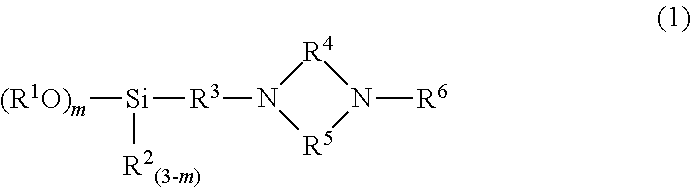
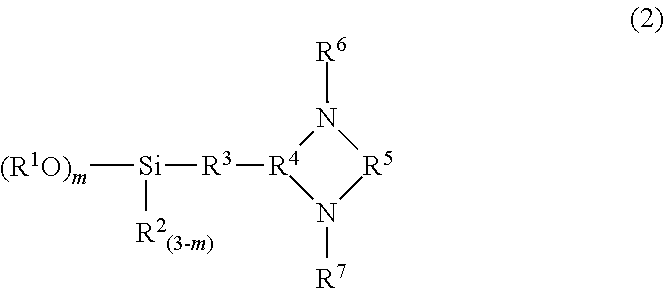
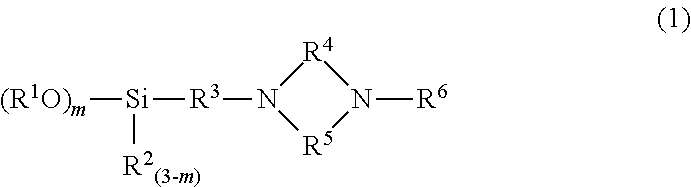
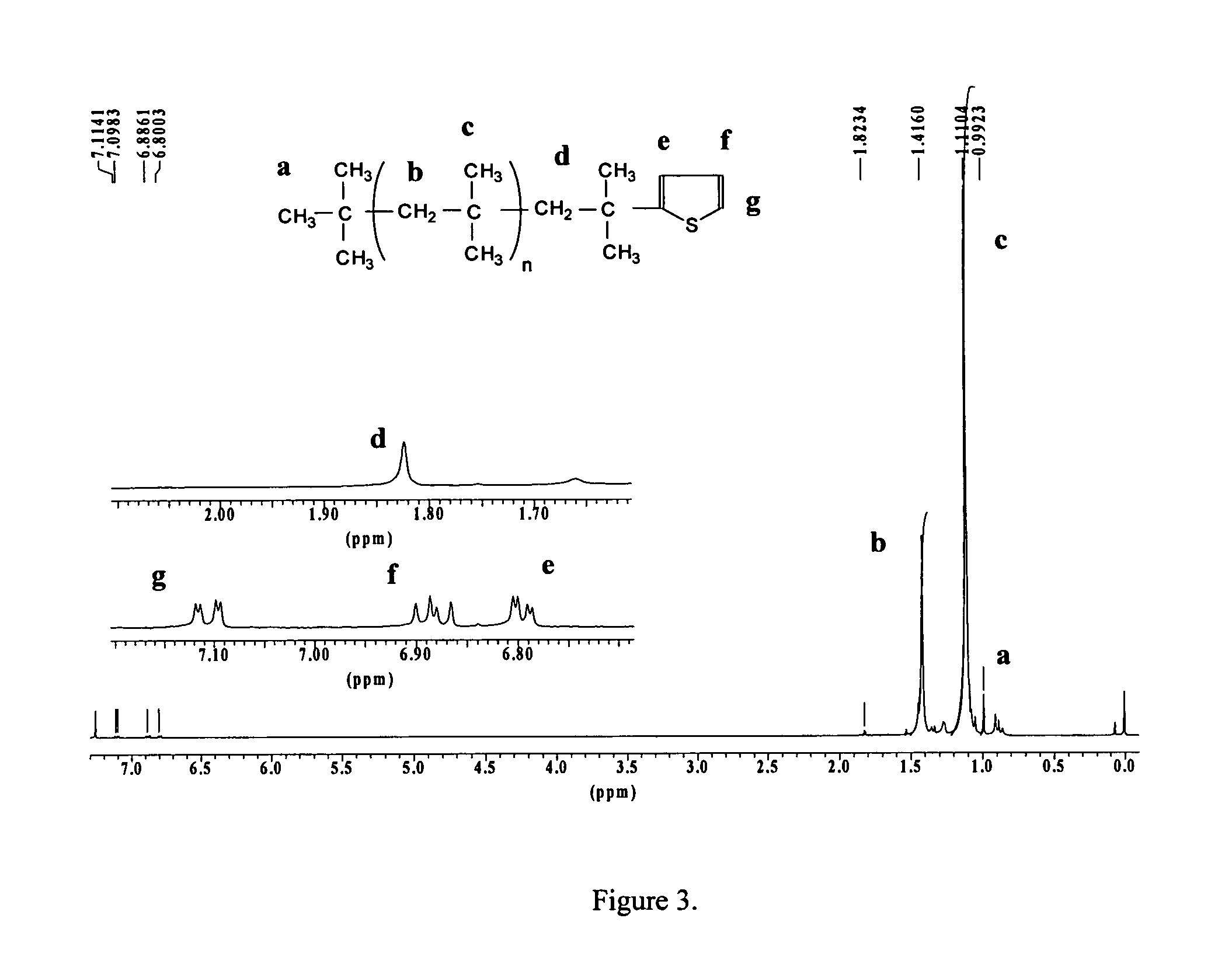
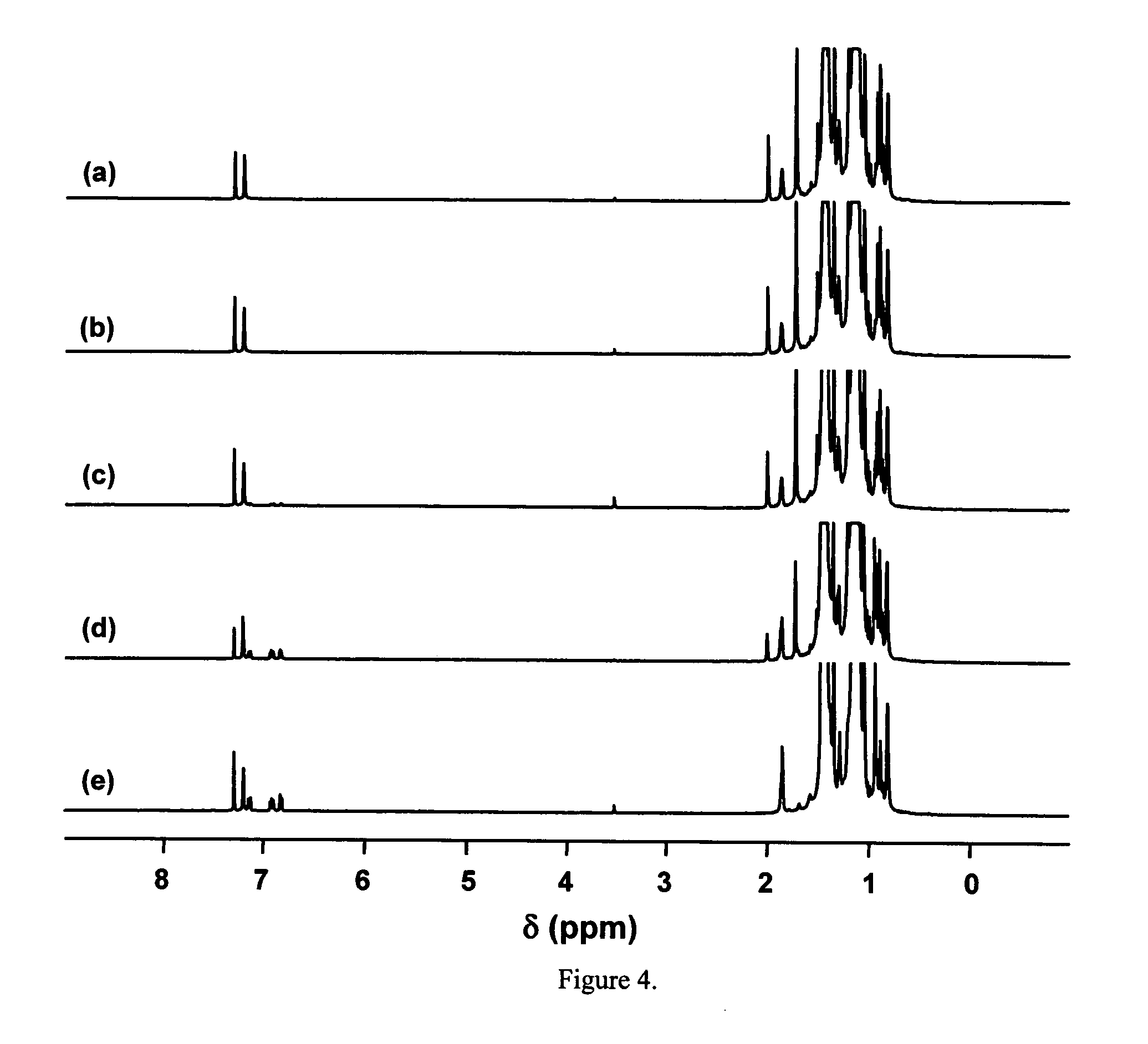
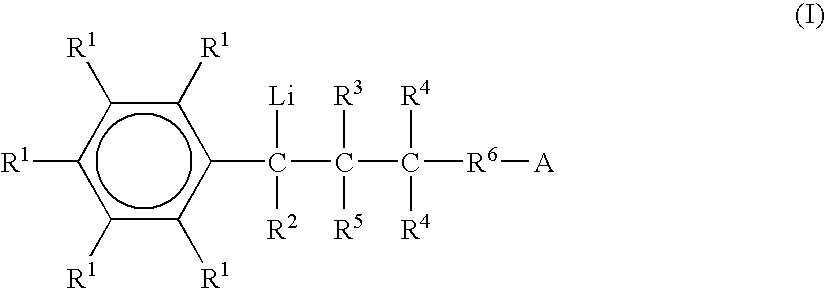
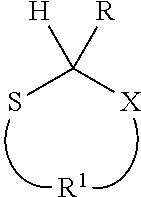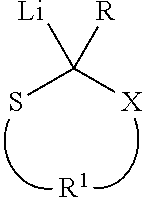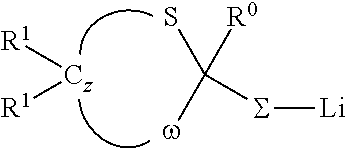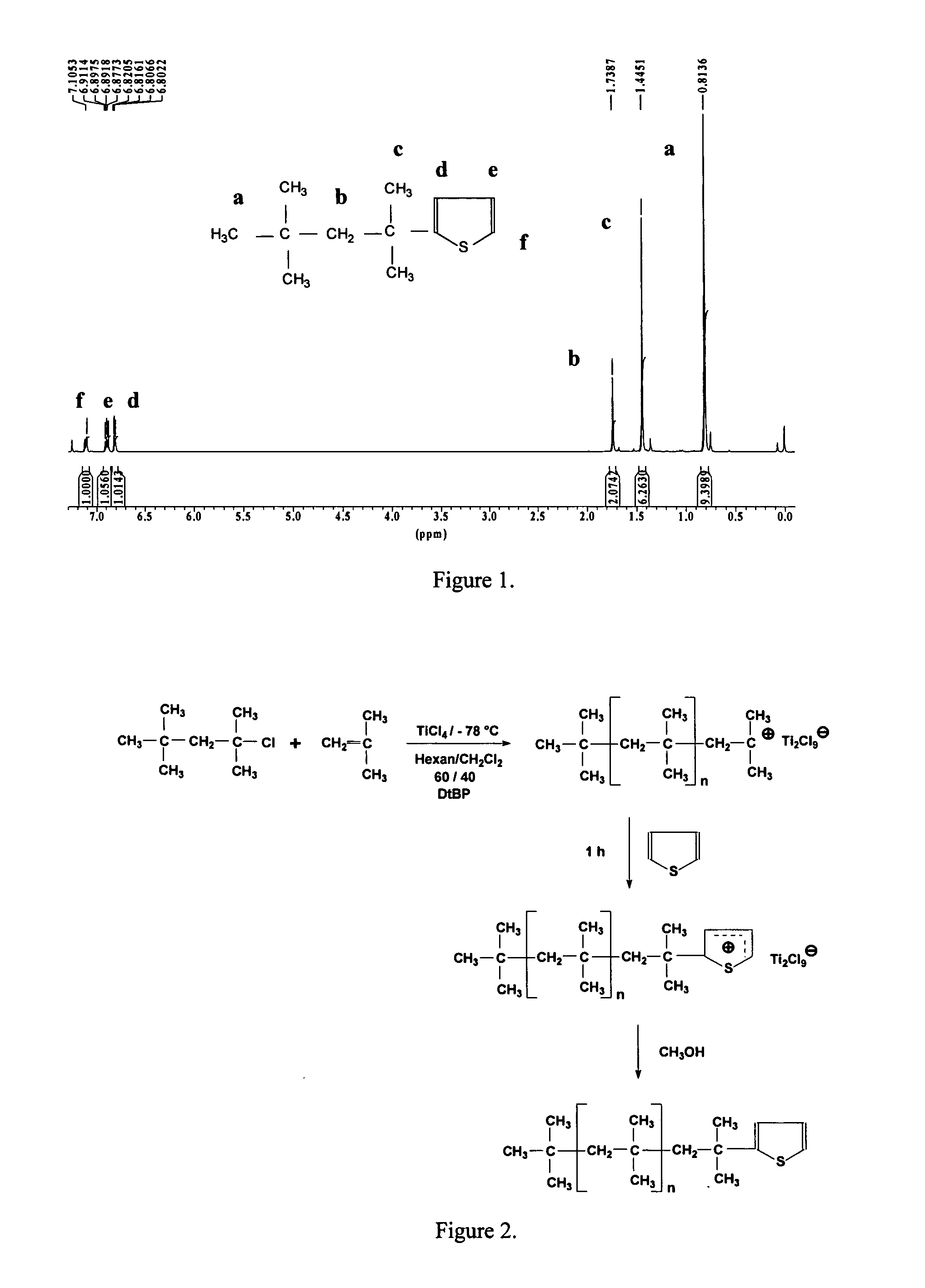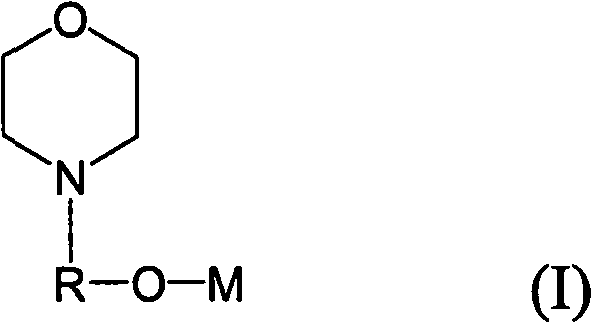Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
88 results about "Organolithium compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
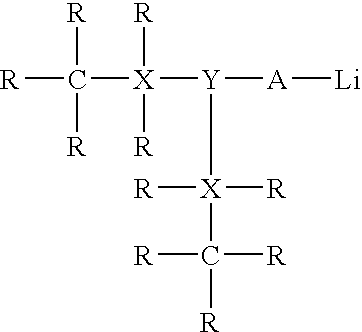
Organolithium reagent. Organolithium reagents are organometallic compounds that contain carbon – lithium bonds. They are important reagents in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom to the substrates in synthetic steps, through nucleophilic addition or simple deprotonation.
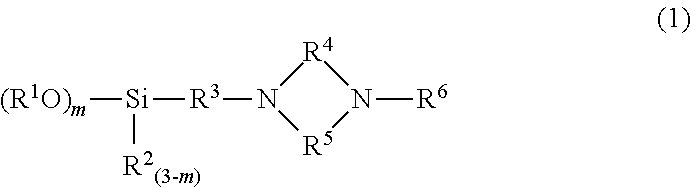
Methods of making siloxy-imine functionalized rubbery polymers and uses thereof in rubber compositions for tires
