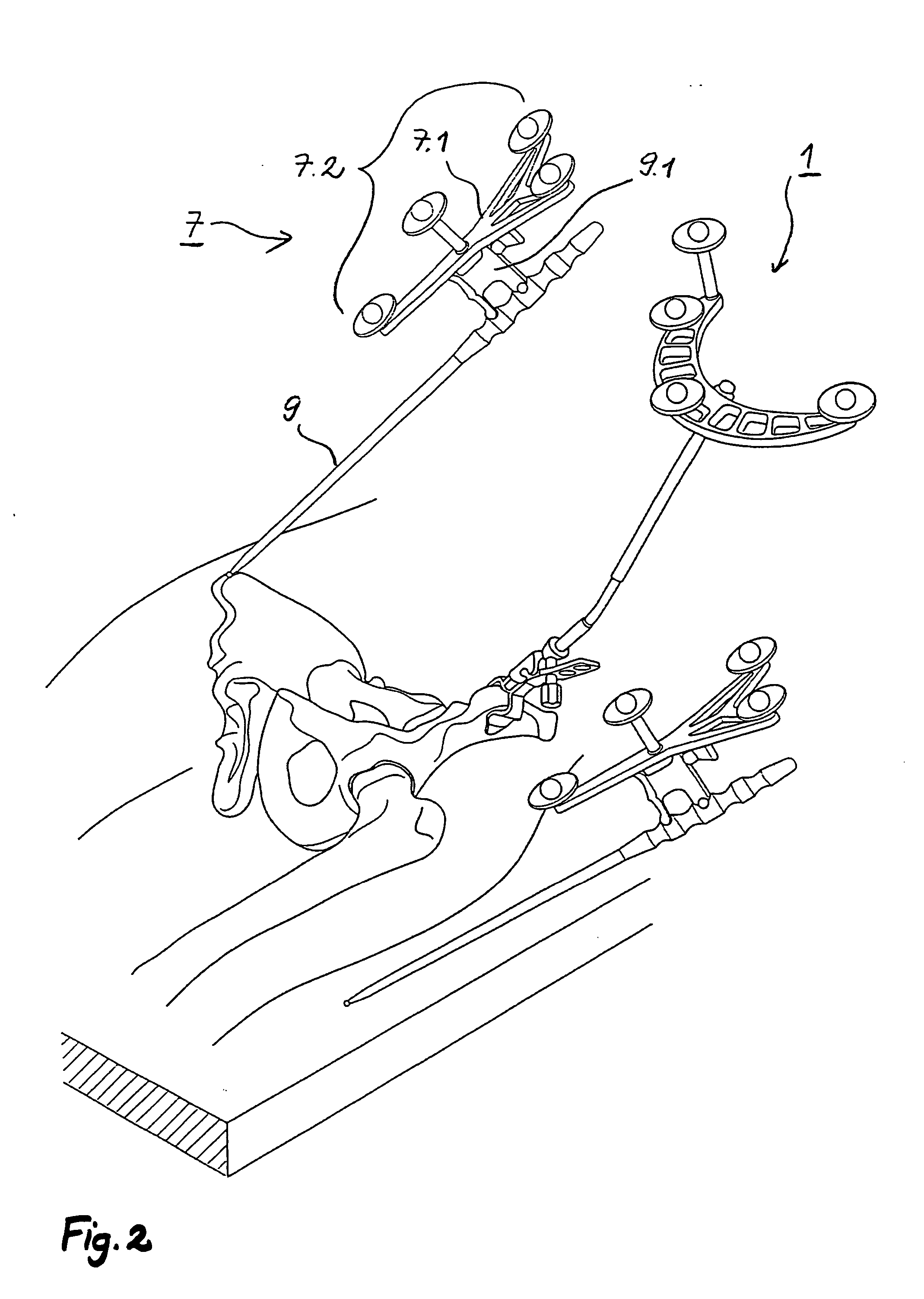
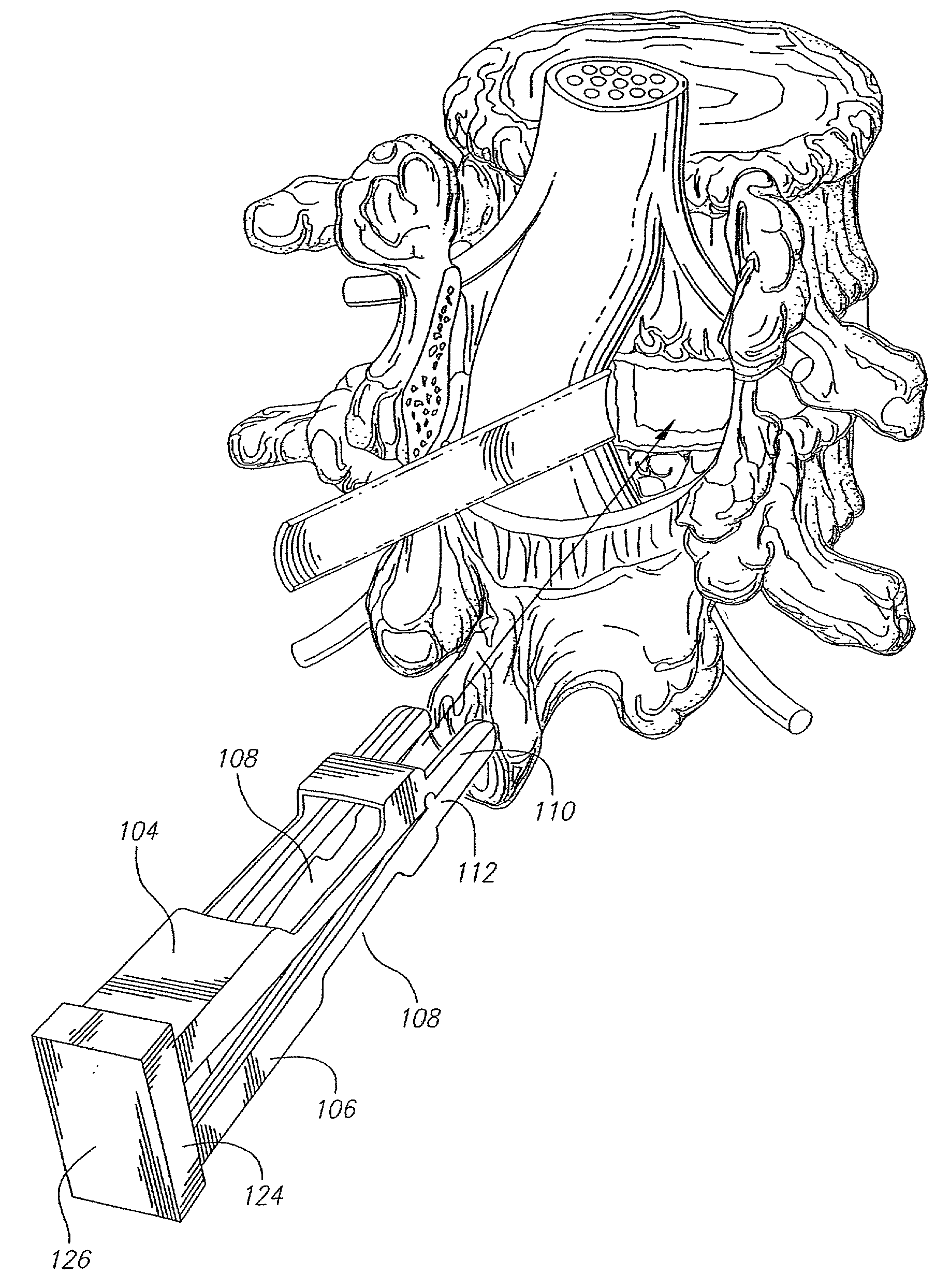
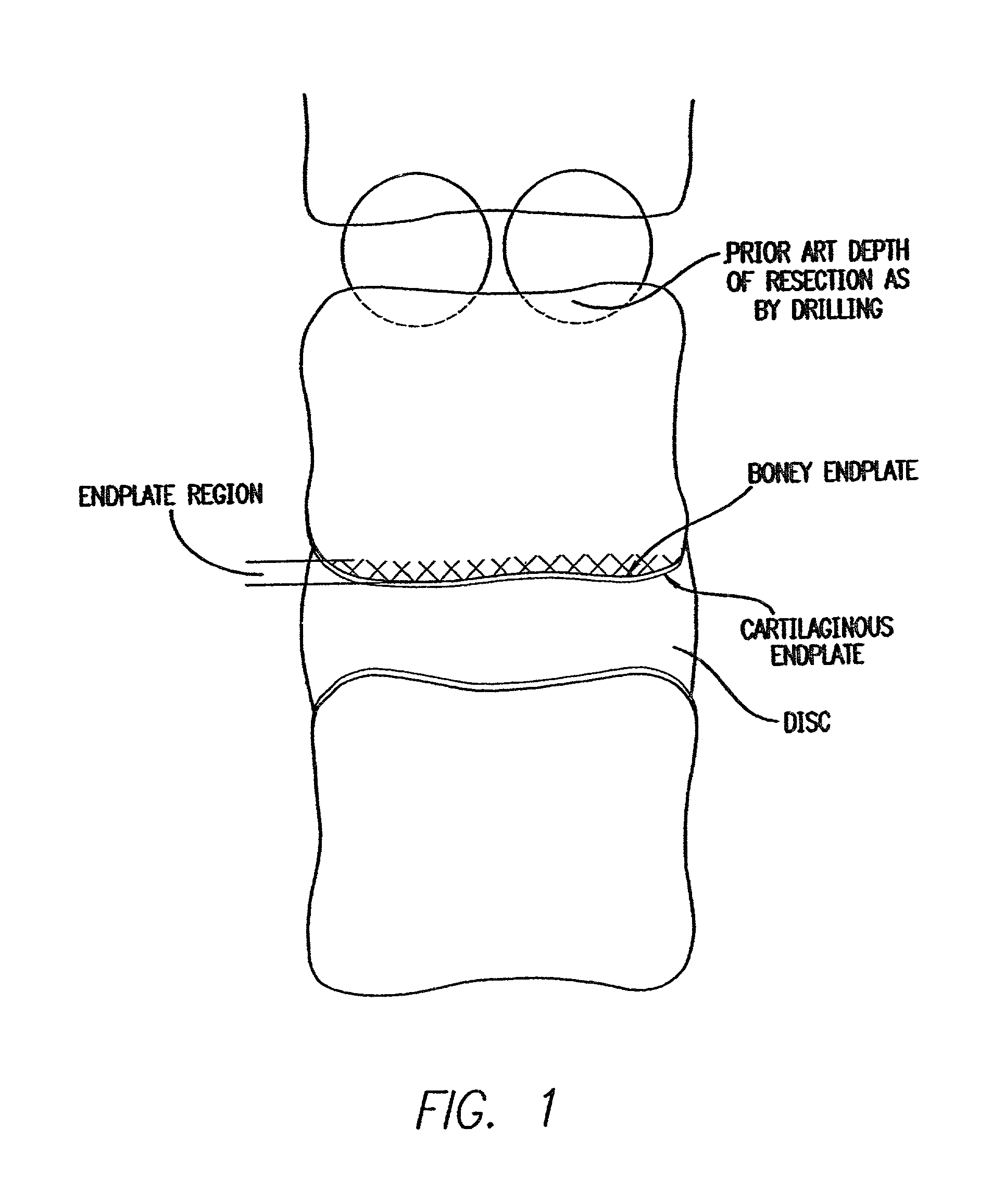
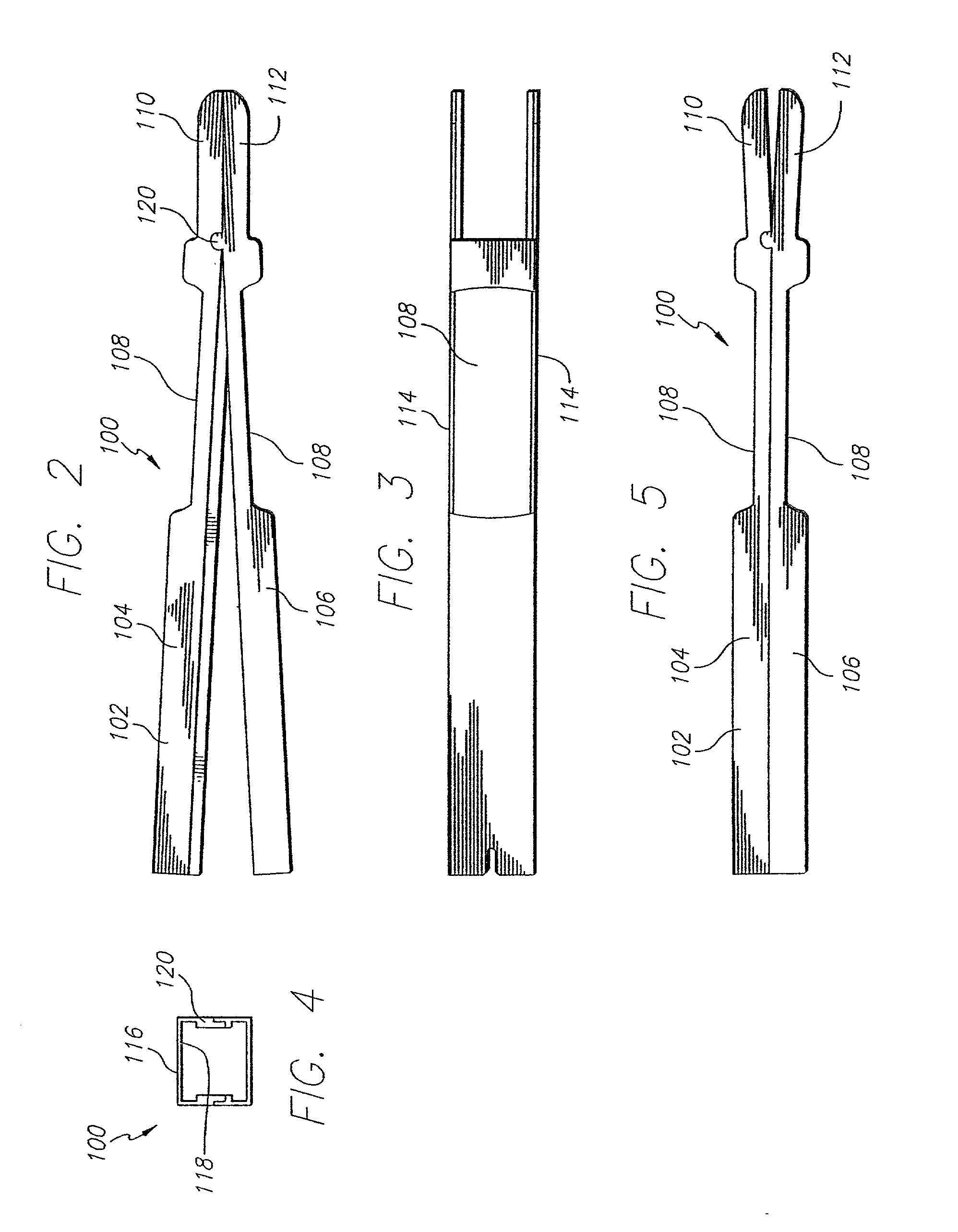
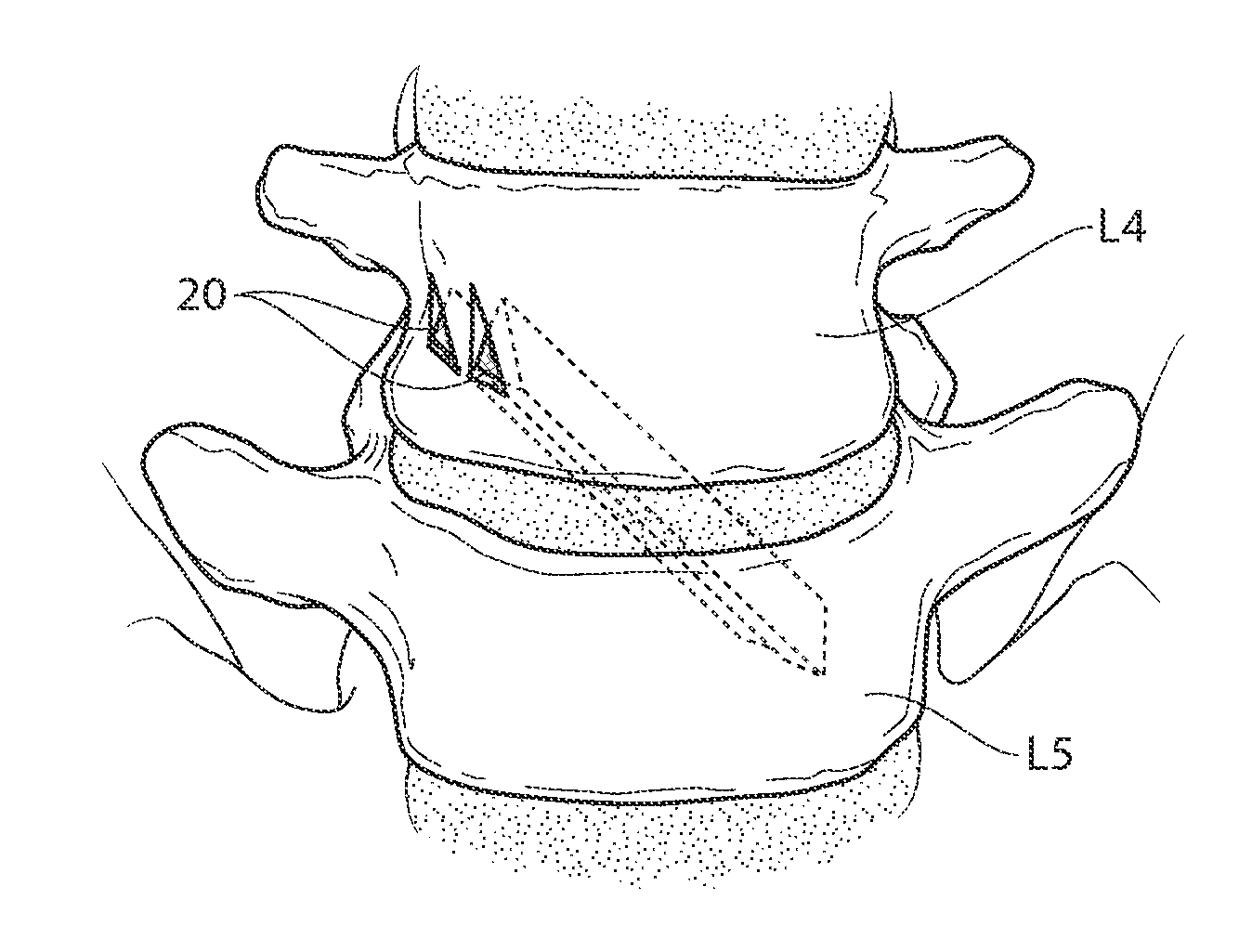
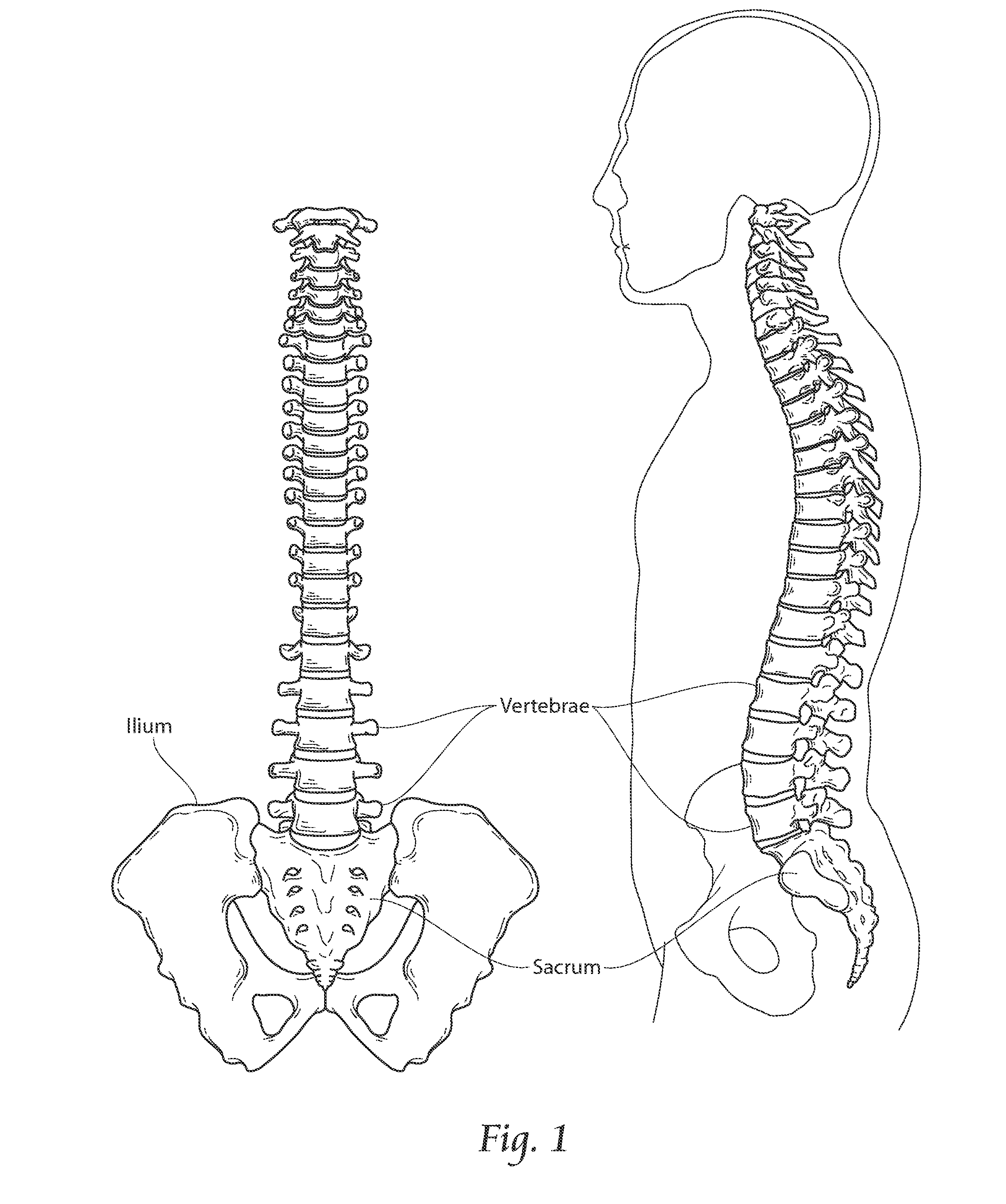
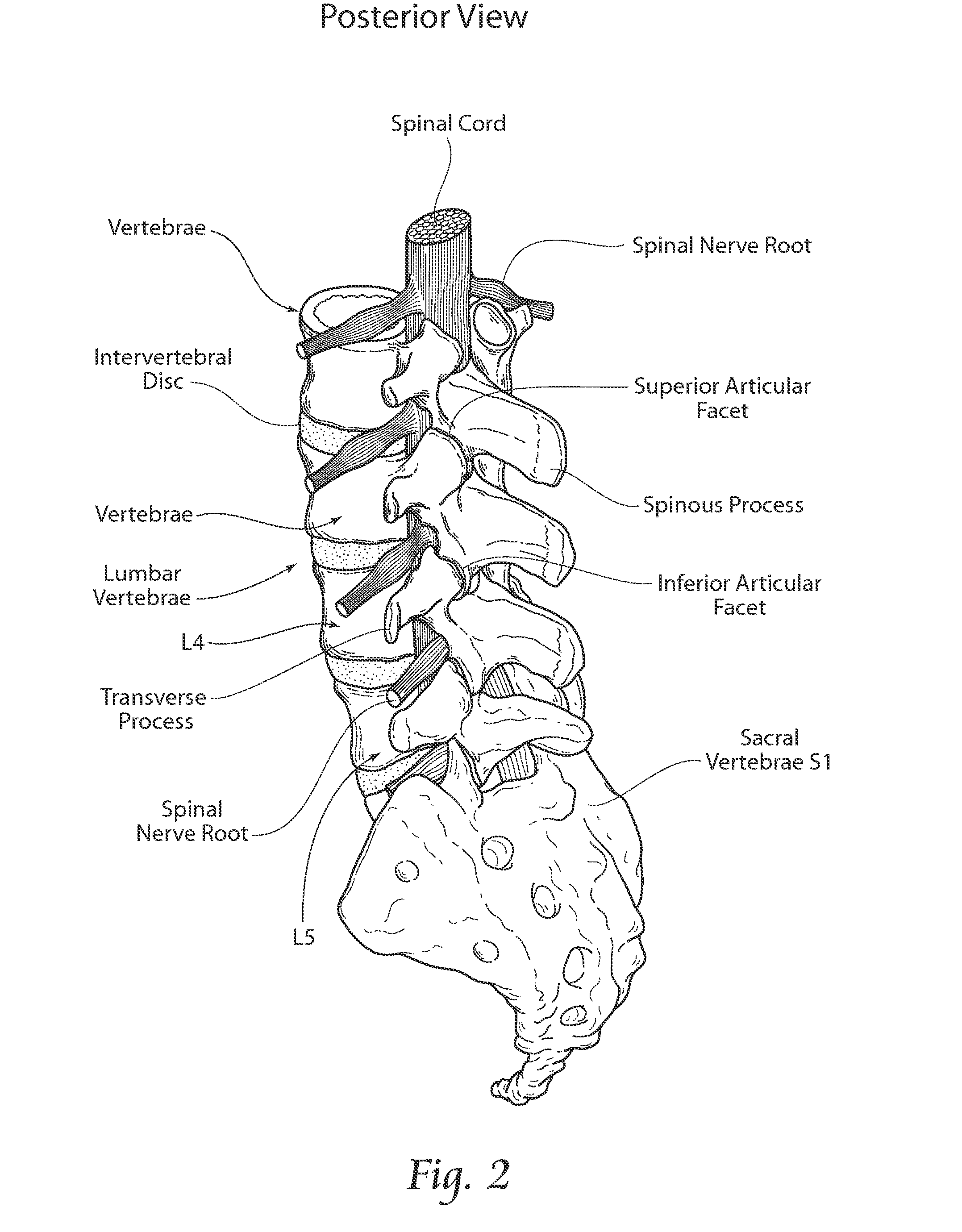
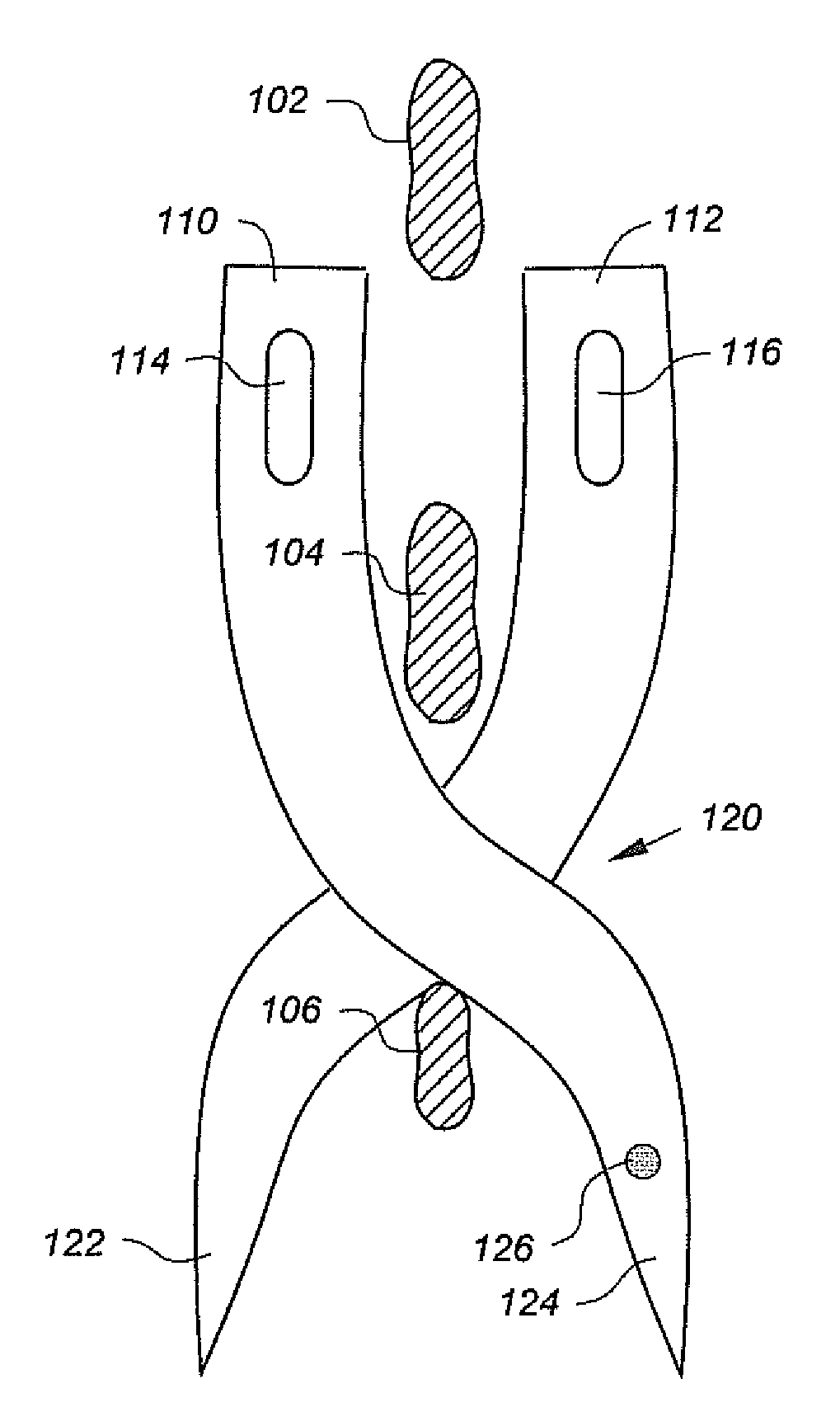
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
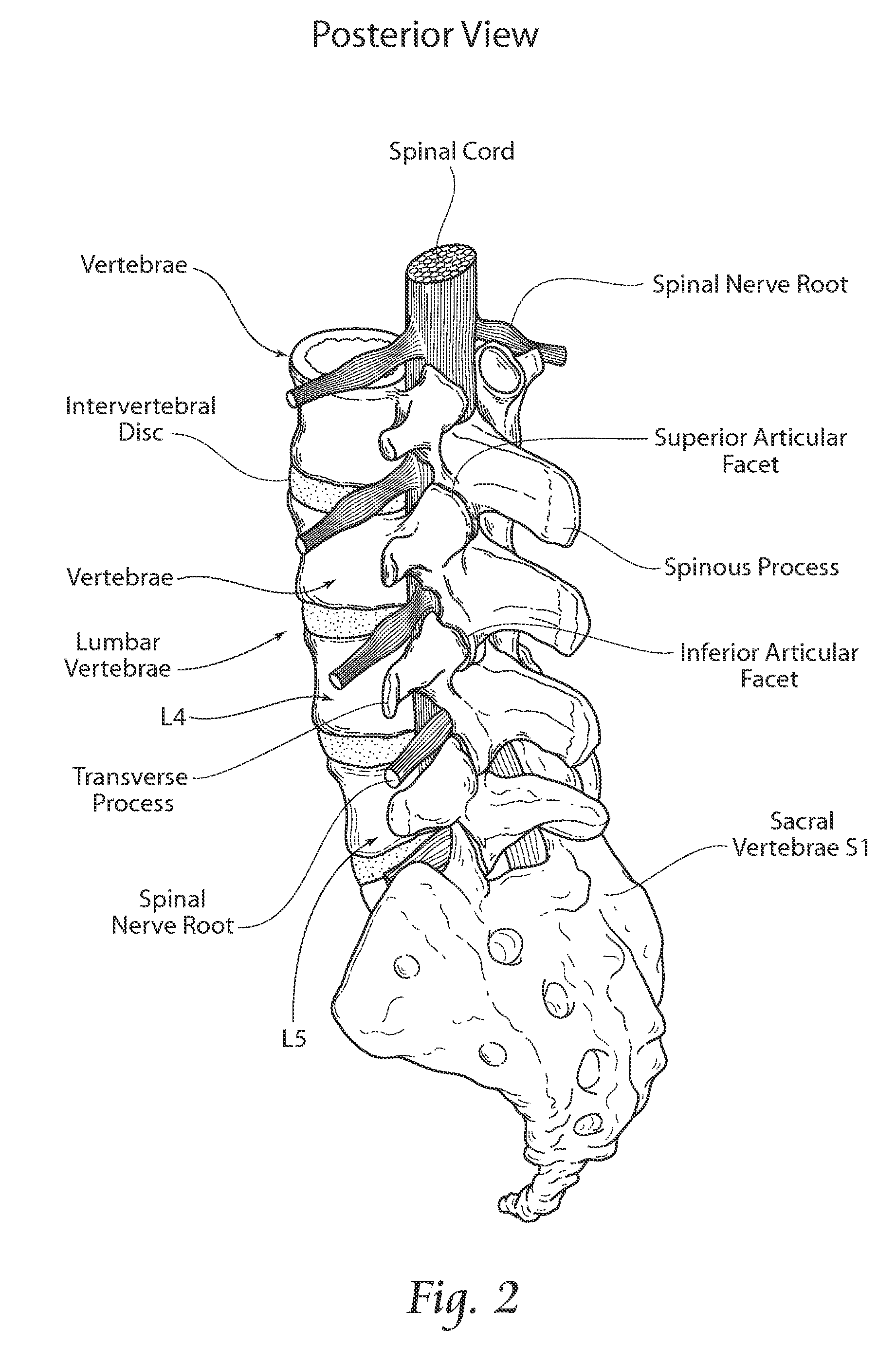
1260 results about "Lumbar spine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
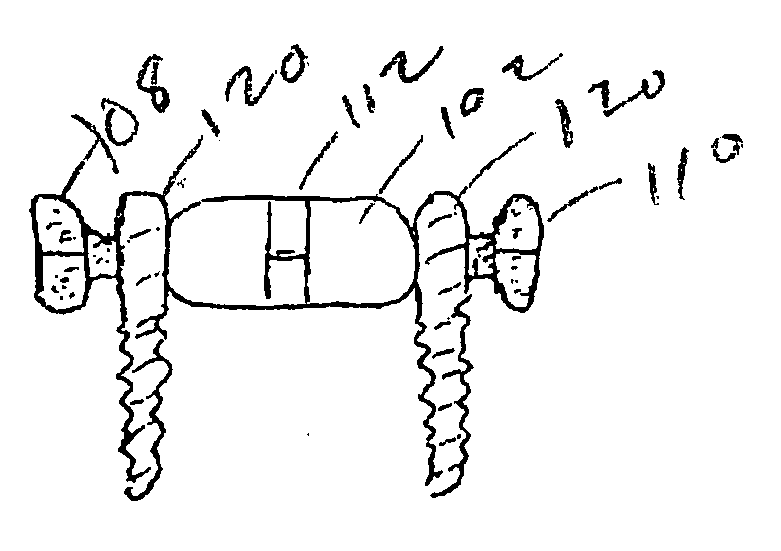
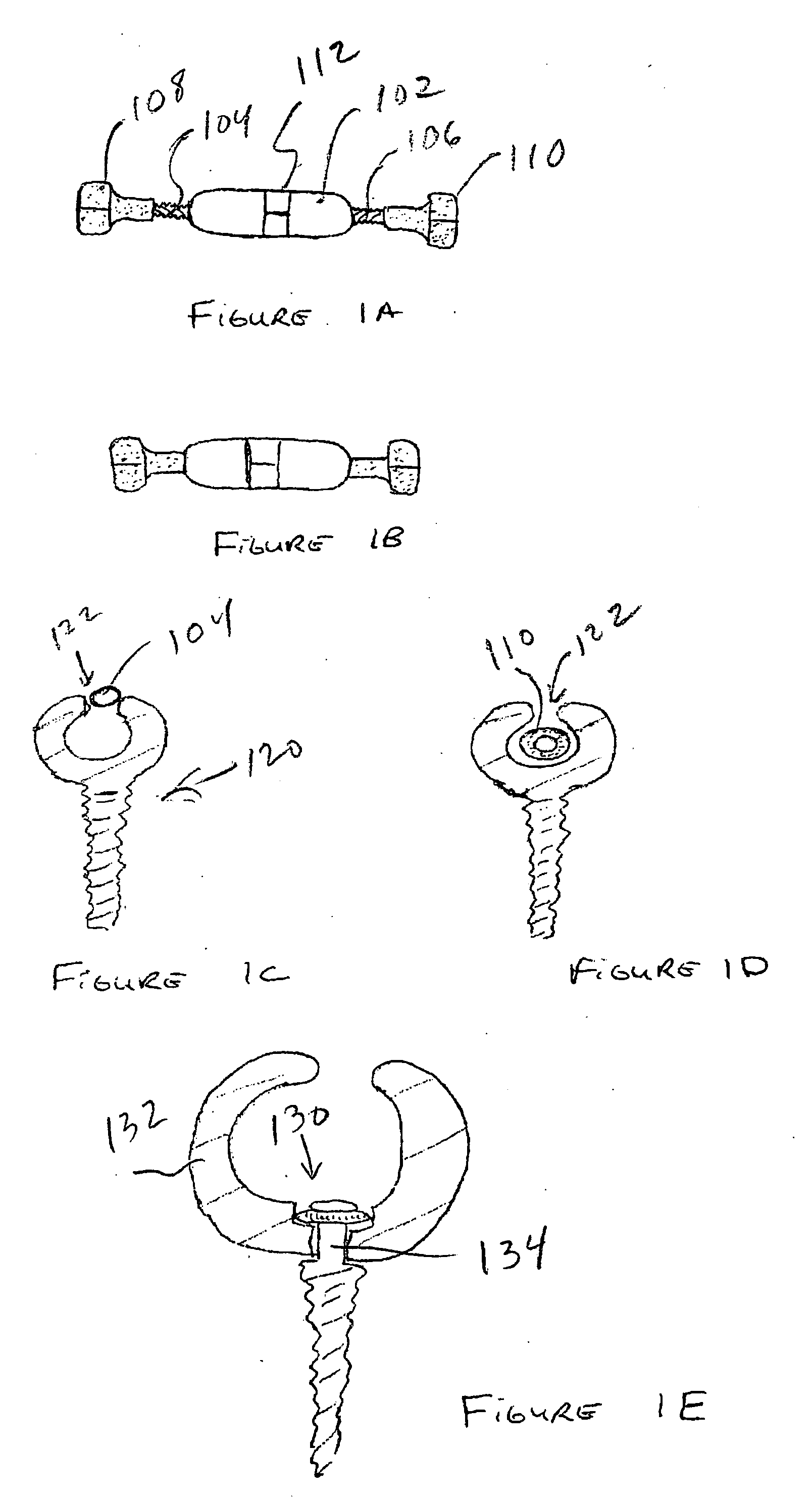
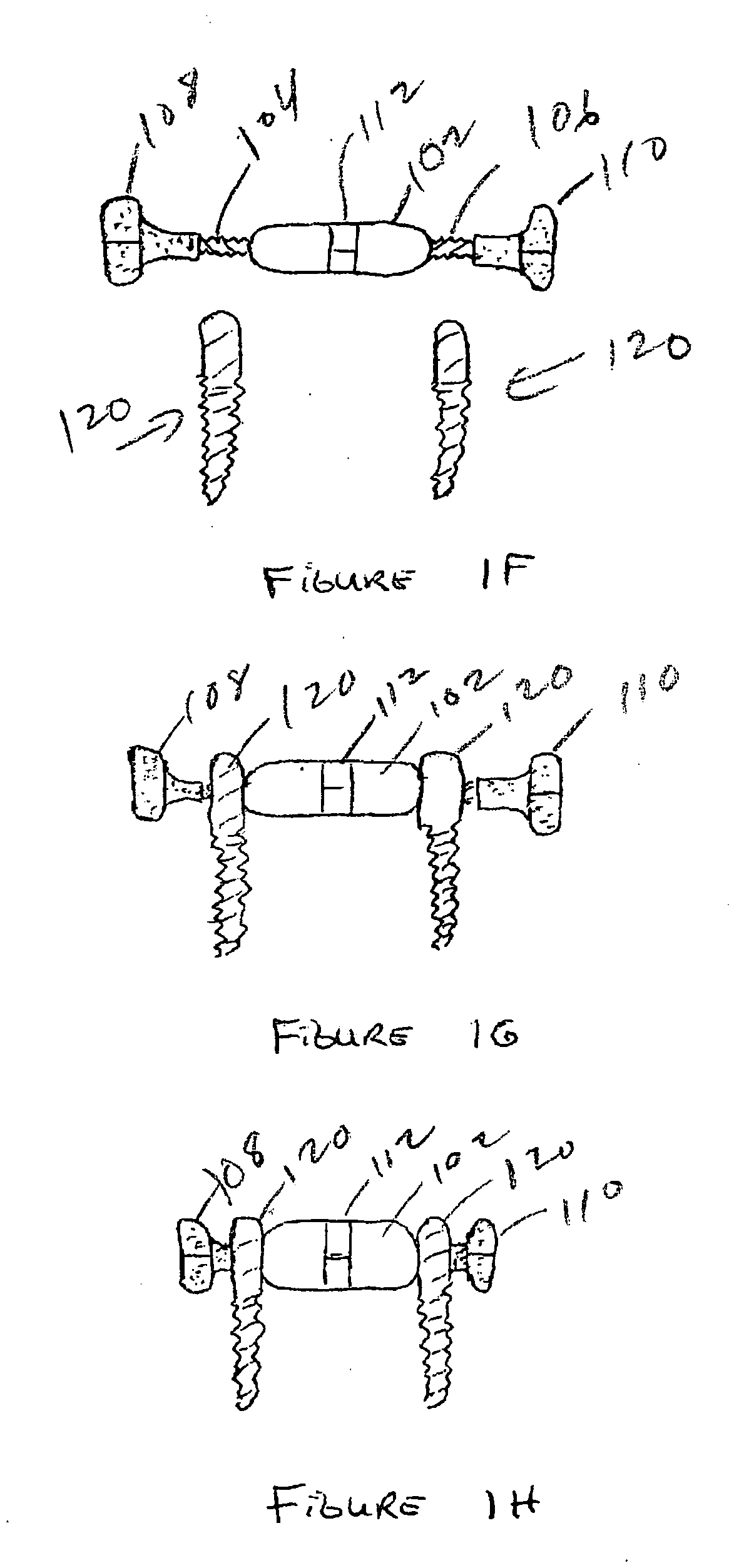
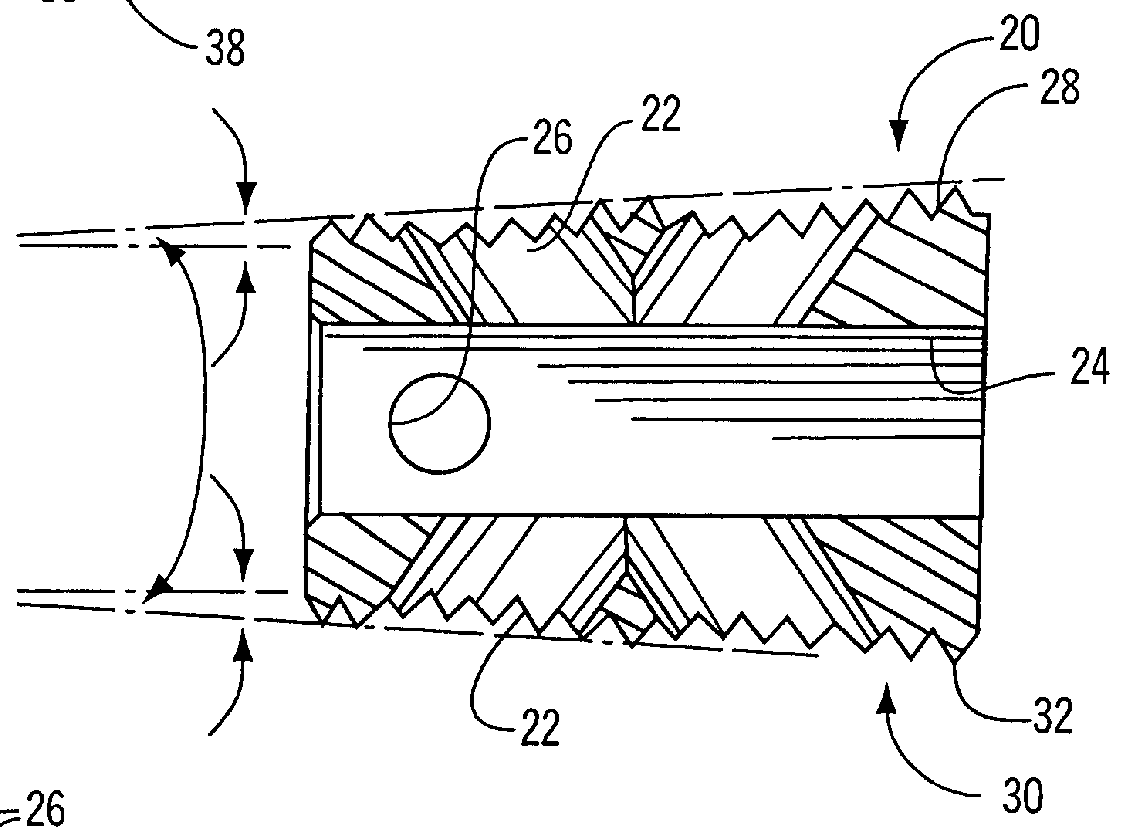
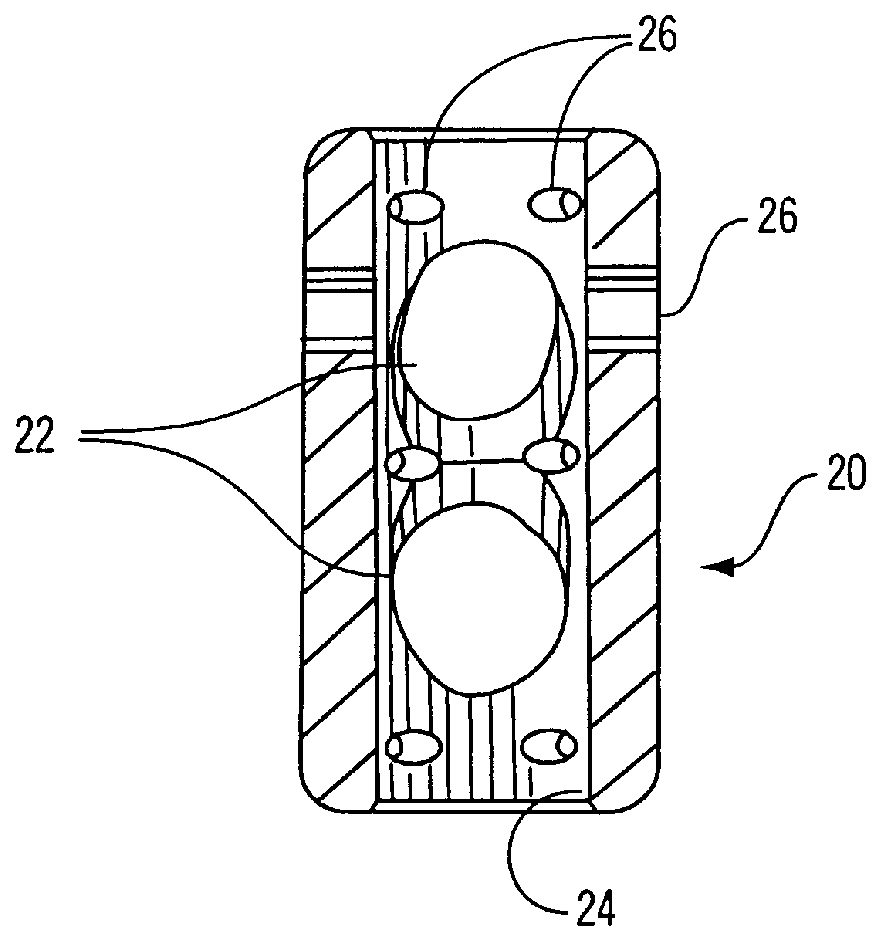
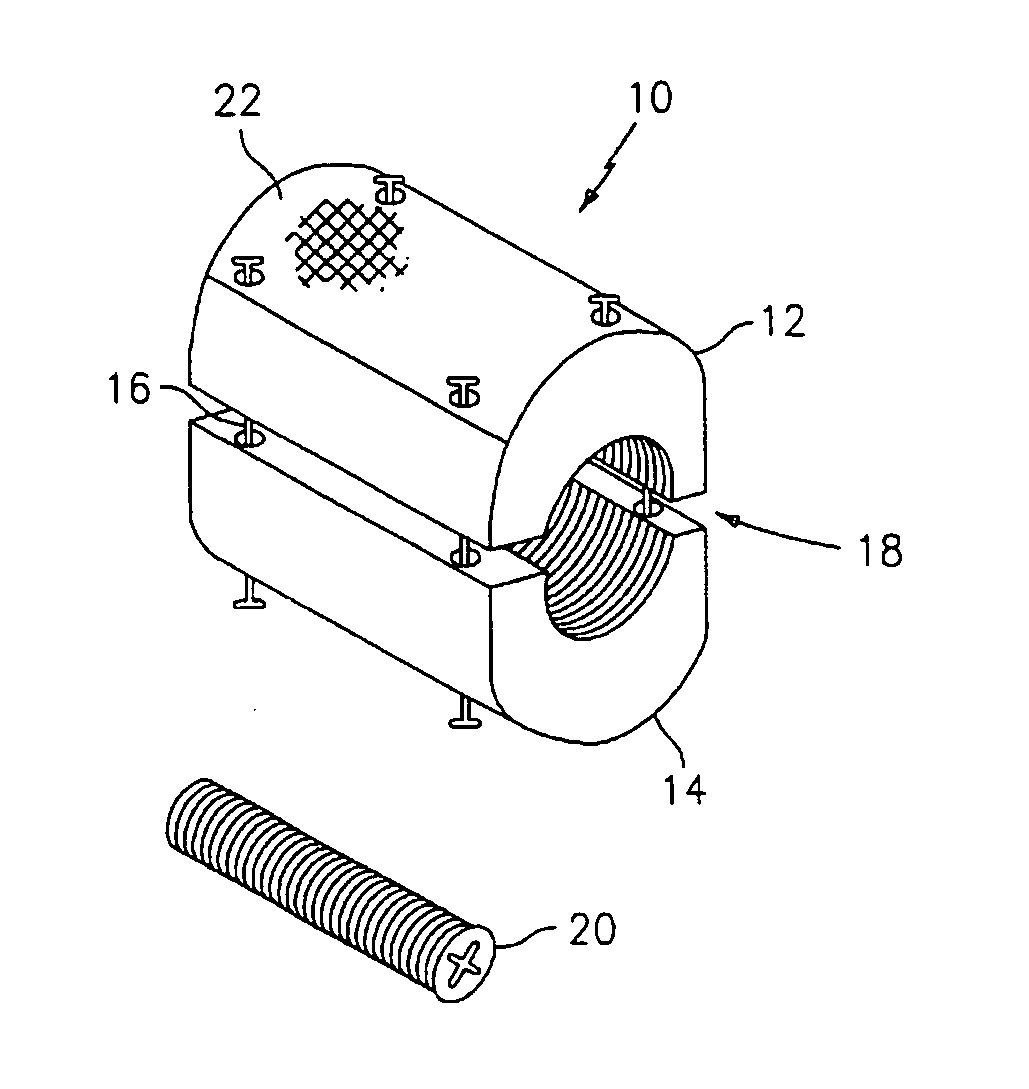
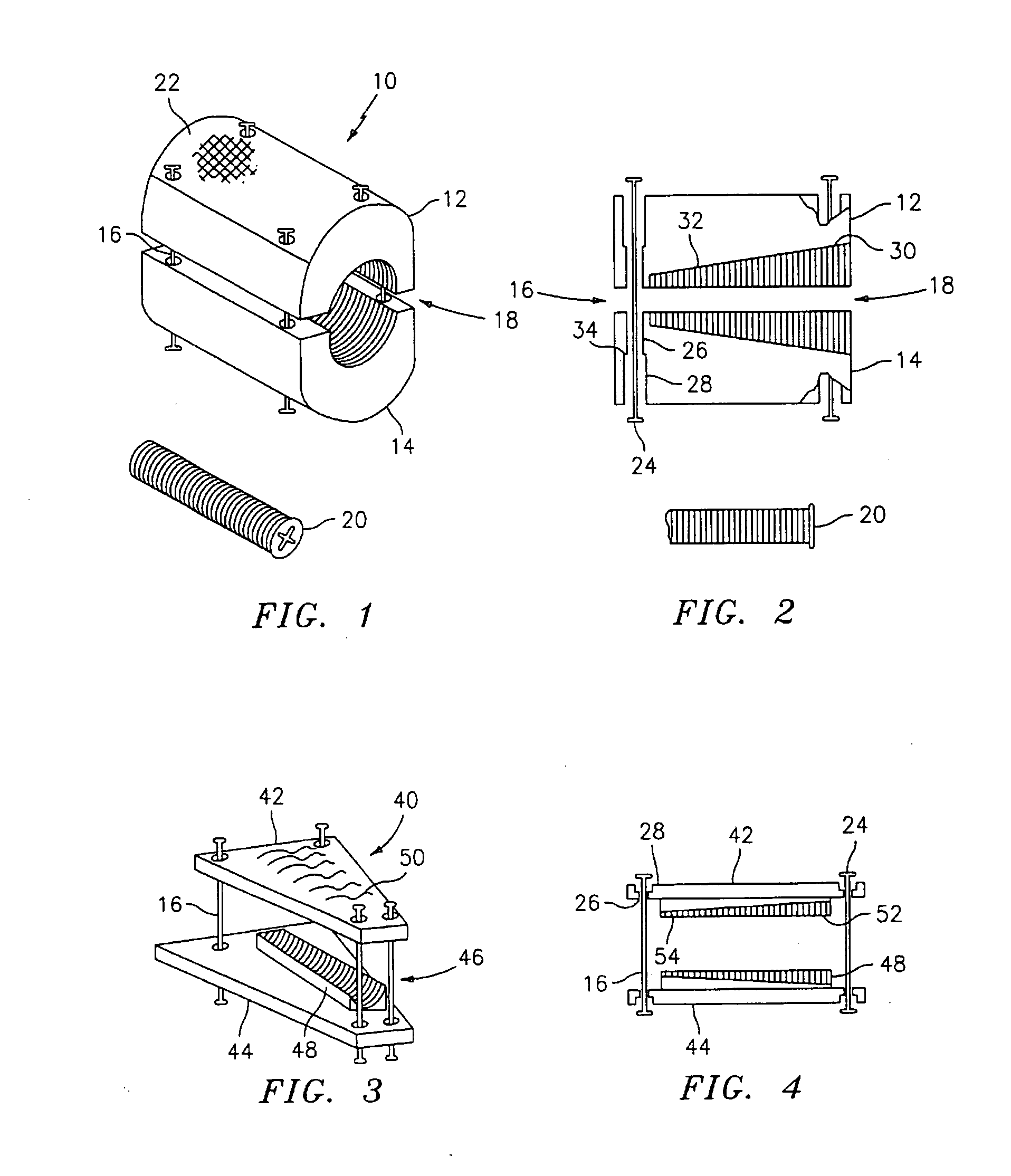
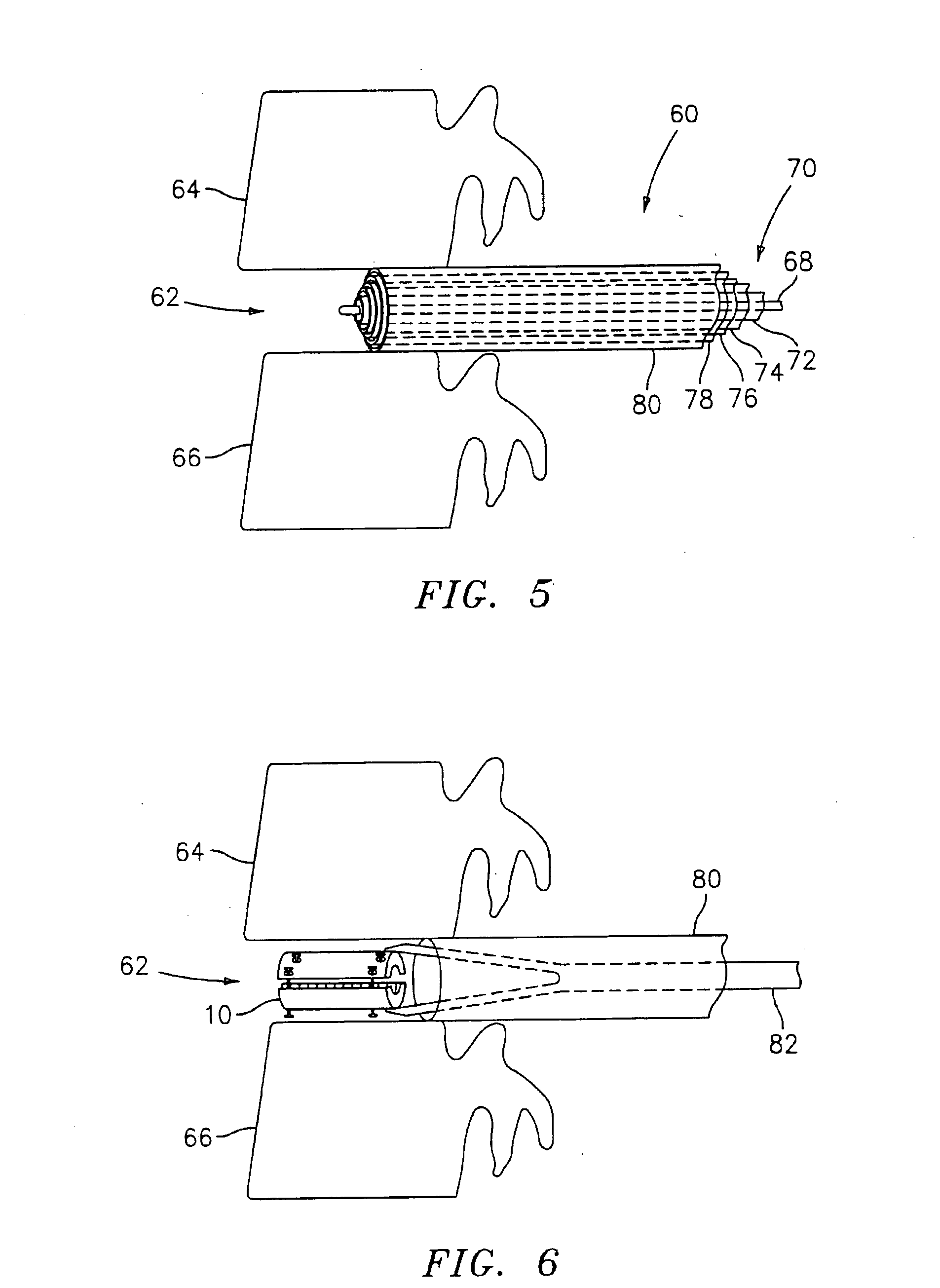
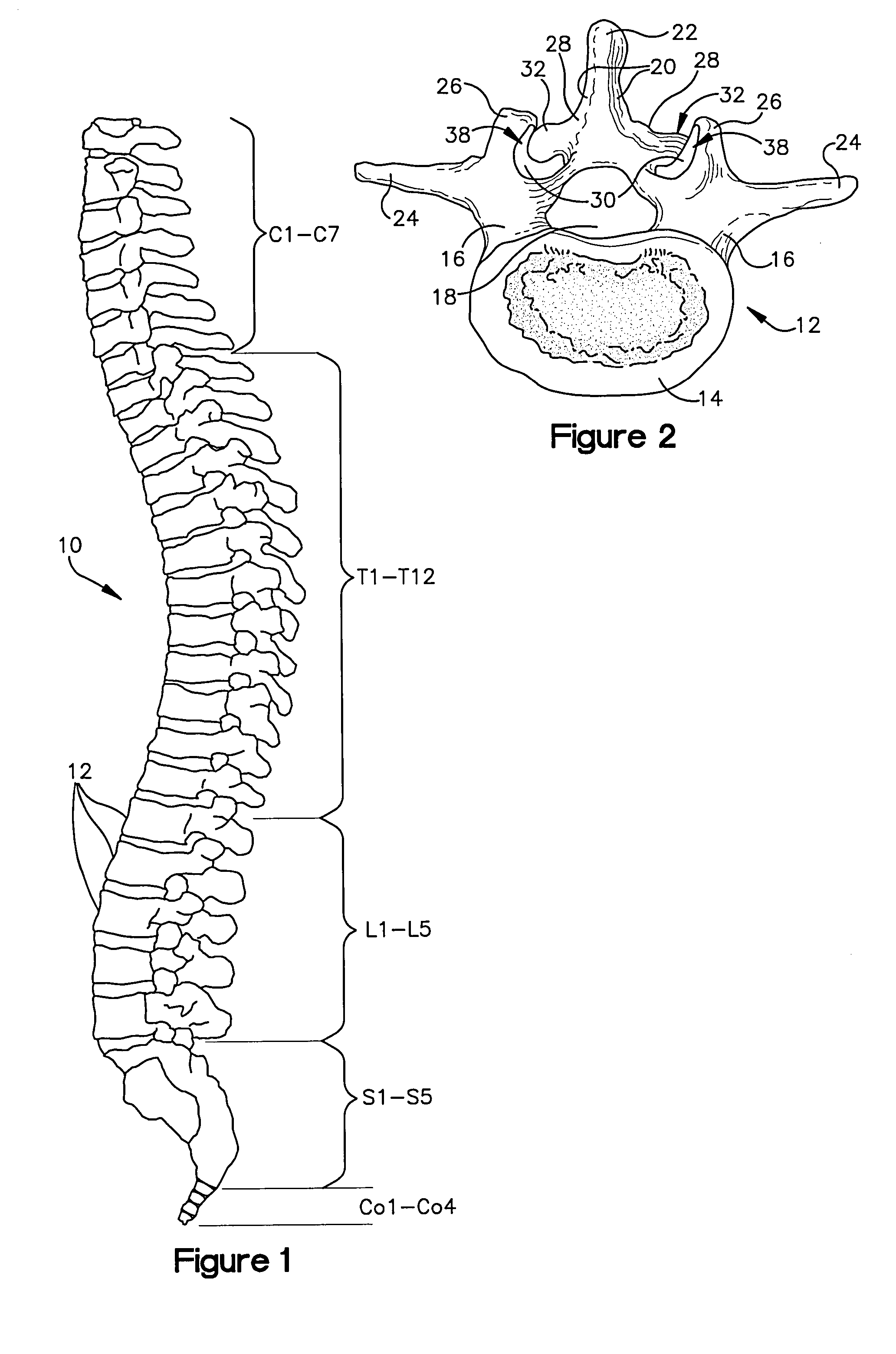
