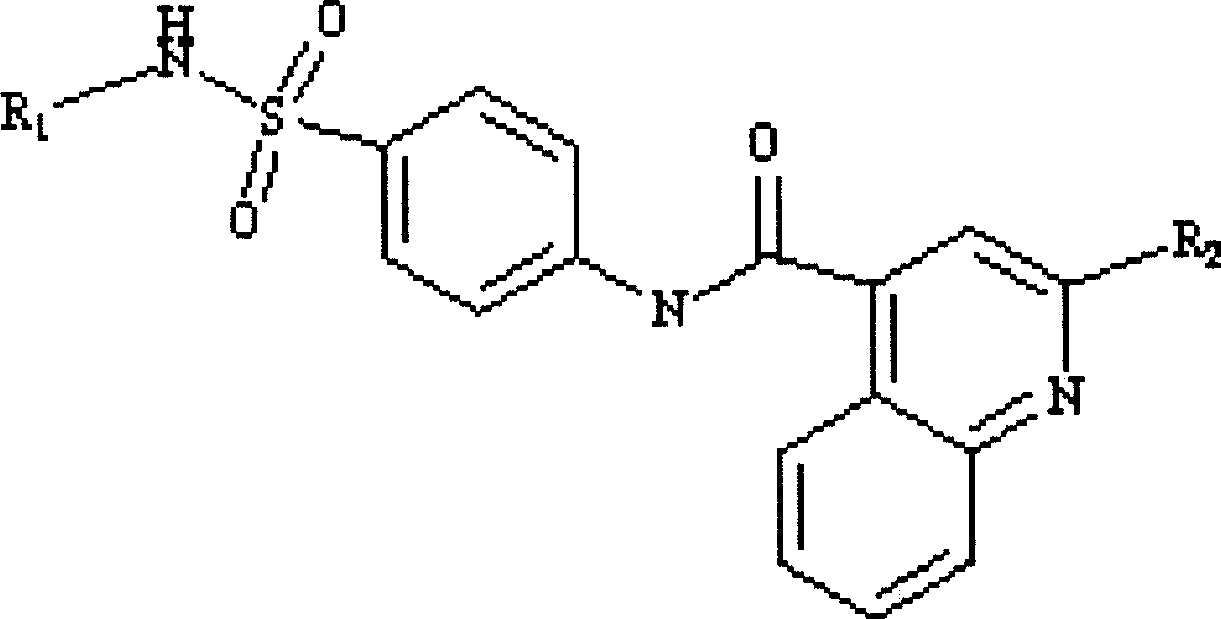
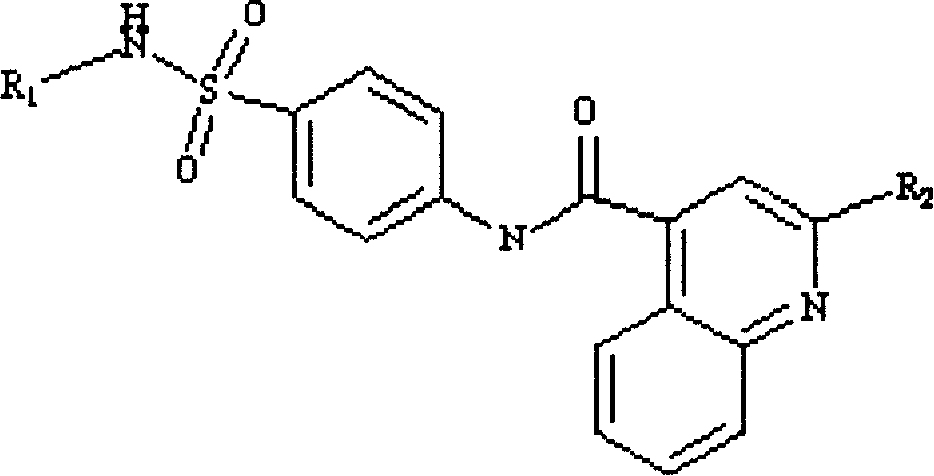
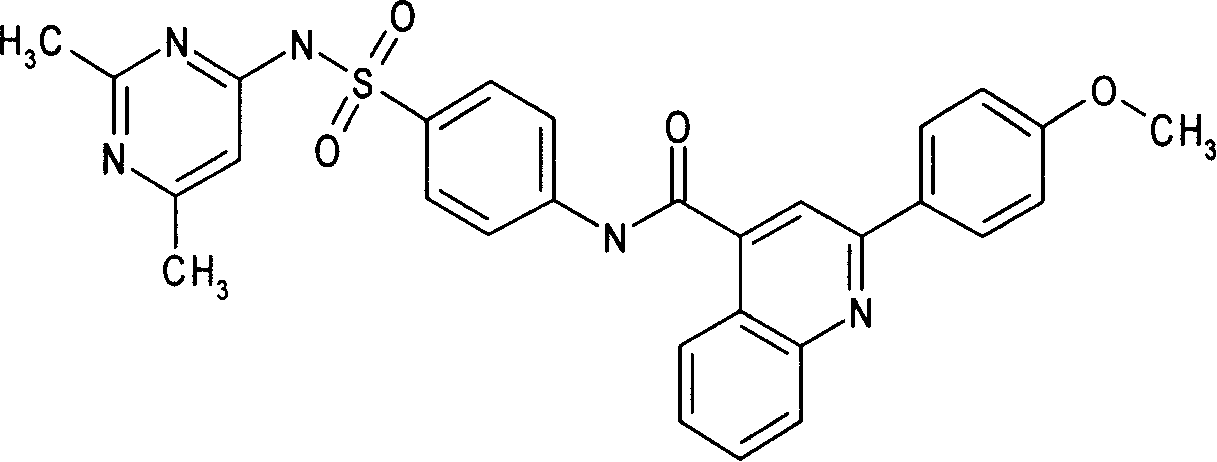
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Interfering virus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A virus which prevents replication of another virus; may be due to blocking of virus attachment sites or the presence of defective interfering particles which block the replication of competent ones.
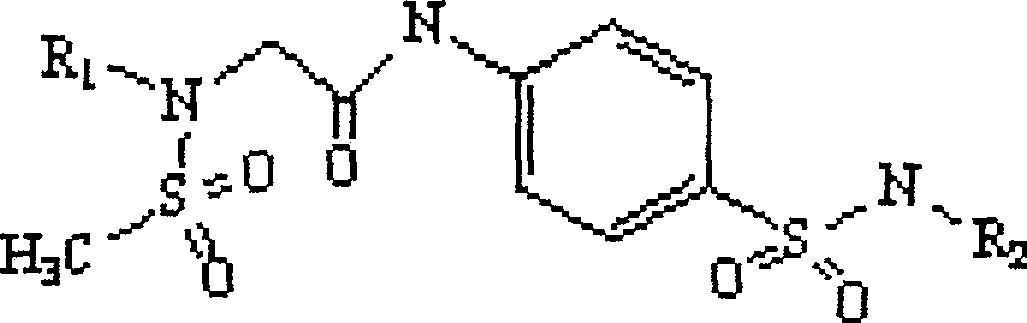
Method for expression of small antiviral RNA molecules within a cell
ActiveUS20030059944A1Prevents sequenceHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneticsViral life cycle
In one aspect, the invention provides methods and compositions for the expression of small RNA molecules within a cell using a retroviral vector. The methods can be used to express double stranded RNA complexes. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) can be expressed using the methods of the invention within a cell, that interfere with a viral life cycle by down regulating either the viral genome, a viral genome transcript, or a host cell that. In another aspect the invention provides methods for treating patients having suffering from infection, particularly infection with HIV.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Lysine demethylase inhibitors for diseases and disorders associated with hepadnaviridae
