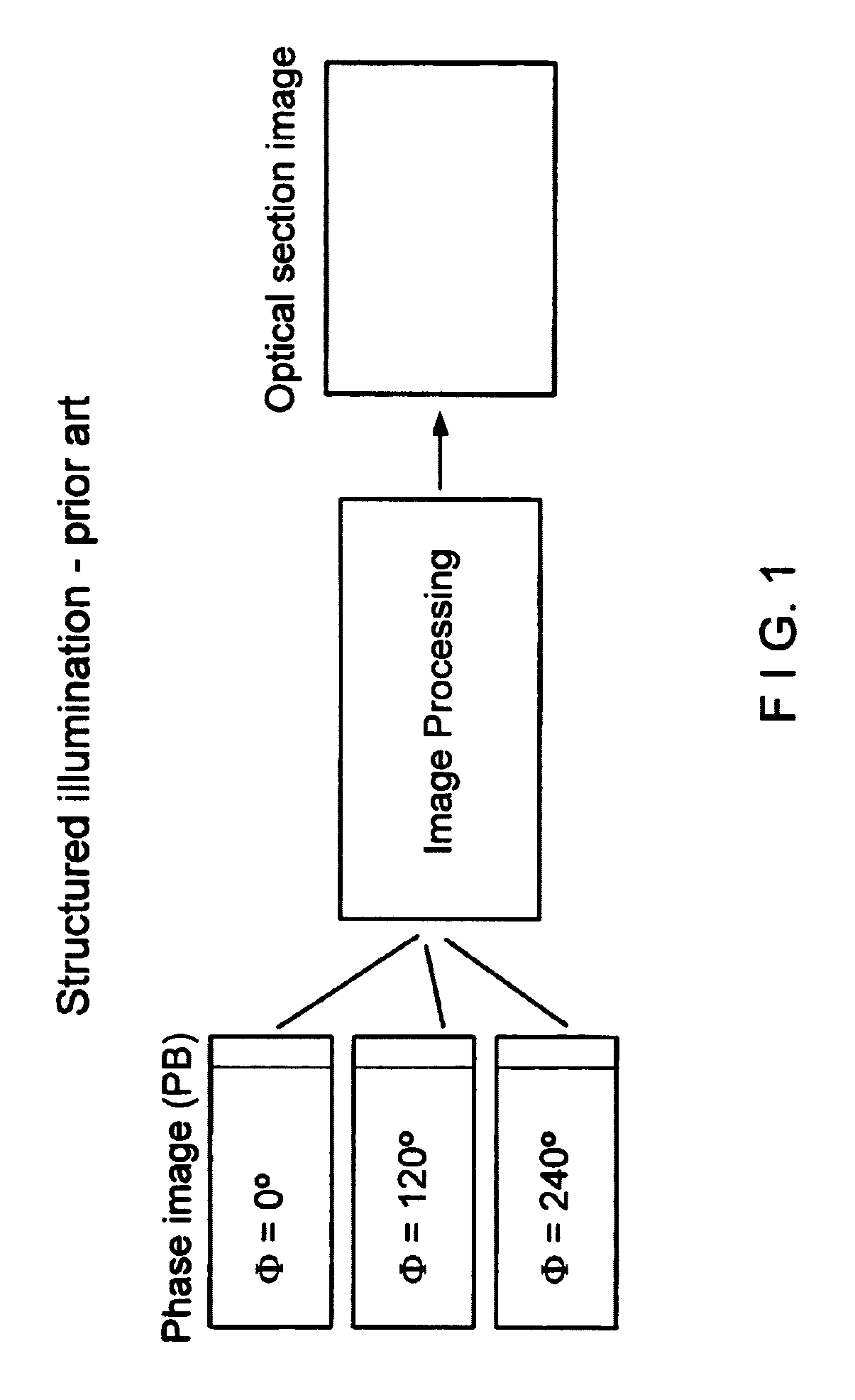
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Optical cross section" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical Cross Section or OCS is a value which describes the maximum amount of optical flux reflected back to the source. The standard unit of measurement is ... Optical cross section of a flat mirror with a given reflectivity at a particular wavelength Where is the cross sectional diameter of the beam.
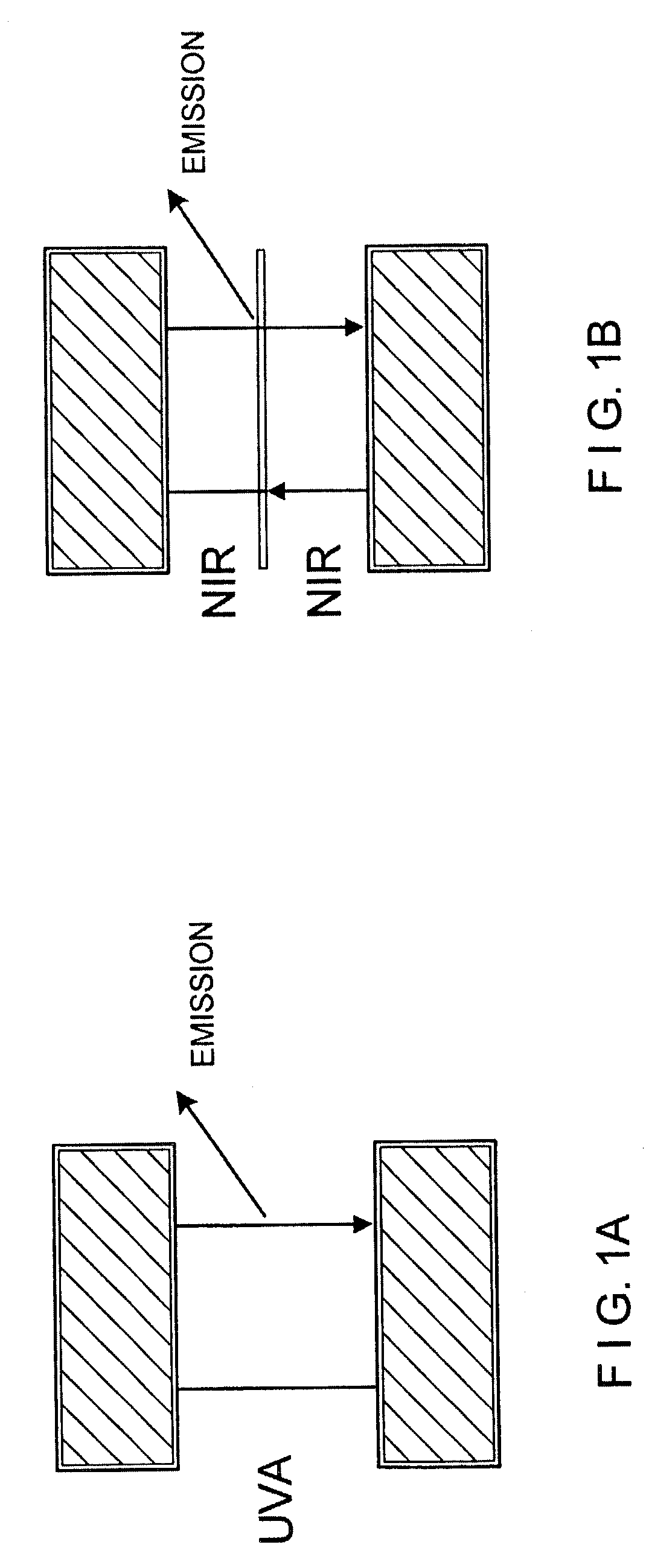
Method and arrangement for the deep resolved optical recording or a sample
InactiveUS20030132394A1Improve optical resolutionHigh resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFluorescenceLength wave
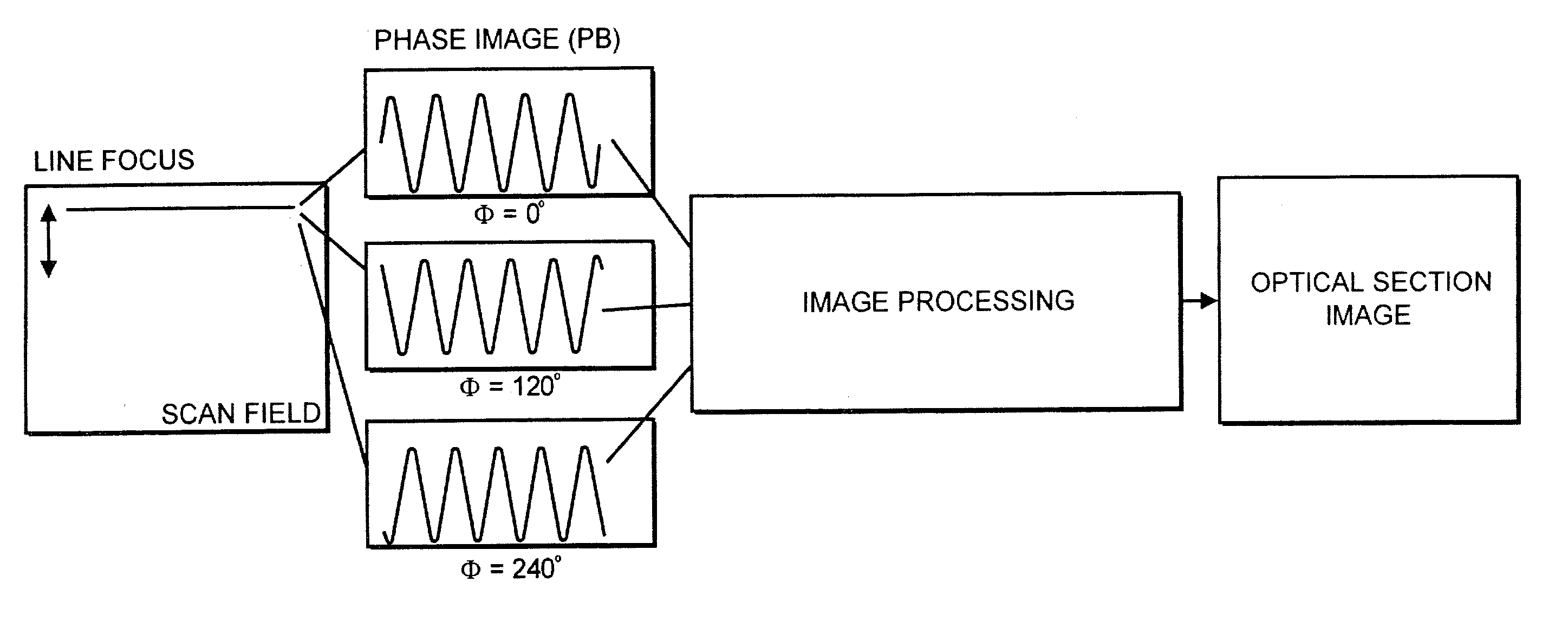
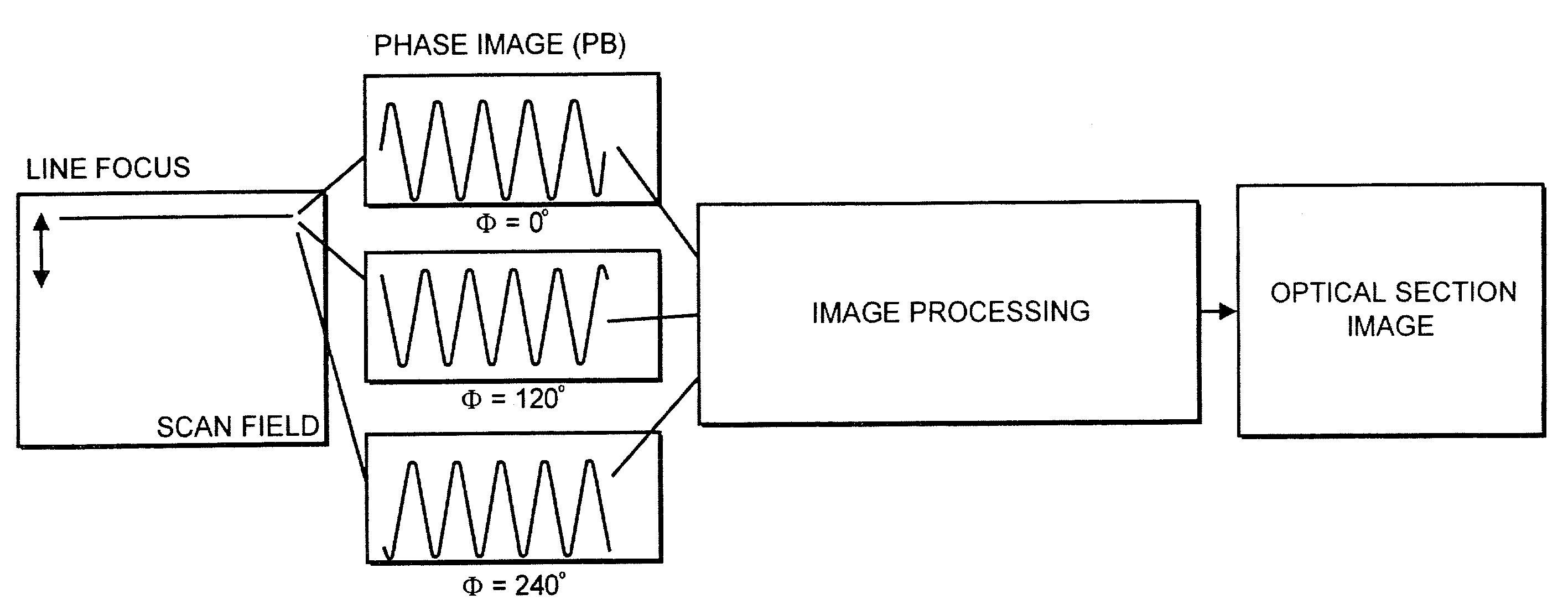
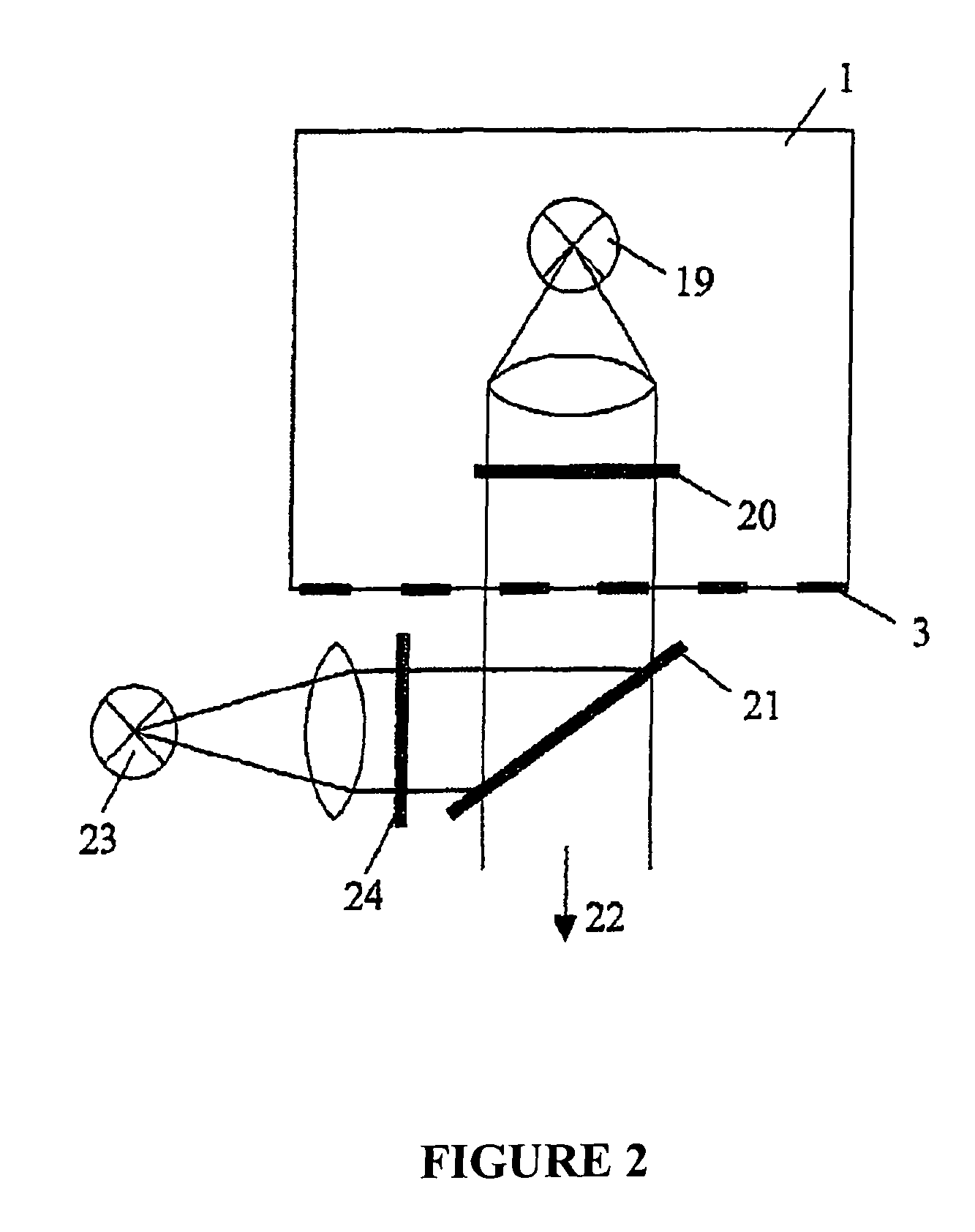
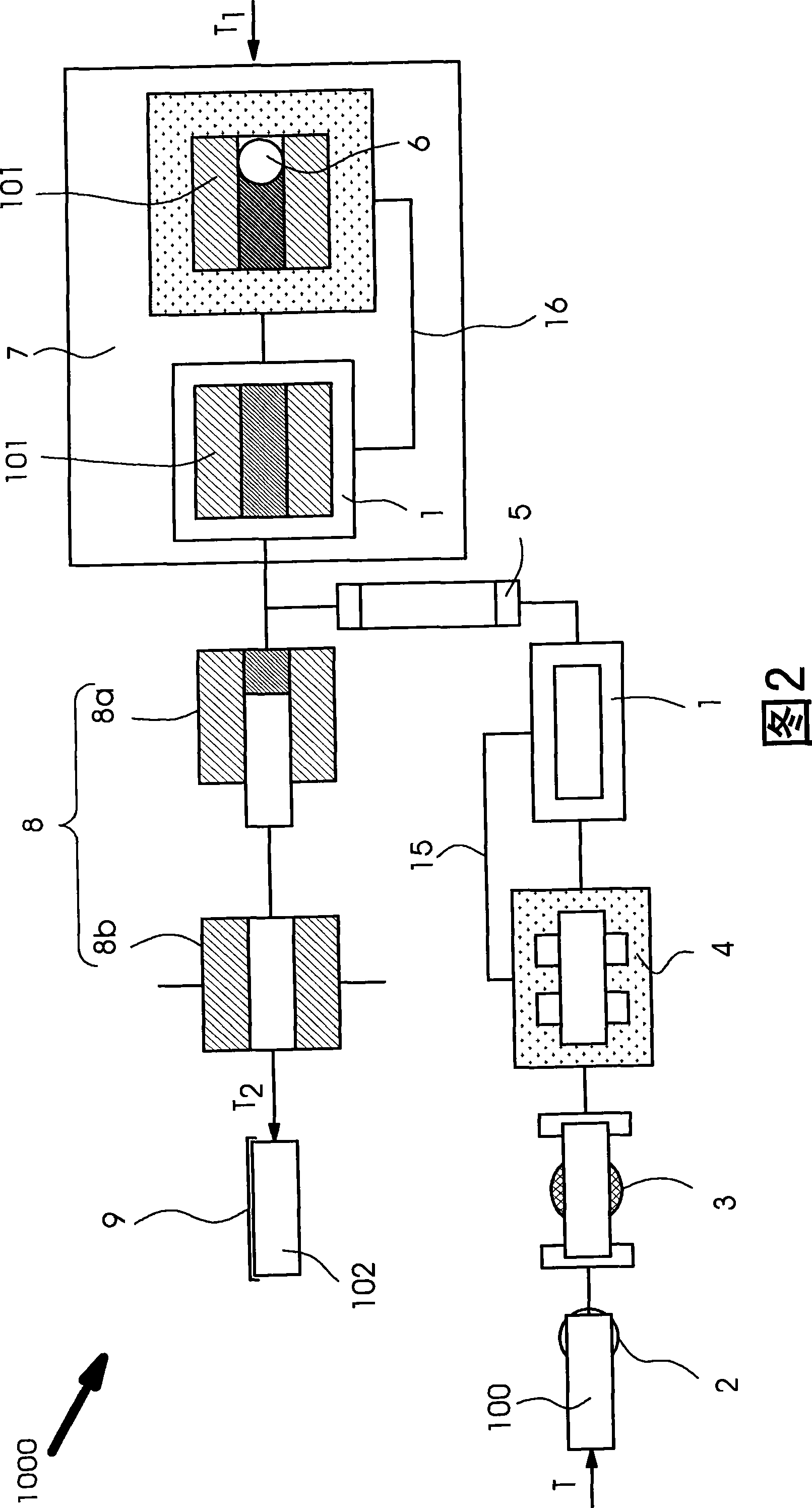
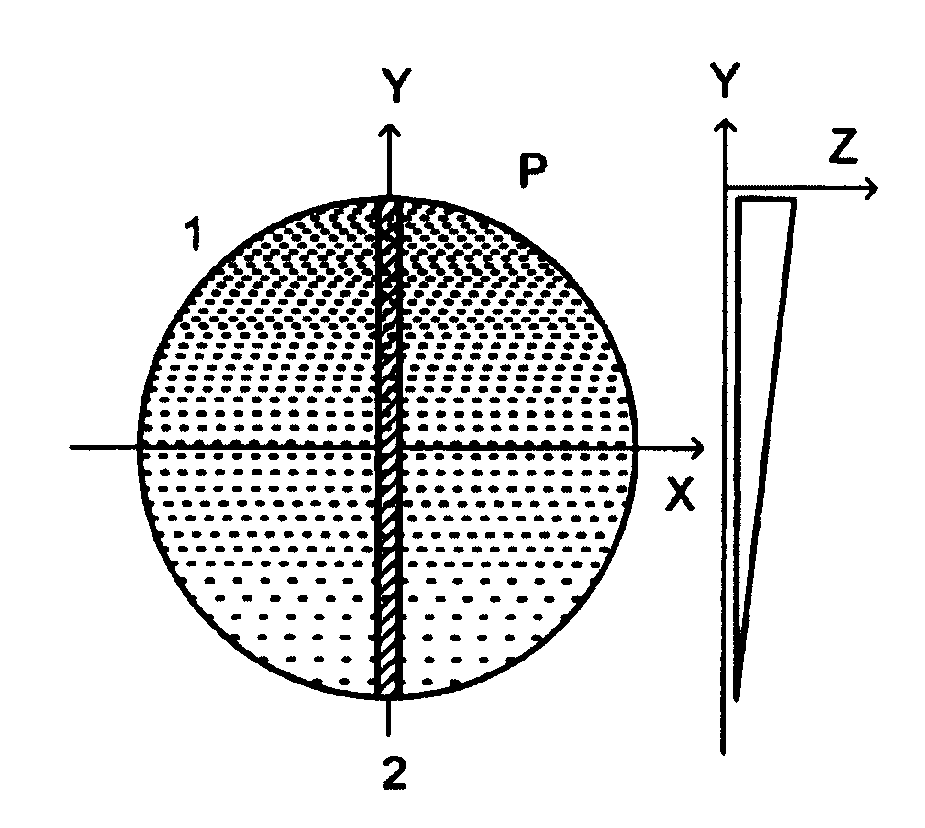
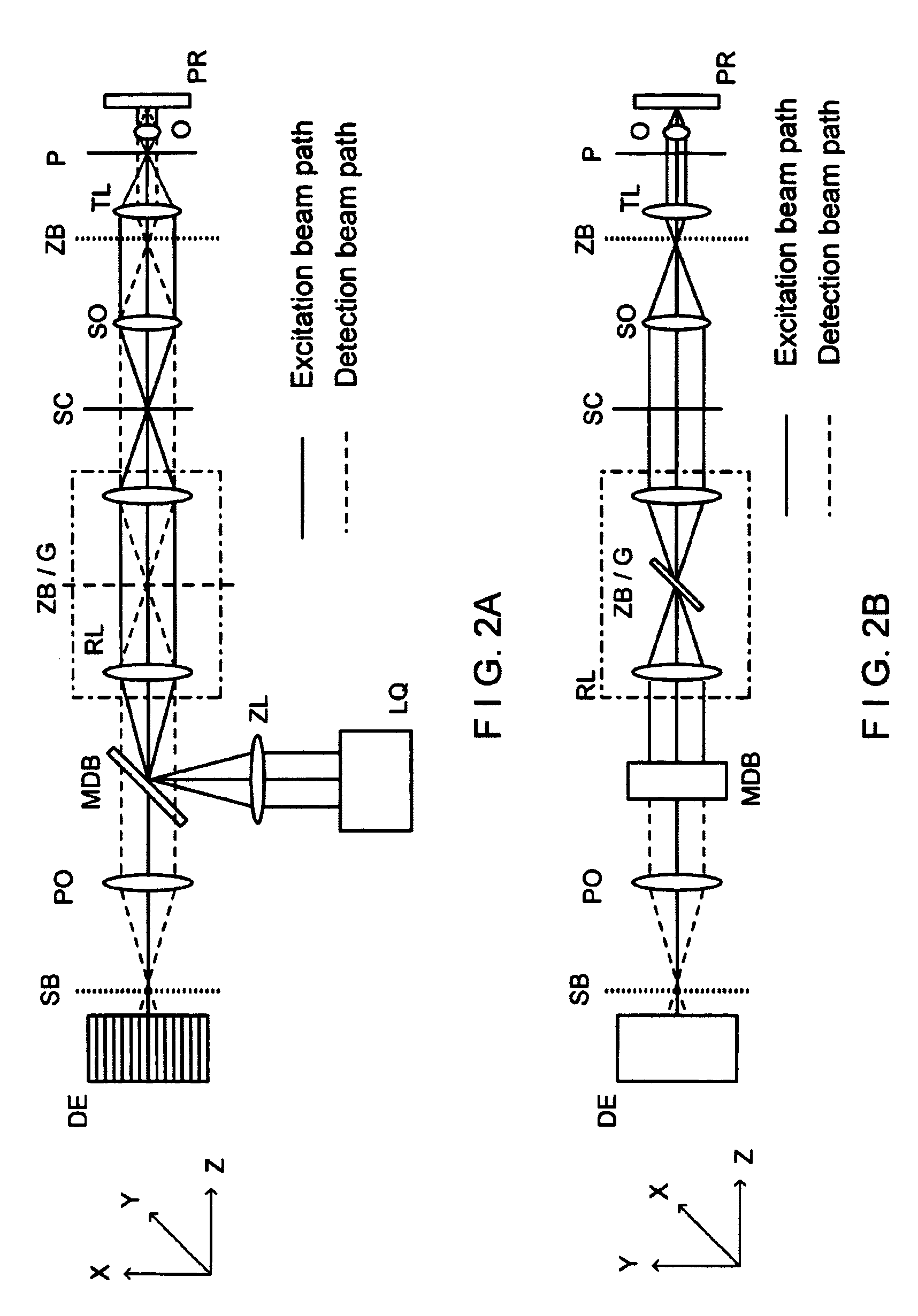
A method for depth-resolved optical detection of a specimen comprises the steps of providing a scanning movement over the specimen or at least a part of the specimen of an illumination light distribution of at least one wavelength which is generated on or in the specimen, providing detection particularly of the light which is influenced based on interaction with the specimen, especially fluorescent light and / or reflected light and / or luminescent light and / or scattered and / or transmitted light, the illumination light having a modulation in at least one spatial direction, and carrying out the scanning movement and detection associated with the scanning with the scanning movement at least in a first and a second different phase position of the modulation and / or first and second frequency of the periodicity of the modulation and calculating at least one optical section image through the specimen or through part of the specimen. Other methods and arrangements are disclosed.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Method and arrangement for the deep resolved optical recording of a sample
A method for depth-resolved optical detection of a specimen comprises the steps of providing a scanning movement over the specimen or at least a part of the specimen of an illumination light distribution of at least one wavelength which is generated on or in the specimen, providing detection particularly of the light which is influenced based on interaction with the specimen, especially fluorescent light and / or reflected light and / or luminescent light and / or scattered and / or transmitted light, the illumination light having a modulation in at least one spatial direction, and carrying out the scanning movement and detection associated with the scanning with the scanning movement at least in a first and a second different phase position of the modulation and / or first and second frequency of the periodicity of the modulation and calculating at least one optical section image through the specimen or through part of the specimen. Other methods and arrangements are disclosed.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Methods, systems and computer program products for calibration of microscopy imaging devices
An imaging system on which a calibration method is practiced includes: a light source; a substrate for supporting an object; a patterning mask that generates a substantially periodic spatial pattern on the object; a phase shifter that adjusts the relative position of the patterning mask and object to shift the position of the pattern on the object; a detector that detects images of the object; and an analyzer that analyzes at least three images of the object, each of which represents a different spatial shift of the pattern, the analyzer being configured to remove the spatial pattern from the images to generate an optically sectioned image of the object. The calibration method includes: calibrating the position of the mask relative to the substrate via a phase-voltage technique; calibrating the position of the mask relative to the substrate via a merit function technique; and operating the calibrated imaging system.
