Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
94 results about "Longitudinal optical" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
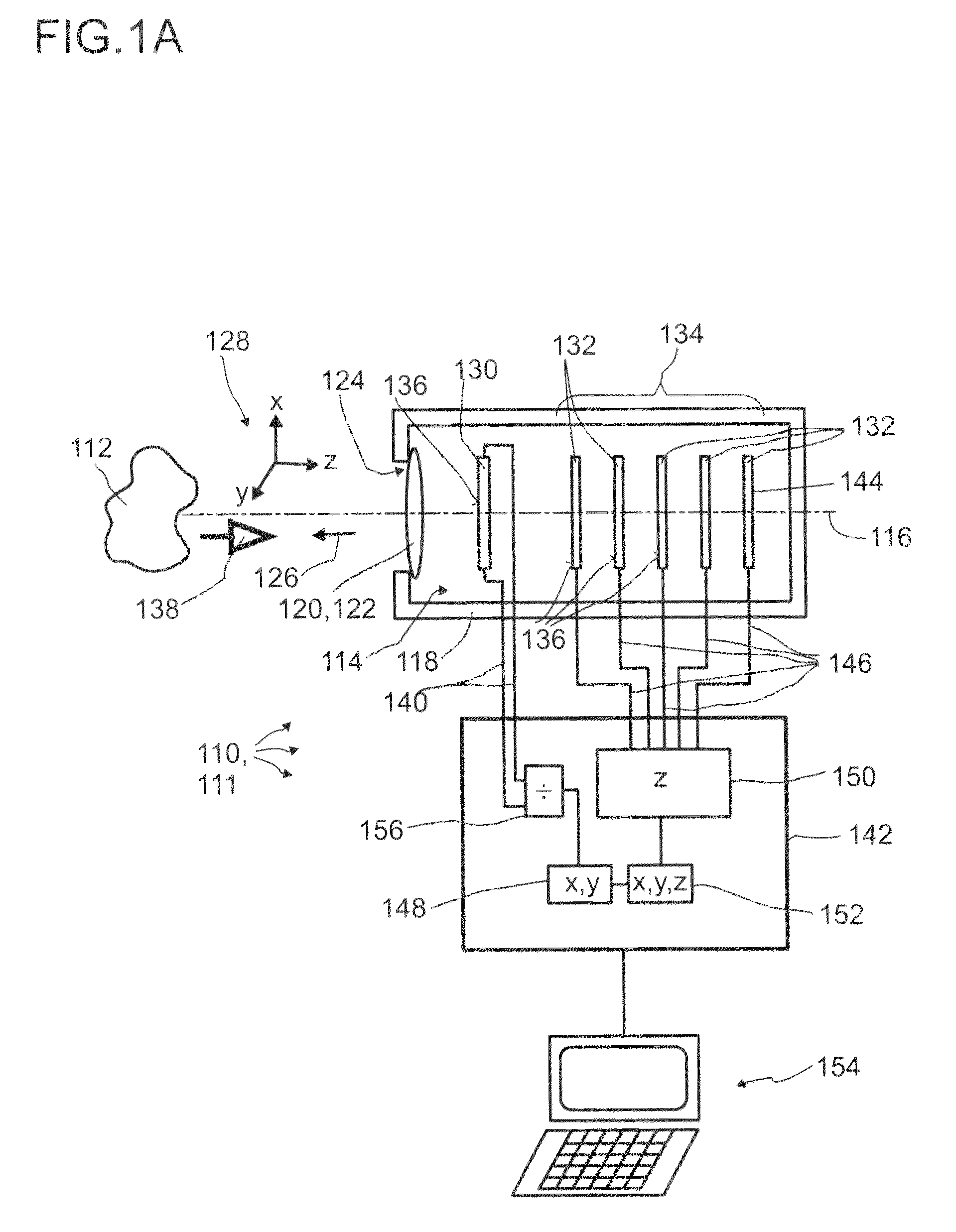
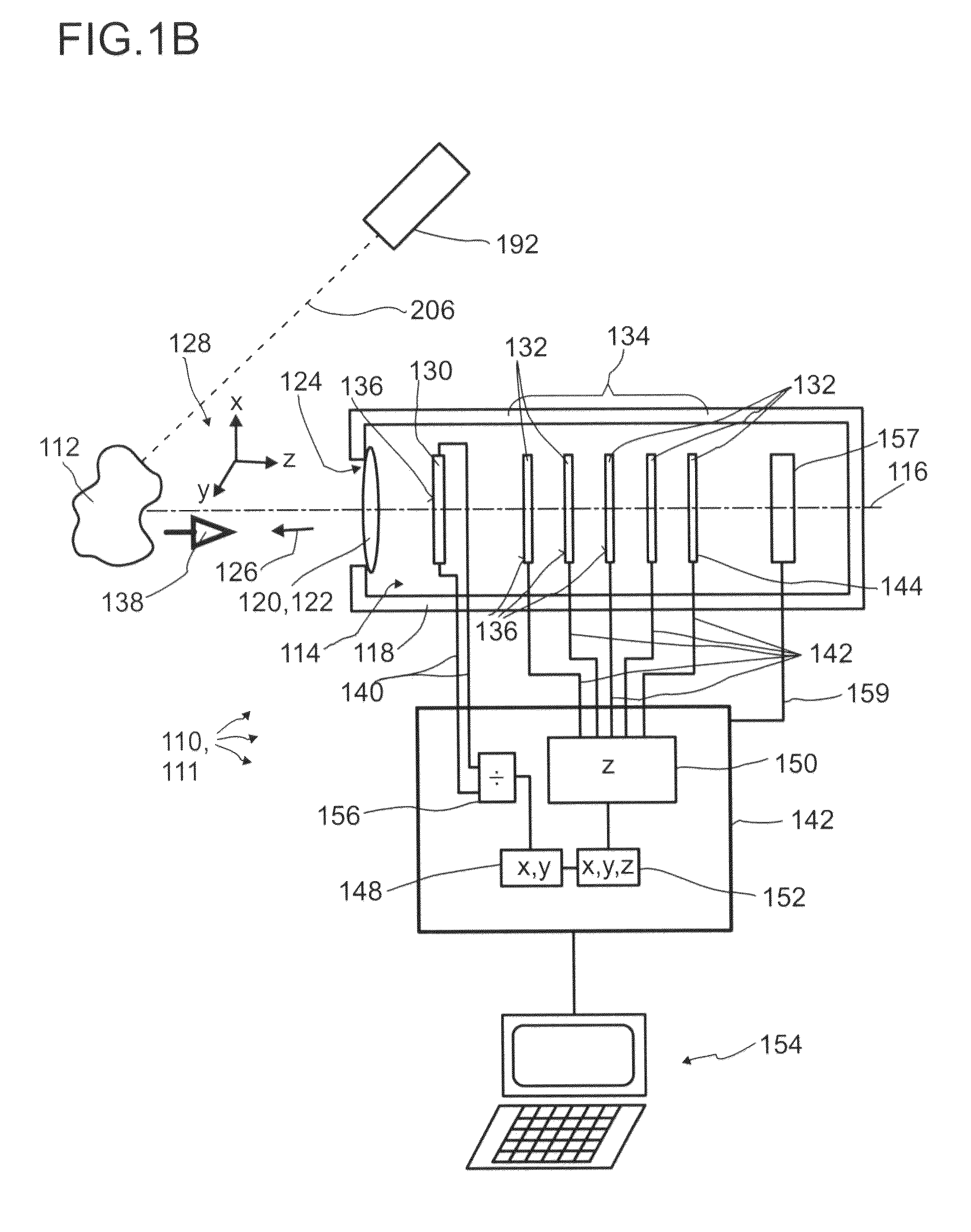
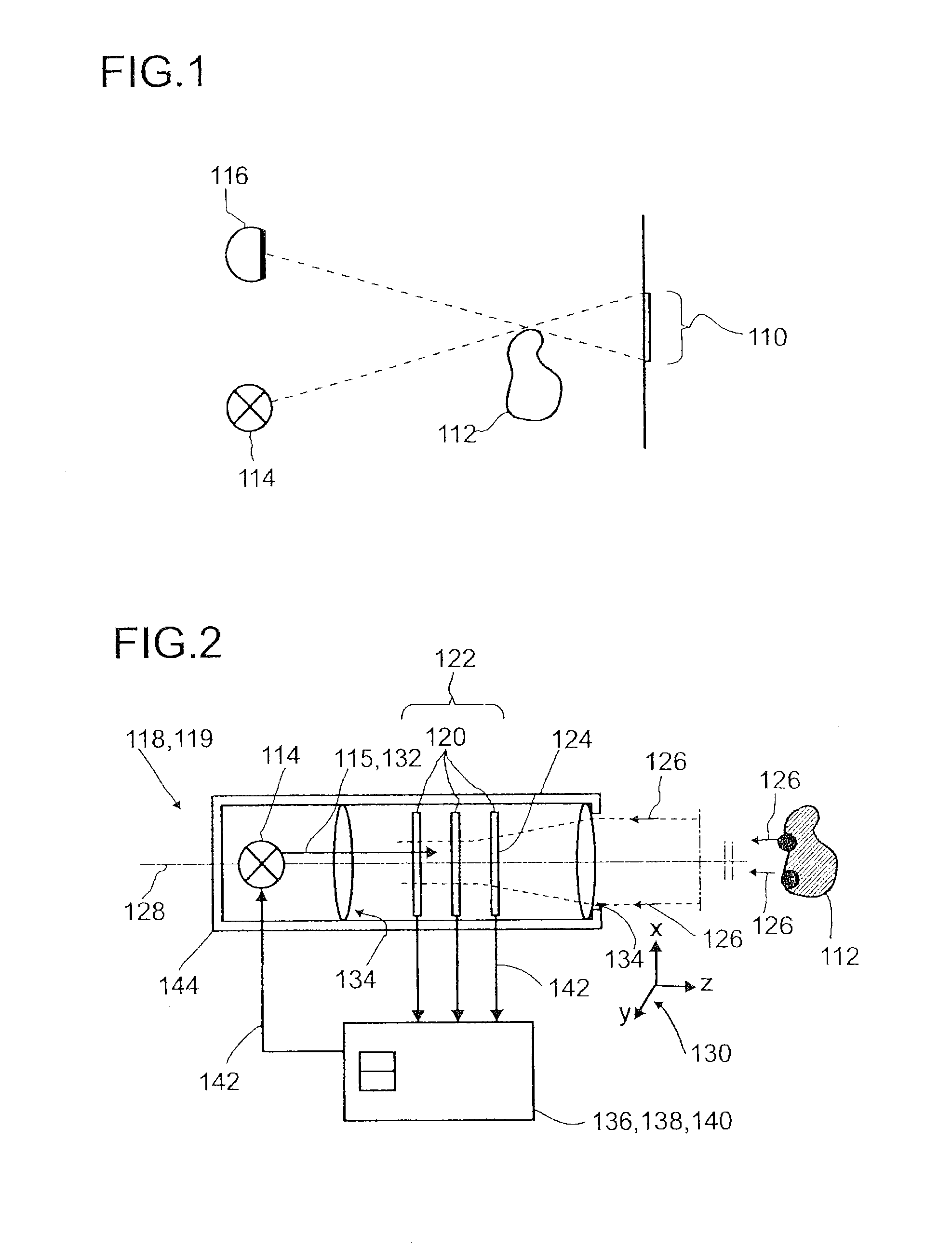
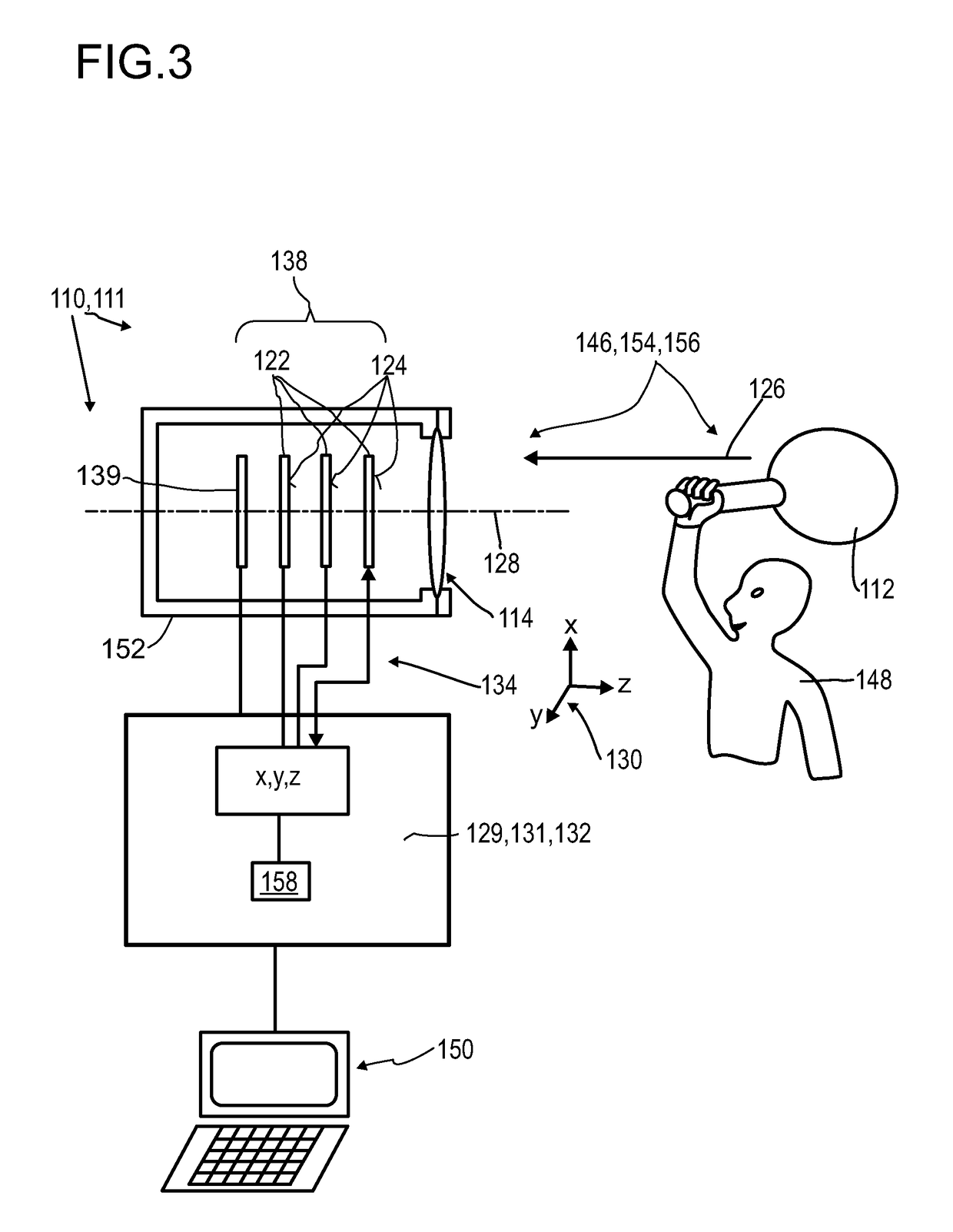
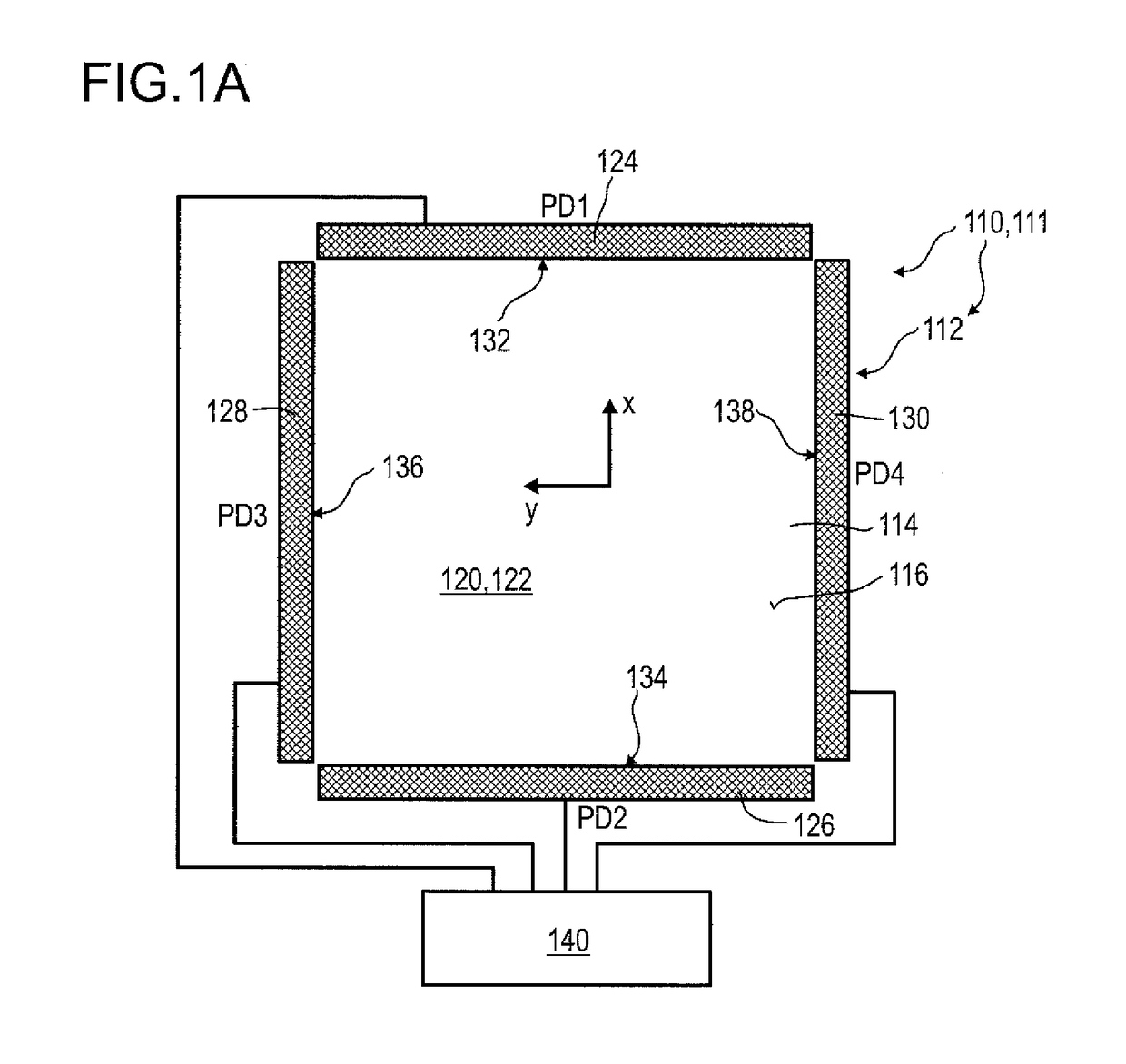
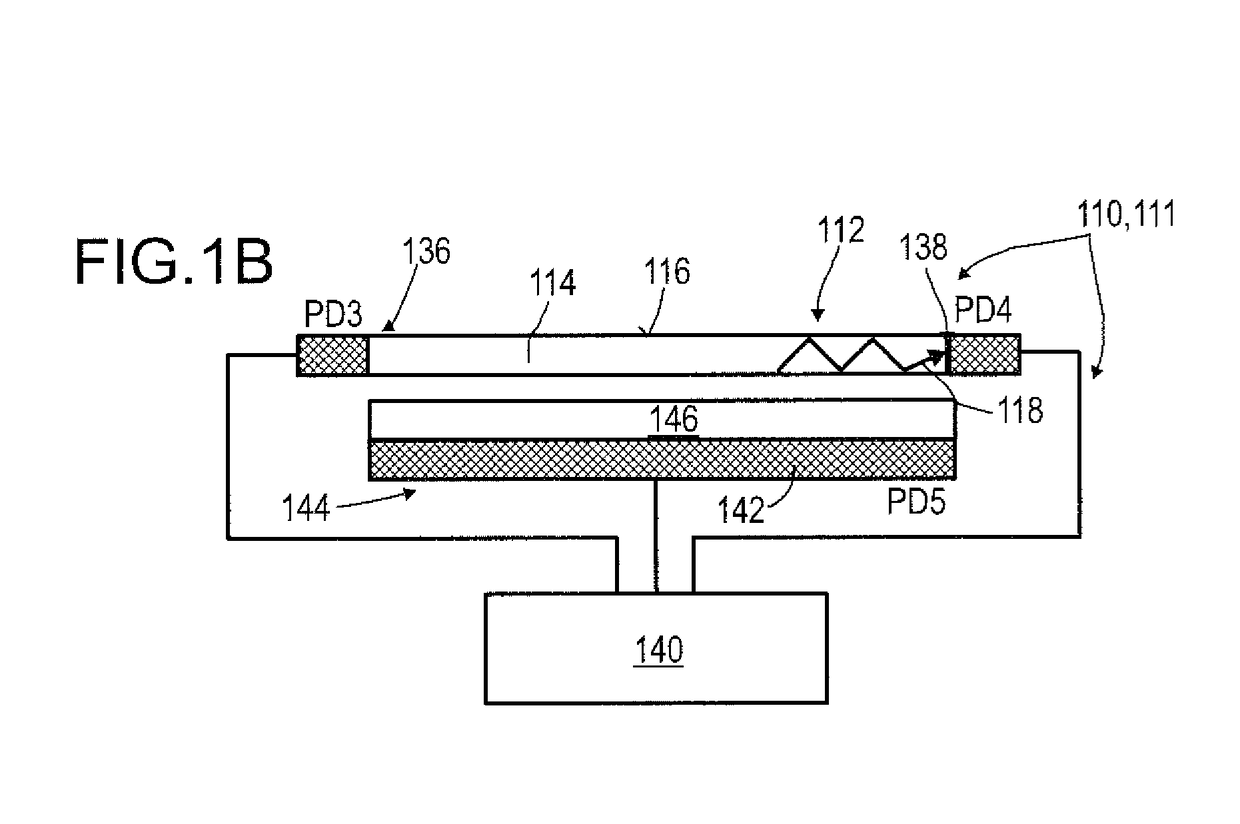
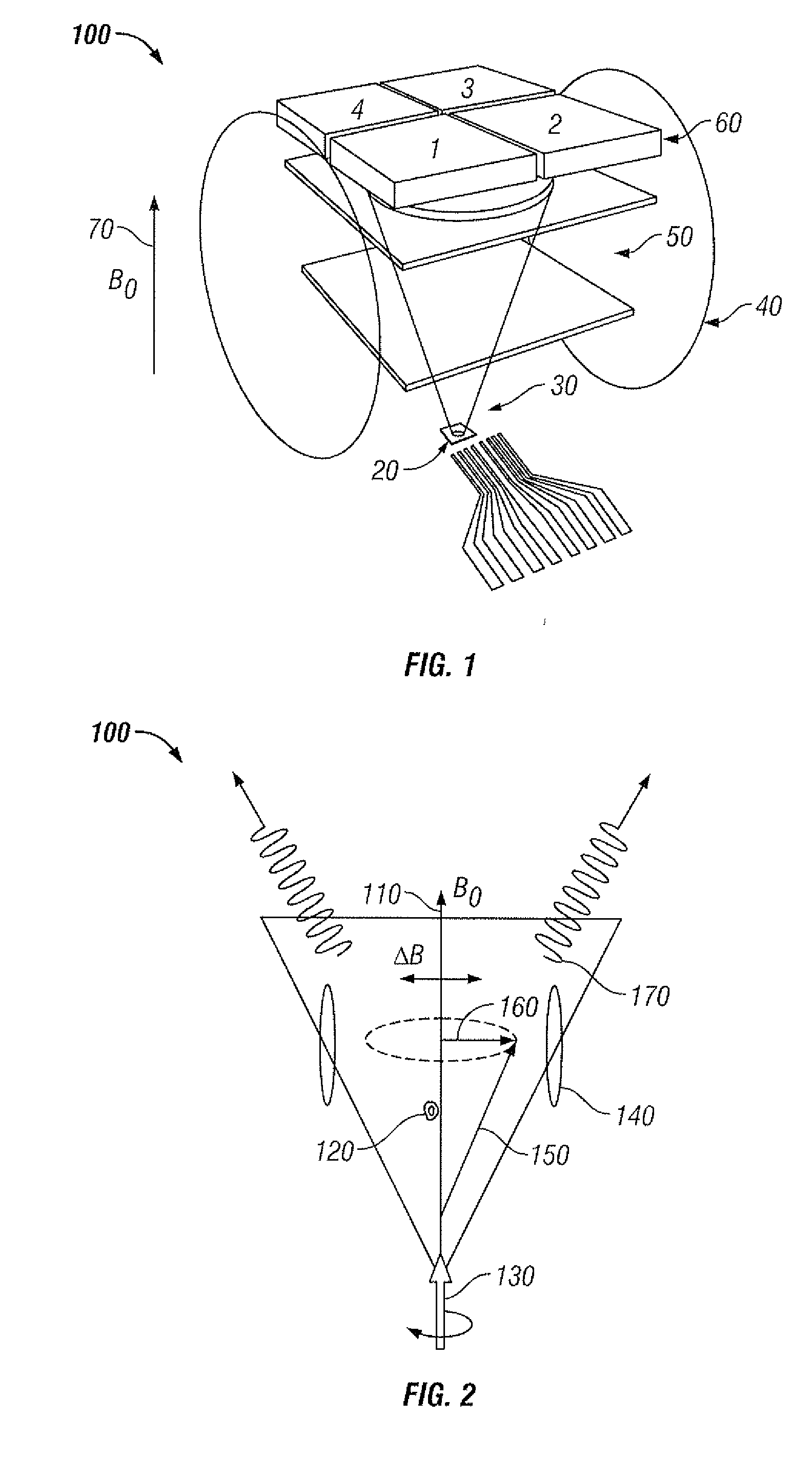
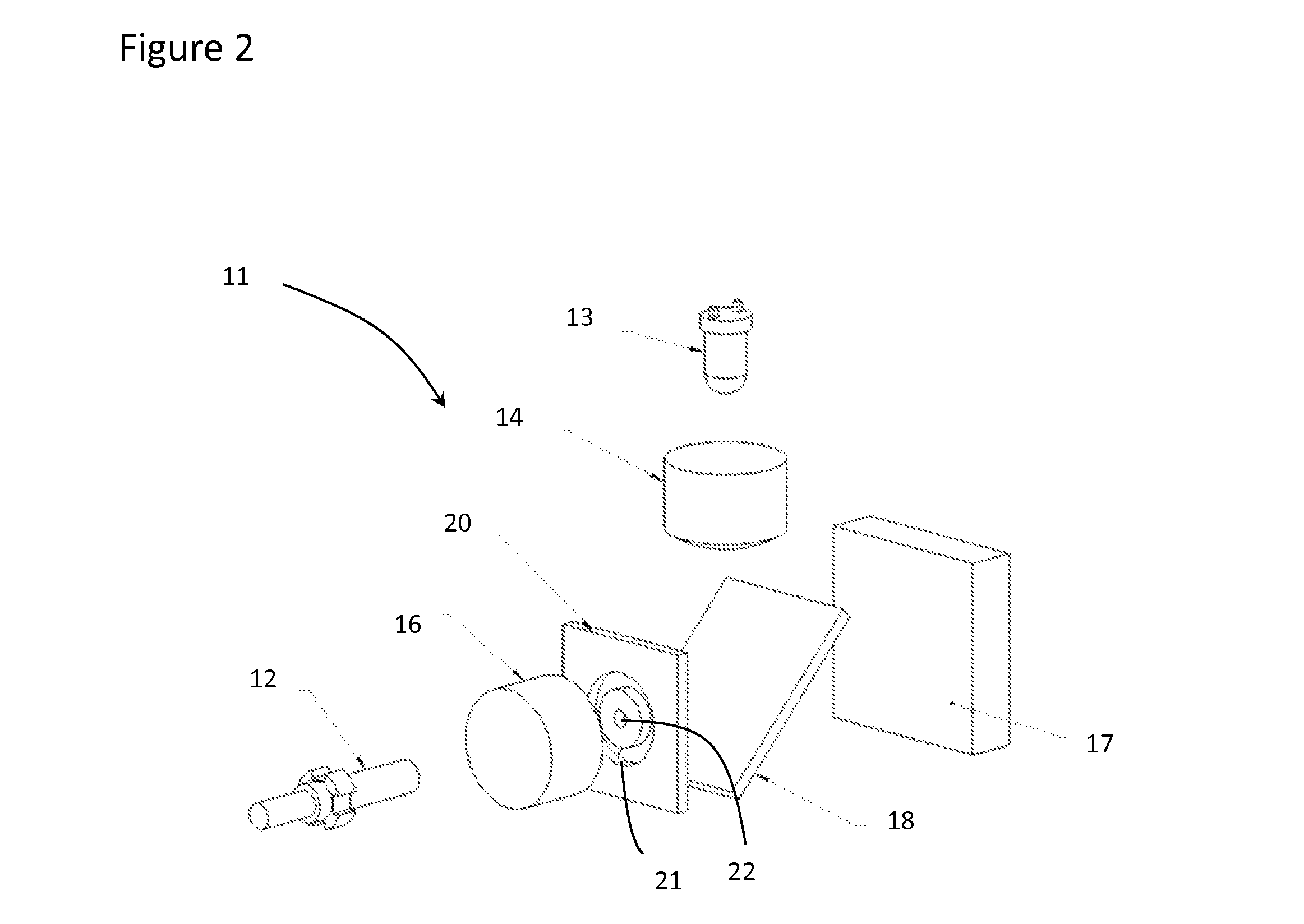
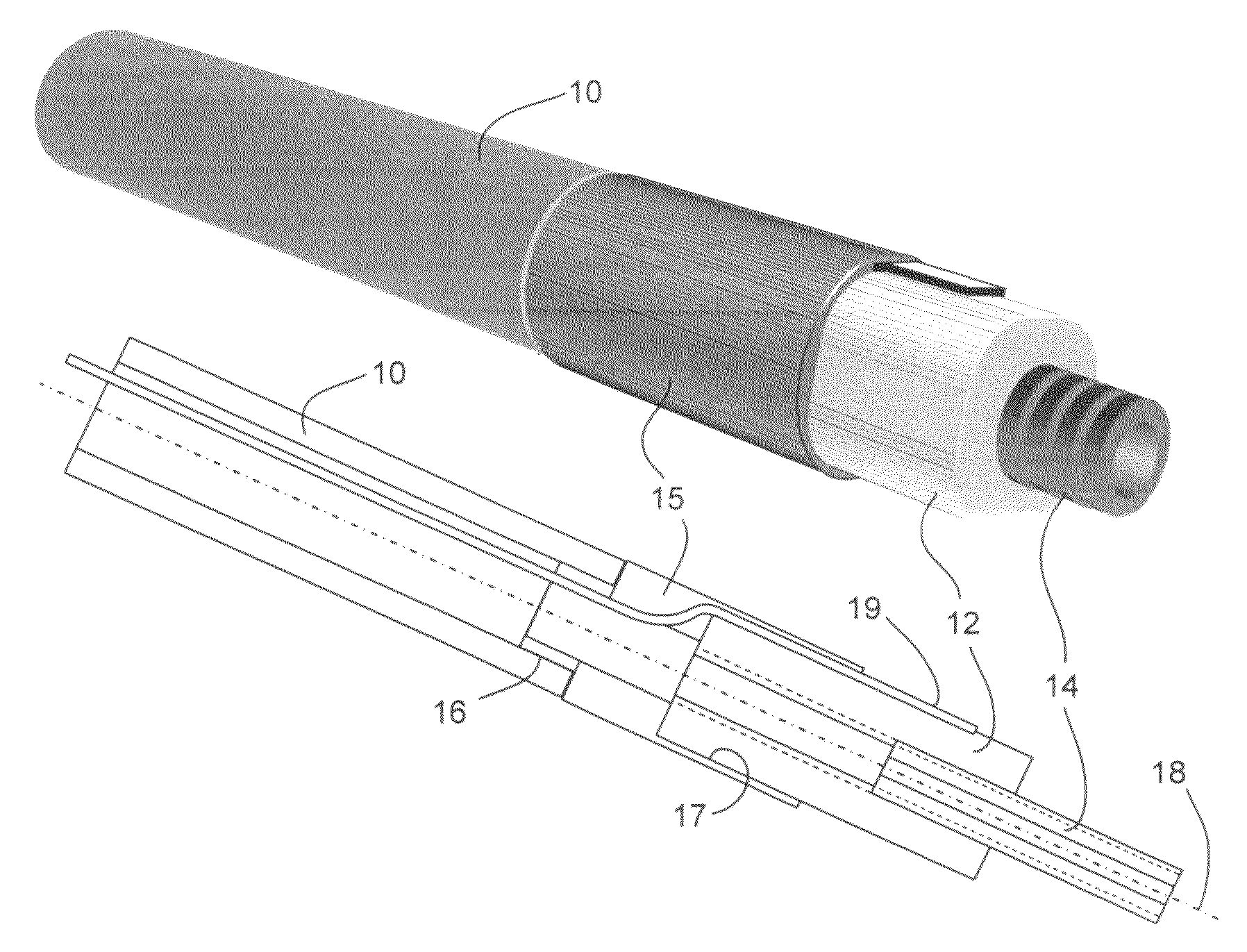
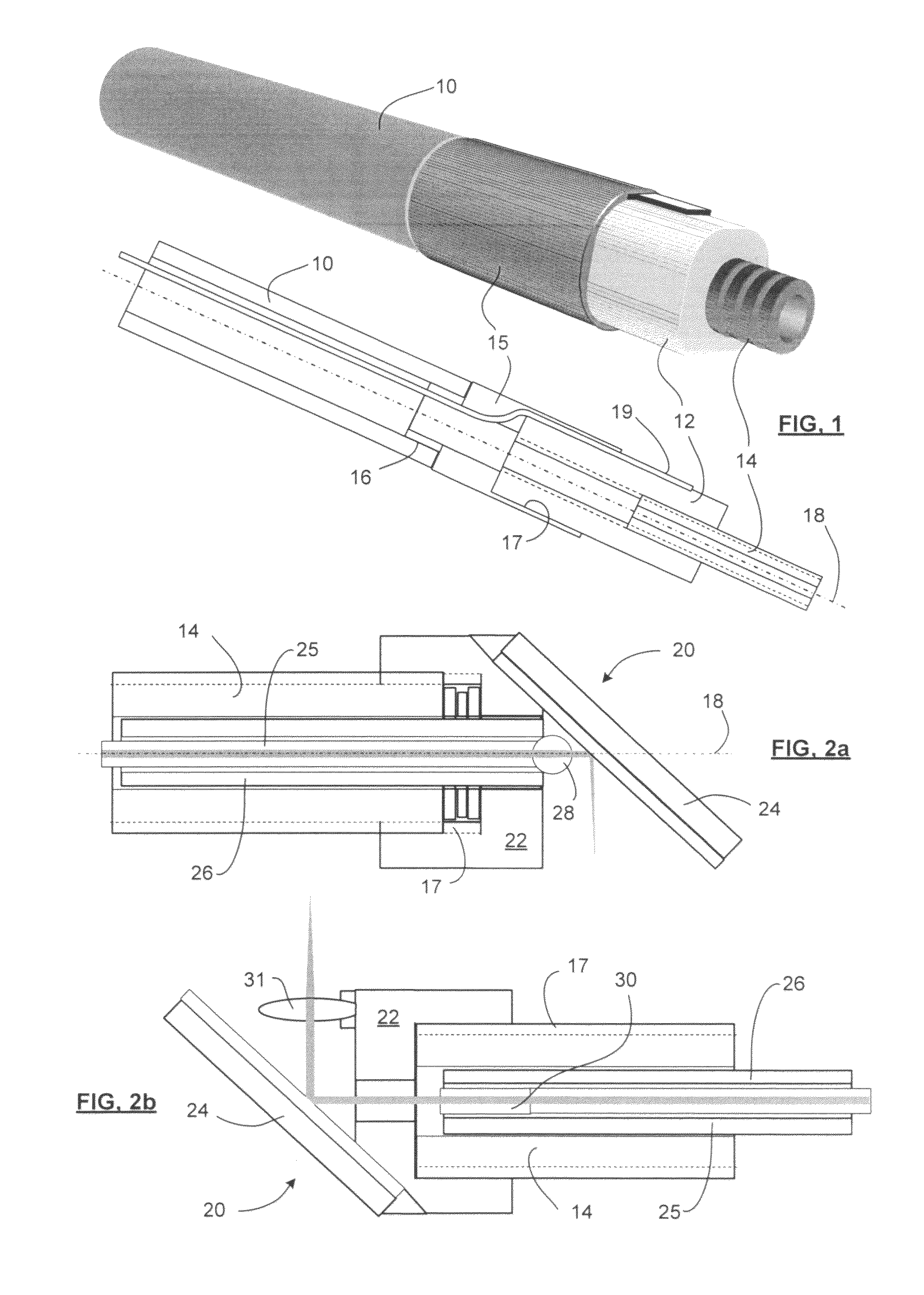
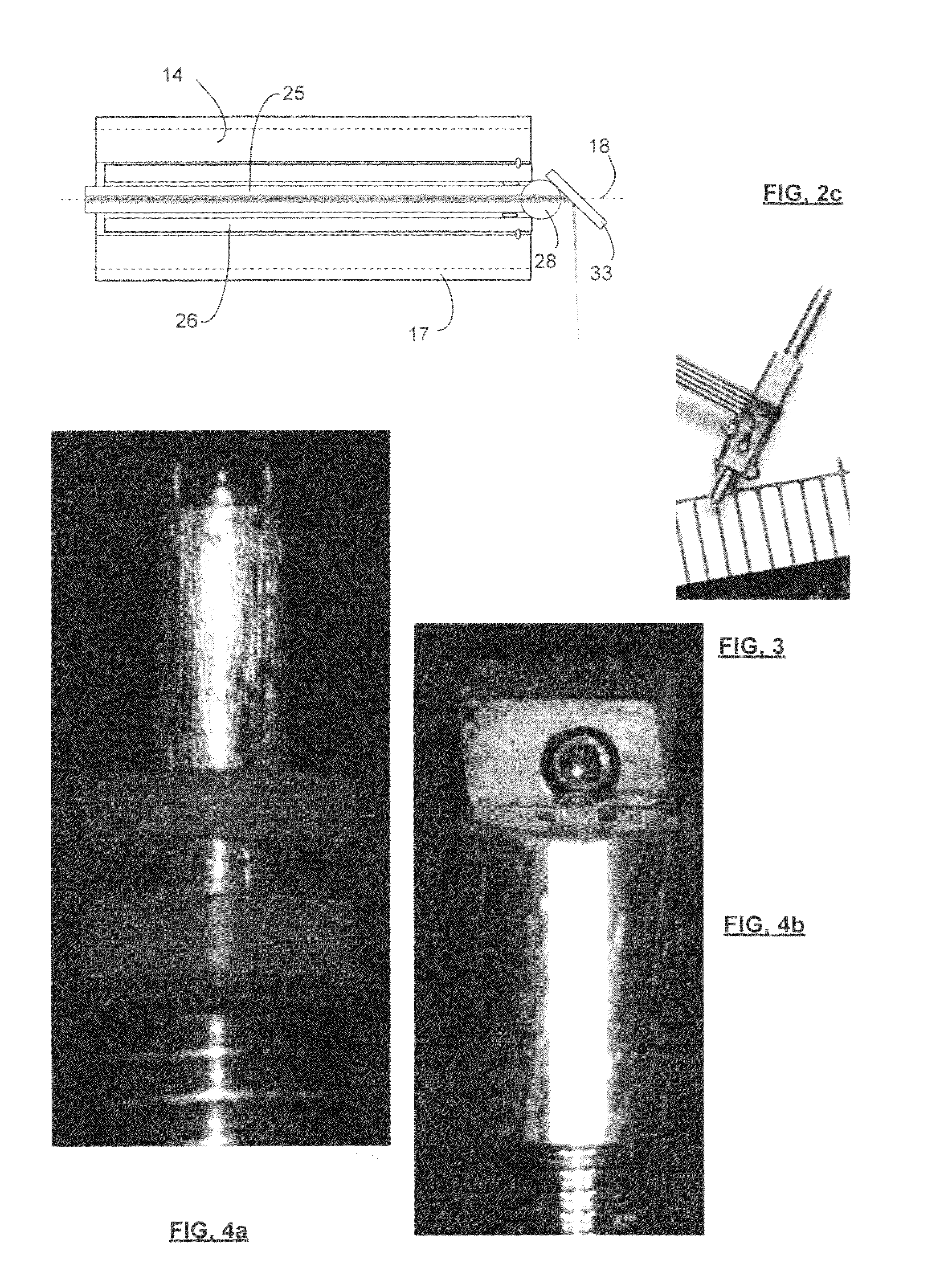
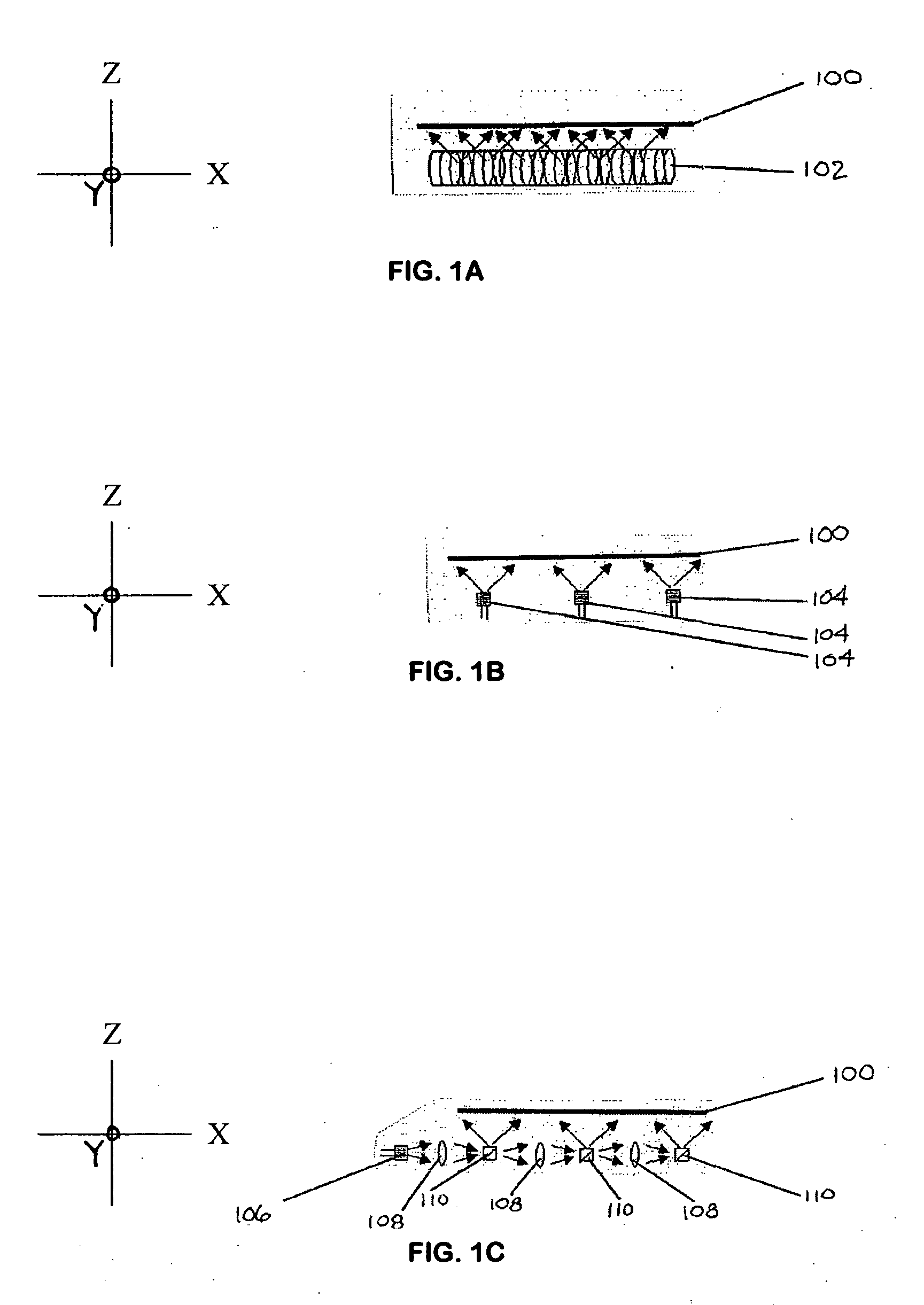
Detector for optically detecting at least one object
ActiveUS20140291480A1Improve long-term stabilityOptical rangefindersMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical axisLight beam
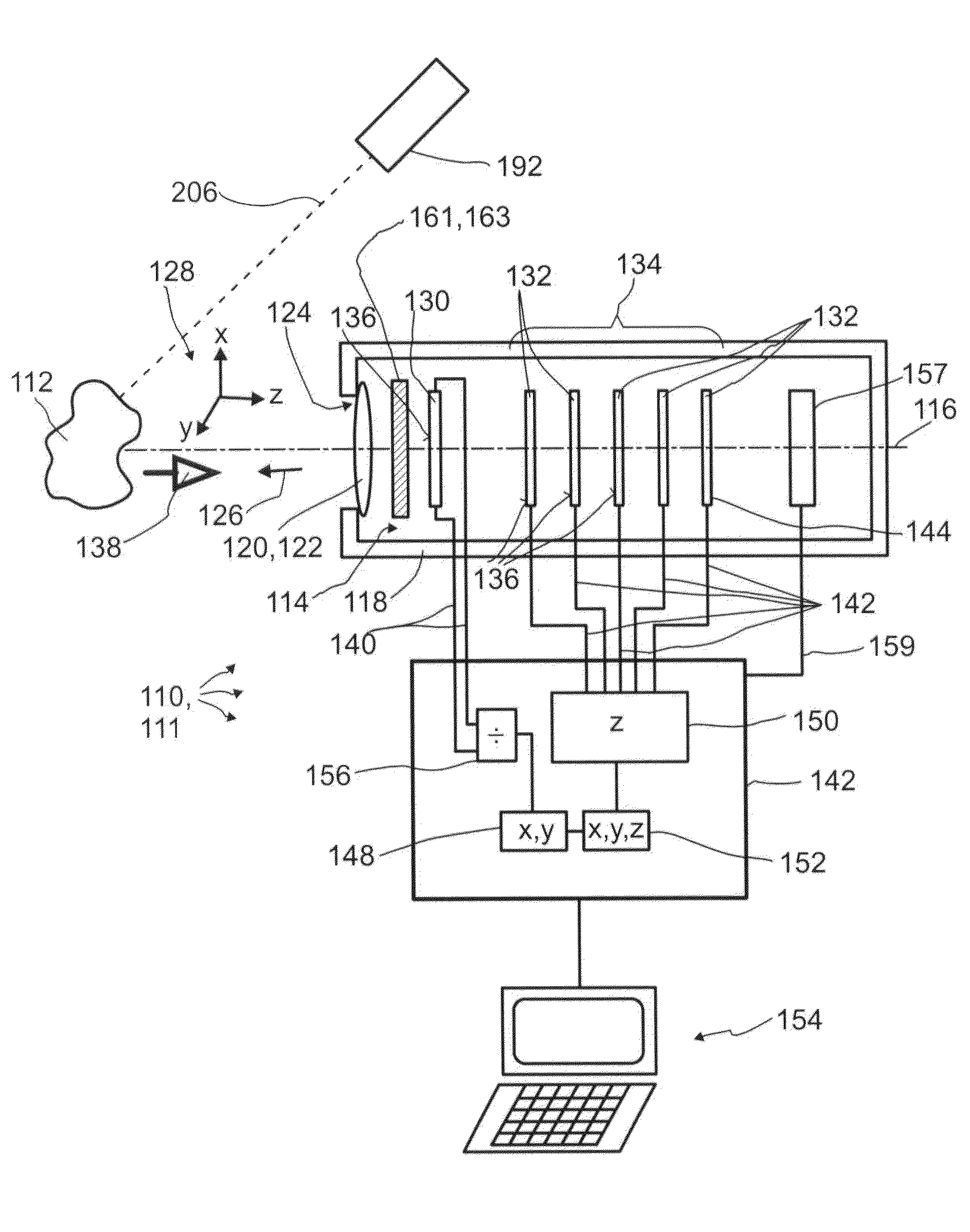
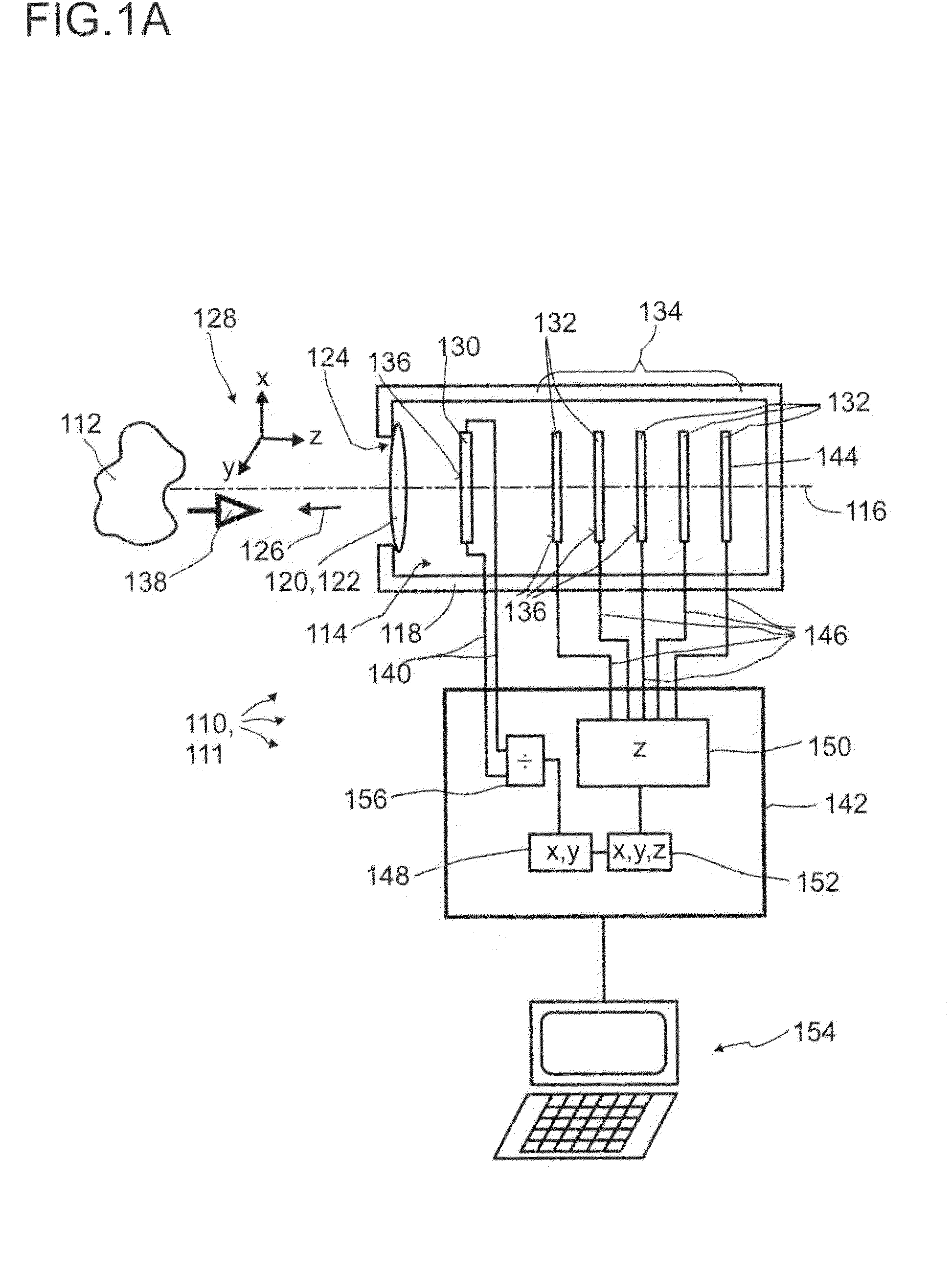
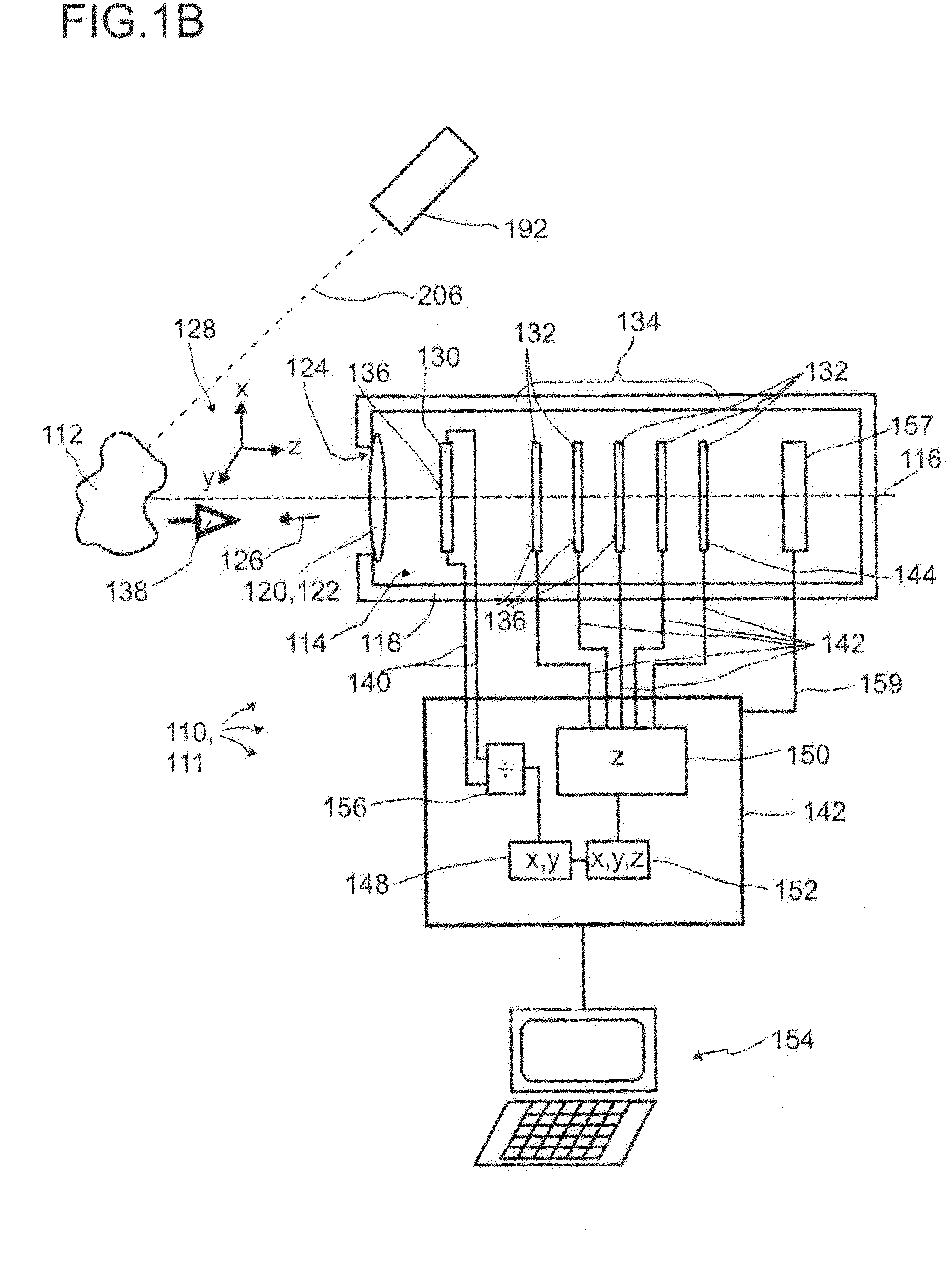
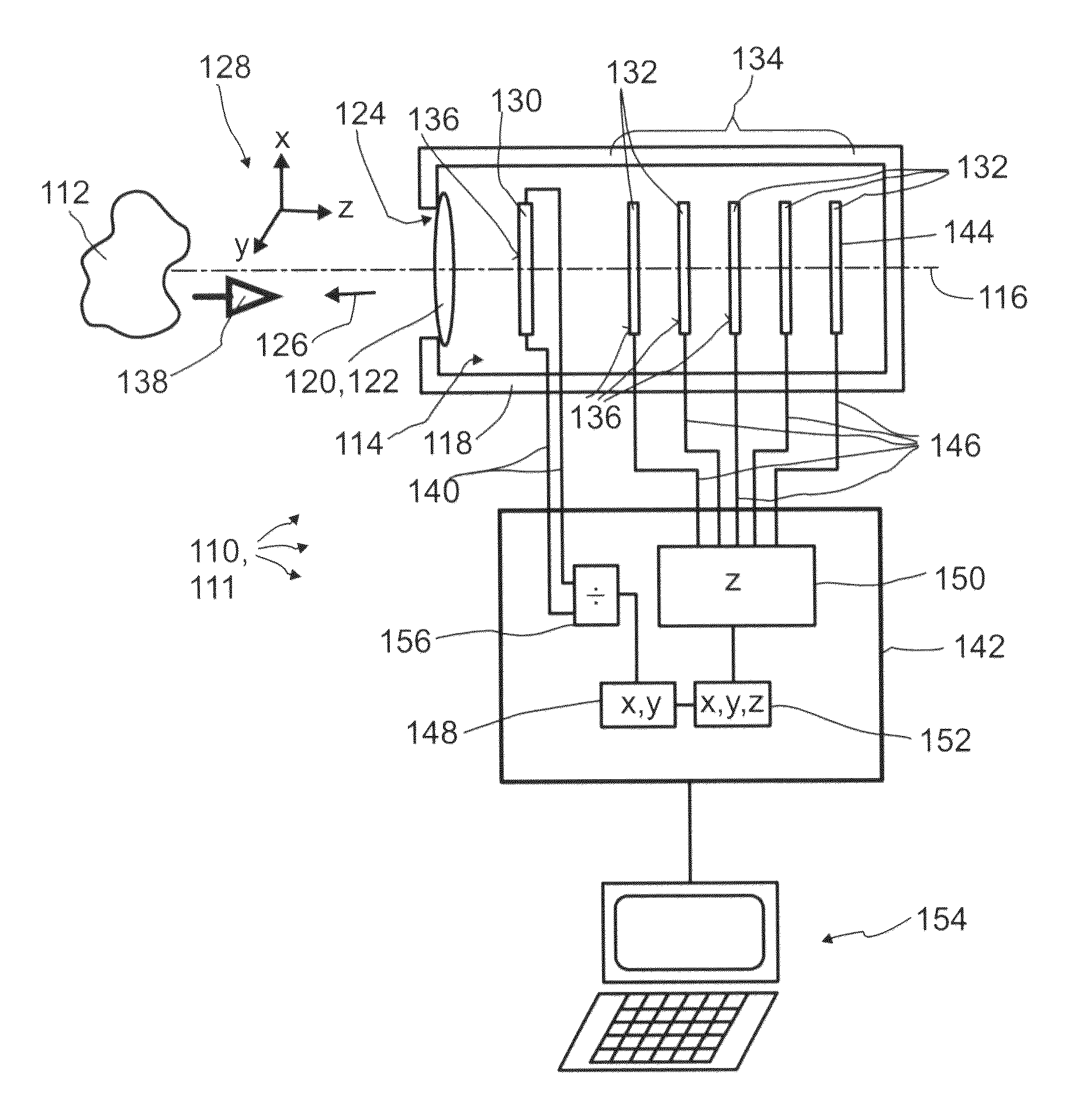
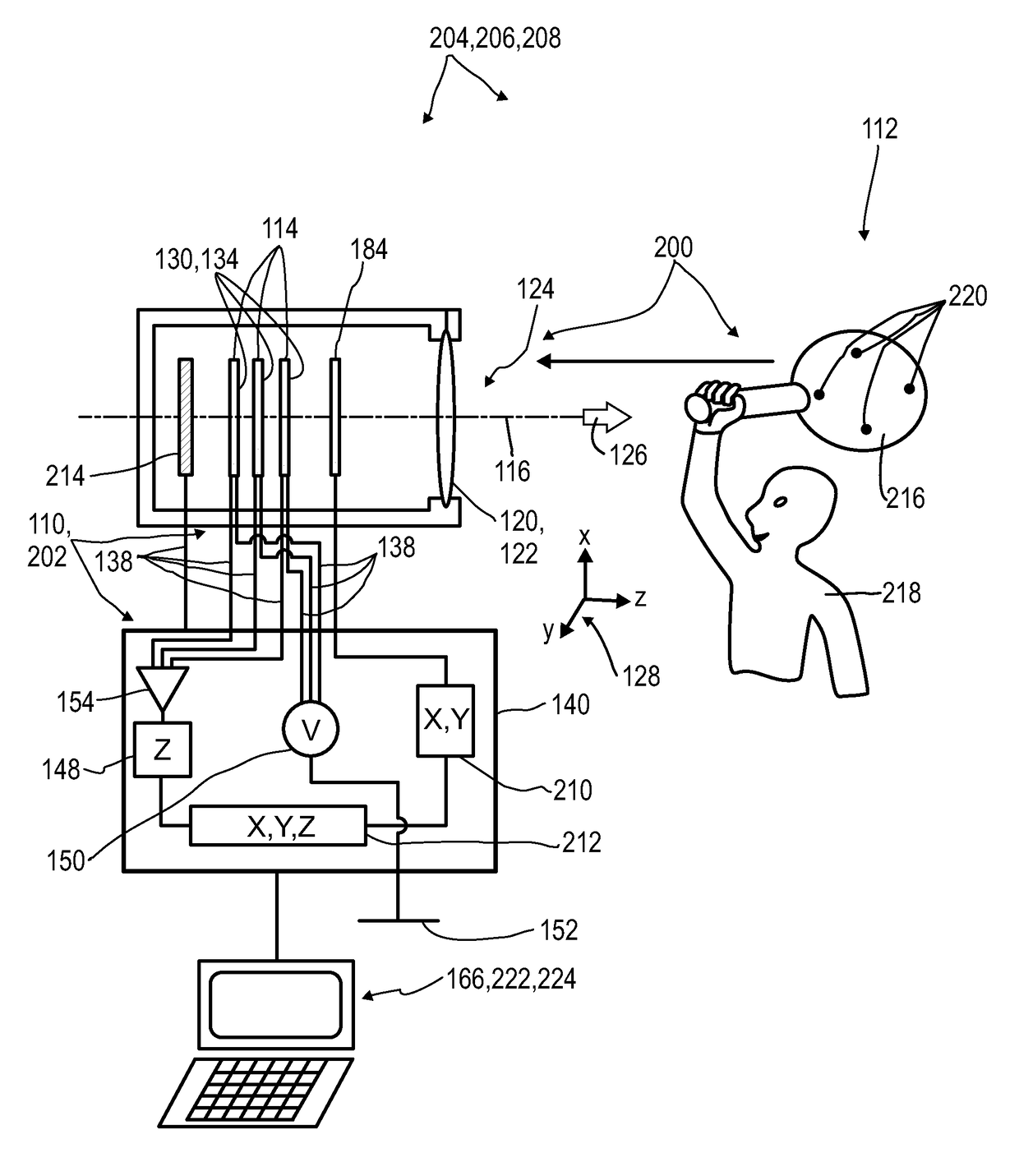
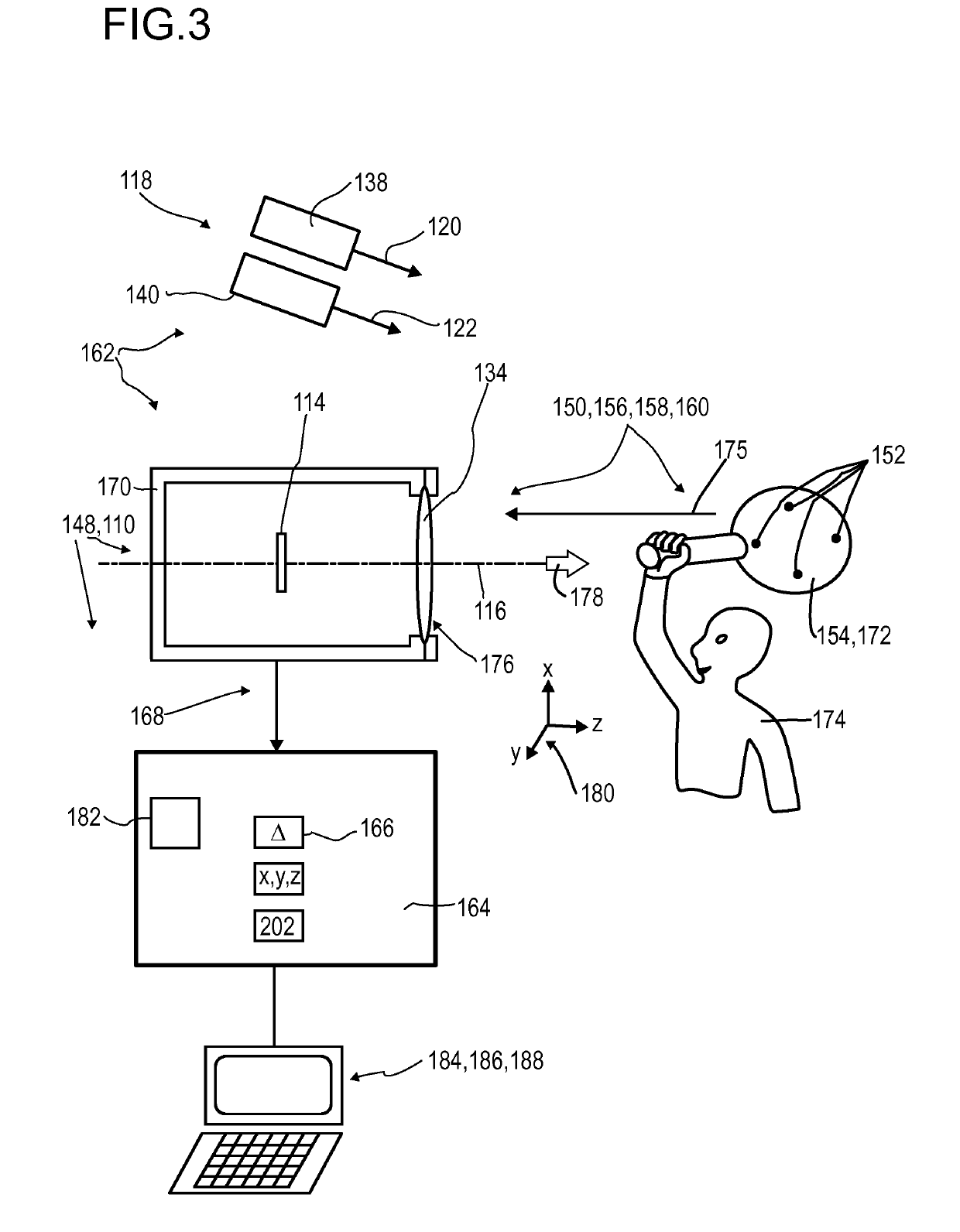
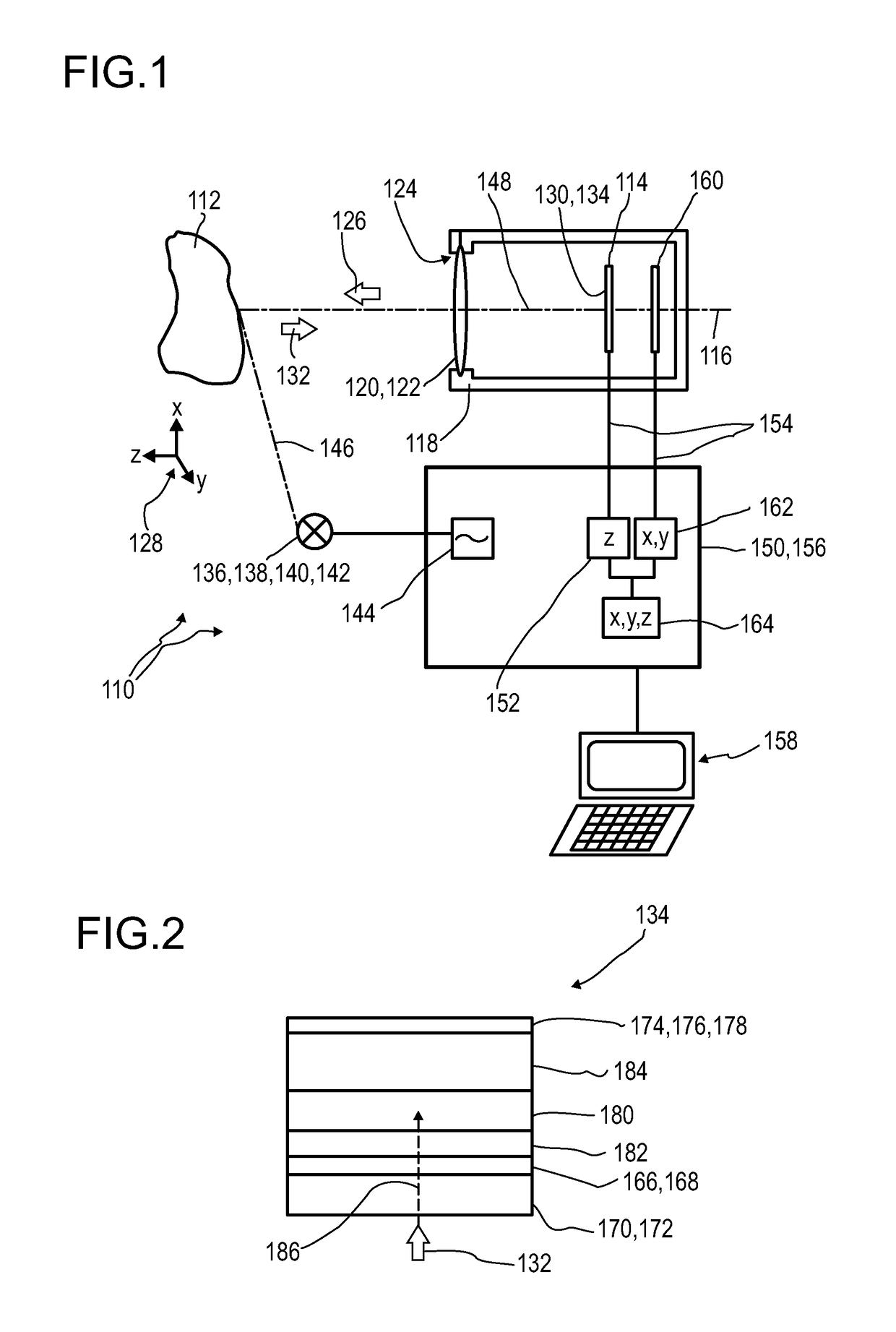
A detector (110) for determining a position of at least one object (112) is proposed. The detector (110) comprises:at least one transversal optical sensor (130), the transversal optical sensor (130) being adapted to determine a transversal position of at least one light beam (138) traveling from the object (112) to the detector (110), the transversal position being a position in at least one dimension perpendicular to an optical axis (116) of the detector (110), the transversal optical sensor (130) being adapted to generate at least one transversal sensor signal;at least one longitudinal optical sensor (132), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (132) has at least one sensor region (136), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (132) is designed to generate at least one longitudinal sensor signal in a manner dependent on an illumination of the sensor region (136) by the light beam (138), wherein the longitudinal sensor signal, given the same total power of the illumination, is dependent on a beam cross-section of the light beam (138) in the sensor region (136);at least one evaluation device (142), wherein the evaluation device (142) is designed to generate at least one item of information on a transversal position of the object (112) by evaluating the transversal sensor signal and to generate at least one item of information on a longitudinal position of the object (112) by evaluating the longitudinal sensor signal.