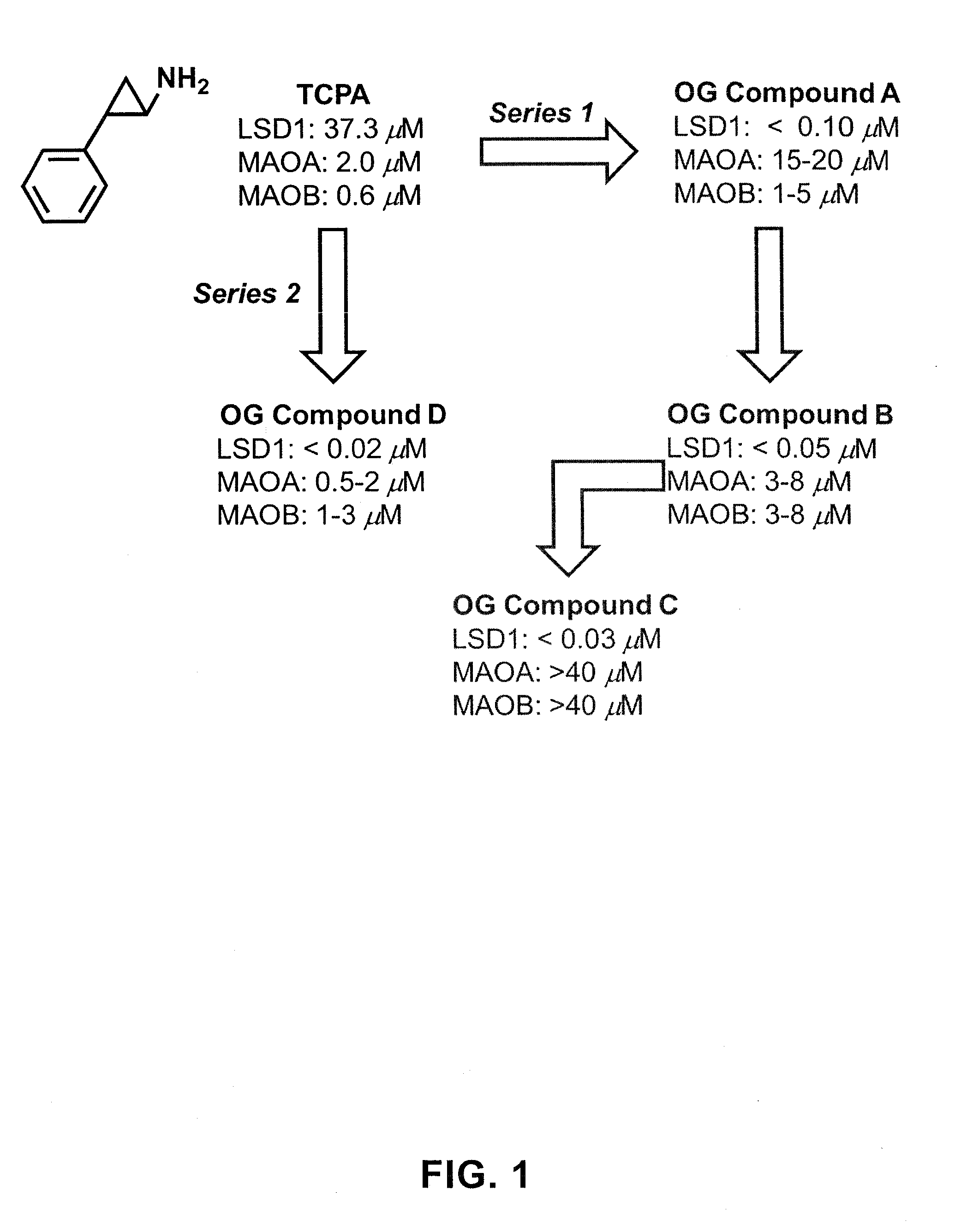
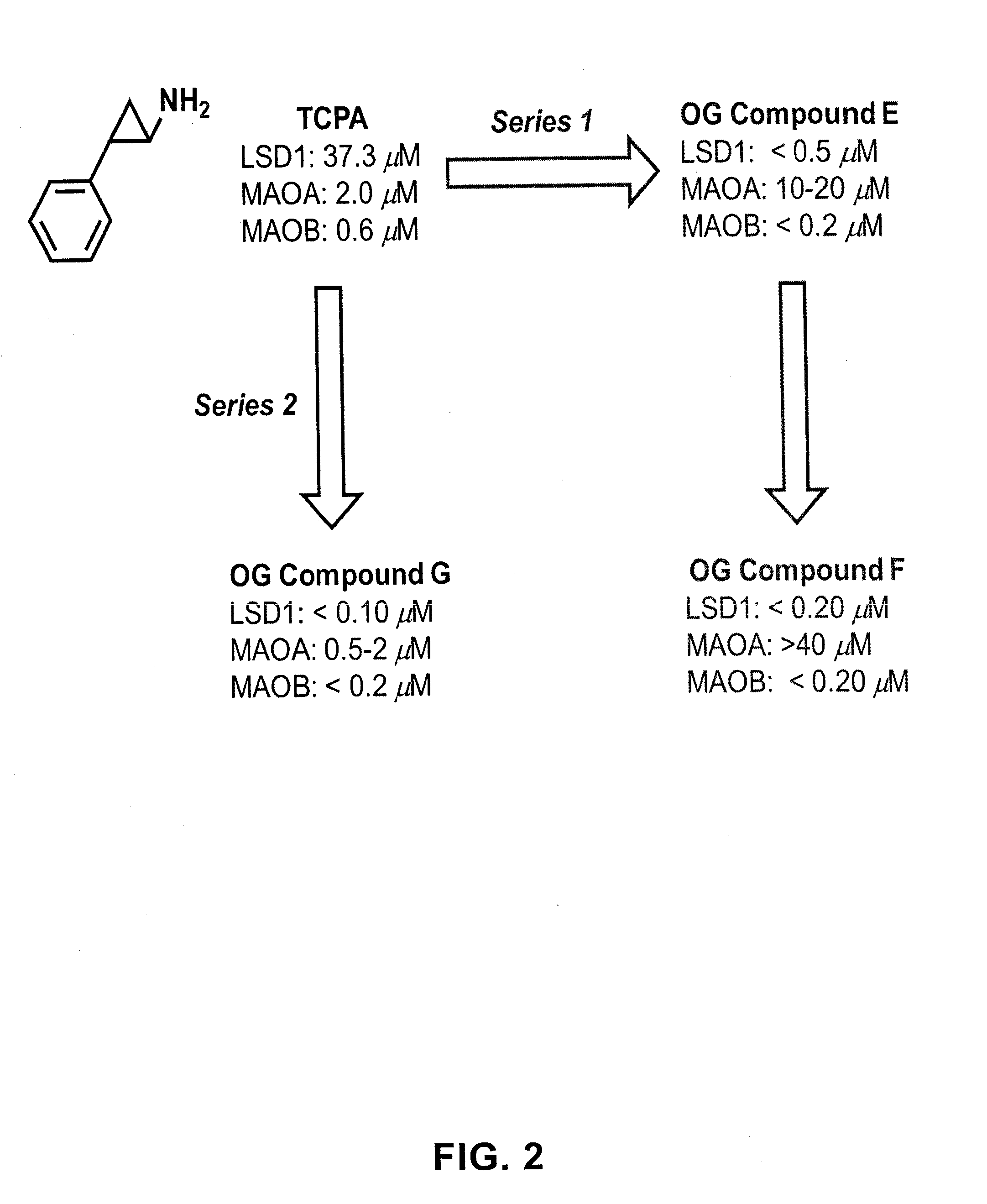
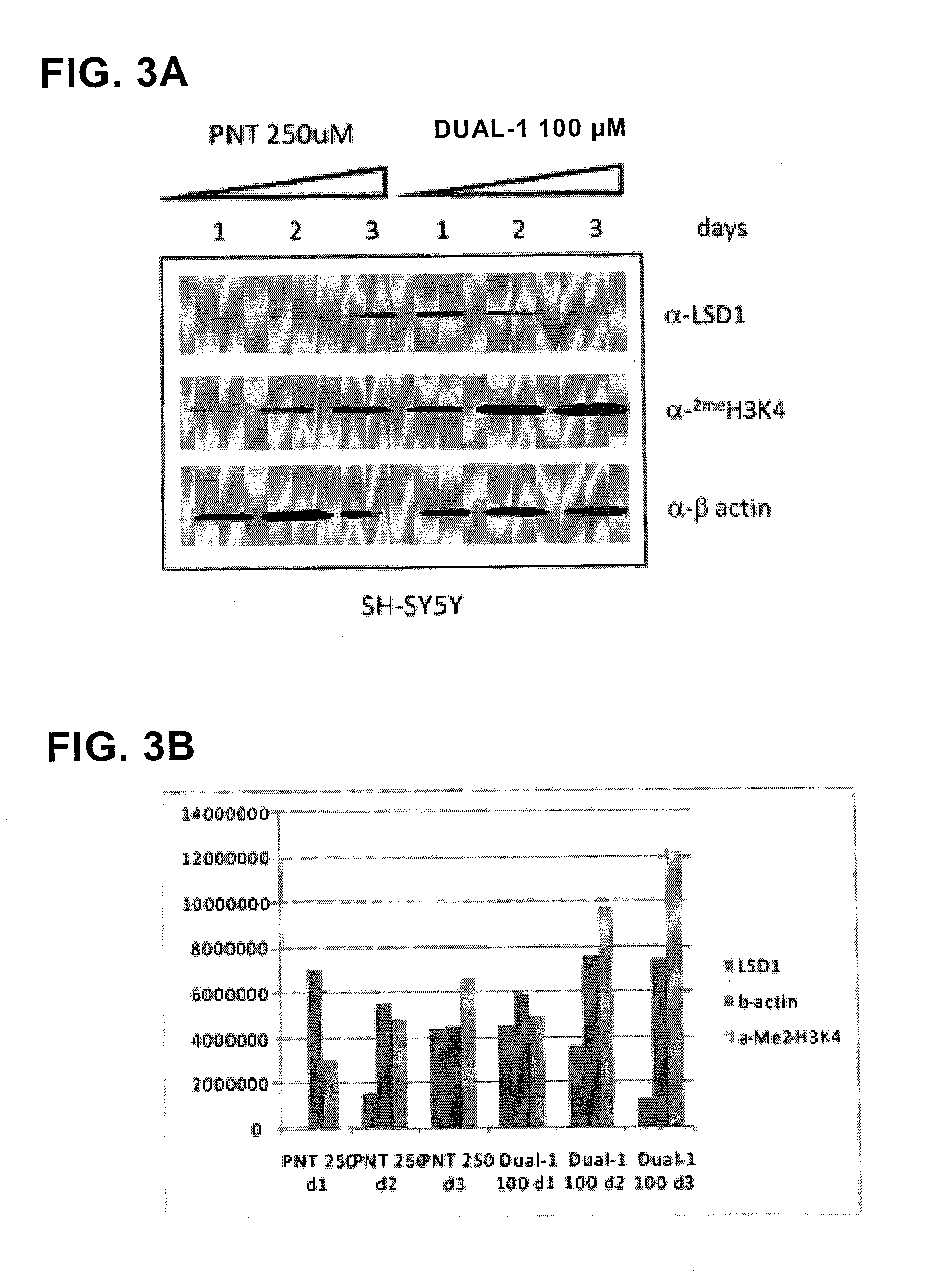
ActiveUS20130095067A1Symptoms improvedReduce probabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMammalHepadnavirus
The present invention provides for the treatment or prevention of Hepadnaviridae infection and disease caused by Hepadnaviridae infection. In particular, the invention provides compositions and methods that affect the ability of Hepadnaviridae to utilize the host's cellular machinery as part of the virus' lifecycle. The invention relates to the discovery that interfering with the normal ability of viruses to utilize the host cell machinery with LSD1 inhibitors reduces HBV replication. Thus, the treatment and prevention of Hepadnaviridae infection and disease caused by Hepadnaviridae according to the invention comprises administering to an individual in need of treatment, a therapeutically effective amount of a LSD1 inhibitor. The individual in need of treatment can be a human or, e.g., another mammal.
