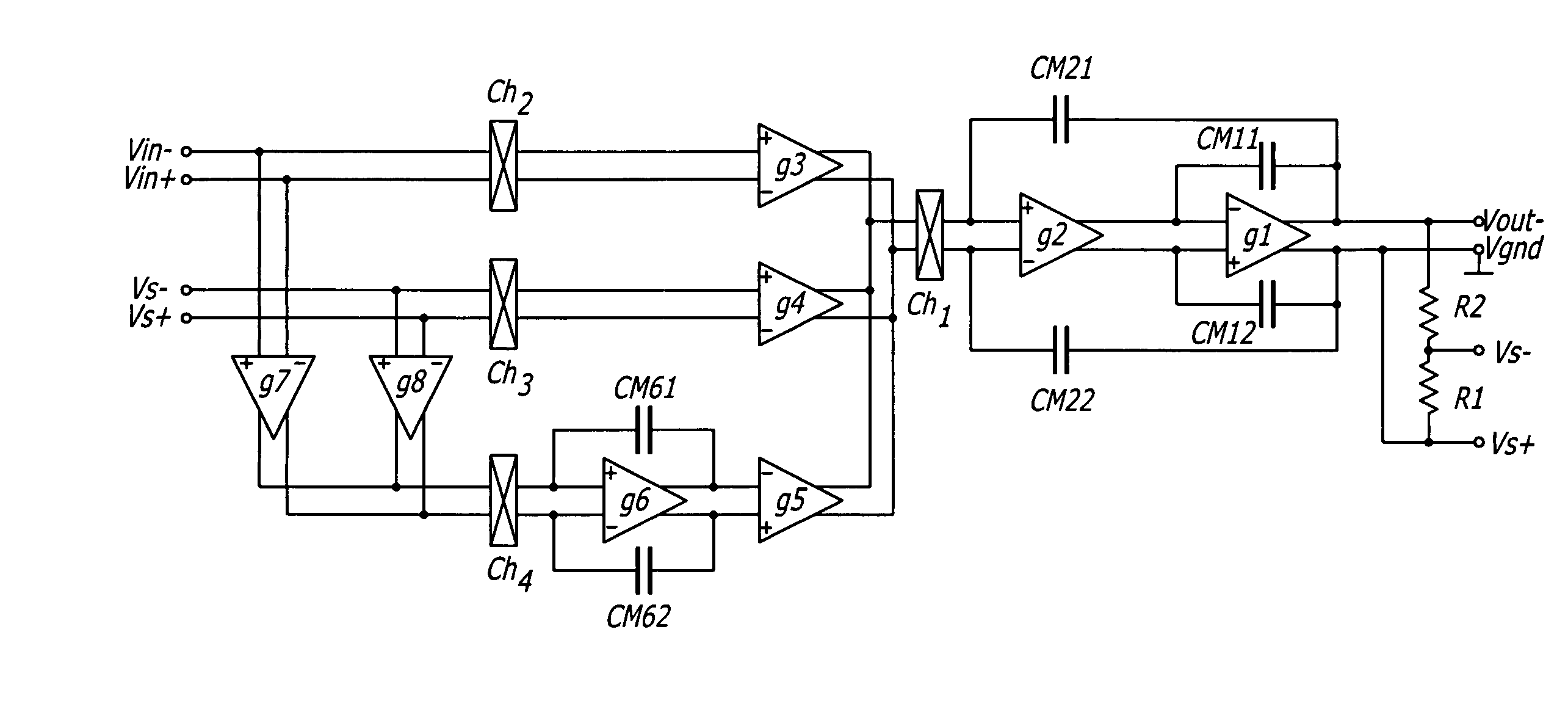
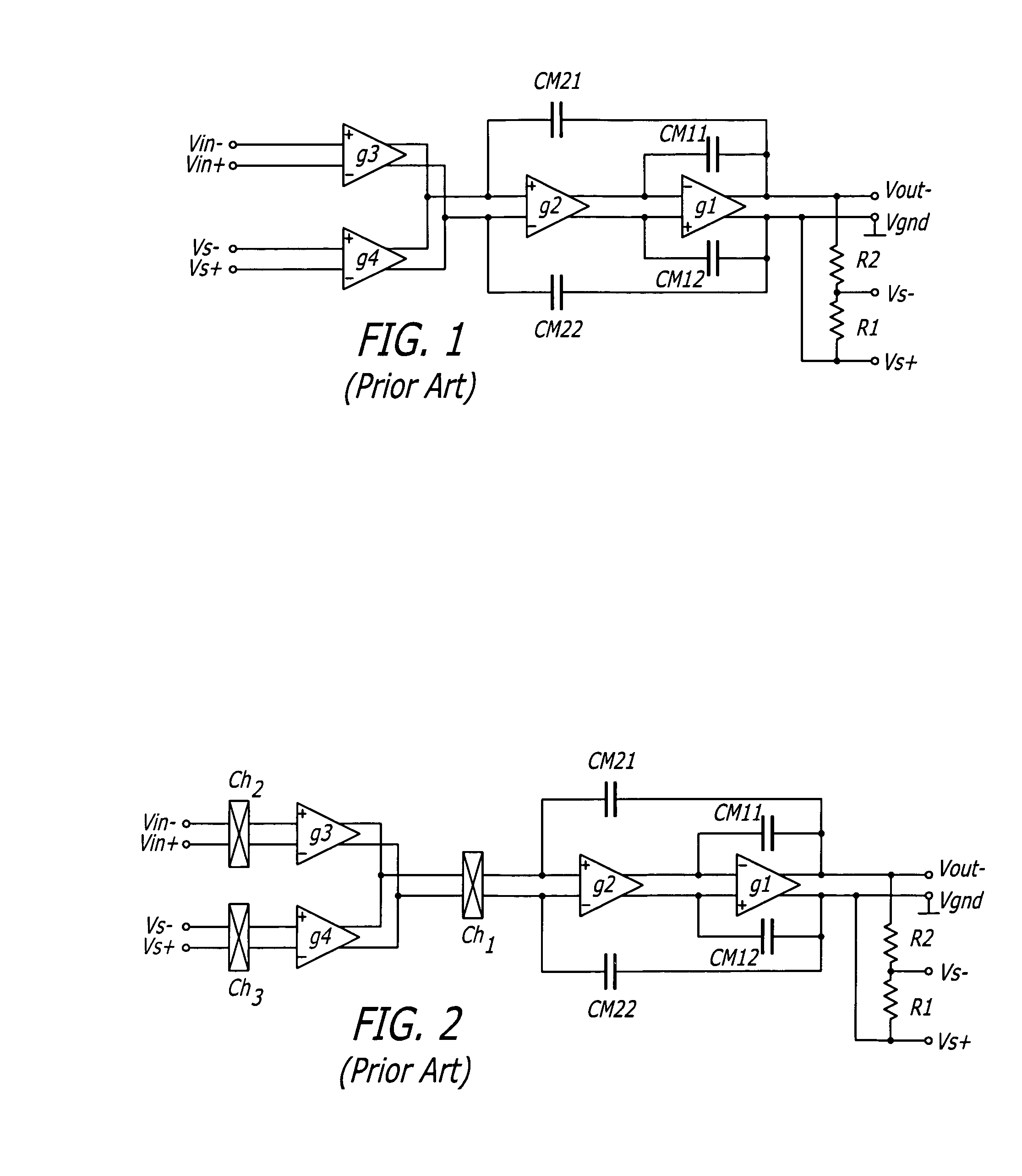
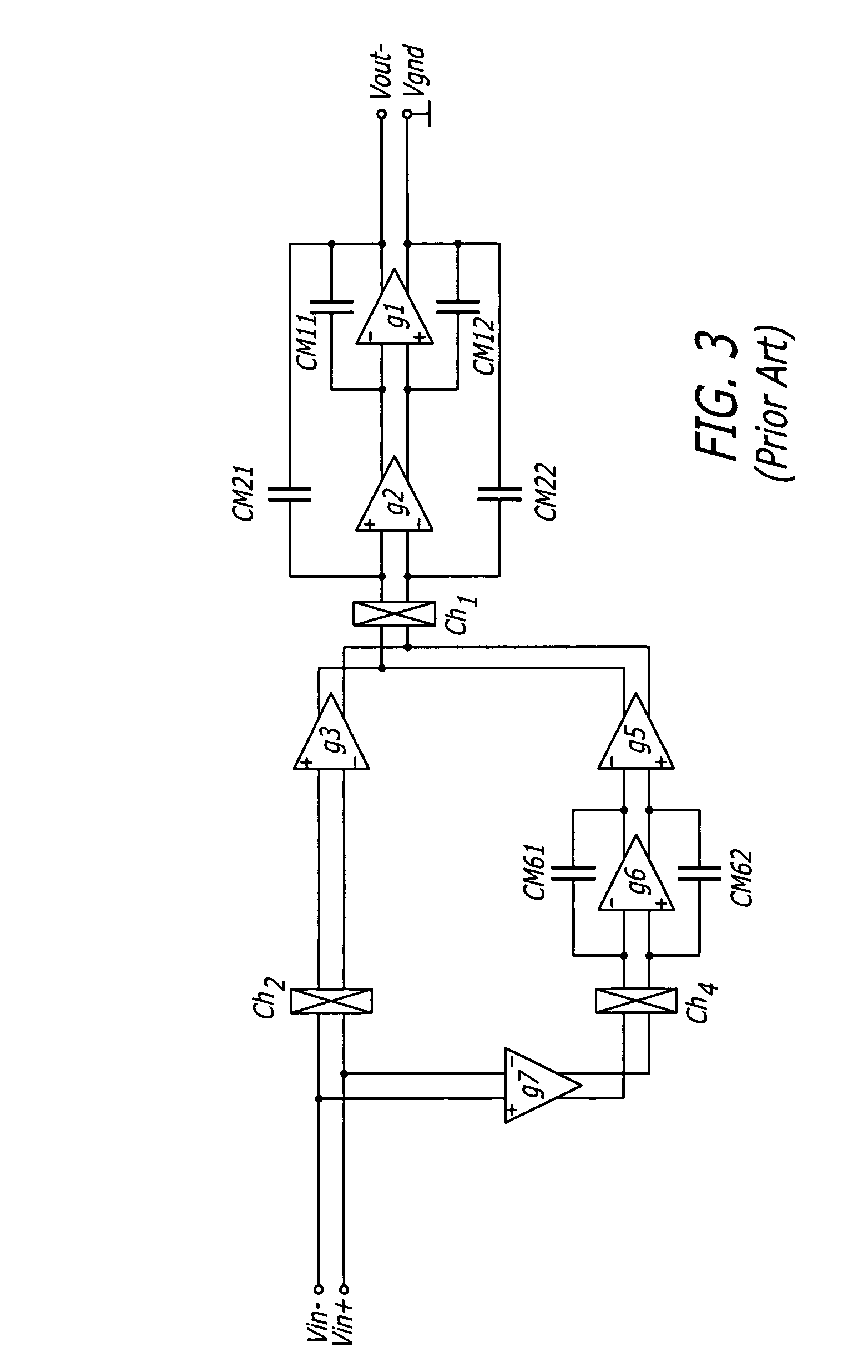
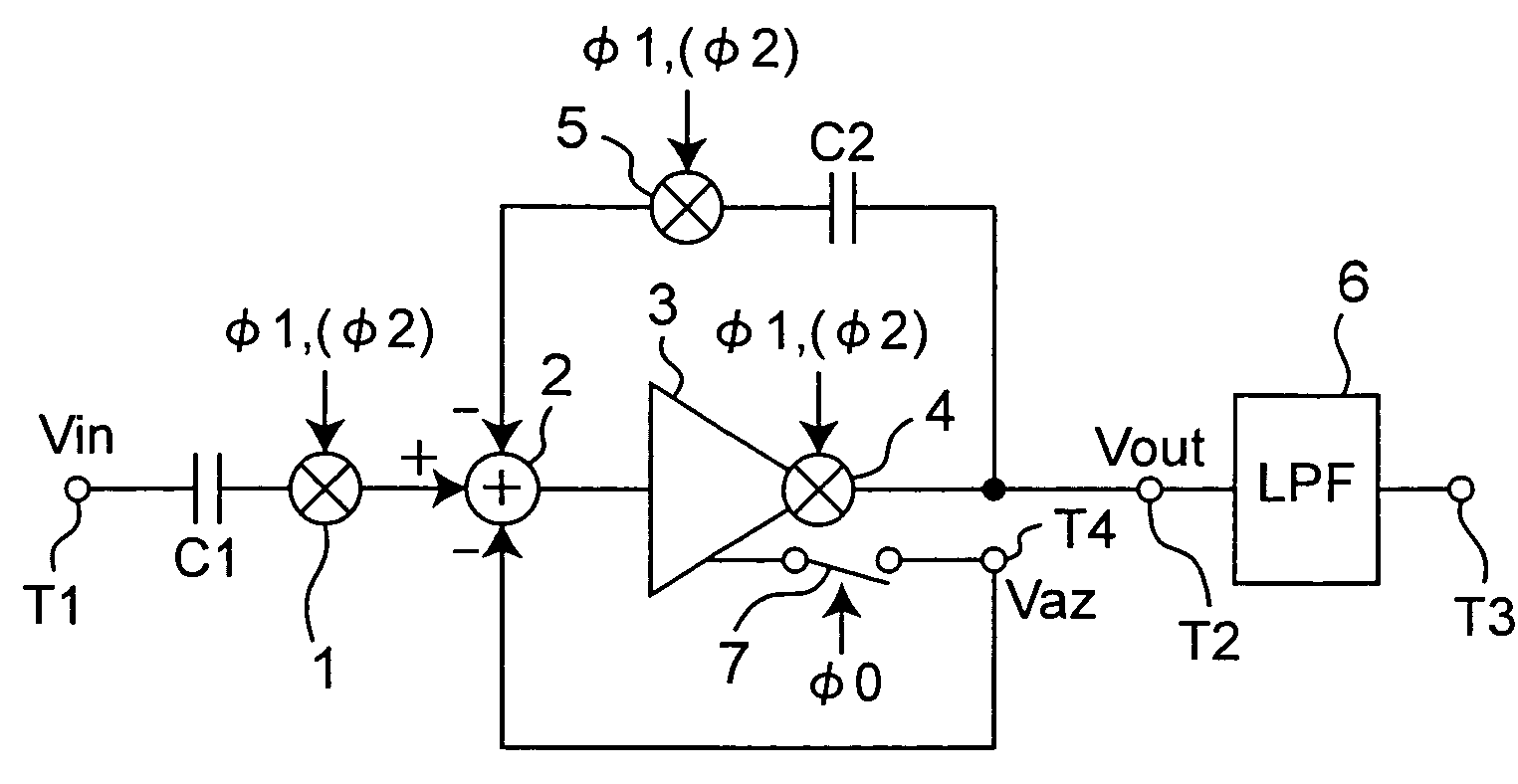
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
110 results about "Chopper amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
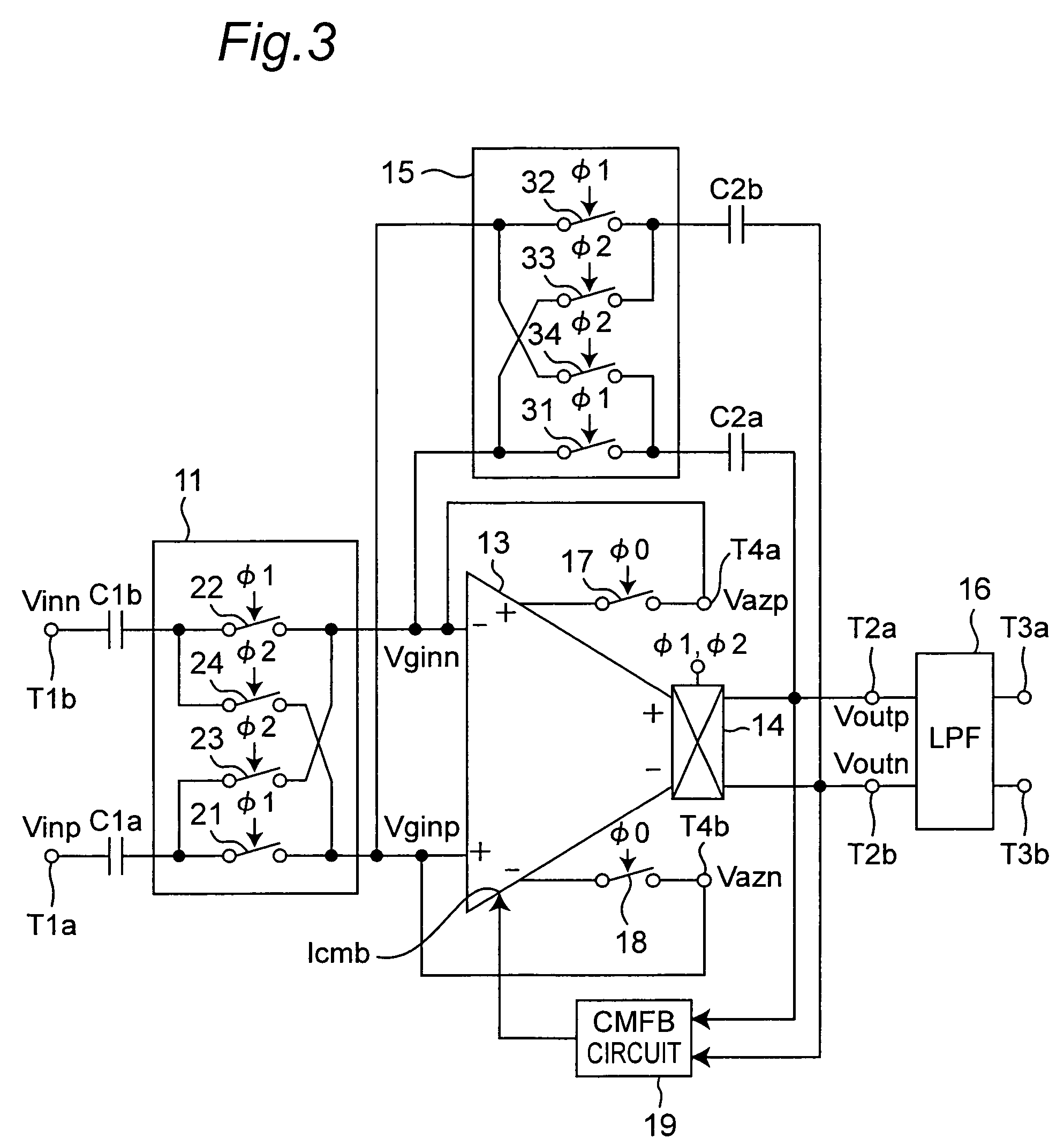
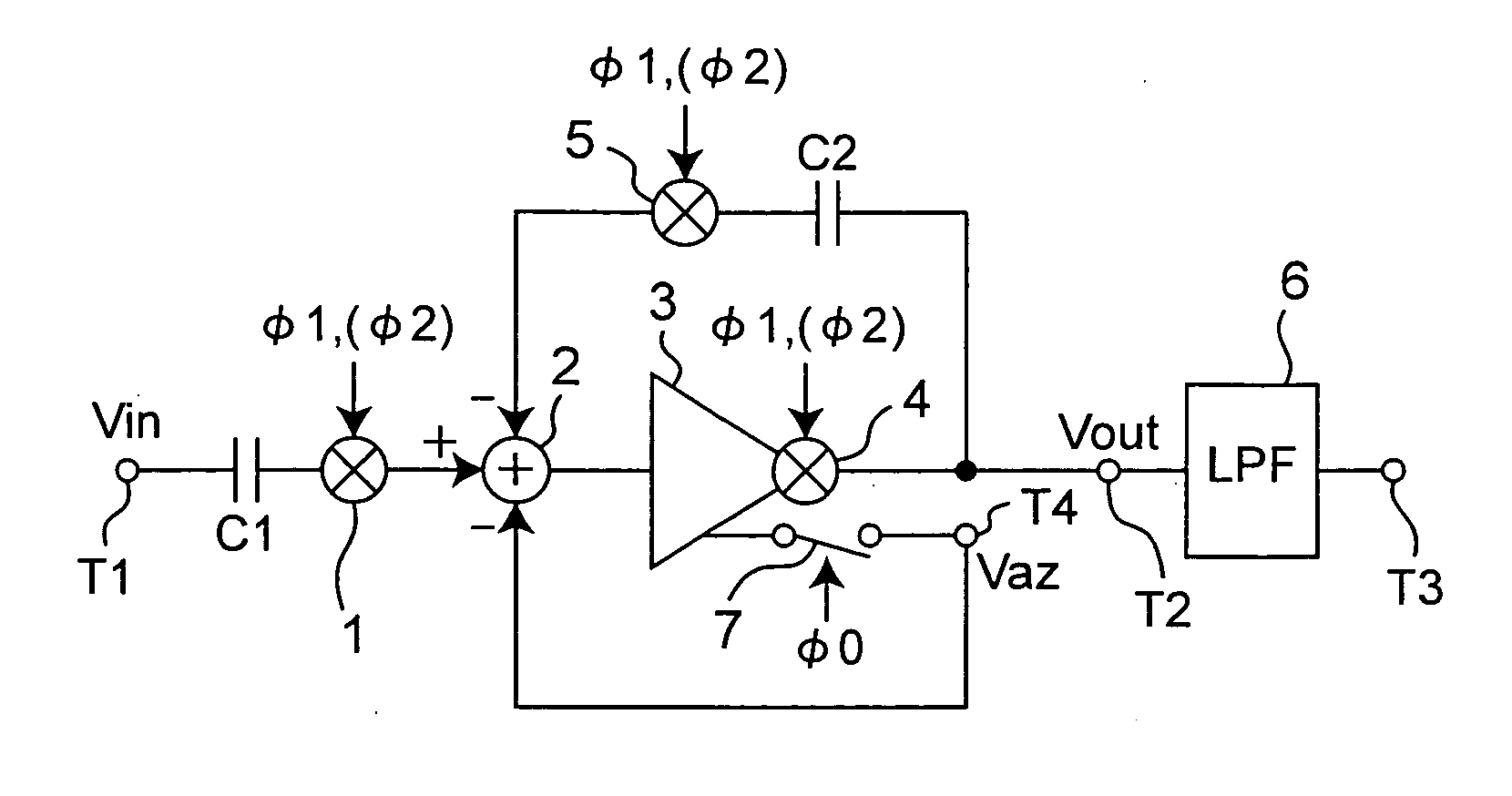
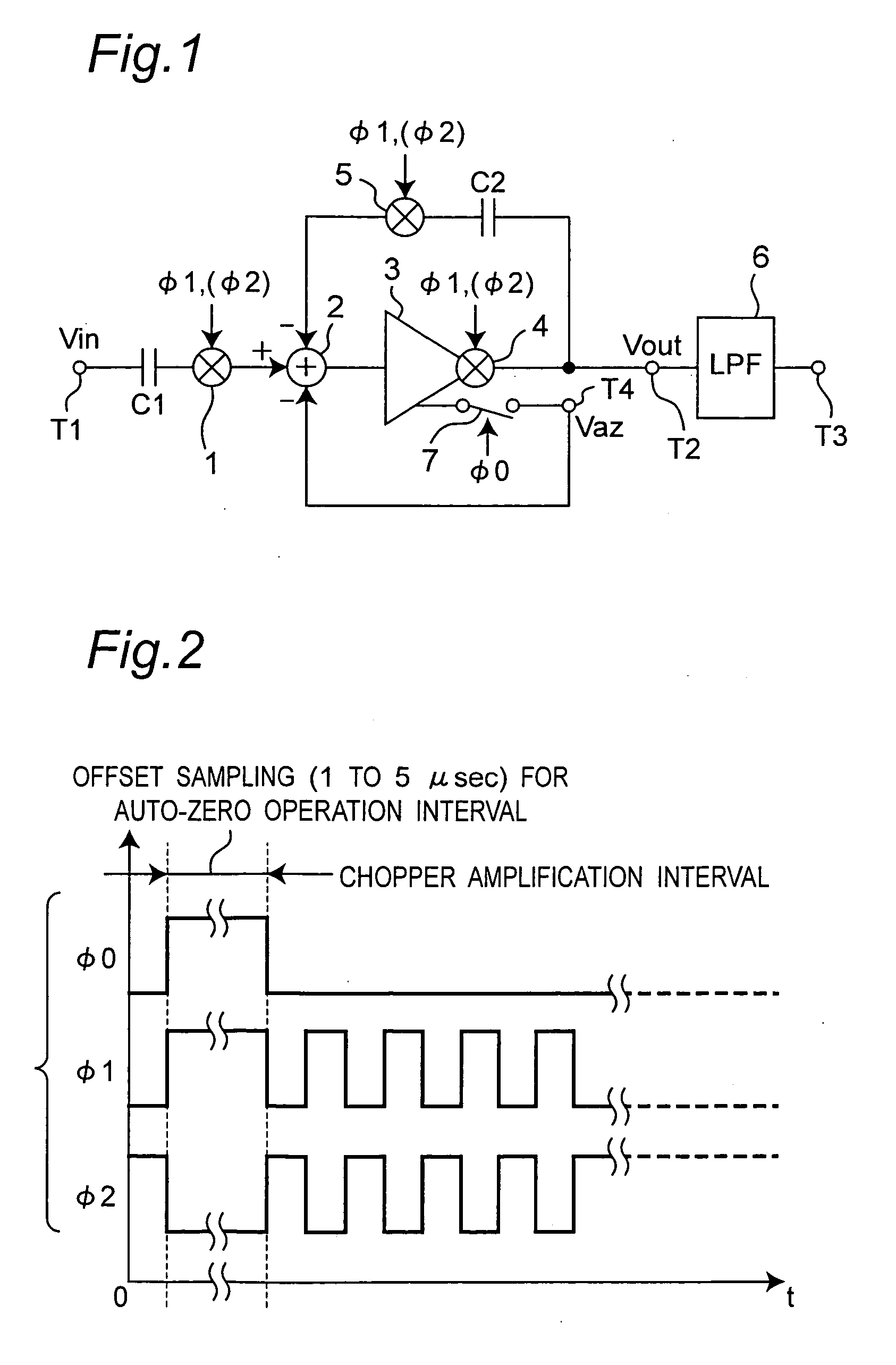
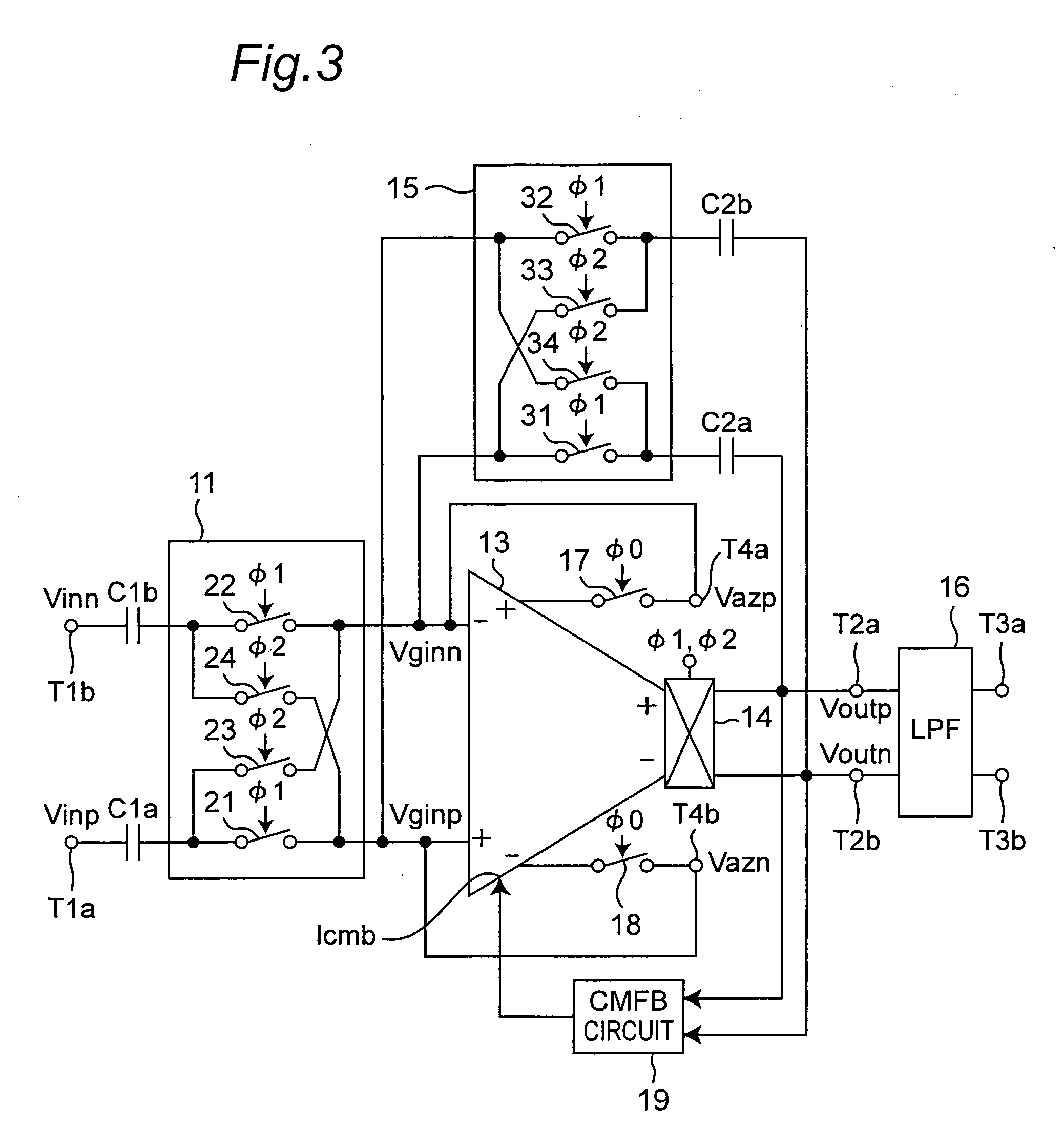
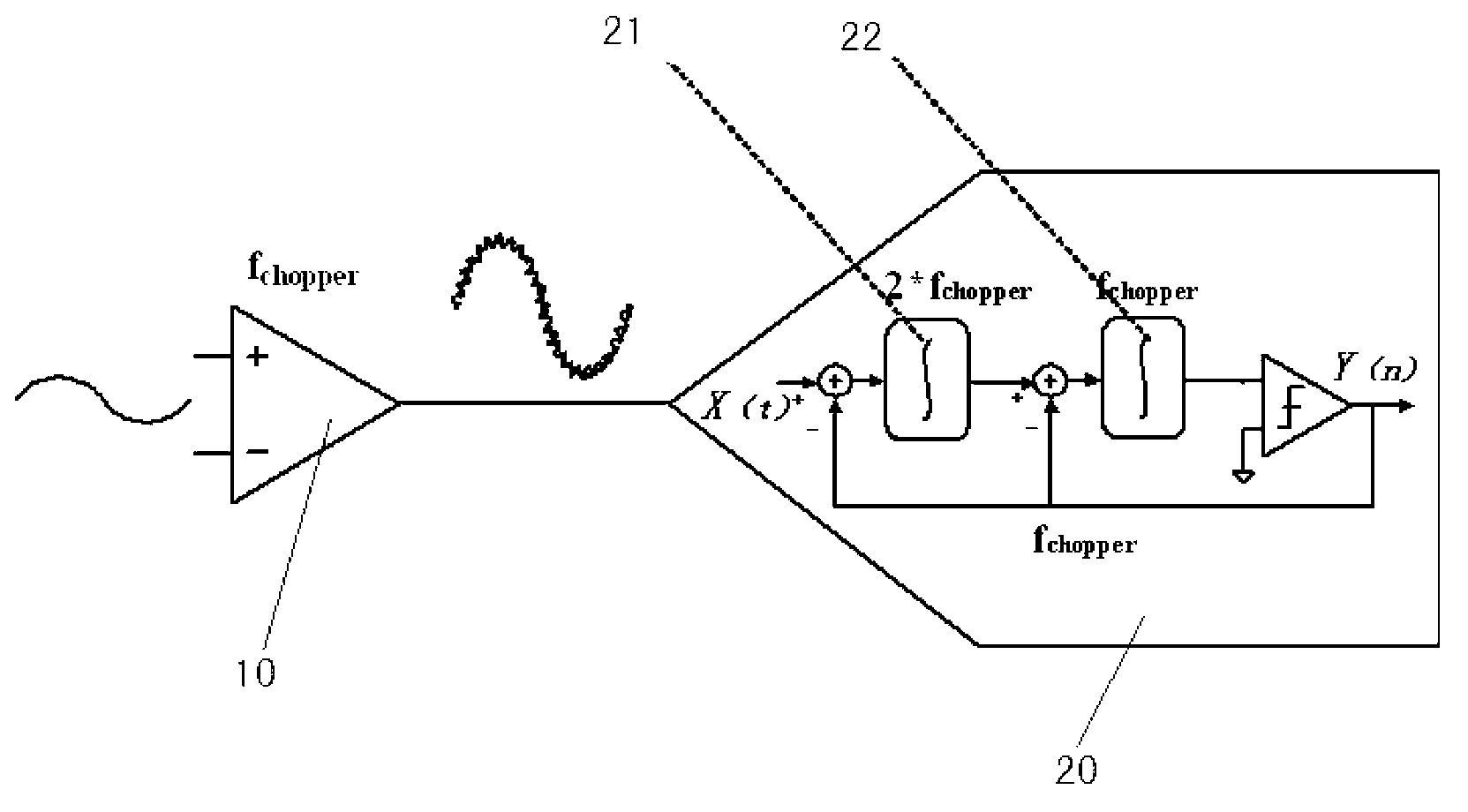
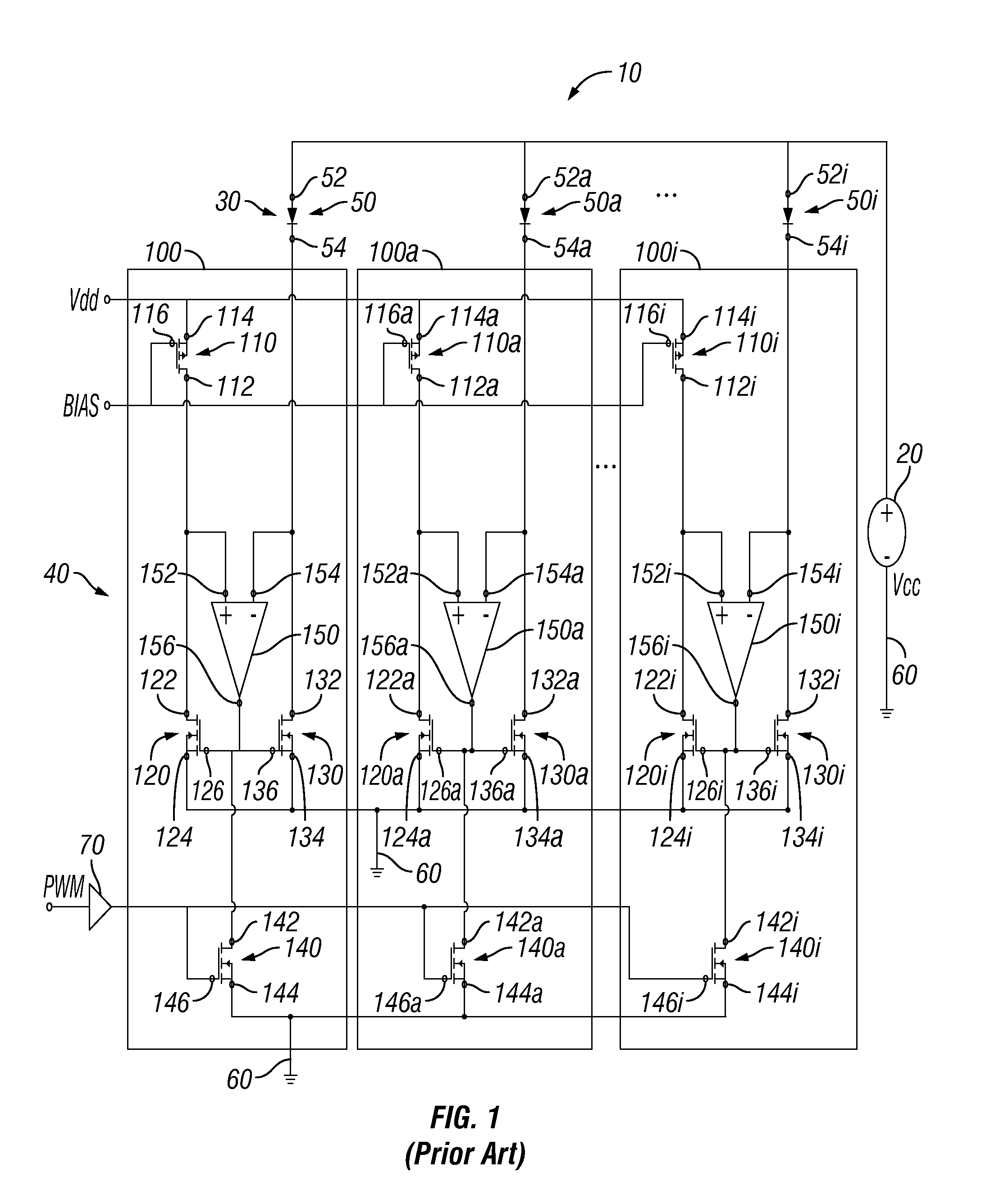
Chopper chopper-stabilized instrumentation and operational amplifiers
ActiveUS7132883B2Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierInstrumentation amplifier
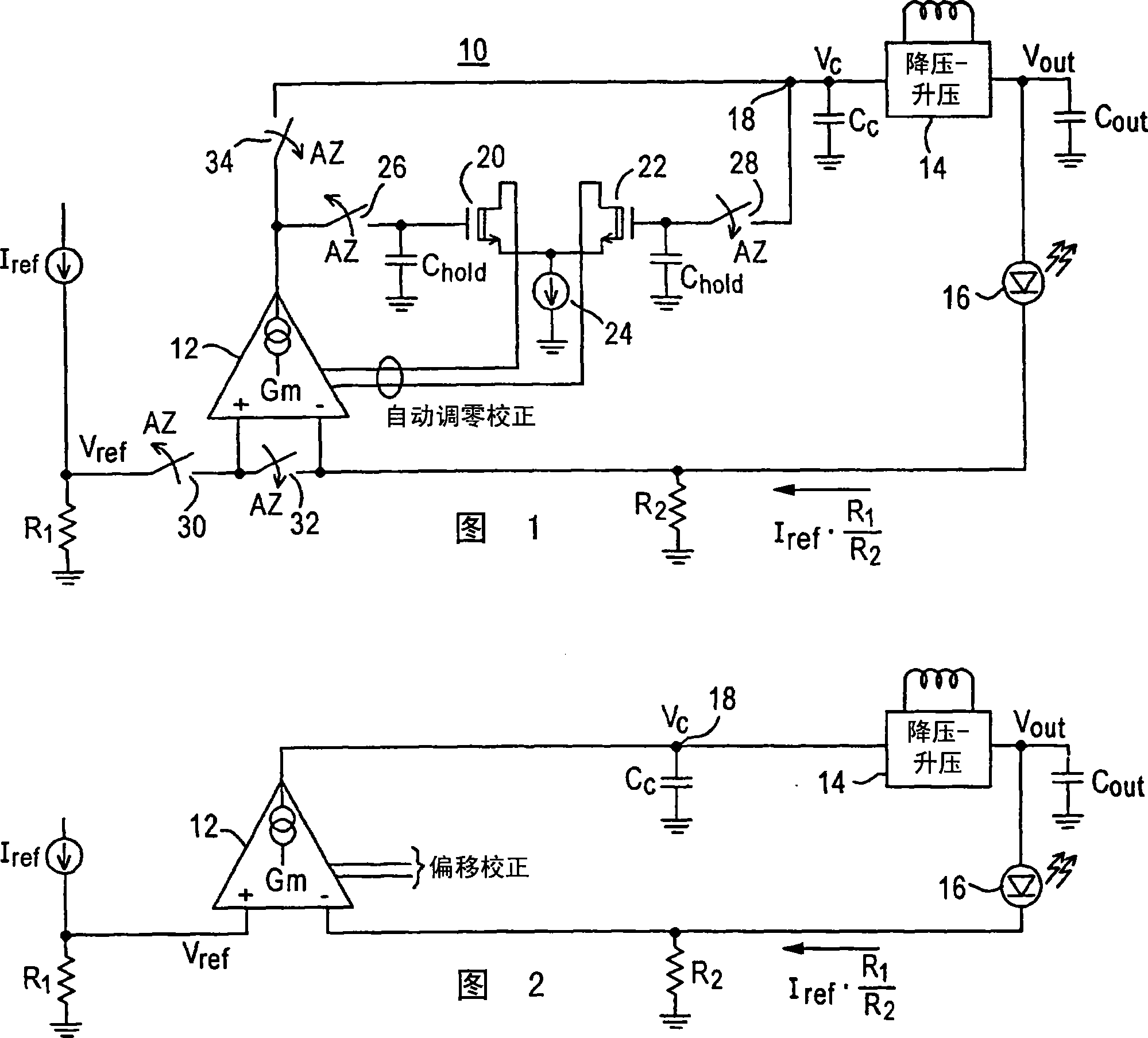
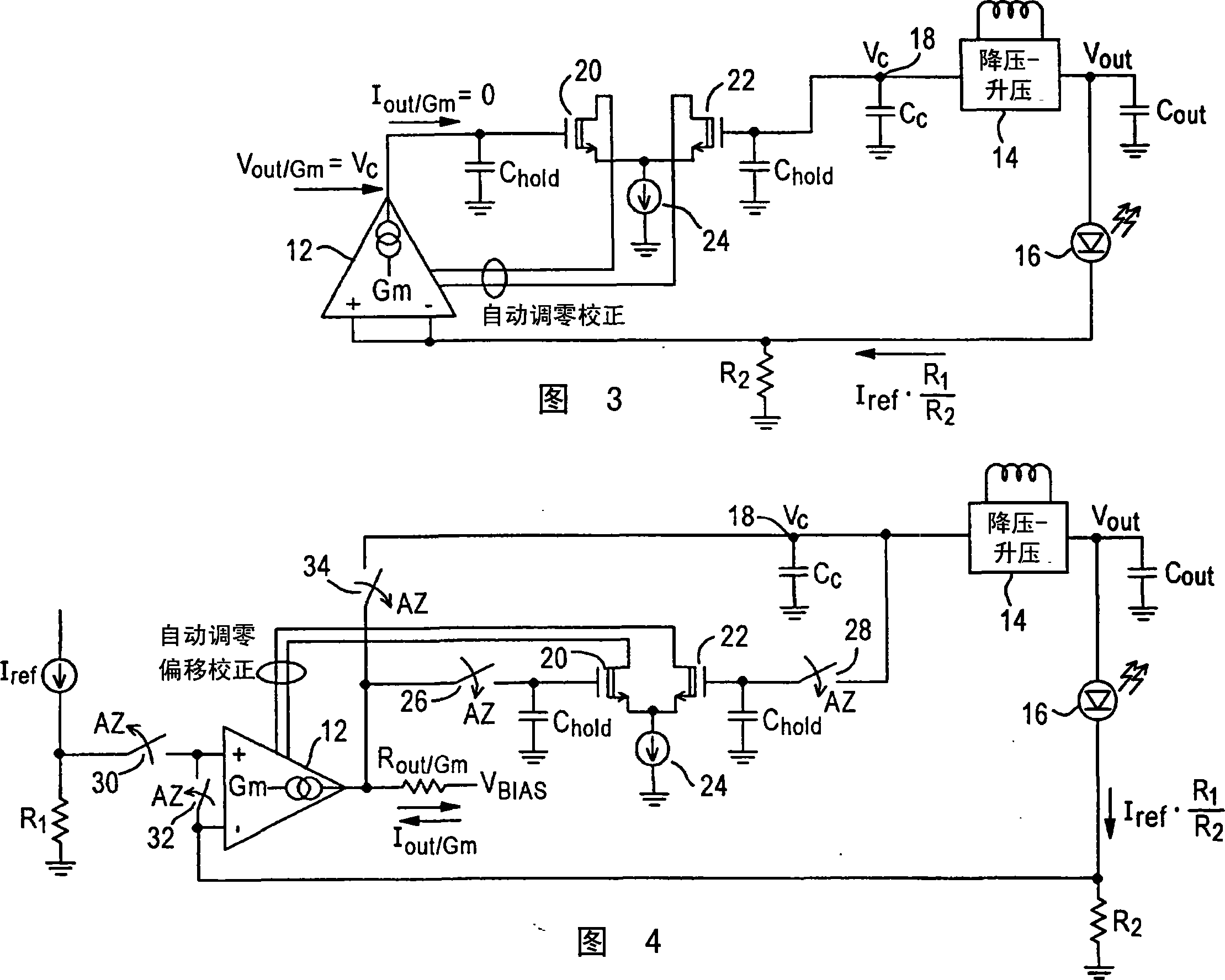
Chopper chopper-stabilized instrumentation and operational amplifiers having ultra low offset. The instrumentation amplifiers use current-feedback, and include, in addition to a main chopper amplifier chain, a chopper stabilized loop for correcting for the offset of the input amplifiers for the input signal and for receiving the feedback of the output voltage sense signal. Additional loops, which may include offset compensation and autozeroing loops, may be added to compensate for offsets in the chopper stabilized loop for correcting for the offset of the input amplifiers. Similar compensation is disclosed for decreasing the offset in operational amplifiers.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Chopper amplifier circuit apparatus operable at low voltage utilizing switched operational amplifier
InactiveUS7336123B2Simple circuit configurationImprove reliabilityAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierLow voltage
In a chopper amplifier circuit operable at a low voltage utilizing a switched operational amplifier, a chopper modulator chopper-modulates an input signal according to a predetermined control signal, and outputs a chopper-modulated signal. An amplifier circuit constituted by the switched operational amplifier amplifies the chopper-modulated signal outputted from the chopper modulator, and outputs an amplified chopper-modulated signal. A chopper-demodulator of the switched operational amplifier chopper-demodulates the amplified chopper-modulated signal outputted from the amplifier circuit according to the control signal, and outputs a demodulated output signal as a chopper-amplified output signal from an output terminal. A chopper modulator chopper-modulates a demodulated signal outputted from the chopper demodulator according to the control signal, and outputs a chopper-modulated signal to an input terminal of the amplifier circuit.
Owner:SEMICON TECH ACADEMIC RES CENT
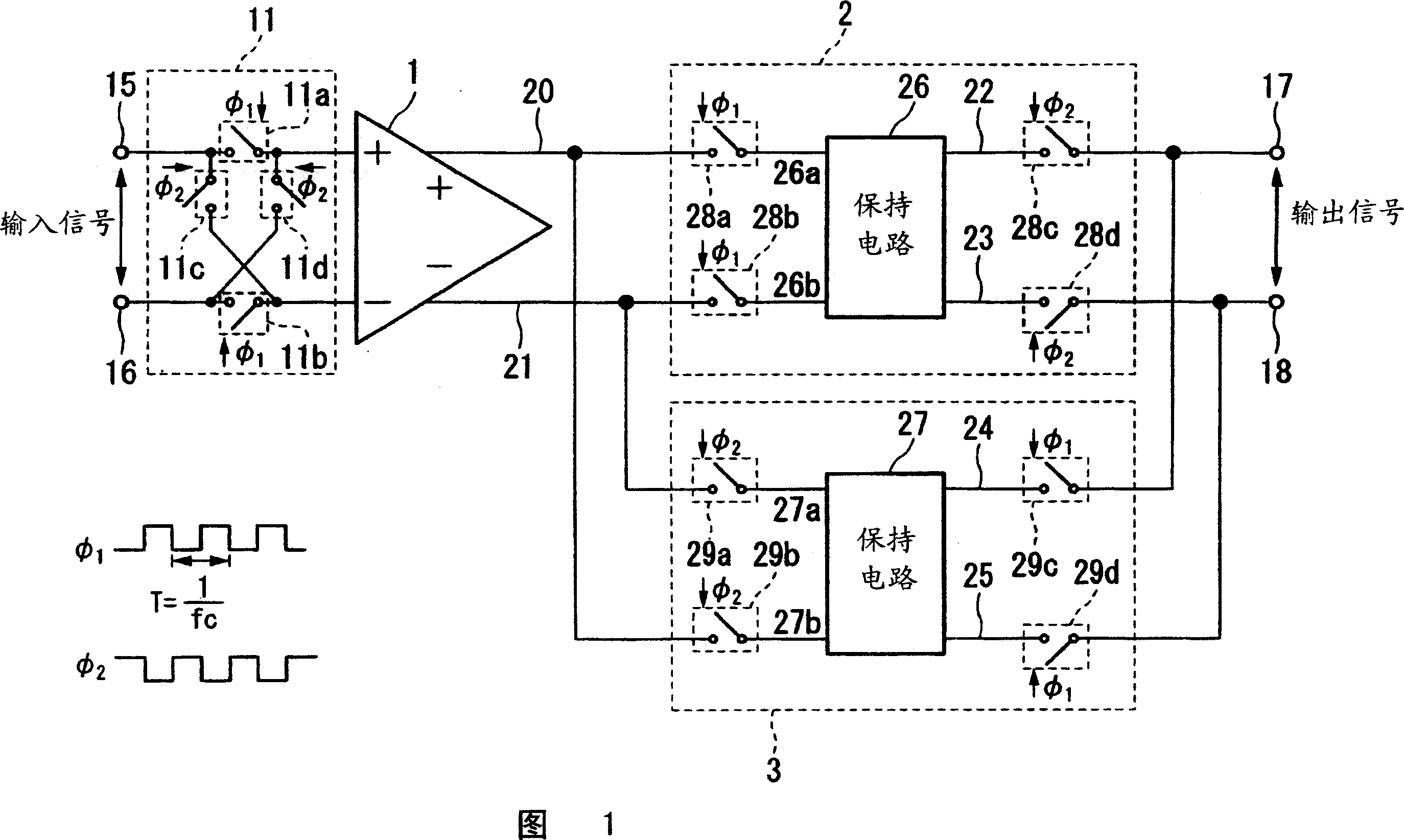
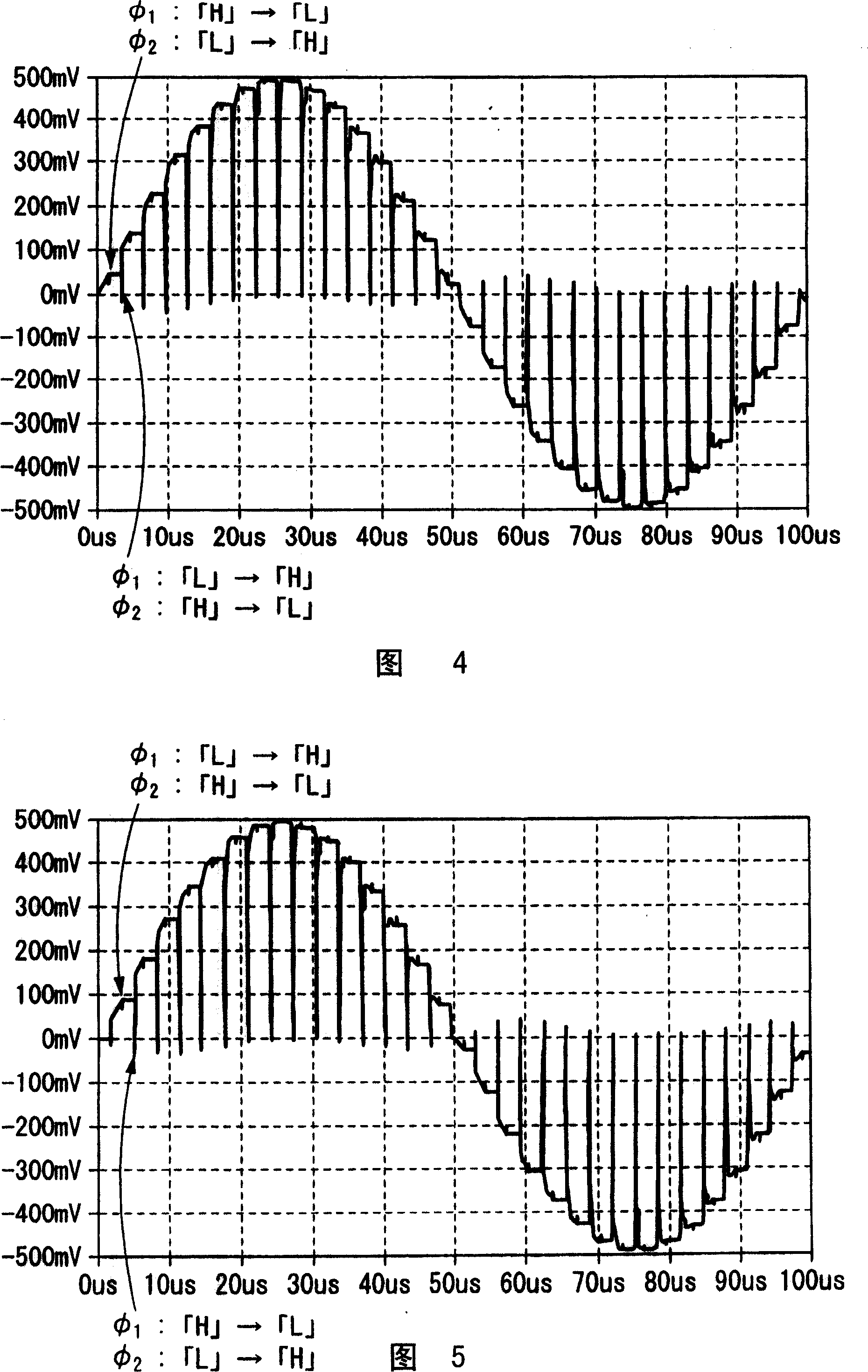
Signal conditioning circuit and dual sampling-hold circuit applying the conditioning method
ActiveCN101394163AAvoid residual dysregulation problemsEasy to integrateDigital technique networkElectric analogue storesSignal conditioning circuitsDigital down converter
The invention discloses a signal conditioning circuit, a conditioning method thereof and a double sampling retaining circuit. The signal conditioning circuit comprises a first chopping switch, a programmable gain amplifier, a second chopping switch, a double sampling retaining circuit, an analog-to-digital converter, and a digital reduction sampling filter which are connected in sequence. The double sampling retaining circuit samples outputs of the programmable gain amplifier in two-phase positions of a chopping clock, and the results of two samplings are added. and an added output voltage is transmitted to and processed by the analog-to-digital converter, and the digital reduction sampling filter. Since the double sampling retaining circuit is added, the invention avoids the residual and off-tune problem in a chopping amplifier. Meanwhile, the invention facilitates the integration of a single chip, without the need of external filtering capacitor. Furthermore, a novel sequential control reduces the consumption of a digital signal conditioning circuit based on a chopping amplifier.
