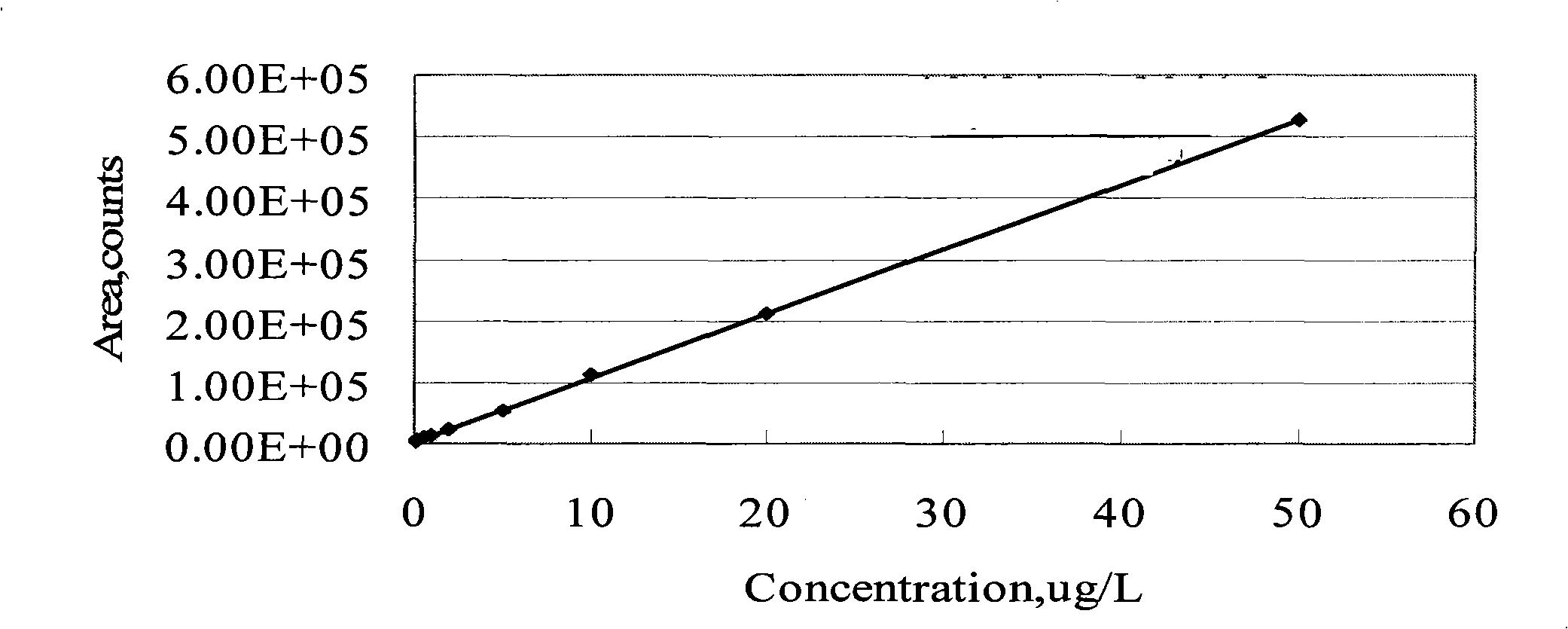
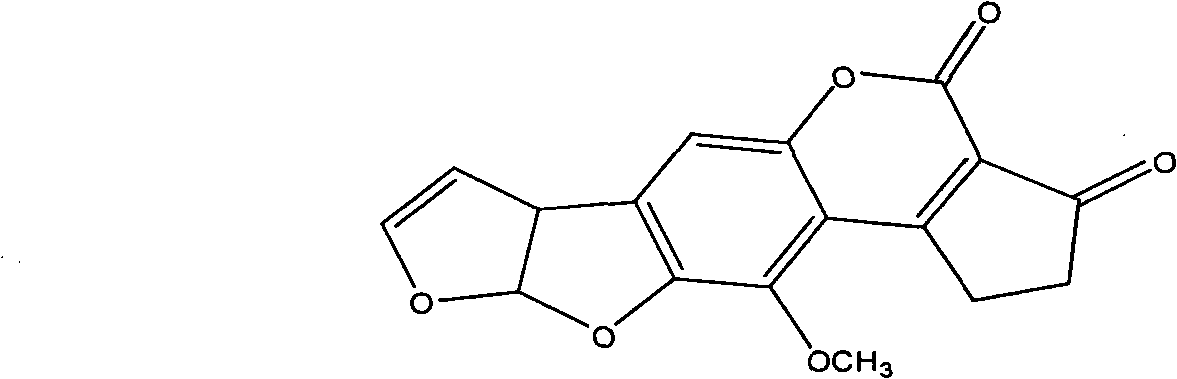
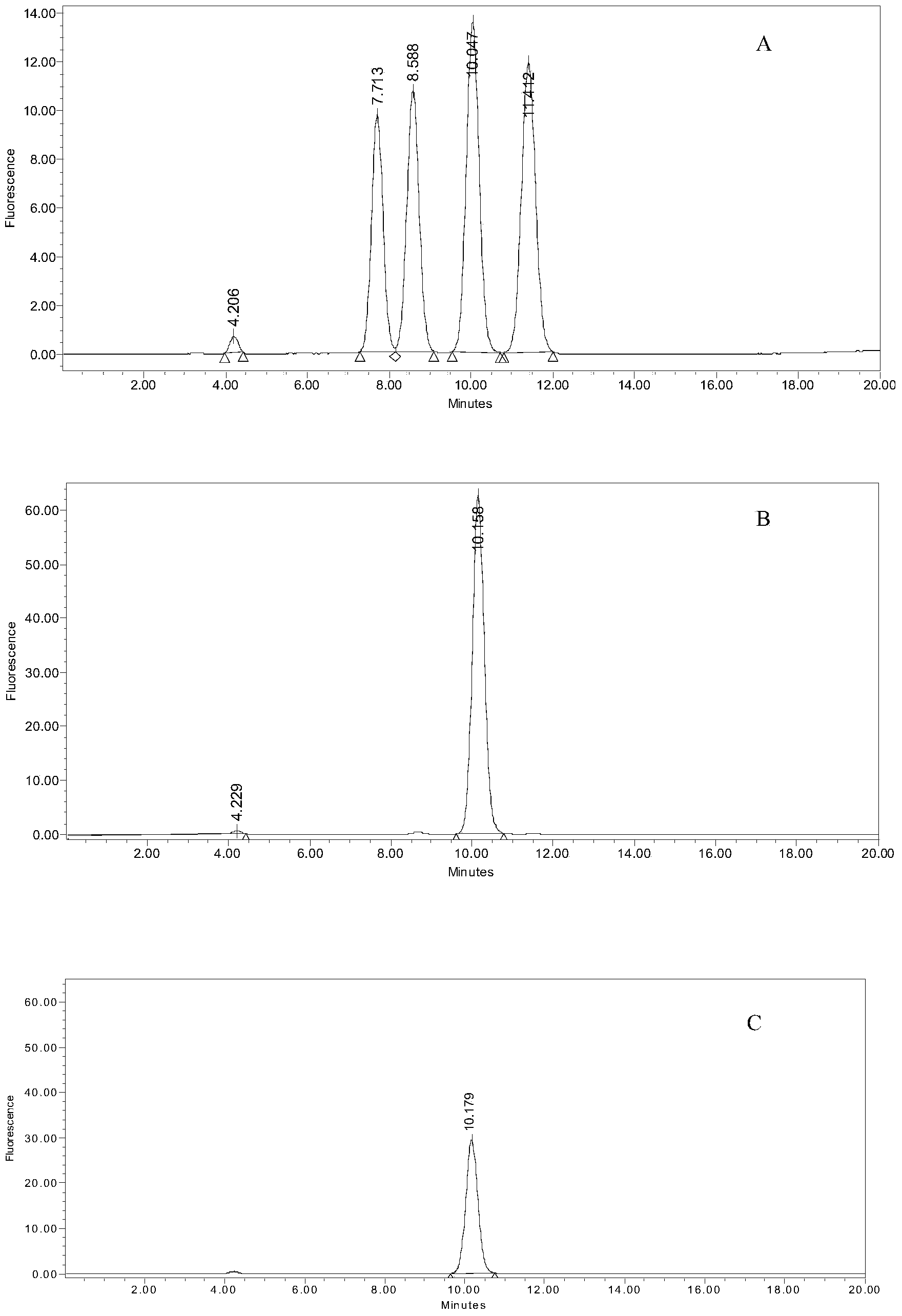
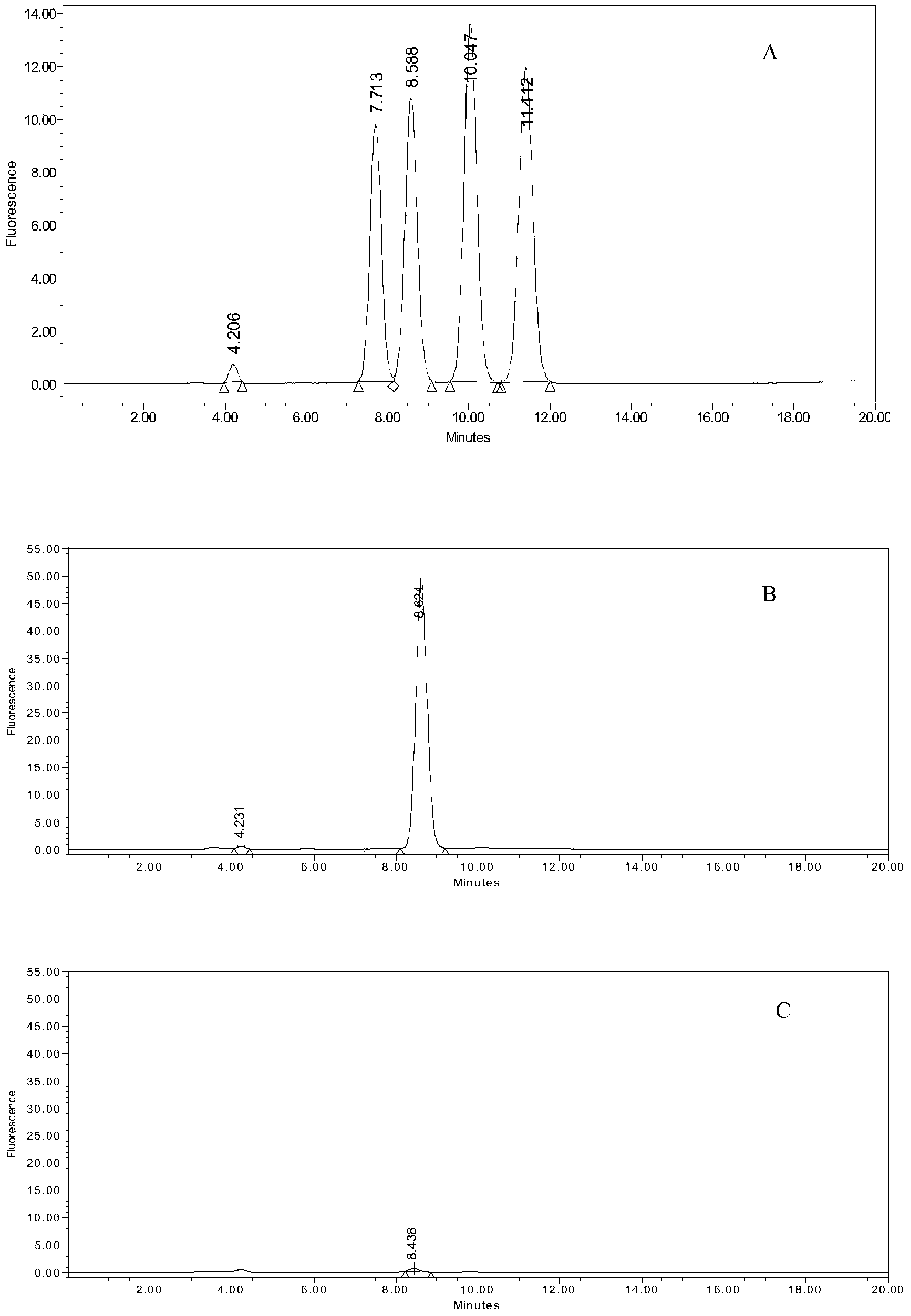
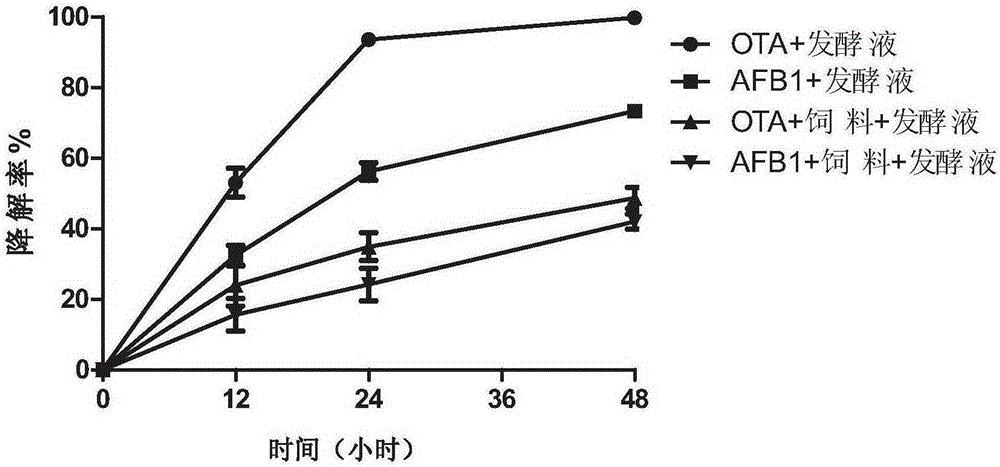
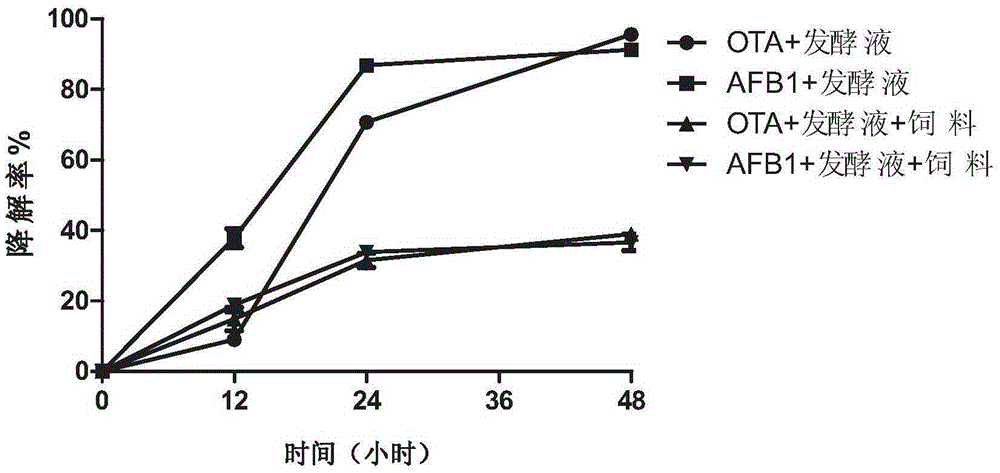
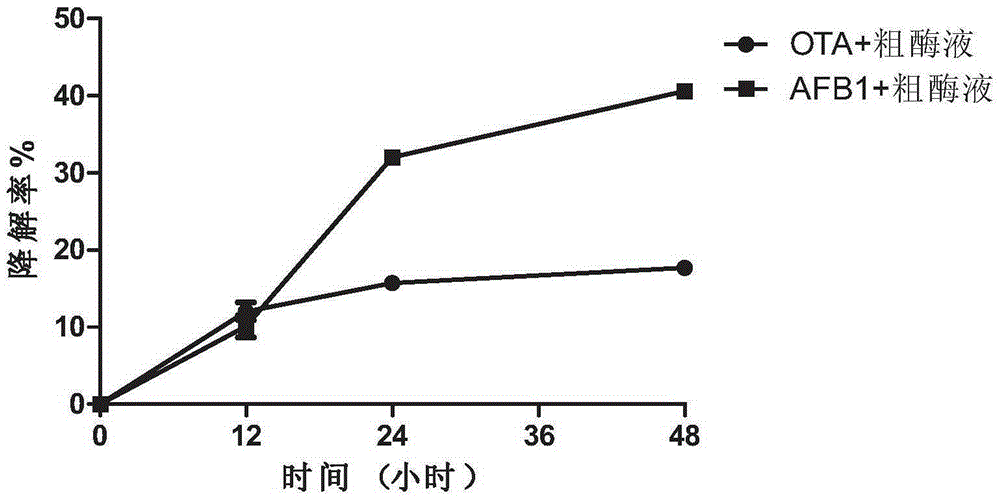
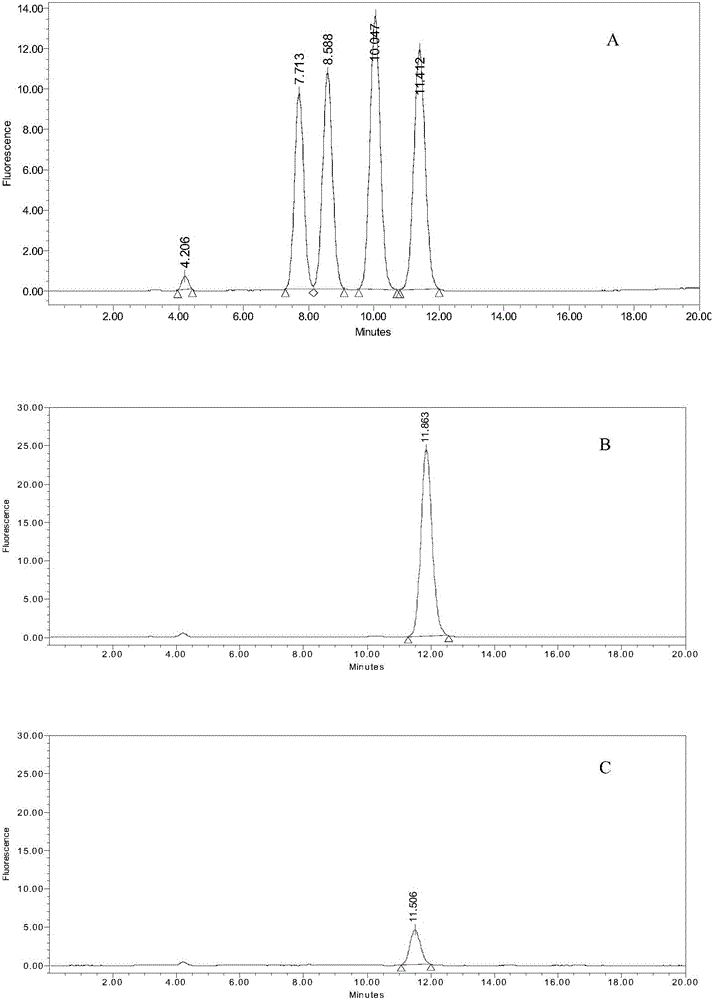
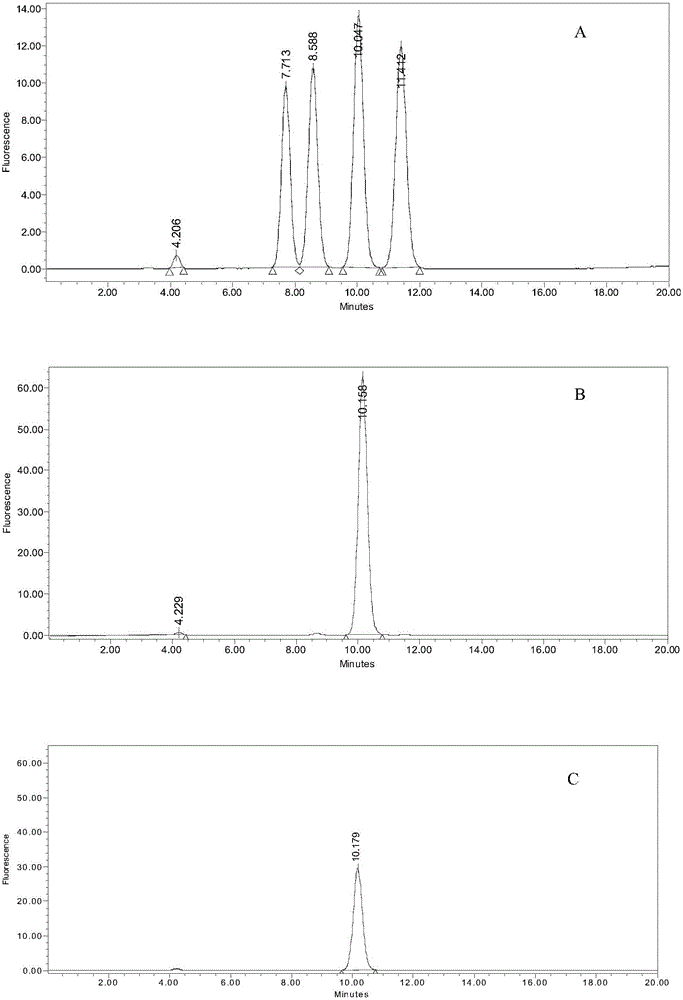
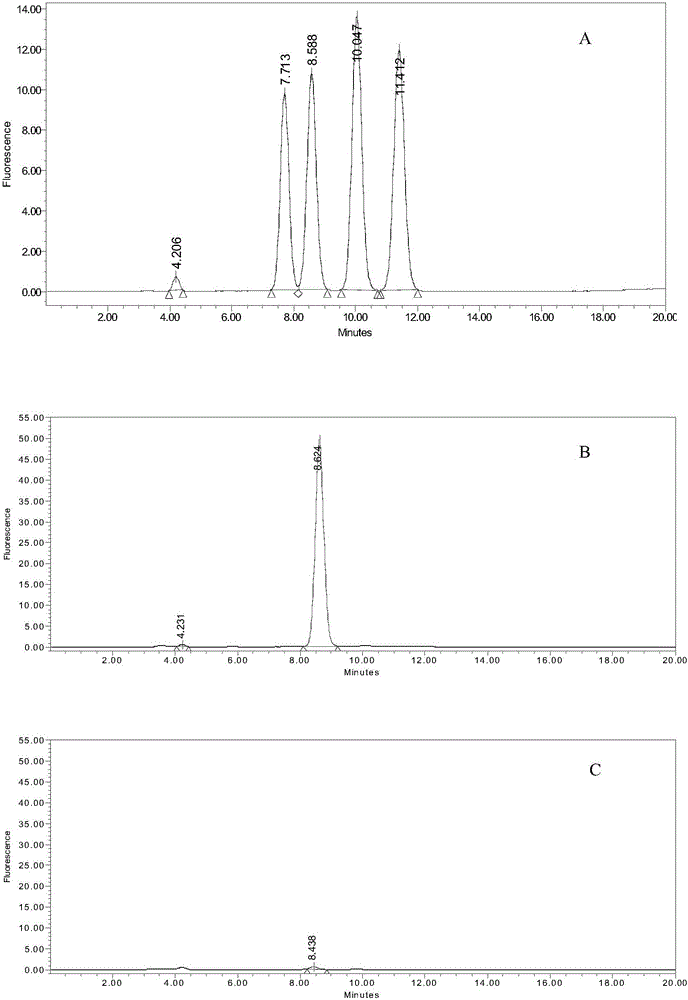
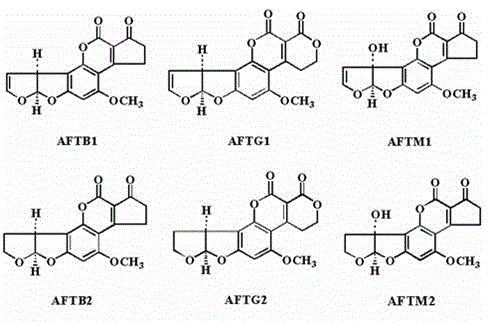
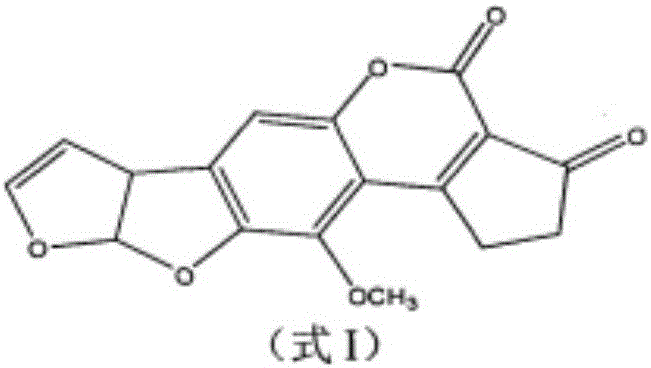
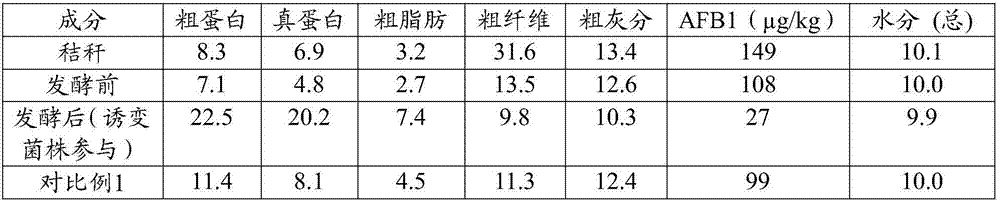
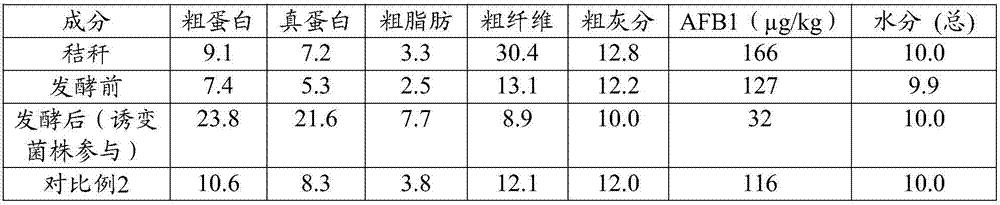
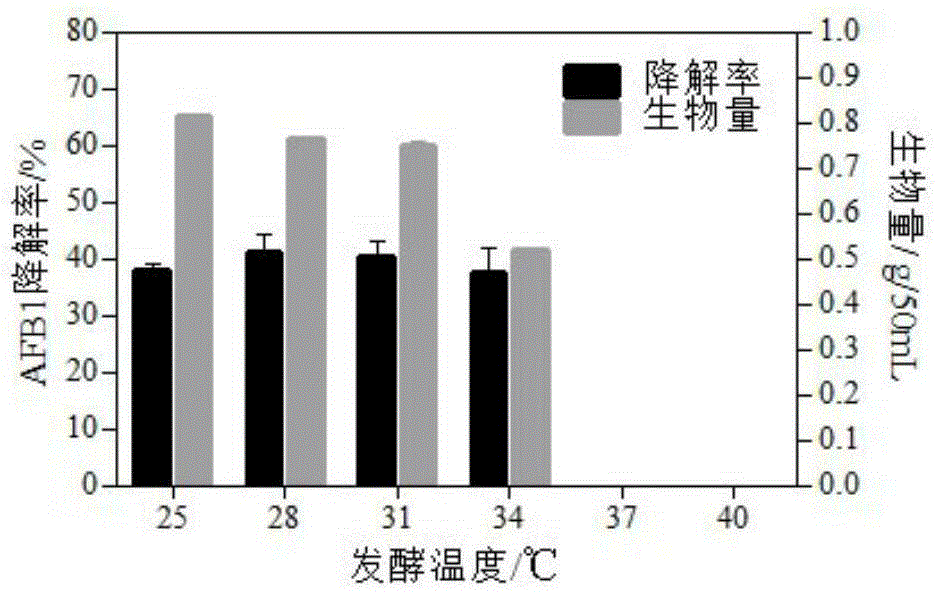
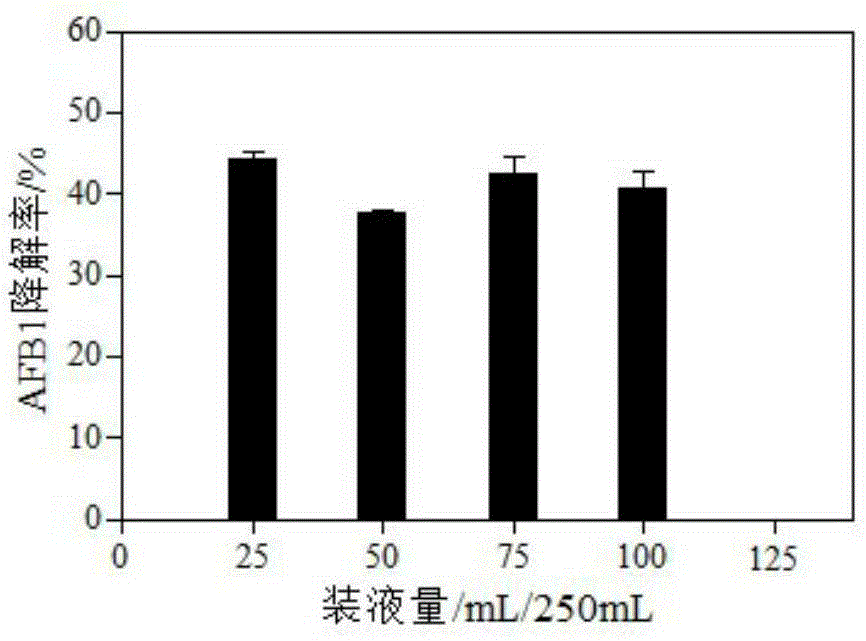
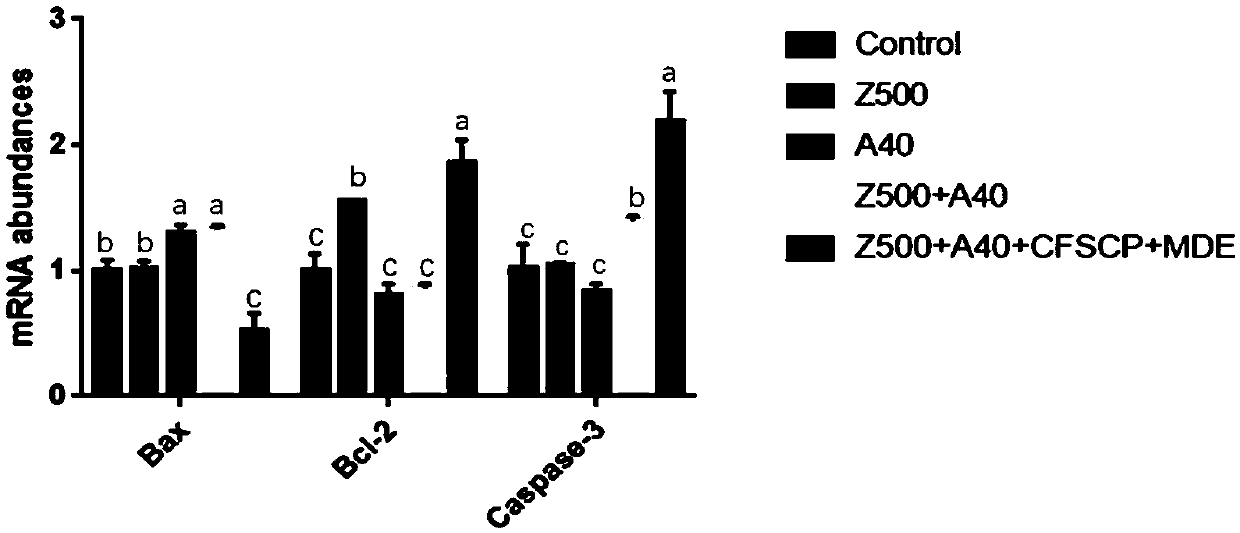
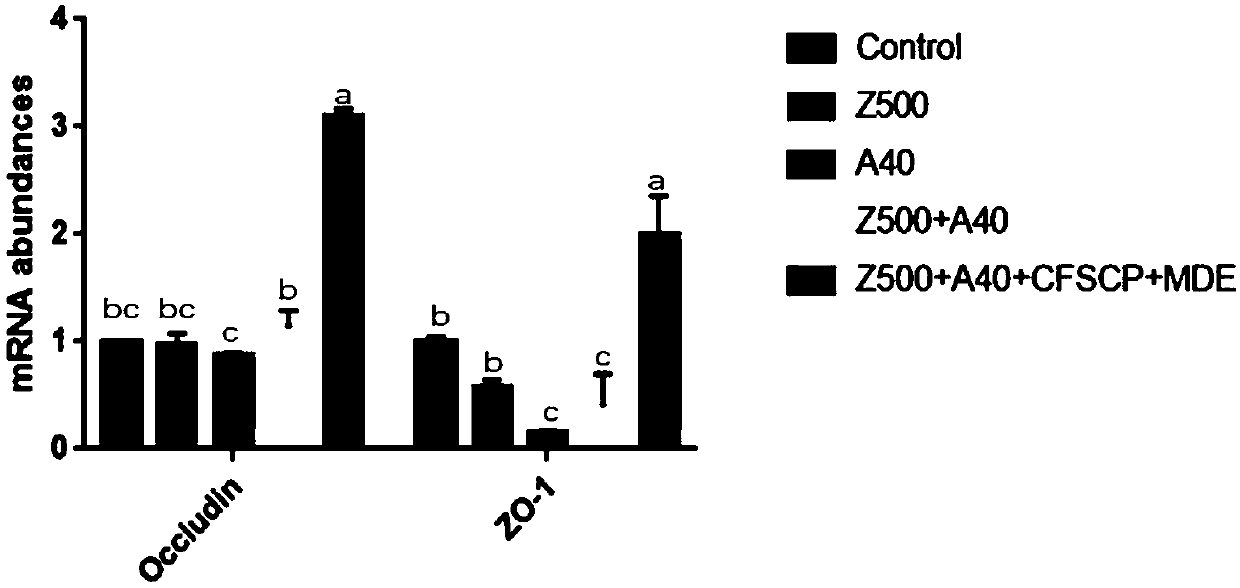
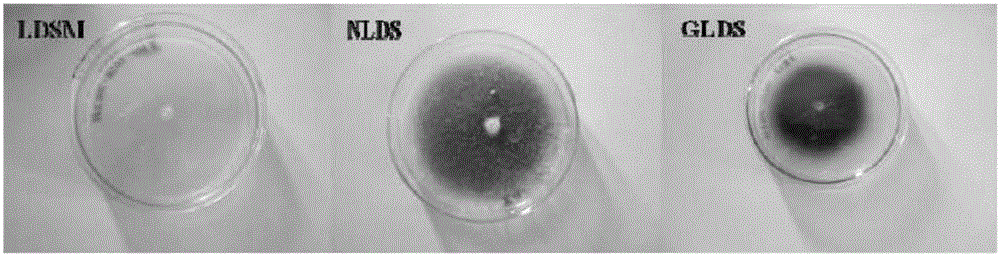
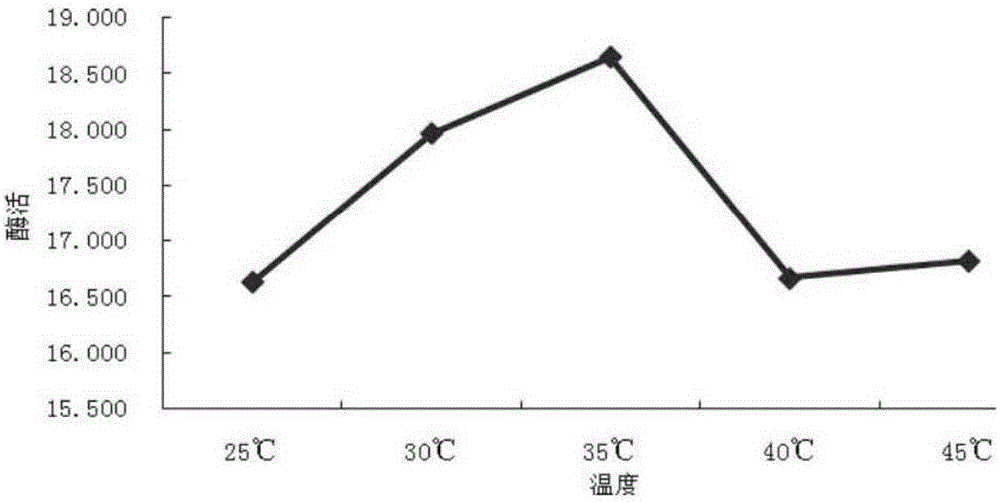
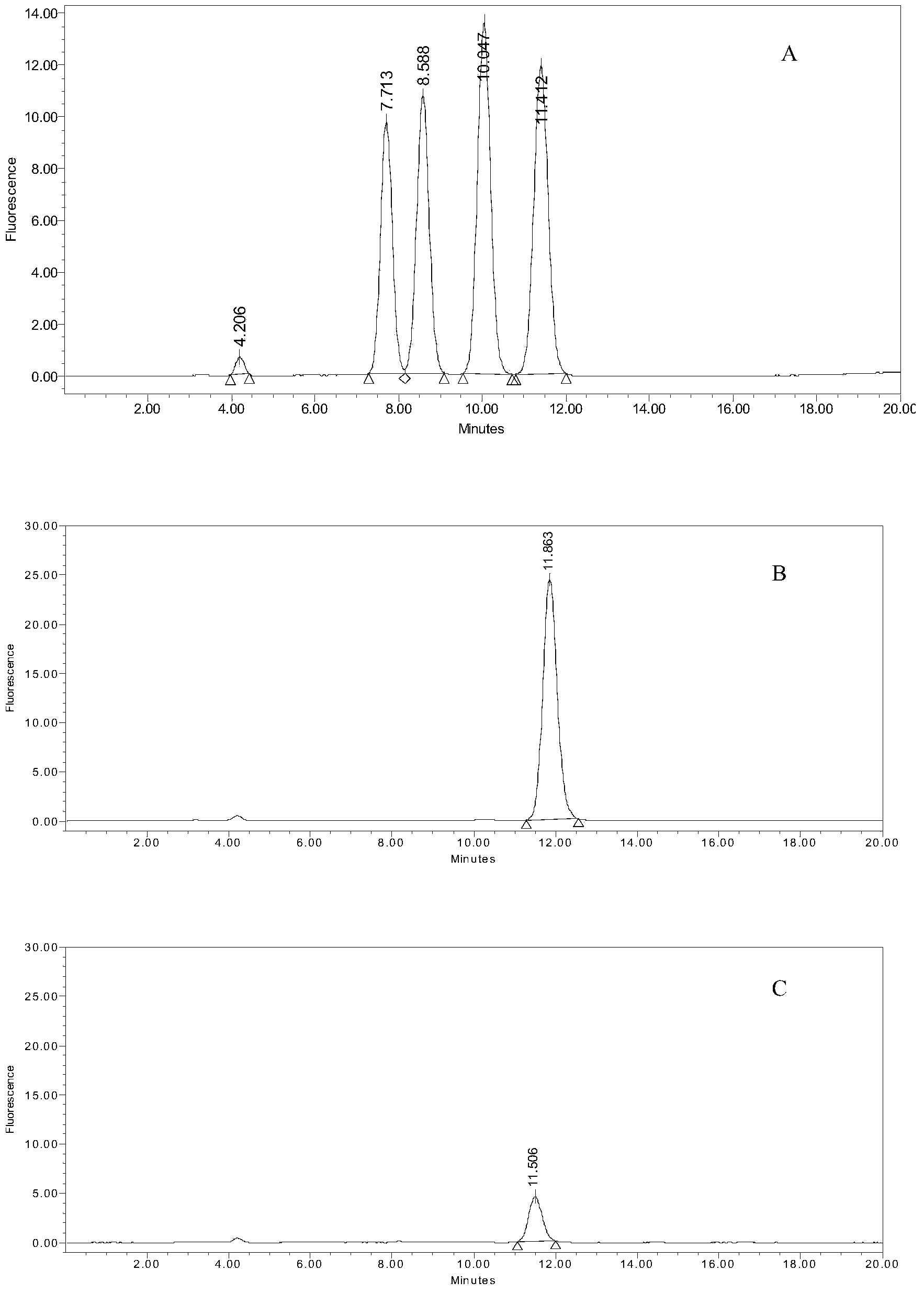Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80 results about "Aflatoxin degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aflatoxin degradation method
The invention discloses a method for degrading aflatoxin, which makes use of gamma rays to irradiate a sample containing the aflatoxin, wherein the gamma rays are generated by a radioactive substance Co, and the irradiation dose is between 0 and 10 kGy not including 0, preferably between 2 and 10 kGy, more preferably between 4 and 10 kGy, particularly preferably between 6 and 10 kGy, and the most preferably 10 kGy. The sample containing the aflatoxin is a farm product containing the aflatoxin or a product obtained by processing the farm product, such as food, feedstuff, and the like. The method is particularly applicable to degrading the aflatoxin B1, not only can kill pathogenic microorganisms but also can degrade biotoxin therein, and does not generate any industrial pollution.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and application of pseudomonas aeruginosa in aspect of degrading aflatoxin
ActiveCN103710292AEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyAflatoxin degradation
The invention discloses pseudomonas aeruginosa and application of the pseudomonas aeruginosa in the aspect of degrading aflatoxin. Preservation No. of the pseudomonas aeruginosa disclosed by the invention is CGMCC No. 8511. The pseudomonas aeruginosa disclosed by the invention can degrade aflatoxin effectively; the bacterium, as a biomaterial for degrading the aflatoxin, has excellent application prospects in development of new biodegradable bacterium or biodegradable sterile preparation.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Lysobacter capable of efficiently degrading aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A and application of Lysobacter
ActiveCN105274028APromote degradationEfficient degradation and detoxification abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLysobacter antibioticusAflatoxin degradation
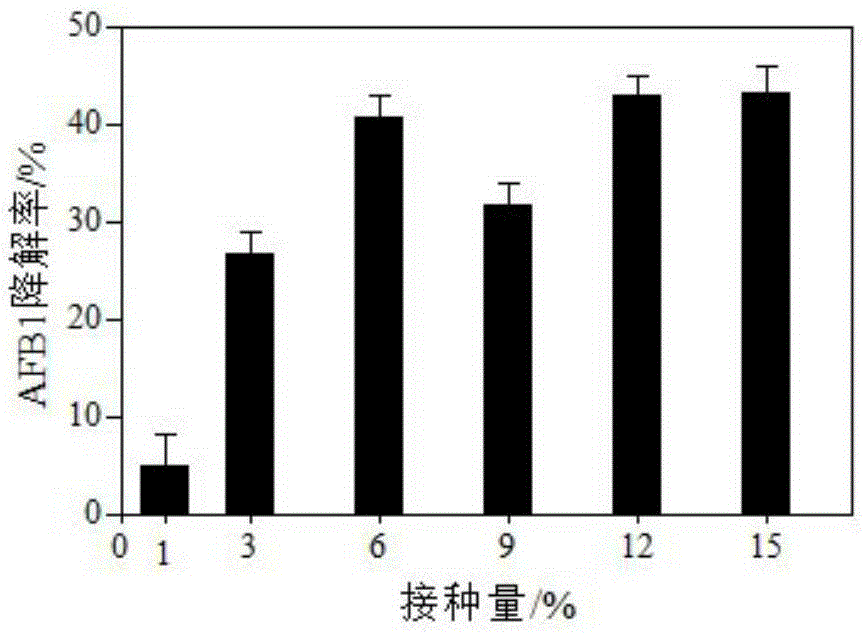
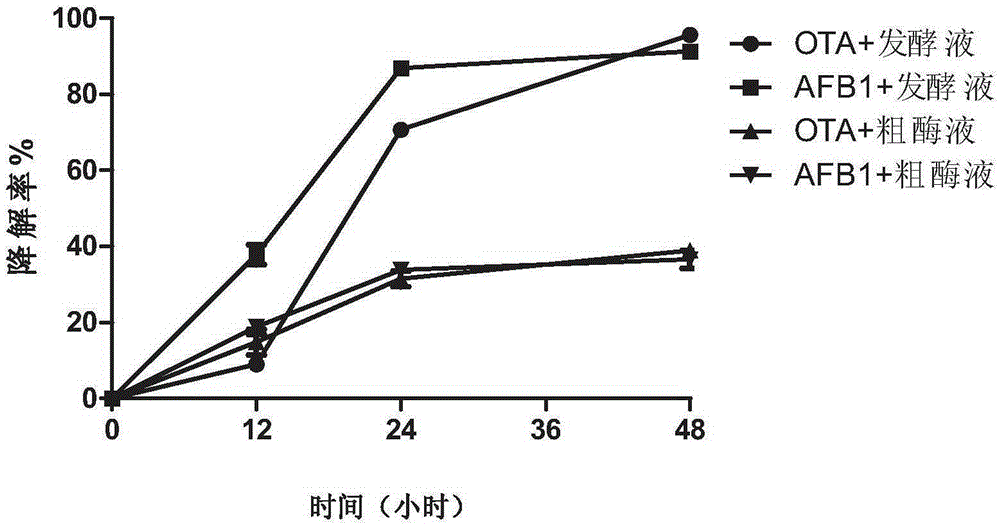
