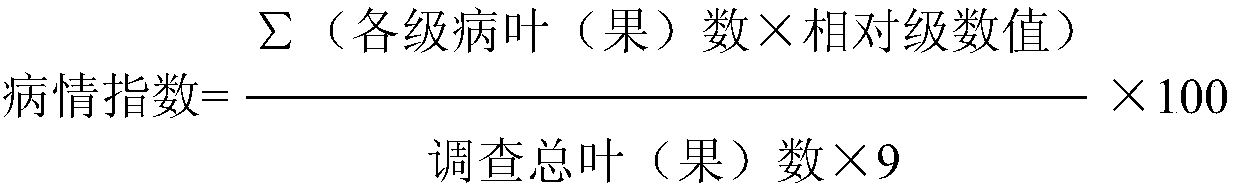
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Colletotrichum acutatum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Colletotrichum acutatum is a plant pathogen. It is the organism that causes the most destructive fungal disease, anthracnose, of lupin species worldwide. It also causes the disease Postbloom fruit drop on many varieties of Citrus, especially Valencia and navel oranges in Florida.
Strain of Paenibacillus jejuni capable of inhibiting anthrax and Fusarium and application thereof
ActiveCN109266589AGood control effectBroad spectrum antibacterialBiocideBacteriaSheath blightFusarium
The invention discloses a strain of Paenibacillus jejuni for inhibiting anthrax and Fusarium and an application thereof. A strain of Paenibacillus jamilae is isolated from the deep sea sediment, the strain was deposited at the General Microbial Center of the China Microbial Culture Collection Management Committee under accession number CGMCC No.16231 on August 8, 2018. The strain has broad-spectrum resistance to many plant pathogens, and has good control effect on fruit tree (citrus, apple, grape) anthracnose caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and vegetable wilt caused by Fusarium oxysporum.
Owner:CHINA KINGDOM AGRITECH QINGDAO
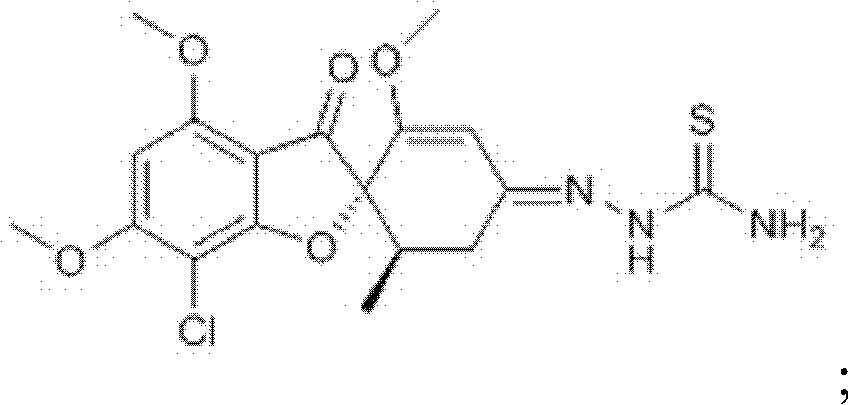
Novel thiosemicarbazone compound and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102219769AEasy to prepareEasy to operateOrganic chemistryFungicidesFusarium oxysporumColletotrichum acutatum
The invention mainly provides a thiosemicarbazone compound which has an inhibition effect on fusarium oxysporum, fusarium moniliforme, fusarium solani and colletotrichum and a preparation method thereof. The chemical structural formula of the compound is shown in the specification. According to the invention, a novel way for preventing and controlling plant diseases caused by fusarium oxysporum, fusarium moniliforme, fusarium solani and colletotrichum is provided; and the preparation method is simple and convenient and has strong operability.
Owner:福建省农业科学院农业生物资源研究所
Huperzia serrata endophytic fungi and its use in production of huperzine a
ActiveCN103103134ASolve bottlenecksSave natural resourcesFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNatural resource
The invention relates to the technical field of microbes and especially relates to huperzia serrata endophytic fungi and its use in production of huperzine a. The huperzia serrata endophytic fungi are named as Colletotrichum sp. SY-1, are preserved in the China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) on August 19, 2011, and have the preservation number CCTCC M2011293. Through fermentation, the huperzia serrata endophytic fungi can produce a huperzine a compound. Through utilization of characteristics of microbe-based huperzine a production and the modern fermentation breeding technology, huperzine a industrial production is realized; bottleneck problems of huperzine a exploitation are solved; and the endangered huperzine a natural resource is protected.
