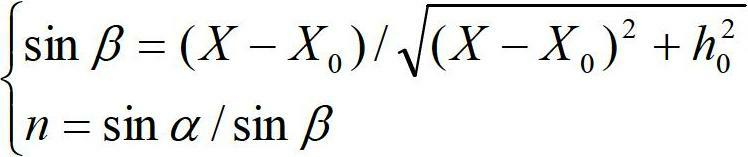Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Density dependent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Density Dependent Factors Definition. Density dependent factors affect a population through increasing or decreasing birth and death rates, in a way that is directly related to the density of the population.
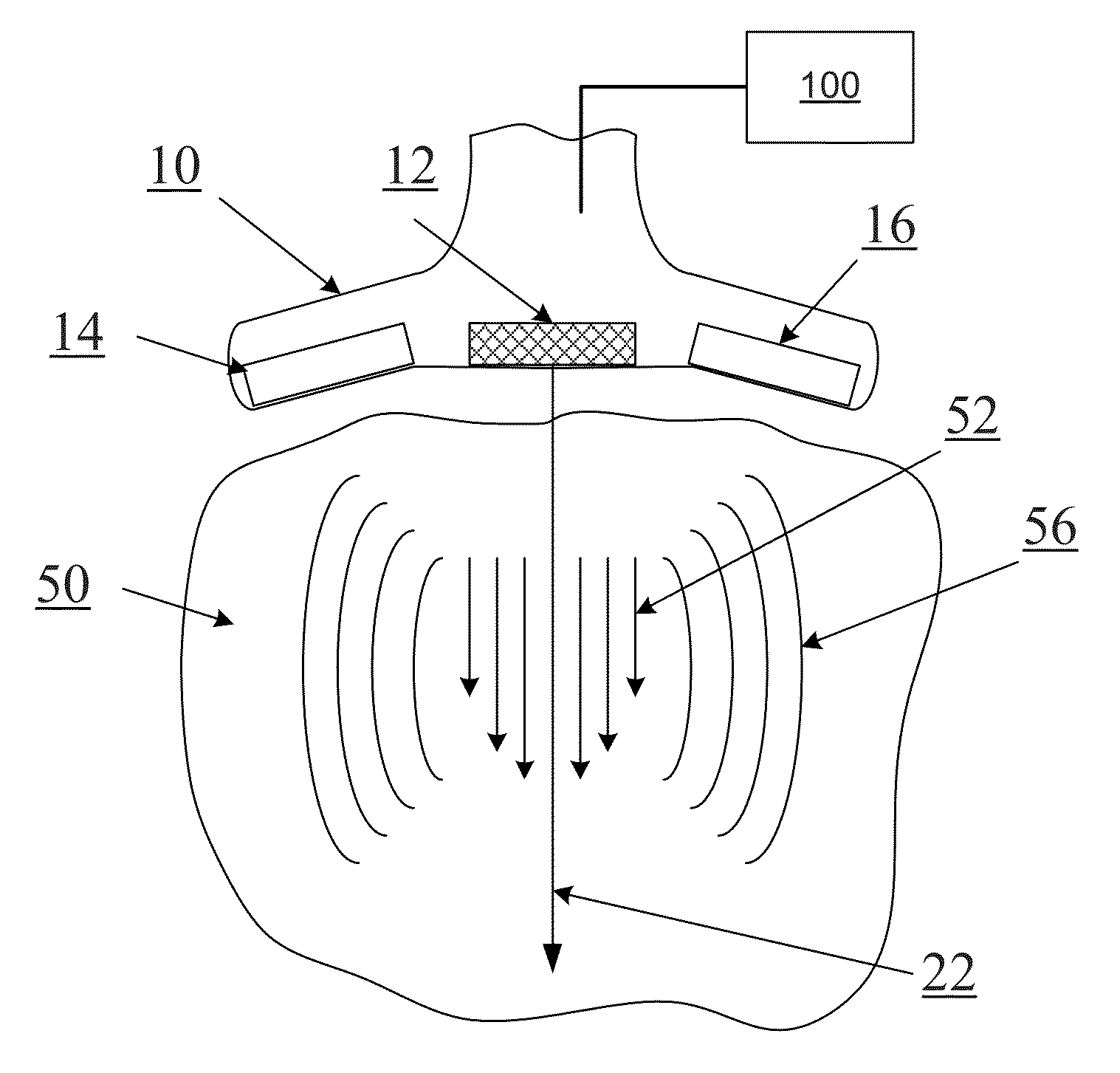
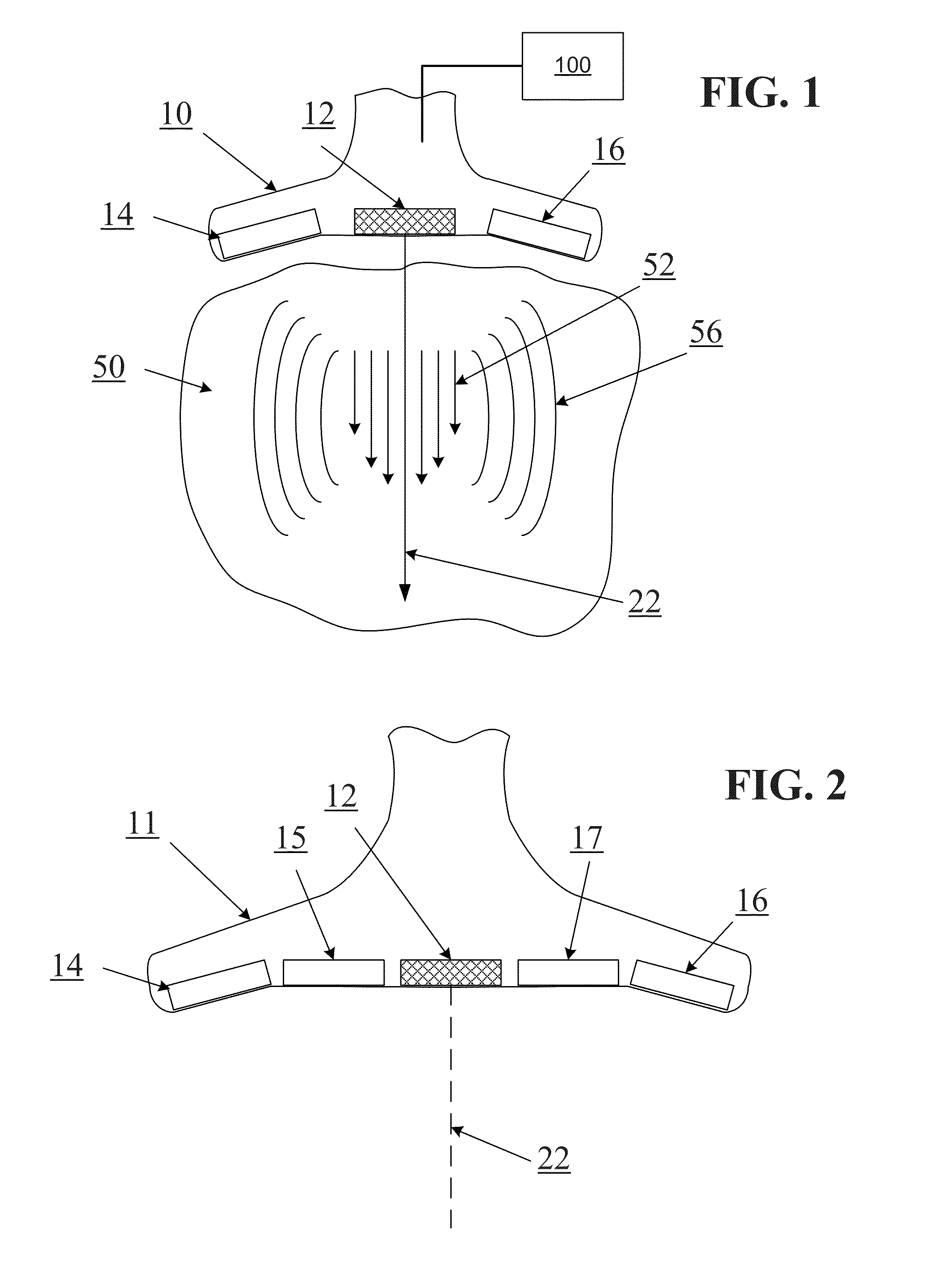
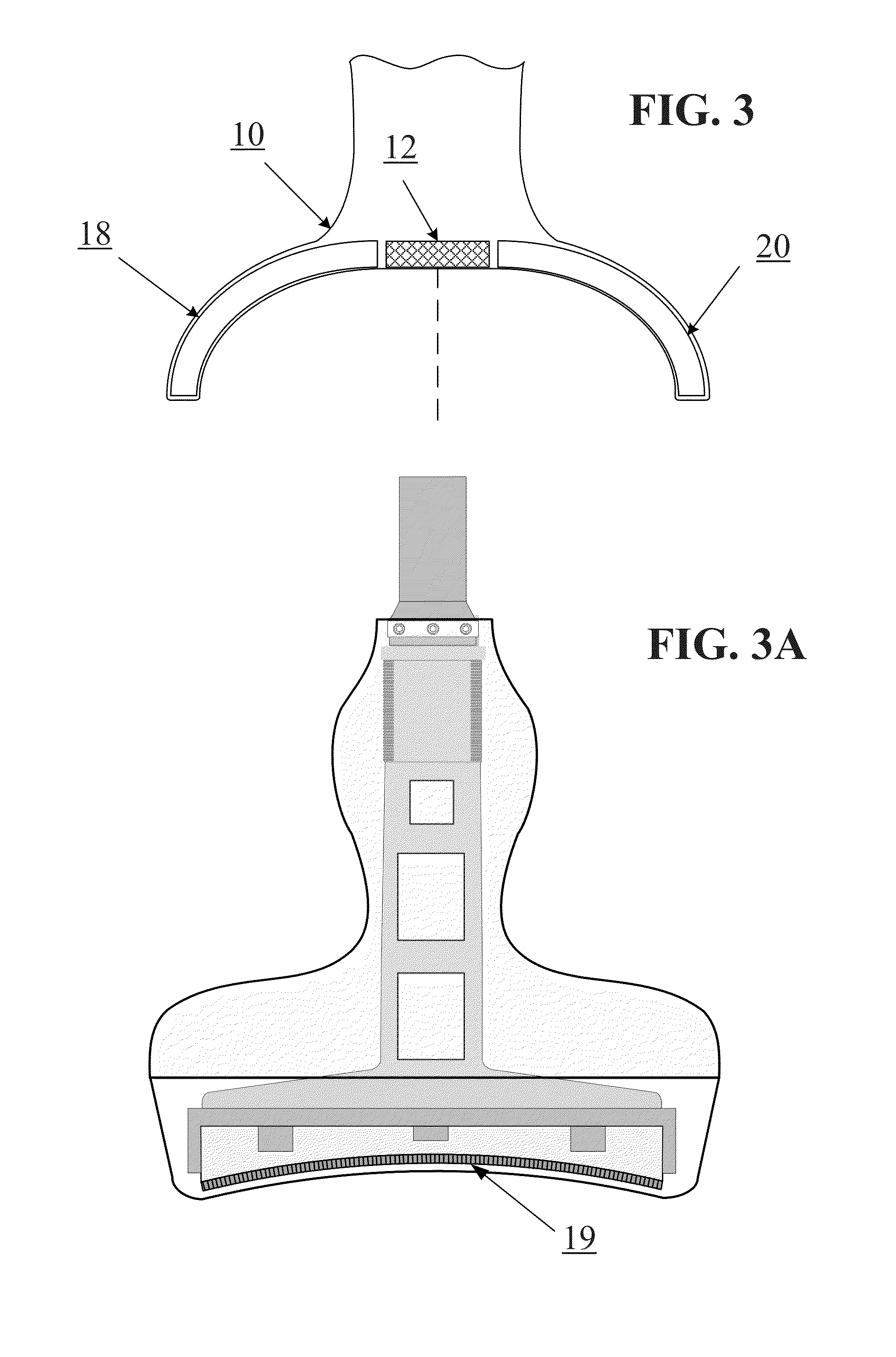
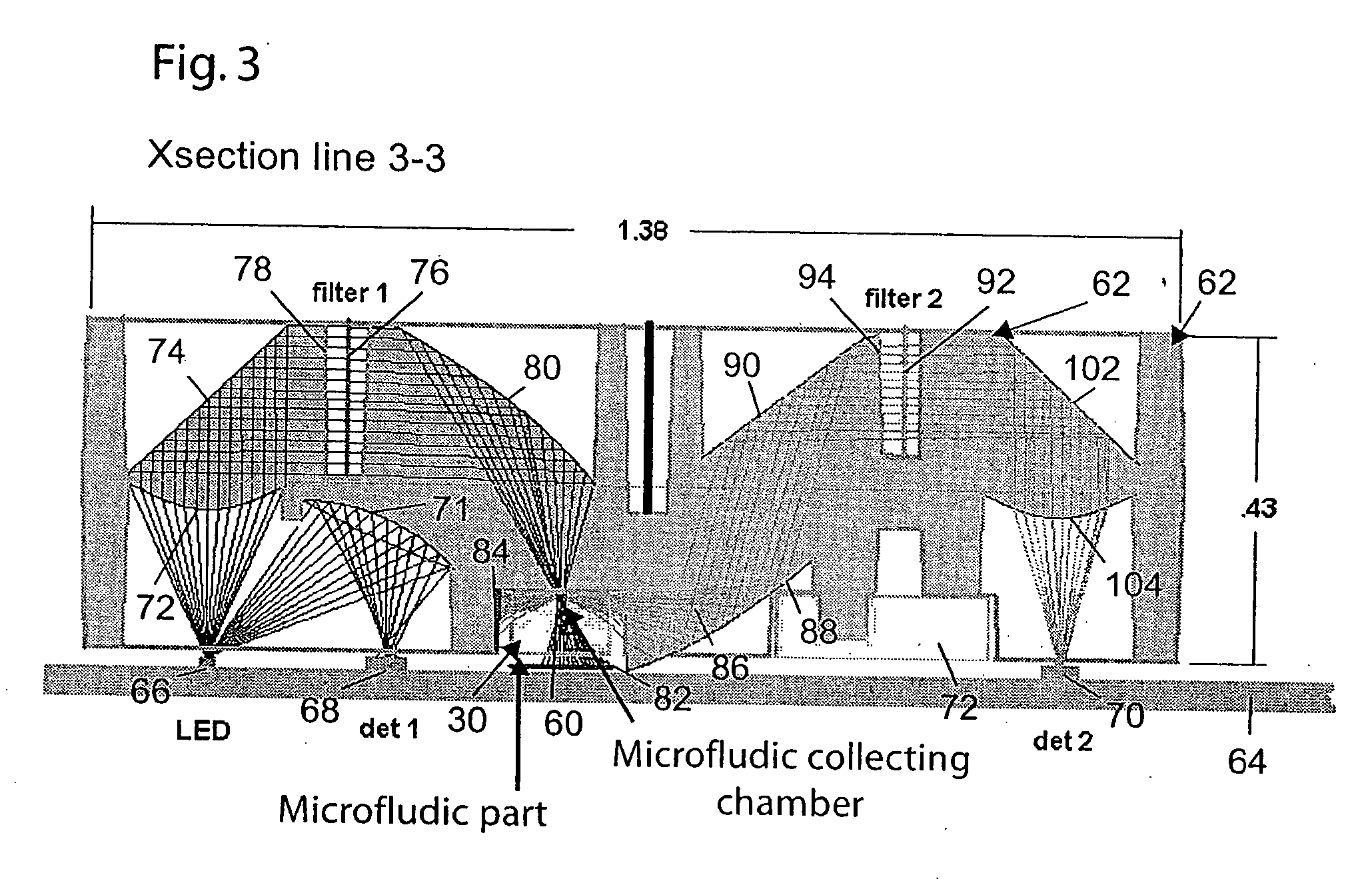
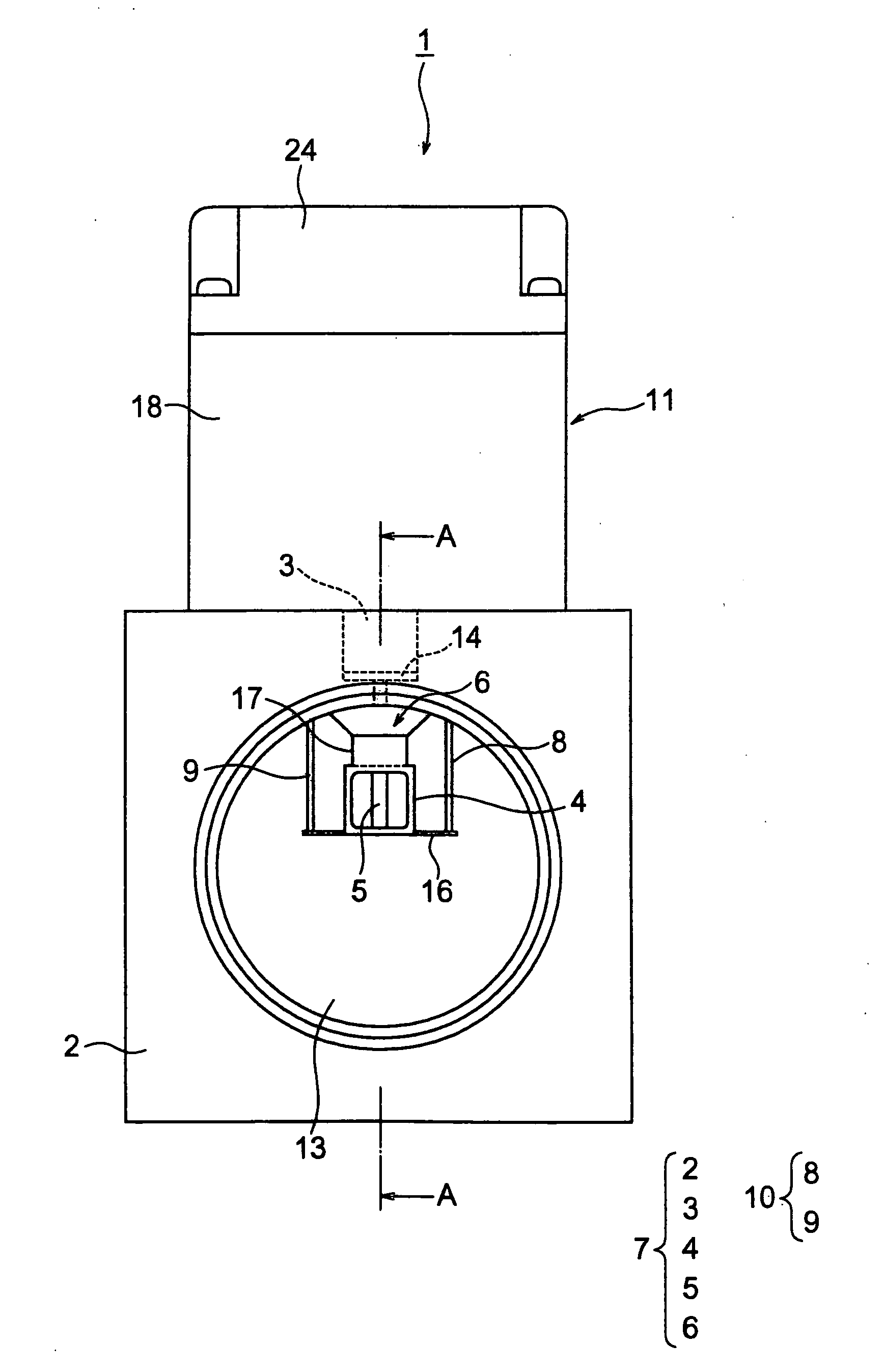
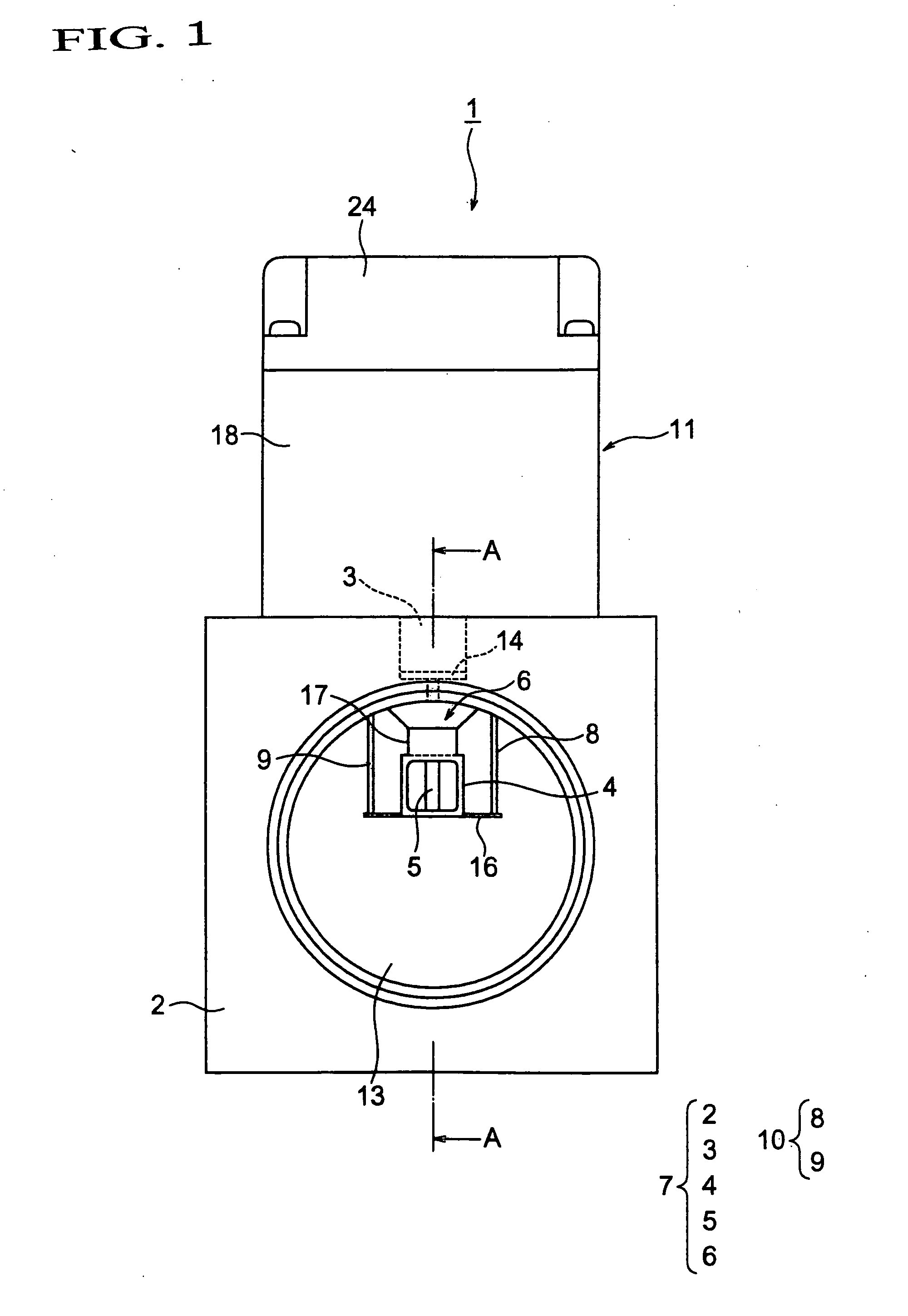
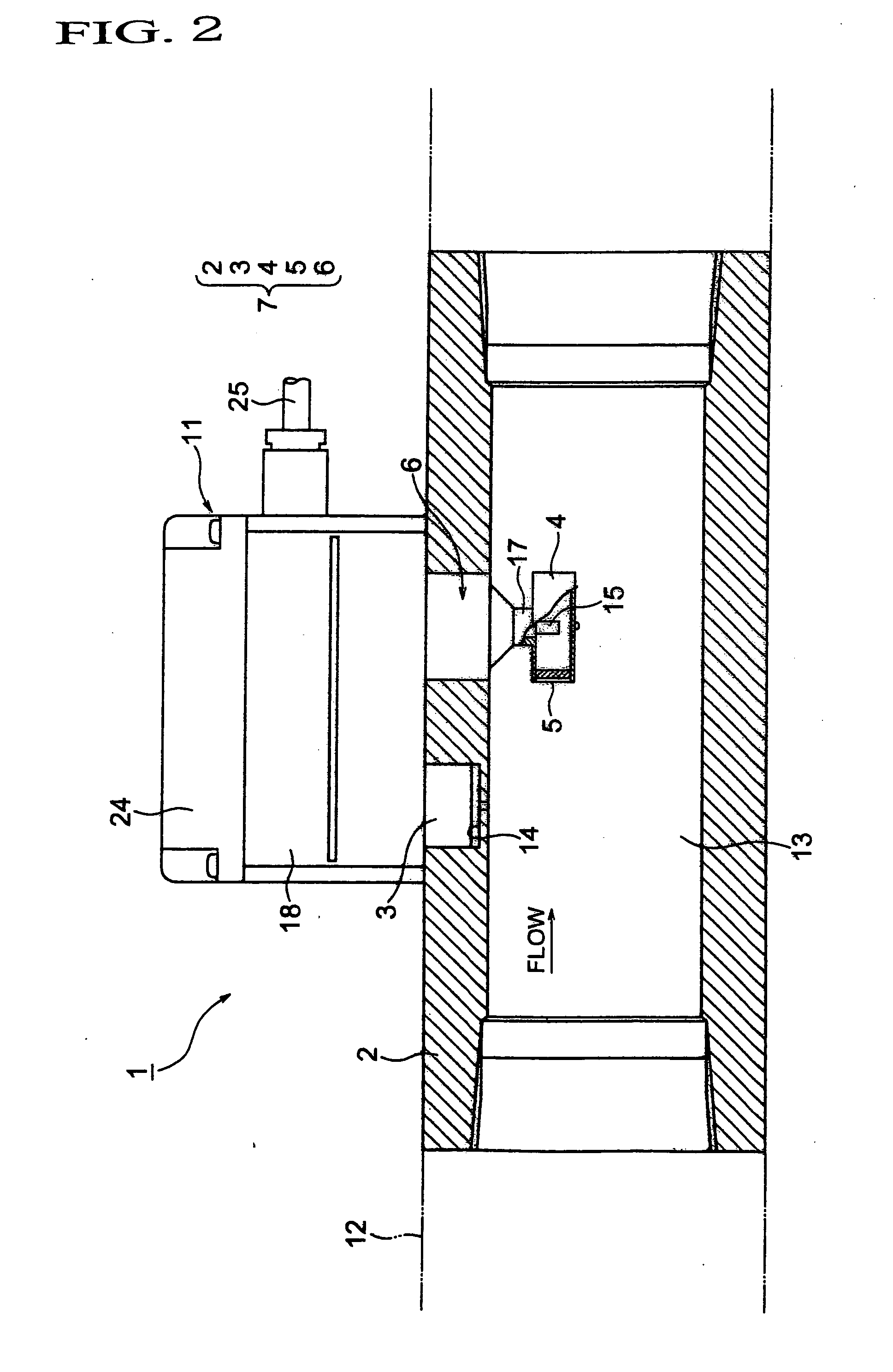
Determining Material Stiffness Using Multiple Aperture Ultrasound
ActiveUS20130218012A1High resolutionHigh imagingOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseSonification
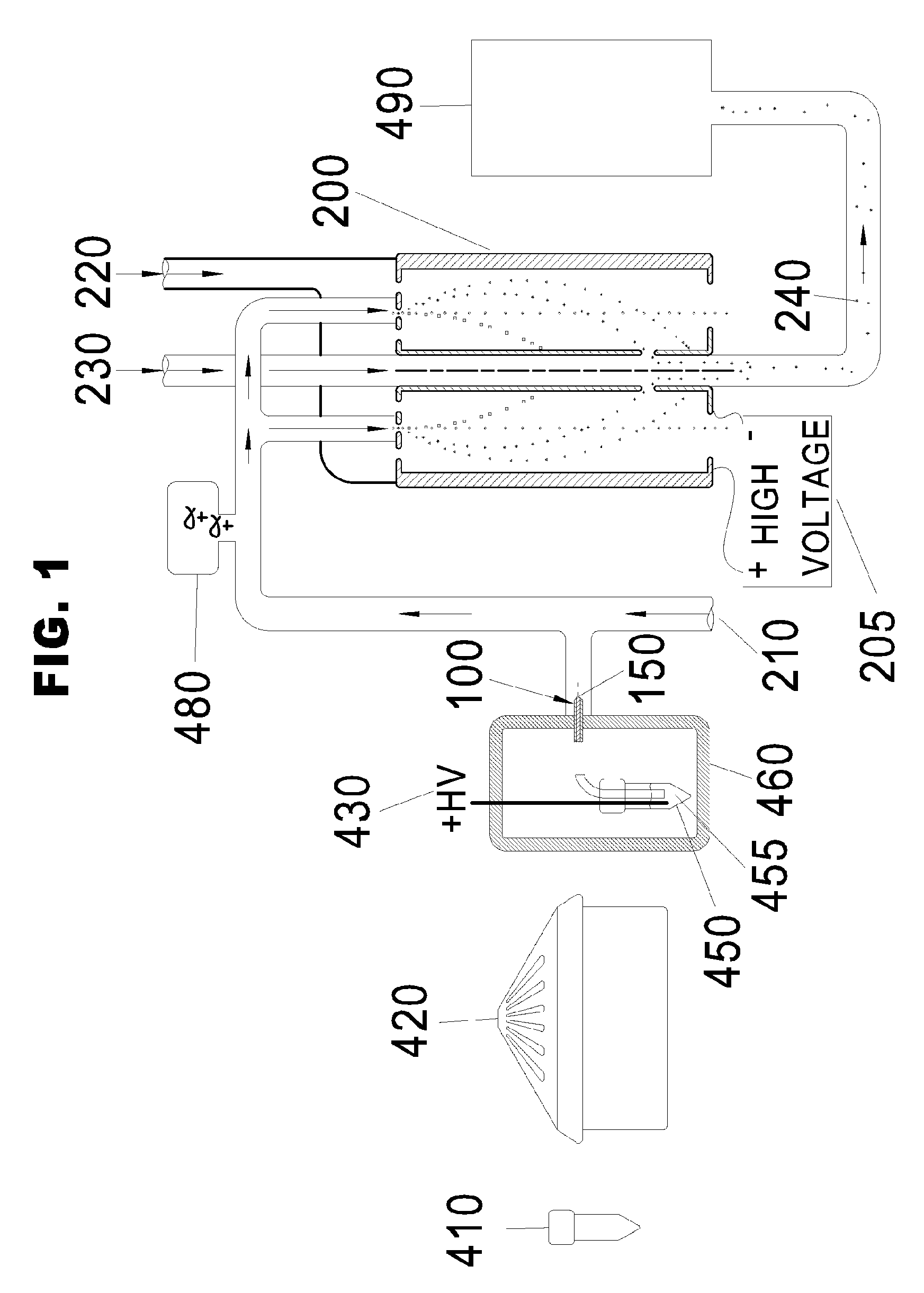
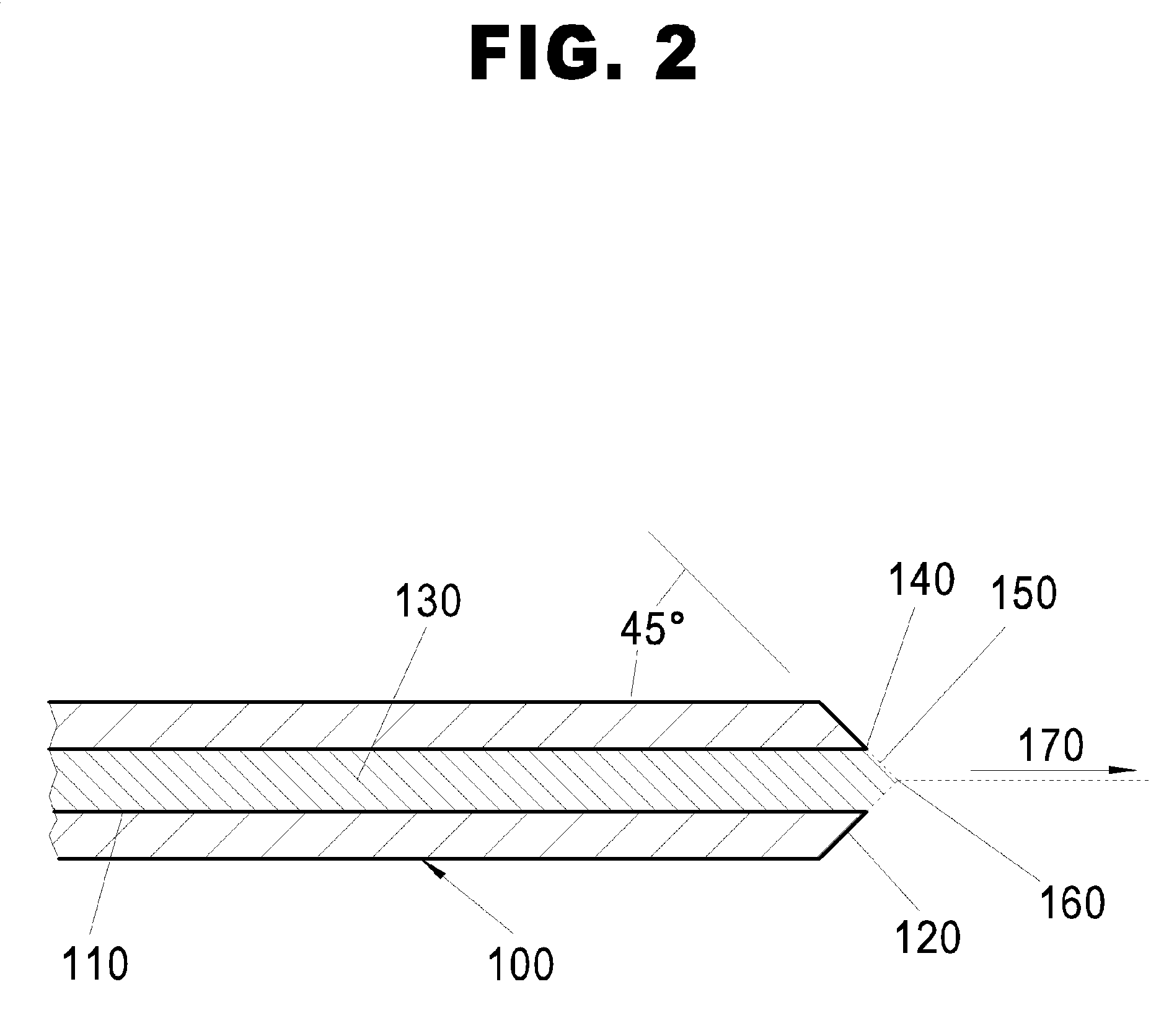
Changes in tissue stiffness have long been associated with disease. Systems and methods for determining the stiffness of tissues using ultrasonography may include a device for inducing a propagating shear wave in tissue and tracking the speed of propagation, which is directly related to tissue stiffness and density. The speed of a propagating shear wave may be detected by imaging a tissue at a high frame rate and detecting the propagating wave as a perturbance in successive image frames relative to a baseline image of the tissue in an undisturbed state. In some embodiments, sufficiently high frame rates may be achieved by using a ping-based ultrasound imaging technique in which unfocused omni-directional pings are transmitted (in an imaging plane or in a hemisphere) into a region of interest. Receiving echoes of the omnidirectional pings with multiple receive apertures allows for substantially improved lateral resolution.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
