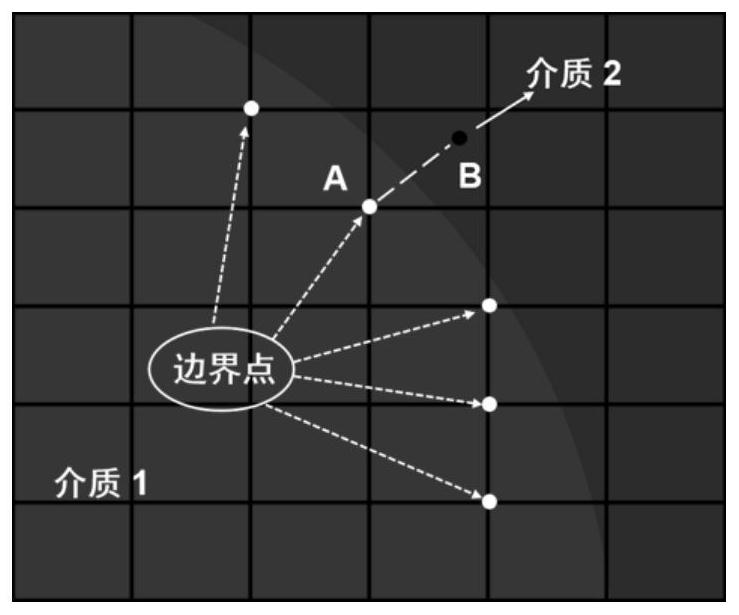
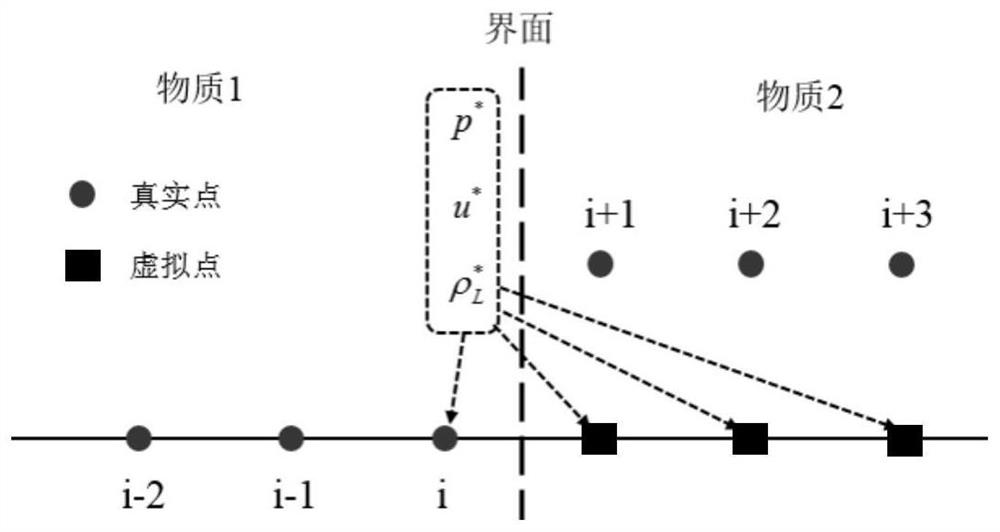
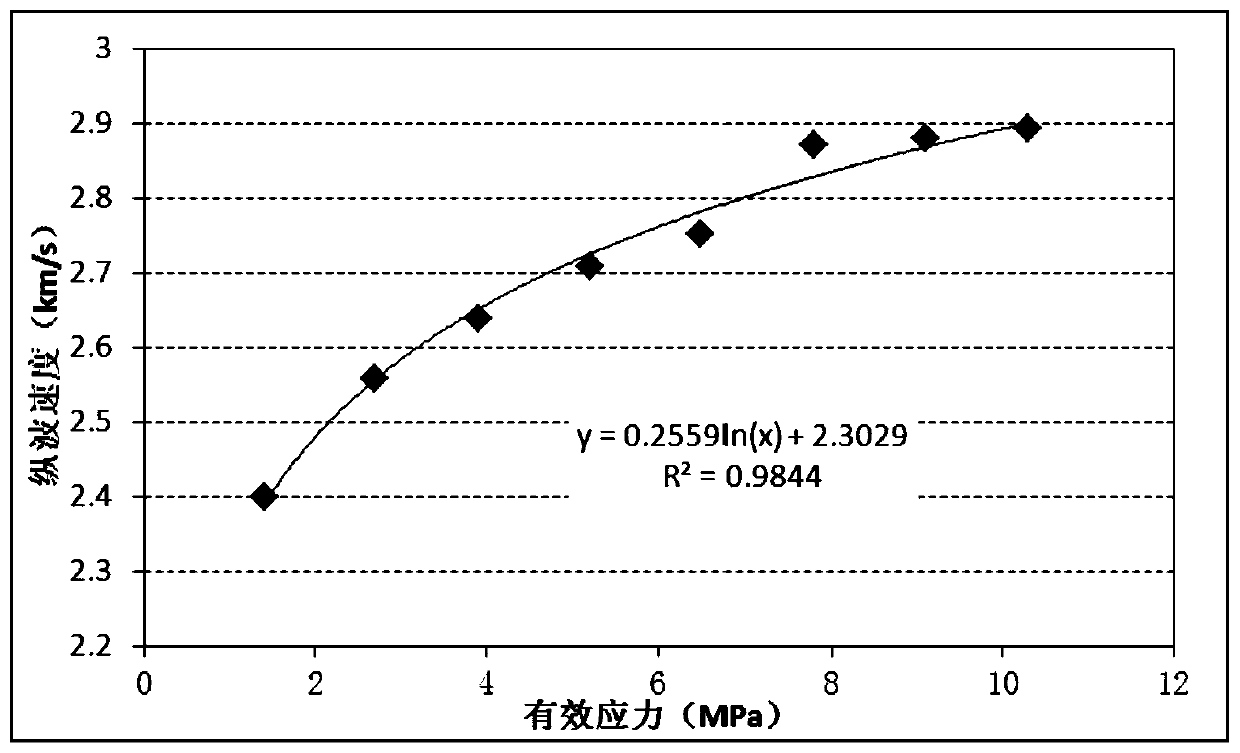
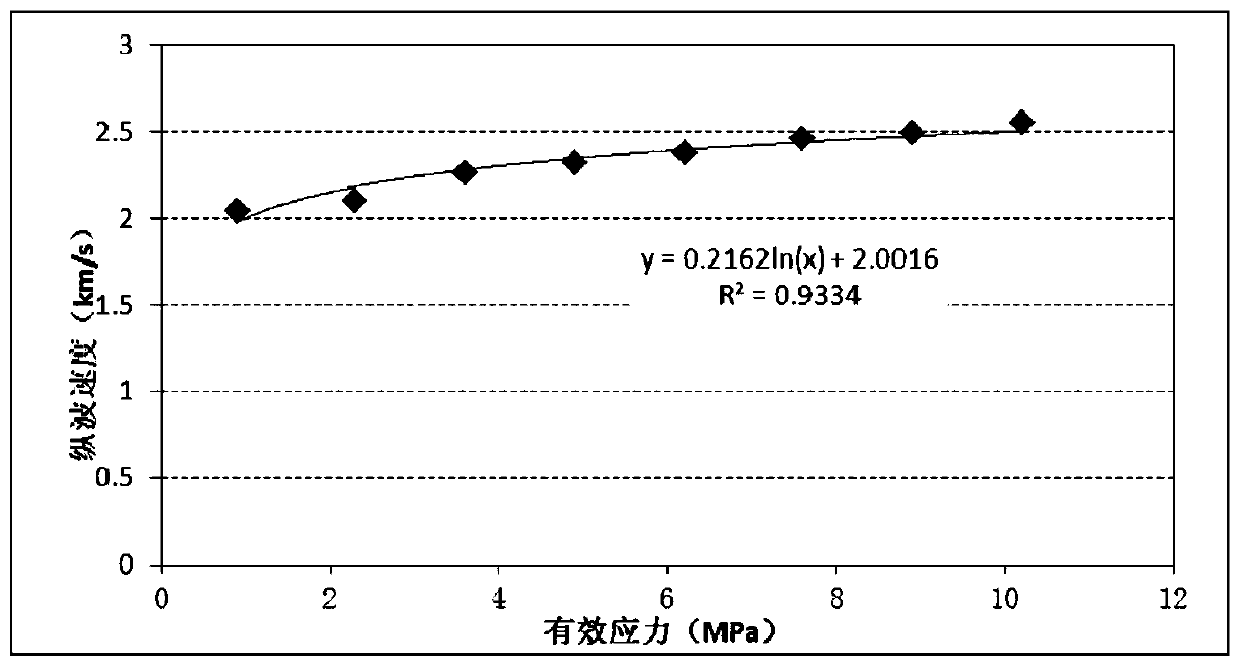
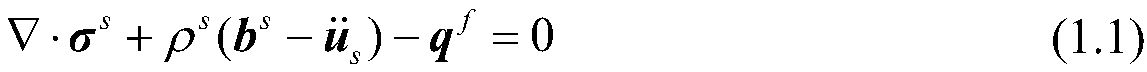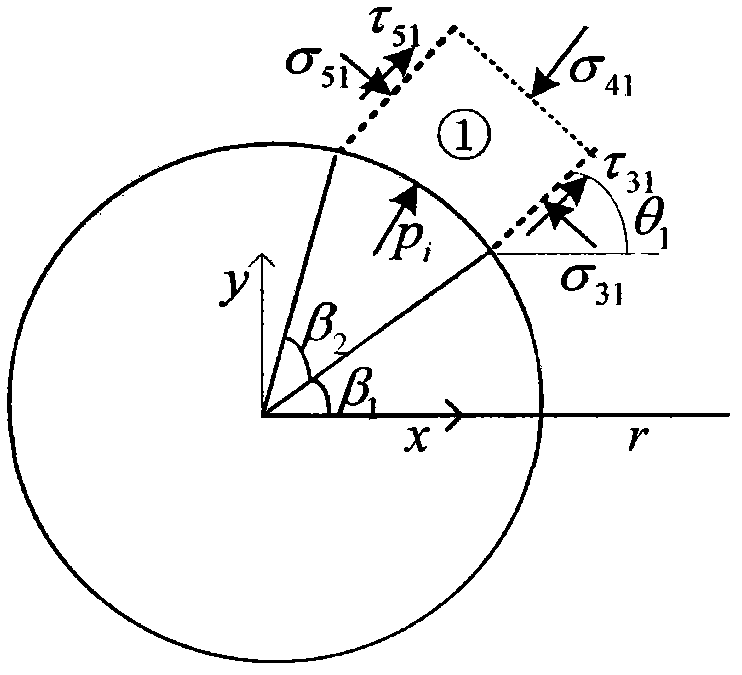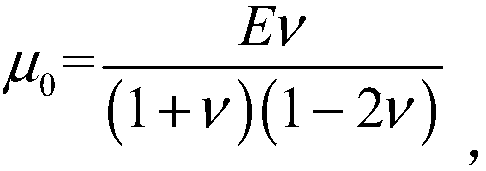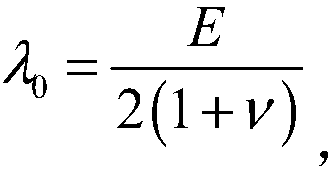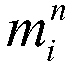Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Continuum mechanics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Continuum mechanics is a branch of mechanics that deals with the mechanical behavior of materials modeled as a continuous mass rather than as discrete particles. The French mathematician Augustin-Louis Cauchy was the first to formulate such models in the 19th century.
Generalized Jet-Effect
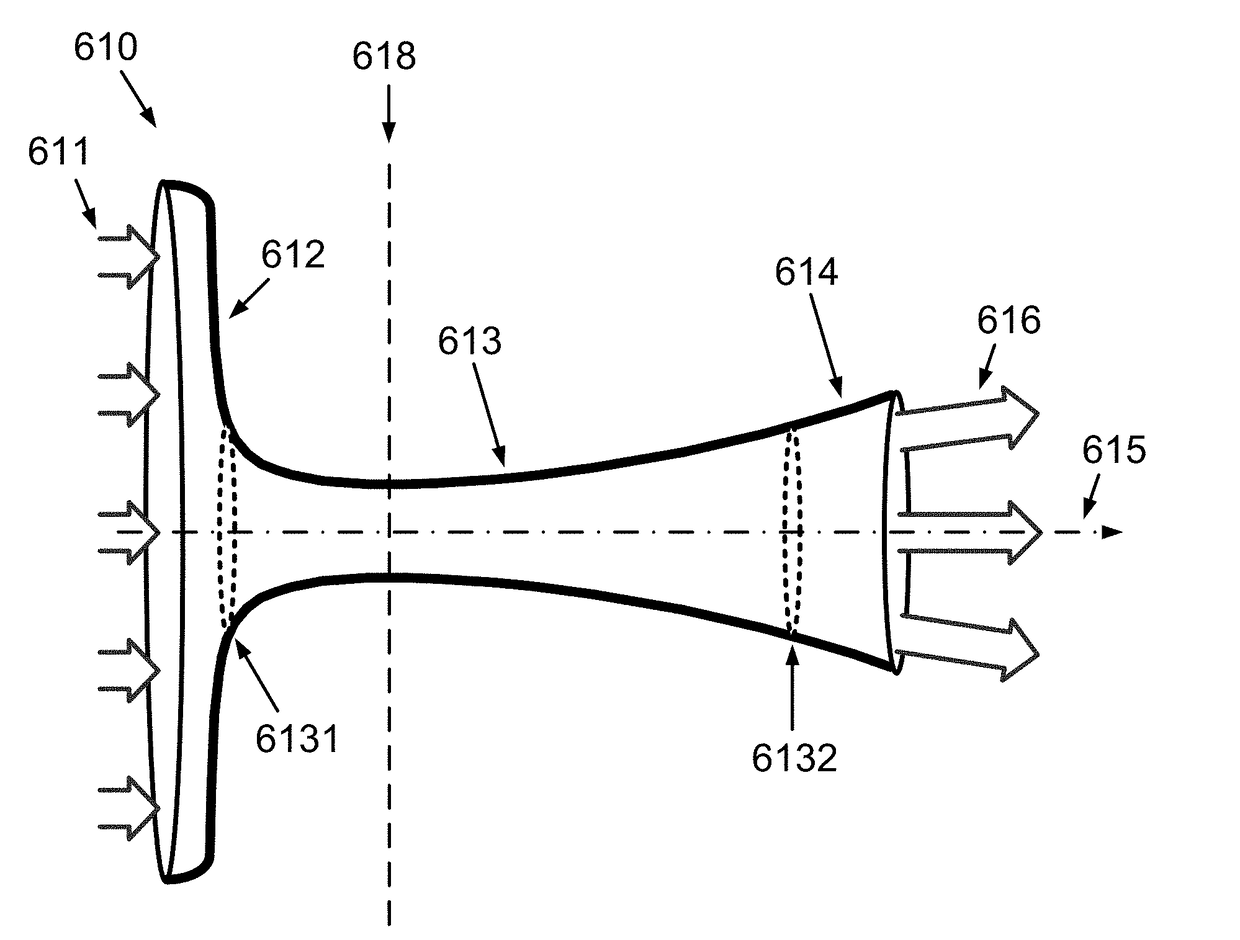
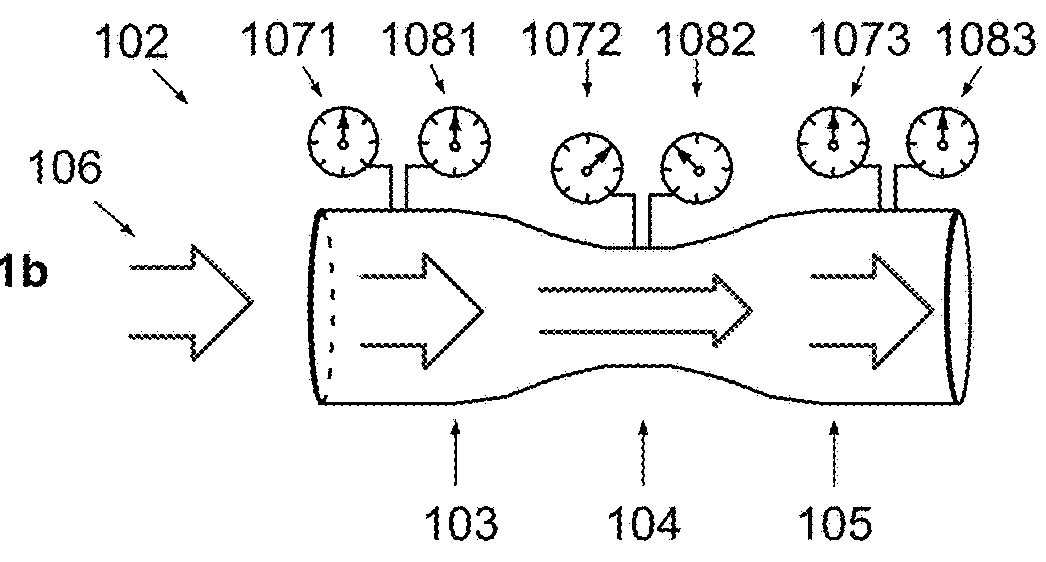
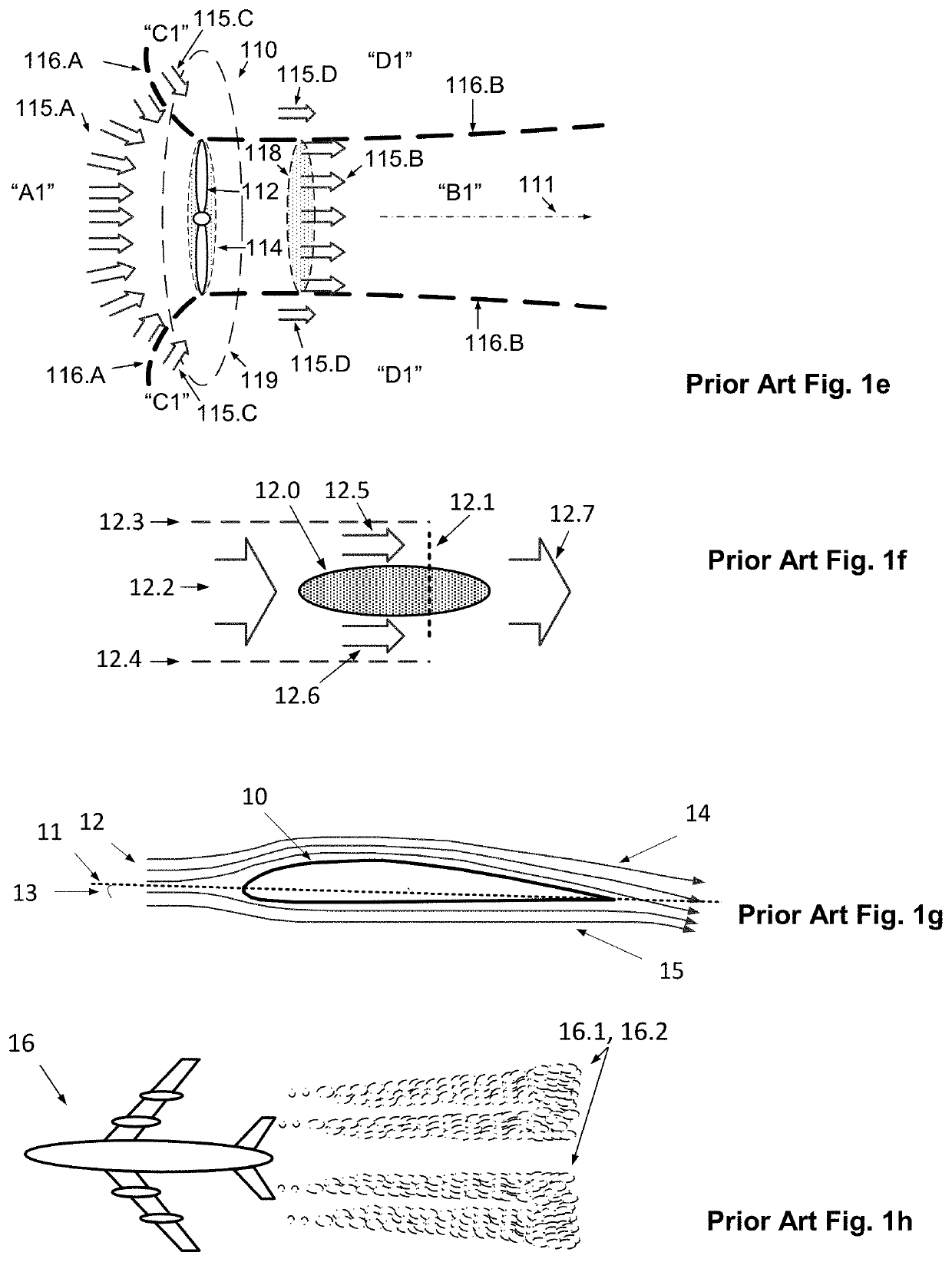
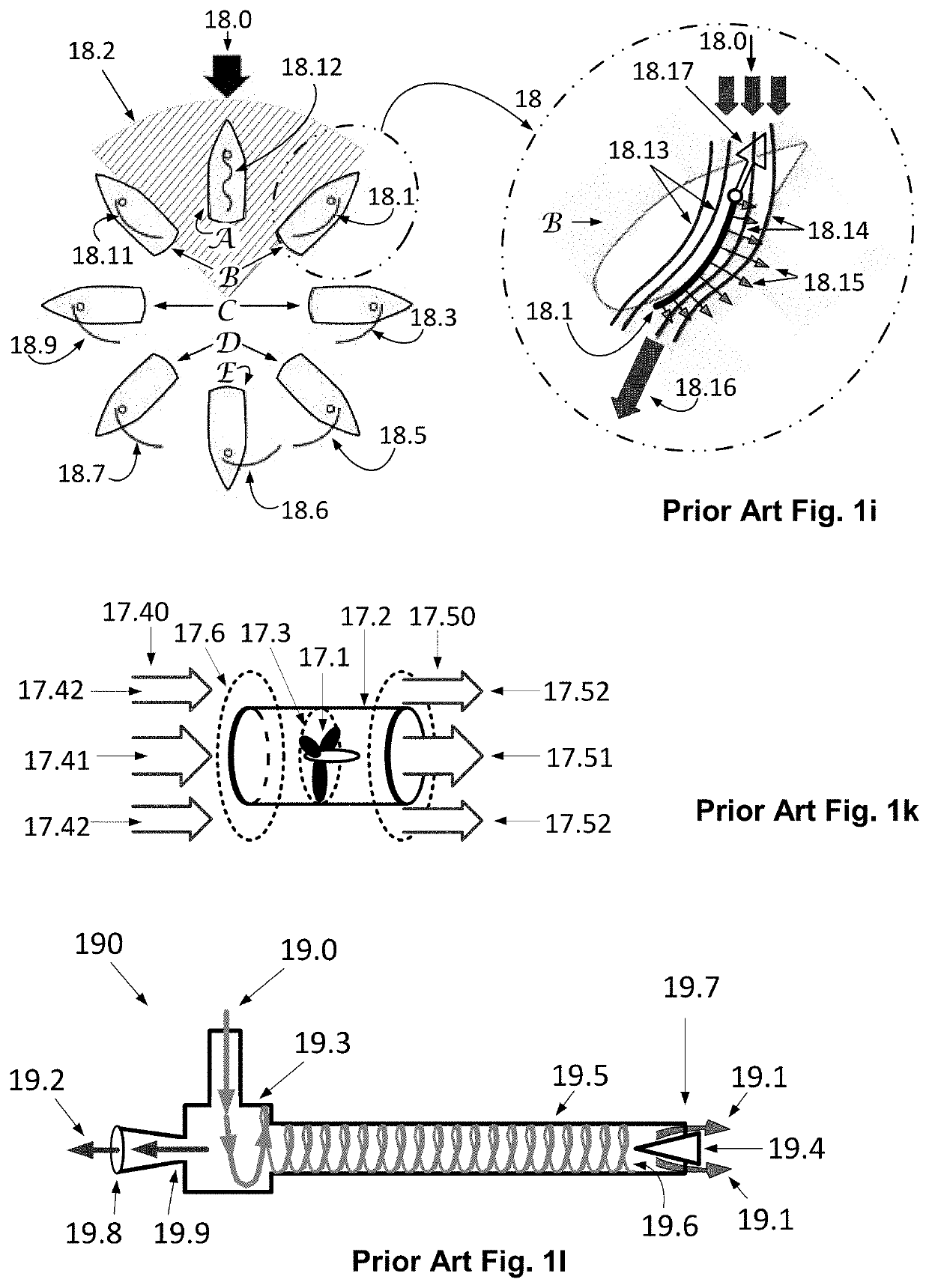
The invention provides a method for computational fluid dynamics and apparatuses making enable an efficient implementation and use of an enhanced jet-effect, either the Coanda-jet-effect, the hydrophobic jet-effect, or the waving-jet-effect, triggered by specifically shaped corpuses and tunnels. The method is based on the approaches of the kinetic theory of matter, thermodynamics, and continuum mechanics, providing generalized equations of fluid motion. The method is applicable for slow-flowing as well as fast-flowing real compressible-extendable fluids and enables optimal design of convergent-divergent nozzles, providing for the most efficient jet-thrust. The method can be applied to airfoil shape optimization for bodies flying separately and in a multi-stage cascaded sequence. The method enables apparatuses for electricity harvesting from the fluid heat-energy, providing a positive net-efficiency. The method enables efficient water-harvesting from air. The method enables generators for practical-expedient power harvesting using constructive interference of waves due to the waving jet-effect.
Owner:SOLITON HLDG CORP DELAWARE CORP
Generalized Jet-Effect and Shaped Tunnel
The invention provides a method for computational fluid dynamics and apparatuses making enable an efficient implementation and use of an enhanced jet-effect, either the Coanda-jet-effect, the hydrophobic jet-effect, or the waving-jet-effect, triggered by specifically shaped corpuses and tunnels. The method is based on the approaches of the kinetic theory of matter, thermodynamics, and continuum mechanics, providing generalized equations of fluid motion. The method is applicable for slow-flowing as well as fast-flowing real compressible-extendable fluids and enables optimal design of convergent-divergent nozzles, providing for the most efficient jet-thrust. The method can be applied to airfoil shape optimization for bodies flying separately and in a multi-stage cascaded sequence. The method enables apparatuses for electricity harvesting from the fluid heat-energy, providing a positive net-efficiency. The method enables efficient water-harvesting from air. The method enables generators for practical-expedient power harvesting using constructive interference of waves due to the waving jet-effect.
Owner:SOLITON HLDG CORP DELAWARE CORP
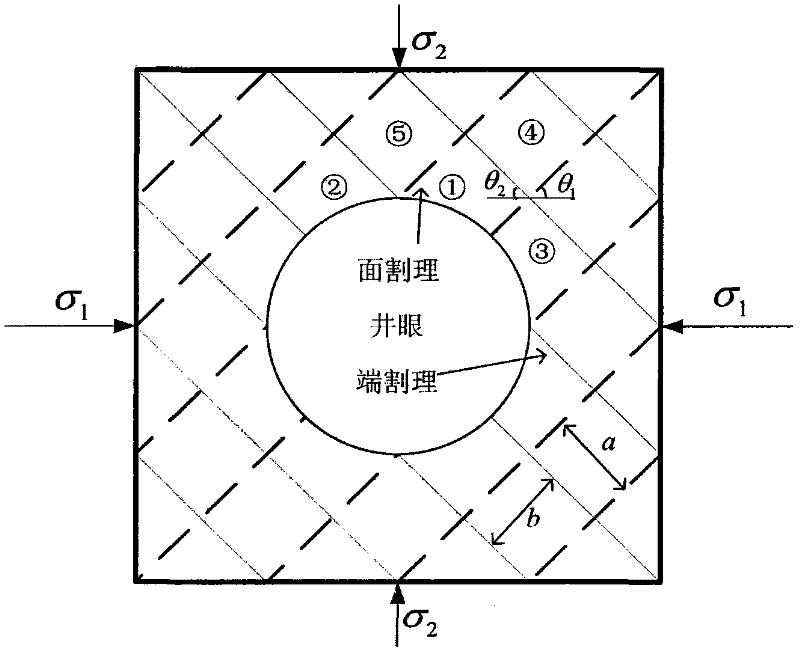
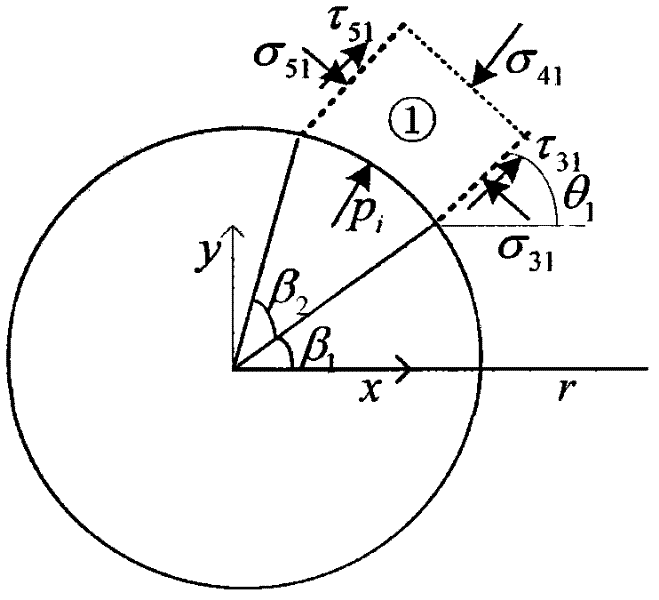
Sidewall stability research method suitable for pressure-depleted formation
