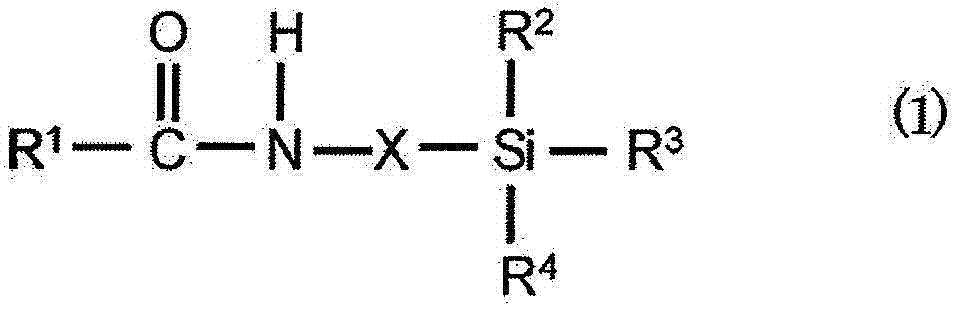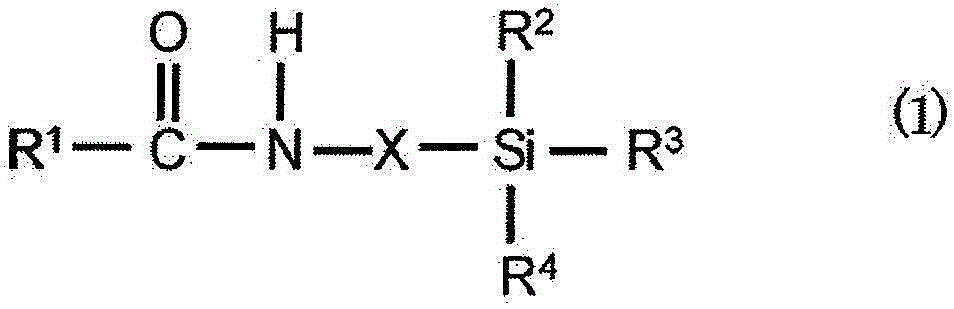Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "Small wavelength dependence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
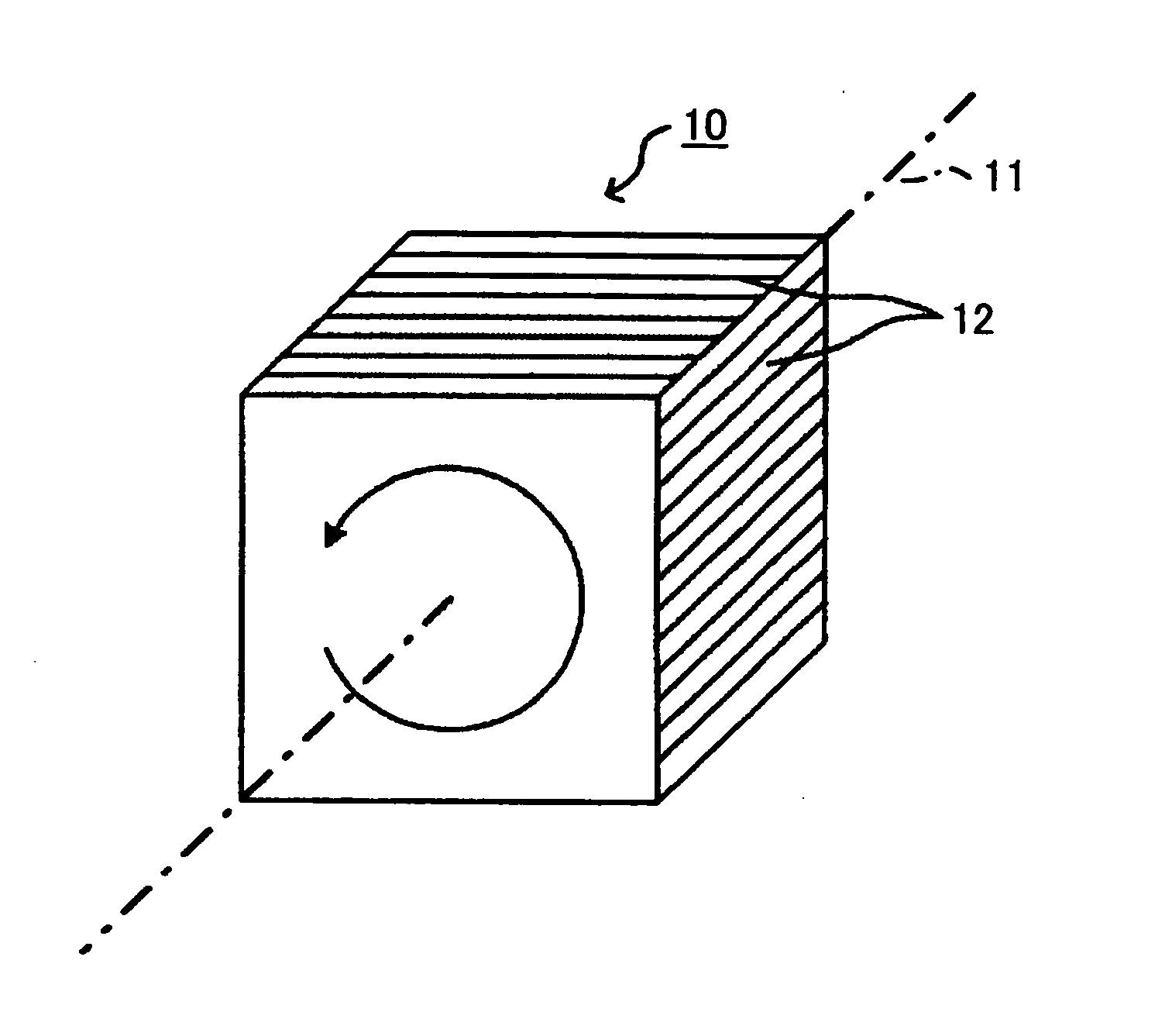
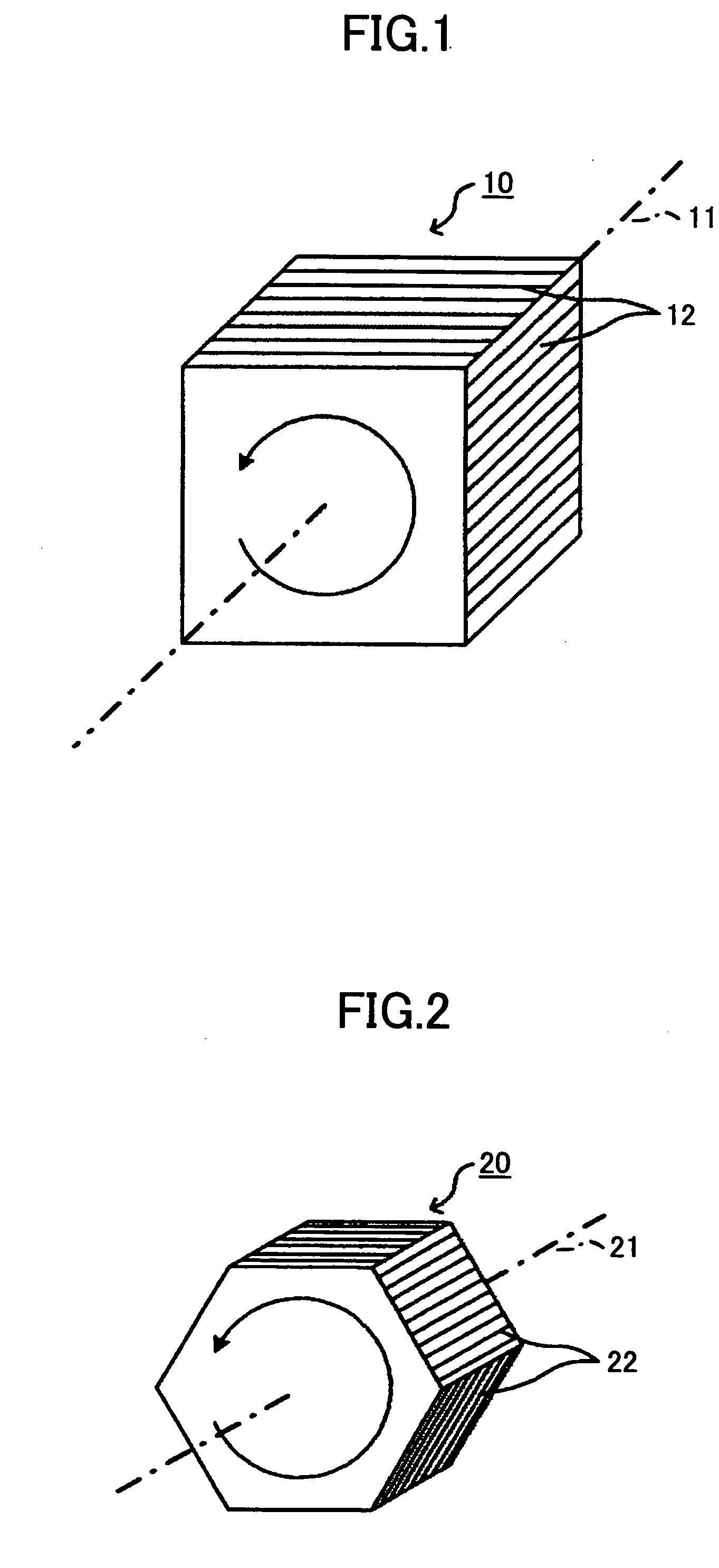
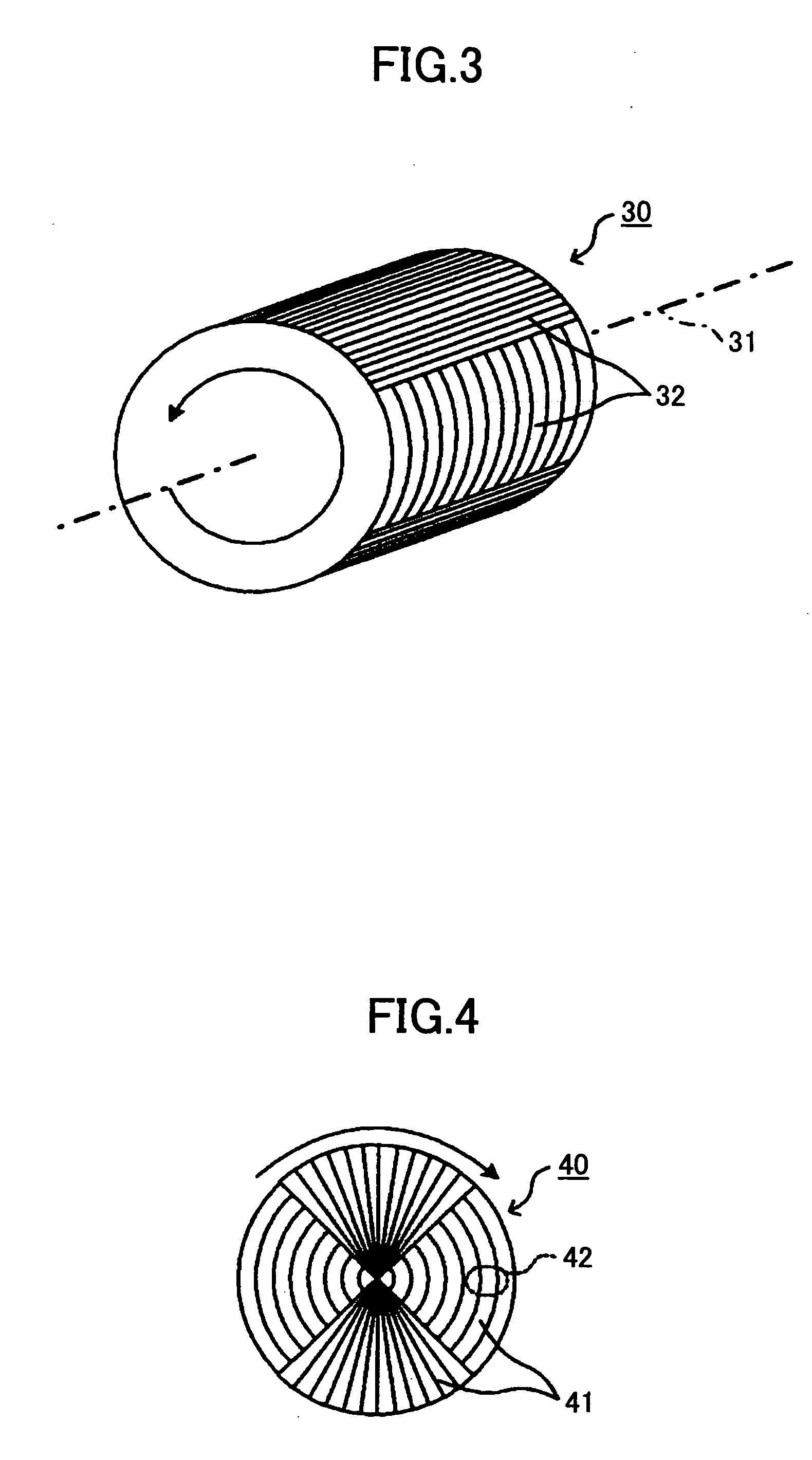
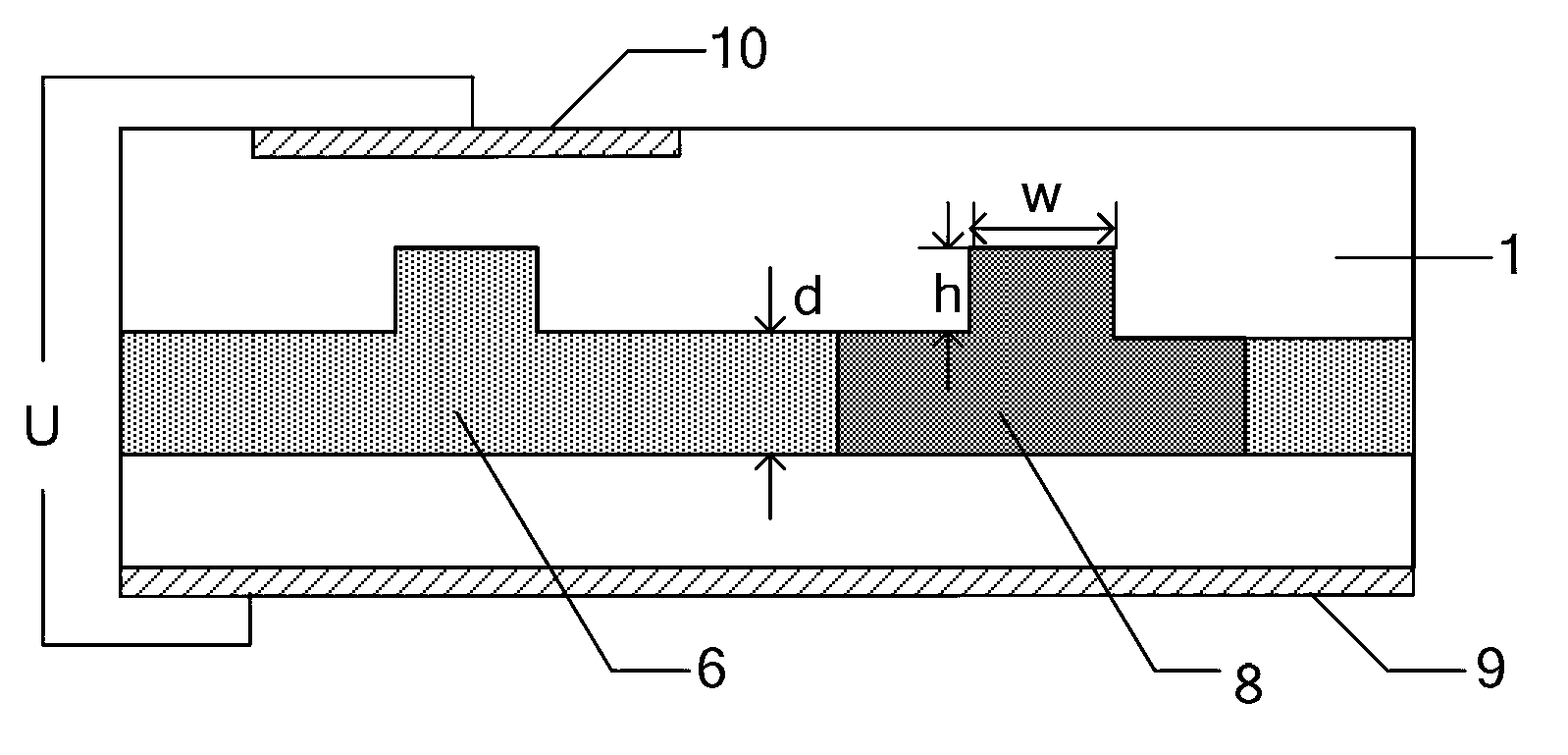
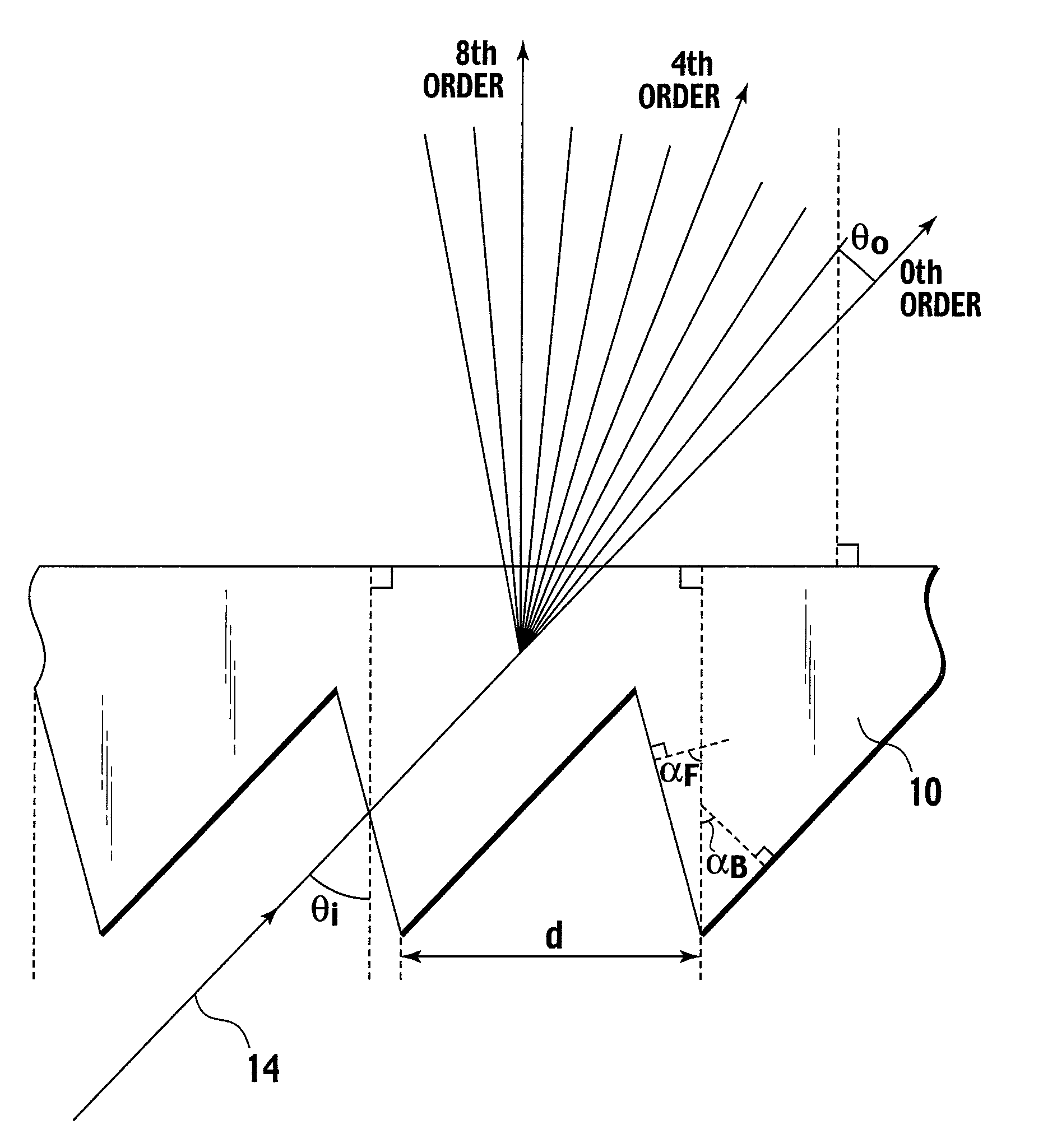
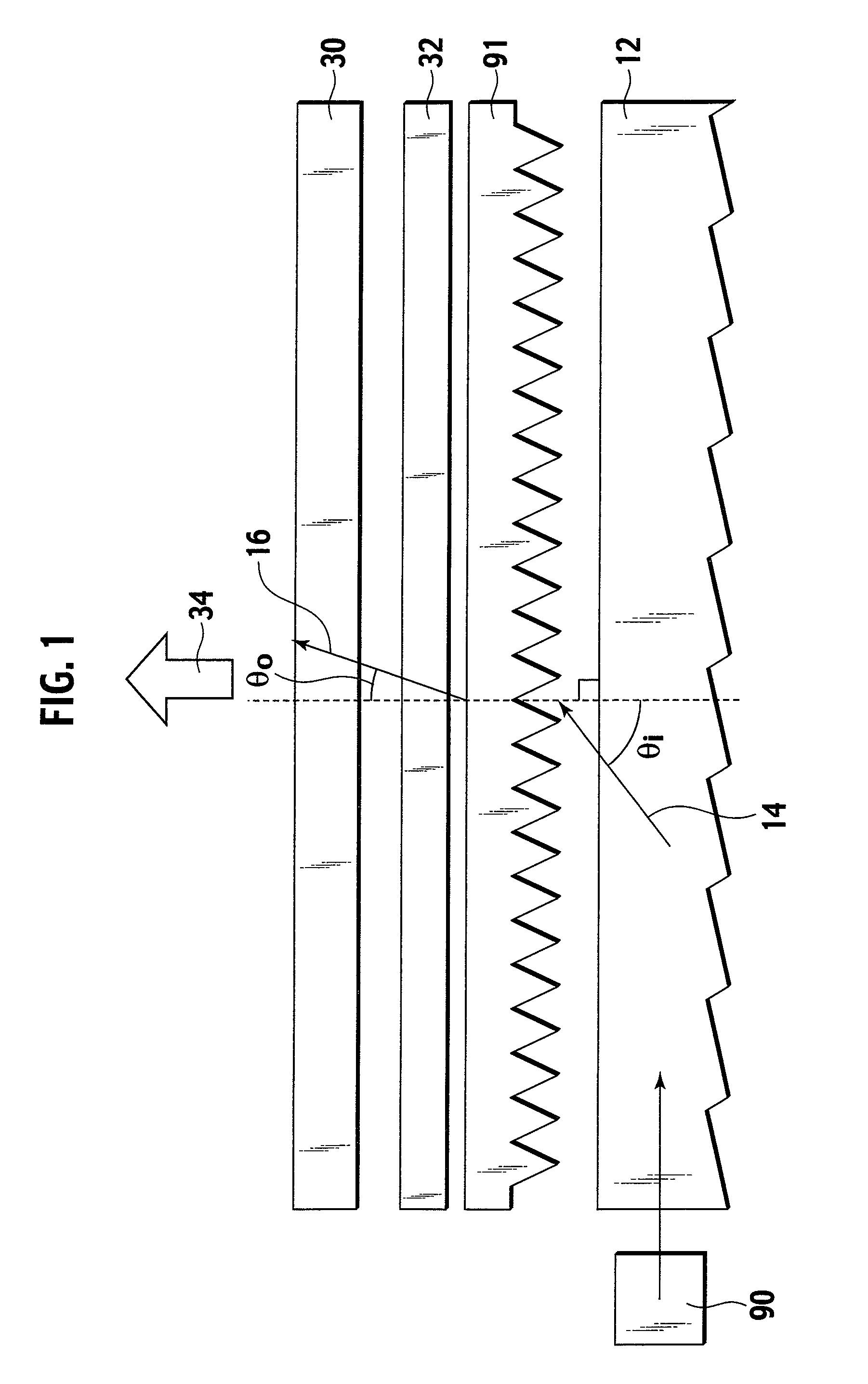
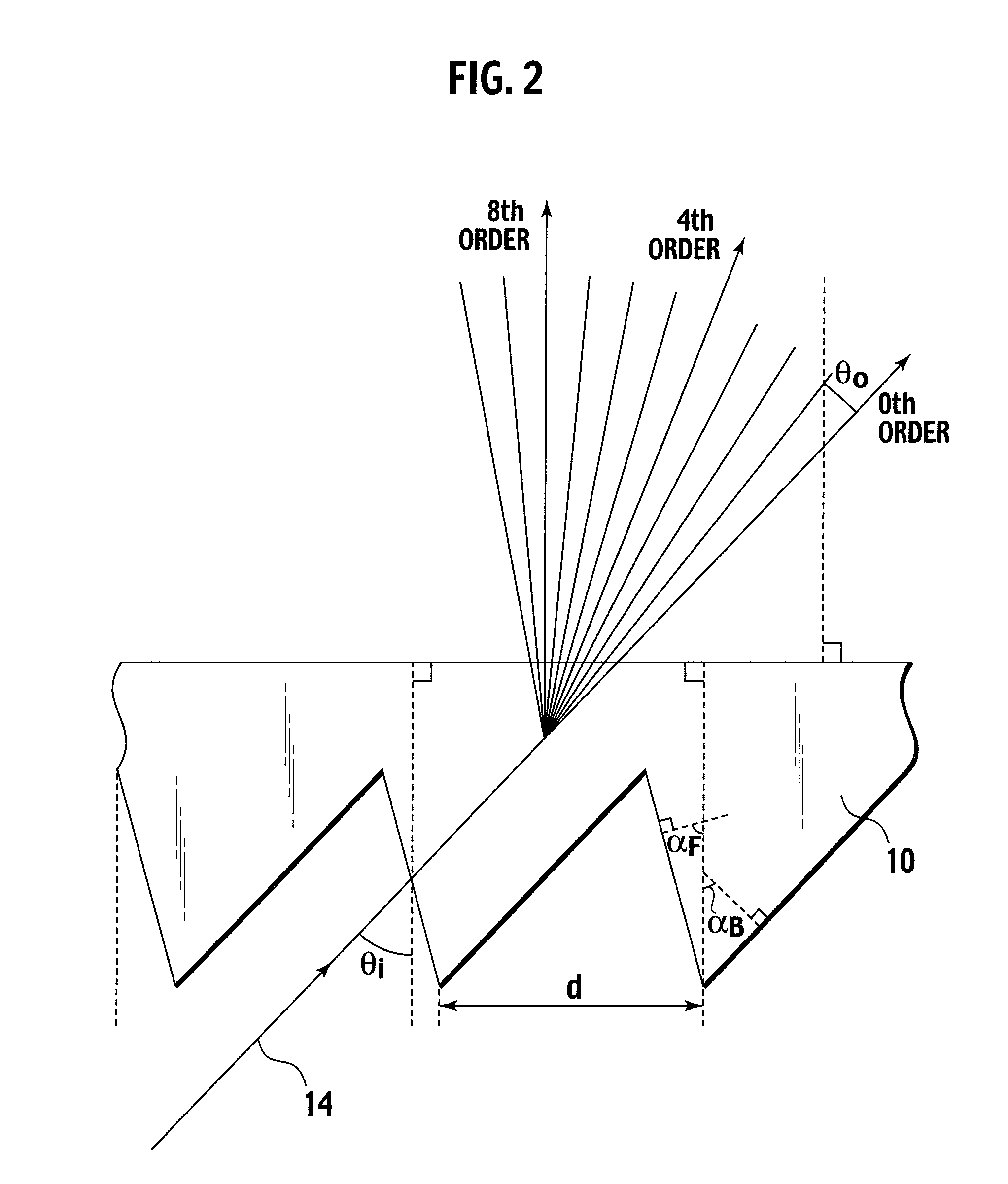
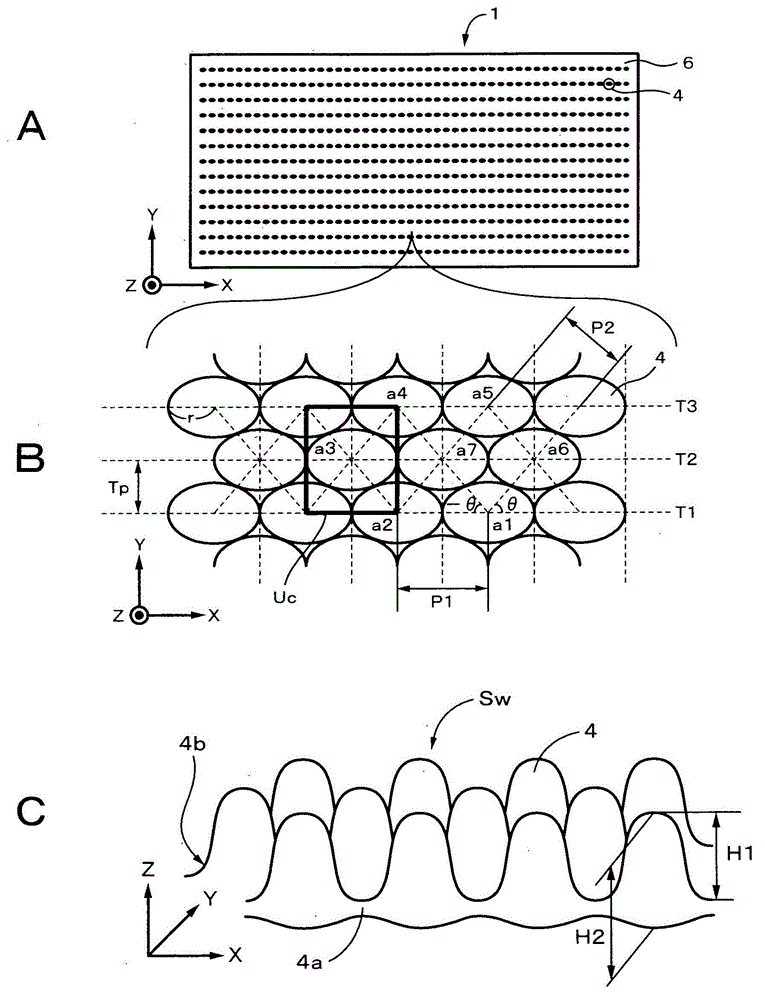
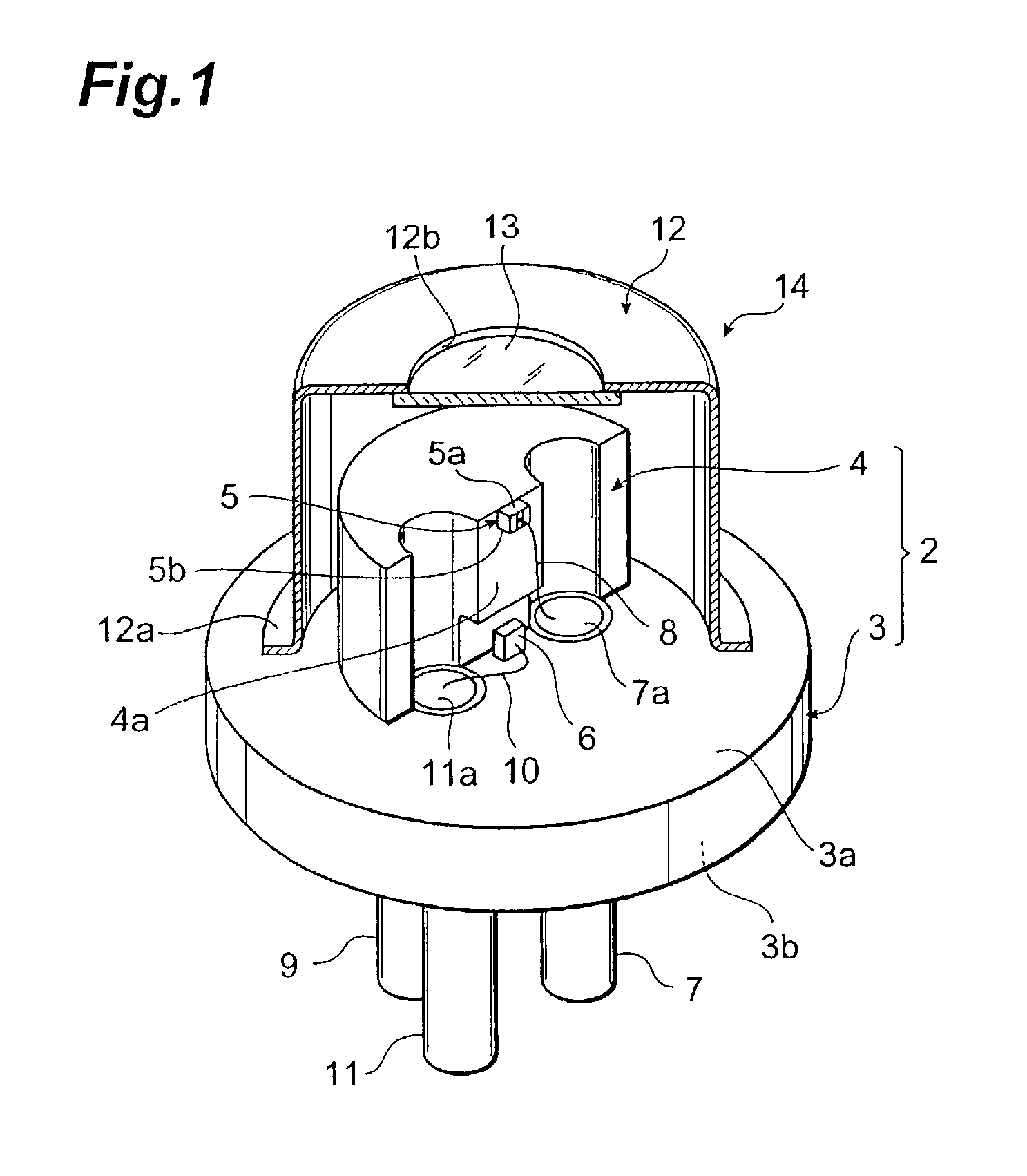
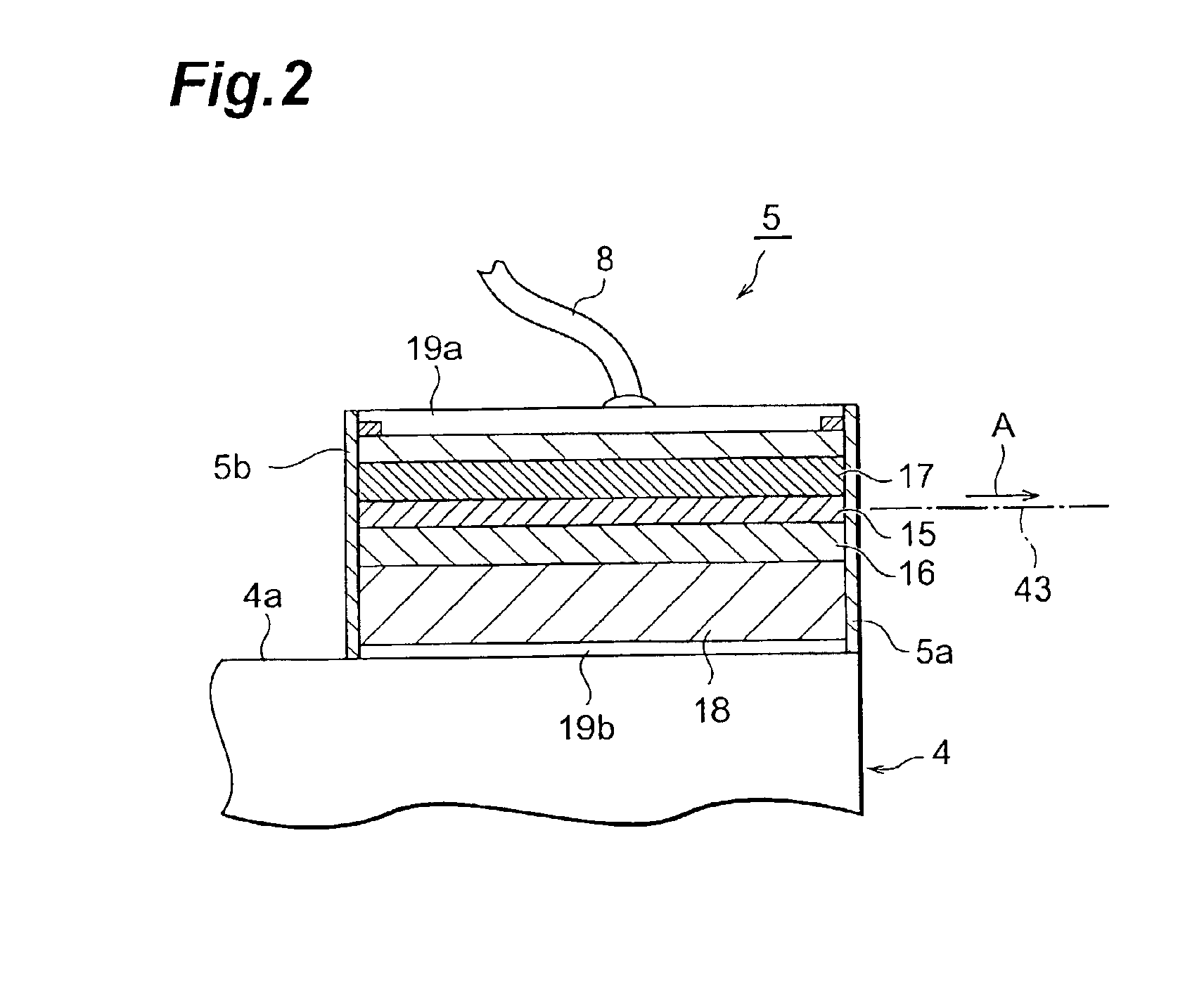
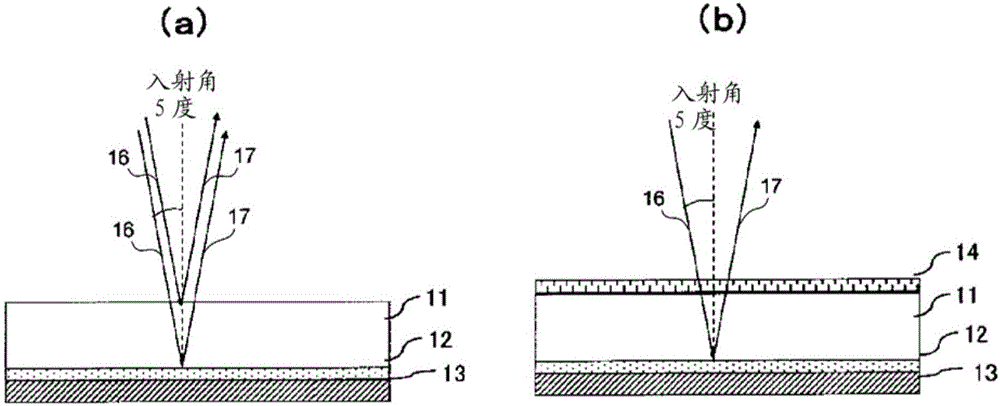
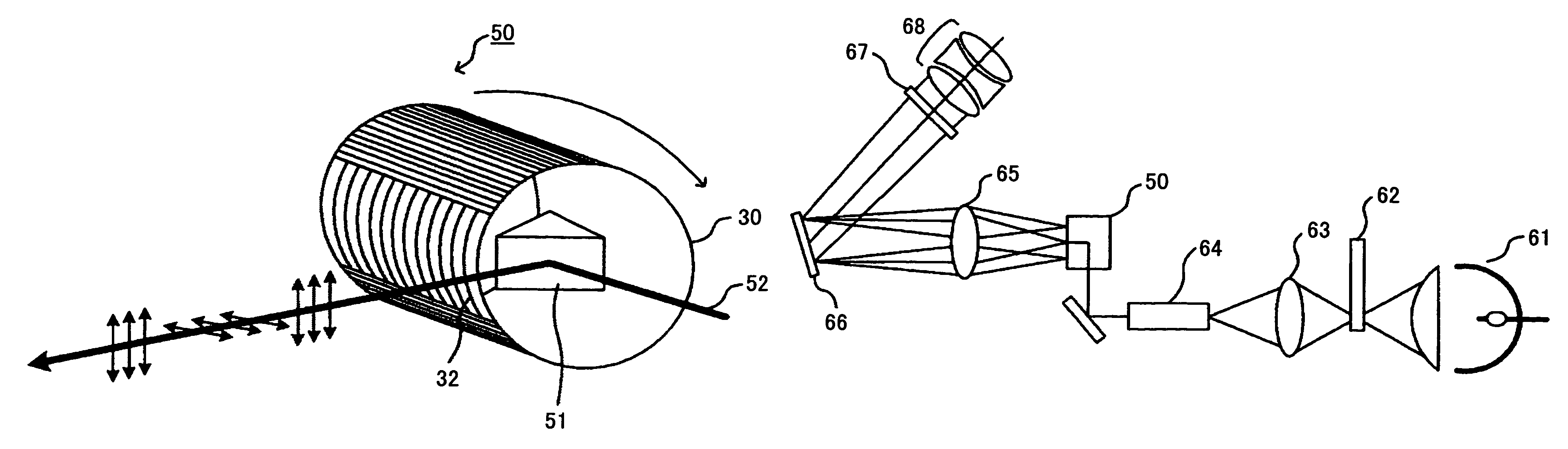
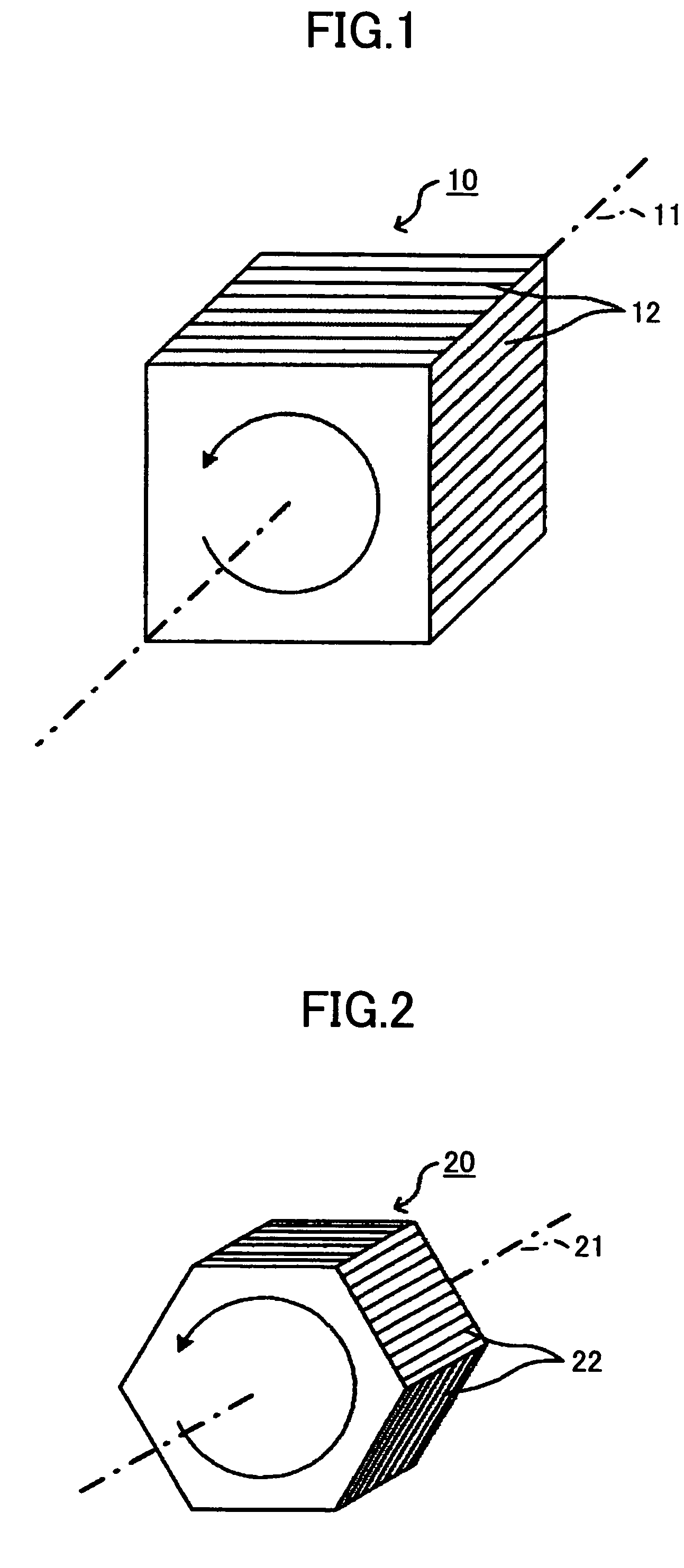
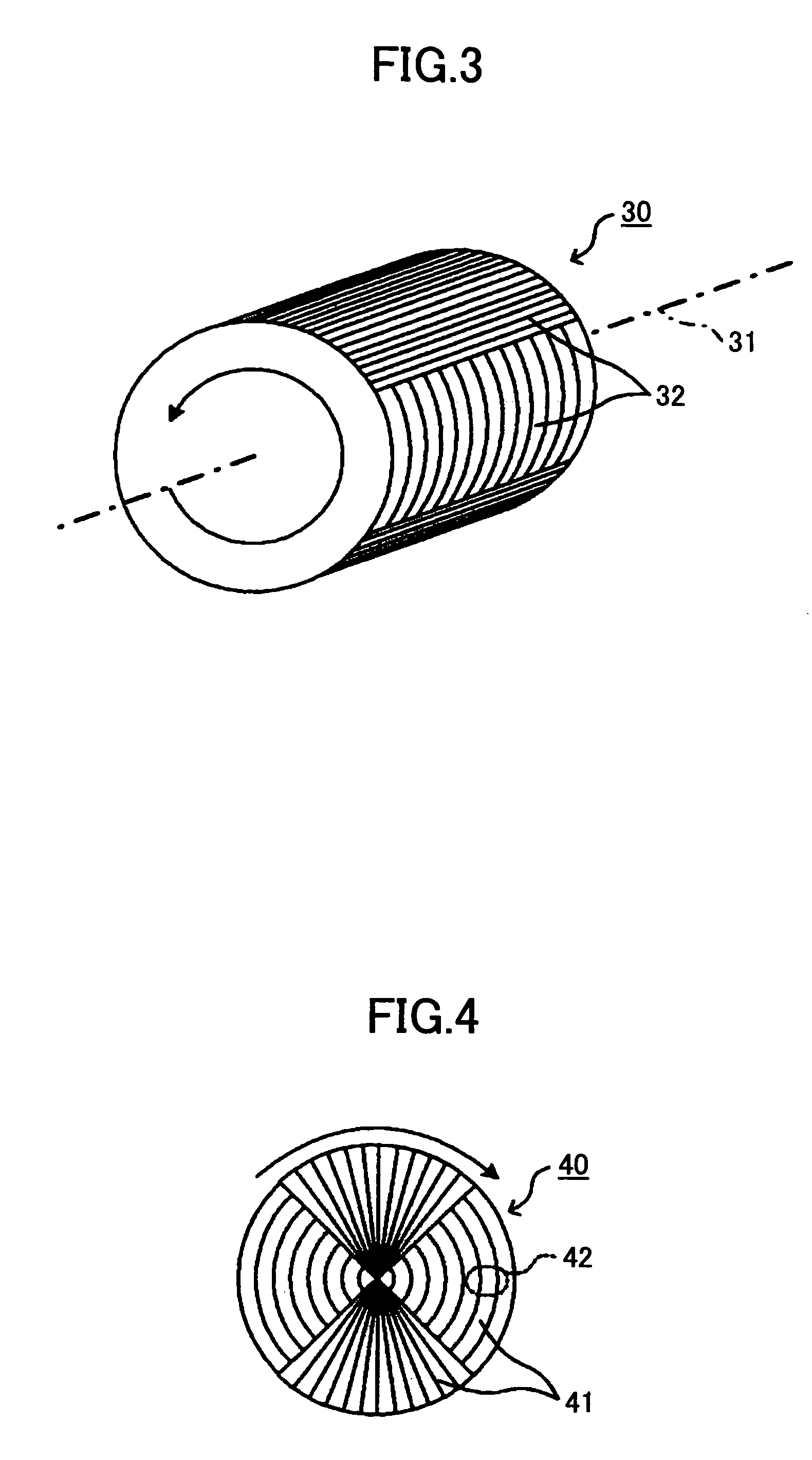
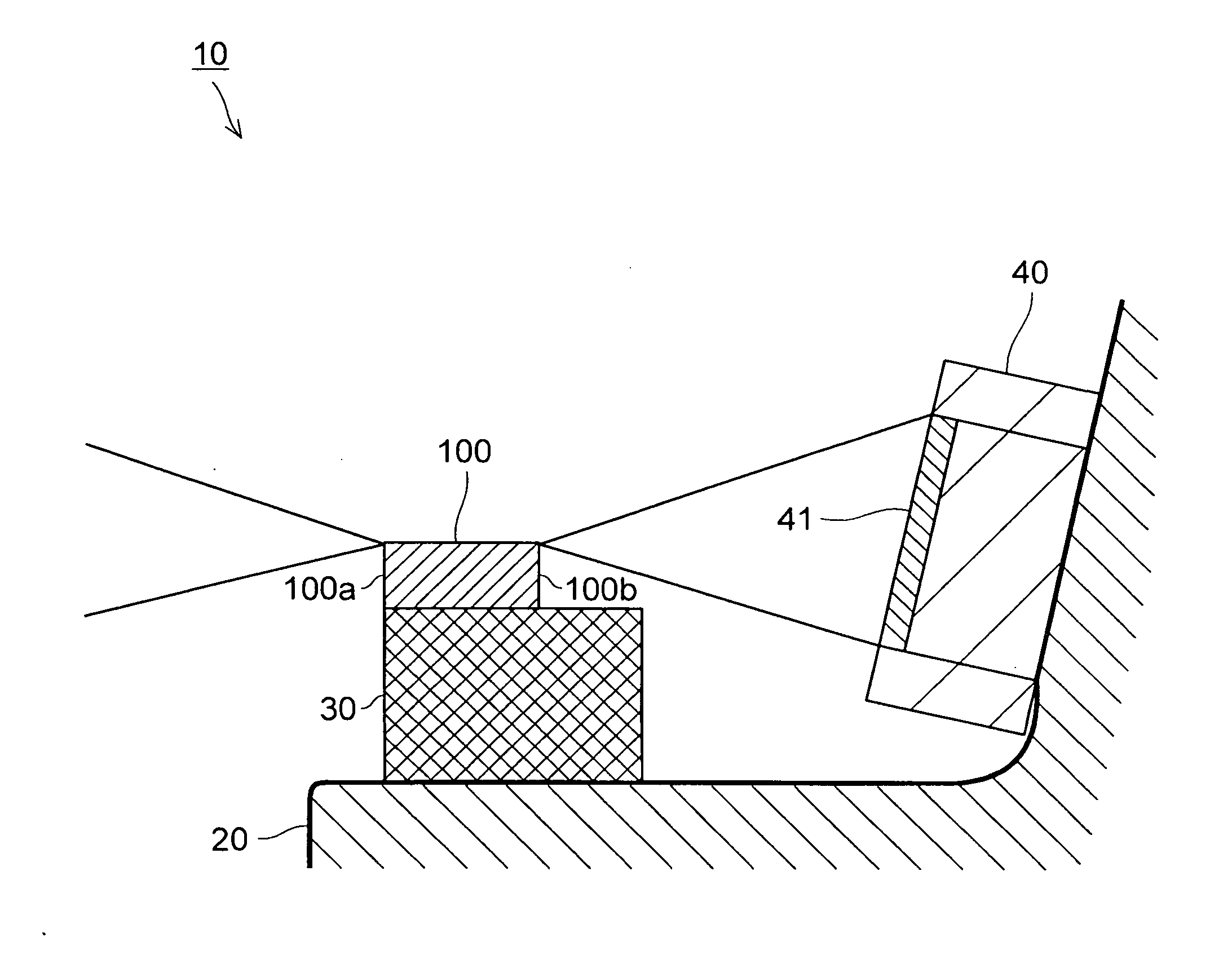
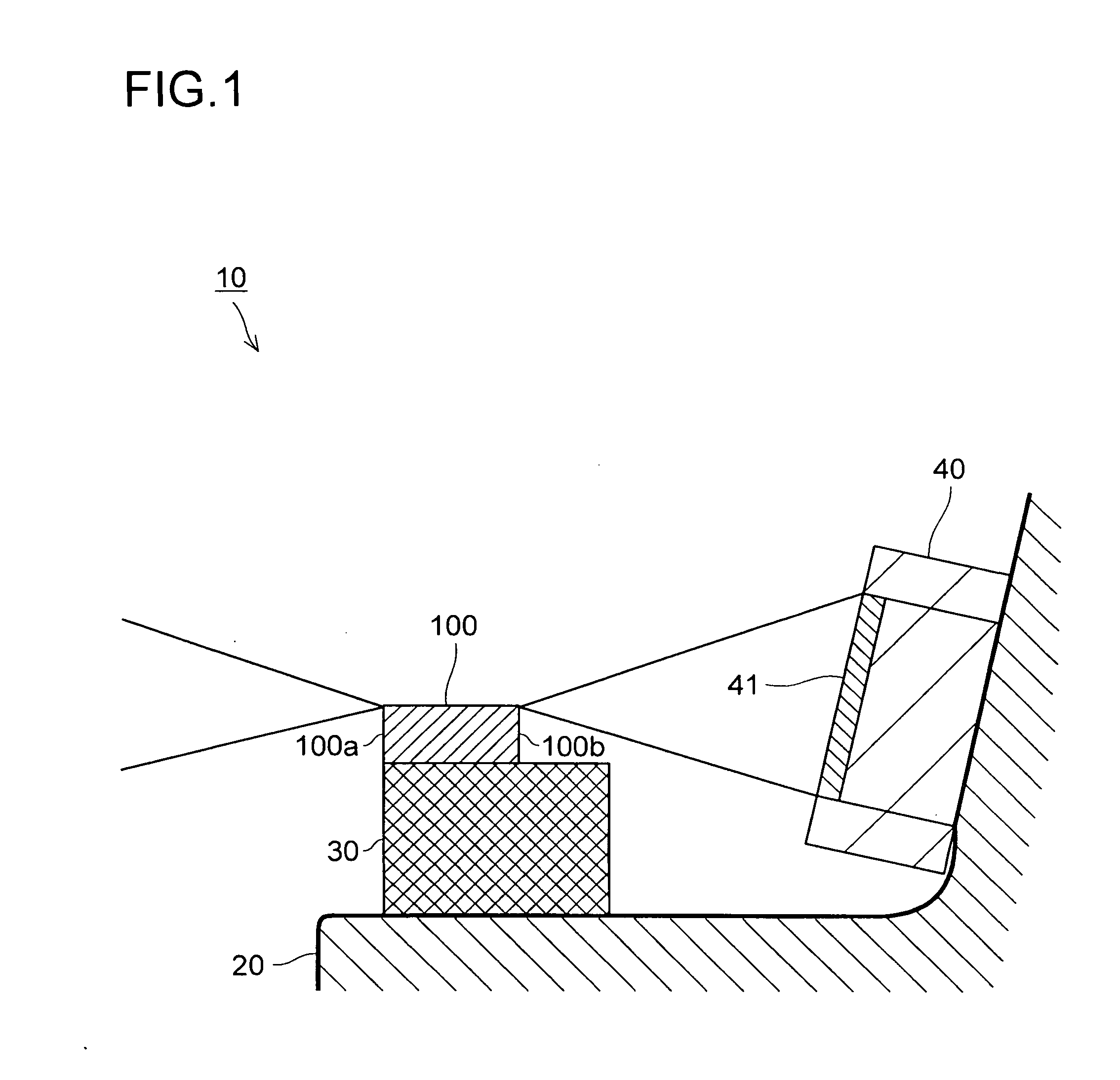
Optical device, display device, and three-dimension image display device
InactiveUS20060039068A1Small wavelength dependenceSuperior in polarization purityProjectorsPolarising elementsRotational axisLight beam
An optical element, an optical device, and a display device are disclosed that are able to change a polarization state in time order and to produce polarized light with little wavelength dependence and superior in polarization purity, and able to perform pixel shift easily and accurately to realize high resolution image display. The