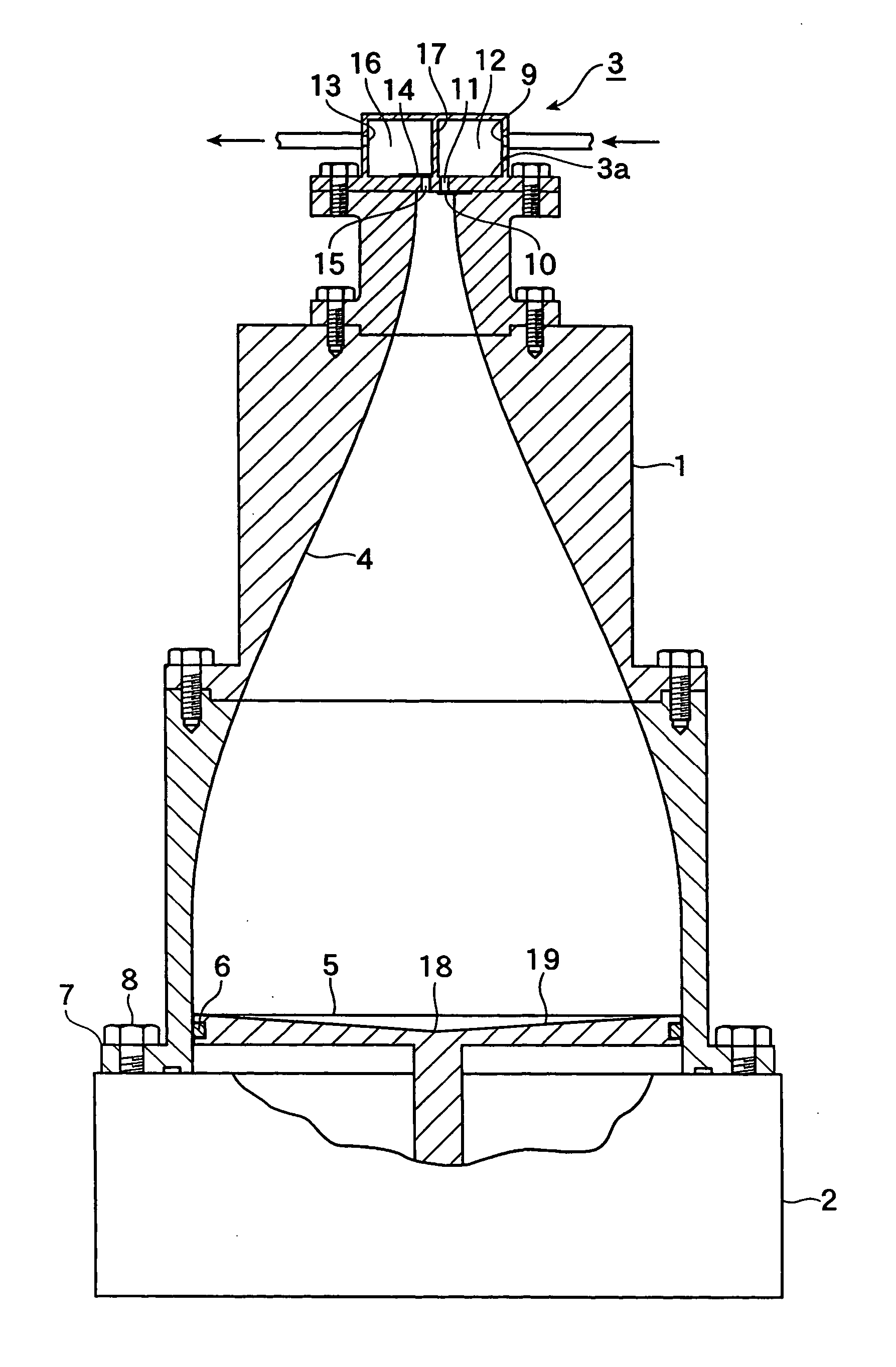
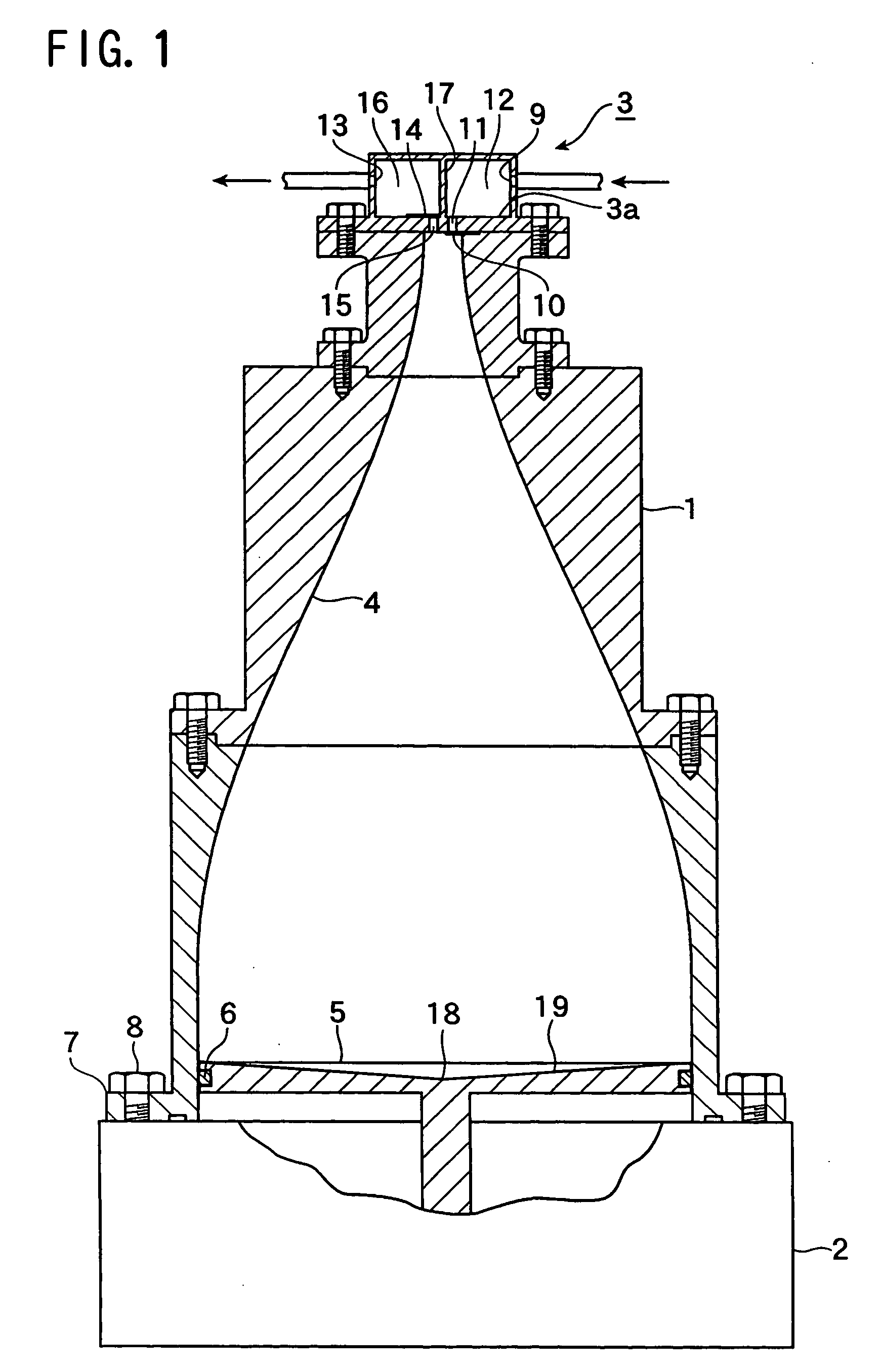
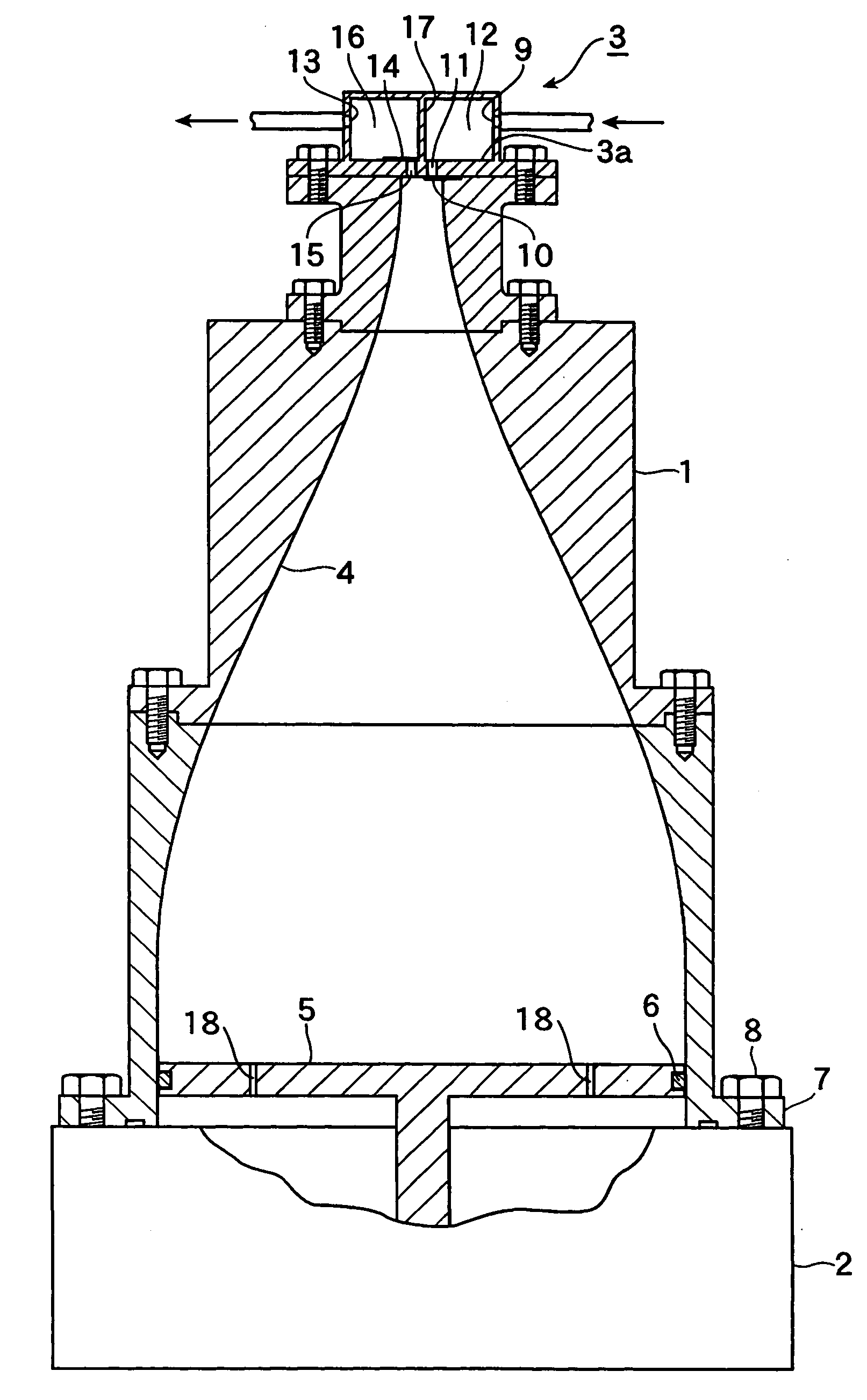
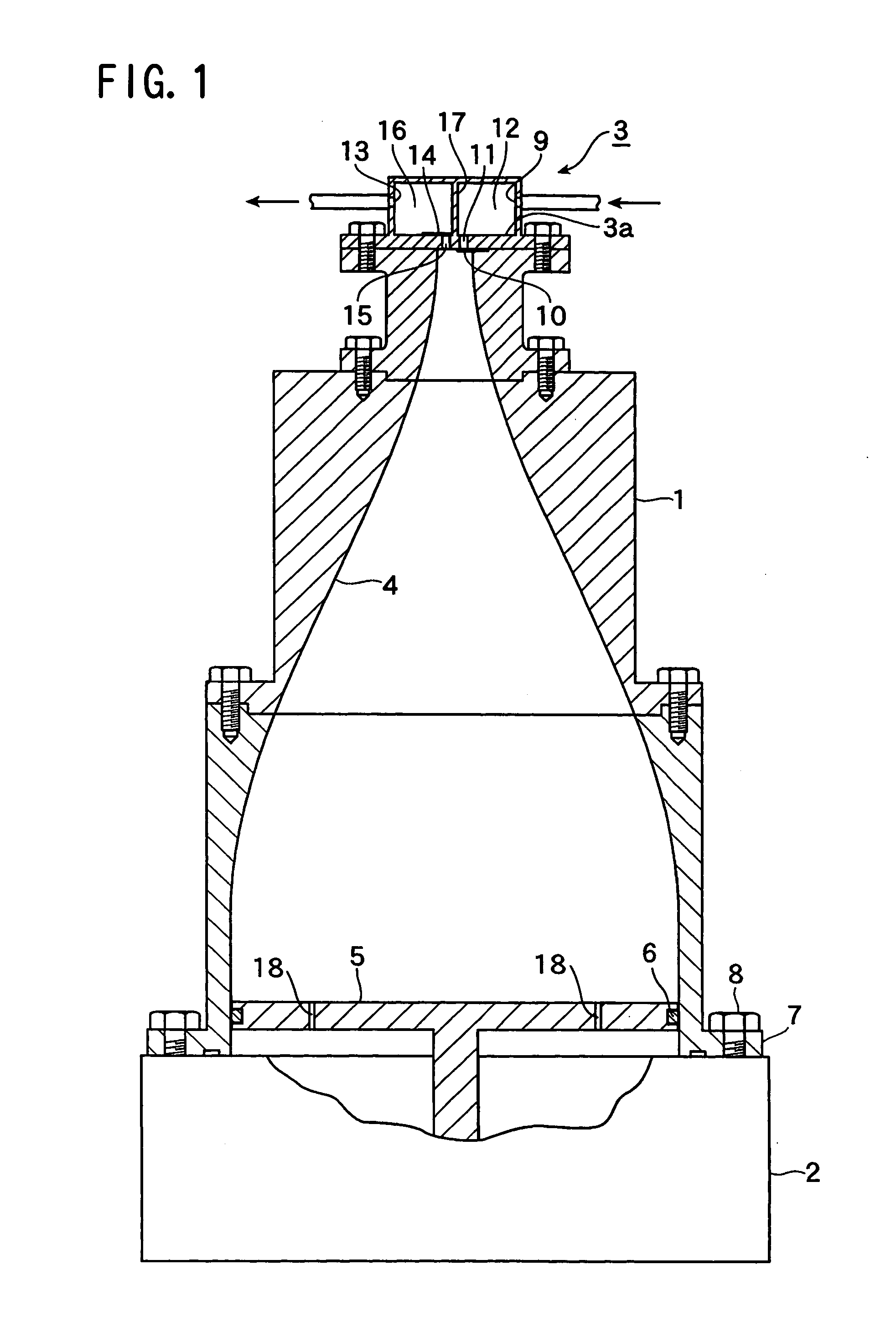
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52 results about "Acoustic Fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
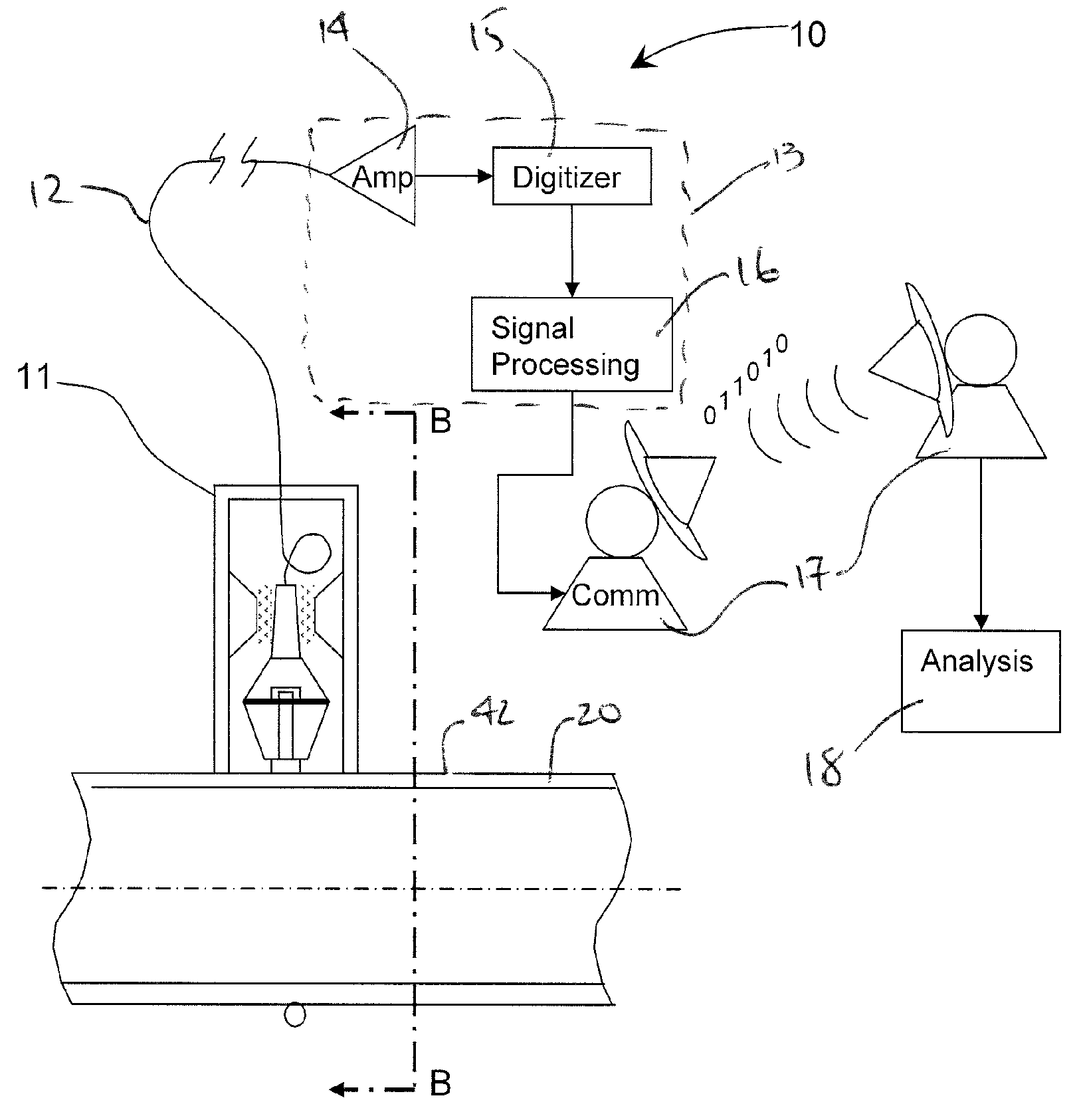
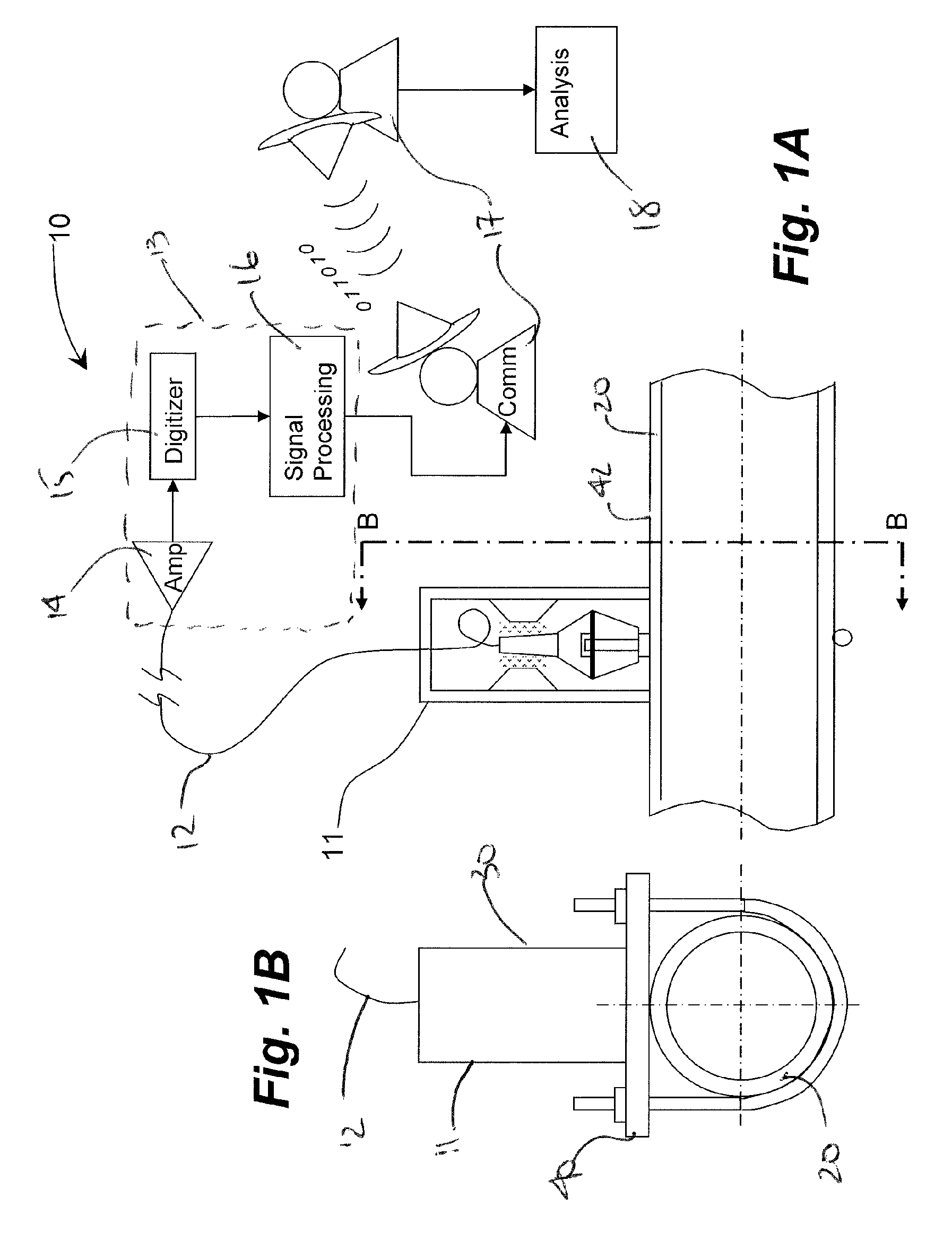
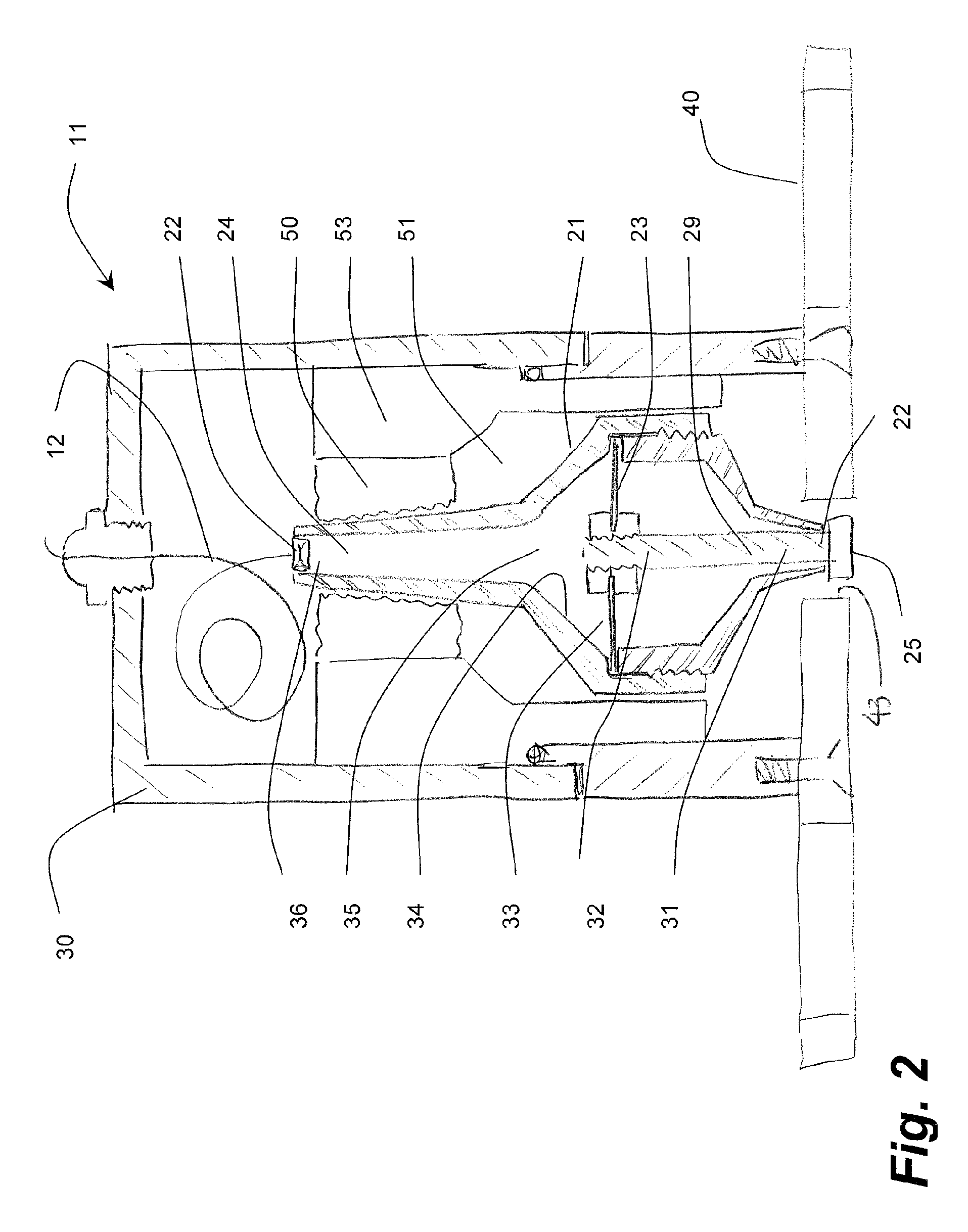
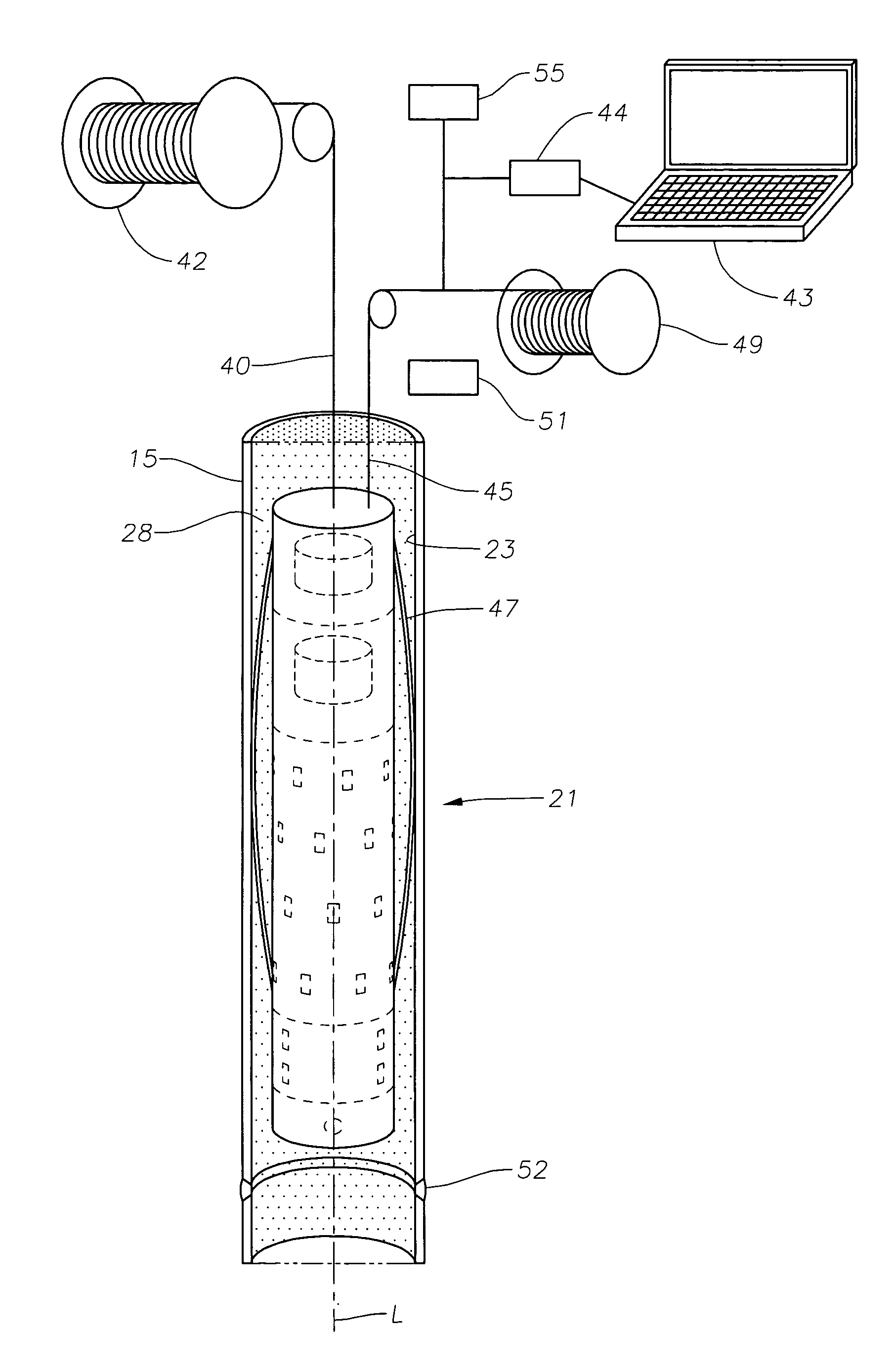
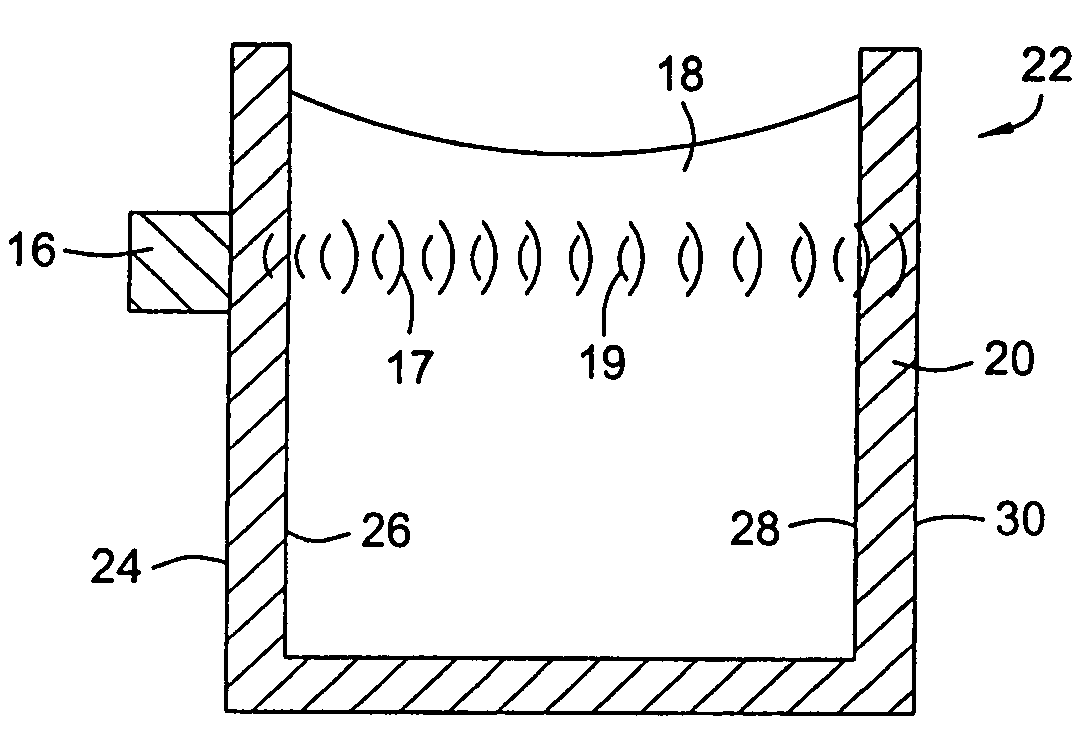
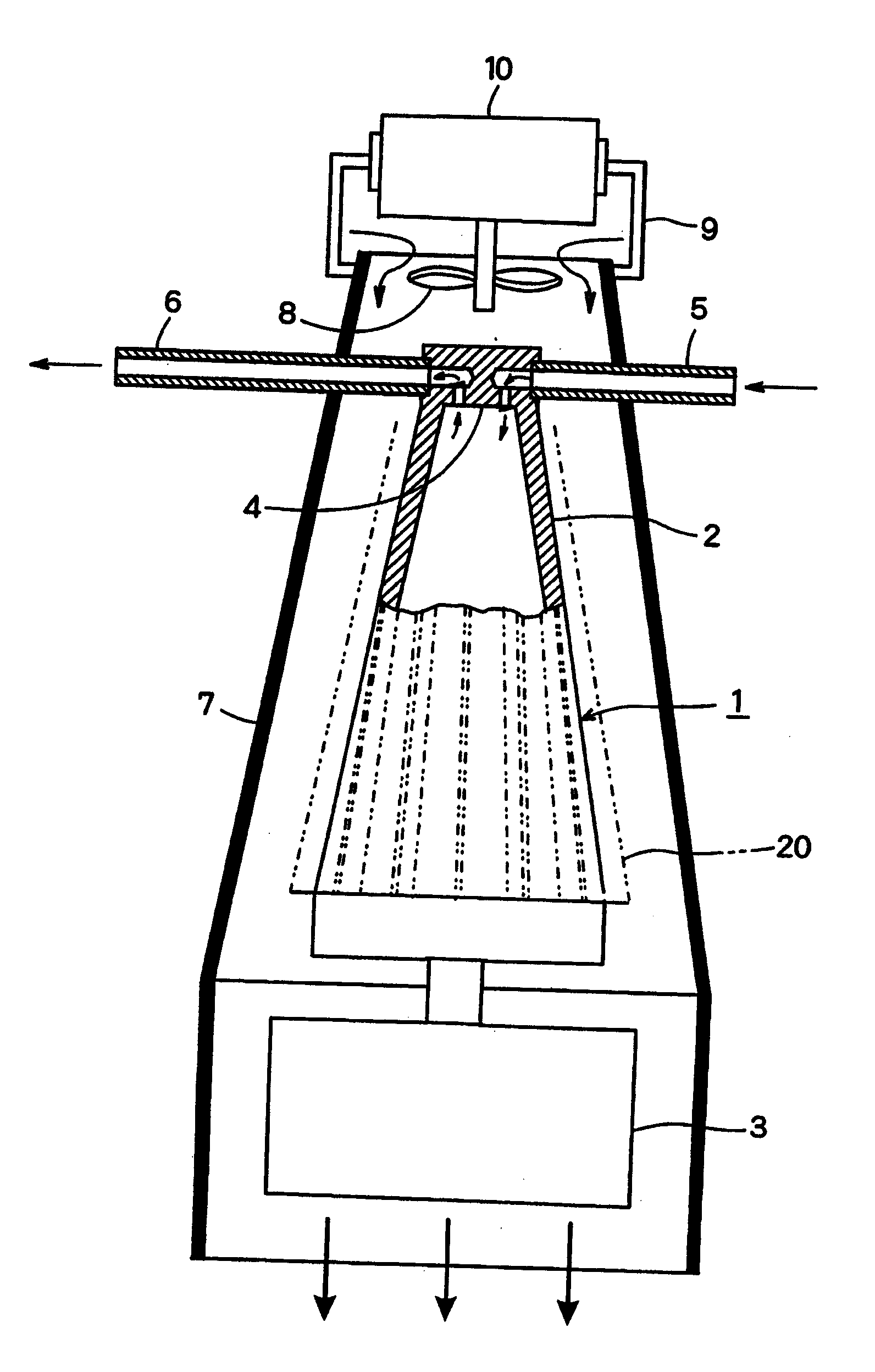
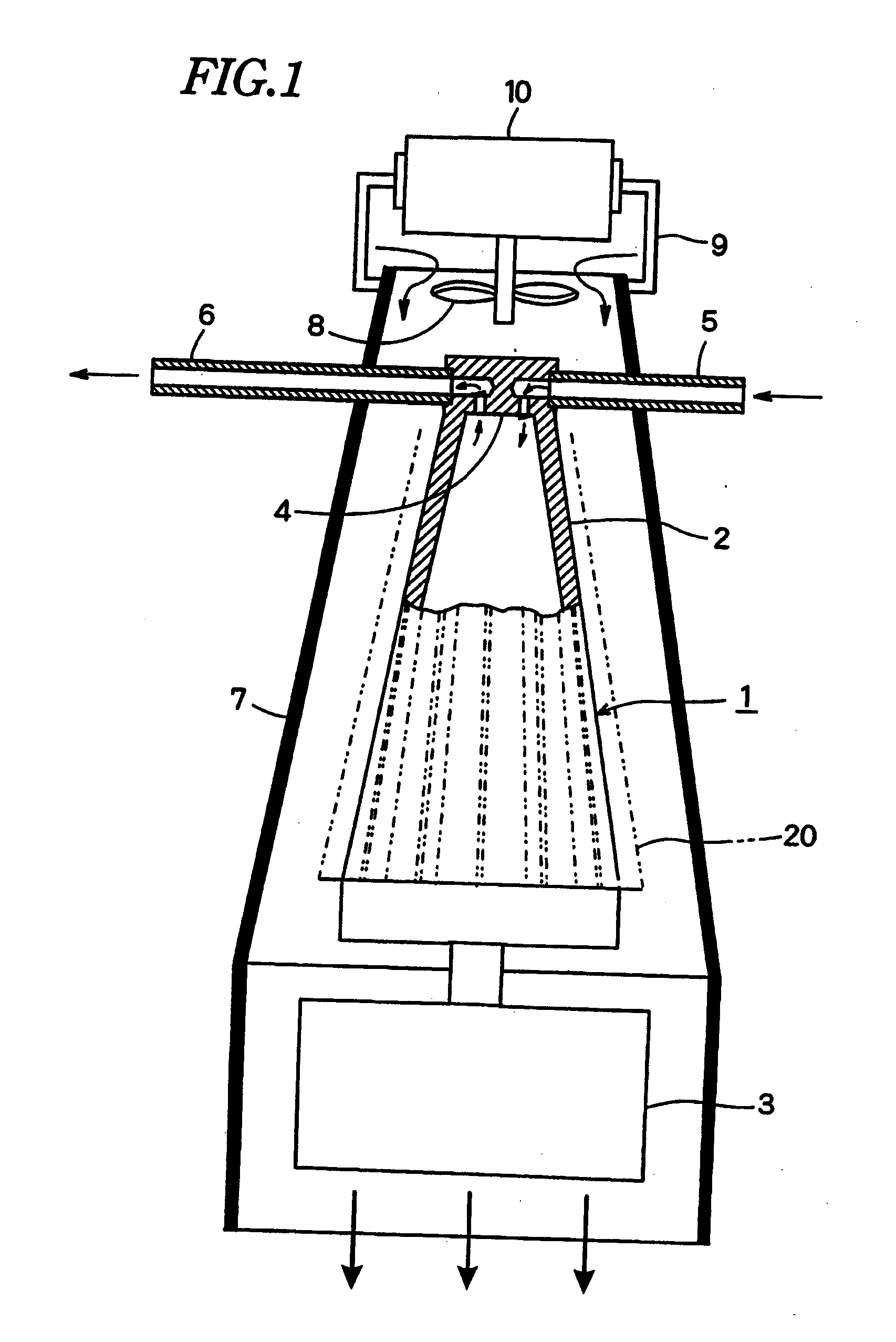
System, method and apparatus for acoustic fluid flow measurement
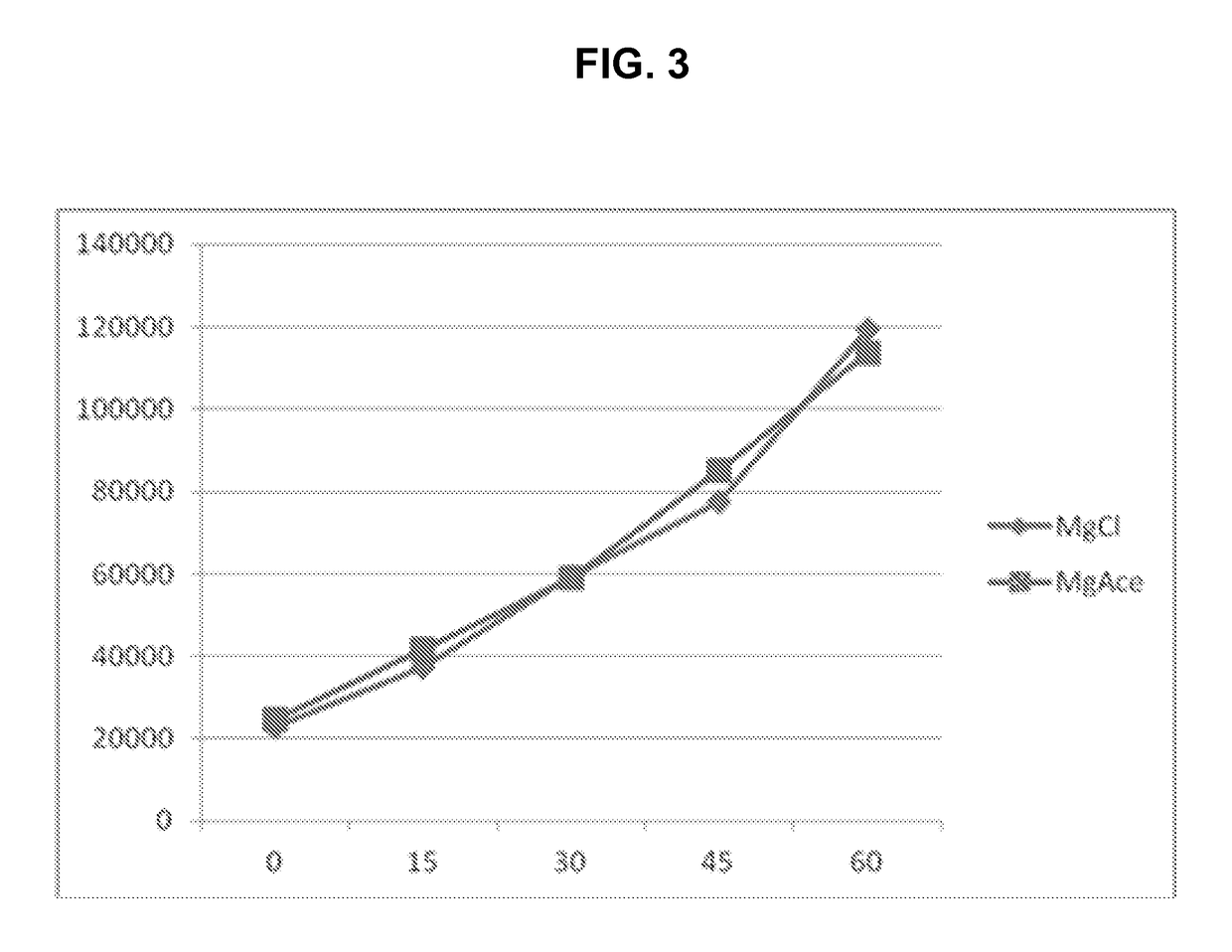
InactiveUS7562584B2Minimal power requirementIncrease signal strengthVolume meteringVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectAudio power amplifierAcoustic energy
An apparatus, system and methodology enable non-intrusive measurement of parameters related to fluid flow in a conduit. An acoustic sensor is located along the conduit and includes a mechanical amplifier having an acoustic input coupled to the conduit and a microphone coupled to the mechanical amplifier. The microphone receives mechanically amplified acoustic energy from the conduit and establishing first signals which are processed for generating second signals which are related to fluid flow in the conduit. The second signals can include quantitative flow data and qualitative data such as change in state and alarms. The second signals can be transmitted wirelessly to a remote site for further processing. Use of low power components and power management enable long term operations on battery power.
