Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Paraspinal Muscle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Paraspinal muscles are thought to play an important role in preventing serious back injuries, such as a herniated disk.When a person experiences a back spasm, it is often a paraspinal muscle tightening up, which is a warning signal that his back is either bearing more weight than it should, or bending and twisting improperly.
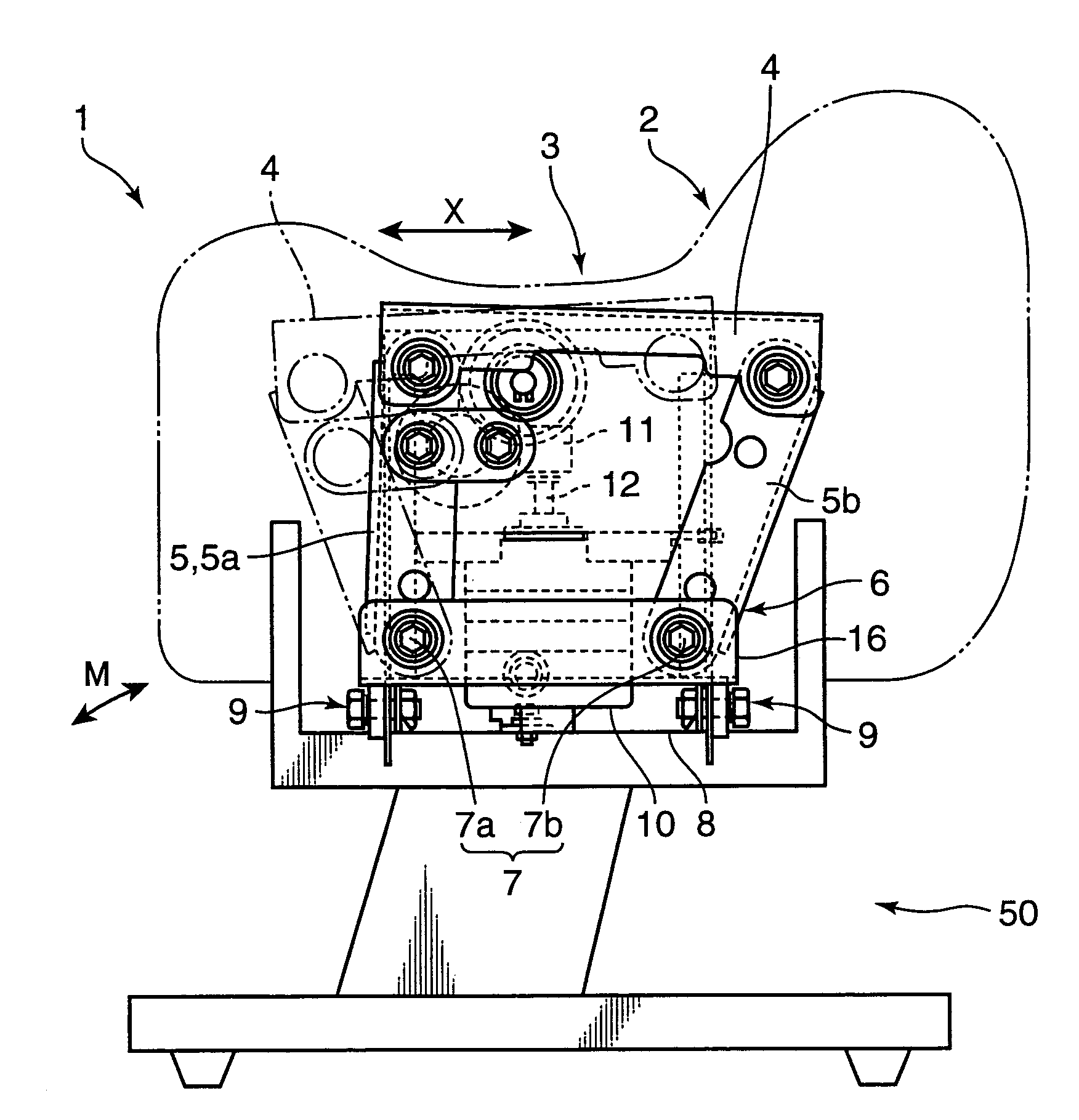
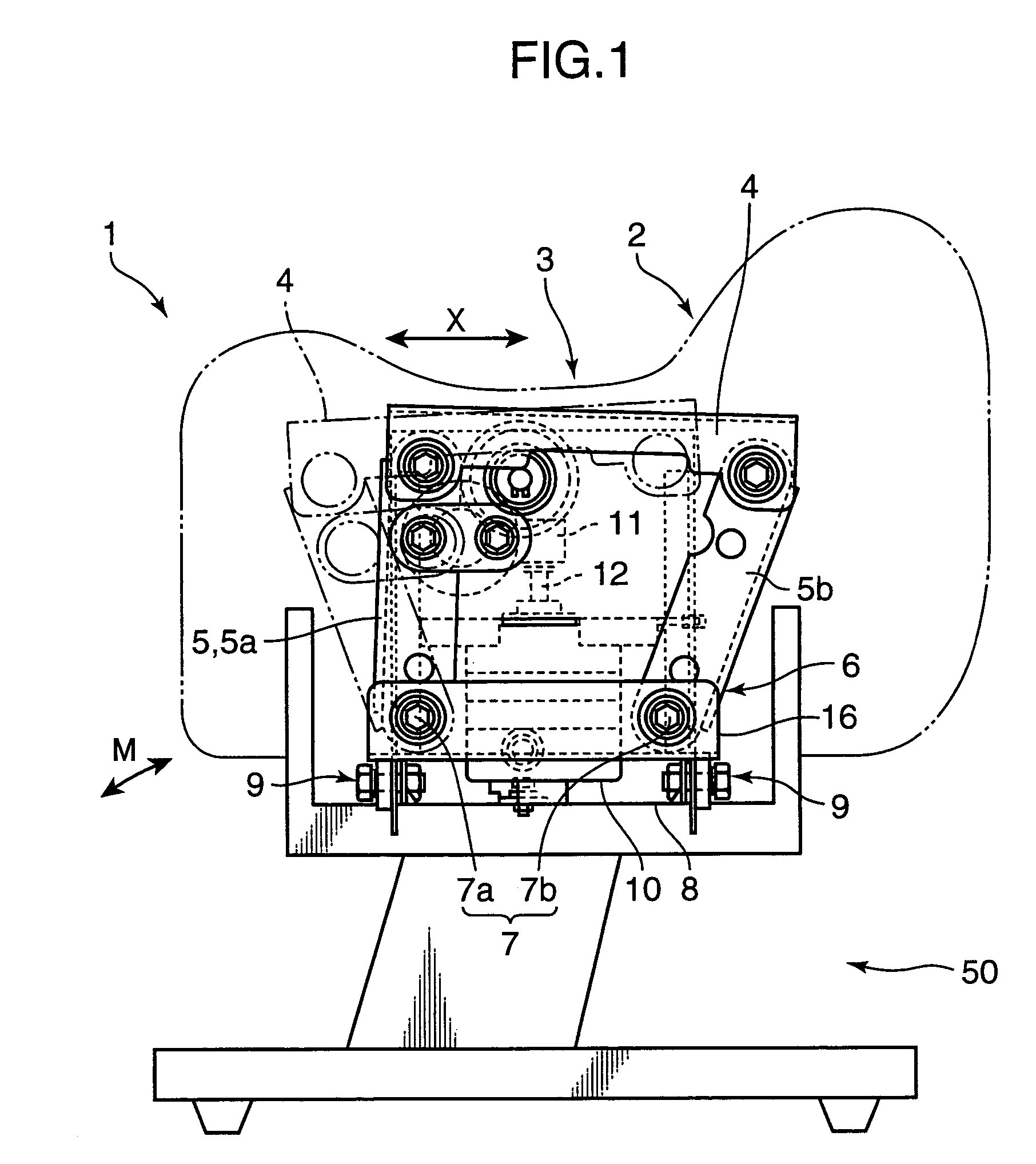
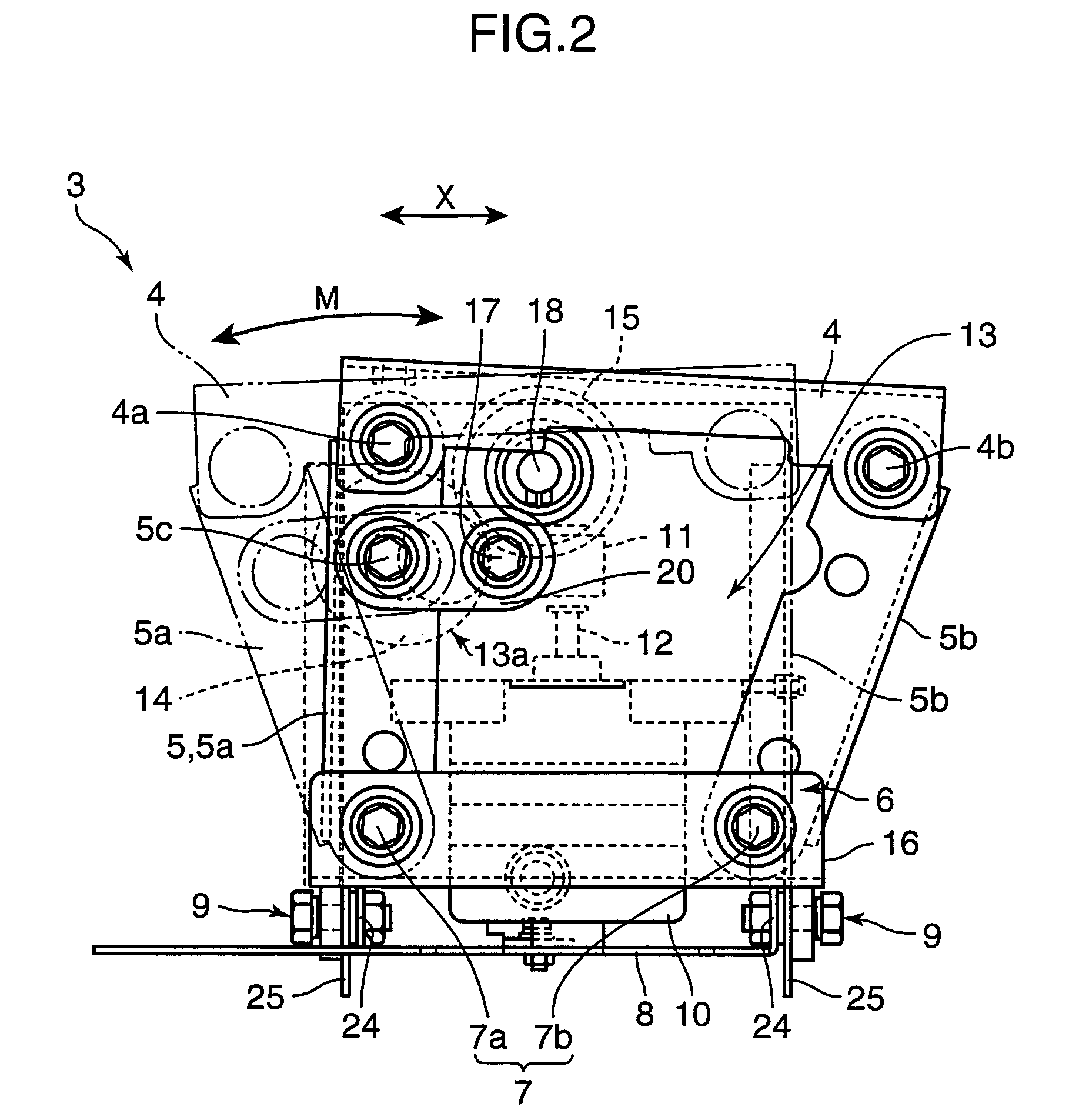
Rocking type exercising apparatus
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
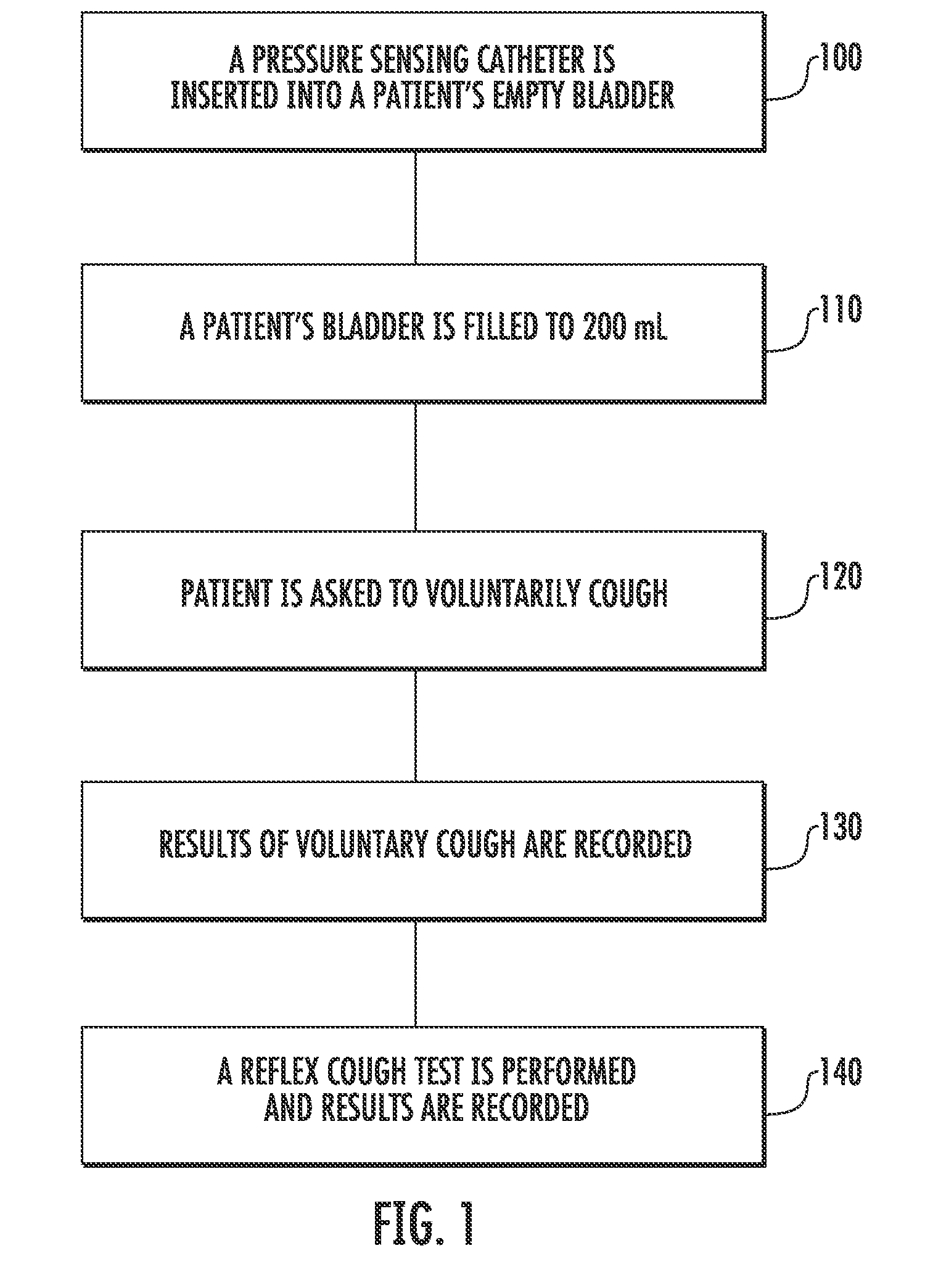
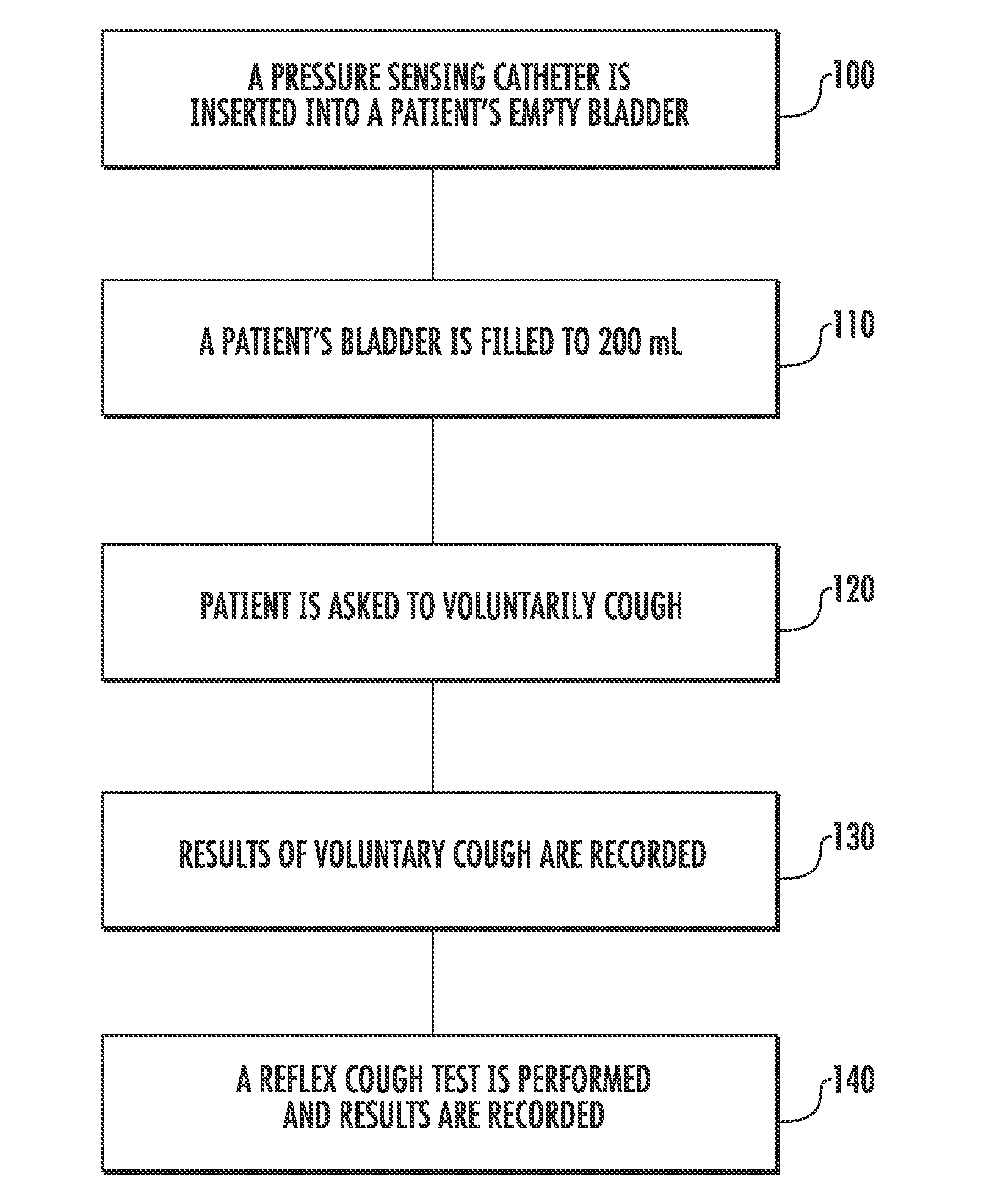
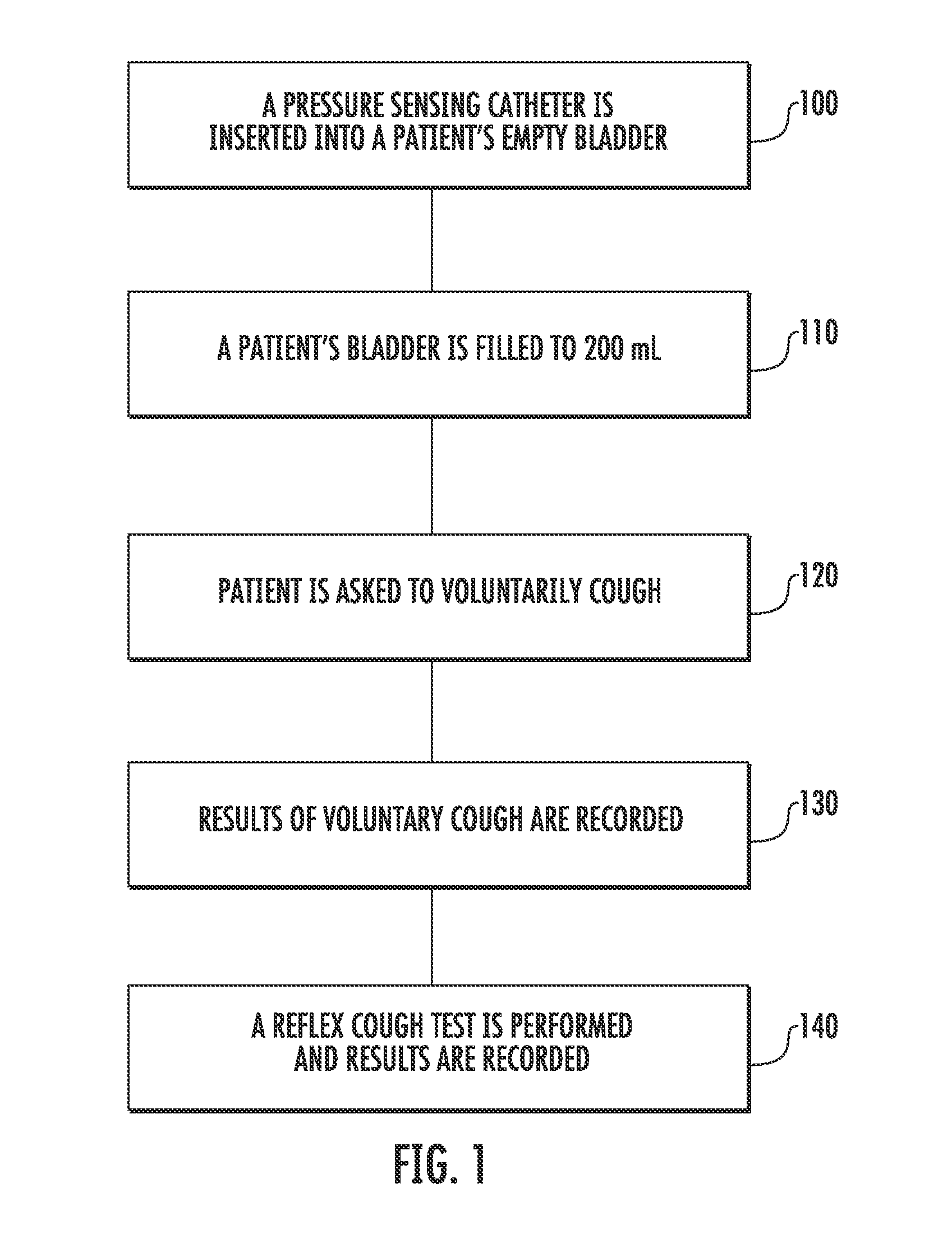
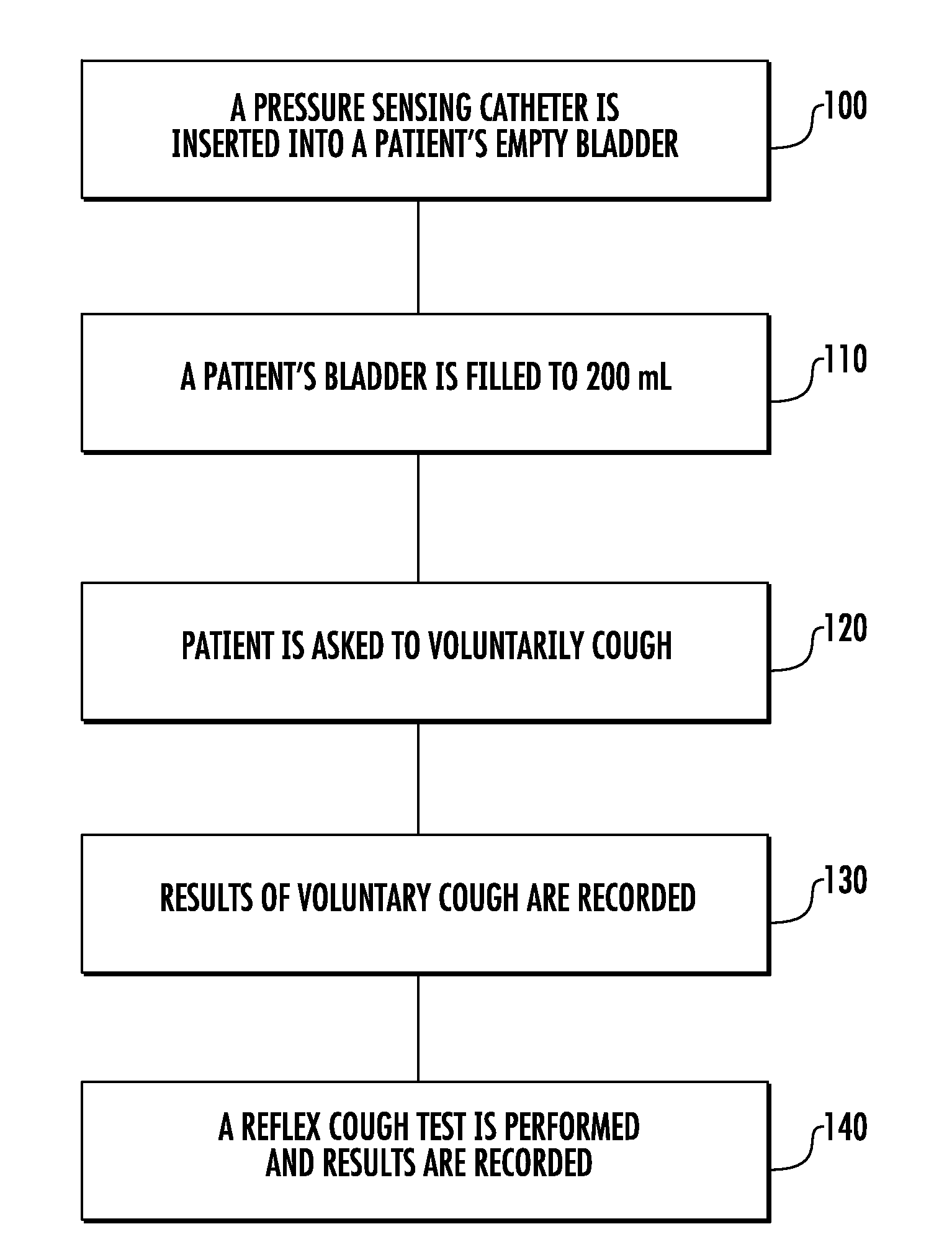
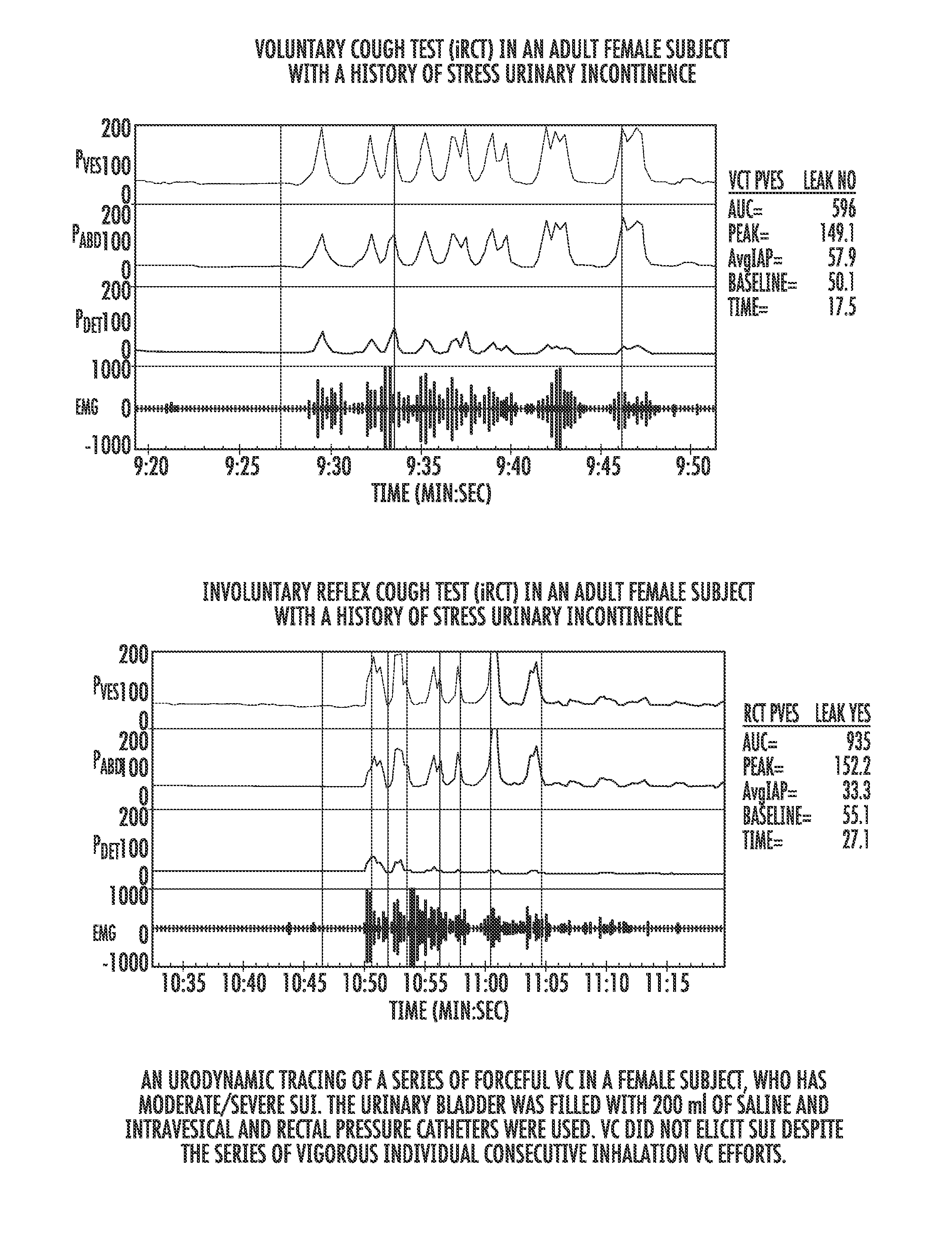
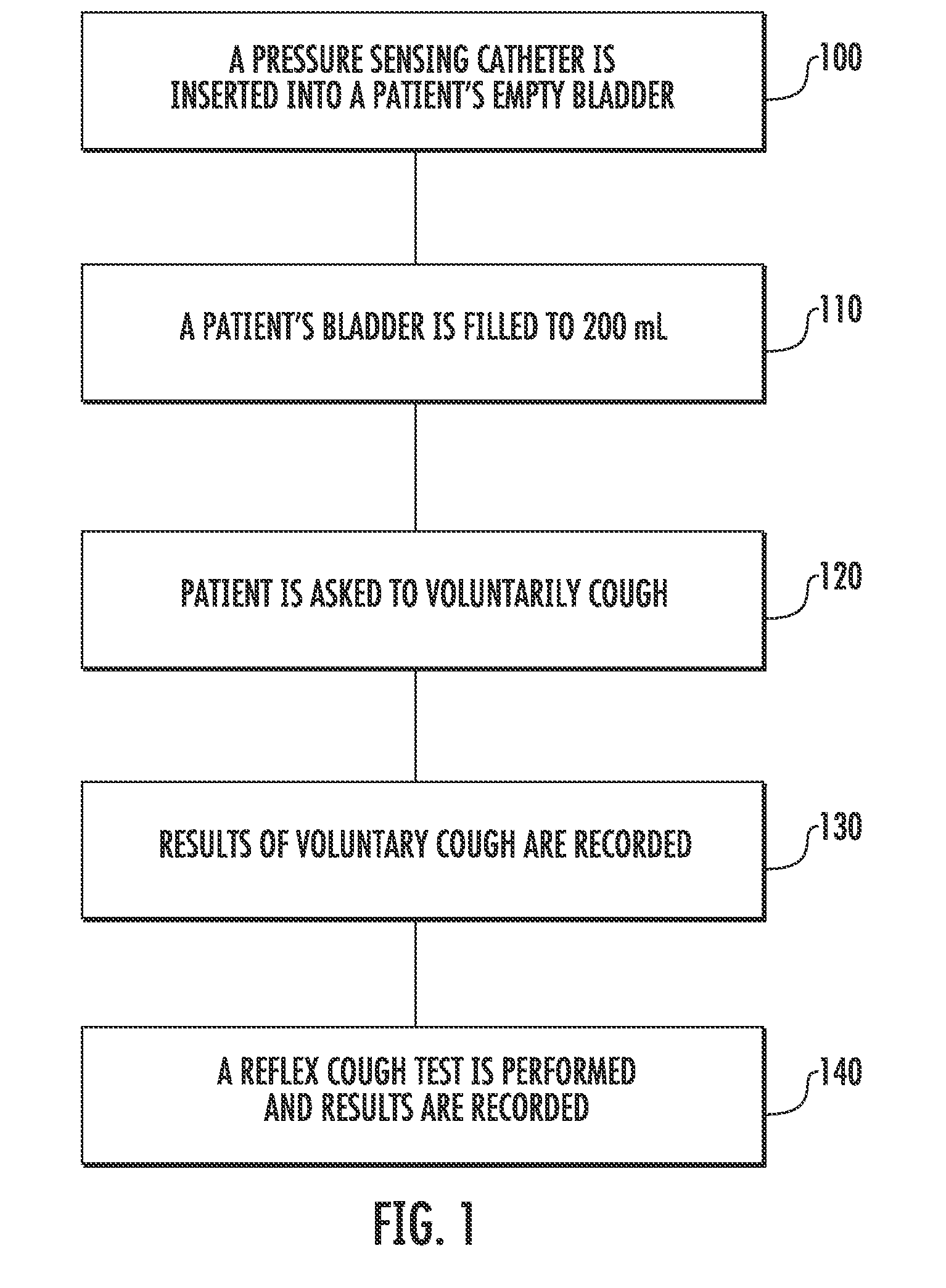
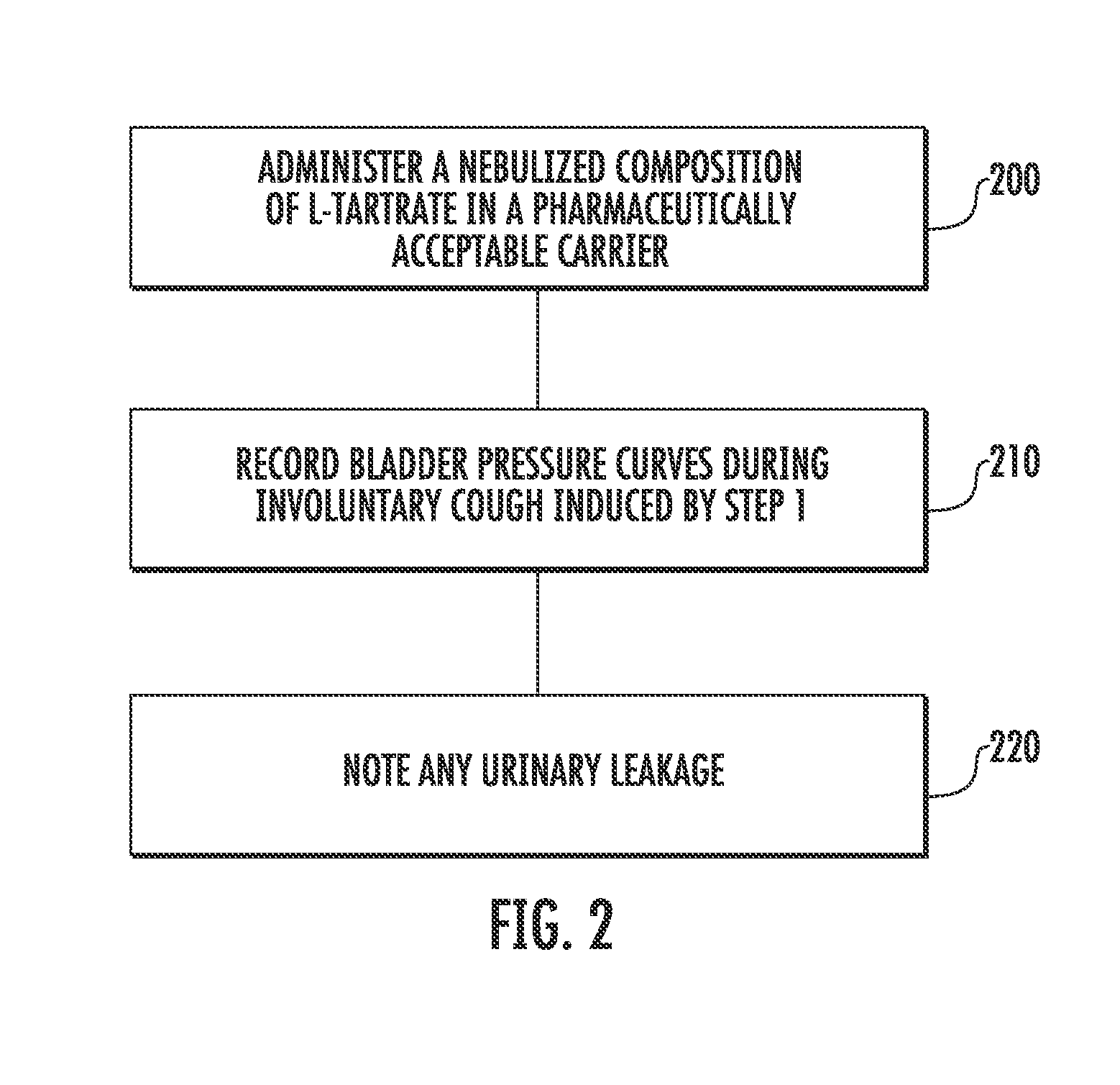
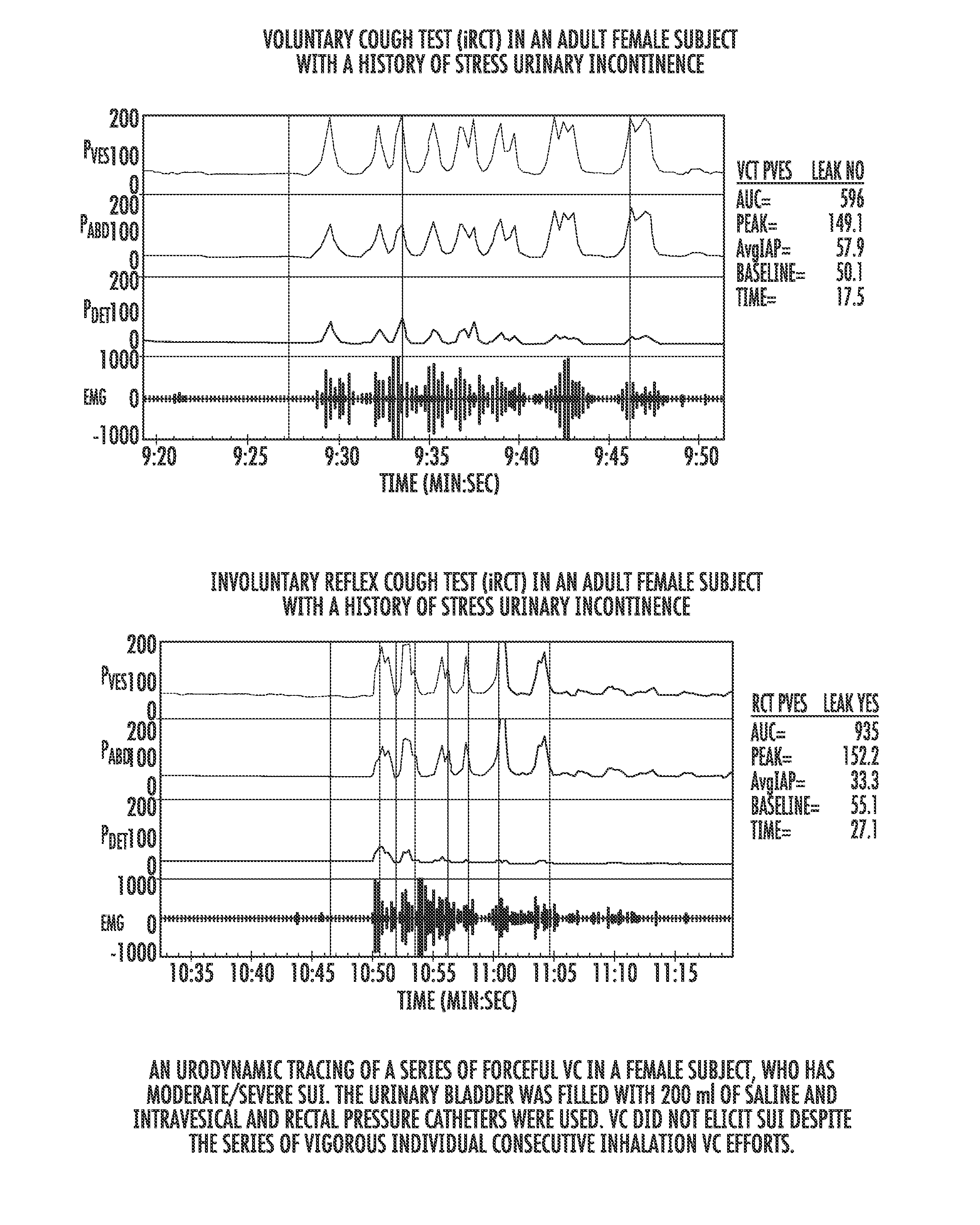
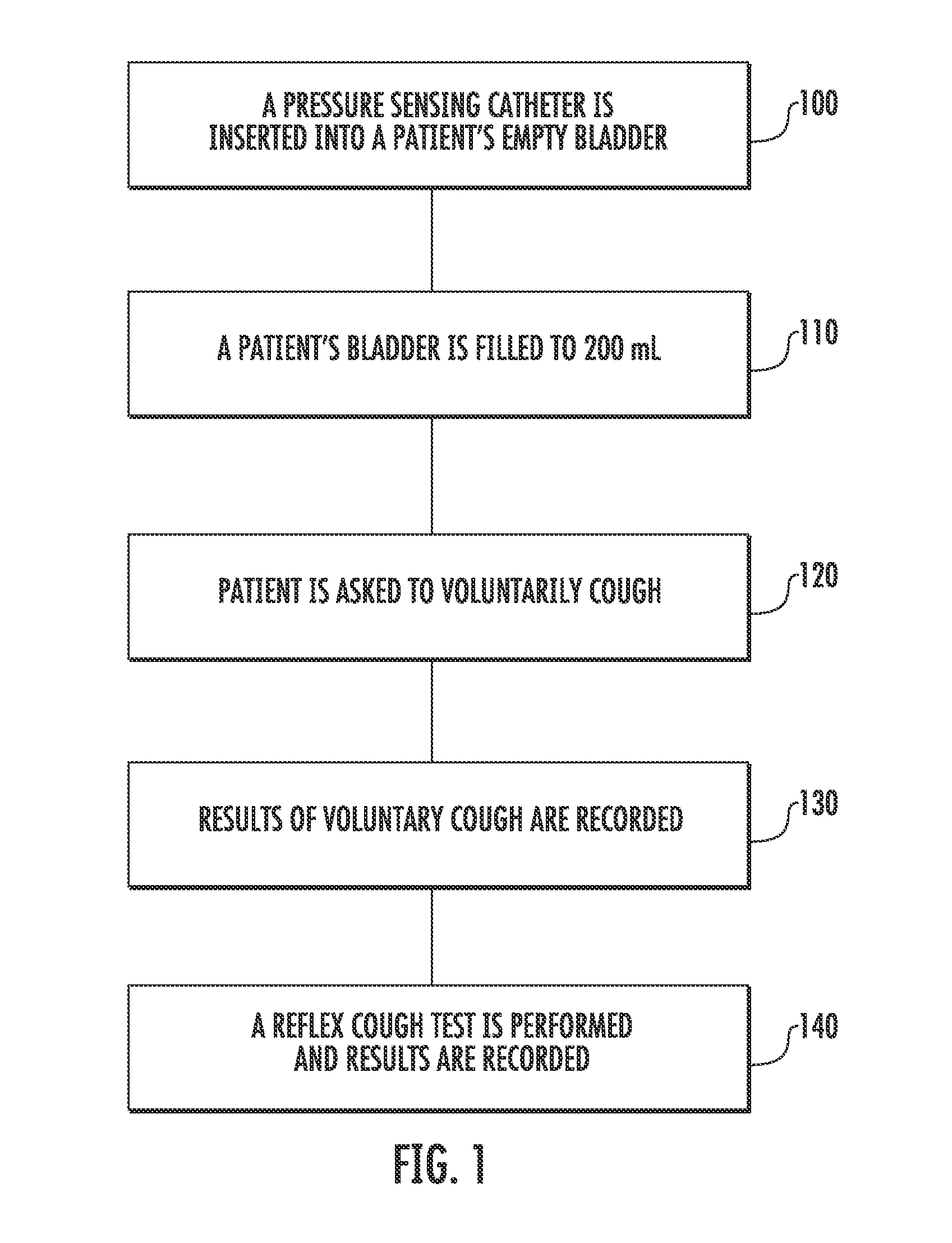
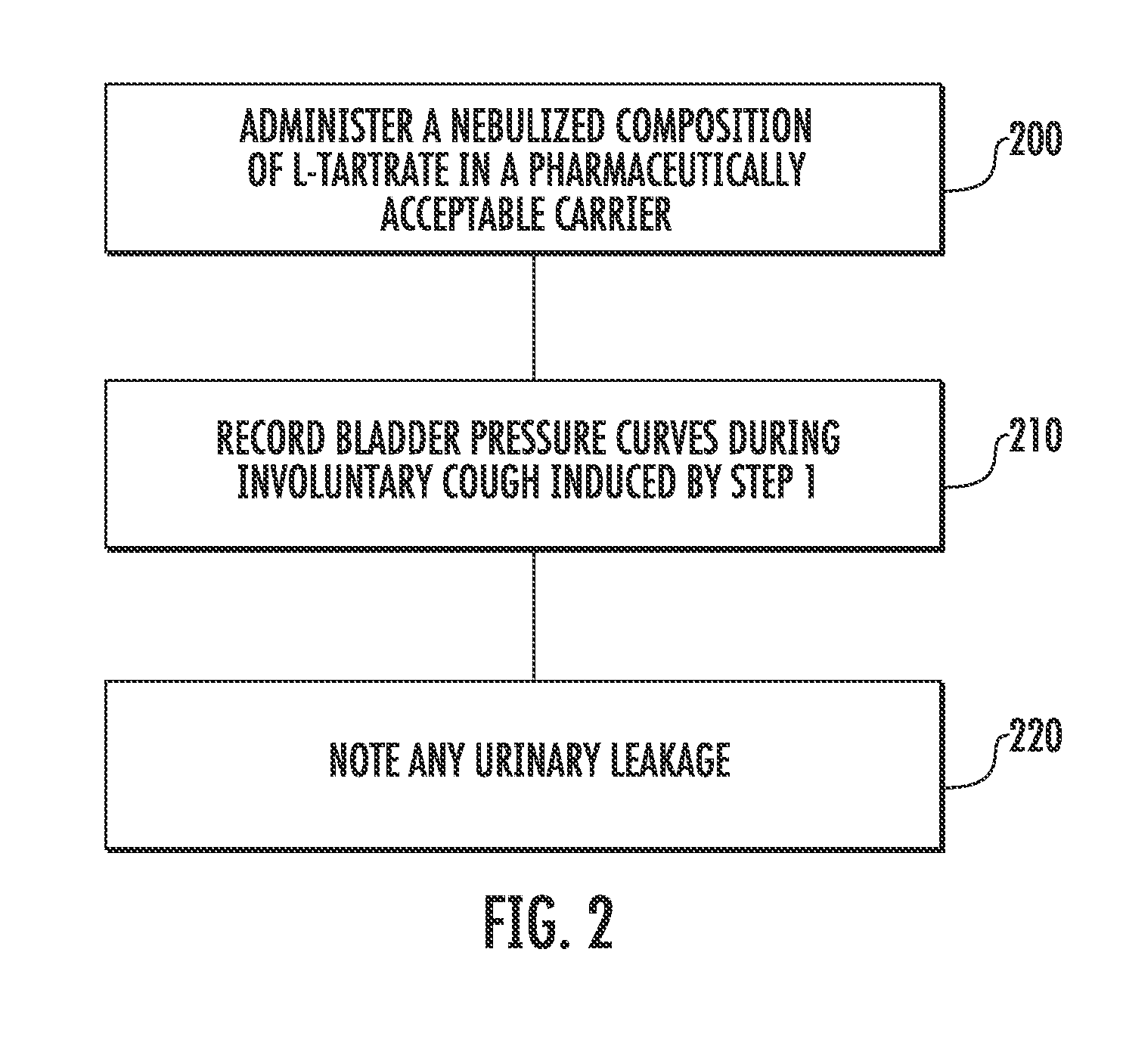
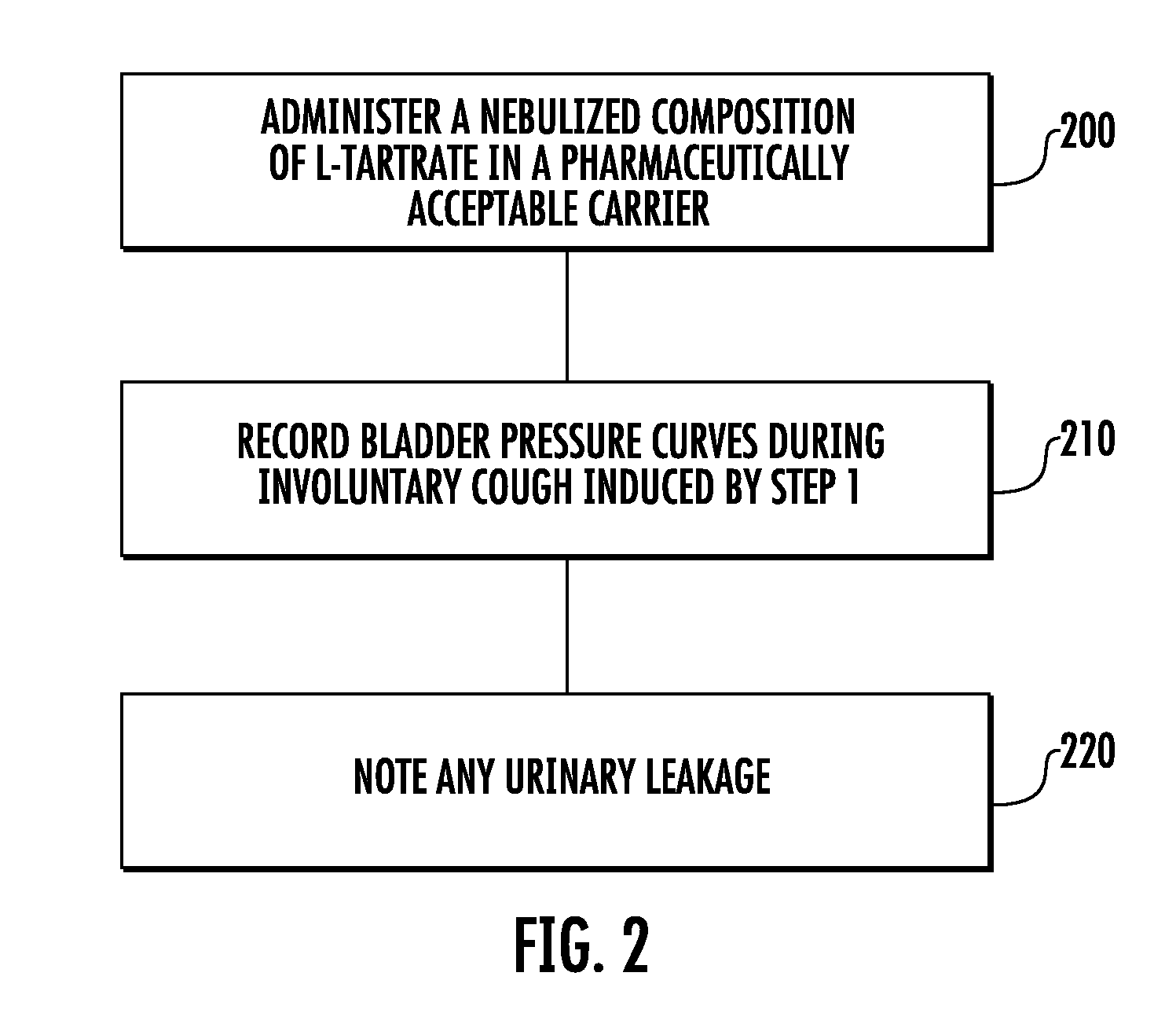
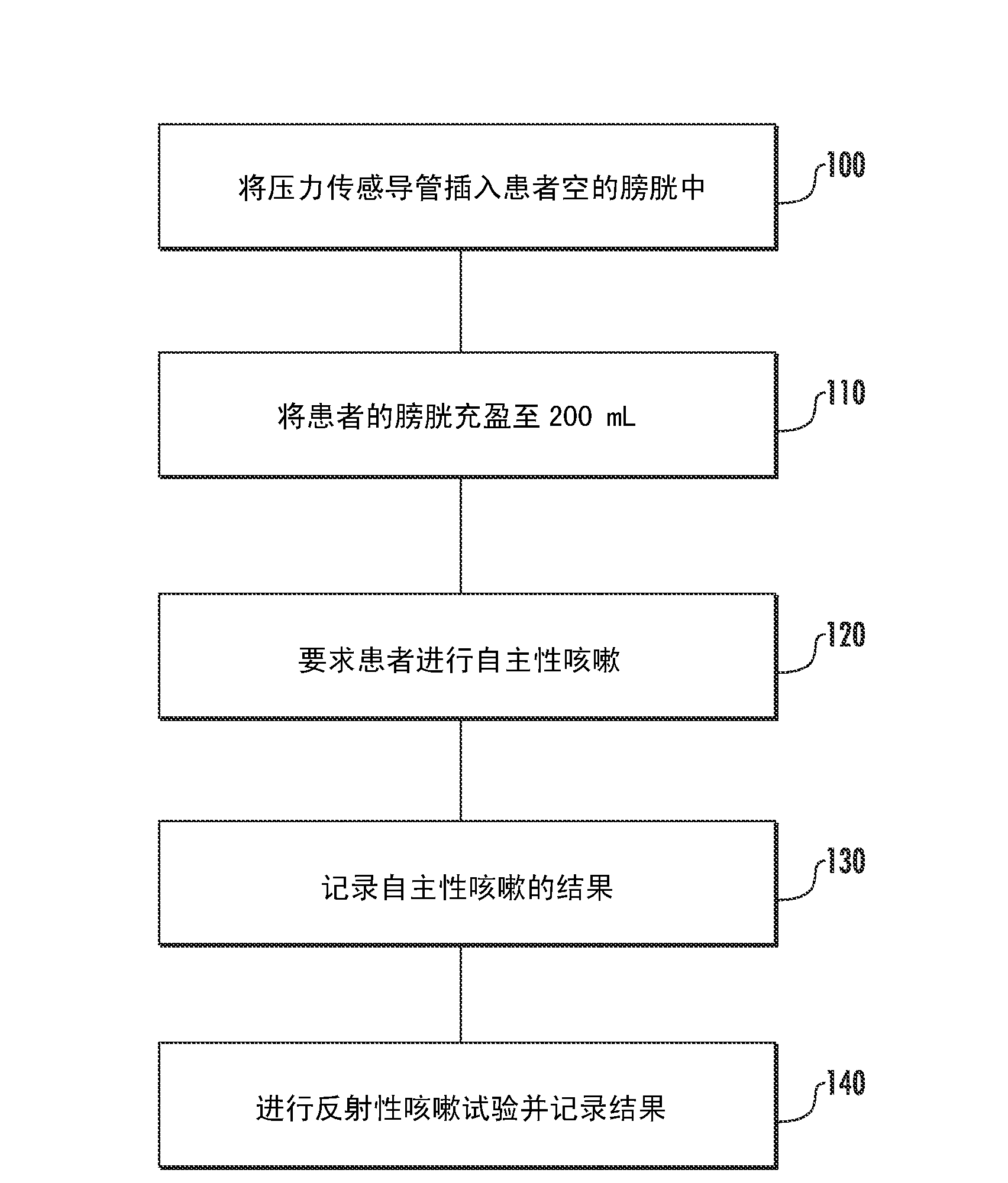
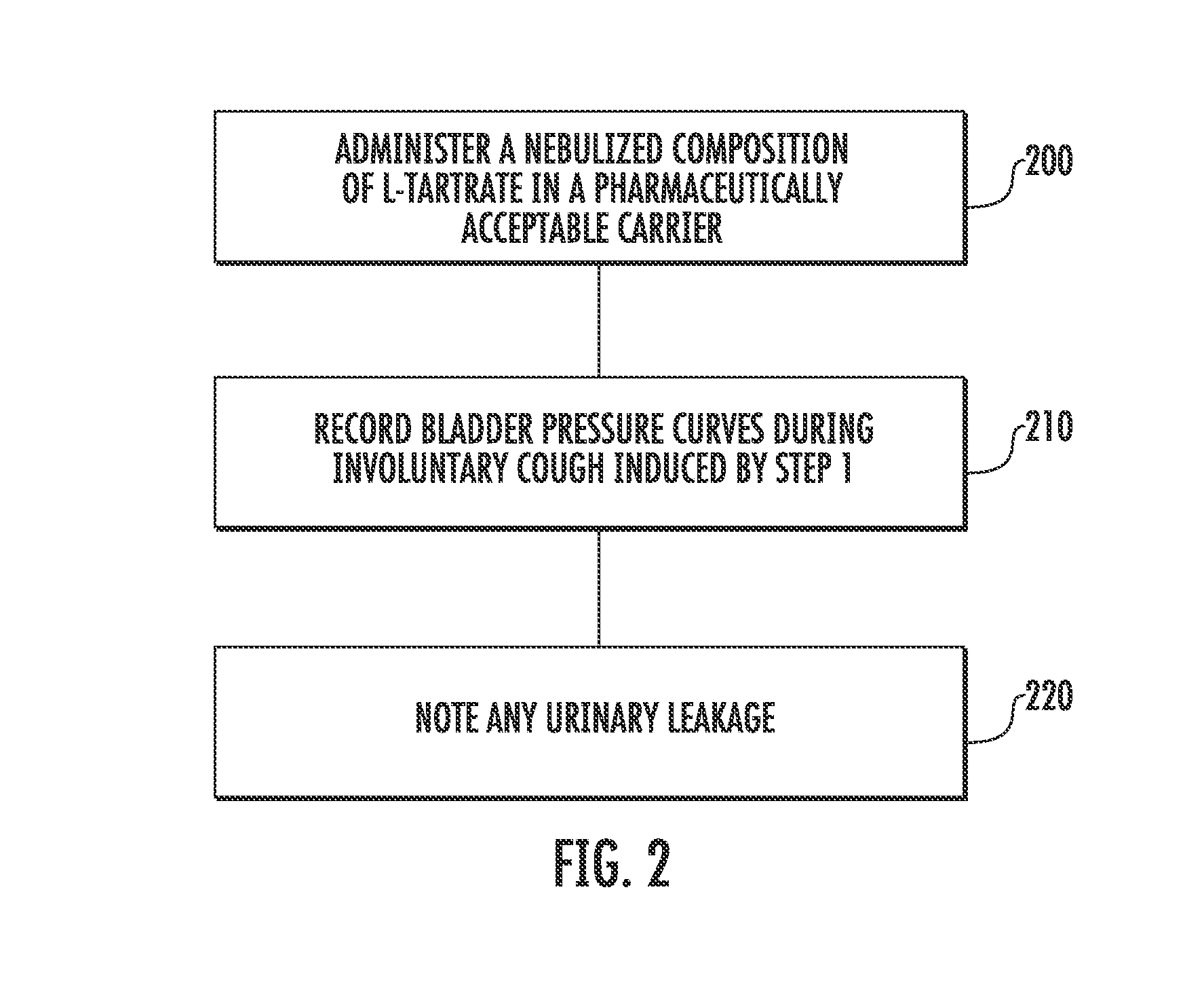
Involuntary contraction induced pressure as a medical diagnostic tool using involuntary reflex cough test
