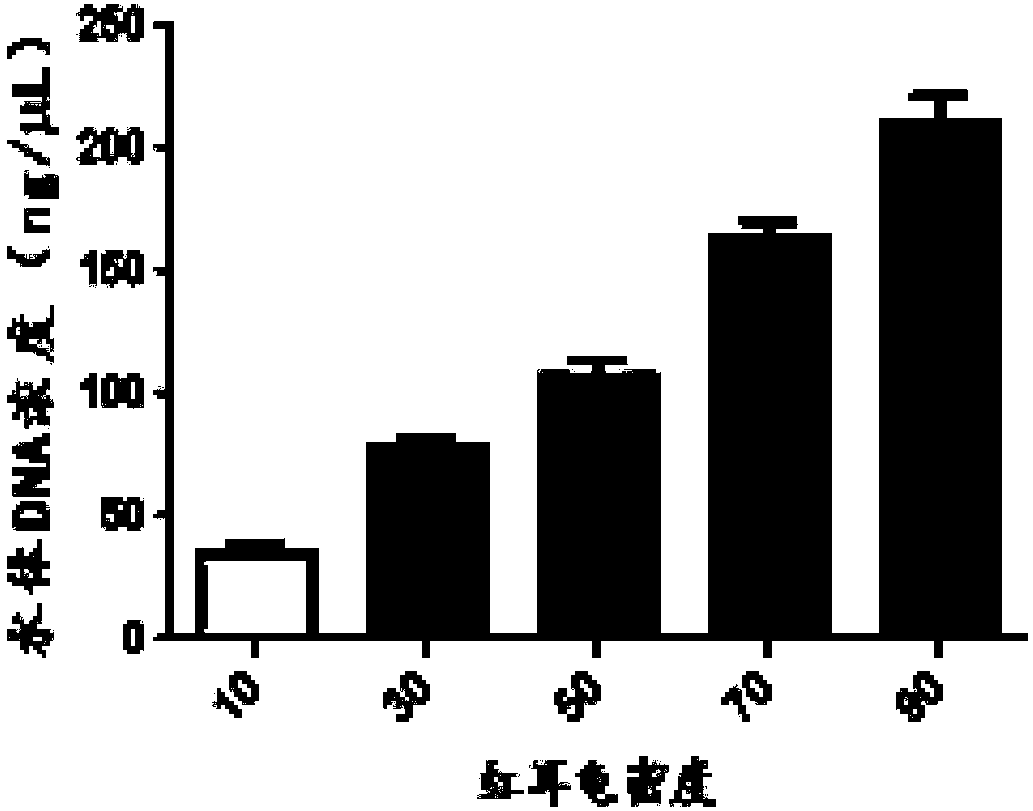
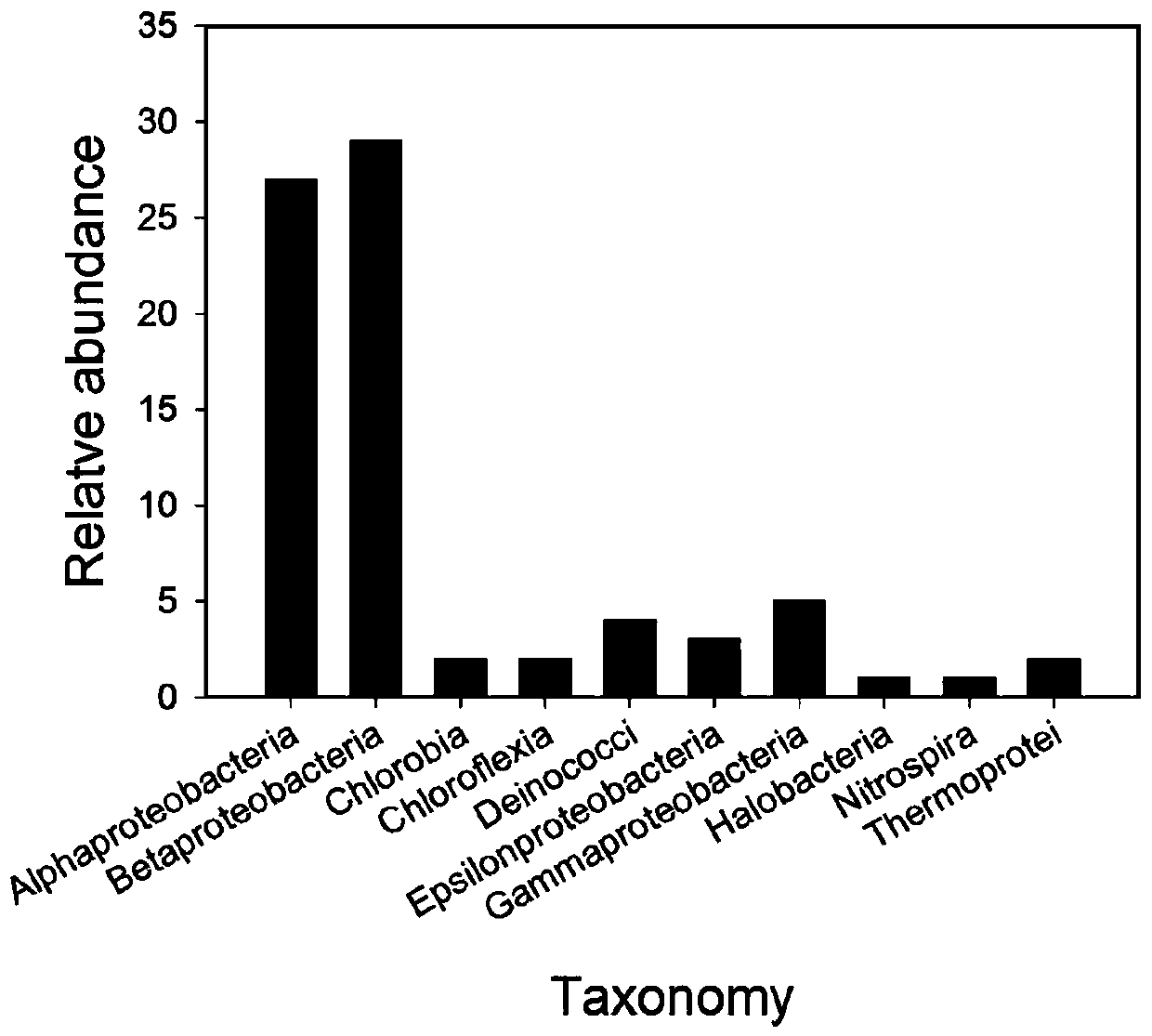
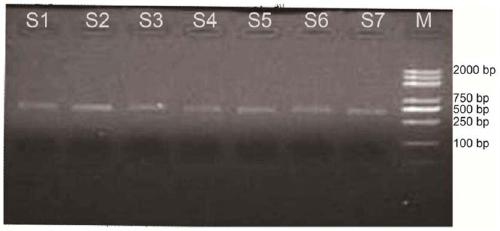
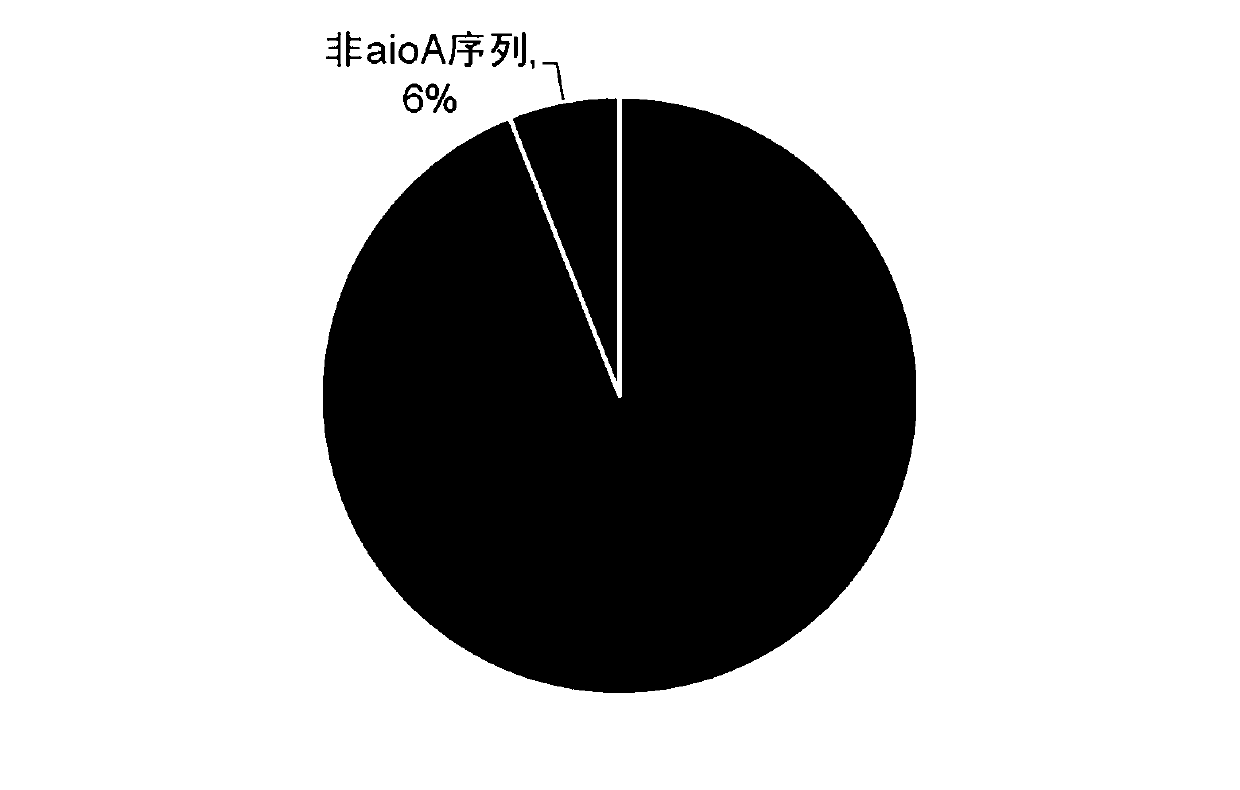
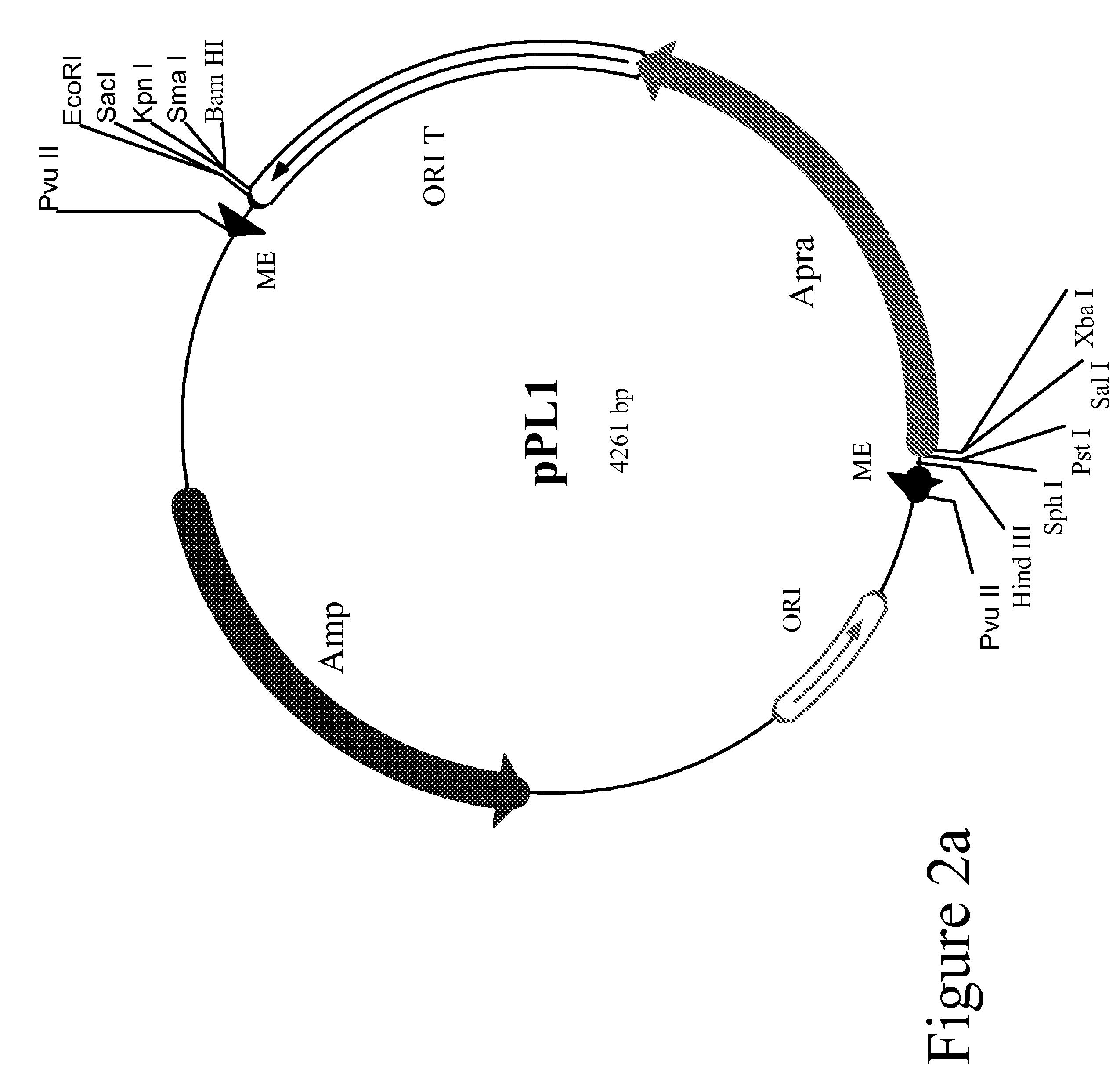
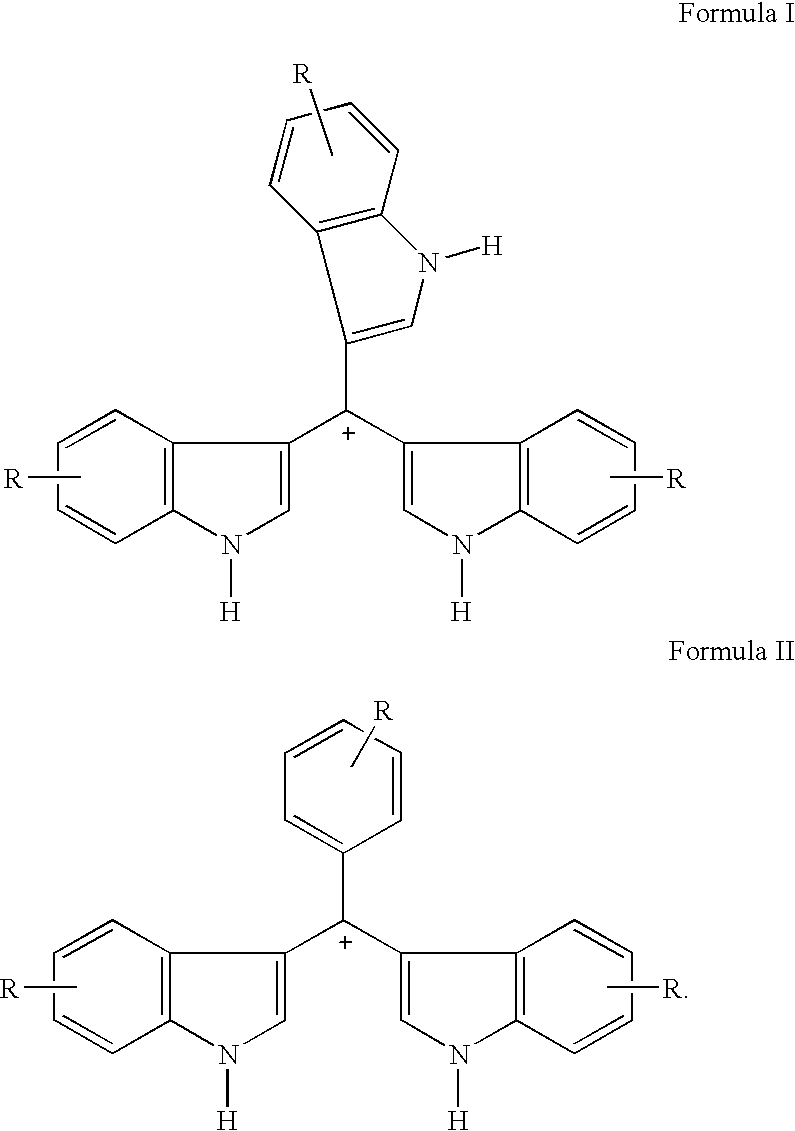
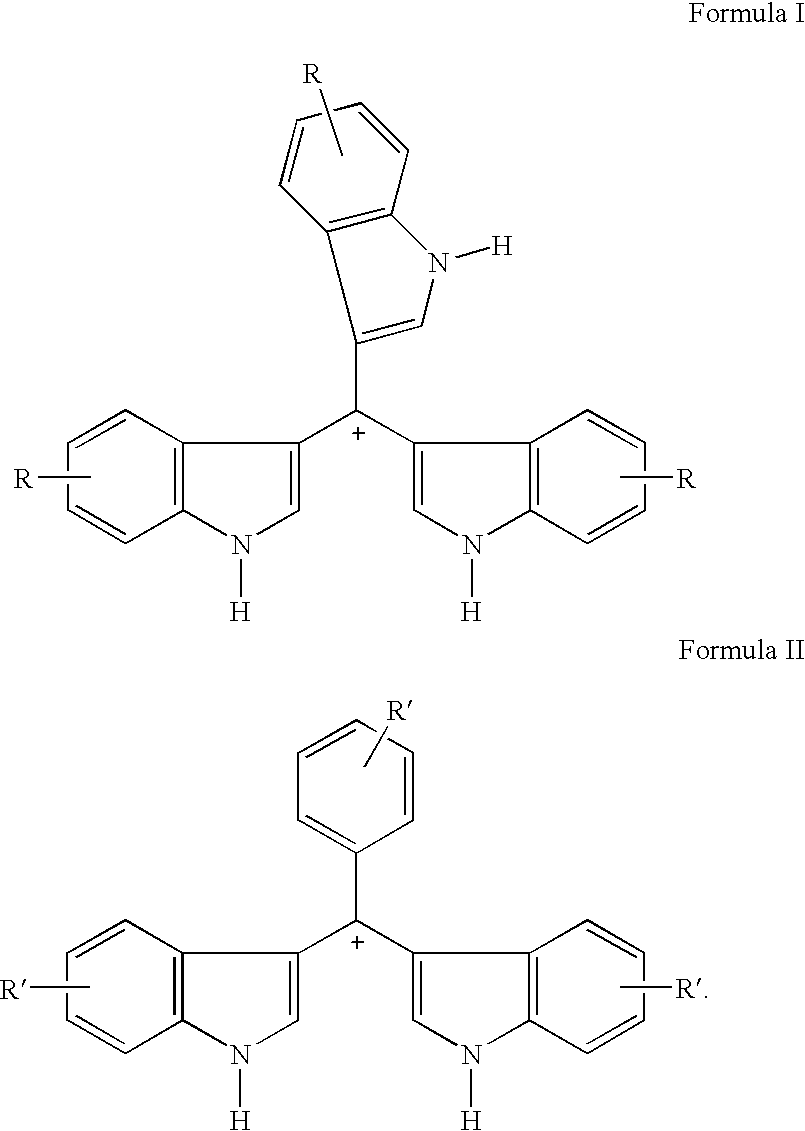
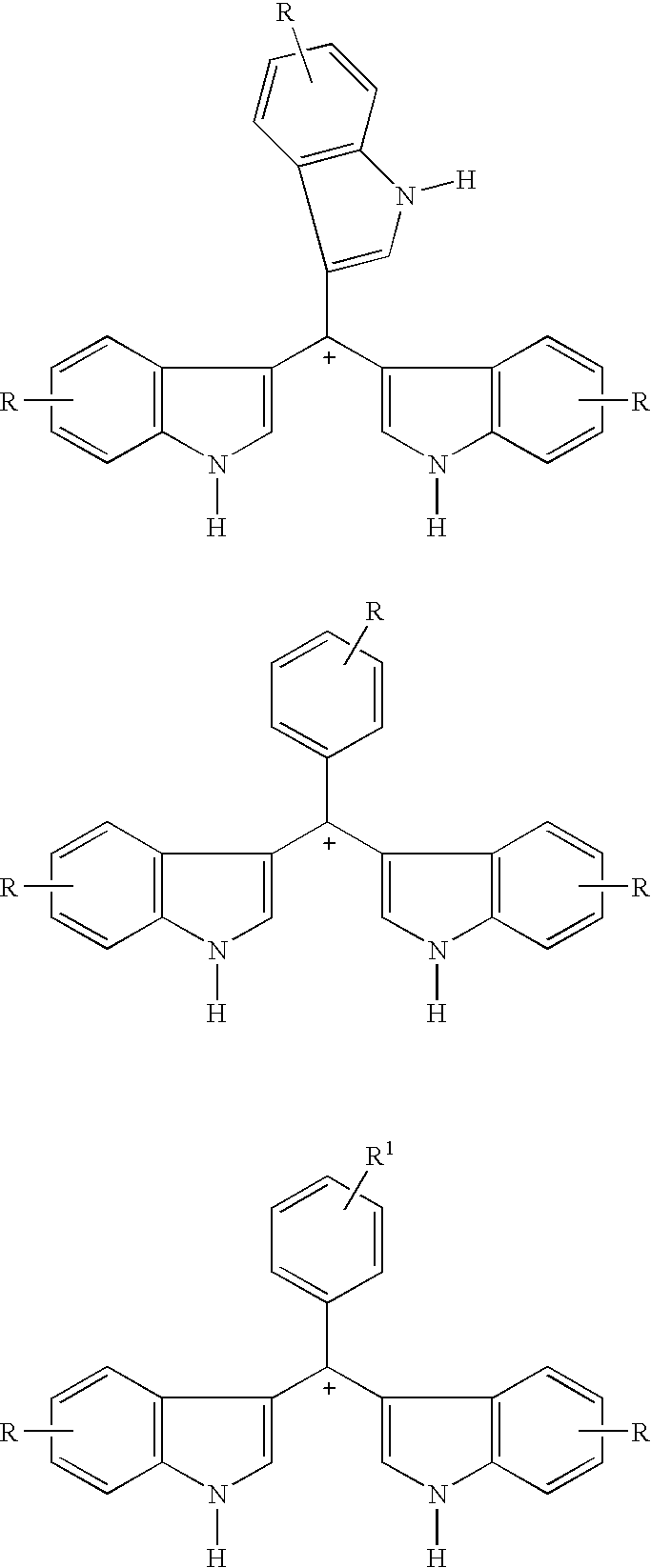
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Environmental DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Environmental DNA or eDNA is DNA that is collected from a variety of environmental samples such as soil, seawater, snow or even air rather than directly sampled from an individual organism. As various organisms interact with the environment, DNA is expelled and accumulates in their surroundings. Example sources of eDNA include, but are not limited to, feces, mucus, gametes, shed skin, carcasses and hair. Such samples can be analyzed by high-throughput DNA sequencing methods, known as metagenomics, metabarcoding, and single-species detection, for rapid measurement and monitoring of biodiversity. In order to better differentiate between organisms within a sample, DNA metabarcoding is used in which the sample is analyzed and uses previously studied DNA libraries to determine what organisms are present (e.g. BLAST). The analysis of eDNA has great potential, not only for monitoring common species, but to genetically detect and identify other extant species that could influence conservation efforts. This method allows for biomonitoring without requiring collection of the living organism, creating the ability to study organisms that are invasive, elusive, or endangered without introducing anthropogenic stress on the organism. Access to this genetic information makes a critical contribution to the understanding of population size, species distribution, and population dynamics for species not well documented. The integrity of eDNA samples is dependent upon its preservation within the environment. Soil, permafrost, freshwater and seawater are well-studied macro environments from which eDNA samples have been extracted, each of which include many more conditioned subenvironments. Because of its versatility, eDNA is applied in many subenvironments such as freshwater sampling, seawater sampling, terrestrial soil sampling (tundra permafrost), aquatic soil sampling (river, lake, pond, and ocean sediment), or other environments where normal sampling procedures can become problematic.