Owner:ADVANCED FLOW TECH
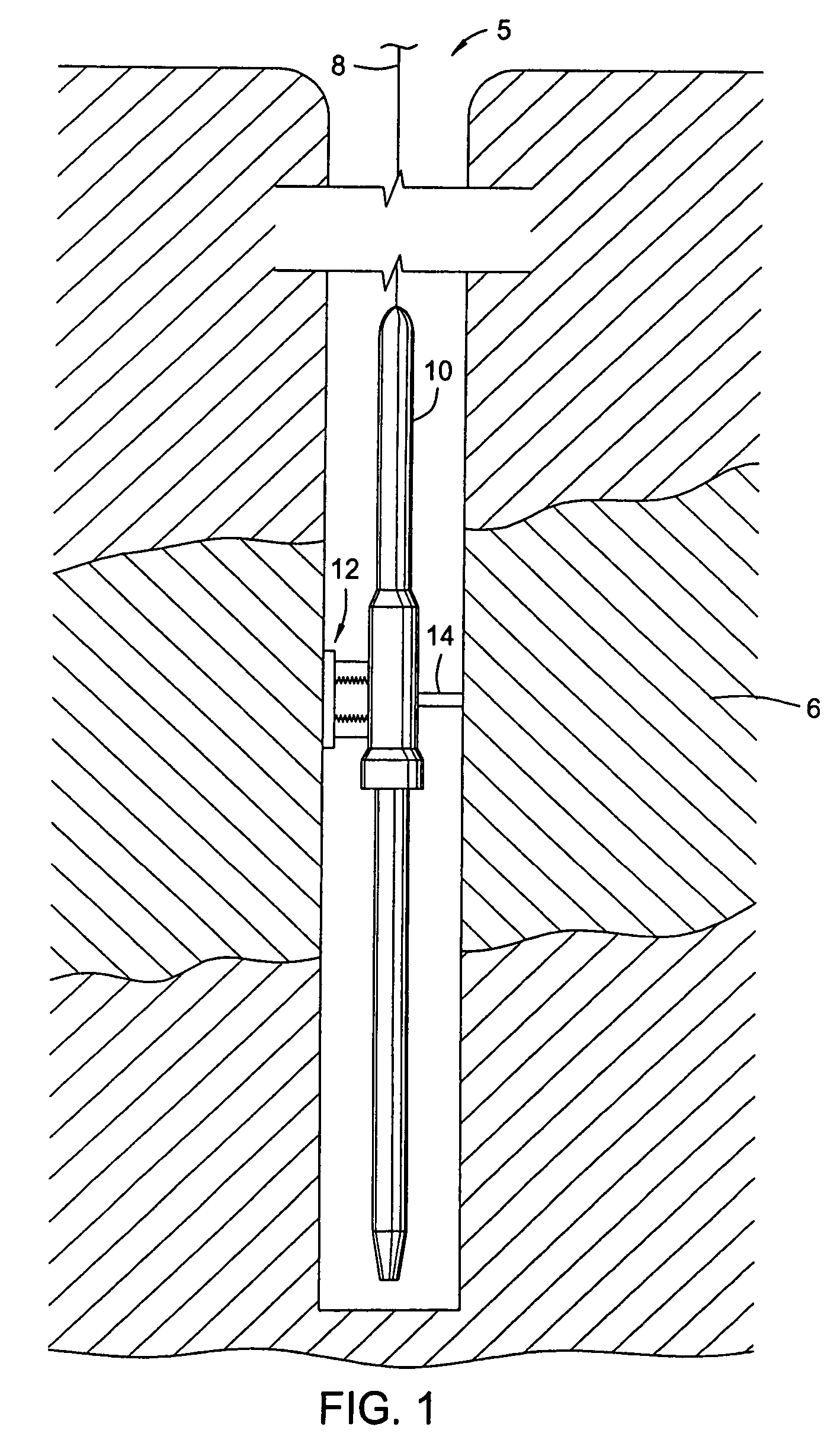
Internal riser inspection device and methods of using same
InactiveUS7082822B2Small outer diameterAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDrilling rodsDiffusionComputer module
An inspection apparatus includes an inspection unit that is lowered into vertically supported pipe filled with seawater. The apparatus includes a pipe weld location detector module carried by the inspection unit. The apparatus also includes a rotating time of flight diffusion (TOFD) module and a non-rotating wall thickness module carried by the inspection unit. The module includes a pair of rotatably mounted weld volume inspection transducers rotatable by an operator and adapted to inspect for and obtain data on weld volume defects. The TOFD module has a fluid carrier positioned within the TOFD module and contains an acoustic fluid. The non-rotating wall thickness module also contains an acoustic liquid and includes a plurality of fixedly mounted wall inspection transducers adapted to obtain data on wall thickness of a portion of the pipe.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
Method for acoustically ejecting a droplet of fluid from a reservoir by an acoustic fluid ejection apparatus
The invention provides apparatuses and methods for acoustically ejecting the fluid from a reservoir contained in or disposed on a substrate. The reservoir has a portion adapted to contain a fluid, and an acoustic radiation generator is positioned in acoustic coupling relationship to the reservoir. Acoustic radiation generated by the acoustic radiation generator is transmitted through at least the portion of the reservoir to an analyzer. The analyzer is capable of determining the energy level of the transmitted acoustic radiation and raising the energy level of subsequent pulses to a level sufficient to eject fluid droplets from the reservoir. The invention is particularly suited for delivering fluid from a plurality of reservoirs in an accurate and efficient manner.
Owner:LABCYTE
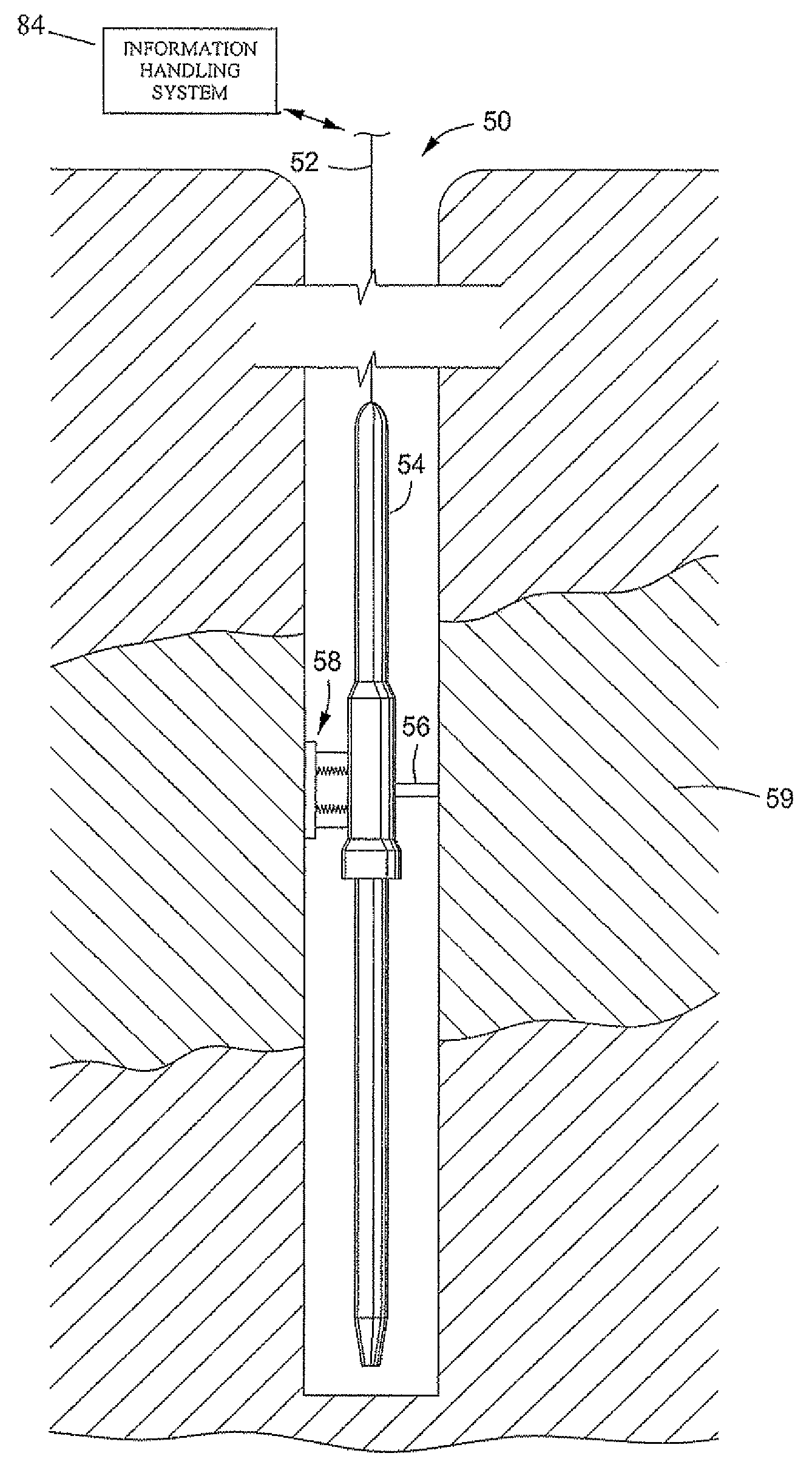
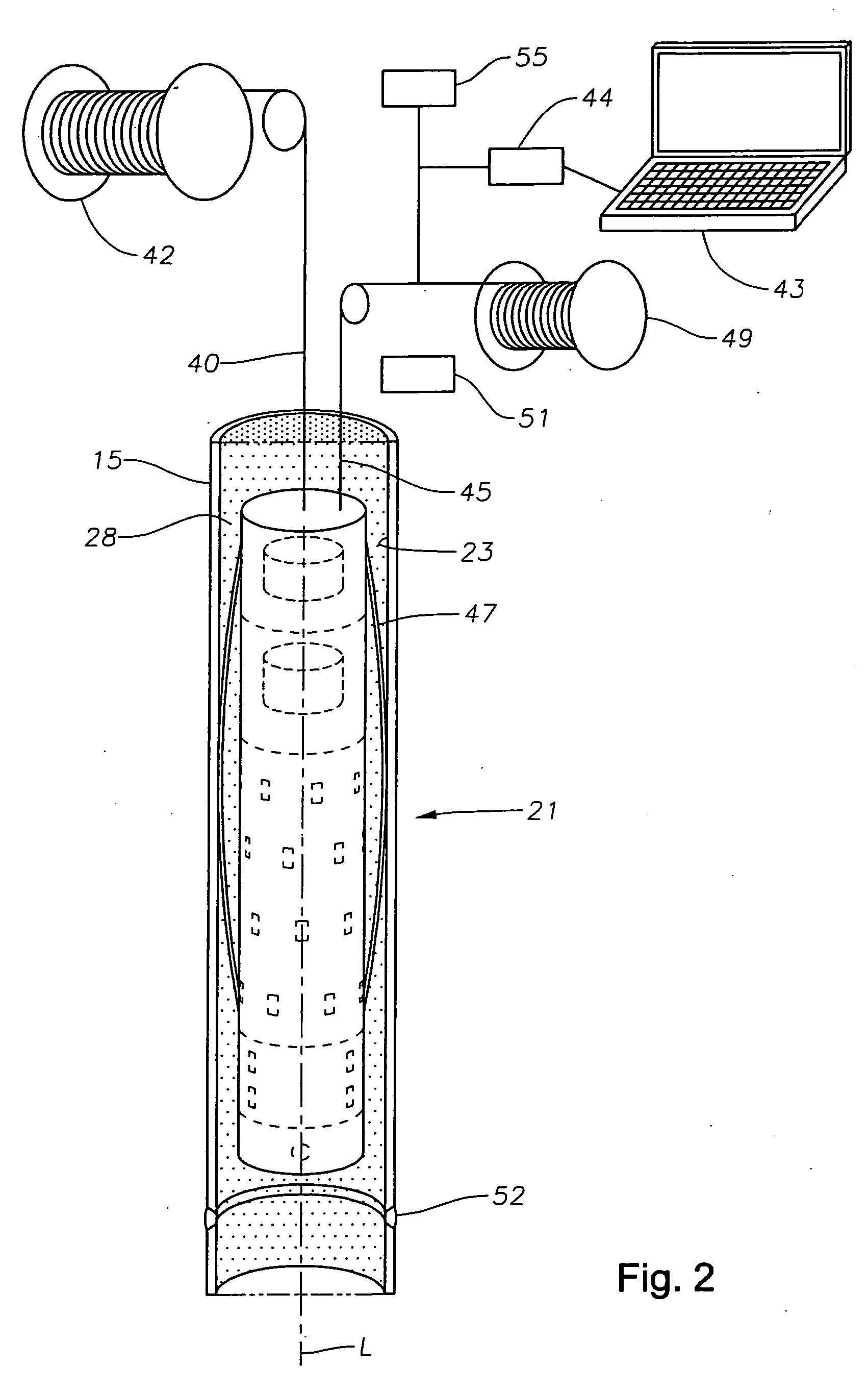
Acoustic fluid analyzer
ActiveUS7523640B2Easy to adaptAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesGas oil ratioFormation fluid
A method of determining properties of a formation fluid based on measurements of fluid sound speed, a measurement of fluid density, or both. The properties include compressibility, thermal conductivity, and gas oil ratio. The compressibility of a fluid is equal to the reciprocal of the product of the sound speed squared and fluid density. The density and the sound speed can be measured acoustically. The method further includes a manner of processing data including applying the Savitzky-Golay method and utilizing a variable thresholding technique.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
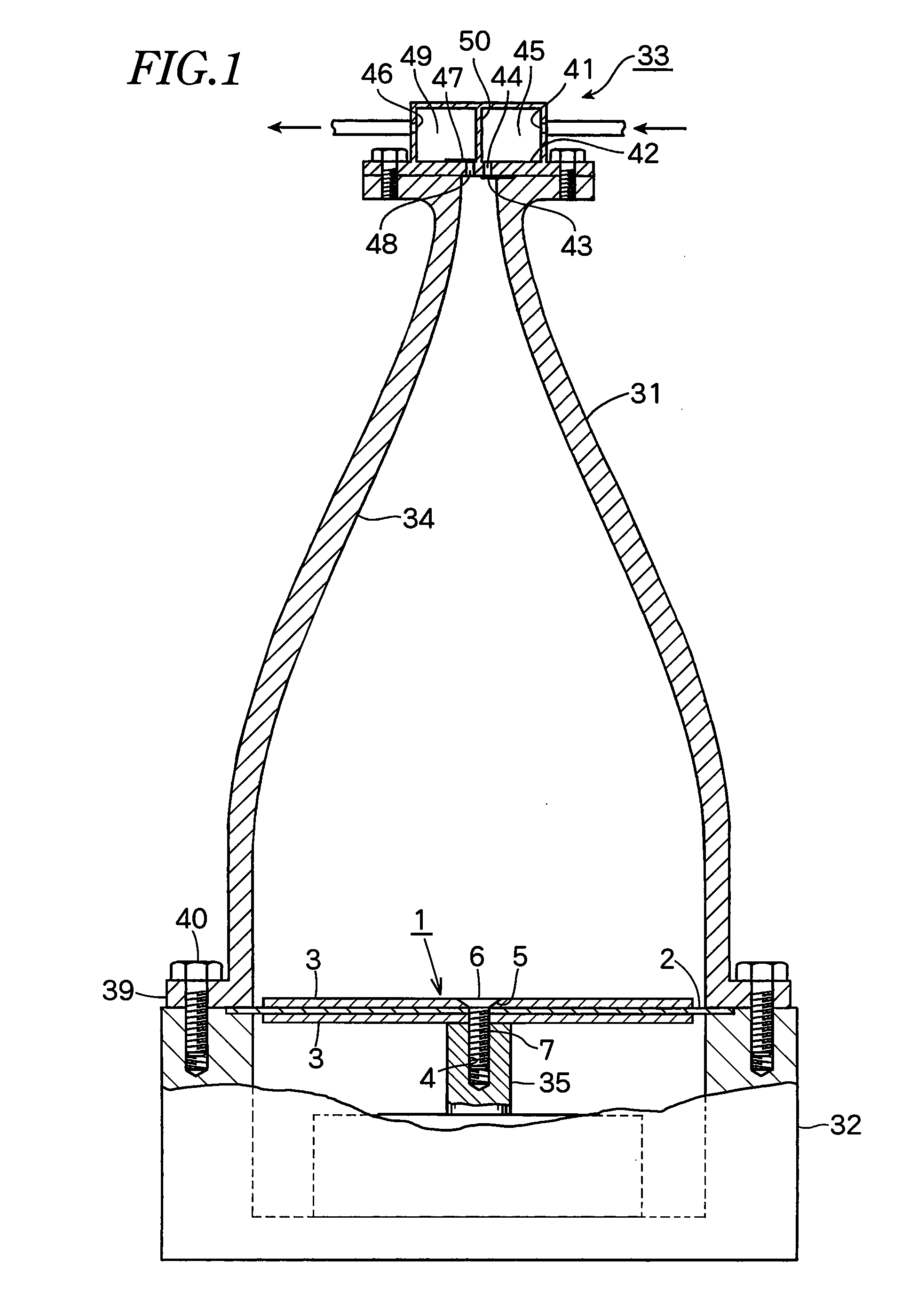
Acoustic fluid level sensor
InactiveUS20070180903A1Simple and reliable processSimple and reliable fluid levelMachines/enginesLubrication indication devicesUltrasonic sensorTransducer
An acoustic fluid level sensor for use in a chamber contained in a surgical cassette. The sensor has an ultrasound transducer mounted on the outside of the bottom of a fluid chamber and is acoustically coupled to the chamber. The transducer sends a pulse ultrasound signal through the chamber and any liquid in the chamber. The signal is reflected back by the air / liquid interface and captured by the transducer. The time required for the signal to travel to and from the transducer will vary with the amount of fluid in the chamber and is indicative of the level of fluid in the chamber.