The invention provides Lysobacter capable of efficiently degrading aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A and application of the Lysobacter and particularly provides double-function Lysobacter sp. CW239 and application thereof to the degradation of low-pollution concentration aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A. Compared with existing aflatoxin degrading bacteria, the Lysobacter sp. CW239 has the advantages that the Lysobacter sp. CW239 can achieve excellent degrading effect under a low-concentration toxin pollution condition; under a liquid fermentation condition, in fermentation broth, which contains the aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A, with the final concentration of 20 microgram / L, the 12-hour ochratoxin A degradation rate of the Lysobacter sp. CW239 is 53.1%, and the 48-hour degradation rate reaches 99.8%; the 12-hour aflatoxin B1 degradation rate of the Lysobacter sp. CW239 is 42.5%, and the 48-hour degradation rate reaches 83.4%; when the Lysobacter sp. CW239 is used for processing feed (with the final concentration of 20 microgram / kg) polluted by toxins, the 48-hour ochratoxin A degradation rate is 68.7%, and the 48-hour aflatoxin B1 degradation rate is 52.1%; the Lysobacter sp. CW239 has substantial application value and significance when being applied to food and feed bio-detoxification.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Aflatoxin degradation method
ActiveCN102934764ARemove completelyAchieve zero detectionAnimal feeding stuffFood preparationChlorine dioxideThird generation
The invention discloses an aflatoxin degradation method. According to the method, substances containing aflatoxin are processed by combining ozone water, chlorine dioxide and ultrasonic to obtain a sample with the reduction of the aflatoxin. The processing method adopted by the invention is as follows: the ozone water contains 1-3g / L of ozone, and the concentration of chlorine dioxide is 3-8g / m<3>; and the aflatoxin and aspergillus flavus in peanuts and rice can be completely removed by ultrasonic intensity being 100w. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the operation is simple, the degradation effect is good, the degradation time is short, and the used chemical reagents are few; and the afatoxin degradation method is used for the degradation of the aflatoxin contained in agricultural products and the like and the control of the content of the aflatoxin contained in the agricultural products, and has extremely high application value and market potential.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Luteimonas sp for degrading alflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A and application of luteimonas sp
ActiveCN105255774APromote degradationEfficient degradation and detoxification abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAflatoxin BAflatoxin degradation
The invention provides luteimonas sp for degrading alflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A and application of the luteimonas sp and particularly provides a strain of difunctional efficient degrading bacteria (Luteimonas sp.) CW574 and application thereof in degrading low-pollution-concentration alflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A. Compared with existing aflatoxin degrading bacteria, the strain CW574 can achieve excellent degrading effects under the condition of low-concentration toxin pollution. Under the condition of liquid fermentation, in a fermentation culture solution containing alflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A with the final concentration being 20 