Owner:吴水生
Chestnut preservation method
ActiveCN106070601AReduce the probability of mildewReduce browning rateEdible seed preservationFreeze-dryingInsect pest
The present invention discloses a chestnut preservation method and belongs to the technical field of chestnut preservations. The preservation method consists of the following steps: (1) fruit selecting: insect pest free, full and harmless chestnuts are selected; (2) preservative treating: the selected chestnuts are soaked with the preservative for 15-35 minutes; (3) clean water soaking: the treated chestnuts in the step (2) are soaked with the clean water at 40 to 50 DEG C for 20-40 minutes; (4) biological treating: the treated chestnuts in the step (3) are soaked with water solution containing endogenetic bacteria for 15-25 minutes, and the soaked chestnuts are air-dried; (5) water content controlling: the treated chestnuts in the step (4) are freeze-dried or cold-air dried to control the moisture content to be 38-44%; and (6) refrigerating: the treated chestnut in the step (5) are put into a cold storage to be preserved at a humidity of 85-95% and a temperature of -4 to 0 DEG C. The endogenetic bacteria are endogenetic bacteria separated from the chestnuts to be preserved and at least have both obvious inhibitions on fusarium solani and colletotrichum gloeosporioides.
Owner:湖北大别山药业股份有限公司
Bacillus substilis BS01 and inoculant thereof, as well as application of bacillus substilis BS01 to inhibition of picked fruit pathogenic bacteria
InactiveCN106434445AOptimizing componentsIncrease contentBiocideBacteriaAntibacterial activityCulture mediums
The invention relates to bacillus substilis BS01 and an inoculant thereof, as well as application of the bacillus substilis BS01 to inhibition of picked fruit pathogenic bacteria. The bacillus substilis BS01 is preserved in Microbial Culture Preservation Center, Guangdong Province (GDMCC) on August, 29, 2016, and the preservation number is GDMCC NO.60069. The in-vitro antibacterial activity of the supernatant of the fermenting liquid of the bacillus substilis BS01 strain provided by the invention on the picked fruit pathogenic bacteria, particularly colletotrichum, can reach 90 percent or above, and is about three times of the antibacterial activity of the supernatant of the fermenting liquid generated by fermentation of the common LB culture medium before optimization; and the inhibition effect of the fermenting liquid of the BS01 strain obtained by the fermentation condition after optimization on anthracnose, such as banana anthracnose, tomato anthracnose and avocado anthracnose, can reach 65 percent or above.