ActiveCN106855897AImprove forecast accuracyHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsBorehole/well accessoriesMeasurement pointAcoustic wave
The invention discloses a sidewall stability research method suitable for a pressure-depleted formation. In the method, knowledge points of multiple disciplines, such as the underground rock mechanics, the borehole geophysics, the continuum mechanics, the elastic mechanics and the mathematical statistics, are integrated, the method starts with microscopic deformation conditions of rock skeleton particles obtained after the formation pressure is depleted till to the macroscopic acoustic response performance, characteristic parameter variation and the like of rocks, makes full use of partial data, such as rock skeleton density logging, shale content logging, actual measurement points of the formation pressure and collapse and fracture pressure and the formation core, obtained when the oilfield formation pressure is not depleted, and finally the collapse and fracture pressure of the pressure-depleted formation is determined, so that guidance and reference are provided for selection of the density of a drilling fluid for pressure-depleted formation drilling. The computing method is high in precision, and just a few of errors exist in fracture pressure prediction.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Three-dimensional digital volume image distortion measuring method
InactiveCN101980304AEfficient solutionReduce complexity3D modellingFast Fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
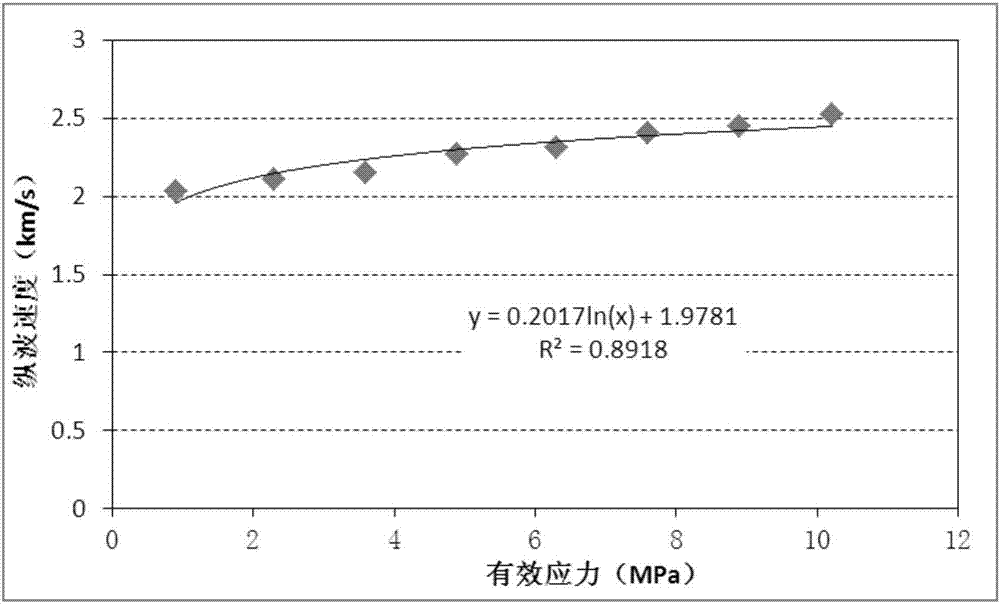
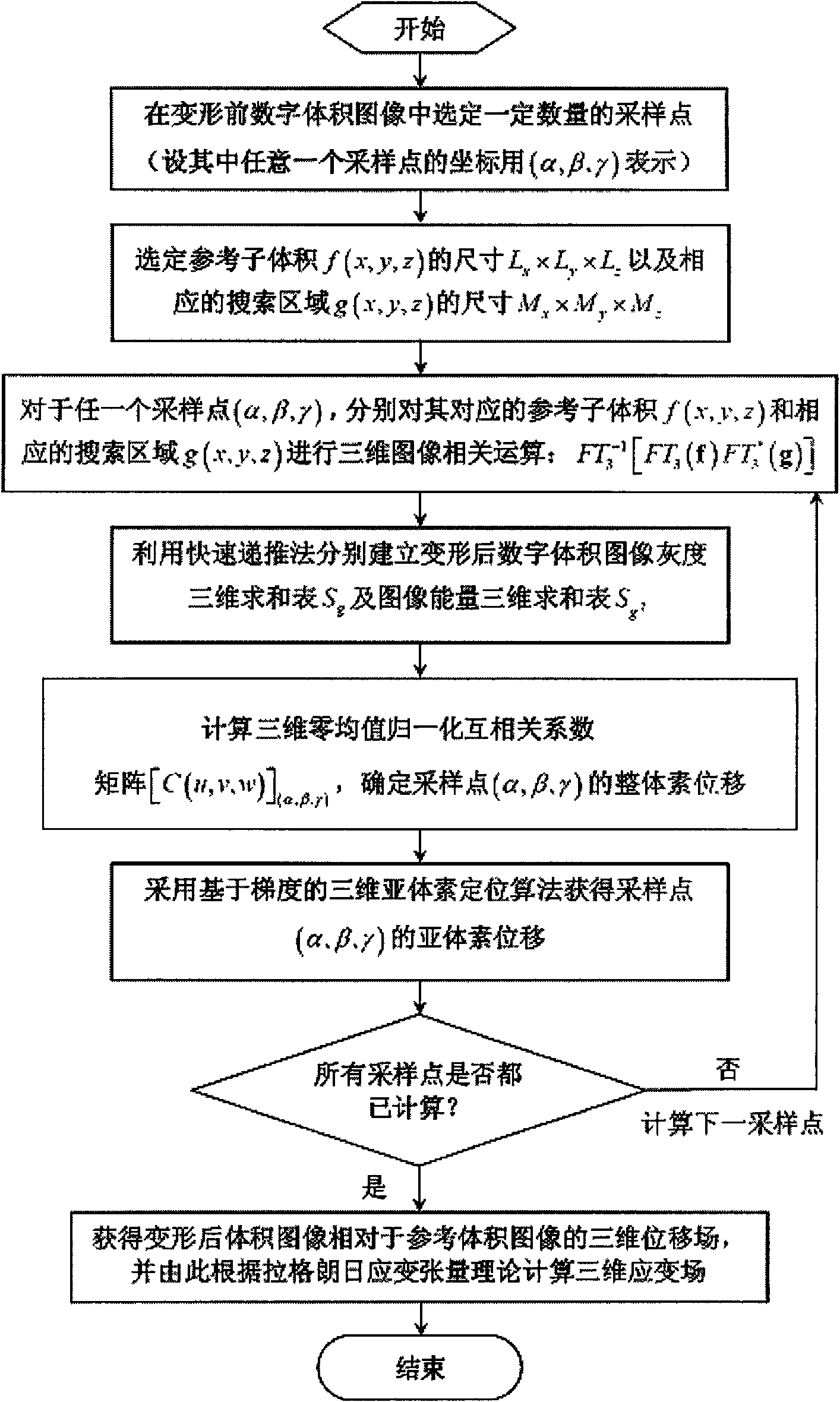
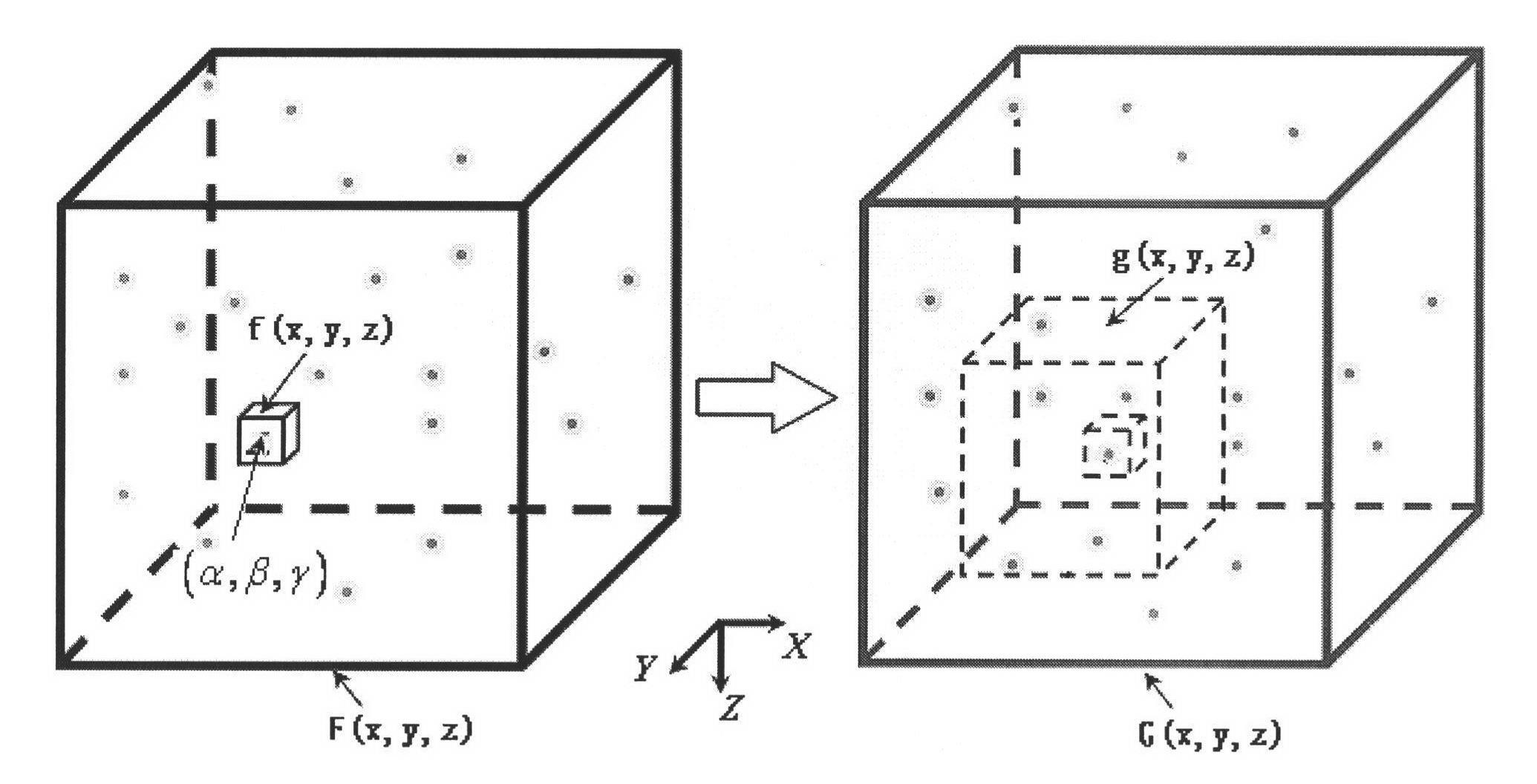
The invention relates to a three-dimensional digital volume image distortion measuring method, which comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting scattered sampling points on a digital volume image before distortion; (2) determining a reference sub-volume and the dimension of a searched area; (3) performing three-dimensional image-related operation on the reference sub-volume and the searched area based on a three-dimensional Fast Fourier Transform method; (4) establishing an image gray three-dimensional summing table and an image energy three-dimensional summing table; (5) solving a three-dimensional zero-mean normalization cross correlation coefficient matrix by using the operational result in the step (3) and the three-dimensional summing tables; (6) calculating subvoxel displacement values of the sampling points by using a gradient-based three-dimensional subvoxel displacement location algorithm; (7) calculating accurate displacement values at all the sampling points according to the steps (3) to (6) so as to obtain a three-dimensional displacement field of the whole distorted volume image relative to the volume image before distortion; and (8) calculating a three-dimensional strain field of the digital volume image according to the Lagrangian strain tensor theory in mechanics of continuous media. The three-dimensional distortion of the digital volume image can be accurately and efficiently measured.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
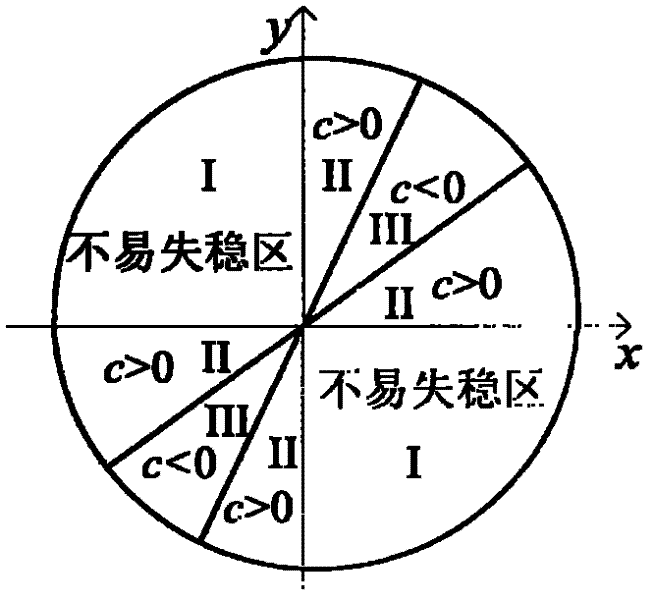
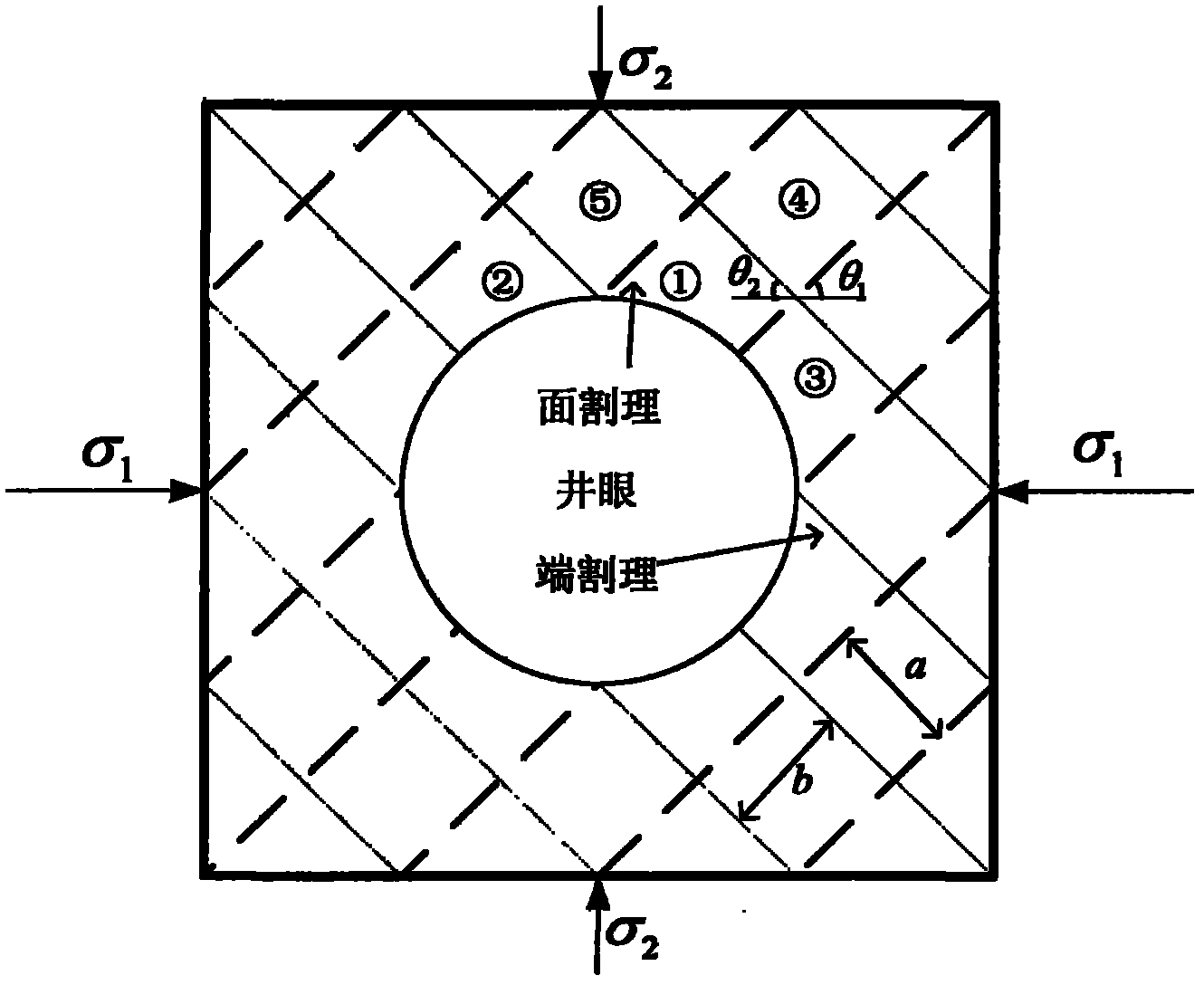
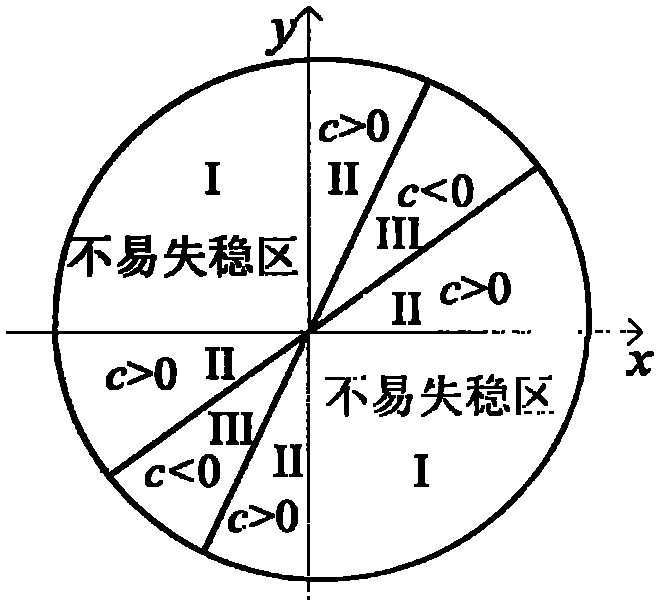
Method for determining safe drilling fluid density of coal bed based on structural element analysis model
InactiveCN102230373ASurveySpecific gravity by measuring pressure differencesCoal briquetteInstability