InactiveUS20090203826A1Improve featuresReduce the heating effectSpecial tyresArylHydrocarbon solvents
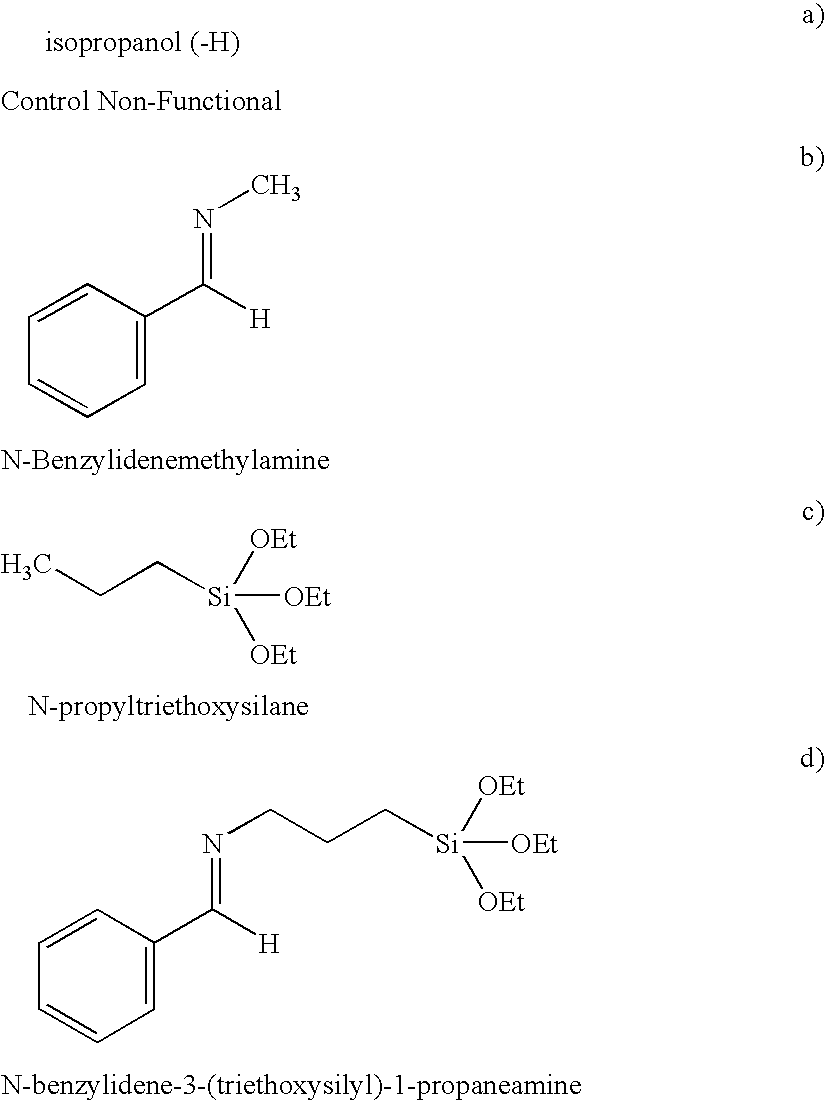
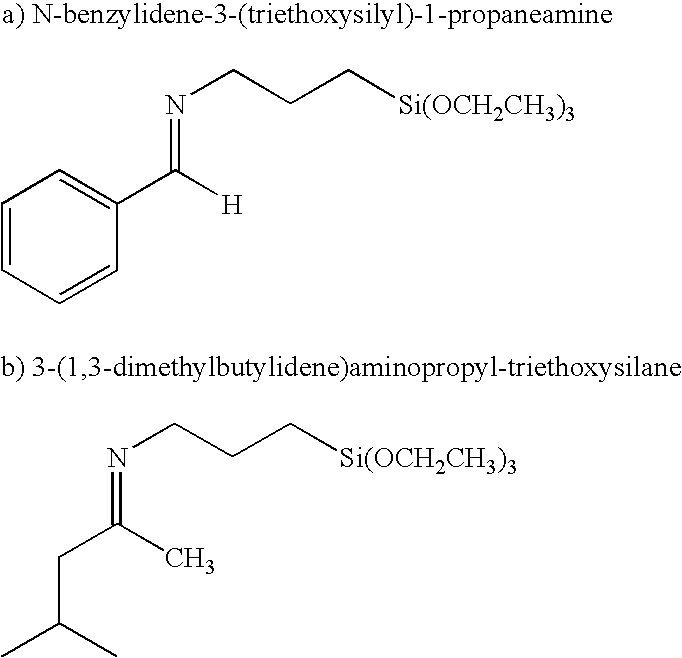
The invention includes a siloxy-imine functionalized rubbery polymer, which exhibits good reinforcing characteristics and filler dispersing effect, a method for making, and a rubber composition including the same. In one embodiment, a process for manufacturing the functionalized rubbery polymer includes polymerizing a conjugated diene monomer using an organolithium compound as an initiator in a hydrocarbon solvent. Next, an active terminal end of the polymer is reacted with a functionalized terminating agent, represented by the general formula:RCH═N(CH2)XSi(OR1)YR23-Y, Formula (1)wherein R represents a group consisting of an aryl or substituted aryl having 6 to 18 carbon atoms, or a heterocycle or heteroaryl having 3 to 18 carbon atoms; R1 and R2 each independently represents a group having 1 to 18 carbon atoms selected from an alkyl, a cycloalkyl, an allyl, and or aryl; X is an integer from 1 to 20; and Y is an integer from 1 to 3.
