Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
99 results about "Memory rank" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
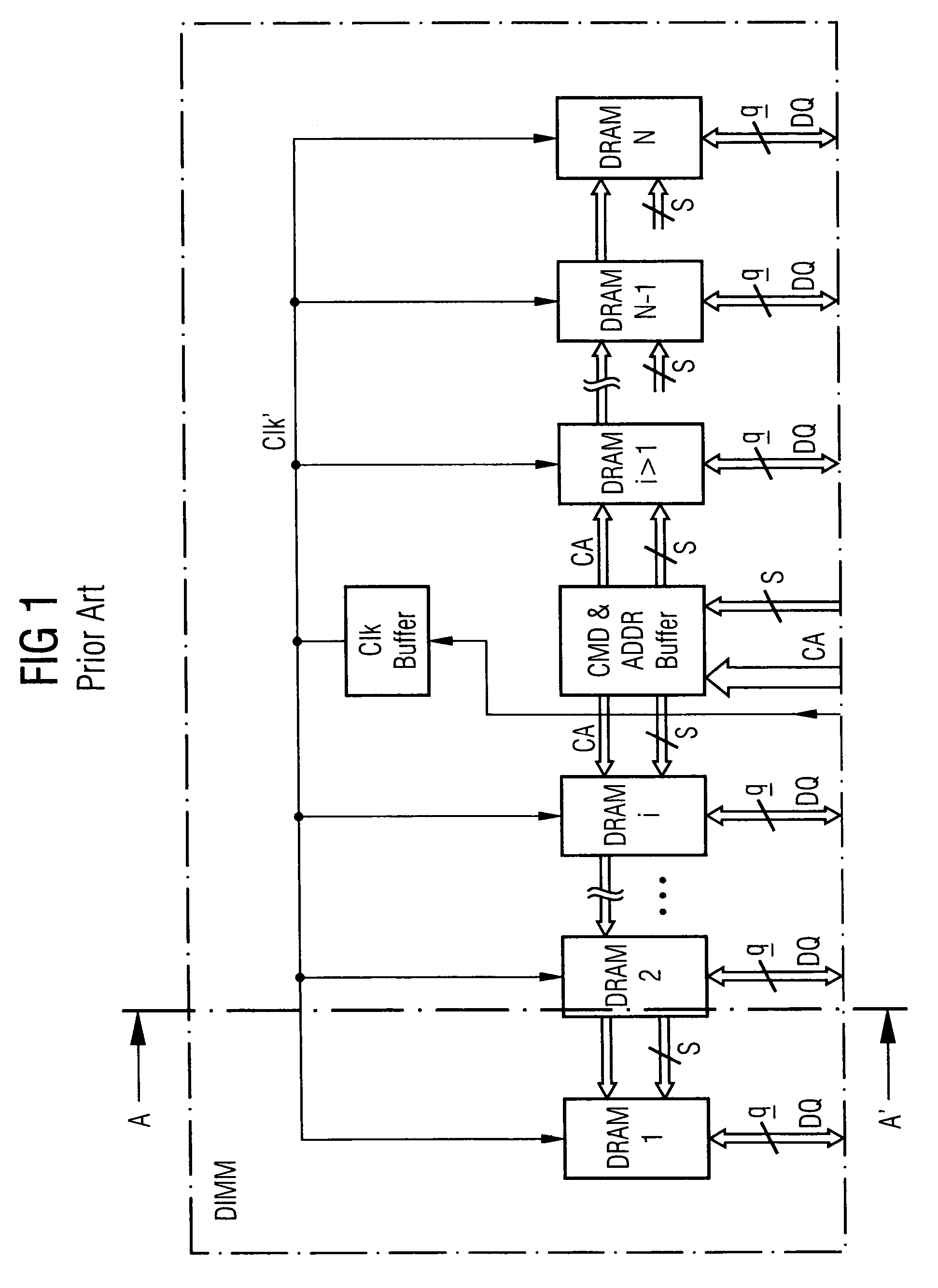
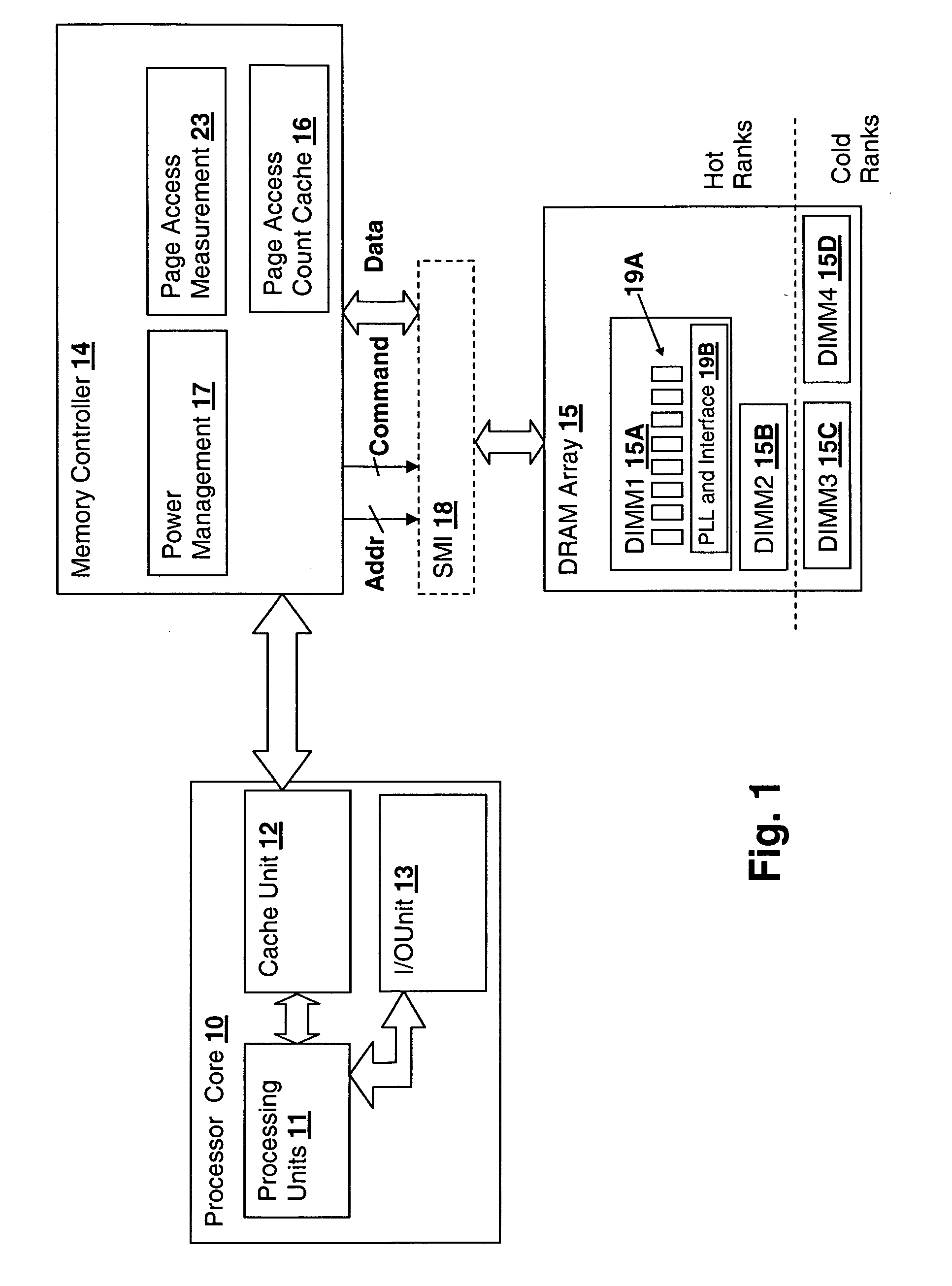
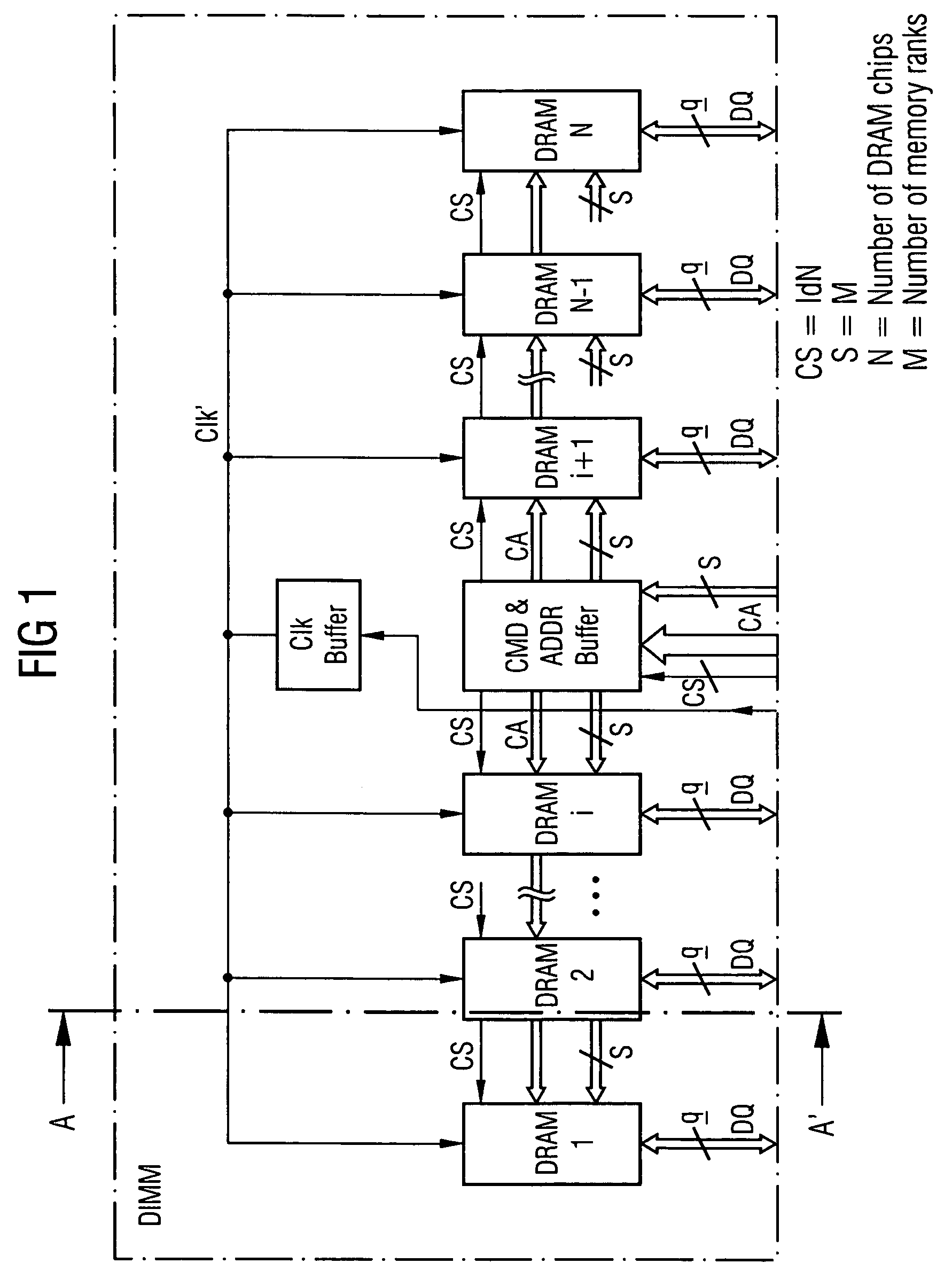
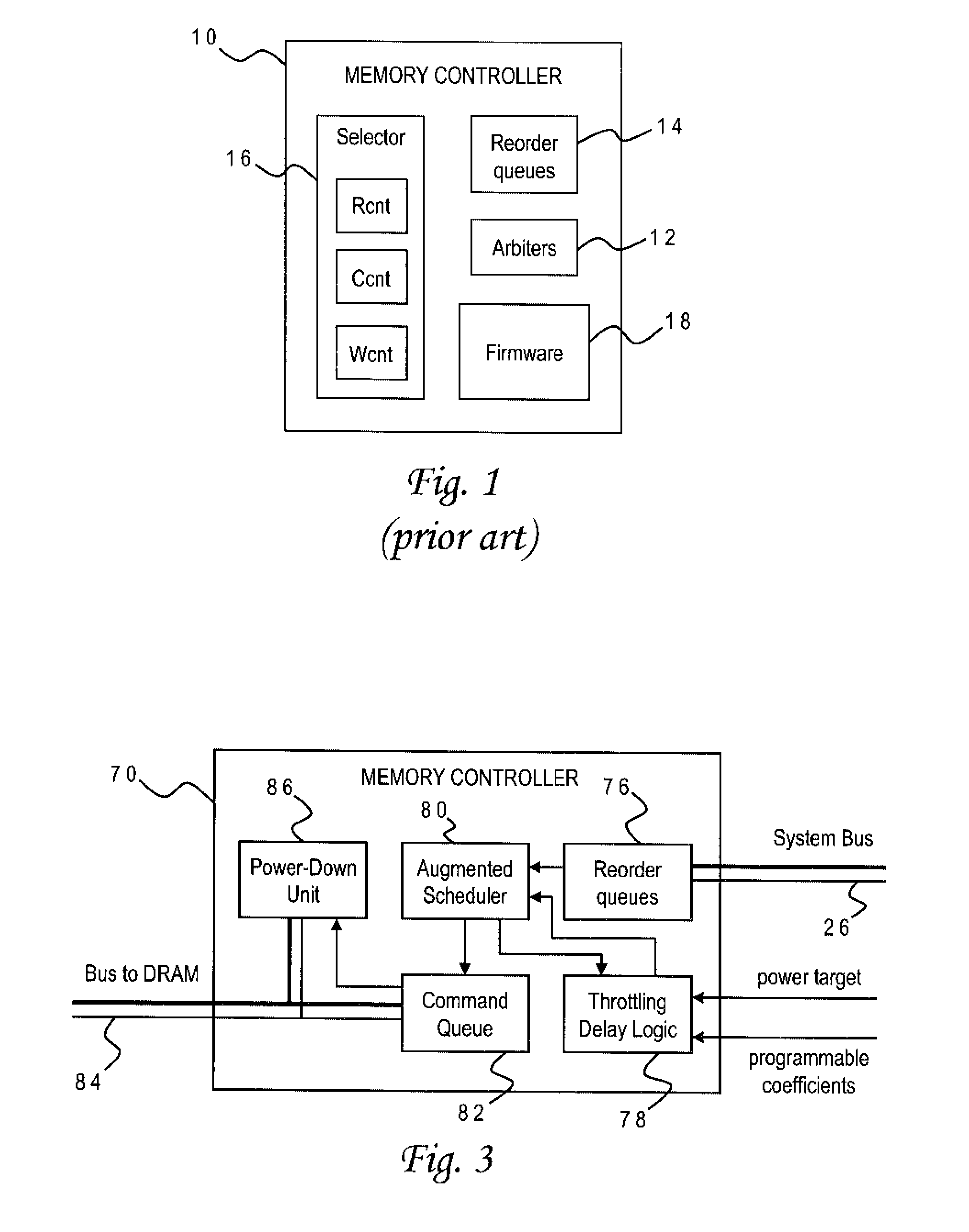
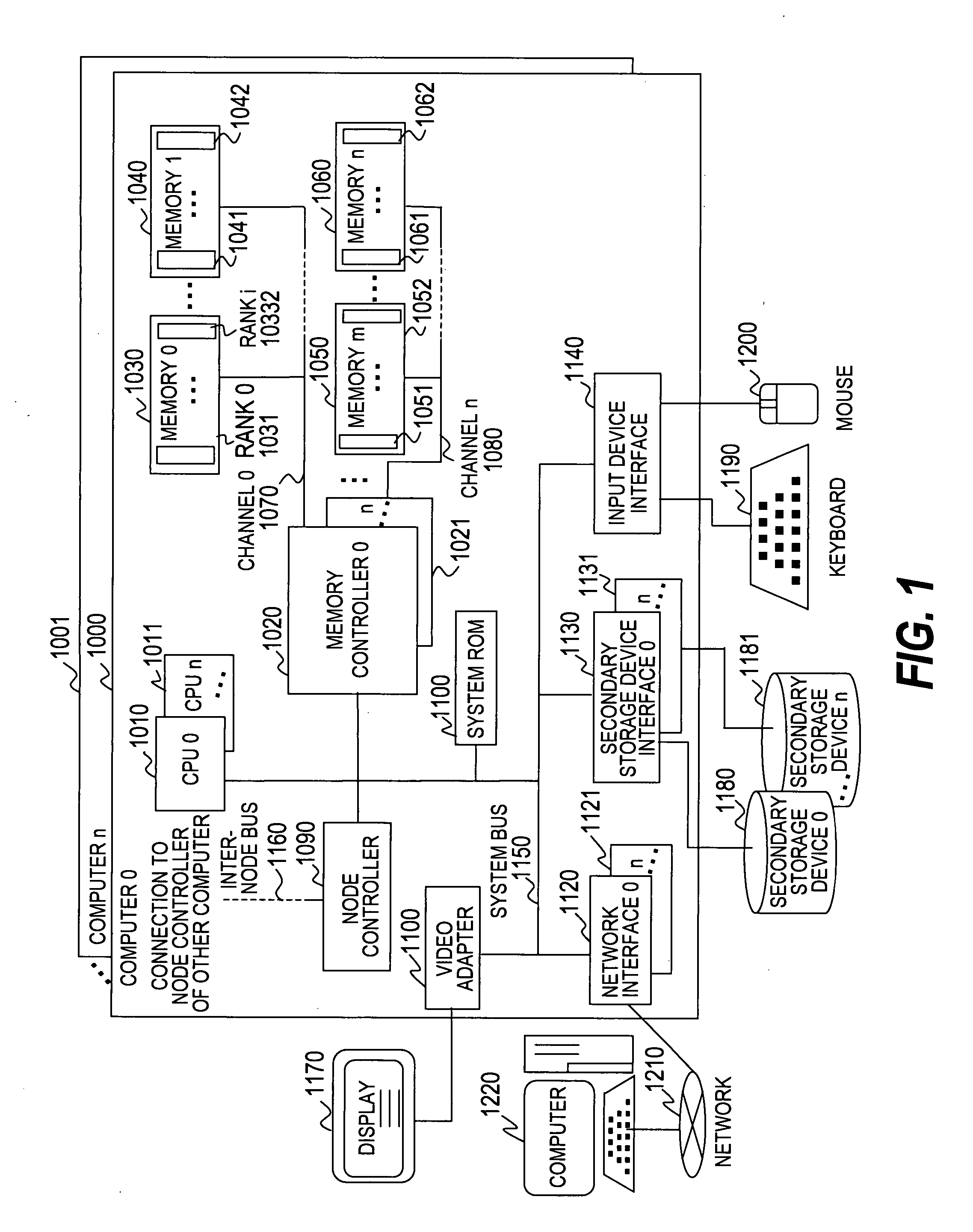
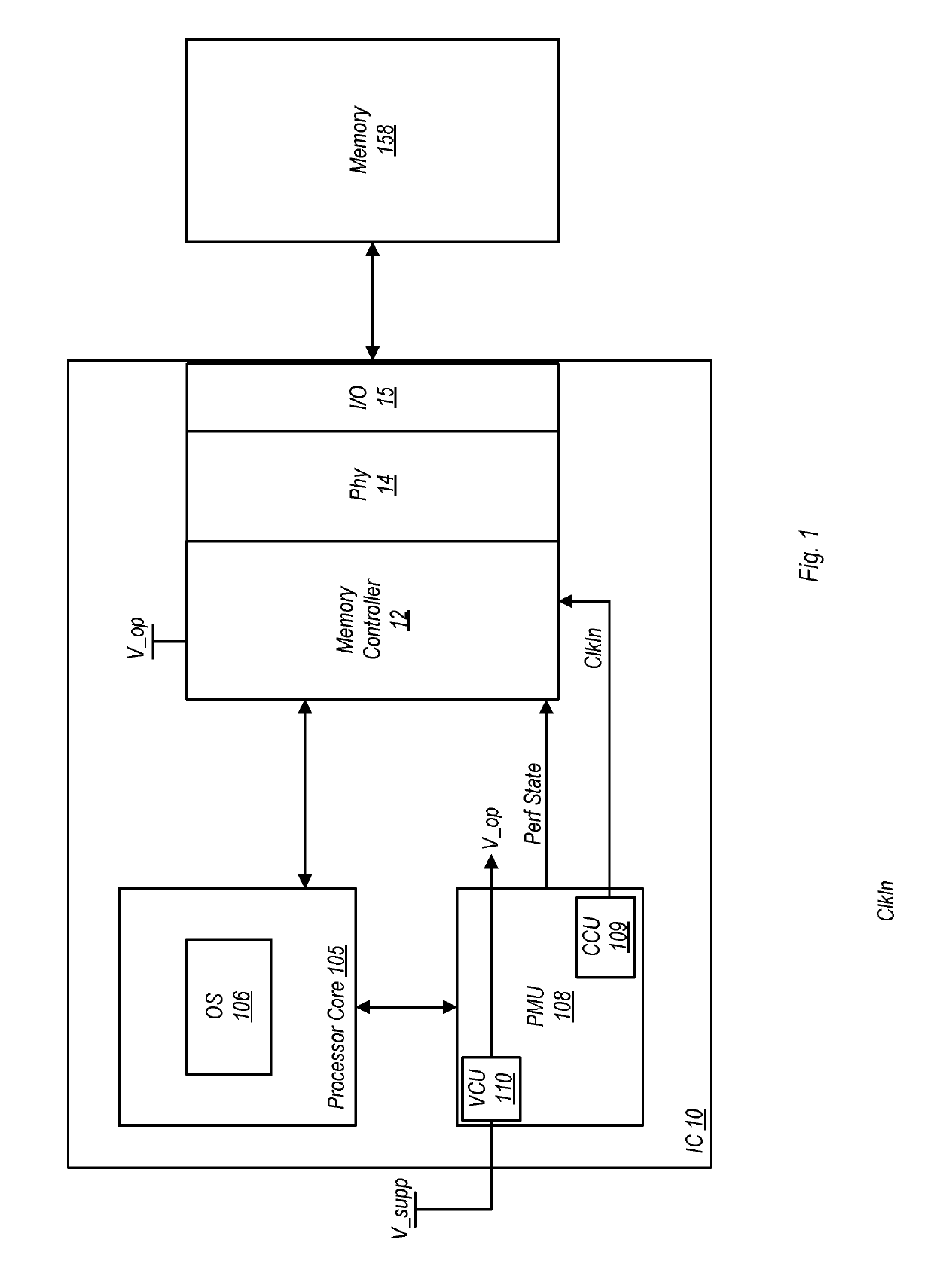
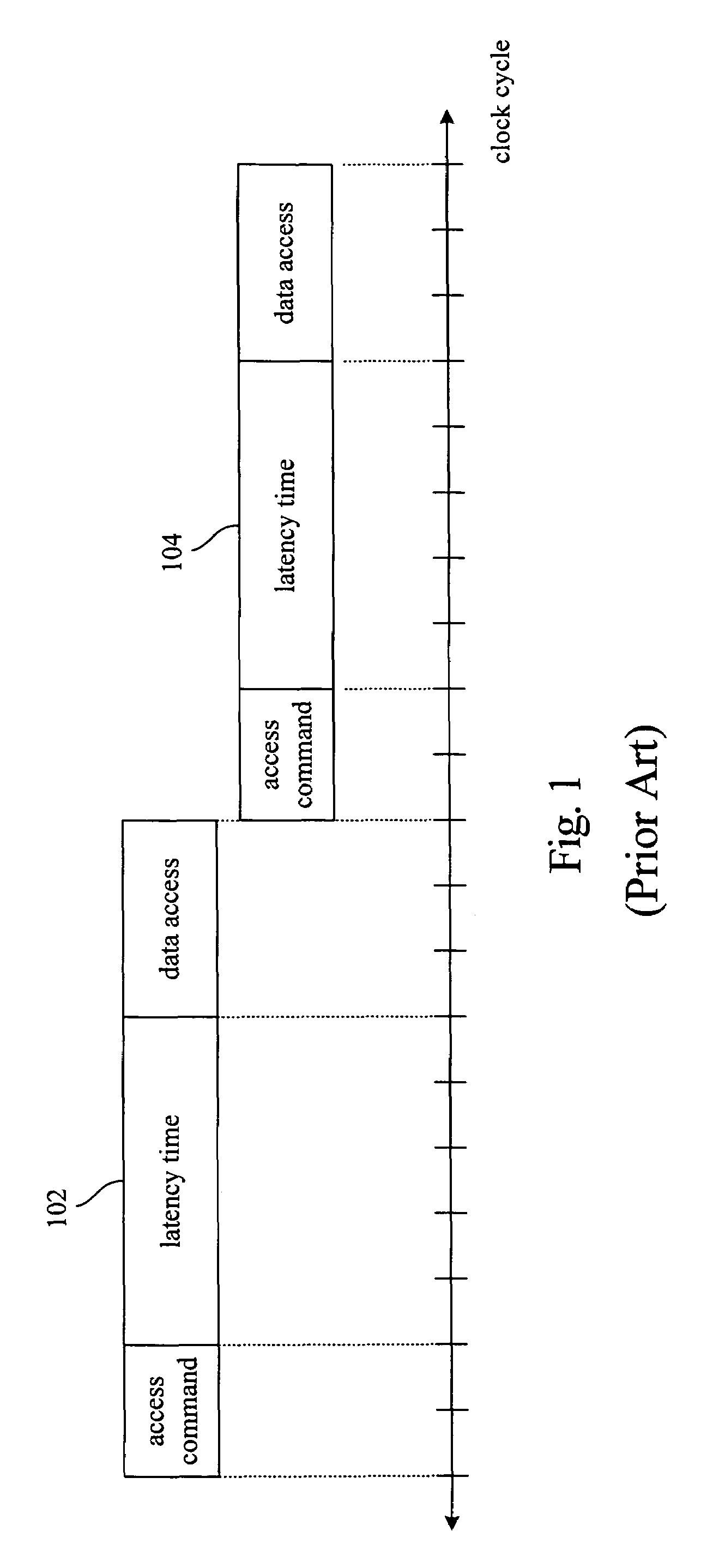
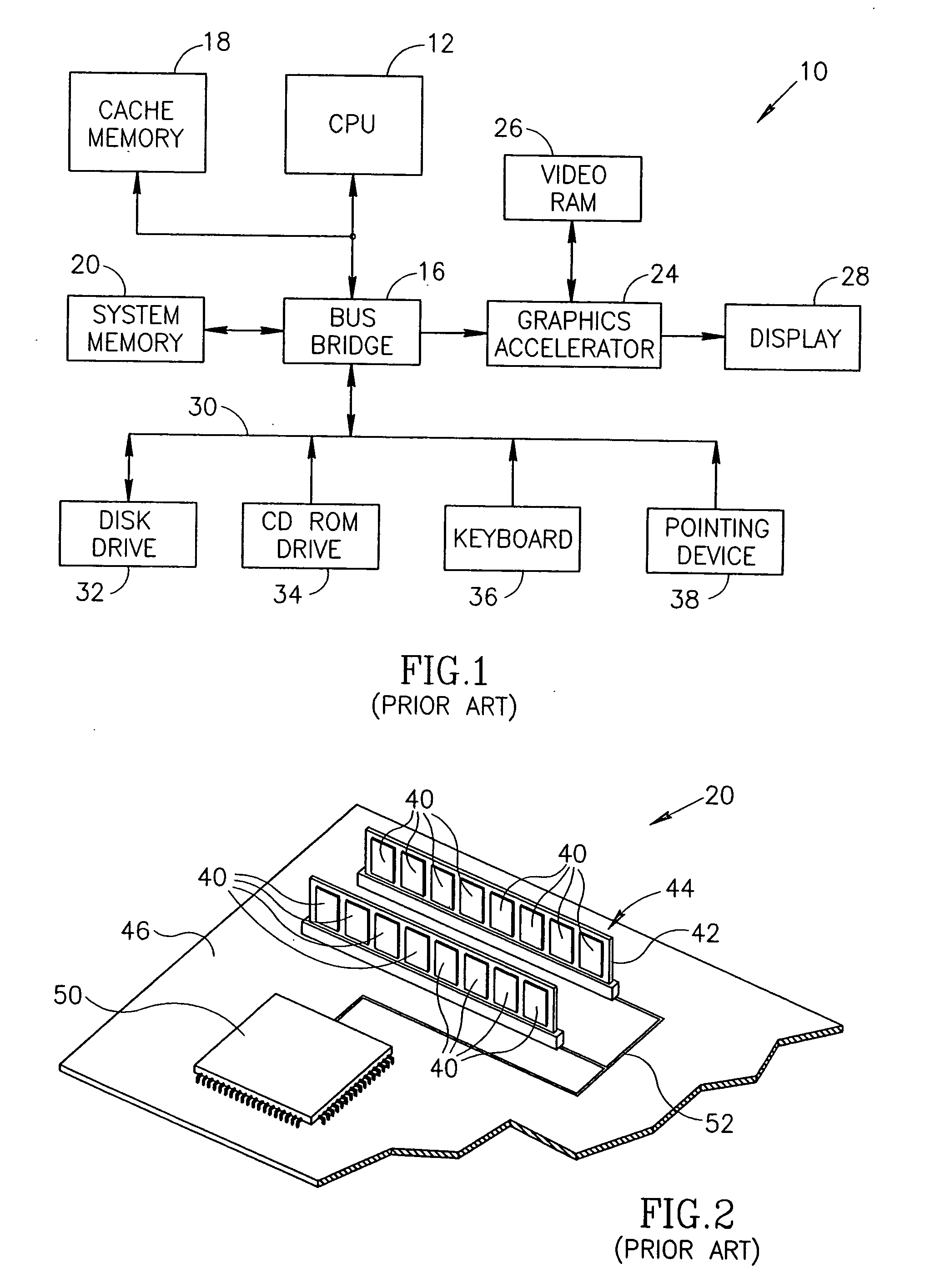
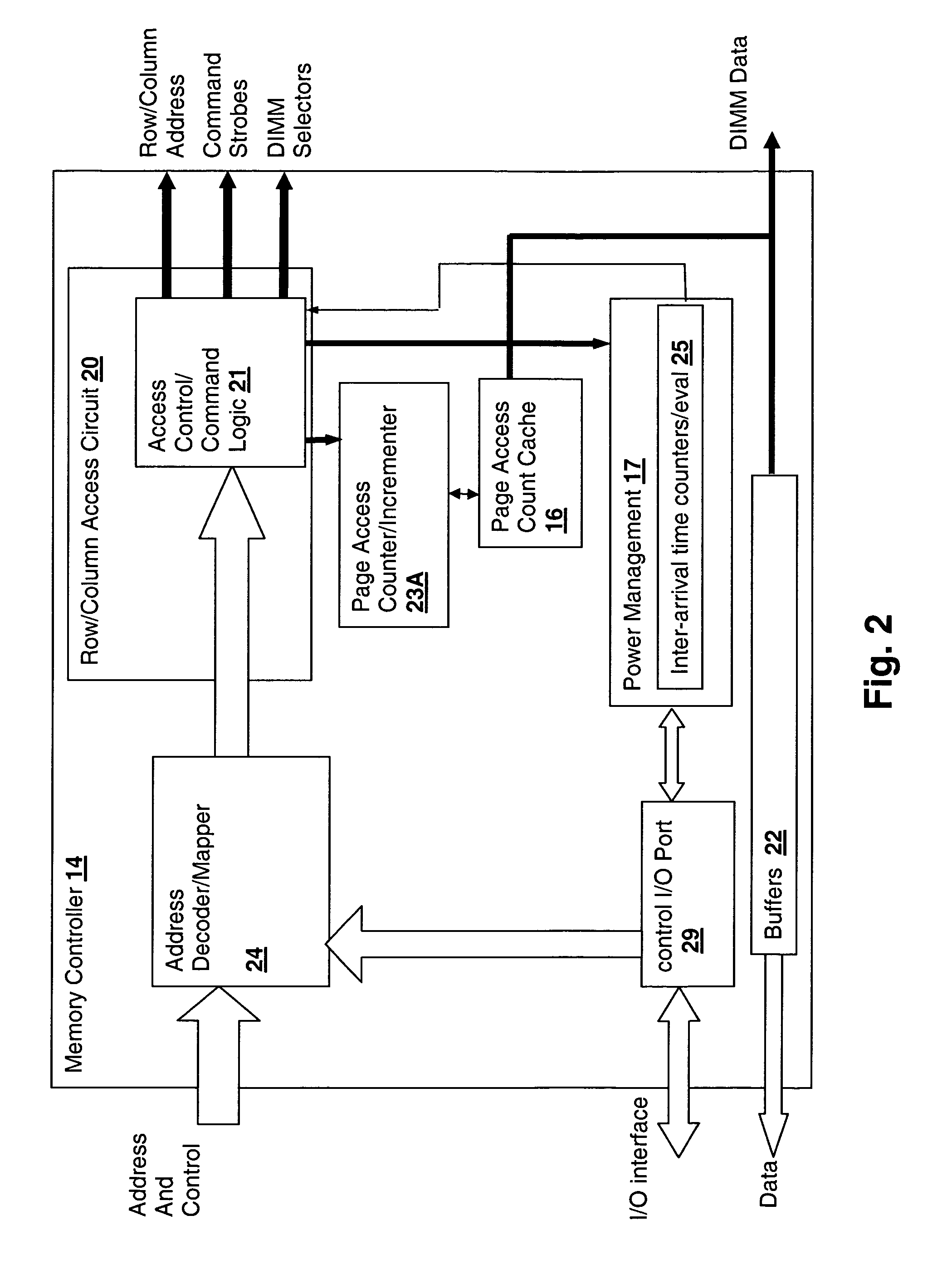
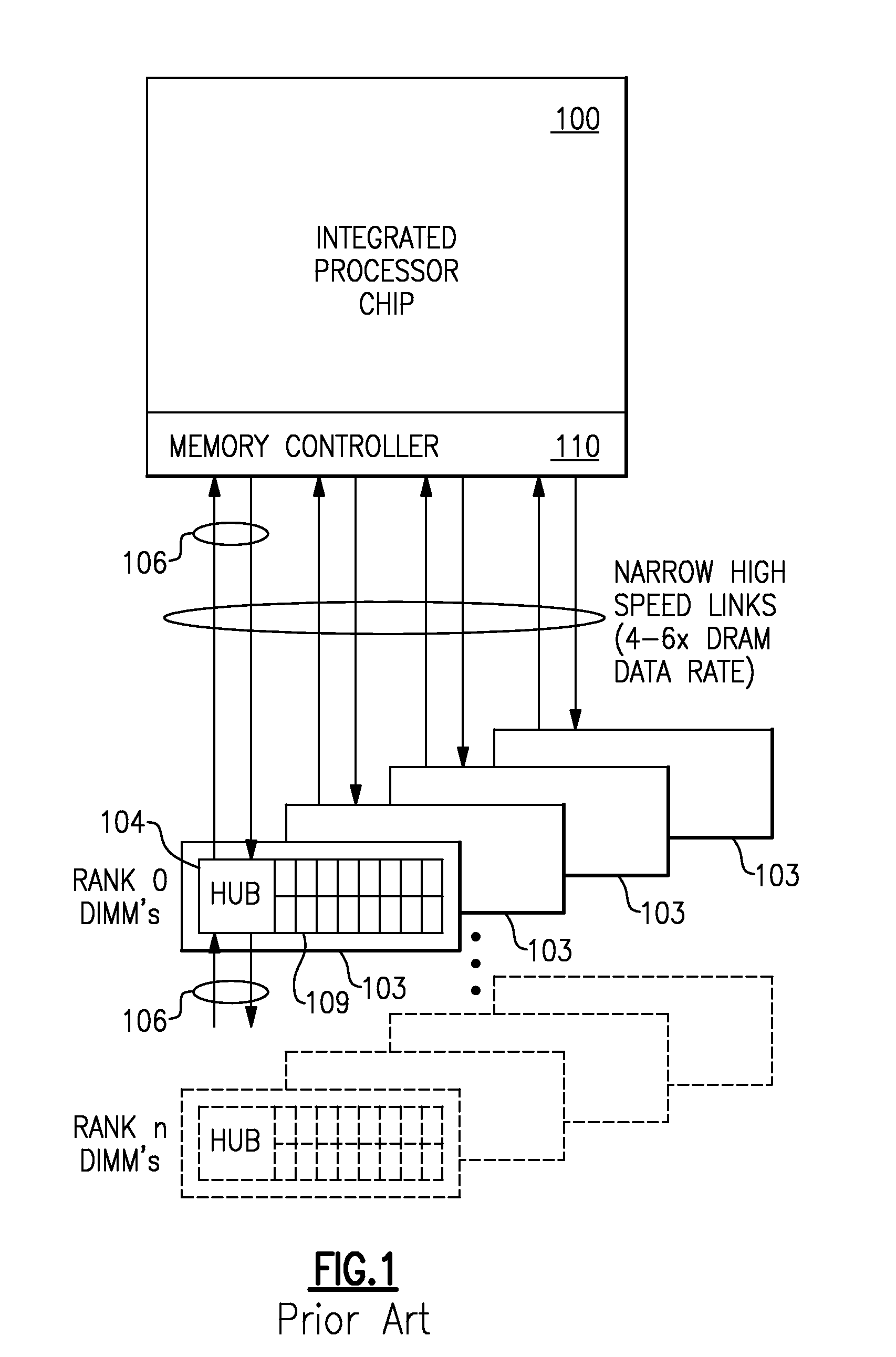