micrograms per liter, the degrading rate of the strain CW574 on ochratoxin A is 90.1% in 48 h; the degrading rate of the strain CW574 on alflatoxin B1 is 85.5% in 48 h. When the strain CW574 is used for treating fodder (the final concentration is 20 micrograms per kg) polluted by toxins, the degrading rate on OTA is 48.3% in 48 h, and the degrading rate on AFB1 is 52.1% in 48 h. The strain CW574 has substantive application value and significance on the application aspects of food and feed biological detoxification.
Owner:江苏奥迈生物科技有限公司
A strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its application in degrading aflatoxin
ActiveCN103710292BEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAflatoxin degradationToxin
The invention discloses pseudomonas aeruginosa and application of the pseudomonas aeruginosa in the aspect of degrading aflatoxin. Preservation No. of the pseudomonas aeruginosa disclosed by the invention is CGMCC No. 8511. The pseudomonas aeruginosa disclosed by the invention can degrade aflatoxin effectively; the bacterium, as a biomaterial for degrading the aflatoxin, has excellent application prospects in development of new biodegradable bacterium or biodegradable sterile preparation.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Gene for coding aflatoxin degradation enzyme and method for obtaining high-efficiency aflatoxin degradation enzyme
InactiveCN103555745AHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFusion Protein Expression
The invention discloses a gene for coding an aflatoxin degradation enzyme and a method for obtaining a high-efficiency aflatoxin degradation enzyme. The nucleotide sequence of the gene for coding the aflatoxin degradation enzyme is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. The method for obtaining the high-efficiency aflatoxin degradation enzyme comprises the following steps: cloning the gene shown as the SEQ ID NO. 1 to a carrier pCold-II; converting to Escherichia coli BL21-PG-Tf2 to obtain expression thallus of the aflatoxin degradation enzyme; inducing expression of the expression thallus by using tetracycline and IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside); collecting the thallus; crushing; purifying by using a fusion protein expressed tag on the pCold-II to obtain the high-efficiency aflatoxin degradation enzyme. The purity of the obtained aflatoxin degradation enzyme reaches over 95 percent by optimizing the expression carrier and the expression condition, and the efficiency for degrading the aflatoxin B1 reaches 161.7 nmol / min / mg.pr.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Solimonas capable of efficiently degrading aflatoxin B1 and application thereof
ActiveCN105255775APromote degradationEfficient degradation and detoxification abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAflatoxin BAflatoxin degradation