Owner:RACHITA MICHAEL JOSEPH +3
Anionic polymerization initiators and polymers therefrom
One or more embodiments of the present invention provides a method for preparing a chain-extended lithiated thioacetal solution, the method comprising (i) preparing a lithiated thioacetal by reacting an initiator precursor compound with an organolithium compound; and (ii) chain extending the lithiated thioacetal by polymerizing monomer including conjugated diene monomer, optionally together with vinyl aromatic monomer, to form a polymeric or oligomeric segment having at least 3 and less than 125 repeat units.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Modified conjugated diene-based polymer, method for producing the same, modified conjugated diene-based polymer composition, and tire
There is provided a modified conjugated diene-based polymer having a silyl group substituted with one or more alkoxy groups, and one or more nitrogen atoms on the chain ends of a conjugated diene-based polymer, the modified conjugated diene-based polymer being obtained by polymerizing a conjugated diene compound, or copolymerizing a conjugated diene compound with an aromatic vinyl compound, by using a polyfunctional anionic polymerization initiator prepared from a polyvinyl aromatic compound and an organolithium compound in a range of a molar ratio (the polyvinyl aromatic compound / the organolithium compound) of from 0.05 to 1.0, so as to obtain the conjugated diene-based polymer, and by reacting a living polymer end of the conjugated diene polymer with the compound having a silyl group substituted with two or more alkoxy groups, and one or more nitrogen atoms.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Nitrogen-doped graphene-silicon composite negative pole material, preparation method thereof, and lithium ion battery
ActiveCN106876689AIncrease gram capacityReduce expansionCell electrodesSecondary cellsOrganolithium compoundsNitrogen doped graphene
The invention relates to a nitrogen-doped graphene-silicon composite negative pole material, a preparation method thereof, and a lithium ion battery, and belongs to the field of lithium ion battery material preparation. The nitrogen-doped graphene-silicon composite negative pole material is of a core-shell structure, the core of the core-shell structure is the nitrogen-doped graphene-silicon composite material, the shell of the core-shell structure is of a double-layer structure, and the double-layer structure consists of a silane coupling agent layer and an organolithium compound layer in sequence from inside to outside; and the silane coupling agent layer is silane coupling agent. By use of the nitrogen-doped graphene-silicon composite negative pole material, the expansion rate of a nanometer silicon material can be lowered, a lithium ion transmission rate and the gram volume of the negative pole material can be improved, and the silane coupling agent layer covers the outer surface of the core to improve the tap density and the structure stability of the material so as to improve the cycle performance of the lithium ion battery of the nitrogen-doped graphene-silicon composite negative pole material; the initial efficiency of the material of the lithium ion battery can be improved by an original lithium compound layer out of the silane coupling agent layer, sufficient lithium ions are provided for a large multiplying power charging and discharging process of lithium ions, and multiplying power performance is improved.
Owner:CHINA AVIATION LITHIUM BATTERY LUOYANG
End-capped polymer chains and products thereof
Methods are described herein for converting carbocationically terminated polymers to anionically terminated polymers. These methods comprise: (a) providing a carbocationically terminated polymeric moiety; (b) reacting the carbocationically terminated polymeric moiety with a heterocyclic compound of the formula where —X— is selected from —S—, —O—, —NH— and —NR—, and where R is an alkyl group or an aryl group, thereby providing an end-capped polymeric moiety; and (c) reacting the end-capped polymeric moiety with an organolithium compound to yield an anionically terminated polymeric moiety. Also described are block copolymers in which a first polymer block comprising cationically polymerized monomers is linked to a second polymer block comprising anionically polymerized monomers by a group, as well as a polymer in which a polymer block comprising cationically polymerized monomers is linked to a halogenated silane residue or a carbosilane residue by a group.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS LOWELL
Preparation of functionalized anionic polymerization initiators
InactiveUS20060036050A1Improve stabilityAvoid the needSilicon organic compoundsLithium organic compoundsOrganolithium compoundsCompound (substance)
