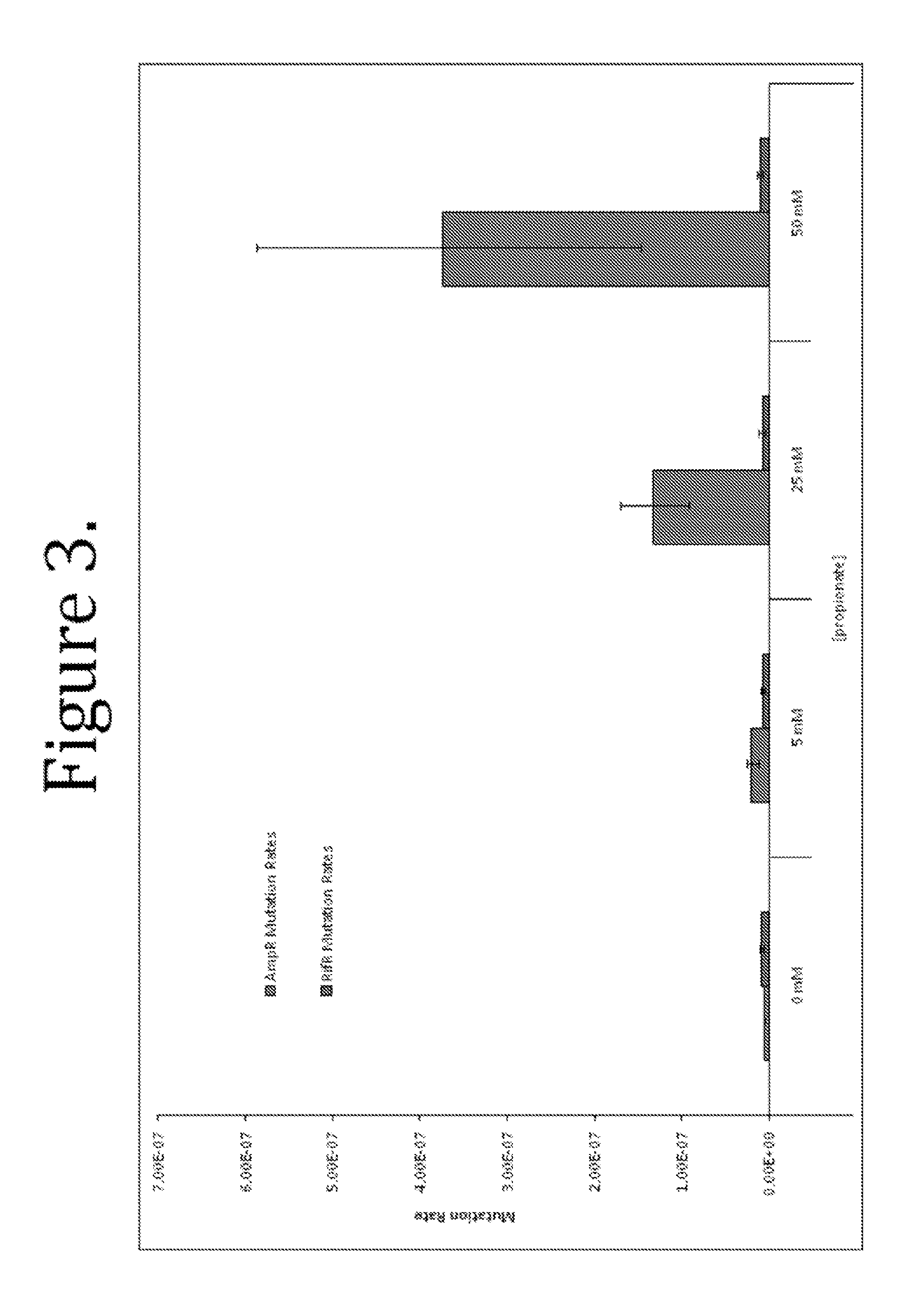
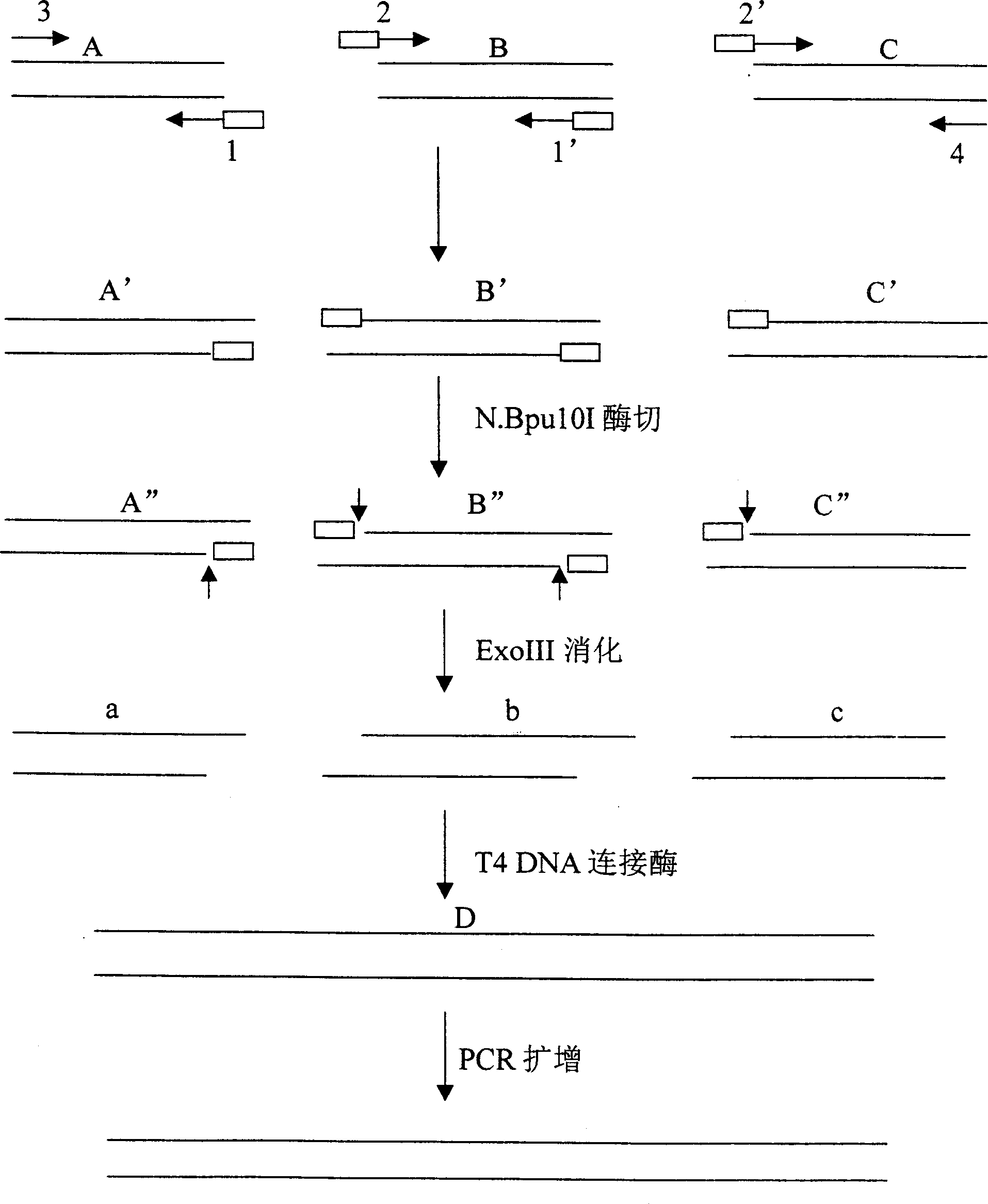
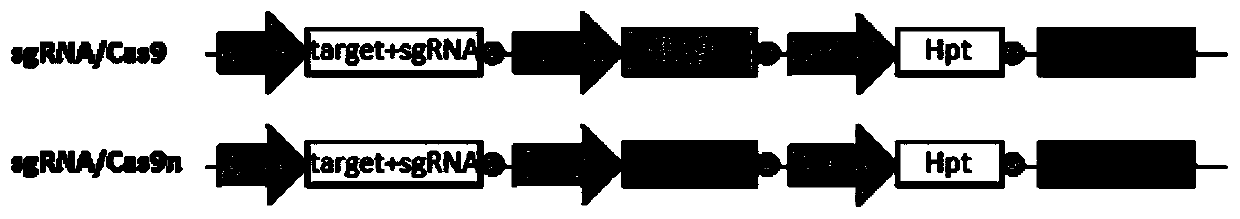
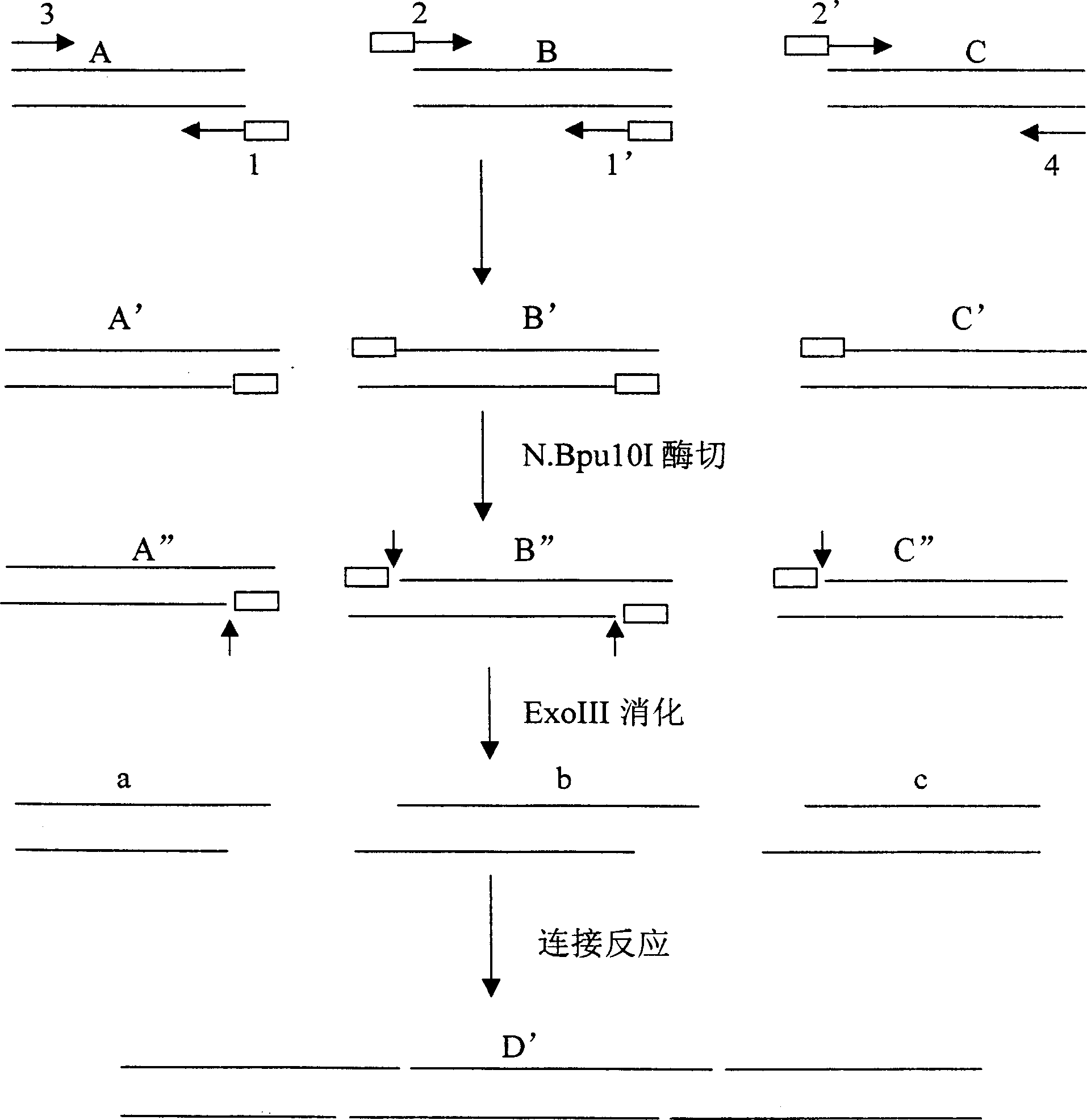Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
70 results about "Nicking enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
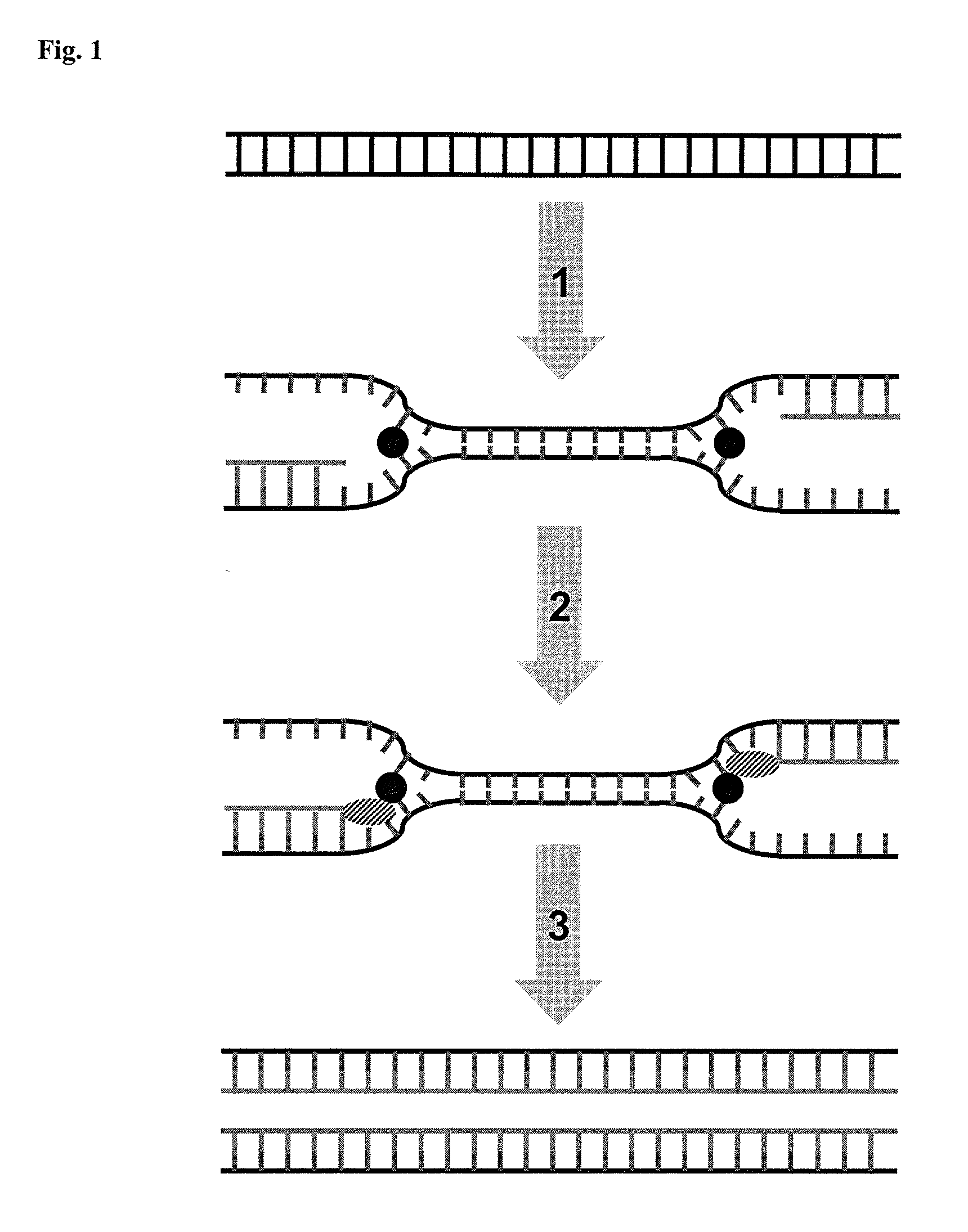
A nicking enzyme (or nicking endonuclease) is an enzyme that cuts one strand of a double-stranded DNA at a specific recognition nucleotide sequences known as a restriction site. Such enzymes hydrolyse (cut) only one strand of the DNA duplex, to produce DNA molecules that are “nicked”, rather than cleaved.