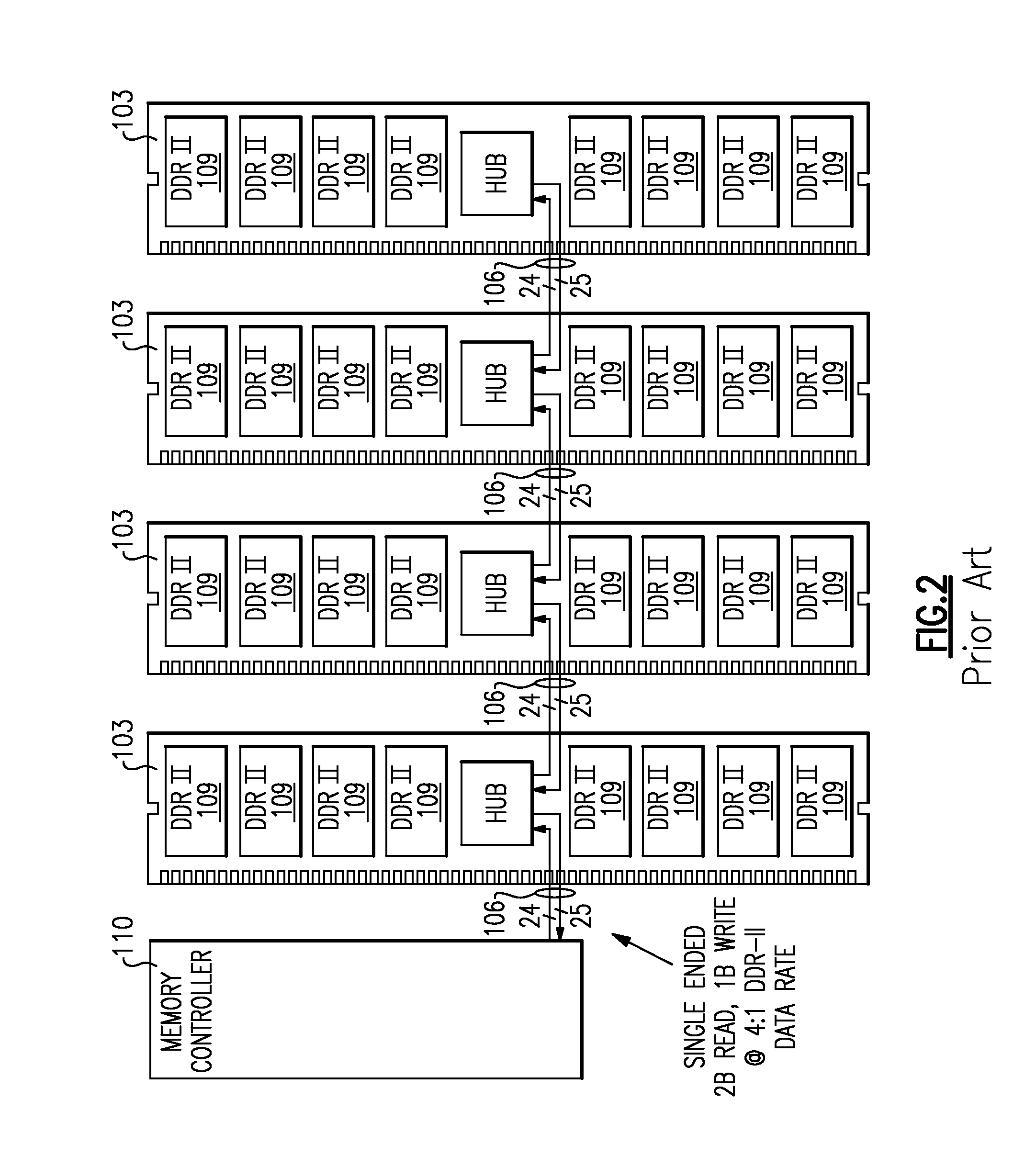
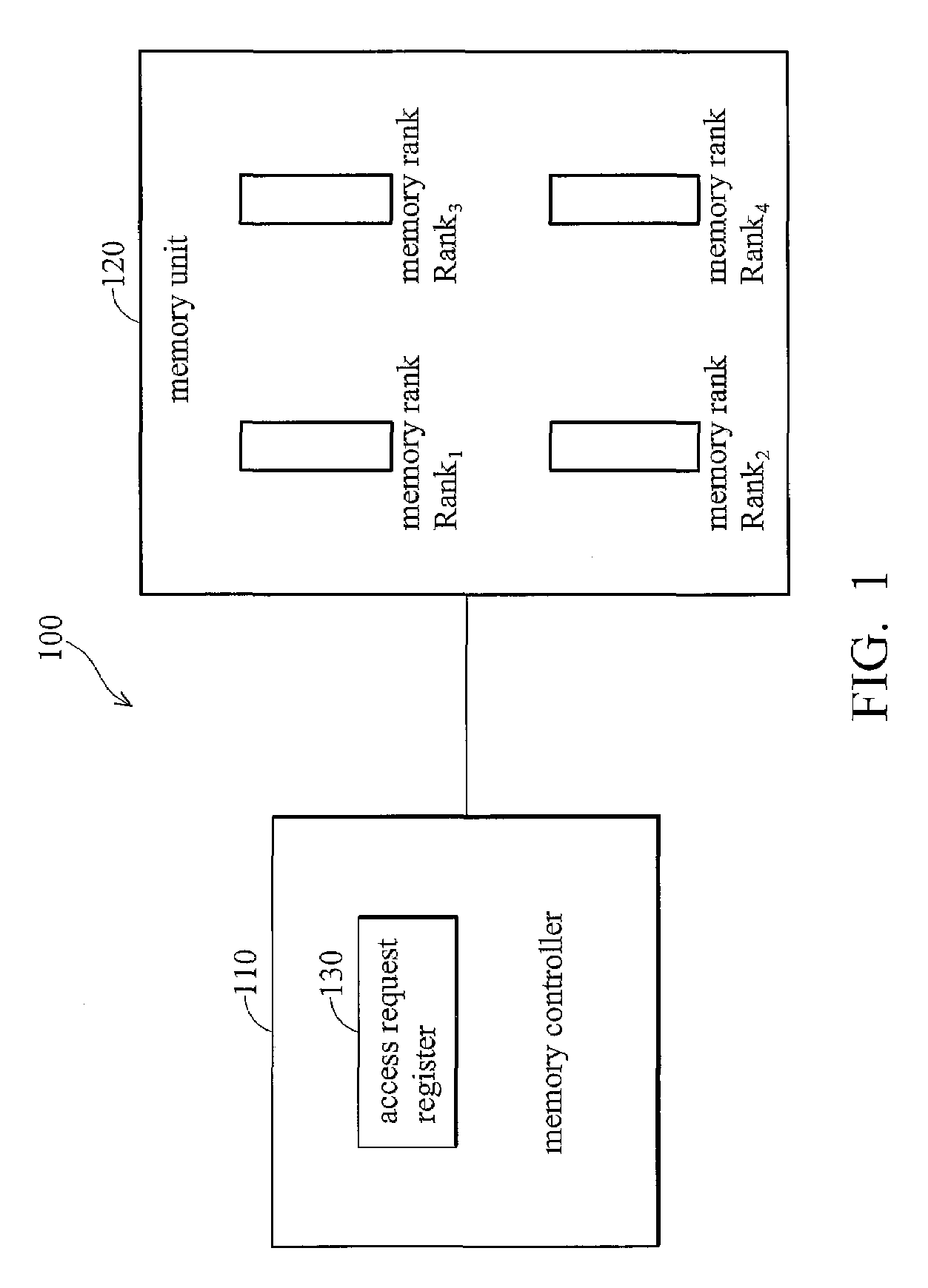
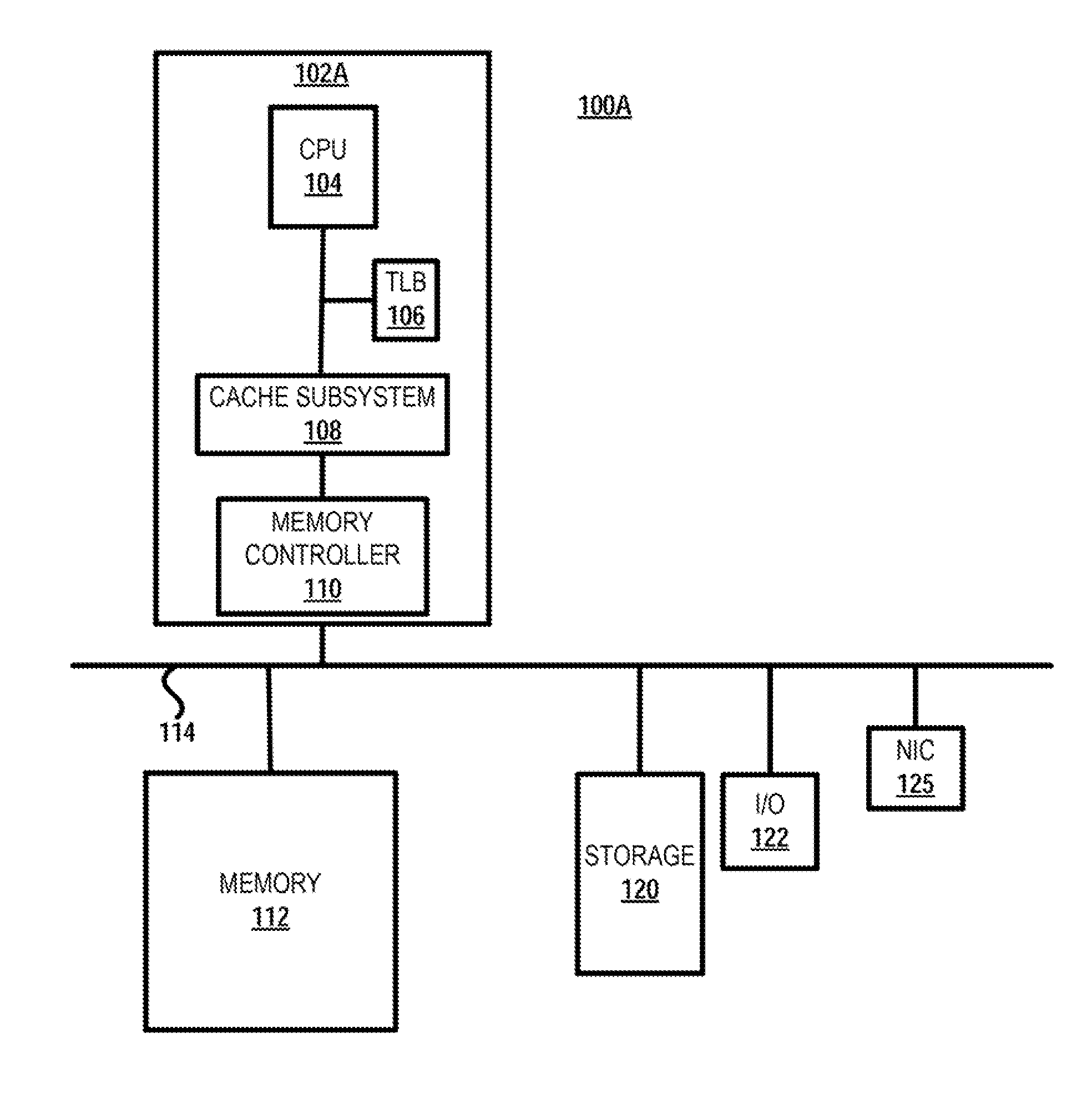
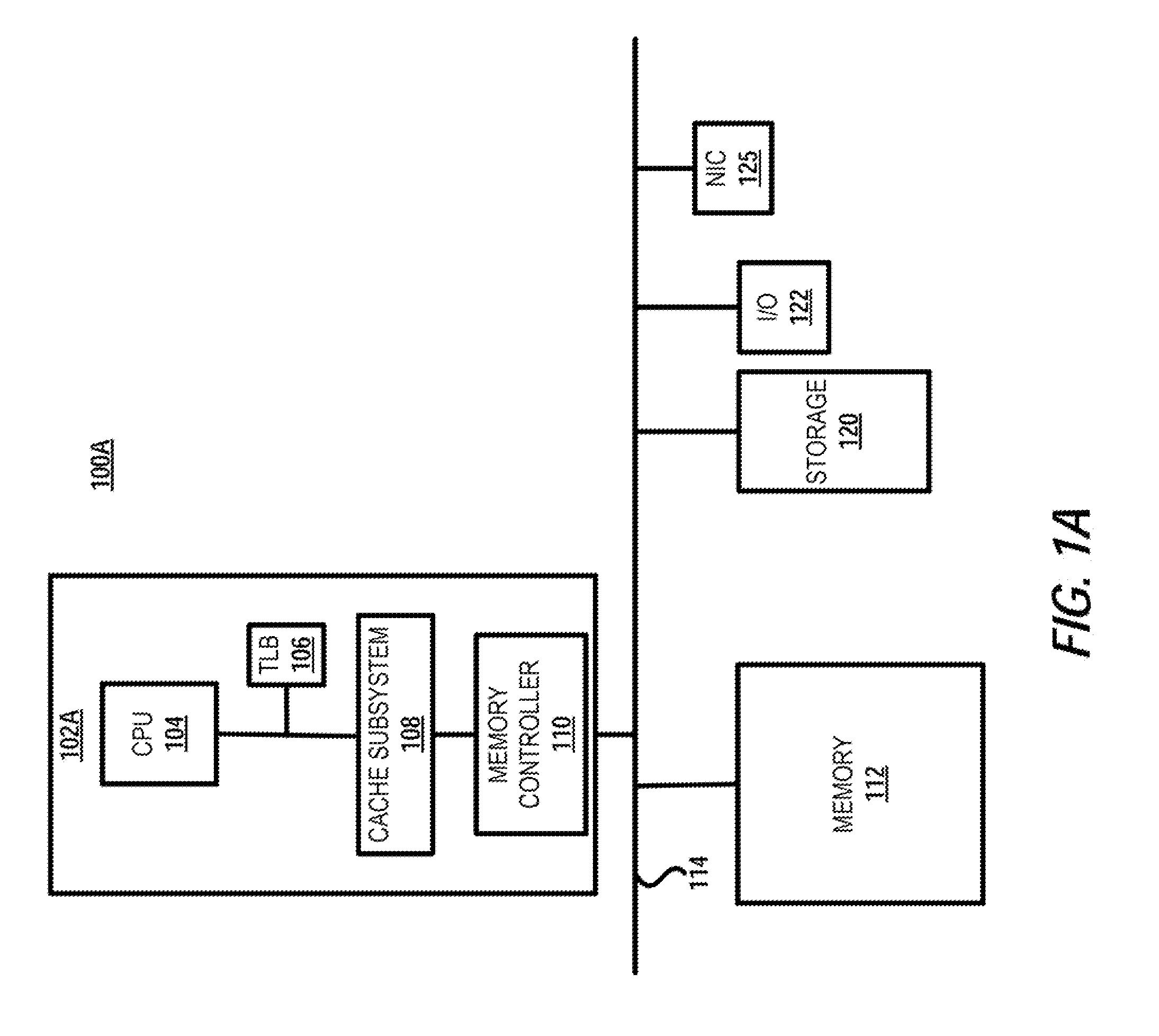
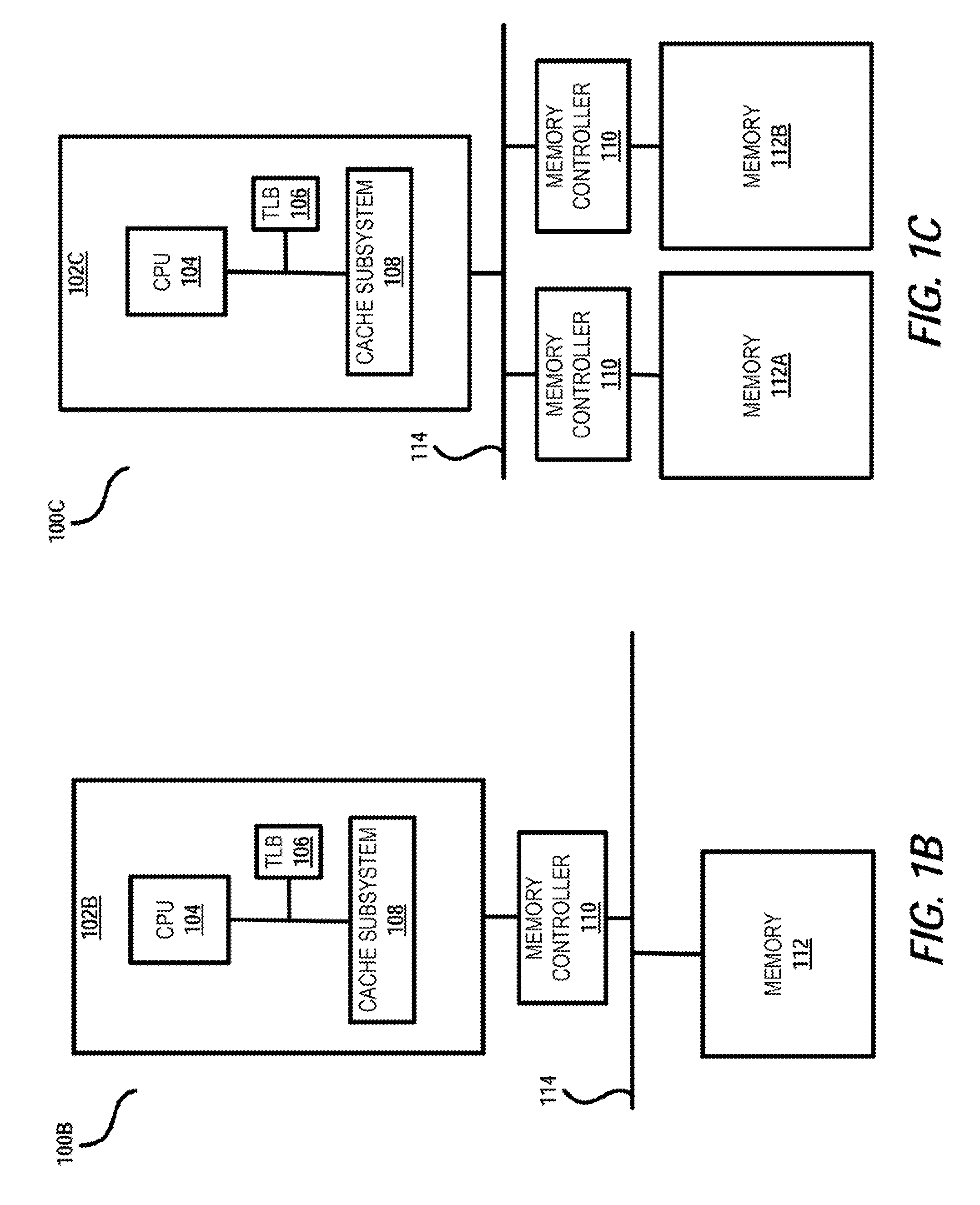
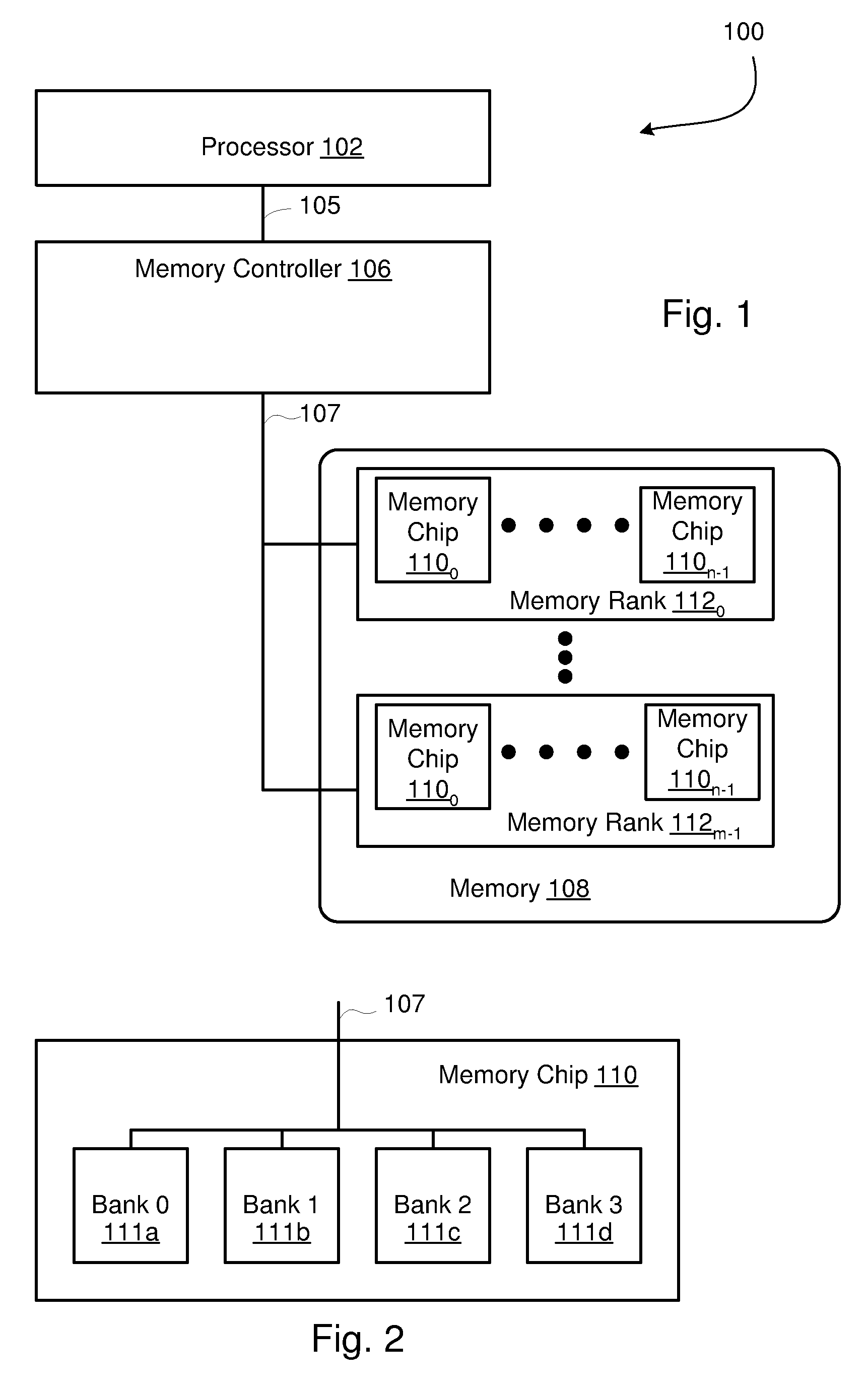
A memory rank is a set of DRAM chips connected to the same chip select, which are therefore accessed simultaneously. In practice all DRAM chips share all of the other command and control signals, and only the chip select pins for each rank are separate (the data pins are shared across ranks).
