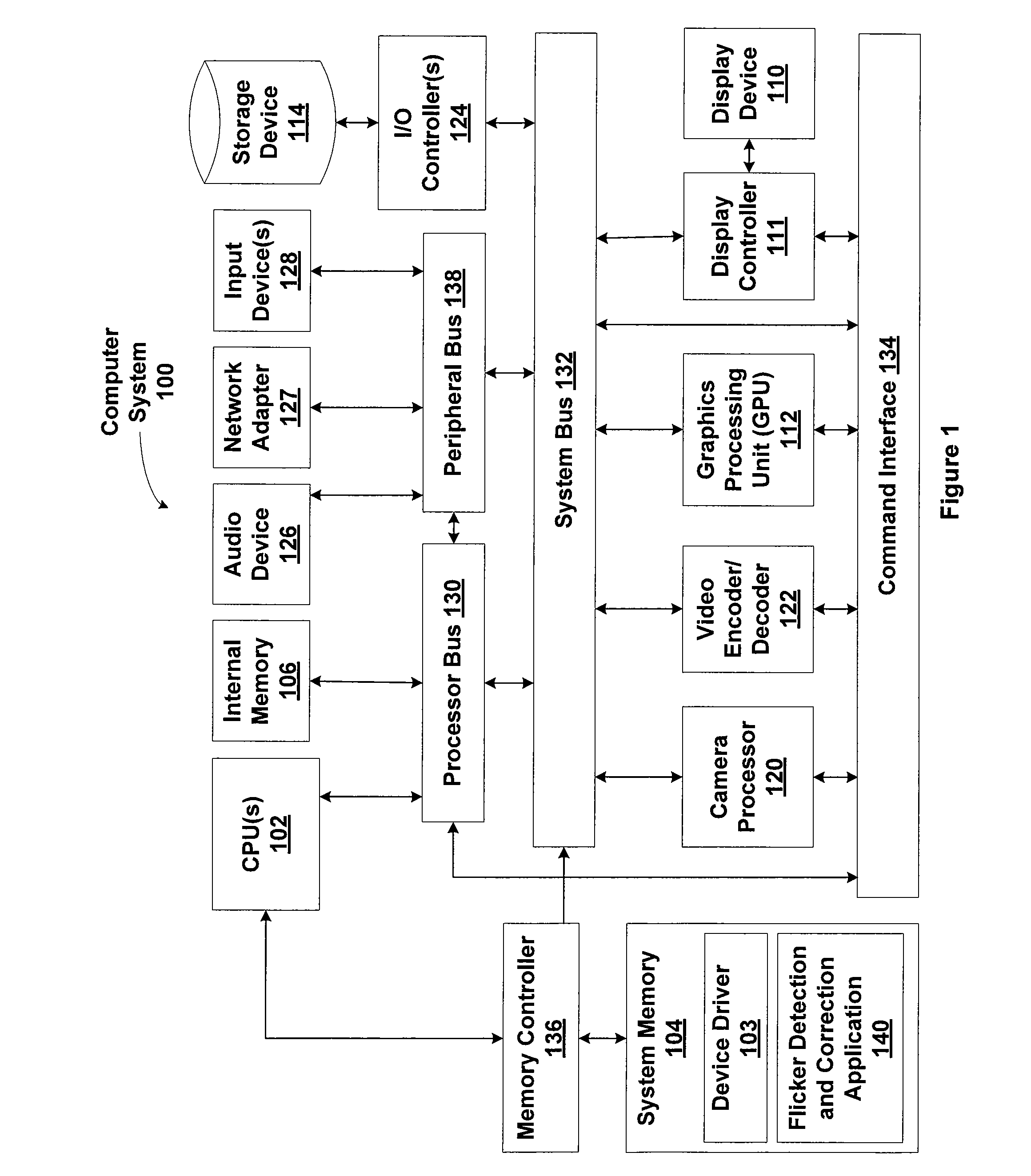
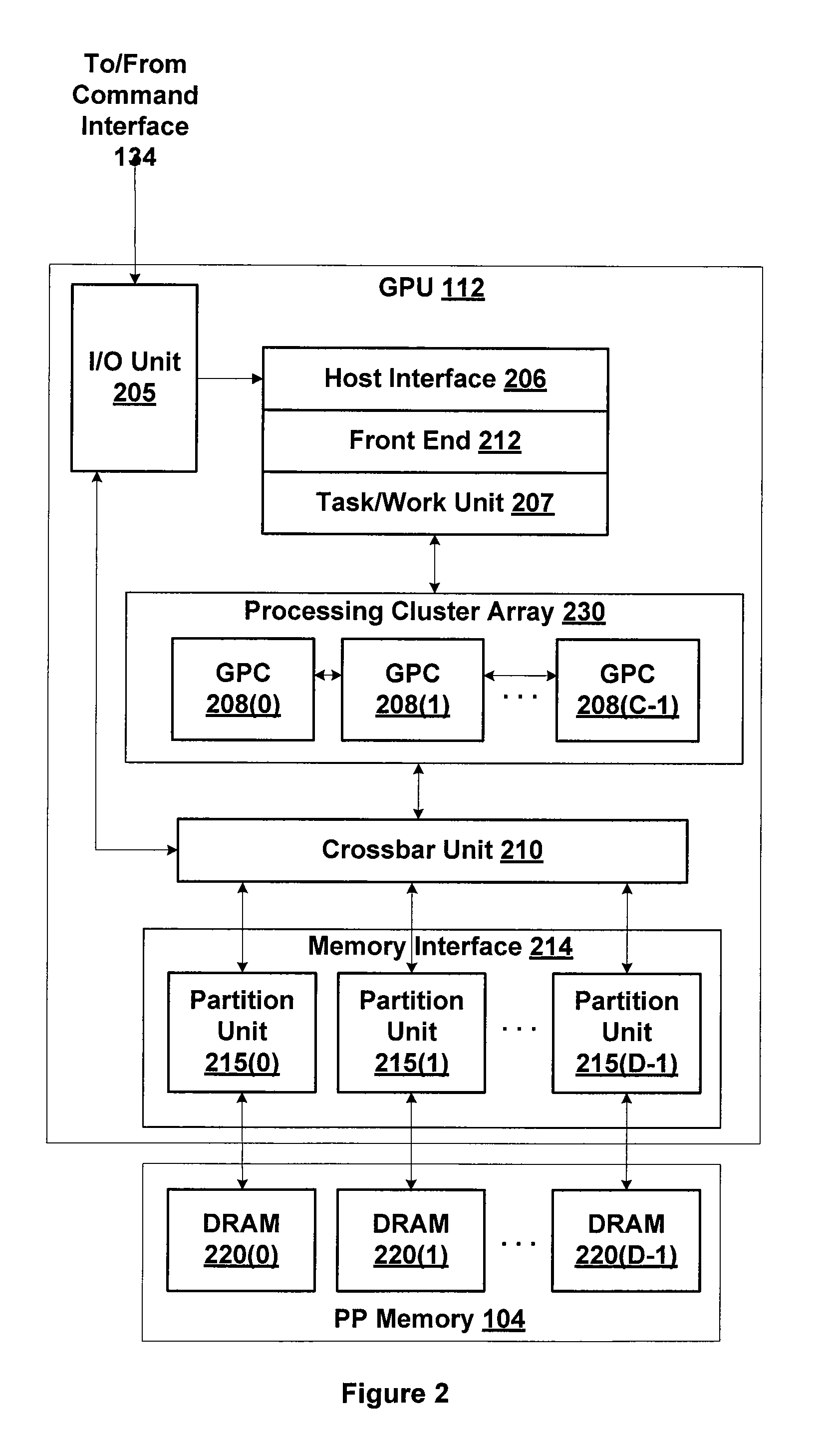
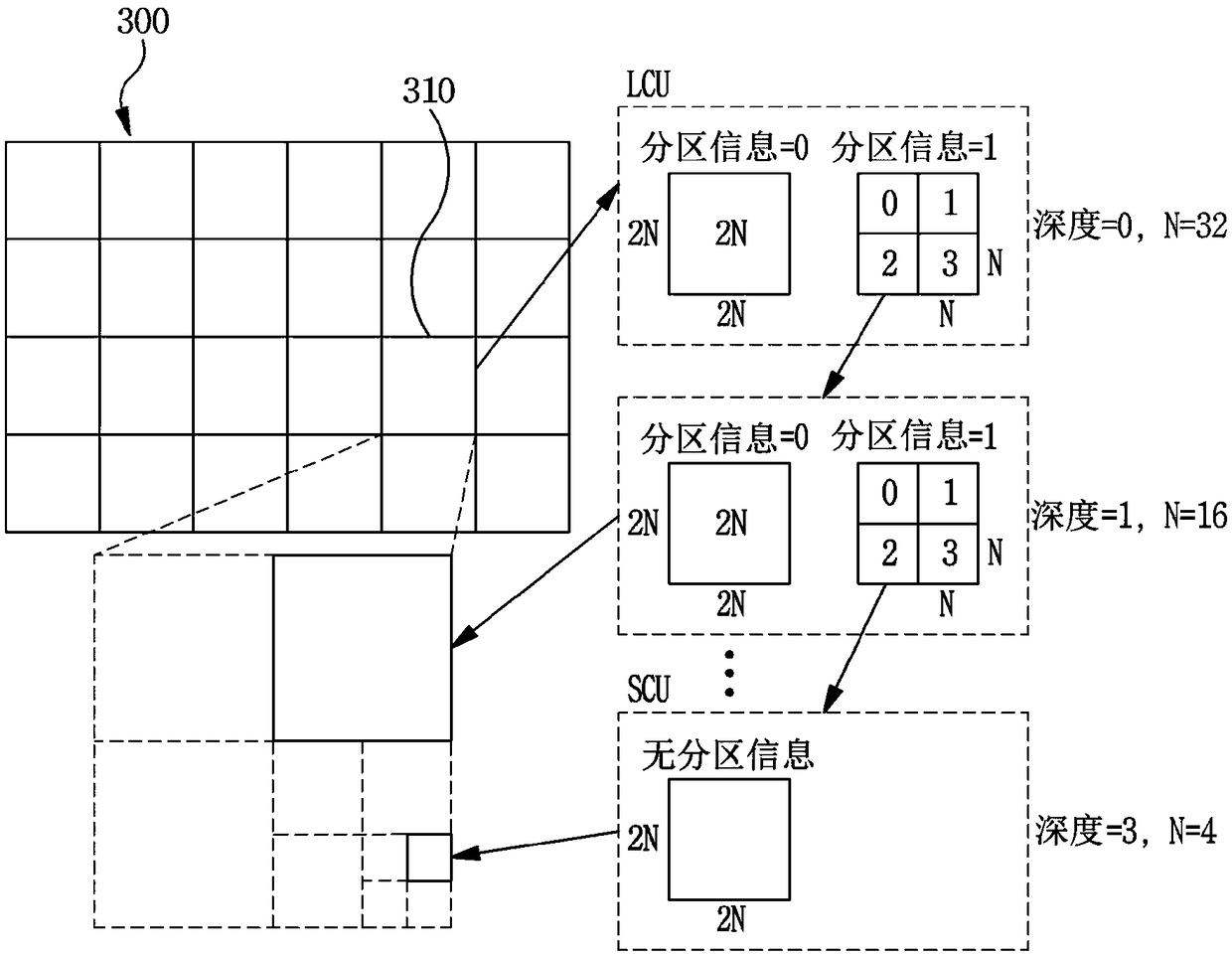
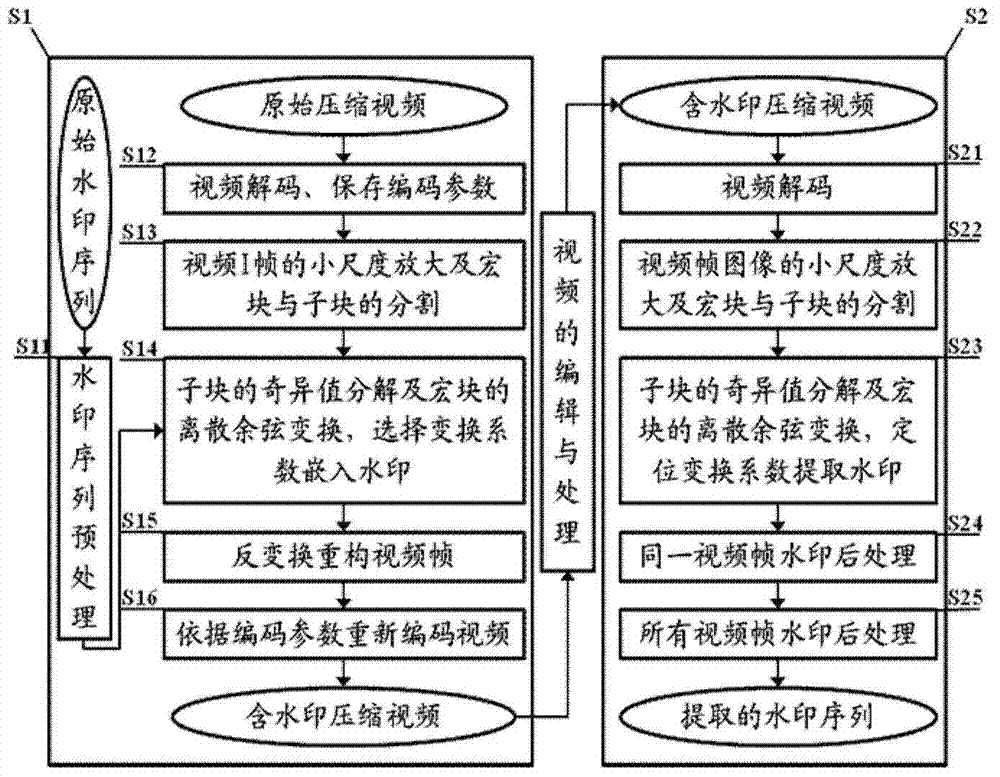
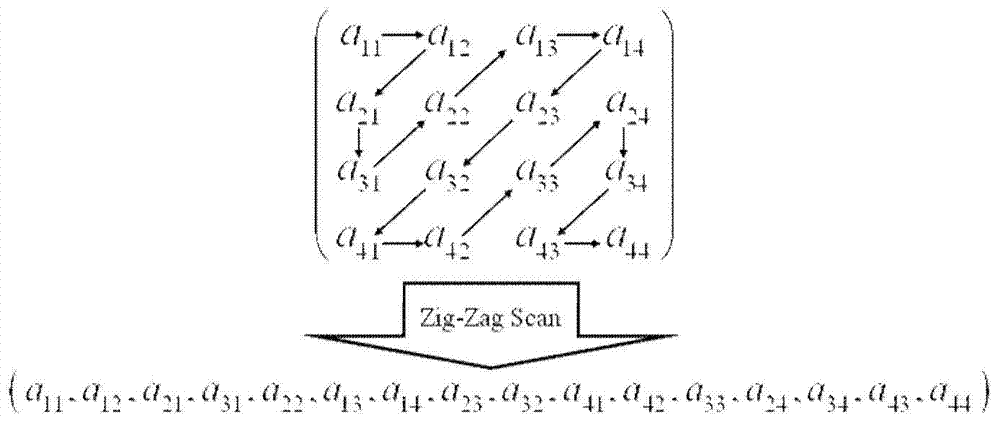
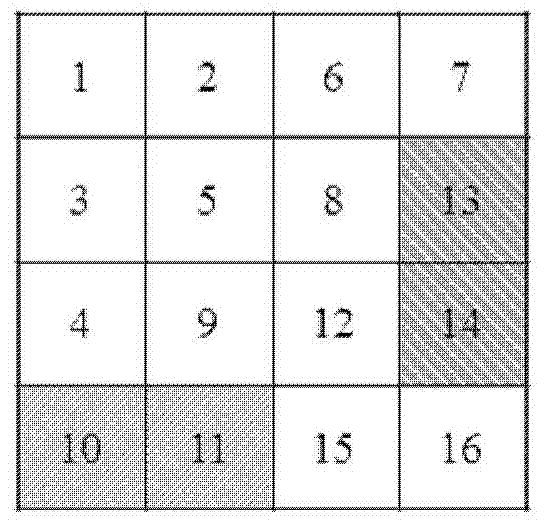
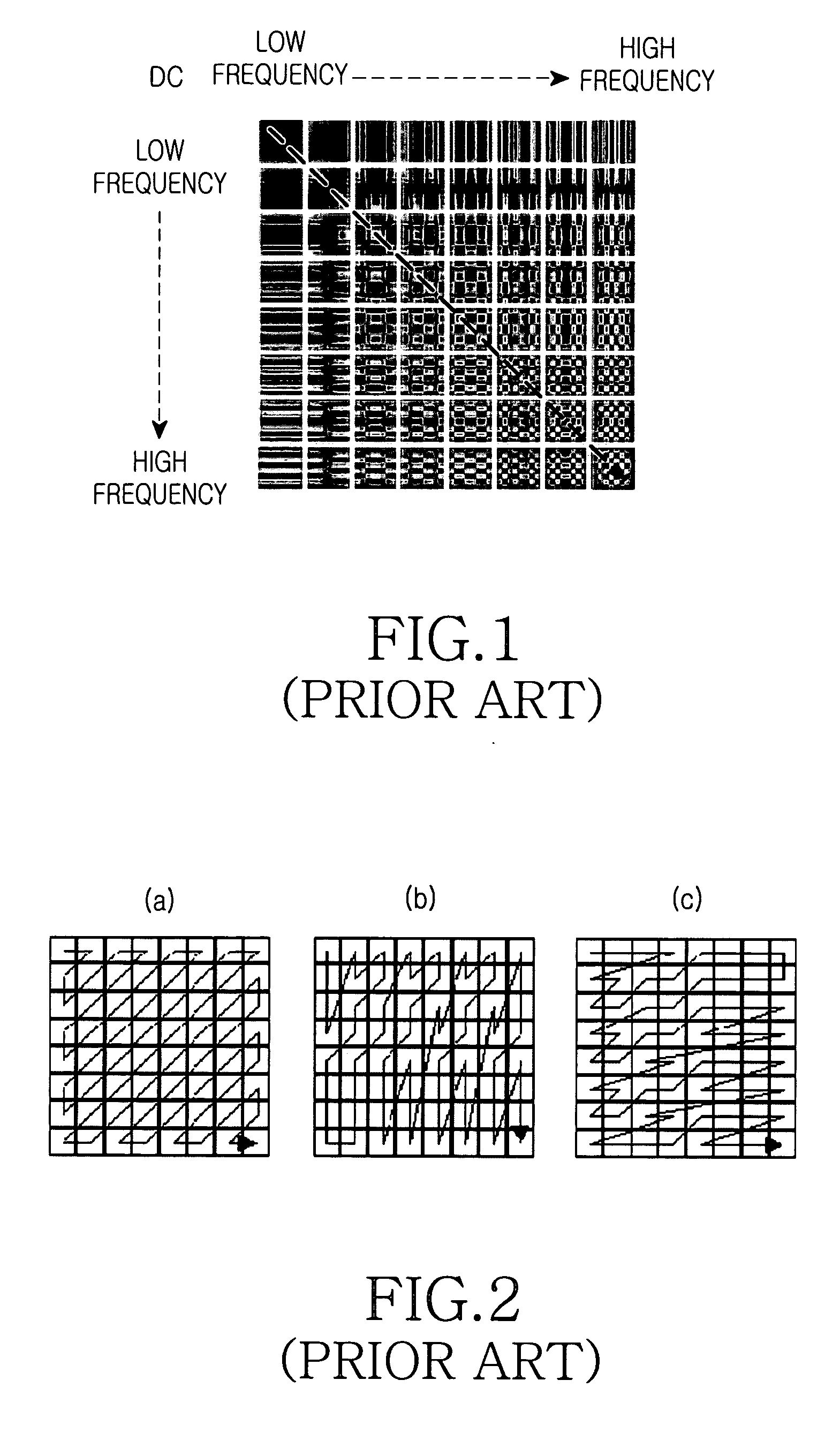
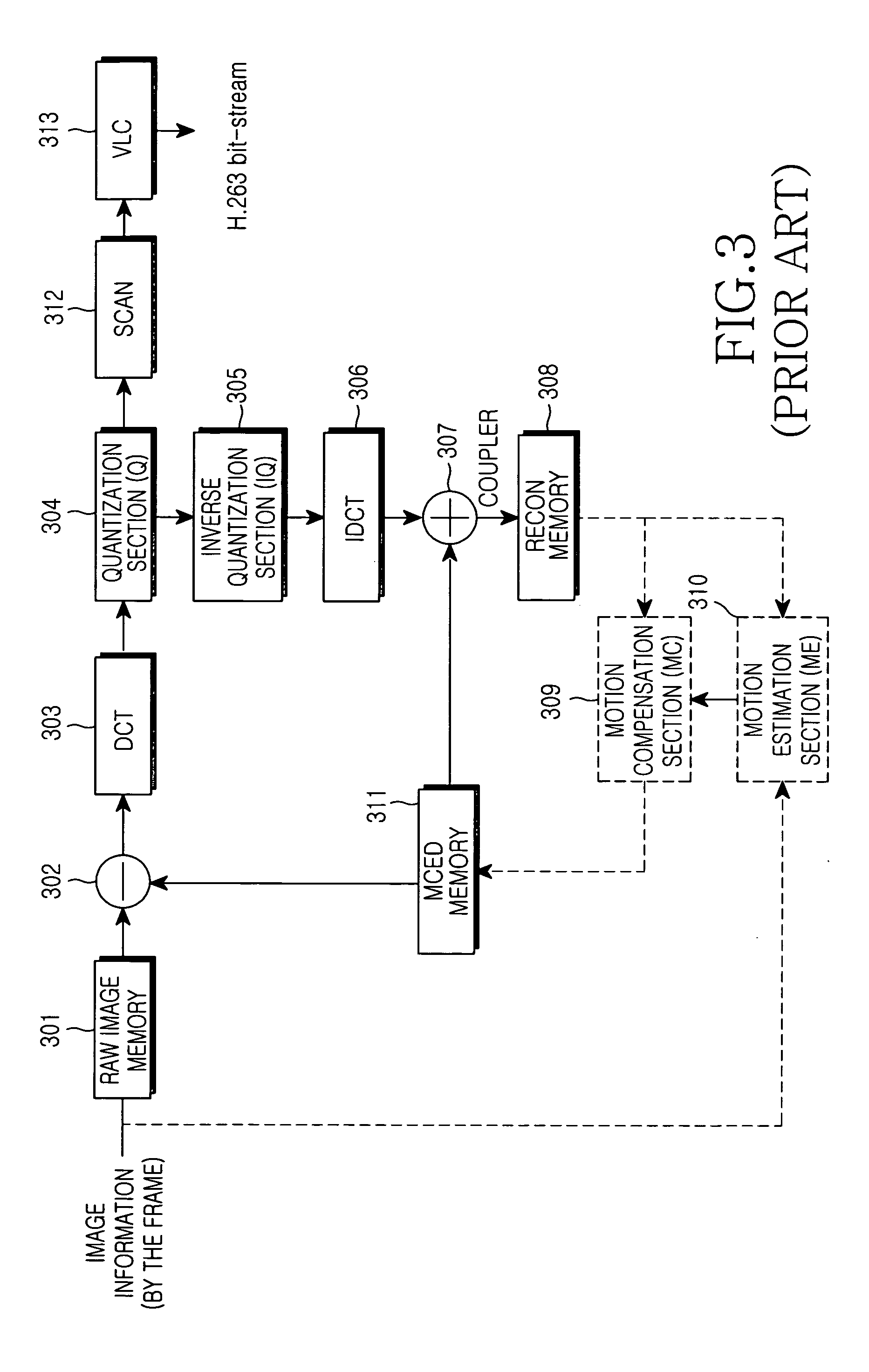
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
291 results about "Discrete cosine transforms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
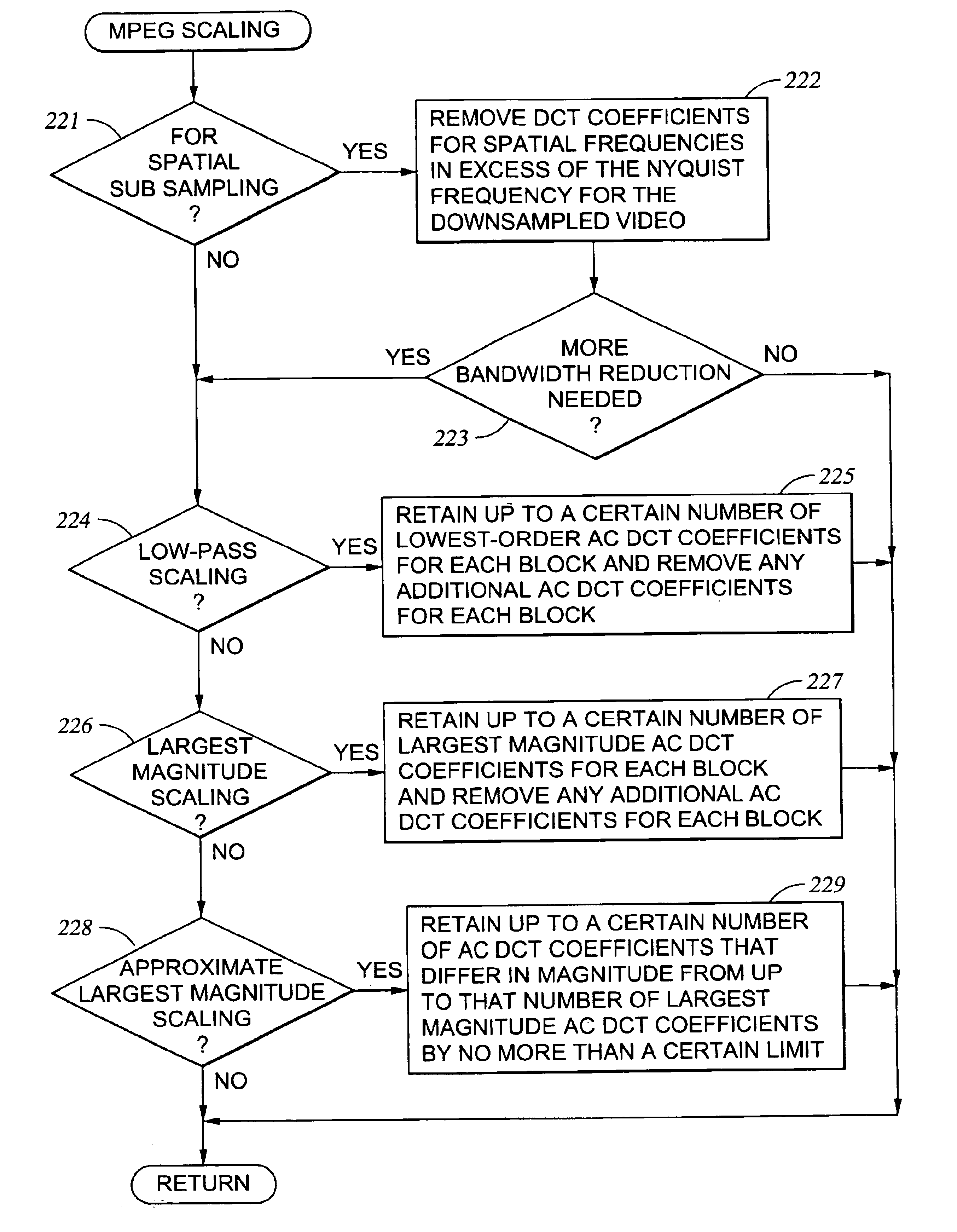
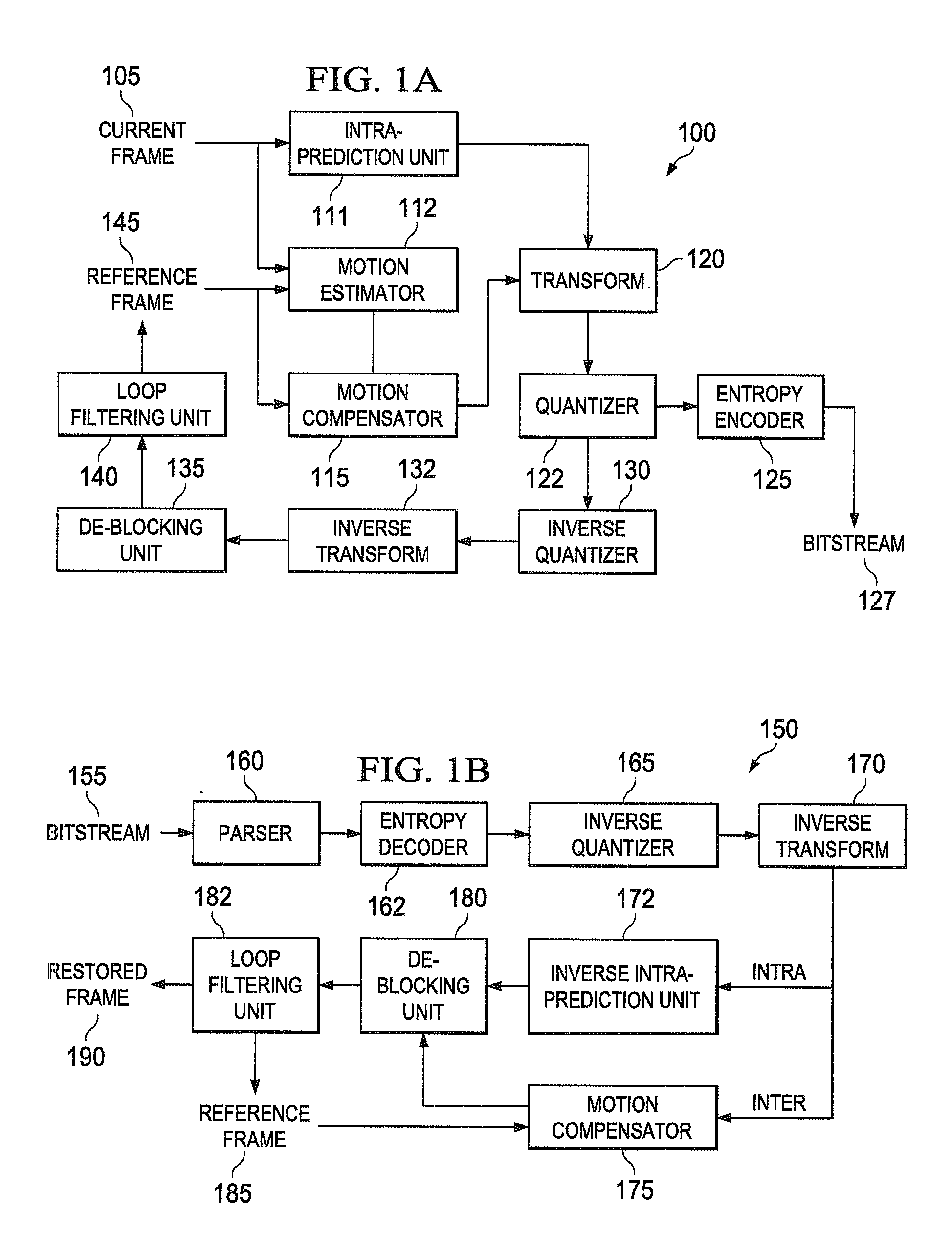
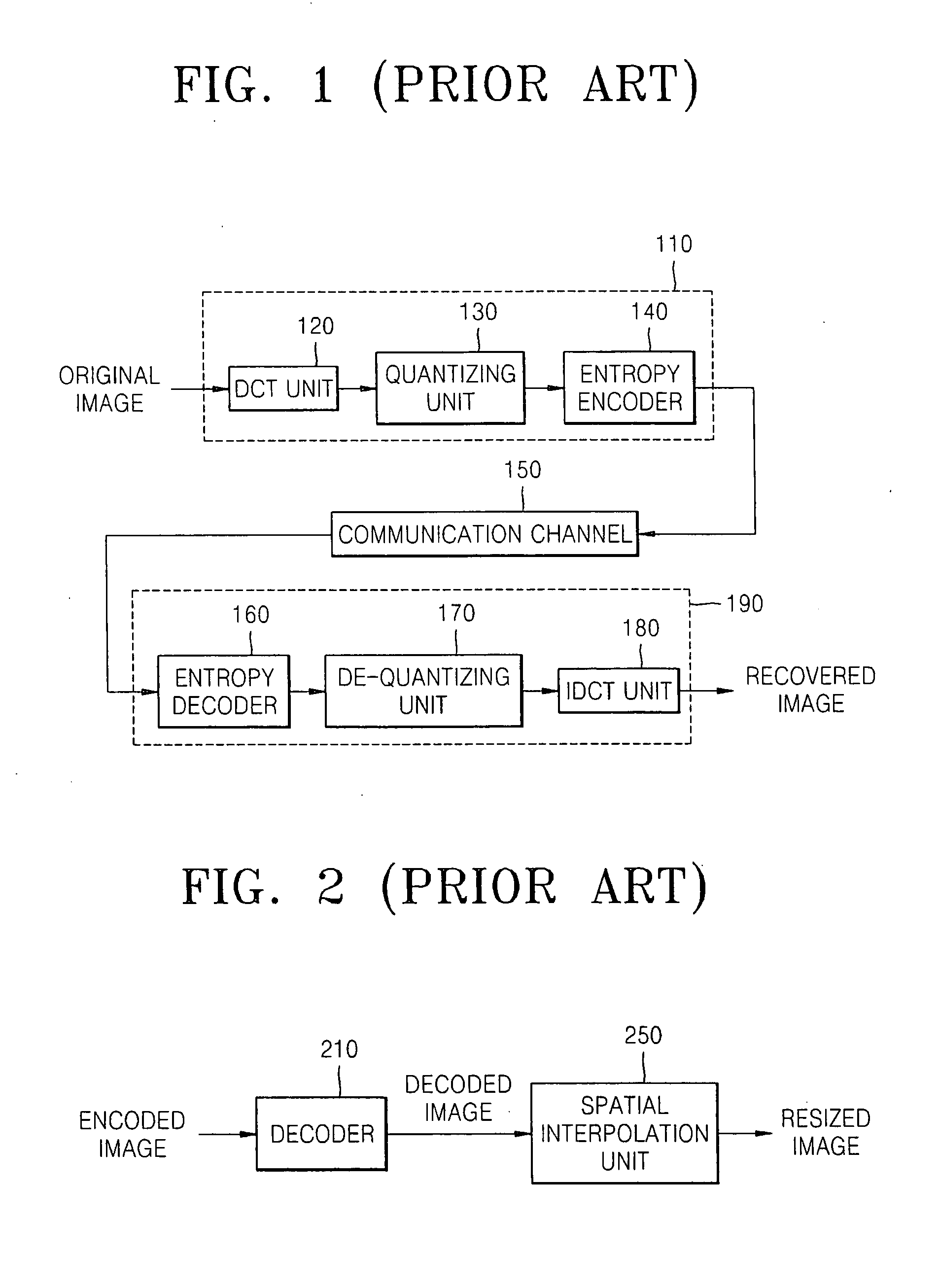
Adaptive bit rate control for rate reduction of MPEG coded video
InactiveUS6937770B1Picture quality be degradeMinimal compute resourceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionFrame sizeSelf adaptive
Original-quality MPEG coded video is processed to produce reduced-quality MPEG coded video at a reduced bit rate. The processing is based on a scale factor between average frame size of the original-quality MPEG coded video and a desired average frame size of the reduced-quality MPEG coded video. For each Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) block of each frame, the processing calculates a size of the block of the reduced frame by scaling the original block size by the scale factor, and removes a sufficient number of bits from the original block to obtain substantially the calculated size. In addition, the processing accumulates excess bits when the block size reduction eliminates more bits from a block than are necessary for the desired reduction of the size of the block, and any excess bits are used for processing a number of following blocks.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
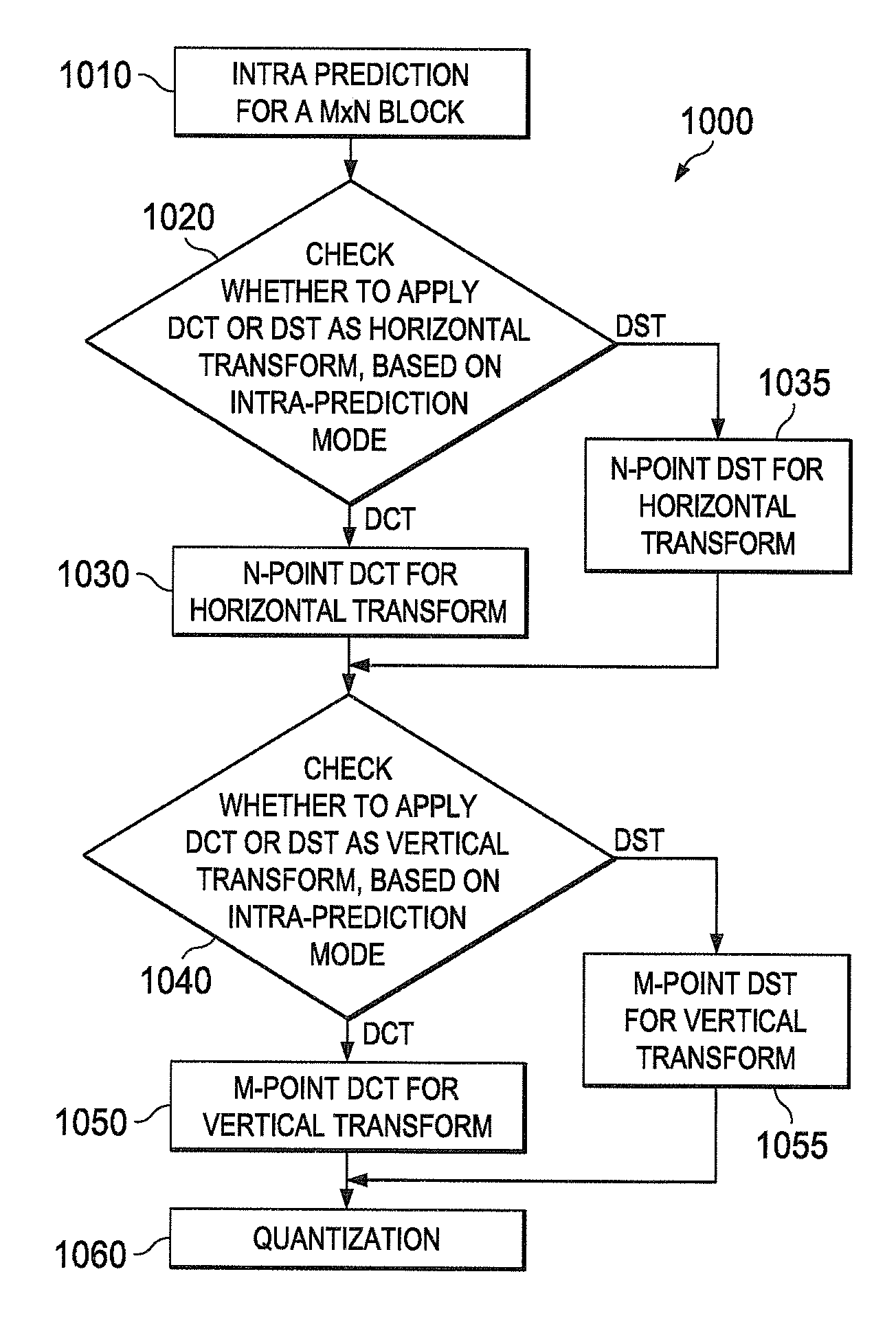
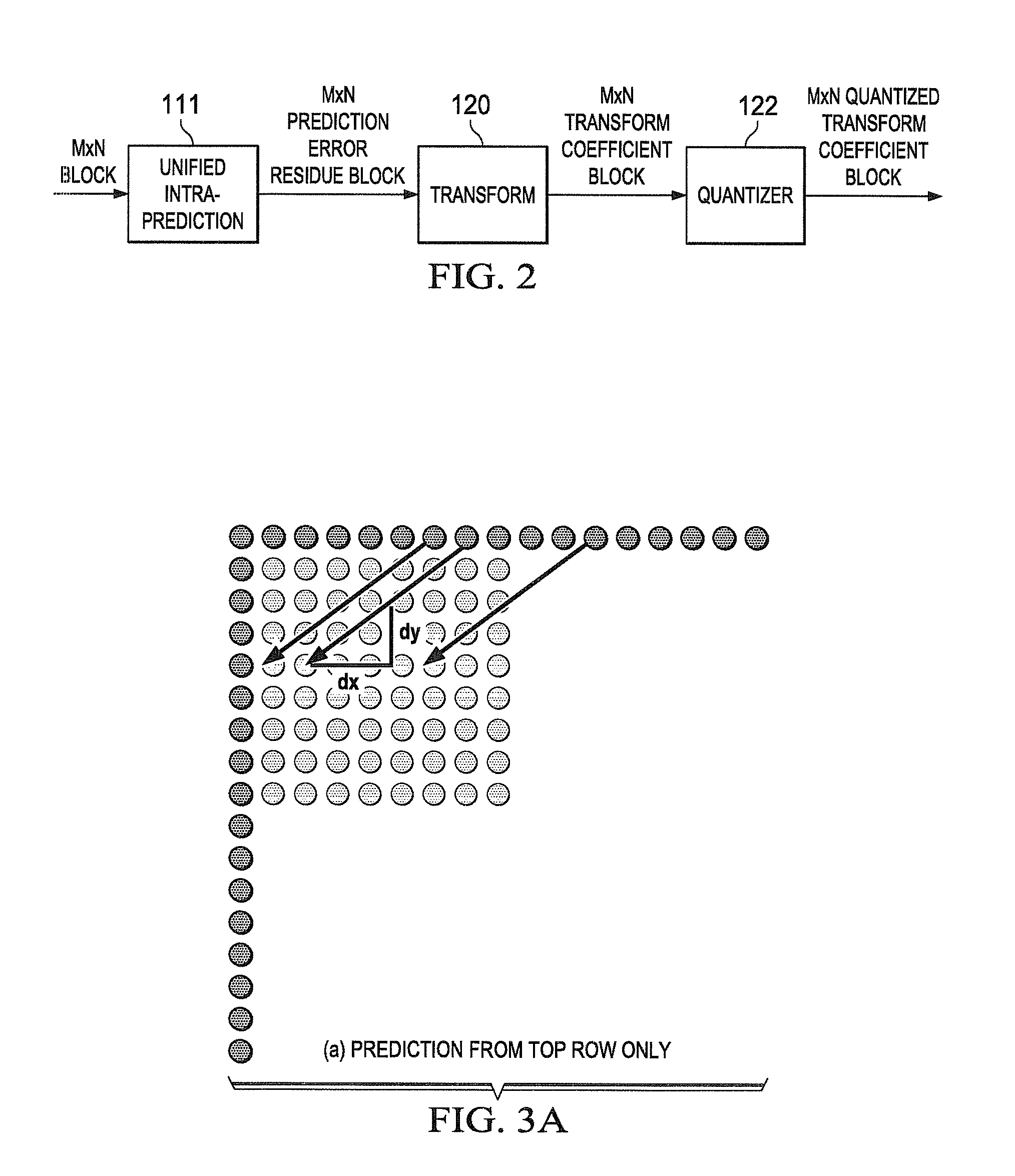
Low complexity transform coding using adaptive dct/dst for intra-prediction
InactiveUS20120057630A1Reduce complexityQuick implementationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo bitstreamSelf adaptive
A method and apparatus encode and decode video by determining whether to use discrete cosine transform (DCT) and DST for each of the horizontal and vertical transforms. During encoding, an intra-prediction is performed based on an intra-prediction mode determined for an M×N input image block to obtain an M×N intra-prediction residue matrix (E). Based on the intra-prediction mode, each of a horizontal transform and a vertical transform is performed using one of DCT and DST according to the intra-prediction mode. During decoding, the intra-prediction mode is determined from an incoming video bitstream. The M×N transformed coefficient matrix of the error residue is obtained from the video bitstream using an inverse quantizer. Based on the intra prediction mode, one of DCT and DST is performed for each of an inverse vertical transform and an inverse horizontal transform.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding using alternative converter accoding to the correlation of residual signal
InactiveUS20090238271A1Increase the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareRate distortion
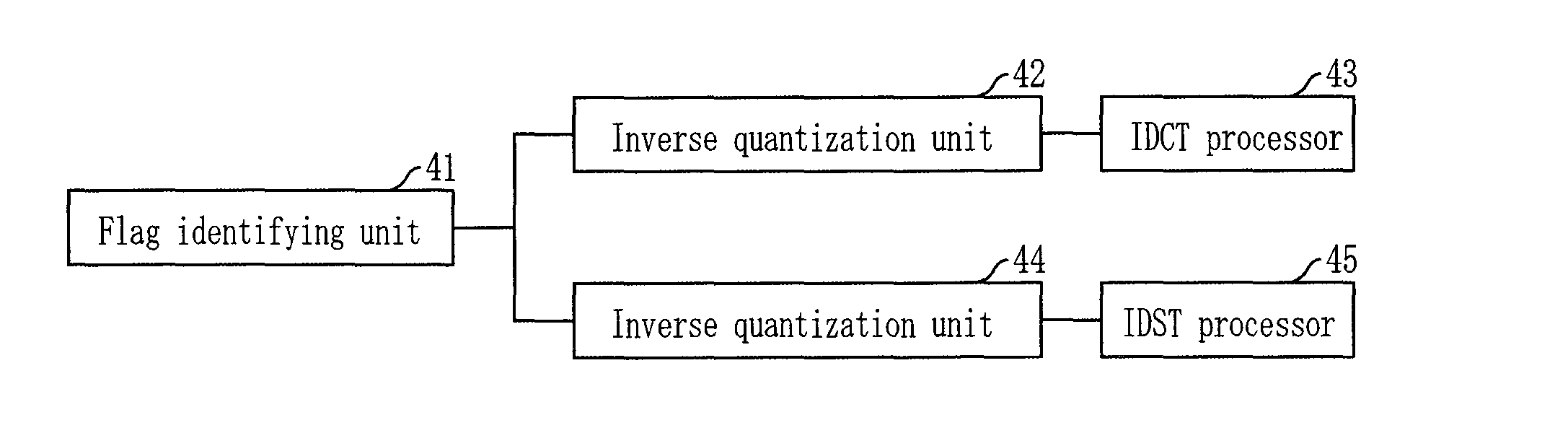
