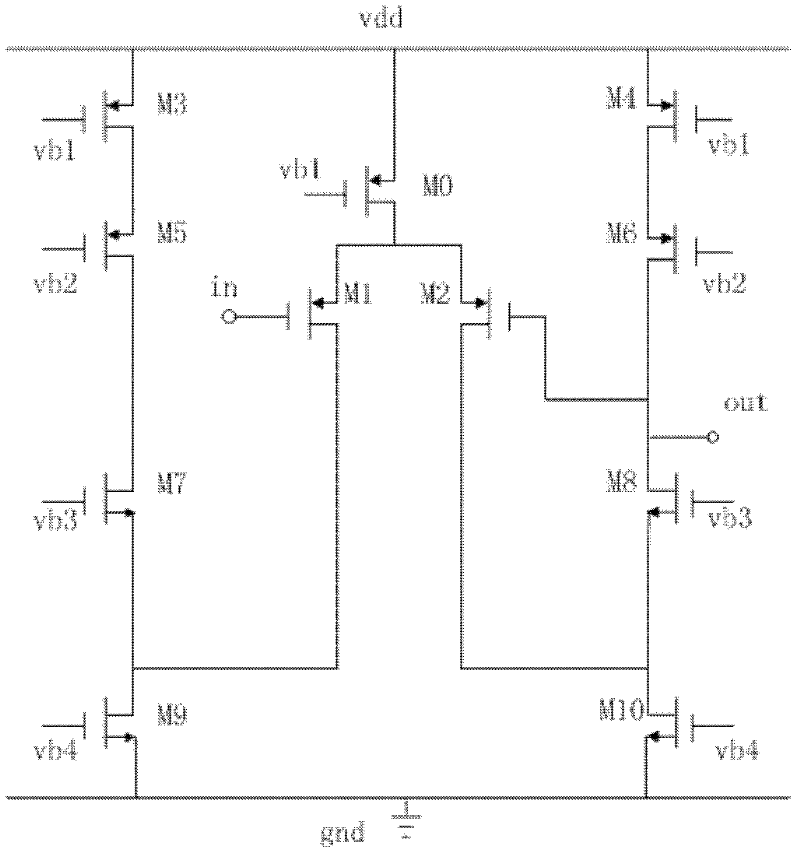
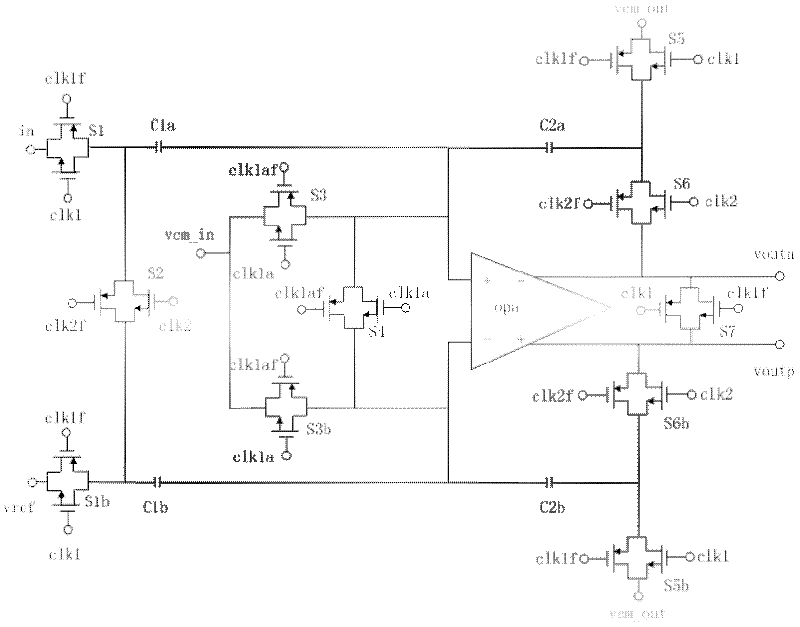
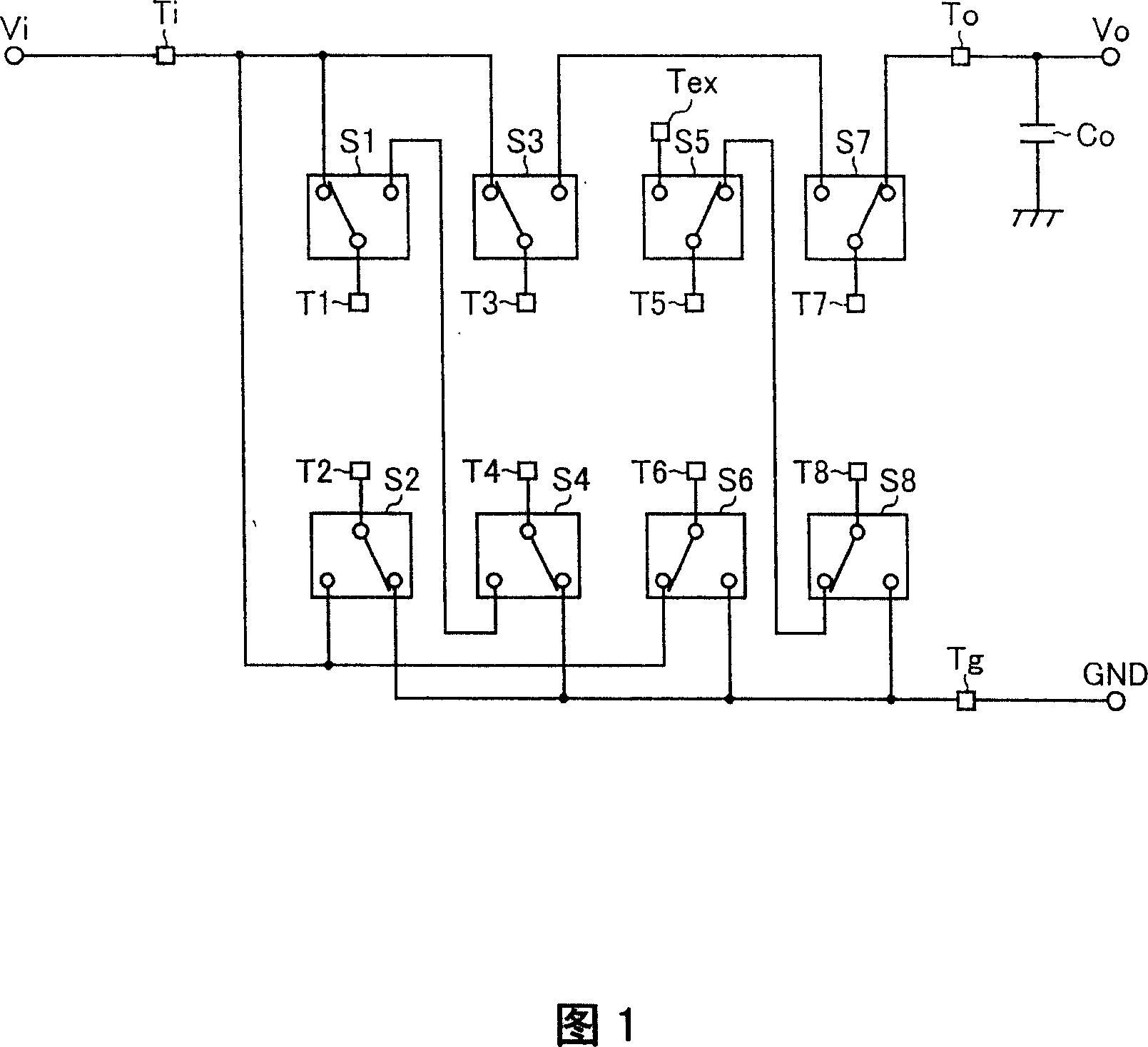
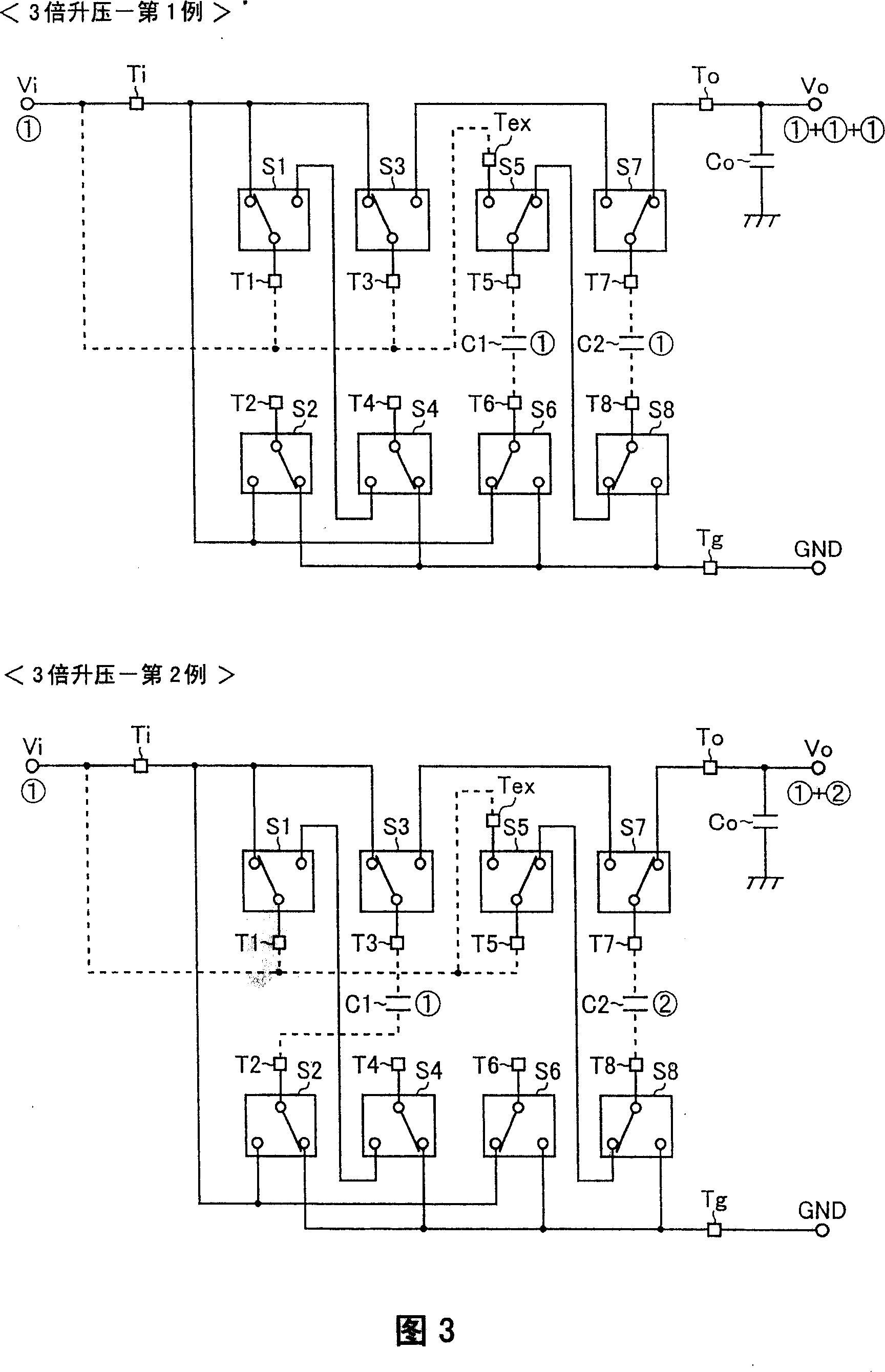
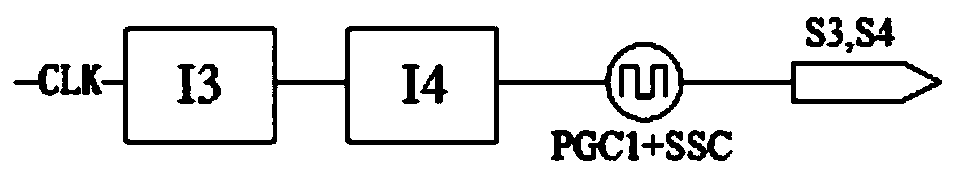
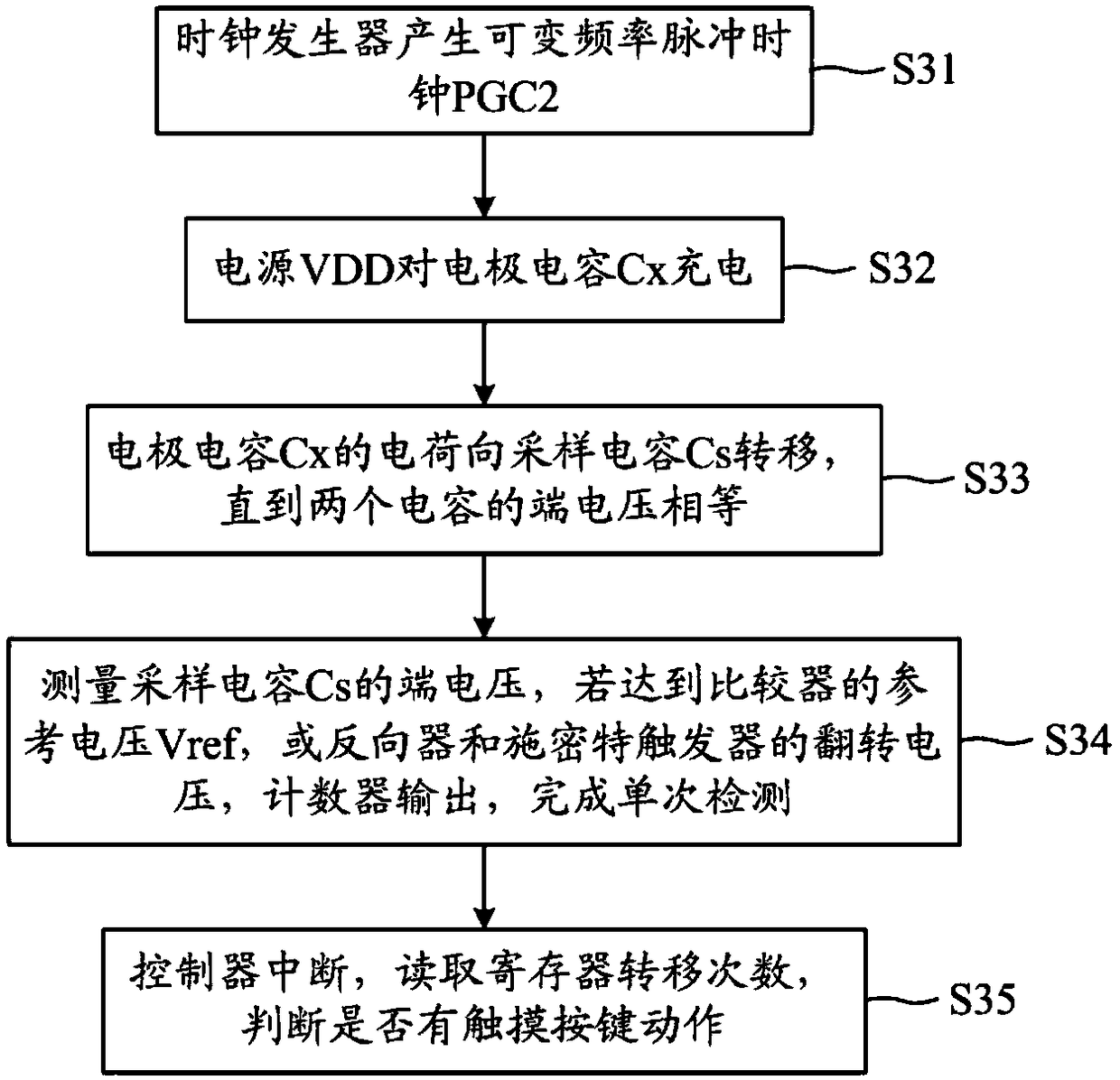
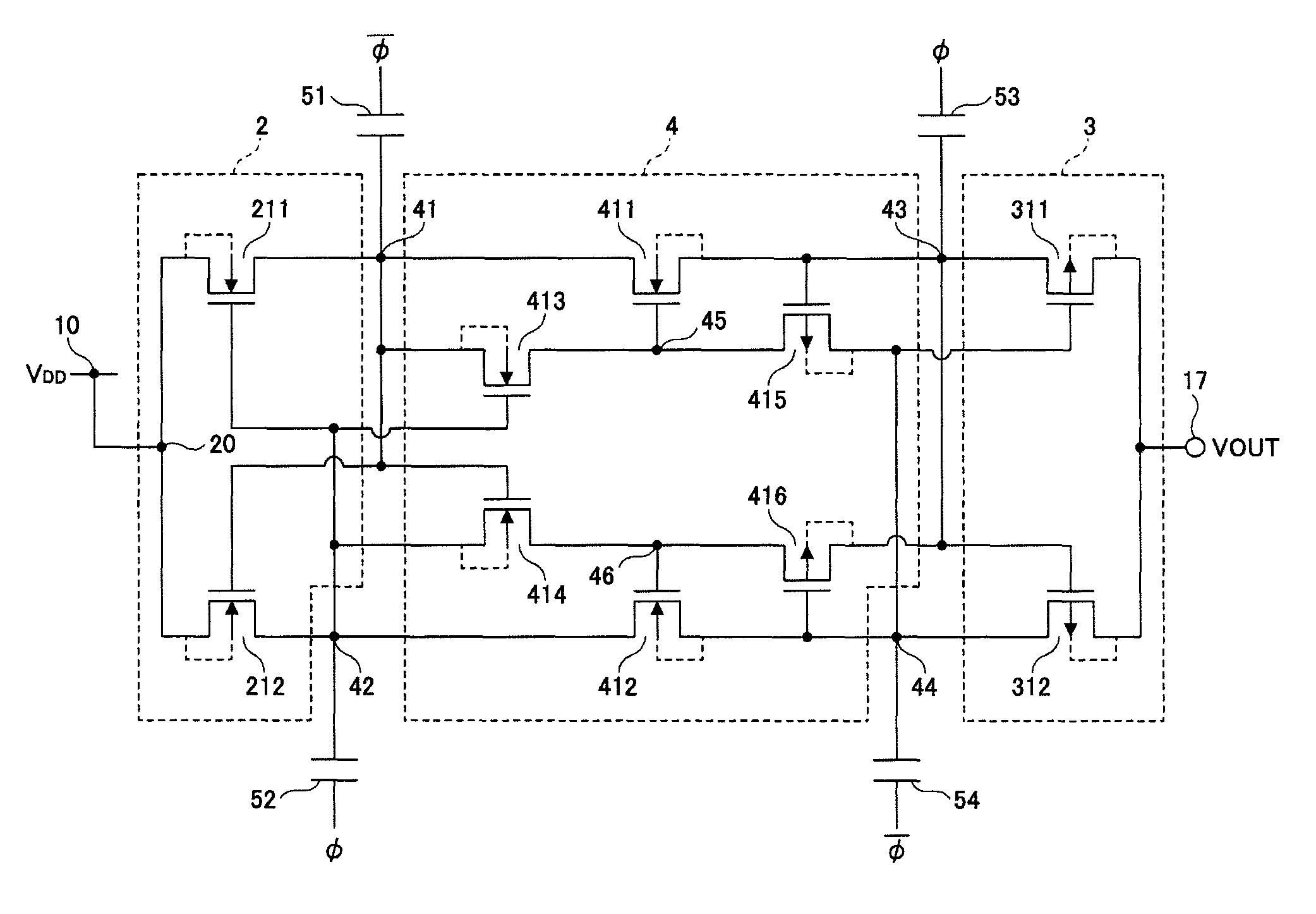
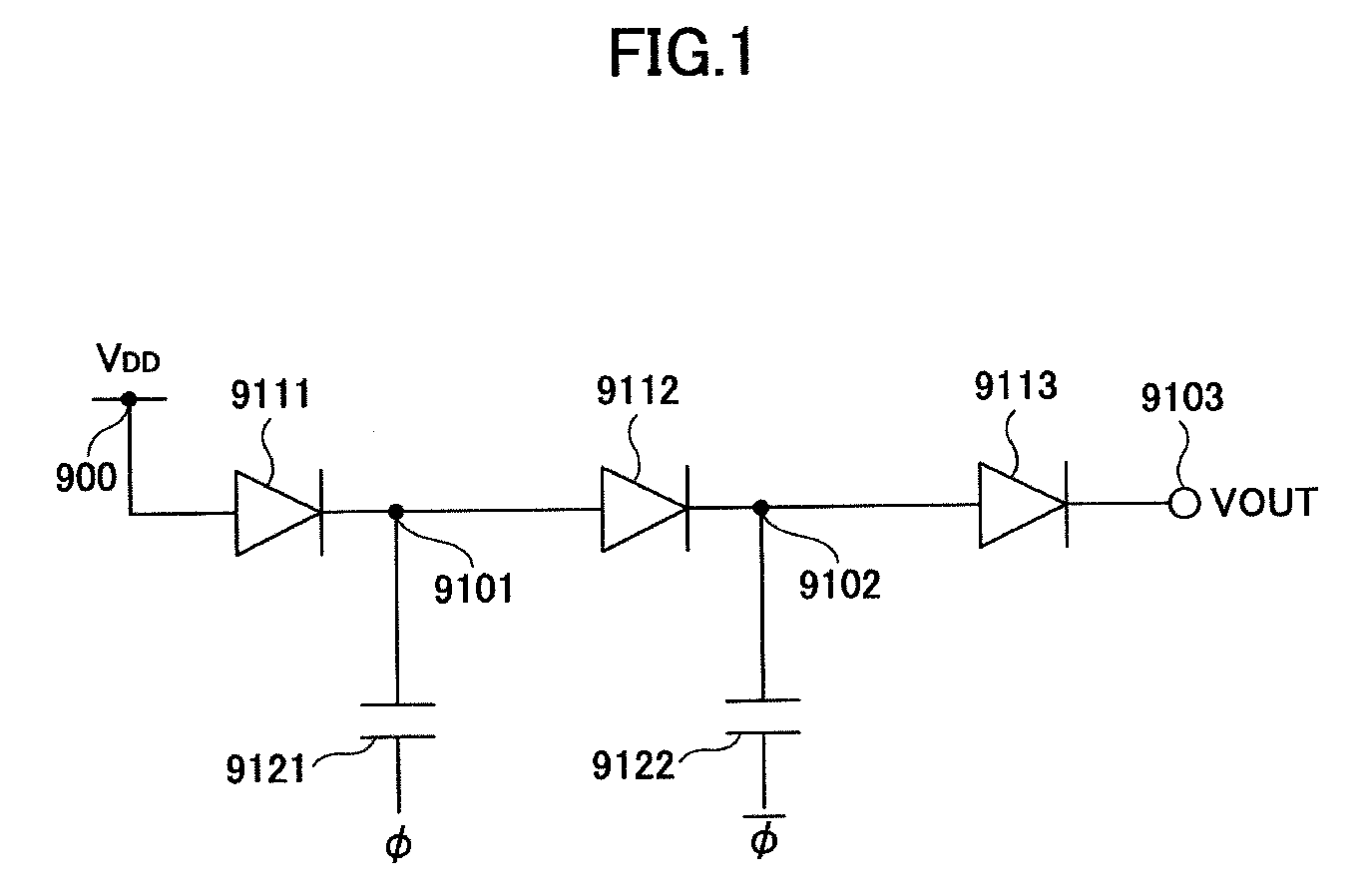
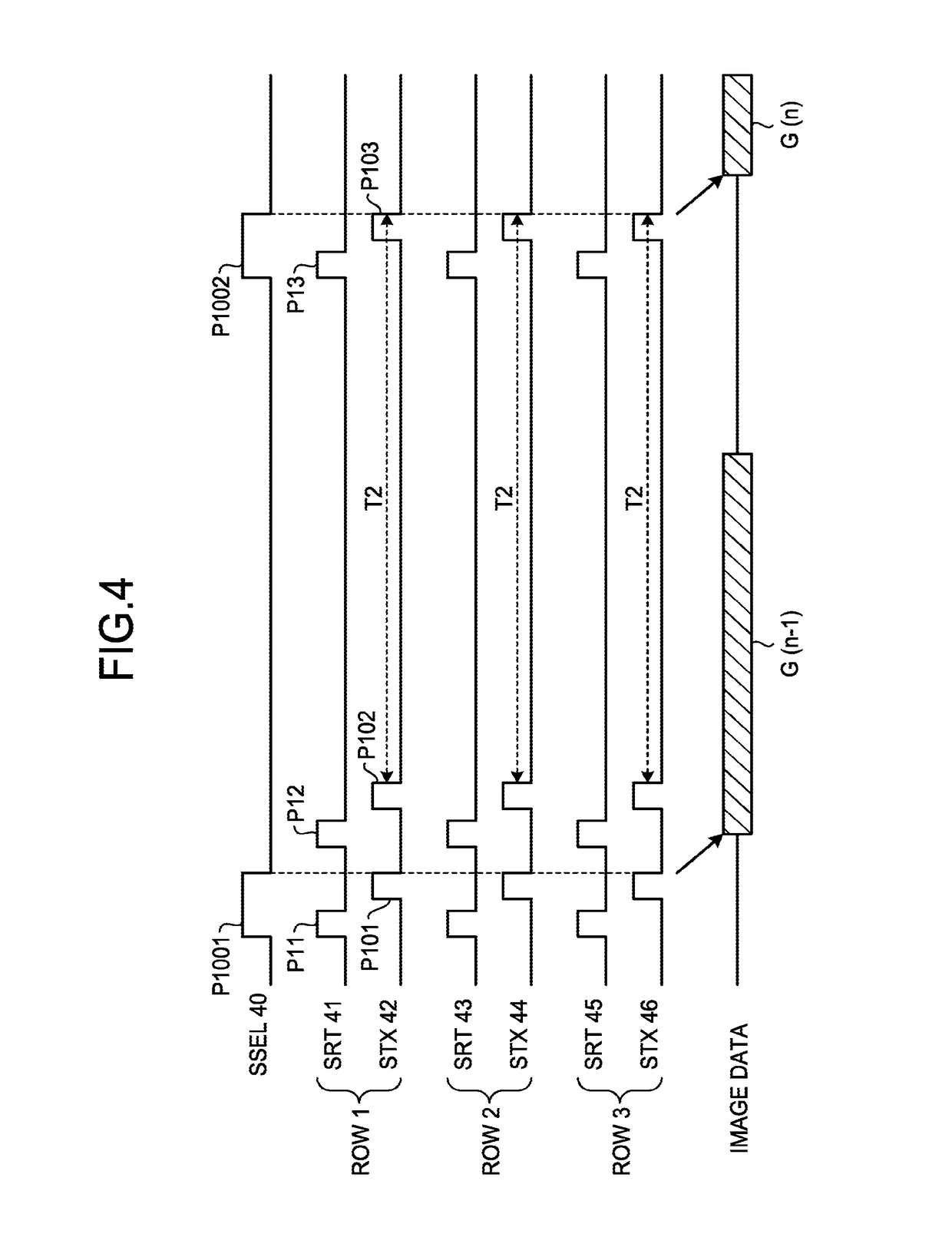
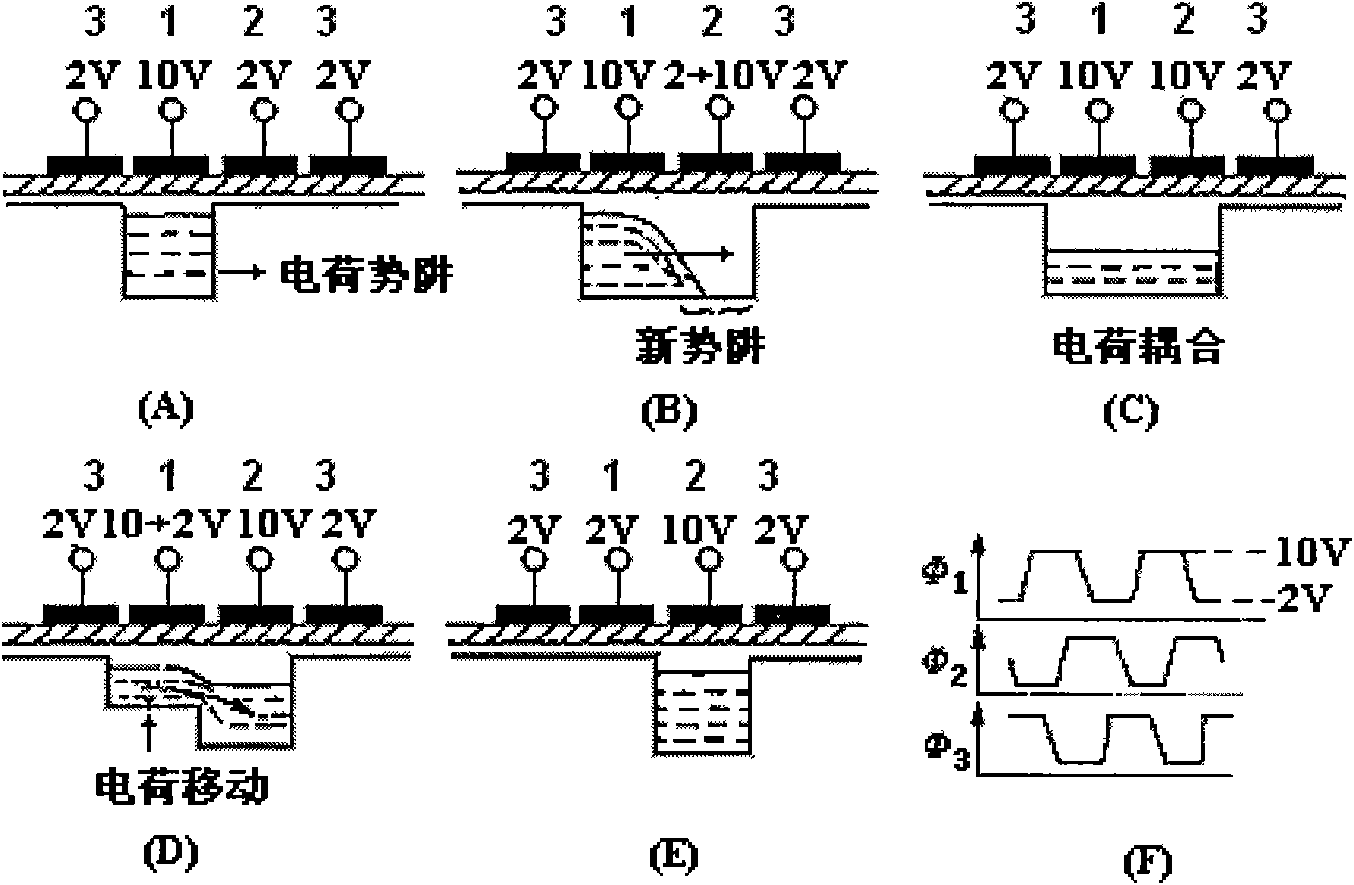
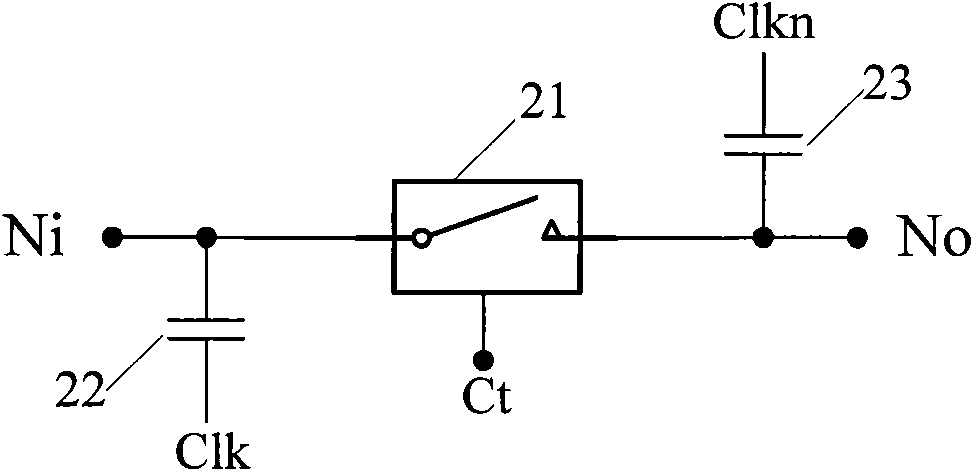
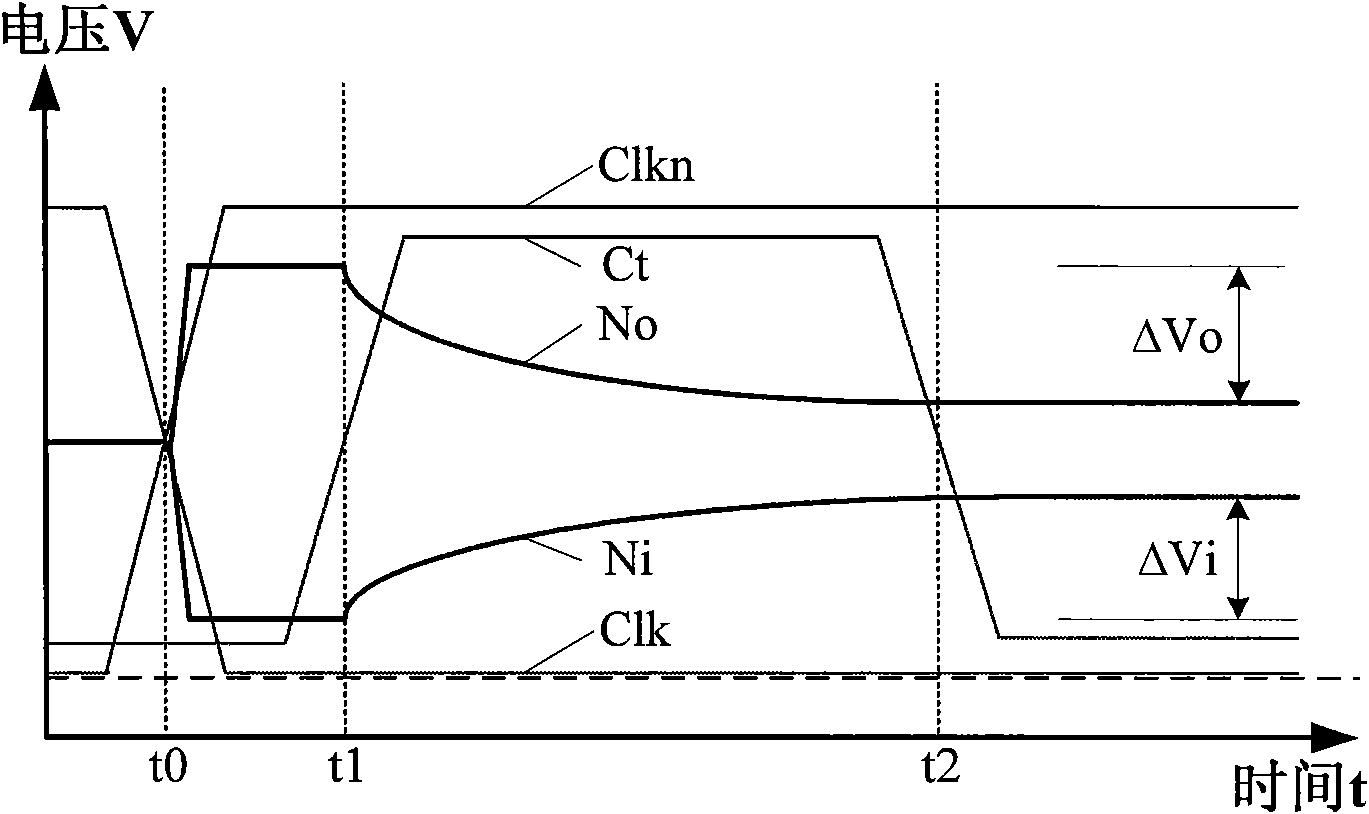
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Charge transfer switch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
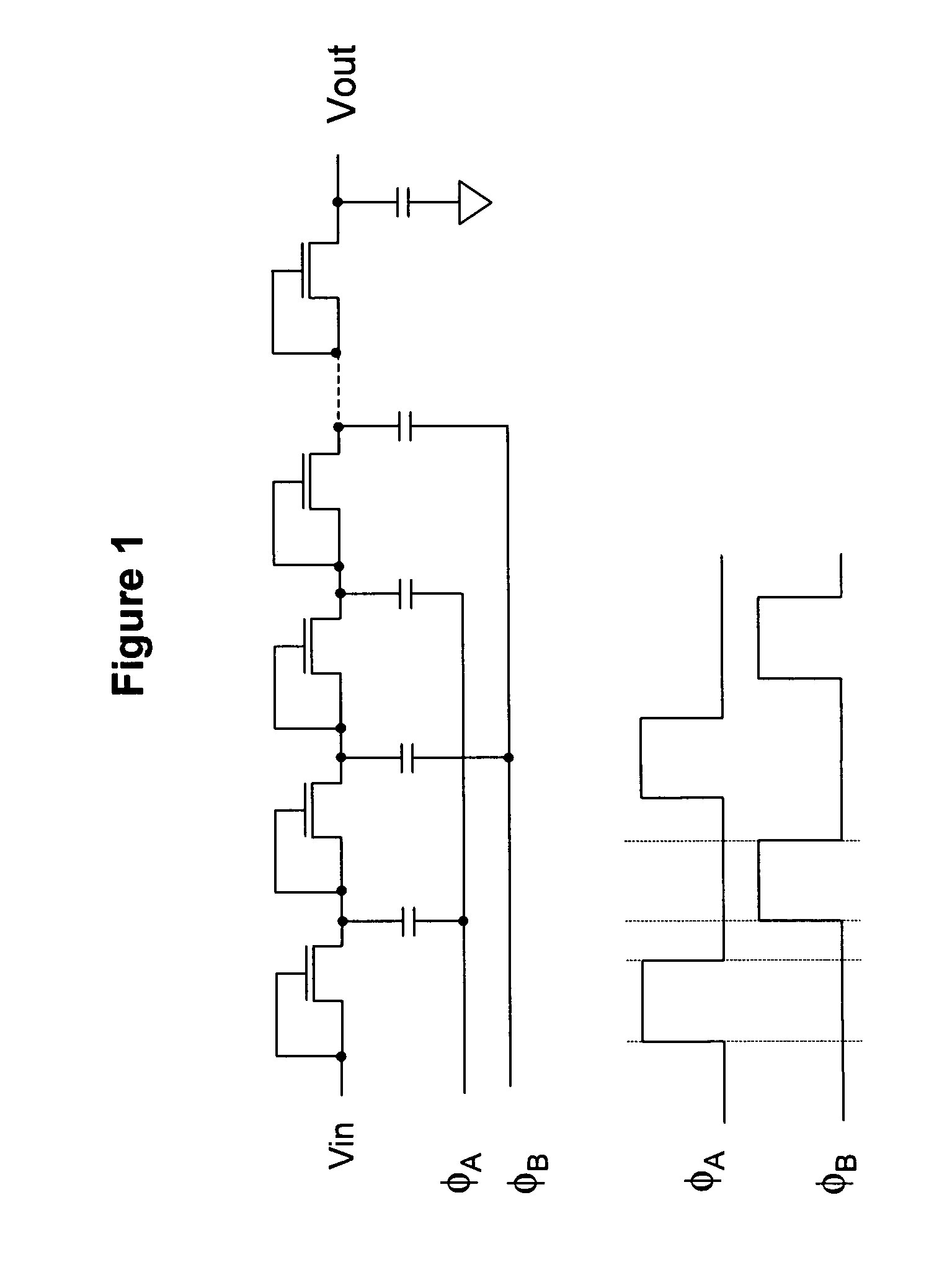
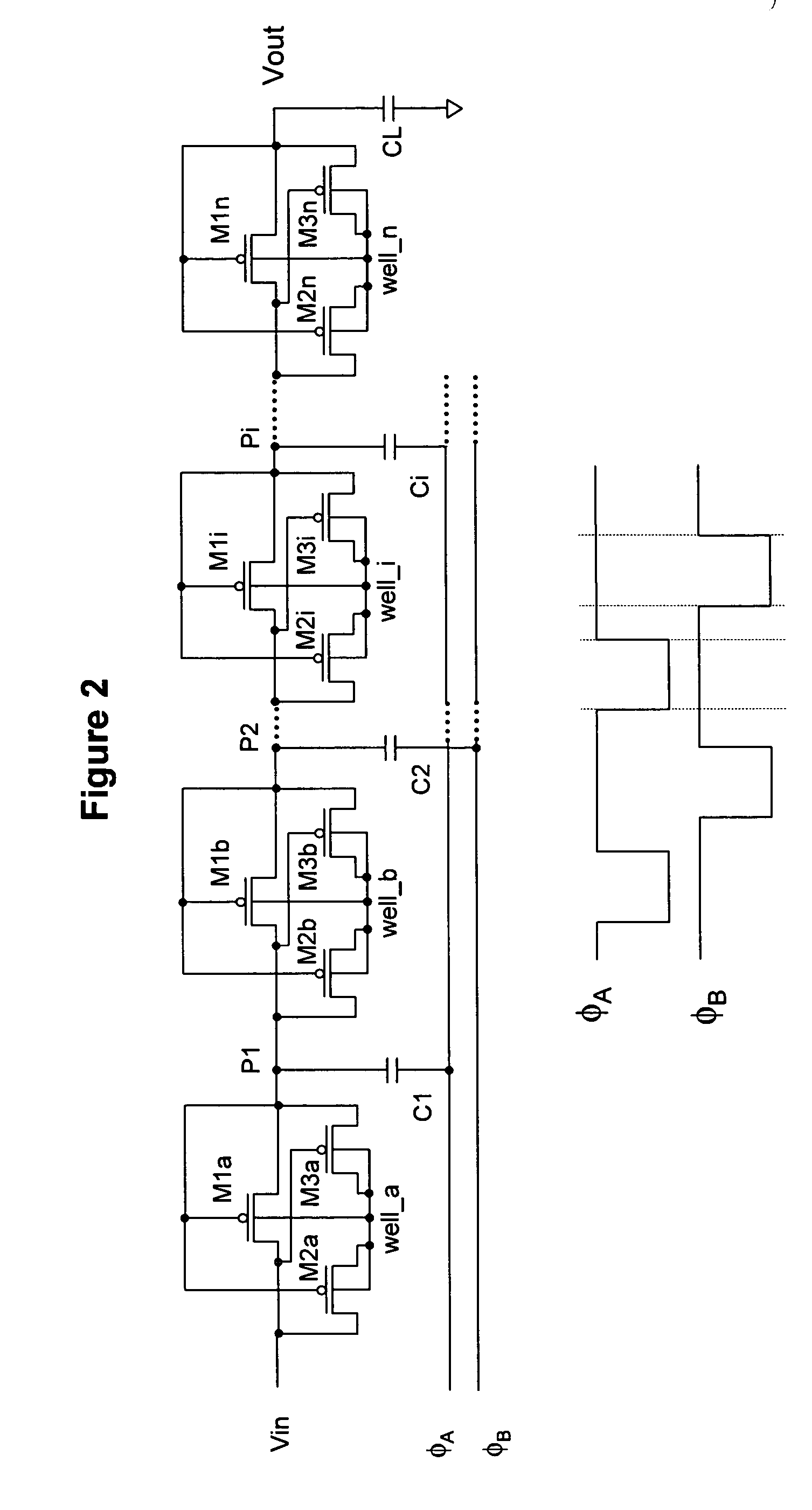
A charge transfer switch OR CTS charge pump is a charge pump that offers better low-voltage performance and "a better voltage pumping gain and a higher output voltage" than previous charge pumps such as the Dickson charge pump.
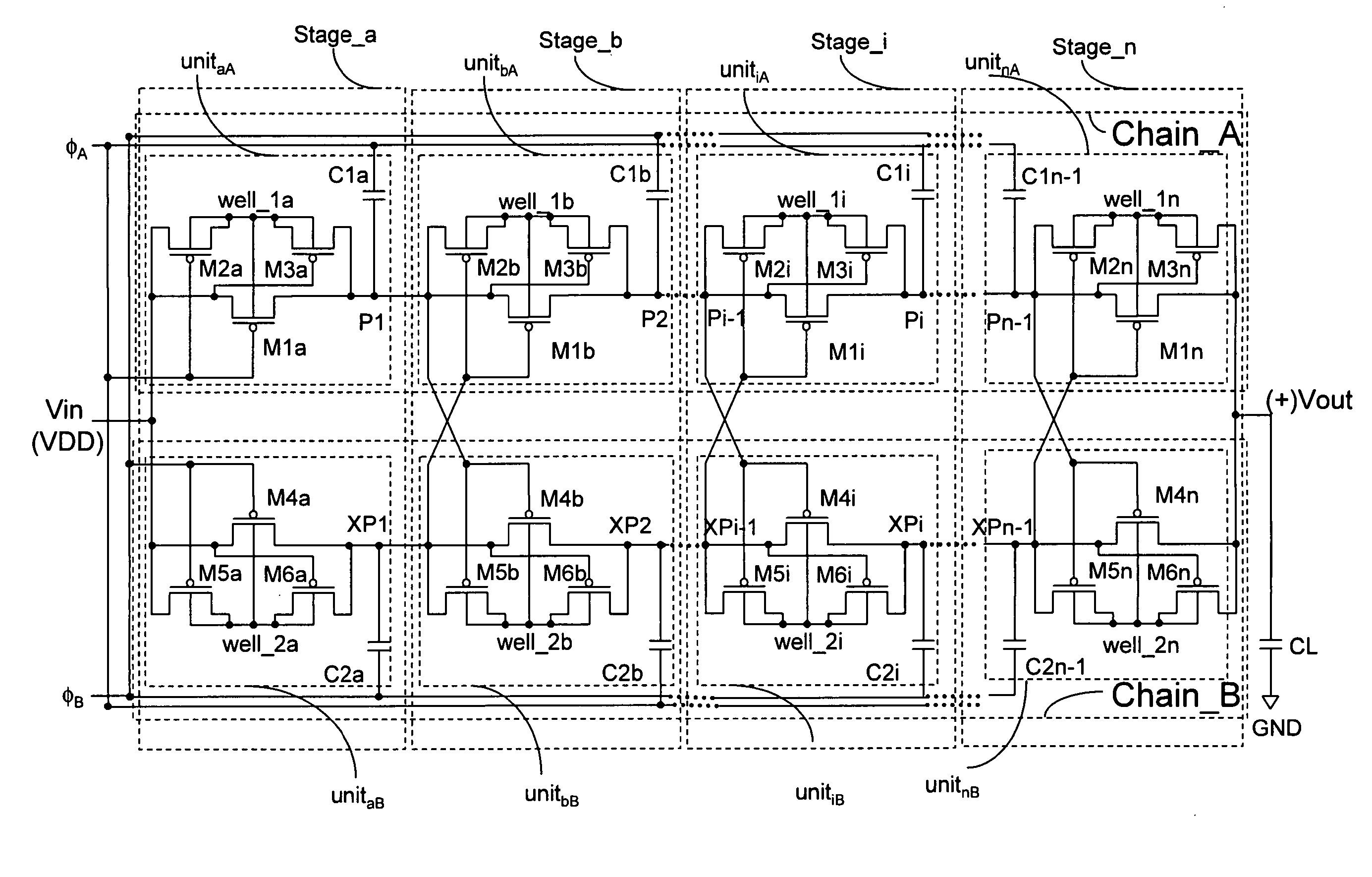
High voltage charge pump with wide range of supply voltage
InactiveUS20070096796A1Easy to implementIncrease lossApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationMOSFETEngineering
A charge pump circuit utilising CMOS or MOSFET (p-channel or n-channel) configured as switches for charge transfer is proposed. Instead of using the conventional diode-connected transistors, CMOS transistors configured as switches are used so that the threshold voltage drop across the stages of the