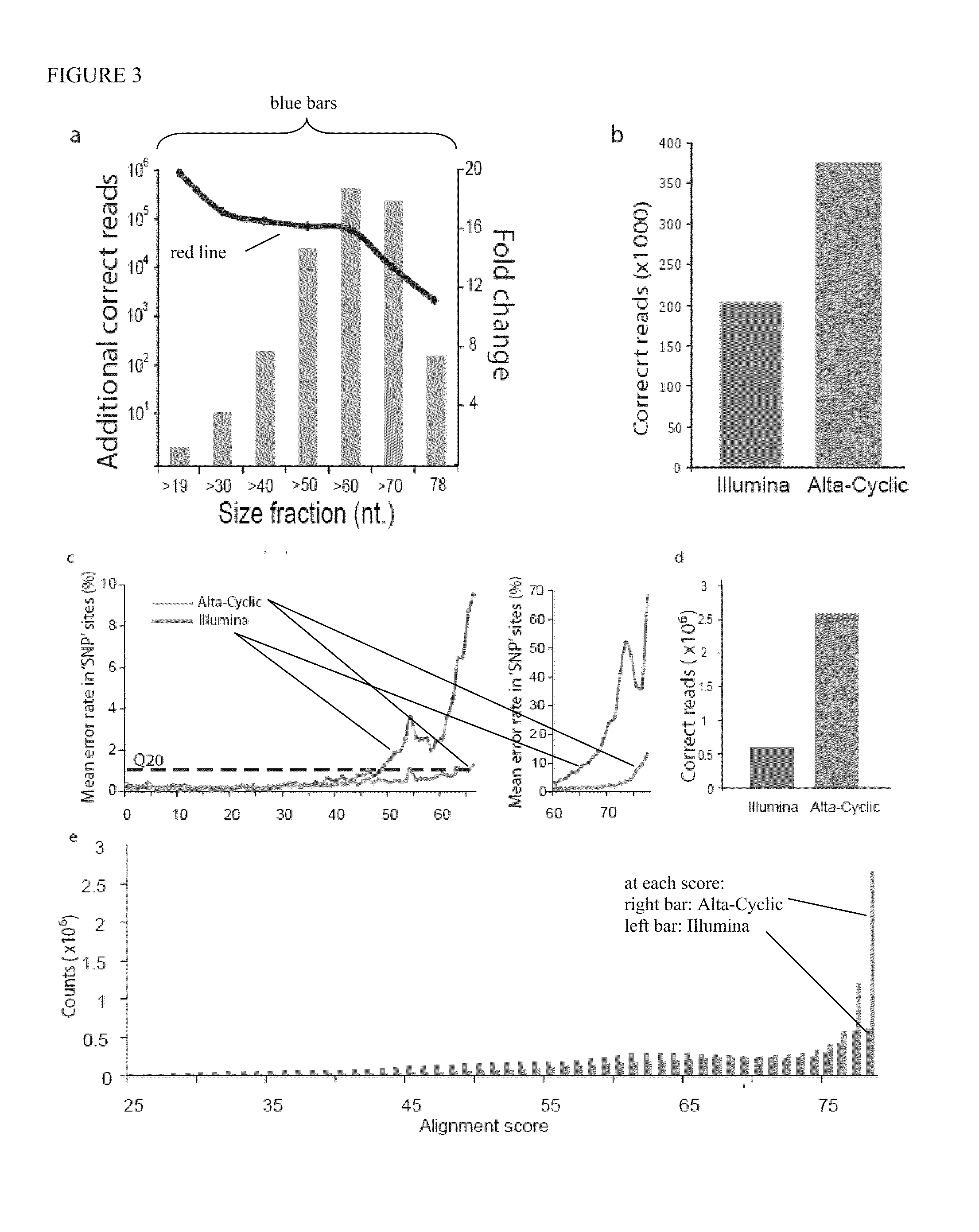
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
90 results about "DNA sequencer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
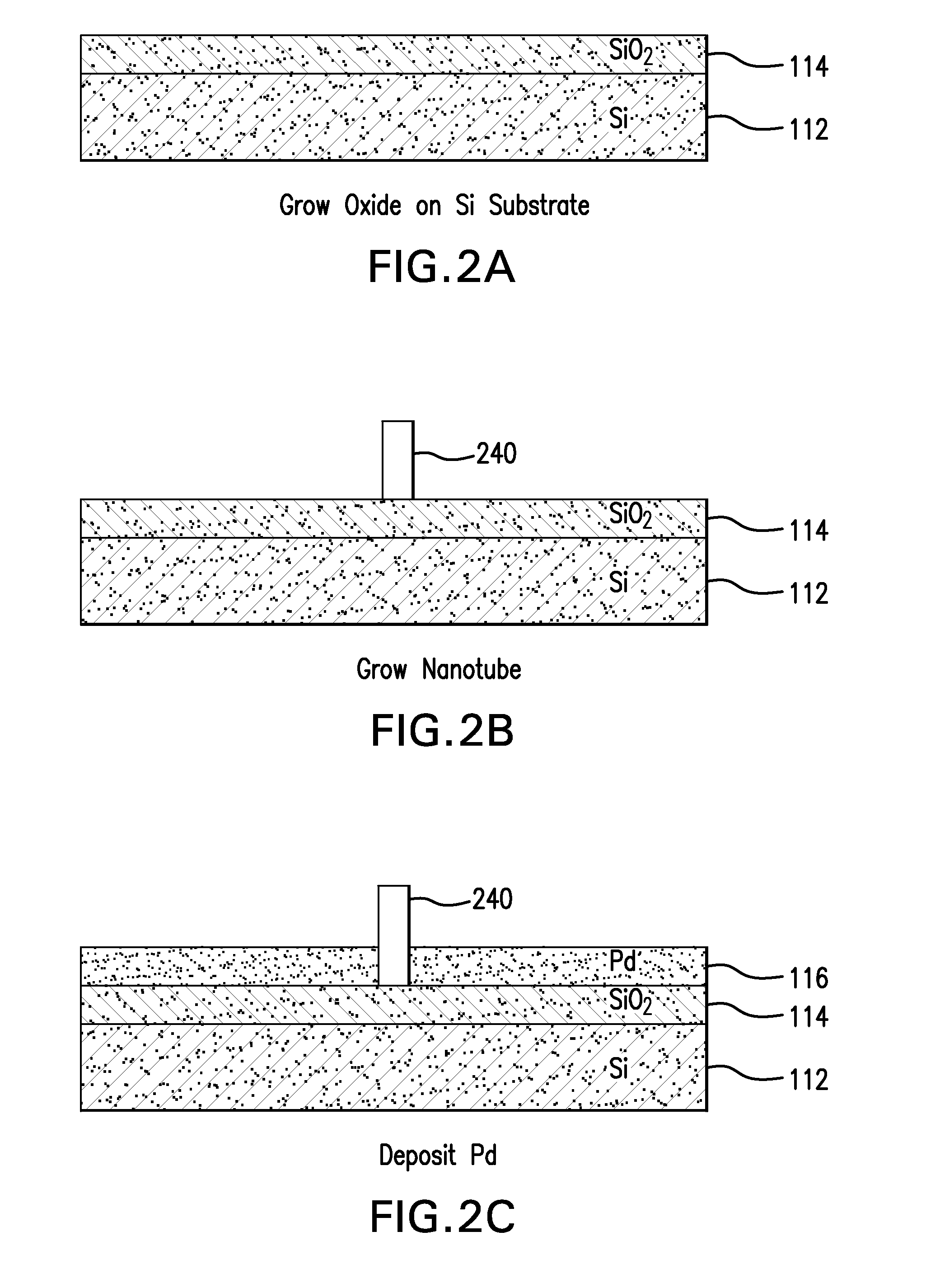
A DNA sequencer is a scientific instrument used to automate the DNA sequencing process. Given a sample of DNA, a DNA sequencer is used to determine the order of the four bases: G (guanine), C (cytosine), A (adenine) and T (thymine). This is then reported as a text string, called a read. Some DNA sequencers can be also considered optical instruments as they analyze light signals originating from fluorochromes attached to nucleotides.
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequencer
ActiveCN102703312AImprove sequencing efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatments3-deoxyriboseBiochemical engineering
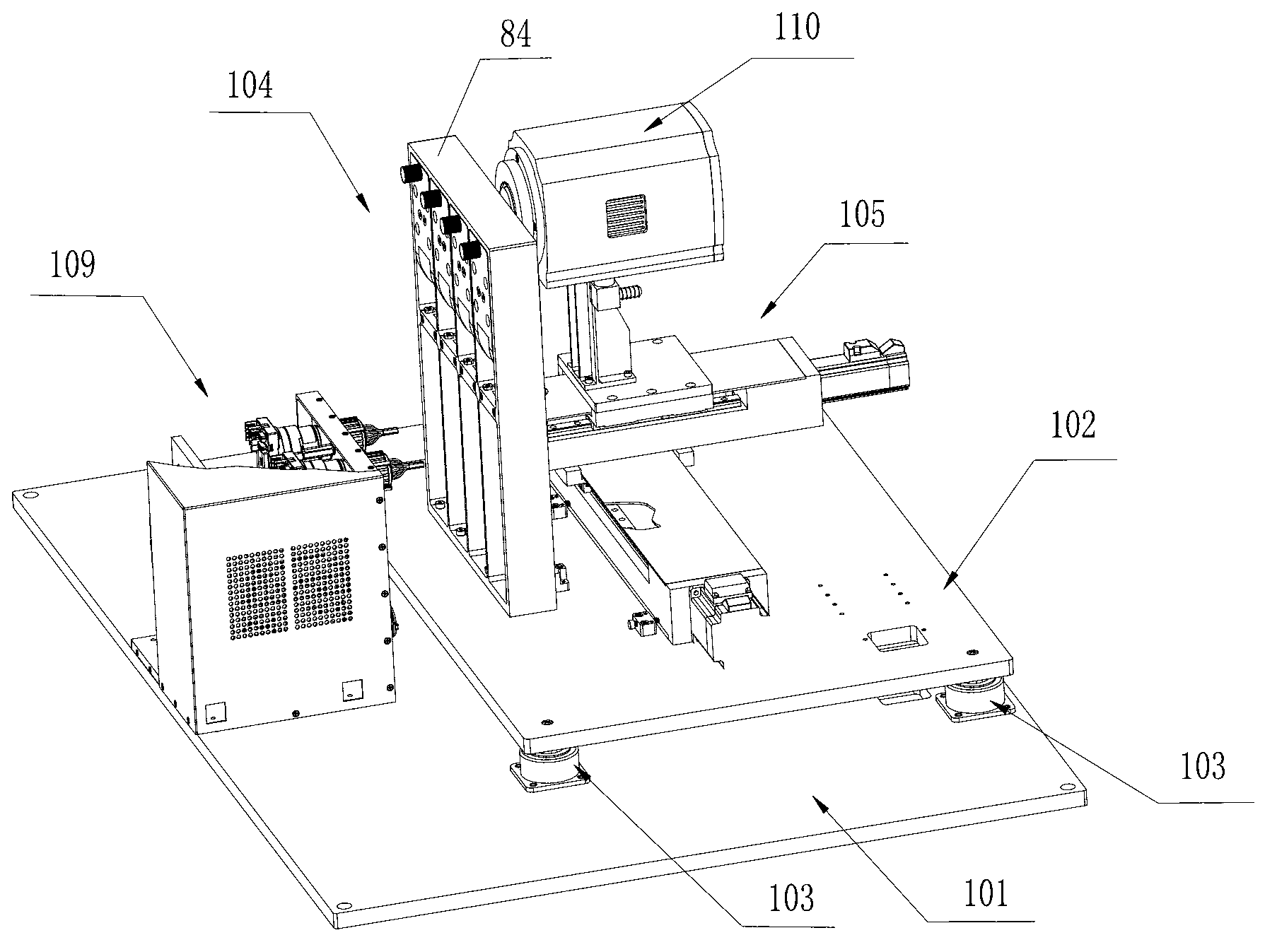
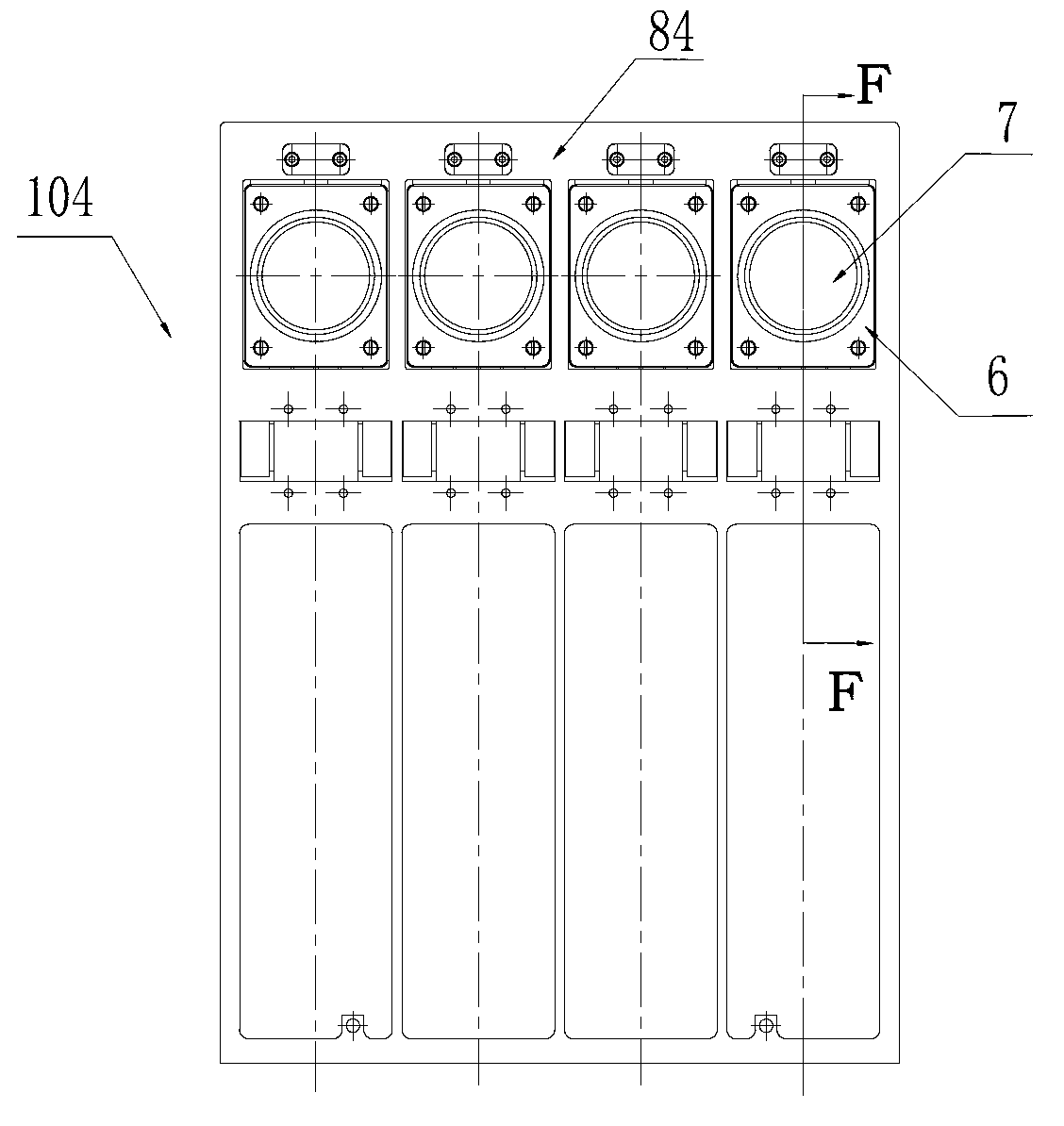
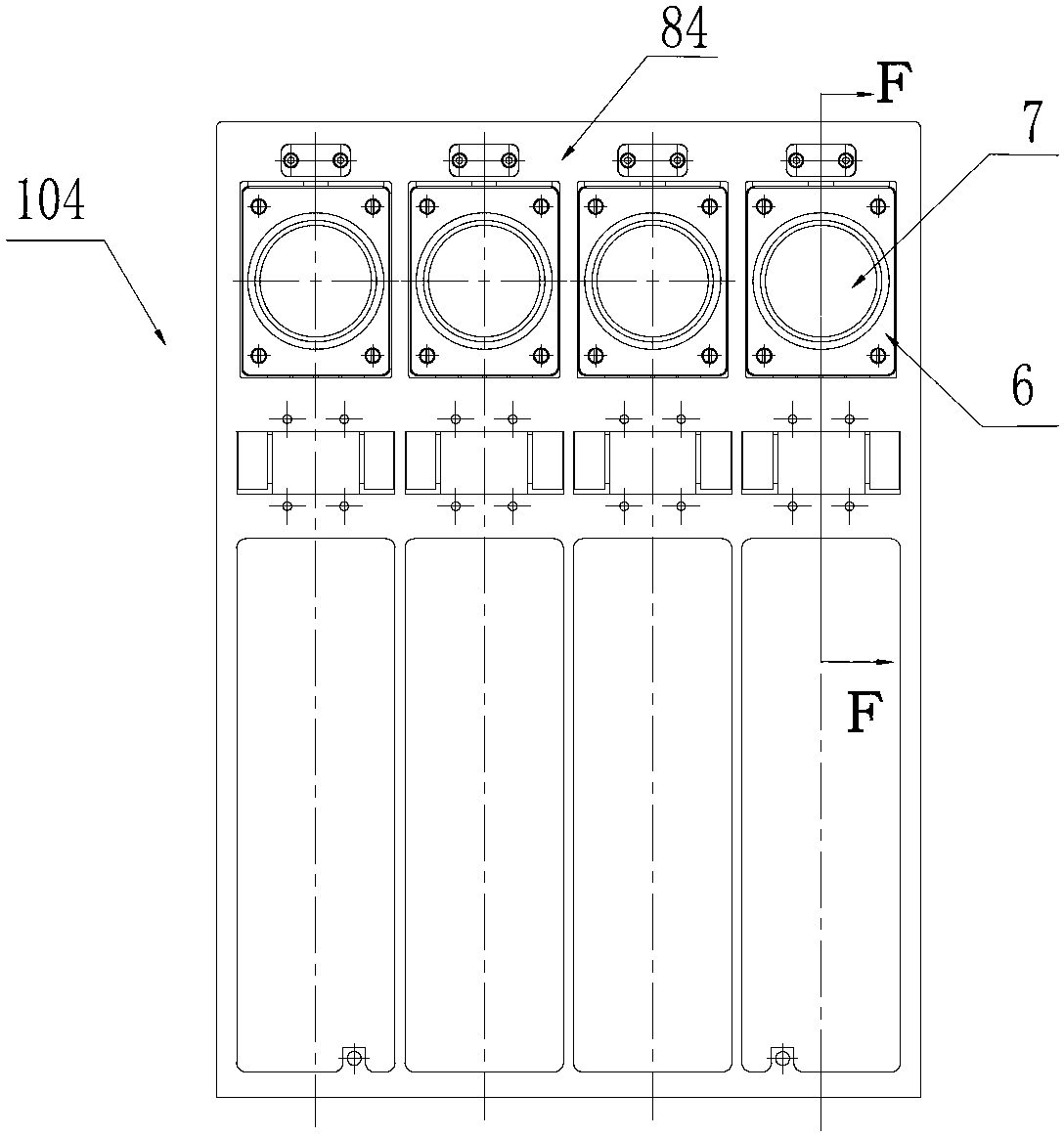
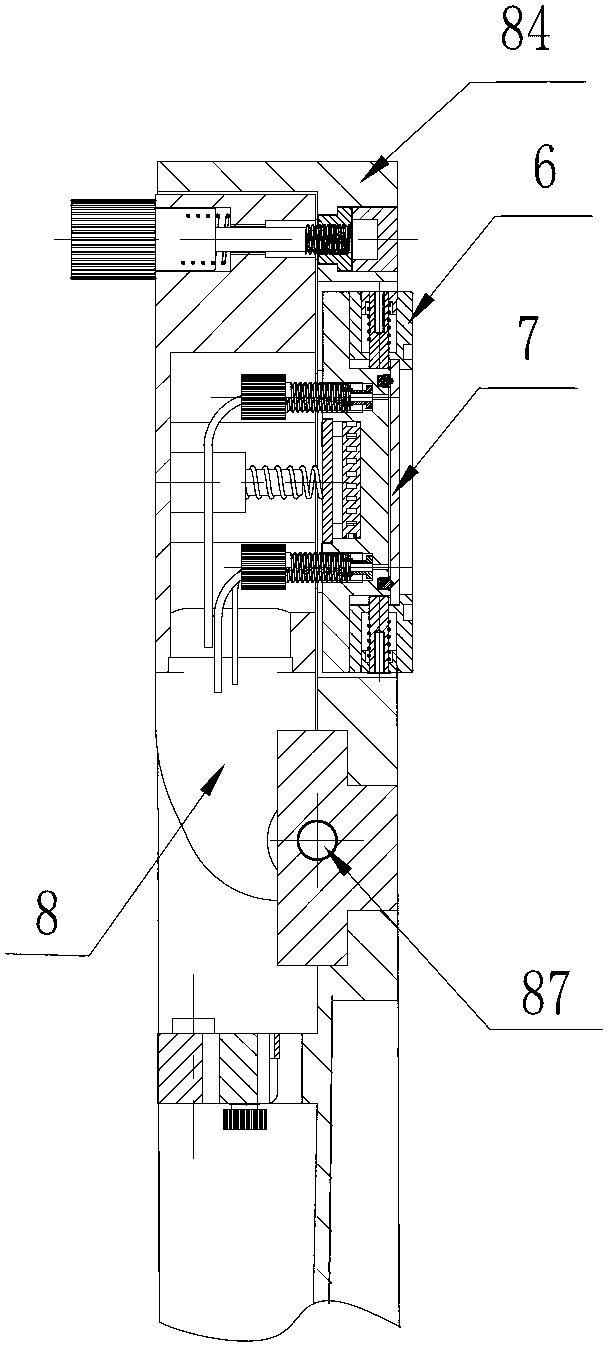
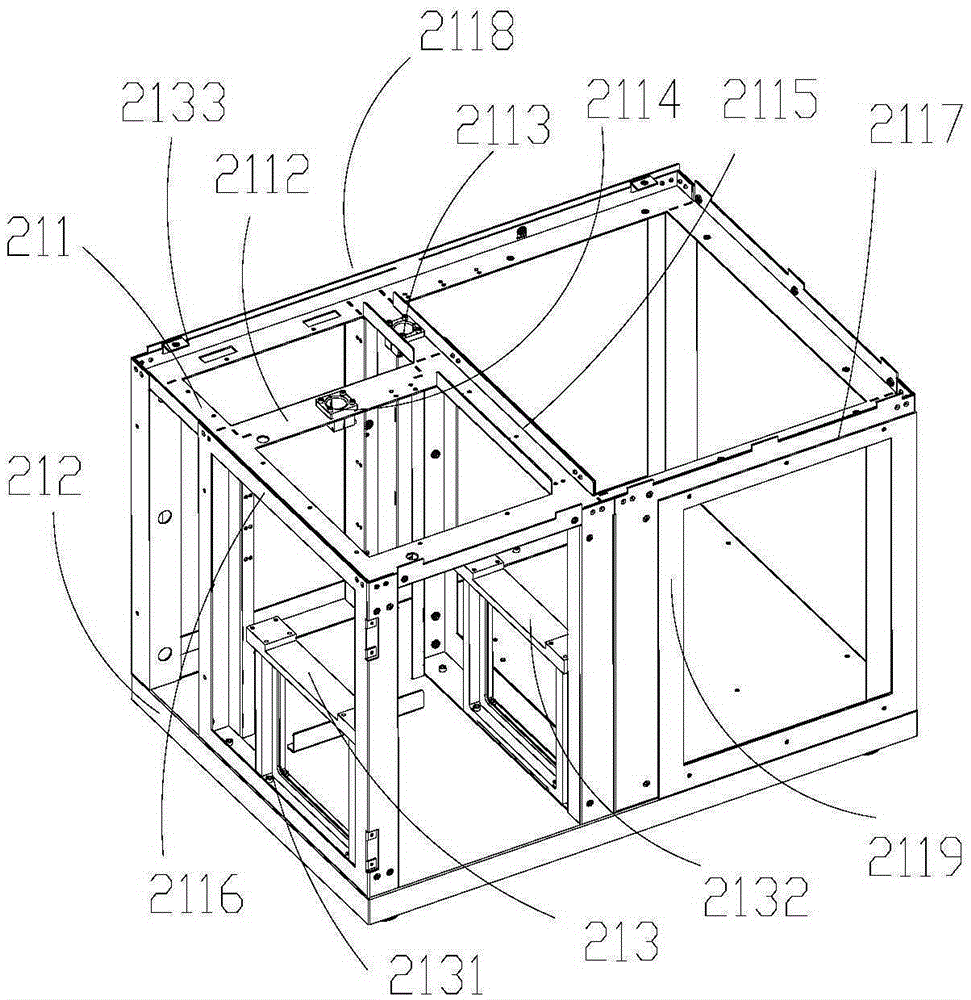
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequencer which comprises a supporting table, a plurality of vibration dampers, a vibration damping plate, a reaction bin assembly, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, a two-dimensional regulation supporting device and a medicament supply assembly, wherein the vibration damping plate is connected with the supporting table by a plurality of vibration dampers; the reaction bin assembly is fixedly arranged on the vibration damping plate and is used for performing the DNA sequencing reaction; the CCD camera is used for acquiring an optical signal; the two-dimensional regulation supporting device is used for supporting the CCD camera; and the medicament supply assembly is arranged on the supporting table and is used for providing reagents and buffer solution for the reaction bin assembly. According to the DNA sequencer disclosed by the invention, by the arrangement of a plurality of reaction bins and the matching of the two-dimensional regulation supporting device capable of carrying out two-dimensional regulation and the medicament supply assembly capable of supplying the reagents for a plurality of reaction bins, the aim of simultaneously performing a plurality of reactions is fulfilled, a plurality of samples can be simultaneously sequenced and the DNA sequencing efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION +1
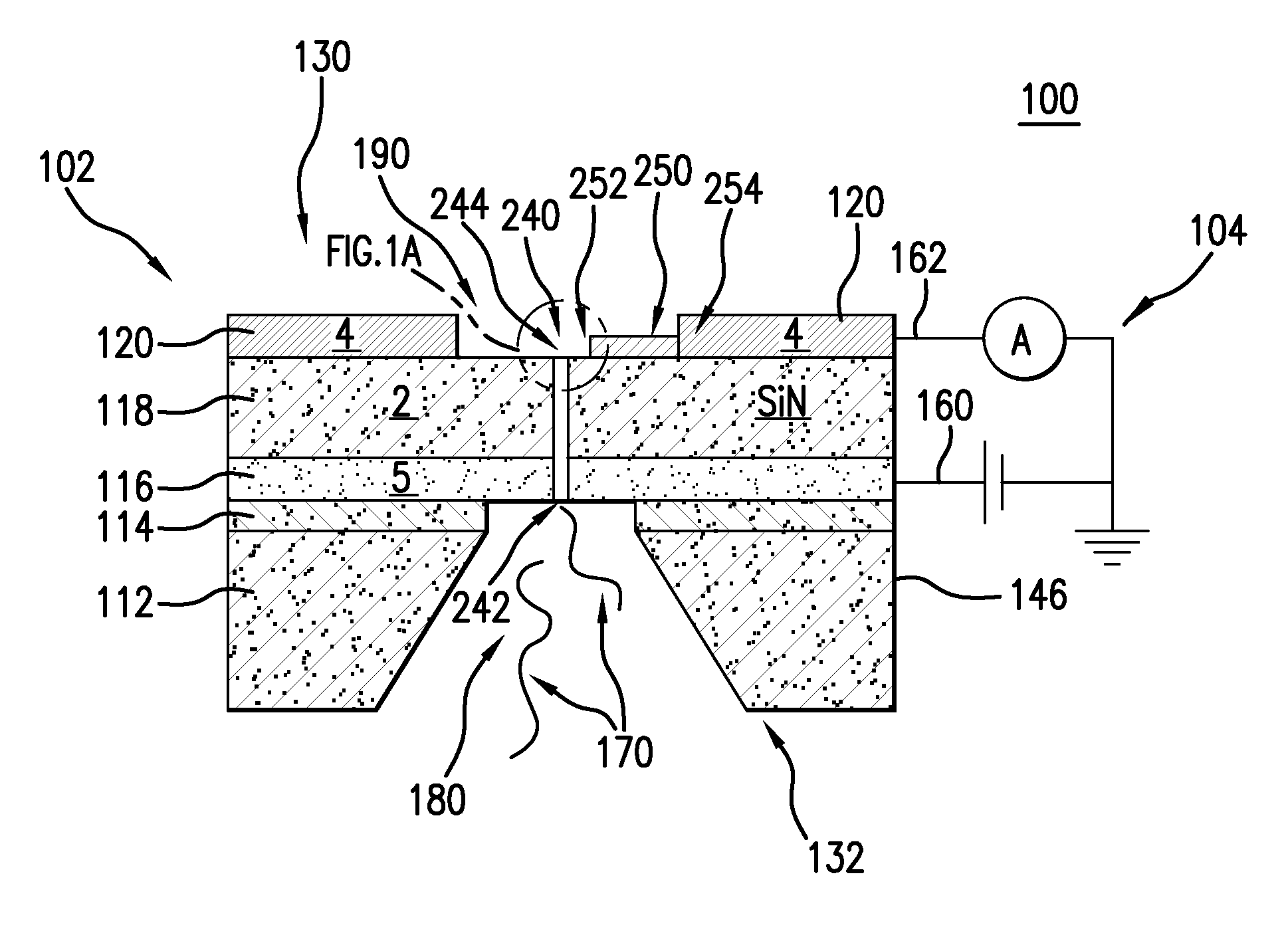
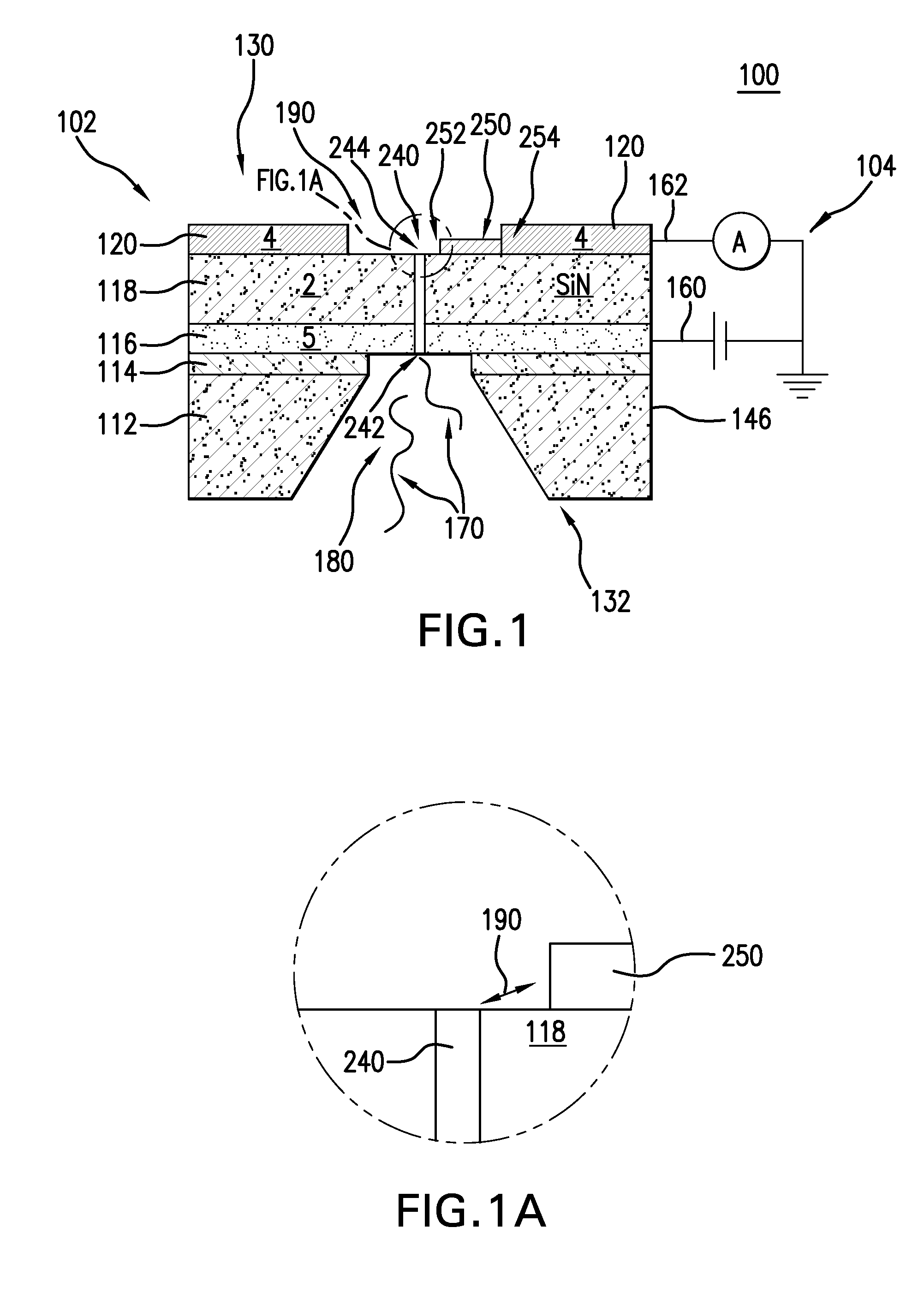
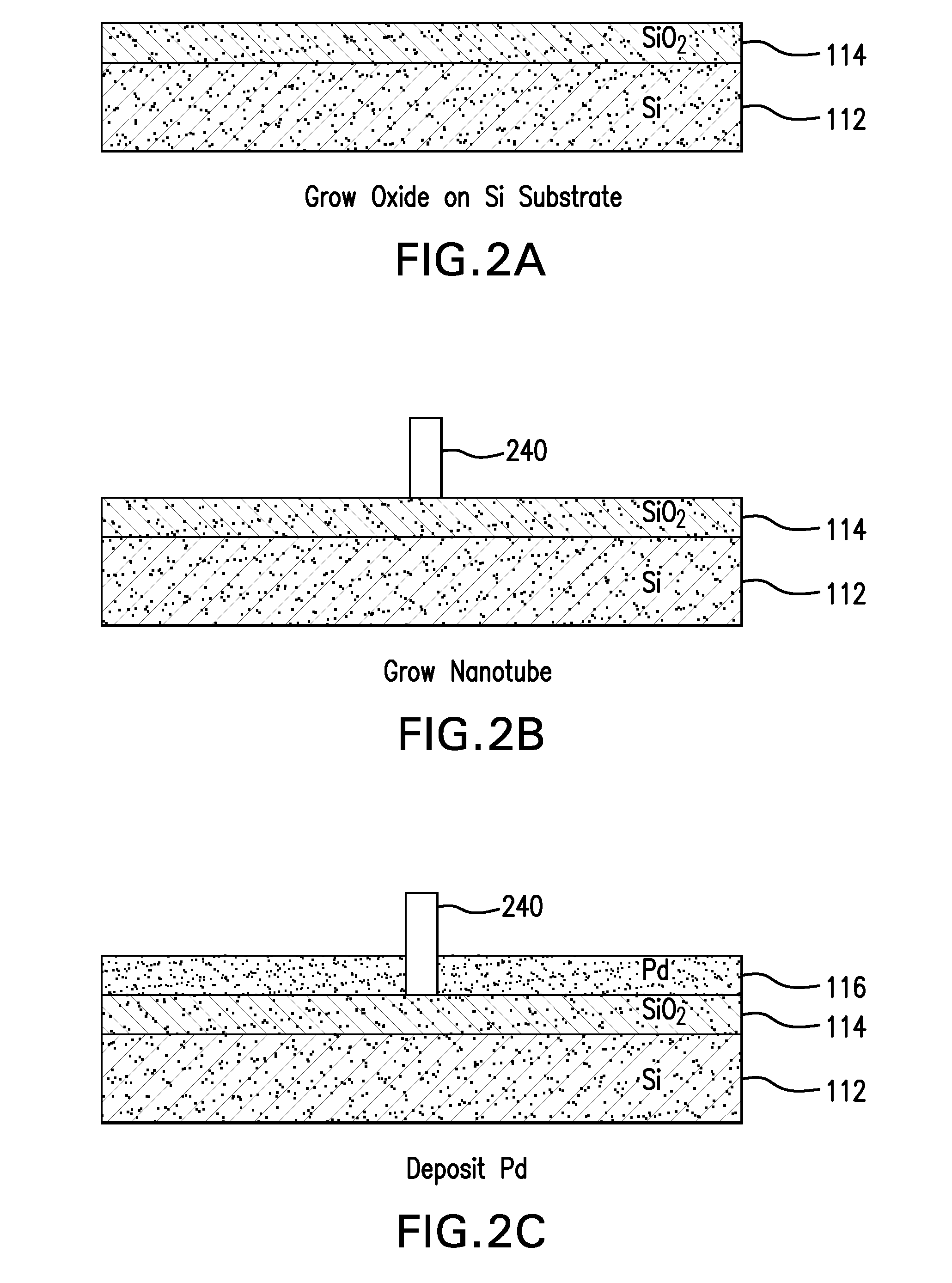
Nanopore and Carbon Nanotube Based DNA Sequencer and a Serial Recognition Sequencer
ActiveUS20110120868A1Volume/mass flow measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsBiopolymerDNA sequencer
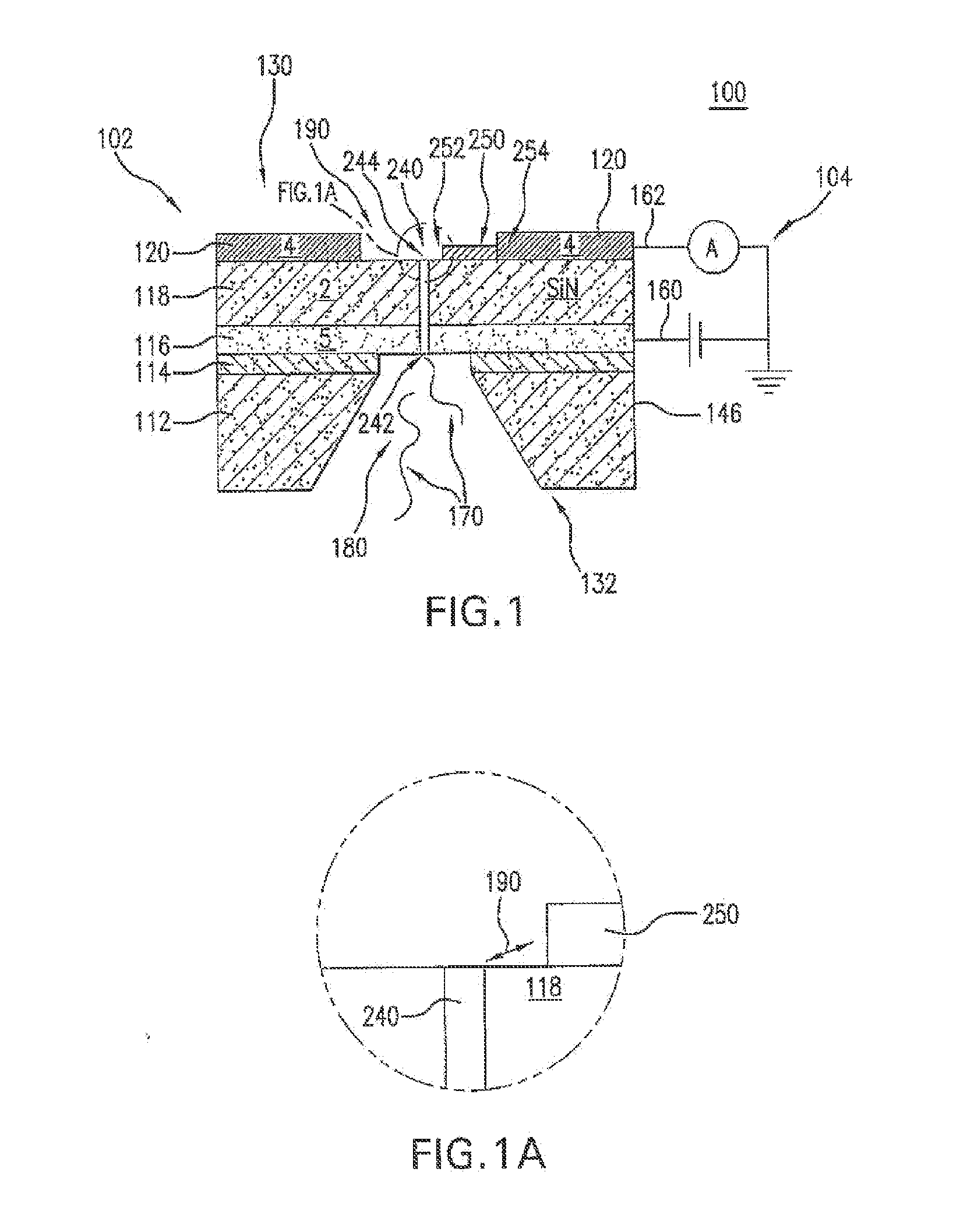
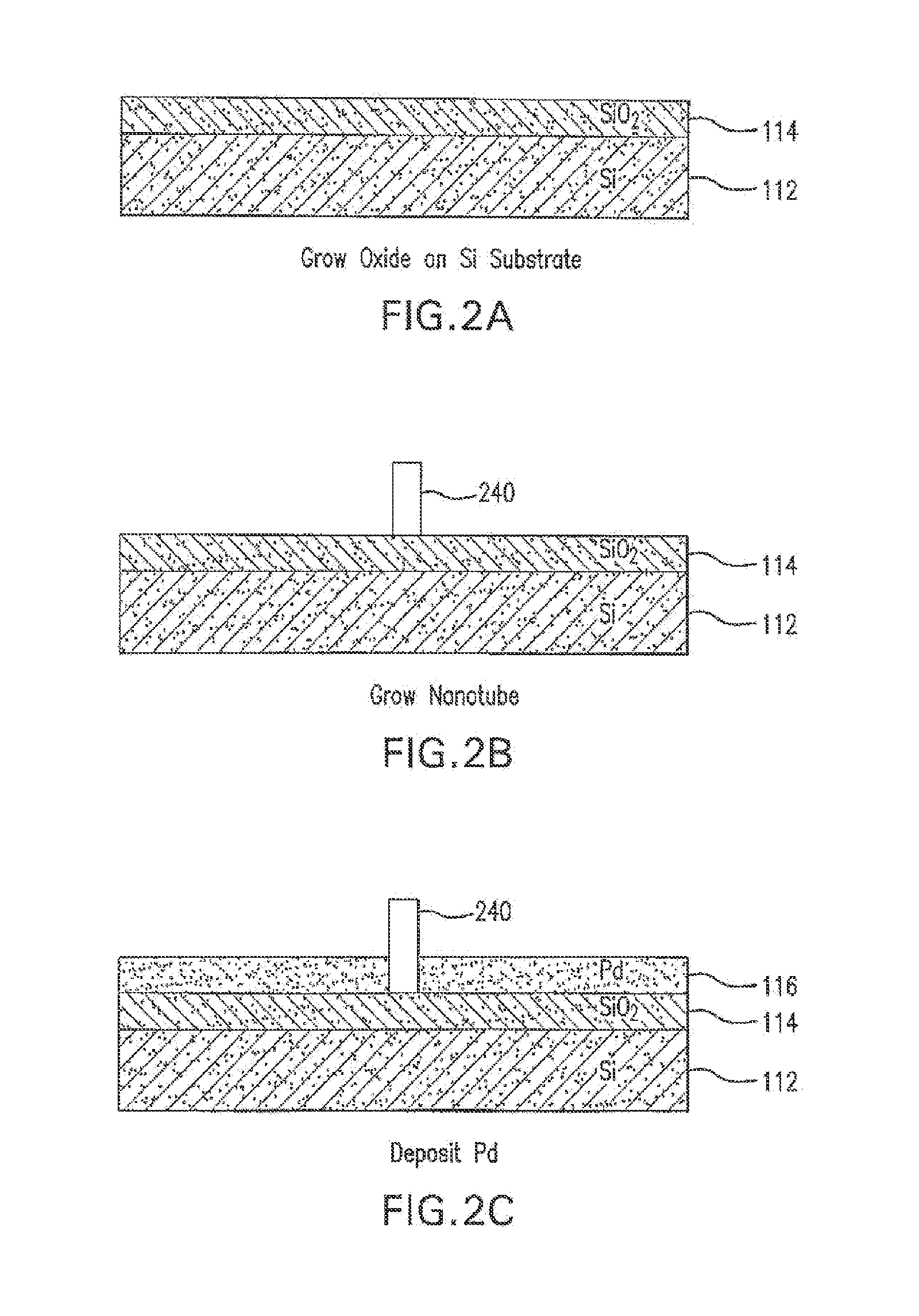
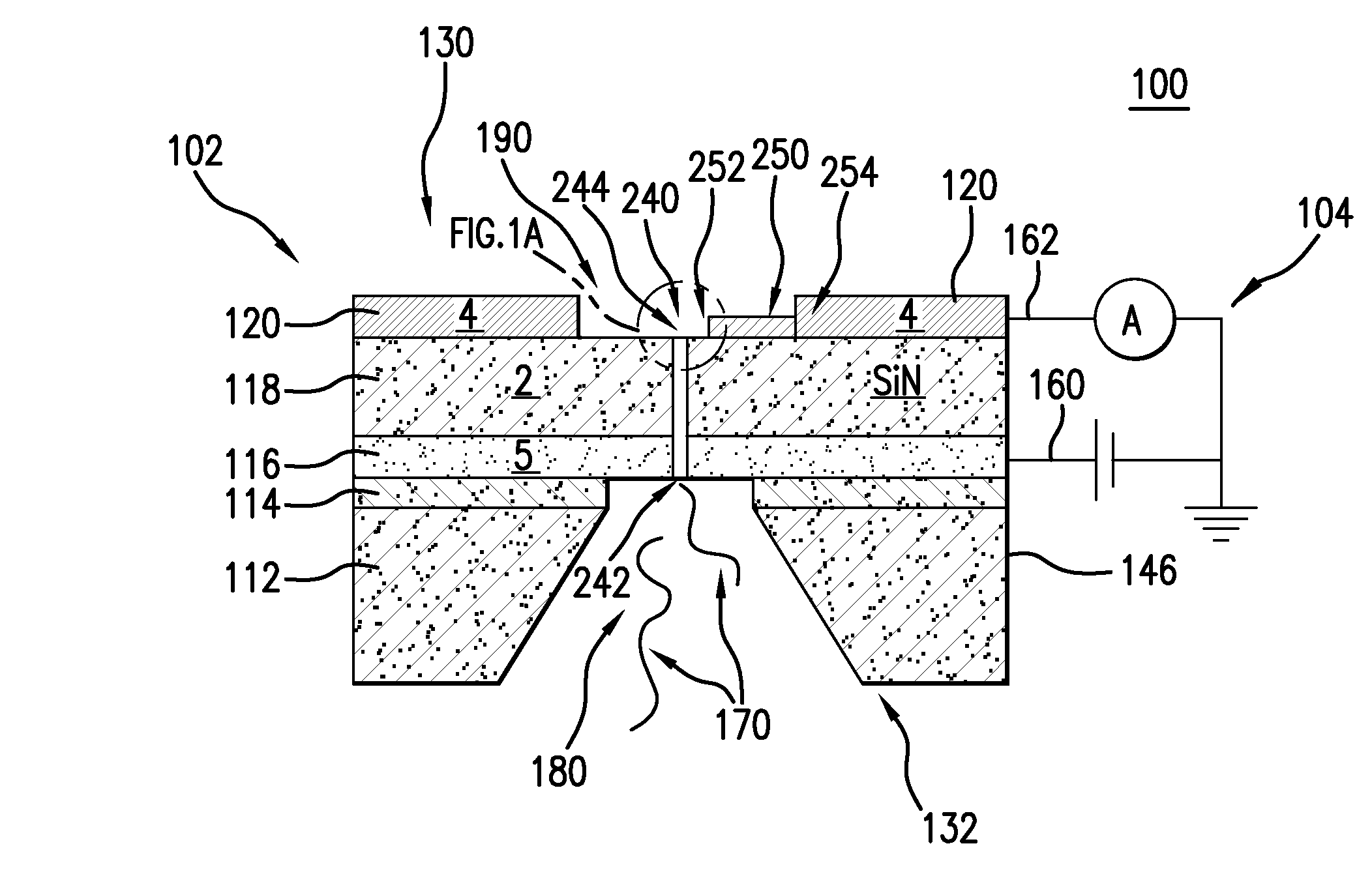
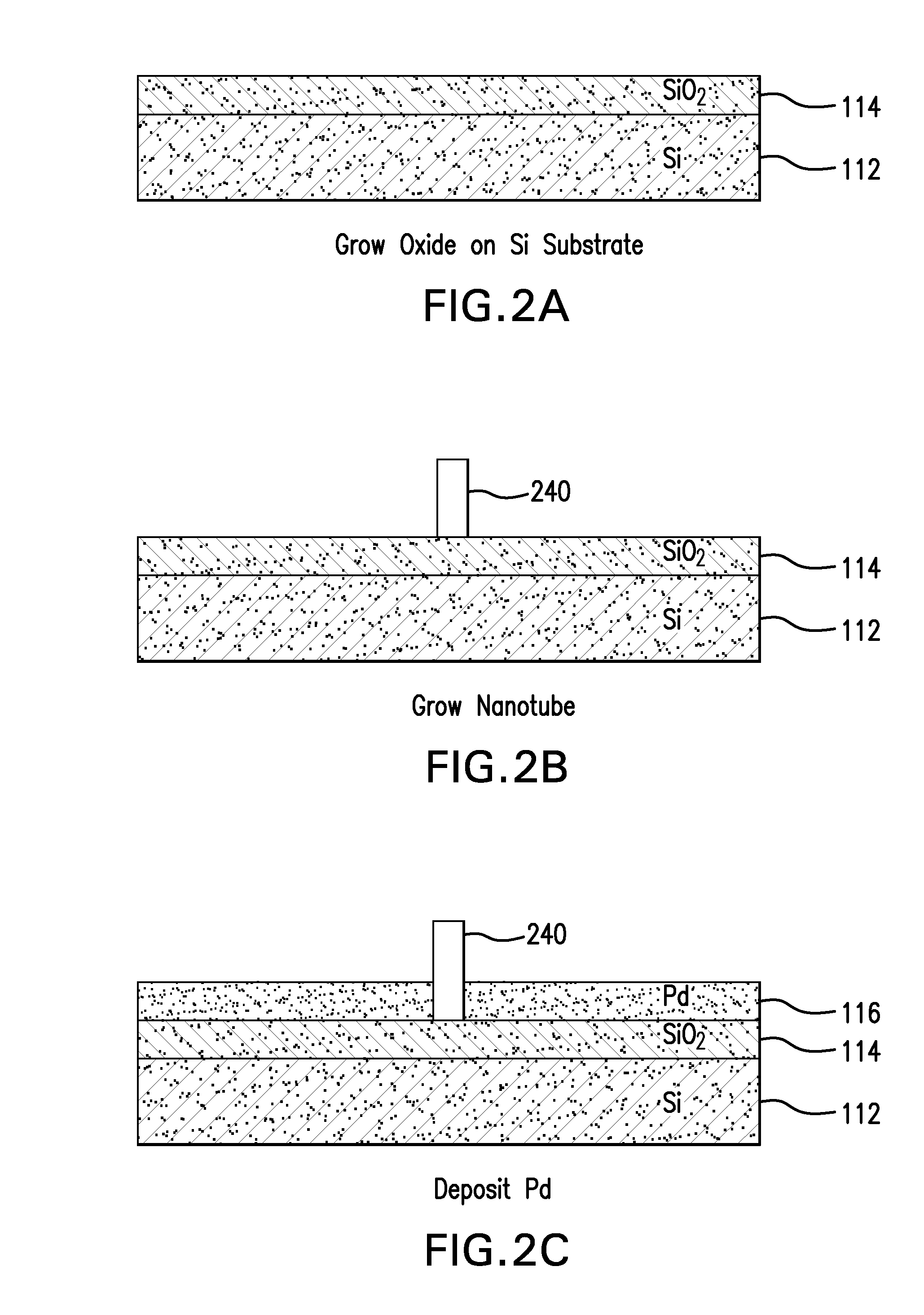
The present invention is directed to systems, devices and methods for identifying biopolymers, such as strands of DNA, as they pass through a constriction such as a carbon nanotube nanopore. More particularly, the invention is directed to such systems, devices and methods in which a newly translocated portion of the biopolymer forms a temporary electrical circuit between the nanotube nanopore and a second electrode, which may also be a nanotube. Further, the invention is directed to such systems, devices and methods in which the constriction is provided with a functionalized unit which, together with a newly translocated portion of the biopolymer, forms a temporary electrical circuit that can be used to characterize that portion of the biopolymer.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
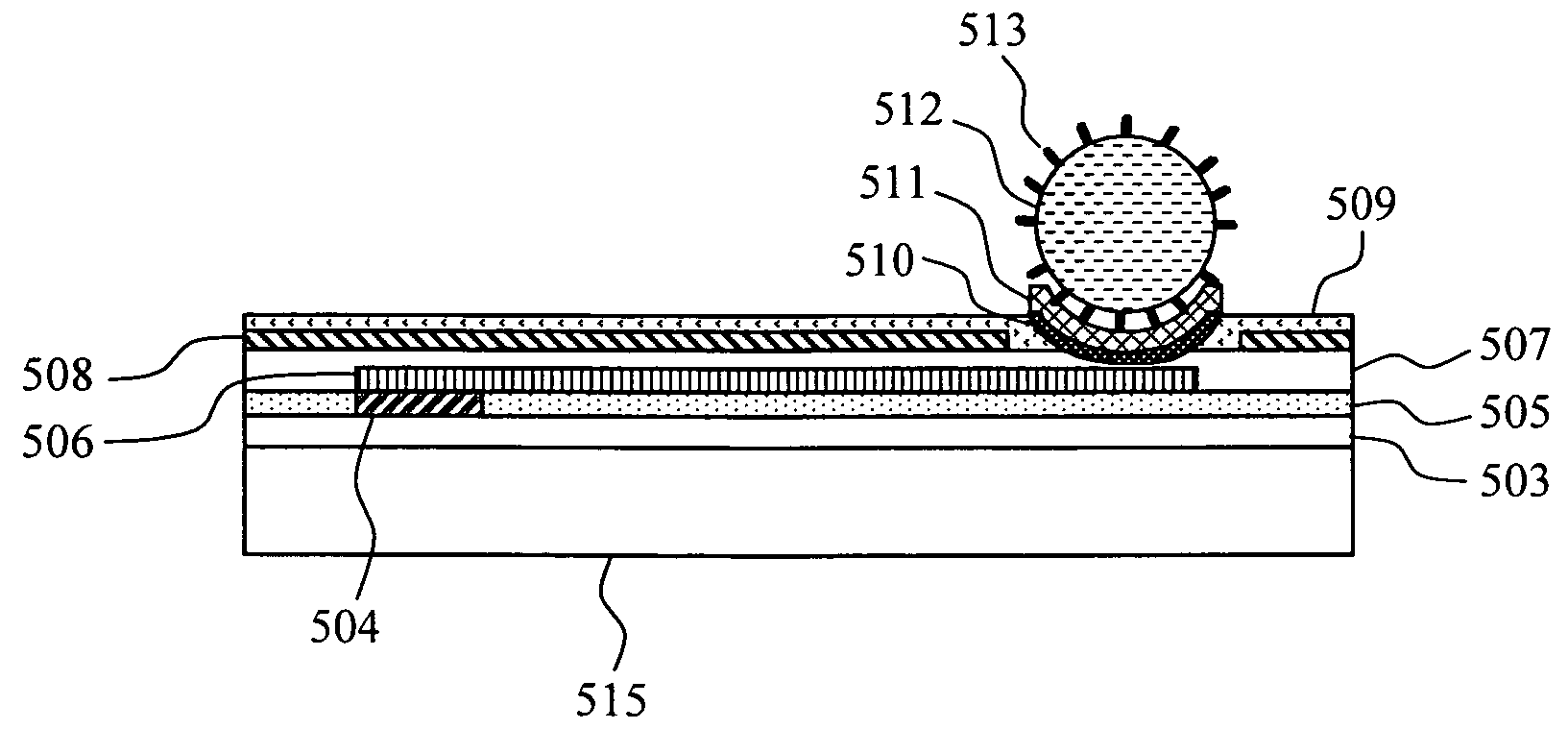
DNA measuring system and method
InactiveUS20080318243A1Suppress deterioration in reproducibility of measurementHigh-precision detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDNA sequencerA-DNA