A system and method allows diagnosis of a patient for physiological abnormality such as a neurological deficiency. An involuntary reflex cough event is induced within the patient that activates the nucleus ambiguus and medial motor cell column of the patient and stimulates involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles in the pelvis of the patient. An electromyogram (EMG) is obtained from the involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles while inducing involuntary reflex cough and determining its duration. The intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) is determined and the IAP is correlated with the EMG duration of the involuntary cough event within a processing device to diagnose a physiological abnormality such as a neurological deficiency within the patient.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Thermal treatment device
InactiveUS20100161014A1Therapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingPhysical medicine and rehabilitationTender point
A thermal treatment device to be worn in close proximity to the skin of a human is disclosed. The thermal treatment device comprises a thermal composition; wherein the device substantially covers the left or right trapezius muscle of the neck and shoulder or the left or right paraspinal muscles in the lower back and the tender point of the respective sacroiliac joint.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
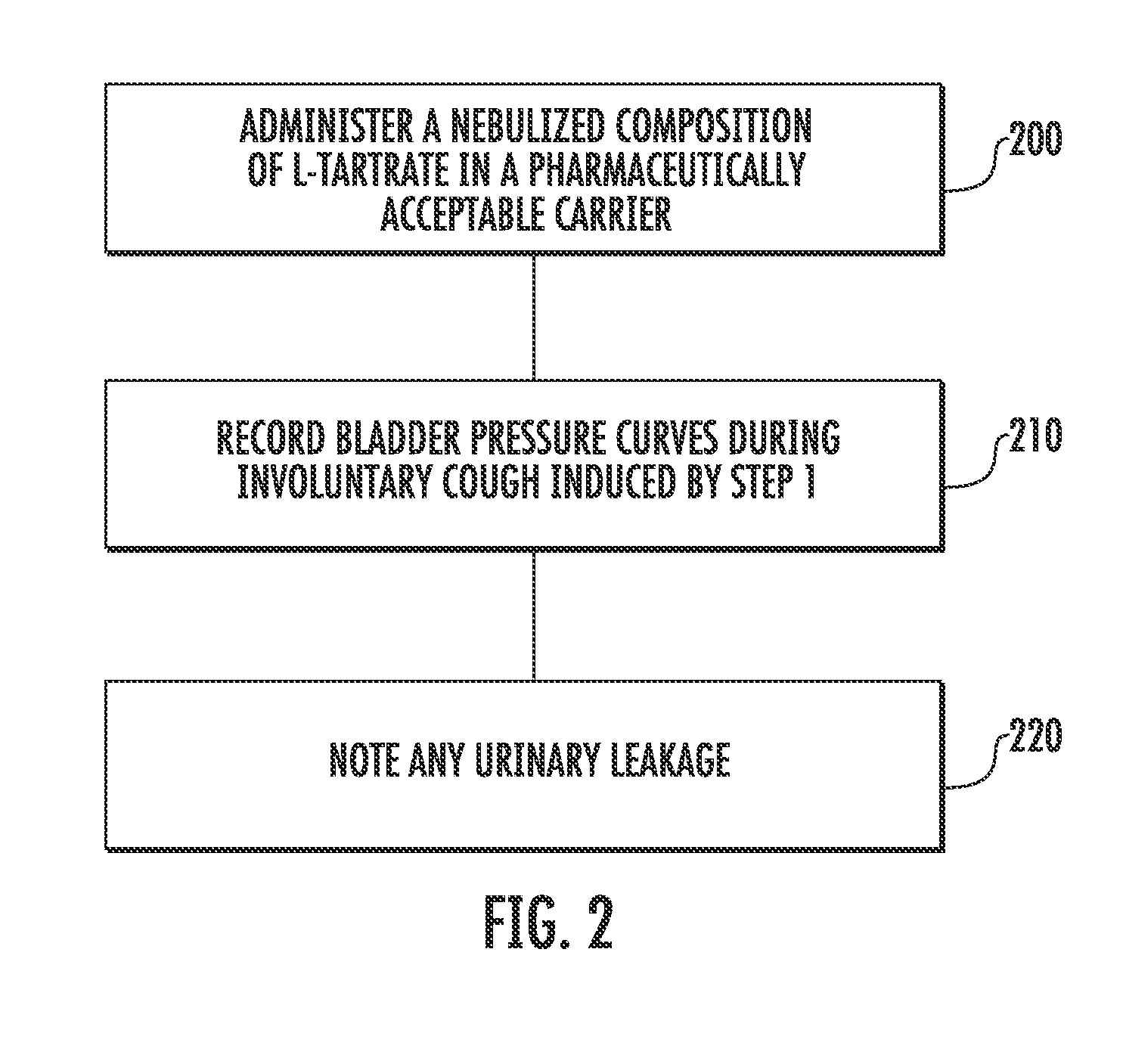
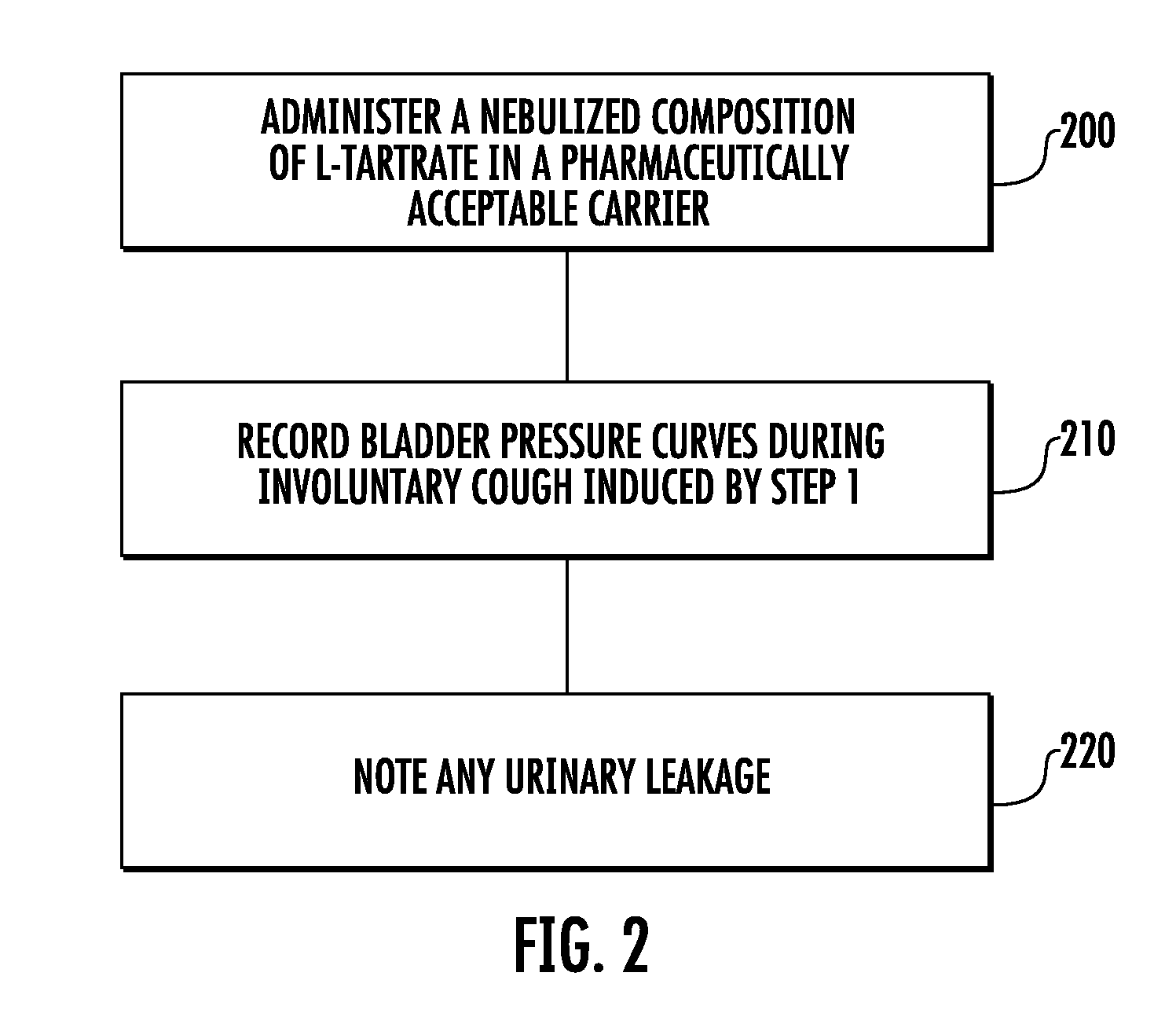
Techniques for evaluating stress urinary incontinence (SUI) using involuntary reflex cough test
ActiveUS20100137737A1Overcome problemsElectromyographyMedical automated diagnosisBacteriuriaUrine leakage
A system and method evaluates a patient for stress urinary incontinence. An involuntary reflex cough event is induced within the patient that activates the nucleus ambiguous and medial motor cell column of the patient and stimulates involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles in the pelvis of the patient. And elecromyogram (EMG) is obtained from the involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles and its duration determined. Any urine leakage time that occurs during the involuntary reflex cough event is identified and correlated within a processor together with the urine leakage time and EMG and duration of cough event to determine stress urinary incontinence.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