The invention discloses a method for determining the safe drilling fluid density of a coal bed based on a structural element analysis model. The method has the advantages of coal bed cleat and fracture development, big rock brittleness, low strength and obvious anisotropy and discontinuity. The borehole wall instability characteristics of the method are different from those of the common sandstone stratum. The phenomenon that the traditional borehole wall stability model based on the mechanics of continuous media is difficult to be successful for solving coal bed instability problems can be eliminated. In the method, the coal bed is composed of discrete blocks. A coal briquette which has the biggest possibility of generating spallation between surface cleats is analyzed to carry out force analysis. A structural element model of collapse pressure is built by the stressed balance condition among pressure stress, shearing strength and shaft pressure. A coefficient c is introduced to judge the stable relationship of borehole pressure and borehole wall so as to judge the range of the safe drilling fluid density.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
An elastic deformation simulation method based on linear differential operator
InactiveCN101216950ATroubleshooting Fast Simulation ProblemsReduce complexityAnimation3D-image renderingEuler–Lagrange equationComputation process
The invention discloses an elastic deformation simulation method based on a linear differential operator. The invention comprises the following steps of using elastic energy based on the linear differential operator defined on the geometric attribute of a deformation gridding model to replace the traditional nonlinear energy based on continuum mechanics, carrying out modeling computation using Euler-Lagrange equation to compute the deformation process of the elastic object in the computer. Meanwhile, according to the calculation model, the invention optimizes the calculation process via further using the techniques of dimension reduction solution, airspace adaptive acceleration, etc, which allows the modeling process to reach the mutual or even real time efficiency and can simulate the elasticity of different materials and the deformation process of plastic objects. The invention reduces the calculation complexity, improves the calculation efficiency of the modeling solution, and keeps the living simulating effect via the model of transform solution based on the deformation energy form of the linear differential operator. The invention solves the rapid simulating problem in the deformation process of the elastic object in the real time or in a mutual virtual simulation system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
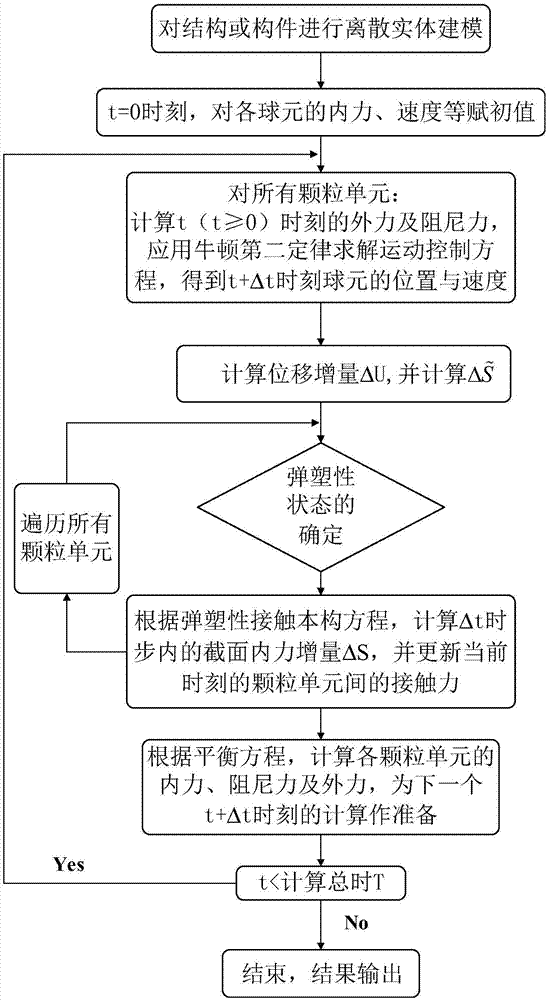
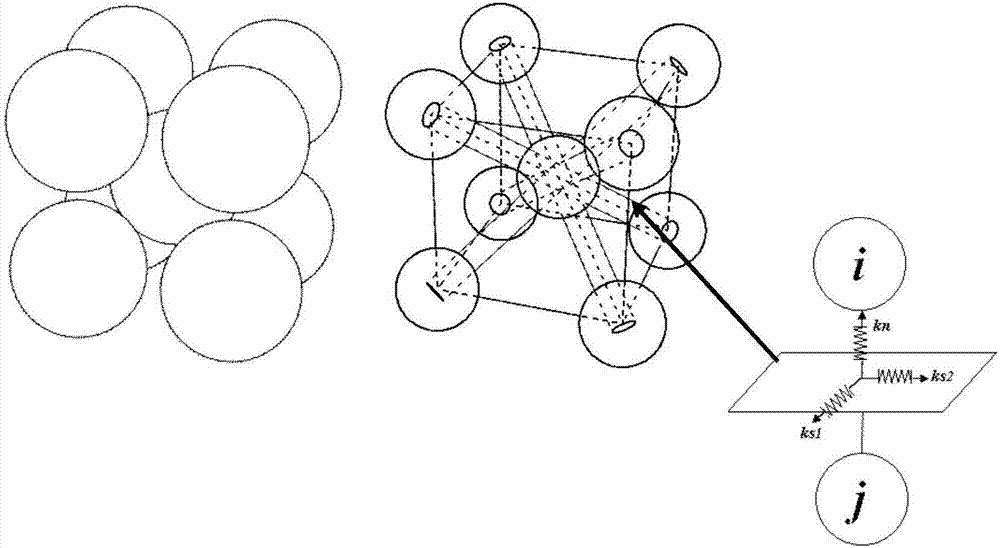
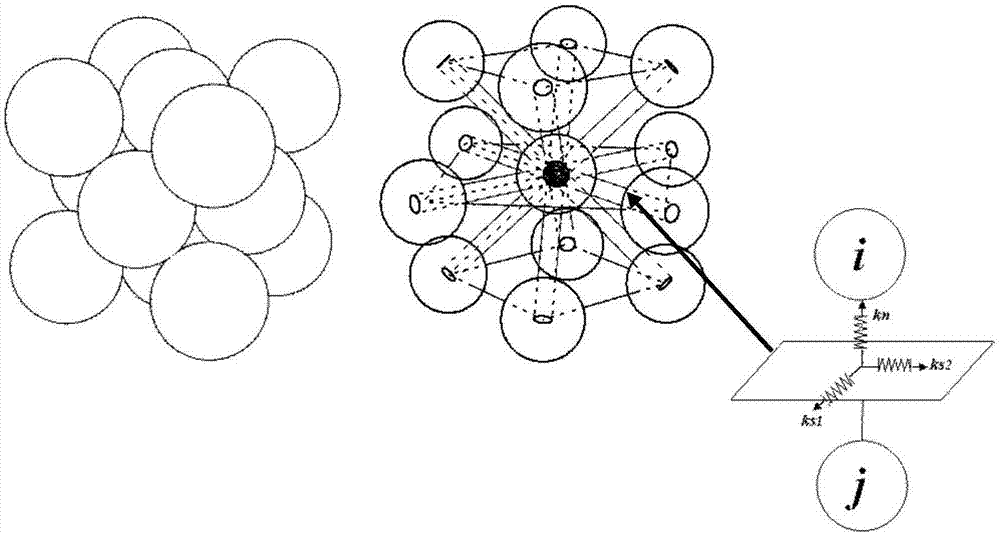
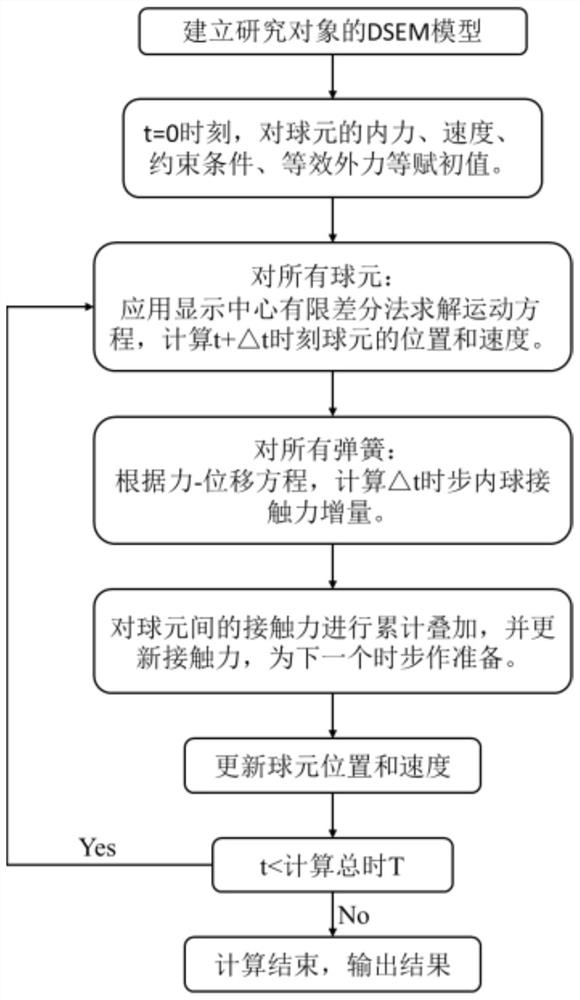
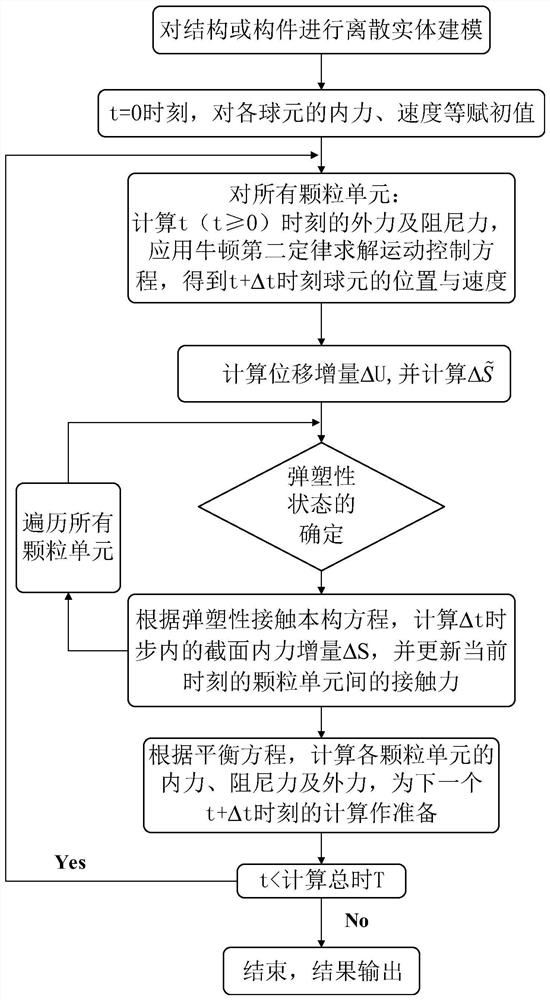
Method for solving nonlinear mechanics problem of continuous medium member by applying three-dimensional discrete entity
ActiveCN107391788ACalculation process is clearThe solution process does not changeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationNonlinear mechanicsElastic plastic
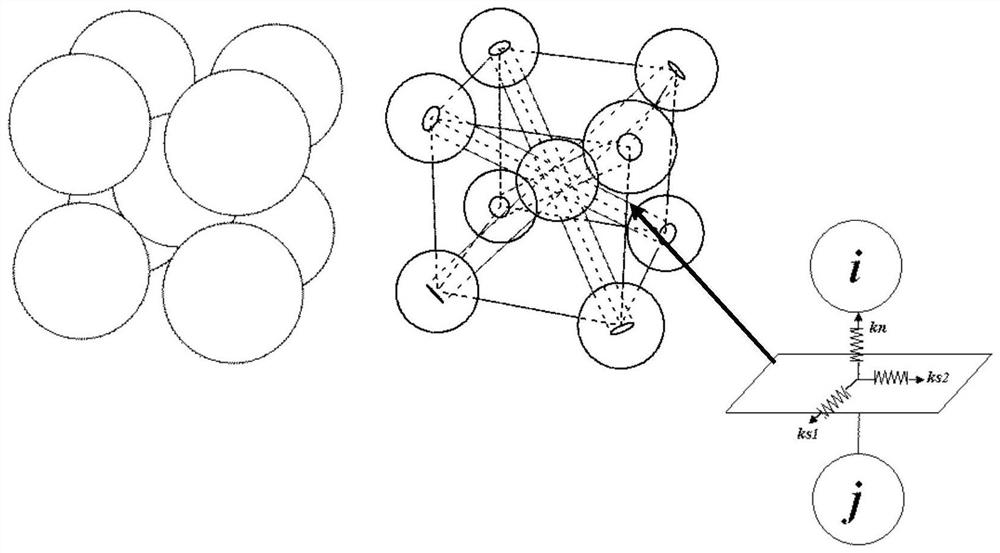
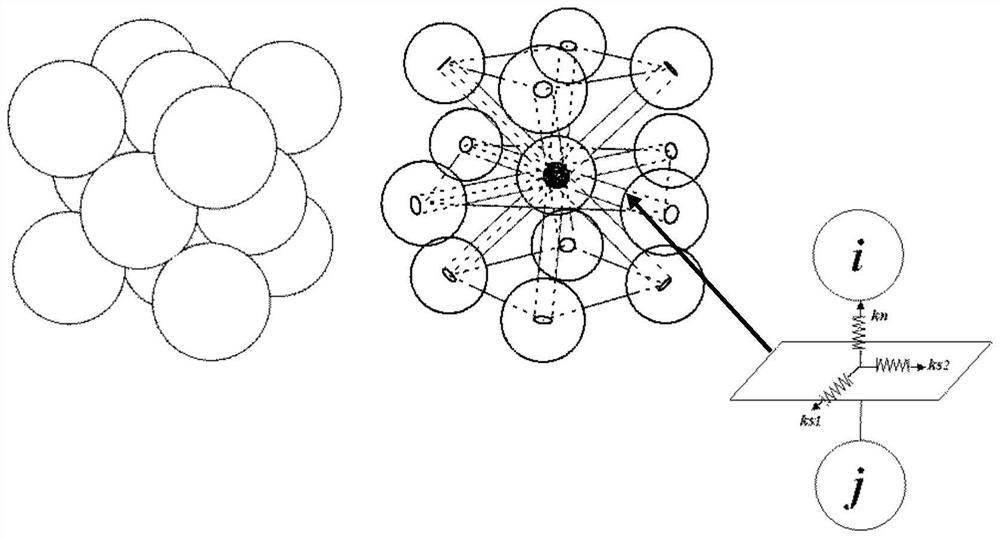