The present invention provides a DNA sequencer using a FET sensor, capable of long-base decoding. Target DNAs are immobilized on the surfaces of spherical fine particles, the fine particles are disposed in the vicinity of metal electrodes each of which is connected electrically to a corresponding one of conductive wirings of the FET sensor and partly has a spherical surface capable of contacting with the fine particles, and the FET sensor detects a change in interfacial potential incident to an extension reaction of DNA molecules containing a hybridization of the target DNA and probe DNA.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Nanopore and Carbon Nanotube Based DNA Sequencer
The present invention provides a device for analyzing the composition of a heteropolymer comprising a carbon nanotube through which the heteropolymer is driven by electrophoresis. The carbon nanotube also serves as one electrode in a reading circuit. One end of the carbon nanotube is held in close proximity to a second electrode, and each end of the carbon nanotube is functionalized with flexibly-tethered chemical-recognition moieties, such that one will bind one site on the emerging polymer, and the second will bind another site in close proximity, generating an electrical signal between the two electrodes when the circuit is completed by the process of chemical recognition.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Methods and systems of DNA sequencing
ActiveUS20100160172A1Quick sortingImprovement in sequence determinationNucleotide librariesLibrary screeningDNA sequencerComputational biology
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Control system for DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequencer
ActiveCN102703314AImprove sequencing efficiencyTimely and accurate supplyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPeristaltic pumpControl signal
The invention discloses a control system for a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequencer, which comprises a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), controllers of first and second servo motors, first and second peristaltic pumps and driving motors of first and second multipass reversing valves, wherein the controllers of the first and second servo motors are electrically connected with the PLC; the first and second peristaltic pumps are respectively and electrically connected with the PLC and are used for receiving control signals of the PLC; a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera is electrically connected with the PLC and is used for receiving a control signal of the PLC; and a plurality of sensors are respectively and electrically connected with the PLC and are used for sending position signals of the CCD camera to the PLC. According to the control system disclosed by the invention, a reagent supply assembly of the DNA sequencer with a plurality of reaction bins timely and accurately supplies reagents and buffer solution for a plurality of reaction bins and the CCD camera can be ensured to timely read an optical signal in each reaction bin, and therefore, the aim of simultaneously performing a plurality of reactions is fulfilled, so that a plurality of samples can be simultaneously sequenced and the DNA sequencing efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION +1
Methods for nucleic acid mapping and identification of fine-structural-variations in nucleic acids
ActiveUS20090325239A1Quick buildEfficient sortingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid mappingA-DNA
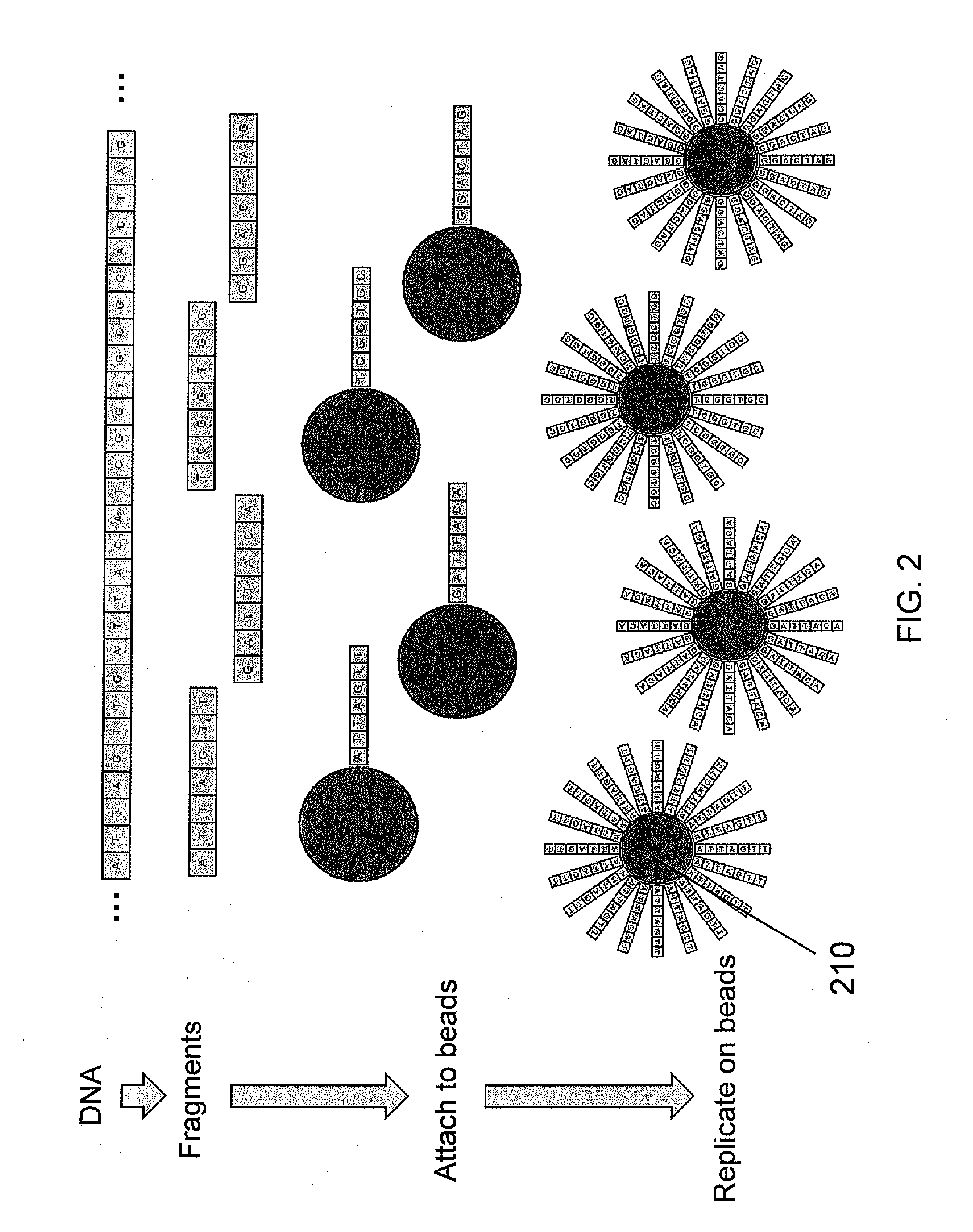
A method of juxtaposing sequence tags (GVTs) that are unique positional markers along the length of a population of target nucleic acid molecules is provided, the method comprising: fragmenting the target nucleic acid molecule to form target DNA insert; ligating the target DNA insert to a DNA vector or backbone to create a circular molecule; digesting the target DNA insert endonuclease to cleave the target DNA insert at a distance from each end of the target DNA insert yielding two GVTs comprising terminal sequences of the target DNA insert attached to an undigested linear backbone; recircularizing the linear backbone with the attached GVTs to obtain a circular DNA containing a GVT-pair having two juxtaposed GVTs; and recovering the GVT-pair DNA by nucleic acid amplification or digestion with endonuclease having sites flanking the GVT-pair. Cosmid vectors are provided for creating GVT-pairs of ˜45- to 50-kb separation sequencable by next-generation DNA sequencers.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Nanopore and Carbon Nanotube Based Dna Sequencer and A Serial Recognition Elements