Owner:豪威国际控股有限公司
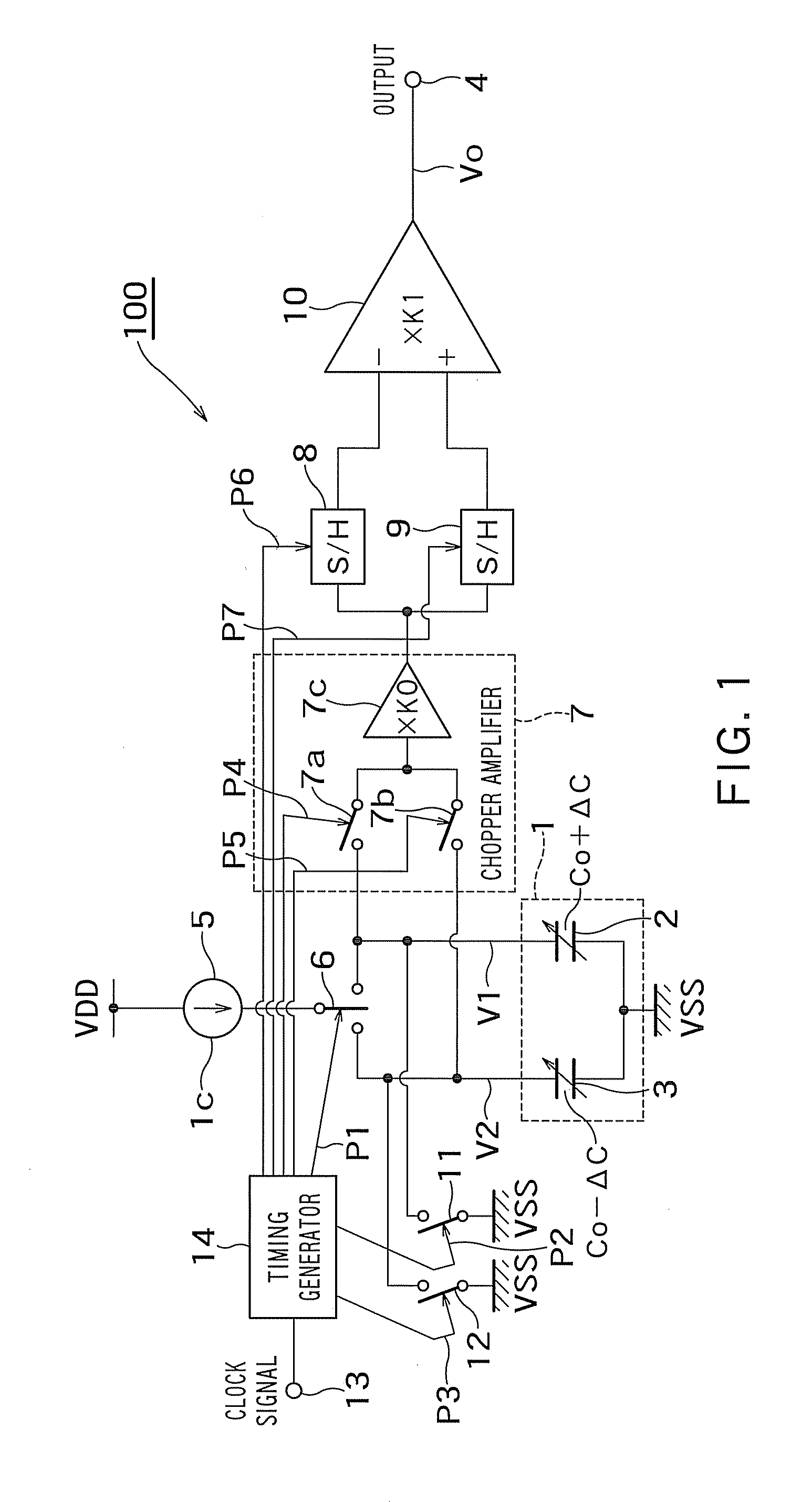
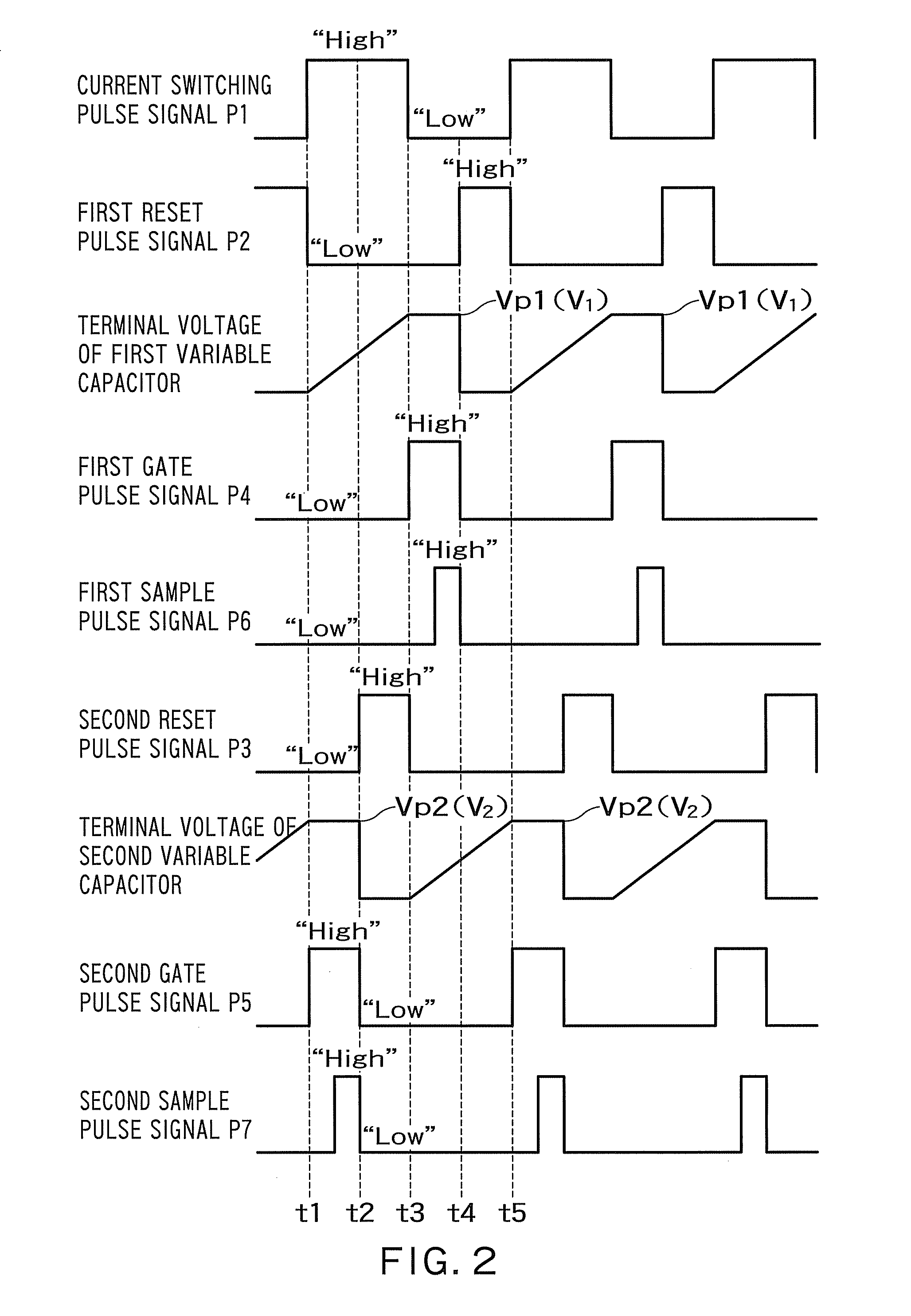
Capacitance difference detecting circuit
A capacitance difference detecting circuit has timing generator that outputs a current switching pulse signal for controlling a switching operation of a current switching circuit, outputs a gate pulse signal for controlling a chopper amplifier so that the chopper amplifier detects the first charging voltage when a first variable capacitor is charged by a first charging voltage and detects a second charging voltage when a second variable capacitor is charged by a second charging voltage, outputs a first sample pulse signal for controlling a first sampling and holding circuit so that the first sampling and holding circuit samples and holds the output signal of the chopper amplifier when the first charging voltage is detected, and outputs a second sample pulse signal for controlling the second sampling and holding circuit so that the second sampling and holding circuit samples and holds the output signal of the chopper amplifier when the second charging voltage is detected.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
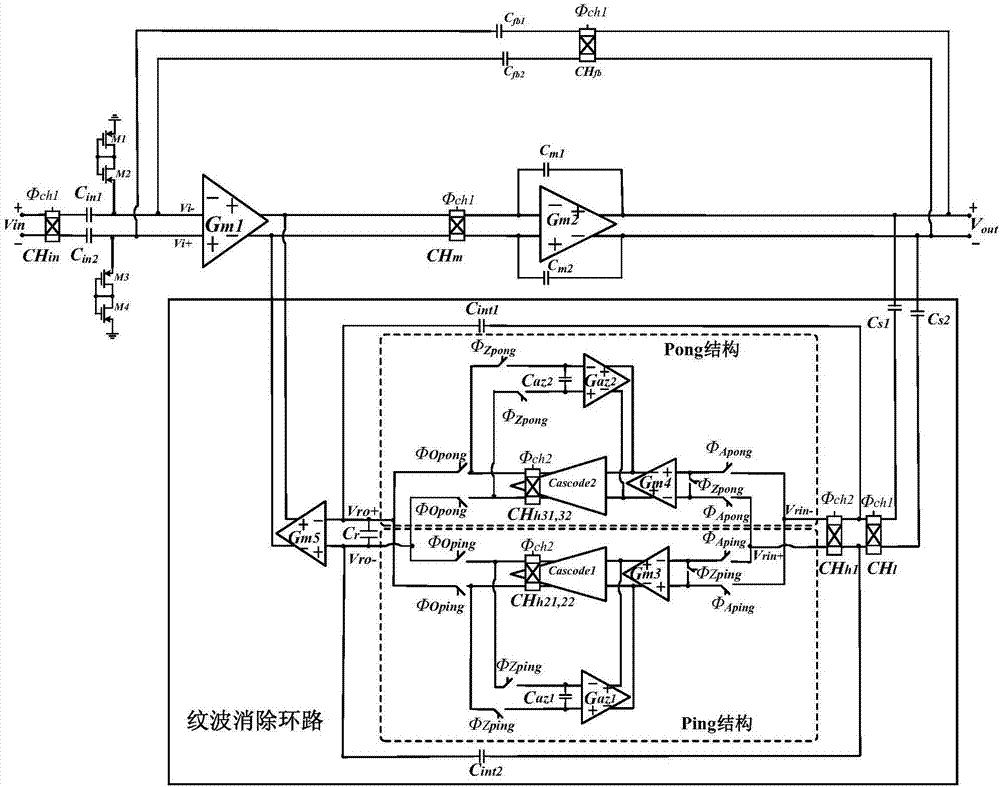
Ripple elimination loop for capacitance coupled chopper amplifier
ActiveCN106972834AOutput Voltage Ripple RejectionOffset Voltage SuppressionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a ripple elimination loop for a capacitance coupled chopper amplifier. An output voltage ripple of a chopper amplifier is converted to an AC signal, the AC signal is modulated to a DC signal, the DC signal is integrated by an integral module to obtain an integral voltage, and the integral voltage is converted to a compensating current through a transconductance module to compensate the offset voltage of the chopper amplifier and suppress the output voltage ripple of the chopper amplifier. In addition, according to the ripple elimination loop disclosed by the invention, the offset voltage of the integral module can be greatly suppressed by using the combination of a high-frequency chopping technology and a Ping-Pong self-zeroing technology in the ripple elimination loop, and thus the accurate integral voltage can be obtained, the accurate compensating current can be formed to suppress the offset current of a main amplifier in the chopper amplifier, and a good effect of suppressing the output voltage ripple of the chopper amplifier can be achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Chopper amplifier circuit apparatus operable at low voltage utilizing switched operational amplifier
InactiveUS20060244521A1Simple circuit configurationImprove reliabilityAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierControl signal
In a chopper amplifier circuit operable at a low voltage utilizing a switched operational amplifier, a chopper modulator chopper-modulates an input signal according to a predetermined control signal, and outputs a chopper-modulated signal. An amplifier circuit constituted by the switched operational amplifier amplifies the chopper-modulated signal outputted from the chopper modulator, and outputs an amplified chopper-modulated signal. A chopper-demodulator of the switched operational amplifier chopper-demodulates the amplified chopper-modulated signal outputted from the amplifier circuit according to the control signal, and outputs a demodulated output signal as a chopper-amplified output signal from an output terminal. A chopper modulator chopper-modulates a demodulated signal outputted from the chopper demodulator according to the control signal, and outputs a chopper-modulated signal to an input terminal of the amplifier circuit.