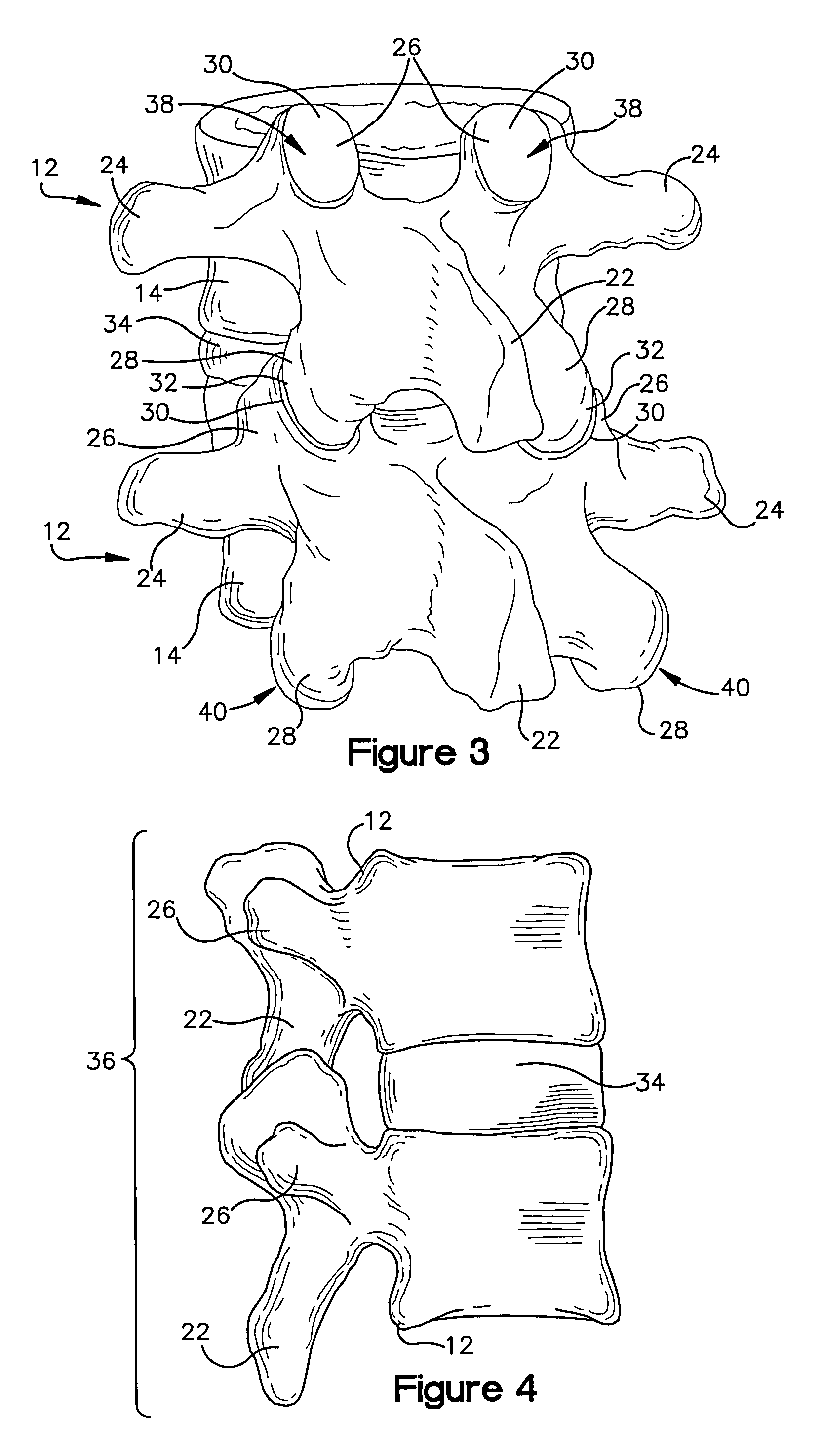
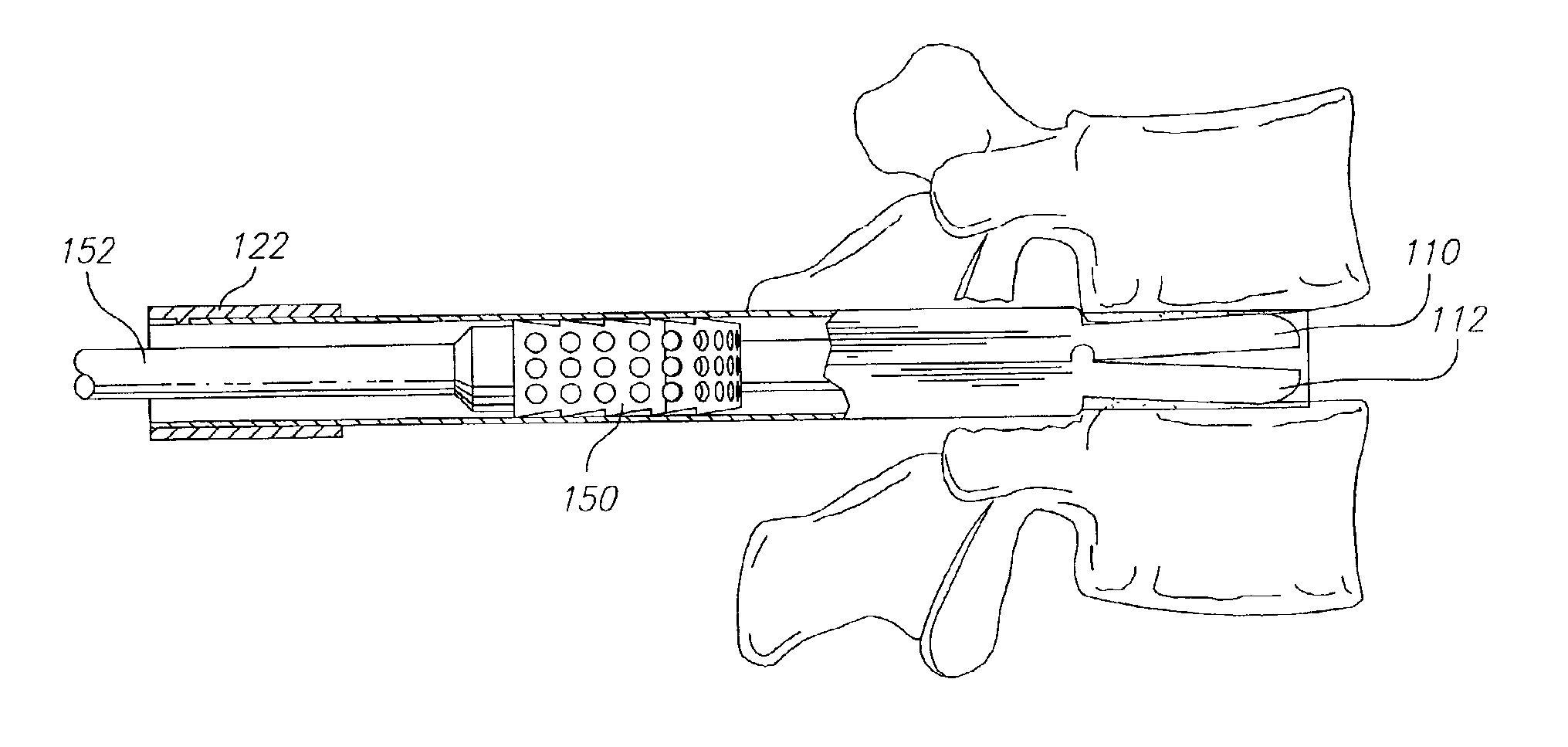
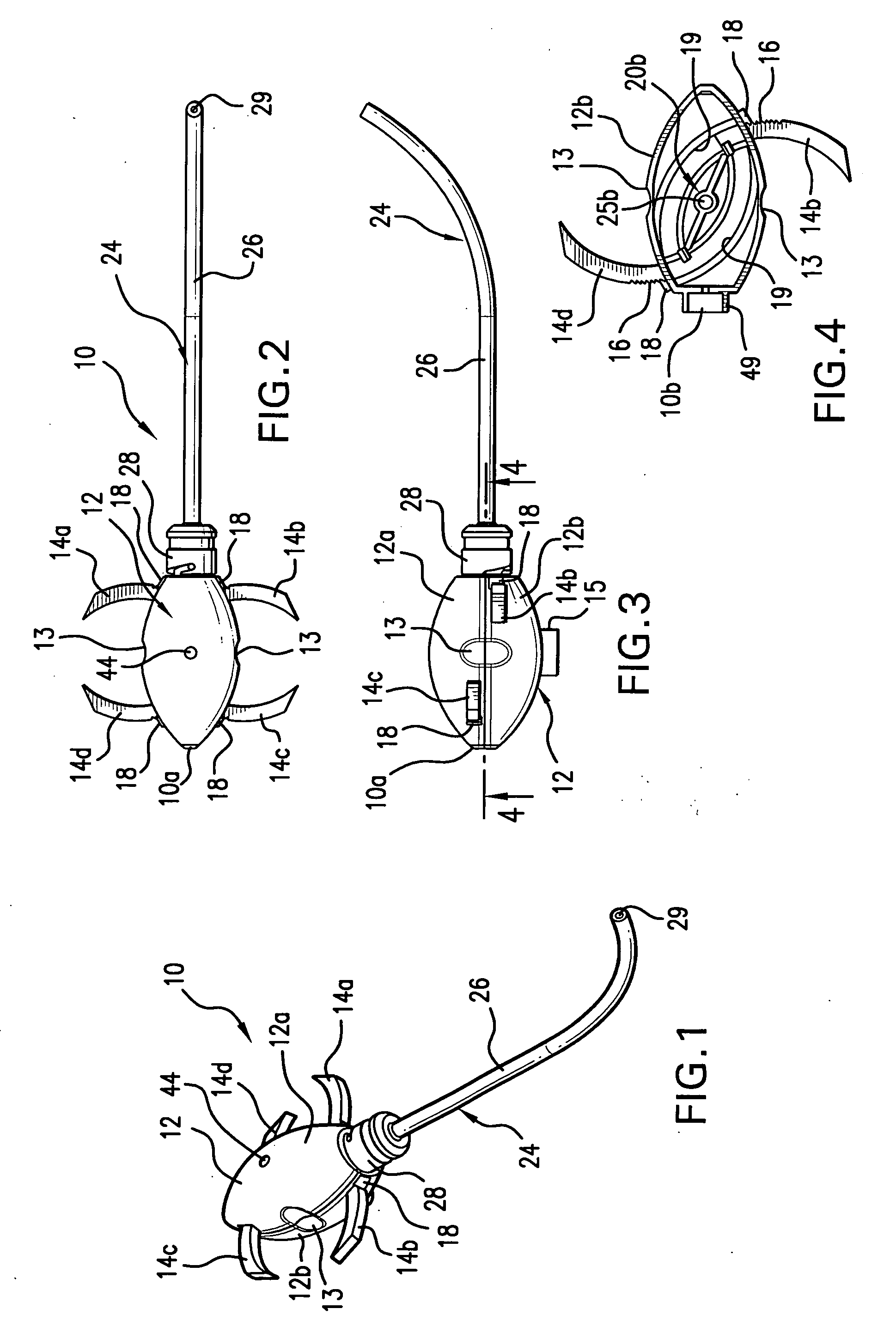
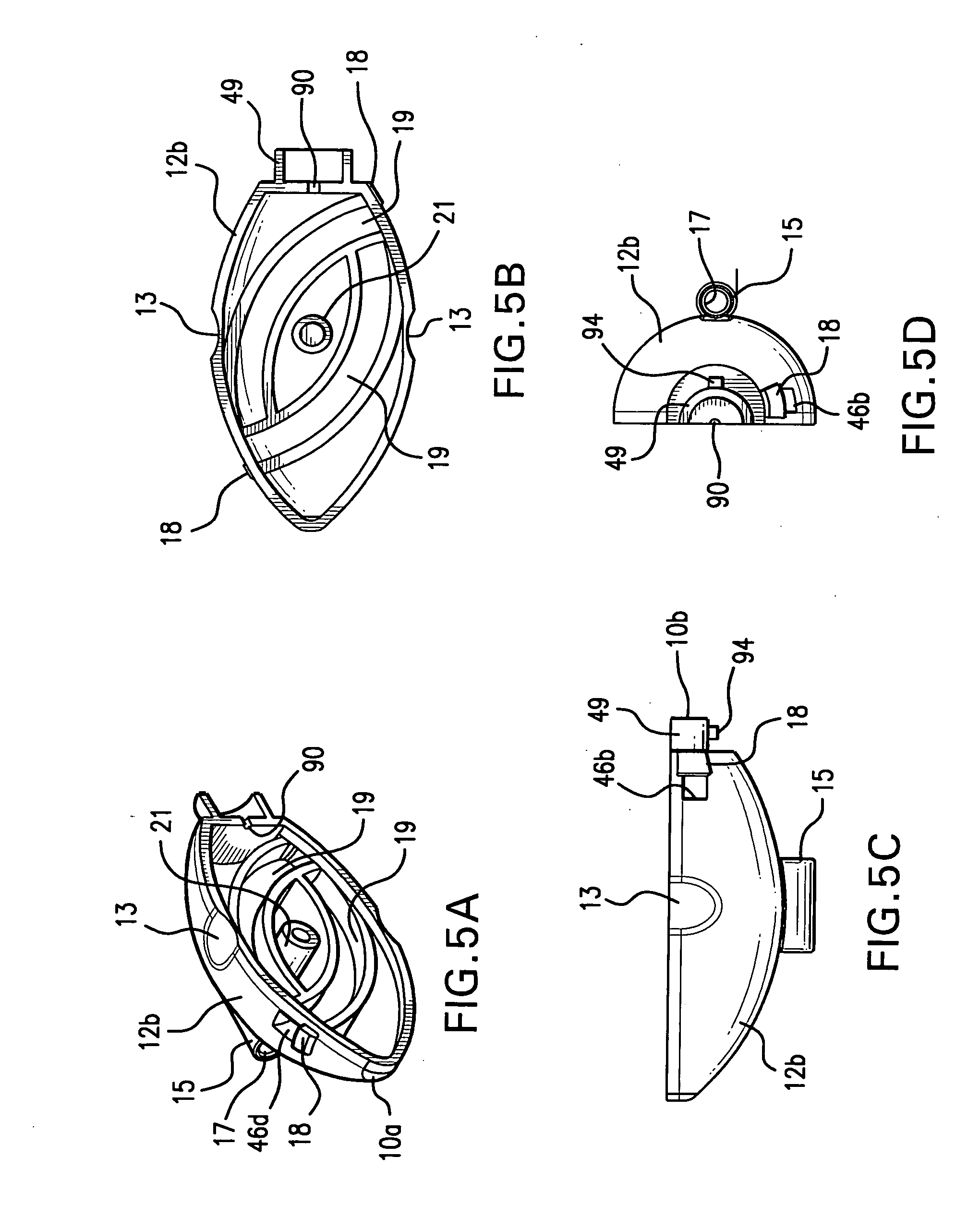
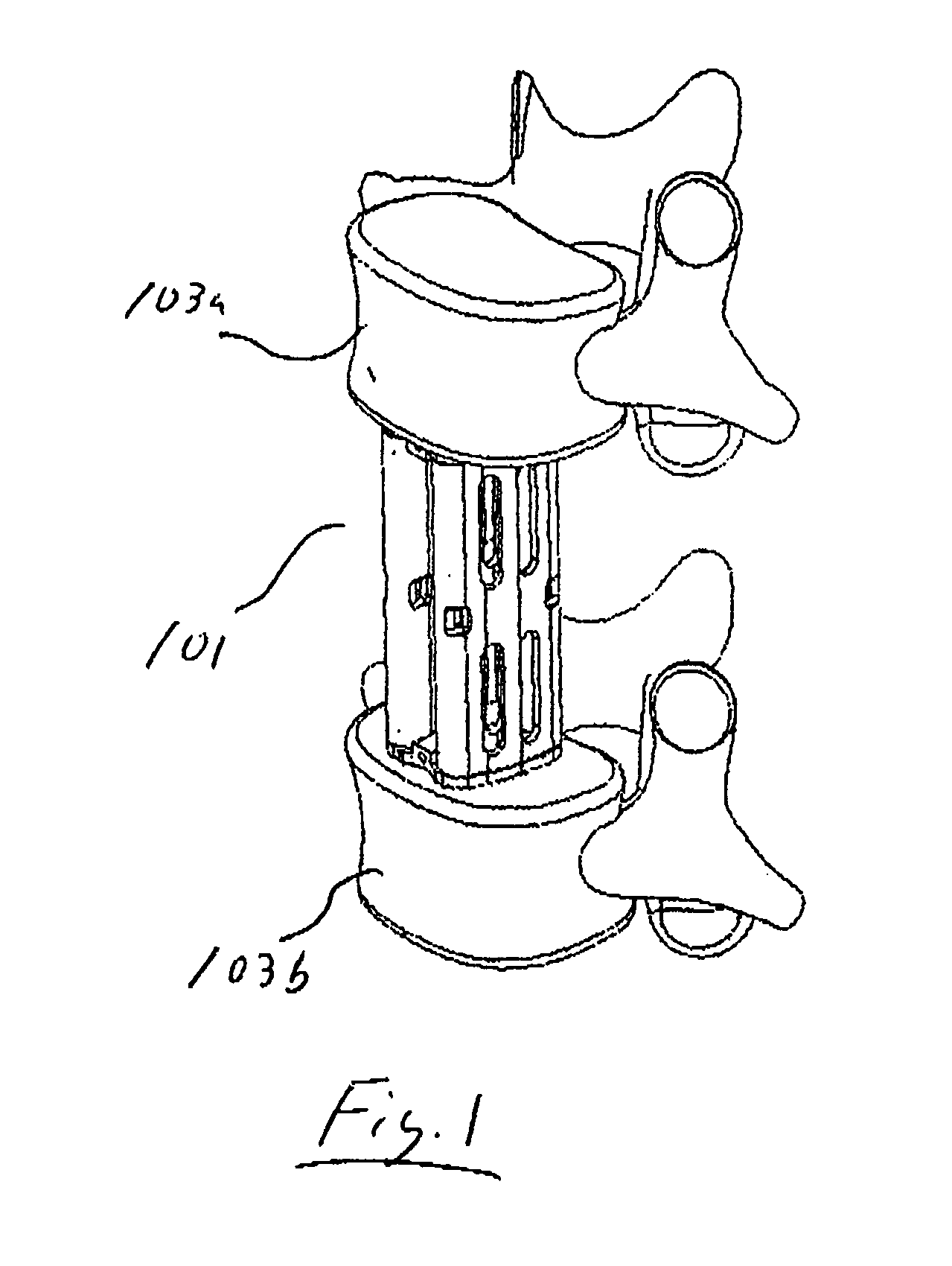
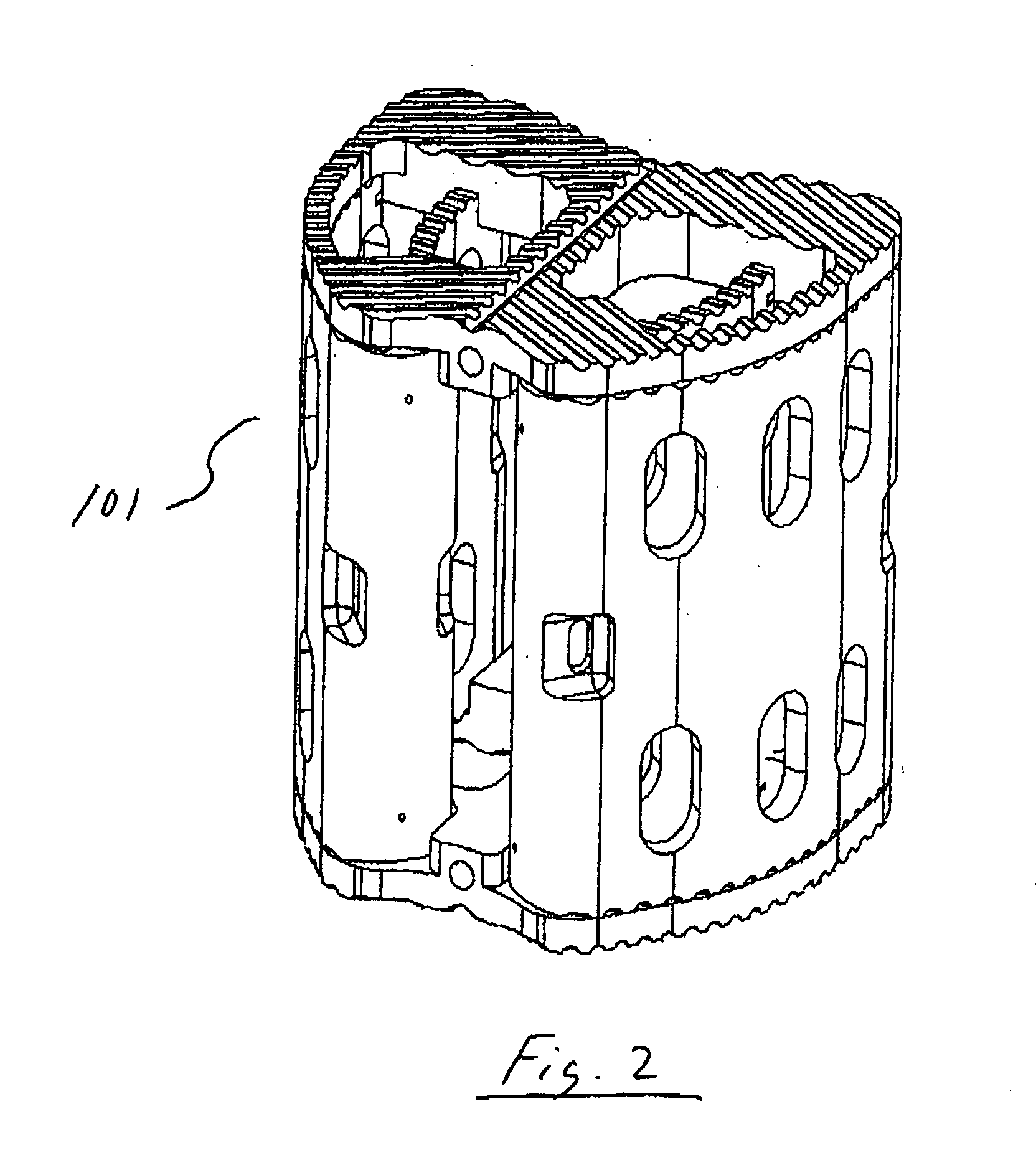
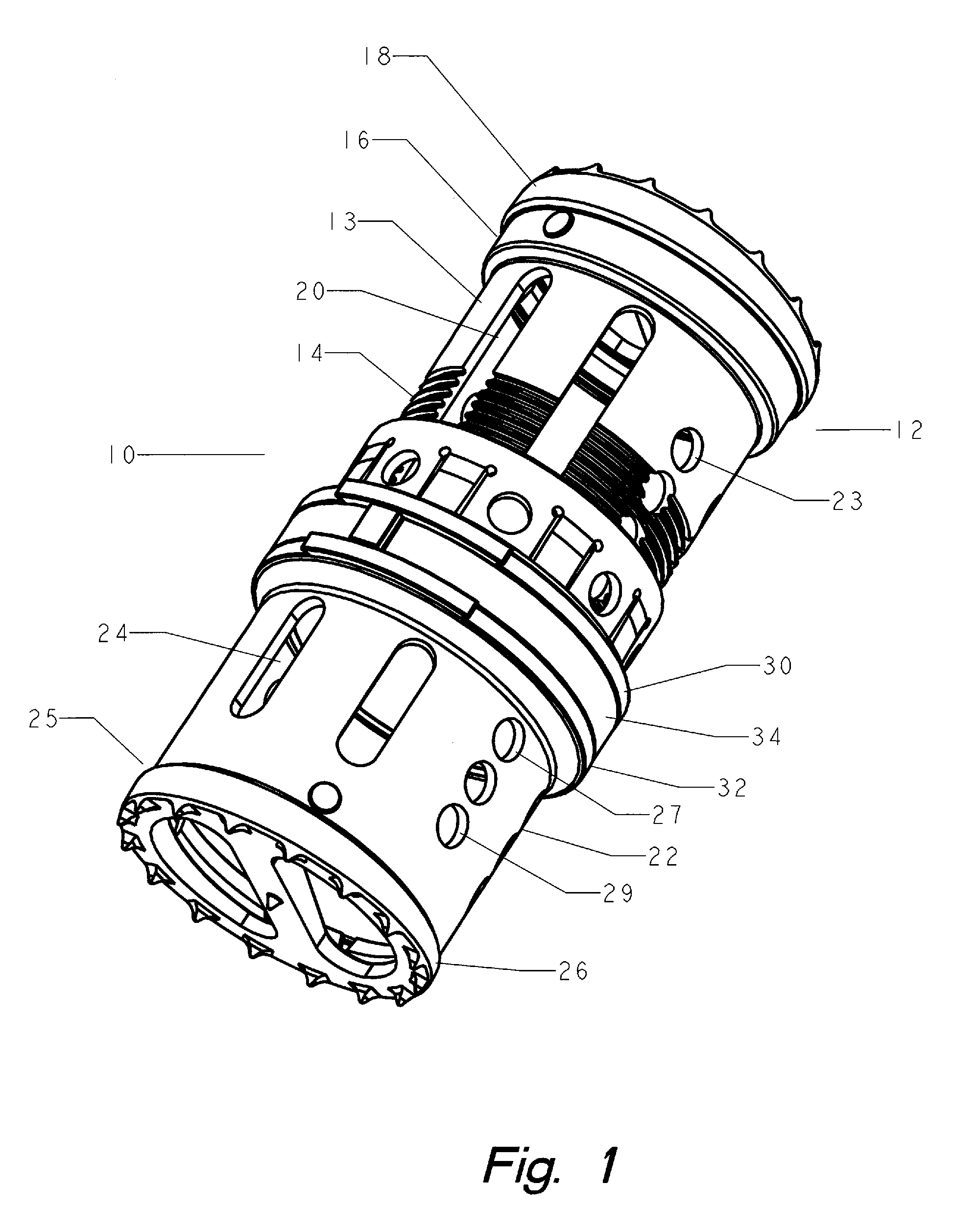
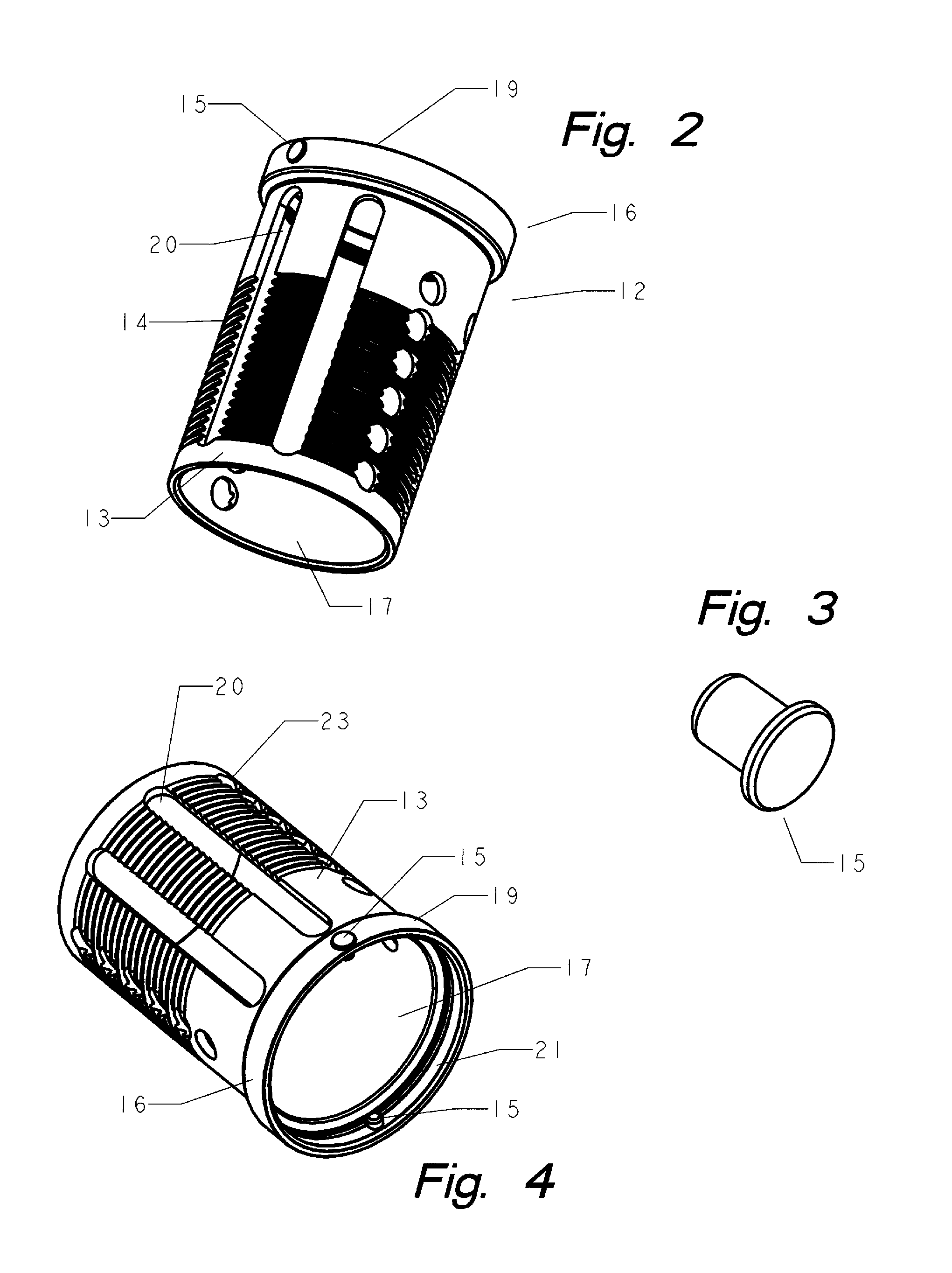
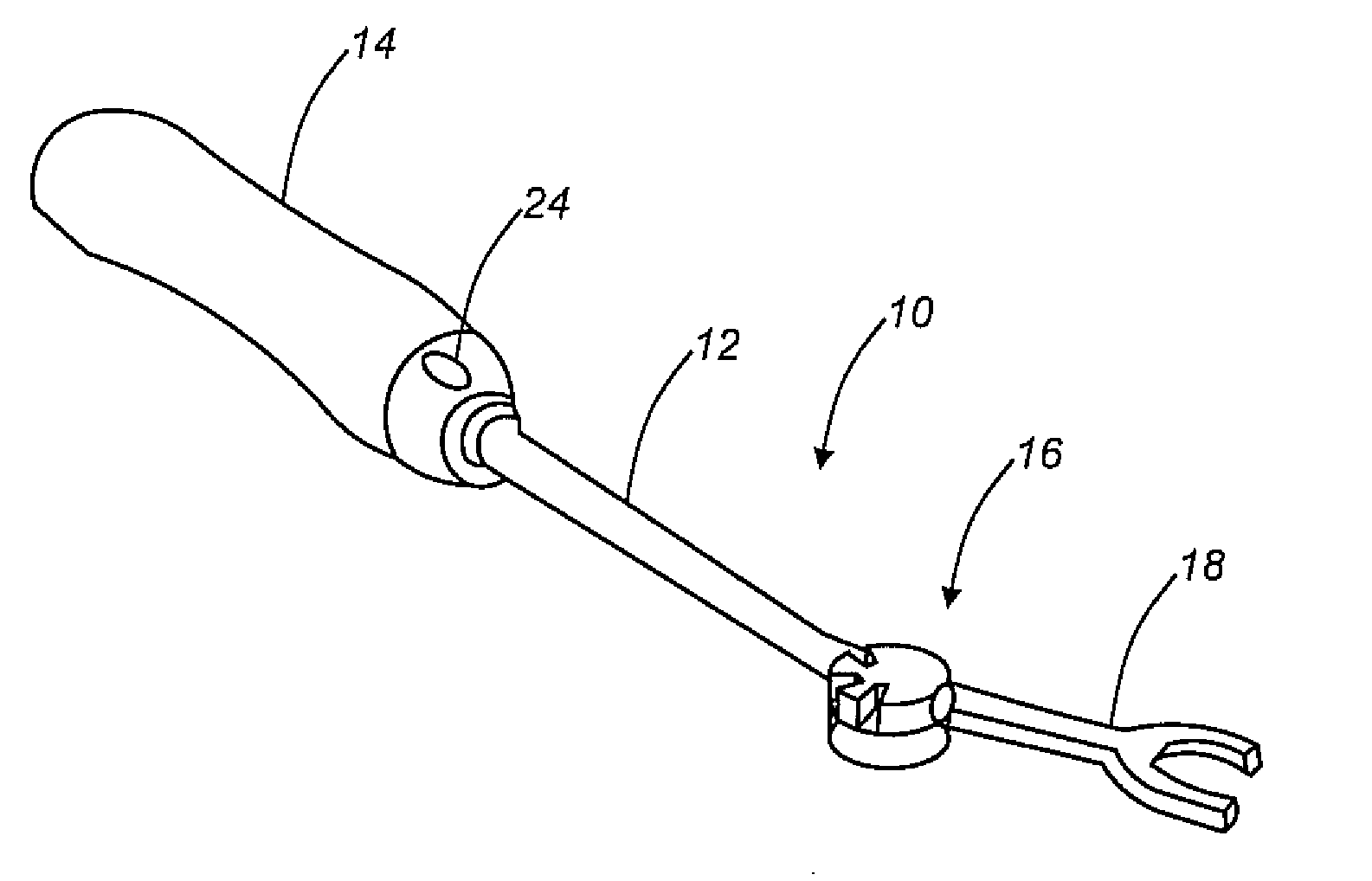
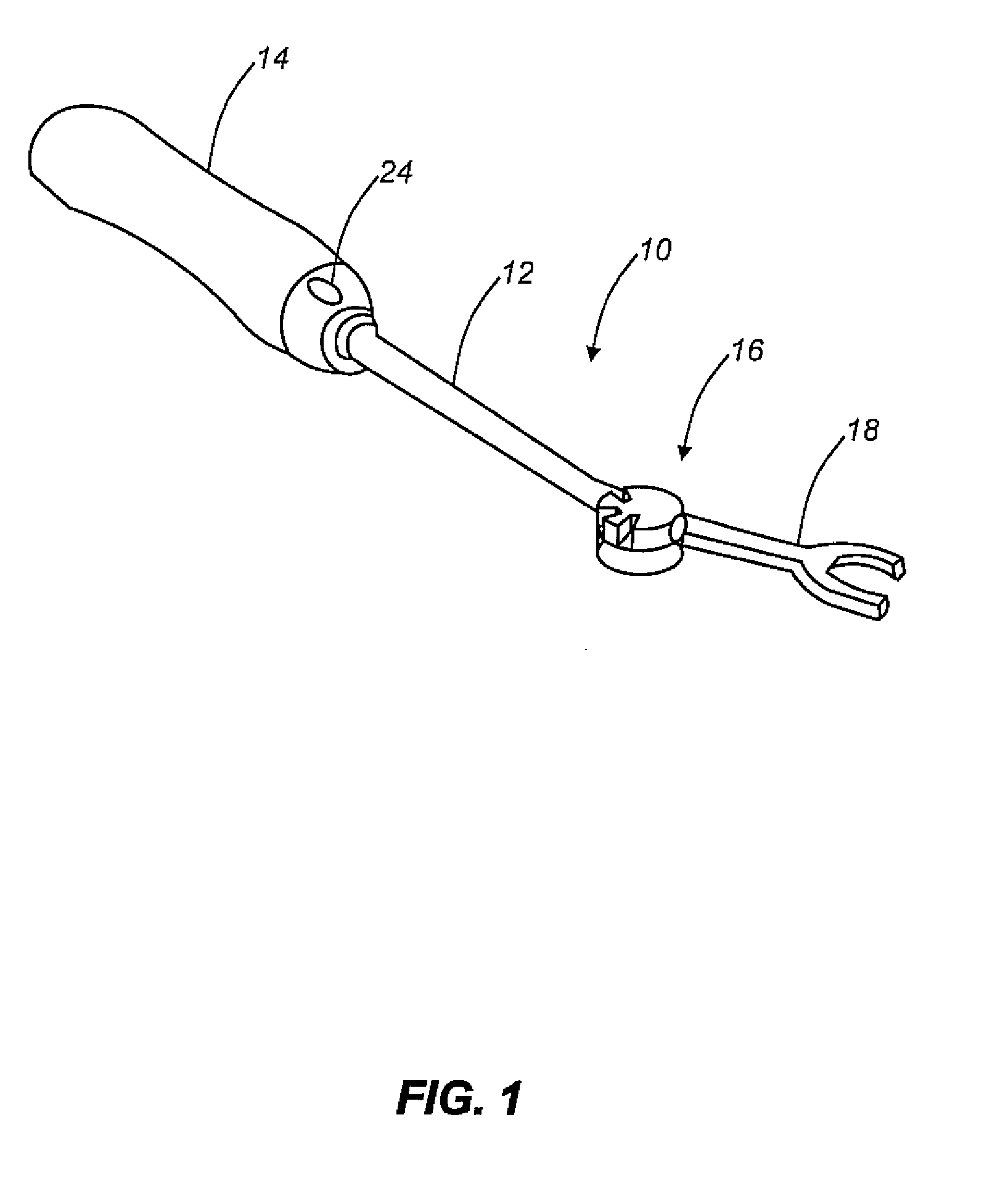
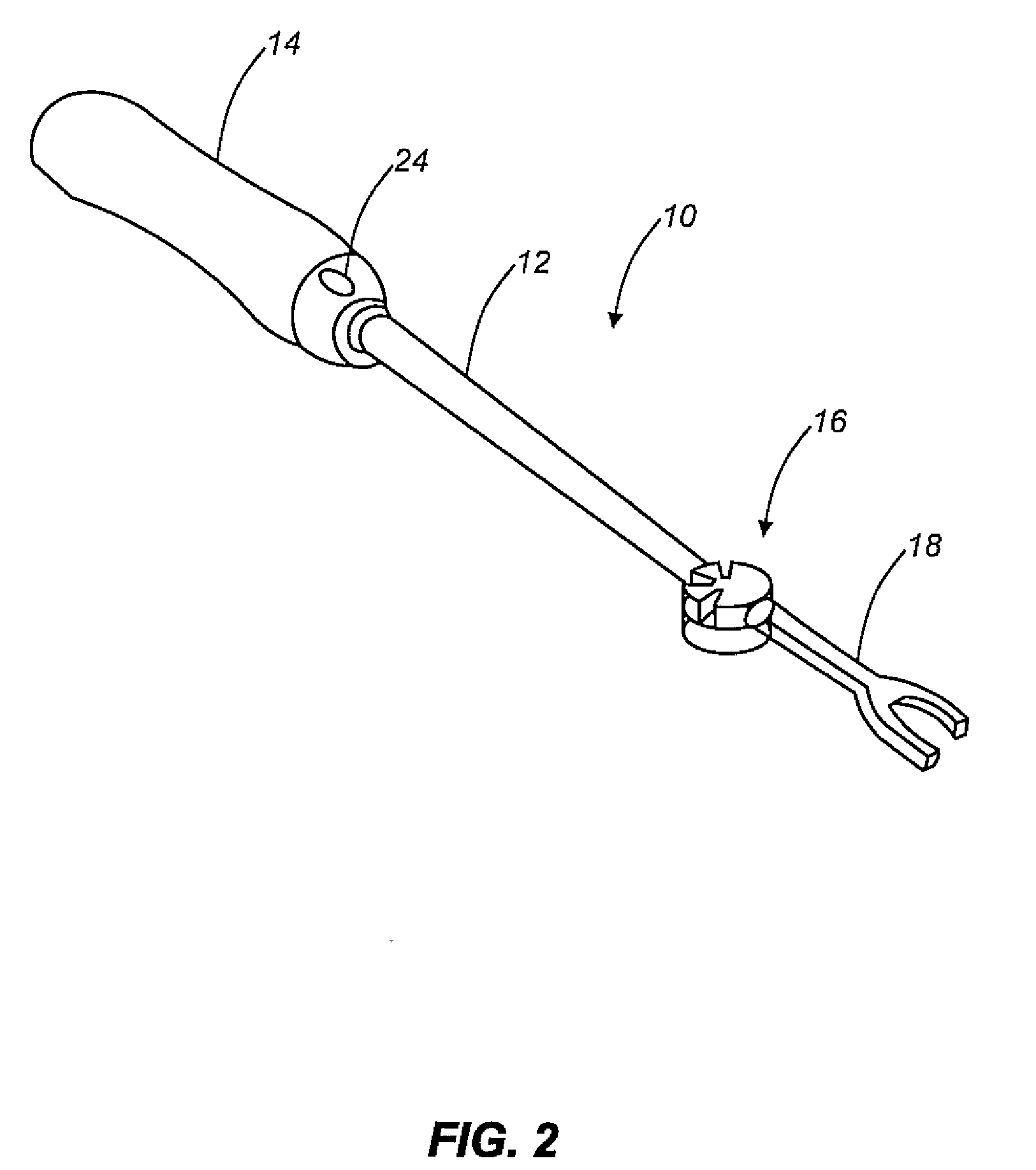
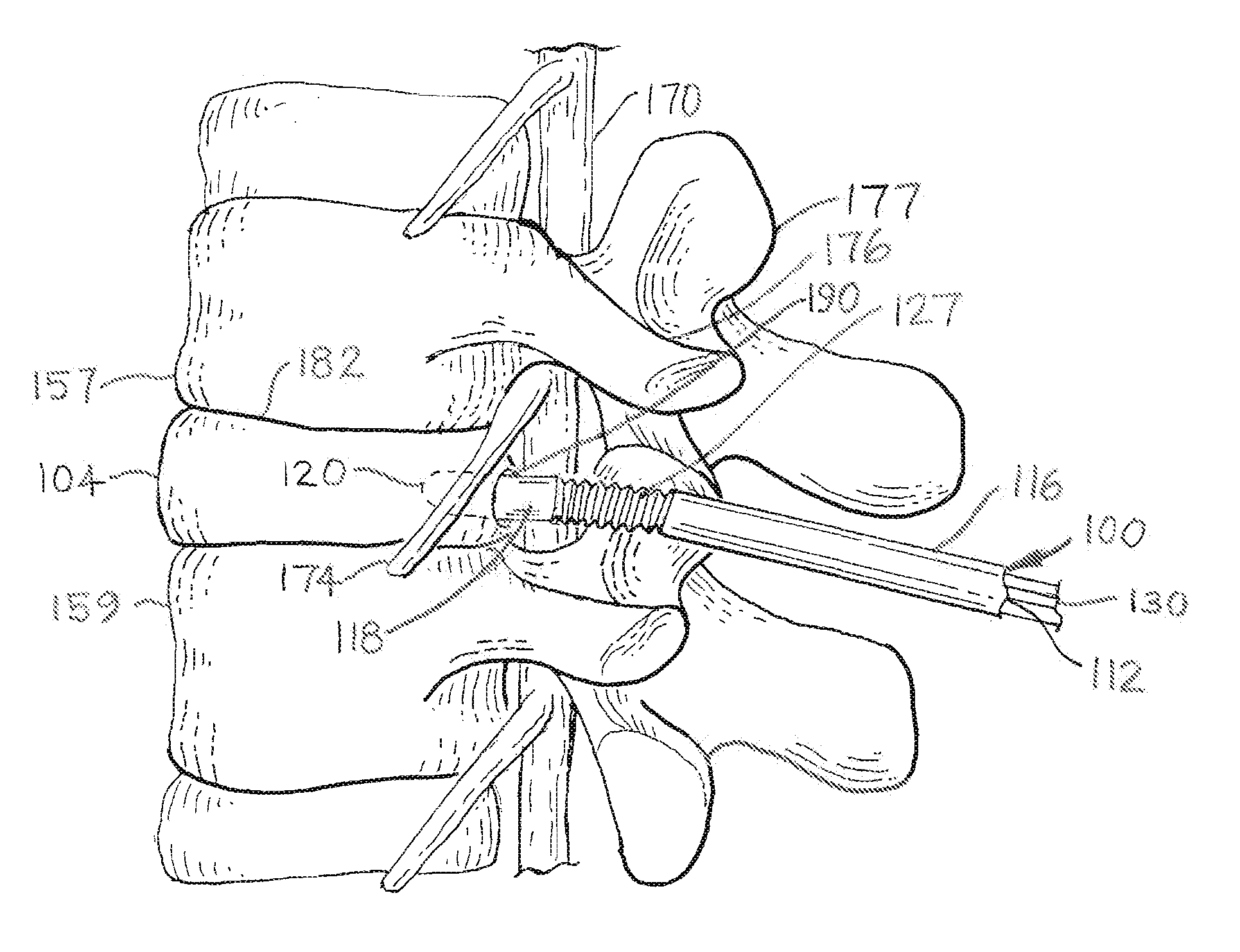
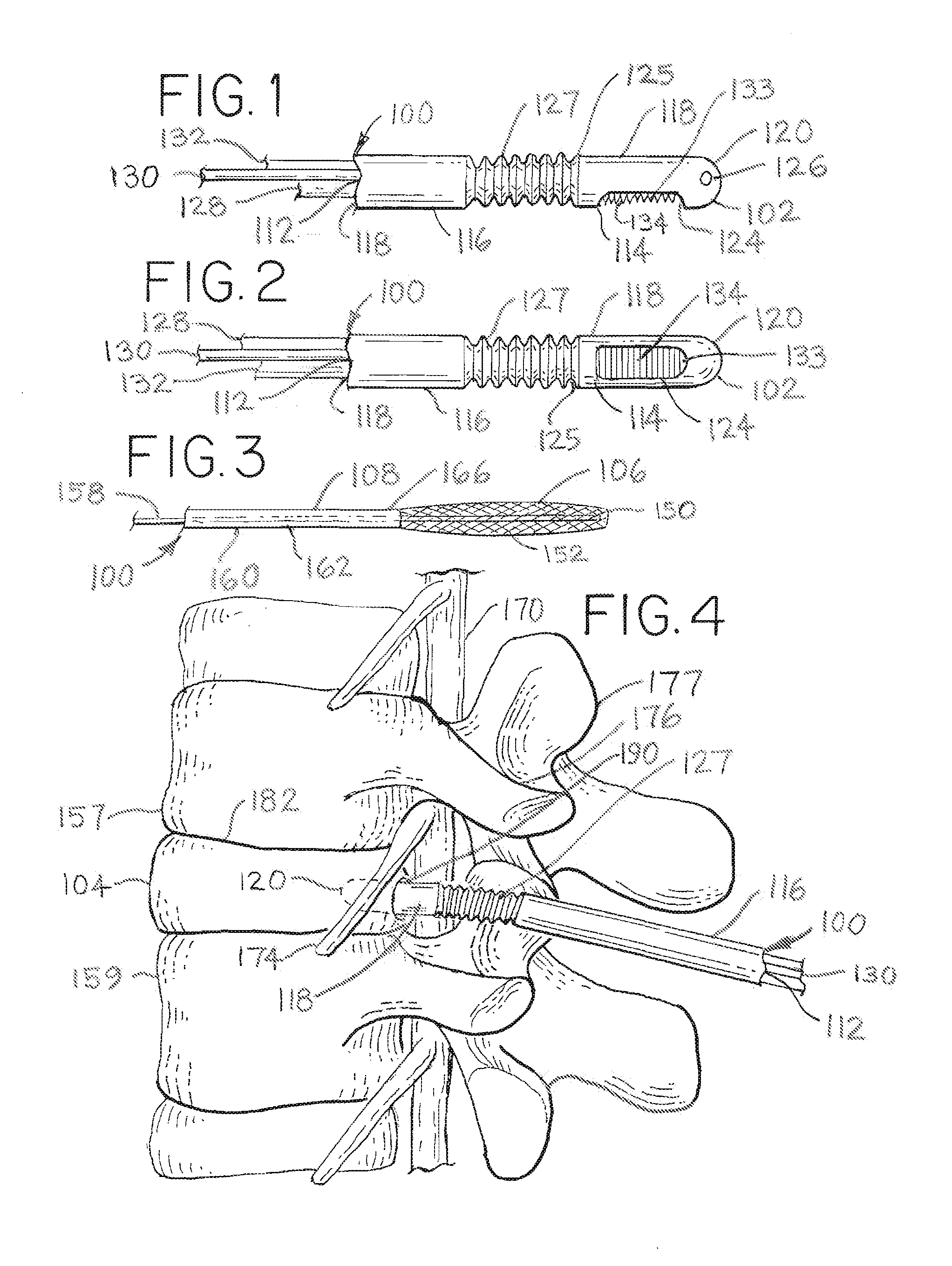
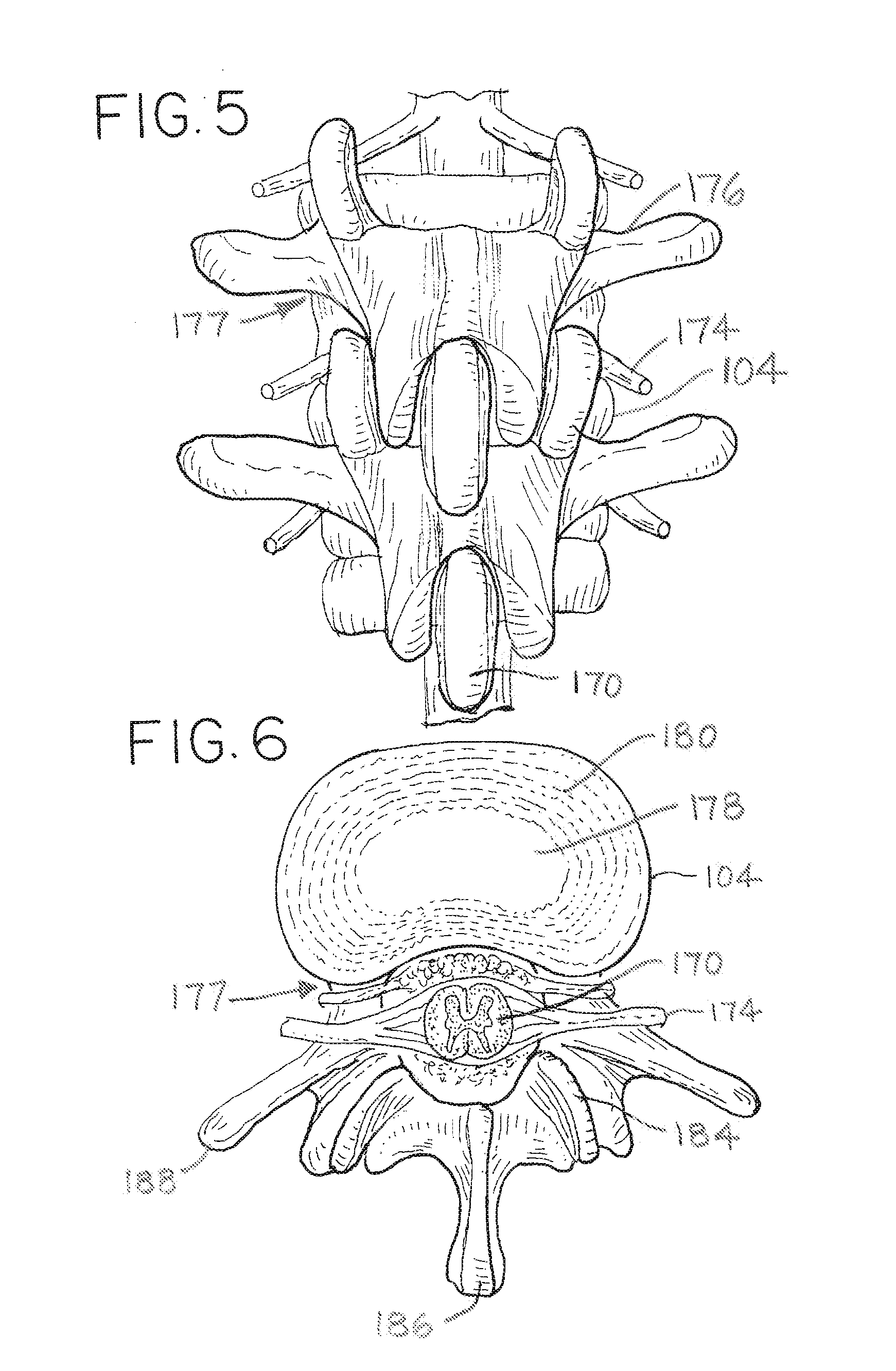
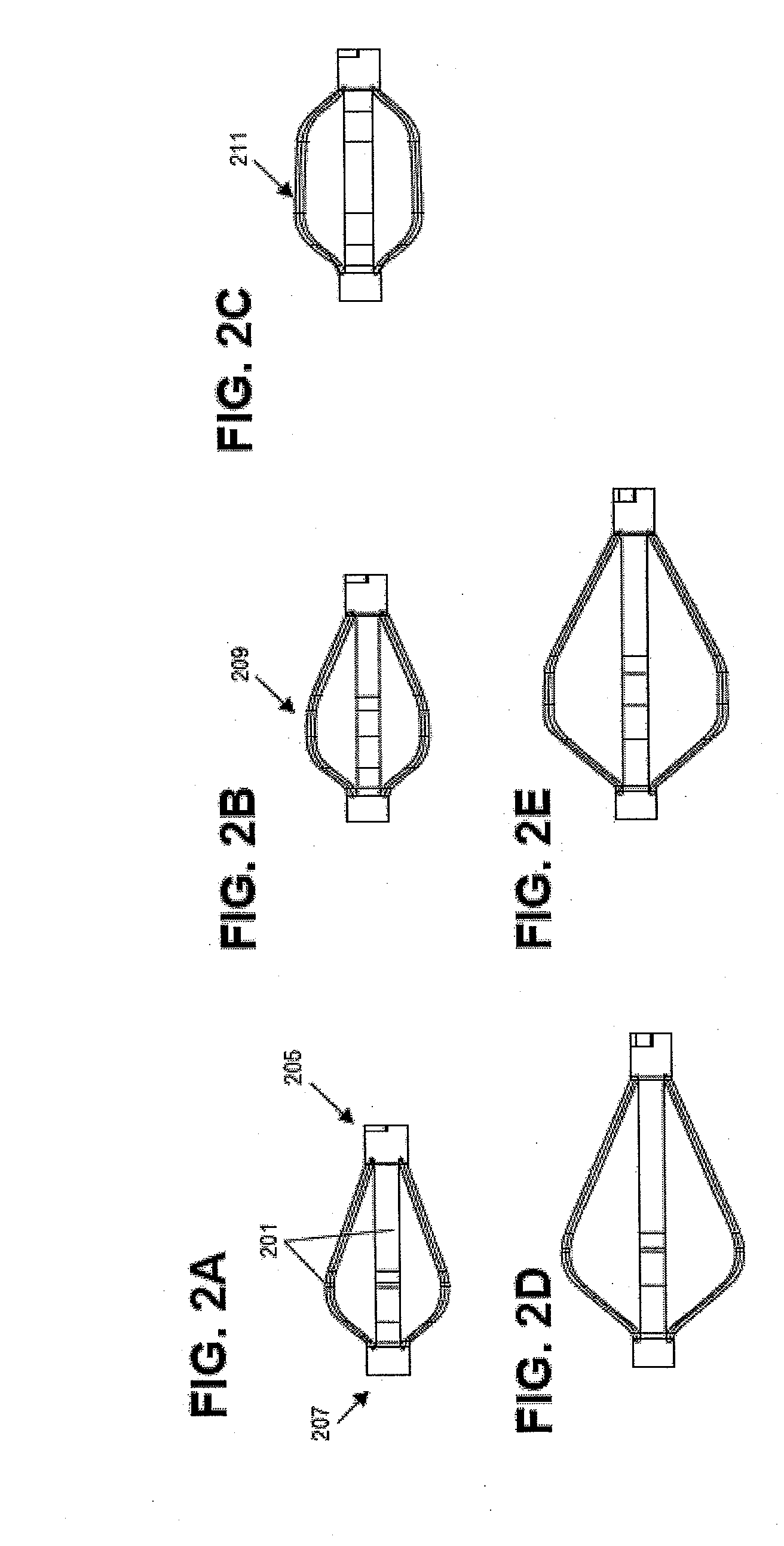
Methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis
InactiveUS20060106381A1Effective treatmentPermit flexionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnDevice form