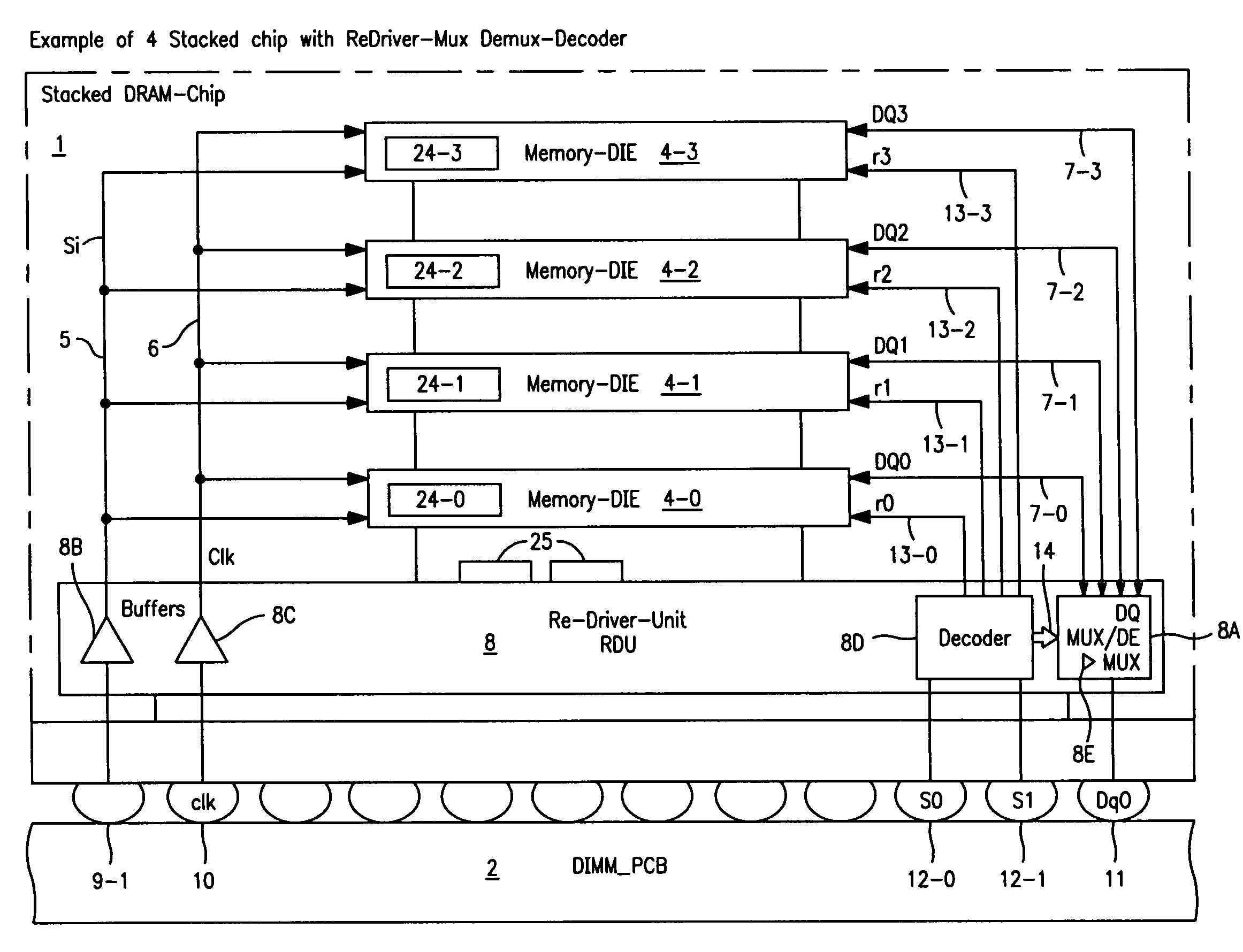
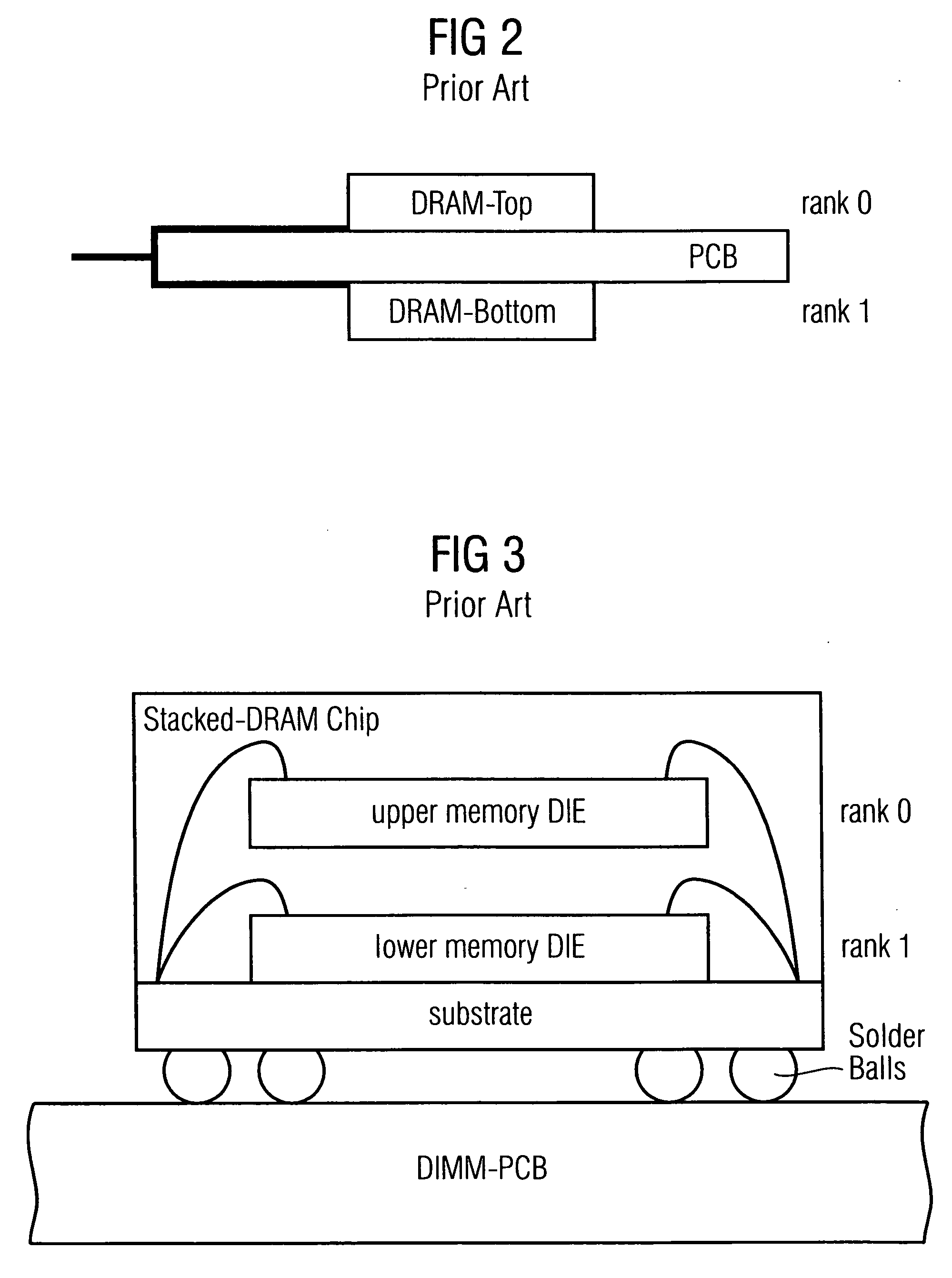
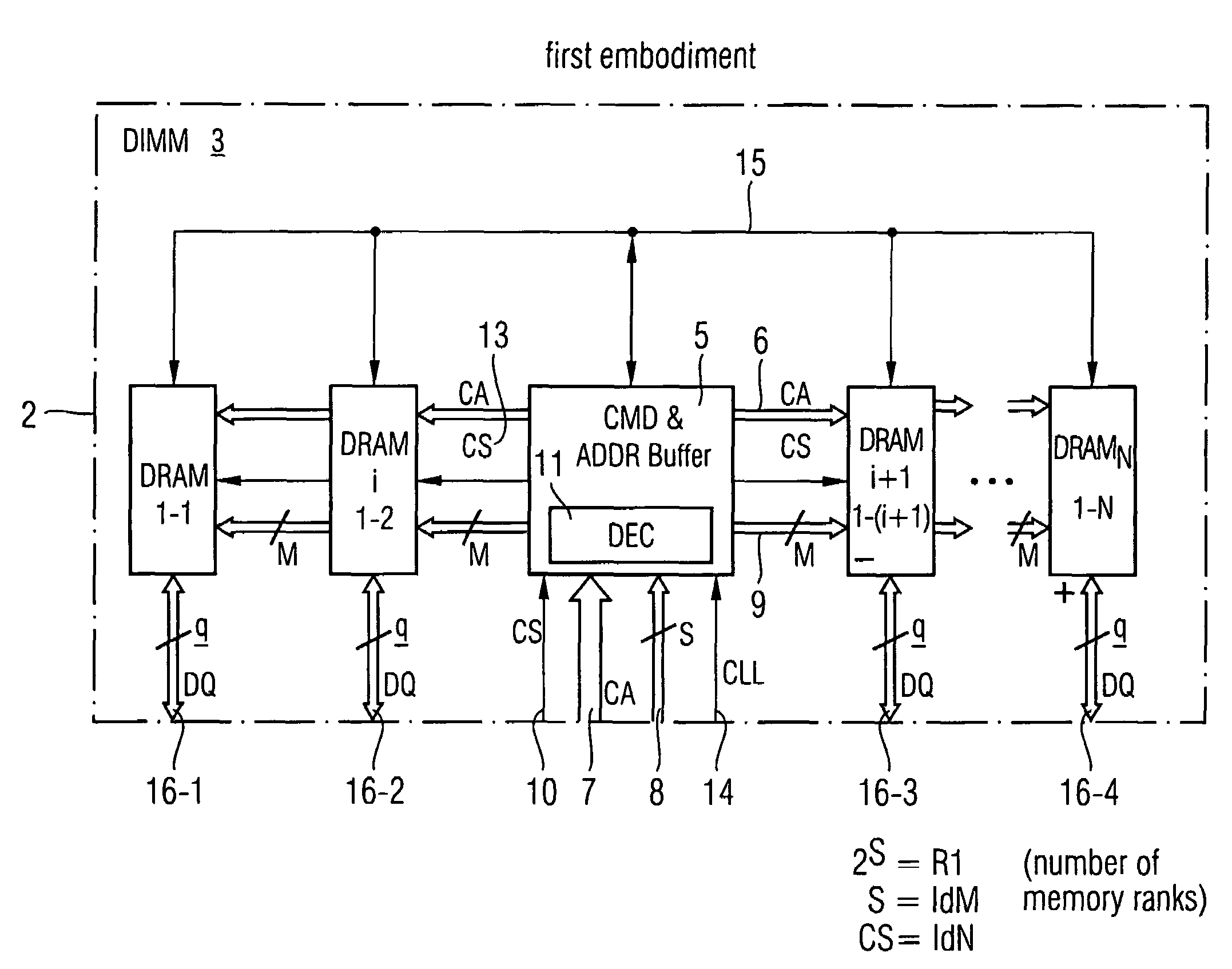
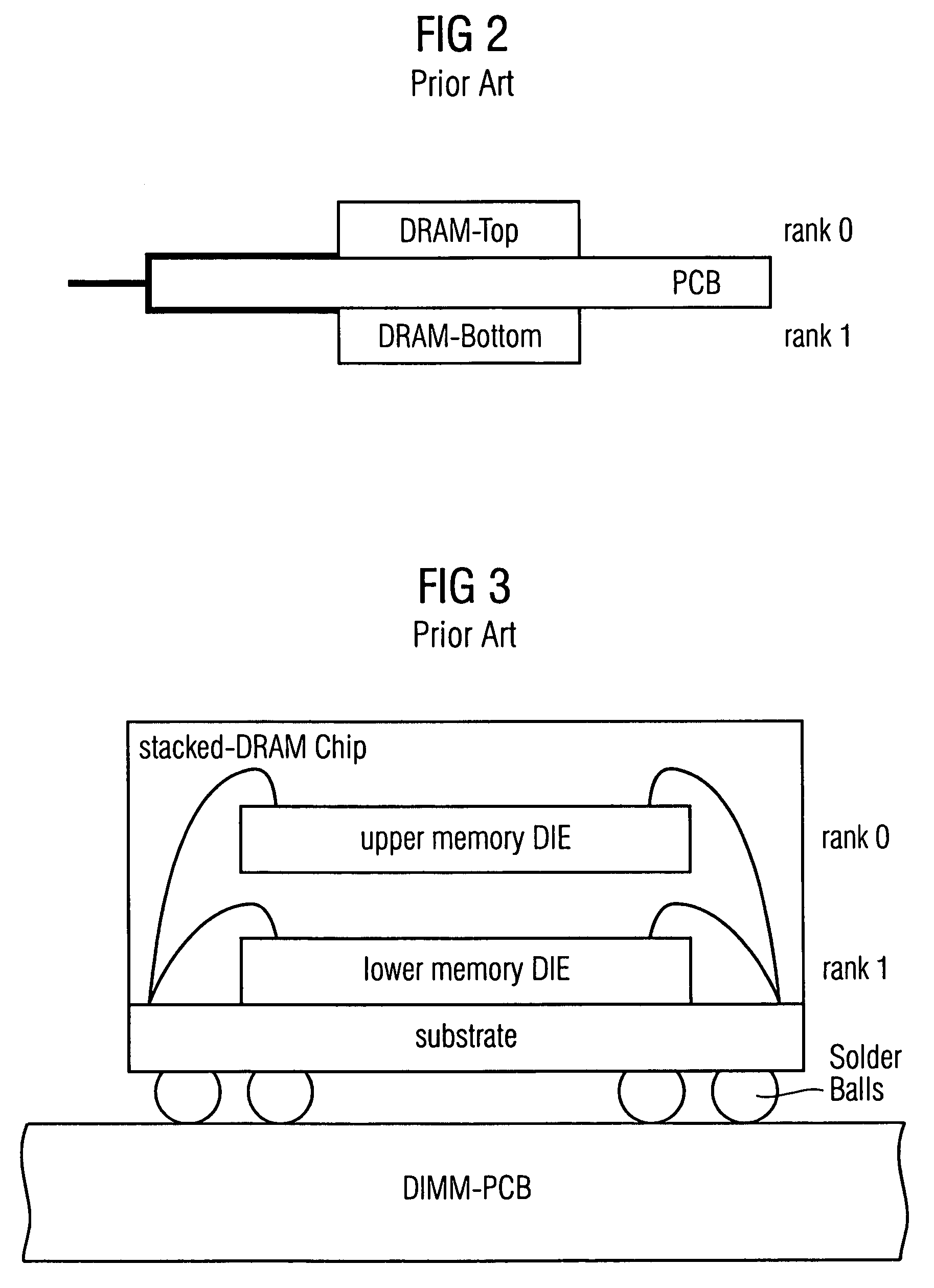
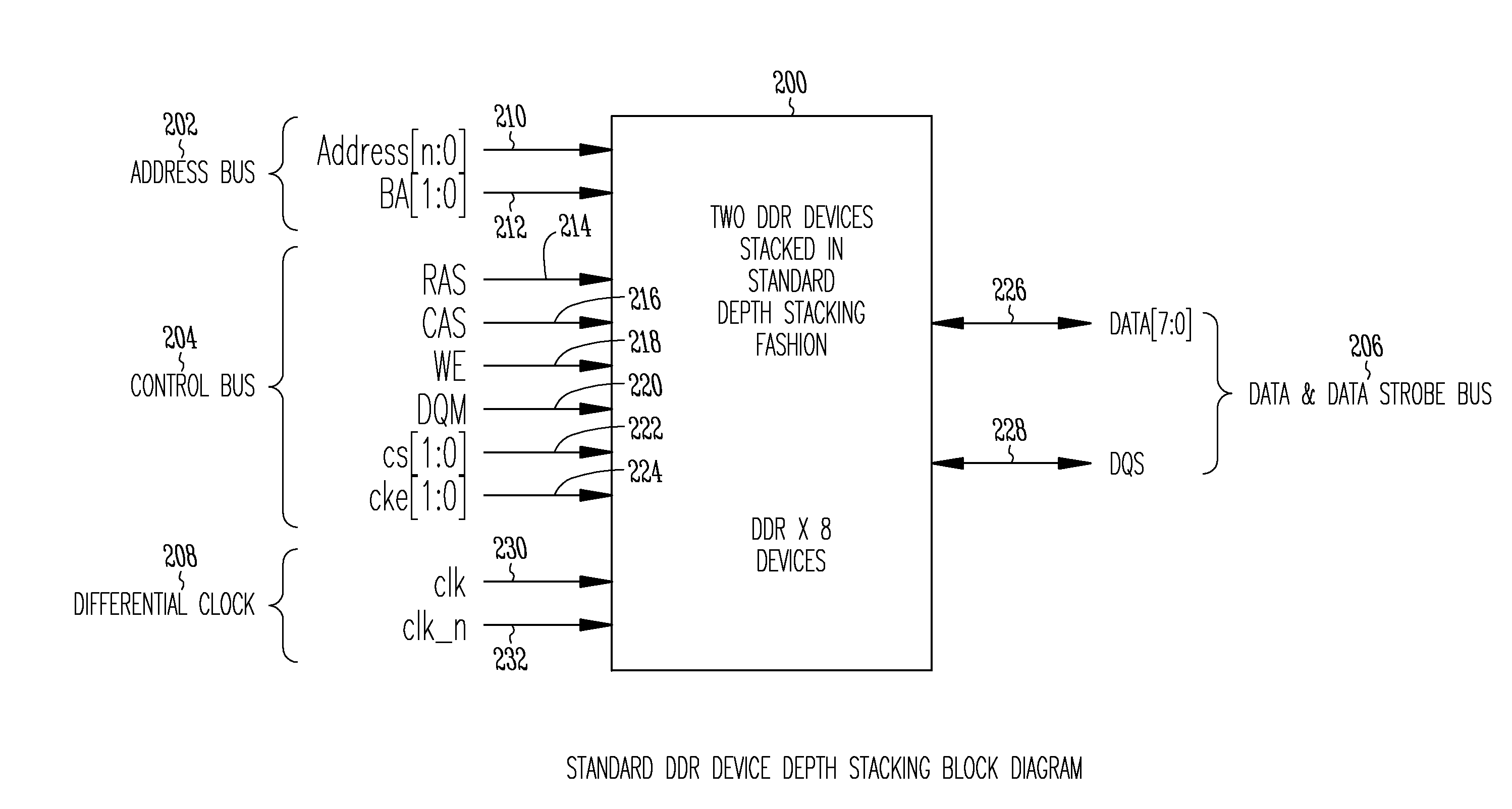
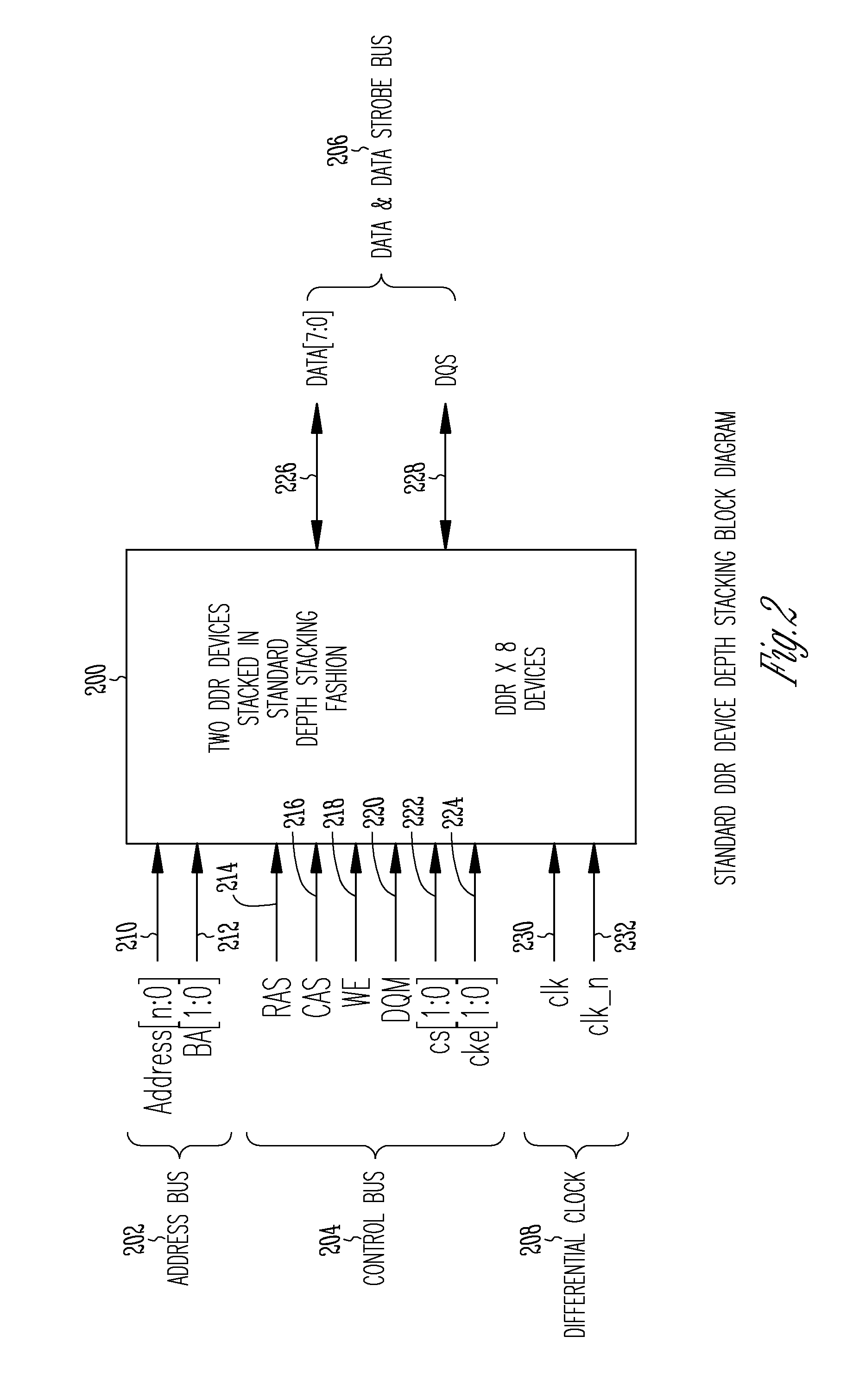
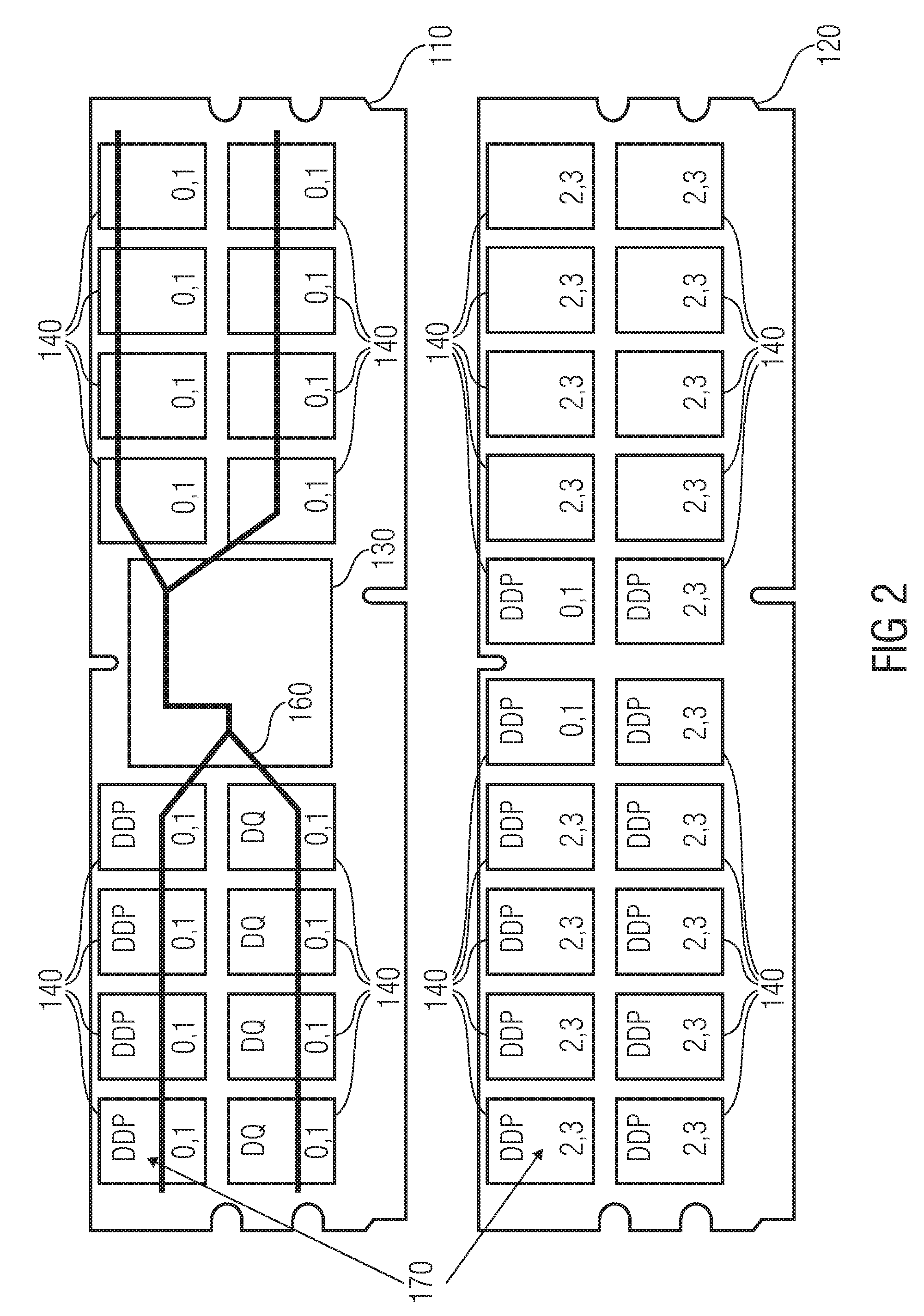
Stacked DRAM memory chip for a dual inline memory module (DIMM)
ActiveUS7200021B2Increase the number ofSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsInternal memoryMemory chip
A stacked DRAM memory chip for a Dual In Line Memory Module (DIMM) is disclosed. According to one aspect, the DRAM memory chip comprises at least four stacked DRAM memory dies. Further, the memory dies are each selectable by a corresponding internal memory rank signal. Each memory die comprises an array of memory cells. A common internal address bus is provided for addressing the memory cells and is connected to all stacked DRAM memory dies. Internal data buses are provided for writing data into the memory cells and reading data out of the memory cells of the DRAM memory dies. An integrated redriving unit comprises buffers for all internal address lines provided for driving external address signals applied to address pads of the DRAM memory chip. A multiplexer / demultiplexer switches the internal data lines of the selected DRAM memory die. A memory rank decoder selects a corresponding memory die.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
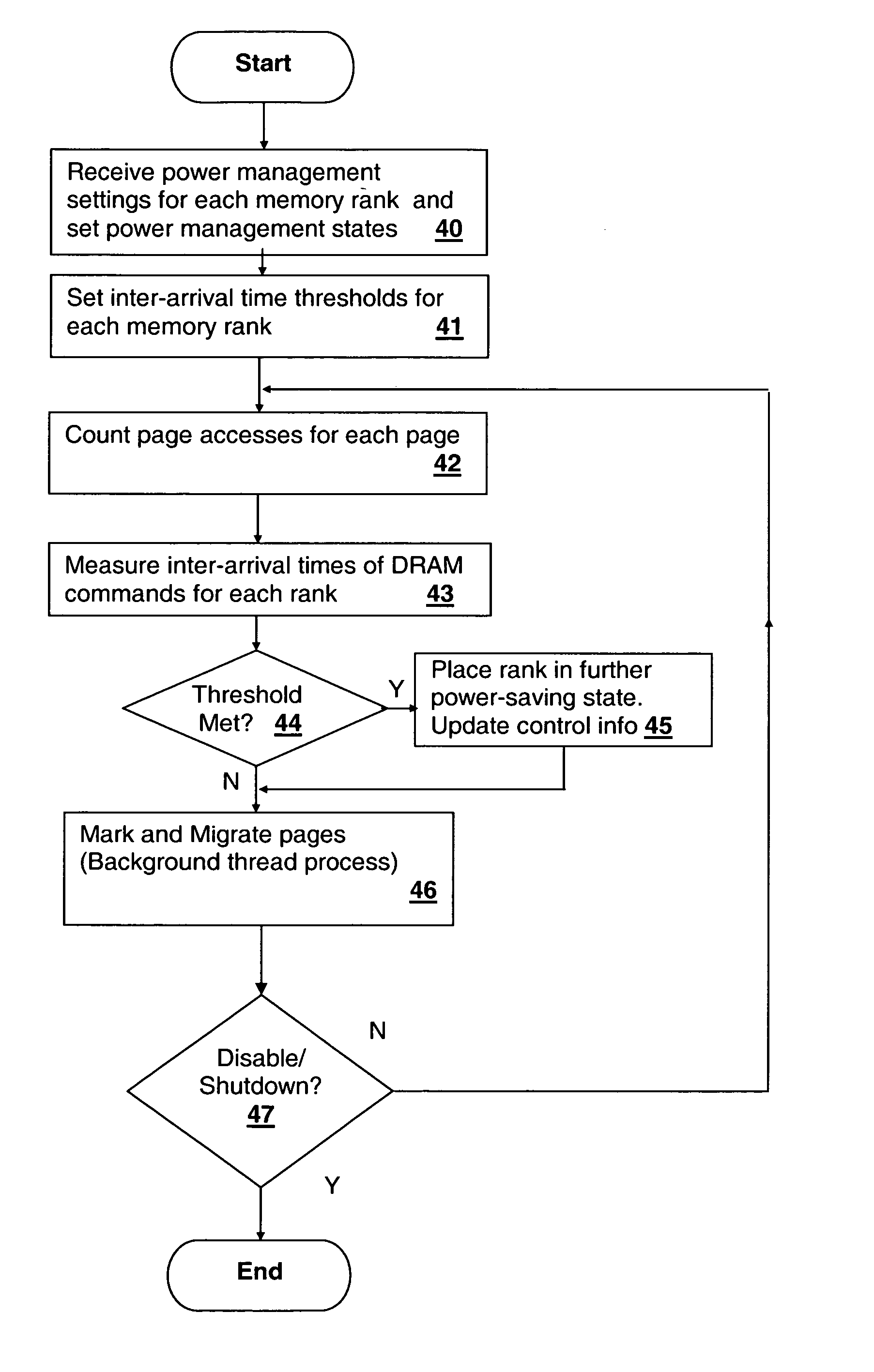
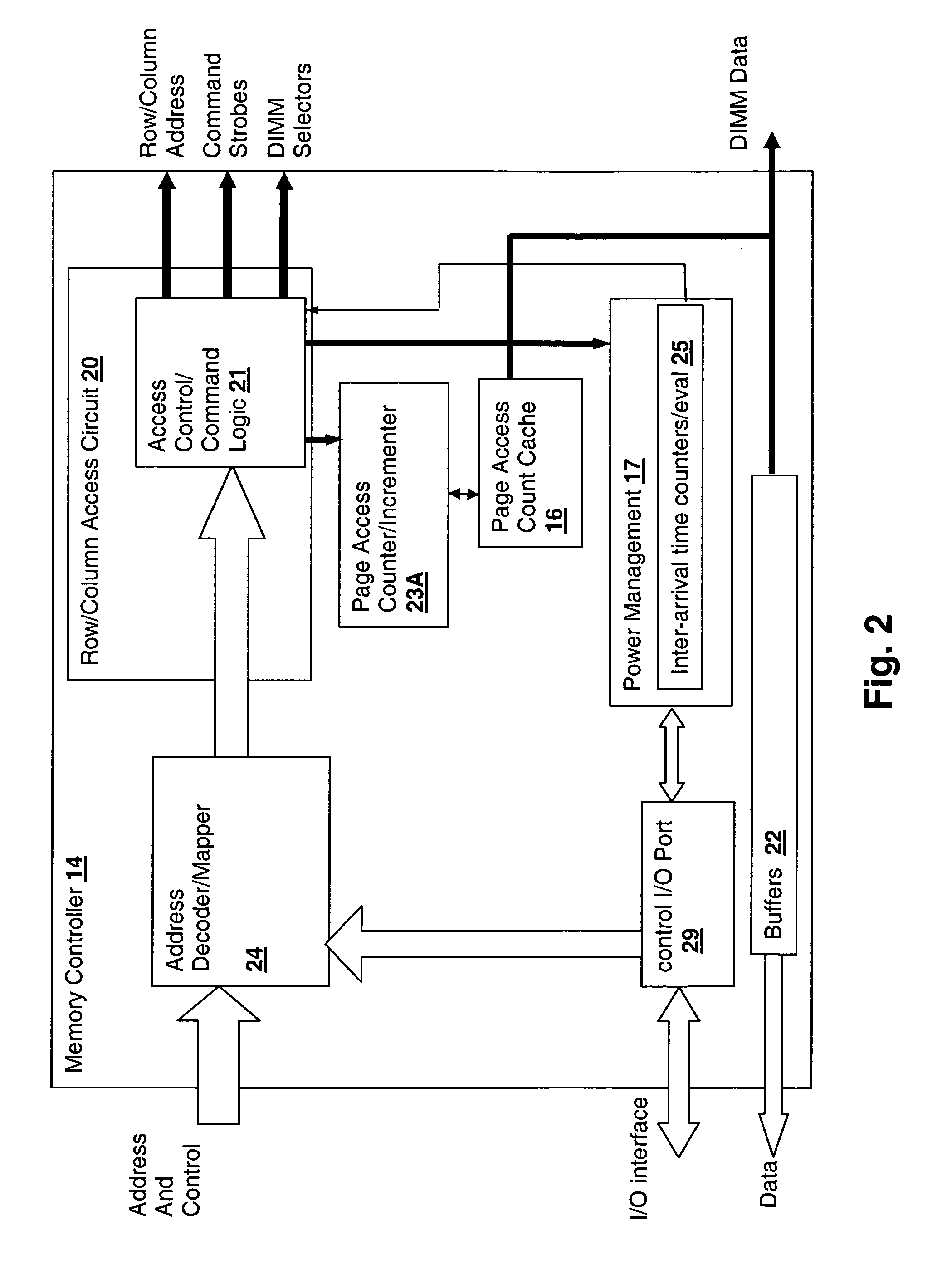
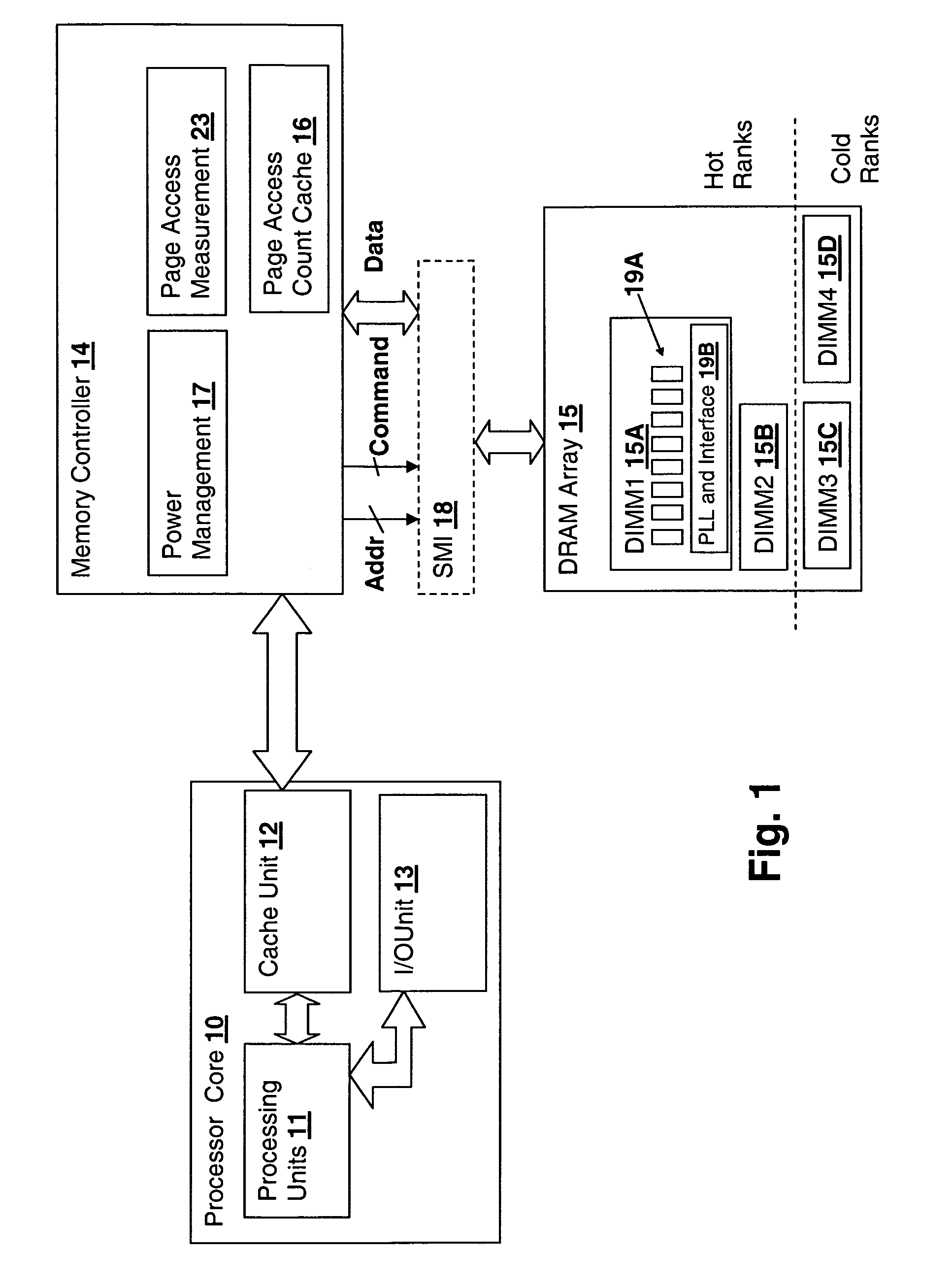
Method and system for decreasing power consumption in memory arrays having usage-driven power management
InactiveUS20070011421A1Reduce power consumptionLow level of activityEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementParallel computingCombined use
A method and system for decreasing power consumption in memory arrays having usage-driven power management provides decreased power consumption in the memory array of a processing system. Per-page usage information is gathered on memory by a memory controller and periodically evaluated by software. The software distinguishes between more frequently accessed pages and less frequently accessed pages by analyzing the gathered usage information and periodically migrates physical memory pages in order to group less frequently accessed pages and more frequently access pages in separately power-managed memory ranks. When used in conjunction with a usage-driven power management mechanism, the ranks containing the less frequently accessed pages can enter deeper power-saving states and / or any power-saving state for longer periods. Operation may be further enhanced by using packed allocation in the memory ranks containing the less-frequently accessed pages and scattered allocation in the memory ranks having more frequently accessed pages.
Owner:IBM CORP
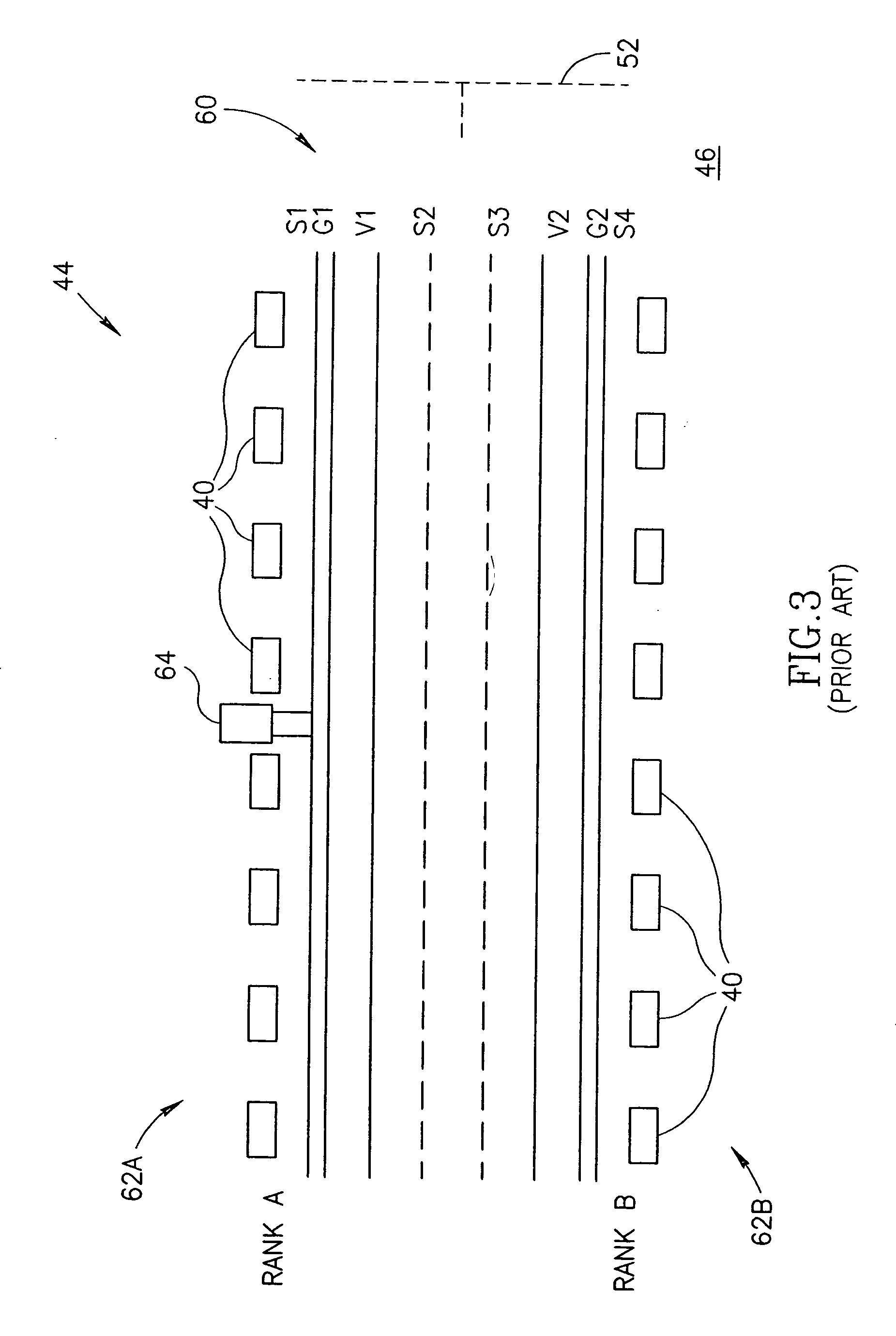
Apparatus and methods for a physical layout of simultaneously sub-accessible memory modules