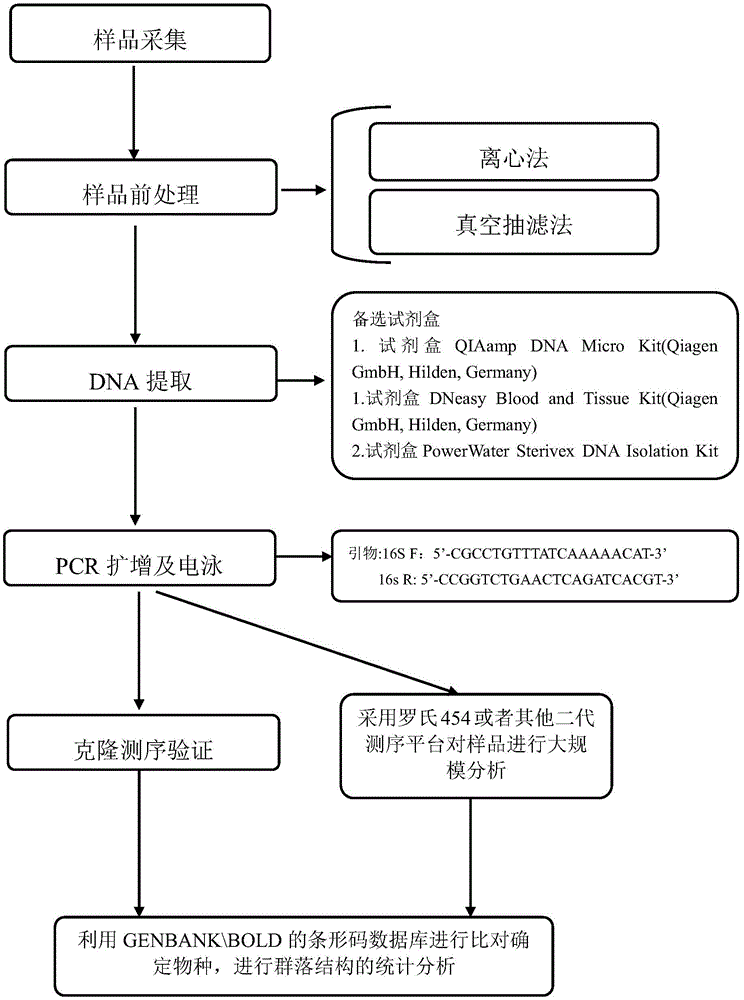
Environment DNA identification method for fish community structure researching
ActiveCN104531879AProtected speciesSave human and financial resourcesMicrobiological testing/measurementCommunity structureNucleotide sequencing
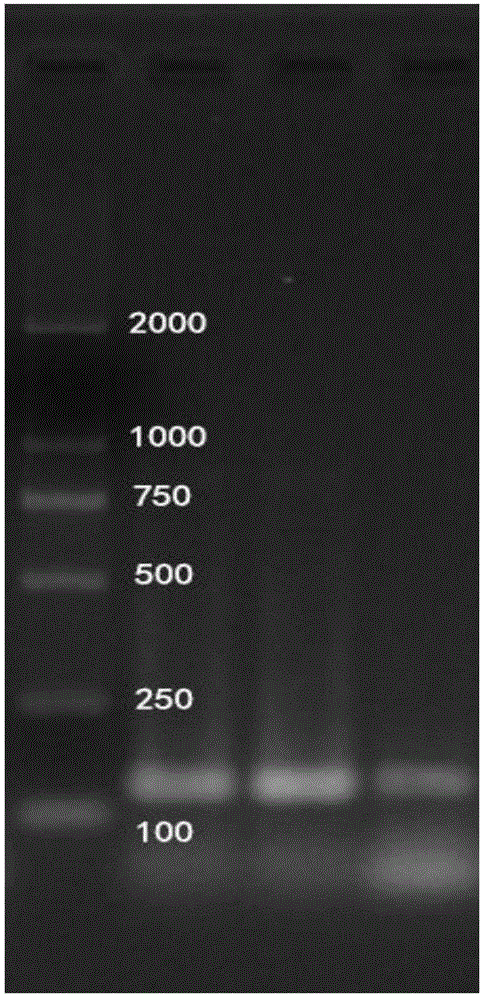
The invention relates to an environment DNA identification method for fish community structure researching. The method is characterized by comprising the steps that 1, water samples are collected according to the size of the water area where a fish community is located; 2, the water samples are processed, and total environment DNA of the processed water samples is extracted; 3, a 16s r DNA sequence with nucleotide sequences being SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 is adopted as a universal primer to carry out PCR amplification on the total environment DNA, and a PCR product is obtained; 4, gel electrophoresis is carried out on the PCR product, and gel with DNA is obtained; 5, gel cutting and clone sequencing are carried out on the gel with the DNA, and then blast comparison is carried out through GENBANK so as to determine whether the DNA is a fish sequence or not; 6, after it is determined that the DNA is the fish sequence, the next-generation sequencing technology is adopted for analyzing composition conditions of the PCR product on a large scale, and therefore the environment DNA fish composition and community structure are determined. The environment DNA identification method is quite easy, convenient and efficient and has the practical value.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
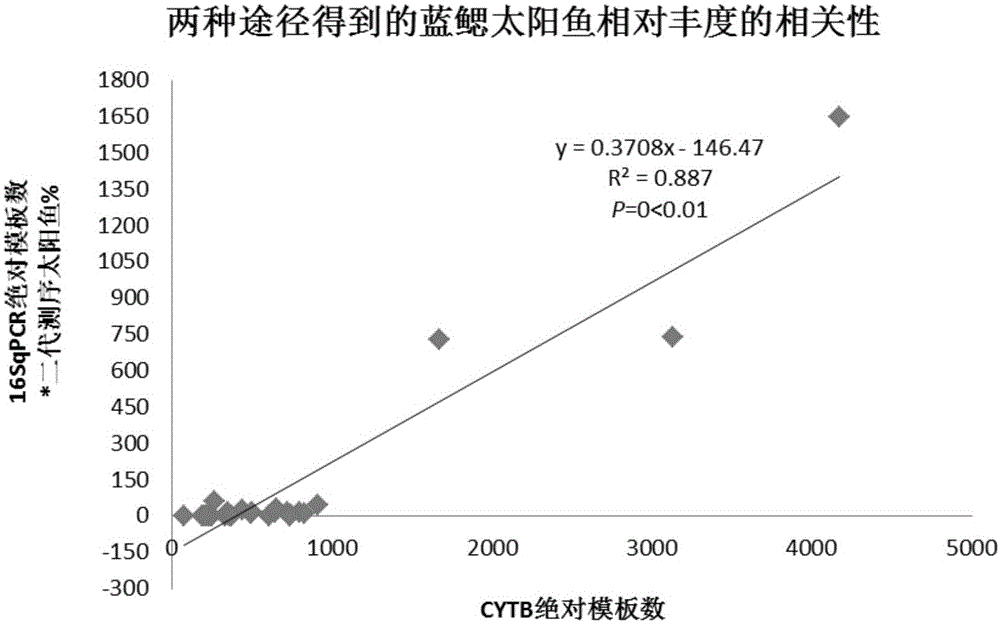
Conjoint analysis method for estimating DNA abundance of fishes based on environment DNA technology
ActiveCN105154564ASampling method is simpleProtect resourcesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisConjoint analysis
The invention relates to a conjoint analysis method for estimating the DNA abundance of fishes based on an environment DNA technology. The conjoint analysis method includes the steps that the total DNA abundance of the fishes is acquired through timed and quantified PCR; the species composition proportion of the fishes is acquired through 454 GS-FLX Titanium sequencing analysis; conjoint analysis of target species is performed through sequencing data and timed and quantified PCR data; a relative distribution diagram of mitochondrial DNA of the fishes in an environment is drawn through sufer 8.0 software. Based on the environment DNA identification technology, weather species exist and how many species exist can be analyzed just by collecting water samples without depending on fish species capturing, a sampling method is simple, and fish resources can be protected to the maximum degree; meanwhile, for some species which are rarely distributed and difficult to capture, the method is still more effective than traditional fishing investigation, the method can effectively solve the problem that effective species specificity primers are difficult to obtain when multiple closely related species exist in samples, and NDA abundance information of all species can be known just by conducting experiment once respectively through the two technologies.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for detecting diversity of fish species on basis of environmental DNA technology
PendingCN109825563ACause some damagesSimple samplingMicrobiological testing/measurementData informationRepresentative sequences
The invention discloses a method for detecting diversity of fish species on the basis of an environmental DNA technology. The method comprises the following steps of (1) conducting sampling; (2) extracting eDNA; (3) performing PCR amplification; (4) recovering and purifying target fragments and constructing a target fragment library; (5) conducting OTU clustering; (6) creating a fish comparison database; (7) conducting comparison analysis on representative sequences of OTUs with data information of the created fish database to determine the species diversity composition of fishes in a to-be-detected water area. According to the method, there is no need to catch the fishes, sampling is simple, and the fish bodies cannot be damaged; detection is convenient, and there is no need to conduct fish appearance identification; detection is simple and fast, the precision is high, and a detection result is accurate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF FRESH WATER FISHERIES
Water environment DNA intelligent collecting device and collecting method
PendingCN109406215AAvoid going toAccurate samplingWithdrawing sample devicesBiological material testing proceduresWater filterOceanography
The invention discloses a water environment DNA intelligent collecting device and collecting method, and belongs to the technical field of environment DNA detection. The water environment DNA intelligent collecting device and collecting method integrate the functions of intelligent control, sample collection, residual liquid emptying, pipeline blockage and pressure relief protection, can collect not only water biological samples but also water samples, can effectively improve the efficiency of the biological sample sampling process and water filtering amount calculation accuracy, ensure the sample timeliness and make the water sample detecting environment closer to the natural environment, thereby having the advantages of being not easy to block, simple in structure, reasonable in design and easy to manufacture.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
PCR amplimer for environmental DNA detection of Chinese sturgeon, detection method using PCR amplimer and application of PCR amplimer
ActiveCN106048065AShort ampliconHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA fragmentationA-DNA
The invention specifically relates to a PCR amplimer for environmental DNA detection of Chinese sturgeon, a detection method using the PCR amplimer and application of the PCR amplimer, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The sequences of ASCB1F and ASCB1R of the PCR amplimer are 5'-ACAATGCCACCCTTAC-3' and 5'-TGTCTGCGTCTGAGTTT-3', respectively. The site of a DNA molecular marker of a Chinese sturgeon species is located in the mitochondrial CYTB gene of the Chinese sturgeon; a DNA fragment has a length of 138 bp and a sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1; the PCR amplimer is used for environmental DNA amplification, an amplification product is compared with the sequence of the site of the DNA molecular marker, and if the non-primer zones of the amplification product and the site sequence are 100% matched, a detected species is the Chinese sturgeon species. According to the invention, identification of the Chinese sturgeon species is realized by using environmental DNA detection, and a sample from a fish body is not needed, so damage to the fish body is avoided.