Method for inhibition of bone growth by anionic polymers
InactiveUS6020326AInhibit bone growthPrevent invasionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCell invasionFibrosis
The present invention relates to the discovery that biocompatible anionic polymers can effectively inhibit fibrosis, scar formation, and surgical adhesions. The invention is predicated on the discovery that anionic polymers effectively inhibit invasion of cells associated with detrimental healing processes, and in particular, that the effectiveness of an anionic polymer at inhibiting cell invasion correlates with the anionic charge density of the polymer. Thus the present invention provides a large number of materials for use in methods of inhibiting fibrosis and fibroblast invasion. Anionic polymers for use in the invention include but are not limited to natural proteoglycans, and the glycosaminoglycan moieties of proteoglycans. Additionally, anionic carbohydrates and other anionic polymers may be used. The anionic polymers dextran sulfate and pentosan polysulfate are preferred. In a more preferred embodiment, dextran sulfate, in which the sulfur content is greater than about 10% by weight, may be used. In a more preferred embodiment, the average molecular weight is about 40,000 to 500,000 Daltons. The present invention provides compositions and methods to inhibit fibrosis and scarring associated with surgery. The invention further provides compositions and methods to inhibit glial cell invasion, detrimental bone growth and neurite outgrowth. In a preferred embodiment, the inhibitory compositions further comprise an adhesive protein.