The invention discloses solimonas capable of efficiently degrading aflatoxin B1 and application thereof, and particularly provides a solimonas (solimonas sp.) strain CW980 and application thereof in degradation of aflatoxin B1 with the low pollution concentration. Compared with an existing aflatoxin degradation bacterium, the strain CW980 can achieve the excellent degradation effect under the low-concentration aflatoxin pollution condition. Under the liquid fermentation condition, in a fermentation culture solution containing the aflatoxin B1 with the final concentration of 20 mug / L, the degradation rate of the strain CW980 to the aflatoxin B1 after 24 h is 37.8%, the degradation rate after 48 h reaches 70.3%, and the degradation rate after 72 h reaches up to 90.4 %. By processing feed polluted by the aflatoxin B1(the final concentration is 20 mug / kg) with the strain CW980 for 48 h, the AFB1 degradation rate is 23.0%, and the AFB1 degradation rate reaches 75.5% after 72 h. The strain CW980 has the substantial application value and great significance in the aspect of biological detoxification application of food and feed.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus siamensis WF2019 strain for degrading aflatoxin B1 and application of bacillus siamensis WF2019 strain
ActiveCN110564640AEfficient degradationImprove degradation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAflatoxin contamination
The invention discloses a bacillus siamensis WF2019 strain for degrading aflatoxin B1 and an application of the bacillus siamensis WF2019 strain. The bacillus siamensis WF2019 strain capable of efficiently degrading the aflatoxin B1 is successfully separated and obtained, is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on June 18th, 2019, and has preservation number of GDMCC NO:60700. The strain can efficiently degrade the aflatoxin B1, and the degradation rate is as high as 98.9%; the environment adaptability is good, the high-temperature resistance is remarkable, and the degradation performance is still remarkable at the temperature of 60 DEG C; meanwhile, fermentation liquor or intracellular substances of the strain can also degrade the aflatoxin B1 and can be applied to detoxification of agricultural products polluted by the aflatoxin B1; in addition, the strain is pollution-free and nuisanceless in the using process. Therefore, the strain is an ideal agricultural product detoxification microorganism, and has good promotion and application prospects in the detoxification aspect of the aflatoxin B1 in the field of feed processing or food processing.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Preparation method of compound enzyme preparation for efficiently degrading aflatoxin B1
InactiveCN106636017AImprove efficiencyEfficient degradationOxidoreductasesFood scienceCentrifugationAflatoxin degradation
Crude enzyme preparations are respectively obtained by a method for centrifugation, concentration, ammonium sulfate precipitation, freezing and drying of fermenting medium solutions for bacillus subtilis and penicillium raistrickii, and are mixed with fungal laccase through a specific component ratio, so that a compound enzyme preparation for efficiently degrading aflatoxin B1 is prepared. The bacillus subtilis crude enzyme preparation and the penicillium raistrickii crude enzyme preparation are mixed with the fungal laccase, the respective component ratio occupied is controlled to be 20-60 percent, and the sum is 1. The prepared compound enzyme preparation can efficiently degrade the aflatoxin B1, and the degrading interval is 76-89 percent. Under the same treatment conditions, the degrading efficiency of the compound enzyme preparation is improved by 25 percent or above as compared with that of each of the three components for the aflatoxin B1. When the ratio of the compound enzyme preparation to the aflatoxin B1 in a system is controlled to be 0.2-0.4 g / L.ppm, compared with any component in the compound enzyme preparation, the compound enzyme preparation shows significant material-saving property.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Pleurotus ostreatus and its application in aflatoxin degradation