ActiveUS6982892B2Improve performanceFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit aspectsMemory interfaceComputer module
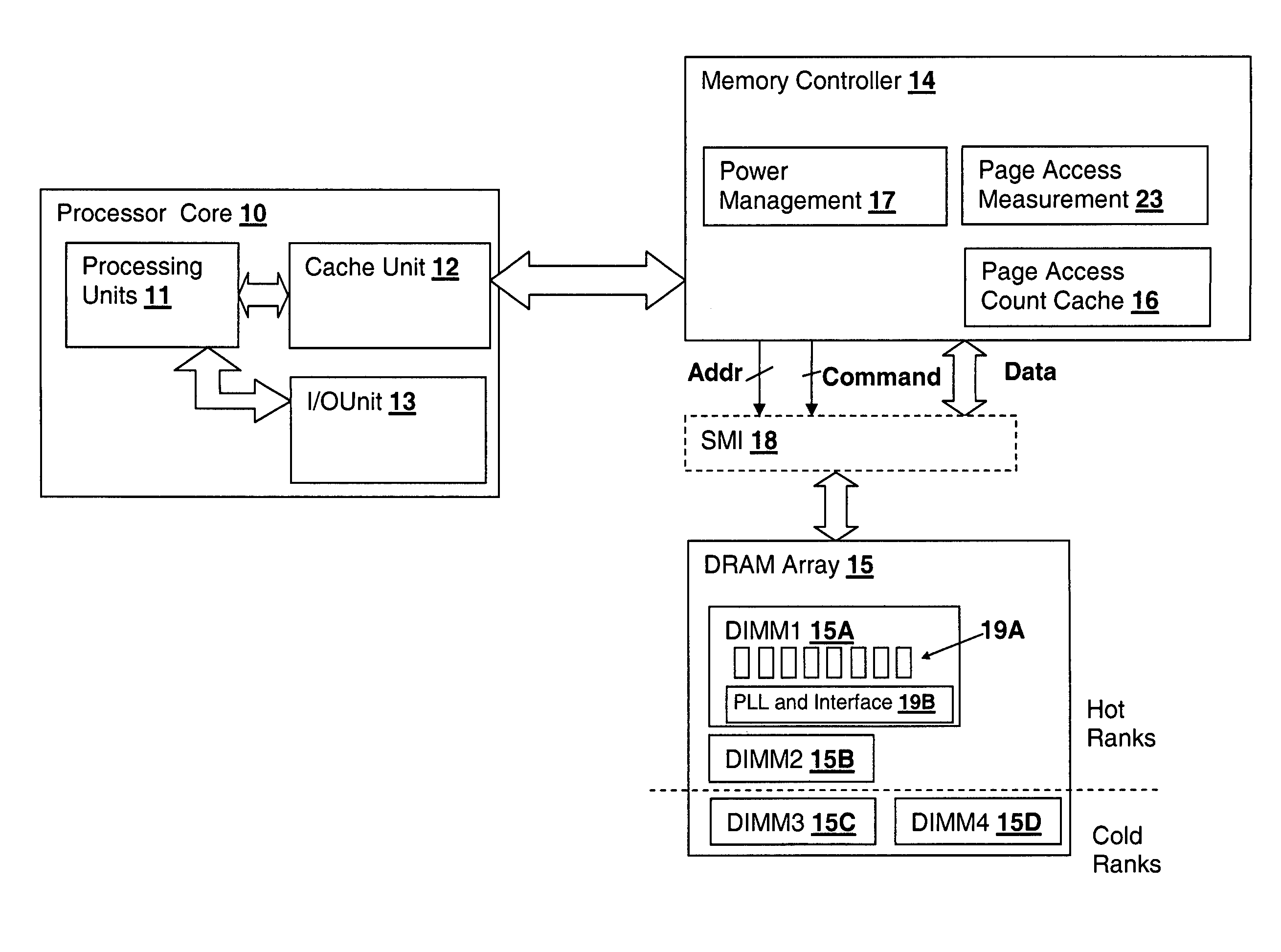
A layout for simultaneously sub-accessible memory modules is disclosed. In one embodiment, a memory module includes a printed circuit board having a plurality of sectors, each sector being electrically isolated from the other sectors and having a multi-layer structure. At least one memory device is attached to each sector, the memory devices being organized into a plurality of memory ranks. A driver is attached to the printed circuit board and is operatively coupled to the memory ranks. The driver is adapted to be coupled to a memory interface of the computer system. Because the sectors are electrically-isolated from adjacent sectors, the memory ranks are either individually or simultaneously, or both individually and simultaneously accessible by the driver so that one or more memory devices on a particular sector may be accessed at one time. In an alternate embodiment, the printed circuit board includes a driver sector electrically isolated from the other sectors and having a multi-layer structure, the driver being attached to the driver sector.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Transparent four rank memory module for standard two rank sub-systems
ActiveUS20060117152A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageParallel computingTerm memory
A transparent four rank memory module has a front side and a back side. The front side has a third memory rank stacked on a first memory rank. The back side has a fourth memory rank stacked on a second memory rank. An emulator coupled to the memory module activates and controls one individual memory rank from either the first memory rank, the second memory rank, the third memory rank, or the fourth memory rank based on the signals received from a memory controller.
Owner:SMART MODULAR TECH
Memory rank decoder for a multi-rank Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM)
The invention refers to a Memory Rank Decoder for a Multi-Rank Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM) having a predetermined number of DRAM memory chips mounted on a printer circuit board (PCB), wherein each DRAM memory chip comprises a predetermined number of stacked DRAM memory dies which are selectable by a memory rank selection signal (r), wherein the memory rank decoder generates the memory rank selection signal (r) in response to external selection signals applied to the dual inline module (DIMM).
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
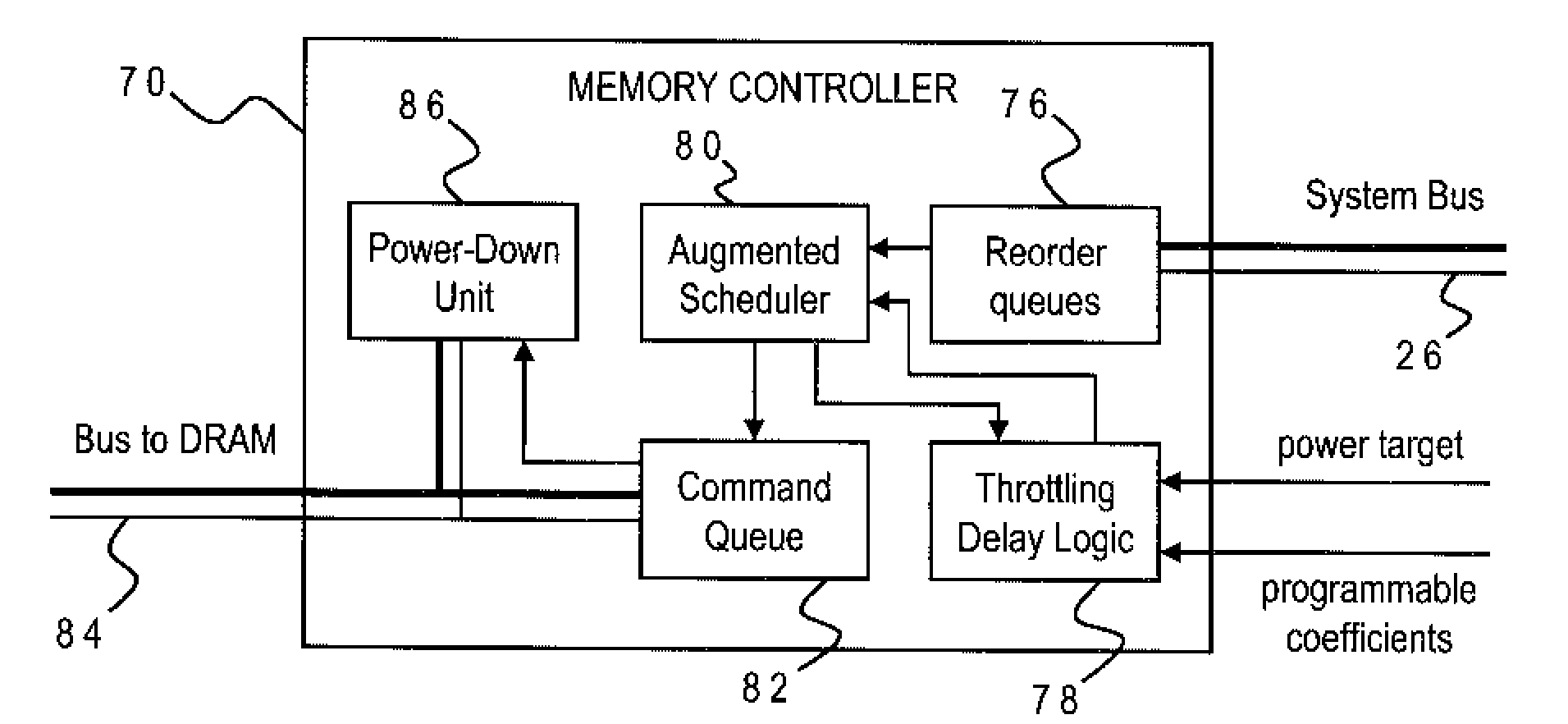
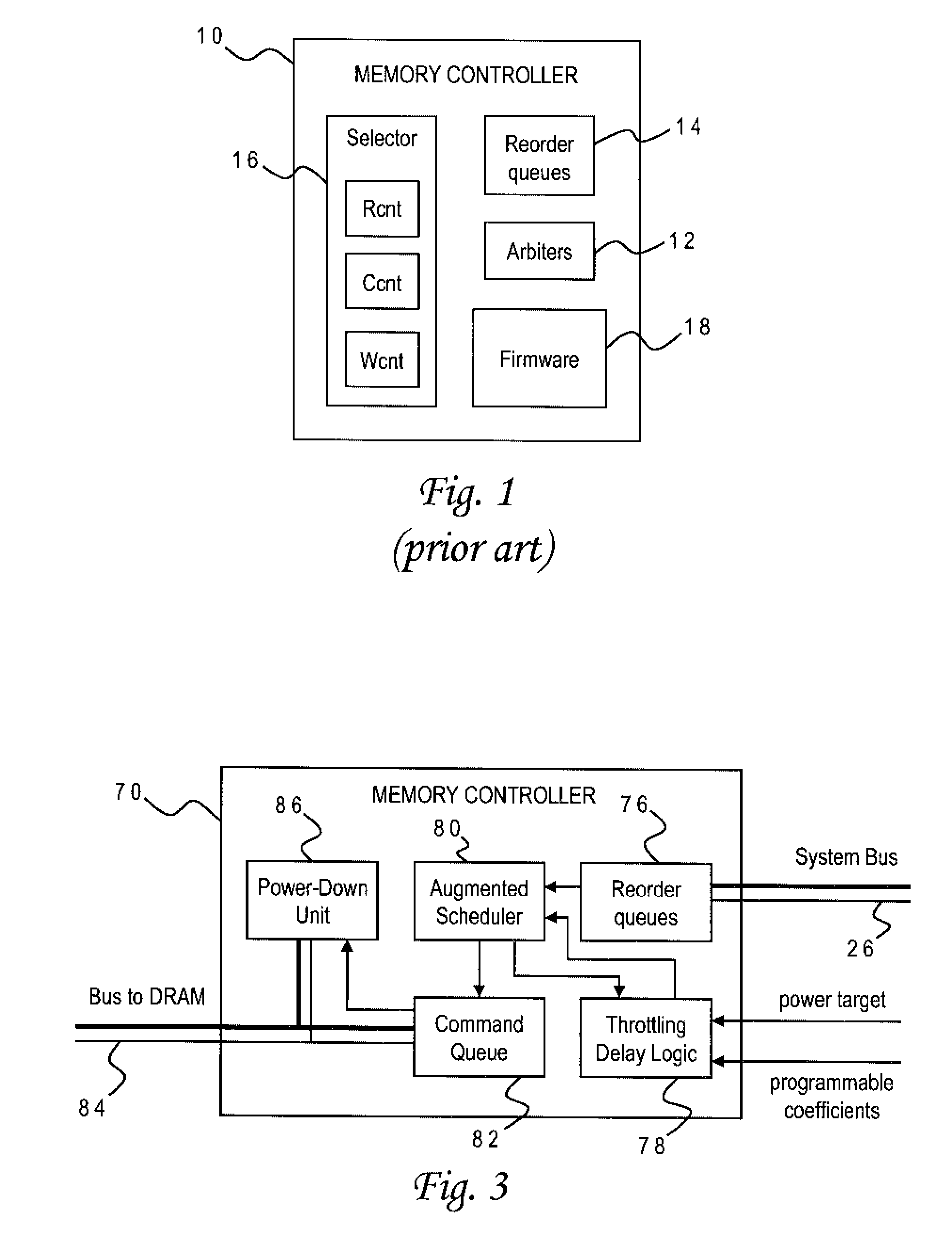
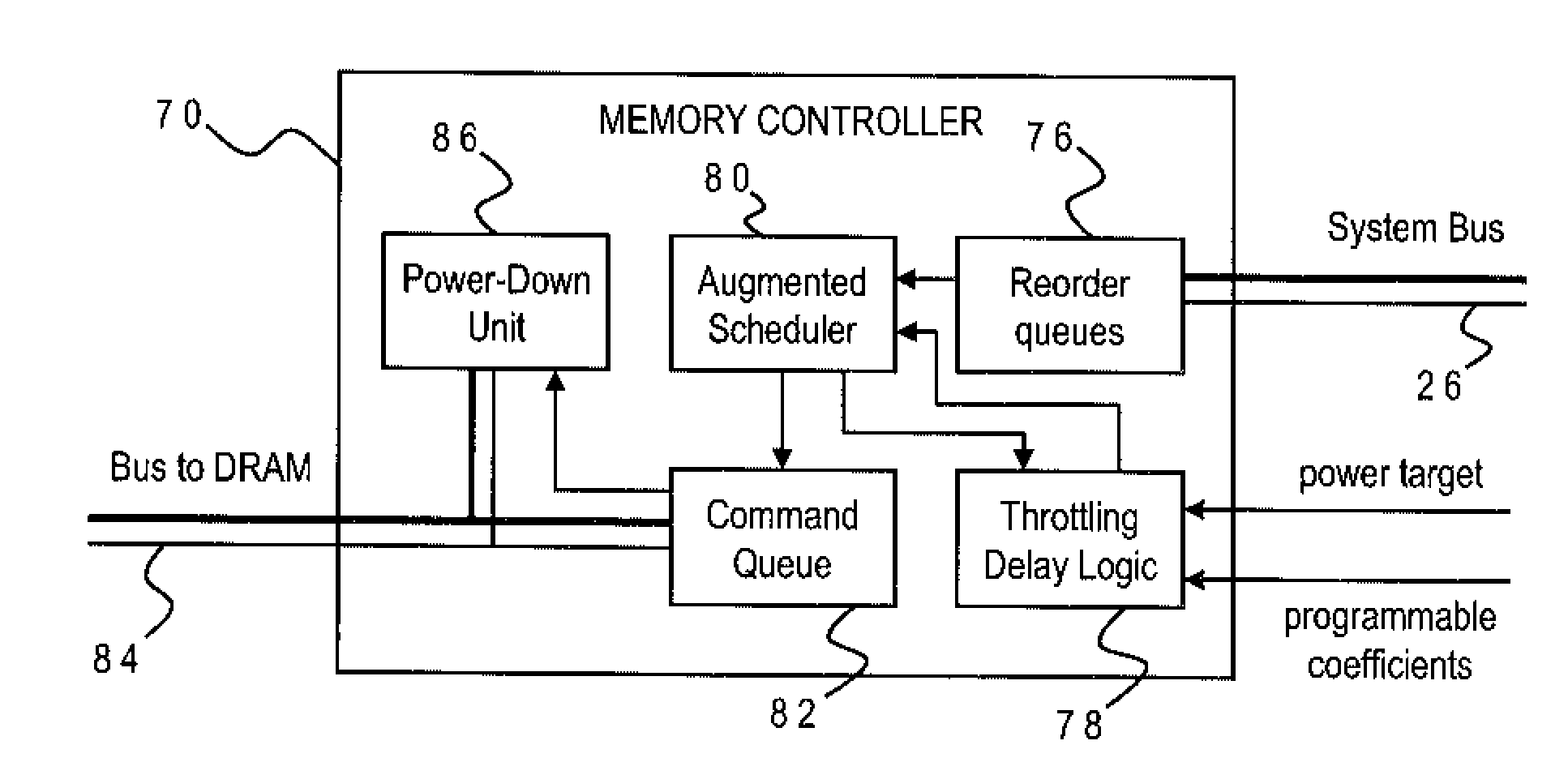
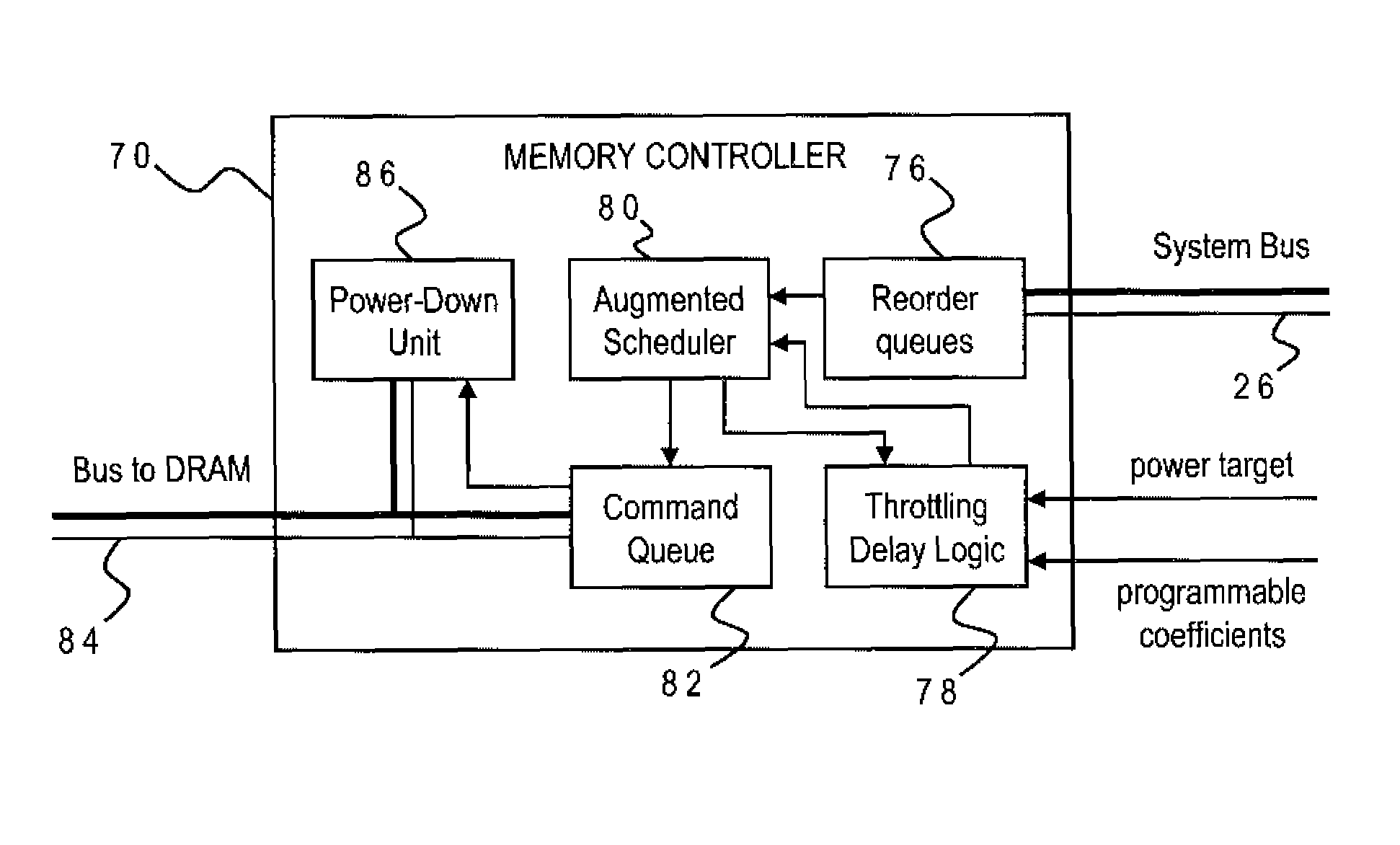
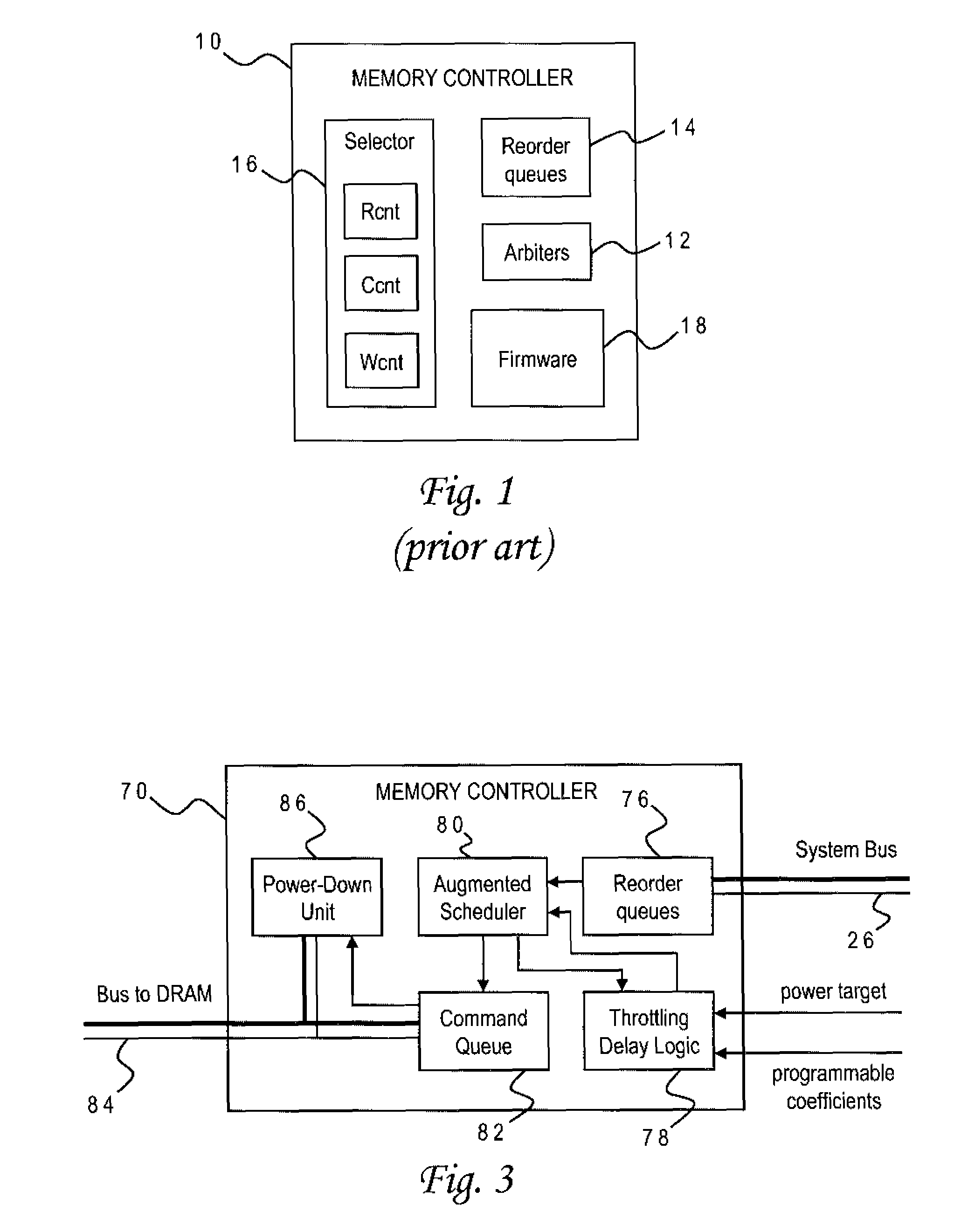
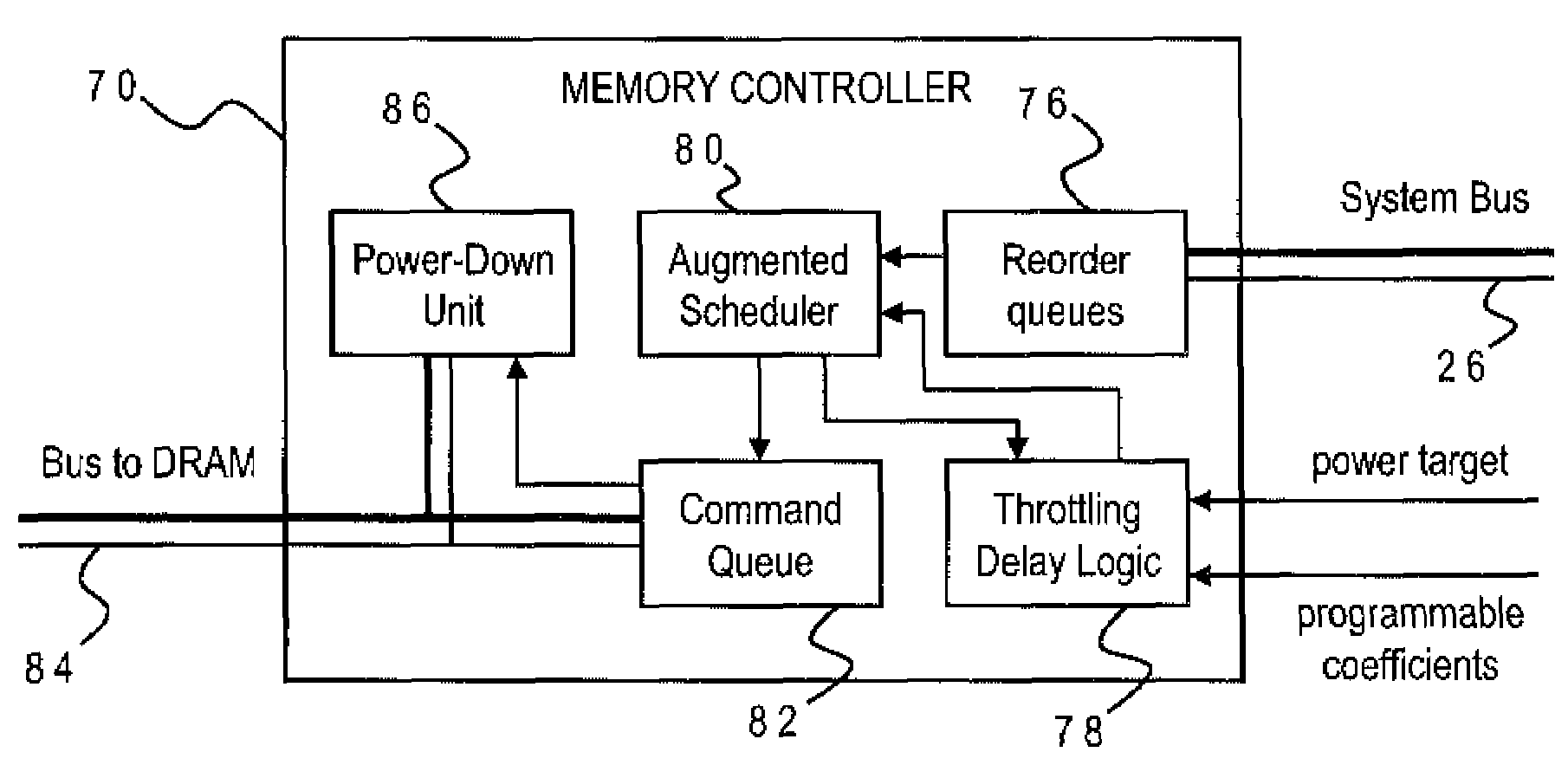
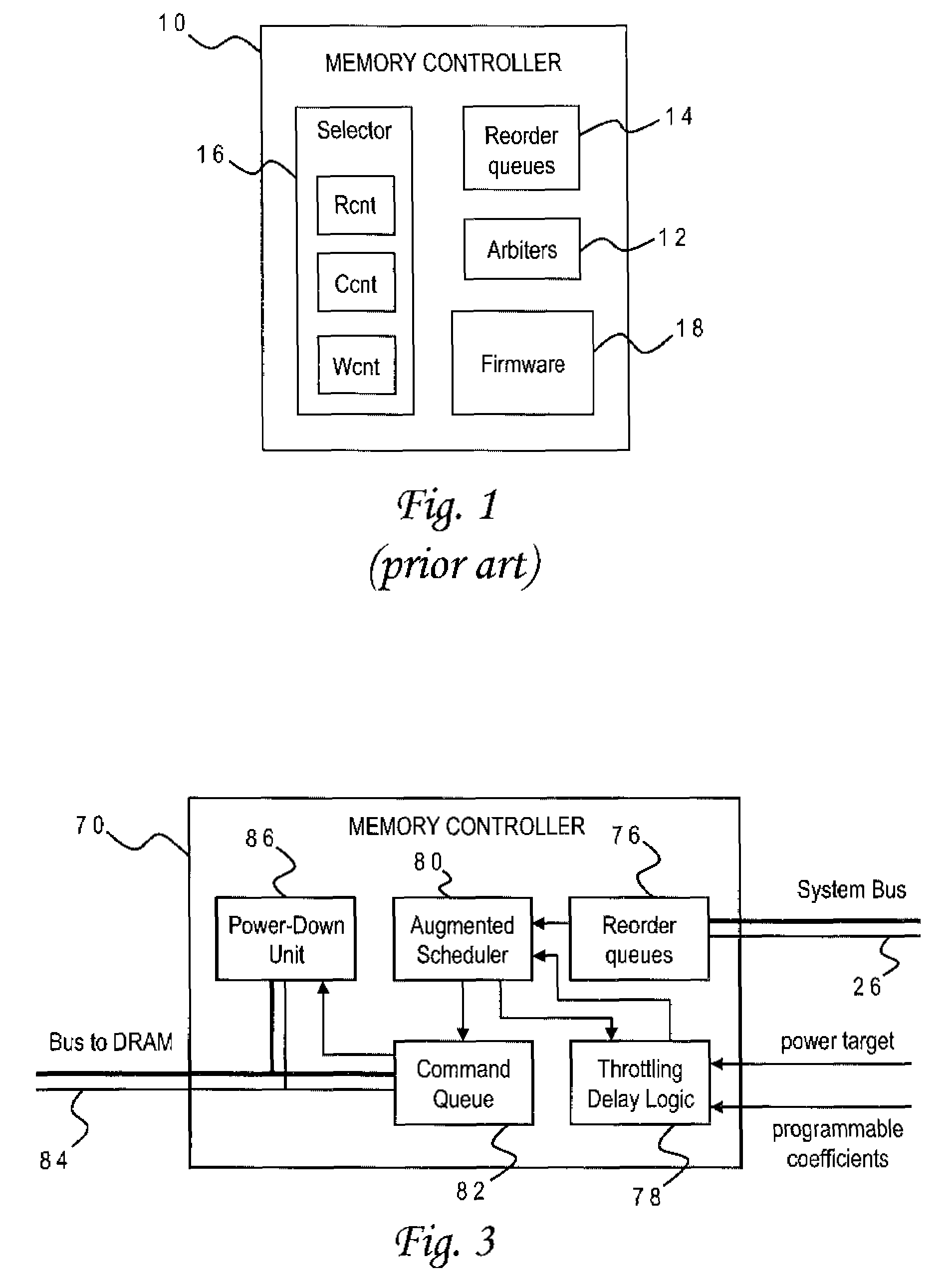
DRAM Power Management in a Memory Controller
InactiveUS20090019243A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTComputer hardwareMemory controller
