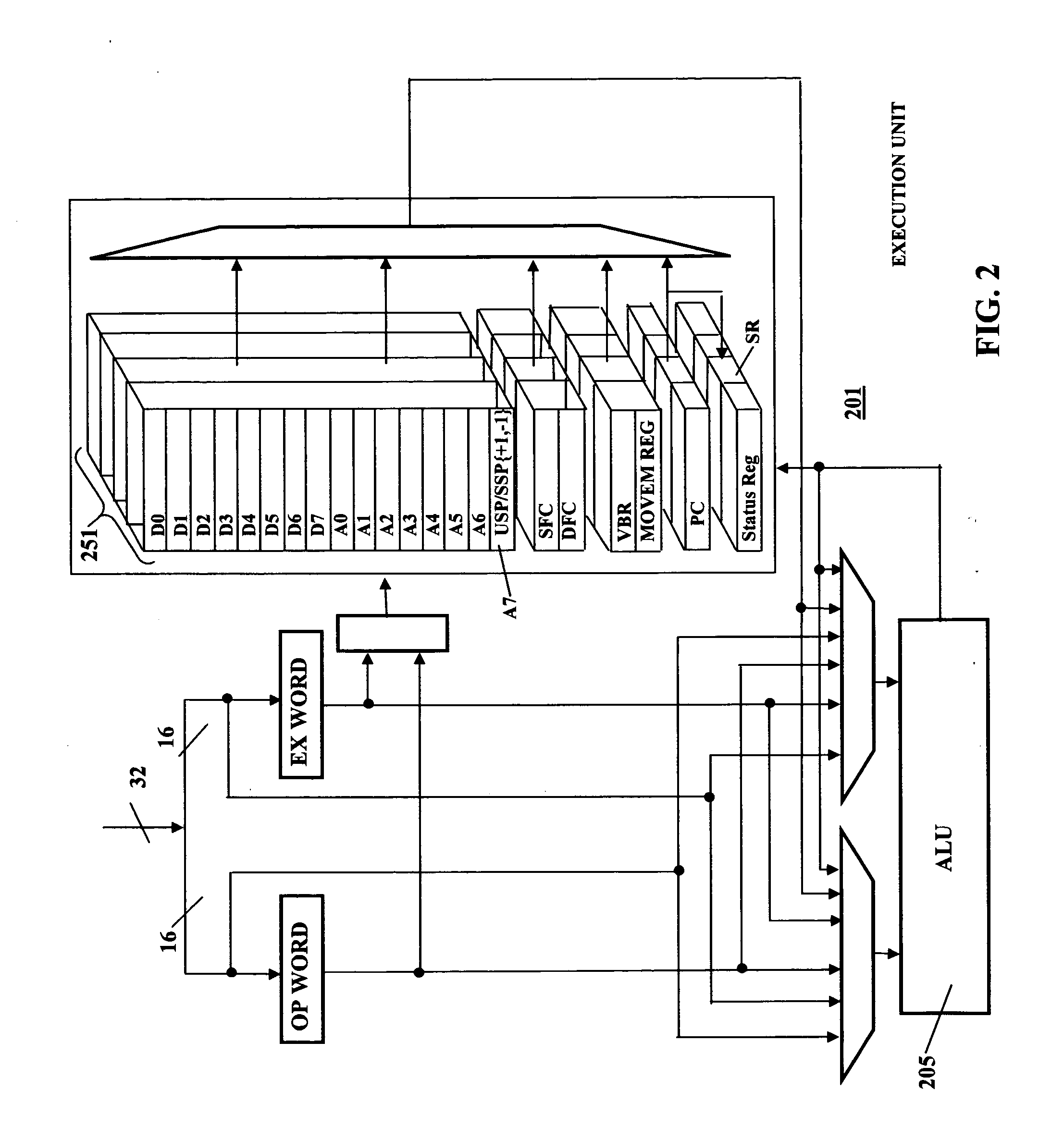
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
150 results about "Memory form" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
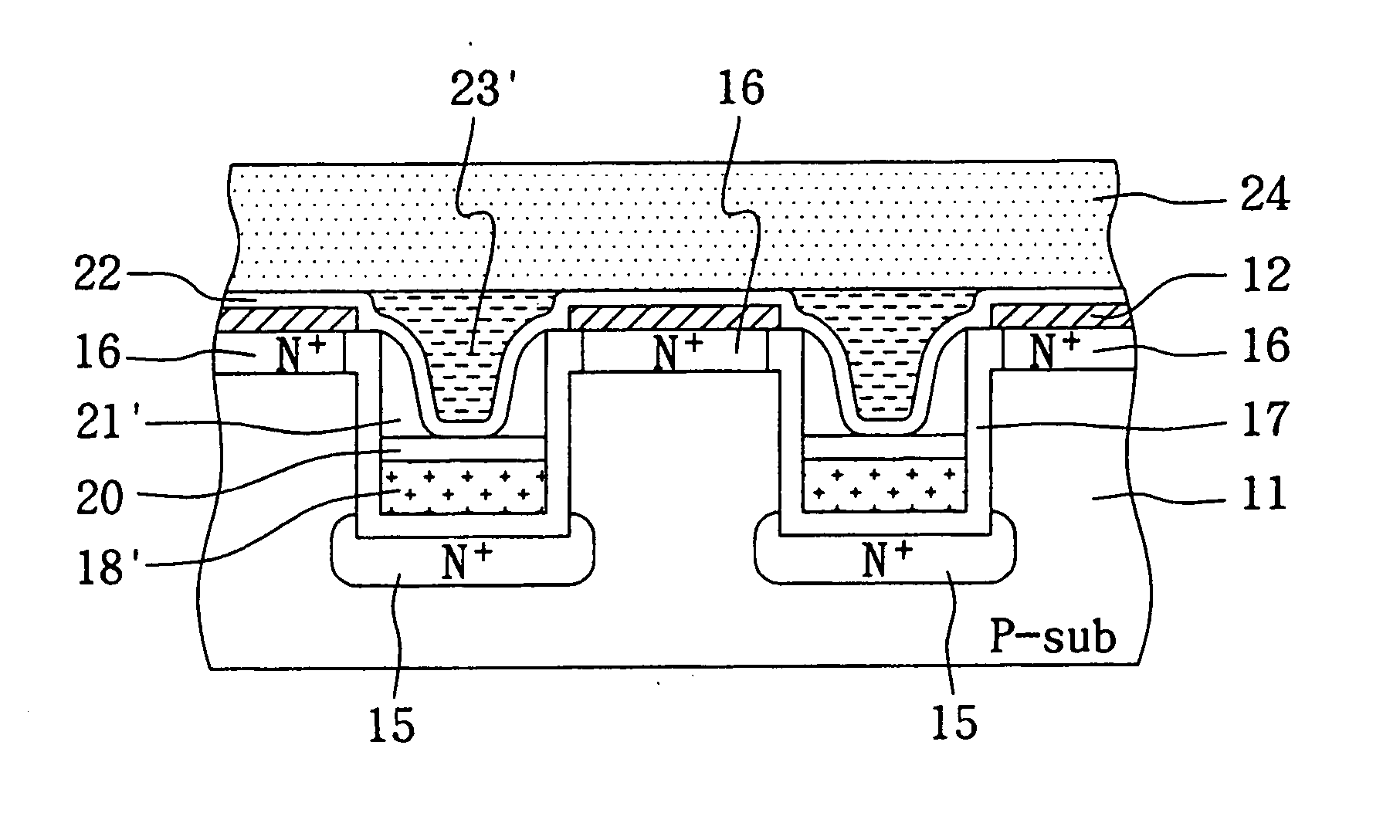
Memory cell comprising switchable semiconductor memory element with trimmable resistance
ActiveUS20070090425A1Solid-state devicesRead-only memoriesHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A nonvolatile memory cell comprising doped semiconductor material and a diode can store memory states by changing the resistance of the doped semiconductor material by application of a set pulse (decreasing resistance) or a reset pulse (increasing resistance.) Set pulses are of short duration and above a threshold voltage, while reset pulses are longer duration and below a threshold voltage. In some embodiments multiple resistance states can be achieved, allowing for a multi-state cell, while restoring a prior high-resistance state allows for an rewriteable cell. In some embodiments, the diode and a switchable memory formed of doped semiconductor material are formed in series, while in other embodiments, the diode itself serves as the semiconductor switchable memory element.
Owner:WODEN TECH INC
Auxiliary display and storage unit
Apparatus and systems, as well as methods and articles, may operate to receive an indication that a housing having an integrated auxiliary display and a memory forming a portion of a redundant array disk storage has been inserted into a recessed housing compartment of a portable computer having an integrated primary display, and to execute a storage operation using the redundant array disk storage.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Cloud-based distributed persistence and cache data model
ActiveUS20130110961A1Improve scalabilityLower latencyDigital computer detailsTransmissionDistributed File SystemWeb service
A distributed cache data system includes a cache adapter configured to reserve a designated portion of memory in at least one node in a networked cluster of machines as a contiguous space. The designated portion of memory forms a cache and the designated portion of memory includes data cells configured to store data. The cache adapter is configured to interface with the data and a distributed file system and the cache adapter is further configured to provide an interface for external clients to access the data. The cache adapter is configured to communicate to clients via a web server, and the cache adapter is further configured to direct data access requests to appropriate the data. A related process of distributing cache data is disclosed as well.
Owner:JADHAV AJAY
Low-cost non-volatile flash-ram memory
ActiveUS20090046501A1Reduced switching currentIncrease memory capacitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer hardwareNon-volatile random-access memory
A flash-RAM memory includes non-volatile random access memory (RAM) formed on a monolithic die and non-volatile page-mode memory formed on top of the non-volatile RAM, the non-volatile page-mode memory and the non-volatile RAM reside on the monolithic die.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Low-cost non-volatile flash-RAM memory
ActiveUS8120949B2Reduced switching currentIncrease memory capacitySolid-state devicesDigital storageComputer hardwareNon-volatile random-access memory
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Portable radio communication apparatus
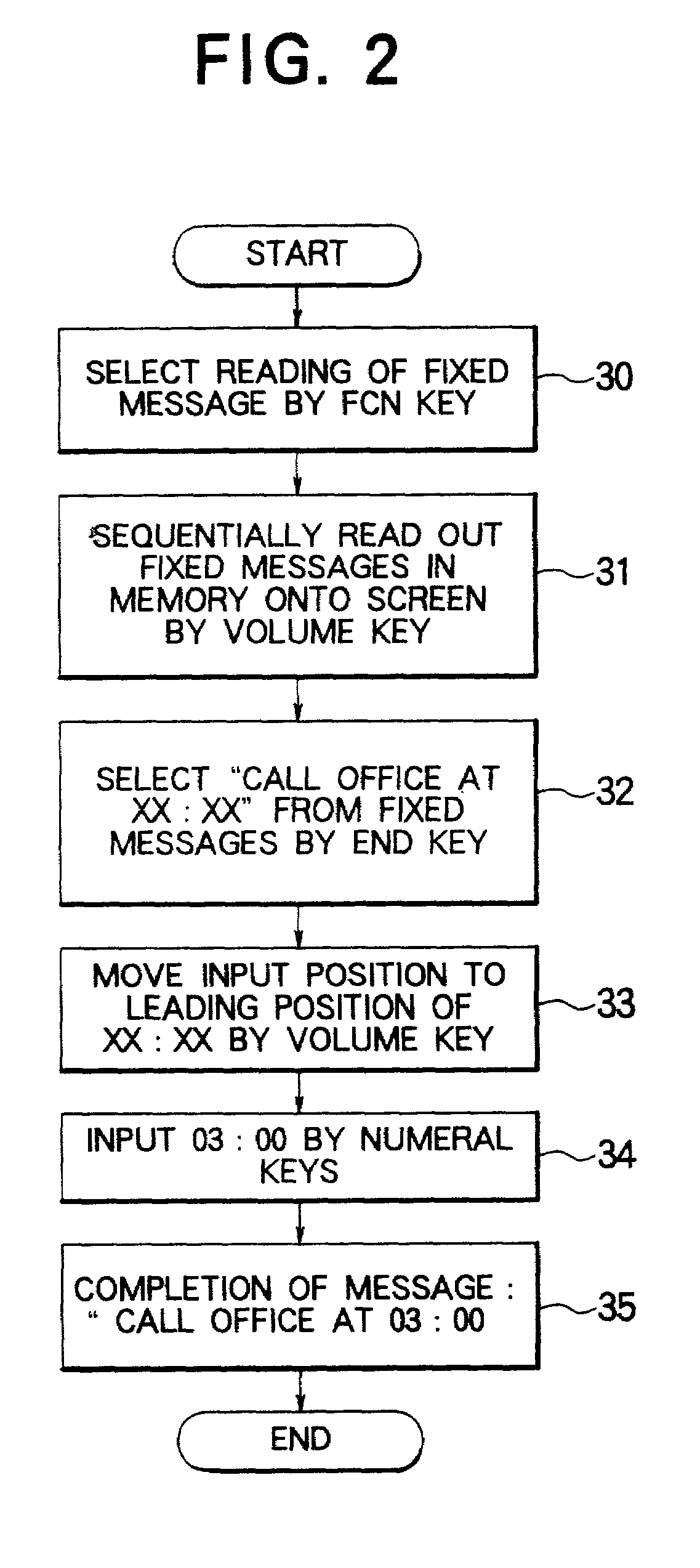
InactiveUS7218916B2Well formedSimple contentDevices with card reading facilityAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingTelecommunicationsMemory form
Owner:APPLE INC
Semiconductor memory device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090050956A1Total current dropReduce areaSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSemiconductor
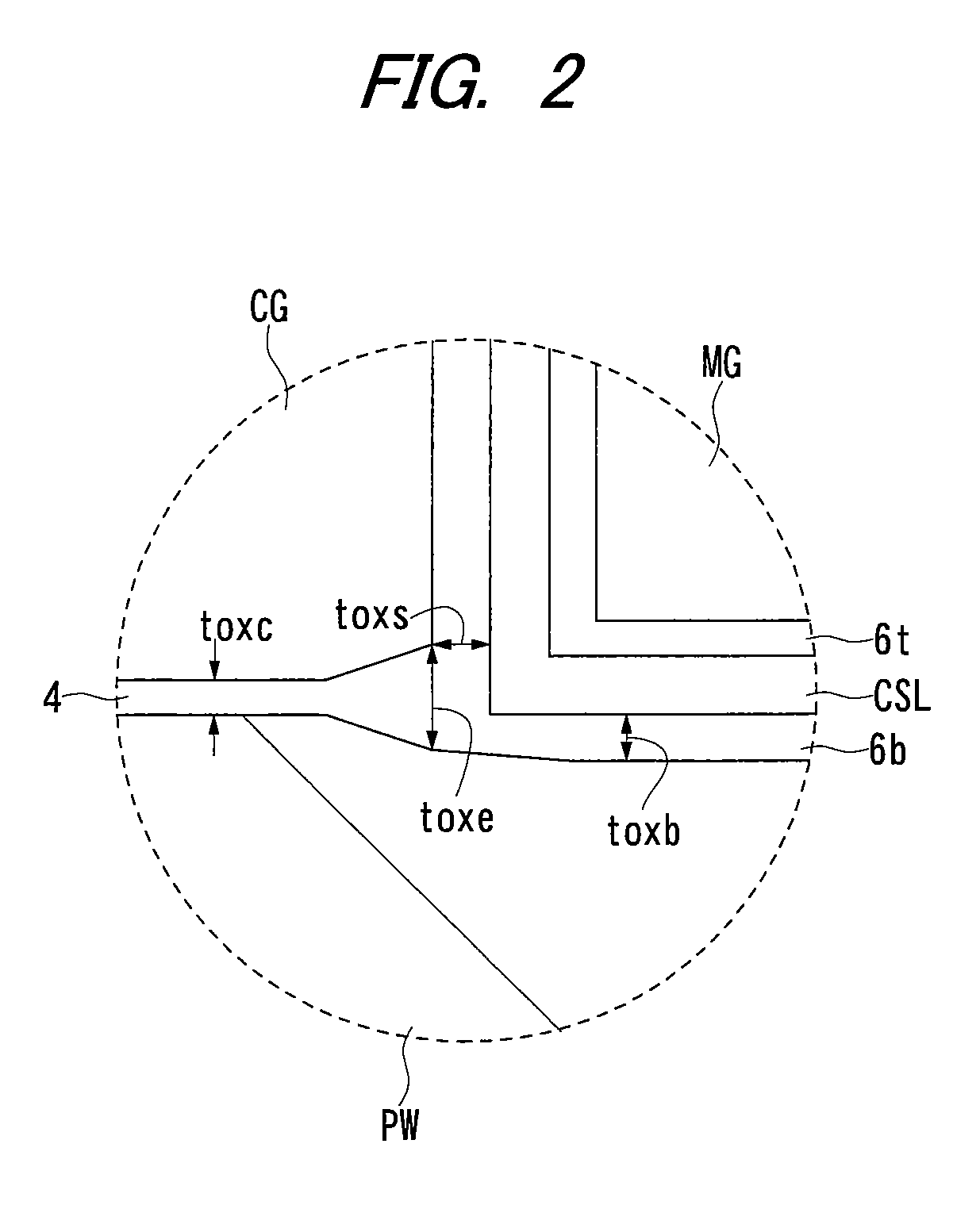
In a memory cell including an nMIS for memory formed on the sides of an nMIS for select and an nMIS for select via dielectric films and a charge storage layer, the thickness of a gate dielectric under the gate longitudinal direction end of a select gate electrode is formed thicker than that of the gate dielectric under the gate longitudinal direction center and the thickness of the lower layer dielectric film that is positioned between the select gate electrode and the charge storage layer and is nearest to a semiconductor substrate is formed 1.5 times or below of the thickness of the lower layer dielectric film positioned between the semiconductor substrate and the charge storage layer.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
In-place transformations with applications to encoding and decoding various classes of codes
InactiveUS7644335B2Reduce running timeLess time accessing memoryError preventionOther decoding techniquesComputer hardwareMemory form
In an encoder for encoding symbols of data using a computing device having memory constraints, a method of performing a transformation comprising loading a source block into memory of the computing device, performing an intermediate transformation of less than all of the source block, then replacing a part of the source block with intermediate results in the memory and then completing the transformation such that output symbols stored in the memory form a set of encoded symbols. A decoder can perform decoding steps in an order that allows for use of substantially the same memory for storing the received data and the decoded source block, performing as in-place transformations. Using an in-place transformation, a large portion of memory set aside for received data can be overwritten as that received data is transformed into decoded source data without requiring a similar sized large portion of memory for the decoded source data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for a controller capable of supporting multiple protocols
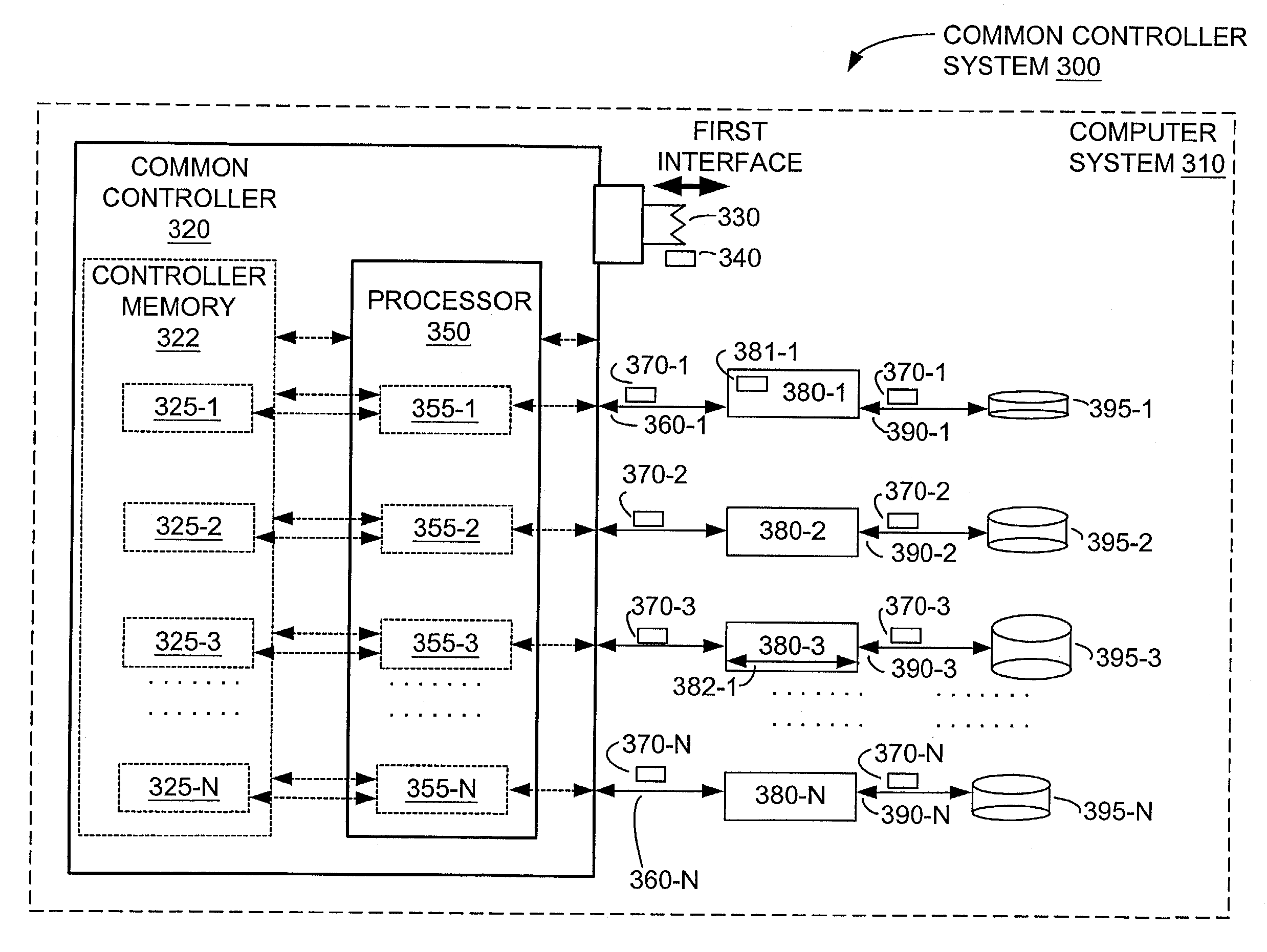
The present invention provides a controller system including a common controller, a first interface, a second interface, and an adapter. The first interface is used to receive and to send data according to a first protocol having a format useable by a computer system. The common controller is coupled between the first interface and the second interface to translate between the first protocol and the second protocol, the second protocol is used by a memory coupled to the common controller. The second interface is used to store and to retrieve data from the memory according to the second protocol. The adapter function can be coupled between the memory and the common controller. The memory forms a response to a request by the computer system, with the response including at least one of (A) storing information, (B) retrieving information, and (C) providing status information.