Provided is an apparatus and method for encoding and decoding using alternative transform units according to the correlation of residual signals. The video encoding apparatus includes a first transforming unit for performing discrete cosine transform (DCT), first quantization, first inverse quantization, and inverse DCT on a block basis onto residual coefficients generated after intra frame prediction or inter frame prediction; a second transforming unit for performing discrete sine transform (DST), second quantization, second inverse quantization, and inverse DST on a block basis onto the residual coefficients; a selecting unit for selecting one having a high compression rate between the first and second transforming units for each block through performing rate-distortion optimization; and a flag marking unit for recording information about the selected transforming unit at a flag bit provided on a macroblock basis.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +2
Switching between coding schemes
ActiveUS20060173675A1Simplify operationEasy to operatePulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSpectral componentPerfect reconstruction
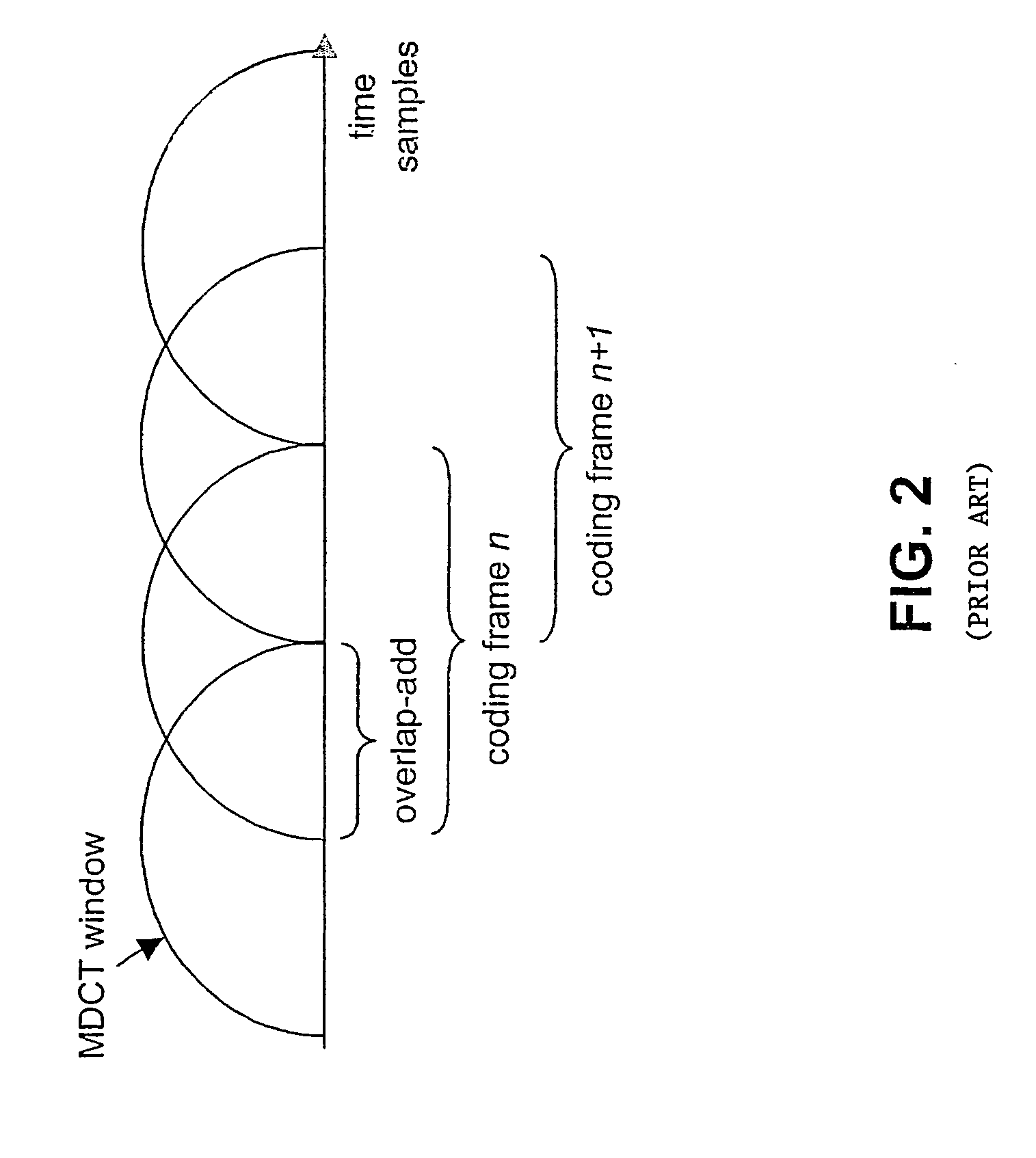
Methods and units are shown for supporting a switching from a first coding scheme to a Modified Discrete Cosine Transform (MDCT) based coding scheme calculating a forward or inverse MDCT with a window (h(n)) of a first type for a respective coding frame, which satisfies constraints of perfect reconstruction. To avoid discontinuities during the switching, it is proposed that for a transient frame immediately after a switching, a sequence of windows (h0(n),h1(n),h2(n)) is provided for the forward and the inverse MDCTs. The windows of the window sequence are shorter than windows of the first type. The window sequence splits the spectrum of a respective first coding frame into nearly uncorrelated spectral components when used as basis for forward MDCTs, and the second half of the last window (h2(n)) of the sequence of windows is identical to the second half of a window of the first type.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Efficient de-quantization in a digital video decoding process using a dynamic quantization matrix for parallel computations
InactiveUS6507614B1Efficient productionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningDigital videoArray data structure
An efficient digital video (DV) decoder process that utilizes a specially constructed quantization matrix allowing an inverse quantization subprocess to perform parallel computations, e.g., using SIMD processing, to efficiently produce a matrix of DCT coefficients. The present invention utilizes a first look-up table (for 8x8 DCT) which produces a 15-valued quantization scale based on class number information and a QNO number for an 8x8 data block ("data matrix") from an input encoded digital bit stream to be decoded. The 8x8 data block is produced from a deframing and variable length decoding subprocess. An individual 8-valued segment of the 15-value output array is multiplied by an individual 8-valued segment, e.g., "a row," of the 8x8 data matrix to produce an individual row of the 8x8 matrix of DCT coefficients ("DCT matrix"). The above eight multiplications can be performed in parallel using a SIMD architecture to simultaneously generate a row of eight DCT coefficients. In this way, eight passes through the 8x8 block are used to produce the entire 8x8 DCT matrix, in one embodiment consuming only 33 instructions per 8x8 block. After each pass, the 15-valued output array is shifted by one value position for proper alignment with its associated row of the data matrix. The DCT matrix is then processed by an inverse discrete cosine transform subprocess that generates decoded display data. A second lookup table can be used for 2x4x8 DCT processing.