Owner:POMOLOGY RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
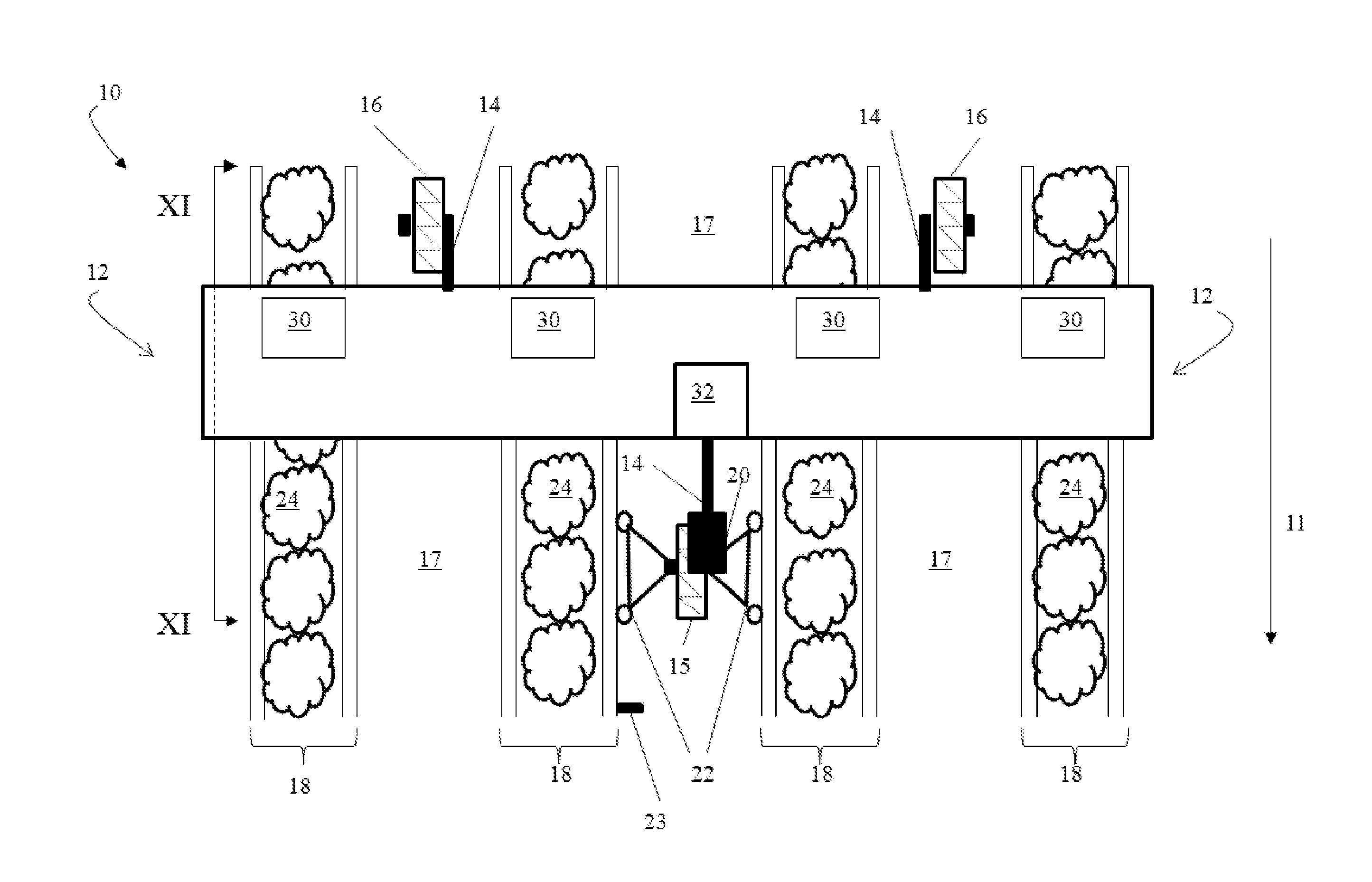
Method for Controlling Fungal Plant Pathogens Using a Combination of UV Radiation Followed by Antagonist Application and Dark Period
InactiveUS20150283276A1Reduced survivalReduce infectionBiocideMaterial analysis by optical meansDiseasePollen
Strawberries are available year-around from production in the field or from controlled environments (e.g. high and low tunnel culture and greenhouse). Diversity of production conditions results in challenges in controlling diseases before, during, and after harvest. Fungicides, traditionally used to control diseases, have limitations. UV-C irradiation followed by a dark period was used to kill two major pathogens of strawberry, Botrytis cinerea and Colletotrichum acutatum. The UV-C irradiation and dark period was followed by repopulation with beneficial biocontrol microorganisms. The 4 hr dark period prevented activation of a light-dependent UV-C damage repair mechanism in the pathogens. This combination protocol makes it possible to use a lower dose of UV-C for reduction and / or elimination of pathogens. A mobile treatment apparatus was designed to provide the appropriately timed UV-C doses, dark period, and sprayable doses of biocontrol microorganisms. The UV-C dose and repeated exposure did not affect pollen germination or cause chlorophyll degradation in strawberry leaves.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Preparation of Streptomyces antibioticus and metabolite thereof and application of Streptomyces antibioticus in aspect of bacterium resistance
The invention discloses preparation of Streptomyces antibioticus and metabolite thereof and application of the Streptomyces antibioticus in the aspect of bacterium resistance. The strain is named as Streptomyces antibioticus PPI-16, the preservation number is GDMCC NO: 60970, and the strain was preserved in the Guangdong Microbiological Culture Collection Center in the fifth floor, No. 59 Building, No. 100 Courtyard, Xianliezhong road, Guangzhou City on March 5, 2020. Active compounds generated by the Streptomyces antibioticus can inhibit various pathogenic fungi such as Colletotrichum lagenarium, Colletotrichum acutatum, Colletotrichum nicotianae and Candida albicans, and new resources are provided for research and development of antibiotic.