Owner:THALES SA
Method and Configuration for Optically Detecting an Illuminated Specimen
InactiveUS20090161208A1High resolutionCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopesImage resolutionLight beam
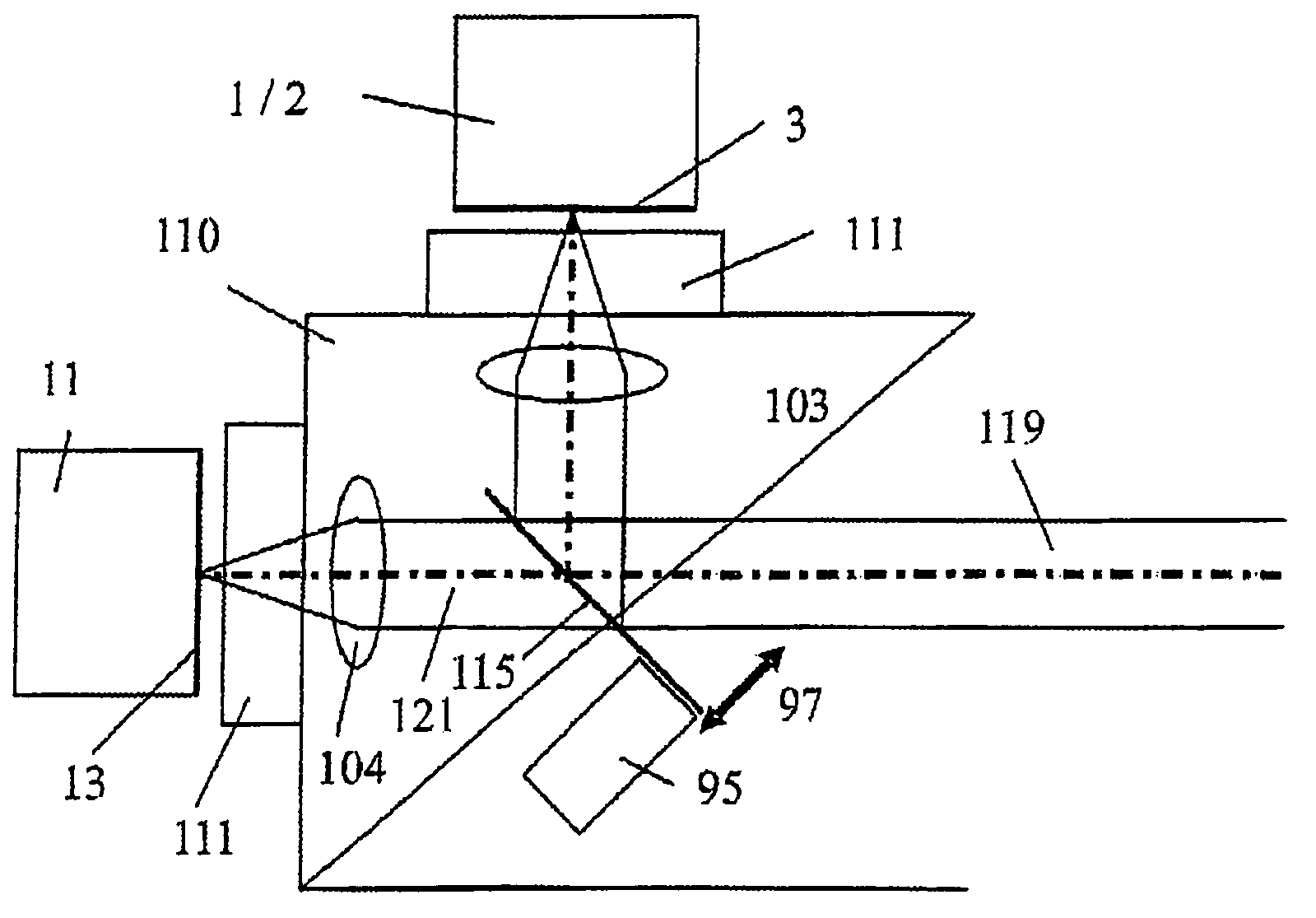
A configuration for the optical detection of a specimen, wherein the specimen or at least part of the specimen is scanned by means of linear illumination by scanning means, means for linear beam shaping of the illuminating light are provided, and the illuminating light has a preferably periodic structure in at least one spatial direction in that means for generating the structure are disposed in the illuminating beam path, light coming from the specimen is detected and images of the specimen are generated therefrom, at least one optical sectional image through the specimen and / or one image with increased resolution is / are calculated from the images, and means for generating the structure are disposed downstream of the scanning means in the direction of the illumination.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
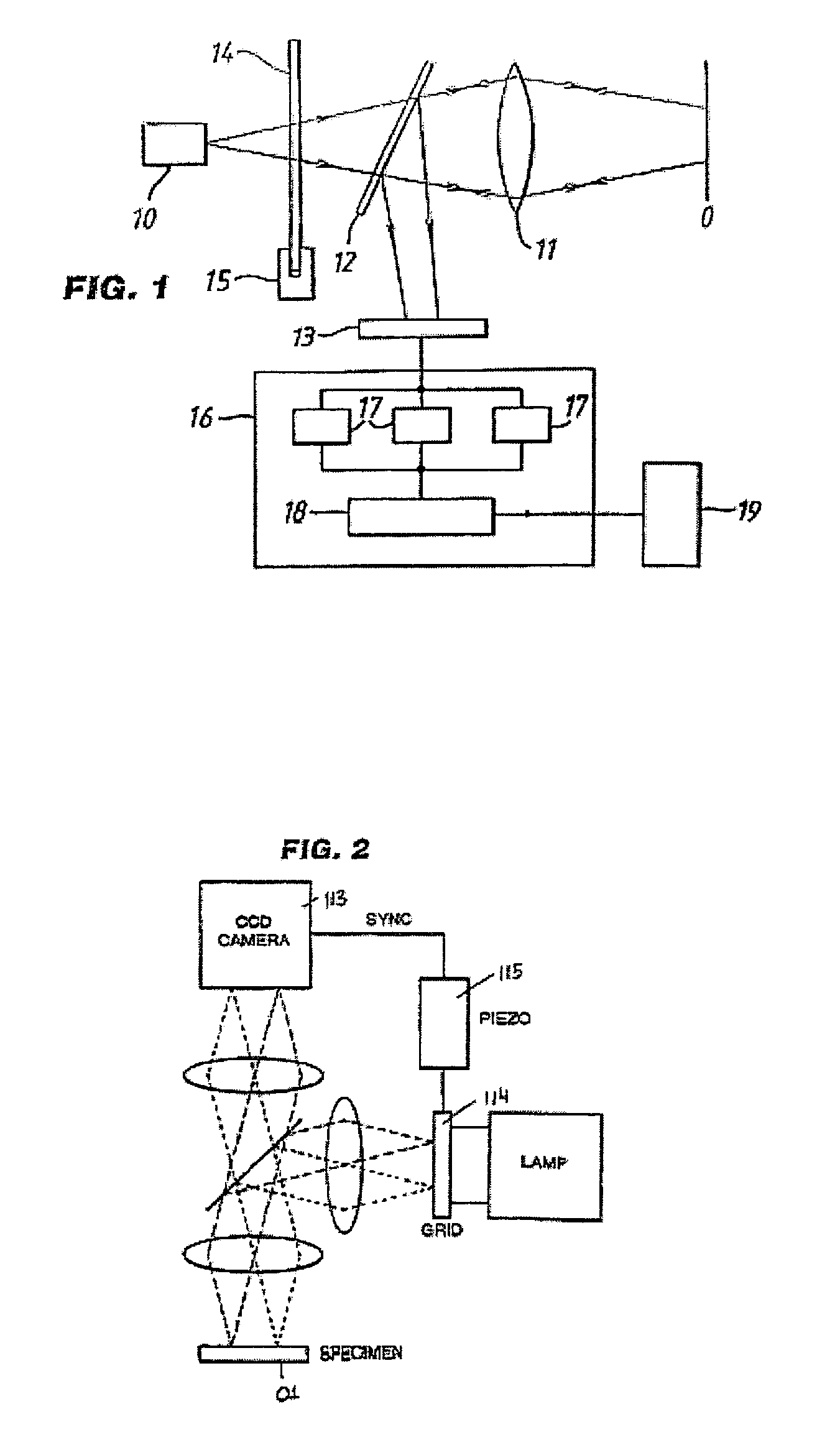
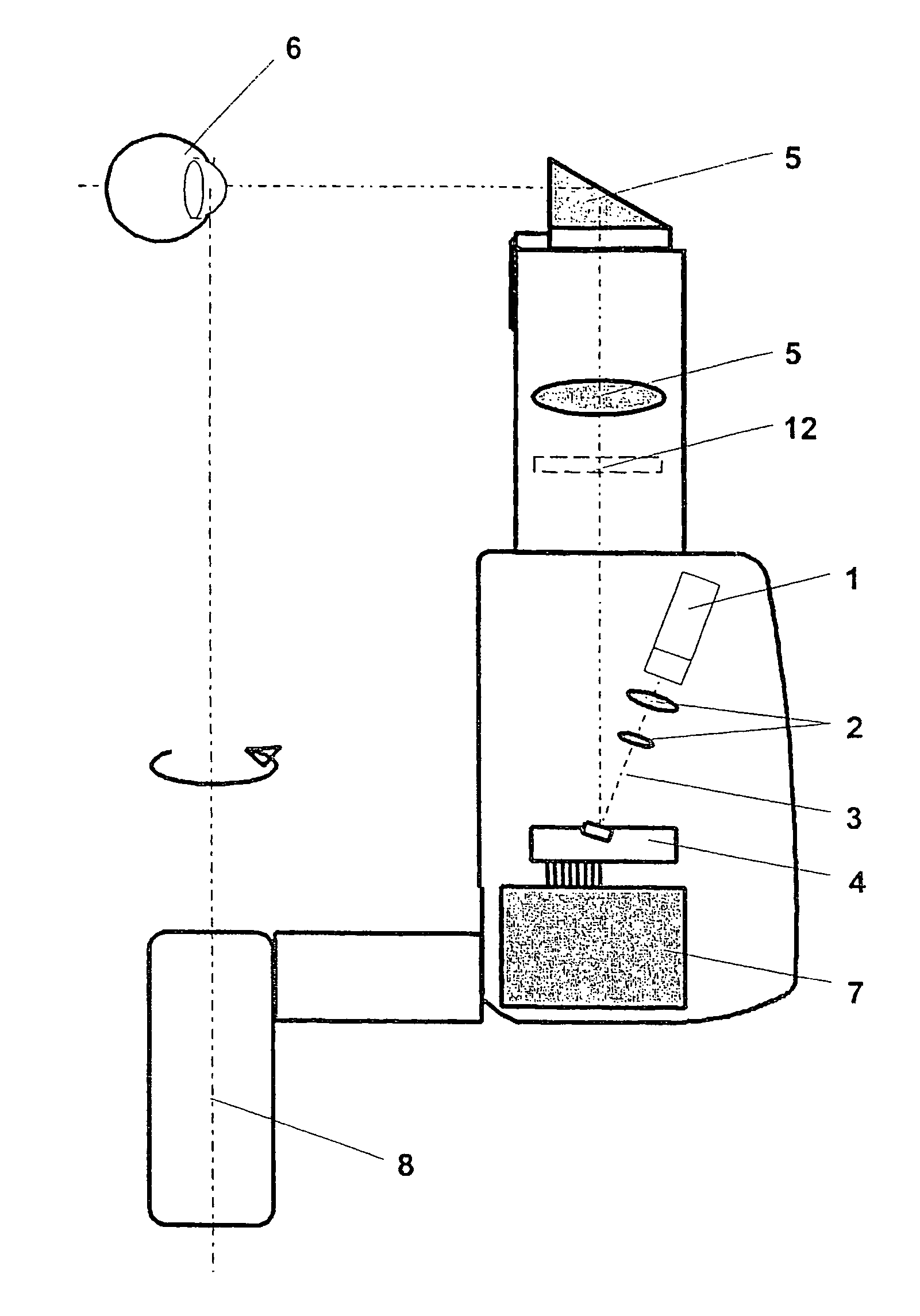
Illumination unit for the generation of optical sectional images in transparent media, in particular in the eye
InactiveUS8277047B2High resolutionSufficient light intensityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsDocumentation procedureImaging processing
Illumination unit for the generation of optical sectional images in transparent media, particularly in the eye is disclosed. In the arrangement according to the invention, the low-divergence beams emitted by a laser serving as illumination source are imaged on or in the eye under examination by a reflection element which is controllable in a defined manner and beam deflection elements present in the beam path. The optical sectional images resulting in and on the eye can be observed and / or recorded, further processed and evaluated with an image processing unit in a known manner. In the solution according to the invention, a sectional image is generated by the deliberate periodic beam deflection of a particularly fine laser beam with high depth of focus, which sectional image remains sharp through the entire dimension of the object to be examined and makes possible an improved evaluation. The intensity of the laser beam bundle can be varied in such a way that it is sufficient for observation and documentation, but so that the diameter of the beam bundle is fine enough for a high detail resolution.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