optical element has a translucent surface parallel to the rotational axis of the optical element, and at least a portion of the translucent surface is formed from an optically anisotropic medium. A polarization state of a light beam transmitting through the translucent surface is switched in time order along with rotation of the optical element.
Owner:RICOH KK
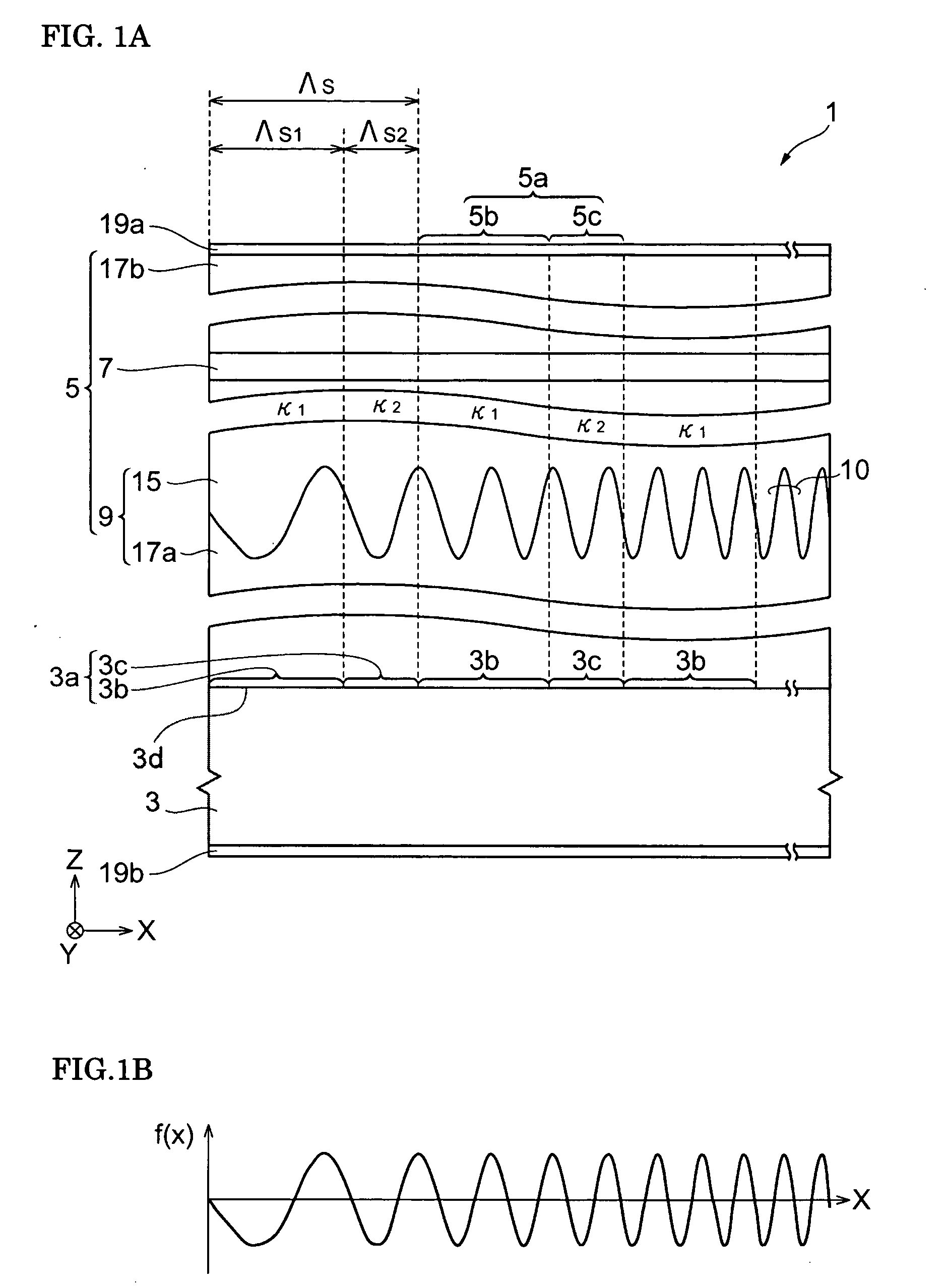
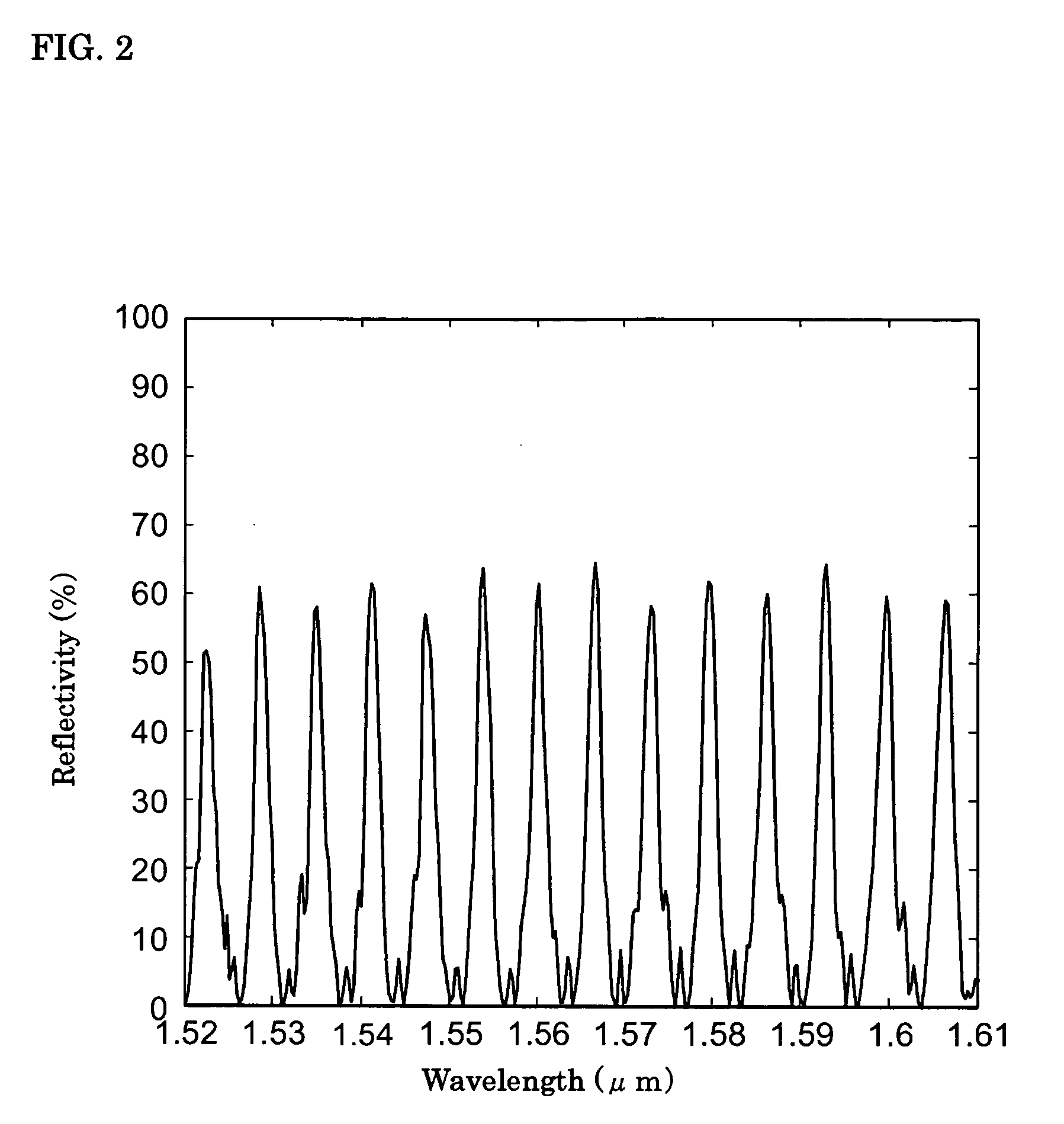
Diffraction grating device, laser diode, and wavelength tunable filter
InactiveUS20090225796A1Small wavelength dependenceReduce widthLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionCouplingLength wave
A diffraction grating device includes a substrate with a primary surface having a plurality of grating areas that are periodically arranged with a constant period in a predetermined axis direction, the grating area including a first area and a second area, a diffraction grating structure providing a chirped grating whose pitch monotonically changes along the predetermined axis direction, a core layer that is optically coupled with the diffraction grating structure with a coupling coefficient, a plurality of grating portions including the diffraction grating structure and the core layer, the grating portion including a first portion and second portion that are arranged on the first area and the second area, respectively, of the primary surface and