Owner:SEMICON TECH ACADEMIC RES CENT
Method and apparatus for reducing noise in a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) having a chopper output stage
ActiveUS7277035B1Reduce noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionSwitched currentDigital analog converter
A method and apparatus for reducing noise in a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) having a chopper amplifier output stage provides improved DAC performance. A switched-current output provided from a digital filter is coupled to the input of a chopper amplifier. The current switches are non-uniform, so that extra zeros are provided at the chopping frequency of the chopping amplifier, thereby reducing noise that would otherwise be aliased in-band at the output of the chopper amplifier. The current switches may include a first set of half-magnitude switches followed by a set of full-magnitude switches and finally by another set of half-magnitude switches having a size equal to that of the first set.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
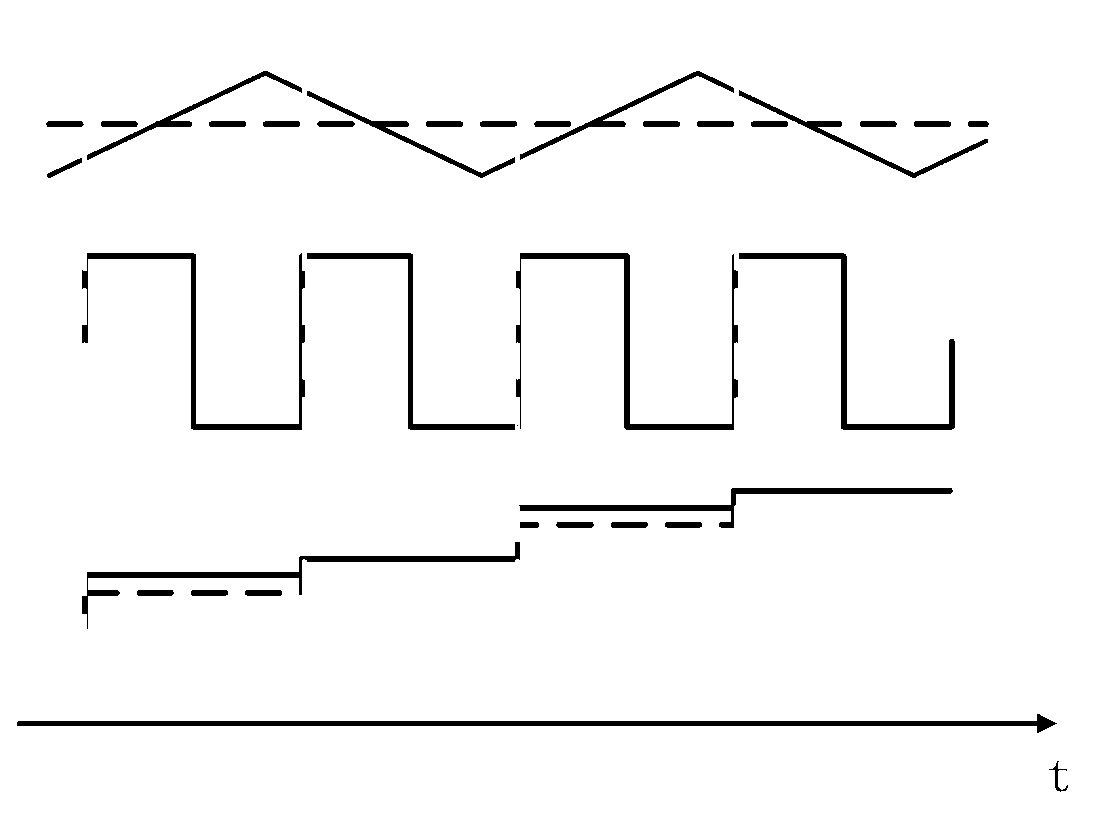
Method for eliminating chopping waves and ripple waves and analogue-digital conversion circuit for realizing method
InactiveCN103023502AThe effect of weakening the precision of the conversionSimple designAnalogue-digital convertersIntegratorLow-pass filter
The invention provides a method for eliminating chopping waves and ripple waves and an analogue-digital conversion circuit for realizing the method. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out two times of sampling on signals in a chopping wave period at an interval which is one half of time of the chopping wave period; and carrying out integration and summation on two times of sampling values so as to keep useful signals and eliminate residual ripple wave signals in the chopping waves. The signal amplification and analogue-digital conversion circuit comprises a chopping wave amplifier and a sigma-delta analogue-digital converter which is cascaded behind the chopping wave amplifier. A switching structure which is embedded into the sigma-delta analogue-digital converter is adopted and an analogue addition function of a first-grade integrator in the analogue-digital converter can be used for carrying out first-order reshaping (voltage summation) on the residual ripple waves of output signals of the chopping wave amplifier, so that the ripple wave amplitude is reduced and influences on the conversion precision of the analogue-digital converter is weakened. The circuit does not need an analogue low-pass filter between the chopping wave amplifier and the analogue-digital converter, so that the power consumption and the area are saved and the design of the circuit is simplified.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Amplifier circuit
InactiveCN101102094AEliminate Slew Rate EffectsReduce Harmonic DistortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceAudio power amplifierHarmonic
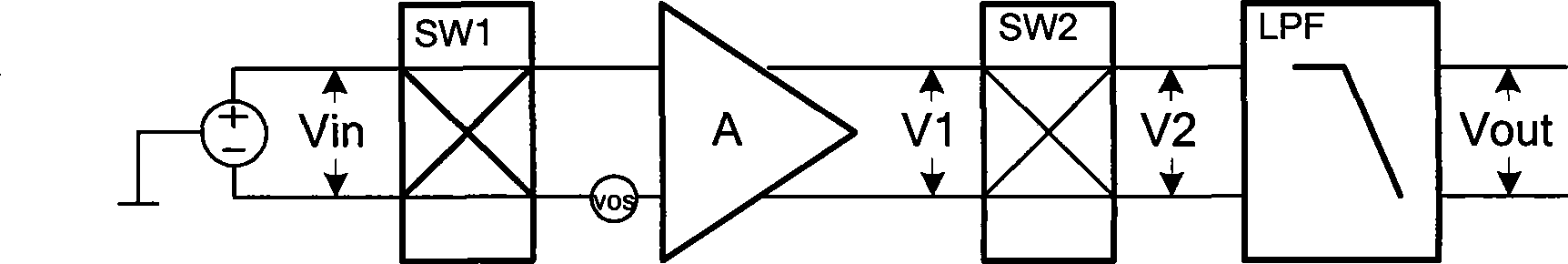
Provided is a chopper amplifier circuit capable of eliminating an influence of a slew rate of an amplifier and suppressing spike generation to thereby obtain an output signal having little harmonic distortion. The chopper amplifier circuit according to the present invention includes: a first chopper circuit for chopping an input signal by a first pulse and a second pulse shifted from each other in phase by a half cycle, switching a relation of connection between an input terminal pair and an output terminal pair at a timing of the chopping, and outputting the input signal as a modulated signal; an amplifier for amplifying the modulated signal and outputting the modulated signal thus amplified as an amplified signal; a first sample hold circuit for holding the amplified signal at the first pulse and outputting the amplified signal at the second pulse; and a second sample hold circuit for holding the amplified signal at the second pulse and outputting the amplified signal at the first pulse.
Owner:SII SEMICONDUCTOR CORP +1
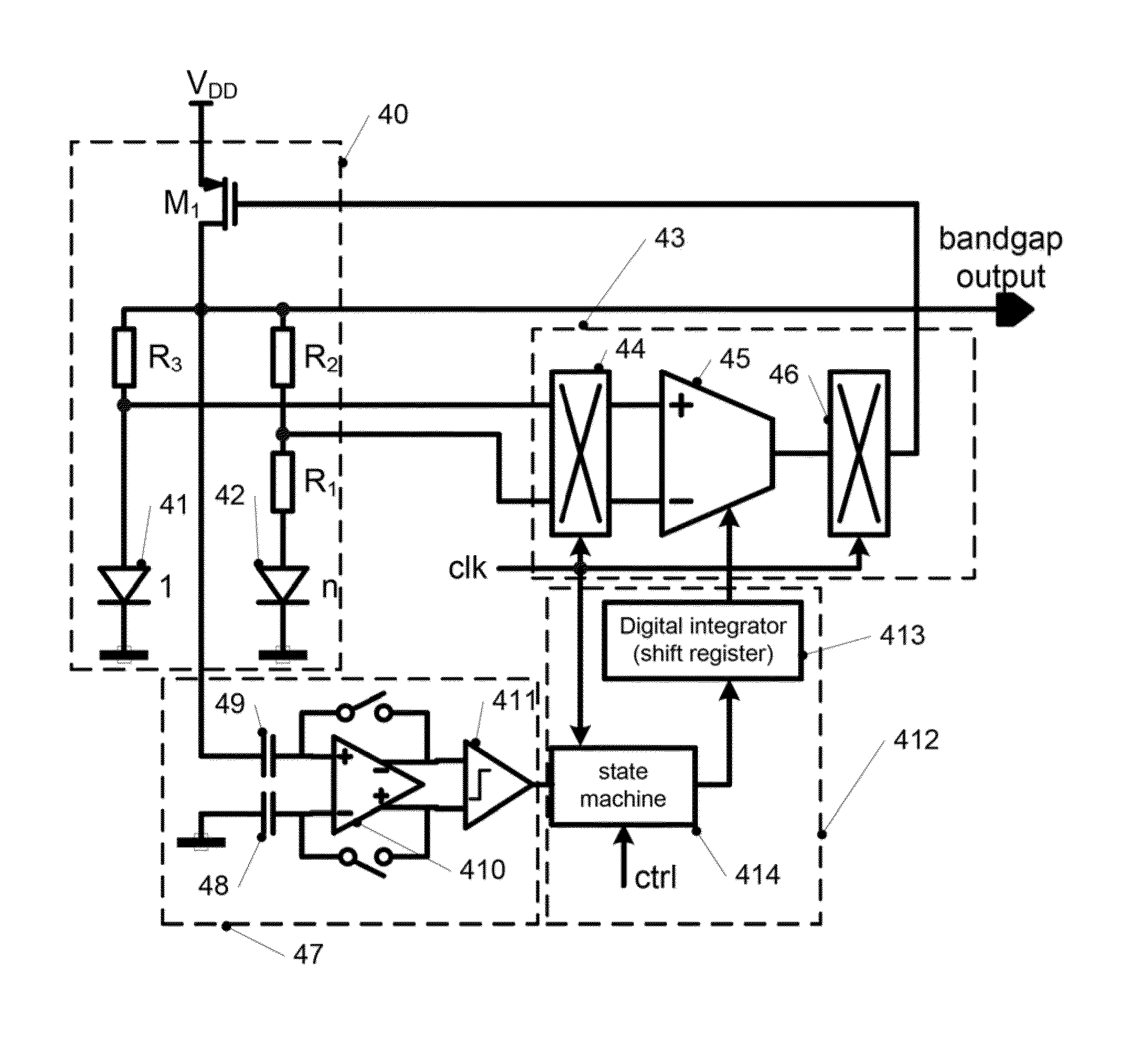
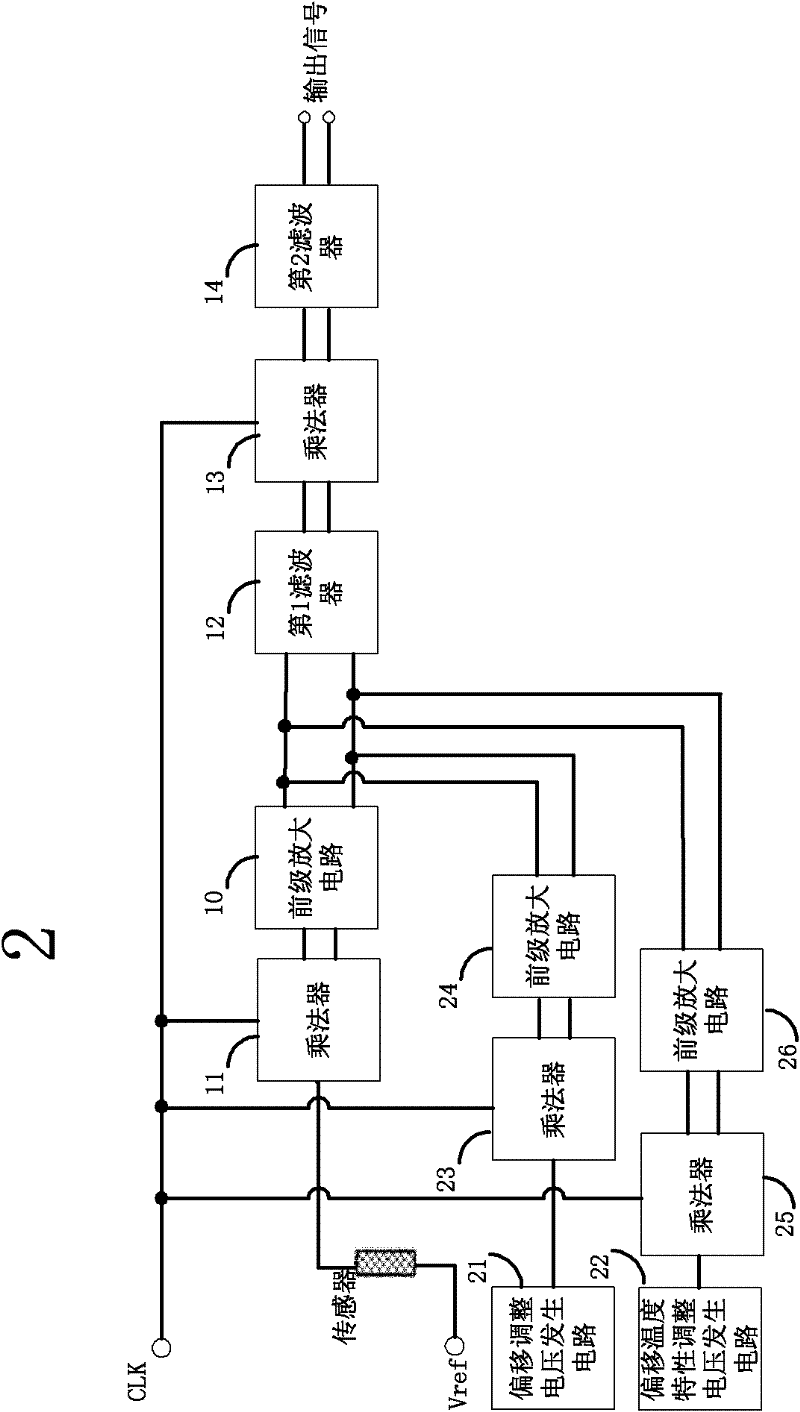
Chopper amplifier circuit and semiconductor device
InactiveCN1929296AAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationLow frequency amplifiersEngineeringChopper amplifier
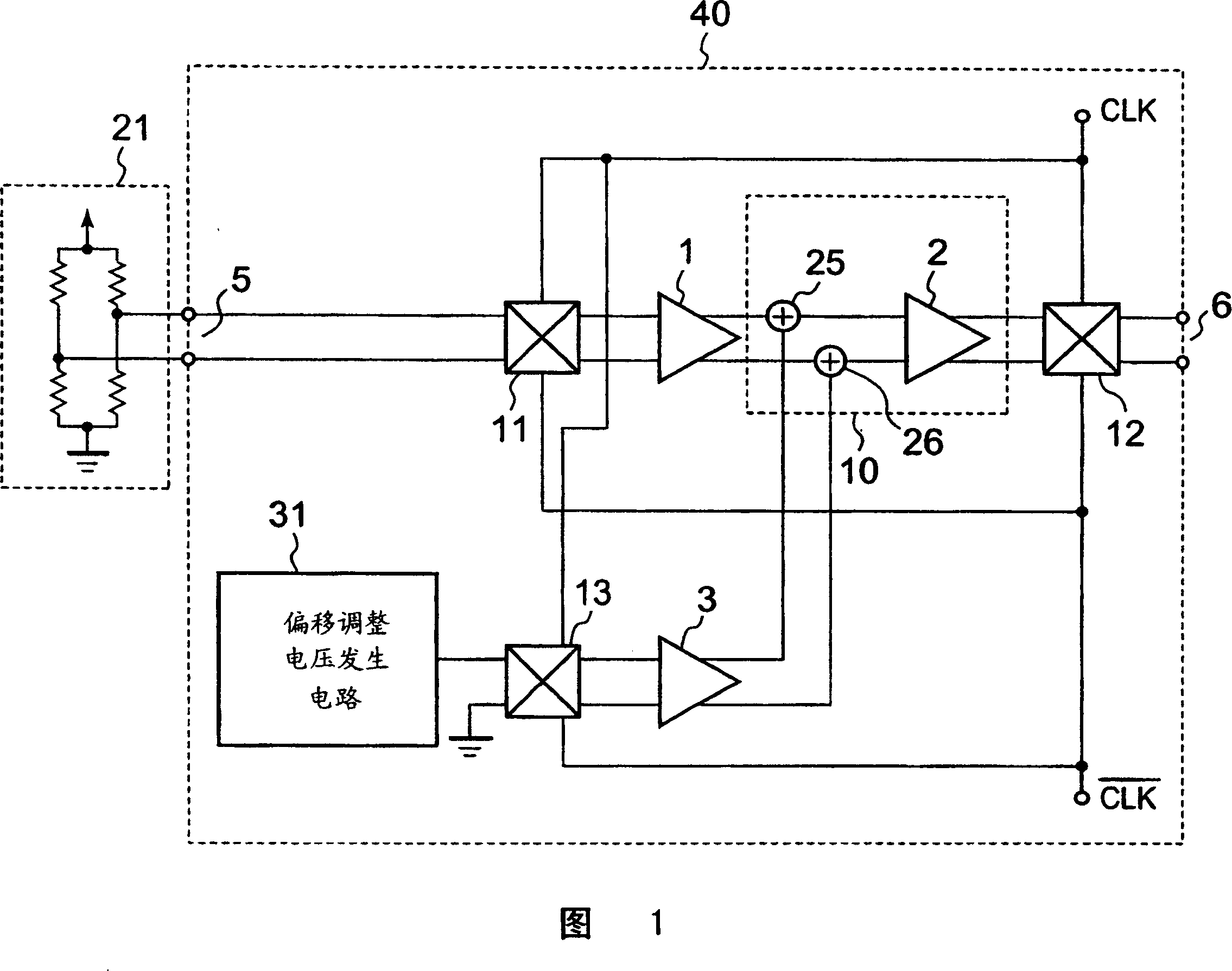
The present invention provides a chopper amplifier circuit capable of reducing the offset voltage of a sensor bridge and the temperature characteristic of the offset voltage. An offset adjustment voltage generating circuit is provided for generating a voltage equal to the offset voltage of the sensor bridge, and an offset temperature characteristic adjusting voltage generating circuit is provided for generating a voltage having the same temperature characteristic as the offset voltage. These output voltages are chop modulated and subtracted from the chop modulated output signal of the sensor bridge.