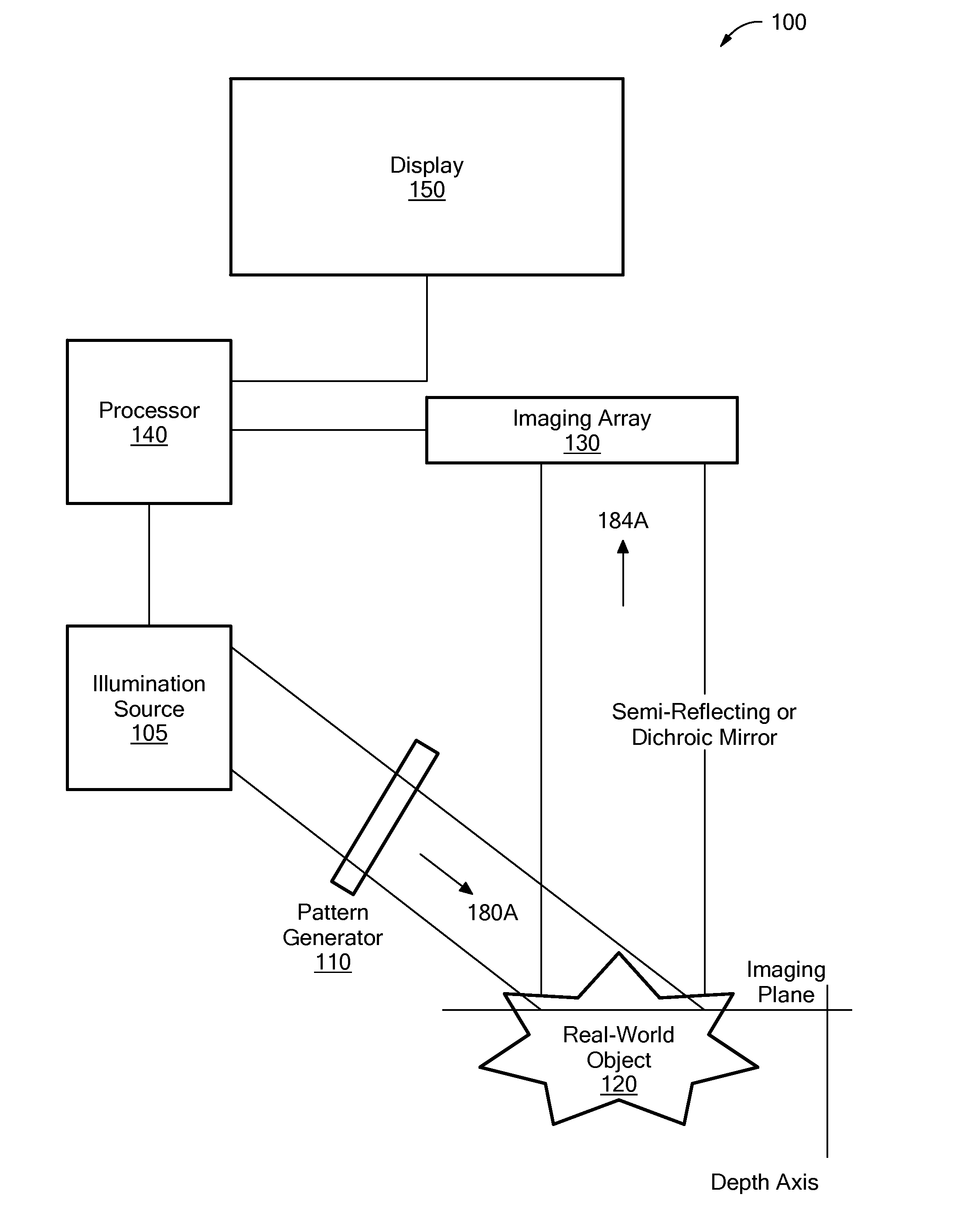
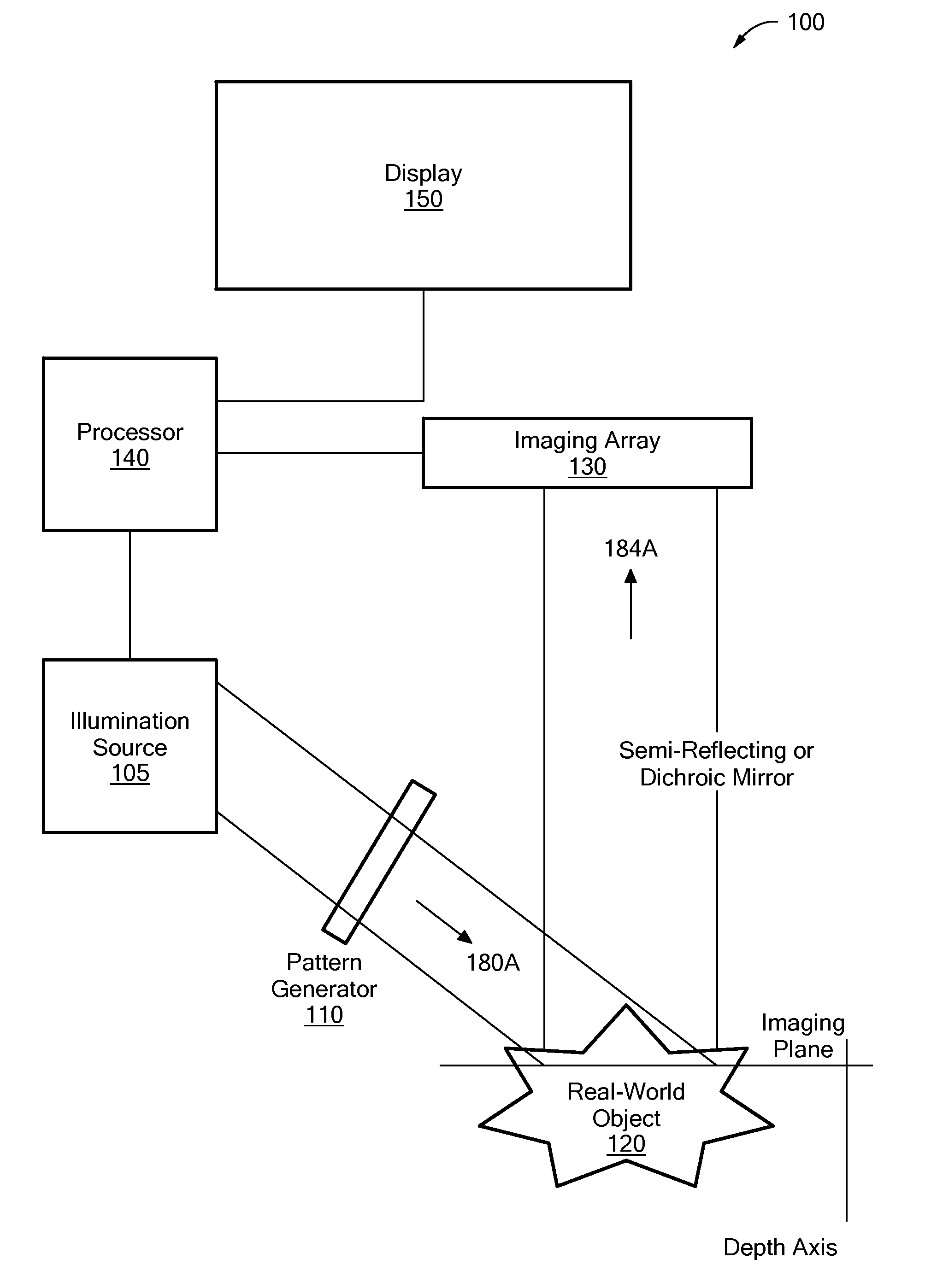
System and Method for Producing an Optically Sectioned Image Using Both Structured and Uniform Illumination
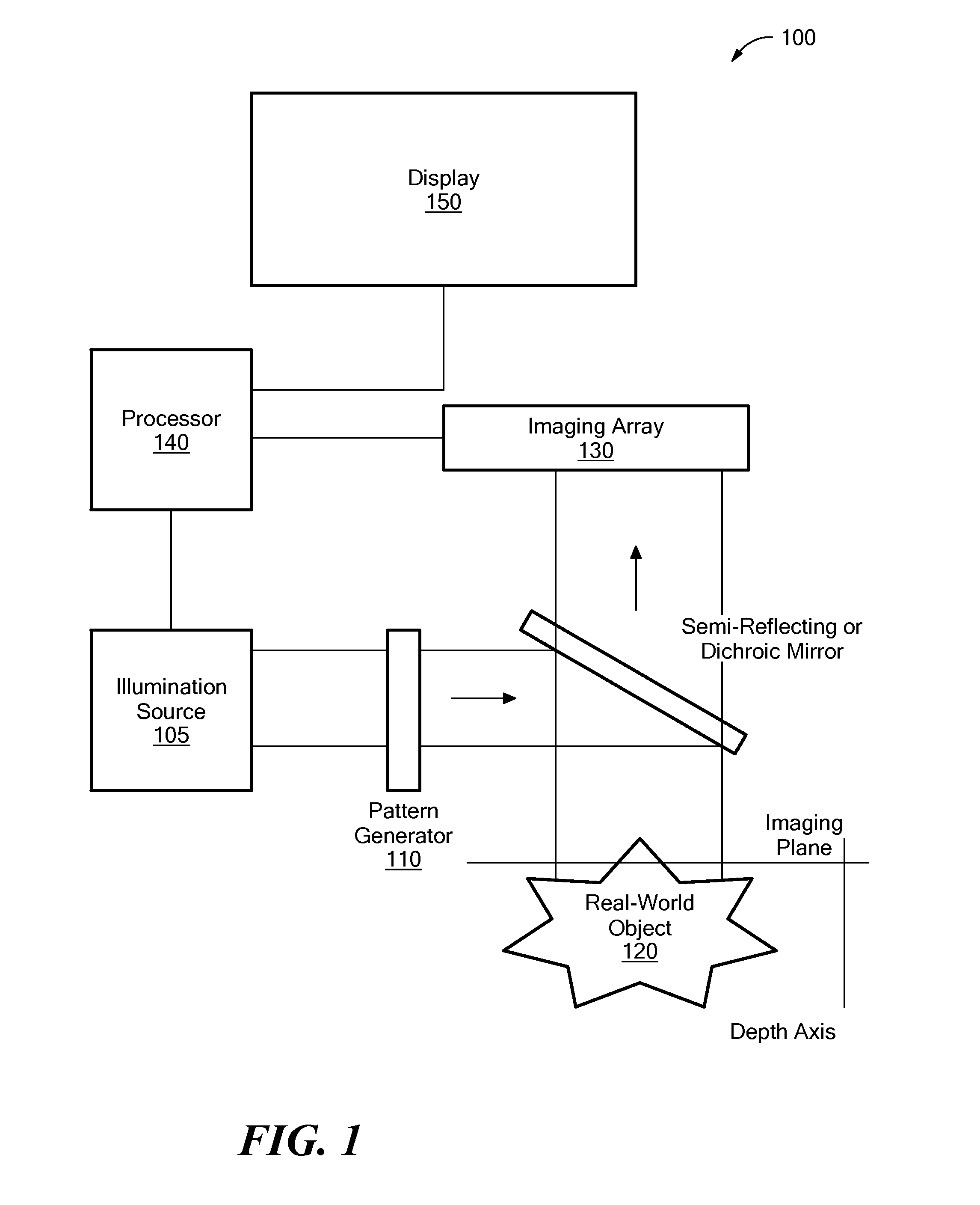
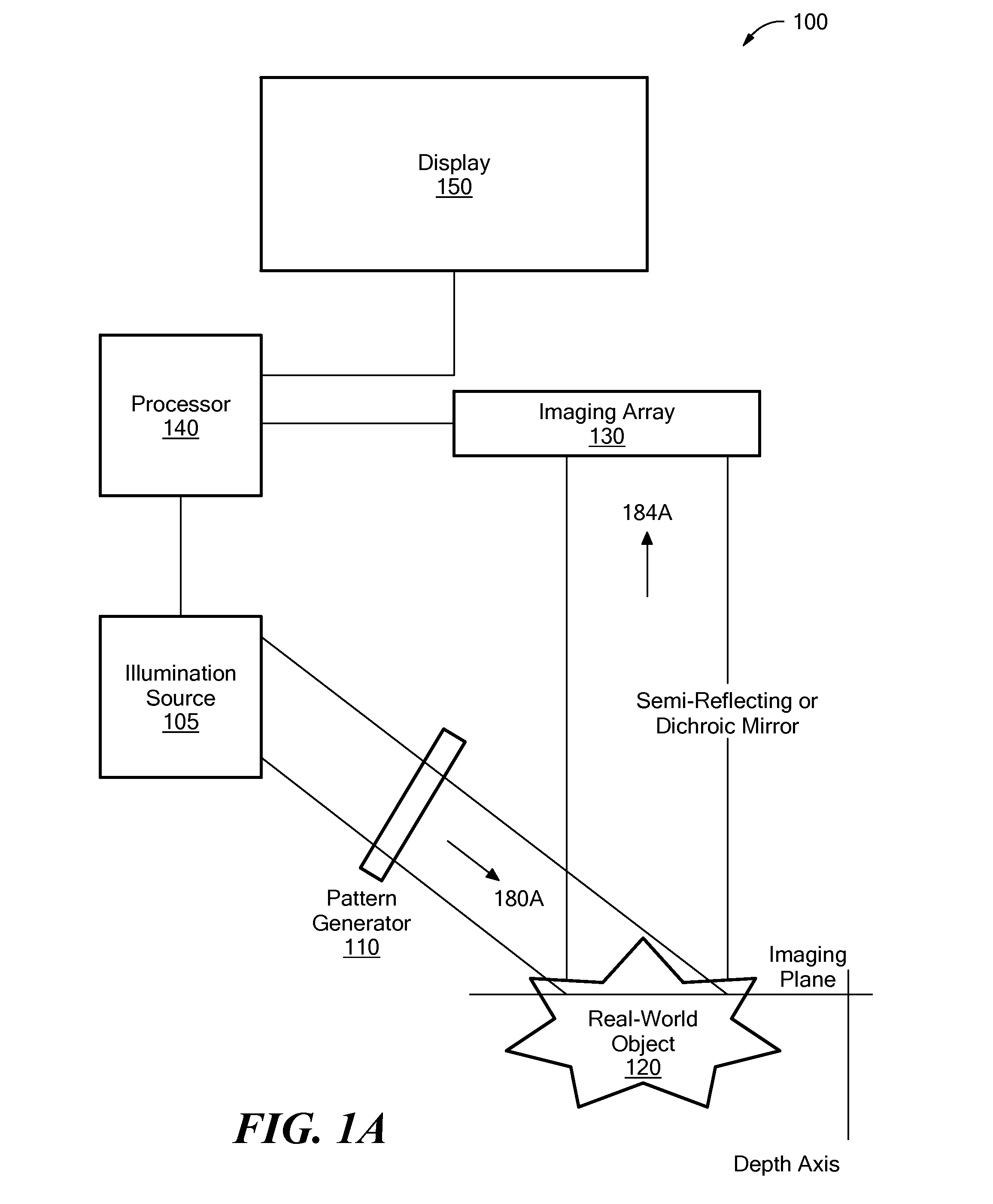
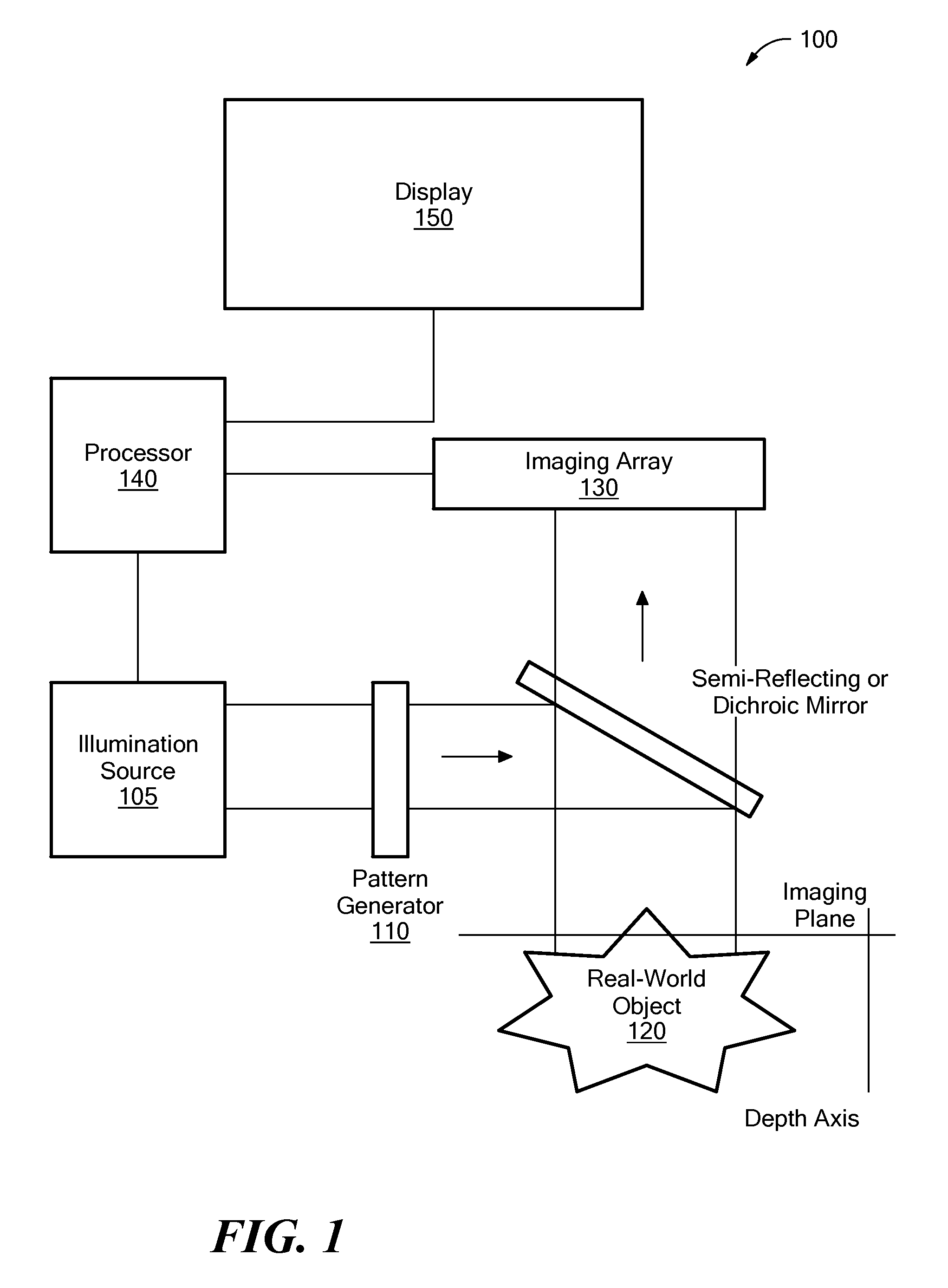
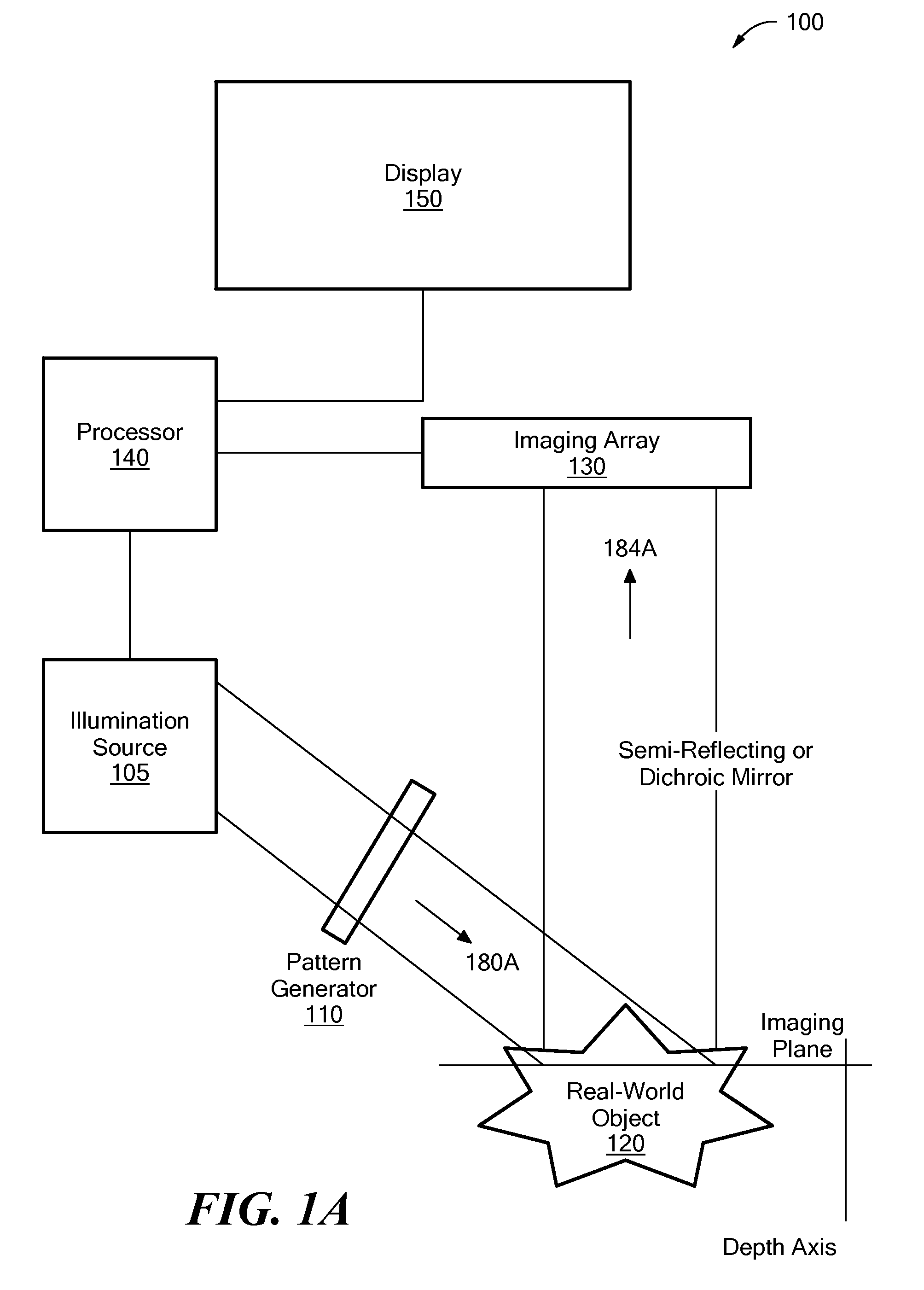
A first image data set of the real-world object is received at a processor where the real-world object was illuminated with substantially uniform illumination. A second image data set of the real-world object is received at the processor where the real-world object was illuminated with substantially structured illumination. A high pass filter is applied to the first-image data set to remove out-of-focus content and retrieve high-frequency in-focus content. The local contrast of the second-image data set is determined producing a low resolution local contrast data set. The local contrast provides a low resolution estimate of the in-focus content in the first-image data set. A low pass filter is applied to the estimated low resolution in-focus data set, thus making its frequency information complementary to the high-frequency in-focus data set. The low and high frequency in-focus data sets are combined to produce an optically-sectioned data set of the real-world object.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
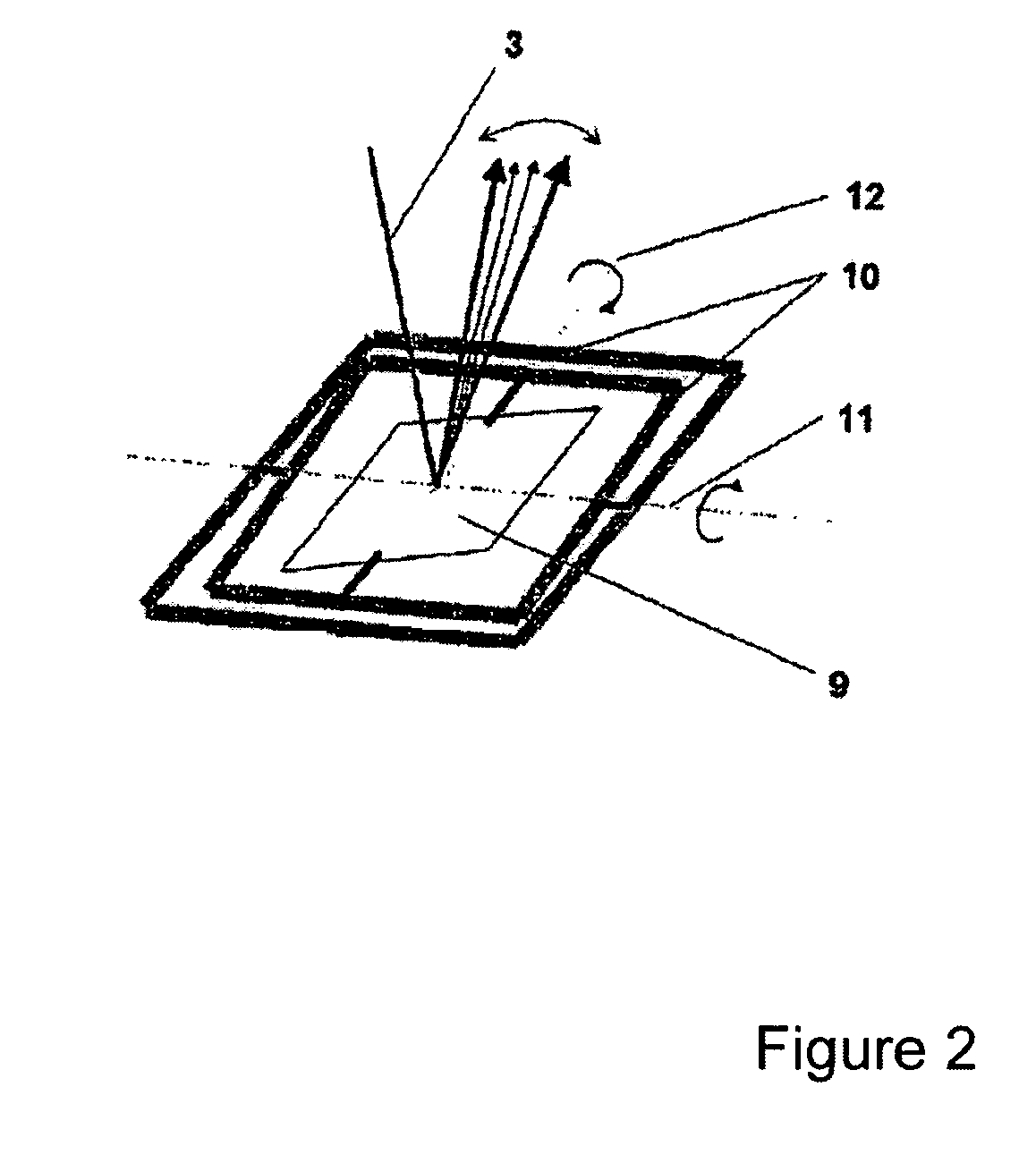
Method and assembly for optical reproduction with depth discrimination
A method and an assembly for generating optical section images permit the three-dimensional, layered optical scanning of spatially extended objects. Illumination patterns with periodicity in at least one direction are projected into a plane and the light from the sample which is reflected and / or scattered and / or emitted fluorescence light is being imaged onto a spatially resolving detector. Initially, there is a calibration step, in which the local phase and / or the local period of the illumination patterns are determined for each location on the detector. In the sample detection mode, for the calculation of each optical section image there are two illumination patterns projected into or onto the sample and the resulting intensity distributions are used to form an image on the detector.