Owner:BASF AG
Method of motion correction in optical coherence tomography imaging
An image data set acquired by an optical coherence tomography (OCT) system is corrected for effects due to motion of the sample. A first set of A-scans is acquired within a time short enough to avoid any significant motion of the sample. A second more extensive set of A-scans is acquired over an overlapping region on the sample. Significant sample motion may occur during acquisition of the second set. A-scans from the first set are matched with A-scans from the second set, based on similarity between the longitudinal optical scattering profiles they contain. Such matched pairs of A-scans are likely to correspond to the same region in the sample. Comparison of the OCT scanner coordinates that produced each A-scan in a matching pair, in conjunction with any shift in the longitudinal scattering profiles between the pair of A-scans, reveals the displacement of the sample between acquisition of the first and second A-scans in the pair. Estimates of the sample displacement are used to correct the transverse and longitudinal coordinates of the A-scans in the second set, to form a motion-corrected OCT data set.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Detector comprising a transversal optical sensor for detecting a transversal position of a light beam from an object and a longitudinal optical sensor sensing a beam cross-section of the light beam in a sensor region
ActiveUS9389315B2Improve long-term stabilityPhotometry using reference valueOptical rangefindersOptical axisLight beam
A detector (110) for determining a position of at least one object (112) is proposed. The detector (110) comprises:at least one transversal optical sensor (130), the transversal optical sensor (130) being adapted to determine a transversal position of at least one light beam (138) traveling from the object (112) to the detector (110), the transversal position being a position in at least one dimension perpendicular to an optical axis (116) of the detector (110), the transversal optical sensor (130) being adapted to generate at least one transversal sensor signal;at least one longitudinal optical sensor (132), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (132) has at least one sensor region (136), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (132) is designed to generate at least one longitudinal sensor signal in a manner dependent on an illumination of the sensor region (136) by the light beam (138), wherein the longitudinal sensor signal, given the same total power of the illumination, is dependent on a beam cross-section of the light beam (138) in the sensor region (136);at least one evaluation device (142), wherein the evaluation device (142) is designed to generate at least one item of information on a transversal position of the object (112) by evaluating the transversal sensor signal and to generate at least one item of information on a longitudinal position of the object (112) by evaluating the longitudinal sensor signal.
Owner:BASF SE
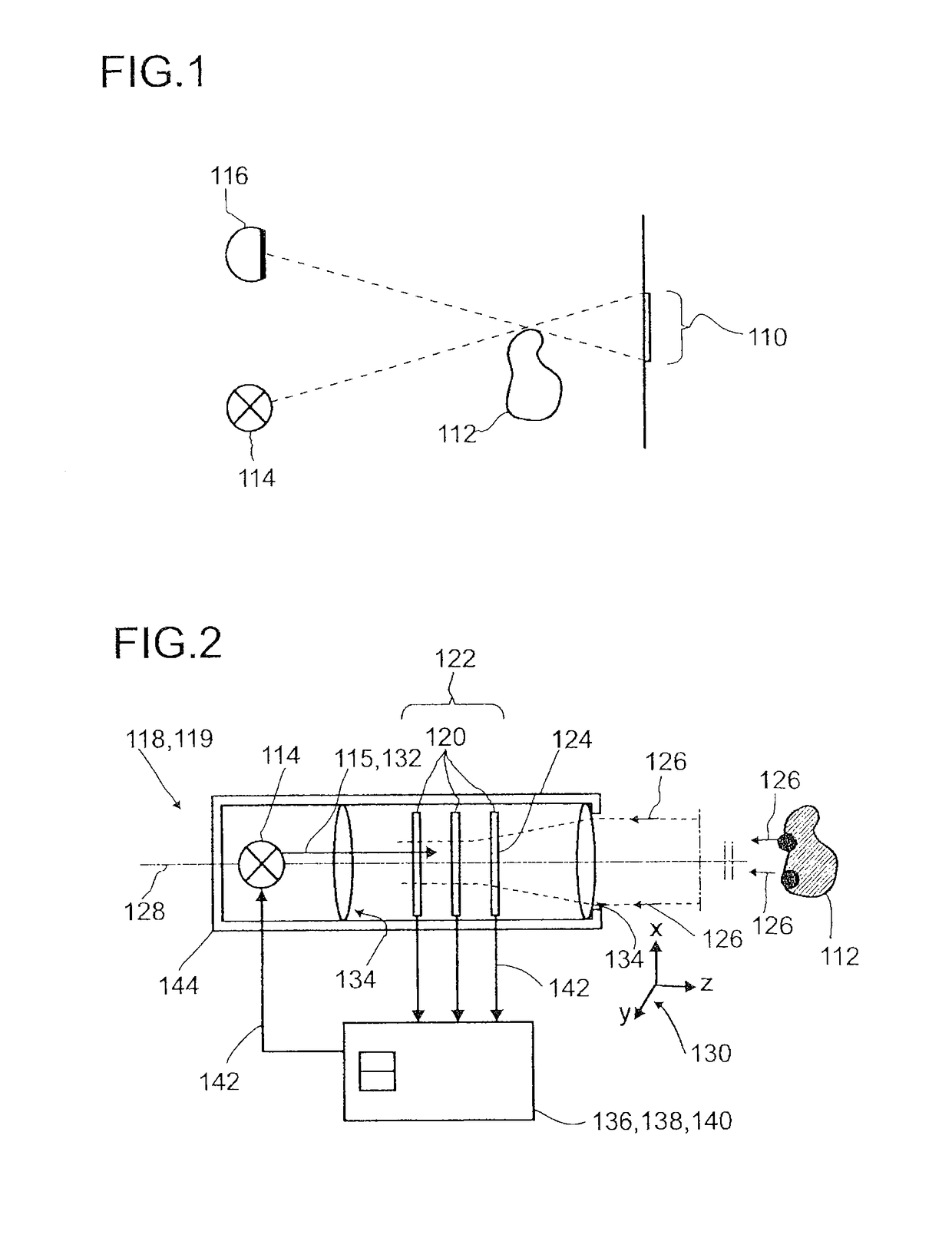
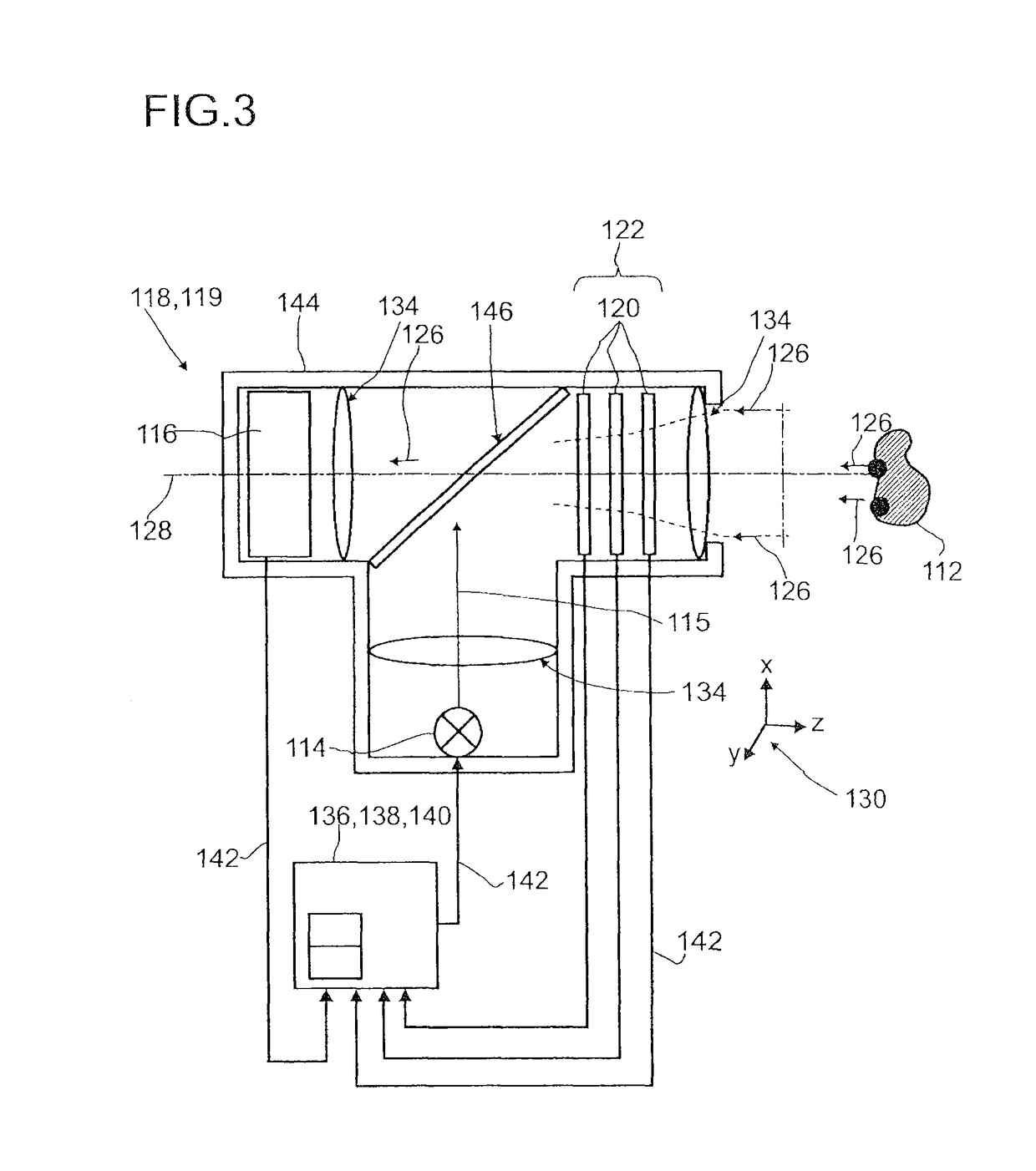
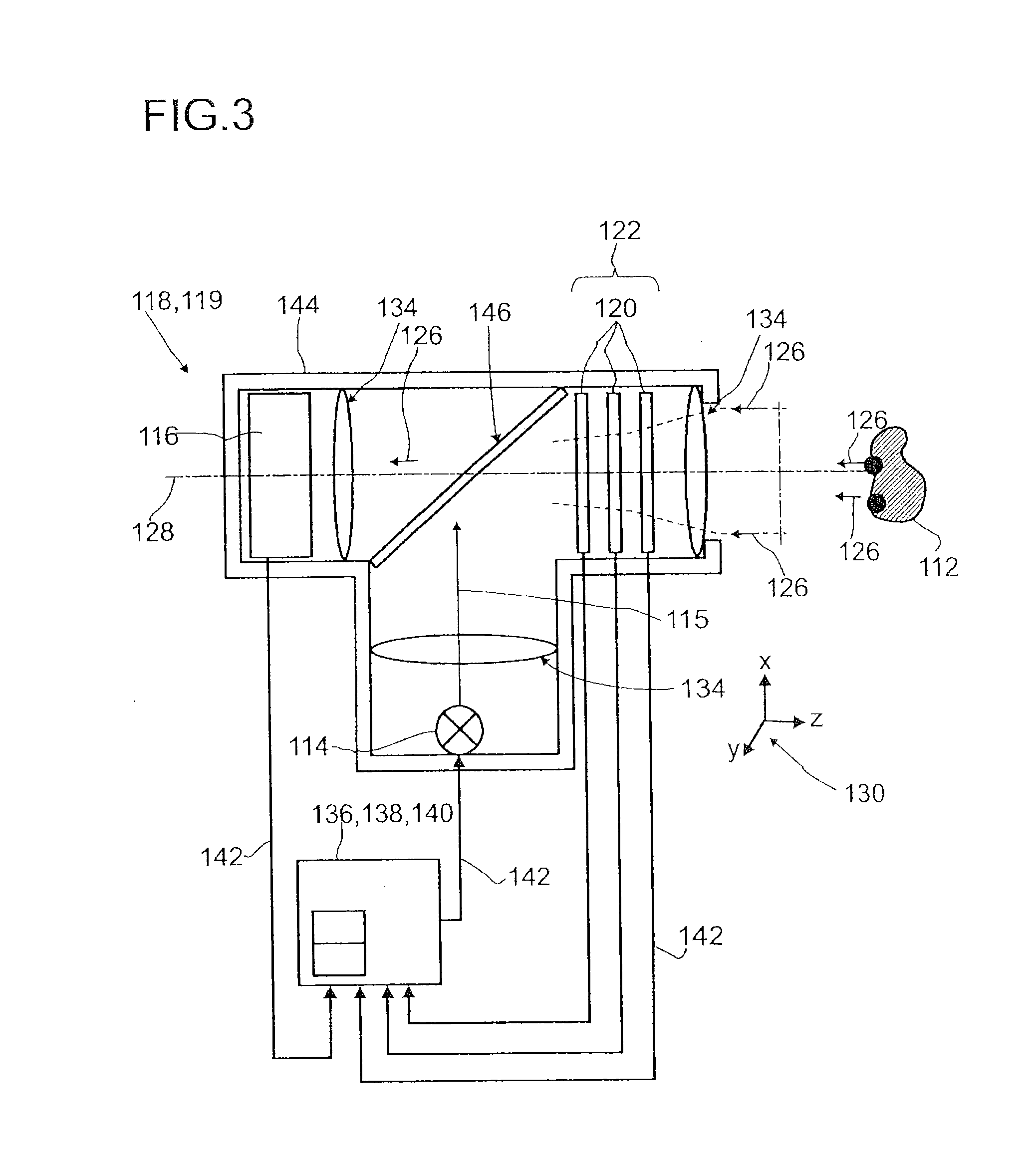
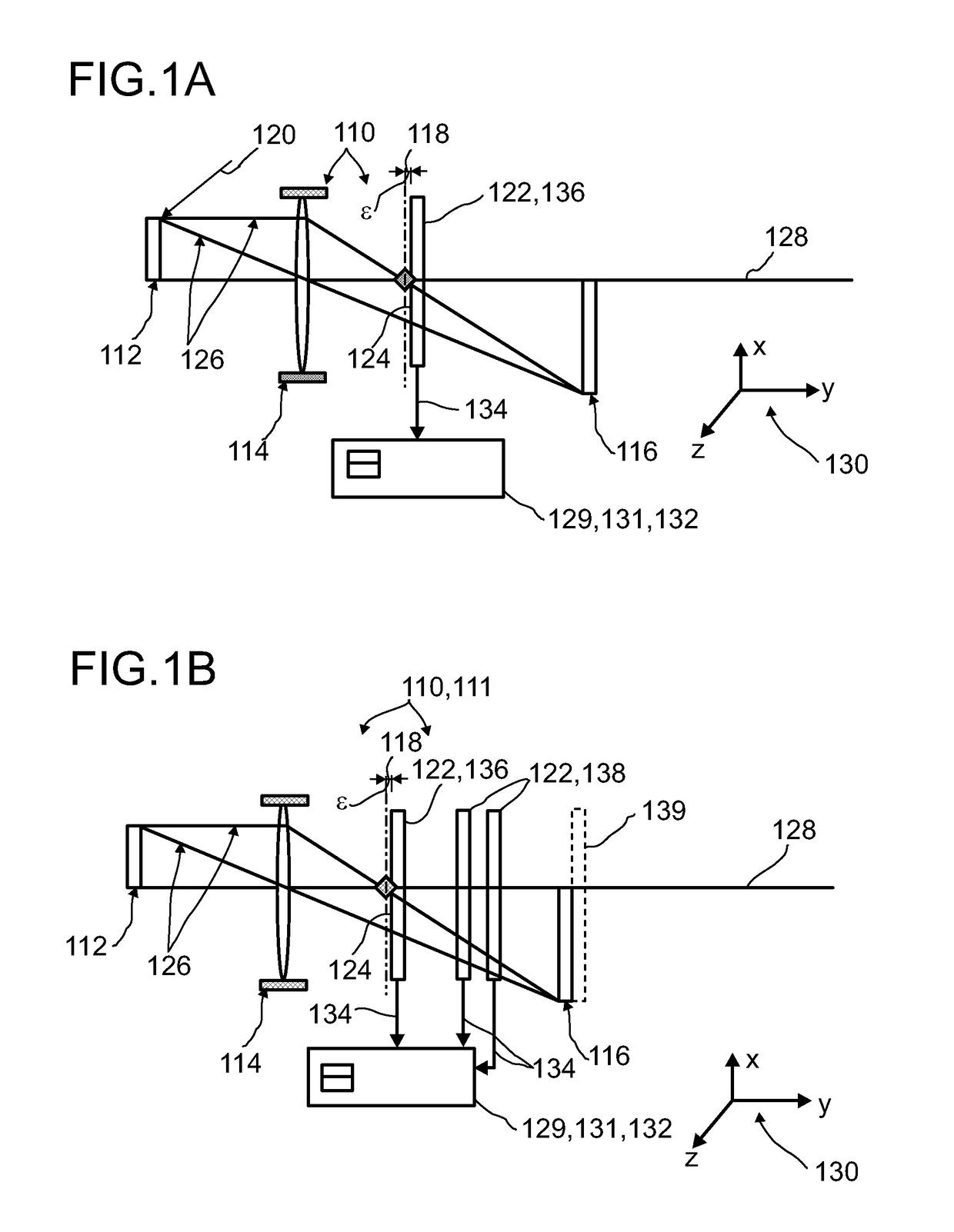
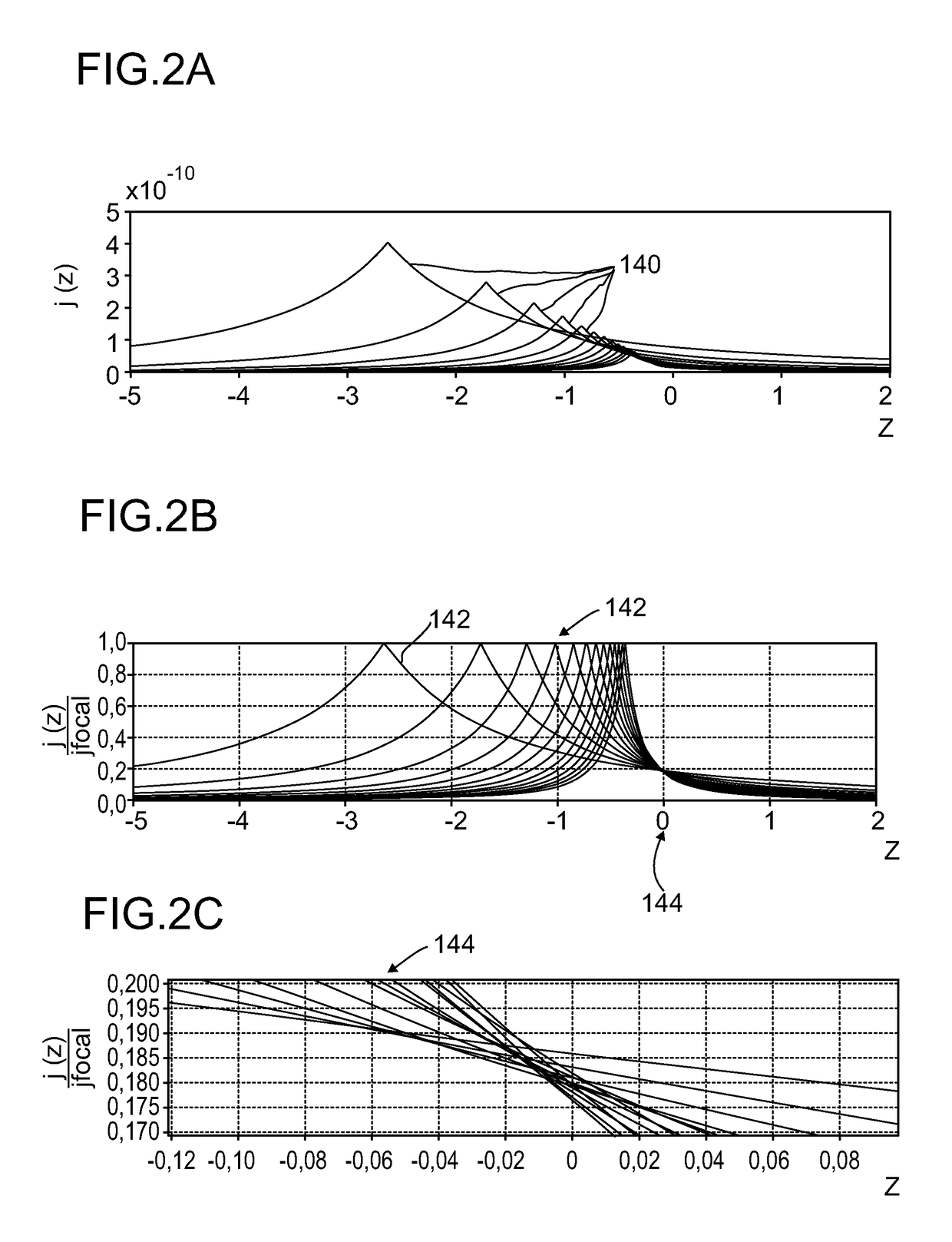
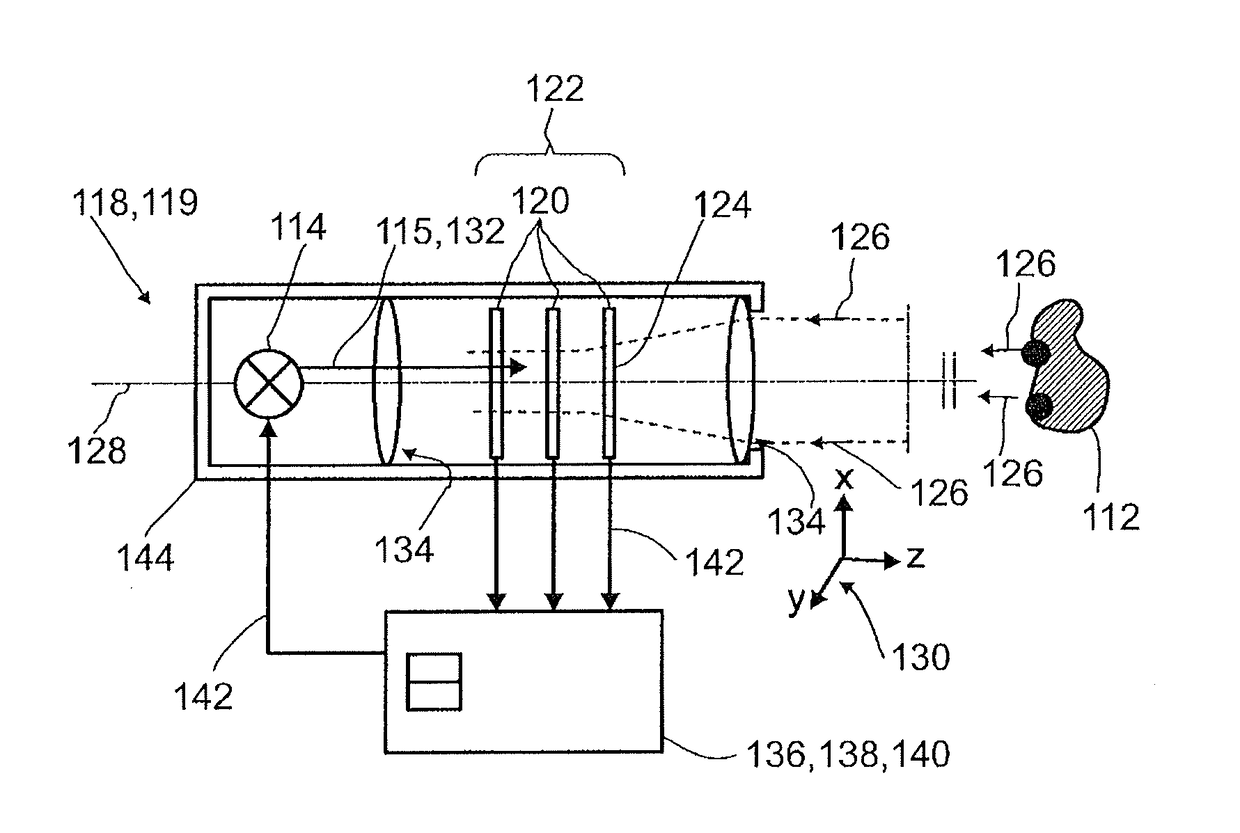
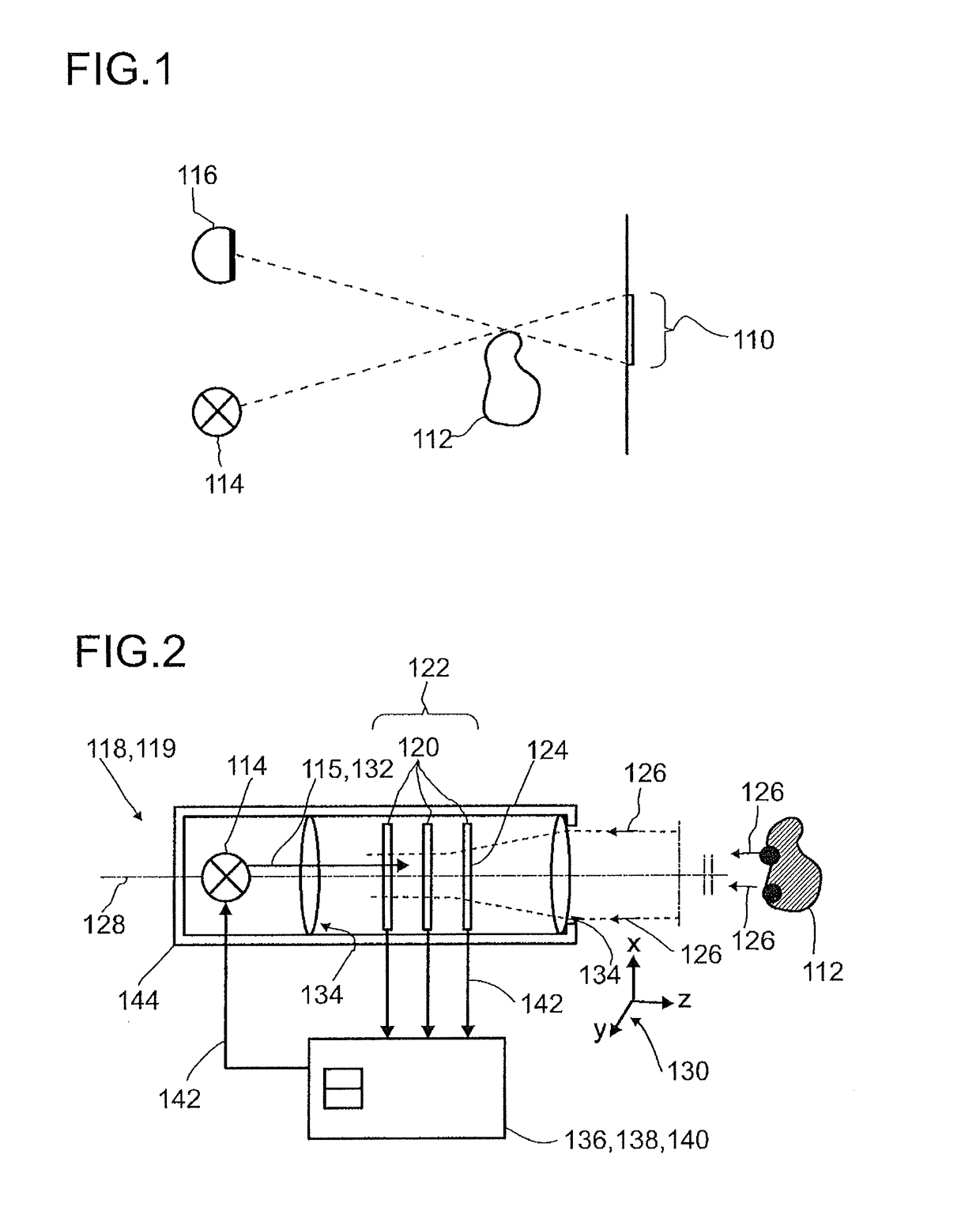
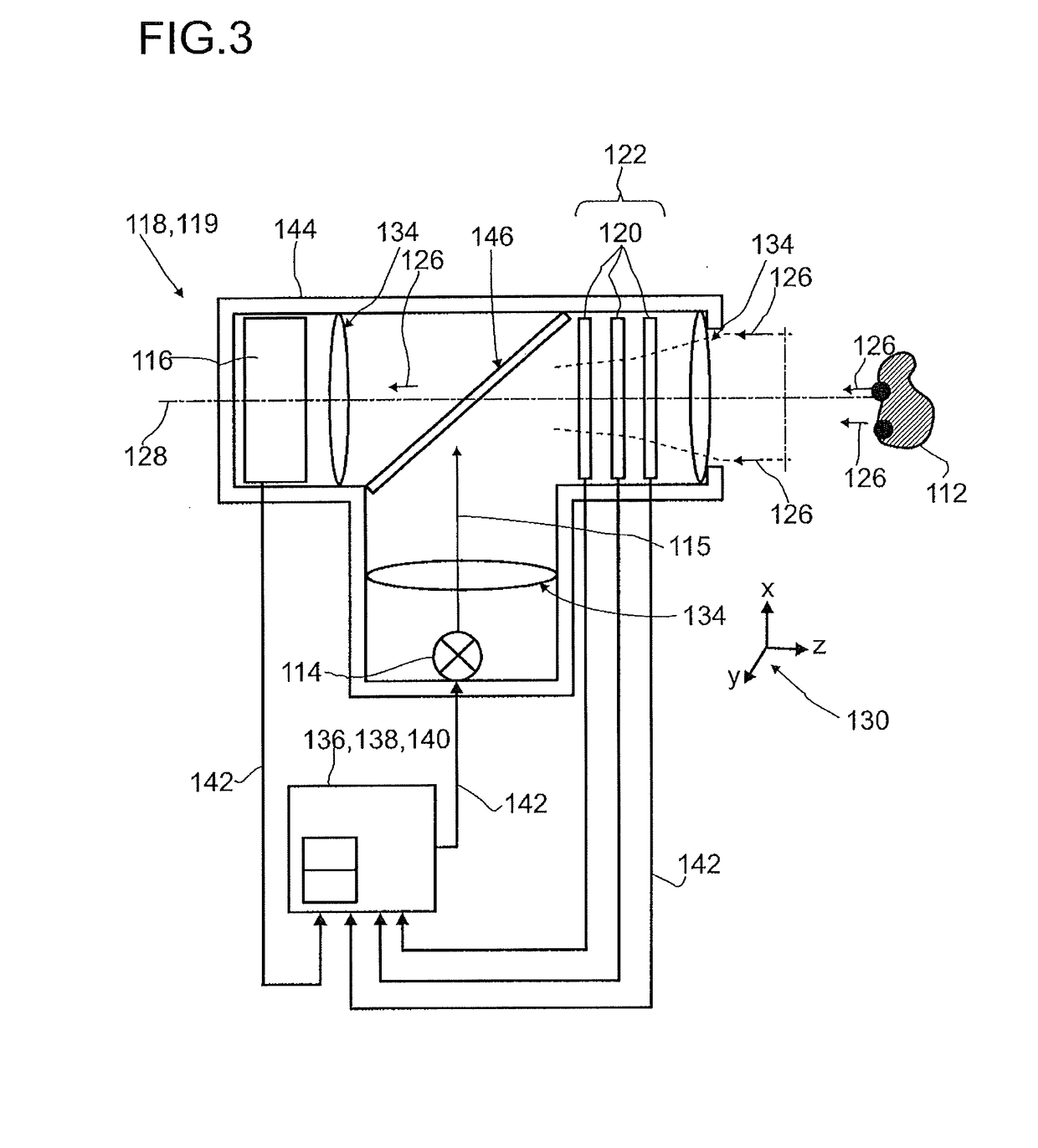
Detector for determining a position of at least one object
ActiveUS9665182B2Reduce measurement errorInput/output for user-computer interactionDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsLight beamBeam cross section
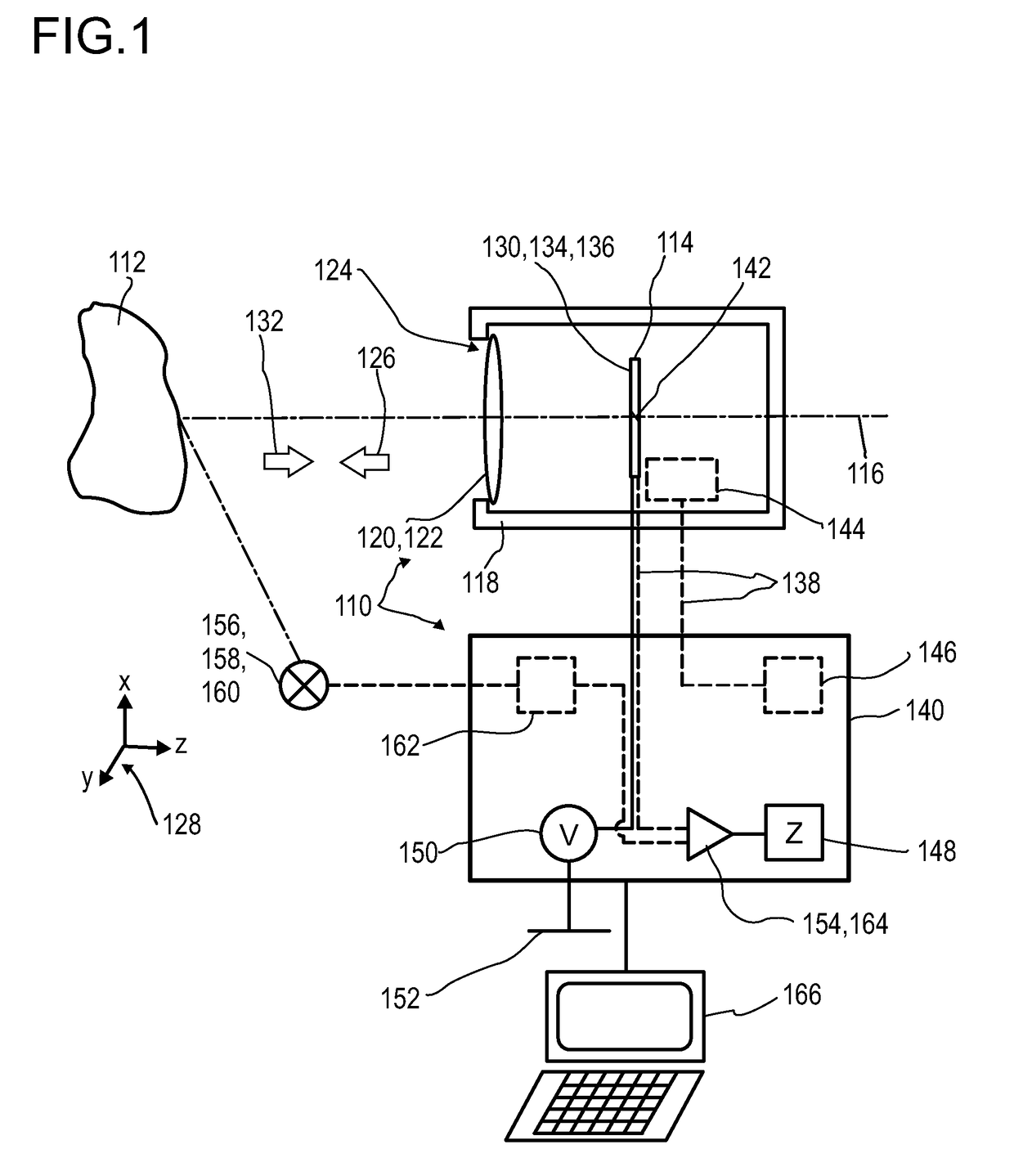
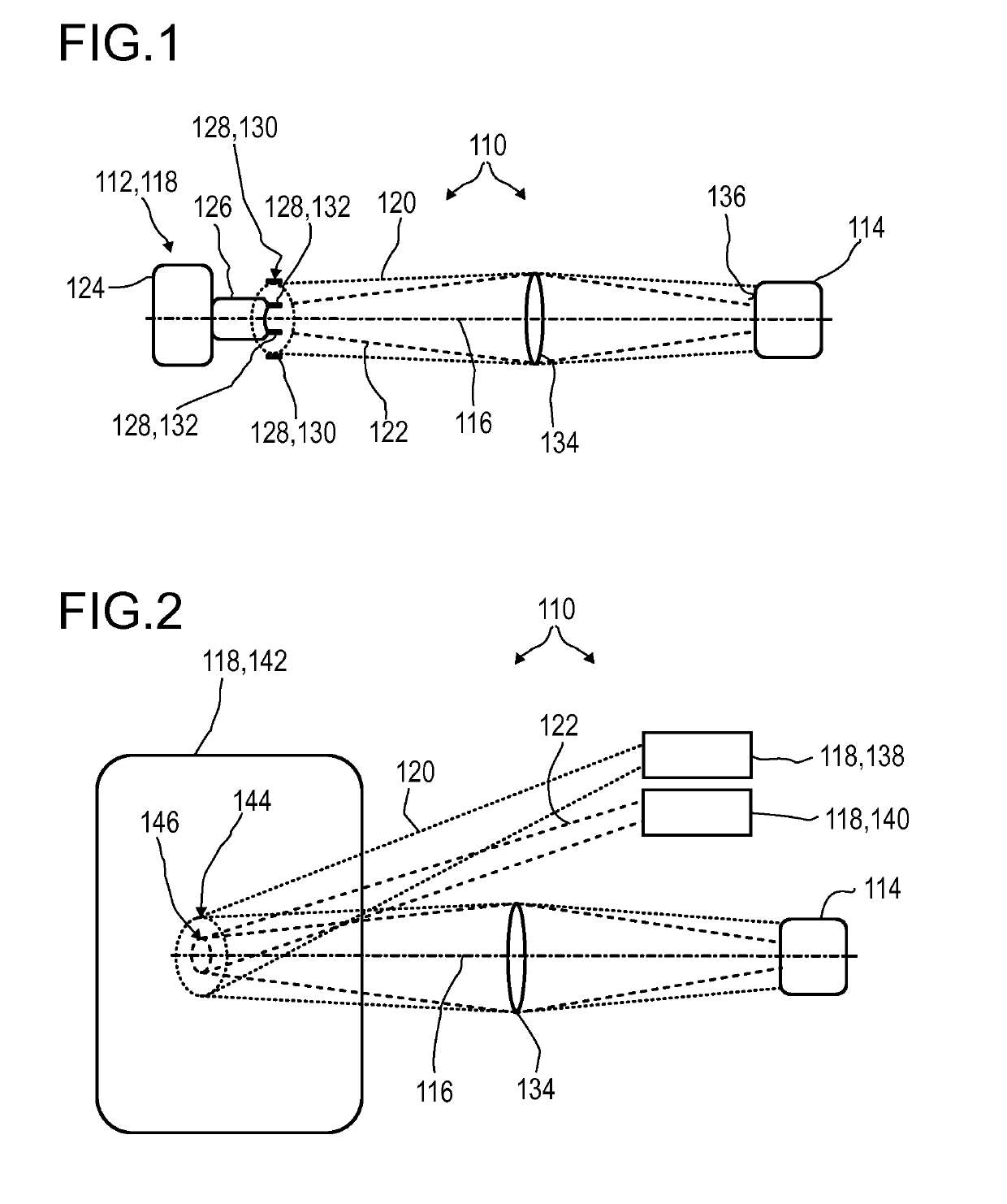
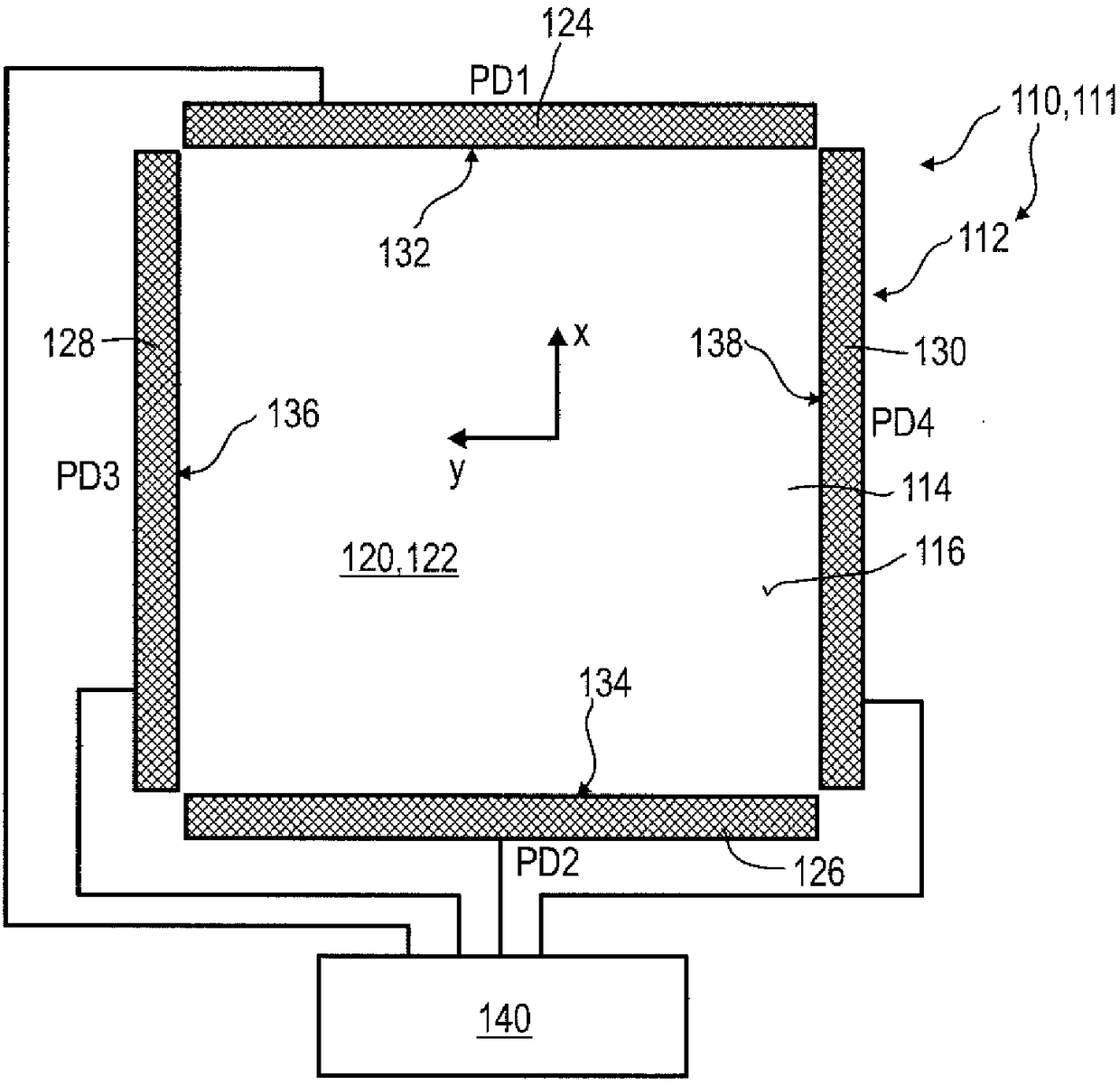
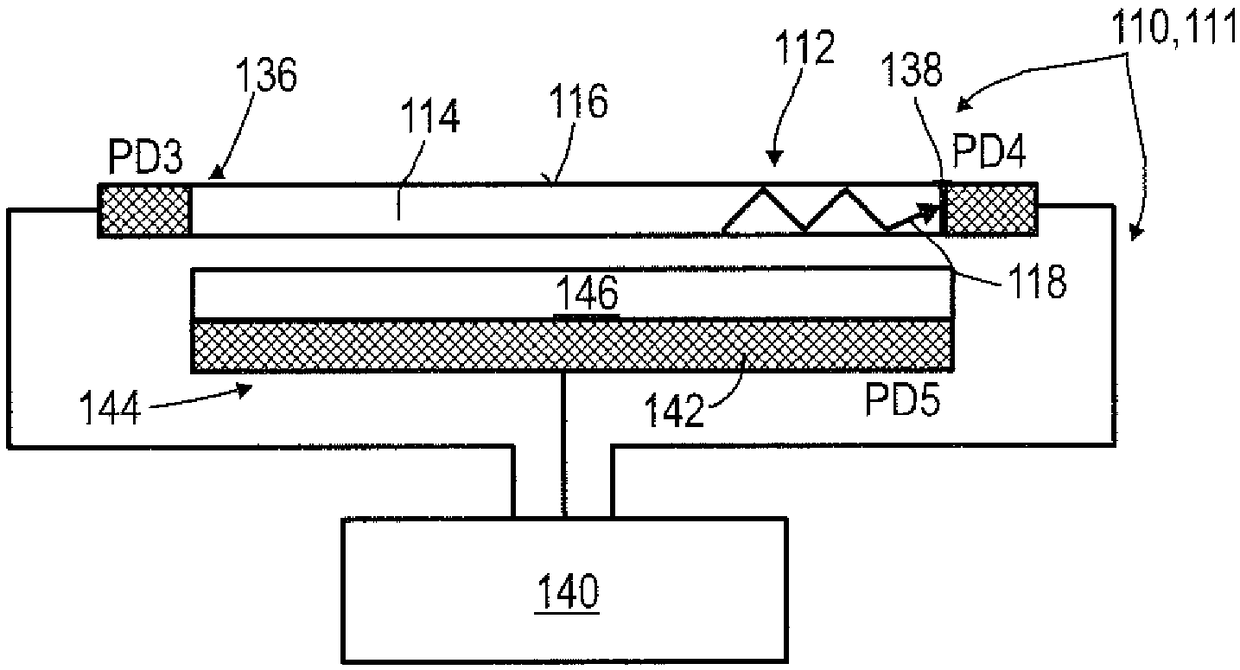
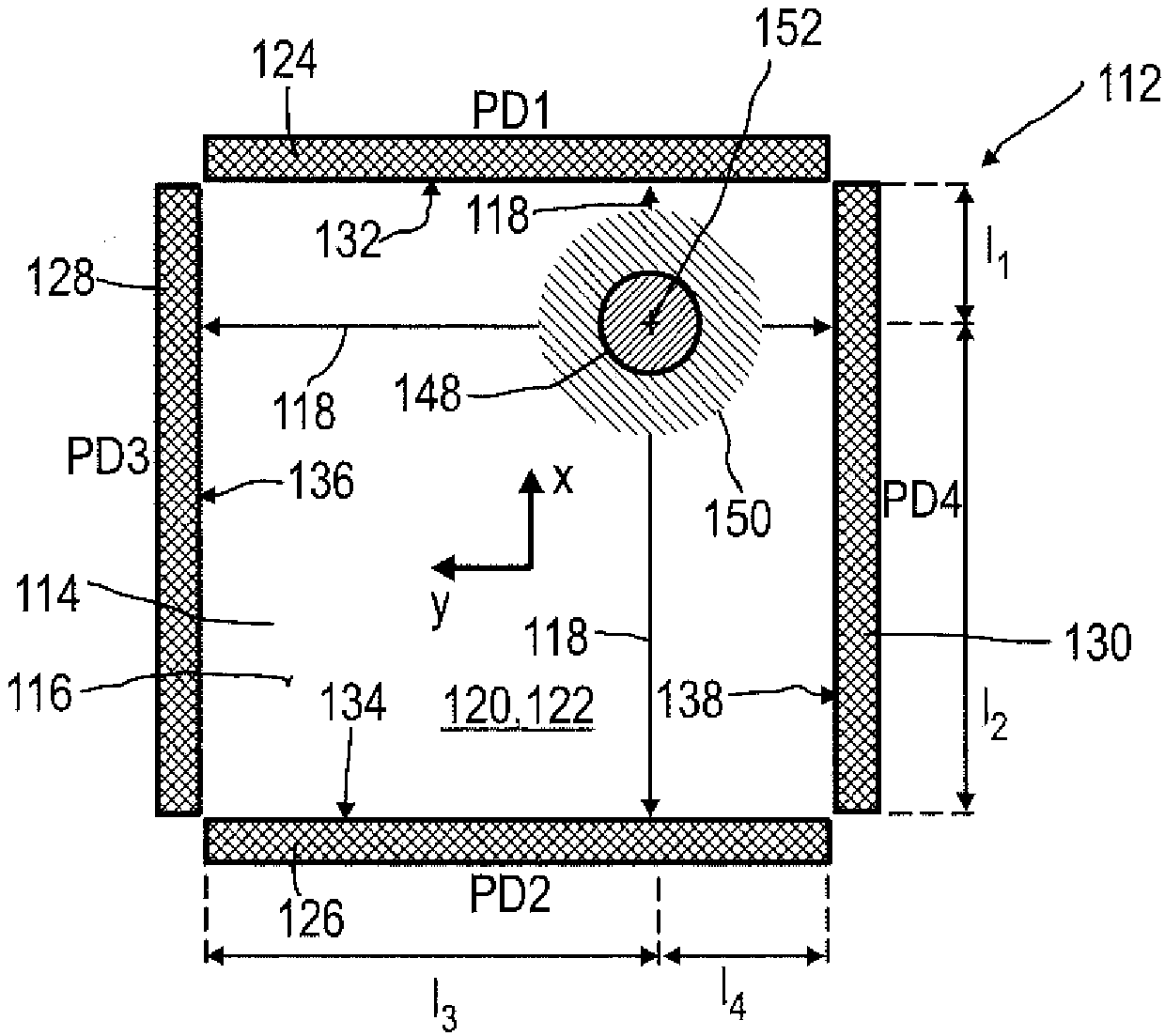
A detector (118) for determining a position of at least one object (112) is disclosed, the detector (118) comprising:at least one longitudinal optical sensor (120), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (120) has at least one sensor region (124), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (120) is at least partially transparent, wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (120) is designed to generate at least one longitudinal sensor signal in a manner dependent on an illumination of the sensor region (124) by at least one light beam (126) traveling from the object (112) to the detector (118), wherein the longitudinal sensor signal, given the same total power of the illumination, is dependent on a beam cross-section of the light beam (126) in the sensor region (124);at least one illumination source (114) adapted to illuminate the object (112) with illumination light (115) through the longitudinal optical sensor (120); andat least one evaluation device (136), wherein the evaluation device (136) is designed to generate at least one item of information on a longitudinal position of the object (112) by evaluating the longitudinal sensor signal.