Owner:WATER ENG ECOLOGICAL INST CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Monitoring method for natural reproduction of fish based on environmental DNA technology
InactiveCN107099595AEasy accessFishing Survey ValidMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA extractionFish species
The invention relates to a monitoring method for natural reproduction of fish based on environmental DNA technology. The method comprises the following steps: acquisition of a water sample; DNA extraction; ddPCR amplification of a target fragment; and concentration analysis. The monitoring method provided by the invention is based on environmental DNA identification technology, does not depend on traditional fishing technology for roe and fries and traditional anatomical technology for oophagous fish and can determine the oviposition behavior of a target species and the position of an oviposition site only through reasonable design of a sampling point, acquisition of a water sample and concentration analysis of the target species. The method maximally protects fish resources and avoids inconvenience caused by restrictive factors like long time for traditional fishing and difficulty in fishing of a part of fish fingerlings.
Owner:CHINESE STURGEON RES INST CHINA THREE GOR
Method for fast extracting AM epiphyte environment DNA in plant rhizosphere soil
The present invention relates to process of fast extracting AM fungal genome DNA in plant rhizosphere soil environment, and belongs to the field of molecular biology and applied microbiology. The process includes the first wet screening to eliminate great amount of PCR proliferation limiting factors from rhizosphere soil, collecting AM fungal related structures of rhizosphere soil for DNA extraction, mechanically breaking wall and adding CTAB to promote DNA release, and further purifying with Chelex-100 resin. The process is easy, simple and fast, and has great DNA extracting amount, capacity of being concentrated and purified and other advantages. The present invention has excellent application foreground.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for detecting diversity of large aquatic plants based on environmental DNA technology
InactiveCN112029896ASimple samplingFast samplingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsAquatic plantEnvironmental DNA
The invention discloses a method for detecting diversity of large aquatic plants based on an environmental DNA technology. The method for detecting the diversity of the large aquatic plants in a waterarea to be detected comprises the following steps: 1) collecting a surface sediment sample of the water area to be detected; 2) extracting environmental DNA (eDNA) in the sediment sample; 3) amplifying the eDNA sample by using an Rbcl primer to obtain a PCR product, and recovering and purifying the product to obtain a purified PCR product; and 3) sequentially performing database building, sequencing, clustering and annotation on the purified PCR product to determine the species composition and / or the species relative abundance of the large aquatic plants in the water area to be detected, so as to realize the detection of the diversity of the large aquatic plants in the water area to be detected. The method disclosed by the invention has the following advantages: the sampling is simple andfast; the detection is efficient, the precision is high, and the detection result is accurate; and the large aquatic plants do not need to be collected, so that the aquatic plant population is protected, and particularly the protection of rare and endangered species is realized.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Primer and method for evaluating biomass of trachemys scripta elegans based on environmental DNA (eDNA) technology
ActiveCN108486227AEasy to classifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTrachemys scriptaLaboratory facility
The invention discloses a primer and a method for evaluating the biomass of trachemys scripta elegans based on an environmental DNA (eDNA) technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a standard curve of DNA concentration and Ct value of the trachemys scripta elegans by a qPCR technology; 2) measuring the eDNA concentration of the trachemys scripta elegans in a water body under different trachemys scripta elegans stocking density environments according to the standard curve; 3) making a corresponding curve of the measured eDNA concentration and the corresponding biomass of the trachemys scripta elegans. The results show that the eDNA concentration and the biomass of the trachemys scripta elegans is of a linear relation, and R2 is 0.9429. The method provided by the invention can quickly identify the trachemys scripta elegans by detecting a water body in laboratory environment and evaluate the biomass of the trachemys scripta elegans according to the eDNA concentration, so as to provide technical support to the field distribution investigation, quantity evaluation and invasion degree and grade evaluation and the like of the trachemys scripta elegans.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
PCR primers and method for detecting composition of environmental microorganism arsenic oxidation gene species
ActiveCN110229917AEfficient analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliForward primer
The invention discloses PCR primers and method for detecting composition of environmental microorganism arsenic oxidation gene species. The forward and reverse primers of the primer pair are as follows: a forward primer: 5'-atctggggbaayracaayta-3'; and reverse primer: 5'-ttcatbgasgtsagrttcat-3'. The method comprises the following steps: using environmental DNA as a template, and amplifying aioA gene by using the primers; after the amplification product is purified, connecting the amplification product to a vector to construct a recombinant plasmid; transforming the recombinant plasmid into Escherichia coli competent cells, smearing bacteria on an LB plate, and performing culturing overnight at 37 DEG C; and selecting monoclonal extraction plasmids, performing sequencing, removing a vectorsequence from a sequencing result, and determining species composition information after comparison with an NCBI-nr database. The aioA primers designed by the application and subsequent molecular biology means can analyze the species composition of arsenic oxidation bacteria in the natural environment efficiently.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Method for quickly and efficiently detecting sepiella maindroni population
InactiveCN108203735AEfficient detectionNo environmental burdenMicrobiological testing/measurementMetapopulationLiving environment
The invention relates to a method for quickly and efficiently detecting a sepiella maindroni population by using environmental DNA to detect the sepiella maindroni population without damaging the environment and the species population. Collected eDNA samples are taken from the soil, sediment and water and the like, no environmental burden is caused to detection points, and no adverse influence iscaused to the living environment of the species. Special primers and probes are utilized to accurately, quickly and efficiently detect the DNA of sepiella maindroni, the efficiency and accuracy of thedetection are improved, and the detection cost is reduced. Compared with a field survey method used by the transmission of the sepiella maindroni population distribution detection, the method has theadvantages of saving time and labor, being low in cost and efficient and causing no harm to target species and no damage to a survey point ecosystem.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