charge pump is eliminated. Two of these charge pump chains are cross-coupled to bias each other at every stage. Consequently, the charge pump presented achieves higher voltage output efficiency with a wider supply voltage range.
Owner:BLUECHIPS TECH PTE
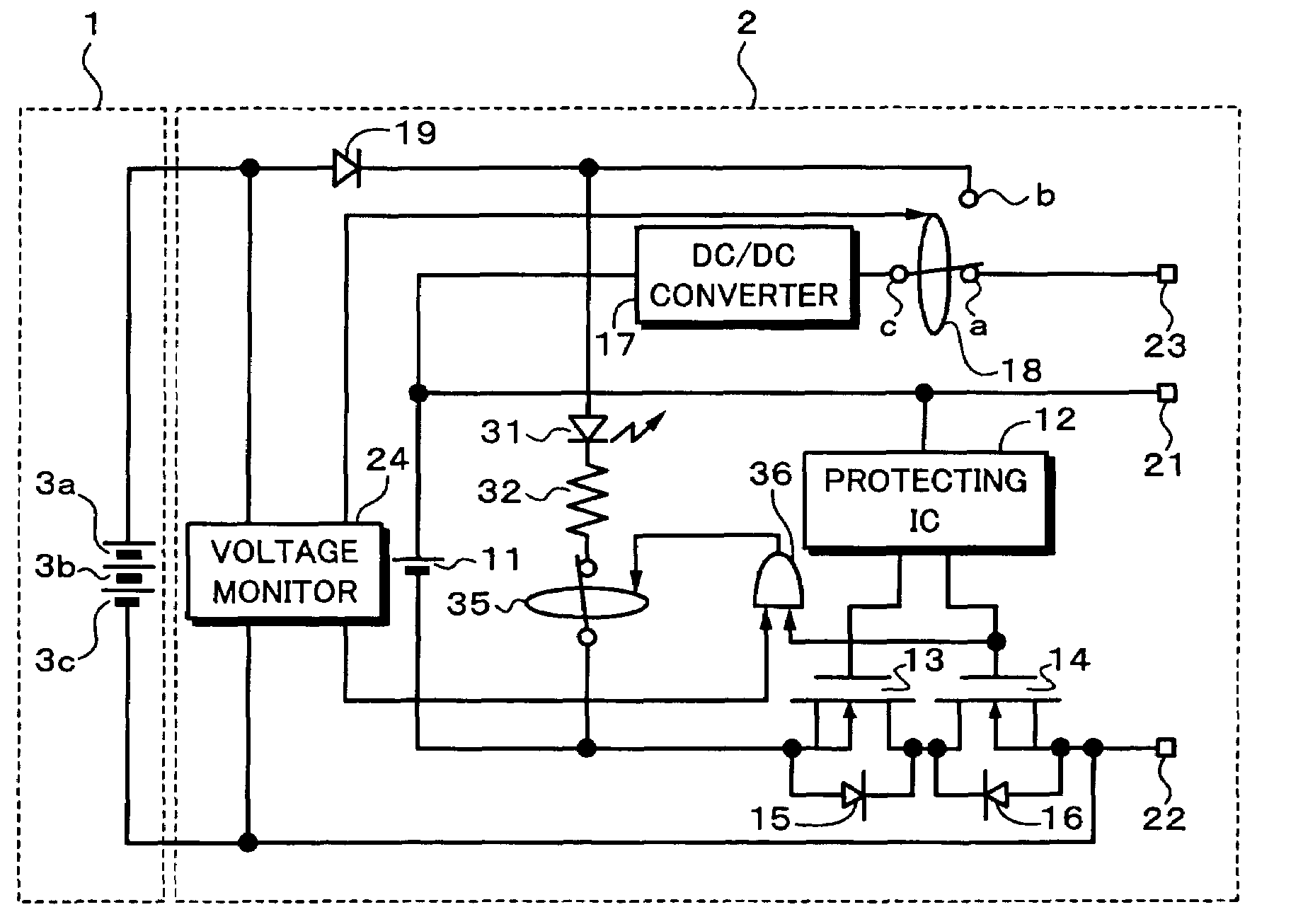
Battery pack
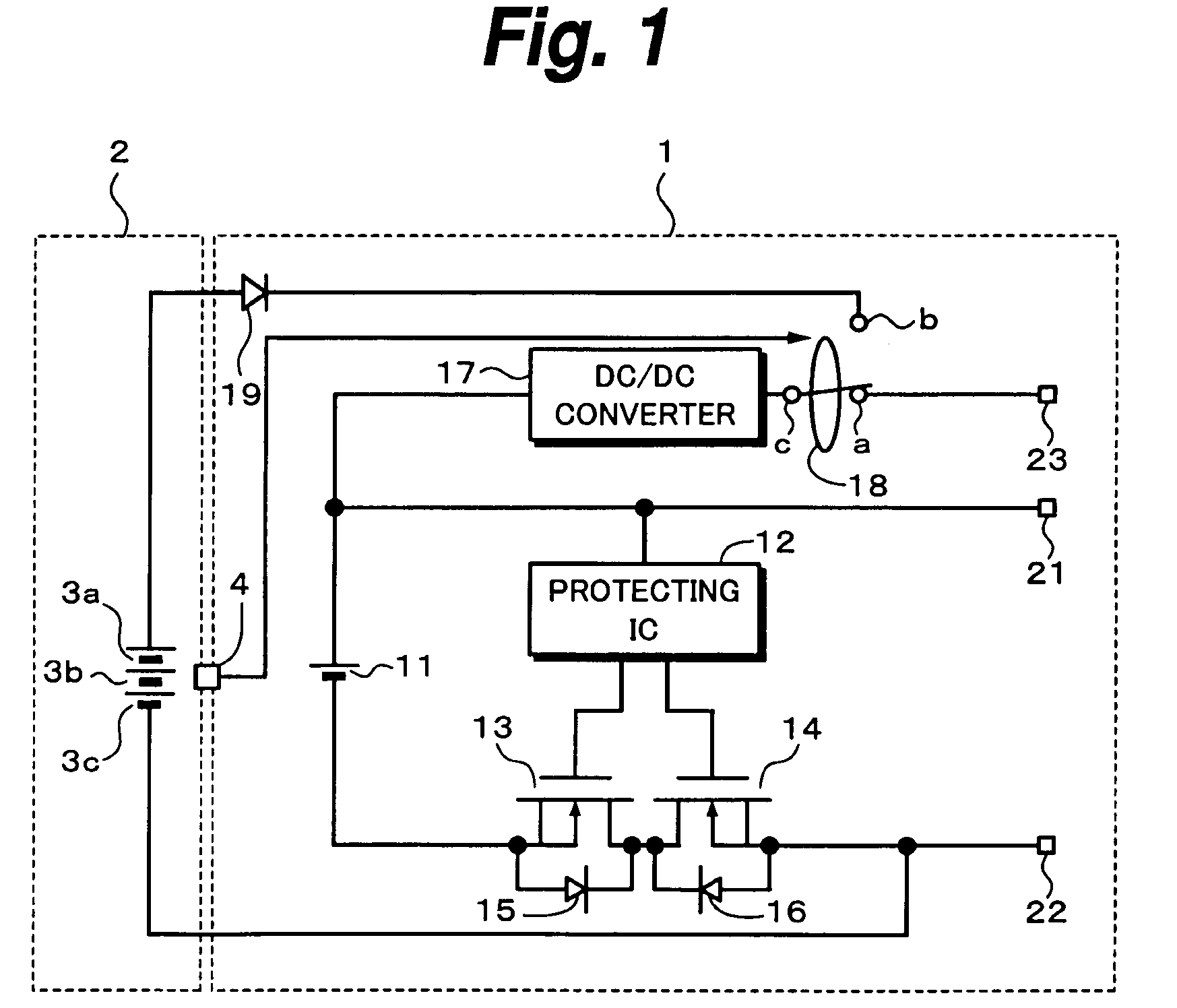
InactiveUS7298113B2Improve efficiencyOverall size miniaturizationBattery charging meansElectrical testingElectrical batteryCharge transfer switch
A detecting switch which is turned on / off in accordance with whether or not primary batteries have been attached to a primary battery holder is provided. In a normal state where no primary battery is attached, terminals (a, c) of a charge change-over switch are connected by a detection signal of the detecting switch, so that a voltage supplied from an external charger is inputted to a DC / DC converter. A secondary battery is charged by a predetermined value output of the DC / DC converter. When the primary batteries are attached, the detecting switch is turned on and terminals (b, c) of the charge change-over switch are connected, so that an output voltage of the primary batteries is inputted to the DC / DC converter. The secondary battery is charged by the predetermined value output of the DC / DC converter. Even when there is no charger, the secondary battery can be charged by the primary batteries and charging power sources are automatically switched.