The invention discloses a method for solving a nonlinear mechanics problem of a continuous medium member by applying a three-dimensional discrete entity. For the limitation of a conventional discrete unit method for calculating a continuous medium problem, discrete element models of two three-dimensional discrete entities are built by taking energy equivalence as a principle based on a mechanics theory of a continuous medium; by adding a contact spring between particle units, the Poisson ratio effect of a material is reflected; and an analytic relationship between a mesoscopic model parameter (spring stiffness) and macroscopic elastic constants (an elastic modulus and a Poisson ratio) is derived, so that a great breakthrough is achieved in simulation of the continuous medium with a large Poisson ratio in PFC software. In addition, a plastic part is added in a contact constitutive equation between the particle units. According to the method, the elastic-plastic problem of the continuous medium can be effectively subjected to simulative calculation analysis by adopting a discrete entity unit method; and the method is suitable for nonlinear mechanics problems of large deformation, damage fracture, collapse destruction and the like of a structure or the member.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Finite-element analysis, monitoring and support method of soft-rock slope stability
InactiveCN107908890ASolving slope stability problemsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMechanical modelsElement analysis
The invention discloses a finite-element analysis, monitoring and support method of soft-rock slope stability. The method includes the following steps: step one, obtaining rock slope failure types, slope stability influence factors and slope reinforcement support measures by induction, establishing a mechanical model of engineering geology simulation analysis under the action of the different influence factors, and analyzing a dominant factor controlling the soft-rock slope stability and a potential mode thereof; and step two, using an approximate equivalent physical model, which is formed bya plurality of mutually associated unit bodies, by a finite-element analysis method of the slope stability to replace actual structures or continua, and establishing equations, which characterize force and displacement relationships, through basic principles of structure and continuum mechanics and physical characteristics of units. The finite-element analysis, monitoring and support method of thesoft-rock slope stability uses the finite-element method to analyze the stability thereof, carries out support and treatment on places where danger may further occur, and has certain guiding significance for solving slope stability problems.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
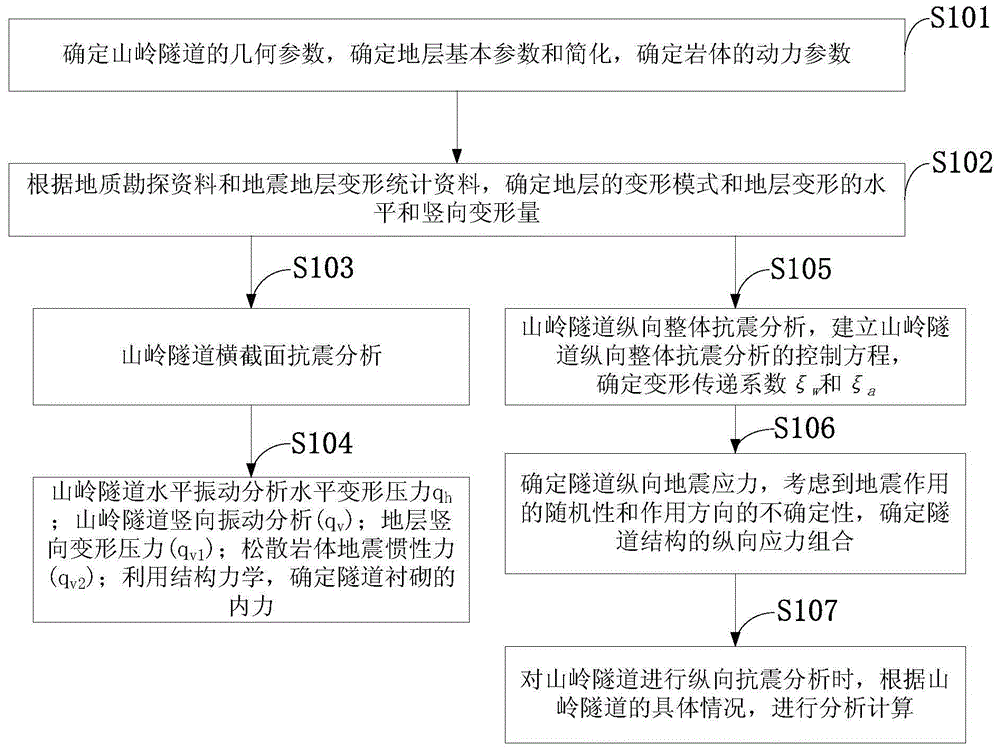
Mountain tunnel anti-seismic analysis method
InactiveCN104992013ALiberation pre-workloadImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsShear deformation theoryDynamic balance
The invention discloses a mountain tunnel anti-seismic analysis method. For the aspect of cross section anti-seismic analysis of a tunnel, based on a stratal elastic shear deformation theory, horizontal stratum deformation, vertical stratum deformation and seismic self-weight inertial force of broken rock bodies at the top of the tunnel are considered at the same time, and related problems of tunnel cross section seismic resistance are studied; and for the aspect of longitudinal overall anti-seismic analysis of the tunnel, an elastic foundation beam is taken as a model, interaction of the tunnel and surrounding rocks is considered, a dynamic