A memory controller uses a power- and performance-aware scheduler which reorders memory commands based on power priorities. Selected memory ranks of the memory device are then powered down based on rank localities of the reordered commands. The highest power priority may be given to memory commands having the same rank as the last command sent to the memory device. Any memory commands having the same power priority can be further sorted based on one or more performance criteria such as an expected latency of the memory commands and an expected ratio of read and write memory commands. To optimize the power-down function, the power-down command is only sent when the selected memory rank is currently idle, the selected memory rank is not already powered down, none of the reordered memory commands correspond to the selected rank, and a currently pending memory command cannot be issued in the current clock cycle.
Owner:IBM CORP
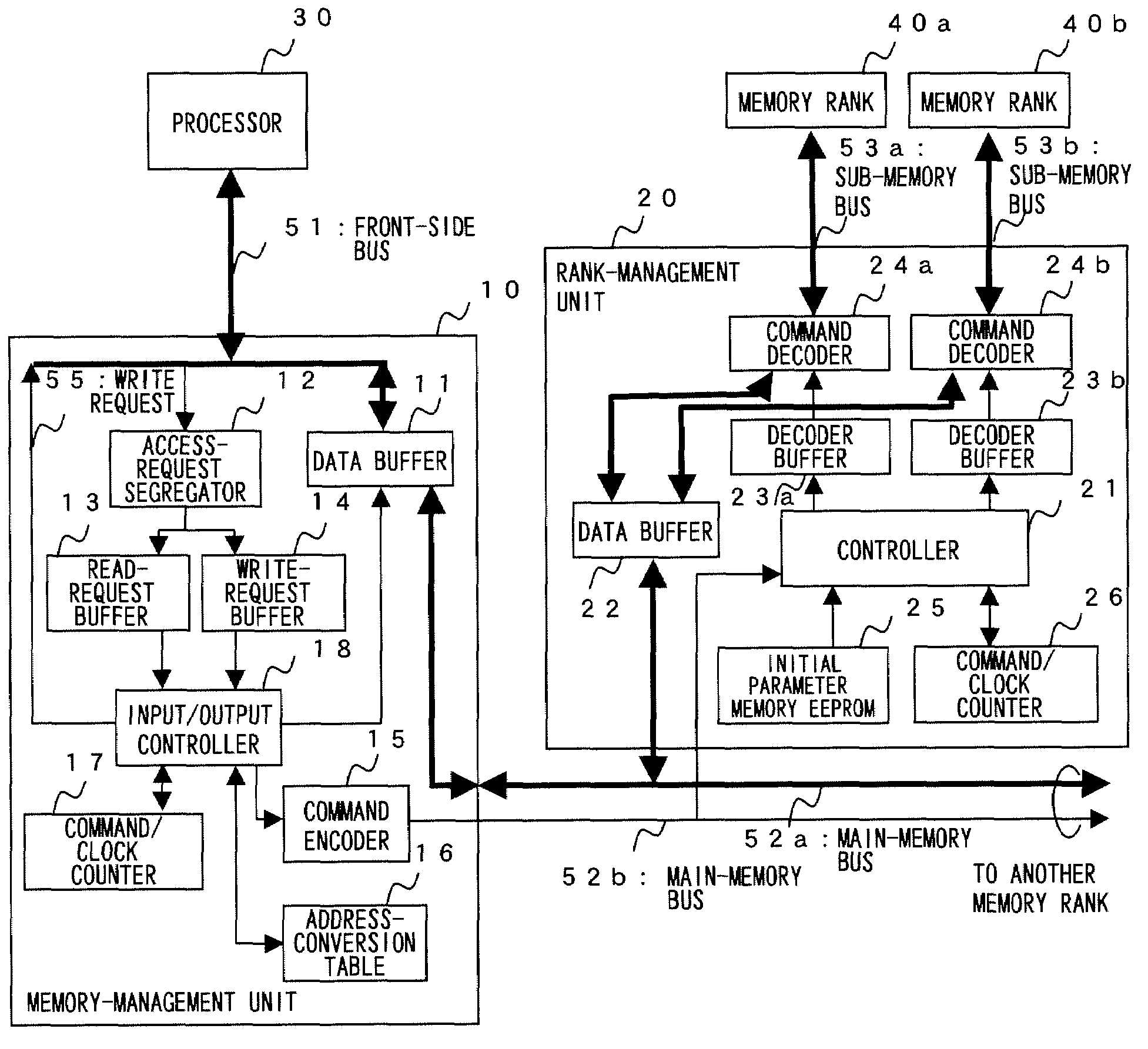
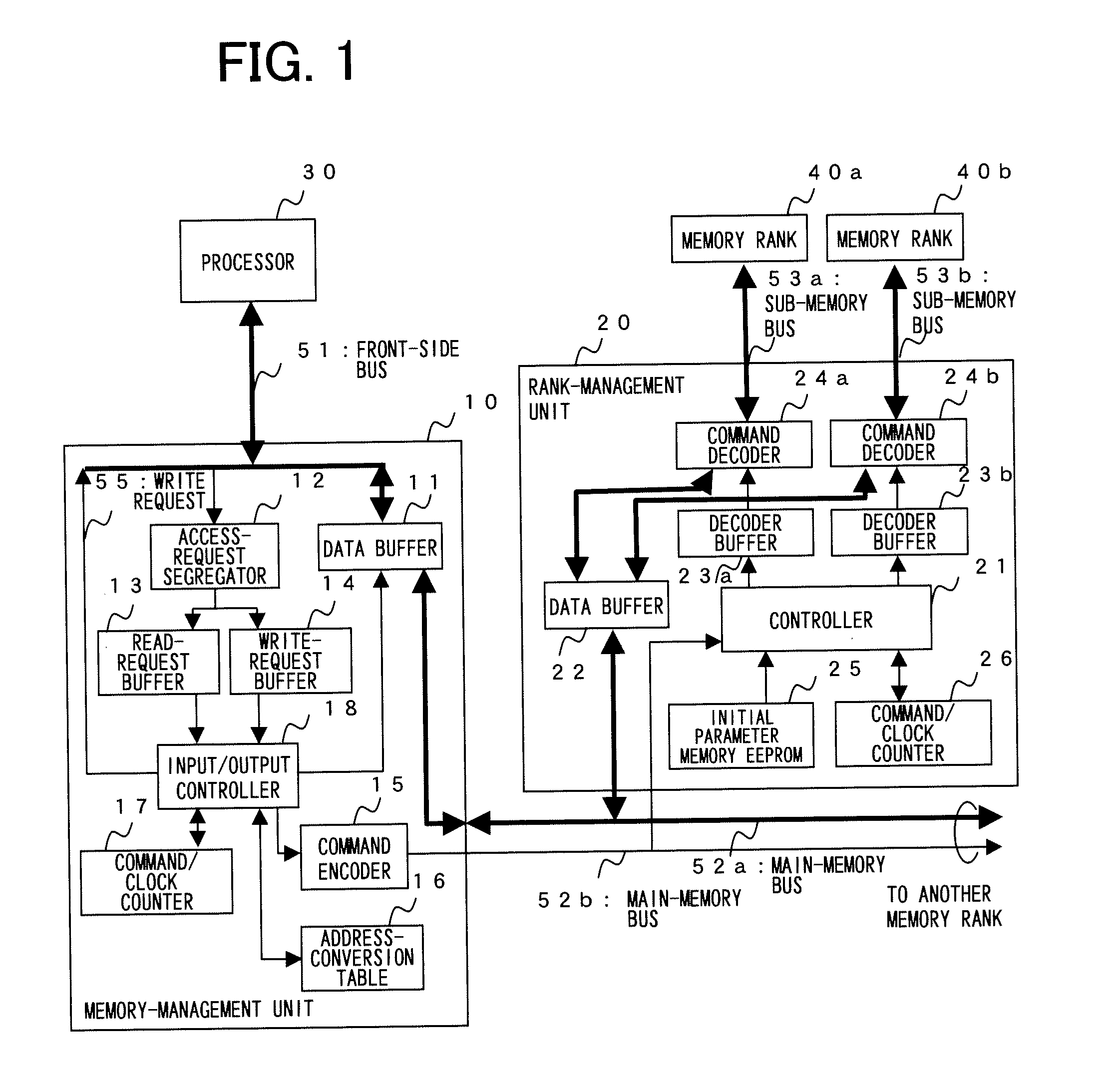
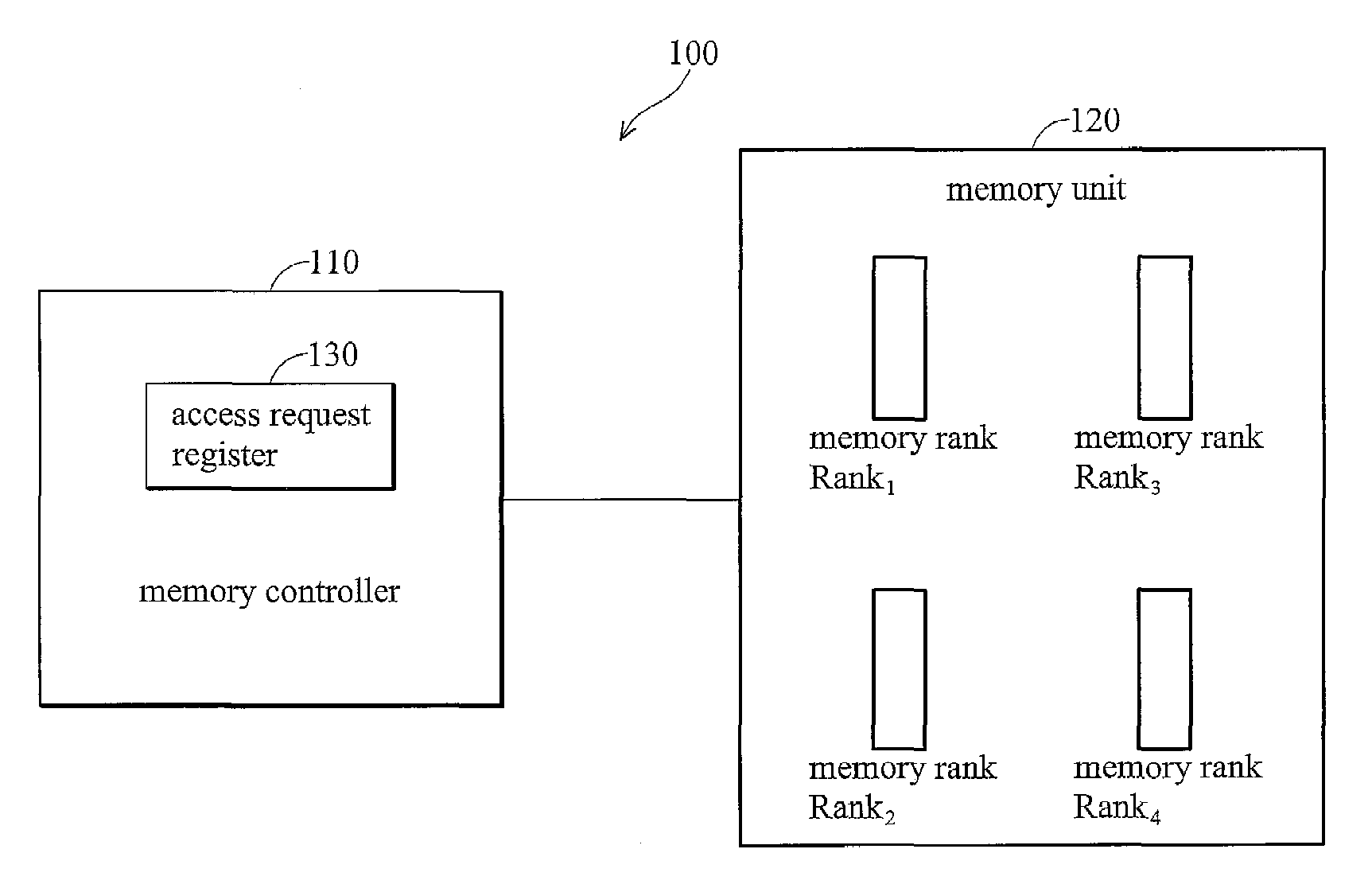
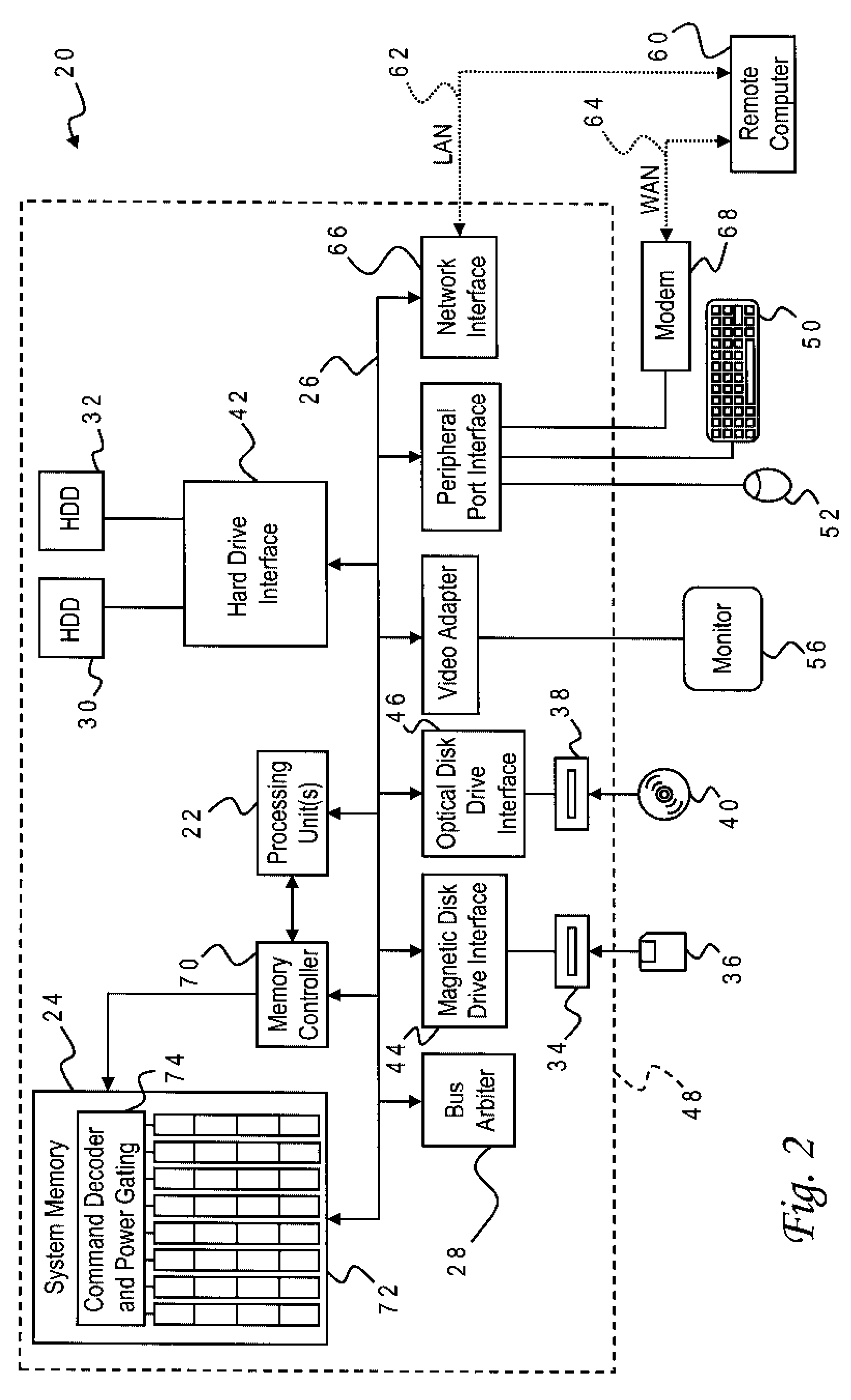
Memory control device
InactiveUS7707366B2Increasing bus utilization efficiencyEasy constructionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGeneral purpose stored program computerManagement unitMemory bus
Improved efficiency of address / data communication over a memory bus. A memory-control device is located between a processor 30 and memory ranks 40a, 40b and controls access to the memory ranks 40a, 40b. A memory-management unit 10 receives and buffers access request from the processor 30 to memory ranks 40a, 40b, and issues access request to a rank-management unit 20 based on scheduling for memory management. A rank-management unit 20 connects the memory ranks 40a, 40b, receives and buffers access request from the memory-management unit 10, and gives access request to a specified memory rank based on scheduling for rank management.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
Memory Controller with Programmable Regression Model for Power Control
InactiveUS20090016137A1Lower performance requirementsAccurate estimateEnergy efficient ICTDigital storageControl storeSystem configuration
A memory controller uses a throttling mechanism which estimates a throttling delay for achieving a target power consumption, and periodically blocks all memory commands for a number of clock cycles corresponding to the throttling delay. Idle memory ranks of the memory device are powered down while the memory commands are blocked. A regression model bases the throttling delay on a plurality of operating factors and a plurality of regression coefficients for the operating factors. In the illustrative implementation the operating factors include power consumption, a current number of bank conflicts, a current number of read commands, and a current number of write commands. Different sets of regression coefficients can be programmably stored for use with different system configurations.