Owner:ORYZON GENOMICS SA
Attenuated influenza NS1 variants
InactiveUS20080050402A1Easy to produceSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocidePhosphatidylinositolPhospholipid
Attenuated influenza virus variants comprising substitutions in NS1 that interfere with viral replication and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation are described. NS1 variant polypeptides, polynucleotides encoding NS1 variant polypeptides, a reverse genetics system for producing attenuated influenza virus NS1 variants, immunogenic compositions comprising live attenuated influenza virus NS1 variants, methods of stimulating an immune response against influenza virus, methods of interfering with influenza virus replication, and methods of treating and preventing influenza virus infection are described.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN
Method to block the infection by flaviviruses, molecules and uses
ActiveUS20110212105A1Modulate the DV infectionReducing and increasing interactionSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsMolecular biologyCarrier protein
The present invention is related to a method for blocking the infection of cells by dengue virus, based on interfering the direct interaction of the viral envelope protein with a cellular receptor or its indirect interaction with said cellular receptor through a carrier protein, as well as related uses; wherein said cellular receptor is the alpha-2 macroglobulin receptor, also known as the low density receptor-related protein or as CD91, and said carrier protein is human alpha-2 macroglobulin.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
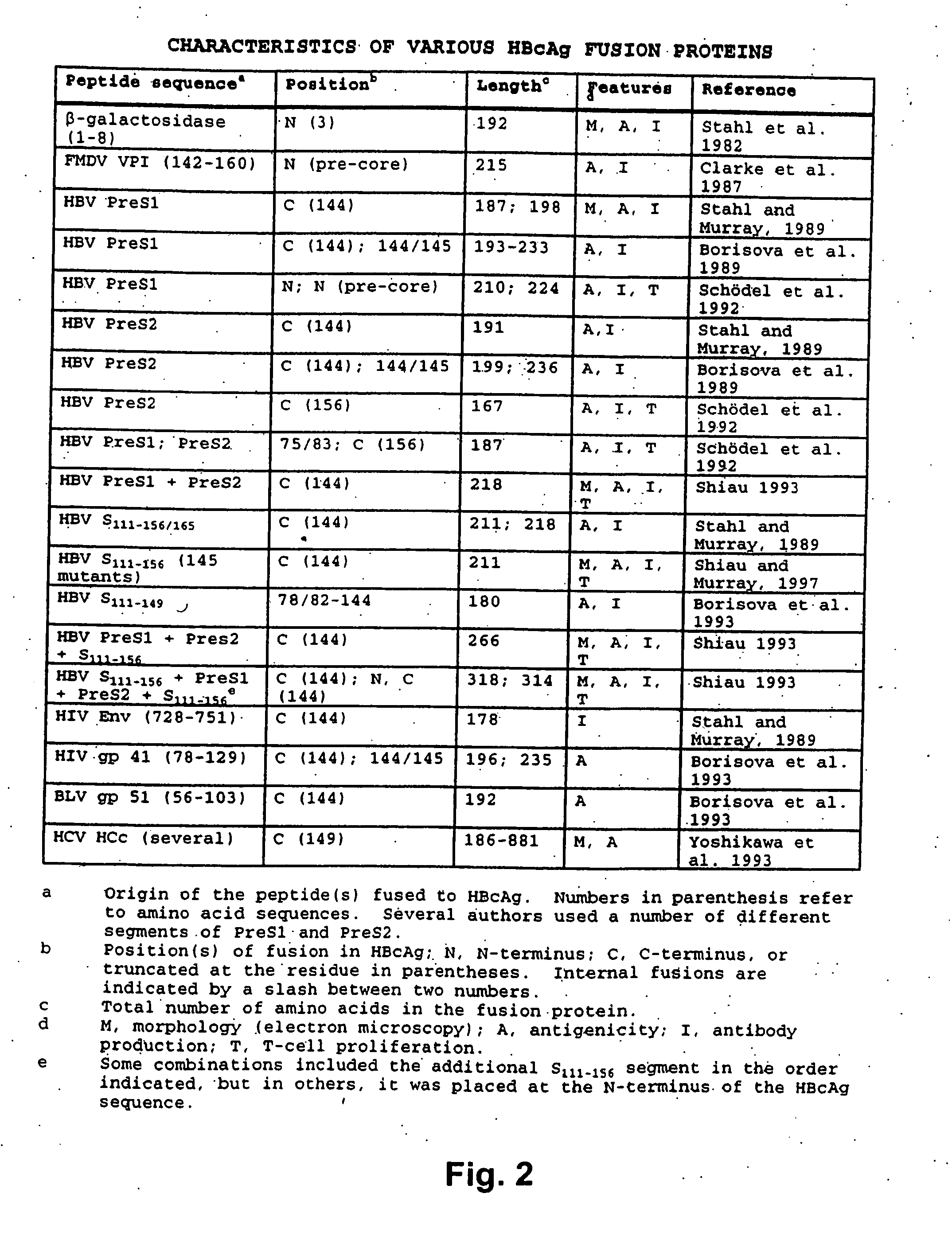
HBV core antigen particles with multiple immunogenic components attached via peptid ligands
InactiveUS20070280962A1Facilitated DiffusionAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsHepatitis B immunizationPeptide ligand
This invention relates to hepatitis B virus (“HBV”) core antigen particles that are characterized by multiple immunogen specificities. More particularly, the invention relates to HBV core antigen particles comprising immunogens, epitopes, or other related structures, crosslinked thereto by ligands which are HBV capsid-binding peptides that selectively bind to HBV core protein. Such particles may be used as delivery systems for a diverse range of immunogenic epitopes, including the HBV capsid-binding peptides, which advantageously also inhibit and interfere with HBV viral assembly by blocking the interaction between HBV core protein and HBV surface proteins. Mixtures of different immunogens and / or capsid-binding peptide ligands may be crosslinked to the same HBV core particle. Such resulting multicomponent or multivalent HBV core particles may be advantageously used in therapeutic and prophylactic vaccines and compositions, as well as in diagnostic compositions and methods using them.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
HBV core antigen particles with multiple immunogenic components attached via peptide ligands
InactiveUS8168190B2Facilitated DiffusionAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsHepatitis B immunizationPeptide ligand