The present invention is directed to systems, devices and methods for identifying biopolymers, such as strands of DNA, as they pass through a constriction such as a carbon nanotube nanopore. More particularly, the invention is directed to such systems, devices and methods in which a newly translocated portion of the biopolymer forms a temporary electrical circuit between the nanotube nanopore and a second electrode, which may also be a nanotube. Further, the invention is directed to such systems, devices and methods in which the constriction is provided with a functionalized unit which, together with a newly translocated portion of the biopolymer, forms a temporary electrical circuit that can be used to characterize that portion of the biopolymer.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Nanopore and carbon nanotube based DNA sequencer
The present invention provides a device for analyzing the composition of a heteropolymer comprising a carbon nanotube through which the heteropolymer is driven by electrophoresis. The carbon nanotube also serves as one electrode in a reading circuit. One end of the carbon nanotube is held in close proximity to a second electrode, and each end of the carbon nanotube is functionalized with flexibly-tethered chemical-recognition moieties, such that one will bind one site on the emerging polymer, and the second will bind another site in close proximity, generating an electrical signal between the two electrodes when the circuit is completed by the process of chemical recognition.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
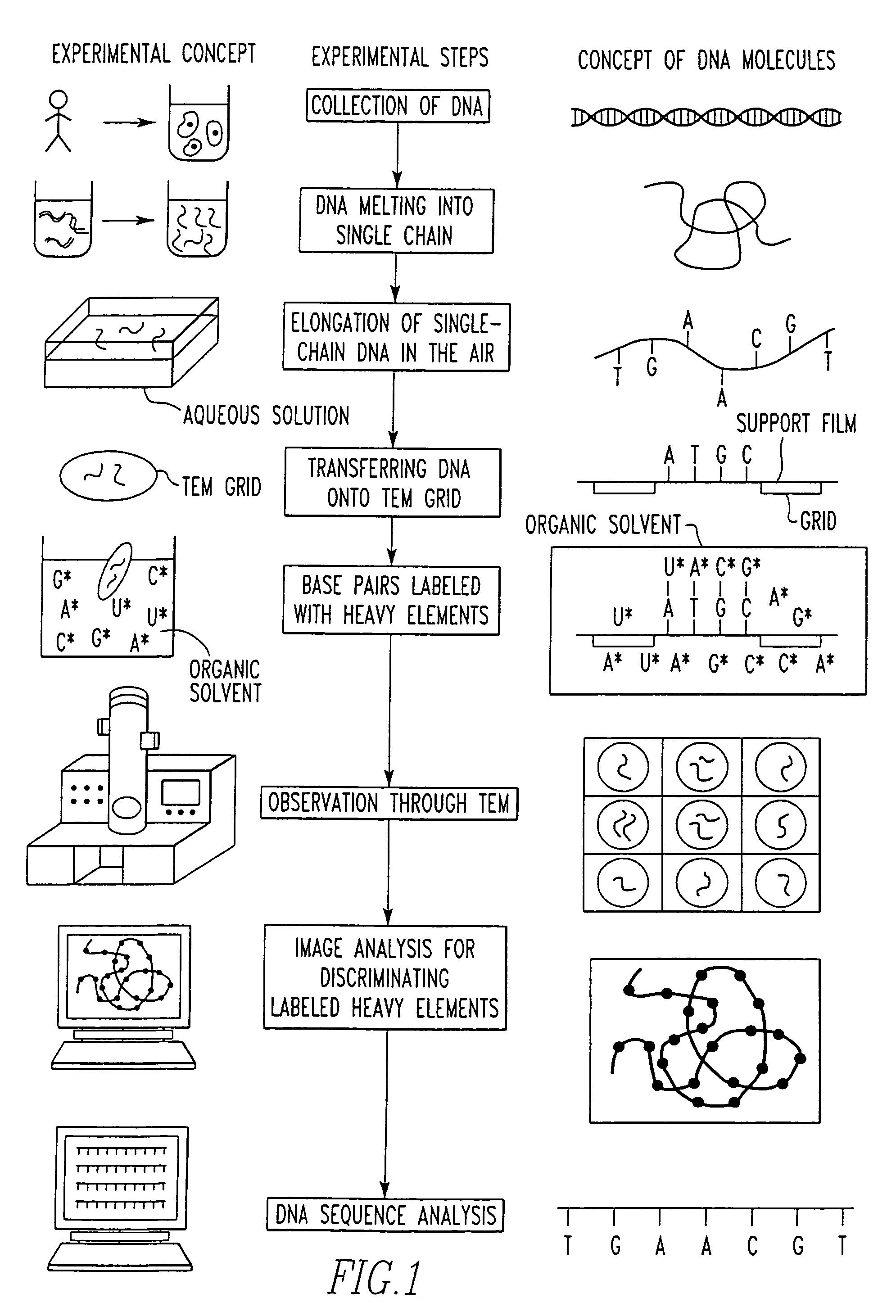
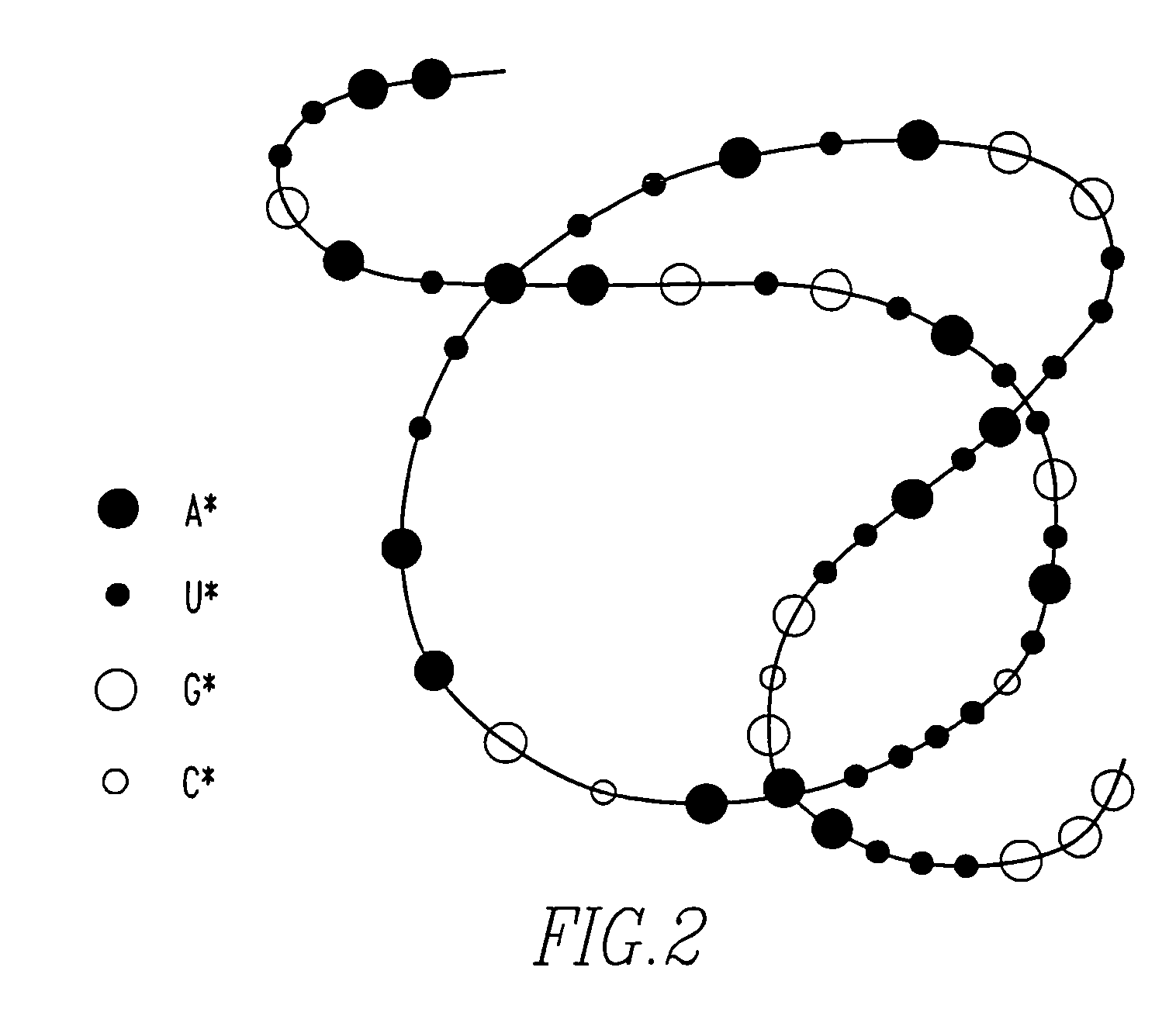
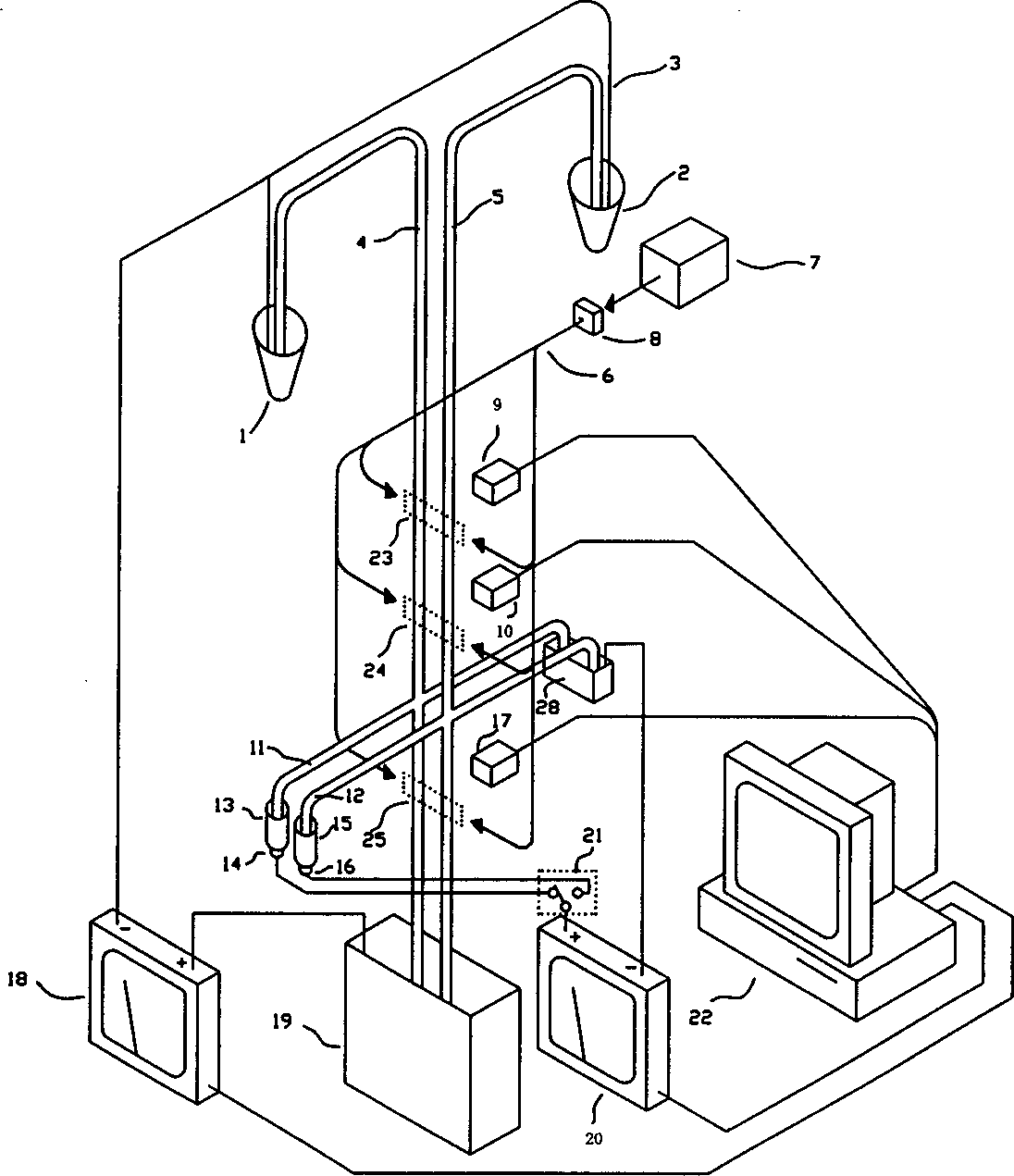
Method of determining base sequence of DNA or RNA using heavy element labeling and imaging by transmission electron microscopy
InactiveUS7332284B2Accurate analysisRemove overlapBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrophoresisDNA sequencer
Novel DNA sequence determination method and DNA sequencer system providing a sequencing speed 103 to 104 times faster than the current DNA sequencing speed (105 bases per day with a lane at maximum) of the existing DNA sequencer based on electrophoresis. The method includes the step of discriminating base-specific labels of heavy elements using a magnified image of elongated single-chain DNA or RNA produced by a transmission electron microscope (TEM). The DNA sequencer system uses this method. The invention provides a DNA sequencing speed that is higher than the existing speed by 3 or 4 orders of magnitude.
Owner:NAGAYAMA IP HLDG
Collector for nucleic acid analysis and its application method
InactiveCN1364940AAutomate analysisRealize automatic collectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA sequencerBioinformatics
The present invention is a kind of collector for nucleic acid analysis and its application method. The collector consists of an integral double-path capillary with sample analyzing path and sample collecting path, three detecting windows in the analyzing path and a sample collecting pipe. The collector is used in automatic fast analysis of nucleic acid segment and high percision and high purity automatic fast collection of different nucleic acid band. The collector has unique structure, and can be used through combining with traditional capillary nucleic acid nucleic acijd analysis technology, such as DNA sequencing instrument technology.
Owner:SHANDONG TUMOR HOSPITAL
Particle sizer and DNA sequencer
InactiveUS6942773B1Ensure sufficient separationEasy to separateSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementFluorescenceElectrophoresis
An electrophoretic device separates and detects particles such as DNA fragments, proteins, and the like. The device has a capillary which is coated with a coating with a low refractive index such as Teflon® AF. A sample of particles is fluorescently labeled and injected into the capillary. The capillary is filled with an electrolyte buffer solution. An electrical field is applied across the capillary causing the particles to migrate from a first end of the capillary to a second end of the capillary. A detector light beam is then scanned along the length of the capillary to detect the location of the separated particles. The device is amenable to a high throughput system by providing additional capillaries. The device can also be used to determine the actual size of the particles and for DNA sequencing.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
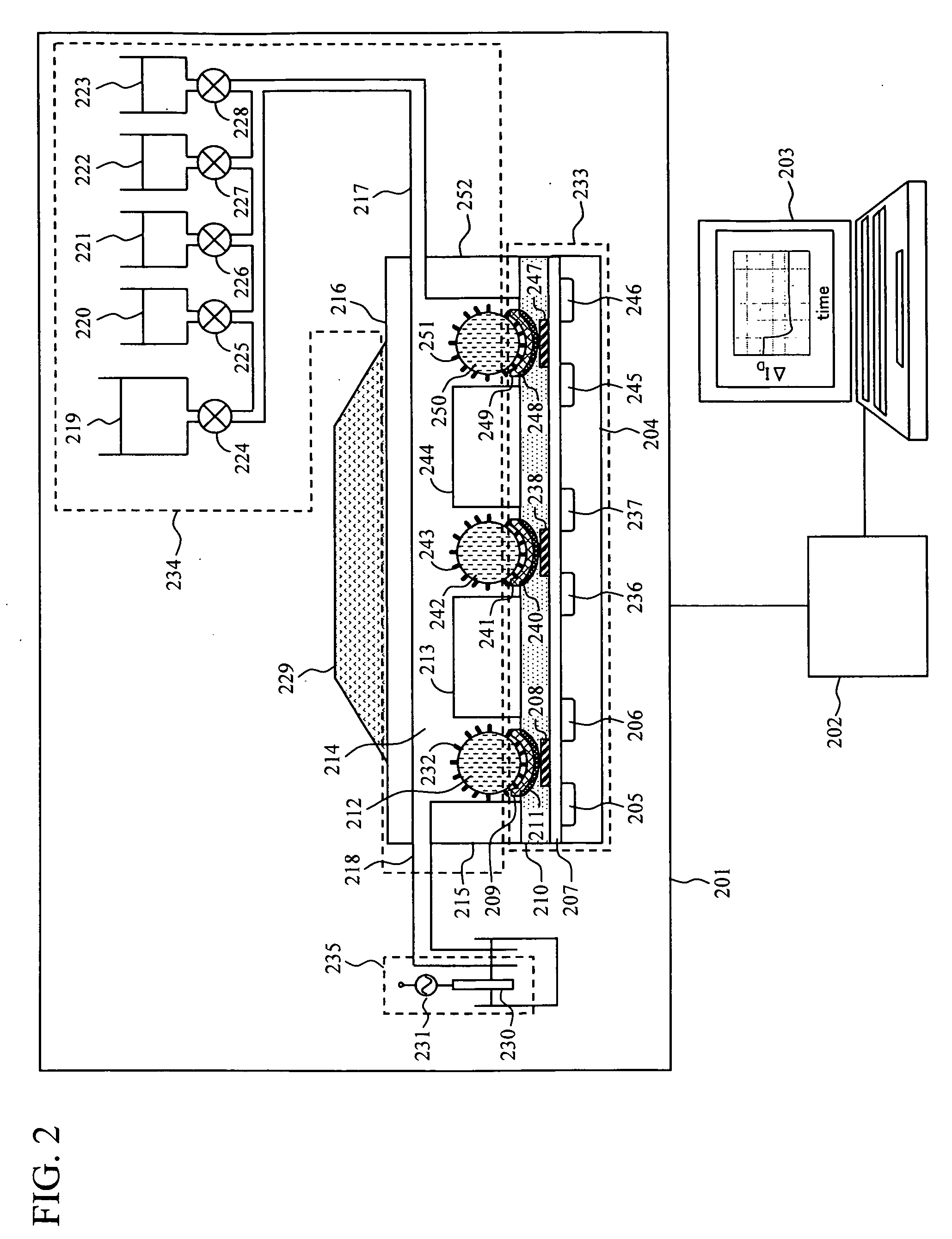
Reagent supply system for DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequencer and control method
ActiveCN102707078AImprove sequencing efficiencyTimely and accurate supplyMaterial analysisPeristaltic pumpDNA sequencer
The invention discloses a reagent supply system for a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequencer. The reagent supply system comprises a preparing pipeline, a buffer pipeline, a main pipeline, a first multi-pass reversing valve, a second multi-pass reversing valve, a first peristaltic pump for extracting a sequencing reaction reagent and a second peristaltic pump for extracting buffer liquid, wherein the preparing pipeline, the buffer pipeline and the main pipeline are connected through a tee connector, inlets of the first multi-pass reversing valve are respectively communicated with reagent bottles; an outlet of the first multi-pass reversing valve is connected with the preparing pipeline through the first peristaltic pump; an outlet of the second peristaltic pump is connected with the buffer pipeline; an inlet of the second multi-pass reversing valve is connected with the main pipe, and outlets of the second multi-pass reversing valve are respectively communicated with a liquid inlet of areaction cabin and a waste liquor bucket. The invention also discloses a control method of the reagent supply system. According to the reagent supply system disclosed by the invention, the reagent and buffer liquid can be immediately and accurately supplied to a plurality of reaction cabins, so a plurality of reactions are carried out at the same time, a plurality of samples can be sequenced at the same time, and the sequencing efficiency of the DNA is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION +1
Methods and systems of DNA sequencing
ActiveUS8407012B2Improve base calling procedureShorten the lengthGeneral purpose stored program computerBiological testingDNA sequencerComputational biology
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Detection device and detection system
InactiveCN101560564AAccurate identification of inspection workLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsProgramming languageDNA sequencer
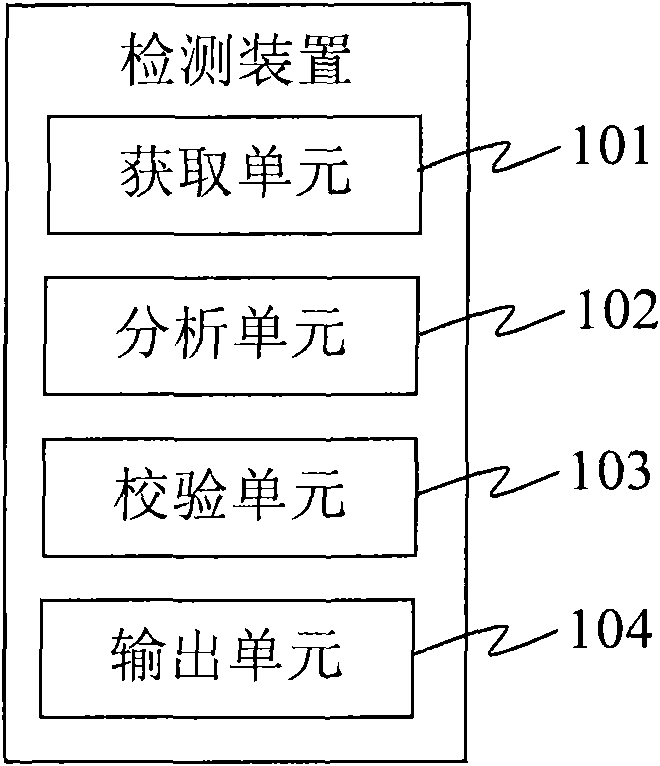
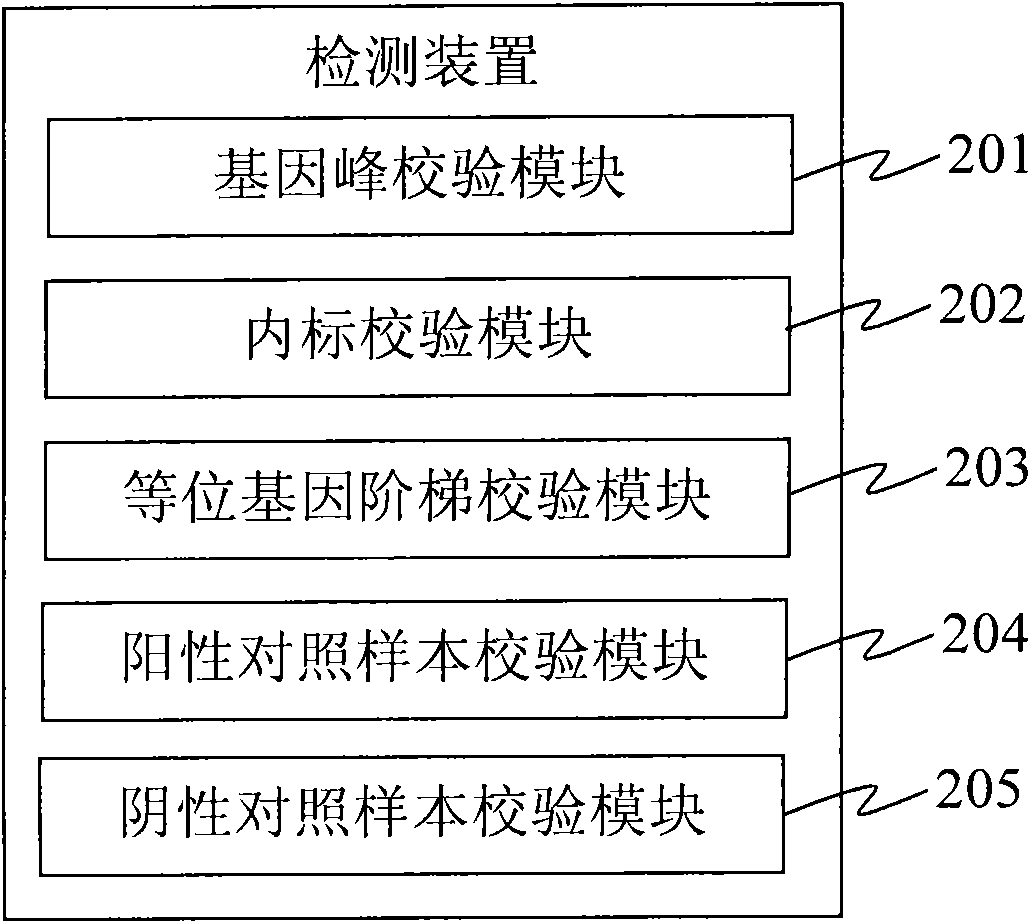
The invention provides a detection device and a detection system. The detection device comprises an acquisition unit, an analysis unit, a check unit and an output unit, wherein the acquisition unit is used for acquiring DNA sample data which is generated by sampling through a DNA sequencer; the analysis unit is used for performing short tandem repeat sequence analysis on the DNA sample data and generating analysis result data; the check unit is used for checking the DNA sample data, verifying whether the DNA sample data has errors, and generating check result data; and the output unit is used for outputting the analysis result data and corresponding check result data. The detection device replaces the manual check process so as to efficiently and accurately finish the identification check work for the identification result and omit the process for analyzing and outputting the short tandem repeat sequence for the DNA sample data with poor check result, and reduces the cost.