Owner:SCHWERTNER MICHAEL
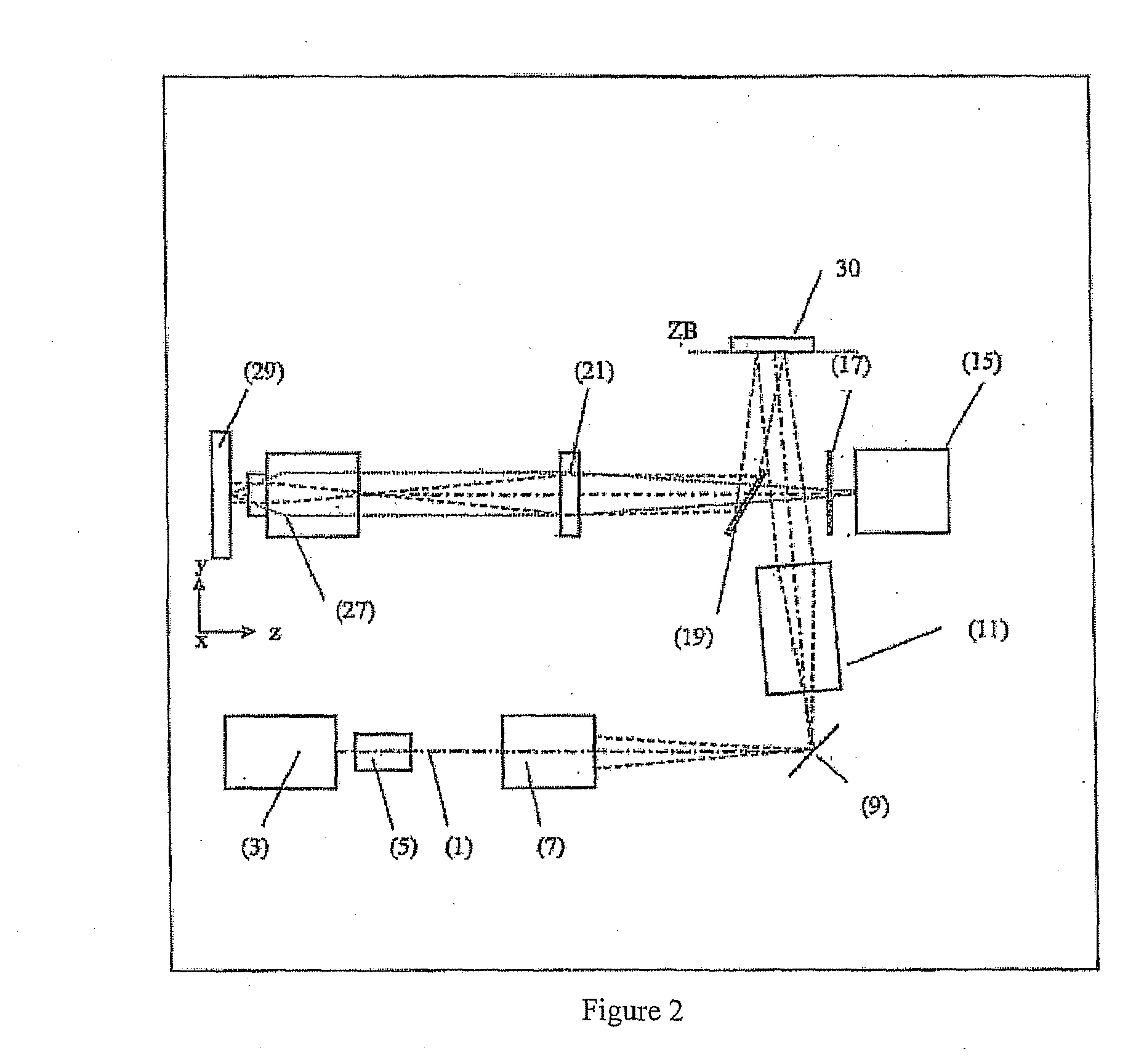
Method and configuration for the optical detection of an illuminated specimen
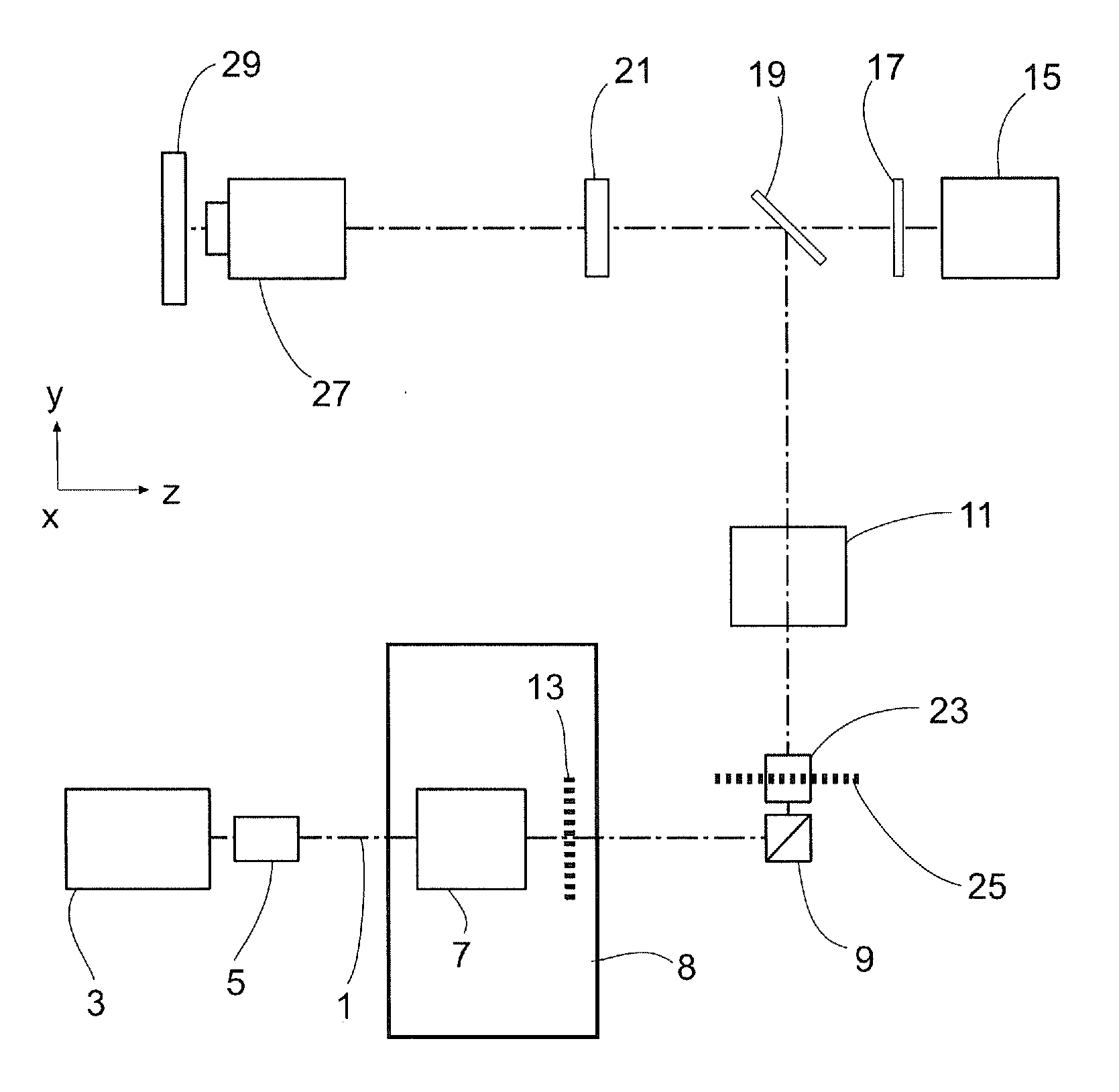
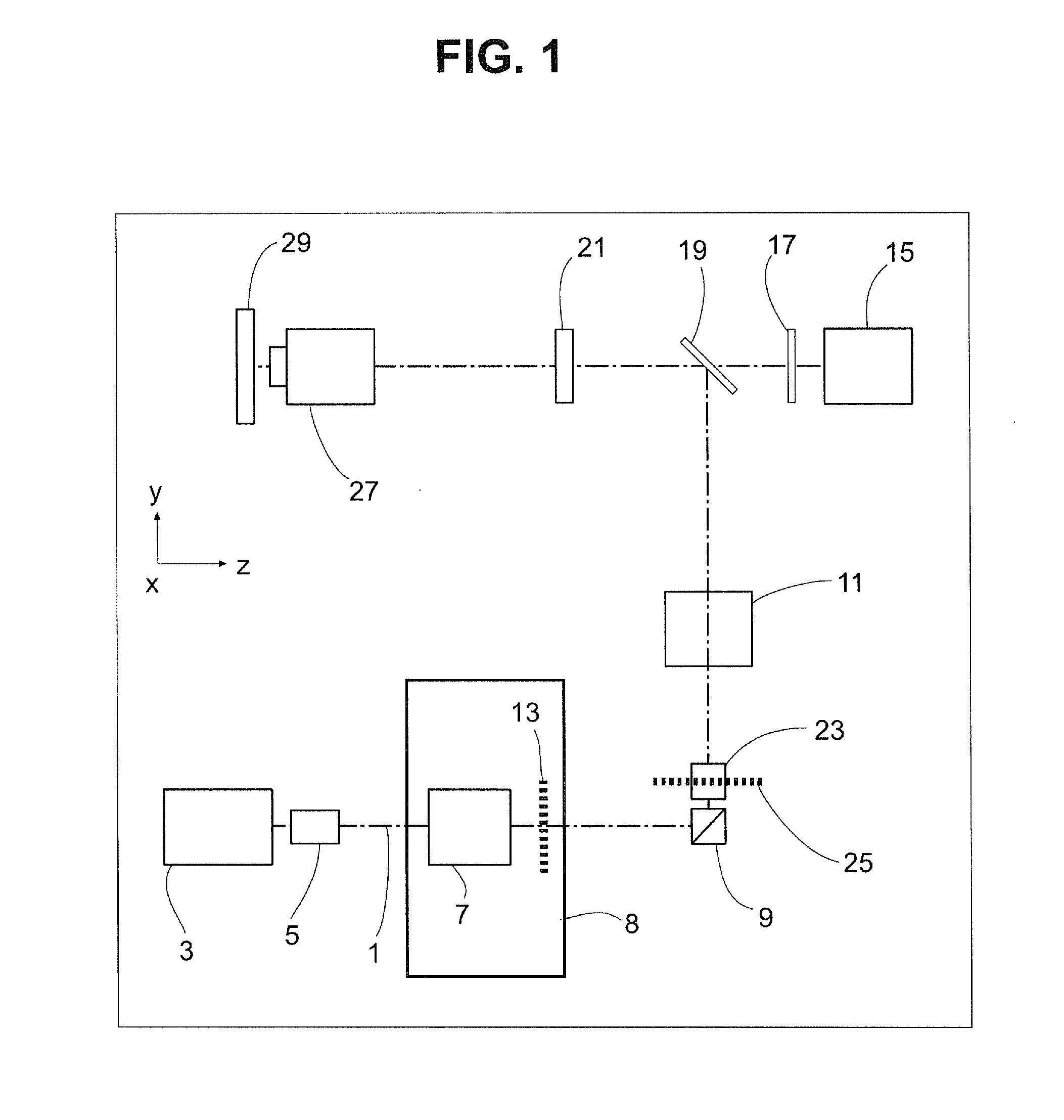
InactiveUS20120019647A1High strengthReduce light lossColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsImage resolutionArea detector
A method and a configuration for the depth-resolved optical detection of a specimen, in which a specimen or a part of the specimen is scanned by means of preferably linear illumination. The illumination of the specimen is periodically structured in the focus in at least one spatial direction. Light coming from the specimen is detected and images of the specimen are generated. At least one optical sectional image and / or one image with enhanced resolution is calculated through the specimen. Images are repeatedly acquired and sectional images are repeatedly blended while changing the orientation of the linear illumination relative to the specimen and / or spatial intervals between lines exposed to detection light from the illuminated specimen region are generated for the line-by-line non-descanned detection on an area detector or a camera and / or, during a scan, light is further deflected upstream of the detector through the line in the direction of the scan of the specimen.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
System and method for optical section image line removal
InactiveUS20070269134A1Character and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansImage basedOptical cross section
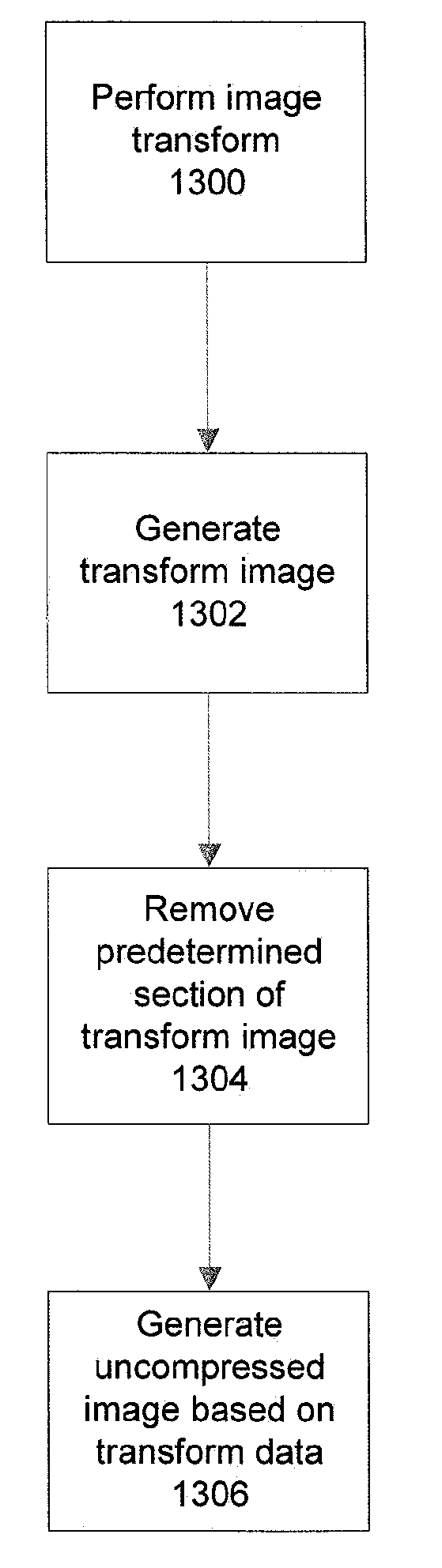
An apparatus, system, and method for generating an image are disclosed. A processor may generate a first output image based on a plurality of input images and remove an artefact, if any, from the first output image to generate a second output image. For example, in an embodiment, the processor may calculate a contribution of the artefact to image intensity values and subtract the calculated contribution from the image intensity values. In another embodiment, the processor may delete a predetermined portion of a transform image representing transform data obtained by applying an image transform to the first output image, thereby modifying the transform data, and may generate a non-transform image based on the modified transform data.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Device for monitoring and regulating an adhesive layer to a be applied when producing printed products
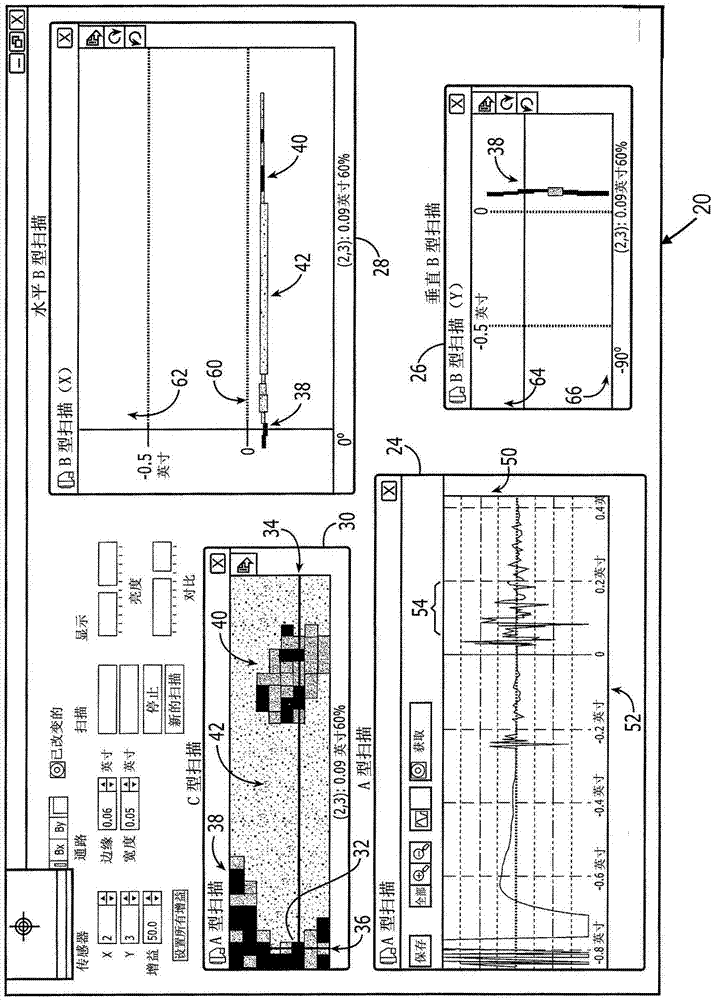
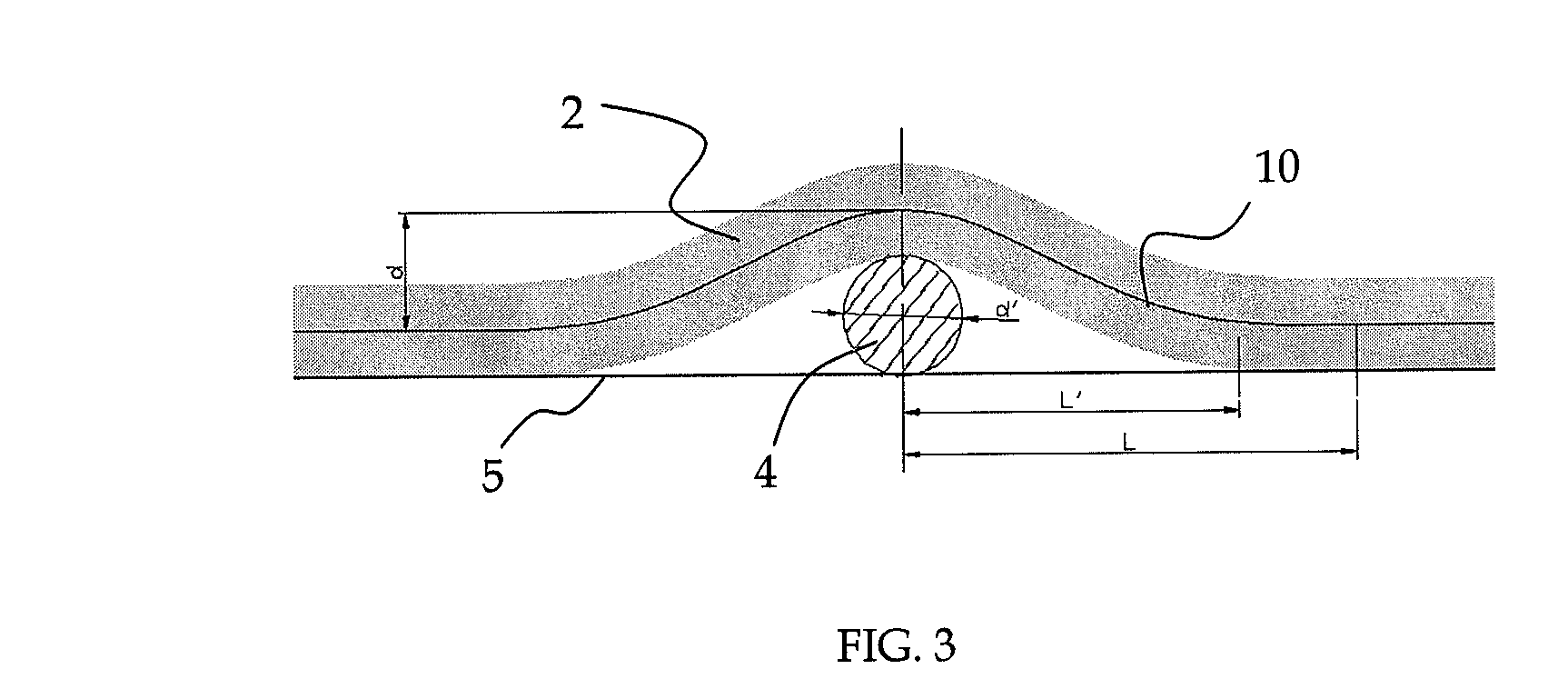
An adhesive layer for bonding each printed sheet on a book block has dominant influence on the quality of perfect binding. The invention relates to a device for controlling the adhesive layer on a product, especially a book block, an envelope and a cover; wherein the device comprises a device for reading in an 3D optical cross-section profile of the adhesive layer by an laser triangulation method and comprising a high-speed camera and a laser projector, and an analyzing-processing device for analyzing and processing the 3D optical cross-section profile by an analyzing-processing program. If the profile is not accordant with the index value, the product is marked or thrown away.
Owner:HEIDELBERGER DRUCKMASCHINEN AG
Method and arrangement for deeply resolved optical detection of a sample
InactiveUS7170696B2Prevents limiting of dynamic rangePreventing modulationImage enhancementPrismsPhase shiftedLength wave
A method and arrangement for the depth-resolved optical detection of a specimen with an illumination light distribution of at least one wavelength generated on or in a specimen and detection particularly of the light that is influenced due to interaction with the specimen, particularly fluorescent light and / or reflected light and / or luminescent light and / or scattered and / or transmitted light, wherein the illumination light has a modulation in at least one spatial direction and the detection light which is modulated like the illumination light is spatially split into two components having a phase shift relative to one another, the components are measured separately and an optical section image of the specimen and / or of part of the specimen is calculated from them.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Imaging lens set with plastic lens element, imaging lens module and electronic device
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical film
ActiveCN1961246AIncrease brightnessAvoid Optical CouplingPrismsDiffusing elementsBrightness perceptionLightness
The present invention relates to an optical film. The optical film comprises a first refraction portion having a plurality of first optical lens patterns that have optical sections for controlling light and are distributed at a predetermined interval in the form of embossment; and a second refraction portion having a plurality of second optical patterns that have optical sections and are arranged linearly at a predetermined interval and formed along patterns surfaces of the first optical lens patterns. Accordingly, there is provided an optical film in which high brightness can be achieved at a wide viewing angle, the wet-out phenomenon can be avoided, and productivity can be improved.