Owner:OPEN INVENTION NEWTORK LLC
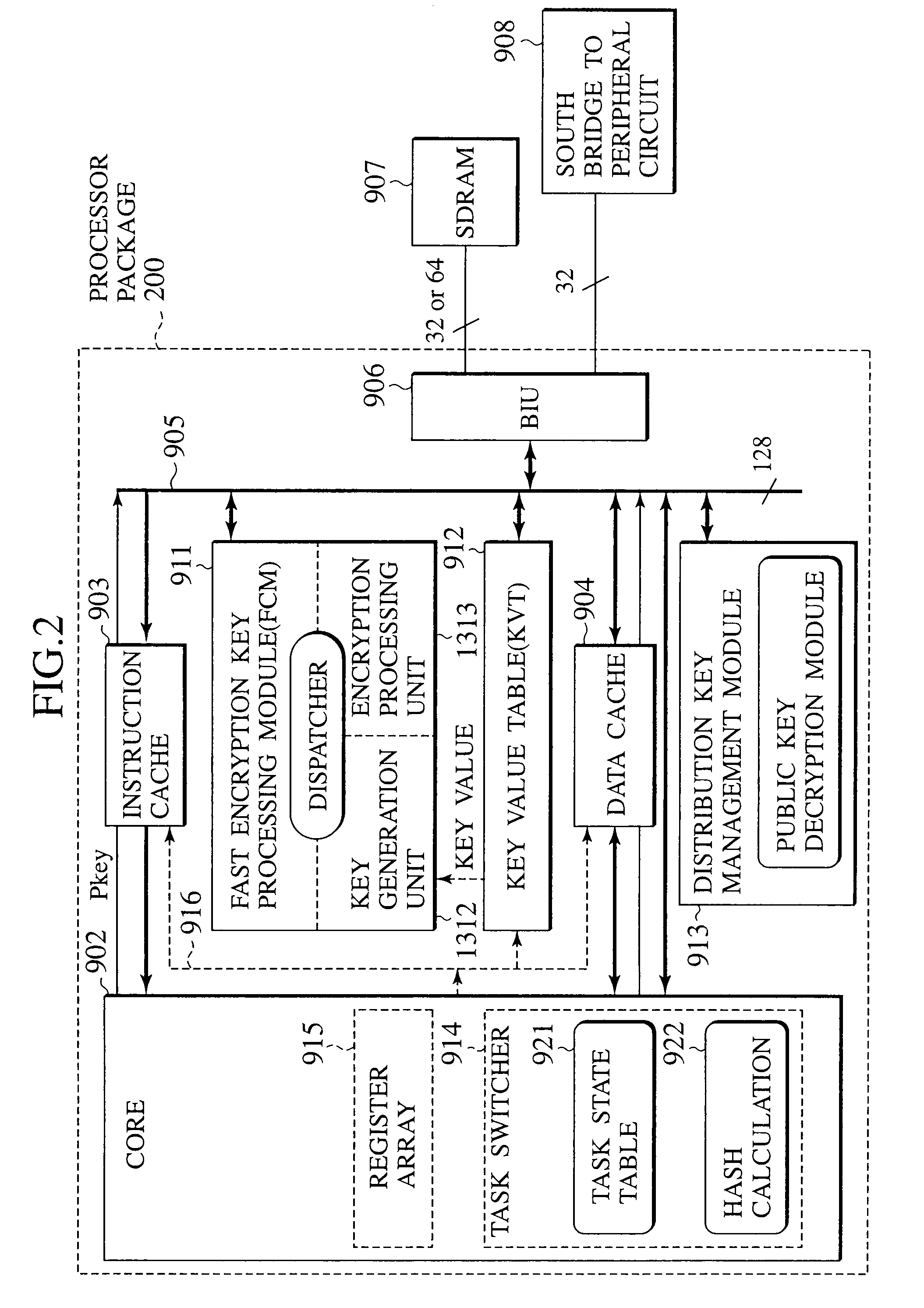
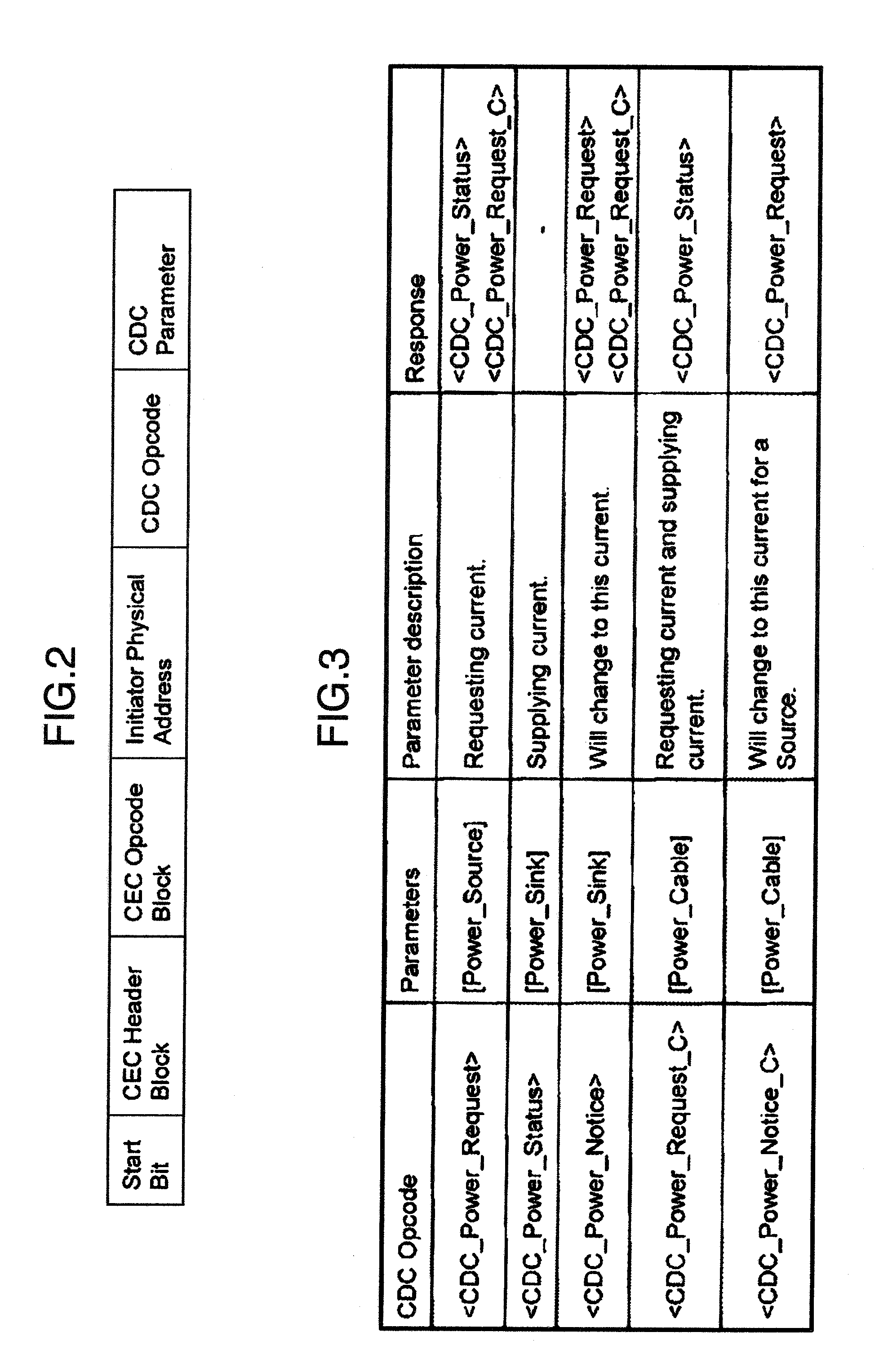
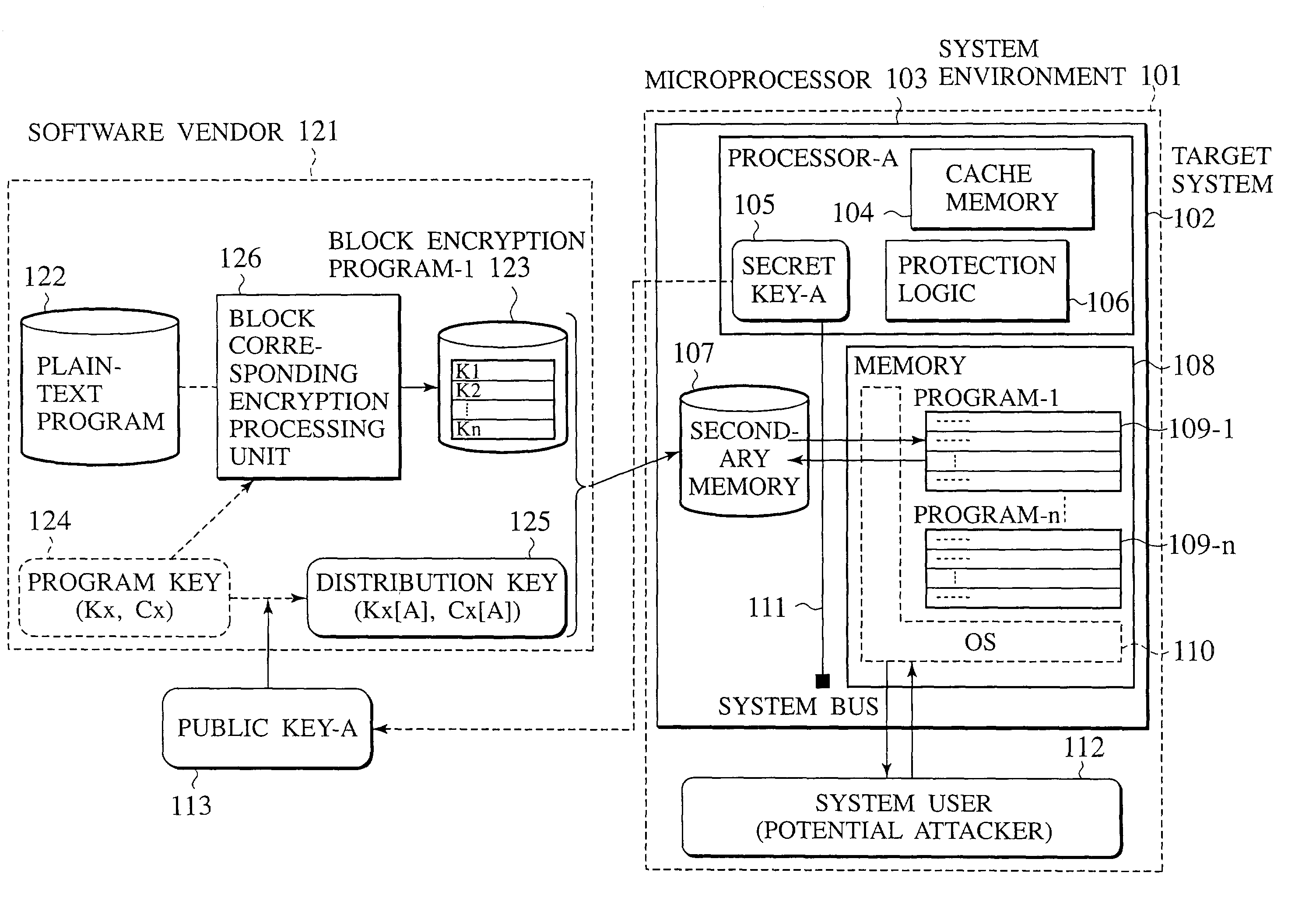
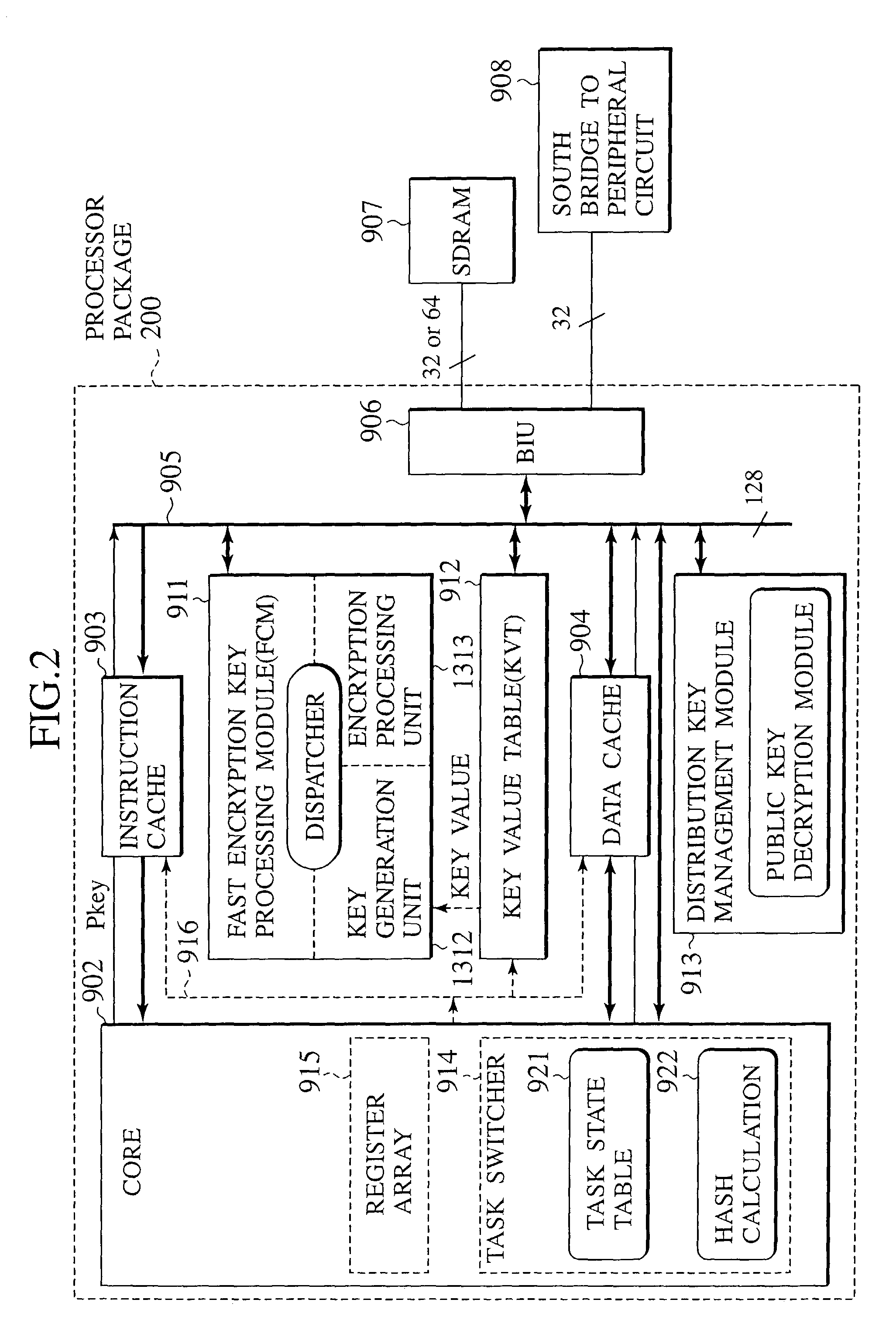
Microprocessor with improved task management and table management mechanism
InactiveUS20090006864A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationExternal storageProcessor register
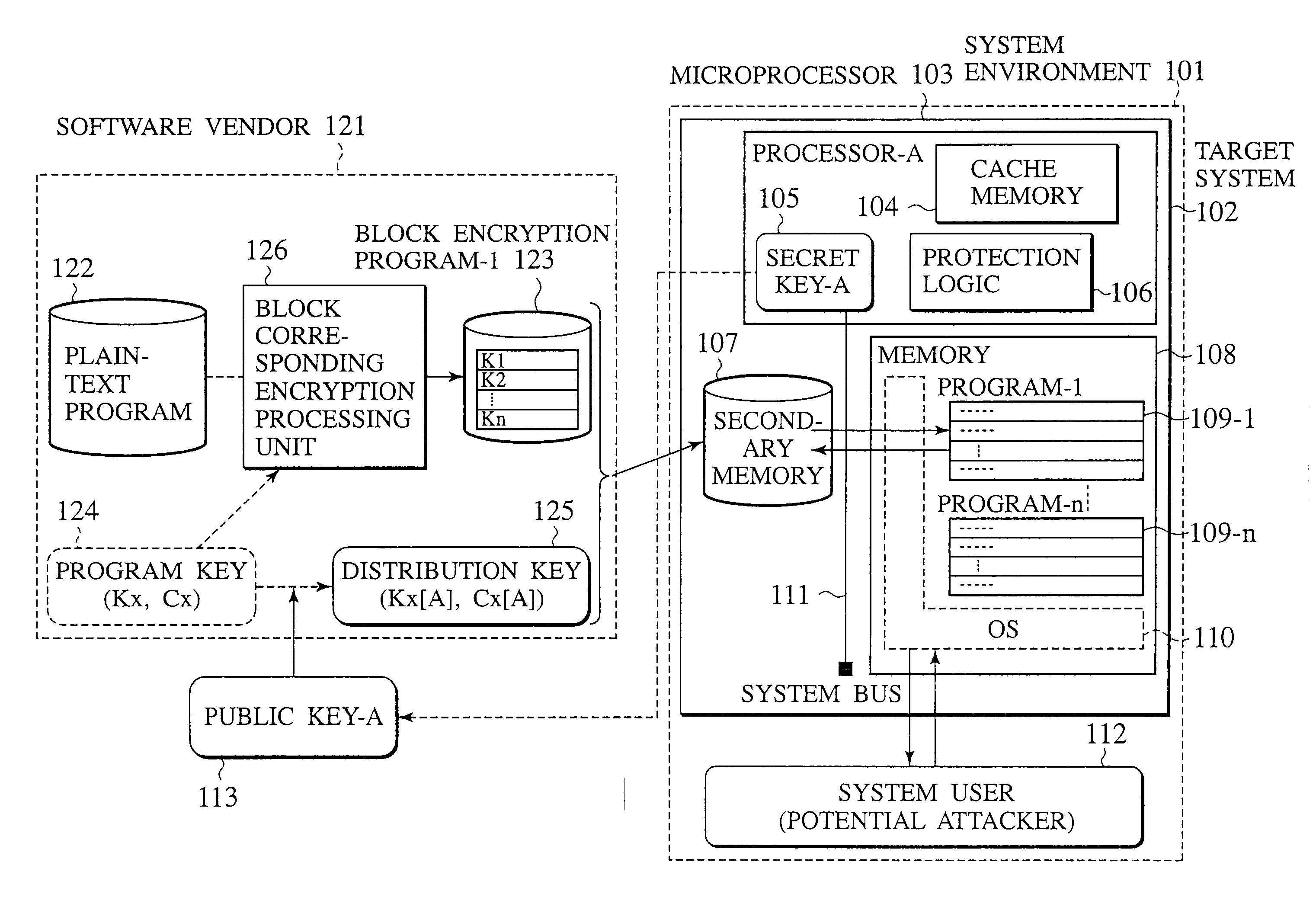
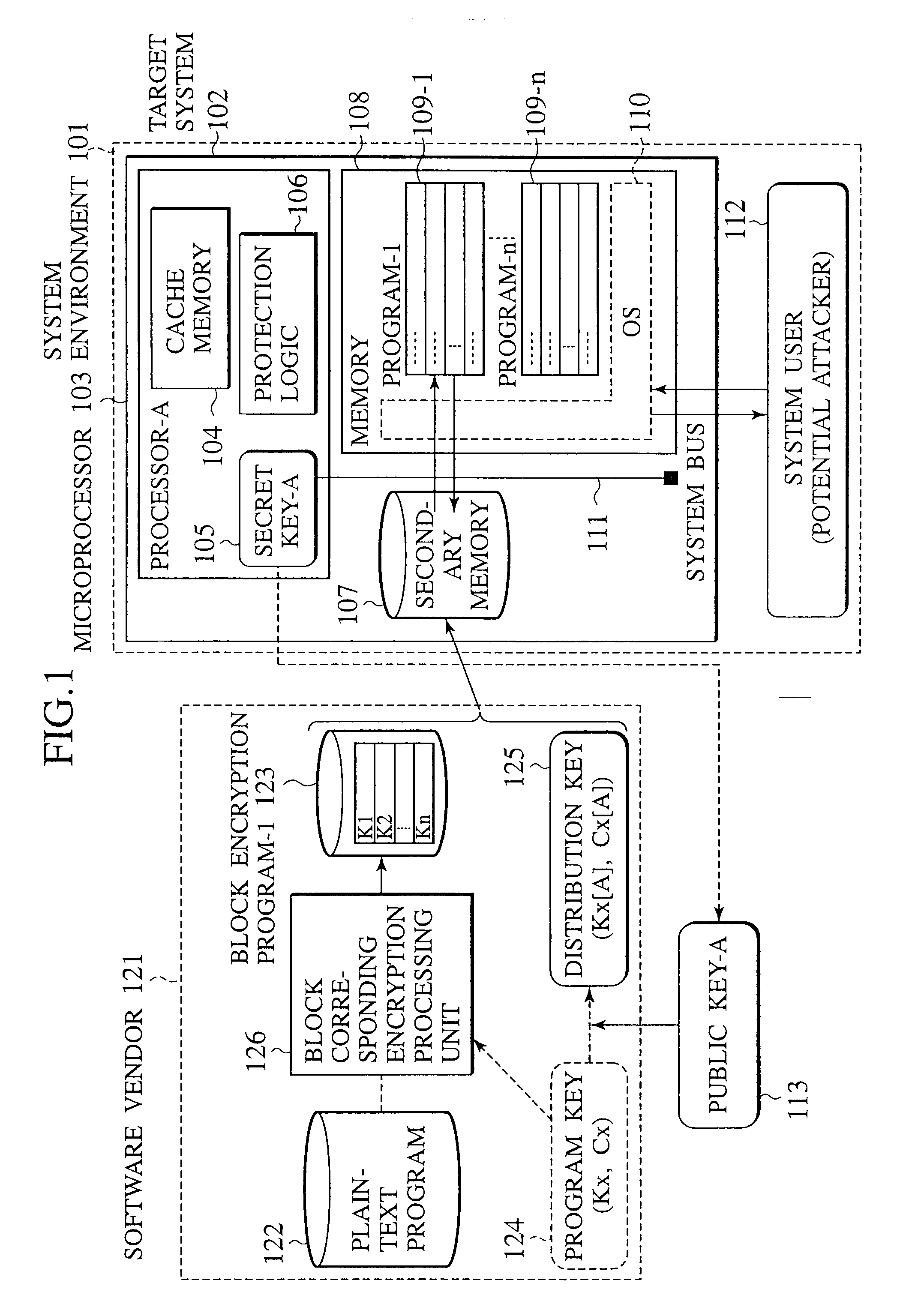
A tamper resistant microprocessor has a task state table for assigning a task identifier to a task that can take a plurality of states, and storing a state of the task in correspondence to the task identifier; a task register for storing the task identifier of a currently executed task; an interface for reading a program stored in a form encrypted by using a program key at an external memory, in units of cache lines, when a request for the task is made; an encryption processing unit for generating decryption keys that are different for different cache lines, according to the program key, and decrypt a content read by the interface; a cache memory formed by a plurality of cache lines each having a tag, for storing the task identifier corresponding to a decryption key used in decrypting each cache line in the tag of each cache line; and an access check unit for comparing the task identifier stored in the tag of each cache line with a value of the task register, and discarding a content of each cache line when the task identifier in the tag and the value of the task register do not coincide.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
In-place transformations with applications to encoding and decoding various classes of codes
InactiveUS20060280254A1Reduce running timeLess time accessing memoryError preventionOther decoding techniquesComputer hardwareTerm memory
In an encoder for encoding symbols of data using a computing device having memory constraints, a method of performing a transformation comprising loading a source block into memory of the computing device, performing an intermediate transformation of less than all of the source block, then replacing a part of the source block with intermediate results in the memory and then completing the transformation such that output symbols stored in the memory form a set of encoded symbols. A decoder can perform decoding steps in an order that allows for use of substantially the same memory for storing the received data and the decoded source block, performing as in-place transformations. Using an in-place transformation, a large portion of memory set aside for received data can be overwritten as that received data is transformed into decoded source data without requiring a similar sized large portion of memory for the decoded source data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
