Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80 results about "Intra abdominal pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
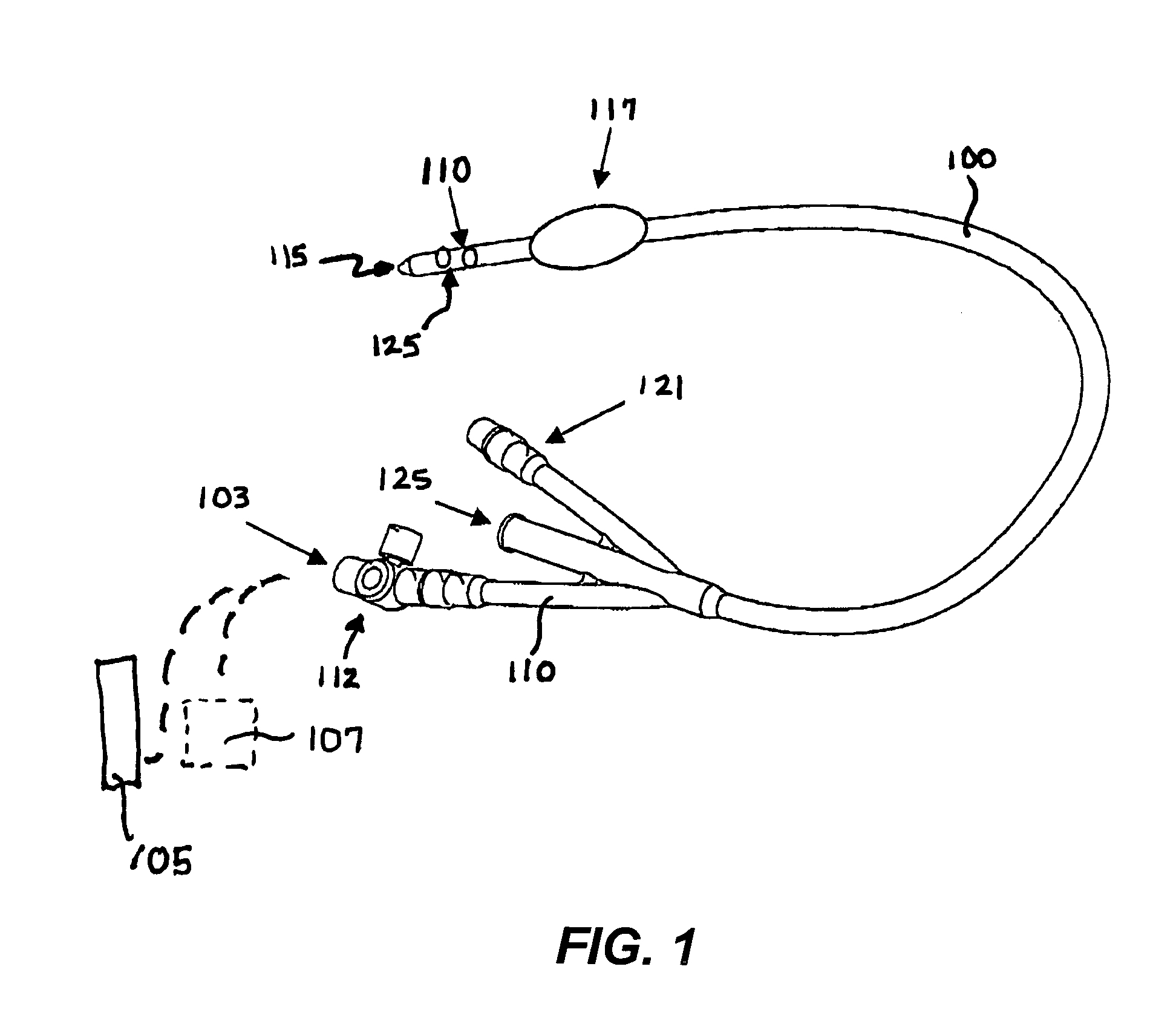
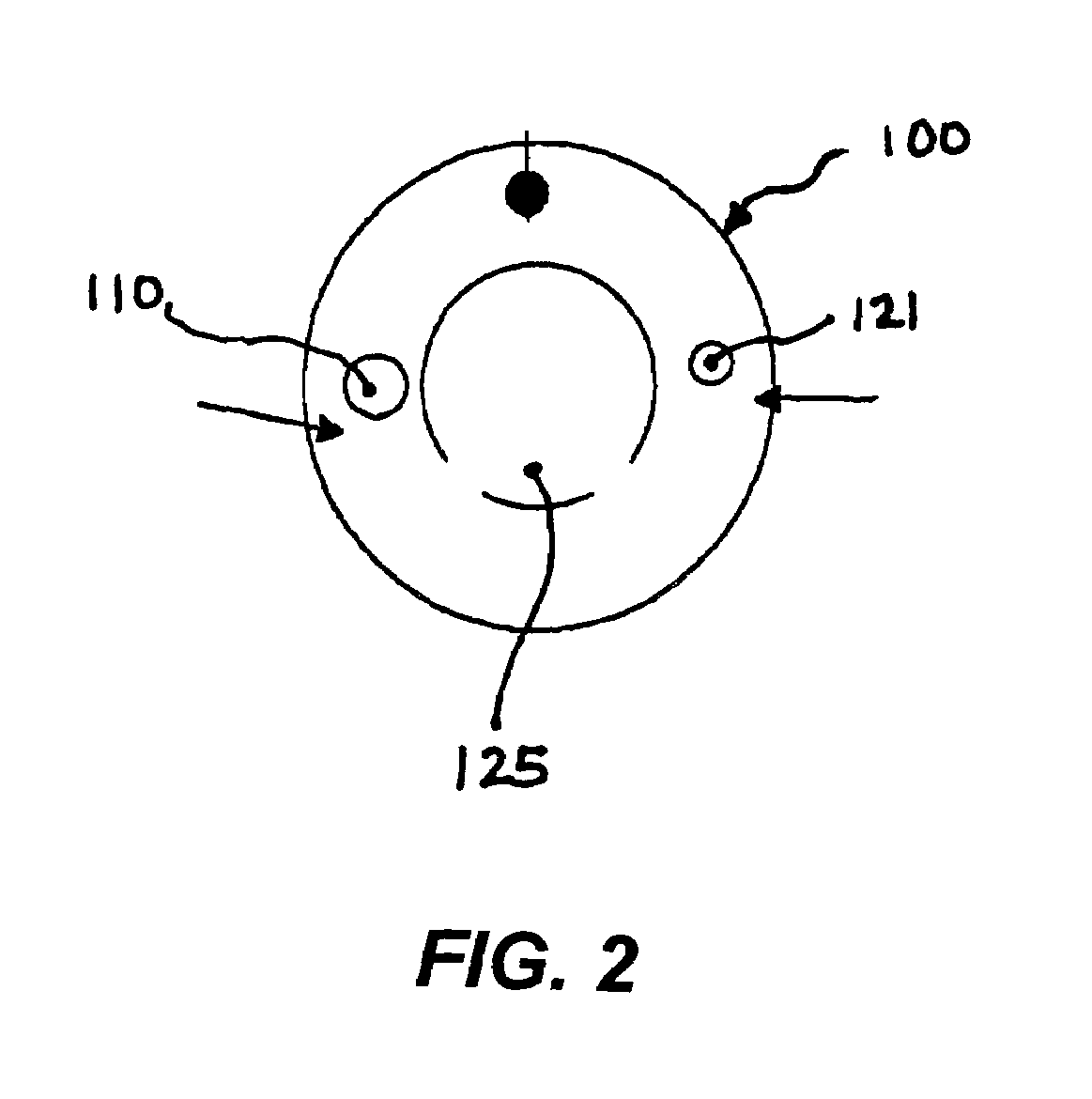
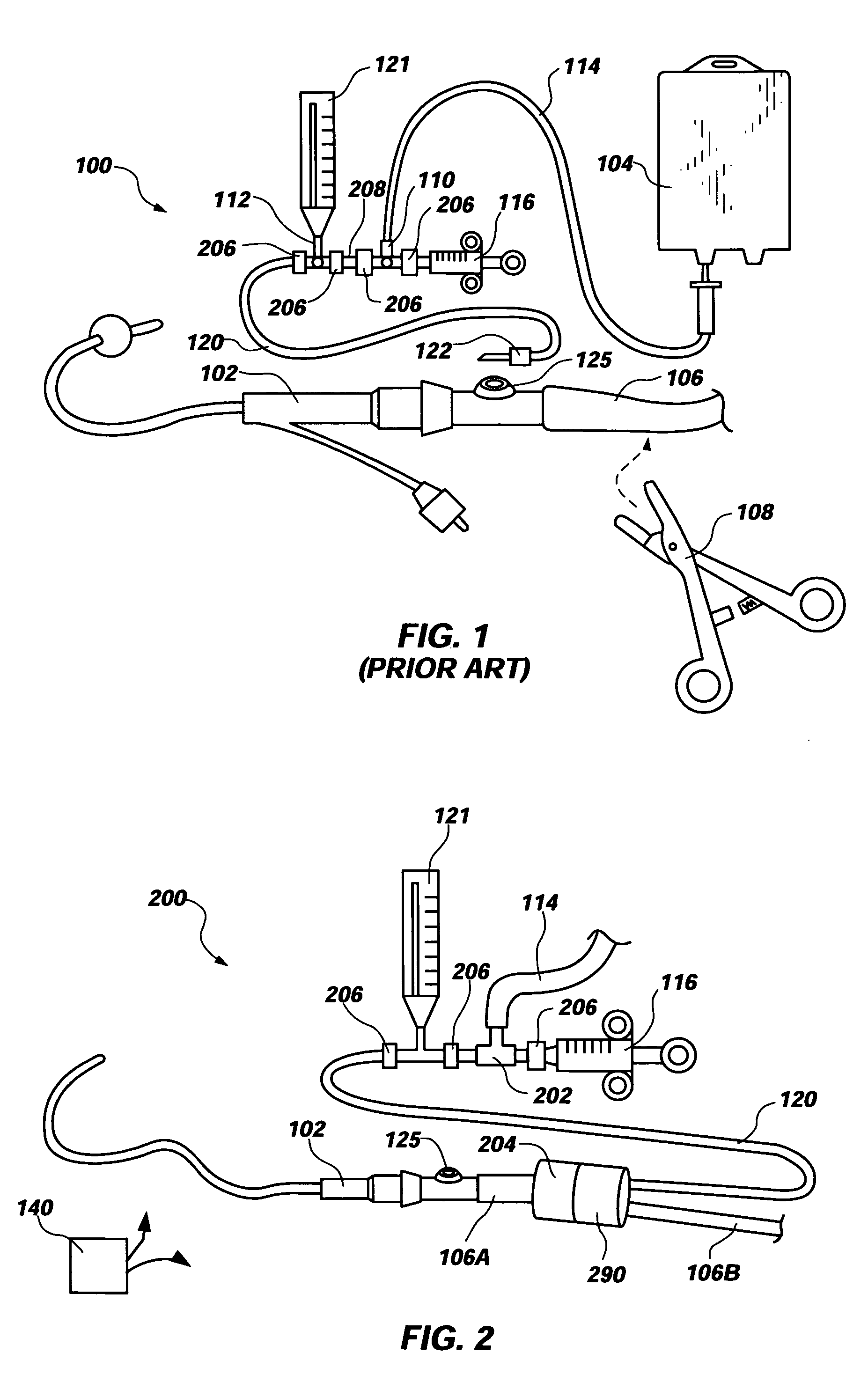
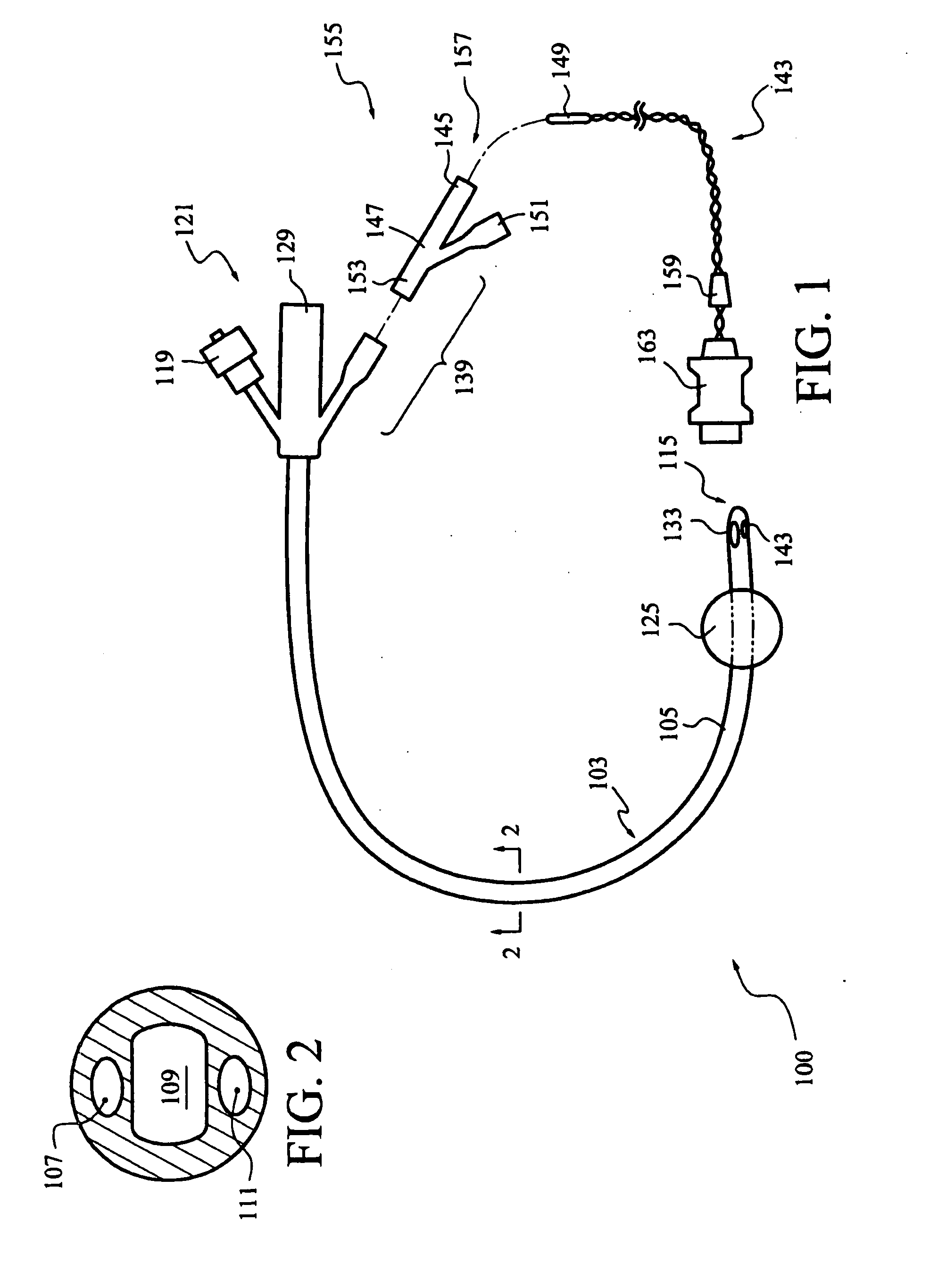
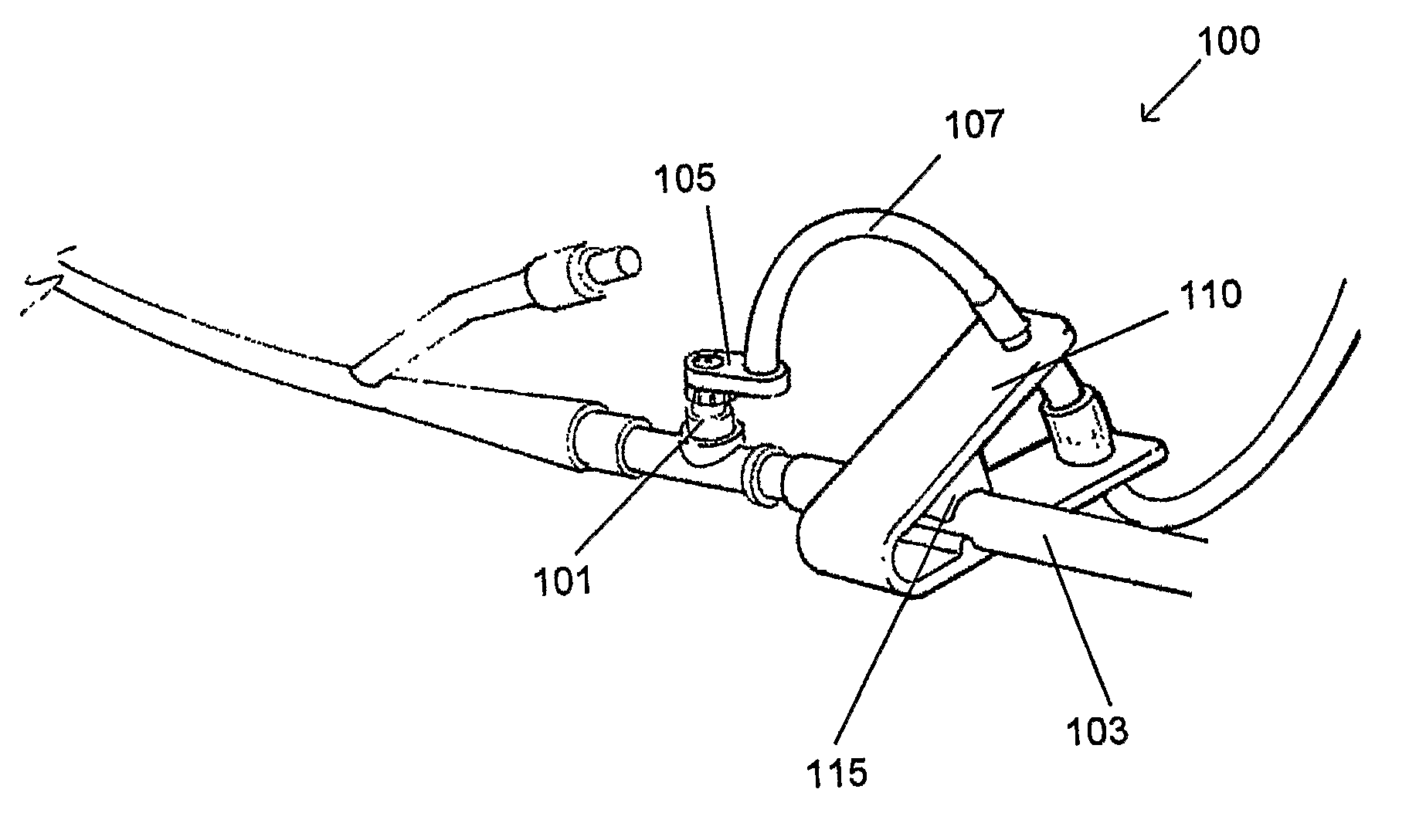
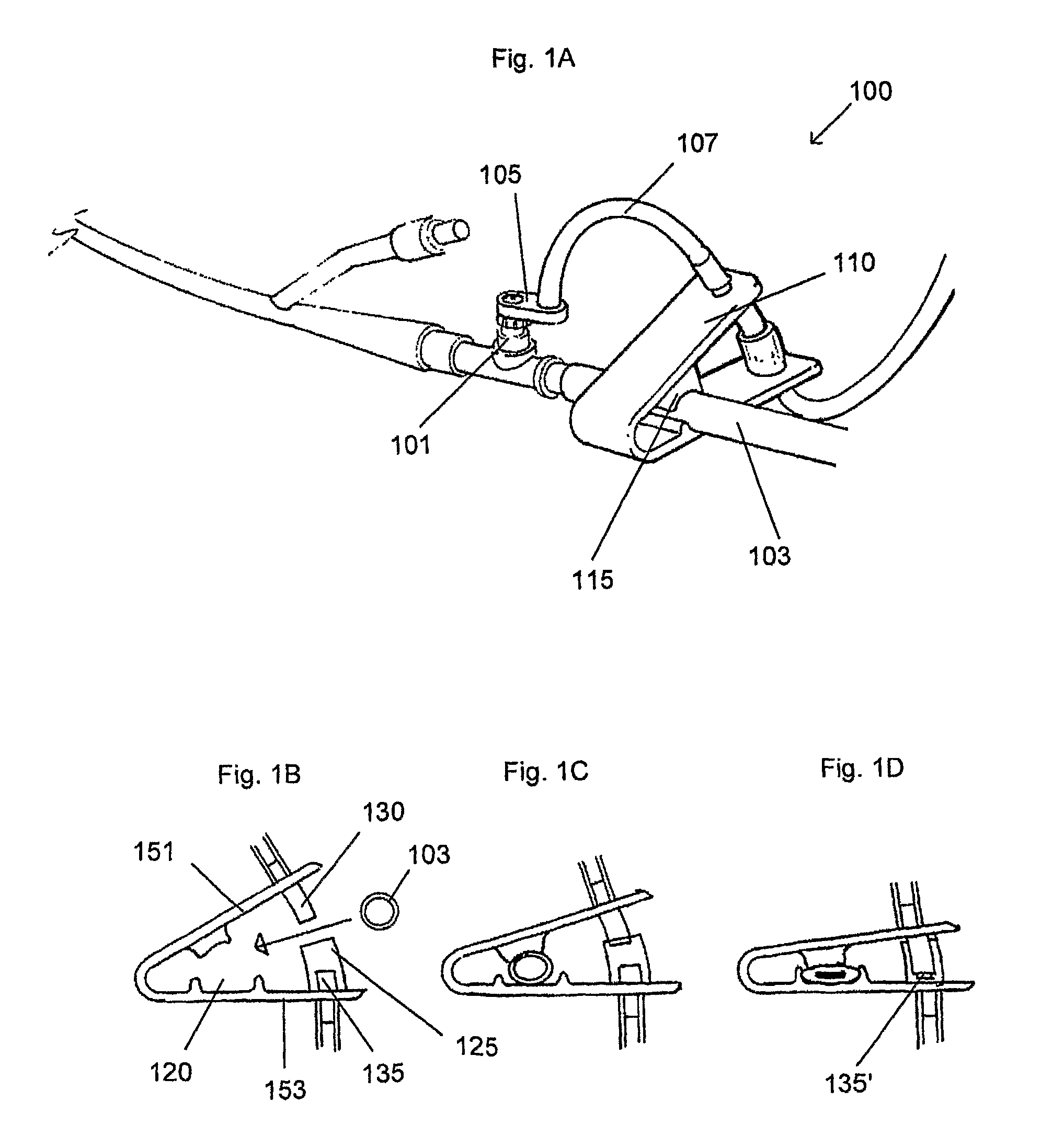
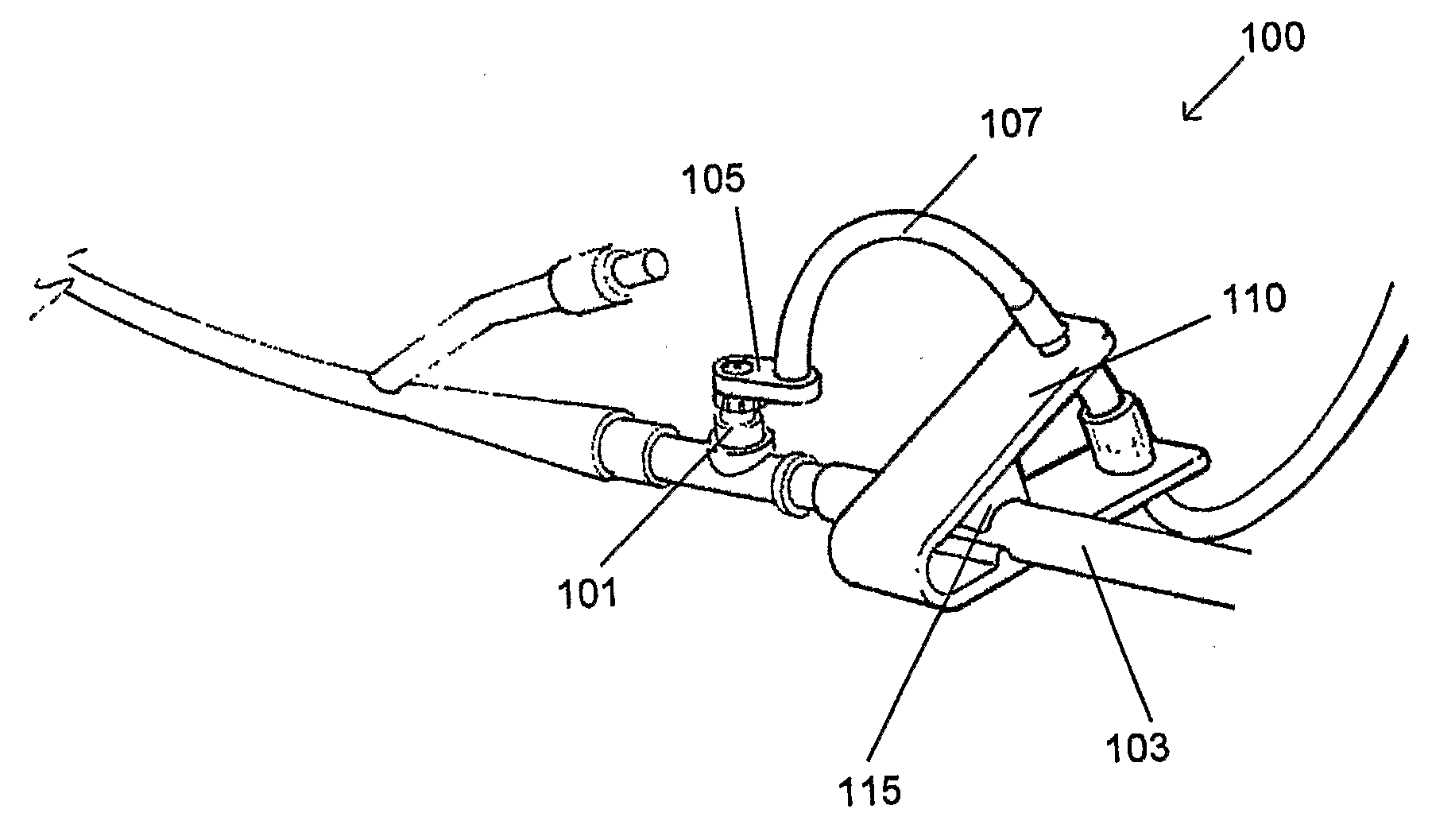
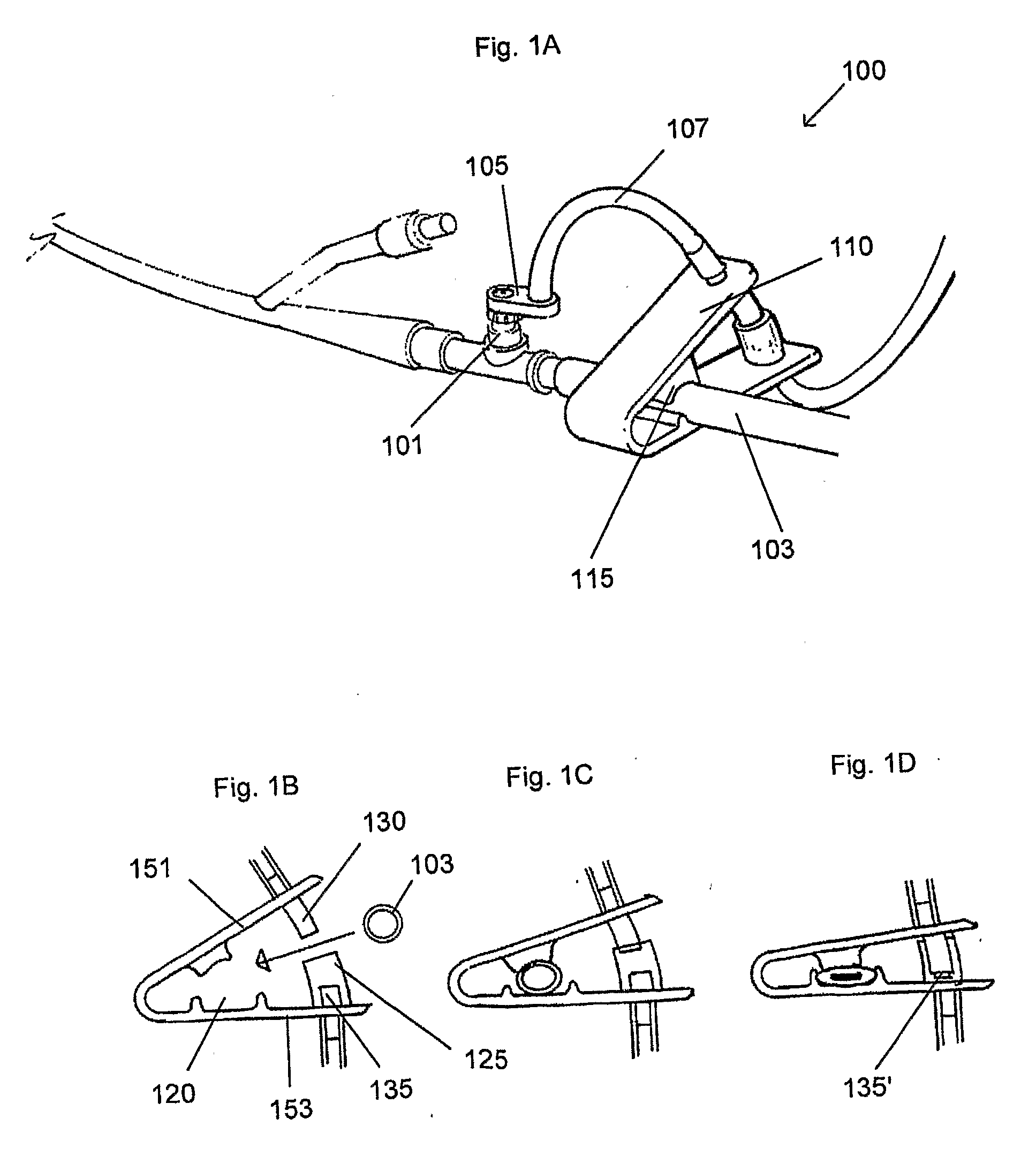
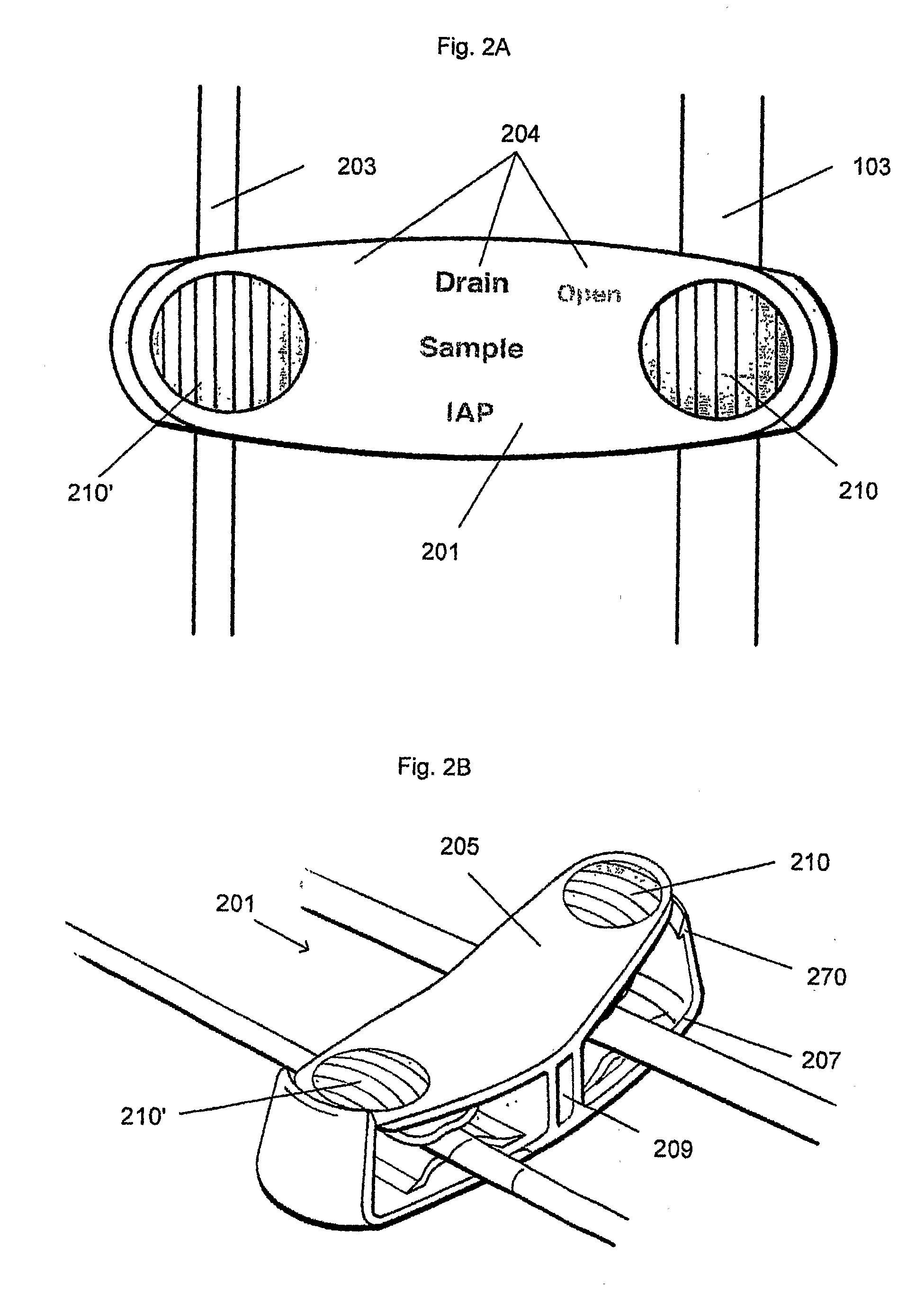
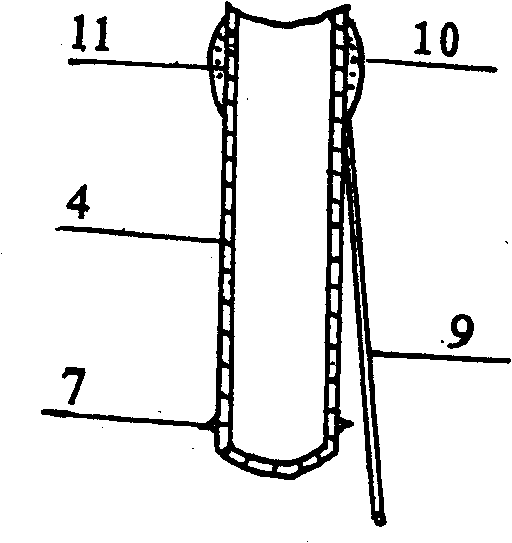
Apparatus for monitoring intra-abdominal pressure
InactiveUS20140088455A1Increase speedFacilitate making pressure measurementCheck valvesEqualizing valvesUrinary catheterHospitalized patients
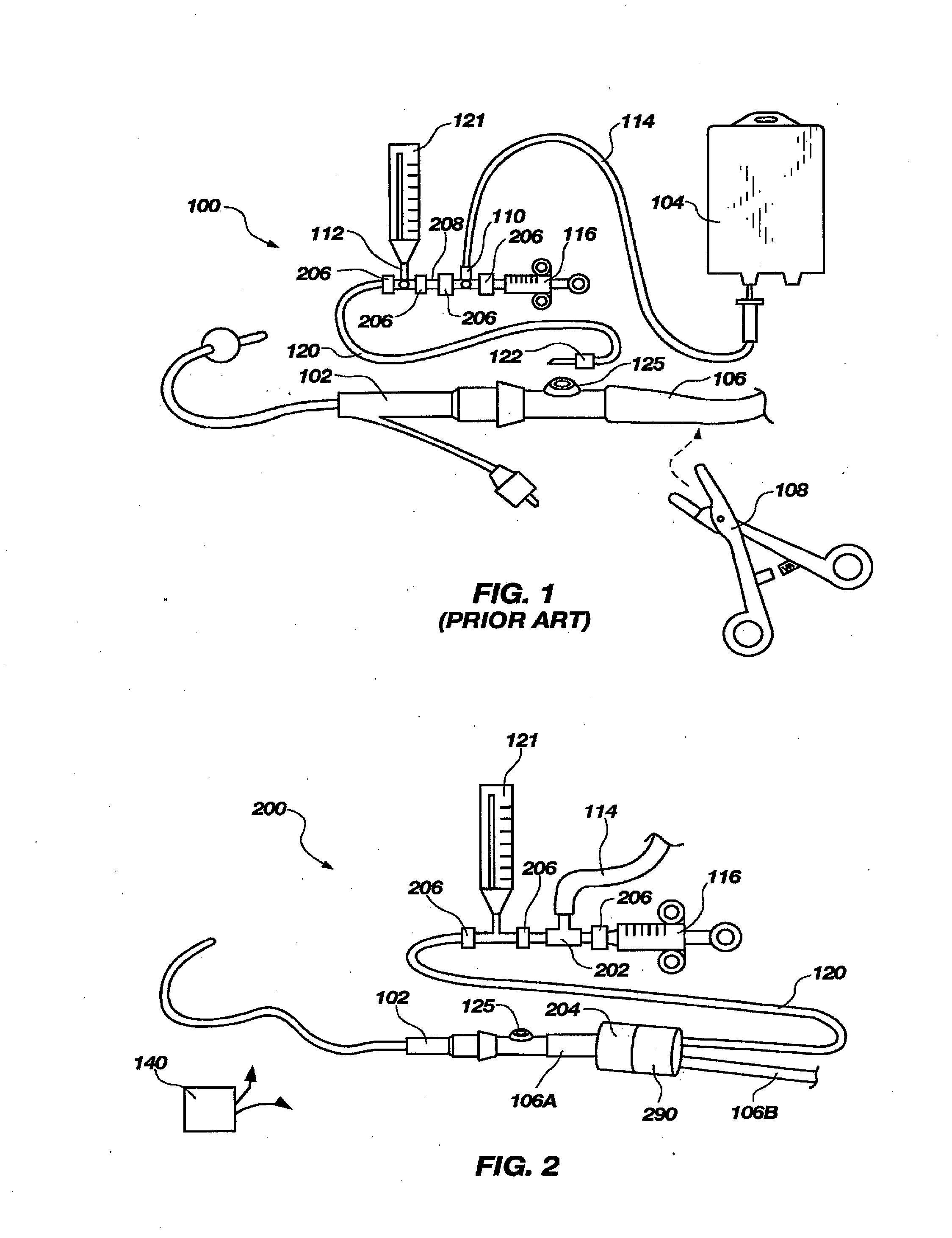
An improved apparatus for monitoring the intra-abdominal pressure of a hospitalized patient includes a urinary catheter connected to a urine valve having selectable communication positions between a discharge end of the urinary catheter and either a drain or a fluid source. Preferably, the urine valve has a housing adapted to resist patient discomfort from leg-valve contact. One operable protective housing may be embodied as a separate tray component. Plumbing structure desirably maintains fluid supply and drain conduits in a substantially parallel arrangement to assist routing those conduits between a patient's legs. When the urine valve is oriented for communication to the fluid source, an infusion pump may be used to introduce a known quantity of fluid through the urine valve and into the patient's bladder where the fluid's pressure can be measured. Desirably, a double check valve is included in a fluid supply path and arranged to permit repetitive operation of a syringe to inject a bolus of fluid into the patient's bladder. Subsequent to making a pressure measurement, the urine valve is returned to the bladder draining position.
Owner:CONVATEC TECH INC
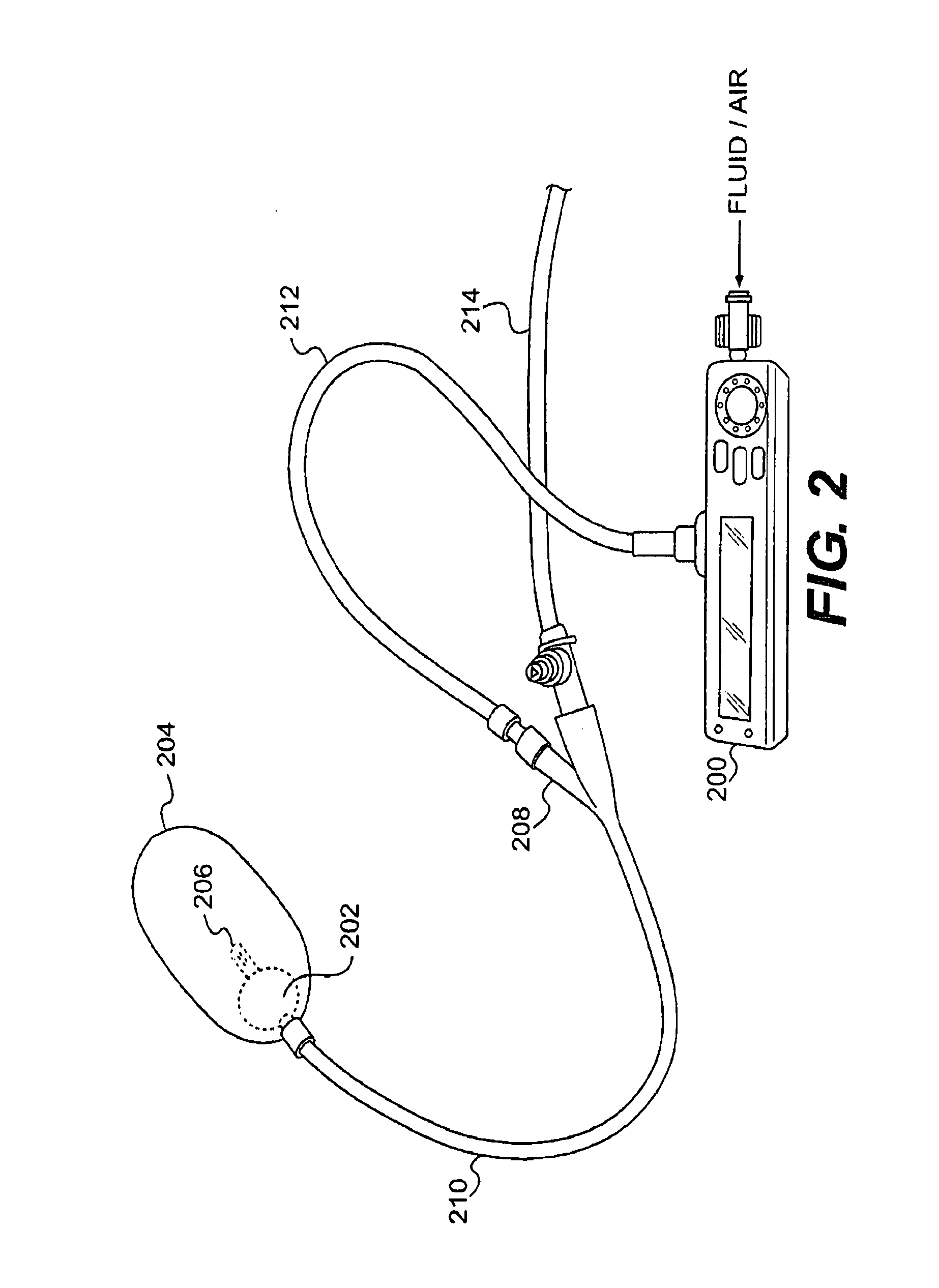
Intra-abdominal pressure monitoring urinary catheter
A urinary catheter and method of its use for measuring the internal pressure of a human or other mammal. The catheter includes three lumens, or channels. The first lumen is dedicated to draining urine, the second lumen is dedicated to a retention balloon, and the third lumen is available for connection to a pressure transducer. In use, the catheter is installed in a patient, the third lumen is filled with a pressure transmitting medium, connected to a pressure sensor, and the patient's intra-abdominal pressure is monitored without interruption of the urine flow.
Owner:CONVATEC TECH INC
Apparatus for monitoring intra-abdominal pressure
ActiveUS7892181B2Increase speedFacilitate making pressure measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsUrinary catheterHospitalized patients