Owner:PLANT PROTECTION RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Methods and products for inhibiting growth of fungal pathogens on turfgrass
Methods and products for inhibiting growth of fungus and fungal disease on a plant. Methods comprise contacting at least a portion of a plant or plant seed together with a fungicidal composition comprising a fungicidal carboxamide. Products comprise any of leaves, crowns, roots, stolons, seed, seedlings, sod, and any combination thereof, treated with a fungicidal carboxamide. Preferred pathogens are of the genus Colletotrichum, preferred disease is anthracnose, preferred fungicides are carboxamides, and preferred plants are turfgrass.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Technique, Method, and Composition for Controlling Plant Pathogens
The present invention relates to a technique, a method, and a composition for controlling plant pathogens comprising a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens KBC1004 strain and a culture medium thereof as active ingredients. Particularly, the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens KBC1004 strain and the culture medium thereof of the present invention have excellent antifungal activity against various plant pathogens such as Rhizoctonia solani AG-2-2(IV) causing turfgrass diseases, Botrytis cinerea causing gray mold rot, Colletotrichum acutatum causing chili pepper anthracnose, Colletotrichum gleosprodes causing sweet persimmon anthracnose, Rhizoctonia cerealis causing yellow patch, Rhizoctonia solani AG-1(1A) causing brown patch, Sclerotium rolfsii causing southern blight, and Phytophthora drechsleri causing kiwifruit phytophthora blight, so that they can be efficiently used as an eco-friendly composition for controlling plant pathogens.
Owner:KOREA BIO CHEM
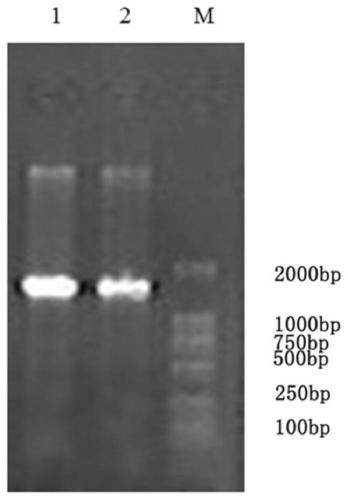
Detection of fungal pathogens using the polymerase chain reaction
InactiveUS20030099946A1Detailed informationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAlternariaOrganism
The present invention relates to the use of primers in polymerase chain reaction assays for the detection of fungal pathogens Colletotrichum acutatum, Alternaria spp., and Cladosporium carpophilum. Specific primers are identified as being useful for the identification of fungal isolates using PCR based techniques. Also described are novel extraction buffer solutions for use in isolating DNA from an organism, methods of extracting DNA from tissue, and methods of performing PCR analysis on DNA extracted from tissue.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Colletotrichum Corda strain and biological herbicide containing spores thereof
InactiveCN101919412ASafe agricultural productionRaw materials are easy to getBiocideFungiBiotechnologyWeed
The invention provides a biological herbicide containing spores produced by a Colletotrichum Corda strain with a collection number of CGMCC No.2867, and a method for preparing the biological herbicide and a method for using the herbicide to remove weeds from crops. The invention particularly provides a biological herbicide for removing digitaria sanguinalis from crops, which comprises the spores produced by the Colletotrichum Corda strain with the collection number of CGMCC No.2867. The biological herbicide can prevent and control weeds in dicotyledons, and prevent and control weeds in monocotyledons; and the strain particularly has 85 to 100 percent of control effect on a target weed digitaria sanguinalis, particularly on plants with less than 3 leaves.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
A kind of chestnut preservation method
ActiveCN106070601BReduce the probability of mildewReduce browning rateEdible seed preservationFreeze-dryingInsect pest
The present invention discloses a chestnut preservation method and belongs to the technical field of chestnut preservations. The preservation method consists of the following steps: (1) fruit selecting: insect pest free, full and harmless chestnuts are selected; (2) preservative treating: the selected chestnuts are soaked with the preservative for 15-35 minutes; (3) clean water soaking: the treated chestnuts in the step (2) are soaked with the clean water at 40 to 50 DEG C for 20-40 minutes; (4) biological treating: the treated chestnuts in the step (3) are soaked with water solution containing endogenetic bacteria for 15-25 minutes, and the soaked chestnuts are air-dried; (5) water content controlling: the treated chestnuts in the step (4) are freeze-dried or cold-air dried to control the moisture content to be 38-44%; and (6) refrigerating: the treated chestnut in the step (5) are put into a cold storage to be preserved at a humidity of 85-95% and a temperature of -4 to 0 DEG C. The endogenetic bacteria are endogenetic bacteria separated from the chestnuts to be preserved and at least have both obvious inhibitions on fusarium solani and colletotrichum gloeosporioides.