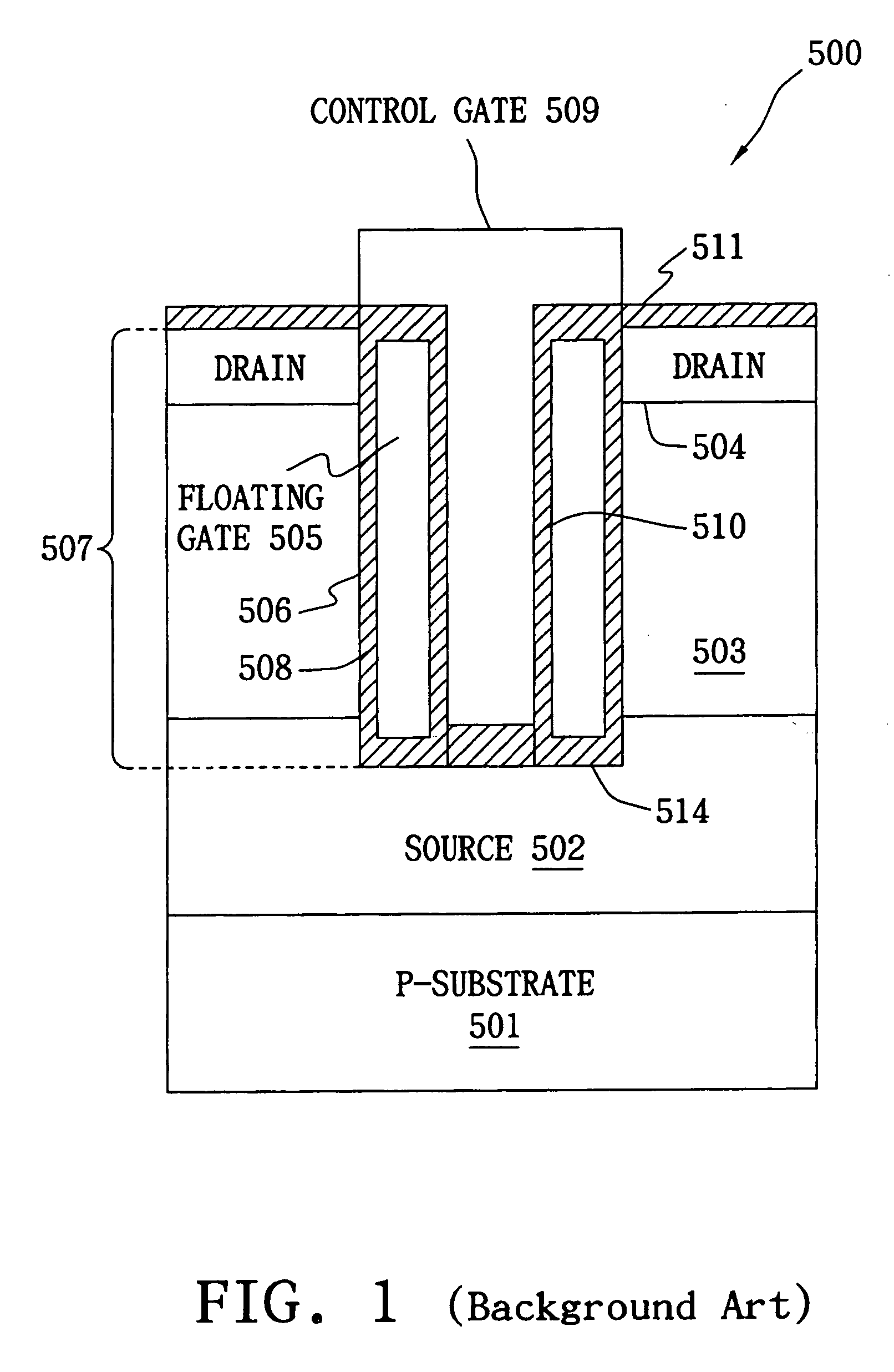
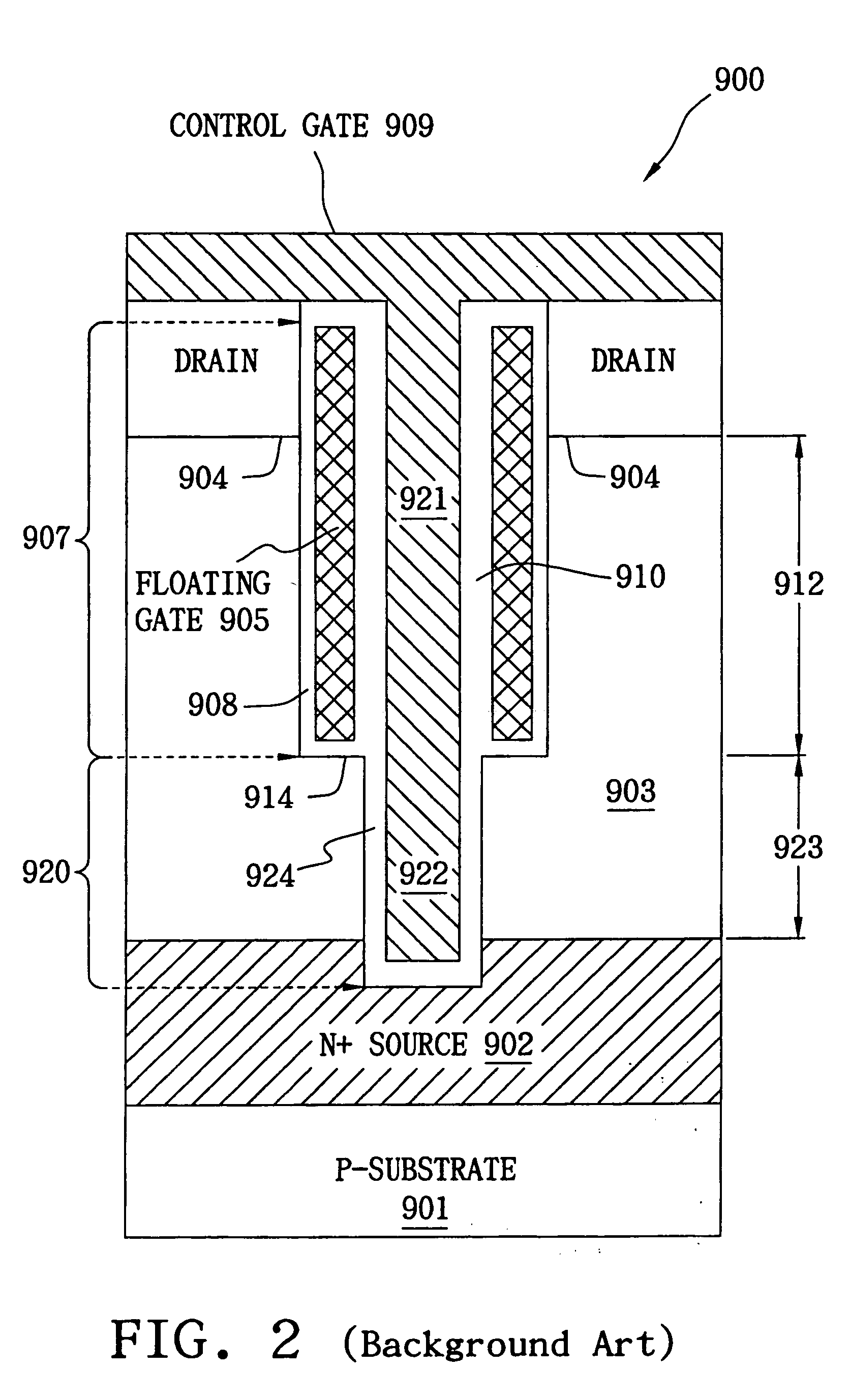
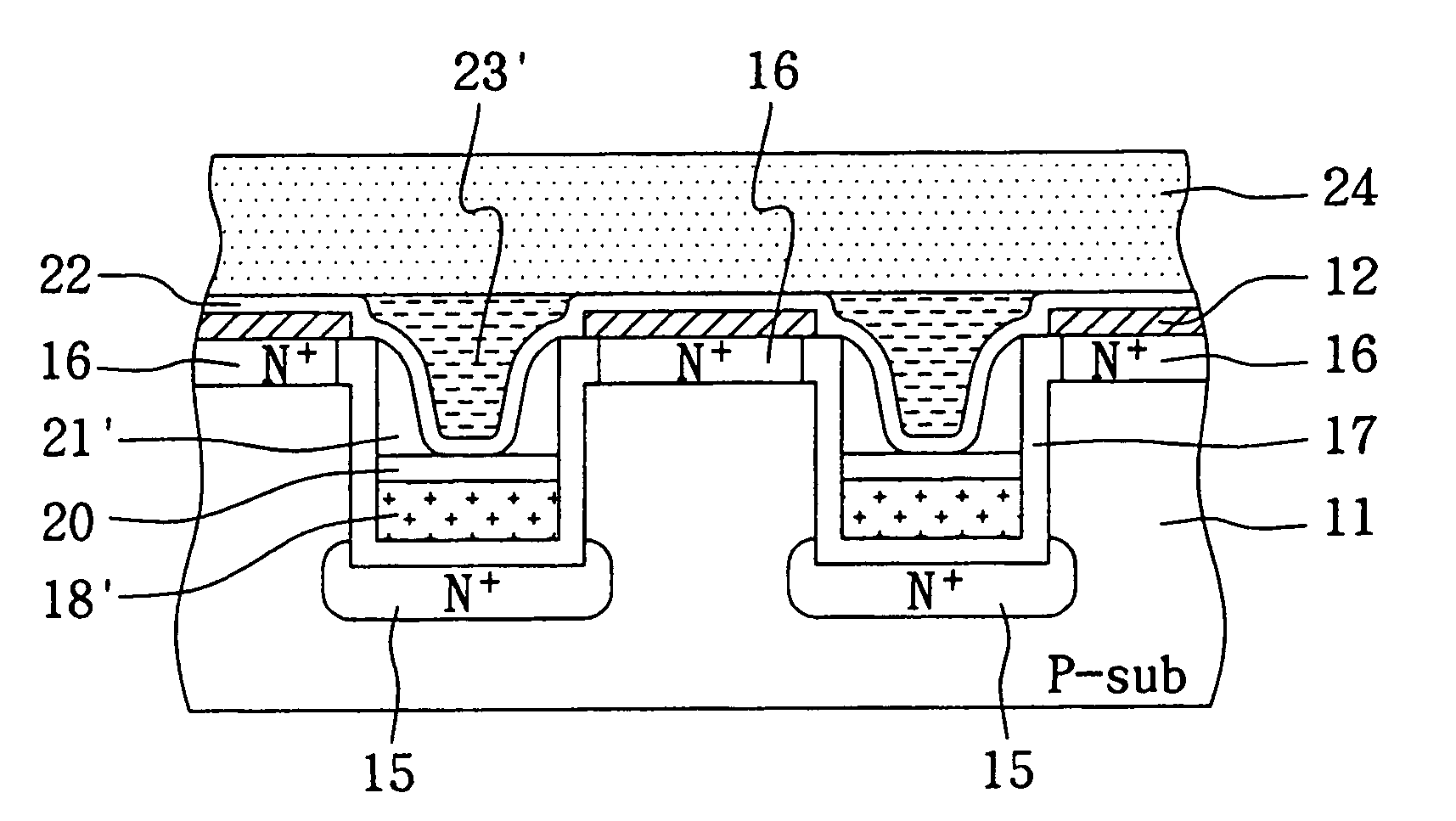
Vertical split gate memory cell and manufacturing method thereof
A vertical split gate memory formed in a trench of a semiconductor substrate comprises a first doping region, a second doping region, a conductive line, a conductive spacer and a conductive plug, wherein the conductive line, conductive spacer and conductive plug serve as a select gate, a floating gate and a control gate of the vertical split gate memory cell, respectively. The first doping region of a first conductive type is underneath the bottom of the trench, whereas the second doping region of the first conductive type is beside the top of the trench. The conductive line serving as the select gate is formed at the bottom of the trench and in operation relation to the first doping region. The conductive spacer is formed beside the sidewall of the trench and above the conductive line. The conductive plug is insulated from the conductive spacer and the conductive line and in operation relation to the conductive spacer.
Owner:SKYMEDI CORPORATION
Low-power-consumption wearable equipment system
ActiveCN103809730AIncrease carrying capacitySmall sizeInput/output for user-computer interactionPower supply for data processingLow power dissipationEmbedded system
The invention provides a low-power-consumption wearable equipment system. Based on a memory formed by a register, a local nonvolatile memory, a main memory and an external high-capacity nonvolatile memory together, a processor of a multi-microcontroller-core structure and a new multi-core management mode are adopted, so that the low-power-consumption wearable equipment system is in an ultra-low-power-consumption state for a long time and is started immediately once awakened, while system performance is improved, the size and consumption of a battery are reduced, achieving cost of the system is reduced, equipment is more microminiaturized, then portability of the wearable equipment is greatly enhanced, and moreover requirements of different users can be met according to usage habits of the different users.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINCHU INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Hybrid bulk/silicon-on-insulator multiprocessors