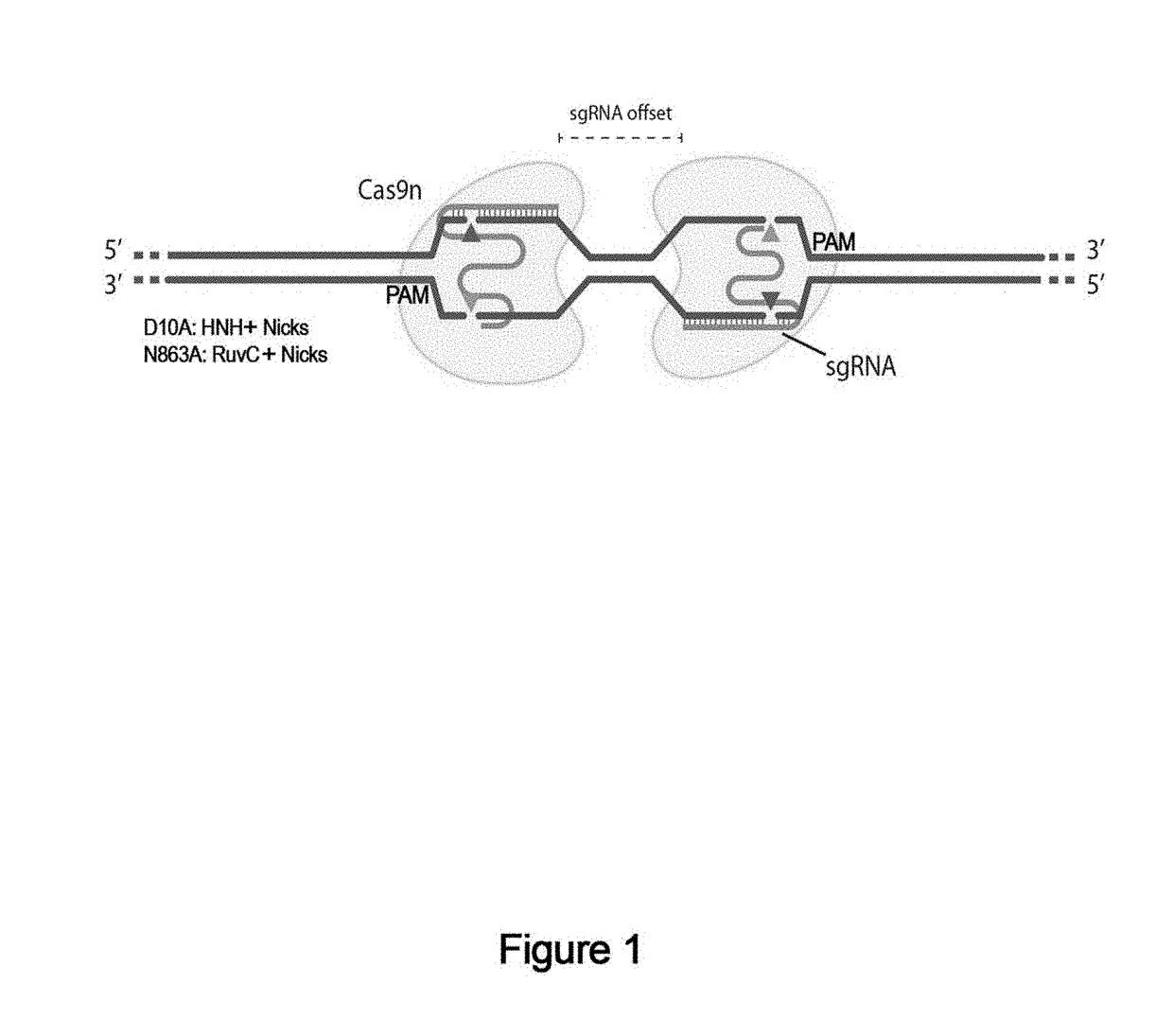
Genome editing using cas9 nickases
InactiveUS20170175144A1Low efficiencyStimulate HDRHydrolasesGenetic material ingredientsGenome editingVector system
The invention provides for delivery, engineering and optimization of systems, methods, and compositions for manipulation of sequences and / or activities of target sequences. Provided are vectors and vector systems, some of which encode one or more components of a CRISPR complex, as well as methods for the design and use of such vectors. Also provided are methods of directing CRISPR complex formation in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells to ensure enhanced specificity for target recognition and avoidance of toxicity.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
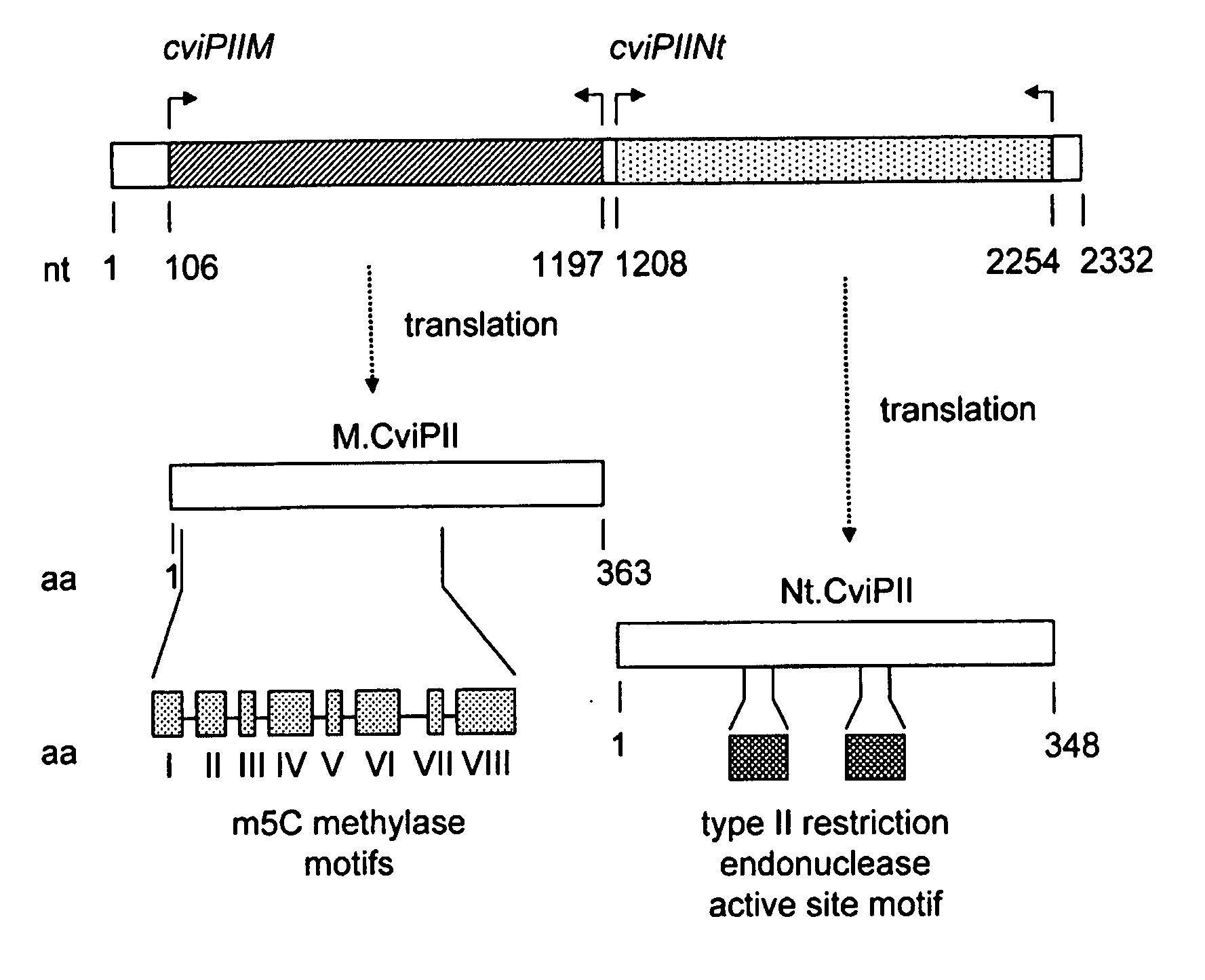
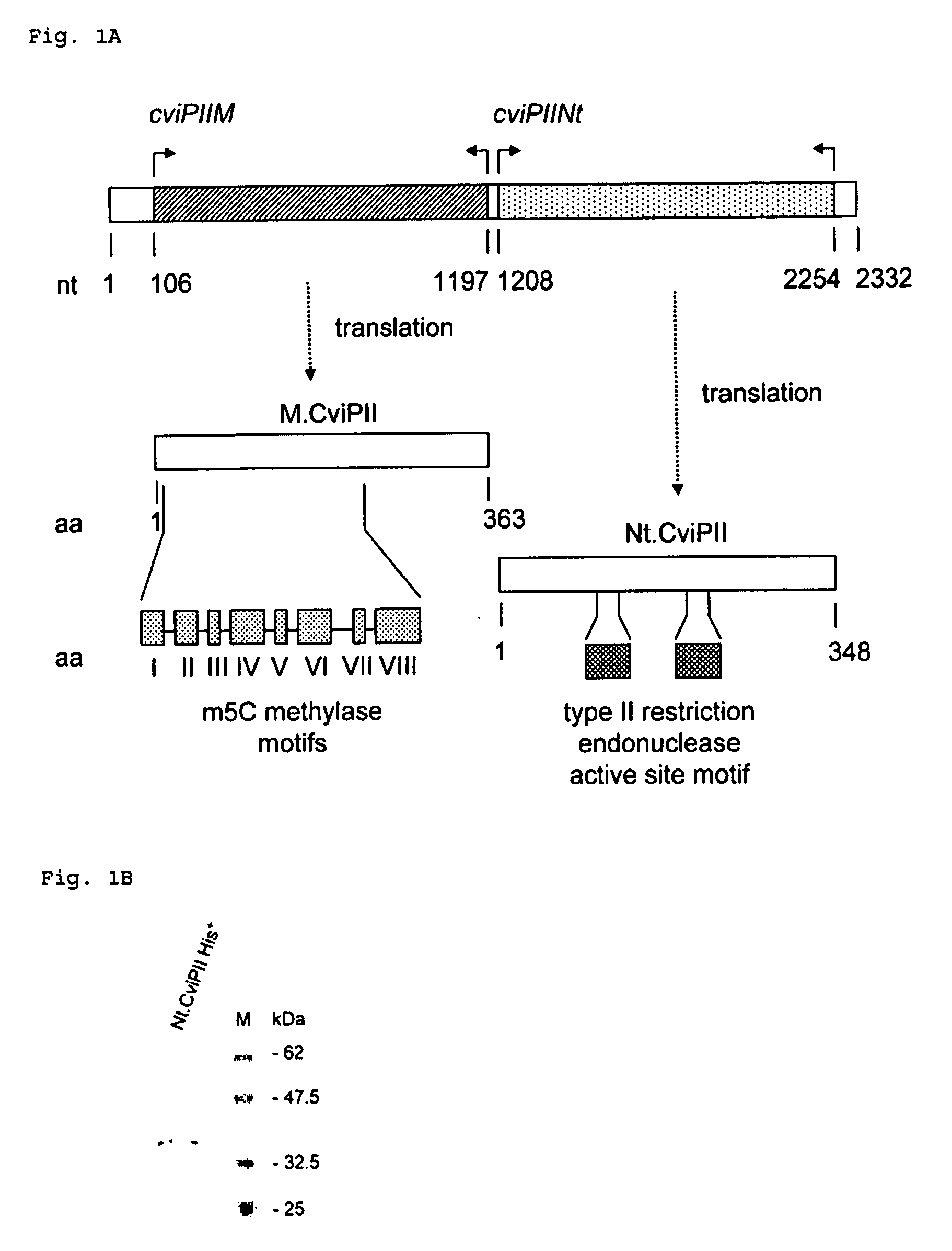
Recombinant Dna Nicking Endonuclease and Uses Thereof
Recombinant nicking endonucleases and associated methylases have been obtained and sequenced and their specificity has been defined. A mutant form of the nicking endonuclease has been cloned where the mutation includes deletion of amino acid sequences at the C-terminal end of the protein. The nicking enzymes have been used for a number of purposes including: amplifying DNA from as few cells as can be found in a single bacterial colony in the presence of a strand displacing polymerase; and for removing genomic DNA in a biological preparation where it is deemed to be a contaminant.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
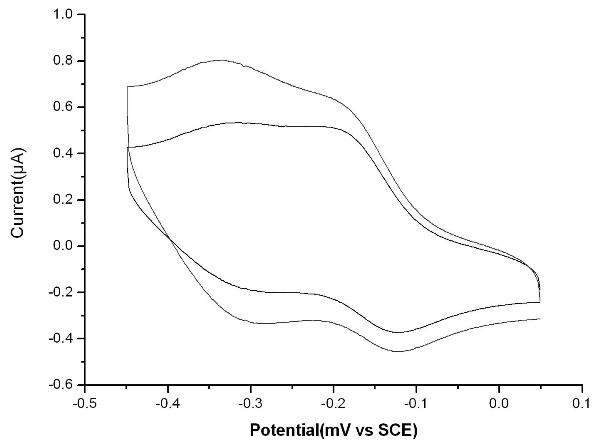
Manufacturing method and application of electrochemiluminescence sensor for detecting thrombin
ActiveCN102507689AHigh sensitivityHigh luminous intensityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSingle strandElectrochemiluminescence
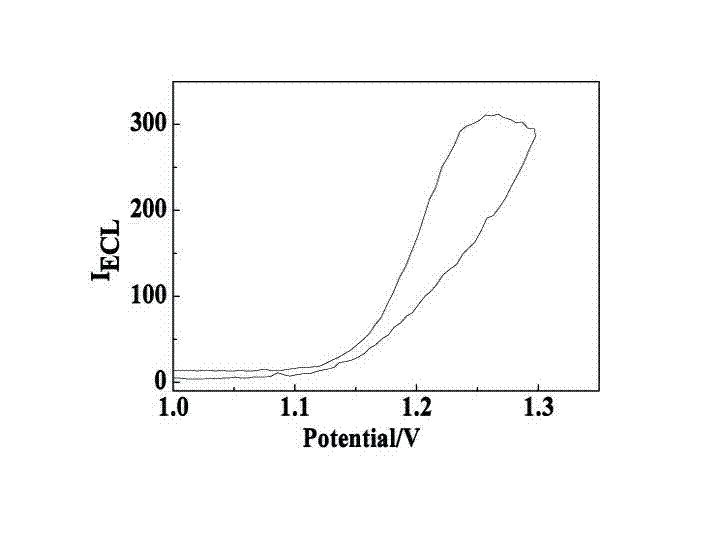
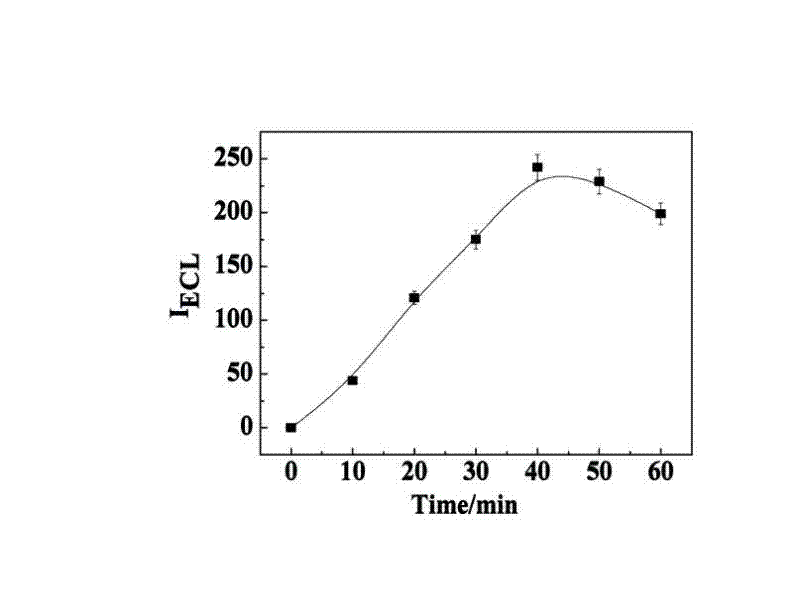
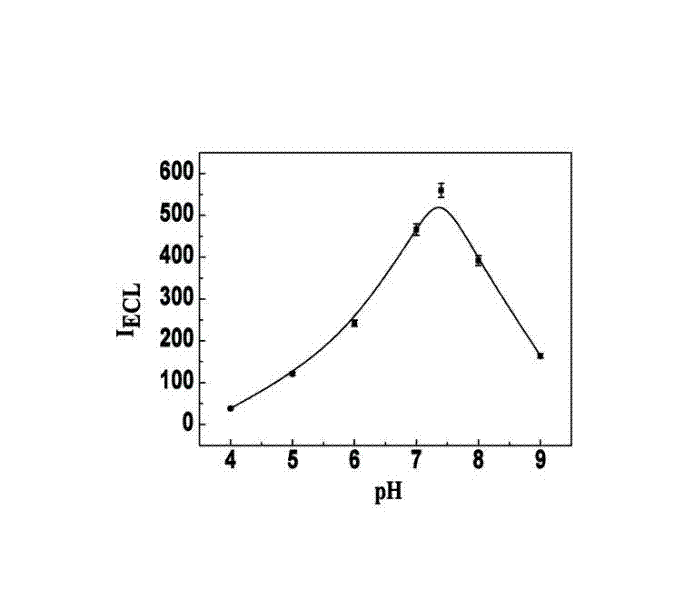
The invention relates to a manufacturing method and application of an electrochemiluminescence sensor for detecting thrombin. Ruthenium bipyridine with active group is modified to the gold nanoparticle surface to form an electrochemiluminescence nanoparticle probe, which plays the role of amplifying electrochemiluminescence, and the upper part DNA single strand is modified on the working electrode surface to constitute an electrochemiluminescence sensor. The target analyte of thrombin is subjected to reaction with partial DNA double strands and then with DNA polymerase, Nb.BbvCI nicking enzyme and partial DNA single strand to obtain DNA hybrid solution which is added into the sensor, so as to increase electrochemiluminescence nanoparticle probes on the electrode surface and further lead to an enhanced electrochemiluminescence signal, and accordingly thrombin determination is realized. The inventive sensor has high selectivity and detection sensitivity.