This invention relates to hepatitis B virus (“HBV”) core antigen particles that are characterized by multiple immunogen specificities. More particularly, the invention relates to HBV core antigen particles comprising immunogens, epitopes, or other related structures, crosslinked thereto by ligands which are HBV capsid-binding peptides that selectively bind to HBV core protein. Such particles may be used as delivery systems for a diverse range of immunogenic epitopes, including the HBV capsid-binding peptides, which advantageously also inhibit and interfere with HBV viral assembly by blocking the interaction between HBV core protein and HBV surface proteins. Mixtures of different immunogens and / or capsid-binding peptide ligands may be crosslinked to the same HBV core particle. Such resulting multicomponent or multivalent HBV core particles may be advantageously used in therapeutic and prophylactic vaccines and compositions, as well as in diagnostic compositions and methods using them.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Identification and use of antiviral compounds that inhibit interaction of host cell proteins and viral proteins required for viral replication
The present invention relates to the identification of host cell proteins that interact with viral proteins required for virus replication, and high throughput assays to identify compounds that interfere with the specific interaction between the viral and host cell protein. Interfering compounds that inhibit viral replication can be used therapeutically to treat viral infection. The invention is based, in part, on the Applicants' discovery of novel interactions between proteins of the influenza virus and a human host cell proteins. One of these host cell proteins, referred to herein as NPI-1, interacts with influenza virus protein NP, and may be an accessory protein required for replication of influenza virus. Another of these host cell proteins, referred to herein as NS1I-1, interacts with influenza virus protein NS1. Compounds that interfere with the binding of the host cell and viral proteins, and inhibit viral replication can be useful for treating viral infection in vivo.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for expression of small antiviral RNA molecules within a cell
InactiveUS20080003658A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsViral life cycleDouble strand
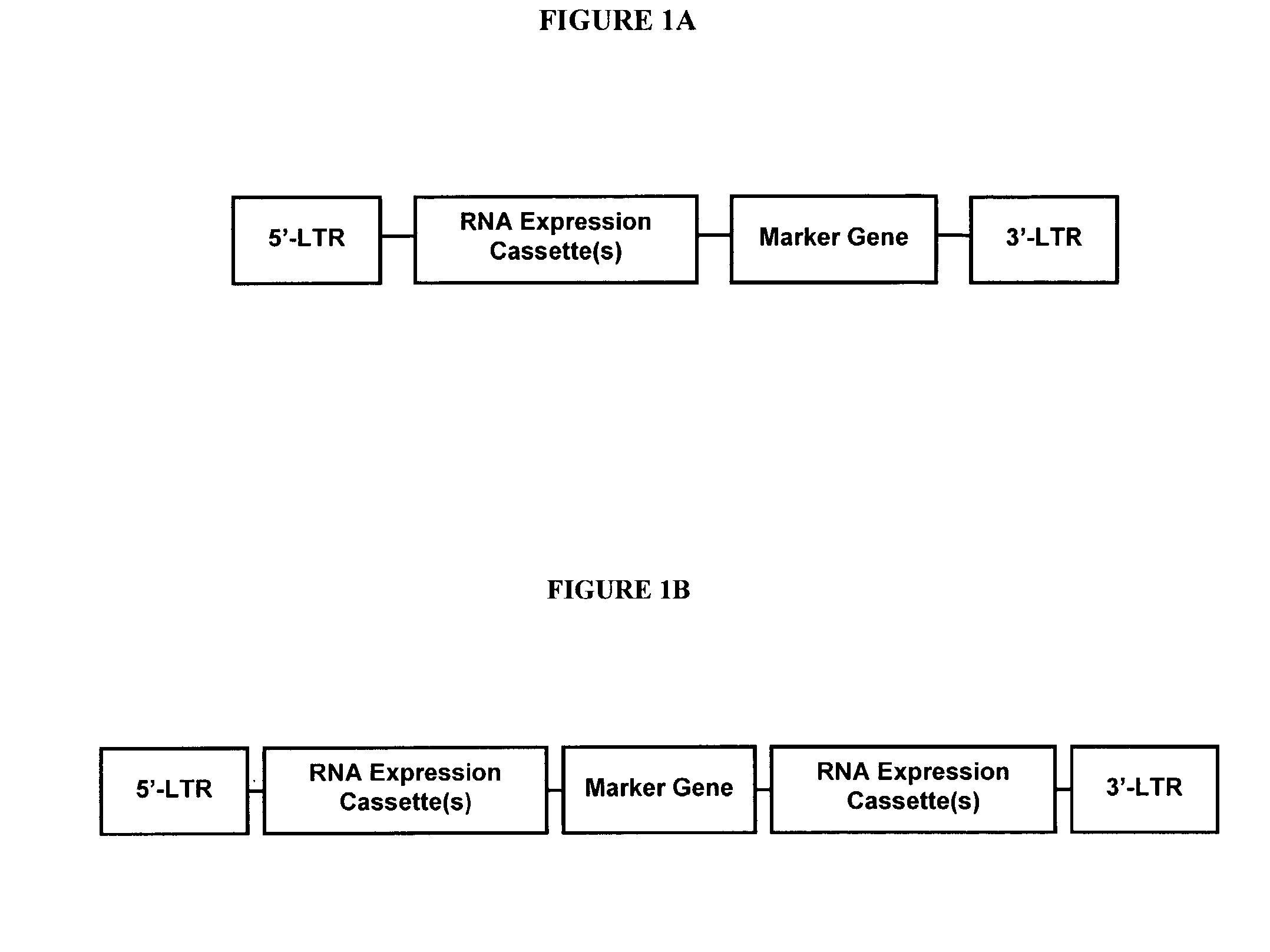
In one aspect, the invention provides methods and compositions for the expression of small RNA molecules within a cell using a retroviral vector (FIG. 1A). The methods can be used to express double stranded RNA complexes. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) can be expressed using the methods of the invention within a cell, that interfere with a viral life cycle by down regulating either the viral genome, a viral genome transcript, or a host cell that. In another aspect the invention provides methods for treating patients having suffering from infection, particularly infection with HIV. In a further aspect, the invention provides methods for producing siRNA encoding lentivirus where the siRNA activity may interfere with the lentiviral life cycle.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
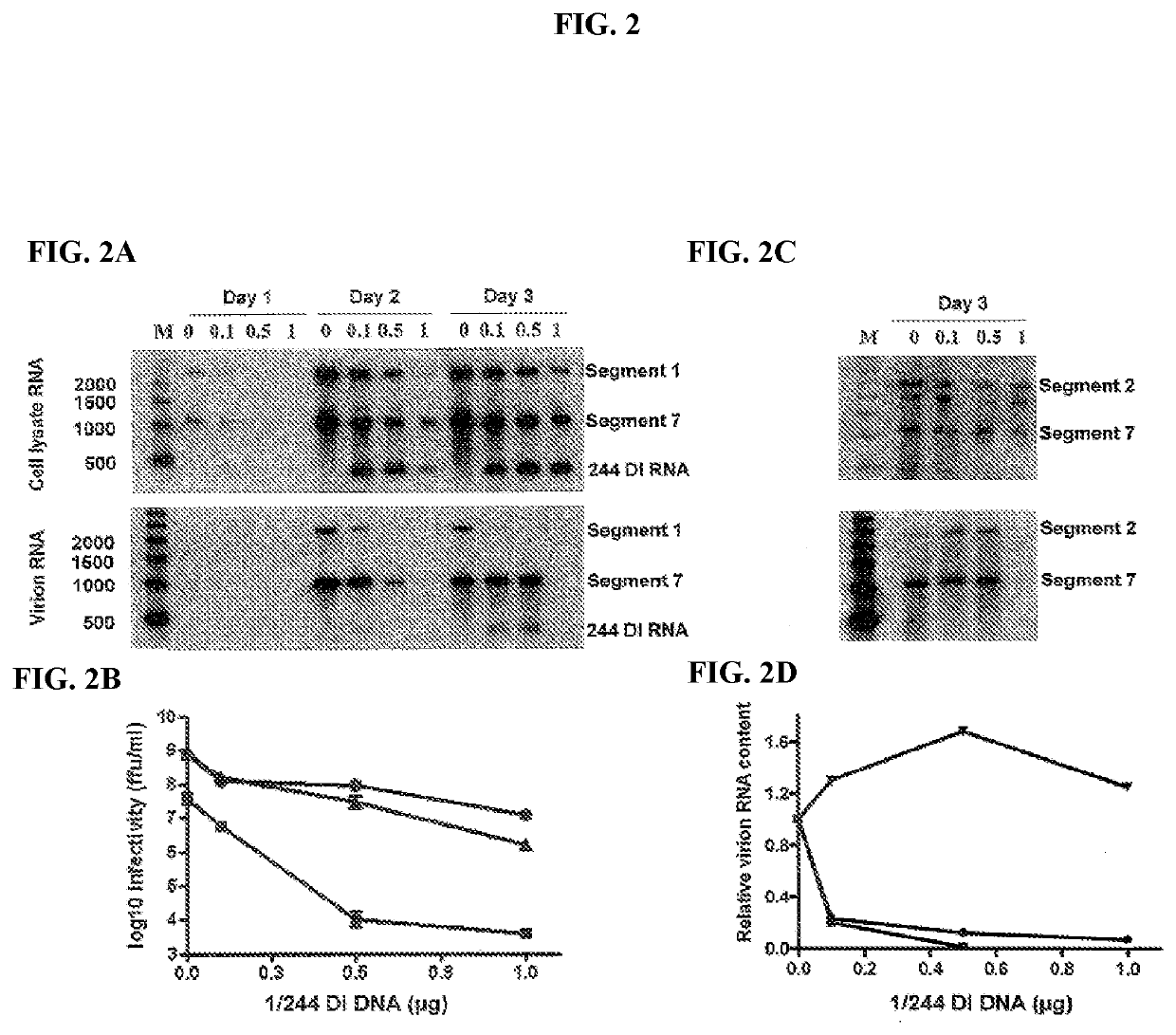
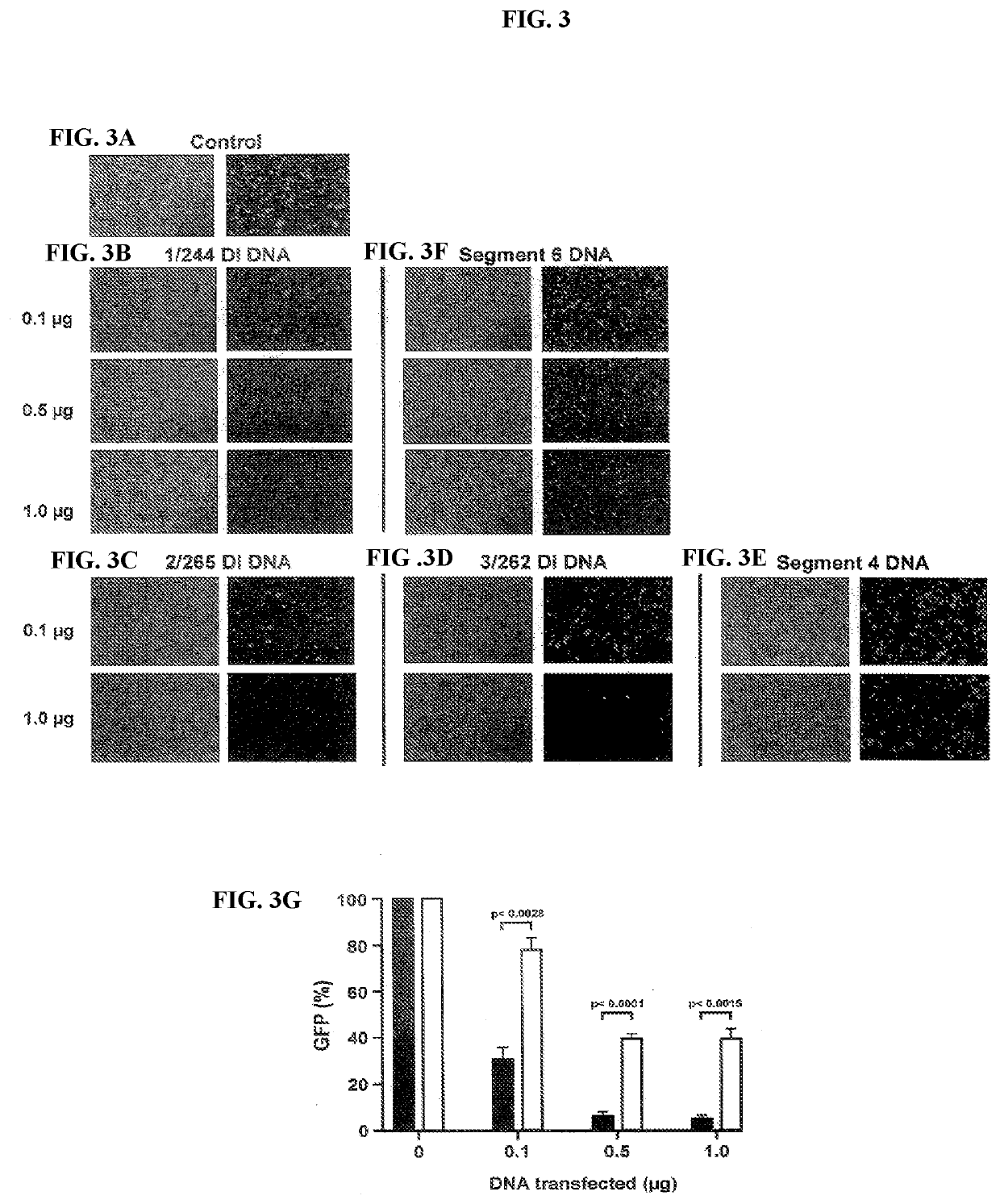
Defective interfering virus
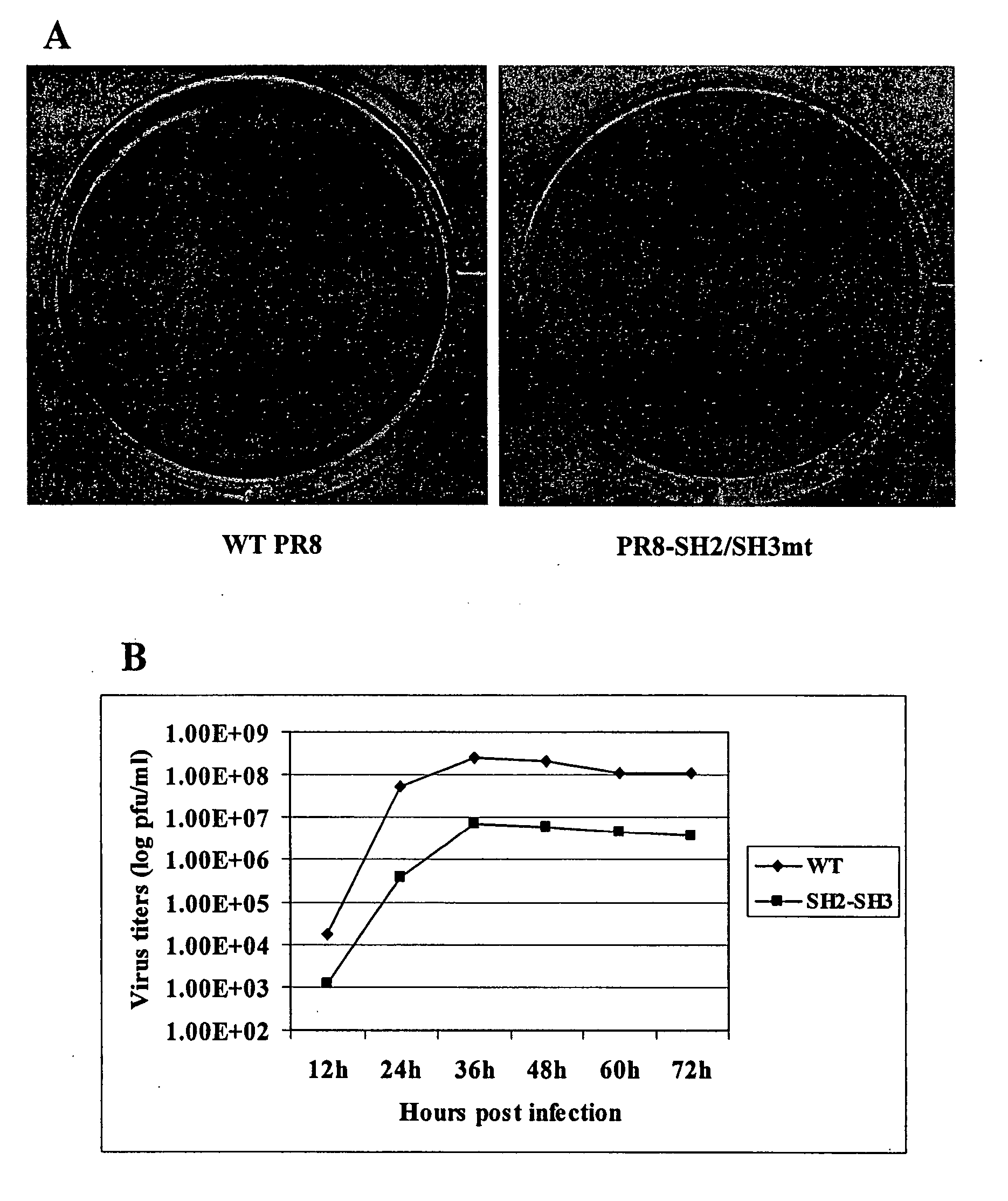
ActiveUS20090191158A1Shorten the progressFaster rateSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideLethal doseWild type