Surgical implants are configured for placement posteriorly to a spinal canal between vertebral bodies to distract the spine and enlarge the spinal canal. In the preferred embodiments the device permits spinal flexion while limiting spinal extension, thereby providing an effective treatment for treating spinal stenosis without the need for laminectomy. The invention may be used in the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine. Numerous embodiments are disclosed, including elongated, length-adjustable components coupled to adjacent vertebral bodies using pedicle screws. The preferred embodiments, however, teach a device configured for placement between adjacent vertebral bodies and adapted to fuse to the lamina, facet, spinous process or other posterior elements of a single vertebra. Various mechanisms, including shape, porosity, tethers, and bone-growth promoting substances may be used to enhance fusion. The tether may be a wire, cable, suture, or other single or multi-filament member. Preferably, the device forms a pseudo-joint in conjunction with the non-fused vertebra. Alternatively, the device could be fused to the caudal vertebra or both the cranial and caudal vertebrae.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Method and device for fixing and correcting spondylolisthesis anteriorly
A method and apparatus for fixation and correction of spondylolisthesis anteriorly includes a disk cage which is inserted into the space between adjacent vertebrae, a drill guide for guiding and aligning a drill bit to angle an opening anteriorly between adjacent vertebrae, a distractor for temporarily aligning the vertebrae to position a disk cage and an elongated hollow screw positioned in said drilled opening through one vertebra, said disk cage and into said adjacent vertebra.