An improved apparatus for monitoring the intra-abdominal pressure of a hospitalized patient includes a urinary catheter connected to a urine valve having selectable communication positions between a discharge end of the urinary catheter and either a drain or a fluid source. Preferably, the urine valve has a housing adapted to resist patient discomfort from leg-valve contact. One operable protective housing may be embodied as a separate tray component. Plumbing structure desirably maintains fluid supply and drain conduits in a substantially parallel arrangement to assist routing those conduits between a patient's legs. When the urine valve is oriented for communication to the fluid source, an infusion pump may be used to introduce a known quantity of fluid through the urine valve and into the patient's bladder where the fluid's pressure can be measured. Desirably, a double check valve is included in a fluid supply path and arranged to permit repetitive operation of a syringe to inject a bolus of fluid into the patient's bladder. Subsequent to making a pressure measurement, the urine valve is returned to the bladder draining position.
Owner:CONVATEC TECH INC
Medical valve and method to monitor intra-abdominal pressure
ActiveUS20070038143A1Reduce flow rateLevel controlEngine diaphragmsUrinary catheterHospitalized patients
An apparatus for monitoring the intra-abdominal pressure of a hospitalized patient includes a urinary catheter connected to a urine valve providing selectable communication between a discharge end of the urinary catheter and either a drain or a fluid source. Preferably, the urine valve is adapted for remote actuation and has a housing adapted to resist patient discomfort from leg-valve contact. Plumbing structure desirably maintains fluid supply and drain conduits in a substantially parallel arrangement to assist routing those conduits between a patient's legs. When the urine valve is oriented to permit communication with the fluid source, an infusion pump may be used to infuse a known quantity of fluid through the urine valve and into the patient's bladder. A pressure transducer desirably is connected in-circuit to indicate the fluid's pressure. To facilitate the infusion process, an automatic flow control device may be included in a fluid supply path and arranged to permit repetitive operation of a syringe to inject a bolus of fluid into the patient's bladder. Subsequent to a period of time in which to make a pressure measurement, preferred embodiments of the urine valve automatically return to a bladder draining position.
Owner:CONVATEC TECH INC
Continuous Intra-Abdominal Pressure Monitoring Urinary Catheter With Optional Core Temperature Sensor
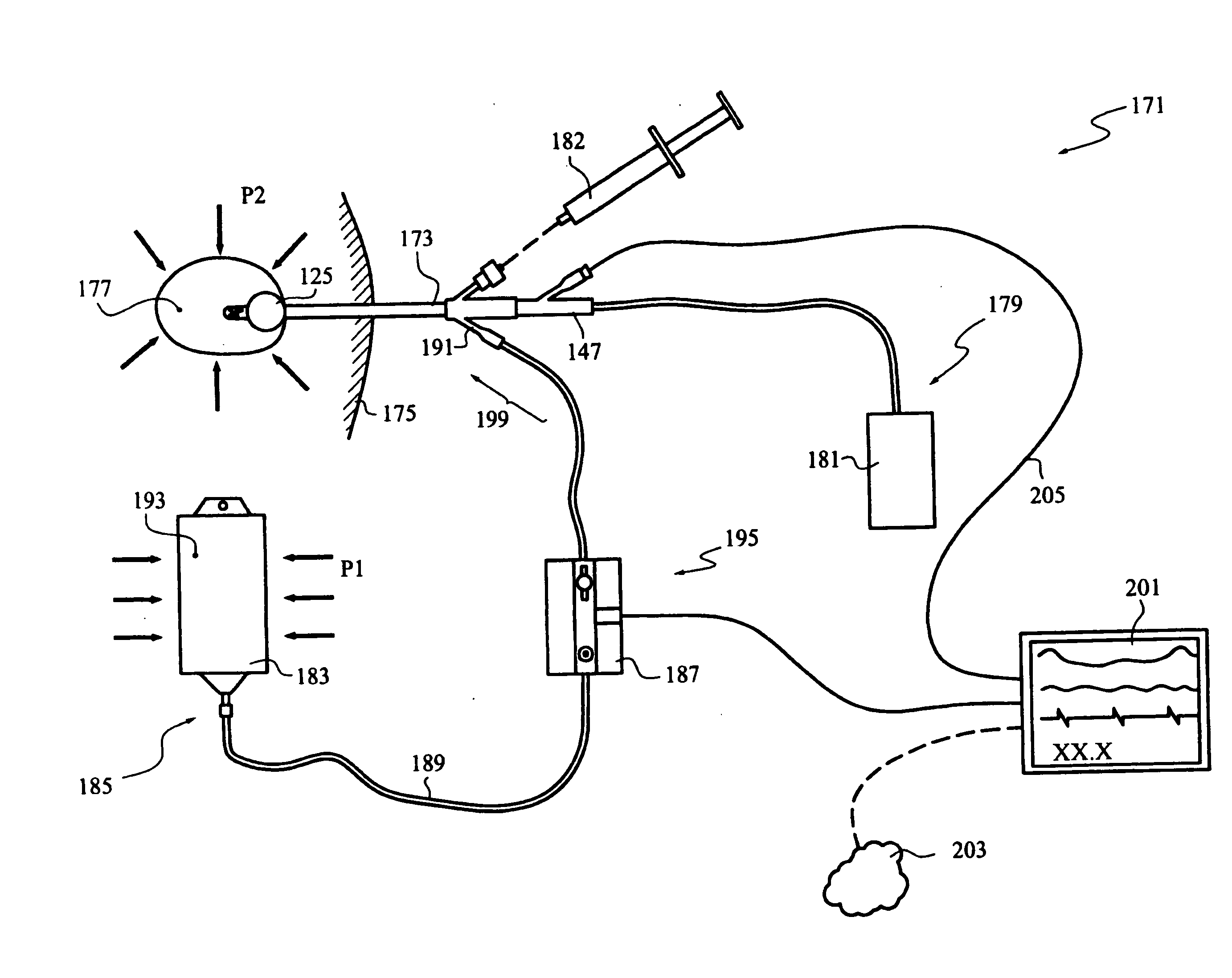
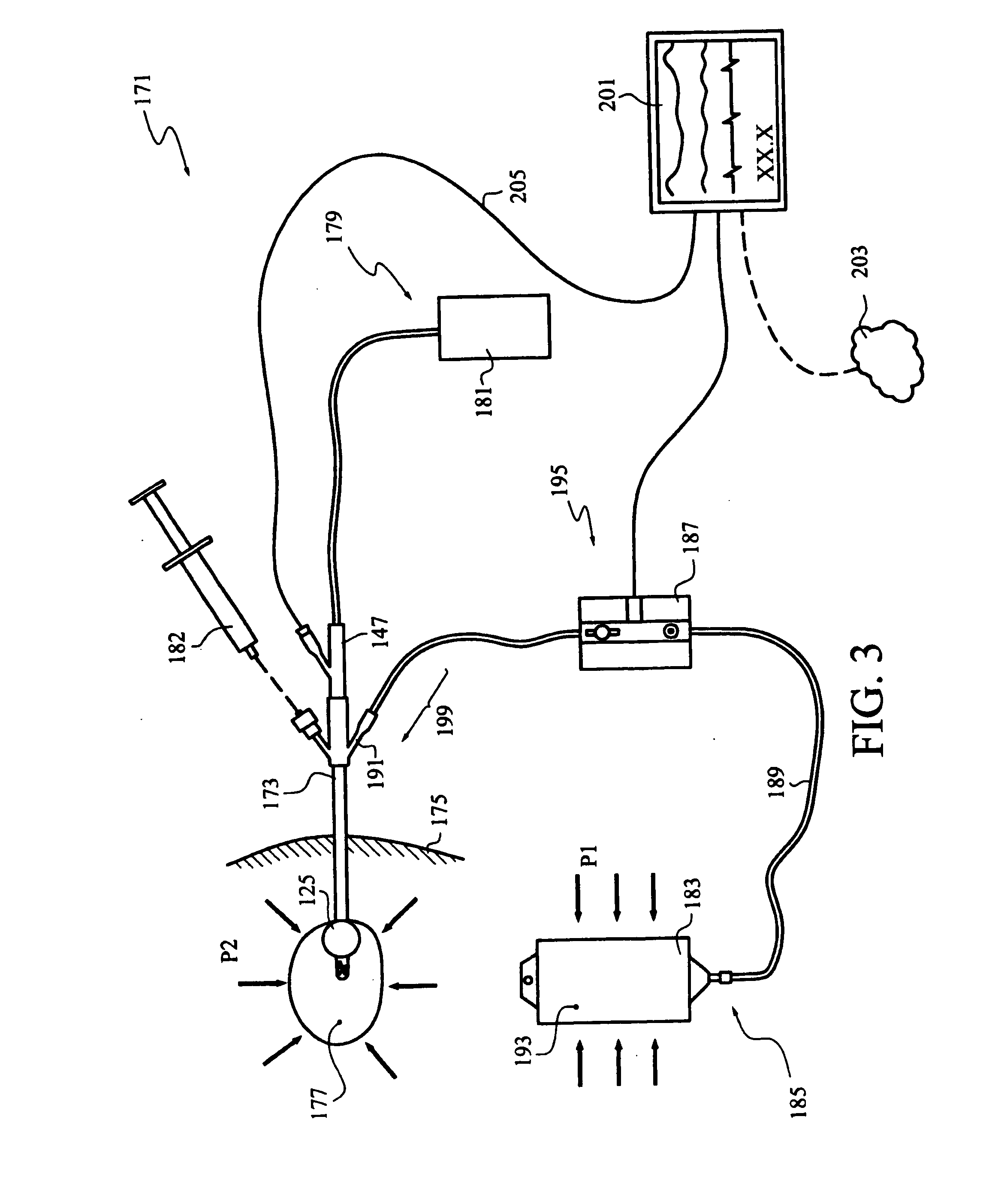
A device structured to generate an input signal to a monitor (201) to visually indicate a value for one or more physiological state variables measured by one or more transducers (203) associated with a medical patient. Preferred embodiments include a pressure transducer (195) placed in fluid communication with the patient's bladder (177) effective to infer intra-abdominal pressure P2. Embodiments may also include a temperature transducer (143) configured to measure the temperature of fluid in / near the bladder (177) to infer core body temperature. Certain embodiments of the invention may include a second pressure transducer (235) configured to measure arterial blood pressure. In the latter case, signals received from the two pressure transducers (177, 235) may be manipulated to produce a third signal corresponding to abdominal perfusion pressure, which can then be indicated on a numeric display device (233).