Owner:SONY CORP
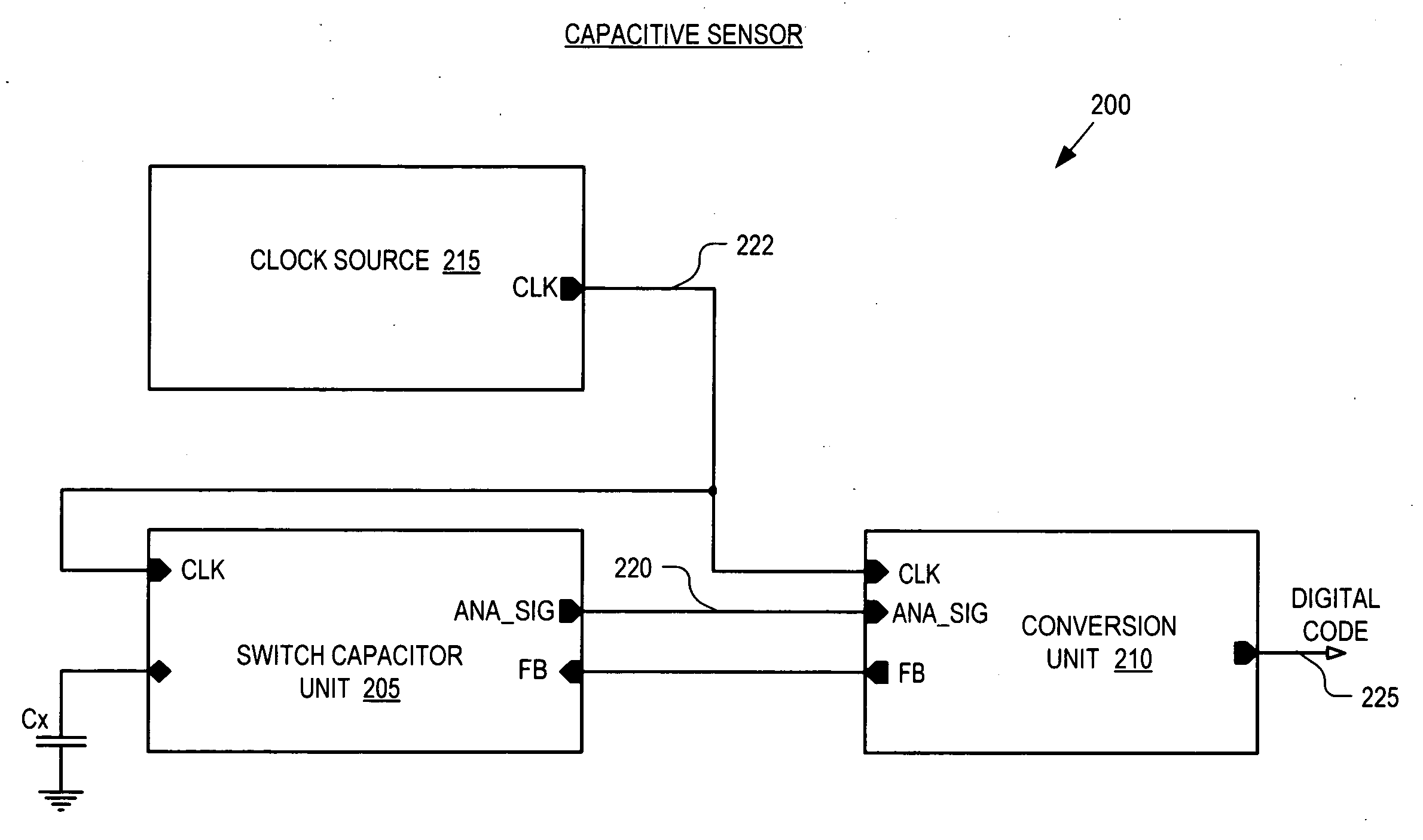
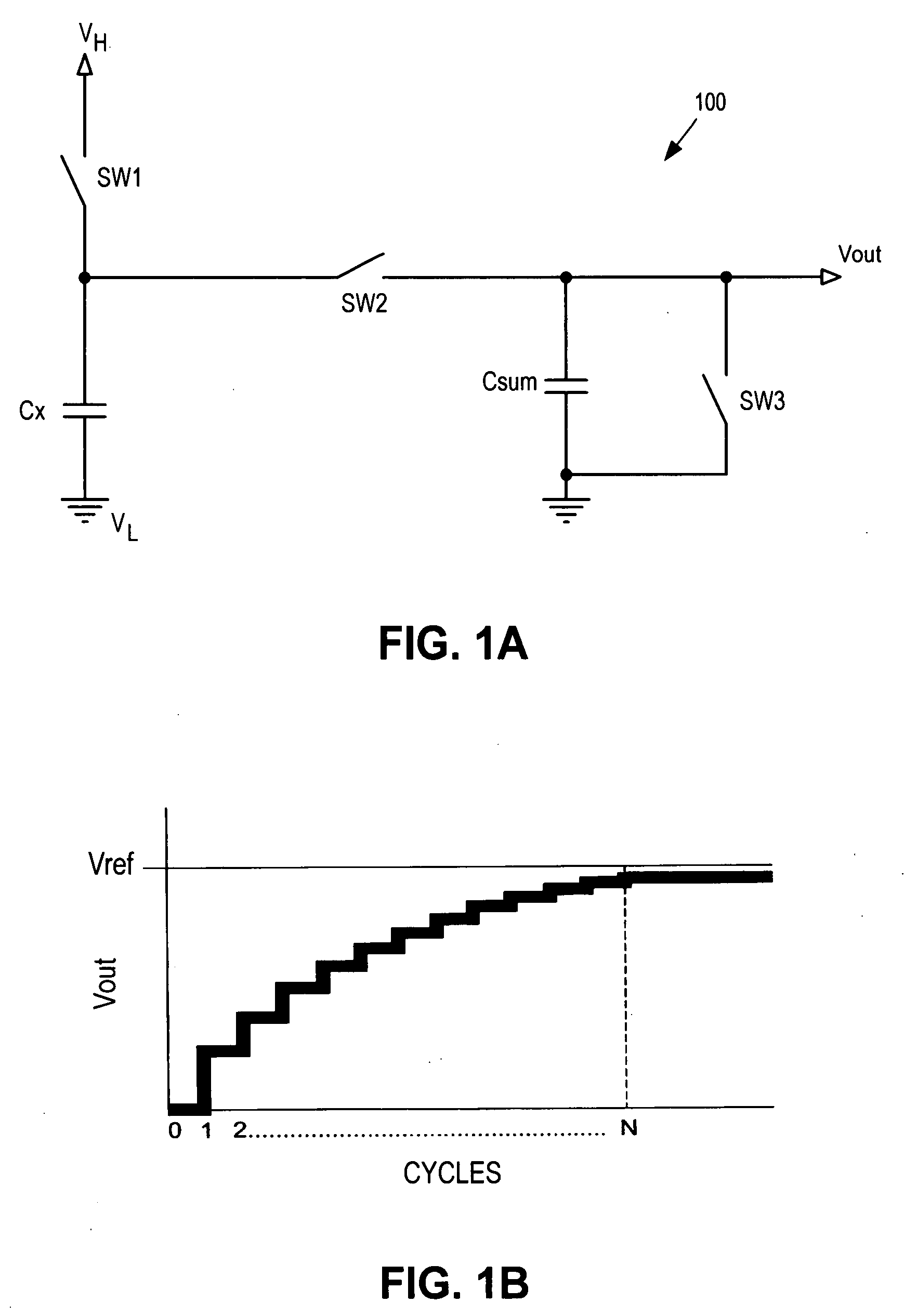
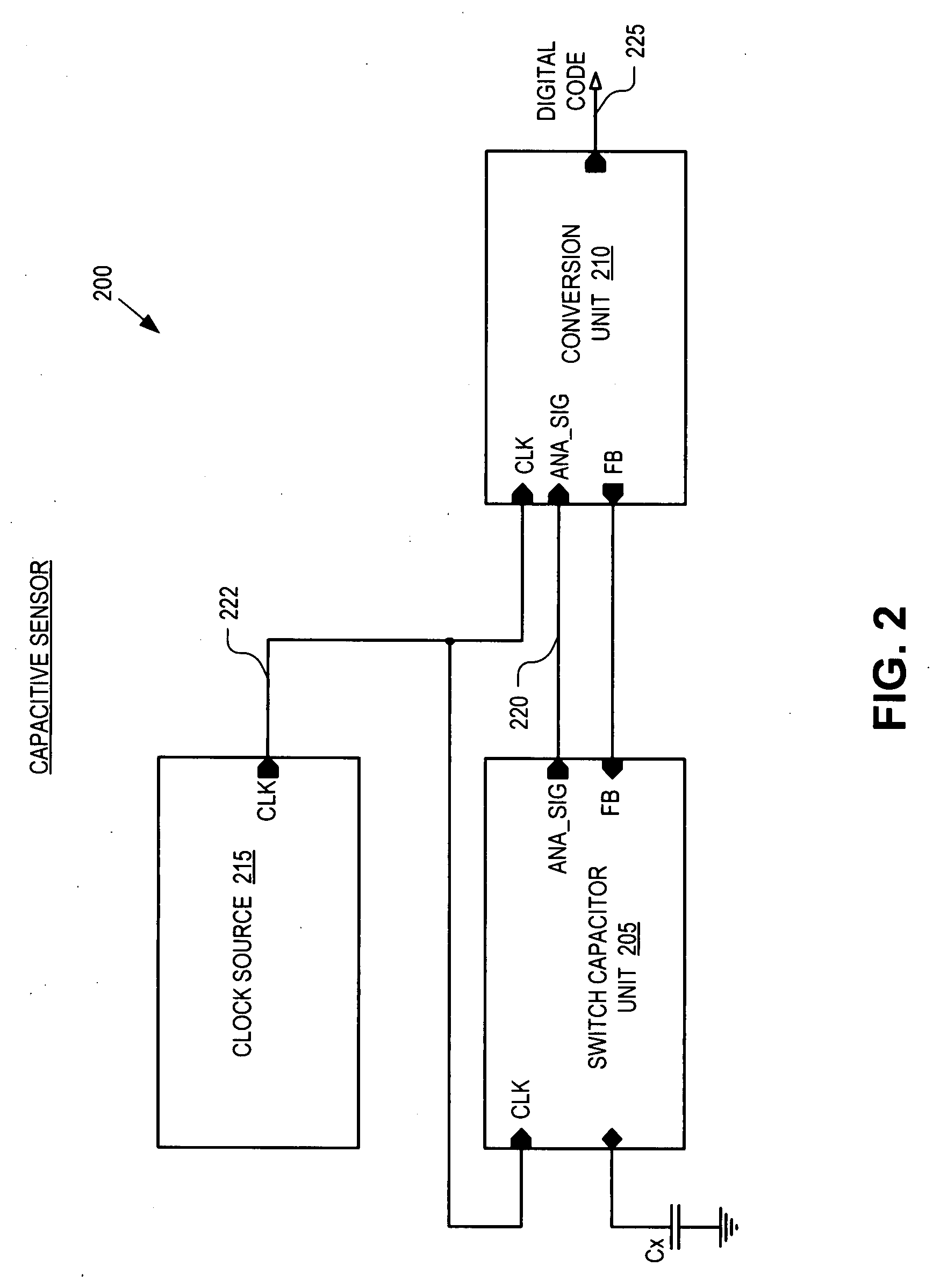
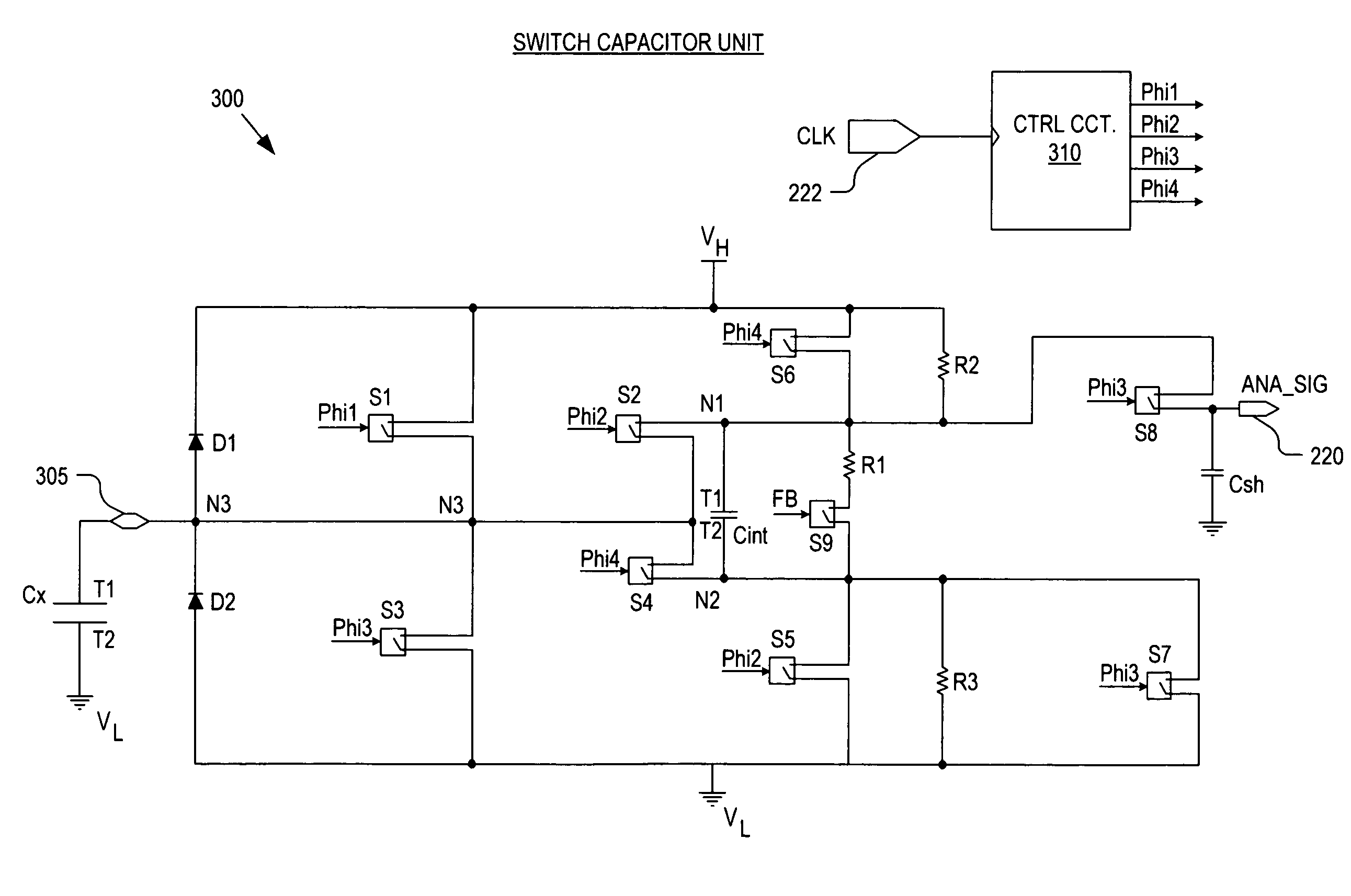
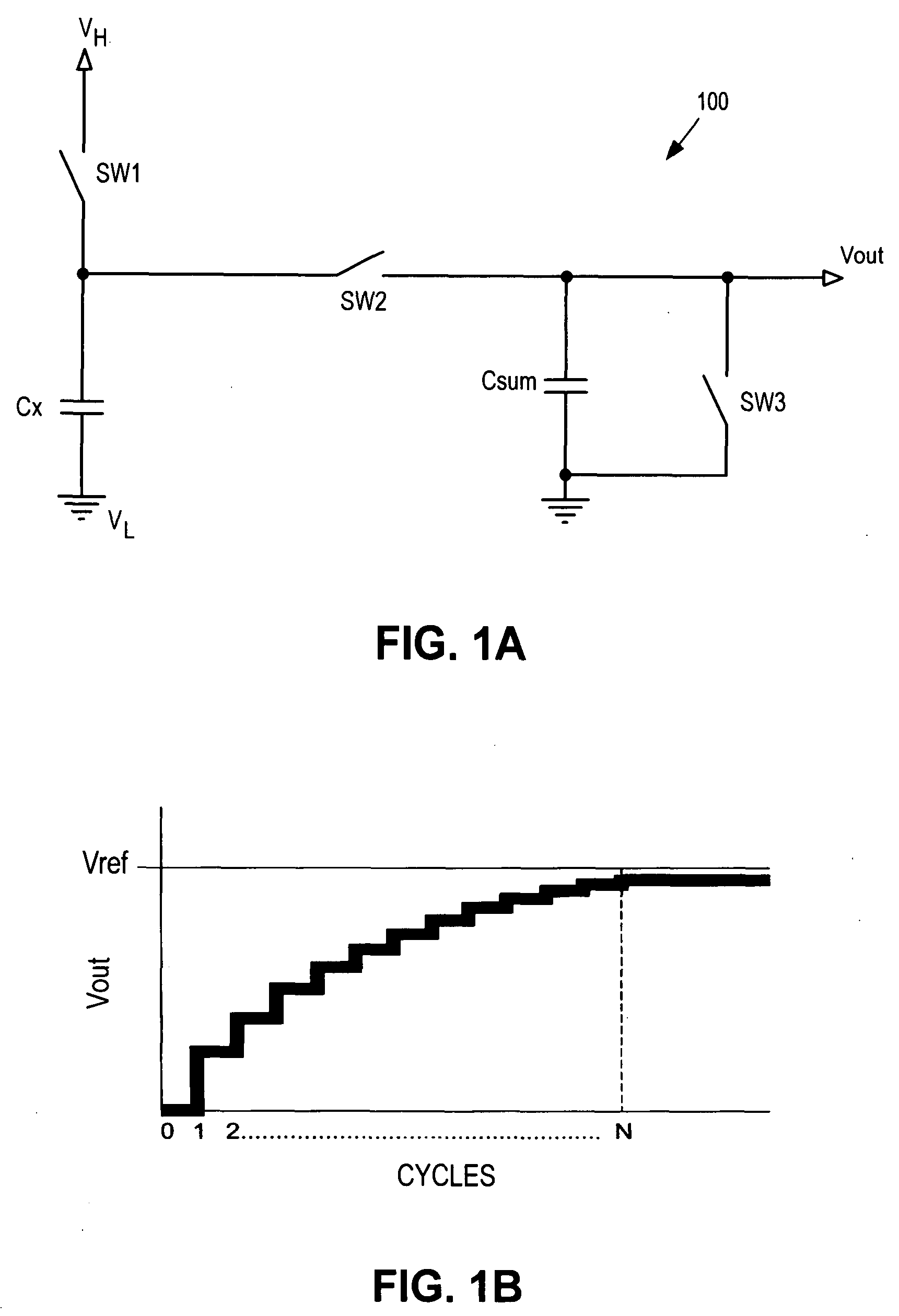
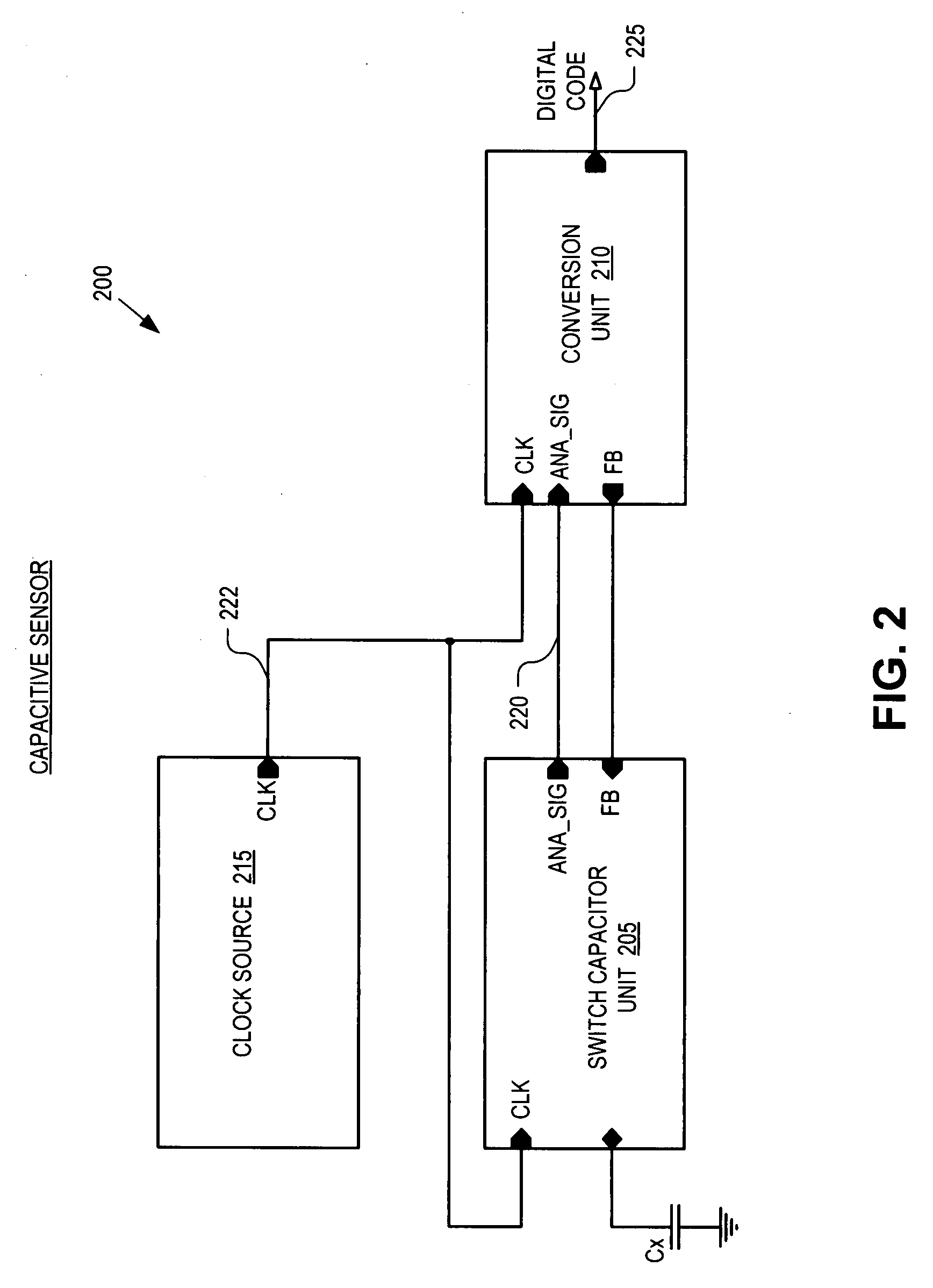
Noise resistant capacitive sensor
ActiveUS20090002206A1Electronic switchingInput/output processes for data processingCharge transfer switchEngineering
A switch capacitor unit for implementing a capacitive sensor includes a charging switch, a charge transfer switch, and a first switch. The charging switch is coupled between a first supply voltage and a circuit node to selectively couple a sensing capacitor to the first supply voltage through the circuit node. The charge transfer switch is coupled between the circuit node and a first terminal of a second capacitor to selectively couple the sensing capacitor through the circuit node to the second capacitor. The first switch is coupled between the circuit node and a second terminal of the second capacitor to selectively couple the second terminal to the sensing capacitor through the circuit node.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Charge transfer circuit suitable for common CMOS process and charge transfer control switch thereof
ActiveCN101977056APrecise addition and subtractionPrecise control of charge sizeAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitanceCharge transfer switch
The invention provides a high-precision charge addition-subtraction transfer circuit suitable for a common CMOS process and a charge transfer control switch thereof. The charge addition-subtraction transfer circuit comprises a charge transfer switch, a first charge storage node, a first charge storage capacitor, a second charge storage node, a second charge storage capacitor and a third storage capacitor, wherein the first charge storage capacitor is connected to the first charge storage node, and the second charge storage capacitor and the third charge storage capacitor are connected to the second charge storage node. The charge addition-subtraction transfer circuit can realize accurate charge addition-subtraction operation and accurately control the quantity of transferred charge, and can be widely used in charge coupled secondary flowing water circuit at all levels in a charge coupled pipeline AD converter.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
Noise resistant capacitive sensor
A switch capacitor unit for implementing a capacitive sensor includes a charging switch, a charge transfer switch, and a first switch. The charging switch is coupled between a first supply voltage and a circuit node to selectively couple a sensing capacitor to the first supply voltage through the circuit node. The charge transfer switch is coupled between the circuit node and a first terminal of a second capacitor to selectively couple the sensing capacitor through the circuit node to the second capacitor. The first switch is coupled between the circuit node and a second terminal of the second capacitor to selectively couple the second terminal to the sensing capacitor through the circuit node.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
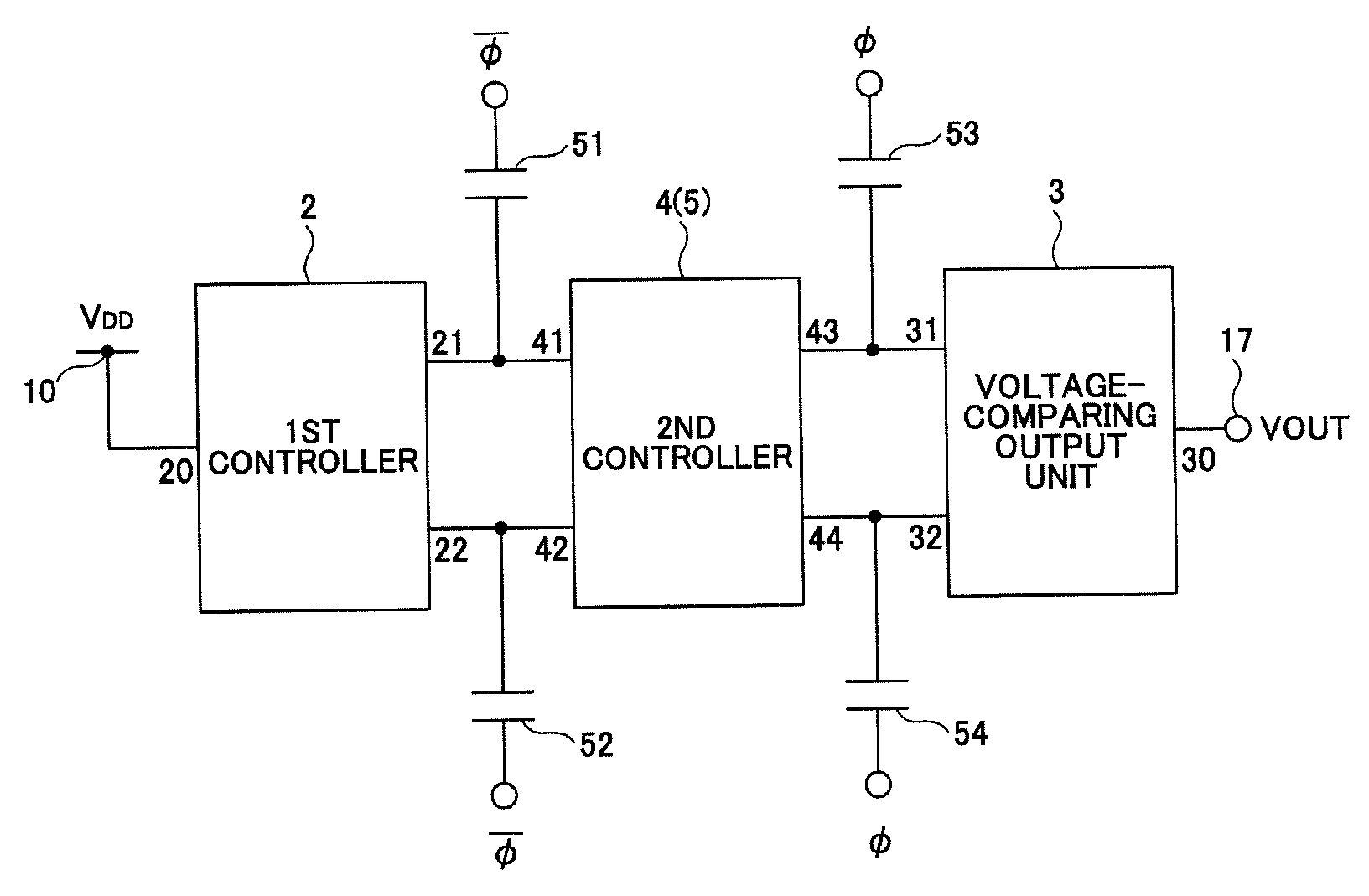
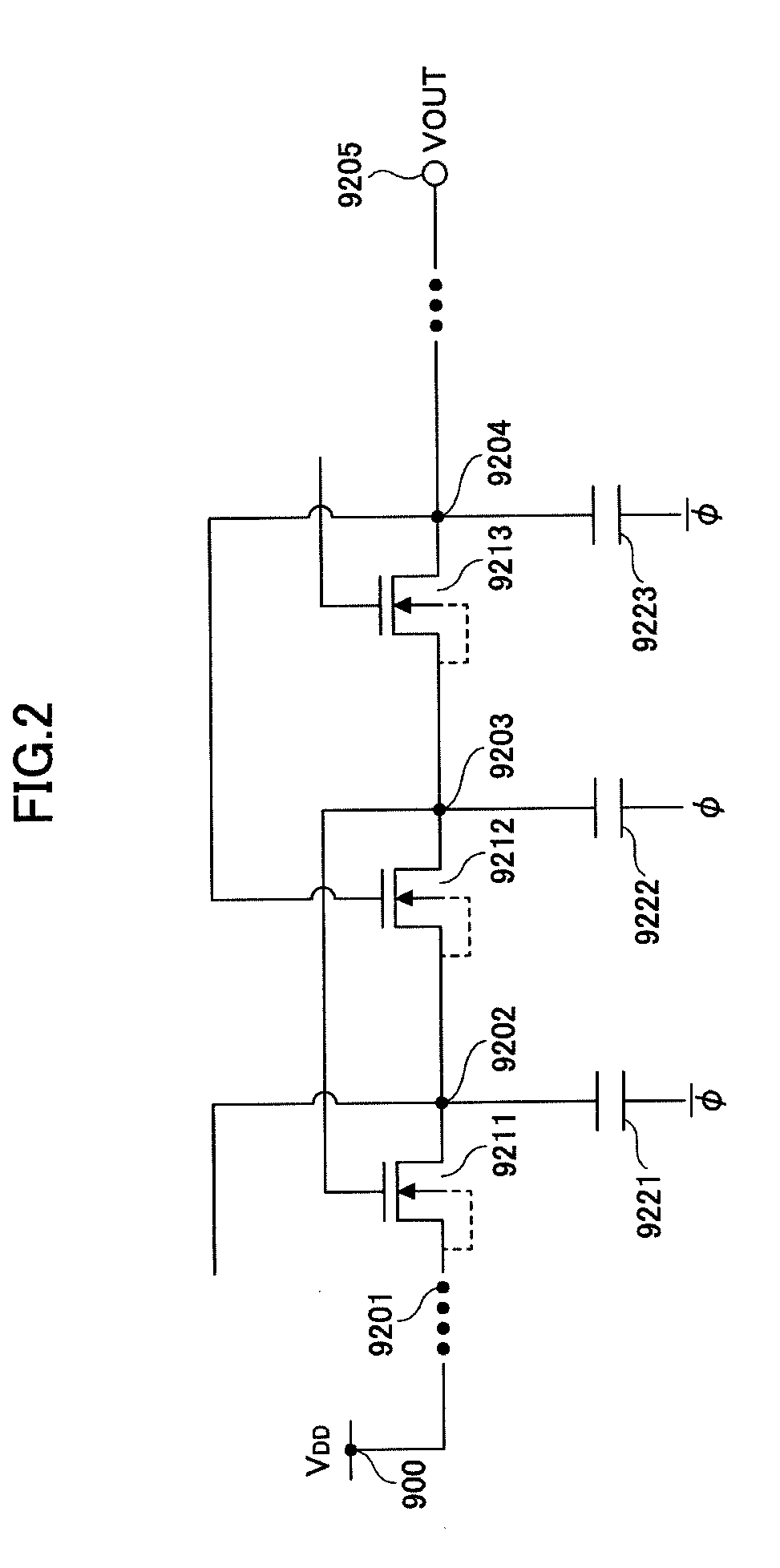
Voltage generating circuit
InactiveUS20090237149A1Eliminate the problemPower Loss MinimizationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCharge transfer switchEngineering
A charge pump provides high boosting efficiency with low power loss even with a heavy load. Plural charge transfer switches are connected in series forming two lines of charge transfer circuits operated by out-of-phase clock signals. Capacitors are connected to each of nodes in the charge transfer circuits. The charge transfer circuits include a first control unit, a second control unit, and a voltage comparison output unit. The second control unit includes a switch unit configured to selectively feed a signal from a previous-stage node or a later-stage node to the gate of a charge transfer switch in the second control unit, depending on the phase of the clock signal.
Owner:RICOH ELECTRONIC DEVICES CO LTD
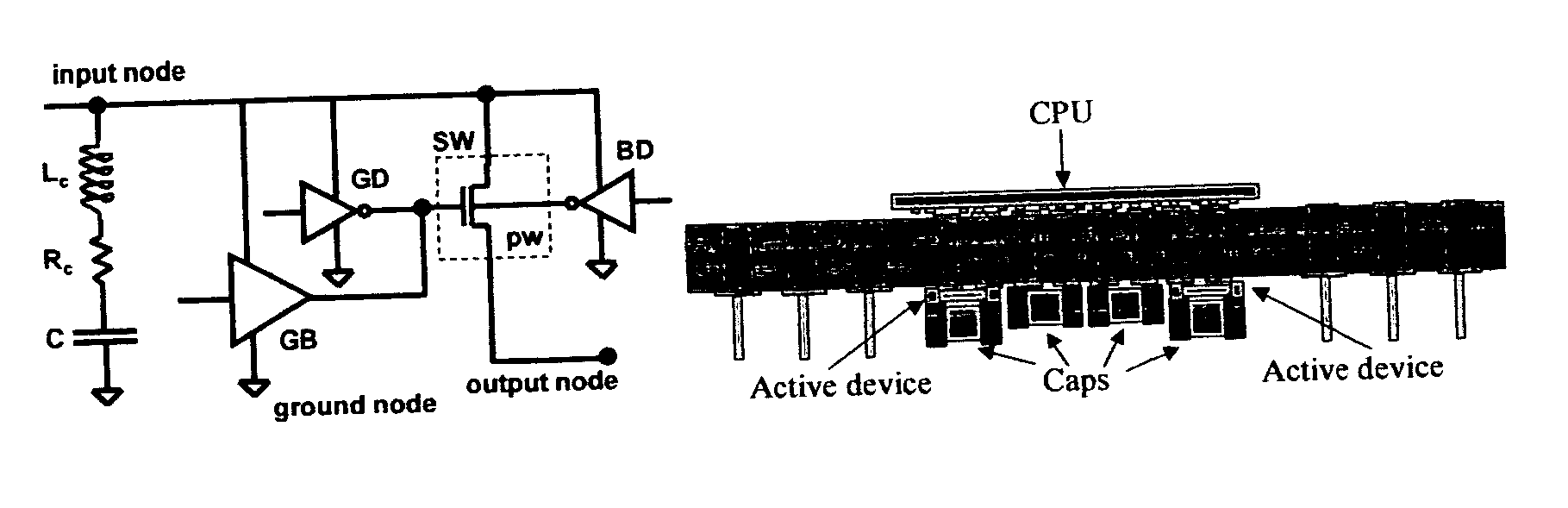
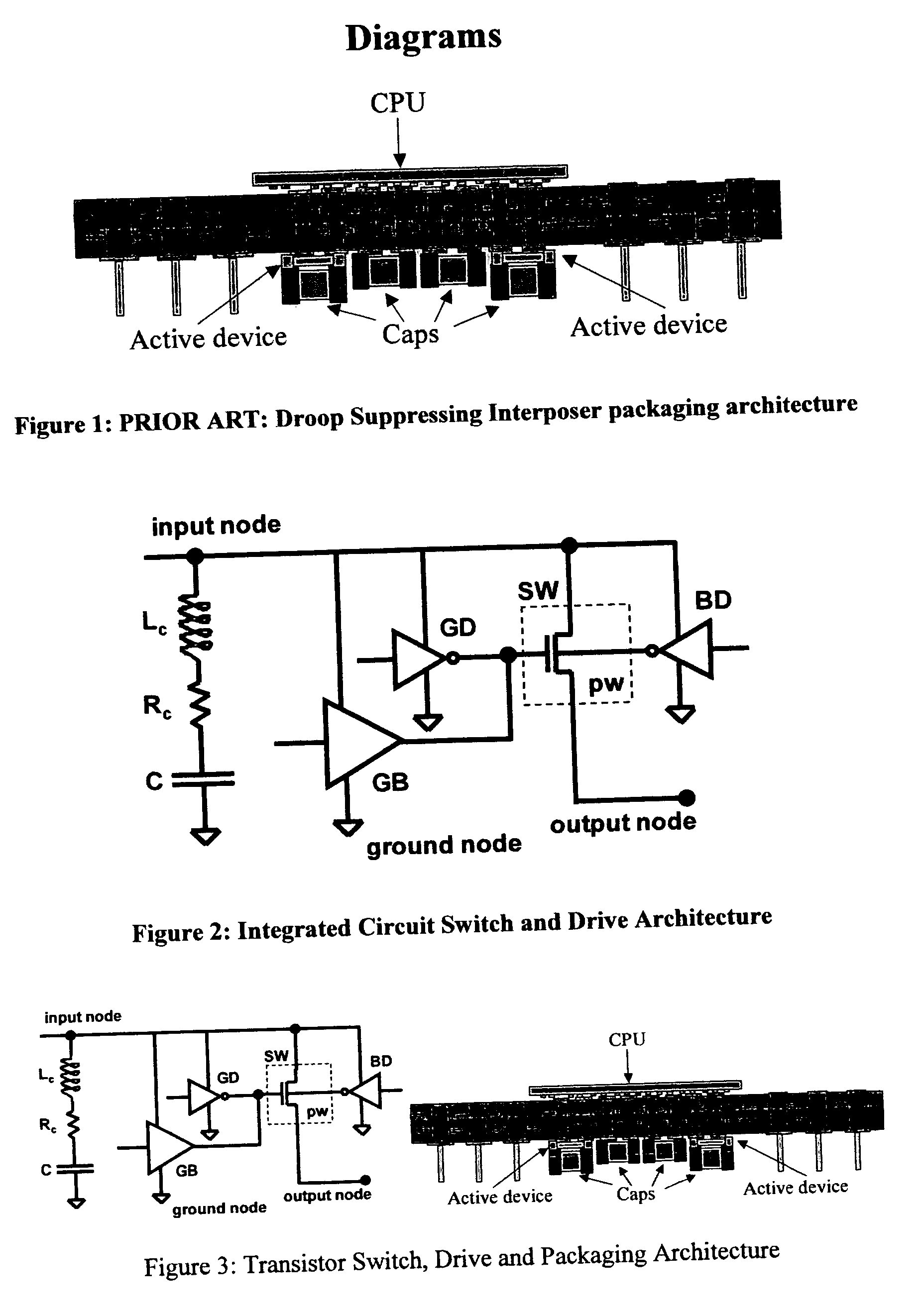
Voltage droop suppressing circuit
InactiveUS20060022733A1Fast turn-on actionImproving voltage droop suppression capabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVolume/mass flow measurementOperating pointElectronic switch
The invention proposes noise suppression circuits that are assembled together with capacitors on a CPU package. Charge is conveyed from the capacitors dedicated to the active noise suppression function through electrical circuit pathways such as controlled electronic switches integrated into a semiconductor substrate. These circuit pathways connect to the capacitor terminals through the package of the active noise suppression semiconductor chip. The circuits within the active device may be any combination of semiconductor switches and / or voltage regulators, and may also contain voltage and current sensing circuitry. The charge transfer switches are designed with control circuitry that dynamically modulate the turn-on threshold voltage of the switches and maintain the switches at an operating point very close to actual turn-on. These enhancements ensure very fast turn-on action for the switches improving voltage droop suppression capability.