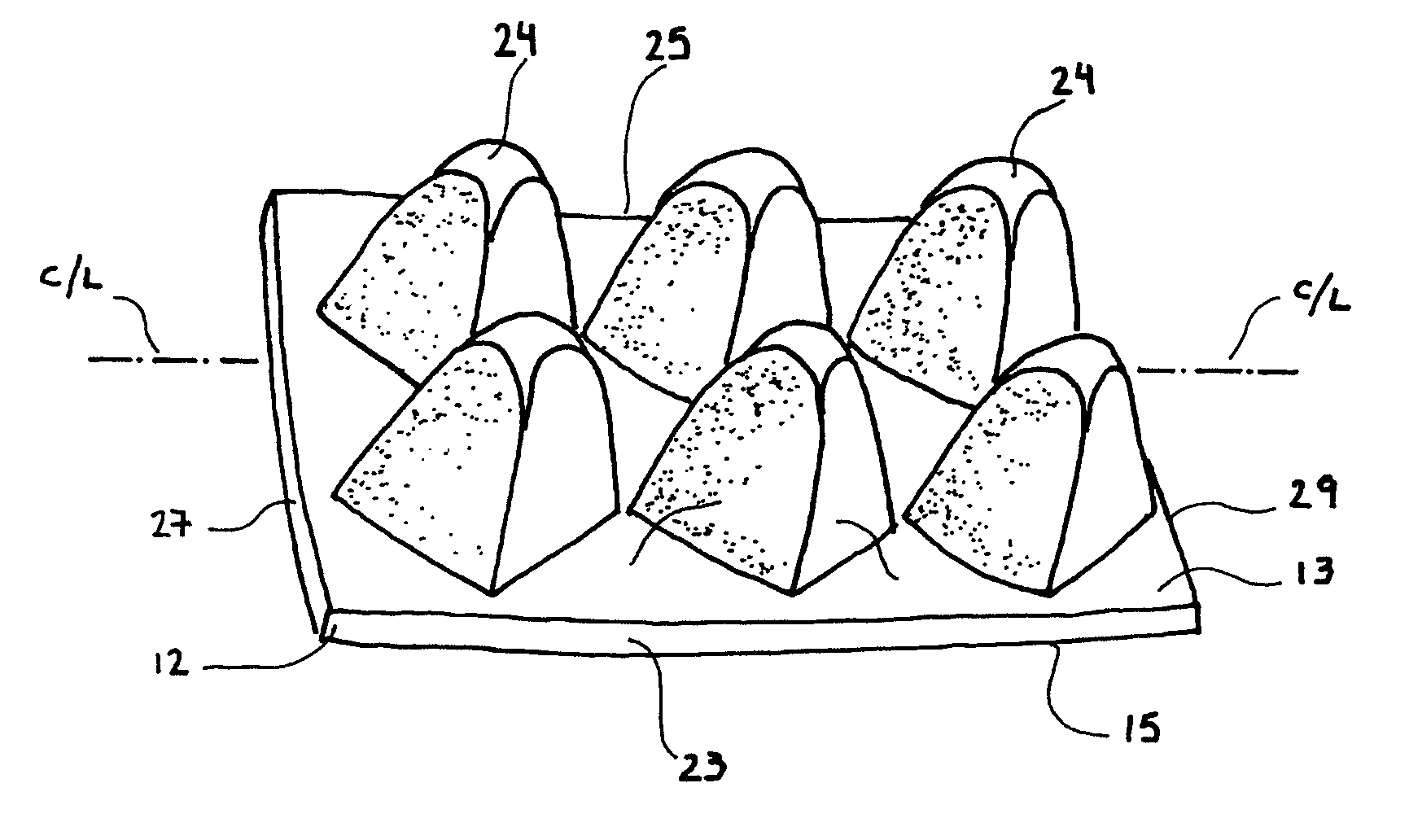
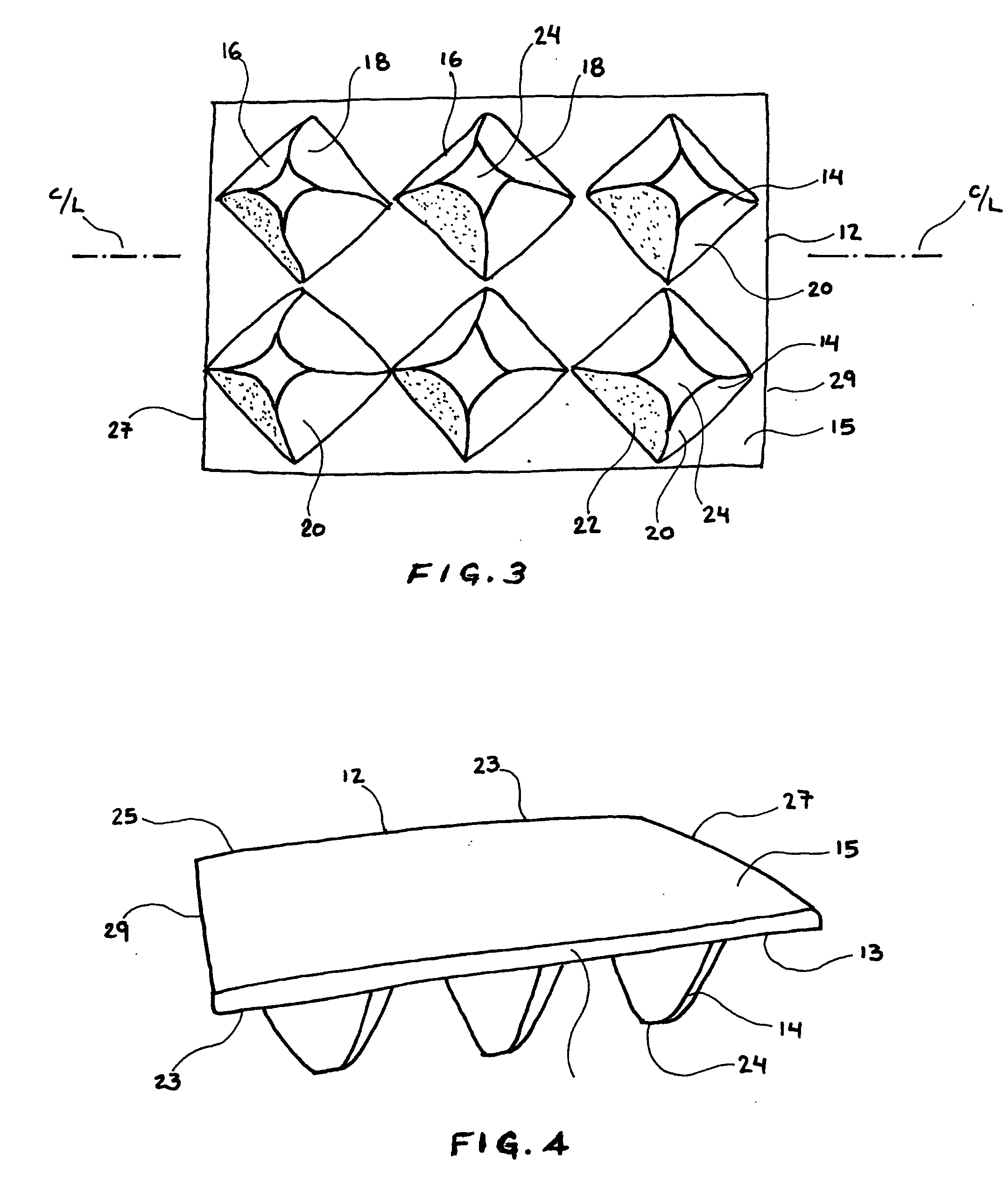
Passive back extensor device to treat trigger point - back pain
InactiveUS20050165450A1Relieve painLess discomfortChiropractic devicesGenitals massageBack painEngineering
A passive back extensor device for treatment of trigger-point back pain has a base substrate having upper and lower generally planar surfaces. A plurality of protuberances are integral with the base substrate and project from the upper generally planar surface and are arranged in substantially evenly spaced relation and define a pair of spaced rows so as to collectively define an elongate space between the rows. Each of the protuberances is of generally pyramid configuration having a rounded end oriented for passive manual pressure engagement with the paraspinal muscles along an individual's back on each side of the spine and with the elongate space receiving the bony protuberances of the spine. Each of the protuberances is arranged with one of its corners located adjacent a side edge or an end edge of the base substrate so that the planar surfaces and base is oriented in angular relation with the side and end edges of the base substrate.