InactiveUS6864524B2Improve chip yieldReduce deleterious diffusionTransistorMemory loss protectionMulti processorParallel computing
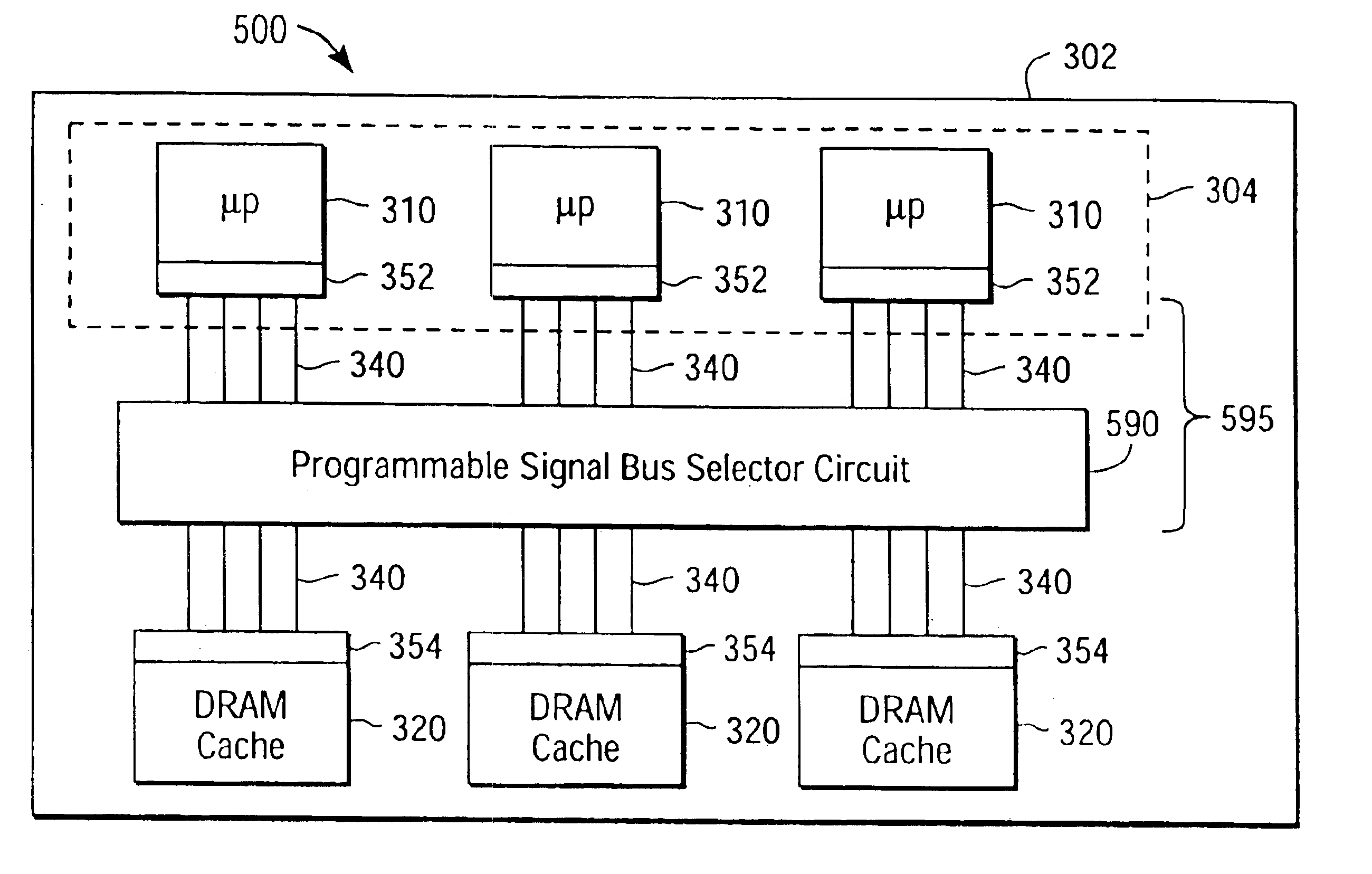
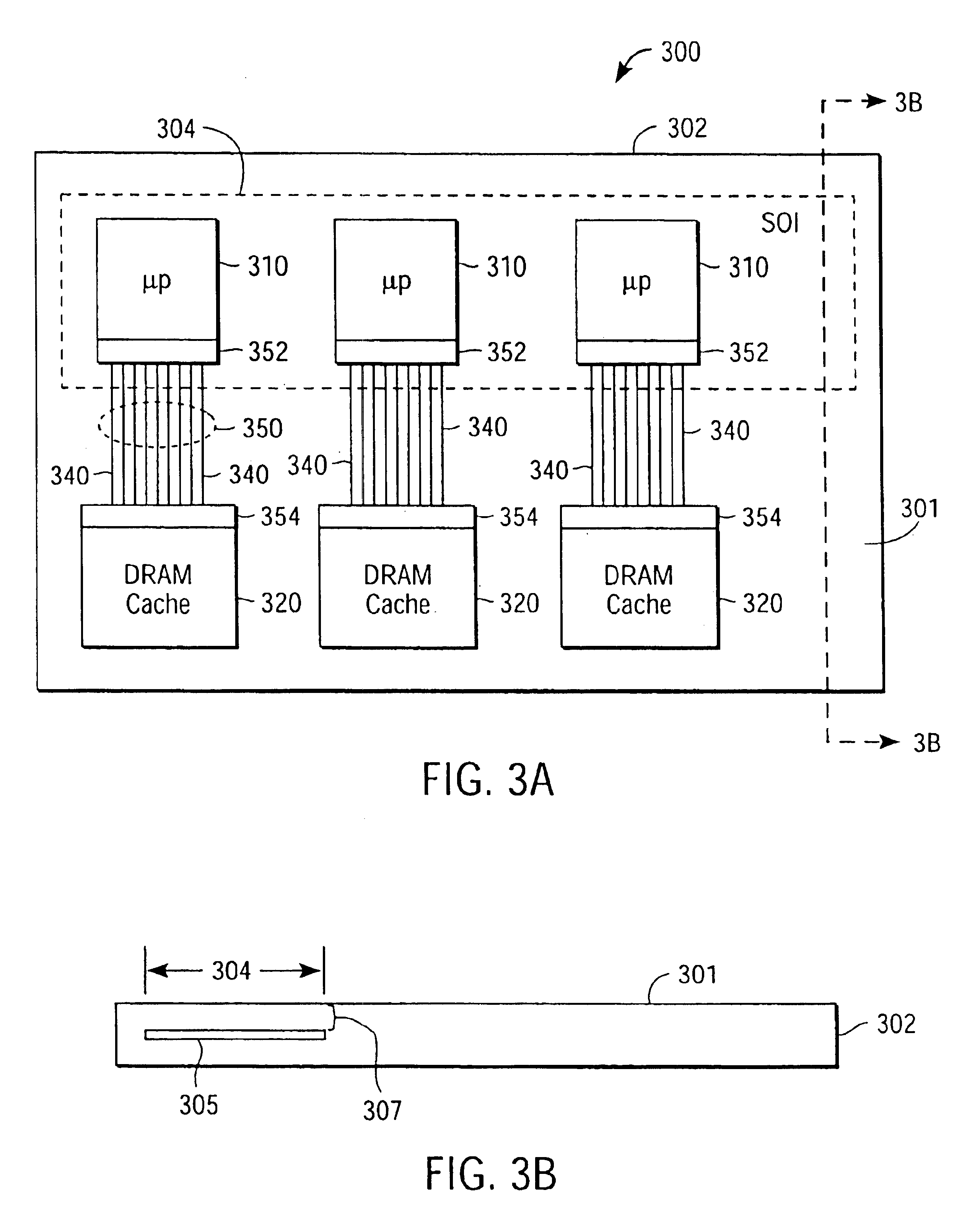
A multiprocessor integrated circuit is disclosed. A preferred embodiment of a multiprocessor chip has microprocessors formed on silicon-on-insulator regions and dynamic random access memory level-2cache memories or level-3 cache memories formed on bulk regions of the chip. A preferred embodiment includes a redundant architecture having a signal bus for coupling the microprocessors to the level-2 or level-3 cache memories in which the signal bus includes a programmable selector circuit for bypassing defective microprocessors or defective level-2 or level-3 cache memories.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Vertical split gate memory cell and manufacturing method thereof
Owner:SKYMEDI CORPORATION
Semiconductor device including nonvolatile memory
A semiconductor device including a nonvolatile memory formed on a semiconductor substrate. According to the semiconductor device, a second gate electrode film is used for a gate electrode film of a logic circuit, and for a control gate electrode film of a nonvolatile memory. As the second gate electrode film is formed at a relatively later step in fabrication, subsequent thermal process may be avoided. The gate structure is suitable for miniaturization of the transistor in the logic circuit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Deterministic microcontroller with configurable input/output interface
ActiveUS20060168429A1Minimal interventionDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsMicrocontrollerData acquisition
A deterministic microcontroller includes a plurality of blocks of cache memories formed on the same integrated circuit as the microprocessor unit. A corresponding plurality of hardware contexts for the microcontroller is provided by the plurality of sets of hardware registers. A context manager controls the selection of the hardware registers such that contexts are changed within one bus cycle and a plurality of hardware contexts are provided. The deterministic microcontroller includes a configurable input / output interface that is programmable to handle any one of a plurality of interfaces that embedded applications might have, including communication protocols and bus interfaces, data acquisition from multiple sensors and actuators, and controls of various motors.