Owner:SONY ELECTRONICS INC +1
Adaptive quantization using code length in image compression
InactiveUS6882753B2Low memory and bus bandwidth requirementImprove processing efficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionLandau quantization
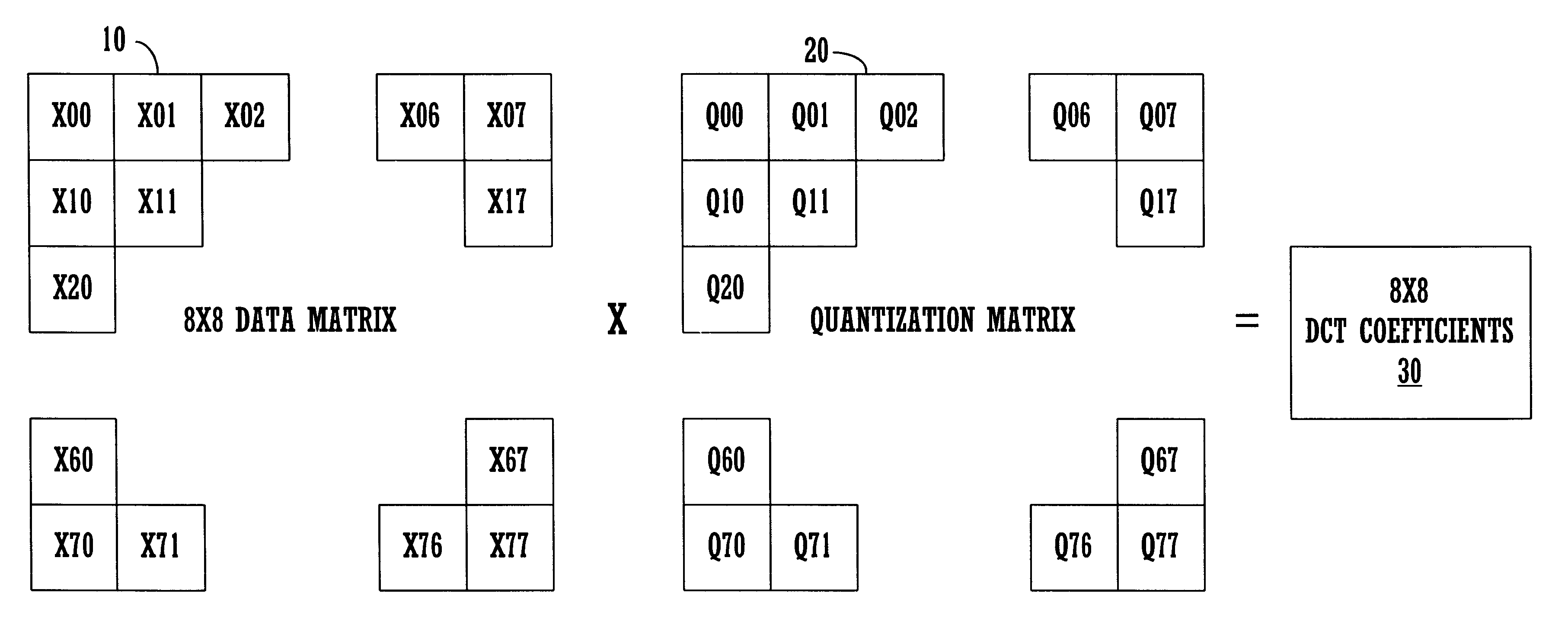
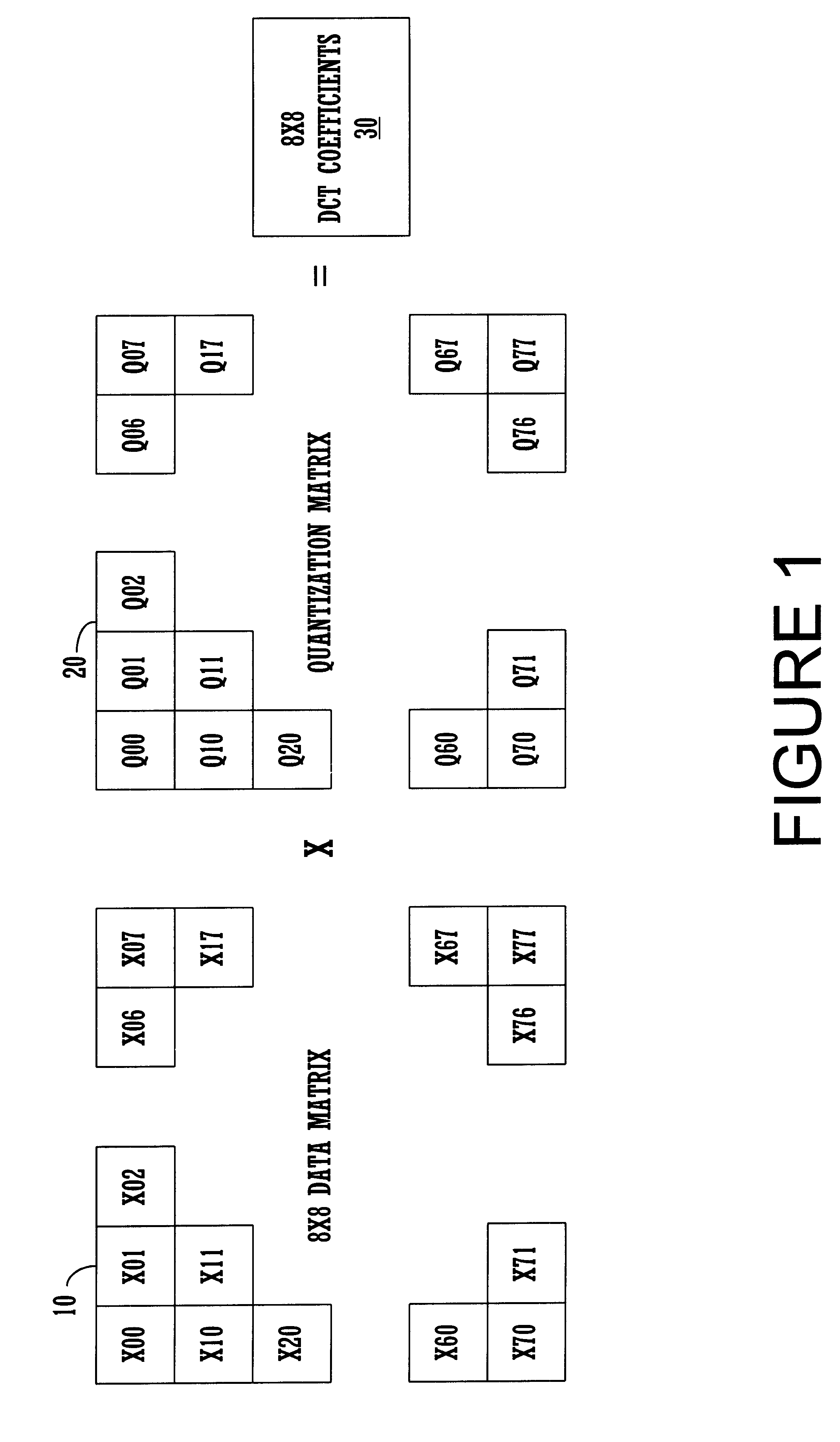
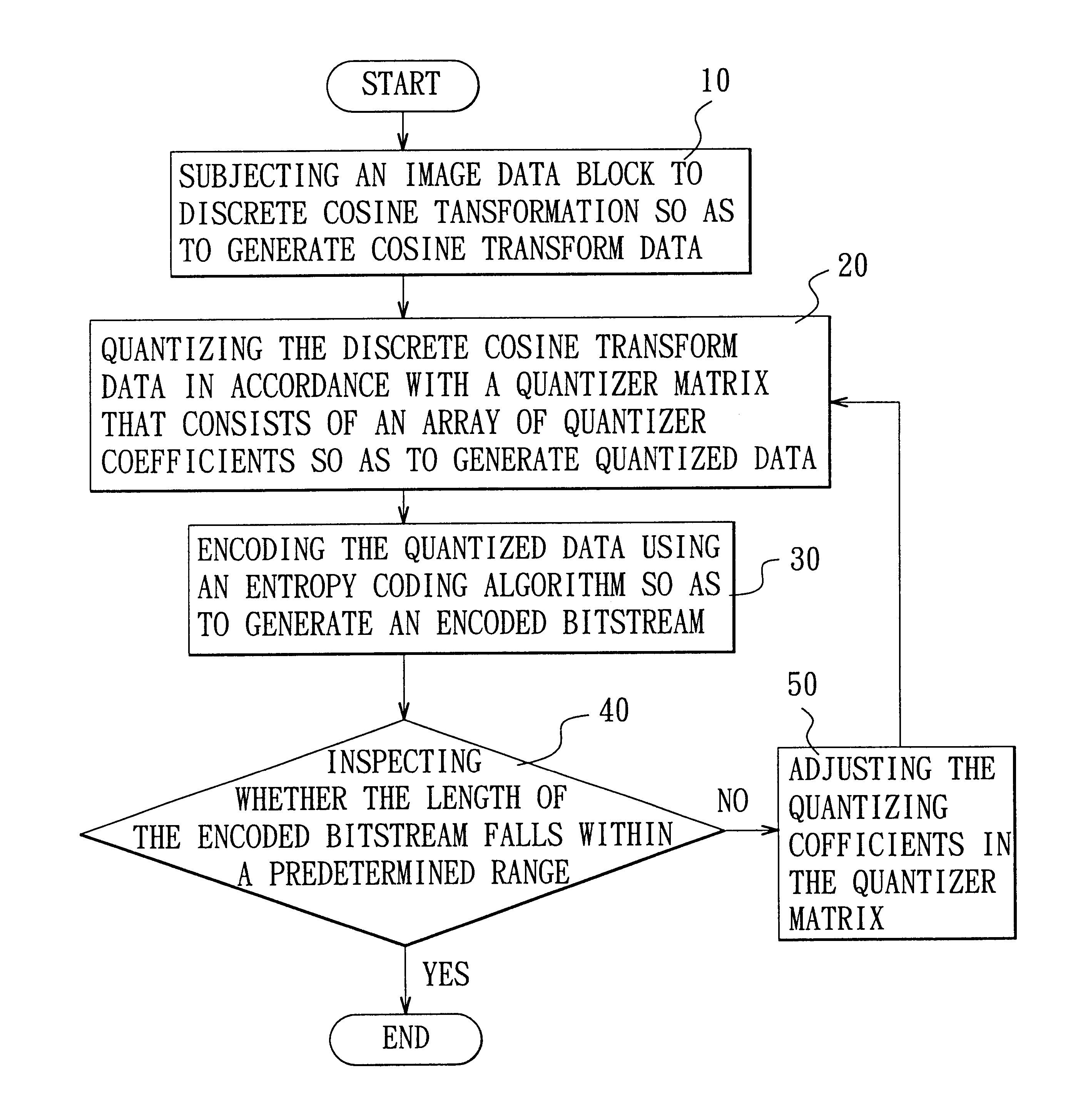
A method is adapted for compressing an image data block, and includes the steps of:(a) subjecting the image data block to discrete cosine transformation so as to generate discrete cosine transform data;(b) quantizing the discrete cosine transform data in accordance with a quantizer matrix that consists of an array of quantizing coefficients so as to generate quantized data;(c) encoding the quantized data using an entropy coding algorithm so as to generate an encoded bitstream; and(d) when the length of the encoded bitstream does not fall within a predetermined range, adjusting the quantizing coefficients in the quantizer matrix and repeating steps (b) and (c) until the length of the encoded bitstream falls within the predetermined range.
Owner:SILICON INTEGRATED SYSTEMS
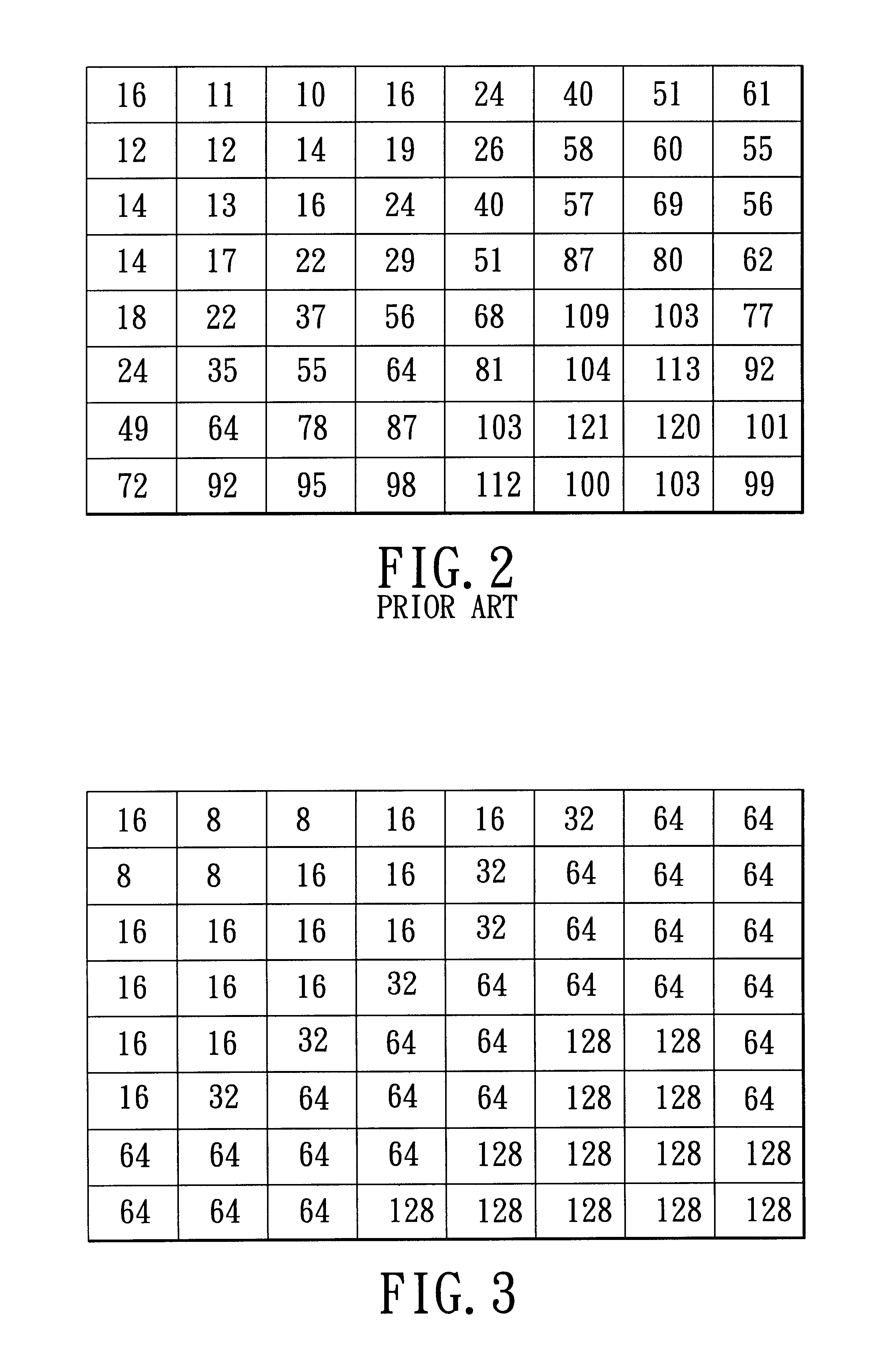
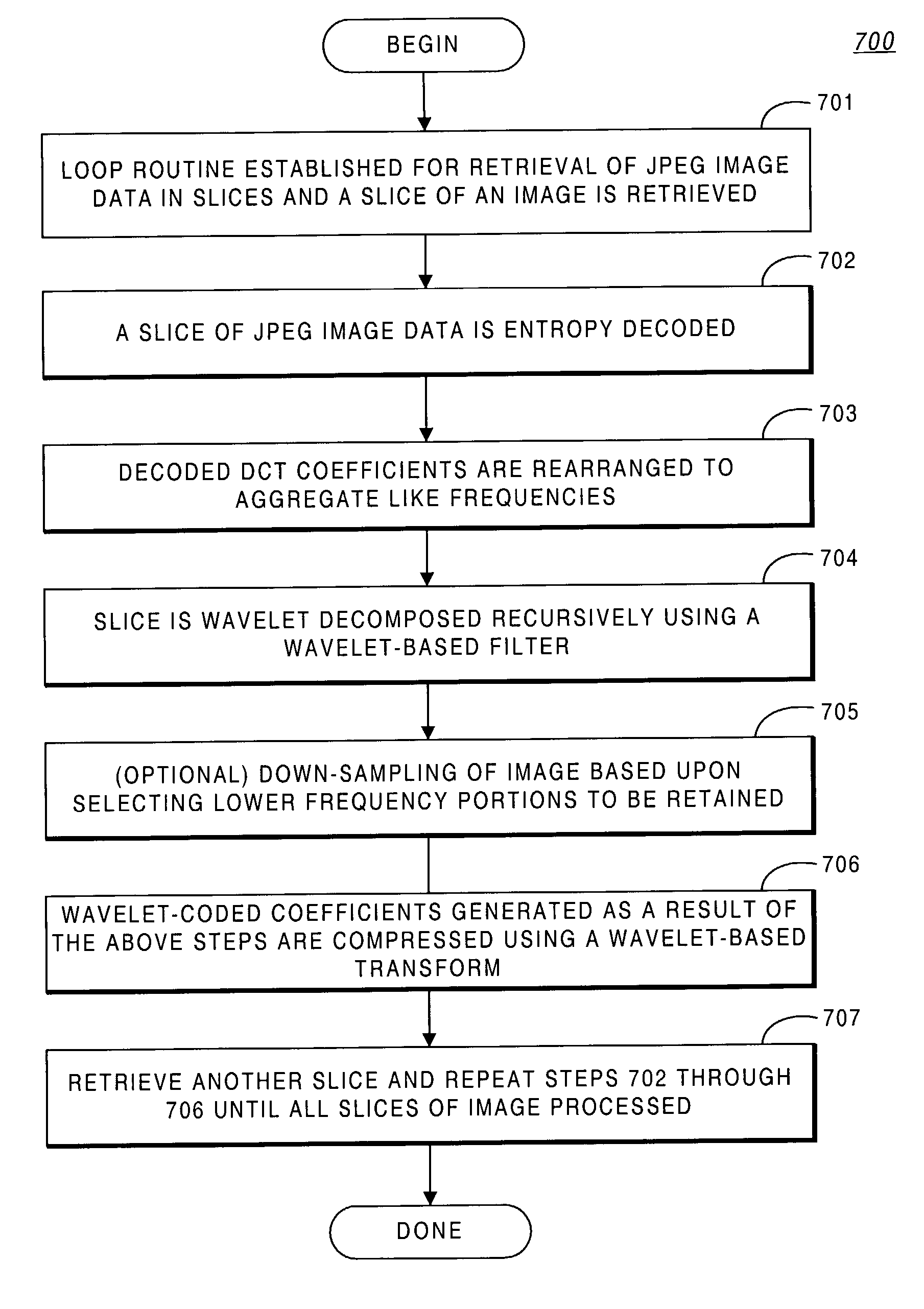
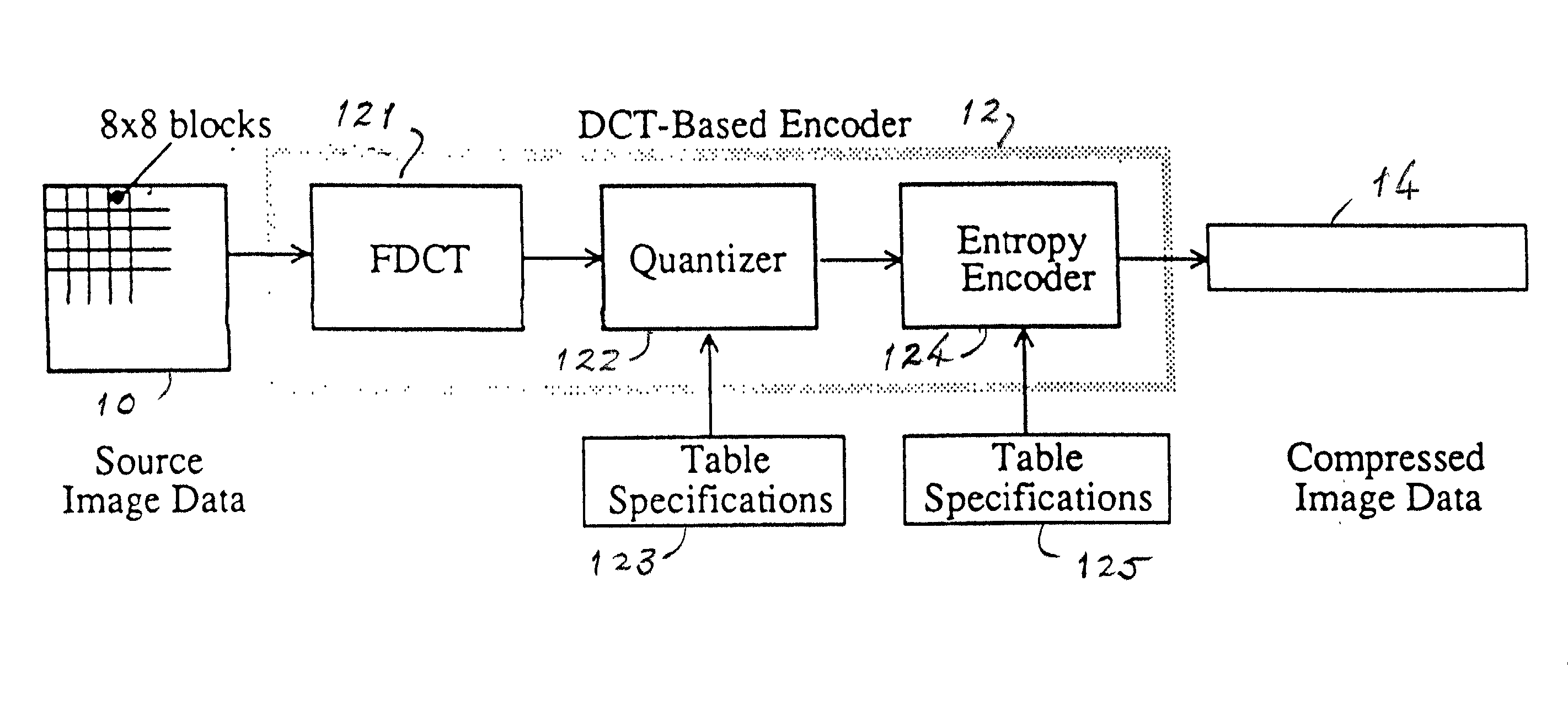
System and method for improved compression of DCT compressed images
A system providing methods for improved compression of images that have been compressed using Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) based compression is described. A digital image that has been compressed using DCT based compression, such as an image compressed using the Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) compression scheme, is received and partially decompressed to generate DCT coefficients of the image. The decoded coefficients of the image are then rearranged to aggregate like frequencies together. After rearrangement, the image is recompressed using a wavelet-based compression scheme.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method of embedding digital watermark, method of extracting embedded digital watermark and apparatuses for the same
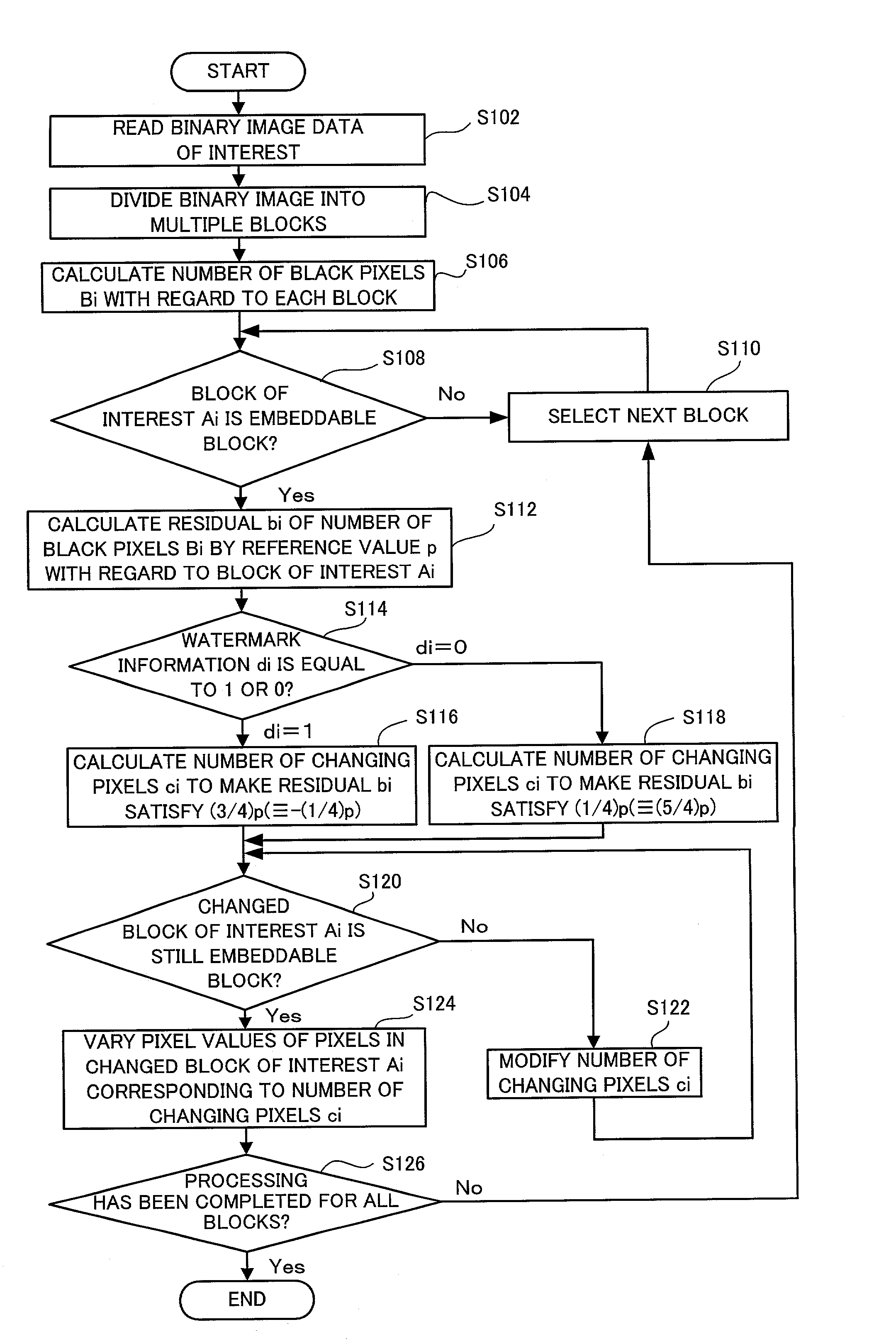
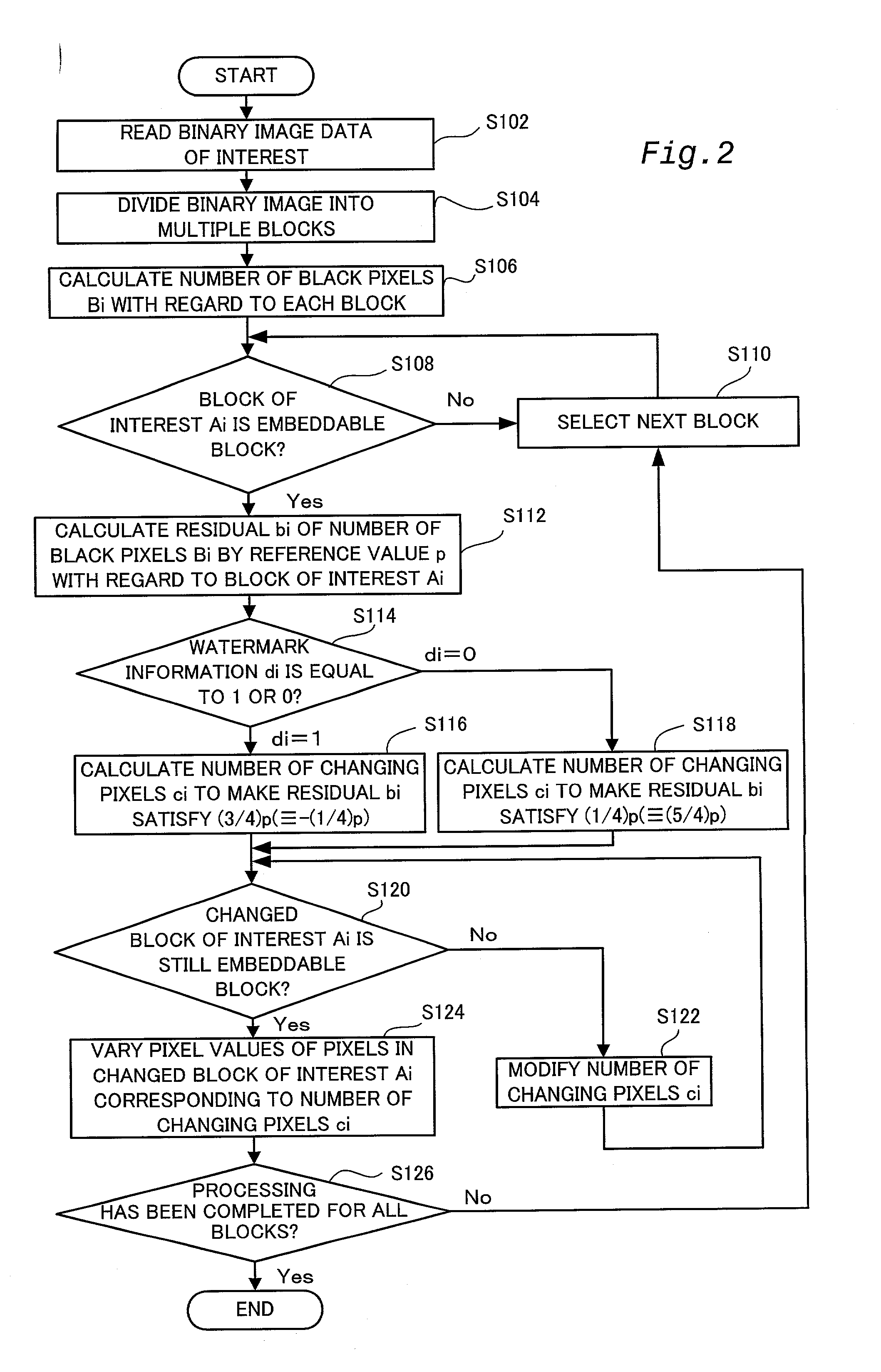
InactiveUS20030076979A1Easy to processIncrease resistanceCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsColor imageColor transformation
A color conversion module 42 carries out color conversion of original color image data Grgb from the RGB color system into the CMYK color system to obtain color-converted original color image data Gcmyk (step S104). A DCT module 44 applies DCT (discrete cosine transform) over the whole color-converted original color image data Gcmyk to generate DCT coefficients Dcmyk (step S106). An embedding module 46 embeds the watermark information s into the components C, M, Y, and K of the DCT coefficients Dcmyk (step S108). An IDCT module 48 applies IDCT (inverse discrete cosine transform) onto DCT coefficients D'cmyk with the watermark information s embedded therein to generate embedding-processed color image data G'cmyk (step S110). The color conversion module 42 carries out color conversion of the embedding-processed color image data G'cmyk from the CMYK color system into the RGB color system to obtain embedding-processed color image data G'rgb (step S112). This arrangement does not require any correction of the position or the shape of image blocks in the process of extracting the embedded watermark information.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
JPEG packed block structure
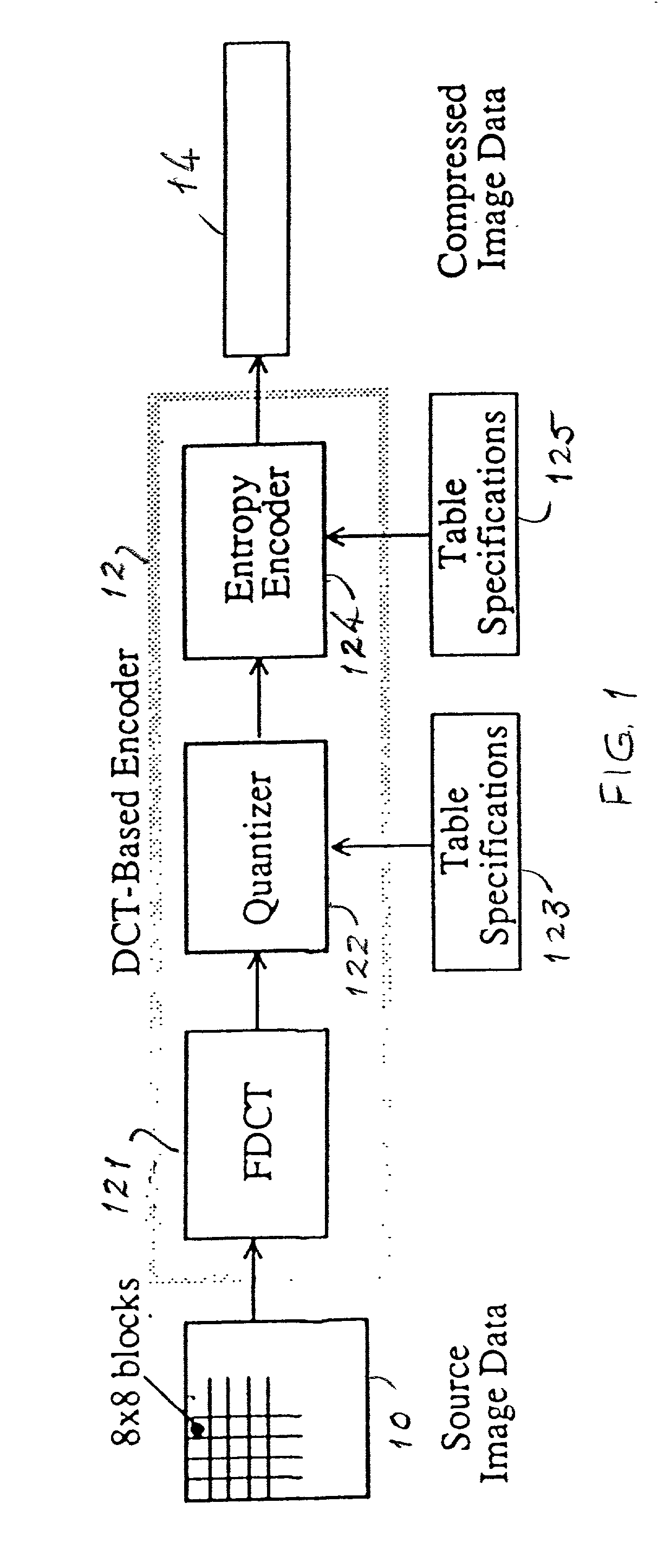
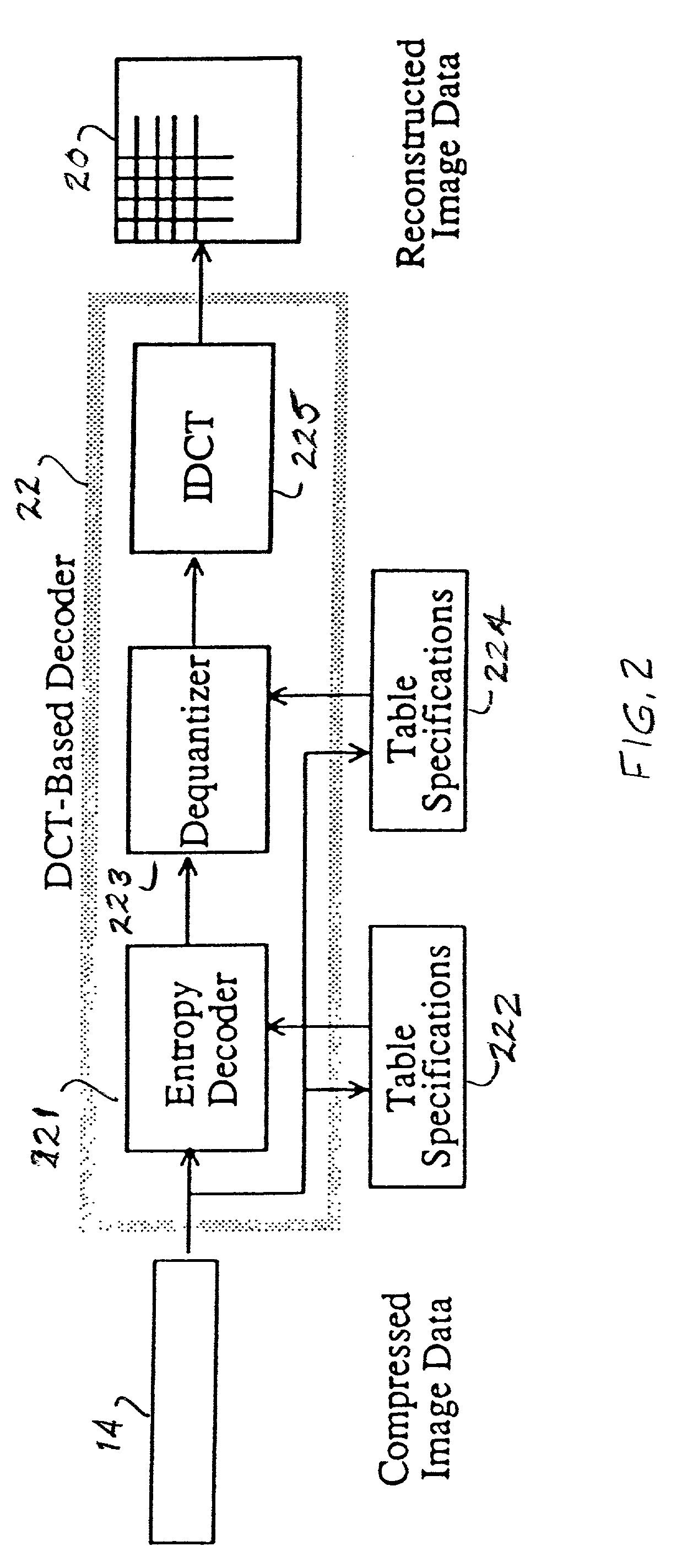
InactiveUS20020076115A1Not impose processing costSpeedCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionENCODEDiscrete cosine transform
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) images are encoded and decoded as fast as possible for a variety of disparate applications. A novel structure stores the 8x8 Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) blocks after entropy decoding in a JPEG decoder or after the Forward Discrete Cosine Transform (FDCT) in the JPEG encoder to use as an intermediate format between transform processes. The format was chosen to speed up the entropy decode and encode processes and is based on the information needed for the JPEG Huffman entropy coding, but lends itself to fast execution of other DCT based transforms, including arithmetic entropy coding.