Cloned, i.e. defined, defective interfering (DI) influenza A virus is produced in embryonated hens eggs using a method which generates large quantities of DI virus material. Cloned DI virus is then used in tests on mice and ferrets given a lethal challenge of wild-type influenza A virus. When cloned DI influenza A virus is co-administered with a lethal dose of virulent influenza A virus, mice are protected compared to a control of inactivated cloned DI influenza A virus. Mice which survived the administration of cloned DI influenza A virus and infective challenge virus are three weeks later still protected against lethal challenge with infective virus. Control mice which received only cloned DI influenza A virus and no lethal challenge are not protected three weeks later on lethal challenge with infective virus.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK
Barley yellow dwarf virus interference virogene expression vector and its construction method and application
InactiveCN101215572AMake up for the vacancyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBarley yellow mosaic virusRestriction site
The invention relates to 'an expression vector of interfering viruses of barley yellow dwart viruses, a constructing method, and the application' and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The invention provides the expressing vector of interfering viruses of barley yellow dwart viruses which is characterized in that a skeleton carrier which is adopted is pMCG161, a sense strand of a coat protein gene of the barley yellow dwart viruses is inserted between two restriction sites of AscI and AvrII which are on the upstream portion of the pMCG161, and an antisense strand of the coat protein gene of the barley yellow dwart viruses is inserted between two restriction sites of SpeI and SgfI which are on the downstream portion of the pMCG161. The expression vector of interfering viruses of barley yellow dwart viruses GAV which is constructed by the invention is transferred into wheat through particle bombardment to obtain a transgene wheat variety which has resistance to the barley yellow dwart viruses GAV. The invention provides a breeding way with high efficiency and a new strategy.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Recombinant pseudorabies live vaccine for preventing African swine fever, and preparation method of recombinant pseudorabies live vaccine
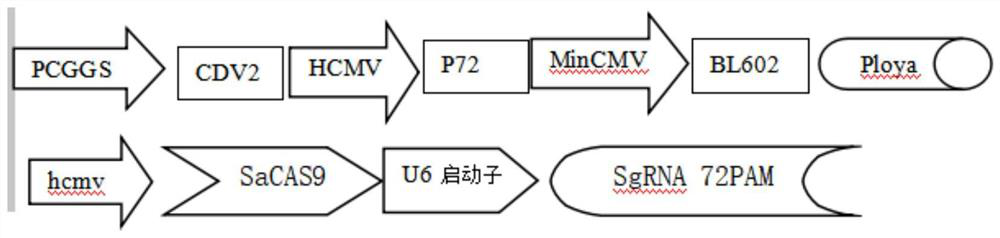
ActiveCN112029736AStable expressionReduce injection stressViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesAfrican swine feverInterfering virus
The invention relates to a recombinant pseudorabies live vaccine for preventing African swine fever, and the preparation of the recombinant pseudorabies live vaccine. The constructed recombinant pseudorabies virus TIE1872V2Sag72 strain containing African swine fever virus CDV2 / P72 / BL602 genes, and a sacas9SgRNA sequence capable of knocking out a wild type P72 gene can express a recombinant CDV2 / P72 / BL602 protein antigen in a BHK cell strain, the expression amount is stable, and meanwhile, an in-vitro cell simulation experiment shows that the method can interfere virus replication. The recombinant strain pseudorabies virus strain is used as a production strain, the recombinant CDV2 / P72 / BL602 protein antigen obtained through suspension micro-carrier culture is used for preparing the live vaccine, and the live vaccine can prevent recently popular African swine fever viruses, and can be prepared into a spray drinking water form to reduce injection stress reaction.