Owner:TRIAD
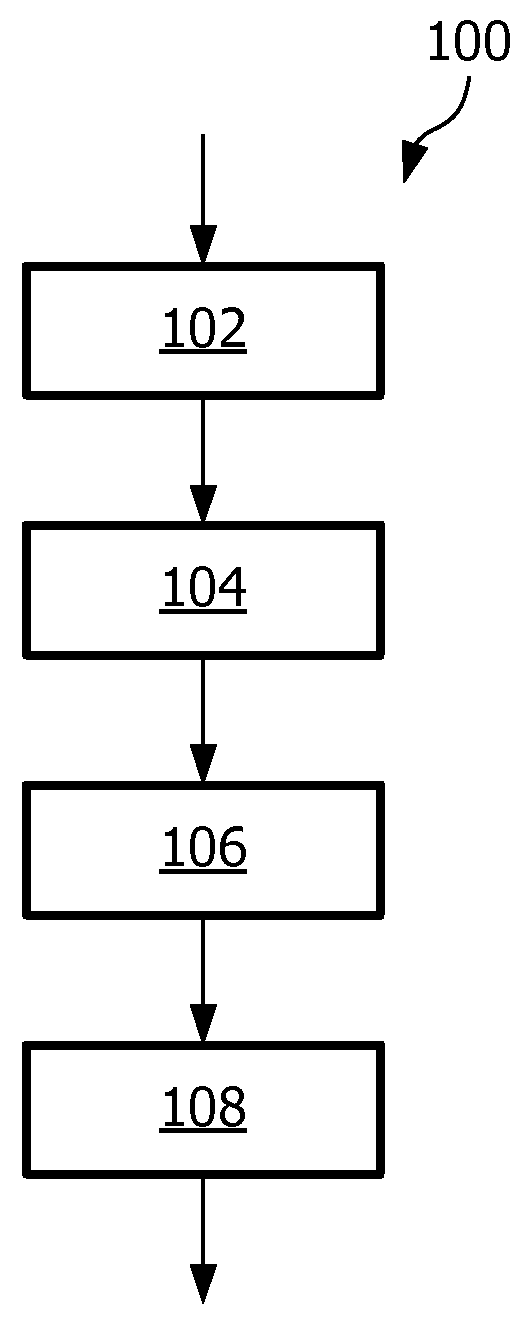
Method of controlling an outdoor lighting system, a computer program product, a controlling device and an outdoor lighting system
ActiveUS20130009569A1Economic controlElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementEngineeringLighting system
A method (100) of controlling an outdoor lighting system, a computer program product, a controlling device for controlling an outdoor lighting system and an outdoor lighting system are provided. The outdoor lighting system comprises outdoor lamps which are distributed over spatial segments of an outdoor space. The emitted light intensity of the outdoor lamps is controllable per spatial segment, and references are used to refer to specific spatial segments. The method (100) comprises the steps of (i) receiving (102) from a detection system an indication of a sub-area of the outdoor space and receiving at least one activity property or the sub-area, the detection system being arranged for detecting activity in the sub-area, the sub-area being different from all the spatial segments, and the indication being used to refer to the sub-area, and the at least one activity property being related to a traffic density in the sub-area (ii) mapping (104) the at least one indication to at least one reference of a respective spatial segment, (iii) determining (106) a light intensity level for the respective at least one spatial segment in dependence on the received at least one activity property, (iv) providing (108) the at least one reference together with the respective determined light intensity to the outdoor lighting system.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
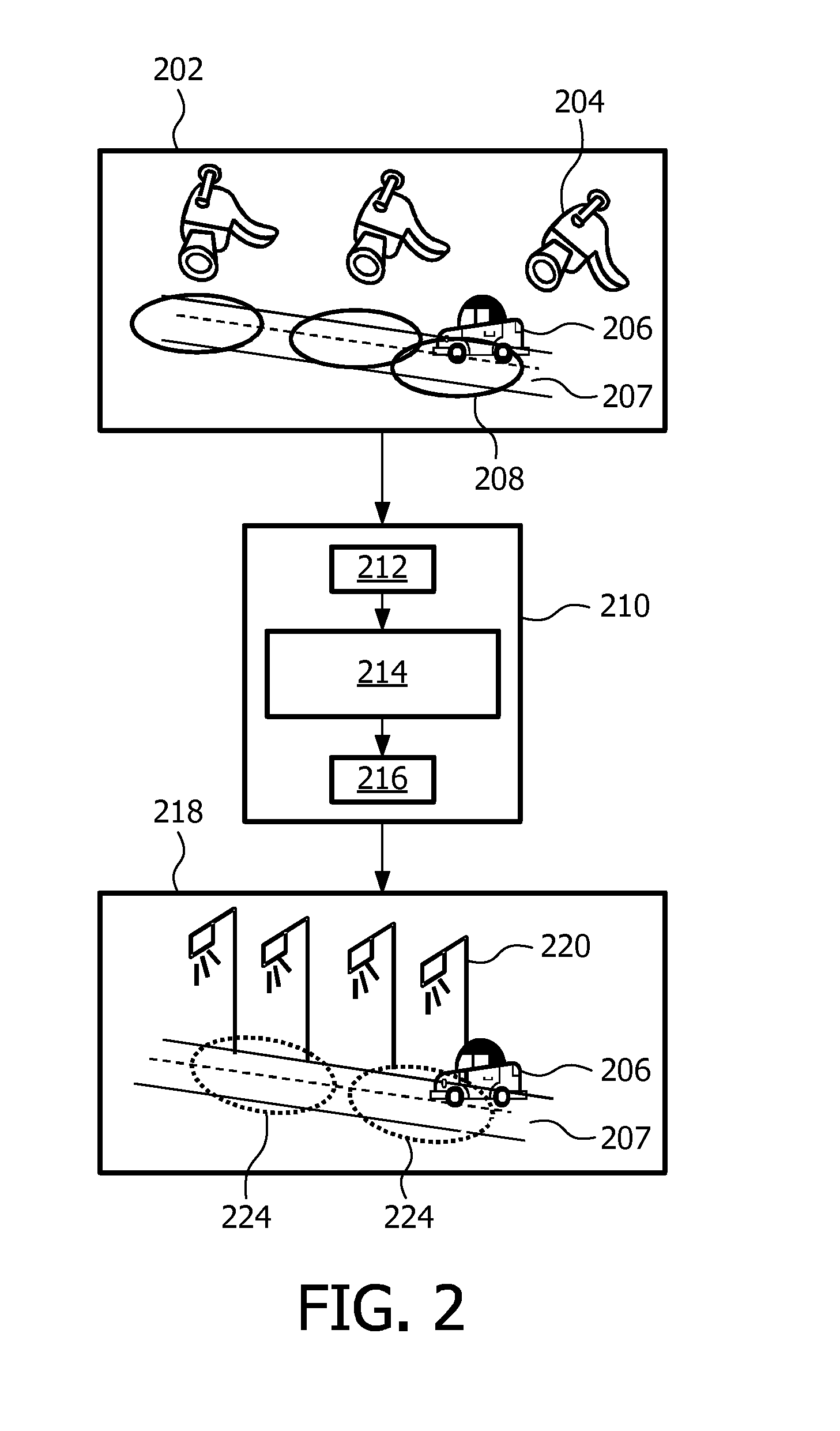
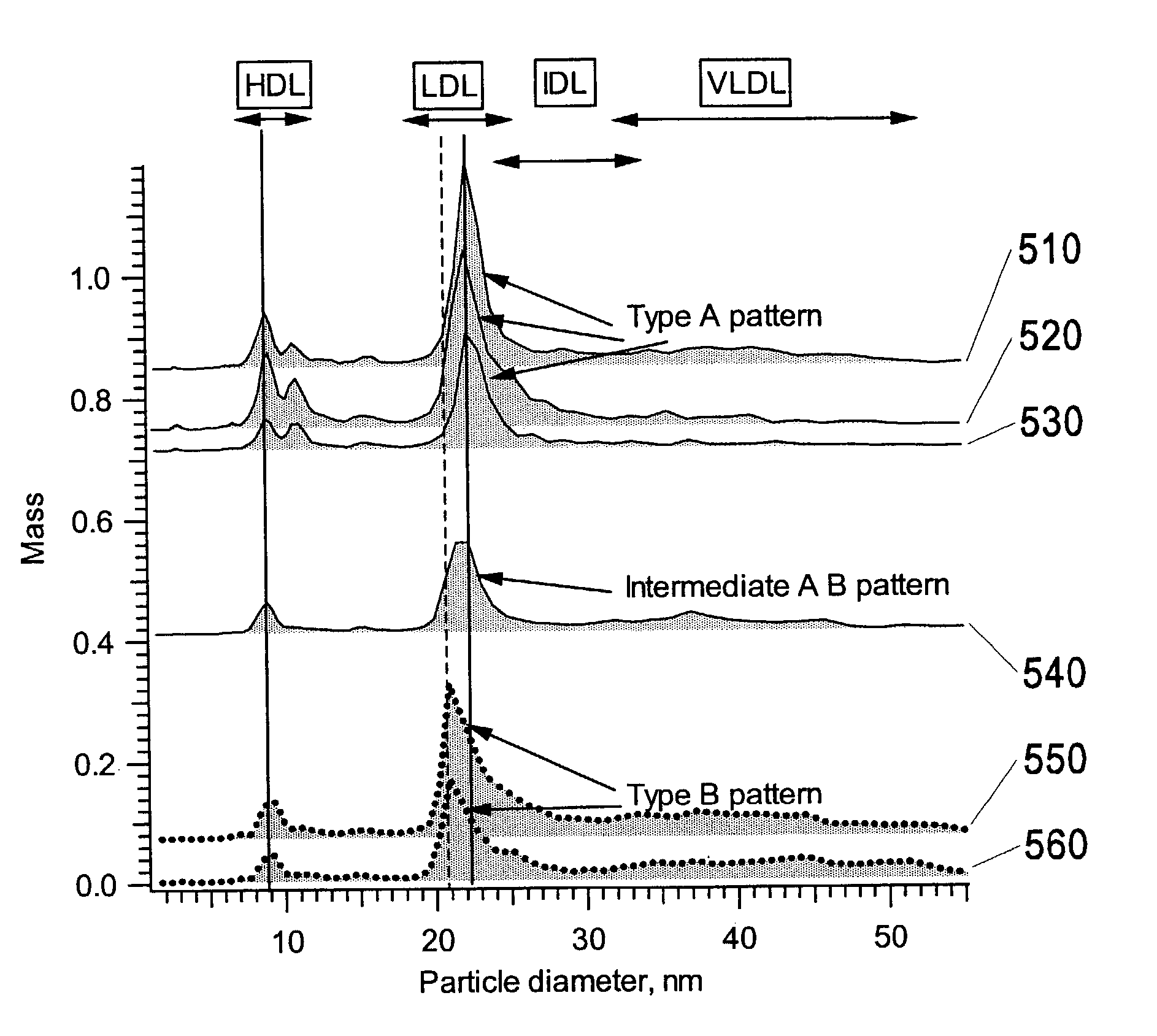
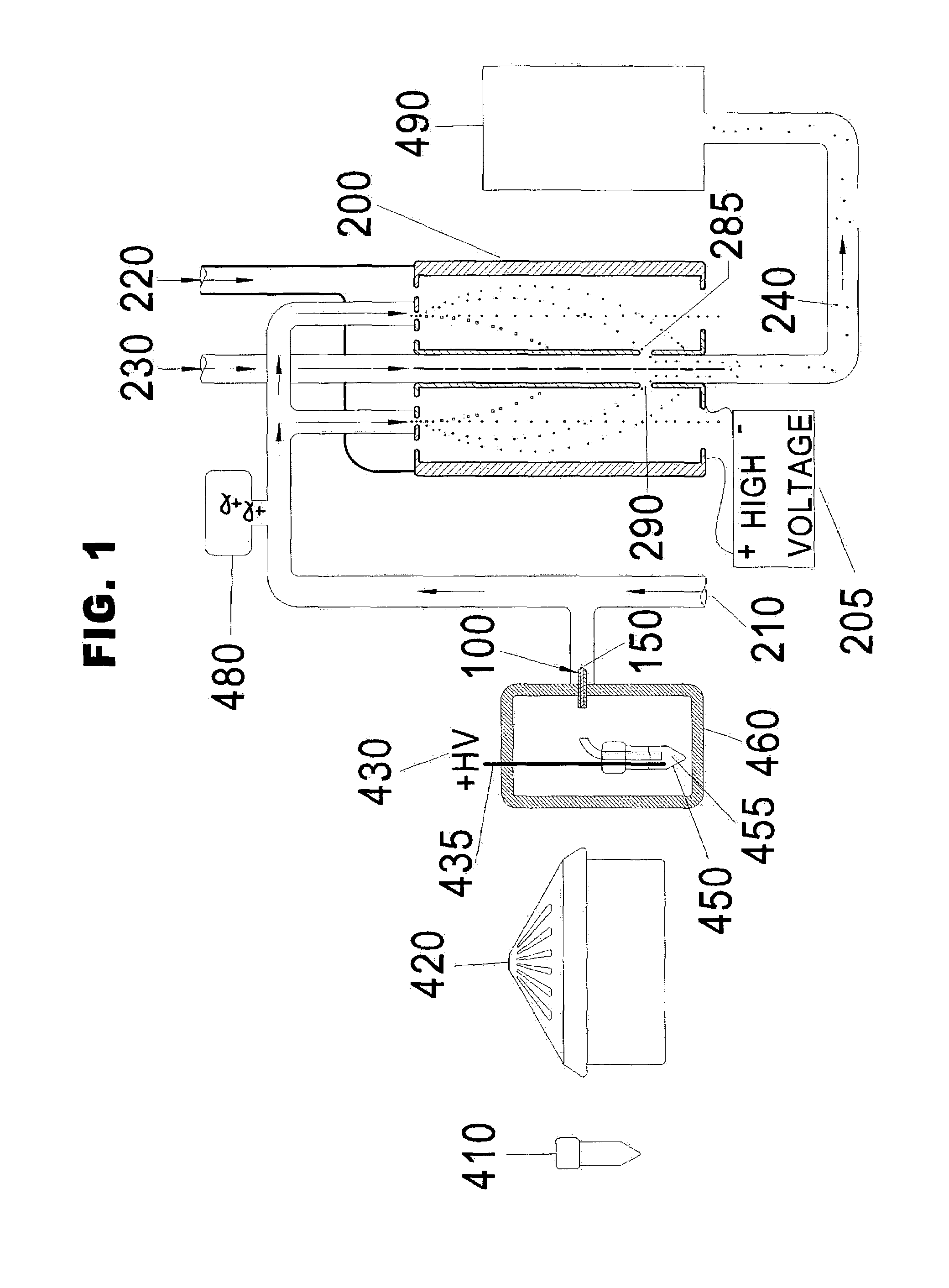
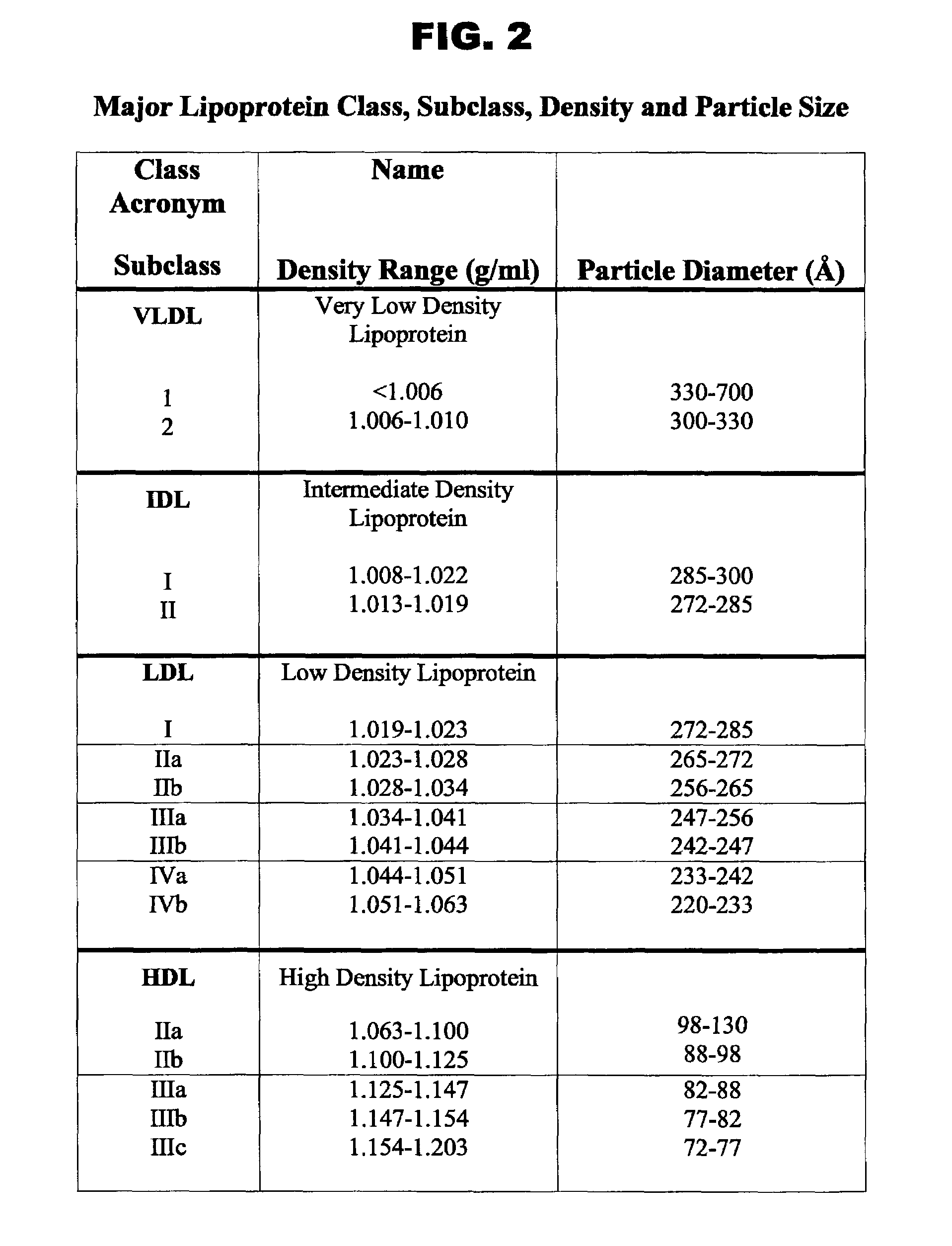
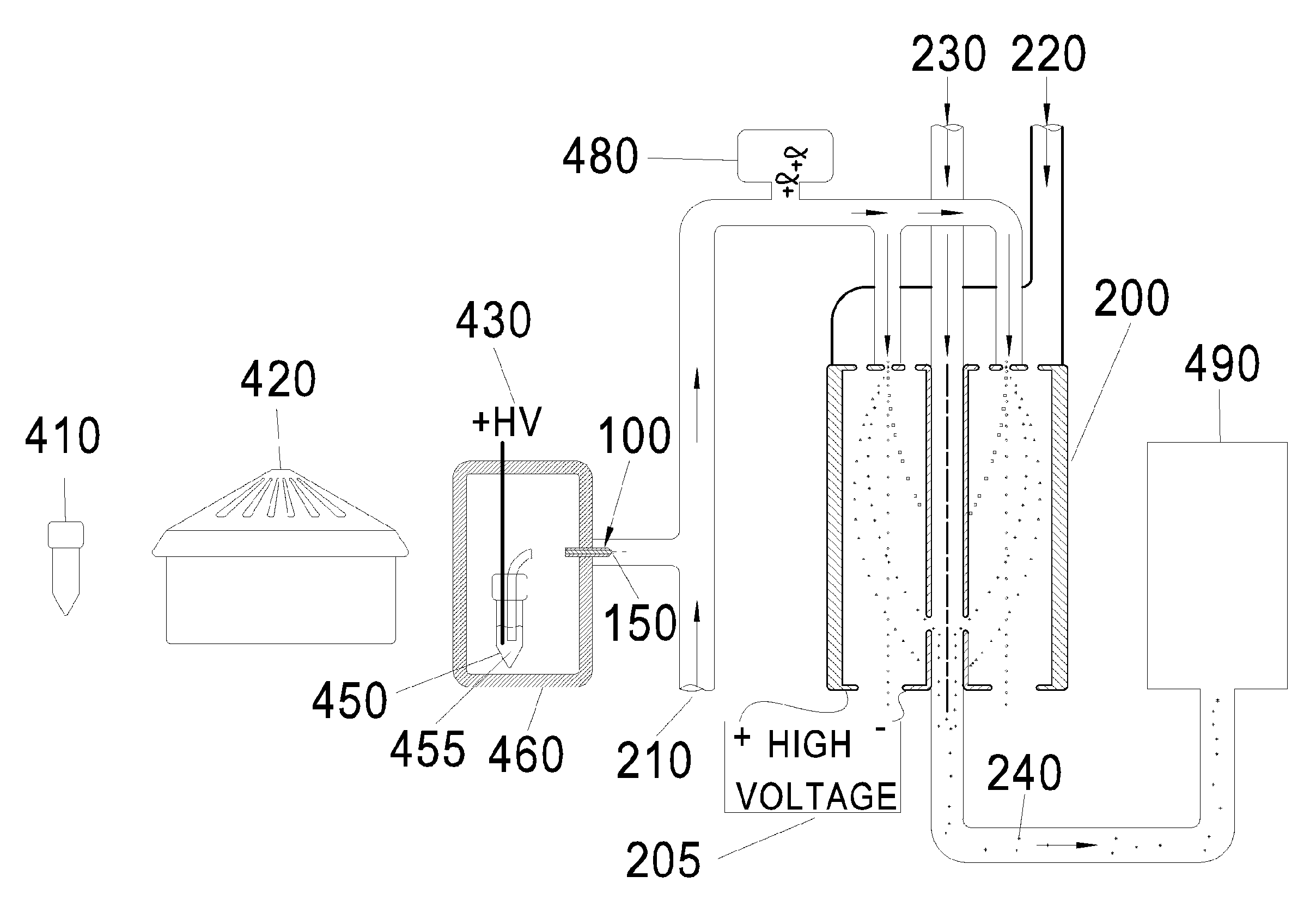
Ion mobility analysis of lipoproteins
A medical diagnostic method and instrumentation system for analyzing noncovalently bonded agglomerated biological particles is described. The method and system comprises: a method of preparation for the biological particles; an electrospray generator; an alpha particle radiation source; a differential mobility analyzer; a particle counter; and data acquisition and analysis means. The medical device is useful for the assessment of human diseases, such as cardiac disease risk and hyperlipidemia, by rapid quantitative analysis of lipoprotein fraction densities. Initially, purification procedures are described to reduce an initial blood sample to an analytical input to the instrument. The measured sizes from the analytical sample are correlated with densities, resulting in a spectrum of lipoprotein densities. The lipoprotein density distribution can then be used to characterize cardiac and other lipid-related health risks.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
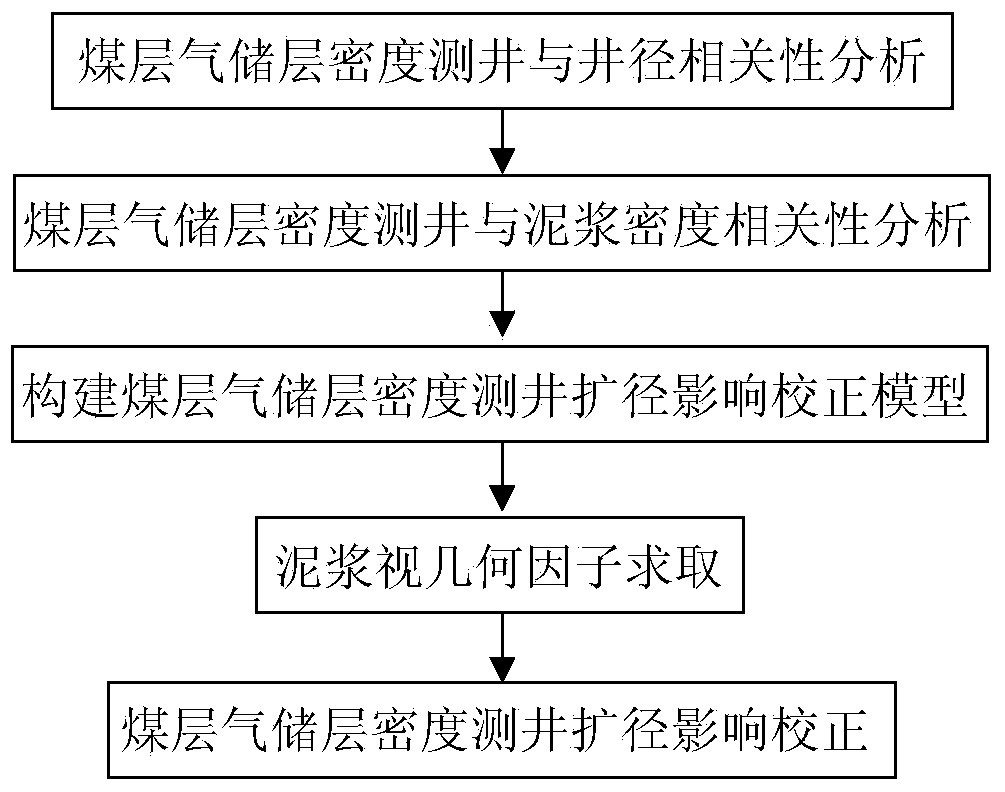
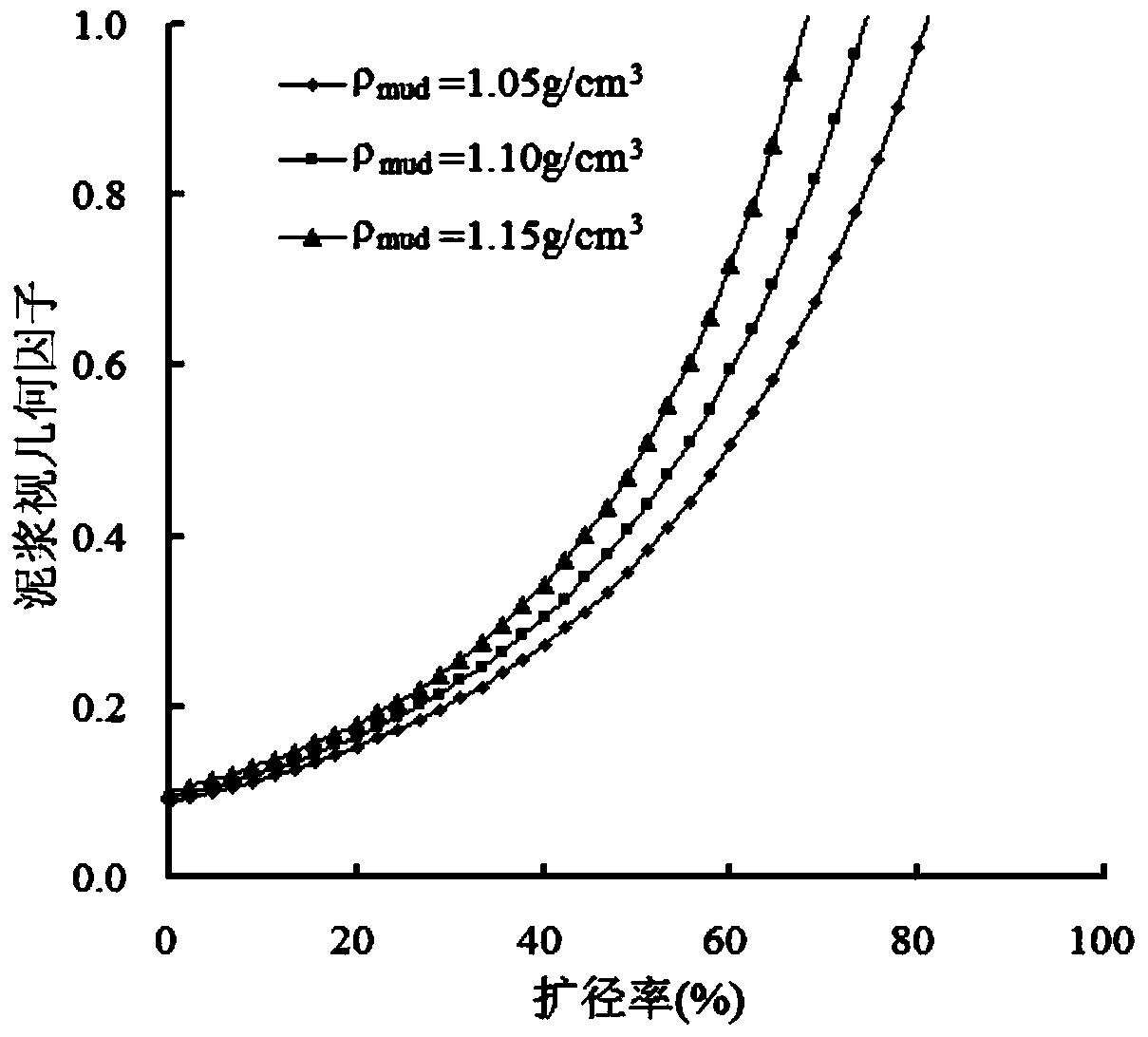
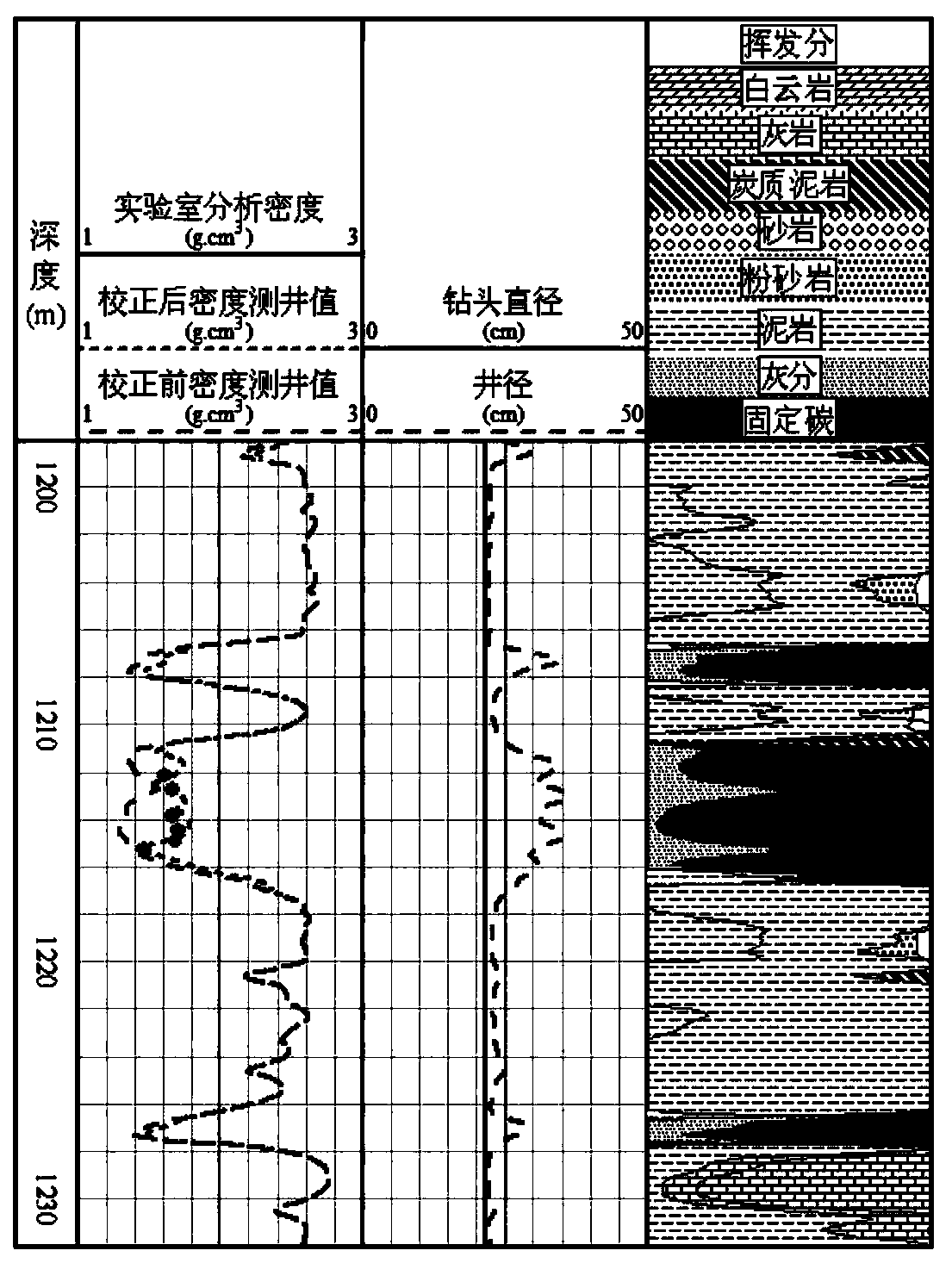
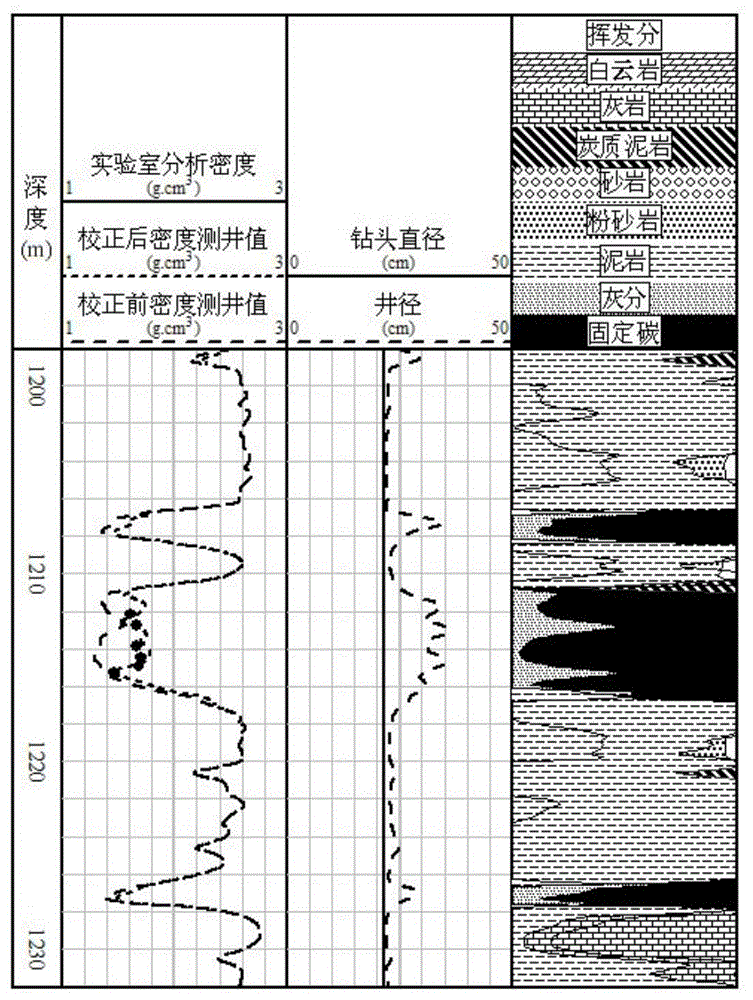
Method for correcting expanding influence of coalbed methane reservoir density logging
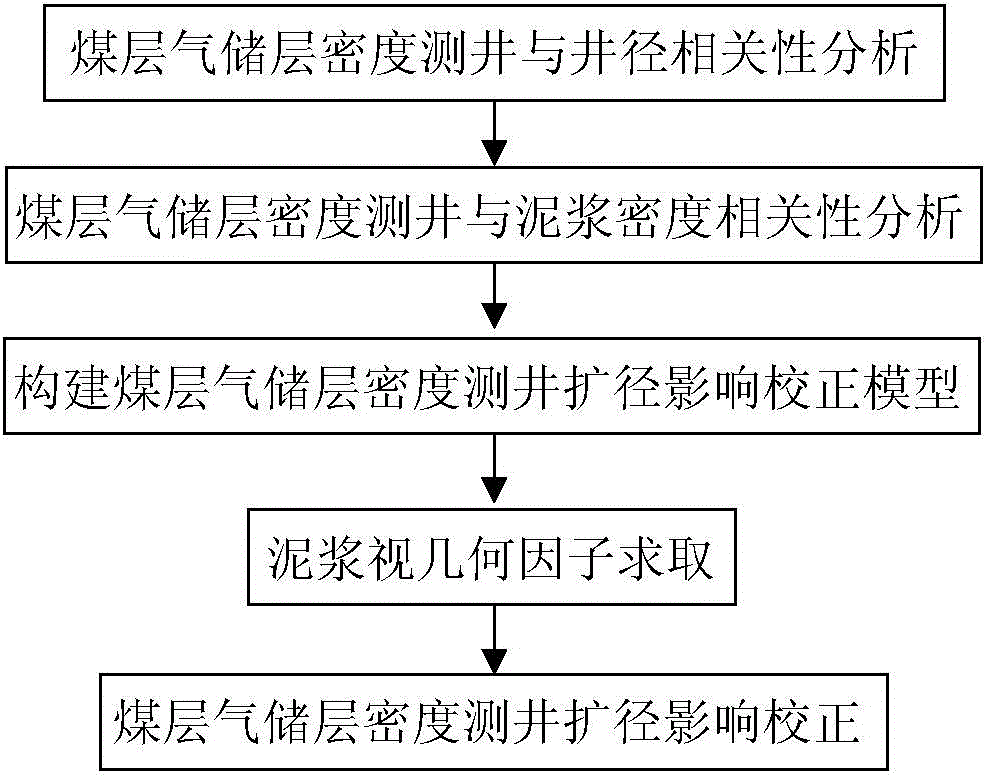
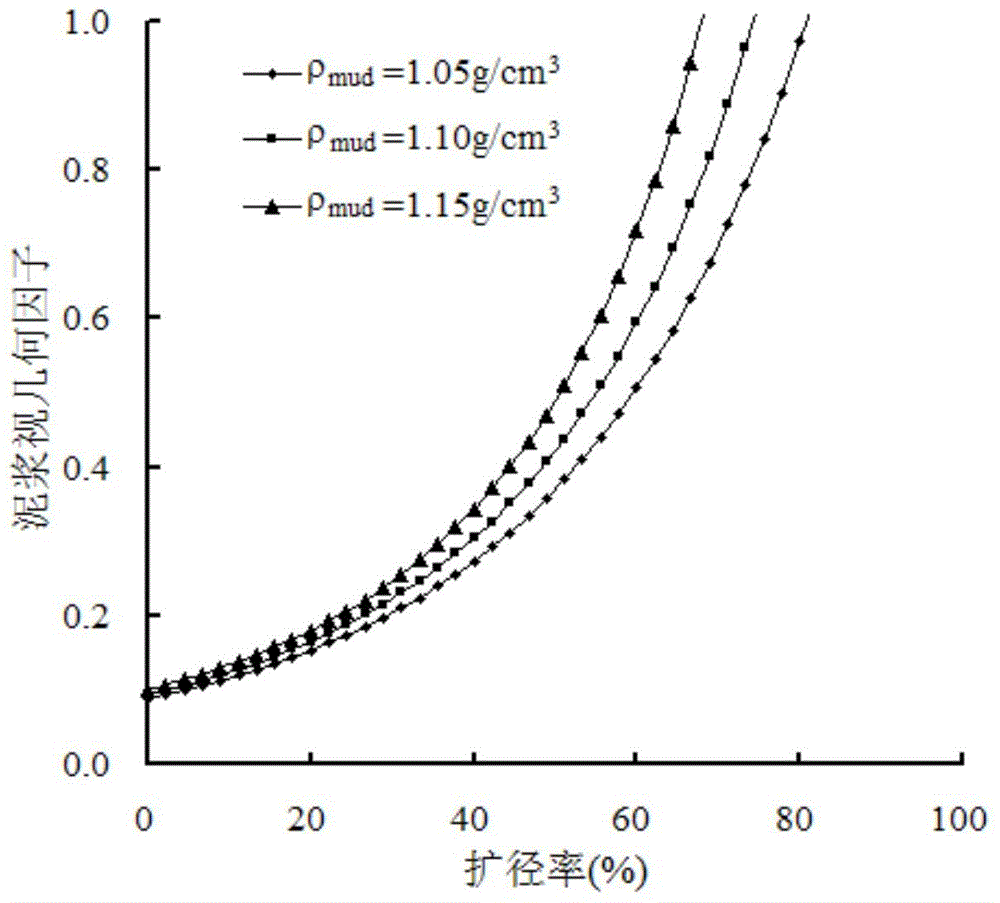
The invention discloses a method for correcting expanding influence of coalbed methane reservoir density logging. The method comprises the following steps of 1, analyzing a correlation between the coalbed methane reservoir density logging and a caliper; 2, analyzing a correlation between the coalbed methane reservoir density logging and mud density; 3, constructing a coalbed methane reservoir density logging expanding influence correcting model; 4, calculating satellite surveillance dilution of mud; 5, correcting the expanding influence of the coalbed methane reservoir density logging. Based on a satellite surveillance dilution theory, internal relations of an expanding ratio, the mud density and a density logging value are fully utilized, the coalbed methane reservoir density expanding influence is corrected, the accuracy of correcting the expanding influence of the coalbed methane reservoir density logging is improved and a guarantee is provided for improving prediction accuracy of coalbed gas content density logging.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Determining material stiffness using multiple aperture ultrasound
ActiveUS9339256B2High resolutionHigh imagingOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseSonification
Changes in tissue stiffness have long been associated with disease. Systems and methods for determining the stiffness of tissues using ultrasonography may include a device for inducing a propagating shear wave in tissue and tracking the speed of propagation, which is directly related to tissue stiffness and density. The speed of a propagating shear wave may be detected by imaging a tissue at a high frame rate and detecting the propagating wave as a perturbance in successive image frames relative to a baseline image of the tissue in an undisturbed state. In some embodiments, sufficiently high frame rates may be achieved by using a ping-based ultrasound imaging technique in which unfocused omni-directional pings are transmitted (in an imaging plane or in a hemisphere) into a region of interest. Receiving echoes of the omnidirectional pings with multiple receive apertures allows for substantially improved lateral resolution.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
Operation method of station based on station density in wireless local area network
InactiveUS20150296370A1Network topologiesWireless commuication servicesTelecommunicationsDensity based
Disclosed are operation methods of station based on station density in wireless local area network. An operation method comprises obtaining density-related information indicating a station density state within a communication area of the first station; and transmitting a notification frame including at least one of an operation mode indication information and a clear channel assessment (CCA) threshold that are set based on the density-related information. Therefore, performance of WLAN can be enhanced.
