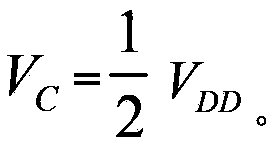Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Conditional equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A conditional equation is one that is solved for only a few numbers. A very simple example: [math] x + 10 = 15 [/math] is a conditional equation, since its only solution is [math] x = 5 [/math]. domain of the pieces in the equation) as a solution. side you obtain [math] x + 10 = x + 10 [/math], which is satisfied by every real number.
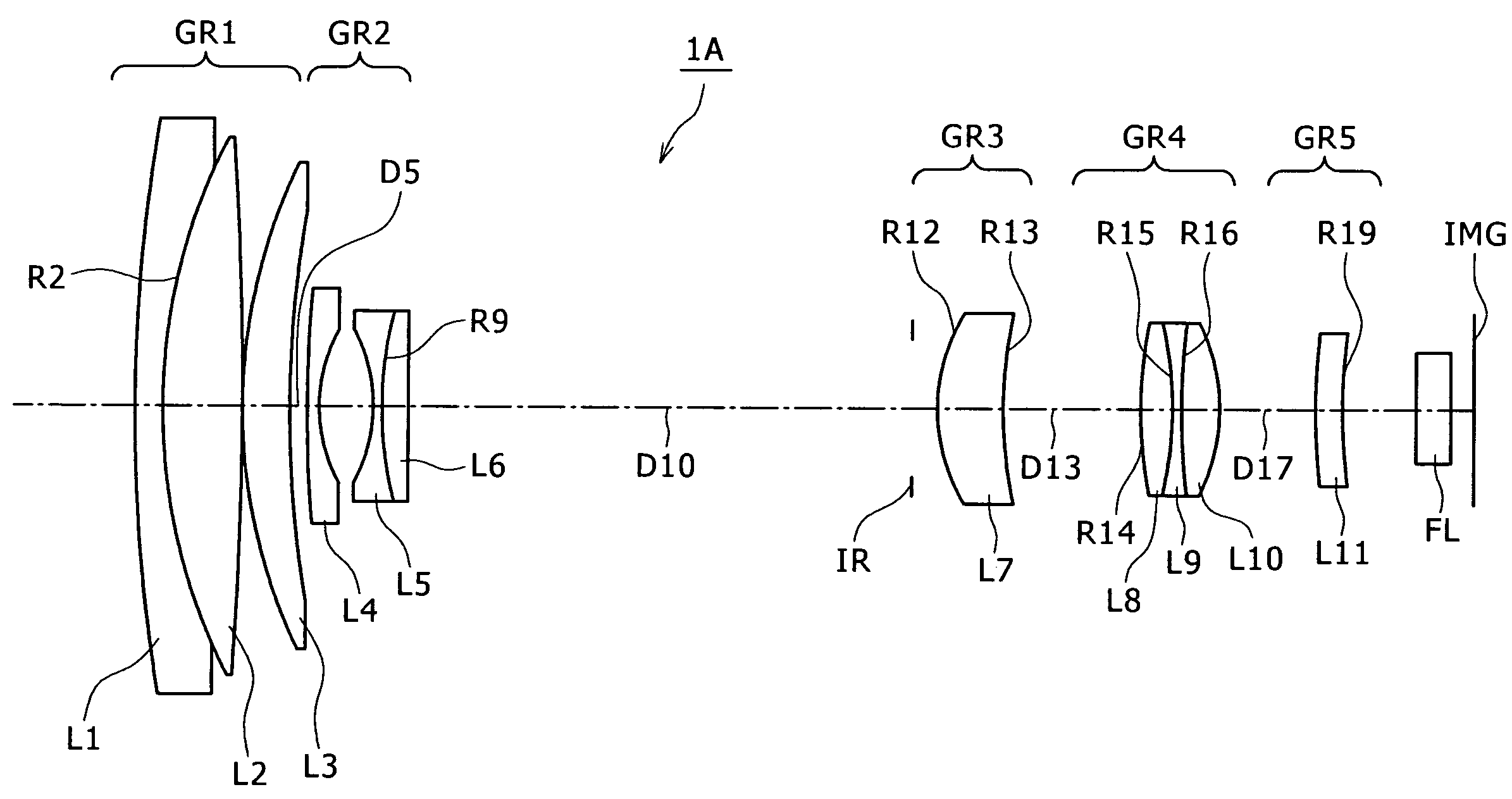
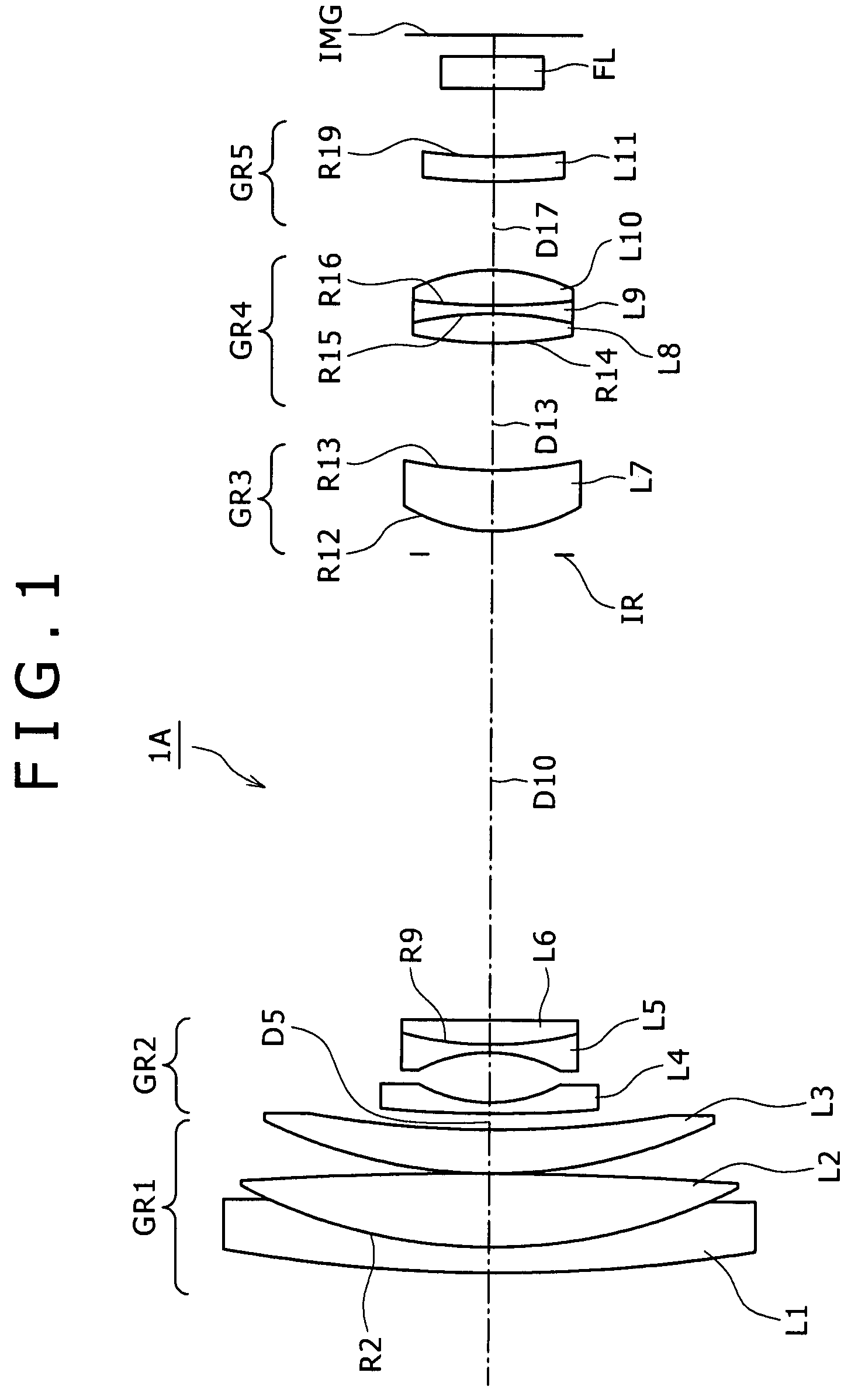
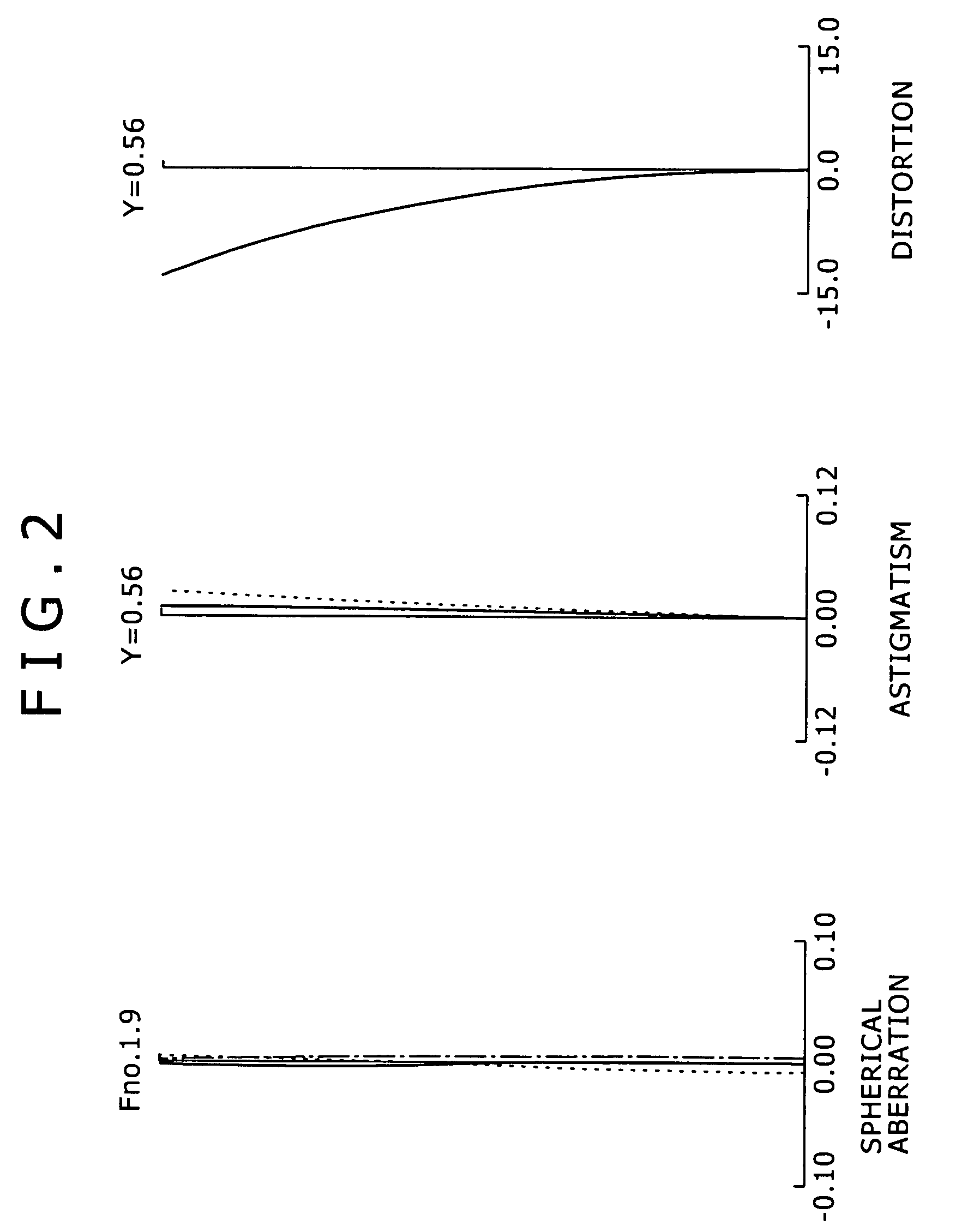
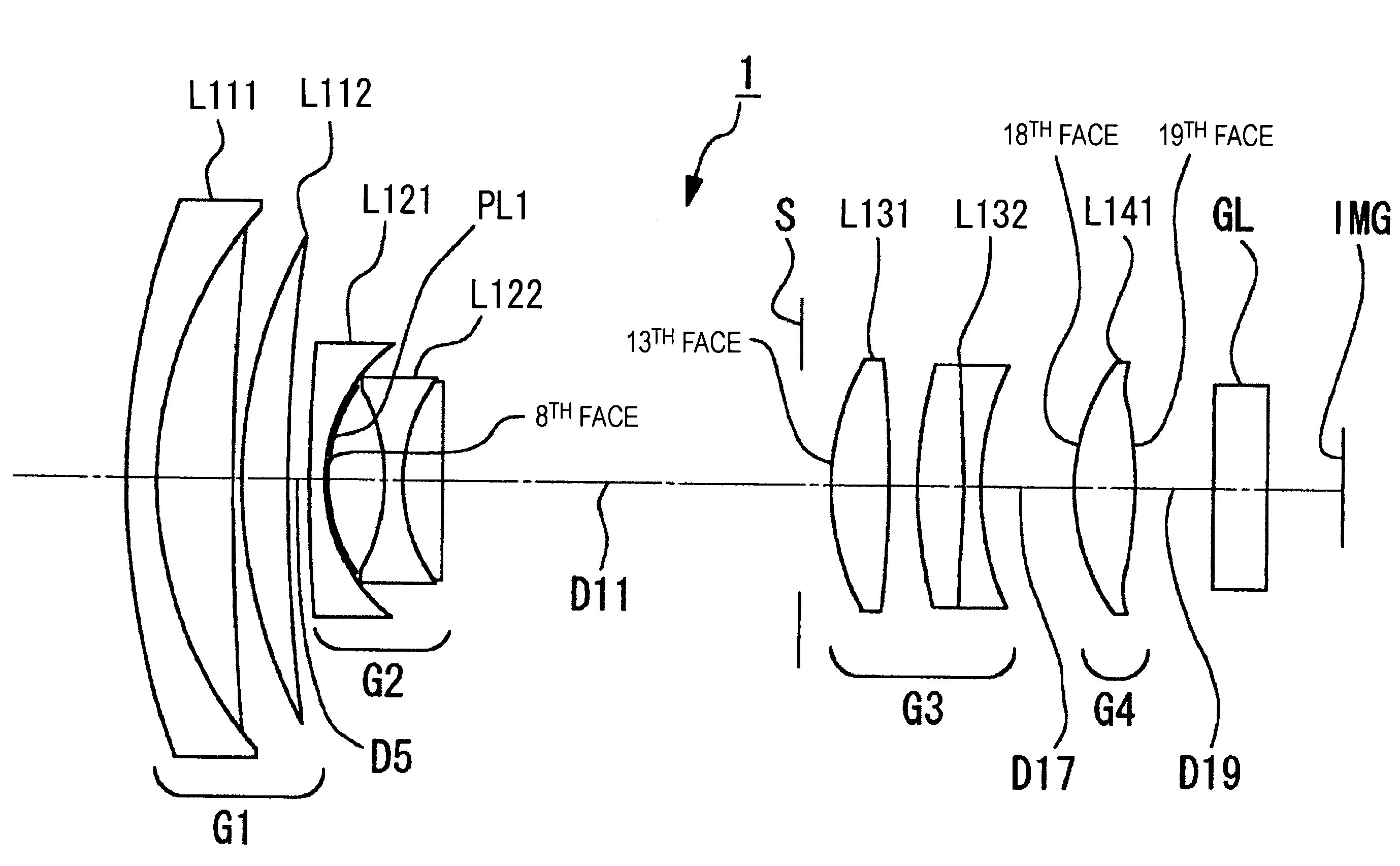
Wide angle lens
Owner:NING ALEX
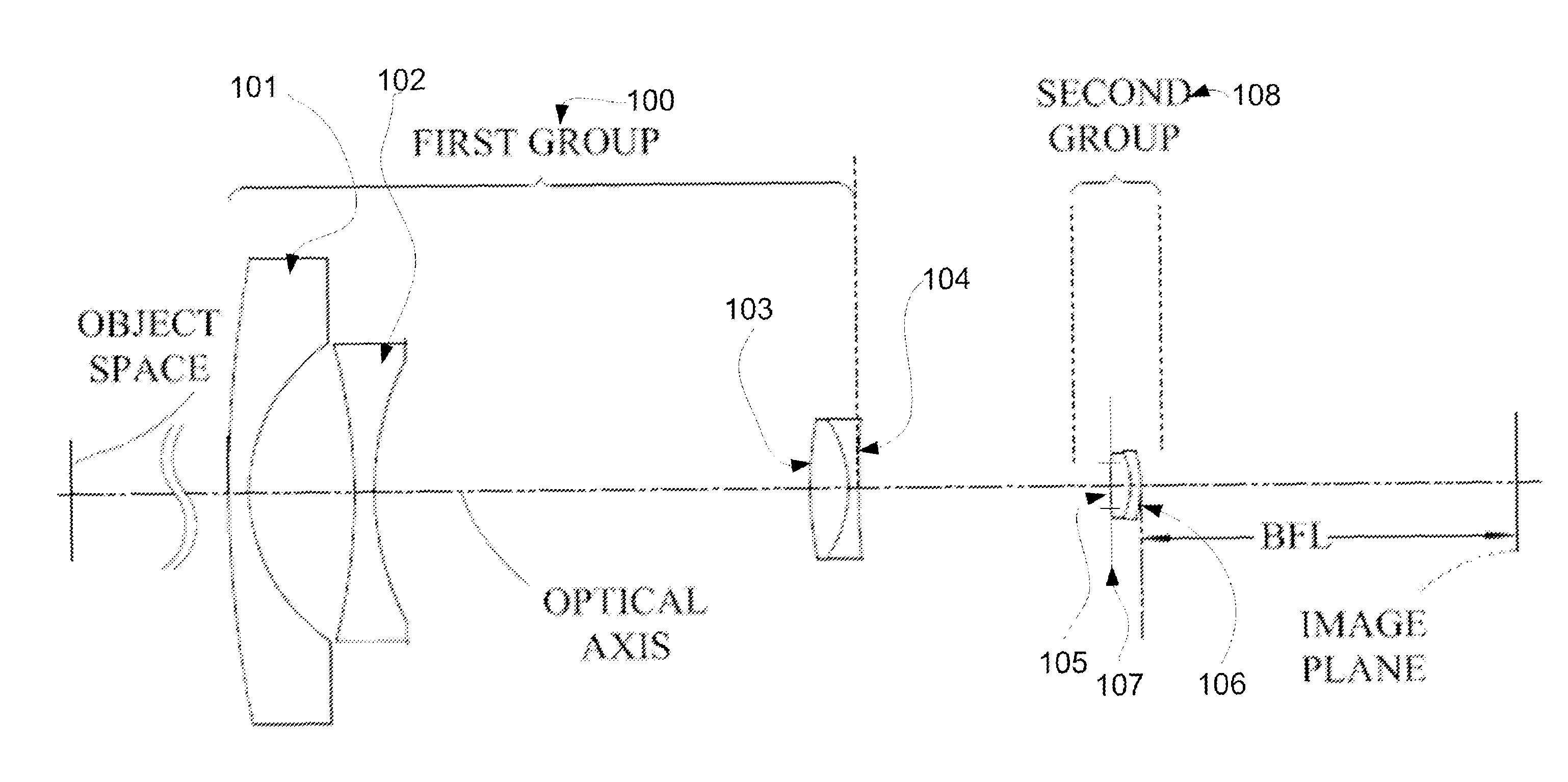
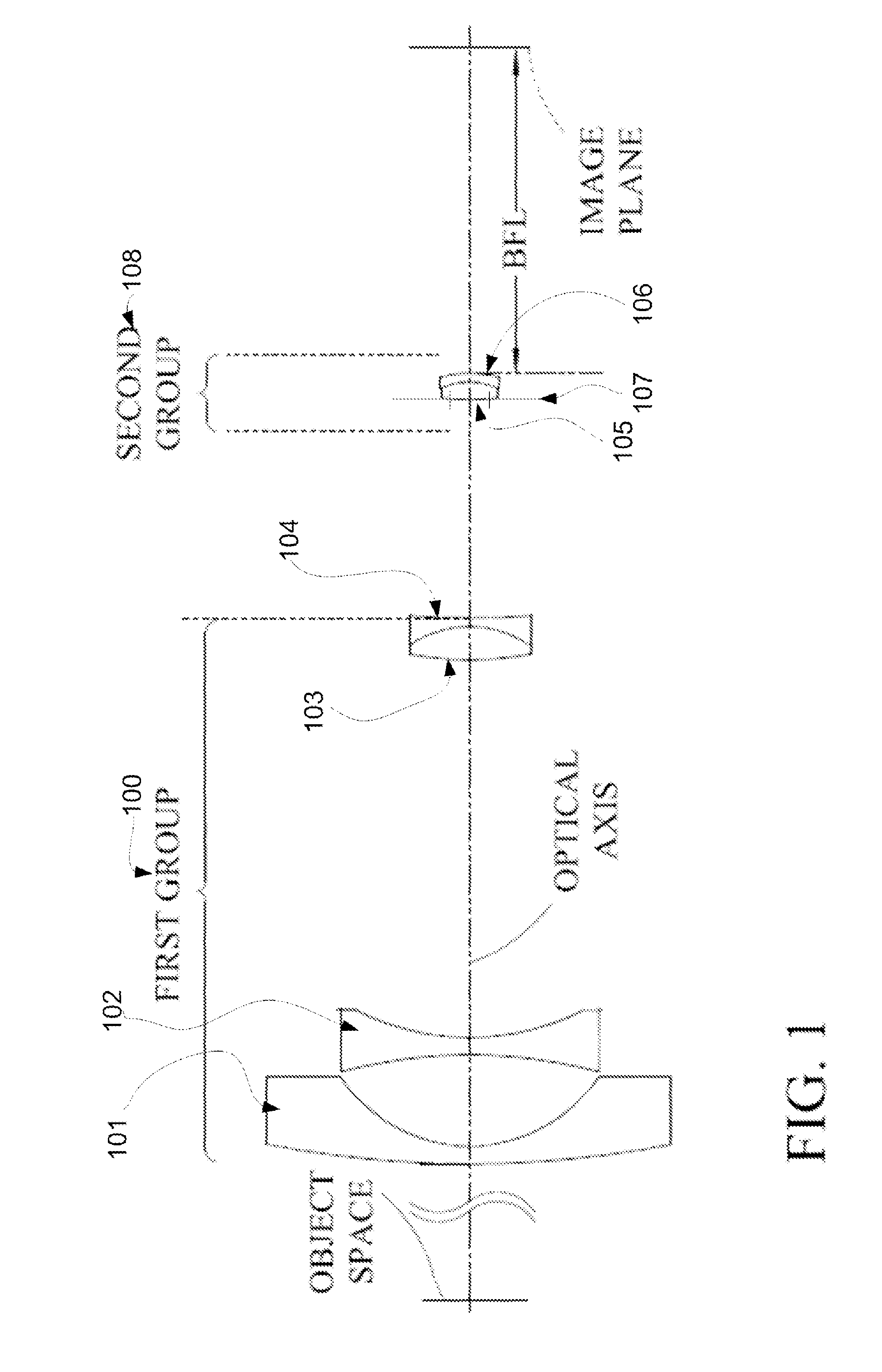
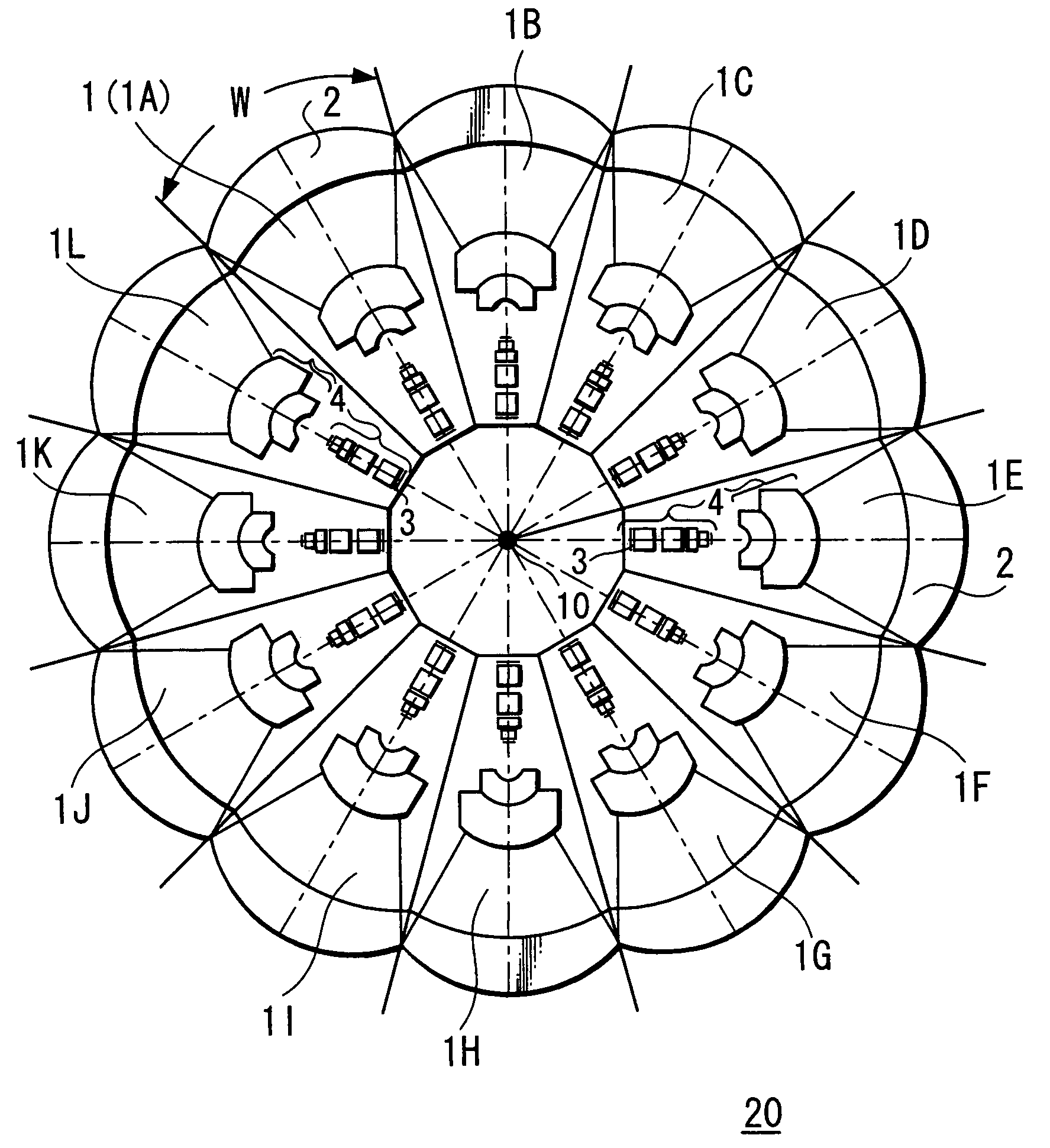
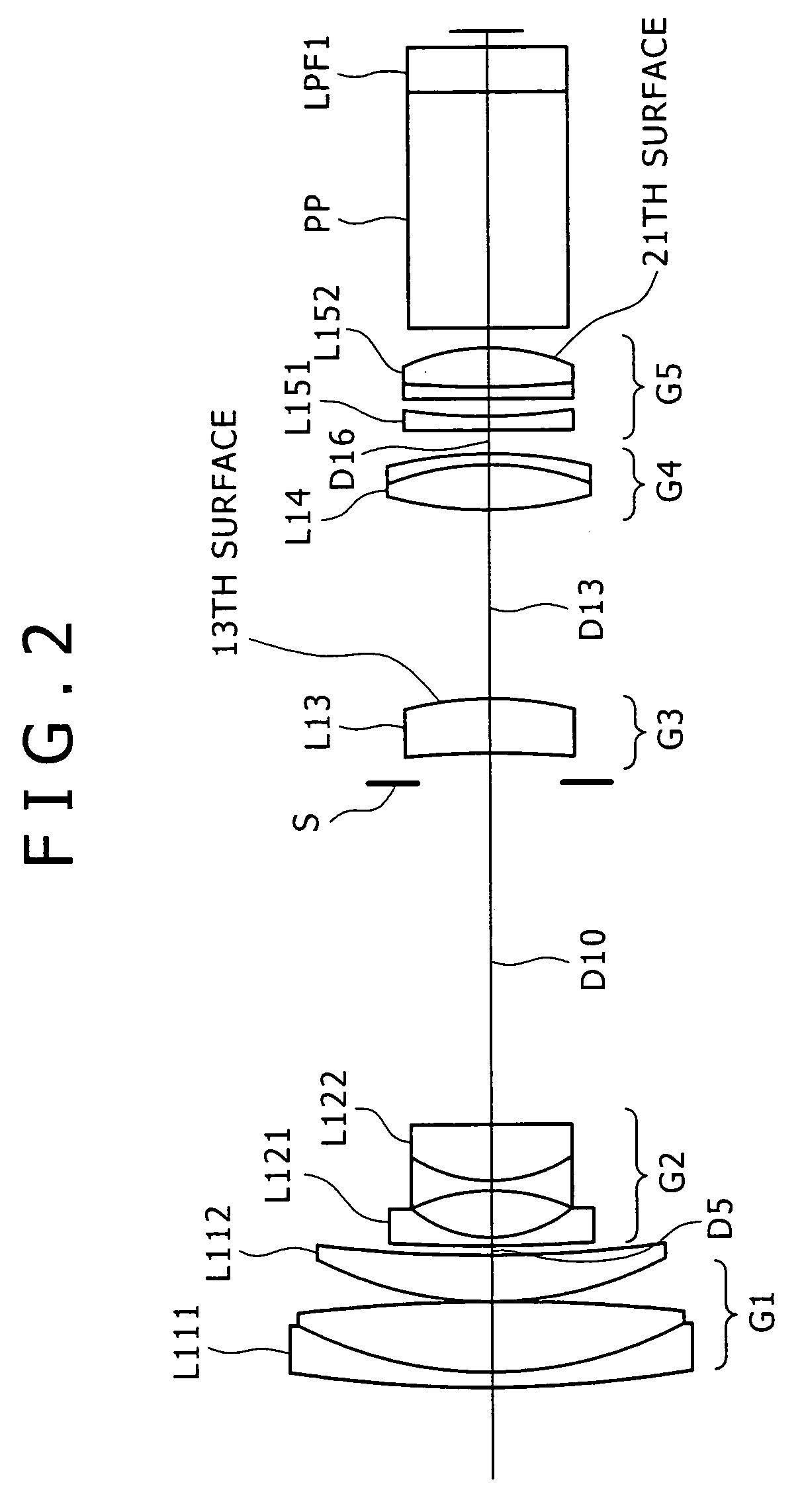
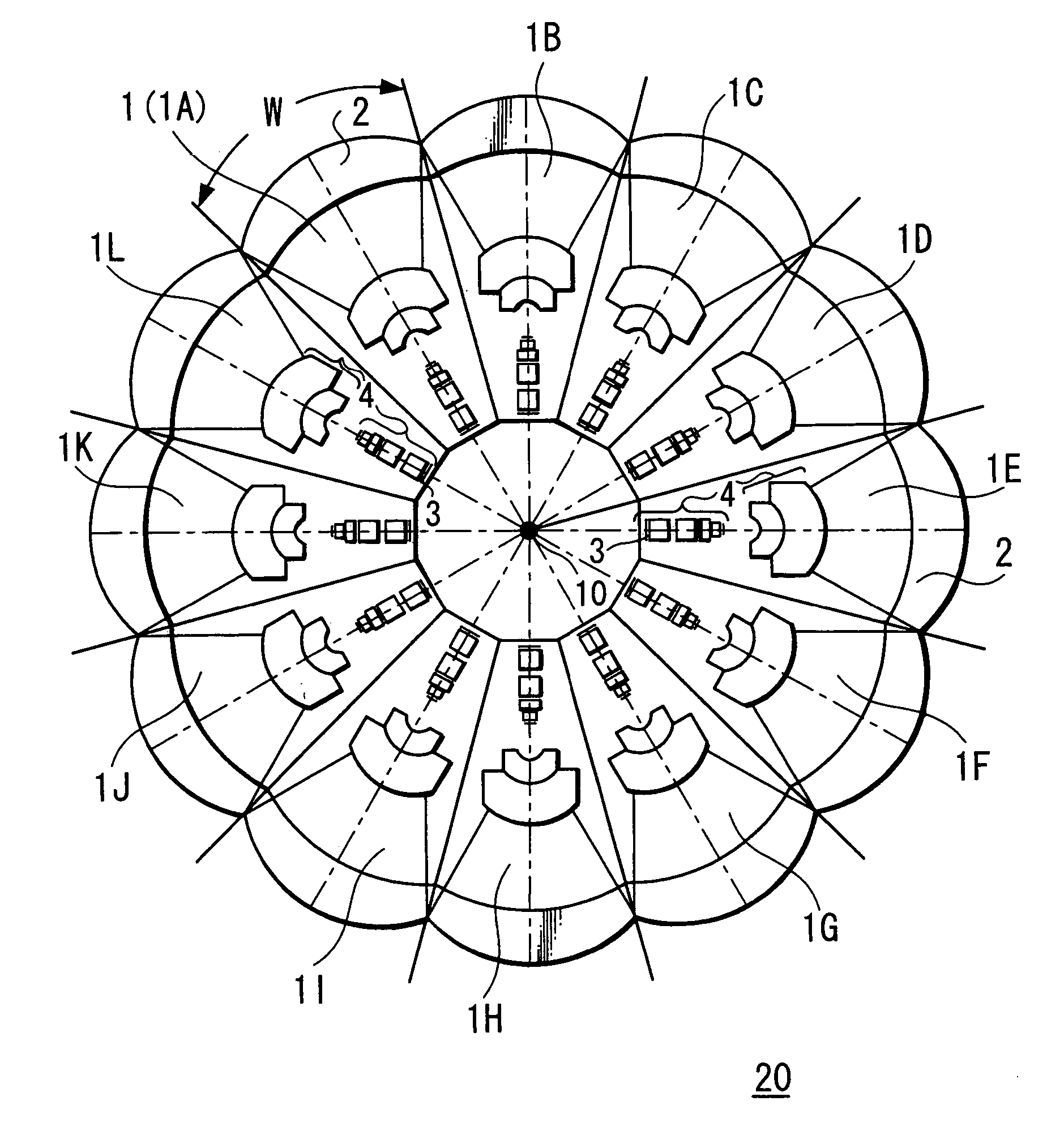
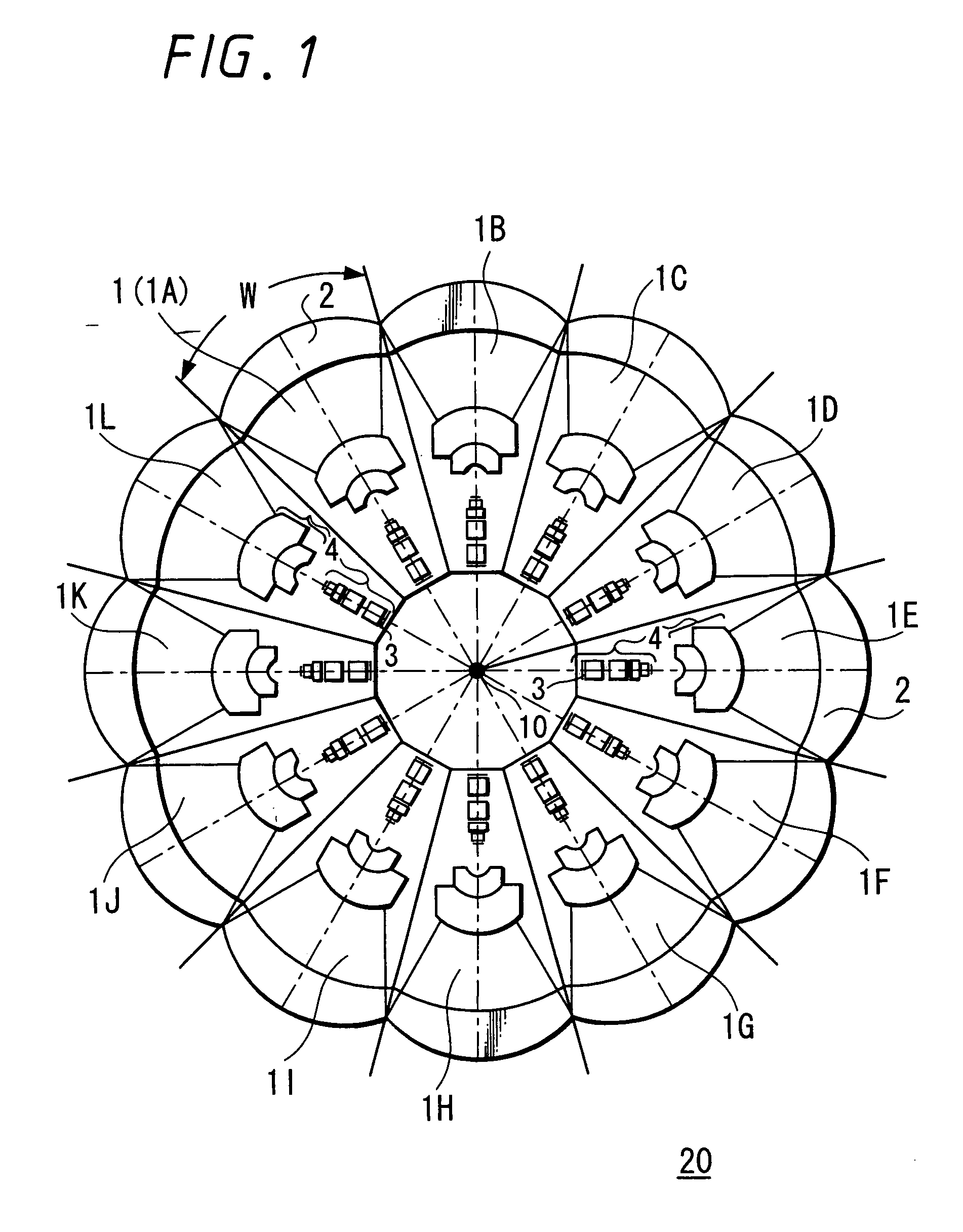
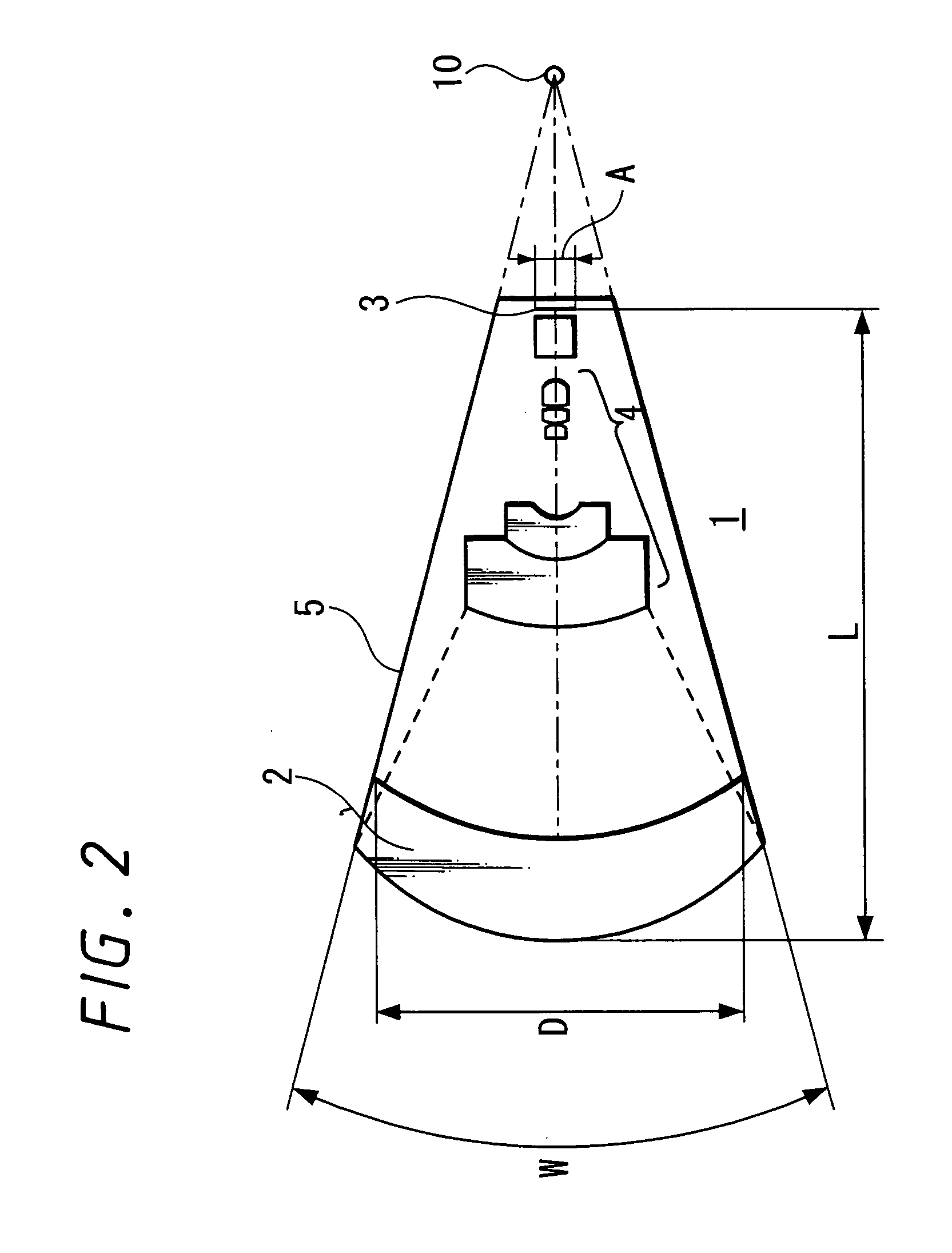
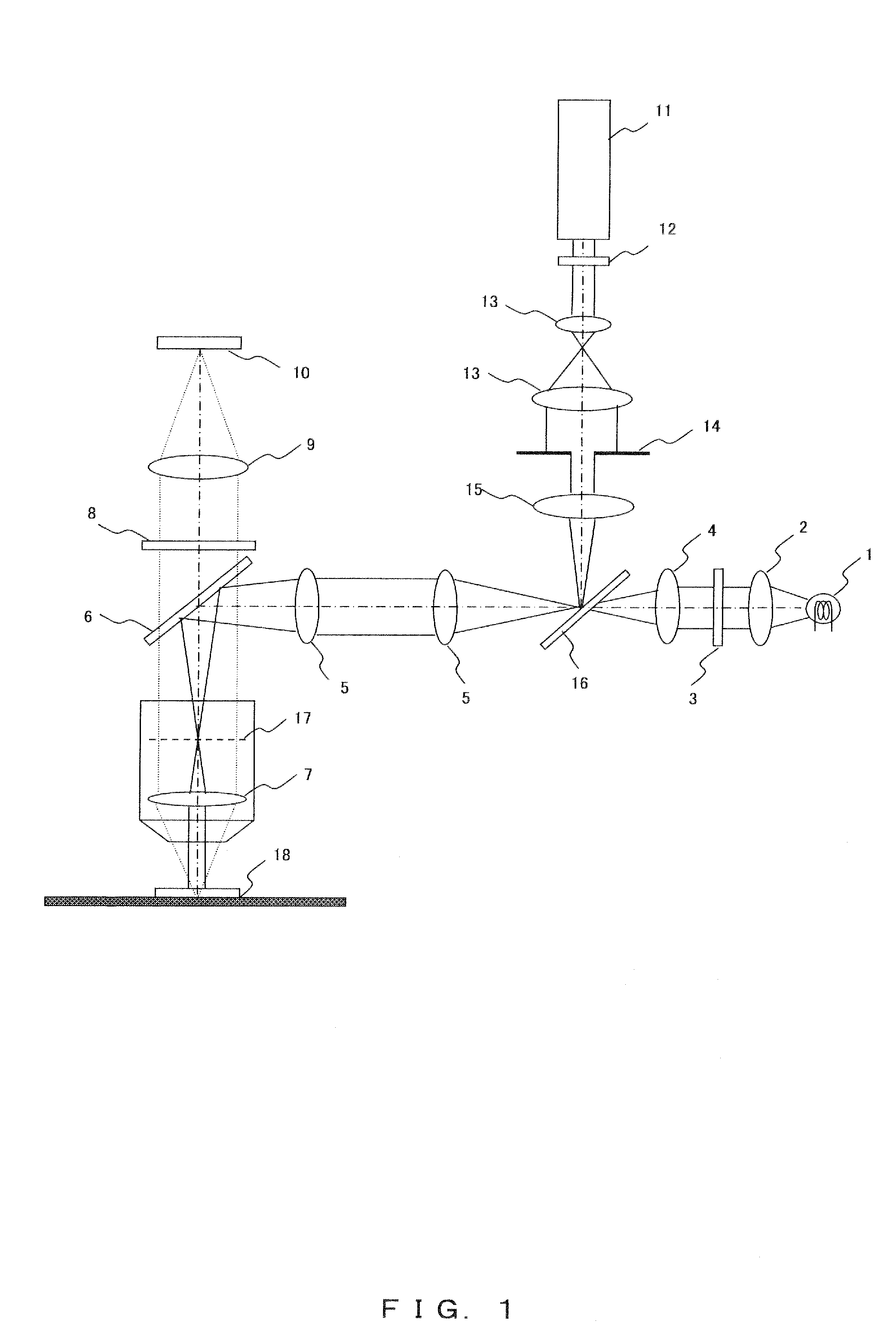
Imaging device
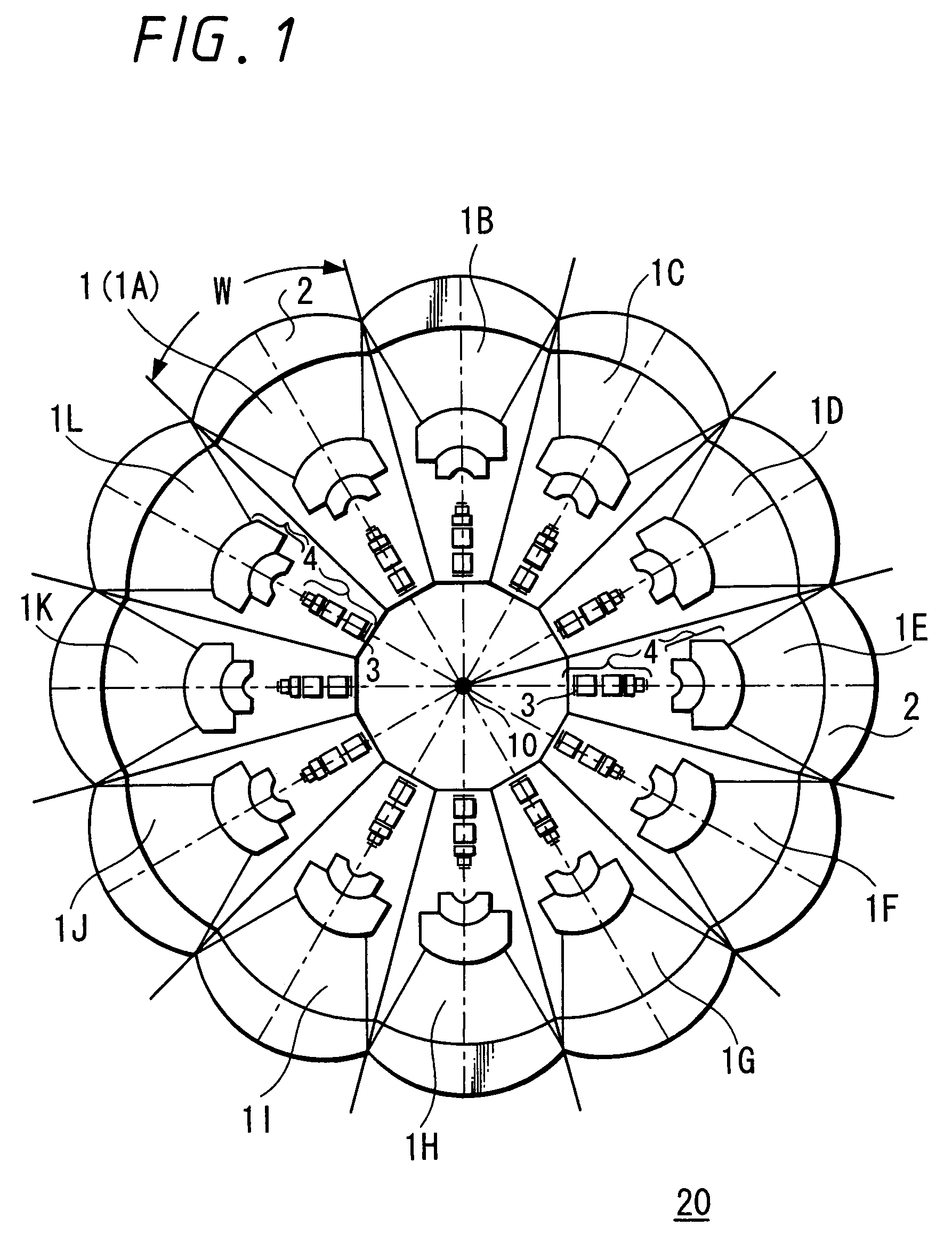
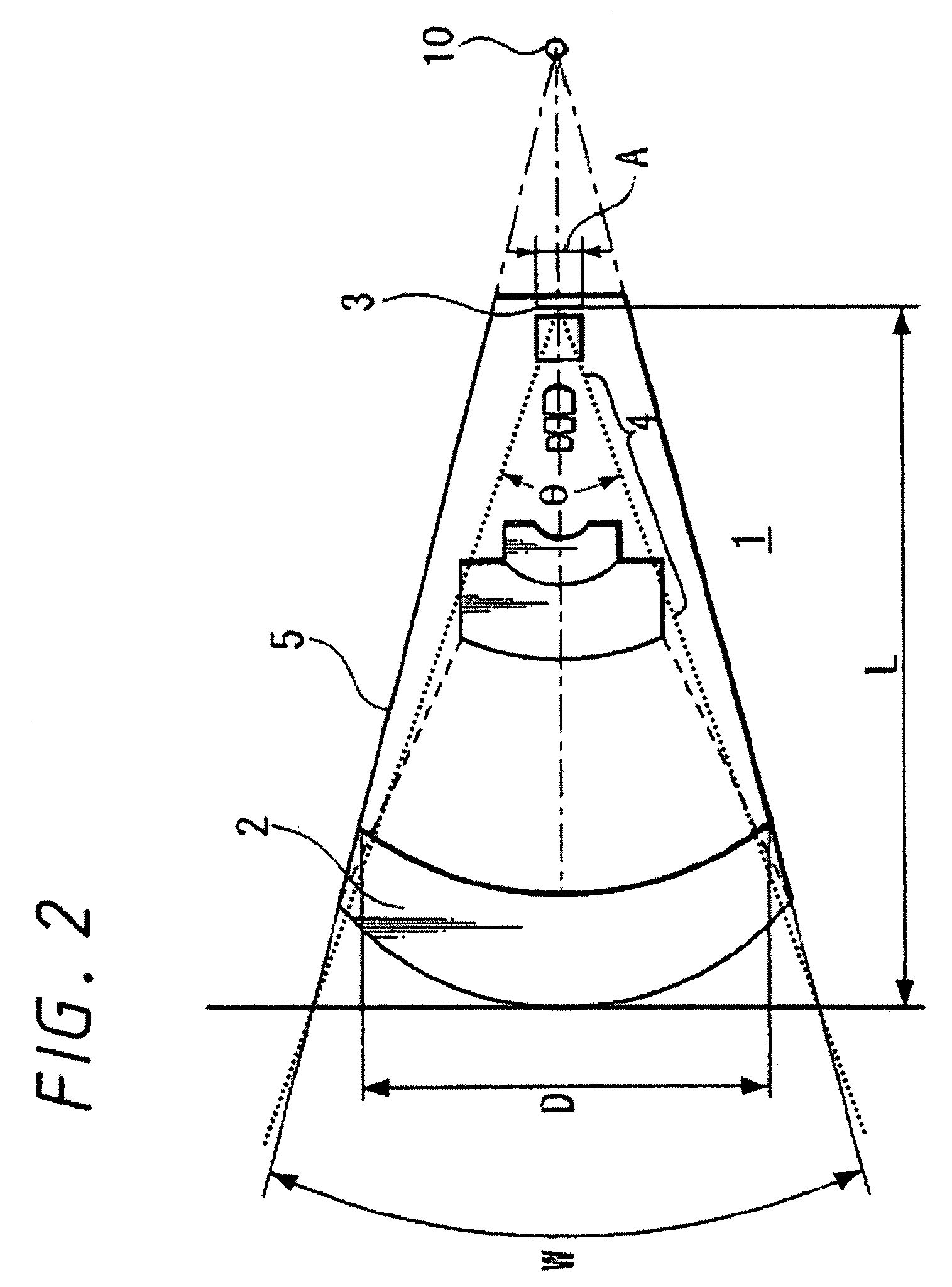
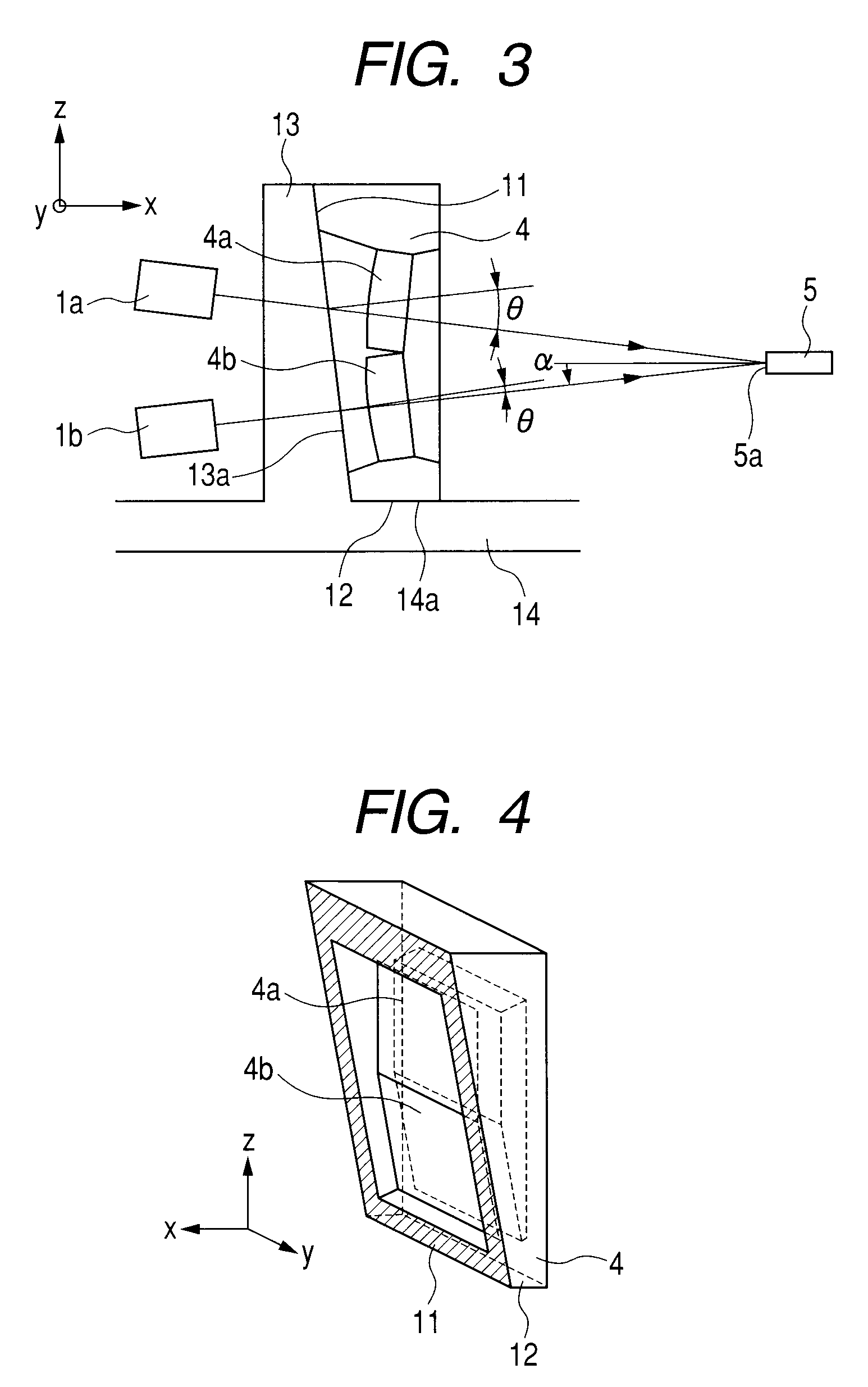
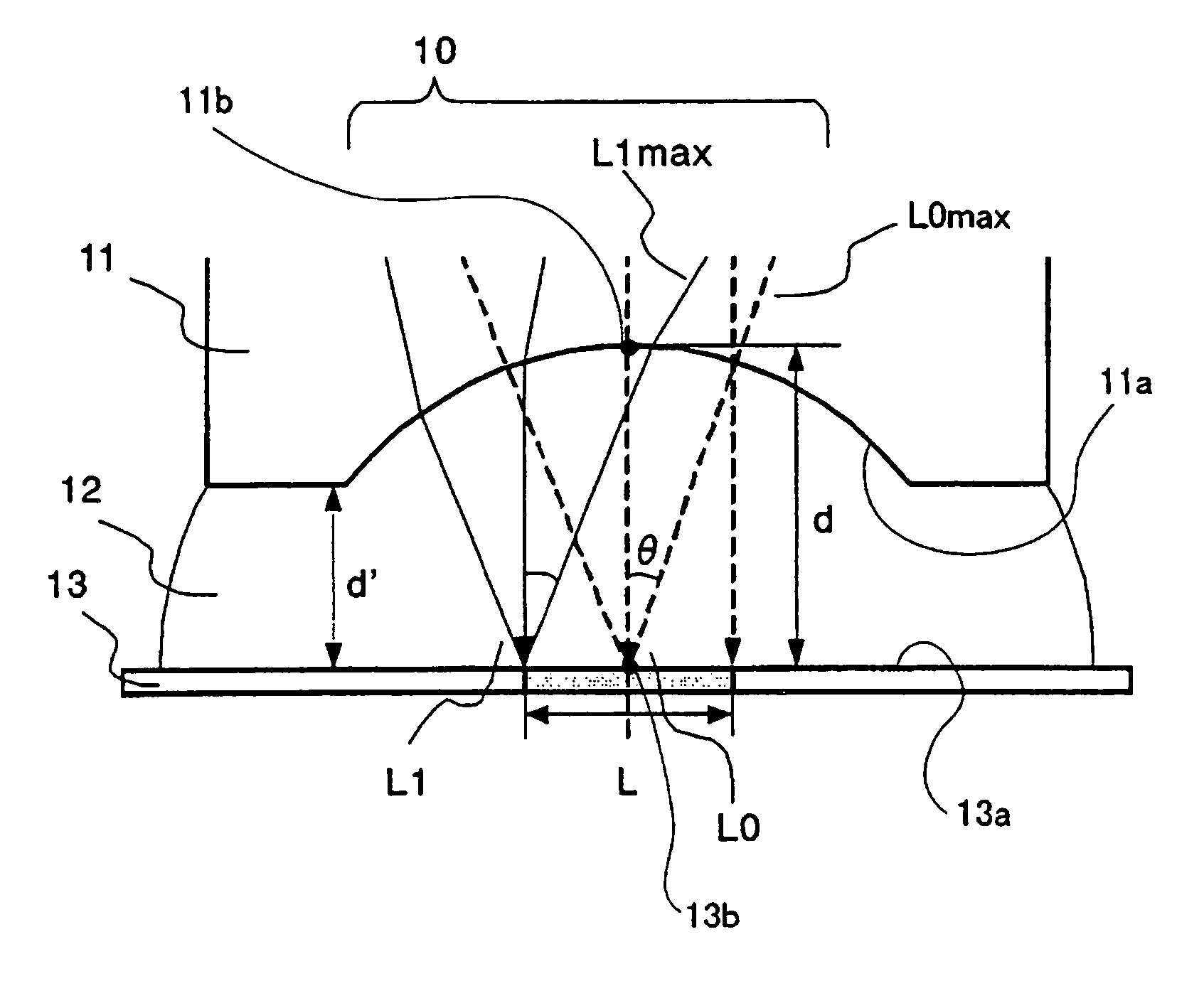
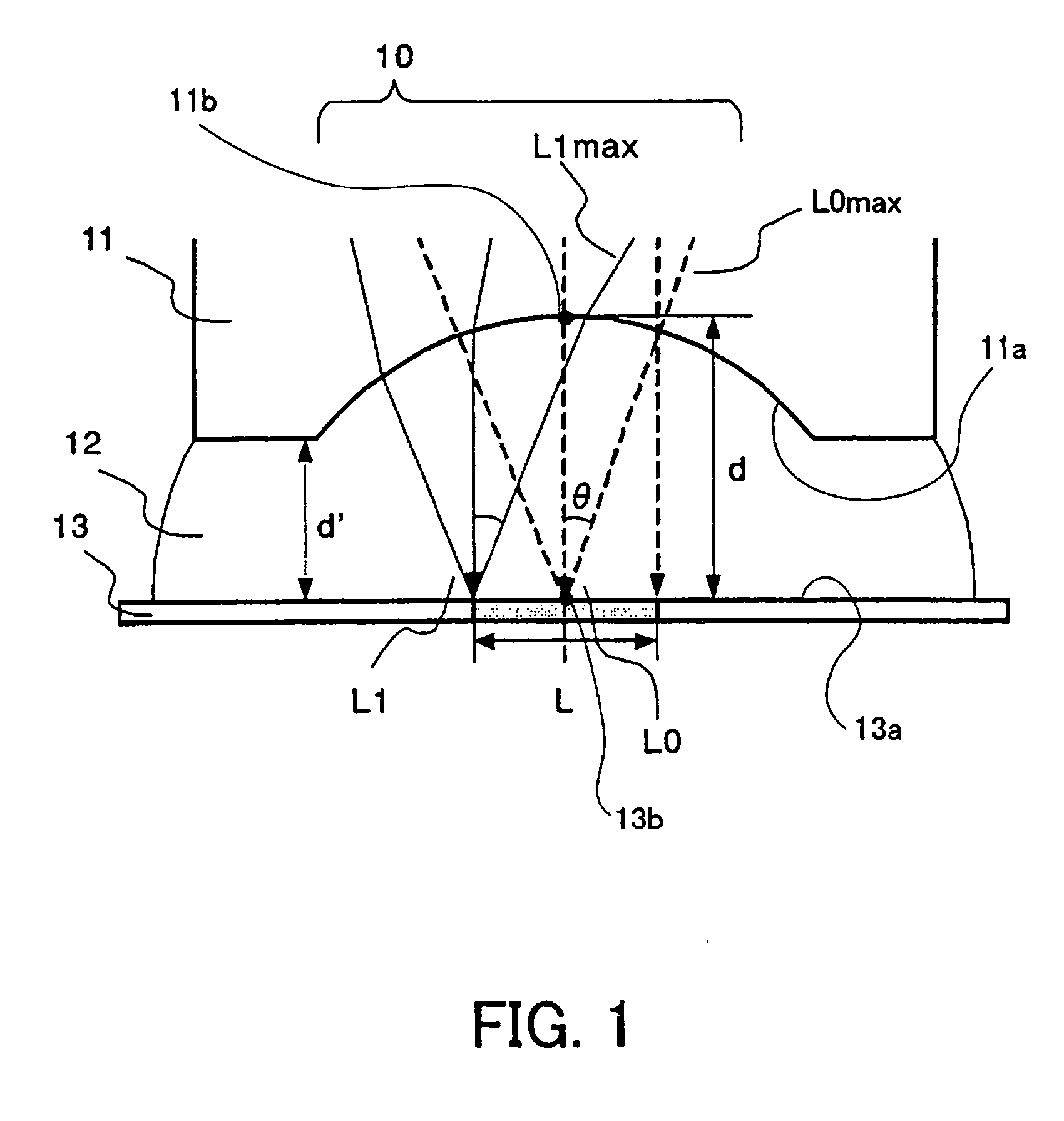
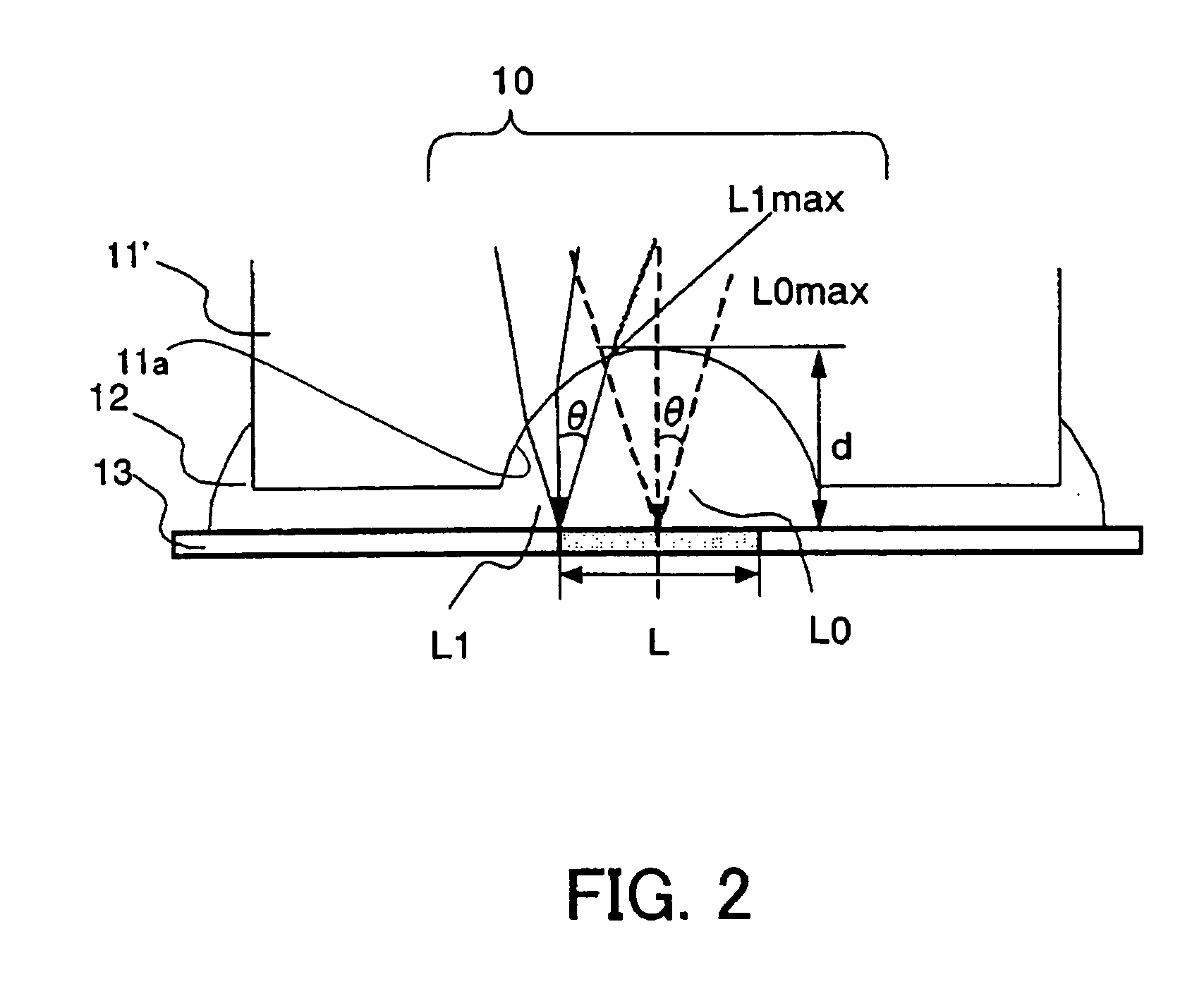
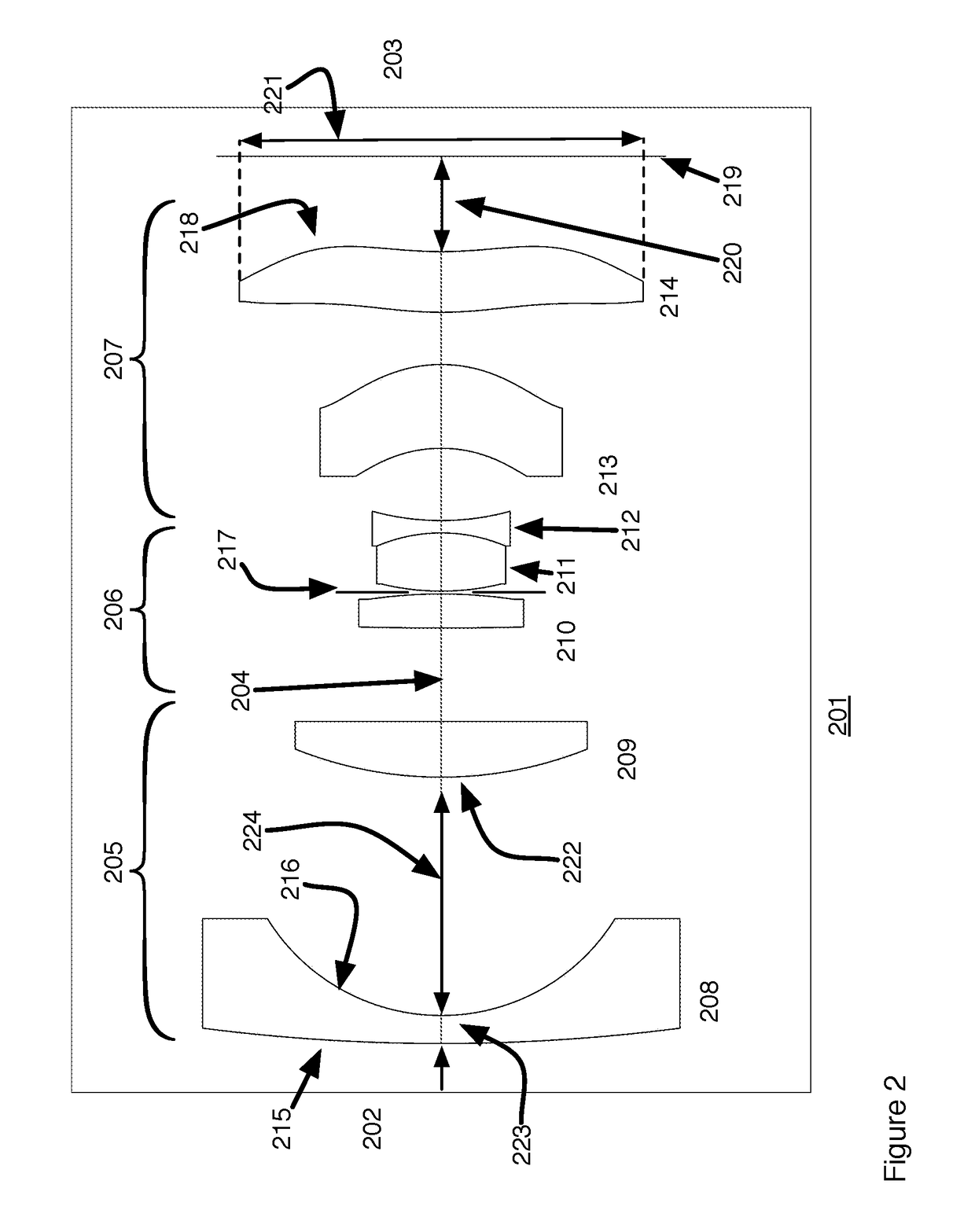
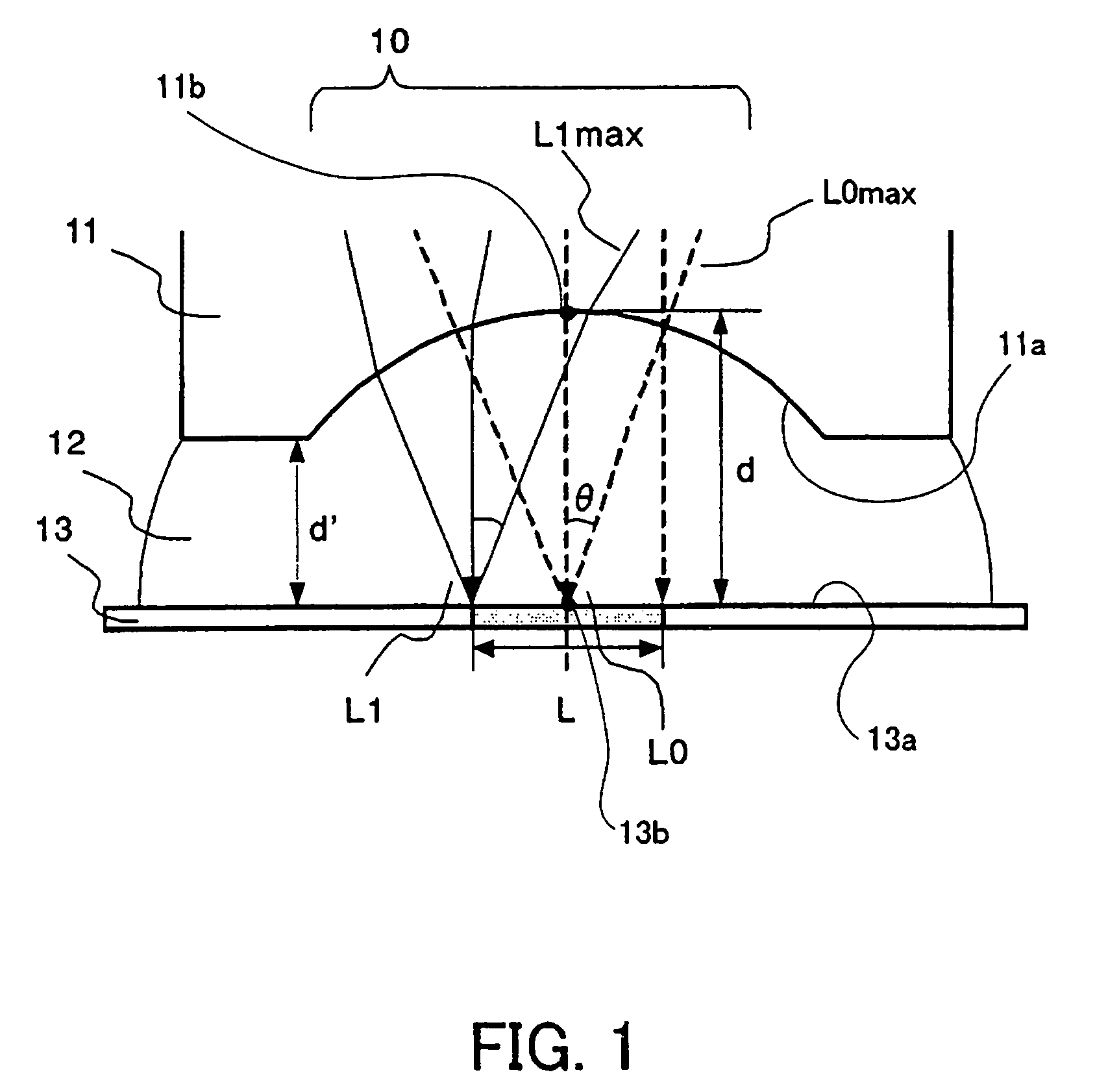
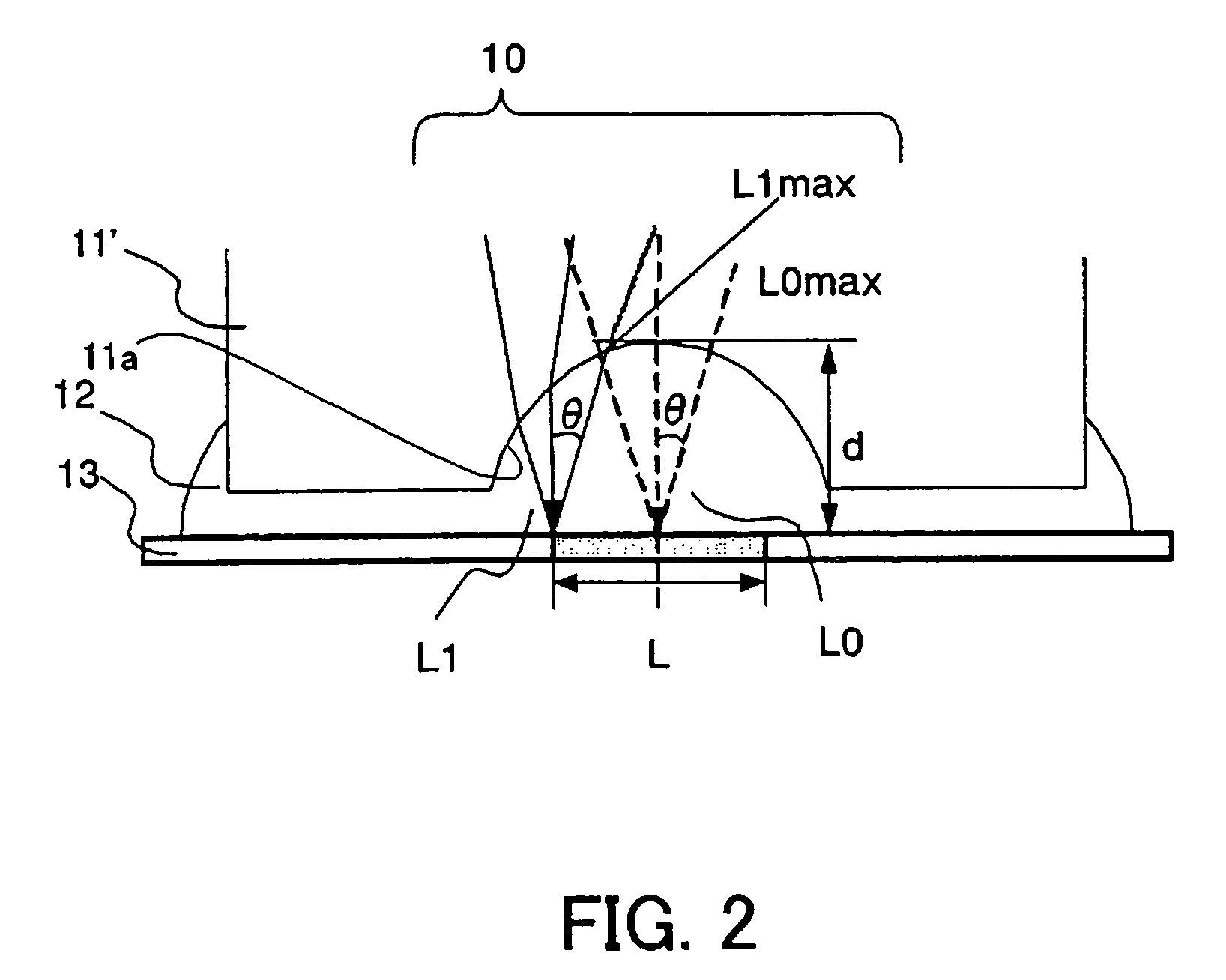
An image pickup apparatus is able to shoot an image of a wide range by a plurality of image pickup units, it is able to obtain excellent image quality and it can be miniaturized. An image pickup apparatus 20 comprises a plurality of image pickup units 1 including an image pickup device 3 and a front lens 2, the adjacent image pickup units 1 being located in such a manner that image pickup areas overlap each other and the image pickup units being located so as to satisfy a conditional equation AL<fD (1) where a cross-section passing a viewpoint center, an image pickup device 3 and a front lens 2 is created in