Owner:武汉菲思特医学检验实验室有限公司
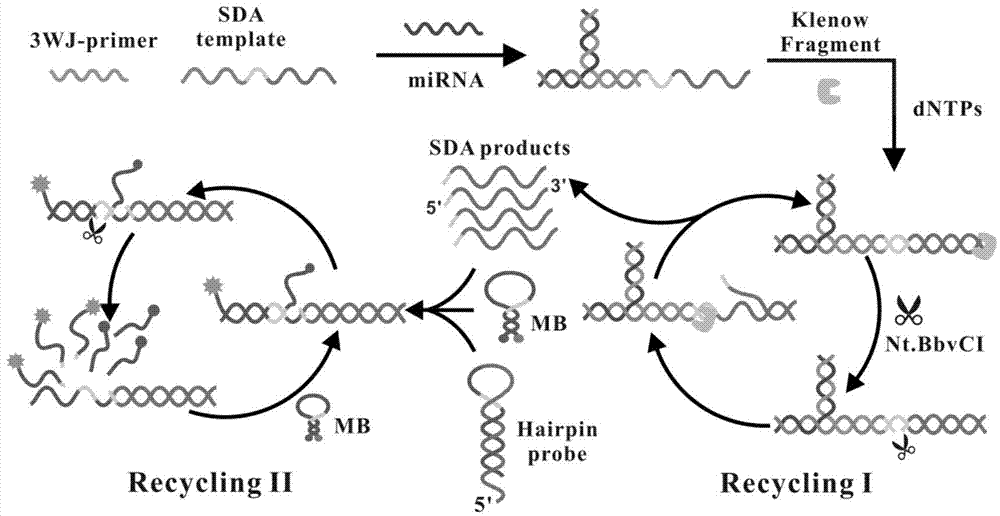
Cascading isothermal amplification based miRNA fluorescence detection kit and miRNA fluorescence detection method
InactiveCN103789435AEasy to distinguishHigh selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceDigestion
The invention discloses a cascading isothermal amplification based miRNA fluorescence detection kit and a miRNA fluorescence detection method. The target miRNA can specifically recognize and form a stable three-way crossing structure with a ternary probe through complementary hybridization of nucleic acids; a ternary primer in the three-way crossing structure performs strand displacement amplification (SDA) along a ternary template and generates a number of SDA template products; the SDA template product can open a difunctional hairpin probe to trigger nickase to perform signal amplification reaction finally; and a cyclophorase digestion molecular beacon can generate cascading amplified fluorescence signals. The kit can detect miRNA low to 100fM; and the detection method has superhigh specificity, can well distinguish highly homologous sequences at different mispairing positions and solves the difficult problem of false positive result caused by poor specificity in the existing detection method.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
DNA nicking enzyme from a homing endonuclease that stimulates site-specific gene conversion
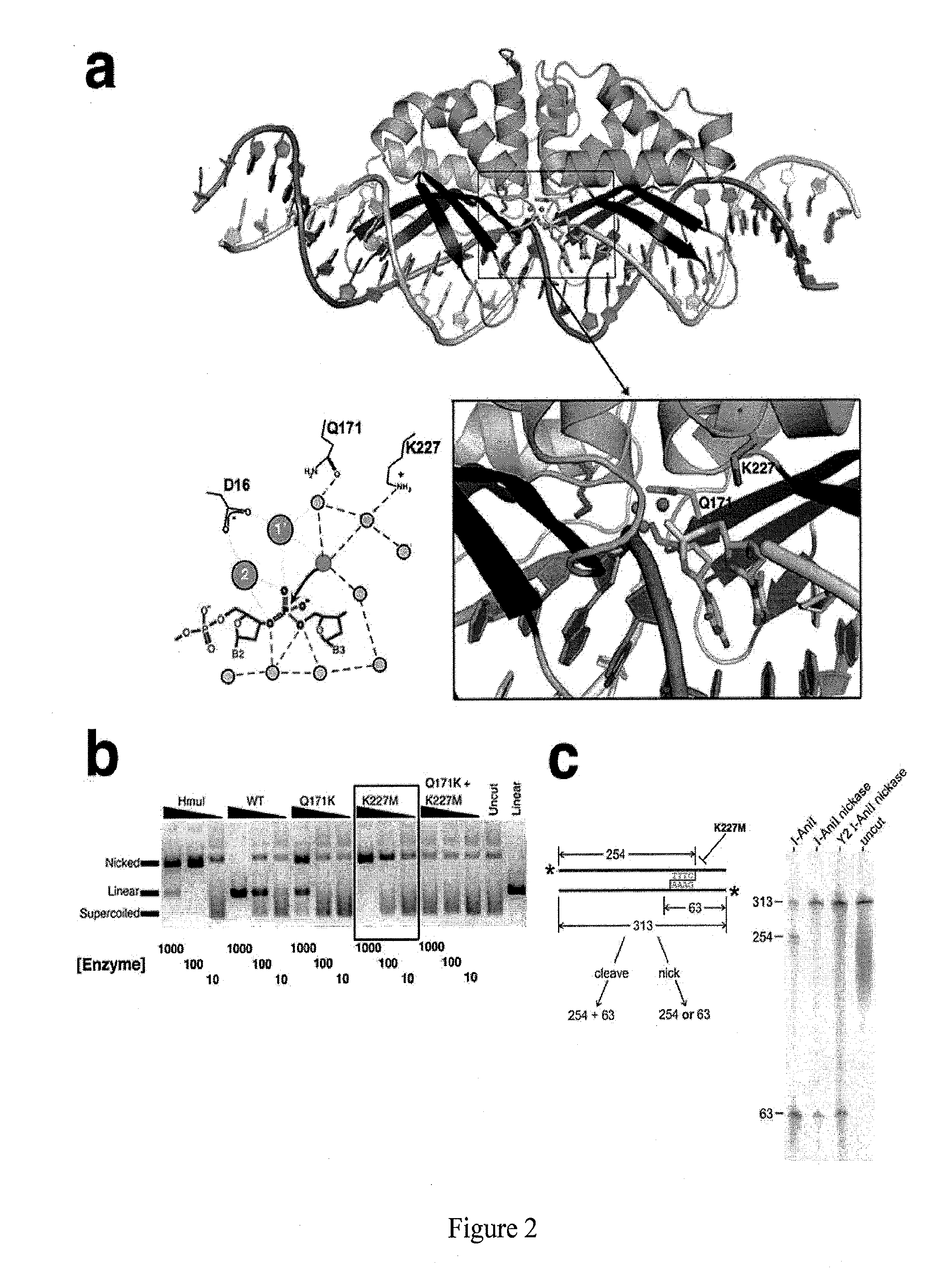
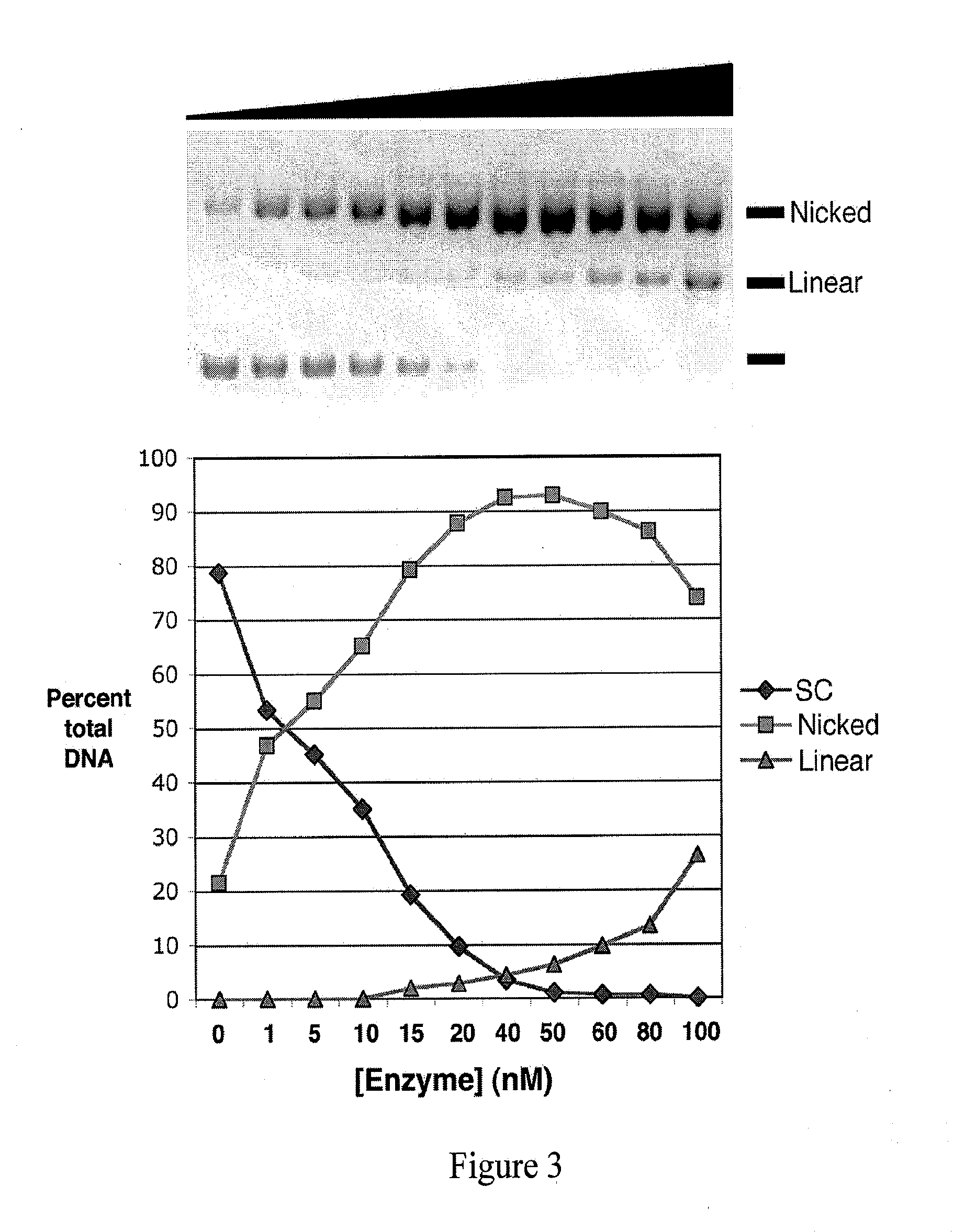
An engineered highly specific DNA-cleavage enzyme delivers a site-specific nick in a double stranded DNA, to cleave one DNA strand within its target site while leaving the opposing DNA strand intact. The engineered enzyme provides the ability to induce a gene conversion event in a mammalian cell. An engineered sequence-specific nickase derived from a LAGLIDADG homing endonuclease is altered by a single amino acid residue, wherein the amino acid residue is involved in the polarization of solvent molecules and acid-base catalysis in the active site without affecting direct contacts between the enzyme and either the bound DNA or bound metal ions. Engineered, site-specific nickase variants, such as of I-AniI and other homing endonucleases, are particularly useful in targeted genome engineering as well as therapeutic, targeted gene repair.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
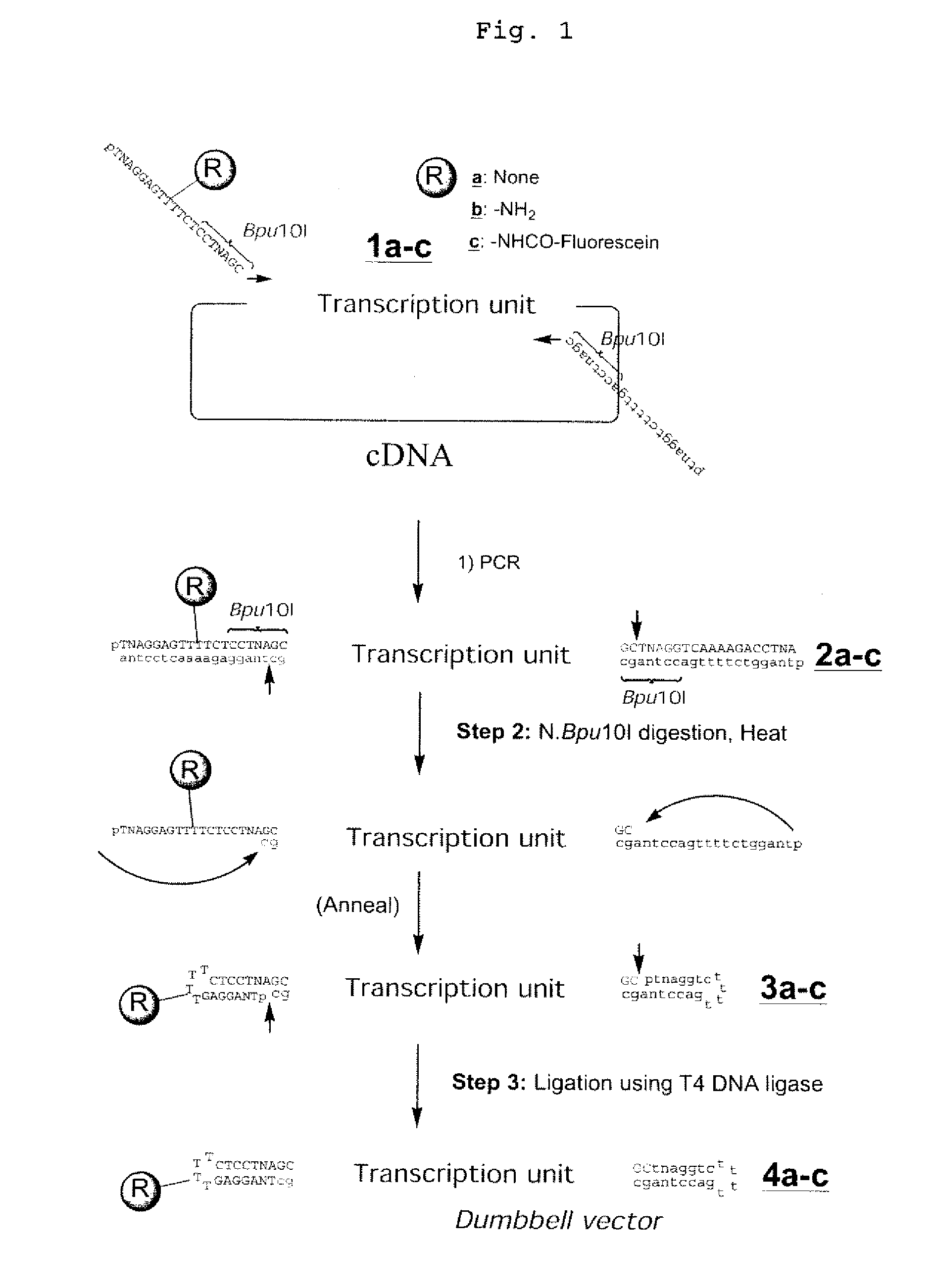
Efficient Process For Producing Dumbbell Dna
InactiveUS20080153763A1Simple methodOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesPhosphorylationAmplification dna
The present invention provides a simple method for producing a dumbbell-shaped DNA.A method for producing a dumbbell-shaped DNA, wherein each of sense and antisense strands is connected at both the 5′ and 3′ ends of a linear-shaped double stranded DNA by a single stranded DNA of loop structure, comprising the steps of;1) amplifying a target DNA in a template DNA by PCR using sense and antisense primers, wherein each of the sense and antisense primers contains the following sequence (a) at the 5′ end and also contains the following sequences (b), (c), and (d) in order from the 5′ end to the 3′ end,(a) a part of a sense sequence of a nickase recognition sequence, comprising the sequence of a region between the site where a nick is introduced by the action of a nickase and the 3′ end,(b) a sequence capable of forming a loop structure from a single strand,(c) the entire antisense sequence of the nickase recognition sequence (a),(d) a sequence complementary to all or part of the sequence of the target DNA;2) treating the amplified DNA product of step 1) with a nickase of (a);3) heating and then annealing the nickase treated amplified DNA product of step 2); and4) treating the heated and annealed amplified DNA product of step 3) with DNA ligase, wherein the sense and antisense primers used in step 1) are phosphorylated at the 5′ end, or the amplified DNA product is phosphorylated at the 5′ end after step 1) but before step 4).