Owner:ATLAS GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and Apparatus for Separating Parts, in Particular Seeds, Having Different Densities
ActiveUS20110049017A1Differential sedimentationMagnetic separationProcess engineeringVolumetric Mass Density
A method for separating seeds of different densities in a process stream, wherein the seeds are introduced into a magnetic process fluid for the formation of the process stream, which process stream is subjected to a magnetic field for the realization of a density stratification in the process stream, such that the individual seeds in the process stream assume a density-dependent position, after which the seeds located in or near a predetermined position or positions in the process stream, are separated from the remaining seeds in the process stream.
Owner:URBAN MINING CORP BV
Methods, systems, and computer program products for measuring the density of material
Methods, systems, and computer program products for measuring the density of material. According to one aspect, a nuclear density gauge is disclosed for measuring the density of a sample construction material. The gauge includes a radiation source positioned in an interior of a sample construction material and adapted to emit radiation from the interior of the sample construction material. Further, a radiation detector is positioned apart from the radiation source. The radiation detector is operable to produce a signal representing an energy level of detected radiation. A material property calculation function is configured to calculate a value associated with the density of the sample construction material based upon the signal produced by the radiation detector. Further, the radiation source may be positioned on a surface of the sample construction material and adapted to emit radiation towards the surface of the sample construction material.
Owner:TROXLER ELECTRONICS LAB INC
Yarn for cell culture scaffold, and fabric including the same for cell culture scaffold
PendingUS20190134271A1Enhance cell viabilityIncrease ratingsNervous system cellsCell culture supports/coatingYarnFiber
Provided is yarn for a cell culture scaffold. The yarn includes ply-twisted fiber strands, and to prevent density-dependent inhibition of cultured cells and increase a cell-contacting specific surface area, at least a part of the plurality of twisted fiber strands are untwisted such that an open space is formed between the fibers. A cell proliferation rate and cell viability may be increased by creating microenvironments suitable for migration, proliferation and differentiation of the cultured cells using the yarn. A large quantity of cells may be simultaneously cultured by creating a cell proliferation space as large as possible in a scaffold space having a limited cell proliferation space, and cell proliferation may be steadily maintained by preventing the inhibition of cell proliferation due to intercellular contact. The cells cultured may be cultured to have a shape / structure suitable for application to an in vitro experiment model or implantation into an animal body.
Owner:AMOLIFESCI CO LTD
Soft-measuring method for density in concentration process of salvia miltiorrhiza injection production
InactiveCN101673096AStrong explanatory abilityInhibition effectProgramme controlComputer controlSalvia miltiorrhizaGas phase
The invention provides a soft-measuring method for density in concentrating process of salvia miltiorrhiza injection production, comprising the following steps: gathering the historical data of each sensor and densimeter in the concentration process of salvia miltiorrhiza, wherein the history data relate to concentrated solution density value and sensor data gathered on line in production process;selecting easily obtained procedure variables including gas phase temperature, liquid phase temperature, pressure and concentrated solution liquid level that have higher degree of correlation with density from each sensor data, and screening representative dataset; using a multivariate analysis method for building a soft-measuring model of density; and gathering the procedure variables on line, and using the soft-measuring model of density to carry out real-time estimation to control the concentration process. Aiming at the problem that the density in the concentration process of salvia miltiorrhiza injection production is difficultly monitored in real time, the invention provides a fast density soft-measuring method with high precision, which makes full use of the history data obtained by each sensor from the production process, and is beneficial to improvement of quality control on salvia miltiorrhiza injection production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for Calibrating Machines for the Analysis of Characteristic Parameters of the Blood Connected To Its Density, Such as Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and/or Red Corpuscles Aggregation Rate
ActiveUS20090120157A1Improve accuracyLimited rangeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansRed blood cellAggregation rate
A method for calibrating machines suitable to effect an analysis of a blood sample by means of measuring the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and / or aggregation of the red corpuscles, wherein said measurement is effected by exploiting the optical density kinetics obtained from the measurement of the variation in the optical density of the blood sample in an interval of time, comprises a measuring step in which, by means of the same machine with which the measurement of the optical density is effected on said blood sample, a measurement is effected of the optical density of two latexes, or turbidimetric samples. Each of the two latexes has a known optical density, reproducible, measurable and different from each other. The method also comprises a comparison step, in which the difference is calculated between the values of optical density of the latexes as obtained from the measurement performed by the machine and the known values of optical density, to allow to determine at least one correction factor usable to calibrate said machine.