Owner:PEREZ TORRENS YNGRID
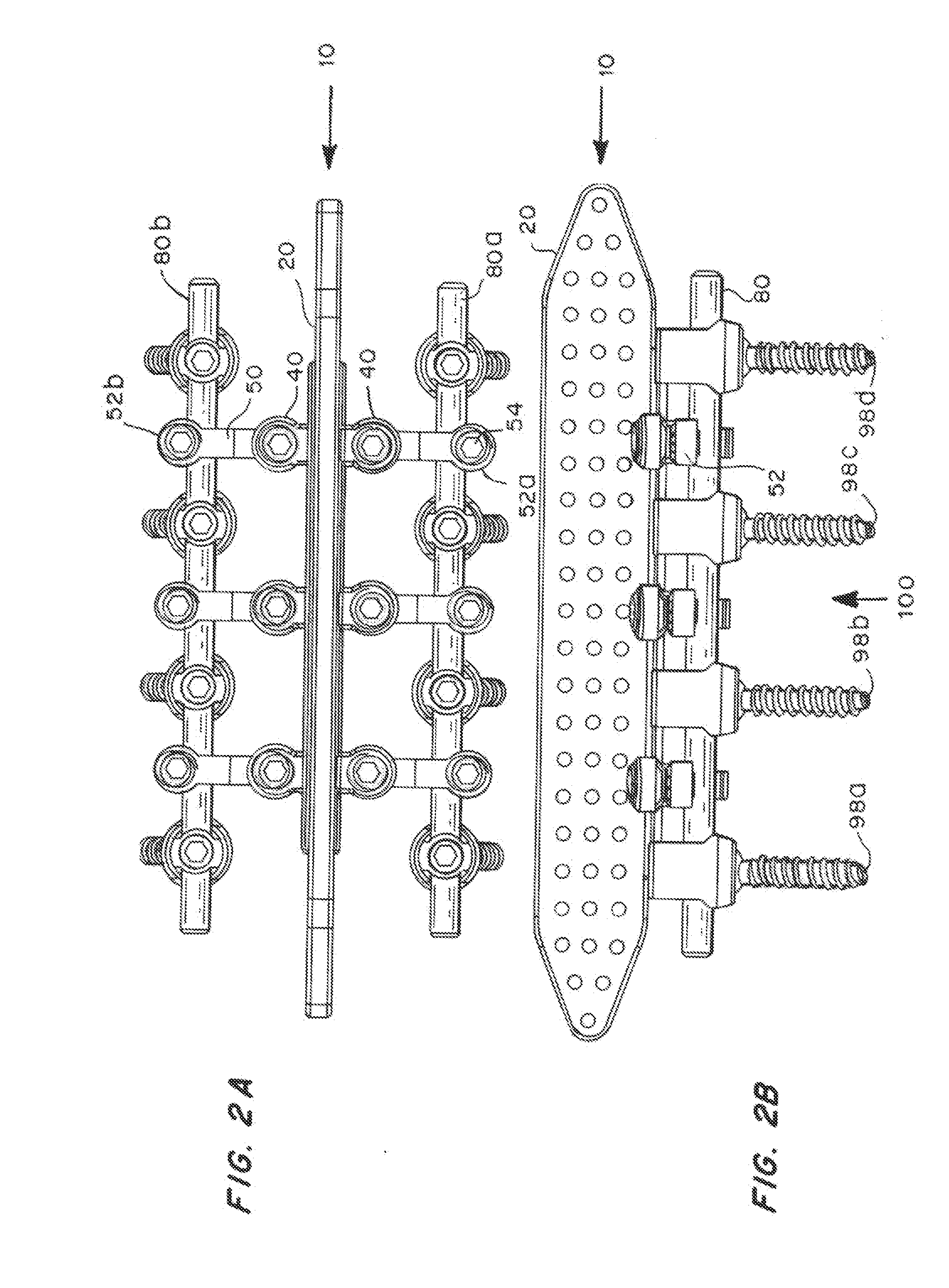
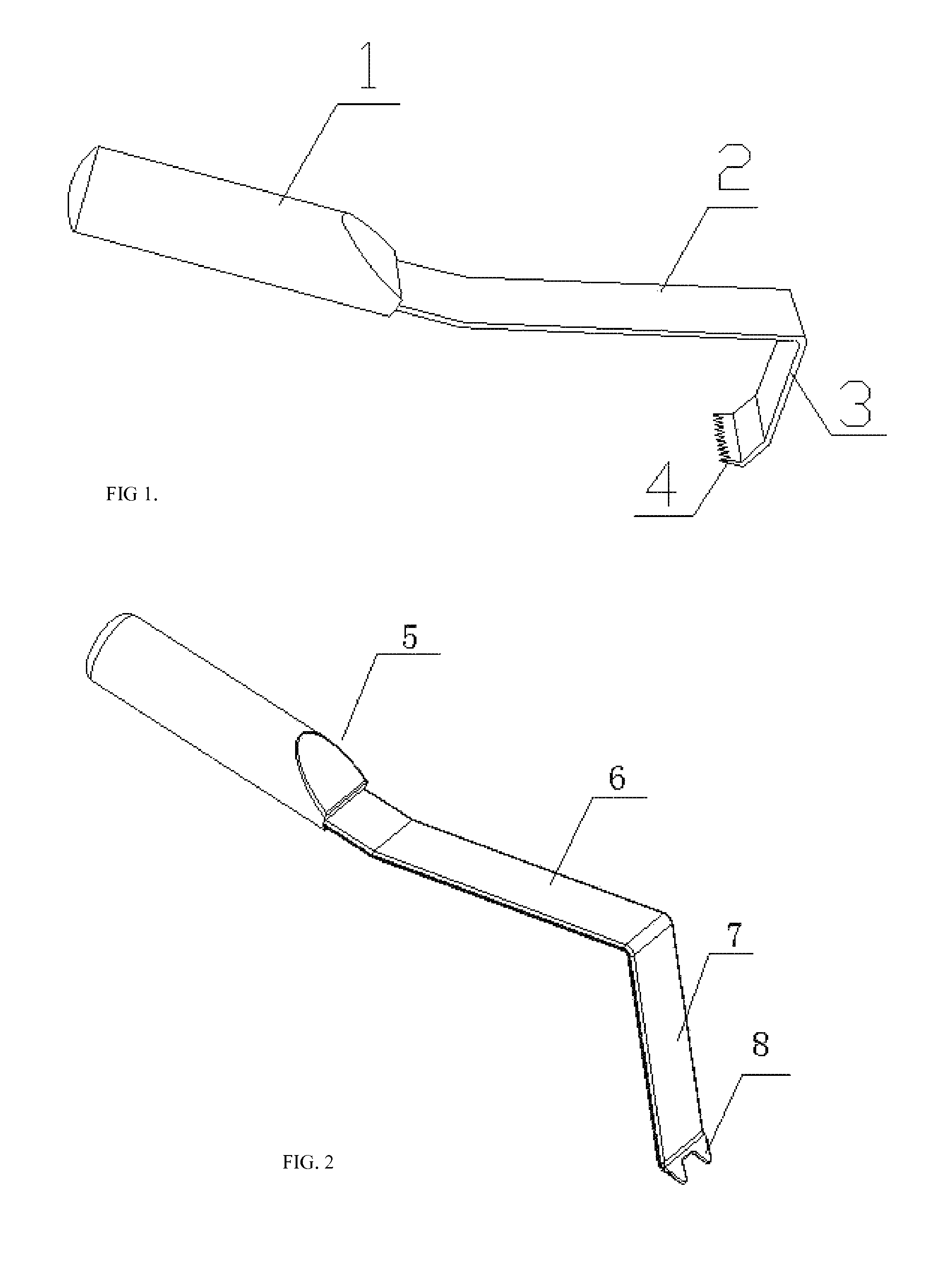
Posterior Spine Attachment Device for Hardware and Paraspinal Musculature
InactiveUS20140052183A1Strengthens and stabilizes spineReduce and prevent formationSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisCross connectionFascia lata
Devices, kits, and methods for stabilizing the spine and replacing spinous processes removed during spine surgery are provided. The device has a suitable configuration to attach to both spine surgery hardware and to the paraspinal muscles and fascia. The device contains a muscle attachment portion, one or more connectors, and one or more cross connectors. Each cross connector contains a pair of connection portions configured to attach to hardware that is implanted in the spine, such as screw heads or rods. The muscle attachment portion contains a plurality of openings for the attachment of the paraspinal muscles and fascia. Following spine surgery, a surgeon attaches the device to the hardware implanted in the surgical site, and sutures the paraspinal muscles to the openings. Thus the device provides a direct attachment to the paraspinal musculature and fascia, and thereby stabilizes the spine.
Owner:FREESETEC
Techniques for evaluating urinary stress incontinence and use of involuntary reflex cough as a medical diagnostic tool
A system permits diagnosis of a patient for a physiological abnormality while protecting their airway. An esophageal airway protection device comprises an elongate device body having a distal end for insertion into the stomach through the esophagus and a proximal end. The device includes a main lumen extending the length of the device and an inflatable esophageal cuff carried by the device body mid-esophagus. Emesis and / or reflux is blocked from passing out of the stomach past the esophageal cuff positioned mid-esophagus when it is inflated to protect a patient's airway during an involuntary cough event. At least one electromyogram (EMG) pad is configured to obtain an EMG from an involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles. A processing device is configured to receive the EMG and process the EMG to determine a physiological abnormality.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Involuntary contraction induced pressure as a medical diagnostic tool using involuntary reflex cough test
A system and method allows diagnosis of a patient for physiological abnormality such as a neurological deficiency. An involuntary reflex cough event is induced within the patient that activates the nucleus ambiguus and medial motor cell column of the patient and stimulates involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles in the pelvis of the patient. An electromyogram (EMG) is obtained from the involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles while inducing involuntary reflex cough and determining its duration. The intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) is determined and the IAP is correlated with the EMG duration of the involuntary cough event within a processing device to diagnose a physiological abnormality such as a neurological deficiency within the patient.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Minimally-Invasive Implant for Opening and Enlargement of Processus Spinosus Interspace and Method of Percutaneously Enlarging Processus Spinosus Interspace Therewith
ActiveUS20090099603A1Simple procedureMinimally invasiveSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisTherapeutic DevicesProcessus spinosus
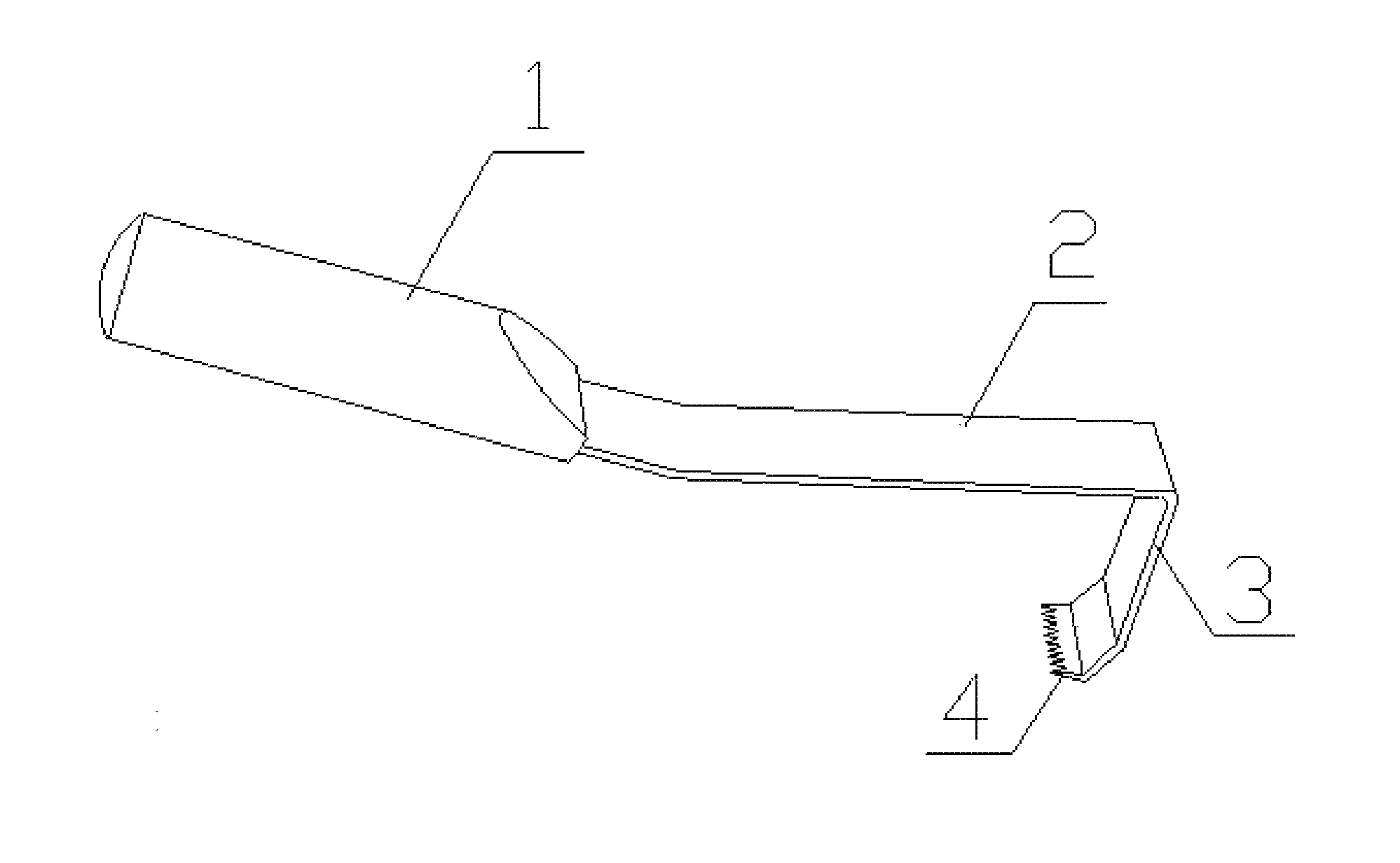
For the purpose of realizing of a method of minimally-invasive therapy for spinal canal stenosis, it is intended to provide a therapeutic device capable of stationing an interspinous process spacer without the need of large skin incision or ligamentous tissue incision and also without the need of detaching of the paraspinal muscle from the spine. There is provided an interspinous process spacer comprising conoid screw region (2) to be screwed into a processus spinosus interspace; spacer region (3) disposed in the longitudinal direction of the screw region (2); head region (4) capable of free interlocking with a tool arbitrarily; and through-hole (5) passing through the axial centers of screw region (2), spacer region (3) and head region (4). The processus spinosus interspace can be smoothly enlarged by screwing of the screw region (2) into the processus spinosus interspace. The spacer region (3) is pinched upon passing of the screw region (2) through the processus spinosus interspace to thereby attain enlarging and fixing of adjacent processus spinosus interspaces. The interspinous process spacer can be guided to an interspinous position by inserting a guide member in the through-hole (5) provided along the axial centers of screw region (2) and spacer region (3) and carrying out penetration into the body along the guide member.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF THE RYUKYUS
System for dynamically adjusting treatment angle under tension to accommodate variations in spinal morphology
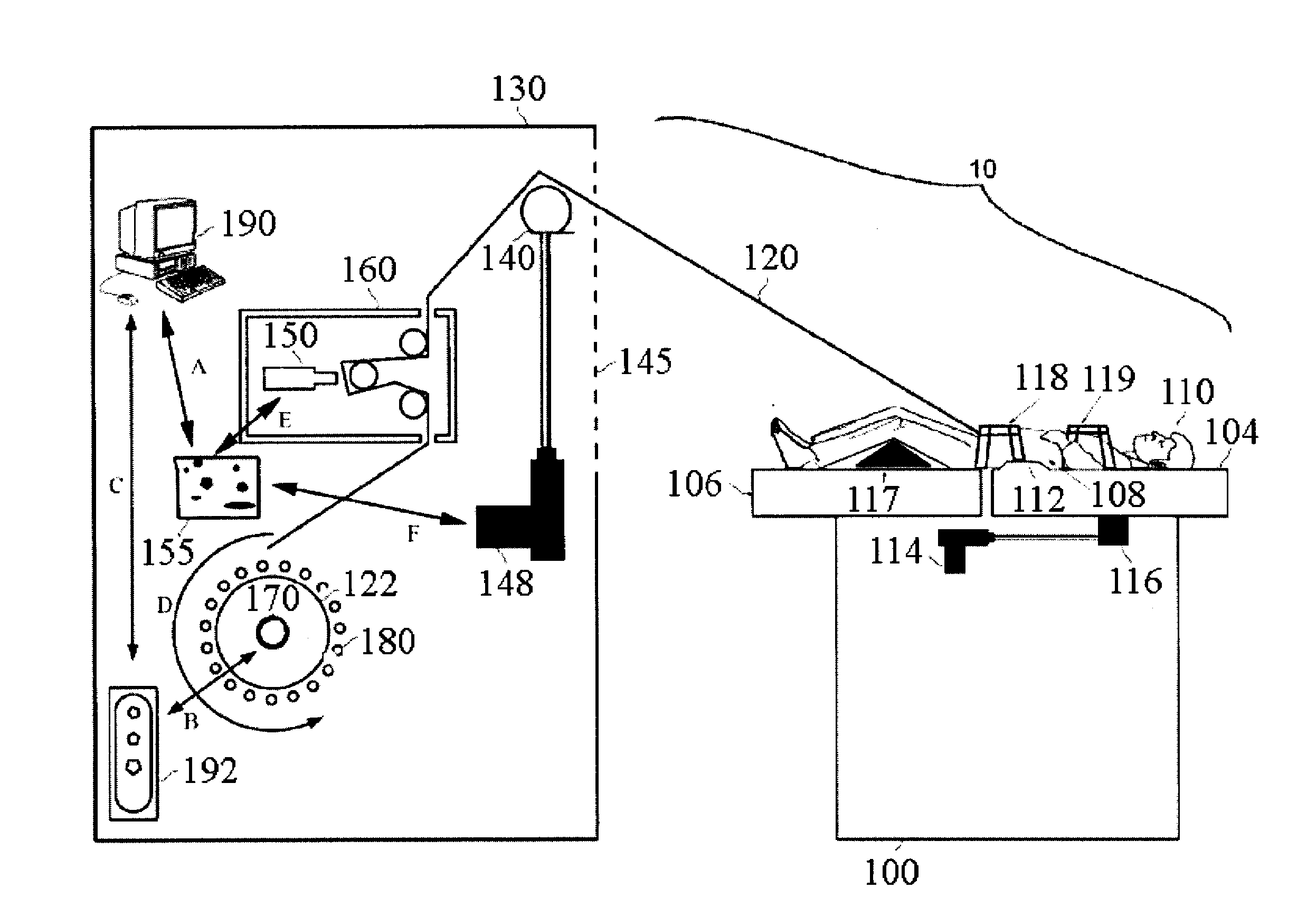
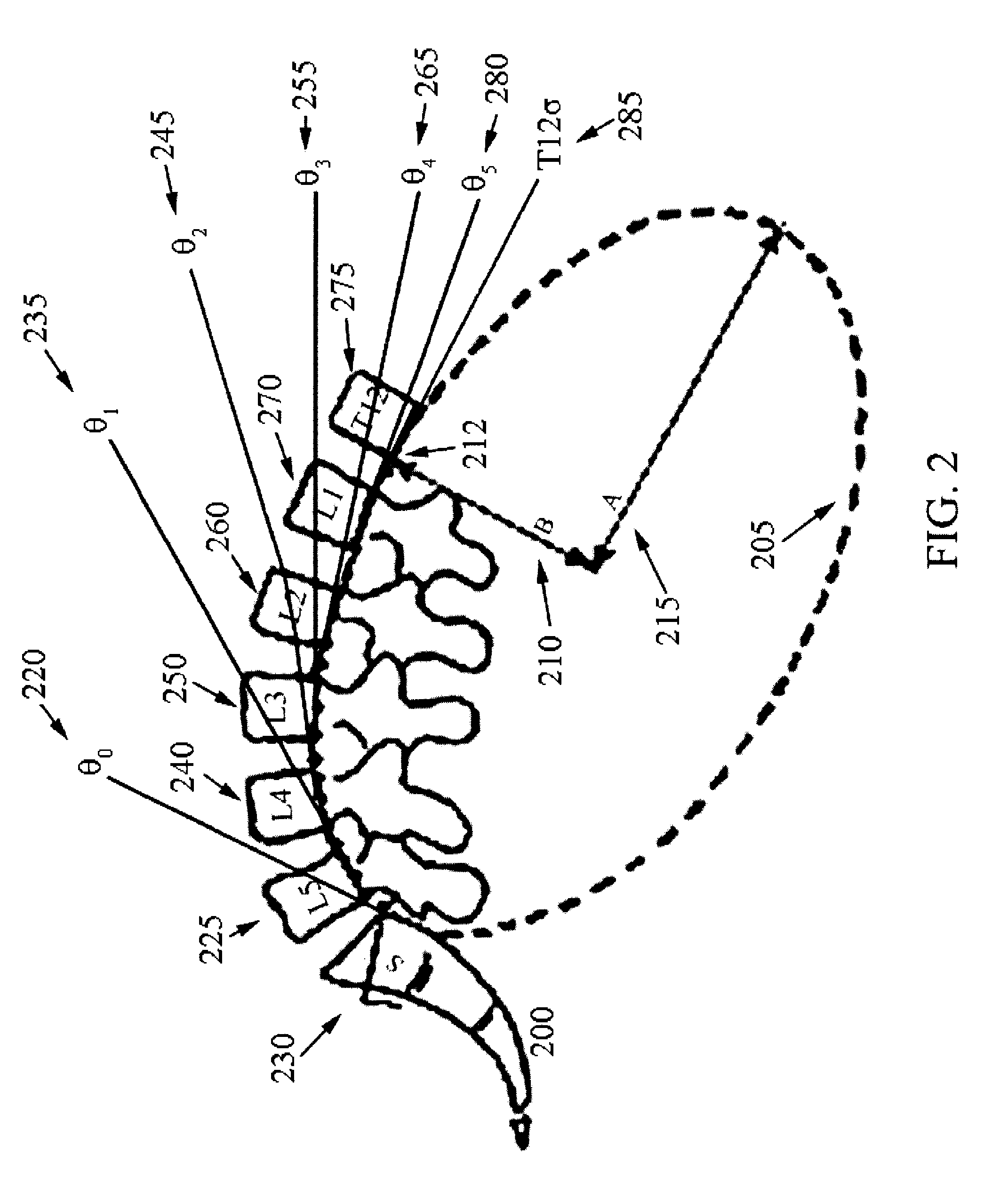
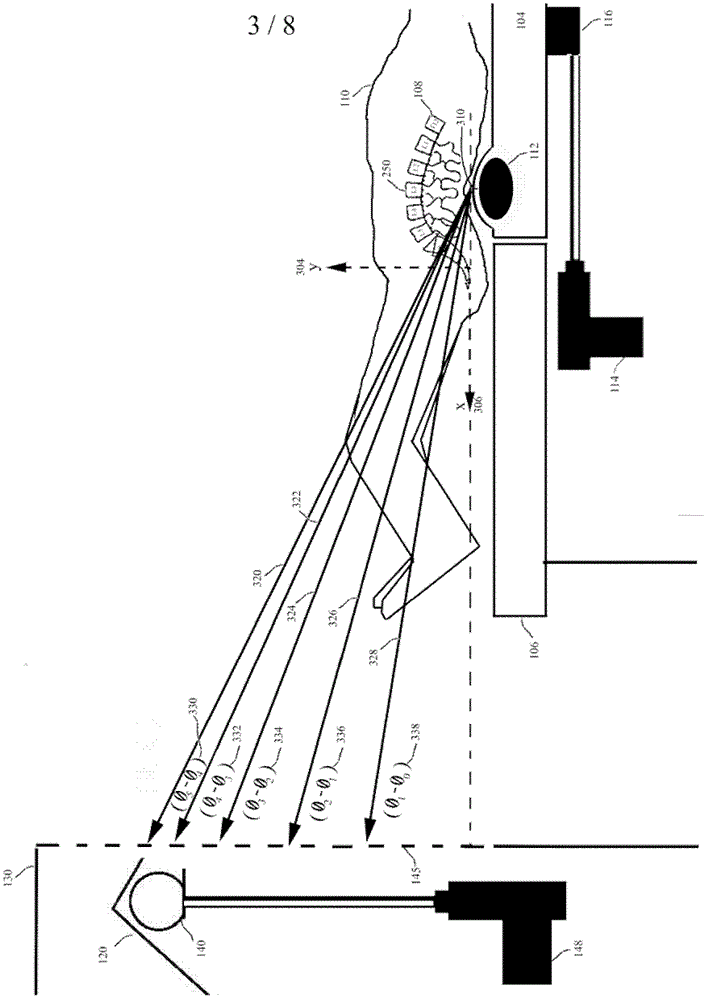
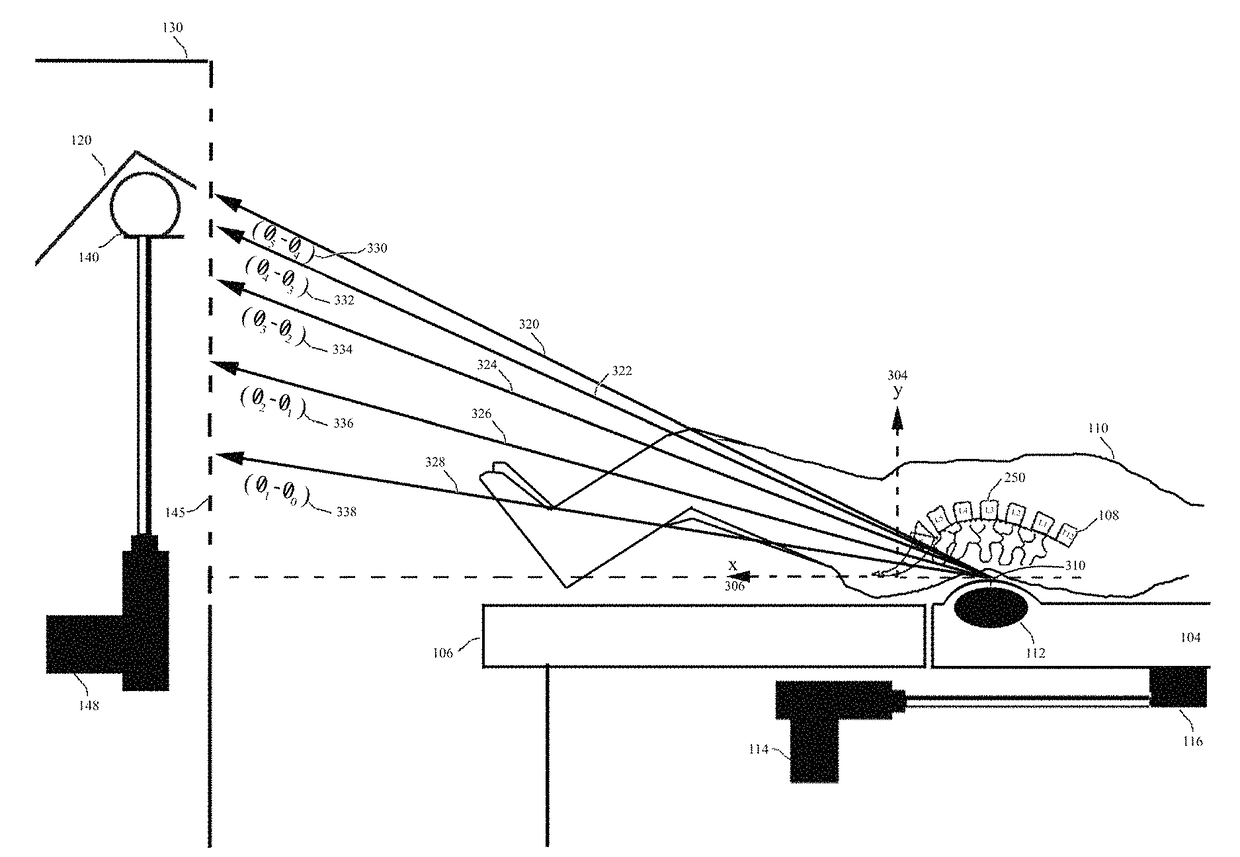
A system for dynamically adjusting treatment angle under tension to accommodate variations in spinal morphology during spinal decompression therapy is provided. It provides a tensioning device including a patient-positioning means, a tension-producing actuator, a positioning device, a patient interface device, a control system and a display. The control system with feedback on the resultant tension vector applied to patient spine operationally configured to allow for adjustment of either tension producing actuator position, patient position, or both while applying tension to the patient spine during non-therapeutic tension levels. The control system automatically adjusts tension producing actuator work levels such that the resultant tension vector magnitude remains ideally constant during adjustment of resultant tension vector angle, reducing the risk of eliciting paraspinal muscle contraction due to changes in resultant tension vector magnitude.