the direction in which the image areas of the adjacent image pickup portions overlap with each other, a cross-section length of the image pickup device 3 is assumed to be A, a cross-section length of the front lens 2 is assumed to be D, a length from the front lens 2 to the image pickup device 3 is assumed to be L and a focal length which results from synthesizing the whole of the lenses within the image pickup unit 1 containing the front lens 2 is assumed to be f and that the viewpoint center of each image pickup unit 1 may lie within a sphere with a diameter of 20 mm.
Owner:SONY CORP
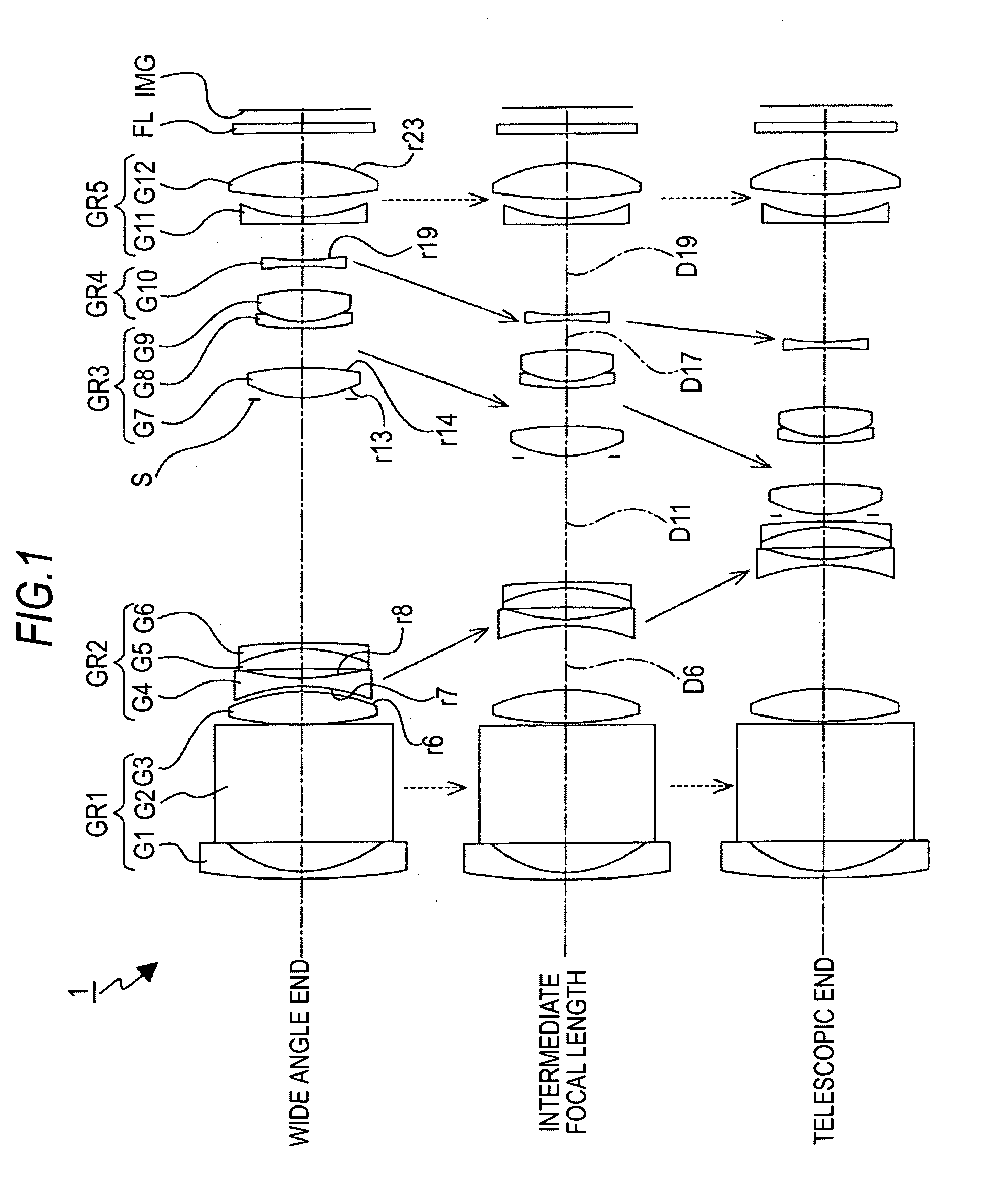
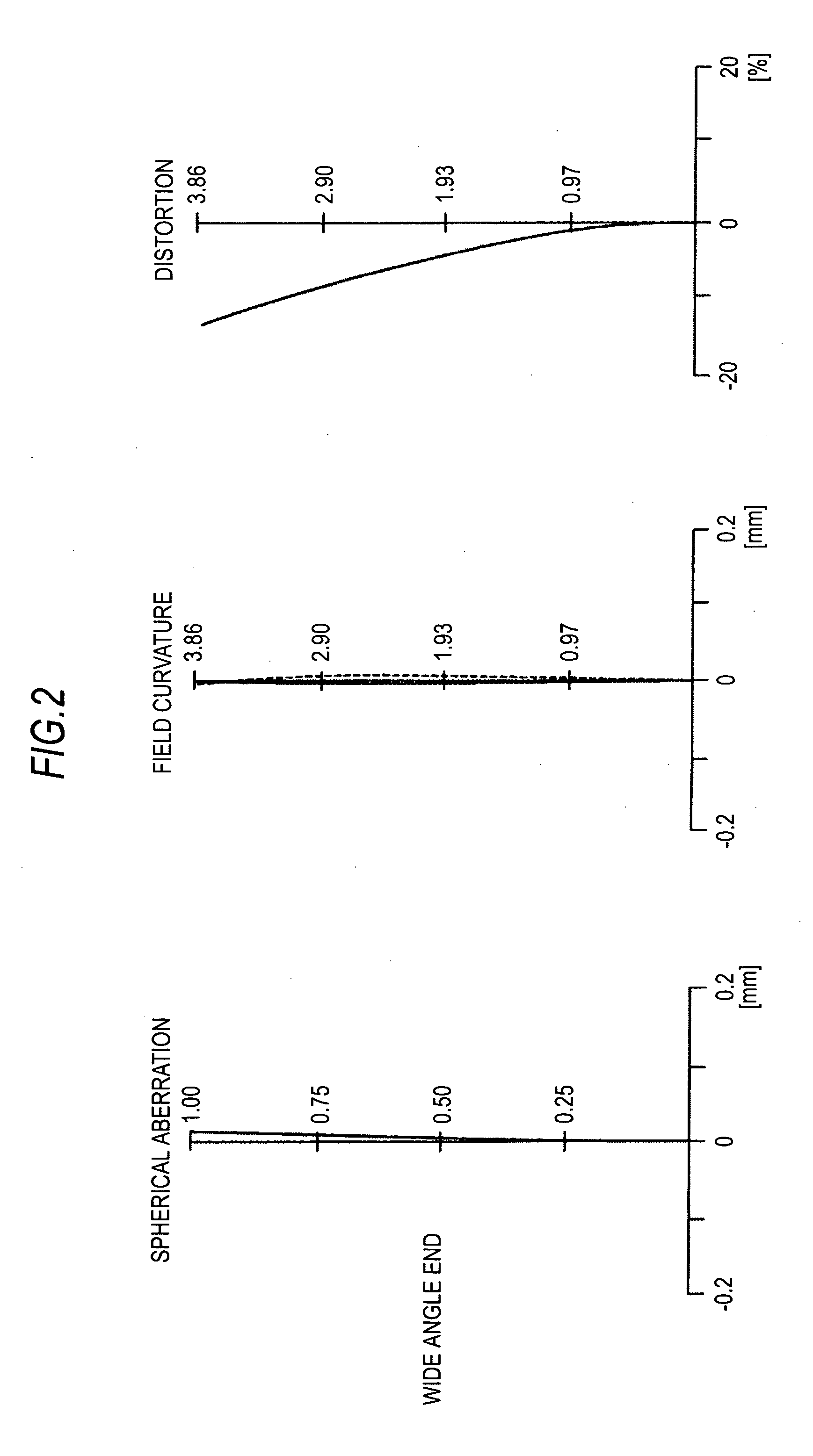
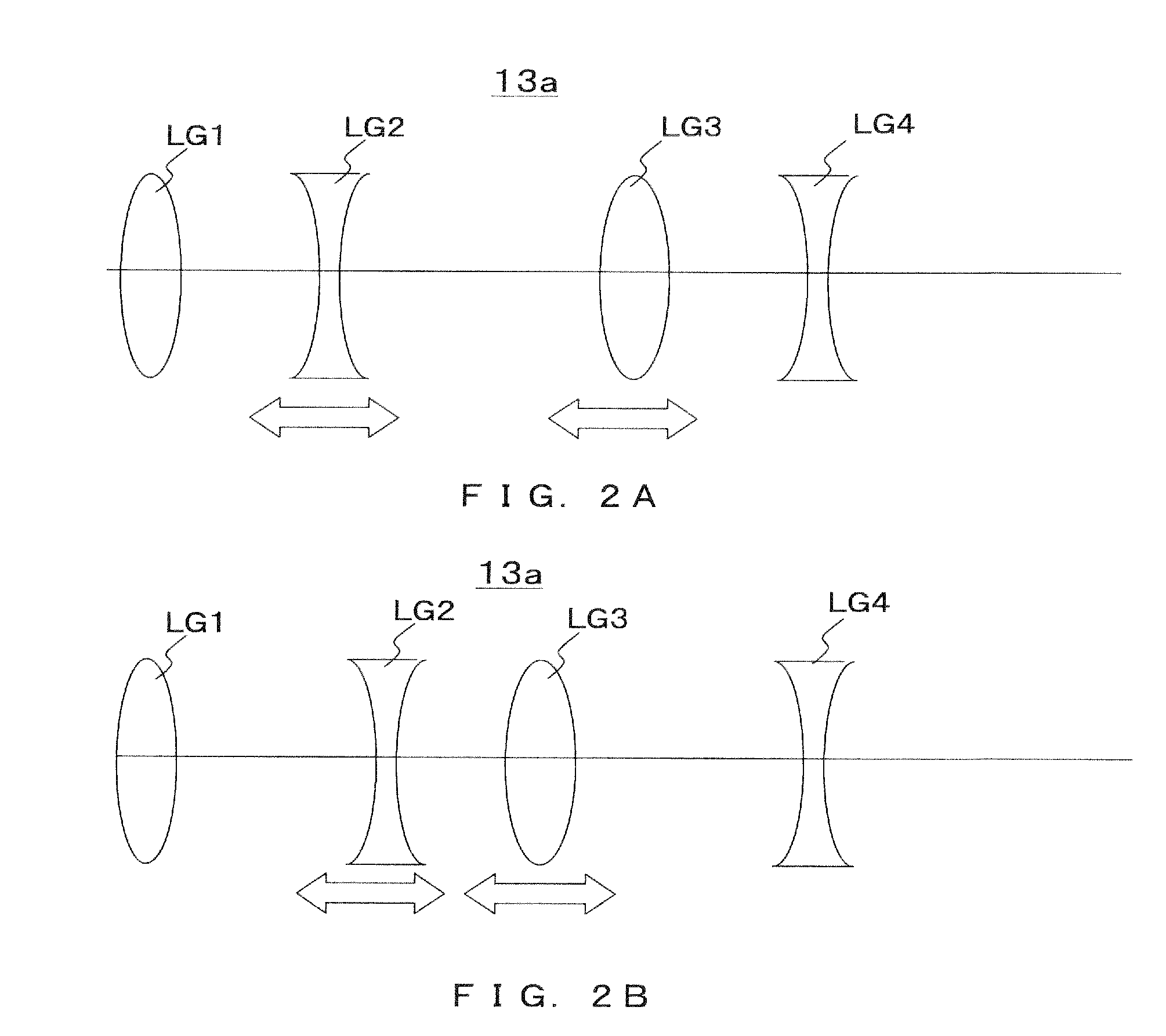
Zoom Lens and Imaging Apparatus
InactiveUS20080212184A1Good optical performanceVarious aberrationCamera body detailsLensCamera lensOptical axis
Provided are a zoom lens and an imaging apparatus using the zoom lens, the zoom lens being suited for achieving compactness without increasing the number of lenses and being capable of implementing motion blur compensation. The zoom lens includes lenses arranged in order from an object side into a first lens group having positive refractive power, a second lens group having negative refractive power, a third lens group having positive refractive power, a fourth lens group having positive refractive power, and a fifth lens group having positive refractive power. In the event of a shift of a lens position mode from a wide angle end mode to a telephoto end mode, the first lens group is fixed along an optical axis direction, the second lens group moves to an image side, the third lens group is fixed along the optical axis direction, the fourth lens group compensates for a fluctuation in an image plane position due to the shift of the second lens group, and concurrently moves along the optical axis direction in a close-distance focusing event, and the fifth lens group is fixed along the optical axis direction. An aperture diaphragm is disposed in the