a perturbing layer disposed at the first portion or the second portion. The perturbing layer changes the coupling coefficient between the diffraction grating structure and core layer. A periodical change in the coupling coefficient is formed along the core layer, and this change in the coupling coefficient affects the light propagating through the core layer in the direction of the predetermined axis.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Waveguide type polarizing beam splitter
InactiveCN102841407AEasy to controlSimple structureOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsLength dependenceBeam splitter
A waveguide type polarizing beam splitter belongs to the technical field of integrated photon devices, is based on the total internal reflection principle and the mode field coupling principle and adopts liquid crystal materials with a large double refraction difference. According to the invention, optical signals of different polarization states can automatically select specific branch waveguides at branch positions to transmit so as to realize effective separation of the optical signals of different polarization states; the refractivity of the liquid crystals at a regulation and control area can be changed through utilizing an electro-optical effect so as to achieve the purpose that the output ports of the optical signals of different polarization states exchange and further realize regulation and control of a polarized light output passage. The polarizing beam splitter provided by the invention has the advantages of simple structure, easiness in design and manufacturing, low wave length dependence, simplicity and convenience in regulation and control, and the like, and has an application prospect in an integrated photon system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Resin composition for light scattering layer, light scattering layer,and organic electroluminescence device
InactiveUS20130331474A1Light extraction efficiency be improveSmall wavelength dependenceElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesOrganic electroluminescencePhysics
Provided is a resin composition for light scattering layer for use in forming a light scattering layer of an organic EL device, including: a binder composition including at least one type of resin (A); and light scattering particles (B). In a resin composition for light scattering layer of the invention, the light scattering particles (B) have an average particle diameter of 200 nm to 500 nm in the resin composition and have a content of 20 vol % or less of particles with a particle diameter of 600 nm or more with respect to a total amount of the light scattering particles (B); and a refractive index difference between the binder composition and the light scattering particles (B) is 0.1 or more.