Owner:SII SEMICONDUCTOR CORP +1
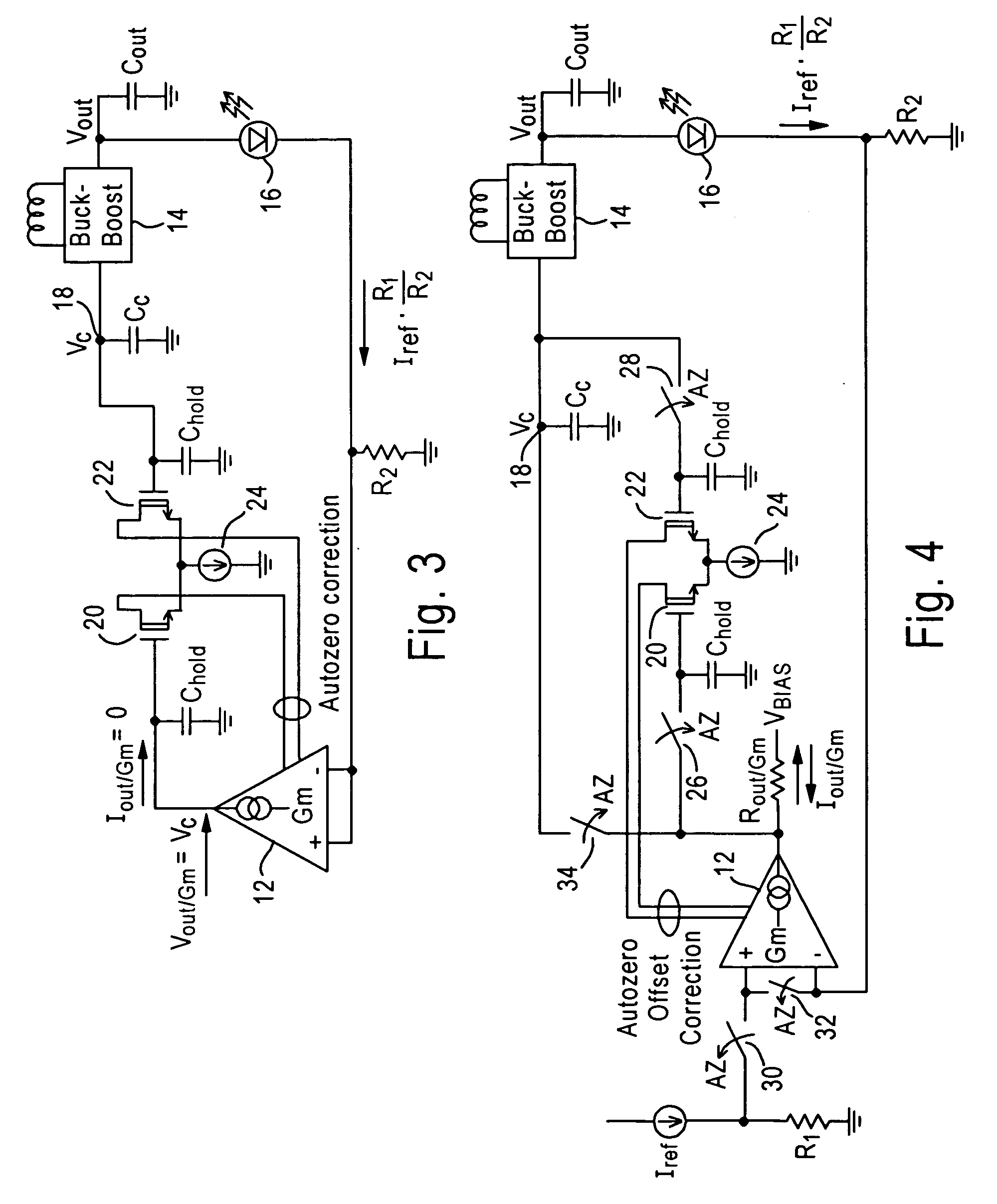
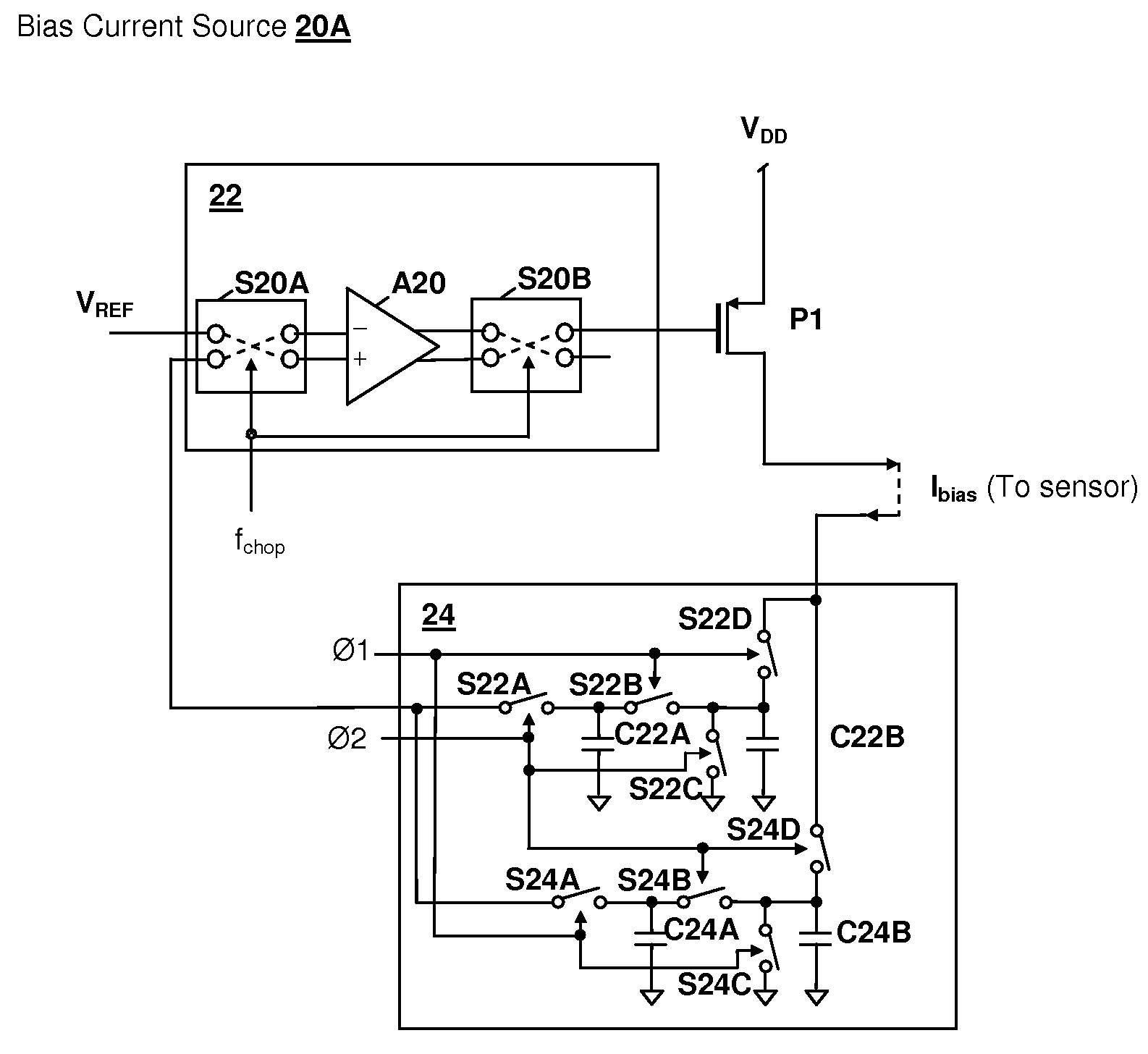
Offset correction circuit for voltage-controlled current source
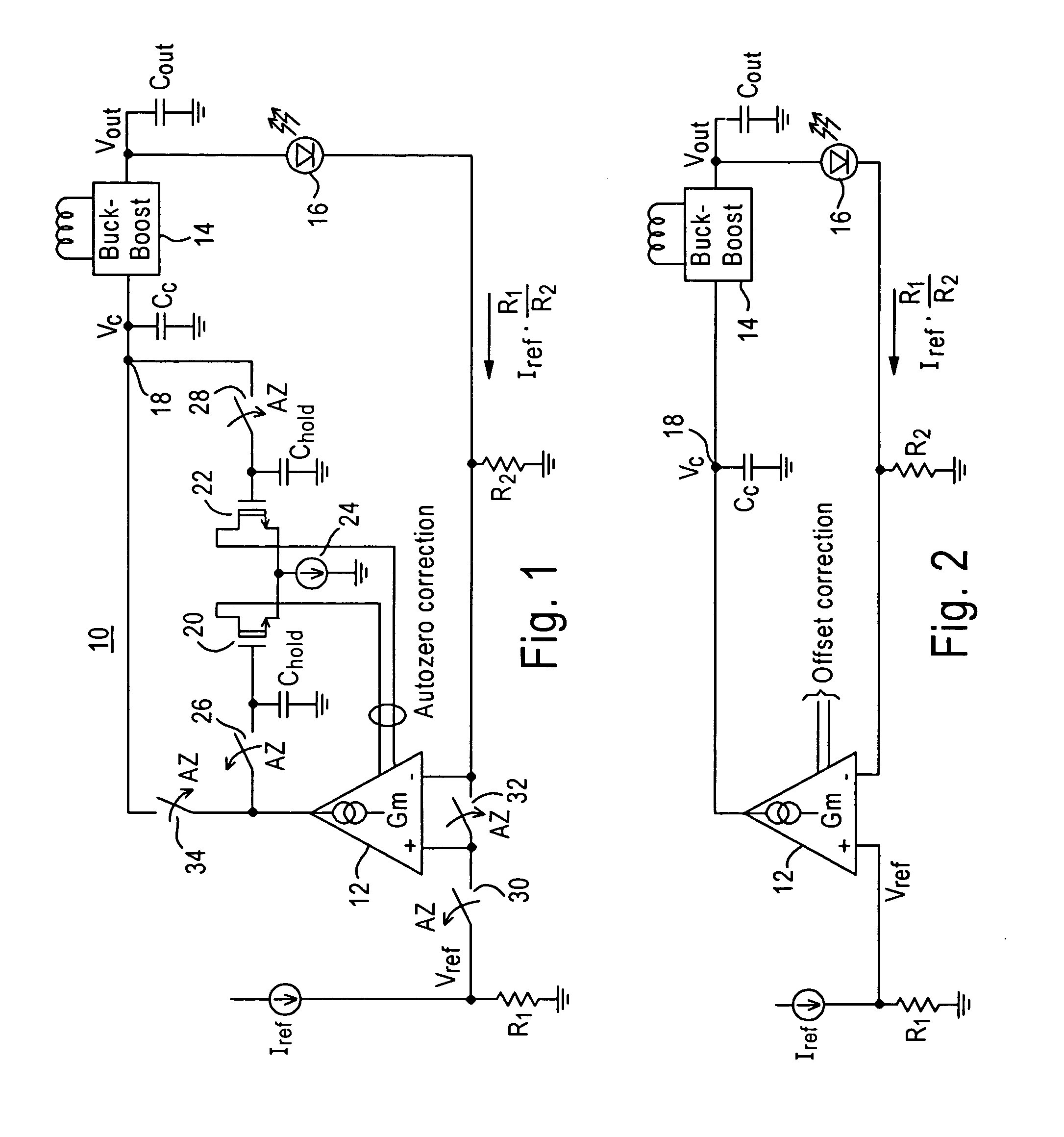
ActiveUS20060226898A1Correct offsetPrevent deviationElectroluminescent light sourcesAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyEngineeringChopper amplifier
Novel circuitry and methodology are provided for correcting the offset associated with a voltage-controlled current source. An offset correction circuit is coupled to the current source to prevent the output current produced by the current source from deviating from a desired level. The current source may include a transconductance amplifier or a chopper amplifier, and may be configured to produce a zero or non-zero value of the output current.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
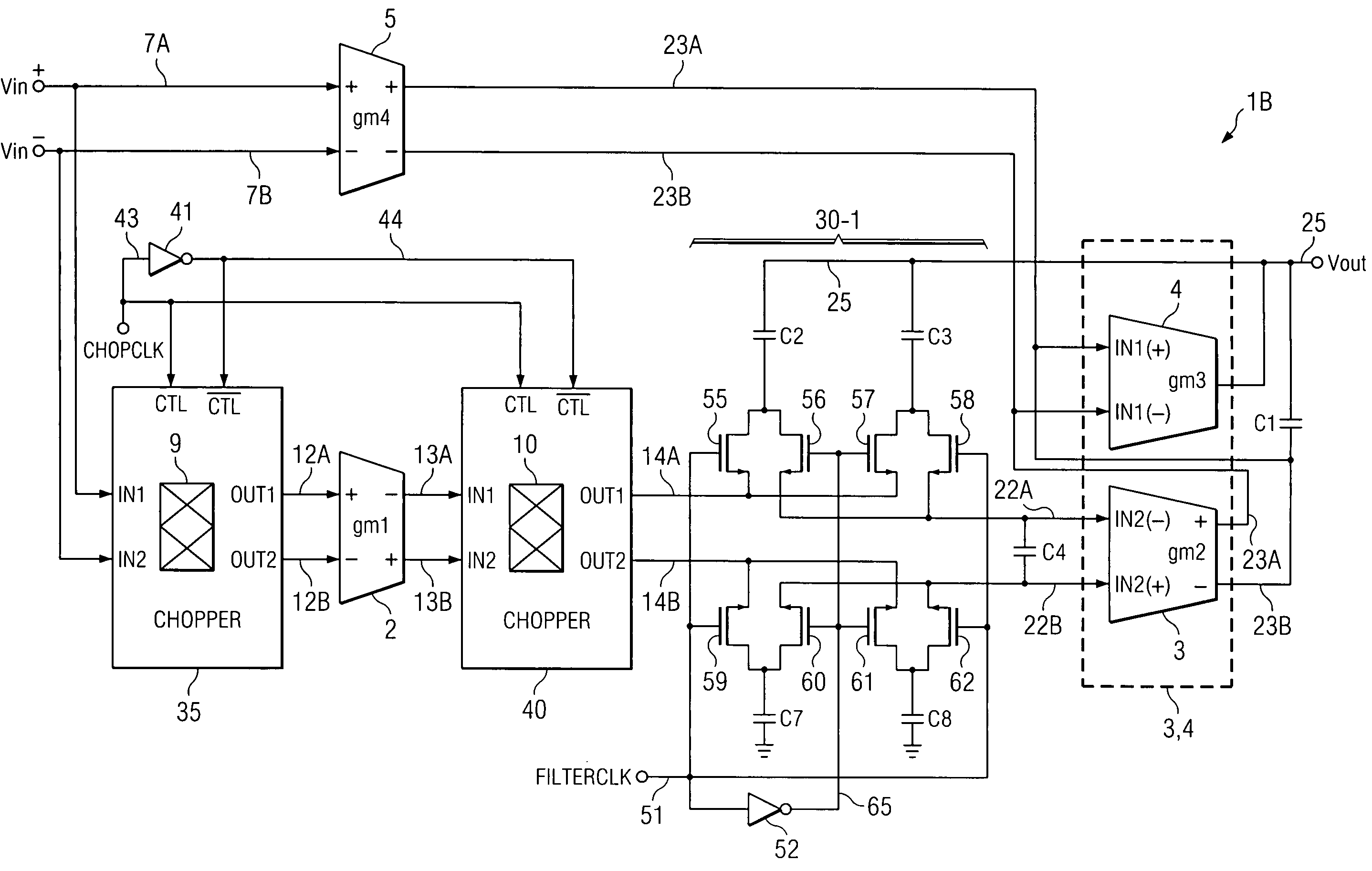
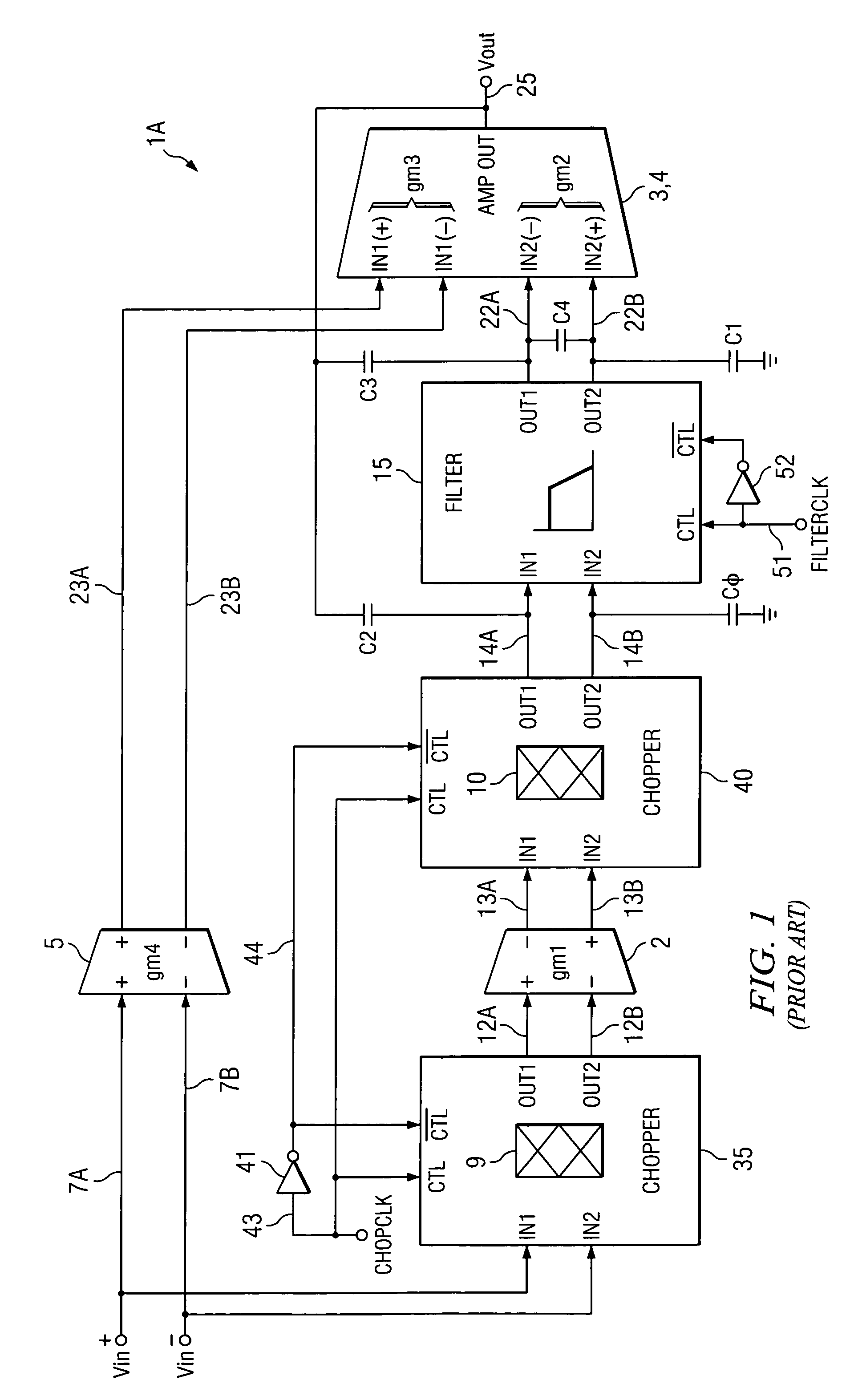
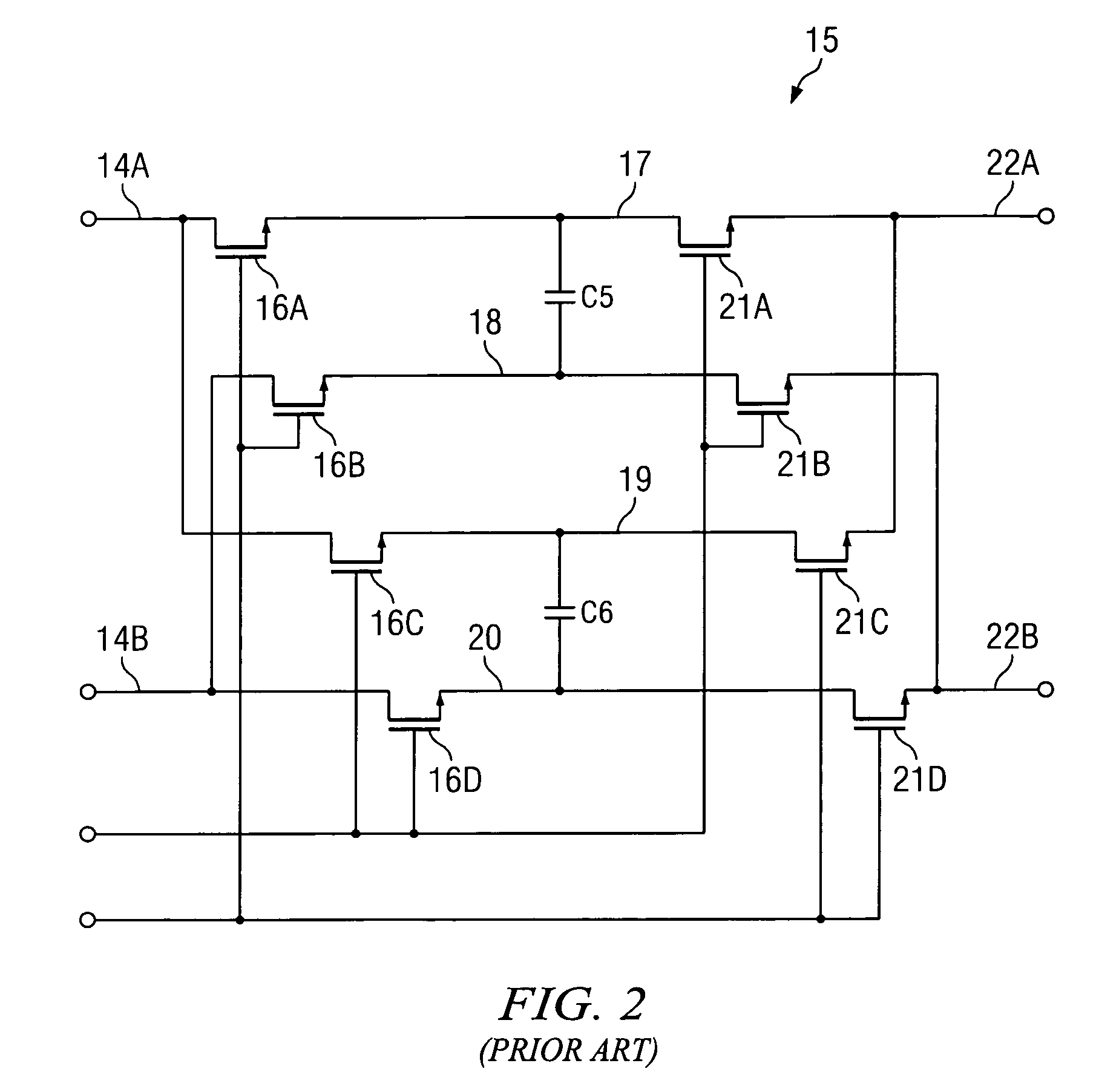
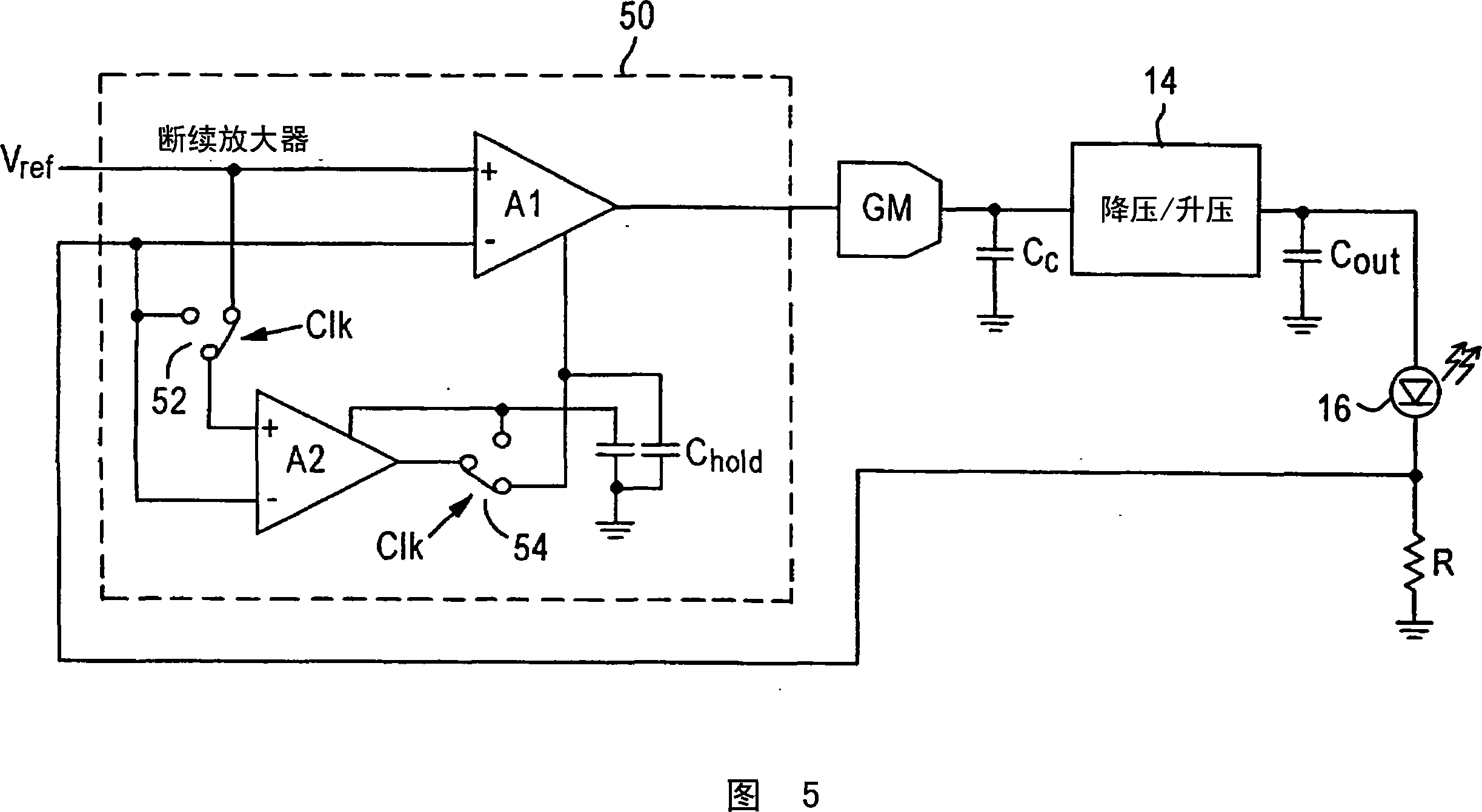
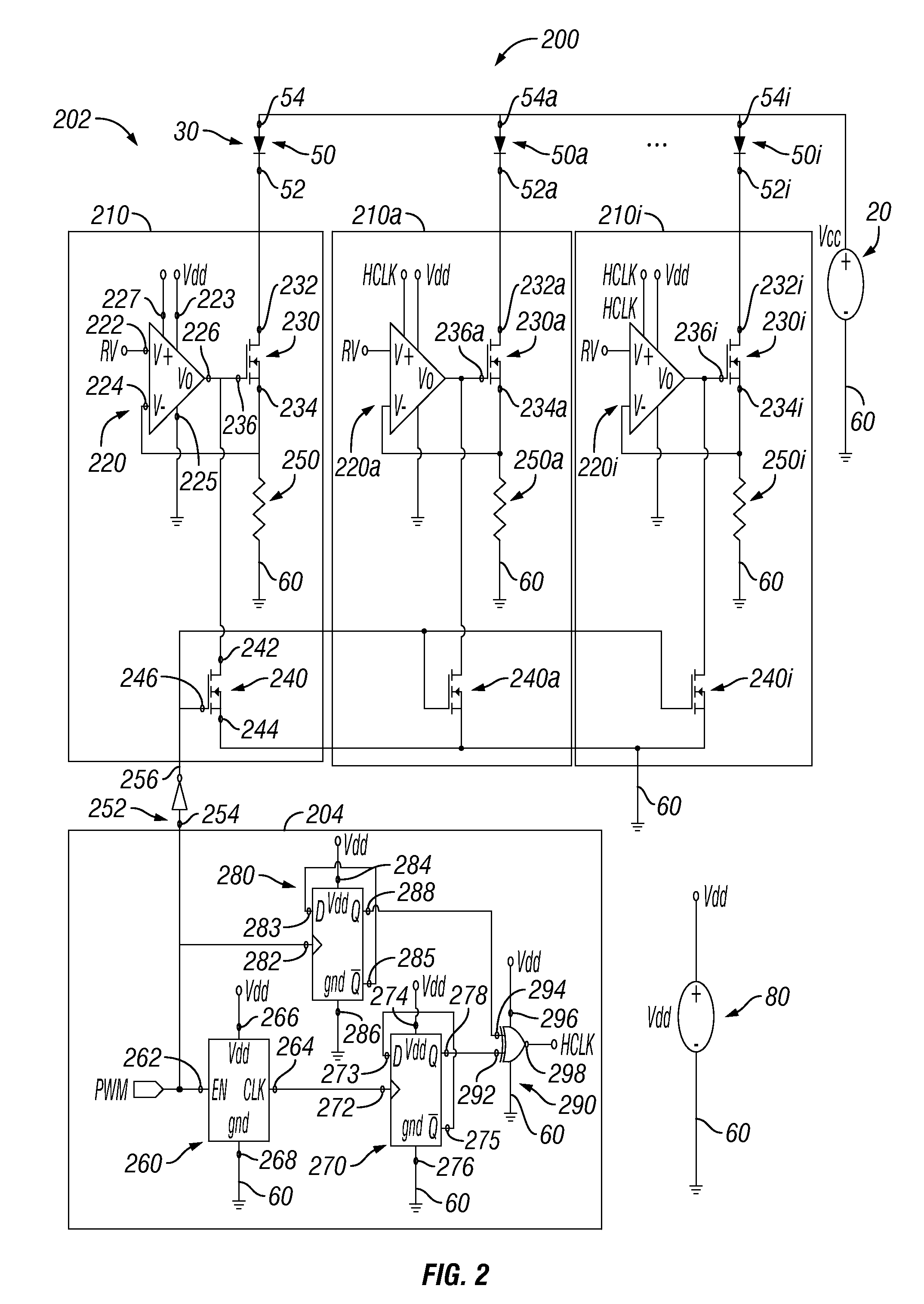
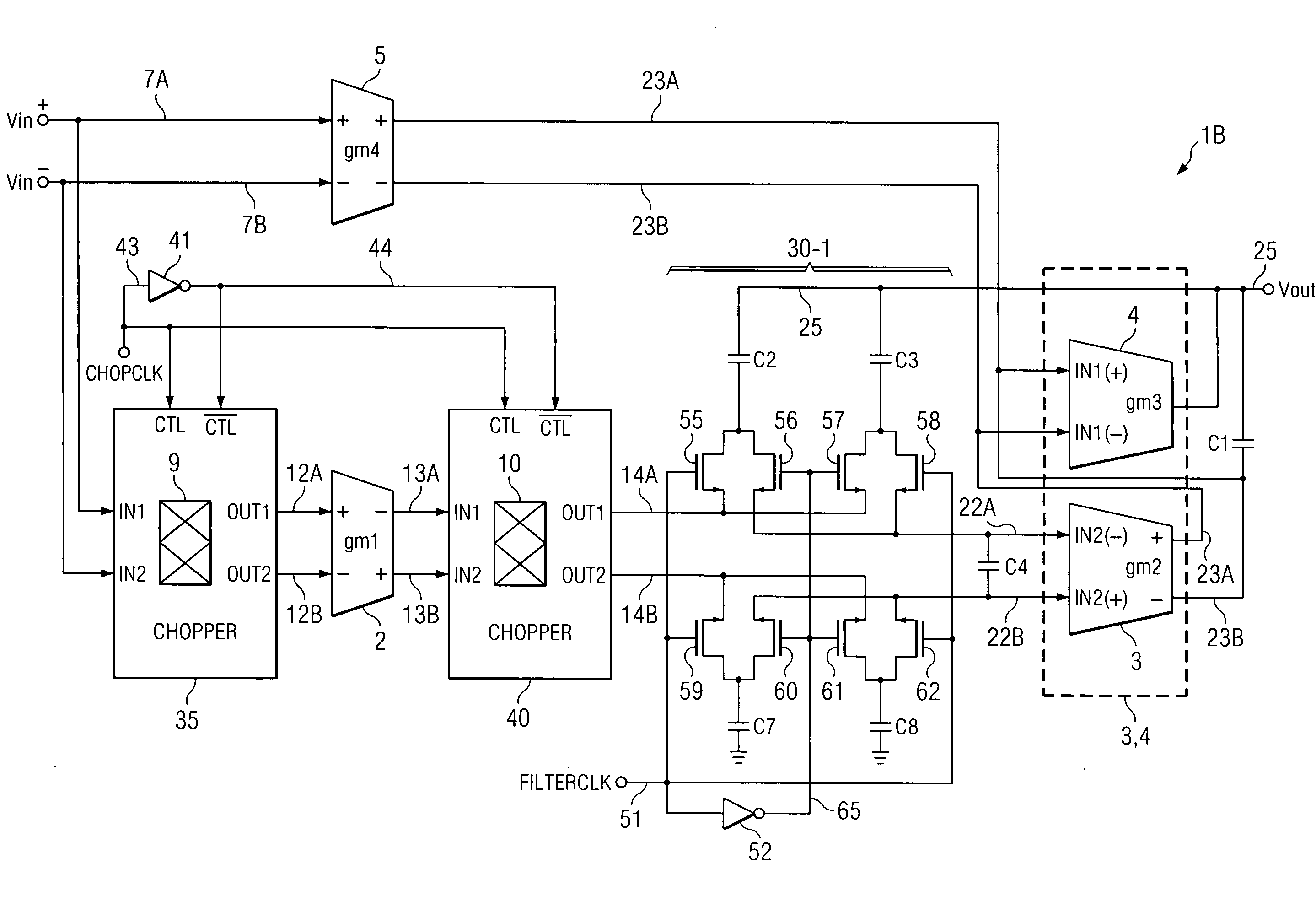
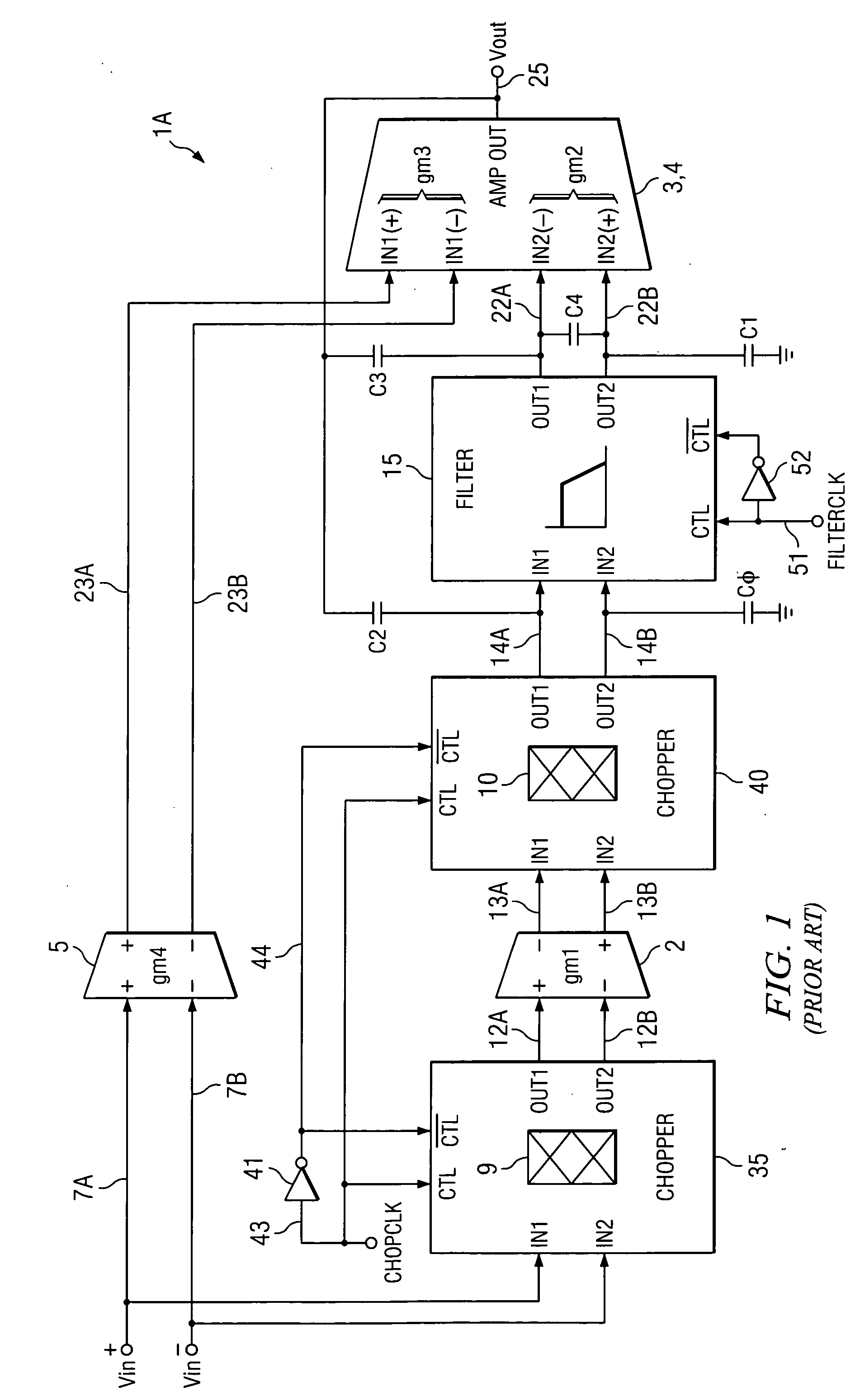
Simultaneous filtering and compensation circuitry and method in chopping amplifier
ActiveUS7586368B2Reduce the amount requiredAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierEngineering
A chopper-stabilized amplifier (1B) having a first output (25) includes an input chopper (9) for chopping an input signal and applying it to the input of a first amplifier (2) and an output chopper (10) for chopping an output signal of the first amplifier and applying it to the input of a switched capacitor notch filter (30-1). Notch filtering of the chopped output signal is performed by coupling a first compensation capacitor (C2) between a first output (25) of the chopper-stabilized amplifier and an output (14A) of