vicinity of the third lens group. The fifth lens group includes a negative sub lens group having negative refractive power and a positive sub lens group having a positive refractive power, wherein the image can be shifted in conjunction with a shift of the positive sub lens group in a direction substantially perpendicular to the optical axis. The zoom lens satisfies conditional equation (1) given as 0.6<f5p / Da<1.4, where f5p is a focal distance of the positive sub lens group disposed in the fifth lens group, and Da is a length extending along the optical axis to a paraxial image position from a most-imagewise surface of the positive sub lens group disposed in the fifth lens group.
Owner:SONY CORP
Imaging device
InactiveUS20060114332A1Television system detailsColor television detailsImaging qualityImaging equipment
An image pickup apparatus is able to shoot an image of a wide range by a plurality of image pickup units, it is able to obtain excellent image quality and it can be miniaturized. An image pickup apparatus 20 comprises a plurality of image pickup units 1 including an image pickup device 3 and a front lens 2, the adjacent image pickup units 1 being located in such a manner that image pickup areas overlap each other and the image pickup units being located so as to satisfy a conditional equation AL<fD (1) where a cross-section passing a viewpoint center, an image pickup device 3 and a front lens 2 is created in the direction in which the image areas of the adjacent image pickup portions overlap with each other, a cross-section length of the image pickup device 3 is assumed to be A, a cross-section length of the front lens 2 is assumed to be D, a length from the front lens 2 to the image pickup device 3 is assumed to be L and a focal length which results from synthesizing the whole of the lenses within the image pickup unit 1 containing the front lens 2 is assumed to be f and that the viewpoint center of each image pickup unit 1 may lie within a sphere with a diameter of 20 mm.