Owner:INNOVASIC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS7313026B2Less element deteriorationMaintain good propertiesSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCapacitancePotential difference
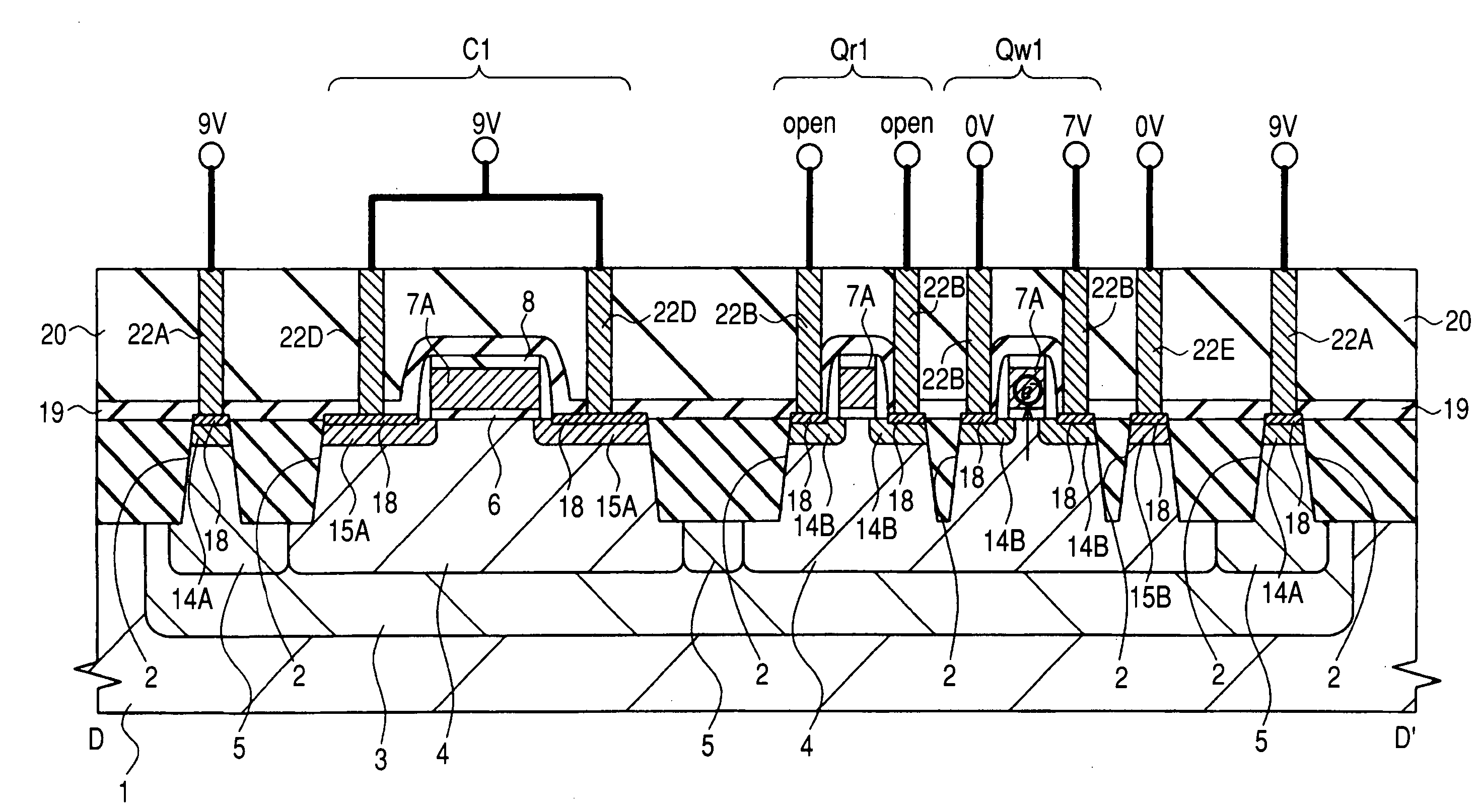
Provided is a nonvolatile memory with less element deterioration and good data retaining properties. In a nonvolatile memory formed by the manufacturing steps of a complementary type MISFET without adding thereto another additional step, erasing of data is carried out by applying 9V to an n type well, 9V to a p type semiconductor region, and −9V to another p type semiconductor region and setting the source and drain of data writing and erasing MISFETs and data reading MISFETs at open potential to emit electrons from a gate electrode to a p well by FN tunneling. At this time, by applying a negative voltage to the p well having a capacitive element formed thereover and applying a positive voltage to the p well having the MISFETs formed thereover, a potential difference necessary for data erasing operation can be secured at a voltage low enough not to cause gate breakage.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20100109990A1Quality improvementReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayElectrical polarity
A liquid crystal display device includes a pair of substrates, a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix and a static memory formed on the substrates. A bit signal corresponding to an image data is written and held in a static memory in the pixel. The polarity of the input bit signal is controlled. A liquid crystal voltage supplied to a liquid crystal layer arranged between the pair of substrates is generated by the bit signal. The polarity of the bit signal is controlled to alternate the liquid crystal voltage, and a transmittance of the liquid crystal layer is changed by supplying the alternated liquid crystal voltage.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
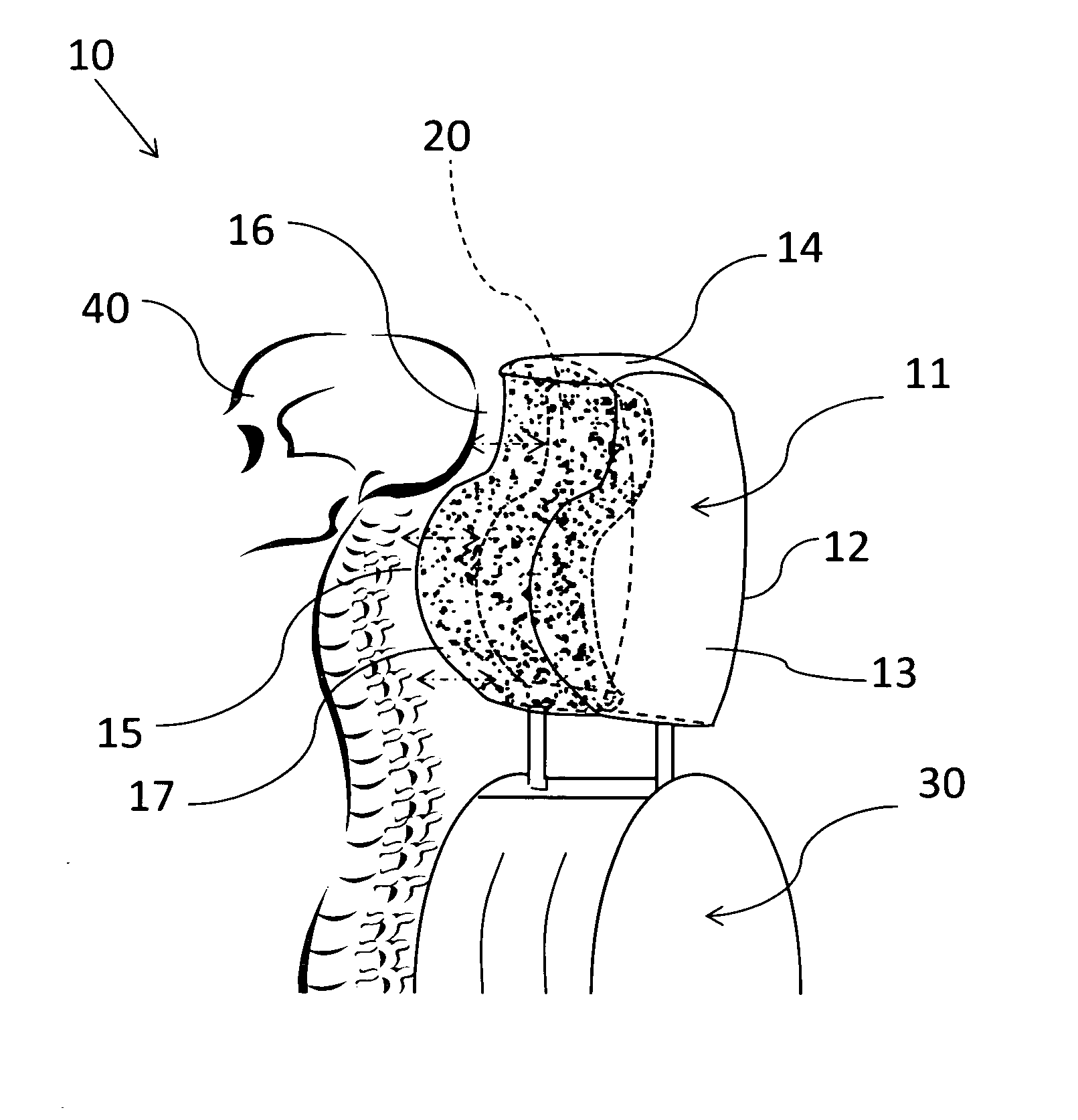
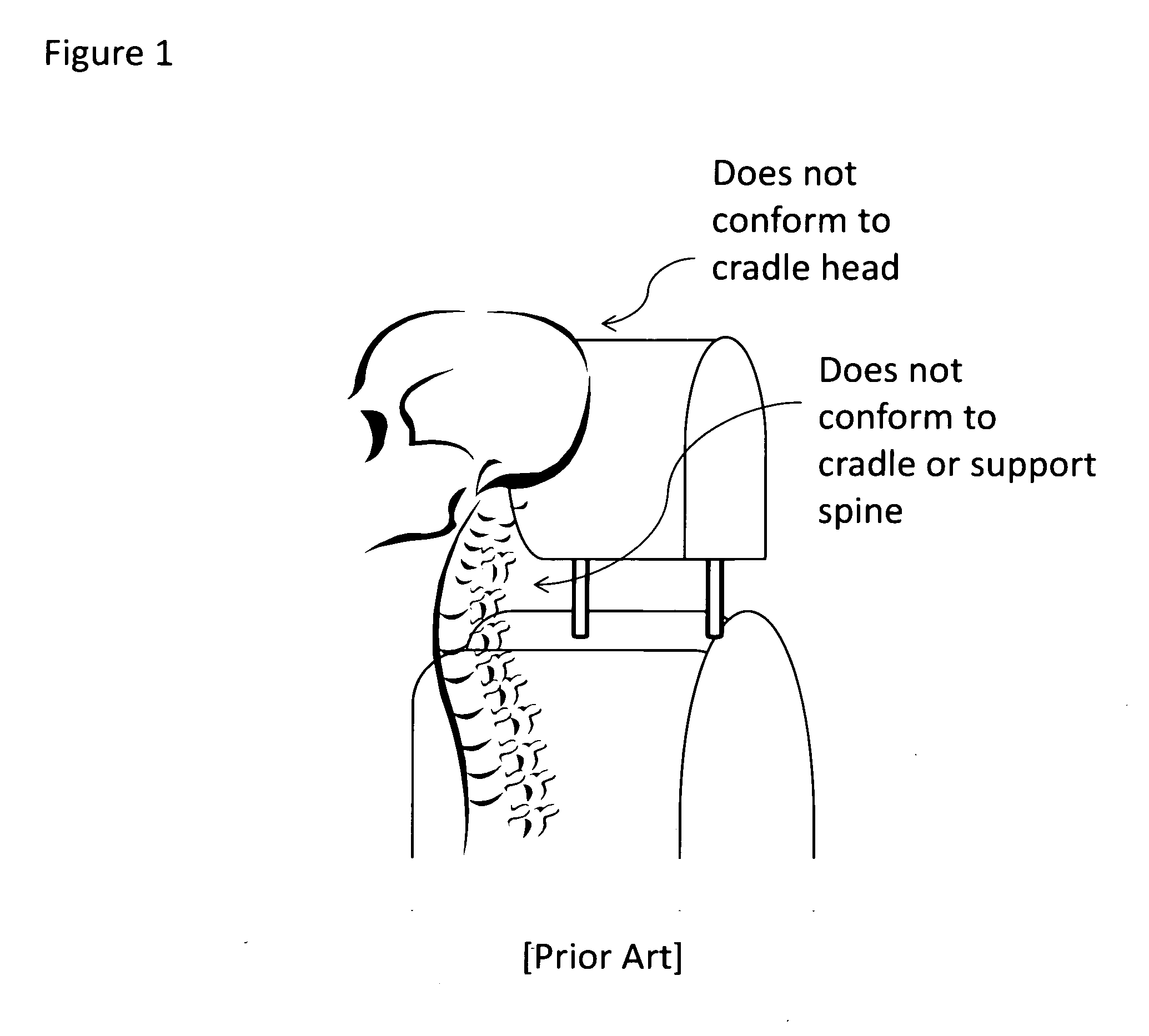
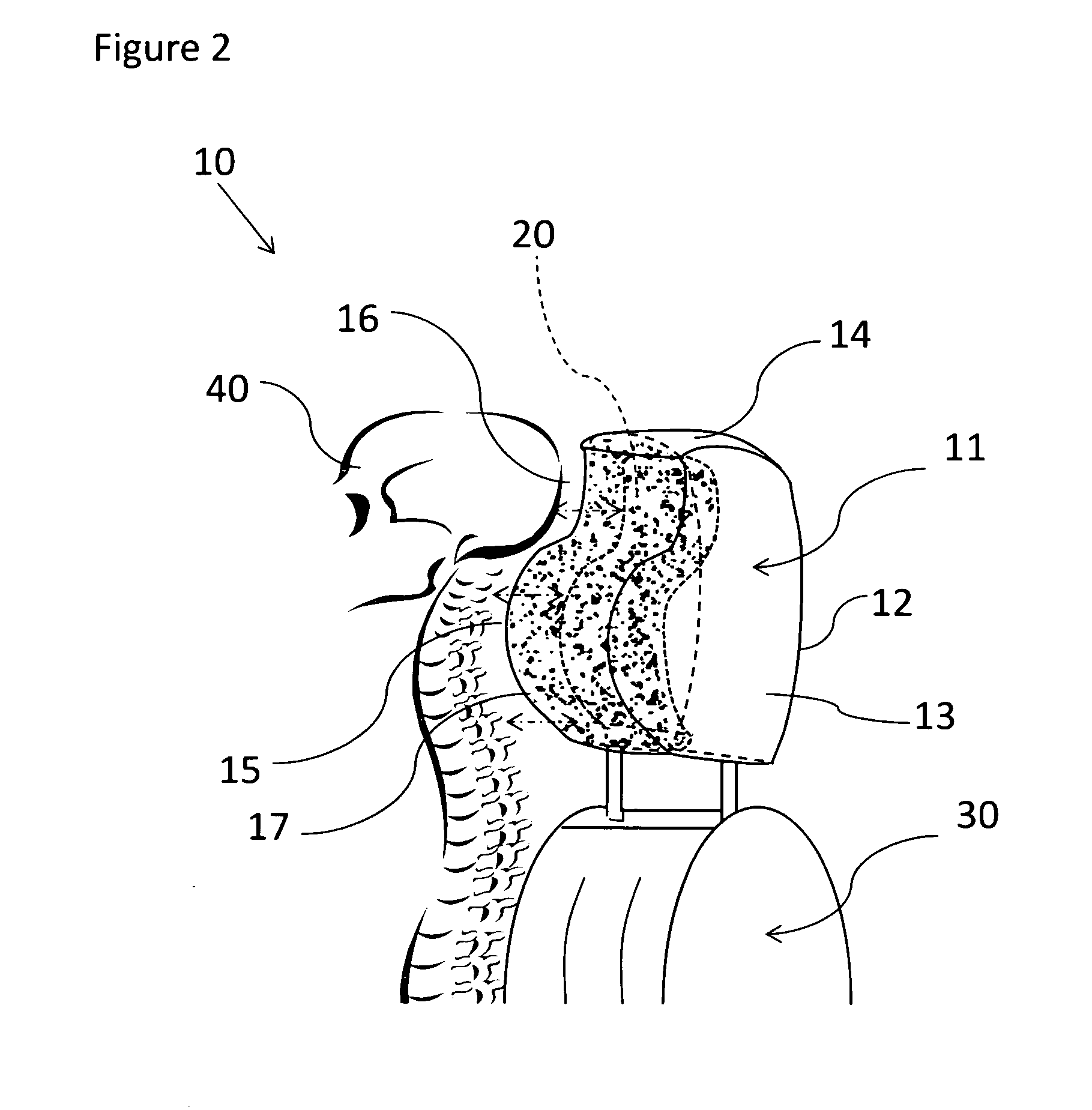
Protective headrest
InactiveUS20130278027A1Enhanced neck injuryImprove protectionVehicle seatsOperating chairsVertical planeBiomedical engineering
A protective headrest for land vehicles provides ergonomic support and protection against injury to a passenger's head and spine. The protective headrest has a back wall, sides, top and front wall. The front wall includes a head support segment co-joined and adjacent to a spine support segment. The head support segment has a semi-spherical concave curvature adapted and shaped to correspond with a passenger's head. The spine support segment is substantially shaped as a convex curvature adapted and shaped to correspond with the passenger's spine region at the neck-head interface. The spine support segment is located proximate and adjacent to the head support segment on a vertical plane. Preferably, the headrest includes a memory foam or other moldable insert within the head support segment and / or the spine support segment.