Owner:ALIFAX
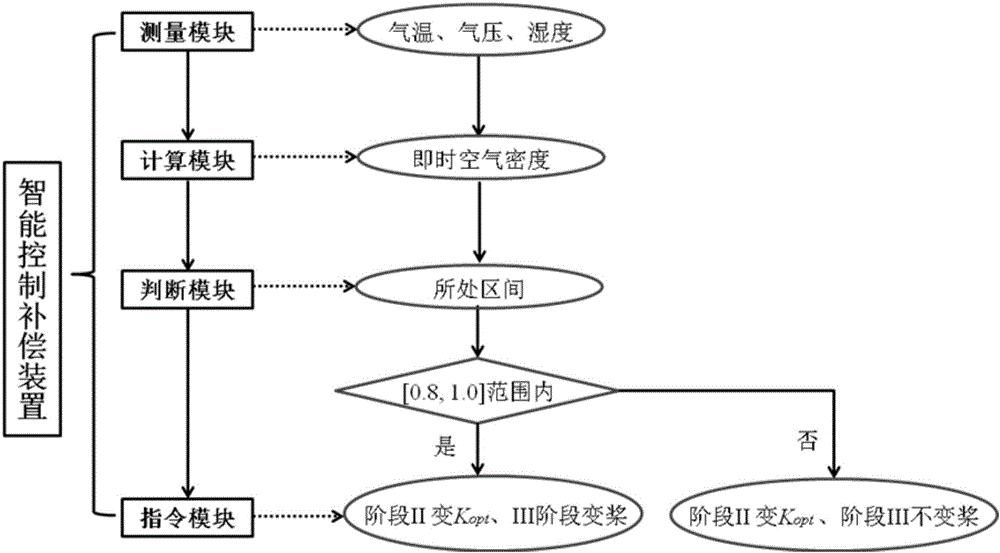
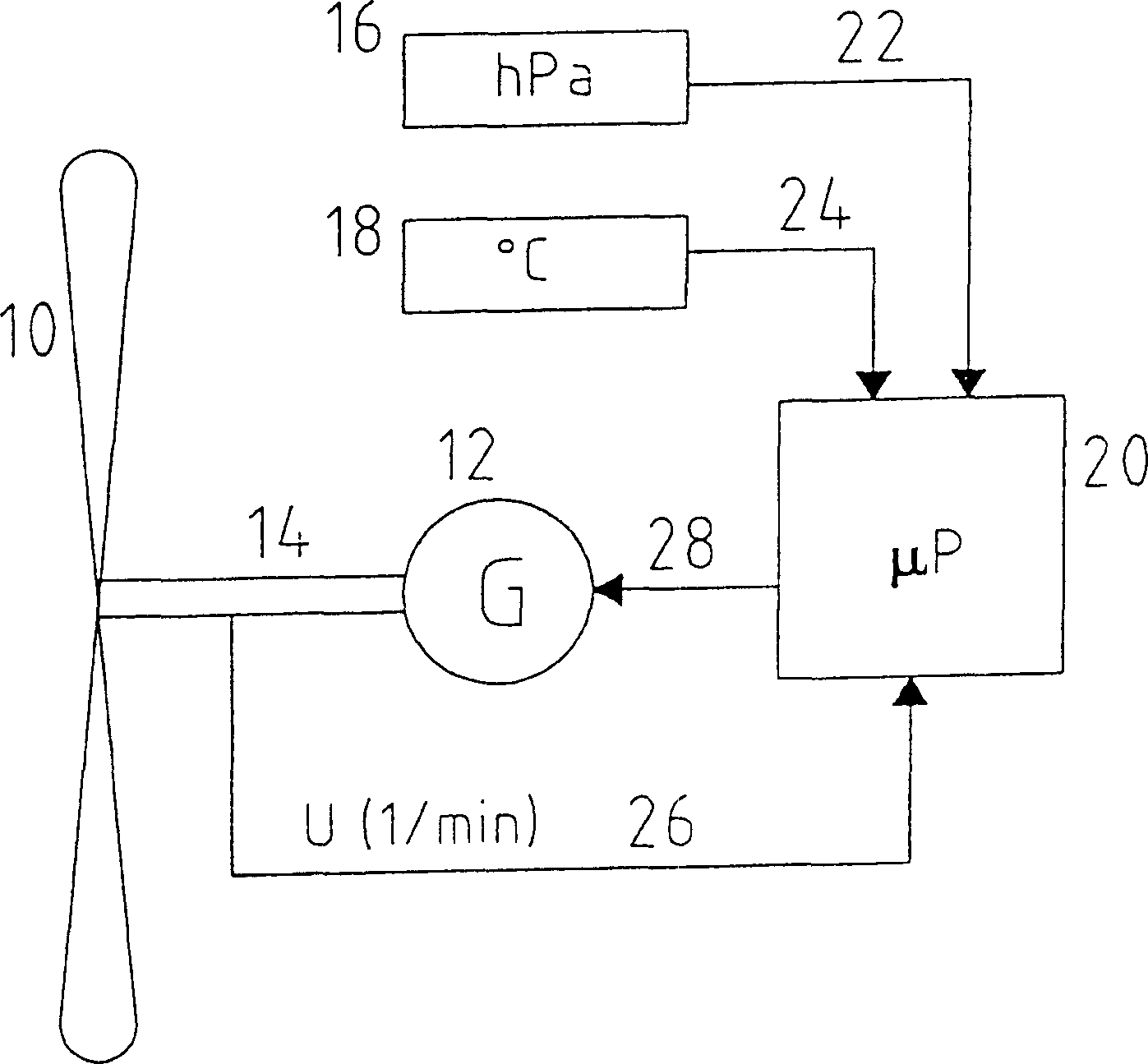
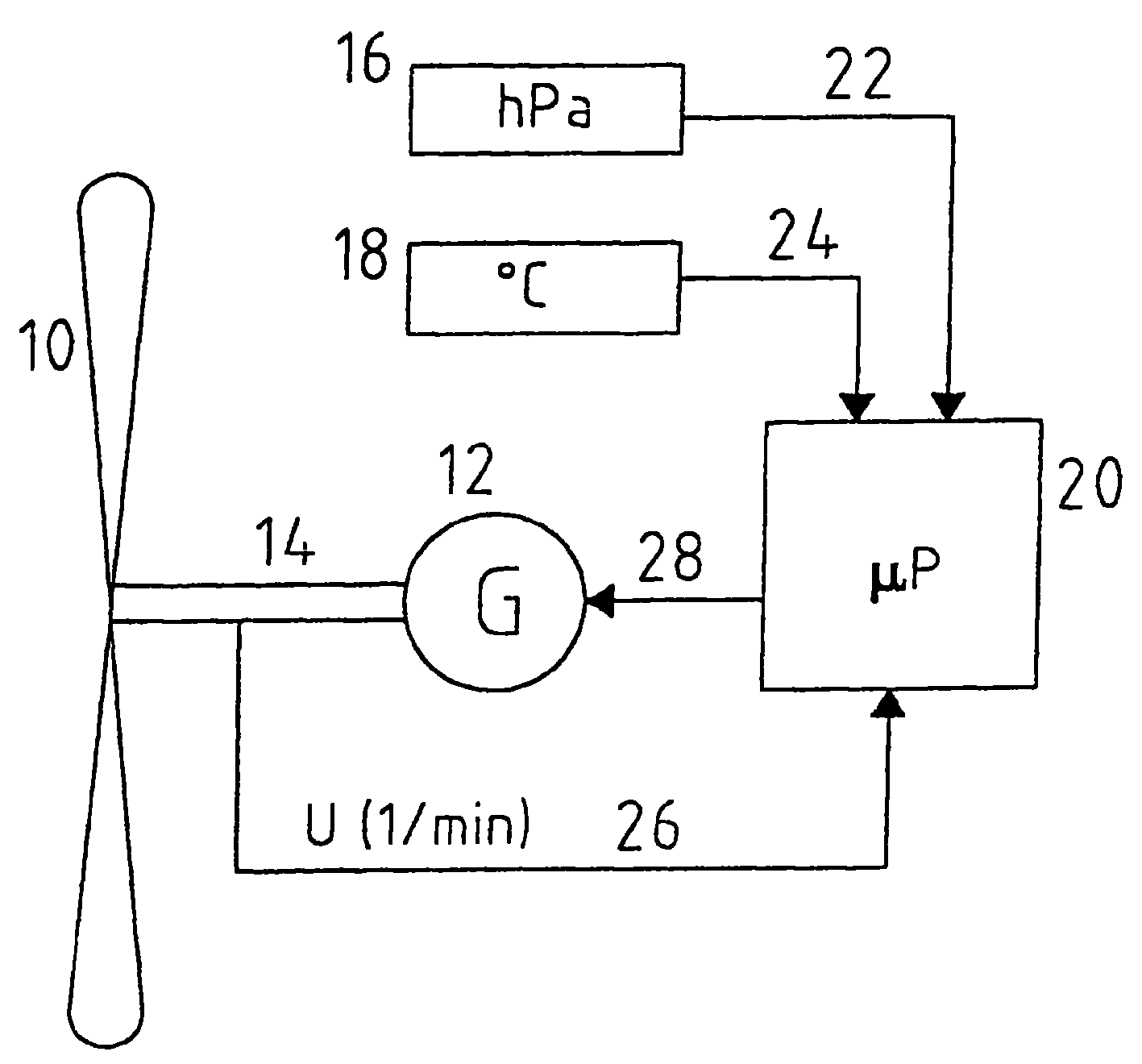
Intelligent control compensation method and device for improving wind energy capturing capacity of wind generating set
InactiveCN106523279AReal-time monitoring of air densityImprove capture abilityWind motor controlMachines/enginesVolumetric Mass DensityEngineering
The invention discloses an intelligent control compensation method for improving wind energy capturing capacity of wind generating set. The method comprises the following steps that (1) the local current air densities are obtained through timing calculation with the period of Tcal by measuring the air temperature, the air pressure and the humidity of a field where the wind generating set is located; (2) discrete air density values obtained through calculation are integrated into a plurality of preset interval ranges, and the densities input into a master control system are assigned according to the interval of the actual density; and (3) according to the interval of the current air density value, parameters of a master control program of the wind generating set relevant to density are corrected, when the air density is lower than a preset threshold, a set blade variable function is started before the wind speed reaches the rated wind speed, and the wind generating unit maintains the optimal working state in the changing environment. The invention further provides an intelligent control compensation device for improving wind energy capturing capacity of wind generating set. The method and device improve the wind energy capturing capacity and achieve output optimization under different working conditions.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WINDEY
Male fertility assay method and device
InactiveUS20050130122A1Prevent outflowPromote absorptionMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologySemen sampleMicrofluidics
A method and device for assaying sperm motility in a forward direction and density of active sperm in a semen sample are disclosed. The device includes a microfluidics structure having a sample reservoir, a downstream collection region and a microchannel extending therebetween. The microchannel is dimensioned to confine sample sperm to single-direction movement within the channel, such that sperm in a semen sample placed in the sample reservoir enter and migrate along the microchannel toward and into the collection region. Also included is a detector for detecting the presence of labeled sperm in the microchannel or collection region, and an electronics unit operatively connected to the detector for (i) receiving detector signals, (ii) based on the detector signals received, determining sperm motility and density in the sperm sample, and (iii) displaying information related to sperm motility and density.
Owner:QN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
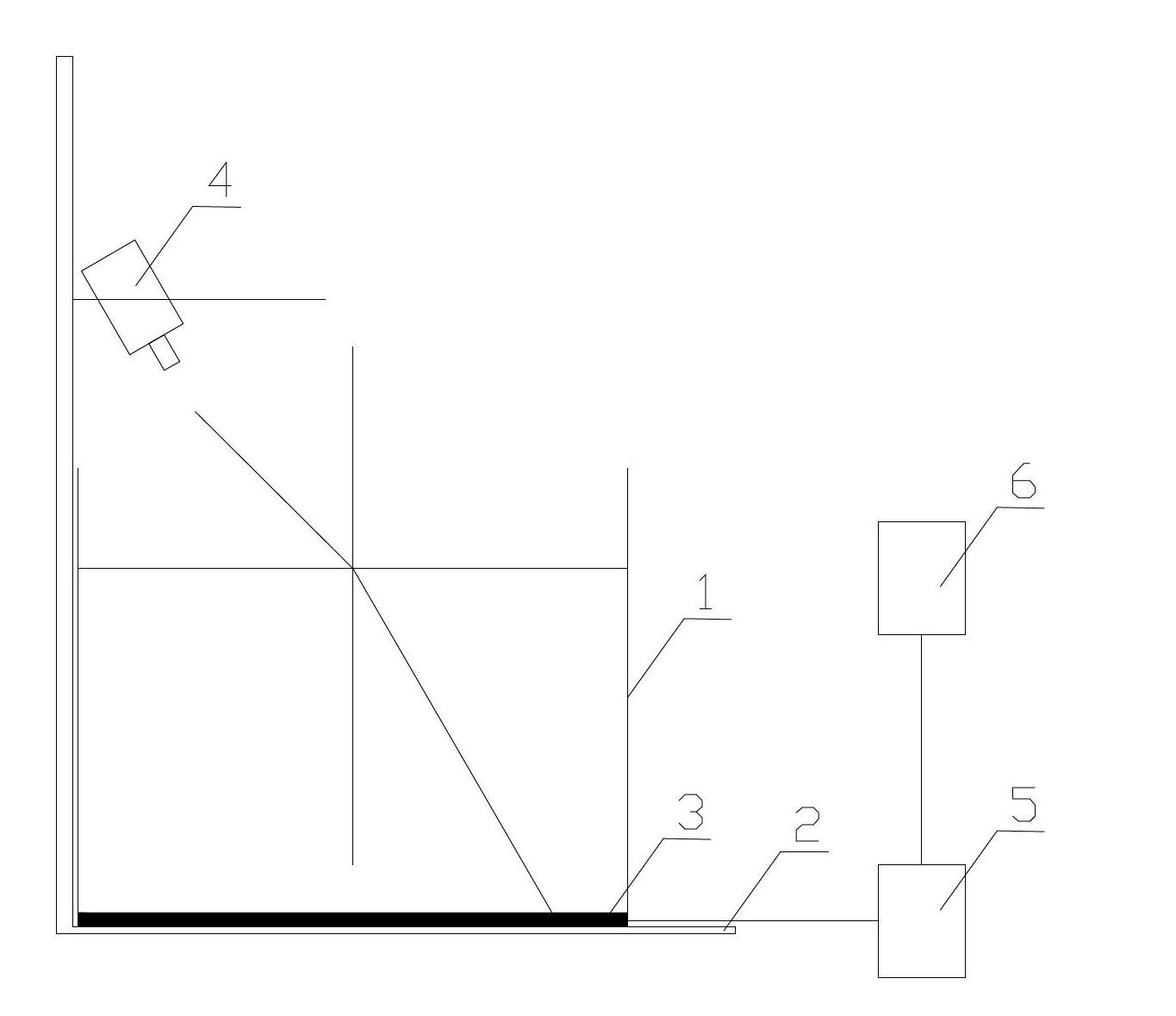
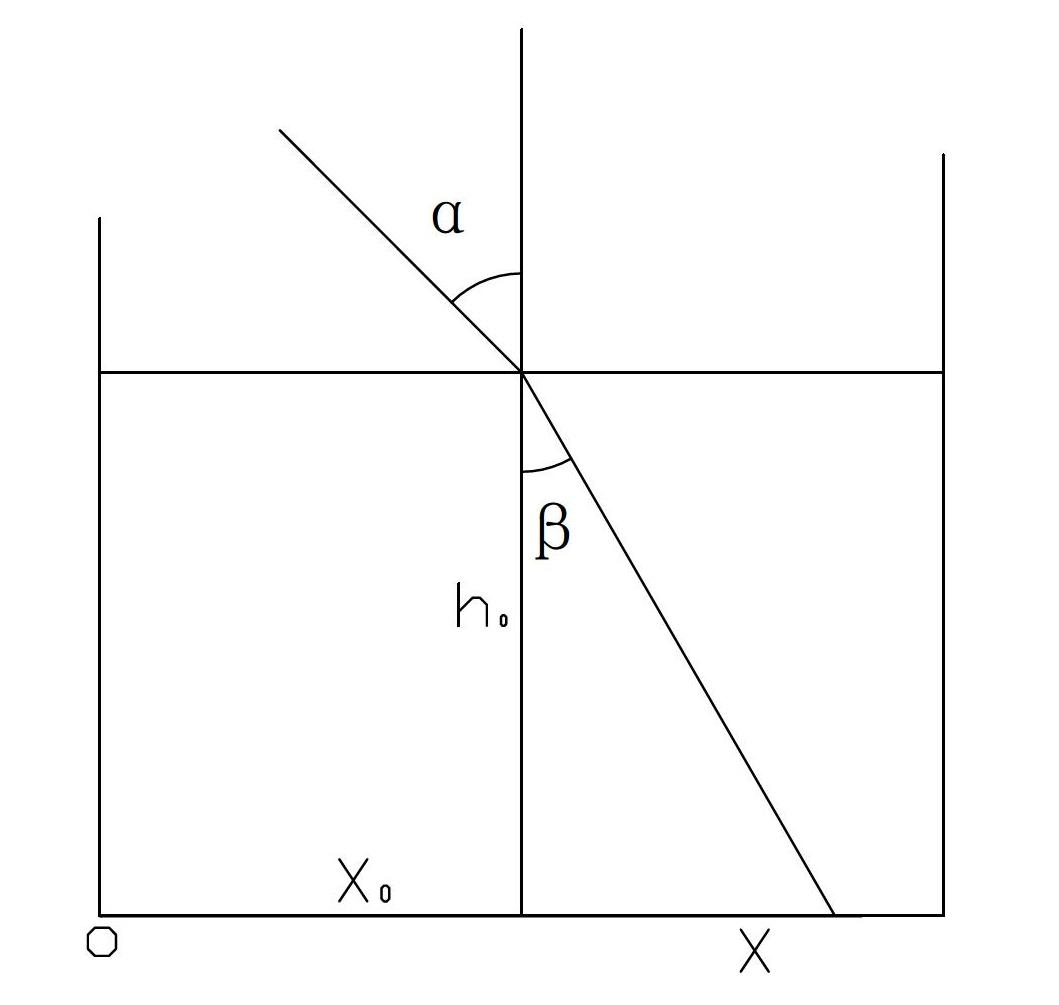
Device and method for measuring sand content of optical sediment solution
ActiveCN102645394AEasy to buildHigh measurement accuracyParticle suspension analysisMeasuring instrumentRefractive index
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring the sand content of an optical sediment solution. The device comprises a measurement cylinder, a regulation base, a black and white linear array charge coupled device (CCD) module and a semiconductor laser, wherein the black and white linear array CCD module is arranged at the bottom of the measurement cylinder, and is connected with a computer by an analog / digital (A / D) conversion card. The method is based on a light refraction law; light refractive index is related to the density which is related to the concentration of the solution with sand content, so that the concentrations of the solution with different sand contents are different from one another, and the concentration has a certain correspondence relationship with the sand content, thus the refractive index corresponds to the sand content of the sediment solution, and the relationship between the concentration of the sediment solution and the refractive index can be established by calibration, so that the concentration of the sand content of the sediment solution can be reversely calculated by utilizing the refractive index according to the calibration relationship. The device disclosed by the invention is easy to build and high in measurement accuracy and degree of automation. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in principle, easy to operate, convenient for manufacturing a sand content measuring apparatus suitable for different occasions and wide in applicability.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
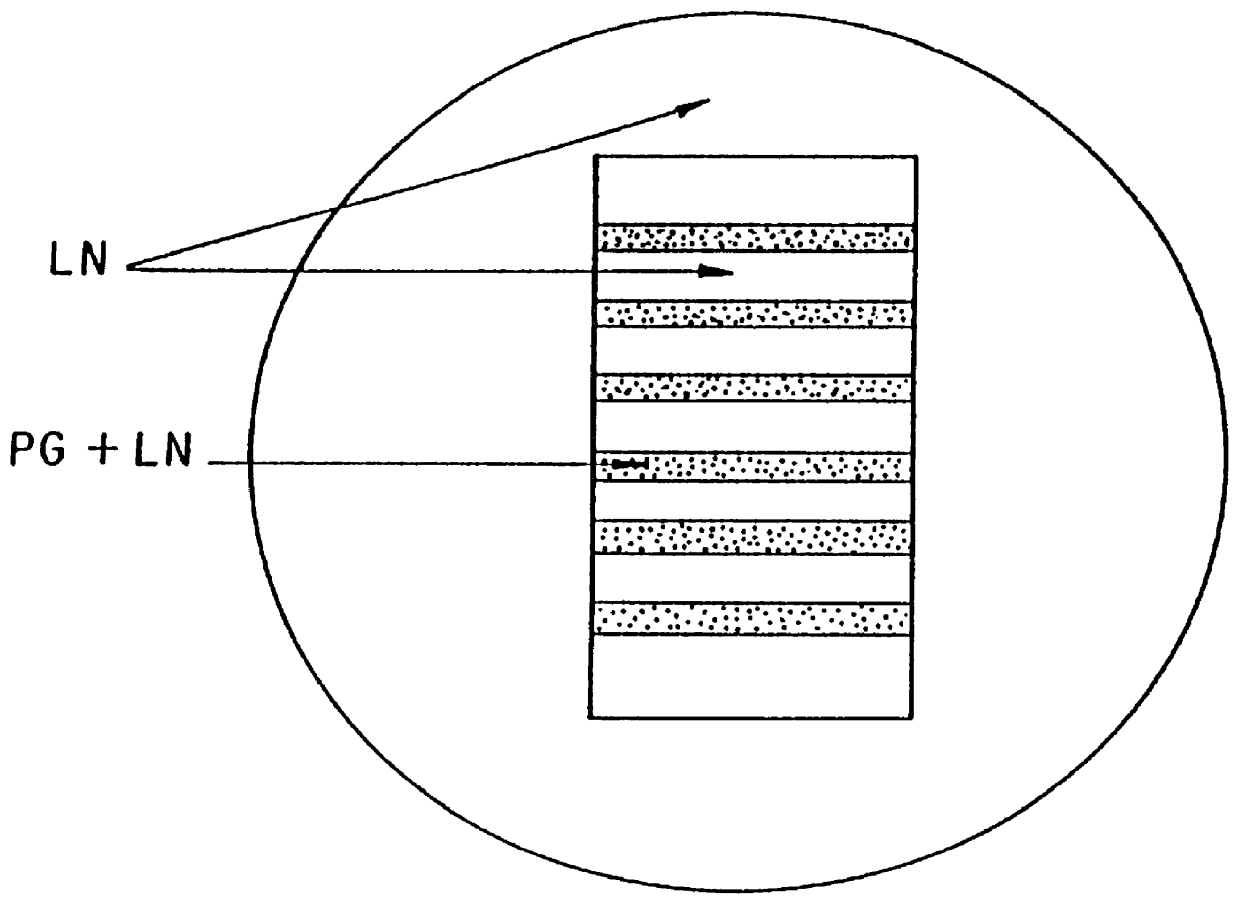
Amorphous metal foam as a property-matched bone scaffold substitute
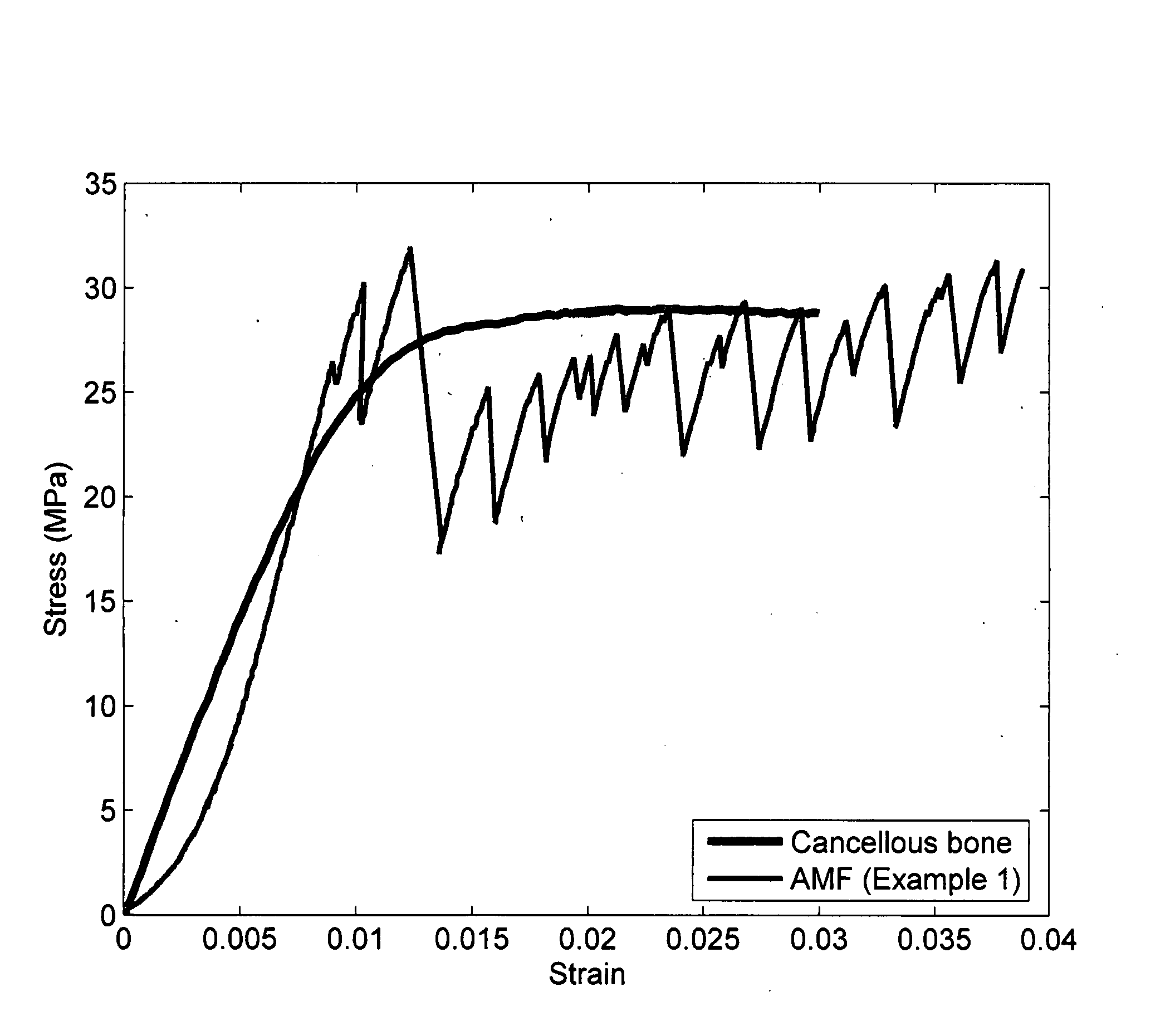
Amorphous metal foams and methods of making the same are provided. The amorphous metal foams have properties matching those of natural bone, enabling their use as bone replacement scaffolds. In one embodiment, for example, an amorphous metal foam has a density-dependent stiffness (or Young's modulus, denoted E) ranging from about 640ρ3.75 τo αβoντ 2900ρ0.78, and a density dependent strength (σy) greater than about 8.1ρ2.57, wherein ρ (the density) is less than about 1.7 g / cc.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Magnetic floating density separation measurement method based on general anti-magnetic properties of materials
InactiveCN107677567AEasy to operateLow costMaterial analysis by observing immersed bodiesVisual observationTest sample