the output chopper by means of a first switch (55) in response to a filter clock (FILTERCLK) and coupling a second compensation capacitor (C3) between the first output and an input (22A) of a second amplifier (3) by means of a second switch (58) in response to the filter clock, and coupling the first compensation capacitor between the first output and the input of the second amplifier by means of a third switch (56) in response to the complement of the filter clock and coupling the second compensation capacitor between the first output and the output (14A) of the output chopper circuit (40) by means of a fourth switch (57) in response to the complement.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
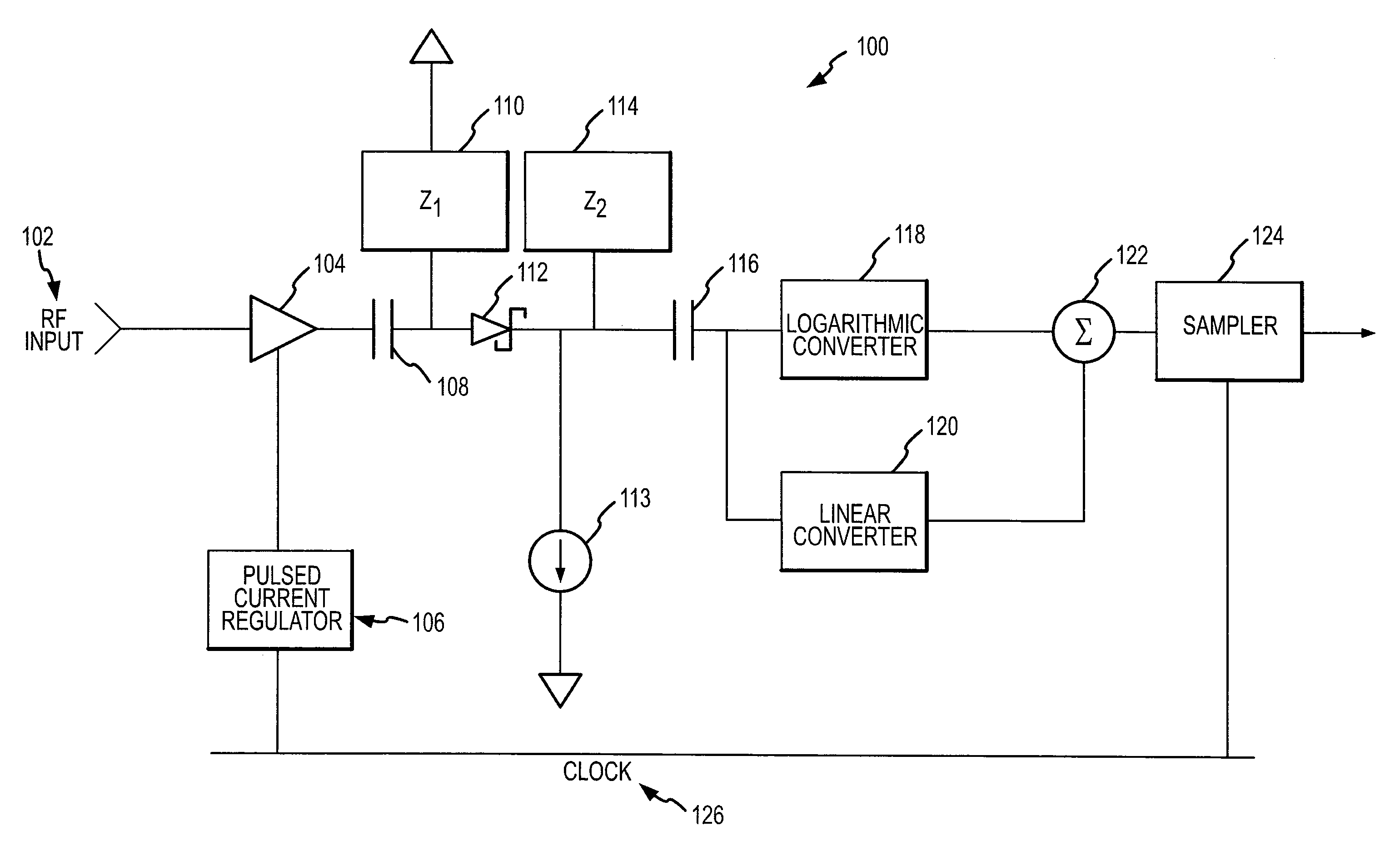
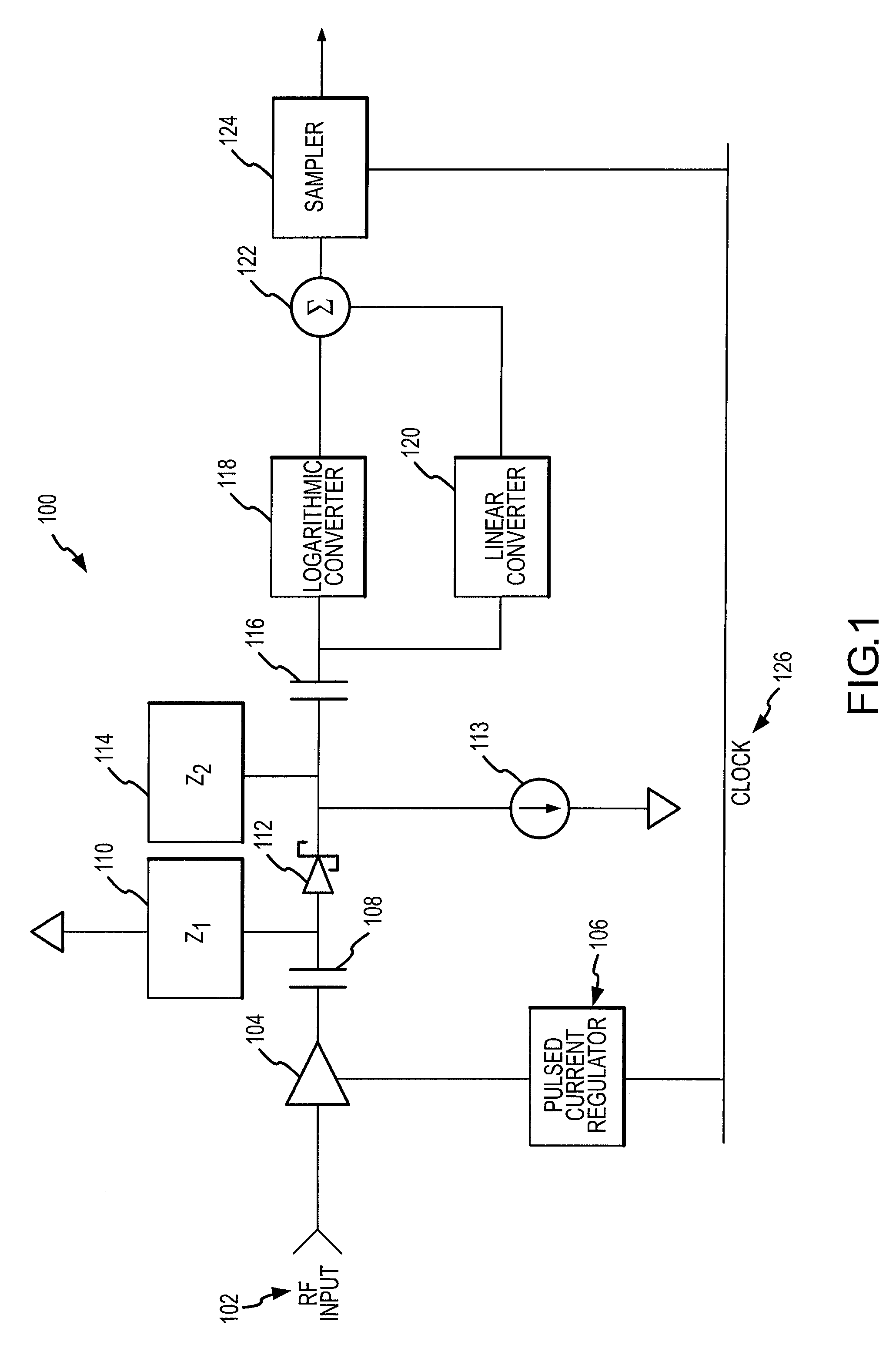
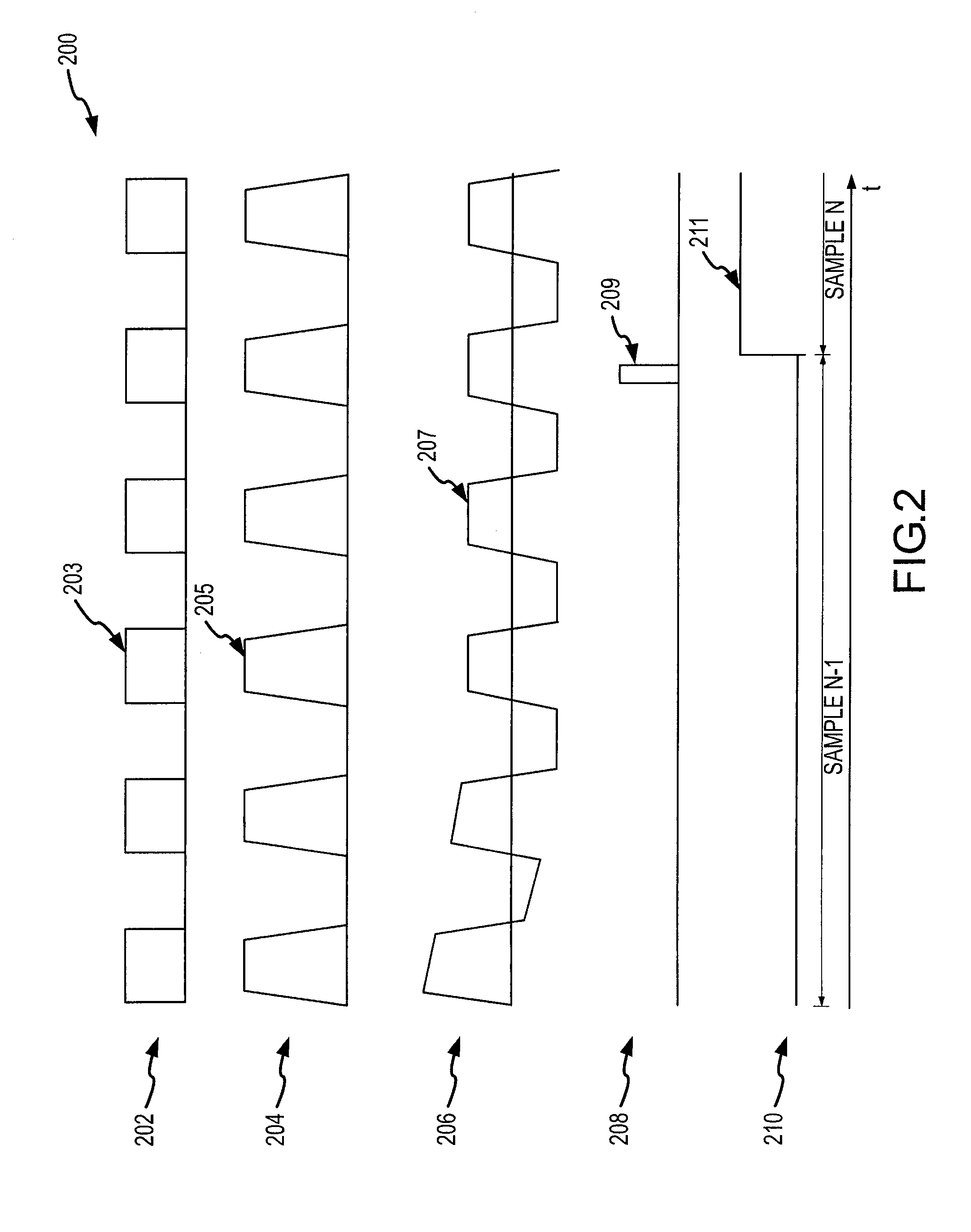
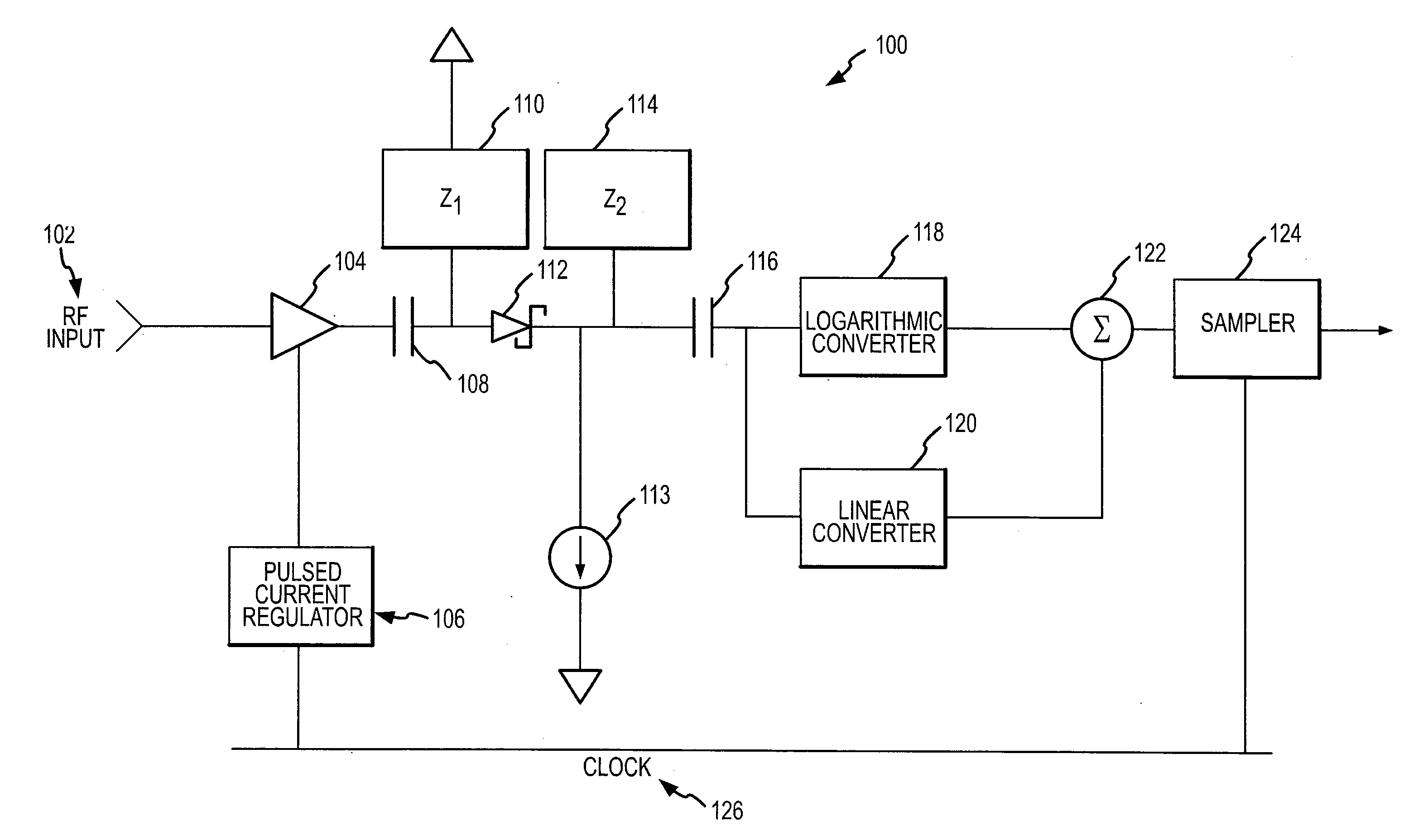
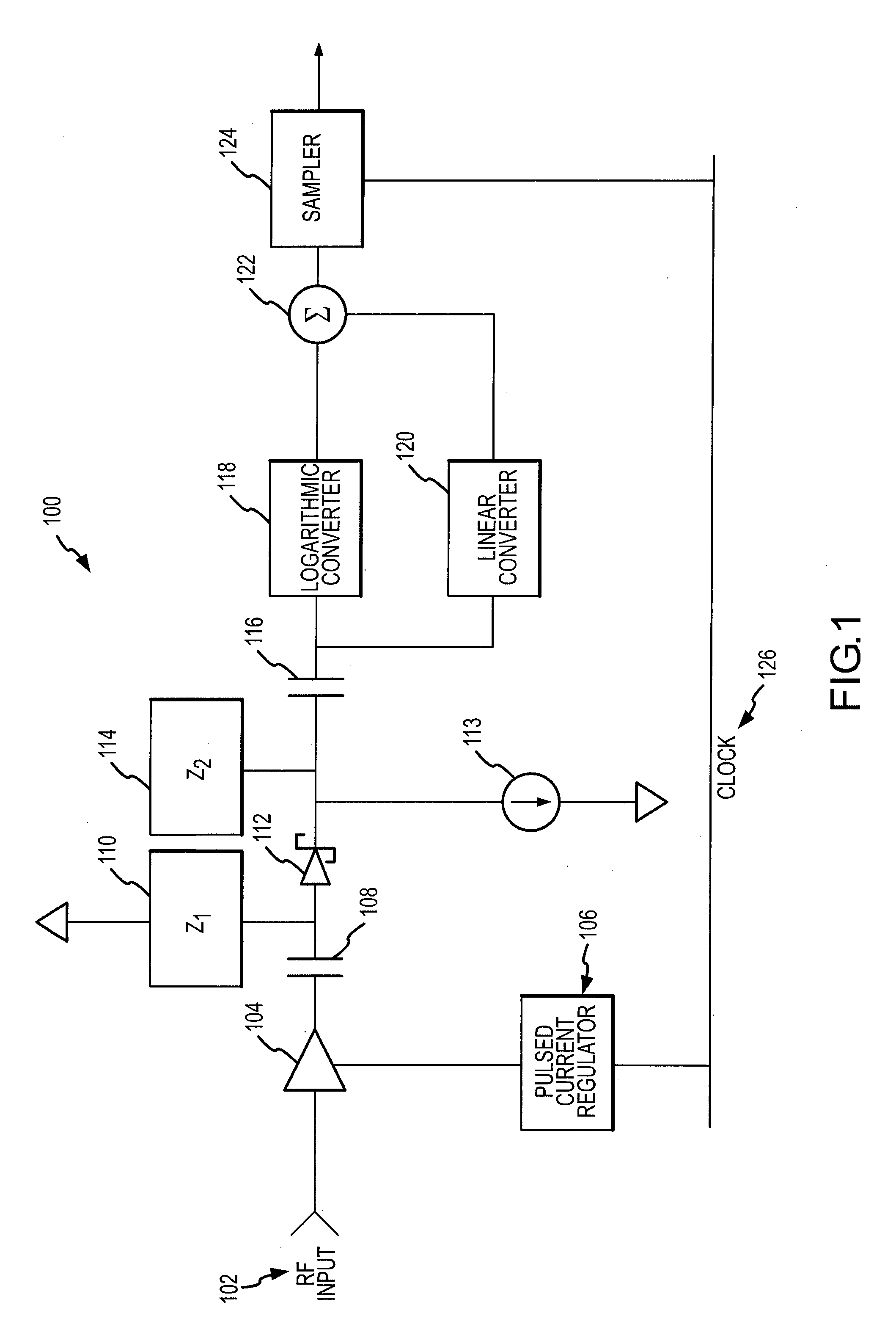
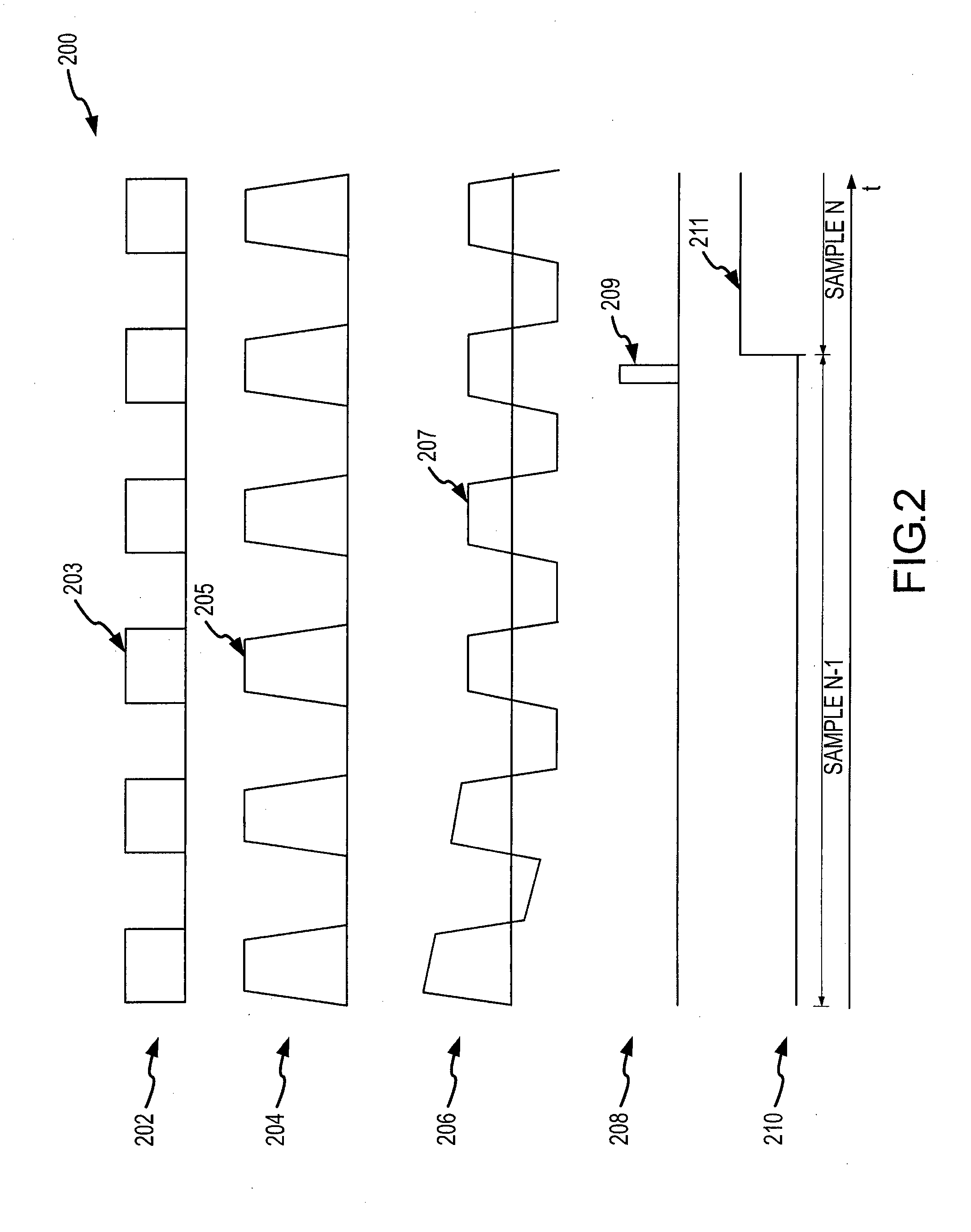
RF power sensor with chopping amplifier
ActiveUS7652464B2Maximize dynamic rangeMaximize signal sensitivityResistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage-current phase anglePower sensorAudio power amplifier
An RF power detector having a wide dynamic range may comprise a chopping amplifier and is configured to detect pulsed high frequency RF signals. The chopping amplifier controlled by a bias current regulator amplifies and chops an RF signal by periodically enabling and disabling the amplifier according to a system clock. The chopped high frequency RF signal feeds a Schottky diode biased to operate in the square law region for weak signals. The Schottky diode voltage is tapped and high pass filtered. The voltage drives a logarithmic and linear converter. The converter outputs are summed to produce an output voltage that is a repeatable and stable monotonically increasing function of the RF power.