Owner:BRUCATO TERRI L
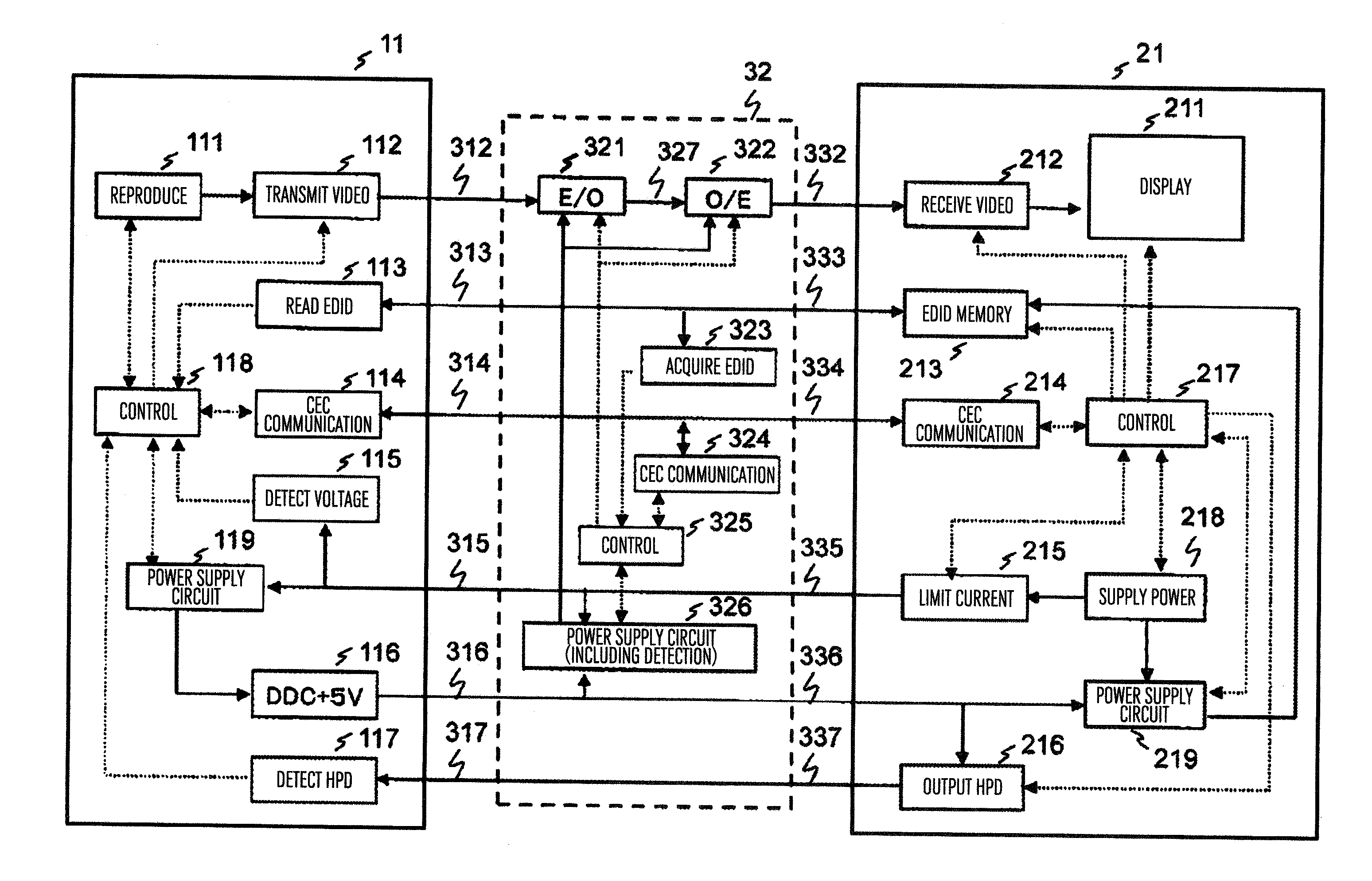
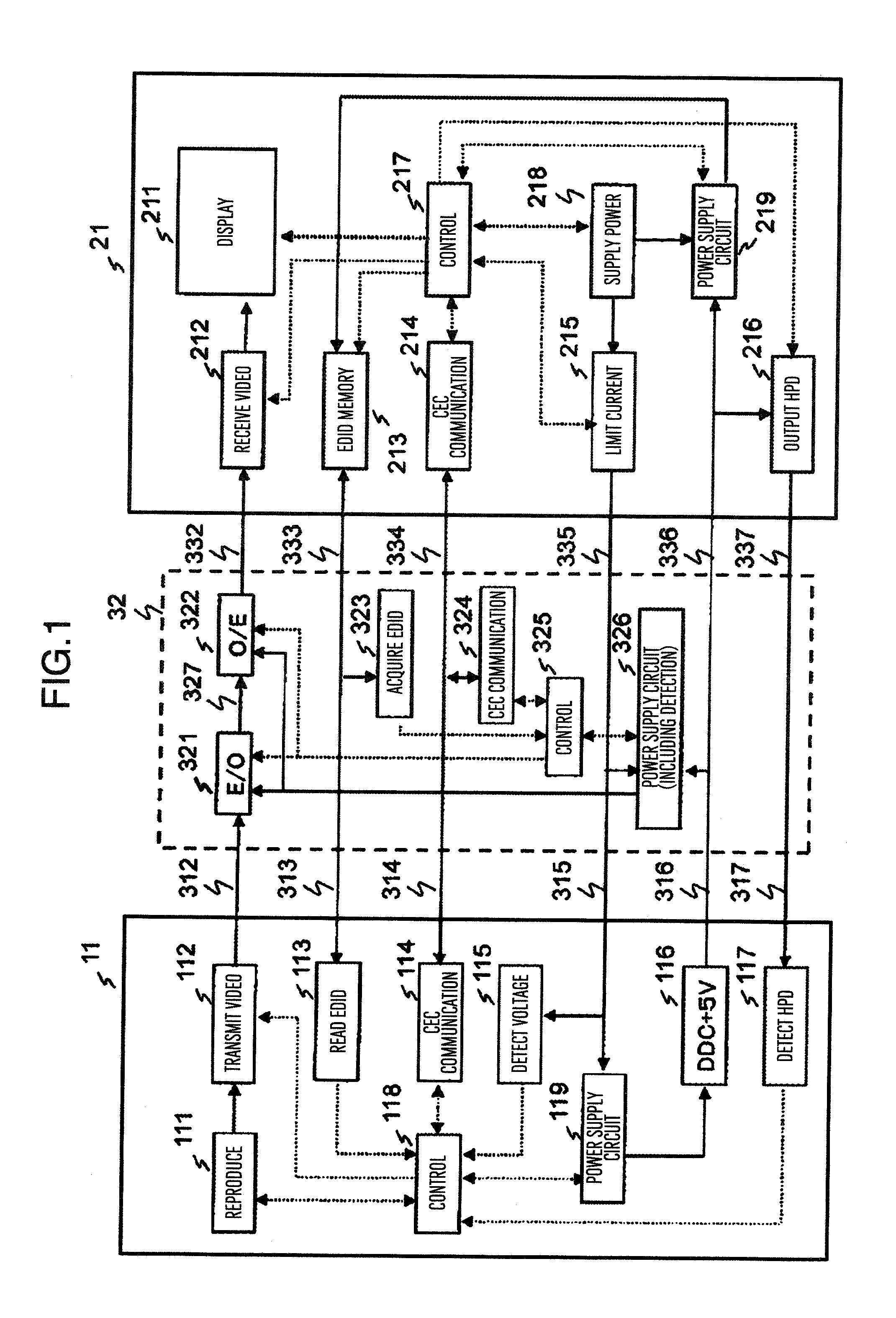
Transmission system and relay device
ActiveUS20120229706A1Improve convenienceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPower flowComputer compatibility
Provided is a system for supplying a power from a sink device to a source device. Not only the source device but also a cable or a repeater device to be connected thereto has compatibility in power supply. A physical address obtained from information of an EDID memory forms a base of CEC message exchange, but a physical address of the cable or repeater device is overlapped with the source device or unknown. The cable or a repeater device uses changes the type of a message while using the same physical address as the source device or use such a message having the physical address information of the source device is described in a parameter of the message using the unknown physical address. The message having a supply or reception current for each device described therein is exchanged with the sink device or the source device to adjust current reception.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Microprocessor with improved task management and table management mechanism
InactiveUS7424622B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationExternal storageProcessor register
A tamper resistant microprocessor has a task state table for assigning a task identifier to a task that can take a plurality of states, and storing a state of the task in correspondence to the task identifier; a task register for storing the task identifier of a currently executed task; an interface for reading a program stored in a form encrypted by using a program key at an external memory, in units of cache lines, when a request for the task is made; an encryption processing unit for generating decryption keys that are different for different cache lines, according to the program key, and decrypt a content read by the interface; a cache memory formed by a plurality of cache lines each having a tag, for storing the task identifier corresponding to a decryption key used in decrypting each cache line in the tag of each cache line; and an access check unit for comparing the task identifier stored in the tag of each cache line with a value of the task register, and discarding a content of each cache line when the task identifier in the tag and the value of the task register do not coincide.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Multibank memory on a die