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Novel method for isothermal amplification detection of double-stranded nucleic acid based on nicking enzyme
ActiveCN104726549AEasy to operateShort reaction timeMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
The invention relates to a novel method for isothermal amplification detection of a double-stranded nucleic acid based on nicking enzyme, belongs to the field of nucleic acid test, and in particular to a method for amplifying a single-chain target from a double-stranded nucleic acid target under the combined action of the nicking incision enzyme and polymerase and carrying out efficient specificity amplification on the target nucleic acid employing two amplification products and a replacement primer in an isothermal condition. Through selection of one amplification primer and an amplification template annealing region, efficient specificity amplification of the target nucleic acid can be finished by only three primers; the 3' end of the template is completely complementary with the primer; the specificity is improved; meanwhile, the problem of refractory amplification due to the fact that the replacement primer occupies the complementary position of the amplification primer in the prior art is avoided; the amplification primer can also be designed into a form of a molecular beacon; and only correctly amplified target sequence can be annealed together with the primer in the form, and generates subsequent fluorescence signals, so that the method has relatively good specificity.
Owner:QINGDAO NAVID BIOTECH CO LTD
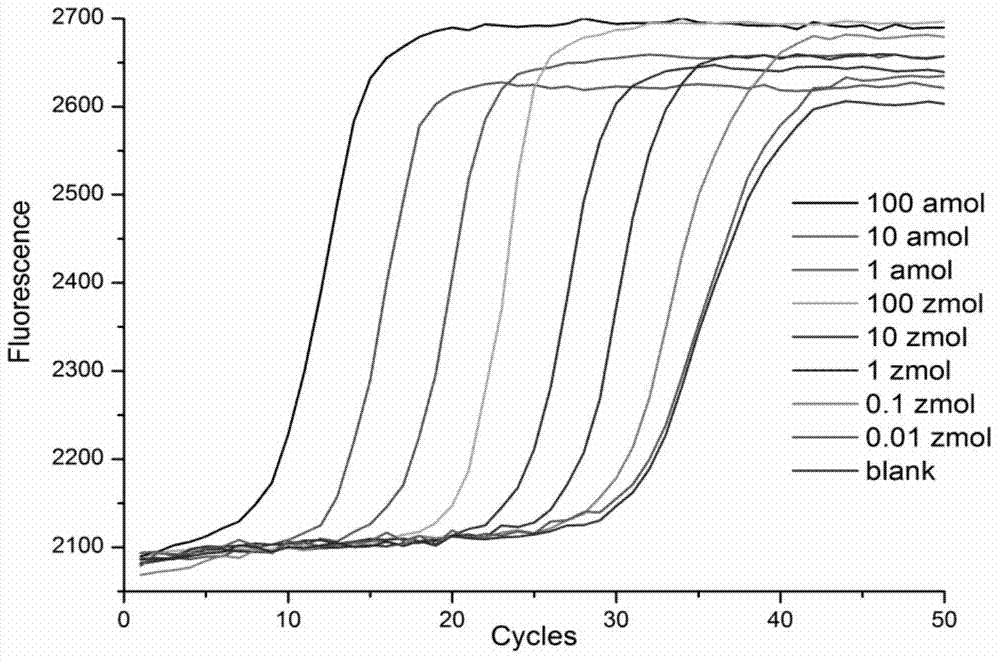
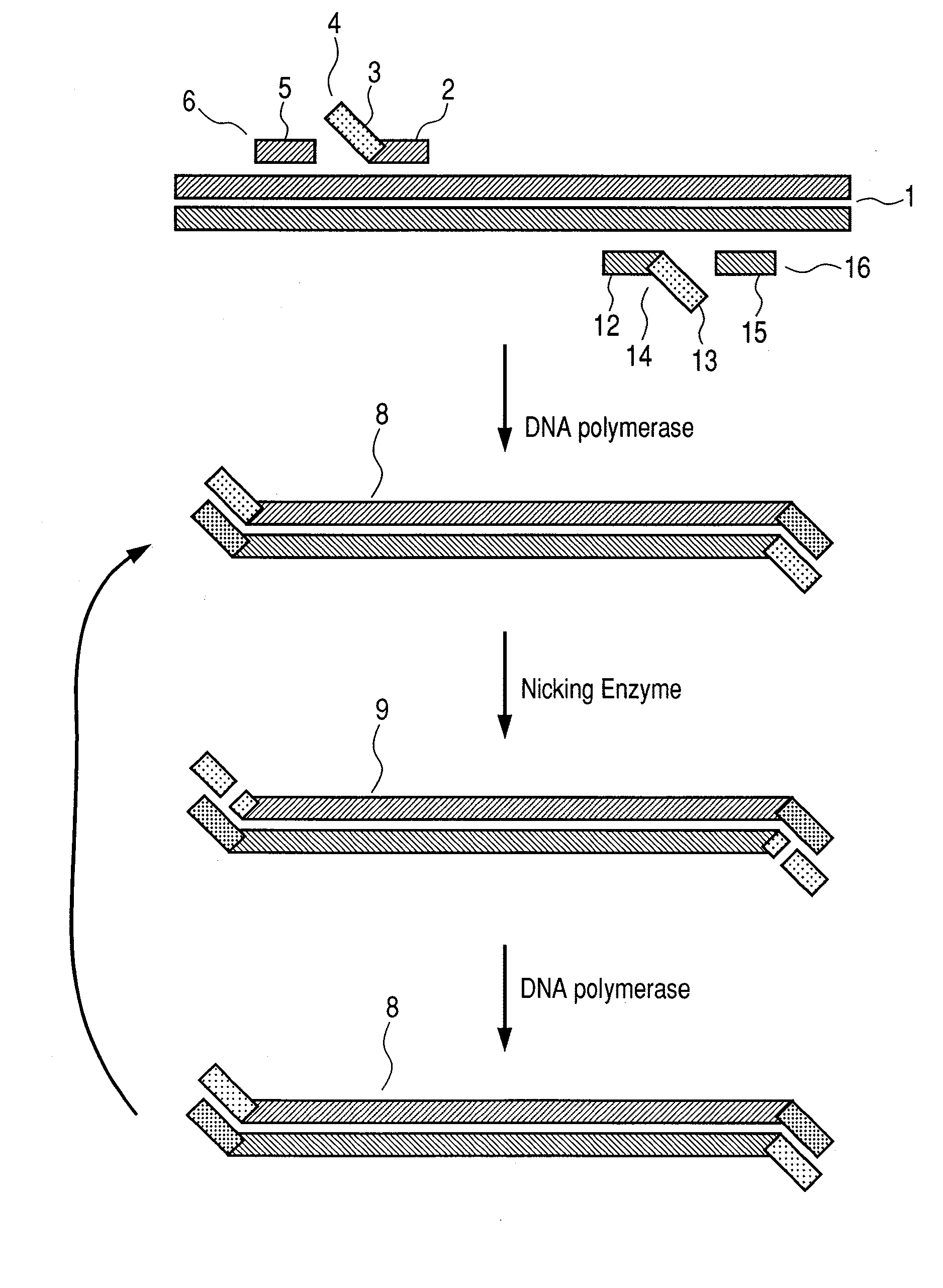
Nucleic acid amplification method
InactiveUS20100255546A1Inexpensive and simple isothermal nucleic acid amplification methodSimplify the design processMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LA-DNA
Disclosed is a novel isothermal nucleic acid amplification method enabling inexpensive and simple and easy detection. The method includes introducing nicking enzyme recognition sequences into an analysis target nucleic acid using nicking enzyme recognition sequence-containing primers and isothermally amplifying a specific region of the target nucleic acid using the primers, a nicking enzyme and a DNA polymerase having strand displacement activity.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
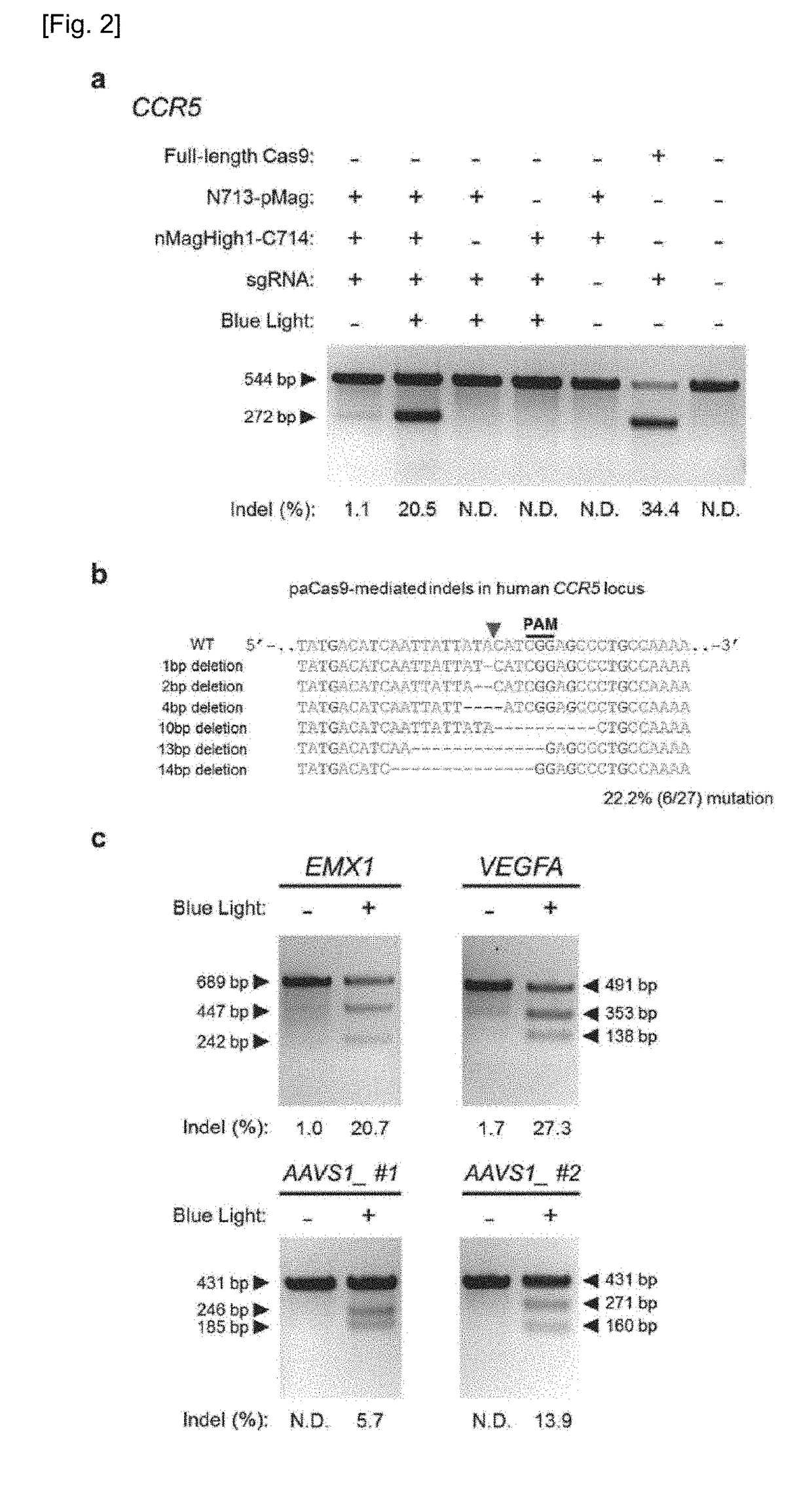
Set of Polypeptides Exhibiting Nuclease Activity or Nickase Activity with Dependence on Light or in Presence of Drug or Suppressing or Activating Expression of Target Gene
The present invention provides, for example, a set of two polypeptides exhibiting the nuclease activity with dependence on light or in the presence of a drug, in which an N-terminal side fragment and a C-terminal side fragment of a Cas9 protein are bound to each of two polypeptides which form a dimer with dependence on light or in the presence of a drug.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Compositions and methods for quantifying a nucleic acid sequence in a sample comprising a primer oligonucleotide with a 3′-terminal region comprising a 2′-modified nucleotide
ActiveUS9096897B2Reduces and eliminates generationExtend detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention features compositions and methods for quantifying detection of a target oligonucleotide in a sample in real time comprising one or more primer oligonucleotides comprising a 5′ nicking enzyme recognition site and a 3′-terminal region comprising a 2′-modified nucleotide. These methods are compatible with target oligonucleotides amplified using a nicking amplification reaction.
Owner:ENVIROLOGIX INC
Method for synthesizing short single strand deoxyribonucleotide probe
ActiveCN103276074AWide range of usesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDiseaseEnzyme digestion
The invention belongs to the field of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) biosynthesis, and in particular relates to a method for synthesizing a short single strand deoxyribonucleotide probe and application thereof. The short single strand deoxyribonucleotide probe can be used for detecting small non-coding ribonucleic acid (RNA) such as micro ribonucleic acid. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing plasmids recombined with template DNA; (2) cutting and connecting the template DNA, performing enzyme digestion on the recombined plasmids to obtain the template DNA, and connecting the template DNA end to end to form a ring; (3) cutting a single strand, performing rolling-circle replication, cutting one strand of the template DNA by using nickase, adding polymerase to perform rolling-circle replication by taking annular DNA with a nick as a template, and amplifying to obtain a DNA single strand containing a neck ring-probe structure; and (4) preparing target short single strand DNA, cutting the product of the step (3) by using a type II incision enzyme to form a target single strand DNA probe and a byproduct DNA, and separating and purifying through PAGE (polyacylamide gel electrophoresis) to obtain a single strand DNA probe without mutation. The short single strand deoxyribonucleotide probe has wide applications in the fields of detection of small non-coding RNA and diagnosis and treatment of small non-coding RNA related diseases.