Owner:湖北大别山药业股份有限公司
Bio-control bacterium Kg2A capable of efficiently inhibiting fusarium and bacillus anthraci and applications thereof
ActiveCN104988096AHas broad-spectrum antibacterial propertiesEasy to trainBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismMicrobial pesticide
The invention belongs to the field of microbial pesticide, and specifically relates to a bio-control bacterium Kg2A and applications thereof on controlling pepper wilt and pepper anthracnose. The bio-control bacterium is Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Kg2A, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.10918. The invention also discloses the molecular biological characteristics, physiological-biochemical characteristics, and culture method of the provided bacterium strain, and proves that the provided bio-control bacterium Kg2A has an activity on inhibiting fusarium that may cause pepper wilt and bacillus anthraci that can cause pepper anthracnose.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Penicillium sp. strain and application thereof
InactiveCN108660083AHigh antagonistic rateStrong antagonistic effectBiocideFungiBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to a penicillium sp. strain and an application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microbe applications. The provided penicillium sp. strain has the collection number of CGMCC No.14142. The provided penicillium sp. strain can have an antagonistic action for colletotrichum, a culture of the penicillium sp. strain has an antagonistic action for colletotrichum throughliquid culture, and the antagonistic rate of colletotrichum is 70%-90%.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof. The strain number of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens is MH71, and the register number of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No.6978. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens has obvious inhibition effect on multiple pathogenic fungi such as botrytis cinerea, fusarium disease, brown rot, root rot and colletotrichum acutatum on fruits and vegetables and pathogenic bacteria such as black rot of Chinese cabbage, brown blotch diseases of oyster mushroom and angular leaf spot of cucumber. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens MH71 is fast in breeding speed, can be artificially cultured and has strong stress resistance capacity and important significance for prevention and treatment of soil-borne diseases such as cabbage wilt disease caused by fungi.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Colletotrichum Corda strain and biological herbicide containing spores thereof
InactiveCN101919412BSafe agricultural productionRaw materials are easy to getBiocideFungiBiotechnologySpore structure
The invention provides a biological herbicide containing spores produced by a Colletotrichum Corda strain with a collection number of CGMCC No.2867, and a method for preparing the biological herbicide and a method for using the herbicide to remove weeds from crops. The invention particularly provides a biological herbicide for removing digitaria sanguinalis from crops, which comprises the spores produced by the Colletotrichum Corda strain with the collection number of CGMCC No.2867. The biological herbicide can prevent and control weeds in dicotyledons, and prevent and control weeds in monocotyledons; and the strain particularly has 85 to 100 percent of control effect on a target weed digitaria sanguinalis, particularly on plants with less than 3 leaves.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Application of camellia oleifera extract in antisepsis and preservation
InactiveCN101543242BGood anti-corrosion and fresh-keeping activityGood fresh-keeping activityFruit and vegetables preservationAlternariaCamellia oleifera
The invention discloses an application of camellia oleifera extract in antiseptic and fresh preservation. The camellia oleifera extract can be applied to post-harvest fruit freshness preservation, and the post-harvest pathogens to fruit include Penicillium italicum Wehmer, Penicillium digitatum Sacc., Geotrichum candidum Link ), banana crown rot (Colletotrichum musae spp), banana anthracnose (Colletorchum musae), litchi downy mildew (Peronophythora litchi), litchi anthracnose (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides Penz.), loquat anthracnose (Colletotrichum acutatum Simmonds), loquat Alternaria Tenuis Nees, Pestalotiopsis eriobotryfolia, etc. have good control effects, and have good fresh-keeping activities on various fruits such as citrus, litchi, banana, loquat, longan, and mango. According to this characteristic of camellia oleifera, an efficient and pollution-free green plant-source fruit preservative can be developed, which has significant social and economic benefits.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Standby form of colletotrichum acutatum laboratory material, and preparation and application method thereof