Owner:TOYO INK SC HOLD CO LTD +1
Diffraction type light-condensing film and planar light source device using the same
InactiveUS20070211342A1Improve abilitiesHigh light transmittancePlanar/plate-like light guidesDiffraction gratingsOptical transmittancePrism
Provided are an easy-to-handle thin diffraction type light-condensing film exhibiting high light transmissivity and condensation ability, and a planar light source device using the film. A hologram optical element using diffraction / interference phenomena based on wave properties of light is used instead of a conventional prism sheet using refraction. As a result, the diffraction type light-condensing film and the planar light source device have high light transmissivity and are thin. In the diffraction type light-condensing film, dependence of bending angle on wave length is low and light entering from an oblique direction is bent in the vertical direction and emitted with spectral separation of white light suppressed. High light-condensation impossible in a conventional optical element is realized by suppressing angular variation in emission light for angular variation in incident light.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Resin compositions for light-scattering layer, light-scattering layer and organic electro luminescence device
ActiveCN103207523ASmall wavelength dependenceHigh light extraction efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic electroluminescenceDouble bond
The invention relates to a light-scattering layer used for forming an organic EL device. The light-scattering layer comprises an adhesive composition containing at least one resin (A) and resin compositions for a light-scattering layer of light-scattering particles (B). In a first resin composition for the light-scattering layer, an average particle diameter of the light-scattering particles (B) is above 200nm and below 500nm, and particles having a particle diameter above 600nm accounts for 20 volume% of the total amount of the light-scattering particles (B), and a refraction difference between the adhesive composition and the light-scattering particles (B) is above 0.1. In a second resin composition for the light-scattering layer, the resin (A) has double bonds and / or a cross-linking group, and has a mass average molecular weight (Mw) above 5,000 and less than 20,000; the light-scattering particles (B) has an average particle diameter above 200nm and below 1.0[miu]m in the resin compositions for the light-scattering layer; and a refraction difference between the adhesive composition and the light-scattering particles (B) is above 0.1.
Owner:TOYO INK SC HOLD CO LTD +1
Diffraction type light-condensing film and planar light source device using the same
InactiveUS7688511B2High light transmittanceEasy to handlePlanar/plate-like light guidesDiffraction gratingsPrismAngular variation
Provided are an easy-to-handle thin diffraction type light-condensing film exhibiting high light transmissivity and condensation ability, and a planar light source device using the film. A hologram optical element using diffraction / interference phenomena based on wave properties of light is used instead of a conventional prism sheet using refraction. As a result, the diffraction type light-condensing film and the planar light source device have high light transmissivity and are thin. In the diffraction type light-condensing film, dependence of bending angle on wave length is low and light entering from an oblique direction is bent in the vertical direction and emitted with spectral separation of white light suppressed. High light-condensation impossible in a conventional optical element is realized by suppressing angular variation in emission light for angular variation in incident light.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Optical information recording medium
InactiveUS20030124459A1Good recording characteristicSmall wavelength dependenceInformation arrangementRadiation applicationsLuminosityLength wave
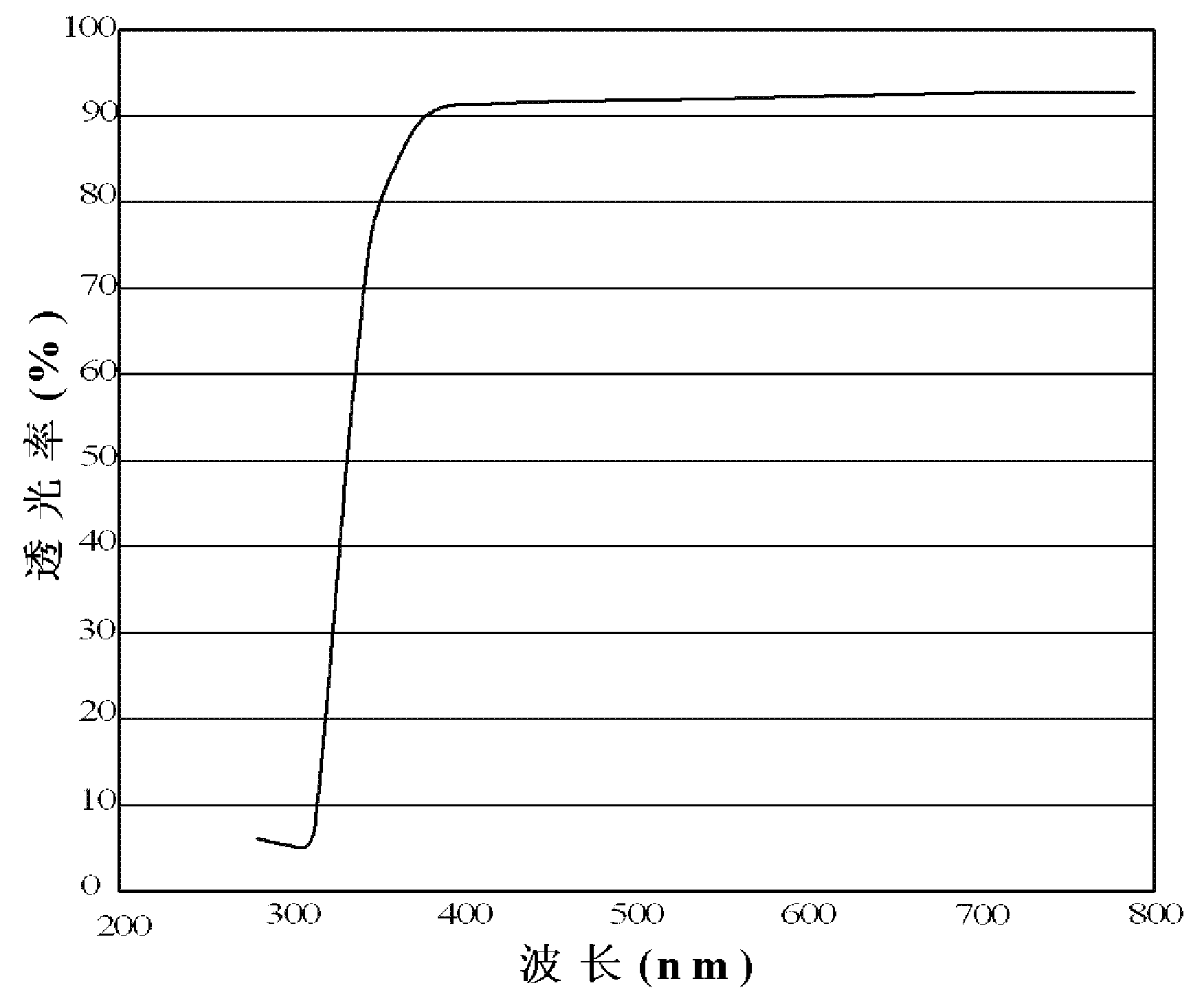
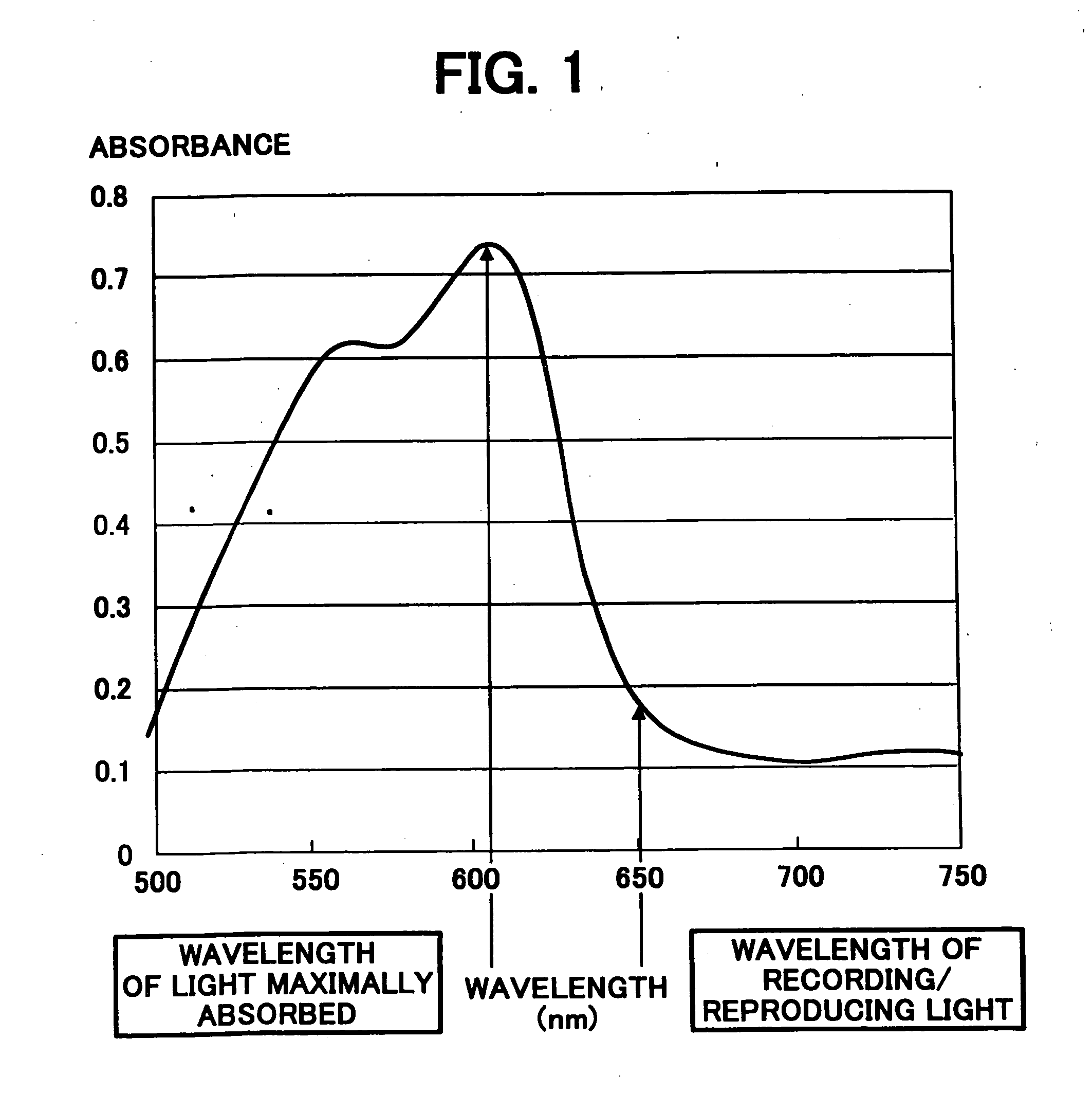
An optical information recording medium including a substrate in which at least one of a groove and a pit is formed; a recording layer located overlying the substrate and including a dye; and a reflection layer located overlying the recording layer, wherein the optical information recording medium has an absorbance curve with an absorbance L of from 10 to 40% against light having a wavelength lambd of from 645 nm to 670 nm, a ratio (Lmax / Lmin) of a maximum absorbance Lmax of the absorbance curve to a minimum absorbance Lmin of from 1.0 to 2.0 at the wavelength range of from 645 nm to 670 nm, and a reflectance of from 45 to 85% against the light having a wavelength lambd of from 645 nm to 670 nm.
Owner:RICOH KK
Light-reflective anisotropic electroconductive adhesive agent and light-emitting device
InactiveCN102482553ASmall wavelength dependenceImprove luminous efficiencyNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesConductive materialBoron nitrideMetal particle