Owner:NAIR RAJENDRAN
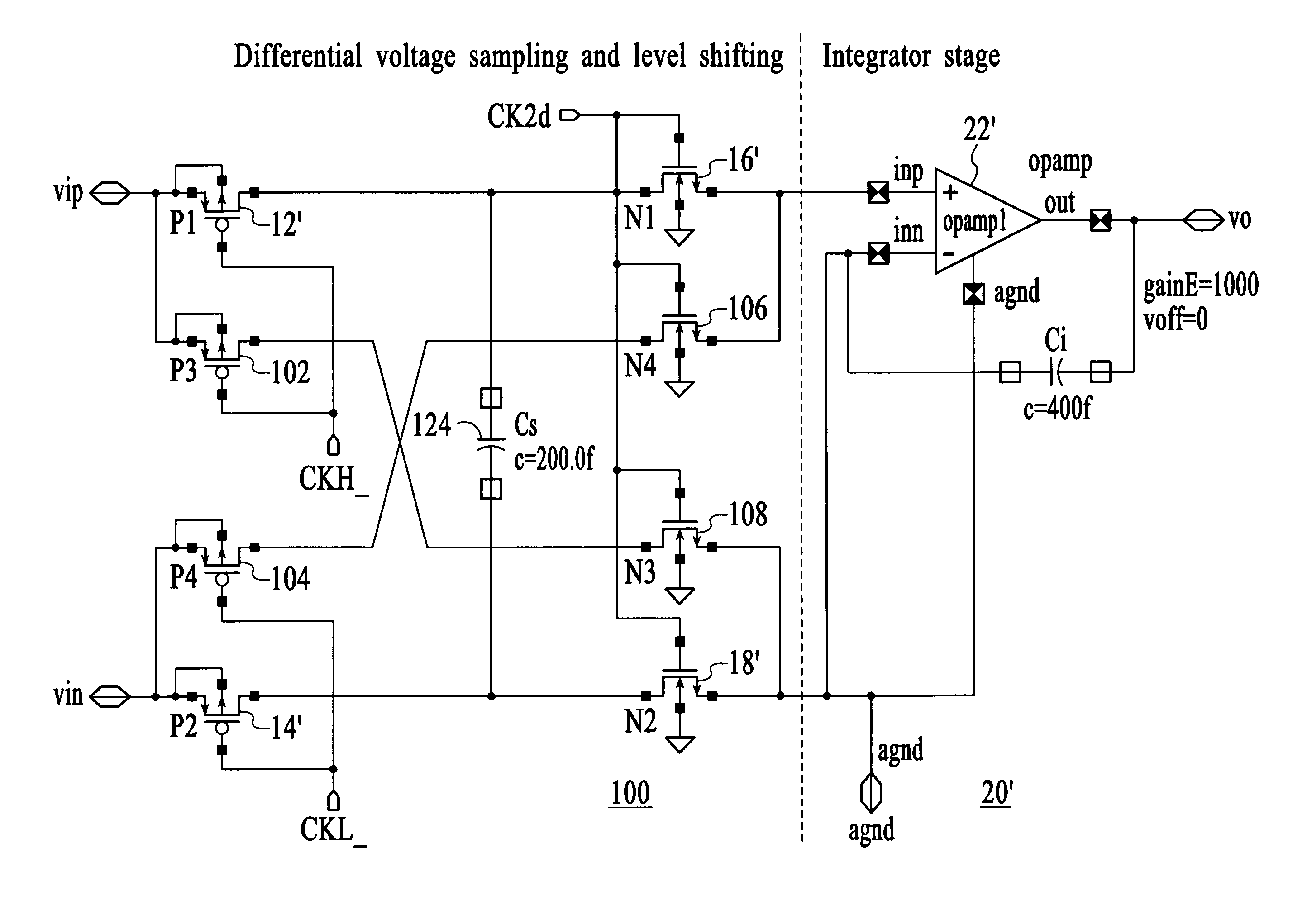
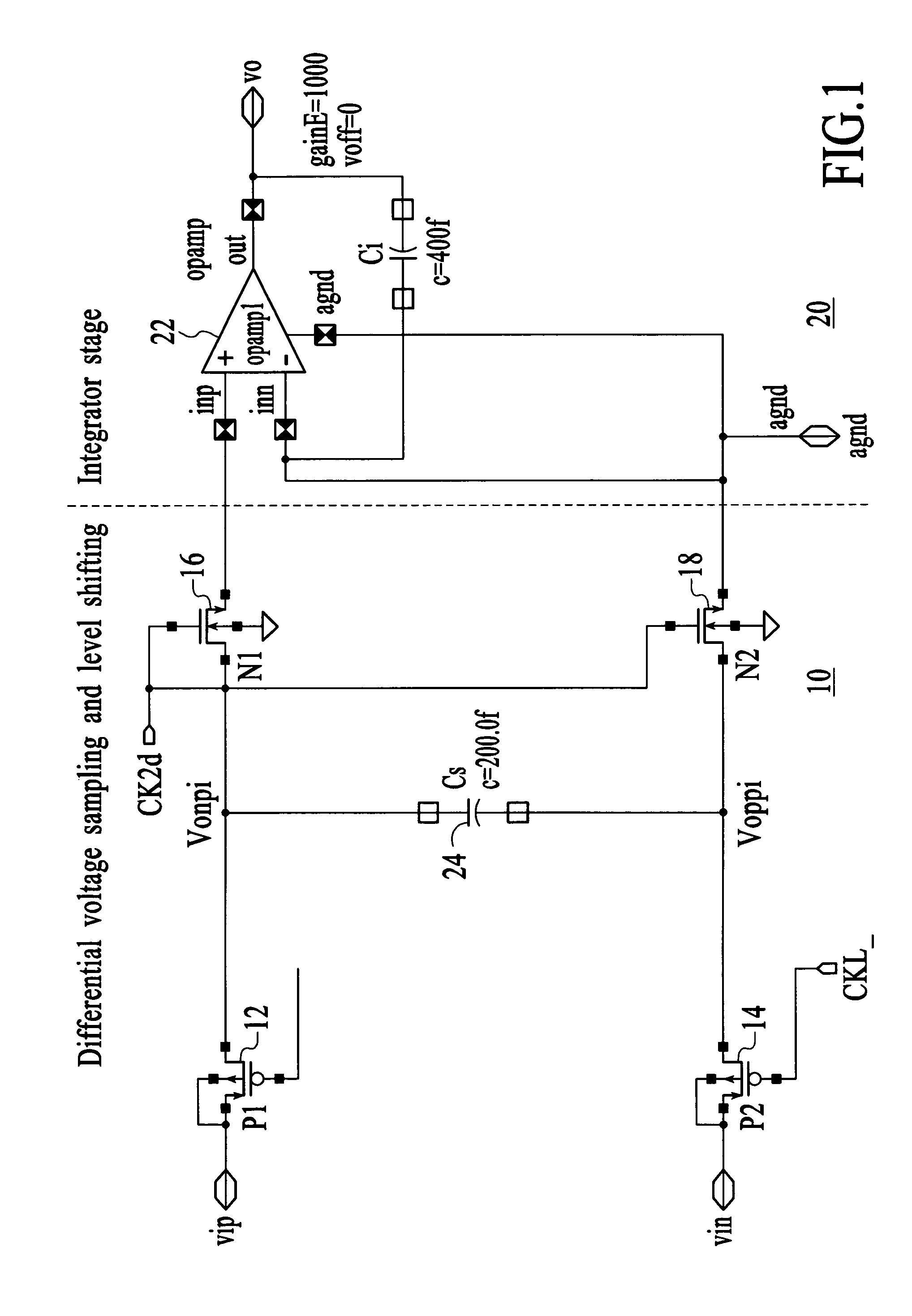
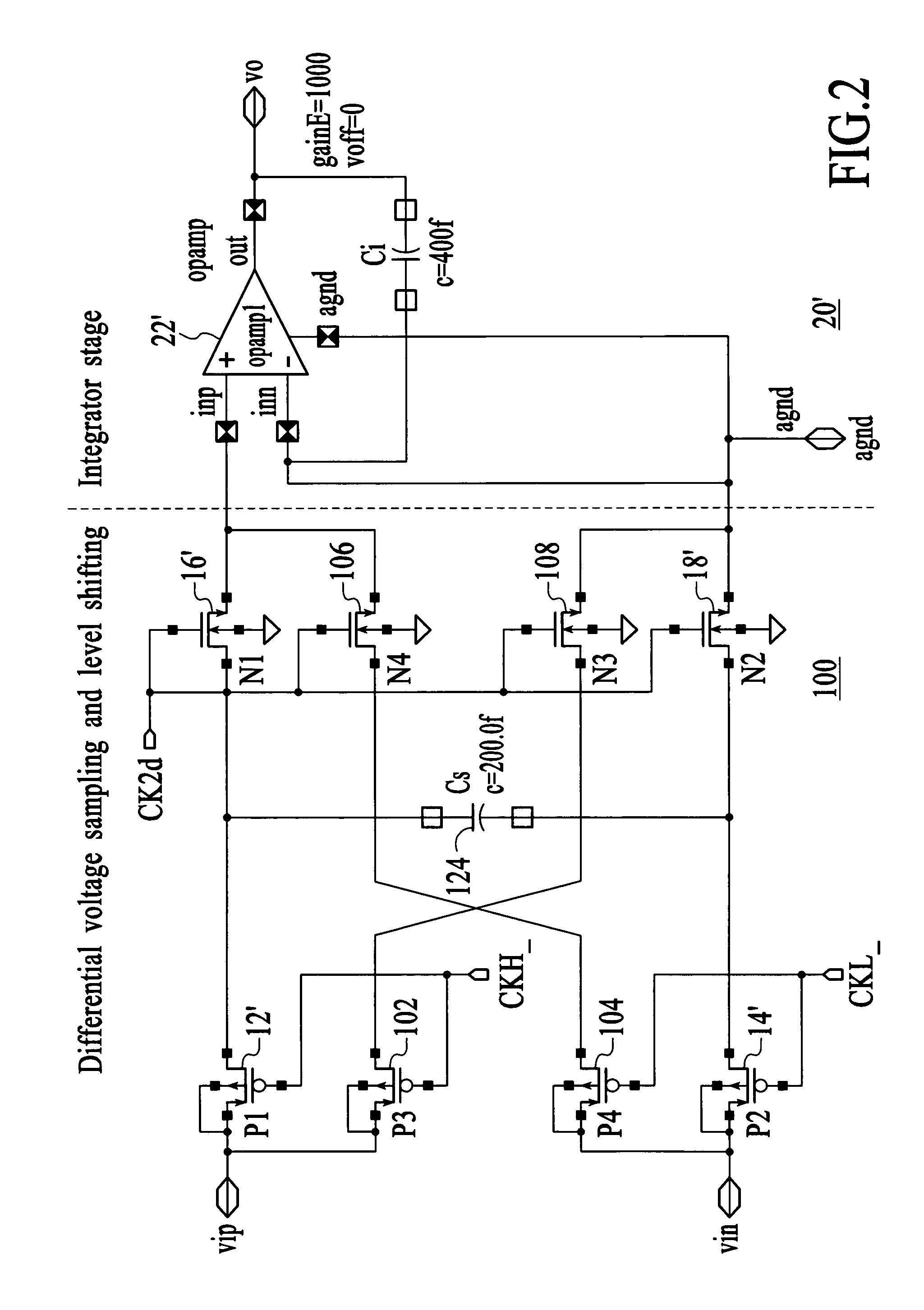
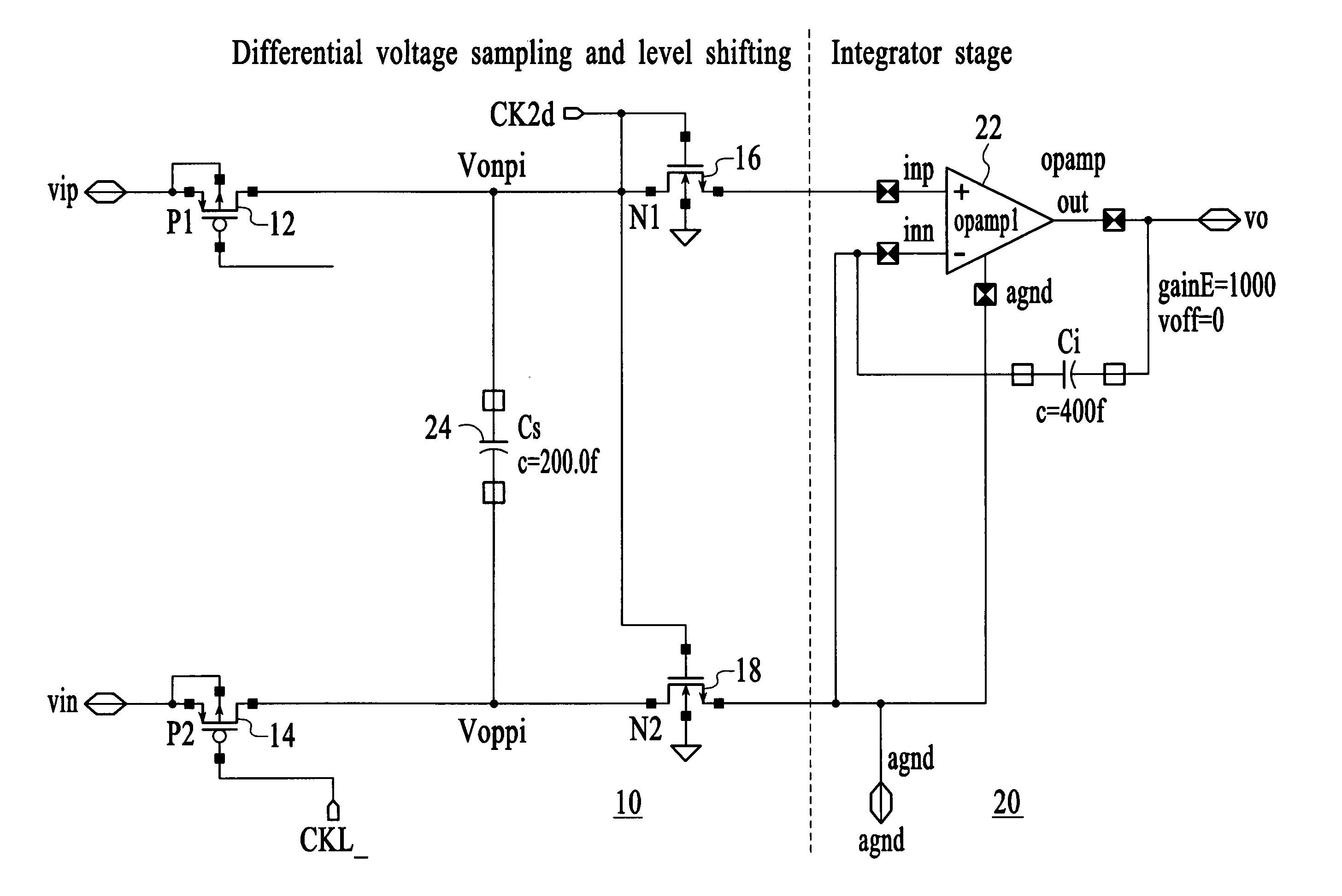
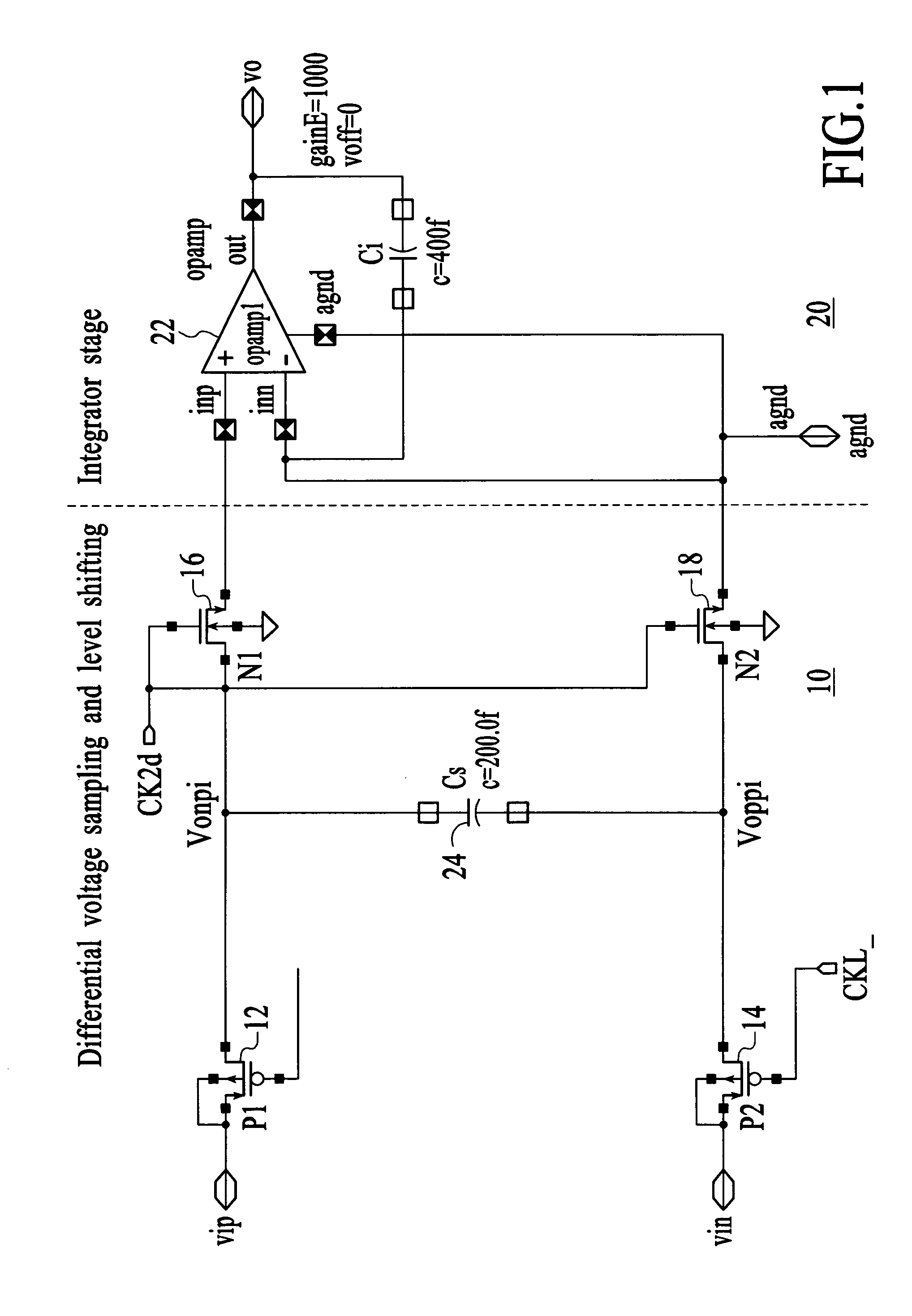
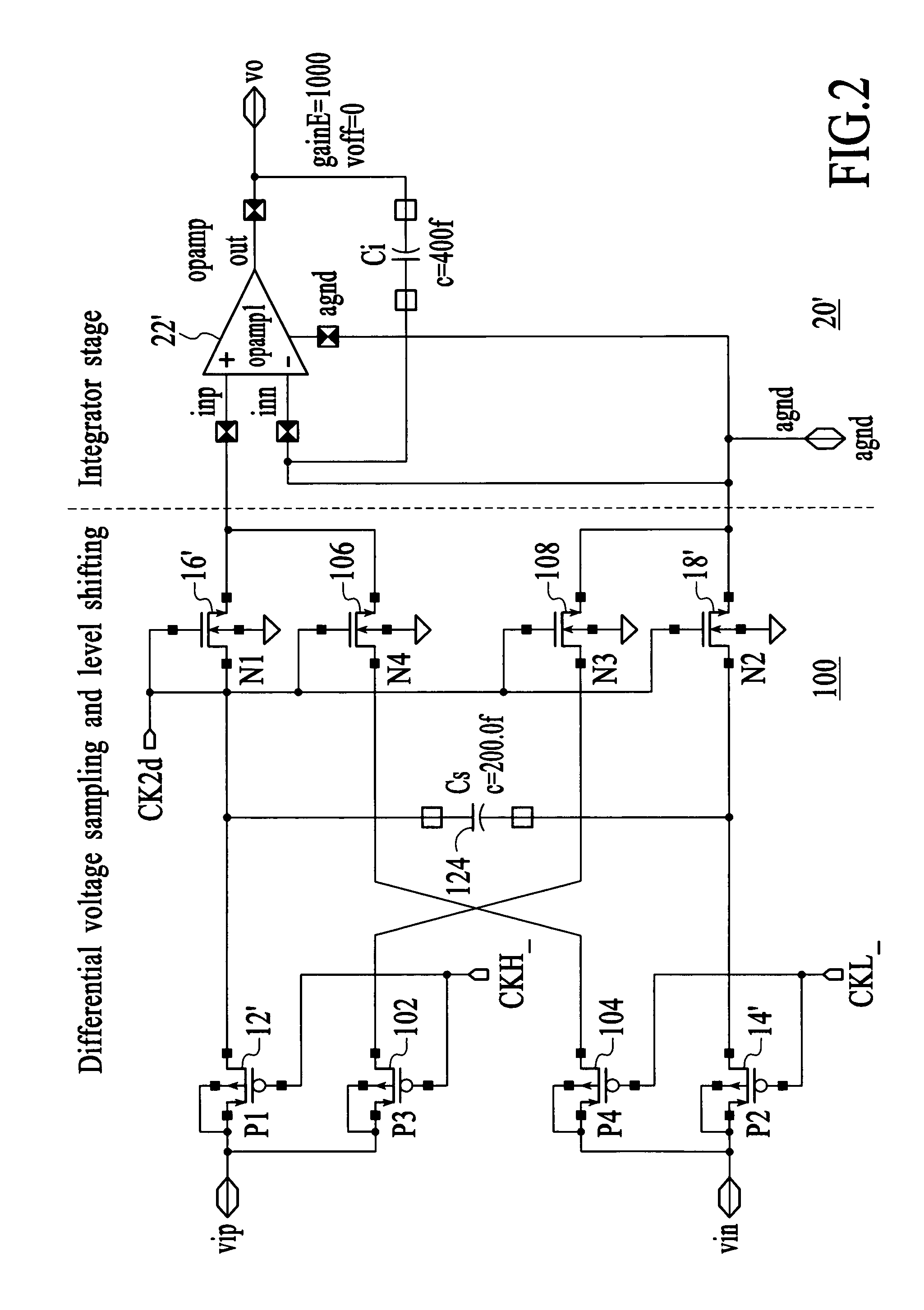
Sampling and level shifting circuit
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Sampling and level shifting circuit
A circuit comprising a first switch for sampling a differential signal and a second switch for level-shifting the sampled differential signal is disclosed. The first and second switches are cross-coupled to cancel a charge injected between the first and second switches and for linearizing the charge transfer; and a capacitor coupled is between the first and second switches. A circuit in accordance with the present invention adds an extra sampling switch to the sampling circuit and an extra charge-transfer switch in the level-shifting circuit. By cross-coupling these extra switches, the result is a cancellation of the charge-injection, and thus linearizing the charge transfer.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit device, charge pump circuit, and electric appliance
InactiveUS20070236972A1Ac-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCharge transfer switchSemiconductor
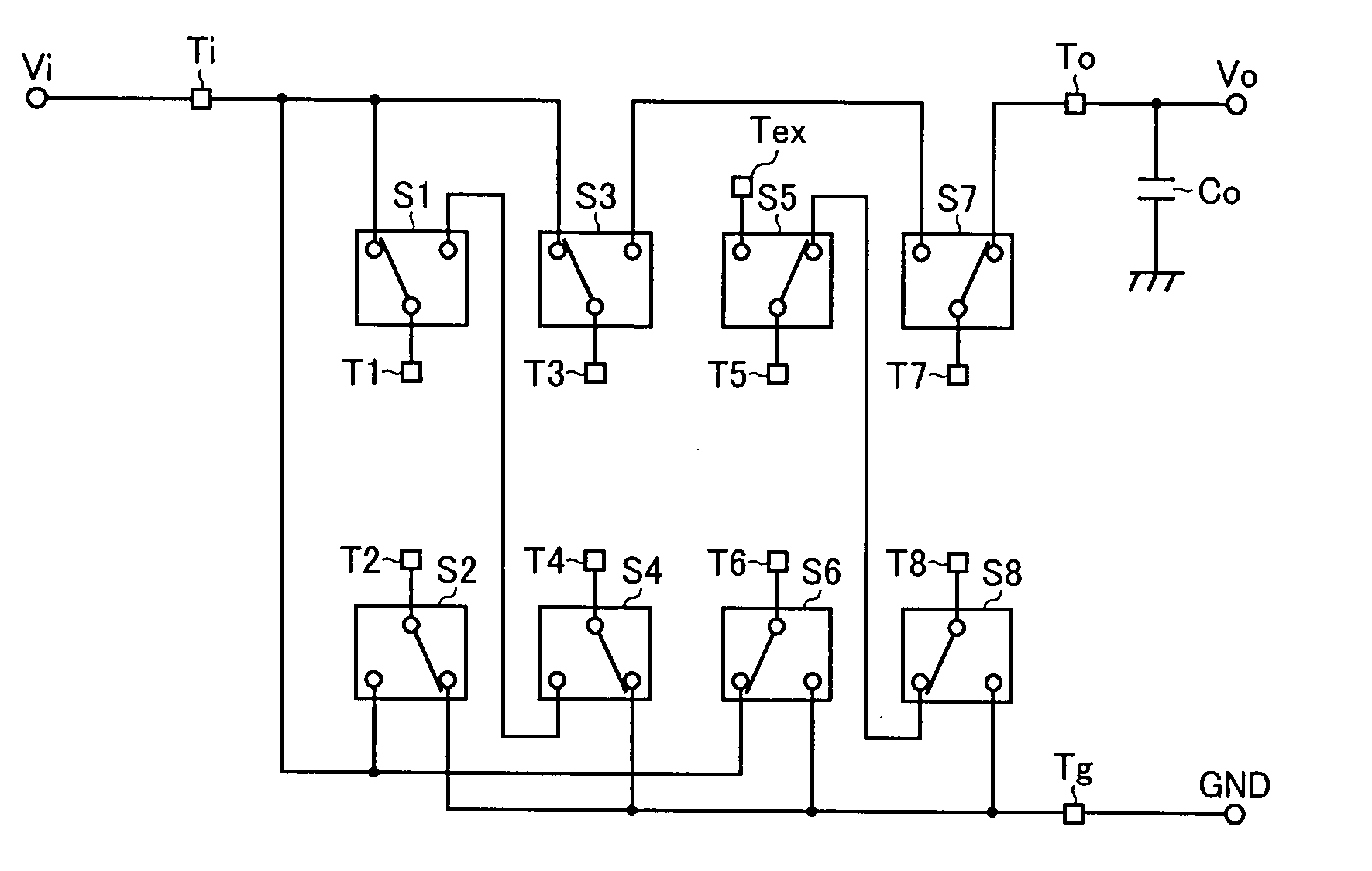
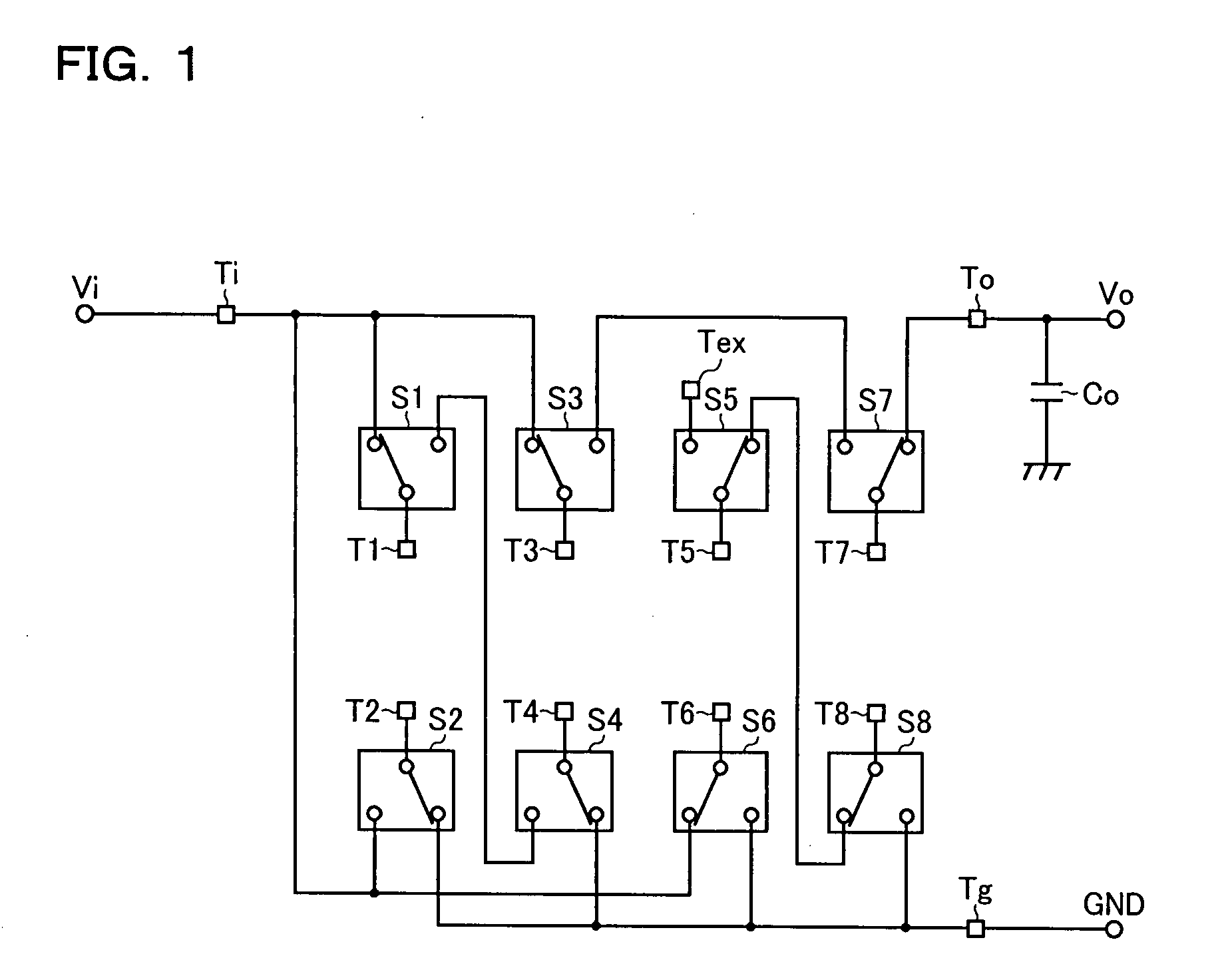
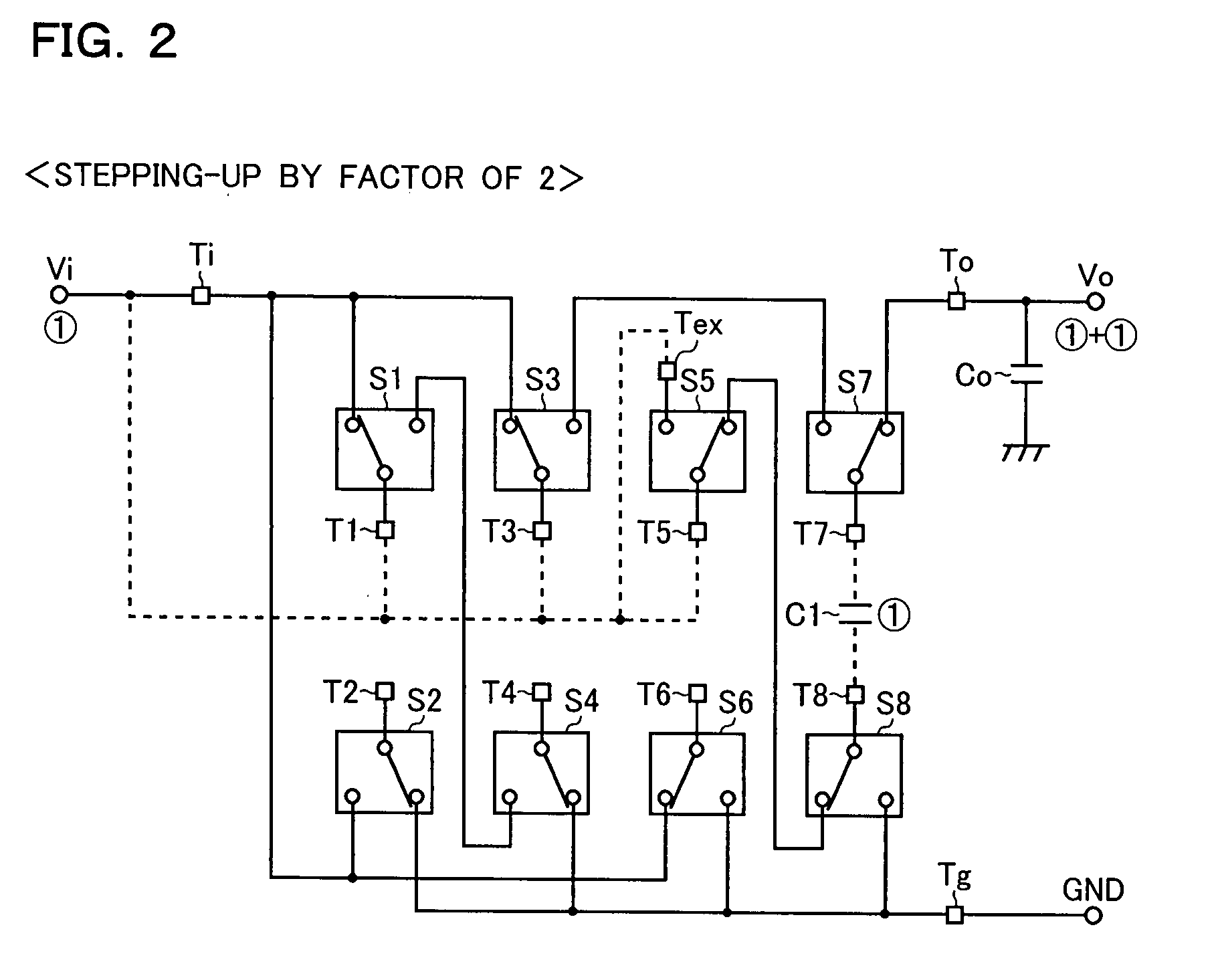
In addition to an input terminal, an output terminal, a ground terminal, a plurality of external terminals, and a plurality of charge transfer switches, a semiconductor integrated circuit device has a step-up factor switching terminal. Here, the plurality of charge transfer switches each have a common contact connected to corresponding one of the plurality of external terminals and two selection contacts alternatively connected to the common contact, and one of the selection contacts of the plurality of charge transfer switches is connected to the step-up factor switching terminal, and each of the other selection contacts is connected to one of the input terminal, the output terminal, the ground terminal, and the rest of the other selection contacts. With this configuration, it is possible to make the semiconductor integrated circuit device versatile so that it can be used to form charge pump circuits having different step-up factors.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
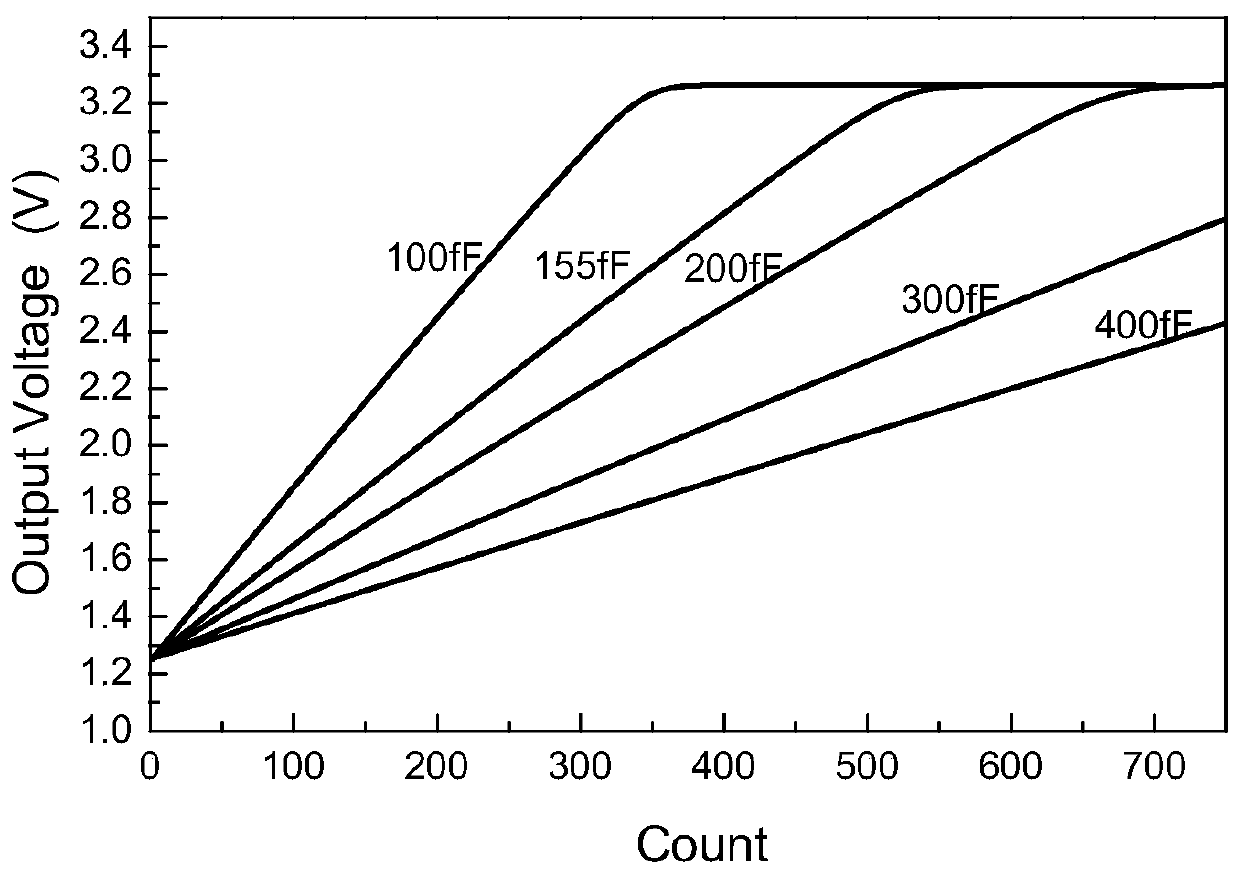
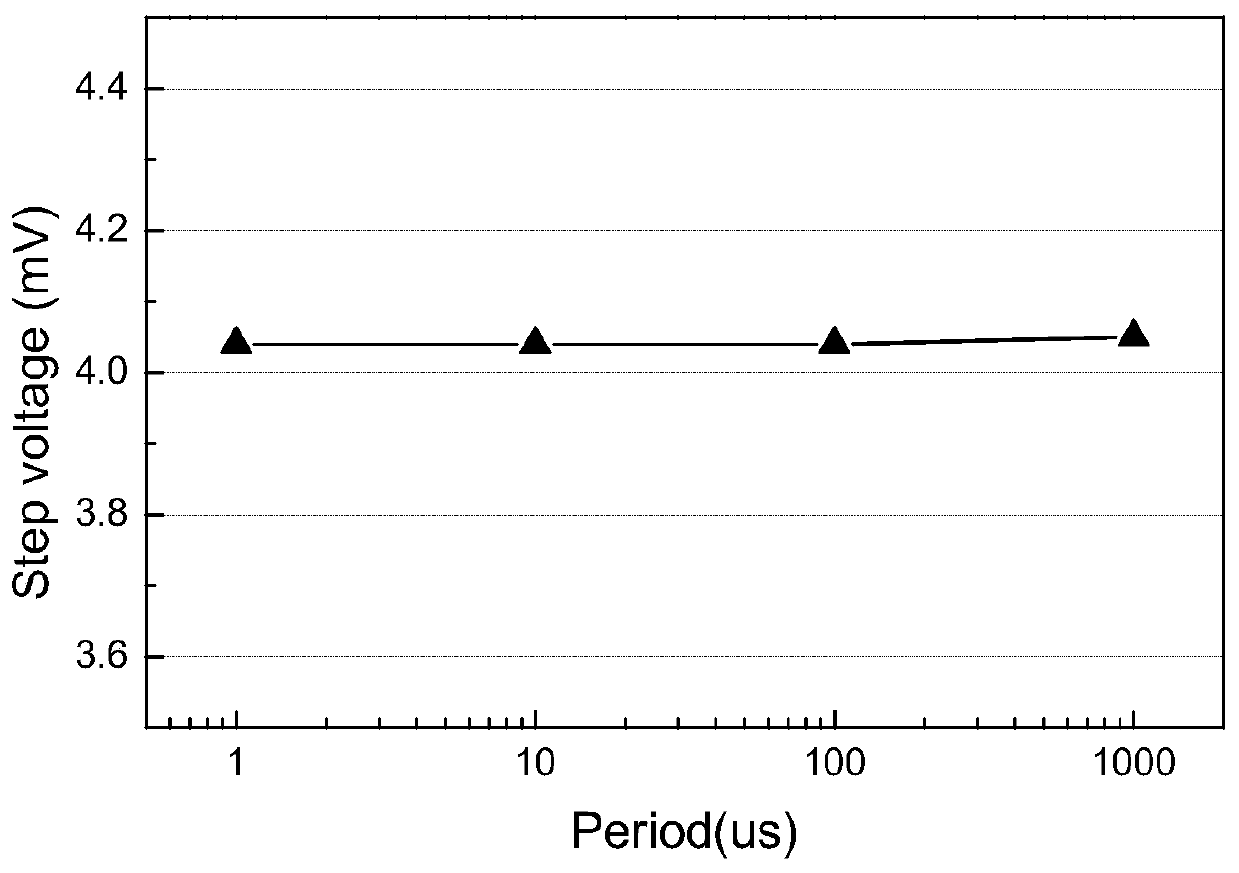
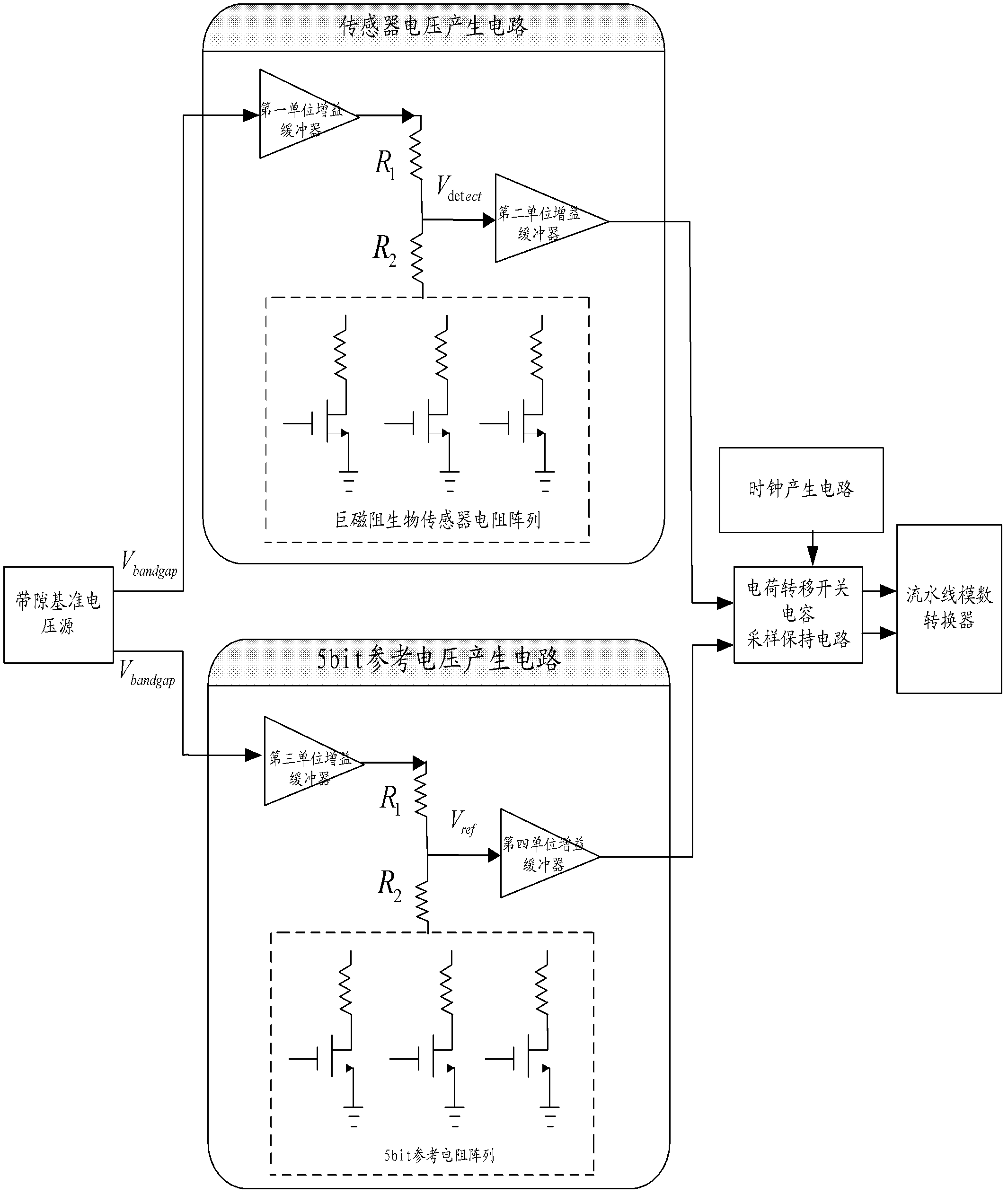
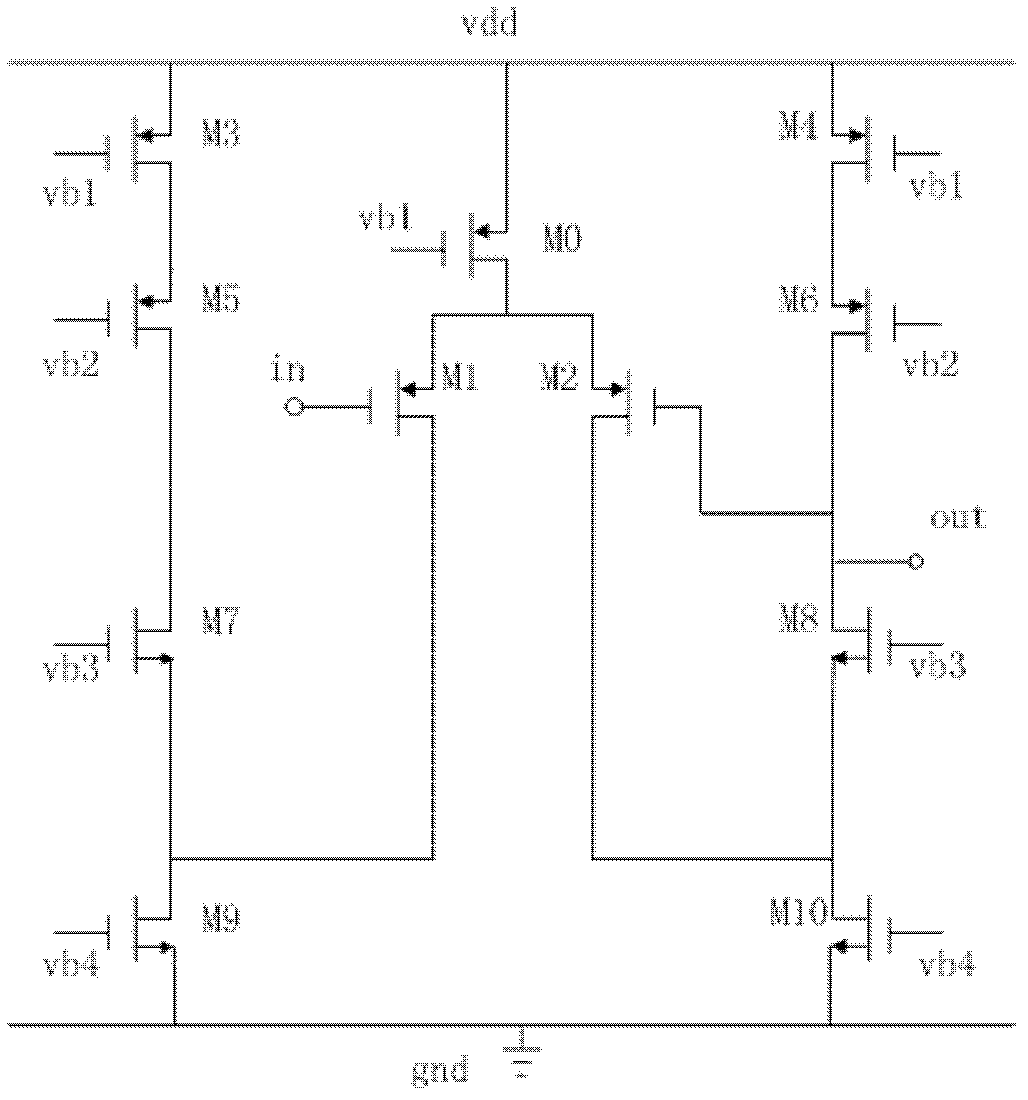
Analog front end detection circuit used for giant magneto-resistive (GMR) biosensor
ActiveCN102339084AAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceVoltage source
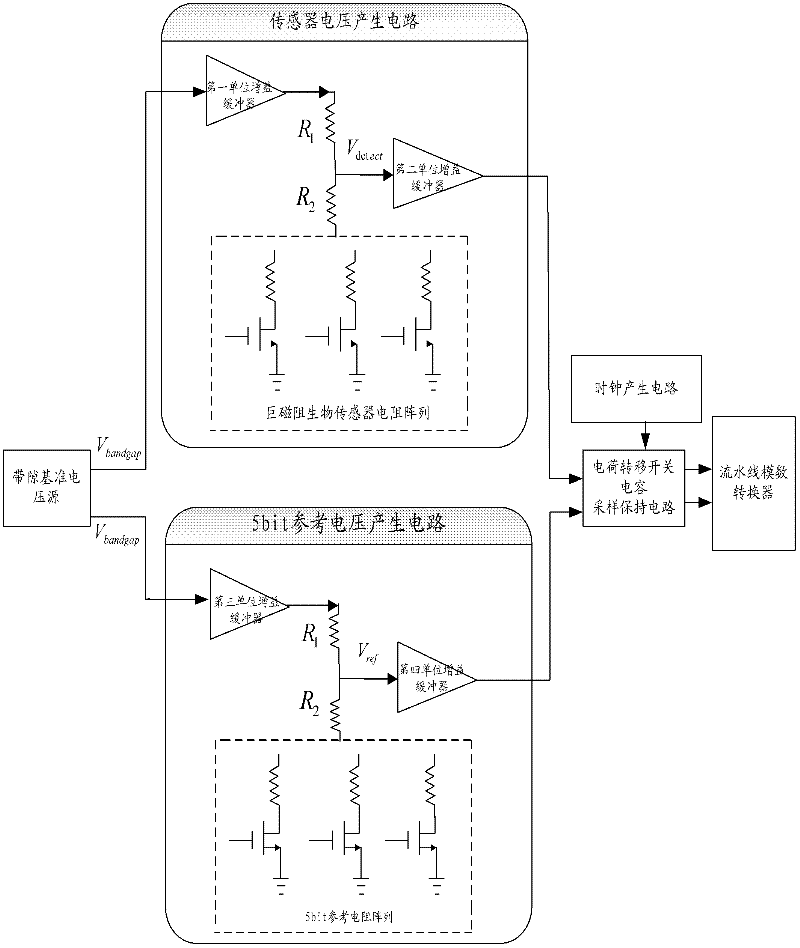
The invention relates to an analog front end detection circuit used for a giant magneto-resistive (GMR) biosensor. The circuit comprises a bandgap reference voltage source, a sensor voltage generating circuit, a 5bit reference voltage generating circuit, a charge transfer switched capacitor sampling / holding circuit and a pipelined analog-to-digital converter. The analog front end detection circuit has the following beneficial effects: the methods of single chip total integration and voltage detection are adopted, thus effectively extracting the weak voltage signals in the GMR biosensor; the charge transfer switched capacitor sampling / holding circuit is utilized to sample the detection voltage of the resistor array of the GMR biosensor and reasonably amplify the detection voltage to the input voltage range of the analog-to-digital converter; and finally, the analog-to-digital converter is used for outputting the digital detection results.
Owner:中科芯未来微电子科技成都有限公司
Semiconductor integrated circuit device, charge pump circuit, and electric appliance
InactiveCN101043178ASolid-state devicesApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCharge transfer switchSemiconductor
In addition to an input terminal, an output terminal, a ground terminal, a plurality of external terminals, and a plurality of charge transfer switches, a semiconductor integrated circuit device has a step-up factor switching terminal. Here, the plurality of charge transfer switches each have a common contact connected to corresponding one of the plurality of external terminals and two selection contacts alternatively connected to the common contact, and one of the selection contacts of the plurality of charge transfer switches is connected to the step-up factor switching terminal, and each of the other selection contacts is connected to one of the input terminal, the output terminal, the ground terminal, and the rest of the other selection contacts. With this configuration, it is possible to make the semiconductor integrated circuit device versatile so that it can be used to form charge pump circuits having different step-up factors.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Charge transfer type analog count reading circuit based on pulse rising edge triggering