Owner:BASF SE
Detector for an optical detection of at least one object
ActiveUS20180017679A1Improve signal qualityImprove signal-to-noise ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLongitudinal opticalOptics
Disclosed herein is a detector (110) containing: at least one longitudinal optical sensor (114), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (114); and at least one evaluation device (140), wherein the evaluation device (140) is designed to generate at least one item of information on a longitudinal position of the object (112) by evaluating the longitudinal sensor signal of the longitudinal optical sensor (114). Also disclosed herein are articles containing the detector (110), and methods for optical detection of objects using the detector (110).
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
Method of motion correction in optical coherence tomography imaging
An image data set acquired by an optical coherence tomography (OCT) system is corrected for effects due to motion of the sample. A first set of A-scans is acquired within a time short enough to avoid any significant motion of the sample. A second more extensive set of A-scans is acquired over an overlapping region on the sample. Significant sample motion may occur during acquisition of the second set. A-scans from the first set are matched with A-scans from the second set, based on similarity between the longitudinal optical scattering profiles they contain. Such matched pairs of A-scans are likely to correspond to the same region in the sample. Comparison of the OCT scanner coordinates that produced each A-scan in a matching pair, in conjunction with any shift in the longitudinal scattering profiles between the pair of A-scans, reveals the displacement of the sample between acquisition of the first and second A-scans in the pair. Estimates of the sample displacement are used to correct the transverse and longitudinal coordinates of the A-scans in the second set, to form a motion-corrected OCT data set.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Compact atomic magnetometer and gyroscope based on a diverging laser beam
InactiveUS7872473B2Improve compactnessLow costTurn-sensitive devicesElectric/magnetic detectionAtomic systemGyroscope
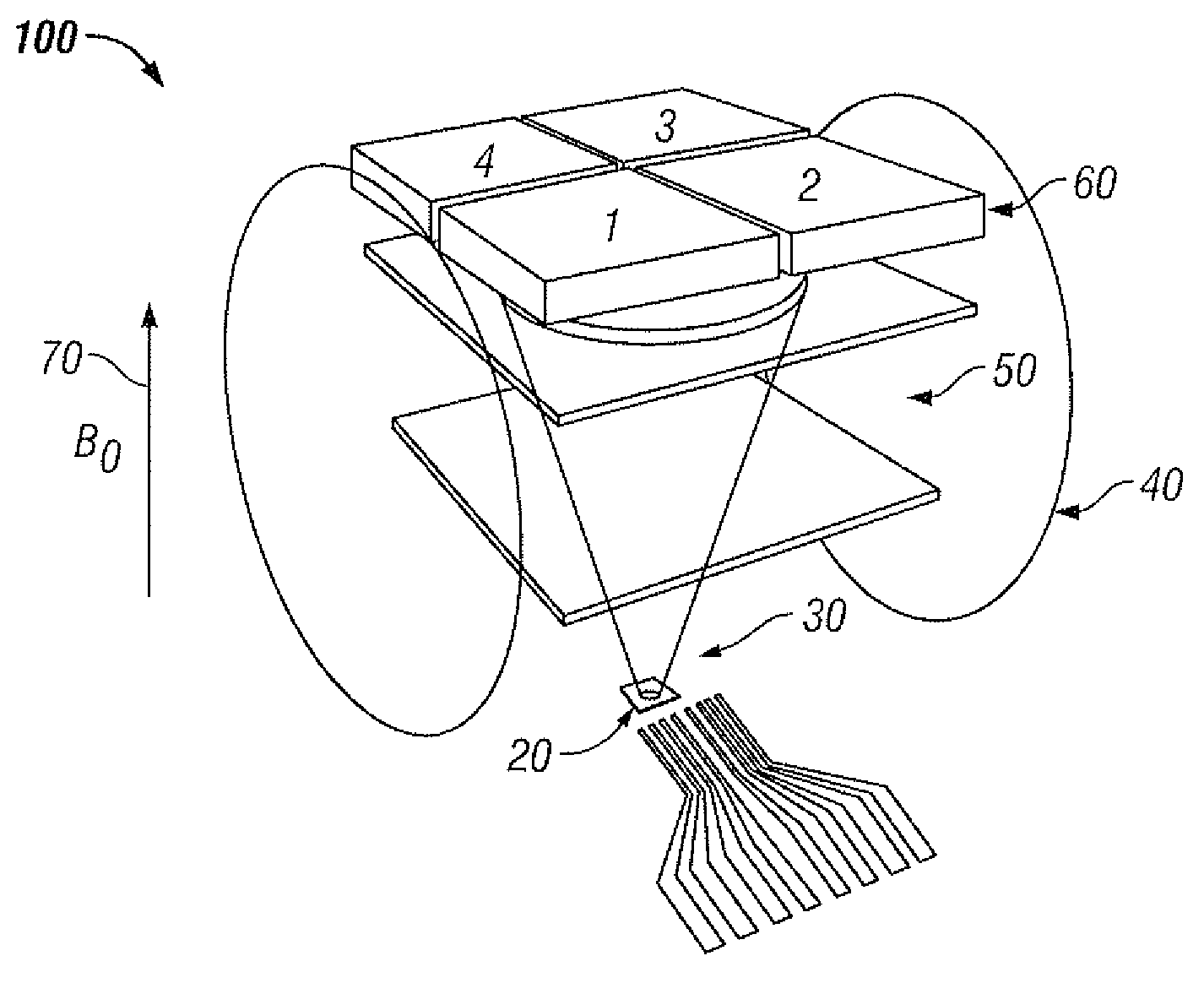
An atomic magnetometer that simultaneously achieves high sensitivity, simple fabrication and small size. This design is based on a diverging (or converging) beam of light that passes through an alkali atom vapor cell and that contains a distribution of beam propagation vectors. The existence of more than one propagation direction permits longitudinal optical pumping of atomic system and simultaneous detection of the transverse atomic polarization. The design could be implemented with a micro machined alkali vapor cell and light from a single semiconductor laser. A small modification to the cell contents and excitation geometry allows for use as a gyroscope.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
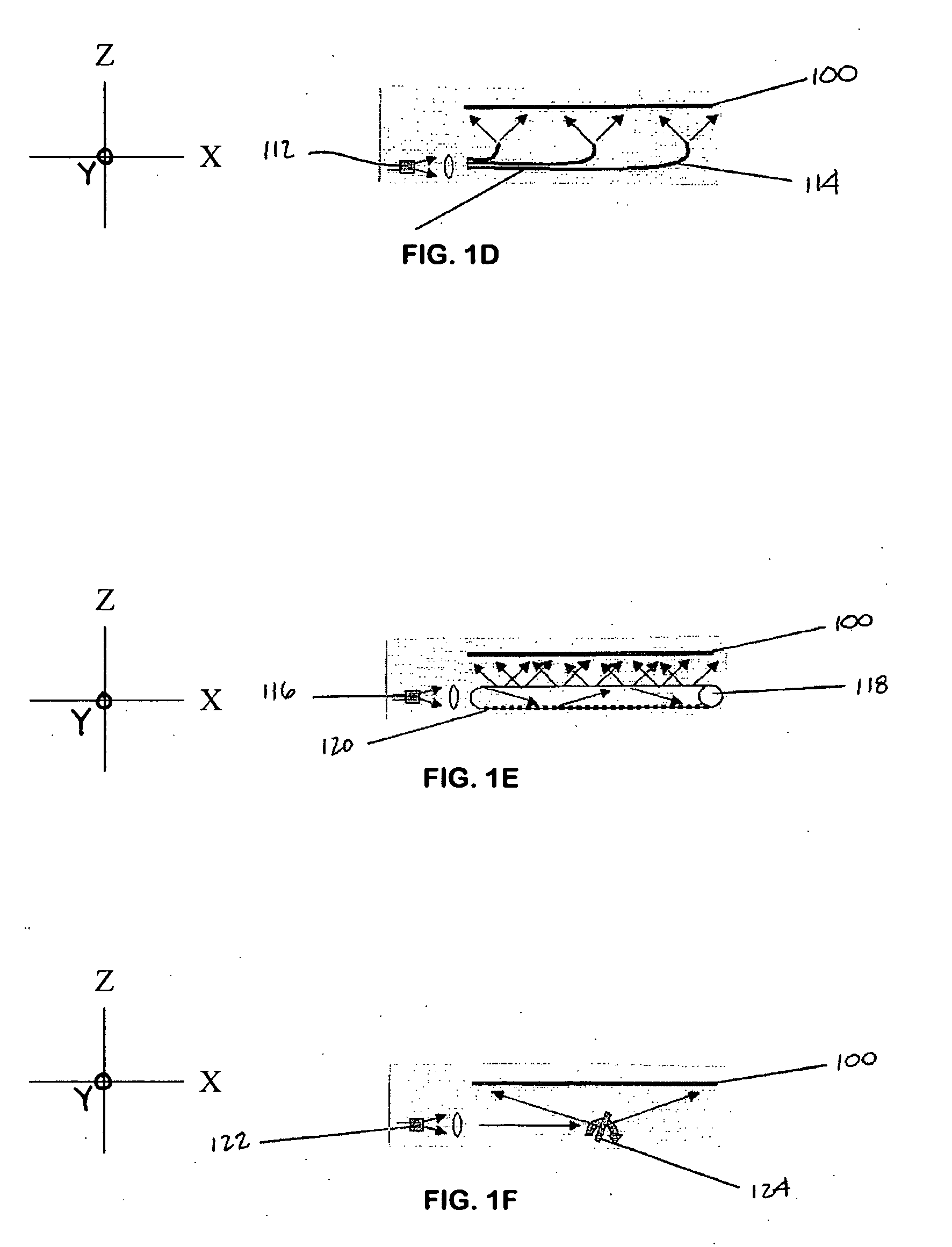
Detector for determining a position of at least one object
ActiveUS20160364015A1Sufficient electrical conductivityReduce measurement errorInput/output for user-computer interactionDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsIlluminanceLight beam
A detector (118) for determining a position of at least one object (112) is disclosed, the detector (118) comprising:at least one longitudinal optical sensor (120), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (120) has at least one sensor region (124), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (120) is at least partially transparent, wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (120) is designed to generate at least one longitudinal sensor signal in a manner dependent on an illumination of the sensor region (124) by at least one light beam (126) traveling from the object (112) to the detector (118), wherein the longitudinal sensor signal, given the same total power of the illumination, is dependent on a beam cross-section of the light beam (126) in the sensor region (124);at least one illumination source (114) adapted to illuminate the object (112) with illumination light (115) through the longitudinal optical sensor (120); andat least one evaluation device (136), wherein the evaluation device (136) is designed to generate at least one item of information on a longitudinal position of the object (112) by evaluating the longitudinal sensor signal.