InactiveCN106754423ALong-term vitalityConvenience to workFungiMicroorganism based processesMyceliumMedicine
The invention discloses a standby form of a colletotrichum acutatum laboratory material, and a preparation and application method thereof. A pure and non-pollution conidium of colletotrichum acutatum is used as the standby form of the laboratory material, and the conidium in the standby form is stored in sterile water. The preparation and application method of the standby form comprises the following steps of (1) using a triangular flask as a culture vessel for preparing the conidium of the colletotrichum acutatum; (2) preparing the standby form of the colletotrichum acutatum material; (3) calibrating the content of the conidium in the standby form of the colletotrichum acutatum material; (4) daily storing the standby form of the colletotrichum acutatum material; (5) applying the standby form of the colletotrichum acutatum material. The standby form of the colletotrichum acutatum laboratory material, and the preparation and application method thereof provided by the invention has the advantages that (1) the growth of the conidium in the standby form can be suspended, but can be back to normal after the conidium is transferred to a culture medium; (2) the conidium in the standby form can be applied in related work at any time, a thallus material can be directly provided for a test link requiring the conidium, and the working procedure of repeatedly preparing and culturing the conidium when a mycelium is used as a standby material can be omitted, so that the work can be carried out conveniently and quickly; (3) the triangular flask is used as the culture vessel, so that the non-pollution conidium liquid can be easily prepared and obtained; (4) the conidium content of the standby conidium liquid can be calibrated, the conidium can be taken and used accurately and quantitatively when being applied, and the standardization of the technical method is facilitated.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for inducing Colletotrichum gloesporioides to generate conidia
ActiveCN108998404AHigh sporulationLarge and stable spore productionFungiMicroorganism based processesDiseaseSpore
The invention discloses a method for inducing Colletotrichum gloesporioides to generate conidia, belonging to the technical field of plant protection. The method comprises the following steps: (1) activation of Colletotrichum gloesporioides: inoculating a culture medium with the Colletotrichum gloesporioides, and carrying out activation culturing so as to obtain activated Colletotrichum gloesporioides; and (2) generation of the conidia by induction: putting the Colletotrichum gloesporioides activated in the step (1) into an oven, carrying out high-temperature culturing, then taking cultured Colletotrichum gloesporioides out of the oven, placing the cultured Colletotrichum gloesporioides into a constant-temperature incubator with a temperature of 27 DEG C, and carrying out constant-temperature culturing for 7 days so as to realize induction of the generation the conidia. According to the invention, the Colletotrichum gloesporioides is successively subjected to high-temperature culturingand constant-temperature culturing for the first time, so the method provided by the invention realizes simple, convenient and large-scale induction of Colletotrichum gloesporioides for generation ofa large number of conidia, and has important significance to researches on determination of pathogenic ability of the Colletotrichum gloesporioides, determination of biological activity of a bactericide of the Colletotrichum gloesporioides, identification of disease resistance of a variety, etc.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Strain S2-16 for growing and secreting secondary metabolites of chlorogenic acid and application thereof
ActiveCN108192830AIn line with the research resultsGood antibacterial effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismChlorogenic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial application, particularly relates to a strain S2-16 for growing and secreting secondary metabolites of chlorogenic acid and application thereof. The strain S2-16 for growing and secreting secondary metabolites of chlorogenic acid has the taxonomy name of Colletotrichum acutatum S2-16, and is collected in CCTCC (China Center For Type CultureCollection) on December 14, 2017. The preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 2017789. A coarse extract of the strain S2-16 can inhibit gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria, and can realize the anti-oxidization and free radical clearing effects; the DPPH clearing rate reaches 77.7 percent.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