The invention discloses a magnetic floating density separation measurement method based on general anti-magnetic properties of materials. The method includes a step (1) of constructing a magnetic floating experimental device, and simulating a magnetic floating effect of a magnetic field on an object by physical modeling; a step (2) of determining the approximate density of a material of a to-be-tested sample, and then determining the density of a paramagnetic medium solution; a step (3) of placing a transparent container containing the to-be-tested sample and the paramagnetic solution in a magnetic flotation device and performing full standing, wherein the magnetic flotation device is provided with an adjustable number of strip-shaped magnets with like poles opposite; a step (4) of obtaining floating height information of the tested sample by means of visual observation and picture collection; and a step (5) of calculating sample density and performing density-related studies. Comparedwith the prior art, the magnetic floating density separation measurement method has the outstanding advantages that a device required by the method is simple and convenient to operate and low in cost, measurement results are easy to observe, measurement accuracy is high, and high-precision density-related test applications can be carried out under limited conditions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Color adjustment method and image forming system using gamma curve associating densities of patches from different printers
ActiveUS8625179B2Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsComputer printingImage formation
Disclosed is a color adjustment method for each of image forming apparatuses, including: a gradation pattern creation step of forming a gradation pattern image including patches different in gradation for each of colors in n pieces of coloring materials; a density detection step of detecting densities of the respective patches, and obtaining density information; a gamma curve creation step of associating the density information of the respective patches in a second image forming apparatus with that in the first, and creating a gamma curve correcting a gradation of received image data so as to obtain densities of the respective patches in the first image forming apparatus; and a color adjustment step of extracting respective color components, deciding output values based on the gamma curve corresponding to the second image forming apparatus, creating output image data, and forming an image on a sheet in the second image forming apparatus.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Multi-Vortex Flowmeter Employing Volume Flow Rate as Switching Point
InactiveUS20090241687A1Improve accuracyGood effectVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectDifferential pressureEngineering
A multi-vortex flowmeter (1) includes a vortex flowmeter for measurement by volume flow rate and a thermal flowmeter for measurement by mass flow rate to selectively use the two flowmeters according to the flow rate of fluid to be measured flowing through a flow channel (13). The multi-vortex flowmeter (1) uses the mass flow rate for a switching point. In other words, the multi-vortex flowmeter (1) has the switching point of two flowmeters based on the mass flow rate. A mass flow rate Qm at the switching point in a range larger than the minimum flow rate of a vortex flowmeter and smaller than the maximum flow rate of a thermal flowmeter is determined by: Qm=K3*√P, (where, P is a pressure of the flow channel (variable), K3 is a constant determined by the area and the vortex differential pressure of the channel (13) and a constant related to the vortex differential pressure, a density at 0° C. and 1 atm, and the pressure at 1 atm). Alternatively, a volume flow rate Q at the switching point in a range larger than the minimum flow rate of a vortex flowmeter and smaller than the maximum flow rate of a thermal flowmeter is determined by: Q=K1 / √P, (where, P is a pressure of the channel (variable), K1 is a constant determined by the area and the vortex differential pressure of the flow channel (13) and a constant related to the density at 0° C. and 1 atm, and the pressure at 1 atm).
Owner:OVAL CORP
Methods of controlling an outdoor lighting system
ActiveUS9386664B2Economic controlElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
A method (100) of controlling an outdoor lighting system, a computer program product, a controlling device for controlling an outdoor lighting system and an outdoor lighting system are provided. The outdoor lighting system comprises outdoor lamps which are distributed over spatial segments of an outdoor space. The emitted light intensity of the outdoor lamps is controllable per spatial segment, and references are used to refer to specific spatial segments. The method (100) comprises the steps of (i) receiving (102) from a detection system an indication of a sub-area of the outdoor space and receiving at least one activity property or the sub-area, the detection system being arranged for detecting activity in the sub-area, the sub-area being different from all the spatial segments, and the indication being used to refer to the sub-area, and the at least one activity property being related to a traffic density in the sub-area (ii) mapping (104) the at least one indication to at least one reference of a respective spatial segment, (iii) determining (106) a light intensity level for the respective at least one spatial segment in dependence on the received at least one activity property, (iv) providing (108) the at least one reference together with the respective determined light intensity to the outdoor lighting system.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
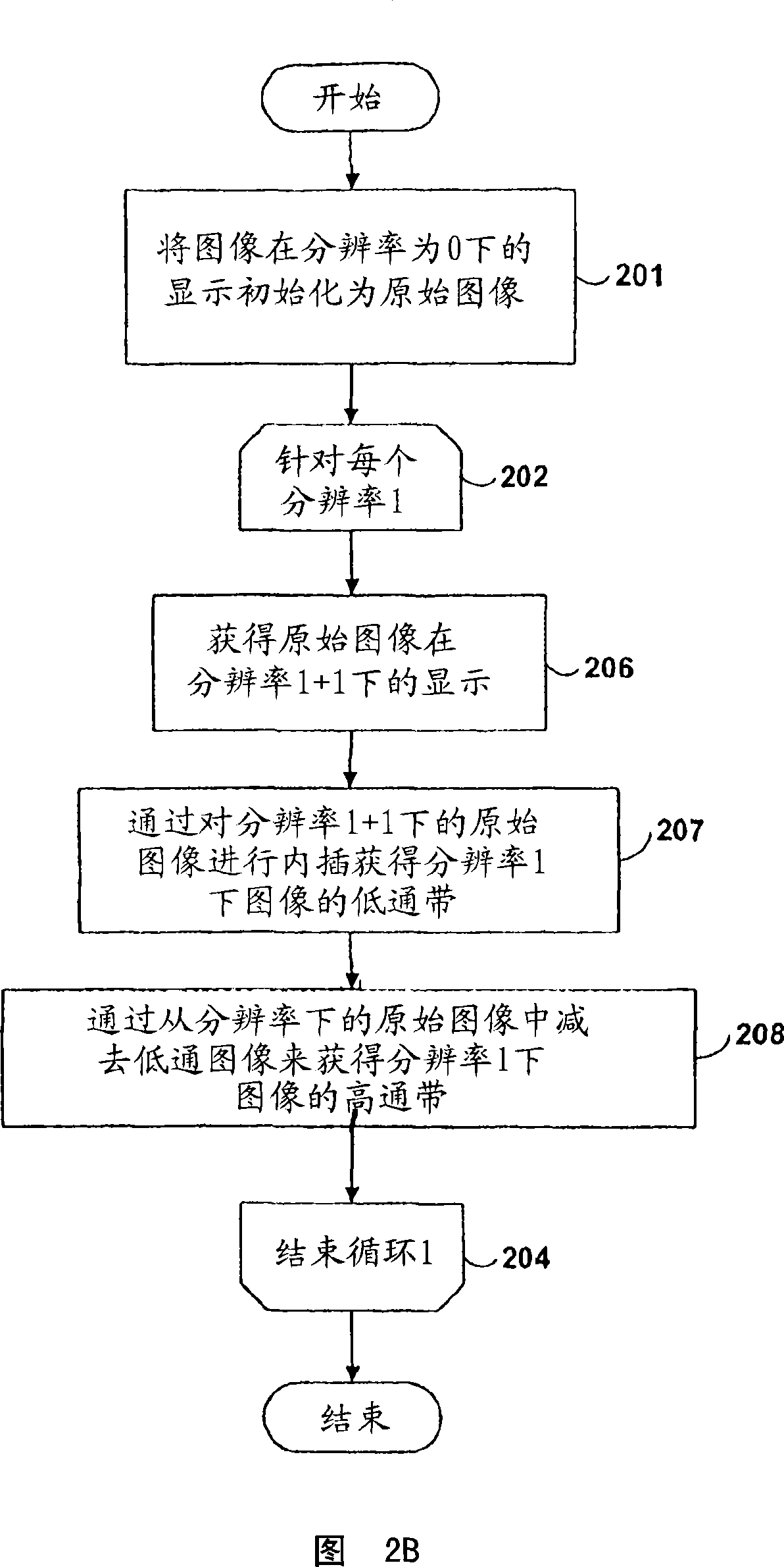
Density-dependent sharpening
InactiveCN101073251AImage enhancementPictoral communicationComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
A sharpening filter is disclosed for performing density-dependent sharpening on digital images. In one embodiment, a digital image to be sharpened is decomposed into a plurality of high-pass versions of the image at different resolutions. These high-pass images are gained at each resolution and recombined with the original image to produce a sharpened version of the image. The gains that are applied at each resolution are density-dependent. As a result, the effects of density-dependent blurring are counteracted, such that the sharpness of the final printed image is independent of the print density. Techniques are disclosed for performing such density-dependent sharpening with a high degree of computational efficiency.