Owner:BASF AG
Detector for determining a position of at least one object
ActiveUS20170205230A1Optimized loading and packing container and vehicleReduce wasteOptical rangefindersPosition fixationLight beamBeam cross section
A detector (110) for determining a position of at least one object (112), the detector (110) comprising: at least one GP transfer device (114) for imaging the object (112) into an image plane (116), the transfer device (114) having a focal plane (118), at least one longitudinal optical sensor (122), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (122) has at least one sensor region (124), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (122) is at least partially transparent, wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (122) is designed to generate at least one longitudinal sensor signal in a manner dependent on an illumination of sensor region (124) by at least one light beam propagating from the object to the detector (110), wherein the longitudinal sensor signal, given the same total power of the illumination, is dependent on a beam cross-section of the light beam in the sensor region (124); and at least one evaluation device (129), wherein the evaluation device (129) is designed to generate at least one item of information on a longitudinal position of the object (112) by evaluating the longitudinal sensor signal. Herein the at least one longitudinal optical sensor (122) comprises a focal longitudinal optical sensor (136), wherein the focal longitudinal optical sensor (136) at least substantially is arranged in the focal plane (118).
Owner:BASF AG
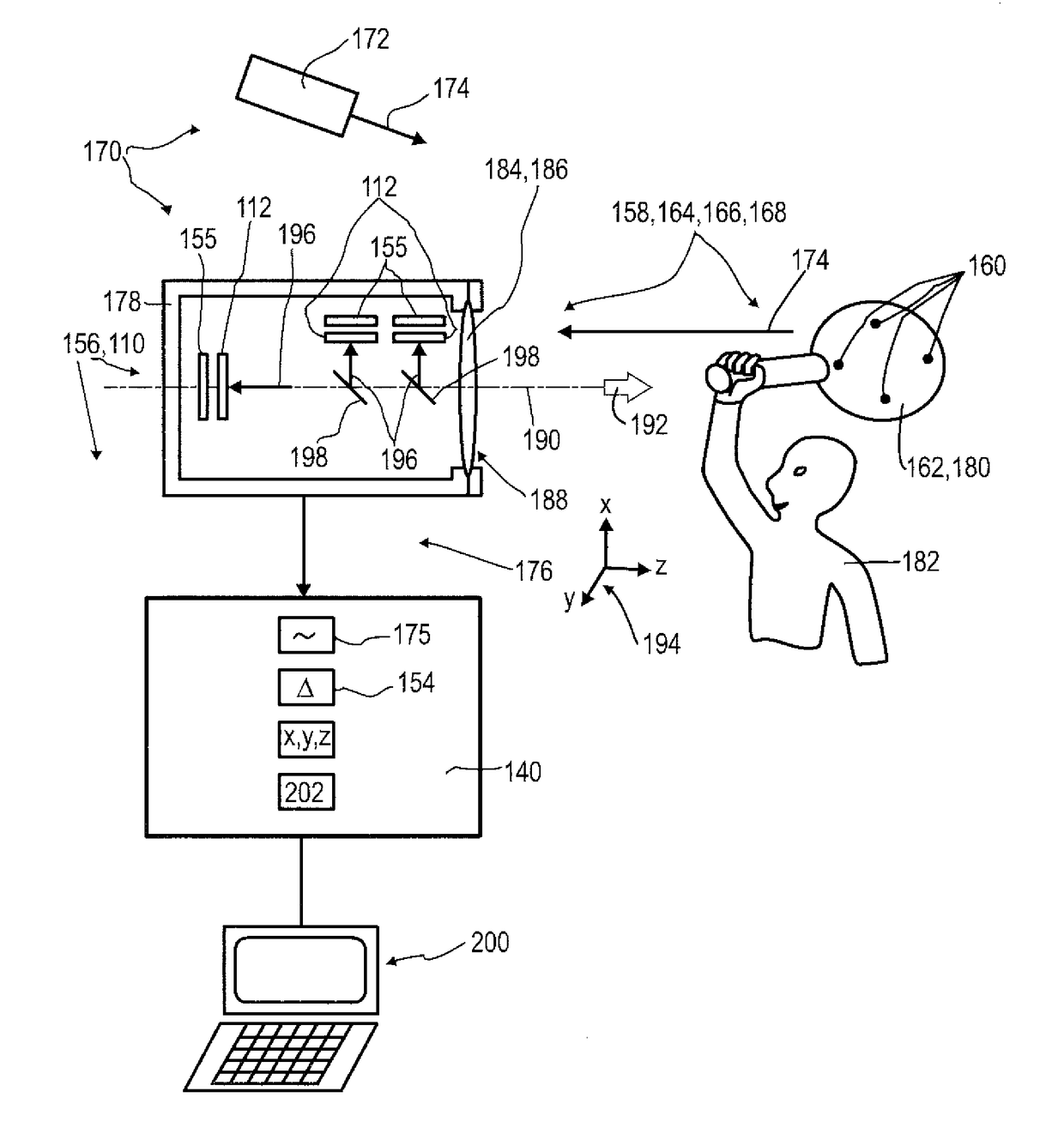
Detector for optically detecting at least one object
InactiveUS20180329024A1Low effortLower requirementInput/output for user-computer interactionPosition fixationLight guideFluorescence
A detector, for determining a position of at least one object, includes: at least one longitudinal optical sensor for determining a longitudinal position of at least one light beam traveling from the object to the detector, at least one transversal optical sensor determining at least one transversal position of the at least one light beam, including at least one fluorescent waveguiding sheet forming a transversal sensitive area, at least two photosensitive elements located at at least two edges of the fluorescent waveguiding sheet capable of detecting fluorescence light guided from the light spot towards the photosensitive elements by the fluorescent waveguiding sheet and capable of generating transversal sensor signals; and at least one evaluation device configured to determine at least one longitudinal coordinate of the object by evaluating the longitudinal sensor signals, and to determine at least one transversal coordinate of the object by evaluating the transversal sensor signals.
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
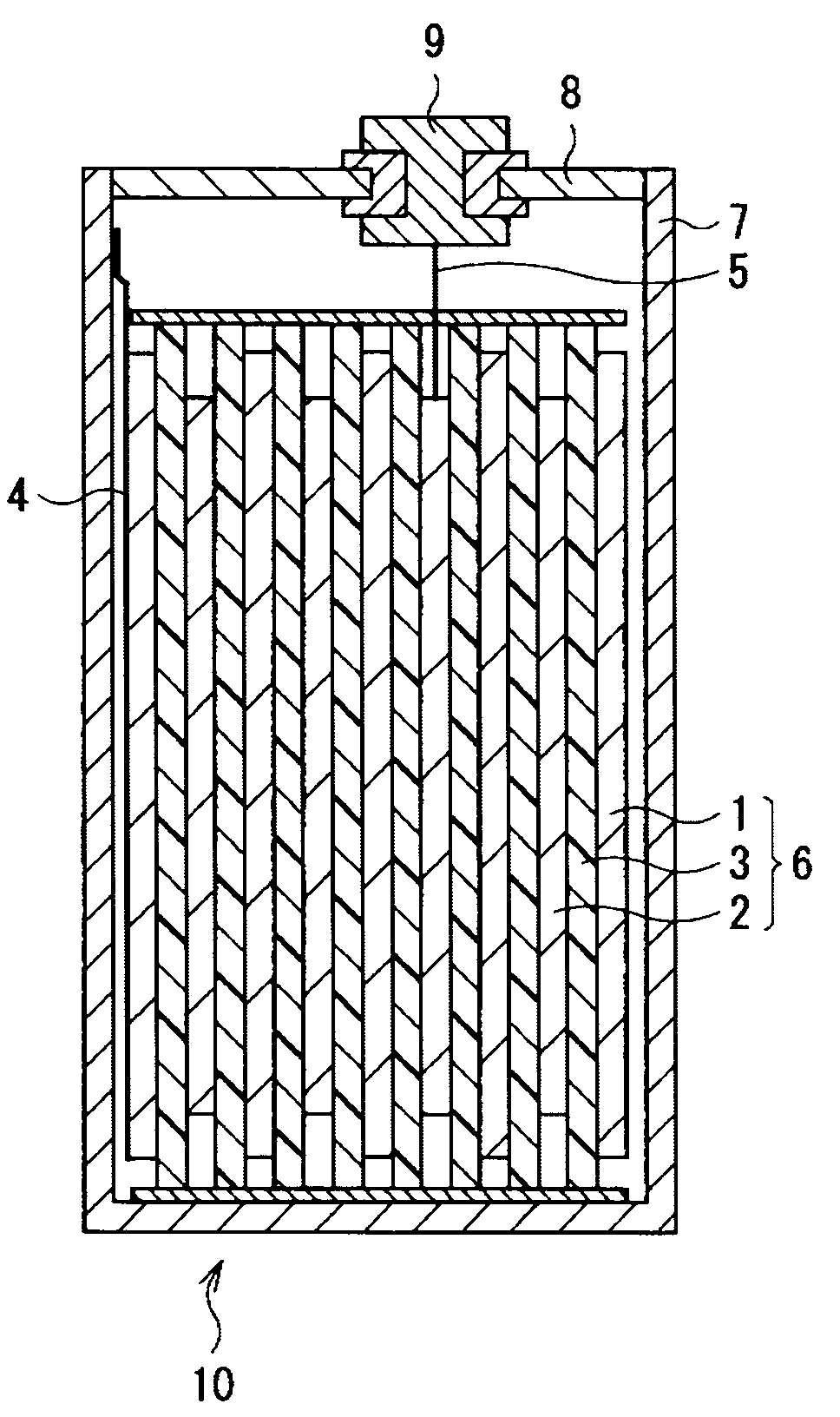
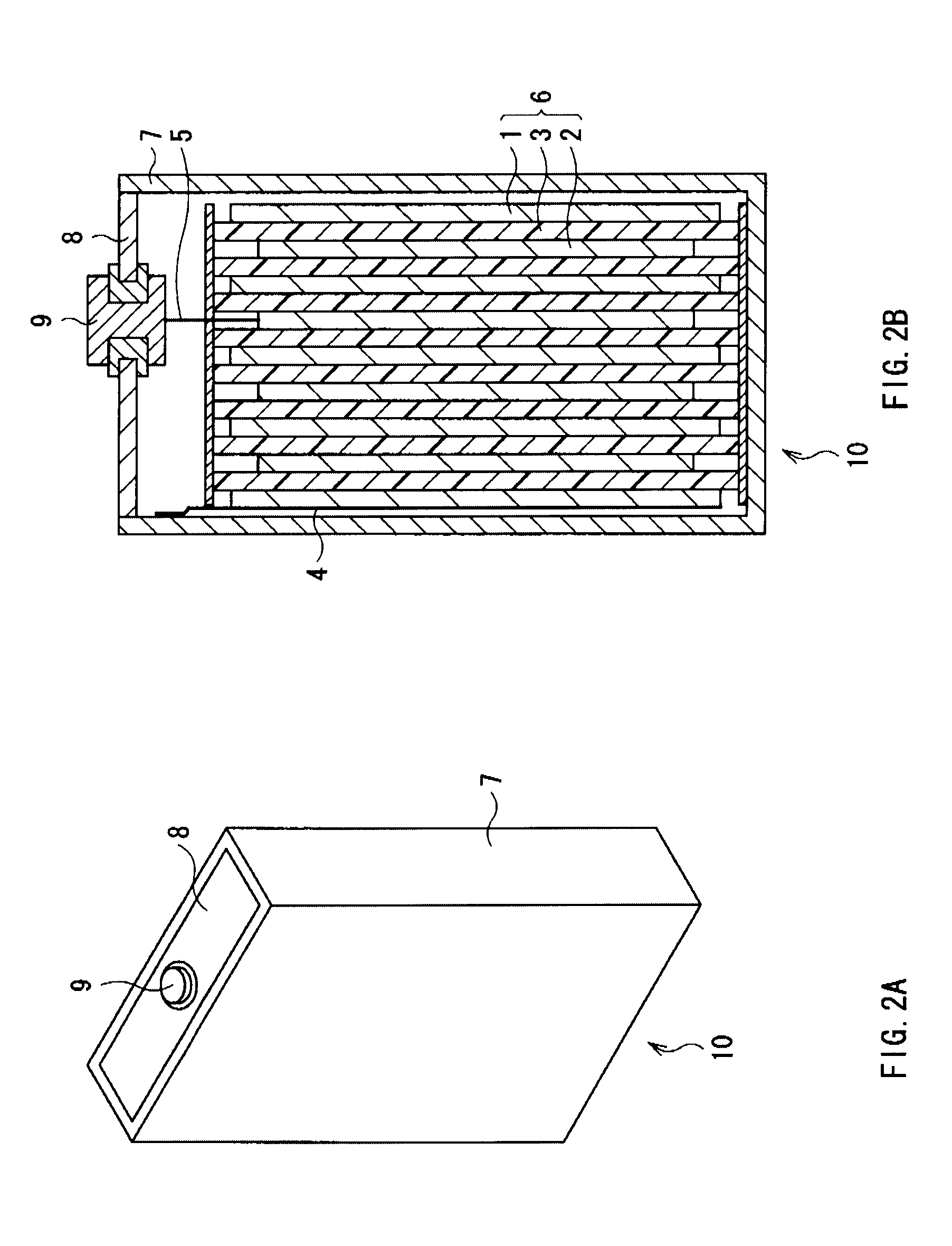
Anode for secondary battery, method of manufacturing it, and secondary battery
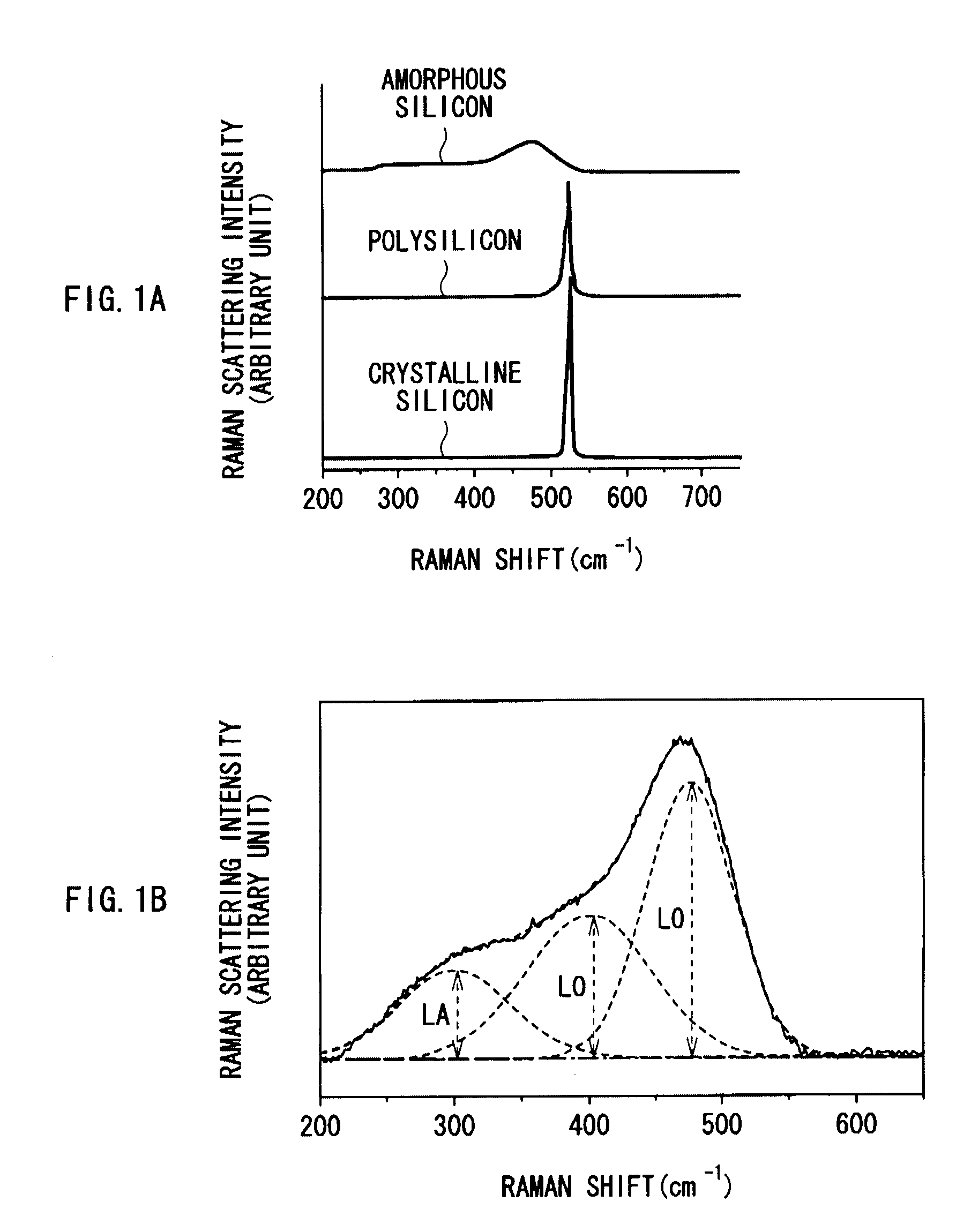
InactiveUS20090068567A1Different degreeLow degreeAlkaline accumulatorsElectrode manufacturing processesAcoustic PhononsSilicon
An anode for secondary battery is provided with an anode active material layer containing silicon on an anode current collector. Silicon in the anode active material has an amorphous structure. In a Raman spectrum of silicon having the amorphous structure after an initial charge and discharge, 0.25≦LA / TO and / or 45≦LO / TO is satisfied, where an intensity of a scattering peak occurred in the vicinity of shift position 480 cm−1 based on scattering due to transverse optical phonon is TO, an intensity of a scattering peak occurred in the vicinity of shift position 300 cm−1 based on scattering due to longitudinal acoustic phonon is LA, and an intensity of a scattering peak occurred in the vicinity of shift position 400 cm−1 based on scattering due to longitudinal optical phonon is LO.
Owner:SONY CORP
Compact atomic magnetometer and gyroscope based on a diverging laser beam
InactiveUS20090039881A1Low costReduce low frequency noiseTurn-sensitive devicesElectric/magnetic detectionAtomic systemGyroscope
An atomic magnetometer that simultaneously achieves high sensitivity, simple fabrication and small size. This design is based on a diverging (or converging) beam of light that passes through an alkali atom vapor cell and that contains a distribution of beam propagation vectors. The existence of more than one propagation direction permits longitudinal optical pumping of atomic system and simultaneous detection of the transverse atomic polarization. The design could be implemented with a micro machined alkali vapor cell and light from a single semiconductor laser. A small modification to the cell contents and excitation geometry allows for use as a gyroscope.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Detector for determining a position of at least one object
ActiveUS20170219694A1Reduce measurement errorInput/output for user-computer interactionOptical rangefindersBeam cross sectionLongitudinal optical
A detector (118) for determining a position of at least one object (112) is disclosed, the detector (118) comprising:at least one longitudinal optical sensor (120), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (120) has at least one sensor region (124), wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (120) is at least partially transparent, wherein the longitudinal optical sensor (120) is designed to generate at least one longitudinal sensor signal in a manner dependent on an illumination of the sensor region (124) by at least one light beam (126) traveling from the object (112) to the detector (118), wherein the longitudinal sensor signal, given the same total power of the illumination, is dependent on a beam cross-section of the light beam (126) in the sensor region (124);at least one illumination source (114) adapted to illuminate the object (112) with illumination light (115) through the longitudinal optical sensor (120); andat least one evaluation device (136), wherein the evaluation device (136) is designed to generate at least one item of information on a longitudinal position of the object (112) by evaluating the longitudinal sensor signal.
Owner:BASF SE
Detector for optically detecting at least one object
InactiveUS20190129035A1Simple and cost-effective setupHigh degreeElectromagnetic wave reradiationLight beamBeam cross section
A detector for optical detection of at least one object includes: at least one illumination source to emit at least one first and second light beams, with different opening angles; at least one longitudinal optical sensor including at least one sensor region and configured to generate at least one longitudinal sensor signal dependent on an illumination of the sensor region by a light beam, and dependent on a beam cross-section of the light beam; and at least one evaluation device configured to differentiate the longitudinal sensor signal of the longitudinal optical sensor into first and second longitudinal sensor signals dependent on the illumination of the sensor region by the first and second light beams, and configured to generate at least one item of information on a longitudinal position of the object by evaluating the first longitudinal sensor signal and the second longitudinal sensor signal.
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
Detector for optically detecting at least one object
InactiveUS20190157470A1Low effortLower requirementFinal product manufactureSolid-state devices3d sensingLight beam
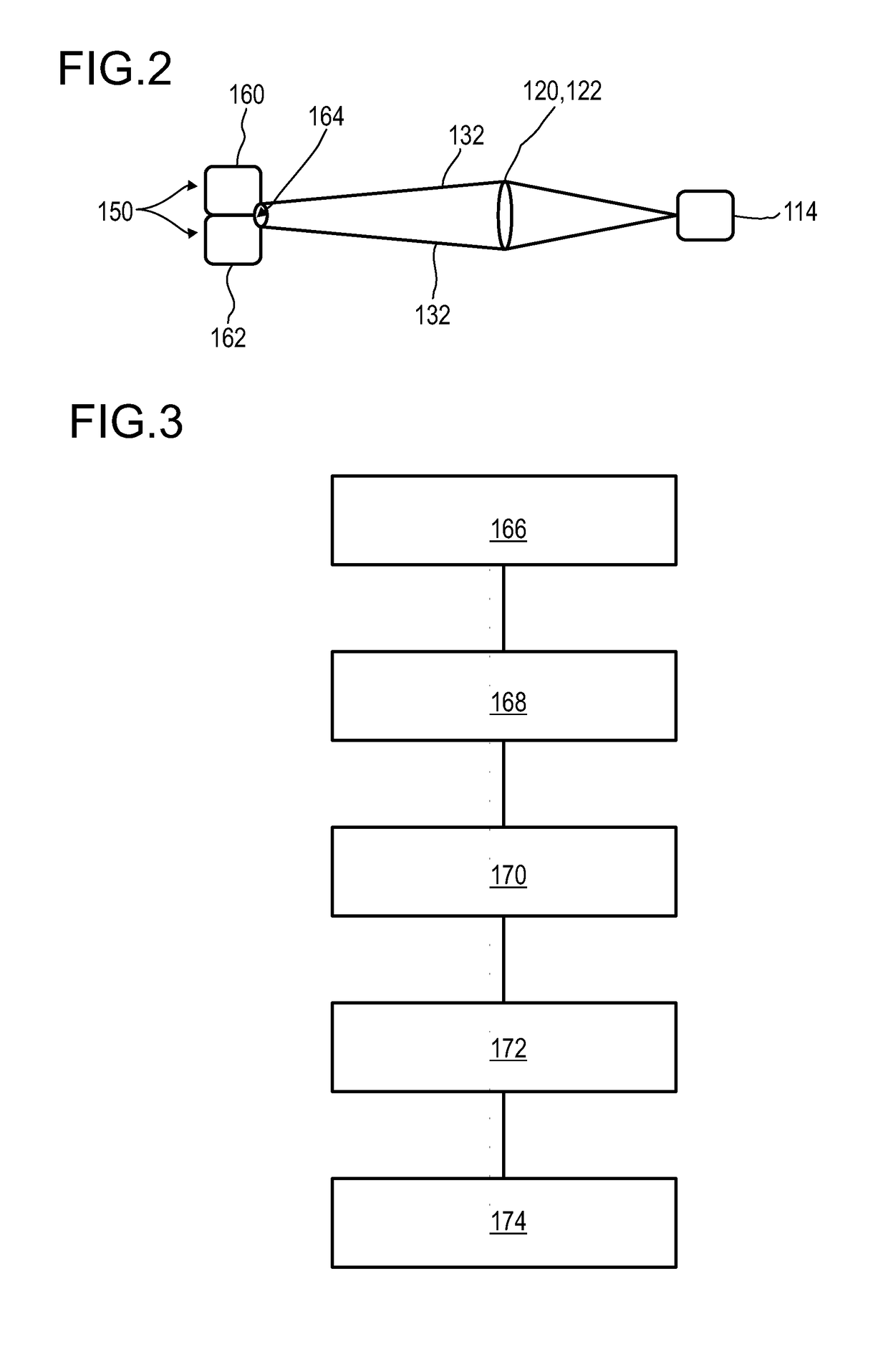
A detector for determining a position of at least one object, in particular for 3D-sensing concepts, is disclosed. The detector comprises a longitudinal optical sensor (110) for determining a longitudinal position of an object by a light beam traveling from the object to the detector and a transversal optical detector (112) which may be designed as an imaging device or a position sensitive detector. The longitudinal sensor (110) has at least two PN structures or PIN structures (138, 140). Each of the PN structures or PIN structures is located between two electrode layers (144), thereby forming photodiodes (146) having a longitudinal sensor region (148) each. Longitudinal sensor signals from the photodiodes (146) are, given the same total power of illumination, are dependent on a beam cross-section of the light beam in the longitudinal sensor regions (148). As an alternative, instead of the transversal optical detector (112) the photodiodes (146) of the longitudinal optical sensor (110) may be adapted to operate as one-dimensional position sensitive detectors each, for determining a transversal x-coordinate and a transversal y-coordinate, respectively.
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
Detector for optically detecting at least one object
InactiveUS20180356501A1Increase probabilityReduced carrier lifetimeDiodeElectromagnetic wave reradiationLight beamBeam cross section
A detector for an optical detection of at least one object is disclosed. The detector contains at least one longitudinal optical sensor and at least one evaluation device. The longitudinal optical sensor has at least one sensor region and is designed to generate at least one longitudinal sensor signal in a manner dependent on an illumination of the sensor region by a light beam. The longitudinal sensor signal, given the same total power of the illumination, is dependent on a beam cross-section of the light beam in the sensor region and further dependent on at least one adjustable property of the longitudinal optical sensor. The evaluation device is designed to generate at least one item of information on a longitudinal position of the object by evaluating the longitudinal sensor signal of the longitudinal optical sensor.