Owner:北京中海生物科技有限公司 +1
Methods and compositions for inhibition of viral replication
InactiveUS20100166704A1Inhibits viral replicationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsInterfering virusViral replication
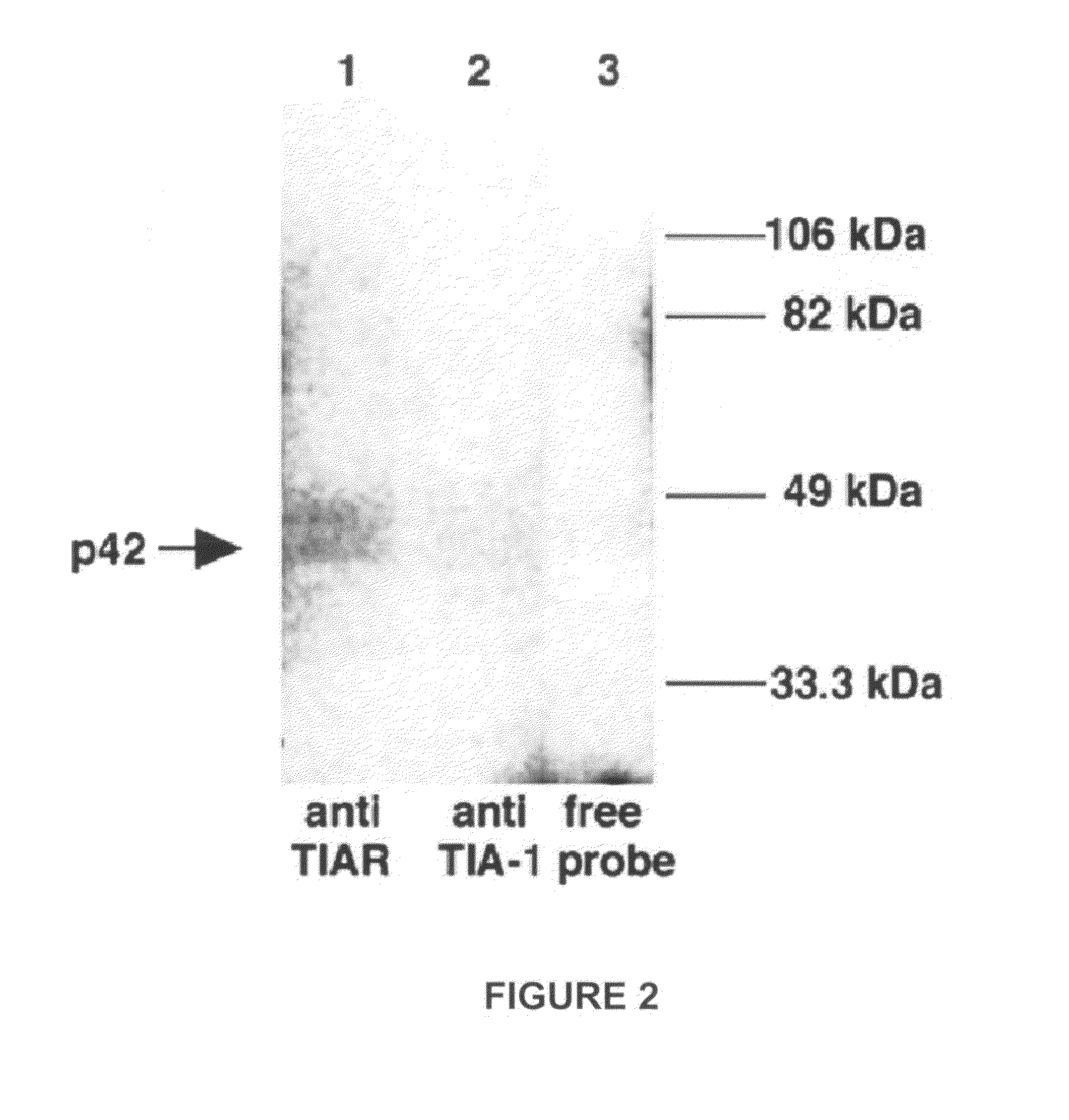
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions that are effective in the inhibition of viral replication. In particular, the methods and compositions are effective at interfering with the activity of host cell proteins required in viral replication. For example, an embodiment of the invention is directed to inhibition of flavivirus replication wherein the replication is affected by changing the normal interactions of the host cell protein TIAR or TIA-1.
Owner:GEORGIA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Defective interfering virus
ActiveCN101454023AEfficient disseminationNot shown to develop resistanceSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsFowlLethal dose
Cloned, i.e. defined, defective interfering (DI) influenza A virus is produced in embryonated hens eggs using a method which generates large quantities of DI virus material. Cloned DI virus is then used in tests on mice and ferrets given a lethal challange of wild-type influenza A virus. When cloned DI influenza A virus is co-administered with a lethal dose of virulent influenza A virus, mice areprotected compared to a control of inactivated cloned DI influenza A virus. Mice which survived the administration of cloned DI influenza A virus and infective challange virus are three weeks later still protected against lethal challange with infective virus. Control mice which received only cloned DI influenza A virus and no lethal challange are not protected three weeks later on lethal challange with infective virus. A therapeutic benefit of administering cloned DI influenza a virus is found when the administration takes place in less than 48 hours after challange with infective virus. Cloned DI influenza A virus of one subtype is found to act in vivo as an effective antiviral against the same or any other sub-type of influenza A virus. The antiviral effect has been found to have both a therapeutic and a prophylactic application against influenza A infection in humans, mammals and birds.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK
Methods and compositions for inhibition of viral replication
ActiveUS8303946B2Inhibits viral replicationBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseInterfering virusViral replication
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions that are effective in the inhibition of viral replication. In particular, the methods and compositions are effective at interfering with the activity of host cell proteins required in viral replication. For example, an embodiment of the invention is directed to inhibition of flavivirus replication wherein the replication is effected by changing the normal interactions of the host cell protein TIAR or TIA-1.