Owner:WOLFE TORY MEDICAL
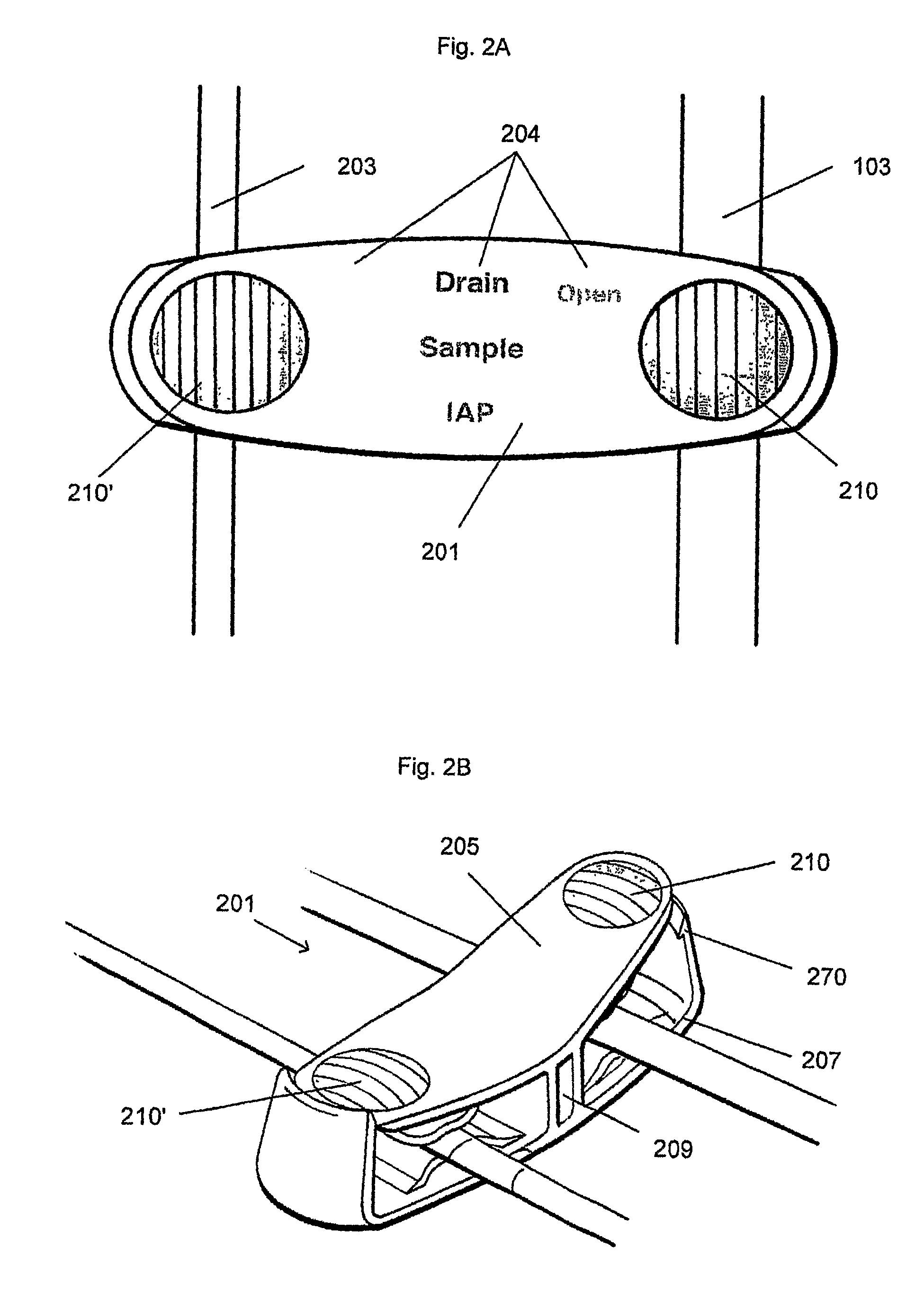
Intra-abdominal pressure monitoring system
ActiveUS8337411B2Avoid flowMaintaining their functionalityWound drainsBagsUrinary catheterDraining tube
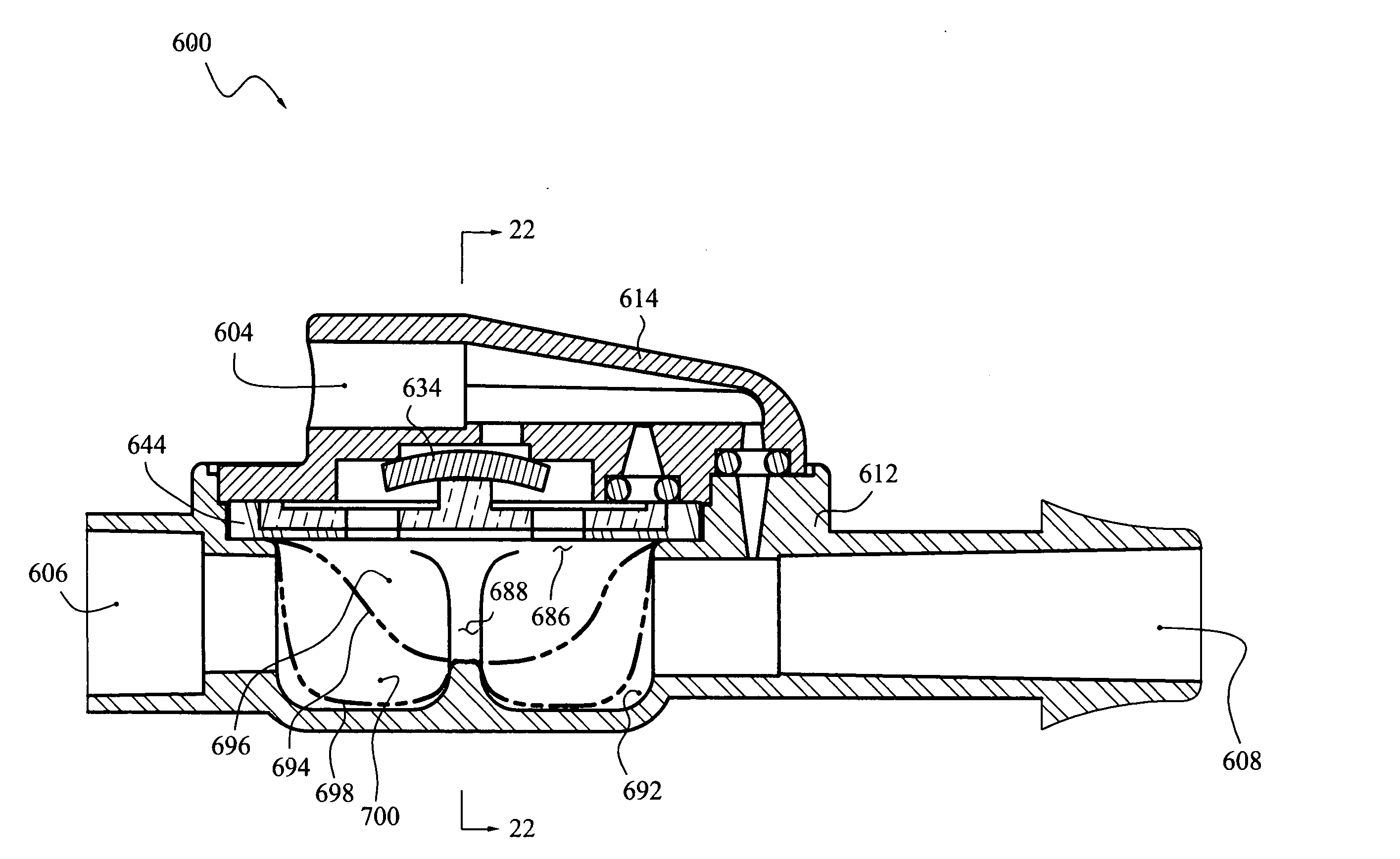
Described herein are devices, systems, kits and methods for measuring intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) from a patient catheterized with a urinary catheter system. Devices may include a bypass lumen configured to connect to a pressure transducer, a sampling port connector connected to the bypass lumen, a drain tube housing configured to at least partially enclose a portion of the drain tube of a urinary catheter system, and a clamp mechanism. The sampling port connector may be configured for removable attachment to the sampling port of the urinary catheter system to form a fluid connection between the urinary catheter system and the bypass lumen of the IAP device. The clamp mechanism may be configured to controllably occlude the lumen of the urinary catheter system drain tube.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Apparatus for monitoring intra-abdominal pressure
InactiveUS20070255167A1Increase speedFacilitate making pressure measurementEqualizing valvesSafety valvesUrinary catheterHospitalized patients
An improved apparatus for monitoring the intra-abdominal pressure of a hospitalized patient includes a urinary catheter connected to a urine valve having selectable communication positions between a discharge end of the urinary catheter and either a drain or a fluid source. Preferably, the urine valve has a housing adapted to resist patient discomfort from leg-valve contact. One operable protective housing may be embodied as a separate tray component. Plumbing structure desirably maintains fluid supply and drain conduits in a substantially parallel arrangement to assist routing those conduits between a patient's legs. When the urine valve is oriented for communication to the fluid source, an infusion pump may be used to introduce a known quantity of fluid through the urine valve and into the patient's bladder where the fluid's pressure can be measured. Desirably, a double check valve is included in a fluid supply path and arranged to permit repetitive operation of a syringe to inject a bolus of fluid into the patient's bladder. Subsequent to making a pressure measurement, the urine valve is returned to the bladder draining position.
Owner:CONVATEC TECH INC
Spinal orthotic devices
InactiveUS7662121B2Property can be increased and decreasedFlexible adaptationOrthopedic corsetsSagittal planeMedicine
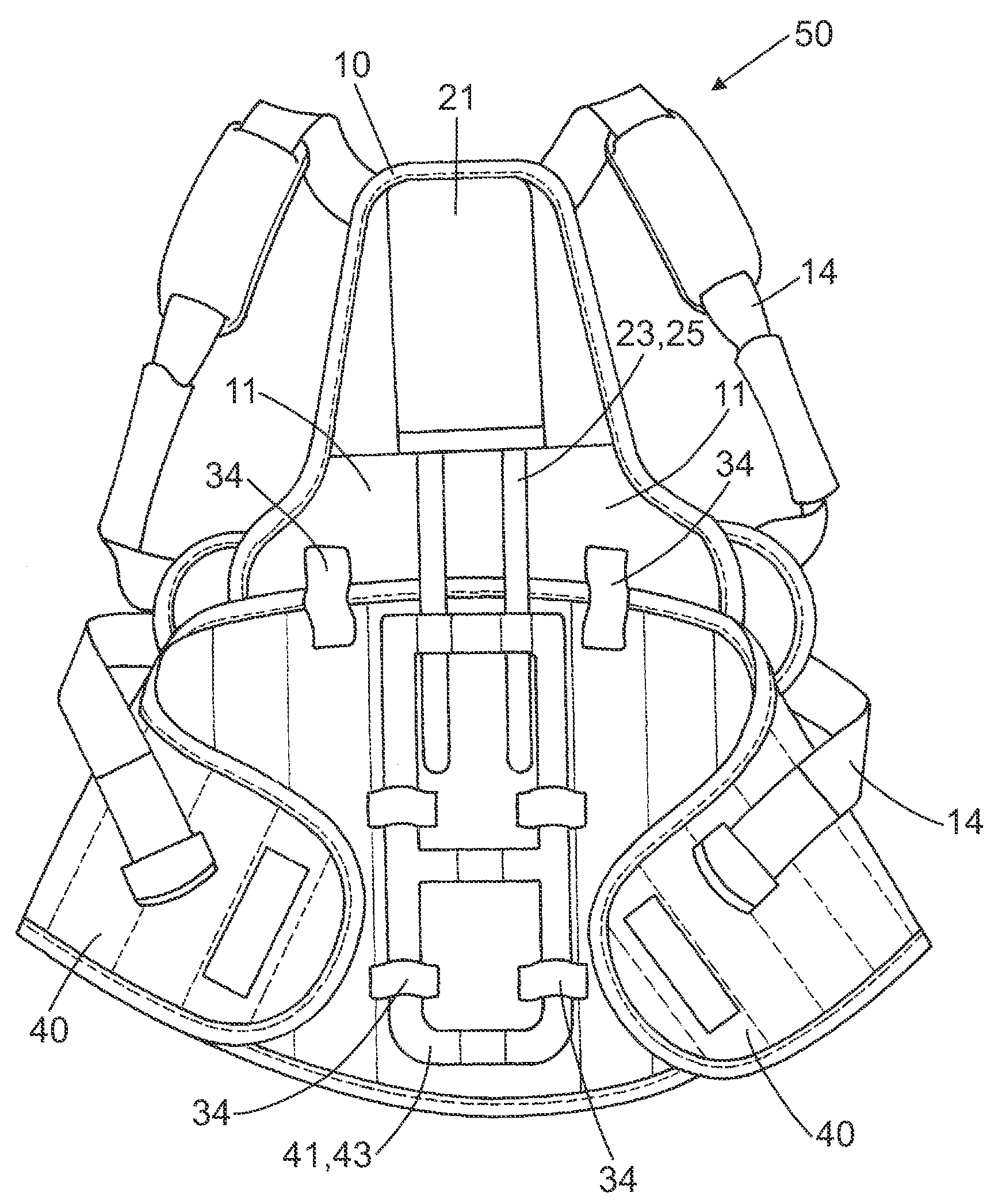
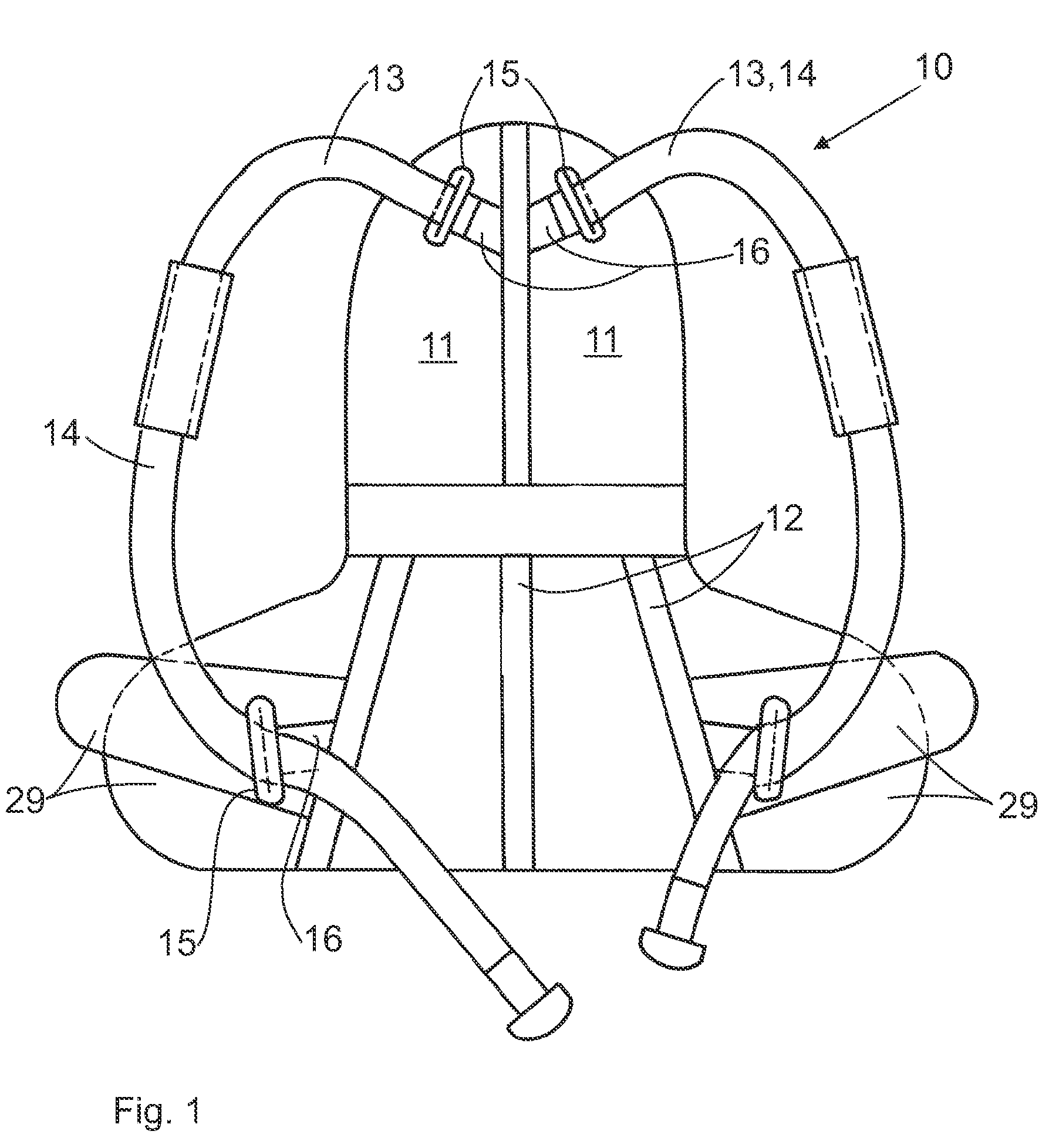
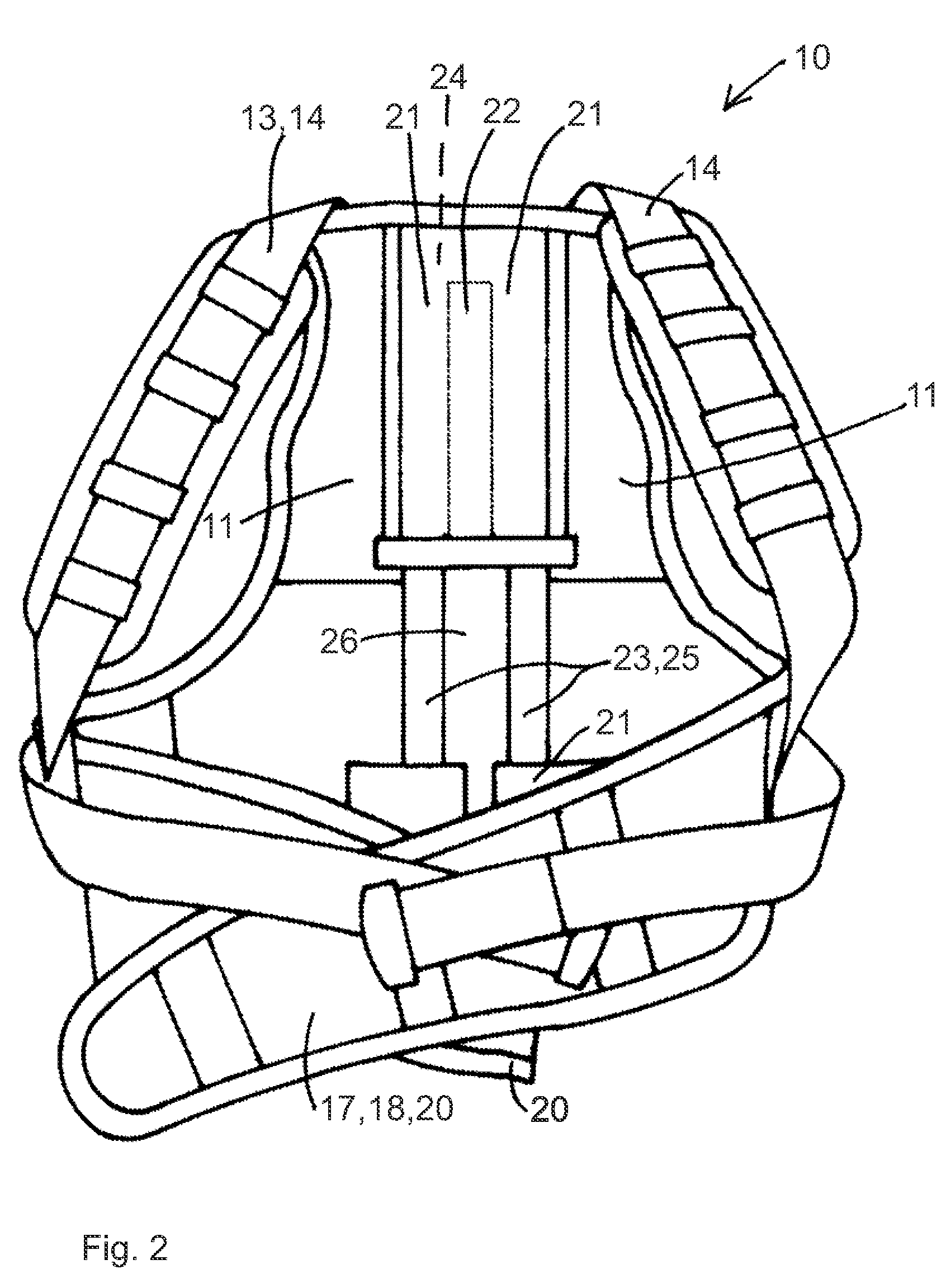
The invention relates to a spinal orthotic device configured from one or more elements of a modular system, comprising the following elements:a lower abdominal corset (40, 120),an upper abdominal corset (17, 130) that can be attached cranially to the lower abdominal corset (40, 120),a corset supporting element (41) that can be secured posteriorly in the lower abdominal corset (40, 120) and is arranged along the lumbar spine, supporting the spine while restricting sagittal mobility,a thoracic spinal corset (10, 200) that can be attached cranially to the lower abdominal corset (40, 120),at least one curved supporting clasp (47) that can be inserted posteriorly optionally into a bandage of a lower abdominal corset (40, 120) and an upper abdominal corset (17, 130) or into an bandage of a lower abdominal corset (40, 120) and a thoracic spinal corset (10, 200), said curved supporting clasp being attached to a corset supporting element (41) for correction of lordosis and for restriction of sagittal and frontal mobility in the area of the lumbar spine,at least one supporting element (23, 160) which can optionally be secured cranially in the thoracic spinal corset (10, 200) and caudally to the corset supporting element (41, 150) and extends laterally along the spine to align and relieve the spine in the sagittal plane,and an abdominal truss pad (190) that can be attached ventrally to a lower abdominal corset (40, 120) for correction of lordosis of the lumbar spine and increasing the intra-abdominal pressure.