A nonvolatile multibank memory on a die with multiple read, write, and erase circuits, allowing more than one bank to be read, written, erased, or tested independently. Such a multibank memory arrangement is used advantageously in a monolithic three dimensional memory formed above a substrate, leaving unused substrate area available in which the additional circuitry and related cache memory can be formed.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Apparatus and method for controlling data write/read in image processing system
InactiveUS8175157B2Reduce data volumeReduce the amount requiredPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImaging processingControl memory
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
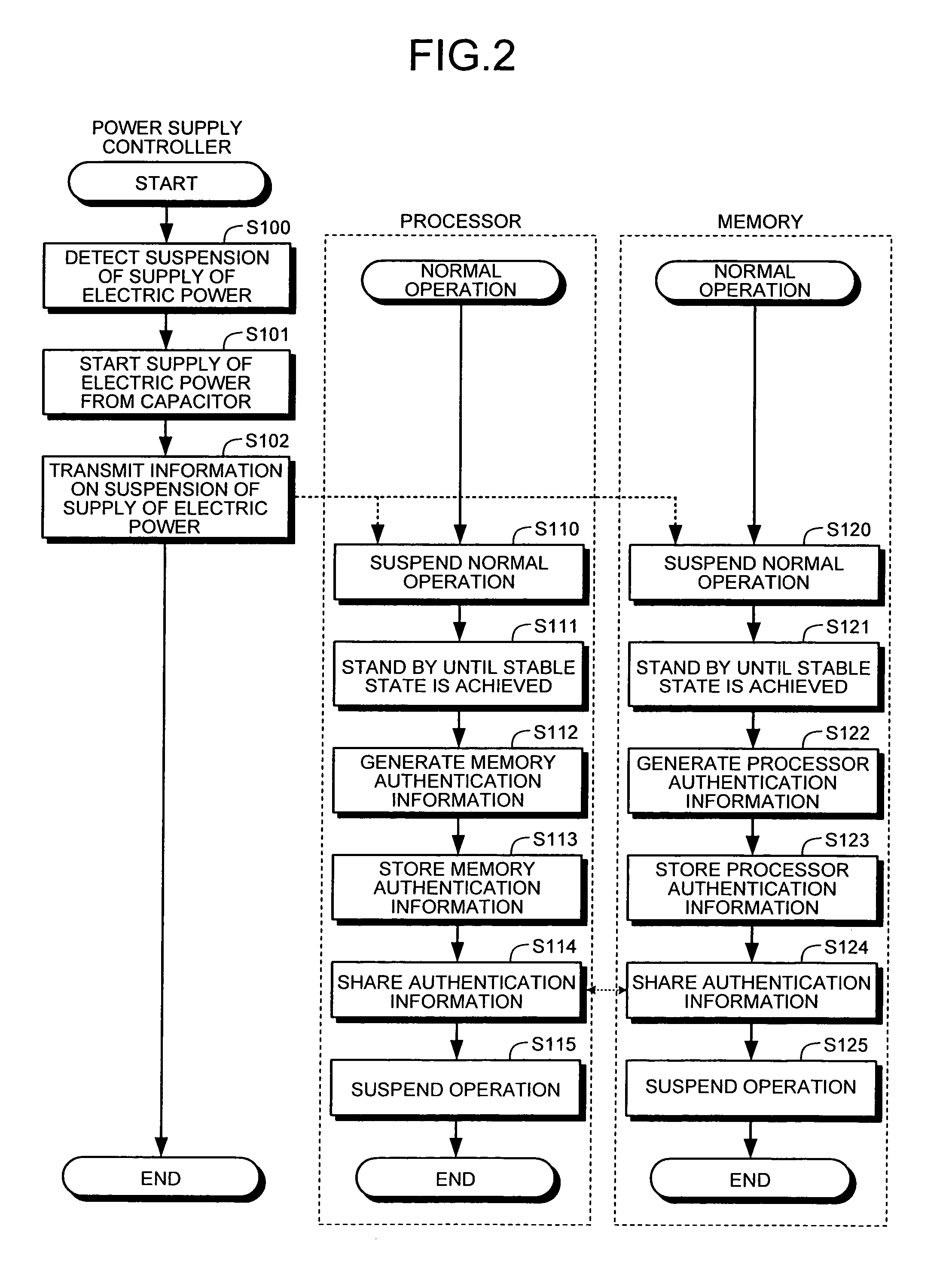
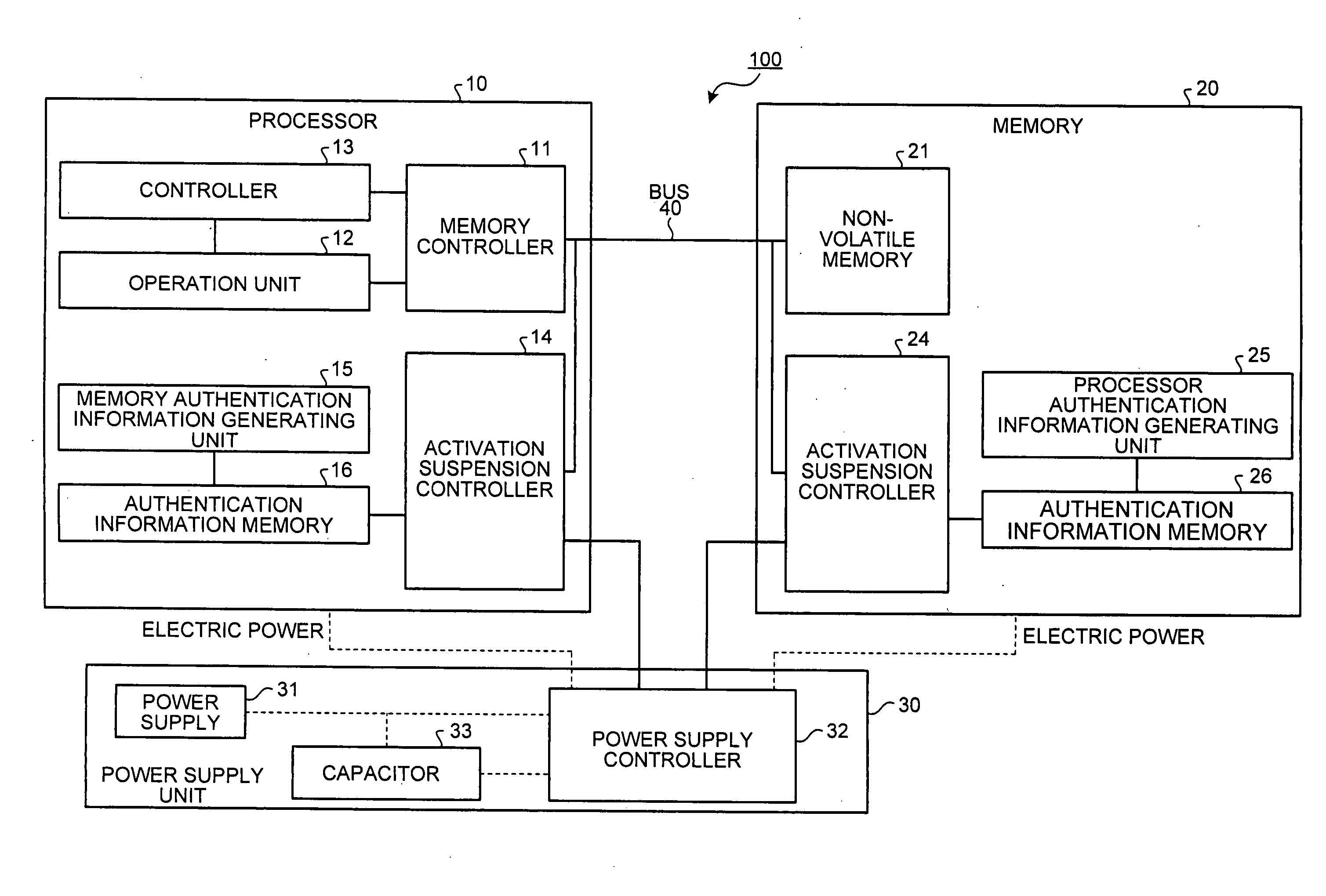
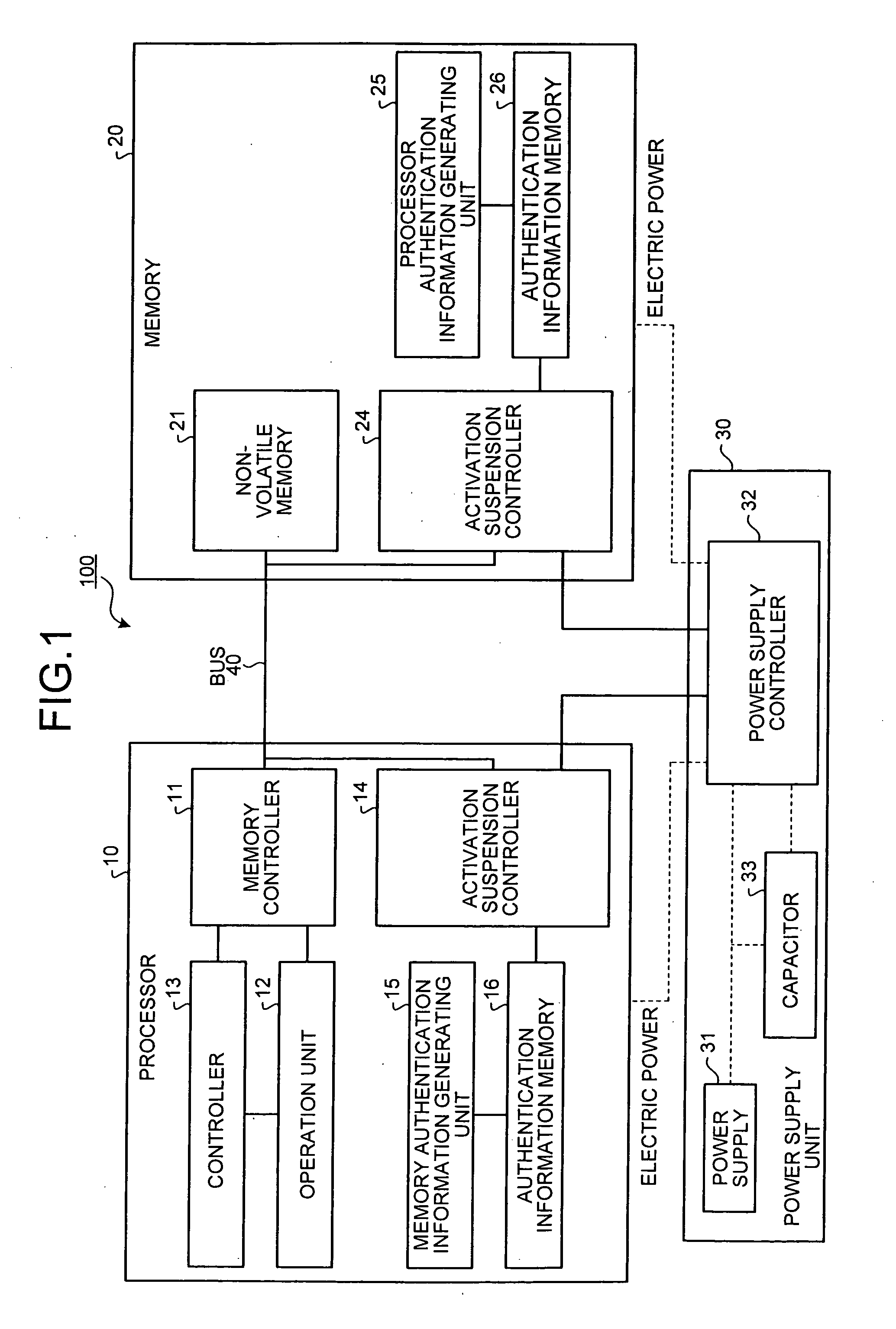
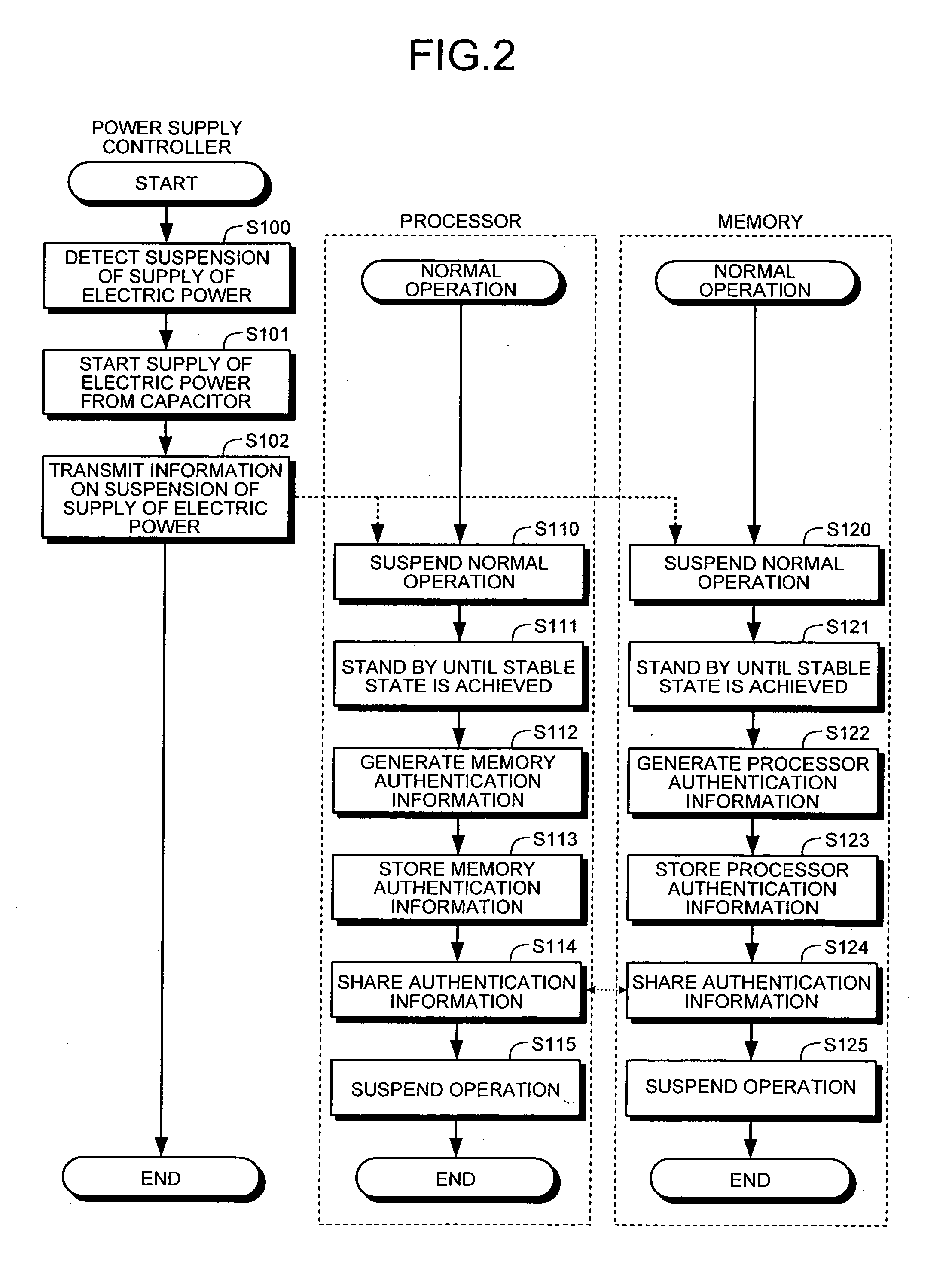
Processor, memory, computer system, system LSI, and method of authentication
InactiveUS8108941B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputerized systemMemory form
A processor, connected to a non-volatile memory storing first memory authentication information for authentication of the non-volatile memory, the processor includes an operation unit configured to perform an operation utilizing information stored in the non-volatile memory; an authentication memory formed integrally with the operation unit, and storing second memory authentication information for authentication of the non-volatile memory; an authentication information acquiring unit configured to acquire the first memory authentication information from the non-volatile memory; a memory authenticating unit configured to compare the first memory authentication information and the second memory authentication information to authenticate the non-volatile memory; and a memory access controlling unit configured to permit an access to the non-volatile memory when the memory authenticating unit succeeds in authentication.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
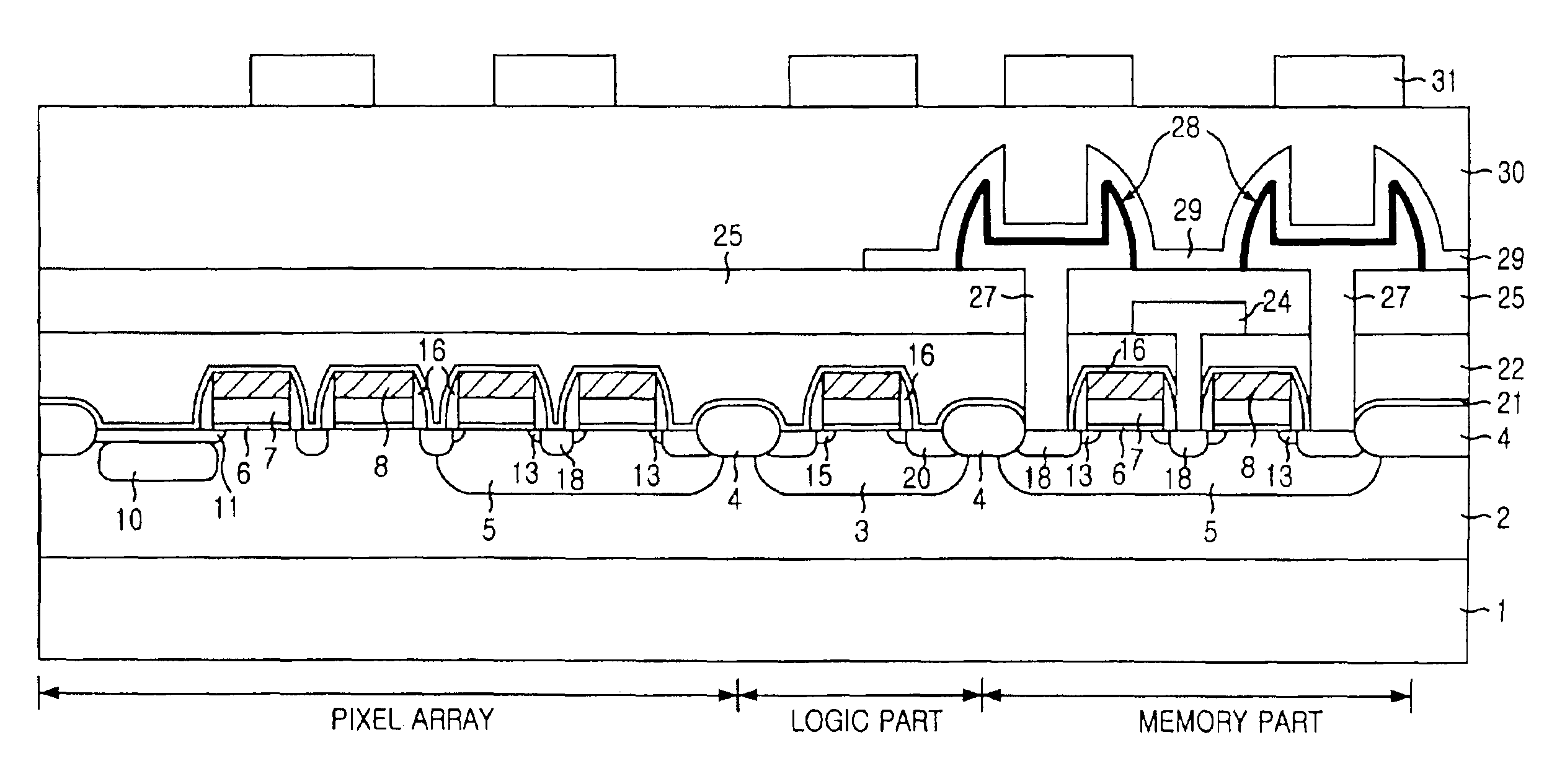
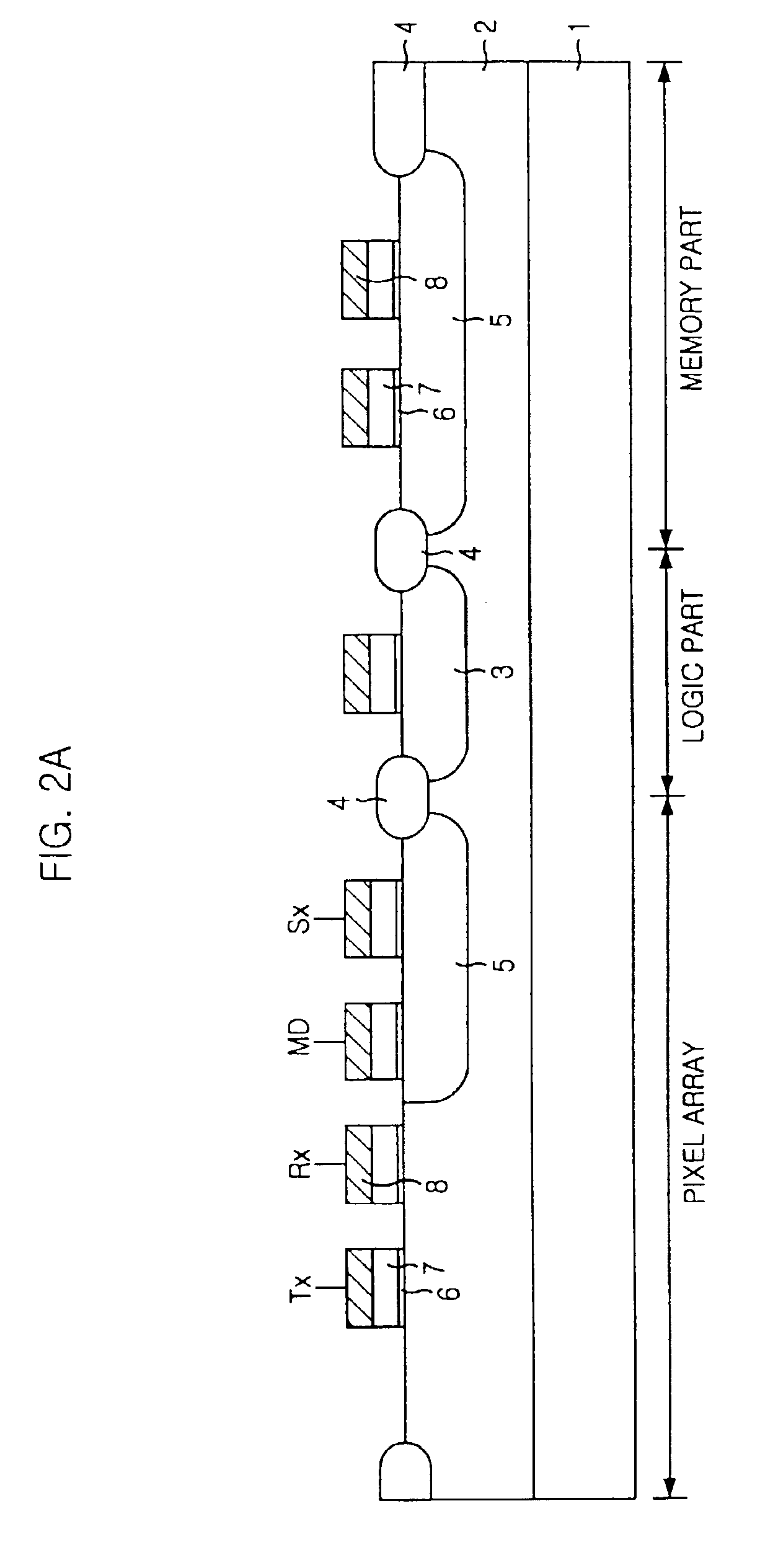
CMOS image sensor integrated together with memory device
The present invention relates to a CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Silicon) image sensor; and, more particularly, to an image sensor integrated into one chip, together with a memory. The CMOS image sensor according to the present invention comprises: a pixel array formed on a chip, having a plurality of unit pixels; a logic circuit formed on the chip to process signals form the pixel array; and a memory formed on the chip to store outputs from the logic circuit, wherein the pixel array, the logic circuit and the memory are isolated from each other by insulating layers, whereby the pixel array, the logic circuit and the memory are integrated on the same chip.