Owner:GEORGIA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Application of a compound in preparing anti-virus medicament
InactiveCN101108186AInhibition of replicationSuitable for life-long medication needsAntiviralsPill deliveryChemical industryAnti virus
The invention relates to the technical field of chemical industry, in particular to a preparation method and application of micromolecule compound with HIV resisting activity. CyPA is able to combine with the Gag polymer protein in HIV-1. Silence or inhibit the activity of CypA with RNAi technology and disturb the replication of virus. The micromolecule compound in the invention refers to a CyPA inhibitor that has the effect of resisting HIV-1 virus. Besides, as the micromolecule compound is designed while aiming at cellular target, the invention is not easy to develop drug resistance, thus meeting the demands of lifetime medication for AIDS patients. Therefore, the micromolecule compound in the invention, which can be developed as a new type anti-AIDS drug, provides a new means for treating and curing AIDS.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
siRNA disturbing rdrp gene function of SARS virus
InactiveCN101113158ASignificant effect and effectOvercoming problems such as expensiveOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesGeneCell biology
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Application of a compound in preparing anti-virus medicament
InactiveCN100502879CInhibition of replicationSuitable for life-long medication needsOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsChemical industryPolymer
The invention relates to the technical field of chemical industry, in particular to a preparation method and application of micromolecule compound with HIV resisting activity. CyPA is able to combine with the Gag polymer protein in HIV-1. Silence or inhibit the activity of CypA with RNAi technology and disturb the replication of virus. The micromolecule compound in the invention refers to a CyPA inhibitor that has the effect of resisting HIV-1 virus. Besides, as the micromolecule compound is designed while aiming at cellular target, the invention is not easy to develop drug resistance, thus meeting the demands of lifetime medication for AIDS patients. Therefore, the micromolecule compound in the invention, which can be developed as a new type anti-AIDS drug, provides a new means for treating and curing AIDS.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Application of myricetin in preparing medicines and health products for preventing and treating diseases caused by herpes simplex virus
InactiveCN109939099ALow toxicityEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsMechanism of actionInterfering virus
The invention provides application of myricetin in preparing medicines and health products for preventing and treating diseases caused by herpes simplex virus. Experiments prove that the myricetin hasthe inhibitory activity on herpes simplex virus infection, has the activity of resisting HSV-1 and HSV-2, and has extremely low toxicity. The protein and mRNA expression of HSV-1 and HSV-2 were significantly inhibited by myricetin treatment. The action mechanism of the myricetin for resisting herpes simplex virus infection is that the myricetin directly interacts with HSV particles to interfere virus adsorption and virus-induced membrane fusion. Experiments prove that the myricetin can be developed into a novel target virus particle anti-HSV preparation and has good market application prospect.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF QINGDAO UNIV +1
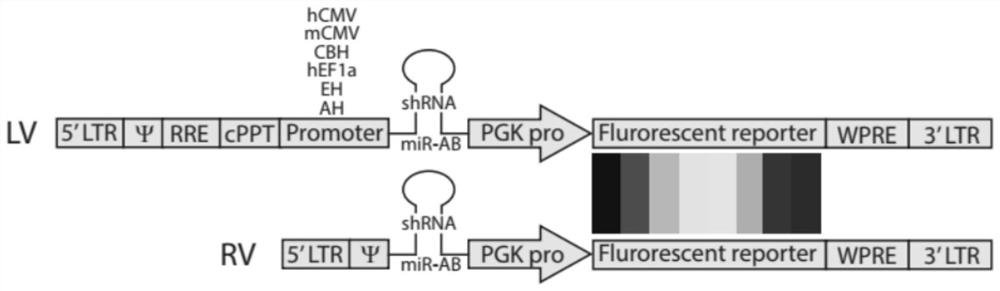
RNA interference virus vector
PendingCN114277058AAvoid cytotoxicityNormal life activitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceViral vectorPromoter
The invention relates to the technical field of RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference, in particular to an RNA interference virus vector which interferes the expression of a target gene by expressing shRNAmir carried by a miR-AB framework based on human miR-30pril-miRNA. The miR-AB sequence is regulated and controlled by a plurality of eukaryotic promoters; the RNA interference virus vector traces cells subjected to RNA interference through fluorescent protein reporter molecules, or screens the cells subjected to RNA interference through antibiotics. According to the present invention, the miR-AB sequence in the RNA interference virus vector is regulated and controlled by a variety of eukaryotic promoters so as to easily achieve the application of the RNA interference virus vector in a variety of eukaryotic cells, and the virus vector can screen the cells subjected to RNA interference through antibiotics by depending on the Puromycin resistance, and can also trace the cells subjected to RNA interference by depending on the fluorescent protein reporter molecule; therefore, a plurality of target genes in the eukaryotic cell can be subjected to single-gene interference and multi-gene arbitrary combination interference at the same time in a multi-virus co-infection mode, so that the functions of the plurality of target genes in the eukaryotic cell are analyzed at the same time.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
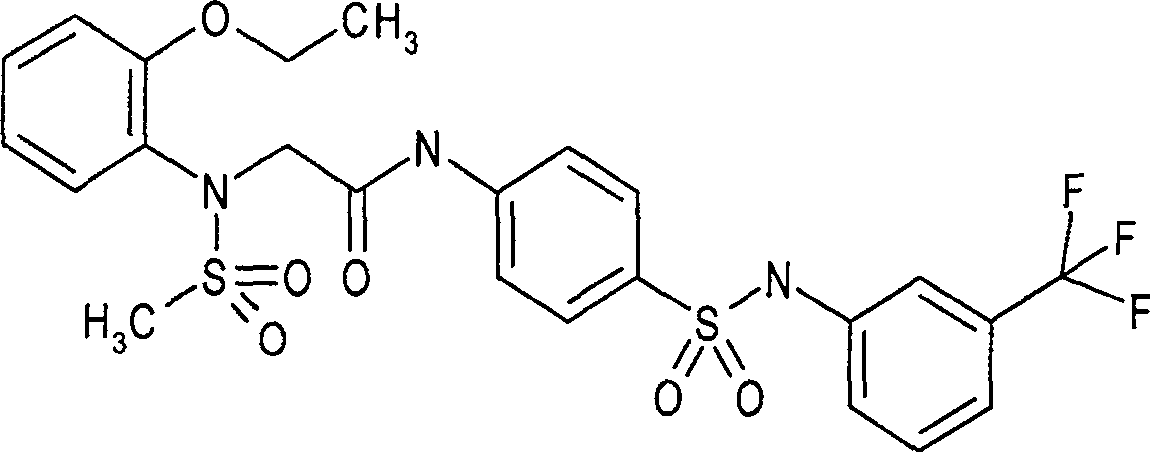
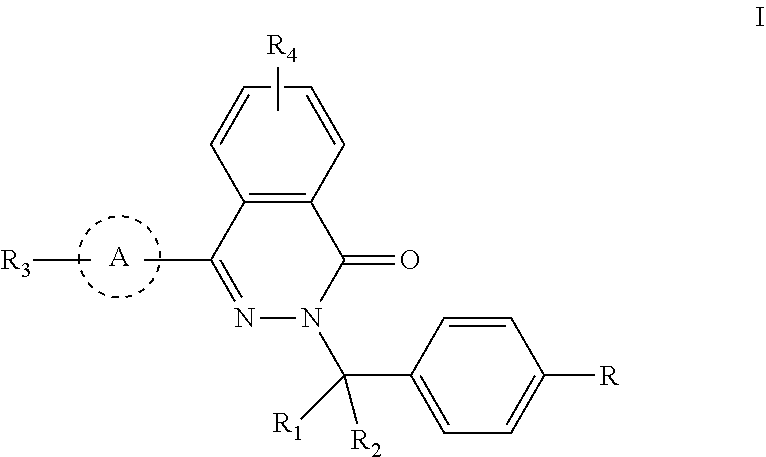
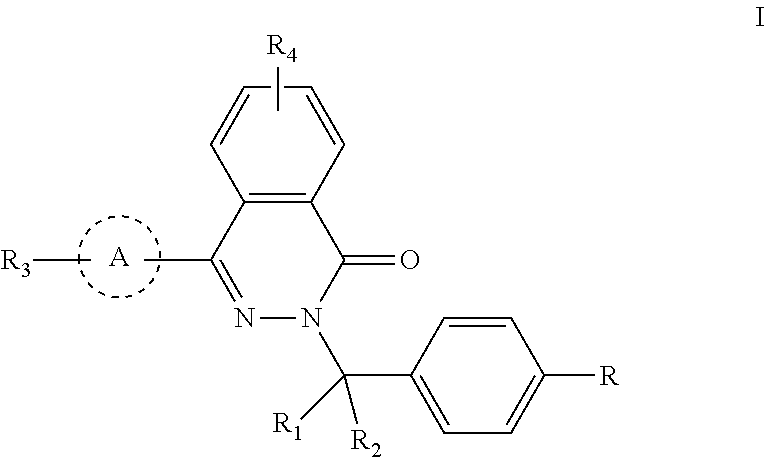
Phthalazinone compound, method for preparation thereof, pharmaceutical composition thereof, and use thereof
ActiveUS20200181109A1High activityLess growth toxicityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAnti-inhibitorMedicine
Provided are a phthalazinone compound, method for preparation thereof, pharmaceutical composition thereof, and a use thereof; the structure of said phthalazinone compound is as represented by formula I; the compound of said formula I is targeted to a viral nucleocapsid; it can inhibit the replication of a virus by means of interference of the viral nucleocapsid, has a potent activity for inhibiting HBV DNA replication and a good liver targeting, can stably exist and enrich in the liver, and is a new and effective anti-HBV inhibitor.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Phthalazinone compound, method for preparation thereof, pharmaceutical composition thereof, and use thereof
ActiveUS11040952B2High activityLess growth toxicityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAnti-inhibitorChemical compound
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Anti-viral peptides
InactiveUS20170298100A1Reducing likelihood and severityPeptide-nucleic acidsPeptide/protein ingredientsInfected cellLysis
Novel antiviral polypeptides are disclosed along with methods for their use to interfere with viral replication cycles by substantially impairing the binding of viruses to target cells, viral replication and assembly in infected cells, and viral egress from infected cells including viral lysis of host cells. The present antiviral peptides exhibit broad specificity across a range of human viral pathogens by virtue of their derivation from selected viral resistance genes and their ability to interfere with conserved mechanisms of host cell-virus interactions.