ActiveCN107425847AHigh resolutionReduce areaCounting chain pulse counters using opto-electronic devicesCounting chain pulse counters using semiconductor devices with 2 electrodesMOSFETCharge injection
The invention discloses a charge transfer type analog count reading circuit based on pulse rising edge triggering. The circuit comprises 13 MOSFET transistors, an integral capacitor and a parasitic capacitor. The MP1 and MP2 are a charge injection switch and a charge transfer switch and are used for controlling generation and transfer of a charge packet. The parasitic capacitor Cgd bridged between a gate and a drain of the MP1 couples an input avalanche pulse signal into the drain of the MP1. The MP4 and MN1 form a reset circuit which is used for discharging charges stored by the integral capacitor. The MP6, MP7, MP8, MN2, MN3 and MN4 form a unit gain amplifier which is used for preventing a voltage of the integral capacitor from being influenced by electric leakage of the MOSFET transistor connected with the integral capacitor C. The MP3 is a source follower transistor. The MP5 is a load. The MP9 is a lien selection transistor. The voltage on the integral capacitor C is read to an external circuit through the MP3 and the MP9. According to the analog count reading circuit, a wide count range can be realized, moreover, an area of SPAD array detector pixel units can be reduced, and the density of an SPAD array detector is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
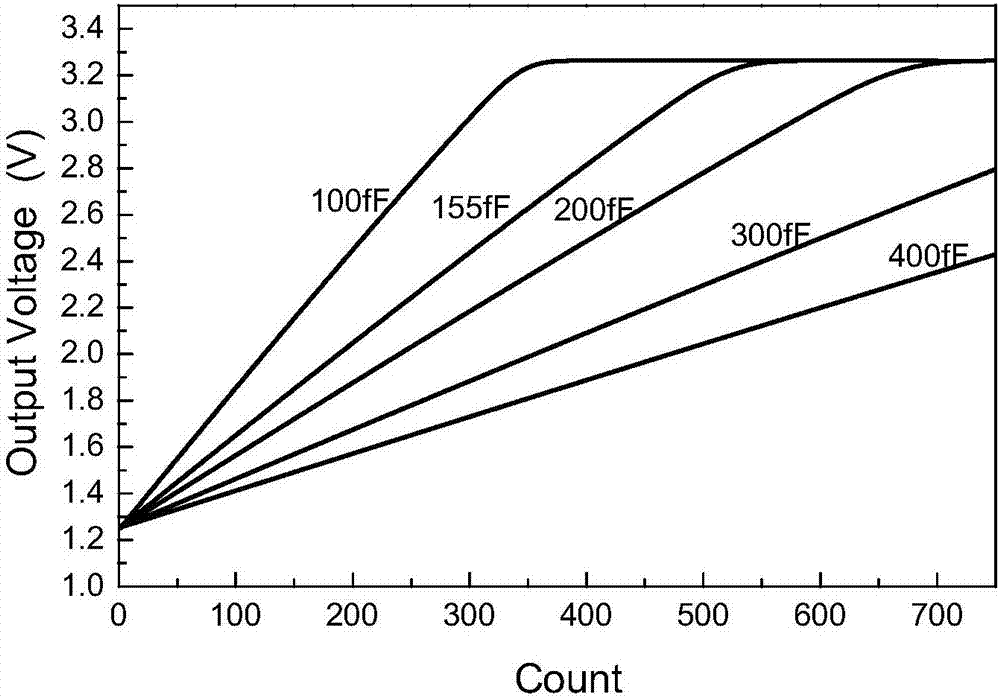
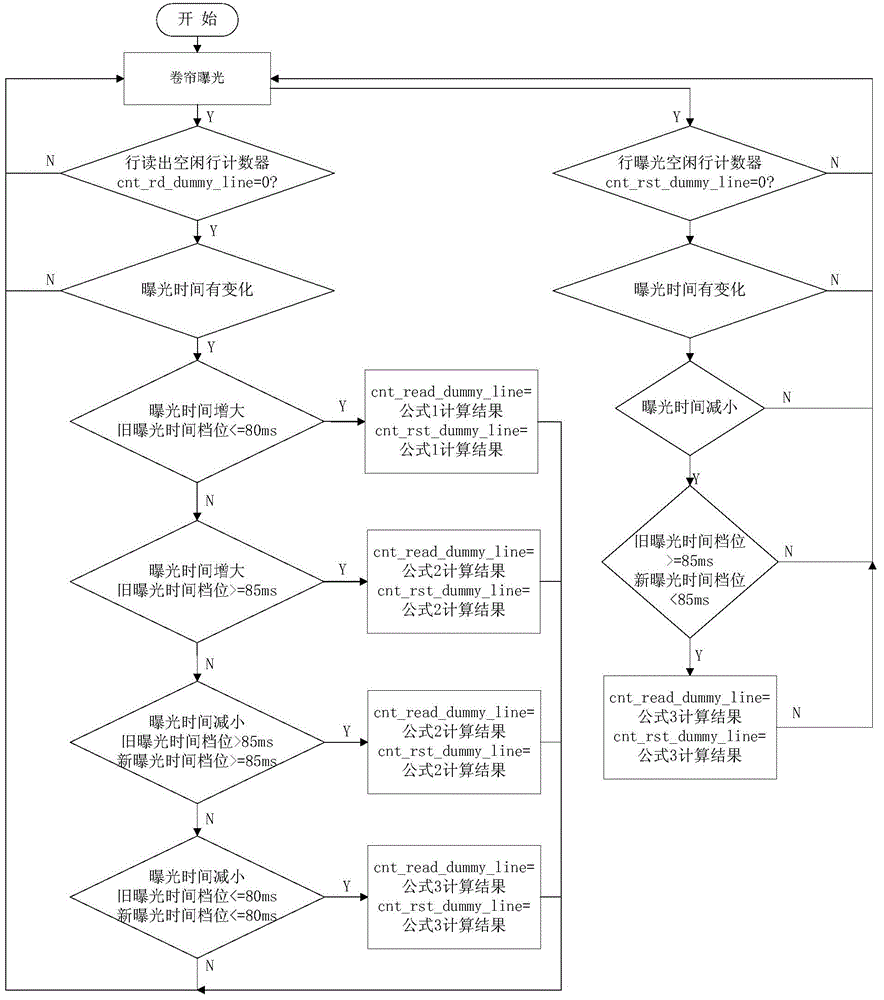
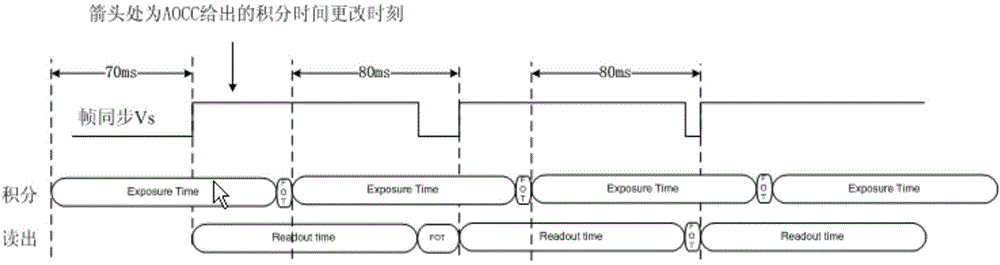
Dynamic exposure time adjusting method for APS (active pixel sensor) star sensor
ActiveCN104567864ATake advantage of flexibilityIncrease or decrease exposure timeNavigation by astronomical meansCMOS sensorProcessor register
The invention discloses a dynamic exposure time adjusting method for an APS (active pixel sensor) star sensor. The method comprises the following steps: (1), the size of a 4T image sensor area array is set, and the time Tus for reading one line is taken as the basic exposure unit; (2), an exposure time gear register is arranged in an FPGA (field programmable gate array), and N-gear exposure time is set; (3), according to a new exposure time gear written by a processor, a corresponding exposure adjusting formula is determined, exposure idle lines and read idle lines are obtained through calculation, read and exposure operation is controlled by switching on and off a pixel charge transfer switch in one-line time, the exposure operation is not performed when exposure is in an idle line, and the read operation is not performed when read is in an idle line; after exposure of the idle lines is finished, a rolling exposure pipeline at a new exposure time gear is entered, and setting of the new exposure time gear is finished. Seamless and dynamic adjustment of multiple-gear exposure time can be realized, the exposure pipeline is not interrupted during dynamic adjustment of the exposure time, and the data read time interval is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Electric vehicle with two-way operating circulation generator
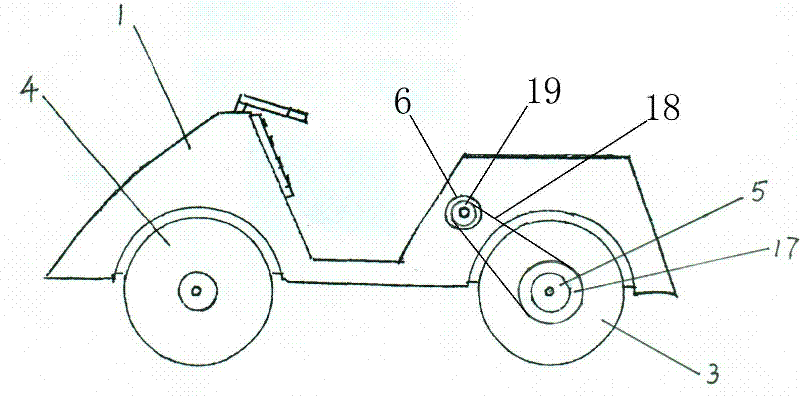
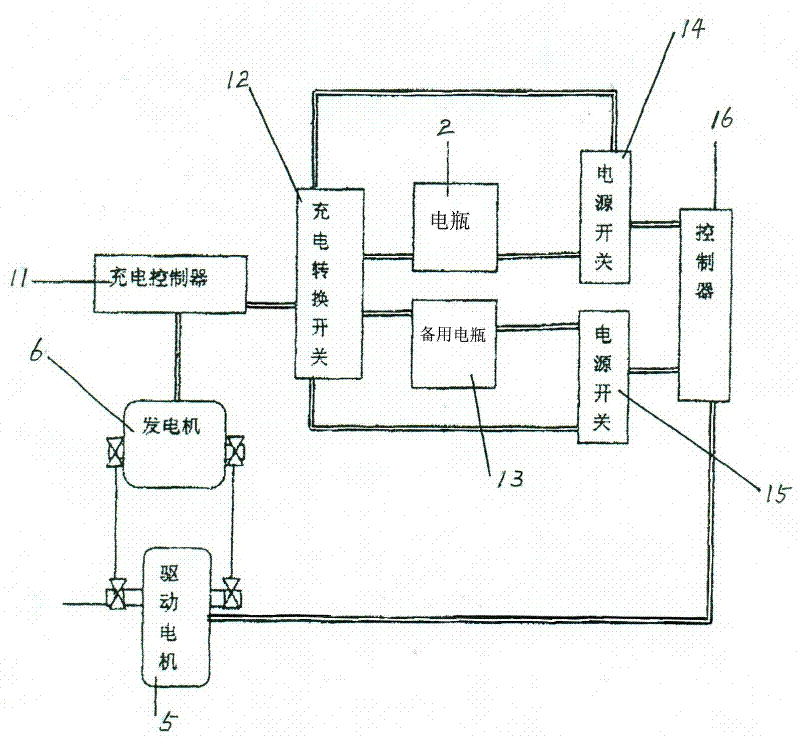
InactiveCN102303537ACompact structureAvoid smallBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric machinesDrive wheelBall bearing
The invention discloses an electric vehicle with a two-way operating circulation generator. In the electric vehicle, a generator (6) is arranged at the other side of a driving wheel (3) and consists of an inner rotor (7) with a winding and an outer rotor (8) which is encircled on the circumference of the rotor and is provided with a magnet; a wheel ball bearing (9) is arranged between the outer rotor and a generator casing; a counter-driving mechanism (10) is arranged between the inner rotor and the outer rotor; the outer rotor is driven by rotating the inner rotor to enable the outer rotor to reversely rotate; a charging controller (11) is arranged and connected with the generator; the charging controller is respectively connected with a battery jar (2) and an arranged standby battery jar (13) through a charging transfer switch (12); and the battery jar (2) and the arranged standby battery jar (13) are respectively connected with a controller through a mains switch (14) and a mains switch (15). According to the invention, the defects that the traditional electric vehicle is frequently charged and the driving range is limited are overcome; and the invention has the remarkable advantages of compact structure, power recovery, energy saving, added charge capacity, reduced driving cost and greatly-increased driving range.