A process for preparing a functionalized polymerization initiator, the process comprising combining a functionalized styryl compound and an organolithium compound.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Liquid rubber and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a liquid rubber and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises: (1) polymerizing alkene under an anionic polymerisation condition and in the presence of an organolithium compound and a nonpolar organic solvent, with a mole ratio of the organolithium compound and the alkene being 1 : 70-1850; and (2) simultaneously or sequentially contacting the polymerized solution in the step (1) with water and / or C1-C6 alcohol and a gas containing 10-100 % by volume of carbon dioxide, and dying by heating or under vacuum the contacted products in the presence of an antioxidant with stirring, wherein relative to 1 mole of the organic lithium compound in the step (1), an amount of the water and / or the C1-C6 alcohol is 0.5-1.5 moles, and an amount of the carbon dioxide is 0.5-2 moles. According to the preparation method of the liquid rubber, the obtained liquid rubber has colorless and transparent appearance which has no obvious changes after aging at a certain temperature.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
End-capped polymer chains and products thereof
According to an aspect of the present invention, a method is provided in which a double diphenylethylene compound is reacted with a polymer that contains a carbocationically terminated chain thereby providing a 1,1-diphenylene end-functionalized chain. Subsequently, an alkylating agent is reacted with the 1,1-diphenylene end-functionalized chain, thereby providing an alkylated 1,1-diphenylene end-functionalized chain. In some embodiments, the method further comprises (a) optionally combining a 1,1-diphenylorganolithium compound with the alkylated 1,1-diphenylene end-functionalized polymer followed by (b) reacting an organolithium compound with the alkylated 1,1-diphenylene end-functionalized polymer. This provides an anionically terminated polymer, which can be used, for example, in subsequent anionic polymerization and coupling reactions. According to another aspect of the present invention, a novel polymer is provided that comprises a polymer chain, which chain further comprises the following: (a) a plurality of constitutional units that correspond to cationically polymerizable monomer species and (b) an end-cap comprising agroup or agroup, where R is a branched or unbranched alkyl group containing from 1 to 20 carbons and R1 is a branched, unbranched, or cyclic alkyl group or an aryl group, containing from 1 to 20 carbons. Other aspects of the present invention relate to novel copolymers that comprise: (a) a first polymer block that comprises a plurality of constitutional units that correspond to isobutylene; and (b) a second polymer block that comprises a plurality of constitutional units that correspond to hydroxyethyl methacrylate.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS LOWELL UNIV OF
Batch process for synthesizing rubbery polymers having a high trans microstructure content
InactiveUS7285605B1High trans microstructure contentSacrificing other performance characteristic(s)Organolithium compoundsLithium compound
The present invention is directed to a batch process for synthesizing rubbery polymers, such as styrene-butadiene rubber, having a high trans microstructure. In one embodiment, the batch process involves mixing a catalyst system with styrene and butadiene monomers in a single reactor, with additional butadiene monomer being added after a desired period of time to further drive styrene conversion and, thus, provide a desirable high trans rubbery polymer, e.g., styrene-butadiene rubber. The copolymerization process can be conducted at a temperature in the range of about 20° C. to about 180° and over a period of about 1 to about 4 hours. The catalyst system can include (a) an organolithium compound, (b) a group IIa metal salt, and (c) an organoaluminum compound. The catalyst system may further optionally include an amine compound and / or an organomagnesium compound.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Preparation process of acrylic acid ester polymer
A process for the preparation of an acrylic acid ester polymer, includes carrying out polymerization of an acrylic acid ester or block copolymerization of an acrylic acid ester and another (meth)acrylic monomer in the presence of an organolithium compound and an organoaluminum compound represented by the following formula (I):AlR1R2R3 (I)wherein R1 represents an alkyl group having at least 3 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having at least 3 carbon atoms or an aryloxy group, R2 and R3 each independently represent an aryloxy group or may be coupled together to form an arylenedioxy group. The process makes it possible to heighten the reaction rate and living properties upon polymerization and heighten the block formation efficiency upon block copolymerization.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Amine containing catalyst system and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7321017B1High trans microstructure contentEasy to wearOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSpecial tyresOrganolithium compoundsNitrogen