Owner:CASCADIA LIFE SCI
Assay and medicament
ActiveUS20200231939A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayInterfering virus
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK
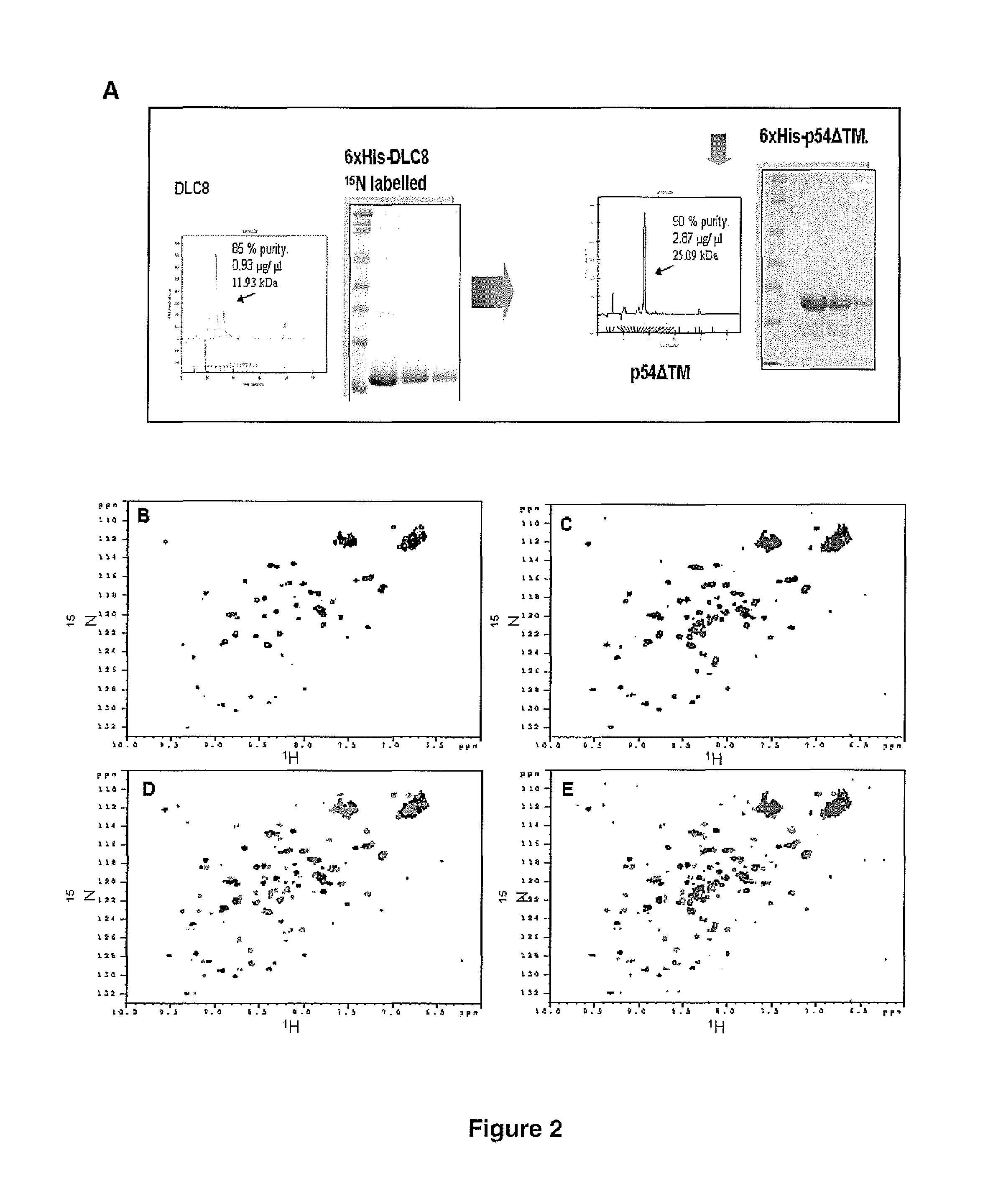
Antiviral peptides from african swine fever virus which prevent the binding of the virus to DLC8
ActiveUS8592552B2Inhibit bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementOut of africaInterfering virus
New antiviral peptides interfering the binding of the virus to DLC8 are provided. A high number of pathogenic agents of viral origin use the dynein based intracellular transport machinery at some point of their infective cycle. The present invention consists of a new antiviral therapy consisting in the inhibition of viral infections produced by those virus that use the dynein system by mechanisms of interference mainly by preventing the interaction between the viral protein and the cellular DLC8 protein. The present invention discloses for the first time the blocking of the function of this interaction by peptides whose sequence comprises or consists of the totality or a partial sequence of the viral protein corresponding to the binding domain with DLC8.
Owner:INST NAT DE INVESTIGACION Y TECH AGRARIA Y ALIMENTARIA INIA +1
A kind of live vaccine against African swine fever recombinant pseudorabies virus and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112029736BStable expressionReduce injection stressViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesAfrican swine feverWild type
The invention relates to a live recombinant pseudorabies vaccine for preventing African swine fever and its preparation. The African swine fever virus CD2V / P72 / B602L gene constructed by the invention and the sacas9SgRNA sequence recombinant pseudorabies virus TIE1872V2Sag72 strain capable of knocking out the wild-type P72 gene are The BHK cell line obtained can express the recombinant CD2V / P72 / B602L protein antigen, and its expression level is stable. At the same time, the in vitro cell simulation experiment shows that this method can interfere with virus replication. The recombinant pseudorabia virus strain is used as the production strain, and the recombinant CD2V / P72 / B602L protein antigen obtained by suspension microcarrier culture is prepared into a live vaccine, which can prevent the recently popular African swine fever virus and can also be made into a spray Drinking water form of the vaccine reduces injection stress.
Owner:北京中海生物科技有限公司 +1
Antibody inhibiting infection of papillomavirus
InactiveUS20090047280A1Avoid infectionViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesEndosomal membraneLysosome
The present invention relates generally to an antibody that binds specifically to a neutralization epitope at the surface of papillomavirus (residues 36-49 of the minor capsid L2) that does not interfere with virus entry into endosomes and lysosomes. This antibody neutralizes infection of the virus in a dose dependent manner.
Owner:ROSALIND FRANKLIN UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE
Methods and compositions for inhibition of viral replication
ActiveUS9572860B2SsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsInterfering virusRNA Sequence
Owner:GEORGIA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Defective interfering virus
ActiveCN101454023BEfficient disseminationNot shown to develop resistanceSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsGenomic SegmentInfected cell
A method for producing a cloned DI influenza A virus comprising: transfecting a cell with (i) a plasmid comprising an RNA segment of an influenza A virus that has a deletion therein and (ii) plasmids which in combination provide RNA segments 1 to 8 of an infectious influenza A virus; culturing the infected cells; introducing an aliquot of less than 100žl of the transfected cell culture medium into an embryonated egg; incubating and recovering virus material from the egg. Also claimed are uses of cloned DI influenza virus as a medicament for the treatment of influenza and isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding genomic segment 1 of a cloned DI influenza virus.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK
Method for significantly increasing lentiviral production
ActiveUS10562939B2Reduce and prevent bindingIncreased maturationPeptide/protein ingredientsVirus peptidesAntigenOxygenase
Increased viral particle maturation and production can be achieved in various methods for producing viral particles from viral proteins, in general, by inhibiting or preventing Heme Oxygenase 2 (HO-2) from binding to the group-specific antigen (Gag) of the viral proteins, thus allowing delivery of the viral proteins to plasma membranes where they can replicate and mature without interference from HO-2. The increase in viral particle maturation and production can also be achieved by minimizing or eliminating the presence of HO-2 to thus reduce or prevent binding of HO-2 to the group-specific antigen (Gag) of the viral proteins. The invention is particularly applicable to the production of lentiviruses from viral proteins wherein the Matrix domain (MA) of the Gag is myristoylated.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Application of a compound in preparing anti-virus medicament
InactiveCN100502865CInhibition of replicationSuitable for life-long medication needsAntiviralsPill deliveryChemical industryPolymer
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com