Owner:IBM CORP
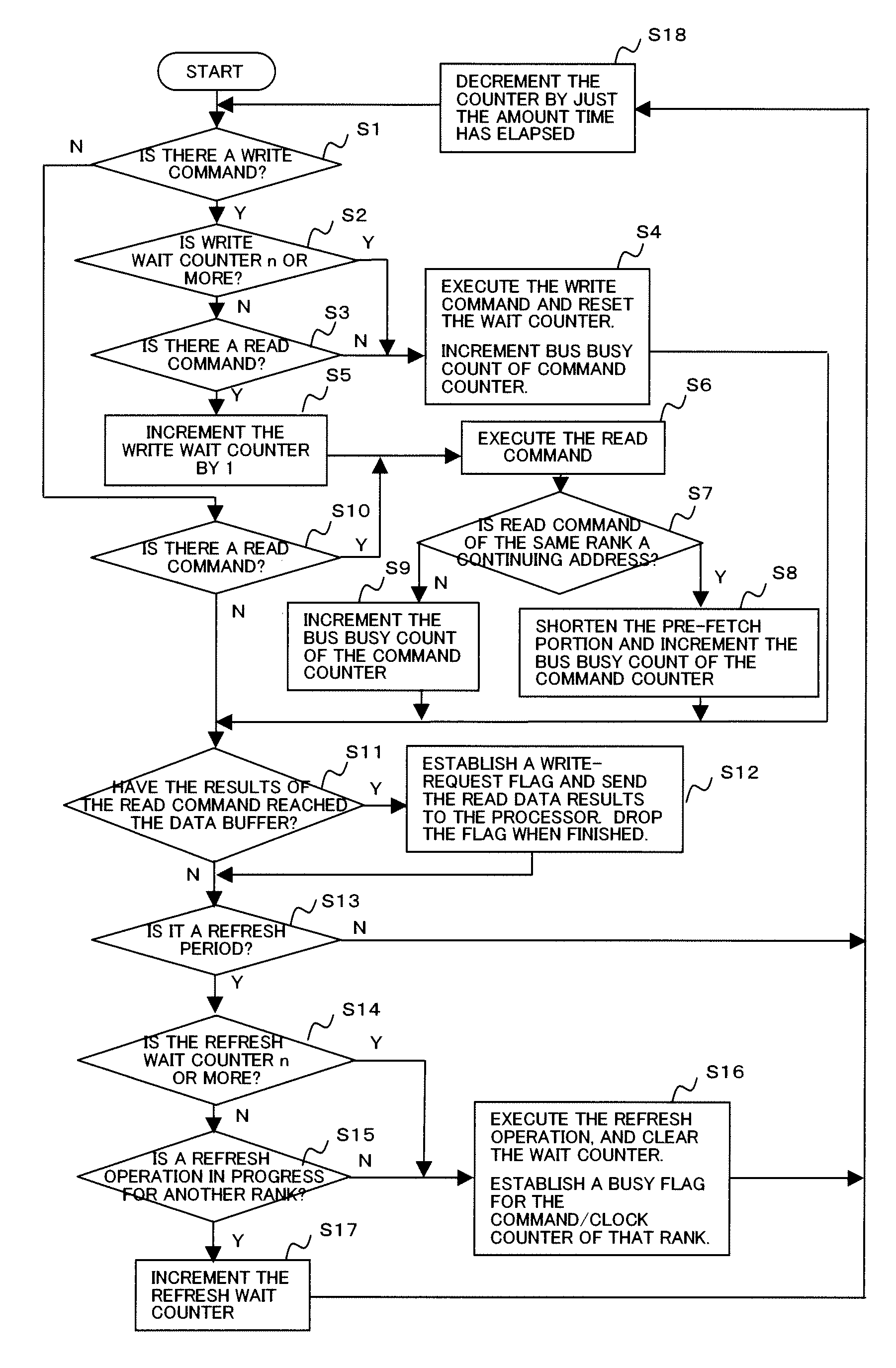
Power consumption decrease memory management method
InactiveUS20070288783A1Suppress power consumptionLow powerVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingTerm memoryActive state
The power consumed by a memory is reduced without affecting the performance whereby a processor accesses the memory. A state of a power supplied to the memory is controlled to one of an active state wherein a storage area included in the memory rank can be accessed from the processor, and an inactive state wherein access cannot be performed without a delay for each memory rank, the basic system software prevents fragmentation in which the allocated storage area spans a plurality of memory ranks, puts the power state of a memory rank which does not include an allocated storage area into the inactive state, and puts the power state of a memory rank which includes a storage area required for allocation first into the active state.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Multi-rank memory module that emulates a memory module having a different number of ranks
A transparent four rank memory module has a front side and a back side. The front side has a third memory rank stacked on a first memory rank. The back side has a fourth memory rank stacked on a second memory rank. An emulator coupled to the memory module activates and controls one individual memory rank from either the first memory rank, the second memory rank, the third memory rank, or the fourth memory rank based on the signals received from a memory controller.
Owner:SMART MODULAR TECH
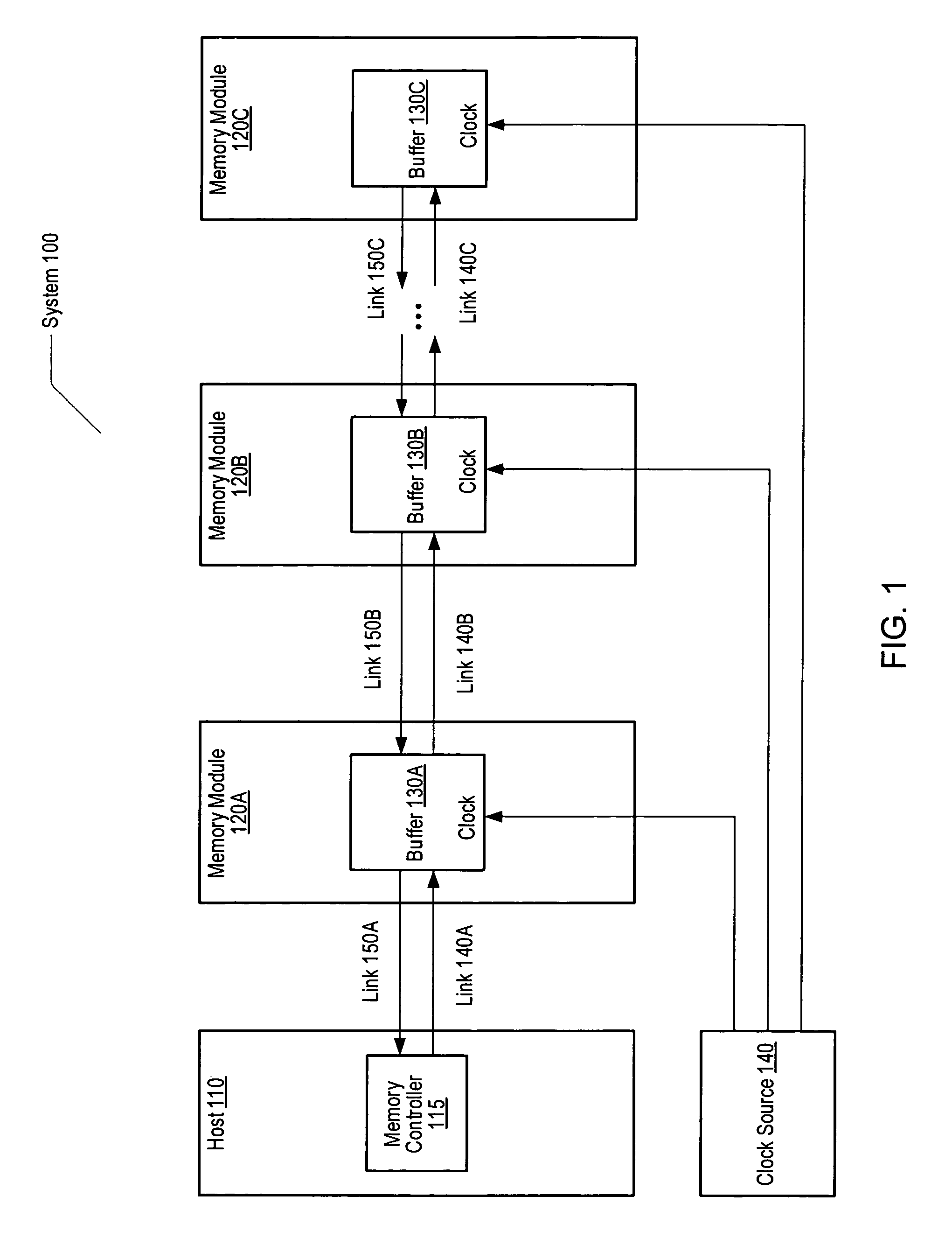
Clock enable throttling for power savings in a memory subsystem
ActiveUS7523282B1Operation be disabledEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementMemory controllerMemory module
A memory subsystem is disclosed. The memory subsystem includes a memory controller coupled to one or more memory modules. Each memory module comprises a buffer coupled to one or more memory ranks. A clock source is coupled to provide a clock signal to each of the memory modules. The memory controller is configured to convey a clock enable (CKE) command to one of the memory modules, the CKE command corresponding to a given memory rank. In response to the CKE command, a memory module buffer associated with the given memory rank is configured to convey a CKE disable signal to the given memory rank. The given memory rank is configured to disable operation of the clock signal within the given memory rank, responsive to the CKE disable signal.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for interrupting memory bank refresh
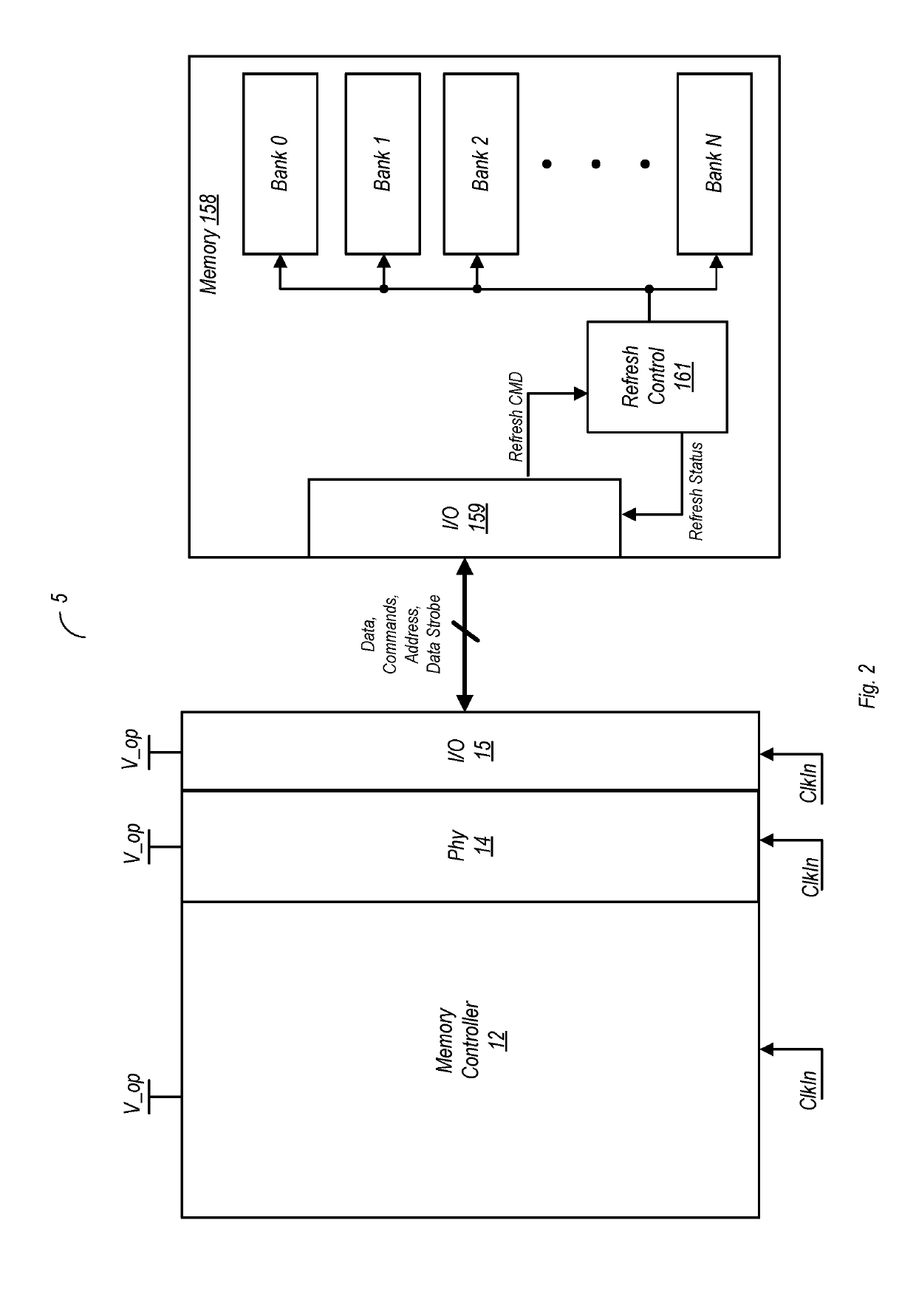
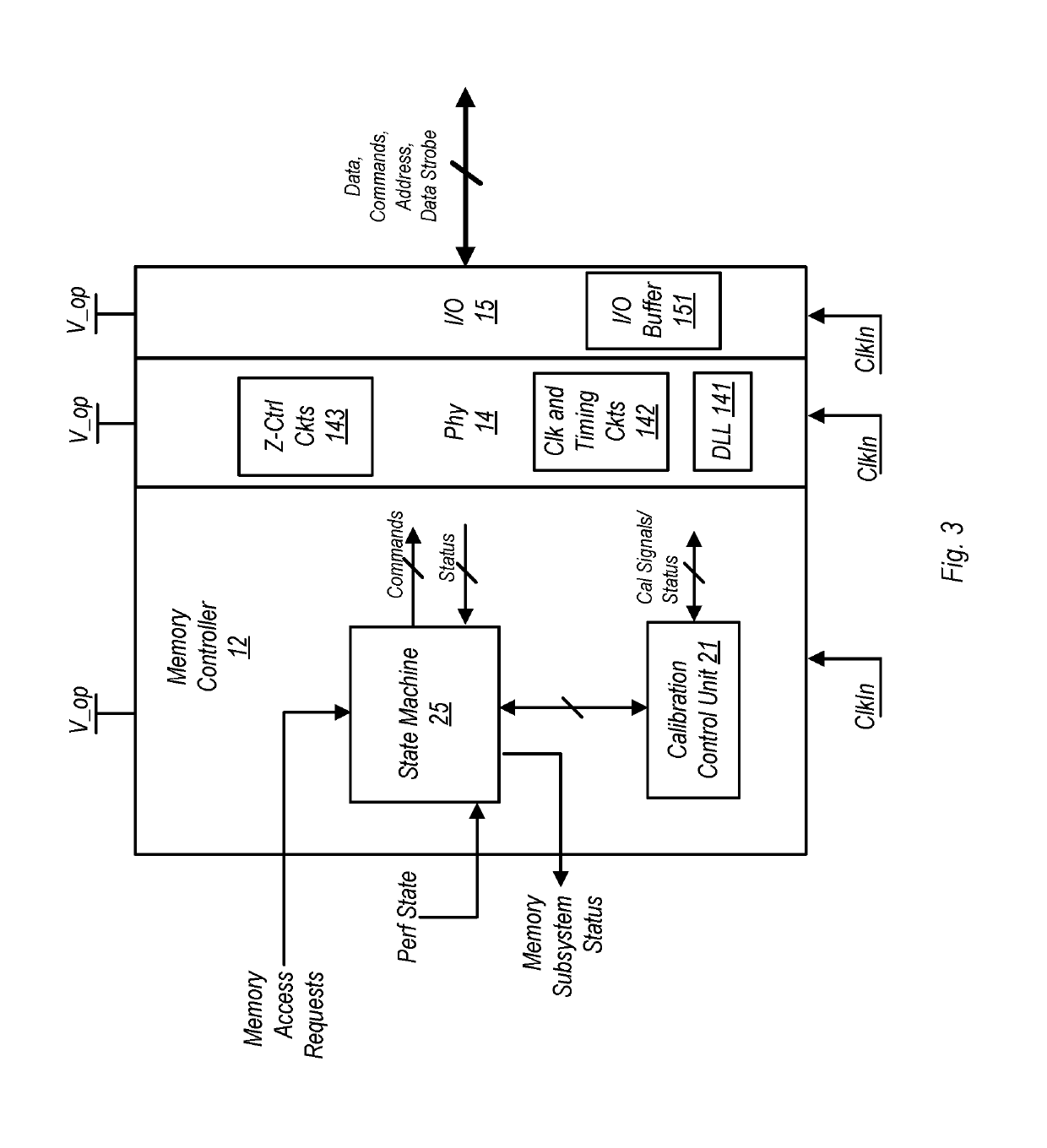
ActiveUS10510396B1Timely controlDigital storageEnergy efficient computingMemory bankMemory controller
A memory controller includes a state machine that initiates a memory refresh of a DRAM (having a number of banks) by sending thereto a refresh command. Responsive to receiving the command, the DRAM may perform a per-bank refresh in which individual ones of the banks are refreshed in succession, one at a time. Upon receiving a high priority transaction, a determination is made as to the number of memory banks that have currently been refreshed in the per-bank refresh. If the number of banks refreshed is less than a threshold value, the per-bank refresh is aborted.
Owner:APPLE INC
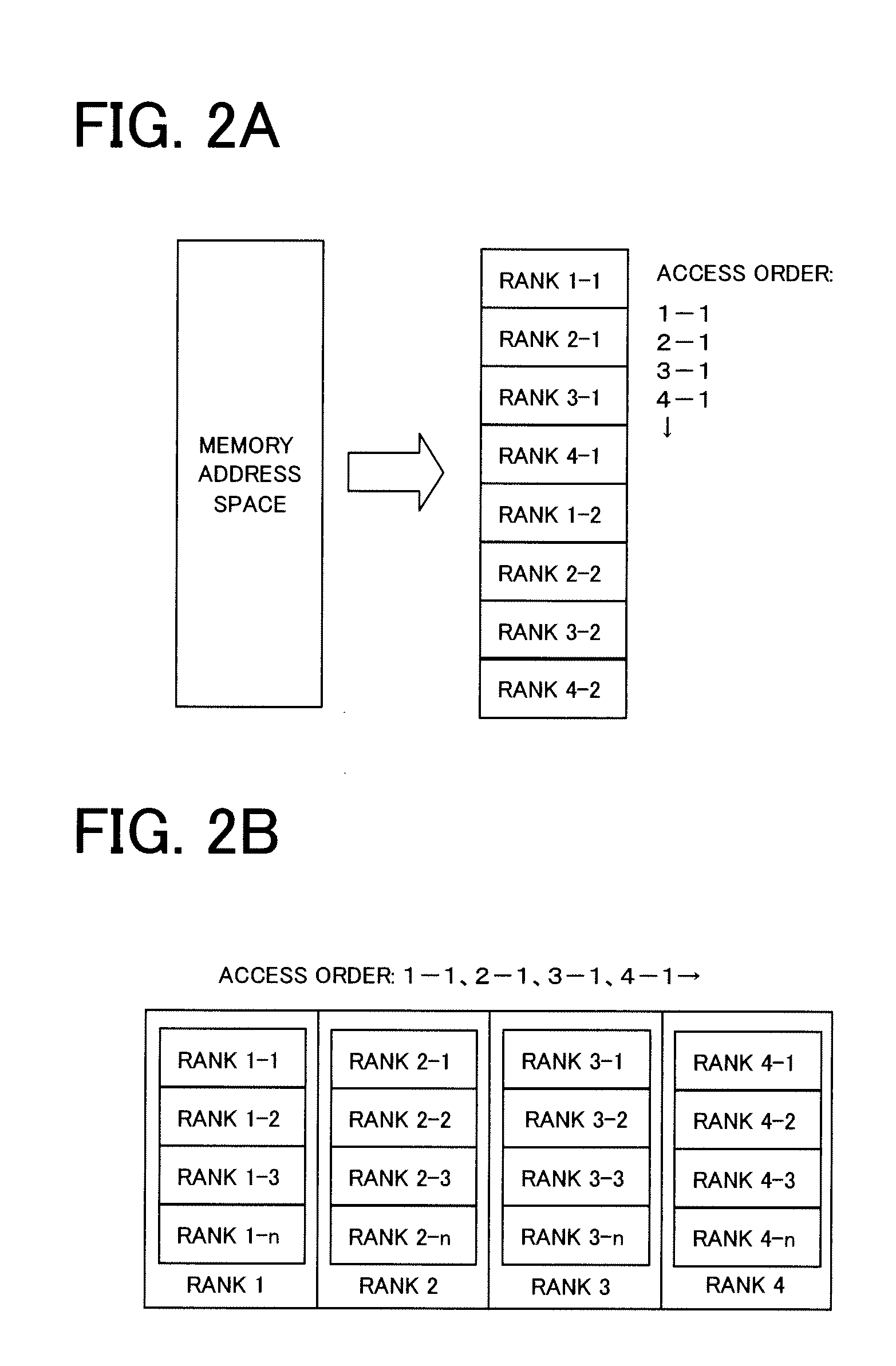
Method of memory space configuration
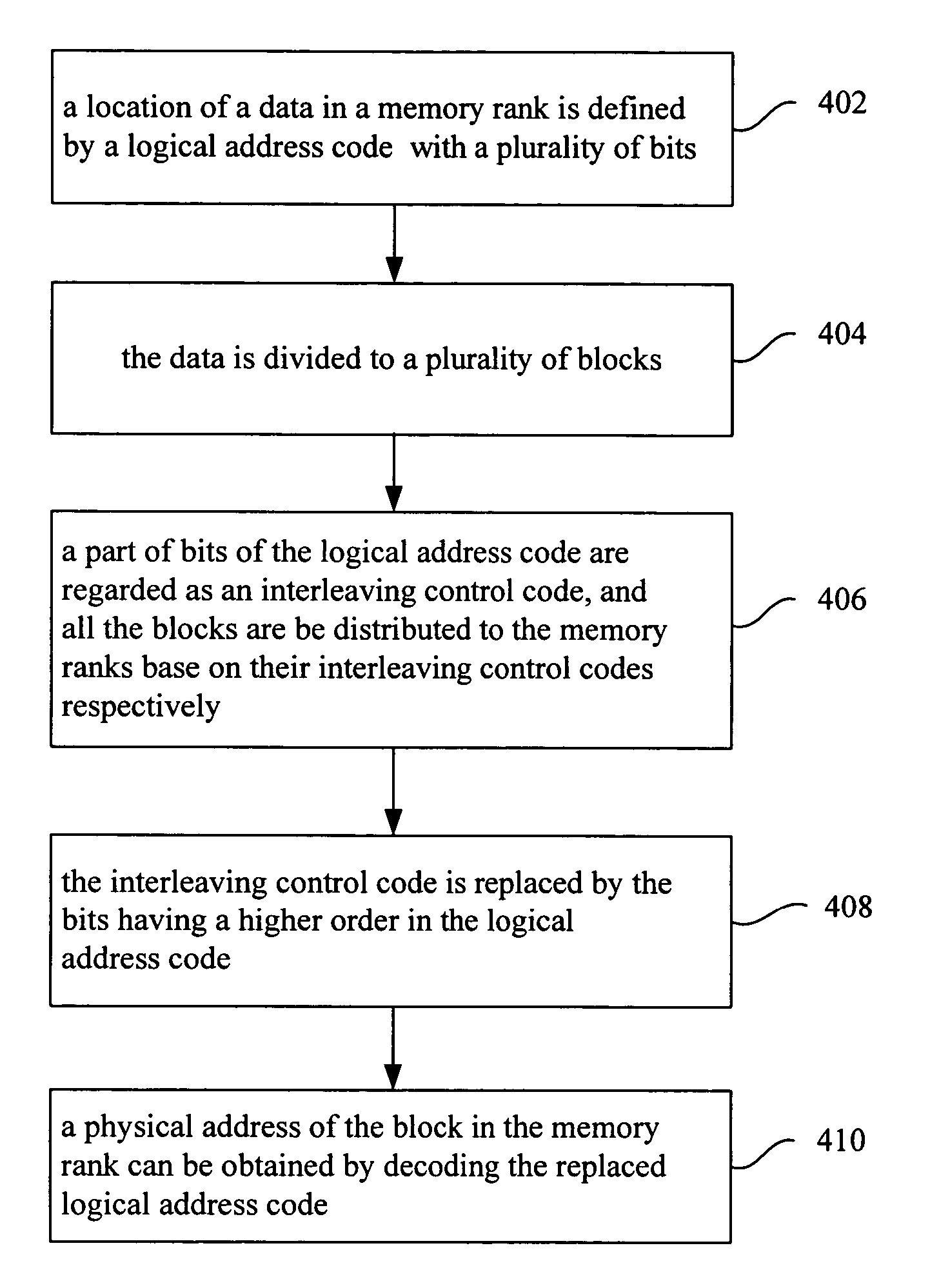
A method is disclosed for utilizing at least one bit within the logical address code of a memory unit formed by Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) to be the control code for interleaving the memory space to different memory ranks. First, the distributive rule of the data is defined. Next, the data is distributed to the memory ranks that the data belongs to according to the rule. Then, the data is physically accessed in one of the memory ranks.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Memory control device
InactiveUS20070162715A1Improve bus utilization efficiencyIncrease speedMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGeneral purpose stored program computerManagement unitMemory bus
Improved efficiency of address / data communication over a memory bus. A memory-control device is located between a processor 30 and memory ranks 40a, 40b and controls access to the memory ranks 40a, 40b. A memory-management unit 10 receives and buffers access request from the processor 30 to memory ranks 40a, 40b, and issues access request to a rank-management unit 20 based on scheduling for memory management. A rank-management unit 20 connects the memory ranks 40a, 40b, receives and buffers access request from the memory-management unit 10, and gives access request to a specified memory rank based on scheduling for rank management.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
Apparatus and methods for a physical layout of simultaneously sub-accessible memory modules
ActiveUS20060215434A1Improve performanceFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit aspectsElectricityDriver/operator
A layout for simultaneously sub-accessible memory modules is disclosed. In one embodiment, a memory module includes a printed circuit board having a plurality of sectors, each sector being electrically isolated from the other sectors and having a multi-layer structure. At least one memory device is attached to each sector, the memory devices being organized into a plurality of memory ranks. A driver is attached to the printed circuit board and is operatively coupled to the memory ranks. The driver is adapted to be coupled to a memory interface of the computer system. Because the sectors are electrically-isolated from adjacent sectors, the memory ranks are either individually or simultaneously, or both individually and simultaneously accessible by the driver so that one or more memory devices on a particular sector may be accessed at one time. In an alternate embodiment, the printed circuit board includes a driver sector electrically isolated from the other sectors and having a multi-layer structure, the driver being attached to the driver sector.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method and system for decreasing power consumption in memory arrays having usage-driven power management
InactiveUS8010764B2Reduce power consumptionImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementCombined useParallel computing
A method and system for decreasing power consumption in memory arrays having usage-driven power management provides decreased power consumption in the memory array of a processing system. Per-page usage information is gathered on memory by a memory controller and periodically evaluated by software. The software distinguishes between more frequently accessed pages and less frequently accessed pages by analyzing the gathered usage information and periodically migrates physical memory pages in order to group less frequently accessed pages and more frequently access pages in separately power-managed memory ranks. When used in conjunction with a usage-driven power management mechanism, the ranks containing the less frequently accessed pages can enter deeper power-saving states and / or any power-saving state for longer periods. Operation may be further enhanced by using packed allocation in the memory ranks containing the less-frequently accessed pages and scattered allocation in the memory ranks having more frequently accessed pages.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
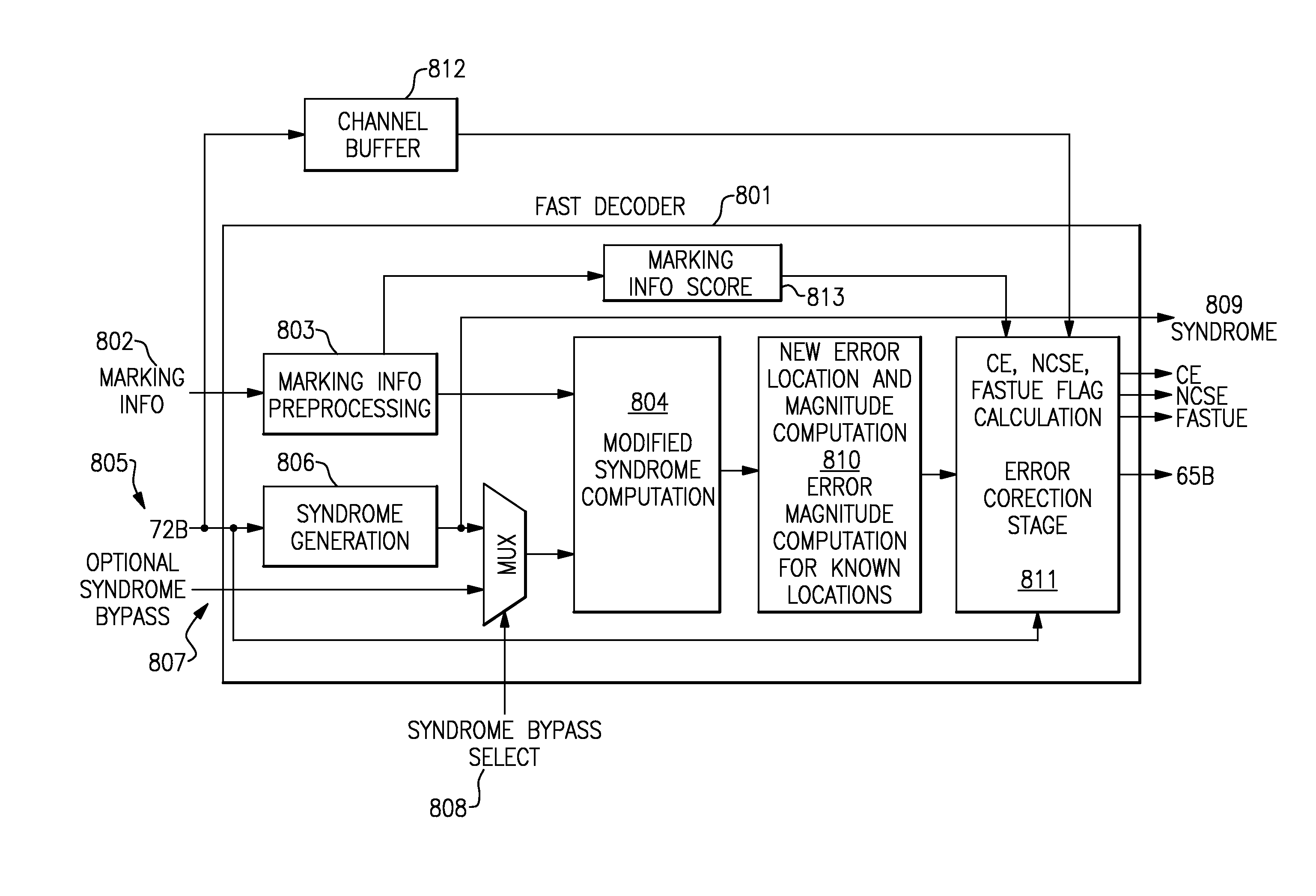
System for Error Control Coding for Memories of Different Types and Associated Methods
ActiveUS20100293436A1Improves error control codingCode conversionUnequal/adaptive error protectionMemory chipEmbedded system
A system to improve error control coding may include memory chips of at least two different kinds. The system may also include error control encoder circuitry to substantially encode data for storage in any memory rank. The system may further include error control decoder circuitry to substantially decode encoded data received from any memory rank. The error decoder circuitry is comprised of a slow decoder and a fast decoder.