Owner:VIASAT INC
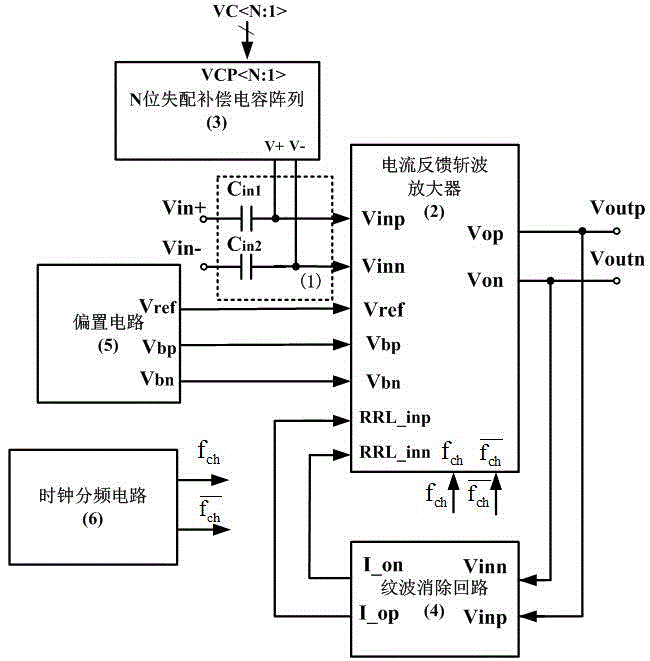
Microcurrent and current feedback chopper modulation instrument amplifier
InactiveCN104320096ACancel offset voltageHigh input impedanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationCapacitanceLow noise
The invention belongs to the technical field of amplifiers, and particularly relates to a current feedback chopper modulation instrument amplifier working under a micro quiescent current. The amplifier consists of a blocking condenser, a current feedback chopper amplifier, an N-bit mismatch compensation capacitor array, a ripple canceling circuit, a biasing circuit and a clock frequency dividing circuit. The microcurrent and current feedback chopper modulation instrument amplifier has the characteristics of alternating current coupling, high input impedance, ultra-low offset voltage, low noise, high common mode rejection ratio, high power supply rejection ratio, micro-power consumption and the like; the circuit is particularly suitable for a wearable health monitoring system biopotential acquisition circuit adopting dry electrodes, and can eliminate semi-potential imbalance between electrodes in a rail-to-rail mode. The simulation result of one embodiment of the invention shows that the common-mode rejection ratio of the instrument amplifier is greater than 120 dB, the equivalent input impedance is greater than 500 M Ohm, and the noise energy efficiency factor NEF is equal to 4.5.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Offset correction circuit for voltage-controlled current source
InactiveCN101147424AAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationElectroluminescent light sourcesAudio power amplifierEngineering
Novel circuitry and methodology are provided for correcting the offset associated with a voltage-controlled current source. An offset correction circuit is coupled to the current source to prevent the output current produced by the current source from deviating from a desired level. The current source may include a transconductance amplifier or a chopper amplifier, and may be configured to produce a zero or non-zero value of the output current.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
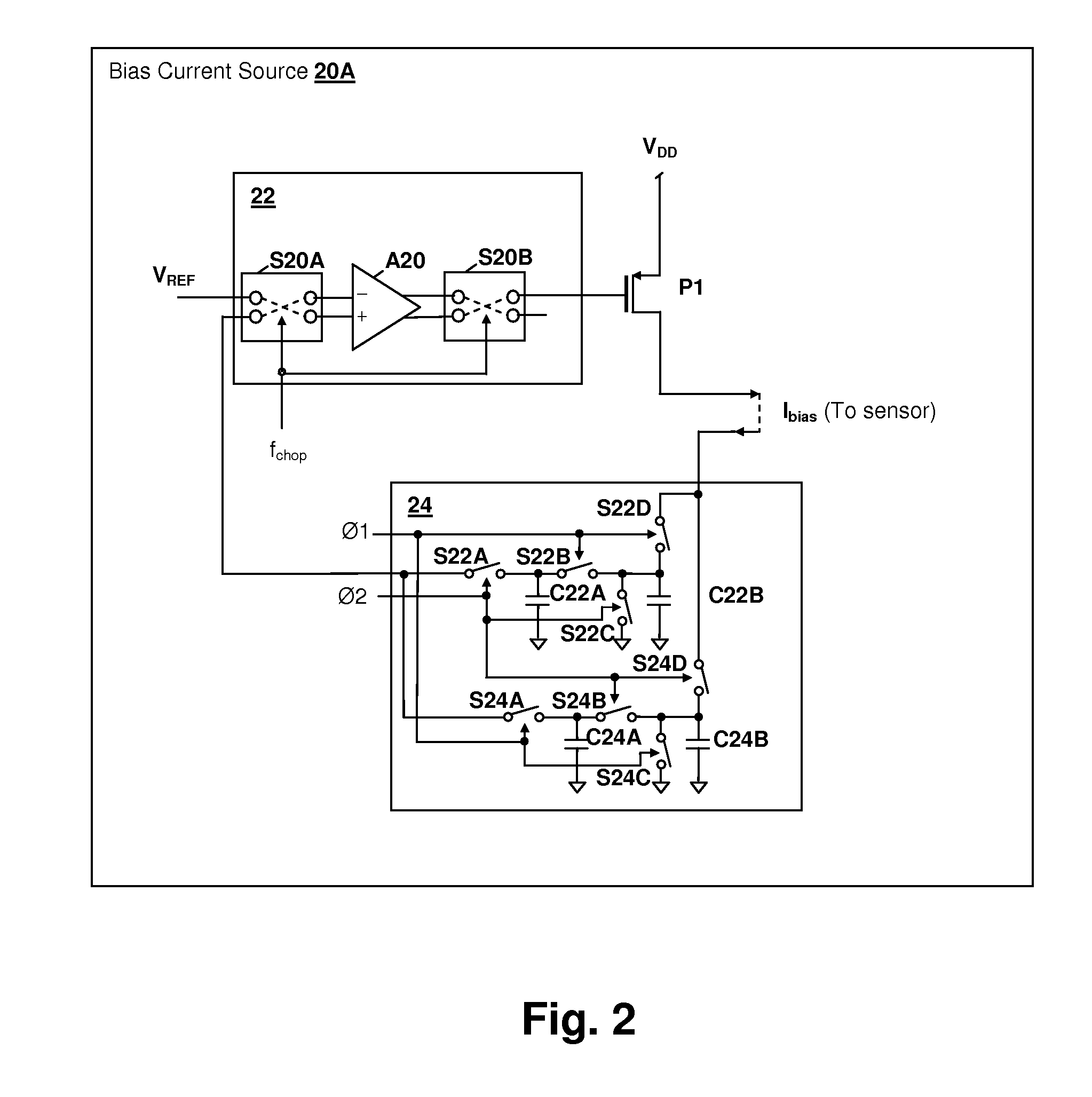
Temperature and process-stable magnetic field sensor bias current source
InactiveUS20090160535A1Less process variationReduce the impactMagnetic measurementsElectric variable regulationReference currentEngineering
A temperature and process-stable magnetic field sensor bias current source provides improved performance in Hall effect sensor circuits. A switched-capacitor sensing element is used to sense either a reference current or the bias current directly. A current mirror may be used to generate the bias current from the reference current, and may include multiple current source transistors coupled through corresponding control transistors that are switched using a barrel shifter to reduce variations in the bias current due to process variation. The current mirror control may be provided via a chopper amplifier to reduce flicker noise and the current mirror control voltage may be held using a track / hold circuit during transitions of the chopper amplifier to further reduce noise due to the chopping action.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
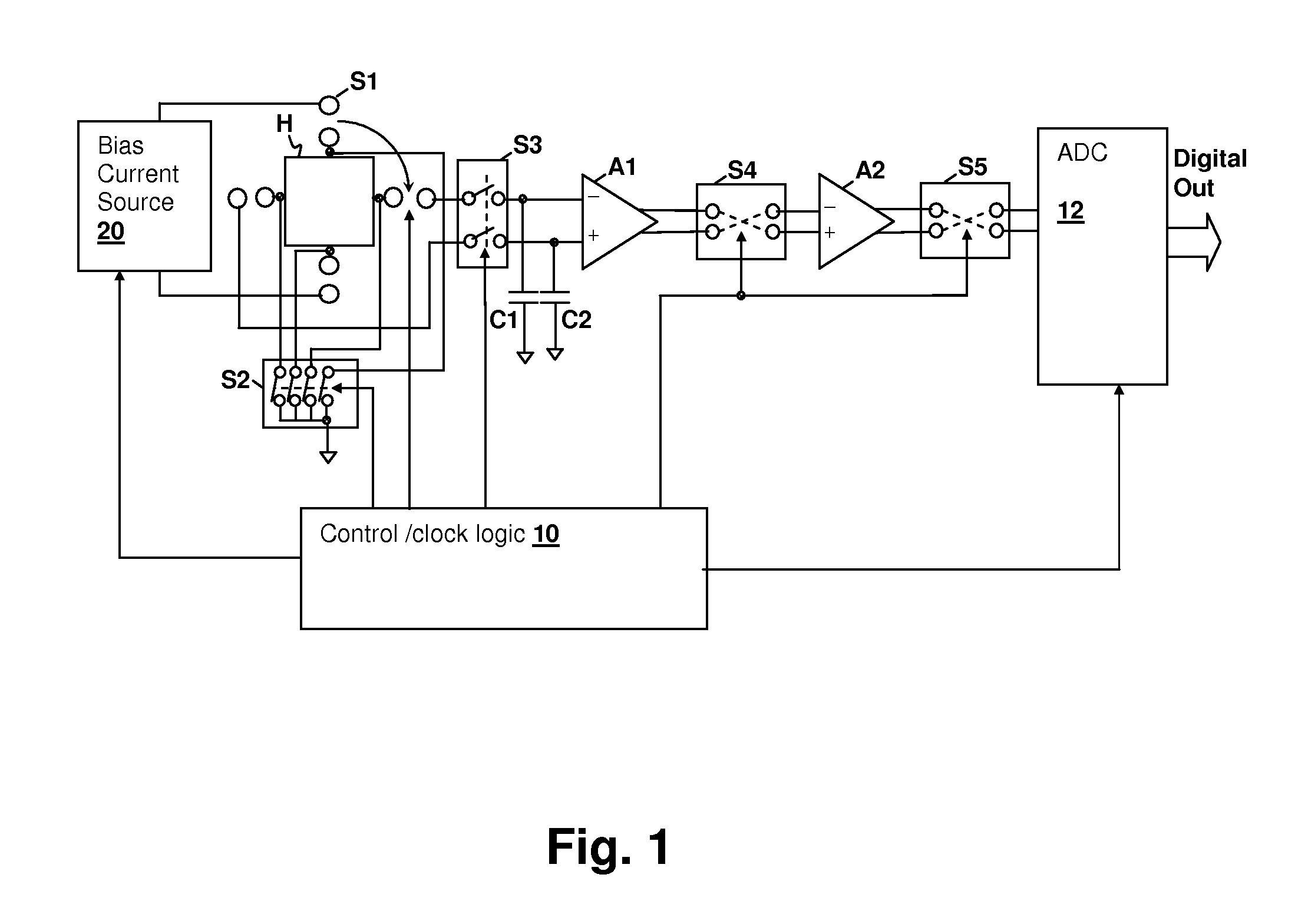
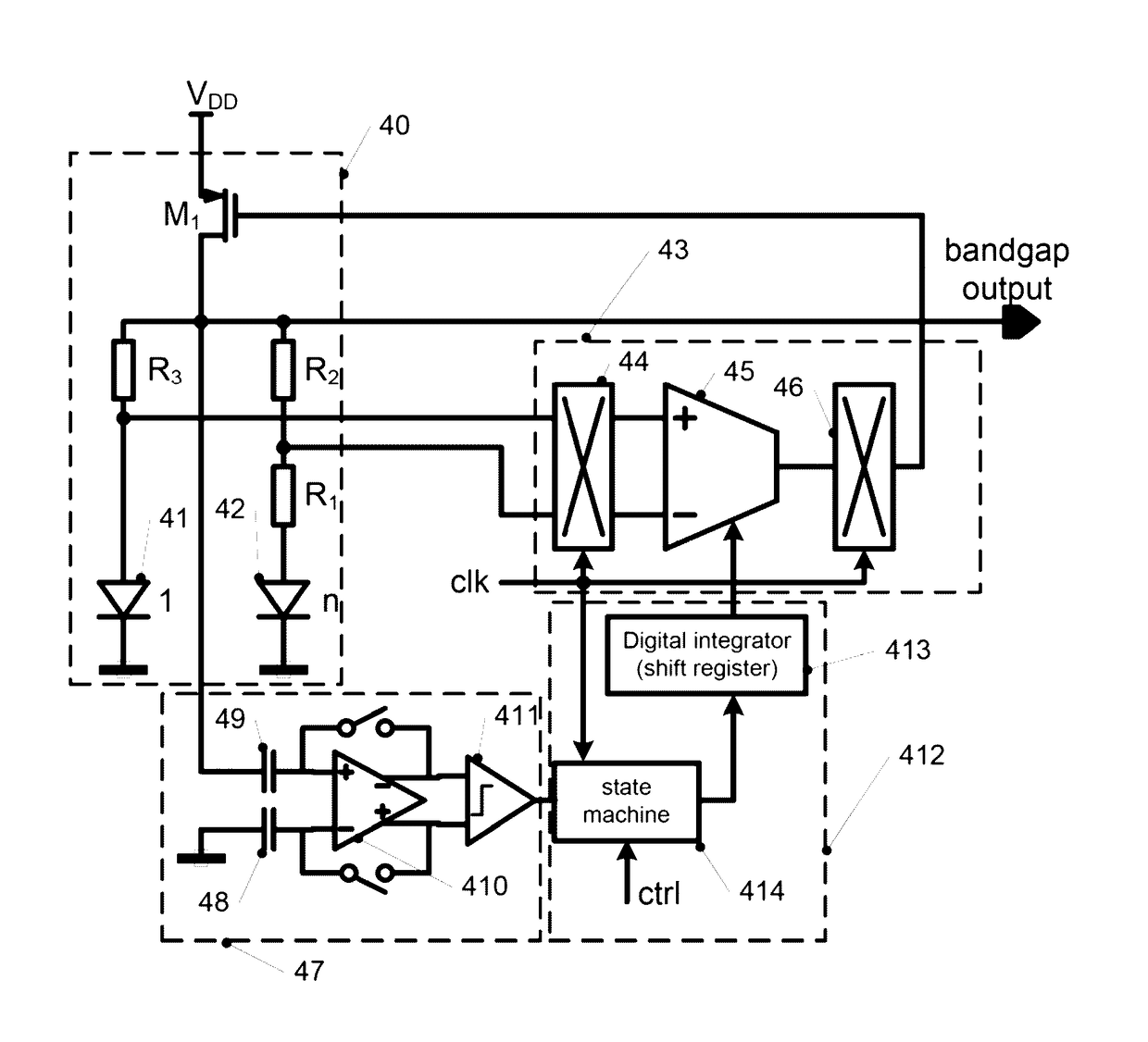
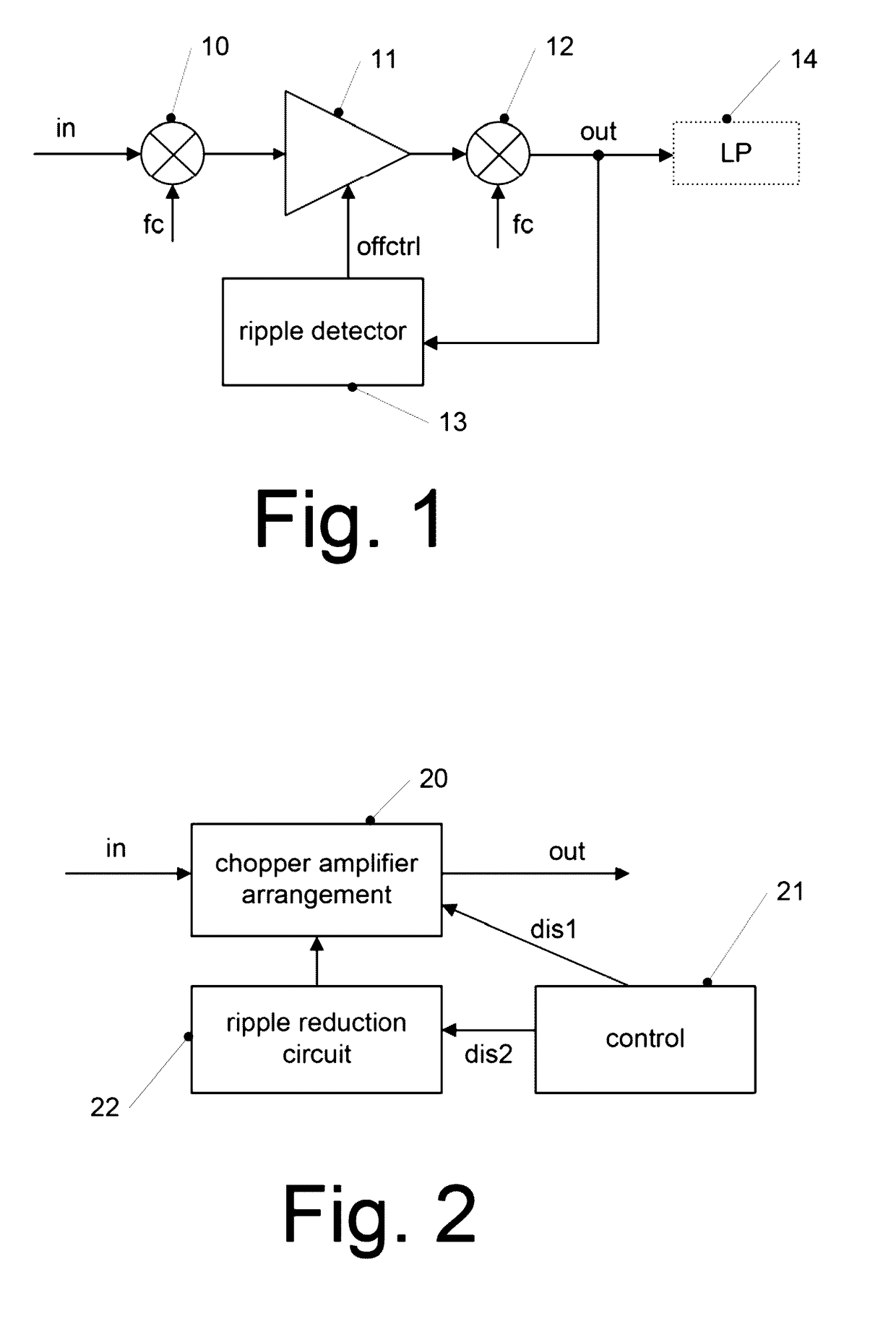
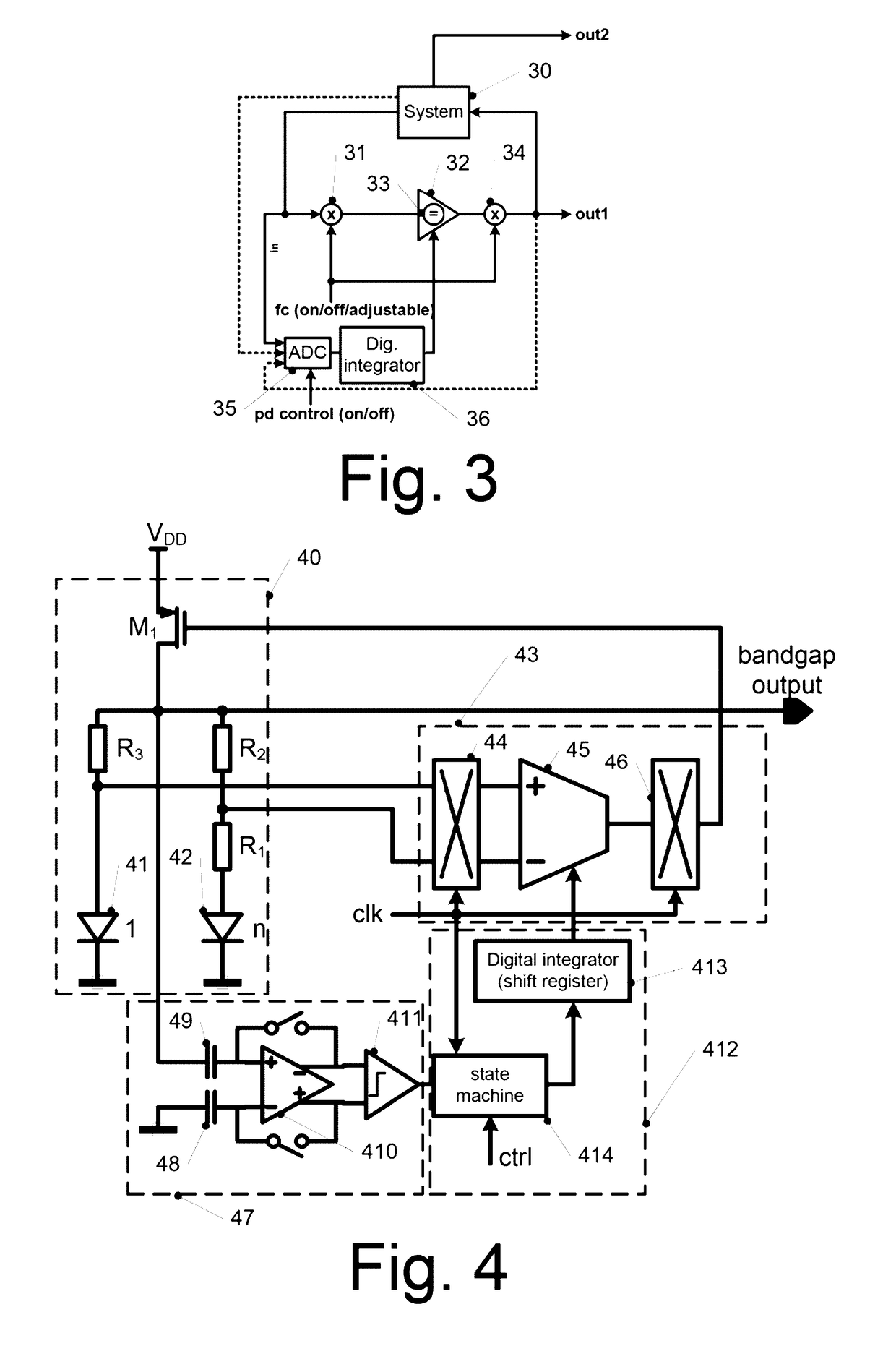
Chopper Amplifier
ActiveUS20140139285A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierChopper amplifier
Various apparatuses and methods are described where a signal is amplified using a chopper amplifier arrangement, and ripples caused by said chopper amplifier arrangement are reduced. In some cases, this reduction of ripples is performed by controlling a voltage offset of an amplifier of said chopper amplifier arrangement. In other embodiments, a detection of ripples or a chopping of the chopper amplifier arrangement is at least temporarily disabled.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Chopper stabilized amplifier with synchronous switched capacitor noise filtering
ActiveUS9473074B1Reduce noiseReduce output noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyCapacitanceSoftware engineering
A chopper stabilized amplifier with synchronous switched capacitor noise filtering is disclosed. In an exemplary embodiment, an apparatus includes a chopper amplifier having an input that receives an input signal and an output that outputs an amplified signal. The chopper amplifier includes an input chopping circuit and an output chopping circuit, where the input and output chopping circuits operate in response to a chop clock. The apparatus also includes a switched capacitor filter having an input that receives the amplified signal and an output that outputs a filtered signal. The switched capacitor filter operates in response to a filter clock. The apparatus also includes a filter timing adjuster that receives a reference voltage and adjusts a phase of the filter clock with respect to the chop clock to reduce chopper noise on that reference voltage.
Owner:LITTELFUSE INC
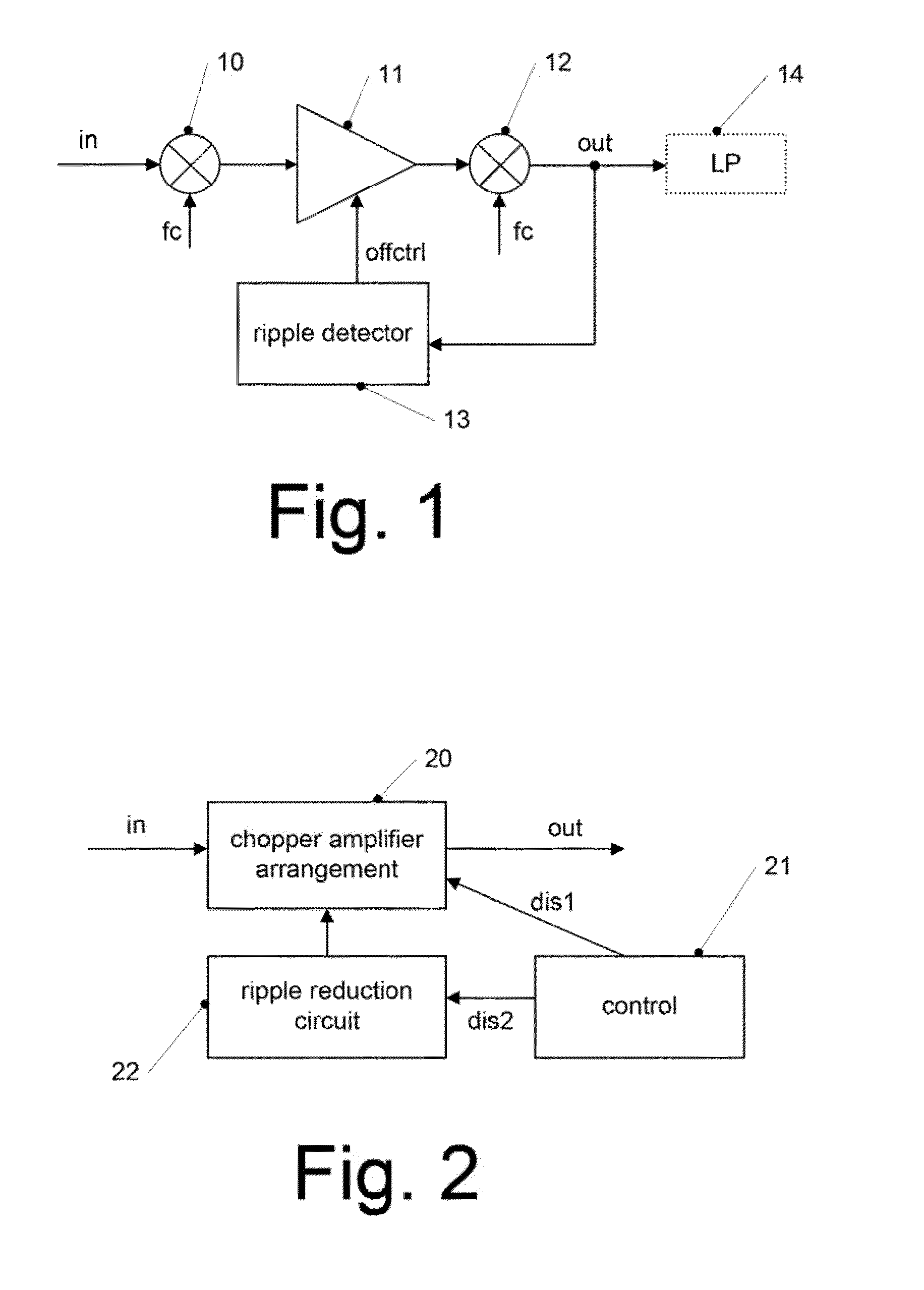
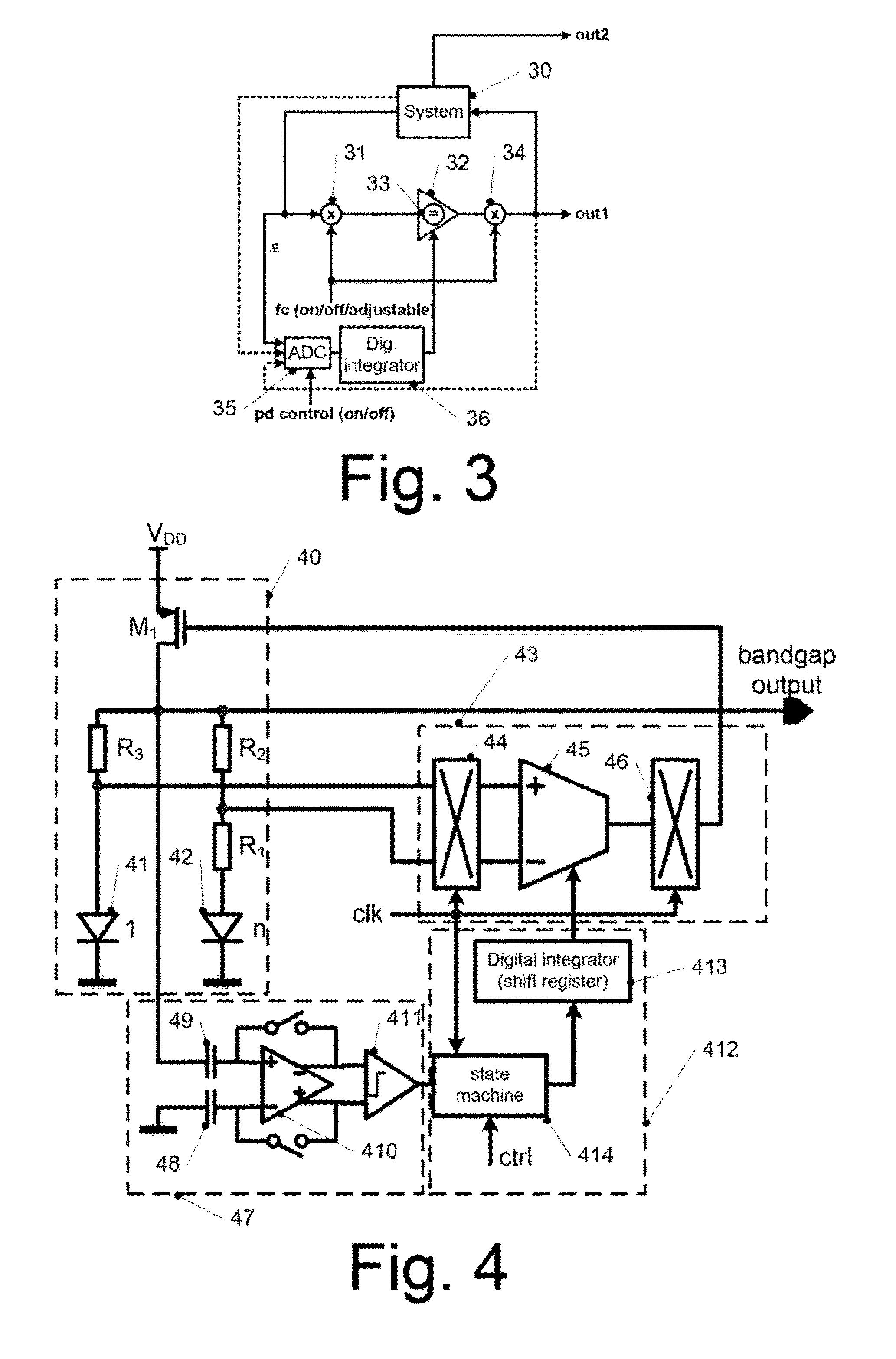
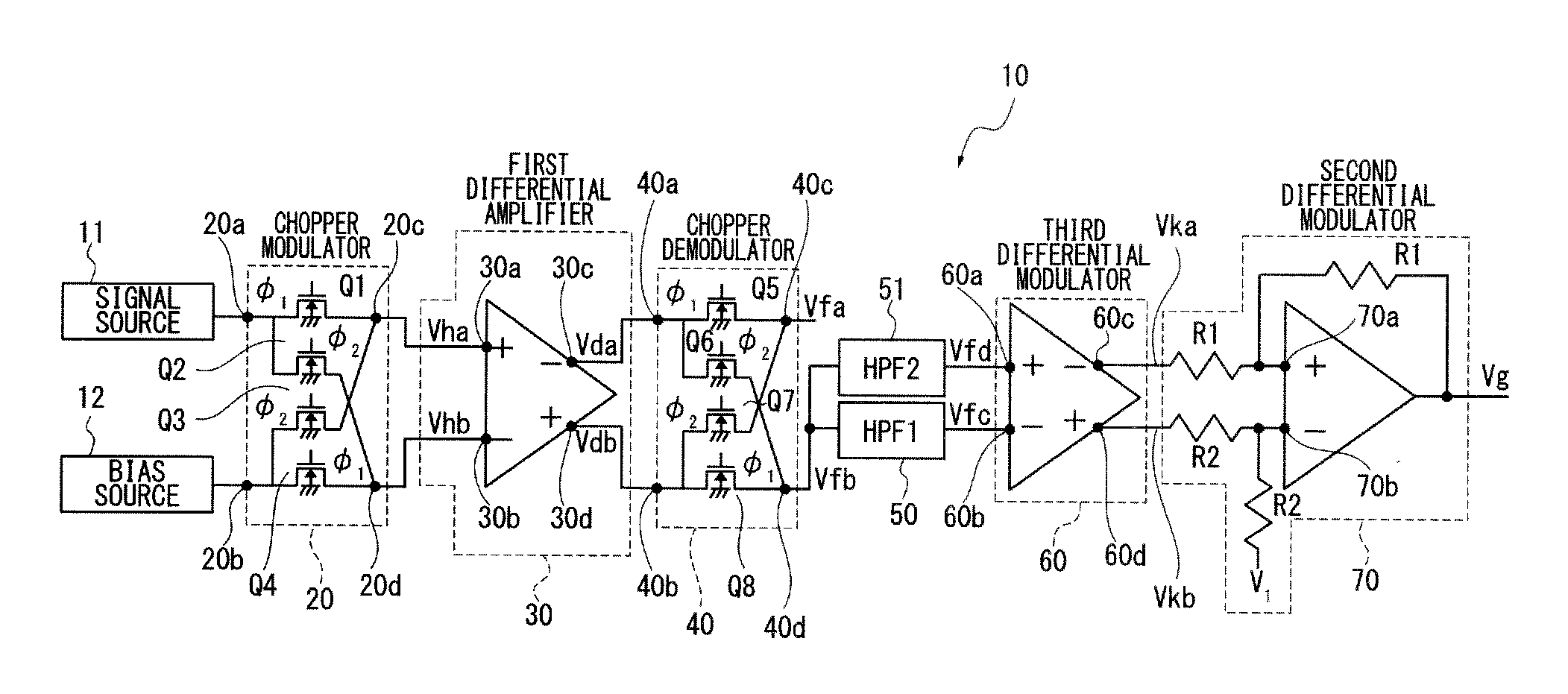
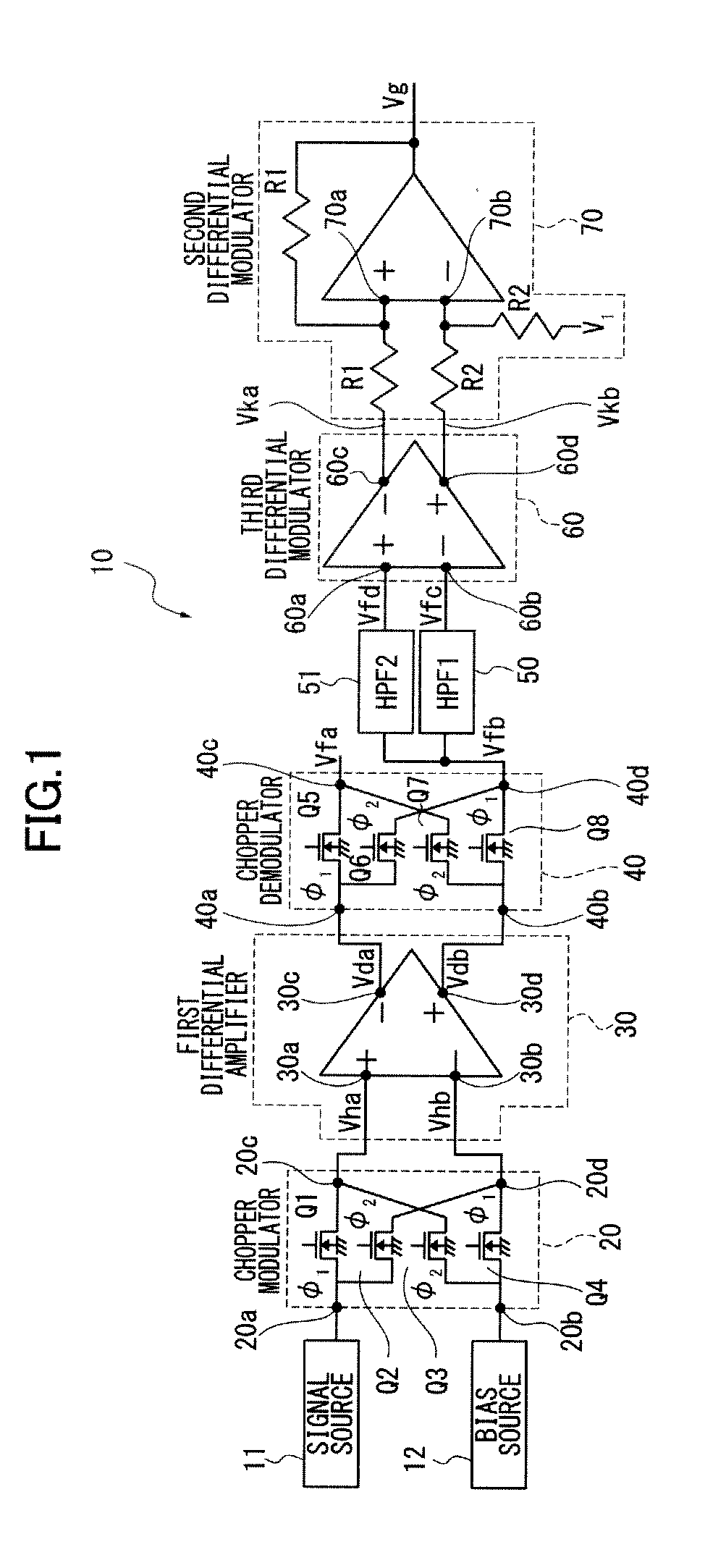
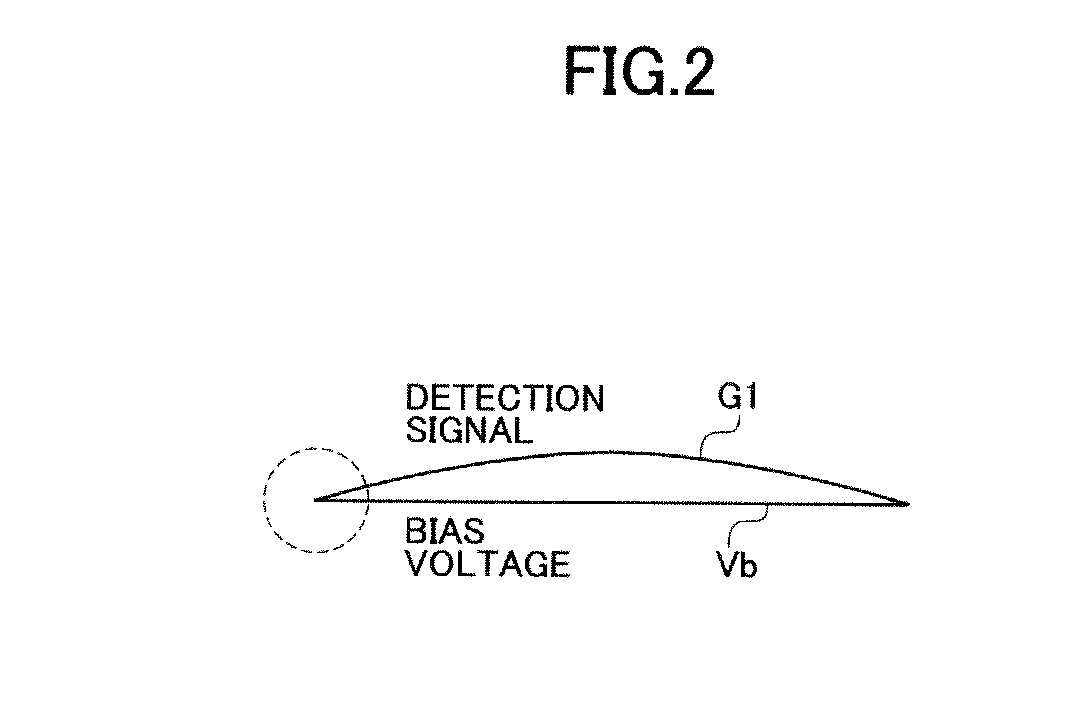
Chopper amplifier
ActiveUS20140312967A1Remove residual offsetRemove offsetAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyLow frequency amplifiersDifferential amplifierChopper amplifier
A chopper amplifier includes a chopper modulator to modulate a certain detection signal and a bias voltage by a certain control signal and output a chopper modulation signal, a first differential amplifier to differentially amplify the chopper modulation signal from the chopper modulator and output a differential modulation signal, a chopper demodulator to demodulate the differential modulation signal from the first differential amplifier by the control signal and output a demodulation signal, a second differential amplifier to extract a detection signal component from the demodulation signal, and a plurality of filters connected at an input terminal of the second differential amplifier and having different cutoff frequencies from each other relative to the demodulation signal.