Owner:深圳弸福科技有限公司
Dual-ring hairpin probe mediate label-free strand displacement amplification method for detecting bleomycin
ActiveCN105385770AReduced stabilityAvoid non-specific hybridizationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescencePolymerase L
The invention discloses a dual-ring hairpin probe mediate label-free strand displacement amplification method for detecting bleomycin. The method includes the steps that when bleomycin exists, a dual-ring hairpin probe fractures at a recognition site, and a triggering sequence is released; the triggering sequence and a ring part of a signal probe are combined and subjected to a strand displacement amplification reaction under the effect of a polymerase and a nicking enzyme, and finally a great number of G-four-chain sequences are generated. At the same time, a primer chain extends to open the signal probe, and therefore the G-four-chain sequences packaged in the neck of the signal probe can be exposed. Finally, NMM molecules are bound to the G-four-chain sequences to generate fluorescence signals, and bleomycin is quantified through the detected fluorescence signals. As the triggering sequence is designed at the neck of the dual-ring hairpin probe, background signals of a detection system are reduced; by combining bleomycin cutting and the strand displacement amplification reaction, bleomycin can be detected sensitively, and the detection limit is 0.34 nm. The method has the advantages of being easy to operate, free of labeling and good in specificity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
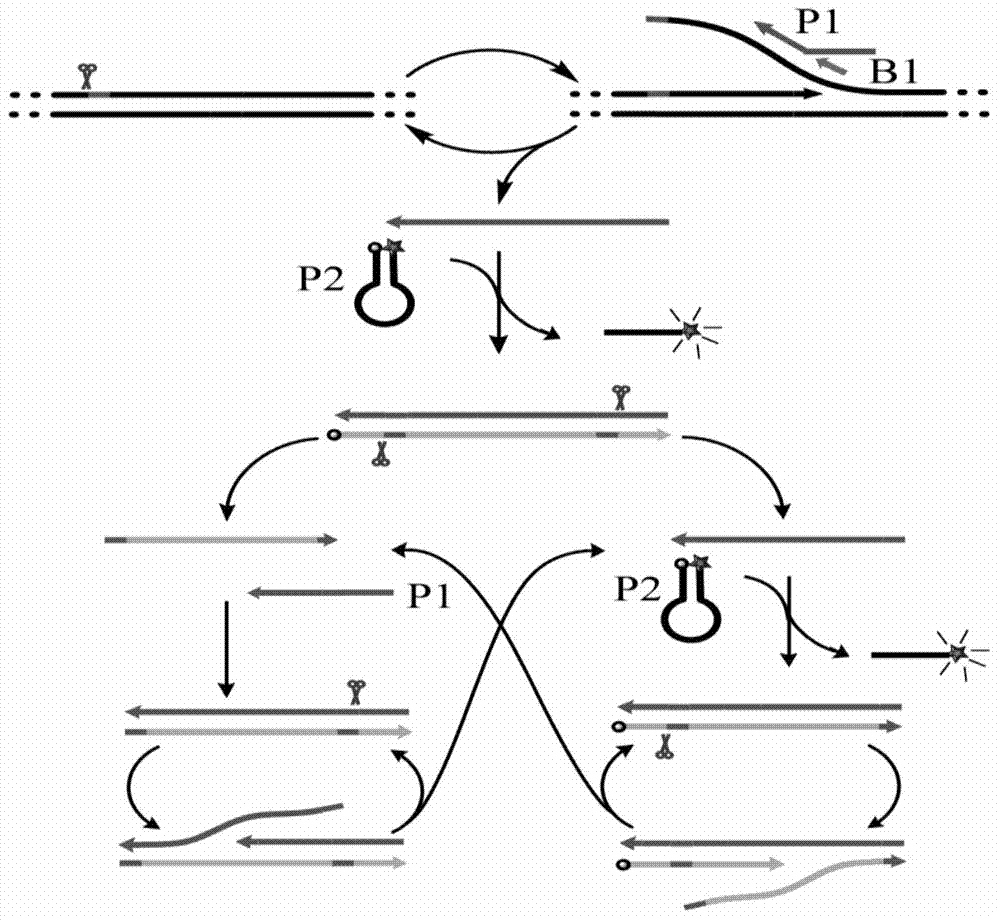
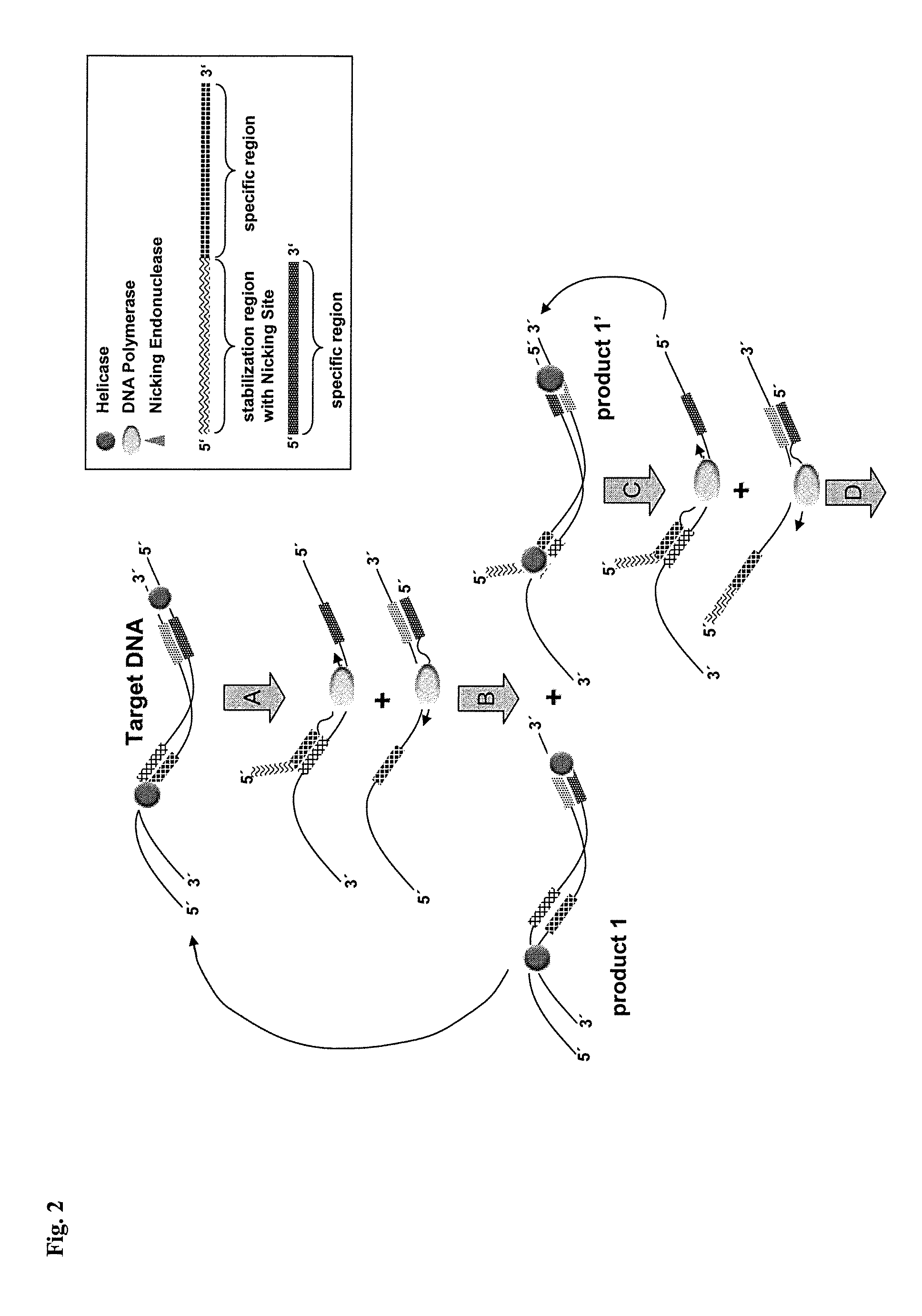
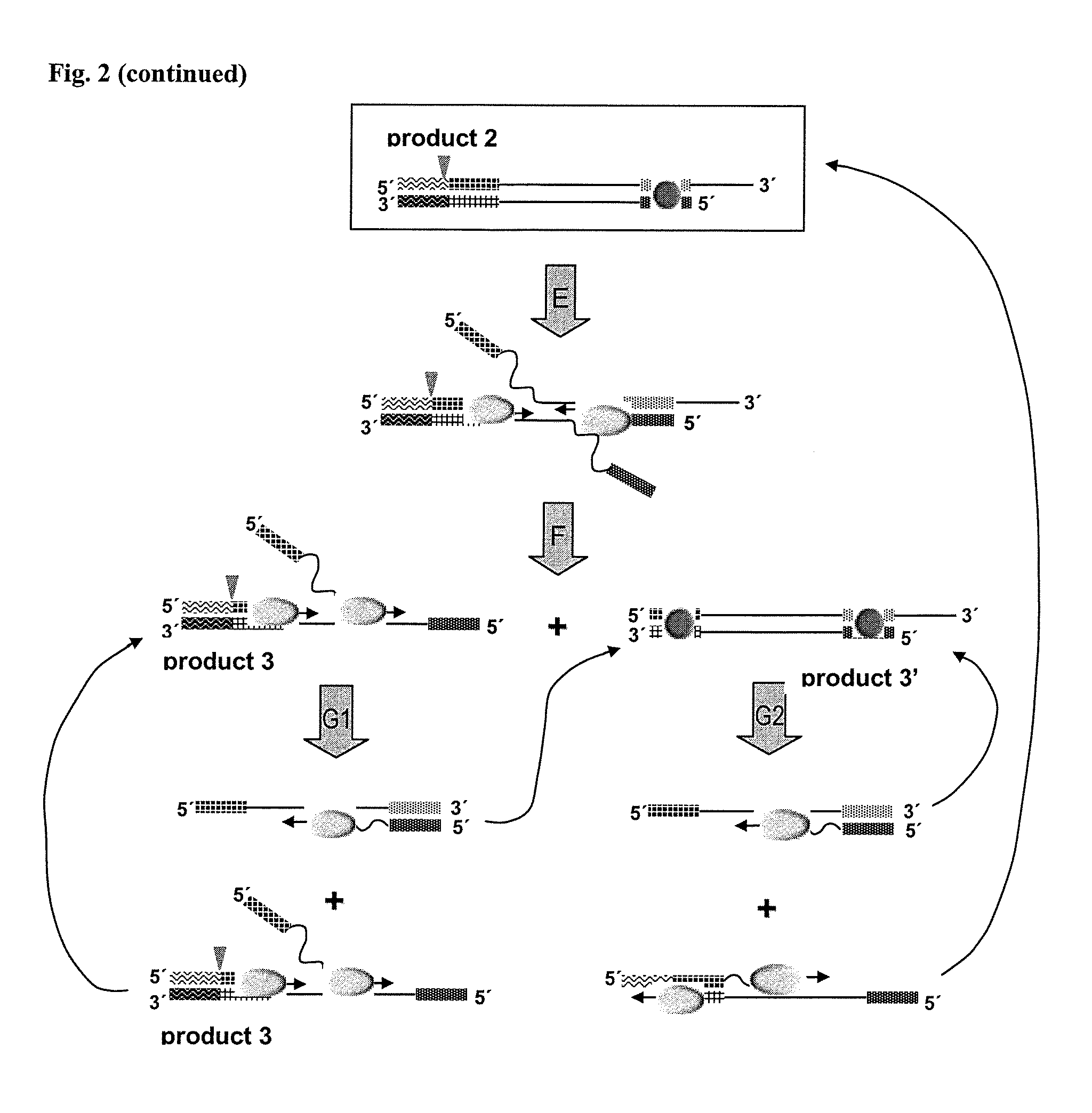
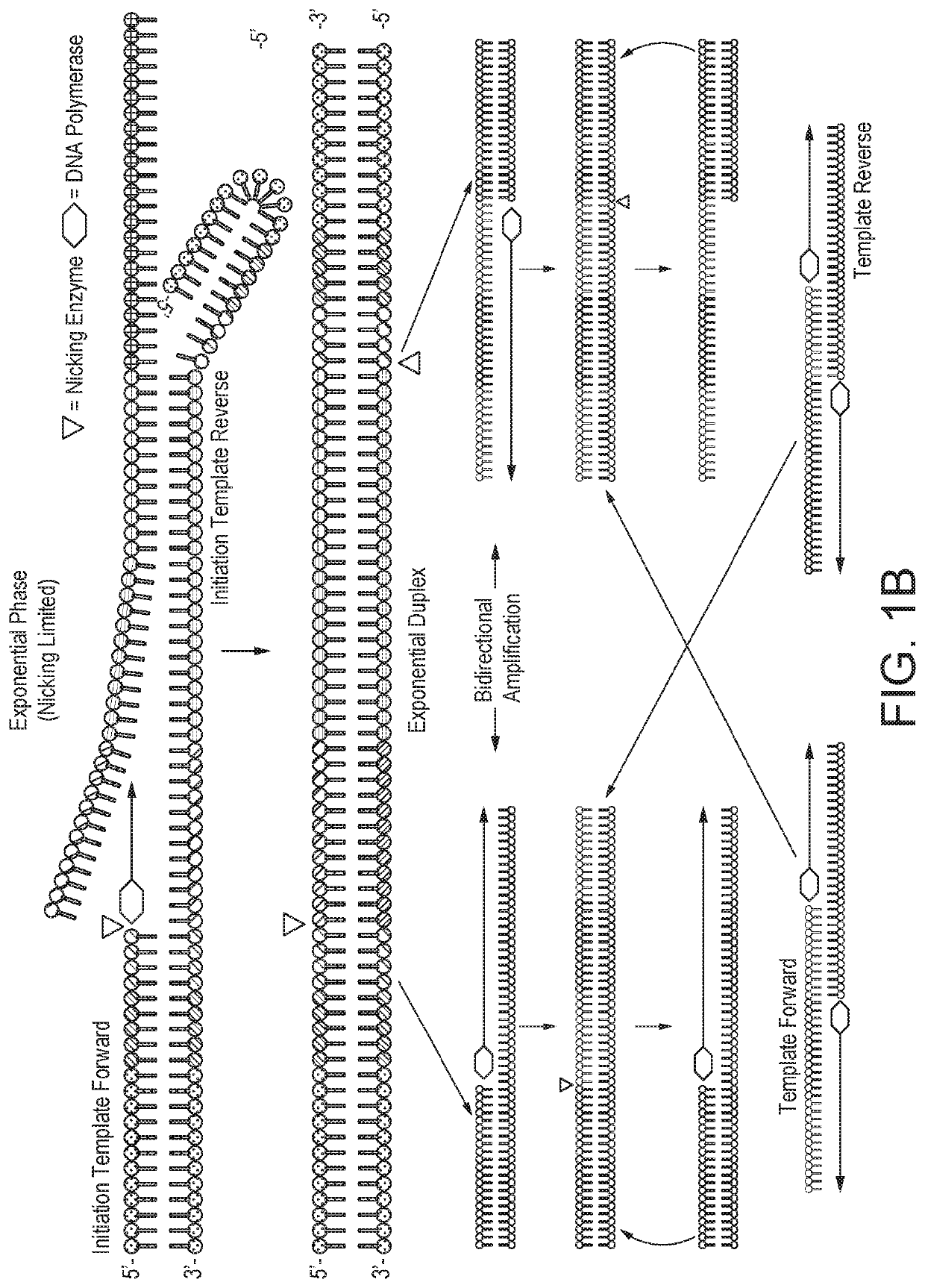
Helicase dependent isothermal amplification using nicking enzymes
ActiveUS20130210019A1Strong specificityAmplify longer template nucleic acidsMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesDna polymerasenDNA unwinding enzyme
The present invention relates to a method for amplifying a template nucleic acid, wherein the method comprises amplifying said template nucleic acid using the helicase dependent amplification (HDA) reaction in the presence of a nicking endonuclease, and wherein said template nucleic acid comprises a sequence recognized by said nicking endonuclease or a sequence recognized by said nicking endonuclease is introduced into the template nucleic acid during the HDA reaction. The invention further pertains to a kit for amplifying a nucleic acid, comprising a nicking endonuclease, a helicase and a DNA polymerase.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Bioelectrochemical sensor for detecting nuclear factor-kappab, its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102262117ARapid quantitative detection is convenientConvenient Quantitative DetectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesNanoparticleSaturated calomel electrode
The invention relates to a novel bioelectrochemical sensor for detecting nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB), its preparation method and its application. The novel bioelectrochemical sensor is a three-electrode system sensor, which is characterized in that the counter electrode in the three electrodes is a platinum electrode, the reference electrode is a saturated calomel electrode, and the working electrode is a gold electrode, and the gold electrode is decorated with strand of DNA. The sensor can successfully identify the lowest concentration of NF-κB at 0.1nM, and the linear detection range is 0.1nM~10nM. The novel bioelectrochemical sensor of the present invention is based on the specific combination of NF-κB and target DNA, and comprehensively uses the dual signal amplification characteristics of Nicking Enzyme (NEase) and gold nanoparticles, as well as the high sensitivity of the electrochemical detection method, so that NF-κB The detection of κB is simple and feasible, and the same principle can also be extended to the detection of other biomolecules, with broad application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for realizing genome editing and accurate and targeted knock-in of genes in fishes
ActiveCN108949830AImprove integration efficiencyLow costMicroinjection basedAnimal husbandryRandom mutationGenome editing
The invention provides a method for realizing genome editing and accurate and targeted knock-in of genes in fishes. A technology of producing DNA single-chain gap based on nicking enzyme is utilized,assisted with a set of homologous recombination repair factor RecOFAR, so as to realize high-efficient, accurate and targeted integration of genome editing and gene knock-in in the fishes. The problems that a current existing method is low in efficiency, and random mutation efficiency of target points is higher are overcome.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
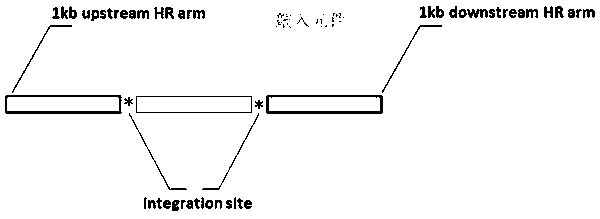
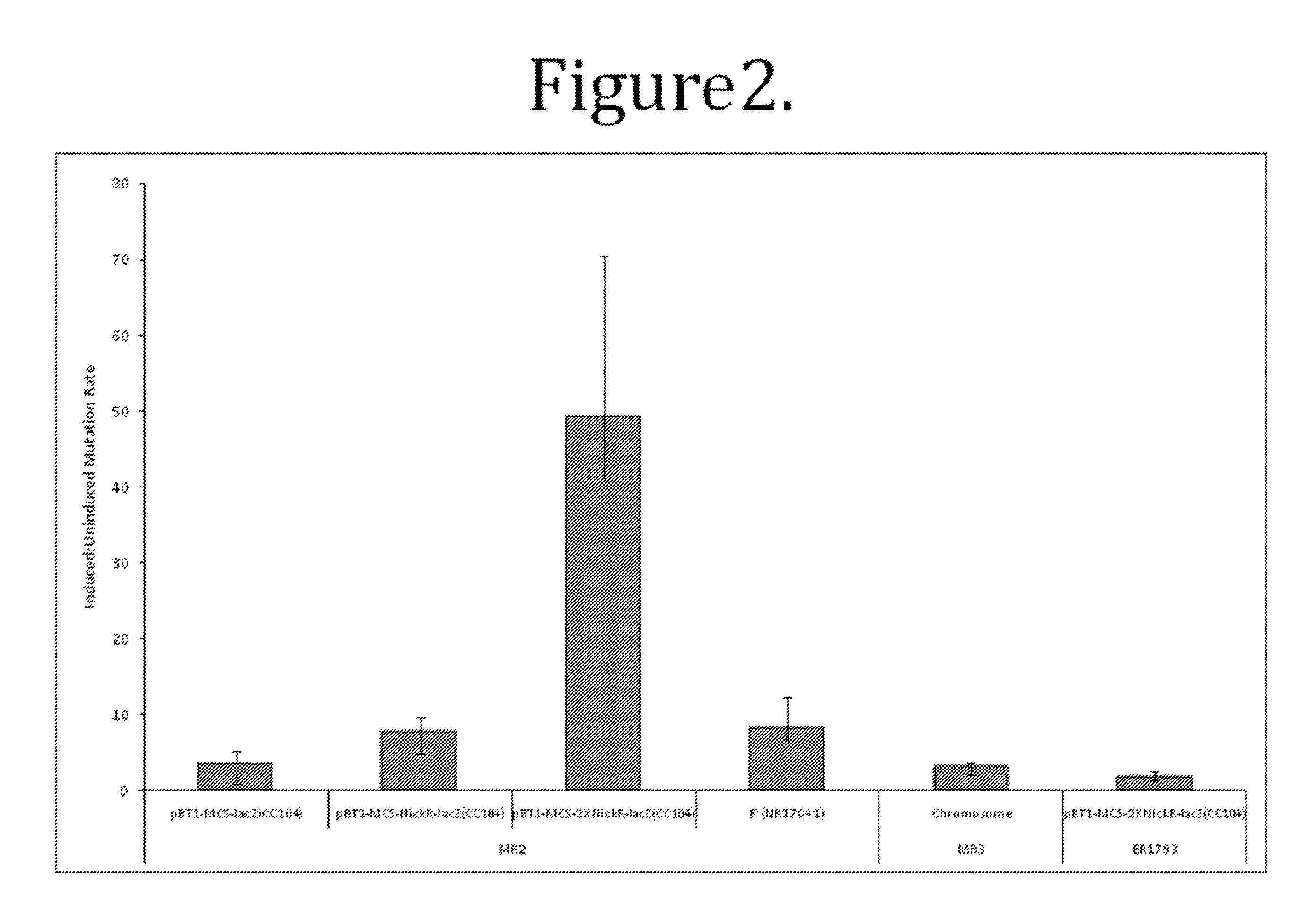
Methods and compositions for targeted mutagenesis in bacteria
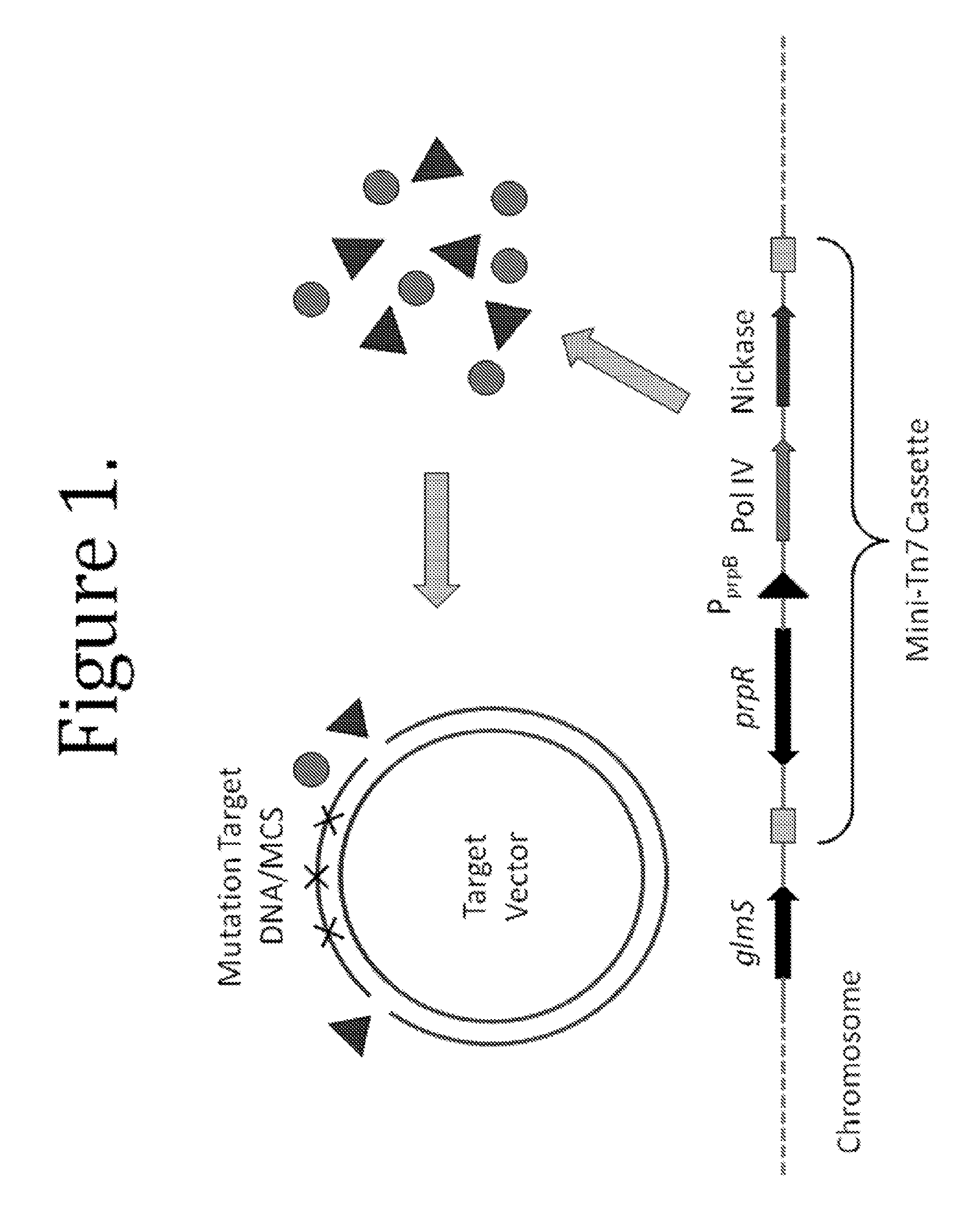
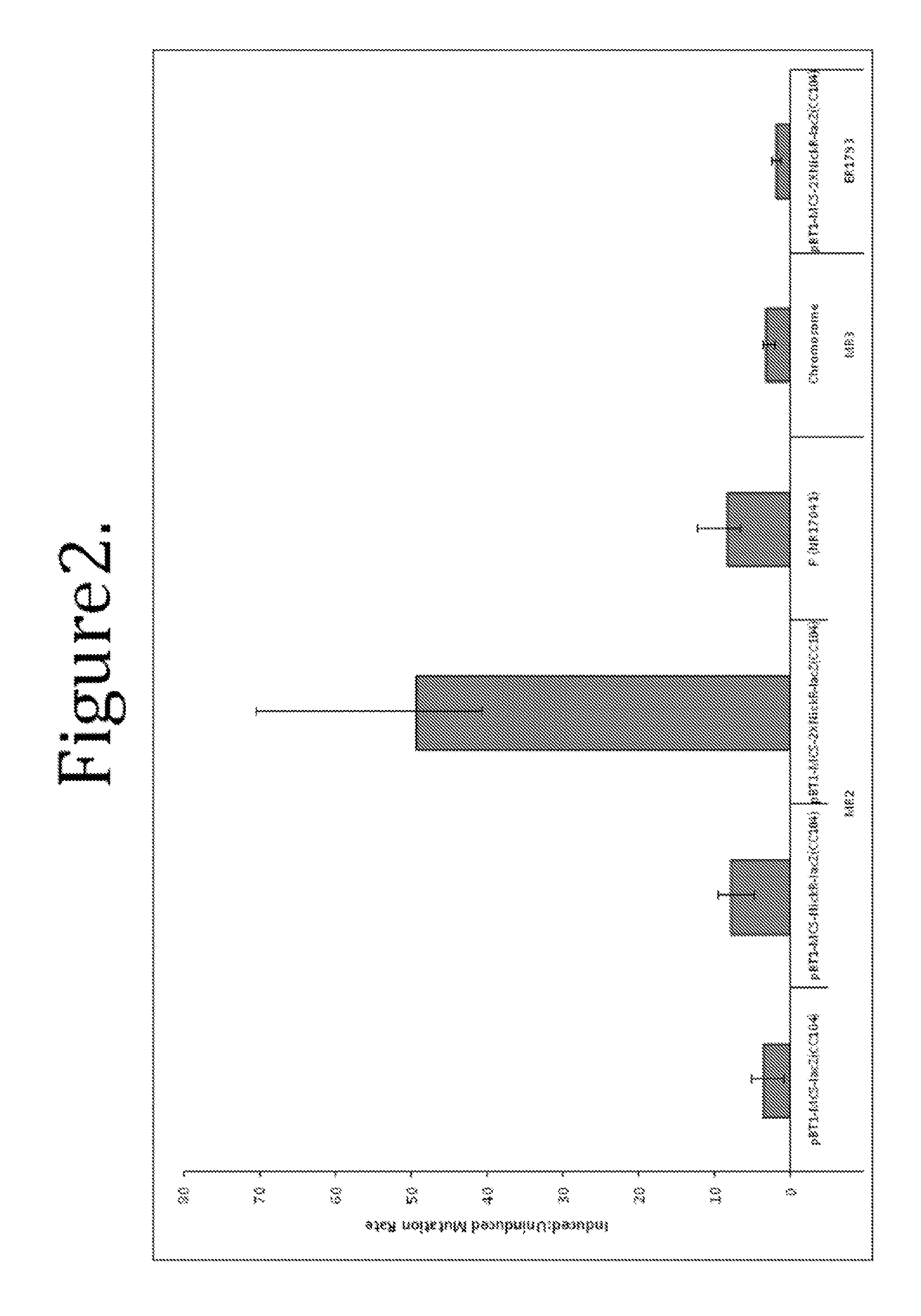