Owner:ALCON INC
Acoustic fluid analysis method
A method of analyzing acoustic data, that includes determining fluid sound speed through connate fluid. The method involves sampling the fluid, sending an acoustic signal into the fluid between a first and a second reflective interface. Data is recorded that represents acoustic signals over time as they are reflecting from the interfaces. A smoothed first derivative with respect to time of the cumulative sum of squares (CSS) of the filtered amplitude data is determined. This first derivative is cross correlated to the time-shifted versions of itself.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Acoustic fluid-gauging system
An aircraft ultrasonic fuel-gauging system has a processing unit that energizes probes and receives signals from transducers arising from energy reflected back from the fuel surface. In addition to determining the time between transmission of a signal from the transducer and reception of its reflection from the fuel surface, the processing unit also determines the time of reception of subsequent reflections caused by reflection back from the lower end of the probe. The processing unit determines whether the subsequent reflected signals are within predetermined limits of the time interval between transmission and reception of the first reflected signal in order to confirm the validity of the first signal. The processing unit also counts the number of subsequent reflected signals received within predetermined time intervals to assign a confidence level and this used to select between different incompatible signals, such as signals from that probe at different times or signals from different probes.
Owner:ONTIC ENG & MFG UK
Device for generating acoustic fluid tweezers
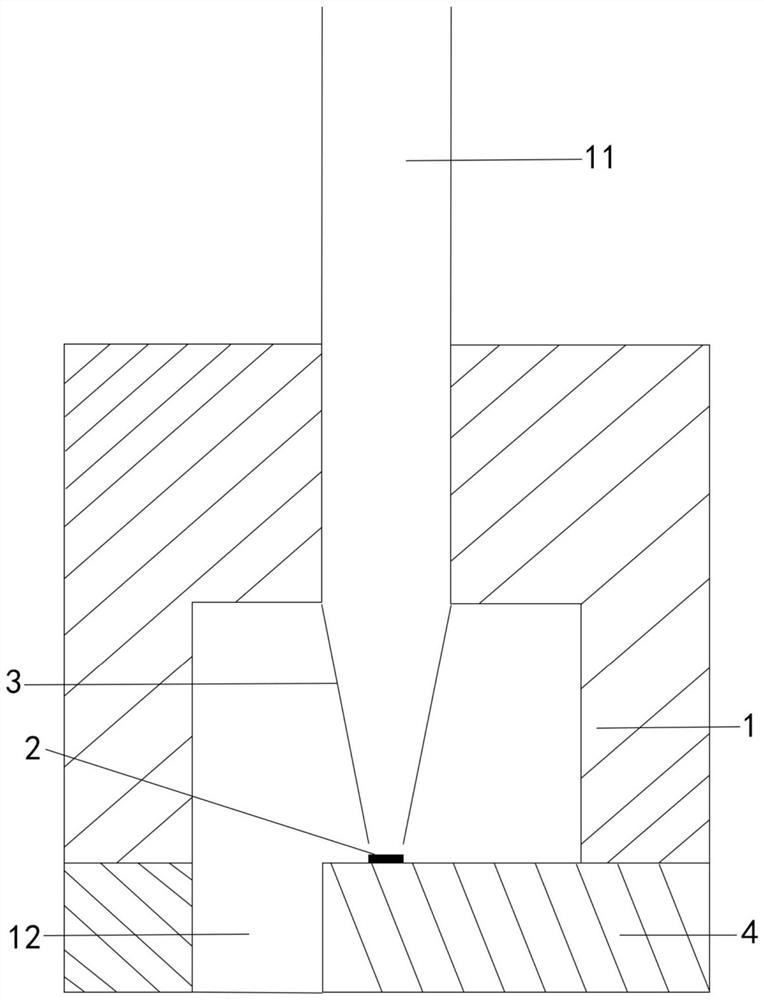
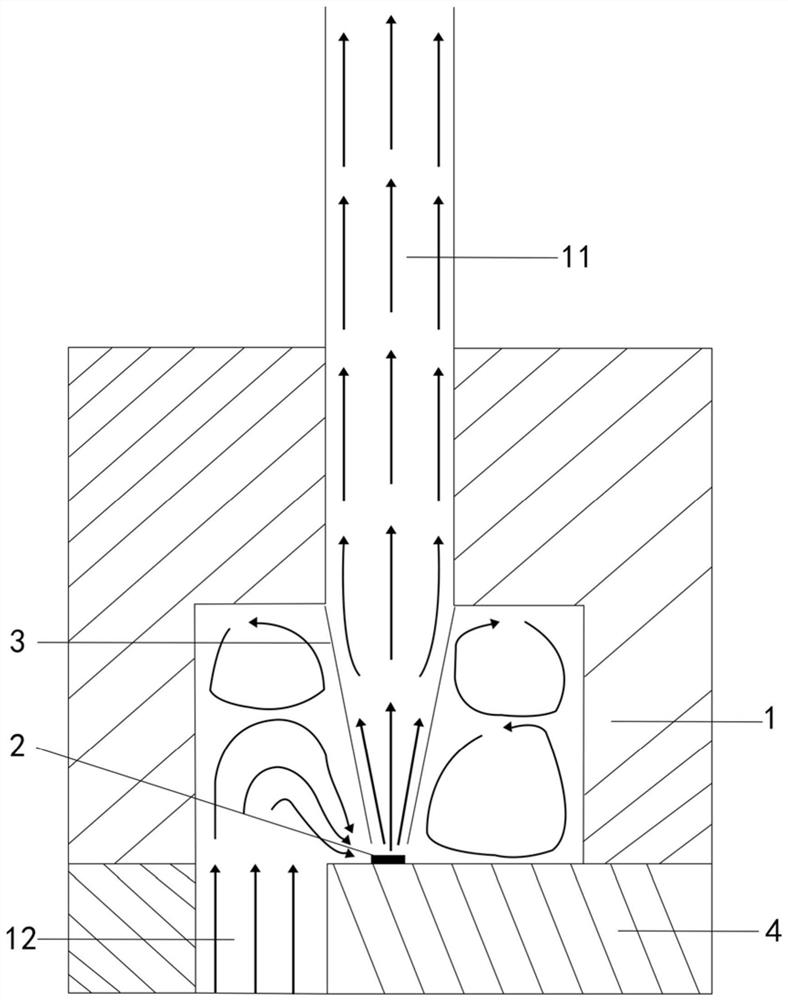
The embodiment of the invention discloses a device for generating acoustic fluid tweezers. The device comprises at least one bulk acoustic wave generating part, an acoustic wave reflection part, a bulk acoustic wave generating area, a bottom lining layer, at least one flow channel and a passivation layer, wherein the bulk acoustic wave generating part comprises a bottom electrode, a piezoelectriclayer and a top electrode which are arranged sequentially from bottom to top; the acoustic wave reflection part is contacted with one side of the bulk acoustic wave generating part; the superposed area of the bottom electrode, the piezoelectric layer, the top electrode and the acoustic wave reflection part form the bulk acoustic wave generating area; the bottom lining layer is used for supportingthe bulk acoustic wave generating part; a part of an area of a flow channel cavity of the flow channel covers an acoustic wave action area of the at least one bulk acoustic wave generating area; and the passivation layer covers a part which is on the piezoelectric layer and does not cover the top electrode. The acoustic fluid tweezers generated by the device can realize accurate operation on objects with molecule, nanoparticle and micrometer size.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Internal riser inspection device and methods of using same
InactiveUS20060137441A1Small outer diameterAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDrilling rodsDiffusionTransducer
An inspection apparatus includes an inspection unit that is lowered into vertically supported pipe filled with seawater. The apparatus includes a pipe weld location detector module carried by the inspection unit. The apparatus also includes a rotating time of flight diffusion (TOFD) module and a non-rotating wall thickness module carried by the inspection unit. The module includes a pair of rotatably mounted weld volume inspection transducers rotatable by an operator and adapted to inspect for and obtain data on weld volume defects. The TOFD module has a fluid carrier positioned within the TOFD module and contains an acoustic fluid. The non-rotating wall thickness module also contains an acoustic liquid and includes a plurality of fixedly mounted wall inspection transducers adapted to obtain data on wall thickness of a portion of the pipe.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