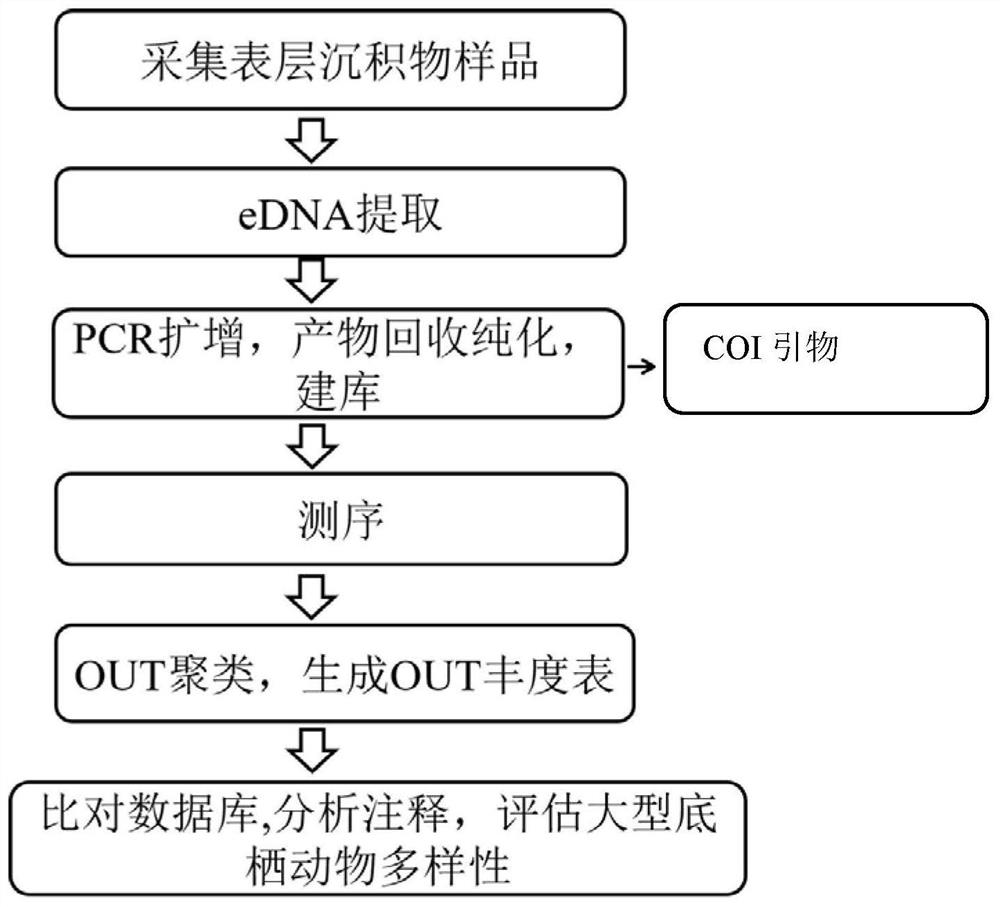
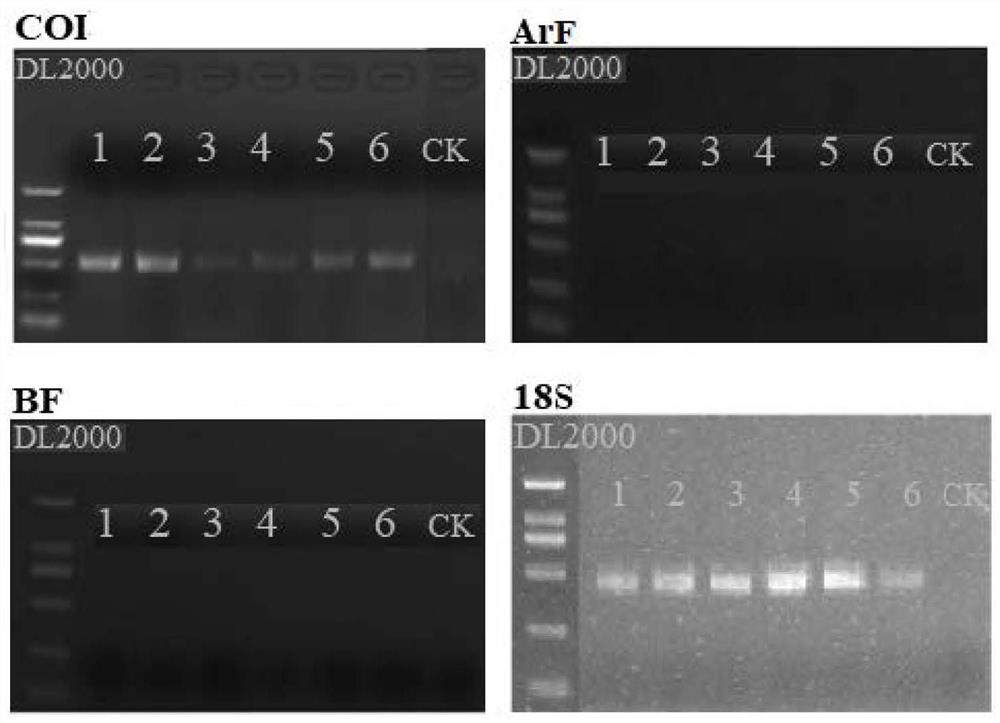
Environmental DNA macro bar code method for researching macrobenthic animal community structure
PendingCN112359119ASimple samplingFast samplingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationZooidFishery
The invention discloses an environmental DNA macro bar code method for researching a macrobenthic animal community structure. One technical scheme to be protected by the invention is the application of the primer pair in detecting the community structure of the macrobenthos in the water area to be detected. The primer pair is named as COI and is composed of a primer 1 and a primer 2, and the primer 1 and the primer 2 can be a sequence 1 and a sequence 2 in a sequence table. Compared with a traditional method, the COI primer provided by the invention is used for amplifying an environmental DNAsample of a to-be-detected water area, and sequencing and annotation analysis are carried out to obtain more obvious species, especially benthonic animal groups which are easy to escape, small in sizeand partial in life history in water; and the method can supplement benthonic animal abundance data which are easy to ignore, difficult to find and small in size in a traditional investigation method, effectively improves the identification level, species detection rate and abundance evaluation accuracy of the large benthonic animals, and is an effective and reliable new method for investigatingthe community structure of the large benthonic animals.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Extraction method for environmental DNA of neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis and application of method
PendingCN108624585ARapid Identification SurveyAccurate Identification SurveyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationNeophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalisMicrobiology
The invention discloses an extraction method for environmental DNA of neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis and application of the method. The method comprises the following steps of collecting water samples of an area to be identified, carrying out filtration treatment, extracting the DNA by adopting kits, carrying out real time PCR amplification and determining whether the neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis exists in the area to be identified or not according to the peak value of a solubility curve. The method has the advantages of being high in efficiency, high in specificity, highin correlation coefficient, wide in linear range and the like; and whether the neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis exists in the surveyed water area can be rapidly and accurately identified.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
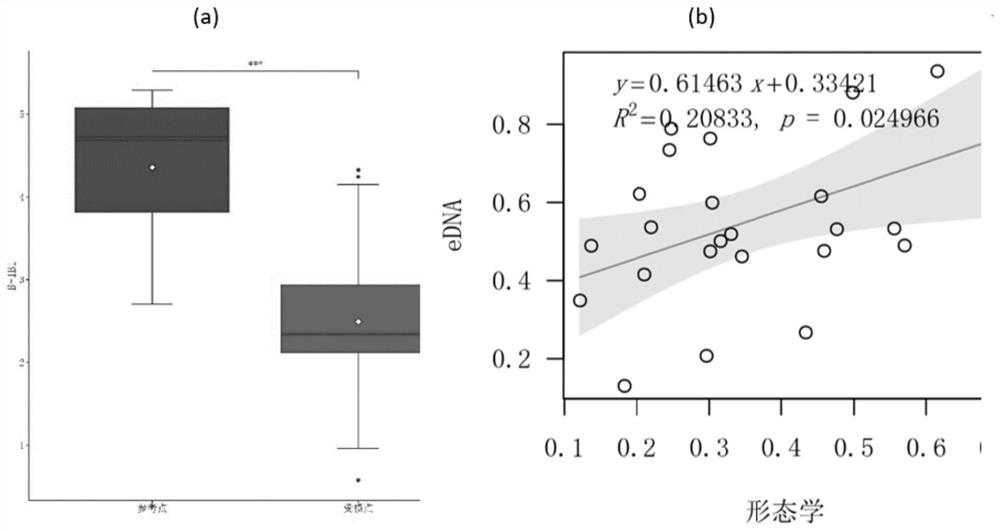
Method for evaluating integrity of benthonic animals based on environmental DNA macro bar code technology
PendingCN113403400AImprove accuracySave human effortGeneral water supply conservationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological integrityFishery
The invention discloses a method for evaluating biological integrity of benthonic animals of a freshwater ecosystem based on environmental DNA macro bar code monitoring data, and belongs to the technical field of biology. Based on the results of monitoring of the benthonic animals through environmental DNA macro bar codes, the method comprises a series of monitoring and evaluation processes including (1) determining a reference point and a damaged point; (2) collecting an environmental DNA sample; (3) performing biological monitoring on an eDNA macro bar code; (4) defining and calculating candidate biological indexes based on the eDNA macro bar code monitoring; (5) screening the candidate indexes; (6) selecting the biological indexes to calculate the biological integrity score of the benthonic animals; and (7) dividing health levels and the like. The method provides complete and easy-to-operate guidance for the evaluation of the biological integrity of the benthonic animals of the freshwater, and can be widely applied to the evaluation of the integrity of the benthonic animals and the evaluation of the water ecological health condition of freshwater ecosystems such as streams, rivers, lakes and reservoirs.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
PCR amplification primer for detecting and identifying northern pacific sea area ommatostrephes species by using environmental DNA as well as detection method and application thereof
PendingCN111440882AEasy to distinguishLess destructiveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPacific oceanFishery
The invention provides a PCR amplification primer for detecting and identifying northern pacific sea area ommatostrephes species by using environmental DNA as well as detection method and applicationthereof. In the PCR amplification primer, the sequence of an upstream primer OMBA-F is 5 '-CGAAGGTTAATCTGTCTCCATCT-3', and the sequence of a downstream primer OMBA-R is 5 '-CCCAATTAAAATTTATATACCACCT-3'. Wherein the DNA molecular marker for detecting the ommatostrephes species is located in the 16S gene of the ommatostrephes; through comparing the environmental DNA detection result with the DNA molecular marker site sequence, the ommatostrephes species can be determined if the comparison result is 100% matching; according to the detection method disclosed by the invention, the detection of thesquid species is realized by only collecting the water sample from the water body, and through DNA sequence comparison, the detection method causes little damage to an ecological system, and the obtained result has the characteristic of high accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Filter membrane assembly and collector for DNA enrichment in water environment and application method
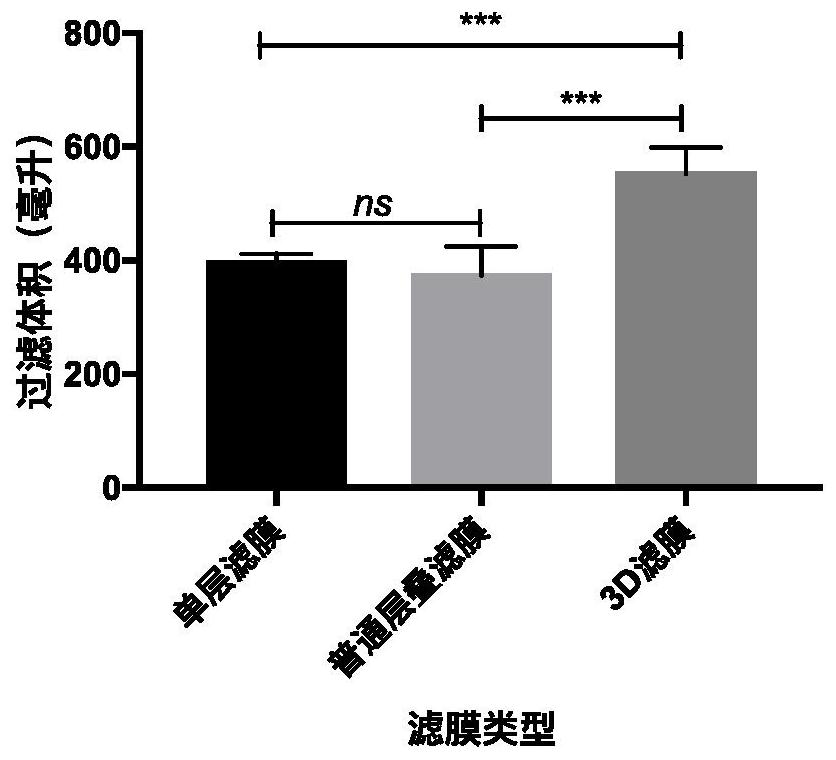
ActiveCN111647594AAvoid cloggingAvoid lostSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisChemical physicsFiltration
The invention discloses a filter membrane assembly and collector for DNA enrichment in water environment and an application method, and belongs to the technical field of environmental DNA detection. The filter membrane assembly includes at least two layers of filter membranes stacked in sequence from top to bottom, the filter pore size of each layer of the filter membrane is arbitrarily selectively reduced linearly or stepwise; and a certain gap is maintained between two upper-lower adjacent layers of filter membranes, and filter holes between the two adjacent layers of the filter membranes are arranged in a staggered manner. By using the filter membrane assembly for DNA enrichment in the water environment, gradient filtration of biological samples in water samples can be achieved, clogging of the filter membranes is avoided, the filtration capacity of the filter membranes is increased, the filtration flux and filtration efficiency of the water samples are increased, and the subsequentDNA extraction efficiency can further be improved.