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
Systems and methods for supplying a distributed light source
Owner:PRINCETON LIGHTWAVE INC
Detector for an optical detection of at least one object
InactiveUS20180231376A1Easy to identifyLess energy consumptionOptical rangefindersFinal product manufactureSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Electron donor
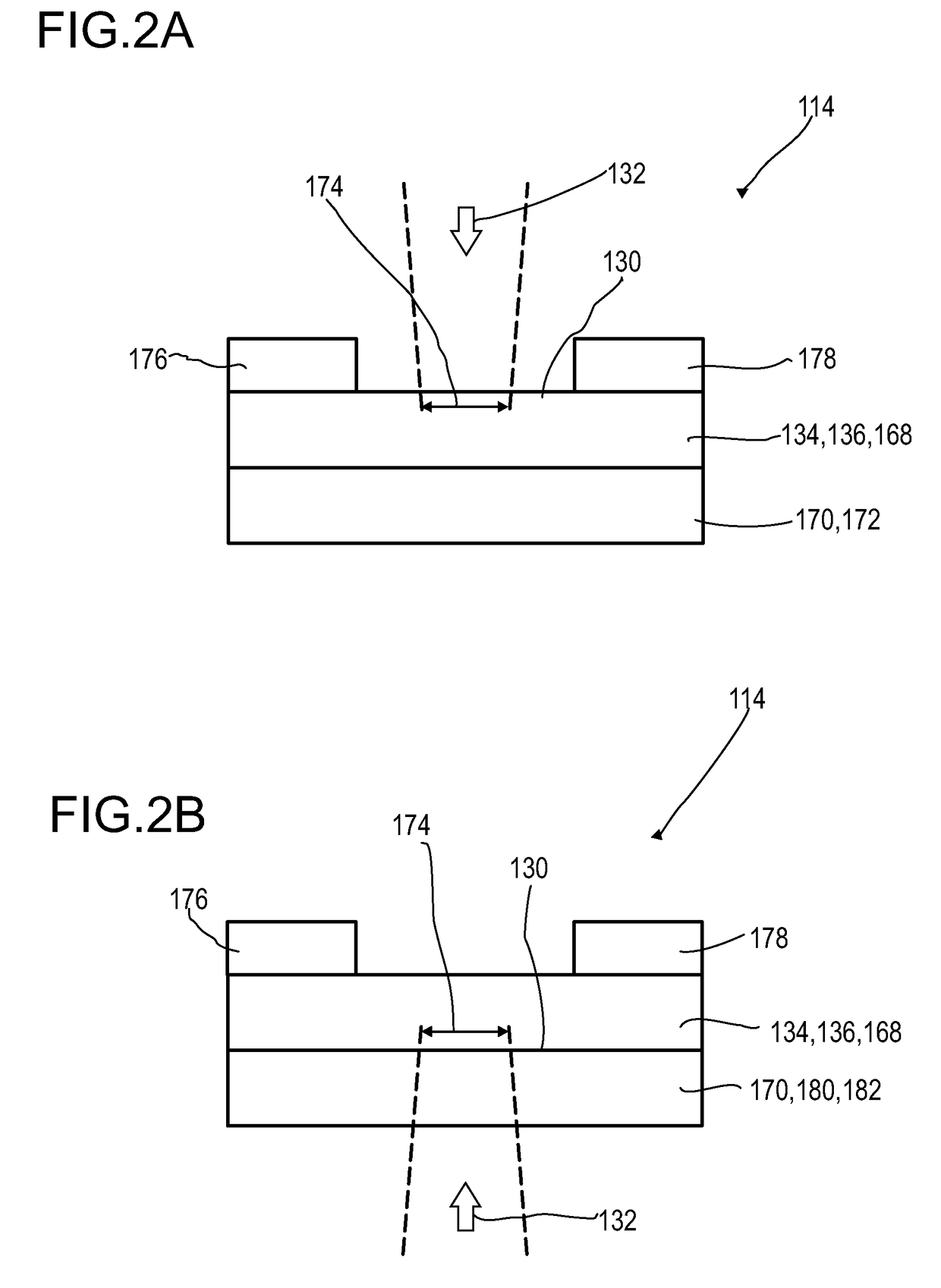
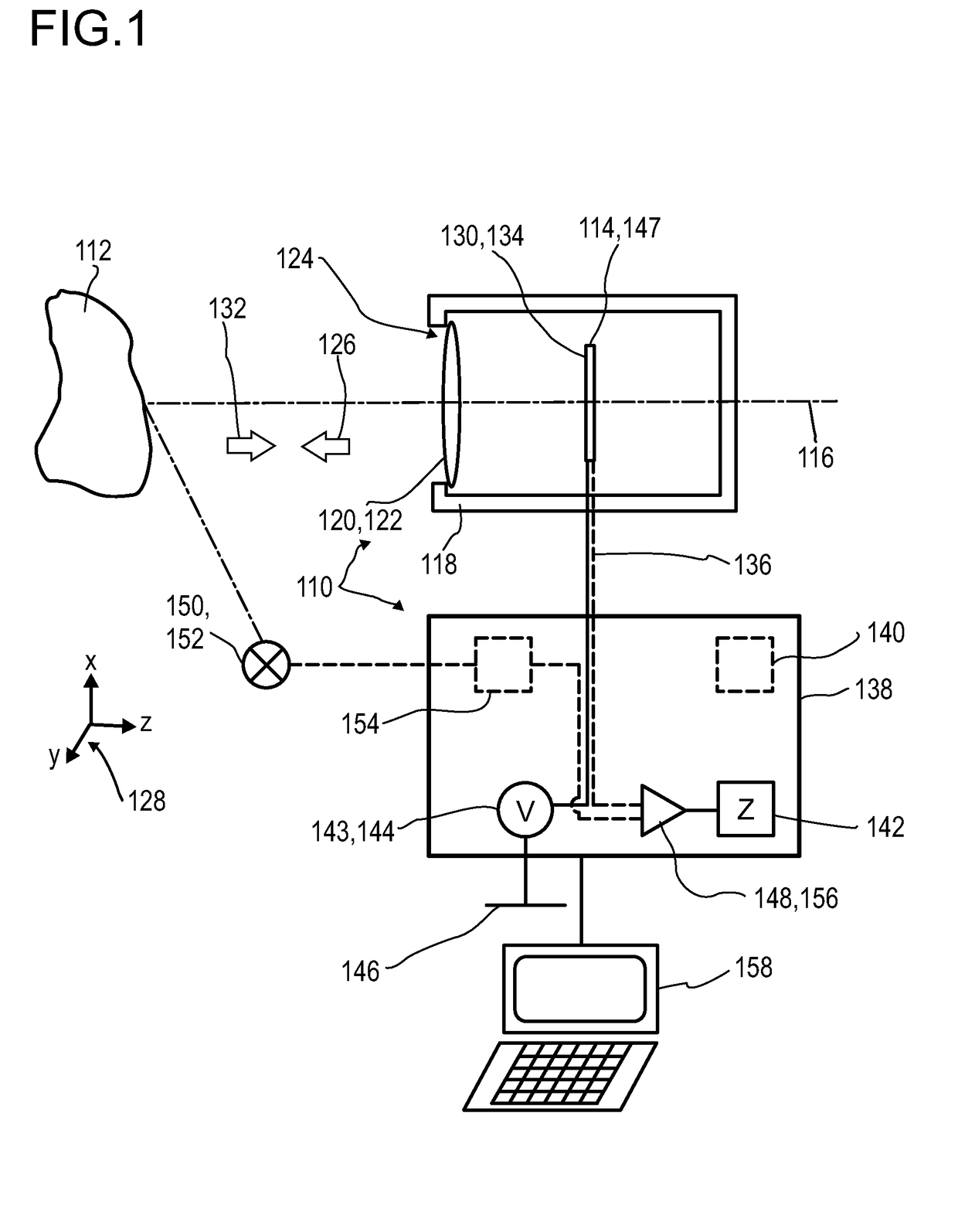
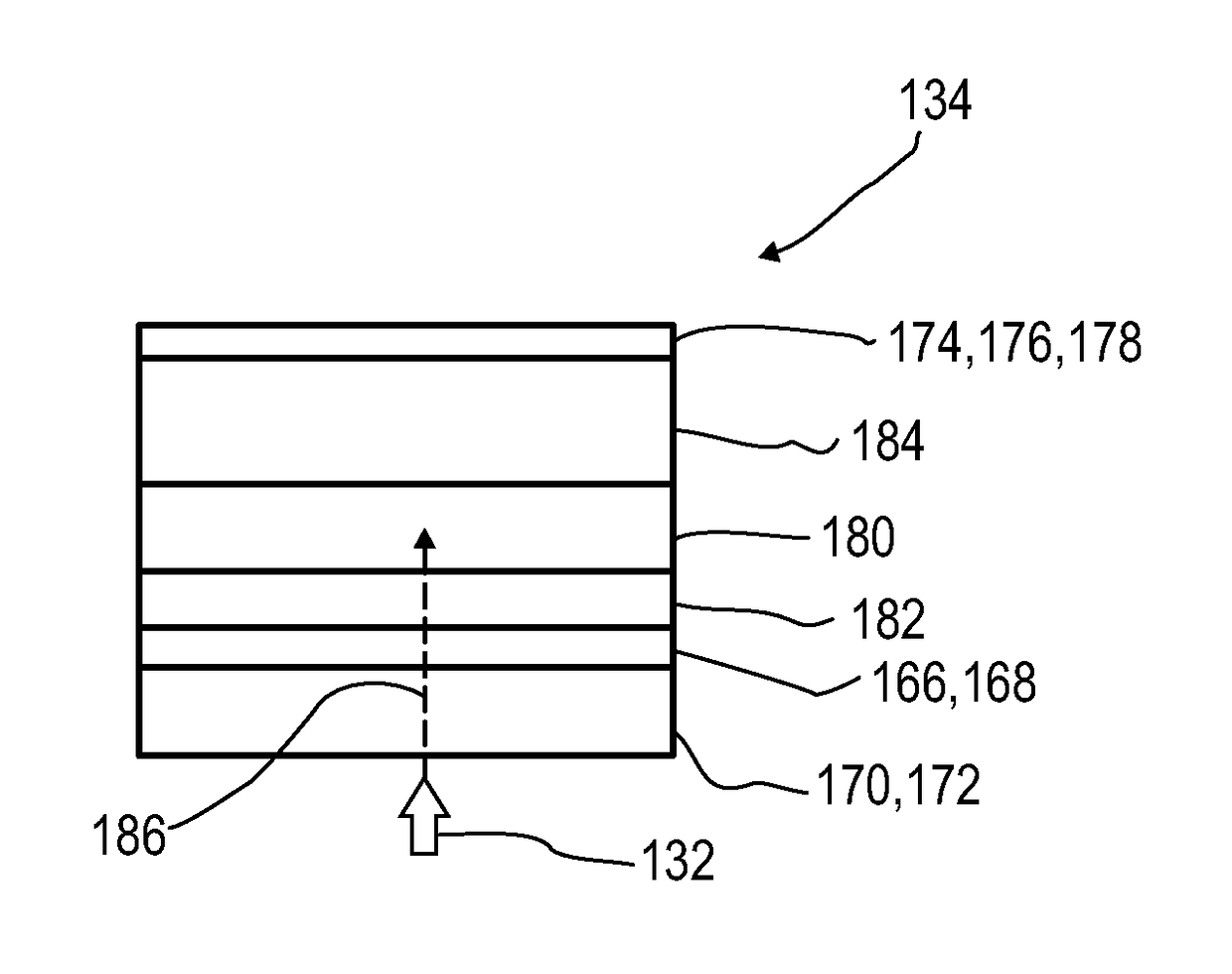
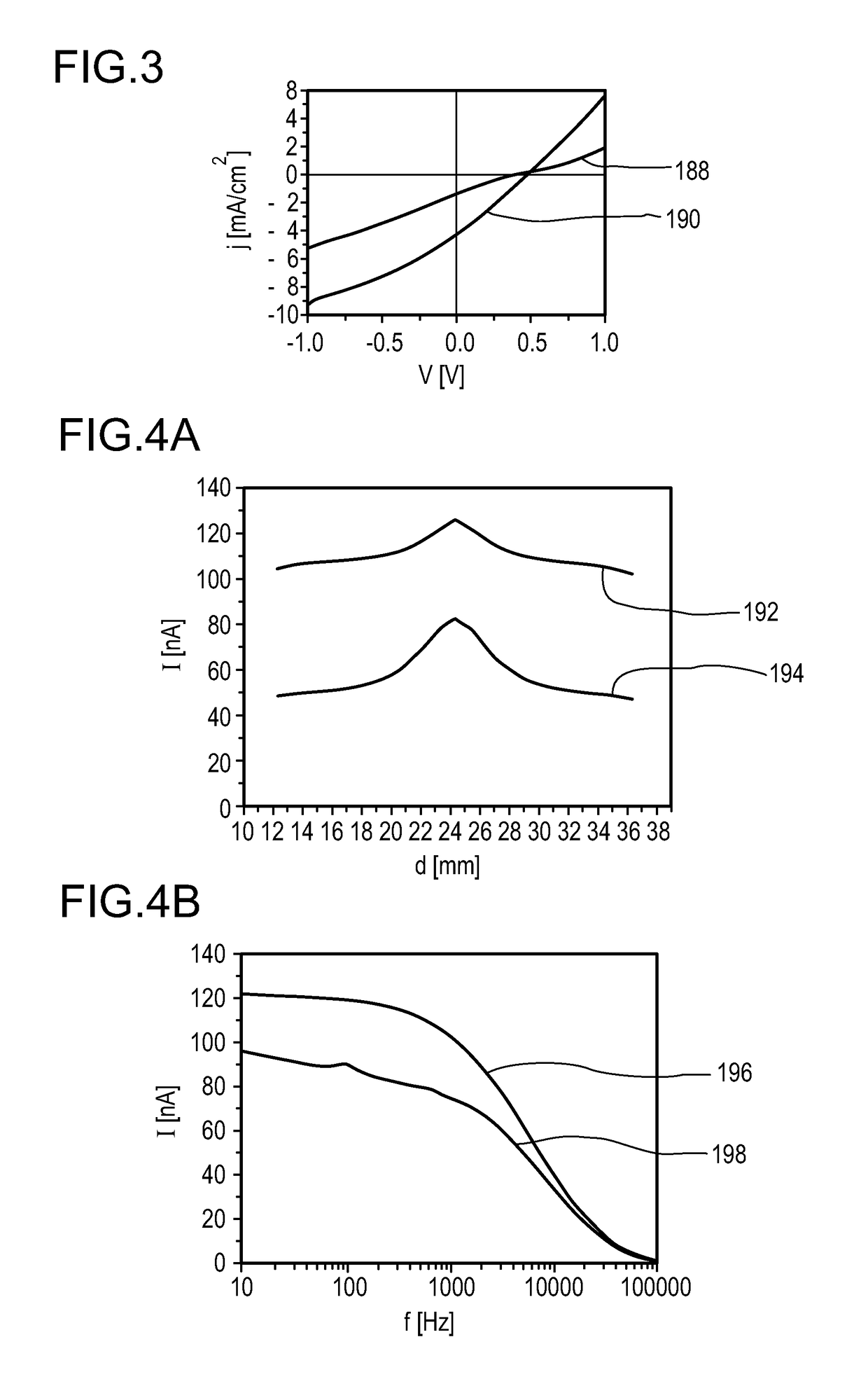
Disclosed herein is a detector (110) for an optical detection of at least one object (112) the detector (110) including: (a) at least one longitudinal optical sensor (114) having at least one sensor region (130), the longitudinal optical sensor (114) containing at least one photodiode (134) the photodiode (134) having at least two electrodes (166, 174), wherein at least one photoactive layer (180) containing at least one electron donor material and at least one electron acceptor material is embedded between the electrodes (166, 174); and (b) at least one evaluation device (150) designed to generate at least one item of information on a longitudinal position of the object (112) by evaluating the longitudinal sensor signal. The detector (110) is efficient for accurately determining of a position of at least one object (112) in space, and exhibits an FiP effect with an improved signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
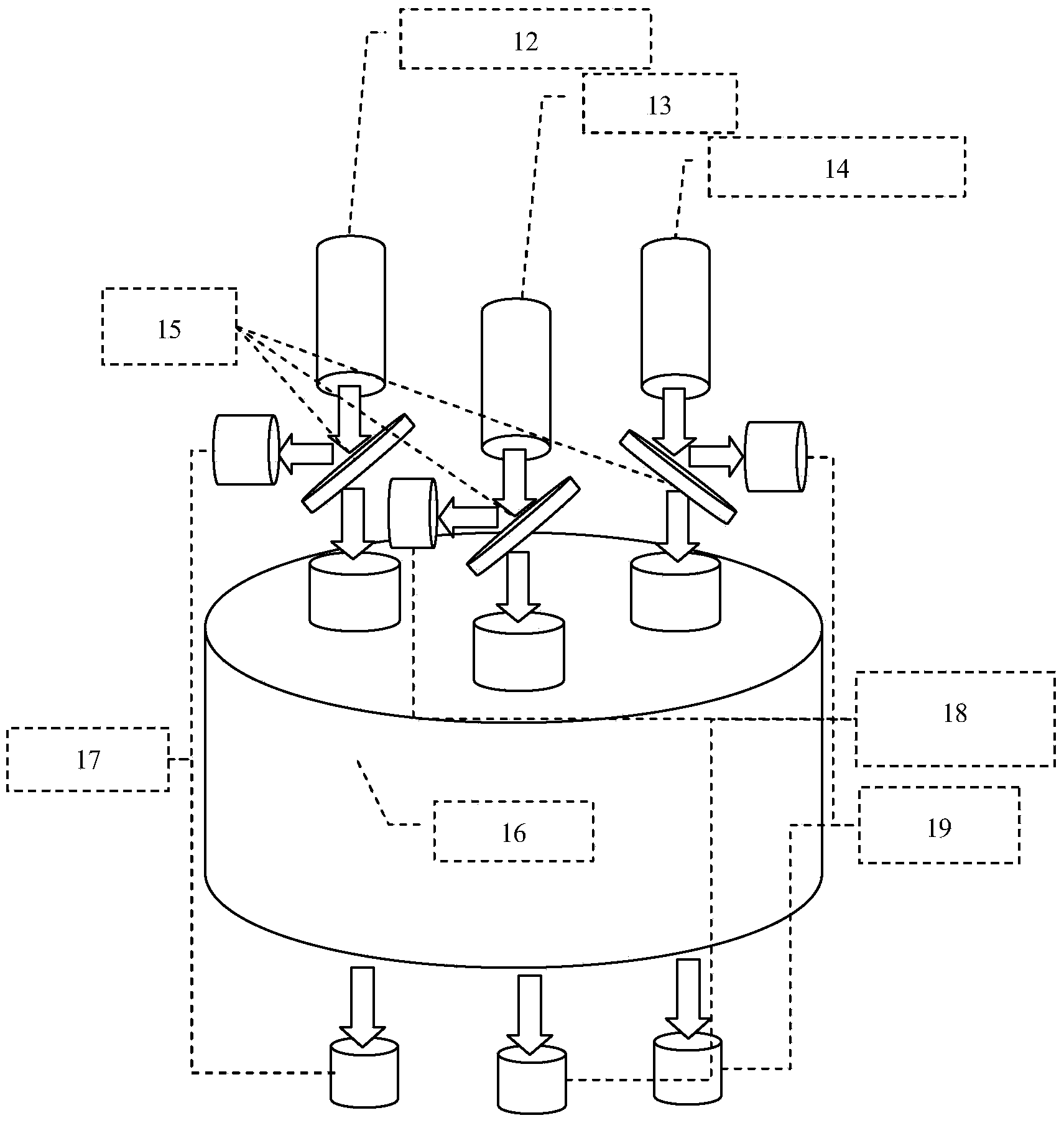
Longitudinal multi-optical-path multi-waveband measuring device for optical transmittance of solid propellant smog
ActiveCN104181129AHigh measurement accuracyReduce the impact of measurement accuracyTransmissivity measurementsCombustion chamberBeam splitting
The invention discloses a longitudinal multi-optical-path multi-waveband measuring device for optical transmittance of solid propellant smog, and is used for solving the problem of a smoke box method that the measure precision of the smog optical transmittance is poor. The longitudinal multi-optical-path multi-waveband measuring device comprises a light source unit, a beam splitting unit, a medium unit, a signal receiving unit, a signal processing unit and a measure and control software unit. Incidence light is split by the beam splitting unit into reference light and measure light, the measure light perpendicularly enters a smog area from a light incidence window on the upper part of a combustion chamber, two beams of light are respectively received by a sensor, and an output signal can be processed to acquire the smog optical transmittance. By designing the longitudinal optical path, the unfavorable influence of the sedimentation effect of the smog on the measure precision can be eliminated. By designing three optical paths, the synchronous measurement of infrared, visible light and laser transmittance of the smog can be realized. The longitudinal multi-optical-path multi-waveband measuring device is suitable for measuring the optical transmittance of the smog which is produced by materials such as a solid propellant, propellant powder and a cladding layer under a given condition and has an important significance on the research of low-characteristic-signal propellants.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
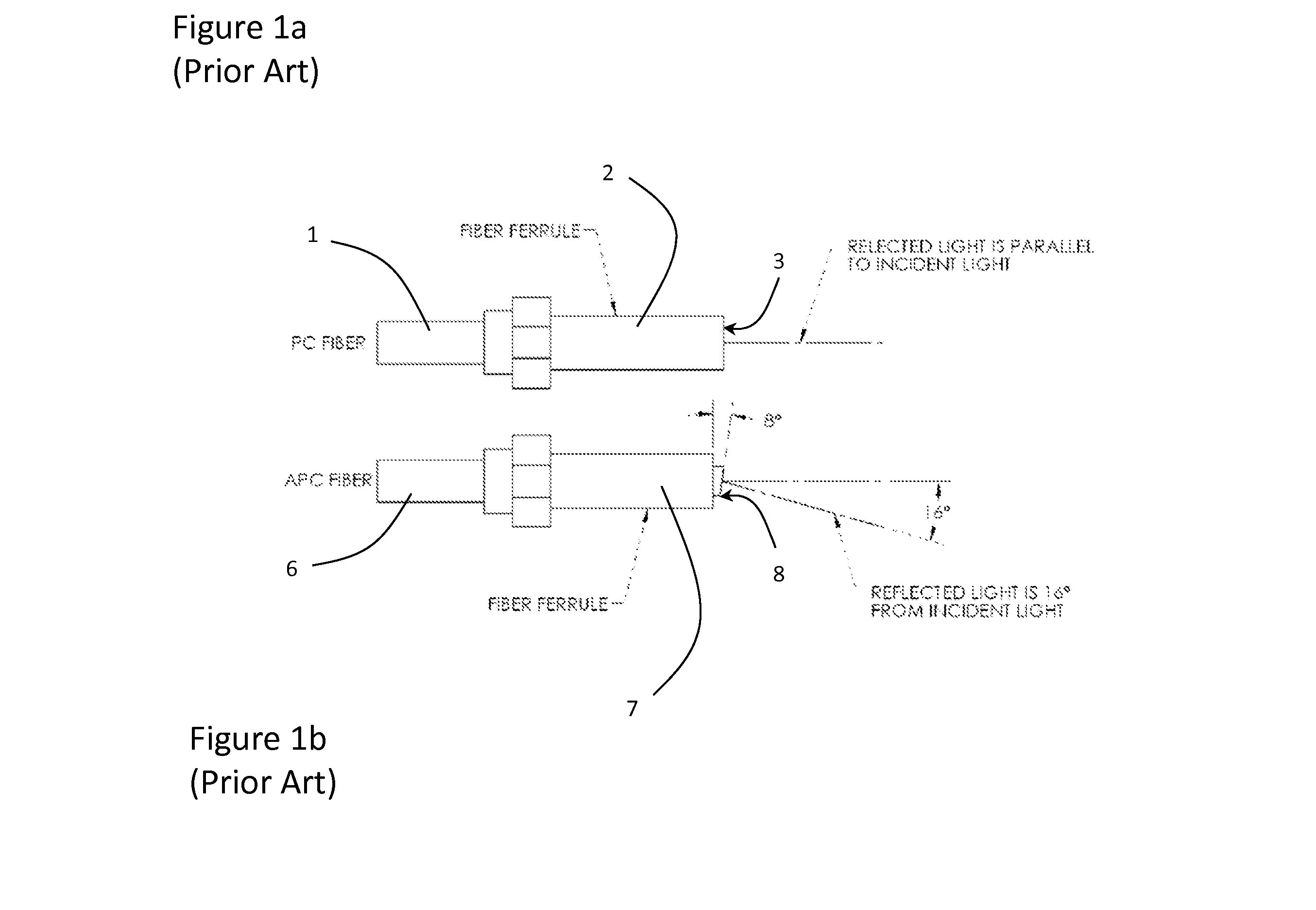
Annulus to create distinct illumination and imaging apertures for an imaging system
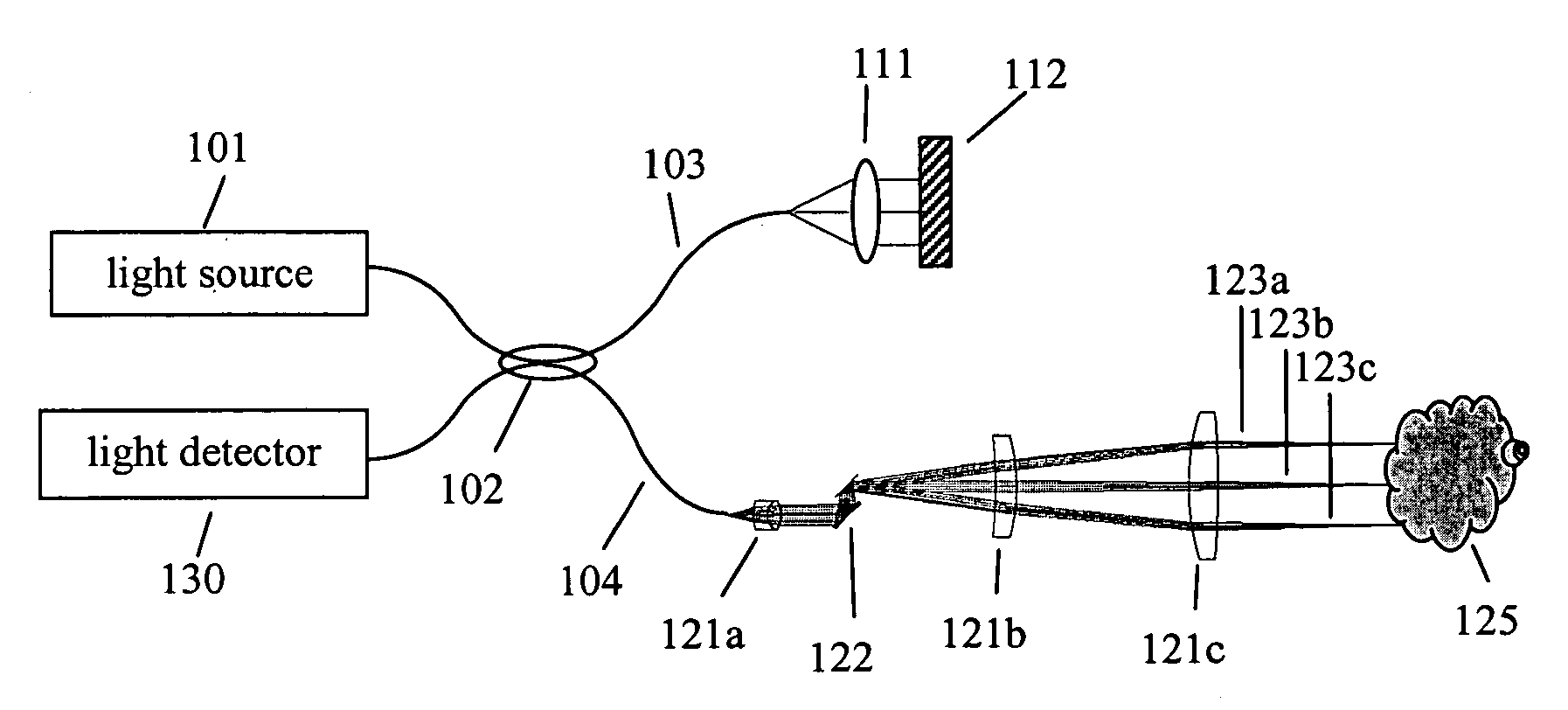
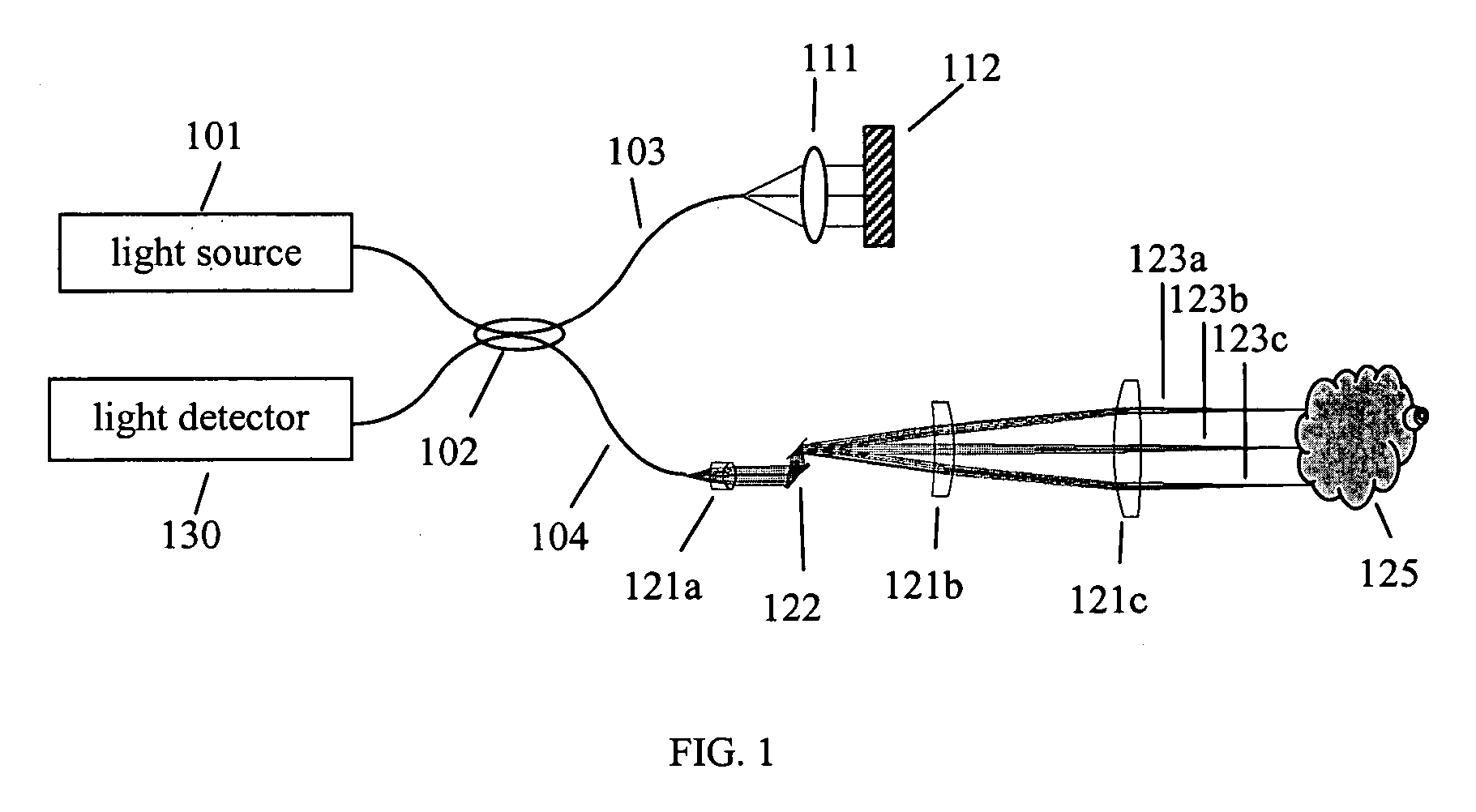
An imaging system for viewing both flat and angled surfaces of a test element, such as the end faces of both PC and APC optical fibers. A light source provides light to the angled surface, while lensing directs a portion of the original light to the angled surface at a second acute angle. A collector, e.g. photodetector, lenses or human eye, receives the portion of the light reflected from the angled surface and generates an image thereof. An annulus is provided in the optical path for managing the light. The annulus includes a transparent outer ring enabling the portion of the light to pass from the light source to the surface at the second acute angle; a central transparent section enabling light reflected from the angled surface to pass to the collector along the longitudinal optical axis; and a first light-blocking ring between the outer ring and the central section for blocking excess light from the light source and reflected from the end surface.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Optical catheter with rotary optical cap
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
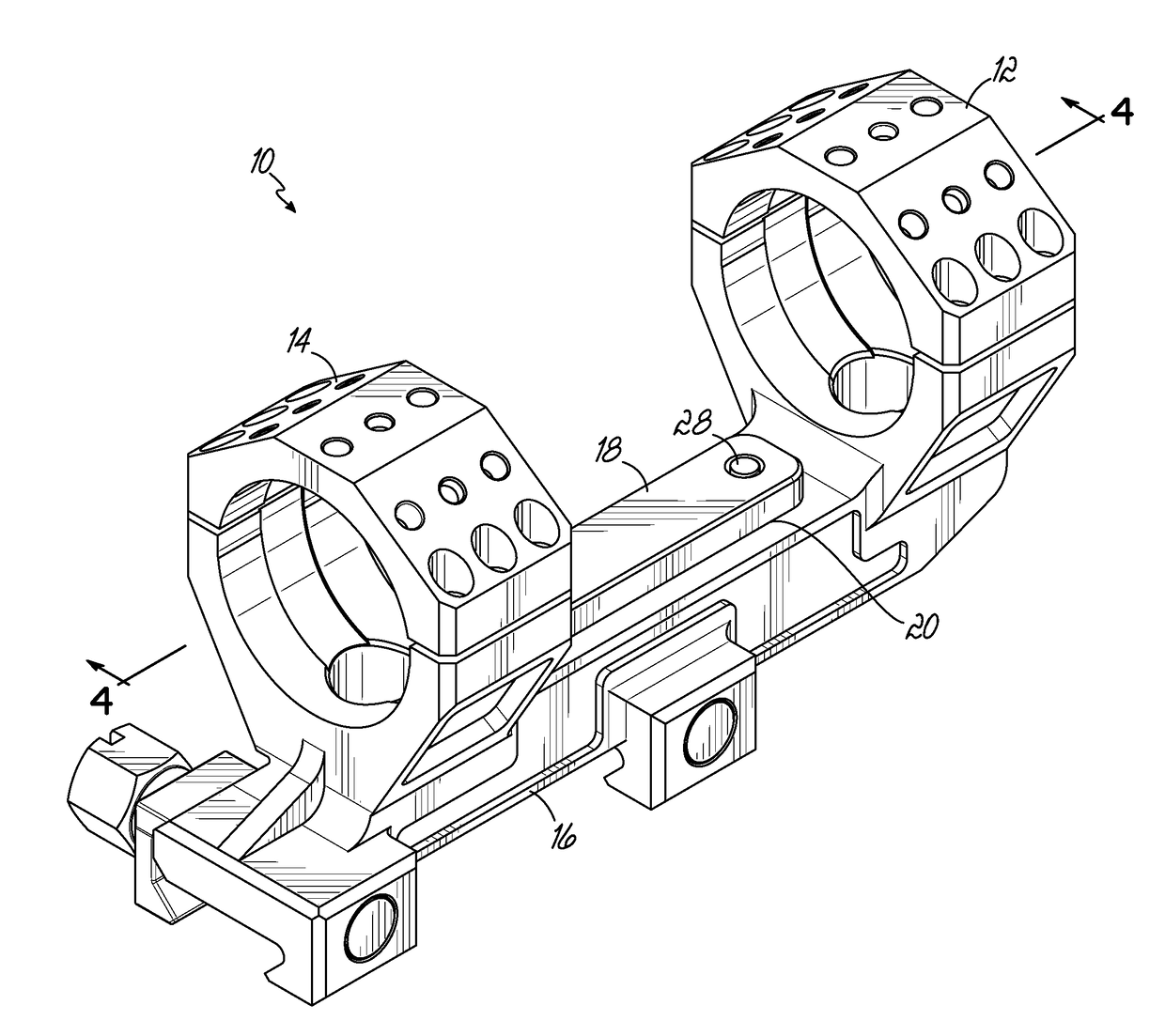
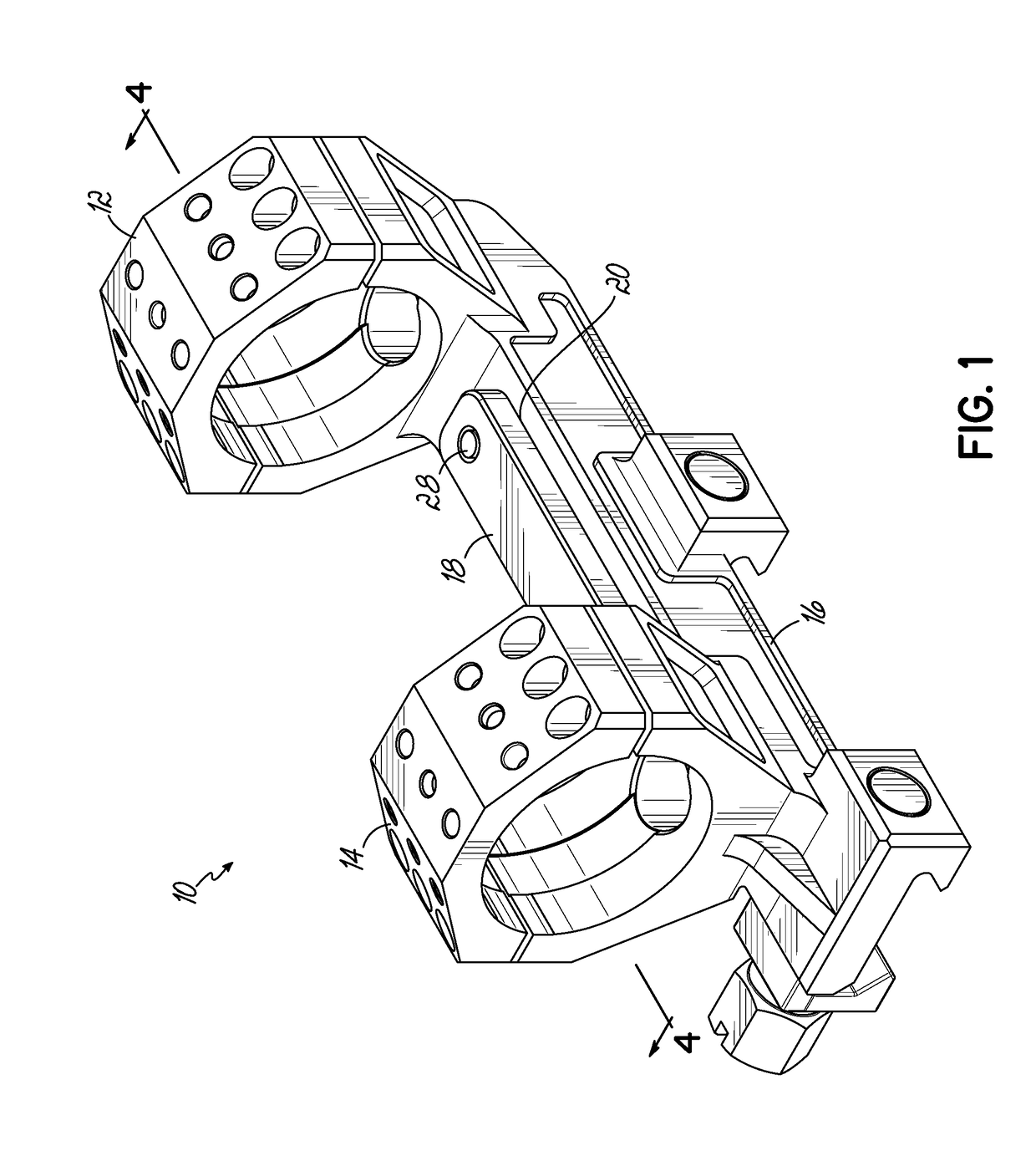
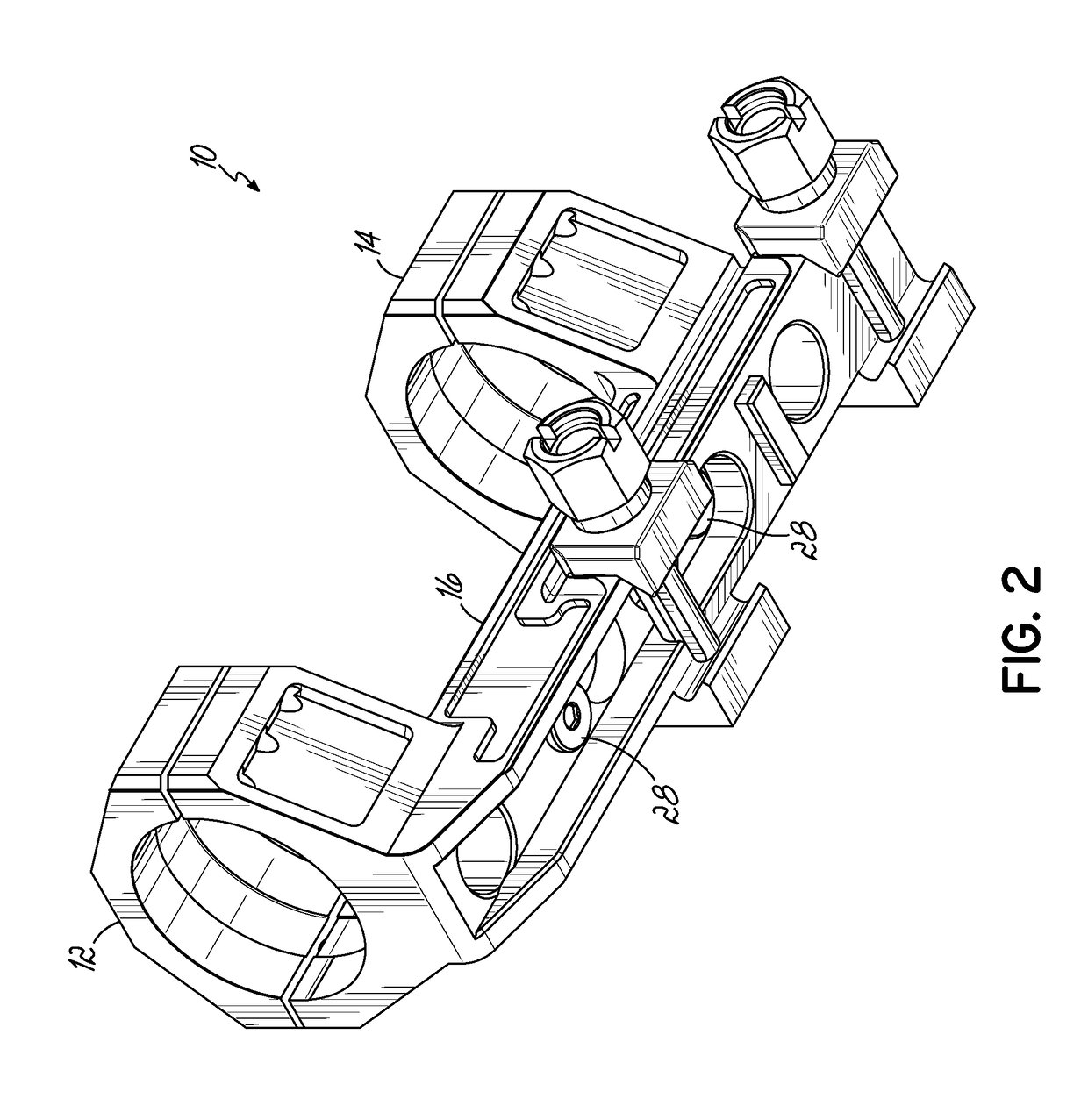
Self-Leveling Scope Mount and Method