Owner:MITCHAM GLOBAL INVESTMENTS
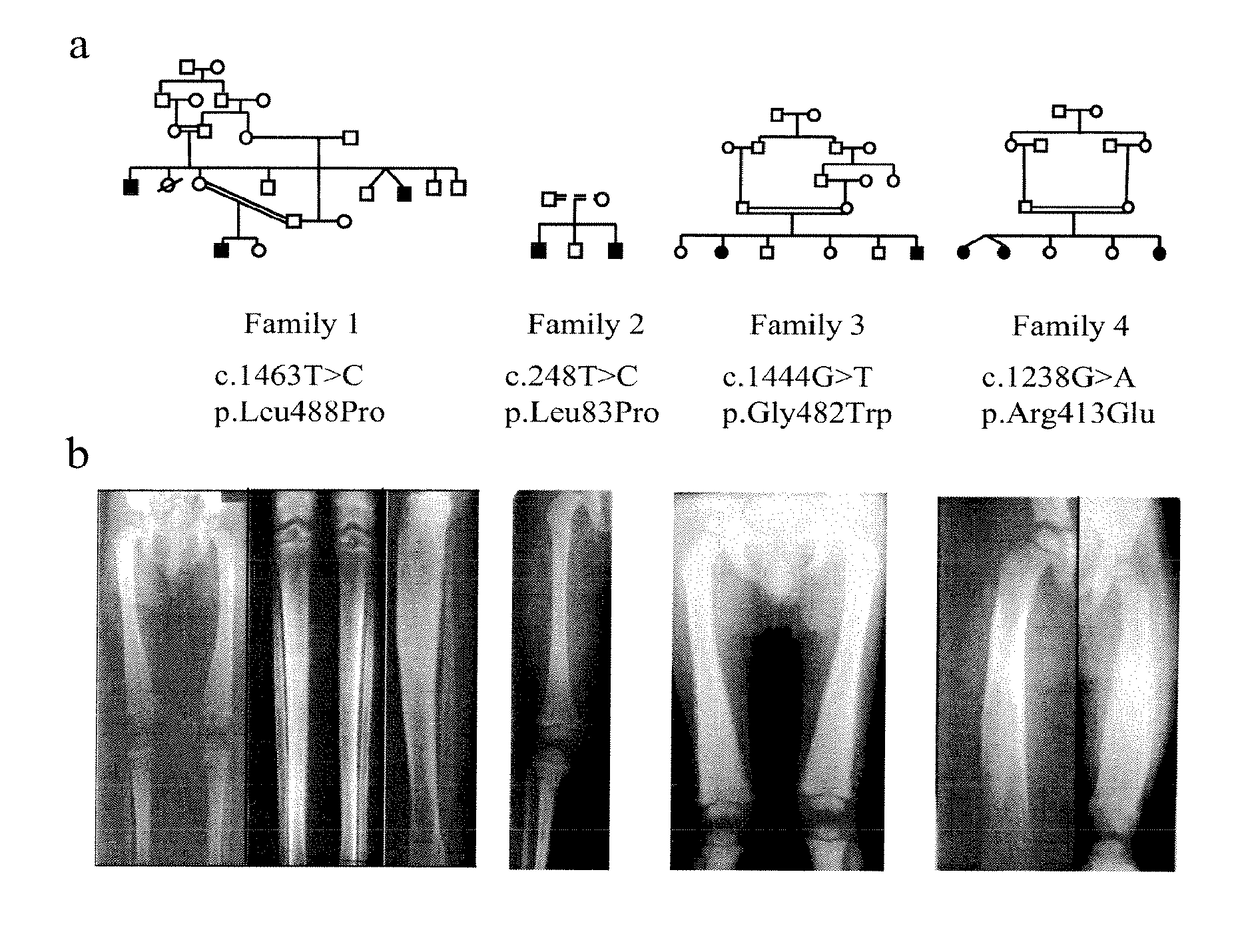
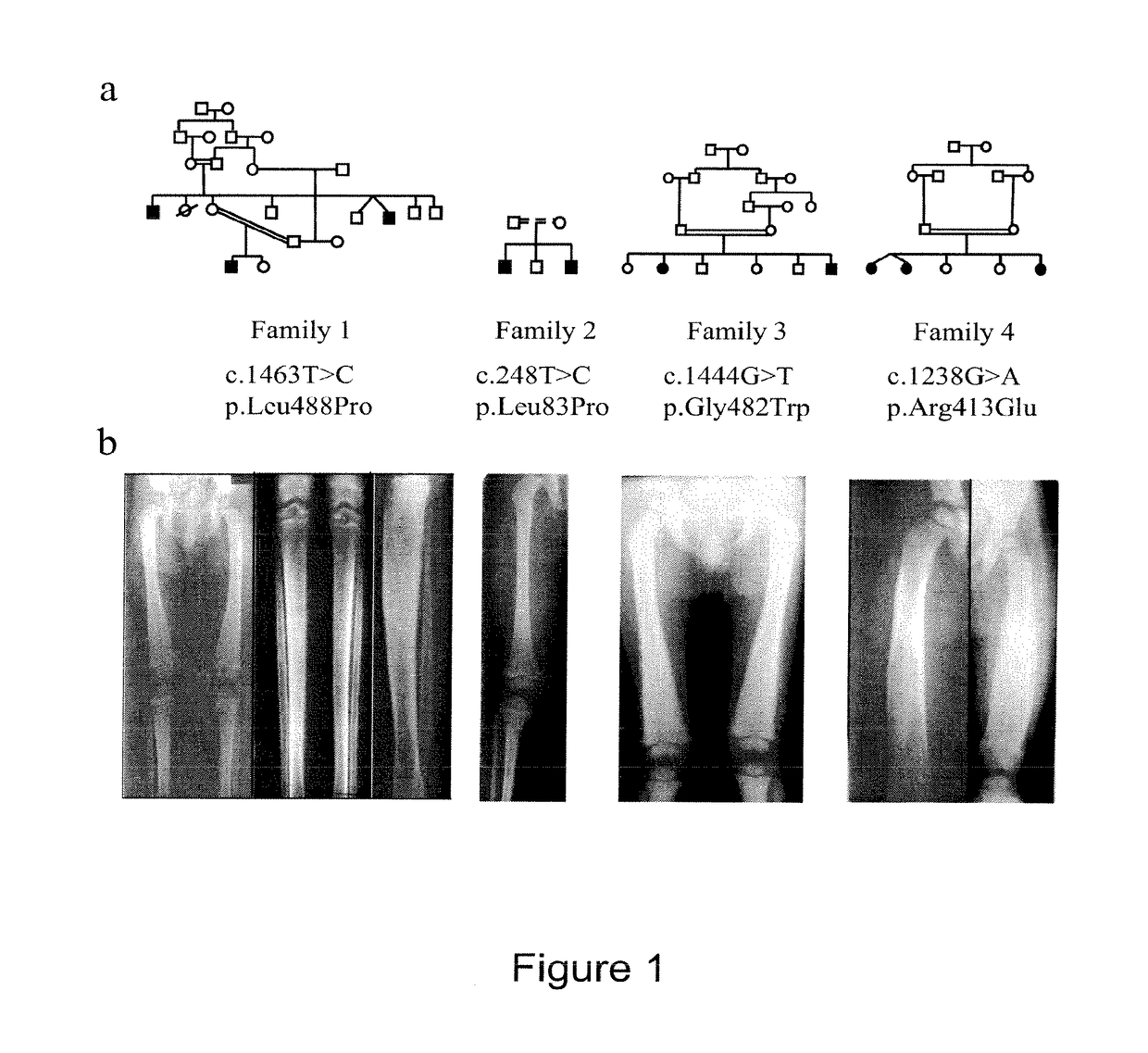
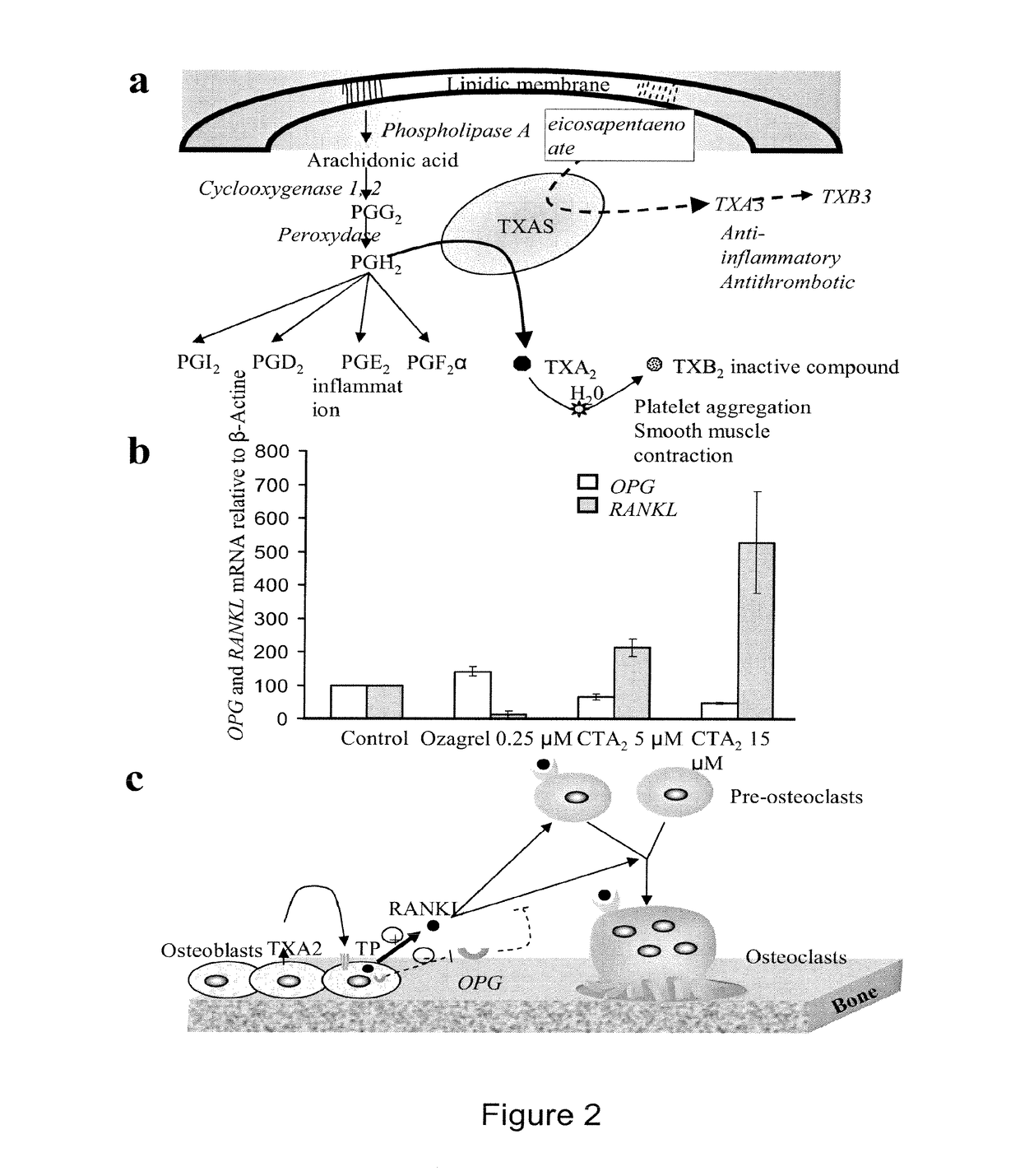
Methods for the treatment and diagnosis of bone mineral density related diseases
ActiveUS9834820B2Simple processAvoid side effectsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsGhosal hematodiaphyseal dysplasiaBone density
Described herein are methods of the treatment and diagnosis of bone mineral density related disorders. More particularly, described herein are methods of diagnosing or predicting a bone mineral density related disease, or a risk of a bone mineral density related disease, in a subject, which method comprises detecting a mutation in the TBXAS1 gene, wherein the presence of such a mutation is indicative of a bone mineral density related disease or of a risk of a bone mineral density related disease. Also described are compounds such as a thromboxane synthase (TXAS) encoding polynucleotide, a TXAS, thromboxane A2 or an analog thereof for treating or preventing a disease associated with an increased bone mineral density (e.g., Ghosal hematodiaphyseal dysplasia syndrome). Additional aspects describe an inhibitor of TBXAS1 gene expression or a thromboxane inhibitor for treating or preventing a disease associated with a decreased bone mineral density (e.g., osteoporosis).
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
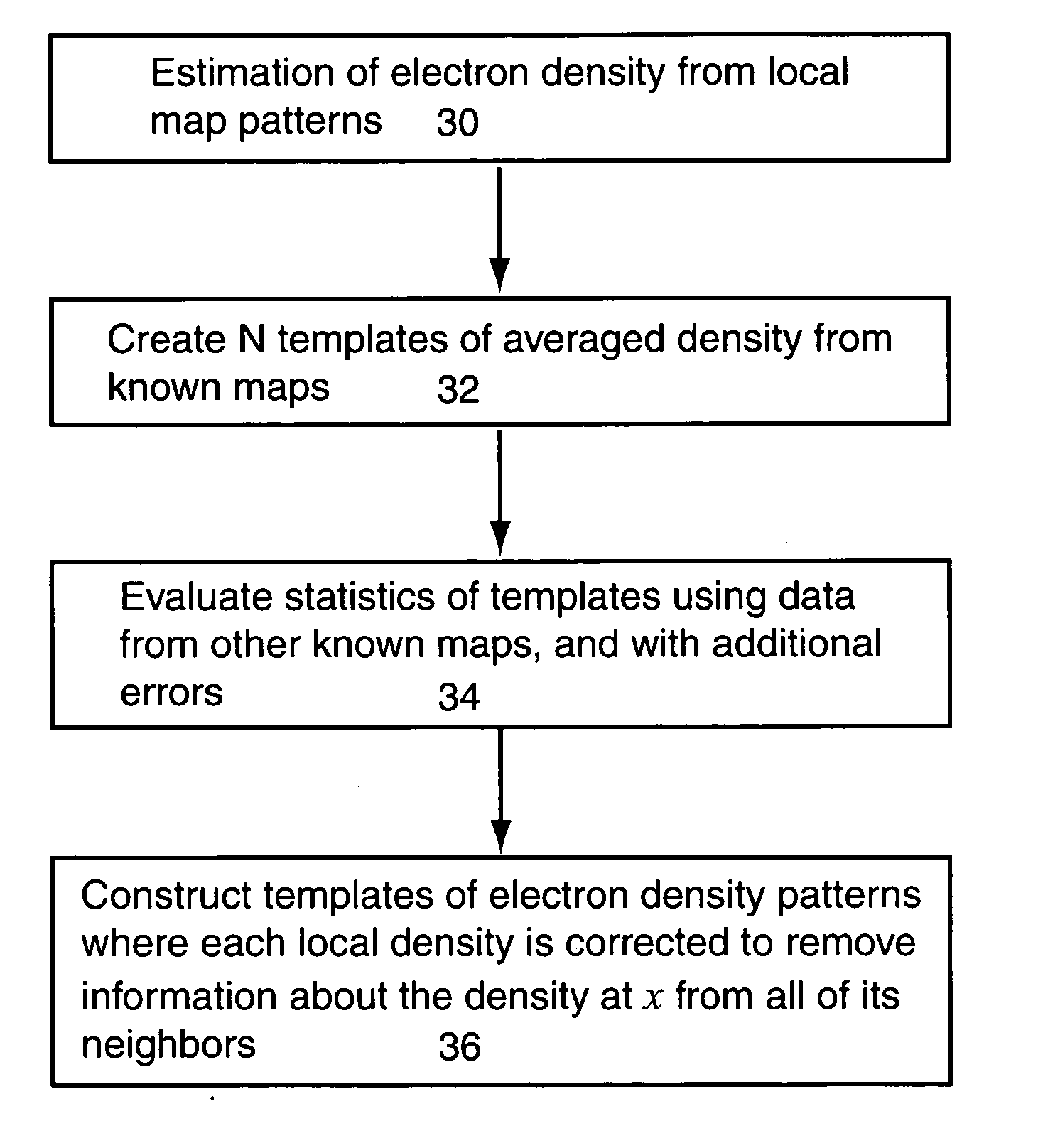
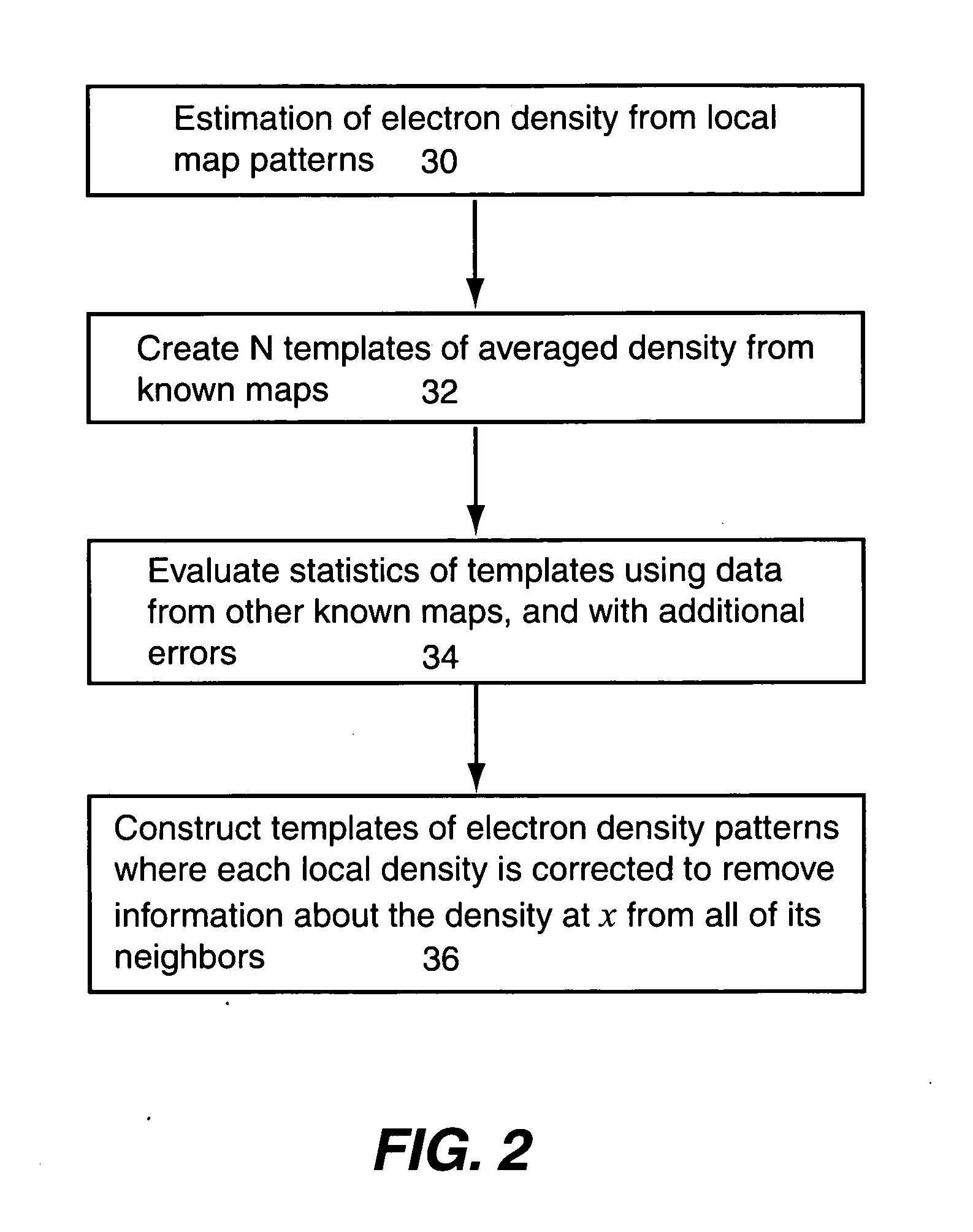
Statistical density modification using local pattern matching
A computer implemented method modifies an experimental electron density map. A set of selected known experimental and model electron density maps is provided and standard templates of electron density are created from the selected experimental and model electron density maps by clustering and averaging values of electron density in a spherical region about each point in a grid that defines each selected known experimental and model electron density maps. Histograms are also created from the selected experimental and model electron density maps that relate the value of electron density at the center of each of the spherical regions to a correlation coefficient of a density surrounding each corresponding grid point in each one of the standard templates. The standard templates and the histograms are applied to grid points on the experimental electron density map to form new estimates of electron density at each grid point in the experimental electron density map.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Method for compensating for deactivated printing nozzles in an inkjet system
A method for automatically compensating deactivated printing nozzles by means of a control computer in an inkjet printing machine has the steps of: printing a test form for a certain combination of materials; analyzing the printing of the test form, and constructing a look-up table including the values from 0 to 1 Compensation probability; detecting inactivated printing nozzles; reading the rated droplet size to be compensated at the position of inactivated printing nozzles from the printing data; calculating the local area density at the position of inactivated printing nozzles; reading from the lookup table by calculating the local area density Compensation probability; calculate the pseudo-random number between 0 and 1 for the right and left adjacent pixels of the pixel to be compensated; if the corresponding pseudo-random number of the right and left adjacent pixels of the pixel to be compensated is less than the pseudo-random number read from the lookup table When the compensation probability is reached, increase the drop size of adjacent pixels; calculate the size of all the rated drop points and adjacent drop points to be compensated on the position of the deactivated printing nozzle, and apply the changed drop point size to the printing data; use the changed printing data Execute printing tasks.
