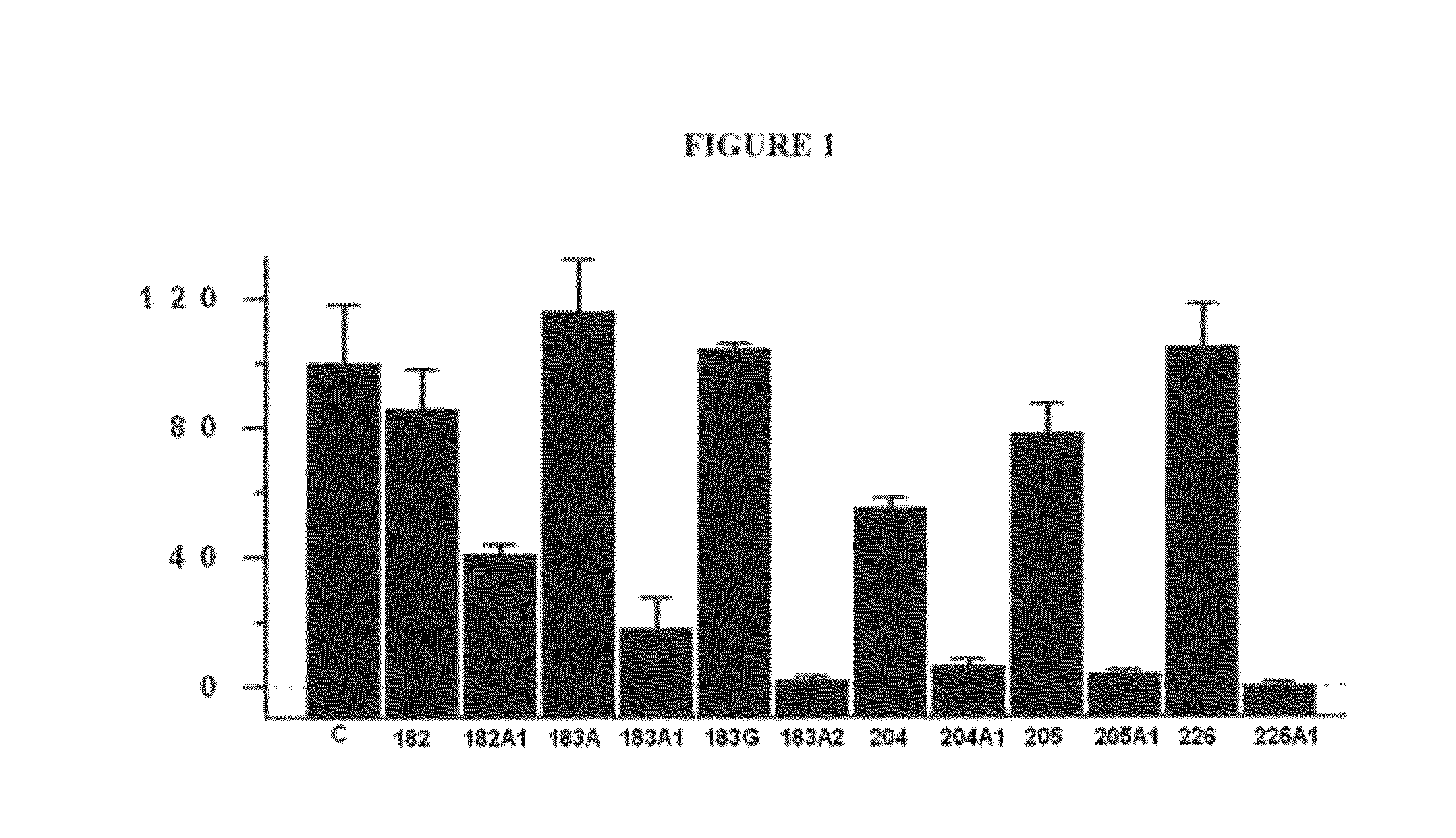
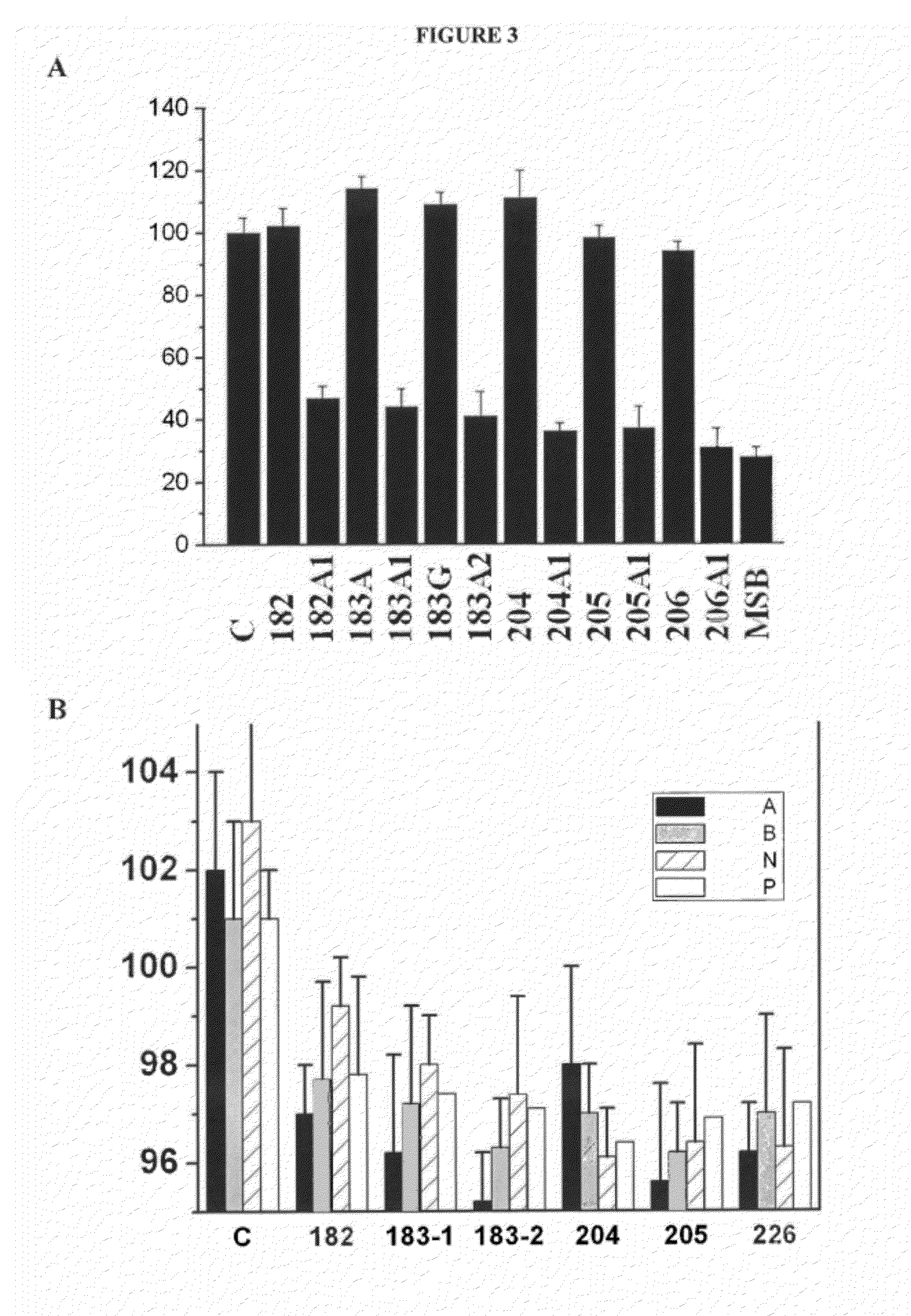
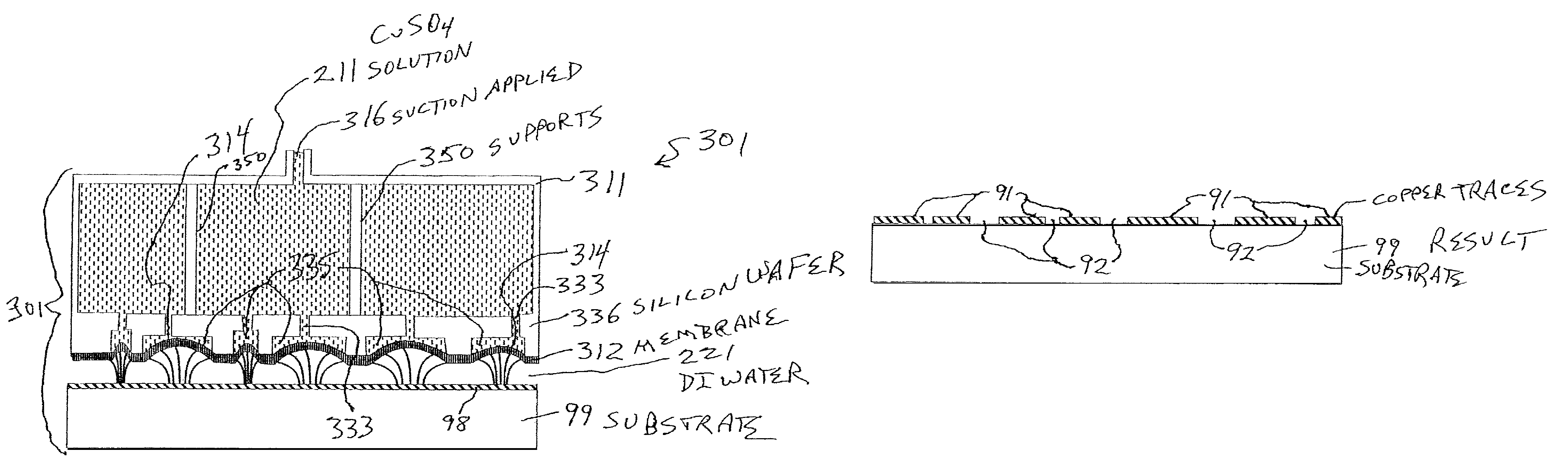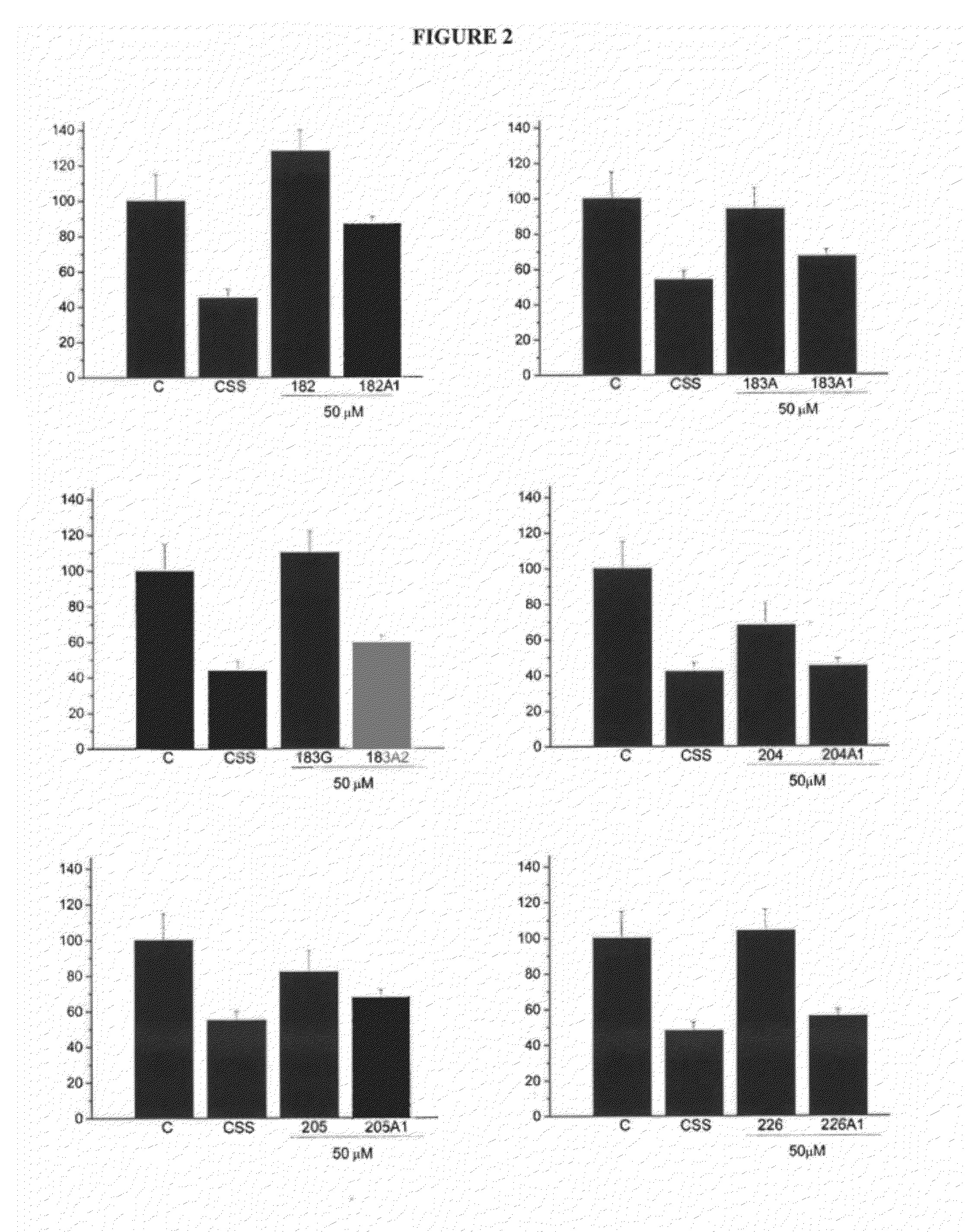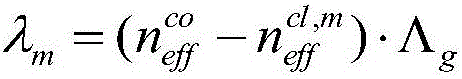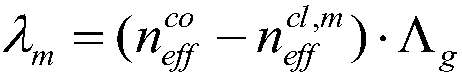Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Membrane interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
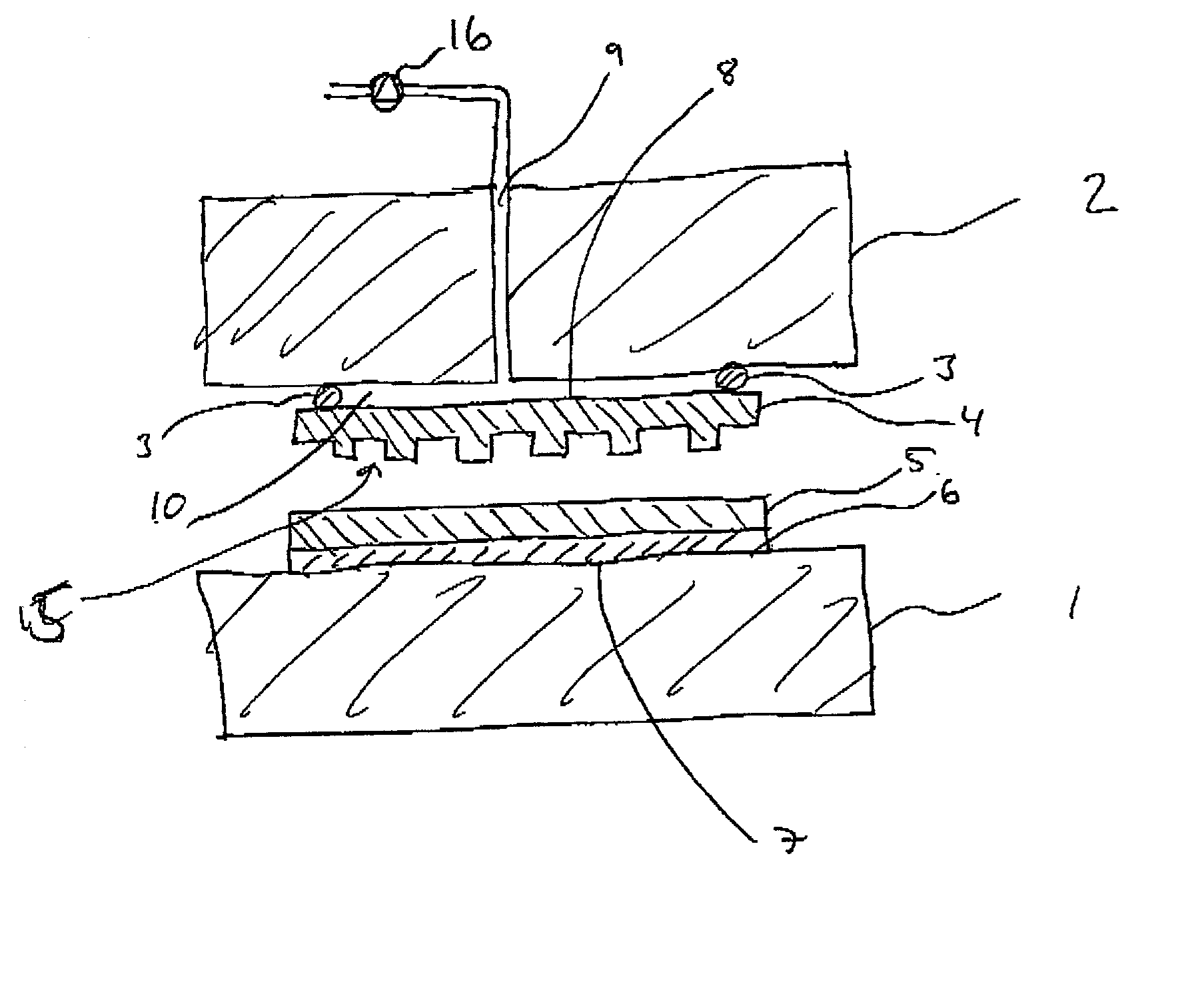
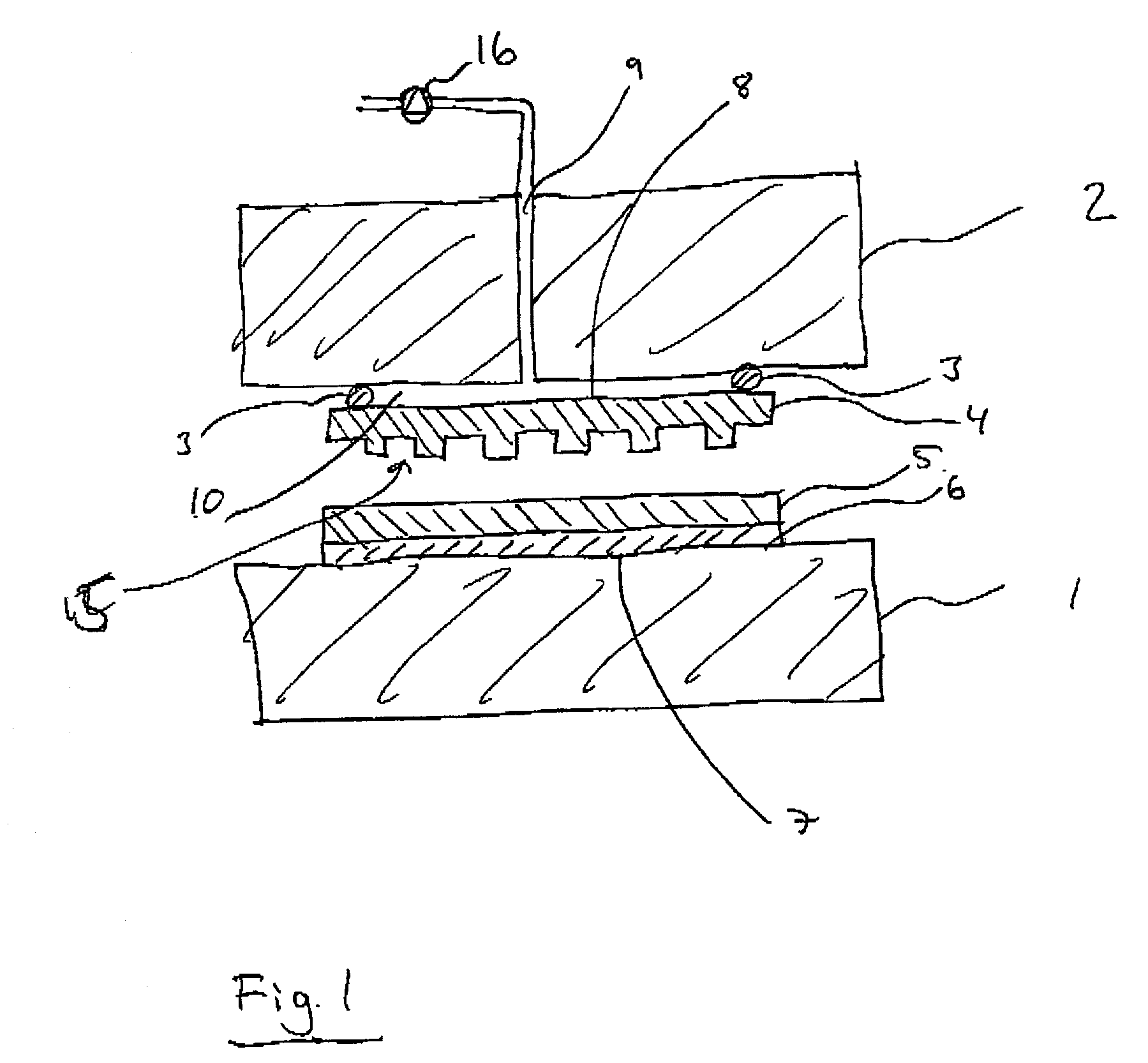
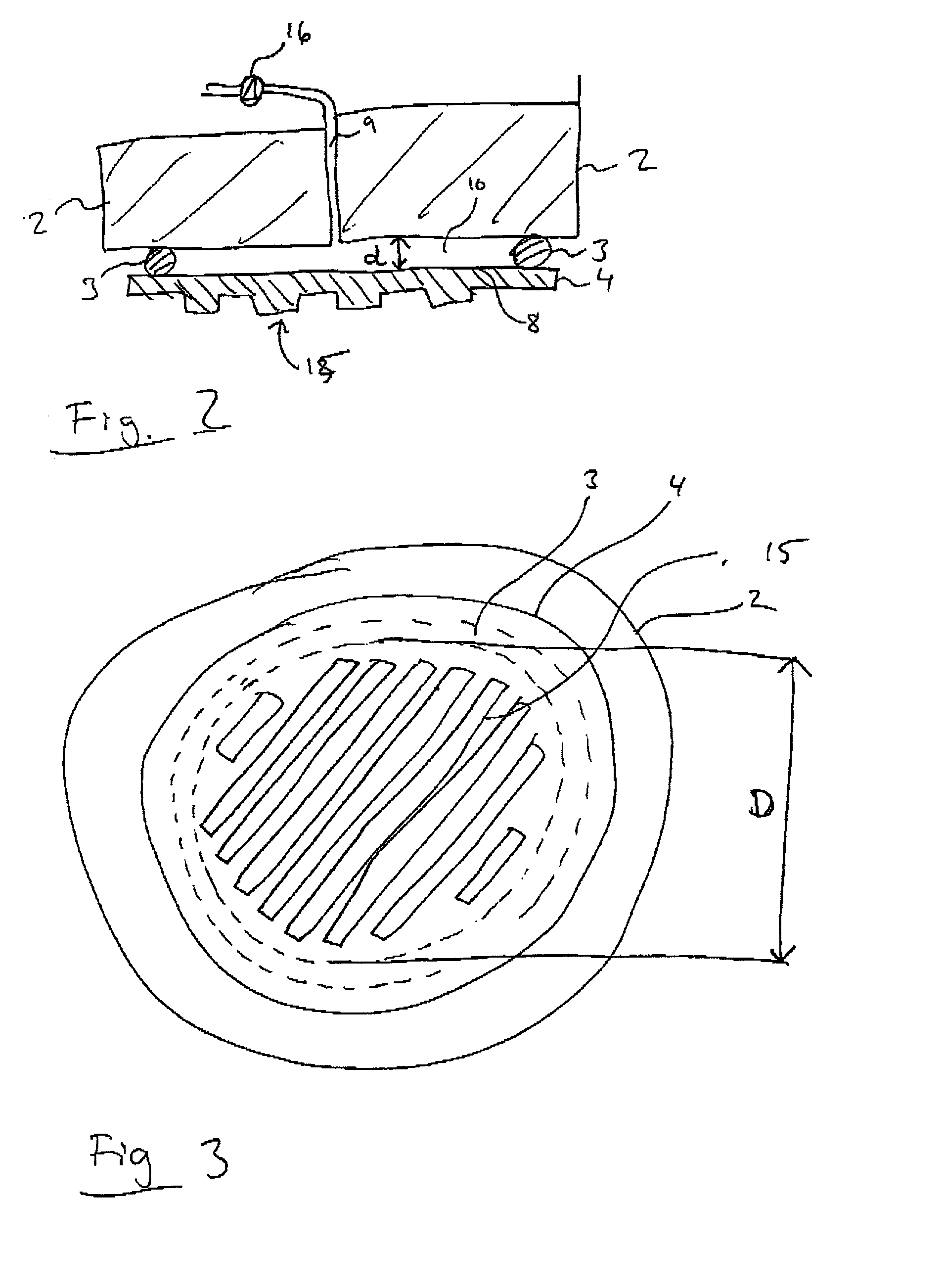
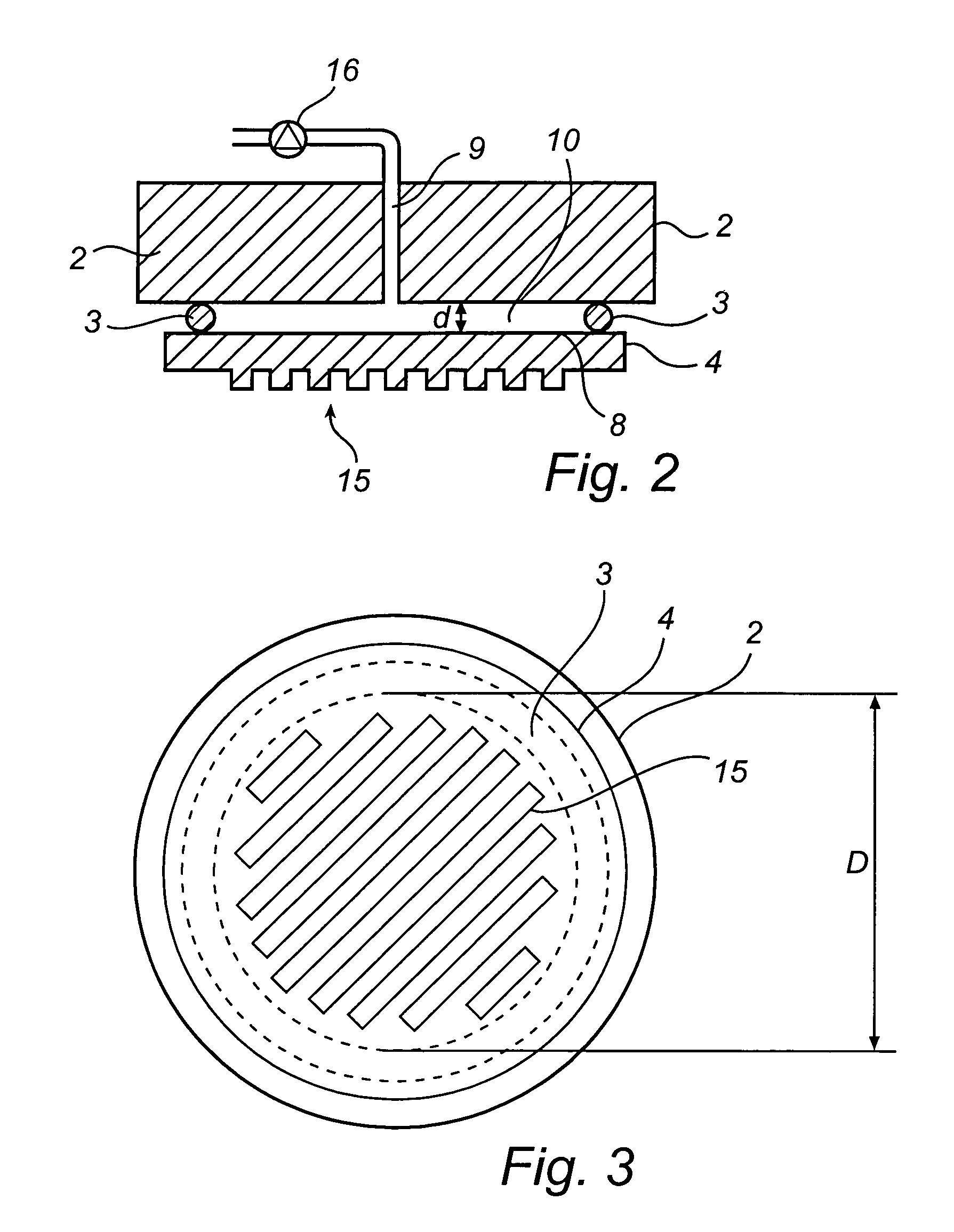
Imprint method and device
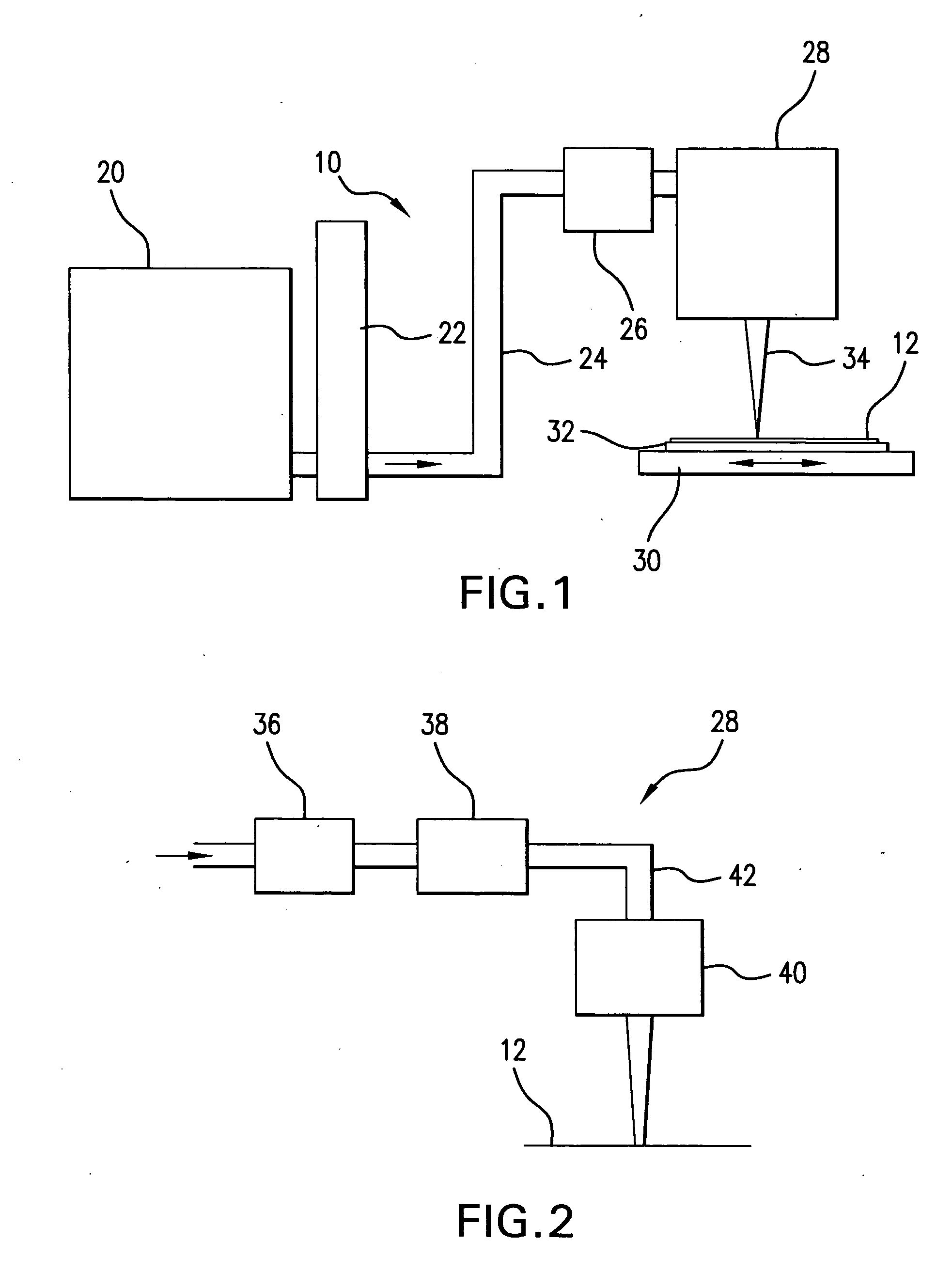
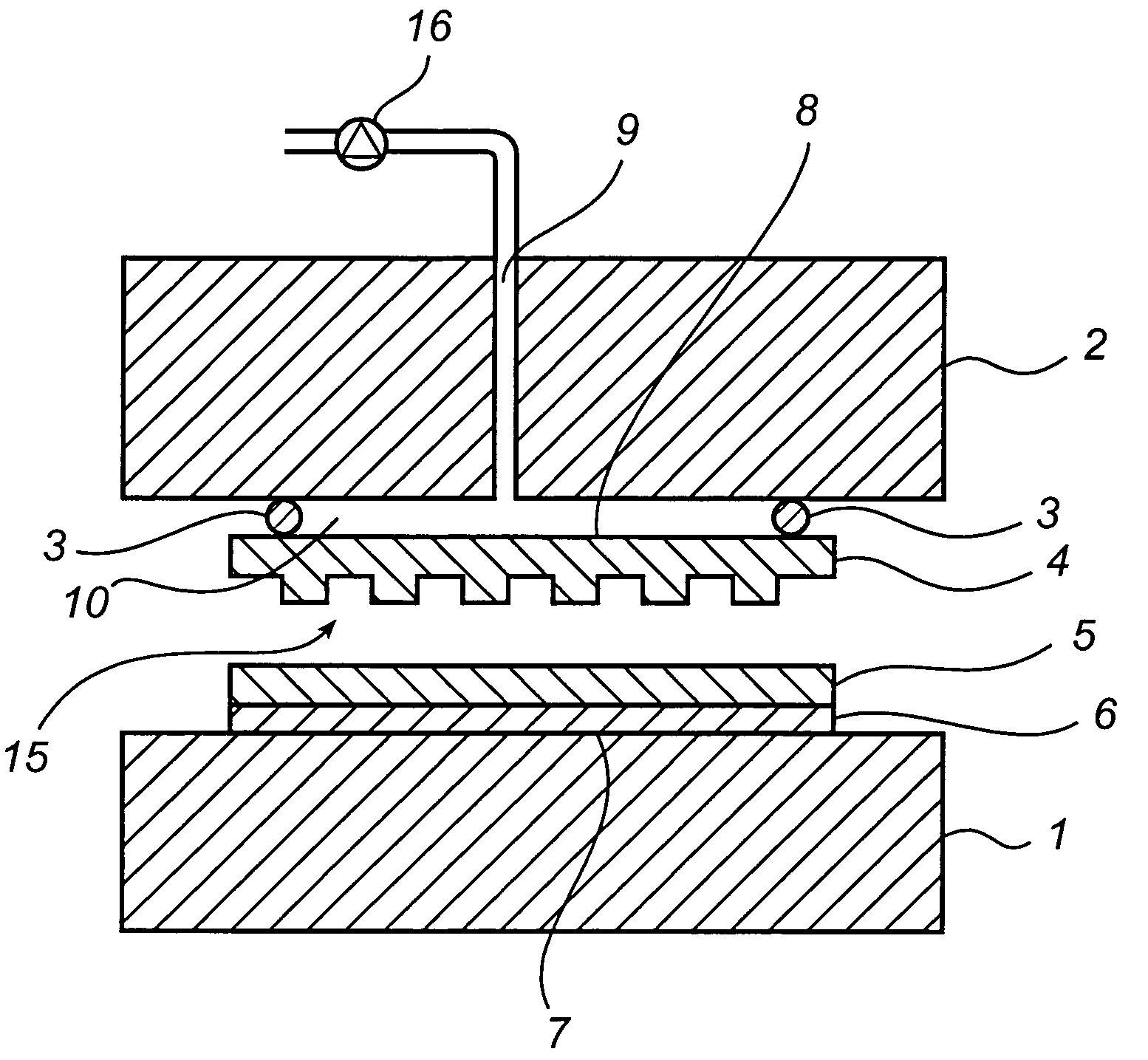
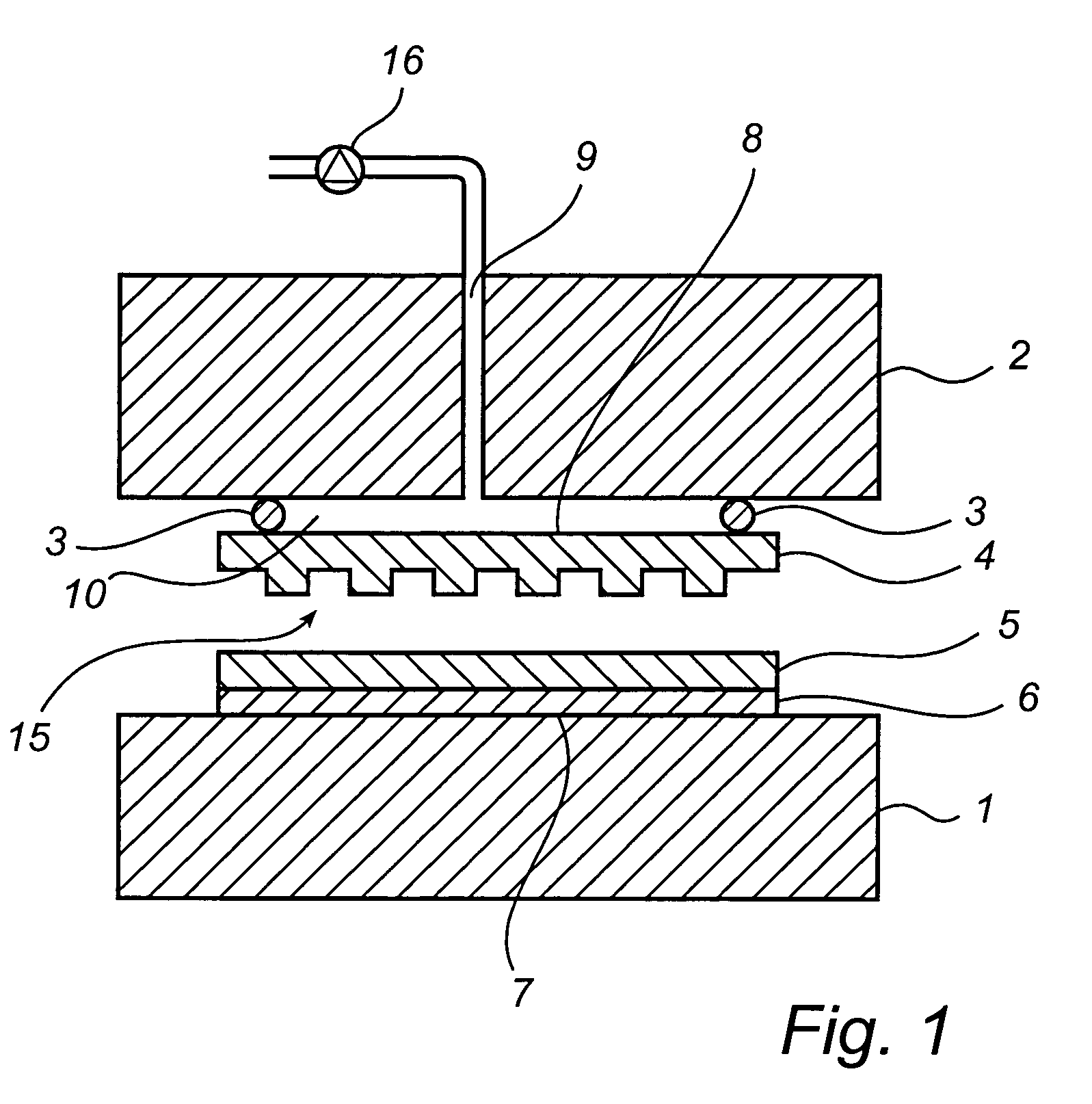
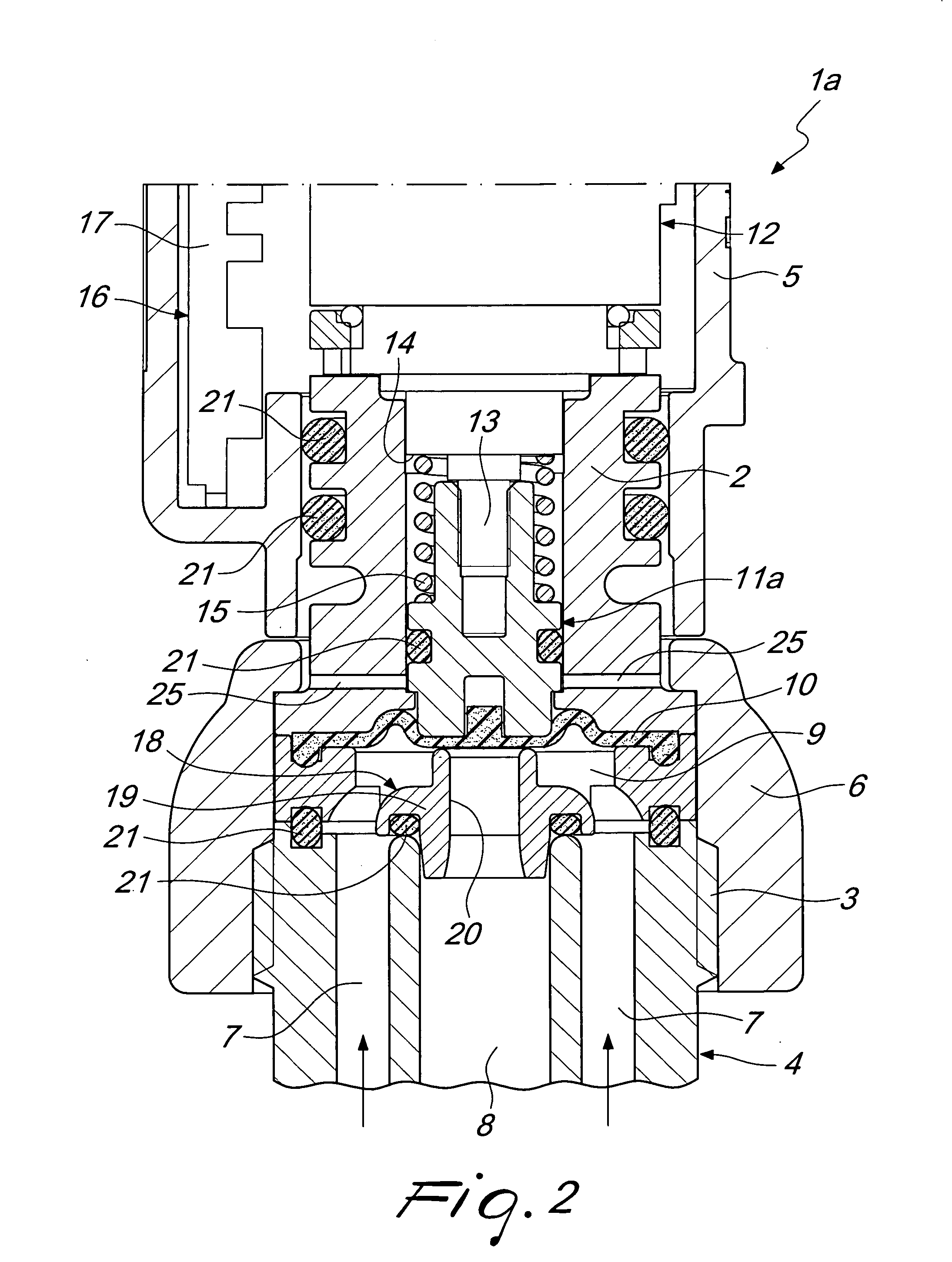
An imprint process comprises the step of aligning a substrate, supported on a first support member, with a template, supported on a second support member. The substrate has at least one essentially plane surface provided with a moldable film. The template has at least one essentially plane surface provided with a relief pattern. The relief pattern is adapted to interact with the moldable film. The process further comprises the step of arranging a sealing gasket between the template and the second support member, such