The present invention is directed to an amine containing catalyst system for synthesizing rubbery polymers, such as polybutadiene rubber and styrene-butadiene rubber, having a high trans microstructure. The catalyst system, in one embodiment, includes (a) an organolithium compound, (b) a group IIa metal salt, (c) an organoaluminum compound, and (d) an amine compound which can be selected from (1) a heterocyclic aromatic compound which includes a ring structure with one or more nitrogen atoms as part of the ring; (2) a heterocyclic non-aromatic compound which includes a ring structure with two or more nitrogen atoms as part of the ring; (3) an aromatic compound including a ring structure substituted with at least one amine and at least one polar functionality containing group selected from a carboxyl group or a hydroxyl group; (4) a bicyclic chelating diamine compound; or (5) an aliphatic amine which includes a C5-C20 alkyl group.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Methods of Making Siloxy-Amine Functionalized Rubbery Polymers and Uses Thereof in Rubber Compositions for Tires
The invention includes a siloxy-amine functionalized rubbery polymer, which exhibits good reinforcing characteristics and filler dispersing effect, a method for making, and a rubber composition including the same. In one embodiment, a process for manufacturing includes polymerizing a conjugated diene monomer using an organolithium compound as an initiator in a hydrocarbon solvent. Next, an active terminal end of the polymer is reacted with a functionalized terminating agent represented by:RN—(CH2)XSi(OR1)3, Formula (I)wherein R, in combination with the nitrogen (N) atom, is a substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic aromatic or non-aromatic compound which includes a ring structure with one or more nitrogen atoms as part of the ring; R1 represents a group having 1 to 18 carbon atoms selected from an alkyl, a cycloalkyl, an allyl, or an aryl; and X is an integer from 1 to 20.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Preparation of functionalized anionic polymerization initiators
InactiveUS7405262B2Highly stabilized carbon-lithium siteAvoid the needSilicon organic compoundsLithium organic compoundsOrganolithium compoundsOrganic chemistry
A process for preparing a functionalized polymerization initiator, the process comprising combining a functionalized styryl compound and an organolithium compound.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Method of homopolymerization of conjugated dienes or copolymerization of conjugated dienes and monovinyl aromatics
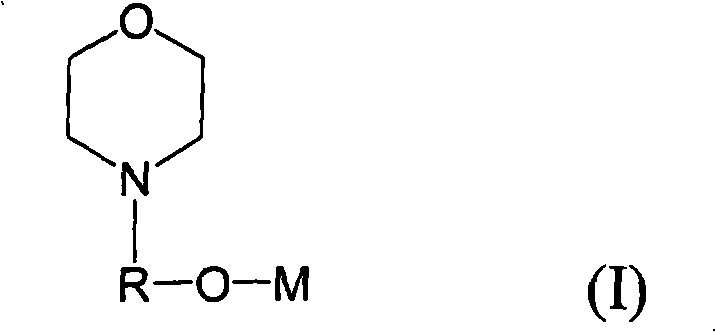
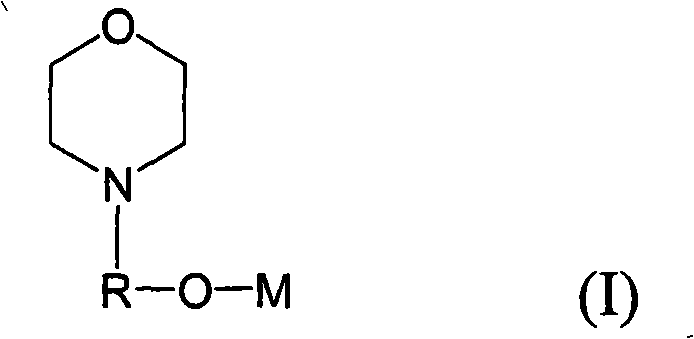
The invention provides a method for homopolymerizing conjugated dialkene or co-polymerizing conjugated dialkene and monovinyl aromatic hydrocarbon. The method comprises the following steps: the conjugated dialkene is homopolymerized or the conjugated dialkene and the monvinyl aromatic hydrocarbon are co-polymerized randomly. The method is characterized in that at least one alkali metal alkoxide compound expressed by the formula (I) is used as a structure regulator; in the formula, R is linear chain or branched chain alkylidene radical having 1 to 10 carbon atoms; M is alkali metal selected from Li, Na, K, Rb and Cs. In addition, the invention further relates to a catalyzer combination used for polymerizing a conjugated dialkene monomer and the anions of an optional mono-vinyl aromatic hydrocarbon into a polydiene polymer having high and medium vinyl content. The catalyzer combination comprises (a) an organolithium compound used as an anionic polymerization initiator, (b) at least an alkali metal alkoxide compound expressed by the formula (I) as a structure regulator. By adopting the compound expressed by the formula (I) as the structure regulator for polymerization of the conjugated dialkene, the dialkene polymer having high and medium vinyl content can be got.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Method of making alkoxy functionalized rubbery polymers
InactiveUS7335706B1Desirable wearDesirable tear characteristicSpecial tyresActive polymerOrganolithium compounds
The present invention is directed to a method for synthesizing rubbery copolymers, such as styrene-butadiene rubber, or rubbery homopolymers, such as polybutadiene rubber, that are alkoxy functionalized, e.g., alkoxysilane functionalized, and provide desirable dispersion of silica in rubber compounds, such as for use in tire treads. To that end, the method, in one embodiment, involves admixing anionically polymerizable conjugated diene monomers with optional vinyl aromatic, an anionic-polymerization initiator, i.e., an organolithium compound, and a lithium alkoxide to form an admixture of living polymers, then adding a halogenated coupling agent to the admixture of living polymers effecting conditions to form an alkoxy functionalized rubbery polymer. The alkoxy functionalized rubbery polymers can be utilized in tire tread rubbers where the rubbery polymers may provide desirable wear properties without substantially sacrificing other performance characteristic(s), e.g., traction properties.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Amino group-containing conjugated diene polymer and method for producing the same, and block copolymer and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20100267918A1Improve the modification rateNarrow in molecularBenzeneOrganolithium compounds