Disclosed is a light-reflective anisotropic electroconductive adhesive agent which is intended to be used for the anisotropic electroconductive connection of a light-emitting element to a wiring board. The light-reflective anisotropic electroconductive adhesive agent comprises a heat-curable resin composition, electroconductive particles, and light-reflective insulating particles. The light-reflective insulating particles are at least one type of inorganic particles selected from the group consisting of titanium oxide particles, boron nitride particles, zinc oxide particles and aluminum oxide particles, or resin-coated metal particles each of which is produced by coating the surface of a scale-like or spherical metal particle with an insulating resin.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Diffraction device
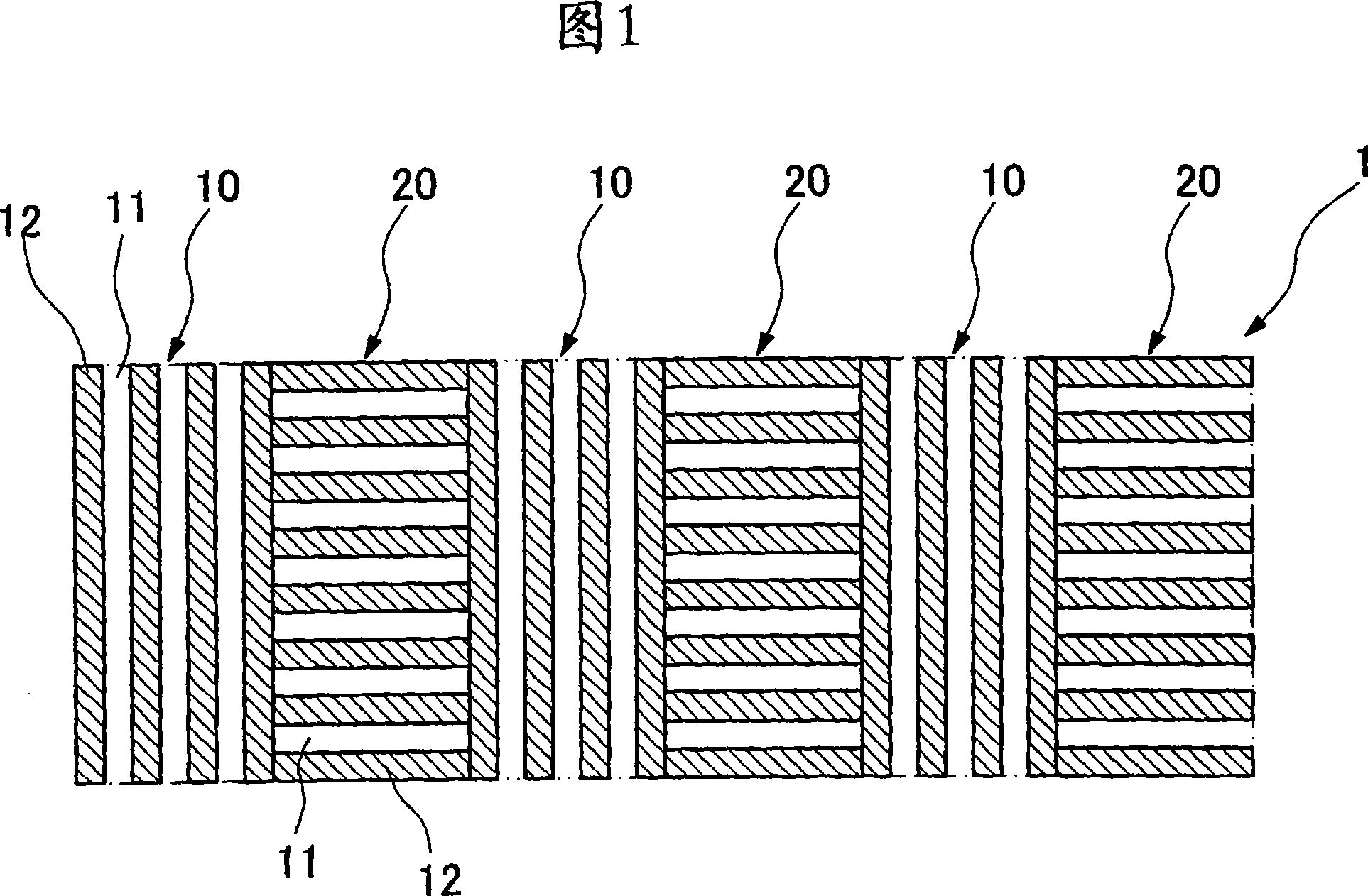
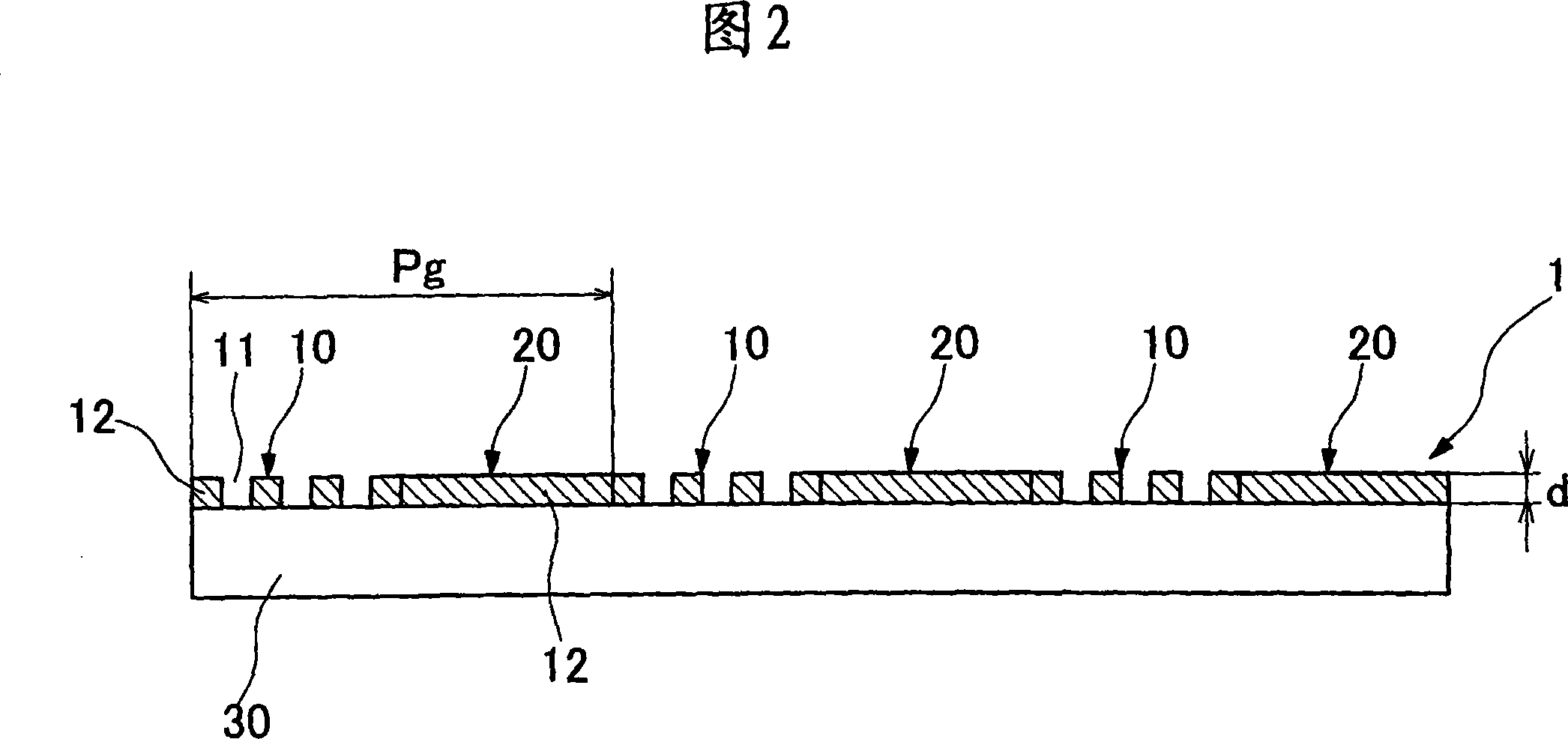
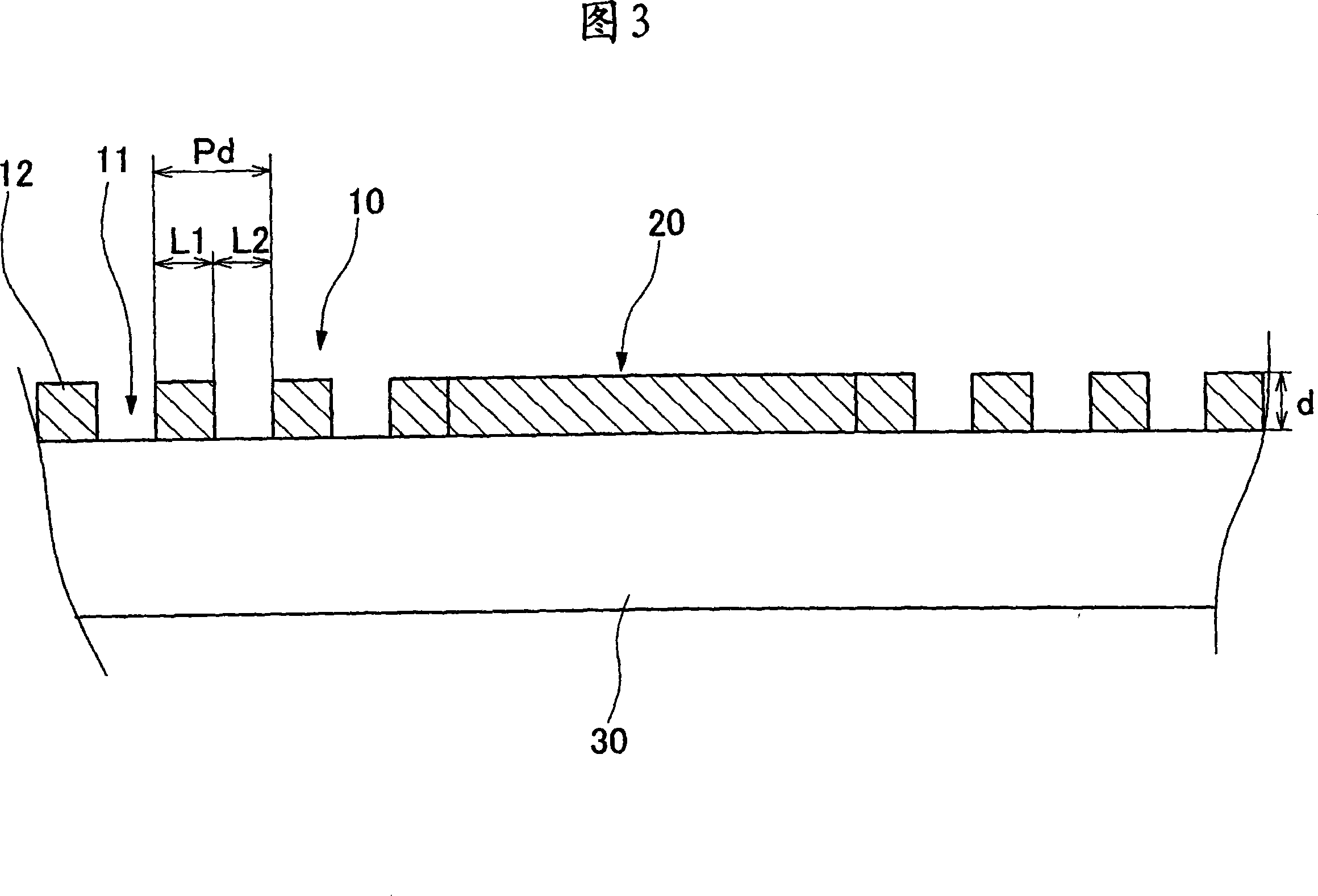
To provide a diffraction element having no wavelength dependency without using a special liquid crystal. In the diffraction element 1 for diffracting incident light, a plurality of first and second phase difference regions 10 and 20 for diffracting incident light are alternately arranged to form a diffraction pattern on a transparent substrate 30. A plurality of fine projecting and recessed structures are arranged in the first and the second phase difference regions 10 and 20 in nano order at a pitch interval shorter than the shortest wavelength of a plurality of wavelength regions for making phase differences of a plurality of wavelengths of incident light even. The fine projecting and recessed structures of the first phase difference region 10 and the fine projecting and recessed structures of the second phase difference region 20 are orthogonal to each other. Phase differences are made even by the fine projecting and recessed structures in the nano order and a diffraction function having diffraction efficiency nearly free from wavelength dependency can be exhibited by the diffraction pattern.
Owner:FUJINON SANO
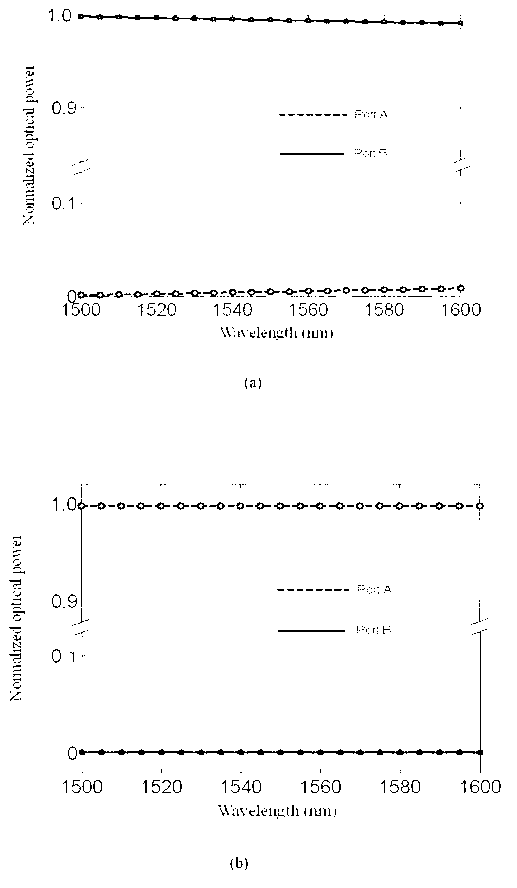
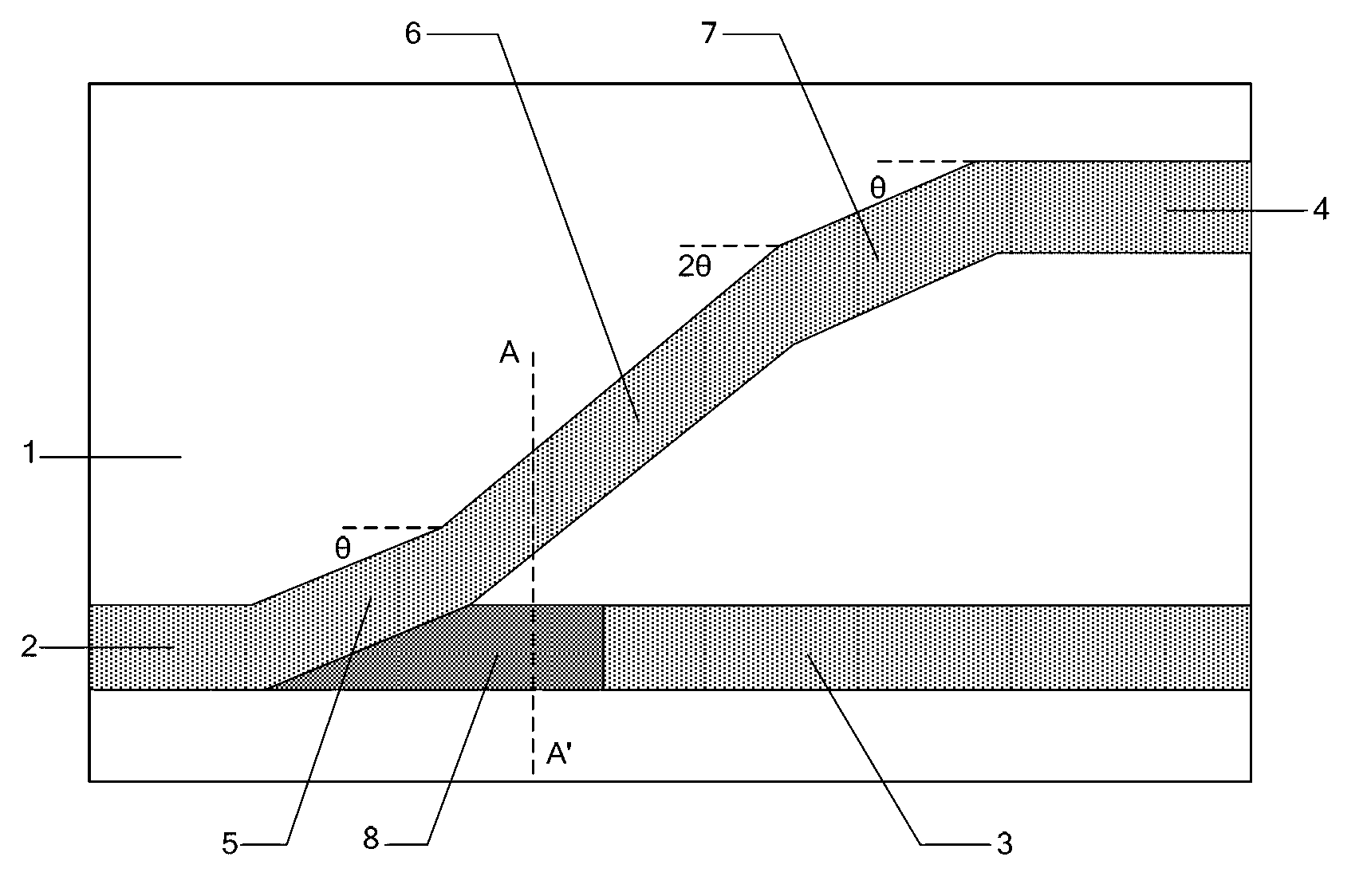
Light branching optical waveguide
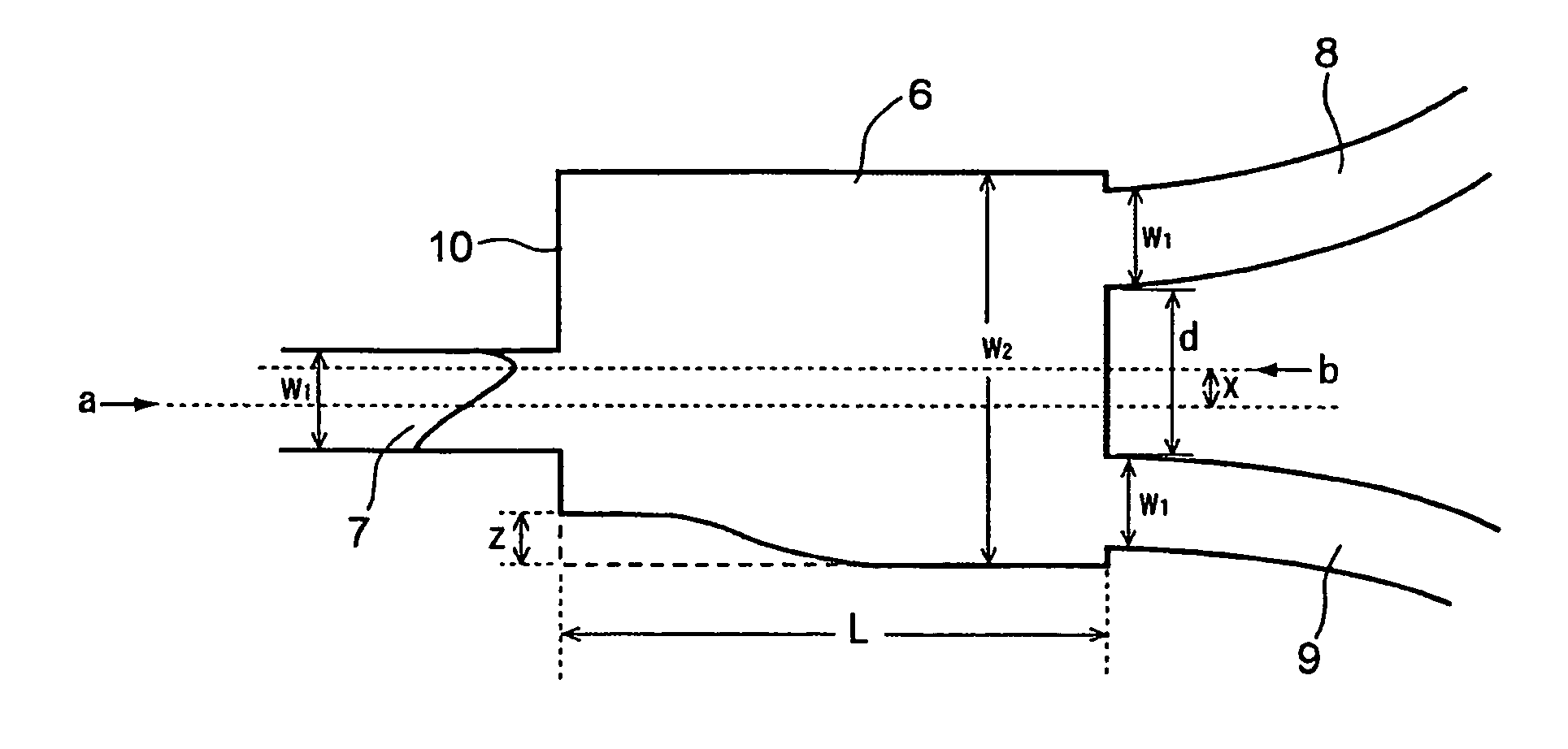
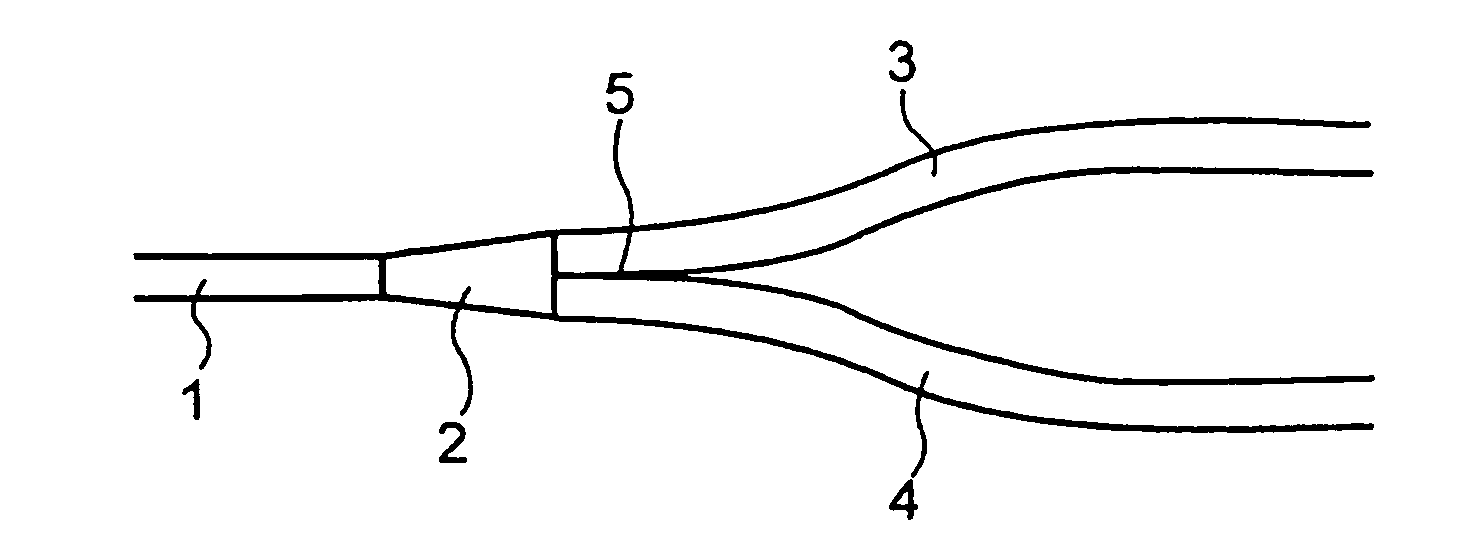
InactiveUS7840108B2Reduced branch lossSmall wavelength dependenceCoupling light guidesLength waveWaveguide
Provided is a light branching optical waveguide including: at least one incident light waveguide (A) optically connected to one end of a multi-mode optical waveguide; and output light waveguides (B) larger in number than the incident light waveguide (A) optically connected to the other end thereof, the light branching optical waveguide being characterized in that: an intensity distribution of light incident from at least one optical waveguide (a) out of the incident light waveguide (A) on the multi-mode optical waveguide at a connecting surface of the incident light waveguide (A) and the multi-mode optical waveguide is asymmetric with respect to a geometrical central axis of the optical waveguide (a); and an extended line of the geometrical center axis of the optical waveguide (a) does not coincide with a geometrical central axis of the multi-mode optical waveguide. Accordingly, it is possible to obtain a low-loss light branching optical waveguide having a reduced branch loss and a reduced variation in branching ratio, and further to obtain a light branching optical waveguide having small wavelength dependence as well as a reduced branch loss and a reduced variation in branching ratio.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
Optical waveguide device, and manufacturing method for optical waveguide device
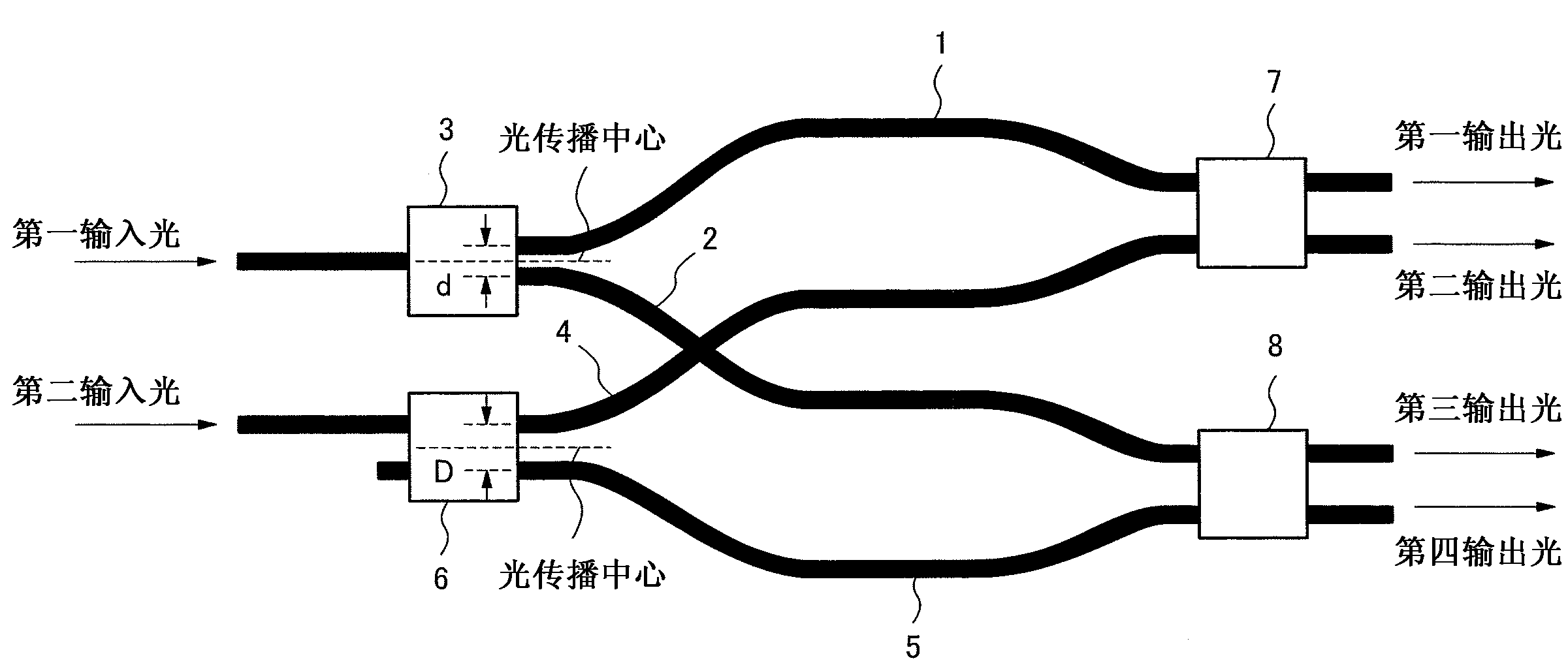
ActiveCN103270440ASmall wavelength dependenceOptical light guidesOptical propagationPhase difference
The present invention reduces the wavelength-dependency of the phase difference applied to optical waves propagating in optical waveguide arms constituting a coherent mixer. The optical waveguide device comprises a 3dB multimode interferometer splitter having: a first optical branching element which branches a first input light and outputs the same to a first and a second optical waveguide; a second optical branching element which branches a second input light and outputs the same to a third and a fourth optical waveguide; a first optocoupler which, after joining the light waves propagating in the first and third optical paths, branches the light to output a first and a second output light; and a second optocoupler which, after joining the light waves propagating in the second and fourth optical paths, branches the light to output a third and a fourth output light. The optical path length of the first and second optical waveguide pair is equal to the optical path length of the third and fourth optical waveguide pair. The first optical branching element has a structure whereby light is input from a position overlapping with the centre of optical propagation of the element. The second optical branching element has a structure whereby light is input from a position further towards the edge side than the centre of optical propagation of the element.
Owner:NEC CORP