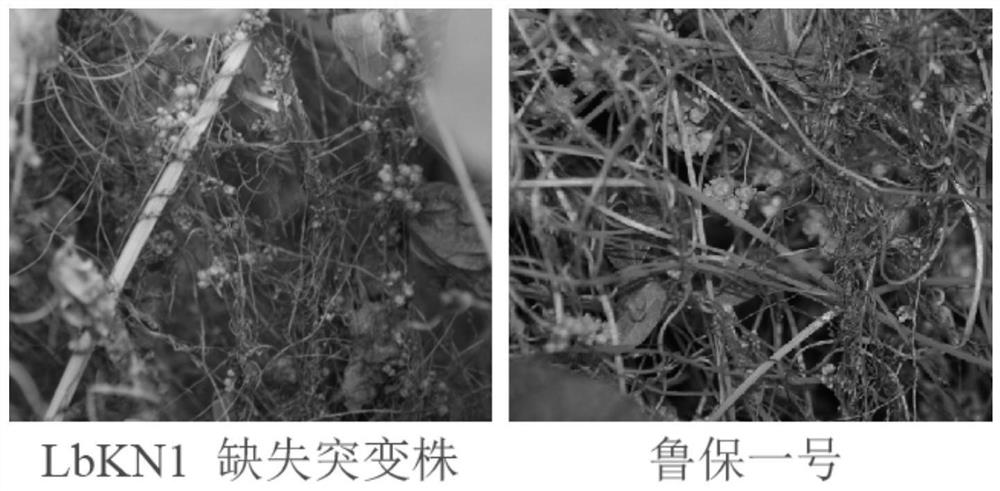
LbKN1 gene derived from Lubao No.1 and application of LbKN1 gene
The invention provides an LbKN1 gene derived from Lubao No.1. An amino acid sequence coded by the LbKN1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The LbKN1 gene can be used for modifying a colletotrichum acutatum dodder specialized type so as to prevent and treat dodder, and the modification is deletion, knockdown or knockout. The LbKN1 gene provided by the invention can be used for regulating and controlling the pathogenicity of colletotrichum acutum dodder seed specialized type (Colletotrichum acutum f. Sp. Cutanea) on the dodder seeds, so that the pathogenicity of the colletotrichum acutum dodder seedspecialized type (Colletotrichum acutum f. Cutanea) on the dodder seeds, specifically, the spore production capacity of the colletotrichum acutatum dodder specialized strain without the LbKN1 gene isremarkably higher than that of a wild strain. The LbKN1 gene participates in a biocontrol bacterium pathogenicity related process, and can be applied to the field of gene engineering for improving the pathogenicity of Lubao No.1 and creating an efficient biocontrol bacterium agent.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A kind of bacillus subtilis bs01, its bacterial agent and its application in inhibiting postharvest pathogenic bacteria of fruits
InactiveCN106434445BEasy to prepareConducive to industrial development and applicationBiocideBacteriaMicrobial agentAntibacterial activity
Owner:POMOLOGY RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Brevibacillus panacihumi bacterial strain and application thereof
ActiveCN108395999AGood control effectBroaden screening sourcesBiocideBacteriaDiseaseTreatment effect
The invention provides a Brevibacillus panacihumi bacterial strain and an application thereof. The bacterial strain is the Brevibacillus panacihumi bacterial strain FJAT-10657, and is preserved in a China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 14th, Jan, 2016 with a preservation number being CGMCC No. 11998. A fermentation supernatant of the Brevibacillus panacihumi bacterial strainFJAT-10657 has inhibition effect on gloeosporium musarum, lasiodiplodia theobromae, Colletotrichum acutatum Simmonds and black spot disease on wax apple, the Brevibacillus panacihumi bacterial strainhas good prevention and treatment effects for gloeosporium musarum, and widens a screening source of a gloeosporium musarum biological control bacterial strain.
Owner:福建省农业科学院农业生物资源研究所
Lubao No.1 mutant strain and application thereof
ActiveCN111440732AStable virulence inheritanceHigh sporulation capacityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySpore
The invention provides a cuscutaspp biocontrol bacterium TB182, i.e., colletotrichum acutatum with a collection number of CGMCC No.17472. The colletotrichum acutatum can be used for preventing and curing Cuscuta chinensis Lam., Cuscuta australis R. Br. Or Cuscuta japonica Choisy. The cuscutaspp biocontrol bacterium provided by the invention is obtained by a molecular biology way, so that the cuscutaspp biocontrol bacterium has a high spore production ability, has stable pathogenicity inheritance for the cuscutaspp, and provides a new tool for the biological prevention and control of the cuscutaspp.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Base fertilizer capable of preventing cotton anthracnose
InactiveCN104496646AReasonably control the amount of inoculationInhibition of reproductive growthFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologyColletotrichum acutatum
The invention relates to a base fertilizer capable of preventing cotton anthracnose. The base fertilizer capable of preventing the cotton anthracnose is prepared by inoculating penicillium in a conventional base fertilizer and simultaneously adding an alkaline copper sulfate solution; the penicillium can be used for killing colletotrichum but also can eb used for killing a plurality of beneficial bacteria in soil, so that based on research carried out for years and by reasonably controlling the inoculation amount of the penicillium in the base fertilizer, the base fertilizer capable of preventing the cotton anthracnose can be used for restraining the propagation growth of the colletotrichum, and can be used for thoroughly and effectively killing the colletotrichum by using the alkaline copper sulfate solution.