Owner:ZOURS CLAUDIA
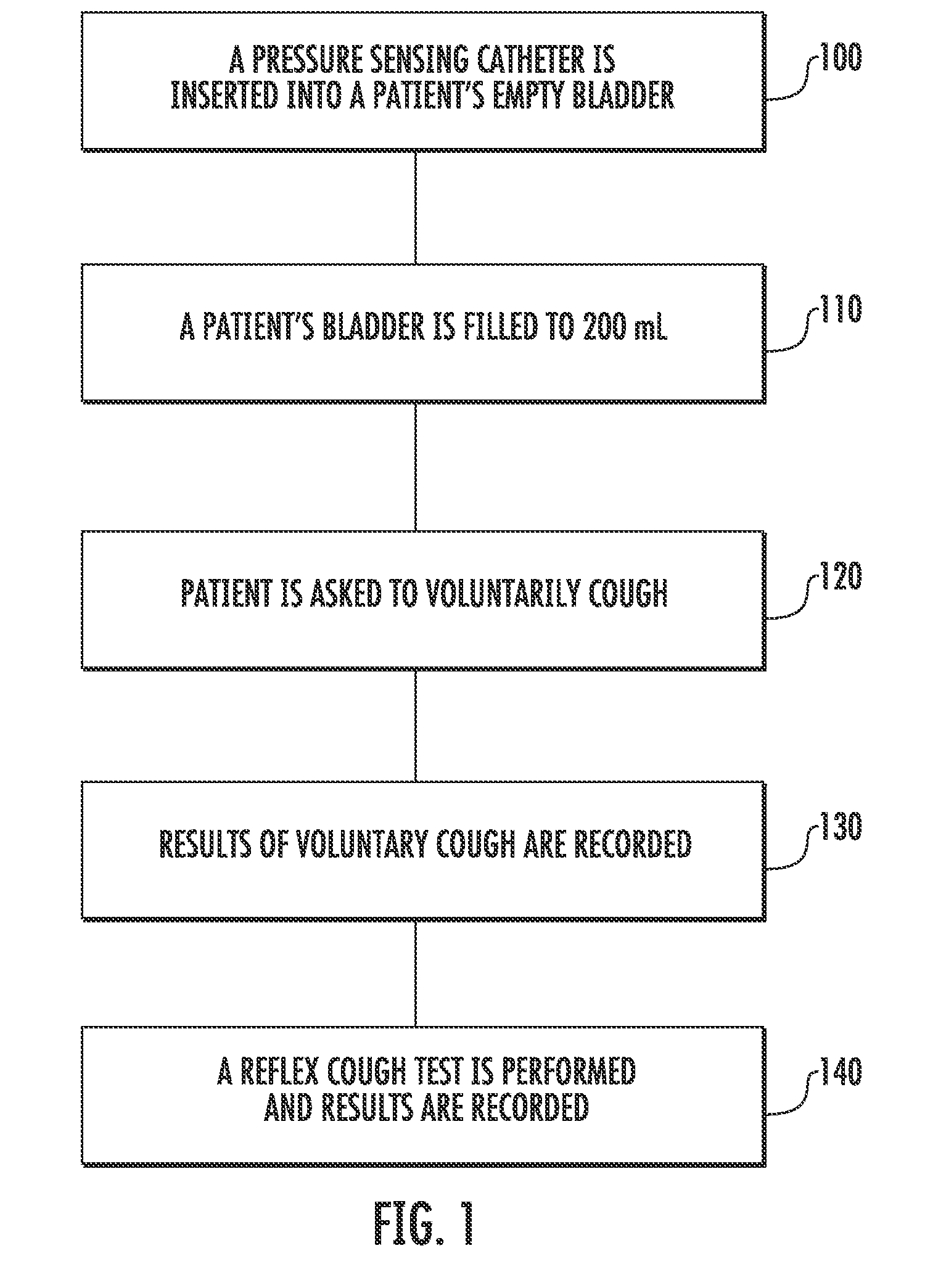
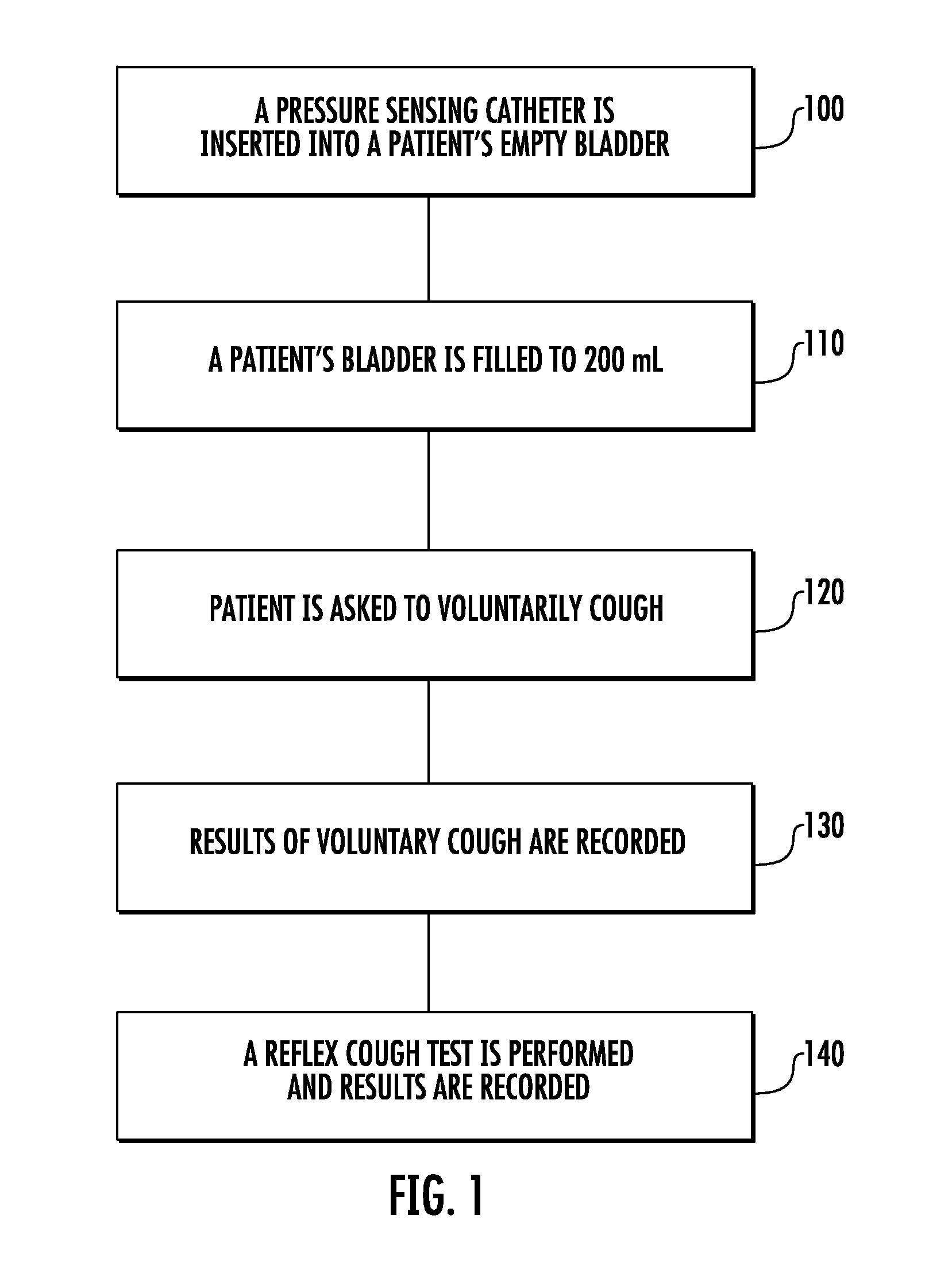
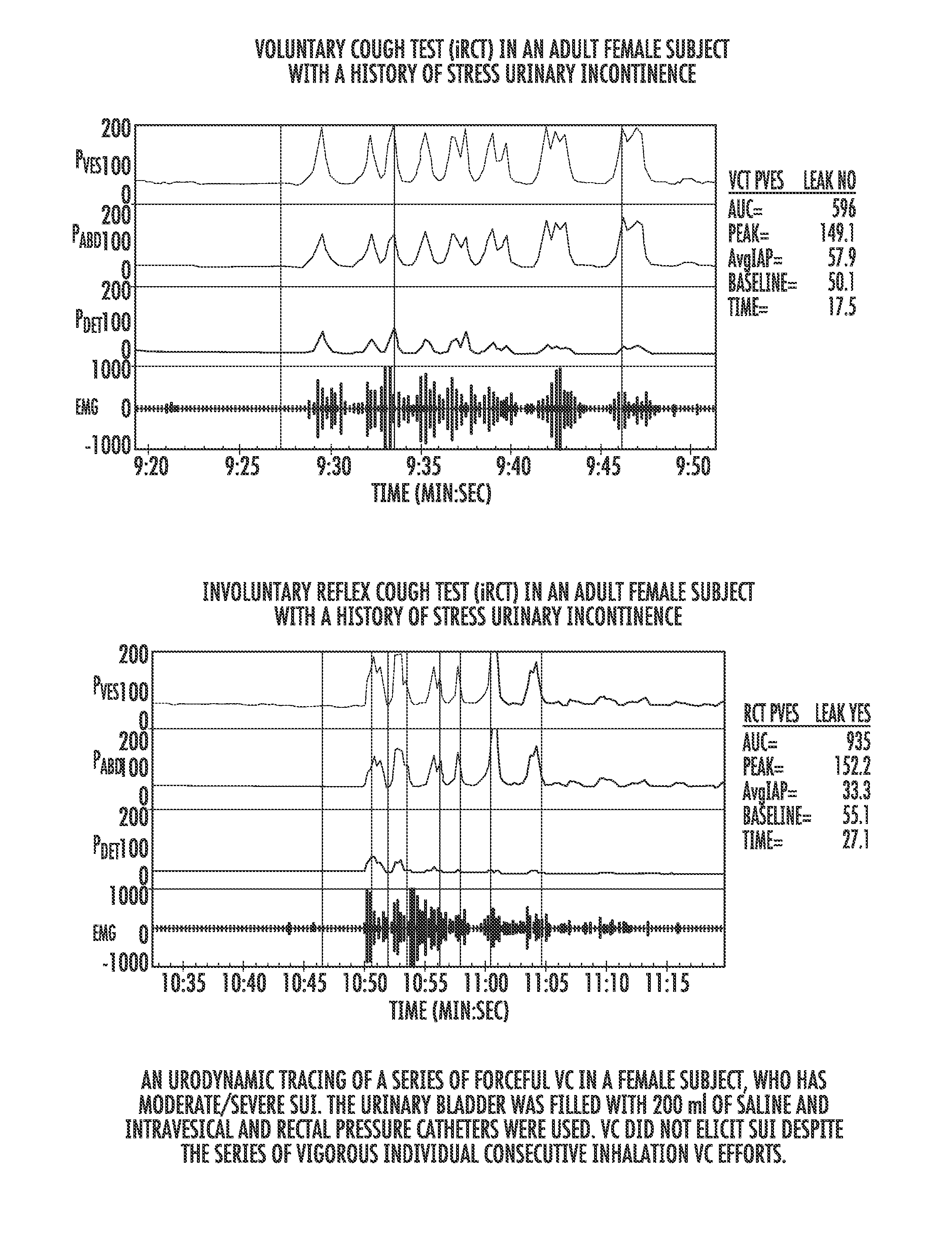
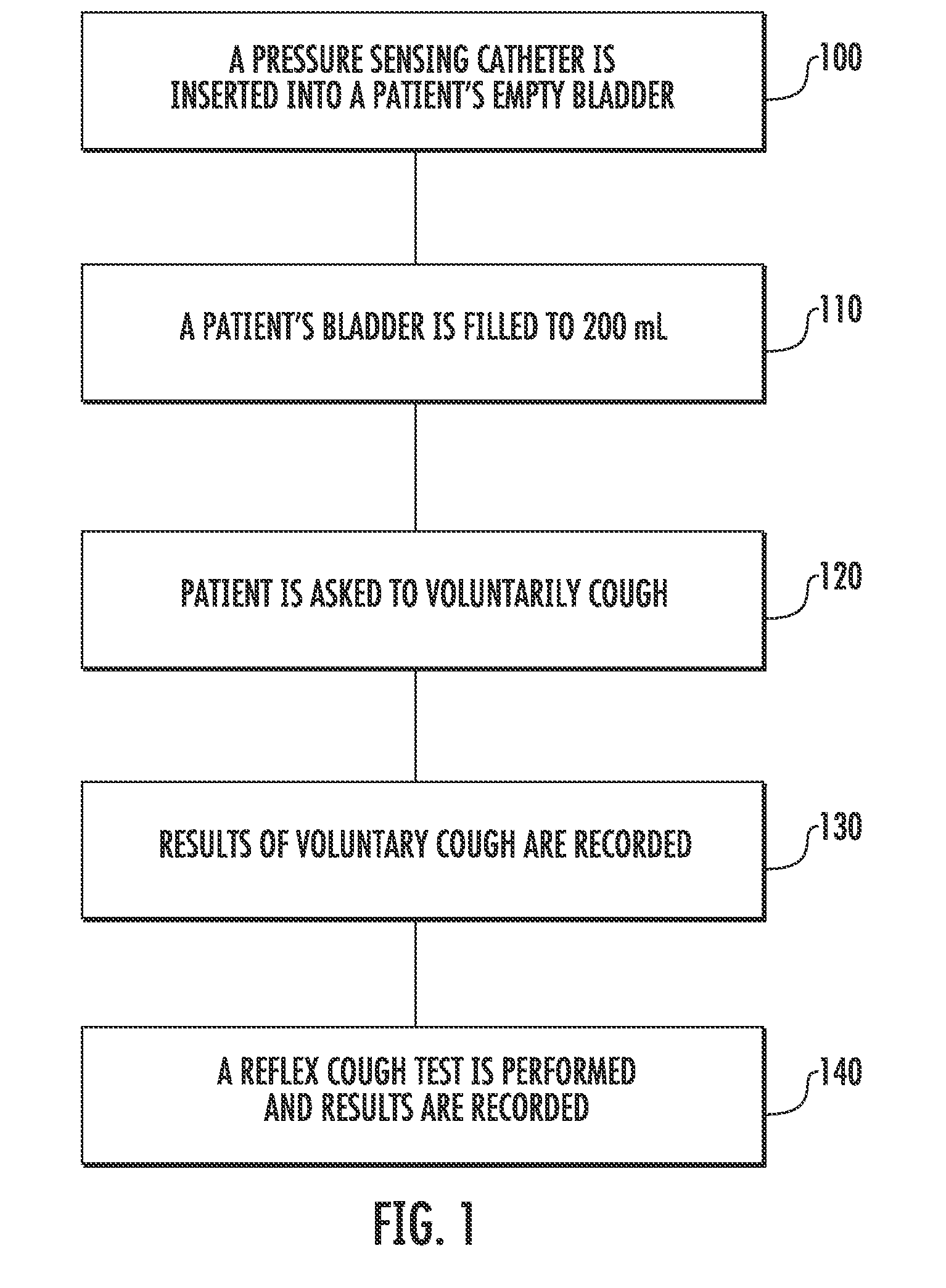
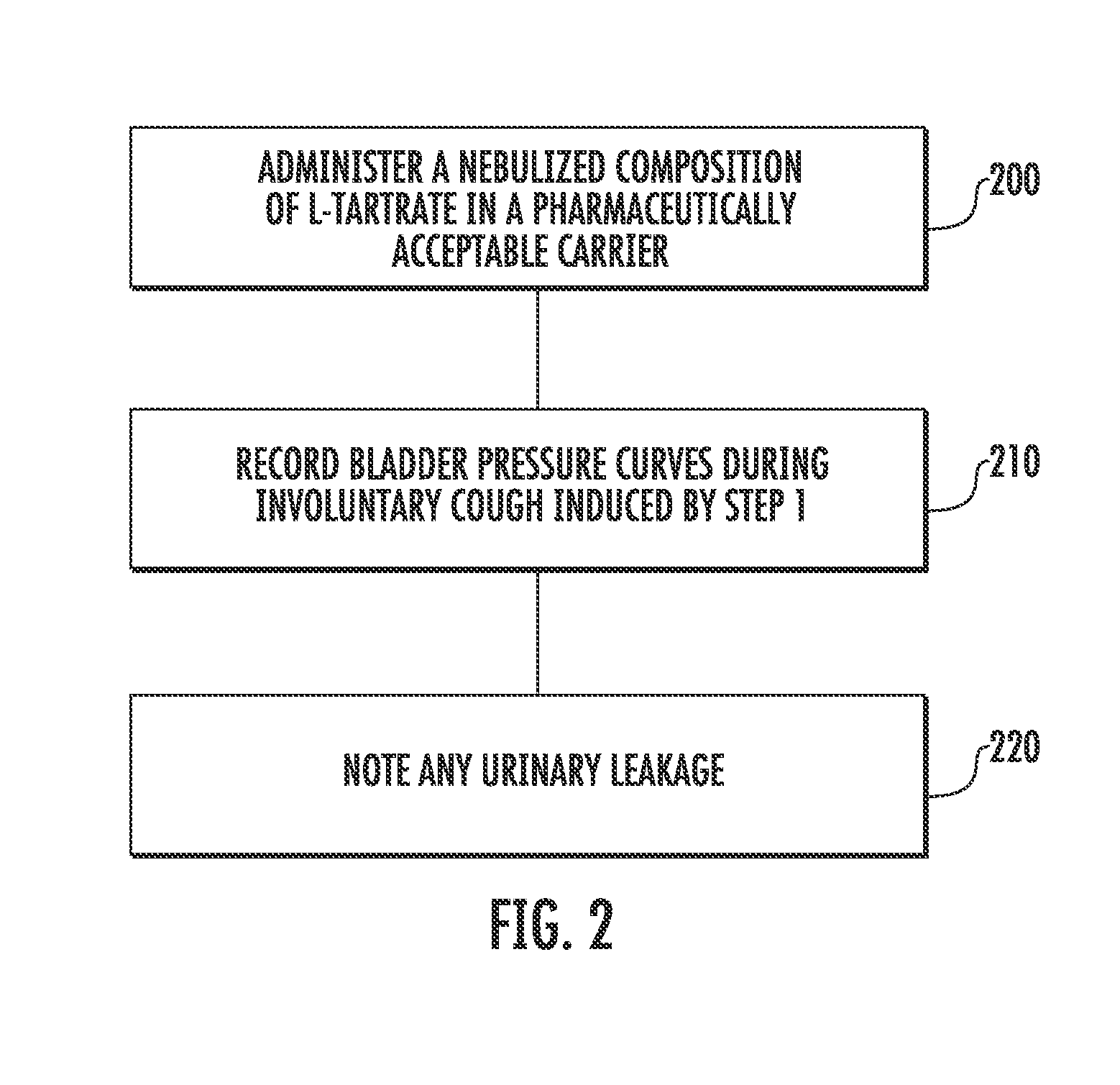
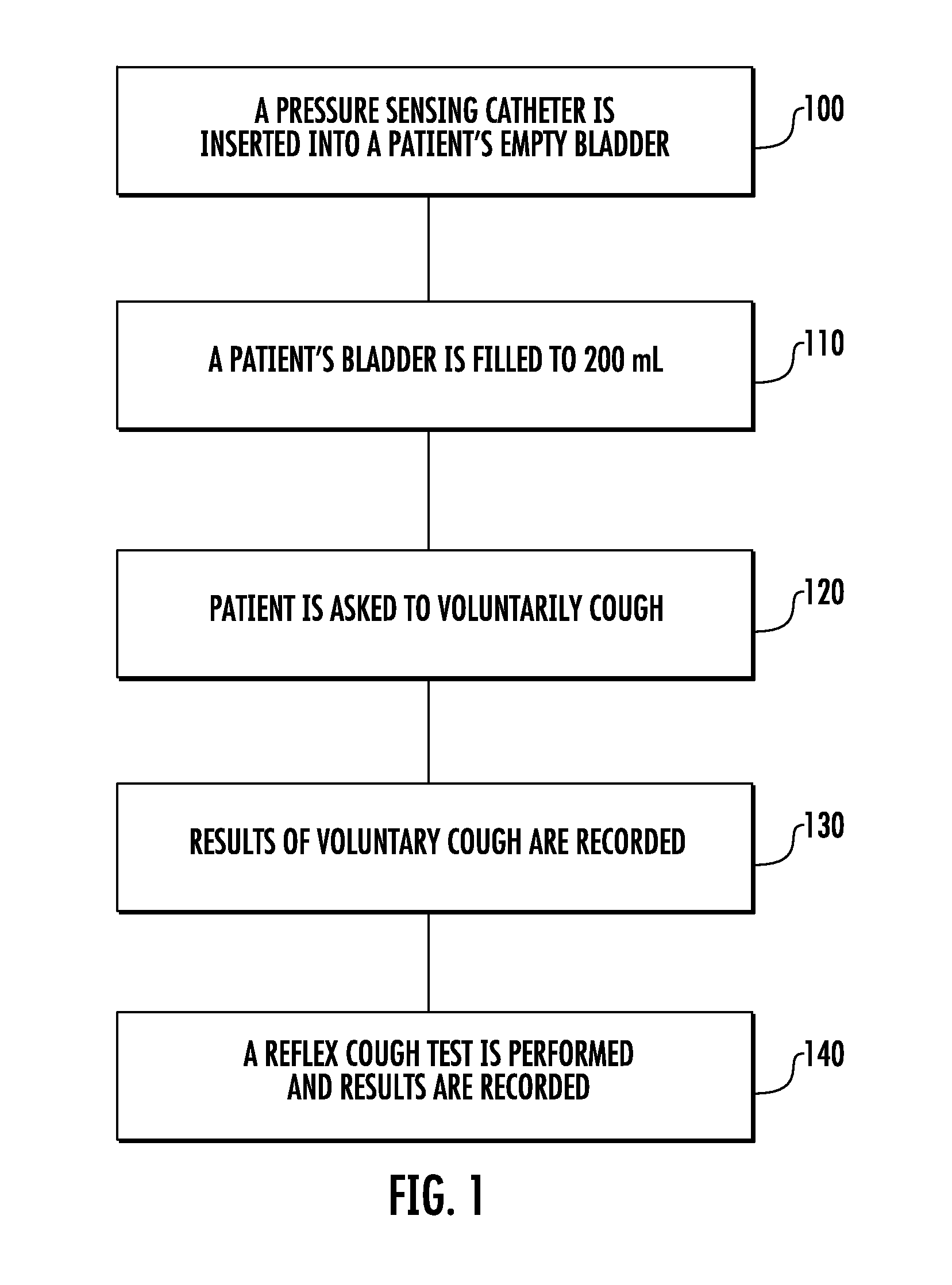
Involuntary contraction induced pressure as a medical diagnostic tool using involuntary reflex cough test
A system and method allows diagnosis of a patient for physiological abnormality such as a neurological deficiency. An involuntary reflex cough event is induced within the patient that activates the nucleus ambiguus and medial motor cell column of the patient and stimulates involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles in the pelvis of the patient. An electromyogram (EMG) is obtained from the involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles while inducing involuntary reflex cough and determining its duration. The intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) is determined and the IAP is correlated with the EMG duration of the involuntary cough event within a processing device to diagnose a physiological abnormality such as a neurological deficiency within the patient.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