Owner:SONY CORP
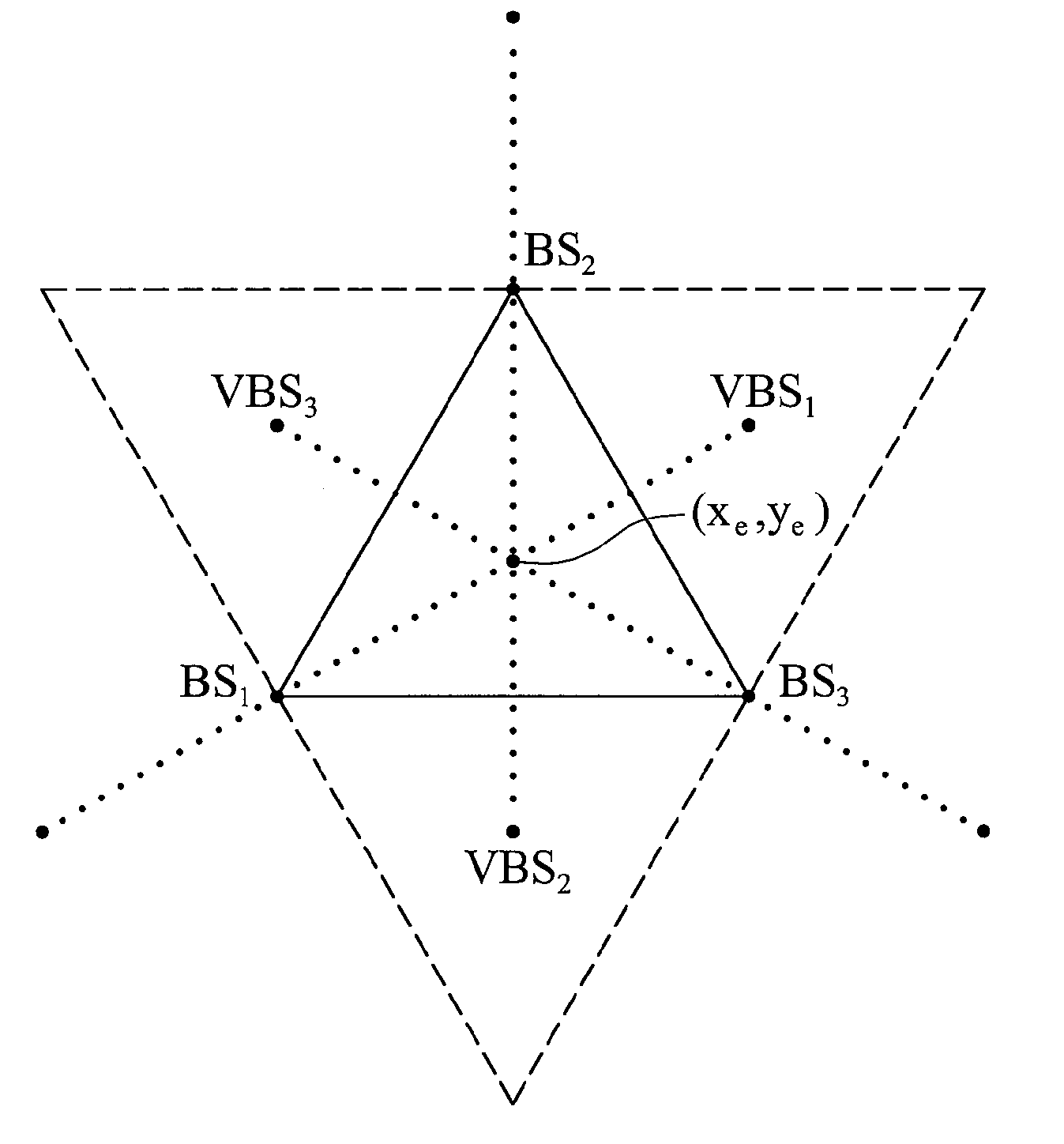
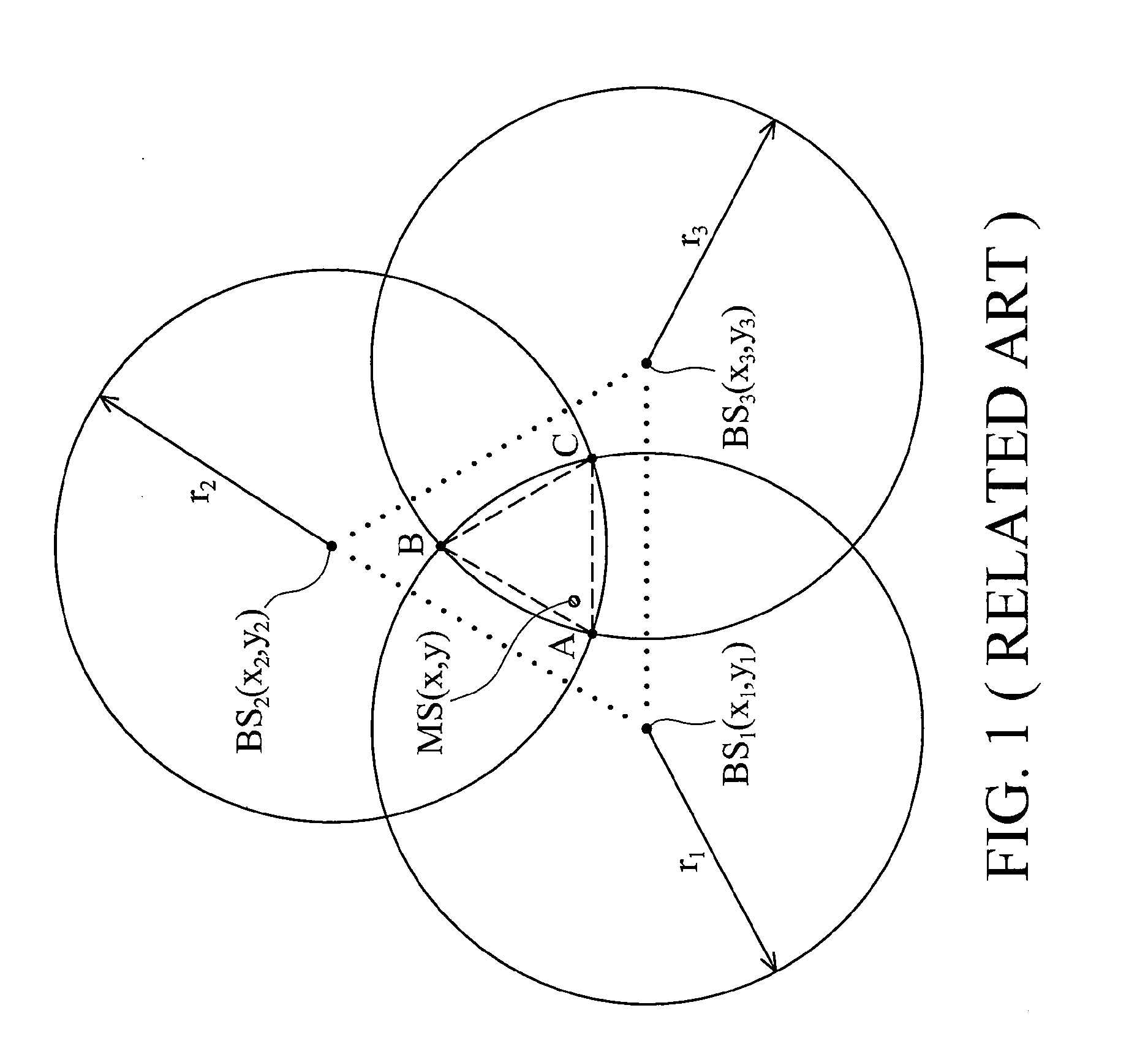
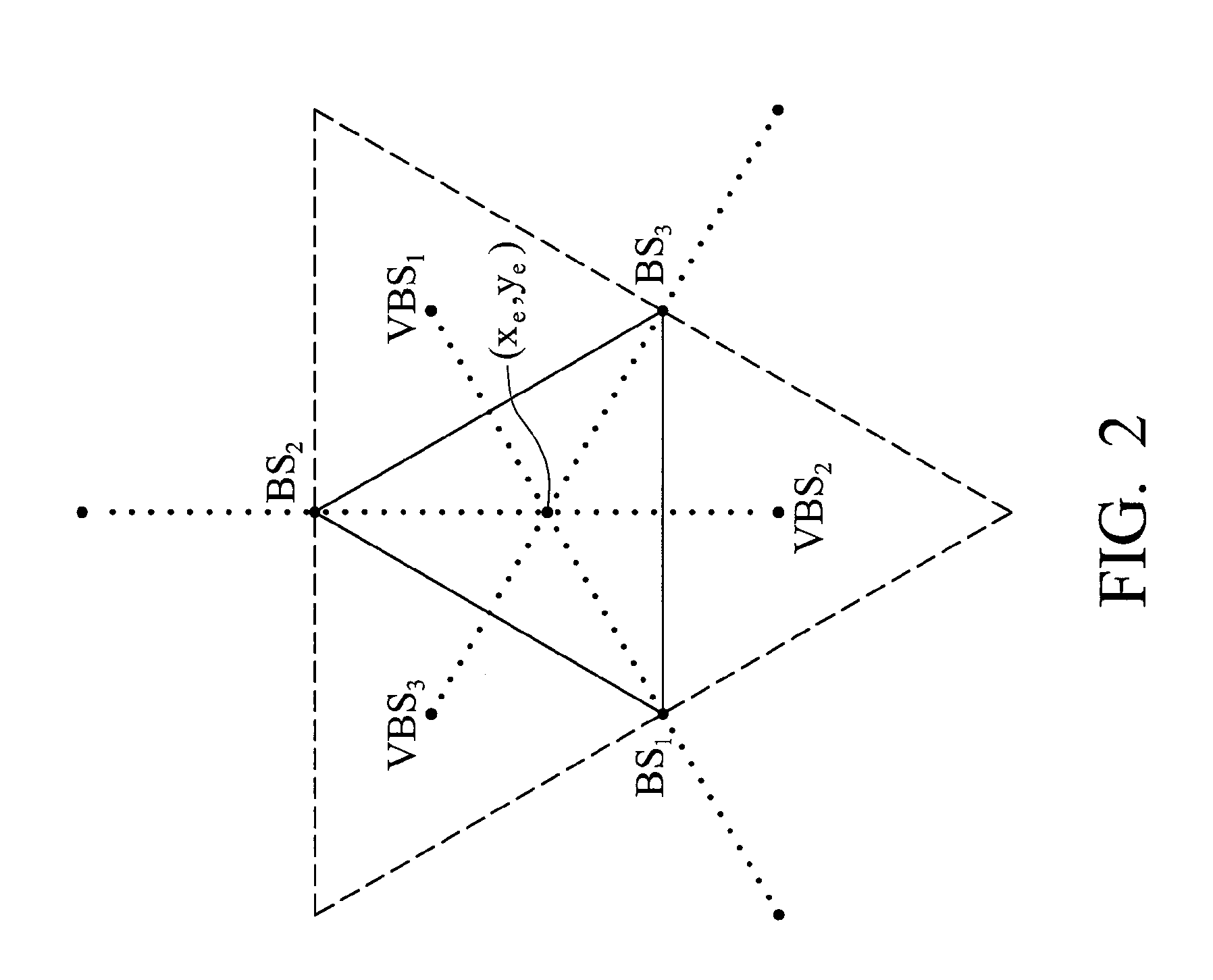
Location estimation method
InactiveUS20070161381A1Telephonic communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsConditional equationEstimation methods
A location estimation method is provided. The method locates coordinates of a mobile station (MS) by referencing a plurality of base stations (BS). A geometric distribution of the BS is analyzed to provide a list of conditional equations. A virtual BS is allocated, having a virtual distance to the MS to provide a constraint equation. The MS location is derived from the conditional equations and the constraint equation.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Liquid droplet ejecting apparatus and liquid droplet ejecting method
A liquid droplet ejecting apparatus having: a liquid droplet ejecting head; and a drive pulse generating unit, wherein the head includes: a nozzle; a pressure chamber which communicates with the nozzle; and a pressure applying section which changes a pressure in the pressure chamber, wherein the generated drive pulse is applied to the pressure applying section so as to change the pressure in the pressure chamber to cause the liquid in the pressure chamber to be ejected from the nozzle, and wherein the drive pulse comprises a rectangular expansion pulse which causes expansion and then contraction of the volume of the pressure chamber and in which the pulse width PW of the expanding pulse is set so as to satisfy the following conditional equation,PW=π-(tan-112πfτ)2πf(1)where f represents an acoustic resonance frequency of a pressure wave in the pressure chamber and τ represents a damping time constant of the pressure wave.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Projection optical system
ActiveUS20100118281A1Increase in sizeShorten the projection distanceProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementProjection opticsMinimum time
A projection optical system satisfies the following conditional equation: 0.01<{(tan θ f1−tan θ f2)−(tan θ n1−tan θ n2)}·(β2 / β1)<0.20. If, however, the normal line and longer side directions of a screen surface are z and x directions, respectively, an incident angle component on an xz-plane with respect to the screen surface is an incident angle θ, the larger incident angle θ of a light ray in light rays incident on respective edges of the upper and lower sides of the screen through the center of a stop is θ; f while the smaller incident angle θ of the light ray is θ n; θ f1 and θ f2: the maximum and minimum incident angles θ f at the maximum and minimum projecting magnification absolute values at a focus adjustment time, respectively, θ n1 and θ n2: the maximum and minimum incident angles θ n at the maximum and minimum projecting magnification absolute values at the focus adjustment time, respectively, and β1 and β2: the maximum and minimum incident magnifications at the maximum and minimum projecting magnification values at the focus adjustment time (if the magnification is negative, the magnification value is that at the absolute maximum or minimum time), respectively.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Array antenna, tag communication device, tag communication system, and beam control method for array antenna
ActiveUS20100295729A1Reduce decreaseReducing the grating lobe and the side lobeSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCommunications systemSide lobe
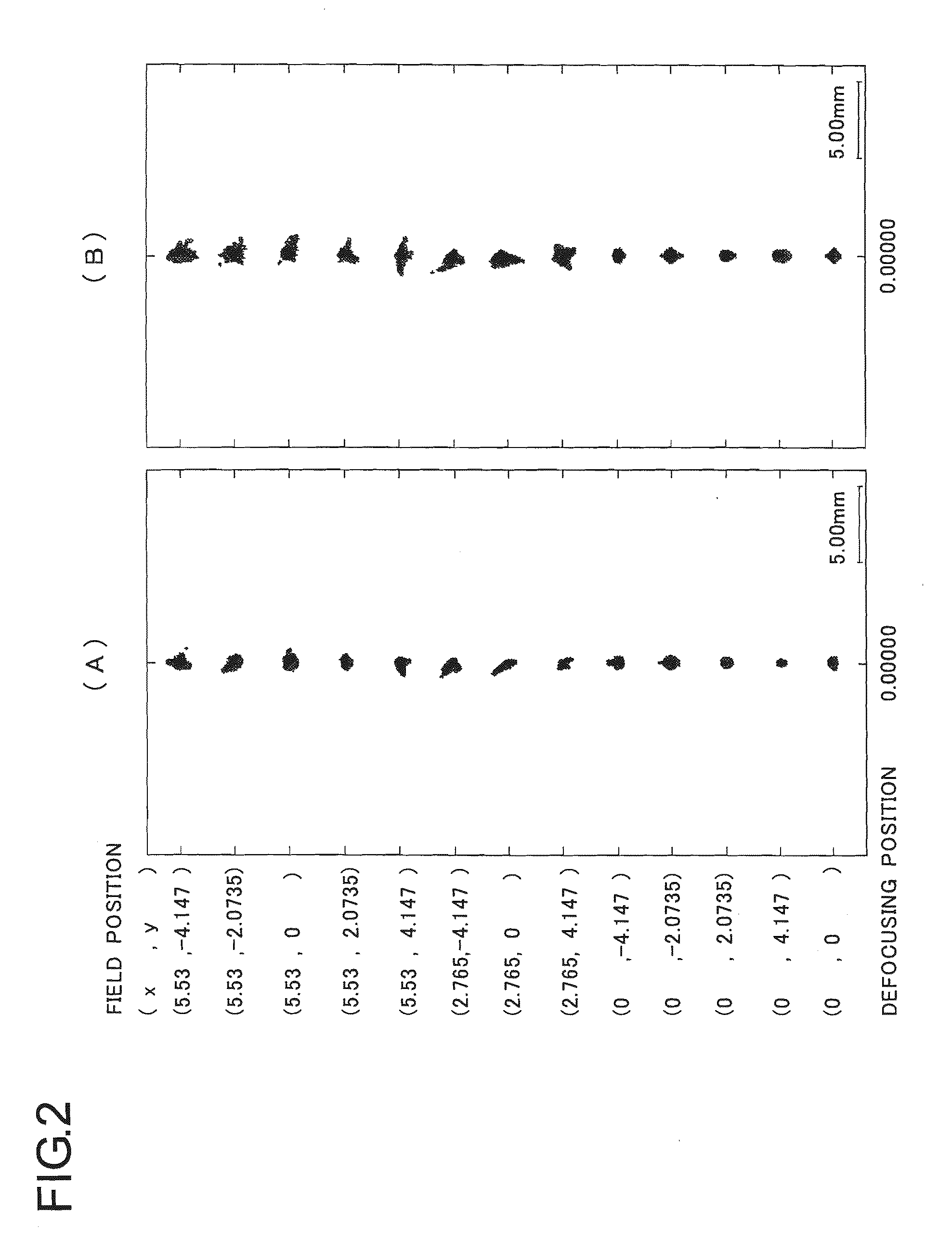
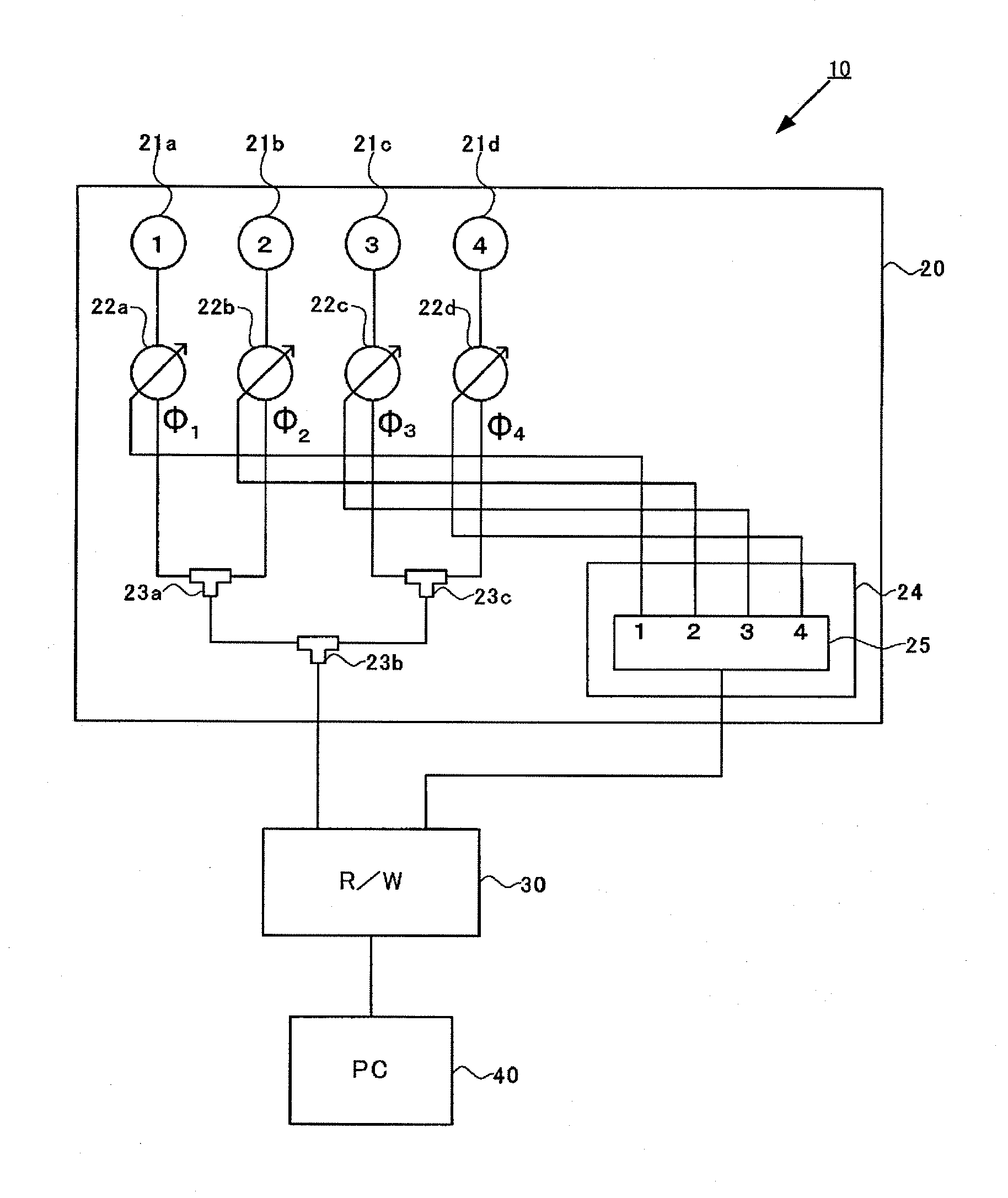
Provided are an array antenna capable of miniaturizing an array antenna while reducing side lobes, a tag communication device and tag communication system provided with the array antenna, and a beam control method for the array antenna. When XY coordinates and a feeding phase of each antenna element (21a to 21d) are defined as the antenna element (21a) (0, Y1)·φ1, the antenna element (21b) (−X1, 0)·φ2, the antenna element (21c) (X2, 0)·φ3, the antenna element (21d) (0, −Y2)·φ4, wavelengths of λ, and directivity directions of θ, each of the feeding phases is set so that the following conditional equations φ1=φ4, φ2=2π·X1·sin(θ) / λ+φ1, φ3=φ1−2π·X2·sin(θ) / λ are all satisfied.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Scanning optical apparatus and image forming apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20100119258A1Image stabilizationImprove image qualityElectrographic process apparatusOptical elementsOptical axisLight flux