Acoustic fluid analyzer
ActiveUS20090229341A1Easy to adaptAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesGas oil ratioFormation fluid
A method of determining properties of a formation fluid based on measurements of fluid sound speed, a measurement of fluid density, or both. The properties include compressibility, thermal conductivity, and gas oil ratio. The compressibility of a fluid is equal to the reciprocal of the product of the sound speed squared and fluid density. The density and the sound speed can be measured acoustically. The method further includes a manner of processing data including applying the Savitzky-Golay method and utilizing a variable thresholding technique.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
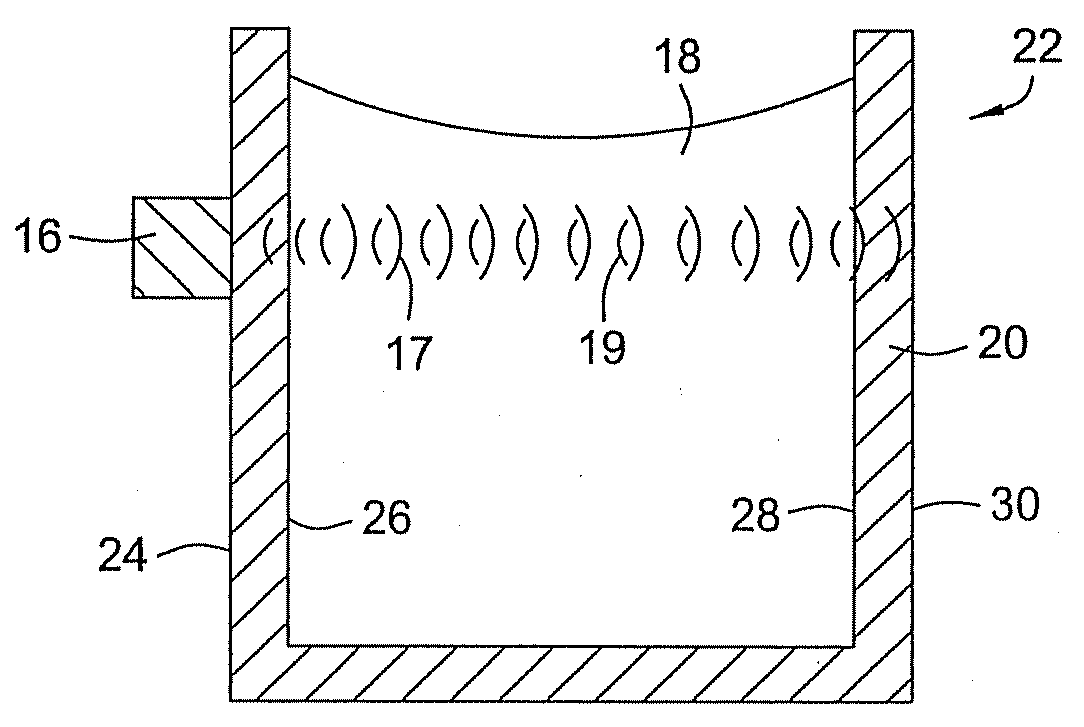
Acoustic fluid machine
InactiveUS20060054382A1Small gradientSilencing apparatusMachines/enginesSmall amplitudeReciprocating motion
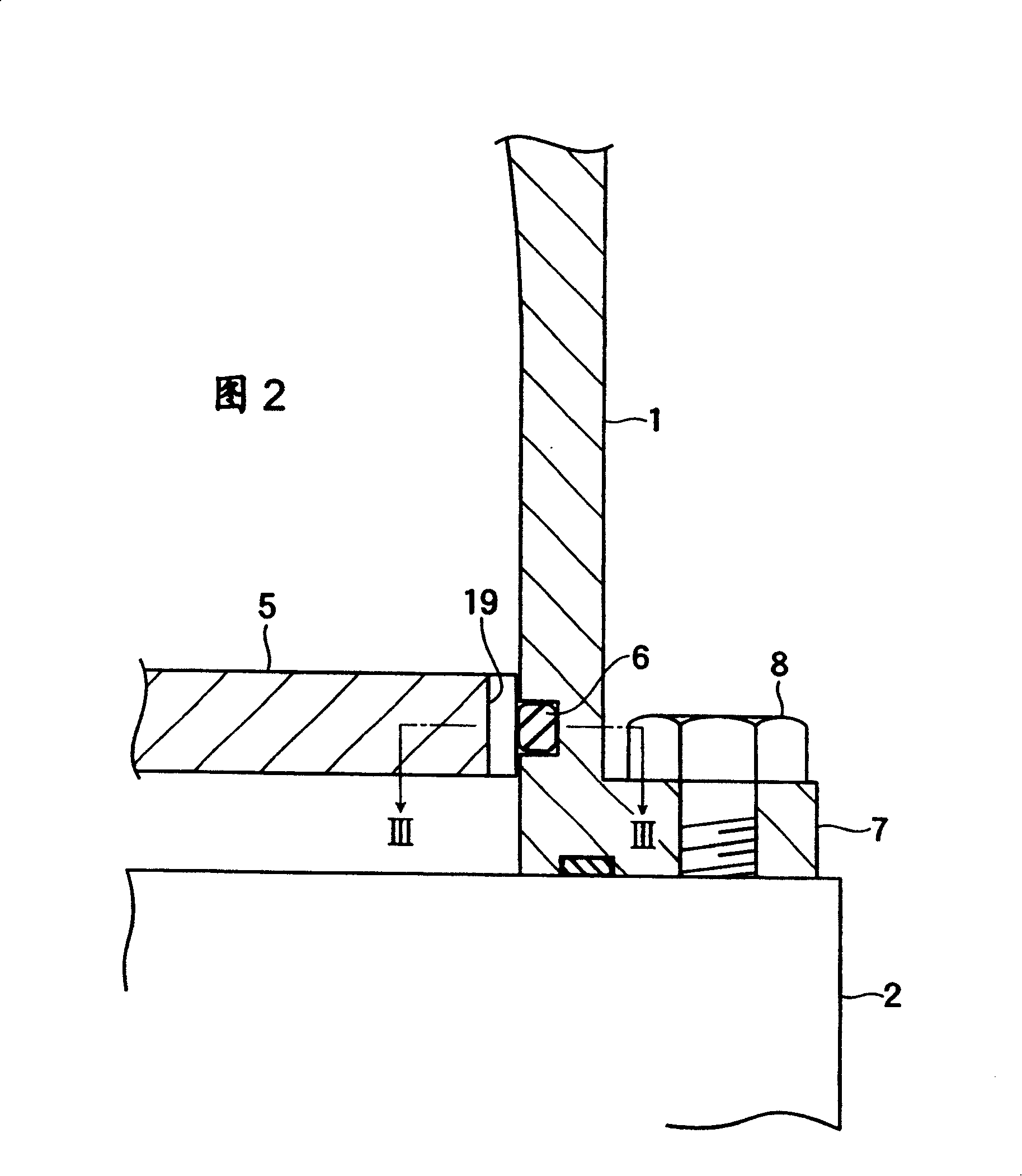
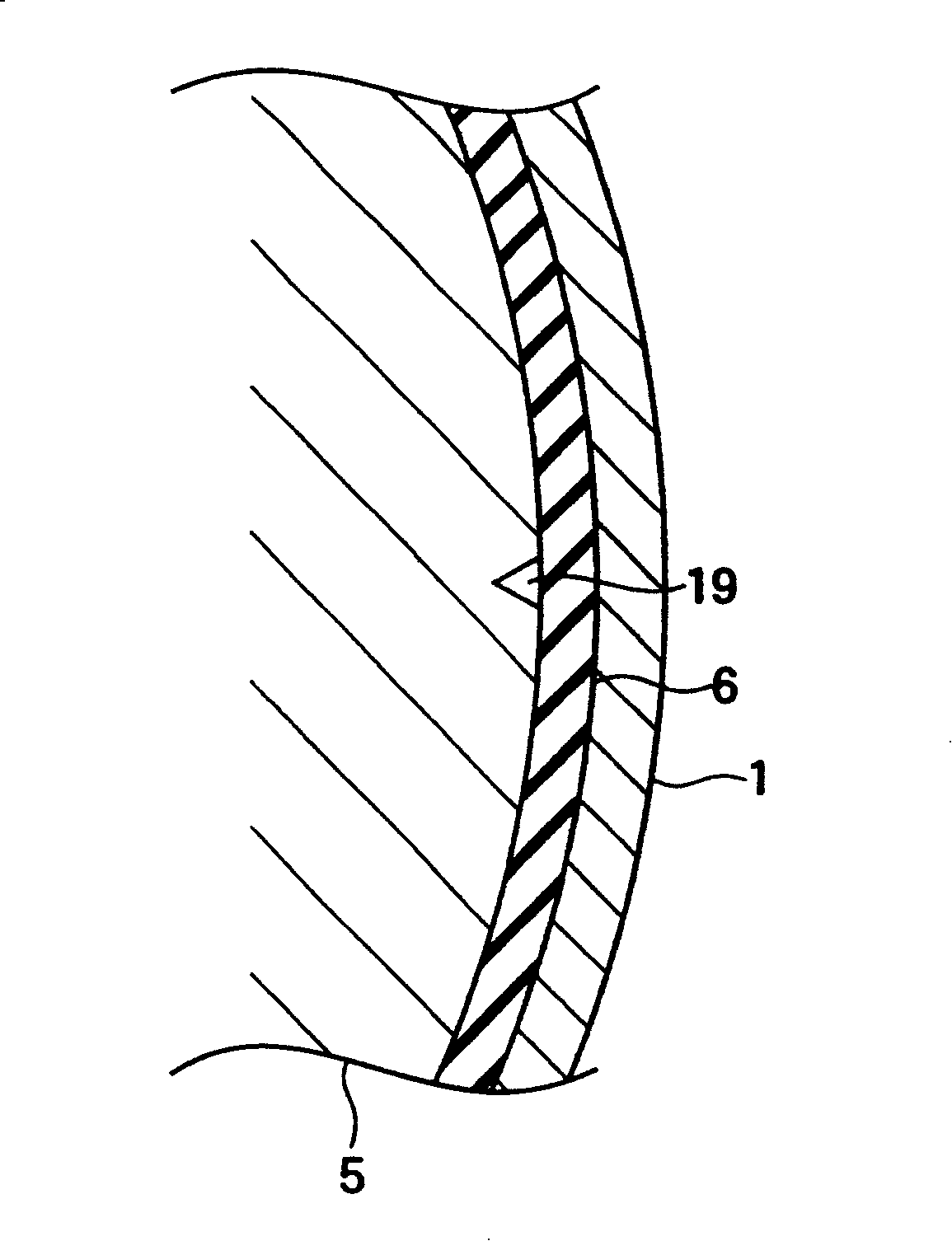
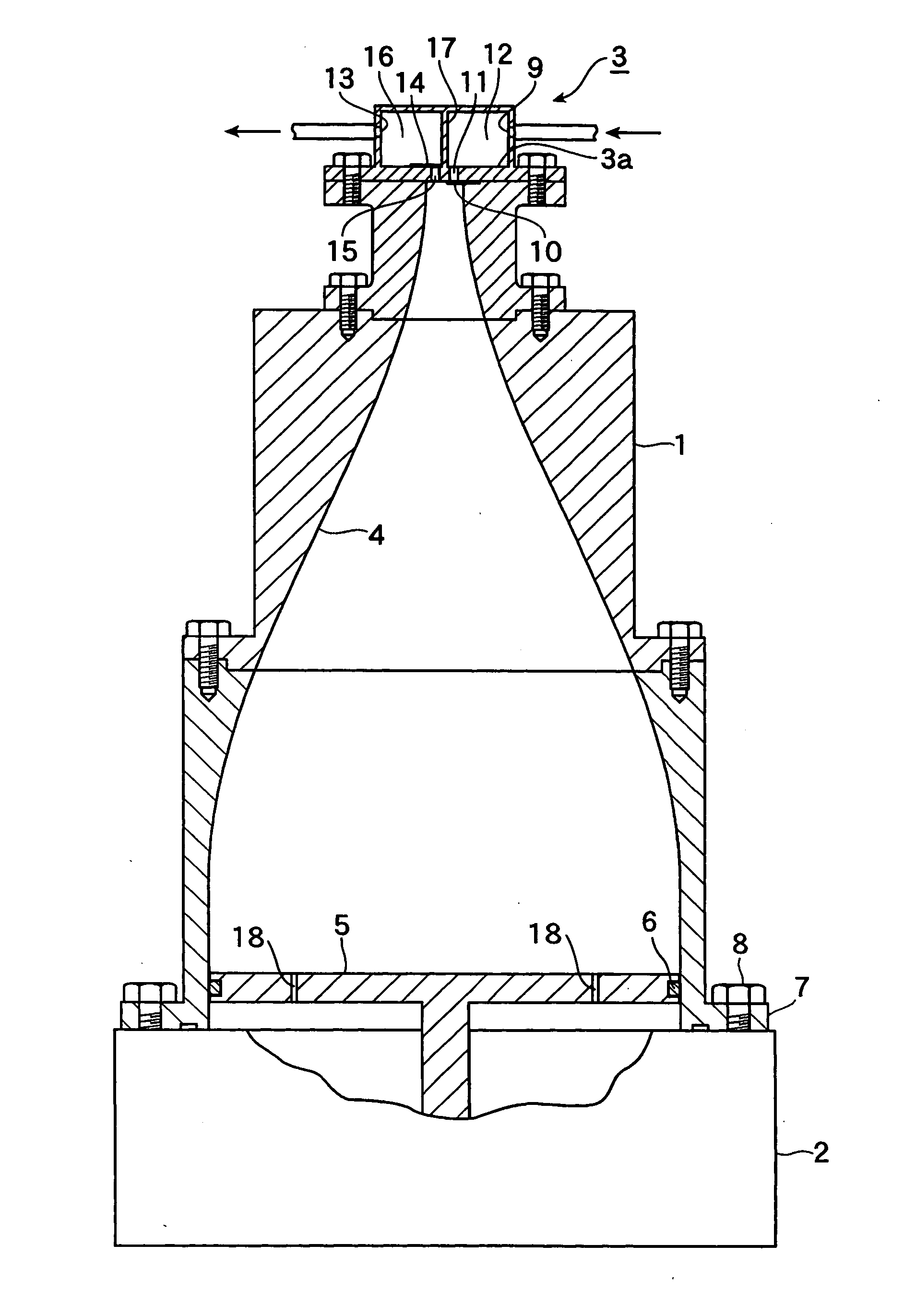
In an acoustic resonator, an actuator allows a piston to reciprocate axially at very small amplitude at high speed. Owing to pressure fluctuation in the acoustic resonator involved by reciprocal motion of the piston, fluid is sucked into and discharged from the acoustic resonator via a valve device at the top end of the acoustic resonator. The acoustic resonator is covered with a gas guide with a space. The valve device is cooled by a fan at the top end of the gas guide.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
Acoustic fluid machine
InactiveUS20060037812A1Reduce waveform strainReduce variationFlexible member pumpsSilencing apparatusResonanceReciprocating motion
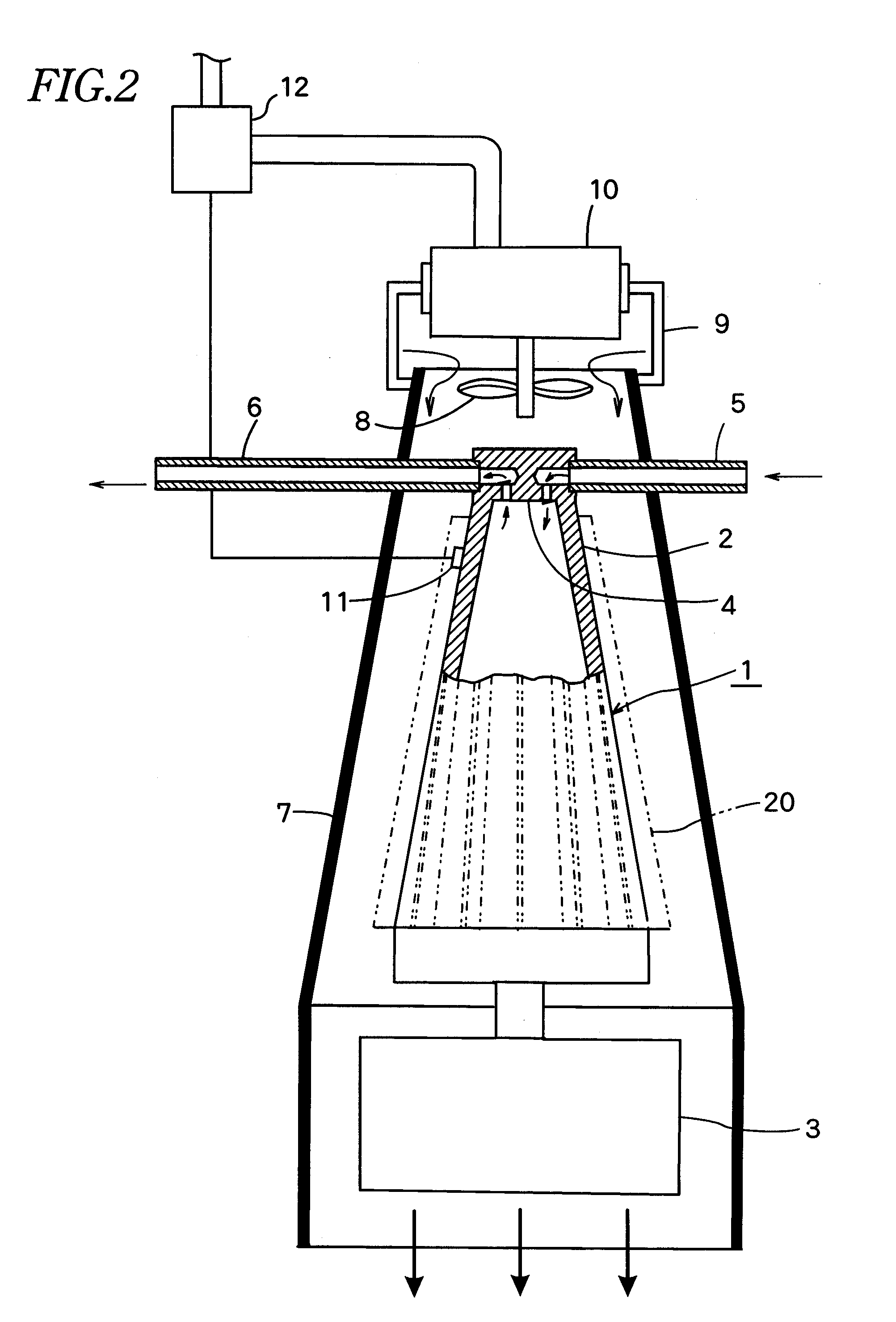
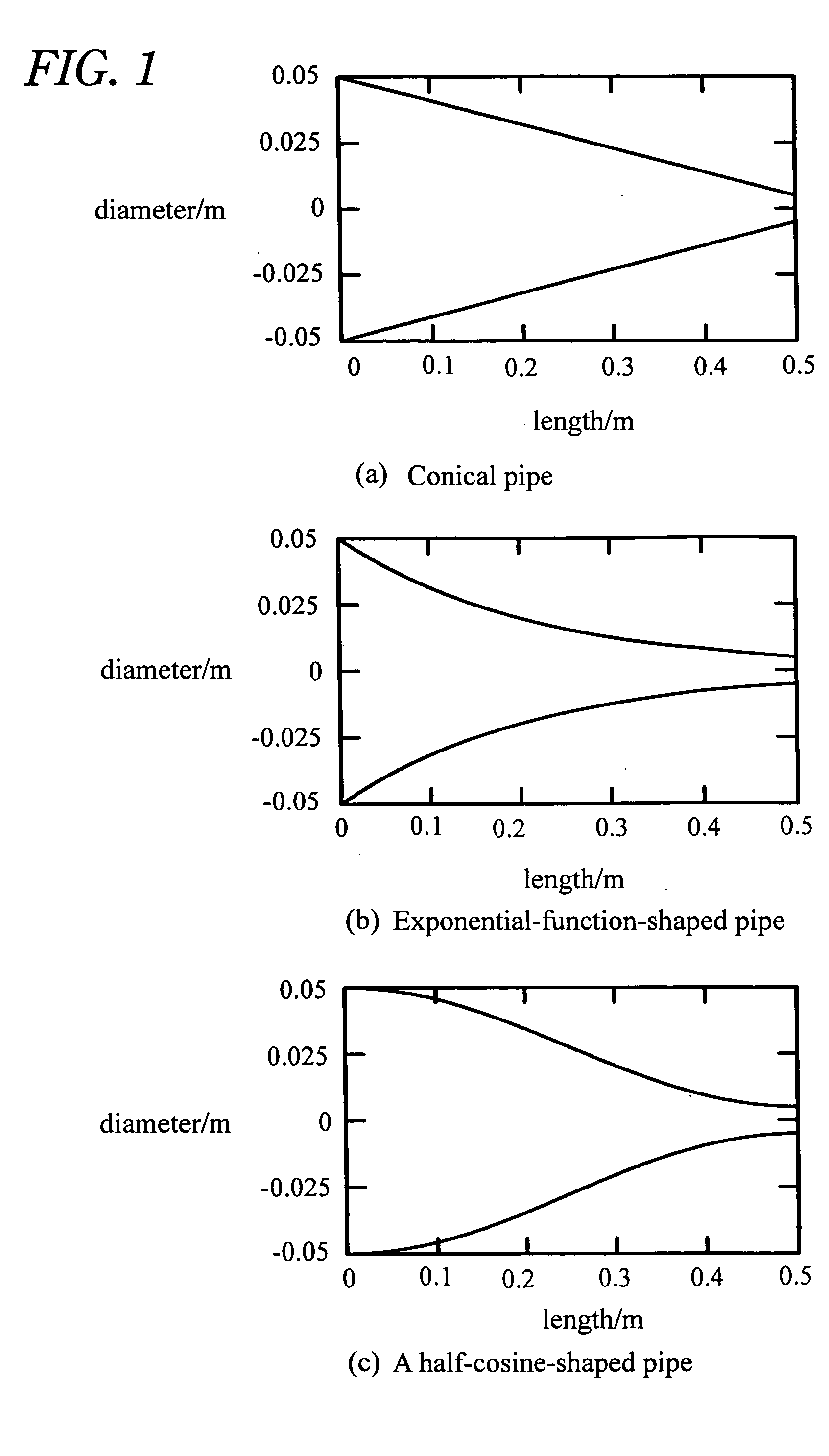
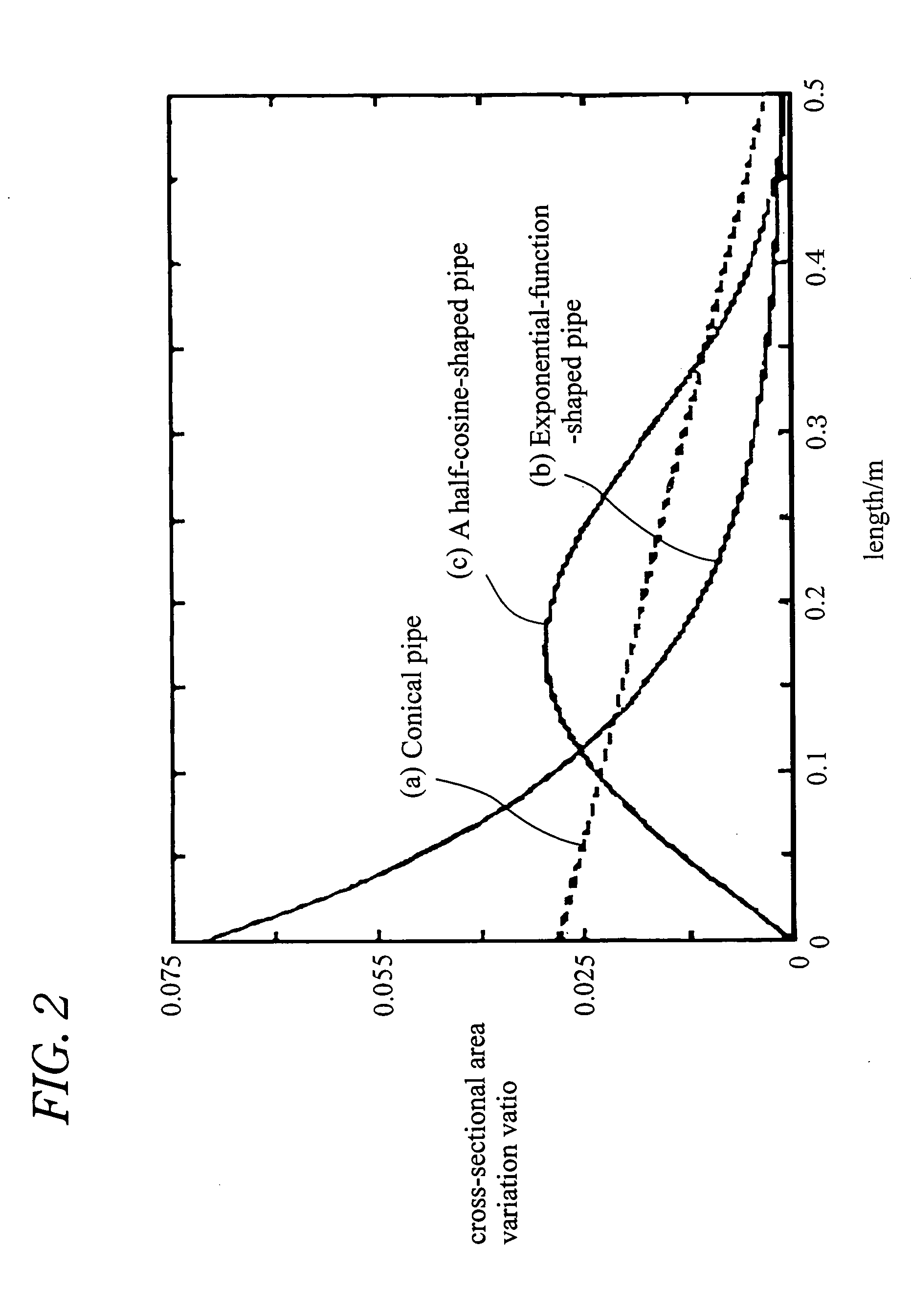
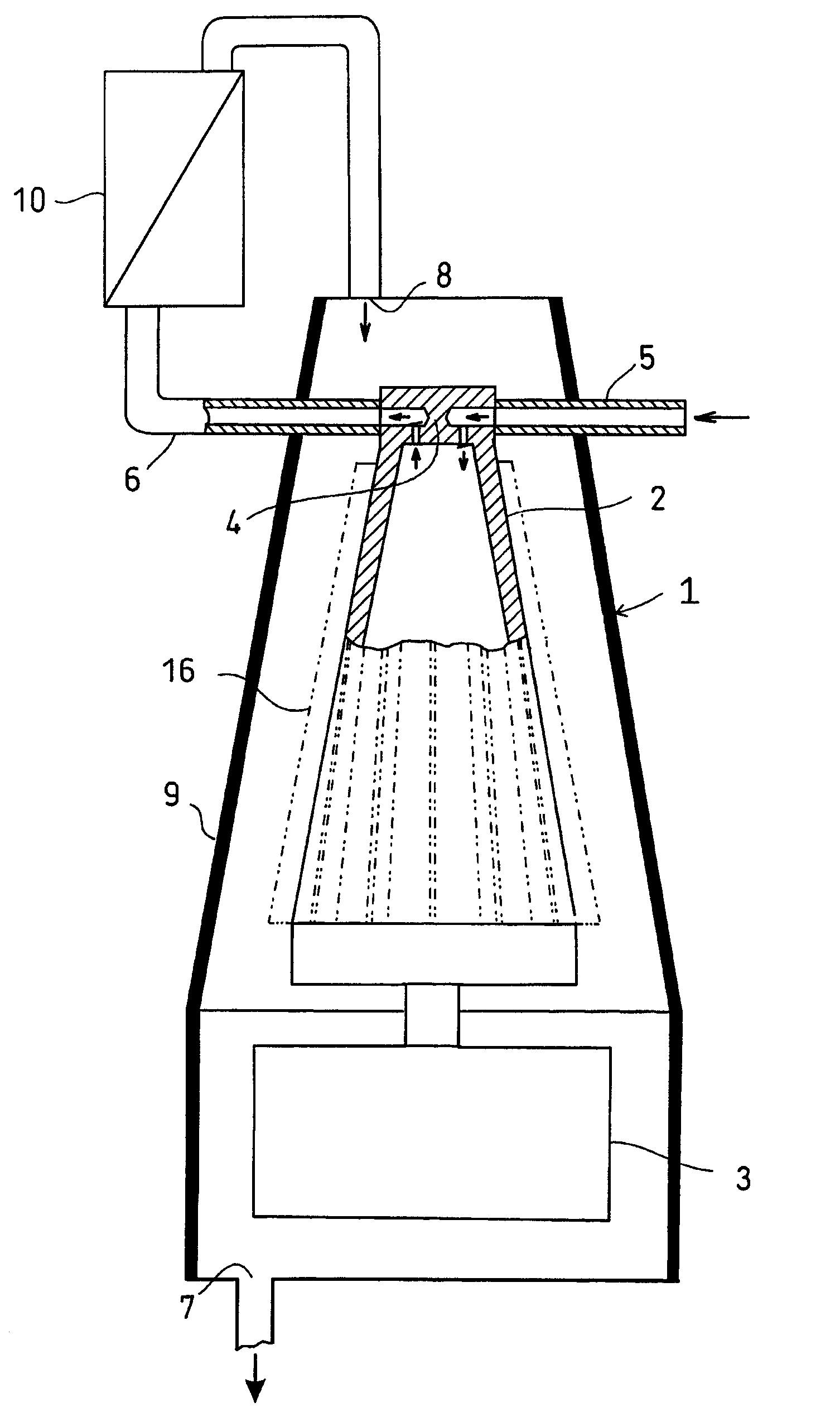
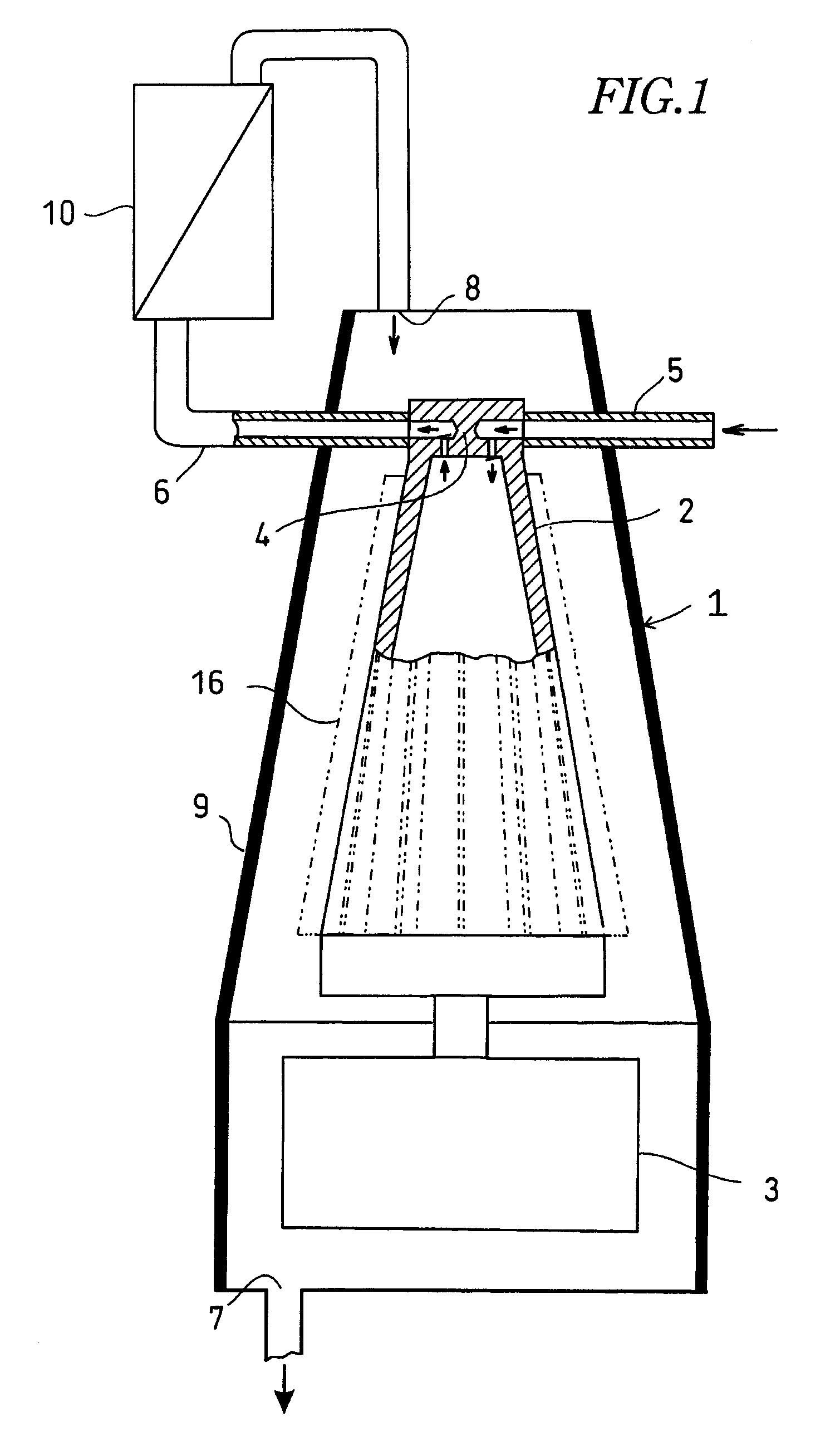
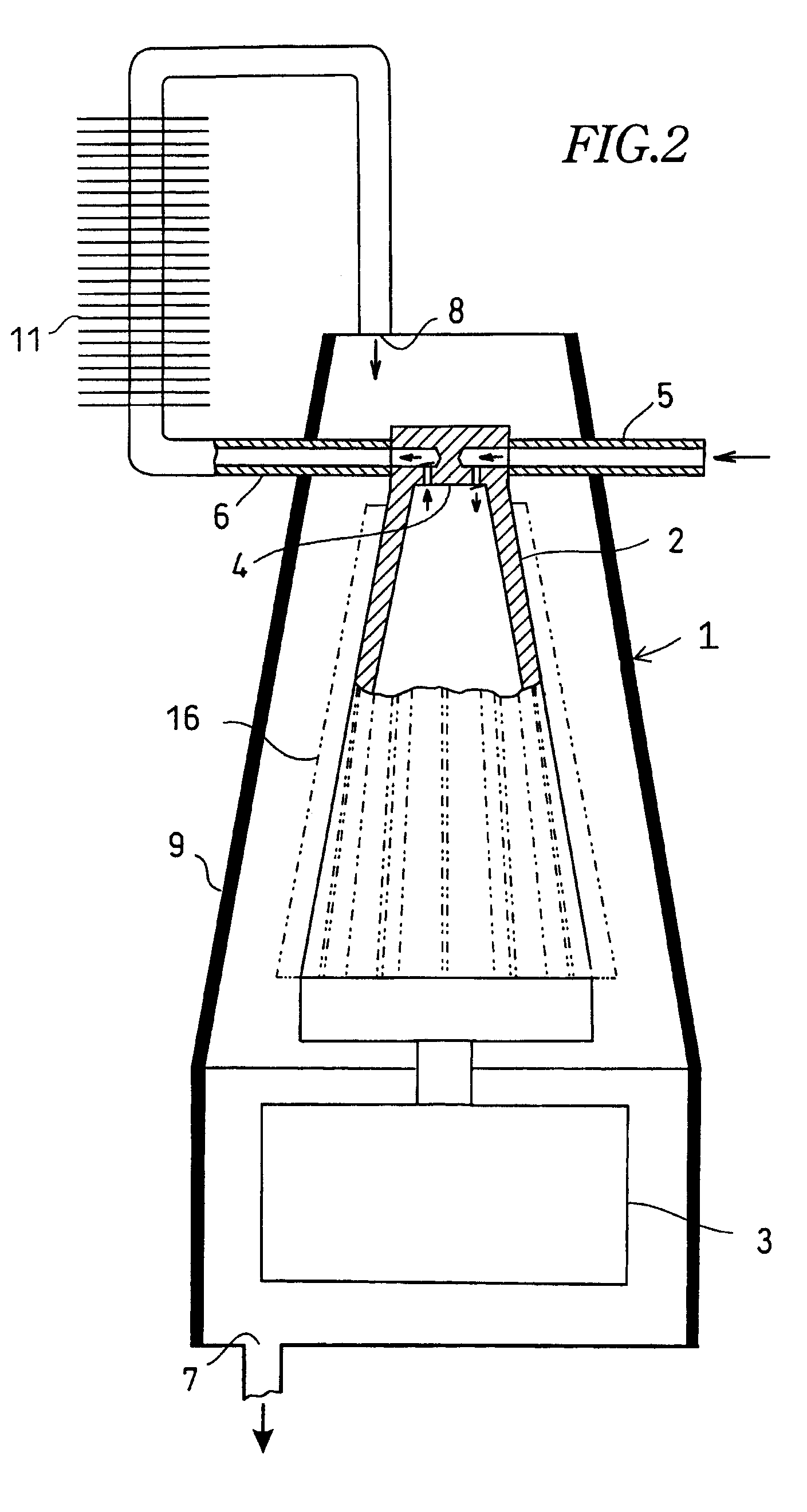
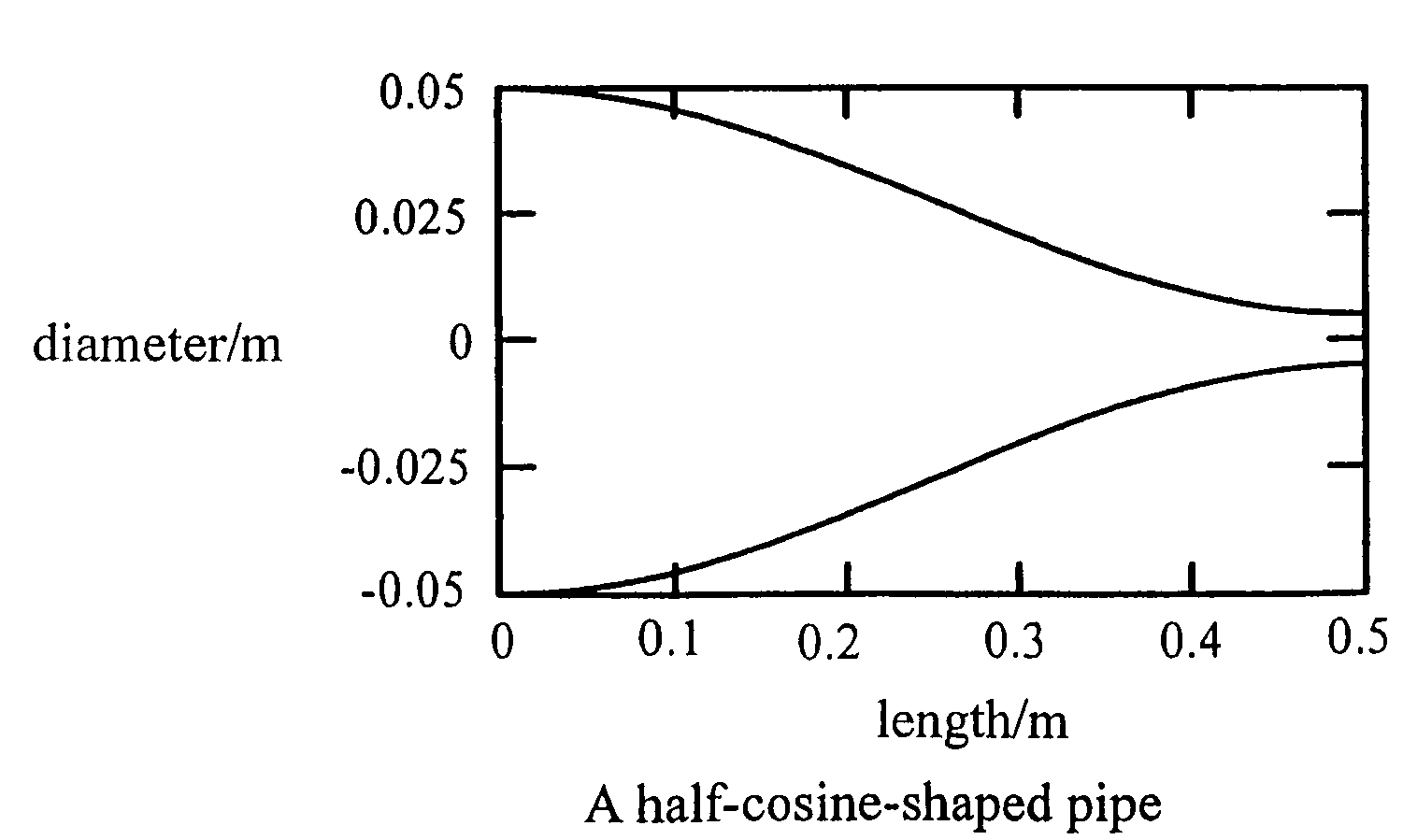
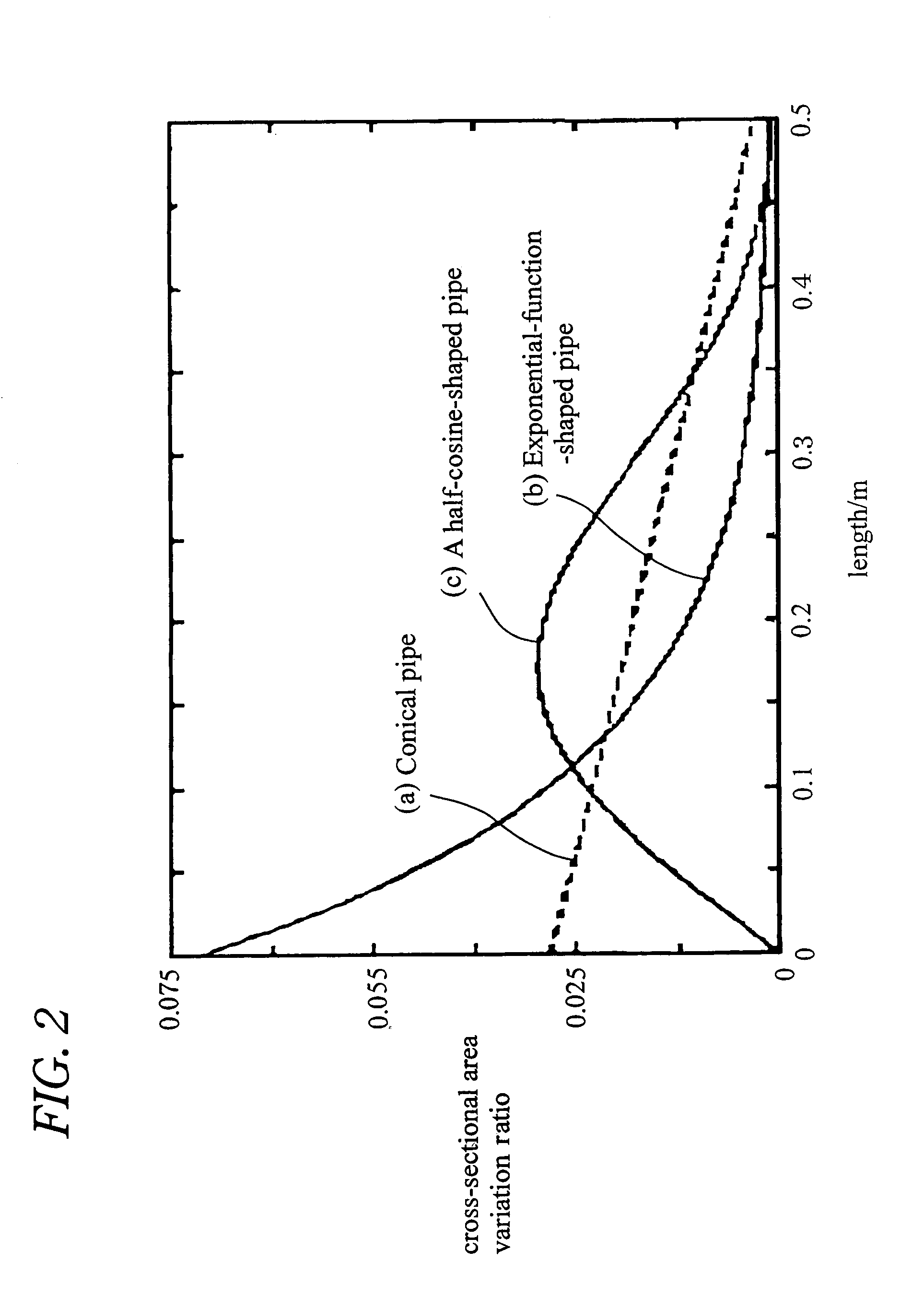
An acoustic fluid machine such as an air compressor comprises an acoustic resonator, a valve device and a piston. Air is sucked into the resonator through the valve device at one end of the resonator. The piston at the other end of the resonator is reciprocated by an actuator to compress the air in the resonator to cause resonance to increase pressure of the air significantly. The inner surface of the resonator is suitably curved to comply with the formula of a half-period cosine function.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
Acoustic fluid machine
InactiveUS20060054383A1Evaporators/condensersCompression machinesSmall amplitudeReciprocating motion
A piston is reciprocated axially at high speed at very small amplitude by an actuator in the larger-diameter base of an acoustic resonator. According to pressure fluctuation in the acoustic resonator involved by reciprocal motion of the piston, fluid is sucked into and discharged from the acoustic resonator via a valve device at the top end of the acoustic resonator. The acoustic resonator is contained in a gas guide. Fluid from the valve device is introduced into the gas guide to cool the valve device.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
Acoustic fluid machine
InactiveUS7252178B2Reduce waveform strain and variationEasy to controlFlexible member pumpsSilencing apparatusResonanceReciprocating motion
An acoustic fluid machine such as an air compressor comprises an acoustic resonator, a valve device and a piston. Air is sucked into the resonator through the valve device at one end of the resonator. The piston at the other end of the resonator is reciprocated by an actuator to compress the air in the resonator to cause resonance to increase pressure of the air significantly. The inner surface of the resonator is suitably curved to comply with the formula of a half-period cosine function.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
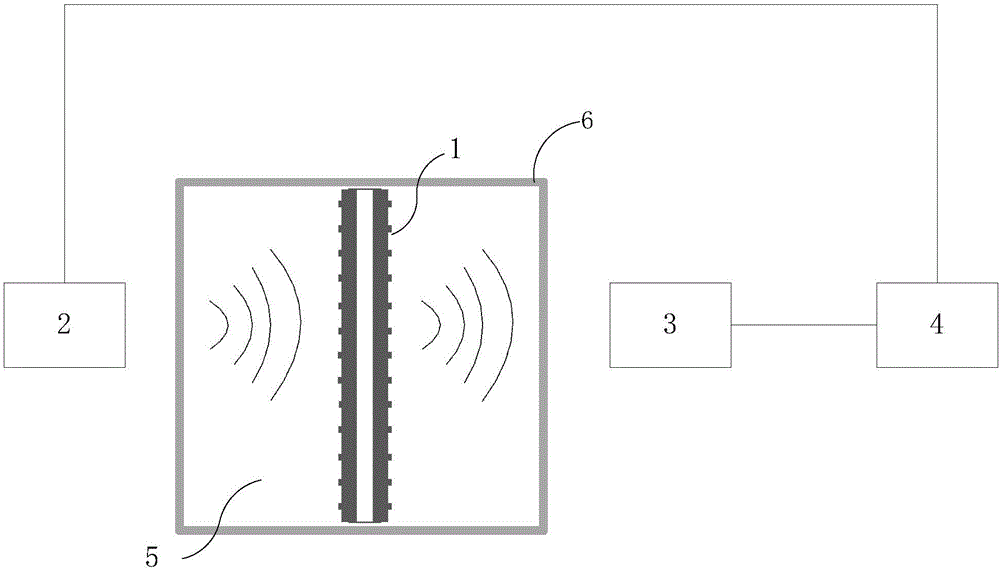
Acoustic fluid sensor