Owner:IBM CORP
Atomic read/write support in a multi-module memory configuration
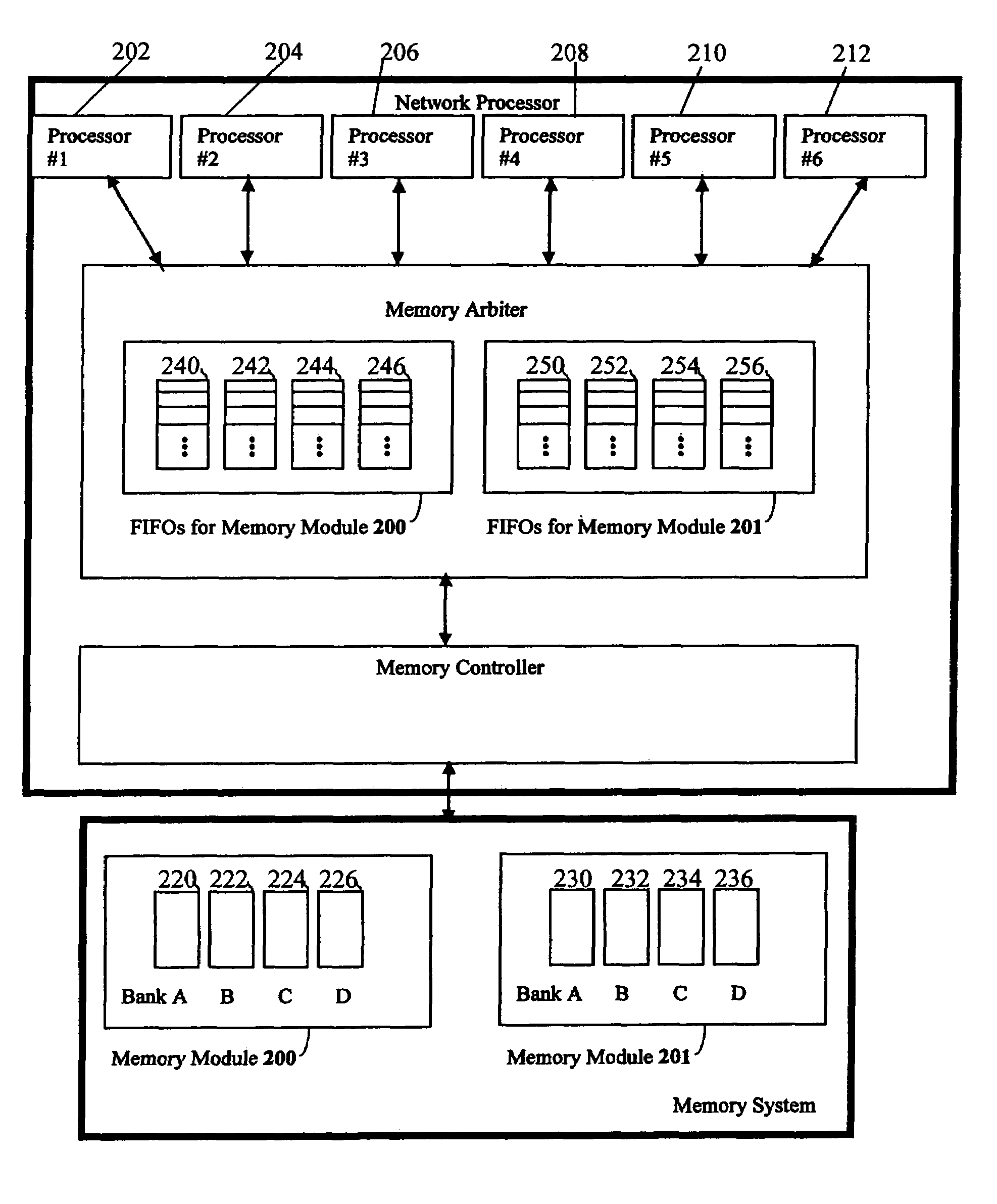
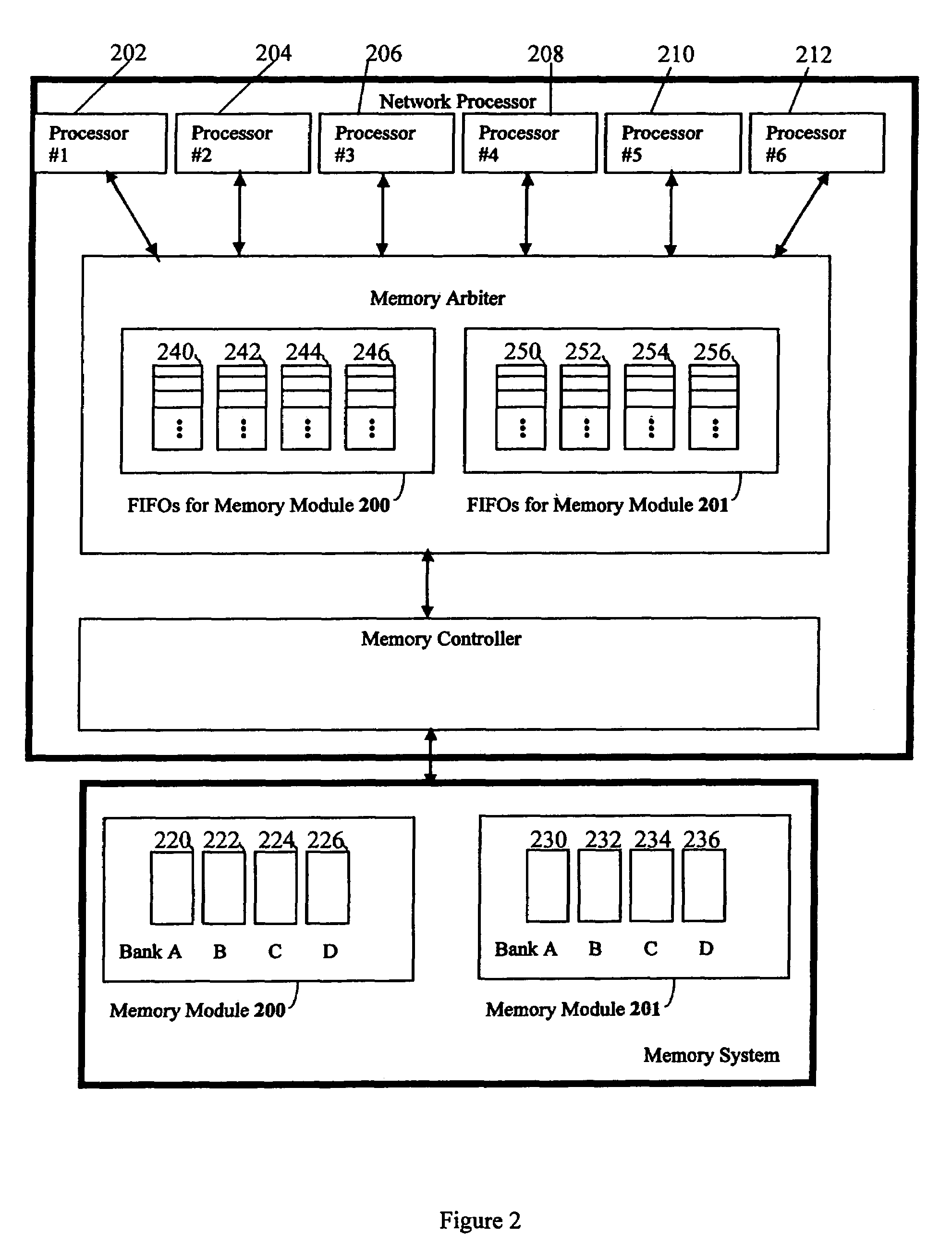
Efficient transfer of data to and from random access memory is described. Multiple request sources and a memory system comprise memory modules having memory banks, each bank containing rows of data. The retrieval comprises transferring all data pursuant to a given request by one source before any data is transferred pursuant to a subsequent request from said second source. This retrieval is achieved using a memory arbiter that implements an algorithm for atomic read / write. Each bank is assigned a FIFO buffer by the arbiter to store access requests. The access requests are arbitrated, and an encoded value of a winner of arbitration is loaded into the relevant FIFO buffer(s) before choosing the next winner. When an encoded value reaches the head of the buffer, all associated data is accessed in the given bank before accessing data for another request source.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
DRAM power management in a memory controller
InactiveUS7739461B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTComputer hardwareElectricity
A memory controller uses a power- and performance-aware scheduler which reorders memory commands based on power priorities. Selected memory ranks of the memory device are then powered down based on rank localities of the reordered commands. The highest power priority may be given to memory commands having the same rank as the last command sent to the memory device. Any memory commands having the same power priority can be further sorted based on one or more performance criteria such as an expected latency of the memory commands and an expected ratio of read and write memory commands. To optimize the power-down function, the power-down command is only sent when the selected memory rank is currently idle, the selected memory rank is not already powered down, none of the reordered memory commands correspond to the selected rank, and a currently pending memory command cannot be issued in the current clock cycle.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
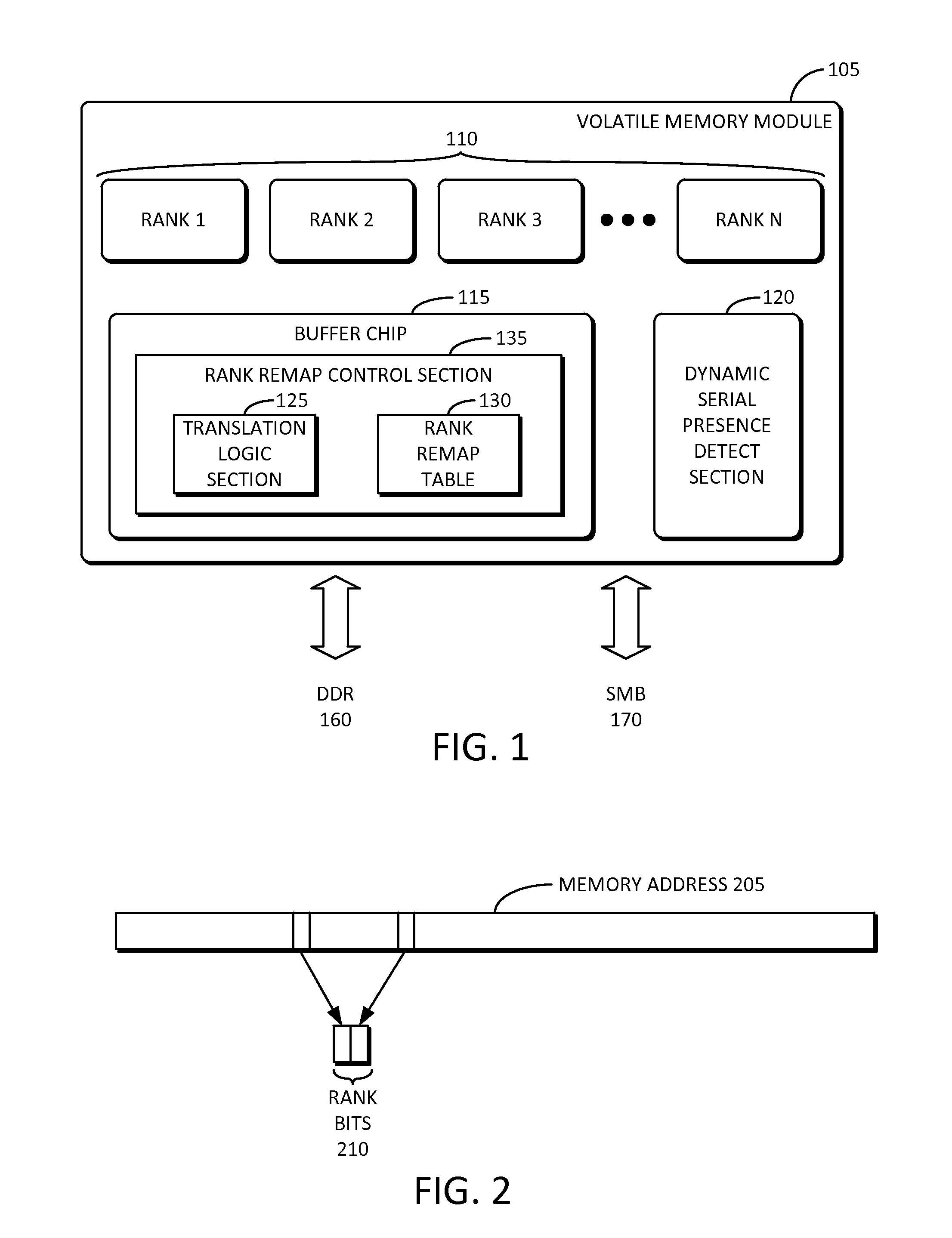
Rank and page remapping logic in a volatile memory
ActiveUS20160147623A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSerial presence detectMemory rank
Embodiments of the inventive concept include a plurality of memory ranks, a buffer chip including a rank remap control section configured to remap a rank from among the plurality of memory ranks of the volatile memory module responsive to a failure of the rank, and a dynamic serial presence detect section configured to dynamically update a stated total capacity of the volatile memory module based at least on the remapped rank. In some embodiments, a memory module includes a plurality of memory ranks, an extra rank in addition to the plurality of memory ranks, the extra rank being a spare rank configured to store a new page corresponding to a failed page from among the plurality of ranks, and a buffer chip including a page remap control section configured to remap the failed page from among the plurality of ranks to the new page in the extra rank.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
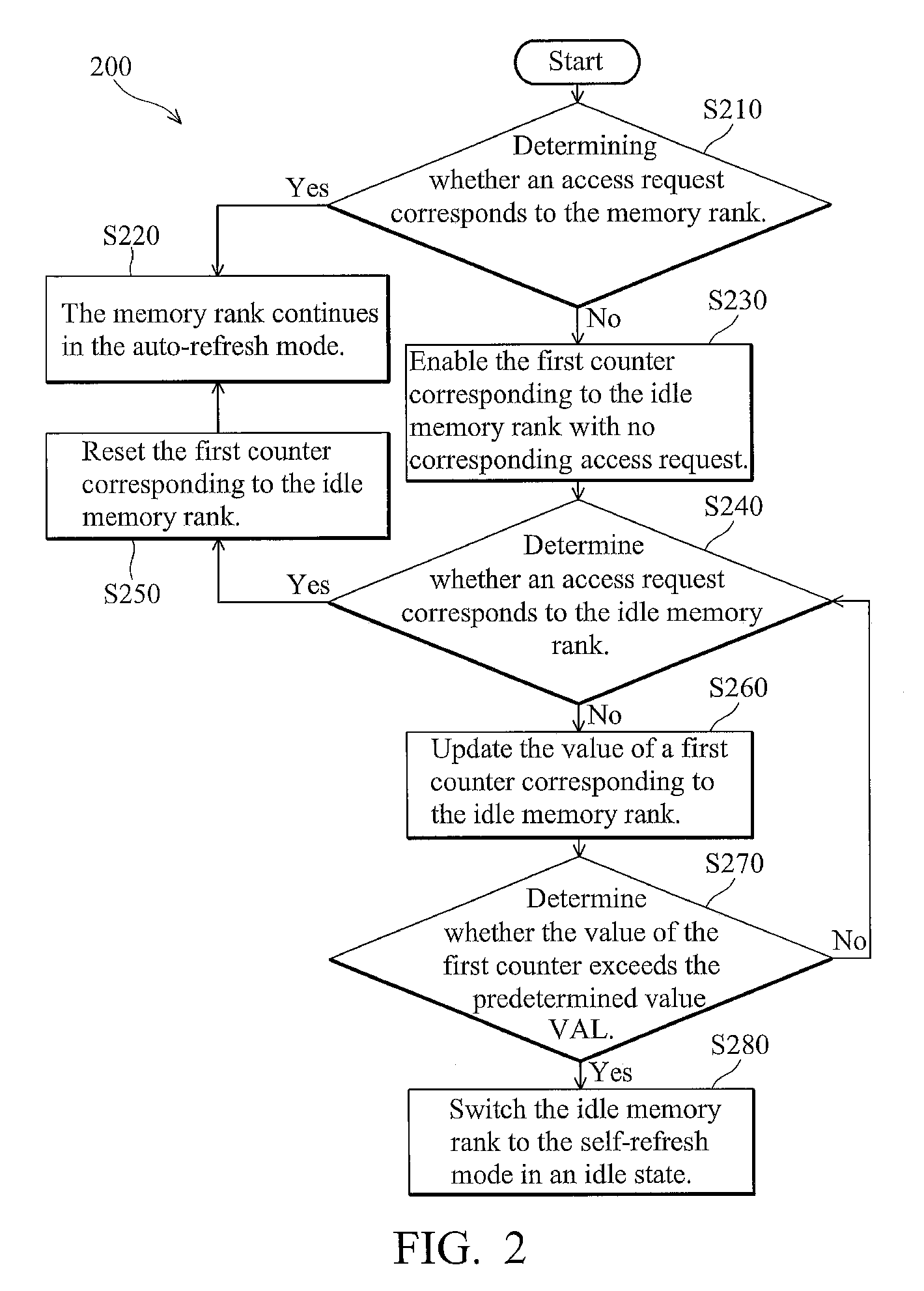
Memory refresh method and system
A memory refresh method applicable in a system memory is disclosed. The memory system comprises a plurality of memory ranks. It is to determine whether an access request corresponds to the memory rank, and an idle auto-refresh number of the memory rank is calculated if there is no access request corresponds to the memory rank. The memory rank is switched from an auto-refresh mode to a self-refresh mode when the idle auto-refresh number of the memory rank reaches a predetermined value.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Accumulator memory for performing operations on block operands
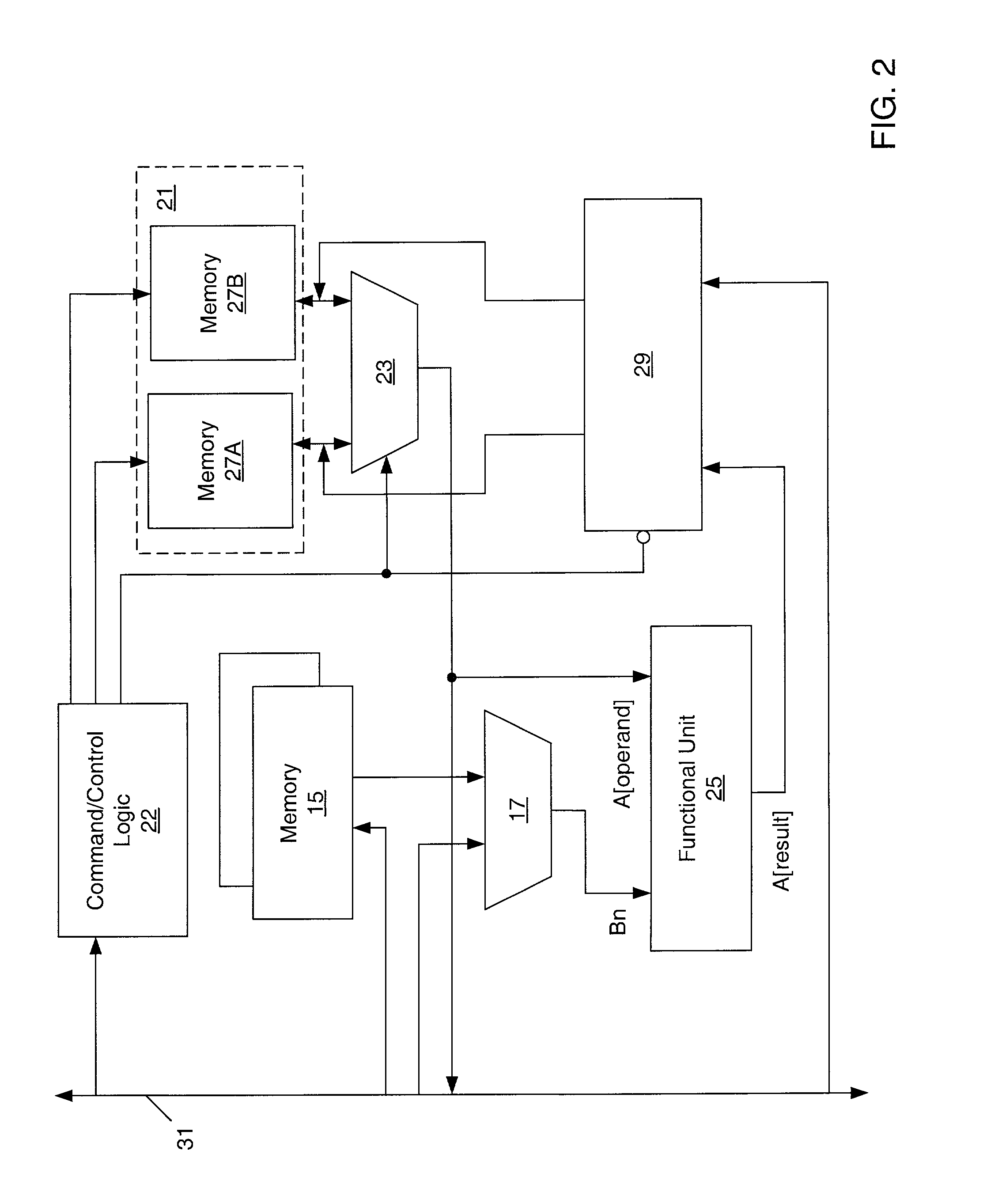
ActiveUS20030014685A1Reliability increasing modificationsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionMemory rankControl unit
An apparatus for performing a block operation includes a functional unit, which performs an operation on one or more block operands, and an accumulator memory. The accumulator memory includes two independently interfaced memory banks. A control unit controls the memory banks in the accumulator memory so that each time the operation is performed, an operand is provided from one of the memory banks and a result is stored in the other memory bank. Since the memory banks are independently interfaced, the operand may be provided at the same time as the result is being stored. Additionally, since the result is stored in a different memory bank than the operand, the operation may be restarted if an error occurs.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Memory recorder queue biasing preceding high latency operations
ActiveUS20130212330A1Latency of operationDigital storageMemory systemsData processing systemParallel computing
A memory system and data processing system for controlling memory refresh operations in dynamic random access memories. The memory controller comprises logic that: tracks a time remaining before a scheduled time for performing a high priority, high latency operation a first memory rank of the memory system; responsive to the time remaining reaching a pre-established early notification time before the schedule time for performing the high priority, high latency operation, biases the re-order queue containing memory access operations targeting the plurality of ranks to prioritize scheduling of any first memory access operations that target the first memory rank. The logic further: schedules the first memory access operations to the first memory rank for early completion relative to other memory access operations in the re-order queue that target other memory ranks; and performs the high priority, high latency operation at the first memory rank at the scheduled time.