The invention discloses a Pleurotus ostreatus and its application in aflatoxin degradation. The Pleurotus ostreatus LY65 provided by the invention is called LY65 for short, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.5428. A broth of the LY65 can be used for degrading aflatoxin B1, has a high degradation capability, and is nontoxic and innocuous to humans and animals because LY65 strains are edible strains. LY65 and its broth have good application prospects in the aflatoxin B1 degradation.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Arthrobacterium and application thereof in degradation of aflatoxin
ActiveCN103981132AEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAflatoxin degradationMicrobiology
The invention discloses an arthrobacterium and an application thereof in degradation of aflatoxin and provides an arthrobacterium (Arthrobacter sp.) L15 which is assigned the accession number CGMCC No.8869. An experiment in the invention proves that the arthrobacterium L15 is discovered in the invention. Aflatoxin can be degraded efficiently when a fermentation liquor of the arthrobacterium L15 is added to the aflatoxin and dissolving and uniform mixing are carried out. The arthrobacterium L15, used as a biological material for degrading aflatoxin, has good application prospects in exploitation of not only novel biodegradation inoculants but also novel biodegradation sterile preparations.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Mycotoxin adsorption degradation agent for pig feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108850783AInhibition of fertilityInhibitionFood scienceAflatoxin degradationAluminosilicate
The invention discloses a mycotoxin adsorption degradation agent for pig feed and a preparation method thereof. The mycotoxin adsorption degradation agent is prepared from the following components inparts by weight: 15 to 25 parts of activated lactic acid bacteria, 15 to 25 parts of bacillus subtilis, 20 to 40 parts of saccharomycetes, 20 to 30 parts of lactic acid bacterium cell wall peptidoglycan, 2 to 6 parts of an aflatoxin degeneration enzyme, 2 to 6 parts of a zearalenone degeneration enzyme, 2 to 6 parts of a vomitoxin degeneration enzyme, 2 to 6 parts of an ochratoxin degeneration enzyme, 2 to 6 parts of a T-2 toxin degeneration enzyme, 100 to 200 parts of hydrated aluminosilicate, 10 to 20 parts of potassium sorbate, 10 to 20 parts of sodium benzoate, 25 to 40 parts of pericarpium citri reticulatae, 25 to 40 parts of fructus crataegi, 25 to 35 parts of cortex cinnamomi and 10 to 25 parts of flos caryophylli. The adsorption degradation agent is subjected to biological adsorption and intestinal degradation, so that mycotoxin in raw materials of the feed and in the feed can be effectively removed and the health and safety of live pigs are ensured.