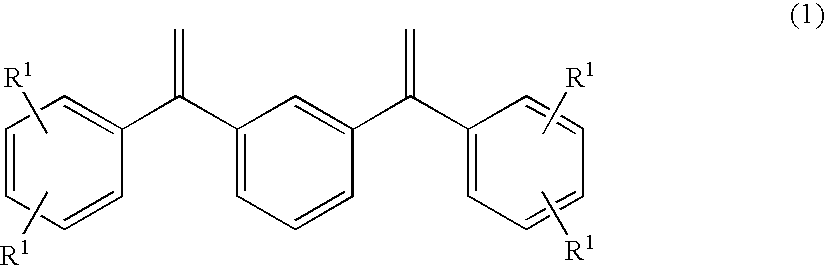
A method for producing an amino group-containing conjugated diene polymer includes polymerizing a conjugated diene compound in the presence of a reaction product of 1,3-bis(diphenylethenyl)benzene or a derivative thereof and an organolithium compound to obtain a conjugated diene polymer, and reacting the conjugated diene polymer with a modifier.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Modified conjugated diene-based polymer, method for producing the same, modified conjugated diene-based polymer composition, and tire
ActiveUS8946339B2Improve balanceLow hysteresis lossSpecial tyresActive polymerOrganolithium compounds
There is provided a modified conjugated diene-based polymer having a silyl group substituted with one or more alkoxy groups, and one or more nitrogen atoms on the chain ends of a conjugated diene-based polymer, the modified conjugated diene-based polymer being obtained by polymerizing a conjugated diene compound, or copolymerizing a conjugated diene compound with an aromatic vinyl compound, by using a polyfunctional anionic polymerization initiator prepared from a polyvinyl aromatic compound and an organolithium compound in a range of a molar ratio (the polyvinyl aromatic compound / the organolithium compound) of from 0.05 to 1.0, so as to obtain the conjugated diene-based polymer, and by reacting a living polymer end of the conjugated diene polymer with the compound having a silyl group substituted with two or more alkoxy groups, and one or more nitrogen atoms.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
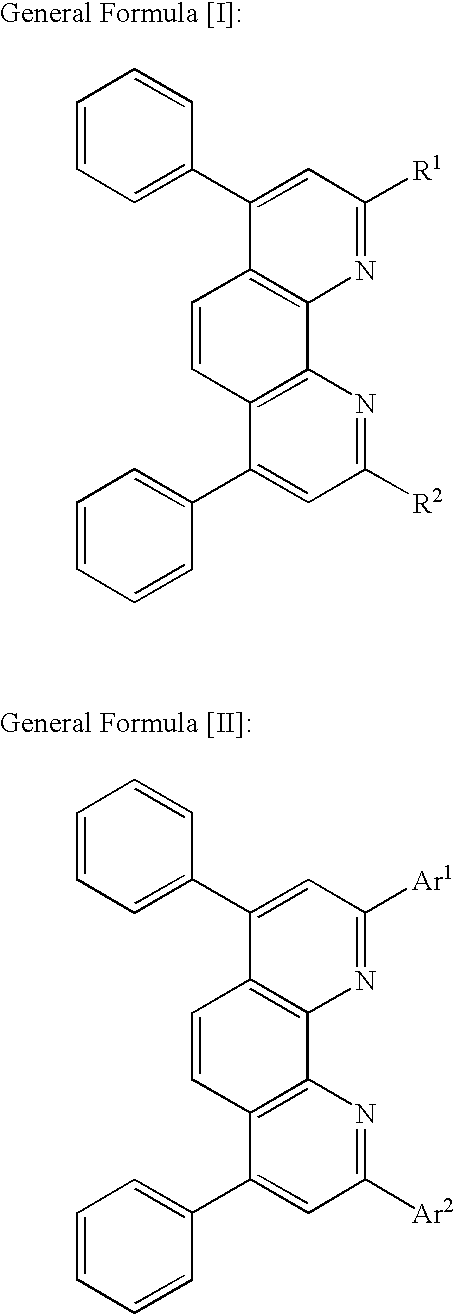
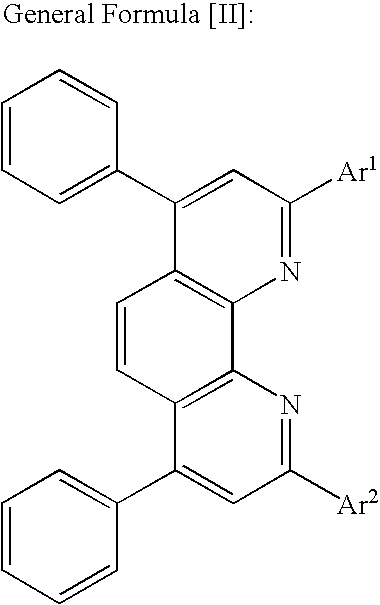
Optical recording medium
InactiveUS20040265626A1Efficient transportOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensArylOrganolithium compounds
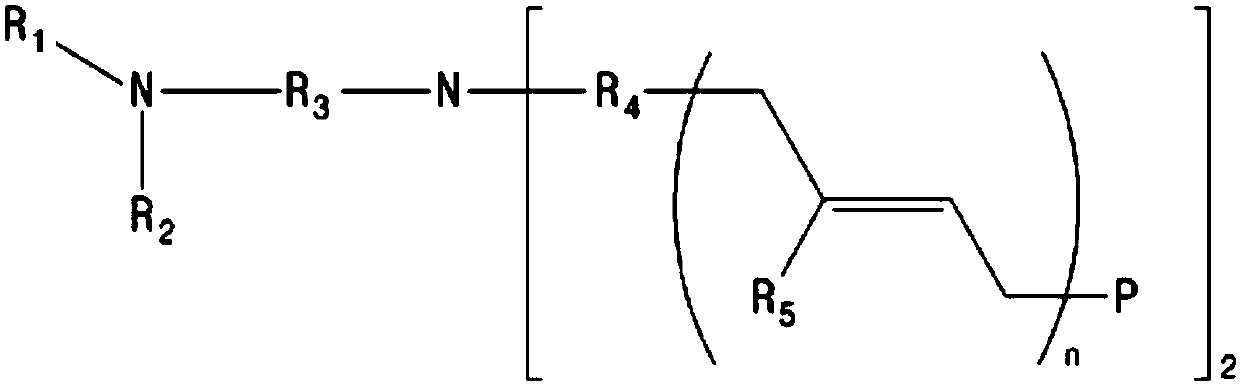
A novel bathophenanthroline compound of the general formula ÄIÜ or ÄIIÜ is provided <CHEM> wherein R<1> and R<2> may be the same or different and independently represent a linear, branched or cyclic, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon group, or a substituted or unsubstituted, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon group provided that at least one of R<1> and R<2> has at least two carbon atoms, and wherein Ar<1> and Ar<2> may be the same or different and independently represent a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group. A process for preparing the compound is also provided wherein bathophenanthroline and an organolithium compound are subjected to nucleophilic substitution reaction to obtain the compound of the above formula ÄIÜ or ÄIIÜ.
Owner:JOLED INC +1
Calcium-based catalyst system
InactiveUS20050181935A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationOrganolithium compoundsOrganic solvent
The process and catalyst system of this invention can be utilized to synthesize a highly random styrene-butadiene rubber having a high trans content by solution polymerization. The styrene-butadiene rubber made by the process of this invention can be utilized in tire tread rubbers that exhibit improved wear characteristics. This invention more specifically reveals a catalyst system for use in isothermal polymerizations which consists essentially of (a) an organolithium compound, (b) a calcium alkoxide and (c) a lithium alkoxide. The subject invention further discloses a process for synthesizing a random styrene-butadiene rubber having a low vinyl content by a process which comprises copolymerizing styrene and 1,3-butadiene under isothermal conditions in an organic solvent in the presence of a catalyst system which consists essentially of (a) an organolithium compound, (b) a calcium alkoxide and (c) a lithium alkoxide. An amine can also be added to the catalyst system to increase the molecular weight (Mooney viscosity) of the rubber.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
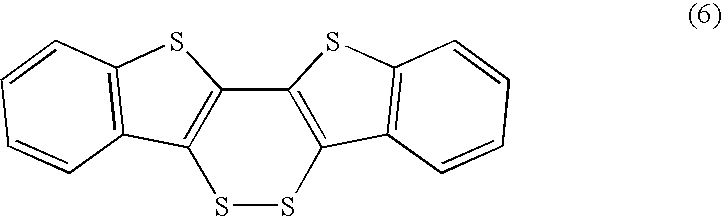
Chalcogen-containing fused polycyclic organic material and method for producing same
ActiveUS20070117973A1Easy to chargeEasy to manufactureOrganic chemistryElectrical apparatusOrganolithium compoundsCompound (substance)
A diacetylene derivative was used as a starting material, and was subjected to dilithiation using an organolithium reagent. The resulting product was allowed to react with an excessive amount of chalcogen. Accordingly, an intramolecular cyclization reaction proceeded simultaneously with formation of skeletons of three rings. As a result, a chalcogen-containing fused polycyclic organic material was found to be obtained which has the three rings and a dichalcogenid bond. Further, by subjecting the resulting compound to a dechalcogenation reaction, a heteroacene was found to be obtained in a satisfactory yield. These synthetic techniques have made it possible to synthesize a series of highly planar chalcogen-containing π-electron system materials. Therefore, it is possible to provide (i) a chalcogen-containing fused polycyclic organic material capable of exhibiting excellent charge-transporting properties and (ii) a method for producing the material.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Calcium-based catalyst system