Owner:RICOH KK
Natural image denoising method based on dictionary learning and block matching
ActiveCN102184526AImprove denoising effectPreserve textureImage enhancementSingular value decompositionDictionary learning
The invention discloses a natural image denoising method based on dictionary learning and block matching, which mainly solves the problems that texture details are easily lost and homogenous areas are not smooth in the conventional natural image denoising. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) setting a denoising target function and inputting a noise-containing image z(x); (2) making an original image equal to the noise-containing image, namely y(x)=z(x), and making a dictionary D be a redundant discrete cosine transform (DCT) dictionary; (3) updating the atoms of the dictionary D and a corresponding coefficient matrix alphaij by using a kernel-singular value decomposition (KSVD) algorithm; (4) denoising the noise-containing image z(x) by using a block matching three-dimensional (BM3D) algorithm to acquire a primary denoising result; and (5) introducing the updated D and alphaij into the estimation formula of the original image to acquire the denoising result of the noise-containing image z(x). Compared with the conventional classic denoising method, the method achieves a better denoising effect and can be used for denoising a natural image; and the homogeneous area is smoothened, and the texture, the profile and the edge detail information of the image can be maintained at the same time.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
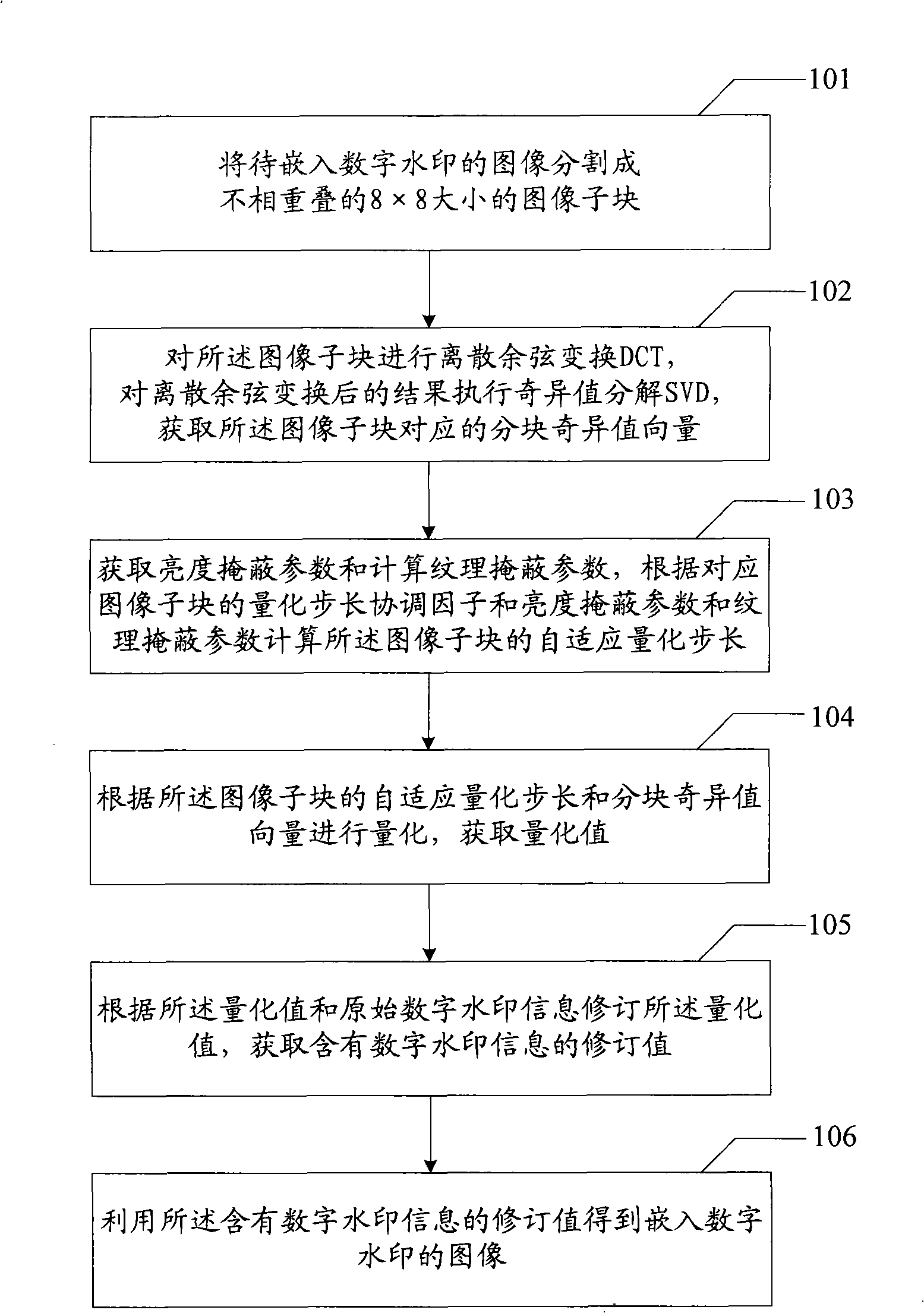
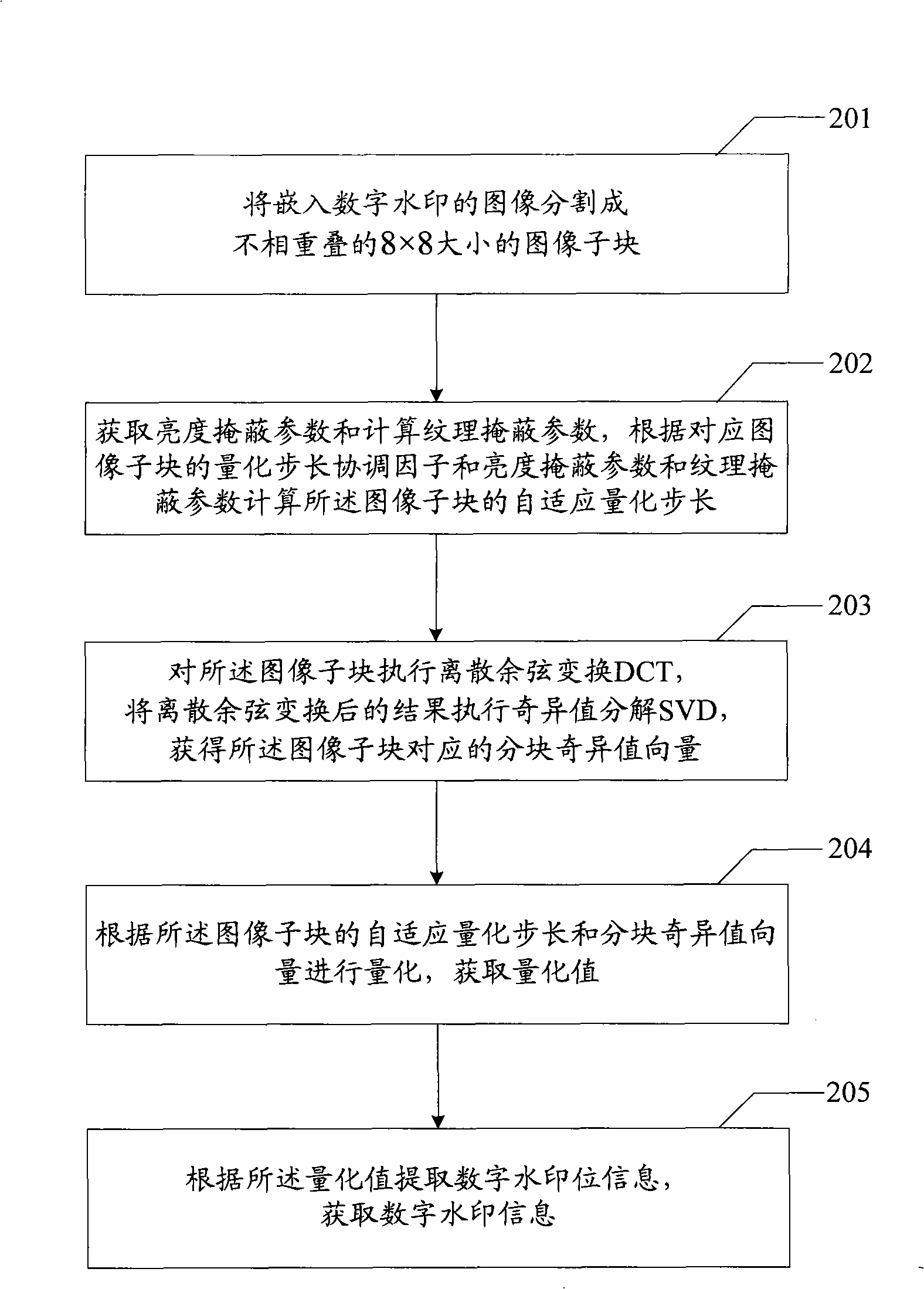
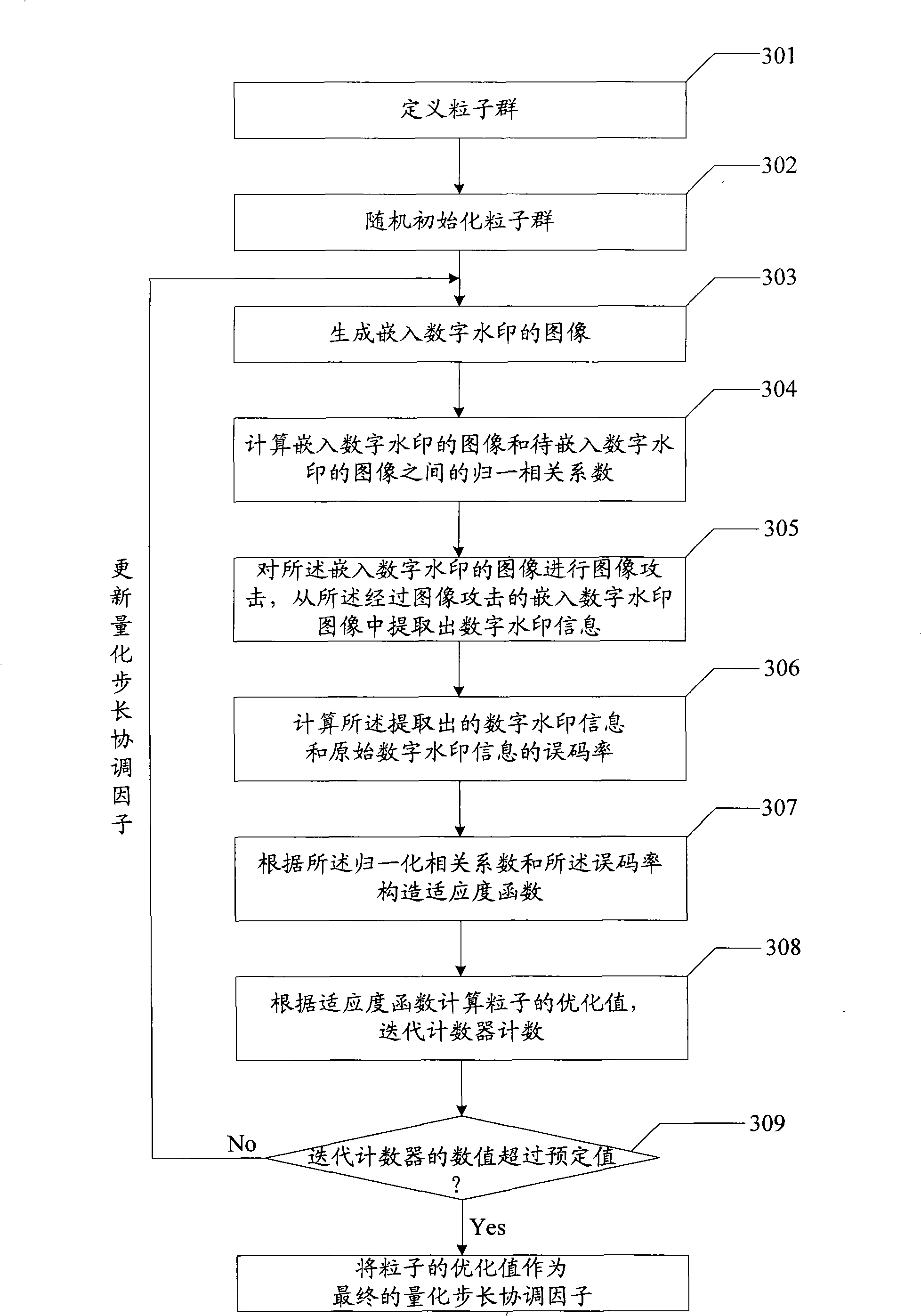
Digital watermarking embedding, extracting and quantizing step size coordinating factor optimizing method and device
The invention relates to an embedding, extracting and quantization step size coordination factor optimizing method of a digital watermark and a device thereof. The embodiment of an embedding method of the digital watermark comprises the steps that: an image to be embedded with the digital watermark is divided into image subblocks with preset size; DCT (discrete cosine transform) is executed to the image subblocks; SVD (singular value transform) is executed to the result after DCT so as to obtain a blocking singular value vector of the image subblocks; a texture masking parameter is calculated to obtain a brightness masking parameter; according to a quantization step size coordination factor, the brightness marking parameter and the texture masking parameter of the image subblocks, a self-adaptive quantization step size of the image subblocks is obtained; the self-adaptive quantization step size of the image subblocks and the blocking singular value vector are quantized to obtain a quantization value; amendment is carried out according to the quantization value and the information of the digital watermark to obtain an amendment value of the information of the digital watermark; and the amendment value containing the information of the digital watermark is utilized to obtain the image embedded with the digital watermark. The embodiment of the invention realizes the balance of the invisibility and the robustness of a digital watermarking method.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
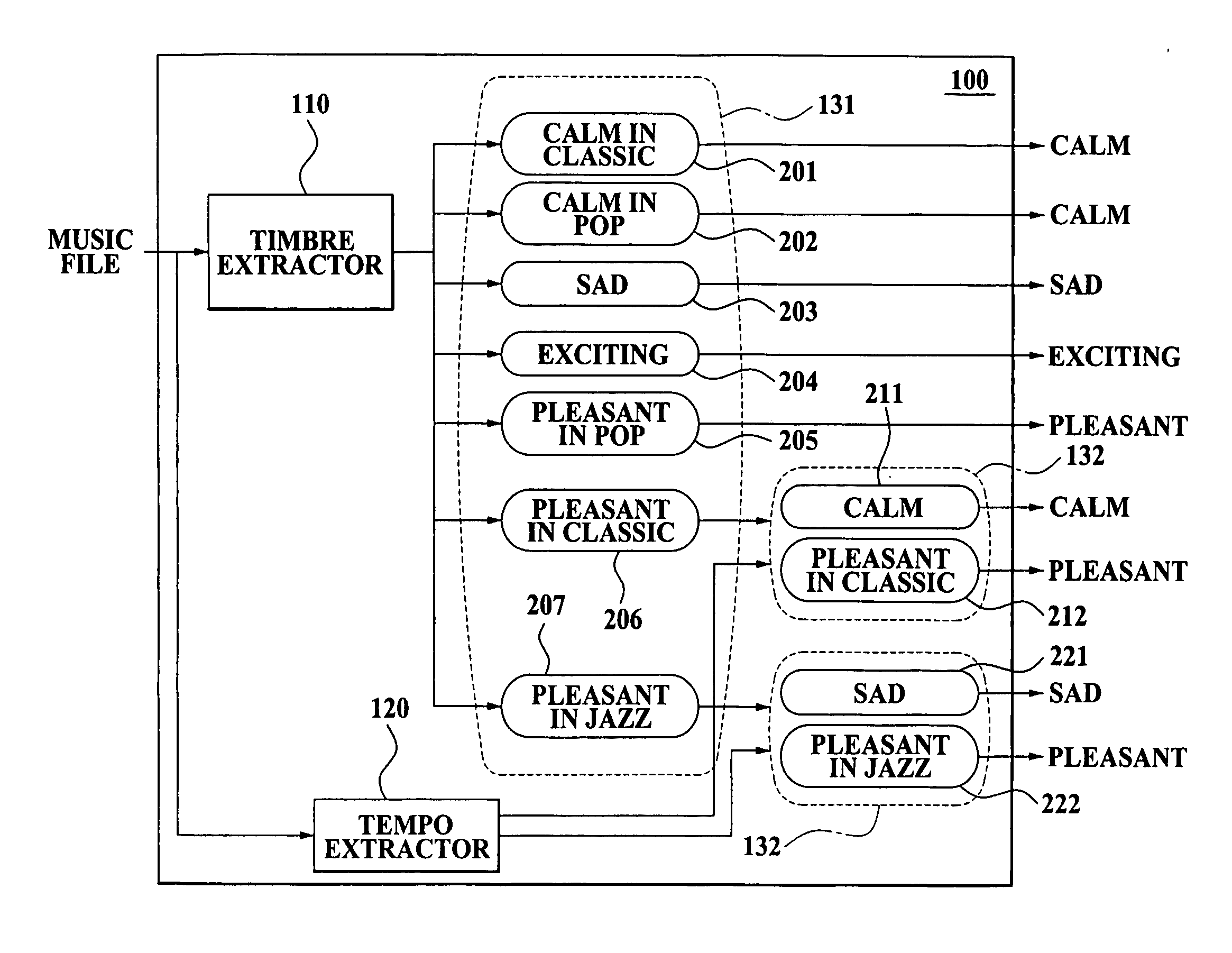
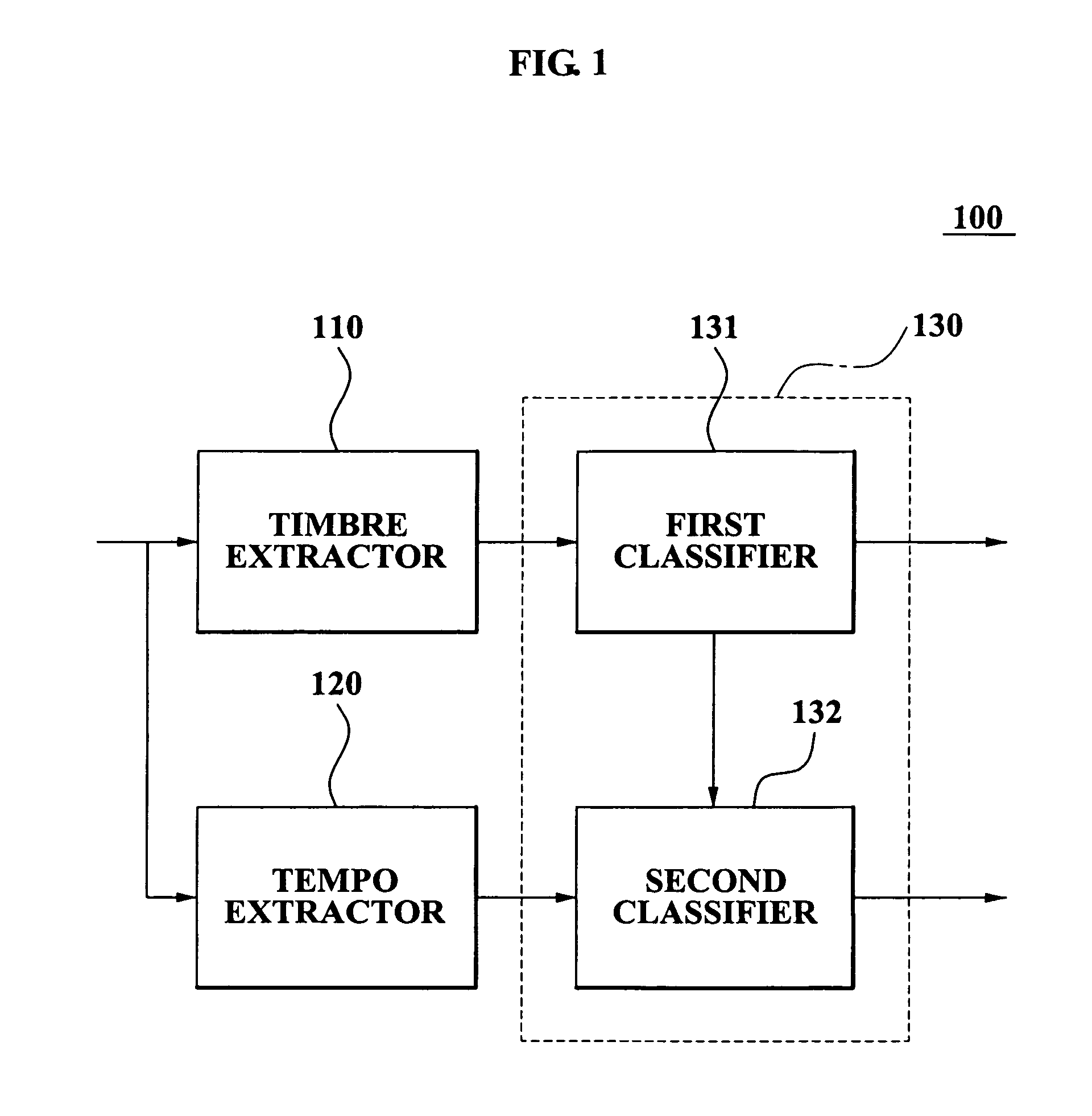
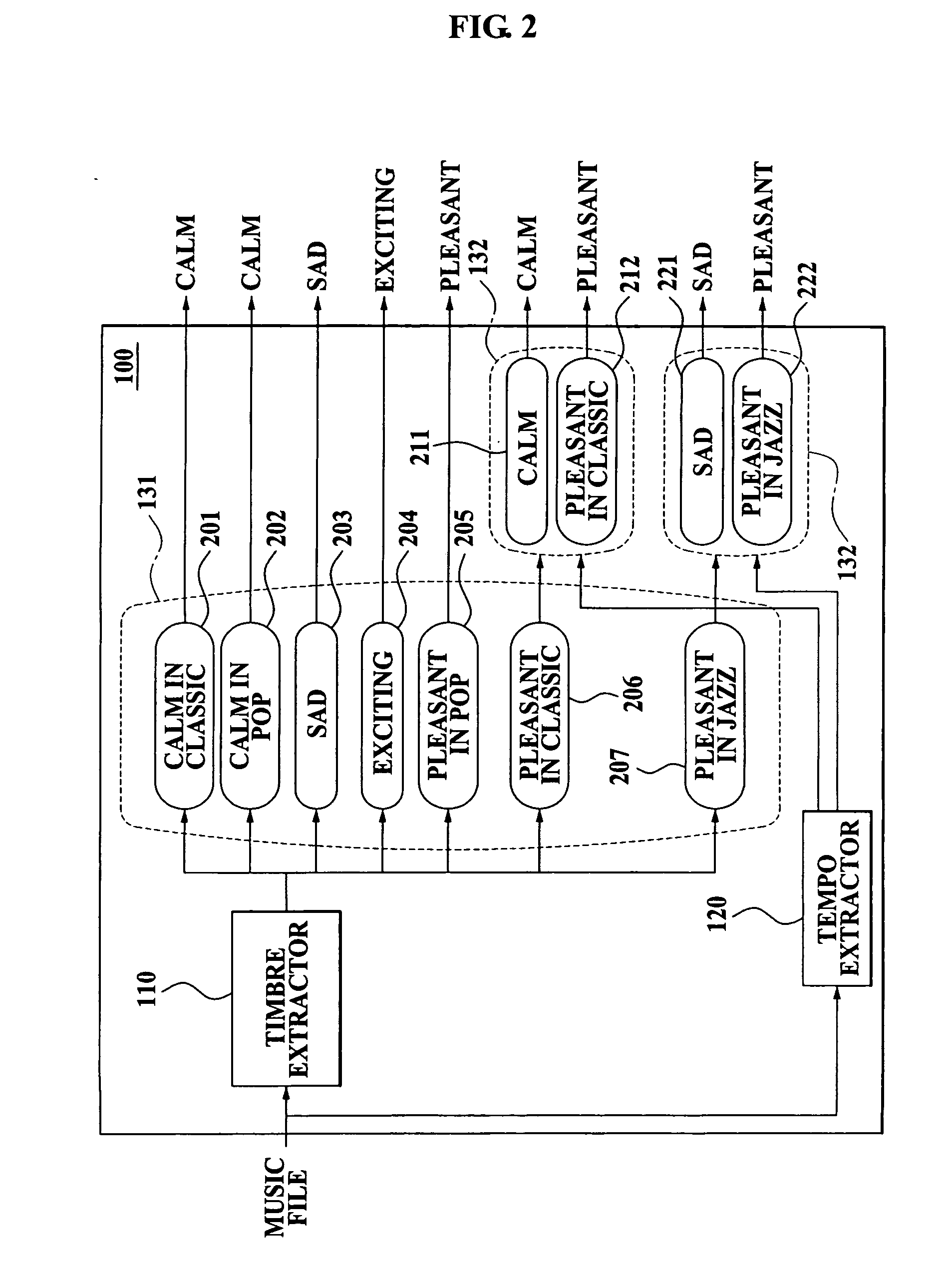
Method and apparatus for classifying mood of music at high speed
ActiveUS20070107584A1Improve reliabilityAccurate classificationElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisPattern recognitionTimbre
A method and apparatus for classifying mood of music at high speed. The method includes: extracting a Modified Discrete Cosine Transformation-based timbre feature from a compressed domain of a music file; extracting a Modified Discrete Cosine Transformation-based tempo feature from the compressed domain of the music file; and classifying the mood of the music file based on the extracted timbre feature and the extracted tempo feature.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image waterprint method for copyright protection
InactiveCN1455578AReduce the amount of calculationAvoid complexityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPattern recognitionImage extraction
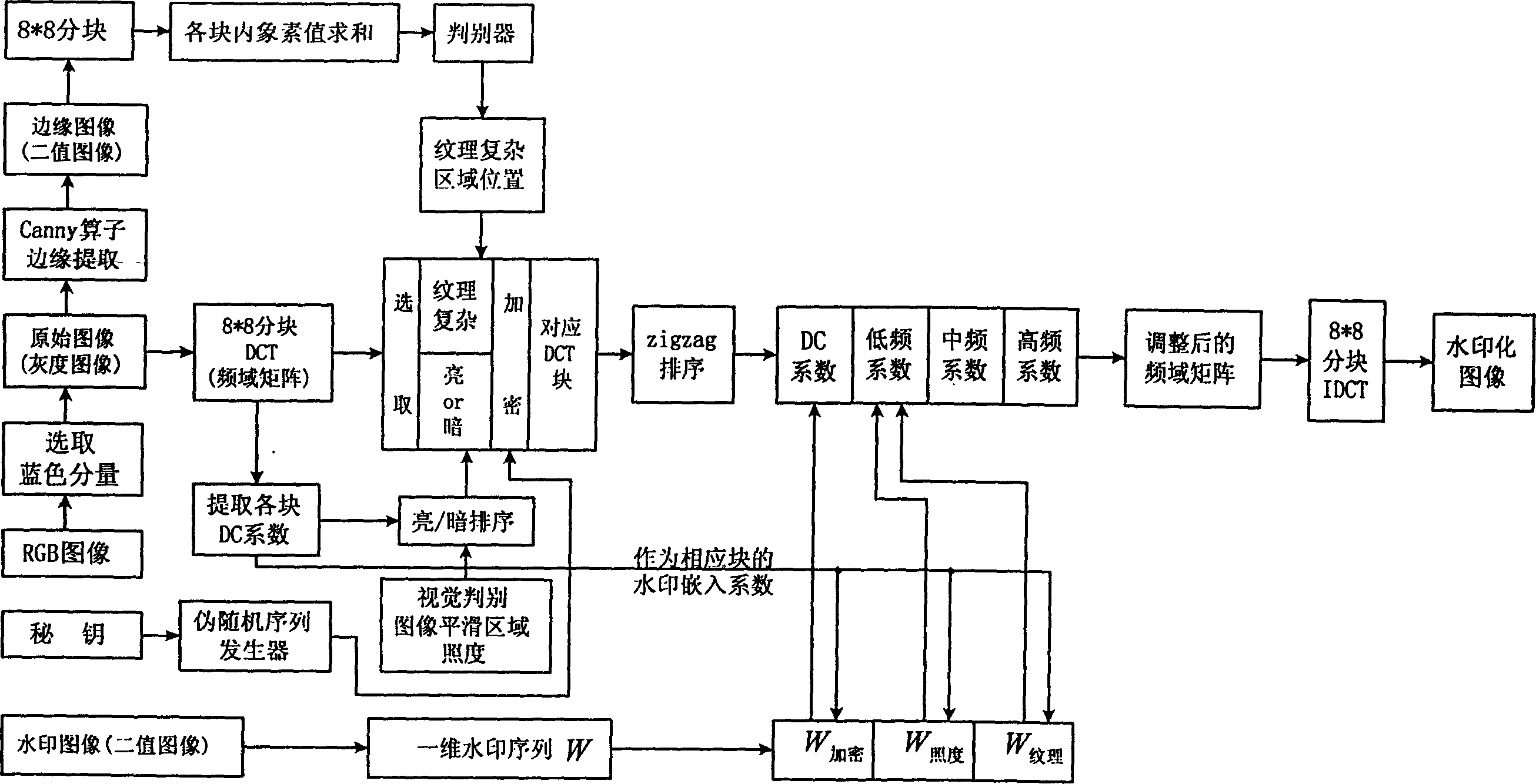
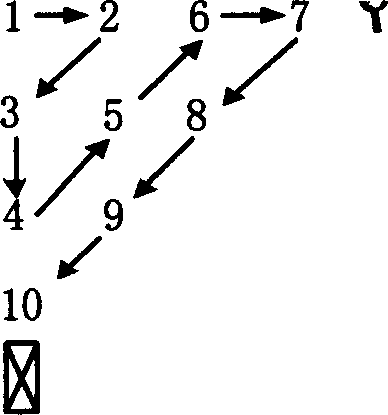
The present invention discloses an image watermark way applied to protecting copyright. It converts two-dimensional pels matrix to a two-value sequence group, splits the original image into 8*8 pels in the pels area, and processes discrete cosine conversion to (DCT) convert every pels area to frequency area. By fake radnom selecting block texture selecting block and illumination selecting block, it can conform which area block need to embed the watermark, and can sort them Zigzag. It embeds the encryption part of the watermark sequence group into the direct-current factor position of the random selecting block, also embeds the texture part and illumination part into respective low frequency factor position.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Embedding and detecting method and system for image data watermark information
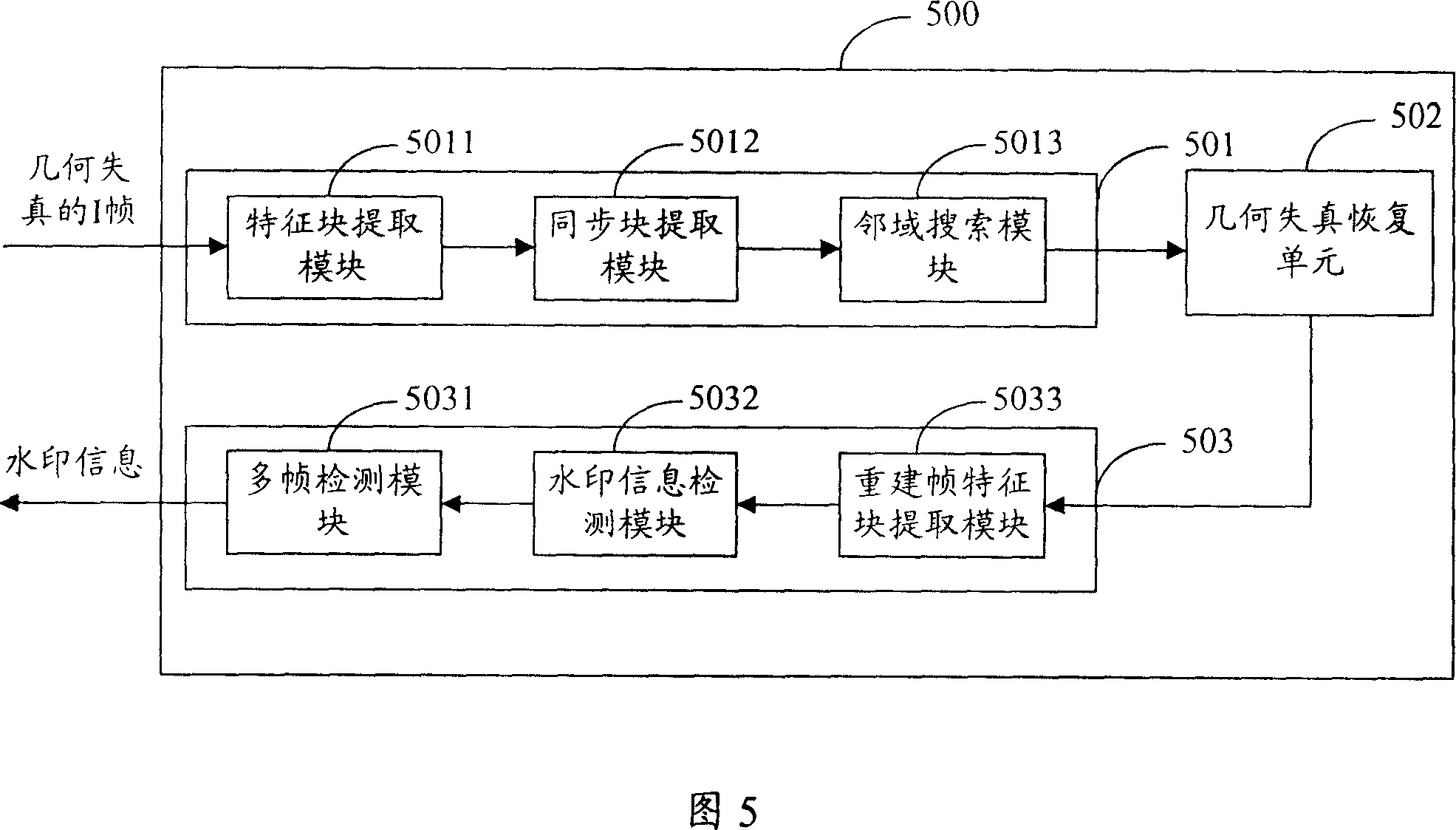
ActiveCN101005615AProtect against geometry attacksReduce complexityTelevision systemsImage data processing detailsIntermediate frequencyDiscrete cosine transform
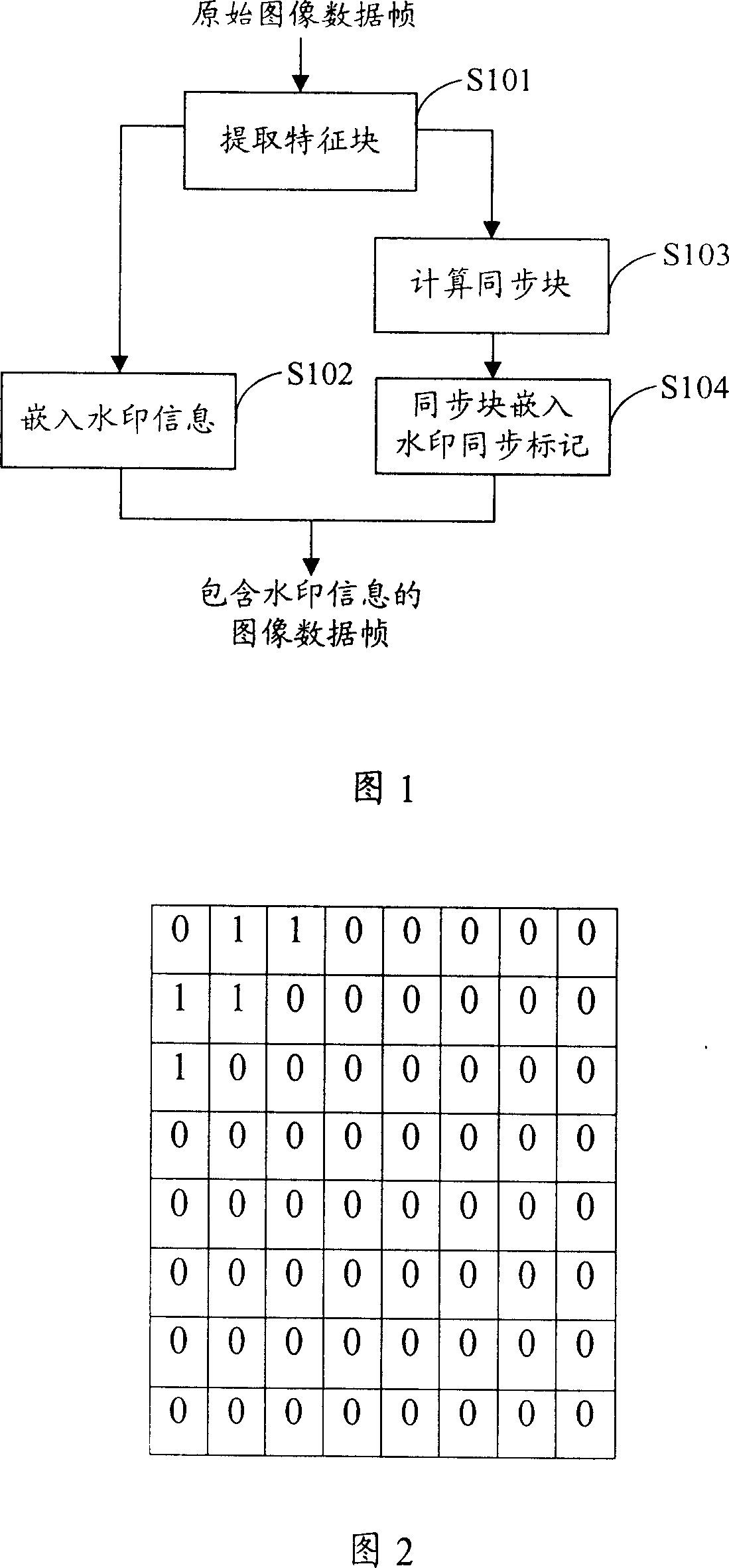