that a pressure cavity is defined by the second support member, the template and the sealing gasket. The process also comprises the step of applying a static gas pressure to the pressure cavity, in order to provide a pressure between the template and the substrate. The pressure is sufficient to form a pattern in the moldable film. An imprint device is also disclosed.
Owner:OBDUCAT AB SE
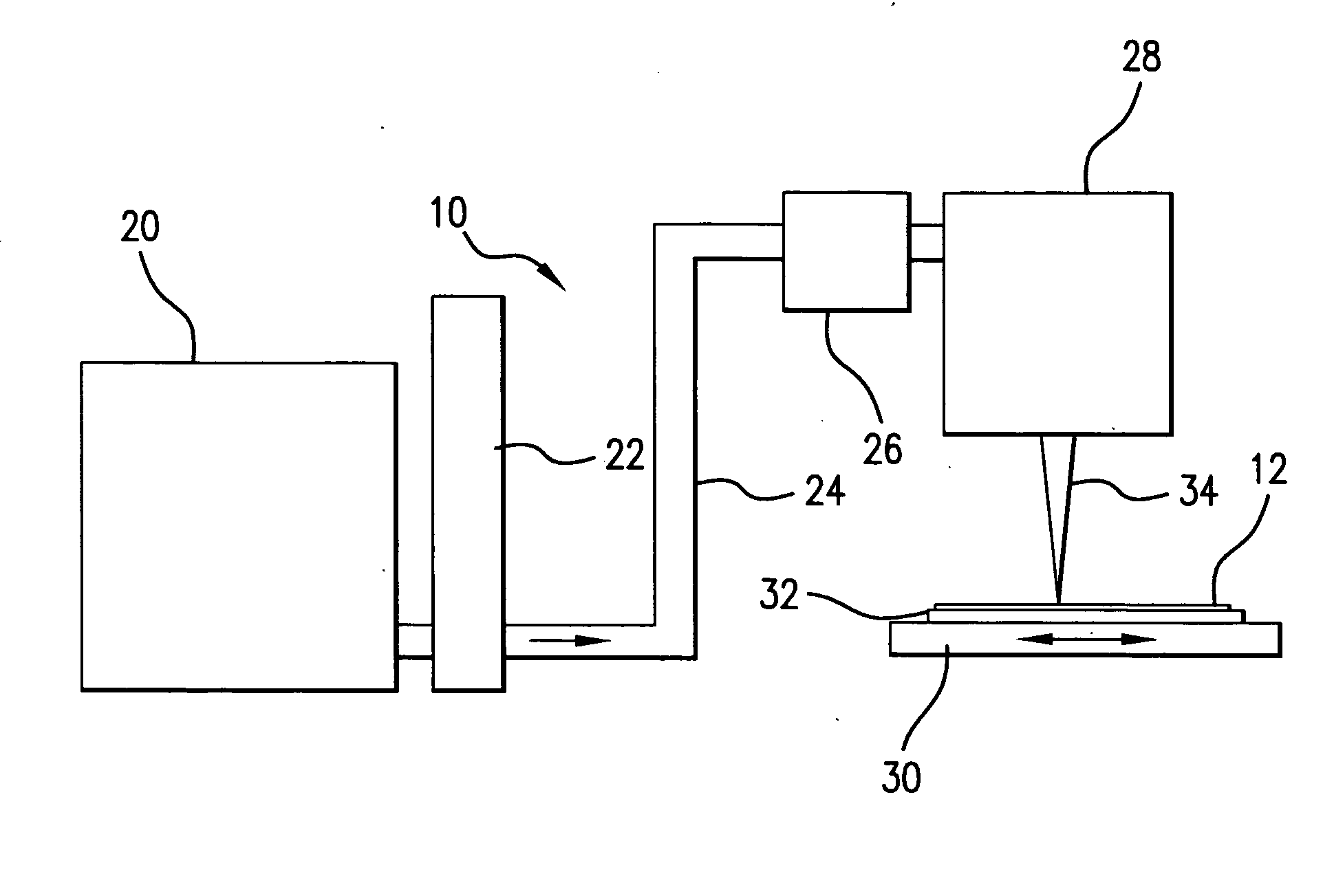
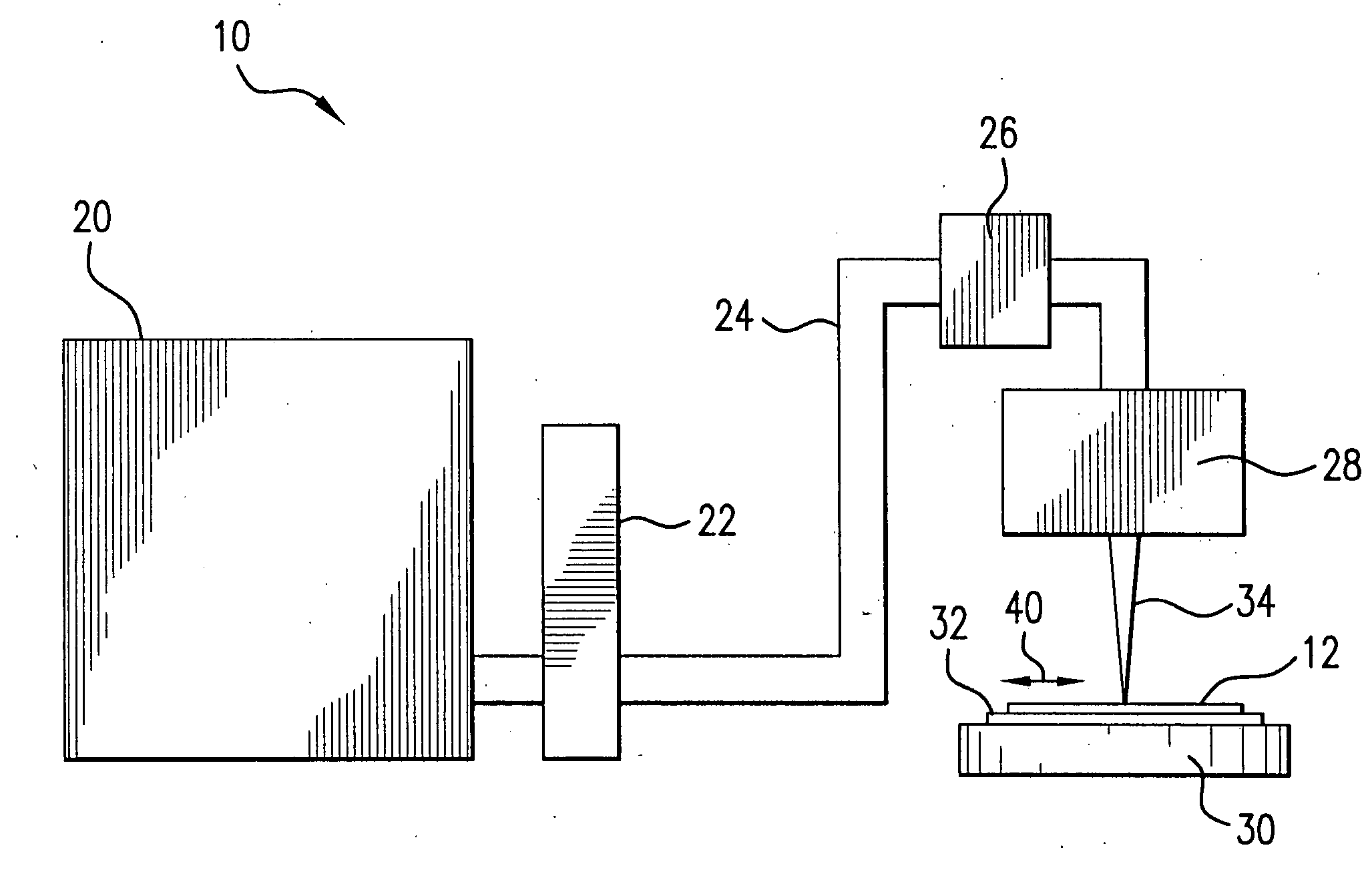
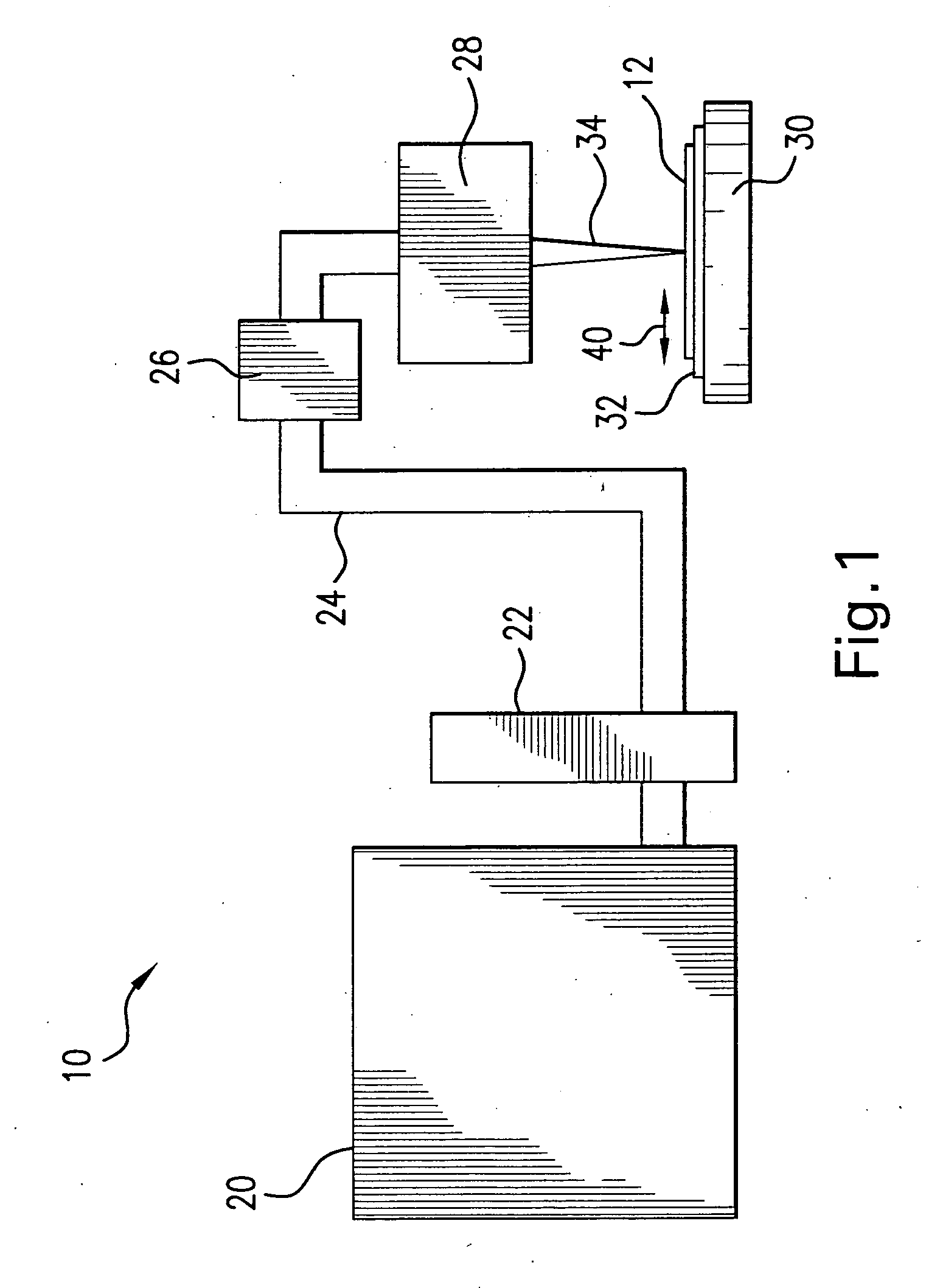
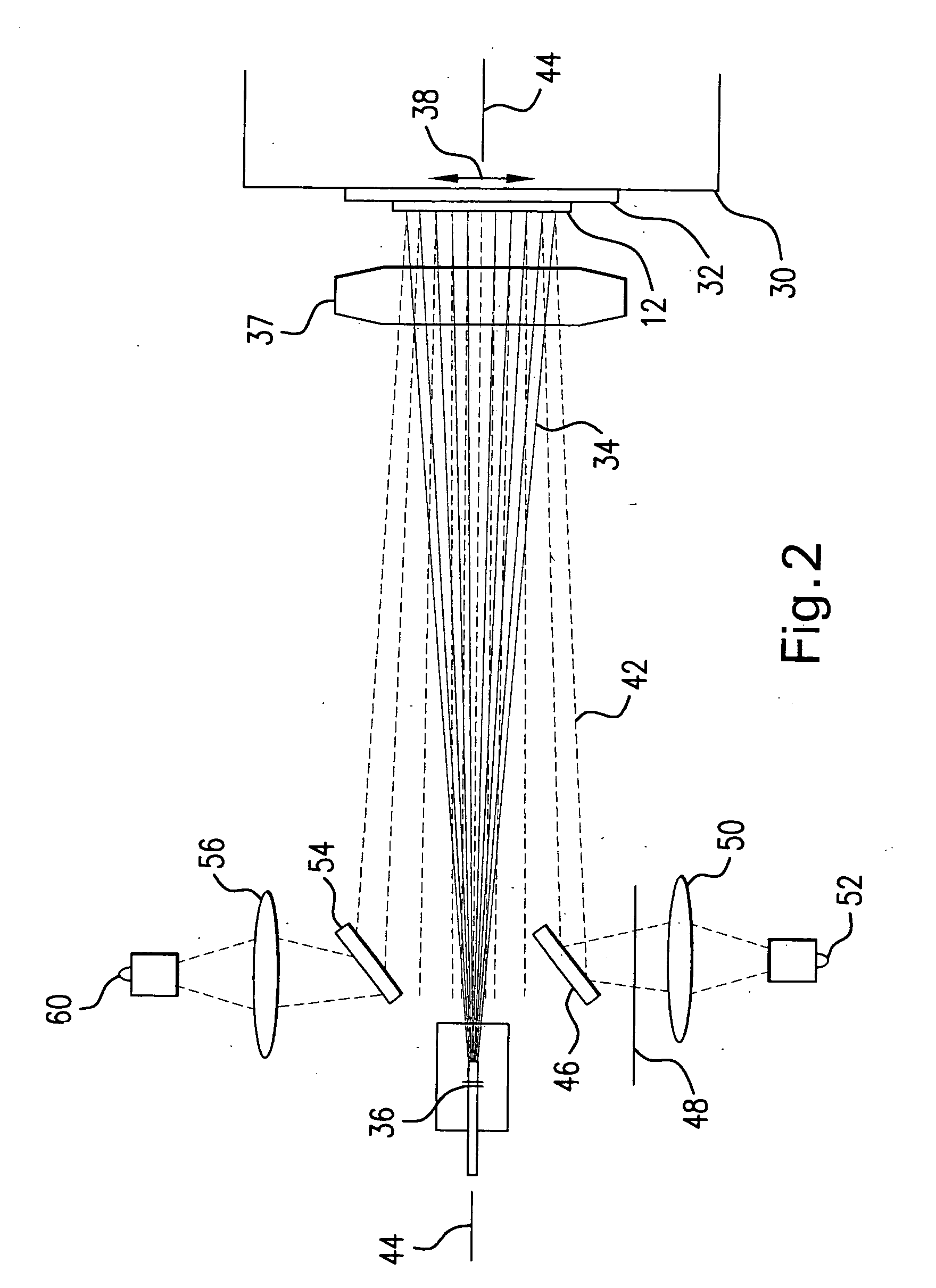
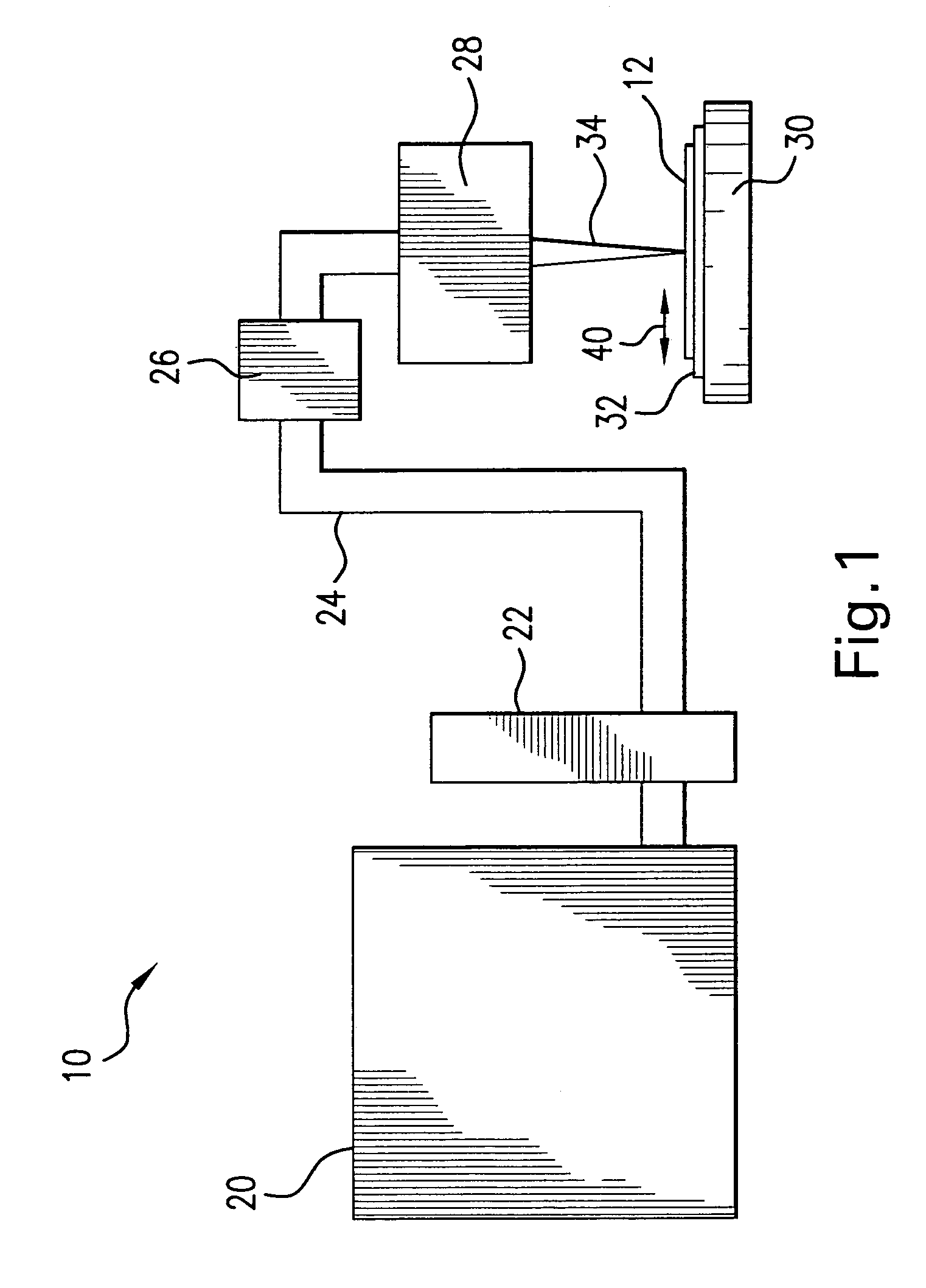
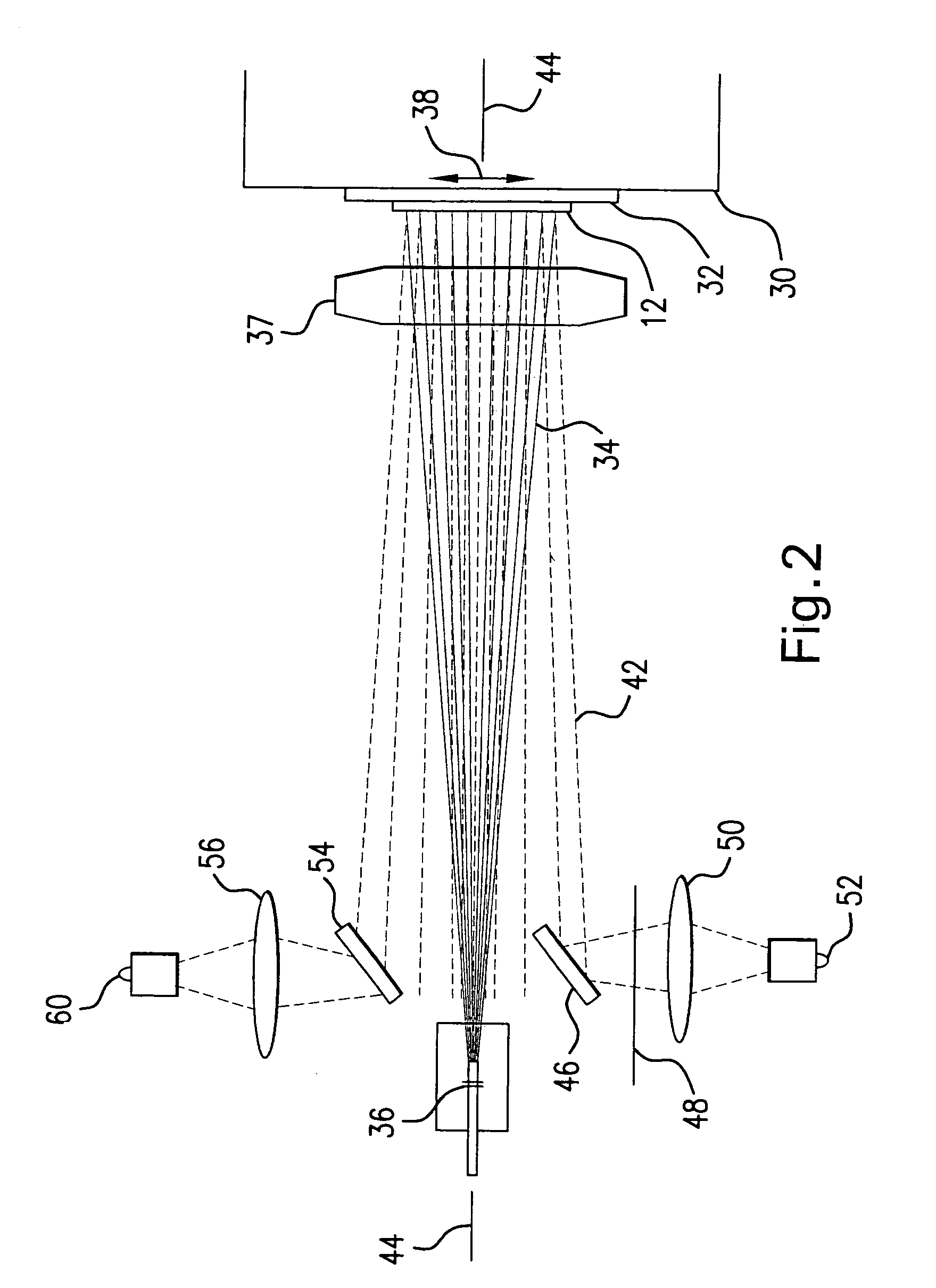
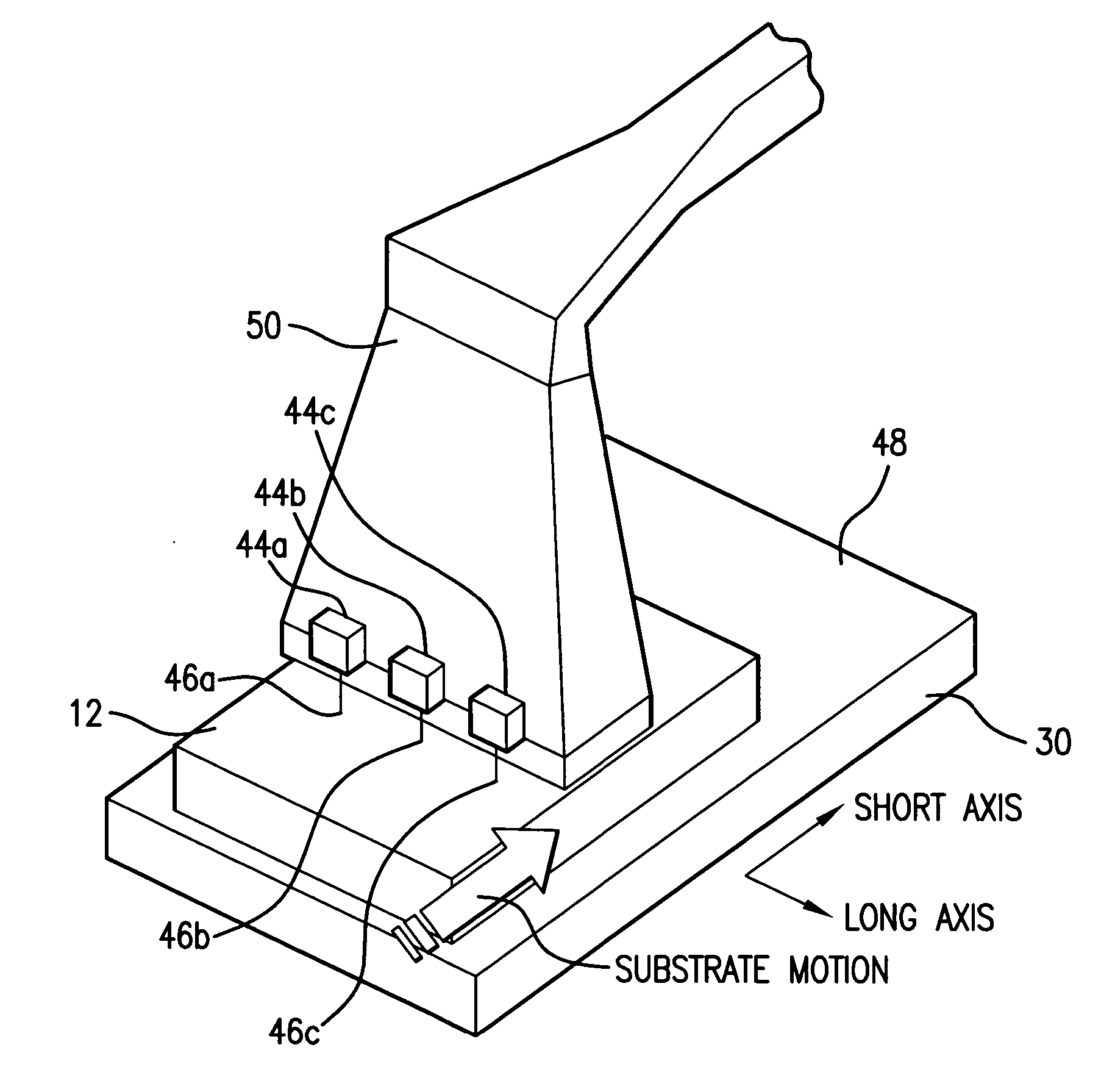
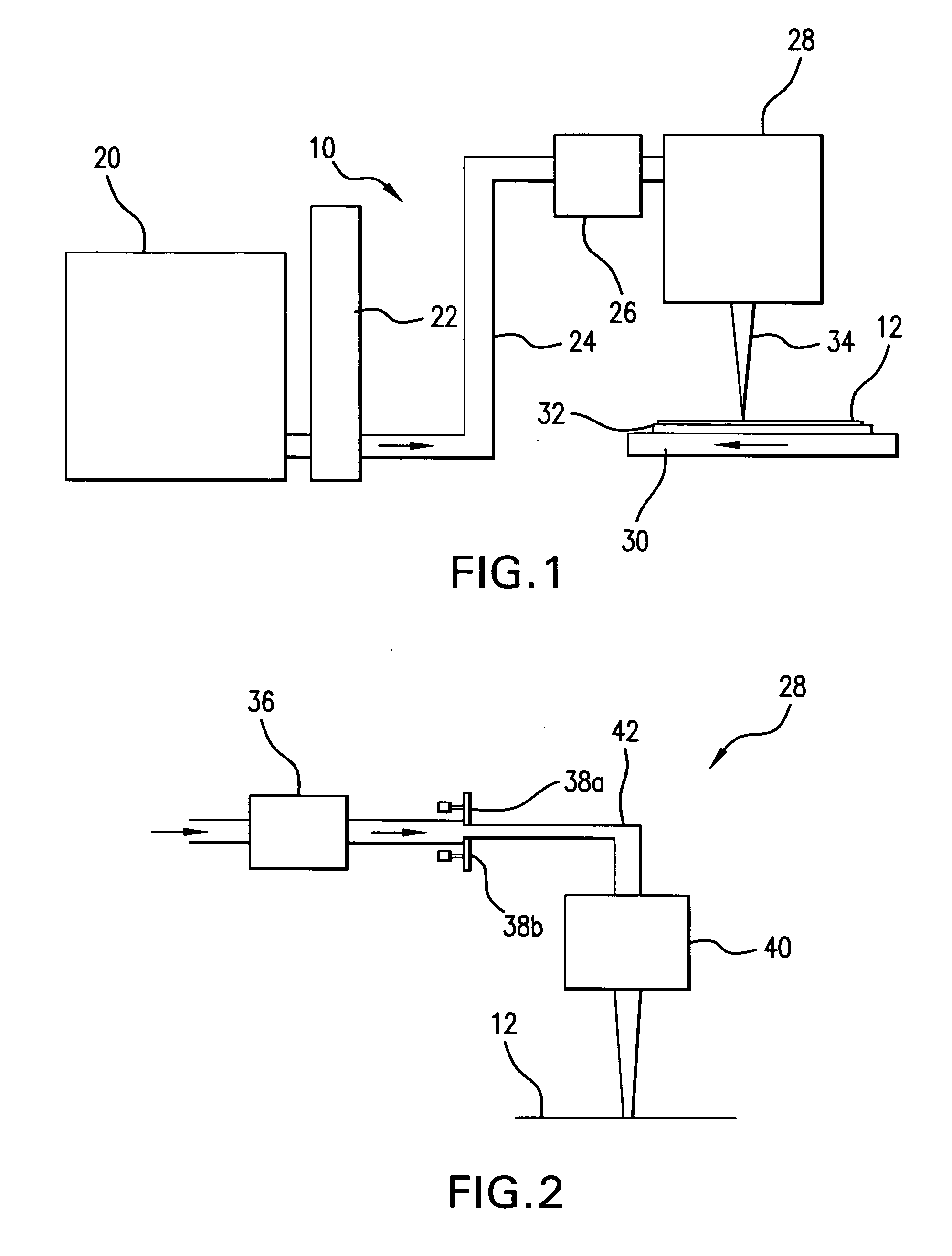
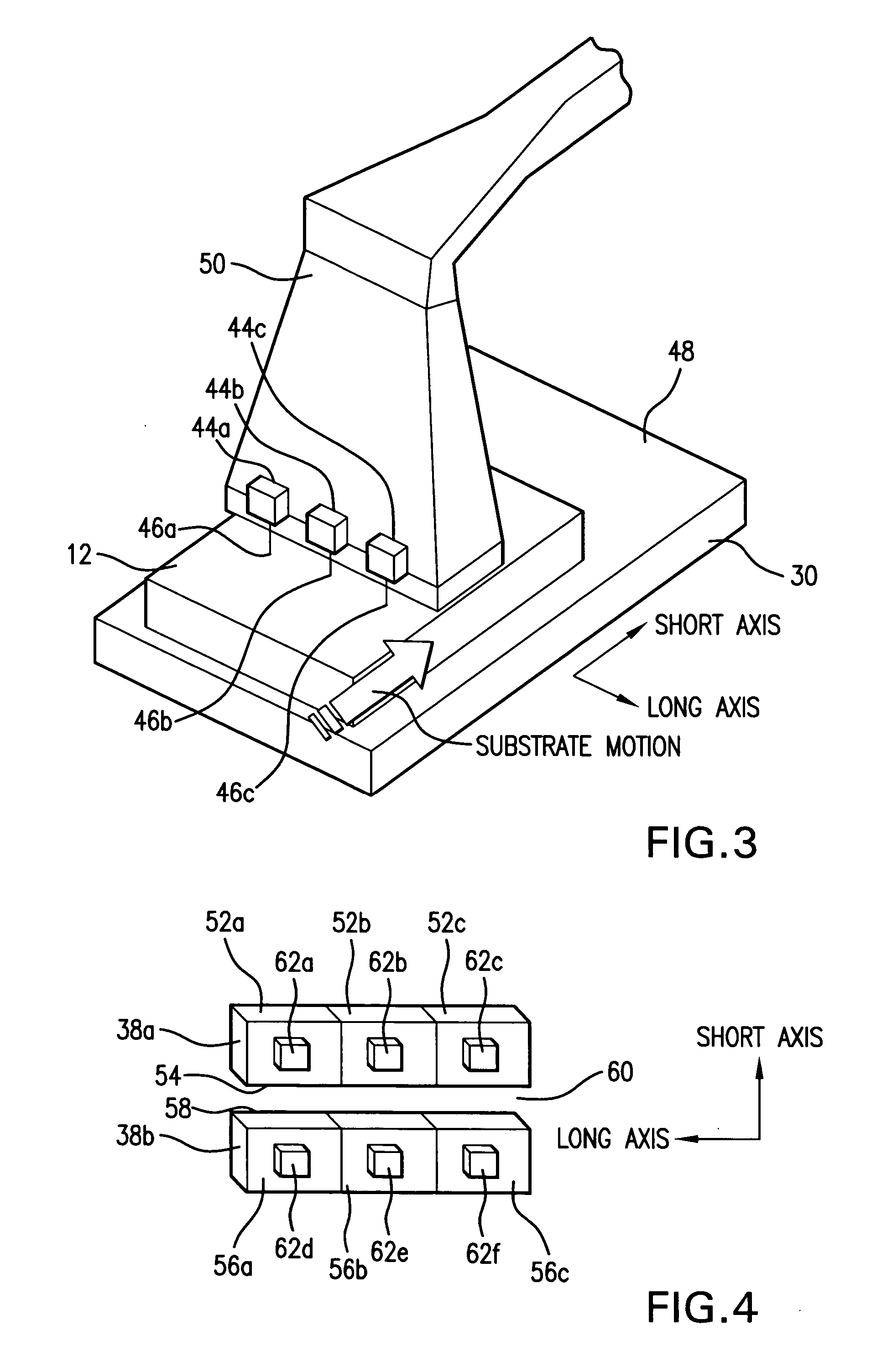
Systems and methods for generating laser light shaped as a line beam
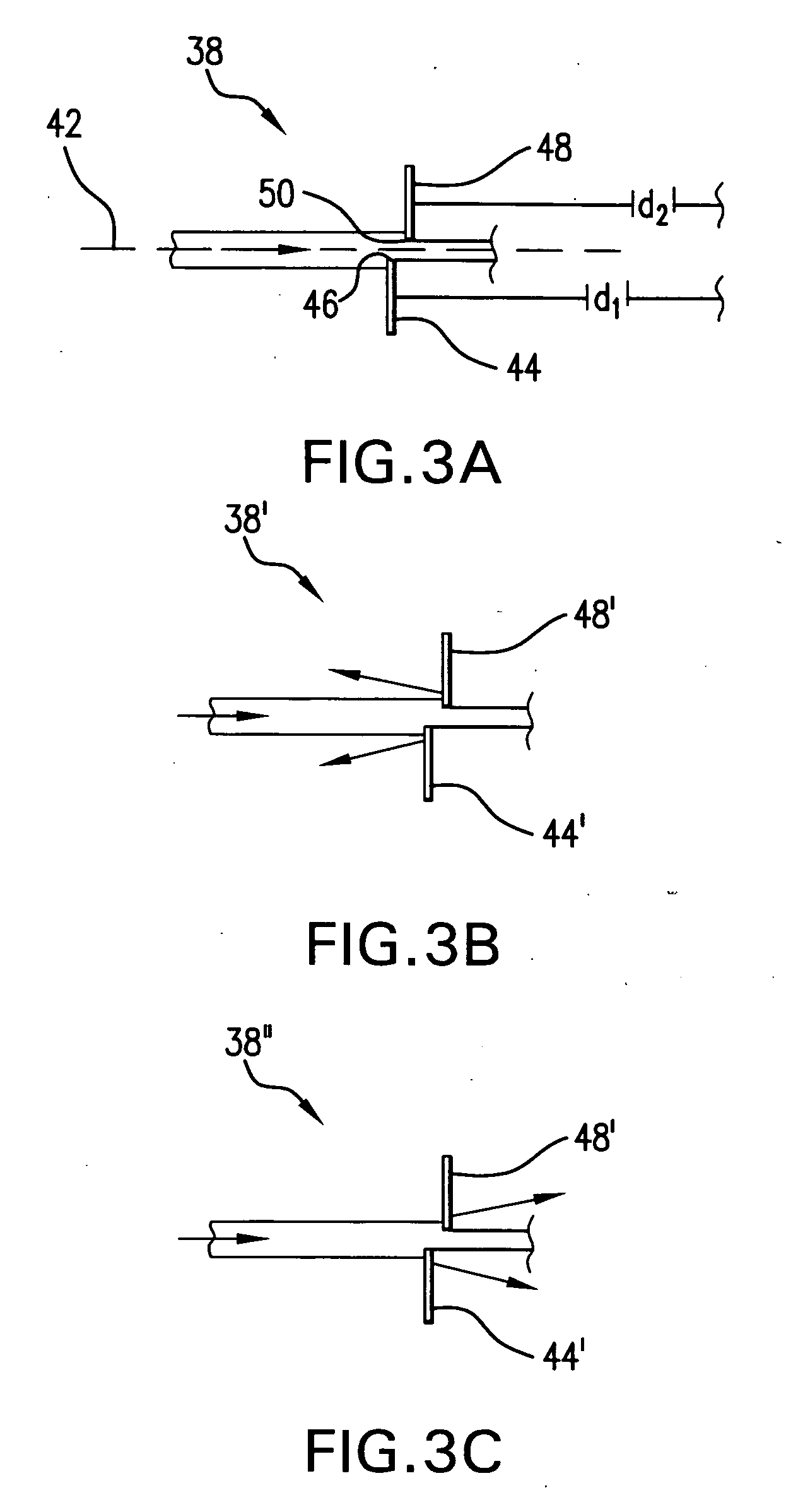
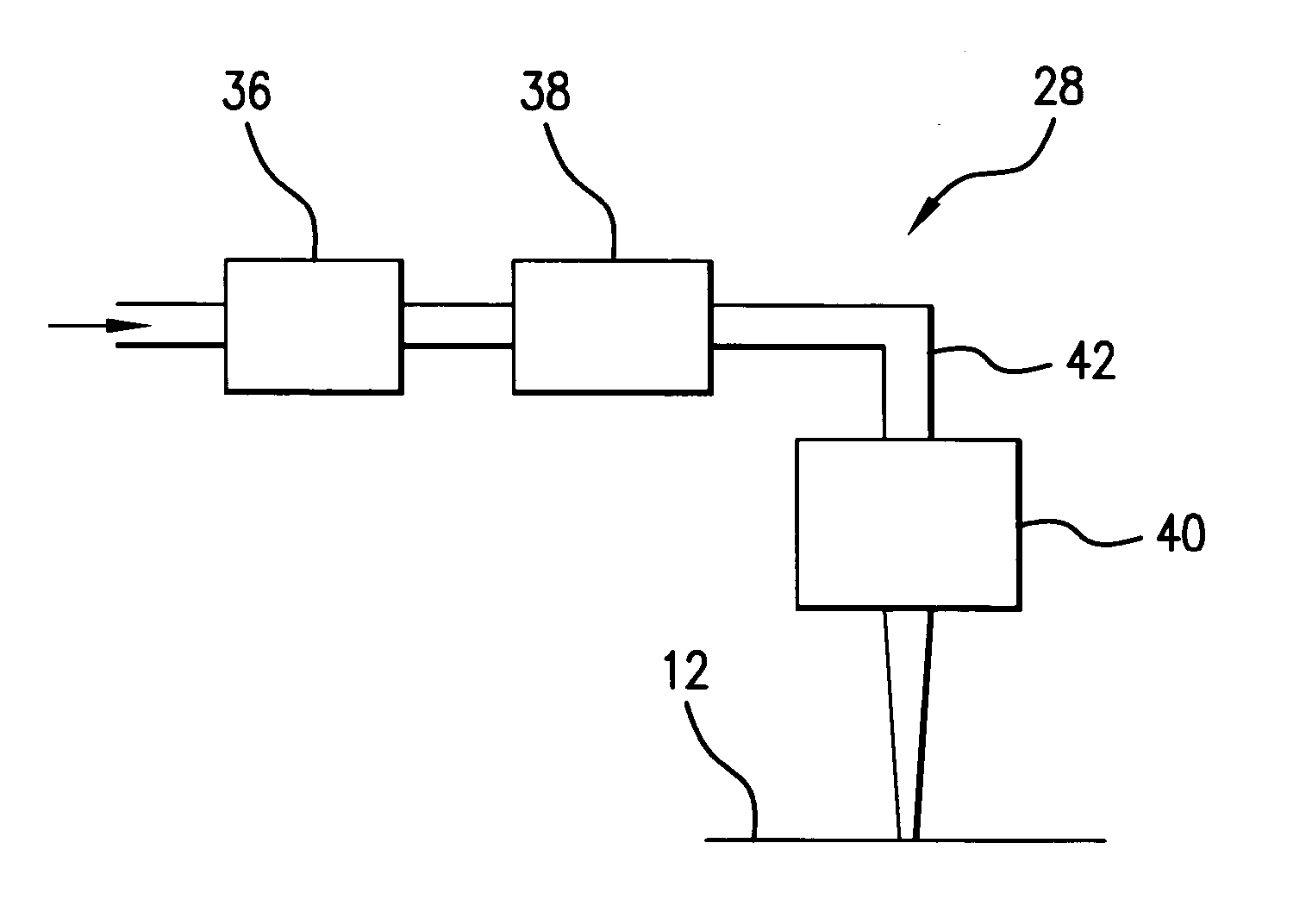
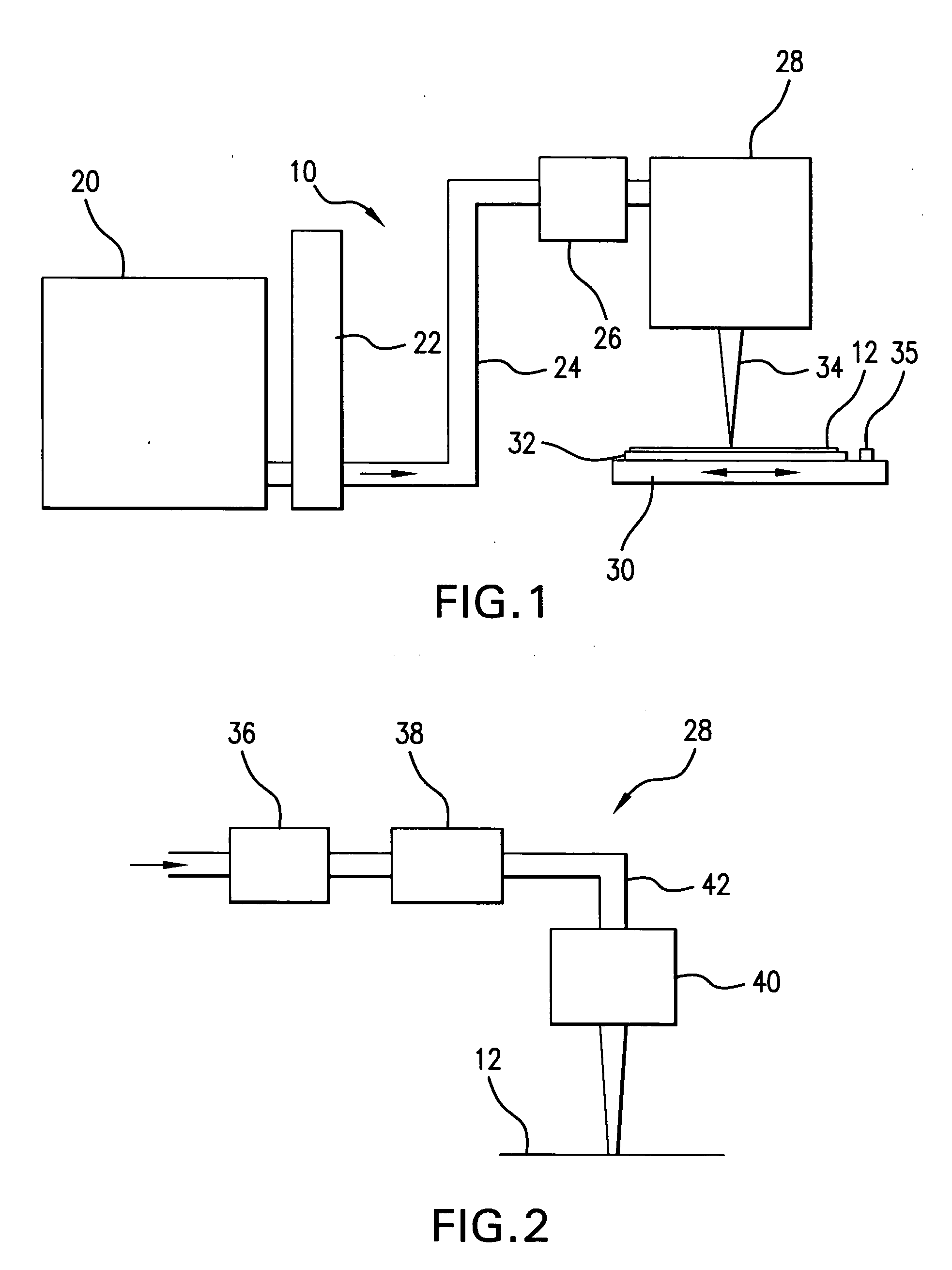
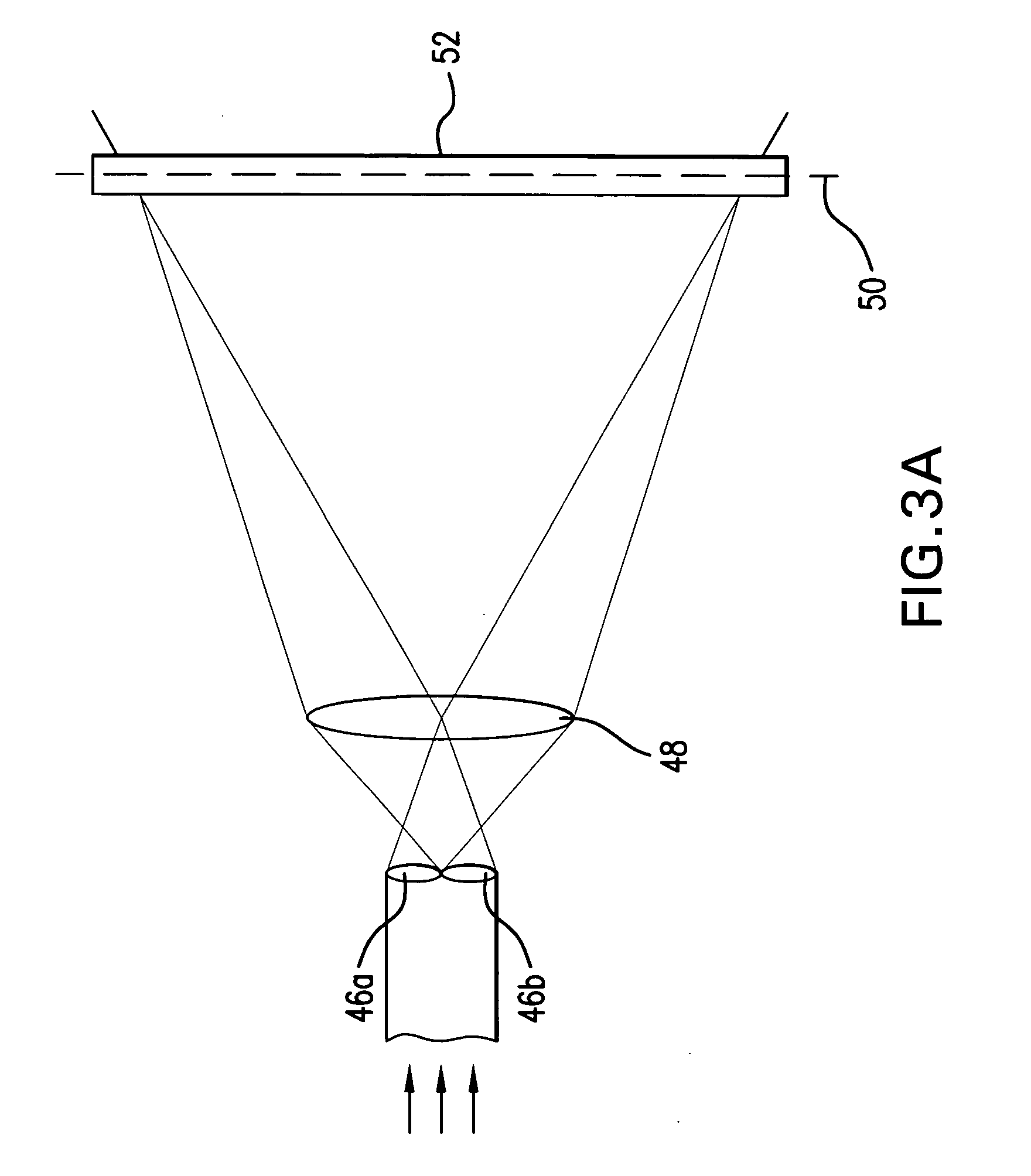
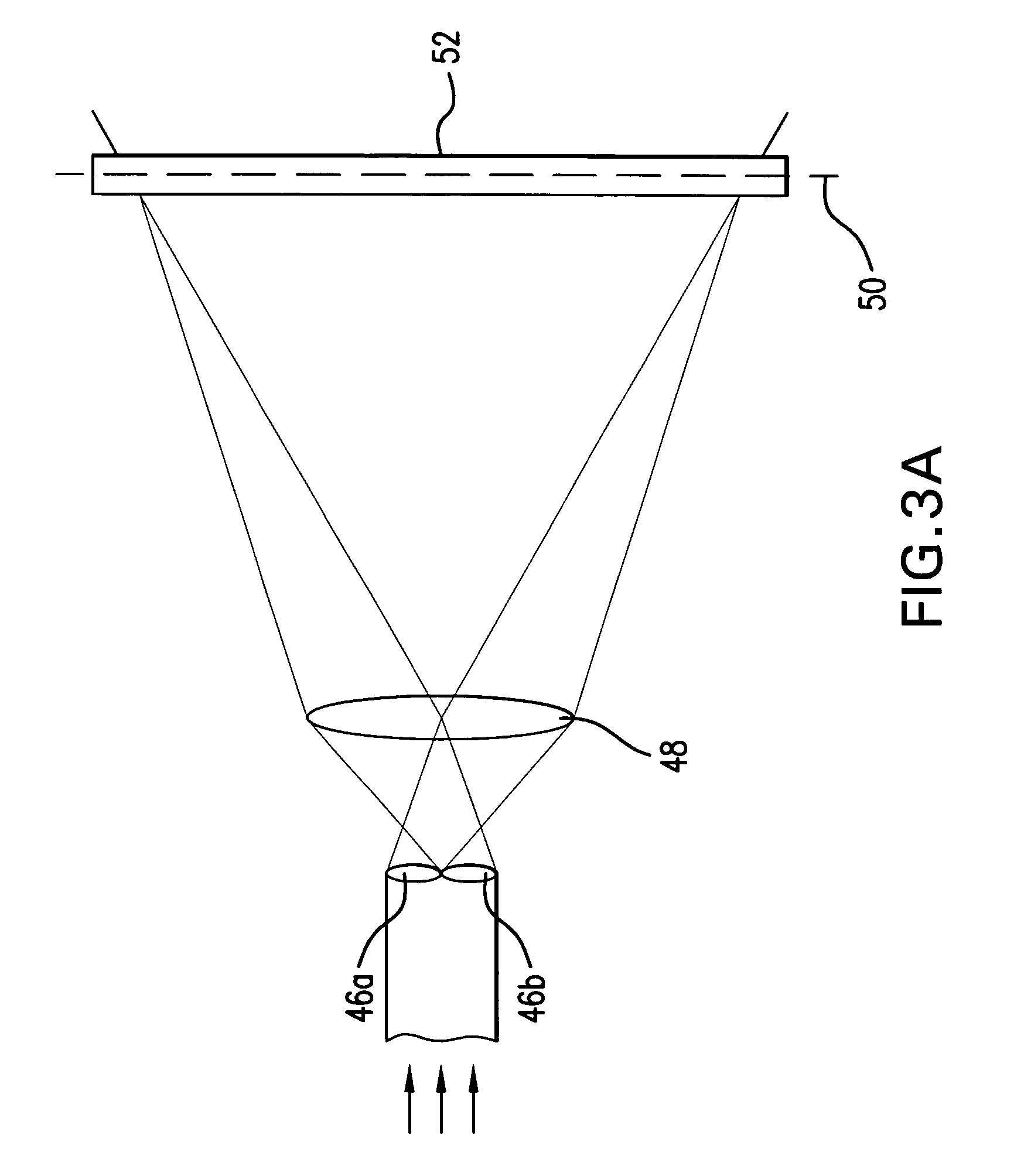
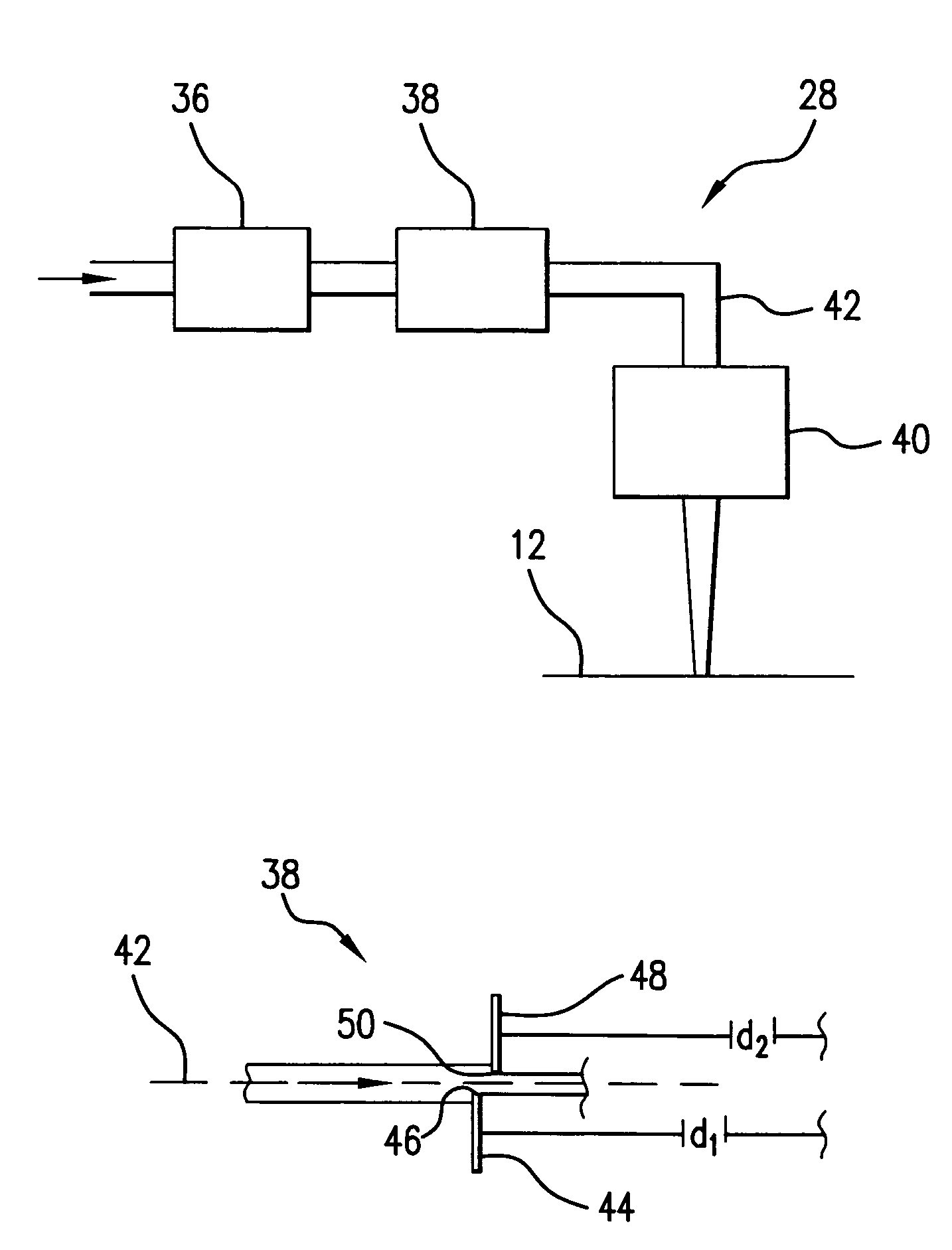
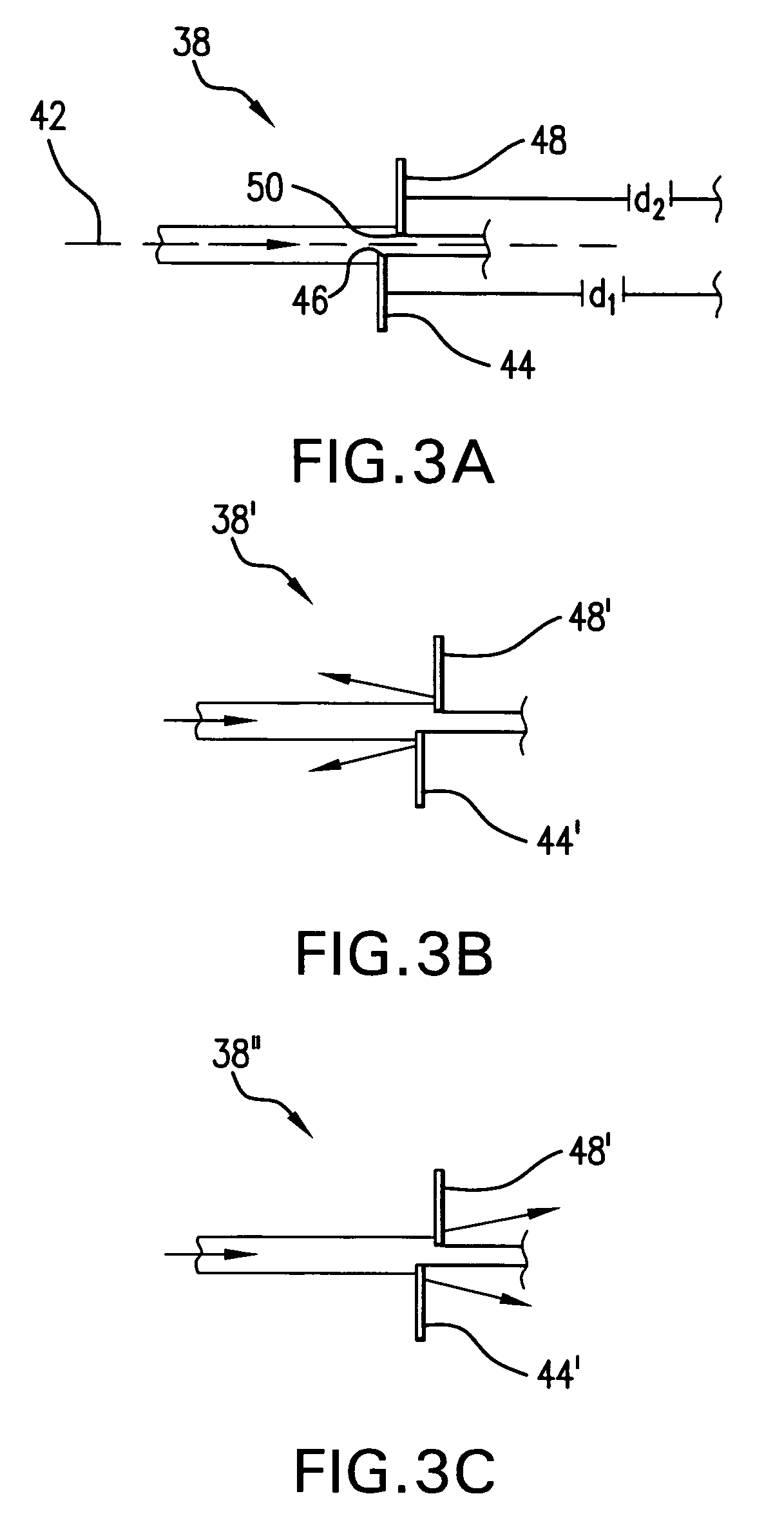
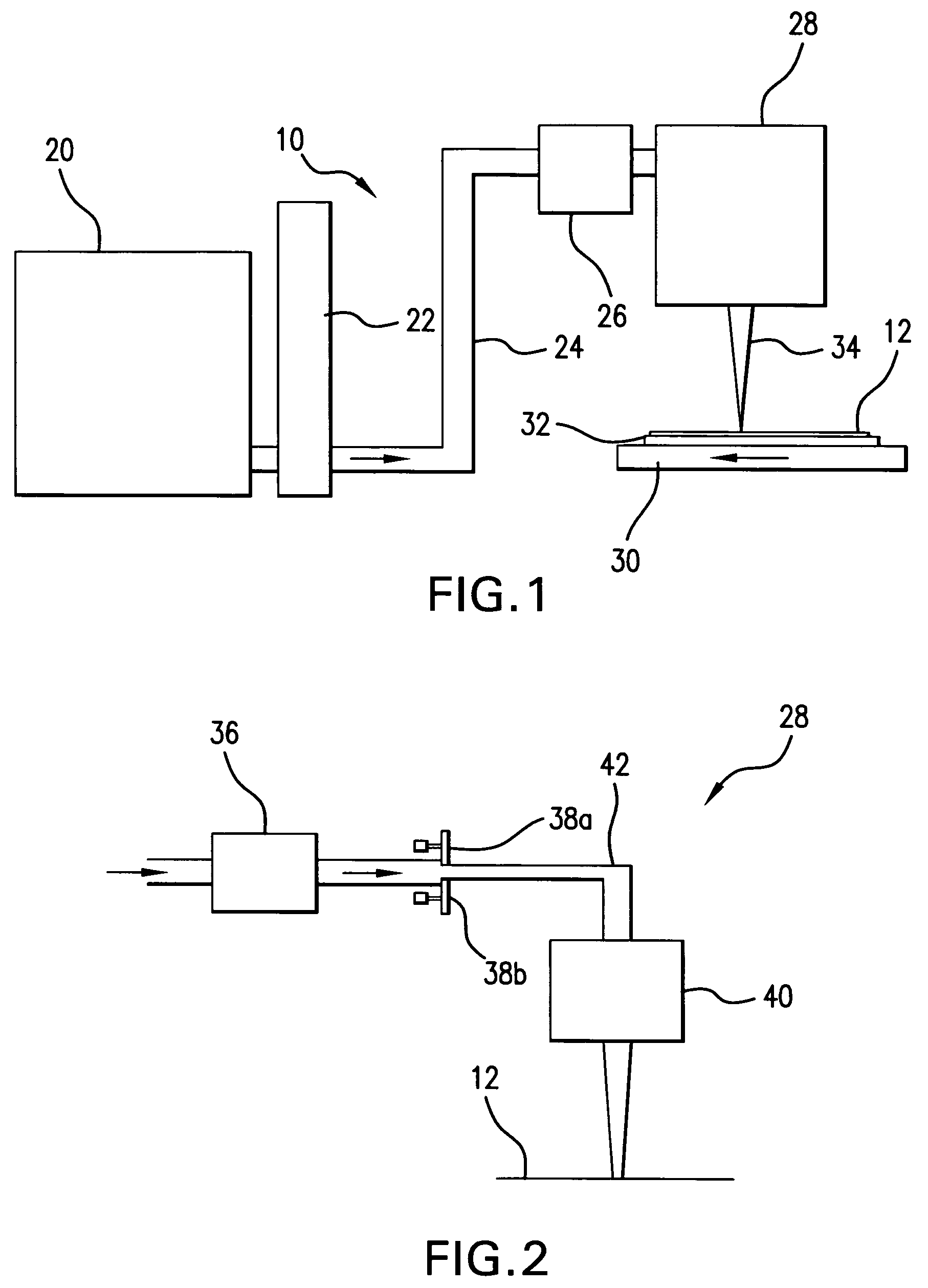
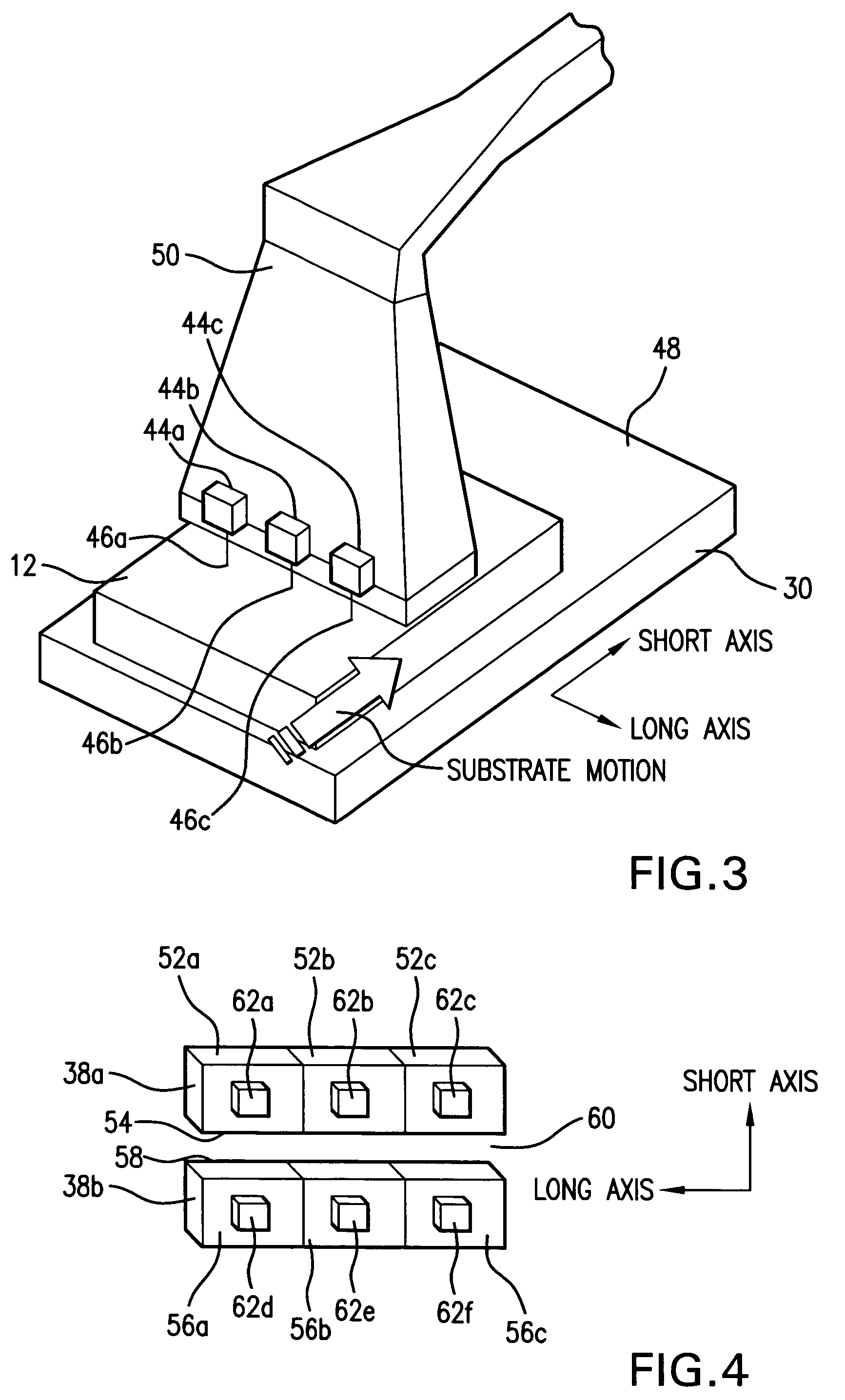