This disclosure provides methods and compositions for targeted mutagenesis of specific genes in a bacterial strain. By inducibly over-expressing error-prone polymerases such as Pol IV or Pol V in conjunction with nickase in a bacterial strain, and housing the targeted gene(s) on an episome or plasmid which contains one or more nickase recognition sequences, the targeted gene(s) can be selectively mutated at rates significantly greater than genes contained on the chromosome. The methods disclosed herein are useful for engineering desirable bacterial phenotypes and novel strains, including for example strains useful for treating or degrading waste and / or environmental contaminants, for optimizing bioprocesses, and for converting low-value feed-stock into value-added products.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Isothermal amplification nucleic acid detection method based on helicase and nicking enzyme and kit
InactiveCN109097448ASignal persistsDisadvantages of Avoiding PollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
Owner:深圳百纳心致生命科学有限公司 +1
Manufacturing method and application of electrochemiluminescence sensor for detecting thrombin
ActiveCN102507689BHigh sensitivityHigh luminous intensityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSingle strandElectrochemiluminescence
The invention relates to a manufacturing method and application of an electrochemiluminescence sensor for detecting thrombin. Ruthenium bipyridine with active group is modified to the gold nanoparticle surface to form an electrochemiluminescence nanoparticle probe, which plays the role of amplifying electrochemiluminescence, and the upper part DNA single strand is modified on the working electrode surface to constitute an electrochemiluminescence sensor. The target analyte of thrombin is subjected to reaction with partial DNA double strands and then with DNA polymerase, Nb.BbvCI nicking enzyme and partial DNA single strand to obtain DNA hybrid solution which is added into the sensor, so as to increase electrochemiluminescence nanoparticle probes on the electrode surface and further lead to an enhanced electrochemiluminescence signal, and accordingly thrombin determination is realized. The inventive sensor has high selectivity and detection sensitivity.
Owner:武汉菲思特医学检验实验室有限公司
Efficient process for producing dumbbell DNA
InactiveUS7972816B2Easy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesPhosphorylationSingle strand
The present invention provides a simple method for producing a dumbbell-shaped DNA.A method for producing a dumbbell-shaped DNA, wherein each of sense and antisense strands is connected at both the 5′ and 3′ ends of a linear-shaped double stranded DNA by a single stranded DNA of loop structure, comprising the steps of;1) amplifying a target DNA in a template DNA by PCR using sense and antisense primers, wherein each of the sense and antisense primers contains the following sequence (a) at the 5′ end and also contains the following sequences (b), (c), and (d) in order from the 5′ end to the 3′ end,(a) a part of a sense sequence of a nickase recognition sequence, comprising the sequence of a region between the site where a nick is introduced by the action of a nickase and the 3′ end,(b) a sequence capable of forming a loop structure from a single strand,(c) the entire antisense sequence of the nickase recognition sequence (a),(d) a sequence complementary to all or part of the sequence of the target DNA;2) treating the amplified DNA product of step 1) with a nickase of (a);3) heating and then annealing the nickase treated amplified DNA product of step 2); and4) treating the heated and annealed amplified DNA product of step 3) with DNA ligase, wherein the sense and antisense primers used in step 1) are phosphorylated at the 5′ end, or the amplified DNA product is phosphorylated at the 5′ end after step 1) but before step 4).
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Method and reagent for constructing nucleic acid double-linker single-strand cyclical library
ActiveUS10479991B2Increase the lengthSimplify construction proceduresSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandNucleobase
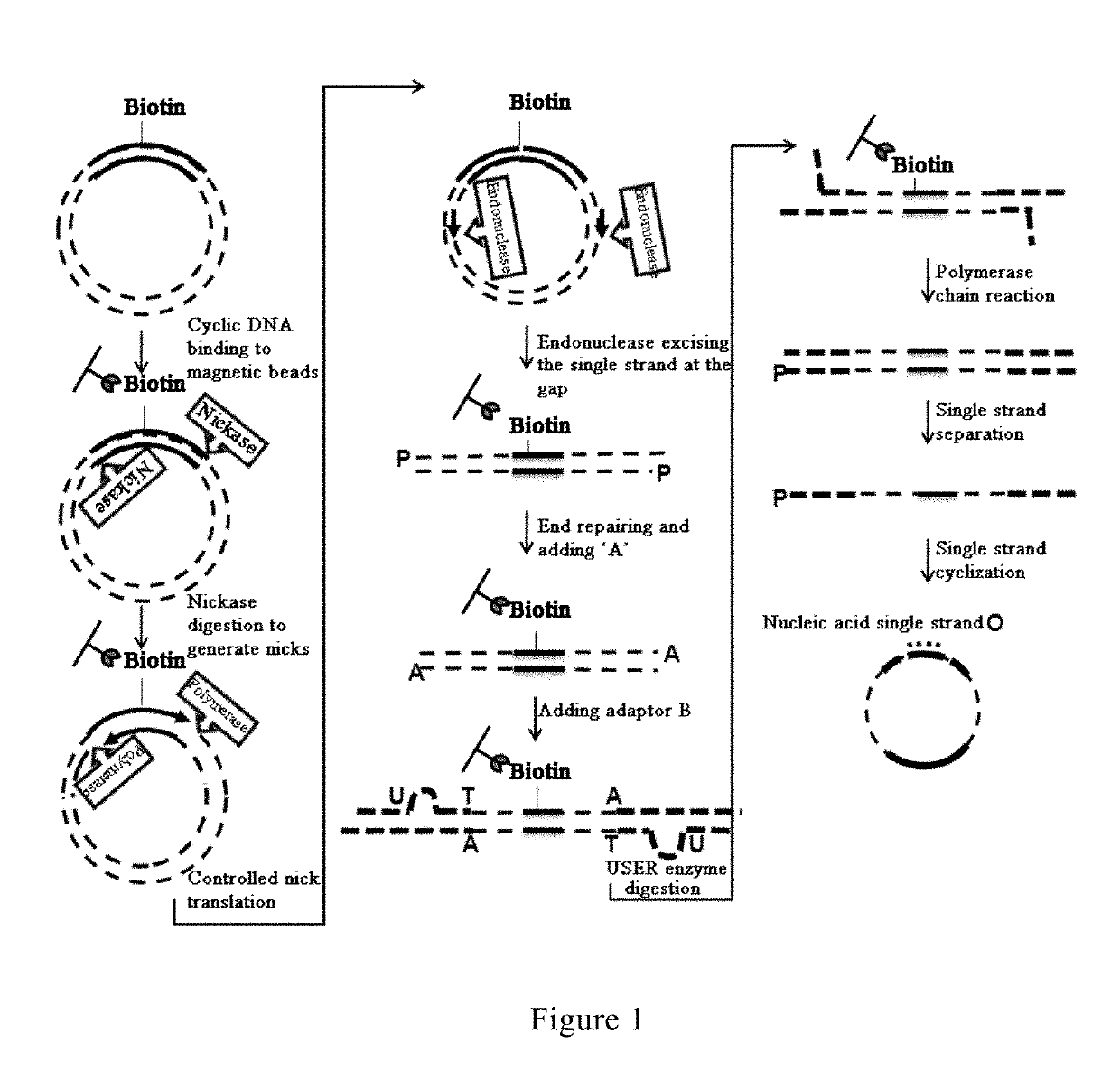
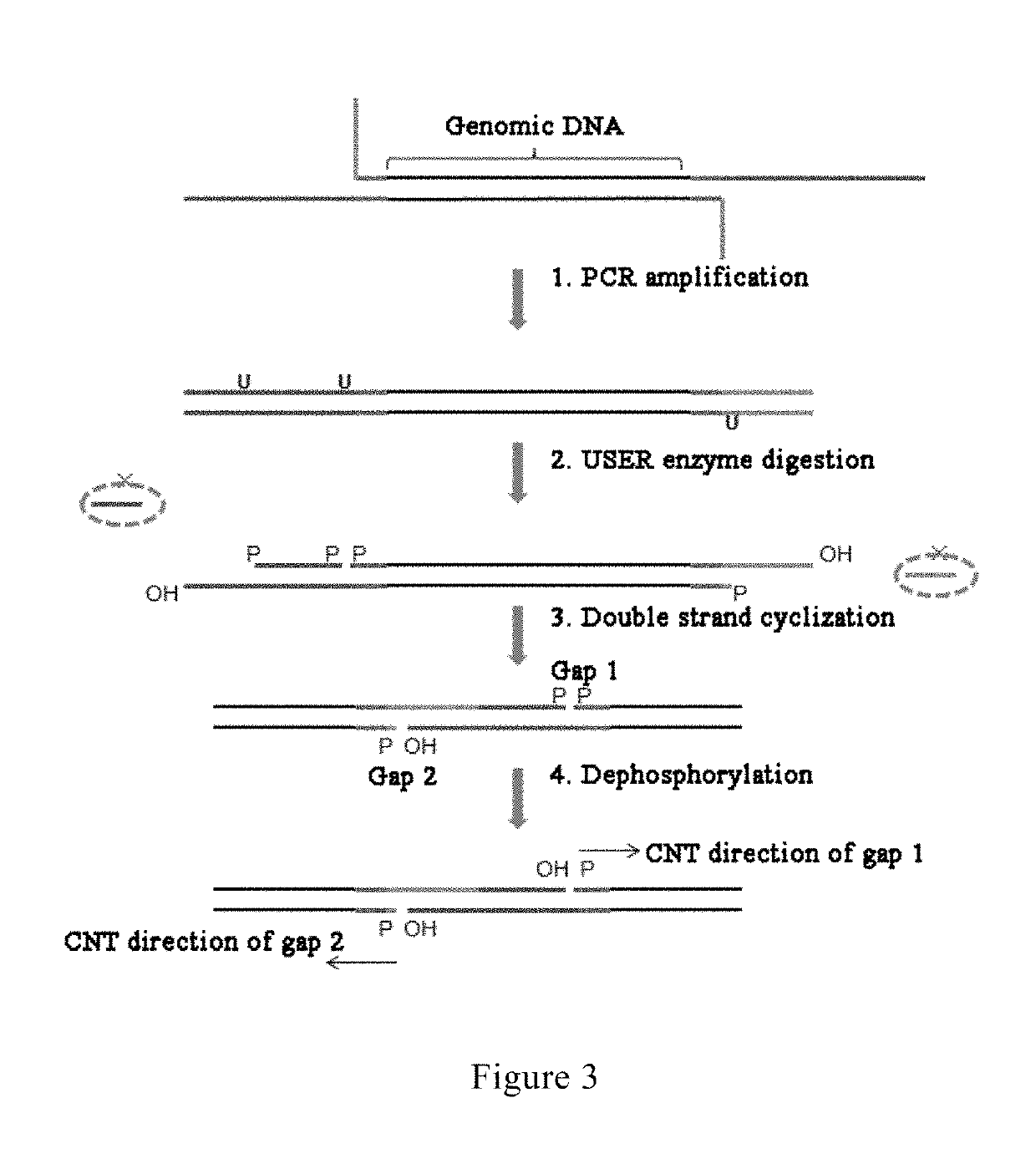
A method and reagent for constructing a nucleic acid double-linker single-strand cyclic library. The method comprises: breaking a nucleic acid into nucleic acid fragments; connecting a first linker sequence; producing by amplification a first product provided with the first linker sequence at either end, where a U nucleobase site is provided on primer sequences and a nicking enzyme recognition sequence is either provided or not provided on same, and a first affinity tag is provided on one of the primer sequences; using USER enzyme to cleave the first product; cyclizing the cleaved first product; treating the cyclization product with either a phosphatase or a nicking enzyme; using a solid-phase vector for combination with a cyclized molecule; performing a restrictive gap translation reaction; removing by digestion any portion that did not undergo the restrictive gap translation reaction; connecting a second linker sequence; producing by amplification a second product provided with the second linker sequence at either end; denaturing the second product, and cyclizing a single-strand nucleic acid molecule. The method allows an increase in the length of library insert fragments, a simplified library construction process, reduced library construction time, and reduced library construction costs.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Methods and compositions for targeted mutagenesis in bacteria