Owner:RICOH KK
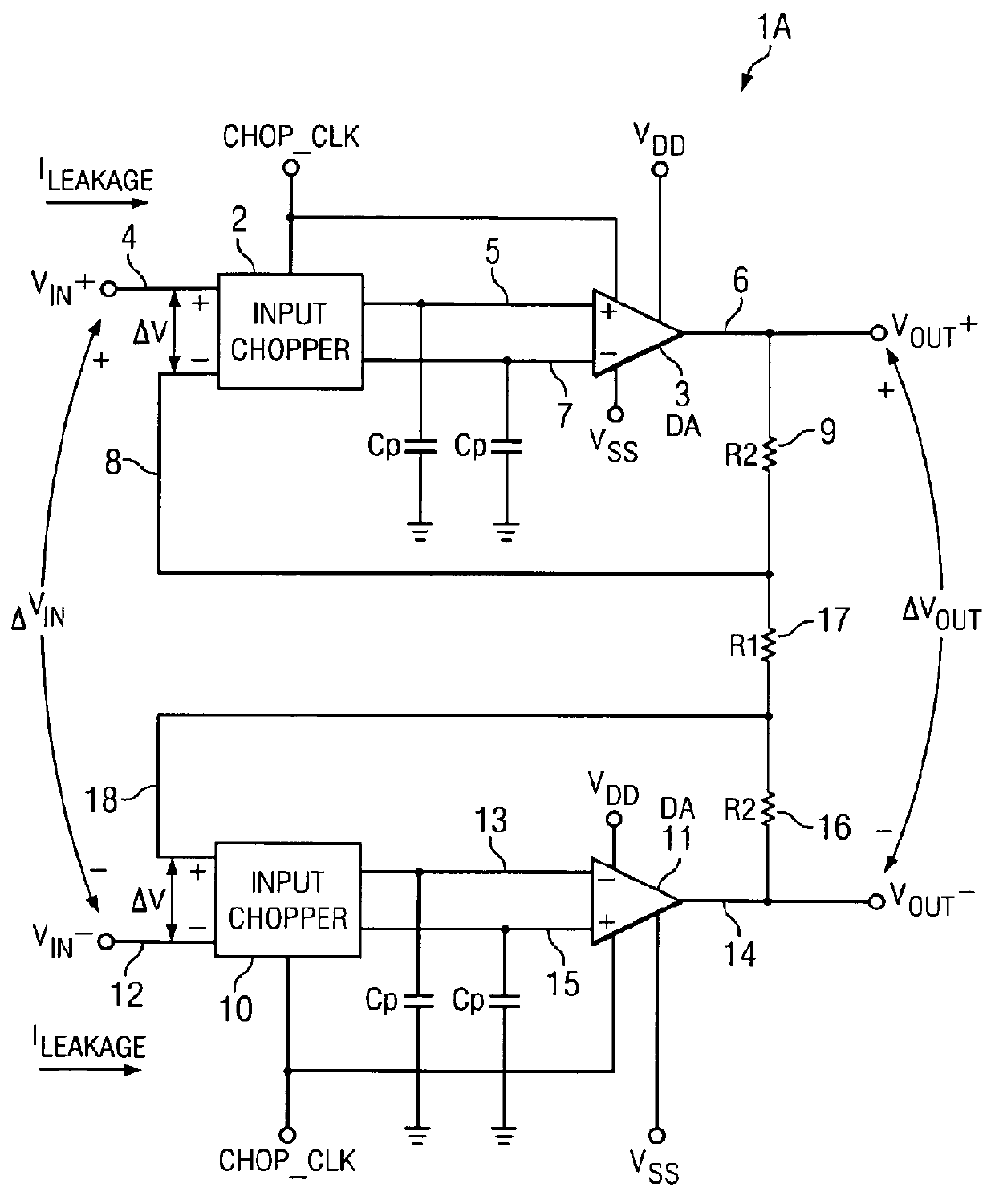
Circuit and method for reducing input leakage in chopped amplifier during overload conditions
ActiveUS8258863B2Low input leakage currentHigh input impedanceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierChopper amplifier
A chopper-stabilized amplifier (20A) includes an amplifier (3), an input chopper (2A) having a first input (4) receiving an input signal (VIN+), an output (5) coupled to a first input of the amplifier, and a feedback resistor (9) coupled to an output (6) of the amplifier to couple a feedback signal (VFB+) to a second input of the amplifier (3). The input chopper operates in response to a chopping clock (CHOP_CLK). If the amplifier (3) is unacceptably close to a saturation condition, the chopping clock (CHOP_CLK) is disabled to reduce input leakage current (ILEAKAGE) of the chopper-stabilized amplifier.
Owner:DURACELL U S OPERATIONS +1
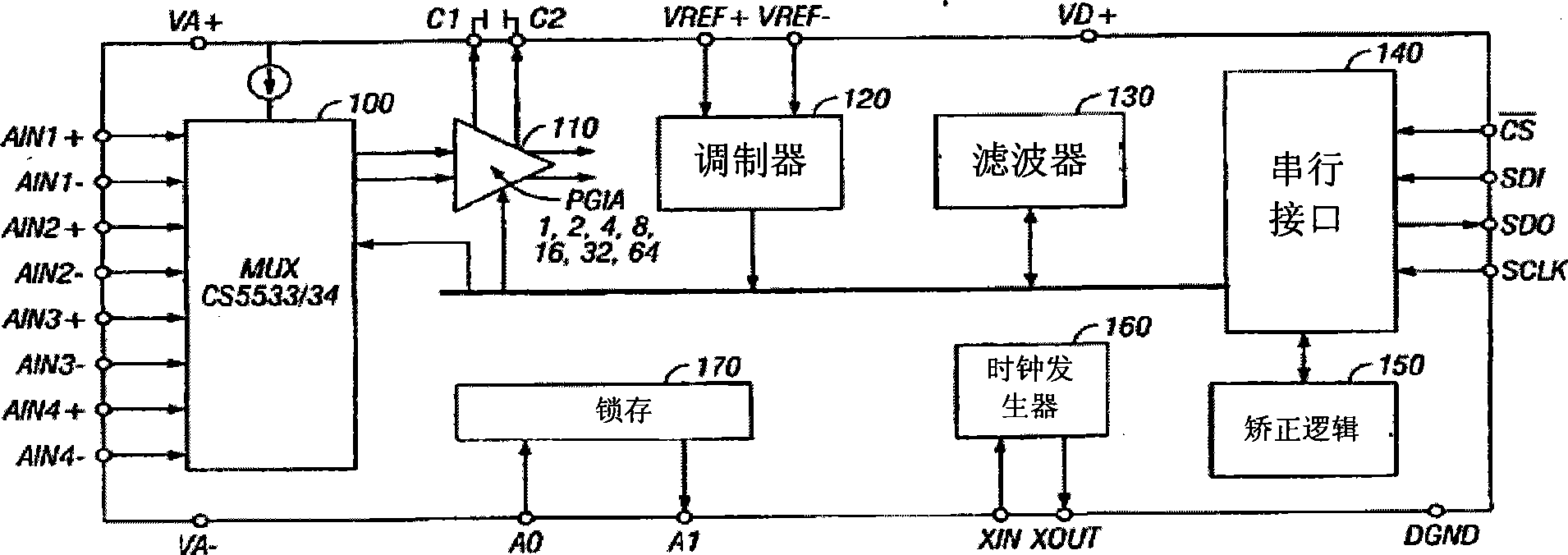
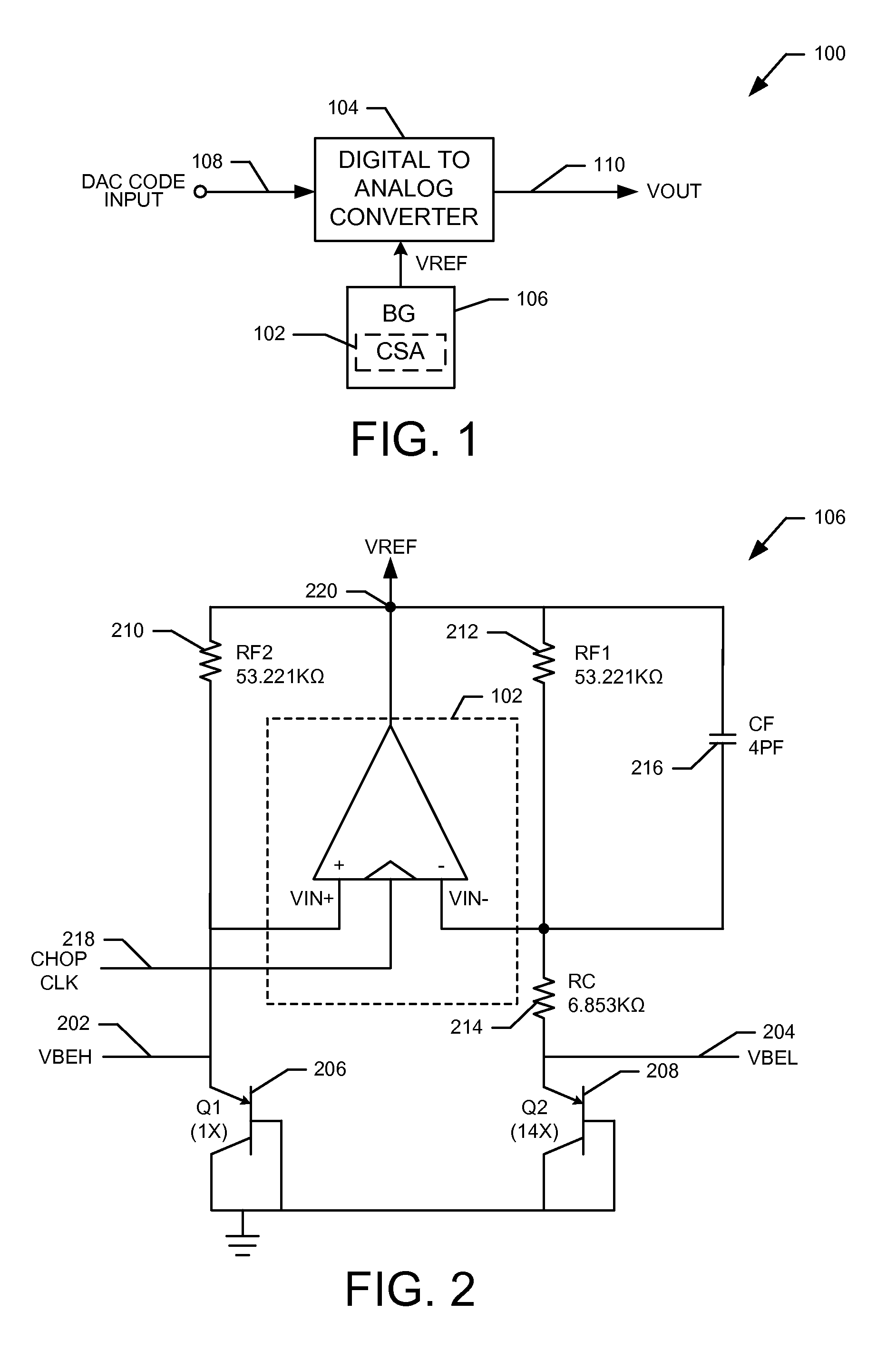
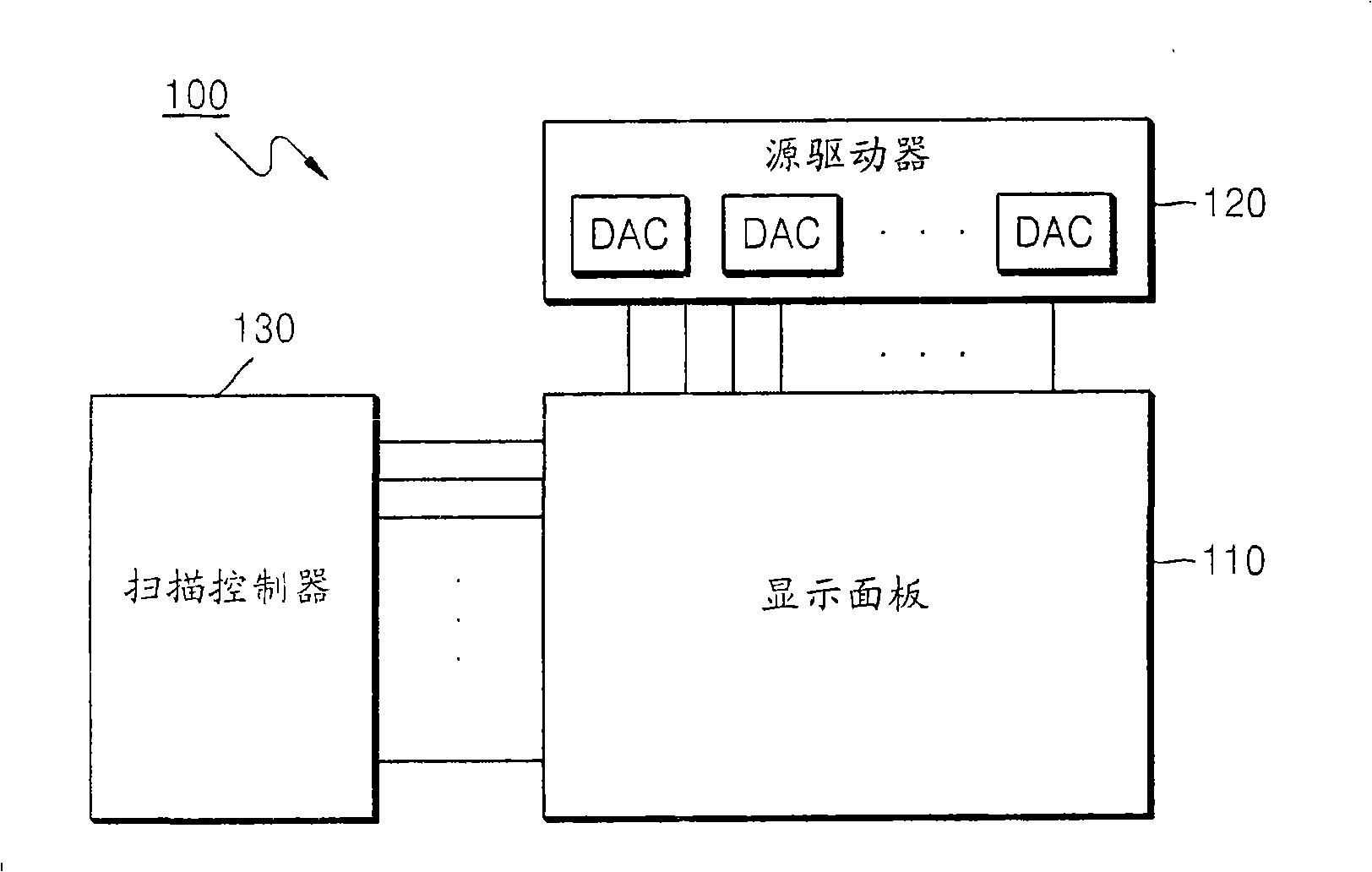
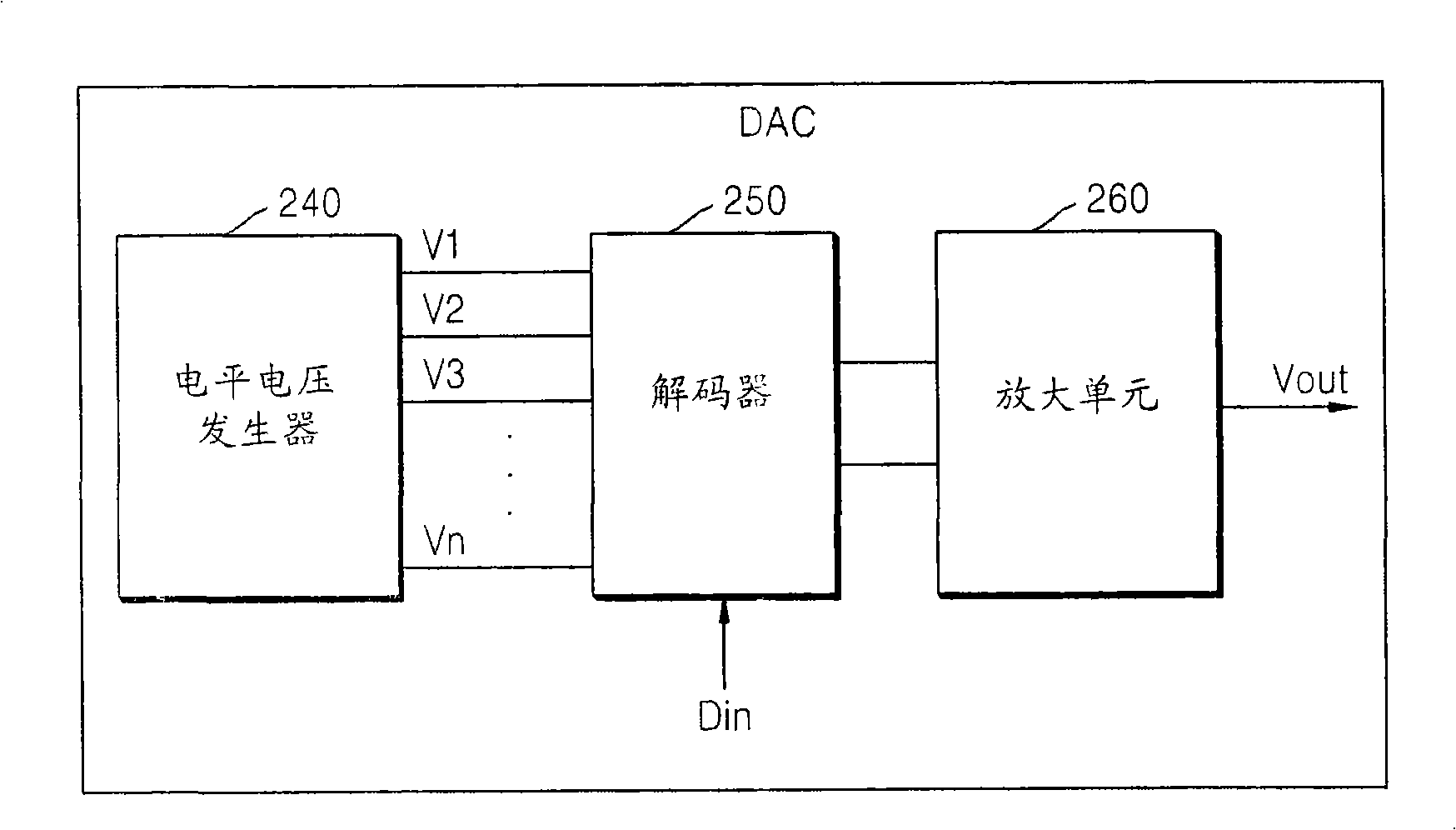
Digital-to-analog converter, display panel driver having the same, and digital-to-analog converting method
InactiveCN101286743AStatic indicating devicesDifferential amplifiersDigital analog converterEngineering
Disclosed is a digital-to-analog converter, a display panel driver containing the same as well as a method for converting digital-to-analog. The digital-to-analog converter outputting an analog data voltage corresponding to n-bit data, includes a chopping amplification unit adapted to receive an upper bit voltage corresponding to upper x bits of the n-bit data and a lower bit voltage corresponding to lower y bits of the n-bit data and to output the analog data voltage. The chopping amplification unit may include a sample and hold capacitor adapted to be charged with the upper bit voltage in a non-inverting mode, and a chopping amplifier adapted to supply the upper bit voltage to the sample and hold capacitor in the non-inverting mode and adapted to output a voltage corresponding to the sum of the upper bit voltage and the lower bit voltage as the analog data voltage in an inverting mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dynamically controllable drive circuit for parallel array of light emitting diodes
ActiveUS8373348B2Reduce variationExact matchElectroluminescent light sourcesAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyControl signalVoltage reference
The present invention relates to a parallel light emitting diode (“LED”) drive circuit and provides a drive circuit configured to drive a parallel array of LEDs. The drive circuit comprises: a switching control signal generator, a plurality of switches, a plurality of sampling resistors, and a plurality of chopper amplifiers. Each switch is coupled to a respective LED in the LED array. Each chopper operational amplifier configured to receive a reference voltage and a switching control signal generated by the switching control signal generator and generate an input offset voltage. Each chopper operational amplifier includes a differential amplifier including an input transistor pair and a current mirror transistor pair, of which the electrical positions can be reserved when the switching control signal is switched between a first state and a second state, wherein the offset voltage, which causes the lightness mismatching in a parallel LED circuit, can be cancelled.
Owner:BCD SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Simultaneous filtering and compensation circuitry and method in chopping amplifier
ActiveUS20090153241A1Reduce the amount requiredAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierEngineering
A chopper-stabilized amplifier (1B) having a first output (25) includes an input chopper (9) for chopping an input signal and applying it to the input of a first amplifier (2) and an output chopper (10) for chopping an output signal of the first amplifier and applying it to the input of a switched capacitor notch filter (30-1). Notch filtering of the chopped output signal is performed by coupling a first compensation capacitor (C2) between a first output (25) of the chopper-stabilized amplifier and an output (14A) of the output chopper by means of a first switch (55) in response to a filter clock (FILTERCLK) and coupling a second compensation capacitor (C3) between the first output and an input (22A) of a second amplifier (3) by means of a second switch (58) in response to the filter clock, and coupling the first compensation capacitor between the first output and the input of the second amplifier by means of a third switch (56) in response to the complement of the filter clock and coupling the second compensation capacitor between the first output and the output (14A) of the output chopper circuit (40) by means of a fourth switch (57) in response to the complement.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
RF power sensor with chopping amplifier
ActiveUS20080012644A1Maximize its weak signal sensitivityMaximize dynamic rangeResistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage-current phase anglePower sensorAudio power amplifier
Owner:VIASAT INC
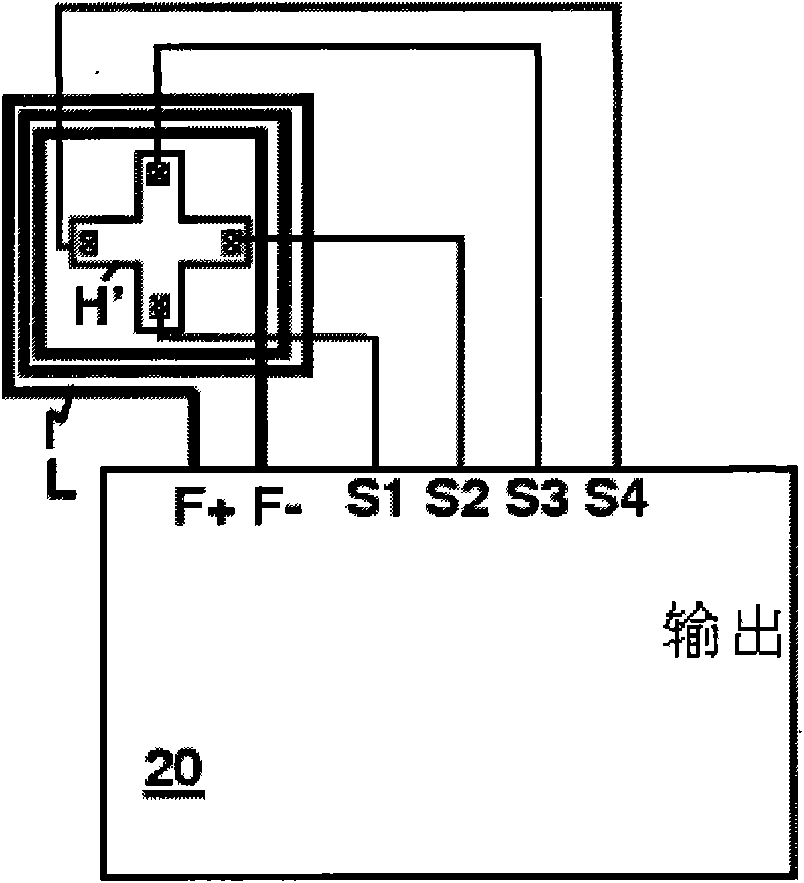
Sensor device
ActiveCN102484458AAnalogue/digital conversionThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsAudio power amplifierChopper amplifier
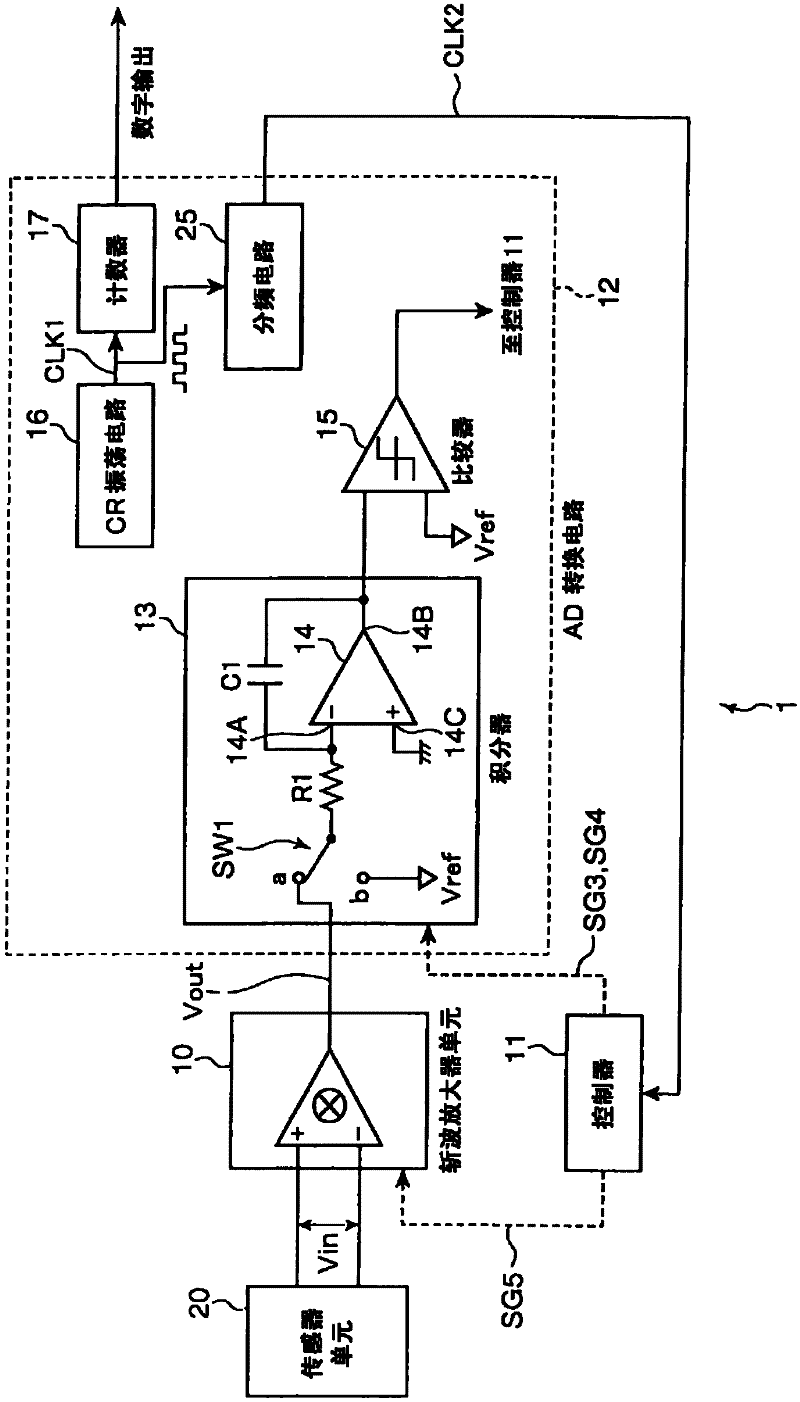
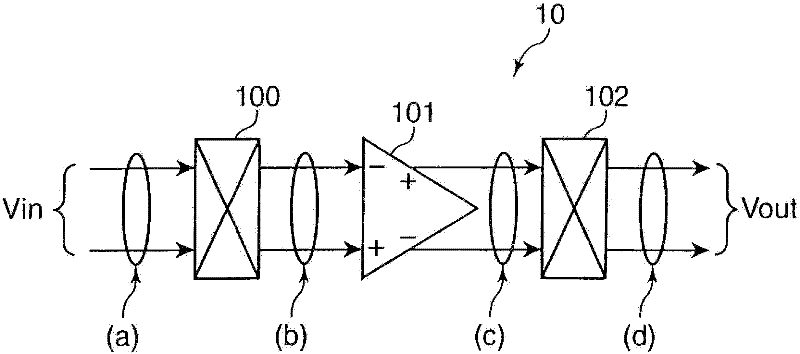
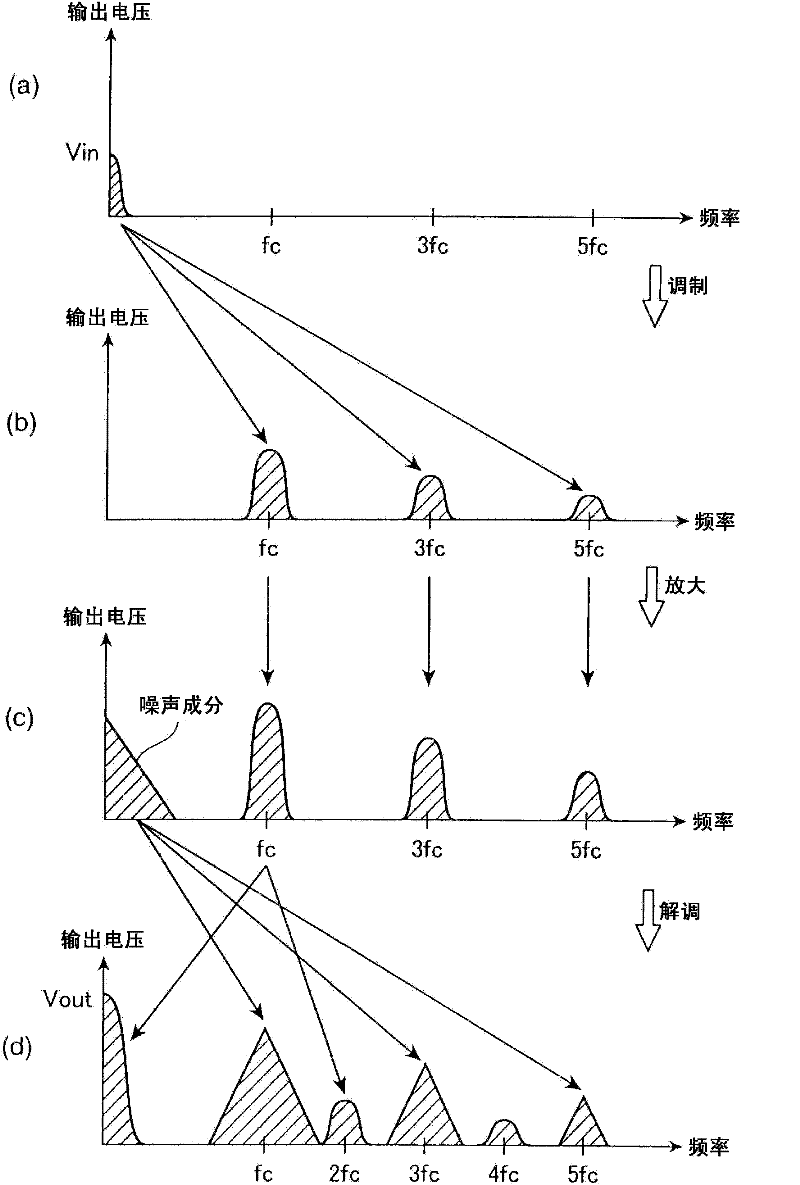
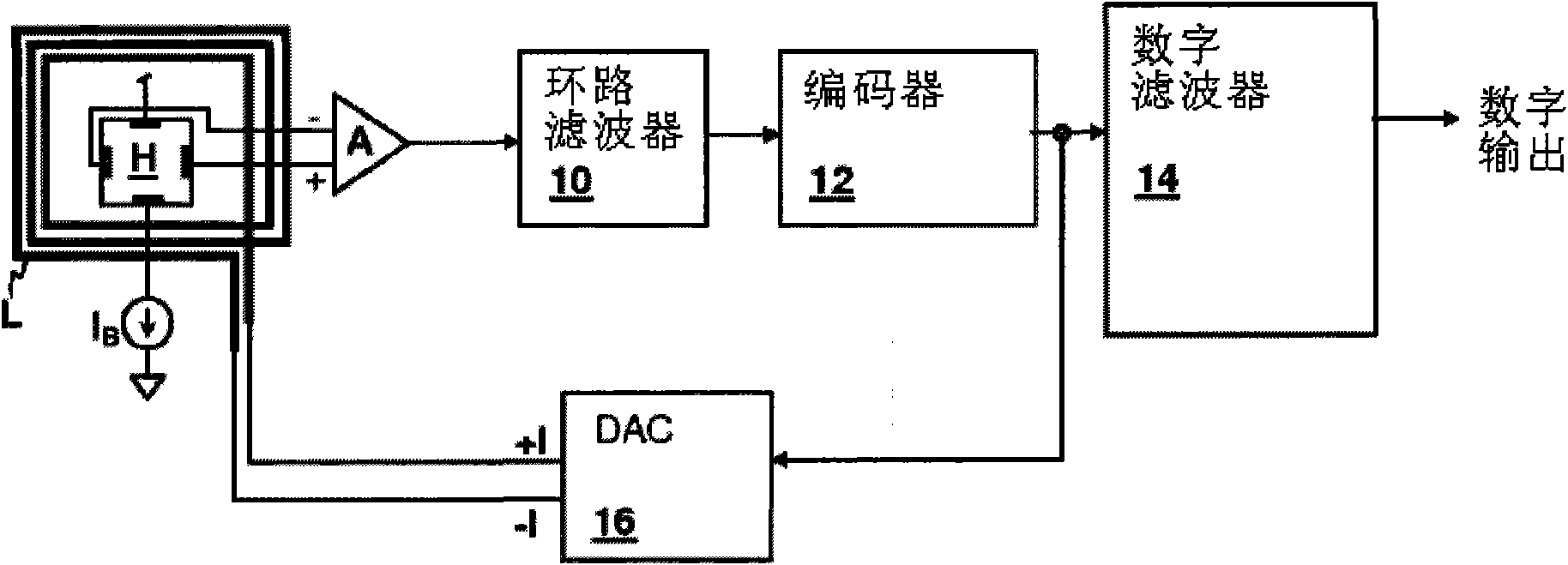