Owner:南京易基诺环保科技有限公司
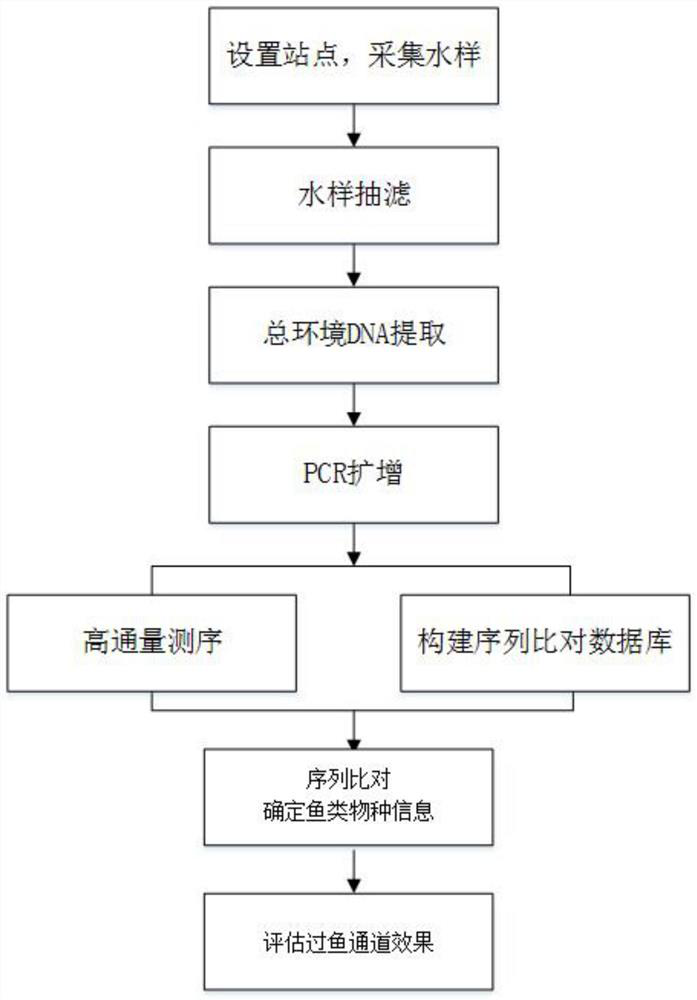
Method for monitoring and evaluating fish passage effects based on environmental DNA
PendingCN111690725AScientific and reasonable structureEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisHigh throughput sequenceZoology
The invention discloses a method for monitoring and evaluating fish passage effects based on environmental DNA. The method comprises the following steps: S1, setting three sampling points at an entrance, exit and rest pool of a fish passage, and collecting water samples and performing storage; S2, performing suction filtration on the collected water samples, and then performing extraction of totalenvironmental DNA; S3, using the extracted total environmental DNA as a template, and using designed primers to PCR amplify a 16S rDNA sequence to obtain a PCR product; S4, recovering and purifying the PCR product, and performing high-throughput sequencing to obtain a PCR product sequence; S5, establishing a fish 16S rDNA sequence alignment database; S6, searching for homologous sequences in theNCBI database and the established database through BLAST, and determining fish species information; and S7, counting the obtained fish species information, and completing the monitoring and evaluationof the fish passage effects. Compared with other existing methods, the method does not need to carry out a large number of fishing operations or instrument operations, is simple in sampling, cannot cause harms to fish, and thereby is conducive to the protection of fish.
Owner:PEARL RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
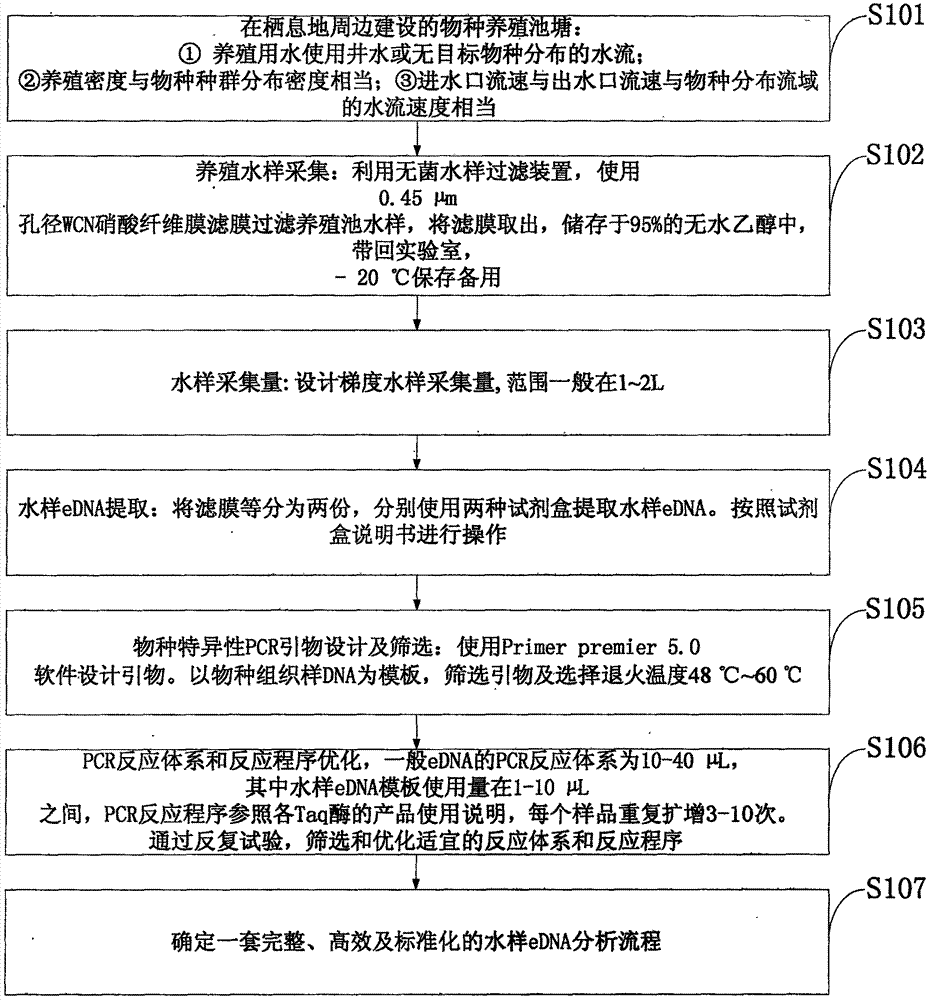
Rare aquatic organismwater sampleenvironment DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) optimization-cultivationwater sample pre-detection method
PendingCN106868117AWide coverageGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAquatic speciesAquaculture
The invention discloses a rare aquatic organismwater sampleenvironment DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) optimization-cultivationwater sample pre-detection method, which comprises the steps of before carrying out endangered aquatic species distribution investigation, making a perfect implementation plan through pre-detection; through acquiring an aquaculture pond water sample, and by taking detection of a target specie as an aim, analyzing water sample eDNA. Compared with water samples in a laboratory and an aquarium, according to the method, the physicochemical propertyof a water sample of an aquaculture pond constructed around a habitat has higher similarity to a water flow of an inhabiting area of species, so that the aquaculture pond water sample is utilized for simulating a habitat water sample, eDNA analysis process optimization of the target specie is carried out, and the reliability and the practicability of a determined operation flow are higher. According to the rare aquatic organismwater sampleenvironment DNA optimization-cultivationwater sample pre-detection method provided by the invention, the work efficiency of aquatic (semi-aquatic) species distributioninvestigation can be effectively improved, the work consumption is reduced, meanwhile, the reliability and the repeatability of an investigated result are ensured, and the sharing and the compatibility of different-source data are realized.
Owner:SHAANXI INST OF ZOOLOGY NORTHWEST INSTOF ENDANGERED ZOOLOGICAL SPECIES
Method for detecting environment DNA of giant salamander distribution
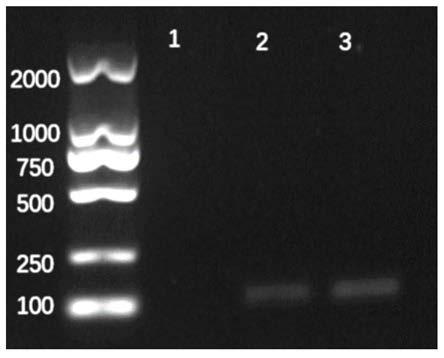
ActiveCN113088574AImprove featuresImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesElectrophoresesChinese giant salamander
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecules, and particularly relates to a method for detecting environment DNA of giant salamander distribution. According to the specific technical scheme, according to the method for detecting the environment DNA of giant salamander distribution, at least one pair of primers is used for conducting PCR amplification detection on a to-be-detected sample, if 158-224 bp positive bands appear in an electrophoresis result, it is considered that giant salamanders are distributed in the environment where the to-be-detected sample is sourced, the primer pair is AdCytbE1, and the sequences are SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2. According to the method, environmental DNA of excrement, skin exfoliates, corpses and the like of Chinese giant salamanders in residual water is utilized, a molecular biological technology is combined, a primer with high specificity, high sensitivity and strong universality is developed, and a method capable of carrying out rapid and standardized detection aiming at the distribution of different species of giant salamanders is established.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Method for detecting diversity of fish species by using environmental DNA technology
PendingCN113355403AEliminate the effects ofThe test result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerNucleotide
The invention provides a method for detecting fish species diversity by using environmental DNA, and relates to the technical field of molecular ecology. The method for detecting fish species diversity by using the environmental DNA comprises the following steps: collecting a water sample of a place to be detected, filtering, extracting eDNA to obtain eDNA of the water sample to be detected, carrying out PCR amplification by using a primer group to obtain an amplification product, carrying out high-throughput sequencing on the amplification product to obtain sequence fragments, splicing the sequence fragments, and carrying out OTU cluster analysis on the species diversity. The primer group comprises an upstream primer and a downstream primer, the nucleotide sequence of the forward primer is as shown in SEQID.NO 1, and the nucleotide sequence of the reverse primer is as shown in SEQID.NO 2. The method has the advantages that the method can be used for detecting the diversity of fish species, especially the diversity of lake aquatic organisms, the detection result is accurate, and multiple species can be detected.