Owner:SPINEOLOGY
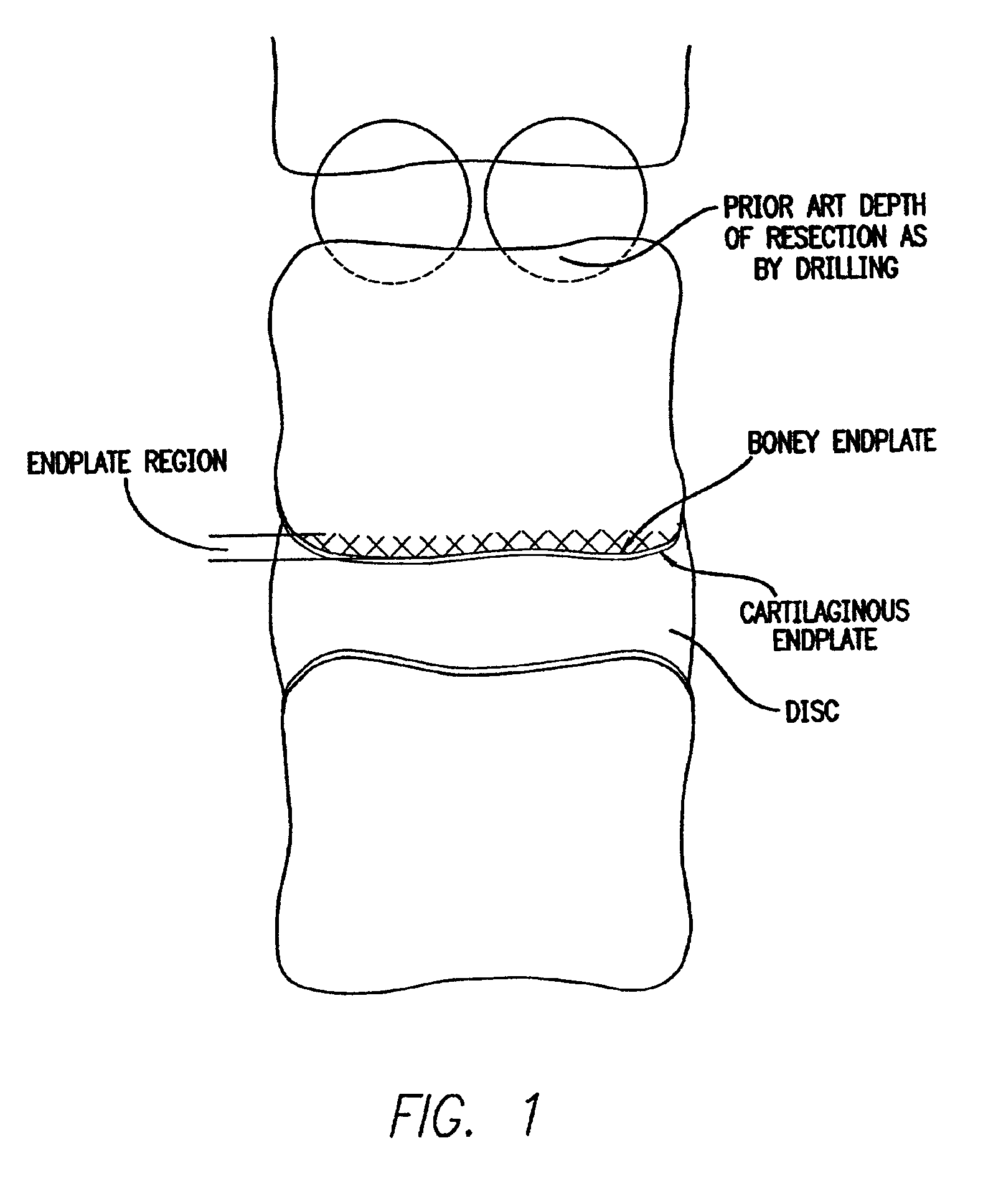
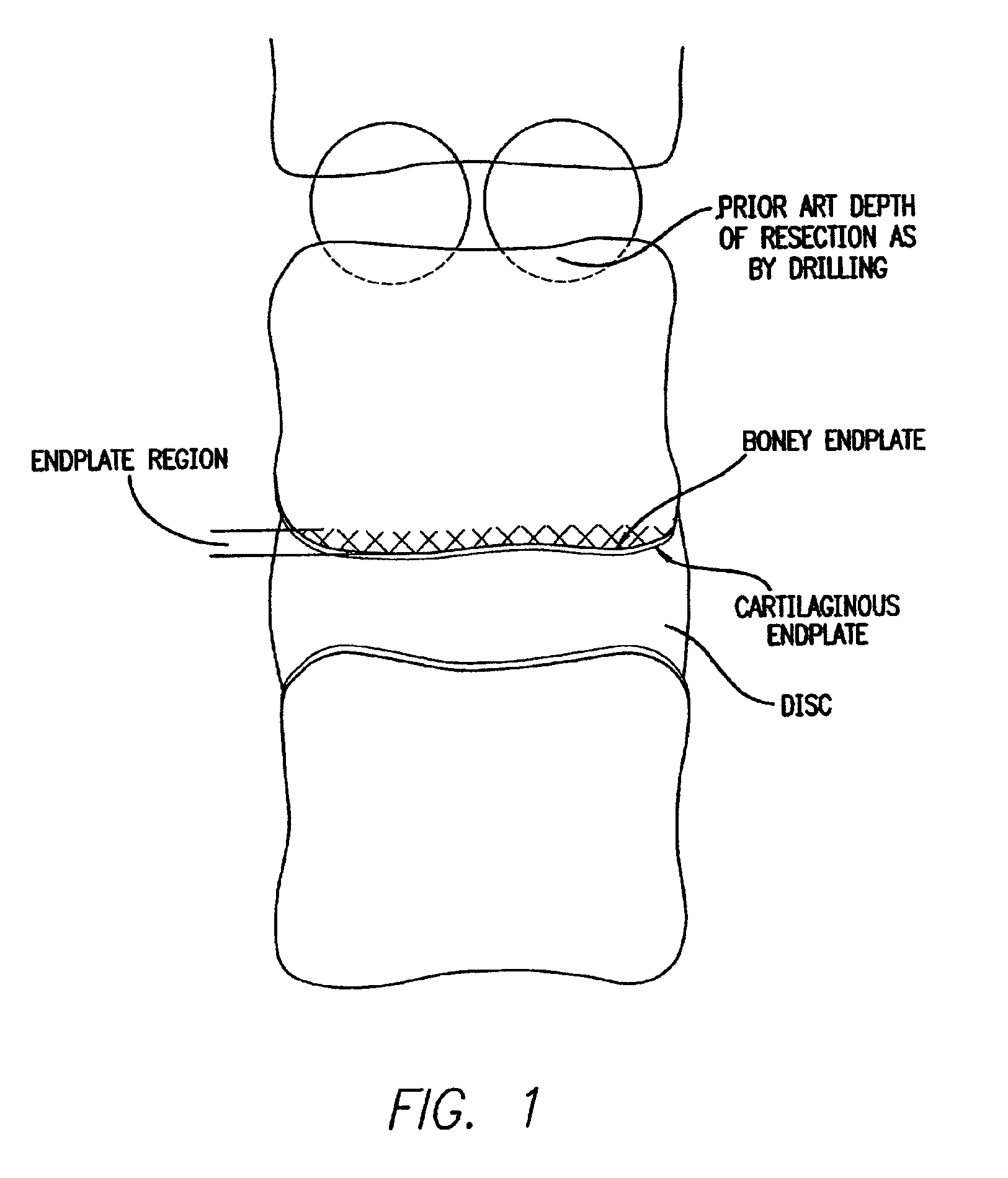
Device for lumbar surgery
InactiveUS20050171541A1Shorten recovery timeReduces the trauma to the patientInternal osteosythesisBone implantDilatorIntervertebral space
A method for performing percutaneous interbody fusion is disclosed. The method includes the steps of inserting a guide needle posteriorly to the disc space, inserting a dilator having an inner diameter slightly larger than the outer diameter of the guide needle over the guide needle to the disc space to enlarge the disc space, and successively passing a series of dilators, each having an inner diameter slightly larger than the outer diameter of the previous dilator, over the previous dilator to the disc space the gradually and incrementally increase the height of the disc space. Once the desired disc height is achieved, the guide needle and all the dilators, with the exception of the outermost dilator, are removed. An expandible intervertebral disc spacer is then passed through the remaining dilator and positioned in the disc space. The disc spacer is expanded to the required disc height, and then a bone matrix is passed through the dilator to fill the disc space. The dilator is then removed. An expandible intervertebral disc spacer is also disclosed, having a tapered bore that causes greater expansion of one end of the spacer with respect to the other. A kit for performing the percutaneous interbody fusion procedure is also disclosed.
Owner:BOEHM FR H JR +1
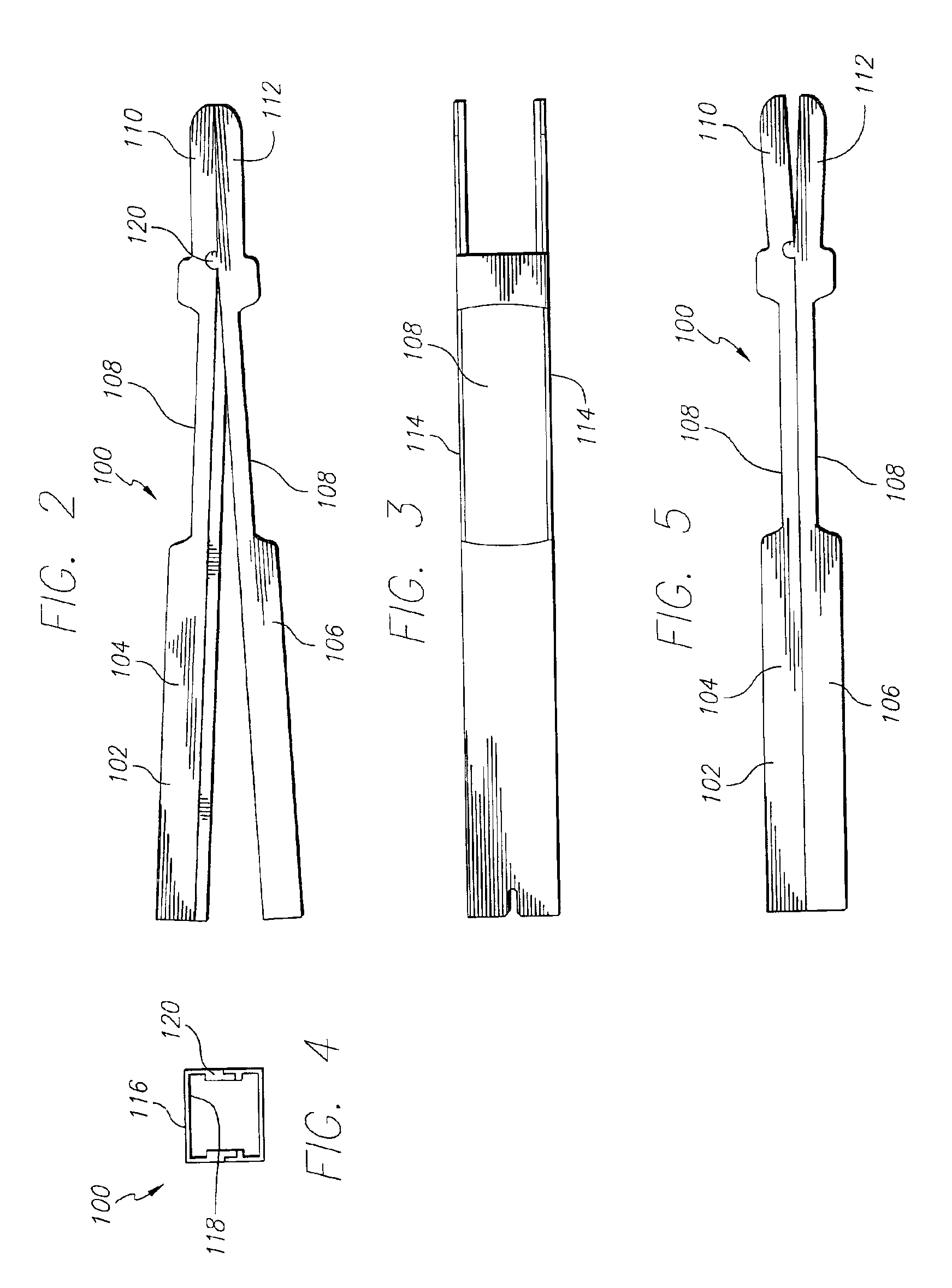
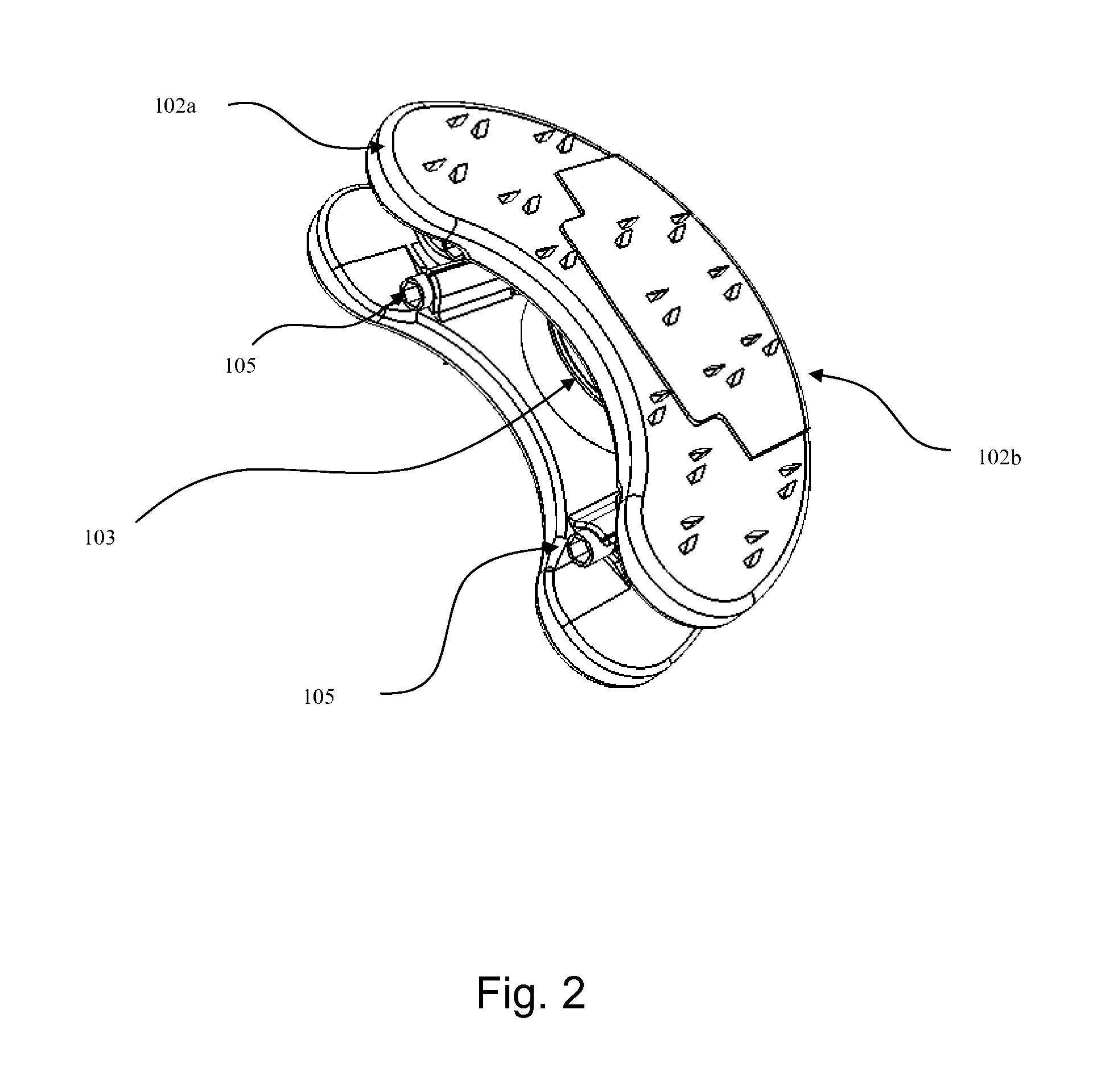
Arcuate dynamic lordotic guard with movable extensions for creating an implantation space posteriorly in the lumbar spine
InactiveUS6896680B2Easy to insertEasy to removeSpinal implantsOsteosynthesis devicesSpinal columnLumbar spine
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method for resurfacing a lumbar articular facet
Methods for treating spinal pathologies, and more specifically methods for treating articulating surfaces of facet joints. The methods involve providing artificial articulating surfaces for facet joint articular facets. In addition, various types of rasps may be used to prepare the articulating surfaces prior to placement of the artificial articulating surfaces.
