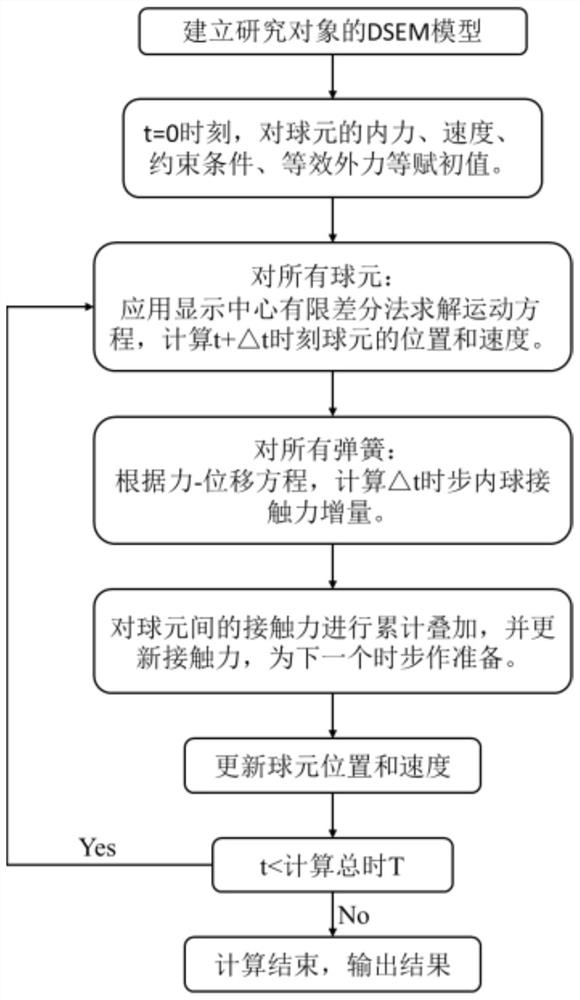
Simulation method for solving mechanics problem of continuum structure through multi-scale discrete entity elements
A technology of structural mechanics and simulation method, which is applied in the field of discrete element analysis, can solve the problems of large number of spherical elements and low calculation efficiency, and achieve the effect of reducing the number, improving calculation efficiency, and simple and clear calculation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] The following example is used to verify the superiority of multi-scale discrete solid element in simulating large deformation of components.
[0069] The cantilever beam is 160mm long, the section size is 30mm×30mm, and the modulus of elasticity is 2.06×10 5 MPa, Poisson's ratio is 0.2, density 7850kg / m 3 , a shear force of 1000MPa is applied at the end of the beam.
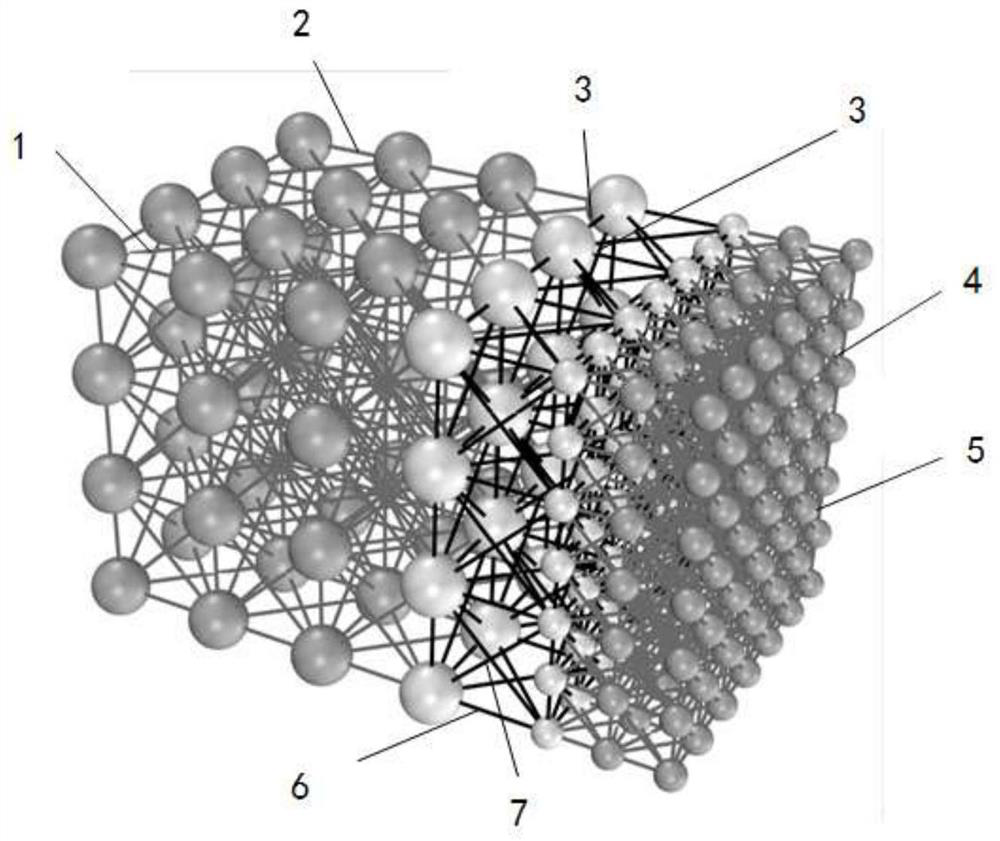
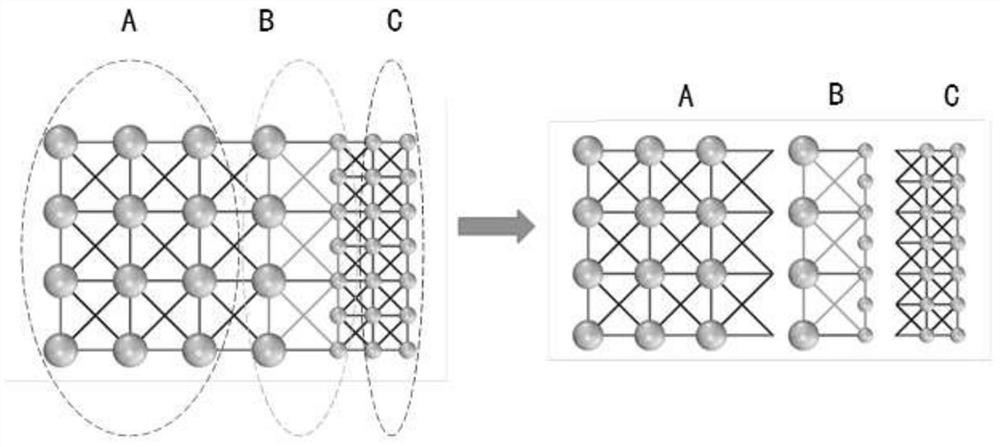
[0070] The radius of the discrete solid element model is 2.5mm, the number of spherical elements is 1617, and the number of connecting springs is 12092×3, such as Figure 4 shown. In the multi-scale discrete solid element model, the length of the large ball area is 80 mm, the diameter of the large ball is 10 mm, the length of the small ball area is 70 mm, the diameter of the small ball is 5 mm, the length of the transition area is 10 mm, the number of ball elements is 879, and the number of connecting springs is 6332×3. Figure 5 shown. In this embodiment, the displacement variation of the Y-direction ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com