Owner:西安默瑞柯生物科技有限公司
Aflatoxin degrading enzyme secreted by Bacillus subtilis, and applications thereof
ActiveCN107760655AStrong specificityImprove degradation efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliTransformation efficiency
The present invention provides aflatoxin degrading enzyme secreted by Bacillus subtilis, and applications thereof. According to the present invention, the aflatoxin degrading enzyme BADE is firstly separated and purified from Bacillus subtilis ANSB060, wherein the amino acid sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO:1, and the gene encoding the enzyme is obtained through cloning; the gene is transformed into an Escherichia coli expression system so as to successfully achieve the expression of the protein in Escherichia coli; and the activity identification results prove that the recombinant rBADE has aflatoxin degrading effect, such that the foundation is established for the development of the aflatoxin degrading enzyme with high specificity and high transformation efficiency.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Strain producing aflatoxin B1 degrading enzyme and application thereof
InactiveCN104498378ASolve pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood safetyAflatoxin contamination
The invention discloses a bacterium Sinomonas sp.HSD8 and application thereof. The preservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO:M2014109. After fermentation culture, the activity of aflatoxin B1 degrading enzyme in the fermentation liquid is improved, the aflatoxin pollution problem in feed and food can be effectively solved, and the animal feed and food safety can be guaranteed.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Microbial fermentation based aflatoxin degradation device
InactiveCN110250403AReduce in quantityPromote fermentationFood scienceMicroorganismAflatoxin degradation
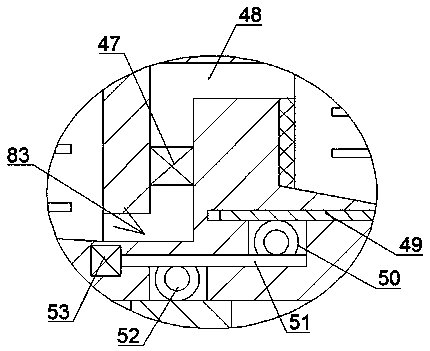
The invention discloses a microbial fermentation based aflatoxin degradation device. The microbial fermentation based aflatoxin degradation device comprises a body and is characterized in that the body is internally provided with a mixing cavity, and a mixing mechanism is arranged in the mixing cavity and capable of well mixing feed with degradation mixed strains to facilitate the next fermentation step. The body on the right side of the mixing cavity is internally provided with a fermentation cavity, and a fermentation mechanism is arranged in the fermentation cavity and enables complete fermentation of the feed with degradation bacteria to further enable complete fermentation degradation of aflatoxin in the feed. The body at the bottom of the mixing cavity is internally provided with a slide cavity, and a power mechanism is arranged in the slide cavity. The aflatoxin degradation device has advantages that by a mixing device for well mixing the feed with the mixed strains, convenience in fermentation is achieved; under the stirring action of second stirring plates and the heating action of a heating layer, the fermentation speed is increased, and time saving is realized.
Owner:象山冰川智能装备有限公司
Method of degrading aflatoxin in peanut meal and synchronously preparing peanut protein peptide
ActiveCN108034690AImproves antioxidant activityHigh nutritional valueMicroorganism based processesFermentationPeanut mealAflatoxin degradation
The invention discloses a method of degrading aflatoxin in peanut meal and synchronously preparing peanut protein peptide and belongs to the field of food safety and nutrition of peanuts. The method includes the steps of: raw material treatment, sectional microbial fermentation, enzymolysis, enzyme deactivation and centrifugation, and spray drying, wherein microorganisms employed in the sectionalmicrobial fermentation comprise coriolus versicolor, bacillus subtilis and aspergillus niger. In the method, the three microorganisms achieve synergistic sectional fermentation and sectional enzymolysis, so that during degradation of the aflatoxin, cyclopiazonic acid is also degraded, and the peanut protein peptide having high anti-oxidizing activity and high nutritional value is prepared. The method is reduced in operation process and shortened in process time, saves cost, has simple operations and is easy to carry out industrially.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
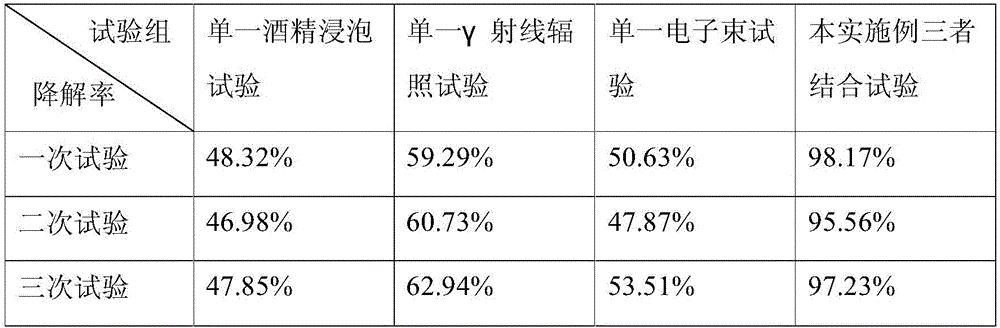
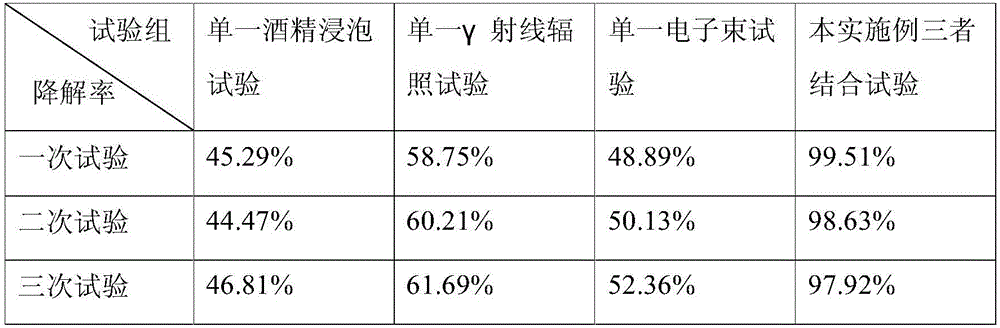
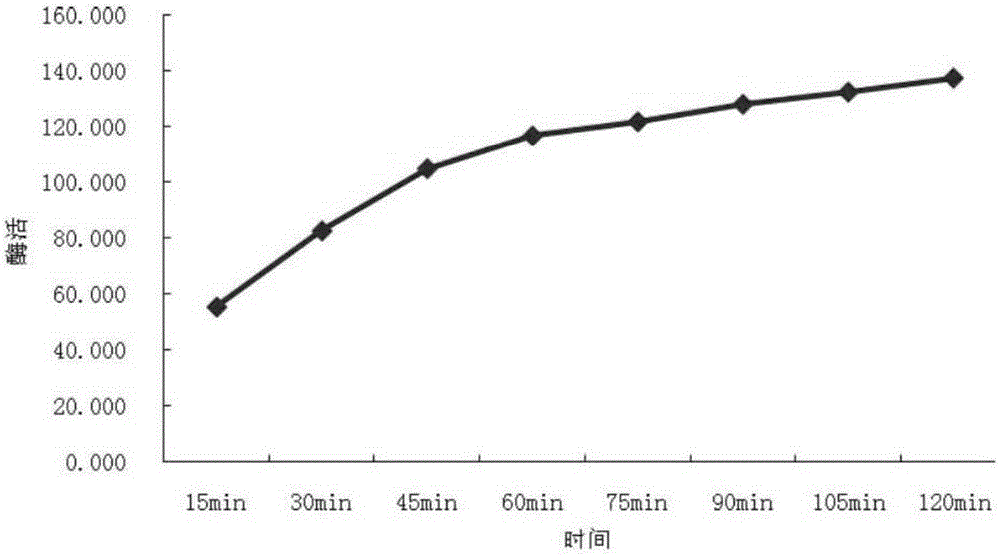
Aflatoxin irradiation degradation method
The invention relates to an aflatoxin degradation method, in particular to an aflatoxin irradiation degradation method. The aflatoxin irradiation degradation method comprises the steps that an asporgillus flavus spore suspension is prepared; an experimental agricultural product is placed under an ultraviolet lamp to be subjected to irradiation sterilization, and the sterilized agricultural product is placed into the asporgillus flavus spore suspension to be mixed evenly and cultured, so that the experimental agricultural product infected with asporgillus flavus is obtained; the experimental agricultural product infected with the asporgillus flavus is placed into alcohol with the volume concentration being 80-85% to be soaked and stirred, and heated in a water bath with the temperature being 70-80 DEG C, and the experimental product which is infected with the asporgillus flavus and degraded preliminarily is obtained; and the experimental agricultural product infected with the asporgillus flavus is placed into a centrifugal tube to be sealed, and the sealed experimental agricultural product infected with the asporgillus flavus is placed into a <60>Co gamma ray radiation field to be irradiated and then placed into an electron beam radiation field to be irradiated. By adoption of the aflatoxin irradiation degradation method, the degradation rate of aflatoxin in the agricultural product is increased, the degrading effect is improved, industrial pollution is reduced, and cost allowance of enterprises in the production process is reduced.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Granulating-dedicated coarse feed composite mildew inhibitor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103416825AExtended storage periodNo toxicityFood preservationAnimal feeding stuffPropionateAflatoxin degradation
The invention discloses a granulating-dedicated coarse feed composite mildew inhibitor and a preparation method thereof, especially relates to a dedicated composite mildew inhibitor for making granulated coarse feed and a preparation method thereof, and aims to solve the problem of no a mildew inhibitor product, which is dedicated for coarse feed in the feed market at present. The formula of the composite mildew inhibitor comprises following components: calcium propionate, potassium sorbate, sodium benzoate, dimethyl fumarate, zeolite powder, aflatoxin degrading enzyme, and carriers. The preparation method comprises following steps: first, weighing 4.5 kg of calcium propionate, 5 kg of potassium sorbate, 4.5 kg of sodium benzoate, 6.0 kg of dimethyl fumarate, and 8.0 kg of aflatoxin degrading enzyme; secondly, pre-mixing the components in a small feed mixing machine for 10 minutes, then adding 27.0 kg of zeolite powder and 45.0 kg of corncob powder, putting the mixture into the small feed mixing machine again, and mixing for another 15 minutes so as to obtain the product. The granulating-dedicated coarse feed composite mildew inhibitor has the advantages of no toxicity, no accumulation in animal bodies, and no affection on nutrition value and palatability of coarse feed.