Systems and methods are disclosed for shaping a laser beam for interaction with a film in which the laser beam travels along a beam path and defines a short-axis and a long-axis. In one aspect, the system may include a first short-axis element having an edge positioned at a distance, d1, along the beam path from the film and a second short-axis element having an edge positioned at a distance, d2, along the beam path from the film, with d2<d1. An optic may be positioned along the beam path between the second element and the film for focusing the beam in the short-axis for interaction with the film. In another aspect, a system may be provided having a mechanism operative to selectively adjust the curvature of one or both of the edges of the short-axis element.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
Imprint method and device
InactiveUS7144539B2Eliminate disadvantagesConfectioneryNanoinformaticsShell moldingMembrane interaction
An imprint process comprises the step of aligning a substrate, supported on a first support member, with a template, supported on a second support member. The substrate has at least one essentially plane surface provided with a moldable film. The template has at least one essentially plane surface provided with a relief pattern. The relief pattern is adapted to interact with the moldable film. The process further comprises the step of arranging a sealing gasket between the template and the second support member, such that a pressure cavity is defined by the second support member, the template and the sealing gasket. The process also comprises the step of applying a static gas pressure to the pressure cavity, in order to provide a pressure between the template and the substrate. The pressure is sufficient to form a pattern in the moldable film. An imprint device is also disclosed.
Owner:OBDUCAT AB SE
Systems and methods for implementing an interaction between a laser shaped as a line beam and a film deposited on a substrate
Systems and methods are disclosed for focusing a beam for an interaction with a film deposited on a substrate wherein the focused beam defines a short axis and a long axis. In one aspect, the system may include a detecting system to analyze light reflected from the film on an image plane to determine whether the beam is focused in the short axis at the film. In still another aspect, a system may be provided for positioning a film (having an imperfect, non-planar surface) for interaction with a shaped line beam.