Owner:刘长华
Microorganism derived from Chinese chestnuts and application thereof as well as microbial agent preparation method
The invention relates to the field of a microorganism, and particularly relates to a microorganism derived from Chinese chestnuts and an application thereof as well as a microbial agent preparation method. The microorganism derived from Chinese chestnuts is collected at the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on November 12, 2013 with the CCTCC No. M2013568, and the collection name of the microorganism is bacillus amyloliquefaciens subspecies CMN1308. The microorganism is an endophyte of Chinese chestnuts and has good effects in the terms of preventing and treating Chinese chestnut seed rot caused by at least one of cryponectria parasitica, fusarium solani, stachybotrys atra, penicillium expansum and colletotrichum, serving as a feed additive to promote the growth of animals and improve the immune ability and the like. Compared with the prior art using chemical pesticides for preventing and treating the seed rot, the microorganism does not cause the harm to human health and environmental pollution, and has important environmental protection significance.
Owner:HUANGGANG NORMAL UNIV
Detection of fungal pathogens using the polymerase chain reaction
The present invention relates to the use of primers in polymerase chain reaction assays for the detection of fungal pathogens Colletotrichum acutatum, Alternaria spp., and Cladosporium carpophilum. Specific primers are identified as being useful for the identification of fungal isolates using PCR based techniques. Also described are novel extraction buffer solutions for use in isolating DNA from an organism, methods of extracting DNA from tissue, and methods of performing PCR analysis on DNA extracted from tissue.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
A lbkn1 gene derived from "Lubao-1" and its application
ActiveCN111549039BModification of pathogenicityBiocideBacteriaGenetic engineeringAntibacterial agent
The invention provides a kind of "Lubao No. 1" wxya Gene, its coded amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. the above wxya The gene can be used to transform the dodder specialized type of anthrax oxysporum to control dodder, and the modification is deletion, knockdown or knockout. provided by the invention wxya Genes capable of regulating dodder specialization of Anthrax oxysporum ( Colletotrichum acutatum f.sp. cuscuta ) for the pathogenicity of dodder, specifically in the sporulation ability: missing wxya The spore production of the Cuscuta oxysporum dodder specialized type was significantly higher than that of the wild-type strain. wxya The gene is involved in the process related to the pathogenicity of biocontrol bacteria, and can be applied in the field of genetic engineering to improve the pathogenicity of "Lubao No. 1" and create high-efficiency biocontrol bacteria.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Detection of fungal pathogens using the polymerase chain reaction
InactiveUS20060166246A1Detailed informationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFungal isolateBiological body
The present invention relates to the use of primers in polymerase chain reaction assays for the detection of fungal pathogens Colletotrichum acutatum, Ateniaria spp., and Cladosporium carpophilum. Specific primers are identified as being useful for the identification of fungal isolates using PCR based techniques. Also described are novel extraction buffer solutions for use in isolating DNA from an organism, methods of extracting DNA from tissue, and methods of performing PCR analysis on DNA extracted from tissue.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Liquid fermentation culture medium for colletotrichum spore production
ActiveCN109355207AReduce the cost of fermentation cultureEasy to getFungiMicroorganism based processesSporeColletotrichum acutatum
The invention provides an excellent culture medium suitable for liquid fermentation culture of colletotrichum. Every 1,000 ml of the culture medium is prepared from 20-40 g of shepherd's purse, 3-6 gof soybean meal, 2-4 g of saccharose, 0.5 g of monopotassium phosphate and the balance 1,000 ml of distilled water, wherein the pH is adjusted to be 6.5. By means of the culture medium, a large quantity of colletotrichum conidiospores can be quickly and efficiently obtained. According to the excellent culture medium, weeds serve as the main component of the culture medium, the cost for fermentation culture of colletotrichum is reduced, and the culture medium for efficient colletotrichum spore production is obtained.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com