Polymerizable liquid crystal compound, polymerizable liquid crystal composition, and oriented film
ActiveCN102630225AHigh optical anisotropyGood chemical resistanceLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryCrystallographyPolarizer
Owner:NISSAN CHEM CORP
Light-reflecting anisotropically conductive adhesive and light emitting device
ActiveCN103415585ASmall wavelength dependenceImprove luminous efficiencyNon-insulated conductorsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesAdhesiveBoron nitride
A light-reflecting anisotropically conductive adhesive, which is used for the purpose of making an anisotropically conductive connection of a light emitting element to a wiring board, contains: a thermosetting resin composition that contains a silicone resin and a curing agent; conductive particles; and light-reflecting insulating particles. The light-reflecting insulating particles are inorganic particles of at least one substance that is selected from the group consisting of titanium oxide, boron nitride, zinc oxide, silicon oxide and aluminum oxide. The silicone resin is a glycidyloxyalkyl-alicyclic alkyl-modified organopolysiloxane.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Transparent conductive element, input device, and display device
InactiveCN102804110ASmall wavelength dependenceImprove visibilityConductive layers on insulating-supportsLayered productsWavefrontDisplay device
A transparent conductive element comprises: an optical layer wherein a wavefront is disposed, further comprising an average wavelength less than or equal to the wavelengths of visible light; and a transparent conductive layer which is formed upon the wavefront to follow the wavefront. With the average wavelength of the wavefront designated [lambda]m, and the average amplitude of the oscillation of the wavefront designated Am, the ratio (Am / [lambda]m) is greater than or equal to 0.2 and less than or equal to 1.0, the average wavelength of the wavefront [lambda]m is greater than or equal to 140 nm and less than or equal to 300 nm, the film thickness of the transparent conductive layer in the location where the wavefront is highest is 100 nm or less, the area of the flat part of the wavefront is 50% or less, and the reflected hue in the chromaticity scheme L*a*b* on the wavefront side is |a*| <= 10 and |b*| <= 10.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
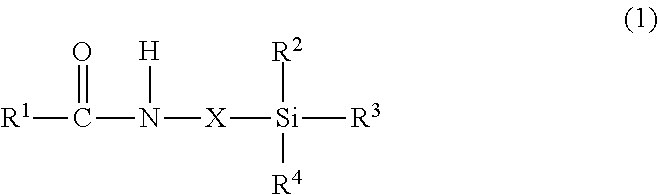
Light-reflective anisotropic conductive adhesive and light-emitting device
ActiveCN104364337ASufficient shear strengthPrevent discolorationNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesConductive materialEpoxyAnisotropic conductive adhesive
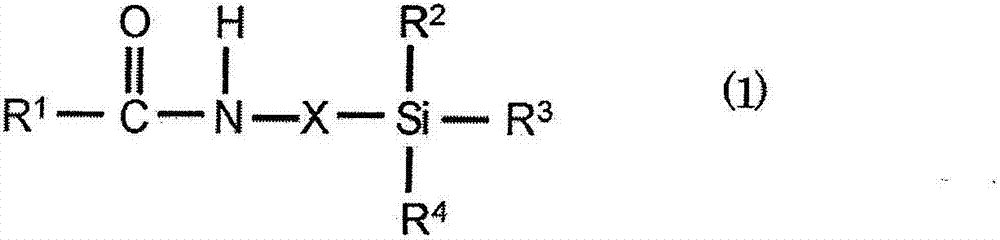
Provided is a light-reflective anisotropic conductive adhesive for use for an anisotropic conductive connection between a light-emitting device and a circuit board, which comprises a thermosetting resin composition, conductive particles and light-reflective insulating particles. The thermosetting resin composition comprises diglycidyl isocyanuryl modified polysiloxane represented by formula (1) and a curing agent for an epoxy resin.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Light branching optical waveguide
InactiveUS20070036486A1Small wavelength dependenceReduce variationCoupling light guidesLength waveWaveguide
Provided is a light branching optical waveguide including: at least one incident light waveguide (A) optically connected to one end of a multi-mode optical waveguide; and output light waveguides (B) larger in number than the incident light waveguide (A) optically connected to the other end thereof, the light branching optical waveguide being characterized in that: an intensity distribution of light incident from at least one optical waveguide (a) out of the incident light waveguide (A) on the multi-mode optical waveguide at a connecting surface of the incident light waveguide (A) and the multi-mode optical waveguide is asymmetric with respect to a geometrical central axis of the optical waveguide (a); and an extended line of the geometrical center axis of the optical waveguide (a) does not coincide with a geometrical central axis of the multi-mode optical waveguide. Accordingly, it is possible to obtain a low-loss light branching optical waveguide having a reduced branch loss and a reduced variation in branching ratio, and further to obtain a light branching optical waveguide having small wavelength dependence as well as a reduced branch loss and a reduced variation in branching ratio.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Optical amplifier
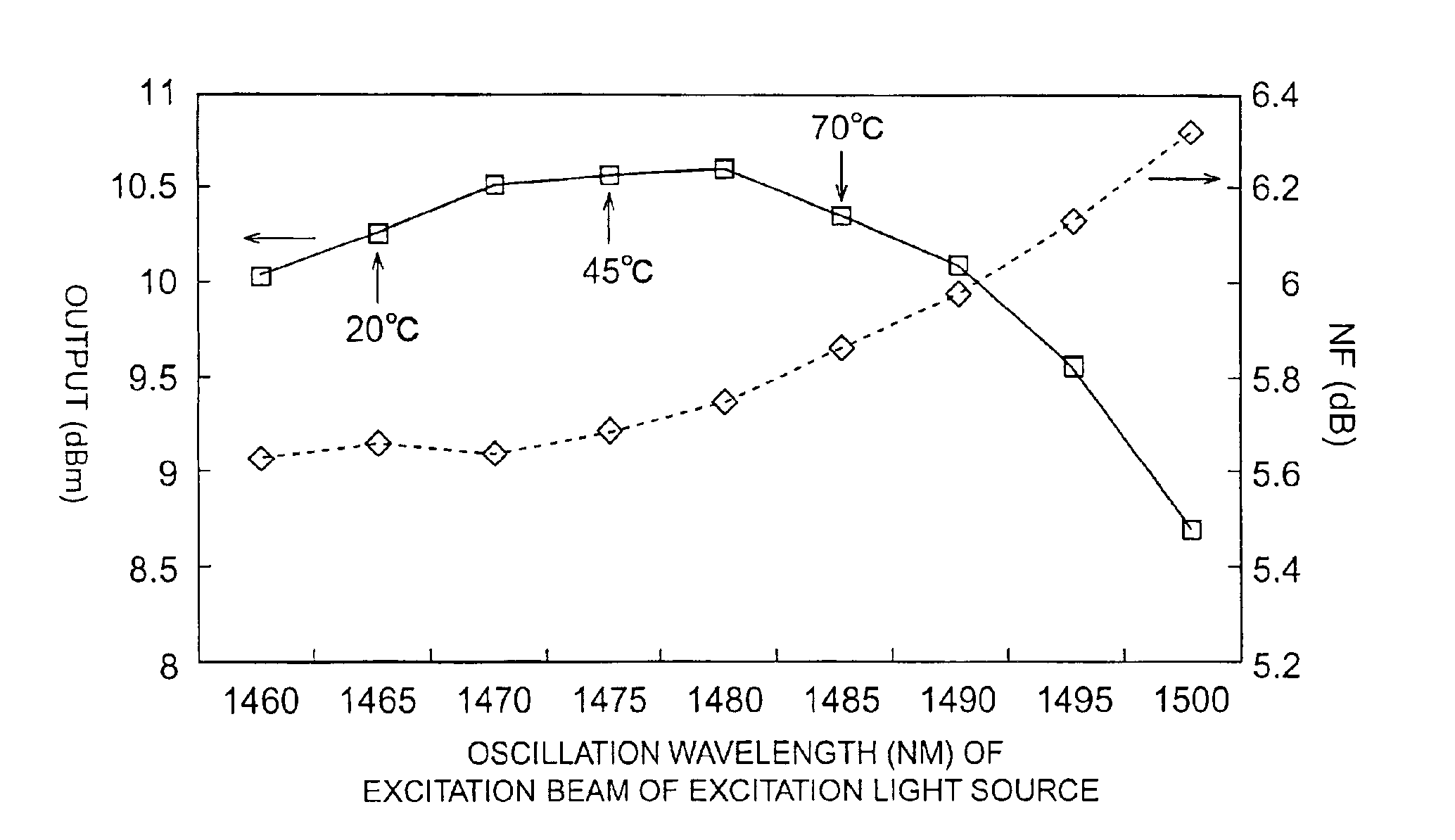
InactiveUS6870667B2Small wavelength dependenceNanoopticsActive medium materialExcitation beamMultiplexer