Owner:LMS SUZHOU MATERIALS CO LTD
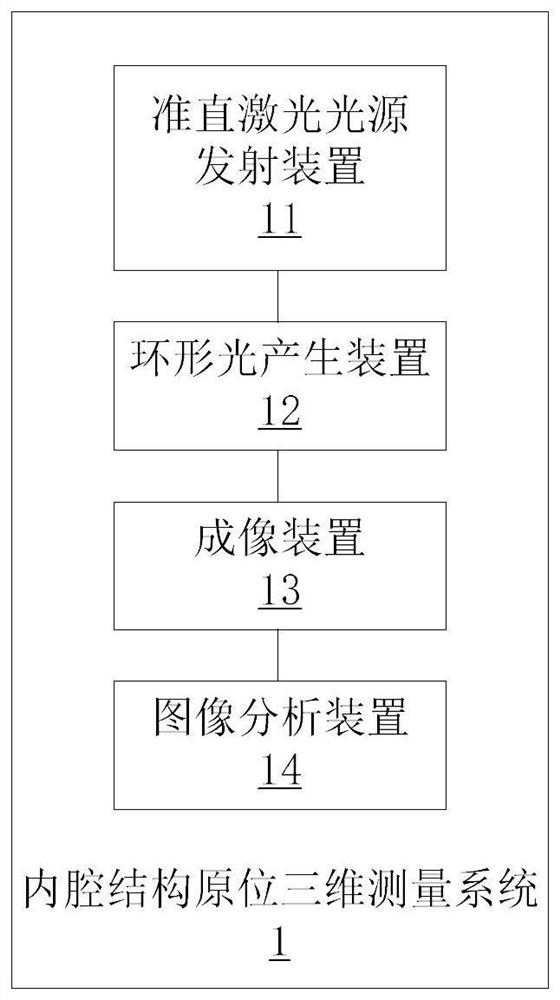
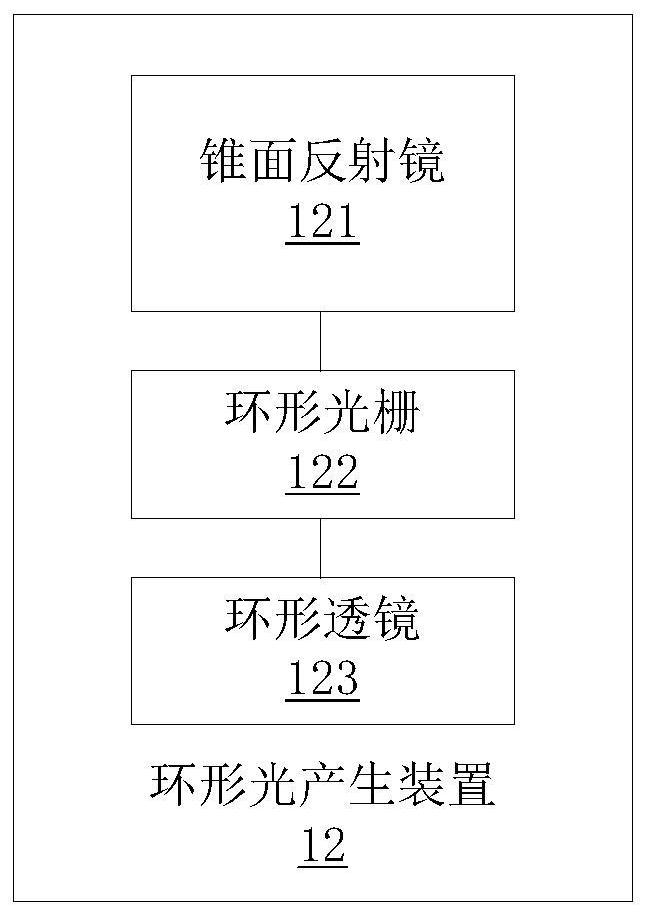
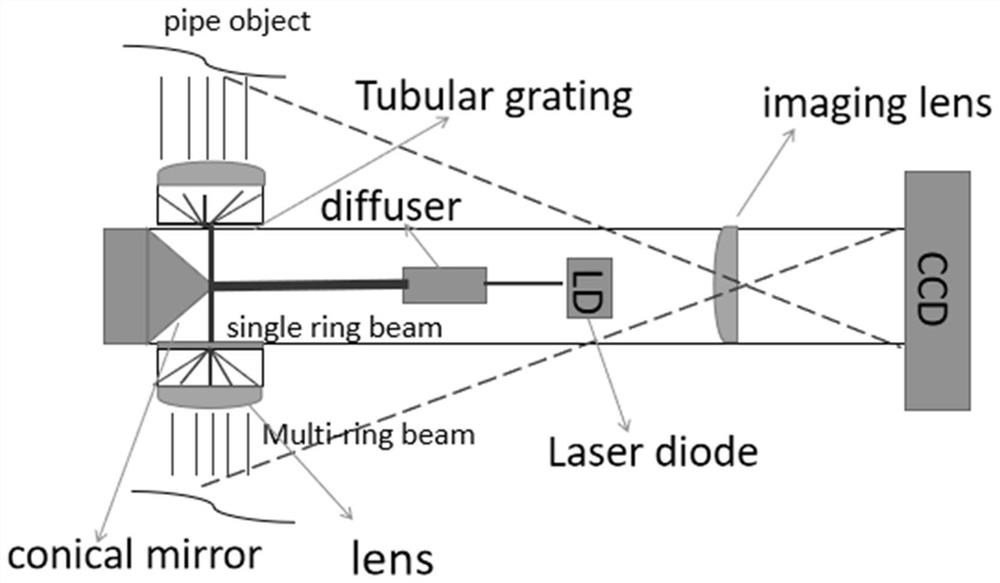
In-situ three-dimensional measurement system and method for inner cavity structure
ActiveCN112393693AResolve accessibilitySolve environmental problemsUsing optical meansOptical elementsOptical axisThree dimensional measurement
The invention provides an in-situ three-dimensional measurement system and method for an inner cavity structure. The system comprises a collimation laser light source transmitting device which is usedfor transmitting parallel laser beams; an annular light generating device which is used for generating multiple paths of parallel annular light distributed along the optical axis at equal intervals according to the laser beams so as to generate multiple inner contour optical sections in a to-be-detected inner cavity structure at the same time; and an imaging device which is used for imaging the inner contour optical sections so as to realize three-dimensional measurement of the to-be-detected inner cavity structure. According to the invention, simultaneous scanning and measurement of a plurality of contour sections of an inner cavity structure are realized, and the problems of difficulty, accessibility, sensitivity to environmental vibration, low measurement efficiency and the like of in-situ measurement by conventional three-dimensional scanning equipment are solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
System and method for producing an optically sectioned image using both structured and uniform illumination
A first image data set of the real-world object is received at a processor where the real-world object was illuminated with substantially uniform illumination. A second image data set of the real-world object is received at the processor where the real-world object was illuminated with substantially structured illumination. A high pass filter is applied to the first-image data set to remove out-of-focus content and retrieve high-frequency in-focus content. The local contrast of the second-image data set is determined producing a low resolution local contrast data set. The local contrast provides a low resolution estimate of the in-focus content in the first-image data set. A low pass filter is applied to the estimated low resolution in-focus data set, thus making its frequency information complementary to the high-frequency in-focus data set. The low and high frequency in-focus data sets are combined to produce an optically-sectioned data set of the real-world object.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
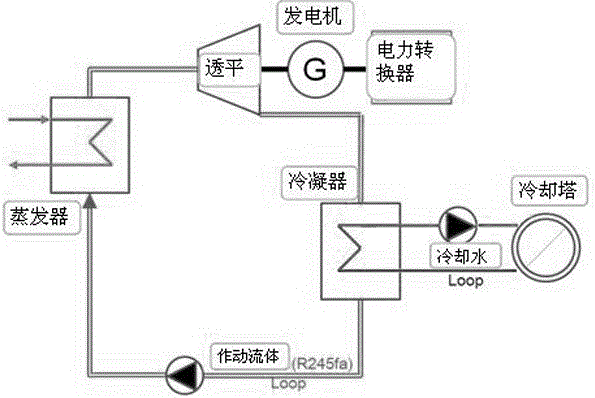
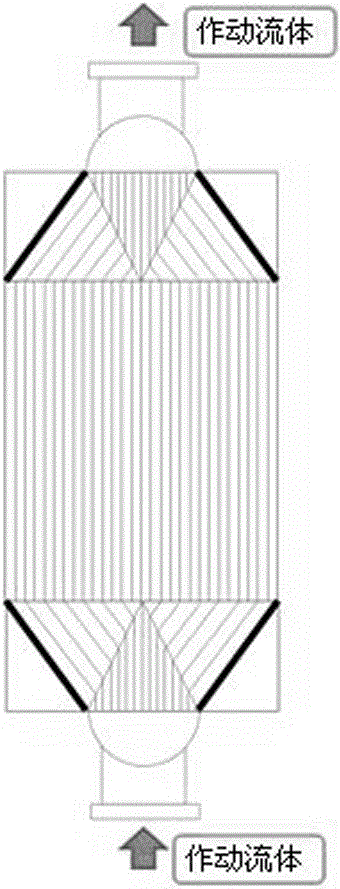
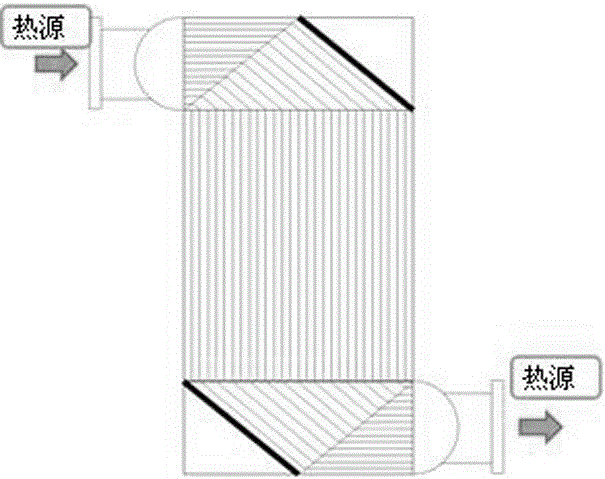
Composite heat exchanger for organic Rankine cycle power generating system
InactiveCN106642831AReduce volumeImprove efficiencyEvaporators/condensersOrganic Rankine cycleGas phase
The invention discloses a composite heat exchanger for an organic Rankine cycle power generating system. The composite heat exchanger comprises a liquid-phase sensible heat area, a gas-liquid latent heat area and a gas-phase sensible heat area, wherein the cross section area of the liquid-phase sensible heat area, the gas-liquid latent heat area and the gas-phase sensible heat area is different. The composite heat exchanger has the advantages that the liquid-phase sensible heat area, the gas-liquid latent heat area and the gas-phase sensible heat area are separated, optical cross section area of the liquid-phase sensible heat area, the gas-liquid latent heat area and the gas-phase sensible heat area is achieved, certain flow speed is maintained, the heat exchanger is reliable and small in size, the efficiency of the organic Rankine cycle power generating system is improved to the maximum extent, and equipment cost is reduced.
Owner:潍坊小禾节能科技有限公司
Method for measuring deformability properties of a fibre
A method for measuring a property of a fibre, such as flexibility, collapsibility and moment of inertia. A fibre is wetted and deformed in its wet state, and an optical section image of the deformed fibre is taken. A measurement is made on the image and the desired property is calculated using the measurement.
Owner:NEW BRUNSWICK UNIV OF
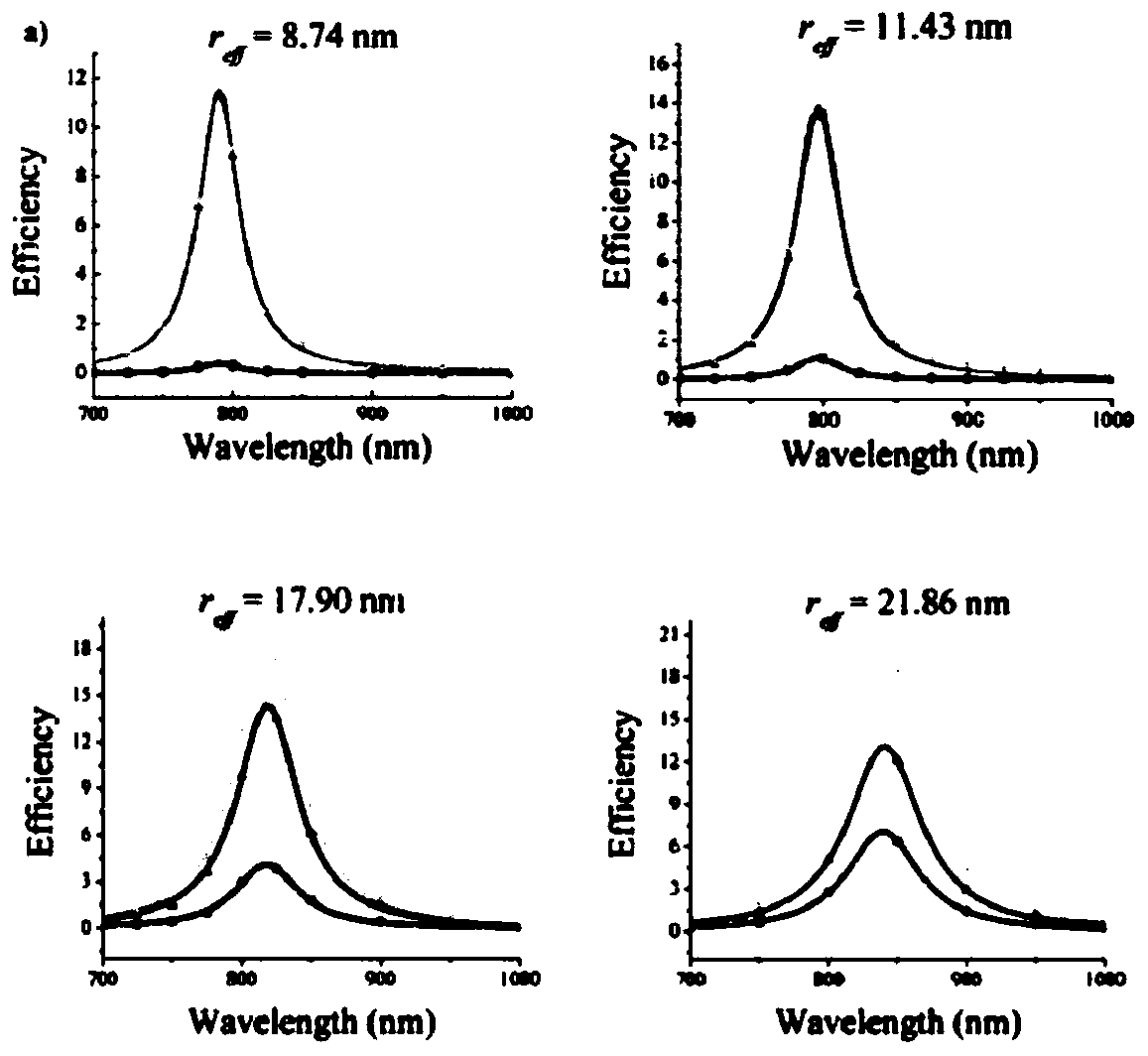
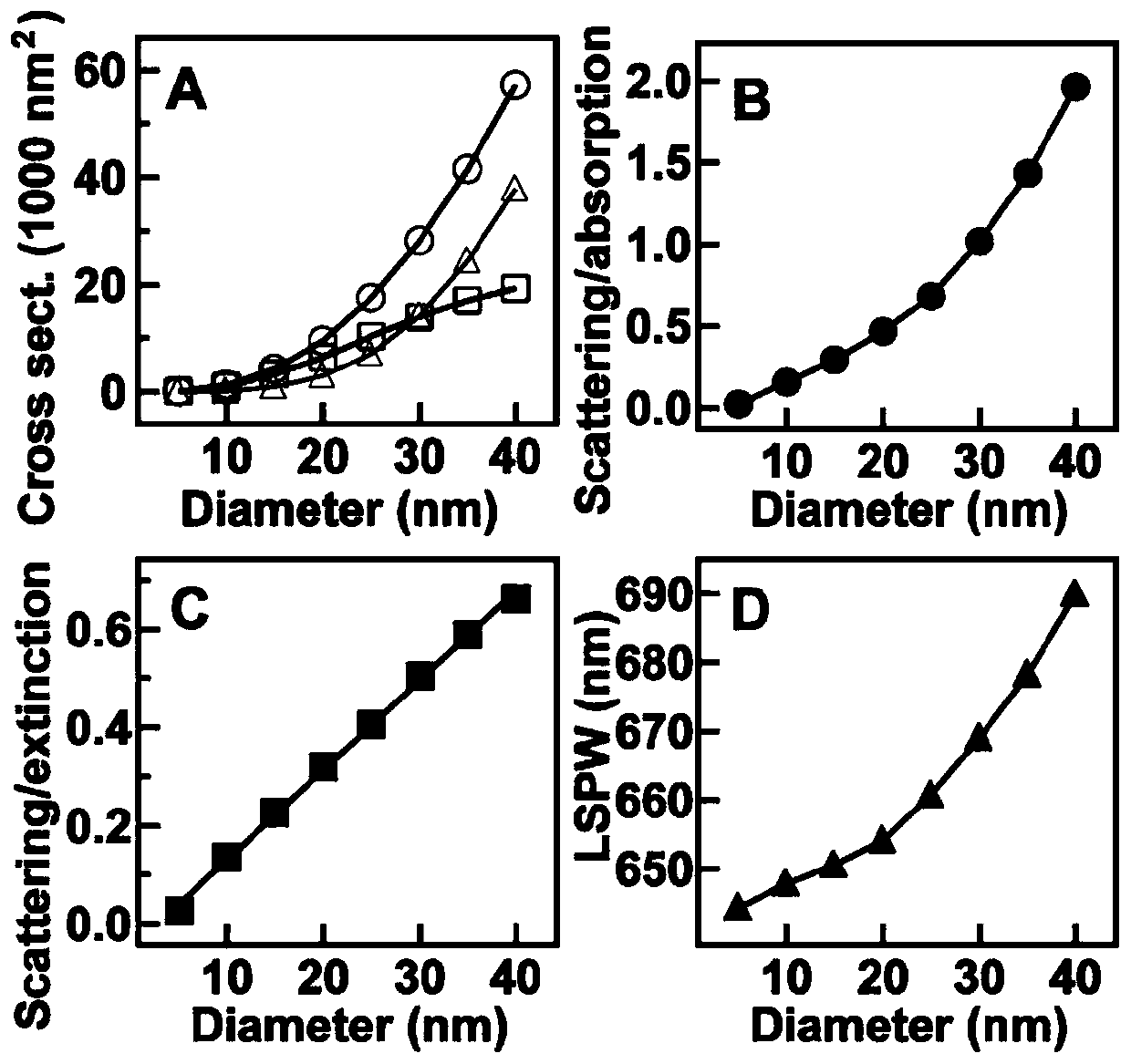
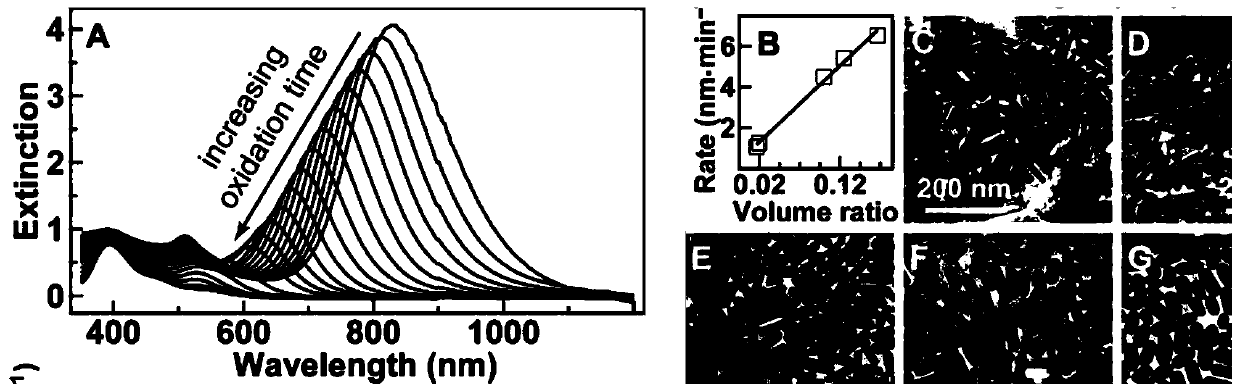
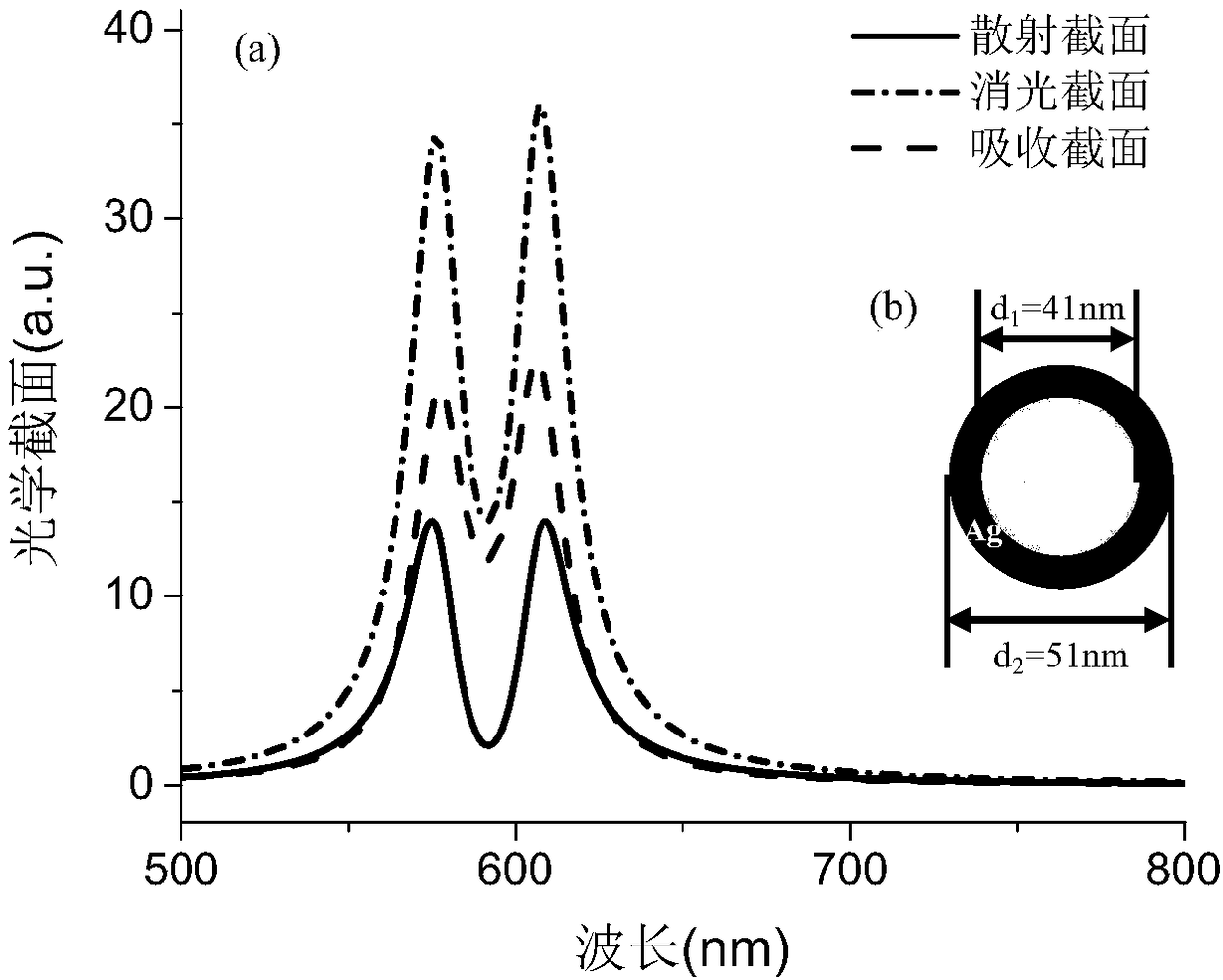
Method for modulating gold nanorod optical section on single wavelength
The invention discloses a method for modulating a gold nanorod optical section on a single wavelength. The method for modulating the gold nanorod optical section on the single wavelength includes thefollowing steps that newly prepared AgNO<3> is added in a mixed liquid of CTAB and 5-bromine salicylic acid, and anti-light standing is conducted; a HAuCl<4>.3H<2>O solution is added, and uniform stirring is conducted; an ascorbic acid solution is added, stirring is conducted until the solution is colorless, and a growth liquid is obtained; the HAuCl<4>.3H<2>O solution is added in a mixed liquid of the CTAB and the 5-bromine salicylic acid, and stirring is conducted; the ascorbic acid solution is added, stirring is conducted until the solution is colorless, and a regrowth liquid is obtained; an original seed crystal solution and the growth liquid are mixed and stirred, and standing is conducted until the color of the solution turns into purple; centrifugation is conducted on the solution,gold nanorods are dispersed in the mixed liquid of the CTAB and the 5-bromine salicylic acid, and a new seed crystal solution is obtained; and the new seed crystal solution and the regrowth liquid aremixed, the volume of the regrowth liquid and the concentration of the 5-bromine salicylic acid are adjusted, then the gold nanorods with the same wavelengths and different optical sections can be obtained. According to the method for modulating the gold nanorod optical section on the single wavelength, the operation is simple, the repetitive rate is high, and scattering and absorbing sections ofthe gold nanorods can be modulated on any single wavelength.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method and configuration for optically detecting an illuminated specimen