Owner:辽宁省畜牧科学研究院
Feed additive capable of decomposing mycotoxin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108967698AAbundant raw materialsTo promote metabolismFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAluminateLycopene
The invention discloses a feed additive capable of decomposing mycotoxin and a preparation method thereof. The feed additive is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 20 to 40 parts of mannan oligosaccharides, 15 to 25 parts of activated lactobacillus, 15 to 25 parts of bacillus subtilis, 20 to 30 parts of lycopene, 2 to 6 parts of aflatoxin degrading enzyme, 2 to 6 parts of zearalenone degrading enzyme, 2 to 6 parts of vomitoxin degrading enzyme, 2 to 6 parts of selenium yeast, 2 to 6 parts of polyglutamic acid, 100 to 200 parts of hydrated silicon aluminate, 10 to 20 parts of flos sophorae immaturus, 10 to 20 parts of herba taraxaci, 25 to 40 parts of pericarpium citri reticulatae, 25 to 40 parts of radix astragali, 25 to 35 parts of cassia bark and 10 to 25 parts offlos caryophylli. According to the feed additive capable of decomposing mycotoxin disclosed by the invention, through biological enteral degradation, mycotoxin in raw materials of the feed and the feed can be effectively removed, and health and safety of live pigs are ensured.
Owner:维康腾达生物科技有限公司
Bacillus subtilis for degrading aflatoxin and application thereof
ActiveCN110878265AEfficient degradationNo side effectsBacteriaFood processingMicroorganismAflatoxin degradation
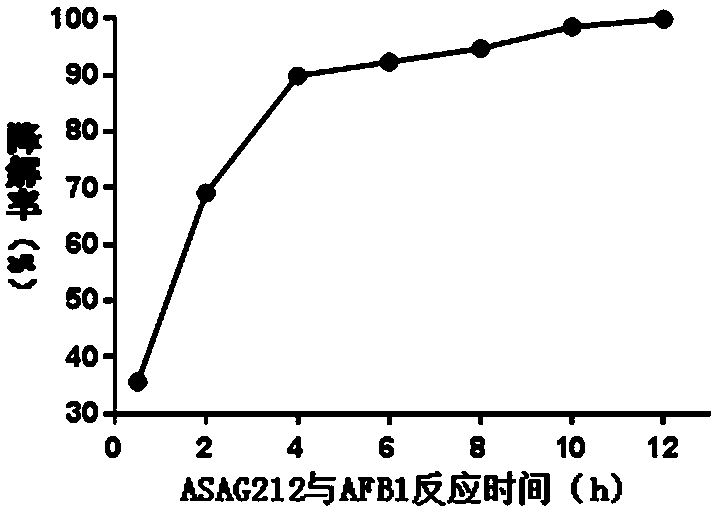
The invention discloses Bacillus subtilis for efficiently degrading aflatoxin and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The Bacillus subtilis is named ASAG212, and was preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 18367. The optimum degradation conditions are as follows: the initial concentration of Bacillus subtilis is 109 CFU / mL, the pH value is 7.2-7.6, the culture temperature is 35-40 DEG C, and the rotational speed is 120 rpm-180 rpm. 10 ug / mL of aflatoxin B1 is degrade into a non-toxic productwithin 4 hours by the strain of the invention, and the degradation rate reaches more than 90%. The invention also provides a bacterial preparation containing the strain and for degrading aflatoxin andan application of the bacterial preparation. The preparation method of the bacterial preparation used by the invention is simple, and the bacterial preparation does not contain antibiotic components,has no toxic or side effects, has no drug resistance, has no pollution, and has remarkable economic benefits and practical application value.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV +2
Capsule rhodobacter strain for degrading aspergillus flavus B1, application of capsule rhodobacter strain, degradation agent and application of degradation agent
ActiveCN107513512AHigh in proteinImprove utilizationBacteriaFood processingBacteroidesAflatoxin degradation
The invention provides a capsule rhodobacter strain for degrading aspergillus flavus B1, application of the capsule rhodobacter strain, a degradation agent and application of the degradation agent, belonging to the technical field of degradation of aflatoxin. The provided capsule rhodobacter strain for degrading the aspergillus flavus B1 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.14603. The capsule rhodobacter strain for degrading aspergillus flavus B1 is applied to the degradation of the aspergillus flavus B1. The aspergillus flavus B1 degradation agent for animal feeds contains the capsule rhodobacter strain. The aspergillus flavus B1 degradation agent is applied to the preparation of the animal feeds. The degradation agent has the properties of the efficient aspergillus flavus B1, and the nutrient contents of crude proteins, true proteins, crude fat and the like in the animal feeds are remarkably increased, so that the feeding value of the animal feeds is greatly increased.
Owner:YIBIN UNIV
Microbe capable of producing aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) degrading enzyme and application thereof
The invention discloses a microbe capable of producing an AFB1 degrading enzyme, i.e., Cladosporium uredinicola HSK8. The microbe is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on March 31, 2015, with an accession number of CCTCC No. M 2015181. The microbe can produce the AFB1 degrading enzyme through fermentation of industrial and agricultural by-products or waste consisting of molasses, corncob powder and orange peel powder, so cost is substantially saved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Spring water monoucleosis for degrading alflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A and application of spring water mononucleosis
ActiveCN105255776APromote degradationEfficient degradation and detoxification abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMononucleosisAflatoxin B
The invention provides spring water monoucleosis for degrading alflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A and application of the spring water mononucleosis and particularly provides a strain of difunctional efficient degrading bacteria (Silanimonas sp.) CW282 and application thereof in degrading low-pollution-concentration alflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A. Compared with existing aflatoxin degrading bacteria, the strain CW282 can achieve excellent degrading effects under the condition of low-concentration toxin pollution. Under the condition of liquid fermentation, in a fermentation culture solution containing alflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A with the final concentration being 20 micrograms per liter, the degrading rate of the strain CW282 on ochratoxin A is 70.7% in 24 h and reaches 95.6% in 48 h; the degrading rate of the strain CW282 on alflatoxin B1 is 86.9% in 24 h and reaches 91.3% in 48 h. When the strain CW282 is used for treating fodder (the final concentration is 20 micrograms per kg) polluted by toxins, the degrading rate on ochratoxin A is 53.2% in 48 h, and the degrading rate on alflatoxin B1 is 58.3% in 48 h. The strain CW282 has substantive application value and significance on the application aspects of food and feed biological detoxification.
Owner:CHACHA FOOD CO LTD
A Strain of Arthrobacter and Its Application in Degrading Aflatoxins
The invention discloses an arthrobacterium and an application thereof in degradation of aflatoxin and provides an arthrobacterium (Arthrobacter sp.) L15 which is assigned the accession number CGMCC No.8869. An experiment in the invention proves that the arthrobacterium L15 is discovered in the invention. Aflatoxin can be degraded efficiently when a fermentation liquor of the arthrobacterium L15 is added to the aflatoxin and dissolving and uniform mixing are carried out. The arthrobacterium L15, used as a biological material for degrading aflatoxin, has good application prospects in exploitation of not only novel biodegradation inoculants but also novel biodegradation sterile preparations.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Composite probiotic fermentation composition and application thereof in preparation of preparation for preventing and treating epithelial cell injury caused by mycotoxin
The invention provides a composite probiotic fermentation composition and application thereof in preparation of a preparation for relieving epithelial cell damage caused by mycotoxin, and belongs to the technical field of mycotoxin degradation. The composite probiotic fermentation composition comprises a compound probiotic fermentation supernatant and an aflatoxin B1 degrading enzyme-zearalenone degrading enzyme compound enzyme solution, wherein the volume ratio of the compound probiotic fermentation supernatant and the aflatoxin B1 degrading enzyme-zearalenone degrading enzyme compound enzymesolution is (2.6 to 3.4) : (1.5 to 2.5). The aflatoxin B1 degrading enzyme activity of the aflatoxin B1 degrading enzyme-zearalenone degrading enzyme compound enzyme solution is 250-350 U / L, and thezearalenone degrading enzyme activity of the aflatoxin B1 degrading enzyme-zearalenone degrading enzyme compound enzyme solution is 25-35 U / L. The composite probiotic fermentation composition can effectively relieve epithelial cell damage caused by aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) and zearalenone (ZEA).