Owner:PHOTONIC IMAGING SOLUTIONS INC
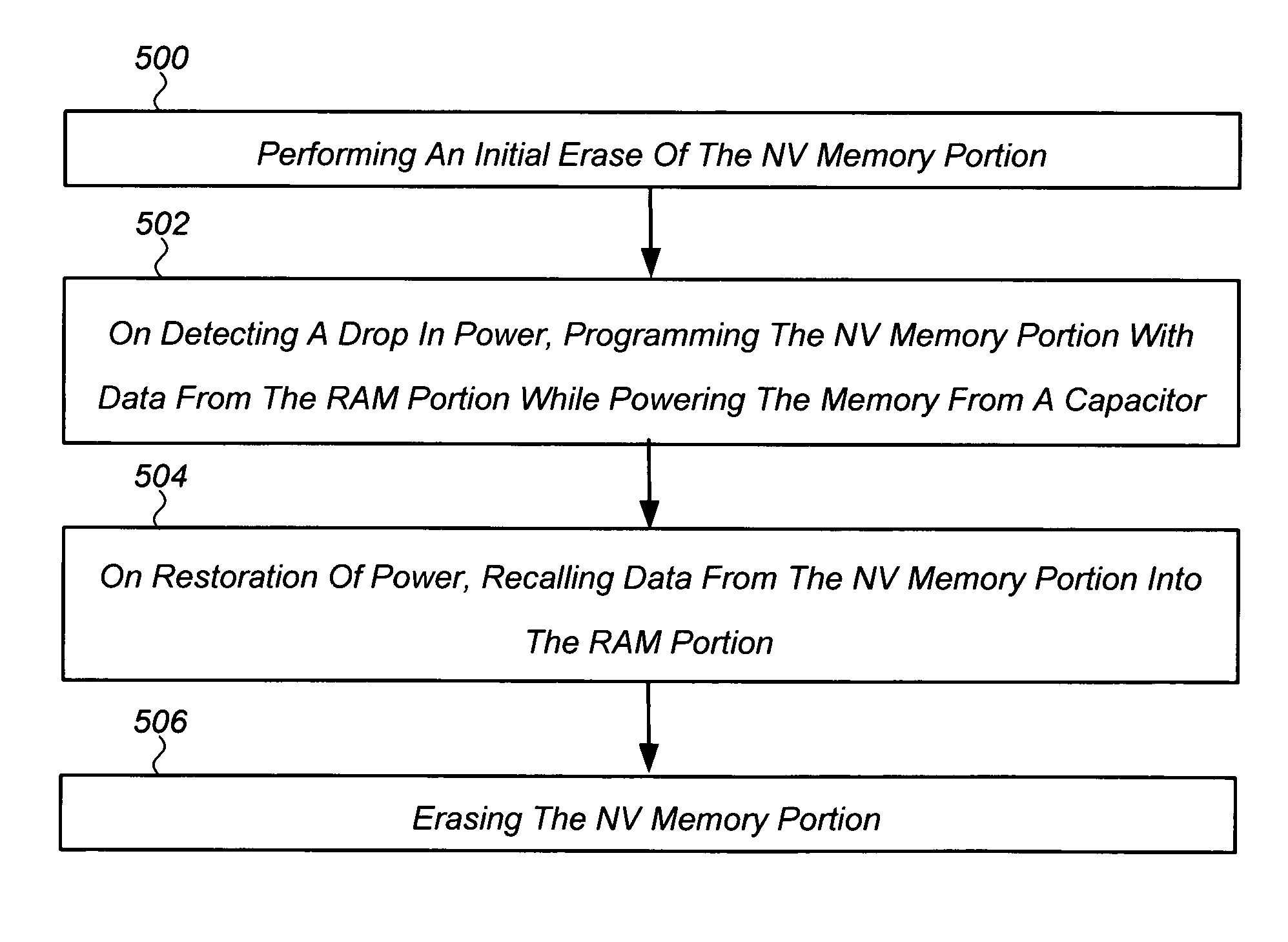
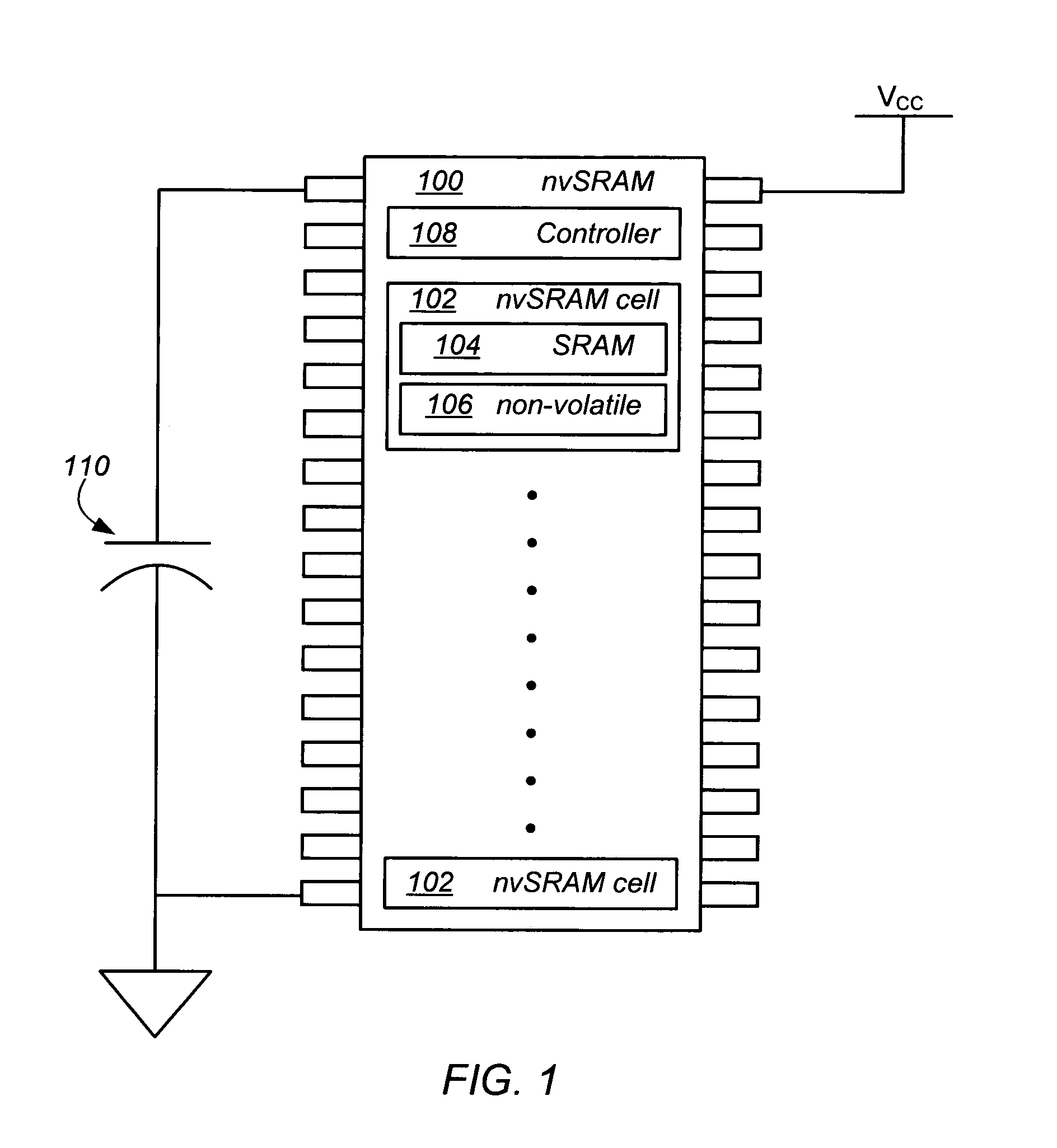
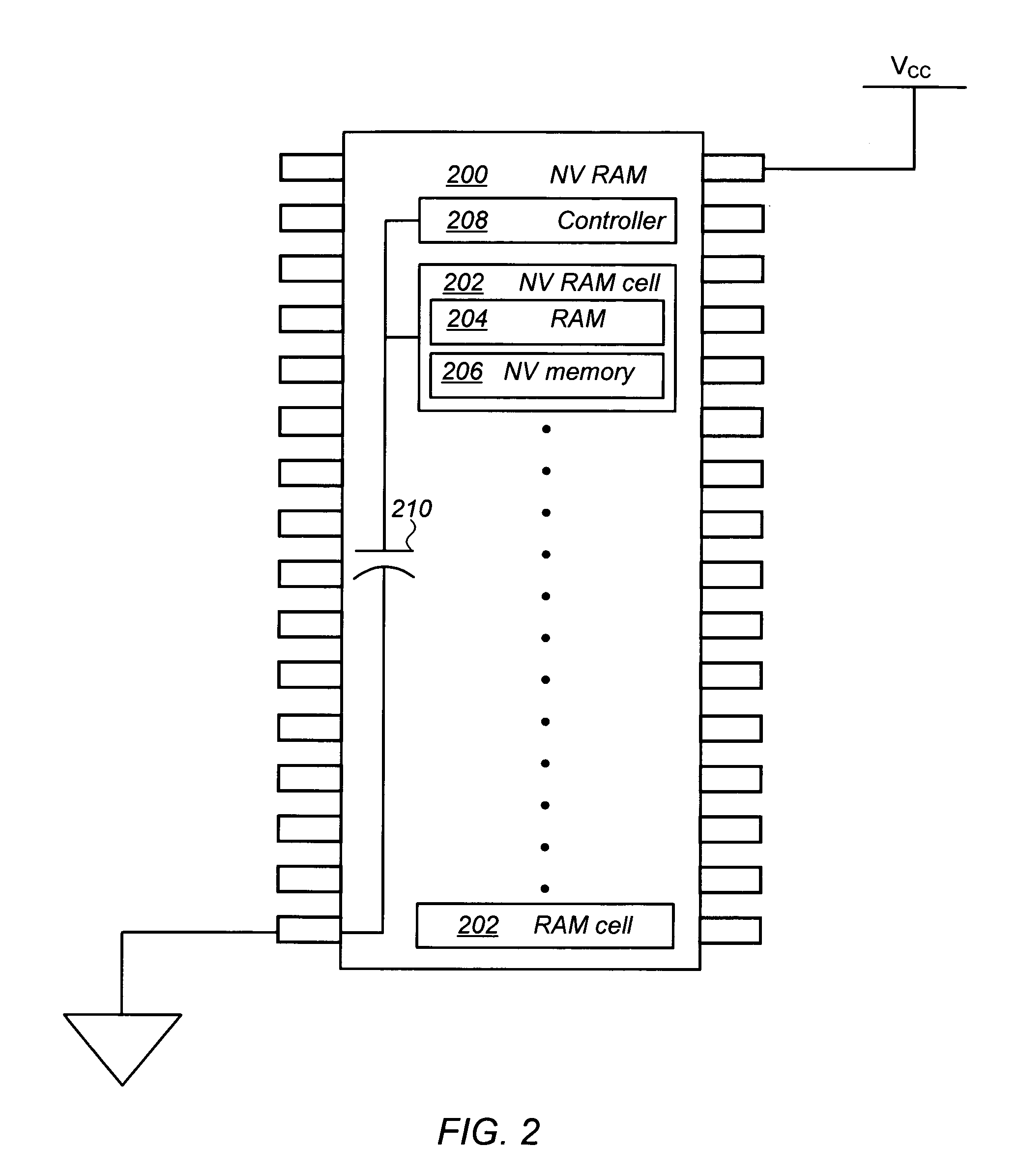
Non-volatile memory and method of operating the same
Non-volatile (NV) semiconductor memories and methods of operating the same to reduce or eliminate a need for an external capacitance are provided. In one embodiment, the memory includes a memory cell comprising a random access memory (RAM) portion and a NV memory portion, and the method comprises steps of: (i) initially erasing the NV memory portion; and (ii) on detecting a drop in power supplied to the memory, programming the NV memory portion with data from the RAM portion while powering the memory from a capacitor. On restoration of power data is recalled from the NV memory portion into the RAM portion, and the NV memory portion erased. Preferably, the capacitor is integrally formed on a single substrate with the NV memory portion and RAM portion. More preferably, the capacitor comprises intrinsic capacitance between elements of the memory formed on the substrate. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
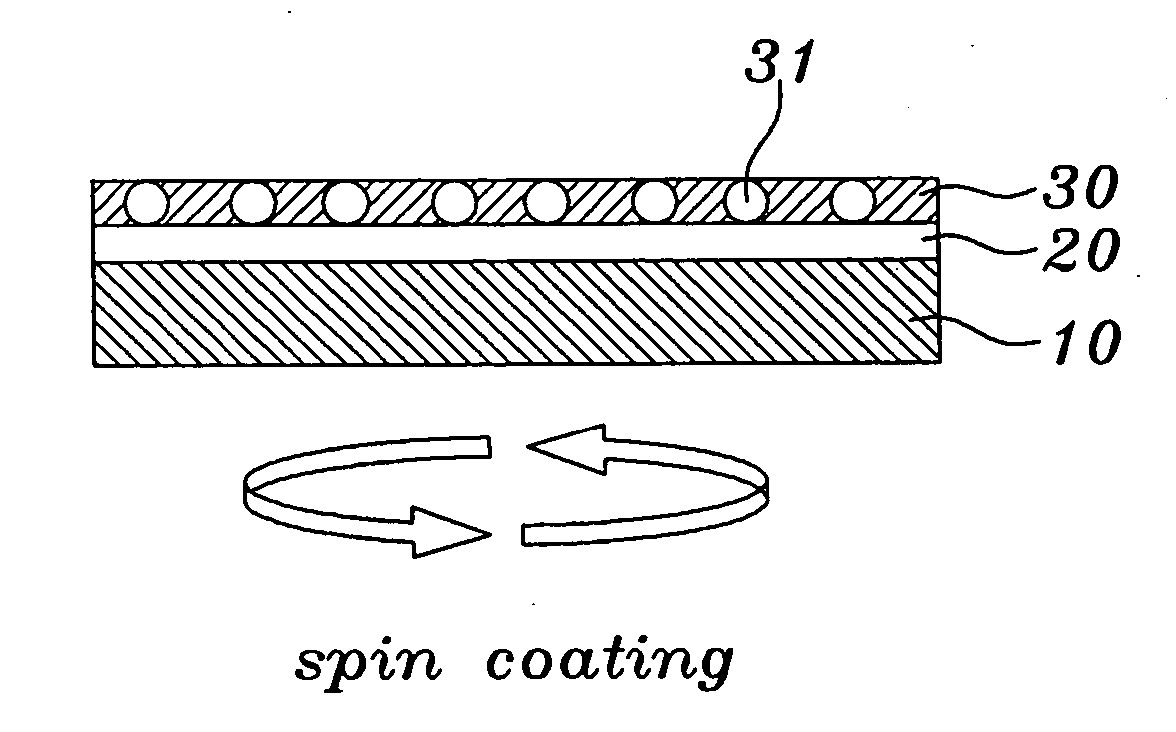
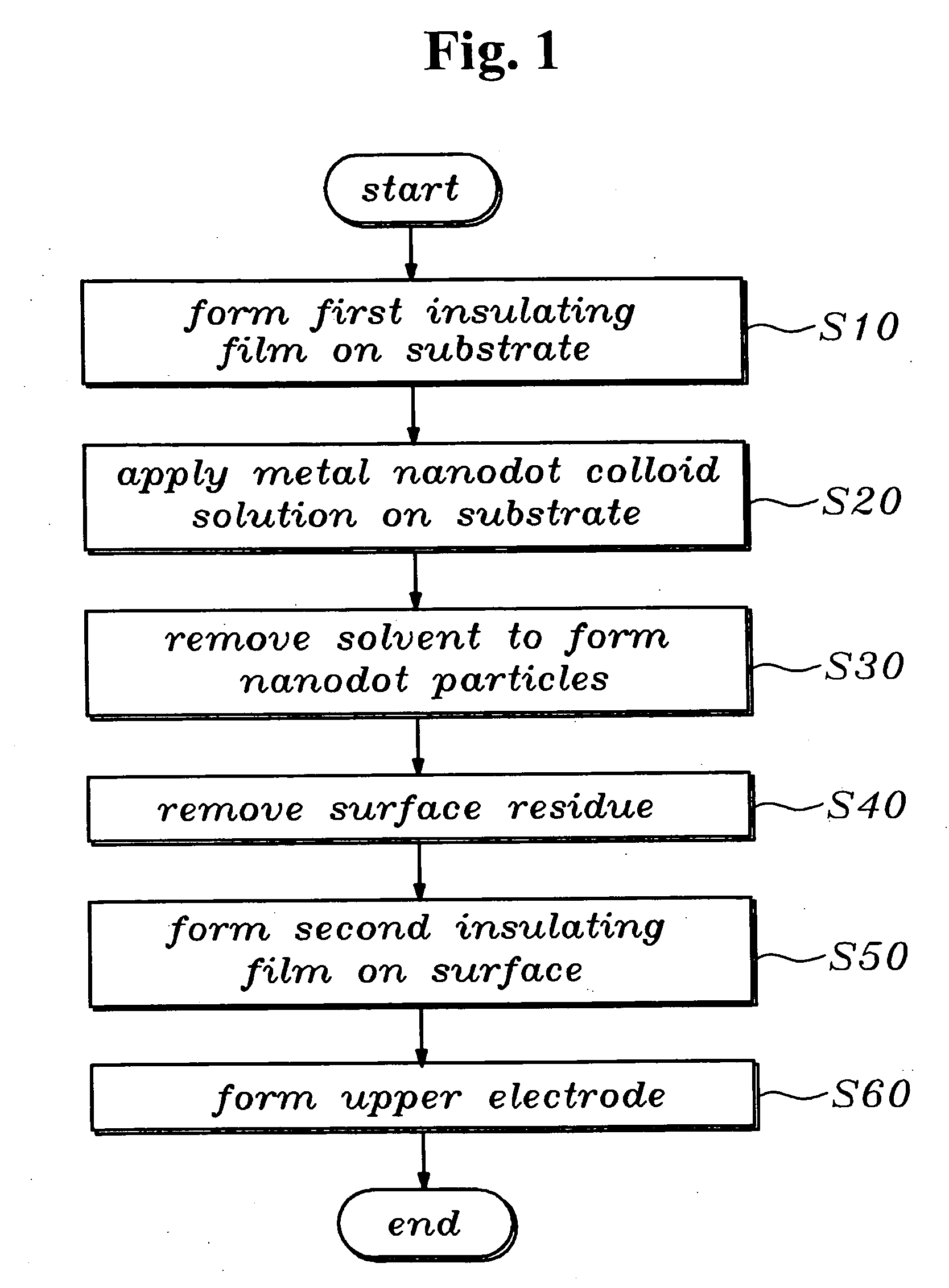
Nanodot memory and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20070054502A1Contamination in device areaReduce pollutionNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanodotColloid
A nanodot memory formed by applying a nanodot colloid solution on a semiconductor substrate to more uniformly arranging nanodot particles with a size of several nanometers on the semiconductor substrate and a fabrication method thereof are provided. In the nanodot memory fabrication method, a first insulating film may be formed on a surface of a substrate. A nanodot colloid solution may be applied on the first insulating film. A solvent in the nanodot colloid solution may be removed such that a nanodot particles layer remains exposed on the first insulating film. A second insulating film may be formed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate, on which the nanodot particles are exposed. The nanodot particles may be formed in a monolayer structure by adjusting a concentration of nanodot particles within the nanodot colloid solution.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor circuit apparatus with power save mode
ActiveUS20050213416A1High speed returnReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityEngineering
A semiconductor circuit apparatus comprises a substrate and a circuit block including a memory formed on the substrate. The circuit block performs regular operations at a first power supply voltage in an active mode, and a part of the circuit block is stopped and the memory keeps stored data at a second power supply voltage smaller than the first power supply voltage in a power save mode. The memory holds the stored data during the power save mode, resulting in higher speed return to a regular active mode, as well as power consumption reduction.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Processor, memory, computer system, system LSI, and method of authentication
InactiveUS20070180536A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsMemory formAuthentication information
A processor, connected to a non-volatile memory storing first memory authentication information for authentication of the non-volatile memory, the processor includes an operation unit configured to perform an operation utilizing information stored in the non-volatile memory; an authentication memory formed integrally with the operation unit, and storing second memory authentication information for authentication of the non-volatile memory; an authentication information acquiring unit configured to acquire the first memory authentication information from the non-volatile memory; a memory authenticating unit configured to compare the first memory authentication information and the second memory authentication information to authenticate the non-volatile memory; and a memory access controlling unit configured to permit an access to the non-volatile memory when the memory authenticating unit succeeds in authentication.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com