This disclosure provides methods and compositions for targeted mutagenesis of specific genes in a bacterial strain. By inducibly over-expressing error-prone polymerases such as Pol IV or Pol V in conjunction with nickase in a bacterial strain, and housing the targeted gene(s) on an episome or plasmid which contains one or more nickase recognition sequences, the targeted gene(s) can be selectively mutated at rates significantly greater than genes contained on the chromosome. The methods disclosed herein are useful for engineering desirable bacterial phenotypes and novel strains, including for example strains useful for treating or degrading waste and / or environmental contaminants, for optimizing bioprocesses, and for converting low-value feed-stock into value-added products.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Cloning-free linear expression vector constituting method
InactiveCN1403575ALow priceReduce use costSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceExonuclease I
The present invention relates to the constitution method of one kind of linear expression vector, and especially relates to the cloning-free constitution method of one kind of linear expression vector. The method includes introducing nickase identifying gene in the primer design, and nickase enzyme incision and nucleic acid exoenzyme degradation after DNA segment proliferation to form connected segment with protruding end and connecting the segments to obtain linear expression vector. The method of the present invention has greatly lowered constitution cost of linear expression vector and the wide application of the constitution method in scientific research and production can provide technological platform for gene expression and protein function research.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for isothermal amplification of nucleic acid target sequence
InactiveCN113481283AGuaranteed specificityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesSingle strandDouble strand
The invention provides a method for isothermal amplification of a nucleic acid target sequence. The method is suitable for the combined reaction of double-stranded DNA, single-stranded DNA and single-stranded RNA, including nickase and strand displacement enzyme, three primers and one probe are adopted during the detection of the double-stranded DNA and the single-stranded DNA, and three primers and one probe or two primers and one probe can be adopted during the detection of the single-stranded RNA. The probe is a molecular beacon, does not degrade in the amplification process, is only used for specifically binding with a target fragment, provides a fluorescence signal and guarantees the specificity of the reaction. According to the invention, a result is judged in real time by adopting the beacon probe which is not overlapped with the primer in the binding area on the target sequence, and beacon probe binding target sequence has very high specificity; meanwhile, a tube is not opened after the reaction, so that false positive is further avoided; the reaction is carried out at a constant temperature, the consumed time is short, the detection can be completed within 8 minutes, and the POCT detection requirements are met better.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOGERM MEDICAL TECH CO LTD BEIJING BRANCH +1
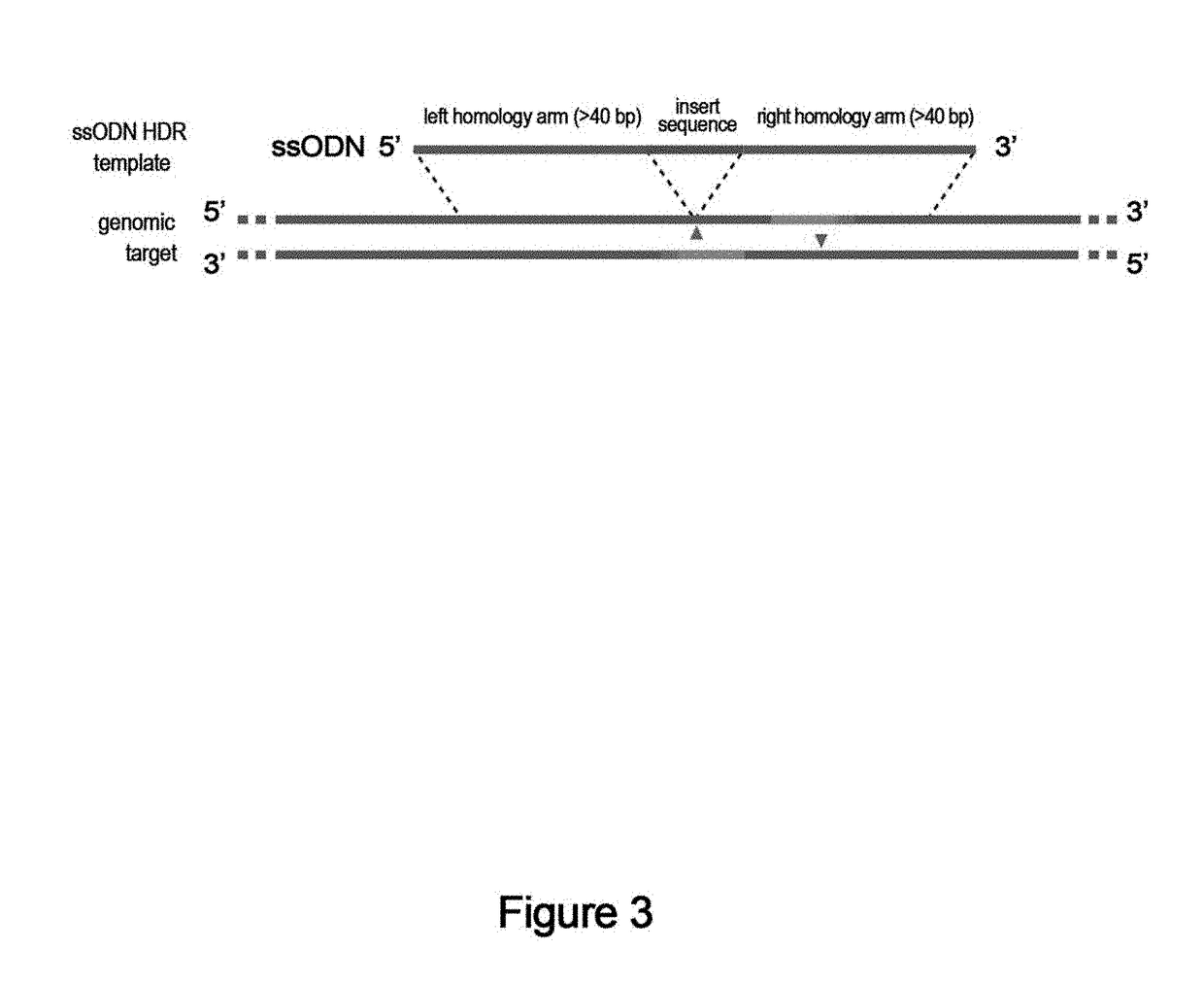
Method for improving plant gene replacing efficiency
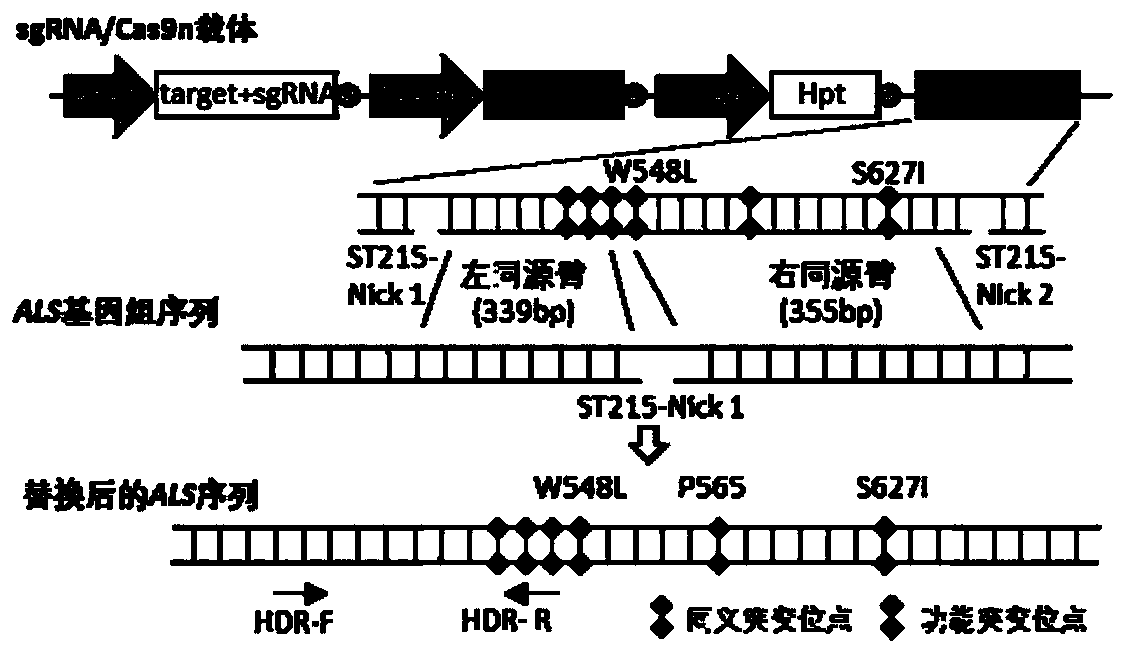
The invention discloses a method for improving plant gene replacing efficiency. The method comprises the following steps of guiding esgRNA, a Cas9 nicking enzyme, a screening agent resistant protein and donor DNA into a purpose plant, enabling the esgRNA to target a DNA fragment A target point sequence, performing coexpression on the Cas9 nicking enzyme and the screening agent resistant protein, wherein the donor DNA sequentially comprises the DNA fragment A target point sequence, a DNA fragment B and a DNA fragment A target point sequence, the DNA fragment B is DNA molecules obtained throughperforming mutation of one or several basic groups on the DNA fragment A, under the guidance of the esgRNA, the Cas9 nicking enzyme produces single-stranded DNA nicking at the DNA fragment A target point sequence in the purpose plant genome and the DNA fragment A target point sequence in the donor DNA, through an in vivo repair mechanism of the purpose plant, the DNA fragment A in the purpose plant genome is replaced with the DNA fragment B, so that plant gene replacement is realized.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for detecting tumor biomarker by using palindrome lock-type probe
InactiveCN108642137AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor BiomarkersBiomarker (petroleum)
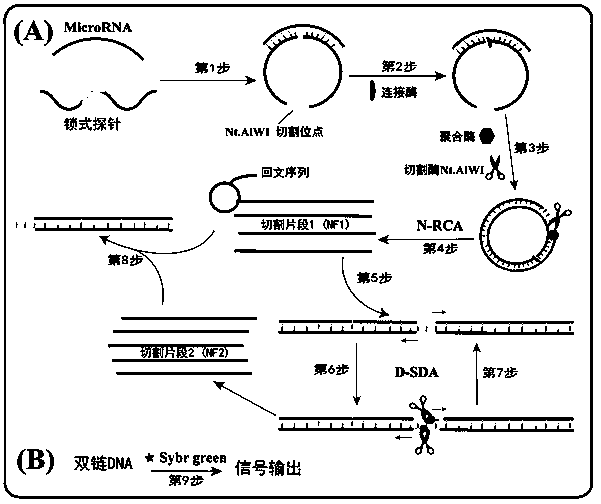
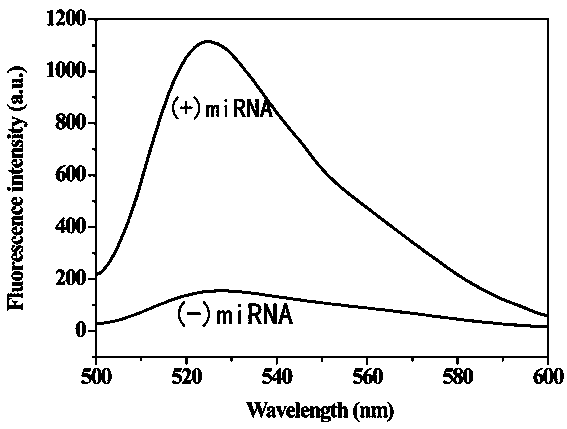
The invention provides a method for detecting a tumor biomarker by using a palindrome lock-type probe. A palindrome-sequence non-fluorescent mark lock-type RCA probe is designed. The probe is composedof a target identification part and a locus cutting part. The target identification part and target miRNA can completely complement each other and is located at a 3' end and a 5' end of the lock-typeprobe; a semi-identification locus of restriction enzyme Nt.AlWI is fused with a palindrome alkali segment. The probe is combined with nicking enzyme, an N-RCA concept is provided, a double-directionchain replacement reaction (D-SDA) is conducted for combination, and the probe is used for detecting the tumor marker miRNA. By means of the method, let-7a miRNA can be efficiently detected through amplification, and the probe is economical and practical and is expected to be applied to development of clinical diagnostic kits.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
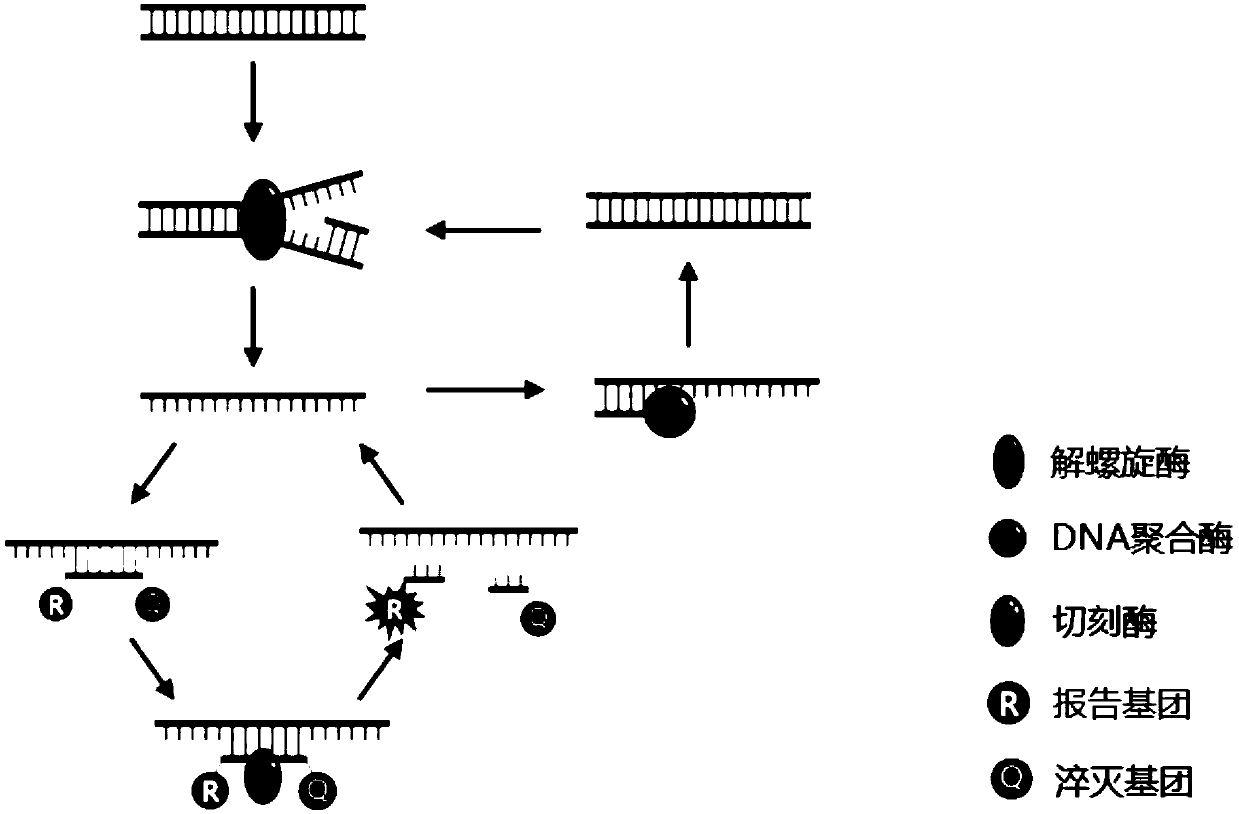