A scanning optical apparatus includes: an incident optical system which is disposed in an optical path between a light source unit and a deflection unit, and includes an optical element for making a light flux emitted from the light source unit enter a deflection surface of the deflection unit with an oblique angle in a sub scanning section; and a positional regulation member for holding the optical element having an x reference surface for performing positional regulation of the optical element in an optical axis direction and a z reference surface for performing positional regulation of the optical element in a sub scanning direction. The optical element is held by a casing so that the x reference surface and the z reference surface contact with the positional regulation member of the casing. The principal ray of the light flux outgoing from the optical element satisfies a conditional equation (1).
Owner:CANON KK
Big relative aperture long-focus image space telecentric zoom lens
InactiveCN101639569AImprove light energy utilizationHigh zoom ratioOptical elementsCamera lensIlluminance
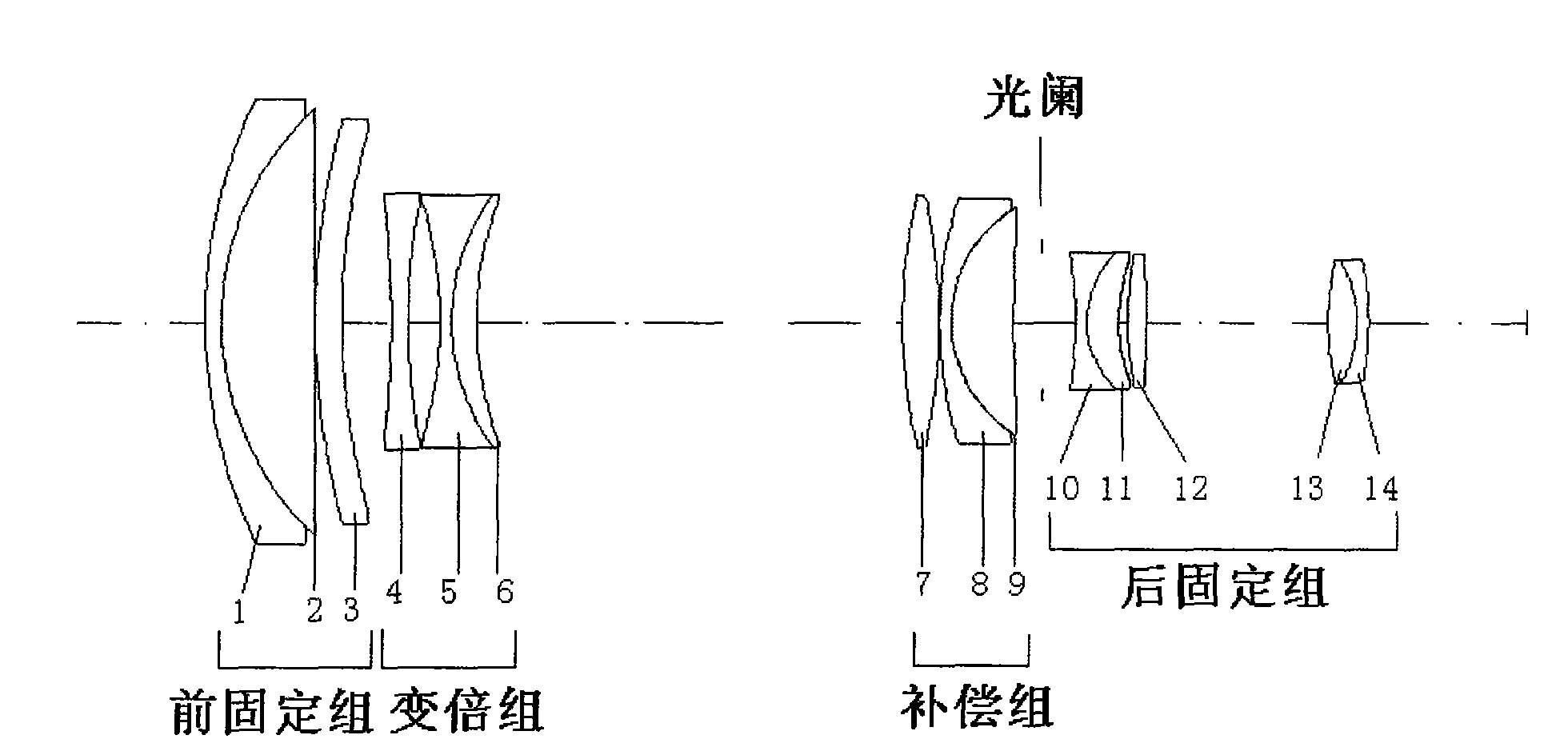
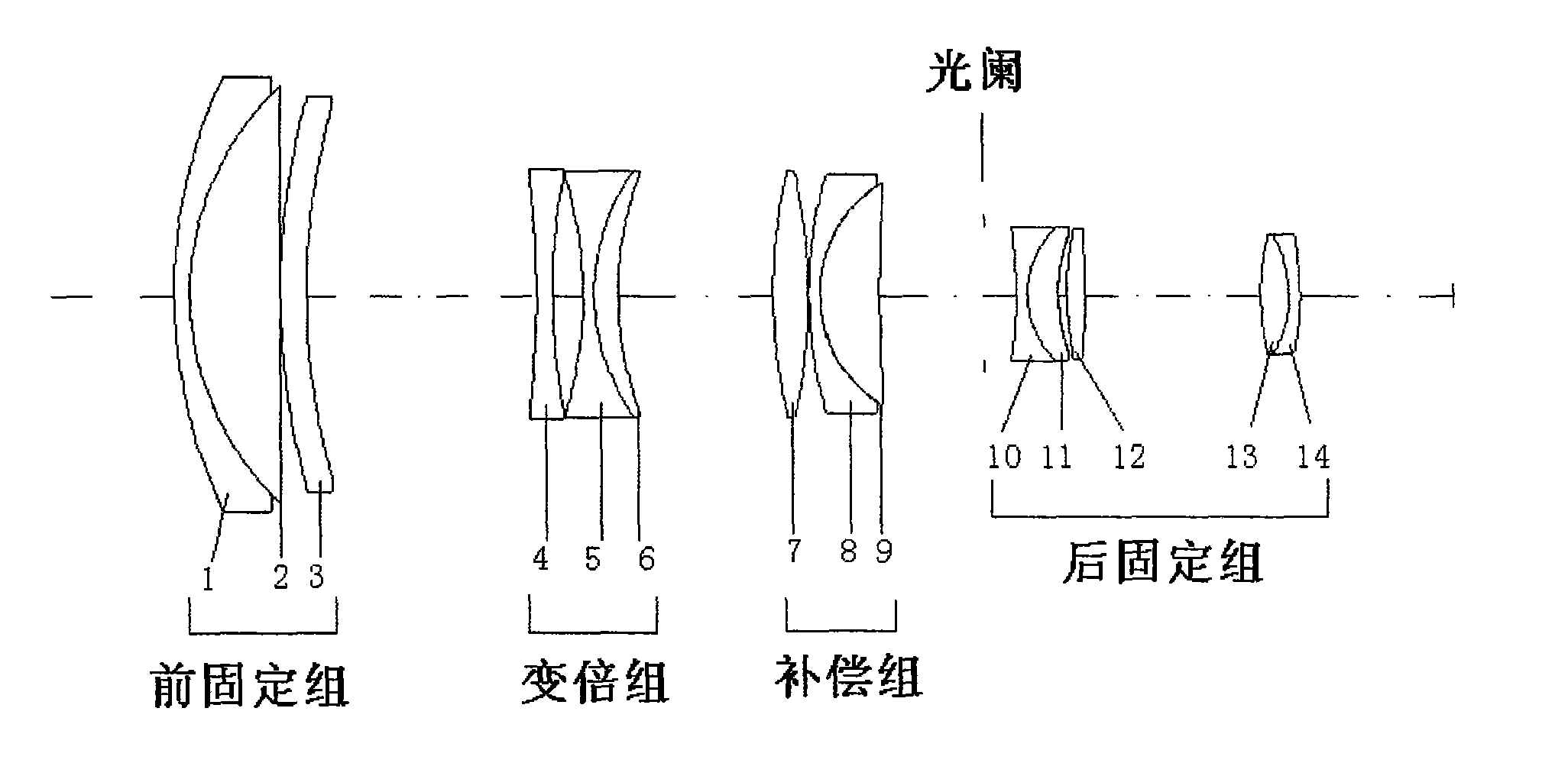
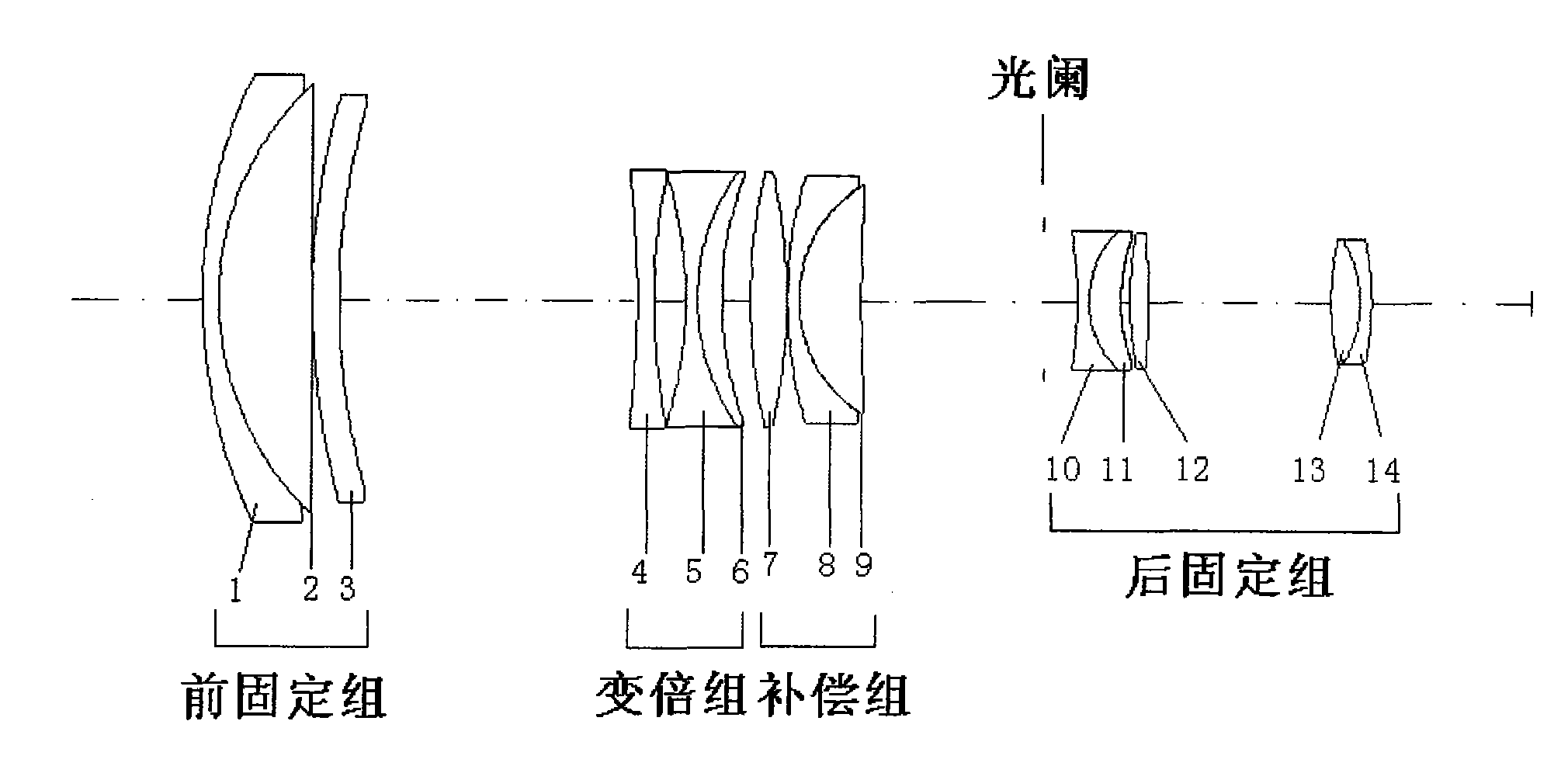
The invention discloses a big relative aperture long-focus image space telecentric zoom lens, sequentially comprising a front fixed group, a zoom group, a compensation group and a back fixed group from the object plane side to the image plane side; the corresponding combined focus satisfies a conditional equation: 3.5<F1 / FW<6, -1.6<F2 / FW<-0.9, 1.1<F3 / FW<2, 1.3<F4 / FW<1.9, wherein FW is the focus ofthe zoom lens in wide angle end state. The invention adopts the design of big relative aperture which reaches 1:2 and keeps constant big relative aperture in zoom process to ensure high light energyutilization rate of lens; bigger zoom ratio and longer focus ensure good imaging quality in zooming process; the lens adopt the image space telecentric design, so that the size of the image plane doesnot change with the movement of the image plane and the illumination is even; and all of the glass are made in China, with low cost. The big relative aperture long-focus image space telecentric zoomlens shows a wide application prospect in the fields of remote sensing, measurement, photography and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
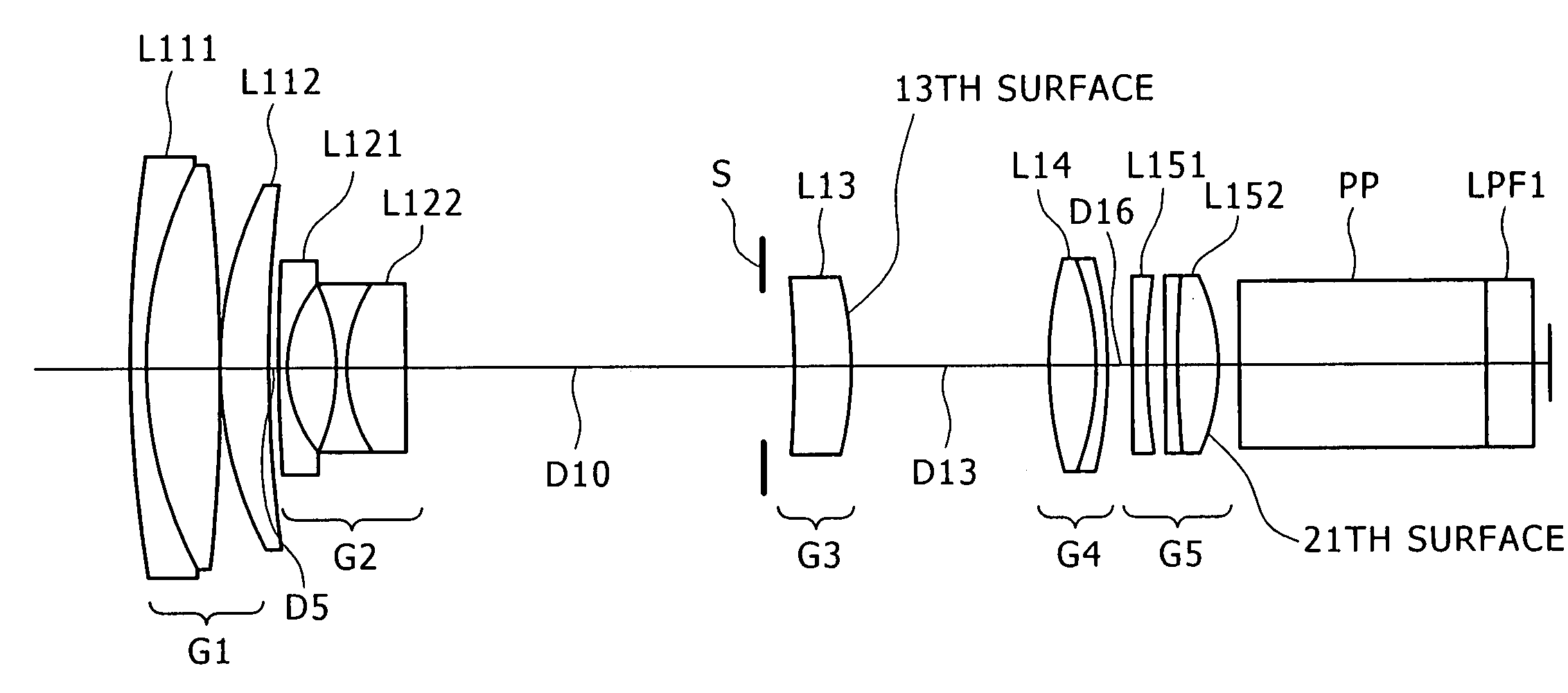
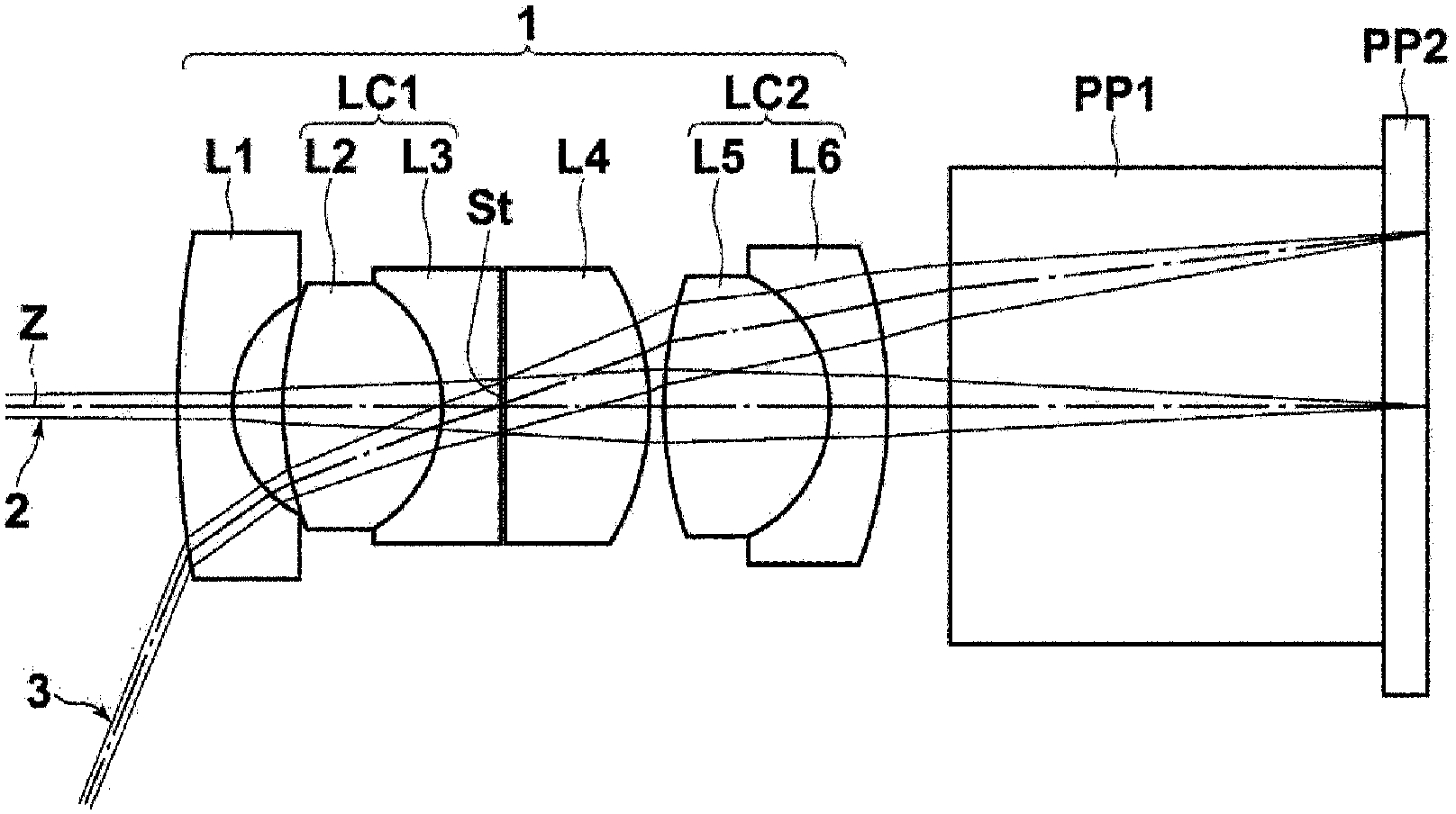
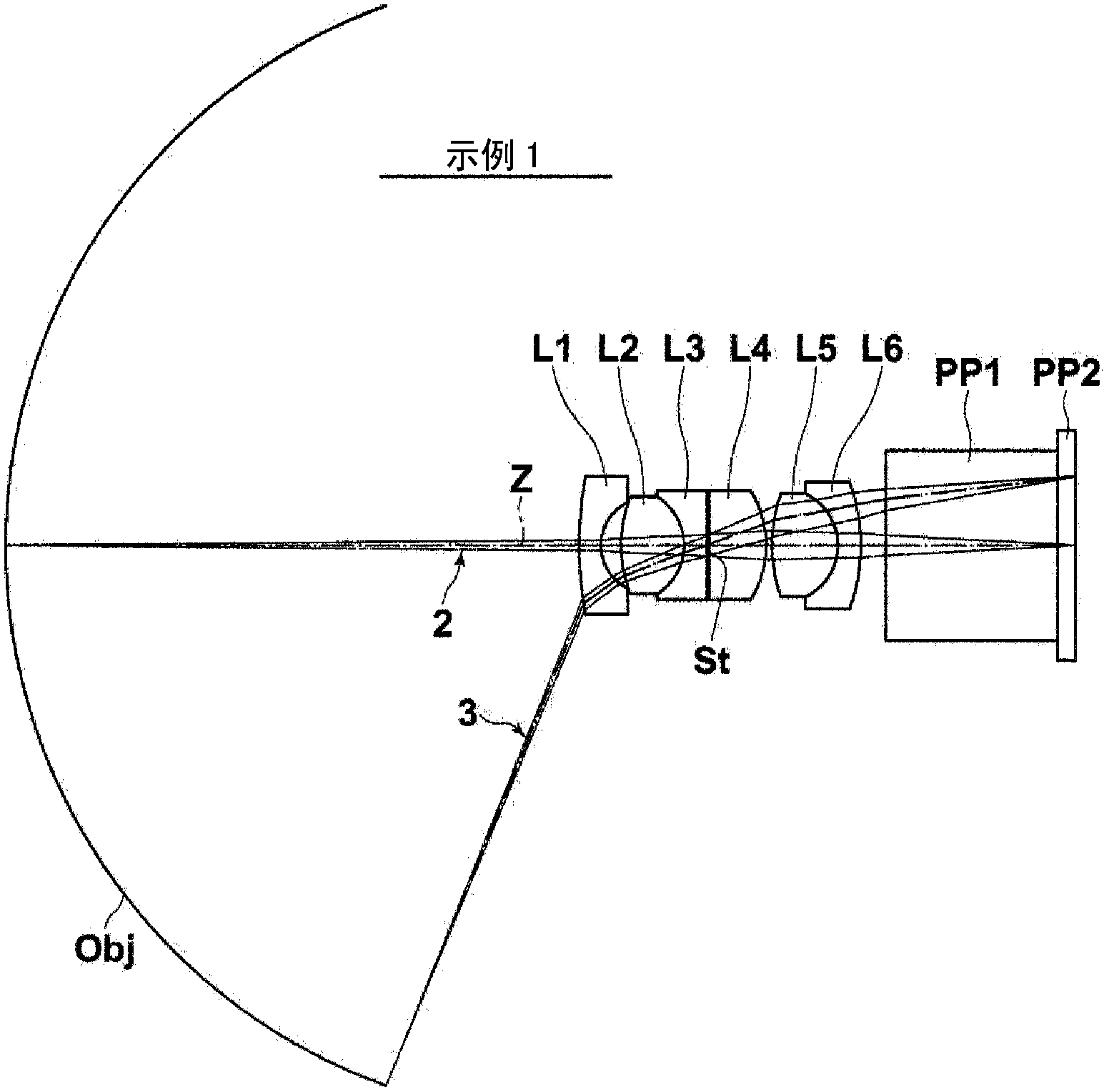
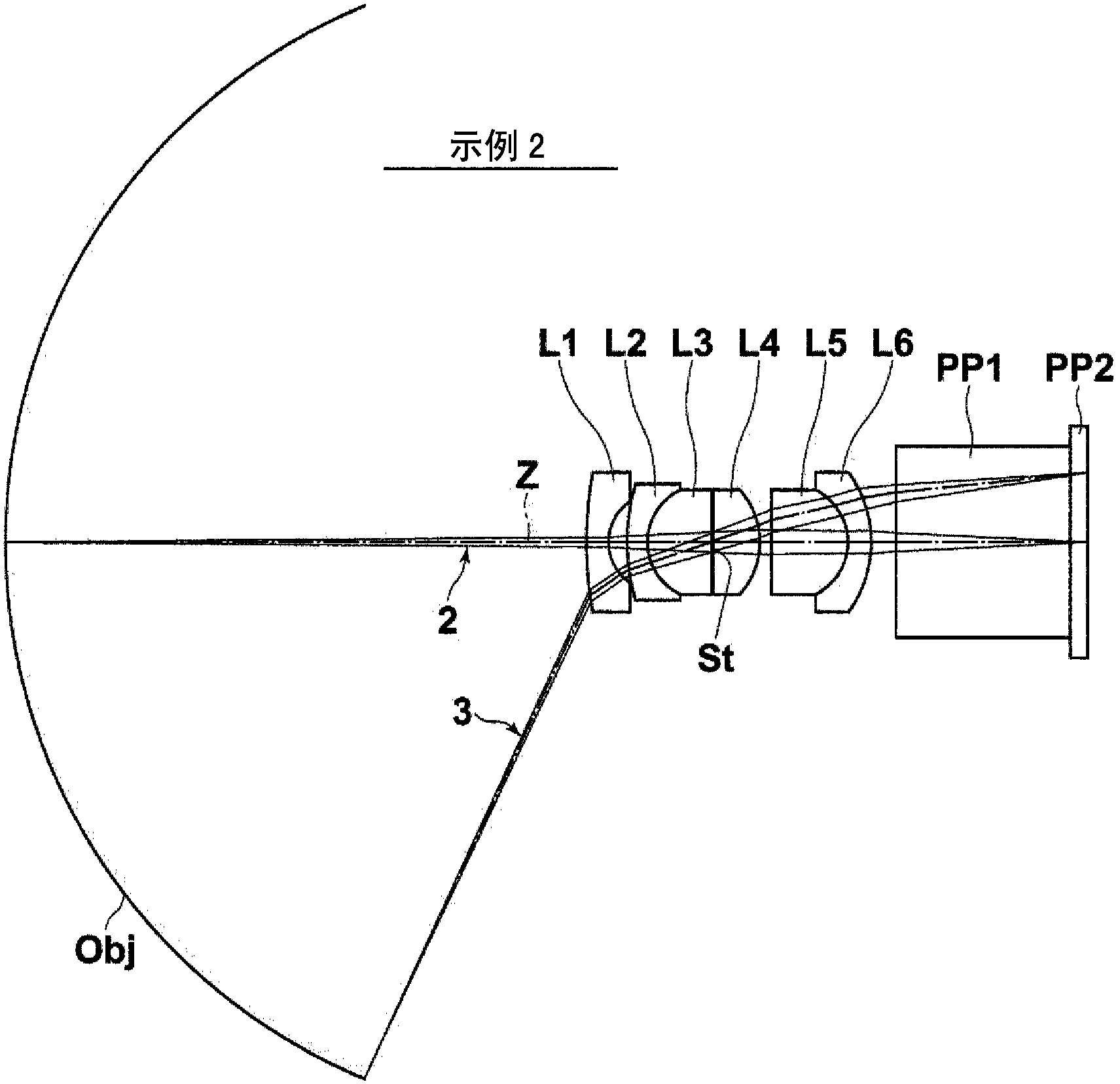
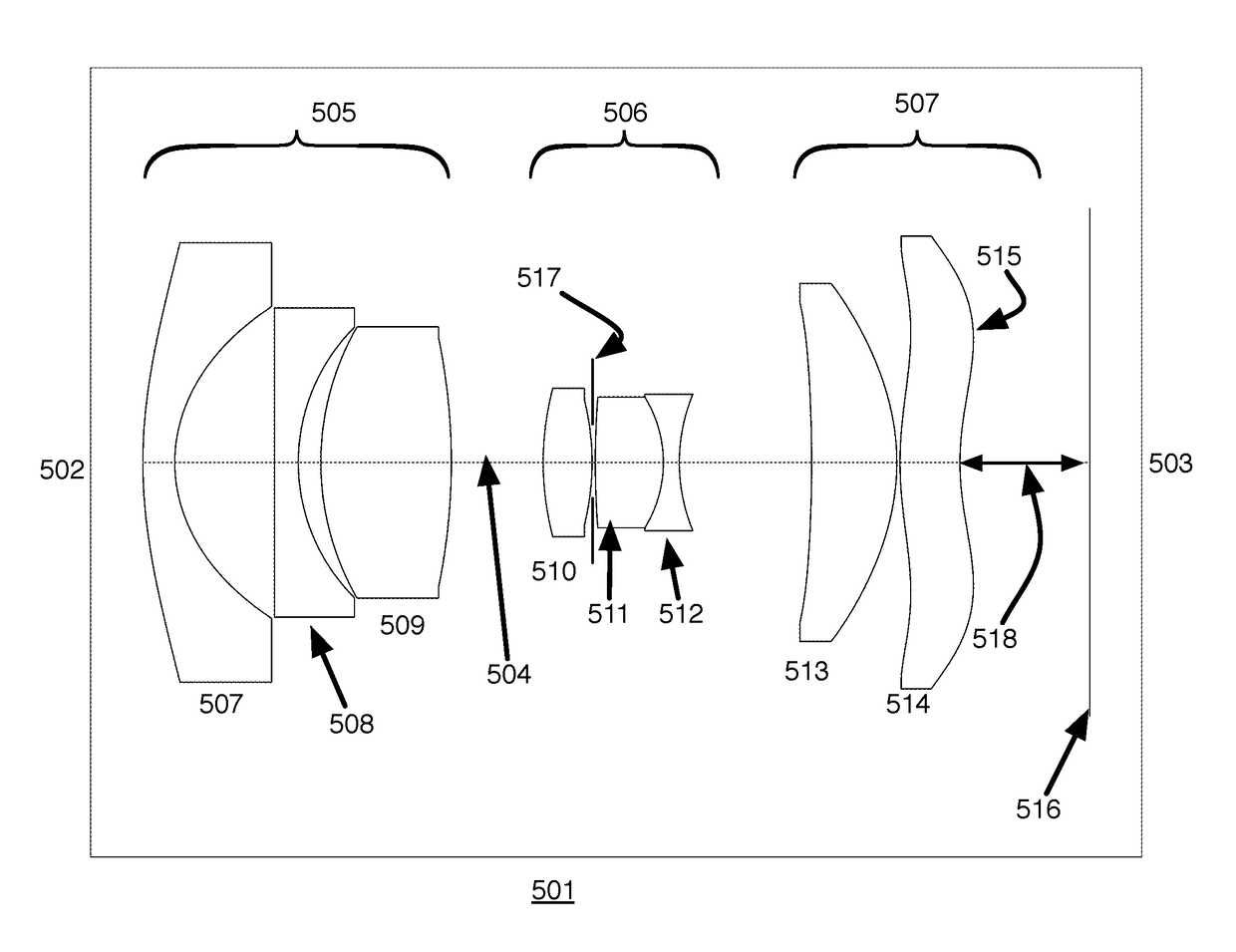
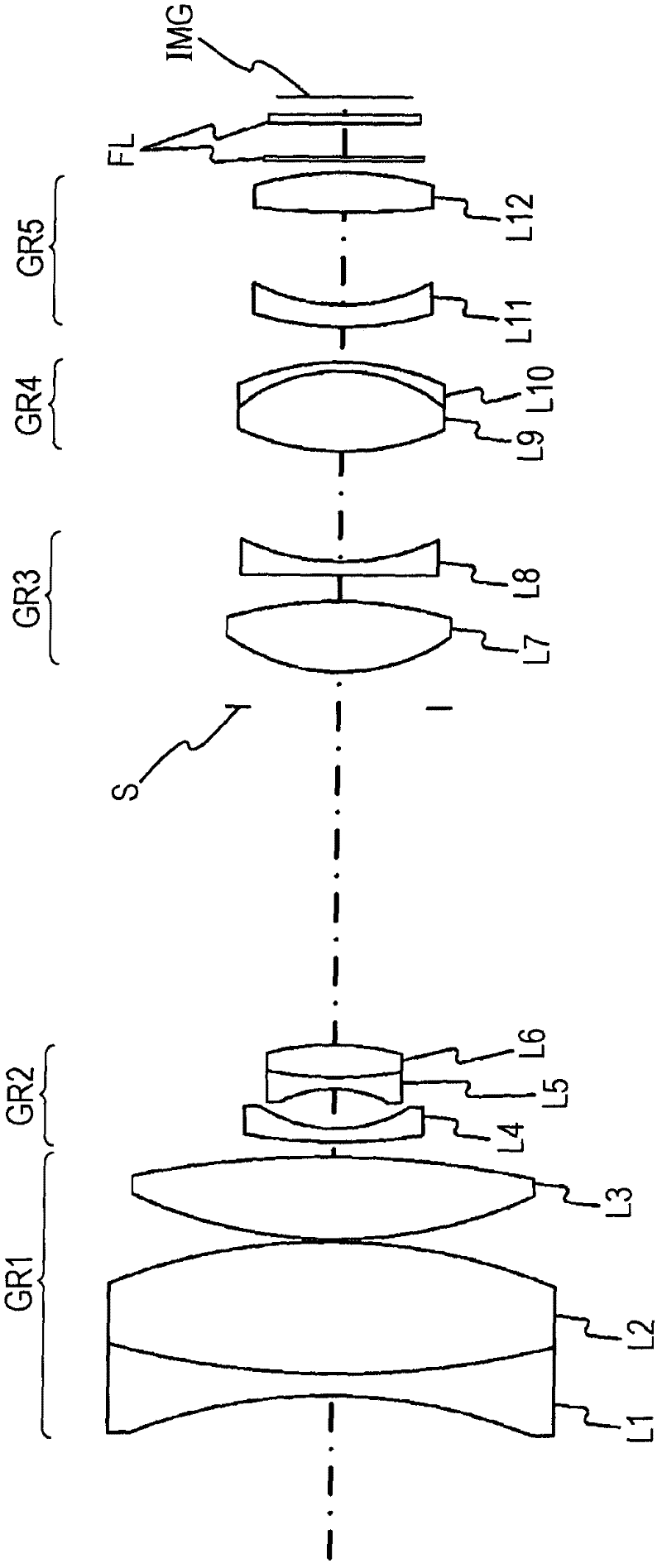
Image pick-up lens and image pick-up device
[Problem] In an image pick-up lens, to achieve both long back focus and a wide angle, and to favorably correct chromatic aberration. [Solution] An image pick-up lens comprising the following, in the following order, starting from the object side: a negative first lens (L1) having a plano-concave or meniscus shape with the concave surface facing the image side; a first cemented lens (LC1) formed by cementing a second lens (L2) and a third lens (L3) with one lens positive and the other lens negative; an opening; a positive fourth lens (L4) with a flat surface or the surface that has the larger radius of curvature absolute value facing the object side; a second cemented lens (LC2) formed by cementing a fifth lens (L5) and a sixth lens (L6) with one lens positive and the other lens negative. The image pick-up lens satisfies a conditional equation related to the ratio between the focal distance of the entire system and the back focus, and the refractive indices and the Abbe numbers of the positive and negative lenses in the first cemented lens (LC1).
Owner:JIANGXI JINGCHAO OPTICAL CO LTD
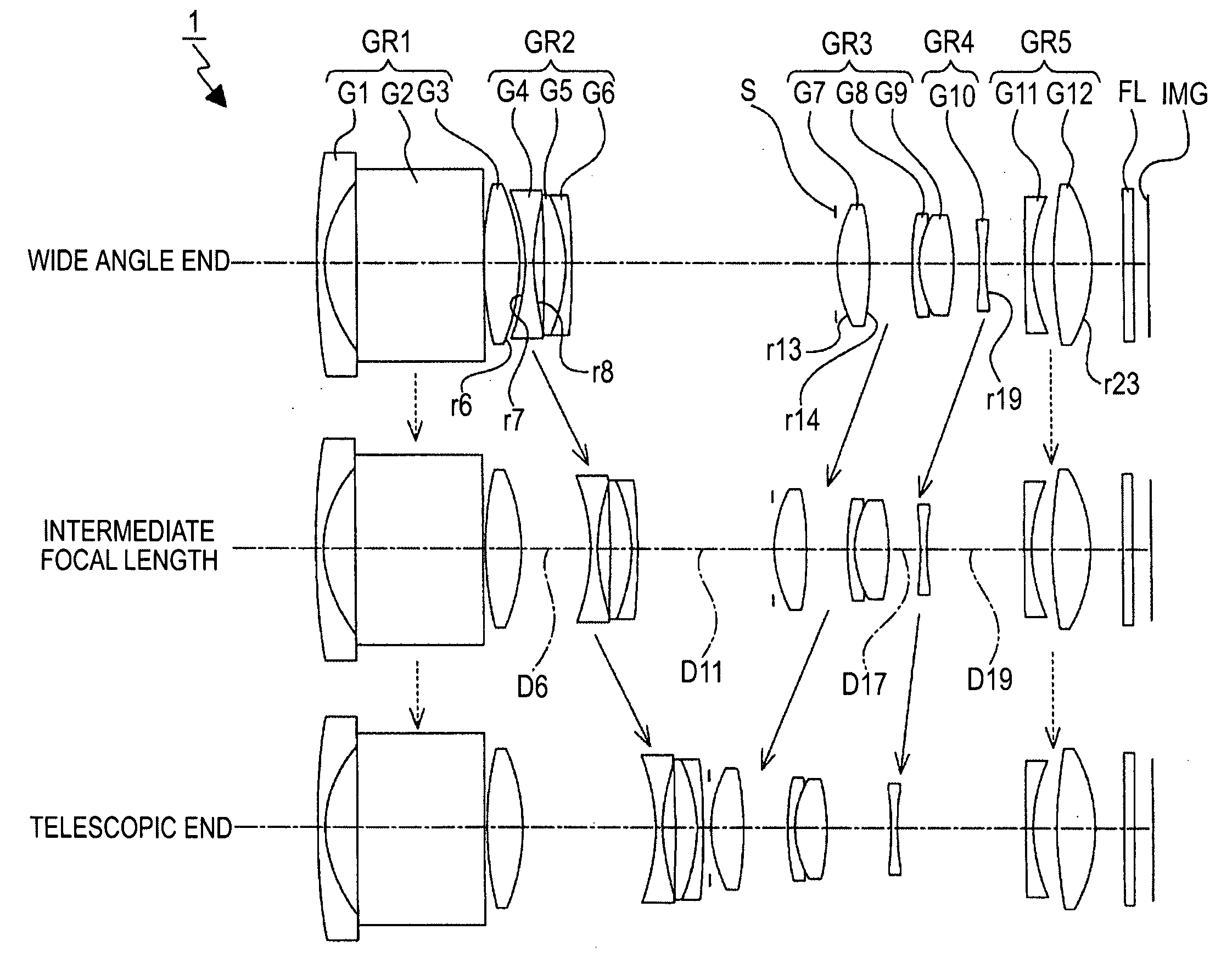
Zoom lens and imaging apparatus
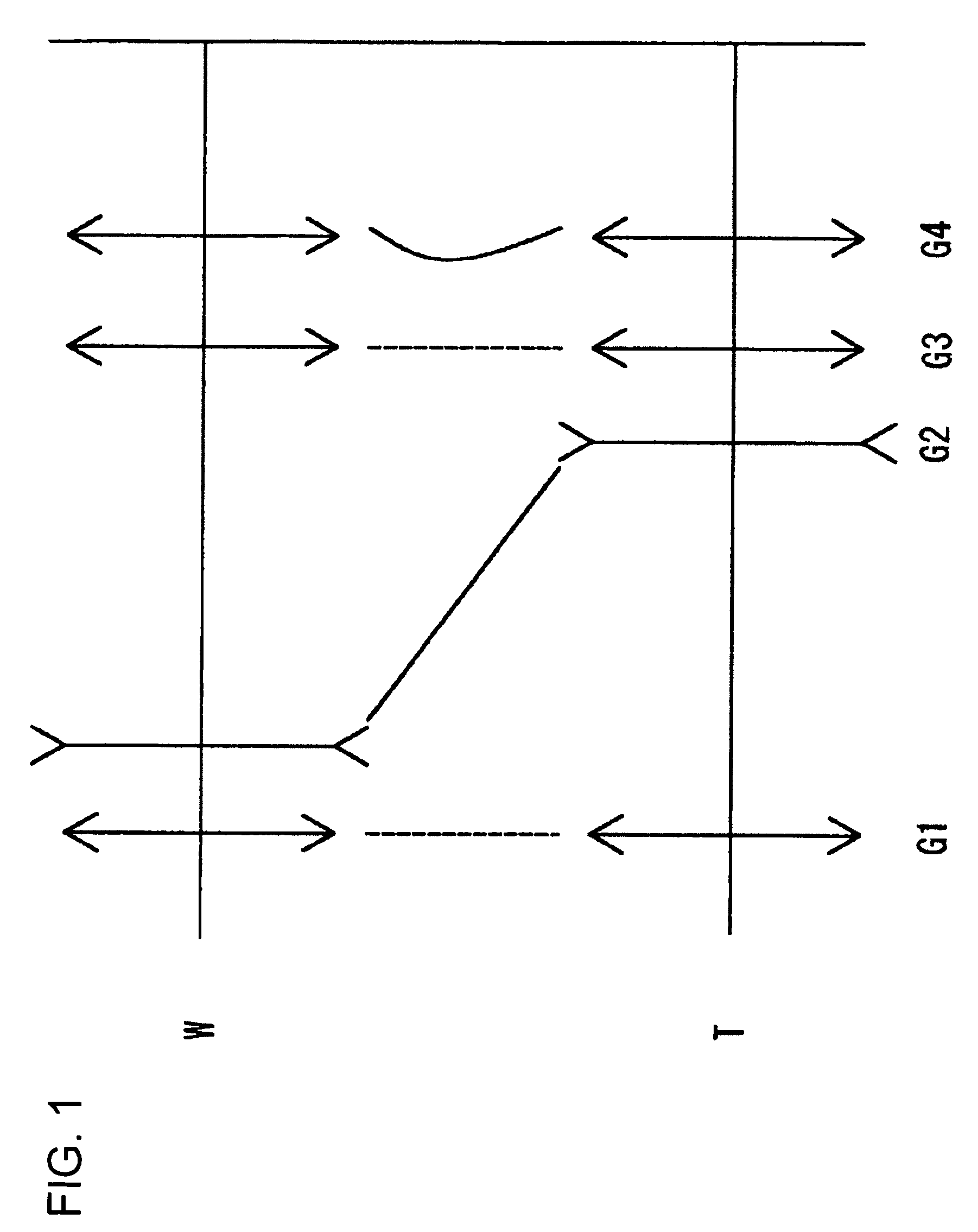
InactiveUS20110194015A1Small sizeSimple configurationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging equipmentZoom lens
A zoom lens includes: a first lens group including a reflection member that deflects an optical path by 90 degrees and having positive refracting power; a second lens group having negative refracting power; a third lens group having positive refracting power; at least one lens group having negative refracting power and at least one lens group having positive refracting power disposed as a fourth lens group and the following lens groups, the first to third lens groups and the fourth and following lens groups arranged in this order from an object side toward an image side; and an aperture diaphragm disposed in the vicinity of the third lens group, wherein in zooming from a wide angle end state to a telescopic end state, the first lens group is fixed, the second lens group is moved toward the image side, and the fourth lens group is moved toward the object side, and the zoom lens satisfies the following conditional equation1<(R1B+R21A) / (R1B−R21A)<20.