ActiveCN109443406AImprove qualityHigh sensitivityConverting sensor ouput using wave/particle radiationCouplingAcoustic Fluid
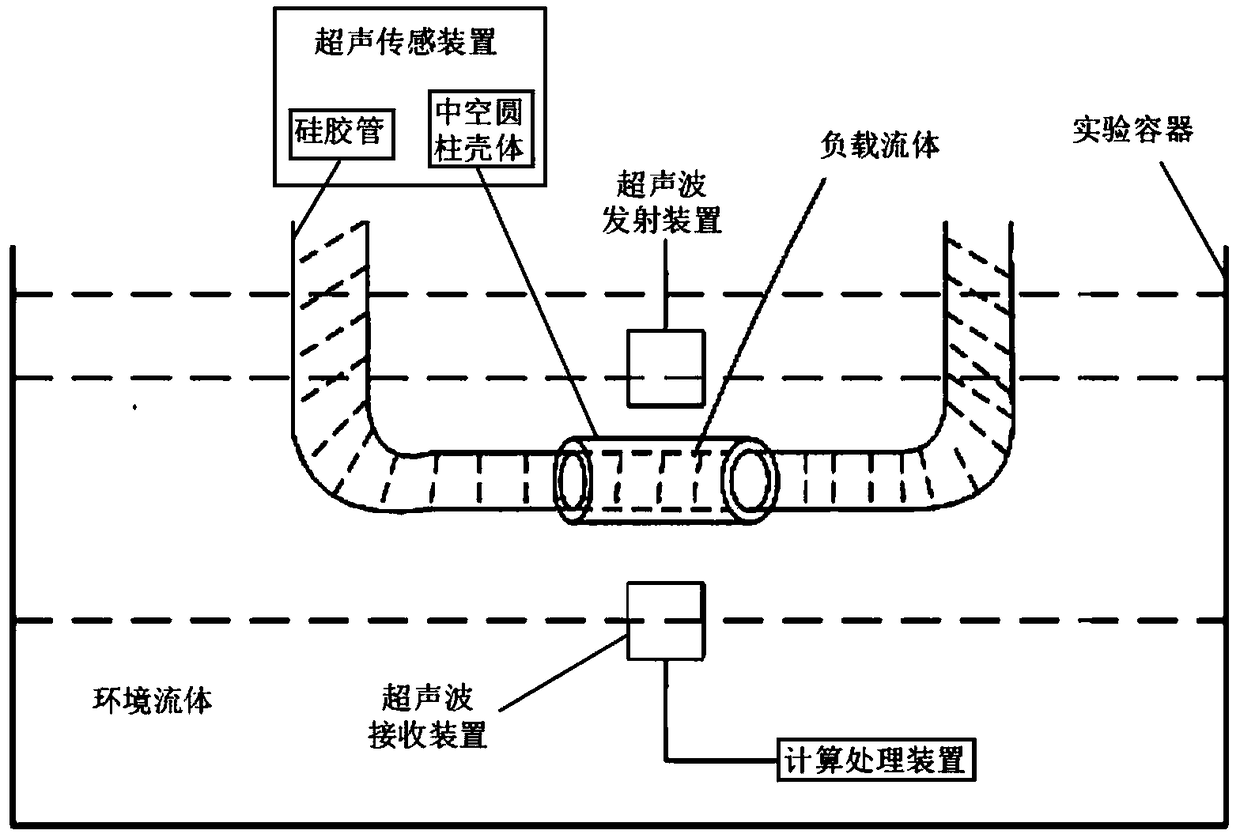
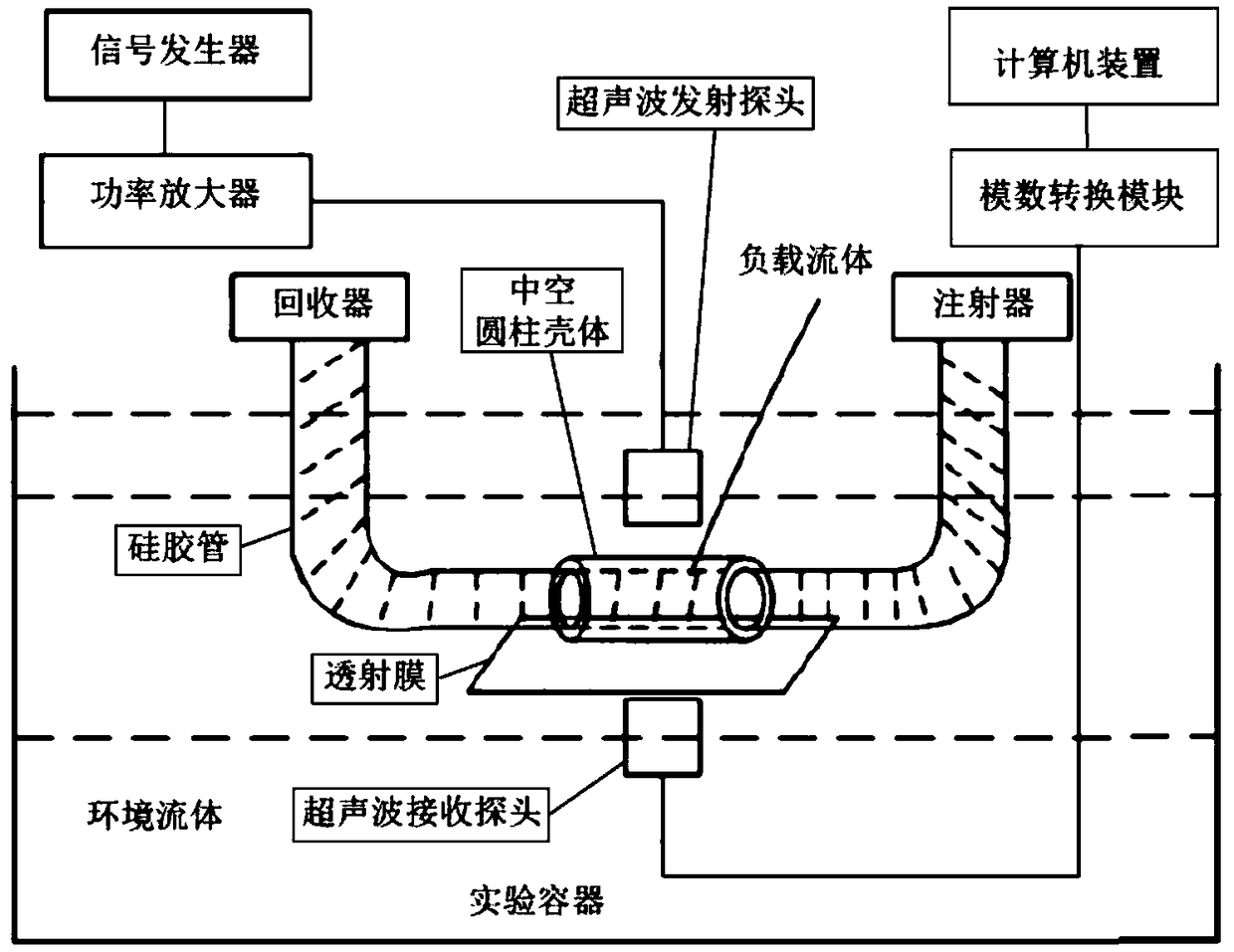
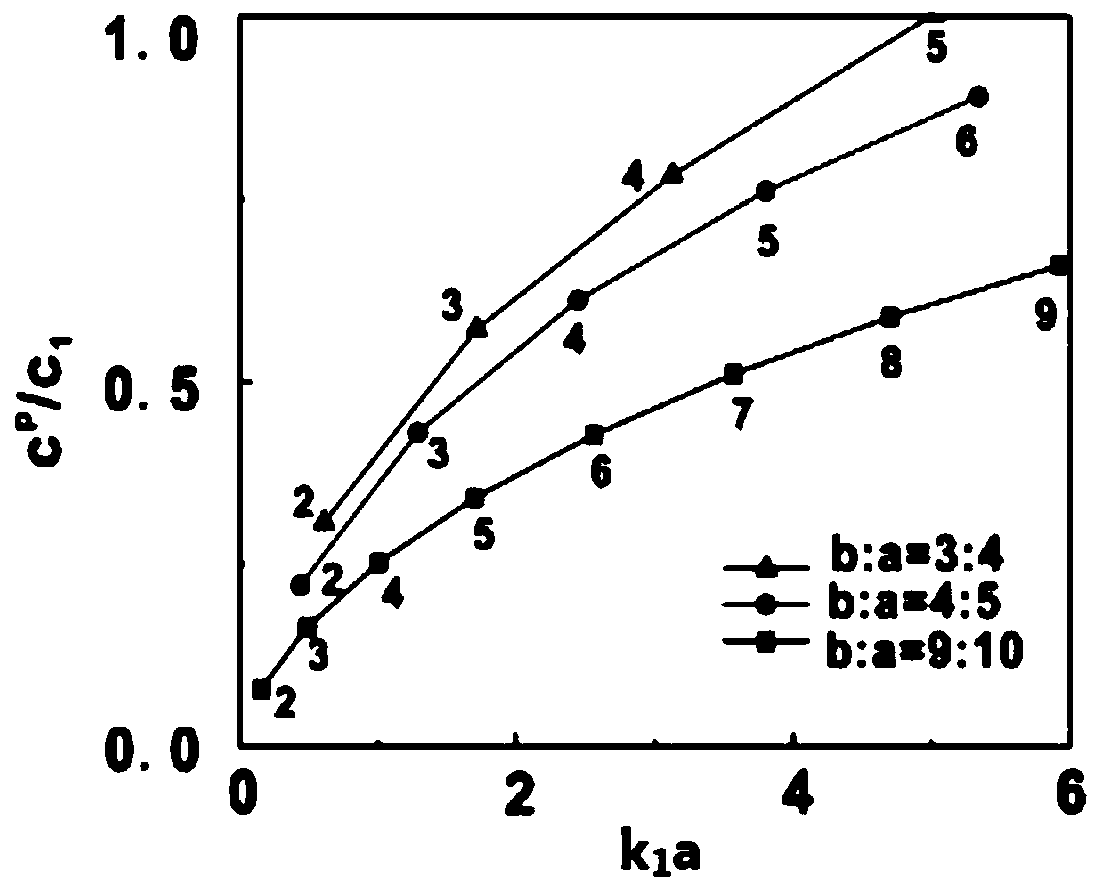
The invention discloses an acoustic fluid sensor. The acoustic fluid sensor comprises an acoustic sensing device, an experimental container, an ultrasonic transmitting device, an ultrasonic receivingdevice and a calculation and processing device; the acoustic transmitting device comprises a hollow cylindrical housing for holding a load fluid, and silicone tubes which are arranged at two ends of the hollow cylindrical housing and constitute a through cavity together with the hollow cylindrical housing; the ultrasonic transmitting device transmits ultrasonic waves into an ambient fluid, excitesthe load fluid in the hollow cylindrical housing to form Scholte-Stoneley circular waves; when the Scholte-Stoneley circular waves satisfy a phase matching condition, standing waves are formed aroundthe hollow cylindrical housing so as to generate a local sound field; and the calculation and processing device determines the quality factor of the acoustic fluid sensor based on normalized transmission spectrum data. The coupling degree of the local sound field generated by the acoustic fluid sensor of the invention and the load fluid is large, and the quality factor and sensitivity of the acoustic fluid sensor can be improved. The acoustic fluid sensor is suitable for the high-sensitivity sensing of a trace fluid.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Acoustic fluid machine
ActiveUS7299894B2Improve applicabilityLow production costSilencing apparatusMachines/enginesSmall amplitudeEngineering
An acoustic fluid machine includes an acoustic resonator, a valve device, a piston, and an actuator. The acoustic resonator has a larger-diameter base and a smaller-diameter upper end. The valve device is provided on the upper end of the acoustic resonator and has a sucking hole and a discharge hole. The piston is provided in the base of the acoustic resonator and has a surface such that the distance between the upper end of the acoustic resonator and the upper surface of the piston is substantially constant over the whole surface of the piston. The actuator is connected to the piston and reciprocates the piston at high speed axially with a very small amplitude so that a gas is sucked into the acoustic resonator via the sucking hole and discharged via the discharge hole by virtue of pressure fluctuations within the acoustic resonator.
Owner:REACTIVE SURFACES +1
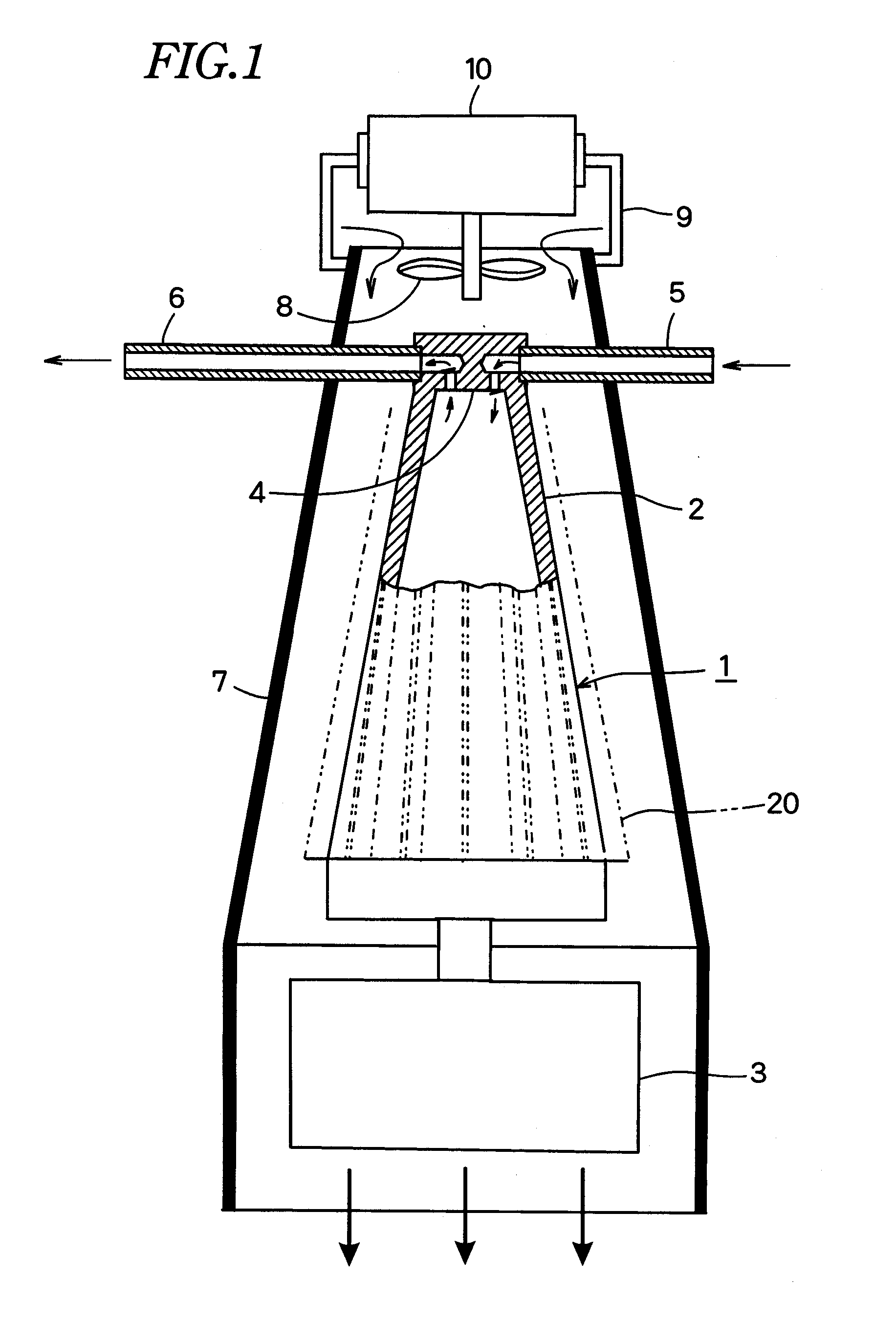
Acoustic fluid flow device for printing system
A printing system includes a liquid drop ejector, a fluid passage, and a fluid flow source. The liquid drop ejector is operable to form liquid drops having a plurality of volumes moving along a first path. The fluid passage includes a wall. A source of acoustic energy is associated with the wall. A fluid flow source is associated with the passage and is configured to provide a fluid flow through the passage. Interaction of the fluid flow and the liquid drops causes liquids drops having one of the plurality of volumes to begin moving along a second path.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Acoustic fluid machine
In an acoustic fluid machine, an acoustic resonator gradually reduces in diameter towards the top on which a valve device is provided to suck a gas into the resonator. The gas is compressed in the resonator by a circular-plate piston at the lower end of the resonator and discharged via an outlet of the valve device. The piston comprises a rubber plate fixed to the resonator and a metal plate attached on the rubber plate.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
Acoustic fluid machine
In an acoustic resonator, an actuator allows a piston to reciprocate axially at very small amplitude at high speed. Owing to pressure fluctuation in the acoustic resonator involved by reciprocal motion of the piston, fluid is sucked into and discharged from the acoustic resonator via a valve device at the top end of the acoustic resonator. The acoustic resonator is covered with a gas guide with a space. The valve device is cooled by a fan at the top end of the gas guide.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