Owner:方子林
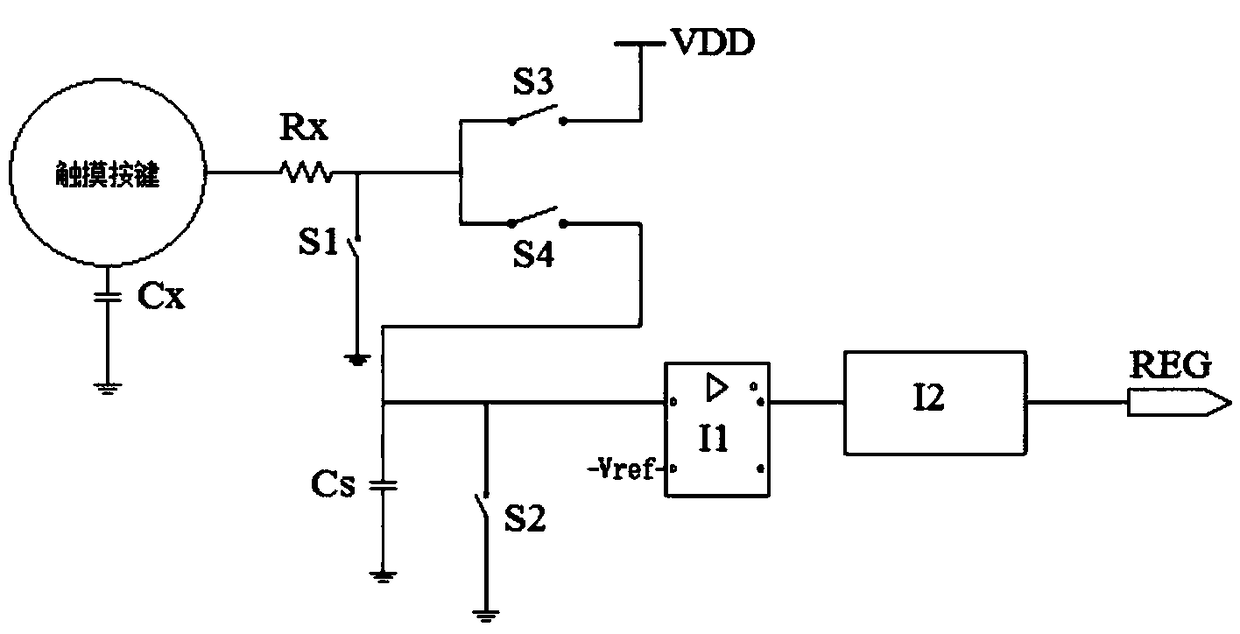
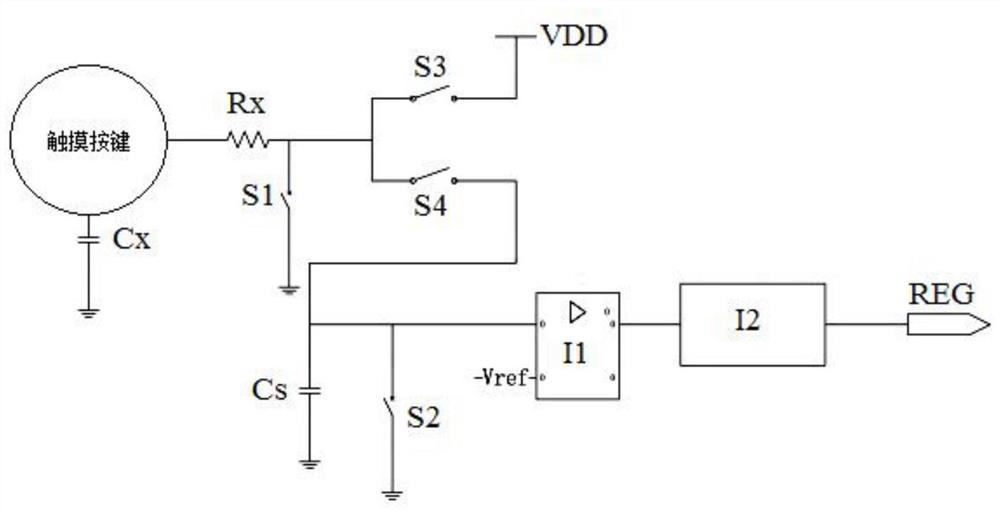
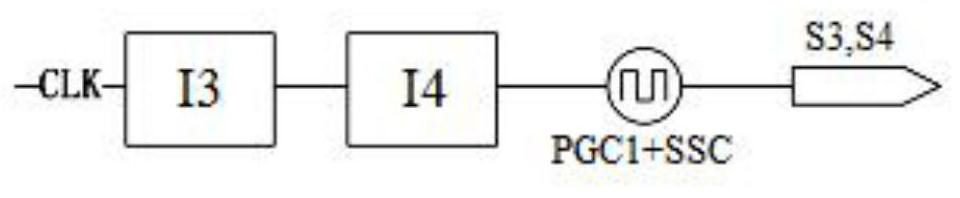
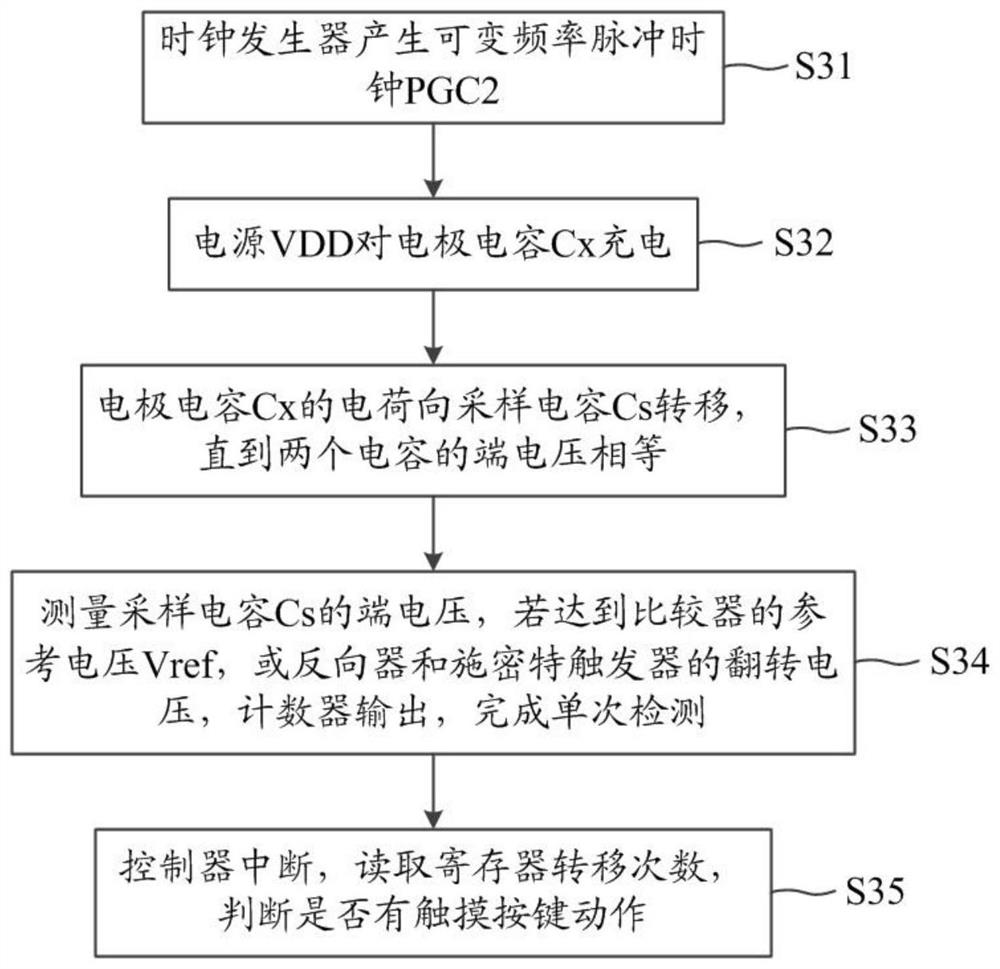
An anti-interference capacitive touch key controller and an implementation method thereof
ActiveCN109039319AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove robustnessElectronic switchingCapacitanceFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an anti-interference capacitive touch key controller and an implementation method, belonging to the technical field of touch sensing. The controller includes a touch key, electrode capacitor, sampling capacitor, antistatic resistor, electronic component, counter and register. One end of the touch key is grounded through the electrode capacitance, and the other end is connected with the first reset switch, the charge switch and the charge transfer switch through the anti-static resistance respectively. The other end of the first reset switch is grounded; The other end ofthe charge switch is connected with a power supply VDD, the other end of the charge transfer switch is connected with a sampling capacitor, a second reset switch and an electronic component. The other ends of both the sampling capacitor and the second reset switch are grounded, and the electronic components are output to the counter, which is connected to the register. Through the pulse clock with variable charging and discharging frequency, the spectrum energy is evenly distributed to a certain range of frequencies, avoiding resonance with the energy peak of high-frequency interference signal, improving the robustness of charge transfer acquisition and detection, and improving the anti-interference ability.
Owner:CHINA KEY SYST & INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Voltage generating circuit
InactiveUS7969230B2Power Loss MinimizationImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCharge transfer switchEngineering
A charge pump provides high boosting efficiency with low power loss even with a heavy load. Plural charge transfer switches are connected in series forming two lines of charge transfer circuits operated by out-of-phase clock signals. Capacitors are connected to each of nodes in the charge transfer circuits. The charge transfer circuits include a first control unit, a second control unit, and a voltage comparison output unit. The second control unit includes a switch unit configured to selectively feed a signal from a previous-stage node or a later-stage node to the gate of a charge transfer switch in the second control unit, depending on the phase of the clock signal.
Owner:RICOH ELECTRONIC DEVICES CO LTD
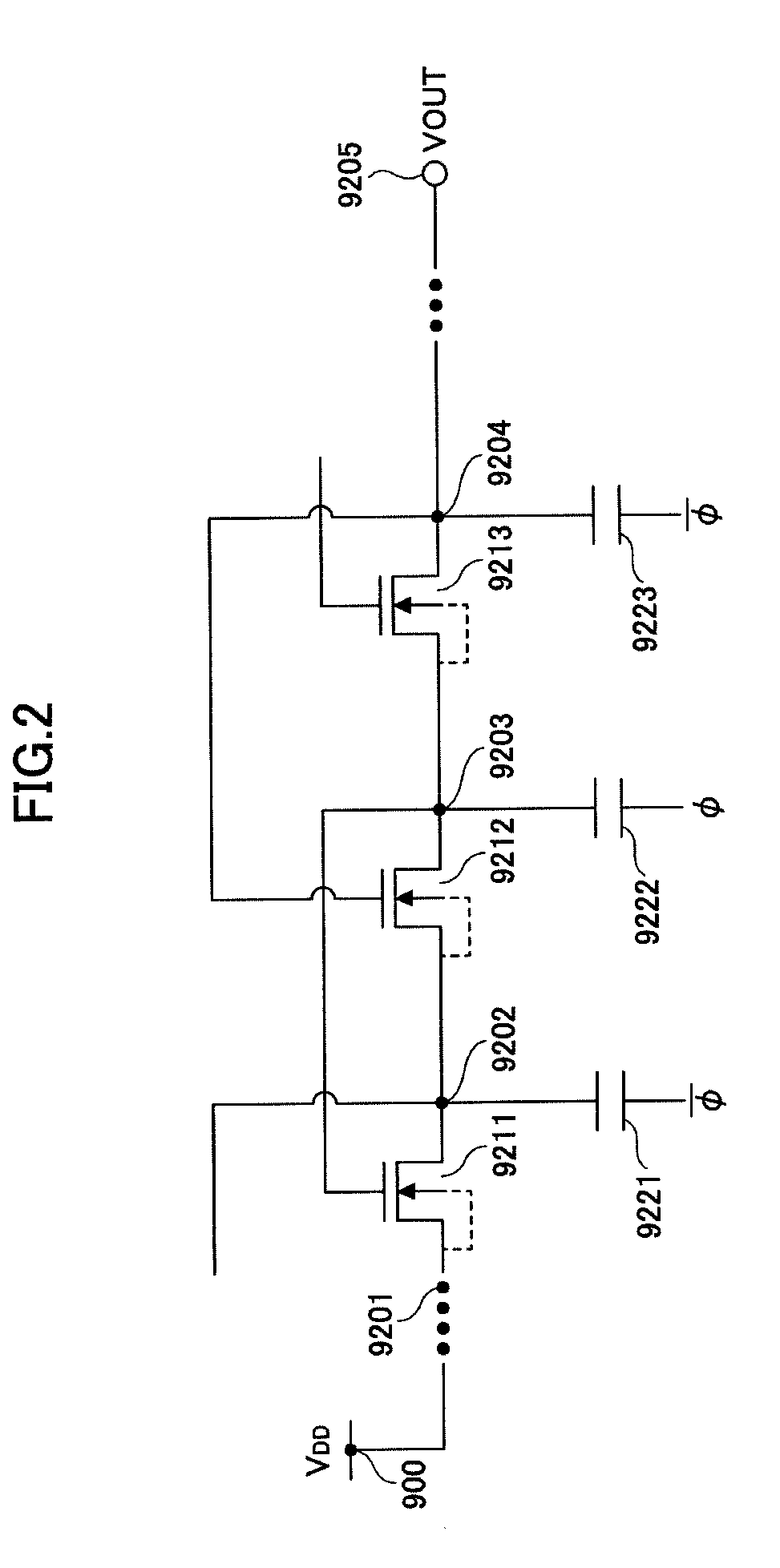
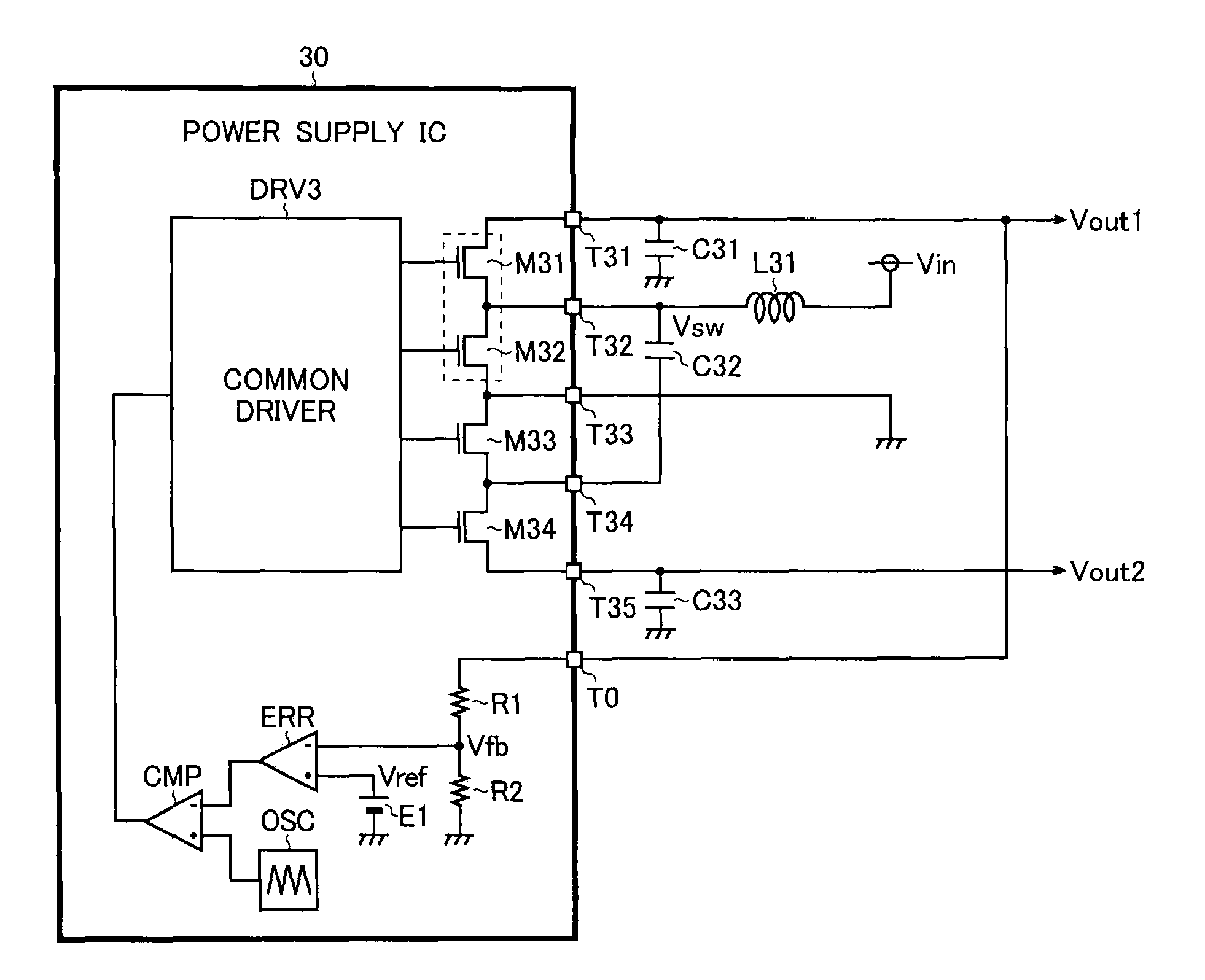
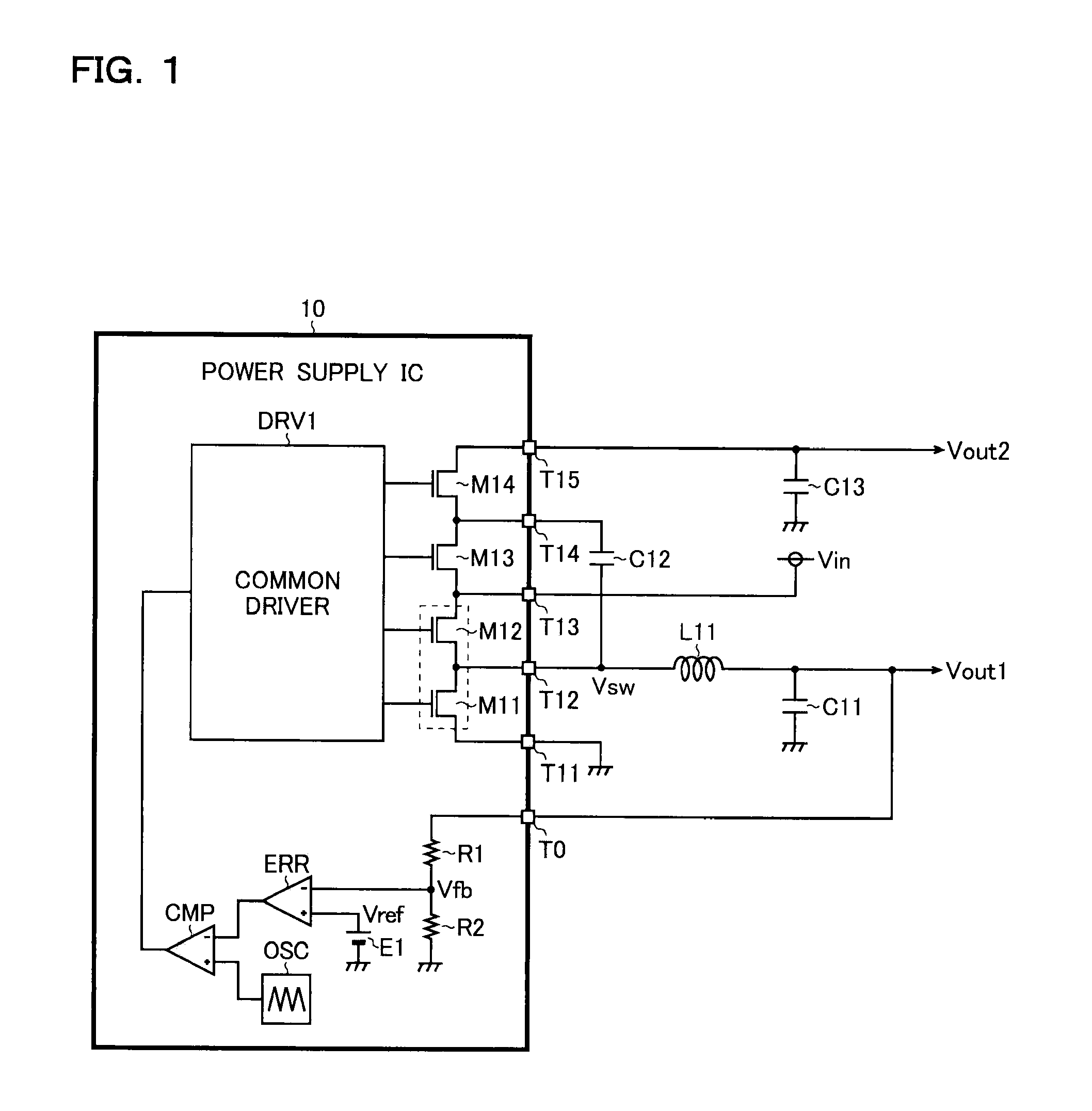
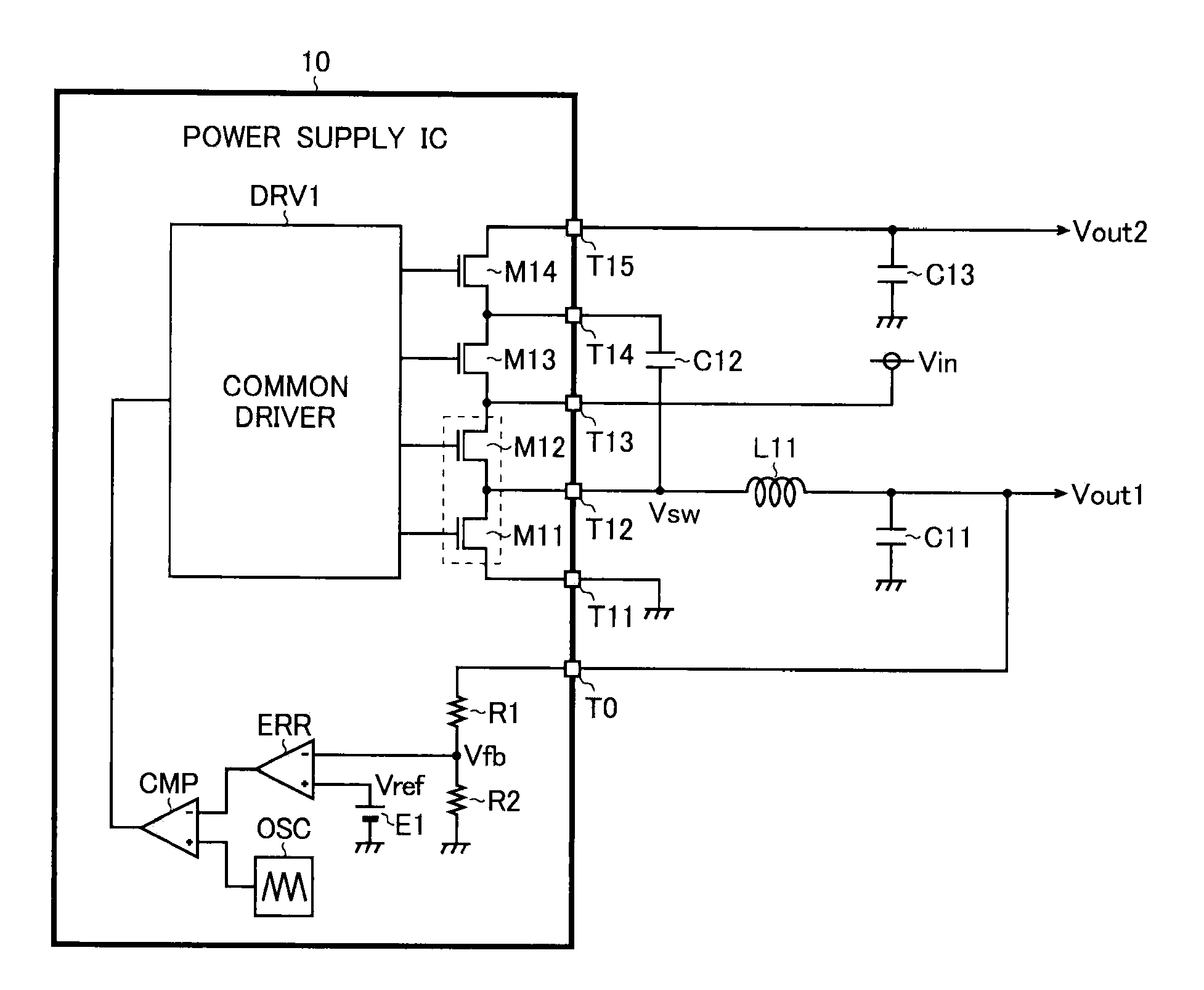
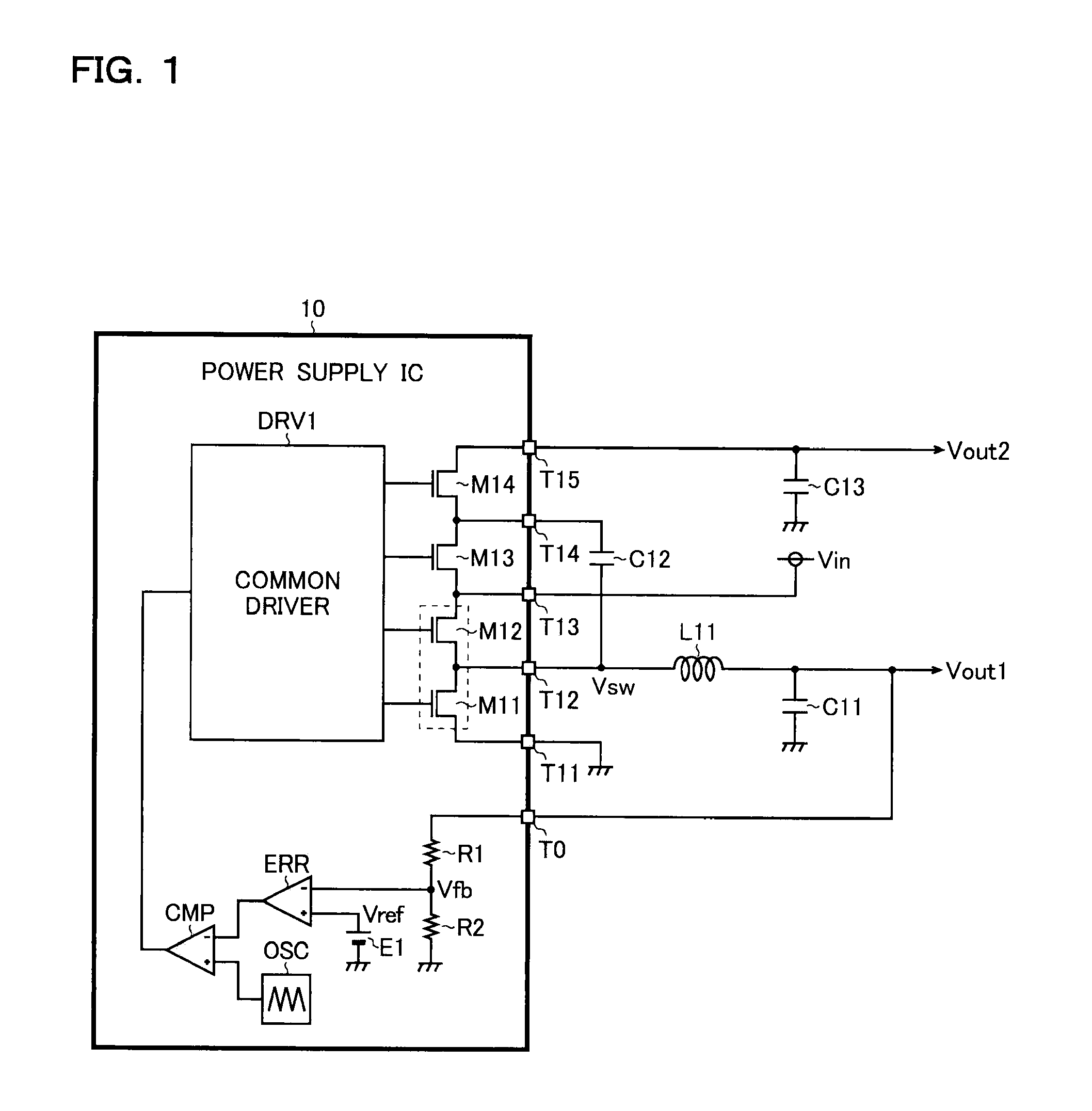
Power supply circuit and semiconductor device for use therein
ActiveUS8159089B2Increase in sizeDc network circuit arrangementsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCharge transfer switchEngineering
A power supply circuit has: a DC / DC converter (M11, M12, L11, C11) which steps down an input voltage Vin to generate an output voltage Vout1 by rectifying and smoothing a pulsing switched voltage Vsw generated by turning on and off output switches (M11 and M12); and a charge pump (M11-M14, C12, C13) which steps up the input voltage Vin to generate an output voltage Vout2 by repeating charging and discharging of a charge accumulation capacitor (C12) by turning on and off charge transfer switches (M11-M14). First end of the charge accumulation capacitor is connected to a terminal from which the switched voltage Vsw is outputted. The output switches are also used as part of the charge transfer switches.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
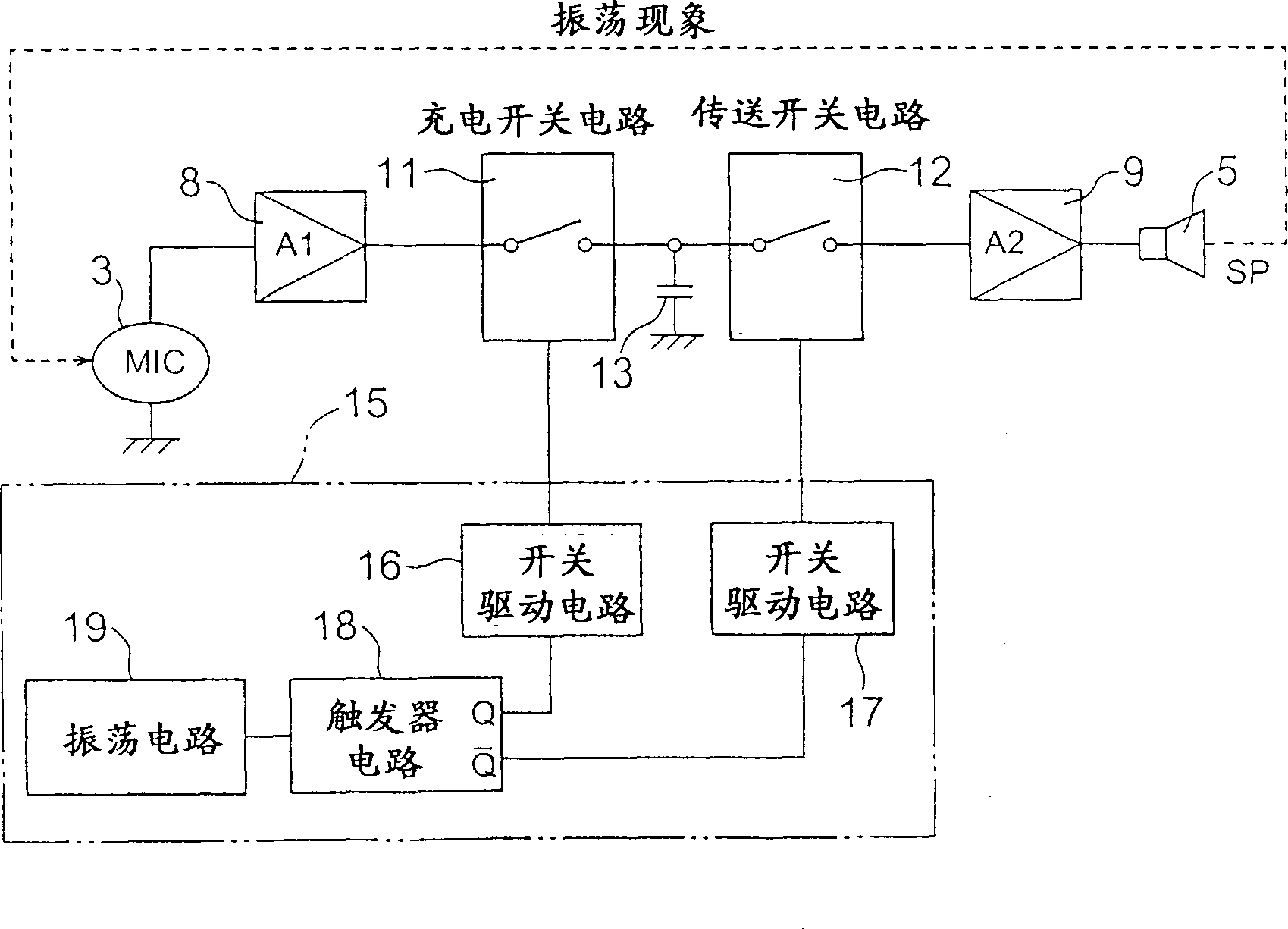
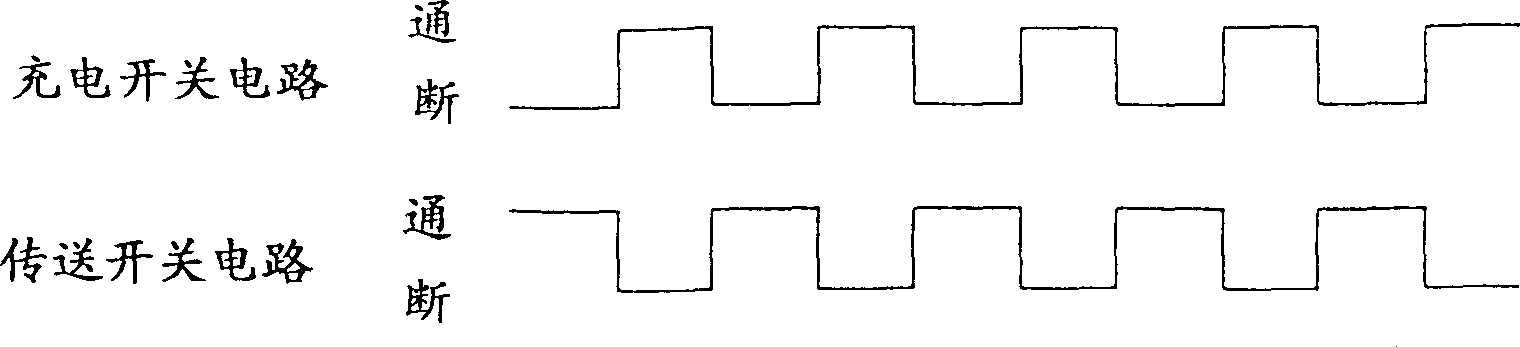
Oscillation preventing circuit
InactiveCN1387387AVolume control without limitAvoid oscillationTransducer acoustic reaction preventionLine-transmissionAudio power amplifierTransfer switch
The oscillation prevention circuit is characterized in that a charge switch circuit and a transmission switch circuit are connected in series between the first amplifier circuit and the second amplifier circuit; The switch circuit is turned "off", and the charging switch circuit is turned "off" when the transfer switch circuit is "on", so as to prevent both switch circuits from being turned "on" at the same time.