Owner:BEIJING RYZUR AXIOM MEDICAL INVESTMENT
Artificial vertebral plate
ActiveCN102551923AAvoid oppressionIntegrity guaranteedSpinal implantsLaminectomy procedureReticular formation
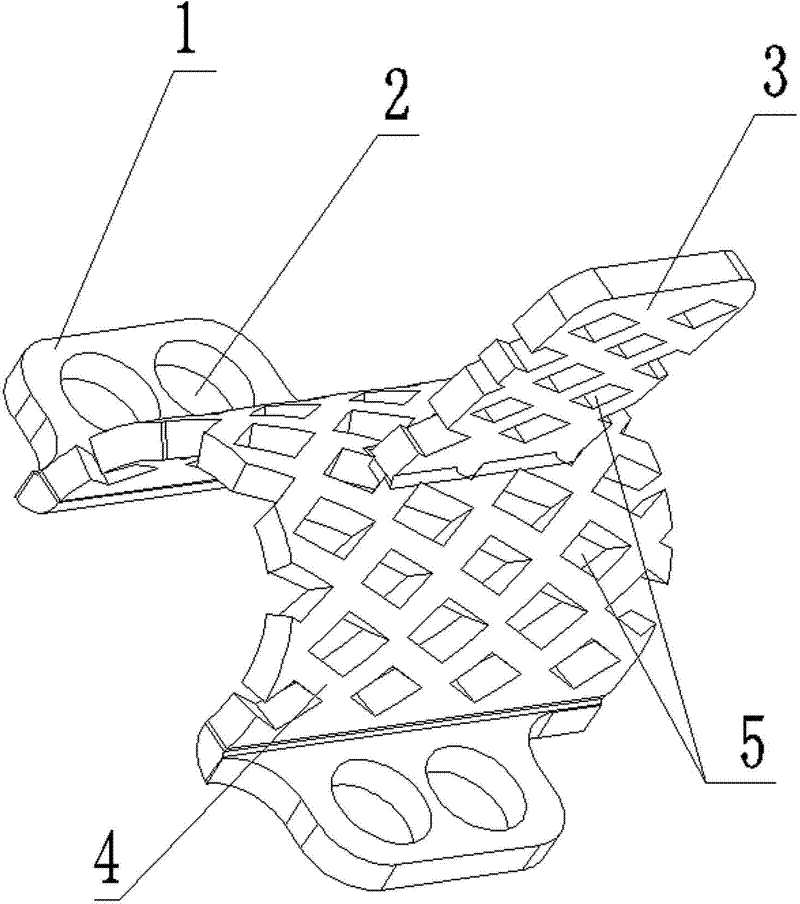
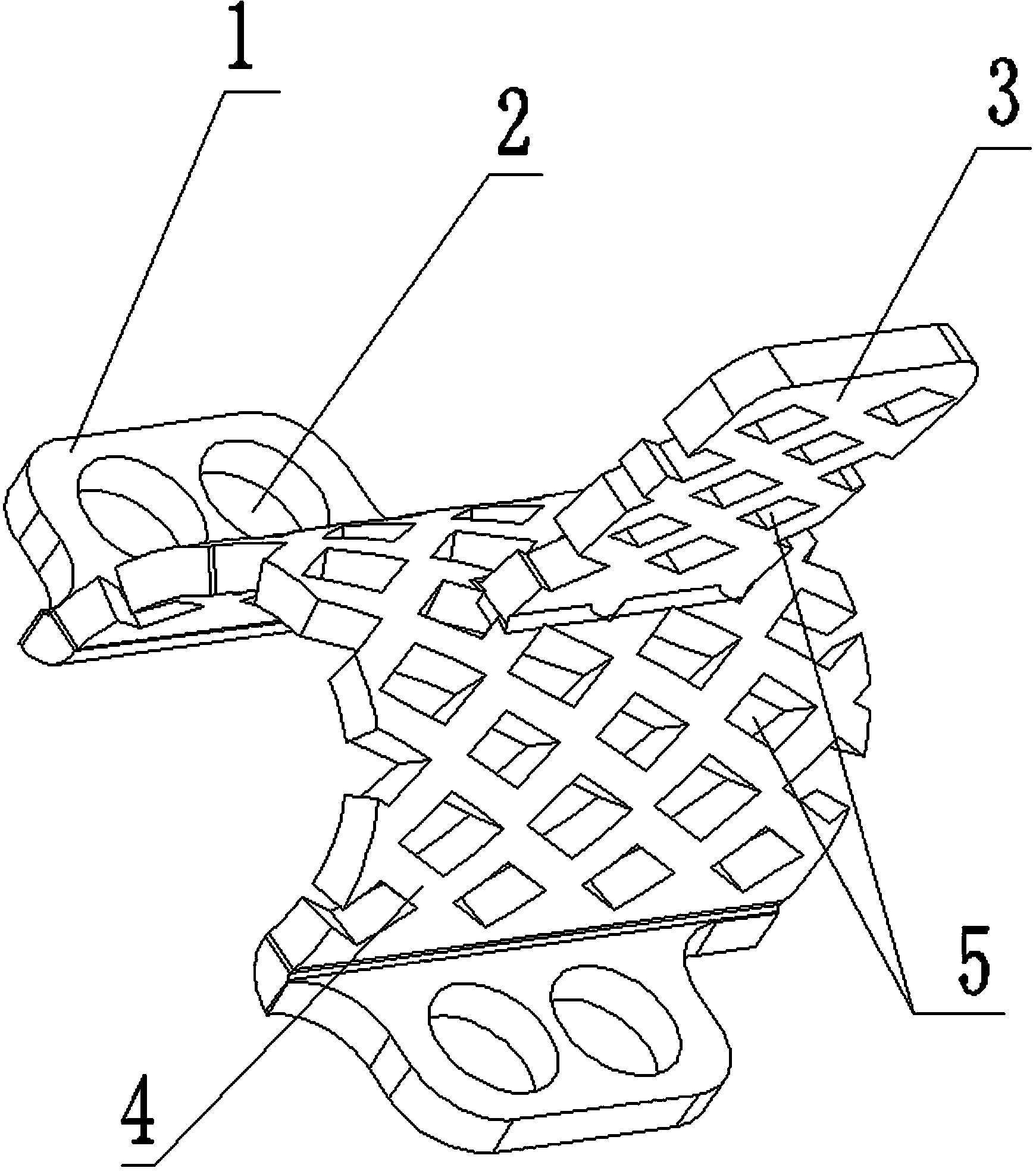
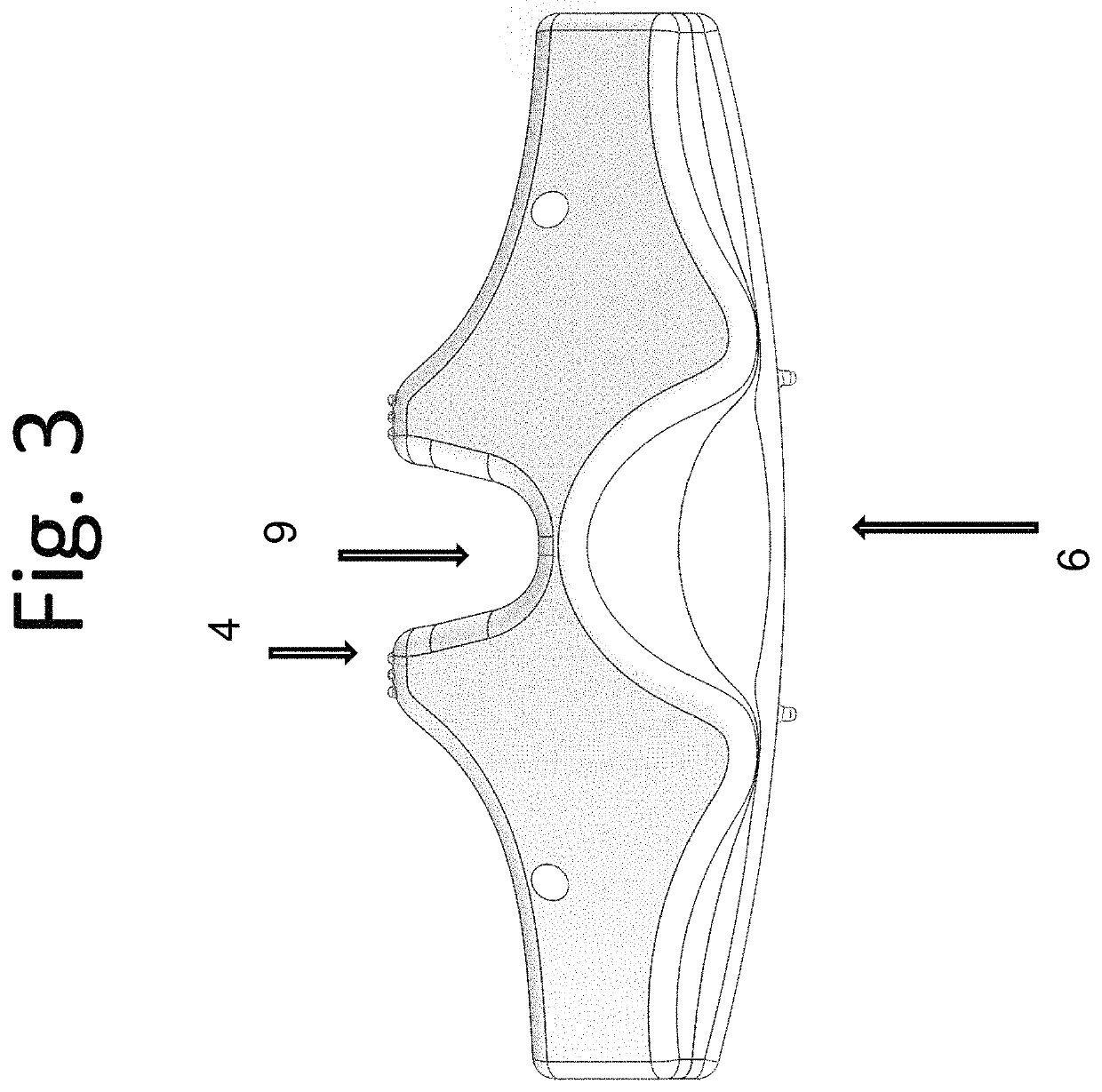
The invention relates to a human body vertebral column implanting appliance, in particular to an artificial vertebral plate, which comprises a vertebral plate body. The artificial vertebral plate is characterized in that the vertebral plate body is an arc-shaped netty vertebral plate, side wings are arranged on two sides of the arc-shaped netty vertebral plate, screw holes are arranged on the side wings, netty bumps are arranged on the back side of the arc-shaped netty vertebral plate, and meshes are arranged on the arc-shaped netty vertebral plate and the netty bumps. The invention is used for reconstruction by the aid of the artificial vertebral plate after laminectomy in posterior spinal surgery for a human body, coloboma of a vertebral plate is repaired, the human body vertebral plate is imitated, spinal cord compression caused by swelling of posterior tissues of the spinal cord of the human body after the surgery is prevented, completeness of a vertebral canal is kept, the vertebral column of the human body is stabilized, and the spinal cord is protected. During usage, the artificial vertebral plate is fixed on a transverse process or a vertebral pedicle of the vertebral column of the human body by screws via the screw holes on the side wings on the two sides, and paraspinal muscle, supraspinal ligament and the like are sewn on the meshes of the netty bumps. The vertebral plate body is the arc-shaped netty structure, so that the volume of the vertebral canal is guaranteed; and the netty structures of the arc-shaped netty vertebral plate and the netty bumps bring convenience for growth of tissues on two sides so as to realize tissue connection.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Techniques for evaluating stress urinary incontinence (SUI) using involuntary reflex cough test
A system and method evaluates a patient for stress urinary incontinence. An involuntary reflex cough event is induced within the patient that activates the nucleus ambiguous and medial motor cell column of the patient and stimulates involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles in the pelvis of the patient. And elecromyogram (EMG) is obtained from the involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles and its duration determined. Any urine leakage time that occurs during the involuntary reflex cough event is identified and correlated within a processor together with the urine leakage time and EMG and duration of cough event to determine stress urinary incontinence.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Techniques for evaluating urinary stress incontinence and use of involuntary reflex cough as a medical diagnostic tool
A system permits diagnosis of a patient for a physiological abnormality while protecting their airway. An esophageal airway protection device comprises an elongate device body having a distal end for insertion into the stomach through the esophagus and a proximal end. The device includes a main lumen extending the length of the device and an inflatable esophageal cuff carried by the device body mid-esophagus. Emesis and / or reflux is blocked from passing out of the stomach past the esophageal cuff positioned mid-esophagus when it is inflated to protect a patient's airway during an involuntary cough event. At least one electromyogram (EMG) pad is configured to obtain an EMG from an involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles. A processing device is configured to receive the EMG and process the EMG to determine a physiological abnormality.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Swing type exercising apparatus
InactiveCN101053690AGet motion effectGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesRectus muscleEngineering
A wedge-shaped tilt provider is attached in contact with the bottom surface of a seat and the upper surface of a seat connection member of a rocking mechanism to set the seat to an initial inclined position relative to a reference position. By setting the seat to a forwardly inclined position from a horizontal position where the seated surface of the seat is set horizontal, the user straddling the seat can increase the amount of muscle activity of his or her rectus muscle of abdomen, or abdominal muscle. Further, by setting the seat to a rearwardly inclined position, the user straddling the seat can increase the amount of muscle activity of his or her back muscle such as paraspinal muscle. With use of a rocking type exercising apparatus having the above construction, a stress of exercise simulating horseback riding is given to the user by changing the position of the seat relative to the reference position by a certain degree of inclination, while rocking the seat which the user straddles, whereby the user is selectively provided with an exercising effect onto a specific site of his or her body.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Techniques for evaluating stress urinary incontinence (SUI) using involuntary reflex cough test
A system and method evaluates a patient for stress urinary incontinence. An involuntary reflex cough event is induced within the patient that activates the nucleus ambiguous and medial motor cell column of the patient and stimulates involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles in the pelvis of the patient. And elecromyogram (EMG) is obtained from the involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles and its duration determined. Any urine leakage time that occurs during the involuntary reflex cough event is identified and correlated within a processor together with the urine leakage time and EMG and duration of cough event to determine stress urinary incontinence.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Thermal treatment device
InactiveCN101756762ATherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingPhysical medicine and rehabilitationTender point
The invention relates to a thermal treatment device, wherein a thermal treatment device to be worn in close proximity to the skin of a human is disclosed. The thermal treatment device comprises a thermal composition; wherein the device substantially covers the left or right trapezius muscle of the neck and shoulder or the left or right paraspinal muscles in the lower back and the tender point of the respective sacroiliac joint.