Owner:HENAN PUAI FEED GRP CO LTD +1
Method for degrading aflatoxins in peanut meal by utilizing solid fermentation of fructificatio amaurodermatis rudae
ActiveCN105166602AEfficient degradationFlourishingFood processingAnimal feeding stuffPeanut mealAflatoxin degradation
The invention discloses a method for degrading aflatoxins in peanut meal by utilizing solid fermentation of fructificatio amaurodermatis rudae. The method comprises the steps of treating raw materials, activating strains, performing solid fermentation, degrading the aflatoxins, determining the aflatoxins and the like. The invention provides an efficient safe method for degrading the aflatoxins in the peanut meal. The degraded peanut meal can be used for producing and processing foods and feeds, and besides, the nutrient value of the peanut meal can also be increased. The method is simple to operate and easy in industrialization.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Aflatoxin degradation device and aflatoxin degradation system
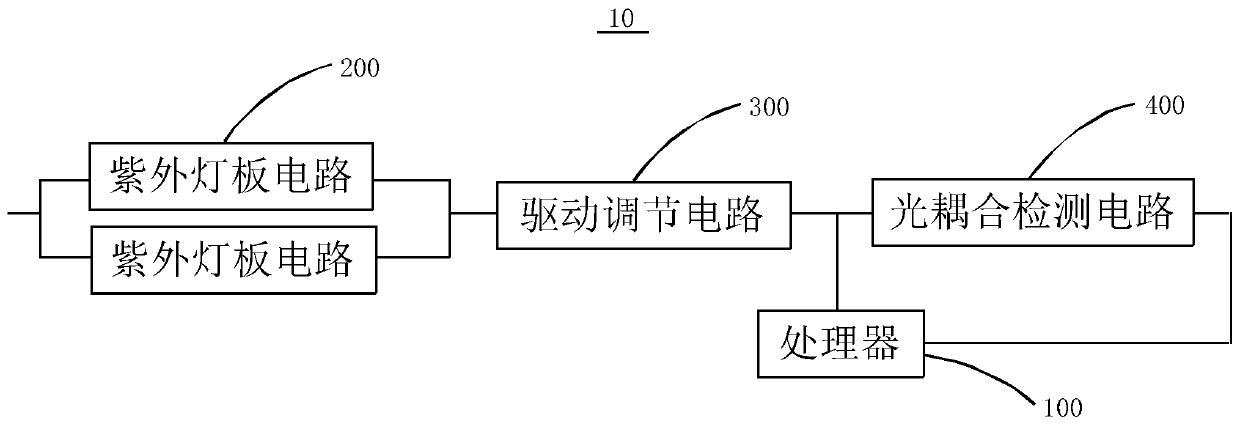
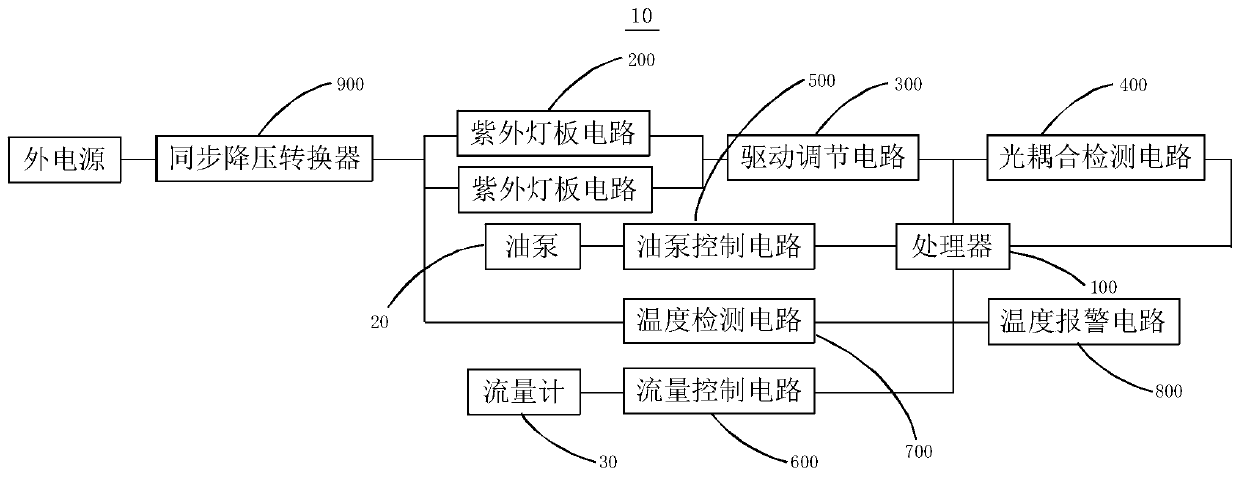
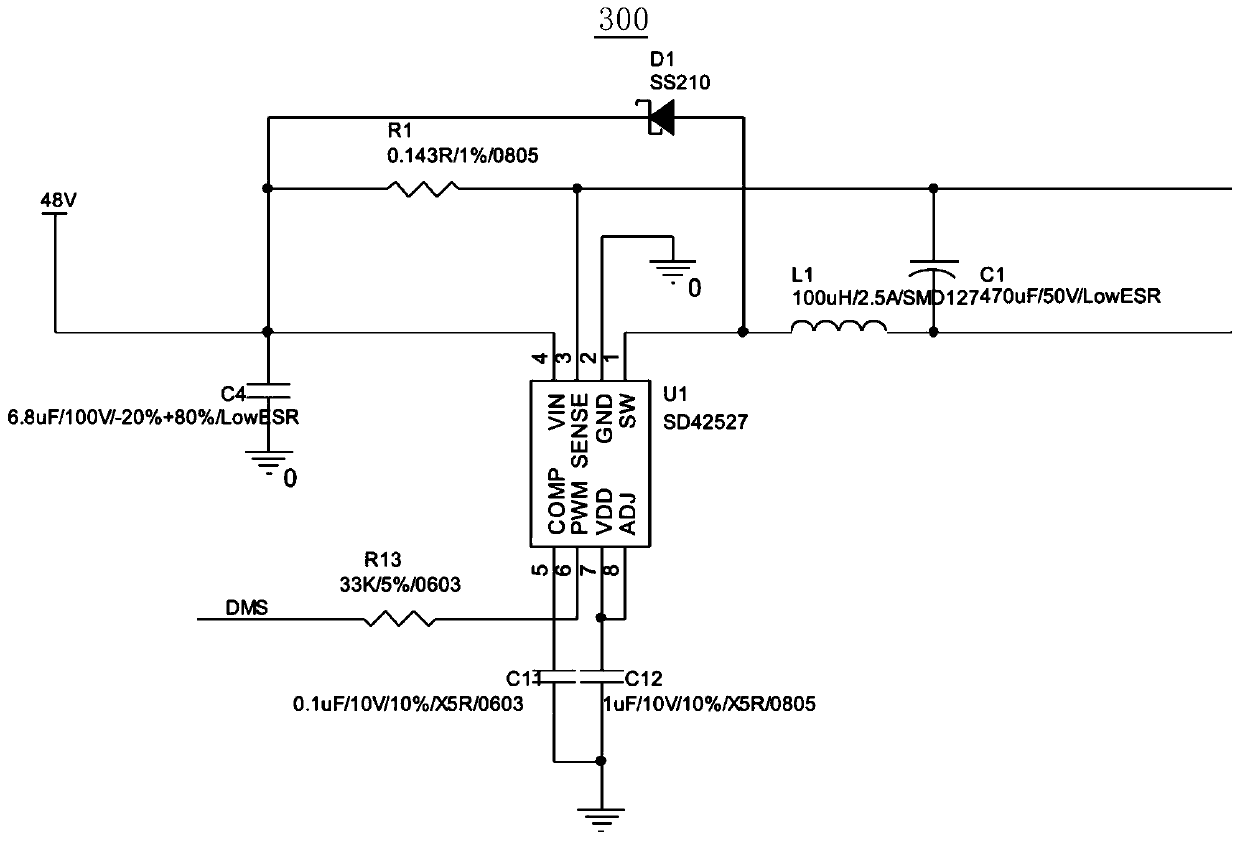
ActiveCN110777001AGuaranteed to workAffect work effectFatty-oils/fats refiningEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesUltravioletEngineering
The invention relates to an aflatoxin degradation device and an aflatoxin degradation system. The aflatoxin degradation device comprises a processor and a plurality of ultraviolet lamp panel circuits.The ultraviolet lamp panel circuits are provided with a driving adjustment circuit and an optical coupling detection circuit. When some ultraviolet lamp panel circuits break down, the drive adjustingcircuit adjusts the working current in each ultraviolet lamp panel circuit to balance the current passing through the remaining ultraviolet lamp panel circuits which do not break down, and the current passing through each ultraviolet lamp panel circuit does not exceed the rated current of each ultraviolet lamp panel circuit, so the aflatoxin degradation device is prevented from influencing the working effect and even being burnt out under the condition that other ultraviolet lamp panel circuits fail, and the technical problem that the whole degradation device cannot be normally used due to faults of some ultraviolet lamp panel circuits of the aflatoxin degradation device is solved, thereby the safety and the stability of the aflatoxin degradation device are improved.
Owner:深圳市银河光生物科技有限公司
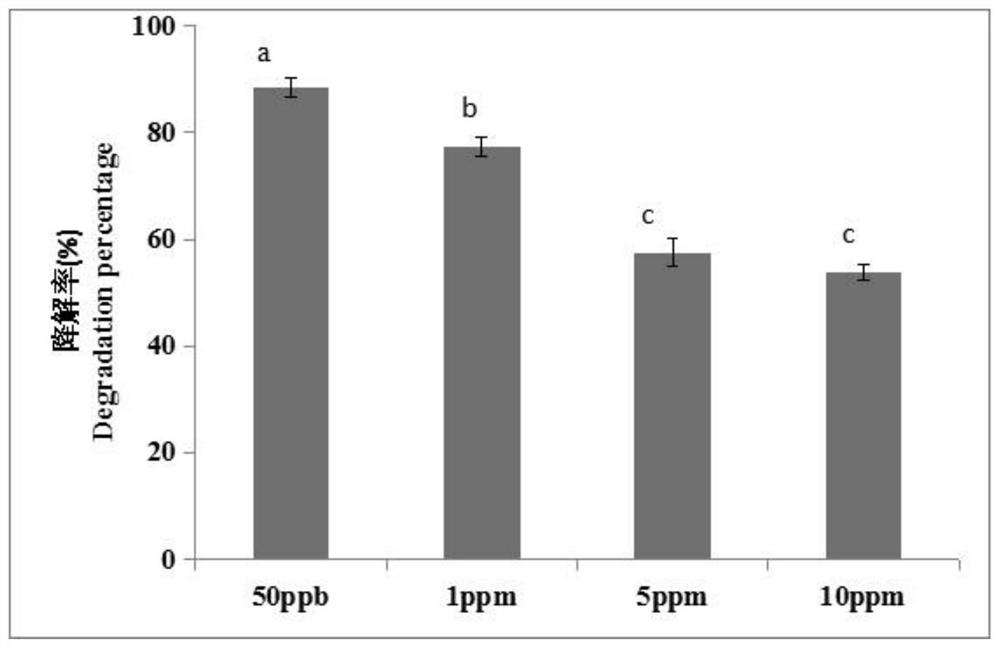
Trichoderma.citrinoviride strain XZ0509 and application thereof
ActiveCN112159764AGood antibacterial effectFungiMicroorganism based processesAflatoxin degradationHypha
The invention provides a trichoderma.citrinoviride strain XZ0509 and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of aflatoxin degradation. The preservation number of the strain XZ0509 is CCTCC M 2020522. The invention further provides the application of the strain XZ0509 in degradation of aflatoxin B1. After the strain XZ0509 is cultured for 3 days, the rate of degradation on an AFB1 solution with the concentration of 50ppt is greater than 80%, after the strain XZ0509 is cultured for 7 days, the AFB1 removal rate is 100%, and after the strain XZ0509 is cultured for 5 days, the rateof degradation on 10ppm AFB1 is still higher than 50%. The strain has strong bacteriostatic and toxin-producing-inhibiting effects at the same time, the inhibition rate on aspergillus flavus hypha is85.6%, and the rate of inhibition on toxin production of aspergillus flavus in peanuts is 92.8%. It is shown that the strain XZ0509 can be applied to degradation of aflatoxin in seriously polluted grain and oil products.
Owner:西藏自治区农牧科学院农业质量标准与检测研究所 +1
Degradation agent of aflatoxin, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108251458ADegradation safetyEfficient degradationMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesAflatoxin degradationFermentation
The invention discloses a degradation agent of aflatoxin, a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of aflatoxin degradation. The degradation agent of the aflatoxin is prepared from the following components: 60-100 g of fresh aloe, 75-125 g of fermentation liquor of fresh lemon, 1% of oleum menthae, 0.1-0.5% of laccase, and 0.2% of Tween-80. Through the mutual coordination among the components, the aflatoxin is adequately degraded. The degradation agent of the aflatoxin is safe in aflatoxin degradation, high-efficient, and mild in reaction conditions, andis capable of degrading the aflatoxin by 96% or above.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com