balance equation of a tunnel structure is created according to an anti-seismic dynamic theory and a deformation transfer theory by utilizing continuum mechanics, and a classic seismic deformation method is a particular case of the method. According to the method, the cross section anti-seismic analysis and the longitudinal overall anti-seismic analysis of the mountain tunnel are performed by adopting unified thought for the first time; the thought is novel; the method is feasible; and through example verification, the method has relatively good applicability for mountain tunnel primary design under the action of strong earthquake.
Owner:EASTERN GANSU UNIVERSITY
Water and soil coupling landslide simulation method based on high-order double-set double-phase material point method
ActiveCN110008599AEffectively characterize and simulate water-soil coupling effectsSolve the problem of mesh distortionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDouble phaseLandslide
The invention provides a water and soil coupling landslide simulation method based on a high-order double-set double-phase material point method, and the method comprises the steps: employing two setsof material point division to disperse solid soil particles and pore fluid, and employing a regular background grid to realize the solving of a control equation; under a continuous medium mechanicalframework, establishing a solid-liquid two-phase substance point method control equation for dividing two sets of substances; realizing interaction between solid-liquid biphase material points and background grid nodes through a high-order B spline primary function; and based on the basic function of the B spline, updating the acceleration, speed, position and other information of the solid-liquidtwo-phase material point, mapping the calculated node information to the material point, updating the material information of the latest solid-liquid two-phase material point, and finally outputtingsimulation information. The method can accurately simulate the large deformation damage process and the water-soil coupling mechanism of the water-soil coupling soil landslide, and provides data support for disaster assessment and prevention of the water-soil coupling soil landslide problem.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
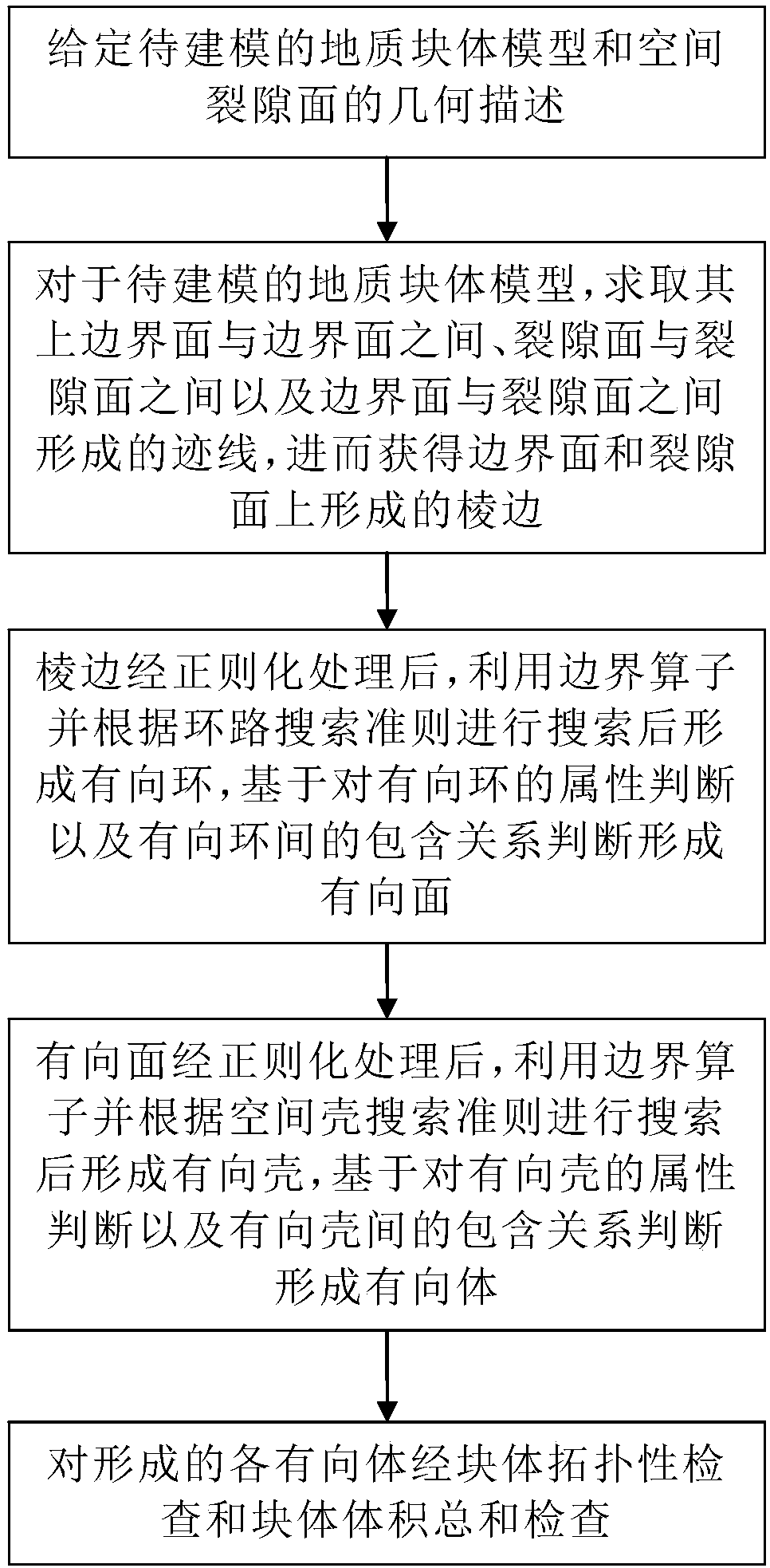
Three-dimensional modeling method for geological mass
The invention discloses a three-dimensional modeling method for a geological mass. The method comprises the steps that a geological mass model to be constructed and geometric description of spatial fissure surfaces are given; for the geological mass model, a trace formed by boundary surfaces and the fissure surfaces is solved, and edges are obtained; the edges are subjected to regularization processing, directed rings are formed after a boundary operator is utilized and search is performed, and directed surfaces are formed based on property judgment on the directed rings and inclusion relation judgment on the directed rings; the directed surfaces are subjected to regularization processing, directed shells are formed after the boundary operator is utilized and search is performed, and directed bodies are formed based on property judgment on the directed shells and inclusion relation judgment on the directed shells; and all the formed directed bodies are subjected to mass topological check and mass volume sum check. According to the method, it is not needed to introduce any artificial hypothesis, the geological mass with arbitrarily complicated space is formed completely according to actual geologic structure surface characteristics, and therefore the method has important application value in engineering practice and has positive theoretical significance for development of a non-continuum mechanic numerical method.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Prediction method for dynamic characteristics of fluid conveying multiwalled carbon nanotube