Owner:CYMER INC +1
Method for patterning nanoscale patterns of molecules on material surfaces
Probe-based methods for patterning a surface of a material are described. In particular, high resolution patterning of molecules on a surface of a material, such as nano-scale patterns with feature sizes of less than 30 nanometers, are described. In one aspect, a method for patterning a surface of a material includes providing a material having a polymer film. A heated, nano-scale dimensioned probe is then used to desorb molecules upon interacting with the film. The film includes a network of molecules (such as molecular glasses) which are cross-linked via intermolecular (noncovalent) bonds, such as hydrogen bonds.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods to shape laser light as a homogeneous line beam for interaction with a film deposited on a substrate
ActiveUS20070096008A1Reduced intensity variationPhotometry using reference valueLaser detailsMembrane interactionLight beam
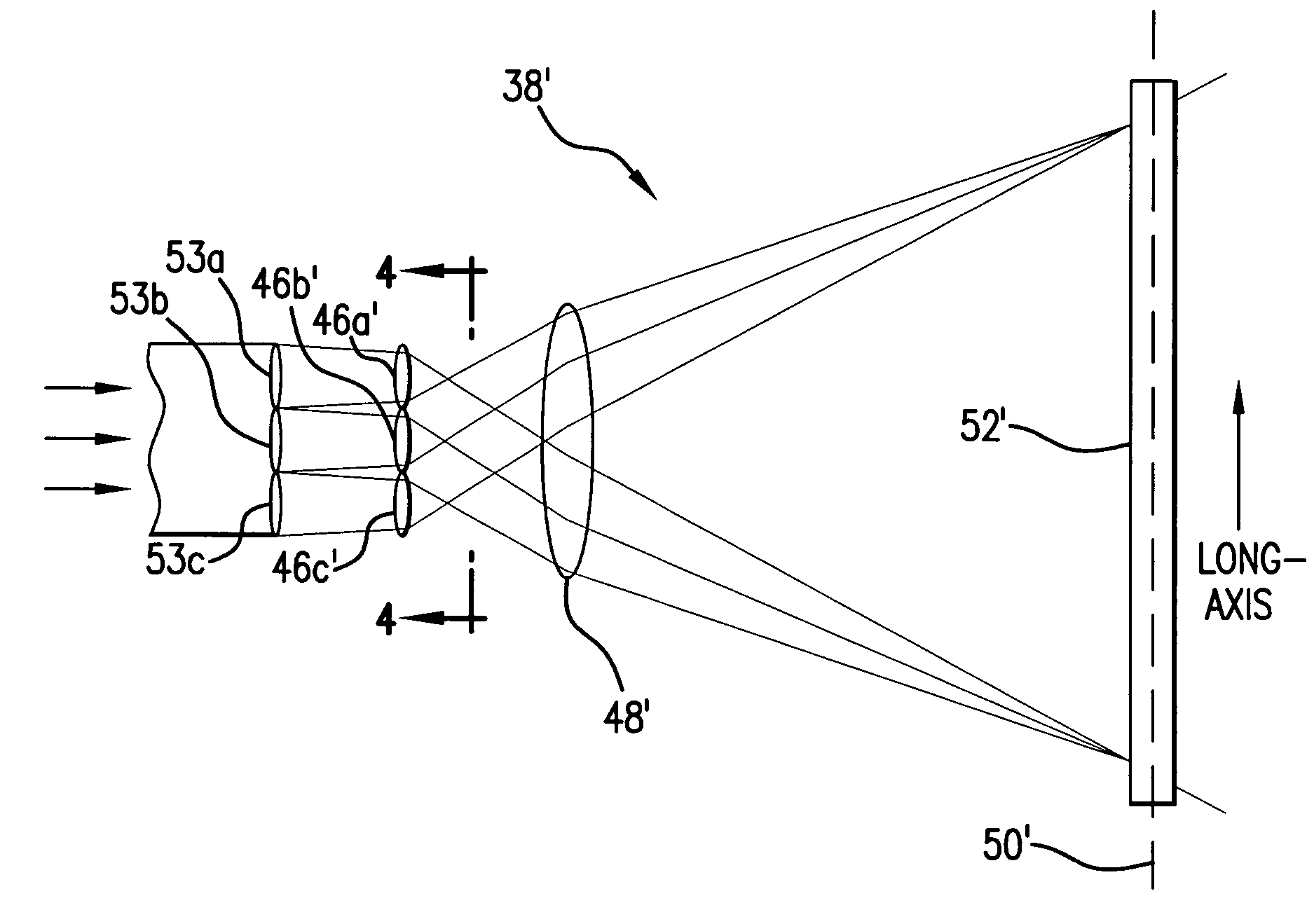
Systems and methods are disclosed for shaping and homogenizing a laser beam for interaction with a film. The shaping and homogenizing system may include a lens array and a lens that is positioned to receive laser light from the lens array and produce a respective elongated image in a plane for each lens in the lens array. In addition, the system may include a beam stop having an edge that is positioned in the plane, and a moveable mount rotating a lens of the lens array to vary an alignment between one of the elongated images and the beam stop edge.
Owner:CYMER INC
Systems and methods to shape laser light as a homogeneous line beam for interaction with a film deposited on a substrate
Owner:CYMER INC
Apparatus for focused electric-field imprinting for micron and sub-micron patterns on wavy or planar surfaces
InactiveUS7998323B1Small sizeEliminate processing stepsElectrolysis componentsElectrical conductorMembrane interaction
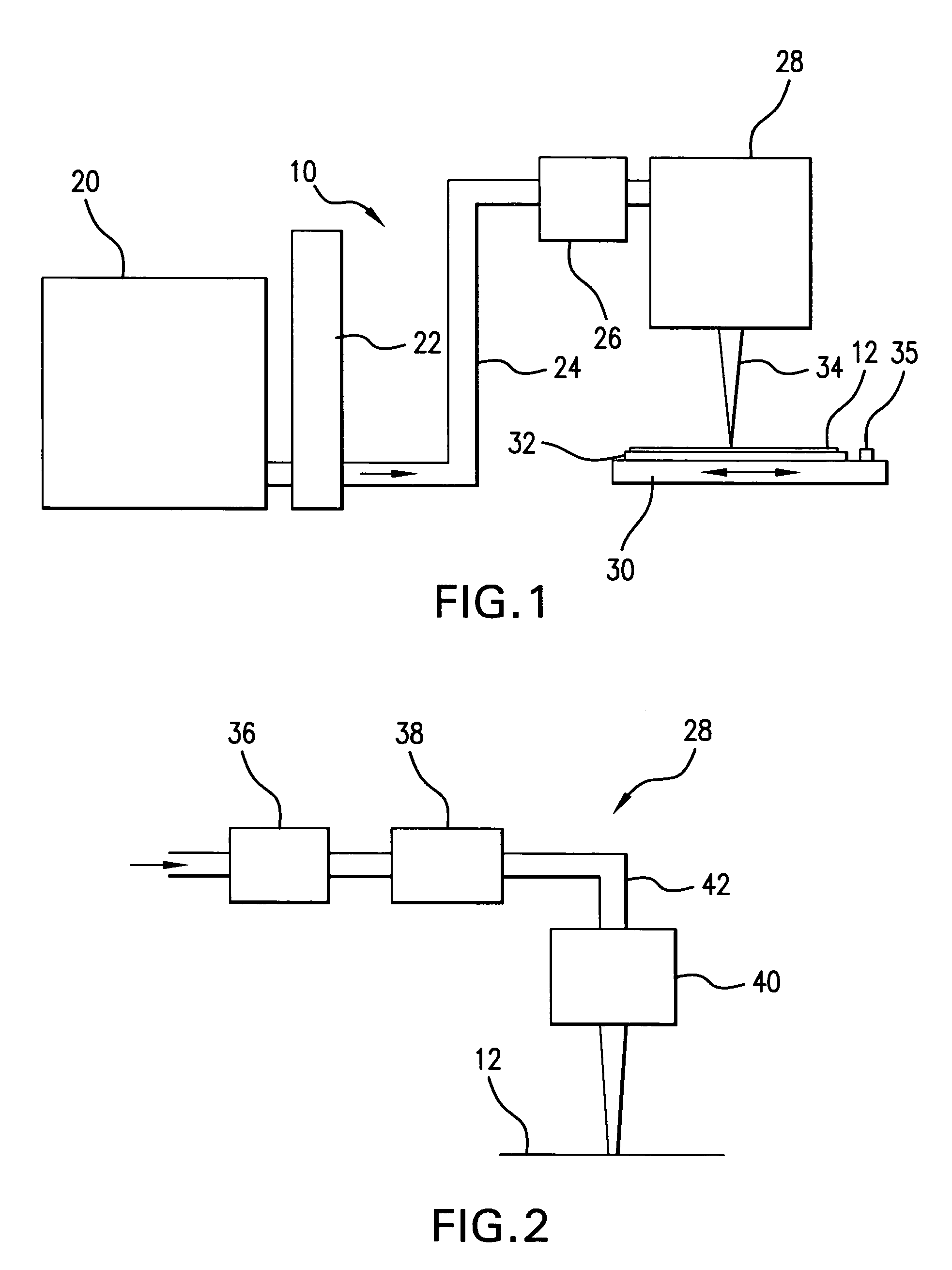
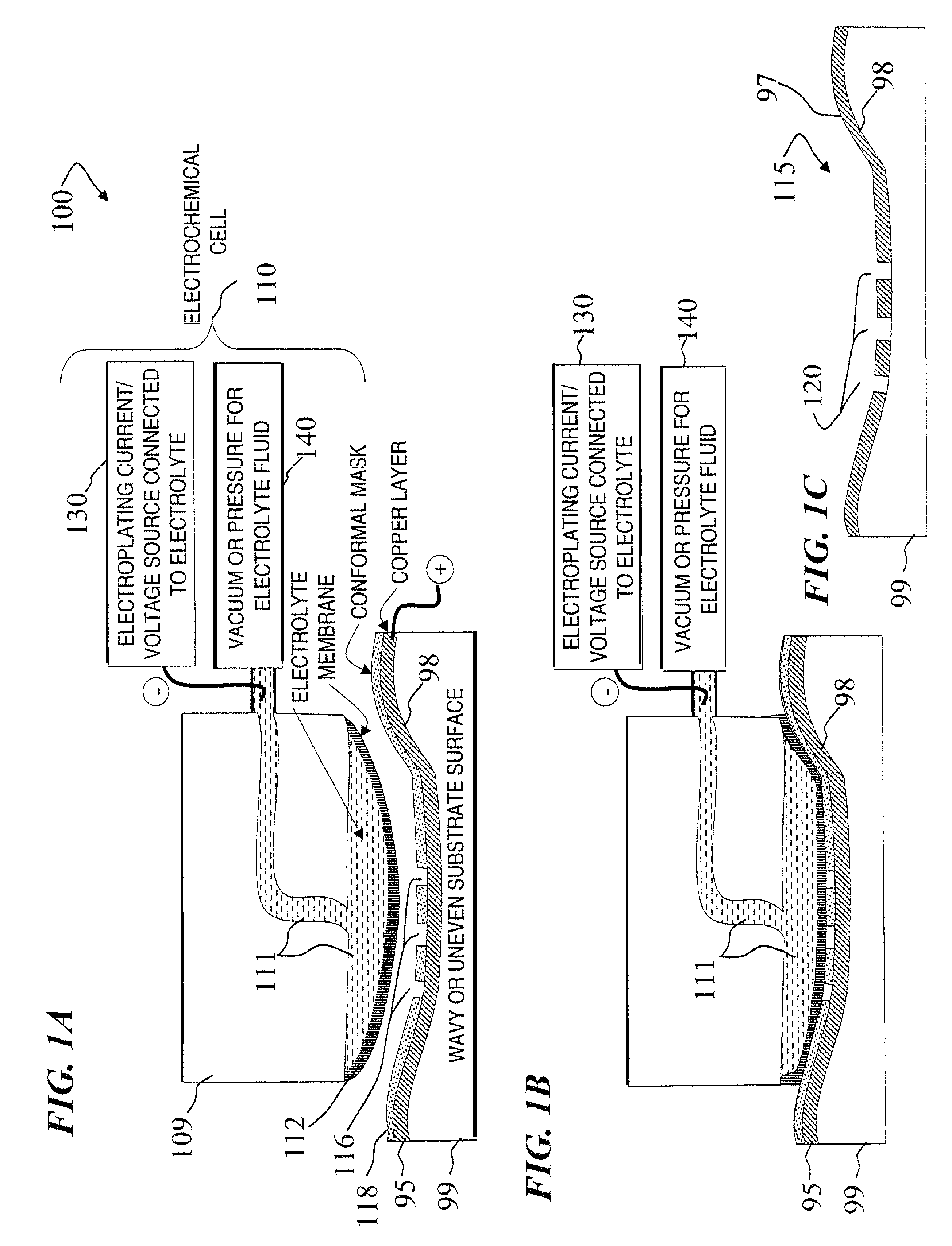
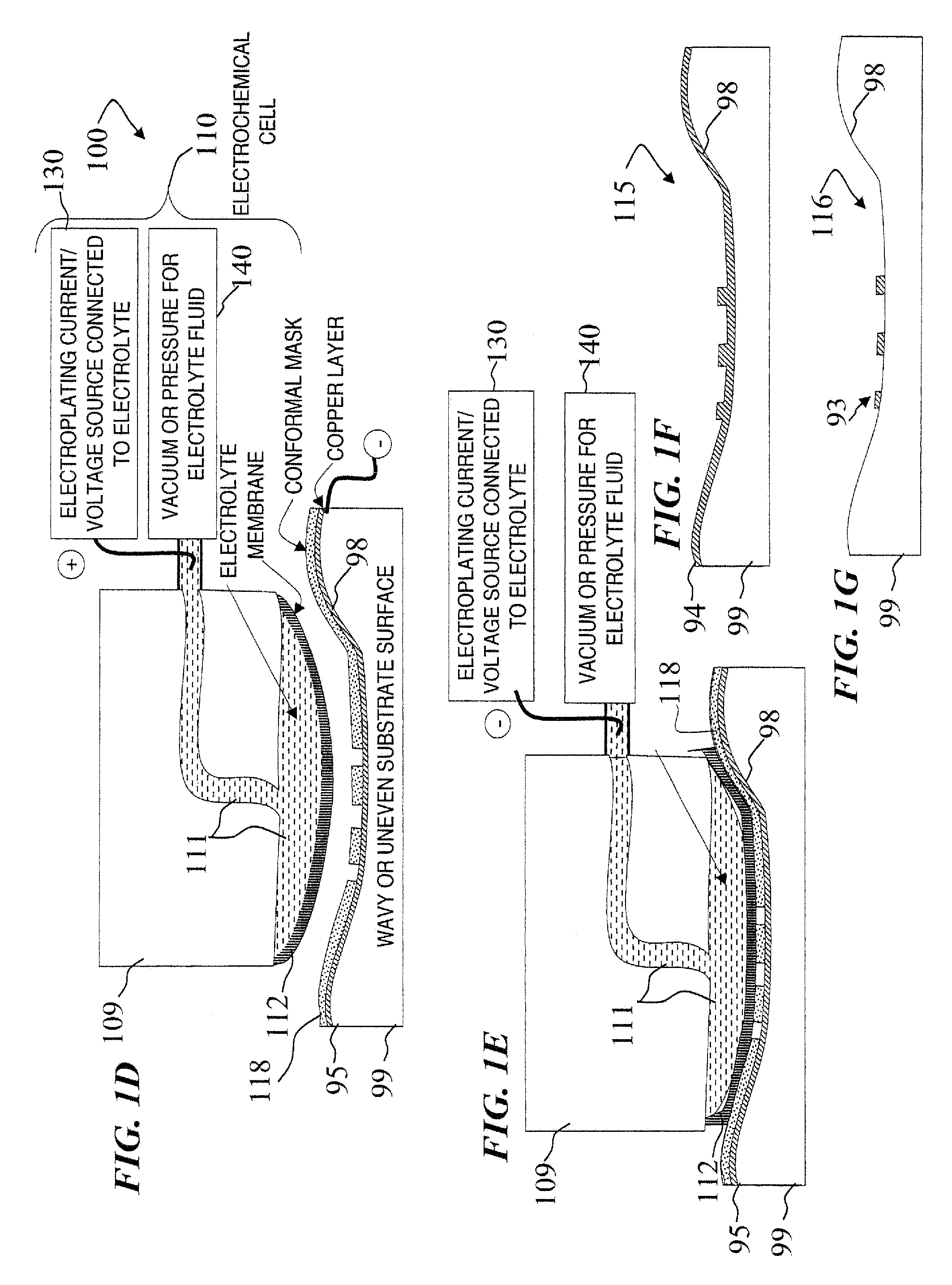
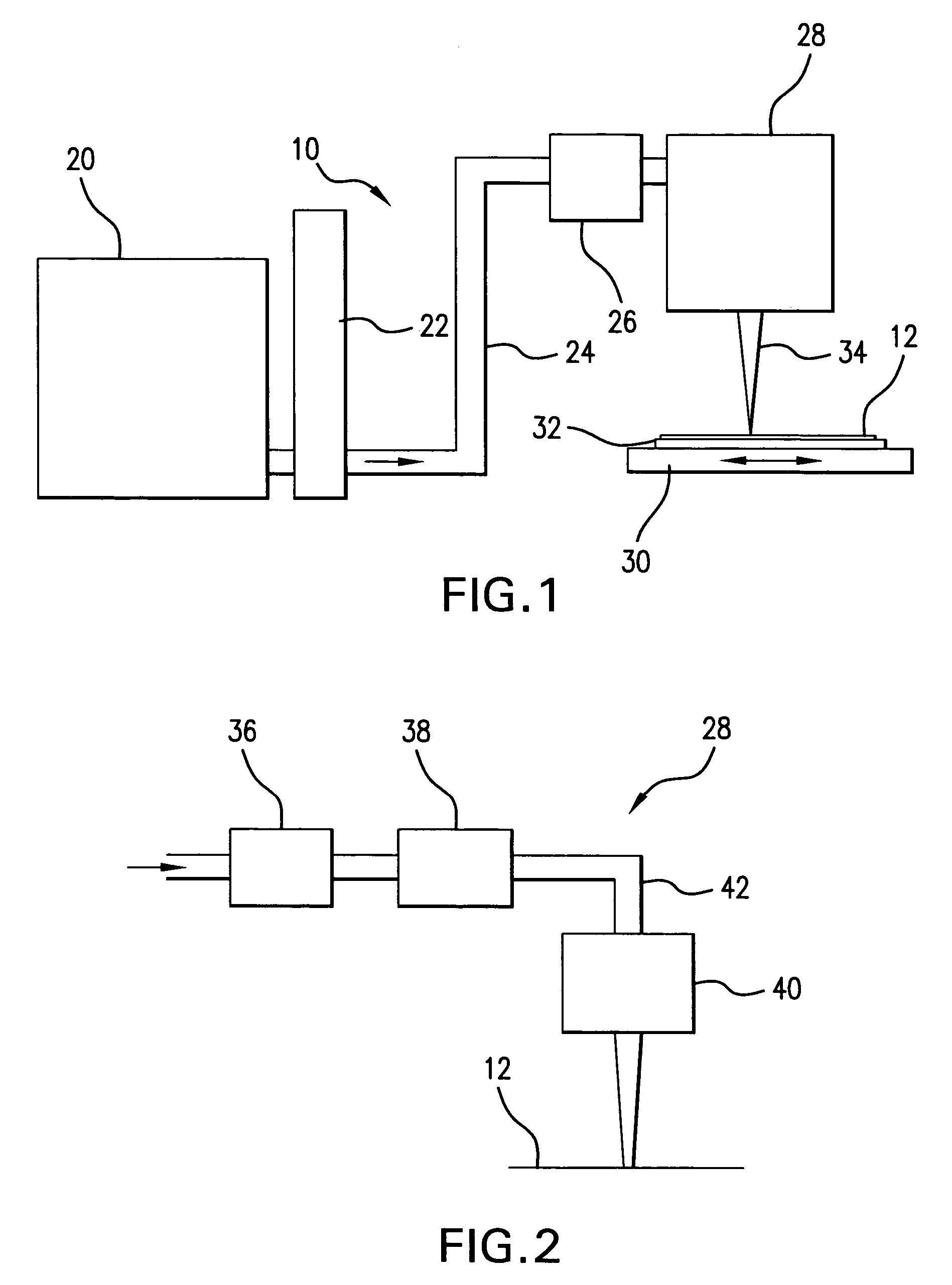
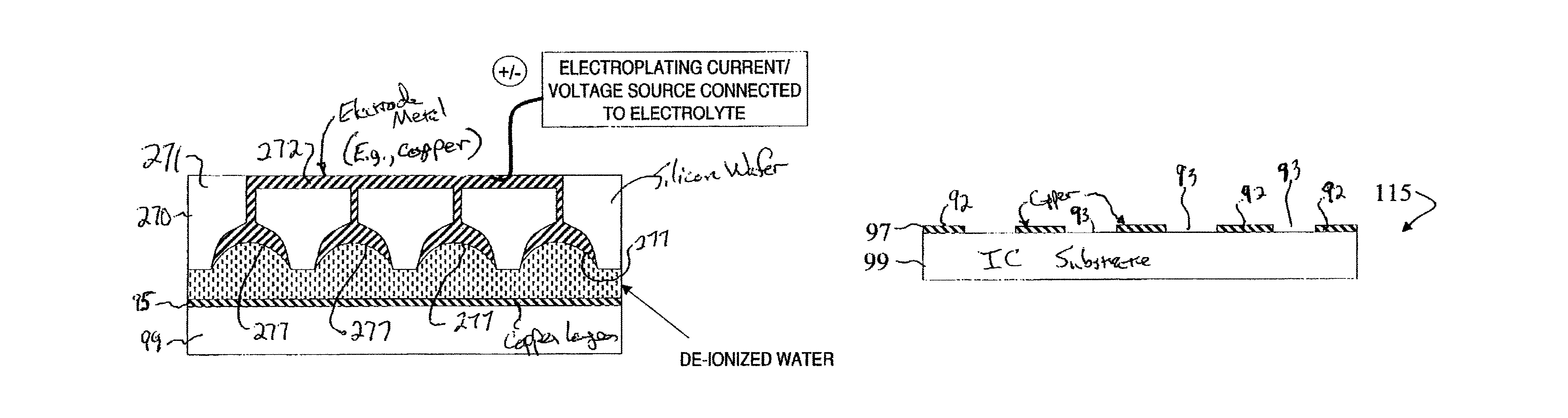
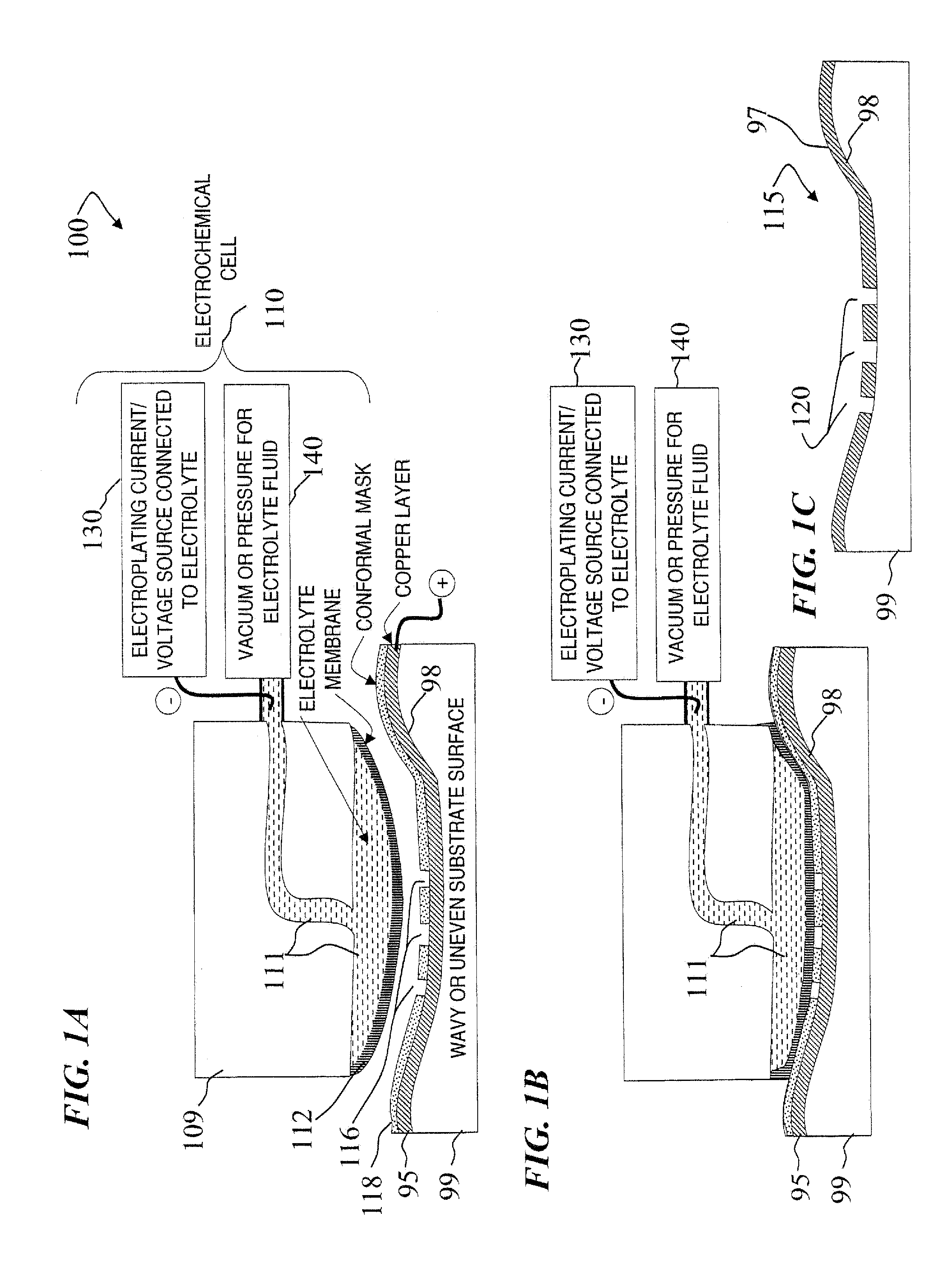
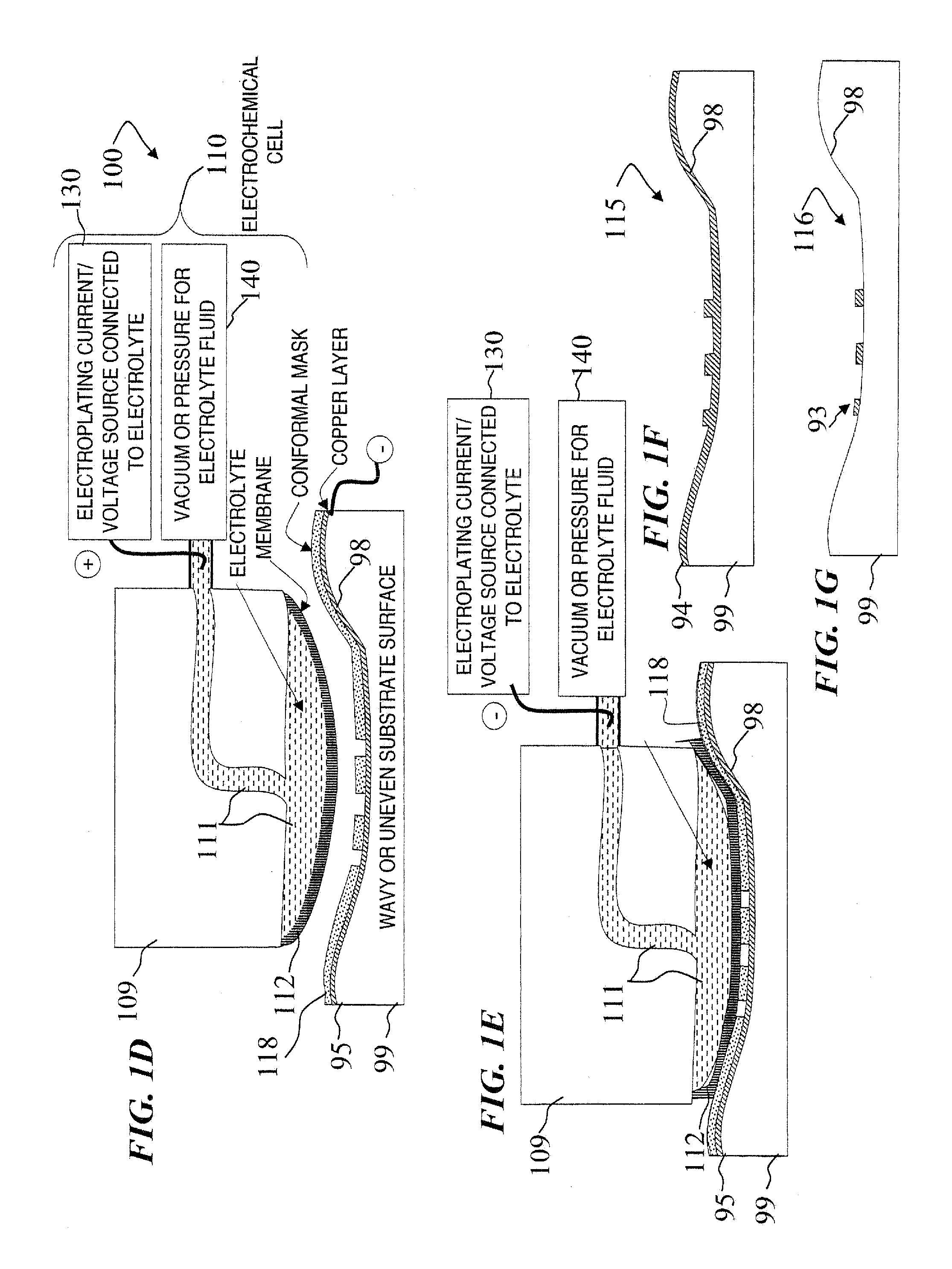
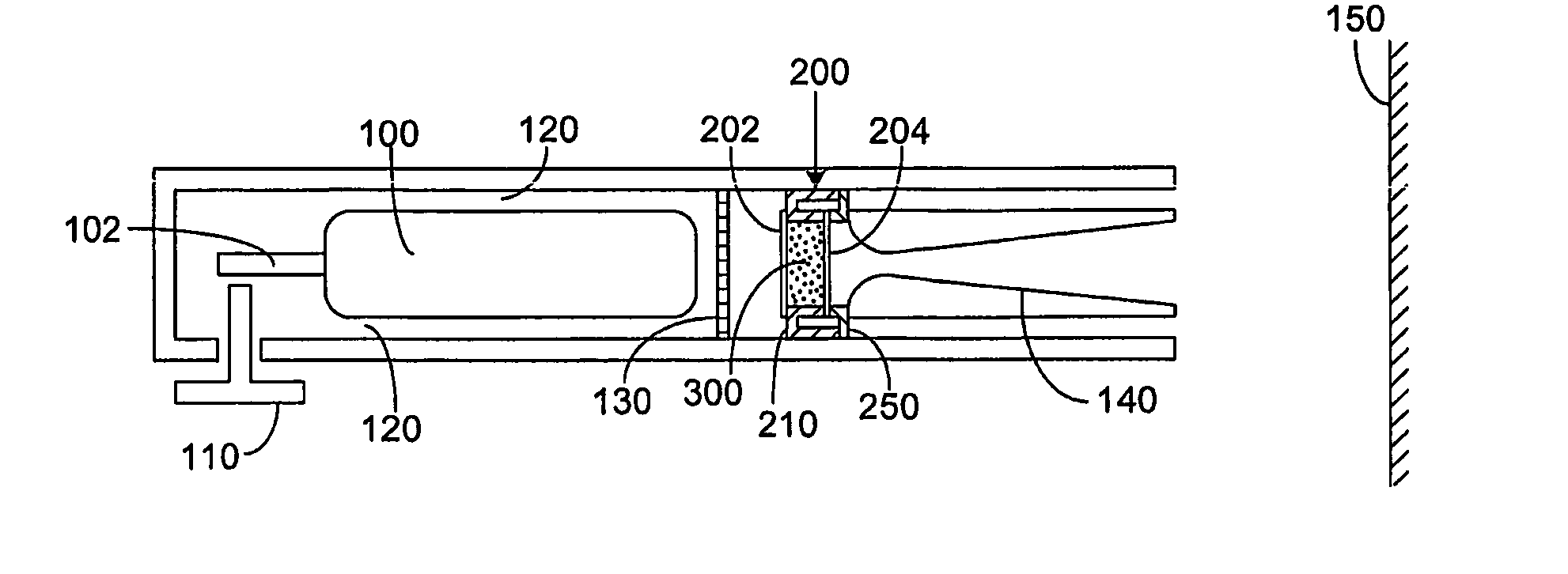
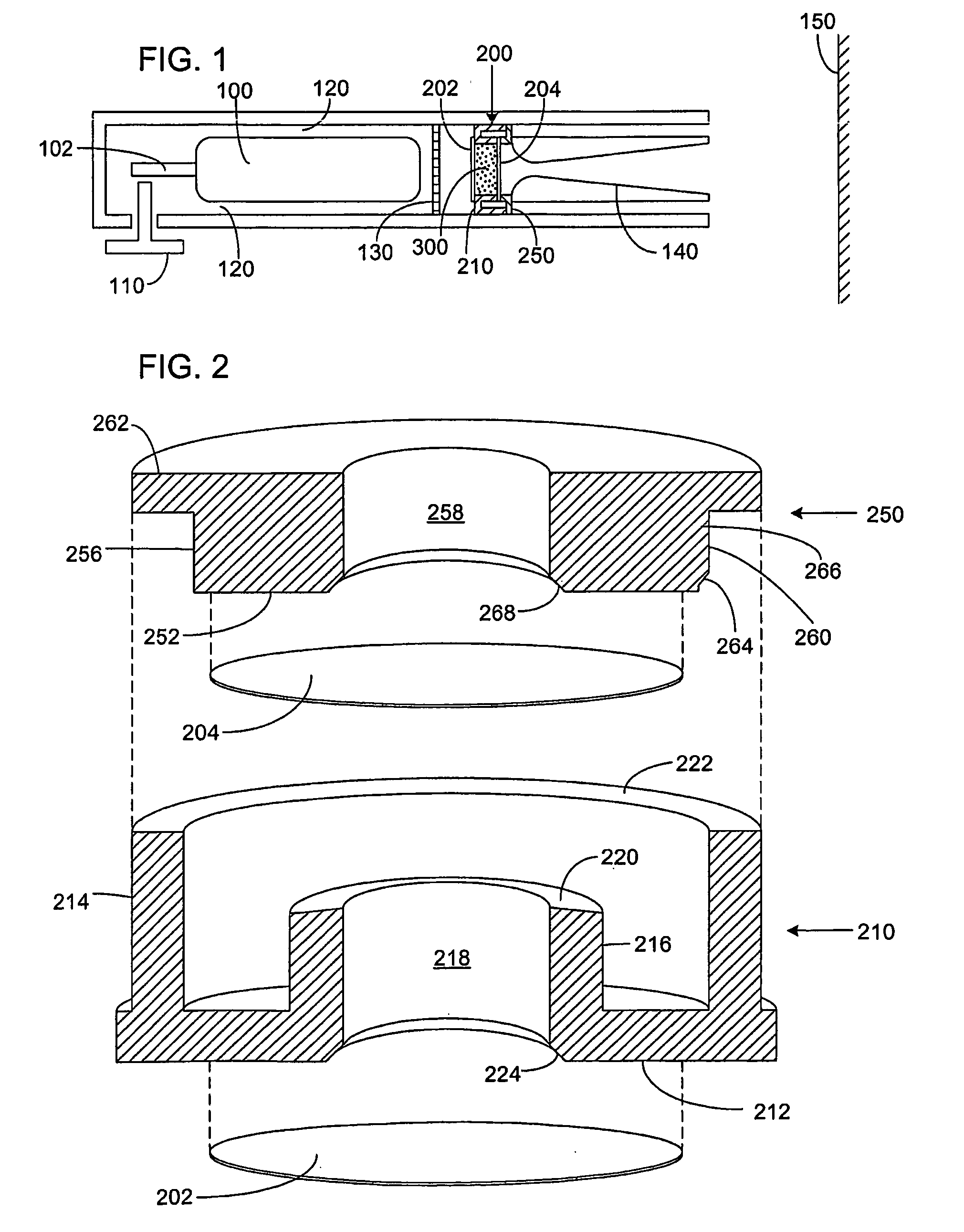
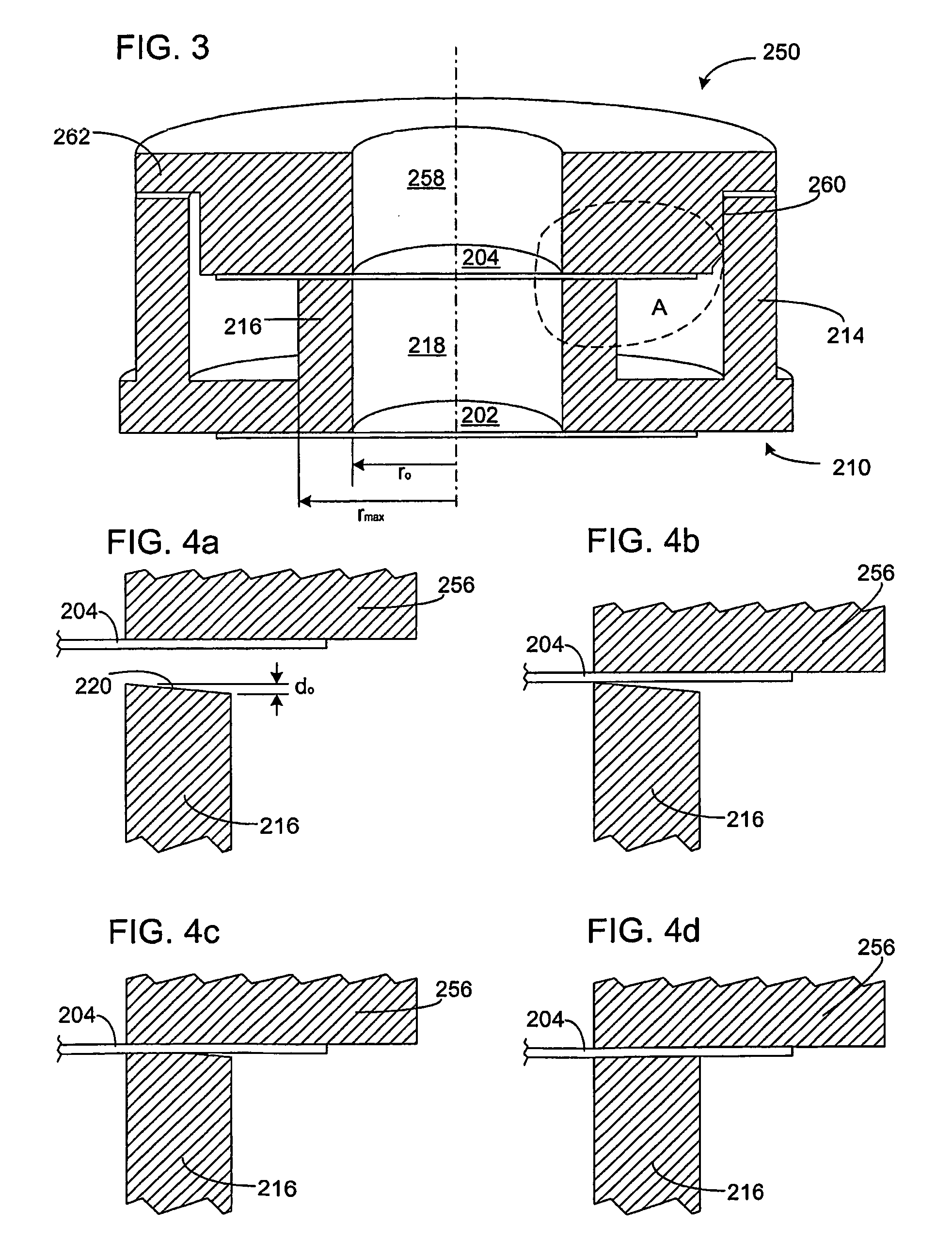
A Focused Electric Field Imprinting (FEFI) process and apparatus provides a focused electric field to guide an unplating operation and / or a plating operation to form very fine-pitched metal patterns on a substrate. The process is a variation of the electrochemical unplating process, wherein the process is modified for imprinting range of patterns of around 2000 microns to 20 microns or less in width, and from about 0.1 microns or less to 10 microns or more in depth. Some embodiments curve a proton-exchange membrane whose shape is varied using suction on a backing fluid through a support mask. Other embodiments use a curved electrode. Mask-membrane interaction parameters and process settings vary the feature size, which can generate sub-100-nm features. The feature-generation process is parallelized, and a stepped sequence of such FEFI operations, can generate sub-100 nm lines with sub-100 nm spacing. The described FEFI process is implemented on copper substrate, and also works well on other conductors.
Owner:ACTUS POTENTIA
Neonatal colorimetric carbon dioxide detector
An application for a neonatal calorimetric carbon dioxide detector has a calorimetric carbon dioxide detector membrane having a pH-sensitive chemical indicator that undergoes calorimetric change in the presence of carbon dioxide. The detector has a patient orifice in fluid communication with the baby's airway and a respiration equipment orifice connected to a breathing system. The patient orifice is connected to a breathing tube and when the breathing tube is inserted correctly into the trachea, as the baby exhales, carbon dioxide interacts with the calorimetric membrane which changes color based upon the concentration of carbon dioxide. The neonatal calorimetric carbon dioxide detector adds a volume of less than or equal to 1 mL after being attached to a breathing circuit.
Owner:MERCURY ENTERPRISES
Use of derivatives of polyunsaturated fatty acids as medicaments
Use of polyunsaturated fatty acid derivatives as medicaments or functional foods. The present invention relates to the use of 1,2-fatty acid derivatives in the treatment or prevention of common diseases whose etiology is based on alterations (of any type) of the cell membrane lipids, for example, changes in levels, in the composition or in the structure of these lipids. In addition, for diseases in which the regulation of lipid composition and of the structure of the membranes (or proteins that interact with membranes) causes the reversion of pathological state.
Owner:LIPOPHARMA THERAPEUTICS
Use of Derivatives of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids as Medicaments
ActiveUS20120108550A1Reduce rateEfficient processBiocideNervous disorderEtiologyMembrane interaction