InactiveUS7087549B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPolymer scienceOrganolithium compounds
This invention reveals a catalyst system for use in isothermal polymerizations which consists essentially of (a) an organolithium compound, (b) a calcium alkoxide and (c) a lithium alkoxide. The subject invention further discloses a process for synthesizing a random styrene-butadiene rubber having a low vinyl content by a process which comprises copolymerizing styrene and 1,3-butadiene under isothermal conditions in an organic solvent in the presence of a catalyst system which consists essentially of (a) an organolithium compound, (b) a calcium alkoxide and (c) a lithium alkoxide. An amine can also be added to the catalyst system to increase the molecular weight (Mooney viscosity) of the rubber.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Organic lithium compound containing tin and its preparation method
InactiveCN1429849ATin organic compoundsLithium organic compoundsPolymer scienceOrganolithium compounds
A Sn-contained organolithium compound as anionic polymerization trigger has a formula R3SnYaZYaLi, where R is C1-C20 alkyl, C3-C20 cycloalkyl, C6-C20 aryl, or substituted aryl, Z is straight-chain orbranch-chain C1-C2 2-valence alkyl, C6-C30 arylidene, or substituted aryldiene, Y is conjugated diene homopolymer group, monovinyl arylhydrocarbon homopolymer group, or conjugated diene and monovinylarylhydrocarbon copolymer group, a is 0-6, and at b=0-6. Its preparing process is also disclosed.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Methods of making siloxy-amine functionalized rubbery polymers and uses thereof in rubber compositions for tires
The invention includes a siloxy-amine functionalized rubbery polymer, which exhibits good reinforcing characteristics and filler dispersing effect, a method for making, and a rubber composition including the same. In one embodiment, a process for manufacturing includes polymerizing a conjugated diene monomer using an organolithium compound as an initiator in a hydrocarbon solvent. Next, an active terminal end of the polymer is reacted with a functionalized terminating agent represented by:RN—(CH2)XSi(OR1)3, Formula (I)wherein R, in combination with the nitrogen (N) atom, is a substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic aromatic or non-aromatic compound which includes a ring structure with one or more nitrogen atoms as part of the ring; R1 represents a group having 1 to 18 carbon atoms selected from an alkyl, a cycloalkyl, an allyl, or an aryl; and X is an integer from 1 to 20.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Method for producing polymer
ActiveUS9738742B2Good colorHigh heat discoloration resistanceHydrocarbon solventsOrganolithium compounds
A method for producing a polymer has: a polymerization step of polymerizing at least a conjugated diene monomer in a hydrocarbon solvent using an organolithium compound as a polymerization initiator, and obtaining a polymer; and, following steps (1) to (4), successively performing after the polymerization step: (1) a step of mixing an acid and water of 20 to 300 parts by mass into the solution containing the polymer of 100 parts by mass, (2) a step of adjusting an amount of the water to 10 parts by mass or less based on 100 parts by mass of the solution containing the polymer, (3) a step of adding a carbon oxide gas and / or a compound to be decarboxylated to the solution containing the polymer, and (4) a step of removing a solvent from the solution containing the polymer until a concentration of the polymer reaches 95 mass % or more.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Efficient and convenient procedure for the synthesis of B-alkylated oxazaborolidines derived from ephedrine and norephedrine
ActiveUS7109345B1Silicon organic compoundsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsAlkyl transferOrganolithium compounds
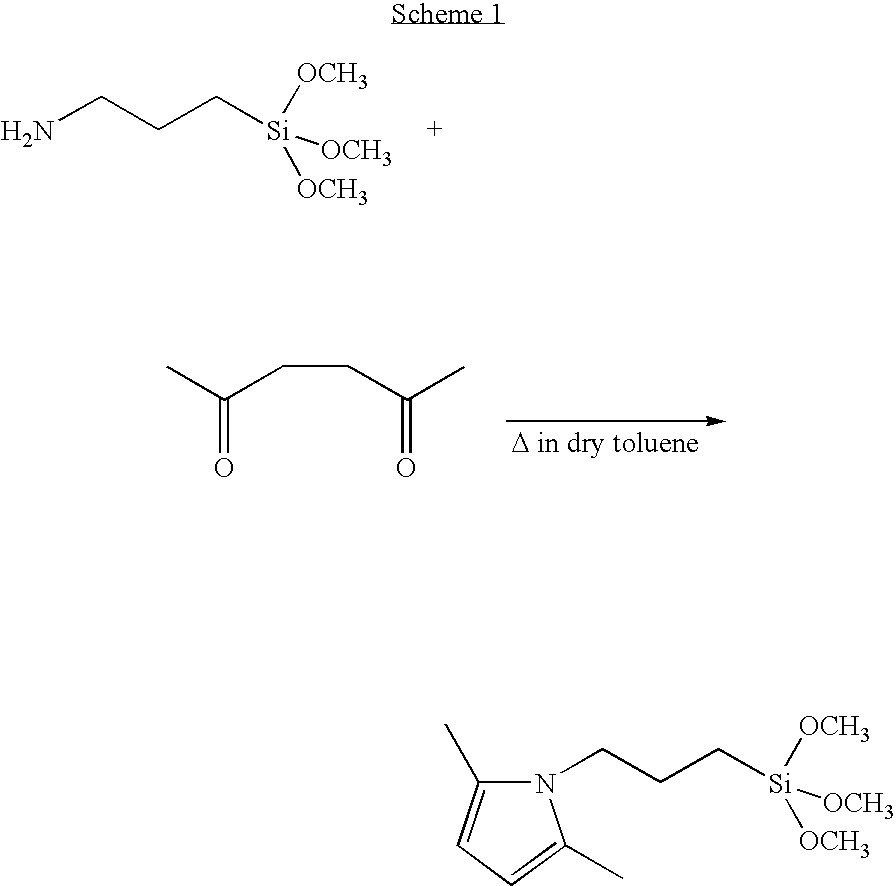
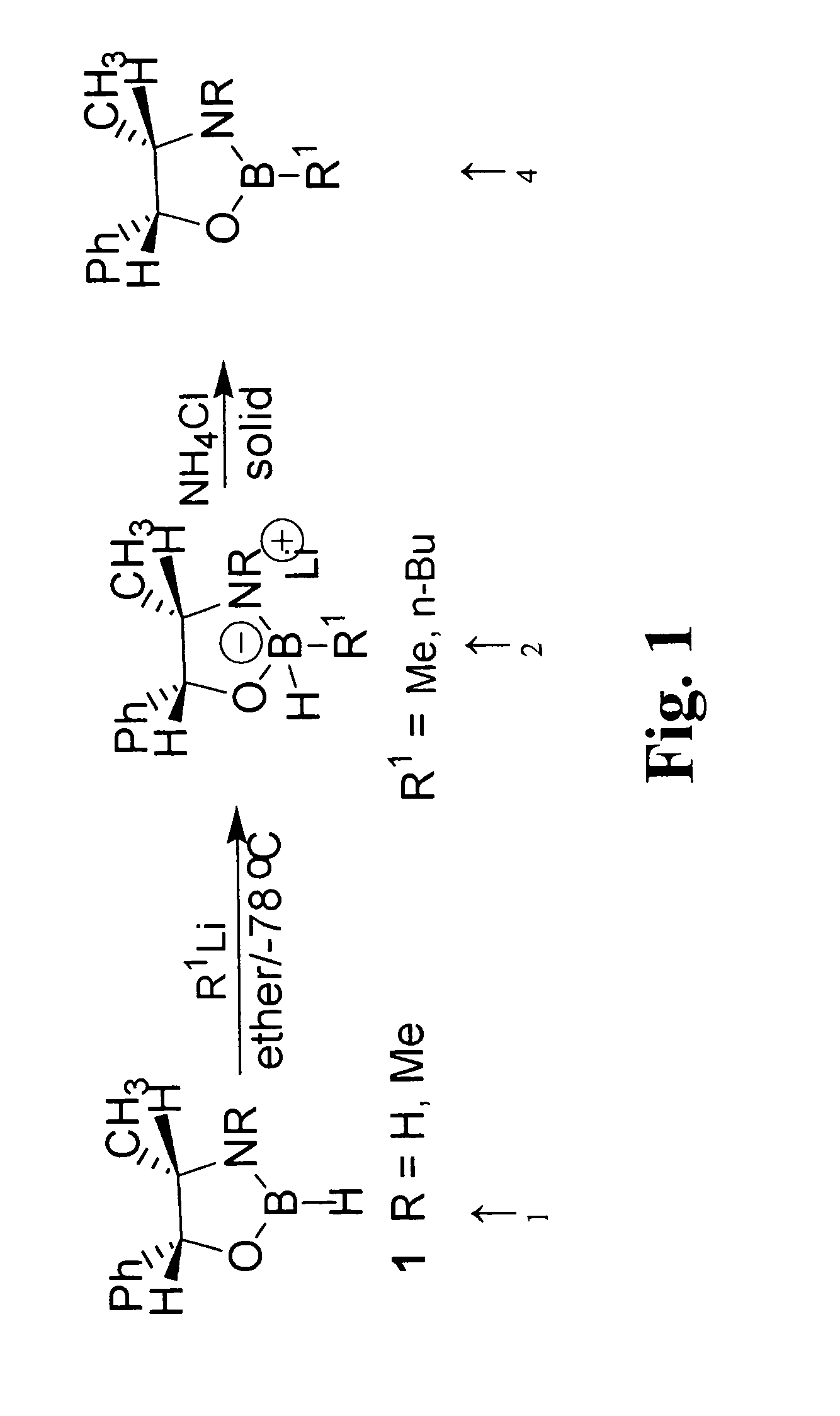
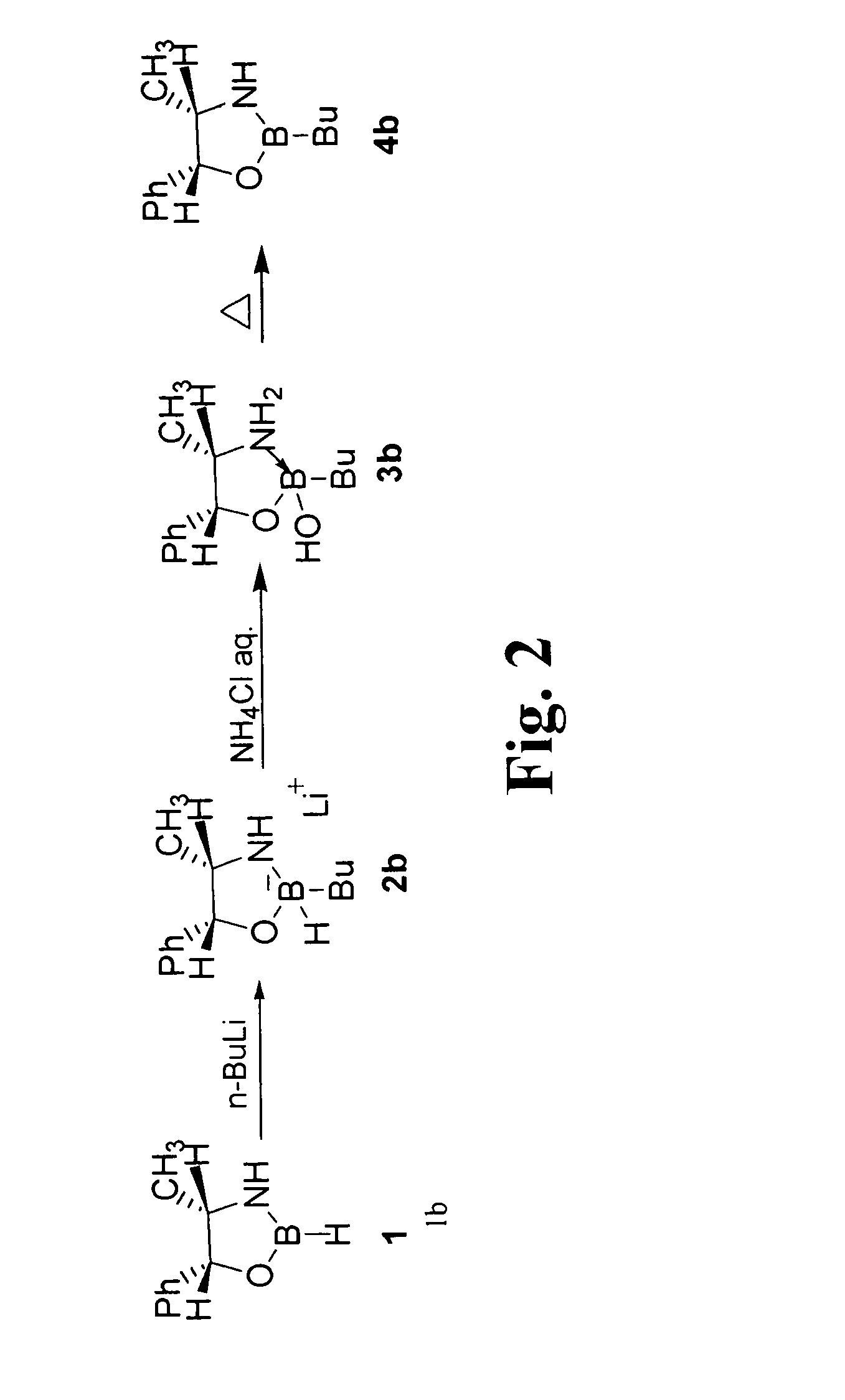
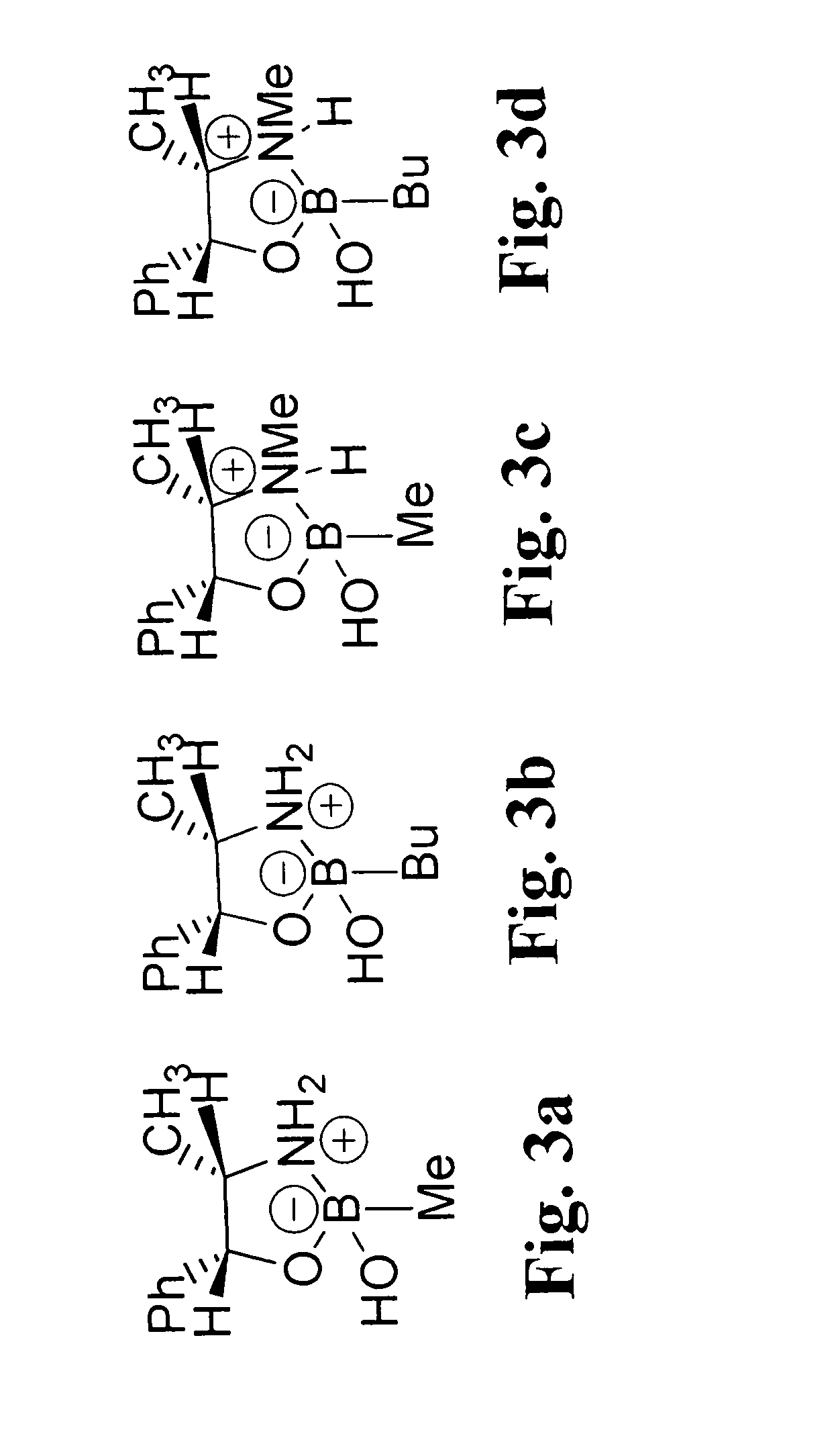
A novel and efficient alkylation procedure of B—H-1,3,2-oxazaborolidines derived from ephedrine and norephedrine has been established. Representative B-butyl- and B-methyl-1,3,2-oxazaborolidines were prepared in good yield and excellent purity by one pot treatment of the parent boraheterocyclic compound with the corresponding organolithium reagent and subsequent hydrolysis of the cyclic borohydride with anhydrous ammonium chloride.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO
Preparation method for aromatic carboxylic acid compounds