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor light-emitting device
ActiveUS20050023539A1Reduce dispersionLittle changeLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionRefractive indexLength wave
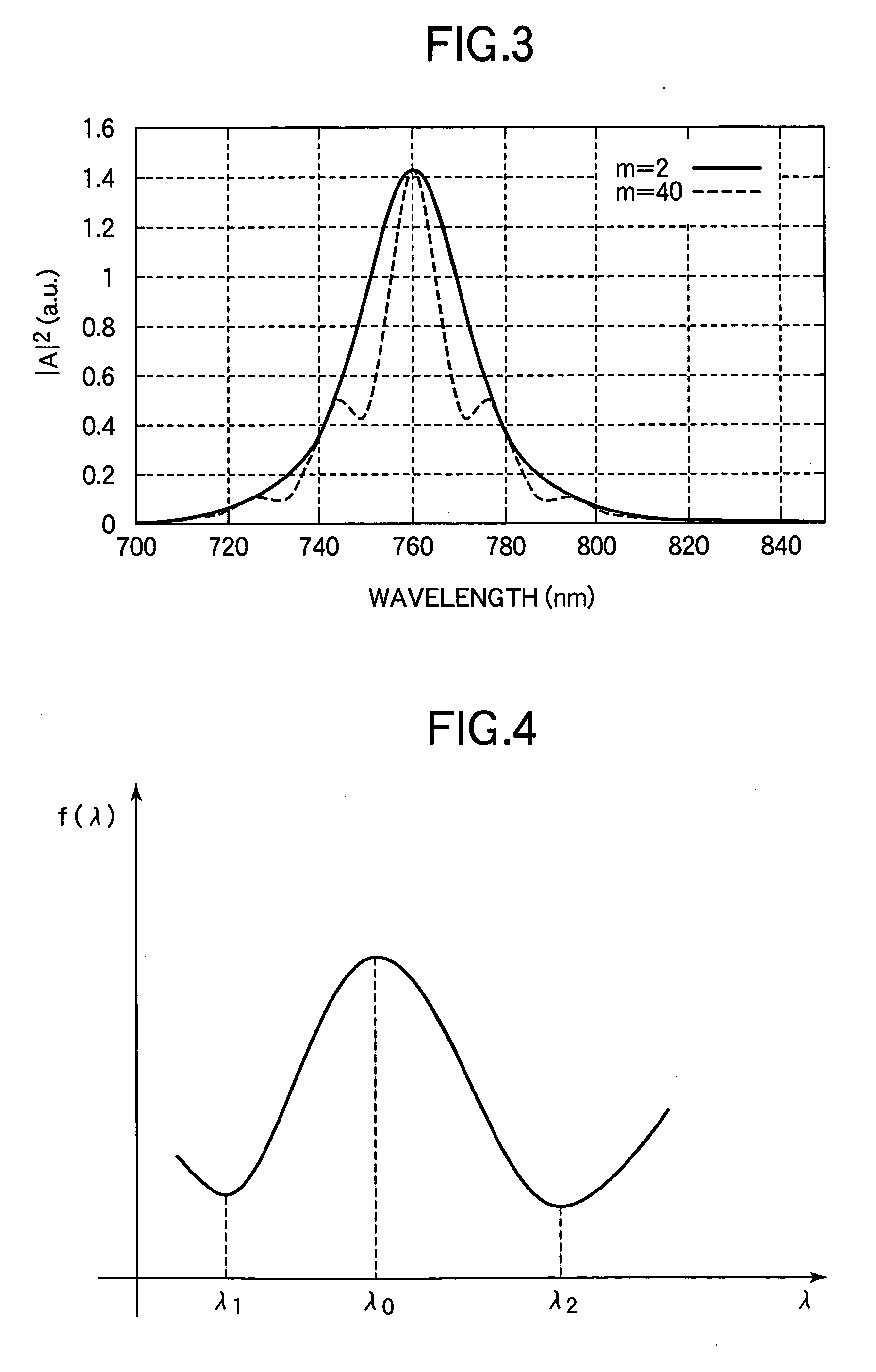
A semiconductor light-emitting device includes a semiconductor light-emitting thin film, the thickness h of which satisfies the following conditional equation: 0.9×(2m+1)λ04n≦h≦1.1×(2m+1)λ04nand m in the conditional equation satisfies the following conditional equation: 2m+1m(m+1)λ02>ξwhere λ0 is a center wavelength of light generated in the semiconductor light-emitting thin film, n is a refractive index of the semiconductor light-emitting thin film, m is 0 or a positive integer, and ξ is a half bandwidth of a light emission spectrum when there is no interference between light rays generated in the semiconductor light-emitting thin film.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Projection optical system and projection type display apparatus using the same
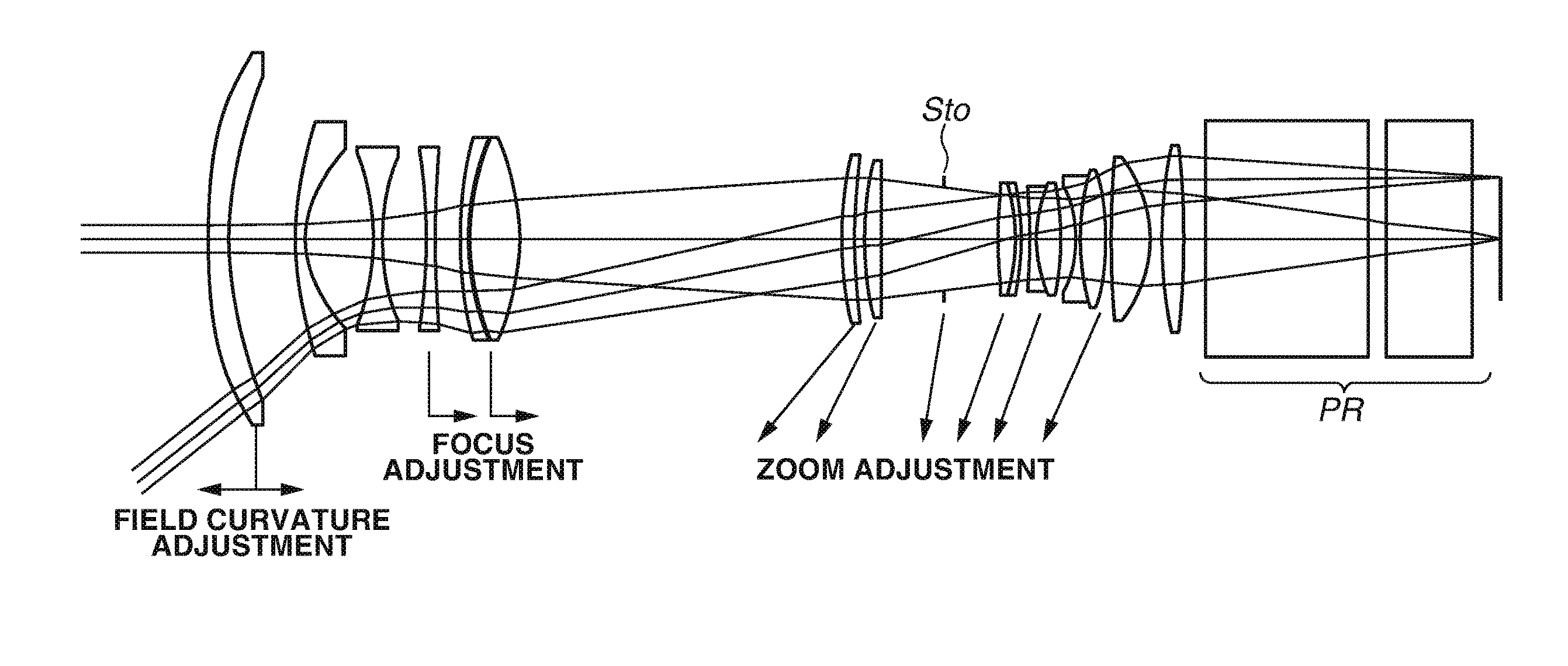
A projection optical system includes a first lens unit that moves in a direction of an optical axis in adjusting an amount of field curvature and a second lens unit located closer to a reduction side than the first lens unit. The first lens unit includes an aspherical lens satisfying predetermined conditional equations.
Owner:CANON KK
Immersion optical system and optical apparatus having the same
InactiveUS20060146662A1Photomechanical apparatusRecord information storageRefractive indexIrradiation
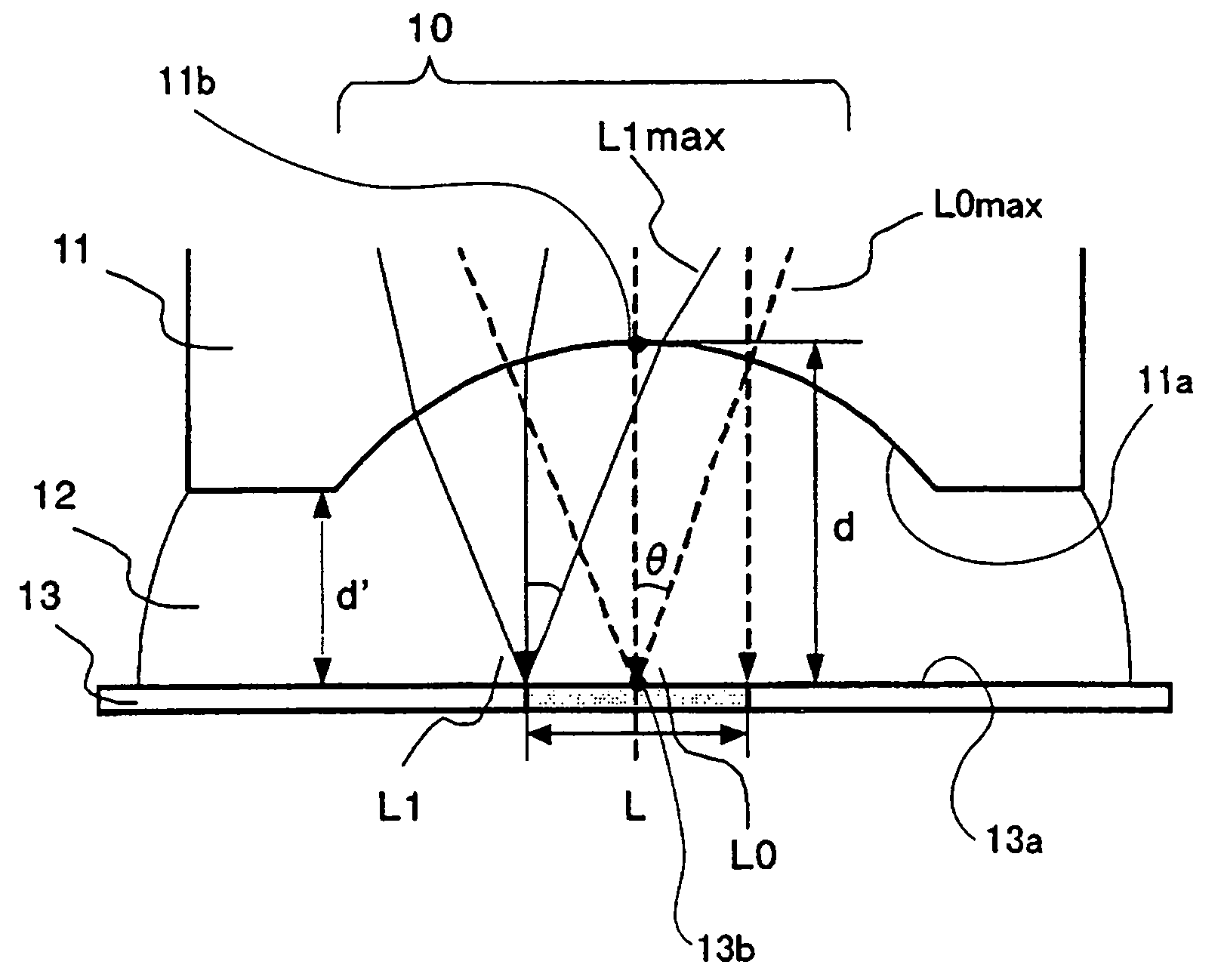
An immersion optical system that condenses light from a light source toward a first surface includes a lens having a concave lens surface closest to the first surface, a liquid being filled in a space between the concave lens surface and the first surface, wherein a conditional equation d>L / [2×tan {arcsin(NA / ni)}] is met, where d is a distance between a first point and a second point when the distance becomes maximum between the first point on the concave lens surface and the second point on the first surface in a direction substantially orthogonal to the first surface, L / 2 is a maximum distance from the second point to an edge of an irradiation area of the light on a first surface, NA is a numerical aperture of the immersion optical system, and ni is a refractive index of the liquid.
Owner:CANON KK
Microscope
A microscope includes a laser light source, an optical system which changes a beam diameter, and a field stop disposed at a position conjugating with a sample plane, in this order beginning from the side of the laser light source. In this microscopes the following conditional equation is satisfied: A≦D / 2 where “A” is the diameter of the field stop, and “D” is the diameter of light incident to the field stop.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Compact Wide Angle Lens
Compact wide angle lens designs are described. The lens has three lens groups and includes complex aspherical lens elements. The lens designs have a field of view of 80° or greater and satisfies at least one of the conditional equations a) BFL / EFL<=0.6 where BFL is the distance from the image surface vertex of the complex aspheric lens element to the image plane, EFL is the effective focal length of the optical lens, and,b) BFL / CA<=0.3 where CA is the clear aperture of the complex aspheric lens element, EFL is the effective focal length of the optical lens, and,c) 3=<TTL / EFL<=6.6 where TTL is the distance from the vertex of the first element of group 1 to the image plane of the lens assembly when focused at infinity, EFL is the effective focal length of the optical lens.
Owner:NING ALEX
Zoom lens and image capturing apparatus
InactiveCN102540428AReduce in quantityHigh zoom ratioTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensOptical axis
The invention relates to a zoom lens and an image capturing apparatus. The inner focus type zoom lens includes a first lens group that has positive refracting power and is normally located at a fixed position, a second lens group that has negative refracting power and is movable in an optical axis direction for zooming, a third lens group that has positive refracting power, a fourth lens group that is movable for correction of a focal position due to the zooming and for focusing, and a fifth lens group that has positive refracting power, in order from an object side, wherein the first lens group includes a negative lens, a first positive lens, and a second positive lens arranged in order from the object side, wherein a first face of the negative lens has a shape of a concave surface turned on the object side, and wherein the zoom lens satisfies the following conditional equation (1) -10.0<G1R1 / fw<-3.0.
Owner:SONY CORP
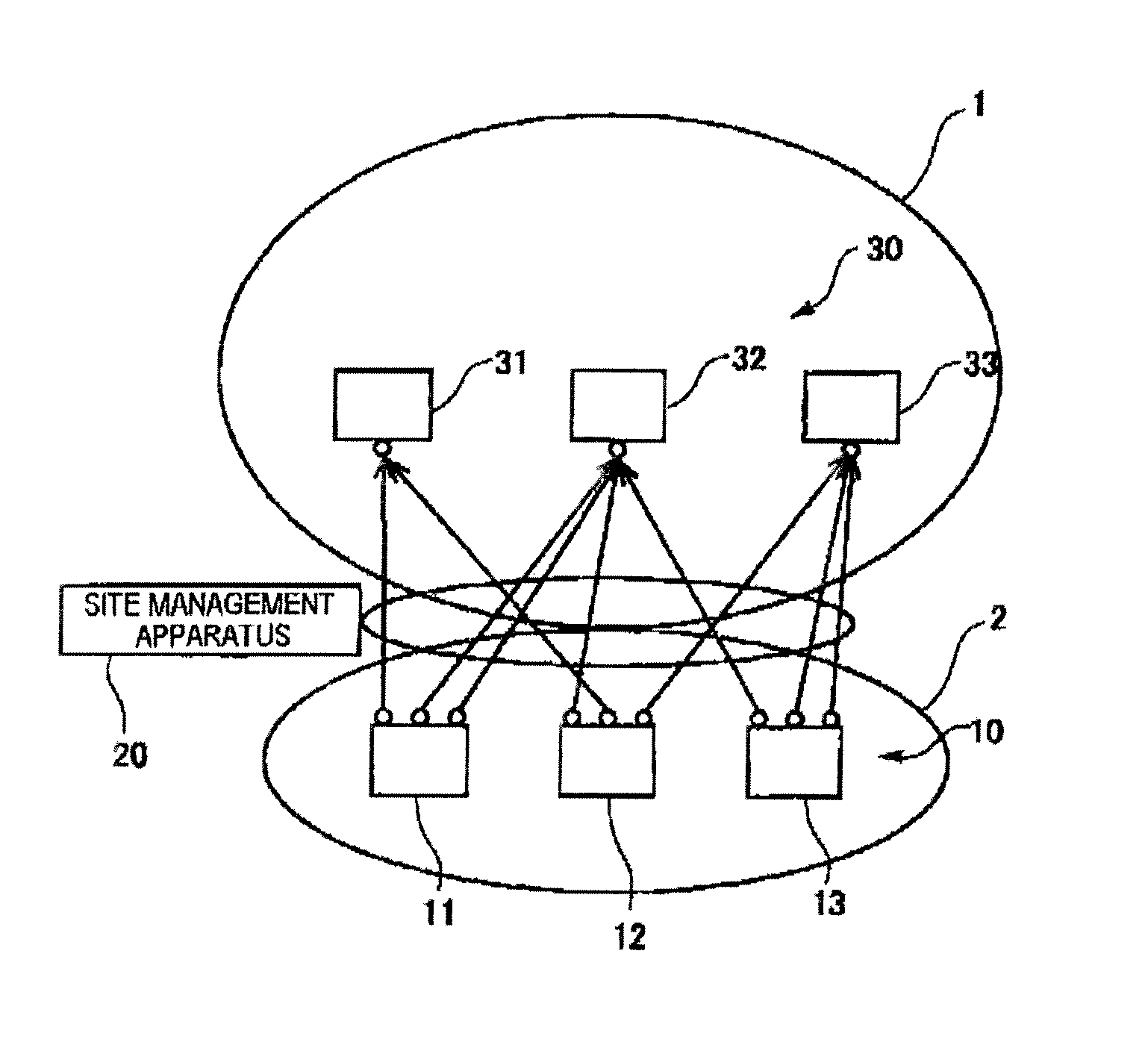
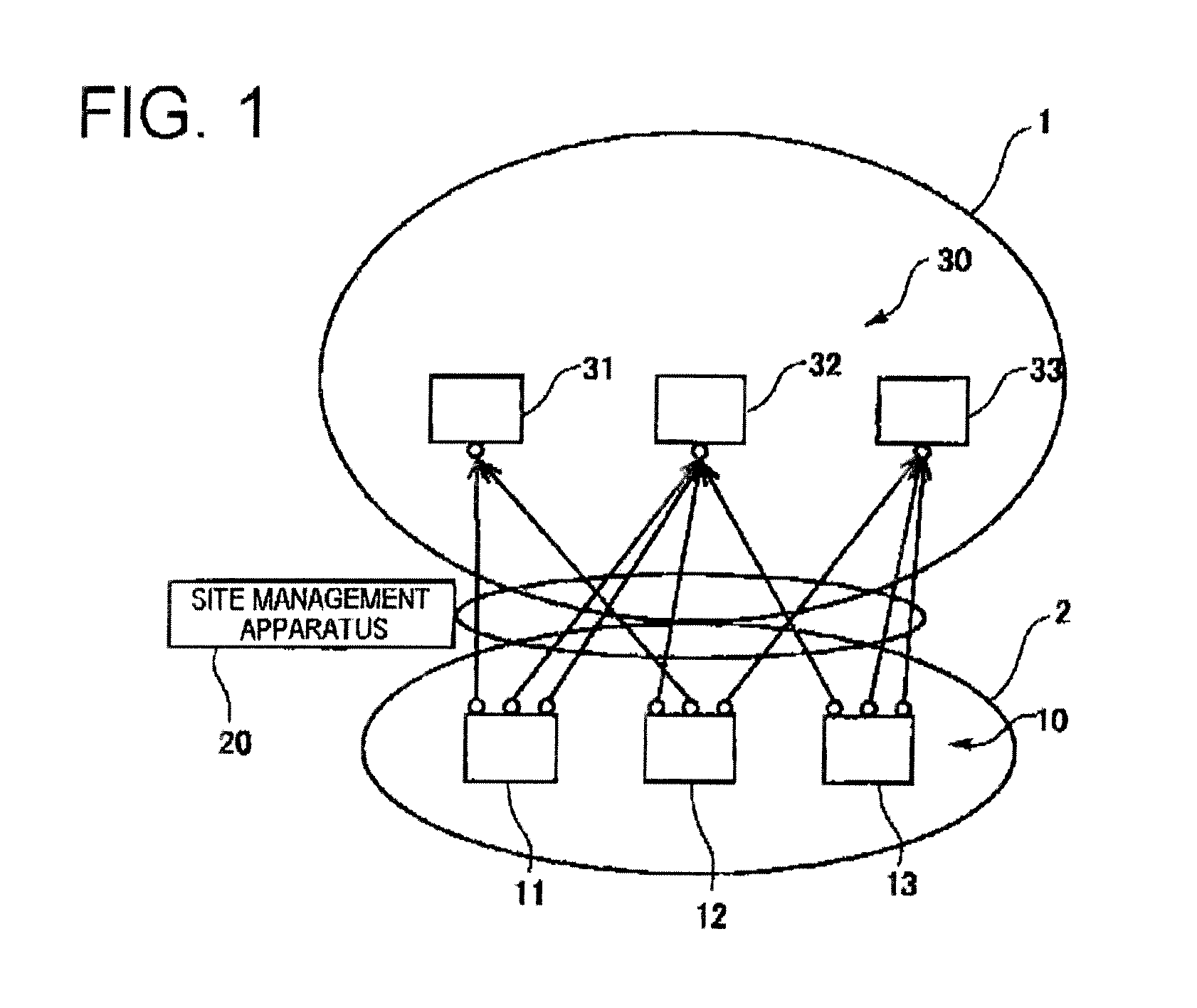
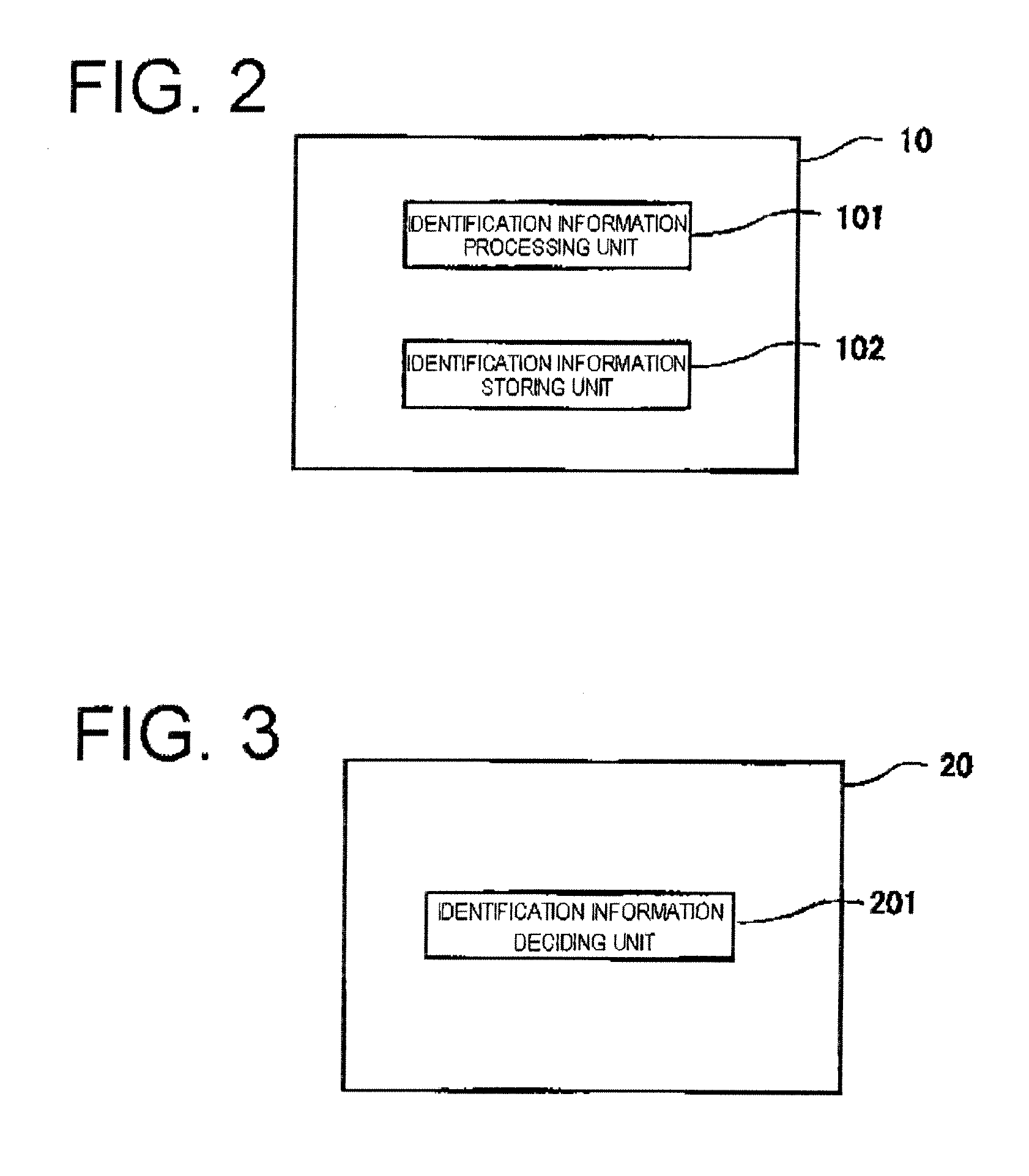
Identification information management system, method of generating and managing identification information, terminal, and generation and management programs
ActiveUS20110241825A1Programme controlElectric signal transmission systemsInformation processingHash function
An identification information management system according to the present invention comprises a plurality of terminals communicable with servers and a site management apparatus which manages site containing the terminals. The terminal has an identification information processing unit which assuming that a one-way hash function is f(x) and a terminal-unique ID is a, generates values x satisfying a conditional equation f(x)=a as identification information.When acquiring multiple items of identification information, the site management apparatus substitutes the identification information as the value x into f(x) and decides whether f(x)=a is satisfied, thereby deciding the terminals.