A configuration for the optical detection of a specimen, wherein the specimen or at least part of the specimen is scanned by means of linear illumination by scanning means, means for linear beam shaping of the illuminating light are provided, and the illuminating light has a preferably periodic structure in at least one spatial direction in that means for generating the structure are disposed in the illuminating beam path, light coming from the specimen is detected and images of the specimen are generated therefrom, at least one optical sectional image through the specimen and / or one image with increased resolution is / are calculated from the images, and means for generating the structure are disposed downstream of the scanning means in the direction of the illumination.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Method for detecting localized environment based on core shell structure nanoparticle strong coupling
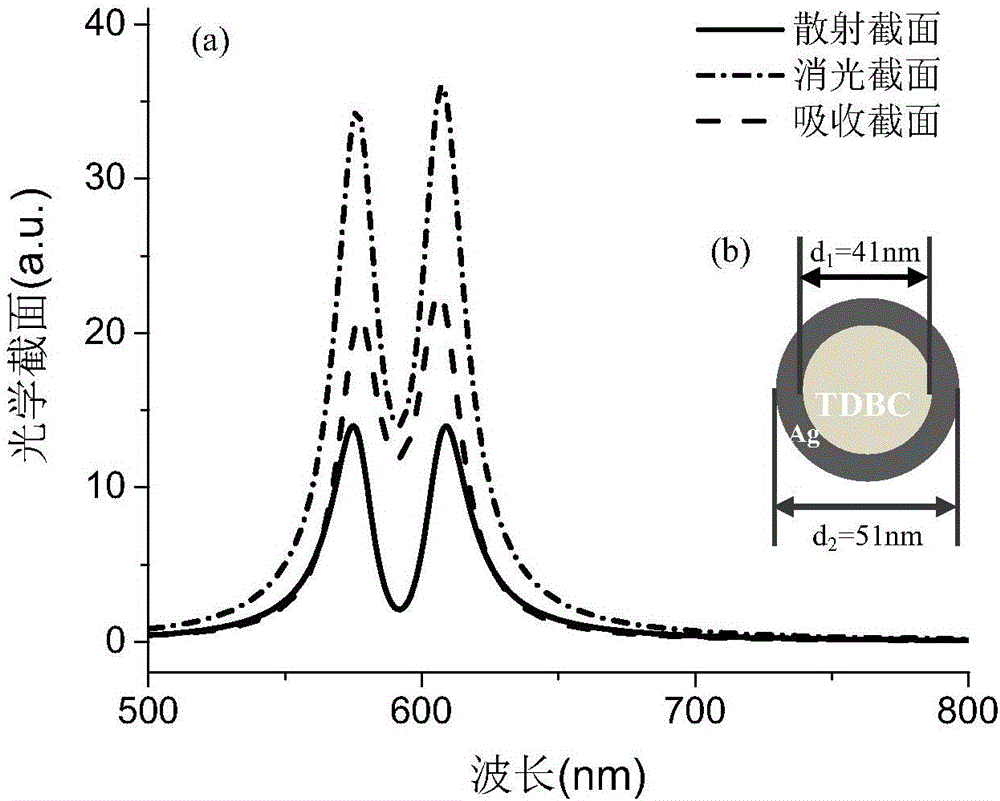
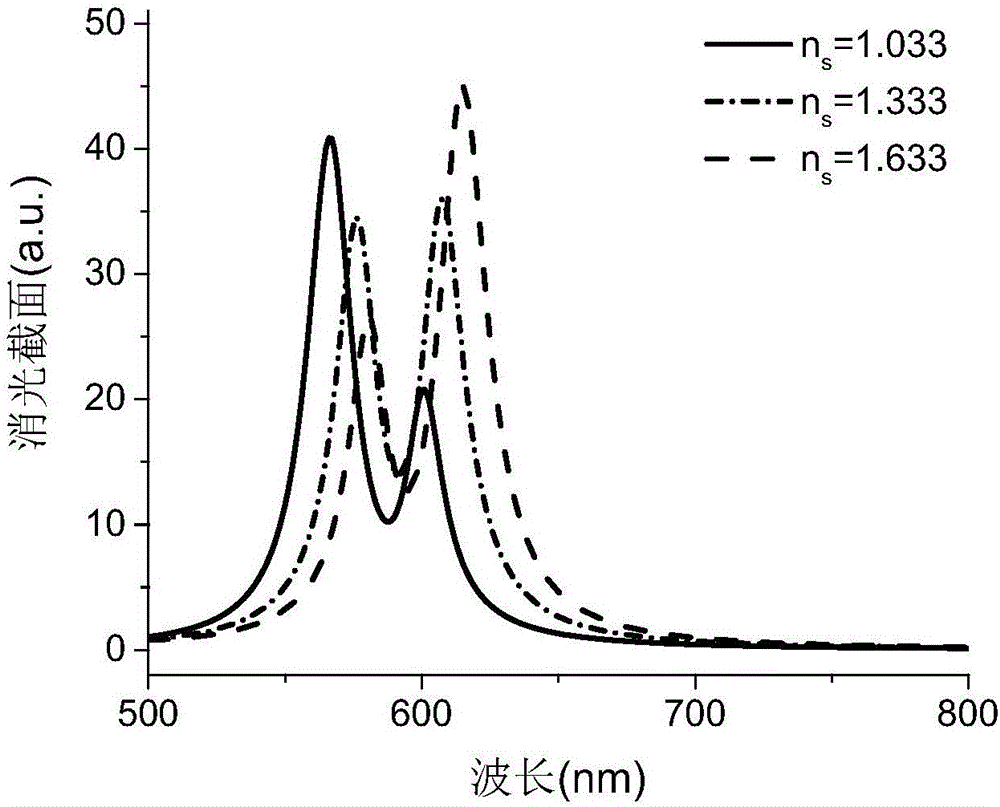
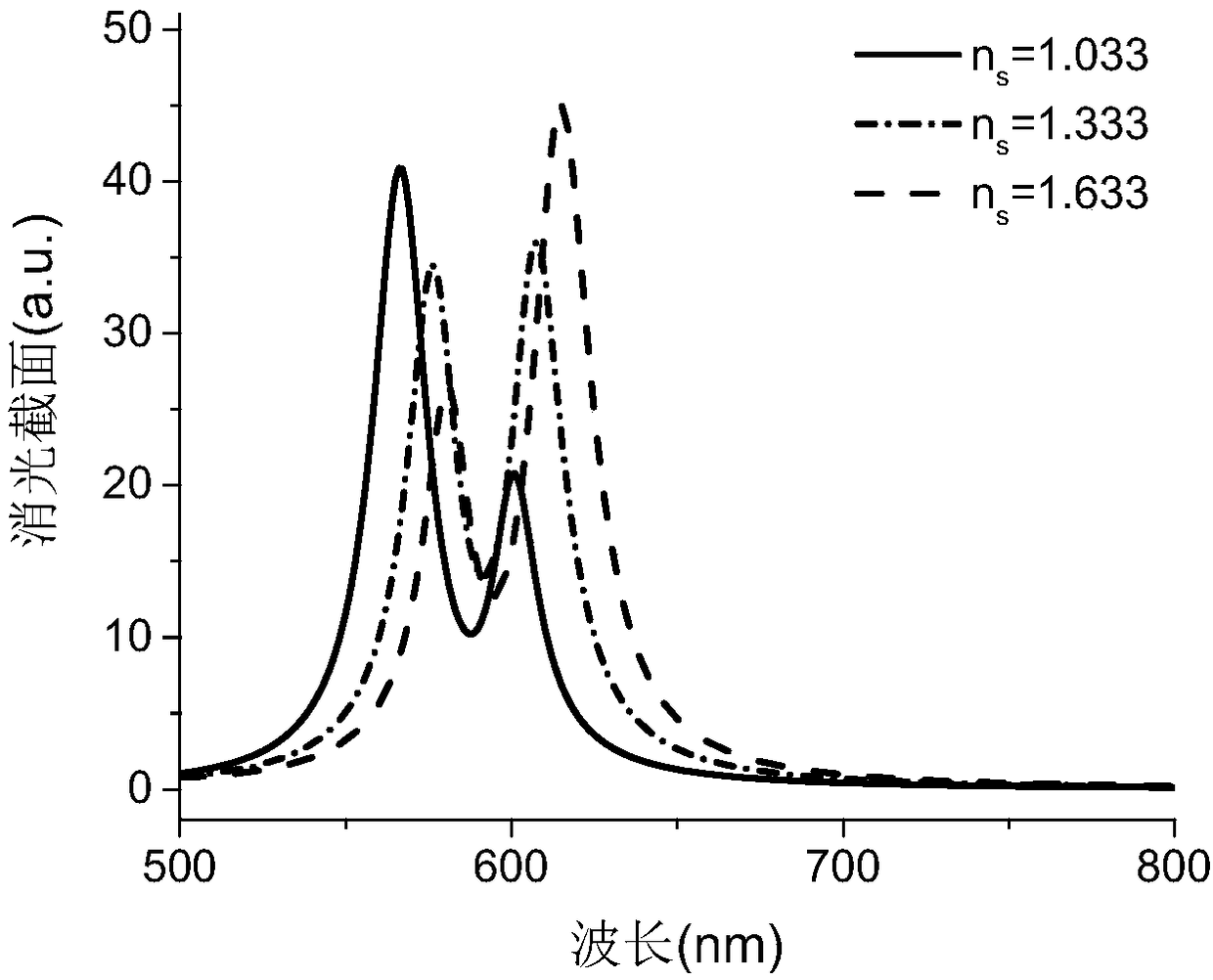
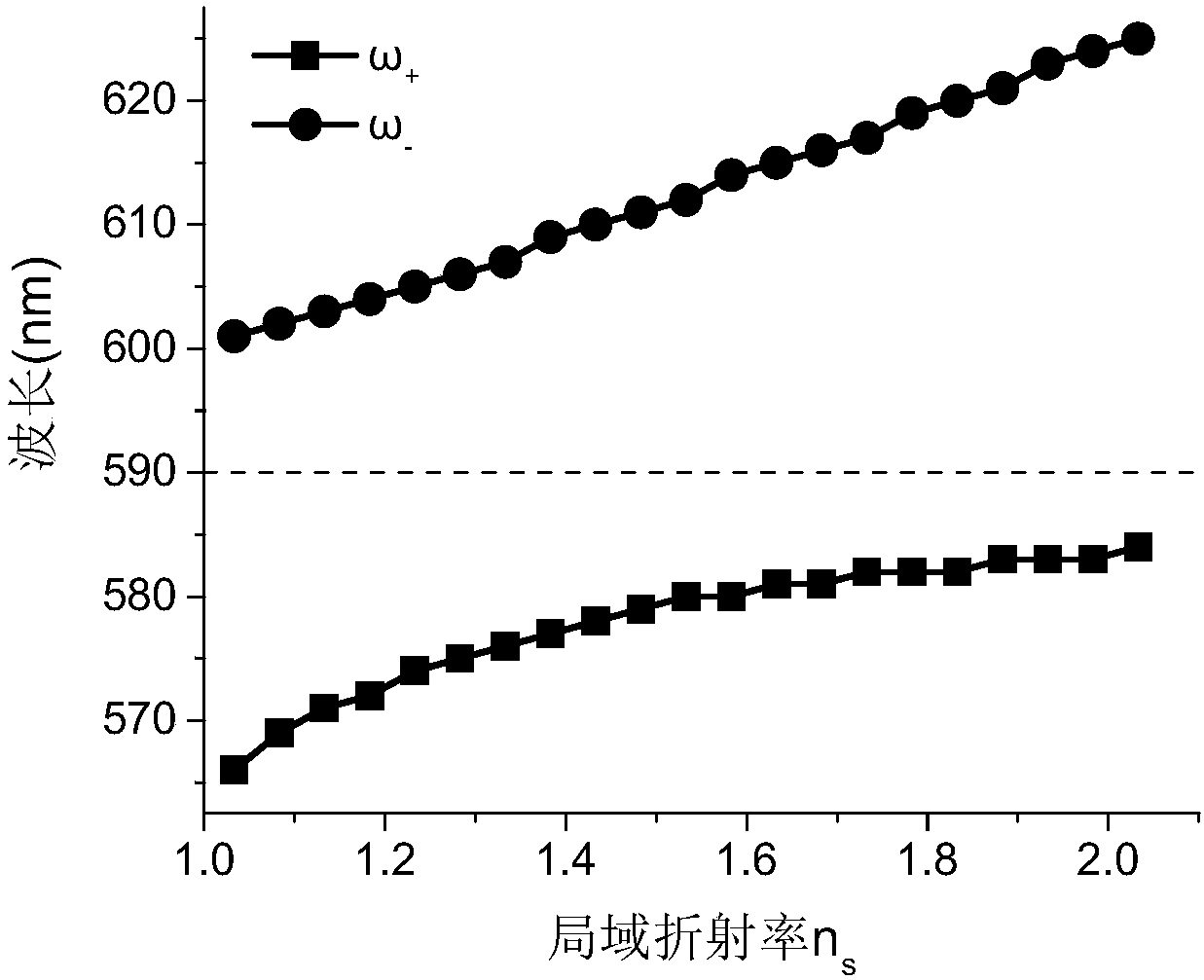
ActiveCN106168574AImplement detectionResponsive to changesPhase-affecting property measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsRefractive indexLocalized surface plasmon
The invention provides a method for detecting a localized environment based on core shell structure nanoparticle strong coupling. The method comprises a step a) of designing a localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) nanoparticle sensor of a core shell structure, wherein after the strong coupling of the LSPR nanoparticle sensor, two peaks of a split extinction cross-section of the LSPR nanoparticle sensor in water are symmetric; a step b) of obtaining relations of two-peak strong of strong coupling splitting varying with a localized environment refractive index around the sensor; a step c) of obtaining a two-peak strength ratio, wherein the ratio is the value obtained by dividing the strength of the peak with a long wavelength by the strength of the peak with a short wavelength and the ratio has a specific law for the variation of the localized environment refractive index; a step d) of fitting the ratio according to the law into a function with respect to the localized environment refractive index; a step e) of detecting a to-be-detected surrounding localized environment according to the law and the fitting function thereof, substituting the measured strength ratio of the spectrum split peak into the fitting function to perform calculation, and obtaining a value of the localized environment refractive index.
Owner:江苏鲲鹏未来光学有限公司
Imaging system for generating vibration region caused by ultrasound wave thereby to obtain optically-sectioned images
ActiveUS20180235474A1Adjust effective frame rateAccurate detectionMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementLight beamSpeckle pattern
An imaging system is configured for generating vibration region caused by ultrasound wave thereby to obtain a plurality of optically-sectioned images. In the imaging system, a stage is operable to be moved along a plurality of scanning imaging positions, and applied to deposit an object with at least one scattering material. When the object receives an ultrasound wave, a shear wave is generated to displace the scattering material thereby to form a vibration region. A laser generating device is configured to transmit a laser beam, which penetrates the vibration region to form a speckle pattern and focused at a focusing position. An optical imaging device is set at the focusing position to receive the laser beam to generate a plurality of scanning optically-sectioned images with respect to the scanning imaging positions.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
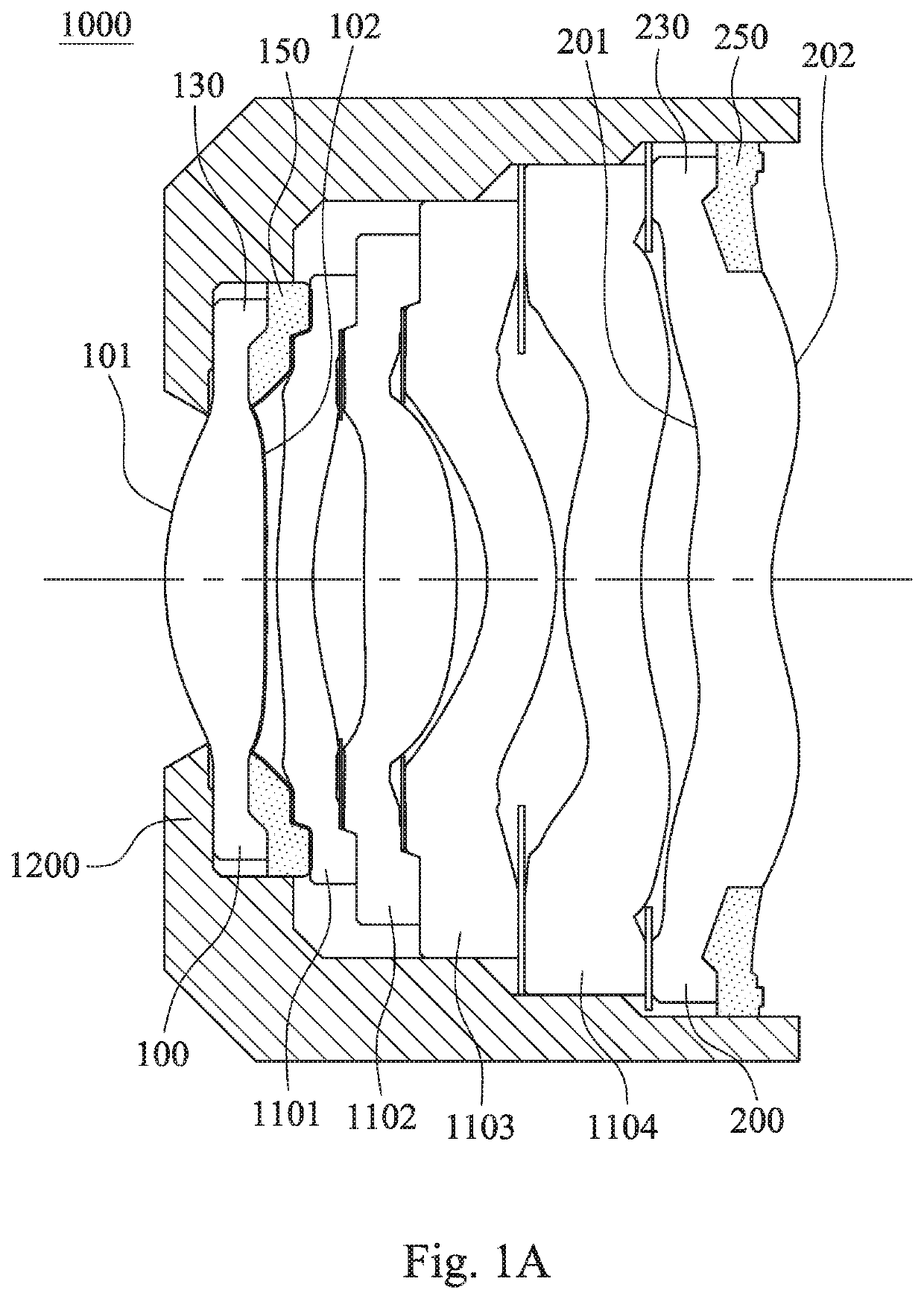
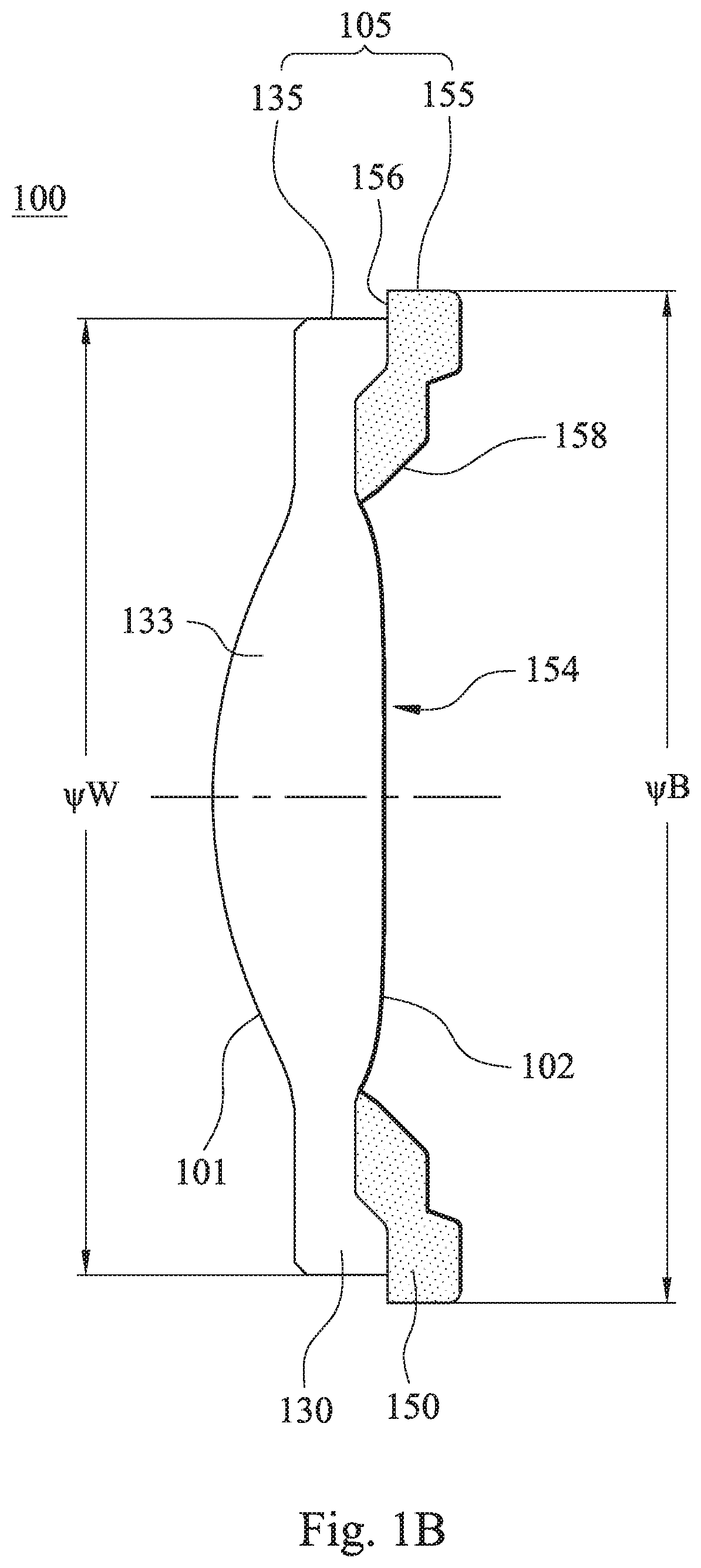
Imaging lens assembly and electronic device
An imaging lens assembly includes a plurality of lens elements, wherein at least one of the lens elements is a dual molded lens element. The dual molded lens element includes a light transmitting portion and a light absorbing portion. The light transmitting portion includes an effective optical section and a first annular surface. The light absorbing portion is located on at least one surface of an object-side surface and an image-side surface of the dual molded lens element, wherein a plastic material and a color of the light absorbing portion are different from a plastic material and a color of the light transmitting portion, and the light absorbing portion includes an opening and a second annular surface. A step surface of the second annular surface is formed by the first annular surface and the second annular surface.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
A detection method for local environment based on strong coupling of core-shell nanoparticles
ActiveCN106168574BImplement detectionResponsive to changesPhase-affecting property measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsRefractive indexLocal environment
The invention provides a method for detecting a localized environment based on core shell structure nanoparticle strong coupling. The method comprises a step a) of designing a localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) nanoparticle sensor of a core shell structure, wherein after the strong coupling of the LSPR nanoparticle sensor, two peaks of a split extinction cross-section of the LSPR nanoparticle sensor in water are symmetric; a step b) of obtaining relations of two-peak strong of strong coupling splitting varying with a localized environment refractive index around the sensor; a step c) of obtaining a two-peak strength ratio, wherein the ratio is the value obtained by dividing the strength of the peak with a long wavelength by the strength of the peak with a short wavelength and the ratio has a specific law for the variation of the localized environment refractive index; a step d) of fitting the ratio according to the law into a function with respect to the localized environment refractive index; a step e) of detecting a to-be-detected surrounding localized environment according to the law and the fitting function thereof, substituting the measured strength ratio of the spectrum split peak into the fitting function to perform calculation, and obtaining a value of the localized environment refractive index.