Owner:邢迎春 +1
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer, reagent or kit and identification method for identifying or assisting in identifying freshwater fish species
PendingCN113564262AAccurate identificationDo not cause interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideZoology
The invention provides a novel PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer (16s 200) for identifying or assisting in identifying freshwater fish species. A nucleotide sequence of the primer is SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table. The PCR primer is applied to eDNA metabolism coding of a fish mitochondrial DNA sequence. The PCR primer is adopted to perform PCR amplification on eDNA in a water body, based on a high-throughput sequencing method, the problem that an effective species specific primer is difficult to obtain under the condition that various closely-related species exist in the water body can be effectively solved, and based on an environmental DNA monitoring technology, an effective technical support is provided for taxonomy research and diversity protection of fishes. The method for identifying the freshwater fish species by using the PCR primer has the advantages of short consumed time, simplicity and convenience in operation, high specificity and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV +1
Method for the expression of unknown environmental dna into adapted host cells
InactiveUS20050282166A1Maintain relatively stableStable propagationSugar derivativesHydrolasesEscherichia coliShuttle vector
The present invention relates to methods for the identification or cloning of polynucleotides encoding a selected phenotype, particularly from environmental DNA. In a specific embodiment, the method comprises (i) cloning environmental DNA fragments into E coli cloning vectors to produce a metagenomic library, (ii) identifying or selecting cloning vectors in said library which contain DNA fragments having a particular characteristic of interest, (iii) modifying the identified or selected cloning vectors into shuttle or expression vectors for transfer and integration in a selected host cell, (iv) transferring the modified cloning vectors into said selected host-cell and (v) identifying or cloning the DNA fragments contained in said modified cloning vectors which encode said selected phenotype in said selected host cell.
Owner:LIBRAGEN SA
Procypris rabaudi real-time fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification primer, probe and detection method based on environmental DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
ActiveCN113667762AShorten detection timeThe monitoring results are accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationNucleotideProcypris
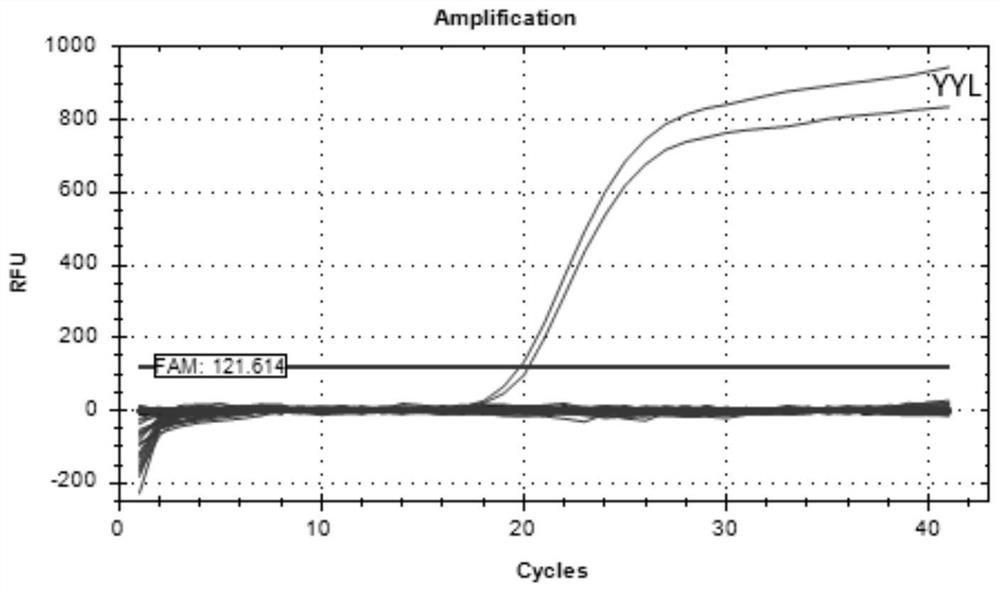
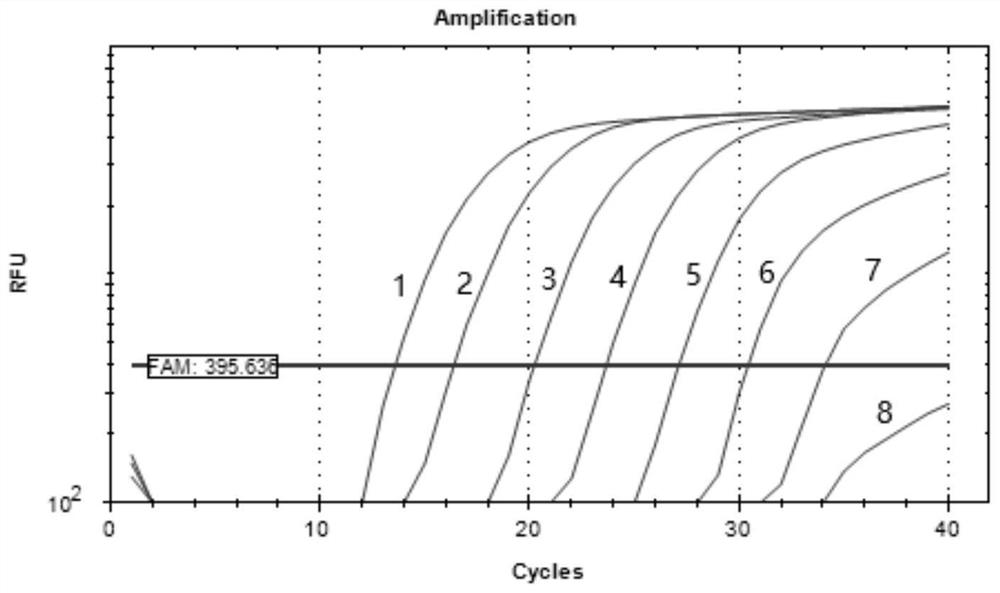
The invention discloses a composition of a primer and a probe for procypris rabaudi real-time fluorescent PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection based on environmental DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid), and establishes a real-time fluorescent PCR detection method of procypris rabaudi to achieve the purpose of accurately identifying procypris rabaudi. A specific primer is designed according to the gene sequence of 12SrRNA in mitochondrial DNA of procypris rabaudi, the nucleotide sequence of an upstream primer YYLF1 is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, the nucleotide sequence of a downstream primer YYLR1 is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, and a probe YYL-MGB1 has the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 3. The probe can be applied to qualitative detection of procypris rabaudi in a water body only by collecting a water sample of a water area in which the procypris rabaudi live, and is high in specificity and good in timeliness; and the density of the procypris rabaudi in the environment can be quantitatively detected, and the biomass and time-space dynamics of the procypris rabaudi at different points can be reflected, so that a reference is provided for artificial release effect evaluation and resource management protection of the procypris rabaudi under the large background of procypris rabaudi without fishery in the Yangtze River.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method for monitoring diversity of freshwater benthic animal communities based on environmental DNA technology
PendingCN112662783ASimple samplingEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisFisheryHigh throughput sequence
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Self-preserving biodegradable environmental DNA filter
ActiveUS20200246755A1Eliminate requirementsPreservation of the environmental DNAMembranesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiochemical engineeringEnvironmental engineering
An inline filter housing with a biodegradable, hydrophilic material that operates in conjunction with a field sampling apparatus to both concentrate field sampled environmental DNA particles from water samples and to automatically preserve the captured DNA via desiccation, thus avoiding filter membrane transfer steps, chemicals or cold storage preservation requirements. The hydrophilic filter housing is capable of rapidly preserving the field sampled environmental DNA captured on the filter membrane at ambient field temperatures.
Owner:SMITH ROOT
Intelligent collection device for environment DNA in marine water body
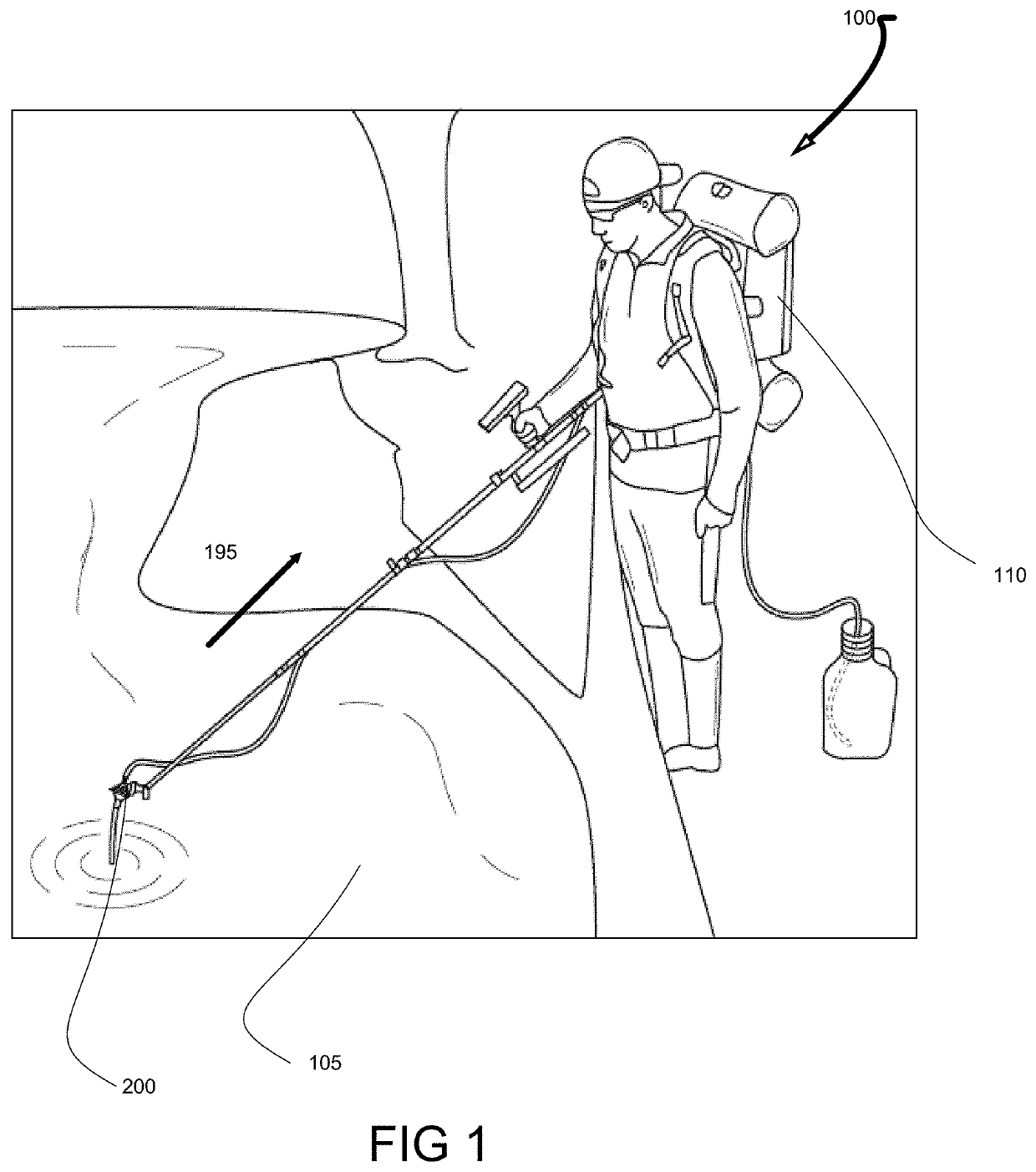
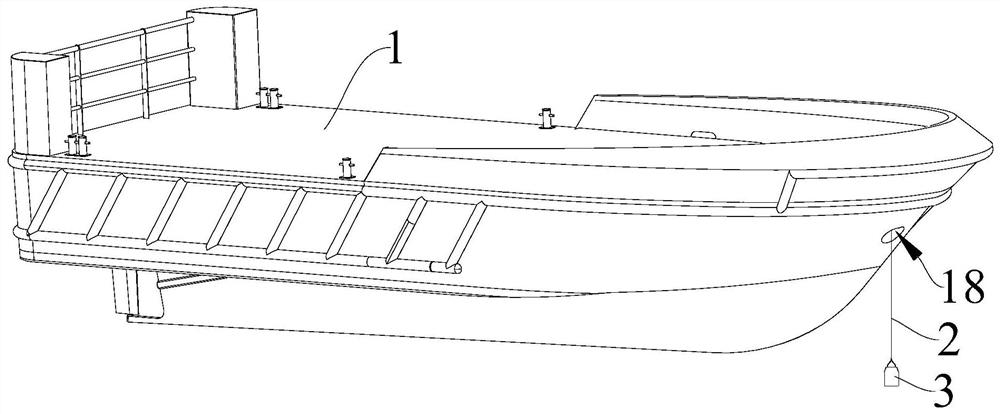
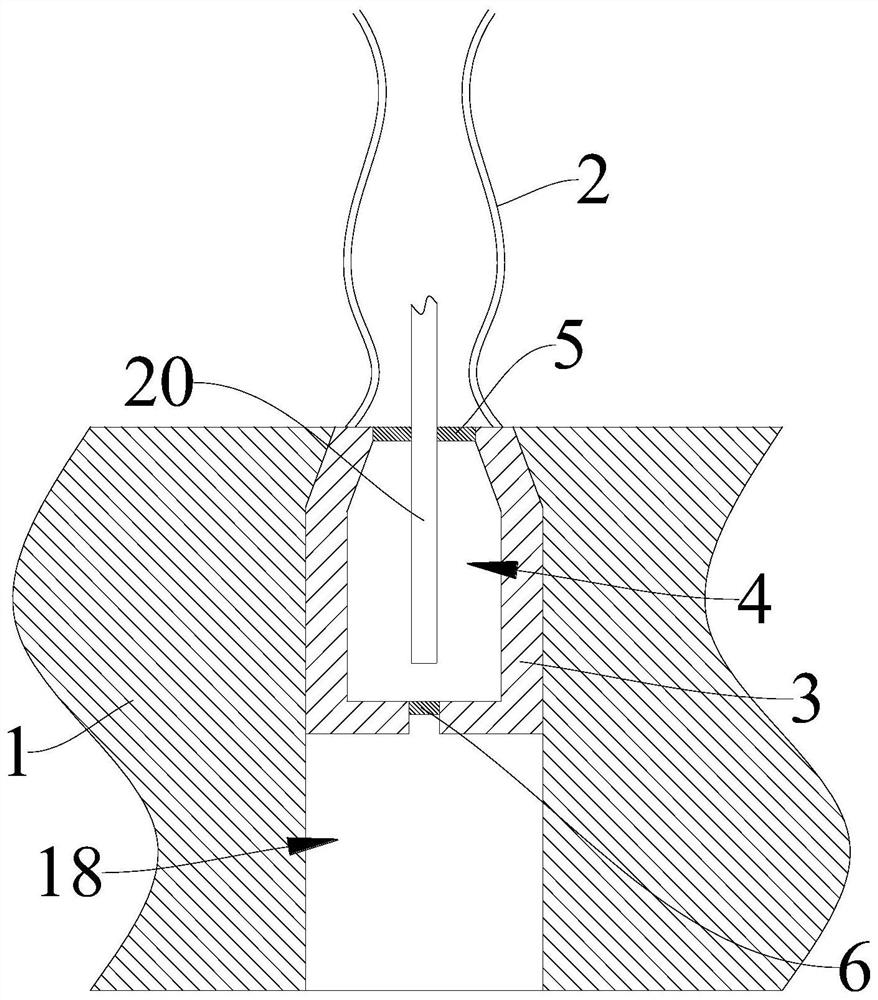