Owner:LANTERNA MEDICAL TECH
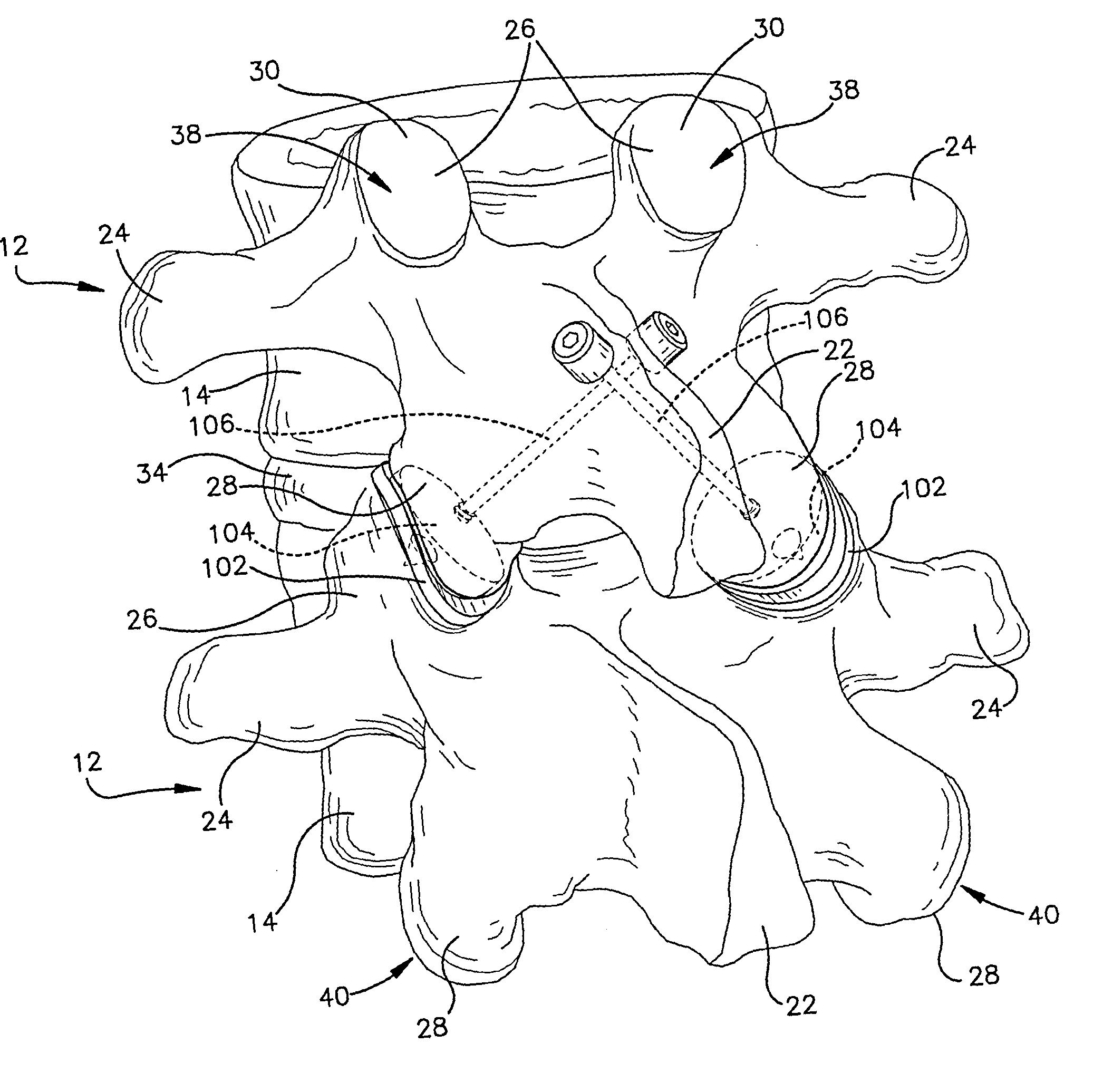
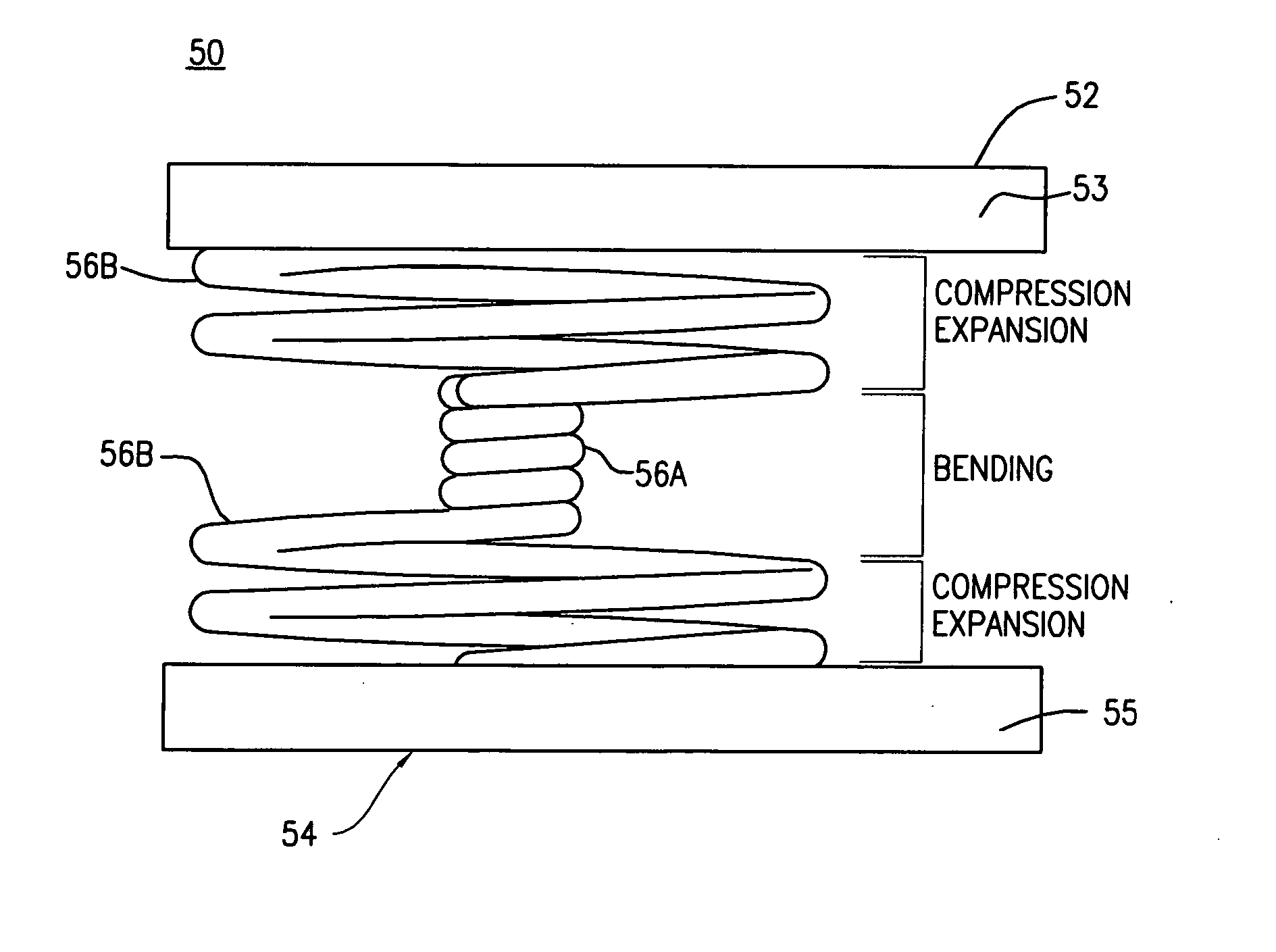
Posterior lumbar intervertebral stabilizer
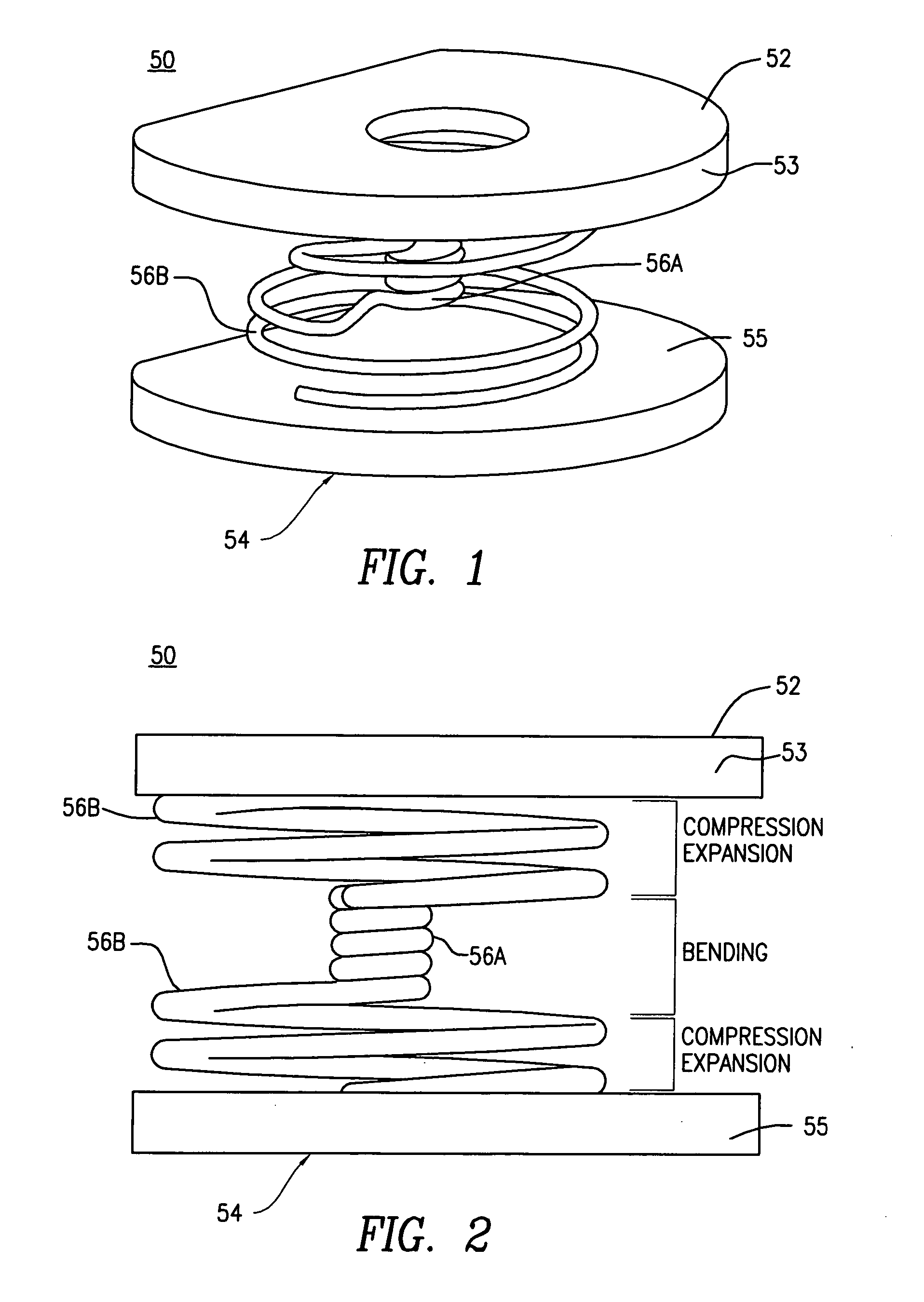
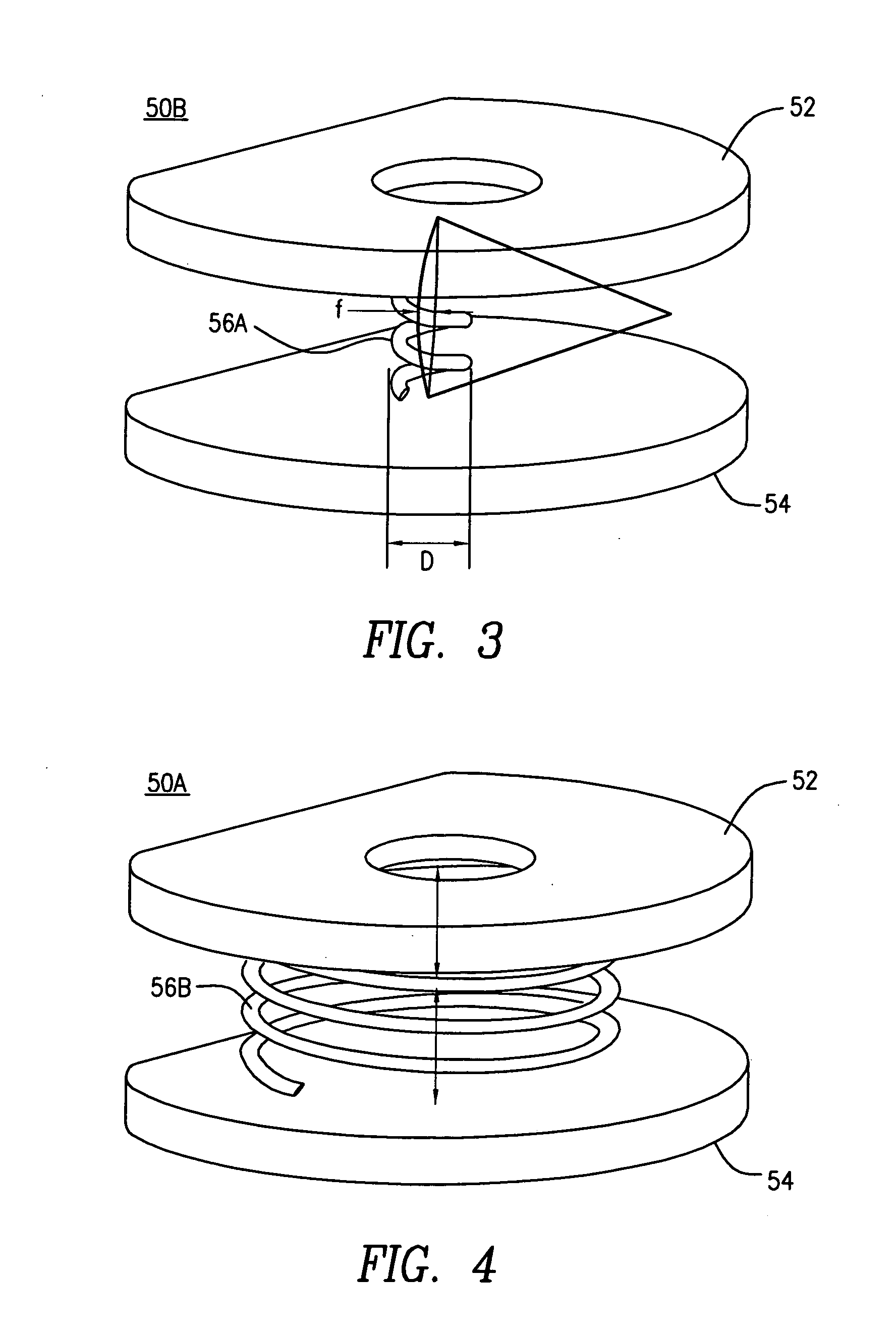
A posterior intervertebral stabilizer includes: a first stabilizing element having: (i) a first surface operable to engage an endplate of a first vertebral bone of a spine, and (ii) a second surface spaced apart from the first surface and operable to engage an endplate of an adjacent second vertebral bone of the spine; a second stabilizing element having: (i) a first surface operable to engage an endplate of the first vertebral bone of the spine, and (ii) a second surface spaced apart from the first surface and operable to engage an endplate of the adjacent second vertebral bone of the spine; and respective spring elements, each including helical coils, disposed between the respective first and second surfaces of the first and second stabilizing elements, each operable to provide a reactive force in response to compression loads from the first and second vertebral bones, wherein at least some diameters of respective turns of the respective helical coils differ.
Owner:CARDO MEDICAL
Arrangement and method for the intra-operative determination of the position of a joint replacement implant
InactiveUS20050149050A1Easy to operateLow risk of errorPerson identificationJoint implantsReference vectorMeasurement point
Arrangement for the intra-operative determination of the spatial position and angular position of a joint replacement implant, especially a hip socket or shoulder socket or an associated stem implant, or a vertebral replacement implant, especially a lumbar or cervical vertebral implant, using a computer tomography method, having: a computer tomography modeling device for generating and storing a three-dimensional image of a joint region or vertebral region to be provided with the joint replacement implant, an optical coordinate-measuring arrangement for providing real position coordinates of defined real or virtual points of the joint region or vertebral region and / or position reference vectors between such points within the joint region or vertebral region or from those points to joint-function-relevant points on an extremity outside the joint region or vertebral region, the coordinate-measuring arrangement comprising a stereocamera or stereocamera arrangement for the spatial recording of transducer signals, at least one multipoint transducer, which comprises a group of measurement points rigidly connected to one another, and an evaluation unit for evaluating sets of measurement point coordinates supplied by the multipoint transducer(s) and recorded by the stereocamera, and a matching-processing unit for real position matching of the image to the actual current spatial position of the joint region or vertebral region with reference to the real position coordinates of the defined points, the matching-processing unit being configured for calculating transformation parameters with minimalization of the normal spacings.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Dynamic lordotic guard with movable extensions for creating an implantation space posteriorly in the lumbar spine and method for use thereof
ActiveUS7211085B2Easy to insertEasy to removeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnProximate
A lordotic guard and method for guiding a bone removal device to form an implantation space in the human spine and, if desired, for inserting a spinal implant into the implantation space. The guard has a body having a first portion and a second portion in pivotal relationship to one another proximate the leading end between an open position and a closed position. The first and second portions define an opening for providing a protected pathway to the disc space and the adjacent vertebral bodies. At least one disc space penetrating extension extends from the leading end of the body adapted for insertion at least in part into the disc space. First and second portions of the extension are in pivotal relationship to one another about an axis that passes through at least a portion of the pathway.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Dynamic lordotic guard with movable extensions for creating an implantation space posteriorly in the lumbar spine
InactiveUS6986772B2Easy to insertEasy to removeJoint implantsSpinal implantsSpinal columnLumbar spine
A lordotic guard and method for guiding a bone removal device to form an implantation space in the human spine and, if desired, for inserting a spinal implant into the implantation space.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
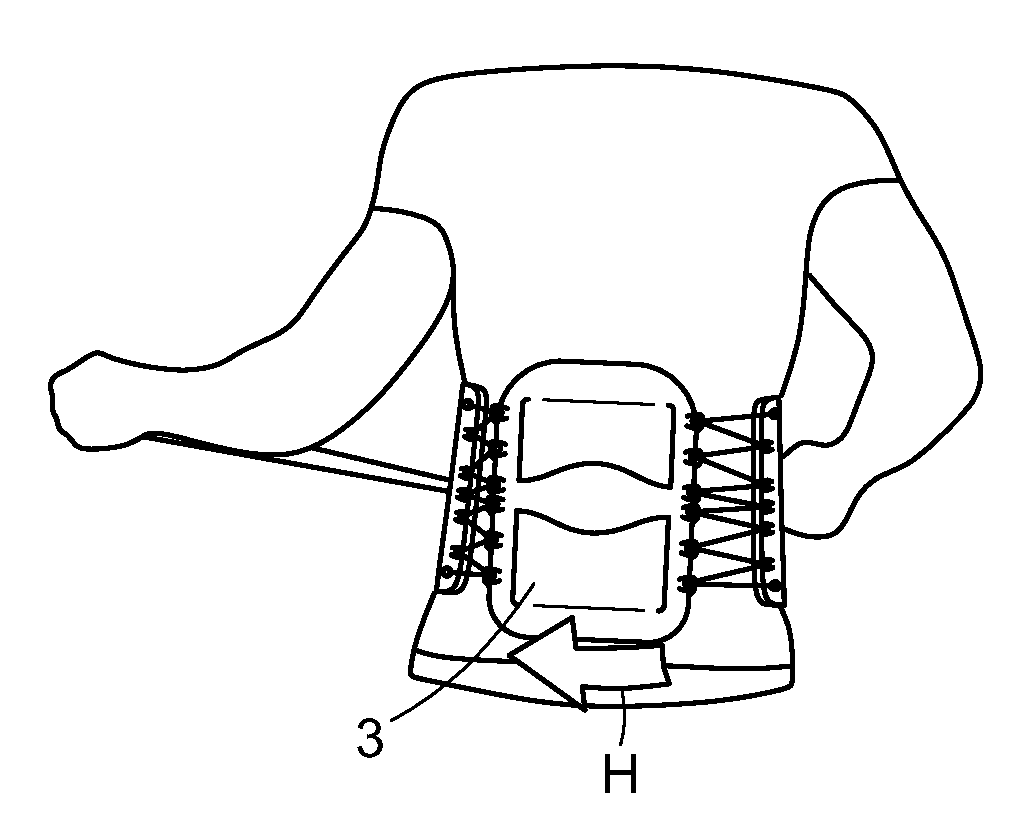
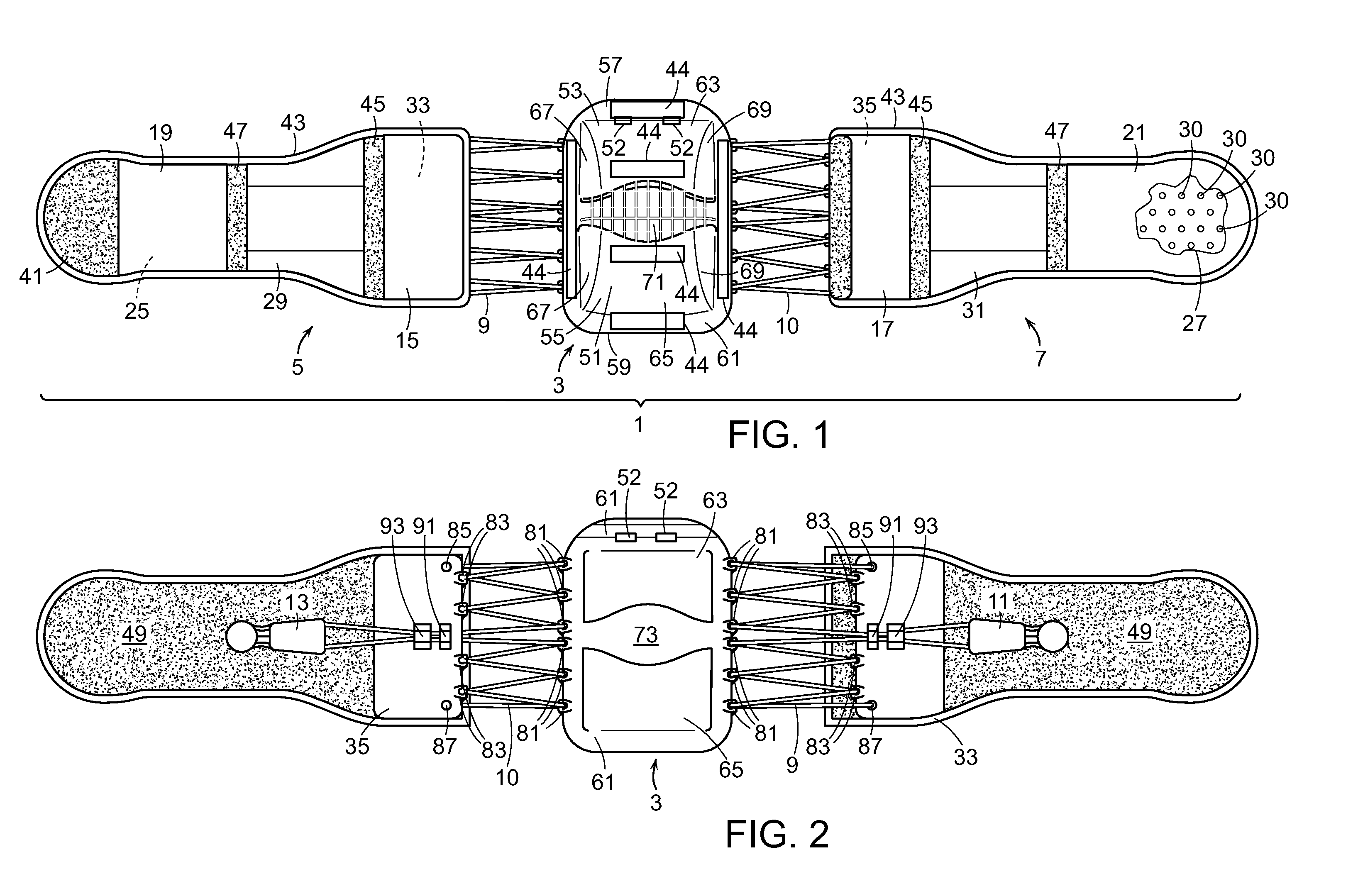
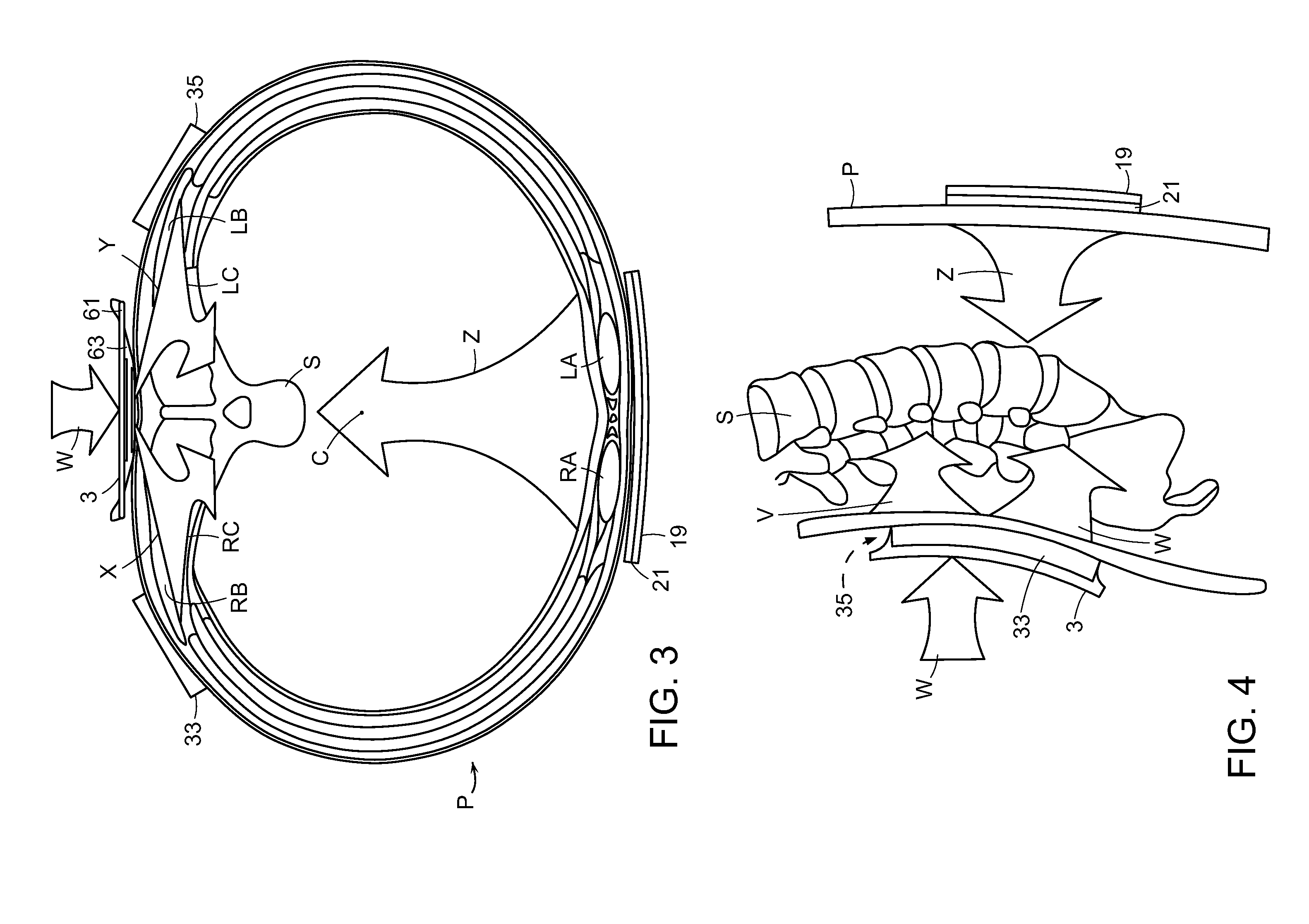
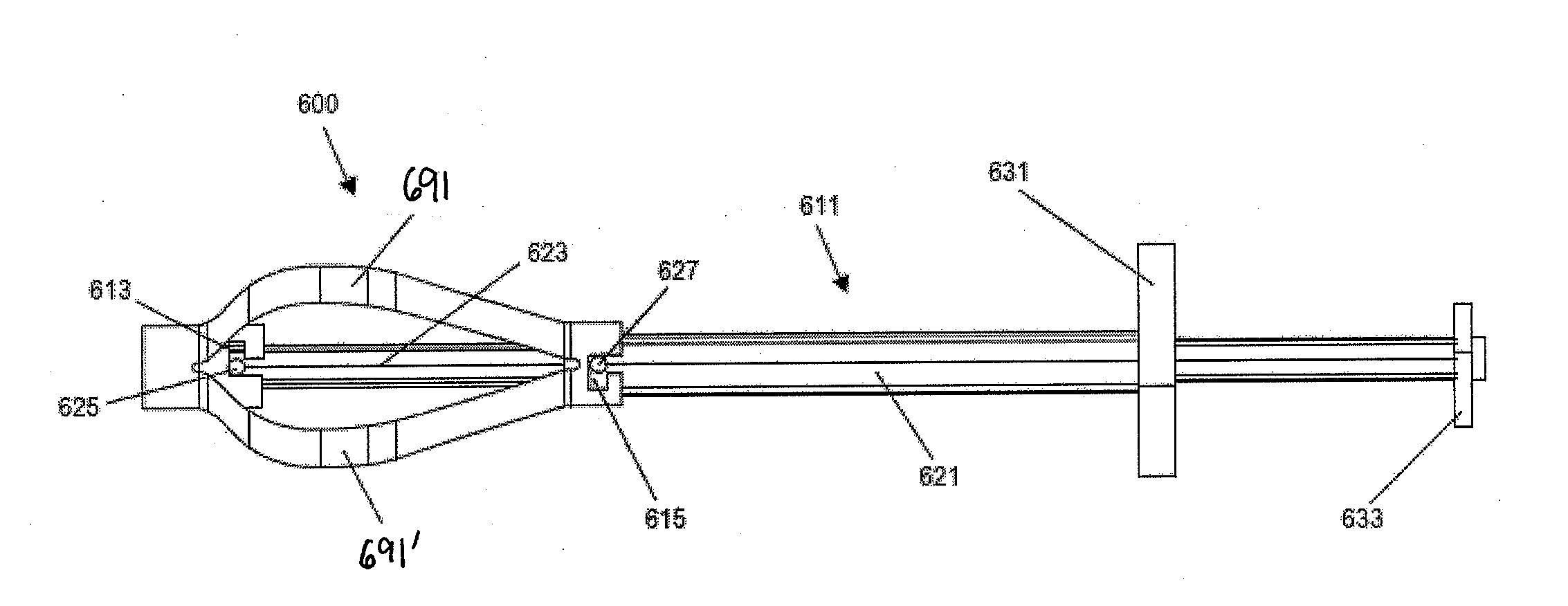
Interspinous implants and methods for implanting same
A spinal implant for treating lumbar spinal stenosis or as an adjunct to spinal fusion. The implant includes a body portion having an interior cavity. A plurality of locking wings are adapted and configured to move between a stowed position retracted within the interior cavity of the body portion and a deployed position extended from the interior cavity of the body portion. In the deployed position, the wings fix the implant in a selected interspinous space. A cable and wheel arrangement moves the plurality of locking wings from the stowed position to the deployed position and a ratchet / pawl assembly prevents backward movement of the wings.
Owner:SPINAL SIMPLICITY
Artificial total lumbar disc for unilateral safe and simple posterior placement in the lumbar spine, and removable bifunctional screw which drives vertical sliding expansile plate expansion, and interplate widening, and angled traction spikes
A total artificial expansile disc and a method for posterior insertion between a pair of vertebral endplates are disclosed. The total artificial expansile disc includes at least one pair of substantially parallel plates that move apart along a first axis, in order to occupy a space defined by the vertebral endplates. In another embodiment, each of substantially parallel plates includes a first plate and a second sliding plate. An expansion device or tool is used to move the substantially parallel pair of plates apart along the first axis. A core is disposed between the pair of plates, and the core permits the vertebral endplates to move relative to one another. A ball limiter or ball extender prevents the core from being extruded from between the substantially parallel plates.