Owner:MCNEIL PPC INC
Methods of screening for compounds for use as modulators of left-right asymmetry in scoliotic subjects and for monitoring efficacy of an orthopaedic device
InactiveUS20100055707A1Efficient transferReliable determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisNODALOrthopaedic device
A method of screening for a compound for treating or preventing adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS), said method comprising: (a) contacting a test compound with a paraspinal skin fibroblast or a paraspinal muscle cell sample from the right and / or left side of the spine of a subject; and (b) determining at least one of Nodal, Notch1, Pitx2, Lefty1 and Lefty2's expression and / or activity in the cell sample; wherein the test compound is selected as potentially useful in treating or preventing AIS if at least one of Nodal, Notch1, Pitx2, Lefty1 and Lefty2's expression and / or activity in the cell sample is different in the presence of the test compound as compared to in the absence thereof.
Owner:CHU SAINTE JUSTINE
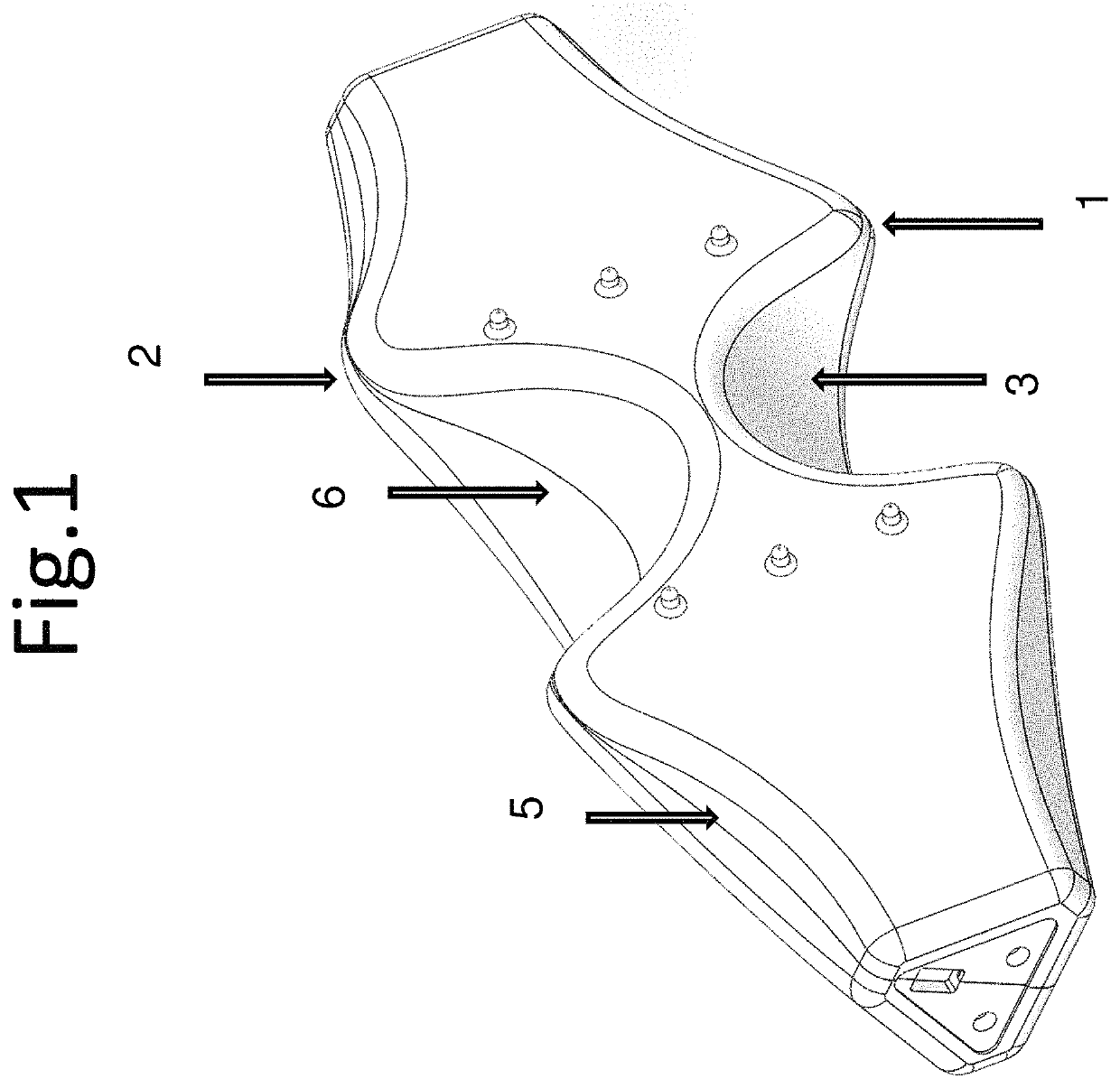
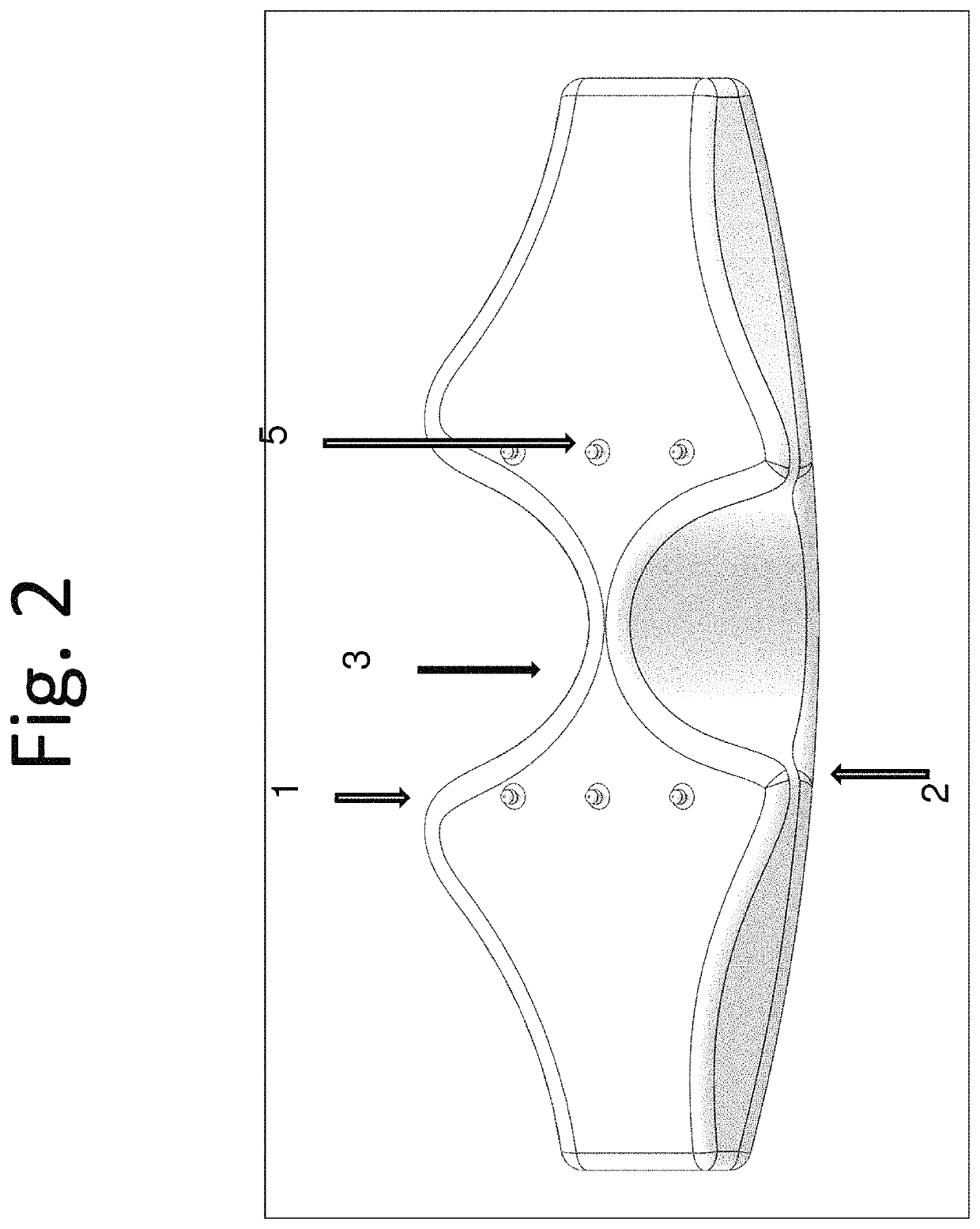
Exposure apparatus for paraspinal muscle clearance approach with posteriorspinal small incision
InactiveUS20150359527A1Easily and atraumatically reachAccurately and quickly and conveniently clearanceDiagnosticsSurgerySpinal columnSurgical operation
An exposure apparatus for a paraspinal muscle clearance approach with a posterior spinal small incision includes a spinous process side vertebral plate retractor and a cooperating vertebral arch outer side retractor is provided. The apparatus can be used to separate a clearance between a multifidus muscle and a longissimus muscle under direct view, easily and atraumatically reach a screw fixation position on a vertebral arch pedicle, expose a facet joint, bluntly separate the multifidus muscle from the vertebral arch, accurately place the retractors, and thereafter locally form a surgical operation tunnel space that externally extends 10 degrees to 15 degrees. A design of angles and structures of retractors effectively protects local soft tissues and prevents a tissue damage while executing traction on local muscles and ensuring an adequate surgical space.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL
Methods of screening for compounds for use as modulators of left-right asymmetry in scoliotic subjects and for monitoring efficacy of an orthopaedic device
InactiveUS20110236889A1Reliable determinationPreserves column mobilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisOrthopaedic deviceSpinal column
A method of screening for a compound for treating or preventing adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS), said method comprising: (a) contacting a test compound with a paraspinal skin fibroblast or a paraspinal muscle cell sample from the right and / or left side of the spine of a subject; and (b) determining at least one of Nodal, Notch1, Pitx2, Lefty1 and Lefty2's expression and / or activity in the cell sample; wherein the test compound is selected as potentially useful in treating or preventing AIS if at least one of Nodal, Notch1, Pitx2, Lefty1 and Lefty2's expression and / or activity in the cell sample is different in the presence of the test compound as compared to in the absence thereof.
Owner:CHU SAINTE JUSTINE
Artificial vertebral plate
ActiveCN102551923BAvoid oppressionIntegrity guaranteedSpinal implantsReticular formationLaminectomy procedure
The invention relates to a human body vertebral column implanting appliance, in particular to an artificial vertebral plate, which comprises a vertebral plate body. The artificial vertebral plate is characterized in that the vertebral plate body is an arc-shaped netty vertebral plate, side wings are arranged on two sides of the arc-shaped netty vertebral plate, screw holes are arranged on the side wings, netty bumps are arranged on the back side of the arc-shaped netty vertebral plate, and meshes are arranged on the arc-shaped netty vertebral plate and the netty bumps. The invention is used for reconstruction by the aid of the artificial vertebral plate after laminectomy in posterior spinal surgery for a human body, coloboma of a vertebral plate is repaired, the human body vertebral plate is imitated, spinal cord compression caused by swelling of posterior tissues of the spinal cord of the human body after the surgery is prevented, completeness of a vertebral canal is kept, the vertebral column of the human body is stabilized, and the spinal cord is protected. During usage, the artificial vertebral plate is fixed on a transverse process or a vertebral pedicle of the vertebral column of the human body by screws via the screw holes on the side wings on the two sides, and paraspinal muscle, supraspinal ligament and the like are sewn on the meshes of the netty bumps. The vertebral plate body is the arc-shaped netty structure, so that the volume of the vertebral canal is guaranteed; and the netty structures of the arc-shaped netty vertebral plate and the netty bumps bring convenience for growth of tissues on two sides so as to realize tissue connection.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
A Convenient Adjustable Minimally Invasive Thoracolumbar Posterior Screw-rod Structure
ActiveCN109717941BNot easy to damageControl insertion depthInternal osteosythesisVertebral pedicleLumbar spine
The invention discloses a minimally invasive thoracolumbar posterior screw rod structure convenient to adjust. The structure comprises a main rod, a first mounting bolt is arranged in the left end ofthe main rod in a penetrating manner, a mounting hole is formed in the left end of an upper positioning block, a breaking block is fixedly connected with the surface of the left end of the upper positioning block, a first vertebral arch hook piece and a second vertebral arch hook piece are mounted on the outer surface of the left side of the main rod, a first pedicle screw is mounted on the outersurface of the middle of the main rod, and the inside of the front end of the first pedicle screw is connected with a third positioning nut through threads. The minimally invasive thoracolumbar posterior screw rod structure convenient to adjust requires no incision for exposure of paraspinal muscle during percutaneous placement of the pedicle screw, cannot damage nerves and blood vessels during placement of a guide needle and is applicable to a thoracolumbar fracture posterior minimal invasion system and patients with posterior longitudinal ligament problems, the insertion depth of the main rod can be controlled by inserting the positioning structure, the length of the main rod is adjustable, and repair length or position of postcentrum is relatively flexible.
Owner:艾奥斯(上海)医疗科技有限公司
Preparation method and application of rat chronic dorsal root neurothlipsis model
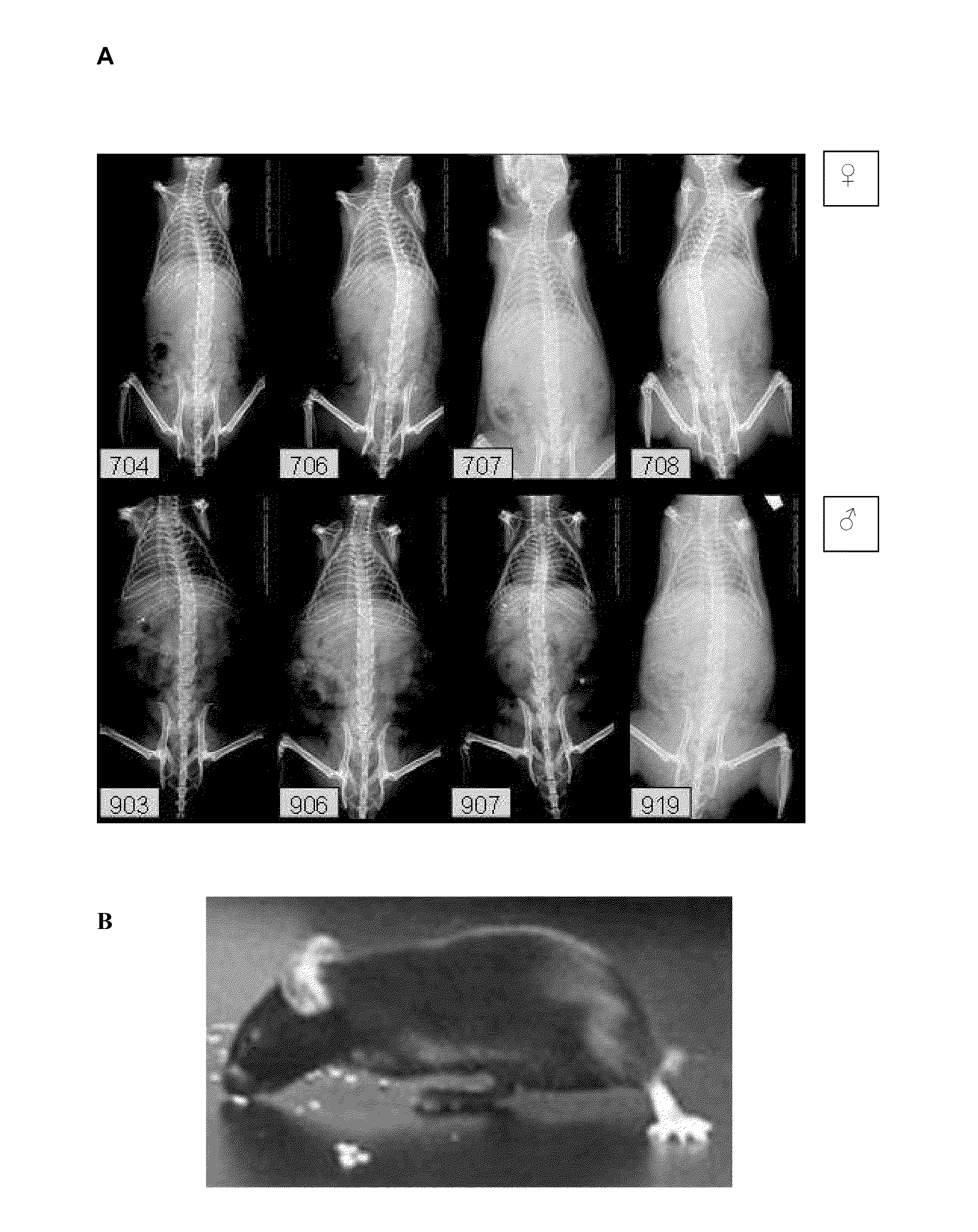
InactiveCN111280124AEasy to measure objectivelyAvoid damageAnimal husbandryEtiologyLumbar intervertebral disc
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a rat chronic dorsal root neurothlipsis model. The method includes the steps: step one, narcotizing a rat; step two, cutting a longitudinal incision on the horizontal left or horizontal right of parts from the 4th lumbar vertebra to the 1st sacrrum, cutting the skin, performing blunt dissection on paraspinal muscles, and exposing the4th lumbar intervertebral foramina and the 5th lumbar intervertebral foramina; and step three, inserting compression elements into the 4th lumbar intervertebral foramen and the 5th lumbar intervertebral foramen on the left or the right so as to obtain the rat chronic dorsal root neurothlipsis model. The compression elements are inserted into the lumbar intervertebral foramina so that continuous and chronic mechanical compression symptoms, caused by protrusions of lumbar disc herniation, of nerve roots are simulated, and the etiology of the symptoms is close to clinical situations; and the preparation method is simple, and has small damage to the animal, good stability and a high success rate. The model which is obtained by using the method can be applied to research of treatment methods and / or imaging detection of lumbar disc herniation.