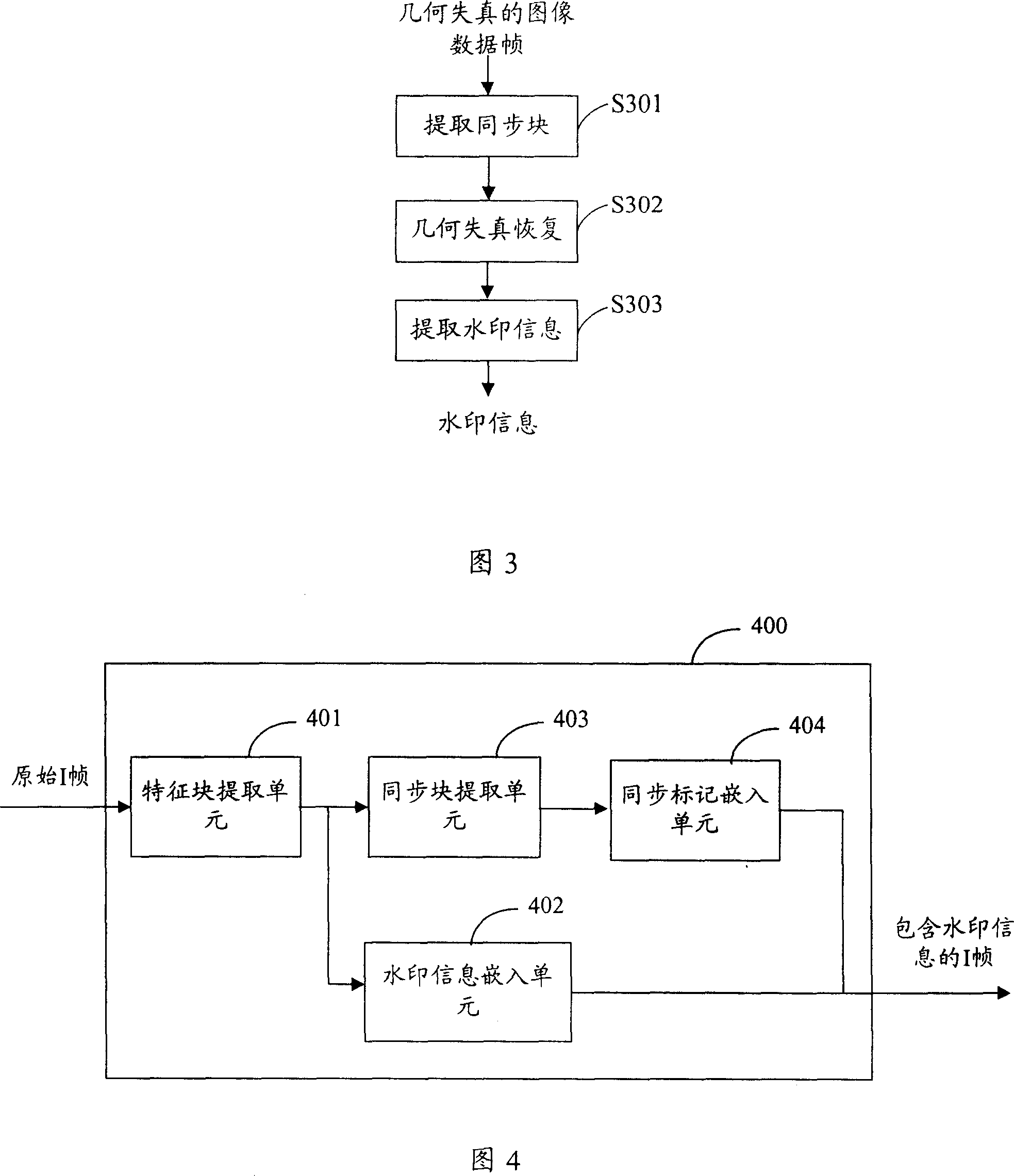
The method thereof comprises: a) using low frequency coefficient of discrete cosine transform (DCT) to extract multi feature blocks from the original image data frame; b) embedding watermark information into the middle frequency of DCT domain of said feature blocks; c) according to said multi feature blocks, determining the position of synchronous block; d) embedding synchronous symbol into the synchronous block. The invention can resist geometrical attack.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
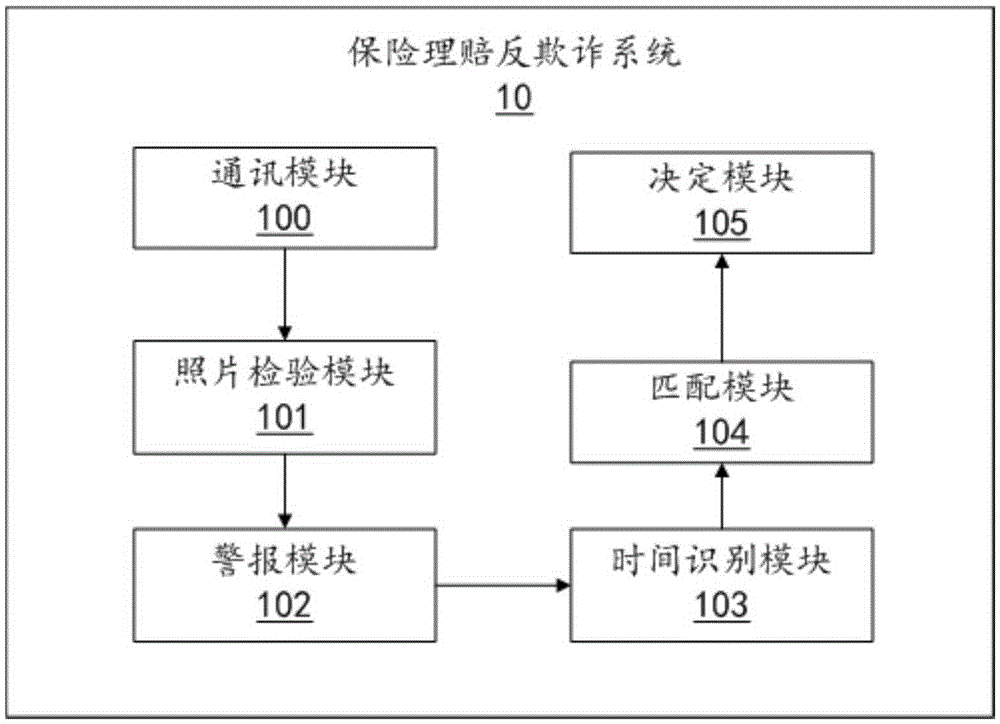
Insurance claim antifraud implementation method based on claim photo deep learning and server
InactiveCN105405054AAutomatically identify claims settlement behaviorImage analysisFinanceDiscrete cosine transformData mining
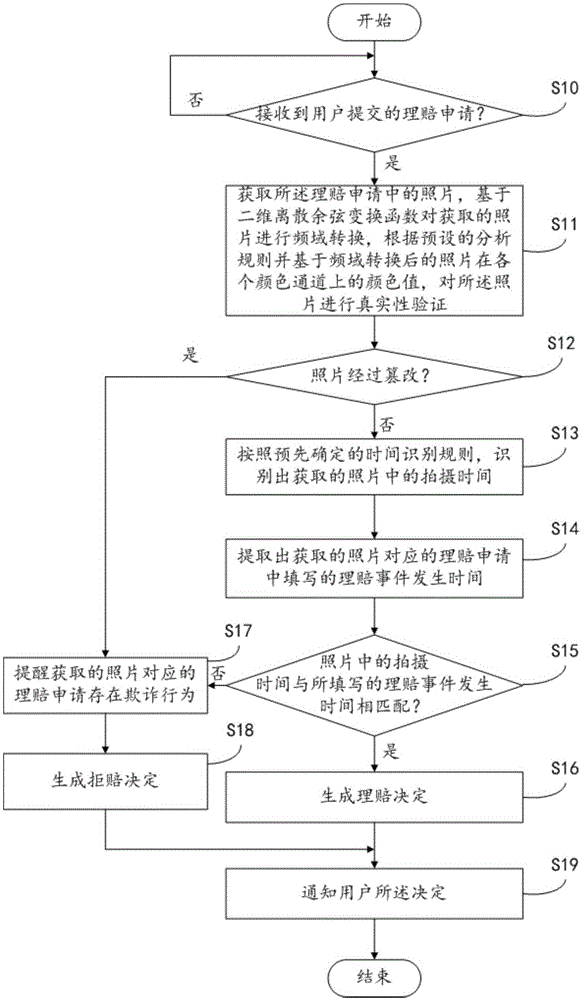
The invention discloses an insurance claim antifraud implementation method based on a claim photo deep learning. The method comprises: when a claim photo submitted by a user is received, performing frequency-domain transforming on the acquired photo based on a two-dimensional discrete cosine transform function, and according to a preset analysis rule and based on a color value of the photo subjected to the frequency-domain transforming in each color channel, performing authenticity verification on the photo; if the acquired photo are unreal, generating reminding information to remind that a fraudulent conduct exists in a claim application corresponding to the acquired photo; if the acquired photo is real, identifying photographing time of the acquired photo; extracting claim event occurrence time filled in the claim application corresponding to the acquired photo; and when the extracted claim event occurrence time does not match with the identified photographing time, generating reminding information to remind that the fraudulent conduct exists in the claim application corresponding to the acquired photo; The present invention also provides a server applicable to the method. The method can automatically identify a fraudulent claim behavior.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
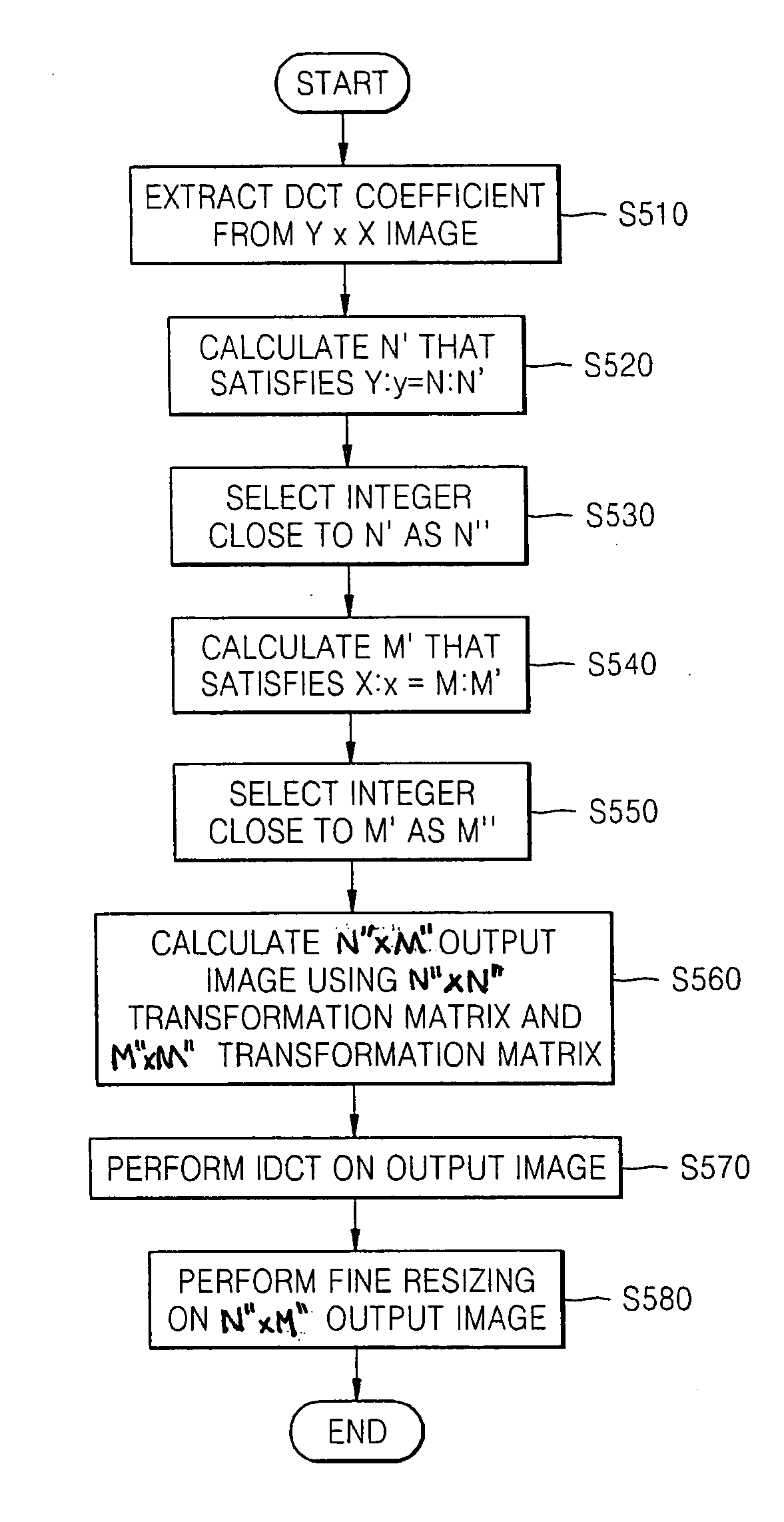
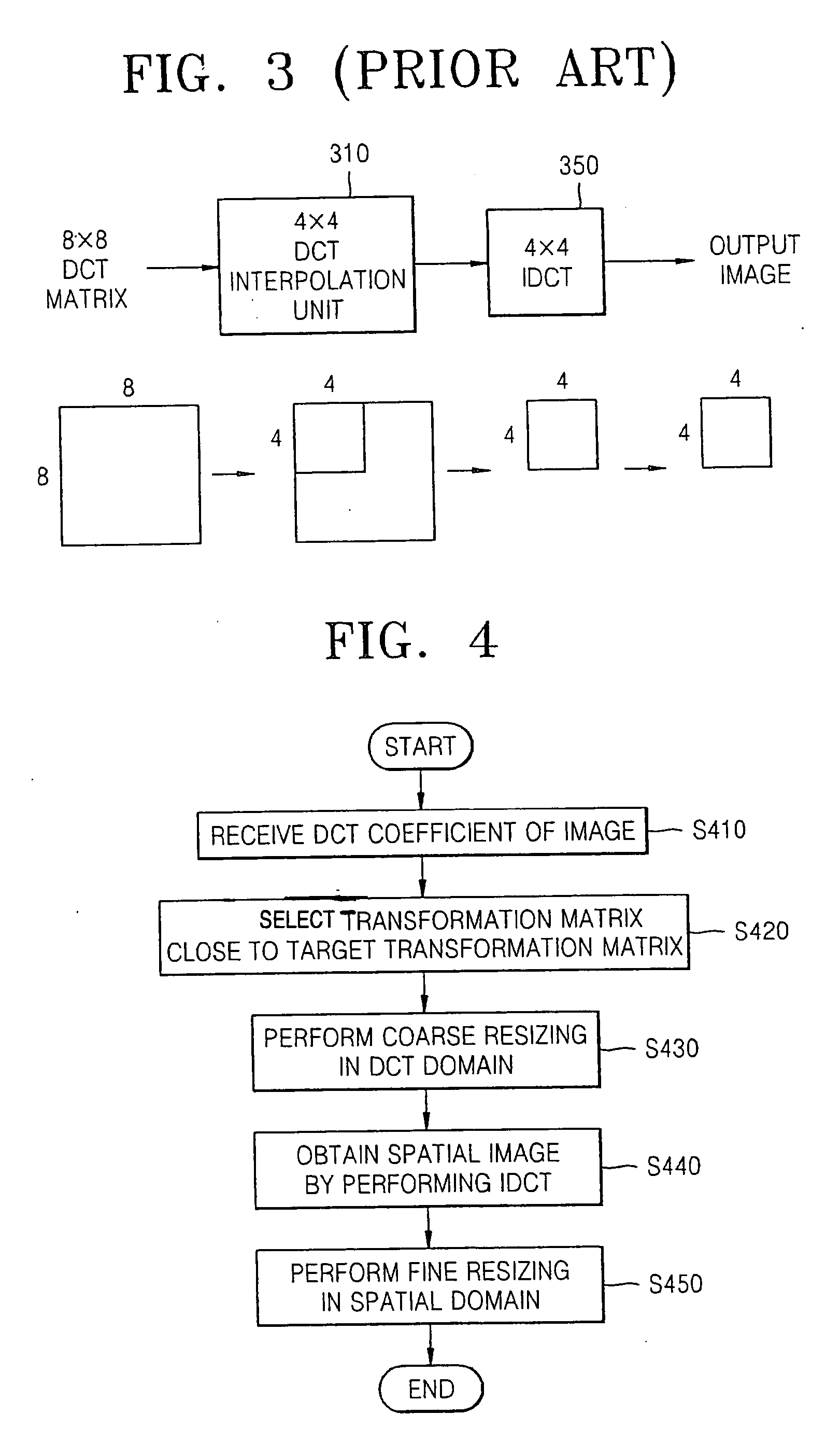
Method and apparatus for resizing images using discrete cosine transform
ActiveUS20070237414A1Geometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDiscrete cosine transform
A method for resizing an image using a resizing ratio may include receiving DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) coefficients of an input image; calculating a transformation matrix for transforming the input image to an integer aspect ratio closest to the resizing ratio; performing a coarse resizing on the input image in a DCT domain using the transformation matrix; obtaining a spatial image by performing an IDCT (Inverse Discrete Cosine Transform) on the coarse-resized domain; and forming an output image by performing a fine resizing on the spatial image in a spatial domain.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND +1
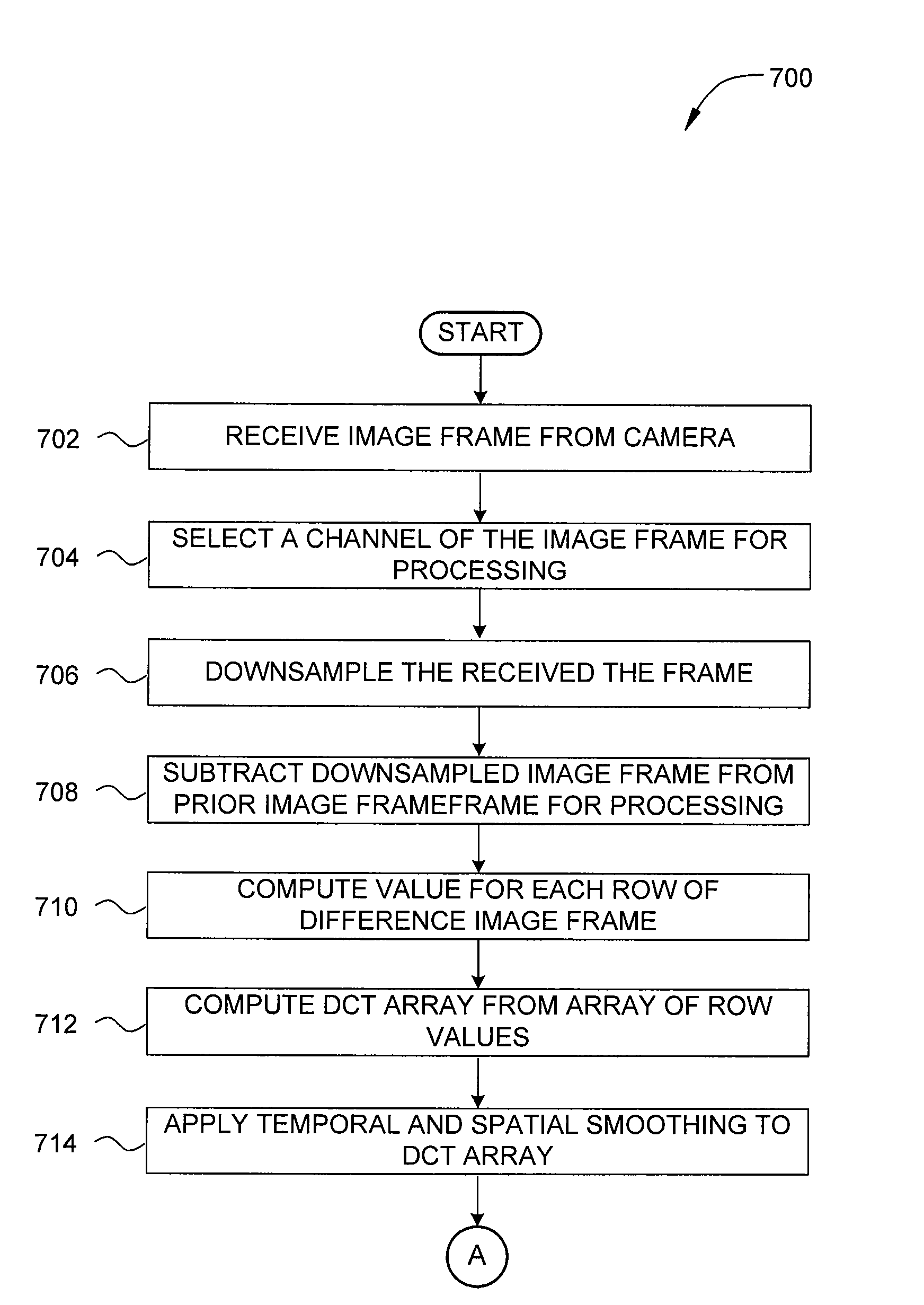
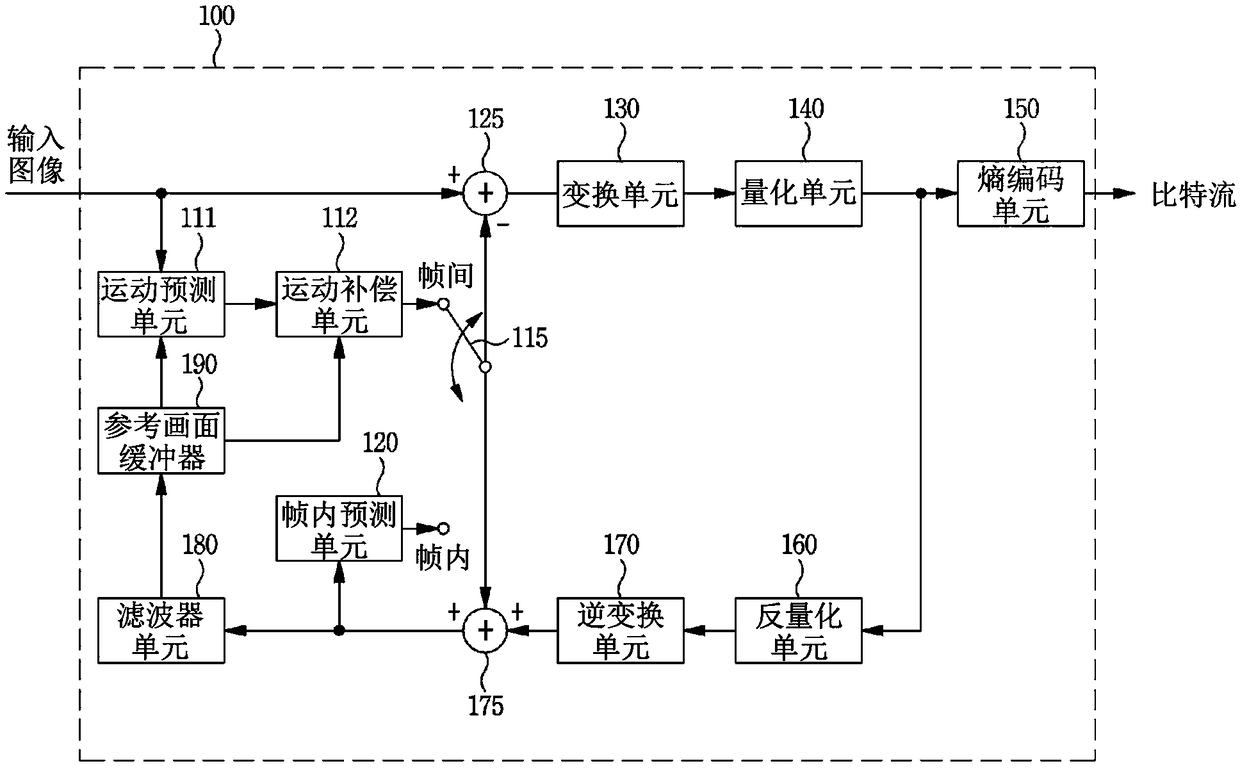
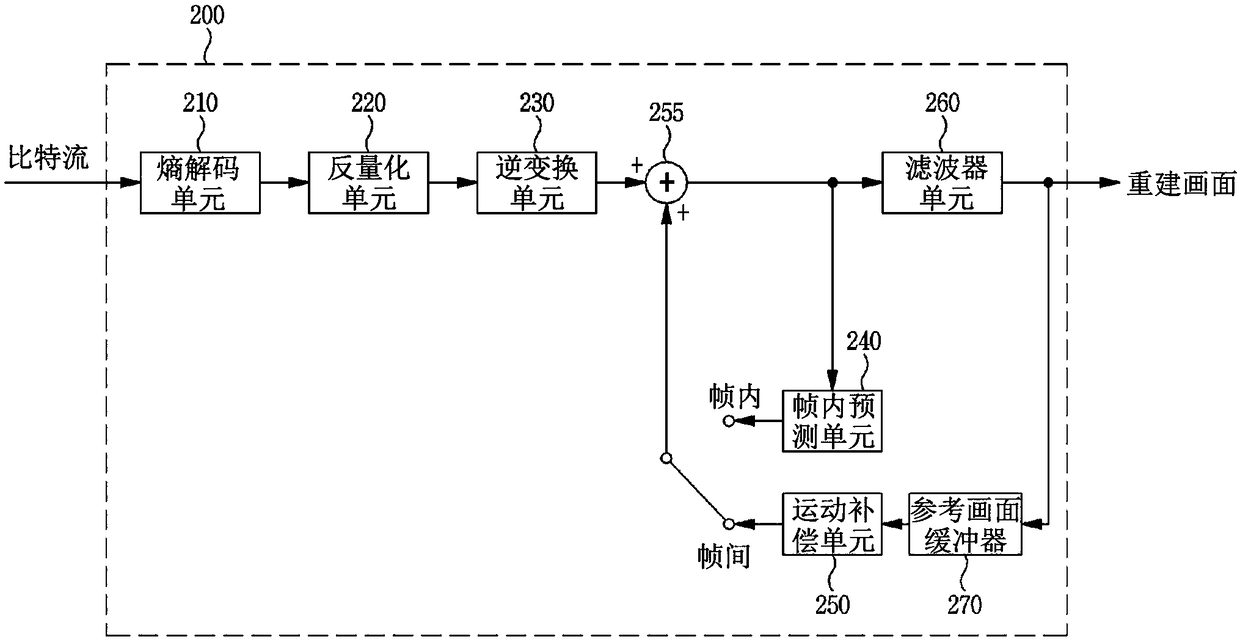
Dct based flicker detection
InactiveUS20150207975A1Accurate detectionReduce flickerTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsRadiologyRolling shutter
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for reducing flicker in image frames captured with a rolling shutter. A flicker detection and correction engine selects a first channel from a first image frame for processing. The flicker detection and correction engine subtracts each pixel value in the first channel from a corresponding pixel value in a prior image frame to generate a difference image frame. The flicker detection and correction engine identifies a first alternating current (AC) component based on a discrete cosine transform (DCT) associated with the difference image frame. The flicker detection and correction engine reduces flicker that is present in the first image frame based on the first AC component. One advantage of the disclosed techniques is that the flicker resulting from fluctuating light sources is correctly detected and reduced or eliminated irrespective of the frequency of the fluctuating light source.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method and apparatus for transform-based image encoding/decoding
ActiveCN109417636AImprove encoding/decoding efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencyDigital video signal modificationCoding decodingDiscrete sine transform
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for transform-based image encoding / decoding. The image decoding method according to the present invention comprises: a step of determining atransform mode of a current block; a step of inversely transforming residual data of the current block according to the transform mode of the current block; and a step of rearranging the residual dataof the current block inversely transformed according to the transform mode of the current block, wherein the transform mode may include at least one of a shuffling discrete sine transform (SDST), a shuffling discrete cosine transform (SDCT), a discrete sine transform (DST) and a discrete cosine transform (DCT).
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Video watermark embedding method and video watermark extracting method
ActiveCN103533458AIncreased Versatility and SecurityImprove efficiencyDigital video signal modificationSelective content distributionSingular value decompositionWatermark embedding