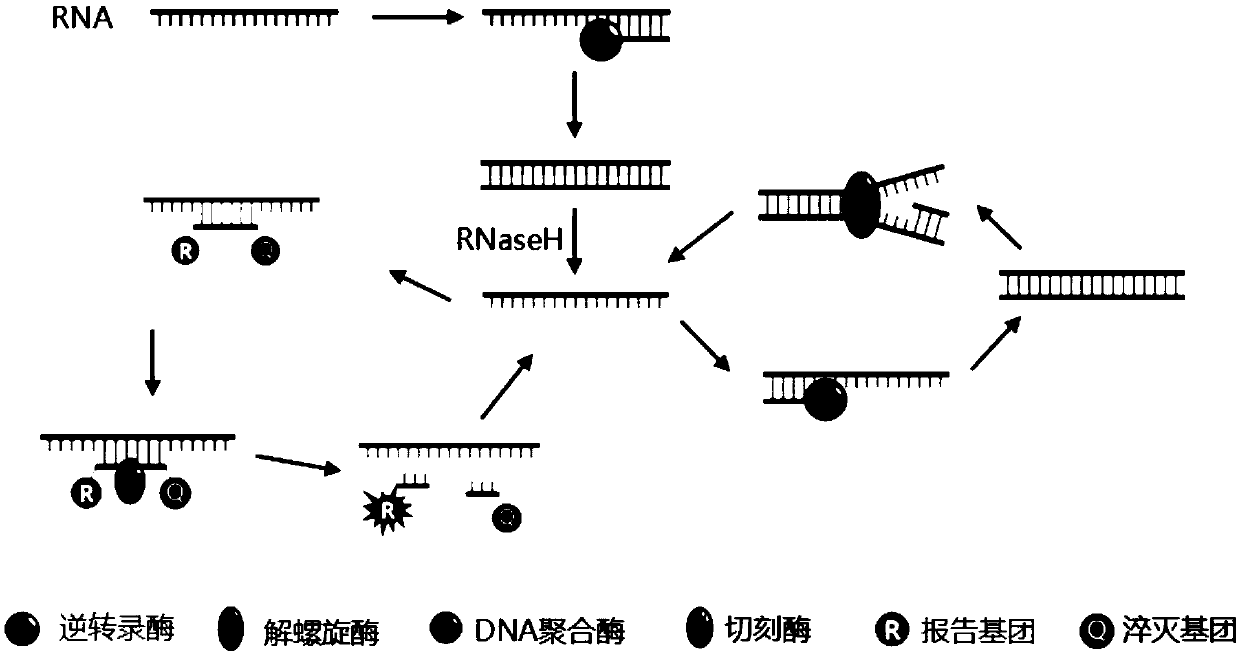
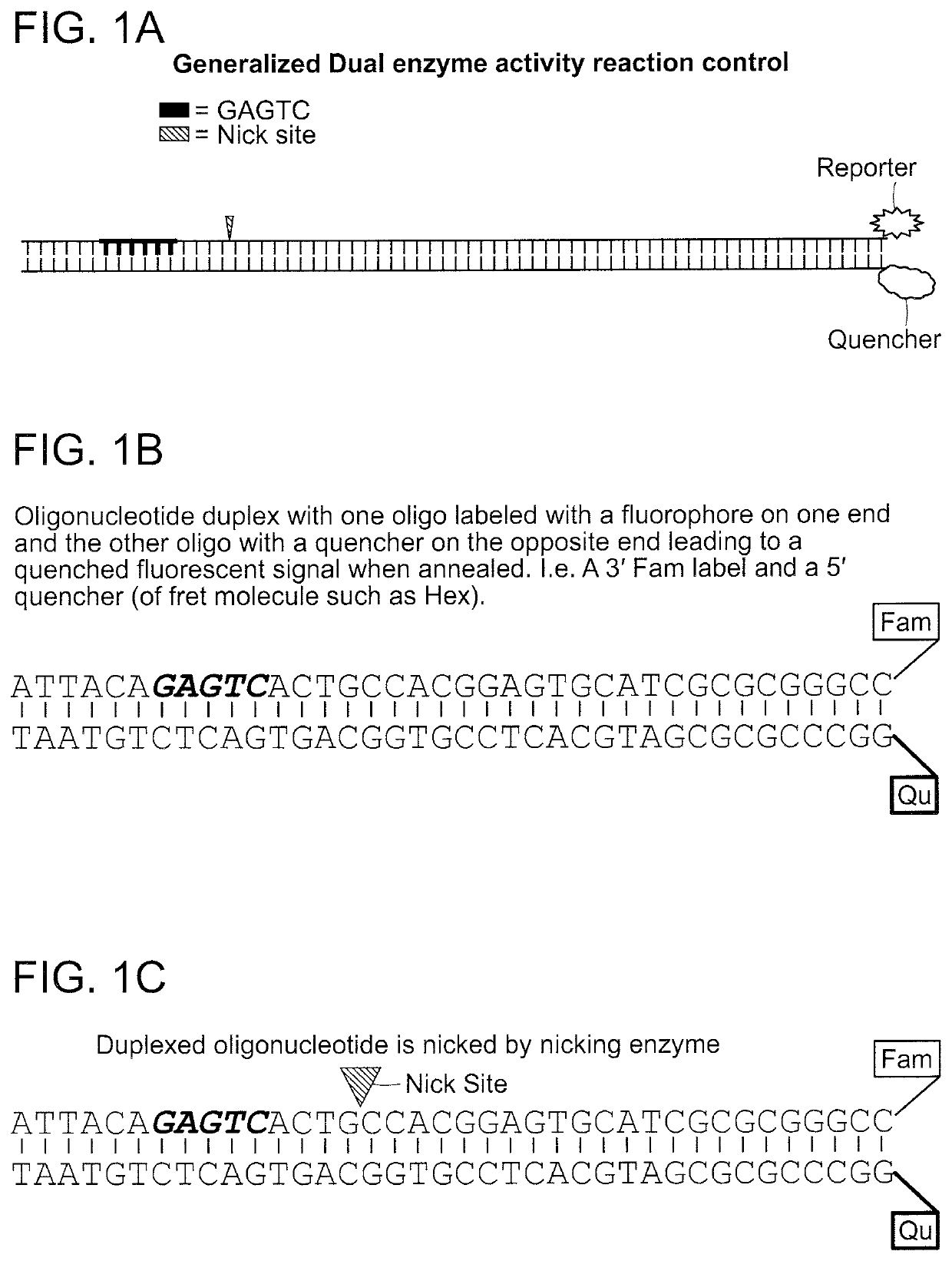
Compositions and methods for detecting nicking enzyme and polymerase activity using a substrate molecule
The present invention provides compositions and methods for assaying the activity of nicking enzyme and polymerase in a reaction involving the use of a nucleic acid substrate molecule that detects nicking enzyme and polymerase extension activities by the release of a detectable reporter (e.g., a fluorophore).
Owner:ENVIROLOGIX INC
Method for generating single-stranded product in isothermal amplification system
InactiveCN107058287AIncrease reaction rateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSingle strandReaction speed
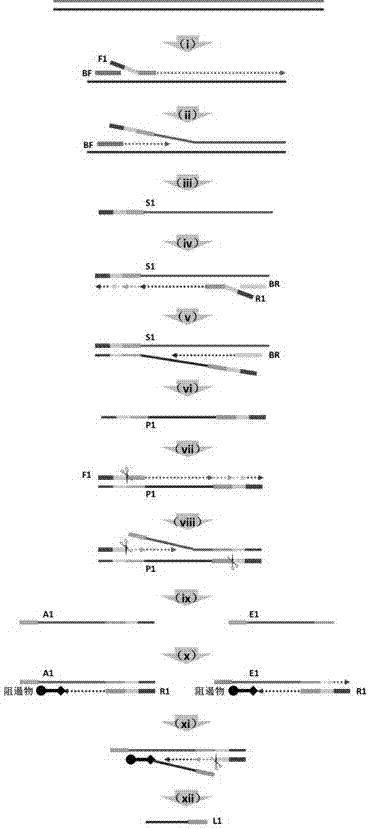
The invention provides a method for generating a single-stranded product in an isothermal amplification system. According to the method for generating the single-stranded product, the isothermal amplification system comprises two pair of primers including F1, R1, BF and BR, wherein each of F1 and B1 includes three parts: a fixed region close to a 5' terminal of the primer, a recognition region which is close to a 3' terminal and capable of specifically bound with a template, and a nickase region between the fixed region and the recognition region. The method has the beneficial effects that the reaction speed is high, the cost is low, the operation is simple and convenient, a single-stranded DNA amplified product can be generated by virtue of an isothermal amplification method, and the technical defects in the background art are overcome.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Improvements in or relating to amplification of nucleic acids
ActiveUS20210292826A1Reduce the temperatureReduce signal noiseMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandDouble strand
Disclosed is a method of performing a non-isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction, the method comprising the steps of: (a) mixing a target sequence with one or more complementary single stranded primers in conditions which permit a hybridisation event in which the primers hybridise to the target, which hybridisation event, directly or indirectly, leads to the formation of a duplex structure comprising two nicking sites disposed at or near opposite ends of the duplex; and performing an amplification process by; (b) using a nicking enzyme to cause a nick at each of said nicking sites in the strands of the duplex; (c) using a polymerase to extend the nicked strands to as to form newly synthesised nucleic acid, which extension with the polymerase recreates nicking sites; (d) repeating steps (b) and (c) as desired so as to cause the production of multiple copies of the newly synthesised nucleic acid; characterised in that the temperature at which the method is performed is non-isothermal, and subject to shuttling, a plurality of times, between an upper temperature and a lower temperature during the amplification process of steps (b)-(d), wherein at the upper temperature, one of said polymerase or nicking enzyme is more active than the other of said enzymes, such that there is a disparity in the activity of the enzymes, and at the lower temperature the disparity in the activity of the enzymes is reduced or reversed.
Owner:LUMIRADX UK LTD
Compositions and methods for detecting huanglongbing
The present invention features compositions and methods for detecting Huanglongbing (HLB) in citrus trees and insects. In one aspect, the invention provides a method of detecting a Huanglongbing (HLB) infection in a citrus grove involving obtaining an extract from a biological sample derived from a citrus grove, contacting the extract with forward and reverse primers that specifically bind a Candidutus nucleic acid molecule in the presence of a nicking enzyme, dNTPs, and a polymerase under conditions permissive for the isothermal amplification of the nucleic acid molecule; and detecting a Candidutus amplicon in the extract.
Owner:ENVIROLOGIX INC
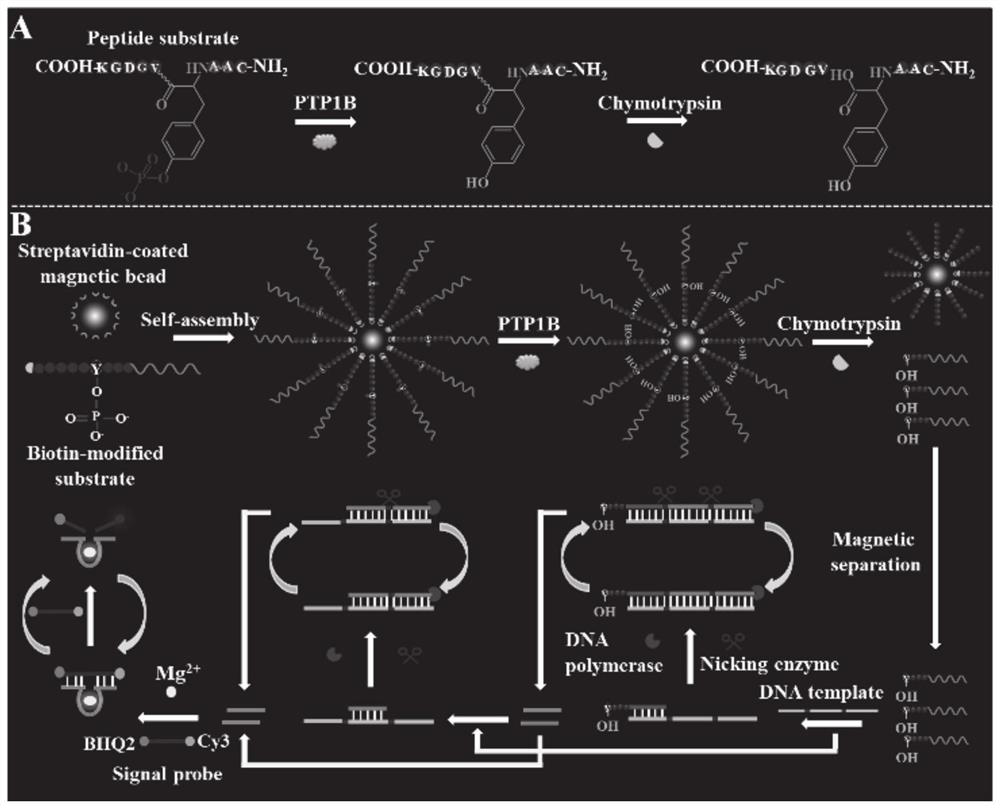
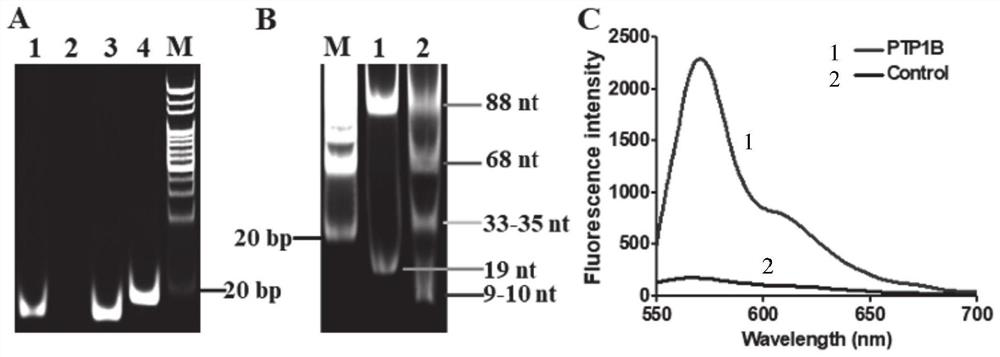
Tyrosine phosphatase biosensor as well as detection method and application thereof
ActiveCN111979295AImprove efficiencyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPhosphorylationNucleotide
The invention discloses a tyrosine phosphatase biosensor as well as a detection method and application thereof. The tyrosine phosphatase biosensor comprises magnetic beads, a peptide-DNA conjugate, aDNA template and a signal probe, wherein one end of a peptide chain in the peptide-DNA conjugate is linked to a 5' end of a first DNA sequence, the peptide chain contains phosphorylated tyrosine, theother end of the peptide chain is used for linking the magnetic beads; the DNA template consists of two second DNA sequences and a third DNA sequence from a 5' end to a 3' end, the third DNA sequencecan be complemented with a first DNA sequence, the DNA template is hybridized and polymerized with the first DNA sequence so as to form double-chain DNA with two nickase recognition sites, and complementary chains of the second DNA sequences are dnazyme; and the signal probe is a nucleotide sequence, fluorophores and quenchers are respectively linked to two ends of the nucleotide sequence, and thenucleotide sequence can be complemented with the dnazyme; and the dnazyme is an RNA sequence capable of realizing cracking and complementation in dependent reaction of divalent cations
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com