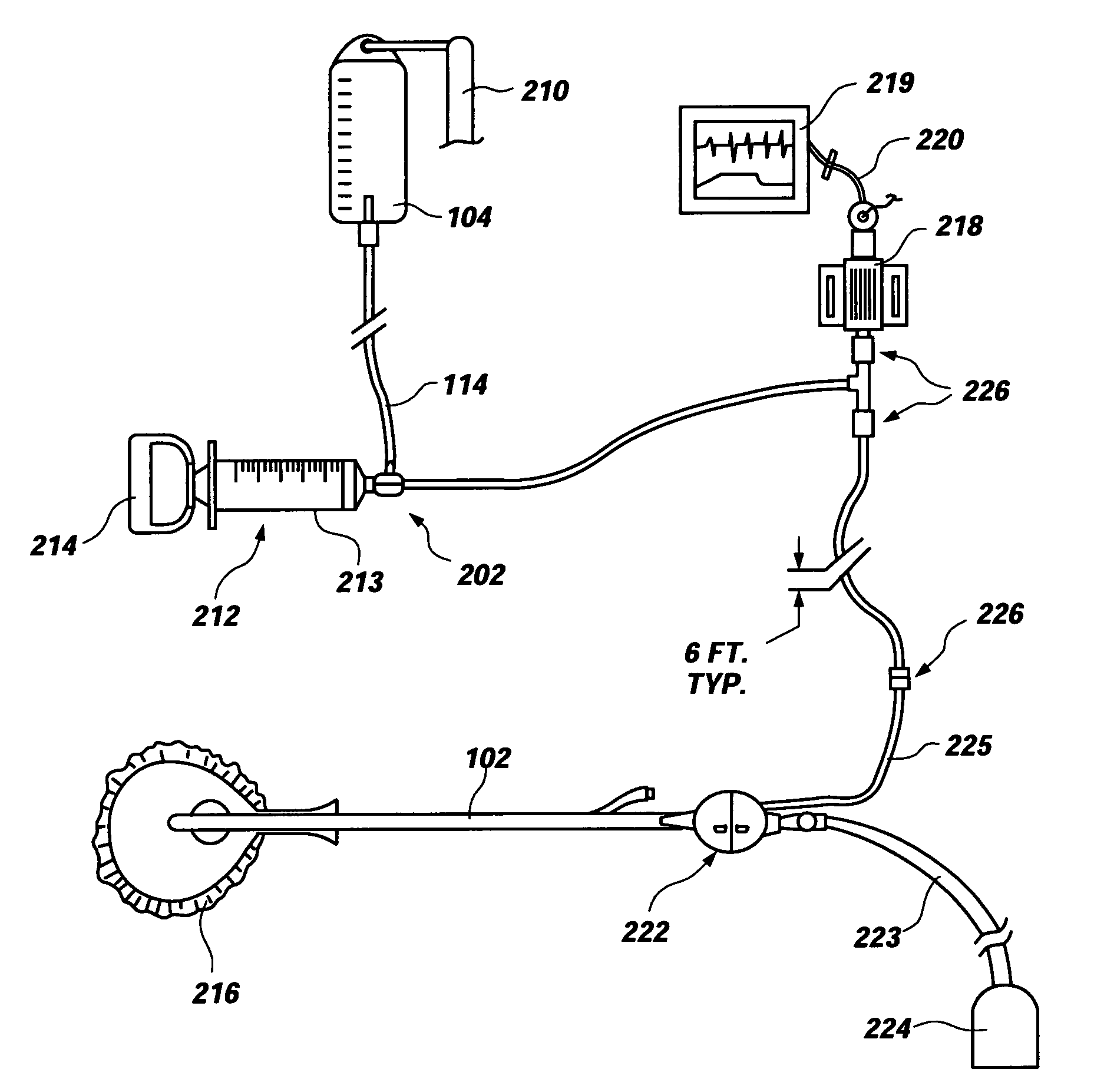
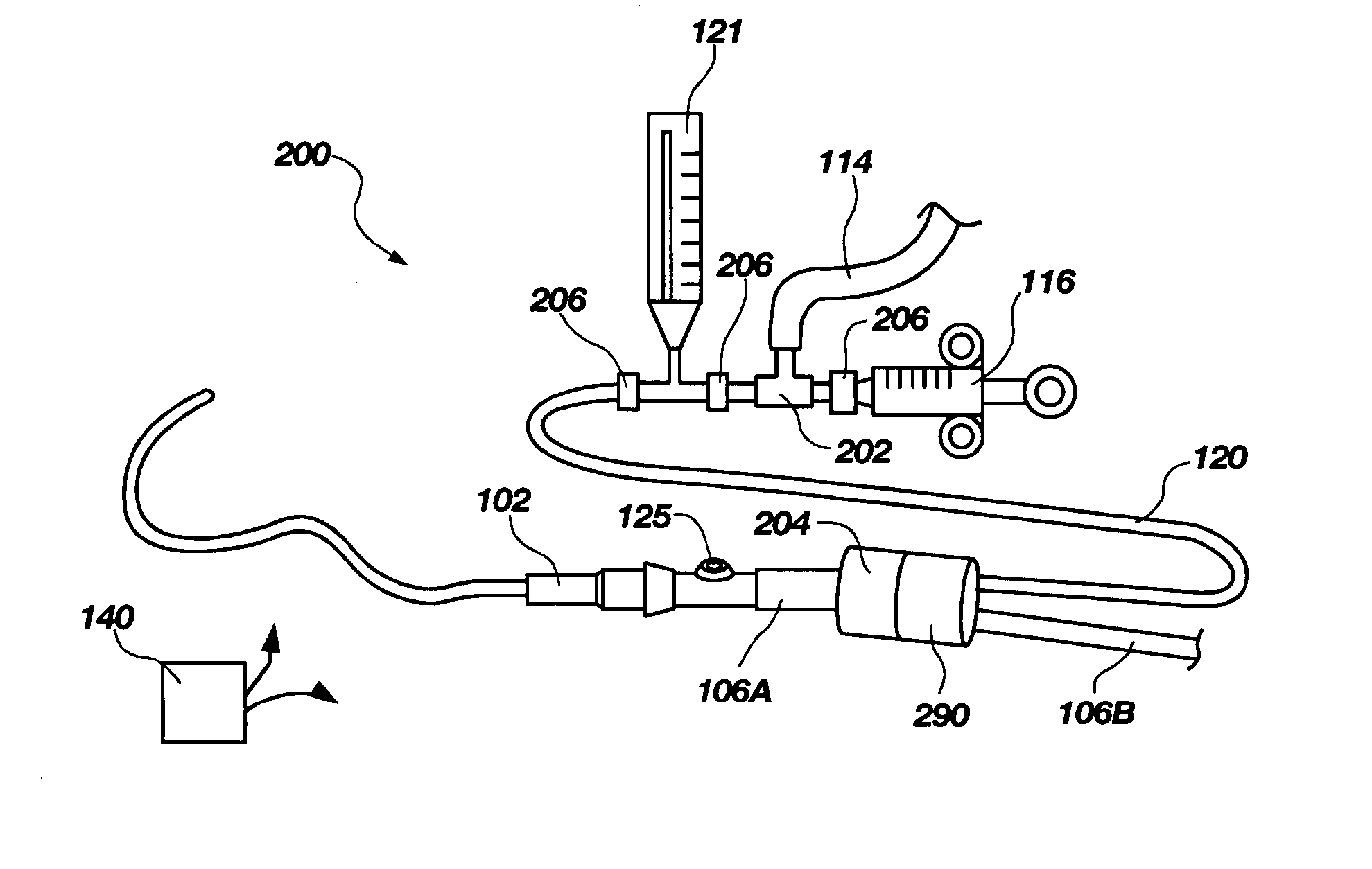
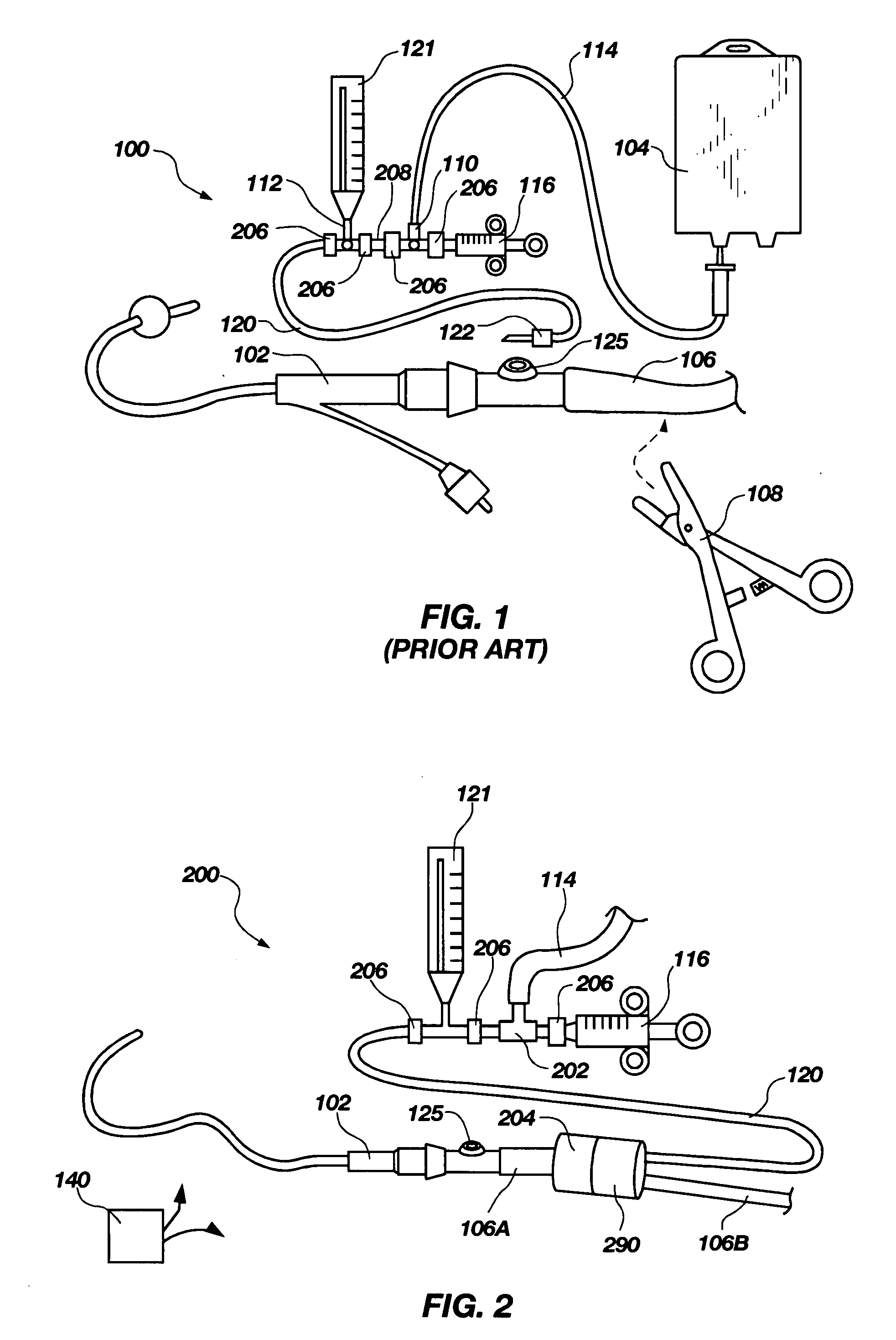
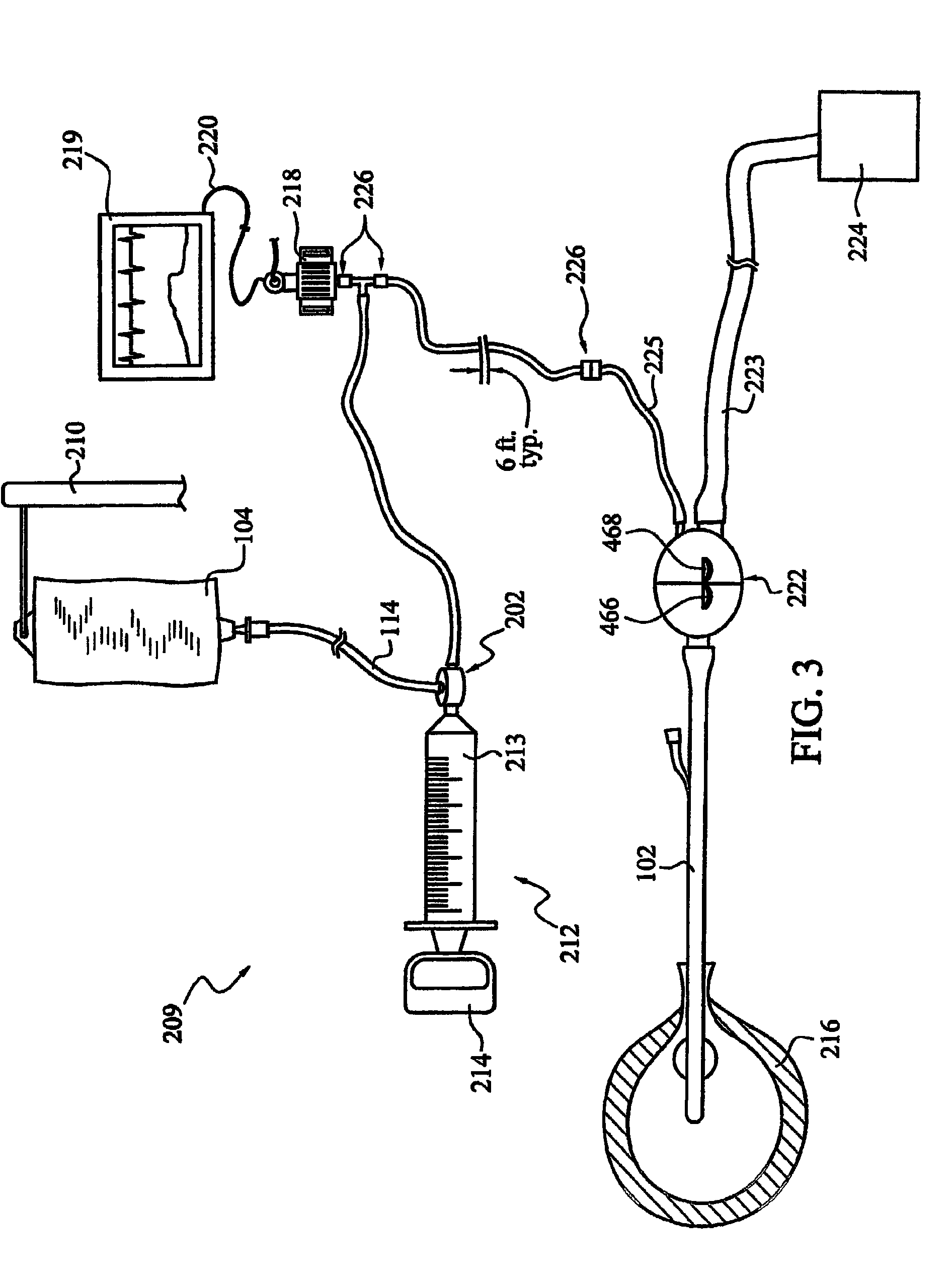
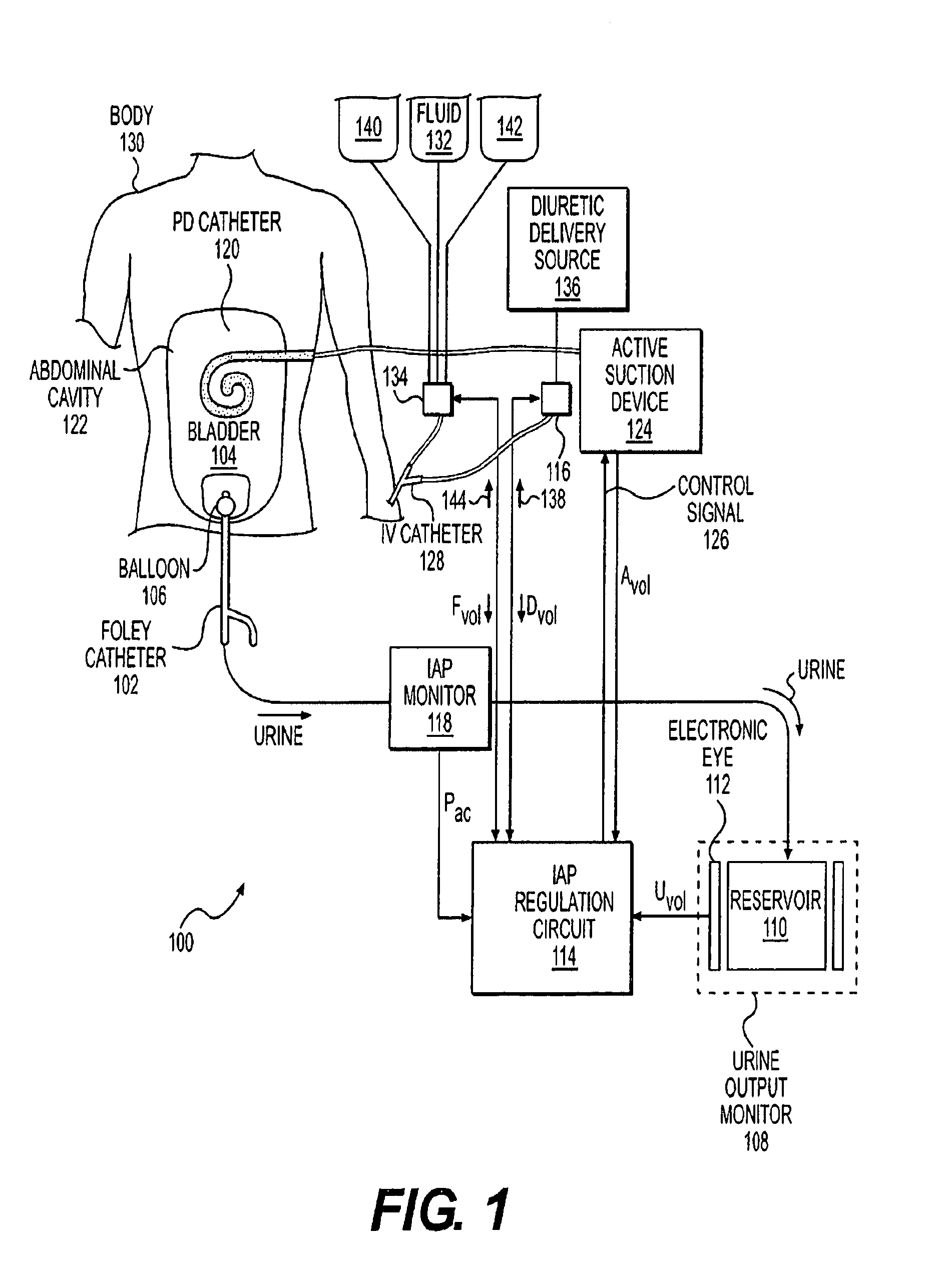
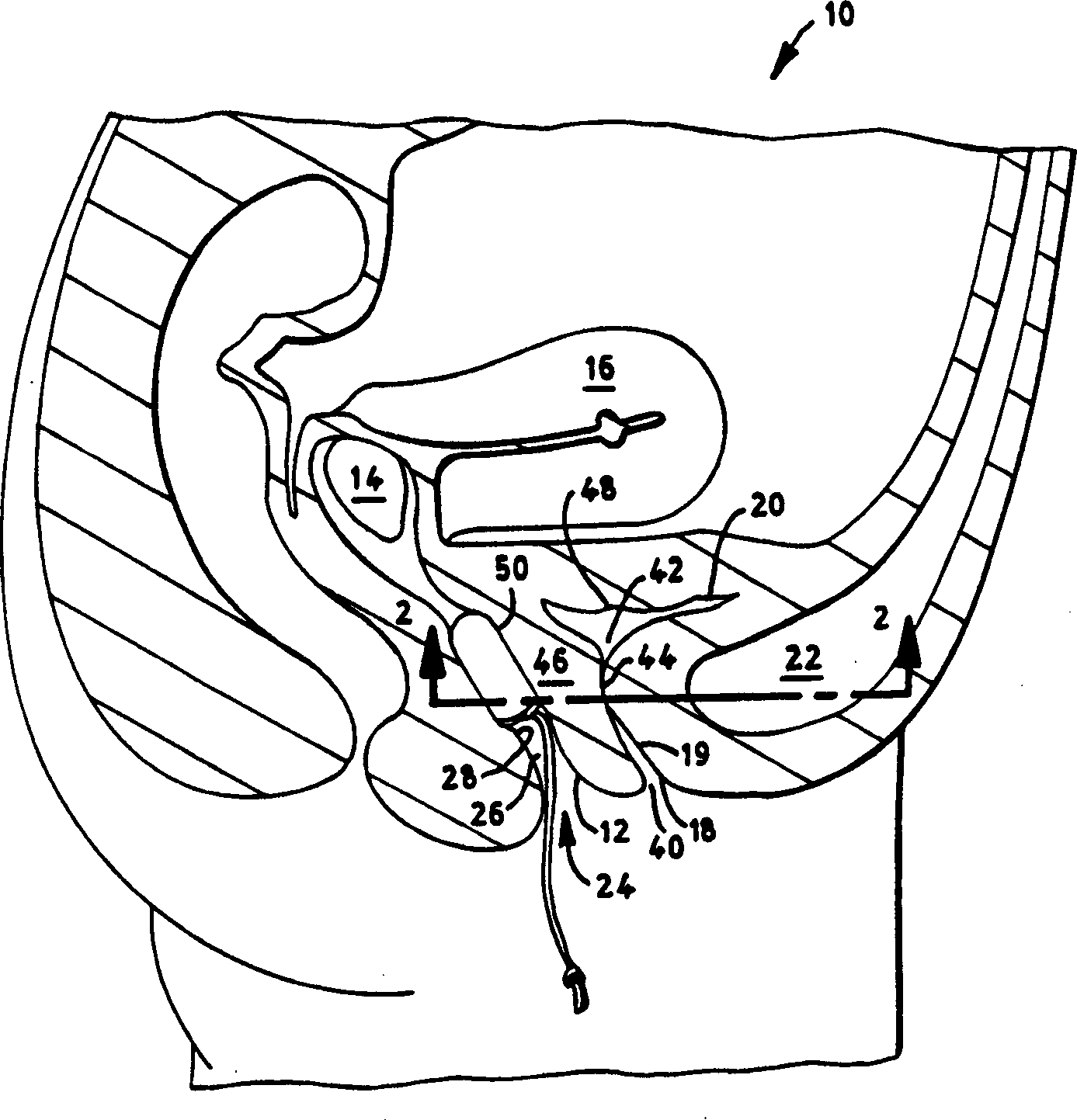
Intra-Abdominal Pressure Monitoring Device and Method
ActiveUS20080114316A1Signal is generatedDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsUrinary catheterTransducer
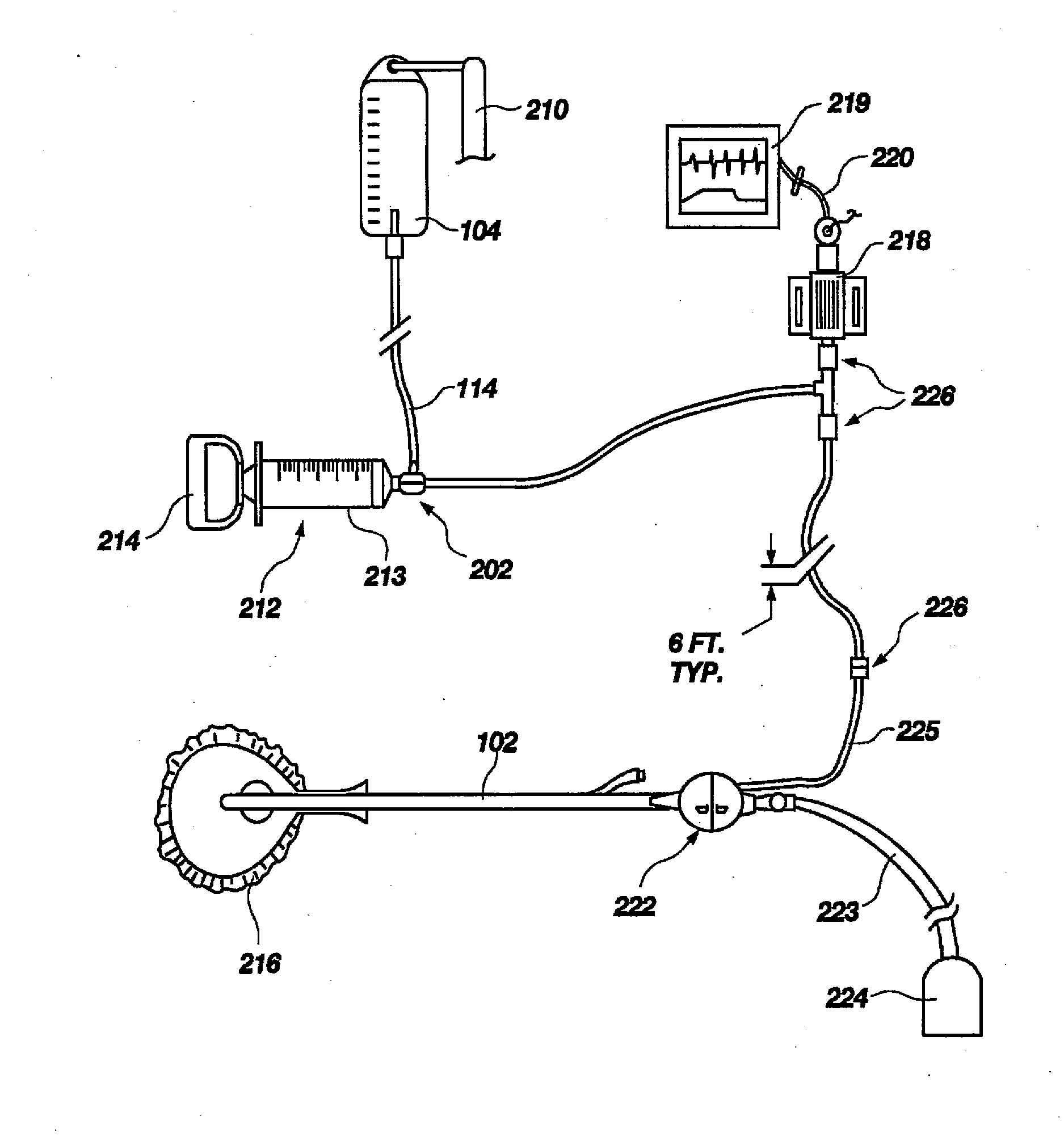
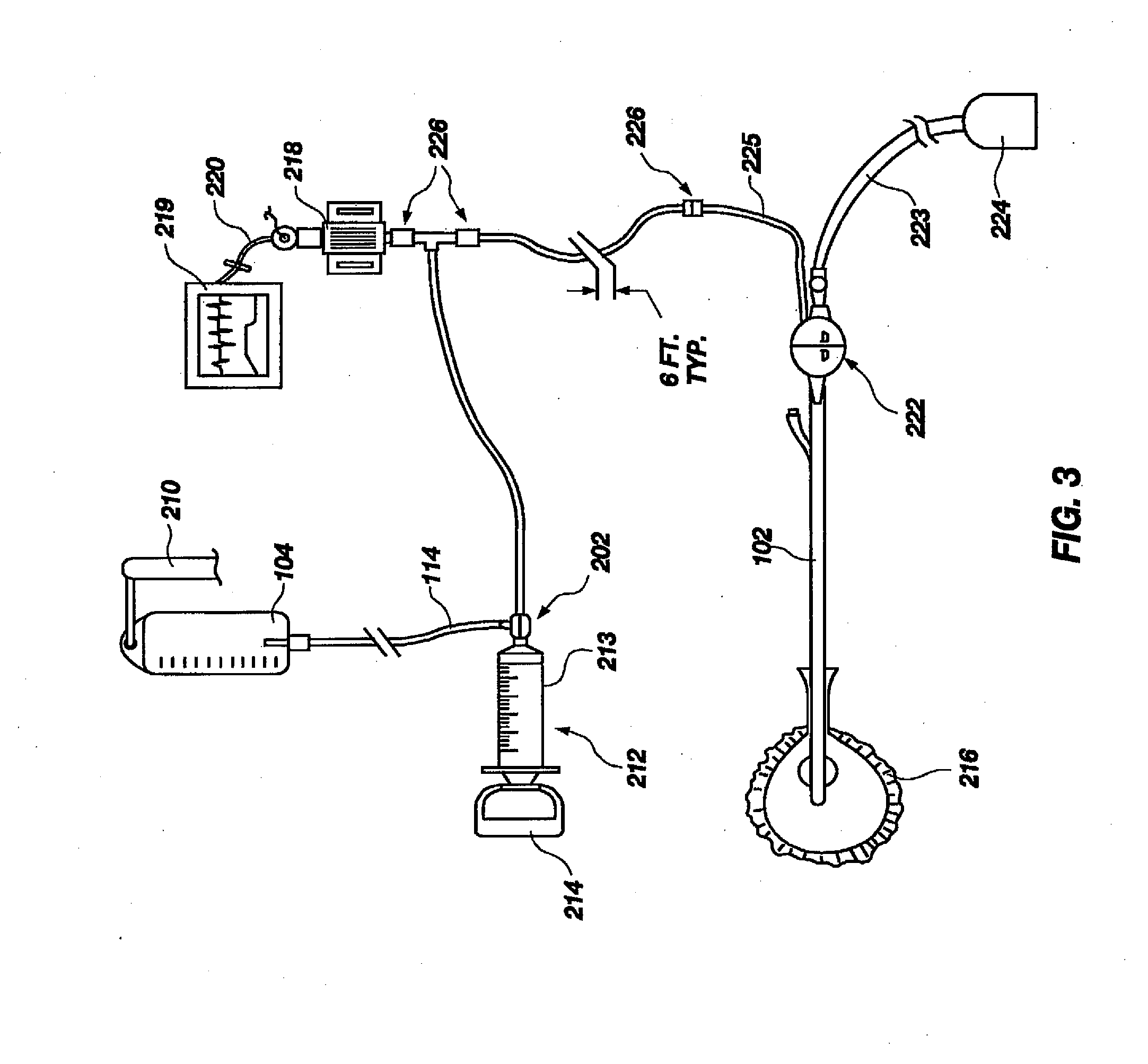
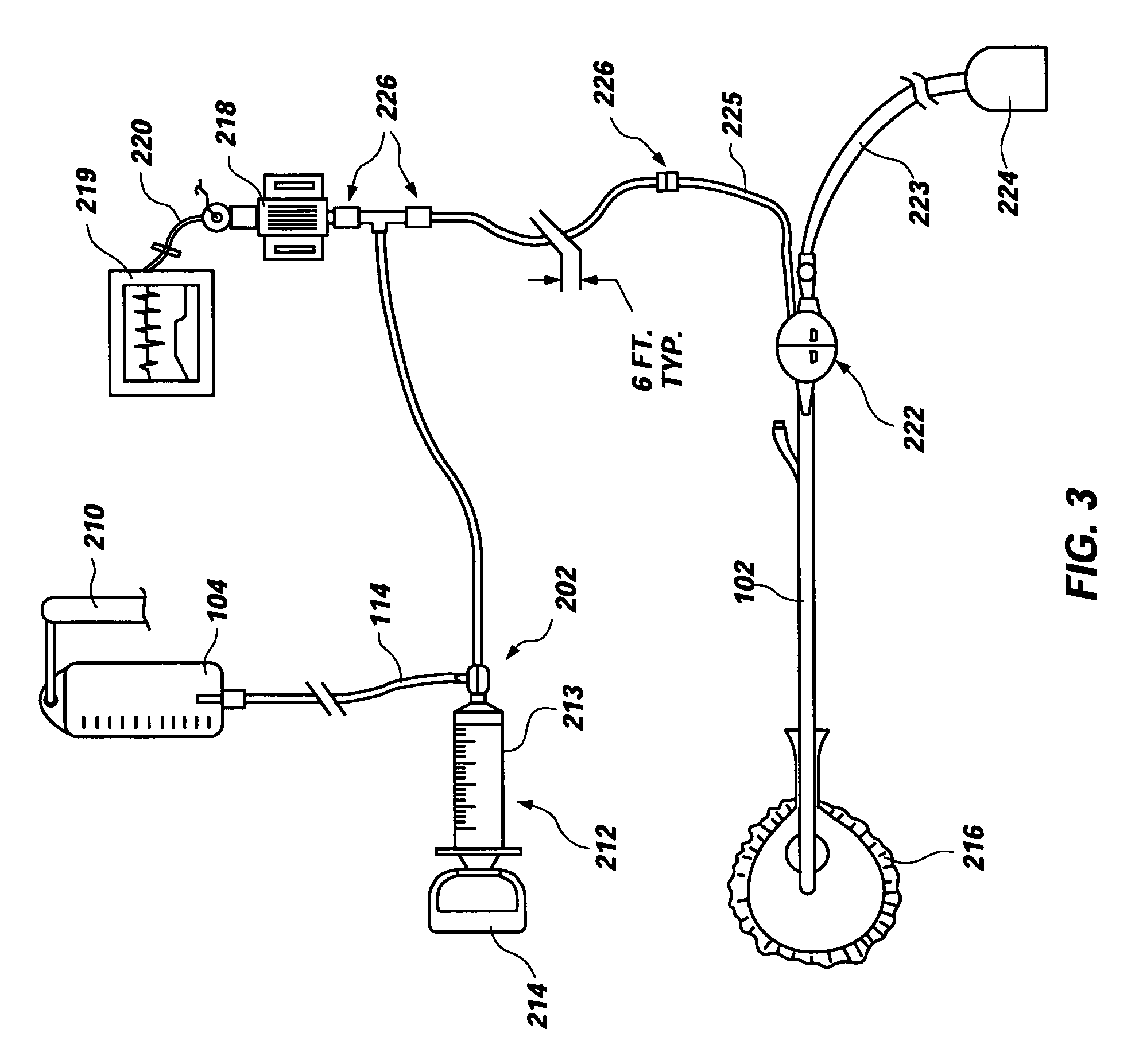
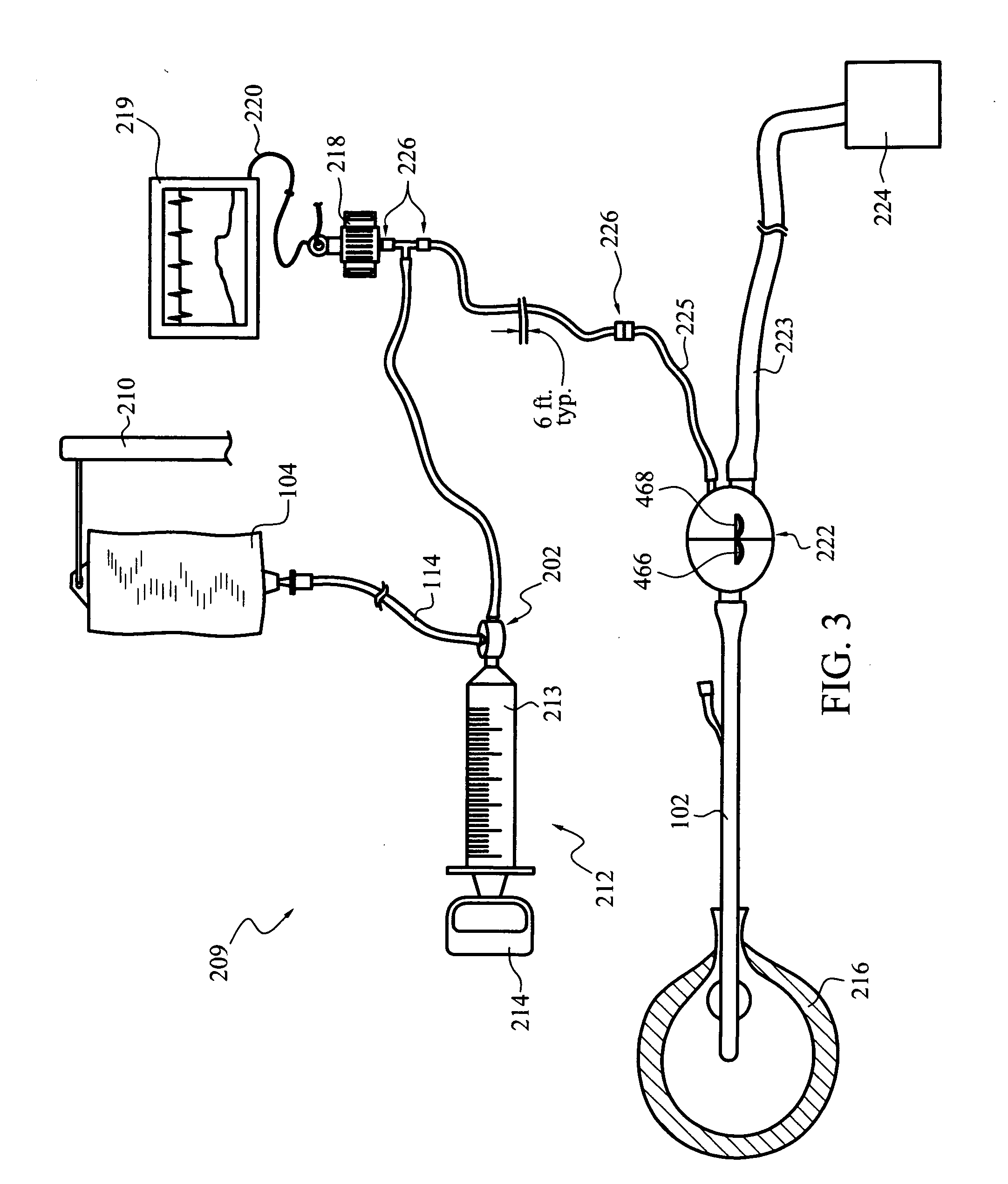
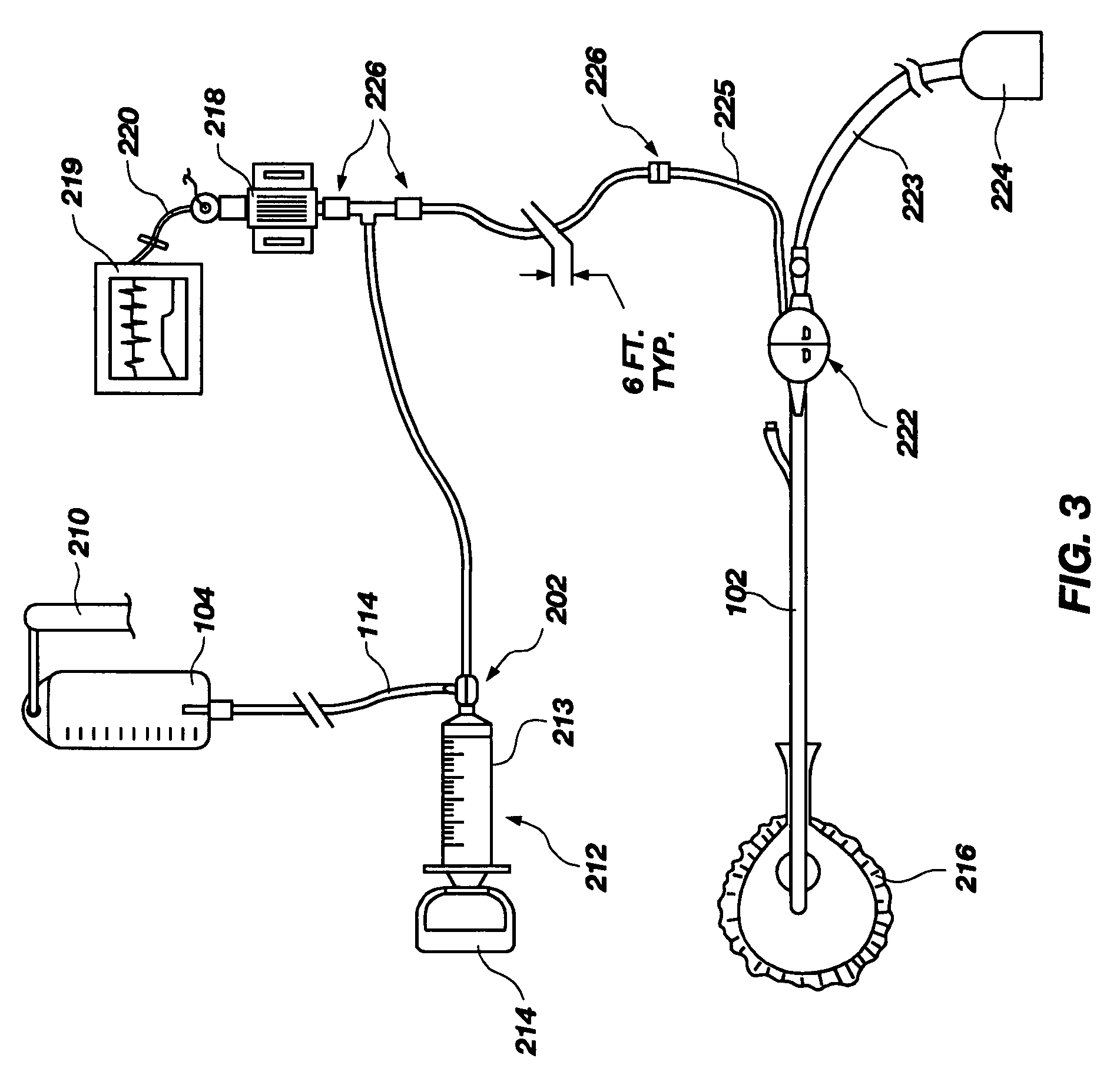
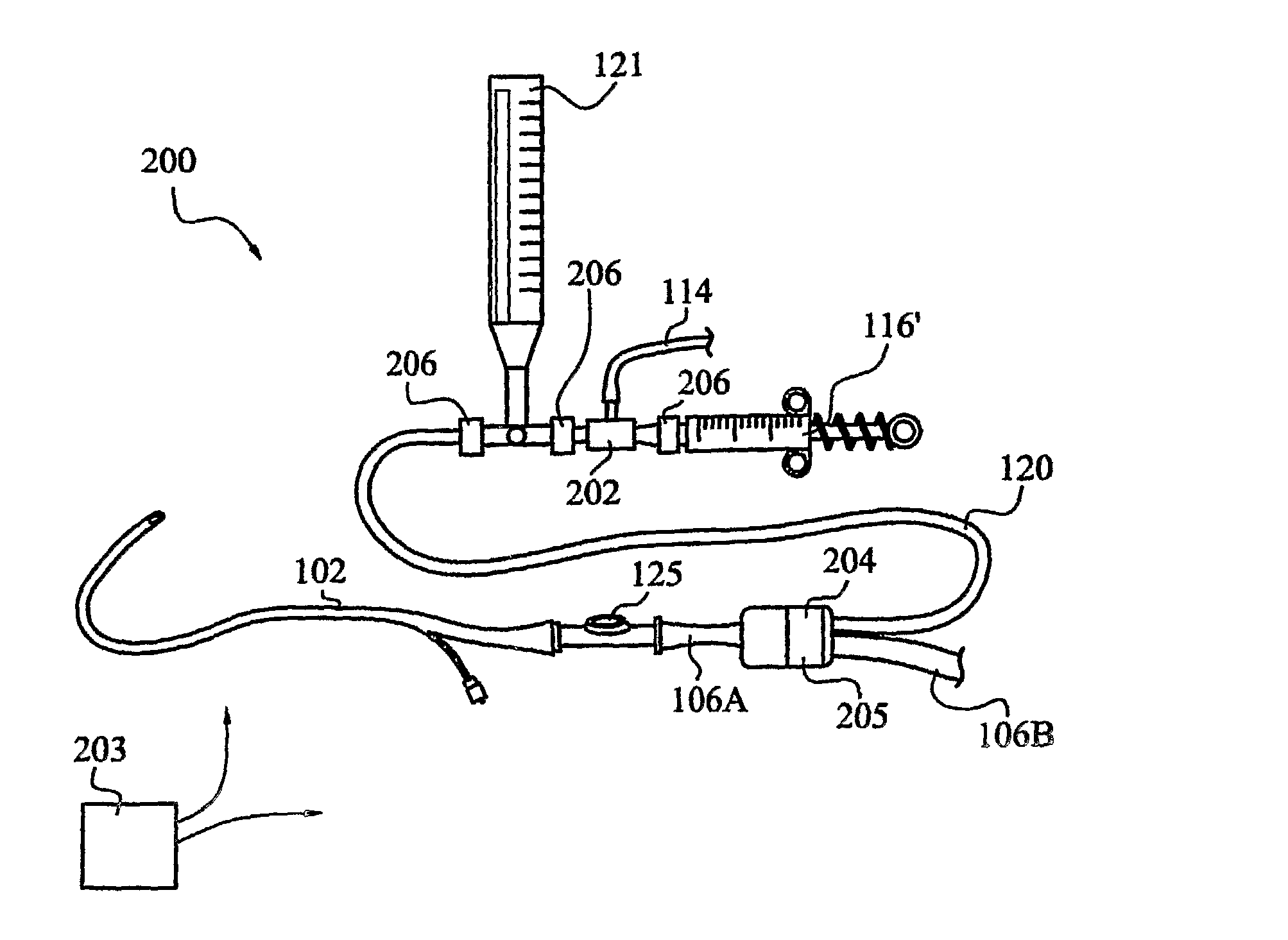
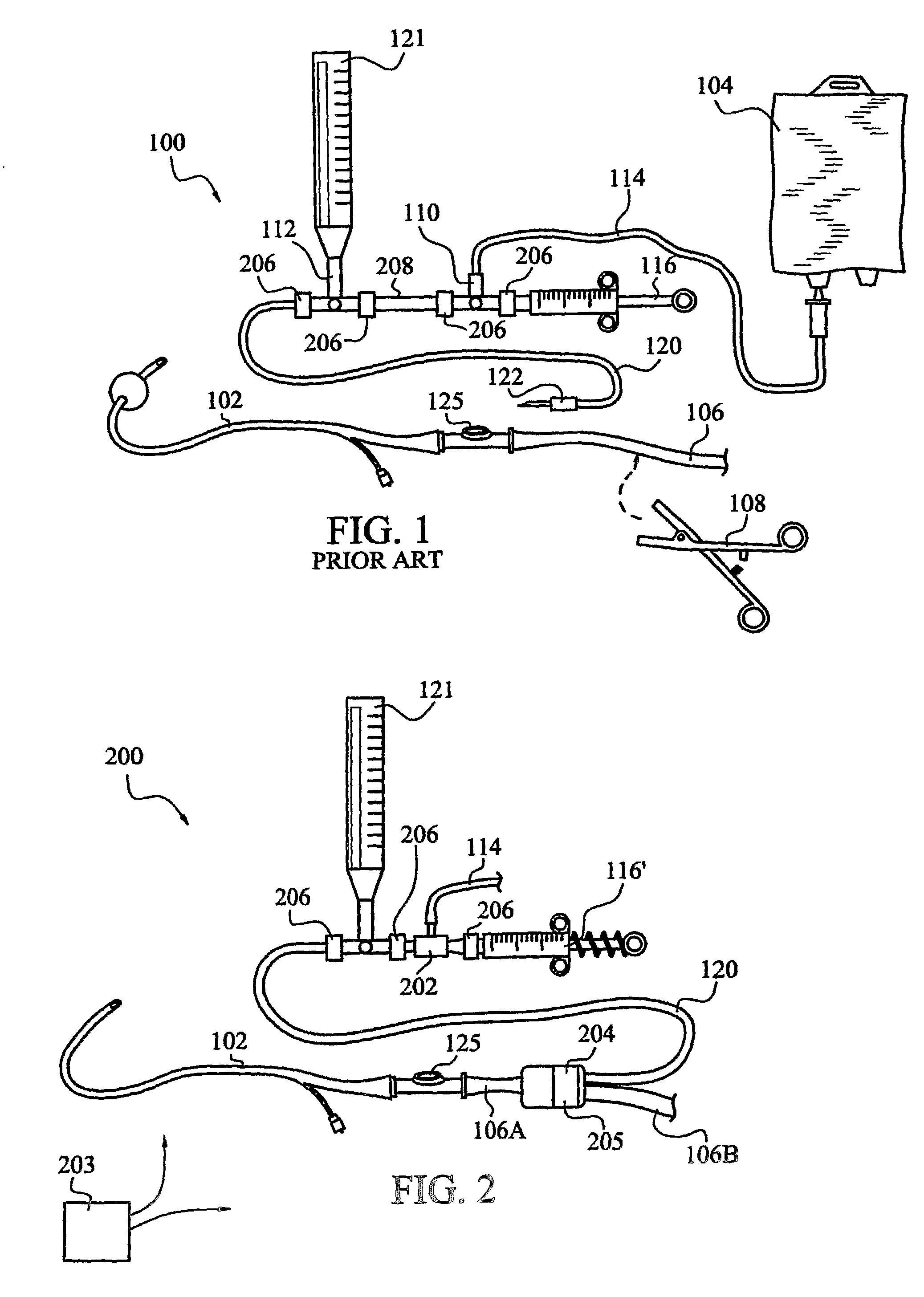
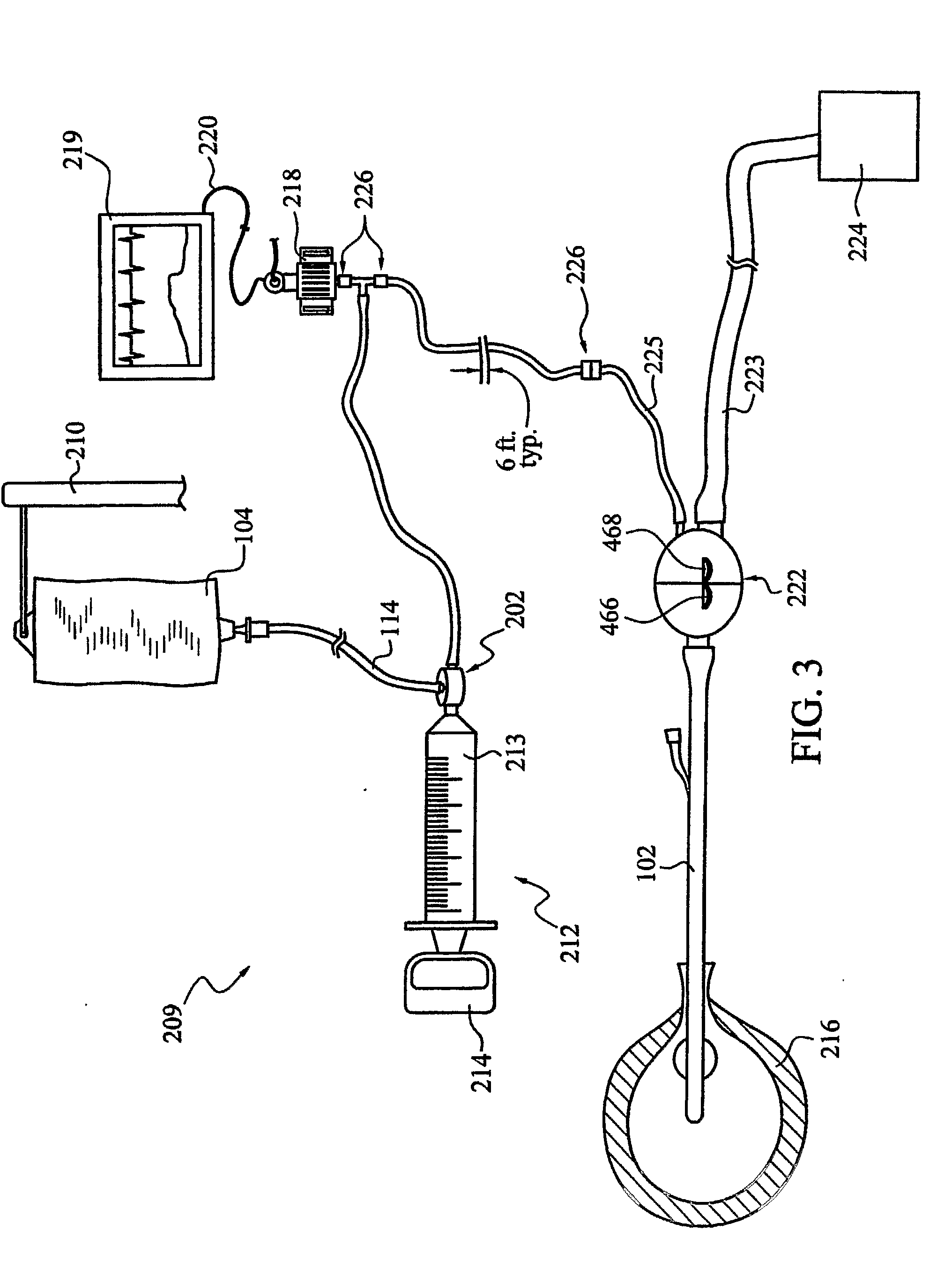
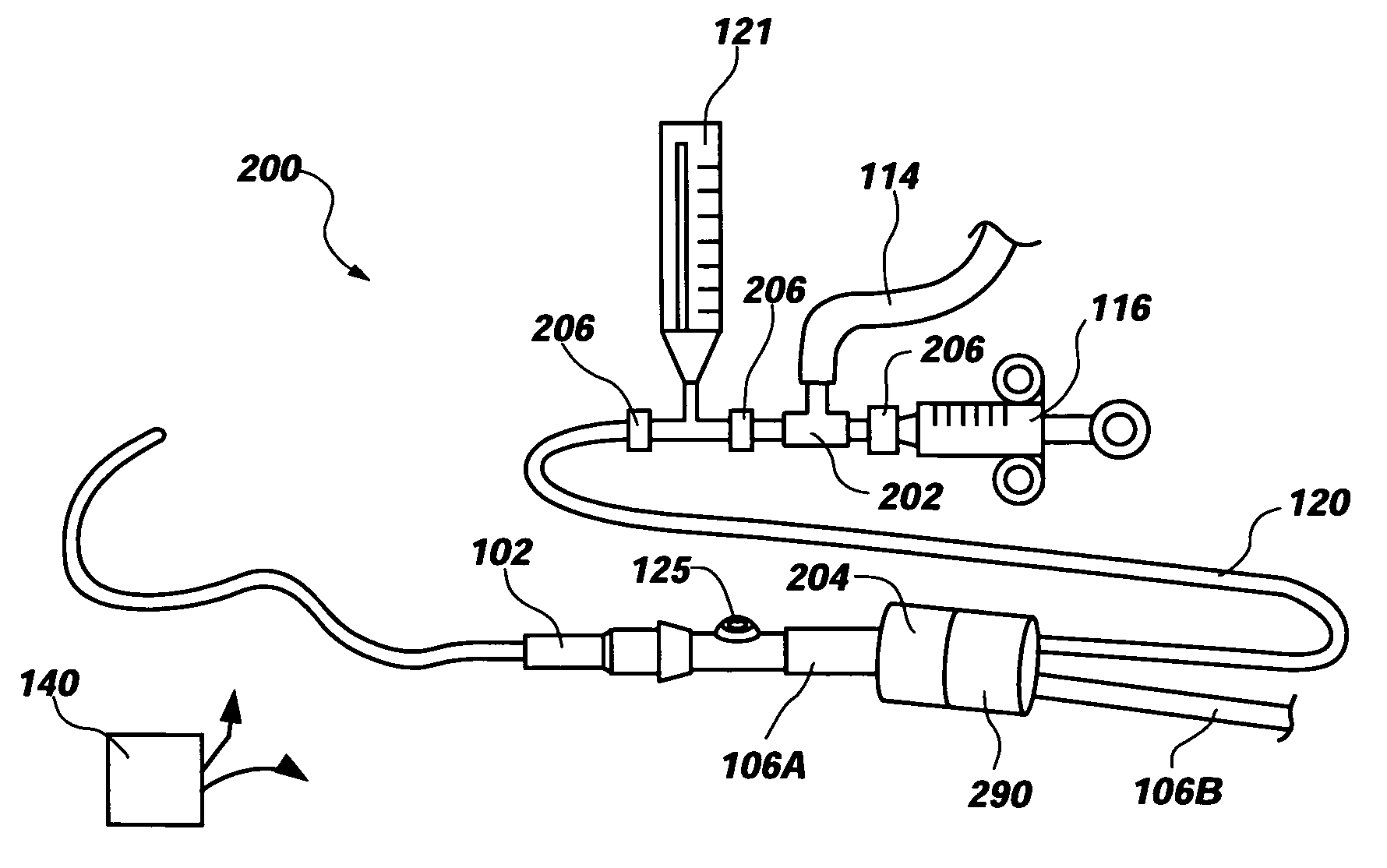
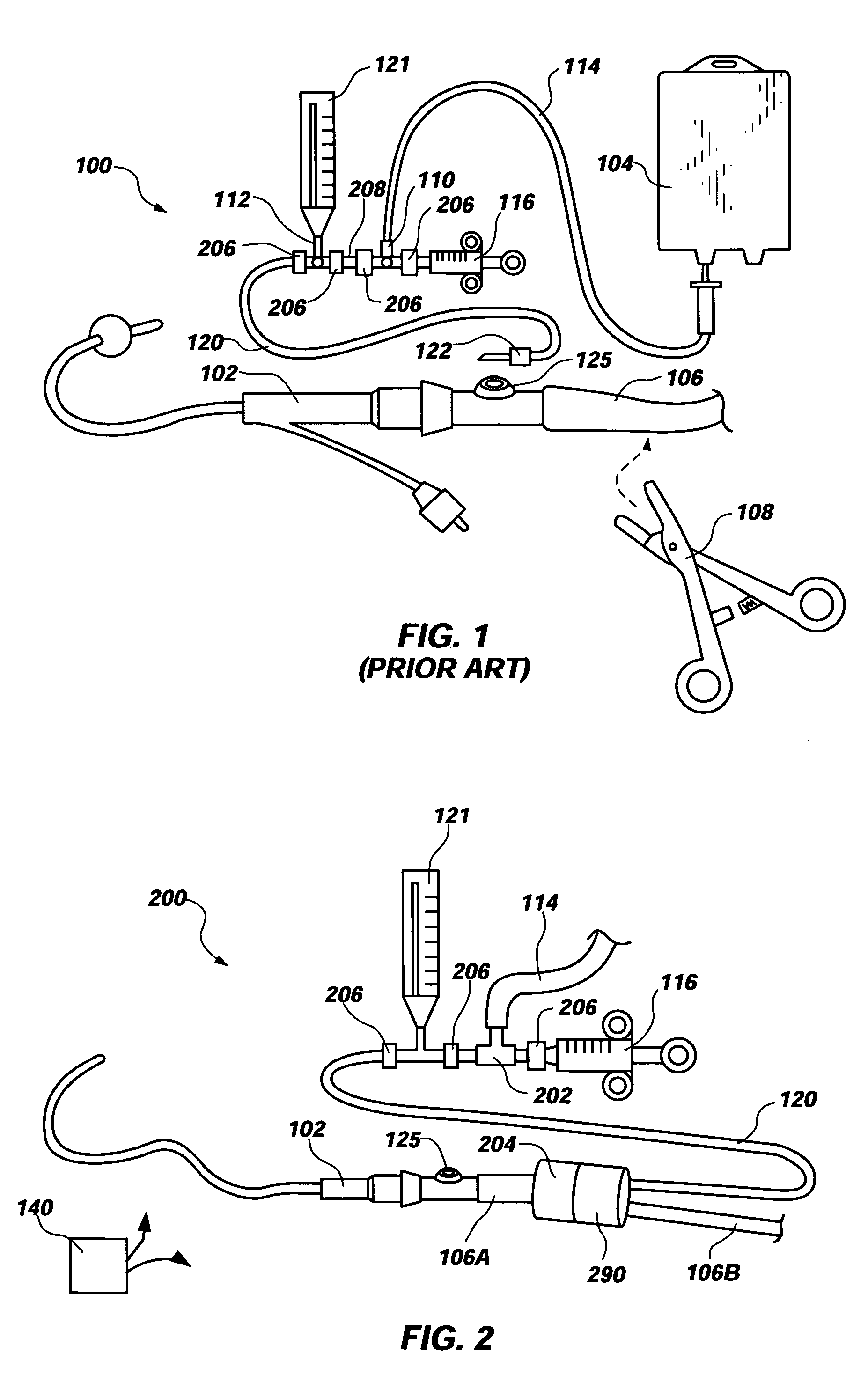
An apparatus for monitoring the intra-abdominal pressure of a patient includes a urinary catheter (102) connected to a urine valve (250) providing selectable communication between a discharge end of the urinary catheter (102) and either a drain (224) or a fluid source (104). Preferably, the urine valve (250) is adapted for remote actuation and has a housing adapted to resist patient discomfort from leg-valve (250) contact. Plumbing structure desirably maintains fluid supply (225) and drain (223) conduits in a substantially parallel arrangement to assist routing those conduits (225, 223) between a patient's legs. When the urine valve (250) is oriented to permit communication with the fluid source (104), an infusion pump (116′) may be used to infuse a known quantity of fluid through the urine valve (250) and into the patient's bladder (216). A pressure transducer (218) desirably is connected in-circuit to indicate the fluid's pressure and avoid pressure fluctuations induced by system components. To facilitate the infusion process, an automatic flow control device may be included in a fluid supply path (225) and arranged to permit repetitive operation of a syringe (116′) to inject a bolus of fluid into the patient's bladder (216). Subsequent to making a pressure measurement, the urine valve (250) is returned to the bladder (216) draining position.