Owner:NEC CORP
Two-dimensional lattice calibrating device, two-dimensional lattice calibrating method, two-dimensional lattice calibrating program and recording medium
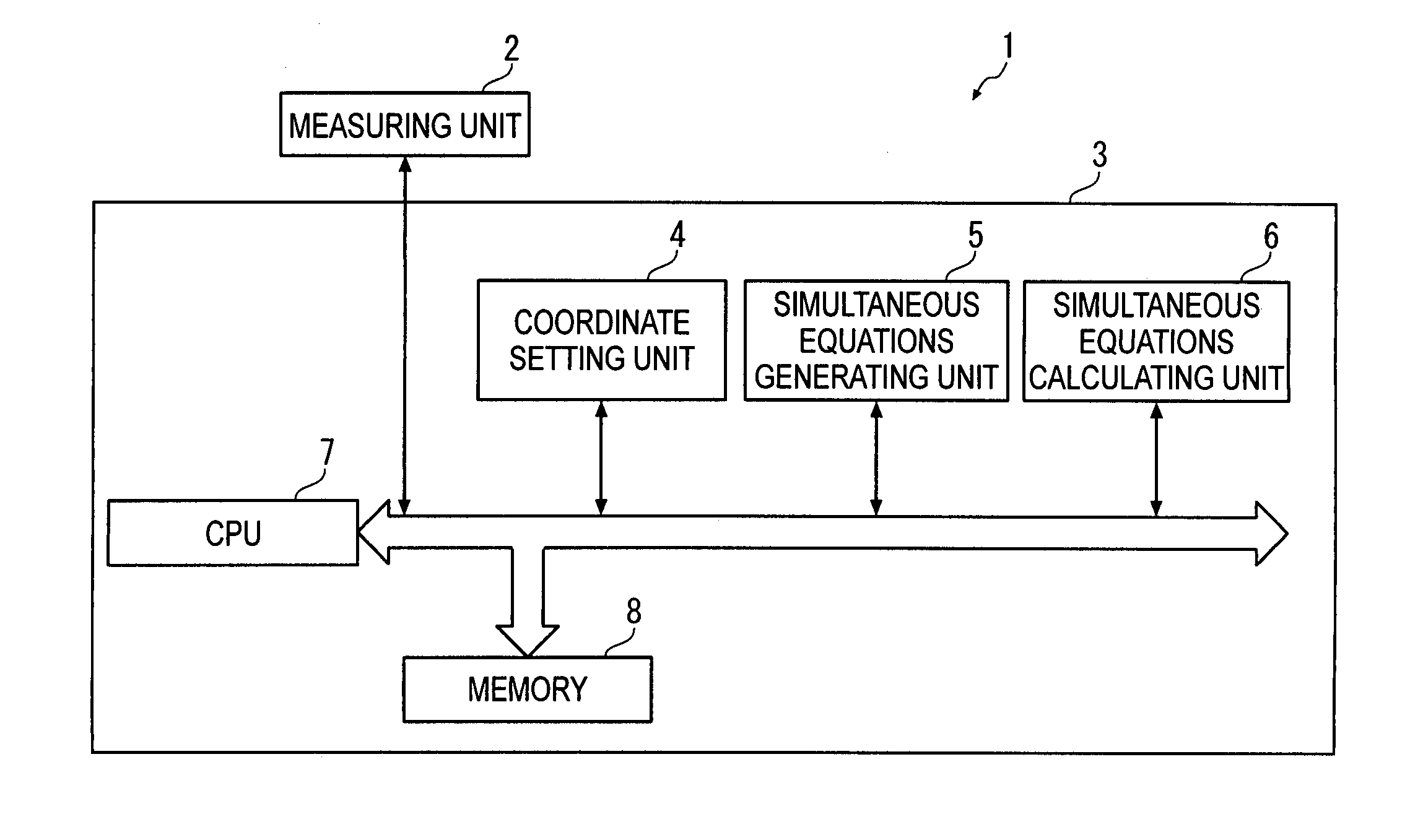
ActiveUS20080294364A1Accurate calculationImprove accuracyTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsDot matrixSimultaneous equations
A two-dimensional lattice calibrating device includes: a measuring unit that measures respective positions of marks for each of a plurality of measurement dispositions; a simultaneous-equations generating unit that generates simultaneous equations for acquiring deviations of the plurality of marks using a coordinate relational equation and a least-squares conditional equation that sets least-squares lines that minimize the deviation of actual position of the marks based on measurement values as coordinate axes of artifact coordinates; and a simultaneous-equations calculating unit that solves the derived simultaneous equations.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
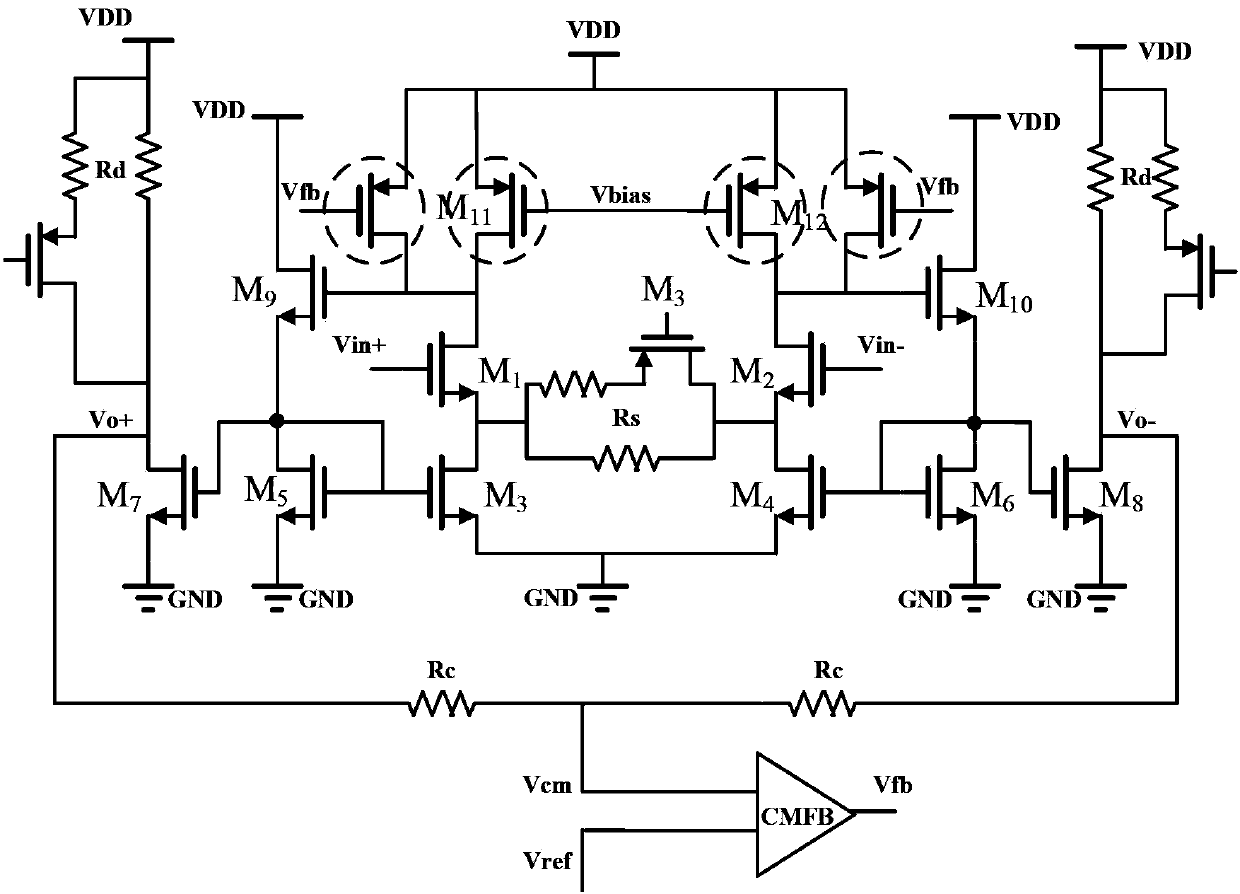
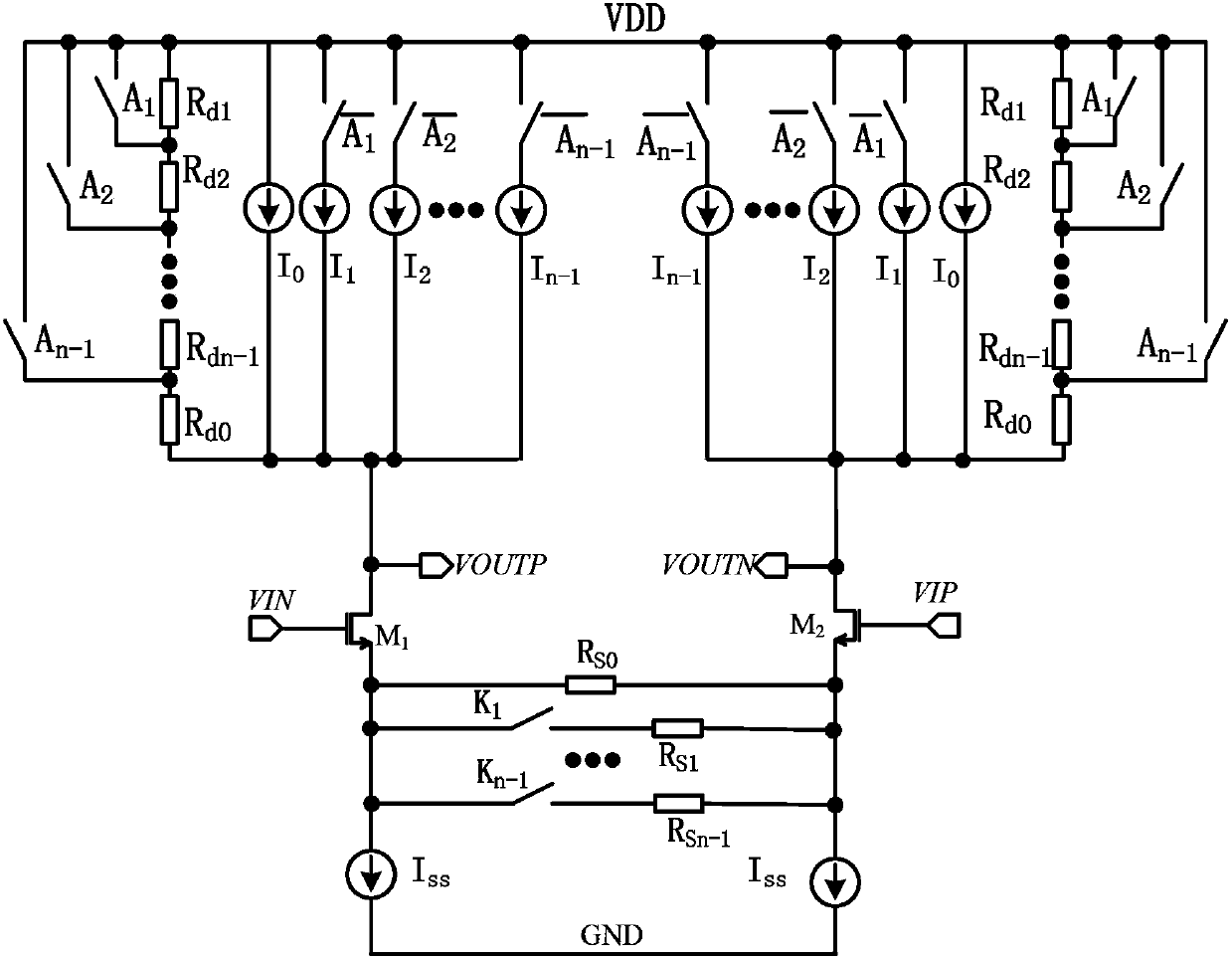
Low-power-consumption variable gain amplifier
ActiveCN103354444AStable outputReduce Design ComplexityGain controlDifferential amplifiersVariable-gain amplifierAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to the field of analogue integrated circuits, and discloses a low-power-consumption variable gain amplifier. The low-power-consumption variable gain amplifier comprises a differential common-source amplification unit, variable load resistor arrays Rd1-Rdn-1, digital control switch arrays A1-An-1, variable current source arrays I1-In-1, variable-source feedback resistor arrays Rs1-Rsn-1, switch arrays K1-Kn-1, a fixed current source I0, a fixed current source ISS, a fixed resistor Rd0 and a fixed resistor Rs0, wherein effective resistance values in the variable load resistor arrays Rd1-Rdn-1 are controlled through the digital control switch arrays A1-An-1, current sources in the variable current source arrays I1-In-1 are controlled through the digital control switch arrays, effective resistance values in the variable-source feedback resistor arrays Rs1-Rsn-1 are controlled through the switch arrays K1-Kn-1, and the output common mode voltage of the variable gain amplifier meets the following conditional equation of . By means of the design mode, the common mode is stably output, a common mode feedback circuit is removed at the same time, and accordingly the complexity and power consumption of the circuits are reduced.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
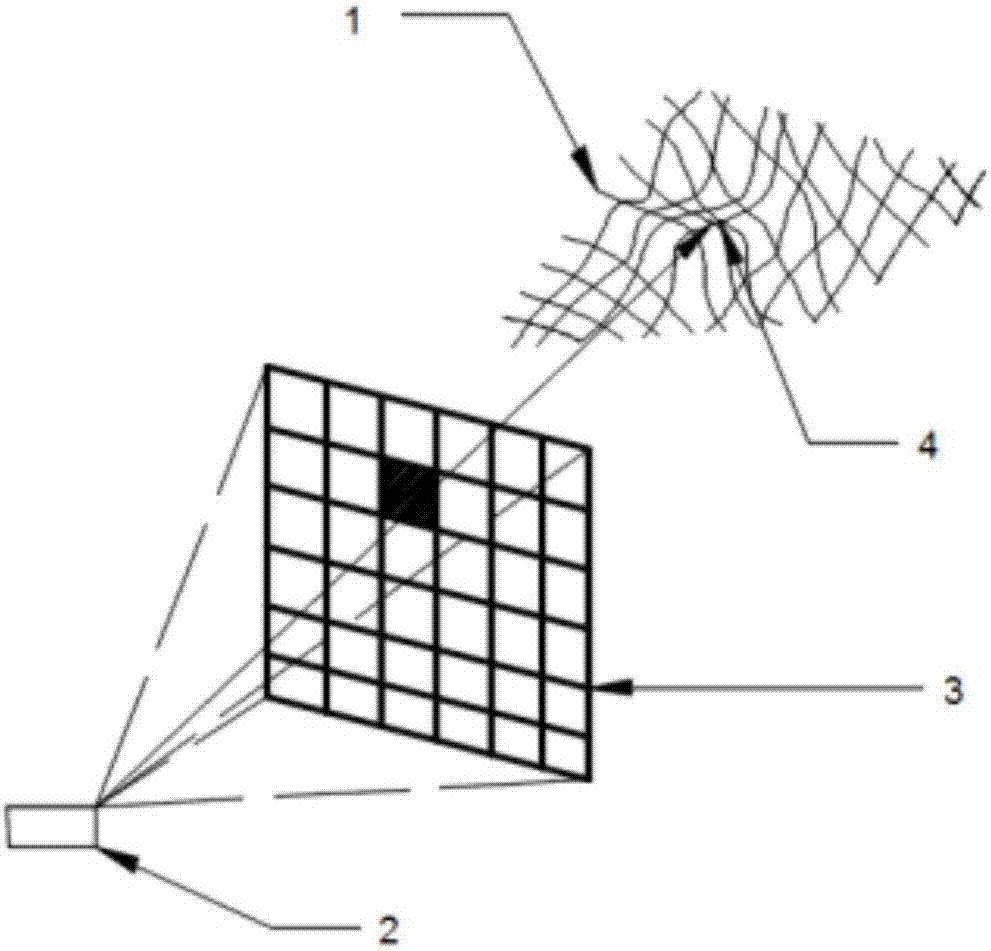
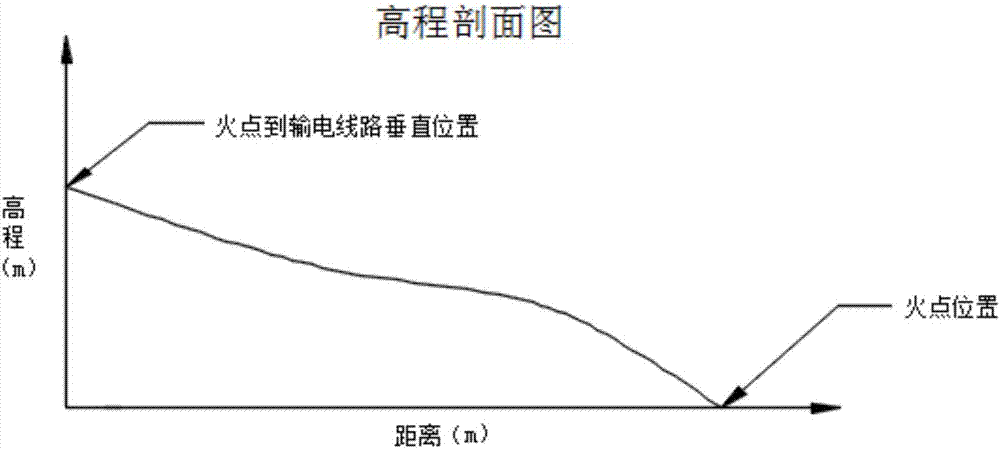
Algorithm for positioning accurate mountain fire and calculating vertical distance between mountain fire edge and overhead transmission line
InactiveCN107967712ASolve positioningSolve real-timeImage analysisPicture interpretationRolling angleConditional equation
The invention discloses an algorithm for positioning the accurate mountain fire and calculating a vertical distance between a mountain fire edge and an overhead transmission line. After the mountain fire is discovered through a camera, a planar two-dimensional coordinate system o-xy, an image space rectangular coordinate system S-xyz, a ground photography coordinate system O-XYZ and an image spaceauxiliary coordinate system S-XYZ are constructed based on the photogrammetry principle, p is an image point, P is a fire point, S is the origin of the camera photographic center, and o is the originof the image center; three-dimensional attitude angles during image shooting are measured through utilizing a three-dimensional electronic compass fixedly mounted on the camera in real time, including the azimuth angle (phi), tehe inclination angle (omega) and the roll angle (kappa); through image point space coordinate transformation, a collinear conditional equation satisfying the image point p, the fire point P and the origin S of the camera photographic center is constructed, and the equal-division search method is utilized to acquire the three-dimensional coordinate of the fire point.
Owner:HAINAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
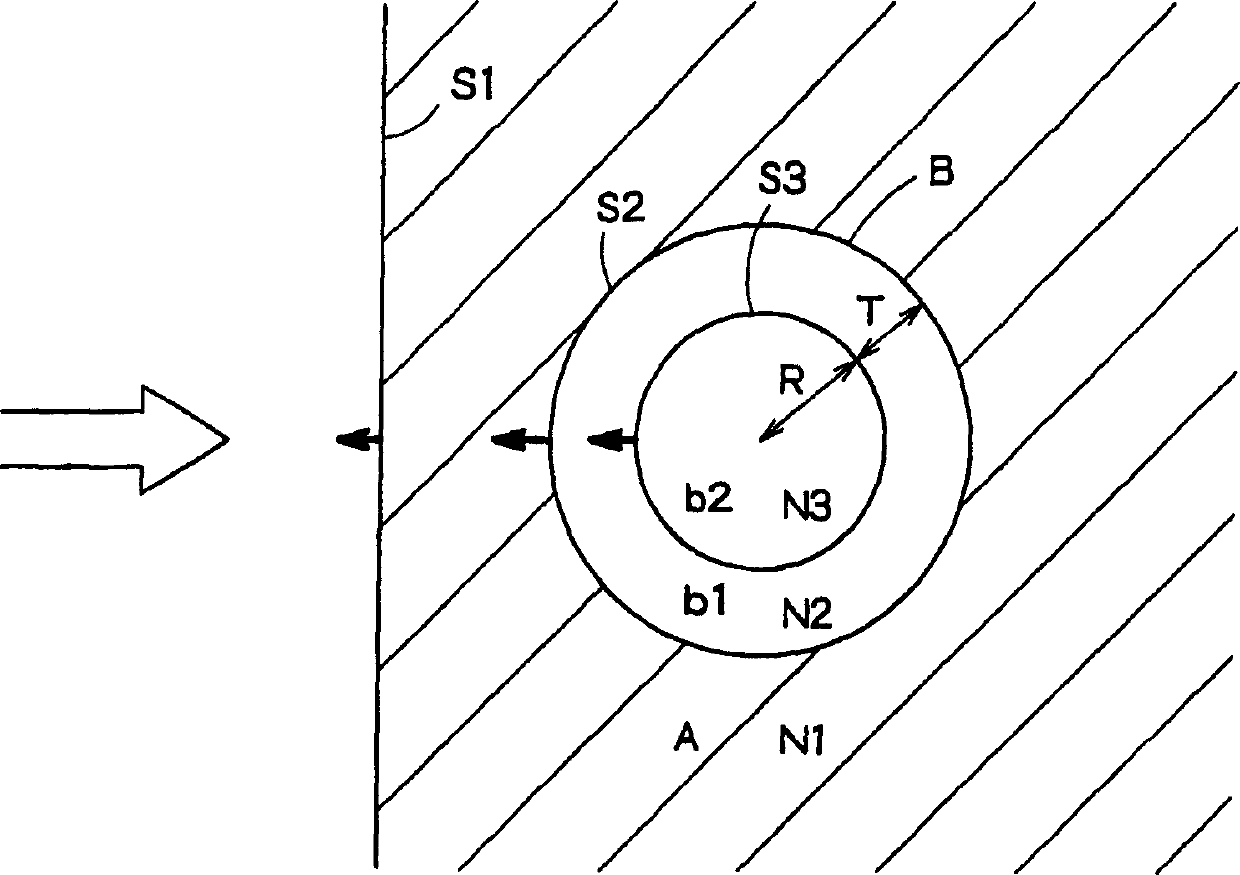
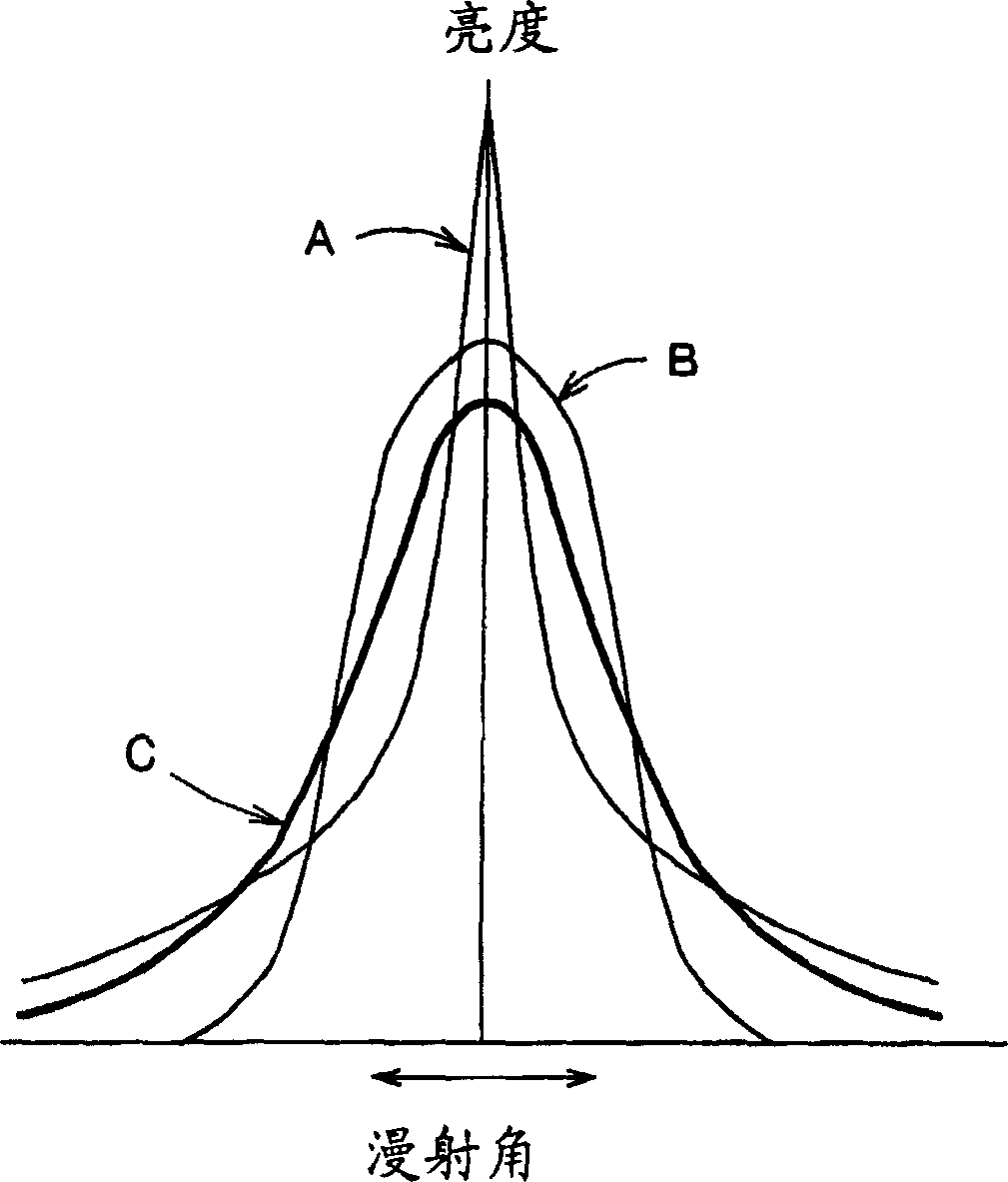
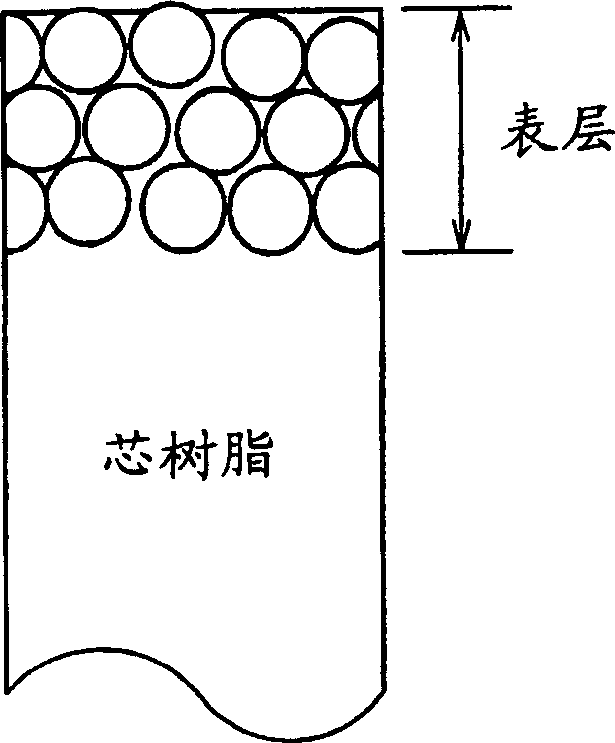
Light diffusing agent, light diffusing sheet, and nonglare sheet
InactiveCN1576901AHigh transparencyLight loss is smallPrismsDiffusing elementsDiffusionRefractive index
Provided is a light diffusion sheet that has high diffusing efficiency and can obtain an excellent image bright with high contrast without dull colors and blur by reducing the unnecessary scattered light, and can realize a high quality image. This is a light diffusion agent to be used by dispersing in a transparent base material, consists of particles and the skin layers covering them, and satisfies the conditional equations (I) and (II). Conditional equation (I): N1 G02B 5 / 02 2 10 2 2004 / 6 / 28 1576901 2005 / 2 / 9 1289924 2006 / 12 / 13 2006 / 12 / 13 2006 / 12 / 13 Dai Nippon Printing Co., Ltd. Japan Honda Makoto gong haijun zhang zhicheng 72001 The Company Ltd. of the Chinese Patent Agency (Hong Kong) Zi Building 22, Yingjun Centre, No.23, Gangwan Road, Hong Kong Wanzi Japan 2003 / 6 / 27 185322 / 03
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
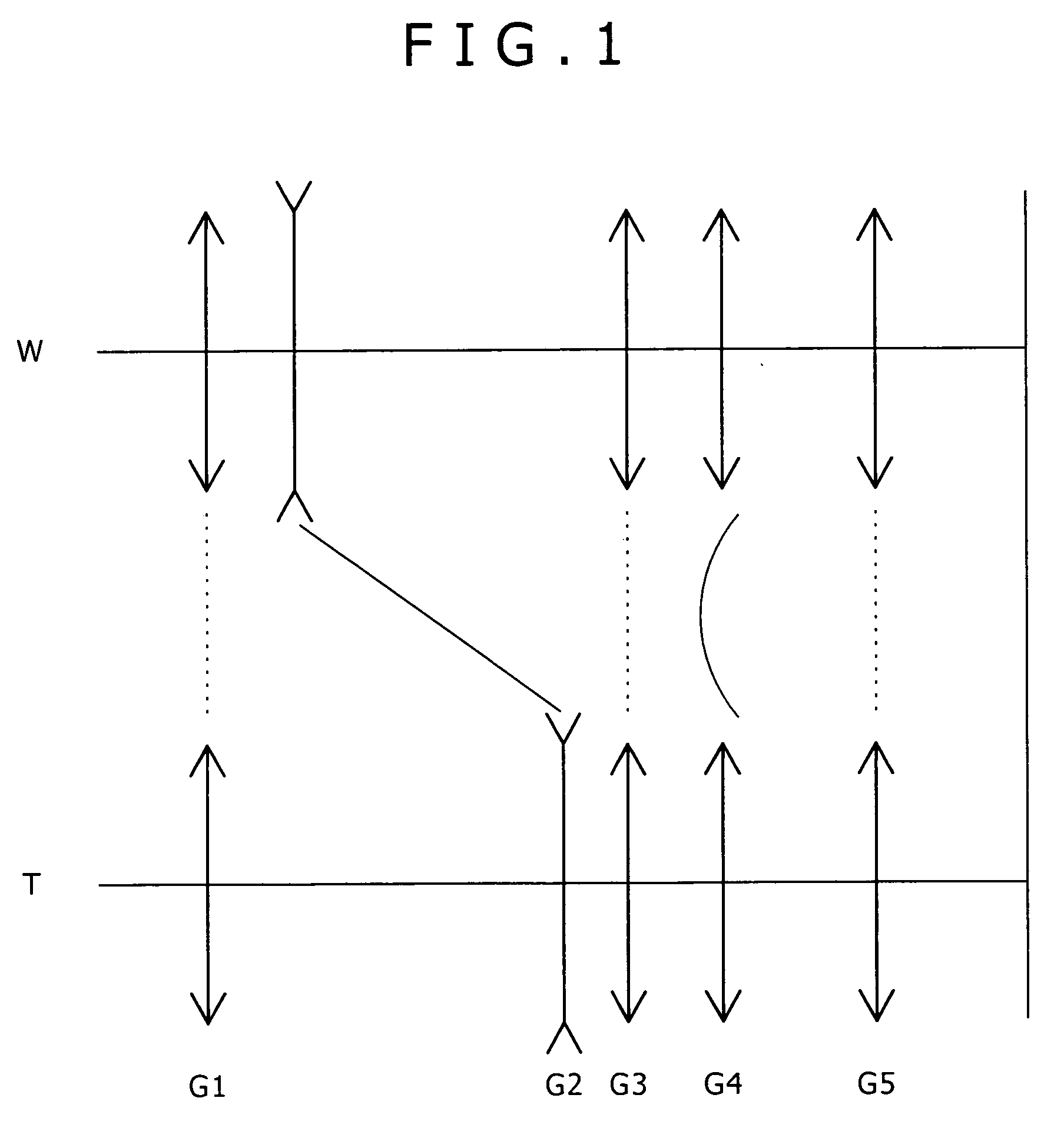
Zoom lens and image capture apparatus
InactiveUS7542212B2High zoom ratioImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsCamera body detailsMagnificationFocal position
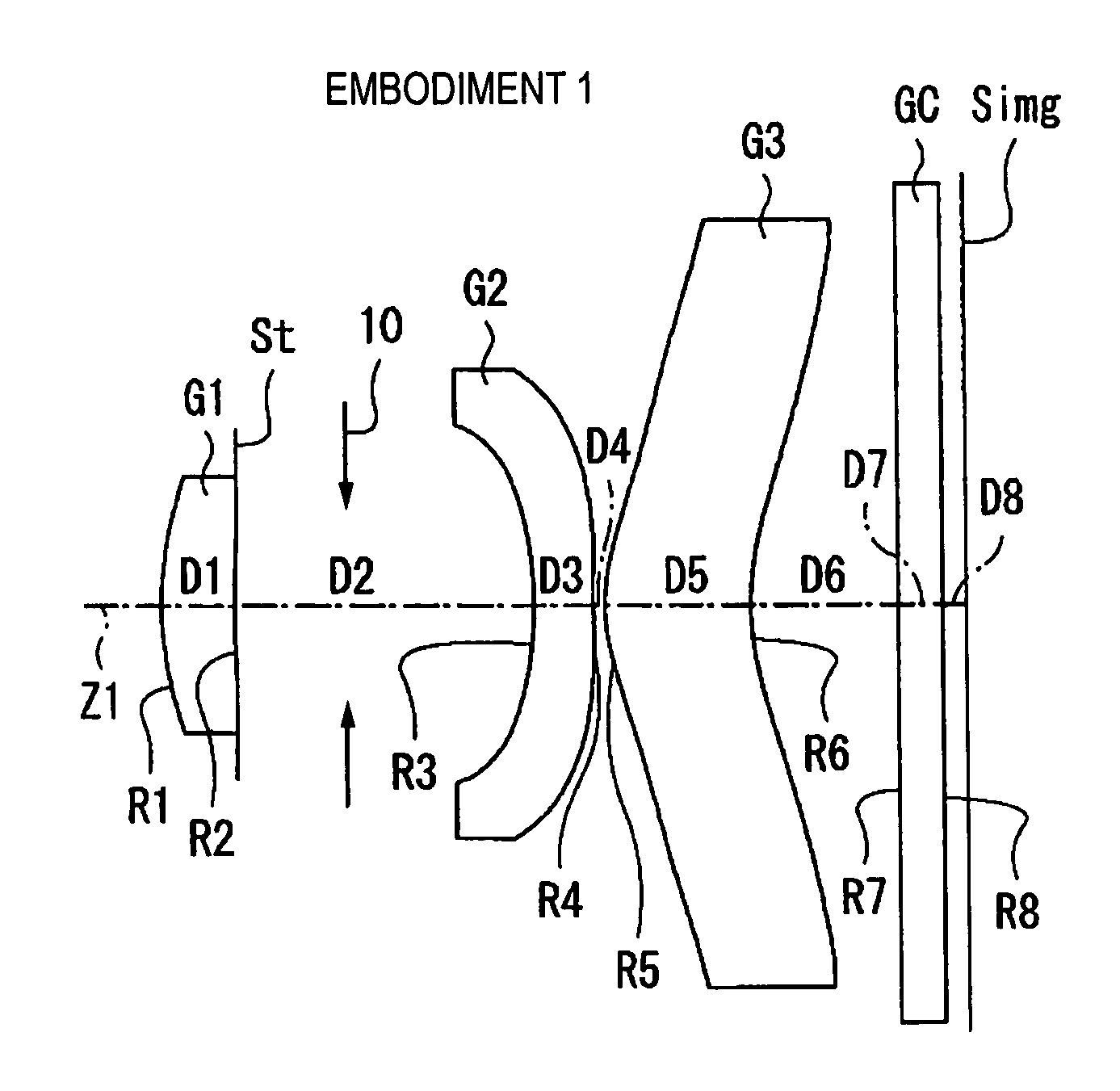
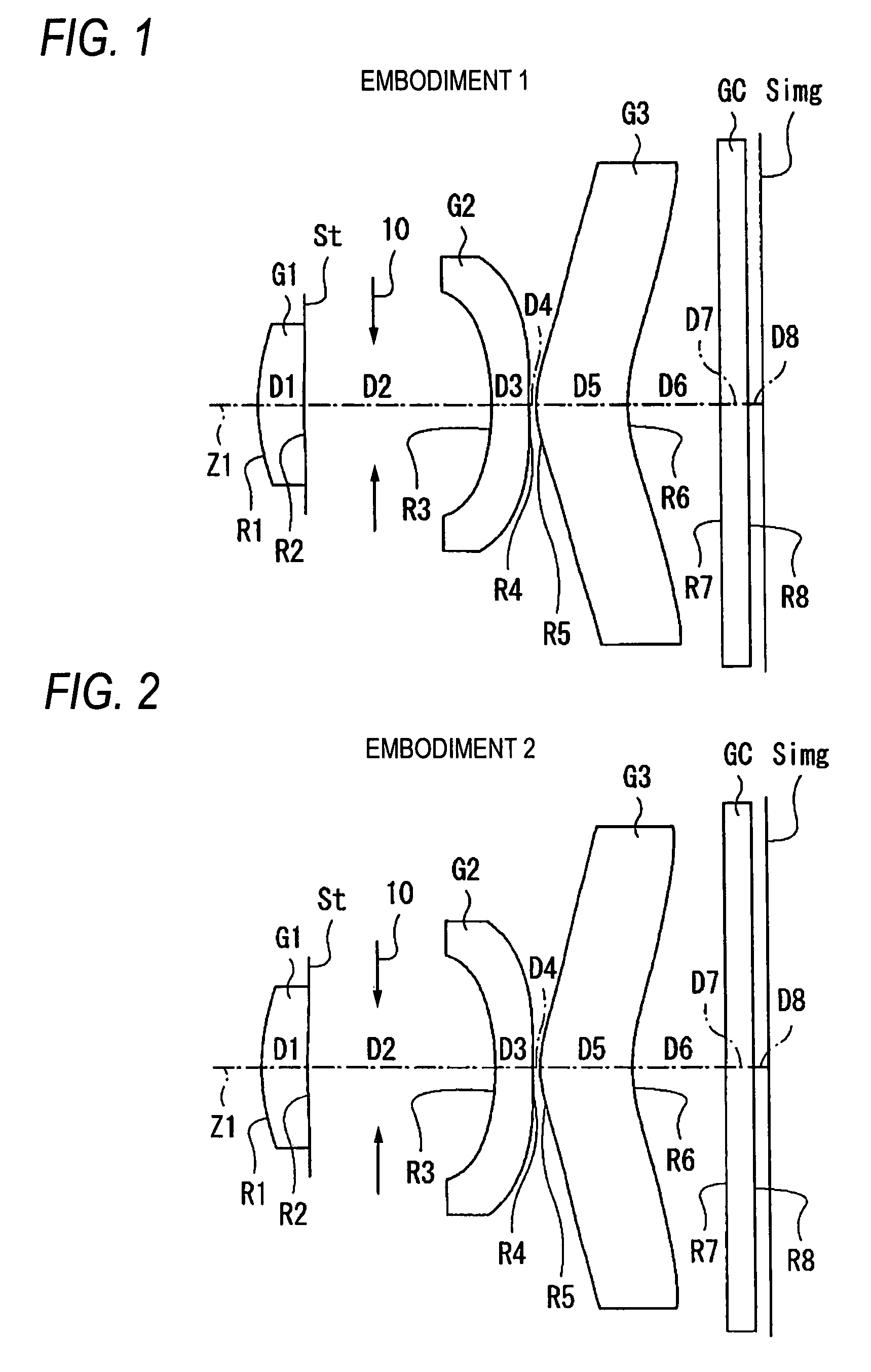
A zoom lens includes in order and from the side of an object, a first lens group having a positive refractive power and fixed in position, a second lens group having a negative refractive power and movable in position for providing mainly zooming, a third lens group having a positive refractive power and fixed in position, a fourth lens group having a positive refractive power and movable in position for performing a focal position correction due to the zooming and for focusing, and a fifth lens group including a single lens fixed in position.Each of the lens groups from the third lens group to the fifth lens group has at least one aspheric surface, and conditional equations (1) and (2) below are satisfied.|f4 / f5|<0.12 (3)0.9<β5<1.2 (4)where f4 is a focal length of the fourth lens group, f5 is a focal length of the fifth lens group, and β5 is a transverse magnification of the fifth lens group.