InactiveCN103853920AJudging Dynamic BehaviorSimplified calculation procedureSpecial data processing applicationsMicro nanoMultiwalled carbon
The invention relates to a prediction method for dynamic characteristics of a fluid conveying multiwalled carbon nanotube, in particular to the field of the dynamic characteristics of carbon nanotube conveying systems in the field of micro nano electromechanical systems. The method comprises the following specific steps: setting a governing equation module, a Galerkin discrete module, a characteristic value solving module and a result output module during a computation process, and finally completing the prediction of the dynamic characteristics of the fluid conveying multiwalled carbon nanotube. Firstly, a method of classical macroscopic continuum mechanics is expanded to research a micro nano conveying system, and secondly, dynamic behaviors of a coupled system are researched by means of the power system bifurcation theory so as to ensure the stability of the micro nano conveying system.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
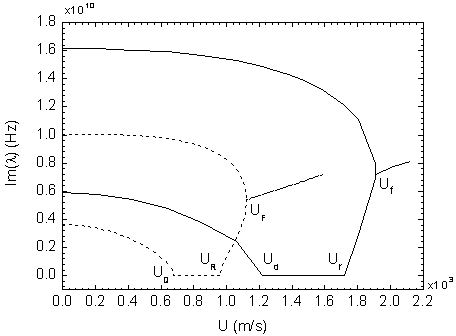
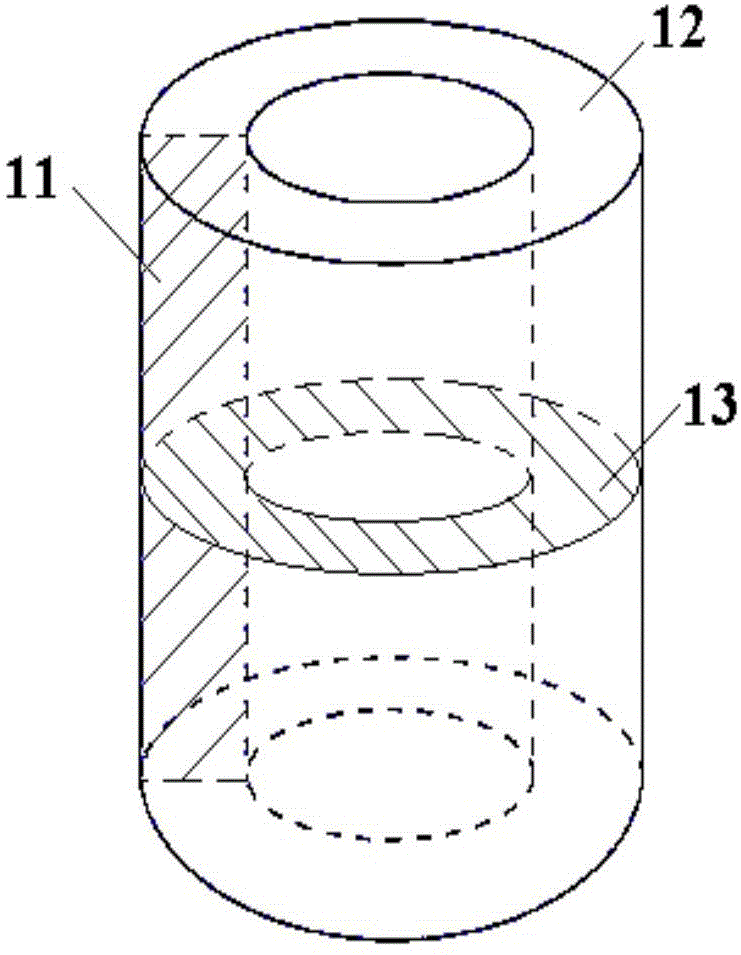
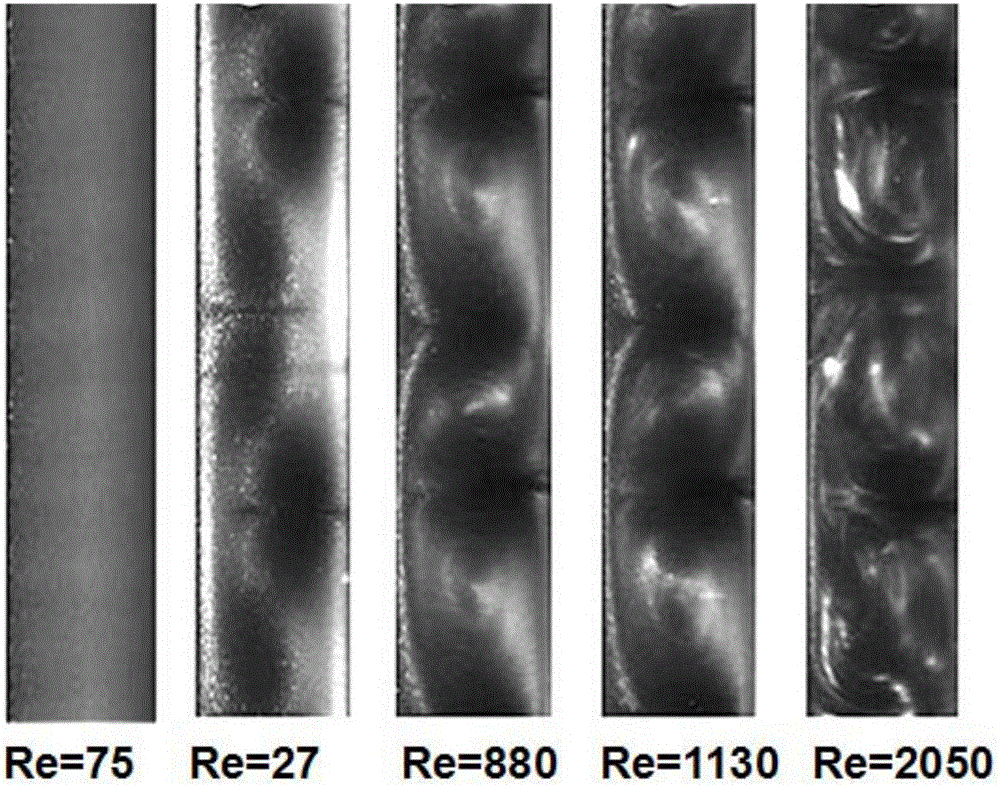
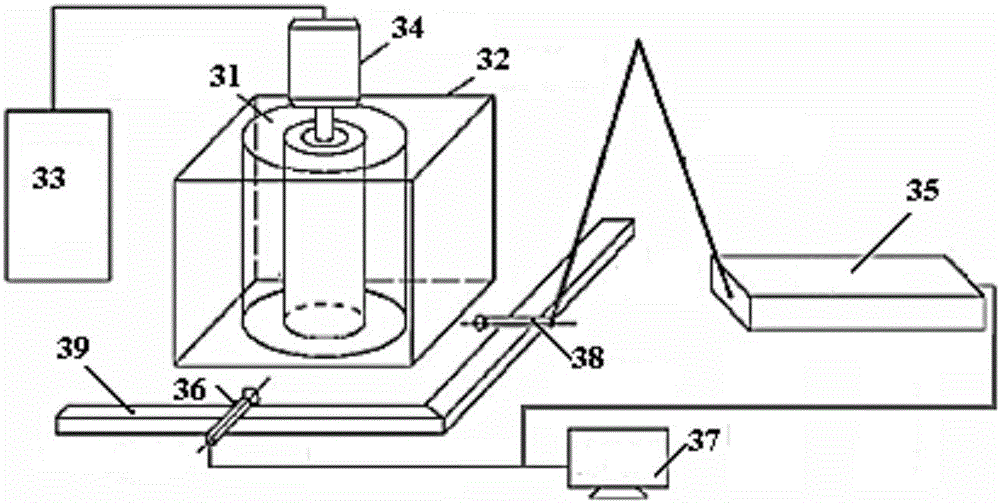
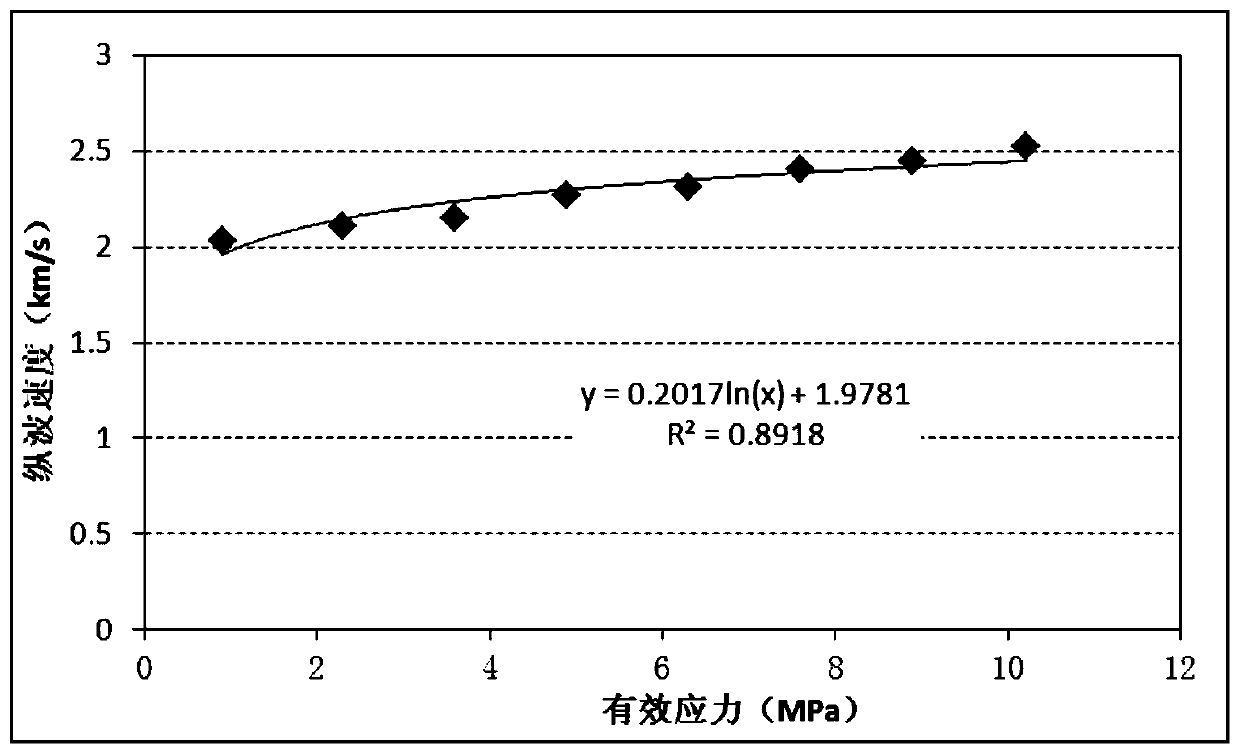
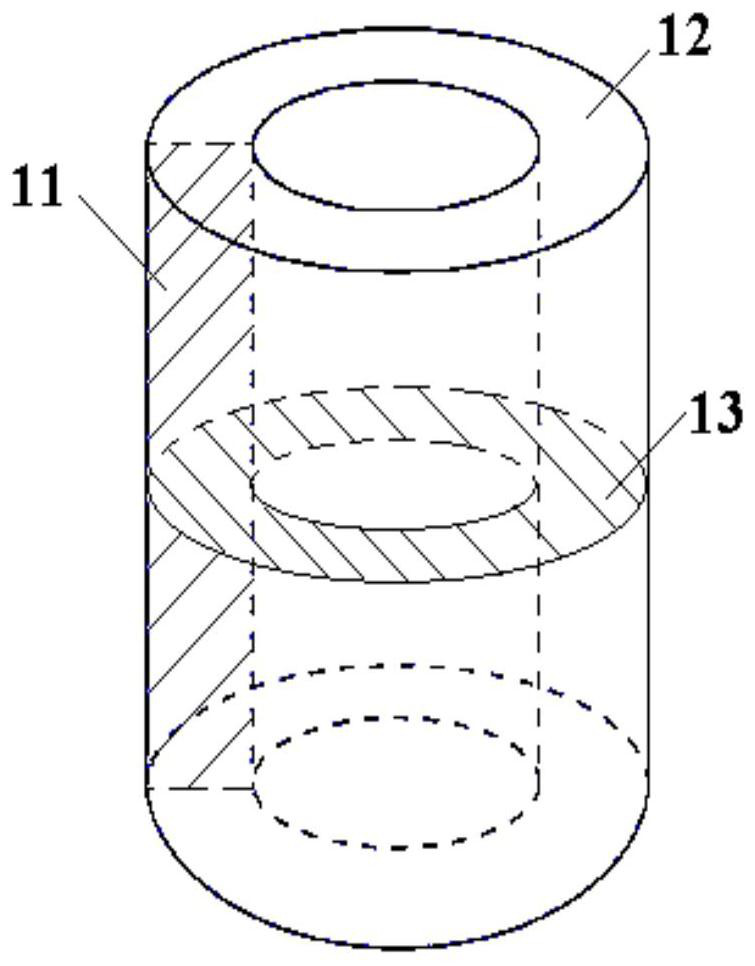
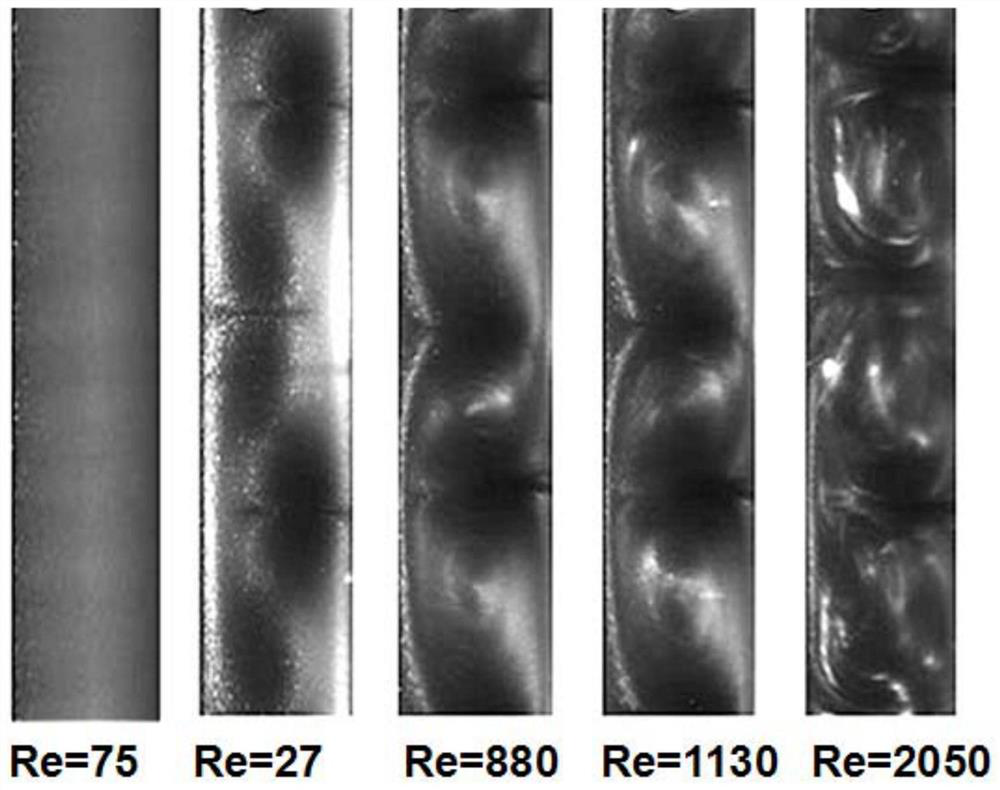
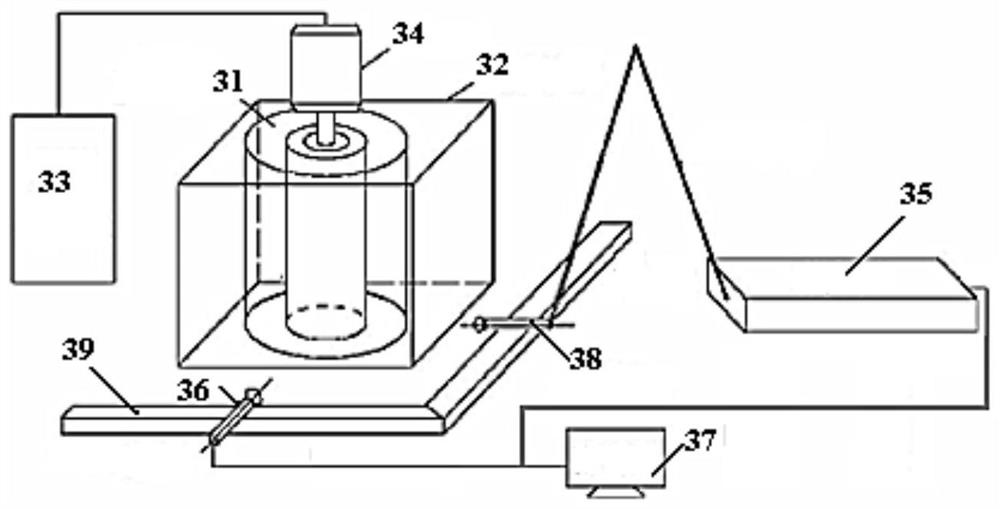
Taylor-Couette experiment device for solid-state medium
The invention discloses a Taylor-Couette experiment device for a solid-state medium and relates to the field of continuum mechanics. The device disclosed by the invention comprises a cylindrical sample chamber composed of inner and outer cylindrical walls and two annular end surfaces, a driving mechanism for driving the inner and outer cylindrical walls of the sample chamber to rotate relatively and a torque sensing recording system for recording relative rotary torques of the inner and outer cylindrical walls of the sample chamber, and further comprises a pressurizing mechanism for applying axial pressure to an end part of an indoor sample of the cylindrical sample chamber, a pressure sensing recording system for recording the axial pressure applied to the end part of the sample and an information acquisition system for recording a rheological condition of the sample solid-state medium. The device disclosed by the invention is simple in structure and easy to realize; the work of researching liquid-state medium rheological behaviors by the Taylor-Couette experiment device can be expanded to rheological researches of the solid-state medium.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
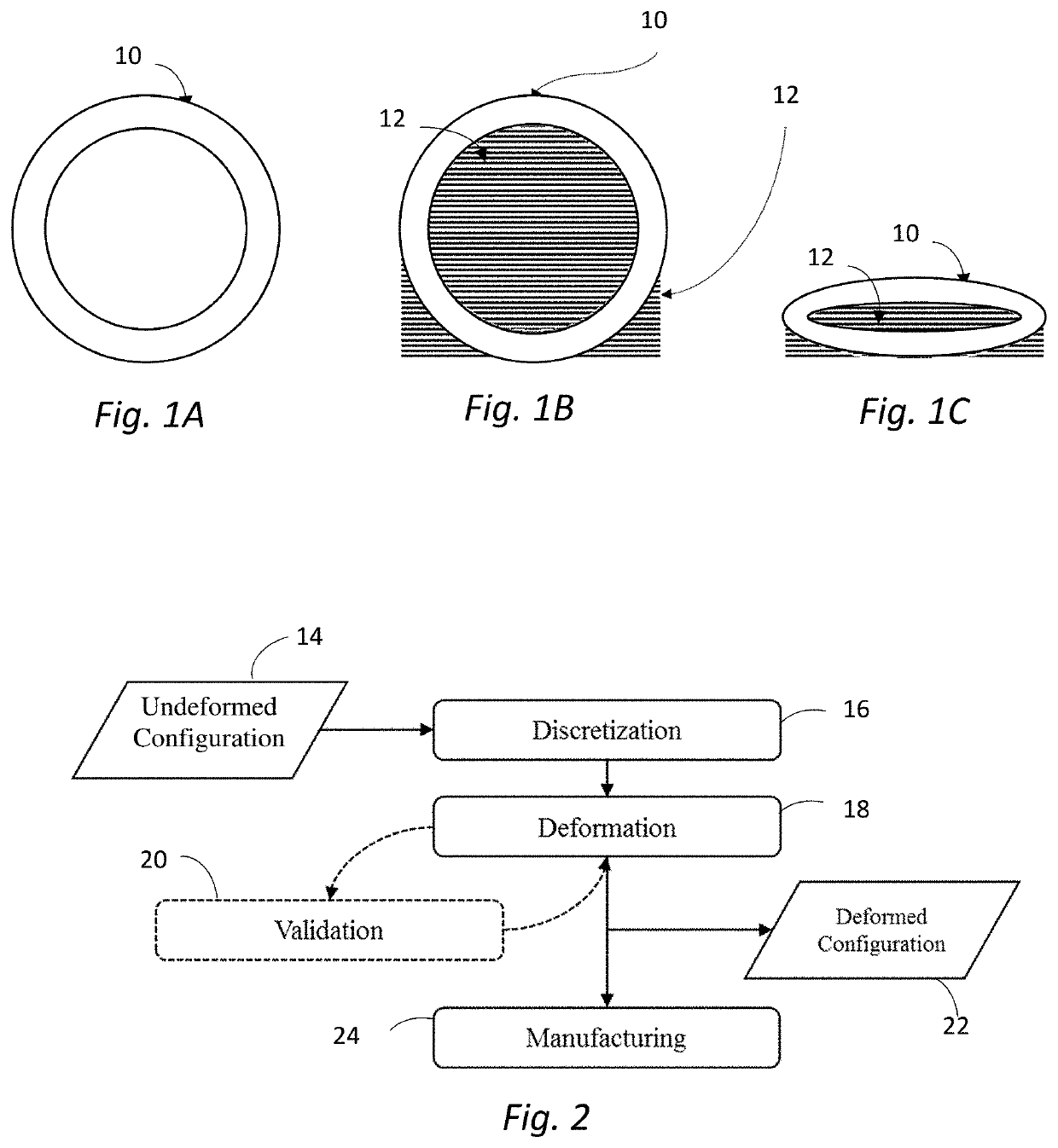
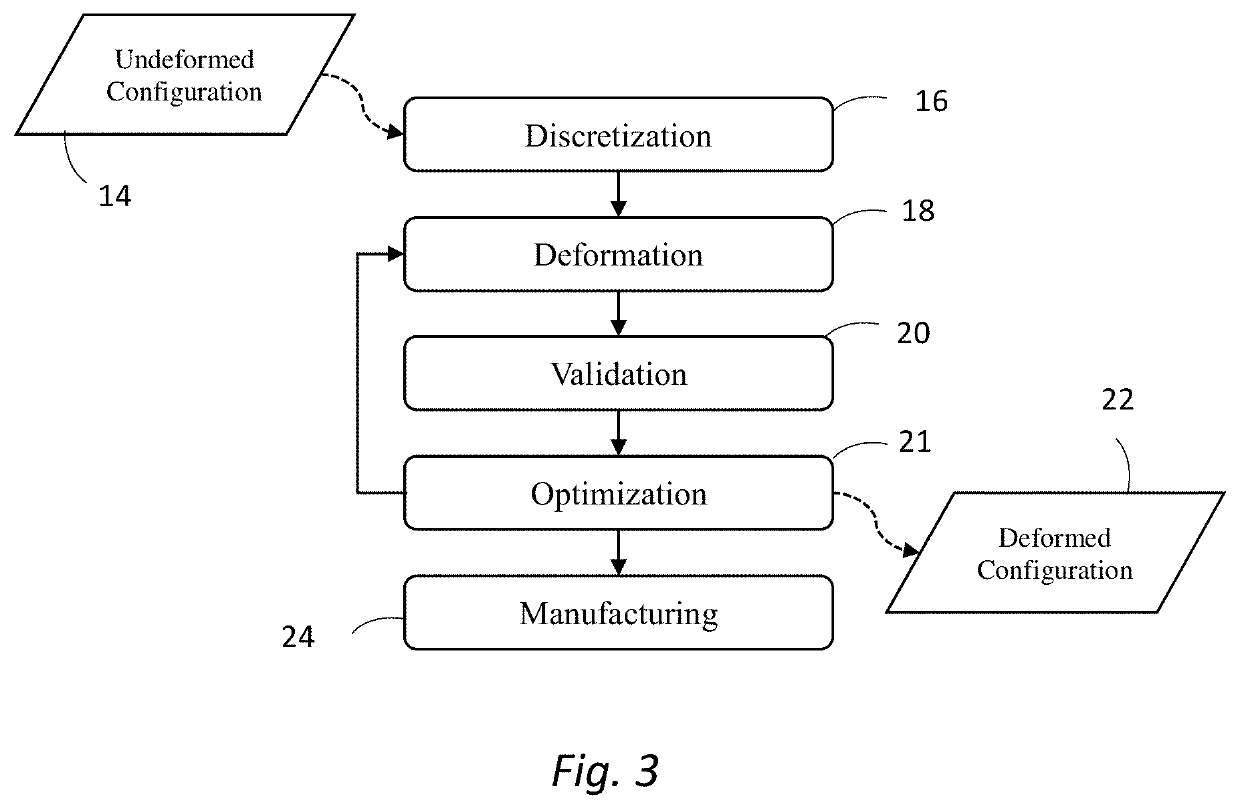
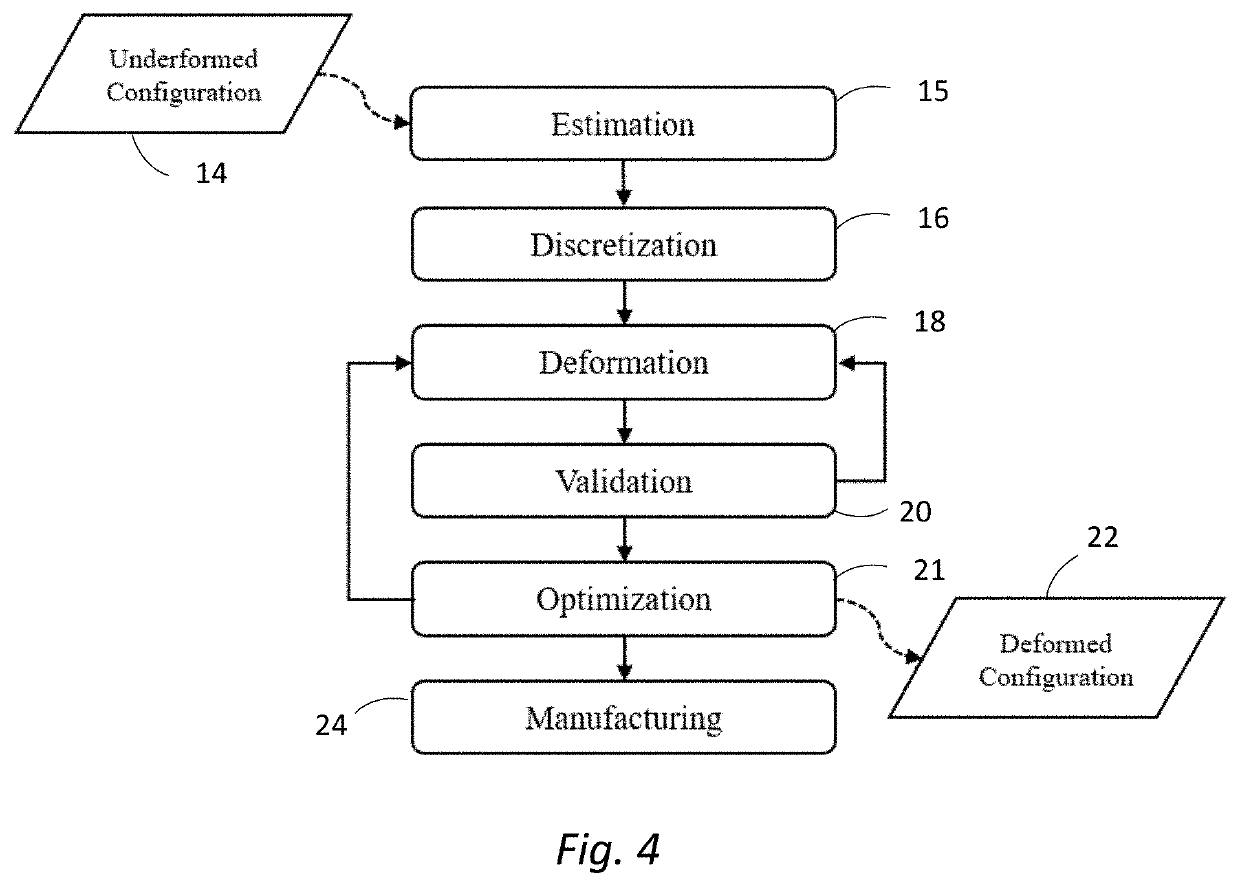
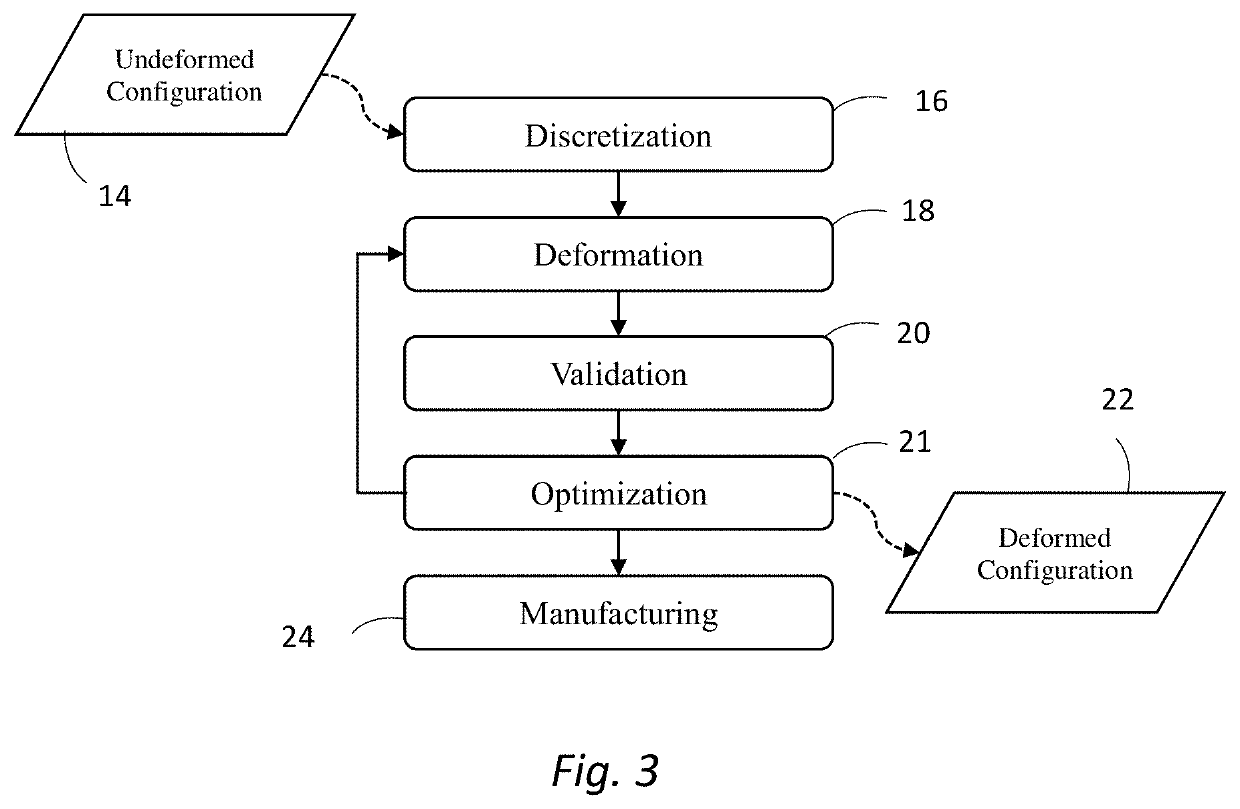
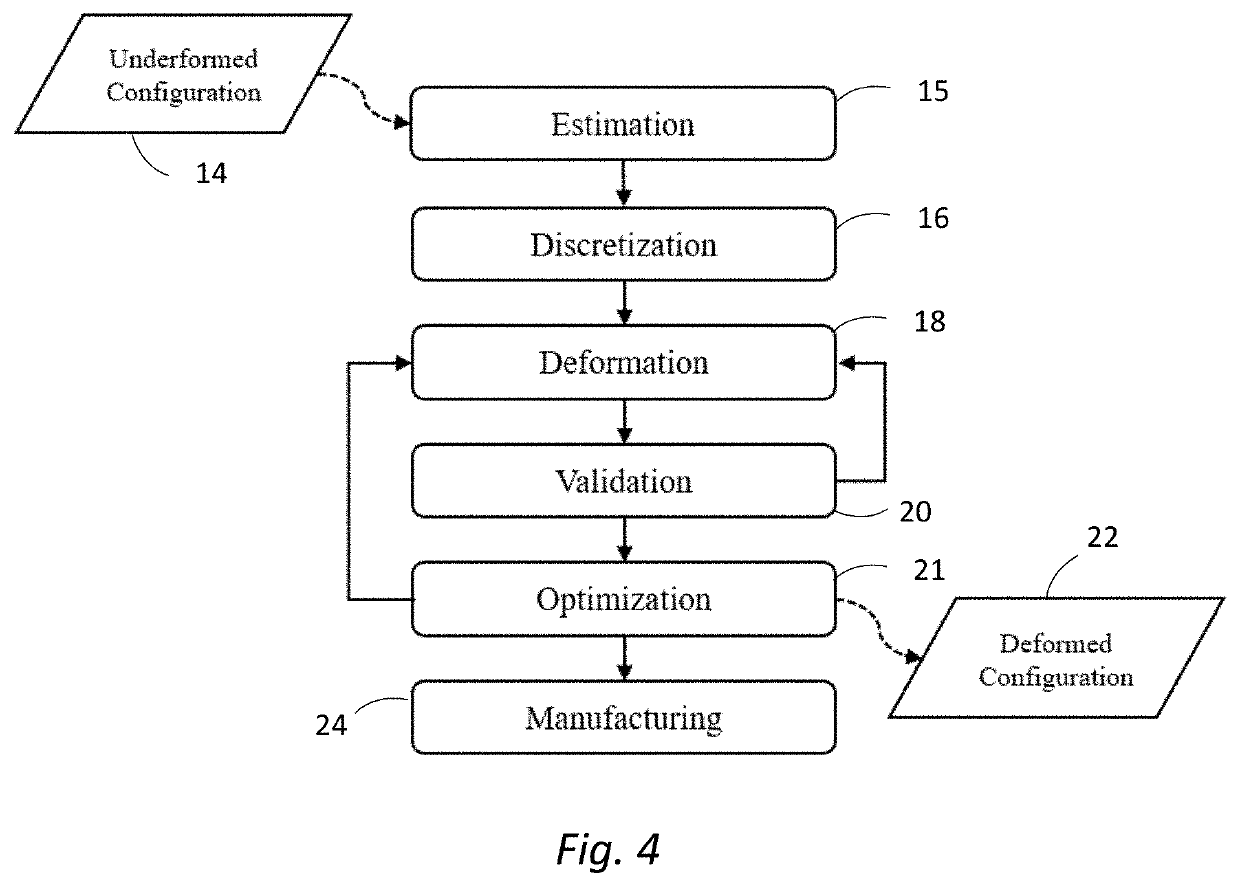
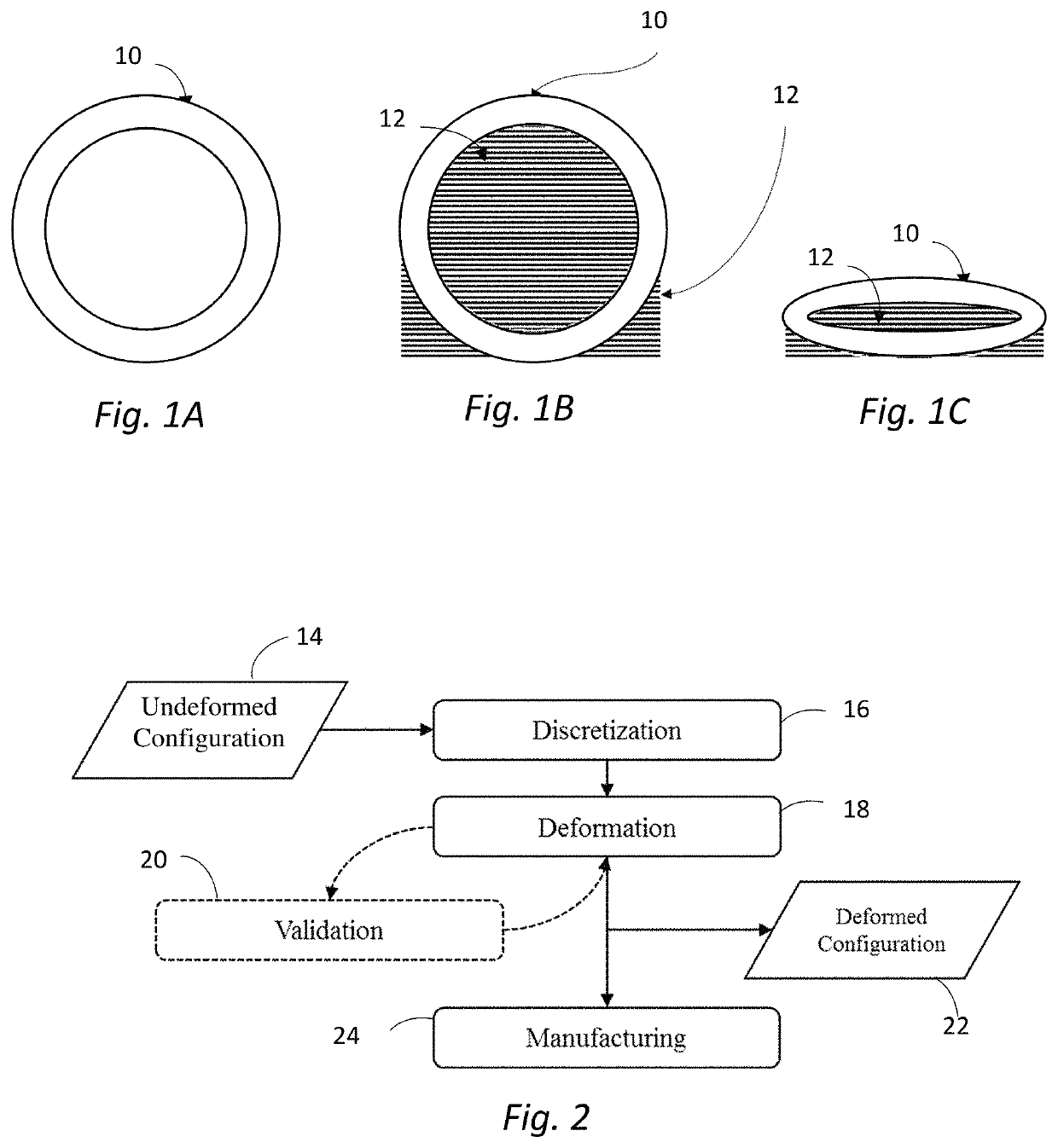
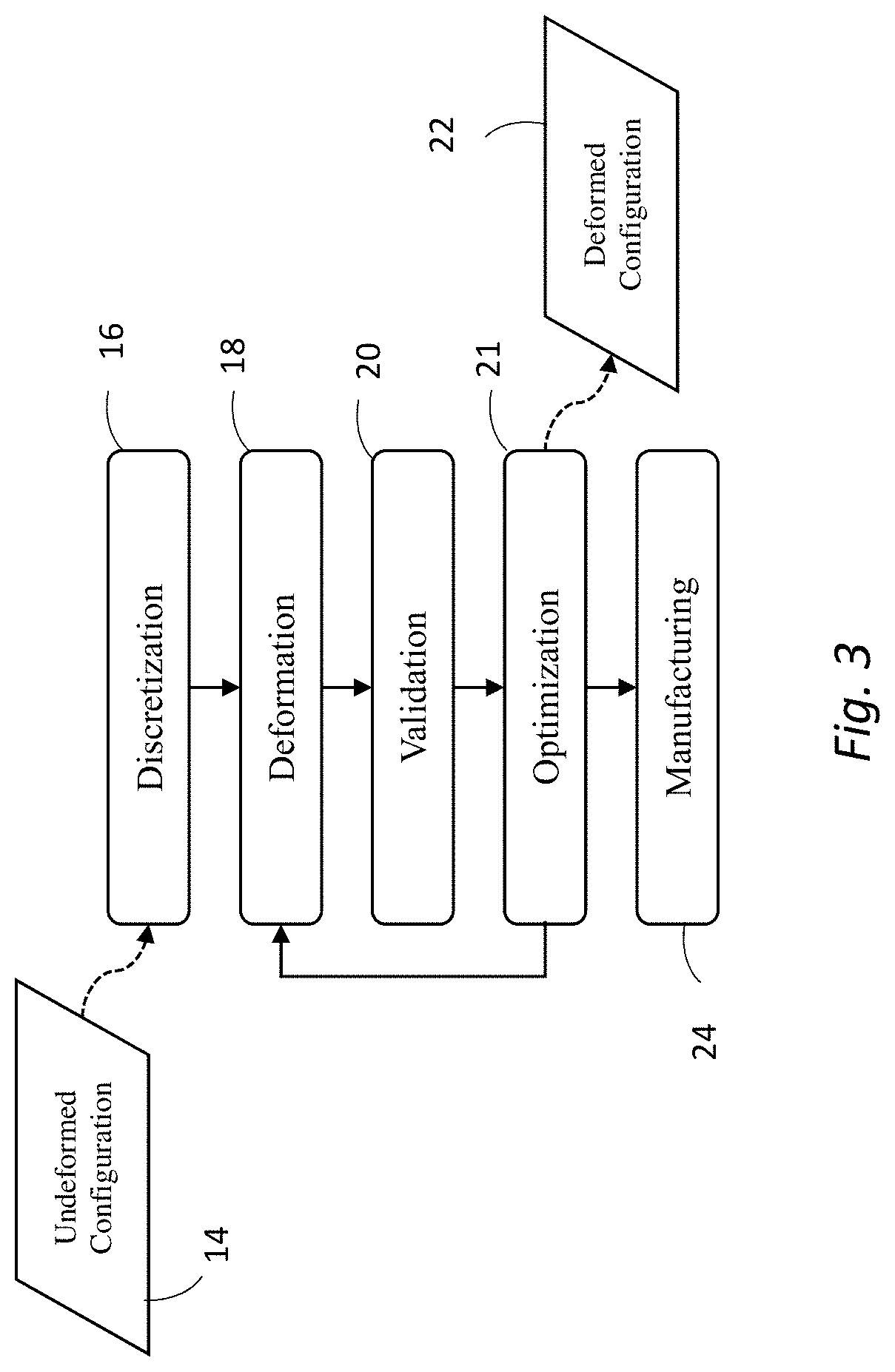
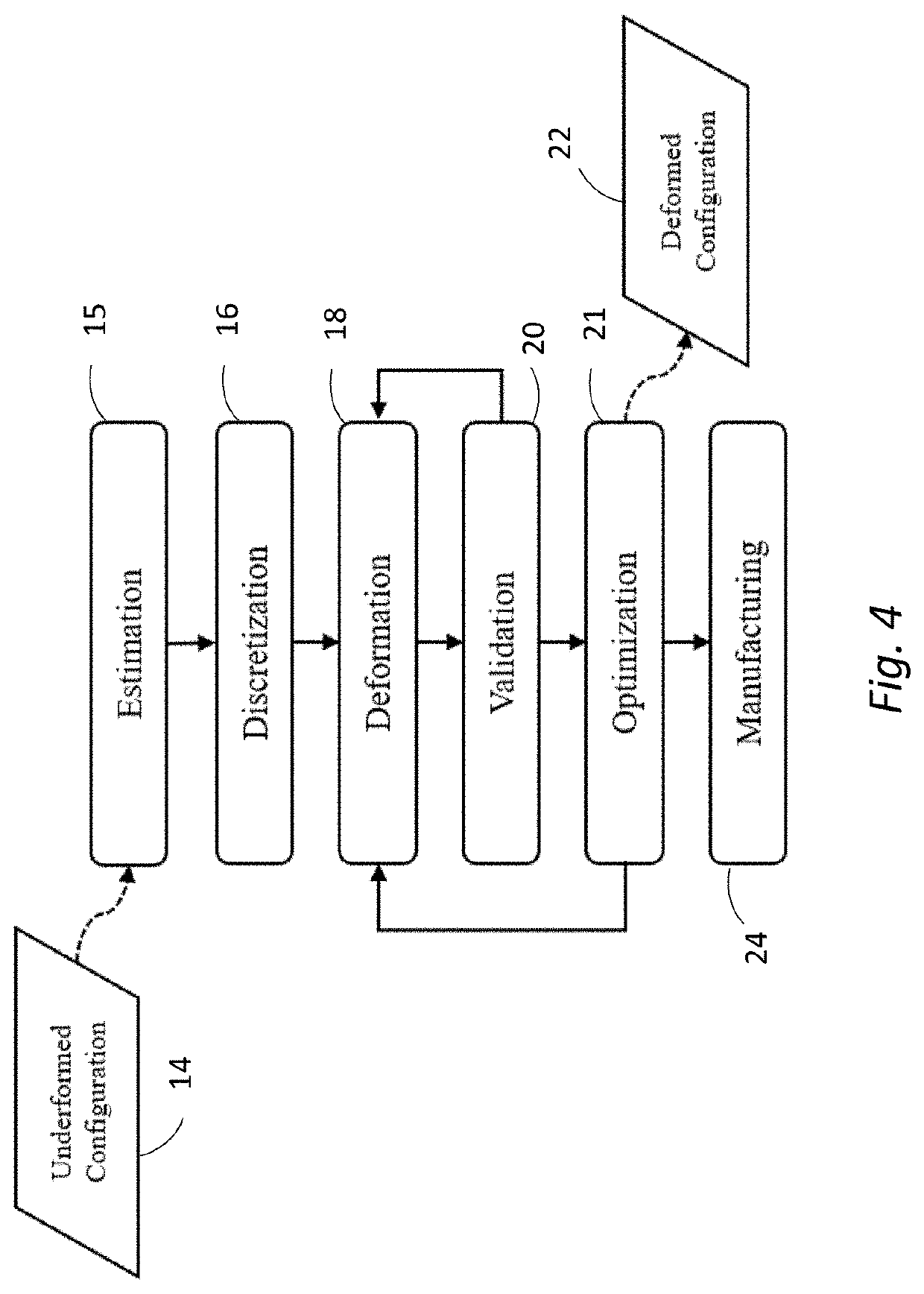