Owner:HEIDELBERGER DRUCKMASCHINEN AG
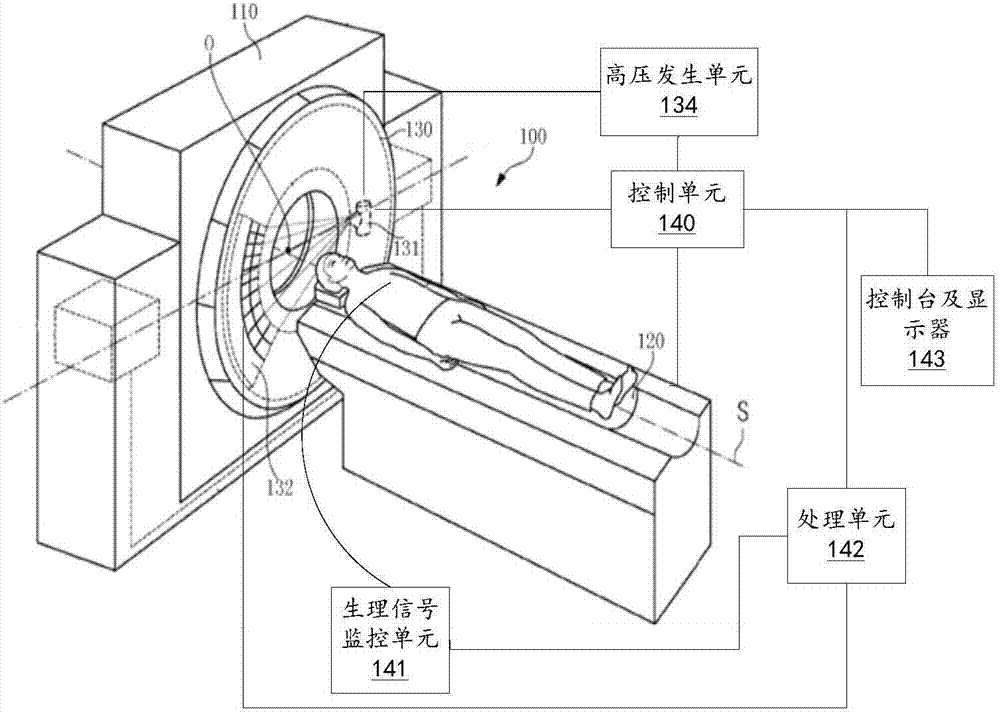
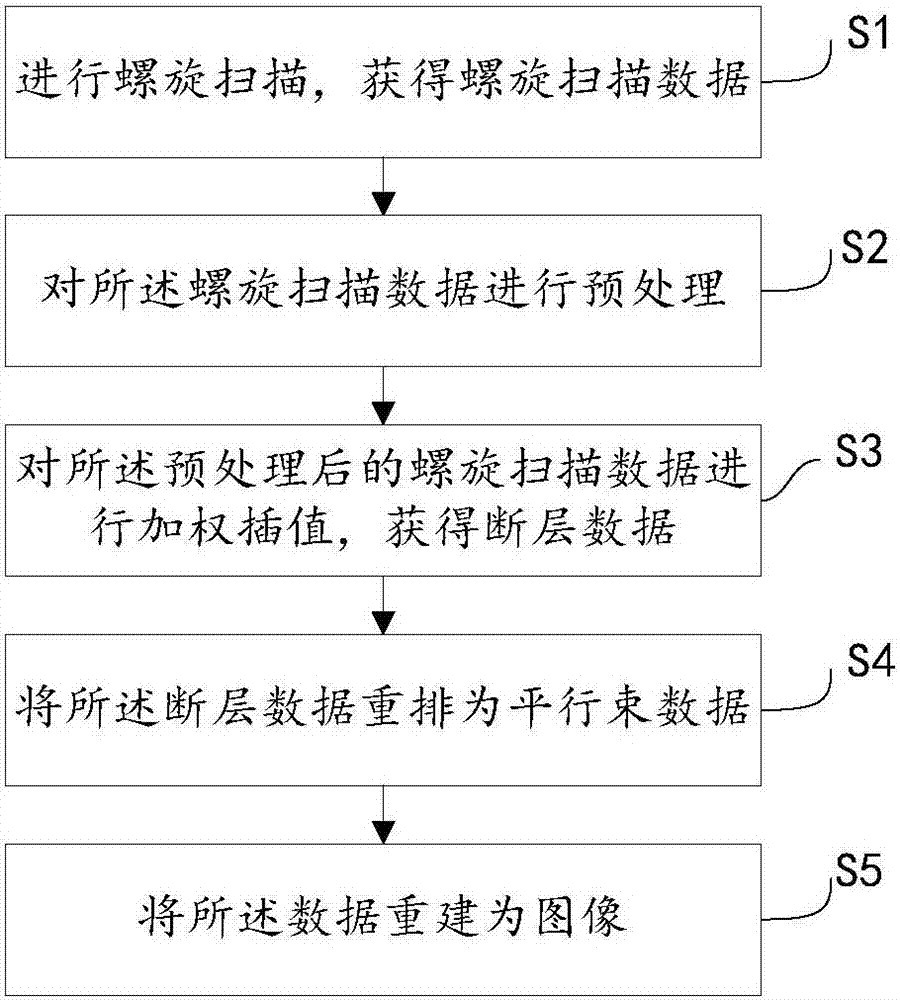
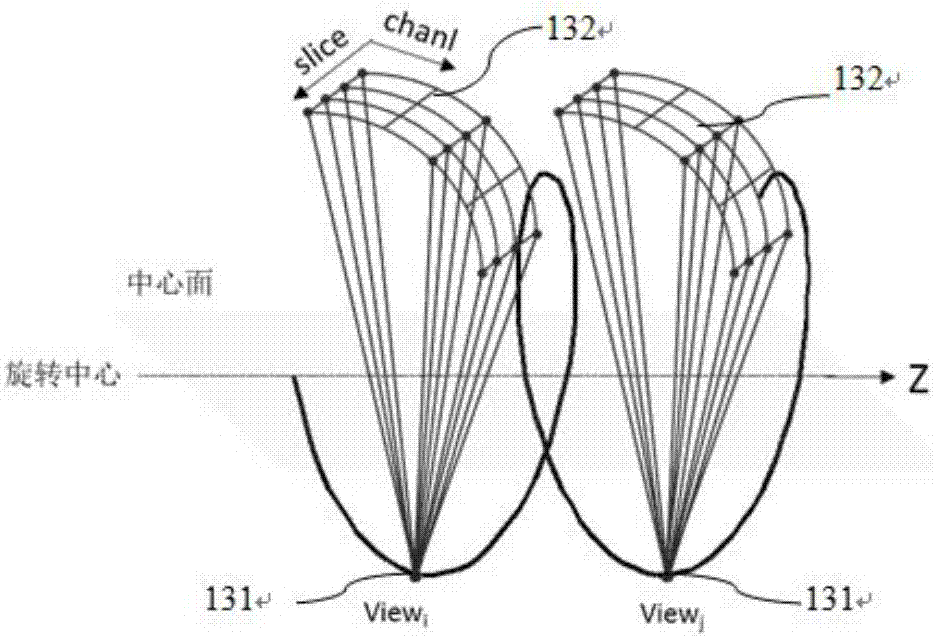
CT (Computed Tomography) helical scanning image reconstruction method and device
ActiveCN107341836AReduce artifactsImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionComputed tomographyReconstruction method
The invention puts forward a CT (Computed Tomography) helical scanning image reconstruction method, which comprises the following steps that: carrying out helical scanning to obtain helical scanning data; obtaining a helical scanning data weighting factor, wherein the helical scanning data weighting factor comprises a first weighting factor, the first weighting factor relates to the density of the helical scanning data in a z-axis direction, and the z-axis direction is the rotation axis direction of the helical scanning; according to the weighting factor, carrying out interpolation on the helical scanning data to obtain segment data; and reconstructing the segment data into an image. By use of the helical scanning image reconstruction method, the distribution nonuniformity of the helical scanning data in the z-axis direction is considered in a weighted interpolation process, the first weighting factor related to the density of the helical scanning data in the z-axis direction is used for weighting the helical scanning data, and image artifacts can be effectively reduced. In addition, the invention also puts forward a CT helical scanning image reconstruction device.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
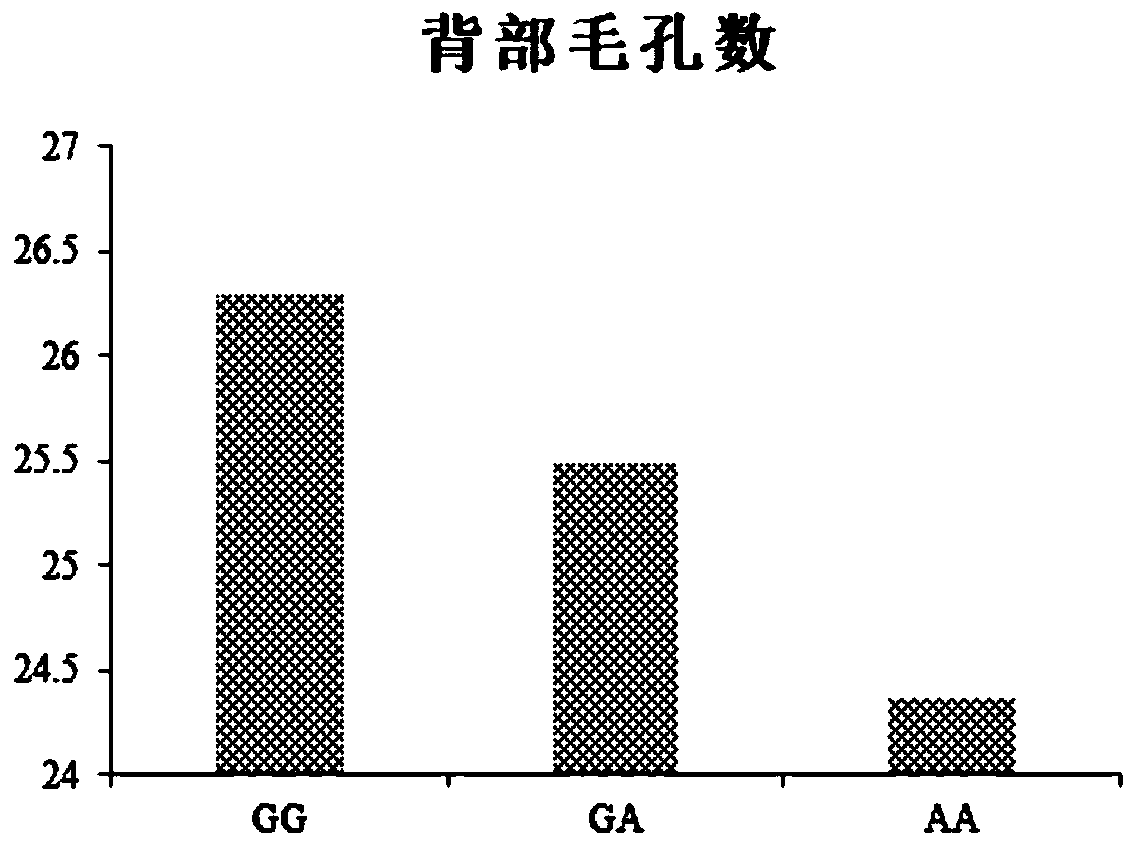
SNP molecular marker related to chicken back pore density and application of SNP molecular marker
ActiveCN110551828ALow densityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAnti stressAgricultural science
The invention discloses an SNP molecular marker related to a chicken back pore density and belongs to the field of molecular markers and genetic breeding. An SNP site of the SNP molecular marker is located at a 169981107 site of a first chromosome of an international chicken reference genome GRCg6a Primary Assembly version, and a base at the site is G or A. The invention further provides a primercombination for detecting the SNP marker and application of the primer composition. By means of the SNP molecular marker and the primer combination, an efficient and accurate molecular marker assistedbreeding method for the back pore density can be established, so that the back pore density is effectively selected, and breeding of the anti-stress chicken breeds is promoted.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF POULTRY SCI
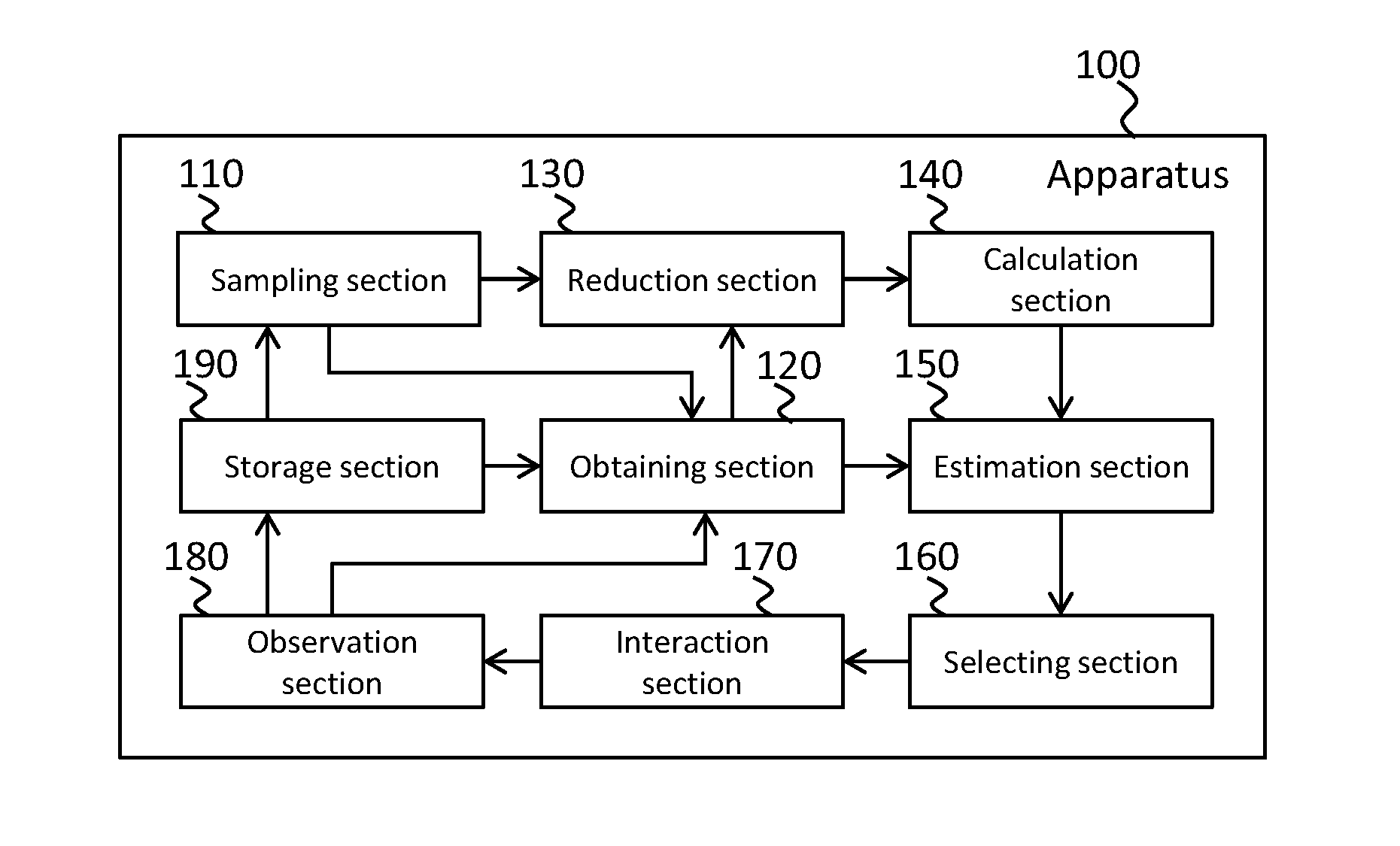
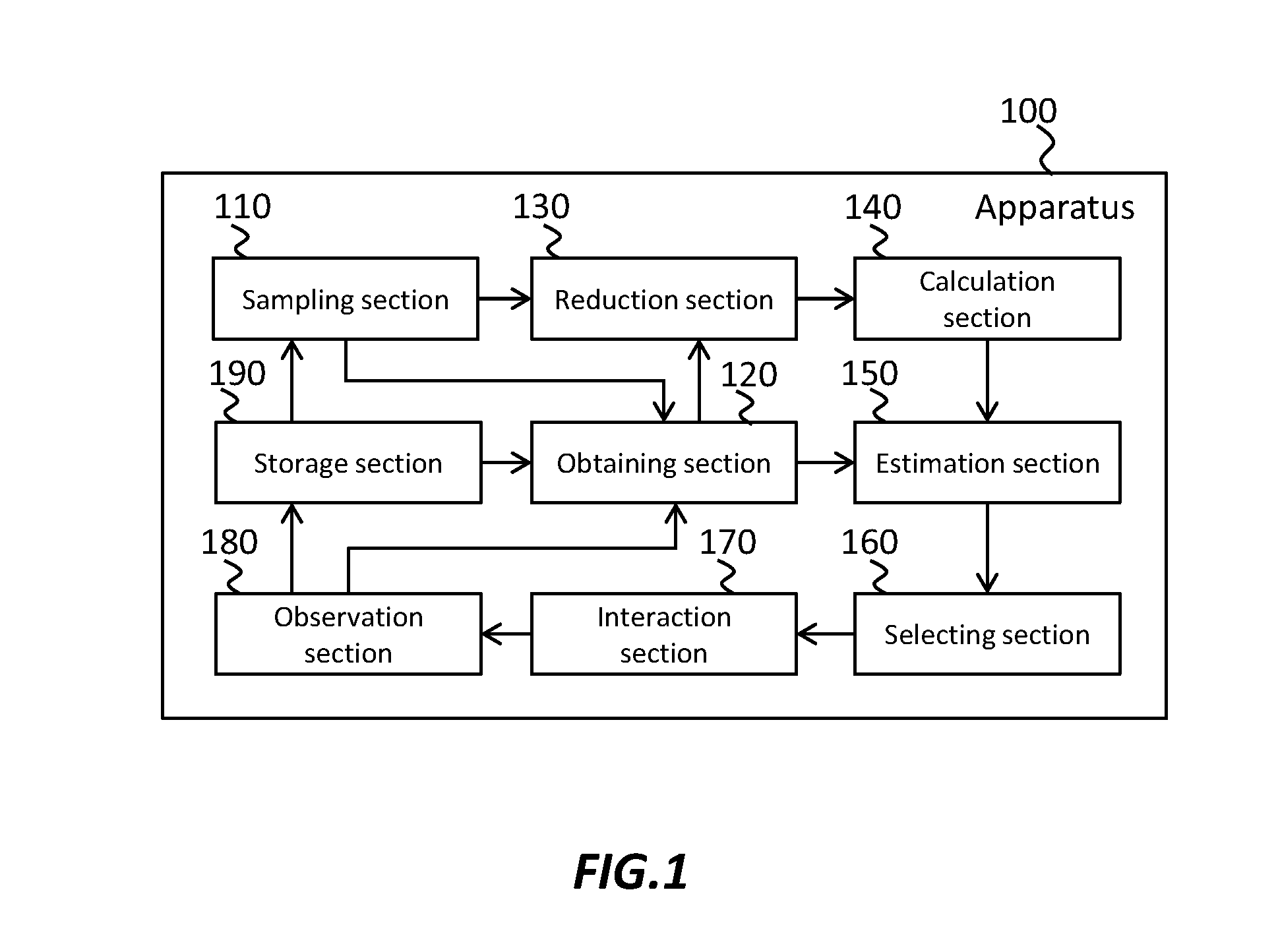
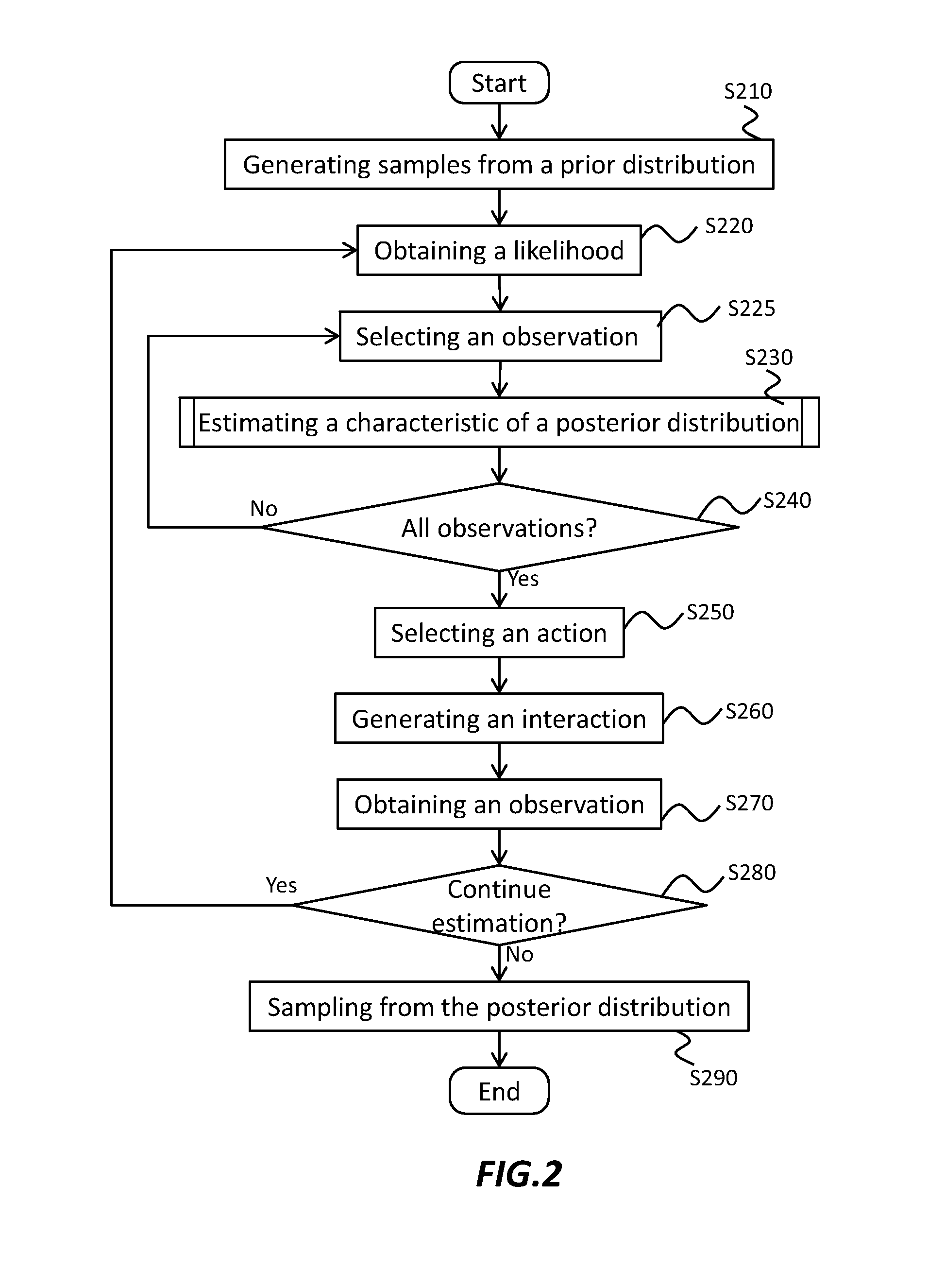
Computational estimation of a characteristic of a posterior distribution
An apparatus for estimating a characteristic of a posterior distribution includes a sampling section configured to generate a plurality of samples from a prior distribution, an obtaining section configured to obtain, for each sample among the plurality of samples, a likelihood of observation given the sample, a calculation section configured to calculate a parameter relating to a density at each sample in the prior distribution, and an estimation section configured to estimate, for the plurality of samples, a characteristic of the posterior distribution based on the parameter relating to the density at each sample and the likelihood of observation for each sample.
Owner:IBM CORP
Ion mobility analysis of lipoproteins
ActiveUS20070287187A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementDisease riskData acquisition
A medical diagnostic method and instrumentation system for analyzing noncovalently bonded agglomerated biological particles is described. The method and system comprises: a method of preparation for the biological particles; an electrospray generator; an alpha particle radiation source; a differential mobility analyzer; a particle counter; and data acquisition and analysis means. The medical device is useful for the assessment of human diseases, such as cardiac disease risk and hyperlipidemia, by rapid quantitative analysis of lipoprotein fraction densities. Initially, purification procedures are described to reduce an initial blood sample to an analytical input to the instrument. The measured sizes from the analytical sample are correlated with densities, resulting in a spectrum of lipoprotein densities. The lipoprotein density distribution can then be used to characterize cardiac and other lipid-related health risks.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for correcting expanding influence of coalbed methane reservoir density logging
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com