Owner:SONY CORP
Zoom lens and image-pickup apparatus
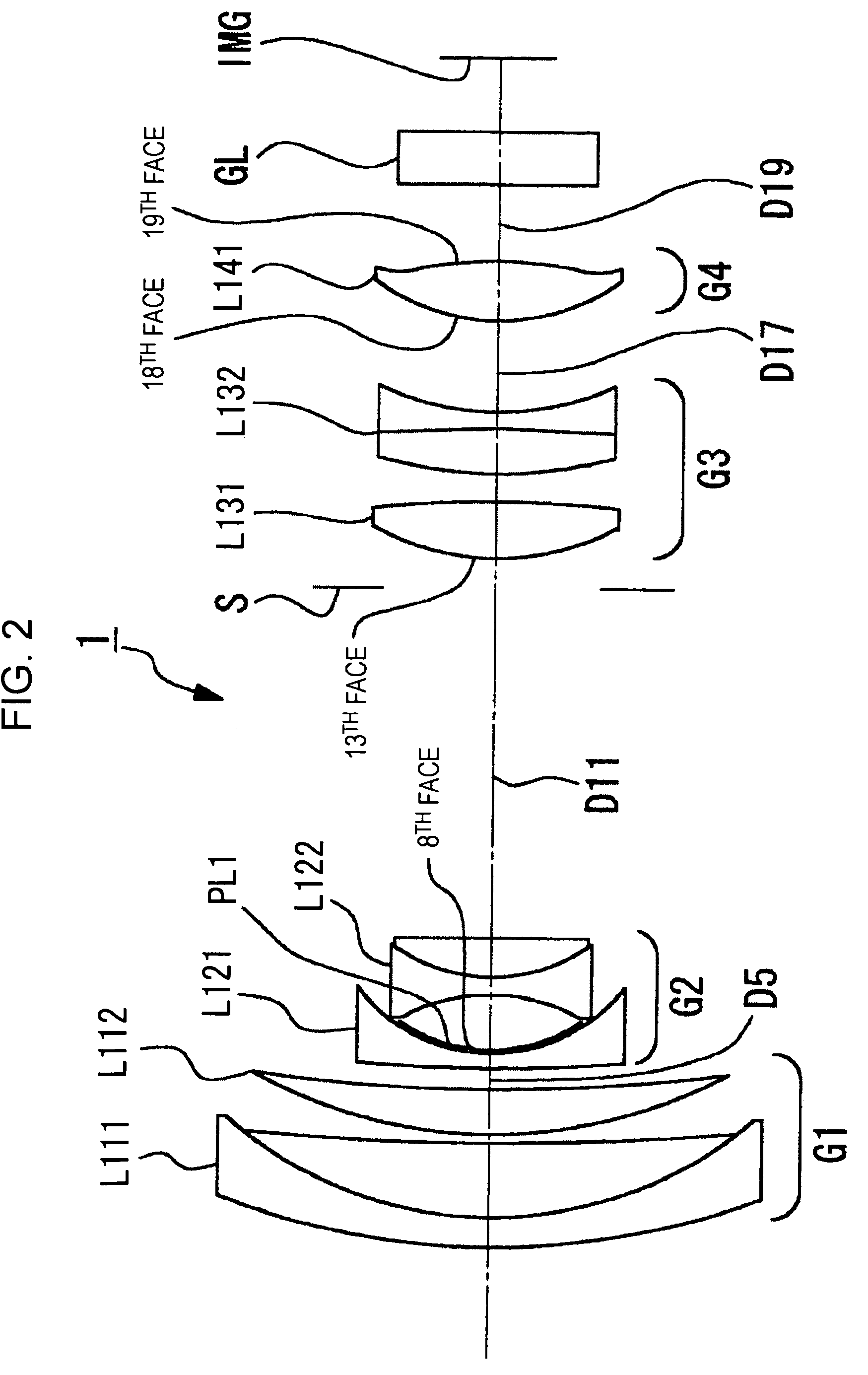
InactiveUS7706080B2Reduce thicknessHigh quality imagingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRefractive indexReversal film
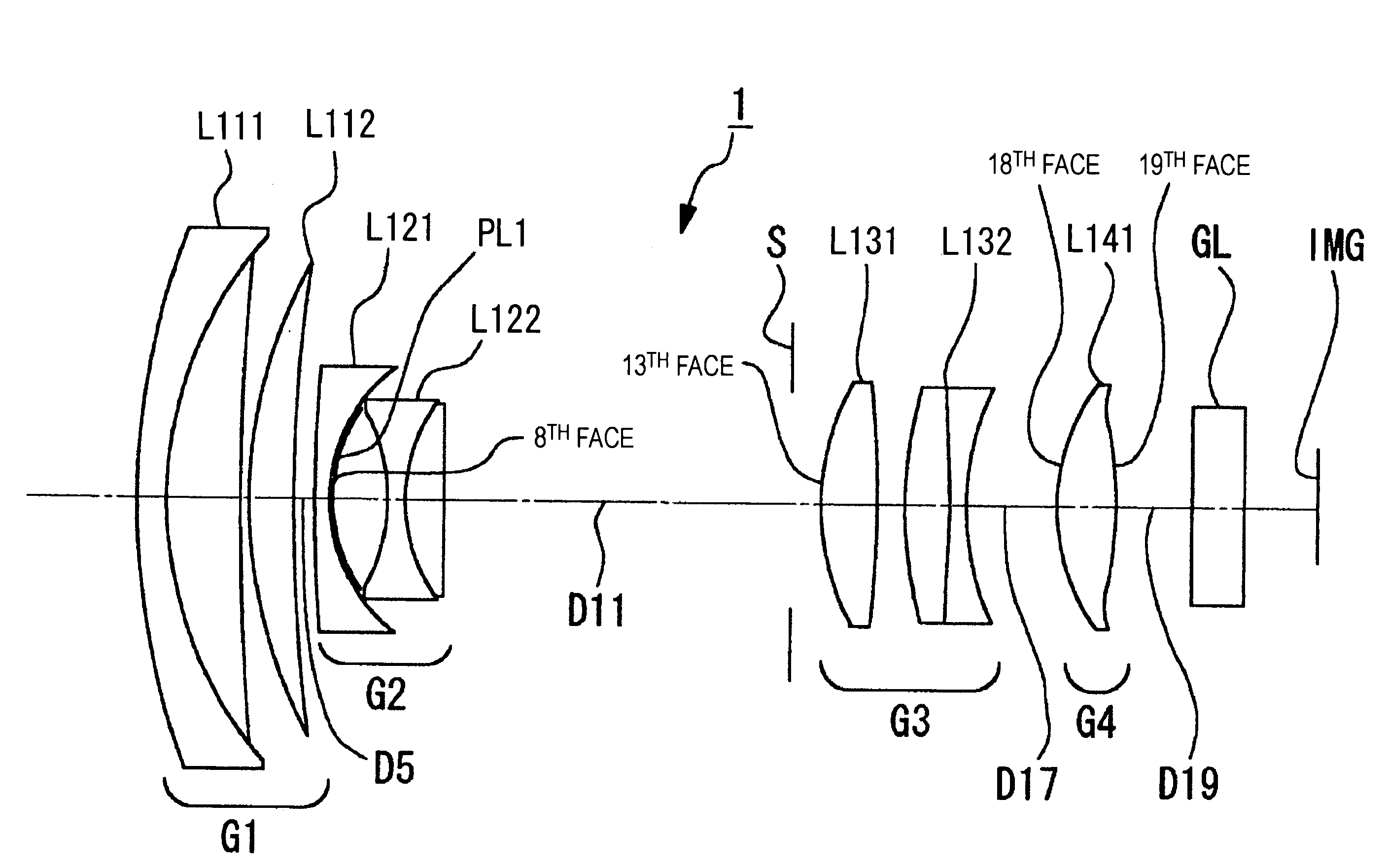
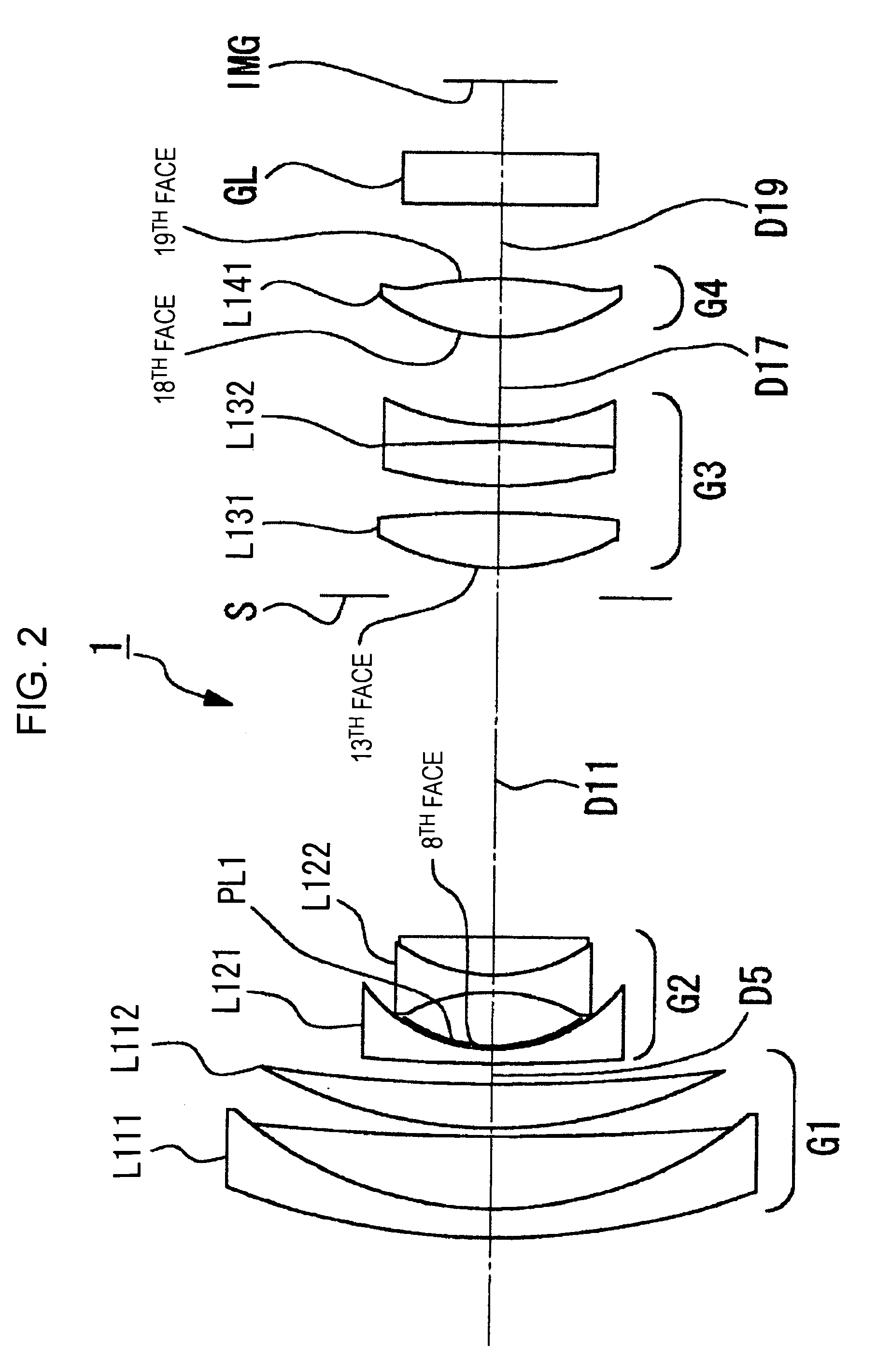
To provide a zoom lens capable of achieving stable optical quality by inhibiting an effect of assemble errors during manufacturing. A zoom lens includes a positive first lens group G1, a negative second lens group G2, a positive third lens group G3, and a positive fourth lens group G4, which are arranged from an object side in that order, and during variation in lens position from a wide angle end state to a telescopic end state, G1 and G3 are fixed, G2 is moved toward an image side, G4 moves so as to compensate fluctuations in image-surface position due to the shift of G2, and an aperture diaphragm S is fixed adjacent to the object side of G3, etc. G2 includes a negative meniscus lens L21 with a concave surface opposing the image side and a cemented lens L22 of a biconcave lens and a positive lens with a convex surface opposing the object side, which are arranged from the object side in that order, and the negative meniscus lens is a compound lens of a glass lens and a resin lens PL formed adjacent to the image side of the glass lens, the lens surface adjacent to the image side of the resin lens is aspheric, and the conditional equation (1) below is satisfied:n2>1.75, (1)where n2 is the average refractive index of glass constituting G2.
Owner:SONY CORP
Two-dimensional lattice calibrating device, two-dimensional lattice calibrating method, two-dimensional lattice calibrating program and recording medium
ActiveUS7765079B2Accurate calculationImprove accuracyTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsSimultaneous equationsRelational equation
A two-dimensional lattice calibrating device includes: a measuring unit that measures respective positions of marks for each of a plurality of measurement dispositions; a simultaneous-equations generating unit that generates simultaneous equations for acquiring deviations of the plurality of marks using a coordinate relational equation and a least-squares conditional equation that sets least-squares lines that minimize the deviation of actual position of the marks based on measurement values as coordinate axes of artifact coordinates; and a simultaneous-equations calculating unit that solves the derived simultaneous equations.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Zoom Lens and Image-Pickup Apparatus
InactiveUS20090109545A1High quality imagingReduce thicknessTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRefractive indexConvex side
To provide a zoom lens capable of achieving stable optical quality by inhibiting an effect of assemble errors during manufacturing. A zoom lens includes a positive first lens group G1, a negative second lens group G2, a positive third lens group G3, and a positive fourth lens group G4, which are arranged from an object side in that order, and during variation in lens position from a wide angle end state to a telescopic end state, G1 and G3 are fixed, G2 is moved toward an image side, G4 moves so as to compensate fluctuations in image-surface position due to the shift of G2, and an aperture diaphragm S is fixed adjacent to the object side of G3, etc. G2 includes a negative meniscus lens L21 with a concave surface opposing the image side and a cemented lens L22 of a biconcave lens and a positive lens with a convex surface opposing the object side, which are arranged from the object side in that order, and the negative meniscus lens is a compound lens of a glass lens and a resin lens PL formed adjacent to the image side of the glass lens, the lens surface adjacent to the image side of the resin lens is aspheric, and the conditional equation (1) below is satisfied:n2>1.75, (1)where n2 is the average refractive index of glass constituting G2.
Owner:SONY CORP
Immersion optical system and optical apparatus having the same
An immersion optical system that condenses light from a light source toward a first surface includes a lens having a concave lens surface closest to the first surface, a liquid being filled in a space between the concave lens surface and the first surface, wherein a conditional equation d>L / [2×tan {arcsin(NA / ni)}] is met, where d is a distance between a first point and a second point when the distance becomes maximum between the first point on the concave lens surface and the second point on the first surface in a direction substantially orthogonal to the first surface, L / 2 is a maximum distance from the second point to an edge of an irradiation area of the light on a first surface, NA is a numerical aperture of the immersion optical system, and ni is a refractive index of the liquid.
Owner:CANON KK
Imaging lens
Owner:TIANJIN OFILM OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical element, optical system and optical apparatus having antireflection coating
ActiveUS20140177059A1Good wavelength band characteristicHigh refractive indexCoatingsOptical elementsRefractive indexLength wave
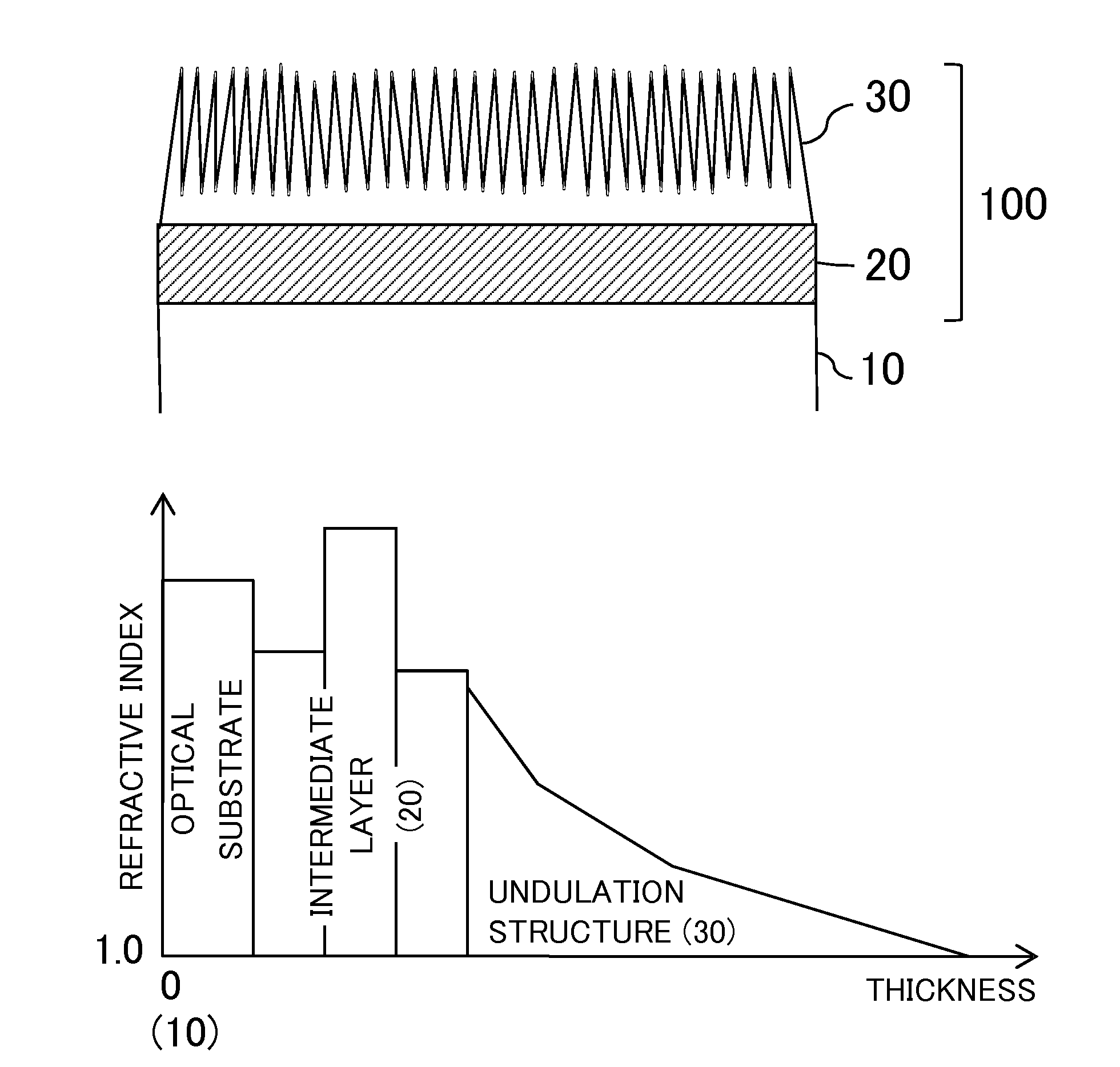
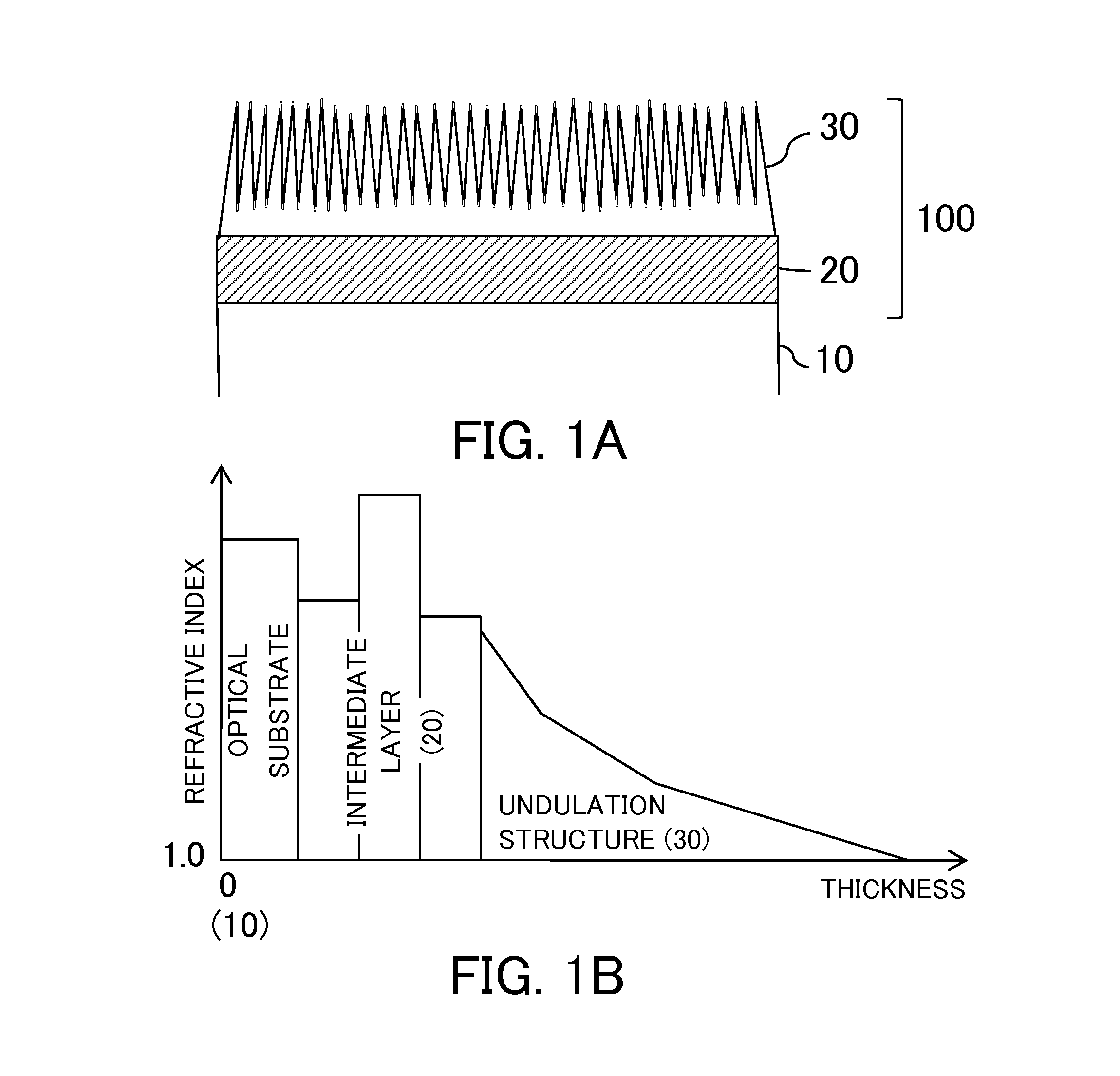
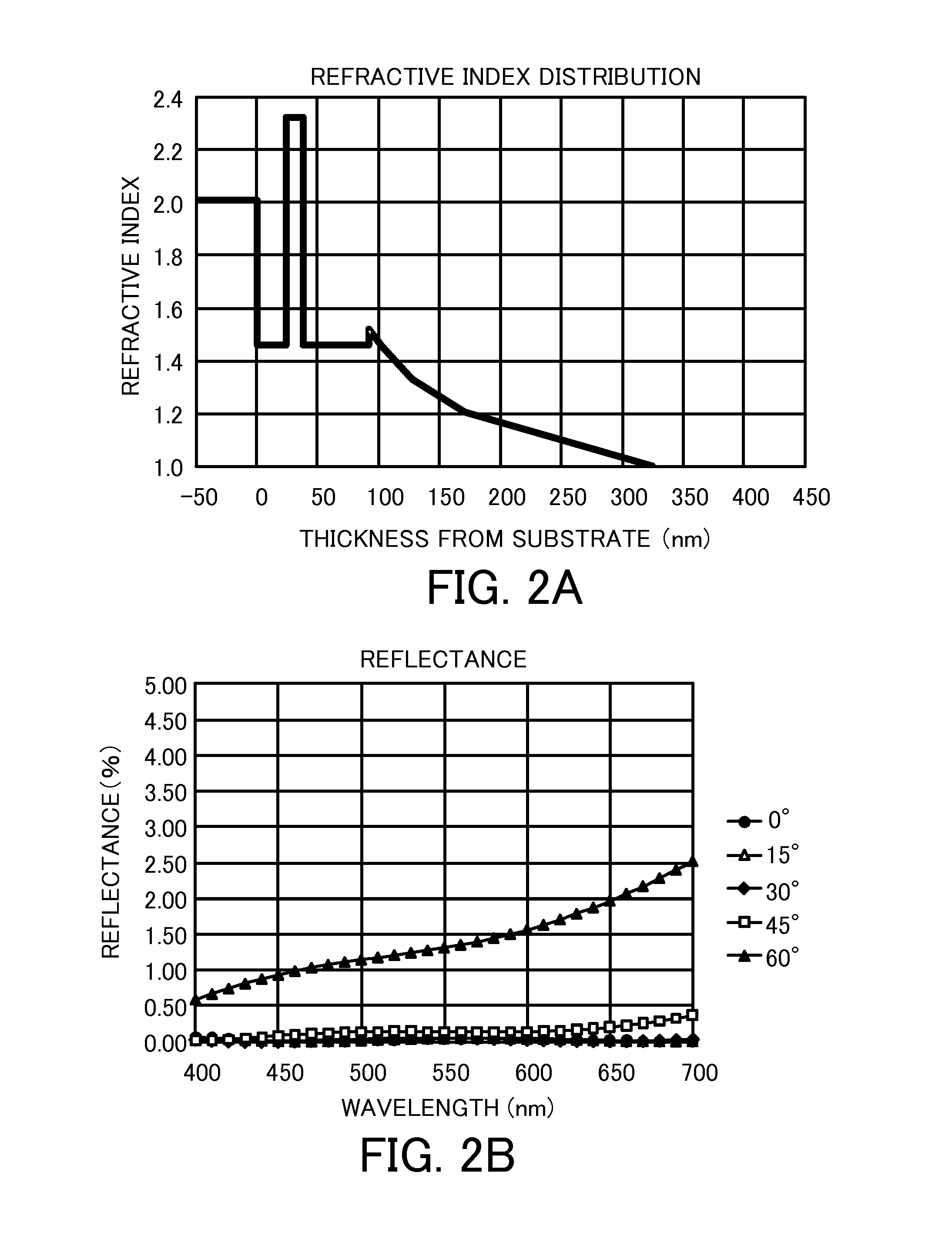
An optical element includes a transparent substrate and an antireflection coating on the substrate. The antireflection coating includes an intermediate layer on the substrate, and an undulation layer that is formed on the intermediate layer and has a plurality of convexes arrayed with spacing shorter than a shortest wavelength. The undulation layer has a portion where refractive index increases from a light incident side to the substrate. The intermediate layer has a first layer closest to the substrate, and a second layer formed on the first layer. A refractive index n1 of the first layer, a refractive index n2 of the second layer, and a refractive index ns of the substrate satisfy the following conditional equations:1.75≦ns≦2.20;n1<n2; andn1<ns.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com