Acoustic fluid sensor
The embodiment of the invention provides an acoustic fluid sensor. The acoustic fluid sensor comprises a slit double-plate acoustic device, an ultrasonic transmitting device, a computing processing device and an experimental vessel; the slit double-plate acoustic device comprises two parallel substrates which are spaced with a slit space which is used for containing to-be-detected fluid, and each substrate is provided with equally-spaced raised lines; the slit double-plate acoustic device is immersed in environmental fluid; the ultrasonic transmitting device transmits ultrasonic into the environmental fluid, the two substrates arranged in the slit double-plate acoustic device are stimulated to form non-leaky A0 mode Lamb waves and form a symmetric strong local mode through resonant coupling in the slit space, and the computing processing device determines parameters of the to-be-detected fluid by computing frequency points and amplitudes of resonant transmission enhancement peaks in an ultrasonic spectrum. According to the acoustic fluid sensor, only a trace amount of to-be-detected fluid is needed, high sensitivity and quality factors can be achieved, and the sensor is particularly sensitive to fluid opposite to density and acoustic velocity change trends.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Blood separation device based on acoustic fluid mechanics
PendingCN112718030ANo damageImprove controllabilityPreparing sample for investigationLaboratory glasswaresMechanical engineeringBiomedicine
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedicine, and provides a blood separation device based on acoustic fluid mechanics. The blood separation device comprises a micro-fluidic chip, a micro-fluidic pump and a sound wave driving system, wherein the micro-fluidic pump is connected with the micro-flow channel of the micro-fluidic chip through a hose, micropores distributed in an array mode are formed in the bottom face of the micro-flow channel, the piezoelectric transducer of the sound wave driving system is fixed to the glass substrate of the micro-fluidic chip, microfluid enters the micro-flow channel under the action of the micro-fluidic pump, particles in the microfluid are separated according to different acoustic flow field forces borne by the particles with different particle sizes in an acoustic flow field, and by controlling the acoustic flow capture force borne by the particles and the thrust of an external flow field, the particles with relatively large particle sizes are captured by the micropores, and the particles with relatively small particle sizes migrate along with the flow field. According to the blood separation device, particles in blood are not damaged, the controllability is high, and target bacteria can be simply and efficiently separated from the blood.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Acoustic fluid machine
ActiveUS20060000669A1High intake/discharge effectShorten the lengthSilencing apparatusEqualizing valvesSmall amplitudeEngineering
An acoustic fluid machine includes an acoustic resonator, a valve device, a piston, and an actuator. The acoustic resonator has a larger-diameter base and a smaller-diameter upper end. The valve device is provided on the upper end of the acoustic resonator and has a sucking hole and a discharge hole. The piston is provided in the base of the acoustic resonator and has a surface such that the distance between the upper end of the acoustic resonator and the upper surface of the piston is substantially constant over the whole surface of the piston. The actuator is connected to the piston and reciprocates the piston at high speed axially with a very small amplitude so that a gas is sucked into the acoustic resonator via the sucking hole and discharged via the discharge hole by virtue of pressure fluctuations within the acoustic resonator.