Owner:北京华生恒业科技有限公司 +1
Method and apparatus for image processing for massive parallel DNA sequencing
InactiveUS20110007981A1Increase speedImprove accuracyImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPattern recognitionPoint spread
Owner:LEVEL SET SYST
Methods for nucleic acid mapping and identification of fine-structural-variations in nucleic acids
ActiveUS8329400B2Quick buildEfficient sortingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNADigestion
A method of juxtaposing sequence tags (GVTs) that are unique positional markers along the length of a population of target nucleic acid molecules is provided, the method comprising: fragmenting the target nucleic acid molecule to form target DNA insert; ligating the target DNA insert to a DNA vector or backbone to create a circular molecule; digesting the target DNA insert endonuclease to cleave the target DNA insert at a distance from each end of the target DNA insert yielding two GVTs comprising terminal sequences of the target DNA insert attached to an undigested linear backbone; recircularizing the linear backbone with the attached GVTs to obtain a circular DNA containing a GVT-pair having two juxtaposed GVTs; and recovering the GVT-pair DNA by nucleic acid amplification or digestion with endonuclease having sites flanking the GVT-pair. Cosmid vectors are provided for creating GVT-pairs of ˜45- to 50-kb separation sequencable by next-generation DNA sequencers.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Method for DNA sequencer to reattach short sequence to genome
InactiveCN102453751AReduce running timeMeet the requirement of 100% recall rateMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsDNA sequencerA-DNA
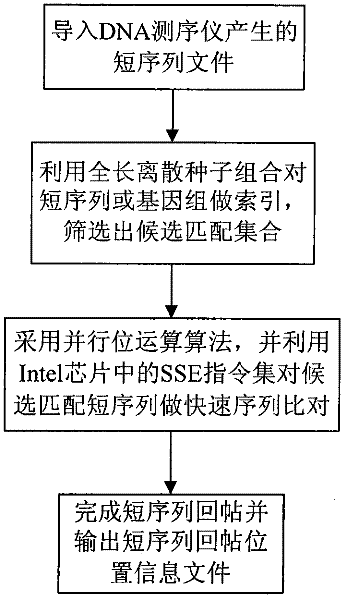
The invention belongs to a method for processing DNA sequencing data. In order to improve the efficiency of reattaching a short sequence to genome, the invention provides a method for a DNA sequencer to reattach a short sequence to genome. 100% recall ratio can be ensured by giving an optimized overall length discrete seed combination, and meanwhile, the efficiency of data processing is improved.
Owner:DINGSHENG TECH BEIJING
Collector for nucleic acid analysis and its application method
InactiveCN1138862CAutomate analysisRealize automatic collectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA sequencerBioinformatics
The present invention is a kind of collector for nucleic acid analysis and its application method. The collector consists of an integral double-path capillary with sample analyzing path and sample collecting path, three detecting windows in the analyzing path and a sample collecting pipe. The collector is used in automatic fast analysis of nucleic acid segment and high percision and high purity automatic fast collection of different nucleic acid band. The collector has unique structure, and can be used through combining with traditional capillary nucleic acid nucleic acijd analysis technology, such as DNA sequencing instrument technology.
Owner:SHANDONG TUMOR HOSPITAL
Semiautomated method for finger-printing bacterial DNA
InactiveUS6395475B1Result is obtainedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide primersBiology
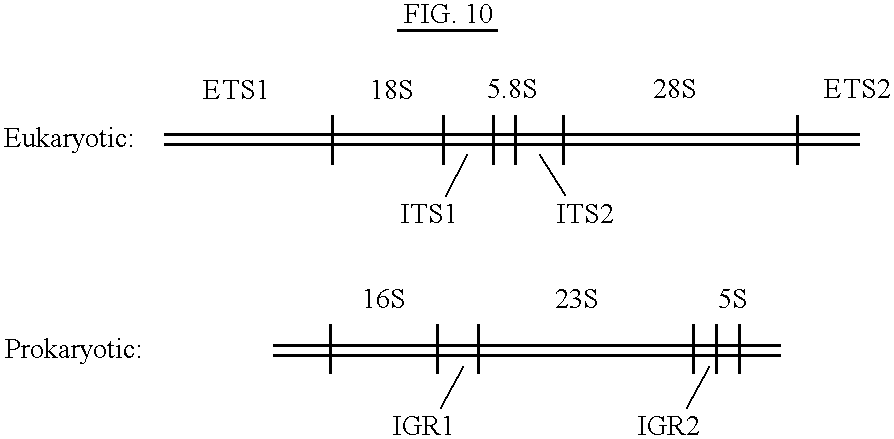
Methods and kits for typing prokaryotes and eukaryotes are disclosed. A specific DNA fragment in the rRNA intergene region is amplified by PCR using two universal oligonucleotide primers. The labeled PCR product is cleaved with a variety of restriction endonucleases and electrophoresed on an automated DNA sequencer. The methods and kits are beneficial in, for example, a clinical laboratory because they allow for rapid strain identification of pathogenic bacteria. The DNA fingerprinting methods and kits of the present invention are more definitive, since genomic bacterial DNA is used. One advantage of the methods of the present invention is the speed with which results are obtained. For example, a preliminary screen by agarose gel electrophoresis of a PCR product can be completed five to six hours after receiving hospital isolates. The preliminary screen can then be confirmed in approximately 24 hours by RFLP analysis on an automated sequencer. The speed of the methods of the present invention provide infection control personnel with adequate information to contain and prevent the spread of nosocomial infections, rather than having analyses done retrospectively.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIVERSITY
System for DNA Identification Hiding Personal Traits
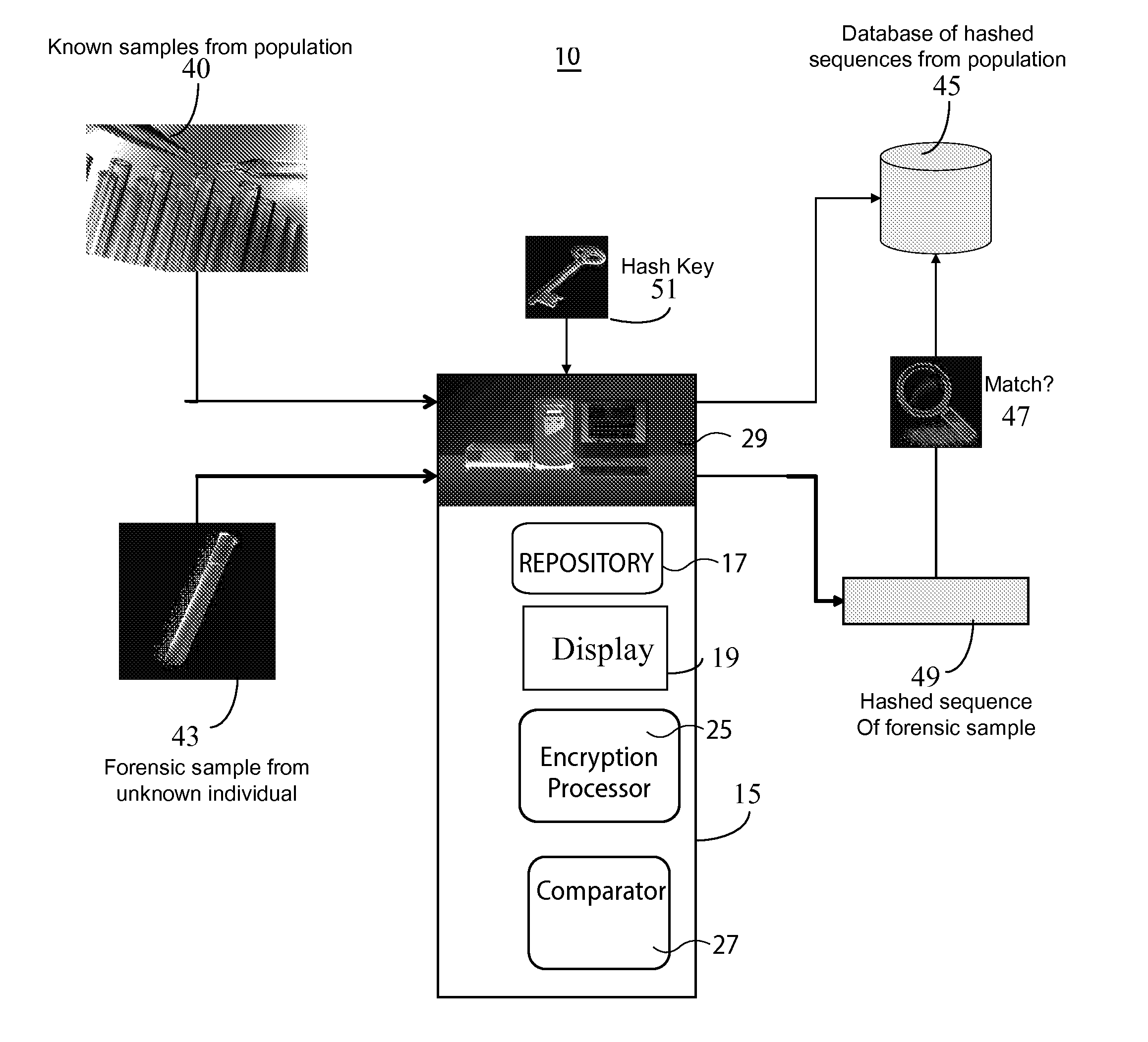
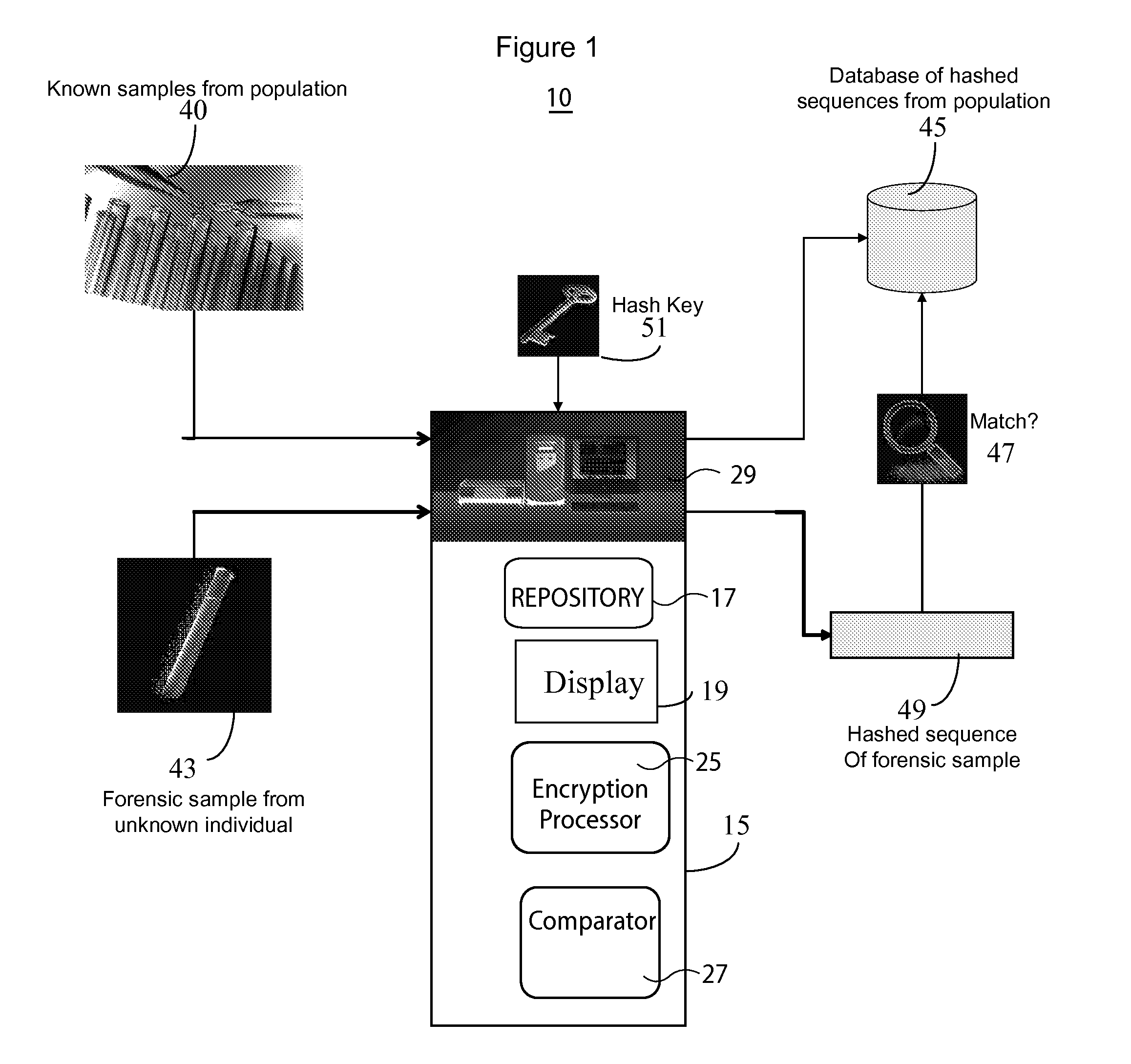
InactiveUS20130266135A1Microbiological testing/measurementComputer security arrangementsGeneticsDNA sequencer
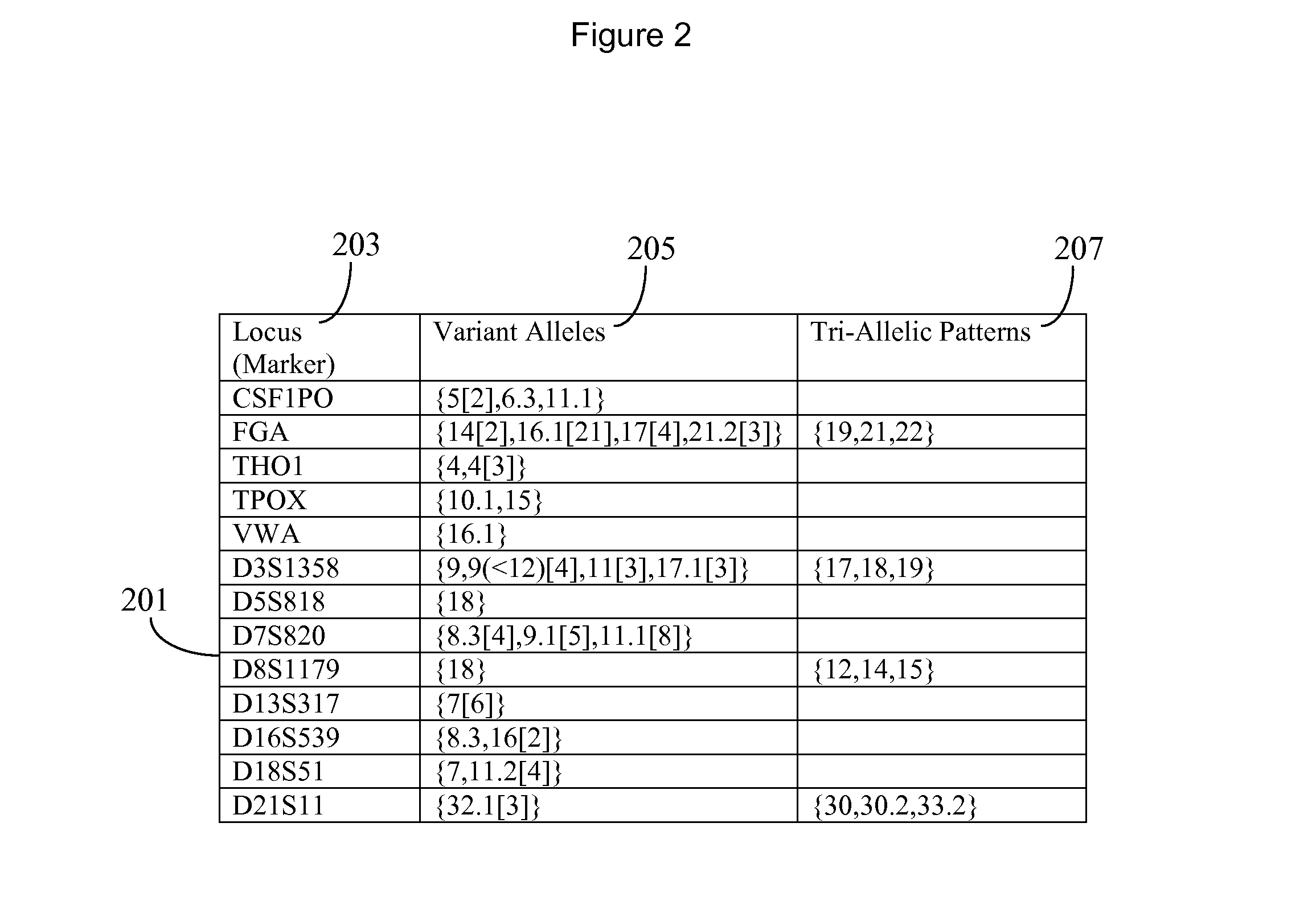
A system for DNA sequence identification hides personal and medical characteristics. A DNA sequencer processes a biological sample to provide genetic data identifying biological sample genetic marker variations of multiple different markers from corresponding reference markers. An encoding processor one way encrypts the genetic data into an encrypted code using an encryption key. A comparator compares the encrypted code with multiple encrypted codes retrieved from storage to identify a match and biological sample source. The multiple encrypted codes are derived by encrypting genetic data of multiple different biological samples using the encryption key and the multiple different biological samples are associated with corresponding identifiers of their respective biological sample sources.