Use of polyunsaturated fatty acid derivatives as medicaments or functional foods. The present invention relates to the use of 1,2-fatty acid derivatives in the treatment or prevention of common diseases whose etiology is based on alterations (of any type) of the cell membrane lipids, for example, changes in levels, in the composition or in the structure of these lipids. In addition, for diseases in which the regulation of lipid composition and of the structure of the membranes (or proteins that interact with membranes) causes the reversion of pathological state.
Owner:LIPOPHARMA THERAPEUTICS
Systems and methods for generating laser light shaped as a line beam
Systems and methods are disclosed for shaping a laser beam for interaction with a film in which the laser beam travels along a beam path and defines a short-axis and a long-axis. In one aspect, the system may include a first short-axis element having an edge positioned at a distance, d1, along the beam path from the film and a second short-axis element having an edge positioned at a distance, d2, along the beam path from the film, with d2<d1. An optic may be positioned along the beam path between the second element and the film for focusing the beam in the short-axis for interaction with the film. In another aspect, a system may be provided having a mechanism operative to selectively adjust the curvature of one or both of the edges of the short-axis element.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
Method for focused electric-field imprinting for micron and sub-micron patterns on wavy or planar surfaces
InactiveUS8617378B1Small sizeEliminate processing stepsElectrolysis componentsElectrochemical machining apparatusElectrical conductorMembrane interaction
Focused Electric Field Imprinting (FEFI) provides a focused electric field to guide an unplating operation and / or a plating operation to form very fine-pitched metal patterns on a substrate. The process is a variation of the electrochemical unplating process, wherein the process is modified for imprinting range of patterns of around 2000 microns to 20 microns or less in width, and from about 0.1 microns or less to 10 microns or more in depth. Some embodiments curve a proton-exchange membrane whose shape is varied using suction on a backing fluid through a support mask. Other embodiments use a curved electrode. Mask-membrane interaction parameters and process settings vary the feature size, which can generate sub-100-nm features. The feature-generation process is parallelized, and a stepped sequence of such FEFI operations, can generate sub-100-nm lines with sub-100-nm spacing. The described FEFI process is implemented on copper substrate, and also works well on other conductors.
Owner:ACTUS POTENTIA
Particle cassettes
ActiveUS8298173B2Ensure sealing performanceAchieving Reliability RequirementsAmpoule syringesJet injection syringesMembrane interactionCompanion animal
A method of producing a particle cassette for a needleless syringe device which alleviates problems of providing a chamber for the confinement of particles which is hermetically sealed from the environment. A predetermined force is applied in the longitudinal direction to push first and second cassette parts together so as to cause plastic deformation of a portion of the first cassette part so as to create said hermetically sealed chamber. The cassette parts are preferably made of PETG and have bonded thereto rupturable membranes preferably made of PET. The sealing is preferably achieved at the end of a protrusion on the first cassette part which is tapered and which interacts with the membrane of the second cassette part.
Owner:POWDER PHARM INC
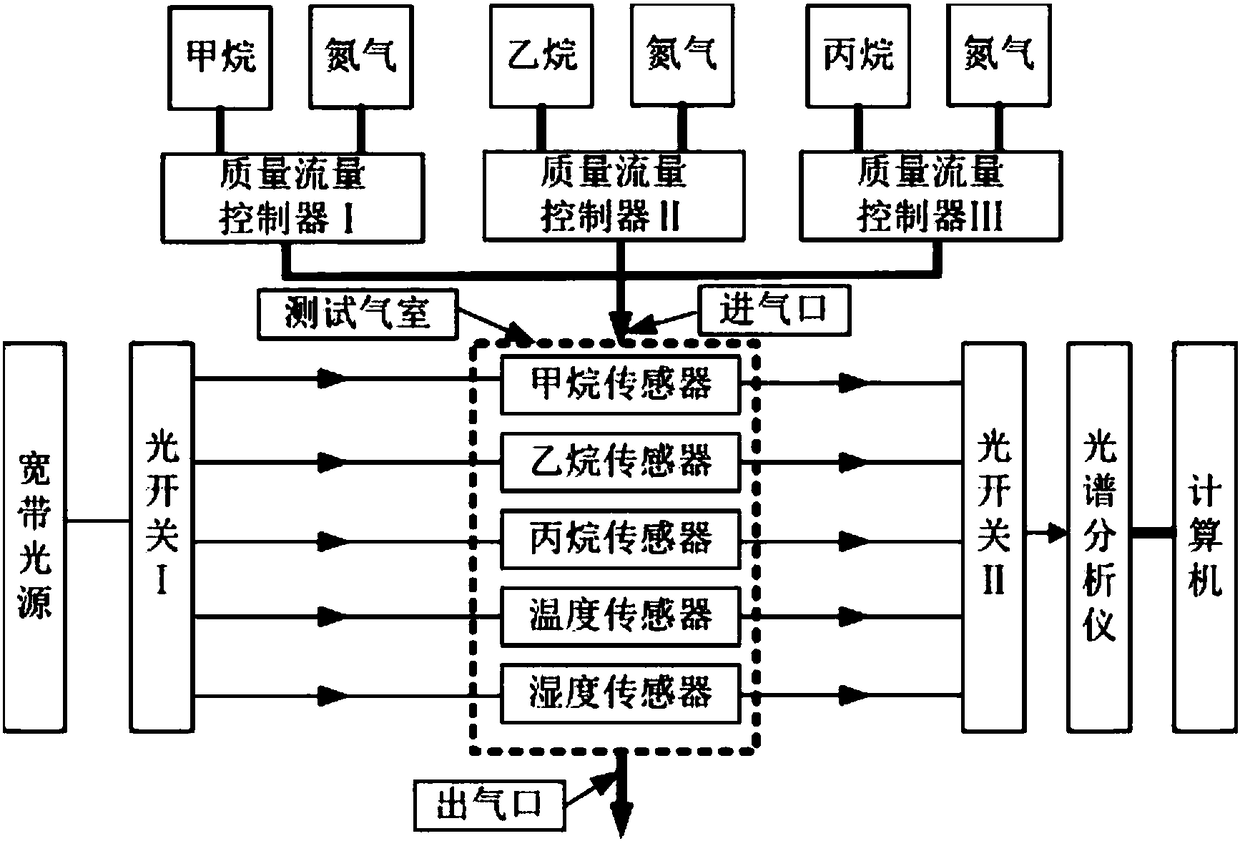
Detection device for multiple parameters of oil and gas concentration
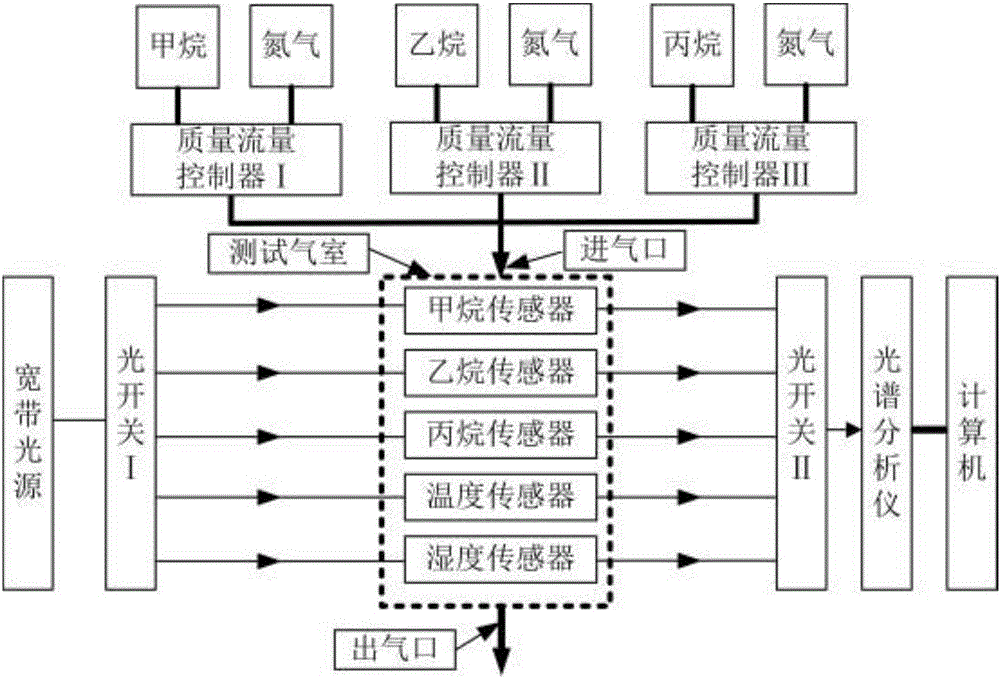
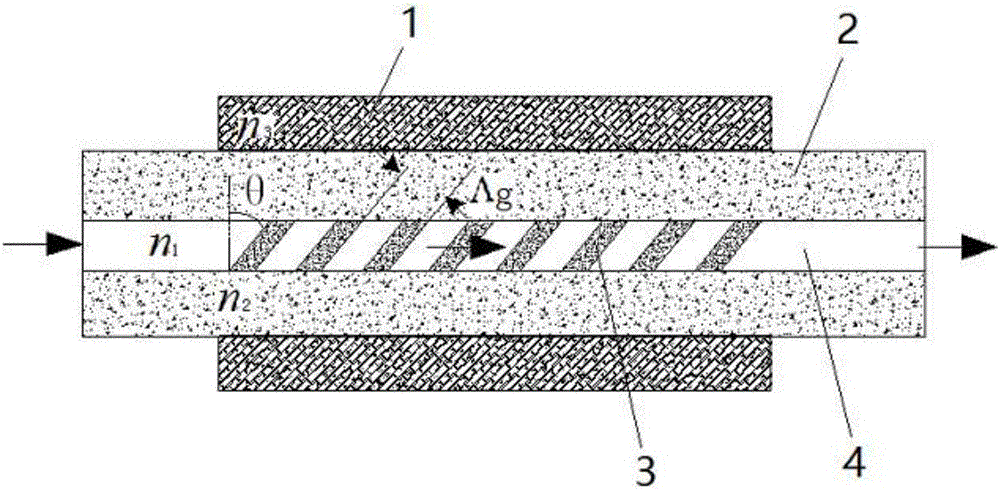
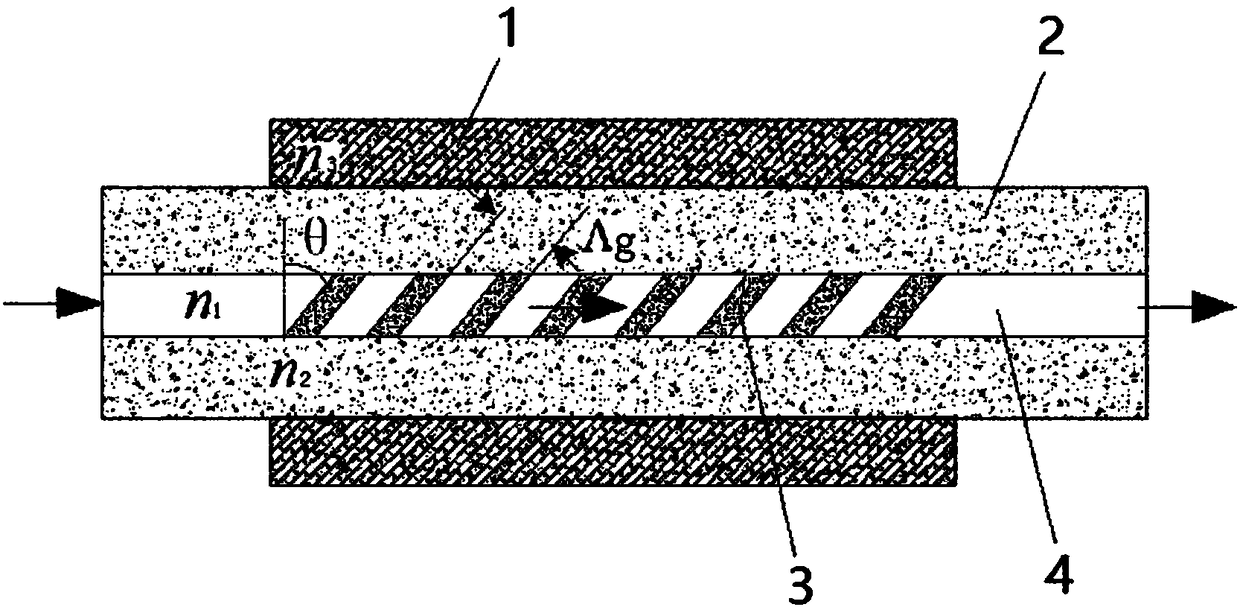
ActiveCN106198409AHigh sensitivityImprove coupling coefficientColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberLong-period fiber grating
The invention discloses a detection device for multiple parameters of oil and gas concentration. The detection device comprises a broadband light source, a methane sensor, an ethane sensor, a propane sensor, a humidity sensor, a temperature sensor, optical switches, a testing gas chamber, a computer, a mass flow controller and the like, wherein the front ends of all the sensors are connected with the broadband light source through the optical switch I; the rear ends of all the sensors are connected with a spectrum analyzer through the optical switch II; all the sensors are positioned in the testing gas chamber; sensitive membranes of the tilted long-period fiber grating methane, ethane and propane sensors are low refractive index ultraviolet-curing fluorosilicone sensitive membranes containing cage molecules (a cage molecule A, a cage molecule E-(OC3H7)6 or a cage molecule M-(OC3H7)6) and graphene; when methane, ethane and propane to be detected interact with the corresponding sensitive membranes, refractive indexes of the sensitive membranes are changed, and transmission spectra of the methane sensor, the ethane sensor and the propane sensor are enabled to drift; by means of the drift amount of the transmission spectra in the spectrum analyzer, the concentrations of the methane, the ethane and the propane can be measured.