Owner:MOSKOWITZ FAMILY LLC
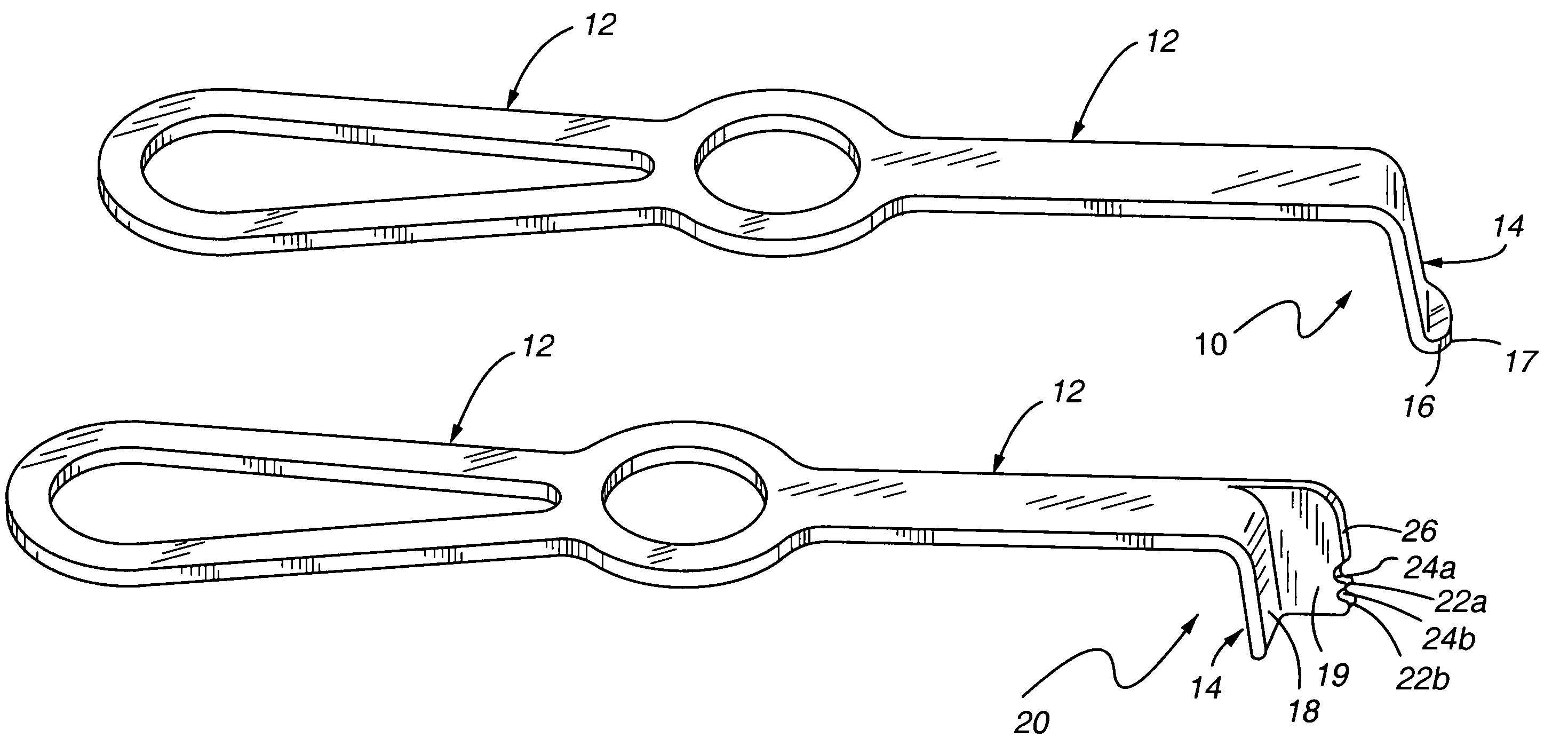
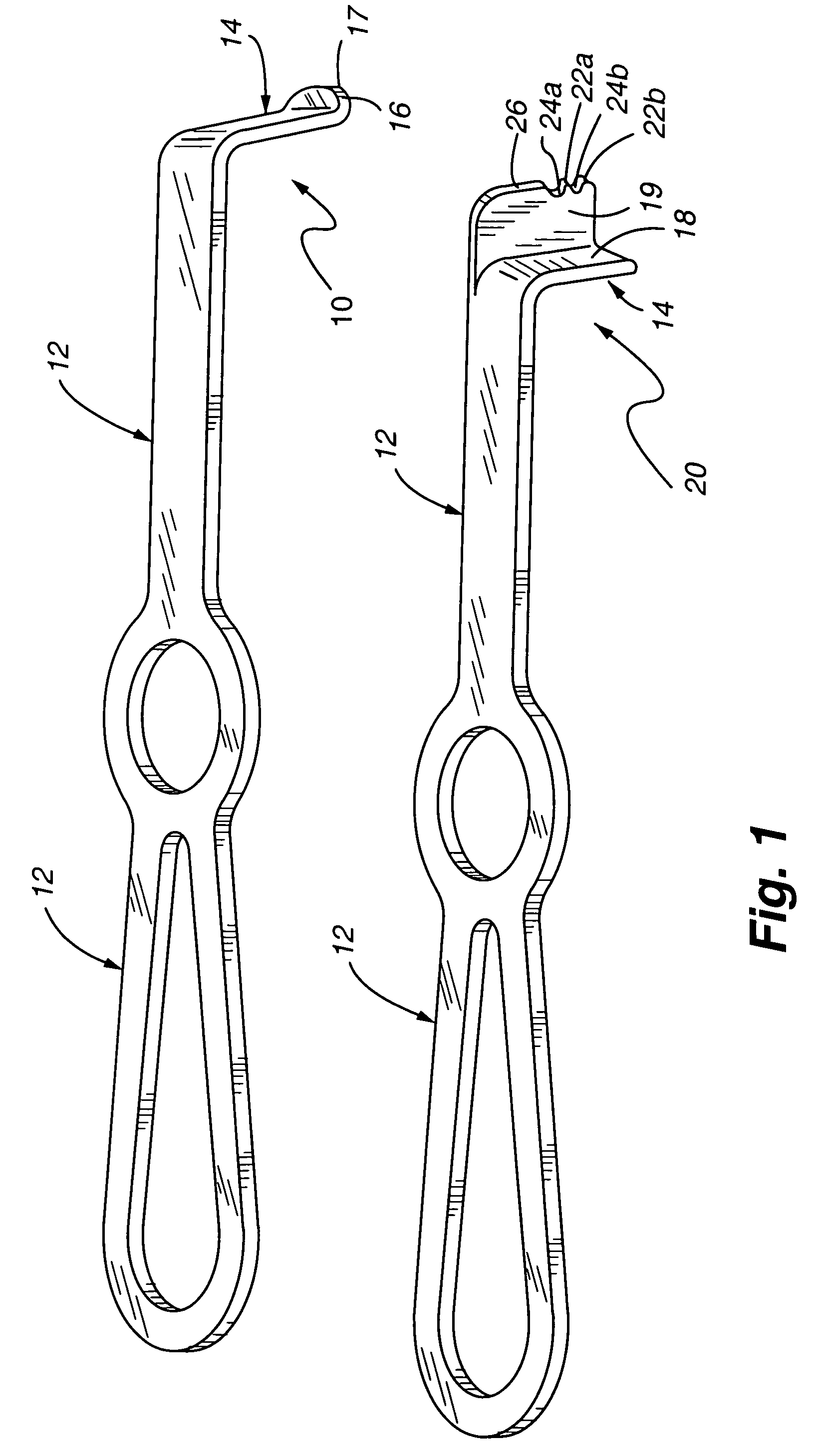
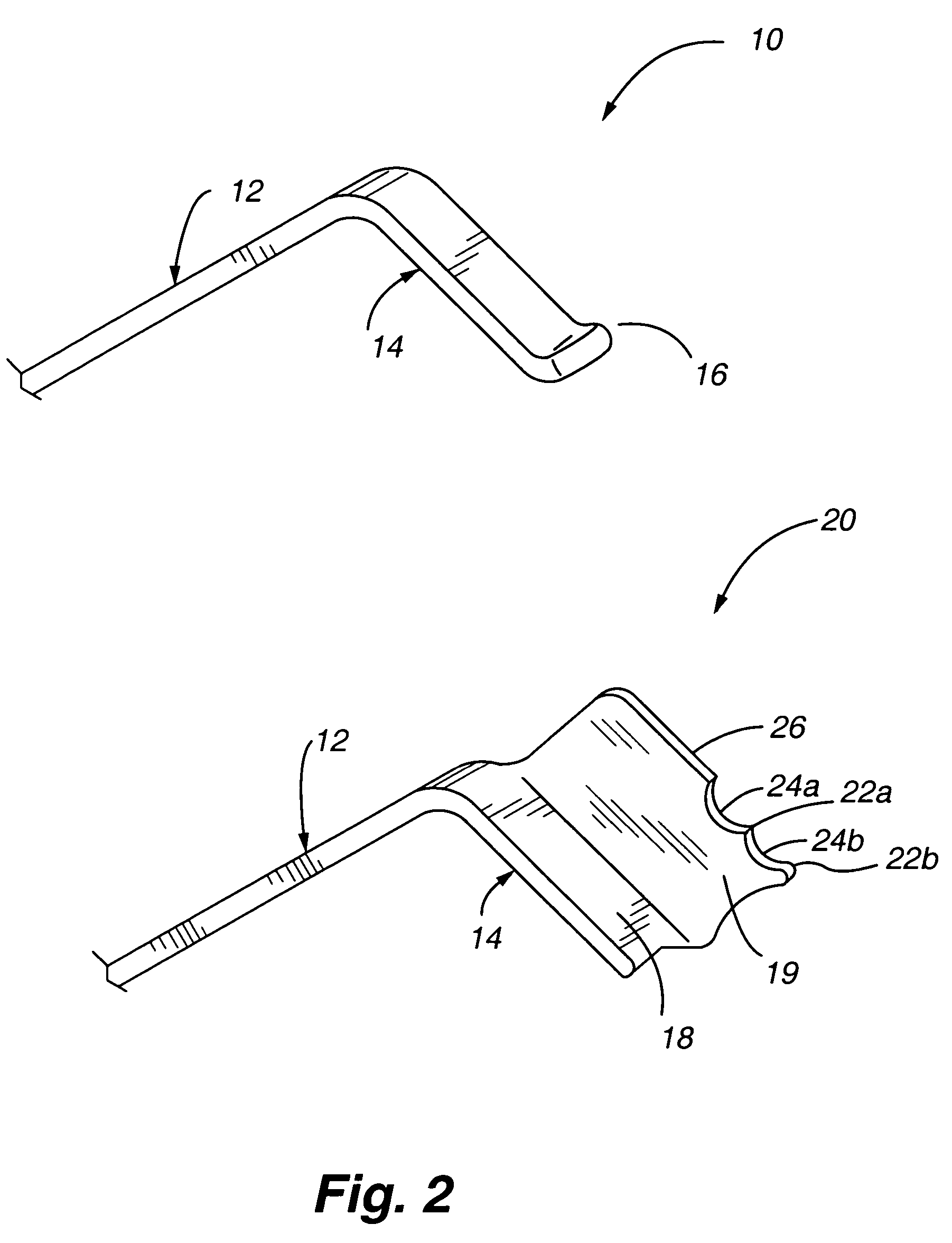
Method and device for retractor for microsurgical intermuscular lumbar arthrodesis
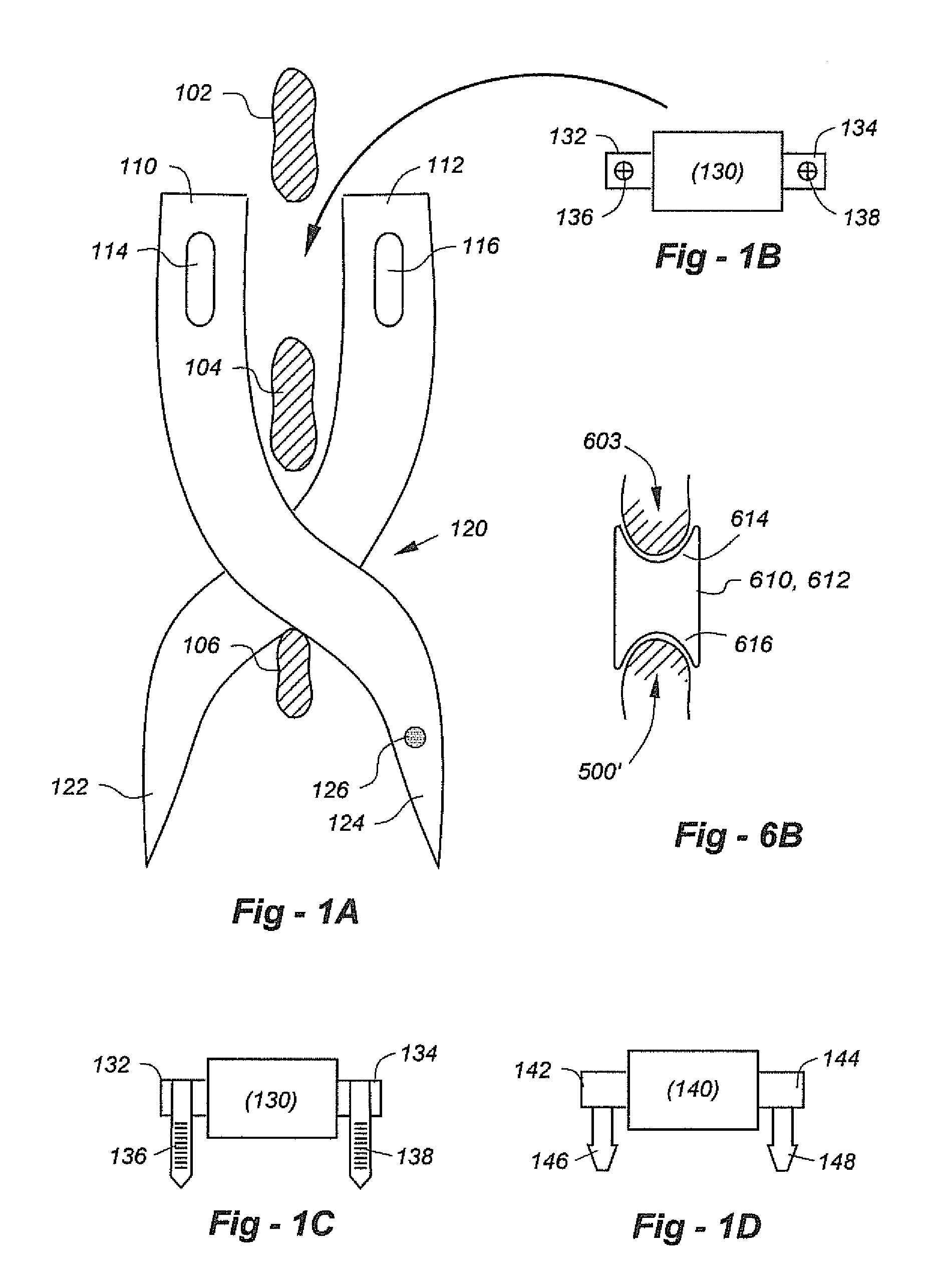
An instrument useful in performing lumbar arthrodesis with a minimal approach which spares the lumbar muscles from surgical disruption and includes one of two retractor designs having blades angled approximately 90° with respect to each respective retractor handle. One blade is bent at an end portion thereof in a direction away from the handle portion. The other blade has first and second blade faces, with the second face having at least two toothed structures located thereon.
Owner:RITLAND STEPHEN
Spinal implants, including devices that reduce pressure on the annulus fibrosis
InactiveUS20050256582A1Promote reconstructionPrevents herniationInternal osteosythesisBone implantFibrosisDiscectomy
The invention broadly facilitates reconstruction of the Annulus Fibrosus (AF) or the AF and the Nucleus Pulposus (NP). Such Reconstruction prevents recurrent herniation following Microlumbar Discectomy (MLD) other procedures. The invention may also be used in the treatment of herniated discs, annular tears of the disc, or disc degeneration, while enabling surgeons to preserve the contained NP. The methods and apparatus may be used to treat discs throughout the spine including the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines of humans and animals. In the preferred embodiment, a spinal repair system according to the invention comprises a first end portion adapted for placement within an intervertebral body, a second end portion adapted for placement within an adjacent intervertebral body, and a bridge portion connecting the first and second end portions, the bridge portion being adapted to span a portion of an intervertebral disc space and prevent excessive outward bulging.
Owner:ANOVA
Vertebral body replacement apparatus and method
Various embodiments of the present invention relate to an apparatus for vertebral body replacement and methods associated therewith. In one embodiment, a vertebral body replacement apparatus may be used to correct and stabilize the spine (e.g., the thoracolumbar spine (T1-L5)). In another embodiment, a vertebral body (e.g., a diseased and / or damaged vertebral body) that has been resected or excised (e.g., for the treatment of a tumor or trauma) may be replaced (with the height of the resected or excised vertebral body being substantially replaced and restored by the apparatus of the present invention).
Owner:BLACKSTONE MEDICAL
Intervertebral disc prosthesis with transversally arched, curved cylindrical articulation surfaces for the lumbar and cervical spine
ActiveUS20060235531A1Easy to integrateMinimize risk of fracturingSpinal implantsCoatingsIntervertebral discLumbar vertebrae
The invention relates to an intervertebral disc prosthesis for the total replacement of a natural intervertebral disc within the lumbar and cervical spine, comprising articulating sliding partners, where the upper sliding partner has means for a firm assembly to an upper vertebral body and the lower sliding partner has means for a firm assembly to a lower vertebral body and at least one sliding surface that is between two sliding partners. According to the invention, functional two- and three part designs are planned and both prostheses have in common, that only a dorsoventral- and rotation movement is possible as a result of laterolaterally aimed, transversally arched, ventrally curved cylindrical convexity(ies) and corresponding concavity(ies), however without an inclination of the sliding partners in a lateral direction. In a further design, the cylindrical articulation surfaces are un-curved, enabling a motion of the sliding partners in only a ventrodorsal direction. According to the invention, the intervertebral disc prostheses are suited for an implantation from lateral and ventrolateral, particularly in revision surgeries.
Owner:BUETTNER JANZ KARIN
Intervertebral disc prosthesis with a motion- adapted edge for the lumbar and cervical spine
ActiveUS20060235527A1Easy to adaptMinimize risk of fractureSpinal implantsEdge regionIntervertebral disc
The invention relates to an intervertebral disc prosthesis for the total replacement of the intervertebral disc within the lumbar and cervical spine. For a two part as well as for a three part intervertebral disc prosthesis, according to the invention, in accordance to the design of the edges of the sliding partners, there are aspects for at least one of the sliding partners, in which there is an wavelike design of the edge, as the respectively differently high edge regions preferably fluently merge. A significant advantage of the two intervertebral disc prostheses, according to the invention, compared to the present state of the art of already known prostheses, is that as a result of a central transfer of load across a large surface area due to the spherical sliding surfaces, the maximally possible inclination of the sliding partners towards each other in a dorsoventral and laterolateral direction and / or the extent of rotation can, according to the invention, be defined through the wavelike design of the edge region.
Owner:BUETTNER JANZ KARIN +1
Apparatus, systems, and methods for achieving trans-iliac lumbar fusion
ActiveUS8414648B2Speed up fusion and stabilization processFusion and/or stabilization of the lumbar spineInternal osteosythesisBone implantLumbar facet jointIntervertebral disc
Assemblies of one or more implant structures make possible the achievement of diverse interventions involving the fusion and / or stabilization of lumbar and sacral vertebra in a non-invasive manner, with minimal incision, and without the necessitating the removing the intervertebral disc. The representative lumbar spine interventions, which can be performed on adults or children, include, but are not limited to, lumbar interbody fusion; translaminar lumbar fusion; lumbar facet fusion; trans-iliac lumbar fusion; and the stabilization of a spondylolisthesis.
Owner:SI BONE INC
Pedicle and non-pedicle based interspinous and lateral spacers
Owner:US SPINE INC
Apparatus, systems, and methods for achieving anterior lumbar interbody fusion
ActiveUS8425570B2Speed up fusion and stabilization processFusion and/or stabilization of the lumbar spineInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsLumbar facet jointIntervertebral disc
Assemblies of one or more implant structures make possible the achievement of diverse interventions involving the fusion and / or stabilization of lumbar and sacral vertebra in a non-invasive manner, with minimal incision, and without the necessitating the removing the intervertebral disc. The representative lumbar spine interventions, which can be performed on adults or children, include, but are not limited to, lumbar interbody fusion; translaminar lumbar fusion; lumbar facet fusion; trans-iliac lumbar fusion; and the stabilization of a spondylolisthesis.
Owner:SI BONE INC
Screw sleeve made of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for augmentation of bone screw insertion in osteoporotic or revision lumbar spine instrumentation
InactiveUS20060129148A1Excellent mechanical propertiesImprove interferenceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisOrthopaedic deviceBone tissue
An orthopaedic device comprising an orthopaedic bone screw and a sleeve of polyetheretherketone material in which the orthopaedic bone screw is received for increasing interference between the screw and bone tissue to increase strength of fixation when the device is installed in bone.
Owner:SIMMONS EDWARD +1
Systems and methods for enhanced implantation of electrode leads between tissue layers
ActiveUS20180008311A1Reduce riskRecovery functionSpinal electrodesSurgical needlesAnatomical structuresMedicine
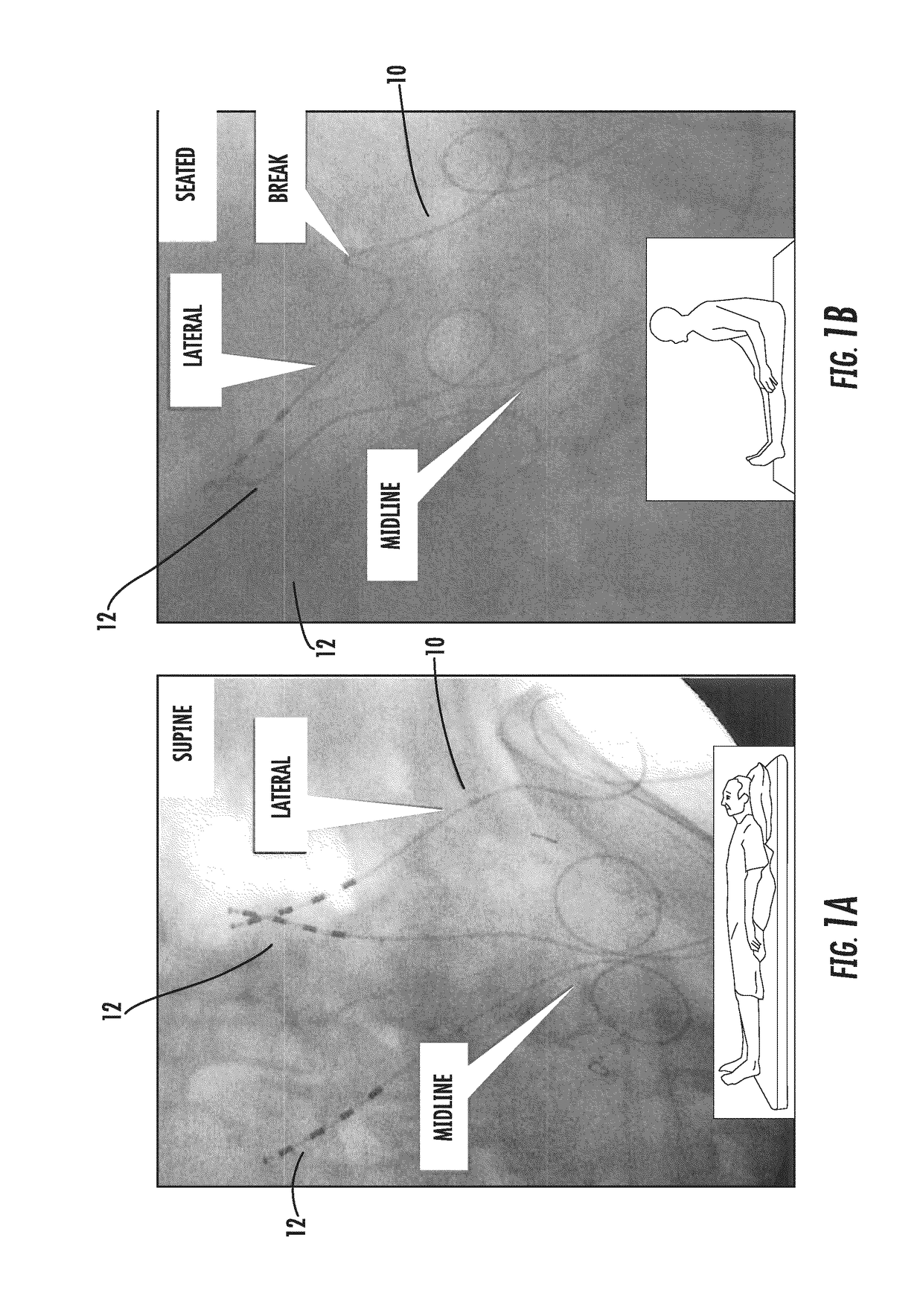
Systems and methods for enhanced implantation of an electrode lead for neuromuscular electrical stimulation of tissue associated with control of the lumbar spine for treatment of back pain, in a midline-to-lateral manner are provided. The implanted lead may be secured within the patient and used to restore muscle function of local segmental muscles associated with the lumbar spine stabilization system without disruption of the electrode lead post-implantation due to anatomical structures.
Owner:MAINSTAY MEDICAL
Spinous process stabilization device and method
InactiveUS20090264927A1Easy to integrateInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsCoronal planeEmbedded teeth
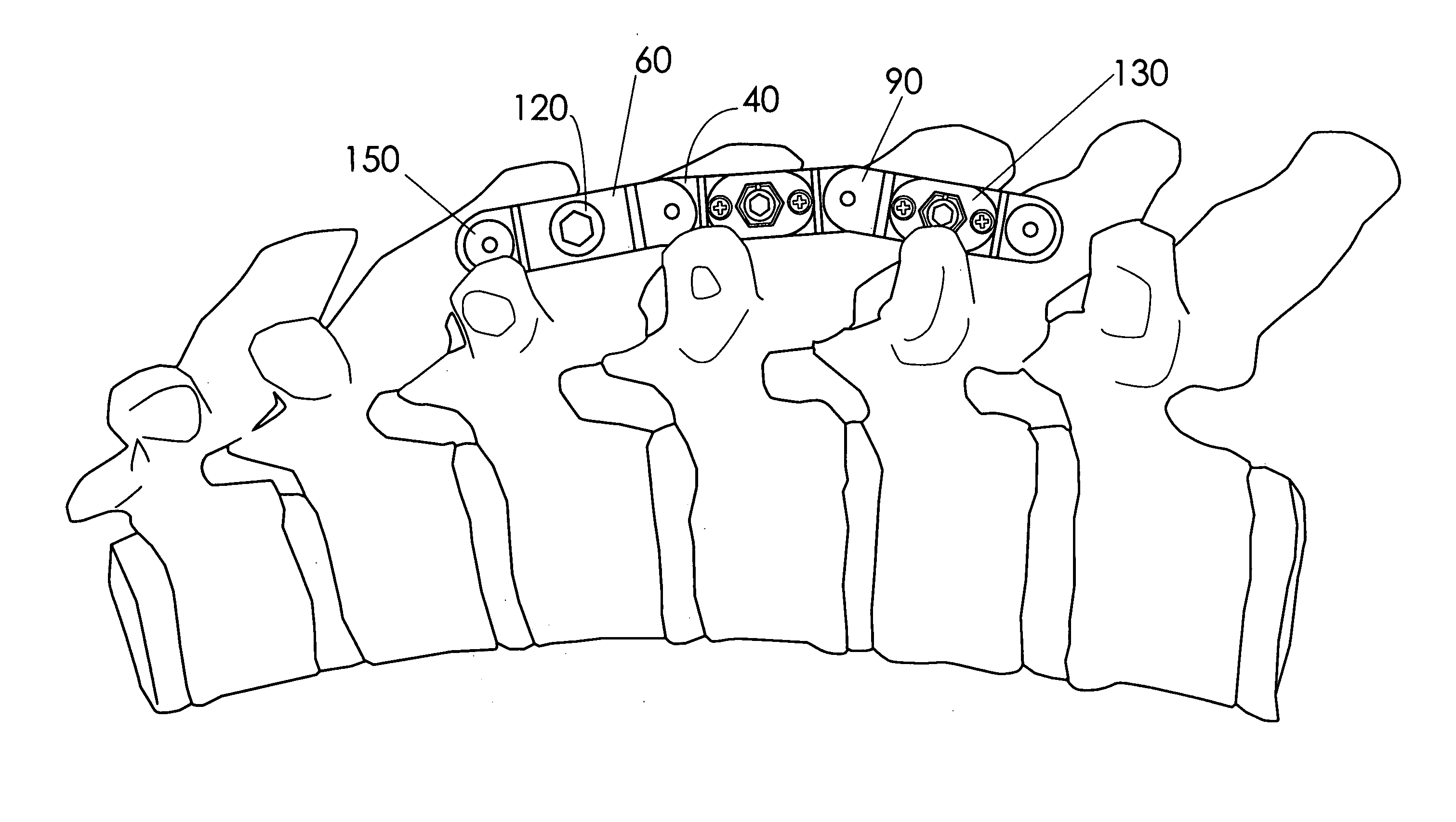
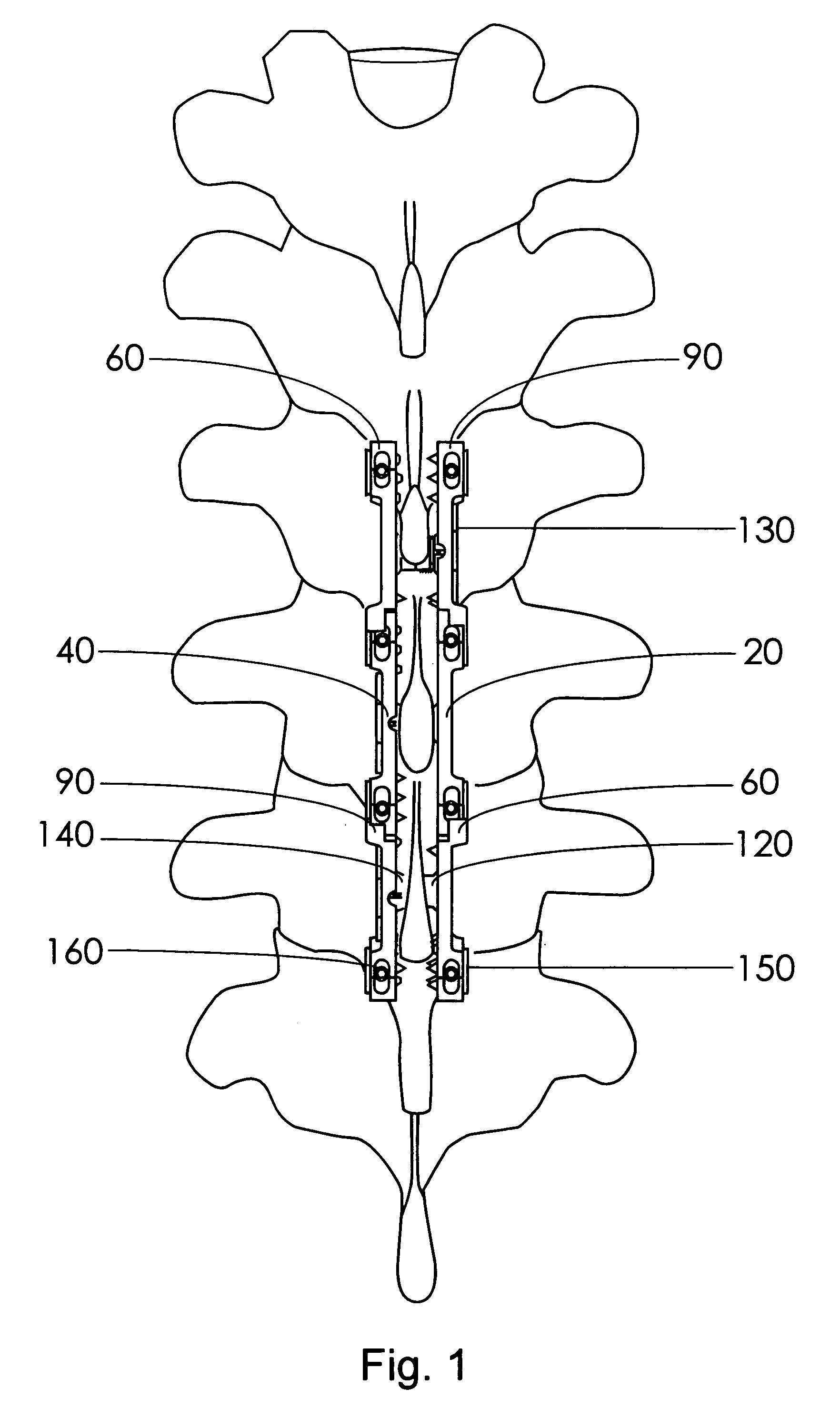
A fixation device to immobilize a spinal motion segment and promote posterior fusion, used as stand-alone instrumentation or as an adjunct to an anterior approach. The device functions as a multi-level fusion system including modular single-level implementations. At a single-level the implant includes a pair of plates spanning two adjacent vertebrae with embedding teeth on the medially oriented surfaces directed into the spinous processes or laminae. The complementary plates at a single-level are connected via a cross-post with a hemi-spherical base and cylindrical shaft passed through the interspinous process gap and ratcheted into an expandable collar. The expandable collar's spherical profile contained within the opposing plate allows for the ratcheting mechanism to be correctly engaged creating a uni-directional lock securing the implant to the spine when a medially directed force is applied to both complementary plates using a specially designed compression tool. The freedom of rotational motion of both the cross-post and collar enables the complementary plates to be connected at a range of angles in the axial and coronal planes accommodating varying morphologies of the posterior elements in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine. To achieve multi-level fusion the single-level implementation can be connected in series using an interlocking mechanism fixed by a set-screw.