Owner:嘉升(上海)生物科技有限公司
System for treating idiopathic scoliosis
InactiveUS20150032185A1Effective treatmentConvenient treatmentElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringPhysical therapyWireless data transmission
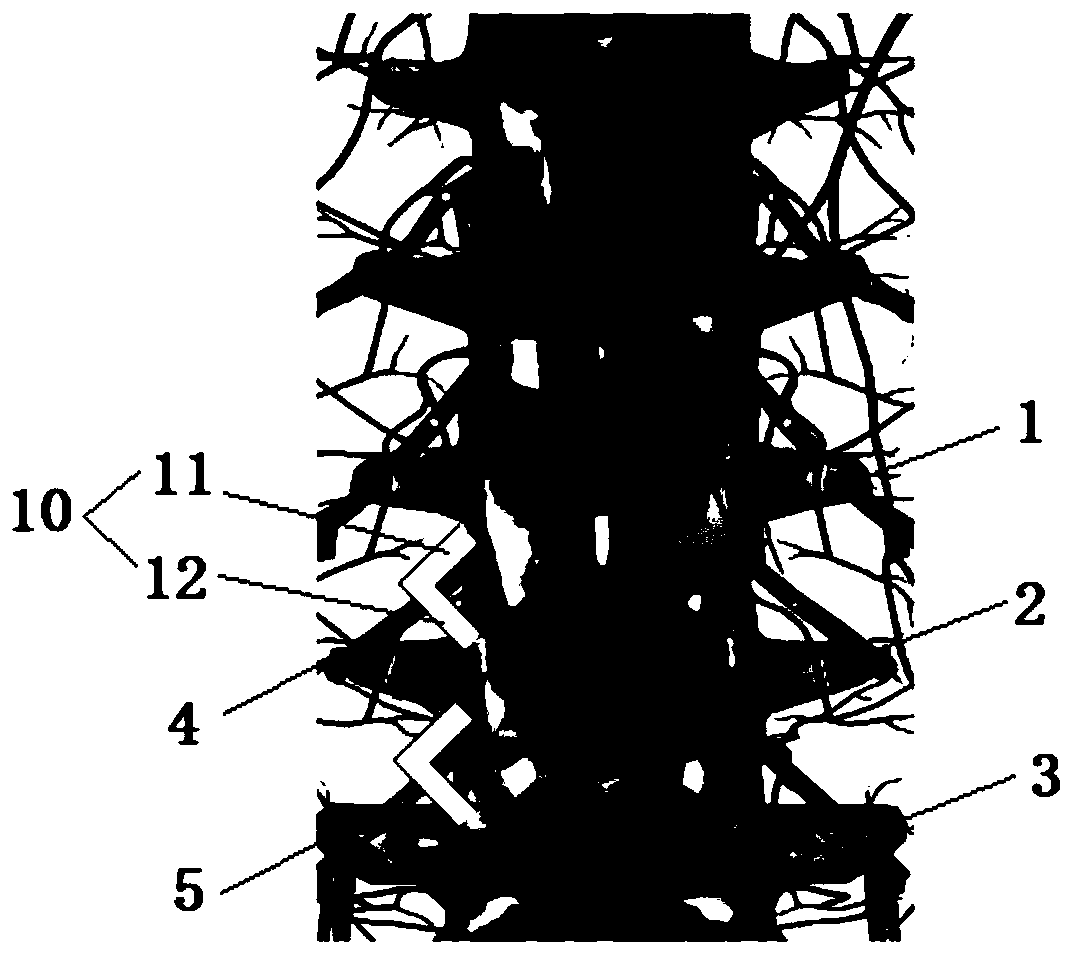
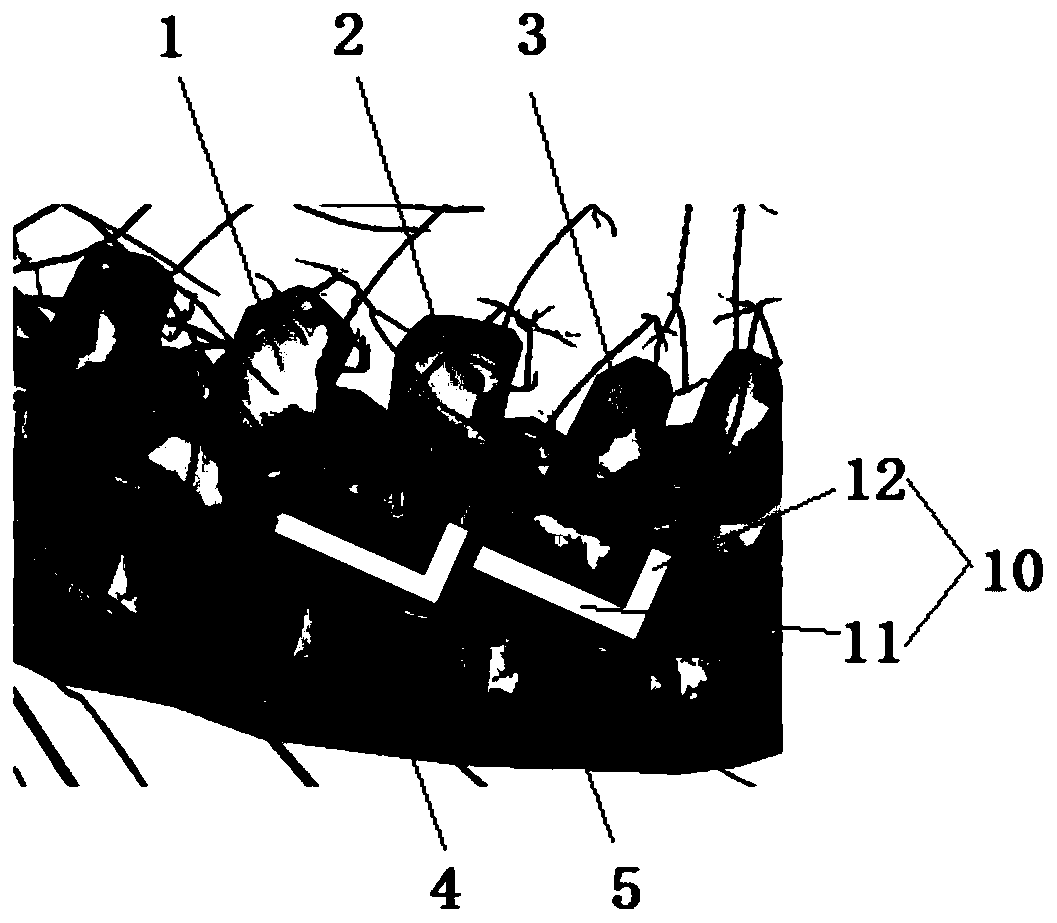
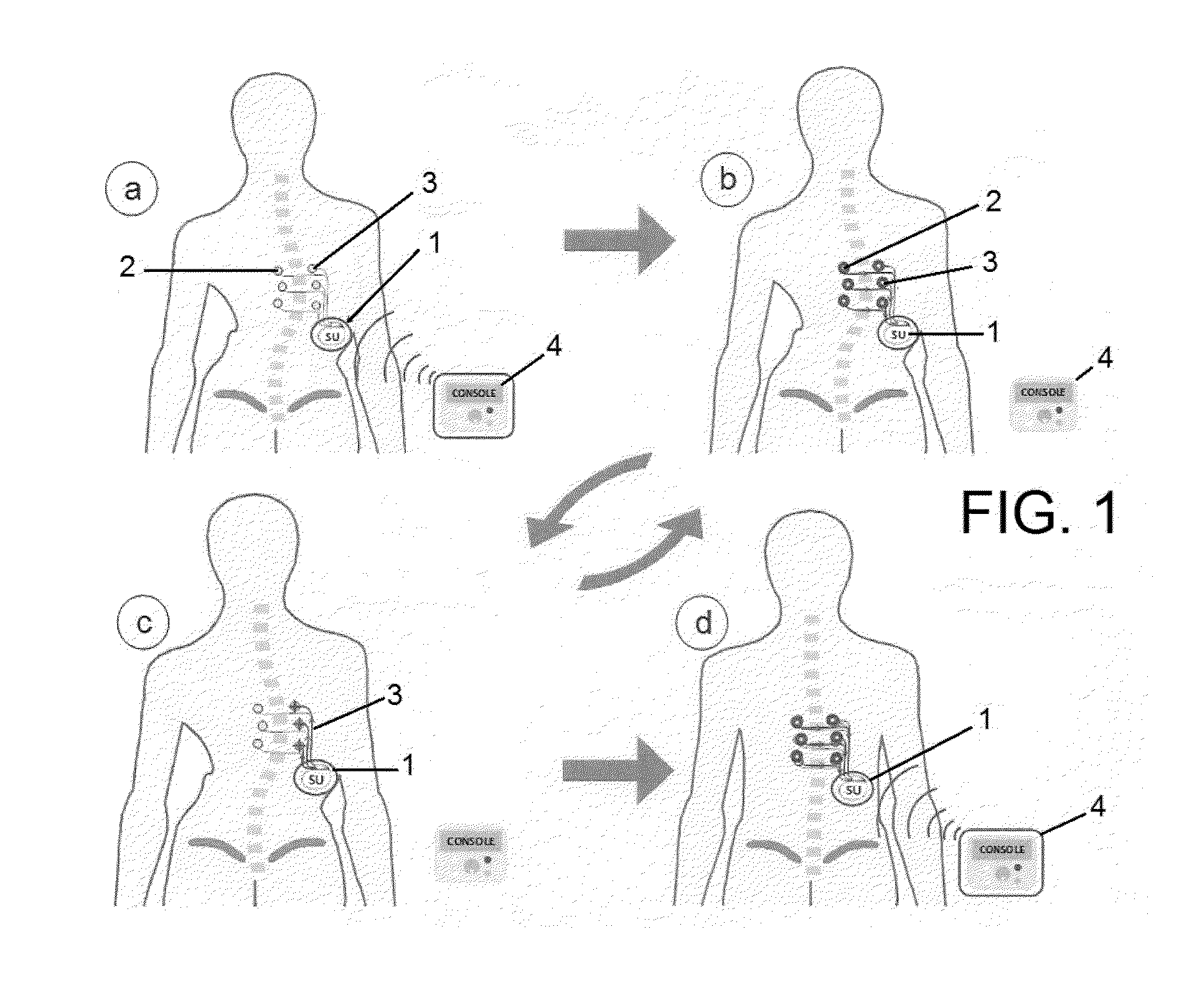
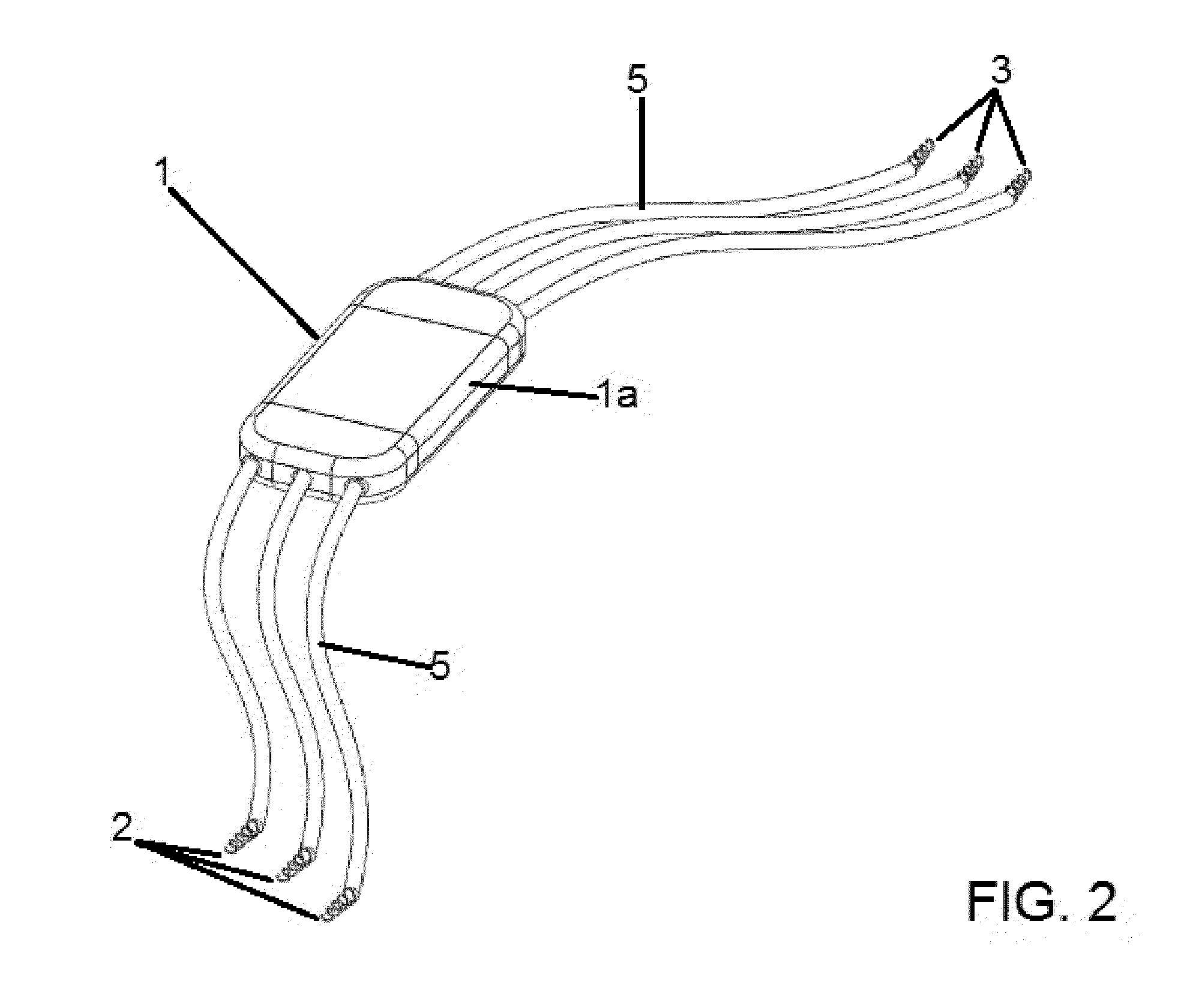
The present invention relates to a system for treating idiopathic scoliosis characterized in that it comprises a programmable subcutaneous or submuscular device (1) connected by means of wiring (5) to a plurality of sensors (2) which are configured to record electromyographic signals and a plurality of stimulators (3) which are configured to stimulate that part of the deep paraspinal muscles that is affected by the pathology, and wherein said device (1) comprises means for wireless data transmission, such that it may be programmed by means of an external console (4), and wherein muscle stimulation is controlled by control logic that comprises a feedback loop algorithm for adjustment of the stimulation based on the results obtained from the sensors (2) for recording the electromyographic signals and according to a musculoskeletal model, for the purpose of creating a suitable stimulus within a set time range.
Owner:TEQUIR
Unit for action on biologically active body points and the relief of paravertebral muscles
A unit has been designed to be applied within the area of physiotherapy and is applicable to both medical and athletic therapeutic programs to provide correction of functional states of the spine and the nervous system to eliminate nervous overloads, fatigue, and stress. Moreover, the unit corrects spinal disorders, paravertebral muscular disorders and can be used as a part of mobilizing procedures to act on biologically active body points, and as a part of therapeutic procedures to relieve the spine.
Owner:YARA LLC
System capable of enabling difference realignment to be carried out on spinal column under tensile force
InactiveCN103156716BMaintain Resultant Pull Vector AngleChiropractic devicesFractureSpinal columnMuscle contraction
A system for differential realignment of vertebra under tension is provided. It provides a tensioning device (10) including a patient-positioning means (100), a tension-producing actuator (170), a positioning device (140), a patient interface device (120) and a control system (190). The control system (190) with feedback on the resultant tension vector applied to patient spine allows for adjustment of either tension producing actuator (170) position or patient position or both while applying therapeutic tension levels to the patient spine. The tensioning device (10) automatically adjusts the resultant tension vector angle such that the resultant tension vector magnitude remains ideally constant during the adjustment of the tension producing actuator (170) position or the patient position, facilitating flexion of spinal segments while reducing the risk of eliciting paraspinal muscle contraction due to changes in resultant tension vector magnitude.
Owner:BEIJING RYZUR AXIOM MEDICAL INVESTMENT
System for dynamically adjusting treatment angle under tension to accommodate variations in spinal morphology
A system for dynamically adjusting treatment angle under tension to accommodate variations in spinal morphology during spinal decompression therapy is provided. It provides a tensioning device including a patient-positioning means, a tension-producing actuator, a positioning device, a patient interface device, a control system and a display. The control system with feedback on the resultant tension vector applied to patient spine operationally configured to allow for adjustment of either tension producing actuator position, patient position, or both while applying tension to the patient spine during non-therapeutic tension levels. The control system automatically adjusts tension producing actuator work levels such that the resultant tension vector magnitude remains ideally constant during adjustment of resultant tension vector angle, reducing the risk of eliciting paraspinal muscle contraction due to changes in resultant tension vector magnitude.
Owner:BEIJING RYZUR AXIOM MEDICAL INVESTMENT
Optical fiber connection optical biological treatment window for rats
PendingCN112656535AIncrease the effective doseGood treatment effectCoupling light guidesLight therapyVisual observationEngineering
The invention discloses an optical fiber connection optical biological treatment window for rats. The optical fiber connection optical biological treatment window comprises an optical fiber channel, an upper end plate and a lower end plate. The end part of the optical fiber extends into the optical fiber channel, and the optical fiber channel is detachably connected with the joint of the optical fiber; and the upper end plate and the lower end plate are fixedly connected to the two ends of the optical fiber channel respectively, the upper end plate is used for being fixedly connected with the skin through a suture line, the lower end plate is used for being fixedly connected with the paravertebral muscle through a suture line, and threading holes allowing the suture line to penetrate through are formed in the upper end plate and the lower end plate. Compared with the prior art, the optical fiber connection optical biological treatment window has the advantages that the effective dose of photobiological therapy reaching the spinal cord injury can be increased, frequent incision treatment does not need to be performed on the spine of the rat, and visual observation of the treatment process is facilitated.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Exposure apparatus for paraspinal muscle clearance approach with posteriorspinal small incision
InactiveUS9439638B2Easily and atraumatically reachAccurately and quickly and conveniently clearanceDiagnosticsSurgerySurgical operationSpinal column
An exposure apparatus for a paraspinal muscle clearance approach with a posterior spinal small incision includes a spinous process side vertebral plate retractor and a cooperating vertebral arch outer side retractor is provided. The apparatus can be used to separate a clearance between a multifidus muscle and a longissimus muscle under direct view, easily and atraumatically reach a screw fixation position on a vertebral arch pedicle, expose a facet joint, bluntly separate the multifidus muscle from the vertebral arch, accurately place the retractors, and thereafter locally form a surgical operation tunnel space that externally extends 10 degrees to 15 degrees. A design of angles and structures of retractors effectively protects local soft tissues and prevents a tissue damage while executing traction on local muscles and ensuring an adequate surgical space.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL
Techniques for evaluating stress urinary incontinence (SUI) using involuntary reflex cough test
A system and method evaluates a patient for stress urinary incontinence. An involuntary reflex cough event is induced within the patient that activates the nucleus ambiguous and medial motor cell column of the patient and stimulates involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles in the pelvis of the patient. And elecromyogram (EMG) is obtained from the involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles and its duration determined. Any urine leakage time that occurs during the involuntary reflex cough event is identified and correlated within a processor together with the urine leakage time and EMG and duration of cough event to determine stress urinary incontinence.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Adjustable gravity loading garment for simulating spine physiological load
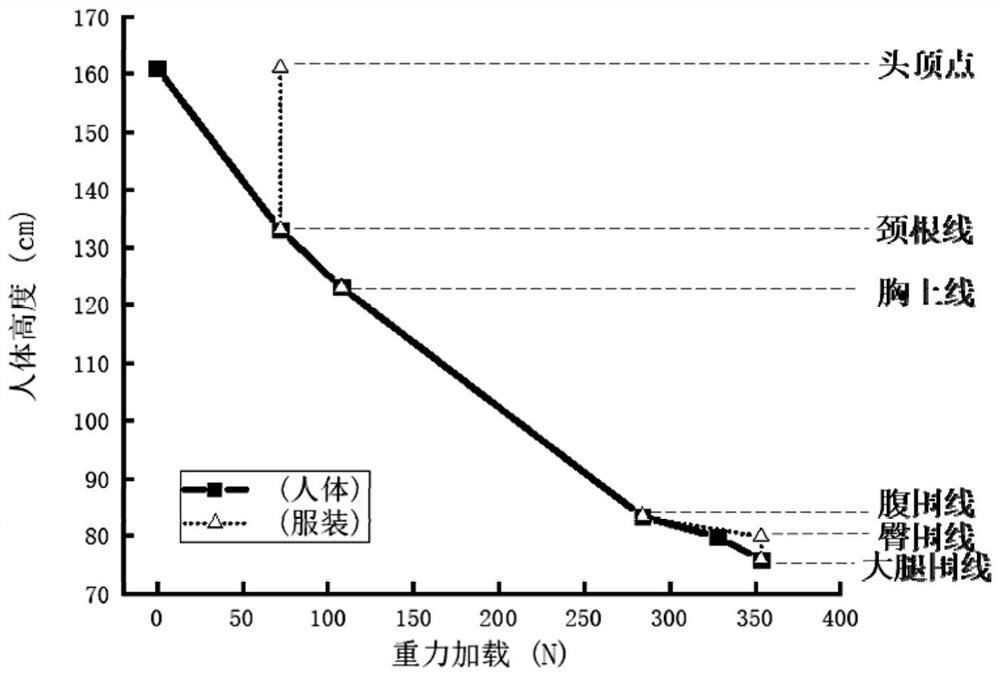
ActiveCN114086300AAvoid Nonspecific Low Back PainAvoid problemsWeft knittingSpace suitsHuman bodySpinal column
The invention relates to an adjustable gravity loading garment for simulating the physiological load of a spine, which is designed for the spine by combining a non-elastic fabric and a variable-elasticity fabric, and compared with the existing elastic material for loading the gravity, the adjustable gravity loading garment can better simulate the physiological load of the spine of a human body. By means of the calculus fabric structure, gravity loading is continuously increased from the neck root line to the thigh girth line, effective confrontation is generated on human body structures such as vertebras, intervertebral discs, paravertebral muscles and intervertebral ligaments, and non-specific lumbago of astronauts or space travelers is avoided. Besides, all-directional pressure loading of the fabric on the human body is fully considered, an axial loading and radial fixing structure is adopted, good wearing comfort in the axial direction and the radial direction is guaranteed, discomfort of other parts of the human body is prevented, and other diseases are avoided. By combining the movable connecting device and the shape memory fabric, high wearing and taking-off performance is guaranteed, wearing and taking-off can be completed by a single person, and meanwhile the gravity loading requirements of different space environments are met.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com