Owner:IBM CORP
Kernel-module memory management method for preventing memory leaks and multiple memory releases
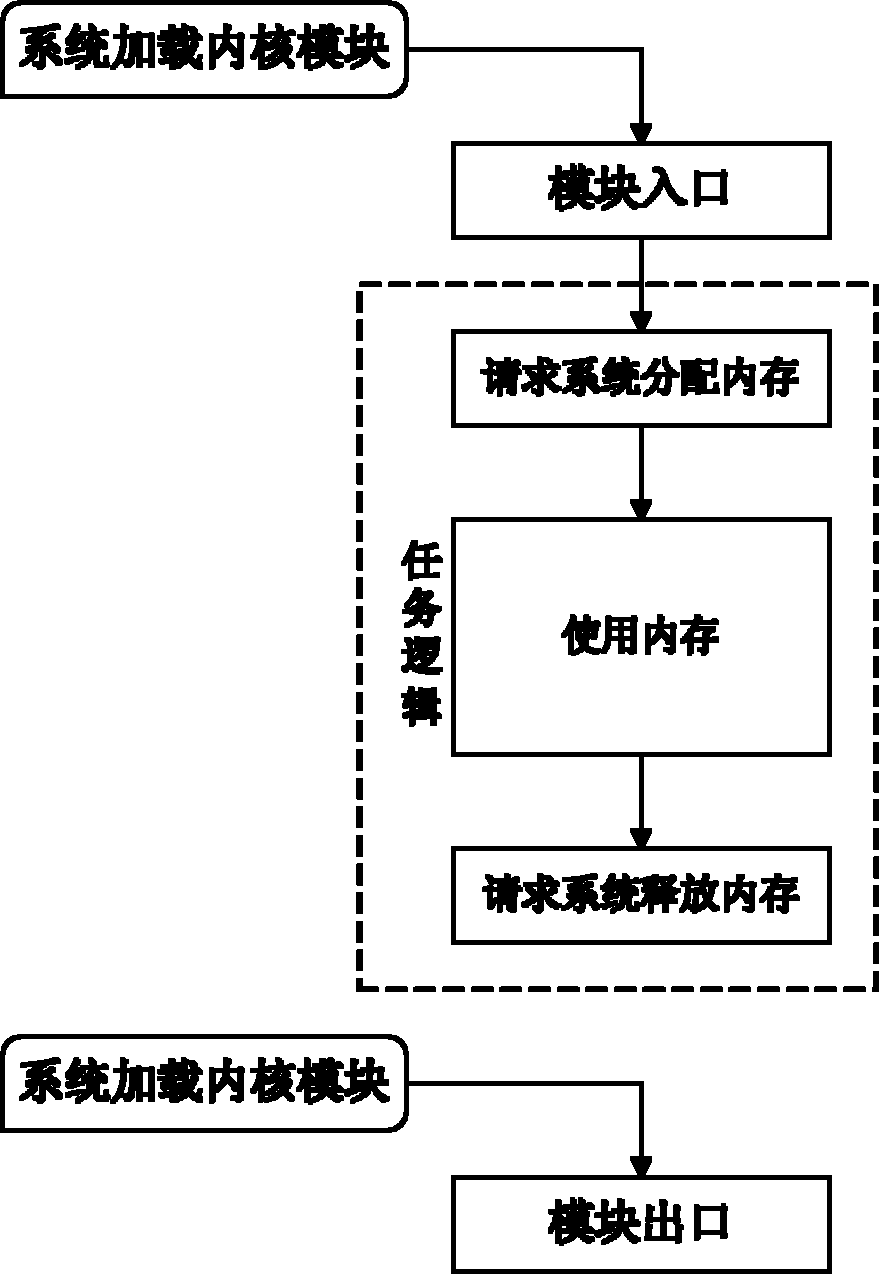
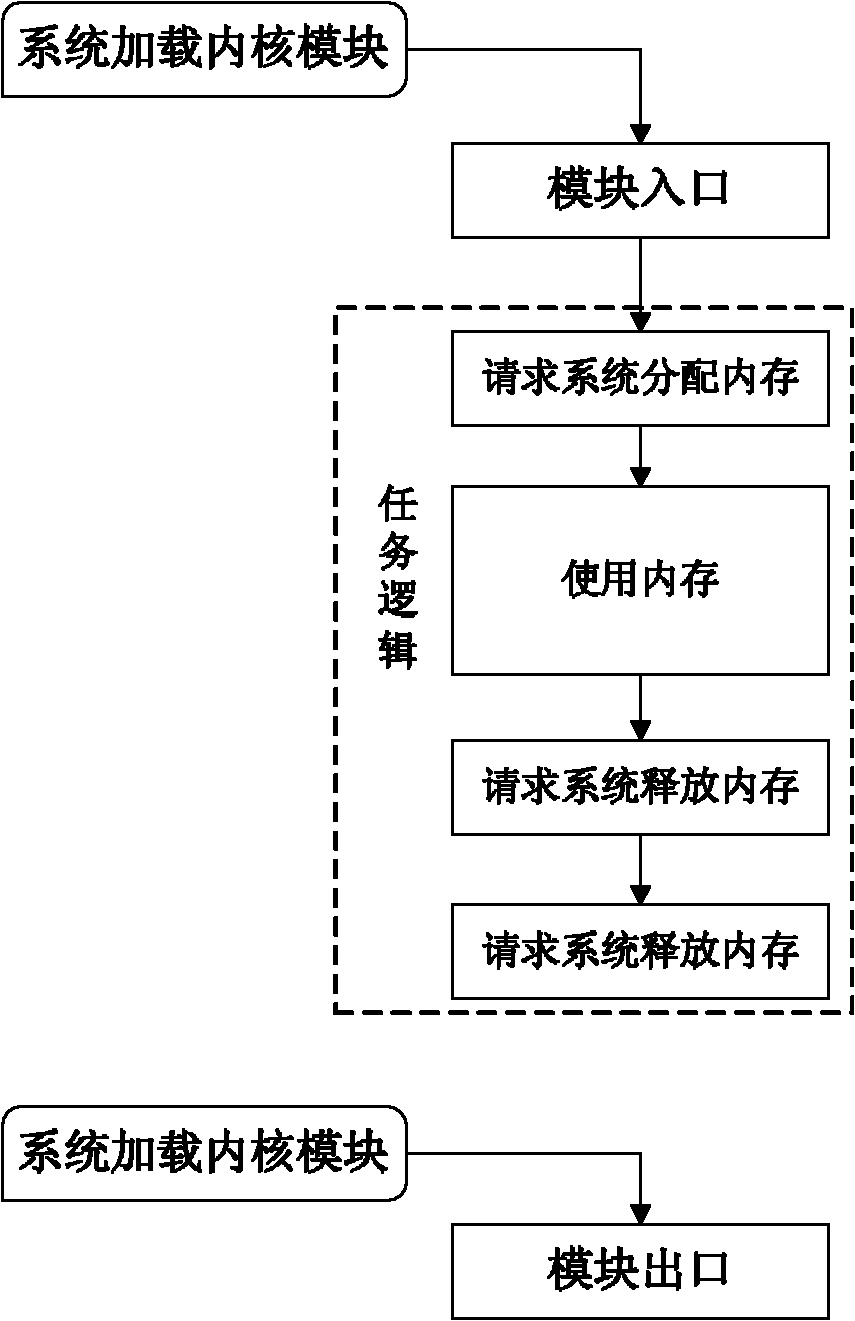
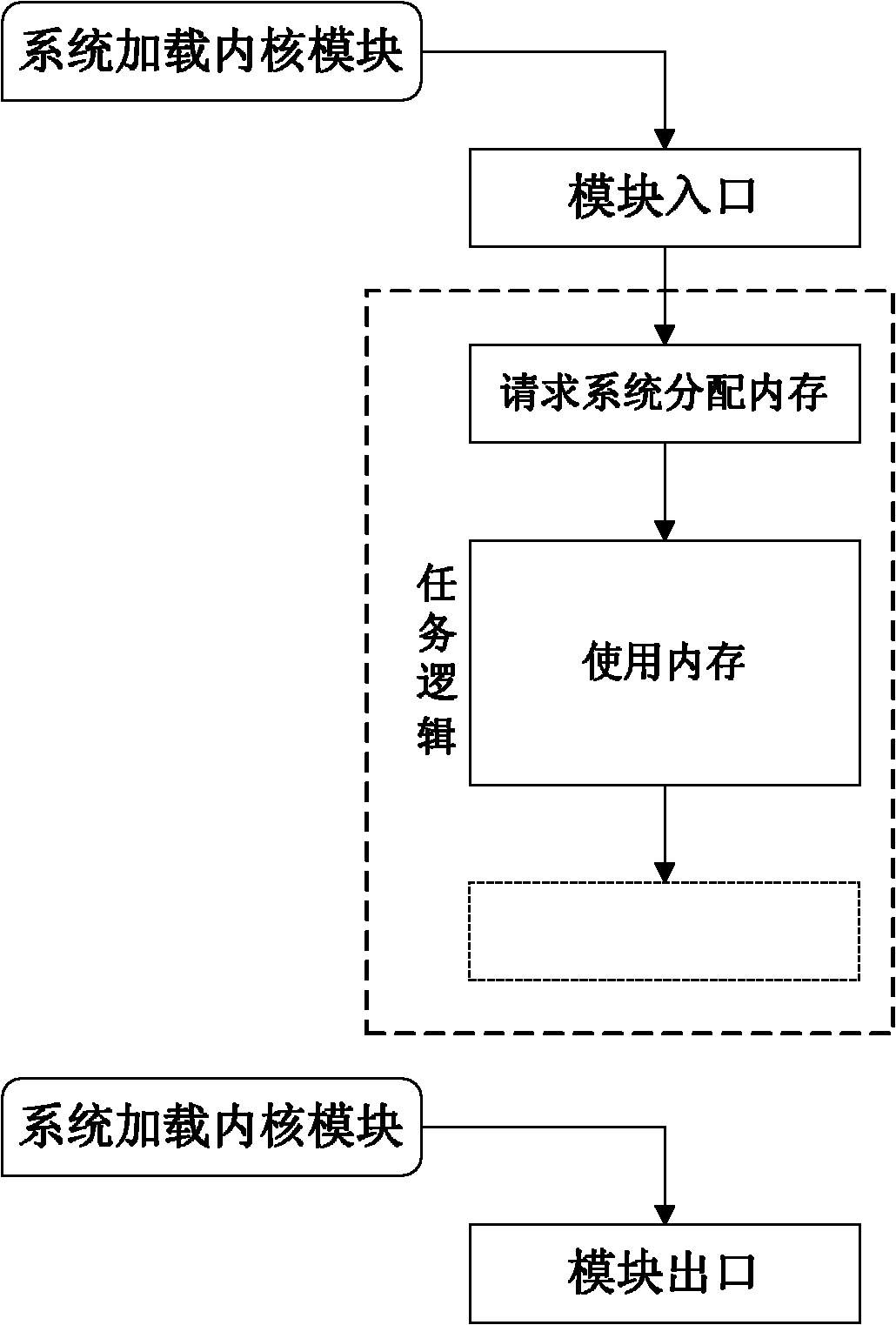
ActiveCN102103541AInhibition releaseTroubleshoot memory management issuesMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperational systemArray data structure
The invention discloses a kernel-module memory management method for preventing memory leaks and multiple memory releases, and the method comprises the following implementation steps: 1) establishing an array of records; 2) when a kernel module requires a system to allocate memories, adding memory allocation records associated with the allocated memories into the array of records; 3) when the kernel module requires the system to release memories, searching memory allocation records associated with the memories to be released in the array of records, if the associated memory allocation records exist, executing memory release, and cancelling the memory allocation records; and if the associated memory allocation records do not exist, issuing an alarm of 'multiple releases'; and 4) when the kernel module exits, scanning the array of records, if the array of records still has memory allocation records, releasing the memories associated with the memory allocation records one by one according to the memory allocation records, and finally, clearing the array of records. By utilizing the method disclosed by the invention, the kernel modules can be prevented from having the phenomena of memory leaks and multiple memory releases; and the method has the advantages of good memory allocation capability, low congestion degree of an operating system, less occupied resources, small memory-footprint, and good adaptability.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Memory controller with programmable regression model for power control
InactiveUS7724602B2Lower performance requirementsAccurate estimateEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsSystem configurationMemory controller
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Memory module having buffer and memory ranks addressable by respective selection signal
A memory module having a board and a plurality of memory elements on the board which belong to different memory ranks, each memory rank being addressable via a respective selection signal. The memory module additionally includes a memory buffer having a memory rank interface coupled to the memory elements of each memory rank, and a selection signal output for the selection signal of each memory rank, the memory elements being arranged in rows on the board and the memory elements of a memory rank extending only over half of the rows.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
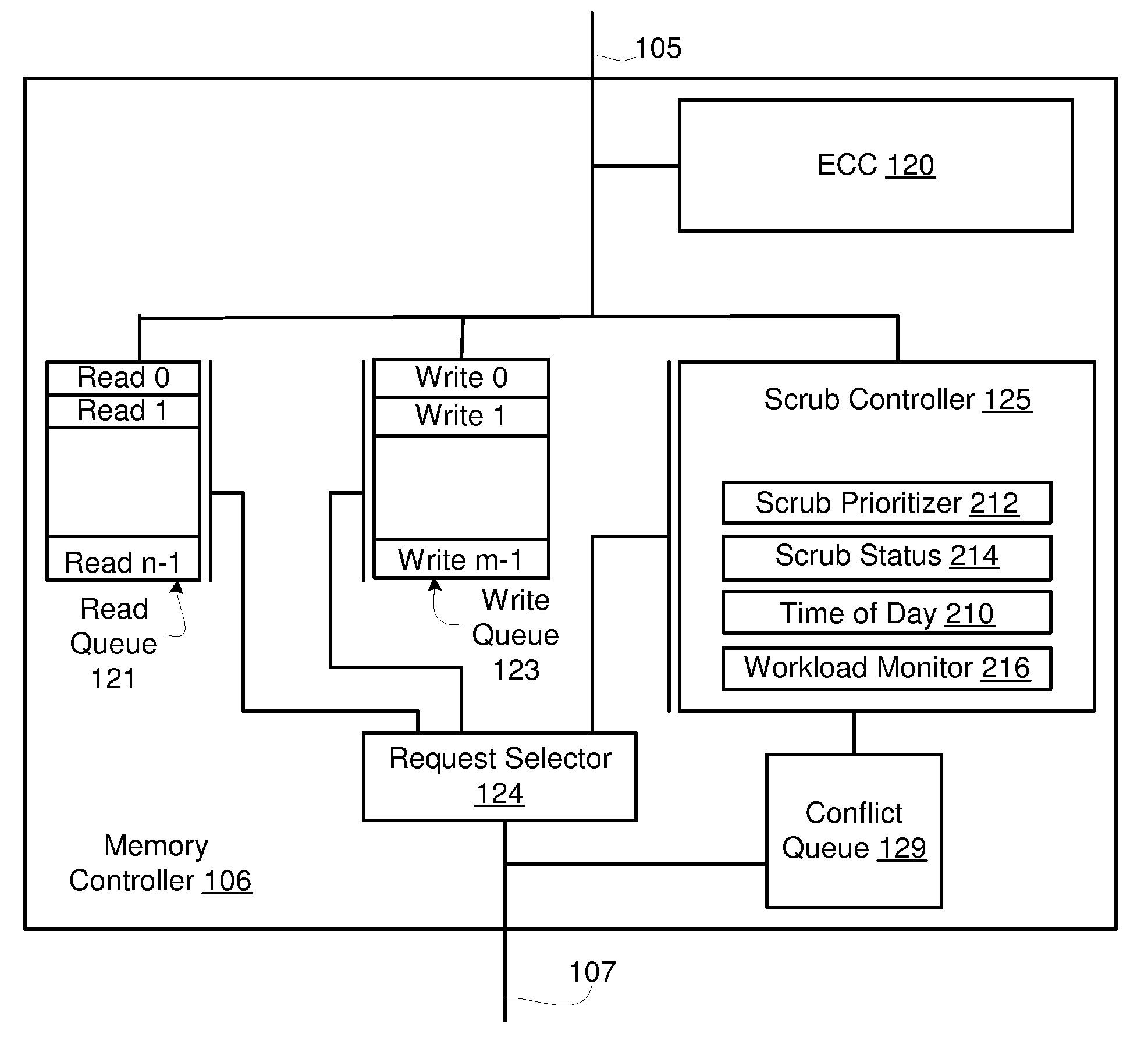
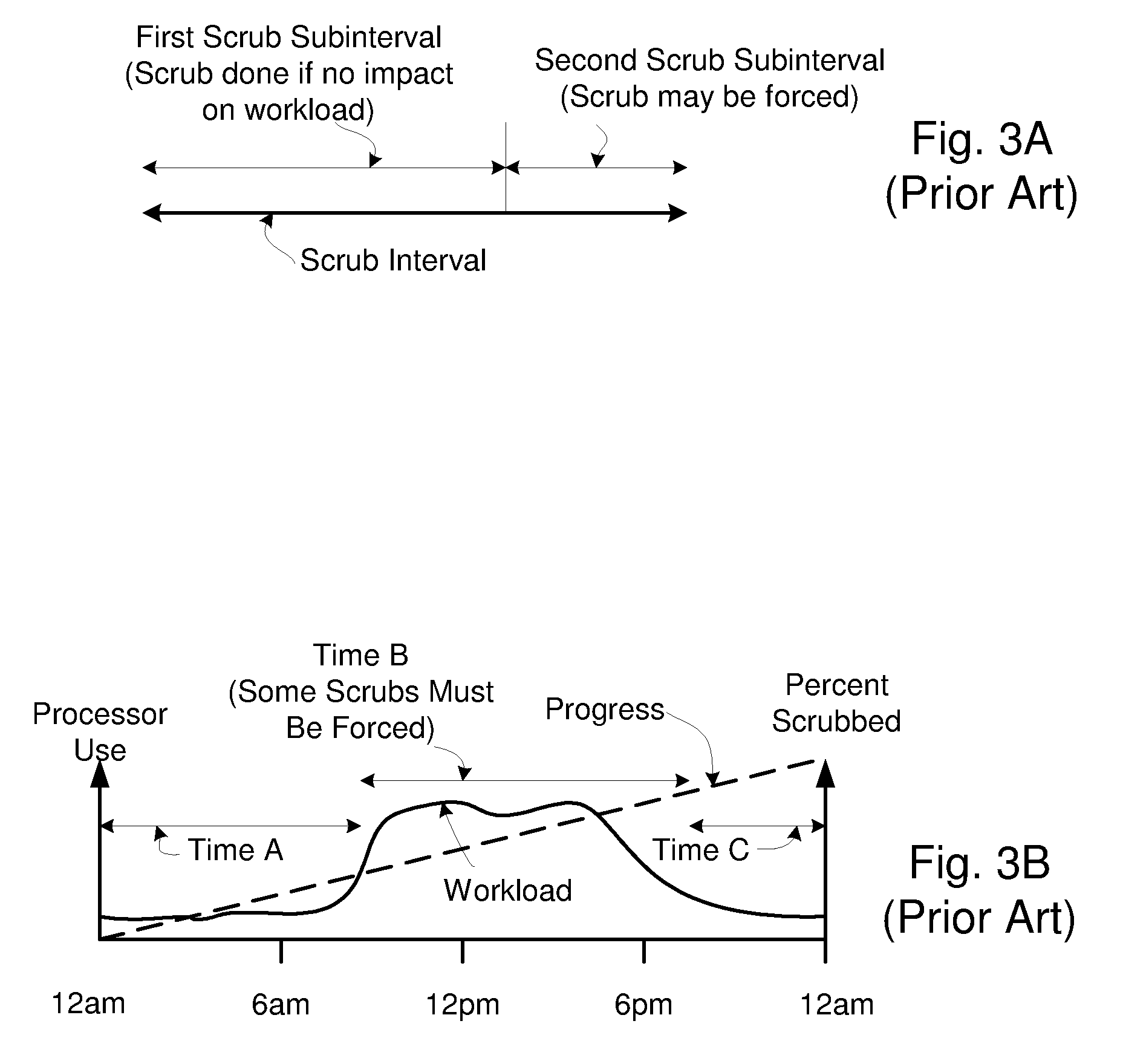
Efficient Scheduling of Background Scrub Commands
InactiveUS20090070648A1Reduce the impactReduce the possibilityError preventionTransmission systemsComputerized systemMemory controller
A method and apparatus to efficiently scrub a memory, during a scrub period, of a computer system that has a memory comprising a number of memory elements. Examples of memory elements are memory ranks and banks. A memory rank may further comprise one or more banks. The computer system has a memory controller that receives read requests and write requests from a processor. The memory controller includes a scrub controller configured to output more than one scrub request during a particular request selector cycle. The memory controller includes a request selector that services a read request, a write request, or one of the scrub requests during a request selector cycle.
Owner:IBM CORP
File server that allows an end user to specify storage characteristics with ease
InactiveUS20080082779A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease powerMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTComputer hardwareMemory controller
A computing node which reduces substantially and effectively reduces the power consumed by a memory is provided without affecting the efficiency whereby a processor accesses the memory. The computing node executes a user program sent by a control node. In case of which a message including the capacity of the memory required to execute a user program is received, a memory rank corresponding to the capacity of the required memory is made active by a memory controller before the user program is loaded into the memory.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Methods and Apparatuses for Idle-Prioritized Memory Ranks
ActiveUS20120102270A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTAccess frequencyMemory rank
Embodiments of an apparatus to reduce memory power consumption are presented. In one embodiment, the apparatus comprises a cache memory, a memory, and a control unit. In one embodiment, the memory includes a plurality of memory ranks. The control unit is operable to select one or more memory ranks among the plurality of memory ranks to be idle-prioritized memory ranks such that access frequency to the idle-prioritized memory ranks is reduced.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
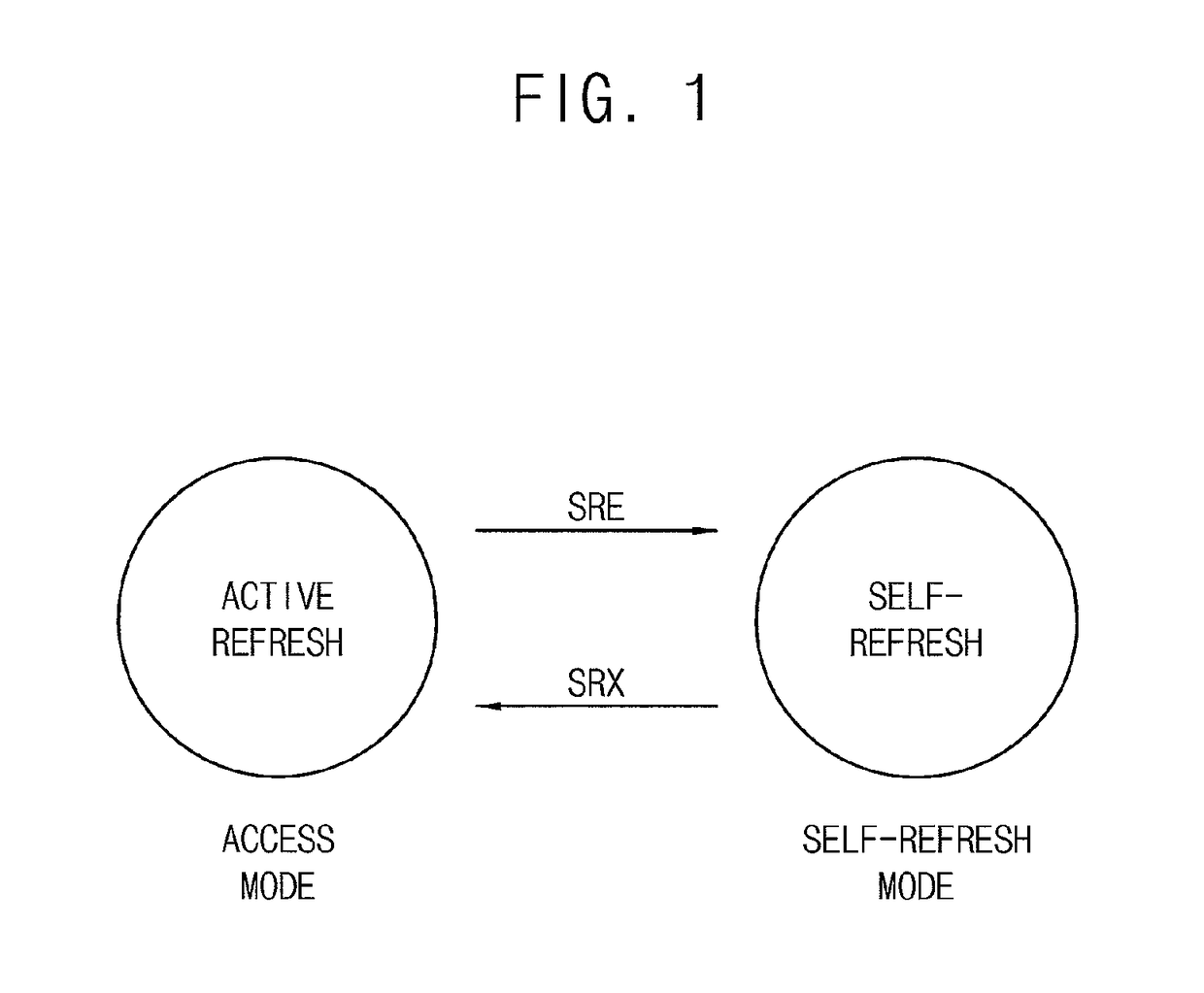
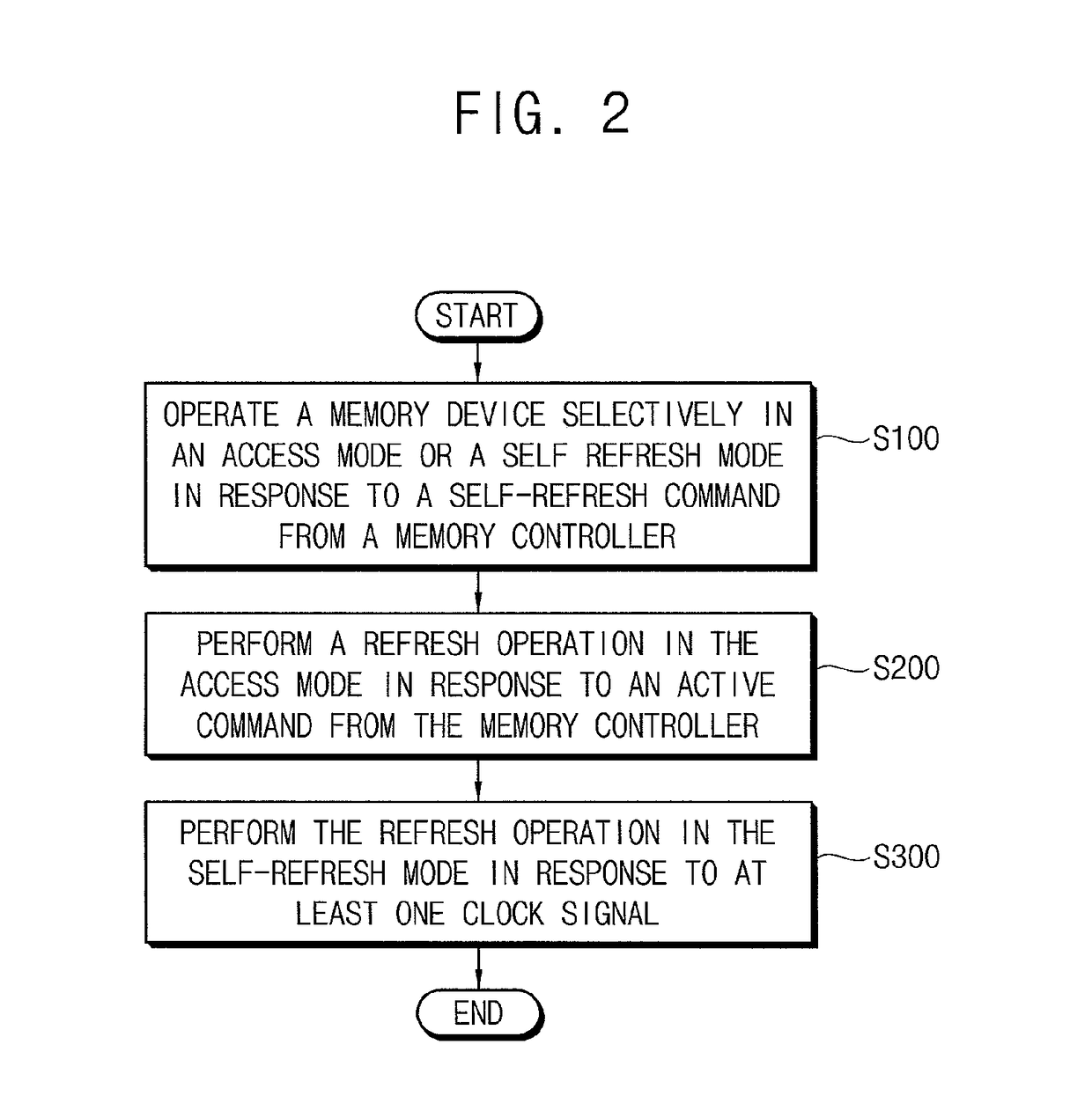
Memory device for refresh and memory system including the same
ActiveUS10115448B2Guaranteed uptimeAvoid collisionInput/output to record carriersDigital storageMemory bankMemory controller
A memory device includes a memory bank including a plurality of memory blocks, a row selection circuit and a refresh controller. The row selection circuit is configured to perform an access operation and a refresh operation with respect to the memory bank. The refresh controller is configured to control the row selection circuit such that the memory device is operated selectively in an access mode or a self-refresh mode in response to a self-refresh command received from a memory controller, the refresh operation is performed in the access mode in response to an active command received from the memory controller and the refresh operation is performed in the self-refresh mode in response to at least one clock signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com