Owner:江苏鲲鹏未来光学有限公司
Imaging lens assembly and electronic device
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
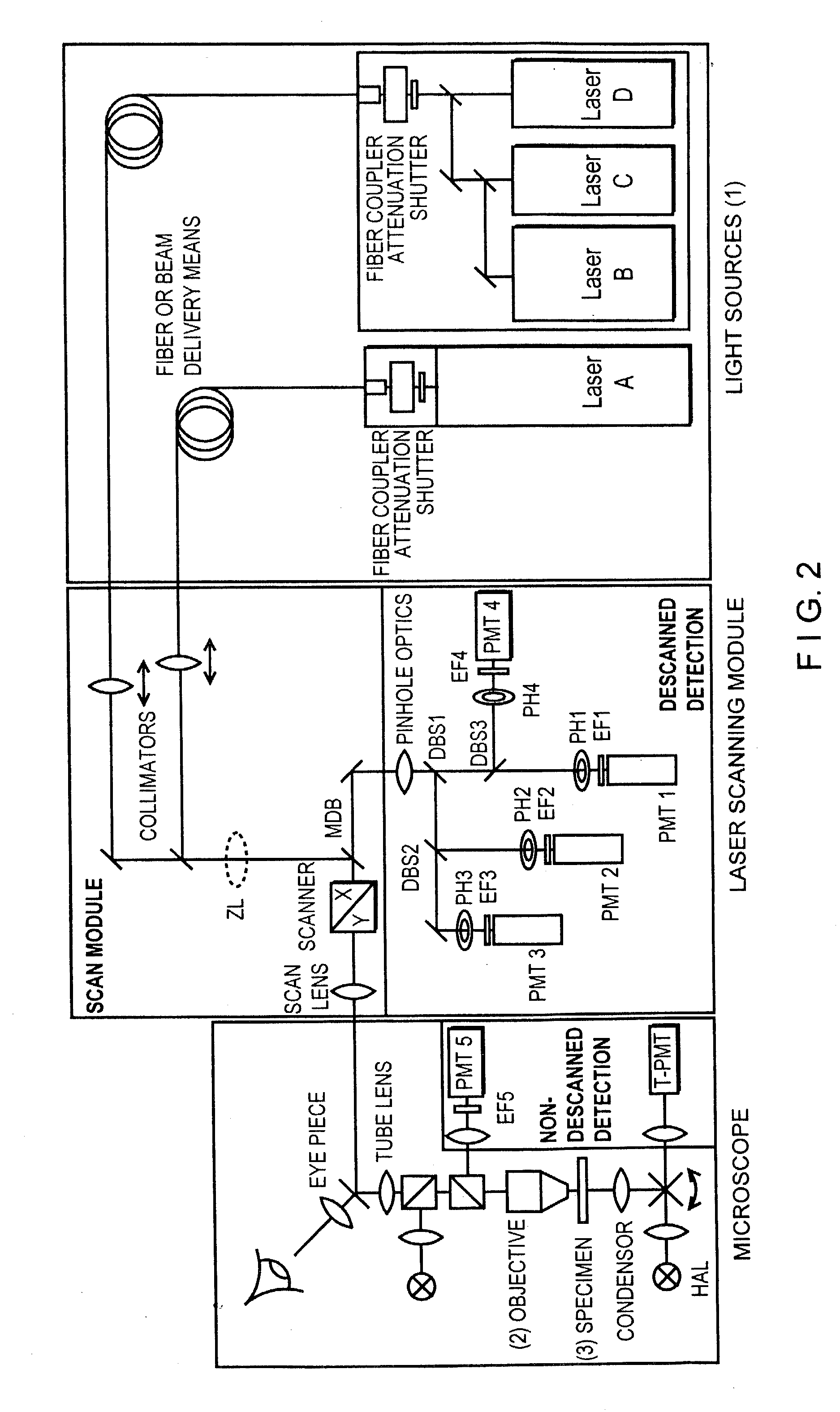
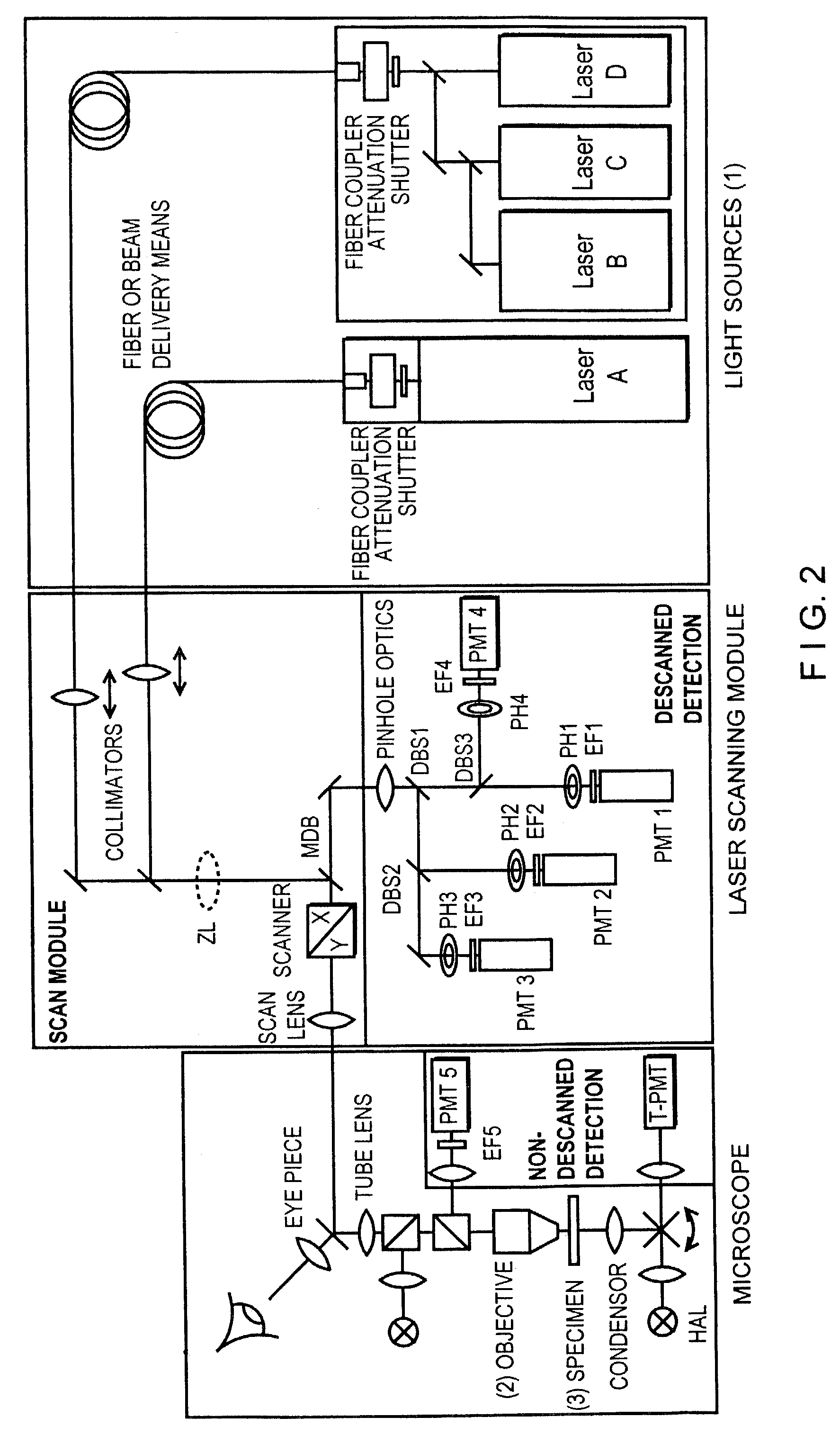
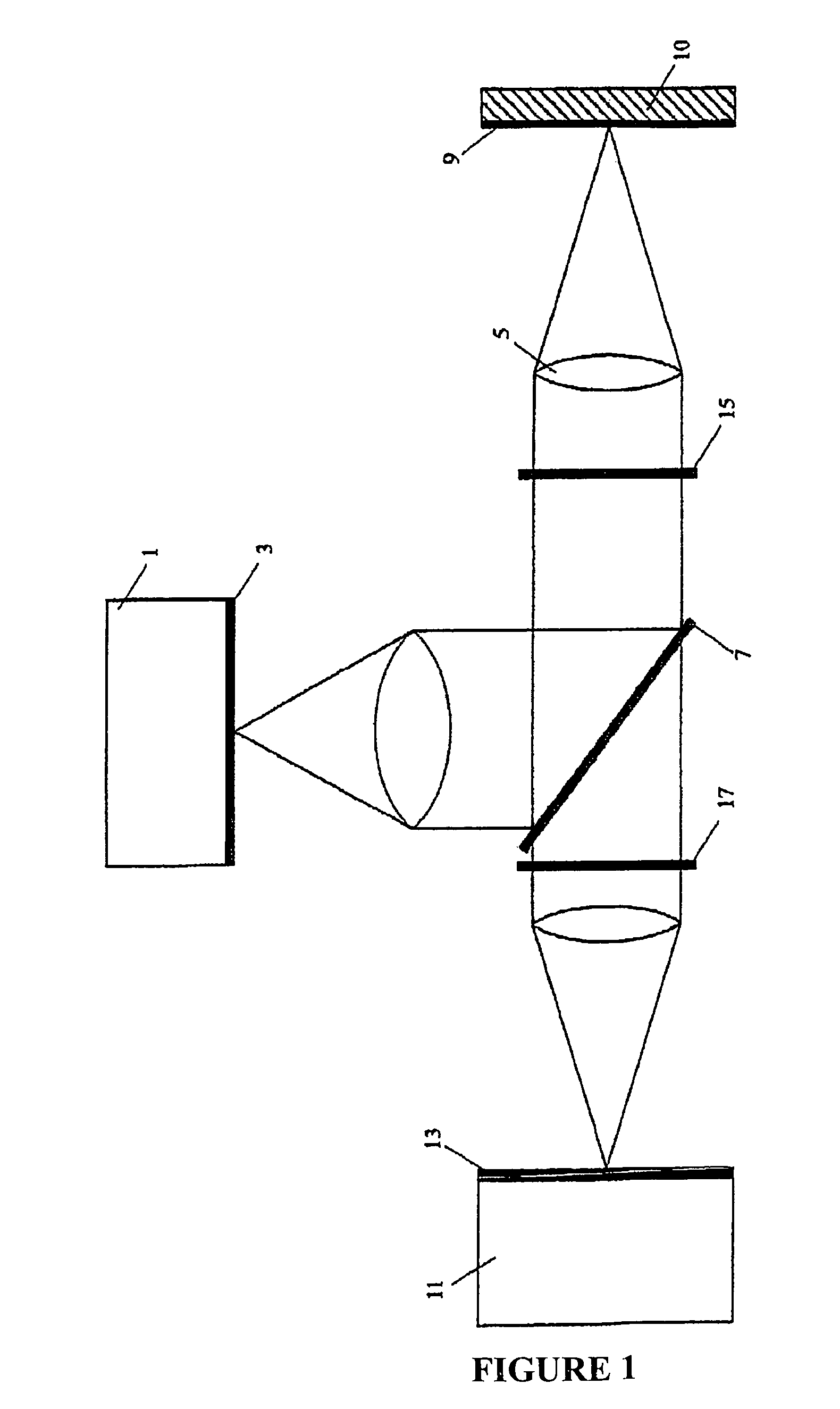
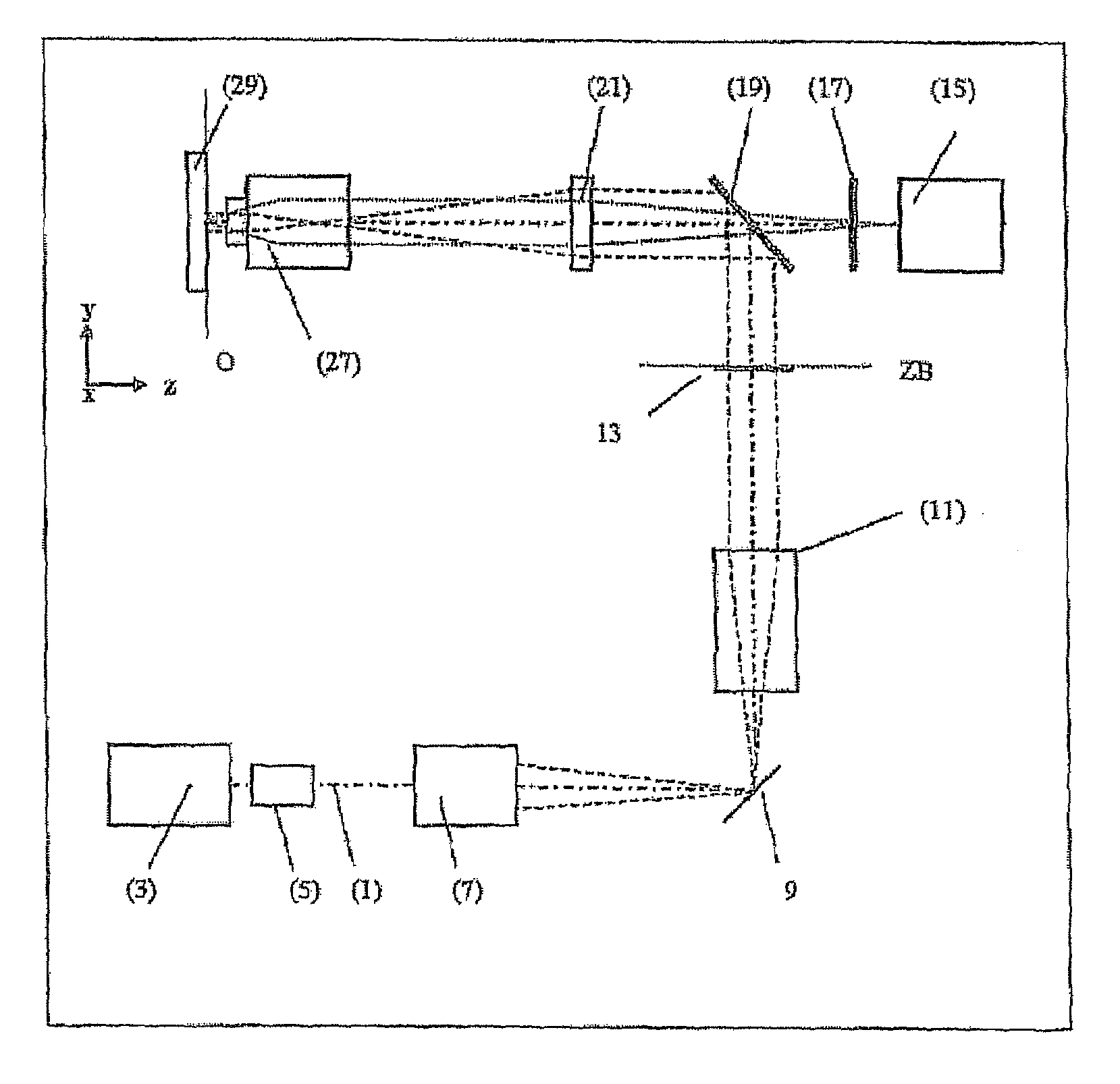
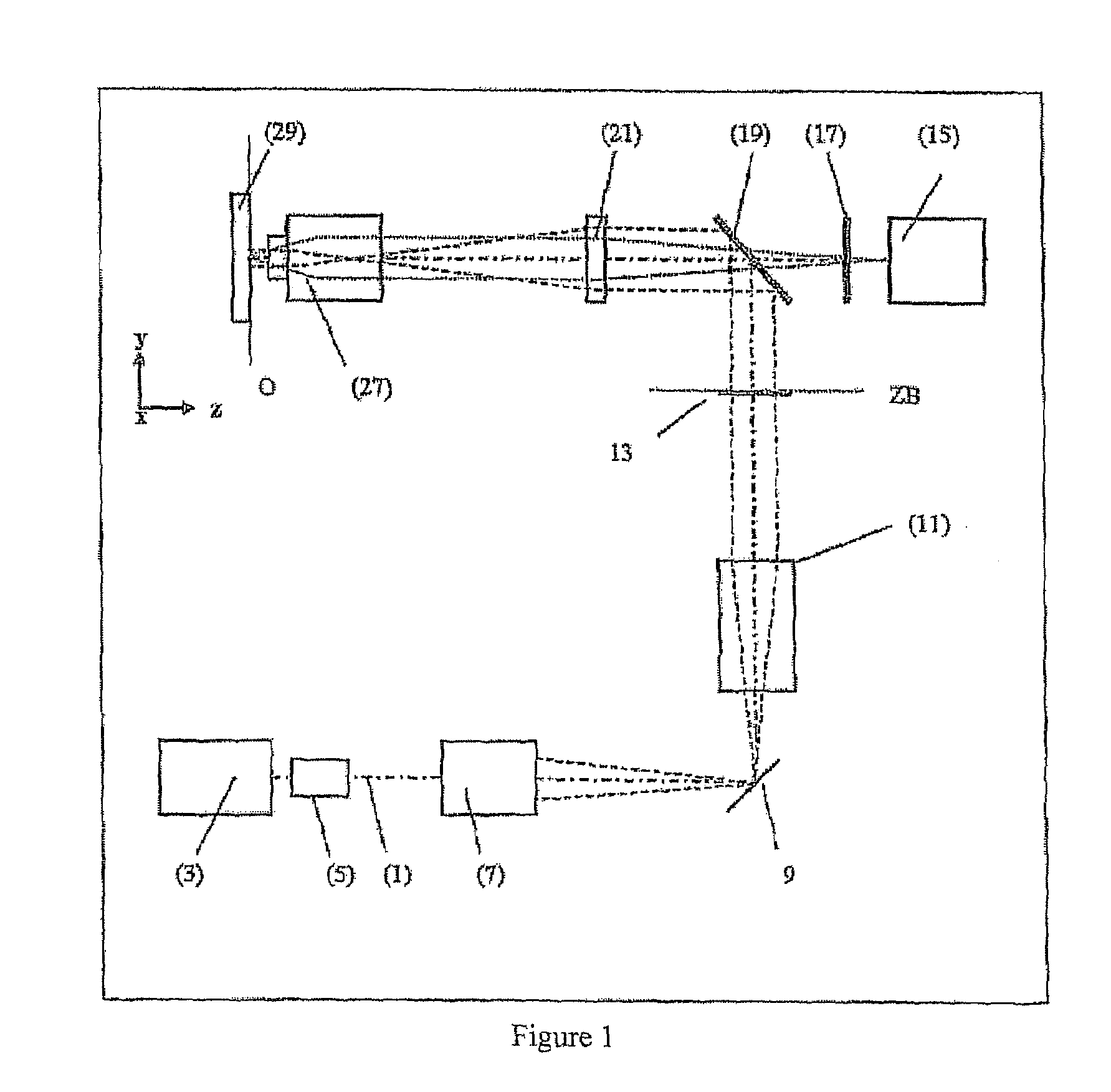
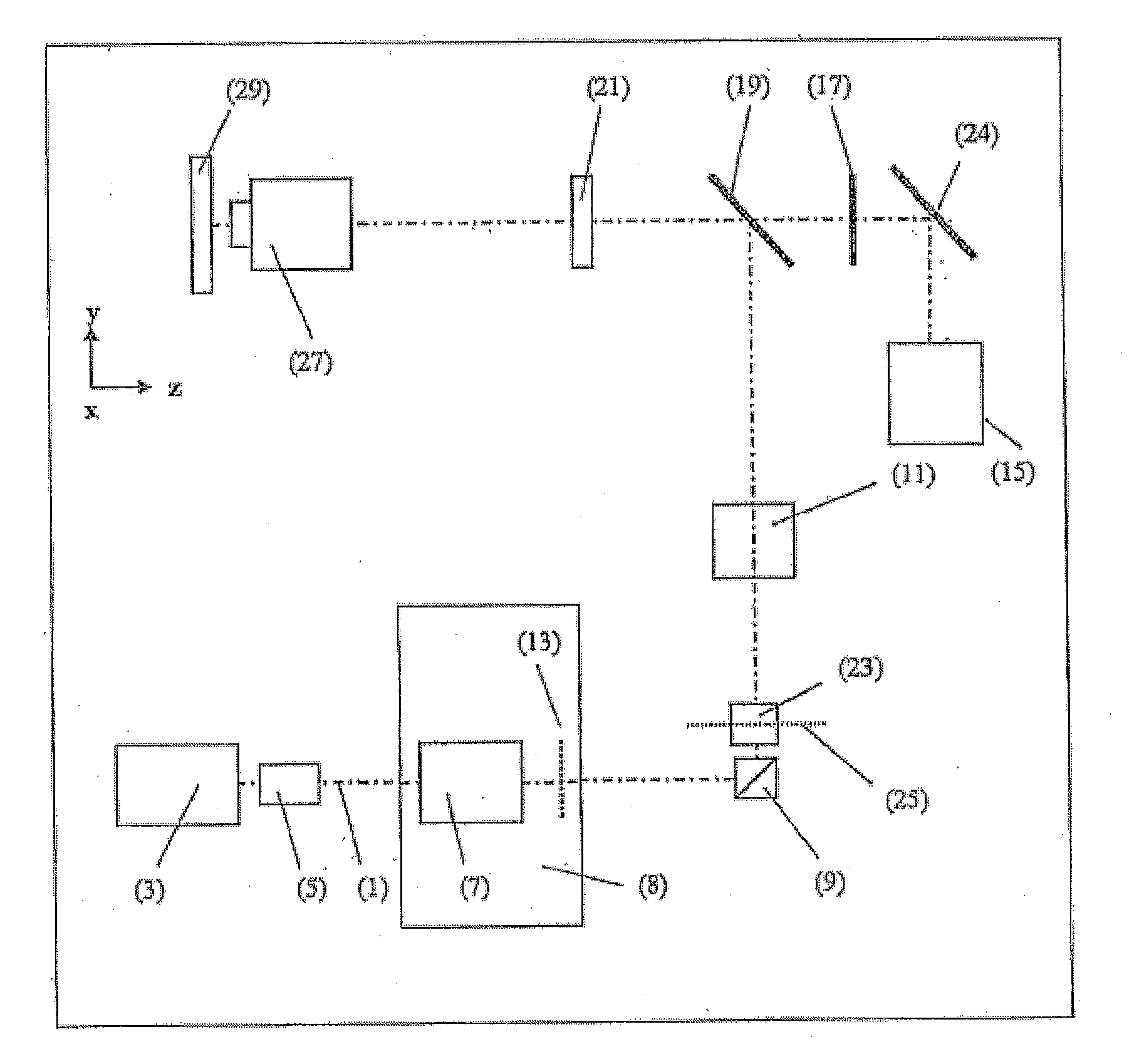
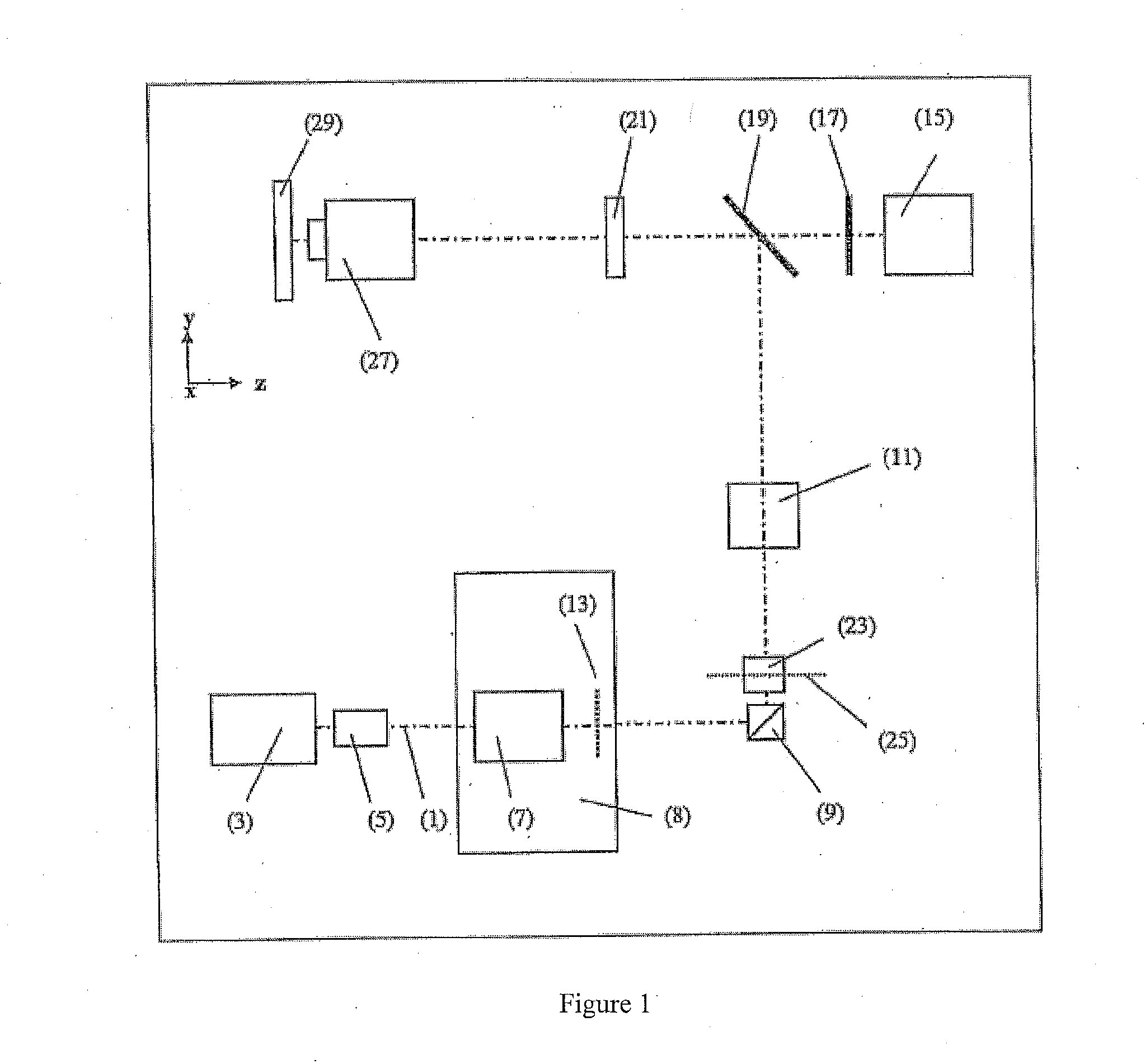
Method and apparatus for optical confocal imaging, using a programmable array microscope
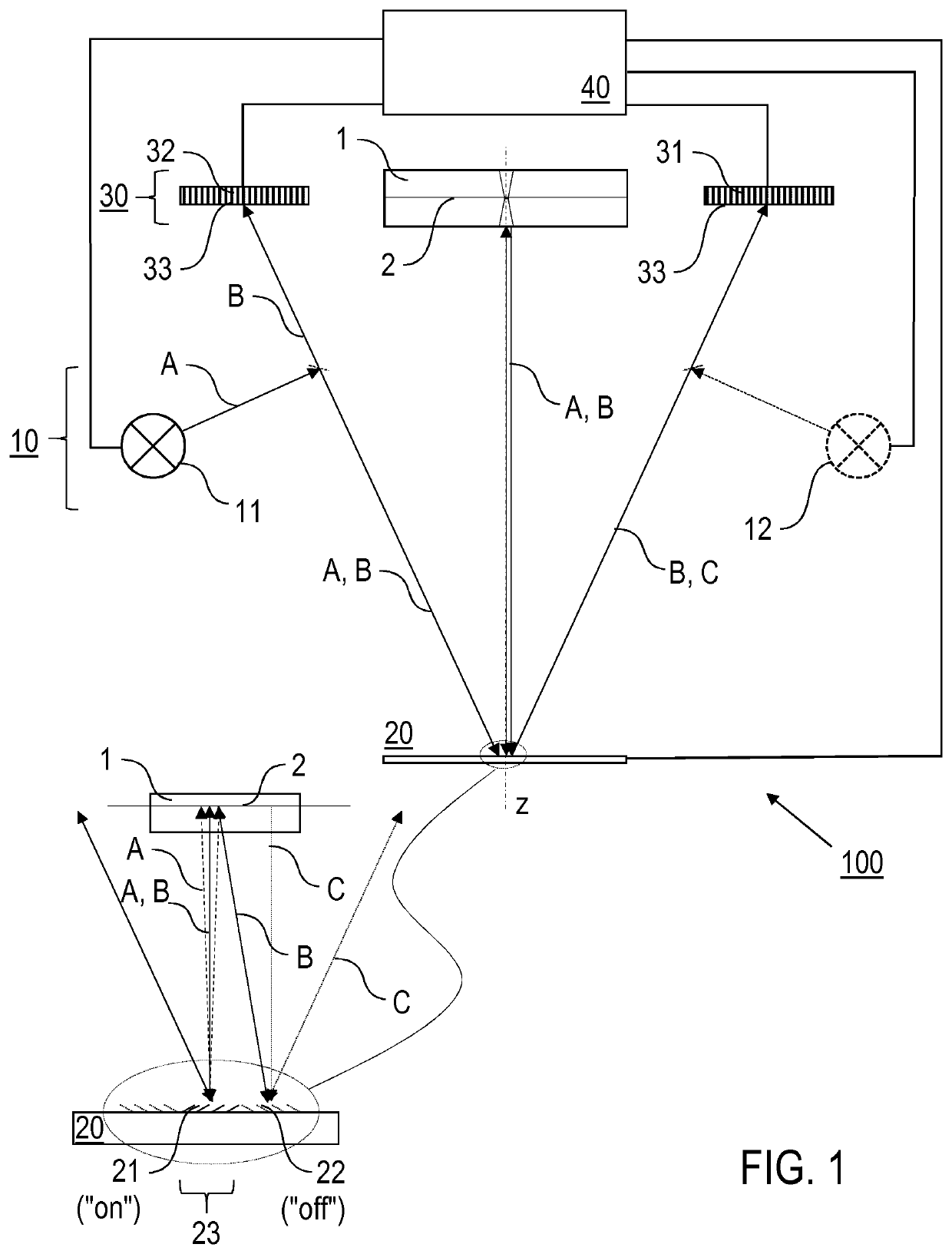
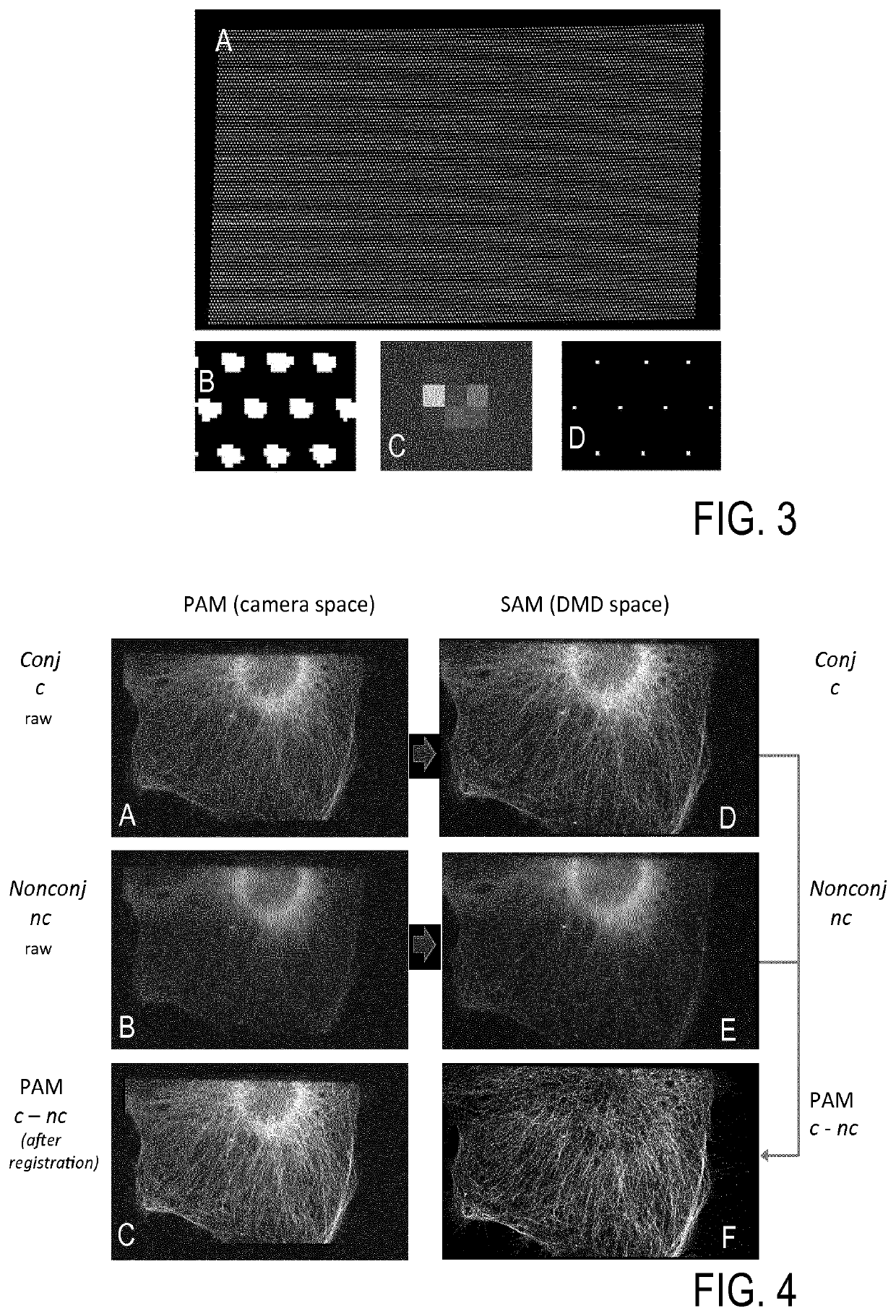
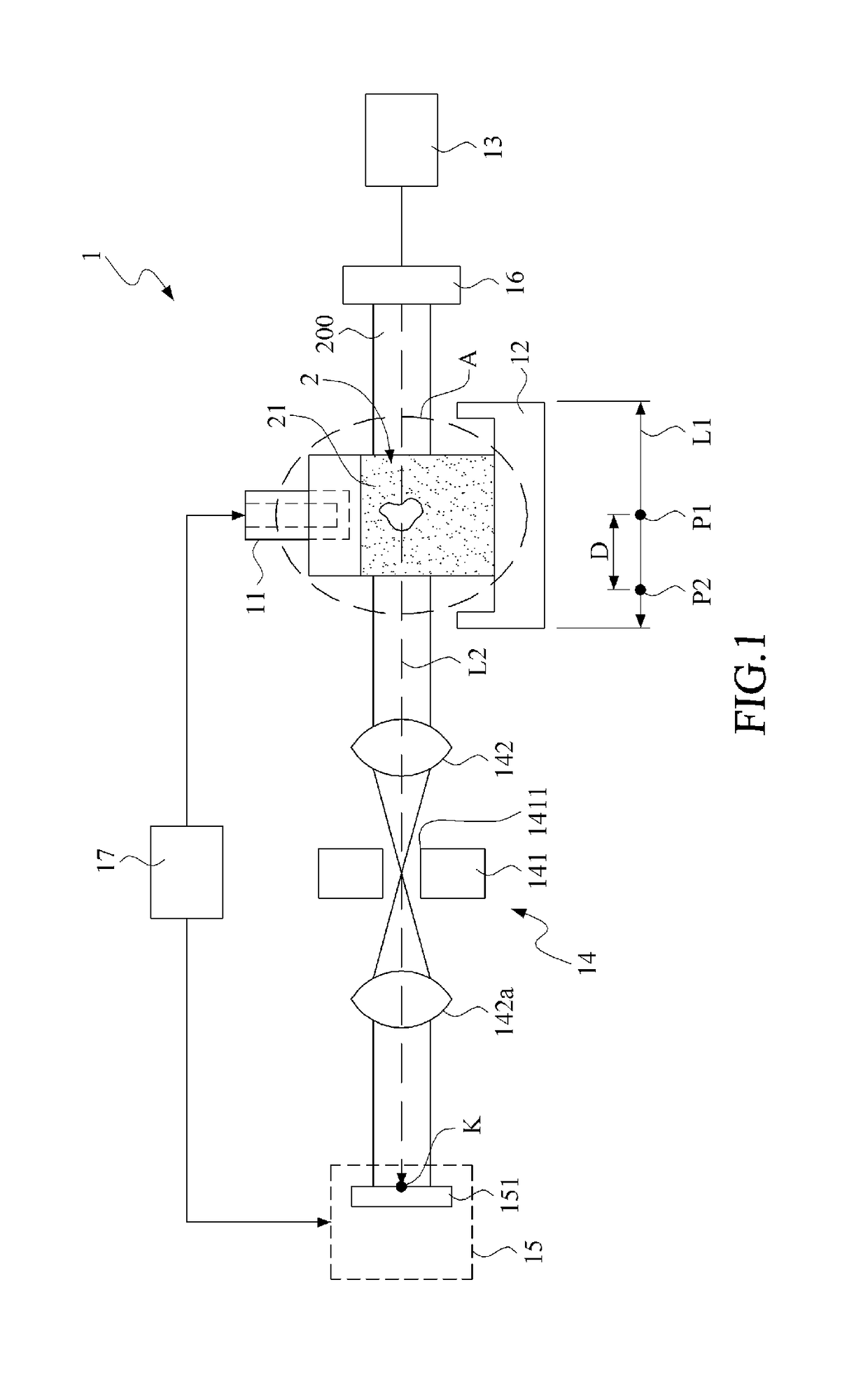
Optical confocal imaging, being conducted with a programmable array microscope (PAM) (100), having a light source device (10), a spatial light modulator device (20) with a plurality of reflecting modulator elements, a PAM objective lens and a camera device (30), wherein the spatial light modulator device (20) is configured such that first groups of modulator elements (21) are selectable for directing excitation light to conjugate locations of an object to be investigated and for directing detection light originating from these locations to the camera device (30), and second groups of modulator elements (22) are selectable for directing detection light from non-conjugate locations of the object to the camera device (30), comprises the steps of directing excitation light from the light source device (10) via the first groups of modulator elements to the object to be investigated, wherein the spatial light modulator device (20) is controlled such that a predetermined pattern sequence of illumination spots is focused to the conjugate locations of the object, wherein each illumination spot is created by at least one single modulator element defining a current PAM illumination aperture, collecting image data of a conjugate image lc, based on collecting detection light from conjugate locations of the object for each pattern of PAM illumination apertures, collecting image data of a non-conjugate image lnc, based on collecting detection light from non-conjugate locations of the object for each pattern of PAM illumination apertures via the second groups of modulator elements (22) with a non-conjugate camera channel of the camera device (30), and creating an optical sectional image of the object (OSI) based on the image data of the conjugate image lc and the non-conjugate image lnc, wherein the step of collecting the image data of the conjugate image lc includes collecting a part of the detection light from the conjugate locations of the object for each pattern of PAM illumination apertures via modulator elements of the second groups of modulator elements (22) surrounding the current PAM illumination apertures with the non-conjugate camera channel of the camera device (30). Furthermore, a PAM calibration method and PAMs being configured for the above methods are described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
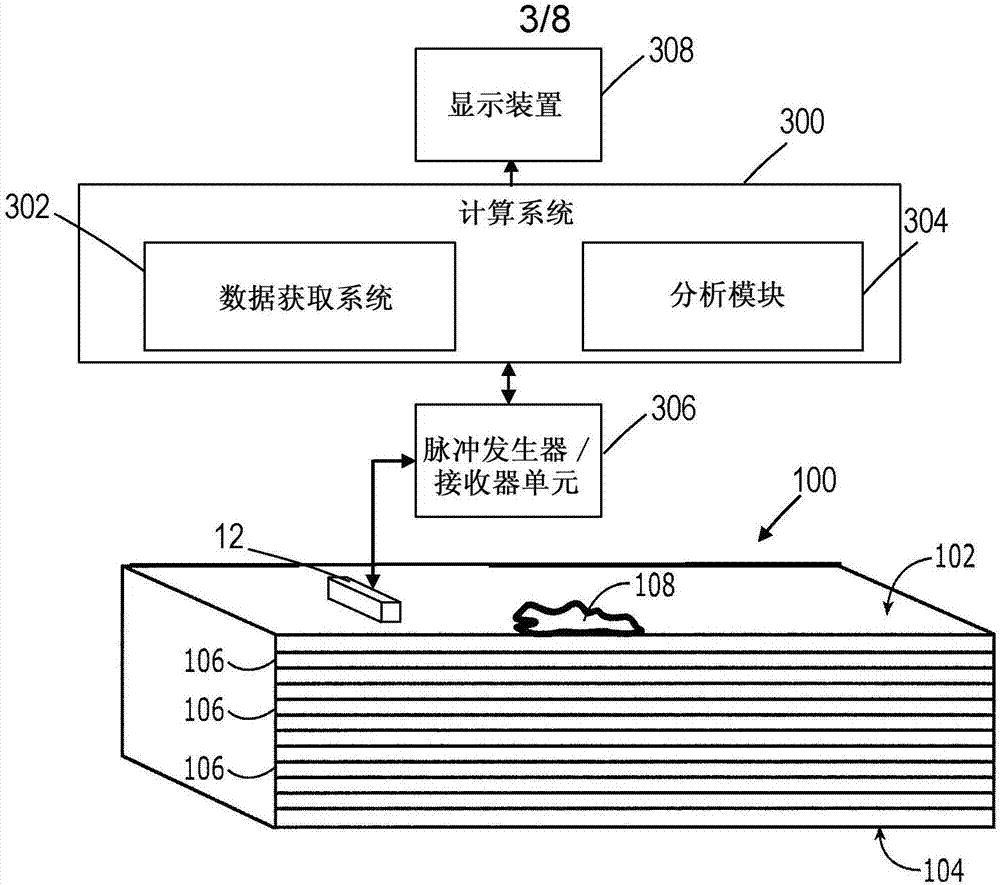
Nondestructive inspection and performance prediction method for composite structures, ultrasonic wave imaging system and calibration method
ActiveCN108008013AShorten the timeAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInvestigating composite materialsElement analysisEngineering
The invention provides a nondestructive inspection and performance prediction method for composite structures, an ultrasonic wave imaging system and a calibration method. In accordance with some embodiments, the method combines the use of B-scan ultrasound data, automated optical measurement of wrinkles and geometry of cross-sections, and finite element analysis of wrinkled composite structure toprovide the ability to assess the actual significance of a detected wrinkle relative to the intended performance of the structure. The disclosed method uses an ultrasonic inspection system that has been calibrated by correlating ultrasonic B-scan data acquired from reference standards with measurements of optical cross sections (e.g., micrographs) of those reference standards.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method for measuring deformability properties of a fibre