Owner:CERNER INNOVATION
High speed DNA sequencer and method
InactiveUS20060188899A1Large separationMinimize collisionTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsMass spectrometryDNA sequencer
This invention relates to a device for the determination of the sequence of nucleic acids and other polymeric or chain type molecules. Specifically, the device analyzes a sample prepared by incorporating fluorescent tags at the end of copies of varying lengths of the sample to be sequenced. The sample is then vaporized, charged and accelerated down an evacuated chamber. The individual molecules of the sample are accelerated to different velocities because of their different masses, which cause the molecules to be sorted by length as they travel down the evacuated chamber. Once sorted, the stream of molecules is illuminated causing the fluorescent tags to emit light that is picked up by a detector. The output of the detector is then processed by a computer to yield of the sequence of the sample under analysis. The present invention improves over the prior art by using photo-detection of the individual molecules instead of measuring the time of flight to a detector that measure collisions. Unlike mass spectrometry, the method of the present invention does not require the extreme sensitivity required to differentiate between very small mass differences in large molecules. The present invention is therefore more robust than the prior art and well suited for extremely high throughput sequencing of large nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:DEWALCH TECH INC
Mutant sequence analyzer
InactiveUS20050164198A1Efficiently obtainedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOptical signal transducersClip seqSequence database
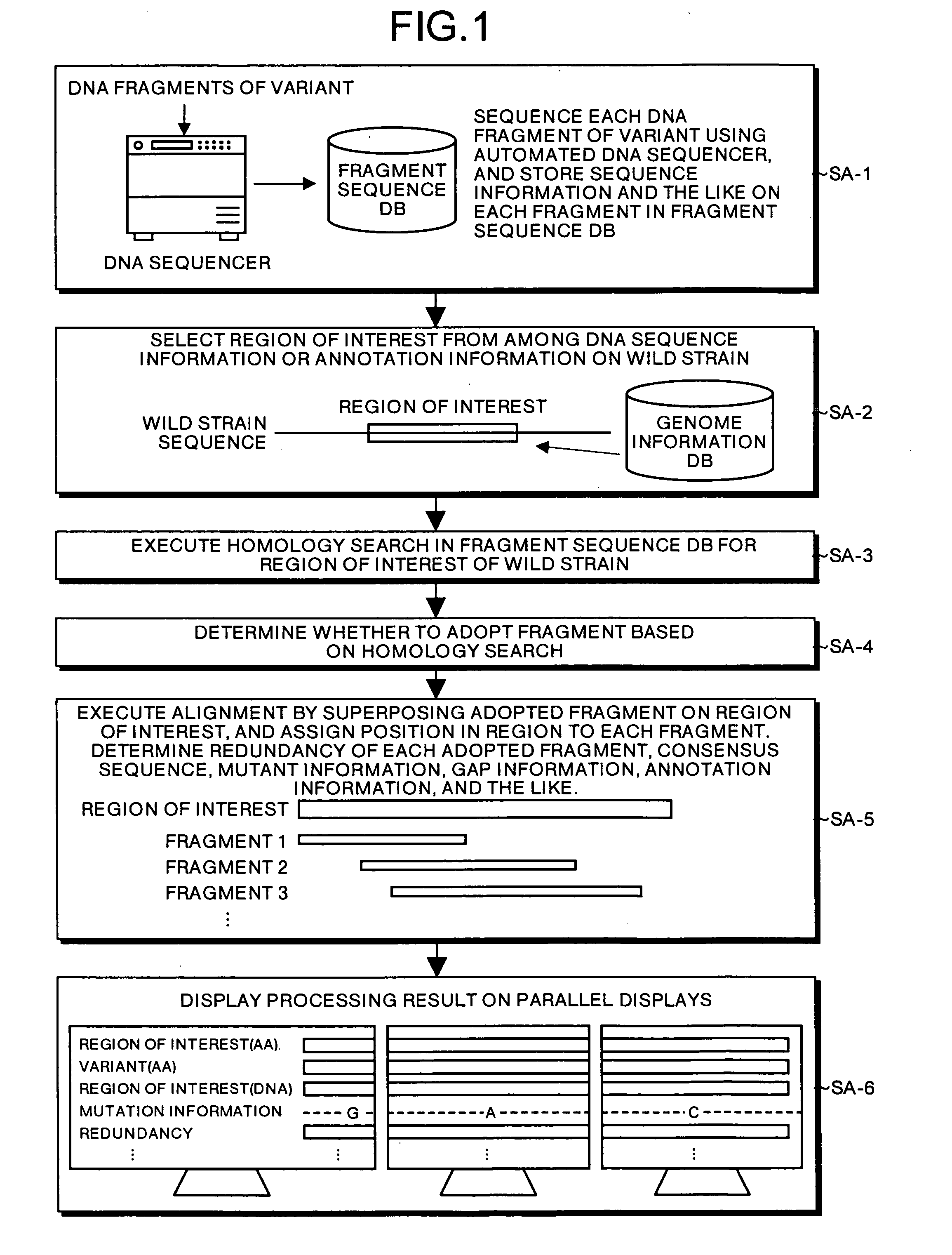
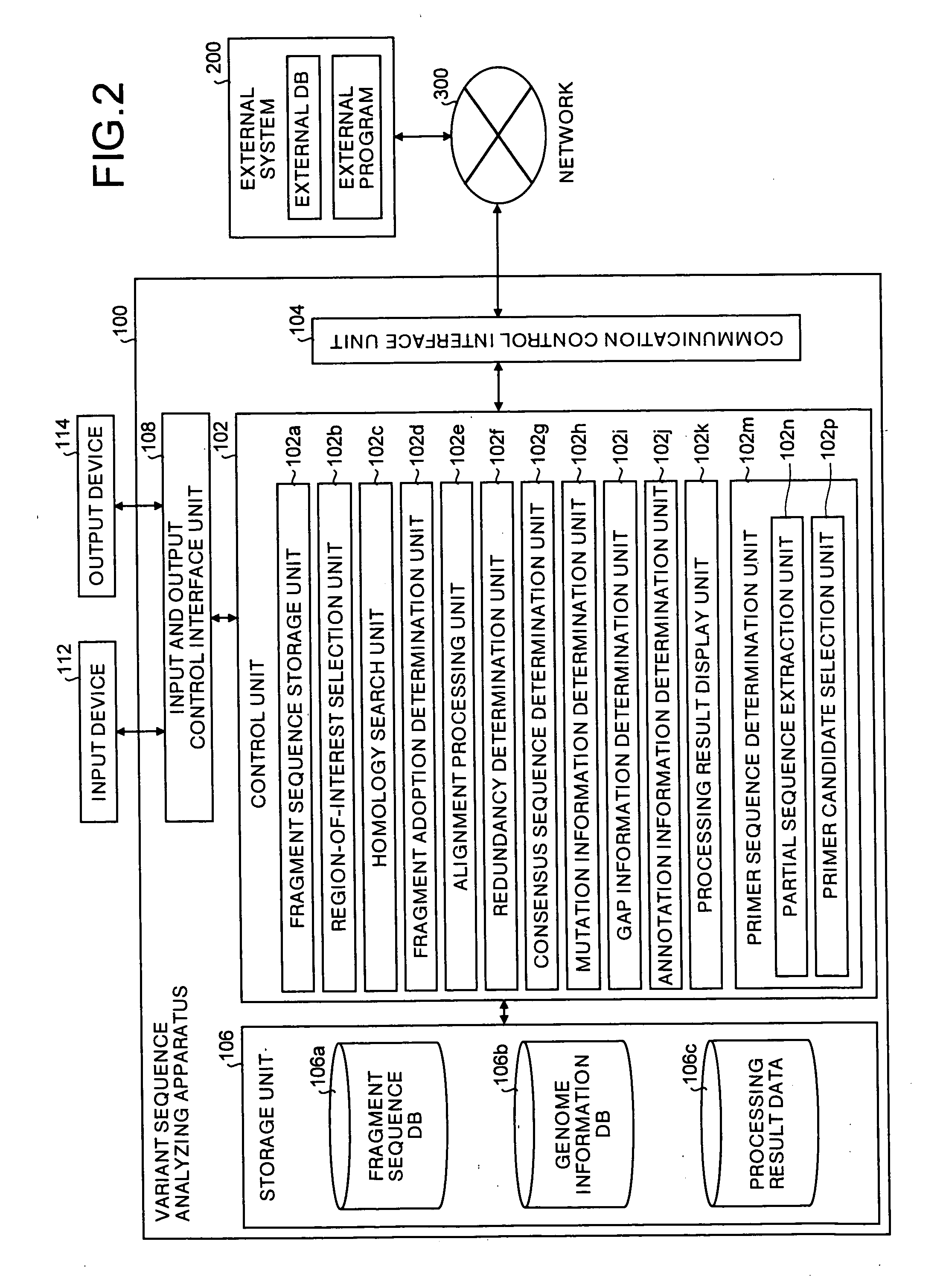
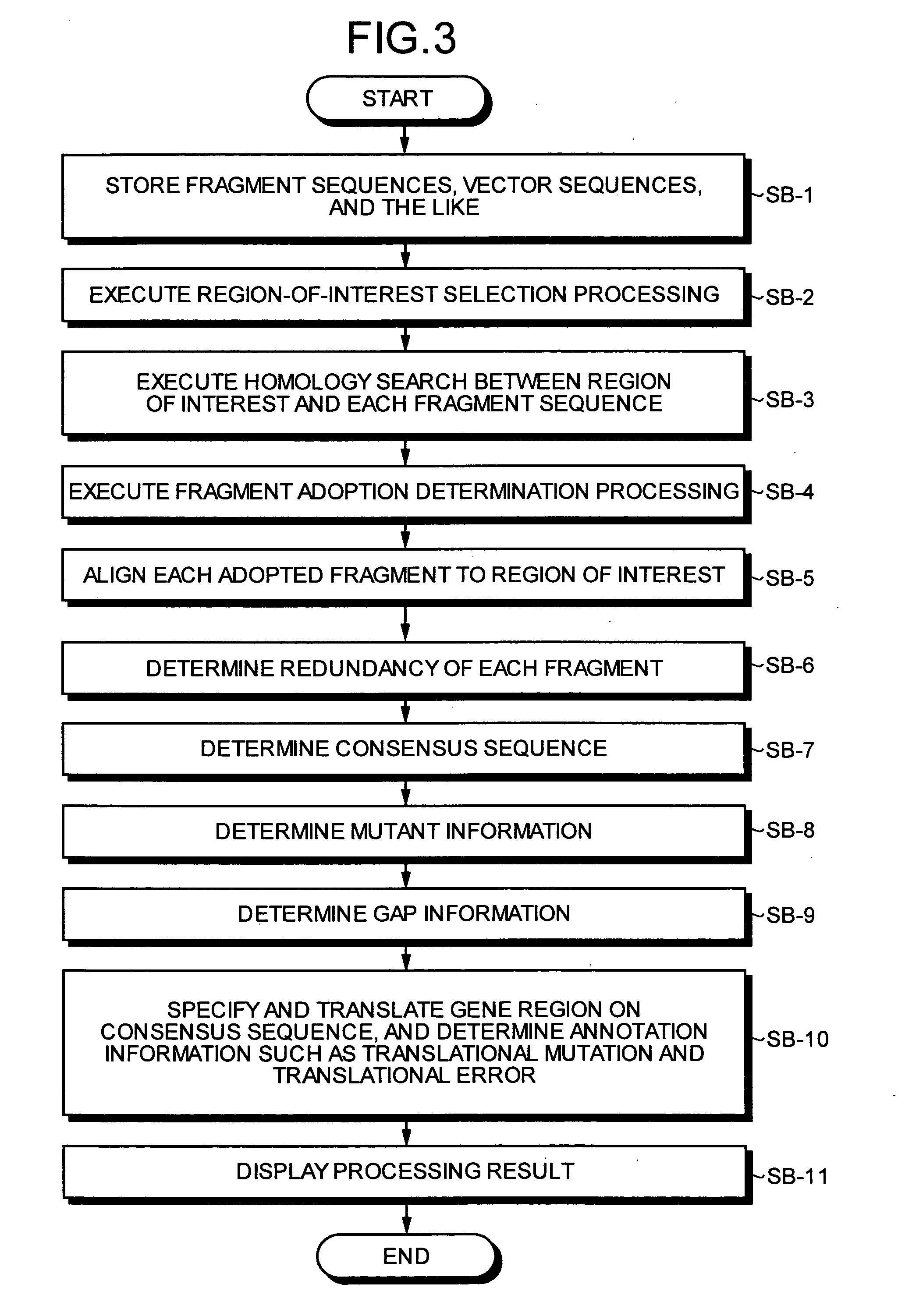
All DNA's of a mutant of a sequencing target organic species (e.g., a resistant bacterium, a tumor cell, or a virus) are extracted, and shotgun libraries are generated for the DNA's. DNA fragments are sequentially fetched from these libraries, and each fragment is subjected to sequencing using an automated DNA sequencer. Fragment sequence information such as base sequences of the respective DNA fragments of the mutant output from the sequencer is stored in a fragment sequence database.
Owner:CELESTAR LEXICO SCI
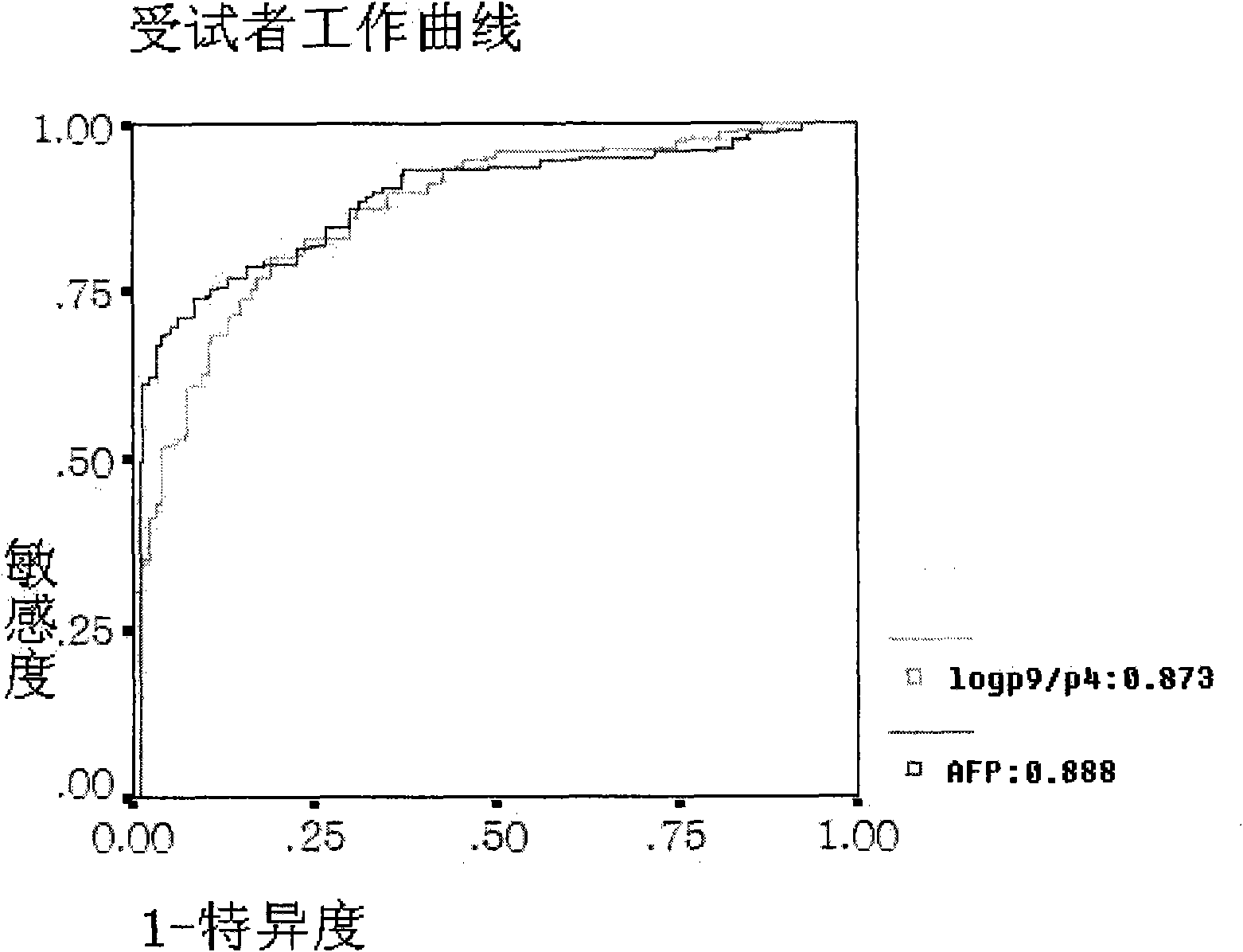
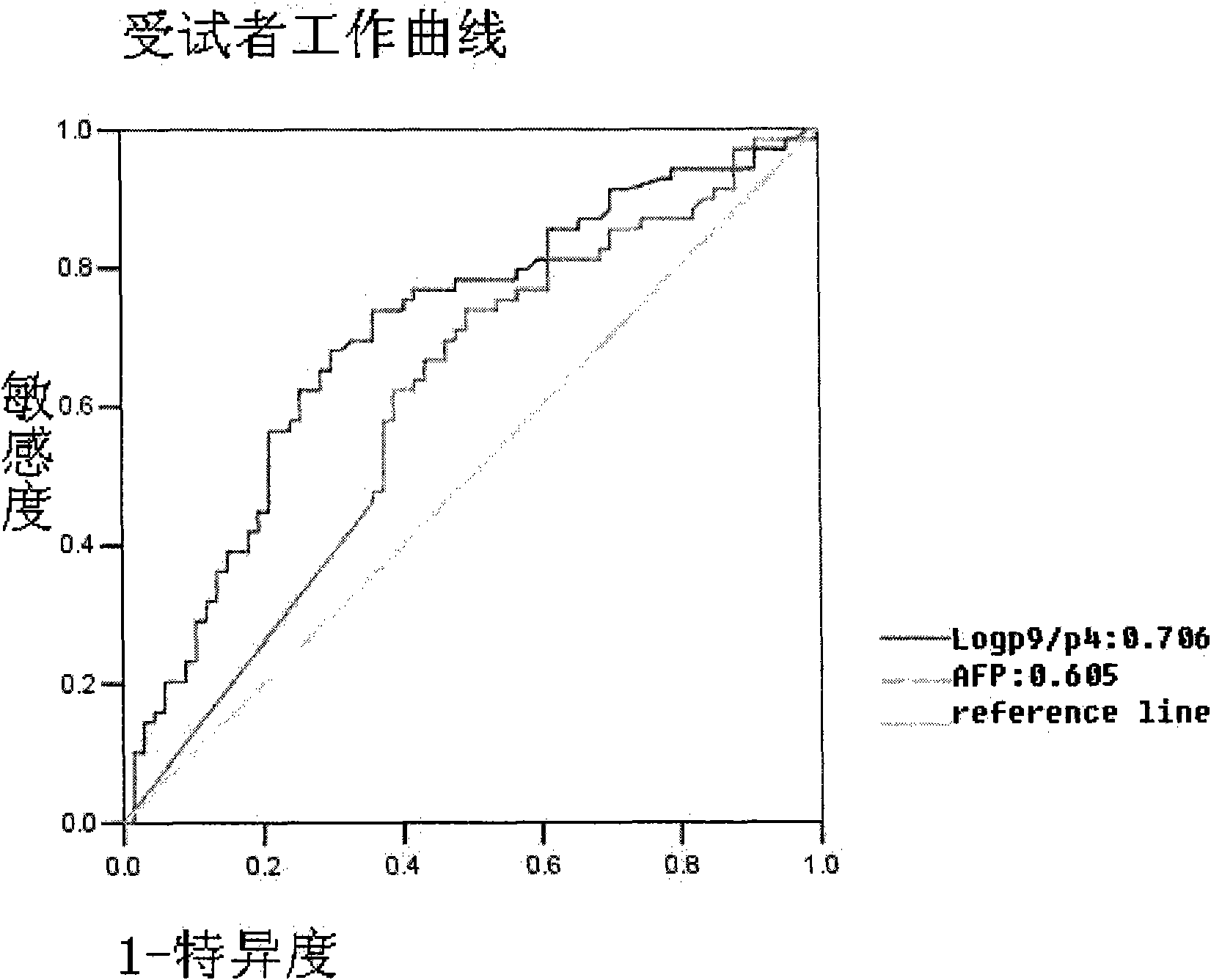
Method for detecting N-glycome log (P9/P4) in serum and detecting system and application thereof
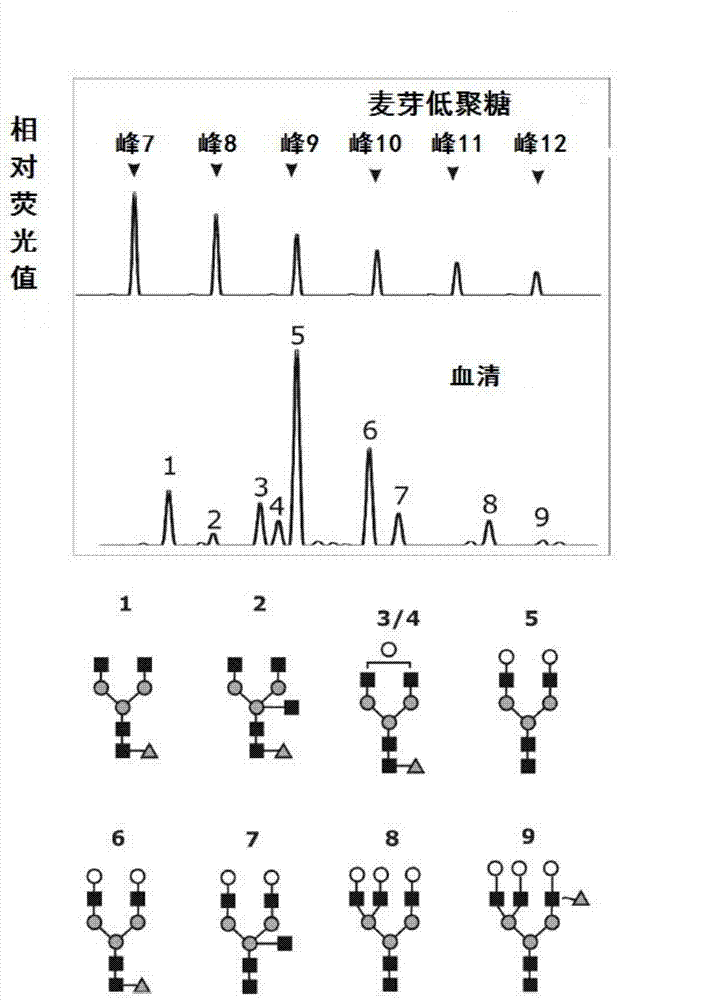
ActiveCN101576495AStrong specificityImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingHigh risk populationsHepatic fibrosis
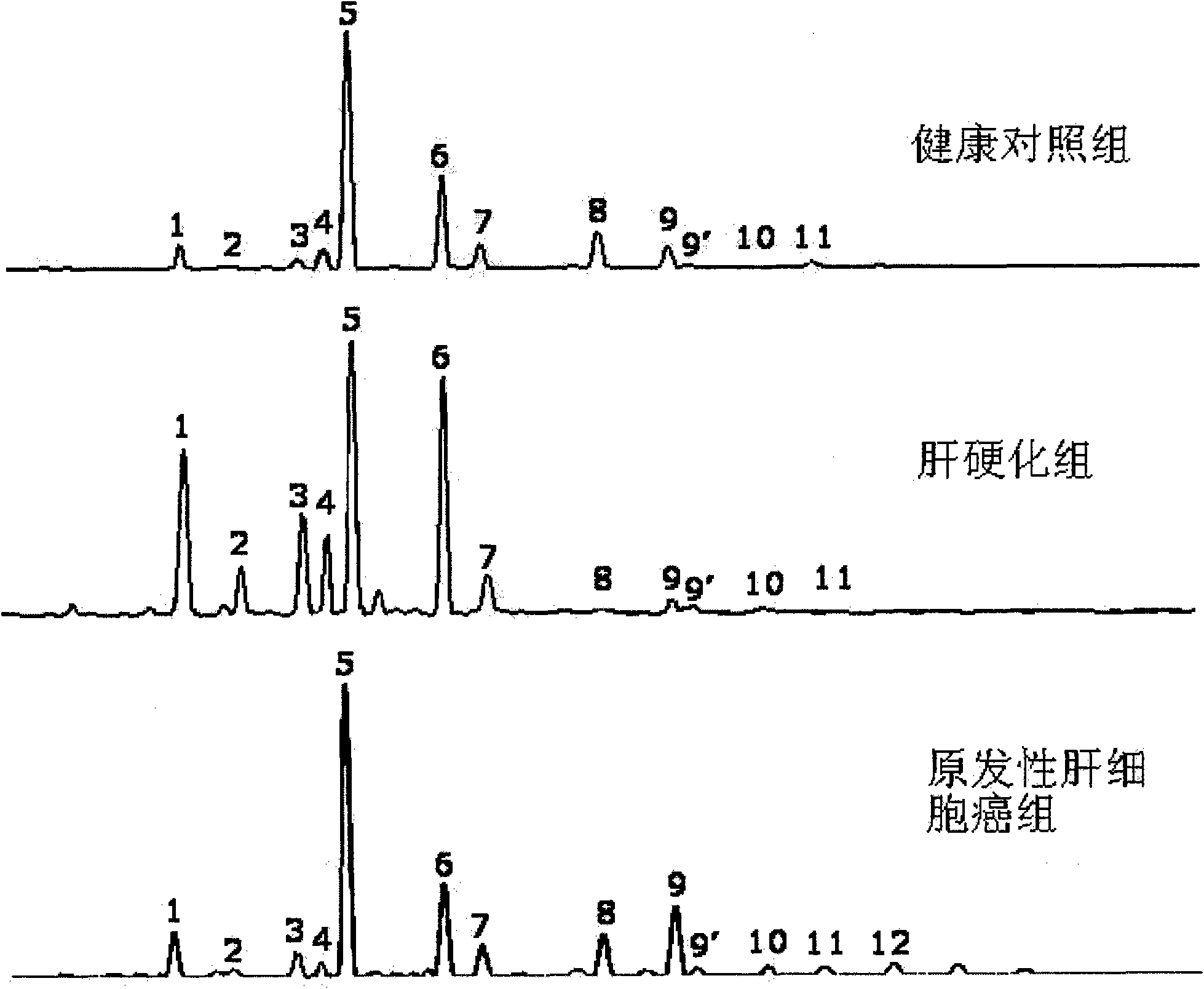
The invention belongs to the diagnostics field of clinical medicine and aims at providing a method for detecting N-glycome log (P9 / P4) in serum so as to overcome defects of prior art that both sensitivity and specificity of AFP detection and supersonic inspection which are adopted to screen high risk group of HCC which is the fifth common malignancy in the world are so low that HCC cannot be detected and treated early. The method is based on DSA-FACE of a DNA sequencer to detect distribution of glycan connected by N-glycosidic bond on glycosidoprotein in serum so as to calculate value of log (P9 / P4). The invention also provides a corresponding detecting system and applies the detecting method and the detecting system to the early screening and diagnosis of HCC, especially to the early screening and diagnosis of tendency of HCC and hepatic fibrosis relevant to HBV inflection. Compared with the AFP detection, the method provided by the invention can raise the specificity and accuracy respectively by 16 percent and 8 percent and has the similar sensitivity.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