The invention discloses a video watermark embedding method and a video watermark extracting method, wherein the video watermark embedding method comprises the steps as follows: magnifying at a small scale a selected video frame image requiring watermark embedding and conducting self-adaption segmentation processing on a macro block and a subblock; selecting a transformation coefficient and embedding a watermark based on singular value decomposition (SVD) of the subblock and discrete cosine transformation (DCT) of the macro block; reconstructing the video frame image through inverse discrete cosine transformation, inverse process of singular value decomposition and small-scale shrinkage of the image. The video watermark extracting method corresponds to the embedding method, and the watermark extracted from a video frame is subjected to a series of post-processing to obtain a final watermark sequence. The methods provided by the invention have good universality, the video frame for watermark embedding and the selection of the transformation coefficient improve the invisibility and the robustness of the watermark, and the watermark embedding and extracting efficiencies are improved while the attacks against transcoding, noises, frame insertion, frame deletion, resolution change and the like are resisted.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
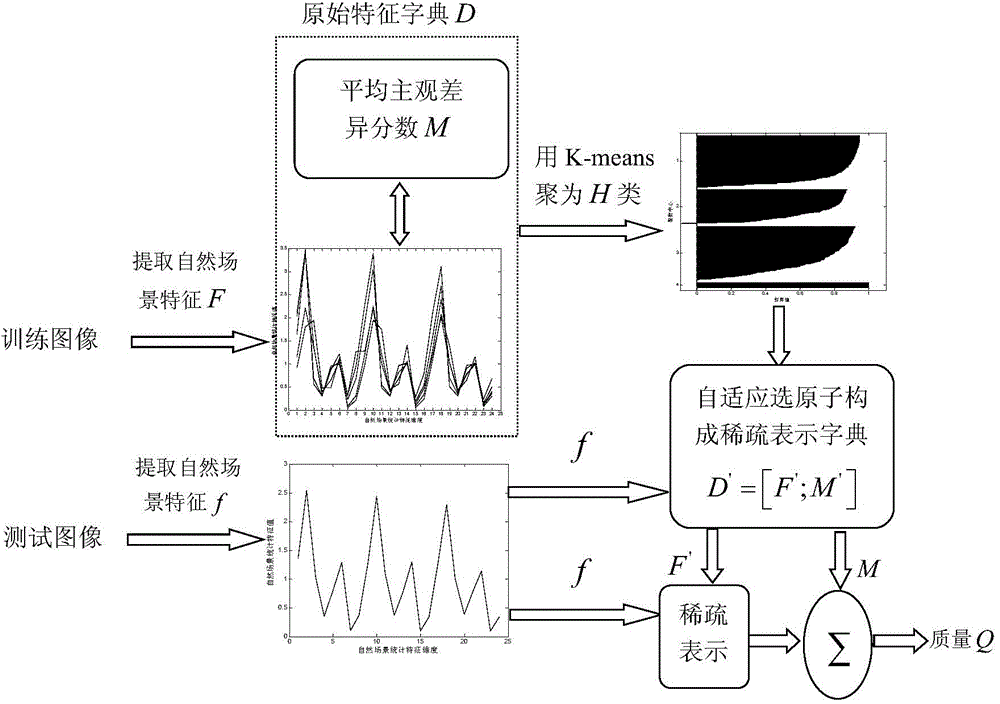
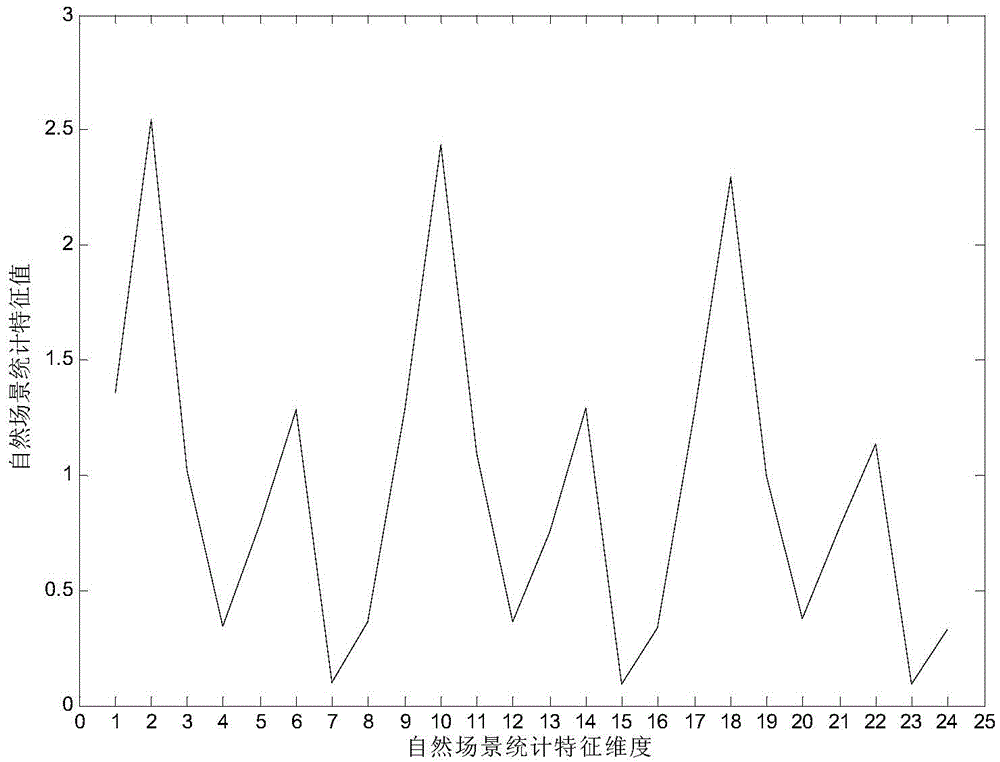
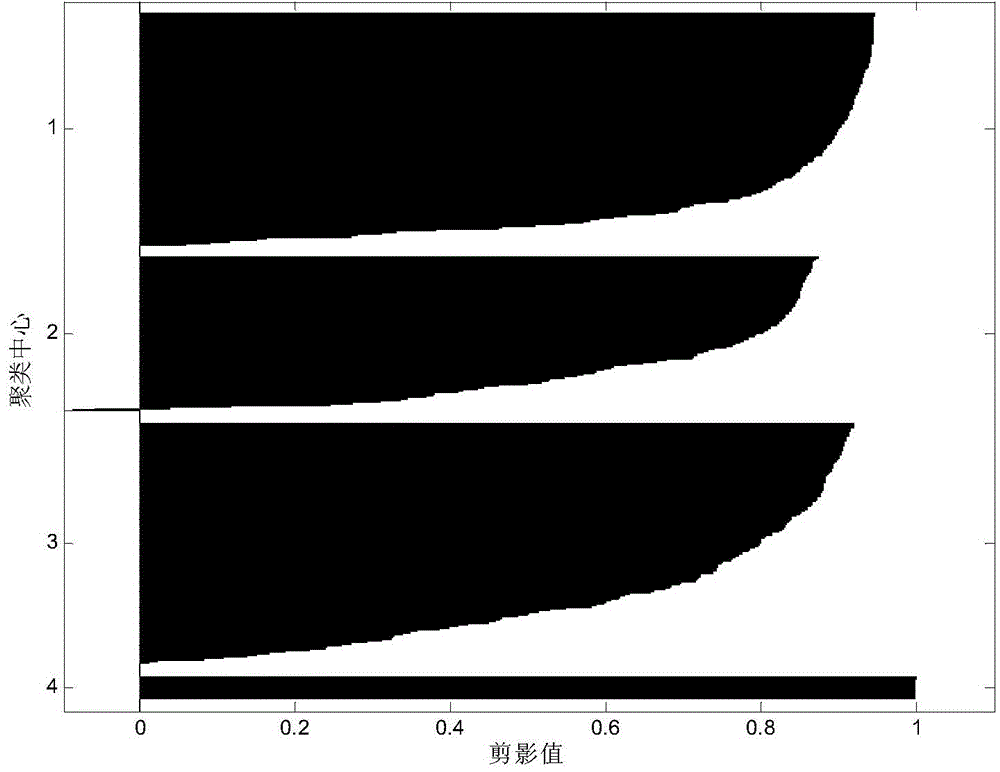
Non-reference image quality evaluation method based on discrete cosine transform and sparse representation
ActiveCN104376565AImprove consistencyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging quality
The invention discloses a non-reference image quality evaluation method based on discrete cosine transform and sparse representation to mainly solve the problem that in the prior art, non-reference image quality evaluation is not accurate. The method comprises the following steps that a gray level image is input, discrete cosine transform is carried out on the gray level image, and natural scene statistical characteristics are extracted; natural scene statistical characteristics of a series of images of different distortion types and different content are extracted, and an original characteristic dictionary is established according to the average subjective difference score; clustering is carried out on the original characteristics dictionary, and atoms are selected in a self-adaptation mode according to the tested image characteristics and the approximation degrees in the original characteristic dictionary to form a sparse representation dictionary; the tested image characteristics are solved and the sparse representation coefficients are calculated through sparse representation in characteristics space, linear weighting summation is carried out according to the subjective evaluation values in the sparse representation dictionary, and the image quality measure is obtained. The method has good consistency with the subjective evaluation result and is suitable for quality evaluation on images with various distortion types.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
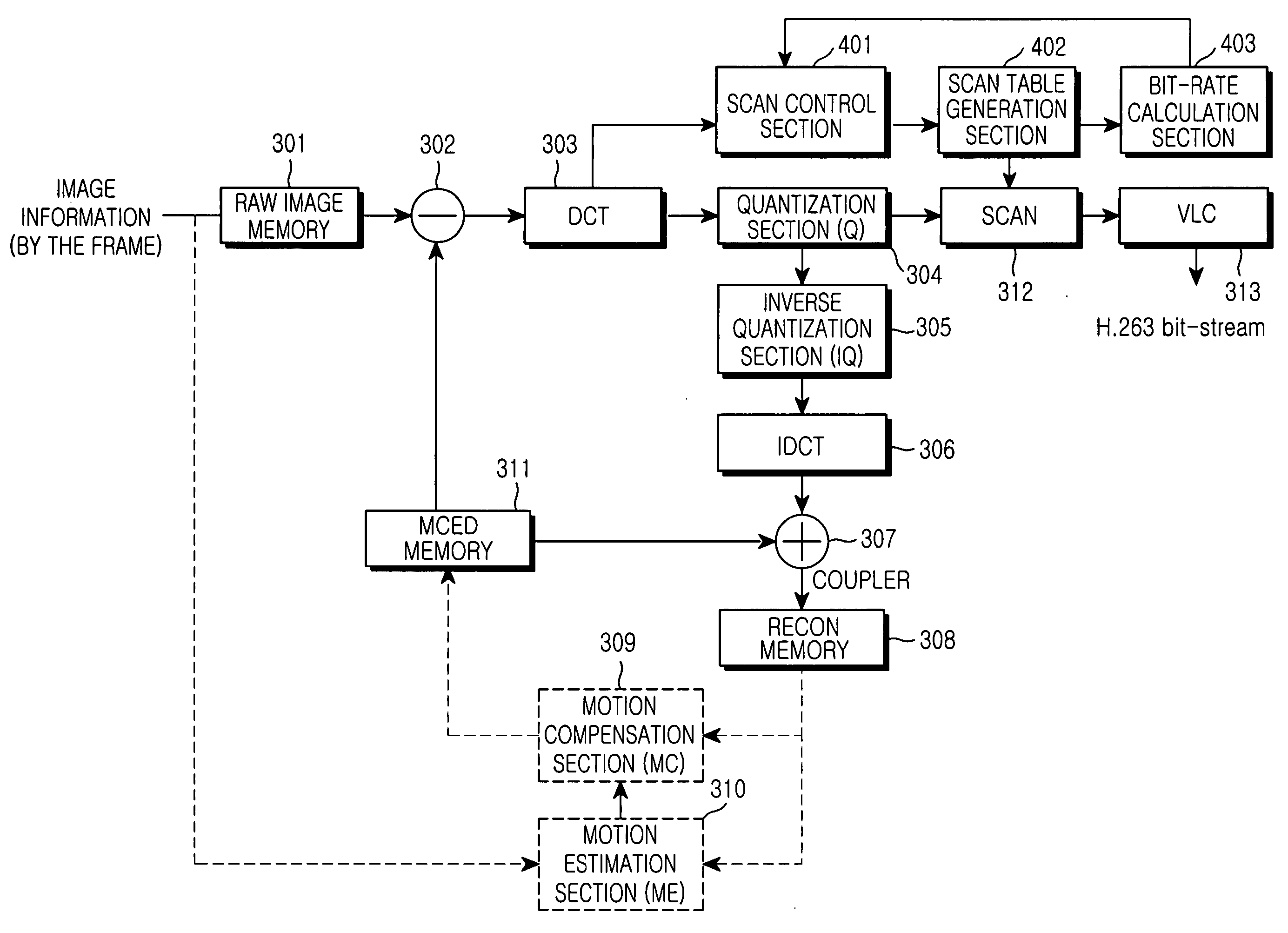
Visual scan method using scan table and discrete cosine transform device employing the same method
InactiveUS20050063462A1Improve defectsIncrease the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDiscrete cosine transformVariable length
Disclosed is a visual scan method using scan table capable of determining an exact scan method according to blocks in discrete cosine transform (DCT) even in special circumstances, and a discrete cosine transform device employing the same method. The discrete cosine transform device includes: a scan table generation section for accumulatively summing absolute values of the coefficients obtained through a DCT operation, in such a manner that the absolute values in pixels located at the same position of each unit video block in a predetermined video block group are summed together by the predetermined video block group with respect to an input video, and then for generating a scan table according to the magnitudes of the summed absolute values; a bit-rate calculation section for calculating an amount of bits by accumulatively summing only bit lengths of a variable length coding (VLC) table, the VLC table being obtained from the values arranged according to the scan table generated in the scan table generation section; and a scan control section for receiving the input video having been discrete-cosine-transformed, inputting the received video to the scan table generation section to generate a scan table by the predetermined video block group, receiving a value of a bit rate according to generation of the scan table from the bit-rate calculation section, and performing a control operation using capacity increase of the scan table and the bit rate to provide a scan table for scanning according to the scan method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
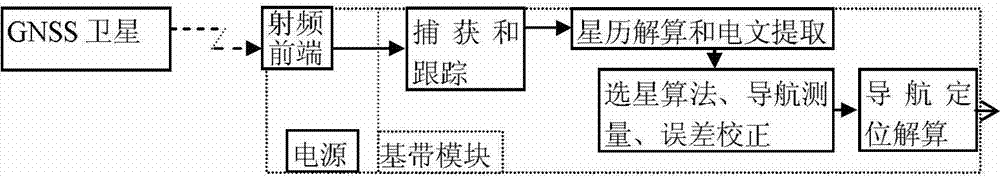
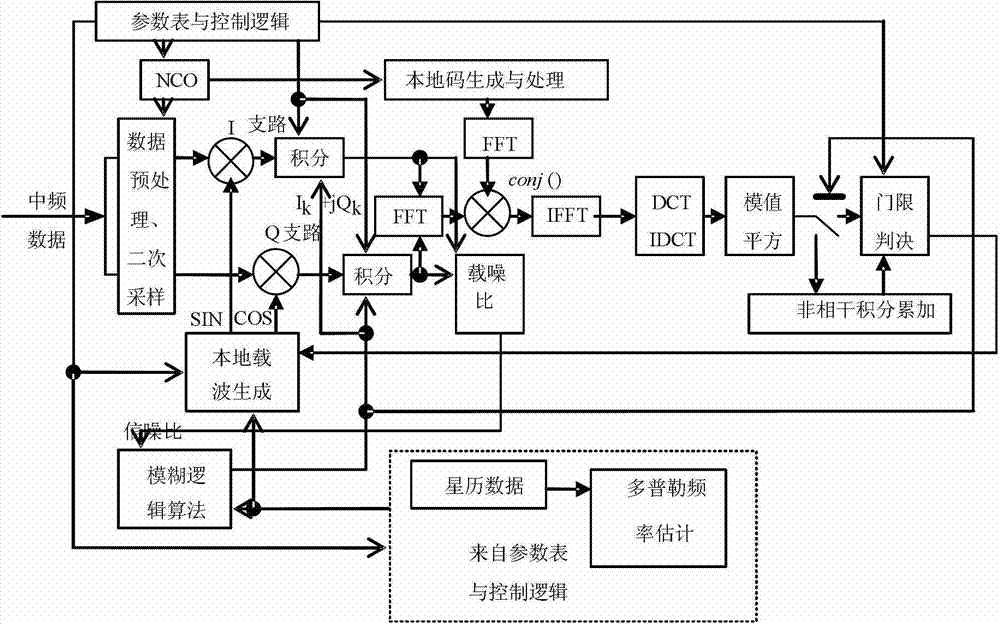
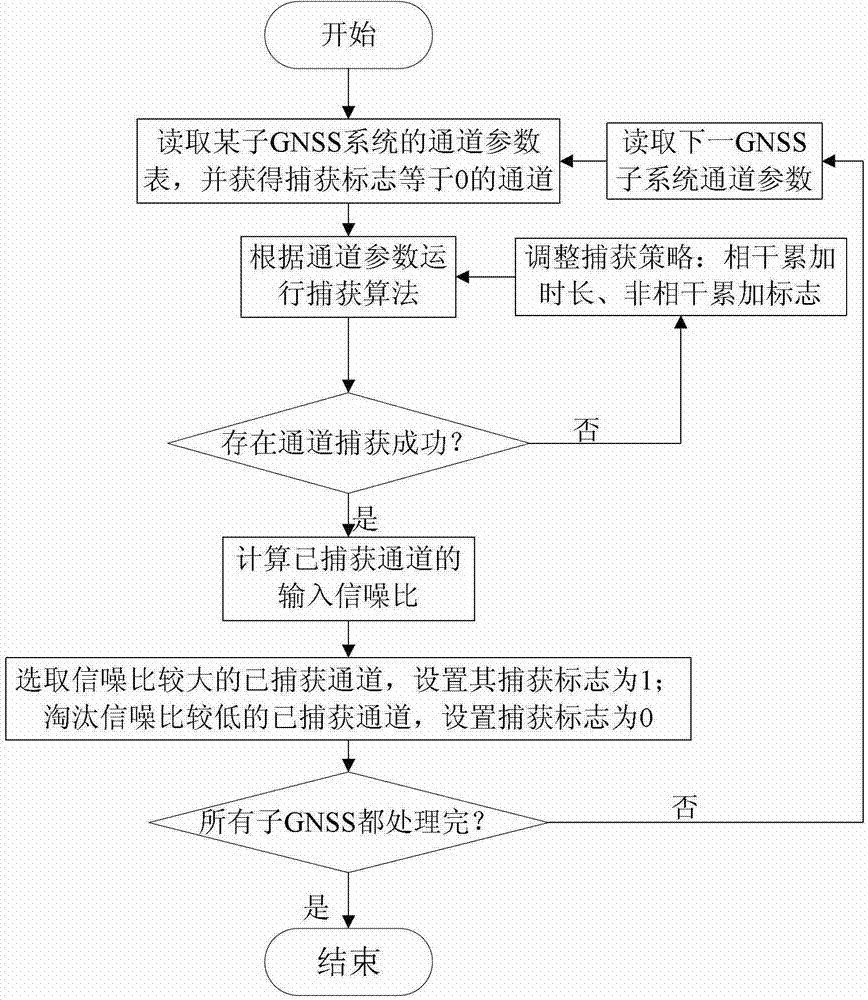
Compatibility capturing method of multi-mode GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) combination receiver
InactiveCN102890280AImprove adaptabilityImprove capture sensitivitySatellite radio beaconingIntermediate frequencyCoded element