Owner:FUKUOKA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
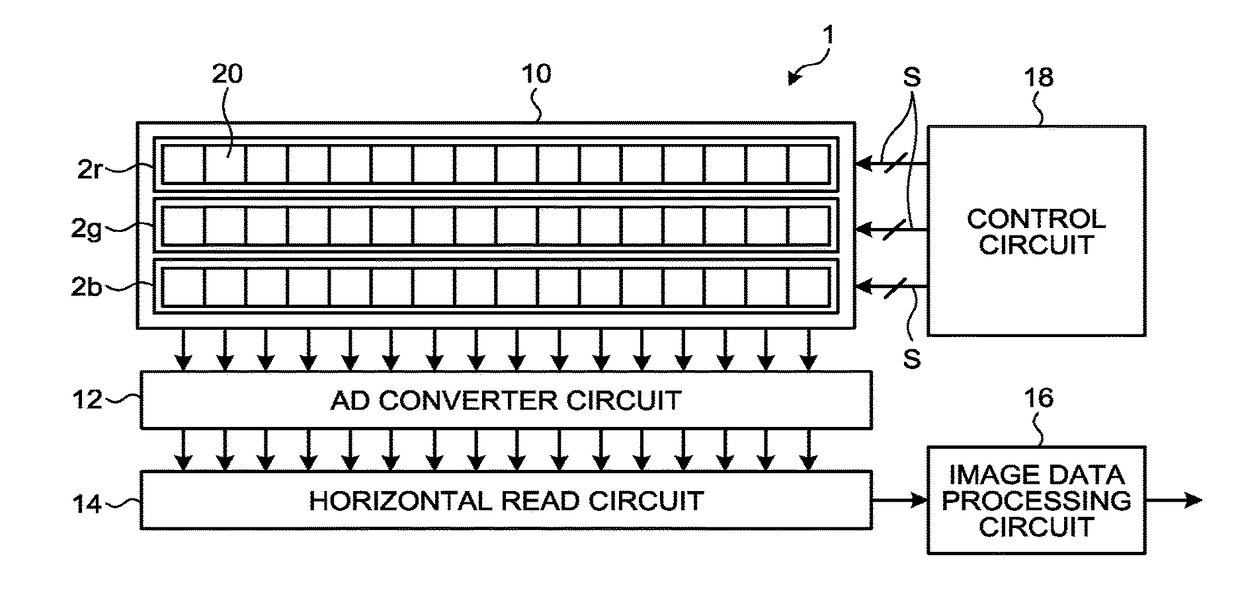
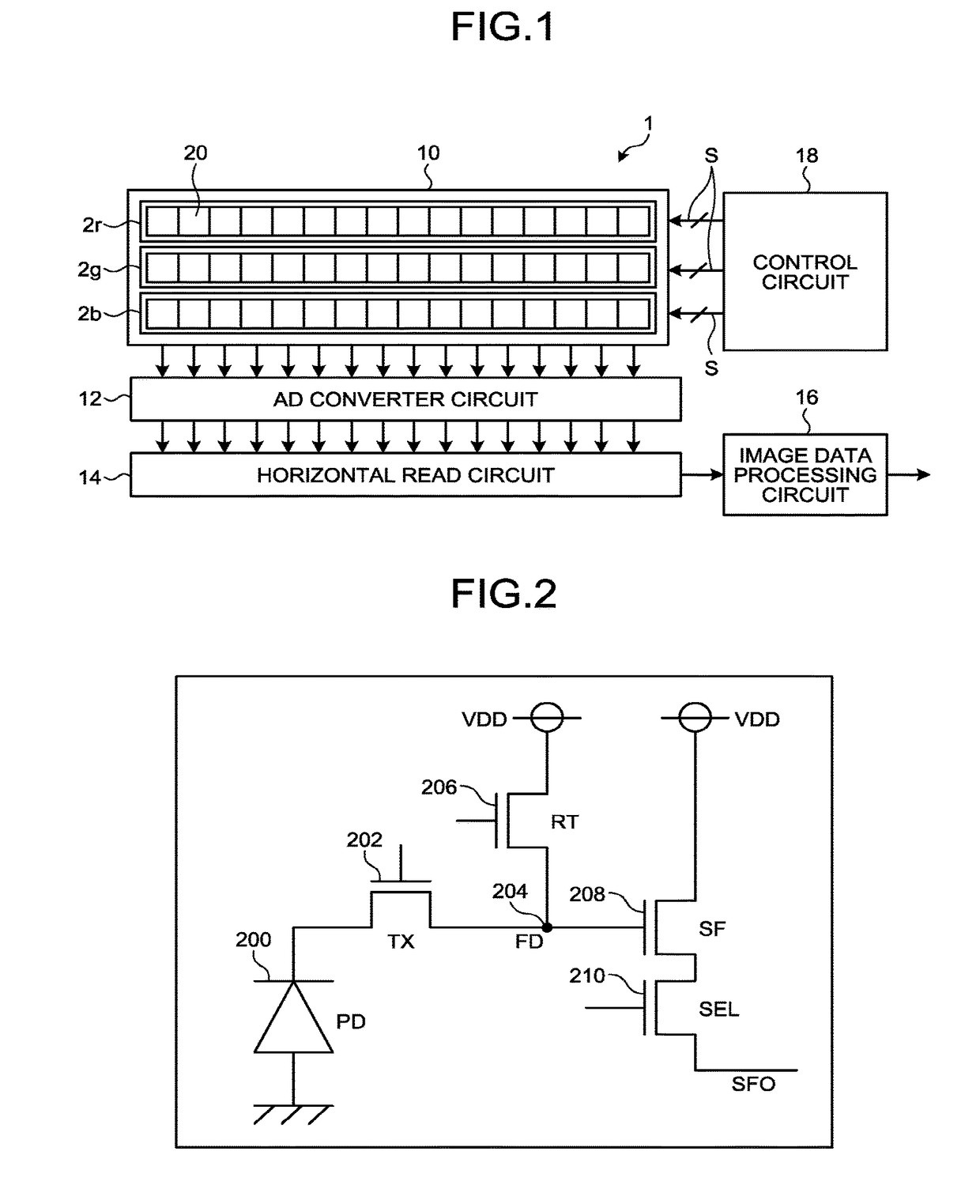
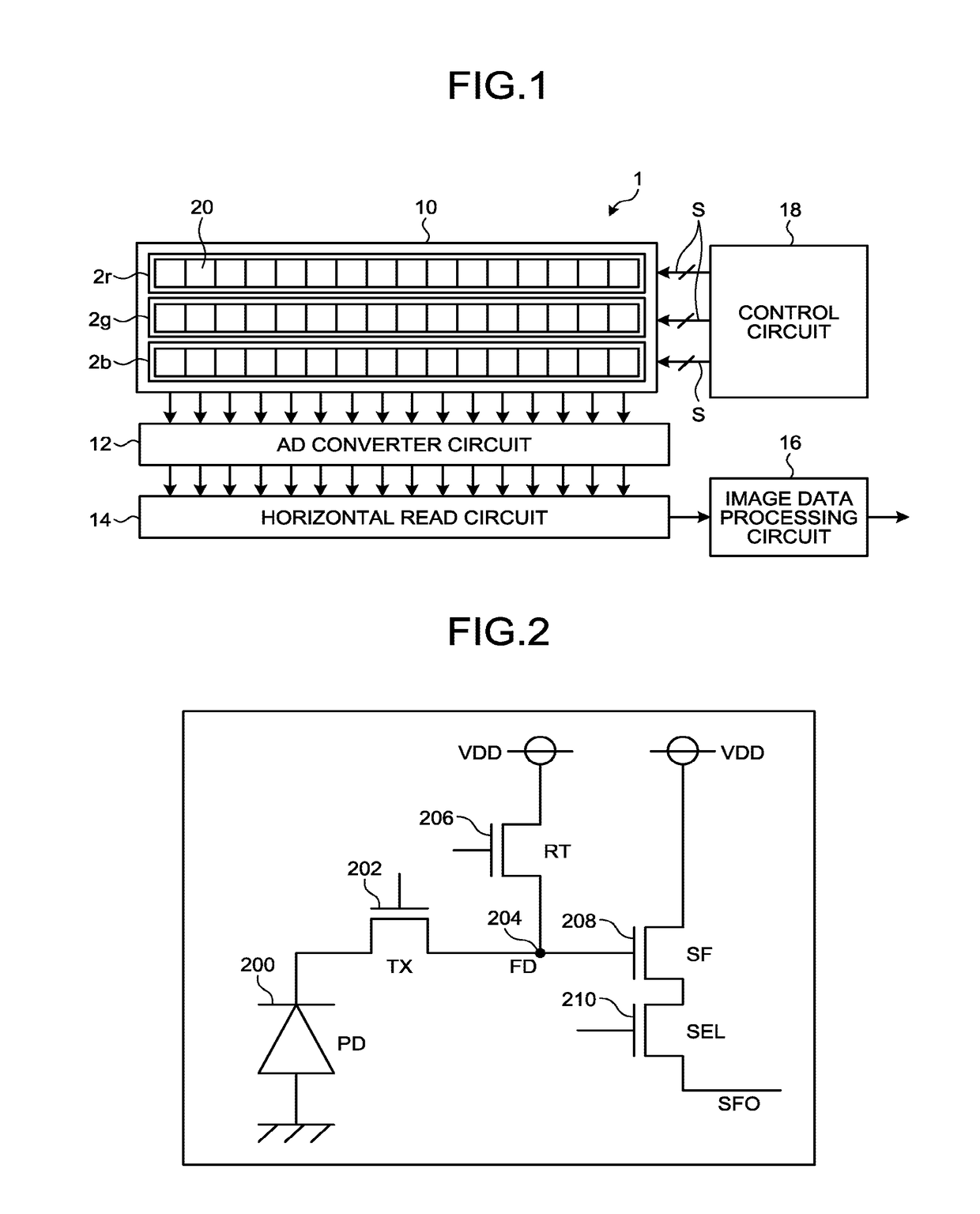
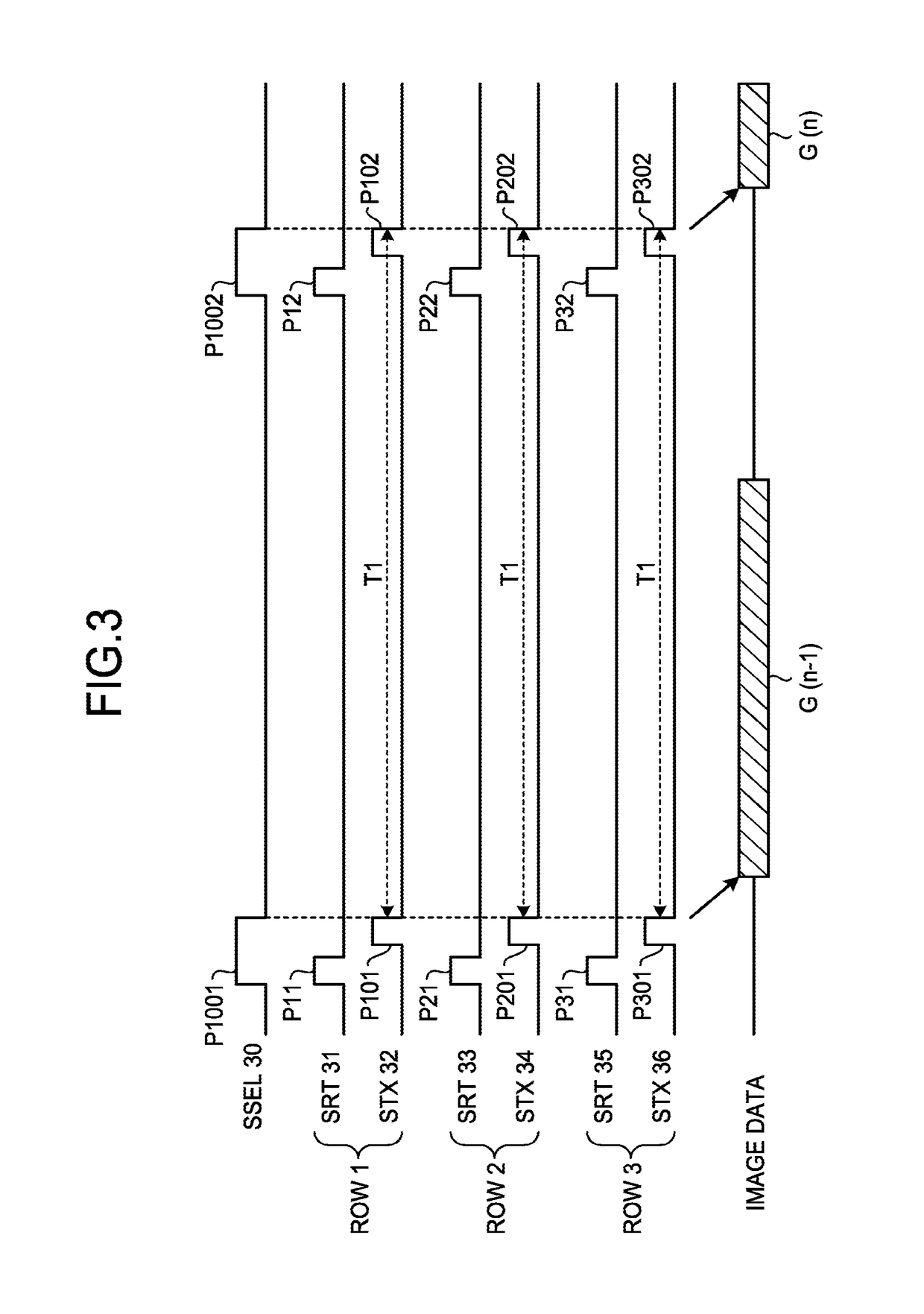
Imaging device
ActiveUS20170256580A1Television system detailsSolid-state devicesCharge transfer switchData acquisition
An imaging device includes a plurality of arranged imaging elements each including: a light-receiving element configured to generate charge from received light by photoelectric conversion, a floating diffusion configured to convert the charge generated by the light-receiving element into voltage, a charge transfer switch configured to transfer the charge from the light-receiving element to the floating diffusion, a reset switch configured to reset the voltage of the floating diffusion, and a source follower configured to amplify the voltage of the floating diffusion. The reset switch is configured to reset the voltage of the floating diffusion a plurality of times for each of predetermined pixel groups in a single image data acquisition period. The charge transfer switch is configured to transfer the charge from the light-receiving element to the floating diffusion a plurality of times for each of the pixel groups in the single image data acquisition period.
Owner:RICOH KK
Power supply circuit and semiconductor device for use therein
ActiveUS20100176784A1Increase in chip sizeIncrease costDc network circuit arrangementsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCharge transfer switchEngineering
A power supply circuit has: a DC / DC converter (M11, M12, L11, C11) which steps down an input voltage Vin to generate an output voltage Vout1 by rectifying and smoothing a pulsing switched voltage Vsw generated by turning on and off output switches (M11 and M12); and a charge pump (M11-M14, C12, C13) which steps up the input voltage Vin to generate an output voltage Vout2 by repeating charging and discharging of a charge accumulation capacitor (C12) by turning on and off charge transfer switches (M11-M14). First end of the charge accumulation capacitor is connected to a terminal from which the switched voltage Vsw is outputted. The output switches are also used as part of the charge transfer switches.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
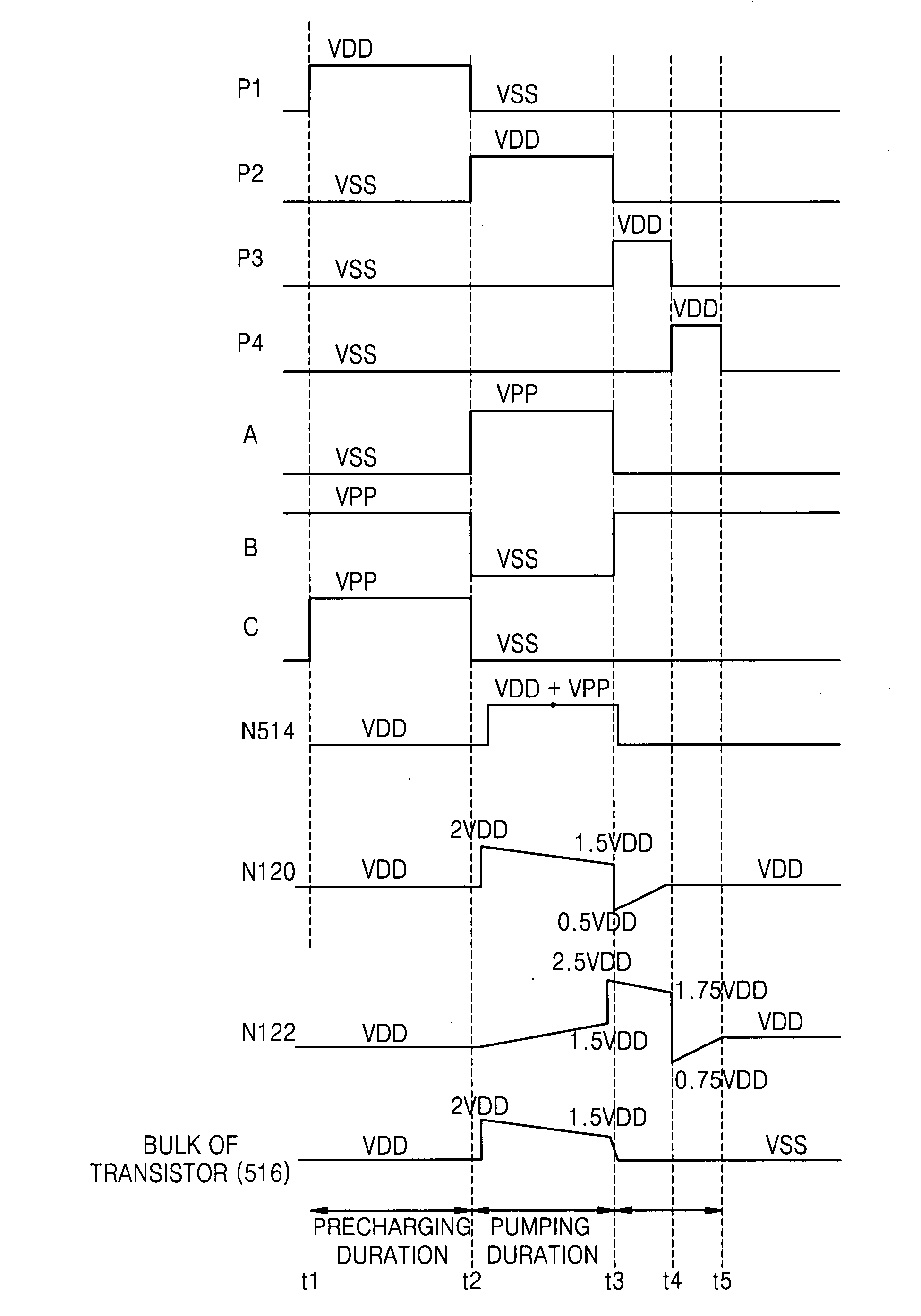
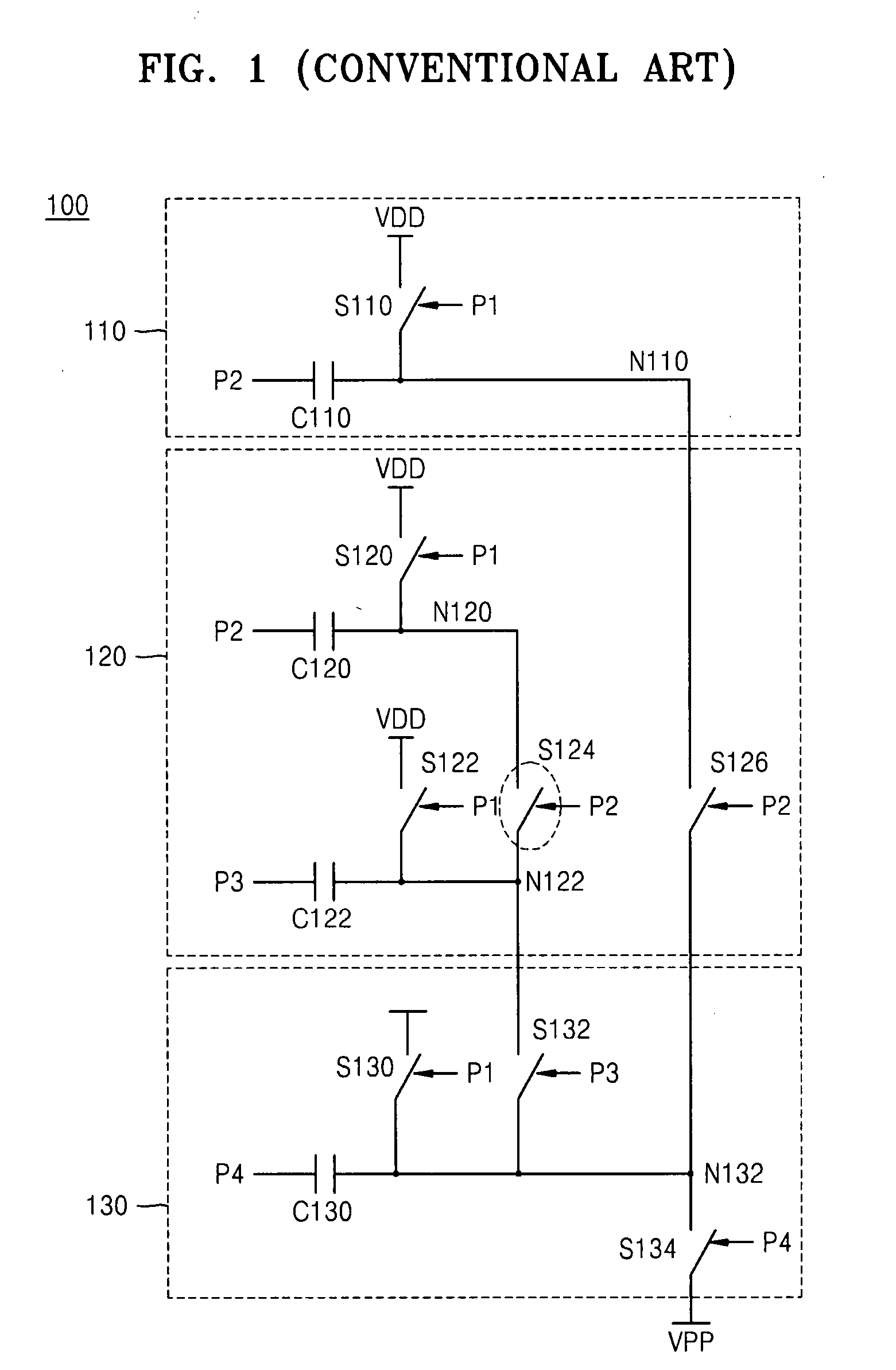
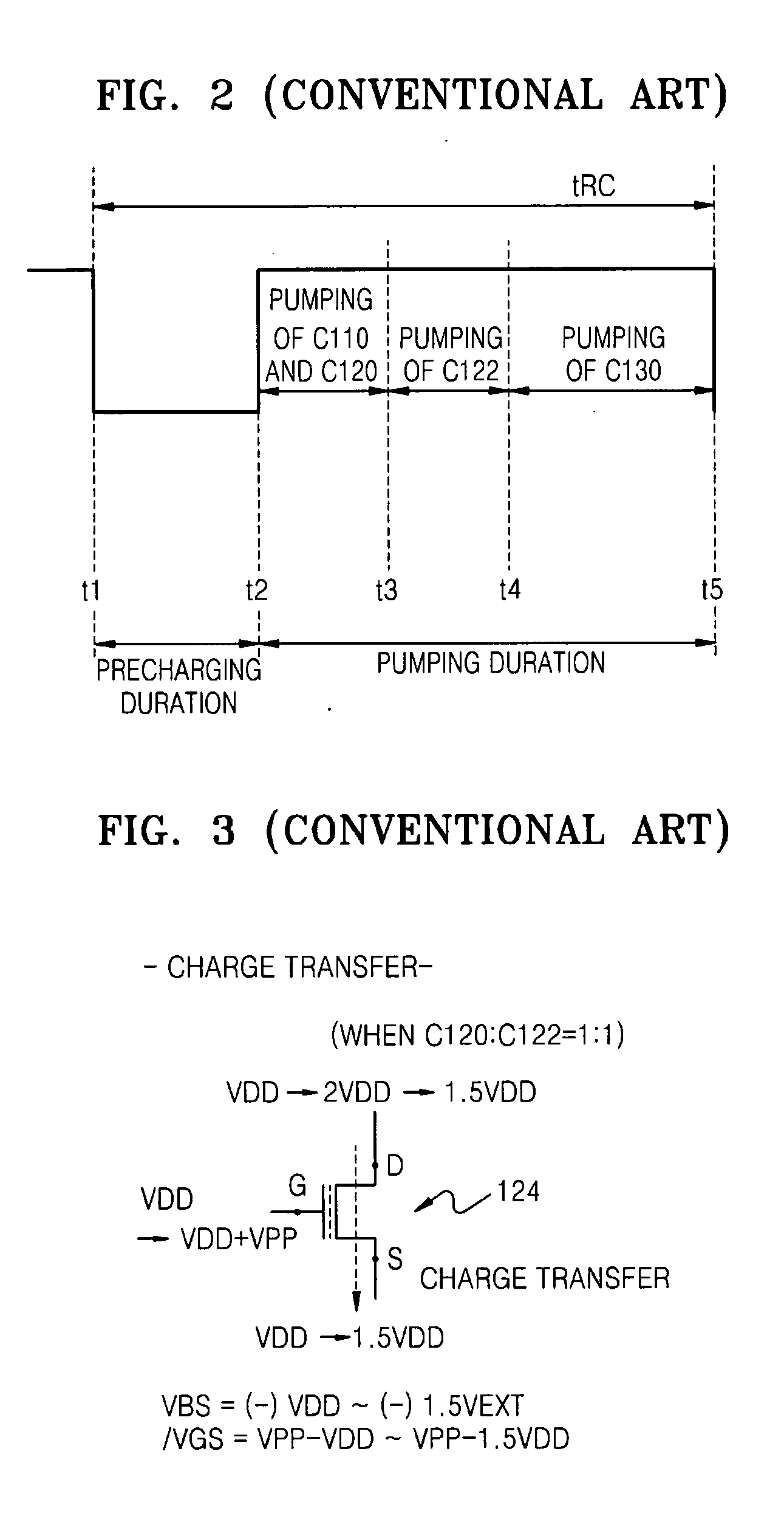
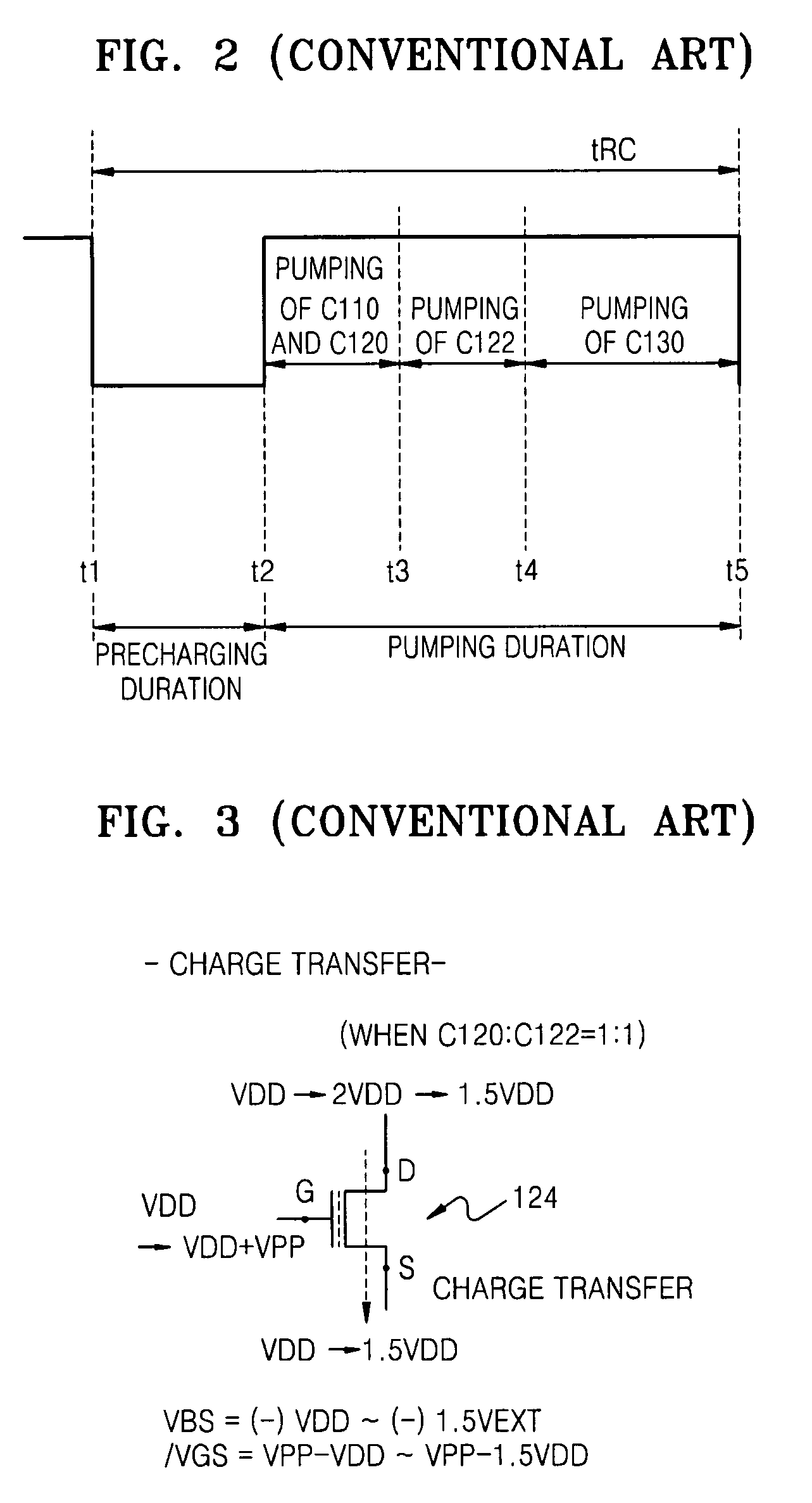
High-voltage generating circuit including charge transfer switching circuit for selectively controlling body bias voltage of charge transfer device
ActiveUS20070286007A1Improve charge transfer efficiencyReducing and preventing backflowElectronic switchingDigital storageControl signalCharge transfer switch
Provided are a charge transfer switch circuit for selectively controlling body bias voltage of a charge transfer device, and a boosted voltage generating circuit having the same. The charge transfer switch circuit may include a capacitor whose voltage is boosted based on first and second control signals, a first transistor connected between a supply voltage and the capacitor and having a gate receiving a precharge signal, a second transistor connected between a first node and a second node and having a gate connected to a terminal of the capacitor, a third transistor connected between the first node and a bulk voltage of the second transistor and having a gate receiving the first control signal, and a fourth transistor connected between the bulk voltage of the second transistor and a ground voltage and having a gate receiving the second control signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
An anti-interference capacitive touch button controller and its realization method
ActiveCN109039319BImprove anti-interference abilityImprove robustnessElectronic switchingCapacitanceFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an anti-interference capacitive touch button controller and a realization method, belonging to the technical field of touch sensing. The controller includes touch keys, electrode capacitors, sampling capacitors, antistatic resistors, electronic components, counters and registers. One end of the touch button is grounded through the electrode capacitance, and the other end is connected to the first reset switch, charging switch, and charge transfer switch through an antistatic resistor; the other end of the first reset switch is grounded; the other end of the charging switch is connected to the power supply VDD, and the charge transfer switch is connected to the other One end is connected to the sampling capacitor, the second reset switch and electronic components; the other end of the sampling capacitor and the second reset switch are both grounded, the electronic components are output to the counter, and the counter is connected to the register. Through the pulse clock with variable charge and discharge frequency, the spectrum energy during touch is evenly distributed within a certain range of frequencies, avoiding resonance with the energy peak of high-frequency interference signals, improving the robustness of charge migration acquisition and detection, and improving the anti-interference ability.