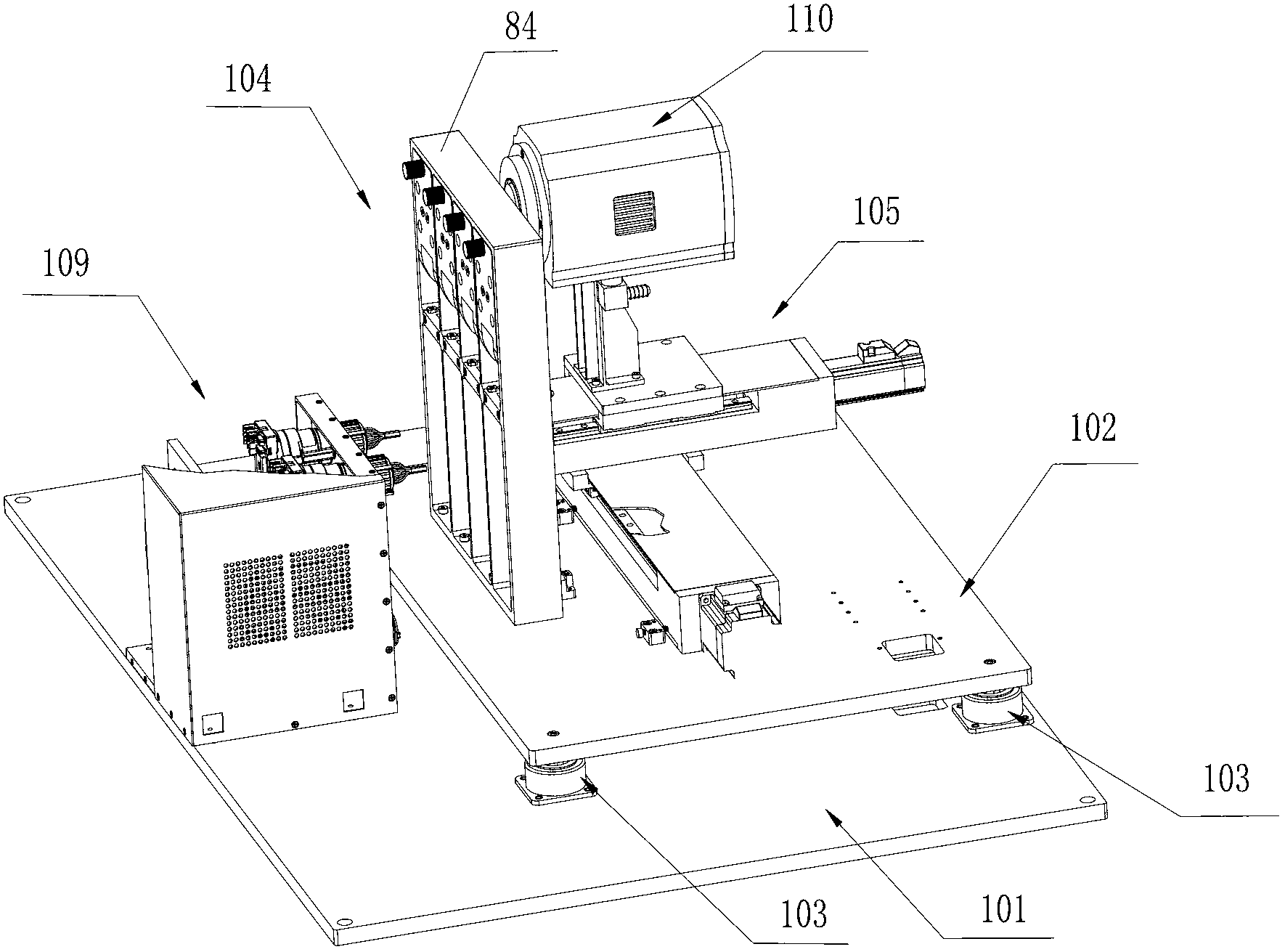
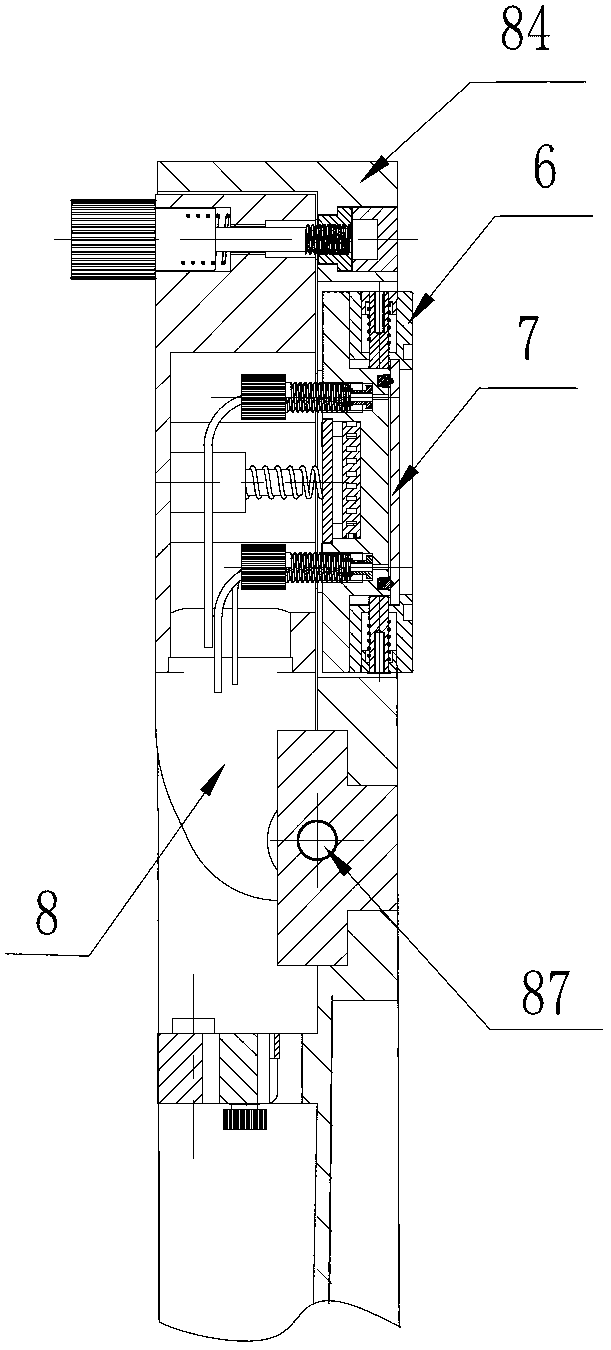
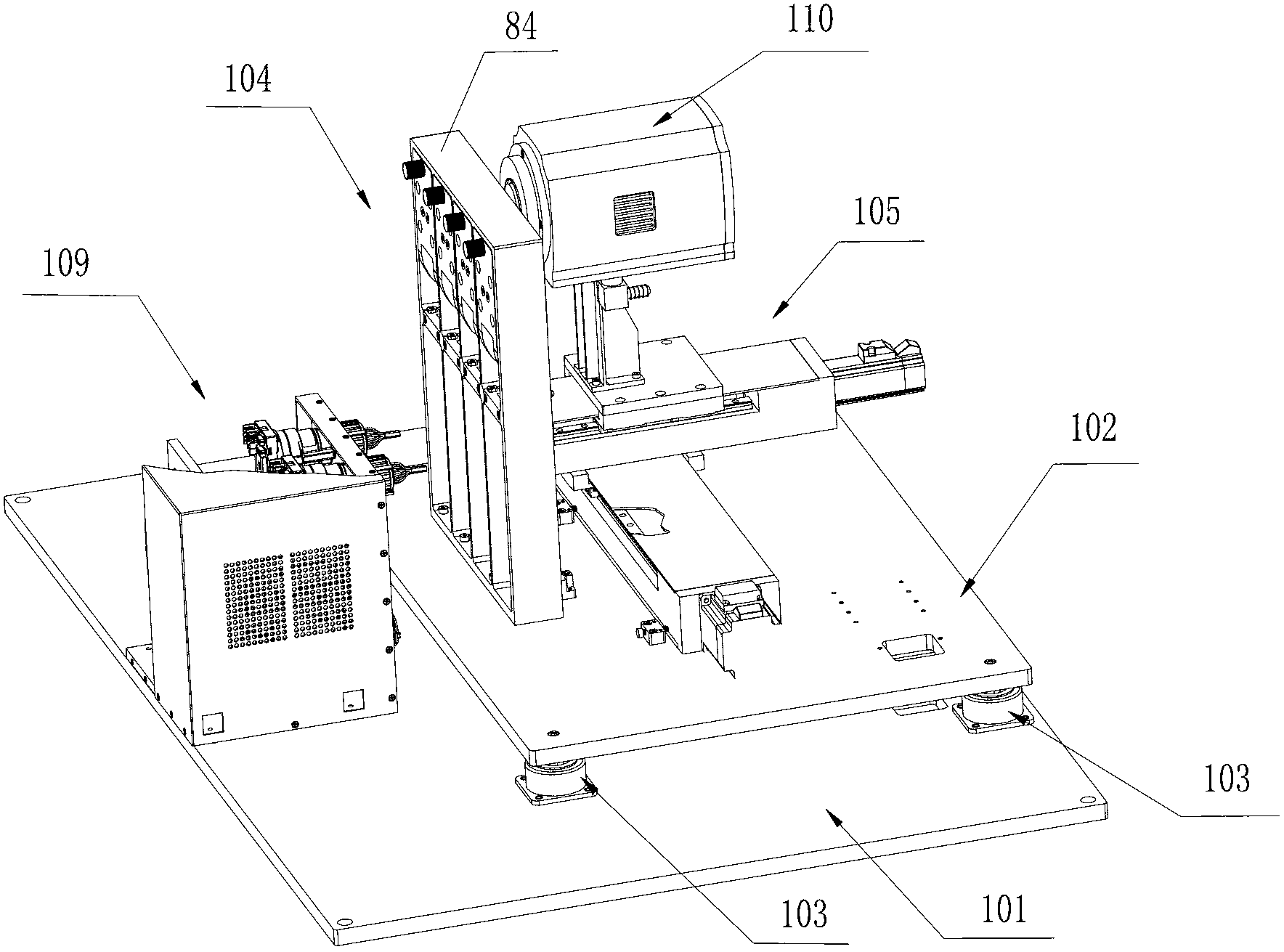
Box-type DNA sequencer with linear feeding CCD camera
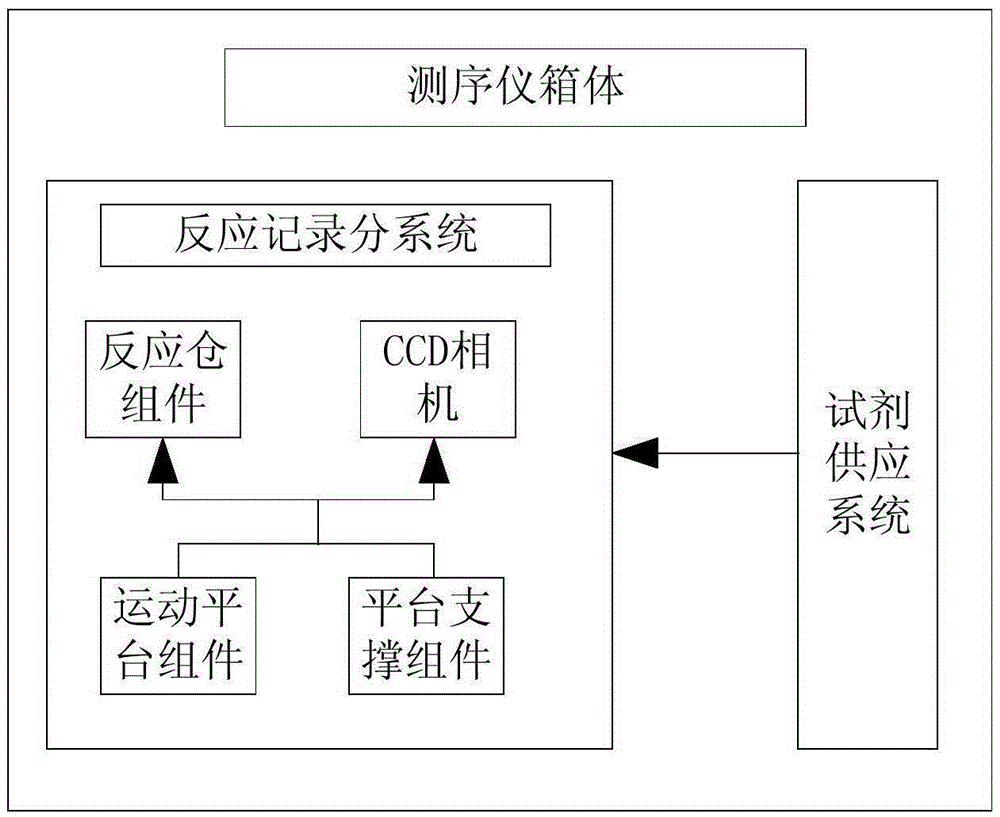
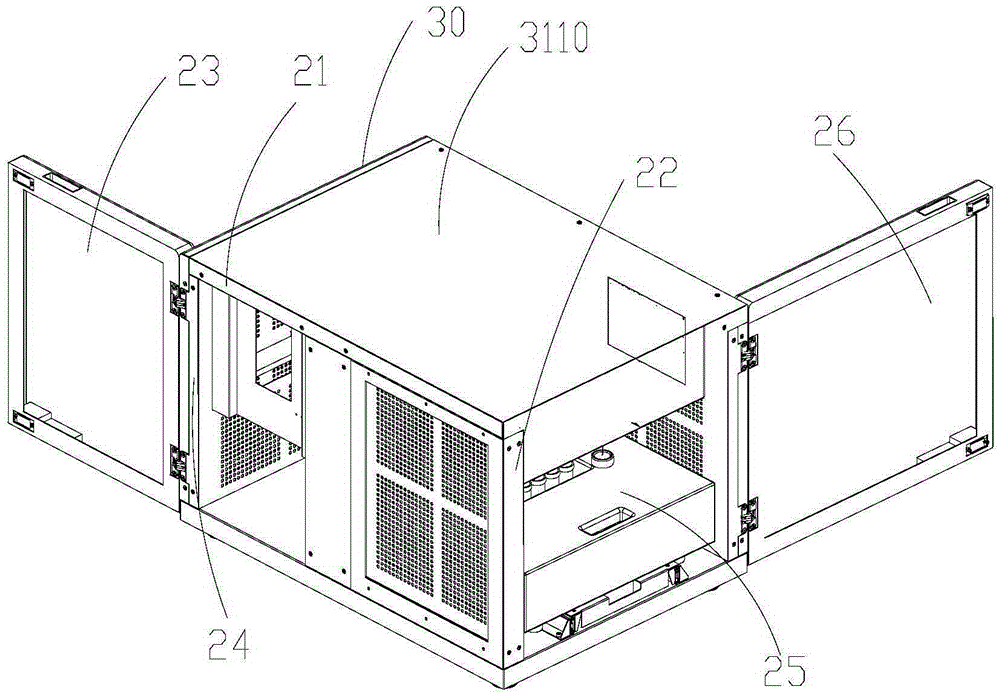
InactiveCN105316228AStable operating environmentClosed operating environmentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl systemDNA sequencer
The invention relates to a box-type DNA sequencer with linear feeding CCD camera. The box-type DNA sequencer comprises a response recording subsystem, a reagent supply system and a control system, as well as a sequencer box body bearing all the systems, wherein the response recording subsystem and the reagent supply system are respectively arranged in a left side section and a right side section of the sequencer box body; the control system is arranged at the rear side of the response recording subsystem in the left side section of the box body; and a motion platform component comprises a motor, a lead screw guide rail component connected with an output shaft of the motor, a support seat supporting the lead screw guide rail component, a detection component and a camera support component. The box-type DNA sequencer is provided with the linear feeding CCD camera and the motion platform component, and feeding and withdrawing of the camera can be finished in the space of the box body structure to complete photographing, so that sampling of the sequencer is finished while the working space is saved.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGKEZIXIN TECH
Preparation method of rare earth cerium doped thermistor material
InactiveCN108640658AThe manufacturing method steps are simpleRaw materials are easy to getHigh resistanceCerium nitrate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a rare earth cerium doped thermistor material. According to the process, rare earth cerium is provided by reaction of cerium nitrate and sodium oxalate,and B value and resistivity of the original thermistor material are changed to a larger extent. The conduction principle of traditional NTC (negative temperature coefficient) thermosensitive ceramicsis the jumping conductance caused by jumping of electrons between different valence-variable ions of the same metal in the position B of a spinel structure, while Mn and Co both have various valenceions, cation distribution of Mn and Co is relatively complex, and various ions such as Mn<4+>, Mn<3+>, Co<3+> and CO<2+> may be present in the position B. Detection shows that after doping of rare earth cerium, the grain size becomes small and the grain boundary increases. In the NTC thermosensitive ceramic material, the grain is a semiconductor, and the grain boundary is a high resistance layer and is the main unit for withstanding voltage. Besides, the thermistor material obtained after doping of rare earth cerium has high stability and good aging resistance, and has greater application prospects in precision instruments such as dialyzers, DNA sequencers, blood analyzers and the like.