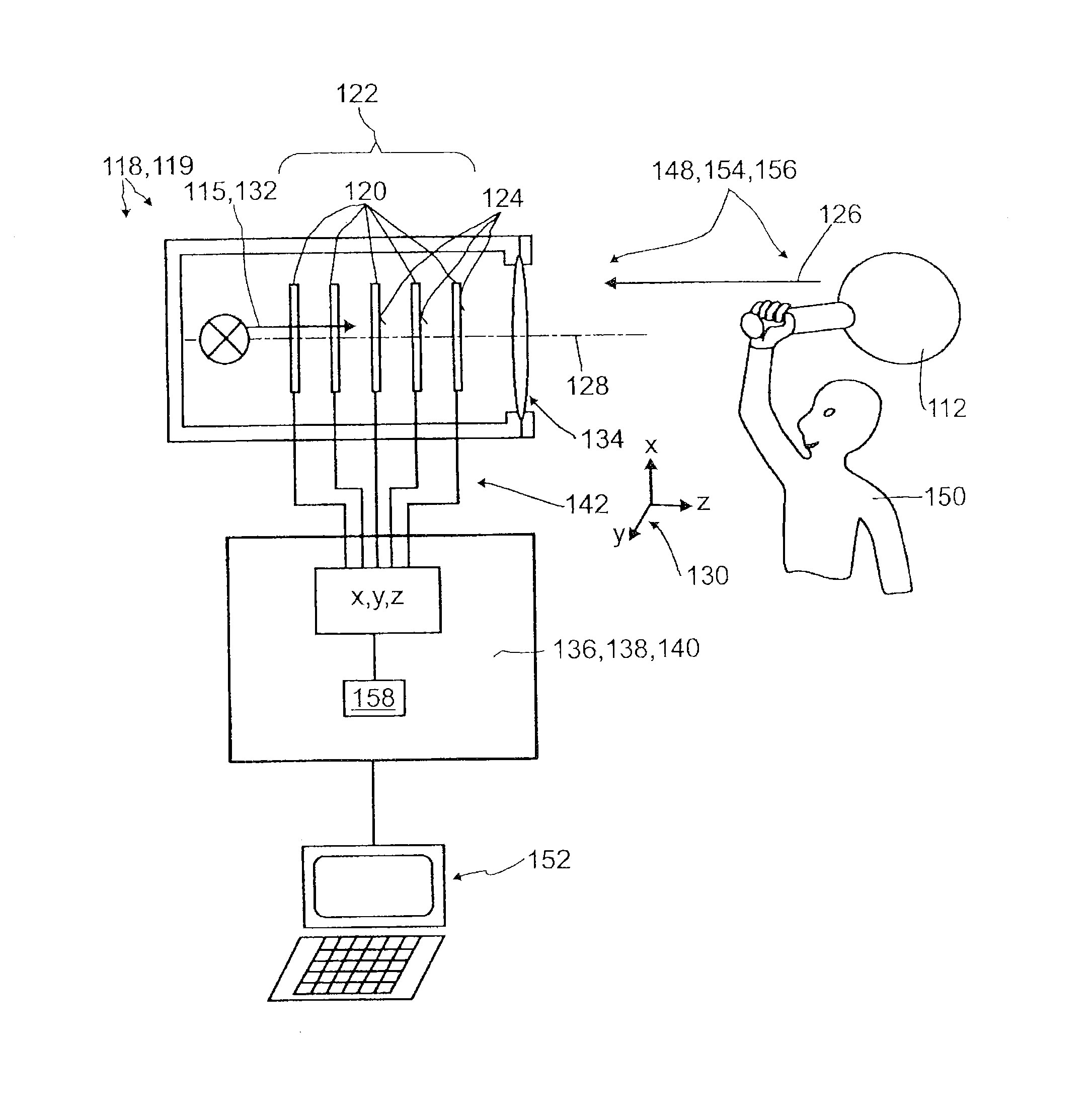
Provided is a self-leveling mount for attaching a sighting scope, having a longitudinal optical axis, to a firearm, having a longitudinal barrel axis. The mount includes a body attachable to a firearm, a pair of scope attachment rings axially spaced apart relative to the body so that at least a portion of the body is situated between the attachment rings, and a vertically movable contact plate on the base between the rings. The plate presents an upper surface that is horizontally perpendicular to the longitudinal axes of a firearm barrel and scope held by the attachment rings. The contact plate makes adjustable alignment contact with a bottom surface of the scope held by the attachment rings to properly orient the scope relative to the firearm.
Owner:LIGHTFORCE USA
Systems and methods for supplying a distributed light source
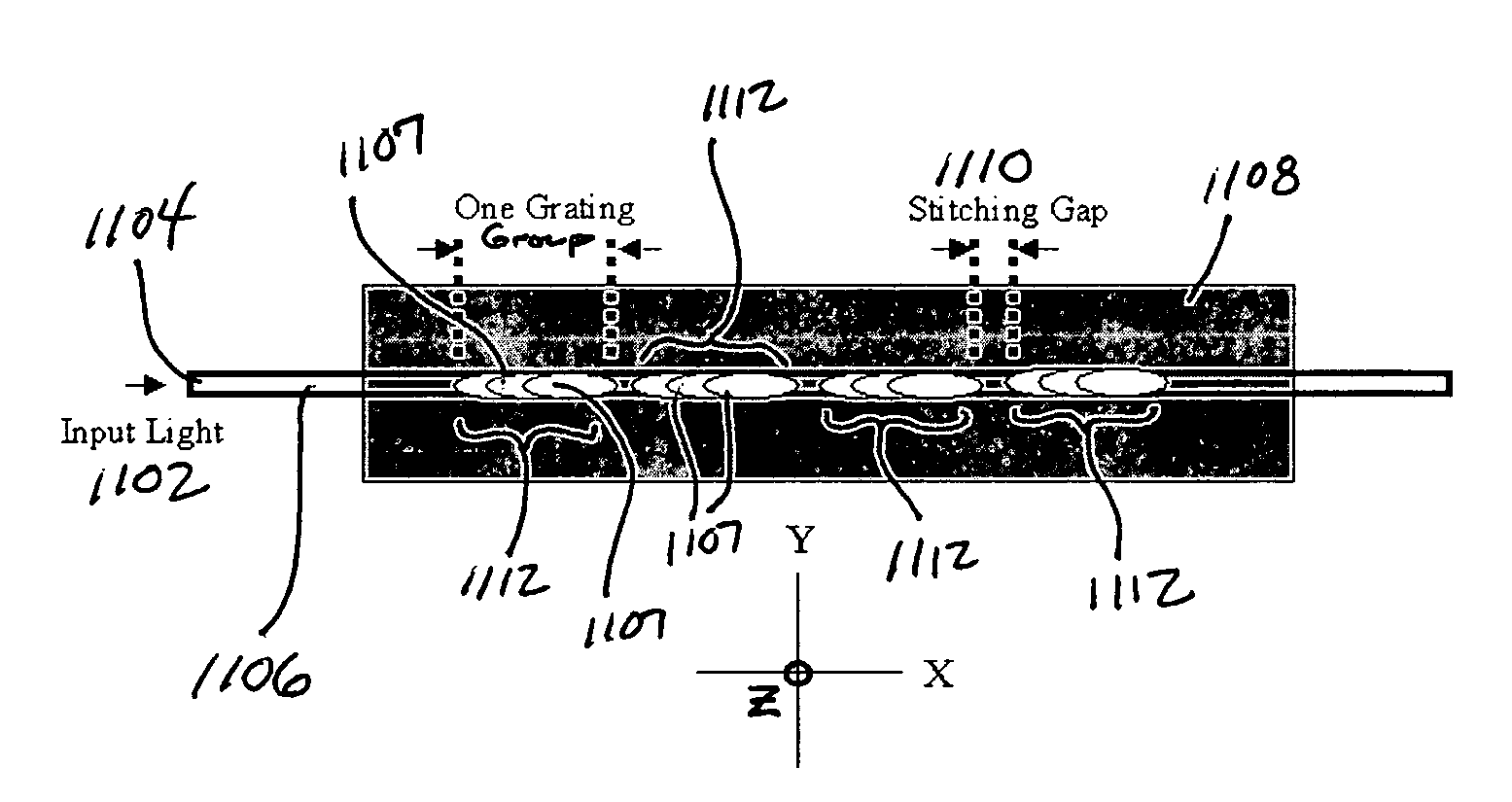
Embodiments of the present invention are directed methods, apparatuses and system for establishing a linear radiant electromagnet energy field. In one embodiment of the invention, a system for providing a linear field of electromagnetic energy includes a laser, at least one length of single mode or multimode optical fiber including a core having a stitched diffraction grating of predetermined pitch for diffracting electromagnetic energy in a predetermined direction, a longitudinal optical element having a convex surface and a length corresponding to the length of optical fiber, wherein the optical element is sized such that the convex surface is positioned at a predetermined distance from the optical fiber and in a direction to receive electromagnetic energy diffracted by the grating of the optical fiber thereby establishing a linear lighting field and a lenticular array.
Owner:PRINCETON LIGHTWAVE INC
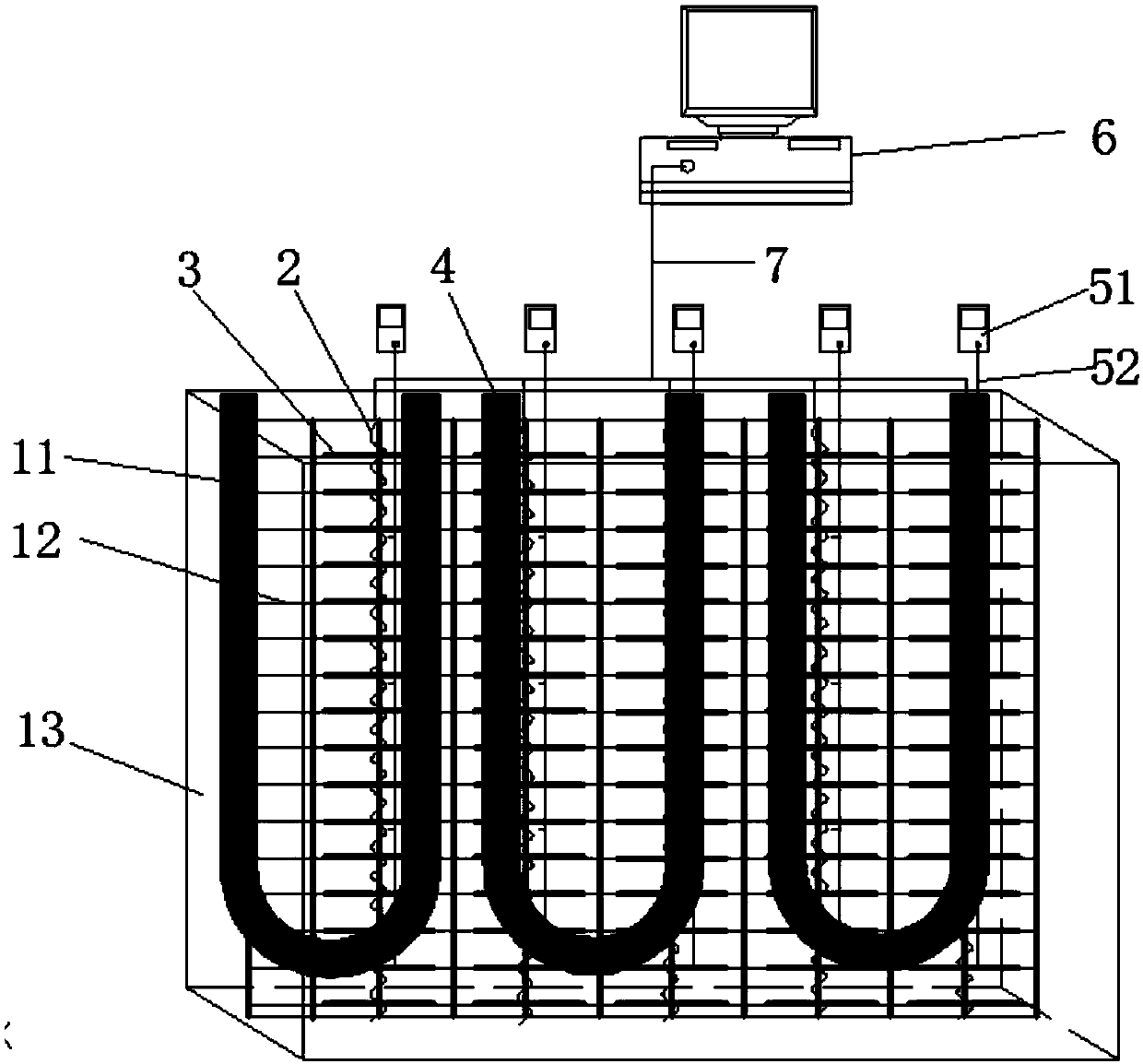
Underground continuous wall seepage detection device based on distributed optical fiber temperature measurement
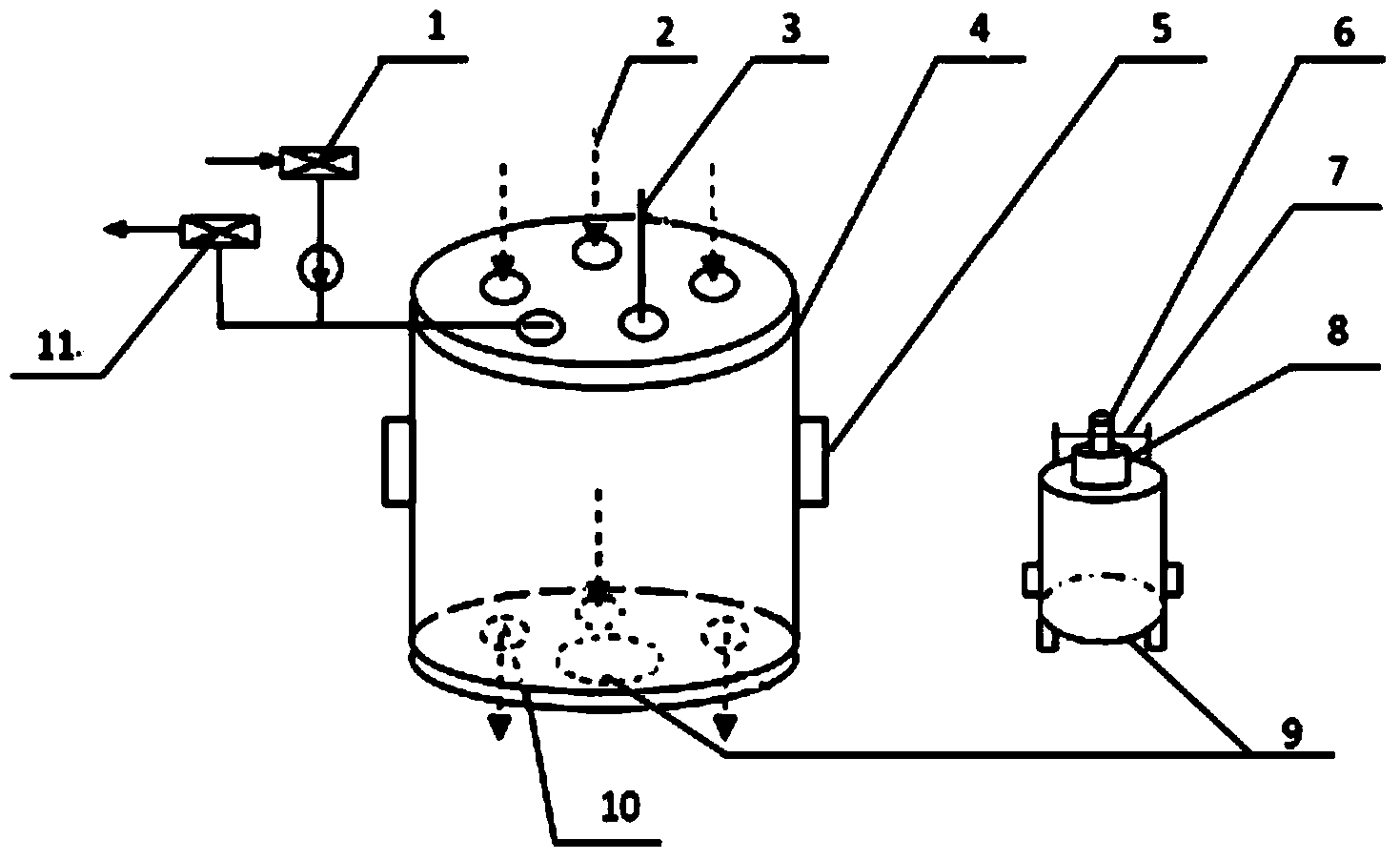
ActiveCN107727271AGuaranteed sensitivityLow costThermometers using physical/chemical changesMaterial flaws investigationSlurry wallFiber
The invention provides an underground continuous wall seepage detection device based on distributed optical fiber temperature measurement, which relates to the field of geotechnical engineering fielddetection and safety protection. The underground continuous wall seepage detection device comprises a heating system, a temperature measurement system and a data processing and analysis system. The heating system is used for heating a soil body behind an underground continuous wall, so that a temperature difference exists between seepage water and optical fibers. The temperature measurement systemis used for measuring an initial temperature value of the optical fibers and a temperature field in the underground continuous wall after heating the soil body. The data processing and analysis system is used for processing temperature data, acquiring a place where the seepage occurs and acquiring a seepage rate of the seepage place. The underground continuous wall seepage detection device makesfull use of a steel reinforcement cage of the underground continuous wall to lay the optical fibers and thermal conductive wires, so that the longitudinal optical fibers and the transverse thermal conductive wires form net-like distributed optical fibers, and the cost is saved. The underground continuous wall seepage detection device further uses the heating system to heat the seepage water, magnifies the temperature difference of the seepage region, does not need to perform surface treatment on the optical fibers, ensures the sensitivity of the optical fibers, and simplifies the process.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
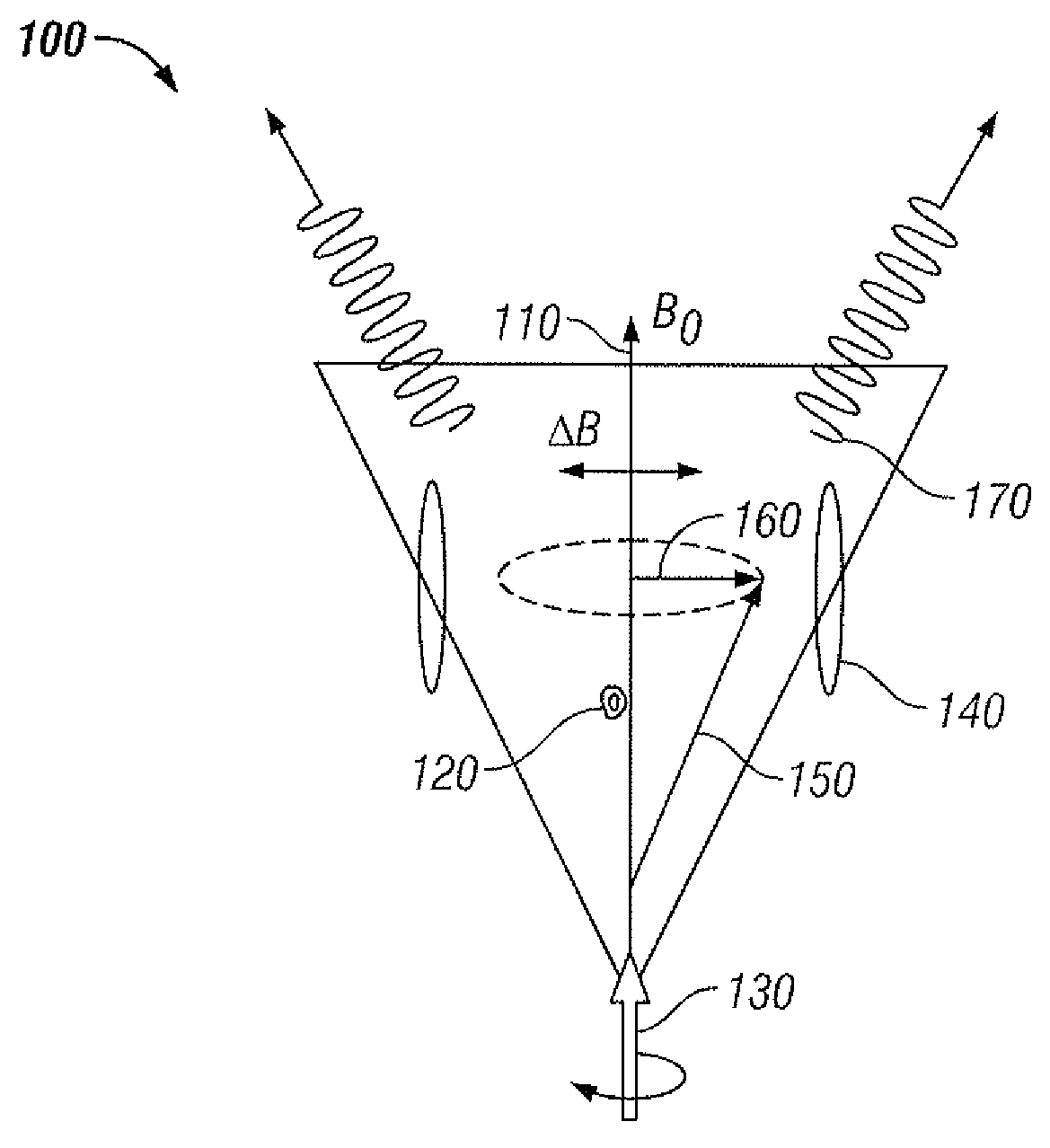
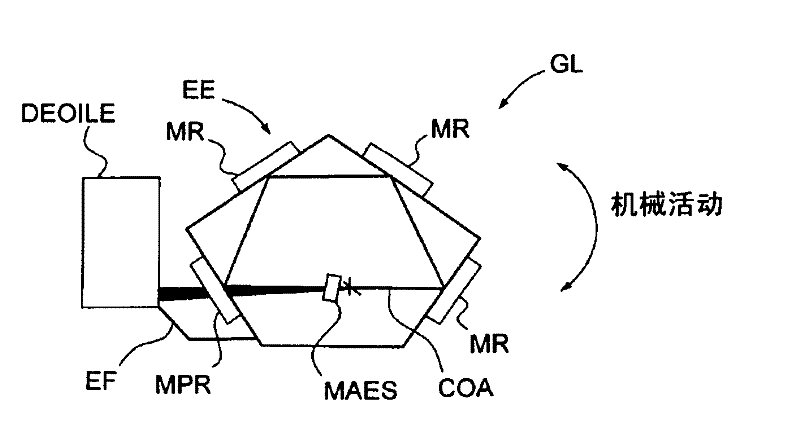
Laser gyro having a solid-state amplifying medium and an optical ring cavity
InactiveCN102177412AUniform gainReduce root causeSagnac effect gyrometersOptical cavityInjection device
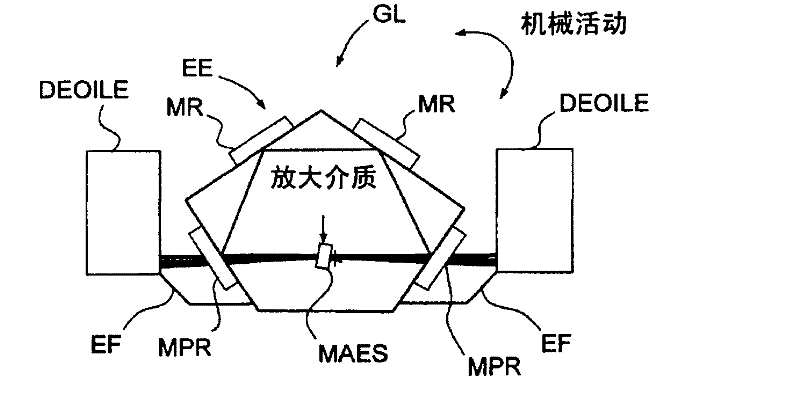
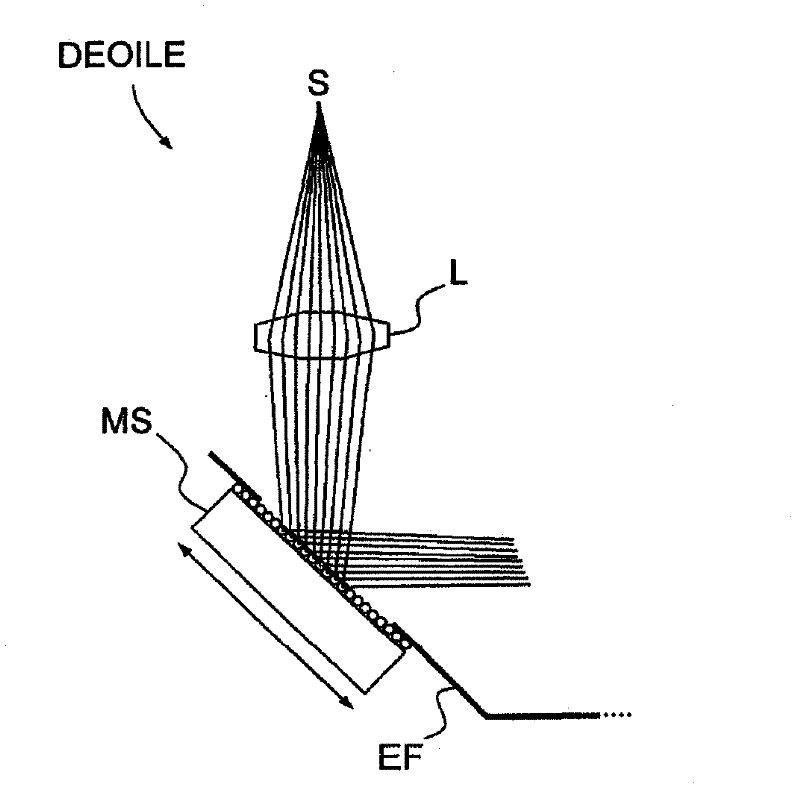
The laser gyro having a solid-state amplifying medium (MAES) and an optical ring cavity (COA) comprises an assembly (EE) containing the optical cavity (COA) and capable of undergoing an oscillatory rotational movement, together with at least one external longitudinal optical energy injection device (DEOILE) for injecting energy into the solid-state amplifying medium (MAES). The laser gyro also includes a fastening assembly (EF) designed to make said assembly (EE) containing the optical cavity and said external longitudinal optical energy injection device (DEOILE) undergo translational and rotational movement as one entity.