A method for measuring a property of a fiber, such as flexibility, collapsibility and moment of inertia. A fiber is wetted and deformed in its wet state, and an optical section image of the deformed fiber is taken. A measurement is made on the image and the desired property is calculated using the measurement.
Owner:NEW BRUNSWICK UNIV OF
Imaging system for generating vibration region caused by ultrasound wave thereby to obtain optically-sectioned images
ActiveUS10184826B2Accurate detectionError in the stiffness estimation of the high elasticity object can be reducedMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementLight beamSpeckle pattern
An imaging system is configured for generating vibration region caused by ultrasound wave thereby to obtain a plurality of optically-sectioned images. In the imaging system, a stage is operable to be moved along a plurality of scanning imaging positions, and applied to deposit an object with at least one scattering material. When the object receives an ultrasound wave, a shear wave is generated to displace the scattering material thereby to form a vibration region. A laser generating device is configured to transmit a laser beam, which penetrates the vibration region to form a speckle pattern and focused at a focusing position. An optical imaging device is set at the focusing position to receive the laser beam to generate a plurality of scanning optically-sectioned images with respect to the scanning imaging positions.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Method and Configuration for Depth Resolved Optical Detection of an Illuminated Specimen
InactiveUS20140118750A1Improve parallelismHigh strengthMicroscopesUsing optical meansImage resolutionArea detector
A method and a configuration for the depth-resolved optical detection of a specimen, in which a specimen or a part of the specimen is scanned by means of preferably linear illumination. The illumination of the specimen is periodically structured in the focus in at least one spatial direction. Light coming from the specimen is detected and images of the specimen are generated. At least one optical sectional image and / or one image with enhanced resolution is calculated through the specimen. Images are repeatedly acquired and sectional images are repeatedly blended while changing the orientation of the linear illumination relative to the specimen and / or spatial intervals between lines exposed to detection light from the illuminated specimen region are generated for the line-by-line non-descanned detection on an area detector or a camera and / or, during a scan, light is further deflected upstream of the detector through the line in the direction of the scan of the specimen.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Backlight module, LCD device and method for improving brightness of backlight source
InactiveCN101246277ADoes not affect uniformityIncrease brightnessNon-linear opticsEngineeringLightness
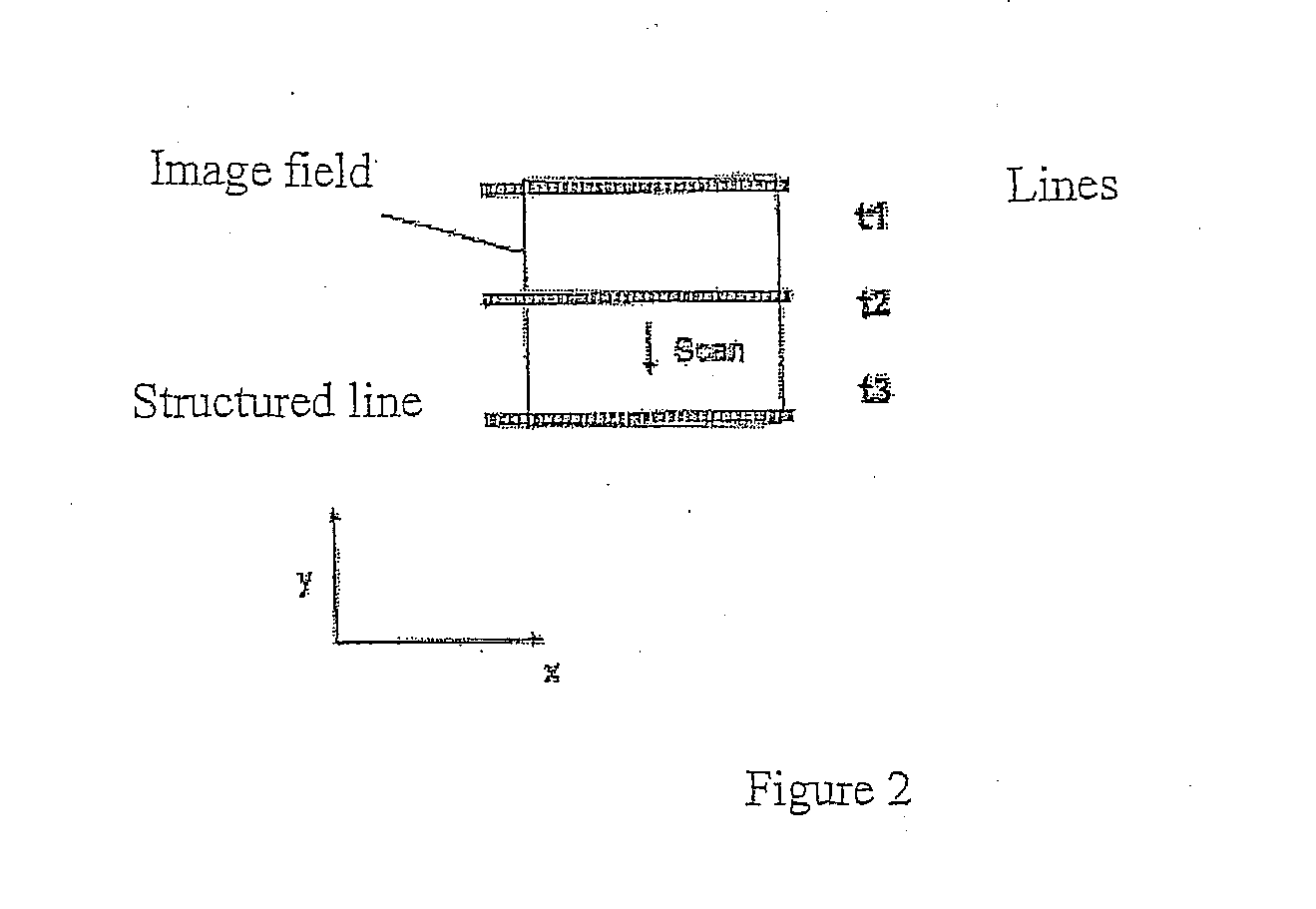
A backlight mould comprises a lamp box, a plurality of lamp source and a diffusing plate. Wherein, the lamp box has opposite a bottom and a out optical cross-section, and the distance from the bottom to the out optical cross-section is H. The lamp source is configured in the lamp box, and the diffusing plate is configured on the out optical cross-section of lamp box. Each lamp source has a first end and a second end, the distance from first end of each lamp box to the bottom of lamp is in the range of 1 / 4 H-3 / 4 H, and at least one distance from first end of lamp source to the bottom is different to other distances. Furthermore, the invention provides another LCD device and a method for hoisting backlight source lightness.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com