ActiveCN102372531AEfficient synthesisImprove tolerancePreparation from nitrilesFunctional group formation/introductionOrganolithium compoundsGrignard reagent
The invention discloses a preparation method for aromatic carboxylic acid compounds. According to the method, corresponding aromatic carboxylic acid compounds are obtained by reacting aryl halides with malononitrile under the conditions of alkali and a copper catalyst. A ligand cocatalyst is also used in the method and is one selected from the group consisting of 2-pipecolic acid, 2-picolinic acid, 2-pralidoxime, glyoxime, 1,10-orthophenanthrolene, N,N-dimethylethylenediamine and L-proline. Compared to the method of oxidation of substituted aromatic hydrocarbons, the method of directly reacting Grignard reagents and organic lithium reagents with carbon dioxide and the method of reacting the compounds of aryl zinc and aryl boron with carbon dioxide under catalysis of transition metals in the prior art, the method provided in the invention has following obvious advantages: the method is based on aryl halides which are easily available; a cheap copper salt is used as a catalyst; little environmental pollution and high yield are realized; high tolerance of a plurality of function groups on aromatic rings is obtained; separation and purification are convenient; etc.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
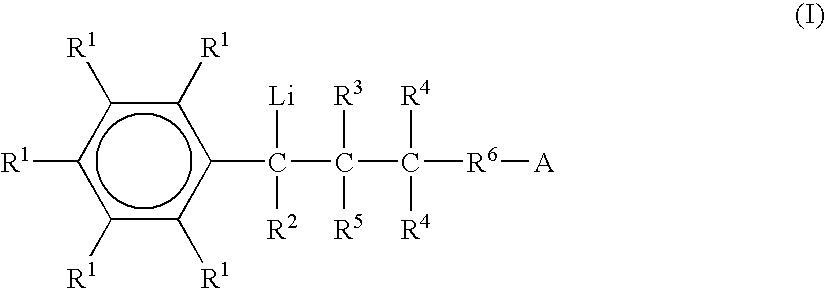
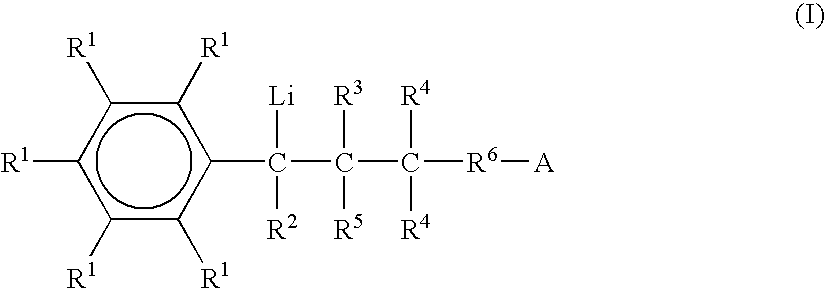
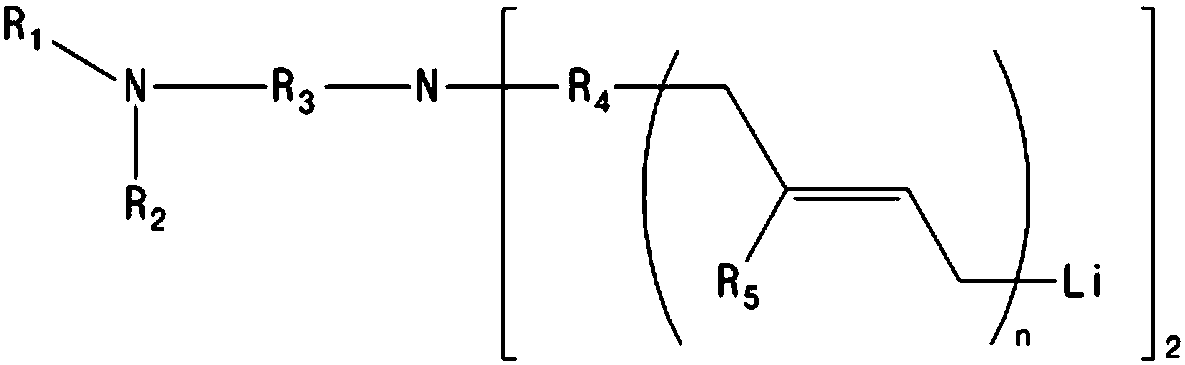
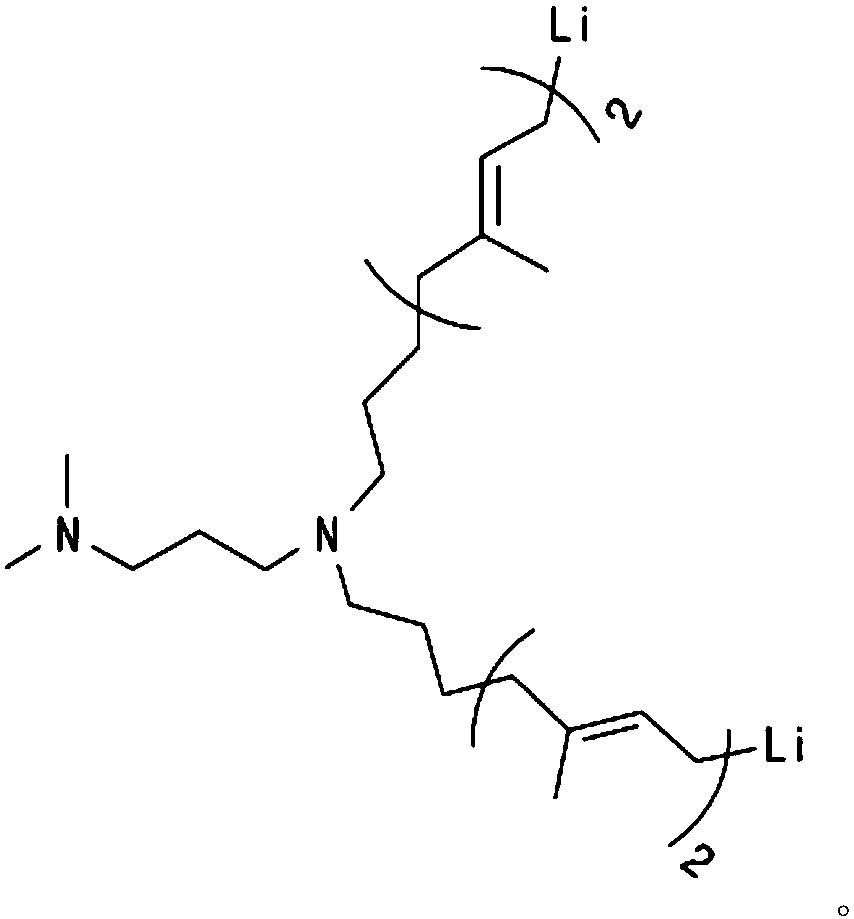
Organolithium compound, method for production of modified conjugated diene-based polymer using same, and modified conjugated diene-based polymer
ActiveCN107614506AHigh affinityEasy to manufactureLithium organic compoundsSpecial tyresPolymer scienceOrganolithium compounds
The present invention relates to an organolithium compound, a method for the production of a modified conjugated diene-based polymer using the same, and a modified conjugated diene-based polymer. Thepresent invention can provide a modified conjugated diene-based polymer having excellent compatibility with an inorganic filler and improved processability, and can provide a tire having excellent exothermic properties, tensile strength, abrasion resistance, low-fuel efficiency, and wet skid resistance, while having low rolling resistance, by using a rubber composition containing the modified conjugated diene-based polymer.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Alkyl group VA metal compounds
InactiveUS6956127B2Suitable for useReduce the temperatureFurnaces without endless coreVacuum evaporation coatingOrganolithium compoundsHalogen
Disclosed are methods of preparing monoalkyl Group VA metal dihalide compounds in high yield and high purity by the reaction of a Group VA metal trihalide with an organo lithium reagent or a compound of the formula RnM1X3−n, where R is an alkyl, M1 is a Group IIIA metal, X is a halogen and n is an integer fro 1 to 3. Such monoalkyl Group VA metal dihalide compounds are substantially free of oxygenated impurities, ethereal solvents and metallic impurities. Monoalkyl Group VA metal dihydride compounds can be easily produced in high yield and high purity by reducing such monoalkyl Group VA metal dihalide compounds.
Owner:SHIPLEY CO LLC
Bathophenanthroline compound and process for preparing same
InactiveUS20050073641A1Efficient transportPoint becomes highLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryArylOrganolithium compounds
Owner:SHIBANUMA TETABUO +3
Preparation method of heterocyclic biphenyl boric acid
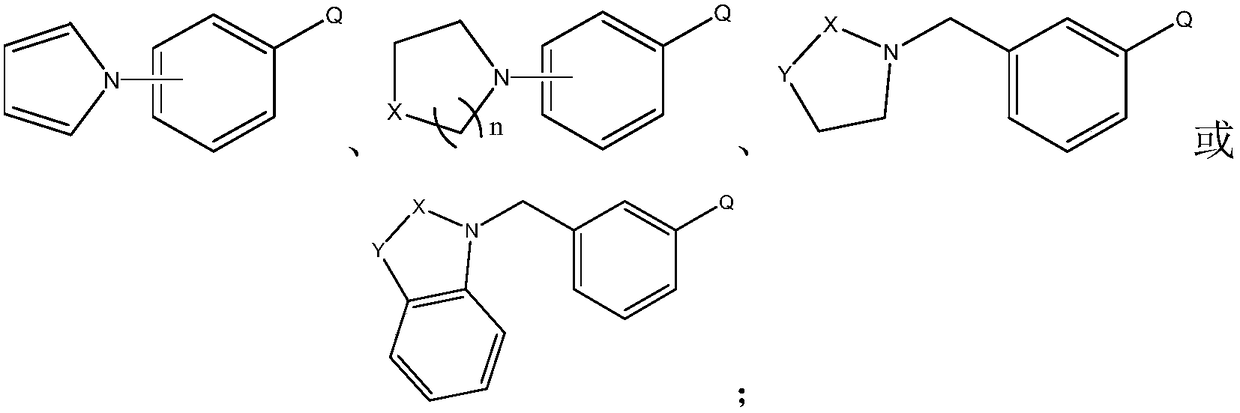
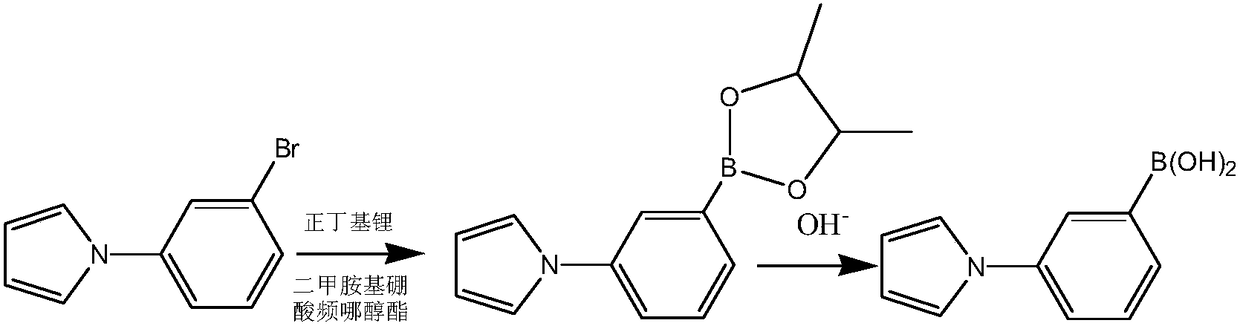
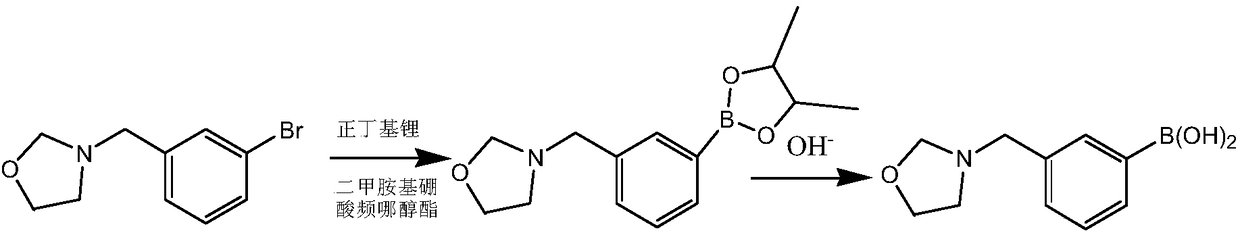
ActiveCN108409767AHigh reaction yieldRaise the reaction temperatureGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsOrganolithium compoundsReaction temperature
The invention provides a preparation method of heterocyclic biphenyl boric acid. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a compound shown in formula I into a solvent A, dissolving a boronizing reagent and an organolithium reagent into a solvent B, then performing continuous flowing feeding reaction on the reagent A and the reagent B, after the reaction is finished, using an alkaline reagent for performing hydrolysis reaction to obtain the heterocyclic biphenyl boric acid; according to the preparation method provided by the invention, a flowing chemical technique is used for synthesizing a heterocyclic biphenyl boric acid compound, compared with the existing conventional reaction method, the reaction yield is increased, the yield of part of the compound can reach upto 82% or above, the reaction time is shortened, the reaction can be rapidly finished within 1 hour, and the reaction temperature is raised, the reaction can be completed at around -20 DEG C to 10 DEG C, energy loss caused by reacting at the ultralow temperature environment can be avoided; the preparation method is an excellent synthetic method, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:上海泰坦科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com