Deformation-based additive manufacturing optimization
ActiveUS20200064812A1Quantity minimizationShorten the timeProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsContinuum mechanics
A system and method that relies on the principles of material science, deformable body mechanics, continuum mechanics and additive manufacturing to reduce the costs associated with additive manufacturing. Physical properties are used by numerical solution methods, such as the Finite Element Method (FEM) or Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH), to deform an original model of an object to be manufactured into a viable configuration that reduces fabrication material, time, and cost when manufacturing an object through additive manufacturing.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
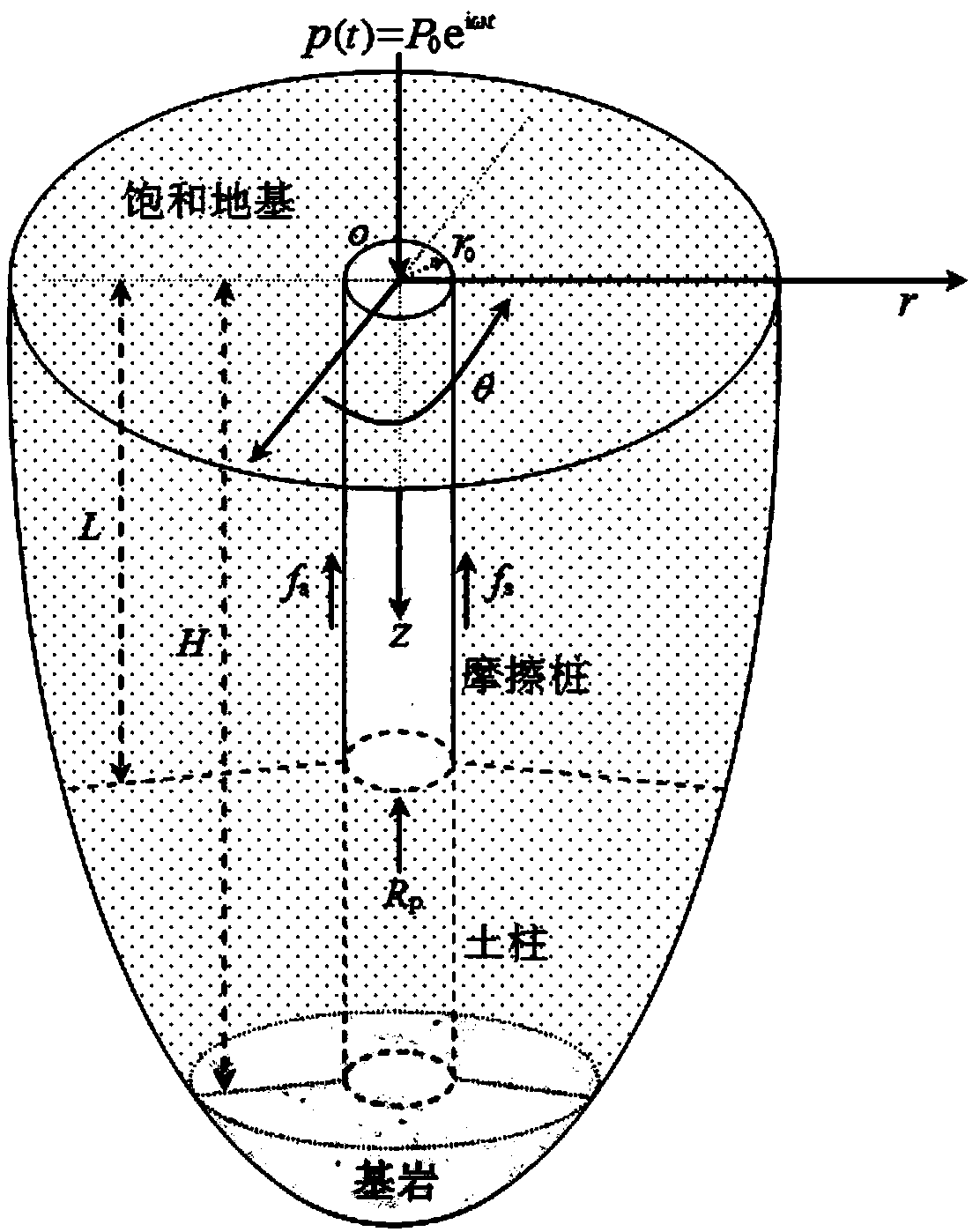
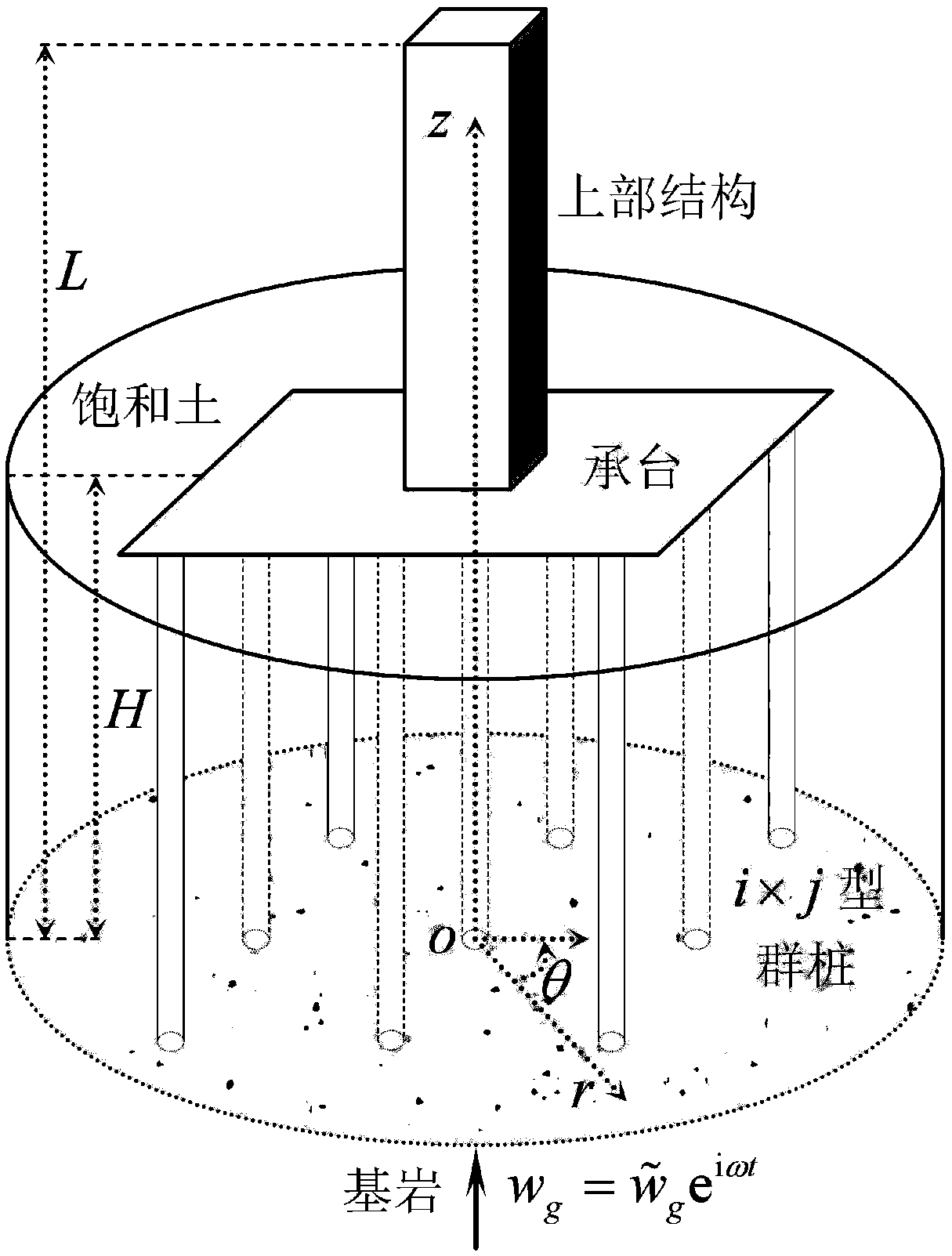
Vertical vibration analysis method of large-diameter friction pile in overlaying bedrock foundation
ActiveCN109056847AAvoid complex formulasFoundation testingComplex mathematical operationsVertical vibrationBedrock
The invention discloses a vertical vibration analysis method of a large-diameter friction pile in an overlaying bedrock foundation, particularly relates to a vertical vibration analysis method of a large-diameter friction pile in a lower horizontal bedrock transverse isotropic saturated viscoelastic foundation, and belongs to the technical field of foundation engineering test analysis. According to the vertical vibration analysis method, de Boer establishes a porous medium theory based on a continuous medium mixture principle and a volume fraction concept, the volume fraction concept is utilized, a plurality of microscopic properties can be directly described through macroscopic properties, and a complex formula in the theory of hybrid mixtures is avoided; the porous medium theory established by de Boer conforms to the continuous medium mechanical and the thermodynamics principles and also has a lot of advantages which are not achieved in the Biot theory; and therefore, the vertical vibration analysis method can provide the theoretical guidance and reference functions for research of more generalized and more complex soil structure dynamic interaction problems.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Generalized jet-effect and fluid-repellent corpus
The invention provides a method for computational fluid dynamics and apparatuses making enable an efficient implementation and use of an enhanced jet-effect, either the Coanda-jet-effect, the hydrophobic jet-effect, or the waving-jet-effect, triggered by specifically shaped corpuses and tunnels. The method is based on the approaches of the kinetic theory of matter, thermodynamics, and continuum mechanics, providing generalized equations of fluid motion. The method is applicable for slow-flowing as well as fast-flowing real compressible-extendable fluids and enables optimal design of convergent-divergent nozzles, providing for the most efficient jet-thrust. The method can be applied to airfoil shape optimization for bodies flying separately and in a multi-stage cascaded sequence. The method enables apparatuses for electricity harvesting from the fluid heat-energy, providing a positive net-efficiency. The method enables efficient water-harvesting from air. The method enables generators for practical-expedient power harvesting using constructive interference of waves due to the waving jet-effect.