Owner:THALES SA
Servo electric cylinder type shockproof exercise simulator
ActiveCN103050026AReduce noiseImprove rigidityCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsOptical axisControl theory
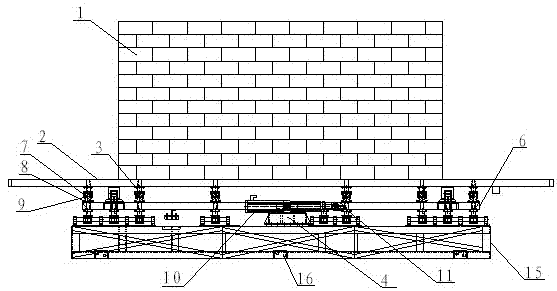
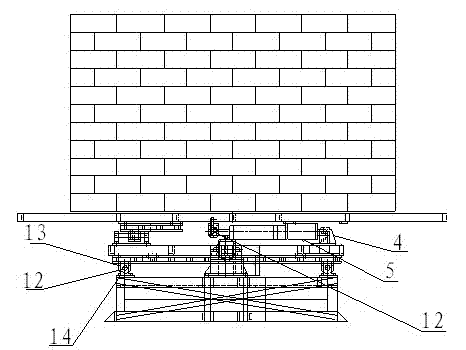
The invention relates to a servo electric cylinder type shockproof exercise simulator which comprises a simulation hut (1), an upper-layer shaking platform (2) fixedly arranged at the lower part of the simulation hut, a base platform (15) which is positioned below the simulation hut and fixedly arranged on a foundation by virtue of footing pieces (16), and a shaking device positioned between the base platform (15) and the upper-layer shaking platform (2); the shaking device comprises a transverse shaking device and a longitudinal shaking device, wherein the transverse shaking device comprises a middle-layer shaking platform (6), two groups of transverse sliding blocks (13), a transverse optical axis (12), a transverse sliding block base (14) and a first servo electric cylinder (10); and the longitudinal shaking device comprises the upper-layer shaking platform (2), two groups of longitudinal sliding blocks (7), a longitudinal optical axis (9), a longitudinal sliding block base (8) and a second servo electric cylinder (5). The invention aims at providing the servo electric cylinder type shockproof exercise simulator which is high in locating precision, stable in movement, low in noise and low in maintenance cost.
Owner:ANHUI NEW HORIZON SCI EDUCATION & CULTURE CO LTD
Rare earth-doped optical fiber perform and preparation method thereof
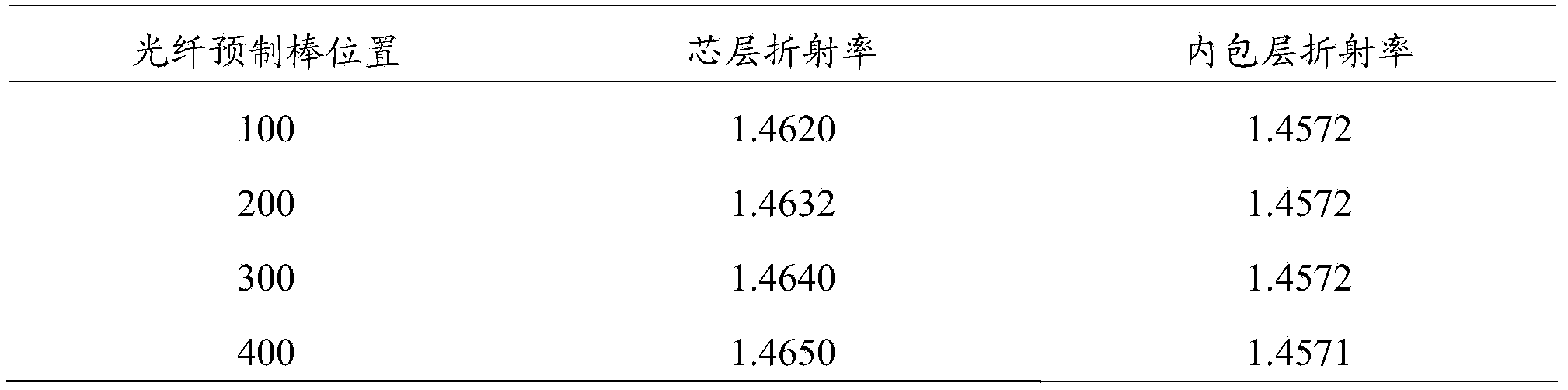
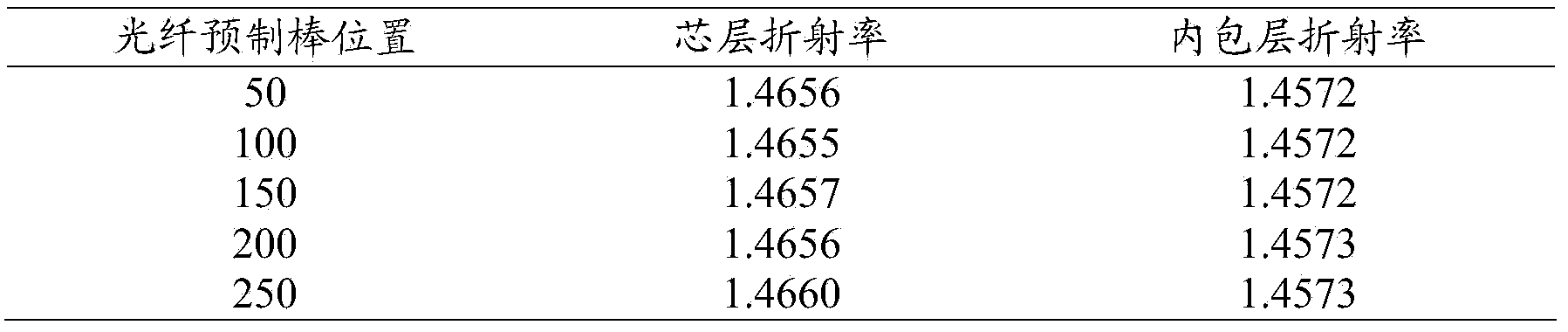
ActiveCN104058587AImprove uniformityImprove longitudinal uniformityGlass making apparatusFiberRare-earth element
The invention provides a preparation method of a rare earth-doped optical fiber perform. The method comprises the following steps: 1) depositing a loose core layer on the inner surface of a quartz deposit tube; 2) soaking the quartz deposit tube with the loose core layer deposited on the inner surface obtained in the step 1) into a solution containing a rare-earth element, and releasing the solution containing the rare-earth element at the release speed obtained in the formula a after soaking the head of the quartz deposit tube, wherein the release speed (mm / min) is L / (3h*L / 400mm-280h.(mm / min) / V) / 60 in the formula a; 3) sequentially drying, sintering and melting the quartz deposit tube soaked in the step 2), so as to obtain the rare earth-doped optical fiber perform. The release speed of the solution containing the rare-earth element is controlled according to the formula a, the doping longitudinal uniformity of the rare-earth element is improved, and energy loss caused by a rare-earth ion cluster is also avoided, so that the longitudinal optical fiber uniformity of the optical fiber perform is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINAOKE CABLE
In-line arrangement for measuring polarization extinction ratio
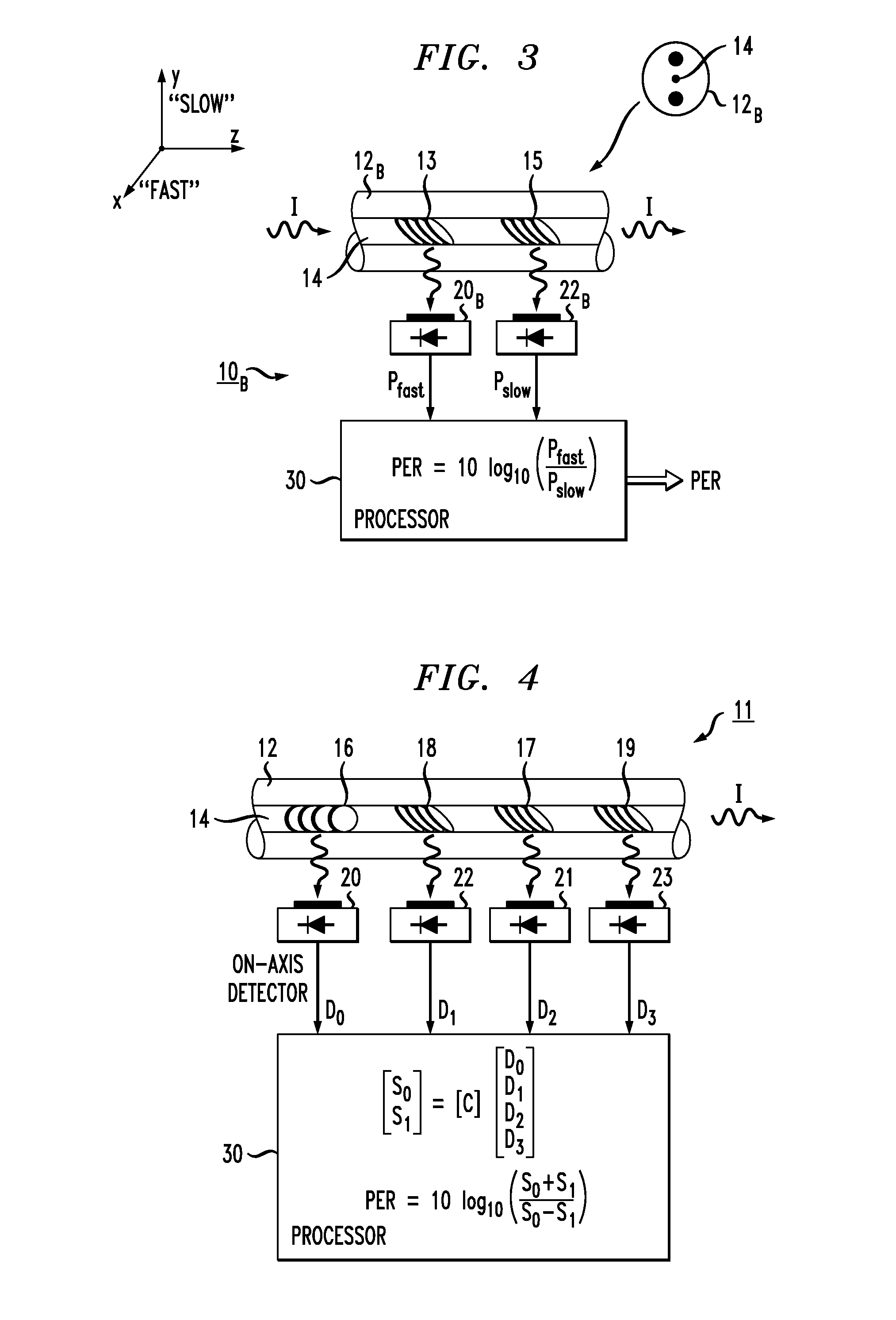
InactiveUS20140218733A1Improve accuracyOptical fibre with polarisationPhotometryFiberMeasurement device
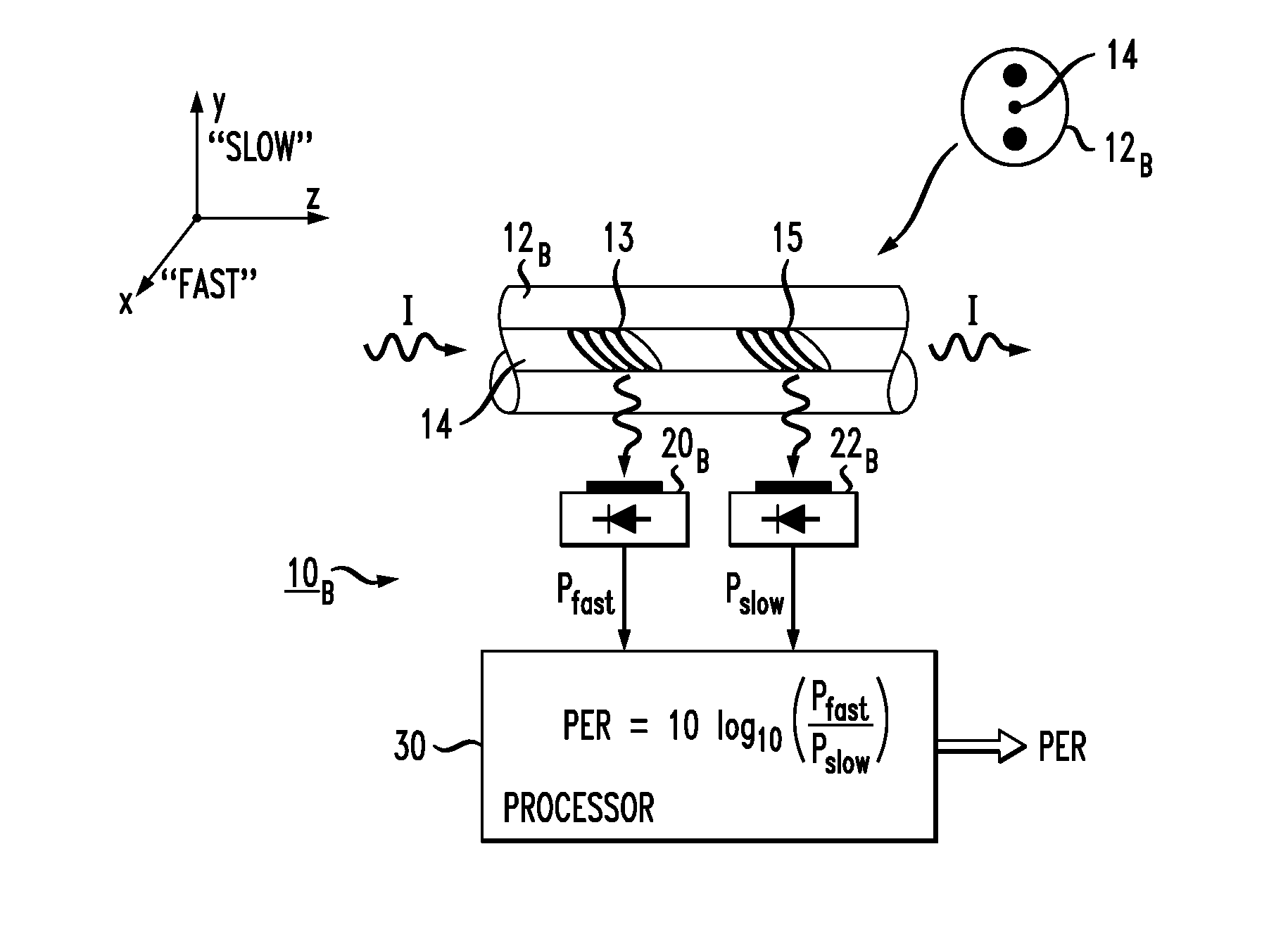
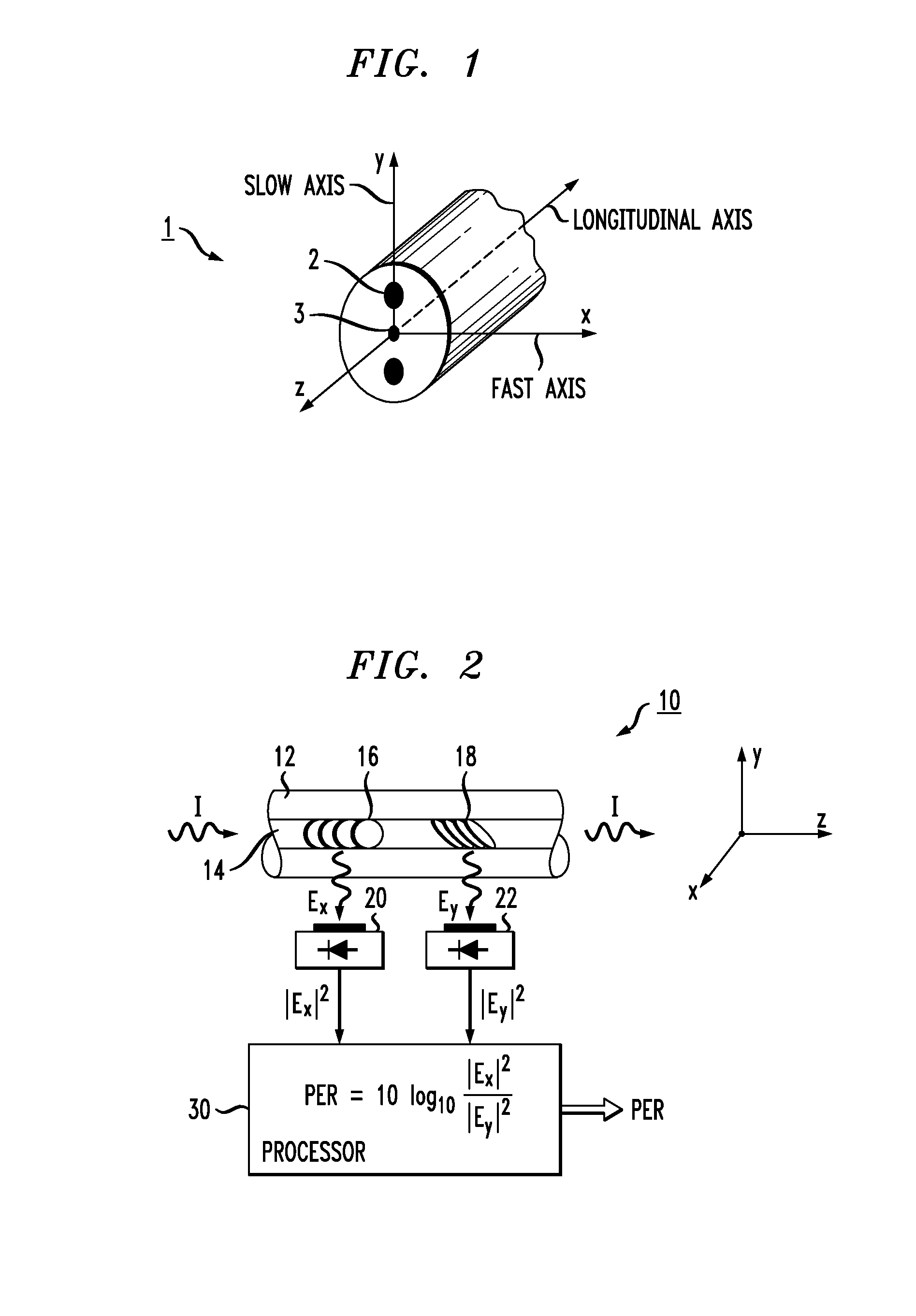
An in-line polarization extinction ratio (PER) monitor that generates a value of an optical signal's PER from a single measurement, without requiring the optical transmission signal path of the system to be directly coupled into a separate measurement device. The polarization extinction ratio may be defined as: 10 log(PEx / PEy), where PEx is the power of the optical signal propagating along the “x axis” and PEy is the power propagating along the orthogonal “y axis” (with the z-axis defined as a longitudinal optical axis of the system and the x-y plane orthogonal to this direction of propagation). The PER monitor comprises a section of optical fiber (preferably birefringent or with induced birefringency), with a pair of gratings formed along the fiber and oriented to out-couple orthogonal components of the propagating signal. Photodetectors are used to convert the scattered light into electrical signal equivalents and then processed to yield the PER value. By properly aligning the axes of the monitor and the optical system, the two measurements are sufficient to provide a one-shot, real-time calculation of the PER of the optical signal propagating through the system.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Detector for optically detecting at least one object
InactiveCN108292175APromote resultsImprove toleranceInput/output for user-computer interactionPosition fixationLight beamEngineering
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
Nitride semiconductor quantum cascade laser
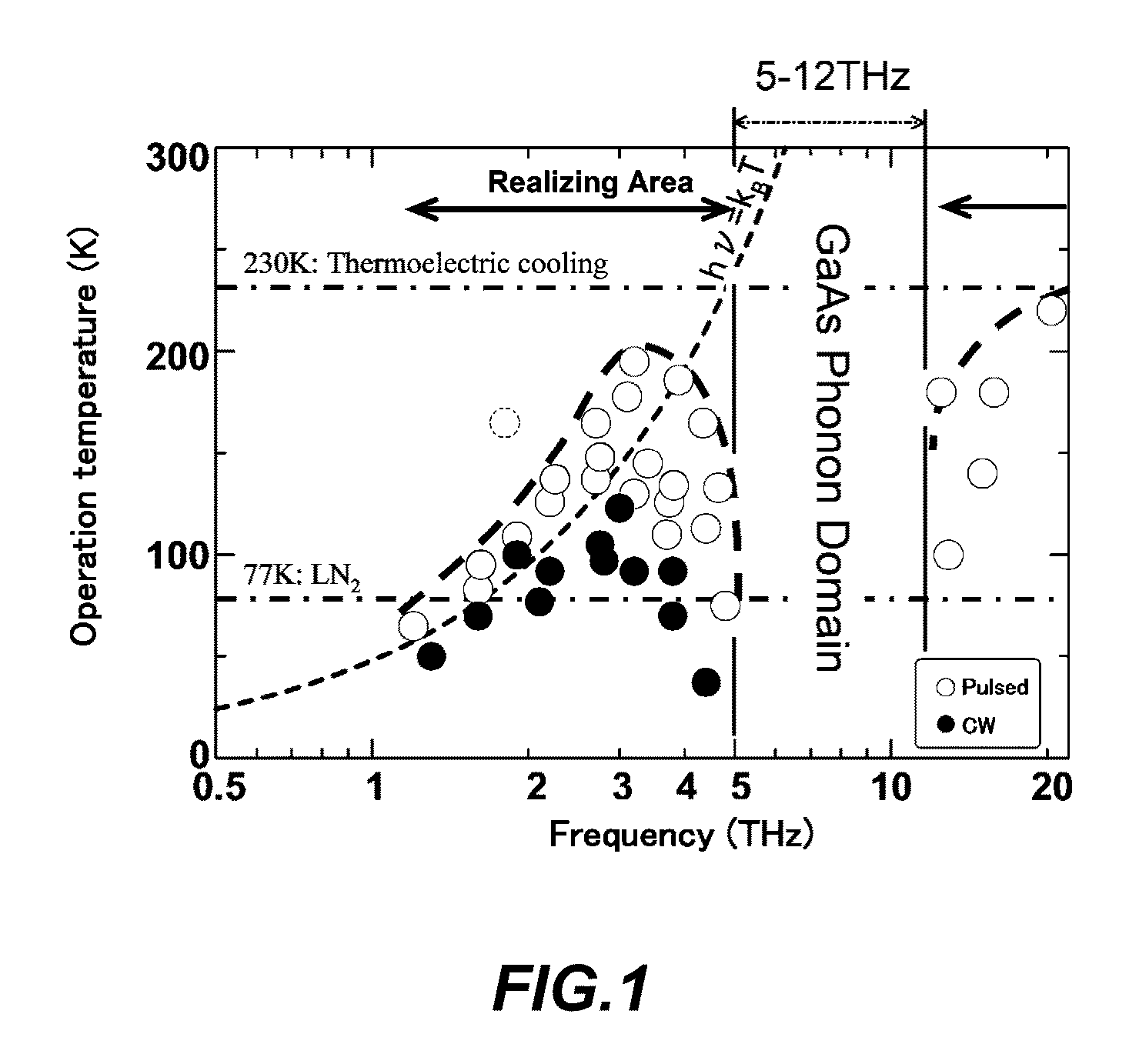
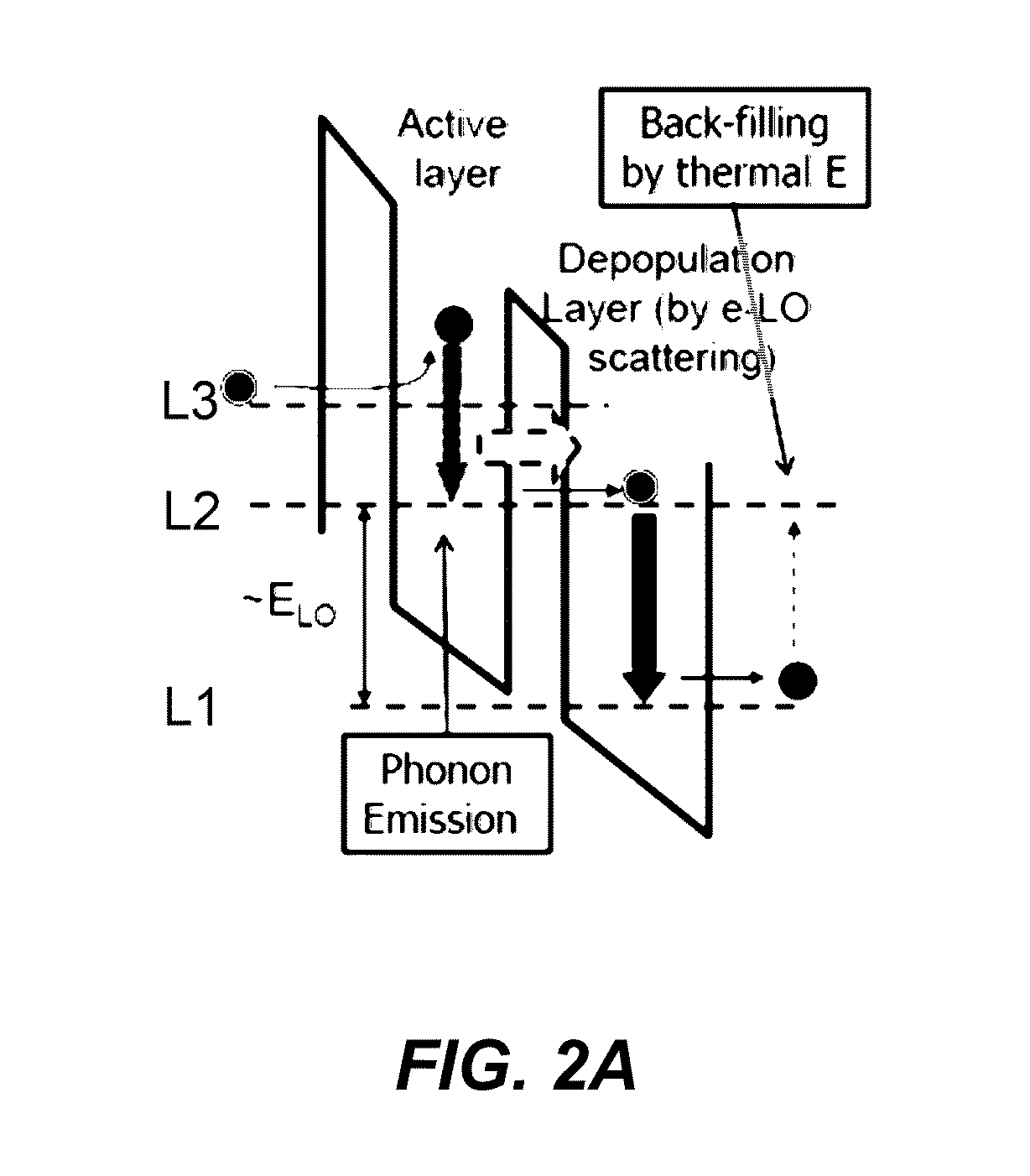
ActiveUS20160064901A1Easy to operateOptical wave guidanceLaser using scattering effectsQuantum cascade laserUnit structure
A terahertz quantum cascade laser (THz-QCL) element operable at an unexplored frequency is obtained. A crystal of a nitride semiconductor is used to fabricate a repeated set of unit structures into a super lattice. Each unit structure includes a first barrier layer, a first well layer, a second barrier layer, and a second well layer disposed in this order. An energy level structure for electrons under a bias electric field has a mediation level, an upper lasing level, and a lower lasing level. The energy value of the mediation level is close to the energy value of either an upper lasing level or a lower lasing level, each belonging to either the unit structure or the other unit structure adjacent thereto, and is separated from the energy value of the other level by at least the energy value of a longitudinal-optical (LO) phonon exhibited by the crystal.
Owner:RIKEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com