Owner:CONVATEC TECH INC
Intra-abdominal pressure monitoring system
ActiveUS20090221933A1Maintaining their functionalityAvoid flowWound drainsBagsMonitoring systemTransducer
Described herein are devices, systems, kits and methods for measuring intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) from a patient catheterized with a urinary catheter system. Devices may include a bypass lumen configured to connect to a pressure transducer, a sampling port connector connected to the bypass lumen, a drain tube housing configured to at least partially enclose a portion of the drain tube of a urinary catheter system, and a clamp mechanism. The sampling port connector may be configured for removable attachment to the sampling port of the urinary catheter system to form a fluid connection between the urinary catheter system and the bypass lumen of the IAP device. The clamp mechanism may be configured to controllably occlude the lumen of the urinary catheter system drain tube.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Intra-abdominal pressure monitoring device and method
ActiveUS8052671B2Signal is generatedMedical devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringUrinary catheterTransducer
An apparatus for monitoring the intra-abdominal pressure of a patient includes a urinary catheter (102) connected to a urine valve (250) providing selectable communication between a discharge end of the urinary catheter (102) and either a drain (224) or a fluid source (104). Preferably, the urine valve (250) is adapted for remote actuation and has a housing adapted to resist patient discomfort from leg-valve (250) contact. Plumbing structure desirably maintains fluid supply (225) and drain (223) conduits in a substantially parallel arrangement to assist routing those conduits (225, 223) between a patient's legs. When the urine valve (250) is oriented to permit communication with the fluid source (104), an infusion pump (116′) may be used to infuse a known quantity of fluid through the urine valve (250) and into the patient's bladder (216). A pressure transducer (218) desirably is connected in-circuit to indicate the fluid's pressure and avoid pressure fluctuations induced by system components. To facilitate the infusion process, an automatic flow control device may be included in a fluid supply path (225) and arranged to permit repetitive operation of a syringe (116′) to inject a bolus of fluid into the patient's bladder (216). Subsequent to making a pressure measurement, the urine valve (250) is returned to the bladder (216) draining position.
Owner:CONVATEC TECH INC
Apparatus for monitoring intra-abdominal pressure
ActiveUS20060058702A1Increase speedFacilitate making pressure measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsUrinary catheterHospitalized patients
An improved apparatus for monitoring the intra-abdominal pressure of a hospitalized patient includes a urinary catheter connected to a urine valve having selectable communication positions between a discharge end of the urinary catheter and either a drain or a fluid source. Preferably, the urine valve has a housing adapted to resist patient discomfort from leg-valve contact. One operable protective housing may be embodied as a separate tray component. Plumbing structure desirably maintains fluid supply and drain conduits in a substantially parallel arrangement to assist routing those conduits between a patient's legs. When the urine valve is oriented for communication to the fluid source, an infusion pump may be used to introduce a known quantity of fluid through the urine valve and into the patient's bladder where the fluid's pressure can be measured. Desirably, a double check valve is included in a fluid supply path and arranged to permit repetitive operation of a syringe to inject a bolus of fluid into the patient's bladder. Subsequent to making a pressure measurement, the urine valve is returned to the bladder draining position.
Owner:CONVATEC TECH INC
Oral-esophageal-gastric device to diagnose reflux and/or emesis
ActiveUS20110040211A1Simplify the viewing processMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesElectromyographyMedicineCatheter
A system and method diagnoses esophageal reflux in a patient. A catheter includes a first pressure sensor configured to measure intra-abdominal pressure when the catheter is inserted into the stomach of a patient. A second pressure sensor is located proximal to the distal tip and configured to measure intra-thoracic pressure. A pH indicator is carried by the catheter body and configured to indicate that reflux has occurred in response to an involuntary reflex cough test. A processing device is configured to receive data regarding the first and second pressure sensors and regarding the pH indicator and process that data and assess if reflux is present during the involuntary epoch.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Continuous intra-abdominal pressure monitoring system
ActiveUS20100249663A1Avoid flowBalloon catheterMulti-lumen catheterUrinary catheterMonitoring system
Described herein are devices, systems, kits and methods for continuously measuring intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) from a patient catheterized with a urinary catheter system Devices may include a lumen configured to connect to a pressure transducer, and a compensation chamber in fluid communication with the lumen and a urinary catheter
Owner:CR BARD INC
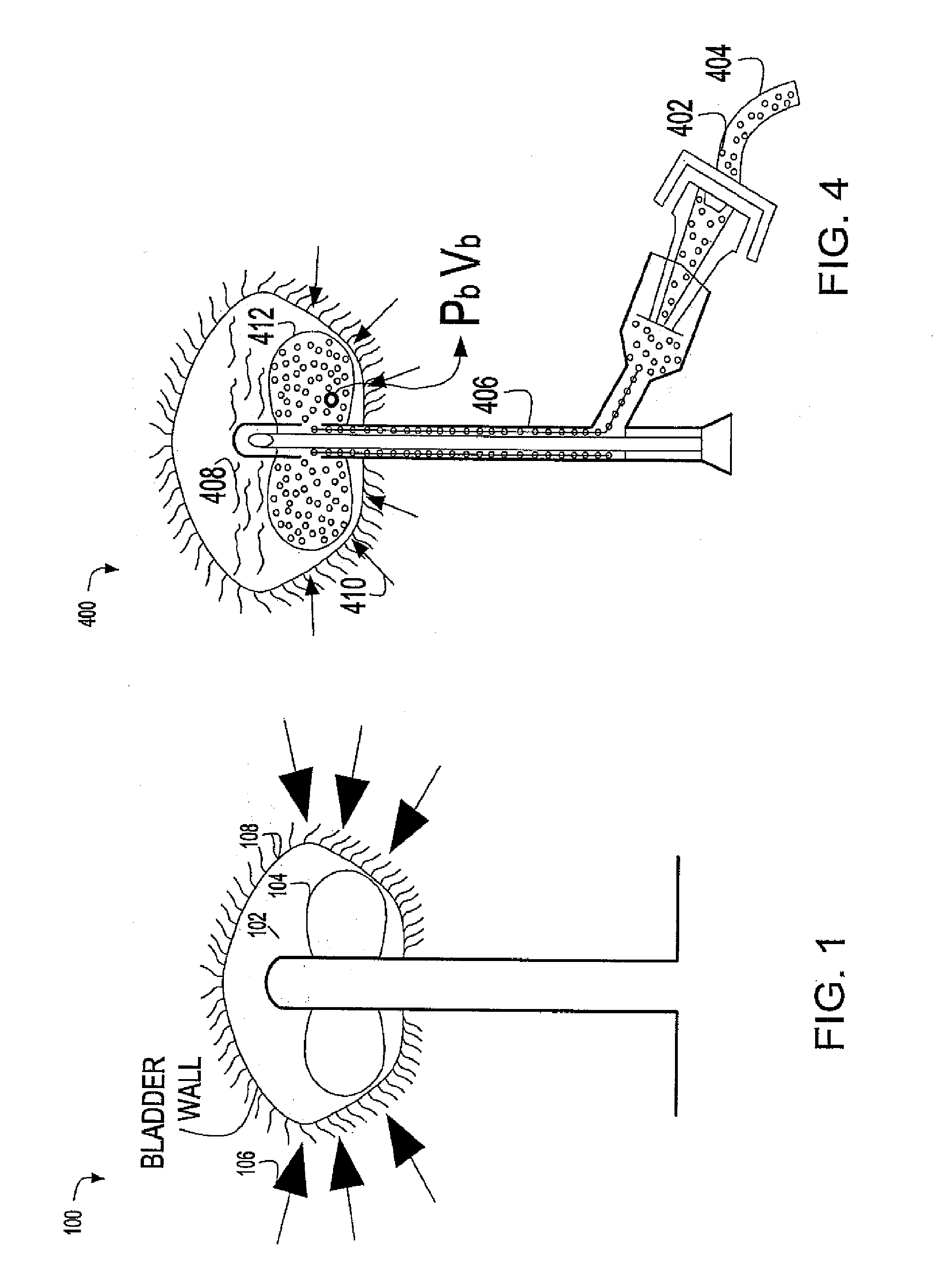
ACS therapy system
An ACS therapy system for continuously monitoring Intra-Abdominal Pressure (IAP) and preventing the onset of ACS. The automated ACS therapy system includes a urine withdrawal device, an IAP regulation circuit, an IAP monitor connected to the urine withdrawal device to supply an IAP value to the IAP regulation circuit, and an abdominal fluid removal device. The abdominal fluid removal device may be connected to an active suction device, which withdraws fluid from the abdominal cavity through the abdominal fluid removal device when activated by the IAP regulation circuit. Based on the IAP value, the IAP regulation circuit may send a control signal that controls the active suction device to turn on and drain fluid from the abdominal cavity. When the IAP value reaches certain levels, the IAP regulation circuit may cause the active suction device to be turned off.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Continuous intra-abdominal pressure monitoring system
Described herein are devices, systems, kits and methods for continuously measuring intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) from a patient catheterized with a urinary catheter system Devices may include a lumen configured to connect to a pressure transducer, and a compensation chamber in fluid communication with the lumen and a urinary catheter.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Medical valve and method to monitor intra-abdominal pressure
InactiveUS20090314973A1Reduce flow rateDiaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesUrinary catheterHospitalized patients
An apparatus for monitoring the intra-abdominal pressure of a hospitalized patient includes a urinary catheter connected to a urine valve providing selectable communication between a discharge end of the urinary catheter and either a drain or a fluid source. Preferably, the urine valve is adapted for remote actuation and has a housing adapted to resist patient discomfort from leg-valve contact. Plumbing structure desirably maintains fluid supply and drain conduits in a substantially parallel arrangement to assist routing those conduits between a patient's legs. When the urine valve is oriented to permit communication with the fluid source, an infusion pump may be used to infuse a known quantity of fluid through the urine valve and into the patient's bladder. A pressure transducer desirably is connected in-circuit to indicate the fluid's pressure. To facilitate the infusion process, an automatic flow control device may be included in a fluid supply path and arranged to permit repetitive operation of a syringe to inject a bolus of fluid into the patient's bladder. Subsequent to a period of time in which to make a pressure measurement, preferred embodiments of the urine valve automatically return to a bladder draining position.
Owner:CONVATEC TECH INC
Acs therapy system
An ACS therapy system for continuously monitoring Intra-Abdominal Pressure (IAP) and preventing the onset of ACS. The automated ACS therapy system includes a urine withdrawal device, an IAP regulation circuit, an IAP monitor connected to the urine withdrawal device to supply an IAP value to the IAP regulation circuit, and an abdominal fluid removal device The abdominal fluid removal device may be connected to an active suction device, which withdraws fluid from the abdominal cavity through the abdominal fluid removal device when activated by the IAP regulation circuit. Based on the IAP value, the IAP regulation circuit may send a control signal that controls the active suction device to turn on and drain fluid from the abdominal cavity. When the IAP value reaches certain levels, the IAP regulation circuit may cause the active suction device to be turned off.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Jack-in excrement cleaning bag inside anus
An anal inserting cleaning feces bag relates to a medical plastic equipment supply which adopts the physical or mechanical operation to remove feces for patients or caregivers and exempt from the harm caused by the increase of the intra-abdominal pressure which is caused by the initiative defecation of the patients or the caregivers by plugging into the anal. The whole structure is formed by connecting a casing, ancillary components and a soft transparent plastic bag. The casing is inserted into the the anal. In order to avoid the injury of the anal mucosa caused by the inserting of the casing, a casing core with the shape of a bullet on the top is inserted into the anal together with the casing. Once the casing is inserted into the anal, the casing core loses the function and is thrown into a plastic bag. The front end of the outer wall of the casing is provided with a ring sponge body sealed by a rubber film and an air duct controlling the incoming and the outgoing of air, so the tightening and the cracking off of the casing inserting into the anal are determined. After the casing is inserted into the anal, the thin feces can be discharged into the connected plastic bags by the casing directly under the peristalsis of intestines, a cleaning spoon arranged in one side of the plastic bag can be used to clean the feces which can not be discharged by the peristalsis of the intestines, or enema is inserted or medicinal oil is filled from an open hole of the other side for infiltration to help cleaning the feces.
Owner:孙波
Method for alleviating female urinary incontinence
InactiveCN1331573ARelieve urinary incontinencePrevent involuntary urinationAnti-incontinence devicesRestraining devicesVaginal canalSymphysis
A method for alleviating female urinary incontinence especially during episodes of increased intra-abdominal pressure is disclosed. The method includes the steps of providing a non-absorbent urinary incontinence device having an initial cross-sectional area, an insertion end and a trailing end. The urinary incontinence device also contains a compressed resilient member which is capable of increasing the cross-section area of the urinary incontinence device when expanded. The urinary incontinence device is inserted into a woman's vagina with the insertion end entering first. The vagina is a canal with an inner periphery made up of right and left lateral walls, an anterior wall and a posterior wall. The urinary incontinence device is inserted such that it contacts at least two of the walls. The urinary incontinence device is positioned in the middle third of the length of the vaginal canal with the insertion end aligned adjacent to a woman's urethral sphincter muscle. The urethral sphincter muscle is a part of the urethral tube. The urinary incontinence device cooperates with a woman's symphysis pubis to sandwich the urethral tube therebetween. The resilient member is allowed to expand within the vaginal canal such that at least a portion of the urinary incontinence device increases in cross-sectional area and contacts all four interior walls of the vaginal canal and provides a supportive backdrop for the urethral tube. The urethral tube is then permitted to be compressed upon itself between the urinary incontinence device and the symphysis pubis thereby limiting involuntary urine flow.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Involuntary contraction induced pressure as a medical diagnostic tool using involuntary reflex cough test
A system and method allows diagnosis of a patient for physiological abnormality such as a neurological deficiency. An involuntary reflex cough event is induced within the patient that activates the nucleus ambiguus and medial motor cell column of the patient and stimulates involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles in the pelvis of the patient. An electromyogram (EMG) is obtained from the involuntary cough activated paraspinal muscles while inducing involuntary reflex cough and determining its duration. The intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) is determined and the IAP is correlated with the EMG duration of the involuntary cough event within a processing device to diagnose a physiological abnormality such as a neurological deficiency within the patient.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Gastric lavage model
The invention relates to a gastric lavage model. The gastric lavage model comprises a microprocessor, a transparent model shell connected with a pump line by a pressure sensor and an electric control valve, a stomach model inside the shell, an electromagnetic coil array on the external surface of the stomach model, an air pocket and an electric control valve at a cardiac line, an electric control valve at a pyloric line, the pressure sensor inside a manifold and a low-frequency excitation source. Cardiac closure and intra-abdominal pressure on the stomach are simulated by aerating the air pocket and a hollow chamber of the model shell, pyloric action is simulated by opening of the electric control valve, and gastric peristalsis is simulated by movement of a stomach wall of the model driven by various groups of coils which are excitated. A plurality of gastric parameters during gastric lavage simulation and gastric lavage training can be adjusted and the gastric lavage effect can be observed at real time, thus improving simulation degree of the gastric lavage to avoid or reduce gastric injury caused by actual gastric lavage.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Intra-abdominal pressure to promote hemostasis and survival
ActiveUS9522215B2Surgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAbdominal cavityIntra abdominal pressure
Systems, methods and kits for treating hemorrhages within cavities are provided. The methods utilize the application of a rapid spike of pressure to the closed cavity, followed by a steady state pressure or pressures.
Owner:ARSENAL MEDICAL
Urinary catheter
InactiveUS20190366038A1Great ease of flow controlMinimize infectionWound drainsMedical devicesBacteriuriaUpper urinary tract infection
There is described a urological device comprising one or more valves within a valve housing, external to the body when in use, with means for connection to an in-dwelling catheter and a means for connection to a urine collection device for the reduction of Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infections (CAUTI's), the valve characterised by having a higher opening pressure than closing pressure, and the urological device having one or more valves movable from a closed position to an open position in response to applied urological / intra-abdominal pressure; and wherein the device is provided with a vent to prevent siphoning action from the urine collection device; and wherein the valve has a region of coaption and the number of valves is varied to provide opening pressures matched to one or more intra-abdominal pressures in one or more patient groups.
