a target cell includes the step of combining, in the target cell, cellular nucleic acid with a synaptic complex that comprises (a) a Tn5 transposase protein and (b) a polynucleotide that comprises a pair of nucleotide sequences adapted for operably interacting with Tn5 transposase and a transposable nucleotide sequence therebetween, under conditions that mediate transpositions into the cellular DNA. In the method, the synaptic complex is formed in vitro under conditions that disfavor or prevent the synaptic complexes from undergoing productive transposition.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com