Owner:REACTIVE SURFACES +1
Acoustic fluid machine
An acoustic fluid machine has an acoustic resonator and a piston reciprocated by an actuator at the base of the acoustic resonator. A valve device is provided on the upper end of the acoustic resonator. External air is introduced into the acoustic resonator through the valve device. The piston has through-holes, through which front space communicates with rear space thereby reducing load applied onto the piston.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
Acoustic fluid machine
InactiveCN100396927CPositive displacement pump componentsPiston pumpsReciprocating motionEngineering
The invention is a sound fluid machine. It has a sound resonator and a piston reciprocating by actuator at the bottom of the sound resonator. A valve device is arranged at the top end of the sound resonator, and external air enters in the sound resonator through the valve device. The piston has a through hole that communicates with front space and back space of the piston, thus reducing the load applied on the piston.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
Acoustic fluid machine
An acoustic fluid machine has an acoustic resonator and a piston reciprocated by an actuator at the base of the acoustic resonator. A valve device is provided on the upper end of the acoustic resonator. External air is introduced into the acoustic resonator through the valve device. The piston has through-holes, through which front space communicates with rear space thereby reducing load applied onto the piston.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
Method and device for facilitating biomolecular sensing and biomolecular sensing system
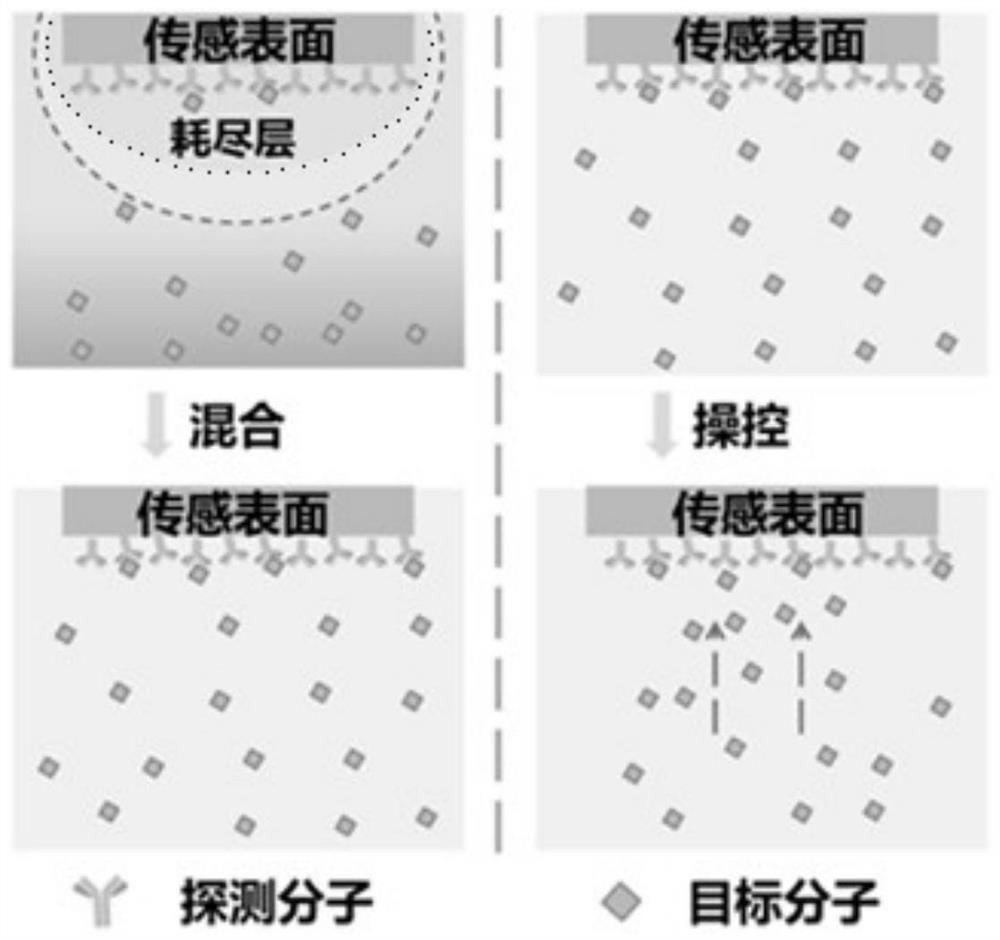
ActiveCN111693600ASufficient Response ConcentrationSave shipping timeAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A method of facilitating biomolecular sensing includes: driving a resonator to generate a gigahertz (GHz) level acoustic fluid in a liquid; and driving biomolecules in a flow field to be transported to a sensing interface of a biosensor in the acoustic fluid action area through the GHz-level acoustic fluid. Also provided is a device for facilitating biomolecular sensing, comprising: an acoustic fluid system portion comprising a resonator for generating an acoustic fluid of GHz level; a cylindrical cavity, positioned in the acoustic fluid action area of the resonator and used for limiting the range of an acoustic fluid field and accommodating a sensing interface of the biomolecular sensor. Correspondingly, the invention also provides a biomolecular sensing system. By using the sensor, the biomolecular sensing function of the sensor can be promoted.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Single cell control system and method, monoclonal cell line construction method, and single cell droplet generation system and method
ActiveCN112746012AEasy to captureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCell dissociation methodsLiquid mediumEngineering
The invention discloses a single cell control system and method based on acoustic fluid tweezers, a monoclonal cell line construction method and a single cell droplet generation method. The single cell control system comprises a sample caching device, an ultrahigh-frequency bulk acoustic wave resonator, a multi-degree-of-freedom motion device and a PLC; the sample caching device is used for fixing and storing different types of samples; the ultrahigh-frequency bulk acoustic wave resonator is connected with the sample caching device through a liquid medium and acts on target cells in the sample caching device; the multi-degree-of-freedom motion device is mechanically connected with the ultrahigh-frequency bulk acoustic wave resonator and controls the ultrahigh-frequency bulk acoustic wave resonator to move; and the PLC is used for adjusting the spatial positions of the ultrahigh-frequency bulk acoustic wave resonator and the cells by controlling the multi-degree-of-freedom motion device and controlling the power and the frequency applied to the ultrahigh-frequency bulk acoustic wave resonator so as to realize stable stripping of adherent single cells and capture of suspension cells, controlling the multi-degree-of-freedom motion device so that the cells move along with the movement of the ultrahigh-frequency bulk acoustic wave resonator, and controlling the release of the captured single cells by controlling the on-off of the power applied to the ultrahigh-frequency bulk acoustic wave resonator.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method and system for determining the concentration of an analyte in a fluid sample
ActiveUS9939352B2Accurate concentrationQuick buildSamples introduction/extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementNitrogen gasSpectrometer
Owner:LABCYTE
Acoustic fluid micro pump based on micro electro mechanical technology
ActiveCN112963326AReduce energy consumptionImprove applicabilityPumpsPositive-displacement liquid enginesEngineeringSignal generator
The invention discloses an acoustic fluid micro pump based on a micro electro mechanical technology. The pump comprises a pump cavity with an inlet and an outlet; a GHz-level resonator is arranged in the pump cavity; and a pipeline which extends from the outlet to the resonator and is not in contact with the resonator is arranged. According to the pump, the GHz-level resonator and the non-contact pipeline over the resonator are arranged in the pump cavity, the power amplifier and the signal generator are externally connected, stable and rapid one-way acoustic jet can be obtained, and efficient and continuous pumping of liquid is achieved. The pump has the advantages of miniature size, simple structure, low power consumption, wide application, compatibility with a semiconductor process, portability through a wireless driving mode and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
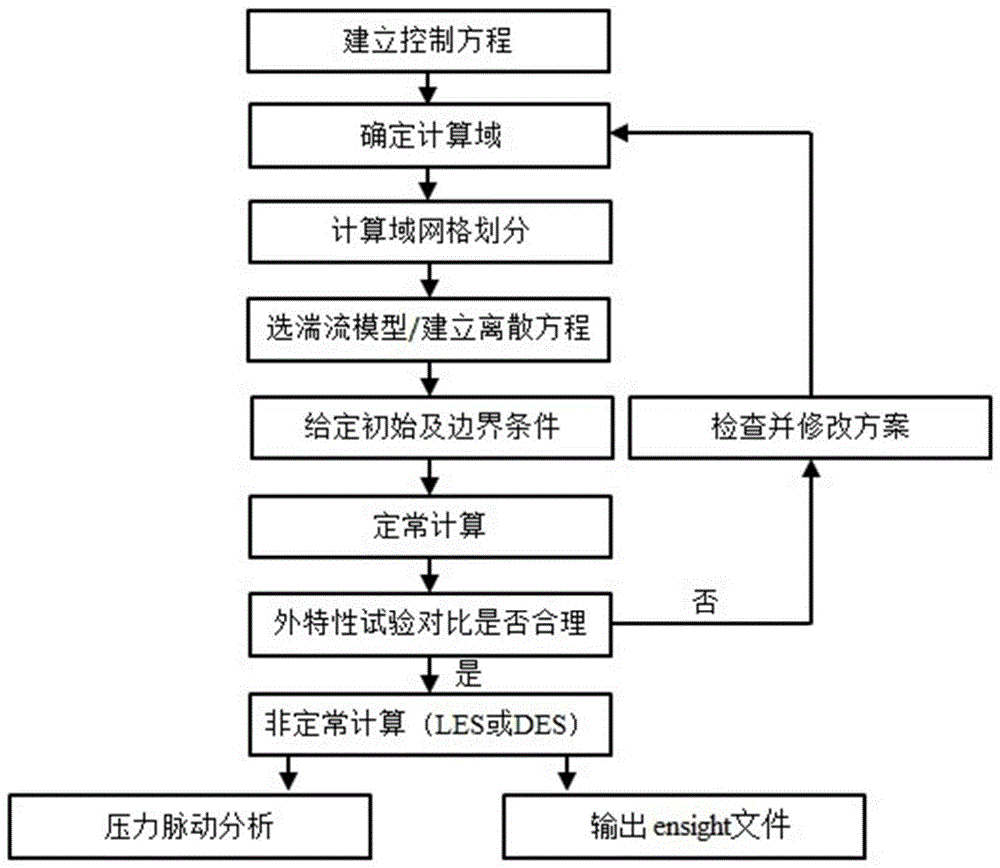
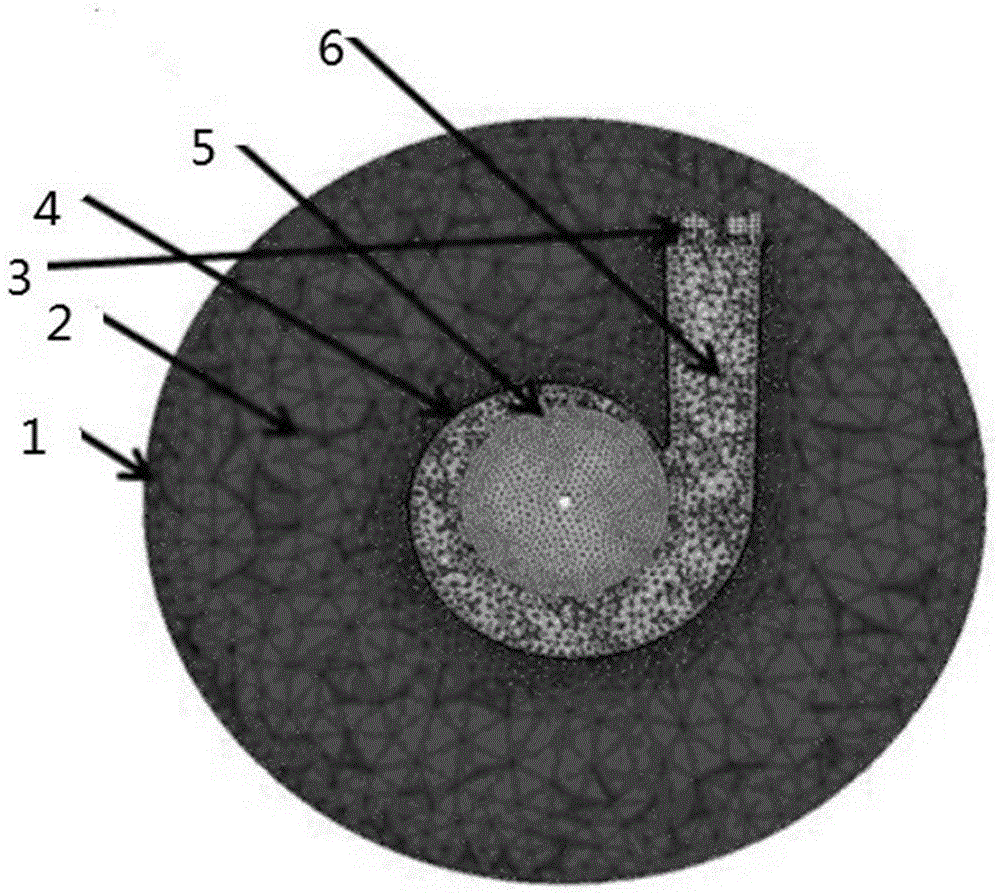
A Numerical Prediction Method for Flow-Induced Noise of Centrifugal Pumps
ActiveCN103631989BImprove design qualityEasy to modify laterSpecial data processing applicationsLow noiseBroadband noise
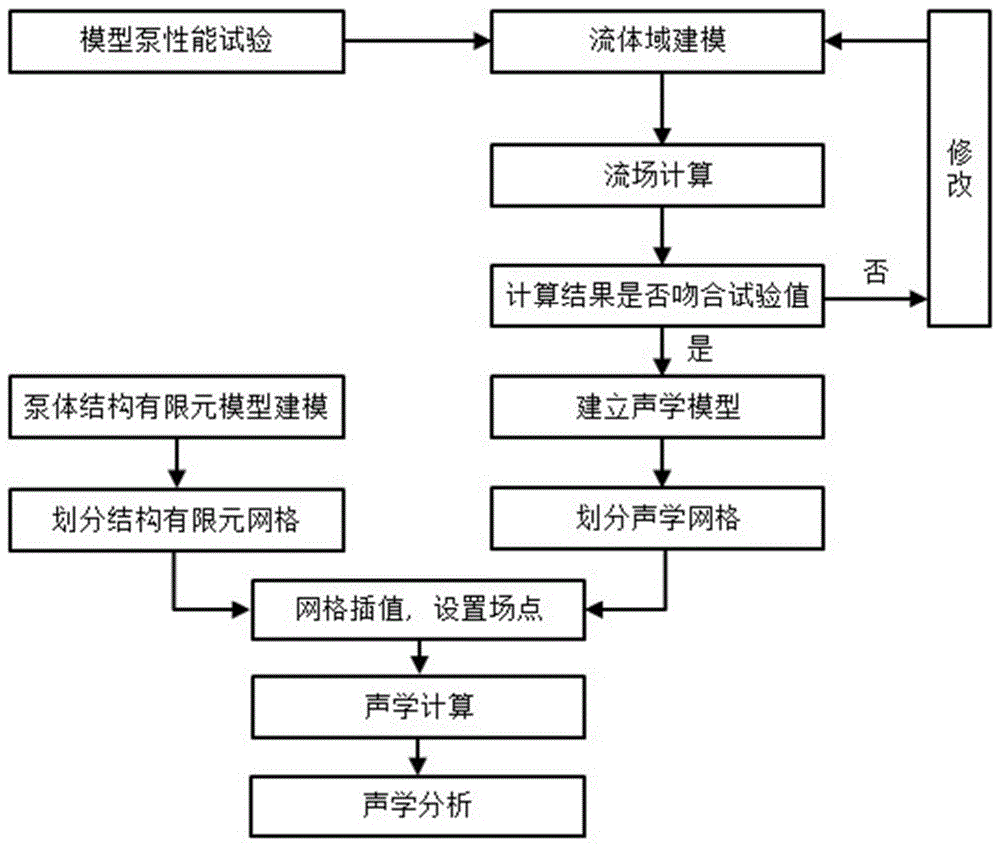
The invention discloses a numerical prediction method of the flow-induced noise of a centrifugal pump. The invention provides a numerical prediction method of the flow-induced noise of a centrifugal pump by calculating the sound source characteristics of the flow noise on the basis of the test results of the performance test of the centrifugal pump. Moreover, this method can better overcome the shortcomings of the traditional calculation method that does not consider the influence of the pump body structure on the sound propagation and ignores the broadband noise of the eddy current. Applying the analysis of the internal flow of the centrifugal pump and the calculation results of the far-field noise value to the low-noise hydraulic design of the centrifugal pump can reduce the number of tests, shorten the development cycle, save development costs, and effectively improve the design quality of the centrifugal pump; fluid grid and acoustics The interpolation method between the grids can preserve the sound source information of the flow field calculation to the greatest extent; the GREEN analysis can be used to obtain the contribution of different parts of the shell to the noise. Research on this can be used for the preliminary design or Post-modification for optimization.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com