Owner:RAINBOW MEDICAL ENG
Method and device for reflecting intra-abdominal pressure by measuring pressure in bladder
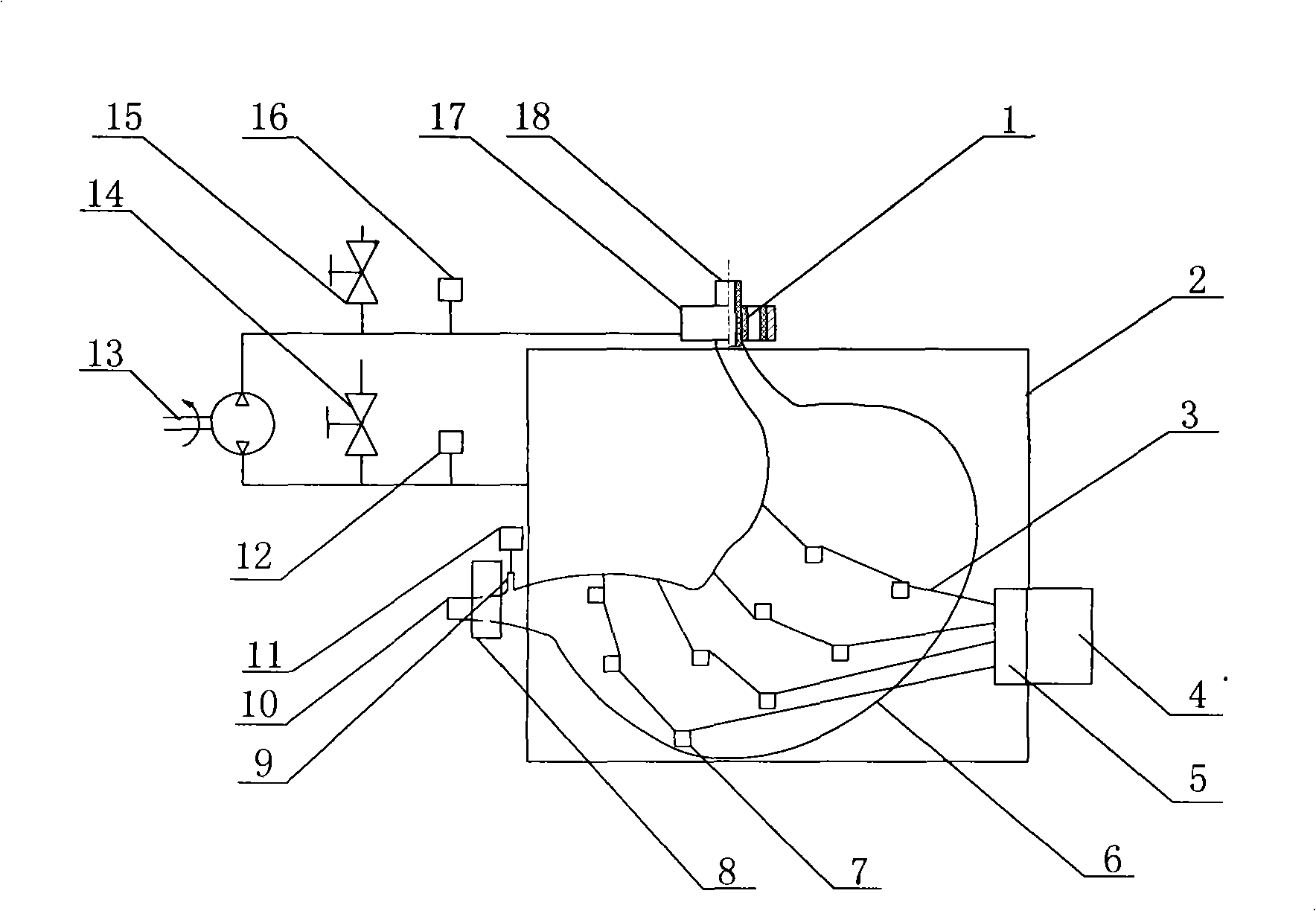
ActiveCN105559769ARelieve painReduce the risk of infectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMeasurement deviceCvd risk
The invention discloses a method and a device for reflecting an intra-abdominal pressure by measuring a pressure in the bladder. The method comprises the following steps: 1) emptying liquid in the bladder; 2) measuring the amount of urine generated in the bladder in unit time and obtaining the speed of generating the urine; 3) calculating the time required for accumulating the amount of the urine generated in the bladder to be 50ml and starting timing; 4) after the timing is finished, performing measurement to obtain the bladder pressure and converting the bladder pressure into the intra-abdominal pressure; and 5) repeating the steps to finish periodic measurement. The device comprises a catheter, a urine amount measurement device, a bladder pressure measurement device, a main control board, a display screen and a controller, wherein the catheter is communicated with the urine amount measurement device and the bladder pressure measurement device; the urine amount measurement device comprises a urine discharge electromagnetic valve, a drainage bag and a weighing sensor; and the bladder pressure measurement device comprises a Luer cock valve and a pressure sensor. The device is simple in structure and convenient to operate, relieves the pain of patients and lowers the infection risk of the patients.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACAD OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
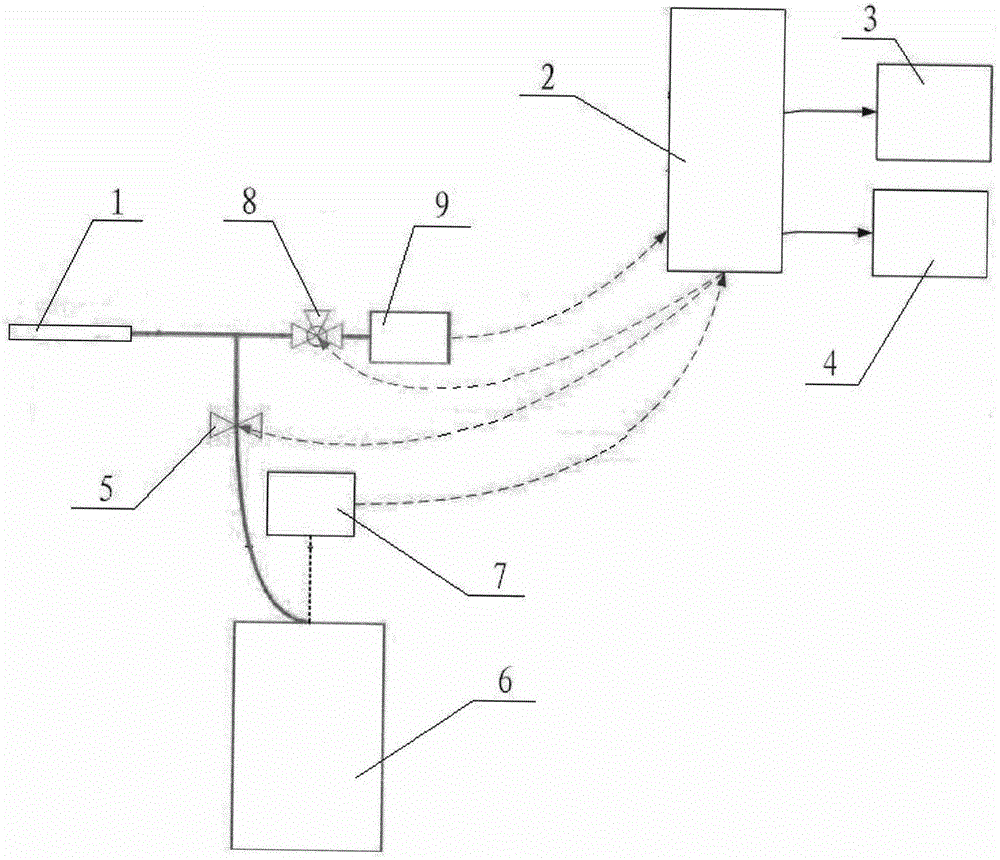
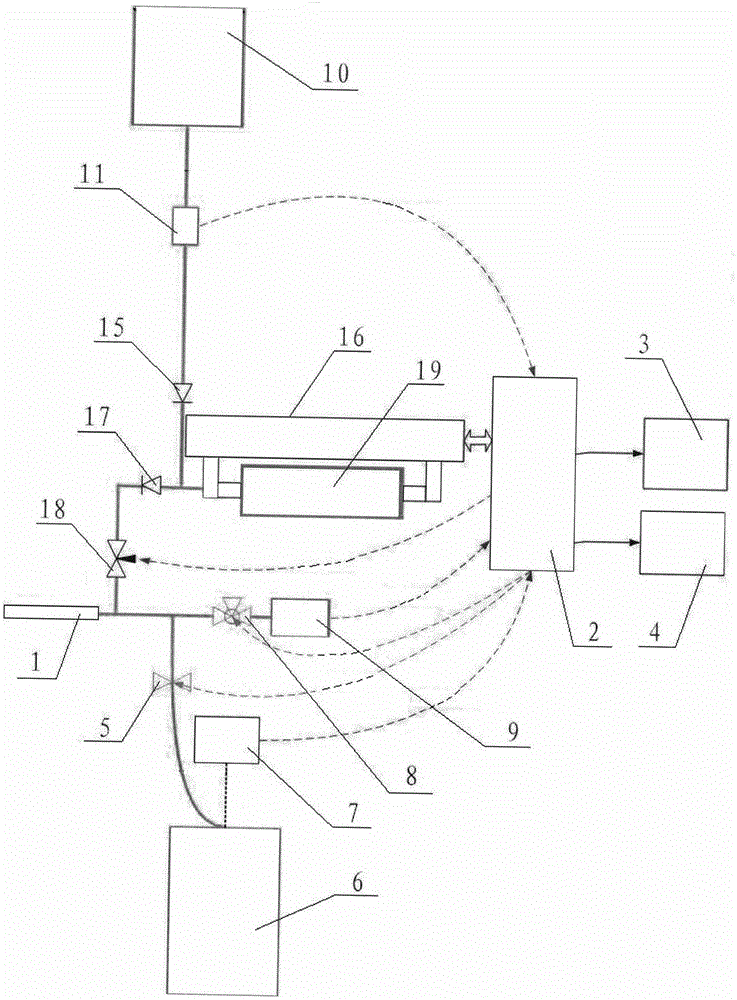
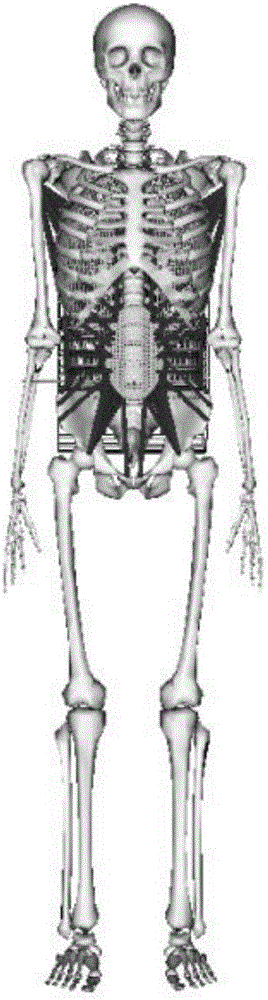
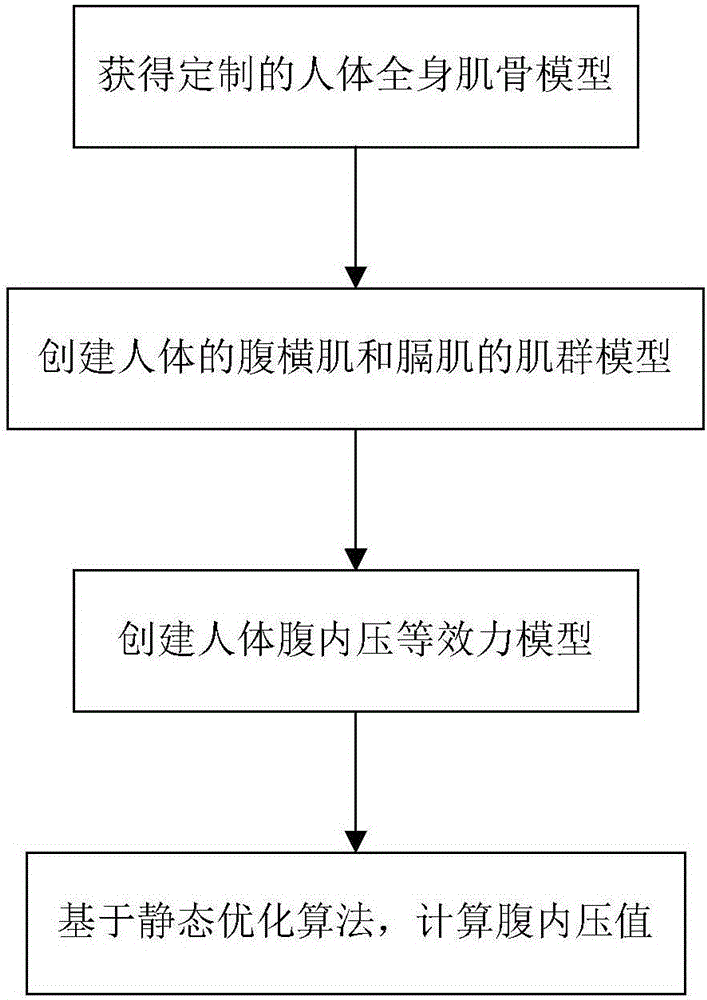
Human intra-abdominal pressure testing method based on musculoskeletal biodynamics
InactiveCN106333697AHigh solution accuracyMedical simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHuman bodyModel composition
The invention relates to a human intra-abdominal pressure testing method based on musculoskeletal biodynamics. The human intra-abdominal pressure testing method comprises the steps of acquiring a human whole body musculoskeletal model customized according to a human body; establishing musculus trasversus abdominis to surround a contact rigid body, representing a musculus trasversus abdominis group and a diaphragm muscle group through a muscle-tendon model, and further creating a muscle group model of musculus trasversus abdominis and diaphragm muscle of the human body; enabling intra-abdominal pressure to be equivalent to equivalent intra-abdominal pressure in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction so as to create a human intra-abdominal pressure equivalent force model; and capturing each posture joint angle of a certain standing posture of a tester, and inputting each posture joint angle into a human musculoskeletal biodynamics model formed by combination of the established models; and calculating the intra-abdominal pressure value under the posture. The method can be used for solving the problems that under different postures or actions, the intra-abdominal pressure is unknown, and is difficult to directly measure, the measuring cost is high, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING MECHANICAL EQUIP INST
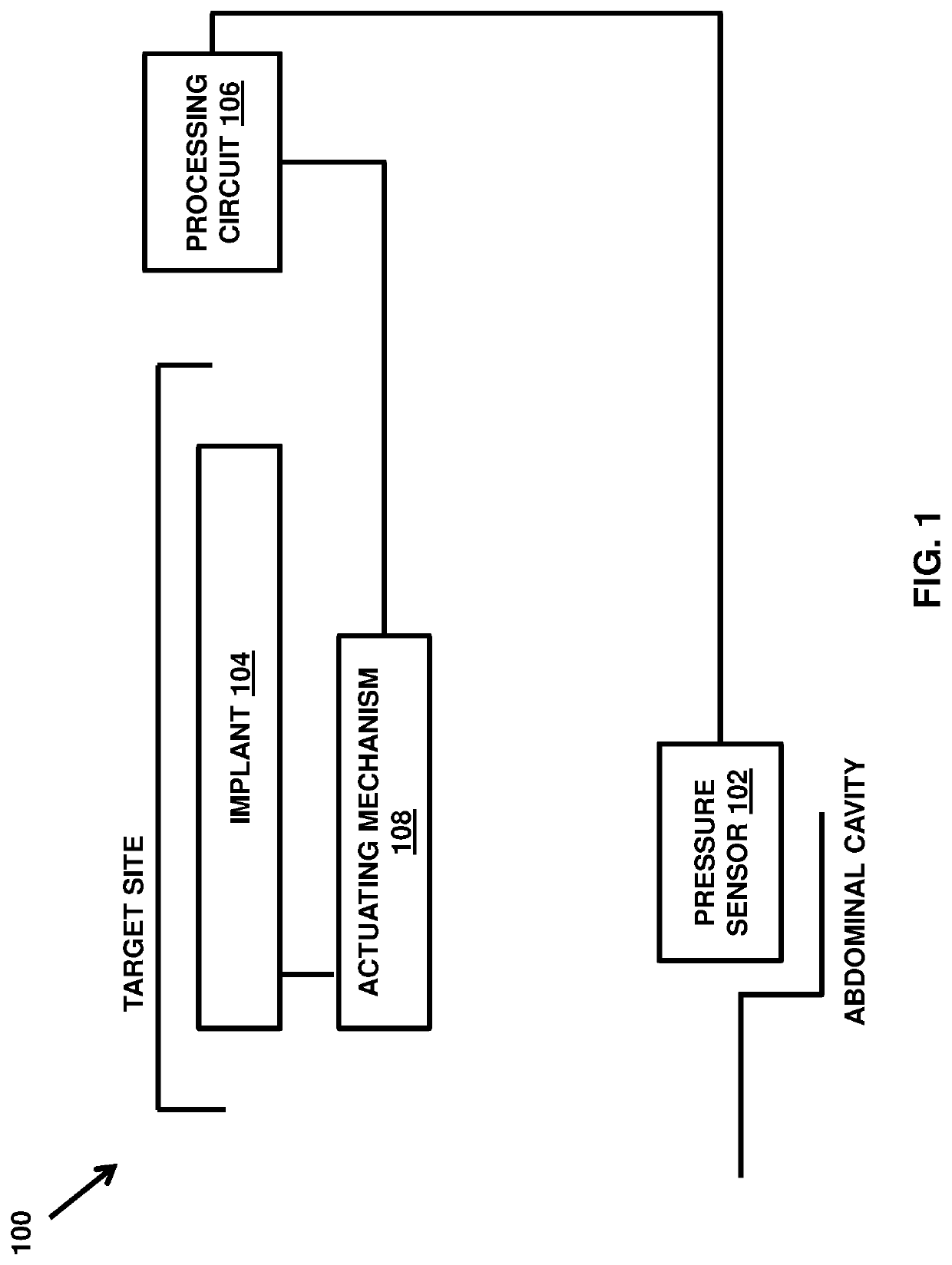
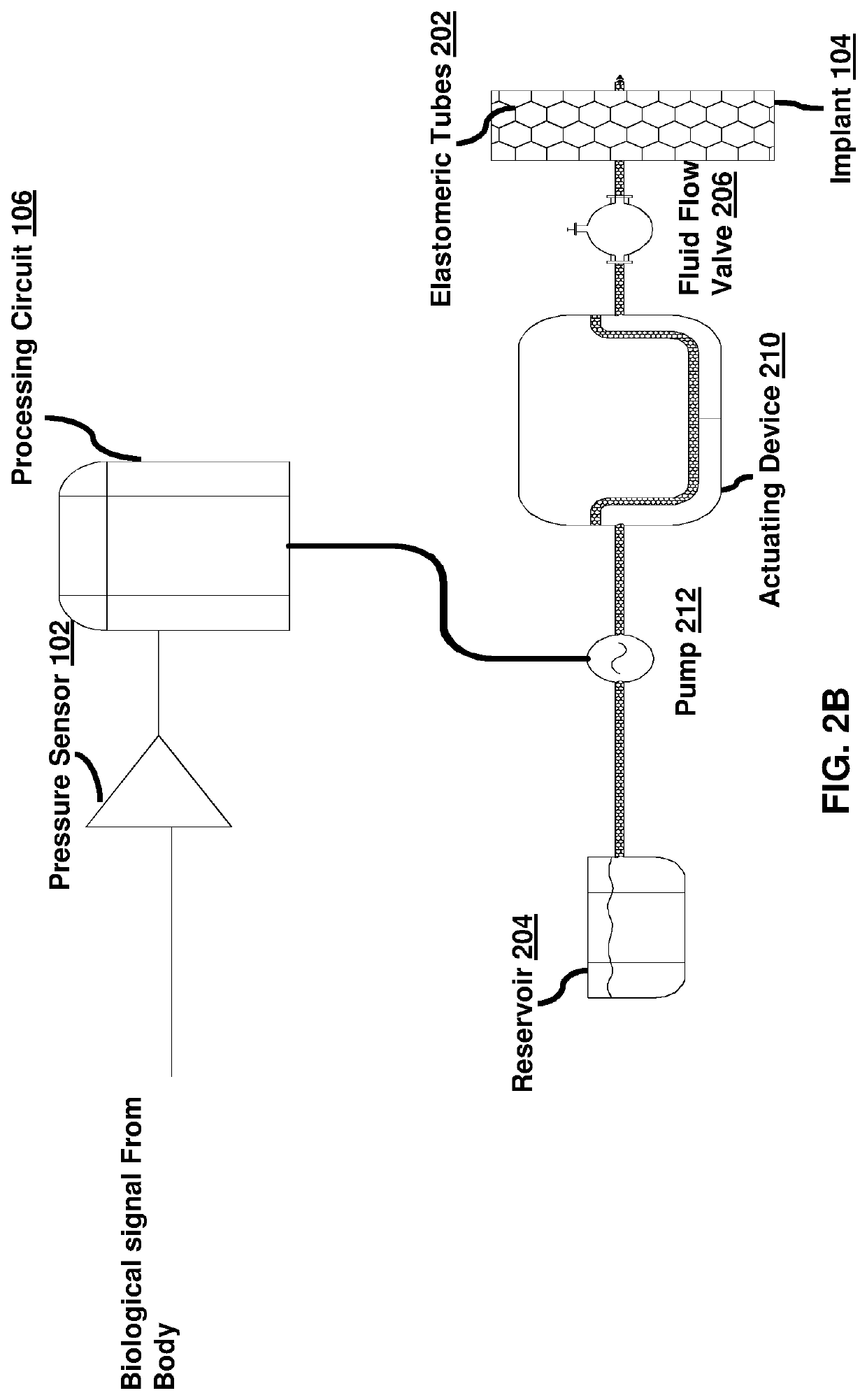
Implantable medical system
ActiveUS10682214B2Prevent leakageIncrease pressureAnti-incontinence devicesSurgical needlesSignal processing circuitsUrethra
Owner:IPENGINE MANAGEMENT INDIA
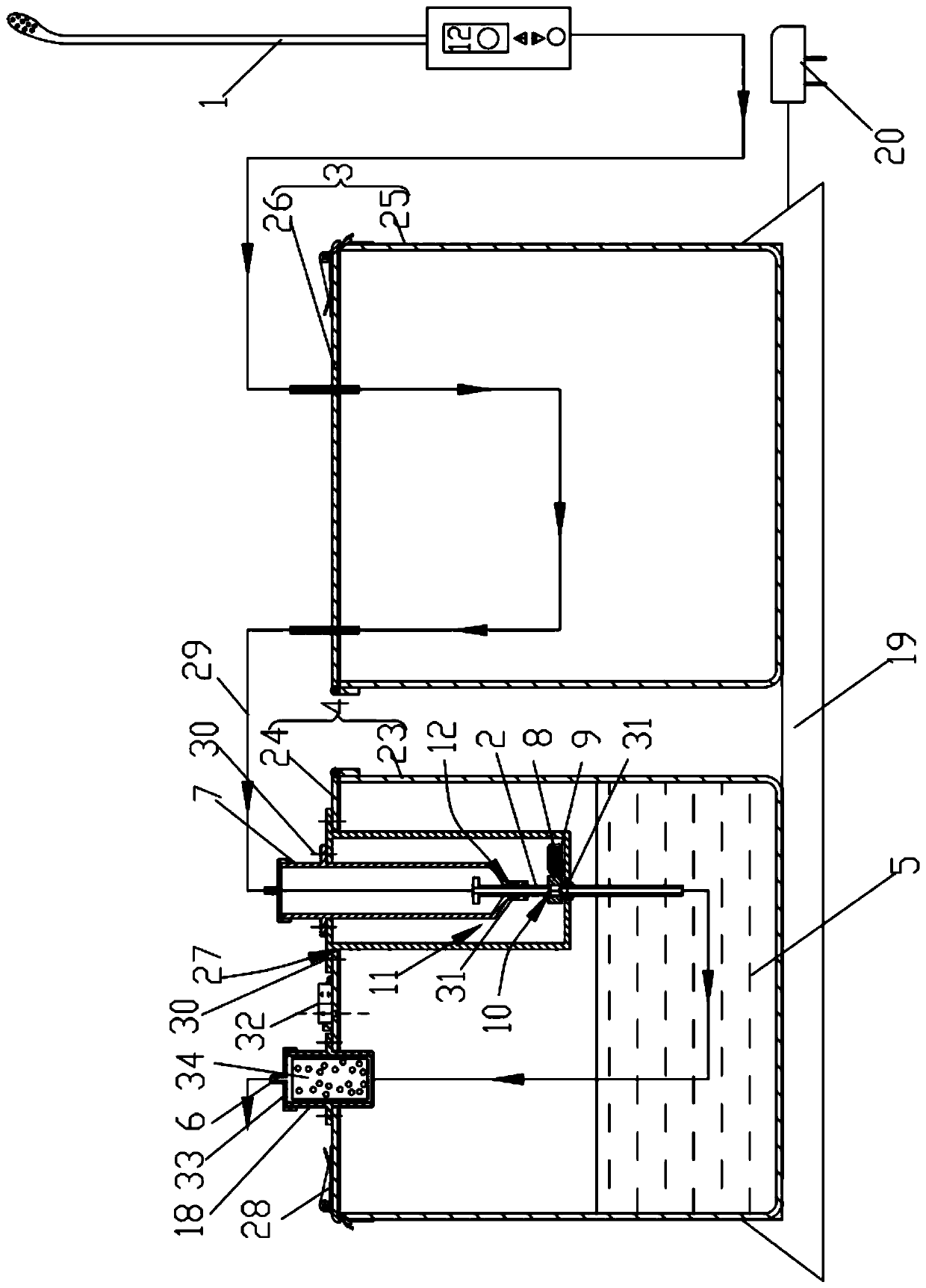
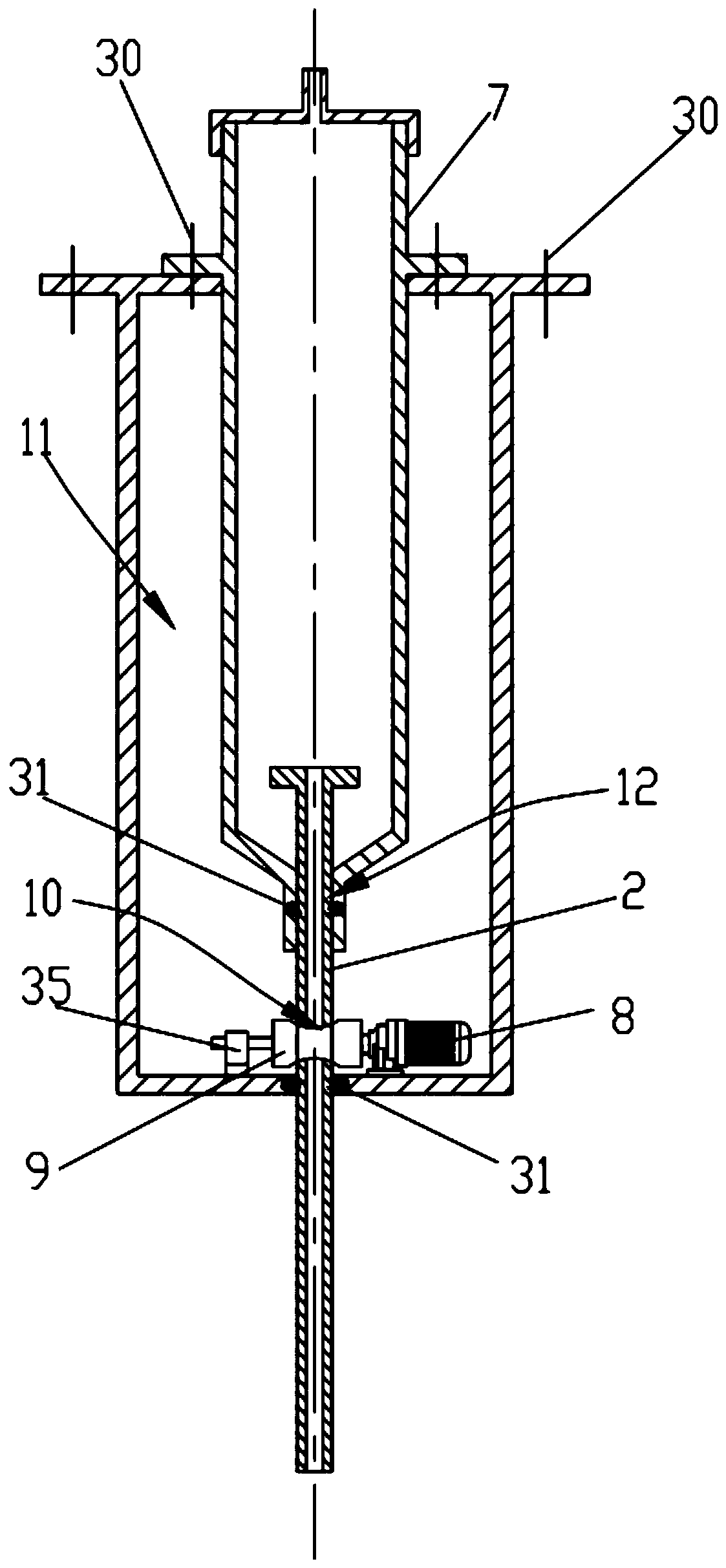
Constant-pressure and adjustable discharge system for endoscopic surgery
The present invention discloses a constant-pressure and adjustable discharge system for endoscopic surgery. The constant-pressure and adjustable discharge system for the endoscopic surgery comprises an aspirator, an adjusting tube, a waste liquid collecting bottle and a pressure adjusting bottle, liquid is arranged in the pressure adjusting bottle, an upper end of the adjusting tube communicates with one end of an upper side of the waste liquid collecting bottle, the other end of the upper side of the waste liquid collecting bottle communicates with the aspirator, a lower end of the adjustingtube extends into the pressure adjusting bottle, an upper side of the pressure adjusting bottle is provided with a negative pressure interface, the liquid in the pressure adjusting bottle is relatively movable with the adjusting tube, and an air venting valve communicating inside and outside is arranged on the pressure adjusting bottle. Active suction and passive discharge can be freely converted;a discharge speed and an intra-abdominal pressure are stable, operators can conduct convenient and visual adjustment, thus the constant-pressure and adjustable discharge system greatly compensates shortcomings of existing aspirators in the endoscopic surgery and is more convenient and secure.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Oral-esophageal-gastric device to diagnose reflux and/or emesis
A system and method diagnoses esophageal reflux in a patient. A catheter includes a first pressure sensor configured to measure intra-abdominal pressure when the catheter is inserted into the stomach of a patient. A second pressure sensor is located proximal to the distal tip and configured to measure intra-thoracic pressure. A pH indicator is carried by the catheter body and configured to indicate that reflux has occurred in response to an involuntary reflex cough test. A processing device is configured to receive data regarding the first and second pressure sensors and regarding the pH indicator and process that data and assess if reflux is present during the involuntary epoch.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com