A sensor device is provided with a voltage detection type sensor unit (20) for converting a physical quantity into a voltage value and outputting a voltage signal indicating the voltage value; a chopper amplifier unit (10) for generating a modulation signal by chopping the voltage signal output from the sensor unit with a predetermined chopping frequency, amplifying the modulation signal into an amplification signal, then demodulating the amplification signal and outputting it as an output signal; an integration unit (13) including an operational amplifier (14) for amplifying a voltage difference between a voltage at a non-inverting input terminal and a voltage at an inverting input terminal, an input resistor (R1) connected to the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier and a capacitor (C1) connected between the inverting input terminal and an output terminal of the operational amplifier (14) and adapted to sample the output signal output from the chopper amplifier unit (10) at a predetermined sampling frequency and integrate the sampled output signal; and a digital conversion unit for converting the output signal integrated by the integration unit into a digital signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
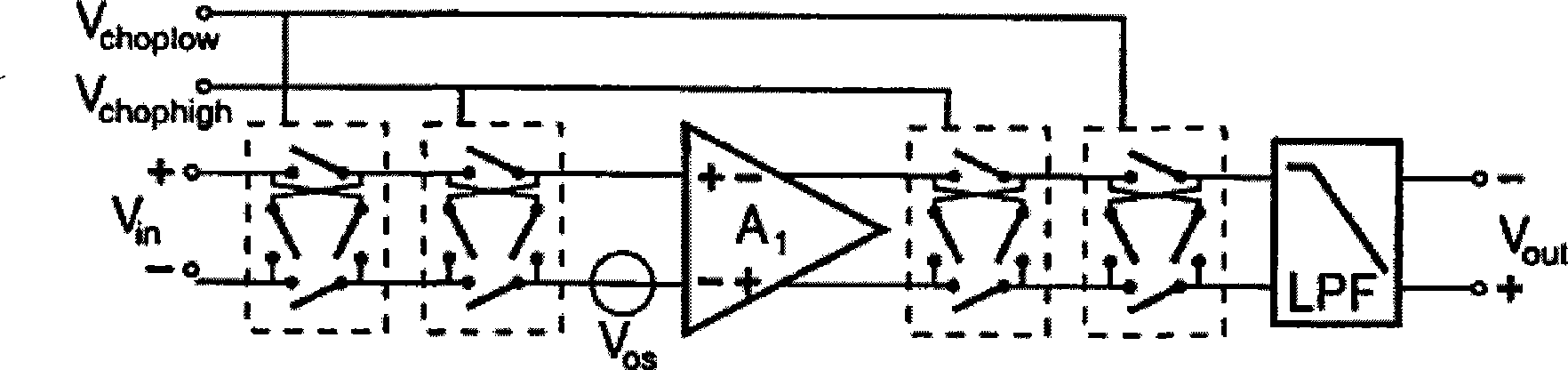
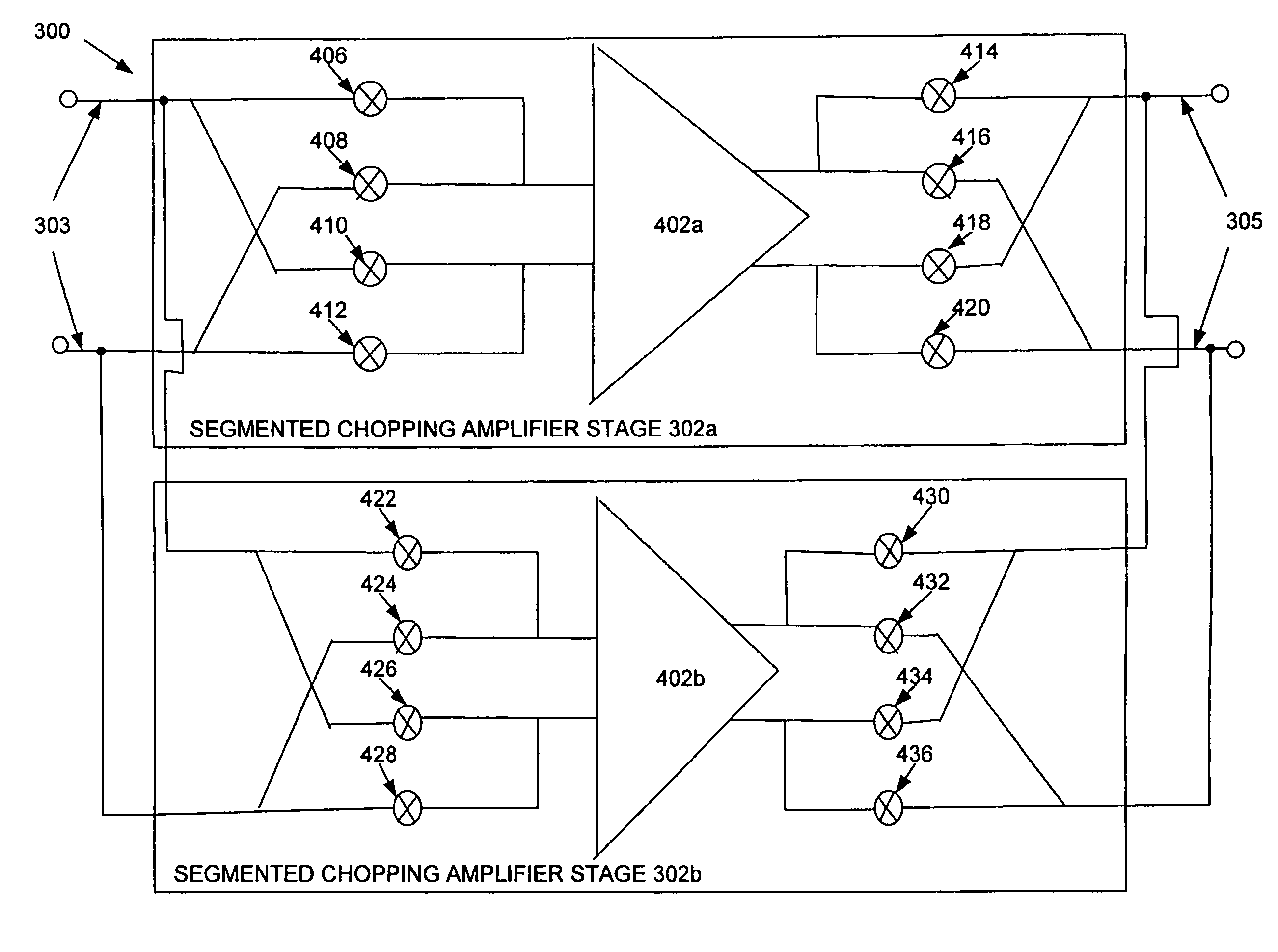
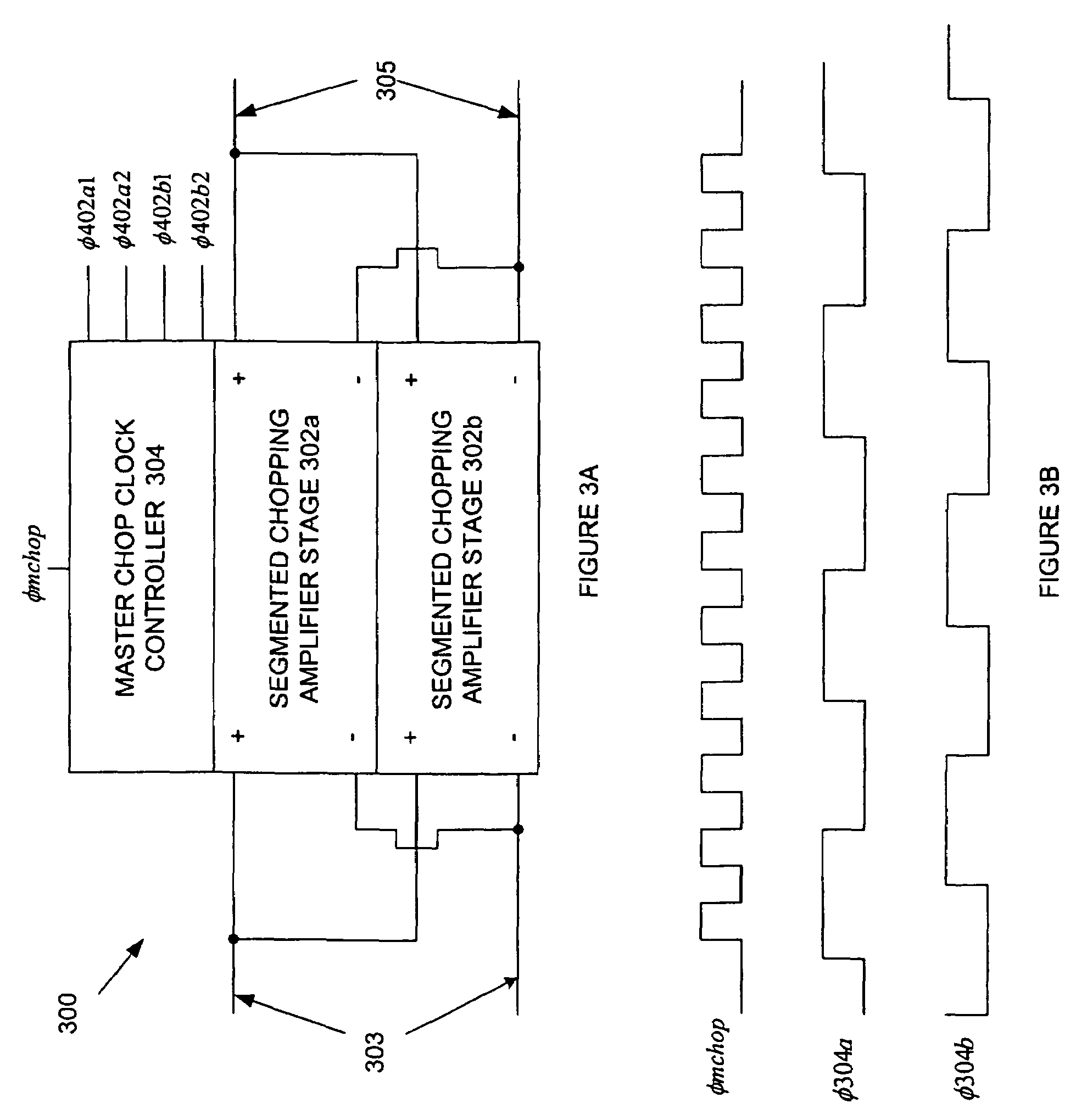
Segmented chopping amplifier
InactiveUS7224216B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower amplifiersAudio power amplifierClock rate
A chopping amplifier and method for chopping an input signal are disclosed. The chopping amplifier and method utilize at least two chopping amplifier stages. A chopping operation of an input signal is segmented across two or more chopping amplifier stages, and the two or more chopping amplifier stages are responsive to a master controller. Chop clock signals of the chopping amplifier stages are staggered so that they have non-overlapping periods and at least one of the chopping amplifier stages is not operating in an open loop at any given time. The non-overlapping periods are periodic so that a master chop clock of the master controller can be operated at a lower chop clock frequency. For every doubling of N number of chopping amplifier stages, magnitudes of chopping artifacts and aliased components are each respectively reduced by 3 dB.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
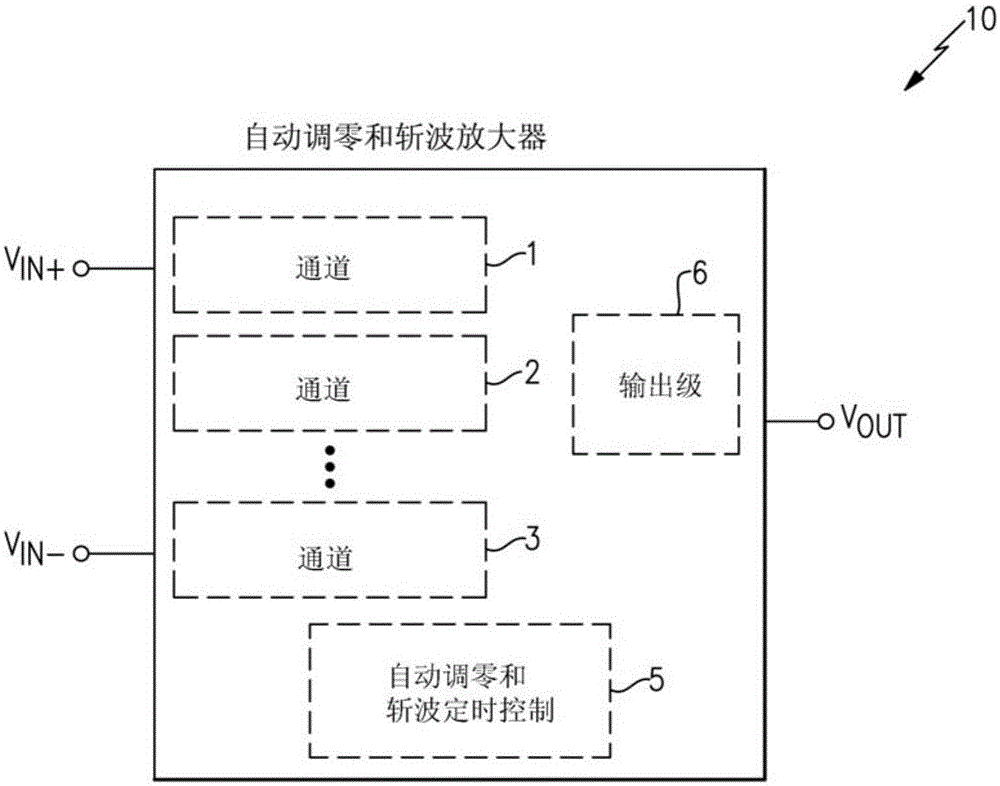
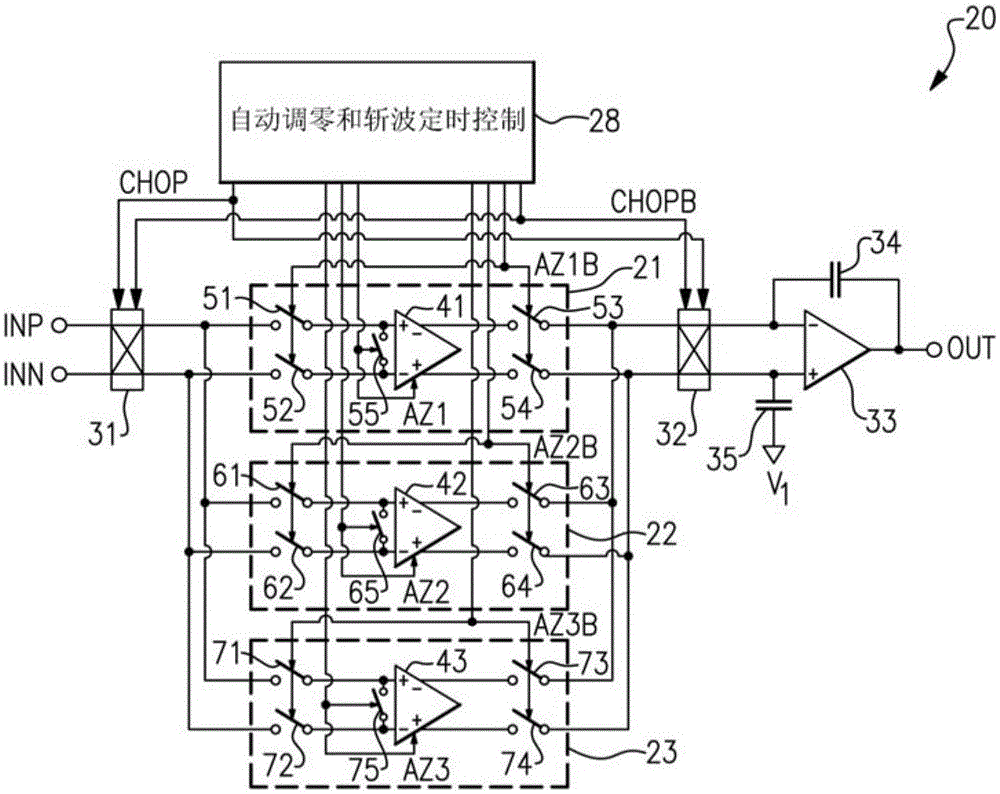
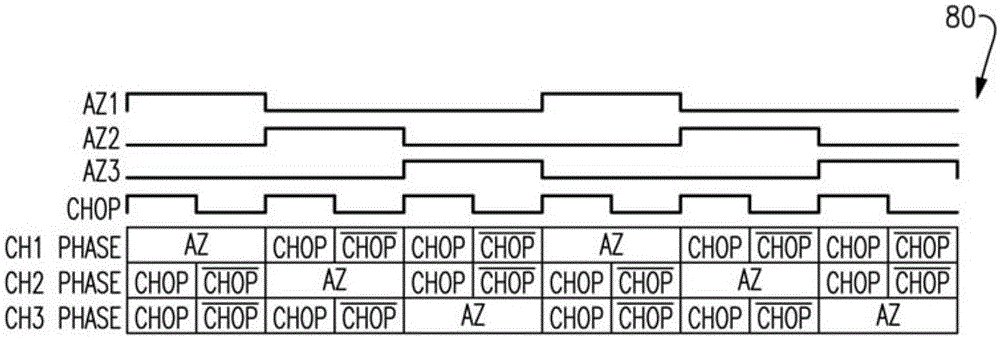
Apparatus and methods for multi-channel autozero and chopper amplifiers
ActiveCN105007047AAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
Apparatus and methods for multi-channel autozero and chopper amplifiers are provided herein. In certain configurations, an amplifier includes at least three channels that operate using multiple phases, including at least a non-inverting chop phase, an inverting chop phase, and an autozero phase. The amplifier further includes an autozero and chopping timing control circuit, which at least partially interleaves or staggers timing of the channels' phases. For example, in certain configurations, when one or more of the channels are being autozeroed at a certain time instance, at least some of the remaining channels operate in the non-inverting chop phase or the inverting chop phase.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Chopper amplifier
ActiveUS9595922B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierChopper amplifier
Various apparatuses and methods are described where a signal is amplified using a chopper amplifier arrangement, and ripples caused by said chopper amplifier arrangement are reduced. In some cases, this reduction of ripples is performed by controlling a voltage offset of an amplifier of said chopper amplifier arrangement. In other embodiments, a detection of ripples or a chopping of the chopper amplifier arrangement is at least temporarily disabled.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
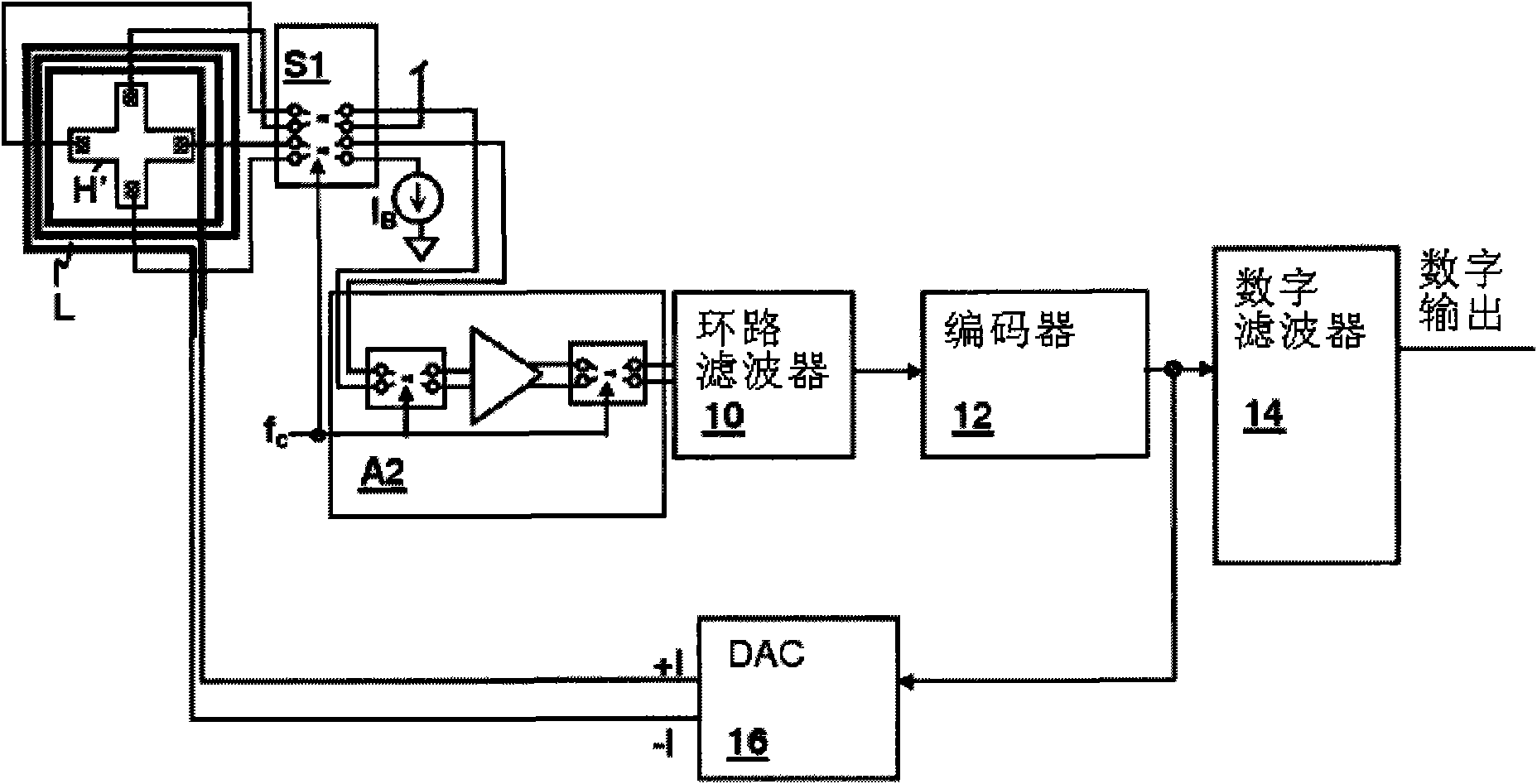
Magnetic field feedback delta-sigma modulator sensor circuit
A magnetic field feedback delta-sigma modulator sensor circuit, provides accurate magnetic field measurements without requiring complex additional calibration circuitry. The output of the semiconductor magnetic field sensor, which may be a Hall effect sensor, is coupled to the input of the delta-sigma modulator loop filter. The output of the quantizer of the delta-sigma modulator is magnetically coupled to the magnetic field sensor, producing a field that causes the output of the sensor to be canceled for frequencies in the band of the modulator loop filter. The output of the quantizer is provided to a current output digital-to-analog converter, which feeds a current loop that is inductively coupled to the sensor body. A chopper amplifier can be provided between the output of the sensor and the modulator loop filter input to reduce 1 / f noise and bias current and output terminals can be rotated to further reduce 1 / f noise and offset.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
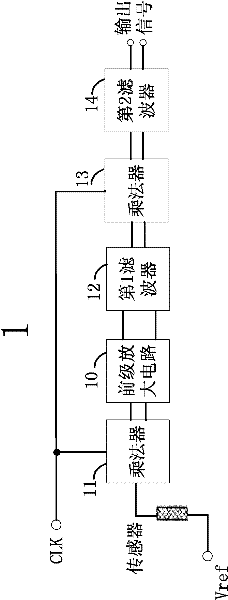
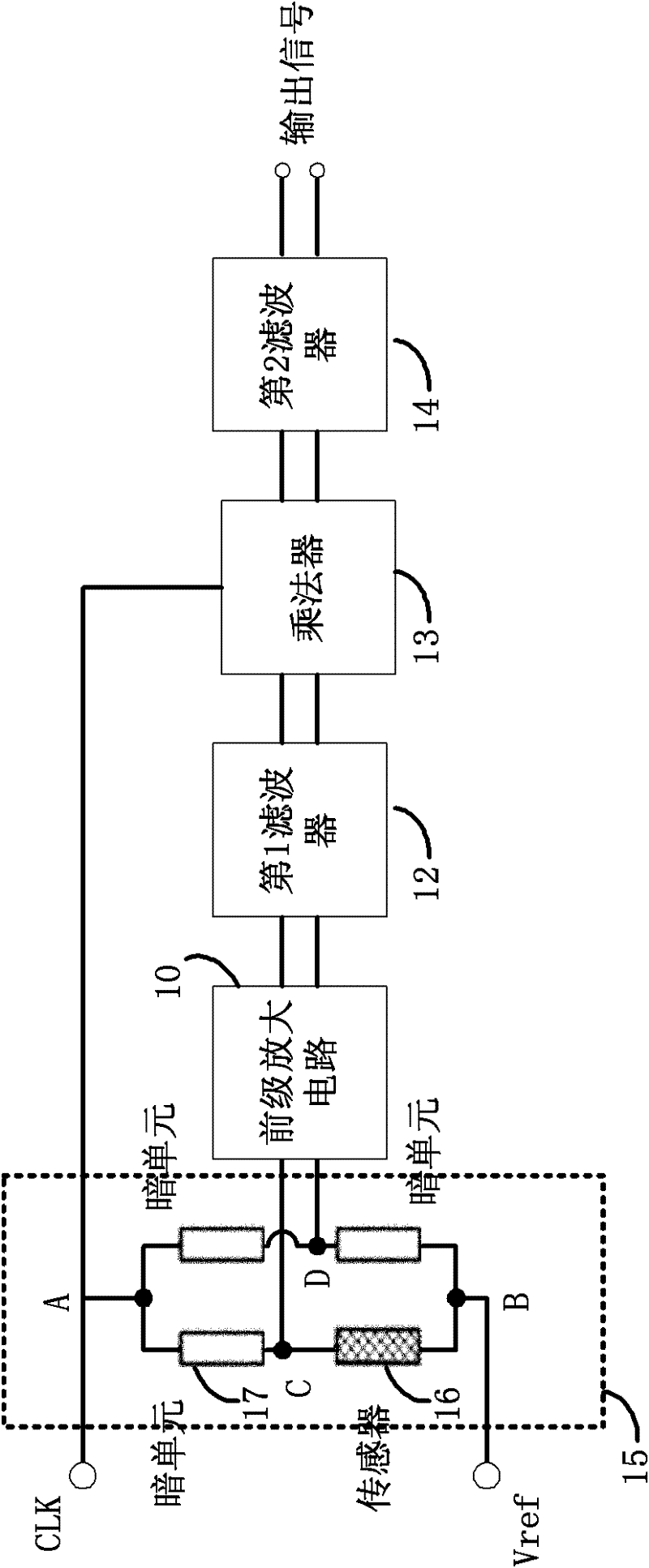
Chopping amplifier circuit coupled with sensor
ActiveCN102694510AImprove signal-to-noise ratioAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationLow frequency amplifiersSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention provides a chopping amplifier circuit coupled with a sensor. Without an additional offset voltage regulating circuit and an additional offset temperature characteristic regulating circuit, the reduction of the offset voltage of the sensor and the influence of the temperature characteristic of the offset voltage are realized, and also low frequency noise of the sensor is effectively reduced. A Wheatstone bridge composed of one sensor and three dark units is also provided, and electrical signals are adjusted to high frequency by controlling a clock signal CLK. The offset voltage and the low frequency noise of the signals are filtered with a filter, and the signals are demodulated back to low frequency with a multiplier. The chopping amplifier circuit not only is simpler than conventional circuits, but also has a higher signal-to-noise ratio than the conventional circuits do.
Owner:锐立平芯微电子(广州)有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com