Owner:SOLITON HLDG CORP DELAWARE CORP
Modular wire-driven continuum robotic arm
The invention provides a modularized cord-driven continuum mechanical arm. The modularized cord-driven continuum mechanical arm comprises a plurality of modularized single bodies, a first hinge joint part and a second hinge joint part are arranged on the opposite surfaces of every two adjacent modularized single bodies respectively, the first hinge joint part of one modularized single body and the second hinge joint part of the other corresponding modularized single body form a hinge joint structure, the modularized single bodies are sequentially in hinge joint through the hinge joint structures to form mechanical arm joints, and the modularized single bodies are provided with function holes and cord passing holes arranged circumferentially sequentially. The modularized cord-driven continuum mechanical arm has the advantage that through different connecting and locking modes adopted between every two adjacent modularized single bodies, different continuum mechanical arms different in flexibility and load capacity can be obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Dynamic response analysis method for saturated soil-group pile-upper structure system
ActiveCN108875157AAvoid complex formulasGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsPorous mediumSoil horizon
The invention relates to a dynamic response analysis method for a saturated soil-group pile-upper structure system, and belongs to the technical field of pile foundation mechanical analysis. Accordingto a porous media theory established by de Boer based on a continuum mixture axiom and a volume fraction concept, by utilizing the volume fraction concept, a plurality of microscopic properties can be described directly through macroscopic properties, and complex formulae in a hybrid mixture theory are avoided. The porous media theory established by the de Boer not only conforms to continuum mechanics and thermodynamics principles, but also has numerous advantages which a Biot theory does not have. In addition, for the situation that the research of pile-soil-upper structure dynamic interaction is limited to single-phase soil, little saturated soil is involved. Due to the existence of a liquid phase, the propagation and dissipation of energy and waves in the saturated soil and the single-phase soil are different; the influences of the filtering and amplifying effects of a soil layer on seismic waves under the action of seismic loads on structure seismic response characteristics are different; and the method is of great practical significance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Deformation-based additive manufacturing optimization
ActiveUS10838402B2Low costShorten the timeProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsContinuum mechanics
A system and method that relies on the principles of material science, deformable body mechanics, continuum mechanics and additive manufacturing to reduce the costs associated with additive manufacturing. Physical properties are used by numerical solution methods, such as the Finite Element Method (FEM) or Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH), to deform an original model of an object to be manufactured into a viable configuration that reduces fabrication material, time, and cost when manufacturing an object through additive manufacturing.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Deformation-based additive manufacturing optimization
ActiveUS11281186B2Low costShorten the timeProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsContinuum mechanics
A system and method that relies on the principles of material science, deformable body mechanics, continuum mechanics and additive manufacturing to reduce the costs associated with additive manufacturing. Physical properties are used by numerical solution methods, such as the Finite Element Method (FEM) or Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH), to deform an original model of an object to be manufactured into a viable configuration that reduces fabrication material, time, and cost when manufacturing an object through additive manufacturing.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Method for determining safe drilling fluid density of coal bed based on structural element analysis model
InactiveCN102230373BSpecific gravity by measuring pressure differencesDrilling compositionCoal briquetteInstability
The invention discloses a method for determining the safe drilling fluid density of a coal bed based on a structural element analysis model. The method has the advantages of coal bed cleat and fracture development, big rock brittleness, low strength and obvious anisotropy and discontinuity. The borehole wall instability characteristics of the method are different from those of the common sandstone stratum. The phenomenon that the traditional borehole wall stability model based on the mechanics of continuous media is difficult to be successful for solving coal bed instability problems can be eliminated. In the method, the coal bed is composed of discrete blocks. A coal briquette which has the biggest possibility of generating spallation between surface cleats is analyzed to carry out force analysis. A structural element model of collapse pressure is built by the stressed balance condition among pressure stress, shearing strength and shaft pressure. A coefficient c is introduced to judge the stable relationship of borehole pressure and borehole wall so as to judge the range of the safe drilling fluid density.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Blood coagulation simulation method and system based on mpm
ActiveCN109271696BSimulation is accurateAvoid Neighborhood SearchDesign optimisation/simulationAnimationMedicineContinuum mechanics
The invention discloses a blood coagulation simulation method based on MPM, including: initializing a general data, 2, discretizing the blood into particles and grid; S3, simulating blood coagulationaccording to substance point method. The invention also discloses a blood coagulation simulation method system based on MPM. The present invention can be based on MPM frame, combined with continuum mechanics and fluid mechanics N-S equation and Lame coefficient function is designed according to the blood coagulation rate to accurately simulate the blood coagulation process.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A High-precision Numerical Simulation Method of Fluid-Structure Interaction Based on Continuum Mechanics
ActiveCN109902376BAccurately Predict Fluid-Structure Interaction ProcessesReduce dissipationDesign optimisation/simulationShock (mechanics)Fluid solid coupling
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Wellbore Stability Research Method Applicable to Pressure-Depleted Formation
ActiveCN106855897BImprove forecast accuracyHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMacroscopic scaleWell logging
The invention discloses a sidewall stability research method suitable for a pressure-depleted formation. In the method, knowledge points of multiple disciplines, such as the underground rock mechanics, the borehole geophysics, the continuum mechanics, the elastic mechanics and the mathematical statistics, are integrated, the method starts with microscopic deformation conditions of rock skeleton particles obtained after the formation pressure is depleted till to the macroscopic acoustic response performance, characteristic parameter variation and the like of rocks, makes full use of partial data, such as rock skeleton density logging, shale content logging, actual measurement points of the formation pressure and collapse and fracture pressure and the formation core, obtained when the oilfield formation pressure is not depleted, and finally the collapse and fracture pressure of the pressure-depleted formation is determined, so that guidance and reference are provided for selection of the density of a drilling fluid for pressure-depleted formation drilling. The computing method is high in precision, and just a few of errors exist in fracture pressure prediction.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
A Taylor-Couette experimental setup for solid-state media
The invention discloses a Taylor-Courte experimental device for solid media, which relates to the field of continuum mechanics. The device comprises a cylindrical sample chamber composed of inner and outer cylindrical walls and two annular end faces; and a driving sample The drive mechanism for the relative rotation of the inner and outer cylindrical walls; the torque sensor recording system for recording the relative rotational torque of the inner and outer cylindrical walls of the sample chamber; it also includes a pressurization mechanism that provides axial pressure to the end of the sample in the cylindrical sample chamber; records the sample The pressure sensing recording system for the axial pressure on the end; the information acquisition system for recording the rheological conditions of the solid medium of the sample. The device has a simple structure and is easy to implement, and can extend the research of the rheological behavior of the liquid medium to the rheological research of the solid medium from the classical Taylor-Couette device.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
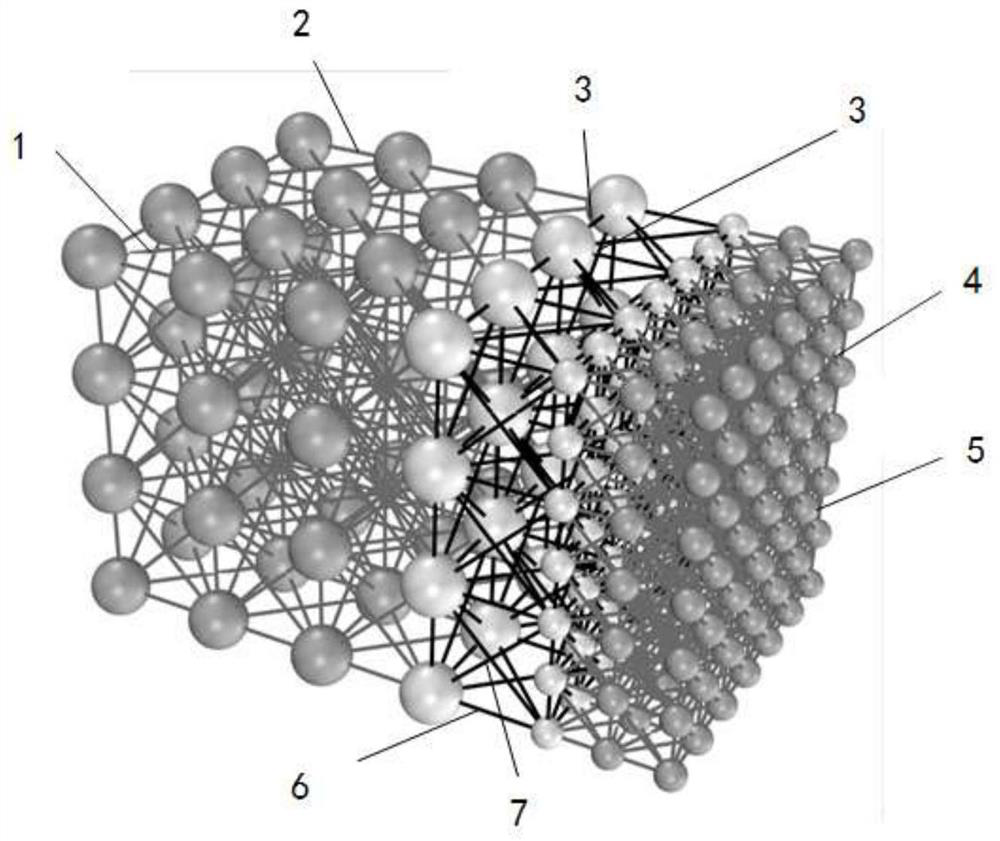
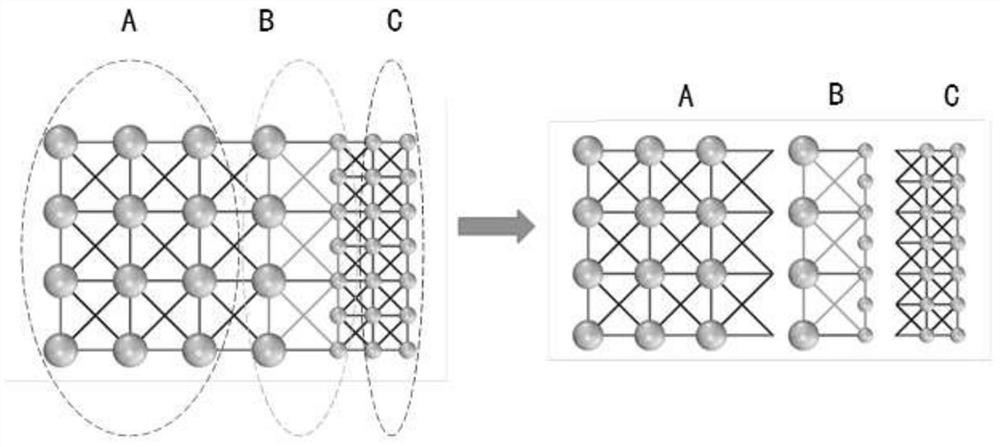
Simulation method for solving mechanics problem of continuum structure through multi-scale discrete entity elements
PendingCN113887094AReduce in quantityImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelMacroscopic scale
The invention discloses a simulation method for solving the mechanics problem of a continuum structure through multi-scale discrete entity elements. A multi-scale discrete entity element model comprises a large ball area, a small ball area and a transition area, ball elements are connected through a spring system, and the spring system comprises an axial spring and tangential springs in two directions. On the basis of a continuous medium mechanics theory and with energy equivalence as a principle, an analytic relationship between a mesoscopic model parameter (spring stiffness) and a macroscopic elastic constant (elastic modulus and Poisson's ratio) is deduced. According to the method, the number of ball elements and springs can be effectively reduced, the calculation efficiency is improved, the discrete entity element method has more possibilities, and the method is suitable for large deformation, damage fracture, collapse damage and other complex mechanical simulation of structures or components.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Blood coagulation simulation method and system based on MPM
ActiveCN109271696ASimulation is accurateAvoid Neighborhood SearchDesign optimisation/simulationAnimationMedicineContinuum mechanics
The invention discloses a blood coagulation simulation method based on MPM, including: initializing a general data, 2, discretizing the blood into particles and grid; S3, simulating blood coagulationaccording to substance point method. The invention also discloses a blood coagulation simulation method system based on MPM. The present invention can be based on MPM frame, combined with continuum mechanics and fluid mechanics N-S equation and Lame coefficient function is designed according to the blood coagulation rate to accurately simulate the blood coagulation process.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A Method for Solving Nonlinear Mechanics Problems of Continuum Components Using 3D Discrete Solids
ActiveCN107391788BCalculation process is clearThe solution process does not changeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMacroscopic scaleAnalogue computation
The invention discloses a method for solving a nonlinear mechanics problem of a continuous medium member by applying a three-dimensional discrete entity. For the limitation of a conventional discrete unit method for calculating a continuous medium problem, discrete element models of two three-dimensional discrete entities are built by taking energy equivalence as a principle based on a mechanics theory of a continuous medium; by adding a contact spring between particle units, the Poisson ratio effect of a material is reflected; and an analytic relationship between a mesoscopic model parameter (spring stiffness) and macroscopic elastic constants (an elastic modulus and a Poisson ratio) is derived, so that a great breakthrough is achieved in simulation of the continuous medium with a large Poisson ratio in PFC software. In addition, a plastic part is added in a contact constitutive equation between the particle units. According to the method, the elastic-plastic problem of the continuous medium can be effectively subjected to simulative calculation analysis by adopting a discrete entity unit method; and the method is suitable for nonlinear mechanics problems of large deformation, damage fracture, collapse destruction and the like of a structure or the member.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for solving critical strain of graphene
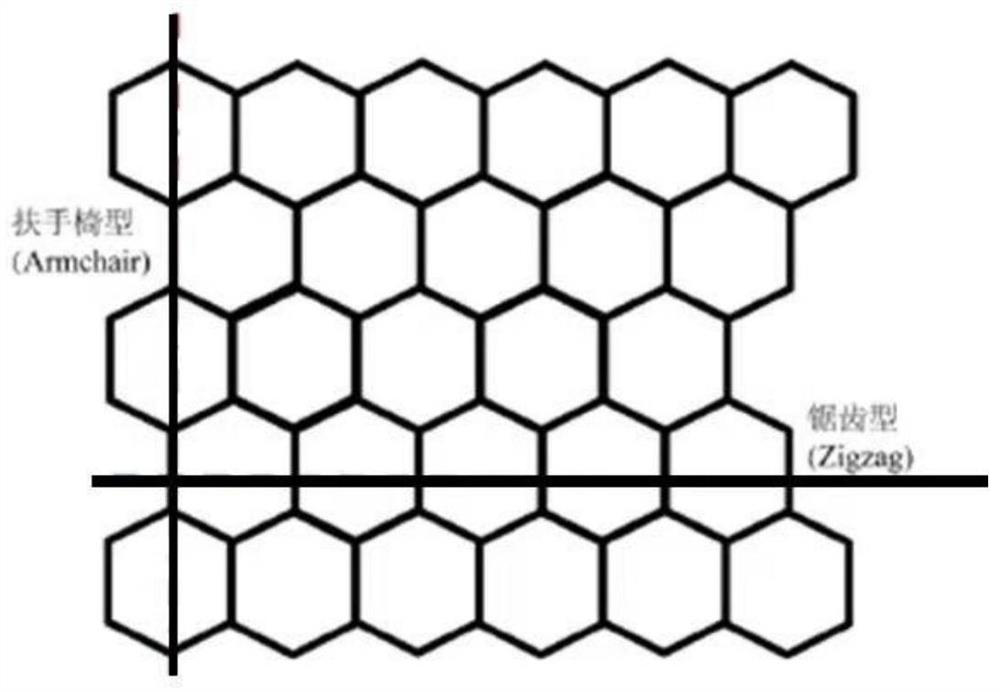
PendingCN113270148AStructure determinationEasy to calculateComputational theoretical chemistryComputational materials scienceStrain energyYoung's modulus
A graphene critical strain solving method applies a load in an Armchair direction or a Zigzag direction to graphene, and comprises the following steps: S1, determining a constitutive relation when the graphene is subjected to the load according to a lowest energy principle; and S2, judging the critical strain of the graphene according to abnormal changes of mechanical property parameters such as Young modulus and Poisson's ratio. According to the method, on the basis of the Cauchy-Born criterion, the strain energy, the Young modulus and the Poisson ratio of graphene are determined through a continuum mechanics method. A constitutive relation is determined when the graphene is loaded according to a lowest energy principle, and a specific structure of the graphene subjected to the load is determined. Through the method, the critical strain of the graphene under the plane load can be calculated more conveniently, and the method can be further expanded to the solution of the loaded critical strain of a novel two-dimensional material.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Large-scale granular material internal stress and crushing simulation analysis method and device
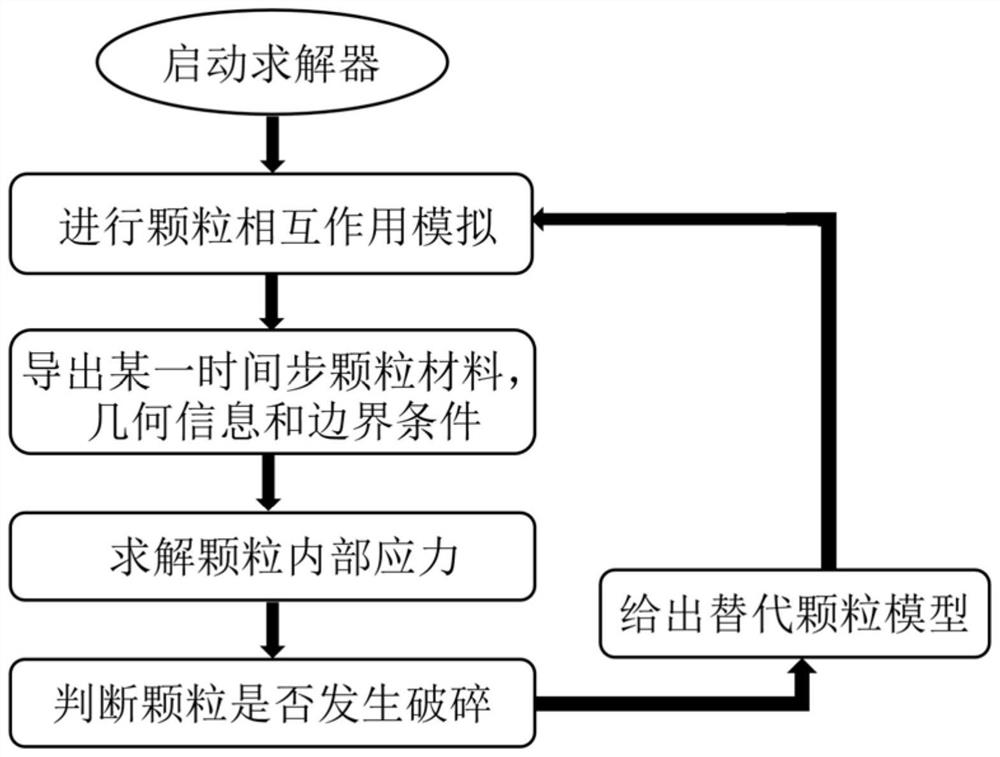
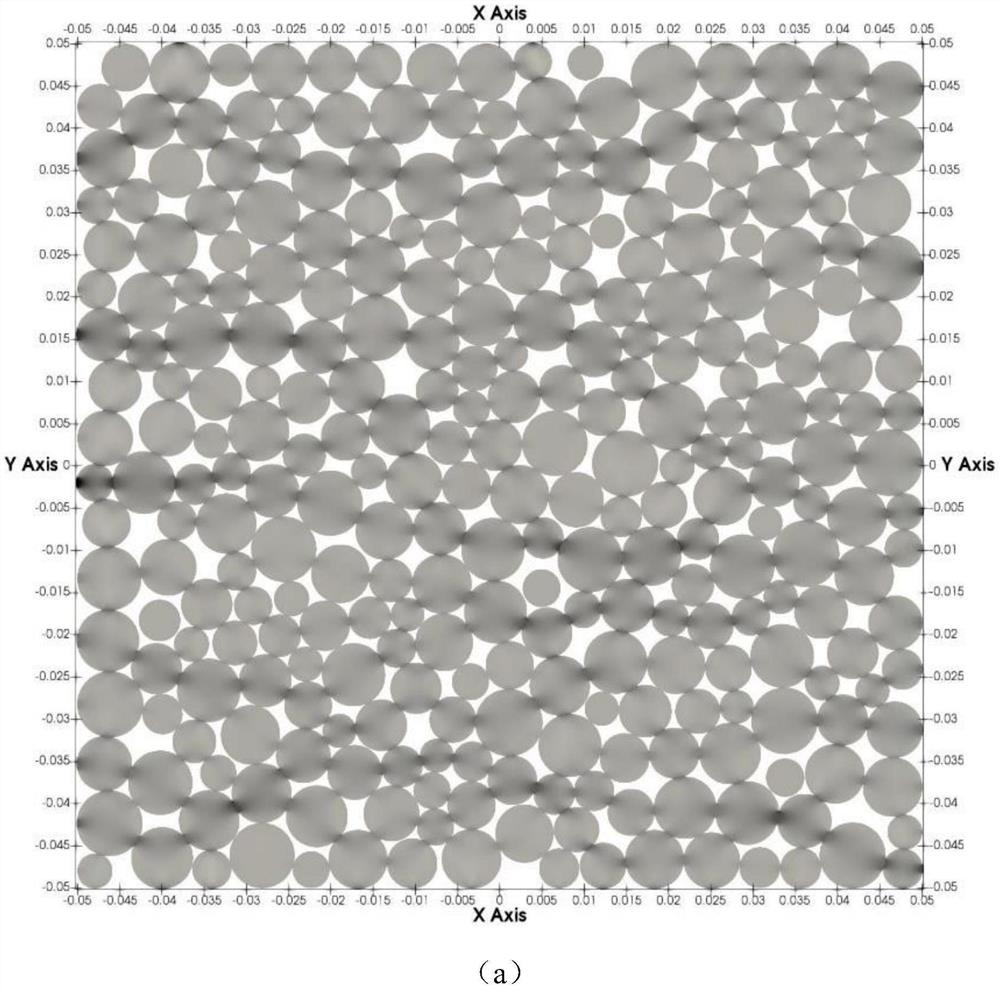
ActiveCN112084647BEasy to solveEnsure safetyDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsDiscrete element methodBoundary element method
The invention discloses a large-scale particle material internal stress and crushing simulation analysis method and device, which belong to the technical field of particle crushing. Based on the basic idea of continuous discrete coupling, the invention combines the boundary element method and discrete element method to carry out large-scale particle crushing research , can use the boundary element method to calculate and analyze the internal stress of the particles, and combine the fracture theory of continuum mechanics, and the Hawke-Brown criterion to judge whether the particles are broken. In addition, when using boundary elements for internal stress simulation, for particle aggregates with similar shapes, such as round particles, the present invention only needs to calculate the coefficient matrix of one particle, and other similar particles obtain the coefficient matrix through coordinate conversion and coefficient scaling. The calculation efficiency is greatly improved. The invention also simulates the internal stress of the circular rockfill material and proves its effectiveness.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com