Owner:GINSBERG HOWARD JOESEPH +2
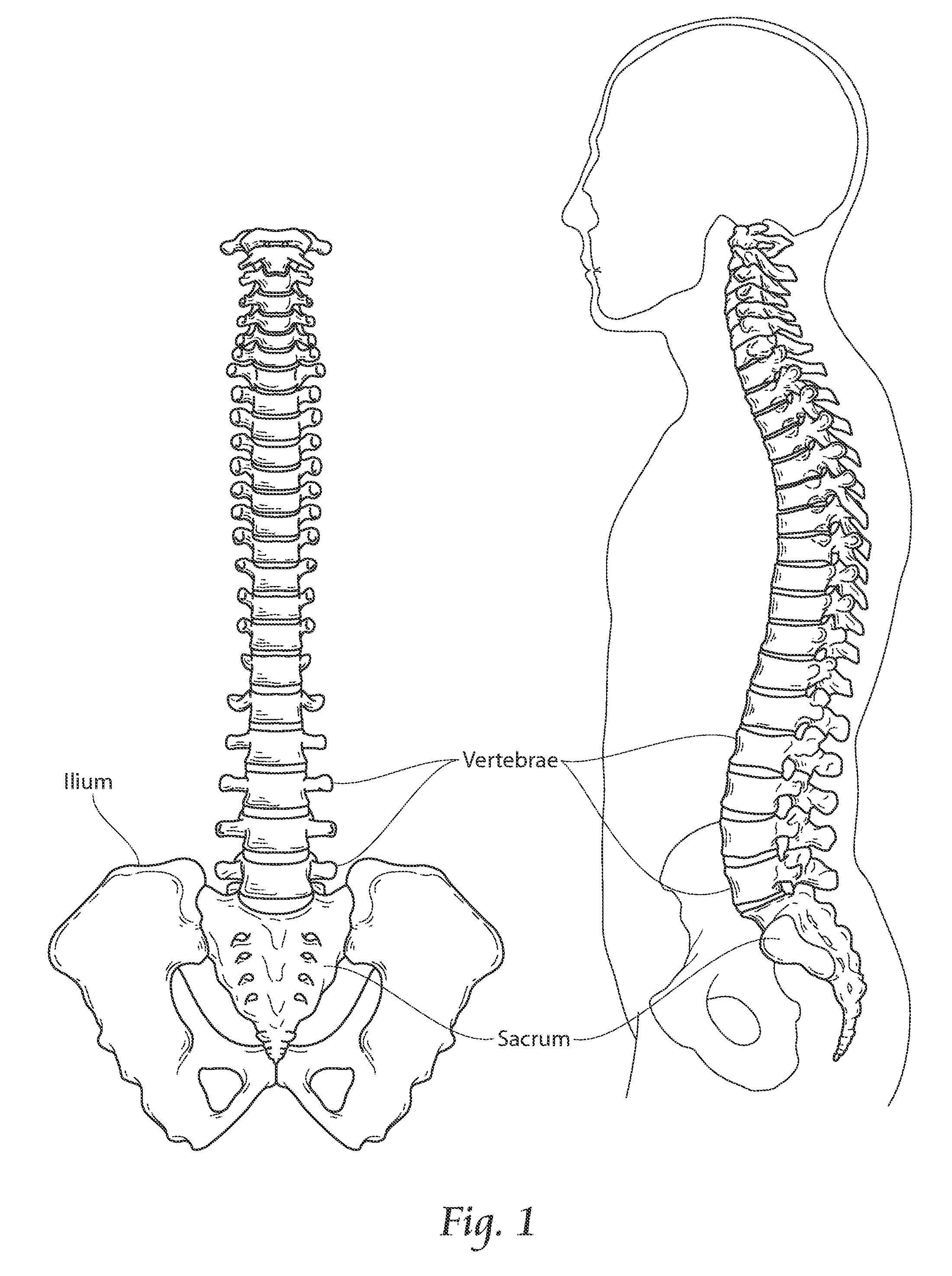
Lumbar flexing seating apparatus
InactiveUS7100983B1Degree of tilt is limitedImprove posturePortable framesOperating chairsButtocksEngineering
A buttocks seat is supported by a post tiltably affixed at a lower end to an upper face of a base. The post is also axially rotatable relative to the base, and threadably engaged with an underside of the seat for supporting the seat on the post, the seat squarely facing upright when the post is vertical. A hand wheel is affixed to the post for rotating the post relative to the seat and the base for selectively raising or lowering the seat relative to the base. A resilient bias urges the post to be vertical unless a seated user flexes his or her lumbar with sufficient force to overcome the bias. Preferably the post is tiltable over a conical range and the bias comprises a resiliently compressible, cylindrical ring coaxial with the post, and extending between and abutting the base and the underside of the seat.
Owner:GANT RICHARD A
Back orthosis and orthotic method
ActiveUS20100168630A1The process is simple and effectiveReduce and eliminate back painRestraining devicesOrthopedic corsetsKnee orthosisEngineering
A lumbar orthosis that includes first and second, separate, opposing and mating front attachment panels; and a separate, laterally adjustable, rigid lumbar compression piece configured for positioning only at the rear of a wearer, wherein pulling of a cord causes the brace both circumferentially to tighten and to concentrate compression and pressure of the separate, laterally adjustable, rigid lumbar compression piece directly and especially upon a spinal region of a wearer's back with the aid of a mechanical advantage dependant upon a number of apertures through which the cord or cords pass. An orthosis and method for correcting lumbar and thoracic back pain and disorders is also disclosed.
Owner:CROPPER DEAN +1
Corpectomy implant
ActiveUS20090138089A1Inhibit migrationEffective recoveryJoint implantsSpinal implantsCorpectomyLumbar spine
The present invention describes an expandable vertebral implant and the method of use. The longitudinally expandable vertebral implant includes telescoping sections adapted for incremental expansion and ease of securement at any desired increment in situ, and constructed and arranged to engage opposing vertebrae. The corpectomy device is a distractible vertebral body replacement for the thoracic and lumbar spine. The device is cylindrical shaped having an inner and outer sleeve made adjustable by use of locking pads formed integral with the outer sleeve for use in engaging parallel circumferential locking grooves formed along the outer side surface of the inner sleeve.
Owner:ORTHO INNOVATIONS
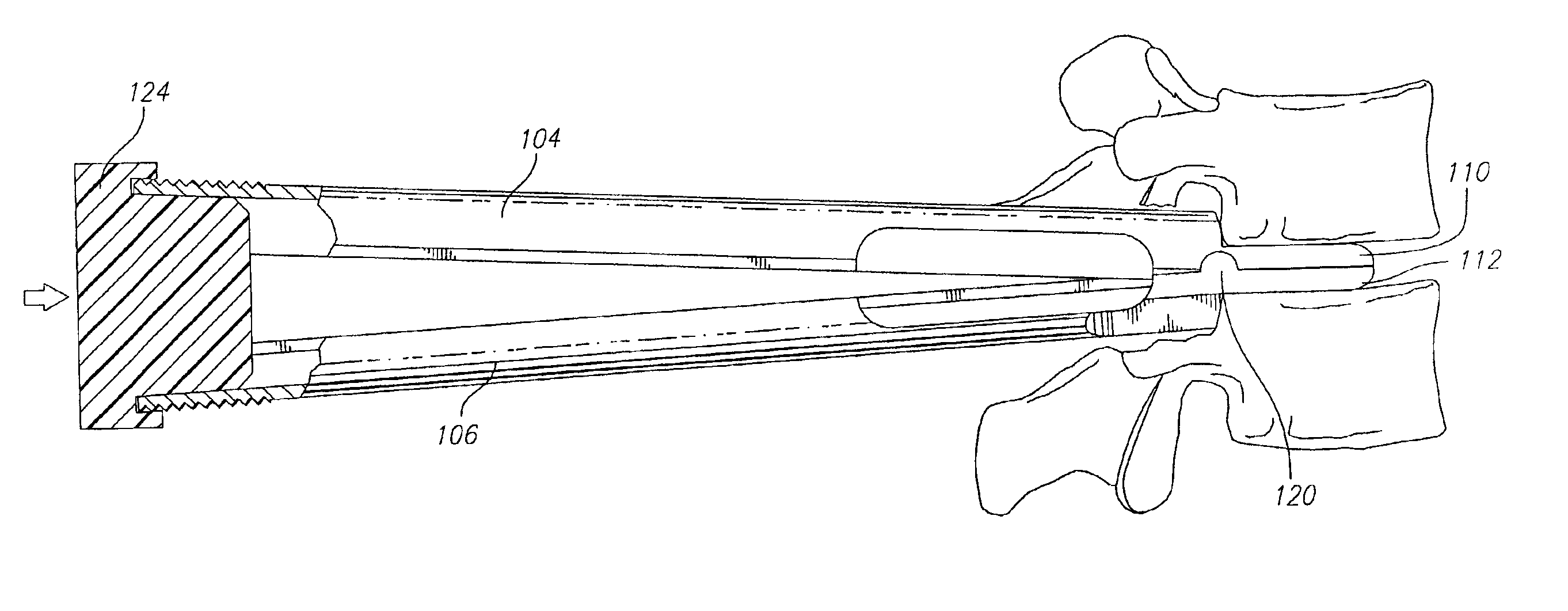
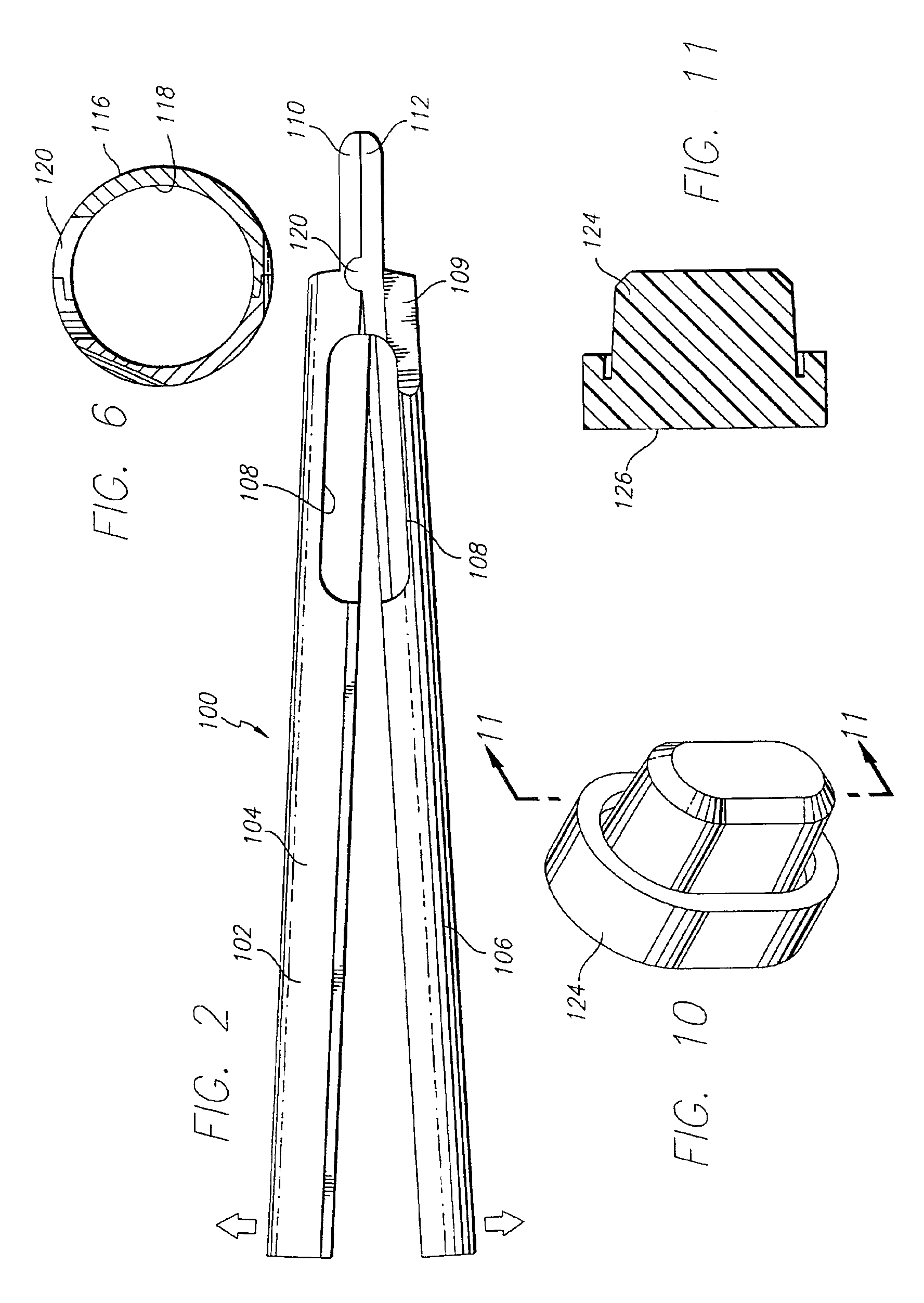
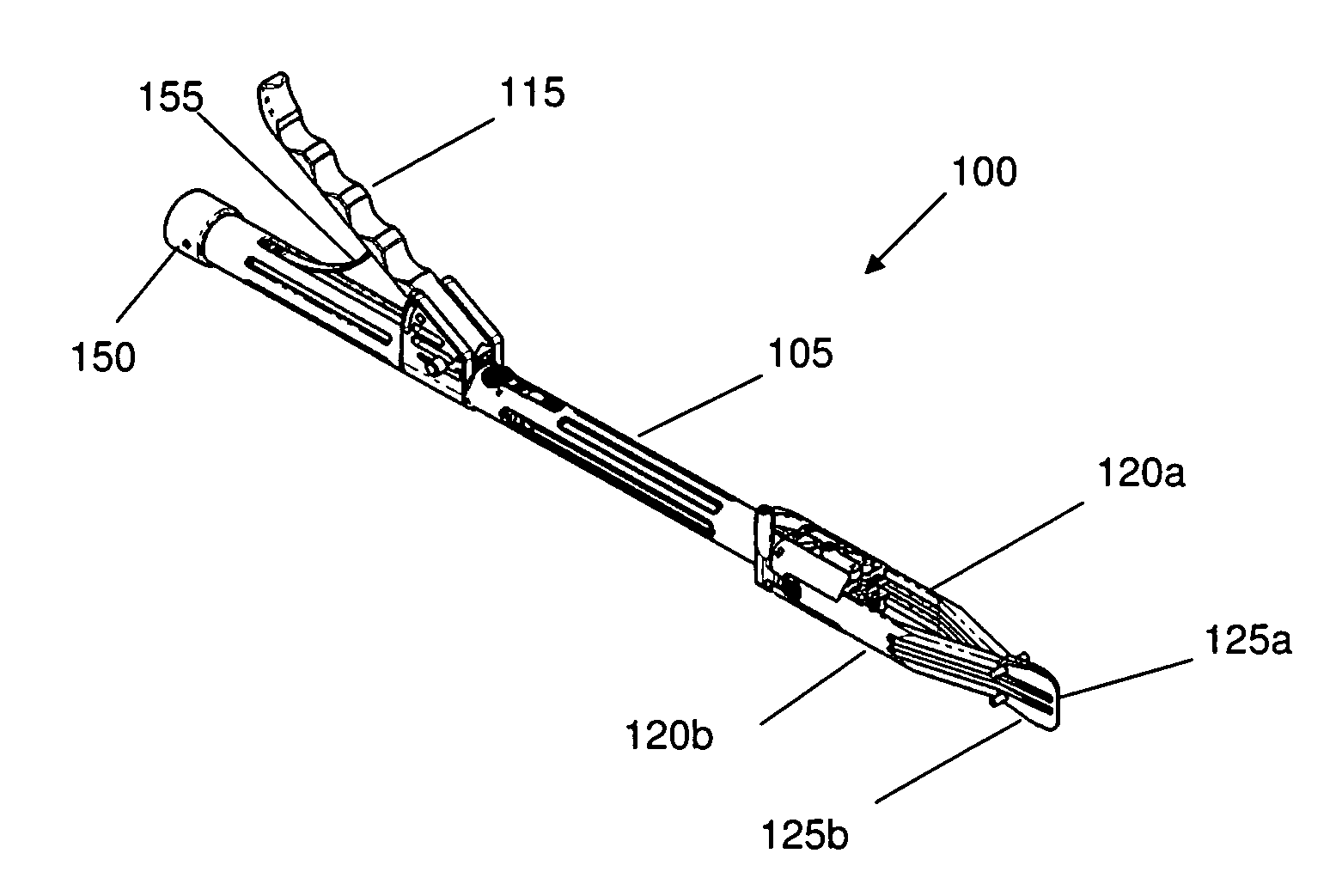
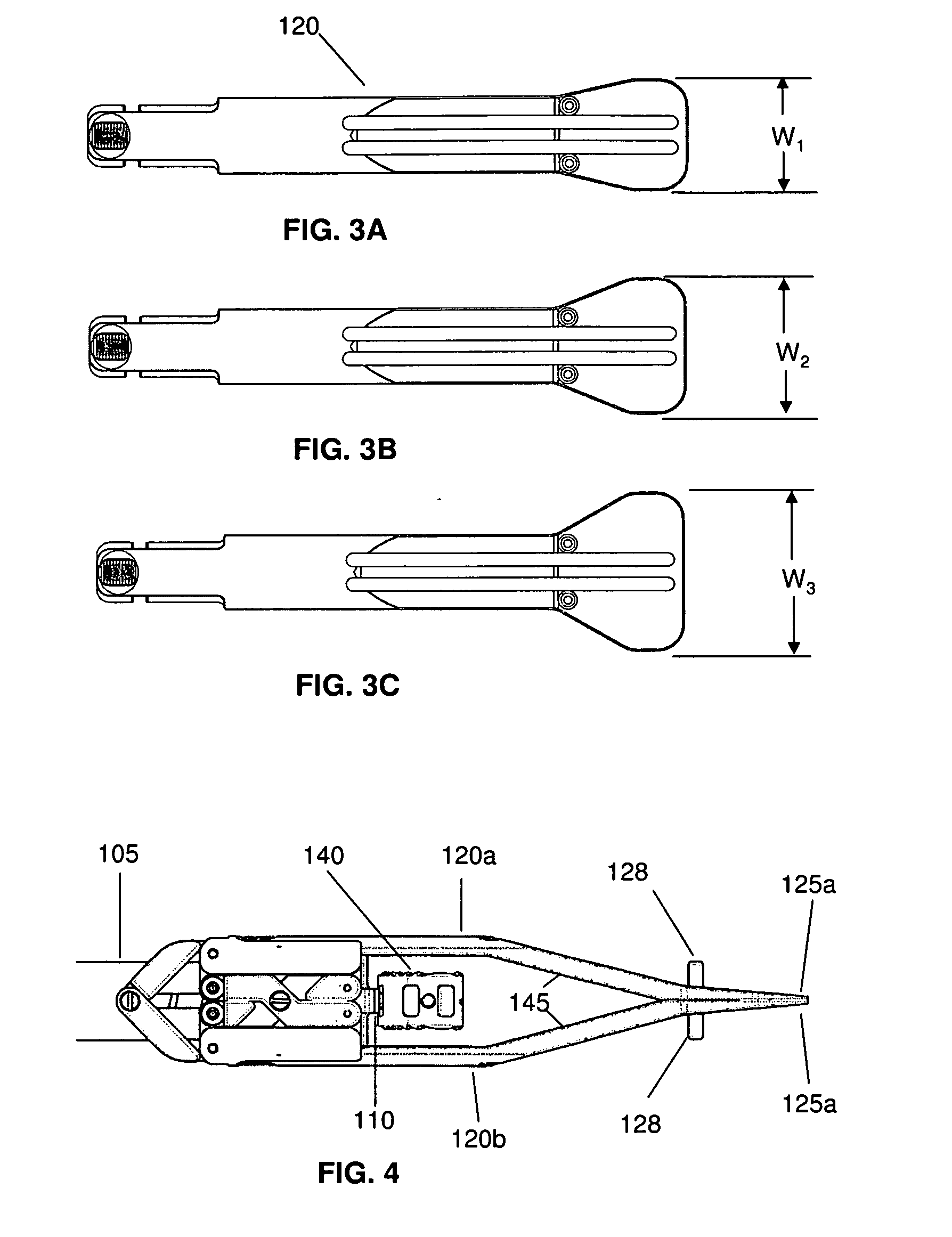
Alif inserter/distractor
Apparatus and method for an instrument for use in an anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) procedure for distraction of adjacent vertebrae and insertion of a vertebral body replacement (VBR) implant. The instrument includes a hollow body having a proximal end and a distal end, an inserter shaft positioned within the body configured to removably engage a VBR implant near the distal end of the body, an actuatable handle coupled to the body, the handle being configured to engage the inserter shaft to advance the VBR implant in a distal direction during handle actuation, and a pair of opposed distraction arms removably coupled to the distal end of the body, the distraction arms having paddle tips configured to fit between adjacent vertebrae, the distraction arms being movable from a closed position to an open position during distal advancement of the VBR implant between the distraction arms.
Owner:ALPHATEC SPINE INC
Articulating Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Inserter Device and Associated Method of Use
InactiveUS20090043312A1Minimal disruptionBig impactSpinal implantsOsteosynthesis devicesSpinal columnIntervertebral space
The present invention provides an articulating TLIF inserter device operable for placing, positioning, and inserting a spinal implant into an intervertebral space with minimum tissue disruption and maximum inline impaction forces, including: an elongate shaft having a proximal end, a distal end, and an axis; an ergonomic handle disposed at the proximal end of the elongate shaft; an articulating joint mechanism disposed at the distal end of the elongate shaft; and an inserter piece coupled to the articulating joint mechanism, wherein the inserter piece is operable for selectively retaining the spinal implant, and wherein the articulating joint mechanism is operable for selectively actuating the inserter piece between one or more substantially off-axis configurations and a substantially on-axis configuration with respect to the elongate shaft. The articulating TLIF inserter device also includes a release mechanism disposed one of at and near the ergonomic handle, wherein the release mechanism is coupled to and operable for selectively actuating the articulating joint mechanism.
Owner:CTL MEDICAL CORP
Minimally Invasive Surgical (MIS) Technique and System for Performing an Interbody Lumbar Fusion with a Navigatable Intervertebral Disc Removal Device and Collapsible Intervertebral Device
InactiveUS20110238072A1Simple technologyEffective and efficient and safeInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsCircular discLess invasive surgery
A technique and system is provided for efficiently, effectively and safely performing an interbody lumbar fusion. The technique and system utilizes: (1) a rotary shaver that provides a shaving cannula; (2) an outflow / insertion cannula which provides a dual purpose cannula; and (3) a fusible balloon which provides a biodegradable intervertebral bag. The patient's disc is shaved and cut out with the shaver while the shavings are sucked out with the dual purpose cannula. Afterwards, the balloon is inserted at the tip of the dual purpose cannula and the balloon is filled with a grafting substance. The balloon assumes the shape of the removed disc. The grafting substance will fuse to the balloon and to the adjacent vertebrae and provide a support where the removed disc was.
Owner:TYNDALL DWIGHT S
Systems, devices and methods for posterior lumbar interbody fusion
InactiveUS20090292323A1Easy to cutEasy to shapeJoint implantsSpinal implantsSurgical operationIntervertebral disc
Described herein are stabilization devices, systems and methods to aid in posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) surgeries. The stabilization devices (“devices”) described herein are typically self-expanding devices that may be implanted into an intervertebral disc and packed with a bone graft or biologic or synthetic material to promote anchoring of the stabilization device and fusion of the vertebrae adjacent to the intervertebral disc.
Owner:SPINEALIGN MEDICAL
System and Methods for Diagnosis and Treatment of Discogenic Lower Back Pain
ActiveUS20150005680A1Inhibit migrationPrevent rotationSpinal electrodesDiagnosticsClosed loopElectrical impulse
Methods and devices to treat discogenic lumbar back pain are disclosed. Electrodes are implanted within the anterior epidural space of the patient. A pulse generator that is connected to the electrodes delivers electrical impulses to sympathetic nerves located within the posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) of the lumbar spine and outer posterior annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc. In alternate embodiments, energy directed to nerves in the PLL may be from light or mechanical vibrations, or the nerves may be cooled. The electrodes may also be used diagnostically to correlate spontaneous nerve activity with spinal movement, fluctuations in autonomic tone and the patient's experience of pain. The electrodes may also be used to generate diagnostic evoked potentials. The diagnostic data are used to devise parameters for the therapeutic nerve stimulation. Automatic analysis of the data may be incorporated into a closed-loop system that performs the nerve stimulation automatically.
Owner:LIPANI JOHN D
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com