Owner:赵娟
Method and apparatus for image processing for massive parallel DNA sequencing
InactiveUS8300971B2Increase speedImprove accuracyImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPoint spreadDNA sequencer
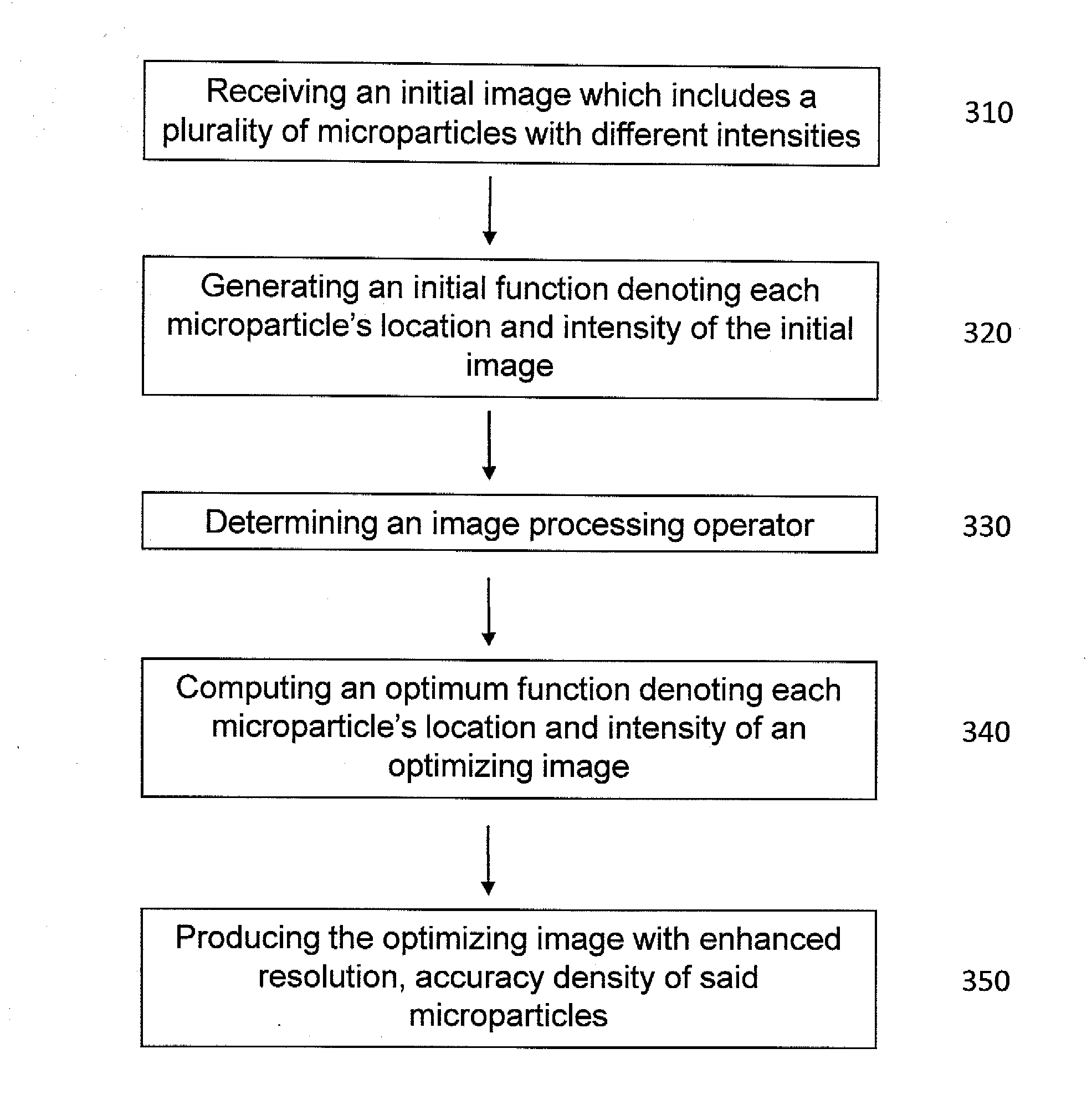
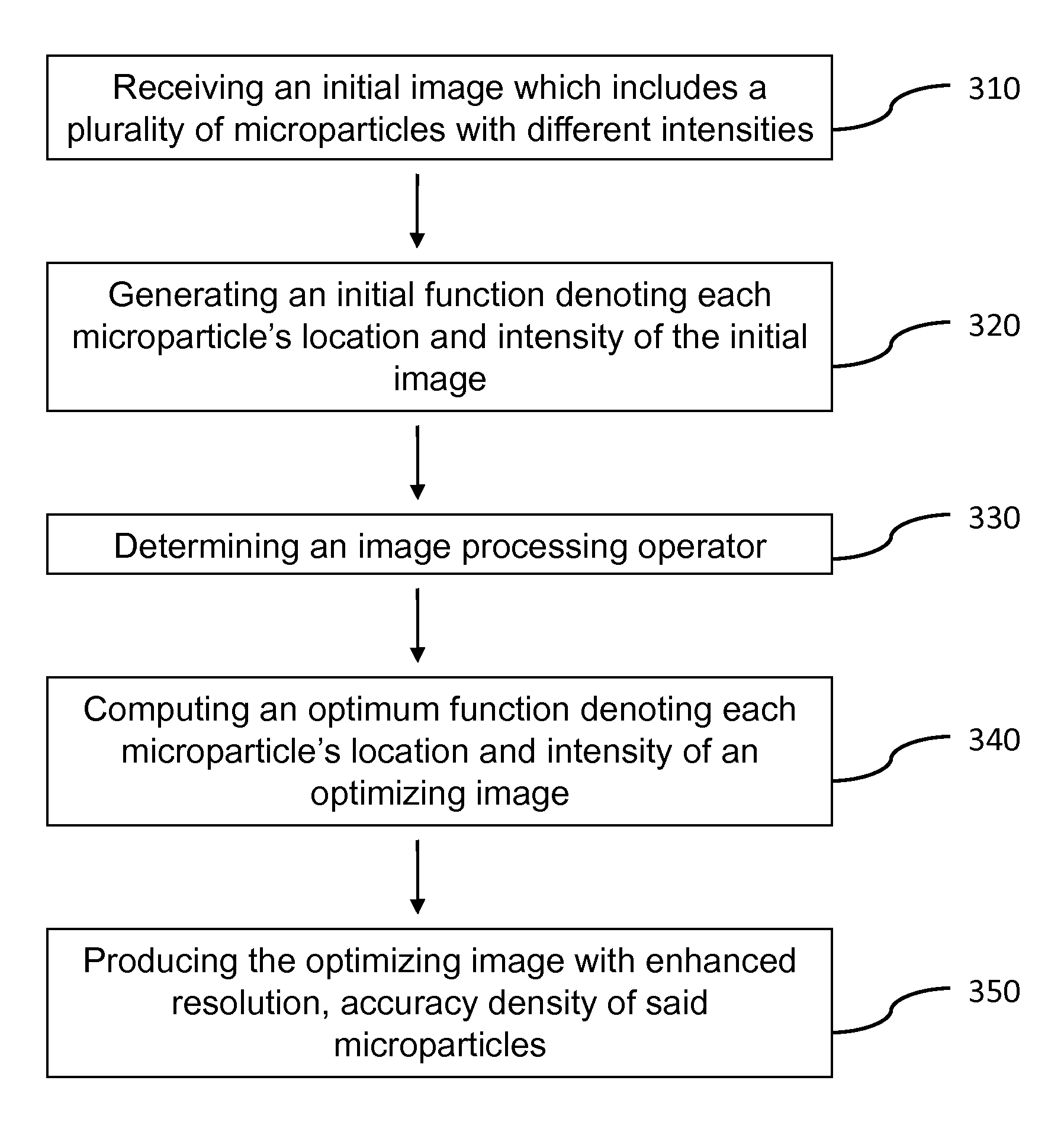
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for image processing, and more particularly, this invention relates to a method and apparatus for processing image data generated by bioanalytical devices, such as DNA sequencers. An object of the present invention is to remove artifacts such as noise, blur, background, non-uniform illumination, lack of registration, and extract pixel signals back to DNA-beads in a way that de-mixes pixels that contain contributions from nearby beads. In one aspect of the present invention, a system for optimizing an image comprises means for receiving an initial image which includes a plurality of microparticles with different intensities; a computing device, comprising a processor executing instructions to perform: generating an initial function denoting each microparticle's location and intensity in the initial image; determining an image processing operator adapted to determine an extent of point spread and blurriness in the initial image; computing an optimum function denoting each microparticle's location and intensity in an optimizing image; and producing the optimizing image with enhanced accuracy and density of the microparticles.
Owner:LEVEL SET SYST
Biomark detection method of Alzheimer's disease
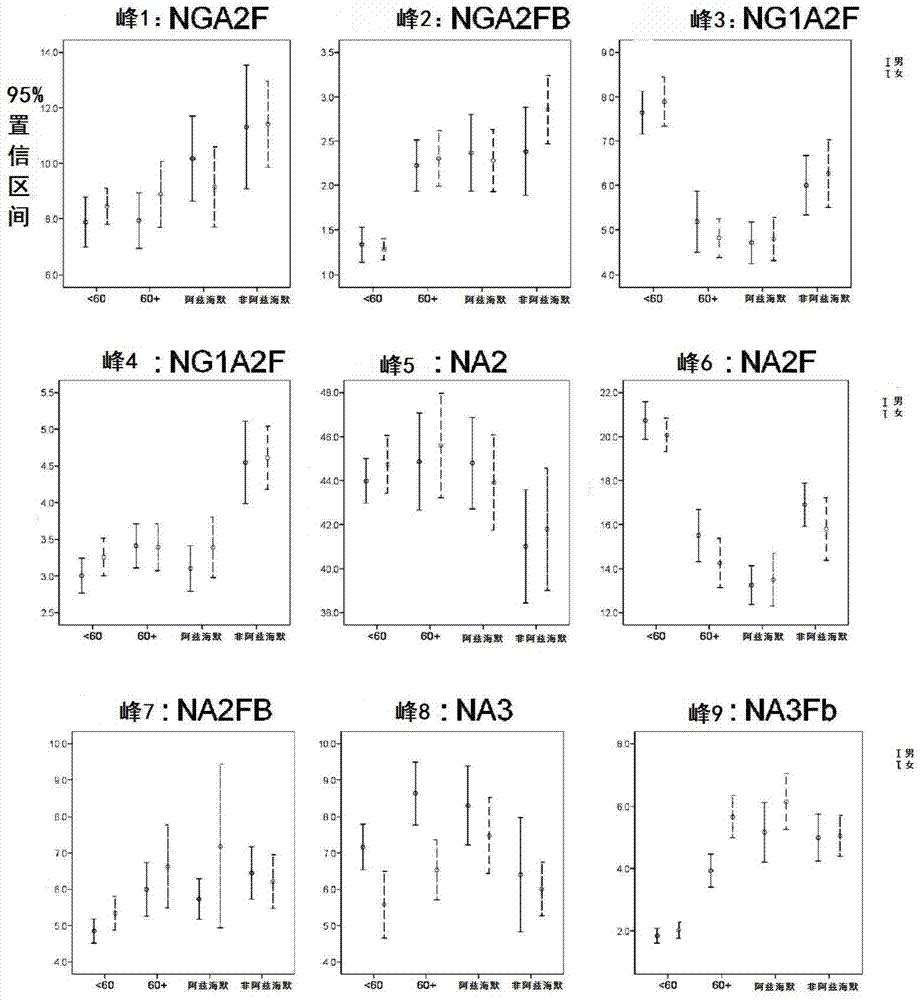
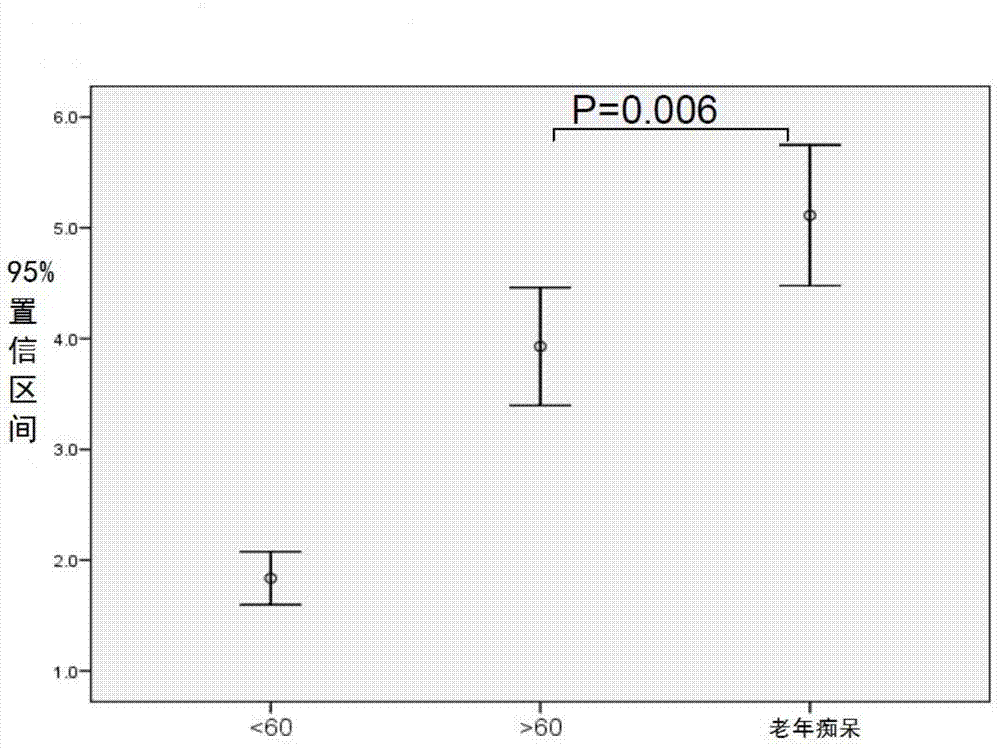
The invention relates to a biomark detection method of Alzheimer's disease, which comprises the following steps: (1) collecting and processing a serum sample; (2) performing fluorescence marking on an oligosaccharide in the serum sample with a fluorophore-assisted carbohydrate electrophoresis (DSA-FACE) technology through a DNA-based sequencer; (3) measuring content of the oligosaccharide subjected to fluorescence marking in the sample by ionophortic separation and obtaining an oligosaccharide fingerprint spectrum; (4) analyzing the oligosaccharide fingerprint spectrum. The difficult detection of the Alzheimer's disease is solved, the Alzheimer's disease can be quantitatively detected and a pathogenetic degree can be quantitatively evaluated.
Owner:XIANSIDA NANJING BIOTECH CO LTD
CCD (charge coupled device) camera directly coupled with sequencing chip
ActiveCN102703310AQuality improvementEasy accessBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsA-DNADNA sequencer
The invention discloses a CCD (charge coupled device) camera directly coupled with a sequencing chip. The CCD camera comprises a sequencing chip clamped in an installation base of a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequencer, a camera body and an optical fiber panel for catching optical signals of the sequencing reaction, wherein one end of the optical fiber panel extends out from the front end of thecamera body and is directly contacted one side of the sequencing chip located on the installation base of the sequencing chip of the DNA sequencer in order to obtain optical signals produced by sequencing reaction at the other side of the sequencing chip. With the adoption of the CCD camera directly coupled with the sequencing chip, due to the optical fiber panel directly coupled with the sequencing chip, the weak visible light produced on the sequencing chip can be directly received by the optical fiber panel to be converted into an electric signal; therefore, the optical coupling efficiencyis improved; the optical coupling efficiency can be more than 70%; and the condition that the high-quality sequencing signal is acquired can be ensured.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION +1
Methods for nucleic acid mapping and identification of fine-structural-variations in nucleic acids
InactiveCN102165073APrecise and fast assemblyHelp with annotationsMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionNucleic acid mappingA-DNA
A method of juxtaposing sequence tags (GVTs) that are unique positional markers along the length of a population of target nucleic acid molecules is provided, the method comprising: fragmenting the target nucleic acid molecule to form target DNA insert; ligating the target DNA insert to a DNA vector or backbone to create a circular molecule; digesting the target DNA insert endonuclease to cleave the target DNA insert at a distance from each end of the target DNA insert yielding two GVTs comprising terminal sequences of the target DNA insert attached to an undigested linear backbone; recircularizing the linear backbone with the attached GVTs to obtain a circular DNA containing a GVT-pair having two juxtaposed GVTs; and recovering the GVT-pair DNA by nucleic acid amplification or digestion with endonuclease having sites flanking the GVT-pair. Cosmid vectors are provided for creating GVT-pairs of -45- to 50-kb separation sequencable by next-generation DNA sequencers.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com