Owner:重庆科知源科技有限公司
Systems and methods for implementing an interaction between a laser shaped as a line beam and a film deposited on a substrate
InactiveUS7277188B2By zone-melting liquidsWelding/cutting auxillary devicesMembrane interactionLight beam
Owner:CYMER INC +1
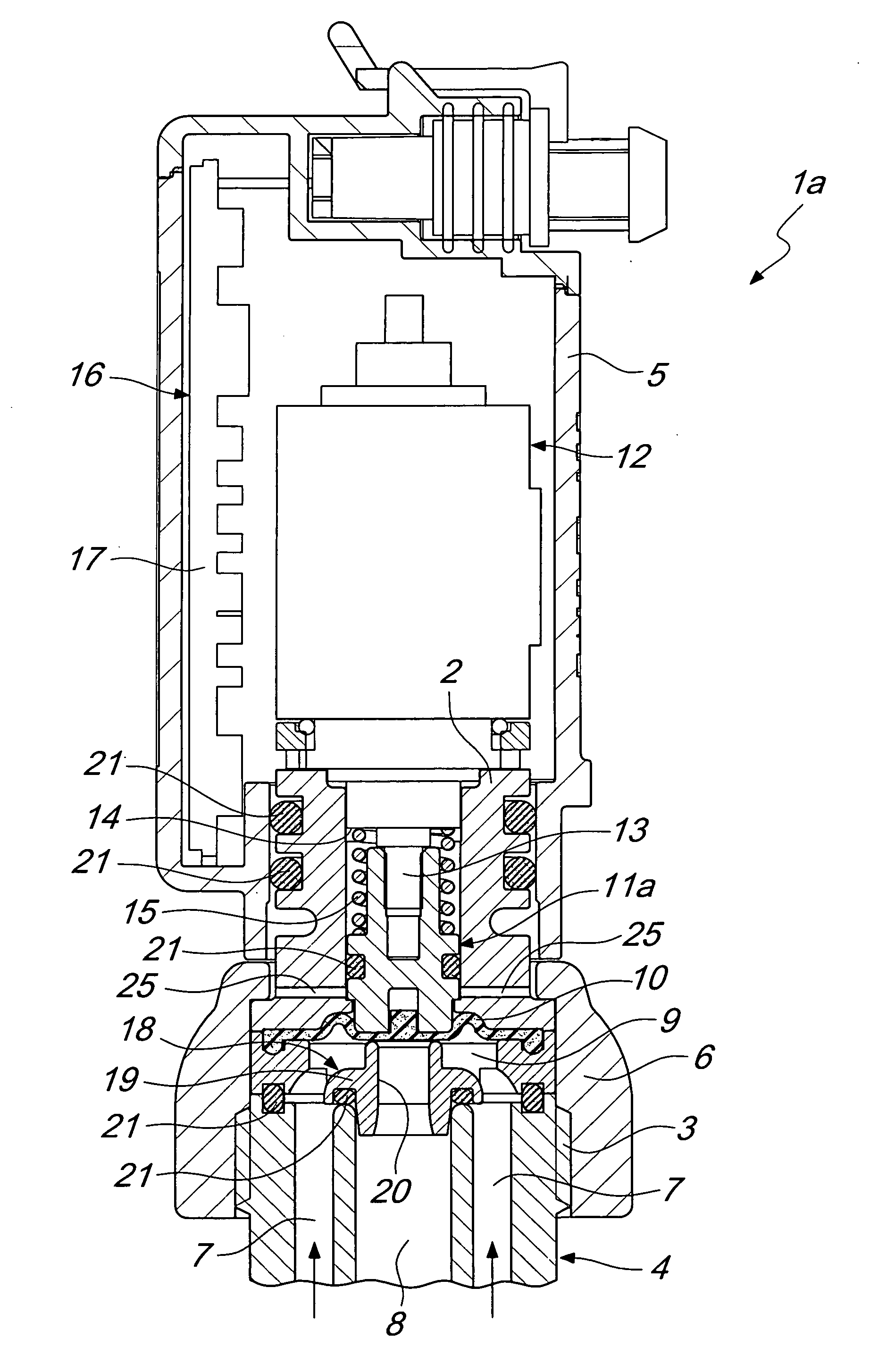
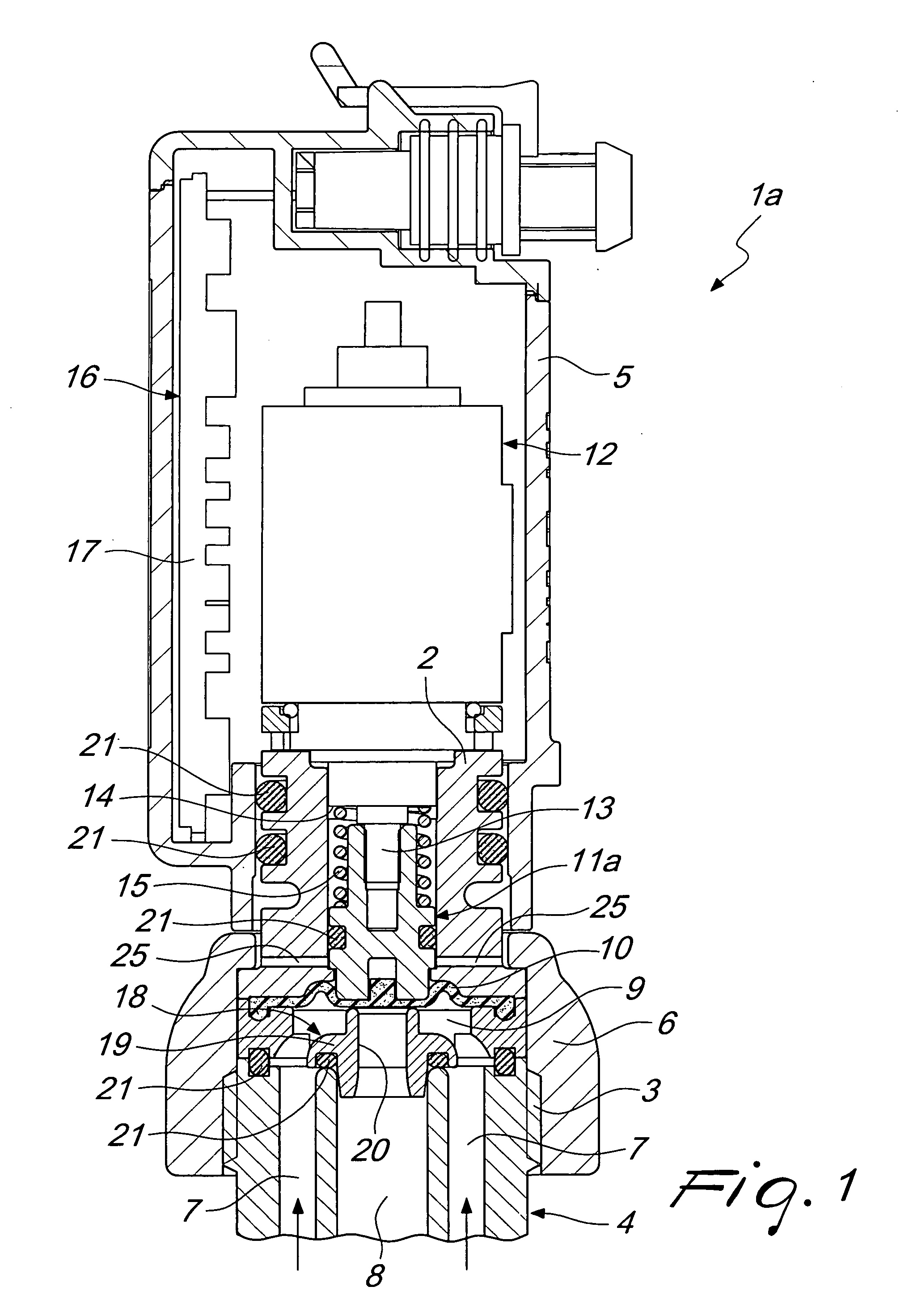
Electromechanically actuated membrane valve for branching ducts of sprinkling and/or weed control systems
InactiveUS20120025115A1Little strengthImprove efficiencyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesValve housingsMembrane interactionControl system
An electromechanically actuated membrane valve, for branching ducts of sprinkling and / or weed control systems, comprising a hollow valve body associated with an end portion of a branching duct of a fluid that contains a piston adapted to interact with a disk-like membrane for blocking the end portion of the branching duct.The piston is movable in the valve body between an open configuration and a closed configuration of the valve. The branching duct comprises an internal duct and an external duct which are mutually coaxial.A passage section reduction element for the internal duct is provided associated with the valve body to interact with the disk-like membrane for the hermetic isolation of the internal duct with respect to the external duct and vice versa.
Owner:ARAG
Apparatus and method for high throughput analysis of compound-membrane interactions
InactiveUS7364905B2Improve developmentAvoid disadvantagesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsControl systemMembrane interaction
An article and method for high throughput and a high content investigation of compound interactions with live tissue or its substitutes under controlled conditions during compound absorption and related processes. In some variations of the illustrative embodiment, the article is a multi-chamber enclosure having at least two chambers separated by a membrane. Membranes can be prepared from live epithelial tissue or from an artificial material with or without attached cells from cell-line cultures. Each chamber is advantageously connected to a fluidic-control system by tubes that pass through a feed fitting. In addition to coupling the chambers with the fluidic-control system, the feed fitting, which is spring-biased, provides a sealing force to seal the enclosure. In some variations, one or more multi-chamber enclosures are installed in a mother chamber, which provides controlled environmental conditions. Operation of the article includes automatic introduction of compounds, buffers, and gases into the chambers, establishing reaction conditions inside the chambers, and individually sampling from the chambers.
Owner:TECHELAN
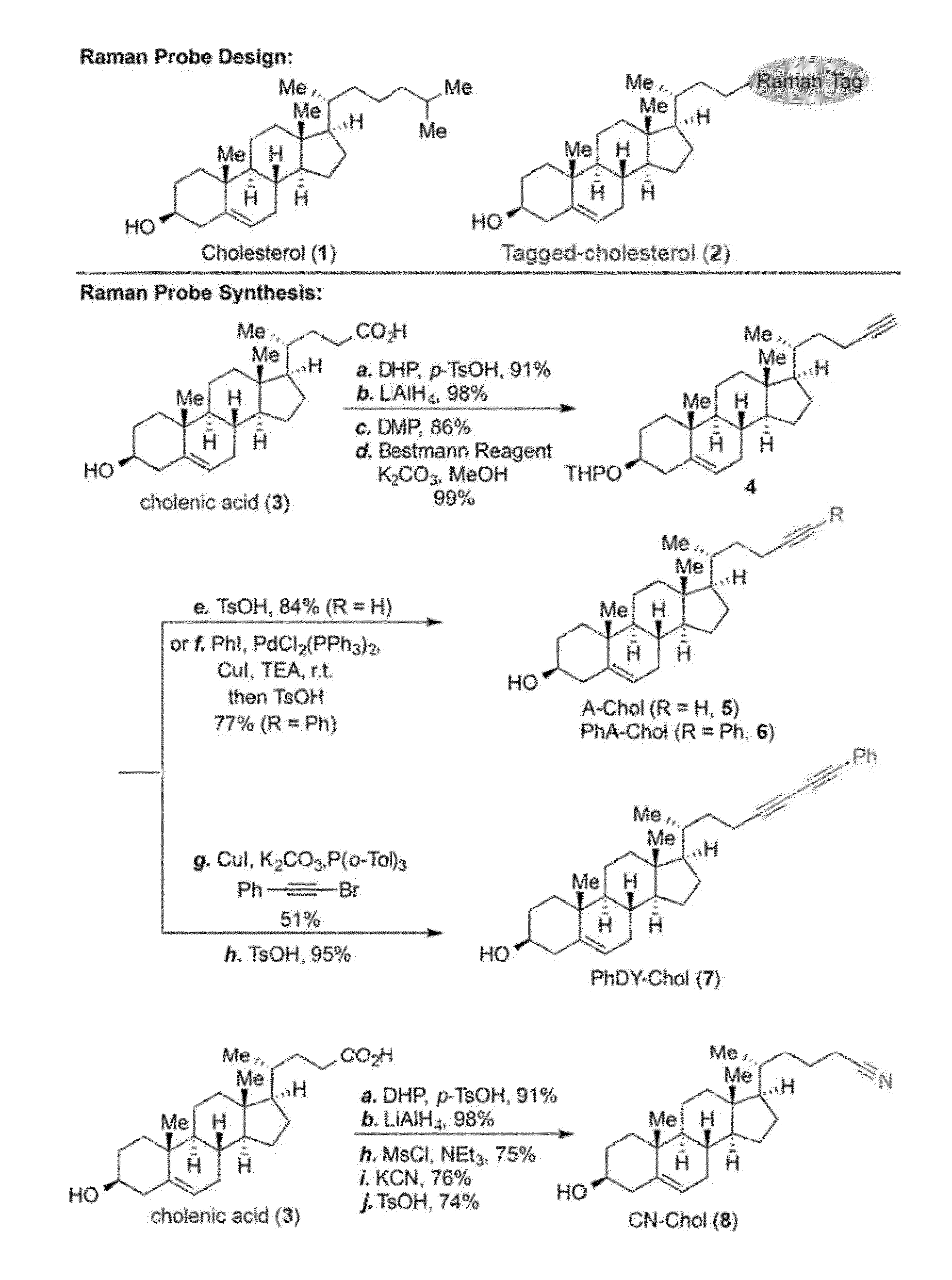
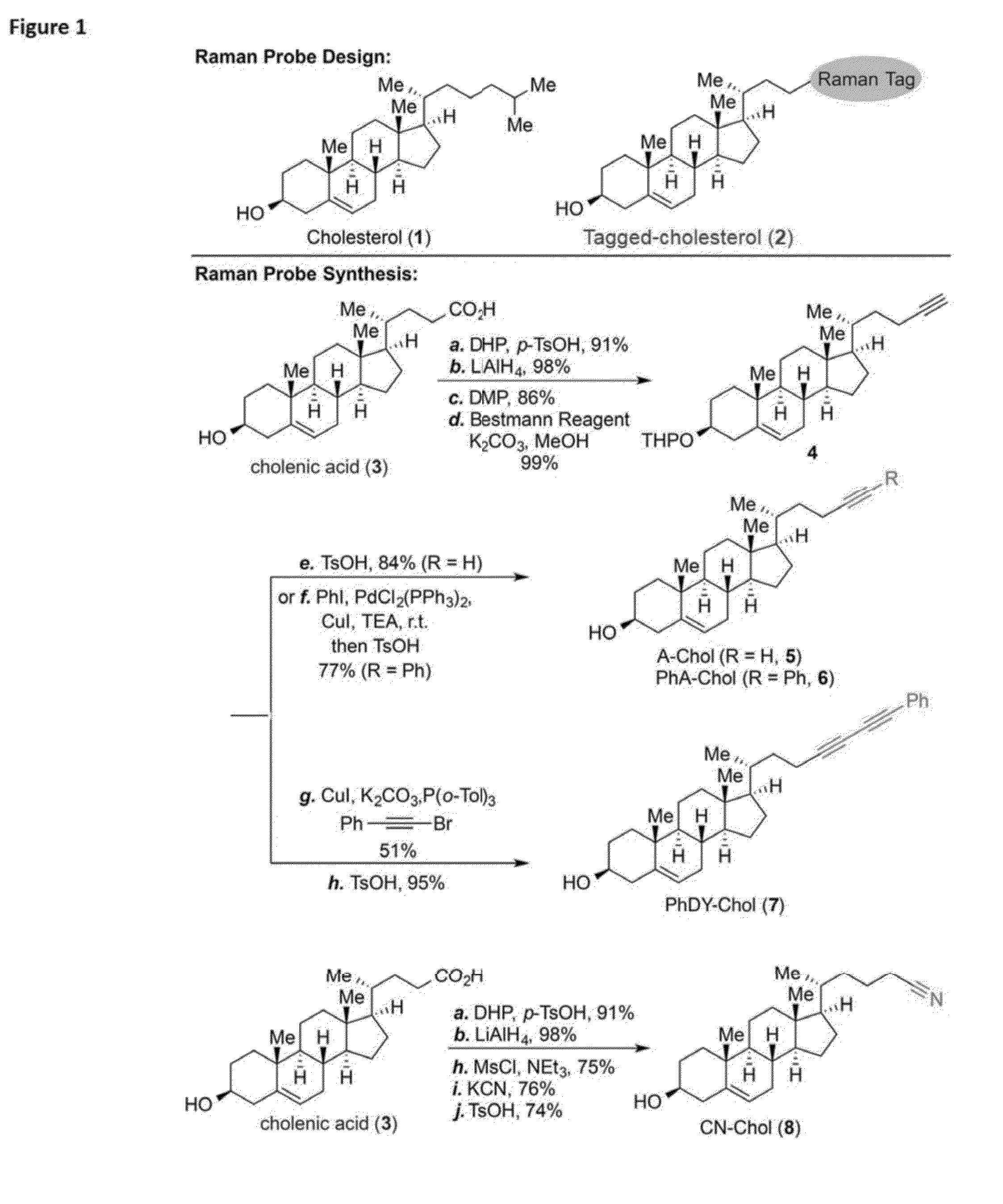
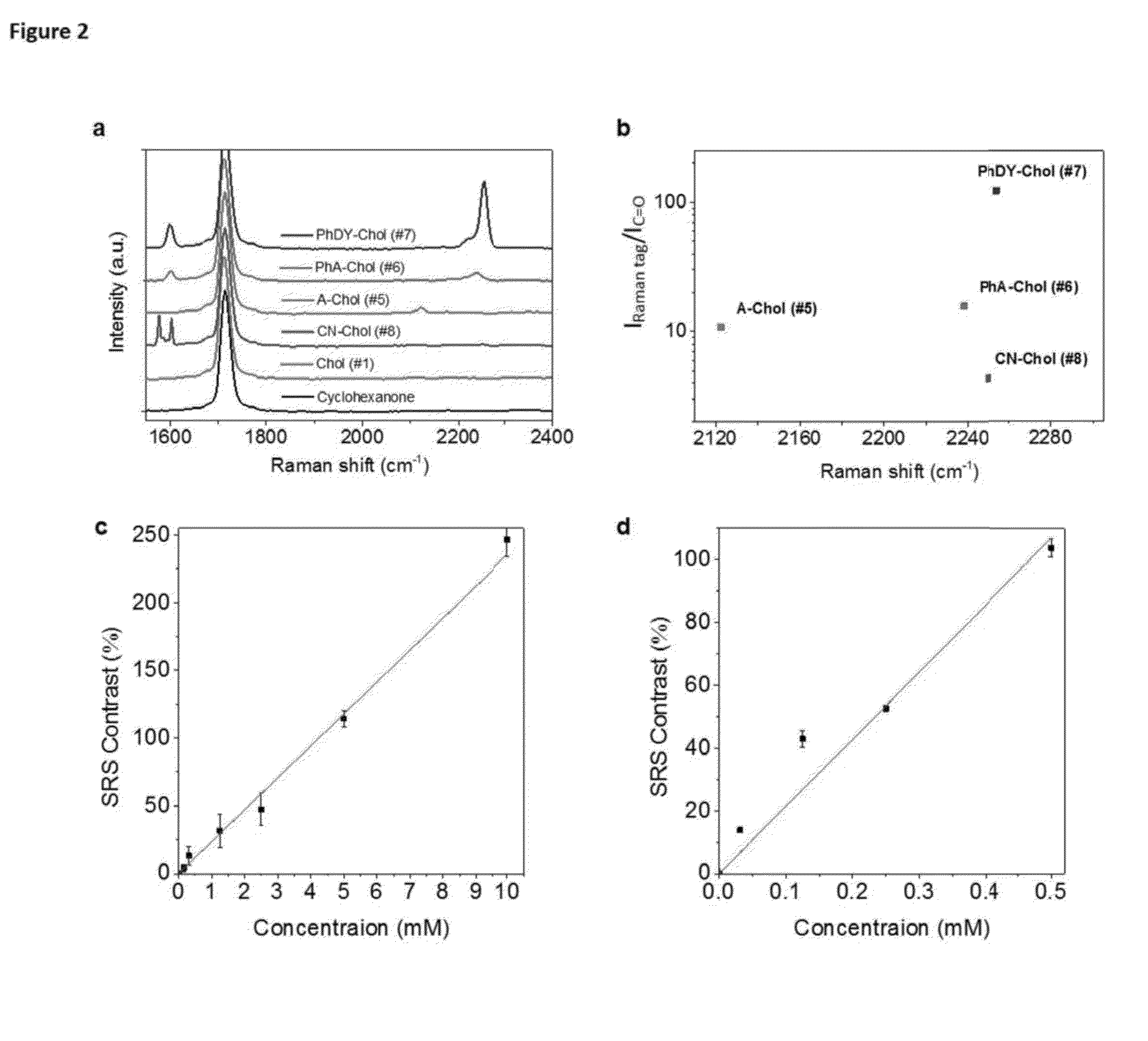
Raman Tag
The present invention provides novel Raman tags for exploring membrane interactions in cells. The tags comprise a phenyl diyne probe where in the dyine is capped with the phenyl group. Methods for using the tags are also provided.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method for preparing edible bacteriostatic membrane
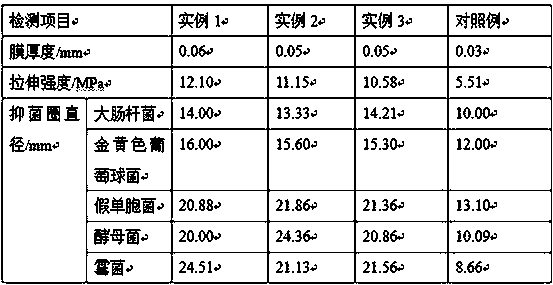
The invention relates to a method for preparing an edible bacteriostatic membrane, and belongs to the technical field of food packaging. Soybean protein isolate, potato starch and konjak glucomannan are adopted as raw materials, and a bacteriostatic agent, a plasticizer and a reinforcing agent are added to prepare the edible bacteriostatic membrane. The konjak glucomannan has a high molecular weight and high water bonding capability so that the konjak glucomannan has good thickening effect, and konjak glucomannan sol has special reversibility. Chitosan, natamycin and lysozyme are adopted as the bacteriostatic agent, and sodium alginate and cellulose acetate fibers are adopted as the reinforcing agent. The antibacterial property of the chitosan is related to positively charged amino, the positively charged amino interacts with the negatively charged microbial cell membrane to increase the permeability of the microbial cell membrane, and destroy the osmotic balance inside and outside thecell membrane so as to cause cell death. The chitosan can inhibit the growth of a plurality of putrefying bacteria, pathogenic bacteria, yeast and mould, and the antibacterial performance of the chitosan can be enhanced through adding the natamycin and the lysozyme.