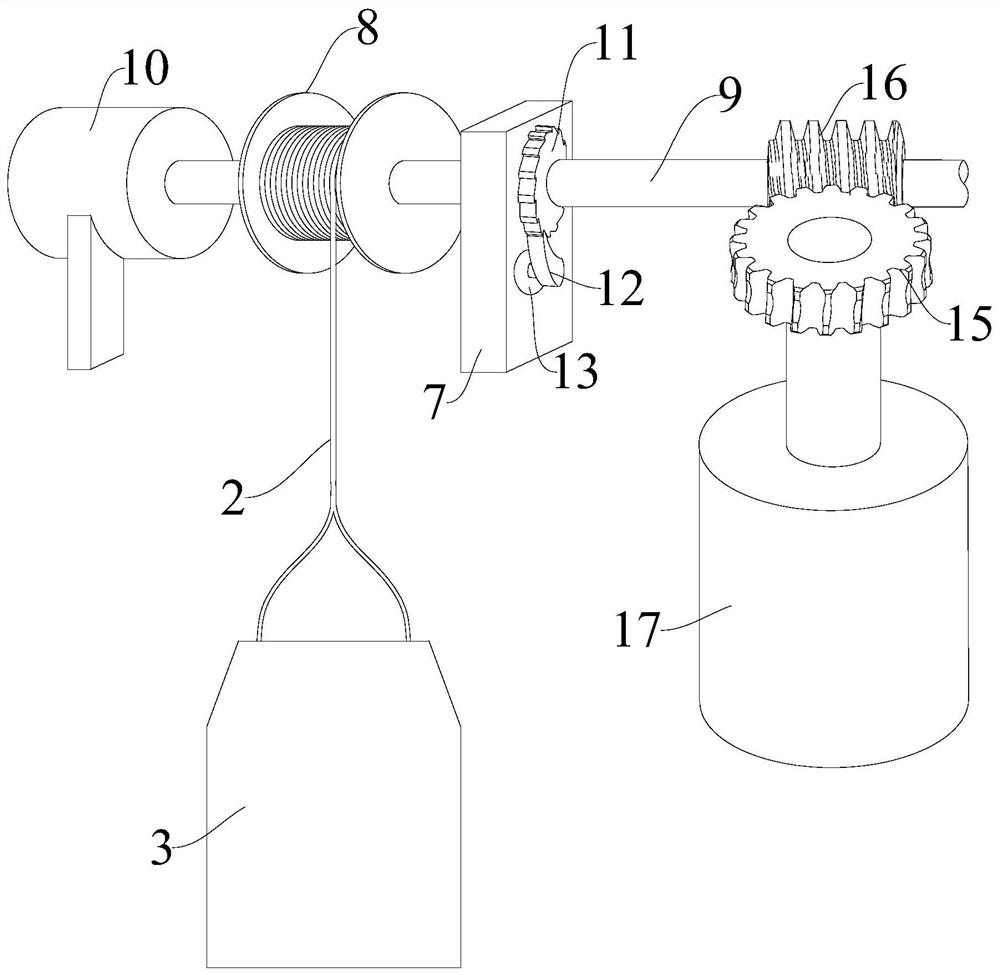
PendingCN113432922AEasy to analyzeEasy to collectWaterborne vesselsWithdrawing sample devicesWater storageRemote control
The invention provides an intelligent collection device for environmental DNA in a marine water body, and relates to the technical field of DNA collection devices. The intelligent collection device for environment DNA in marine water comprises a remote control ship, the remote control ship is provided with a pull rope and a winding and unwinding assembly used for winding and unwinding the pull rope, one end of the pull rope is connected with the winding and unwinding assembly, and the other end of the pull rope is provided with a sampling barrel; a water storage cavity is formed in the sampling barrel, a first opening communicated with the water storage cavity is formed in the top of the sampling barrel, and a first electromagnetic valve is arranged at the first opening; a second opening communicated with the water storage cavity is formed in the bottom of the sampling barrel, and a second electromagnetic valve is arranged at the second opening; and the intelligent collection device further comprises a processor, a power source and a remote control module, the remote control module is wirelessly connected with the processor, and the retractable assembly, the power source, the first electromagnetic valve and the second electromagnetic valve are all electrically connected with the processor. By the adoption of the collecting device, marine water samples can be conveniently collected, operation is convenient and fast, and manpower is saved.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Primer group, kit and method for detecting astronotus ocellatus population
ActiveCN111926088AEfficient detectionFree from destructionMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationFluoProbesNucleotide
The invention provides a primer group, kit and method for detecting an astronotus ocellatus population, and belongs to the technical field of species distribution detection. The primer group comprisesan upstream primer, a downstream primer and a fluorescent probe; the nucleotide sequence of the upstream primer is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, the nucleotide sequence of the downstream primer is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, and the nucleotide sequence of the fluorescent probe is as shown in SEQ ID No. 3. The method comprises the following steps: (1), collecting an environment eDNA sample from a to-be-detected environment; (2), extracting DNA in the environment eDNA sample to obtain a DNA sample solution; and (3), taking the DNA sample solution as a template, carrying out qPCR amplification by using the primer group, measuring a Ct value, and judging a result according to the Ct value. The method can be used for rapidly and efficiently detecting the astronotus ocellatus population by adopting an environmental DNA technology on the premise of not damaging the environment and the indigenous fish population.
Owner:HAINAN TROPICAL OCEAN UNIV
Filter assembly, kit and methods
PendingUS20220081686A1MembranesWithdrawing sample devicesProcess engineeringEnvironmental engineering
The present invention is directed to a filter assembly for capturing environmental DNA (eDNA), a kit comprising the filter assembly, a method of capturing eDNA using the filter assembly, a method of analysing eDNA captured in the filter assembly, and a method of providing biodiversity data by analysing eDNA collected in the filter assembly.
Owner:NATURE METRICS LTD
Method for the expression of unknown environmental DNA into adapted host cells
InactiveUS7910522B2High efficient cloningMaintain relatively stableSugar derivativesHydrolasesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The present invention relates to methods for the identification or cloning of polynucleotides encoding a selected phenotype, particularly from environmental DNA. In a specific embodiment, the method comprises (i) cloning environmental DNA fragments into E. coli cloning vectors to produce a metagenomic library, (ii) identifying or selecting cloning vectors in the library which contain DNA fragments having a particular characteristic of interest, (iii) modifying the identified or selected cloning vectors into shuttle or expression vectors for transfer and integration in a selected host cell, (iv) transferring the modified cloning vectors into the selected host-cell and (v) identifying or cloning the DNA fragments contained in the modified cloning vectors which encode the selected phenotype in the selected host cell.
Owner:LIBRAGEN SA
Triaryl cation antibiotics from environmental DNA
Disclosed are triaryl cationic compounds that exhibit broad spectrum antibiotic and antifungal activity, pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds, and methods of treating bacterial and fungal infections using the compounds. The compounds were initially isolated by screening a 25,000-member bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library of environmental (eDNA) from soil. At least one clone produced a dark brown melanin-like compound that was found to have antibiotic activity. The compounds were isolated and synthesized de novo. From within the positive clone, a single open reading frame that shares extensive sequence similarity with members of the 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate family of enzymes was found to be necessary and sufficient to confer the production of at least one of the subject compounds on E. coli.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com