The invention discloses a compatibility capturing method of a multi-mode GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) combination receiver. The capturing method comprises the following steps of: carrying out corresponding capture process on a satellite signal within coherent integration accumulation time and non-coherent integration accumulation time; adopting a fuzzy logic algorithm in the capture process, dynamically adjusting the coherent integration accumulation time and the non-coherent integration accumulation times according to a carrier-to-noise ratio and a carrier speed; and within the coherent integration accumulation time, carrying out the secondary sampling on a middle frequency signal of the acquired satellite signal, i.e. all data are decomposed into a plurality of groups, and the data points in each group are at one pseudo-random code element, and subsequently the Fourier transform, the Fourier inversion, the DCT (Discrete Cosine Transformation), the IDCT (Inverse Discrete Cosine Transform), the mode value square and threshold judgment process are carried out. With the adoption of the capturing method, the defects that signals cannot be captured as an existing capturing method is low in sensitivity and likely to be interfered are overcome, and satellite signals can be captured normally when a GNSS signal is shielded and strong environment noise exists.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
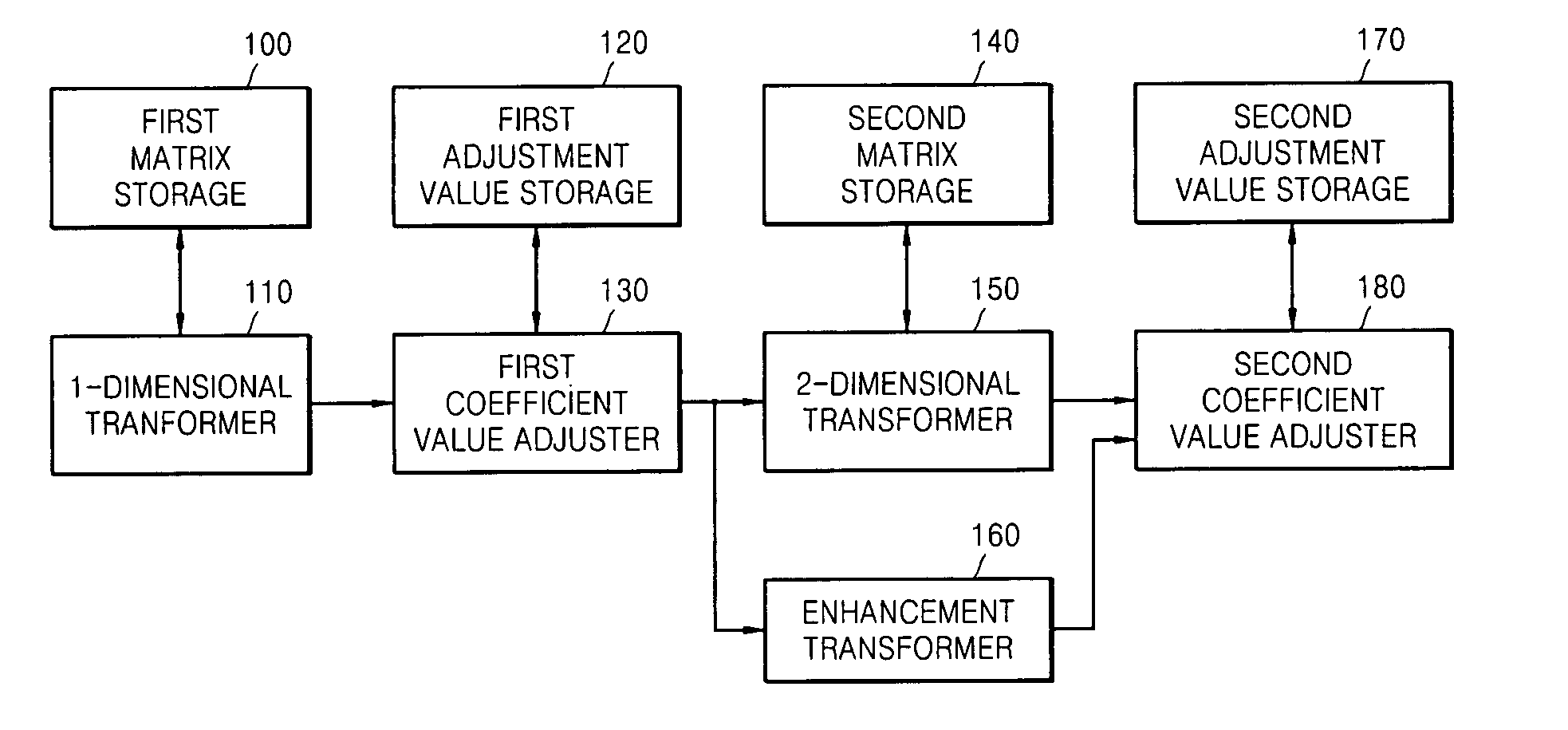
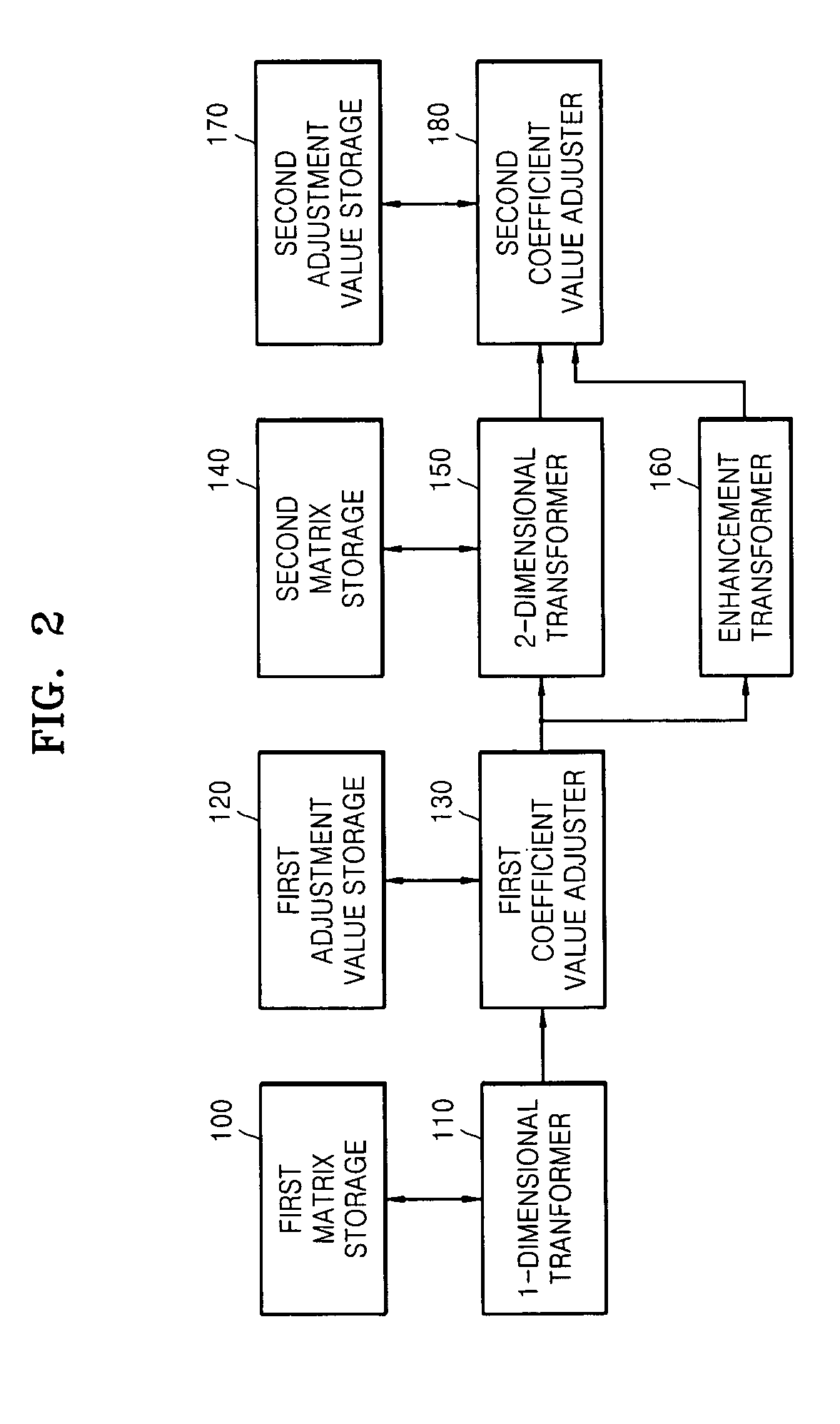
Multi-codec transforming and/or inverse transforming system, medium, and method
ActiveUS20070053604A1Lower the volumeImprove efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationTransformerDiscrete cosine transform
A transforming and / or inverse transforming system, medium, and method for a multi-codec. The transforming system includes a first matrix storage storing 1-dimensional DCT (discrete cosine transform) matrixes corresponding to respective transformation techniques, a second matrix storage storing 2-dimensional DCT matrixes corresponding to the respective transformation techniques, a 1-dimensional transformer 1-dimensionally transforming an input image using a 1-dimensional DCT matrix corresponding to a set transformation technique, a 2-dimensional transformer 2-dimensionally transforming the 1-dimensionally transformed image using a 2-dimensional DCT matrix corresponding to a set transformation technique, and an enhancement transformer enhancement transforming the 1-dimensionally transformed image to improve efficiency of integer transformation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
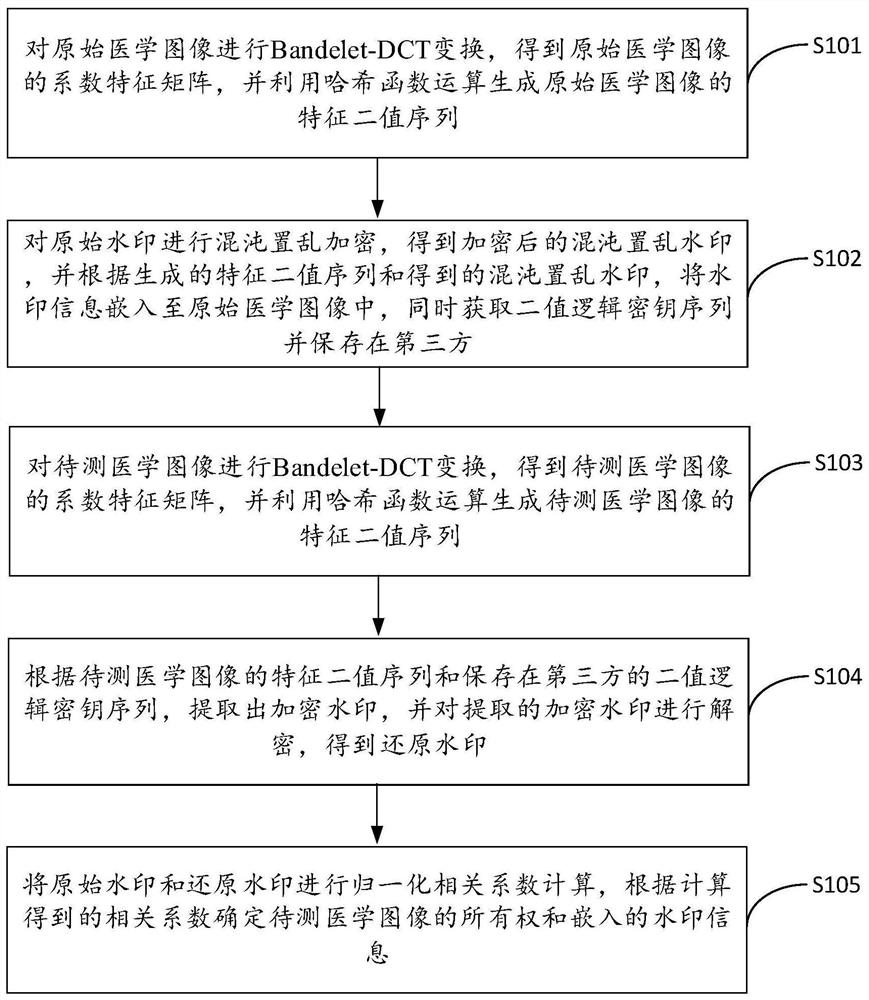
Medical image robust zero-watermark method based on Bandelet-DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform)
PendingCN111968025AGuaranteed safe transmissionEasy extractionDigital data protectionImage watermarkingThird partyHash function
The invention discloses a medical image robust zero-watermarking method based on Bandlet-DCT, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the Bandlet-DCT of an original medical image, obtaining acoefficient feature matrix, and generating a feature binary sequence through Hash function operation; carrying out chaos scrambling encryption on the original watermark to obtain a chaos scrambling watermark, embedding watermark information into the original medical image, and acquiring and storing a binary logic key sequence in a third party; similarly, generating a feature binary sequence of the to-be-detected medical image; extracting an encrypted watermark according to the characteristic binary sequence and the binary logic key sequence, and decrypting the encrypted watermark to obtain areduced watermark; and performing normalization correlation coefficient calculation on the original watermark and the reduced watermark, and determining the ownership of the medical image to be testedand the embedded watermark information. The method has good robustness and invisibility in geometric attack resistance and conventional attack resistance, and can protect the privacy information of apatient and the data security of a medical image at the same time.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
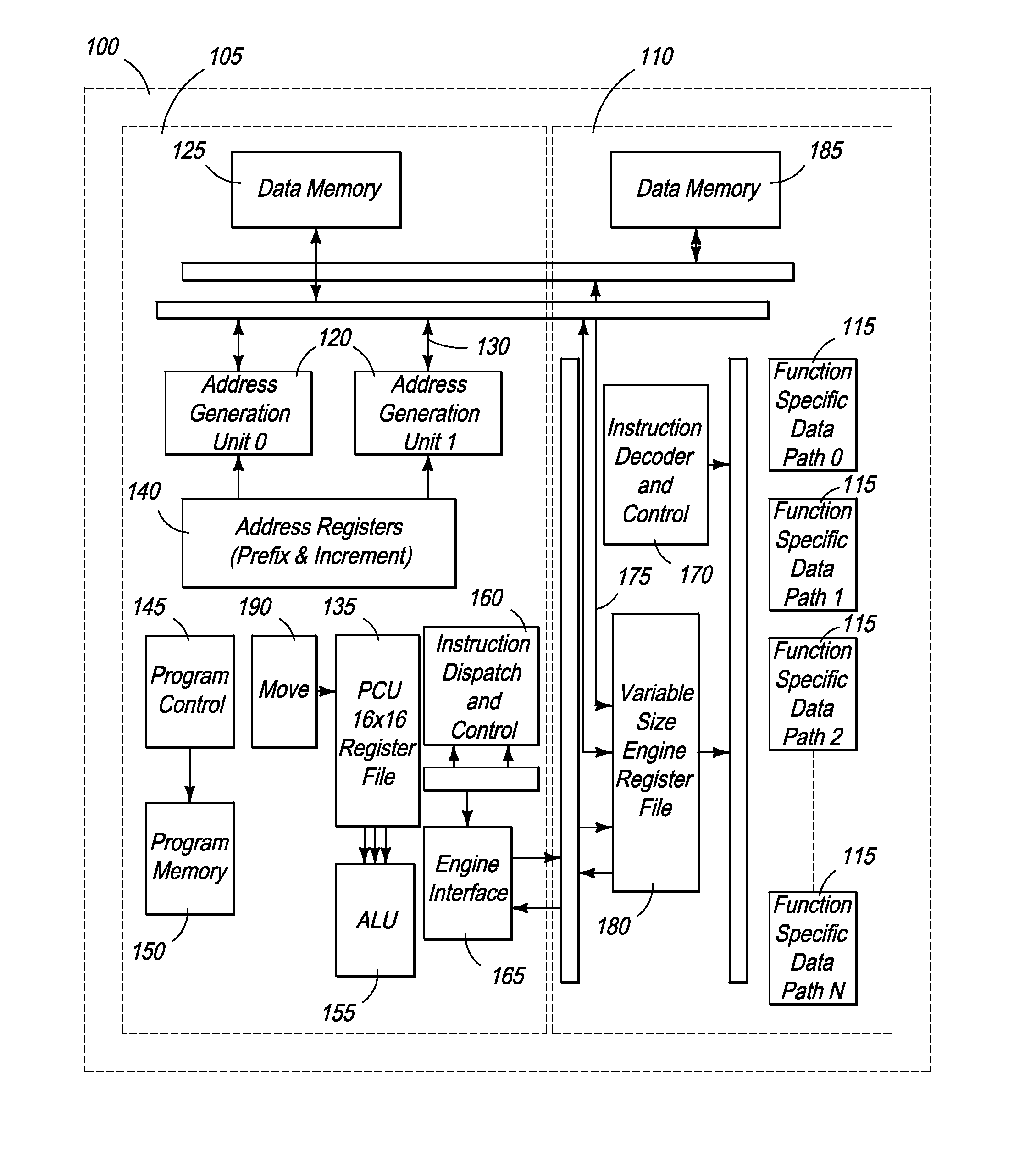
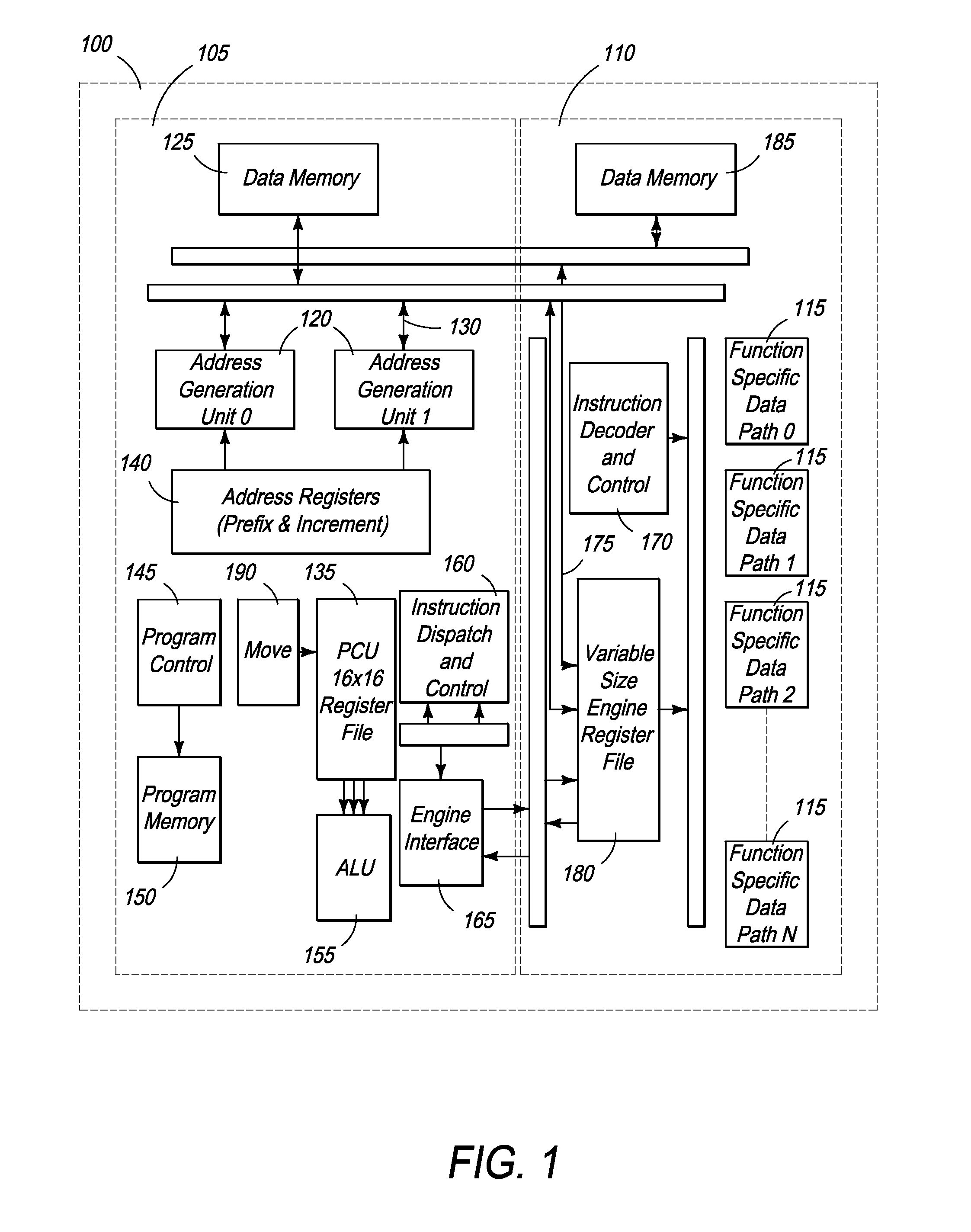
Front End Processor with Extendable Data Path
InactiveUS20100321579A1Easy to processIncrease processing functionTelevision system detailsProgram control using wired connectionsData memoryDiscrete cosine transform
The present specification discloses a processing architecture that has multiple levels of parallelism and is highly configurable, yet optimized for media processing. At the highest level, the architecture is structured to enable each processor, which is dedicated to a specific media processing function, to operate substantially in parallel. In addition to processor-level parallelism, each processing unit can operate on multiple words in parallel, rather than just a single word per clock cycle. Moreover, at the instruction level, the control data memory, data memory, and function specific dath paths can be controlled all within the same clock cycle. Additionally, the processor has multiple layers of configurability, with the extendable data path of the processor being capable of being configured to perform specific processing functions, such as entropy encoding, discrete cosine transform (DCT), inverse discrete cosine transform (IDCT), motion compensation, motion estimation, de-blocking filter, de-interlacing, de-noising, quantization, and dequantization.