Owner:裴文韬
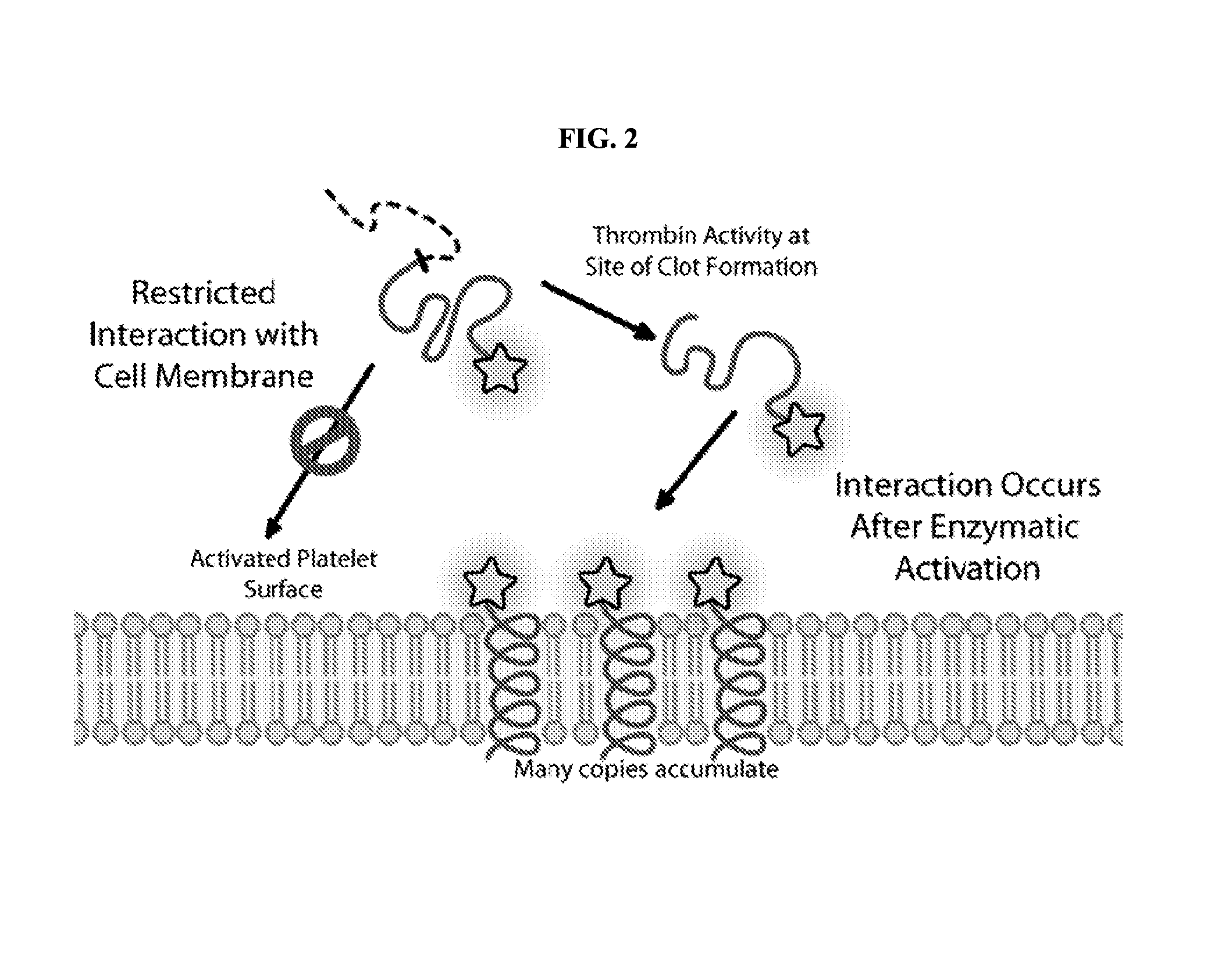
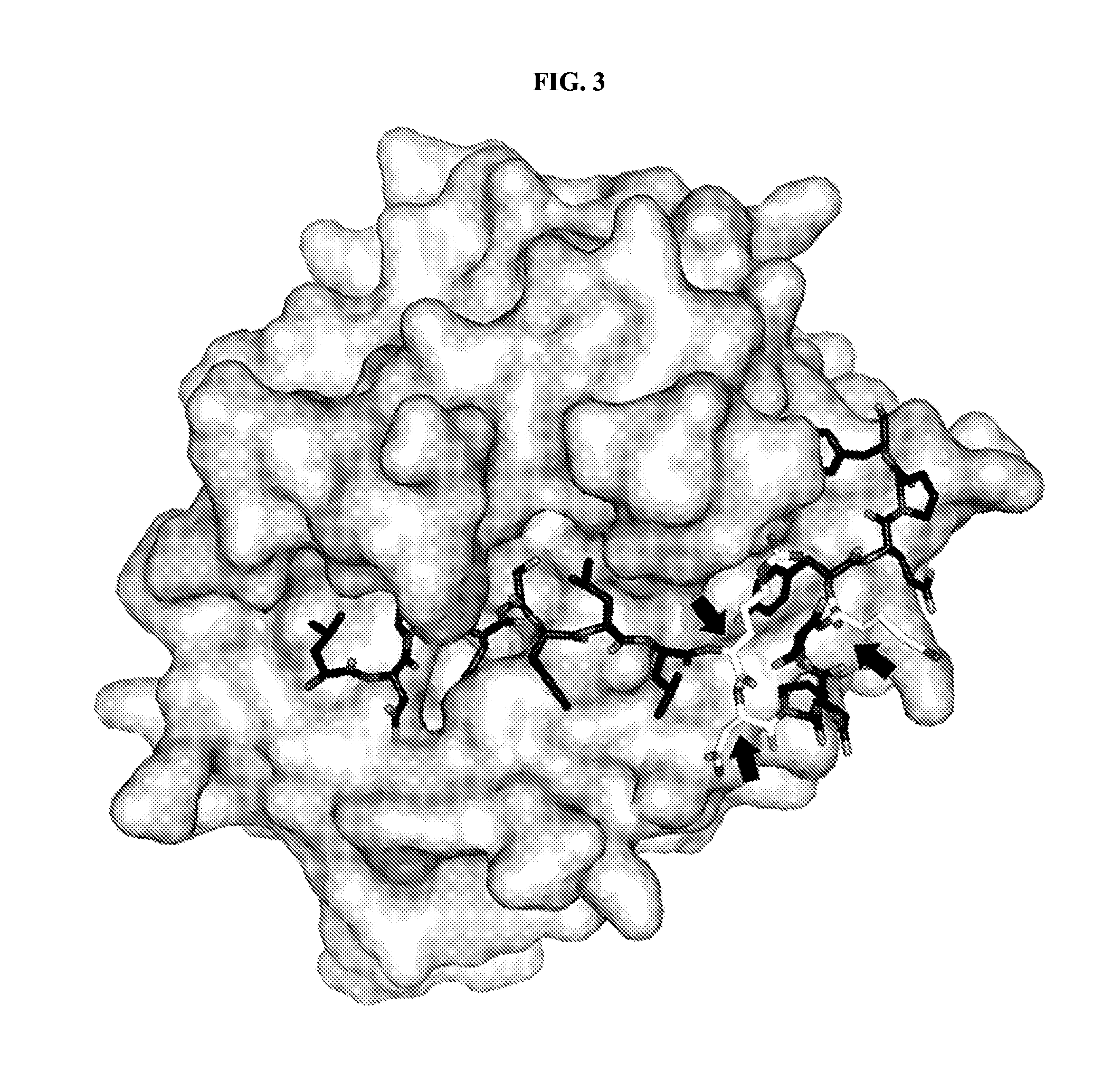
Activatable membrane-interacting peptides and methods of use
ActiveUS9789209B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsCell culture active agentsMembrane interactionCell membrane
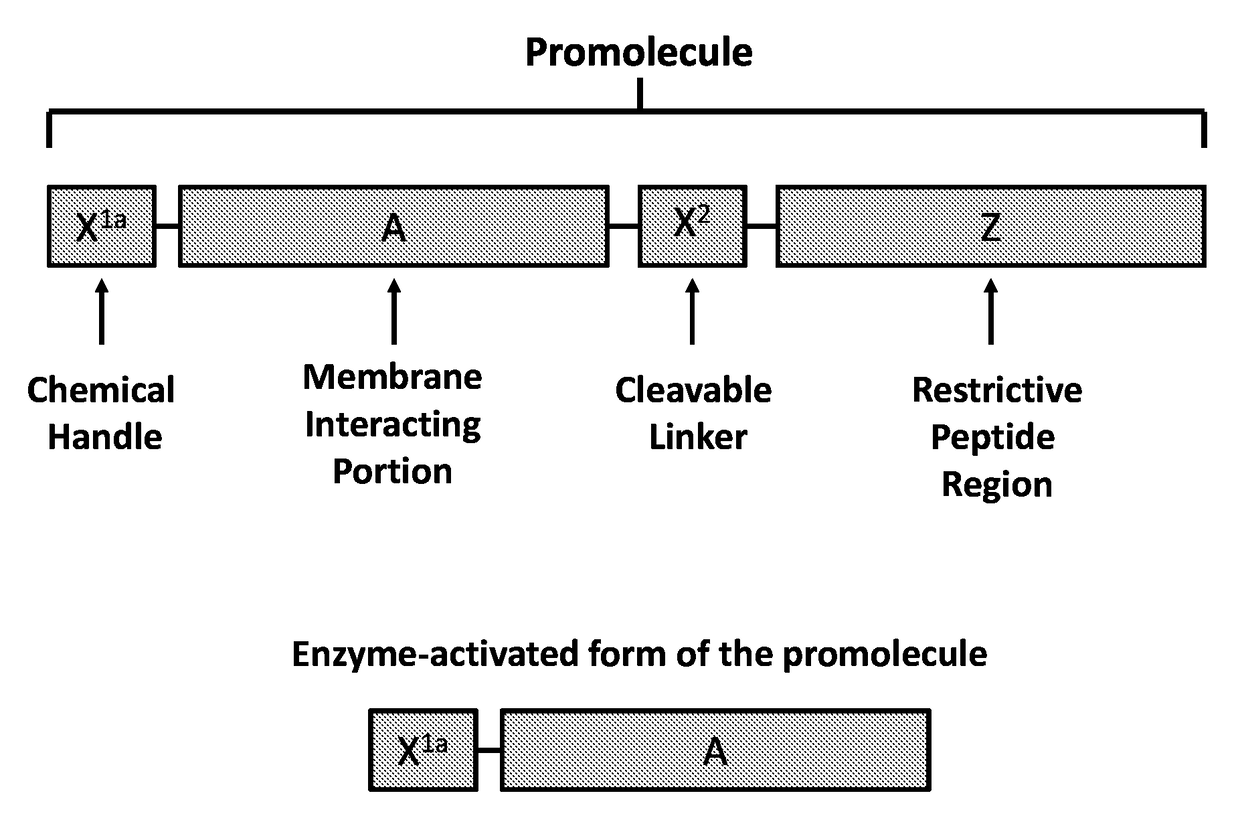
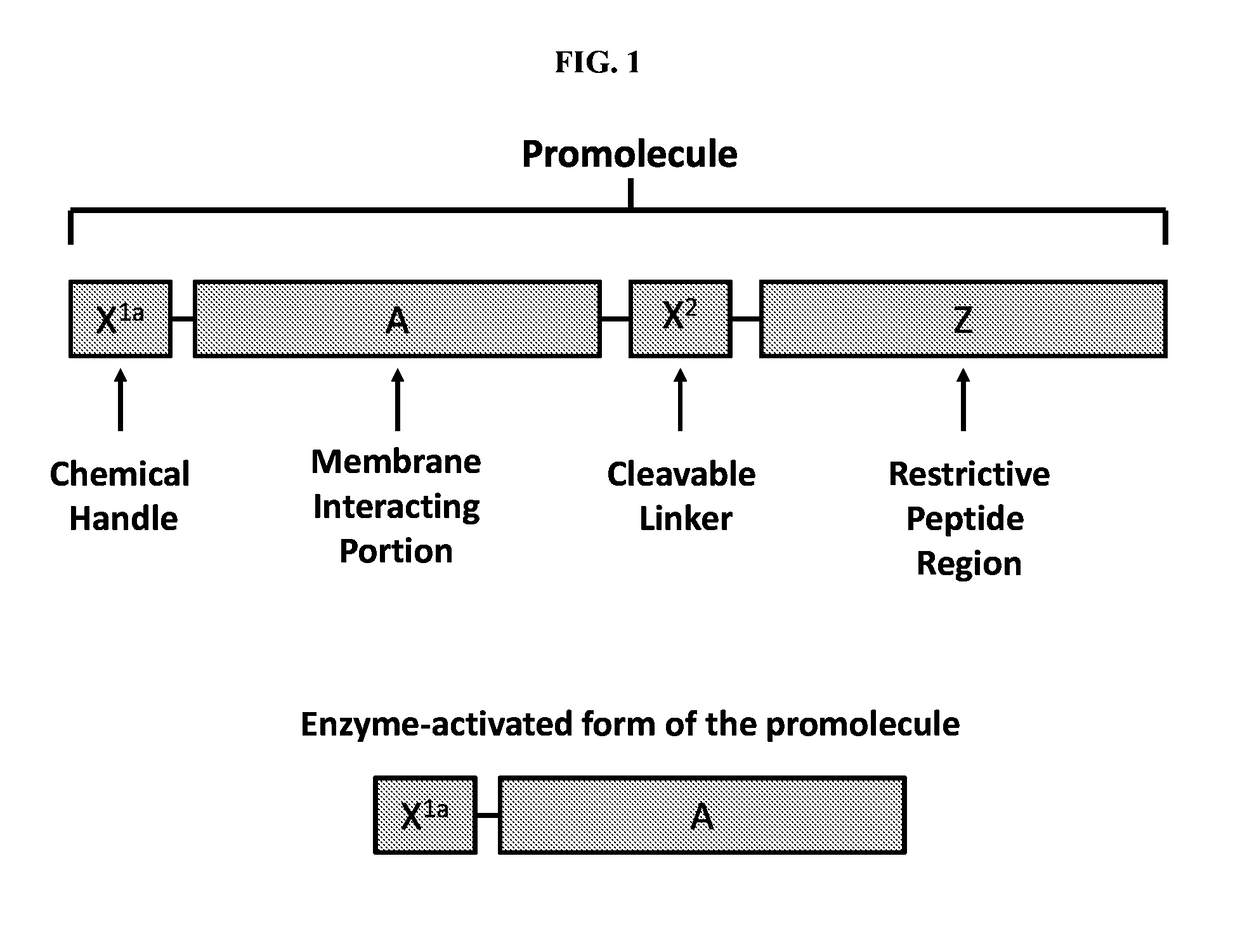
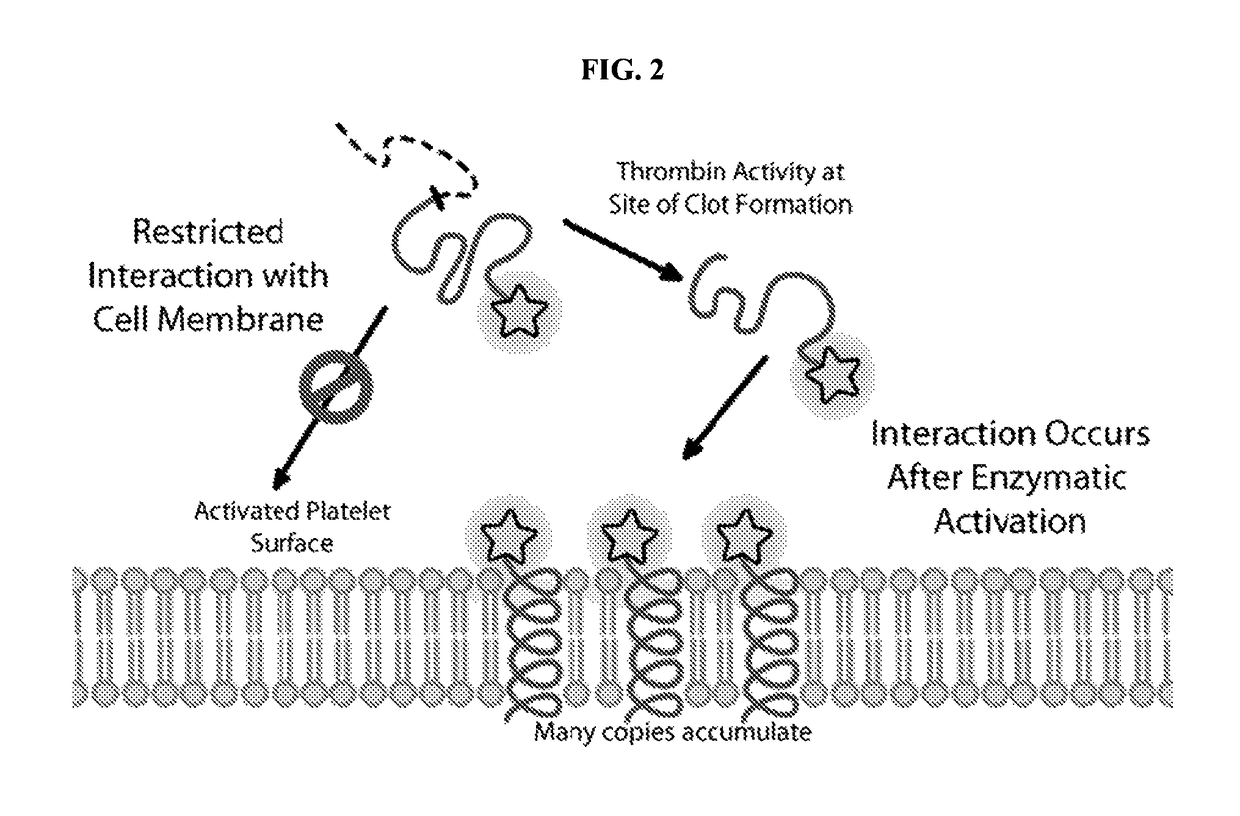
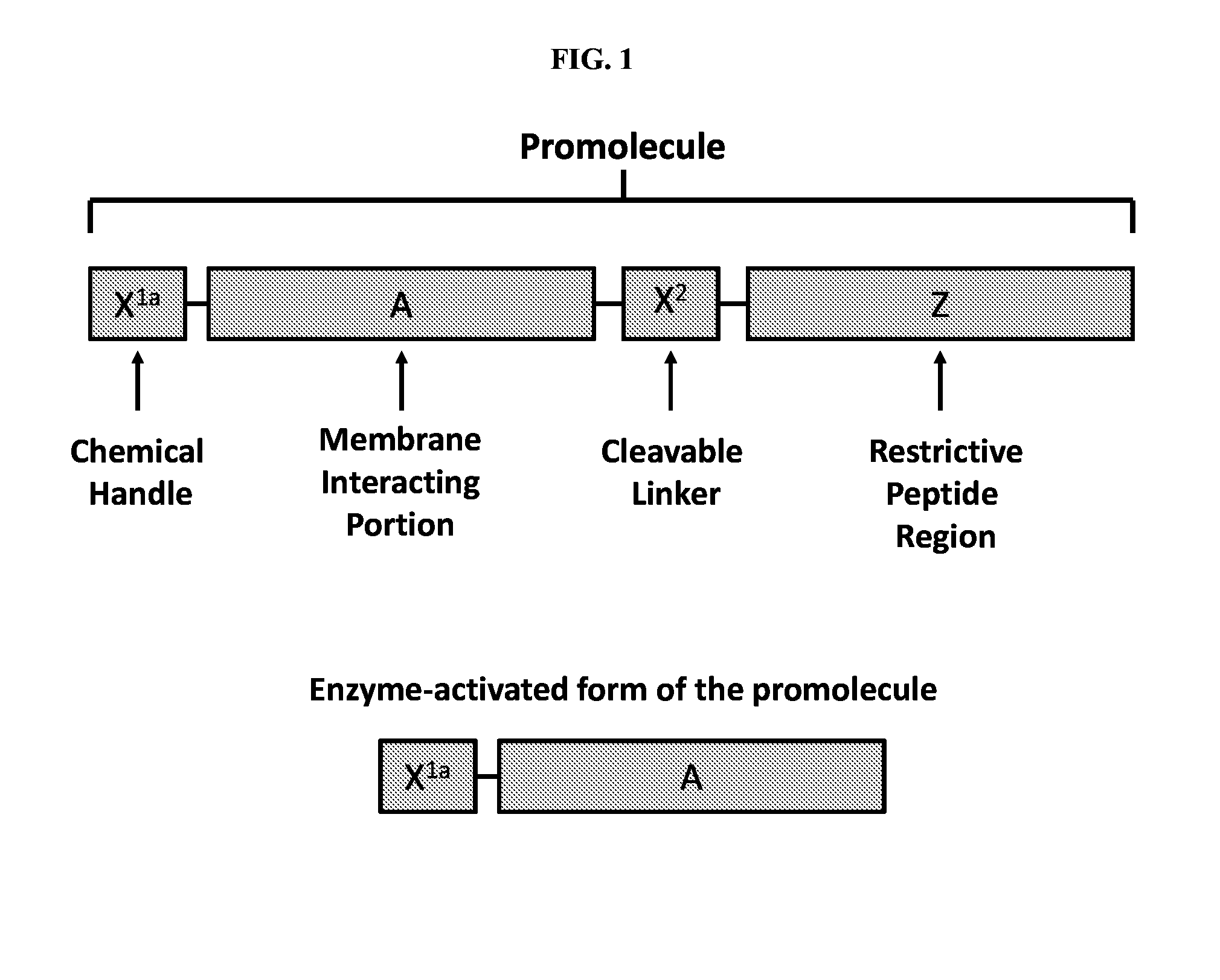
The present disclosure provides activatable and detectable membrane-interacting peptides that, following activation, can interact with phospholipid bilayers, such as cell membranes. The present disclosure also provides methods of use of such compounds. The compounds of the present disclosure are of the general structure X1a-A-X2-Z-X1b, where A is a membrane-interacting peptide region having a plurality of nonpolar hydrophobic amino acid residues that, following separation from portions Z, is capable of interaction with a phospholipid bilayer; Z is an inhibitory peptide region that can inhibit the activity of portion A; X2 is a cleavable linker that can be cleaved to release cleavage products from the compound; and X1a and X1b are optionally-present chemical handles that facilitate conjugation of various cargo moieties to the compound. Prior to cleavage of the composition at X2, the composition acts as a promolecule that does not associate with cellular membranes to a significant or detectable level. Following cleavage at cleavable linker X2, the cleavage product including portion A is free to interact with a phospholipid bilayer (e.g., a cell membrane), and thus accumulate at a site associated with a cleavage-promoting environment. Detection of the membrane-associated cleavage product can be accomplished by detection of a moiety attached through X1a and / or X1b. Such compositions can be used in a variety of methods, including, for example, use in directly imaging active clotting within a subject.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Application of semiconductor nano photosensitive material in preparing visual repair material
ActiveCN110101902AGood effectIncrease the interaction areaPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationRetinal ganglionBiocompatibility Testing
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor nano photosensitive materials, and relates to novel application of a semiconductor nanomaterial with a photosensitive effect, in particular to the application of a semiconductor nano photosensitive material in preparing a visual repair material. The semiconductor nano photosensitive material is similar to a retinal photoreceptor cell and is an ordered one-dimensional gold-modified titanium oxide nanowire array; the semiconductor nano photosensitive material has the advantages of high specific surface area, large material retinal interaction area, large charge mobility and good biocompatibility and stability, and is applied to both isolated retina and a living mouse by replacing a photoreceptor, so that the retina produces a photoreaction; the semiconductor nano photosensitive material can be used for preparing the visual repair material for repairing dysopia. Experiments confirm that the visual repair material can repair retinal ganglion cells to produce the photoreaction, thereby repairing visual cortical nerve cells to produce the photoreaction.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Activatable Membrane-Interacting Peptides and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20160082131A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsMembrane interactionCell membrane
The present disclosure provides activatable and detectable membrane-interacting peptides that, following activation, can interact with phospholipid bilayers, such as cell membranes. The present disclosure also provides methods of use of such compounds. The compounds of the present disclosure are of the general structure X1a-A-X2—Z—X1b, where A is a membrane-interacting peptide region having a plurality of nonpolar hydrophobic amino acid residues that, following separation from portions Z, is capable of interaction with a phospholipid bilayer; Z is an inhibitory peptide region that can inhibit the activity of portion A; X2 is a cleavable linker that can be cleaved to release cleavage products from the compound; and X1a and X1b are optionally-present chemical handles that facilitate conjugation of various cargo moieties to the compound. Prior to cleavage of the composition at X2, the composition acts as a promolecule that does not associate with cellular membranes to a significant or detectable level. Following cleavage at cleavable linker X2, the cleavage product including portion A is free to interact with a phospholipid bilayer (e.g., a cell membrane), and thus accumulate at a site associated with a cleavage-promoting environment. Detection of the membrane-associated cleavage product can be accomplished by detection of a moiety attached through X1a and / or X1b. Such compositions can be used in a variety of methods, including, for example, use in directly imaging active clotting within a subject.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
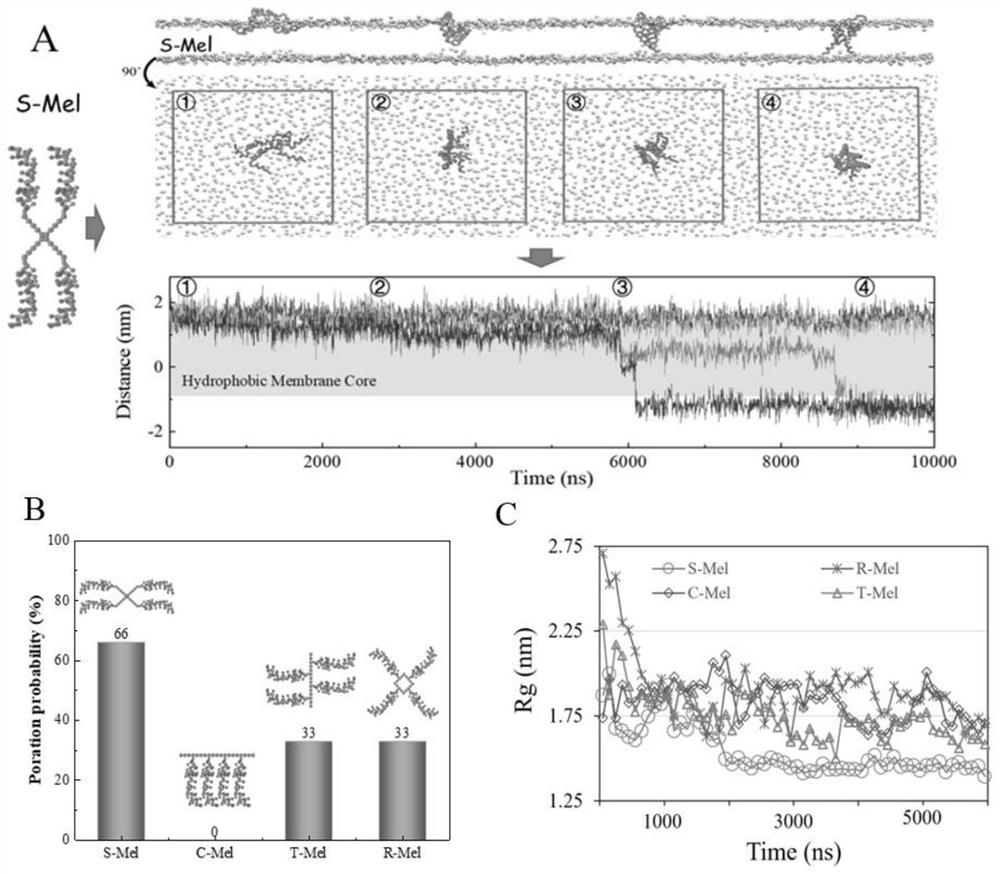
Antibacterial drug based on antimicrobial peptide C-terminal connection
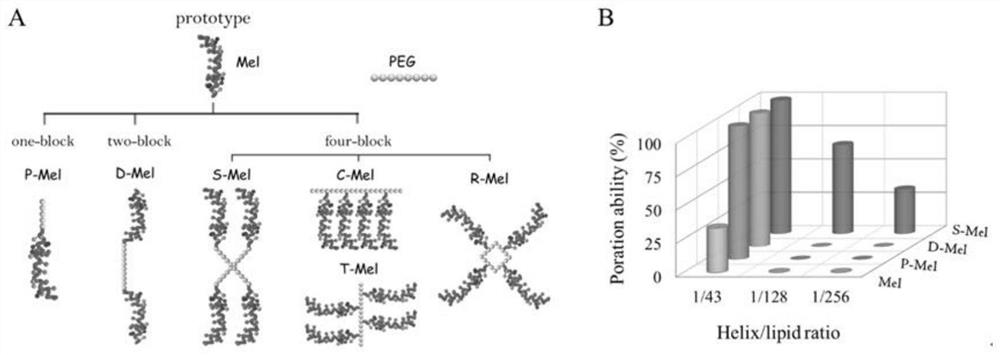
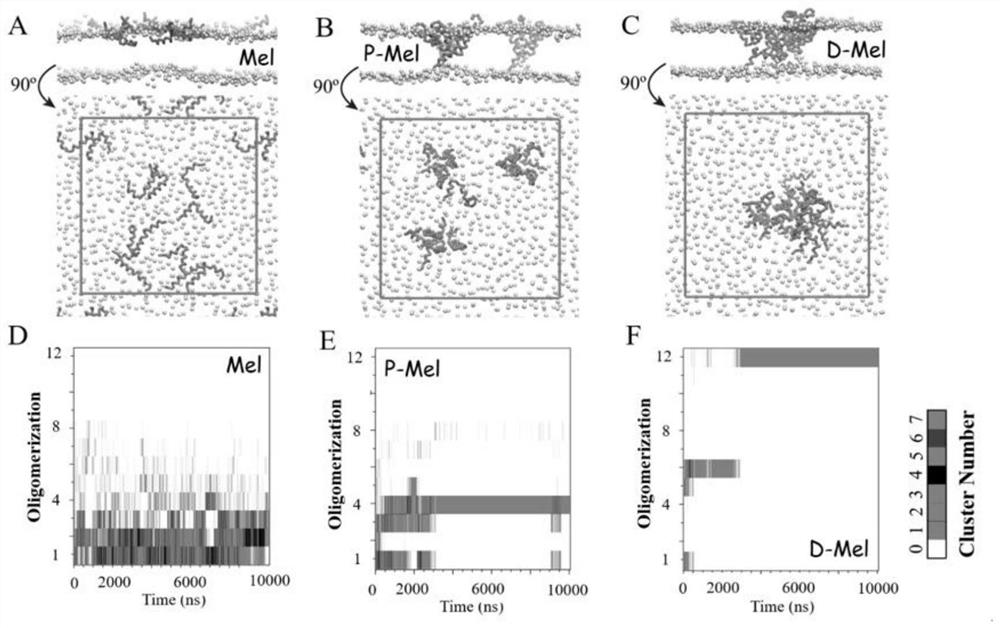
ActiveCN111686256AStrong pore forming abilityUnderstand molecular mechanismsAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial drugAntimicrobial peptides
The invention discloses an antibacterial drug based on antimicrobial peptide C-terminal connection. The antibacterial drug disclosed by the invention has extremely strong membrane rupture and pore-forming ability, and a polypeptide connector S-Mel with a four-arm star-shaped structure shows the highest pore-forming efficiency. A single S-Mel molecule is enough to punch a hole at extremely low concentration, and a plurality of molecules can cooperate to form a larger hole. In addition, the S-Mel has the capability of attacking cell membranes in a specific environment and controlling the pore size. The research of designing an efficient and controllable polypeptide molecular machine is helpful for understanding the molecular mechanism of the interaction between polypeptide and a membrane, and meanwhile, an effective strategy is provided for developing the research of killing specific cells (such as bacteria and tumors) in a targeting manner.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Systems and methods to shape laser light as a line beam for interaction with a substrate having surface variations
Systems and methods are disclosed for shaping laser light as a line beam for interaction with a film that may have an imperfect, non-planar surface. The system may include a beam stop that defines an edge; a sensor that measures a distance between a selected point on a surface of the film and a reference plane and generates a signal representative of the measured distance; and an actuator coupled to the beam stop and responsive to the signal to move a portion of beam stop edge. Movement of the beam stop edge portion shifts a corresponding portion of the focused line beam in a direction normal to the reference plane to produce a line beam that more closely conforms to the surface profile of the film.
Owner:CYMER INC
A centrifugal filter device
InactiveCN104588218BEasy to separateResolve remaining technical issuesCentrifugesParticulatesFiltration membrane
The invention discloses a centrifugal filter device. The centrifugal filter device includes a centrifugal filter and a centrifugal filter sample bottle. The centrifugal filter includes: a drive shaft; a sample turntable fixed on the drive shaft; a bottle carrier arranged on the on the sample turntable and can rotate relative to the sample turntable; the transmission gear is arranged on the drive shaft and can rotate relative to the drive shaft; the rotation gear is fixed on the bottle carrier and is connected to the bottle carrier The transmission gear meshes; the speed regulating device is arranged on the transmission gear; by fixing the centrifugal filter sample bottle on the centrifugal filter instrument, the centrifugal filter sample bottle is driven to rotate and Revolution, so that the suspension can interact with the filter membrane and the membrane cavity to fully separate the particles of different diameters, the large particles are left in the membrane cavity, and the filtration process is completed, which solves the problem that cannot be fully achieved in the prior art. Technical problems of separating large particles of impurities.
Owner:朱思龙
Systems and methods to shape laser light as a line beam for interaction with a substrate having surface variations
Owner:CYMER INC
A Simulation Method of Nuclear Material in Molten Salt Reactor
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cell culture bottle for co-culturing attached cells and suspension cells
PendingCN107937271ASolve the problem of co-cultivation that cannotAchieve experimental resultsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMembrane interactionSemipermeable membrane
The invention discloses a cell culture bottle for co-culturing attached cells and suspension cells. The cell culture bottle comprises a bottle body, wherein the bottle body is provided with a bottle opening and a bottle cap; the bottle body is internally provided with a nano semipermeable membrane; the nano semipermeable membrane is used for separating a space in the bottle body into two parts which are used as a culture container of the attached cells and a culture container of the suspension cells respectively; the bottle cap is an air permeable bottle cap. According to the cell culture bottle disclosed by the invention, the two types of cells do not influence each other in an operation process; however, cell factors secreted between the two types of cells can interact through the nano semipermeable membrane, and can really reflect mutual effects and influences between the two types of cells in a certain sense.
Owner:湖北省银丰鼎诚生物工程有限公司 +1
A multi-parameter detection device for oil and gas concentration
ActiveCN106198409BHigh sensitivityImprove coupling coefficientColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberLong-period fiber grating
The invention discloses a detection device for multiple parameters of oil and gas concentration. The detection device comprises a broadband light source, a methane sensor, an ethane sensor, a propane sensor, a humidity sensor, a temperature sensor, optical switches, a testing gas chamber, a computer, a mass flow controller and the like, wherein the front ends of all the sensors are connected with the broadband light source through the optical switch I; the rear ends of all the sensors are connected with a spectrum analyzer through the optical switch II; all the sensors are positioned in the testing gas chamber; sensitive membranes of the tilted long-period fiber grating methane, ethane and propane sensors are low refractive index ultraviolet-curing fluorosilicone sensitive membranes containing cage molecules (a cage molecule A, a cage molecule E-(OC3H7)6 or a cage molecule M-(OC3H7)6) and graphene; when methane, ethane and propane to be detected interact with the corresponding sensitive membranes, refractive indexes of the sensitive membranes are changed, and transmission spectra of the methane sensor, the ethane sensor and the propane sensor are enabled to drift; by means of the drift amount of the transmission spectra in the spectrum analyzer, the concentrations of the methane, the ethane and the propane can be measured.
Owner:重庆科知源科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com