Owner:CHINA KEY SYST & INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Imaging device
An imaging device includes a plurality of arranged imaging elements each including: a light-receiving element configured to generate charge from received light by photoelectric conversion, a floating diffusion configured to convert the charge generated by the light-receiving element into voltage, a charge transfer switch configured to transfer the charge from the light-receiving element to the floating diffusion, a reset switch configured to reset the voltage of the floating diffusion, and a source follower configured to amplify the voltage of the floating diffusion. The reset switch is configured to reset the voltage of the floating diffusion a plurality of times for each of predetermined pixel groups in a single image data acquisition period. The charge transfer switch is configured to transfer the charge from the light-receiving element to the floating diffusion a plurality of times for each of the pixel groups in the single image data acquisition period.
Owner:RICOH KK
Charge transfer circuit suitable for common CMOS process and charge transfer control switch thereof
ActiveCN101977056BPrecise addition and subtractionPrecise control of charge sizeAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitanceCharge transfer switch
The invention provides a high-precision charge addition-subtraction transfer circuit suitable for a common CMOS process and a charge transfer control switch thereof. The charge addition-subtraction transfer circuit comprises a charge transfer switch, a first charge storage node, a first charge storage capacitor, a second charge storage node, a second charge storage capacitor and a third storage capacitor, wherein the first charge storage capacitor is connected to the first charge storage node, and the second charge storage capacitor and the third charge storage capacitor are connected to the second charge storage node. The charge addition-subtraction transfer circuit can realize accurate charge addition-subtraction operation and accurately control the quantity of transferred charge, and can be widely used in charge coupled secondary flowing water circuit at all levels in a charge coupled pipeline AD converter.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
A charge-transfer analog counting readout circuit based on pulse rising edge trigger
ActiveCN107425847BHigh resolutionReduce areaCounting chain pulse counters using opto-electronic devicesCounting chain pulse counters using semiconductor devices with 2 electrodesMOSFETParasitic capacitor
The invention discloses a charge transfer type analog count reading circuit based on pulse rising edge triggering. The circuit comprises 13 MOSFET transistors, an integral capacitor and a parasitic capacitor. The MP1 and MP2 are a charge injection switch and a charge transfer switch and are used for controlling generation and transfer of a charge packet. The parasitic capacitor Cgd bridged between a gate and a drain of the MP1 couples an input avalanche pulse signal into the drain of the MP1. The MP4 and MN1 form a reset circuit which is used for discharging charges stored by the integral capacitor. The MP6, MP7, MP8, MN2, MN3 and MN4 form a unit gain amplifier which is used for preventing a voltage of the integral capacitor from being influenced by electric leakage of the MOSFET transistor connected with the integral capacitor C. The MP3 is a source follower transistor. The MP5 is a load. The MP9 is a lien selection transistor. The voltage on the integral capacitor C is read to an external circuit through the MP3 and the MP9. According to the analog count reading circuit, a wide count range can be realized, moreover, an area of SPAD array detector pixel units can be reduced, and the density of an SPAD array detector is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Analog front end detection circuit used for giant magneto-resistive (GMR) biosensor
ActiveCN102339084BAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceVoltage source
The invention relates to an analog front end detection circuit used for a giant magneto-resistive (GMR) biosensor. The circuit comprises a bandgap reference voltage source, a sensor voltage generating circuit, a 5bit reference voltage generating circuit, a charge transfer switched capacitor sampling / holding circuit and a pipelined analog-to-digital converter. The analog front end detection circuit has the following beneficial effects: the methods of single chip total integration and voltage detection are adopted, thus effectively extracting the weak voltage signals in the GMR biosensor; the charge transfer switched capacitor sampling / holding circuit is utilized to sample the detection voltage of the resistor array of the GMR biosensor and reasonably amplify the detection voltage to the input voltage range of the analog-to-digital converter; and finally, the analog-to-digital converter is used for outputting the digital detection results.
Owner:中科芯未来微电子科技成都有限公司
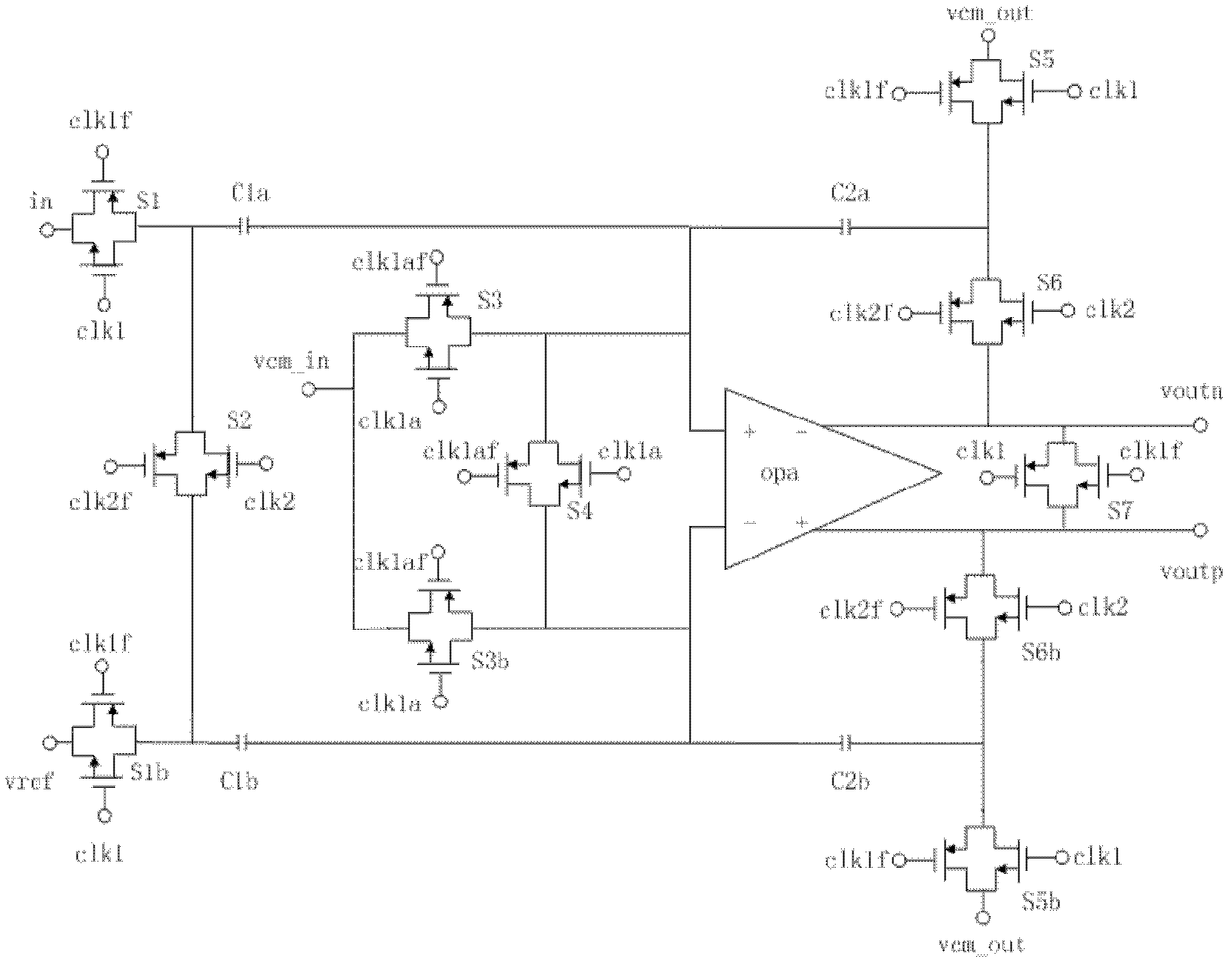
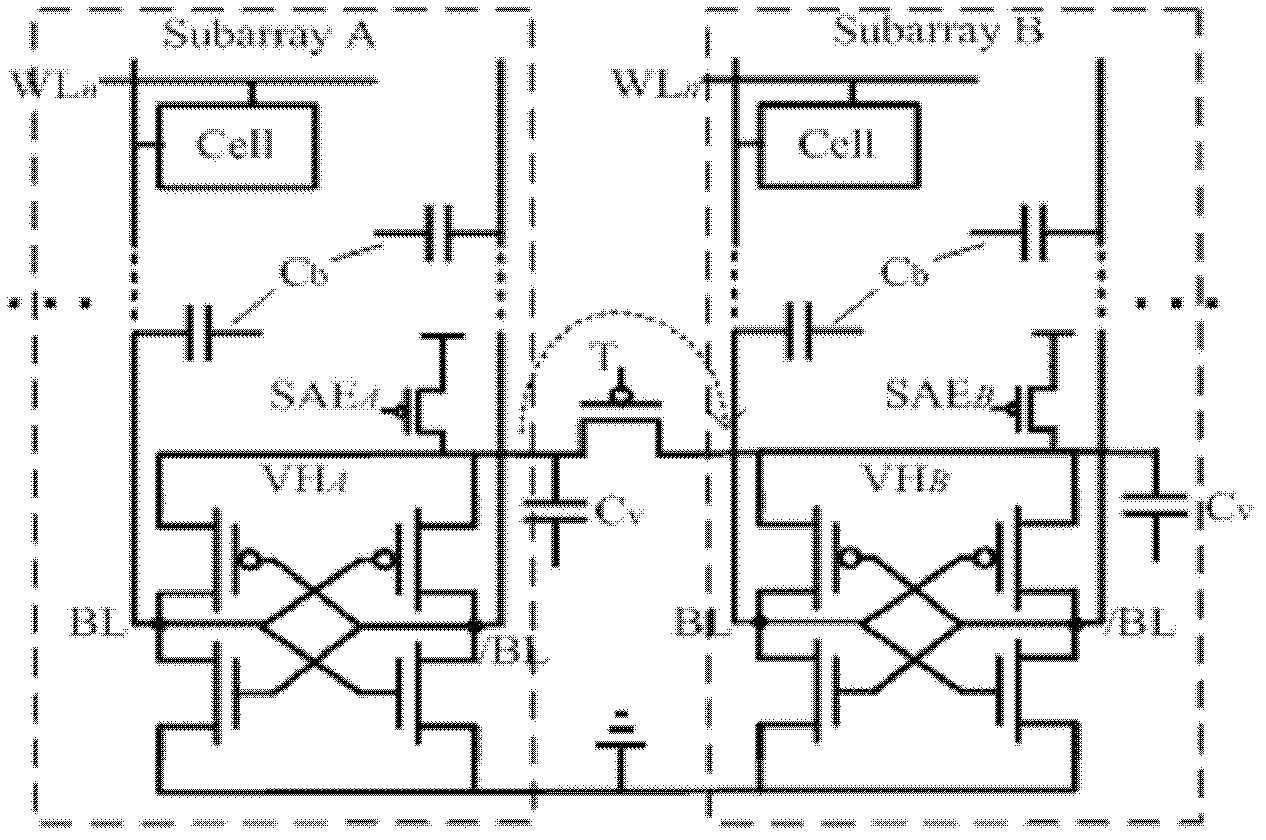
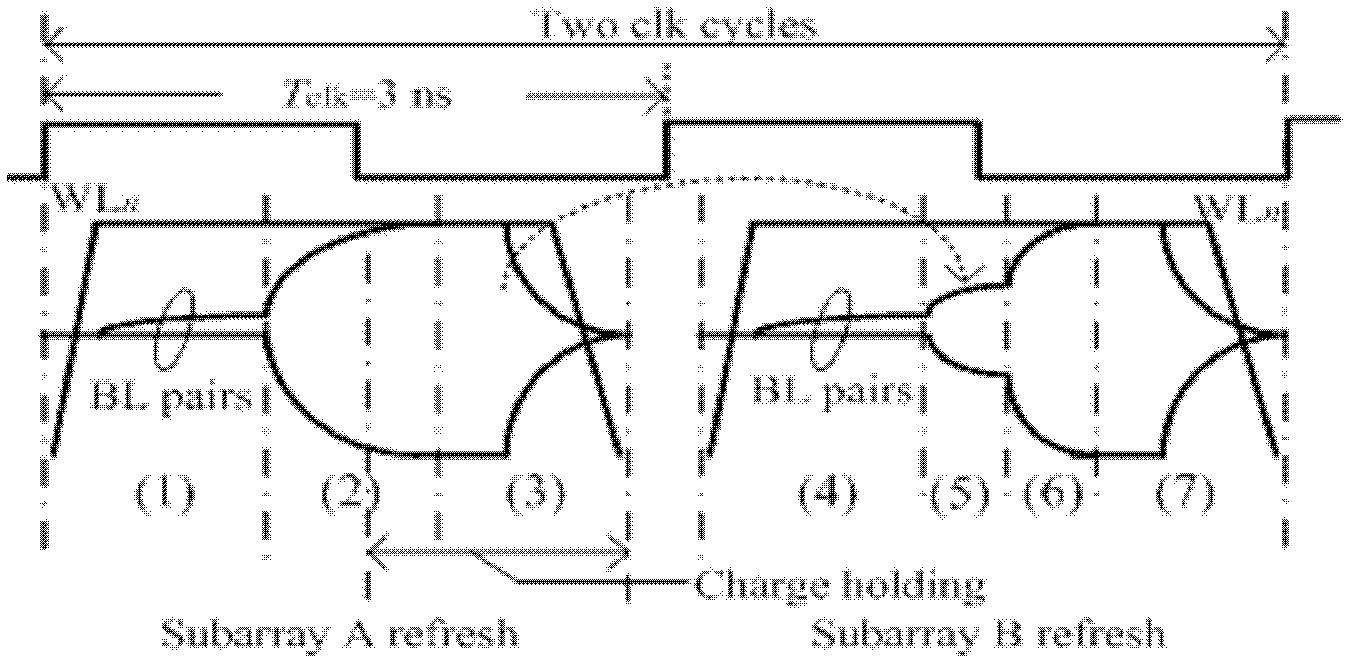
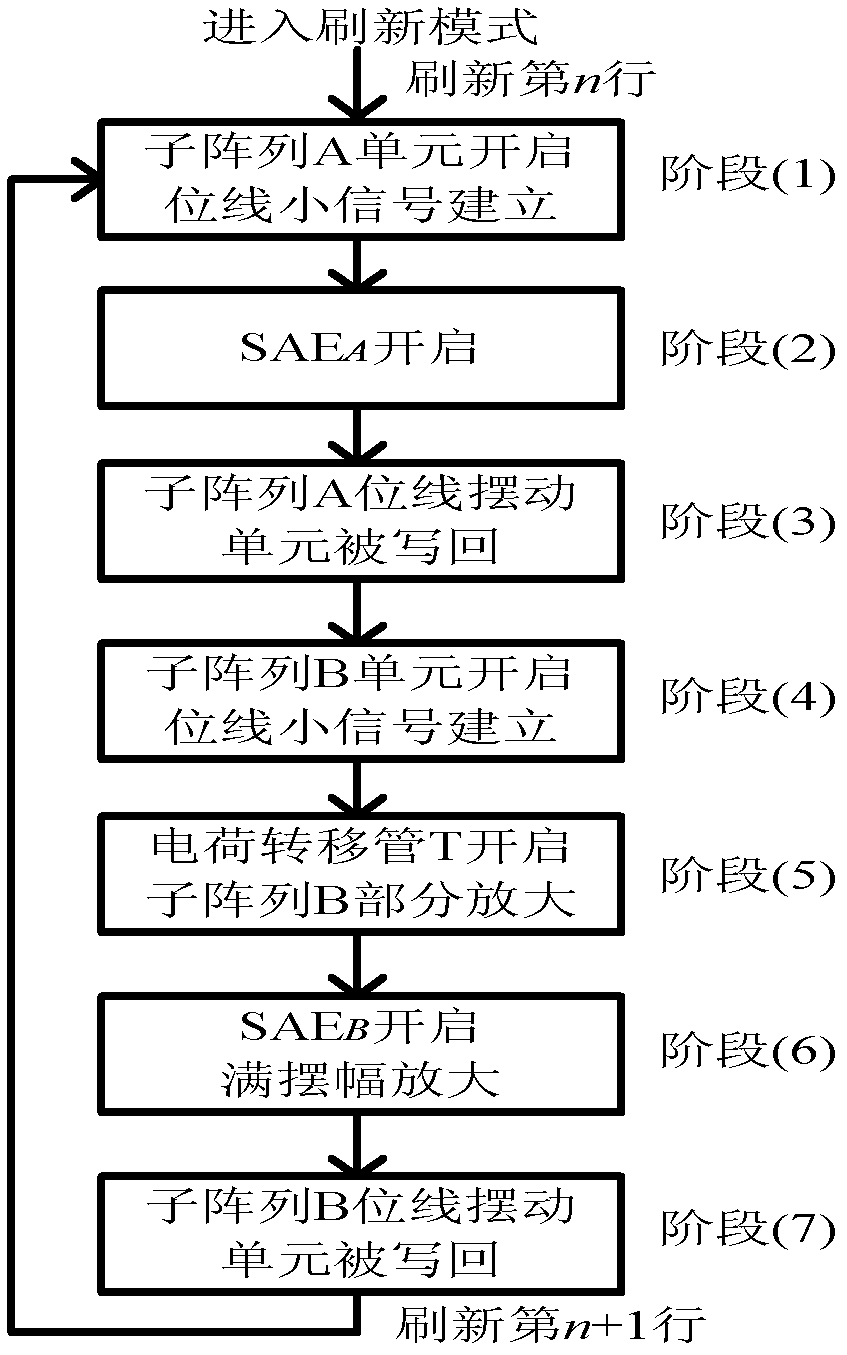
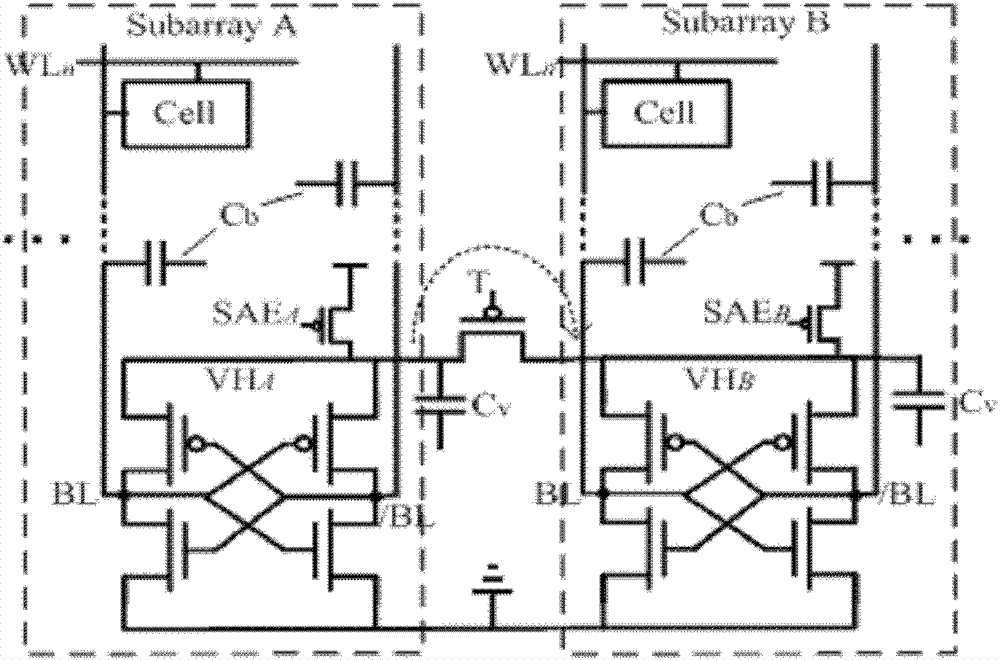
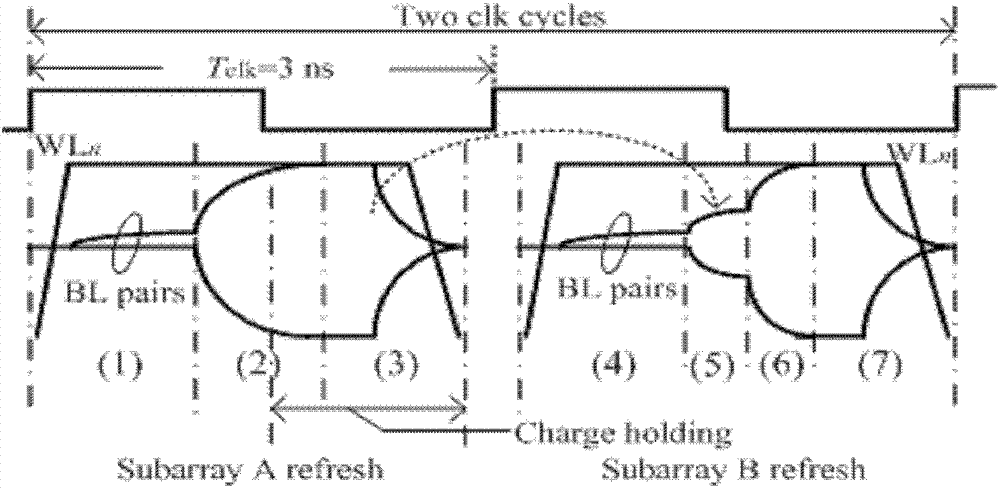
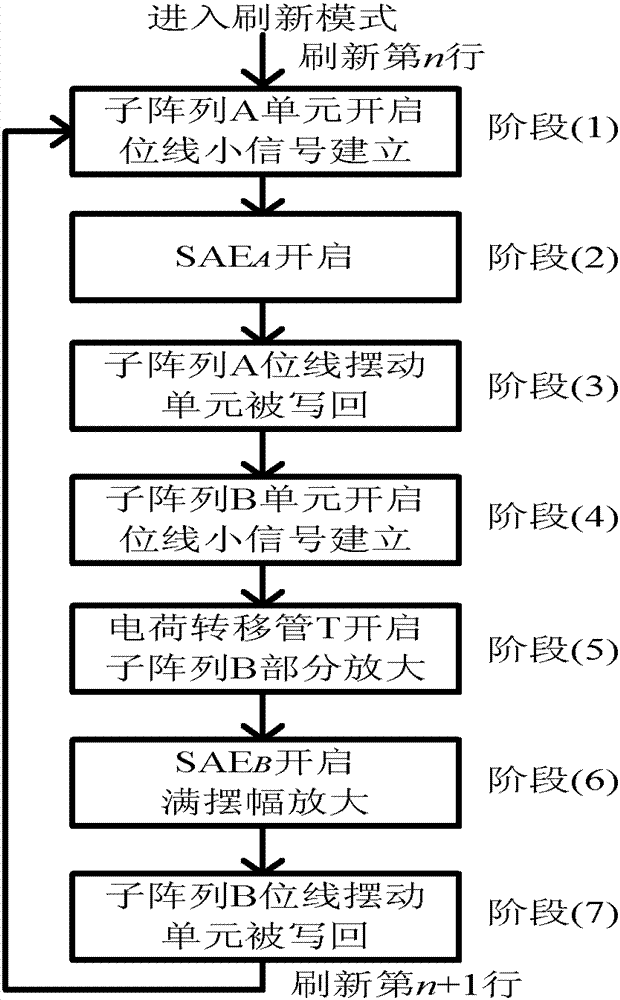
Compact charge transfer refresh circuit and refresh method thereof
ActiveCN103021450ARefresh steps compactly overlapSave refresh power consumptionDigital storageAudio power amplifierCharge transfer switch
The invention belongs to the technical field of memories and especially relates to a compact charge transfer refresh circuit and a refresh method thereof. The compact charge transfer refresh circuit comprises an array of M*N. The array is divided into t subarrays of M*(N / t) in a row direction. The serial numbers of the subarrays are in a range of 1 to n. Virtual power ends VHn of sense amplifiers of the subarrays are connected. Virtual power ends VHn between the subarrays are connected by charge transfer switches Tn. M, N, n and t represent natural numbers. The virtual power ends of the sense amplifiers of the subarrays are connected and VHn represents the virtual power ends. The virtual power ends VHn between the subarrays are connected by the charge transfer switches Tn. The compact charge transfer refresh circuit reduces refresh power consumption, obviously reduces refresh time, has a simple control circuit and has no additional area cost.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Compact Charge Transfer Refresh Circuit and Refresh Method
ActiveCN103021450BRefresh steps compactly overlapSave refresh power consumptionDigital storageSoftware engineeringCharge transfer switch
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
High-voltage generating circuit including charge transfer switching circuit for selectively controlling body bias voltage of charge transfer device
ActiveUS7492213B2Improve charge transfer efficiencyReducing and preventing backflowElectronic switchingDigital storageControl signalCharge transfer switch
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com