Owner:QUARTICS
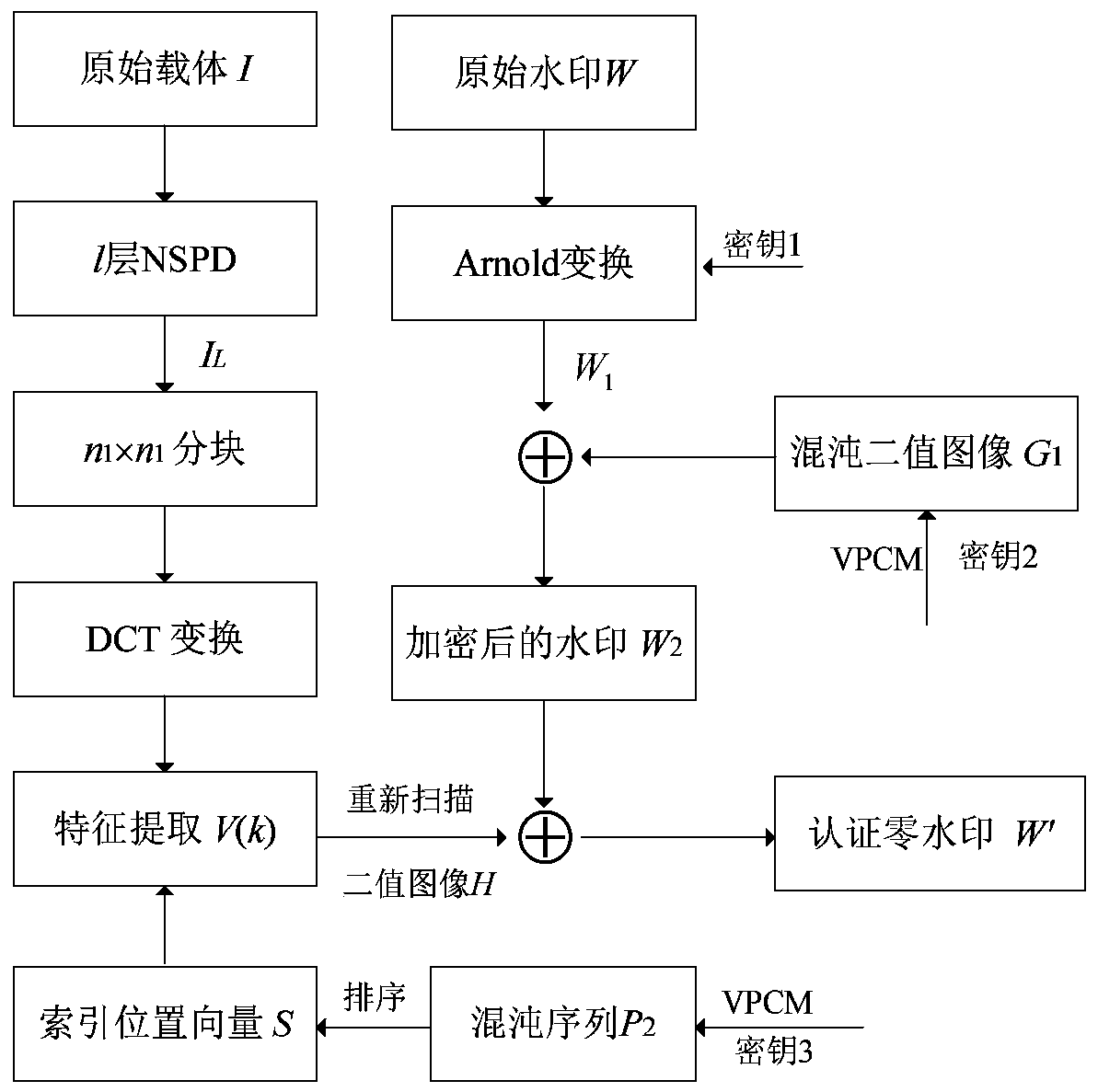
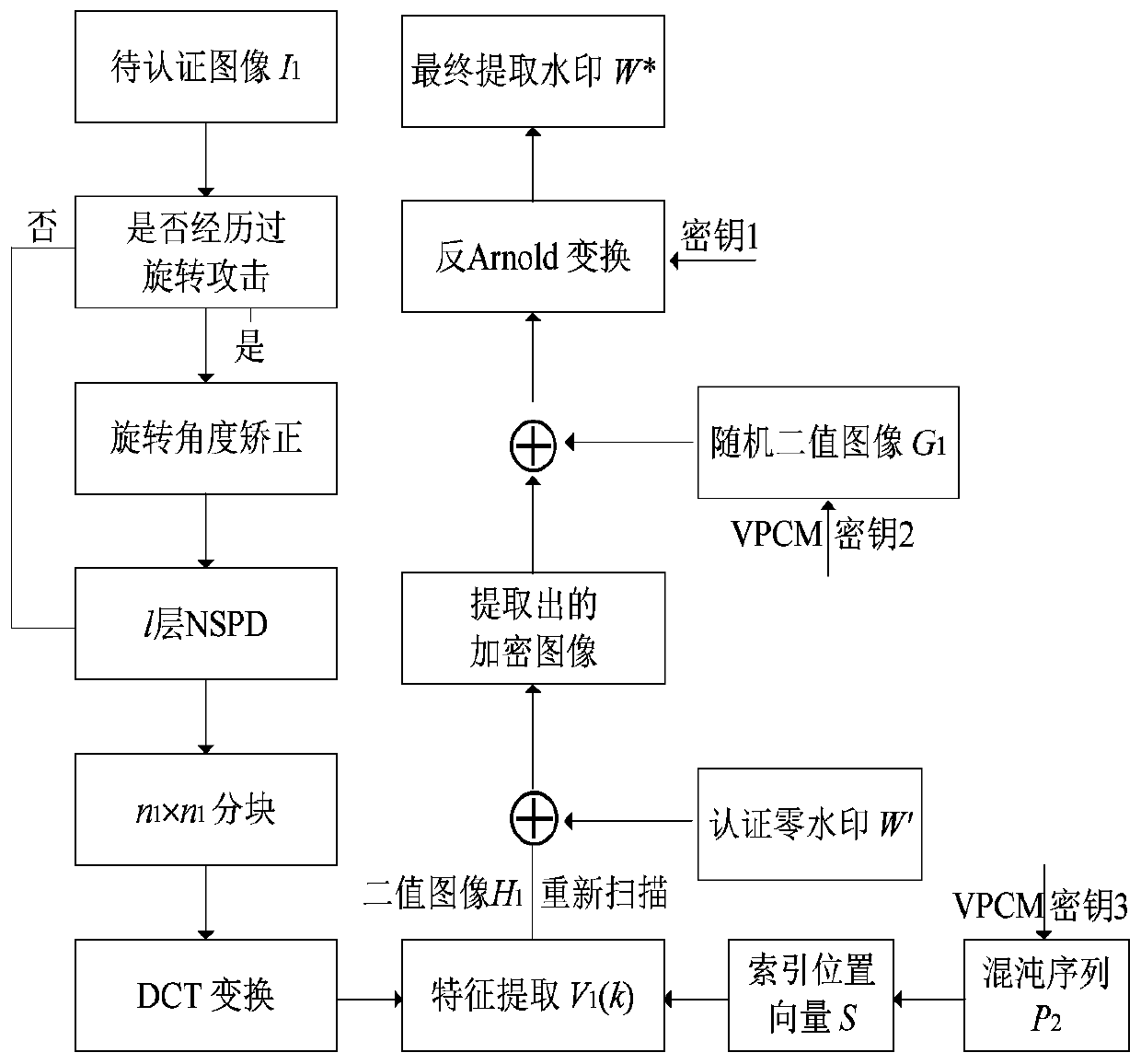
Hybrid transform domain image zero-watermarking method based on variable parameter chaotic mapping
ActiveCN109859093ANovel methodSimple methodImage data processing detailsPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention discloses a hybrid transform domain image zero-watermarking method based on variable parameter chaotic mapping. The method comprises a zero watermark embedding process and a zero watermark detection process. The embedding and detection of the zero watermark are both completed in a non-subsampled pyramid decomposition and discrete cosine transform hybrid transform domain. The translation invariance characteristic of non-subsampled pyramid decomposition of the image and the stability of the alternating current coefficient symbol at the special position in each coefficient block after the image is subjected to block discrete cosine transform are fully utilized, so that the method has relatively good robustness. Experimental results show that the method has good robustness for resisting various common image processing attacks, such as noise addition, filtering, JPEG compression, scaling, rotation attacks at any angle and the like, and has effectiveness and certain practical value.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Non-uniform image defect inspection method
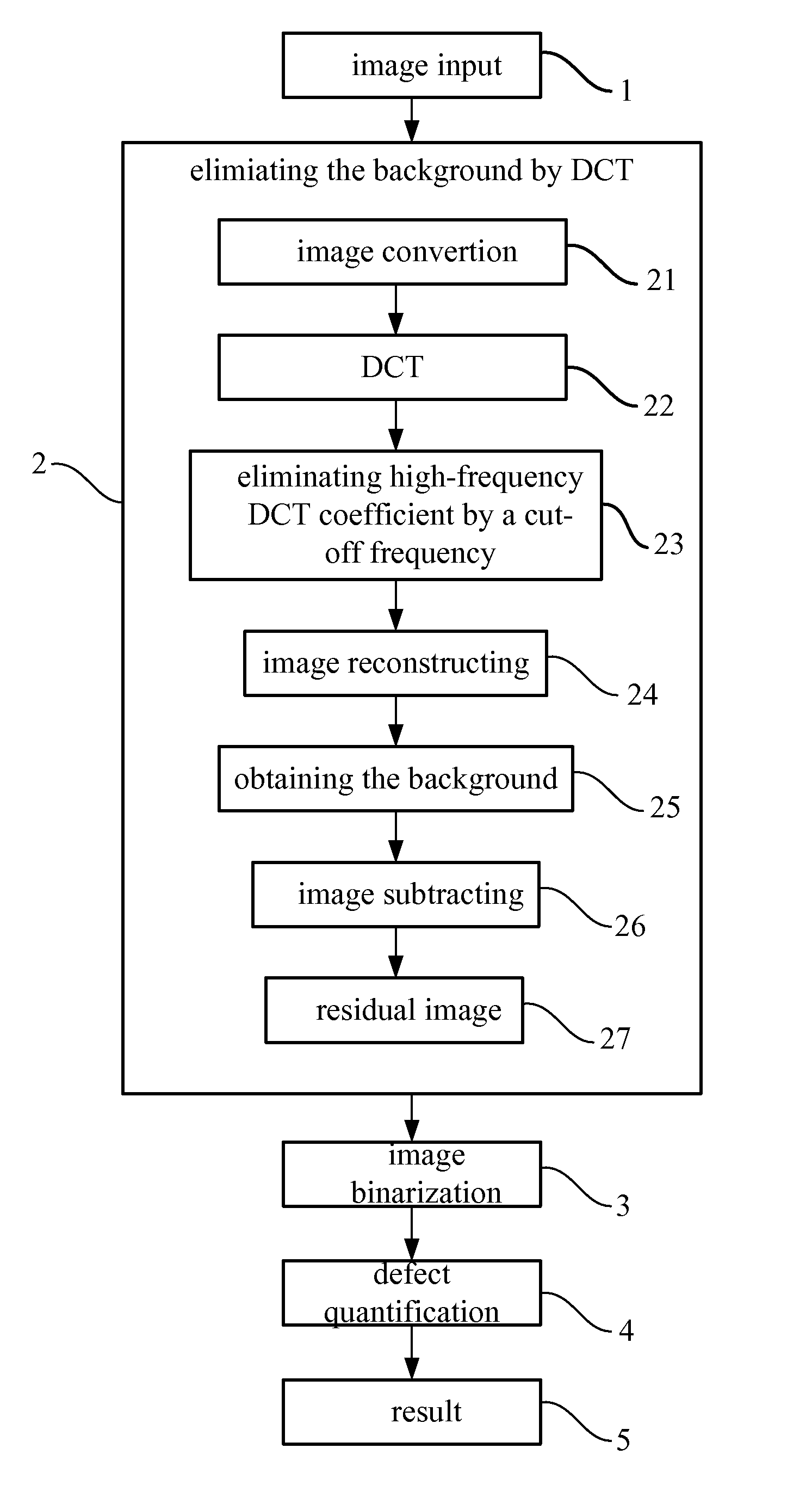
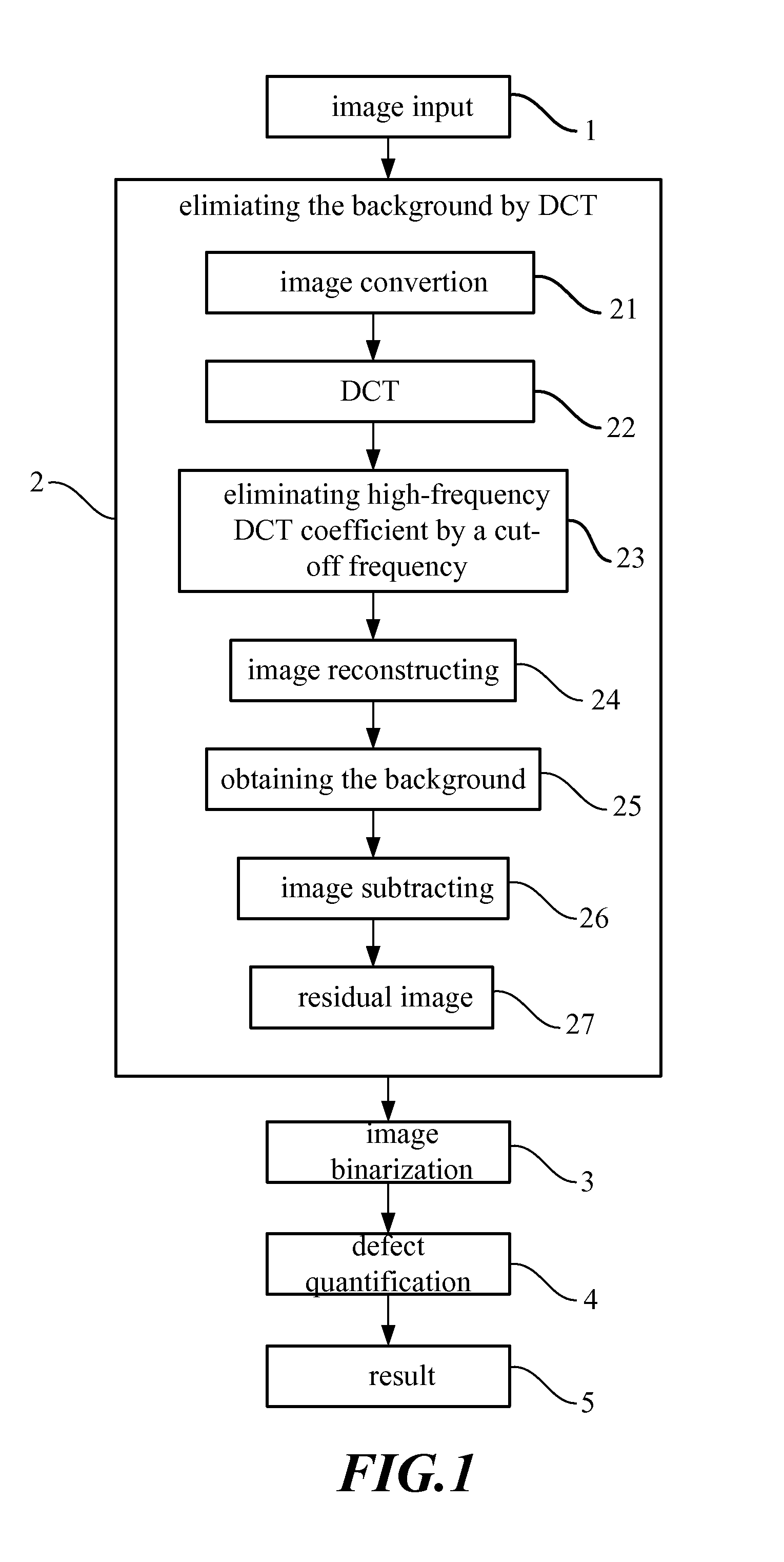
ActiveUS8145008B2Improve inspection efficiencyInspection speed is fastImage enhancementImage analysisDiscrete cosine transformBackground image
A non-uniform image defect inspection method includes steps of inputting an original two-dimensional image; separating a non-uniform background image from the original two-dimensional image by Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) to obtain a residual image without the non-uniform background image; binarization segmenting the residual image to extract defects from the residual image, wherein the segmented defects are the inspection results.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
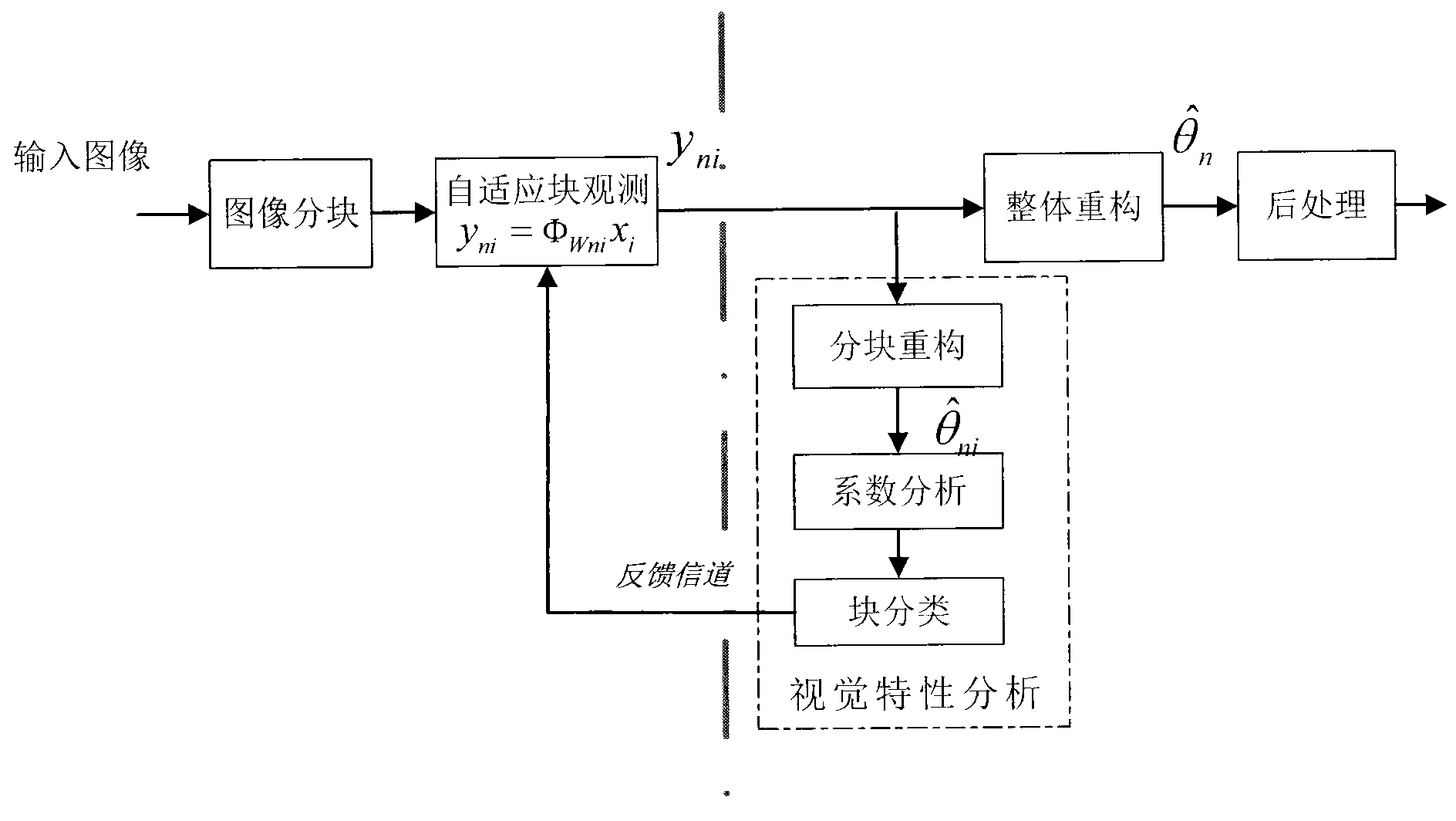
Adaptive block compressing sensing image coding method based on visual perception
InactiveCN103037212AImprove visual qualityImprove recovery qualityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionSelf adaptive
Disclosed is a low-complex adaptive block compressing sensing image coding method based on visual perception. The low-complex adaptive block compressing sensing image coding method based on visual perception is characterized in that I. Block compressing sensing: 1. Coding: reading images and separating images; block observing; sending observed values and observed rates to decoding end; 2. Decoding: measurement matrix is obtained from the observed rates; finding an initial solution; wiener filtering; updated by procedural language (PL); discrete cosine transform (DCT) switching; bivariate threshold denoising disposing; inverse discrete cosine transform (IDCT); updated by the PL; repeated till finish of initial phrase; II. Visual analysis: analyzing each refactoring DCT coefficient block; classifying blocks; entering feedback channel; III. The adaptive block compressing sensing instructed by visual perception: 1. Coding: adaptive observe according to feedback results;sending observed values and observed rates to decoding end; 2. Decoding: combining the observed values; last phrase recover image as a first value; wiener filtering; updated by PL; DCT switching; bivariate threshold denoising disposing; IDCT; updated by the PL; till end of the decoding; next phrase analysis, adaptive observe and refactoring, till the recover image meets the need.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
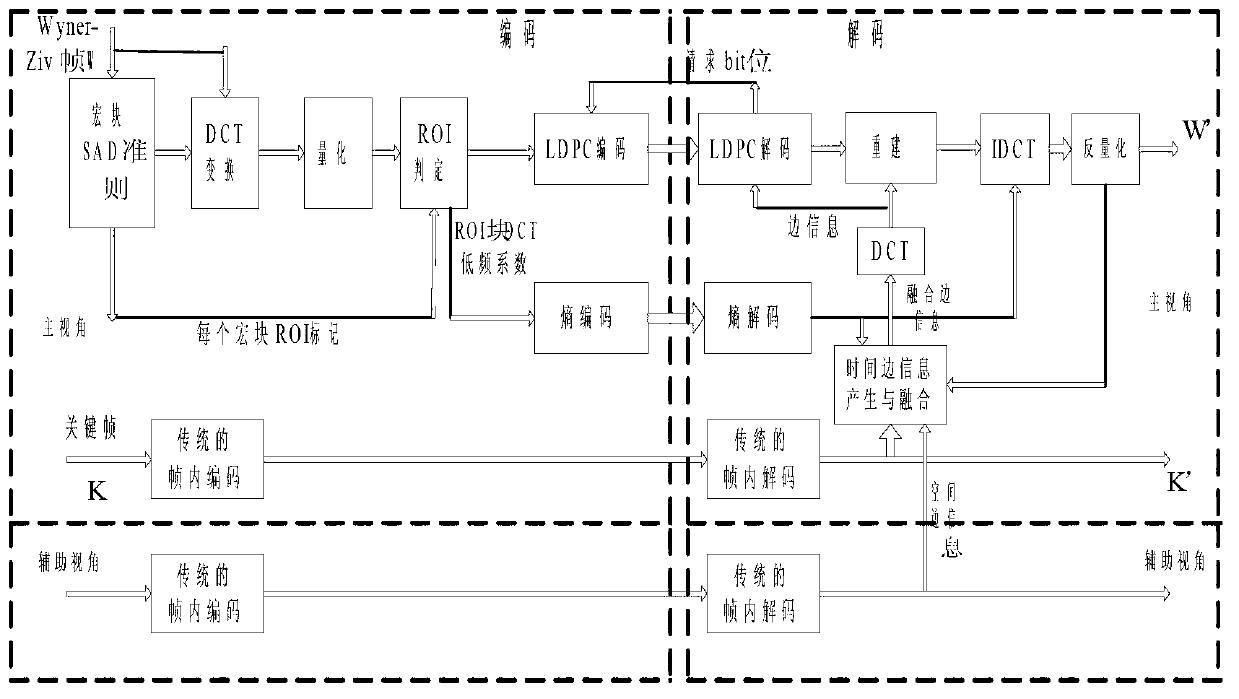
Multi-view distributed video compression side information generation method
InactiveCN103002283AIncrease storage capacityStrong computing powerEnergy efficient ICTTelevision systemsLine sensorInformation space
A multi-view distributed video compression side information generation method facing to a wireless multi-media sensing network is a technical scheme directing to multi-media multi-view data compression in the wireless multi-media sensing network. The method comprises extracting discrete cosine transform (DCT) low frequency coefficients in an area-of-interest (ROI) macro block of a non-key frame (Wyner-Zicframe, WZ) in a main visual angle to conduct entropy coding and decoding, using received the DCT low frequency coefficients to conduct both-way motion estimation interpolation on the decoding end of the ROI macro block to generate ROI macro block side information, using encoded frames to conduct motion compensation frame interpolation (or extrapolation) on a non-ROI area to generate non-ROI macro block side information, and further generating best non-key frame time side information. Space side information is generated by using a homography matrix method. Finally the time side information and the space side information are merged. By means of the improvement, code rate is reduced, quality of decoding images is improved, energy consumption of sensor nodes is reduced, and service life of the wireless sensor network is prolonged.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Reversible transform for lossy and lossless 2-D data compression
2D transformations and their inverses have implementations as a series of lifting steps arranged to reduce computational complexity (ie reduce the number of non-general operations). This pair of transforms has energy-compact properties similar to discrete cosine transforms (DCTs), and is also lossless and scale-independent. Compared to a separable DCT transformation implemented as a 1D DCT transformation applied separately to the rows and columns of a 2D data block, the transformation operation is rearranged as a basic transformation consisting of a 2×2 Hadamard transformation and a 2×2 transformation adding lifting rotation series. These basic transformations have implementations as sequences of lifted operations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com