Optical amplifier according to the present invention is provided with an EDF, a light source device having a semiconductor laser element that generates an excitation beam and a housing that accommodates this, and an optical multiplexer having an input optically coupled with light source device, an input that receives the signal beam, and an output that provides an excitation beam and signal beam to EDF. Semiconductor laser element has an active layer, provided between cladding layers and including compound semiconductors of mutually different conductivity types, that includes a compound semiconductor and is constructed such that the oscillation wavelength at 20° C. of this semiconductor laser element is less than 1470 nm but not less 1440 nm. If this is done, the change of gain in EDF with respect to oscillation wavelength can be made satisfactorily small and the NF can be made satisfactorily small.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Wavelength dispersion compensating filter
InactiveUS6847759B2Improve manufacturabilityLow costCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideOptical propagationMach–Zehnder interferometer
A 2-input, 2-output optical circuit is constructed by serially connecting two or more Mach-Zehnder interferometers possessing a structure in which two waveguides are embraced by two couplers. One output and one input of the two 2-input, 2-output optical circuit are connected by an optical propagation path to thereby construct a loop circuit. The waveguides of the Mach-Zehnder interferometers as well as the loop circuit are each provided with an optical path-length adjustment portion, thereby constructing a wavelength dispersion compensating filter.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Substrate with light-blocking material, color filter, liquid crystal display device and coloring resin composition for forming said light-blocking material
InactiveCN106233164AIncrease production capacityReduce reflexesOptical filtersNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayRefractive index
The present invention provides a substrate with a light-blocking material, which achieves excellently low reflectivity, while having good productivity. The substrate of the present invention is a substrate with a light-blocking material, which comprises a light-blocking material on a transparent substrate. The light-blocking material contains (A) a colorant and (B) an organic binder, and satisfies the following requirements (1) and (2). (1) The light-blocking material contains (C) fine particles having a refractive index of from 1.2 to 1.8 (inclusive). (2) The concentration of the fine particles in the light-blocking material differs in the thickness direction, and the concentration on the side opposite to the transparent substrate side is lower than the concentration on the transparent substrate side.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Optical device, display device, and three-dimension image display device for changing a polarization state of a light beam in time
InactiveUS7495831B2Small wavelength dependenceImprove polarizationProjectorsPolarising elementsRotational axisDisplay device
Owner:RICOH KK
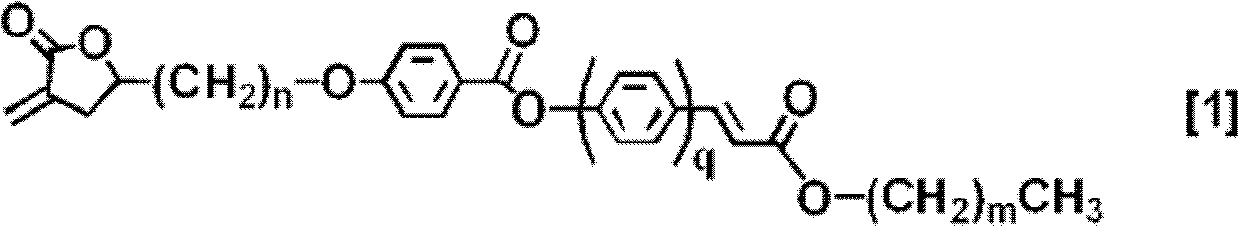
Fumaric acid diester based resin for retardation film and retardation film comprising the same
ActiveUS9266988B2Excellent optical propertiesHigh out-of-plane retardationPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsIn planeFilm plane
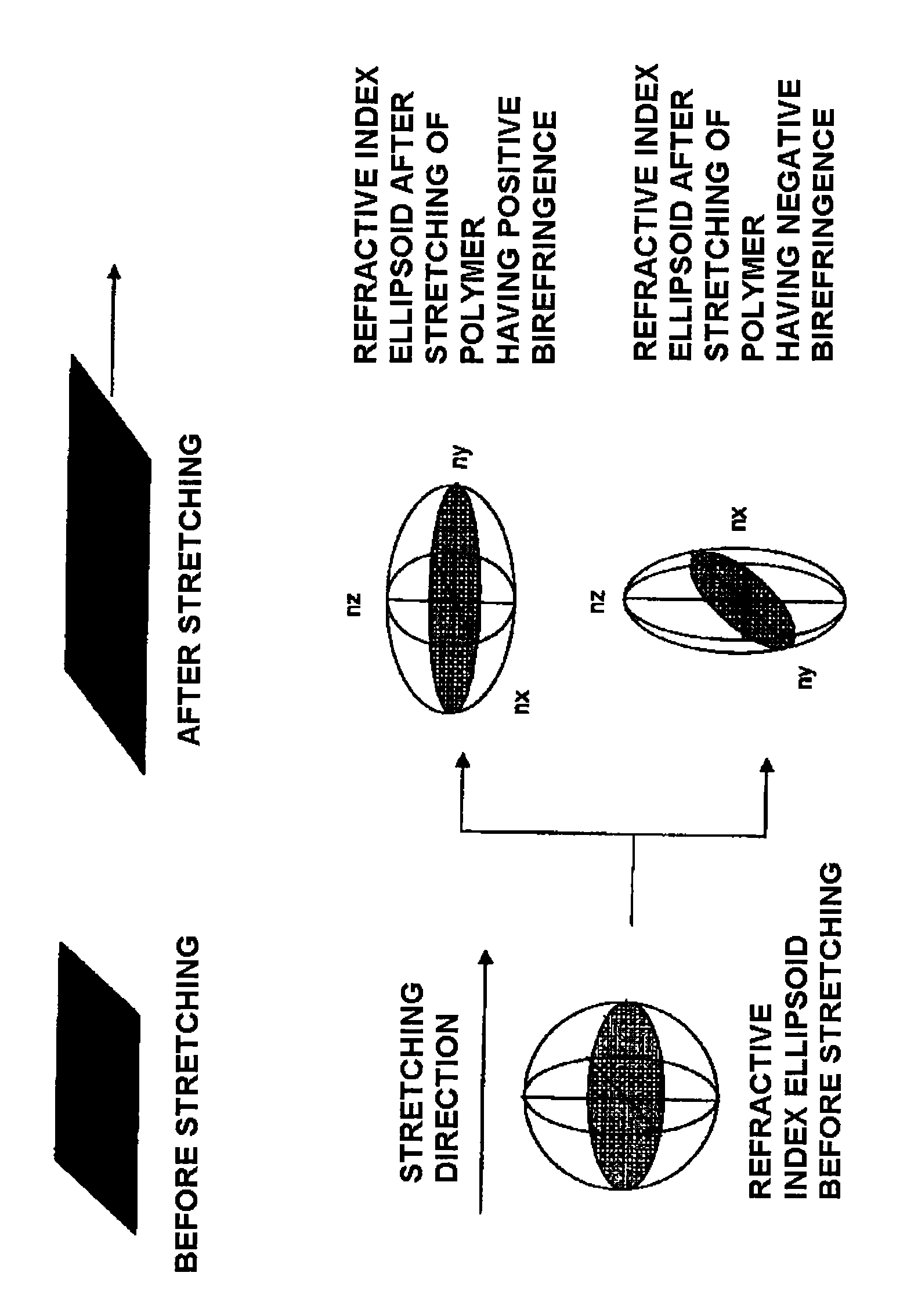
A fumaric acid diester based resin containing a dipropyl fumarate residue unit and a fumaric acid diester residue unit having a C1 or C2 alkyl group, wherein in a retardation film composed of the resin, when a refractive index in the fast axis direction within the film plane is designated as nx, a refractive index in the film in-plane direction orthogonal thereto is designated as ny, and a refractive index in the thickness direction of the film is designated as nz, the respective refractive indices are satisfied with a relationship of (nx≦ny<nz) and a relationship between a film thickness and an out-of-plane retardation measured at a wavelength of 550 nm and expressed by the specific equation is 4.5 nm / film thickness (μm) or more in terms of an absolute value.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Semiconductor laser device
ActiveUS20100303118A1Wavelength dependenceSmall wavelength dependenceOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsReflectivityResonator
A semiconductor laser device has structure including: a semiconductor laser chip having an emission surface and a reflection surface which are opposing end surfaces of a resonator; and a photodiode for detecting light that exits from the reflection surface side, the photodiode being used in a wavelength band where a sensitivity of the photodiode rises as a wavelength lengthens, in which the emission surface has a first dielectric multilayer film formed thereon and the reflection surface has a second dielectric multilayer film formed thereon, and in which, when a wavelength at which a reflectance of the first dielectric multilayer film peaks is given as λf and a wavelength at which a reflectance of the second dielectric multilayer film peaks is given as λr, a relation λf<λr is satisfied.
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
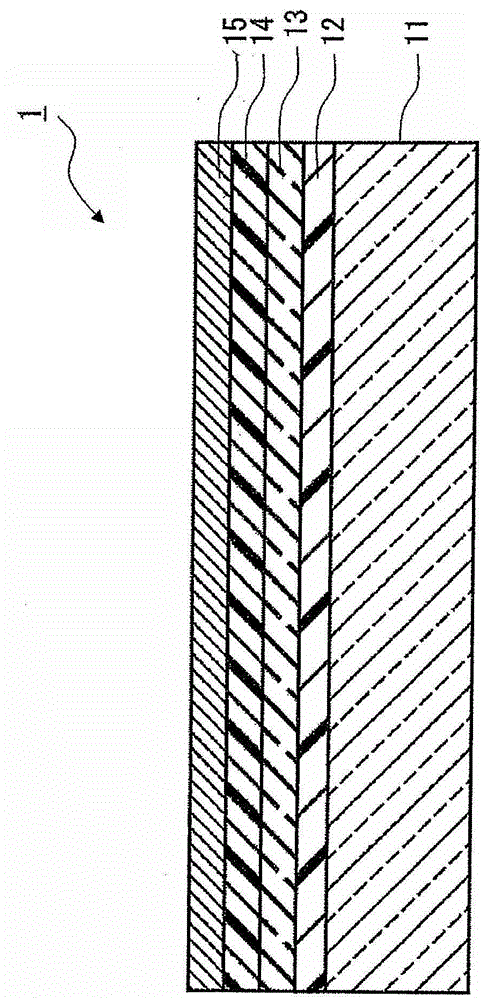
Optical diffraction element and endoscope
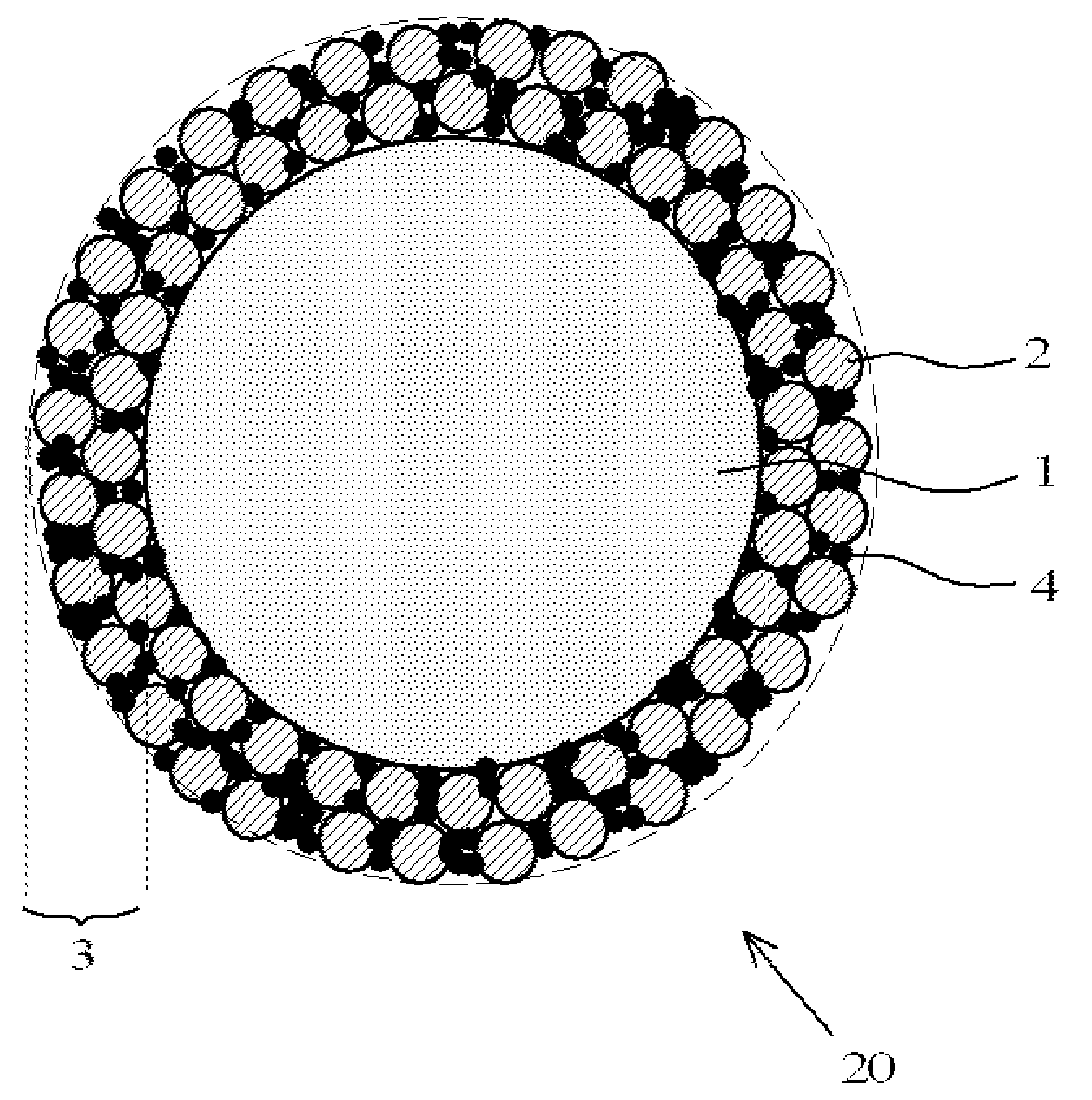
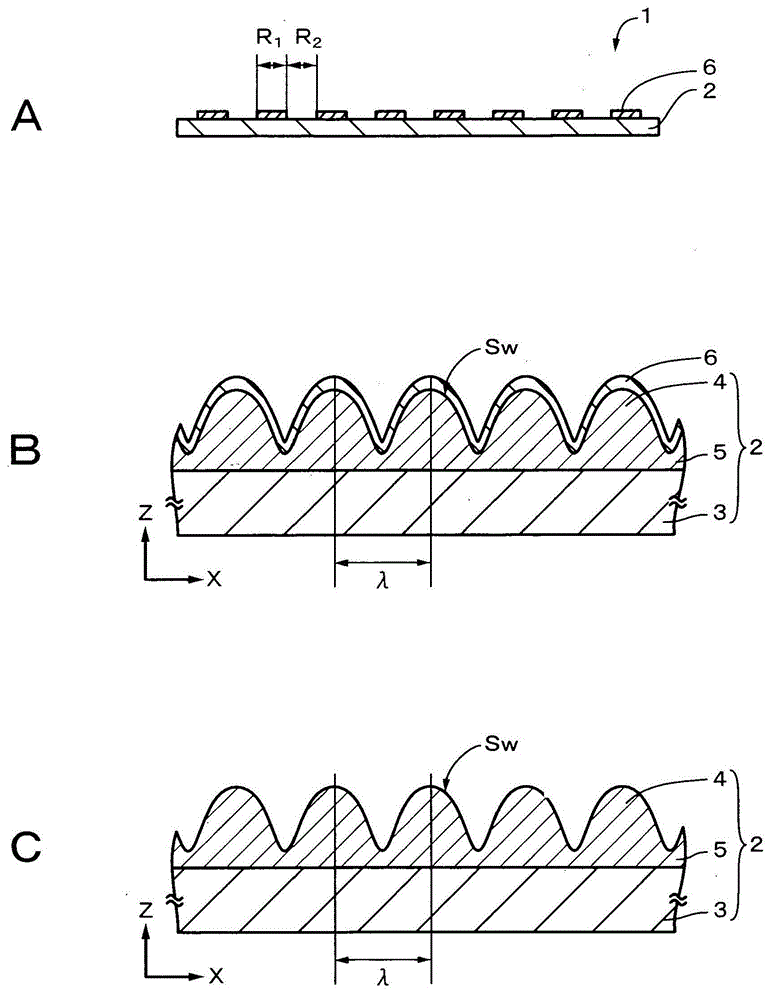
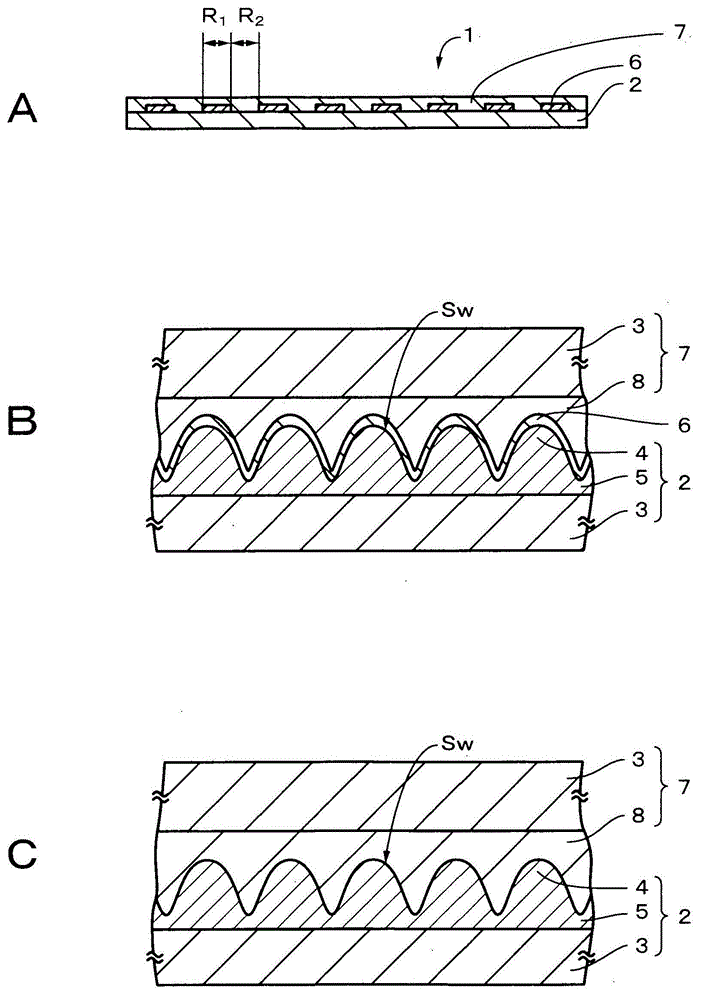
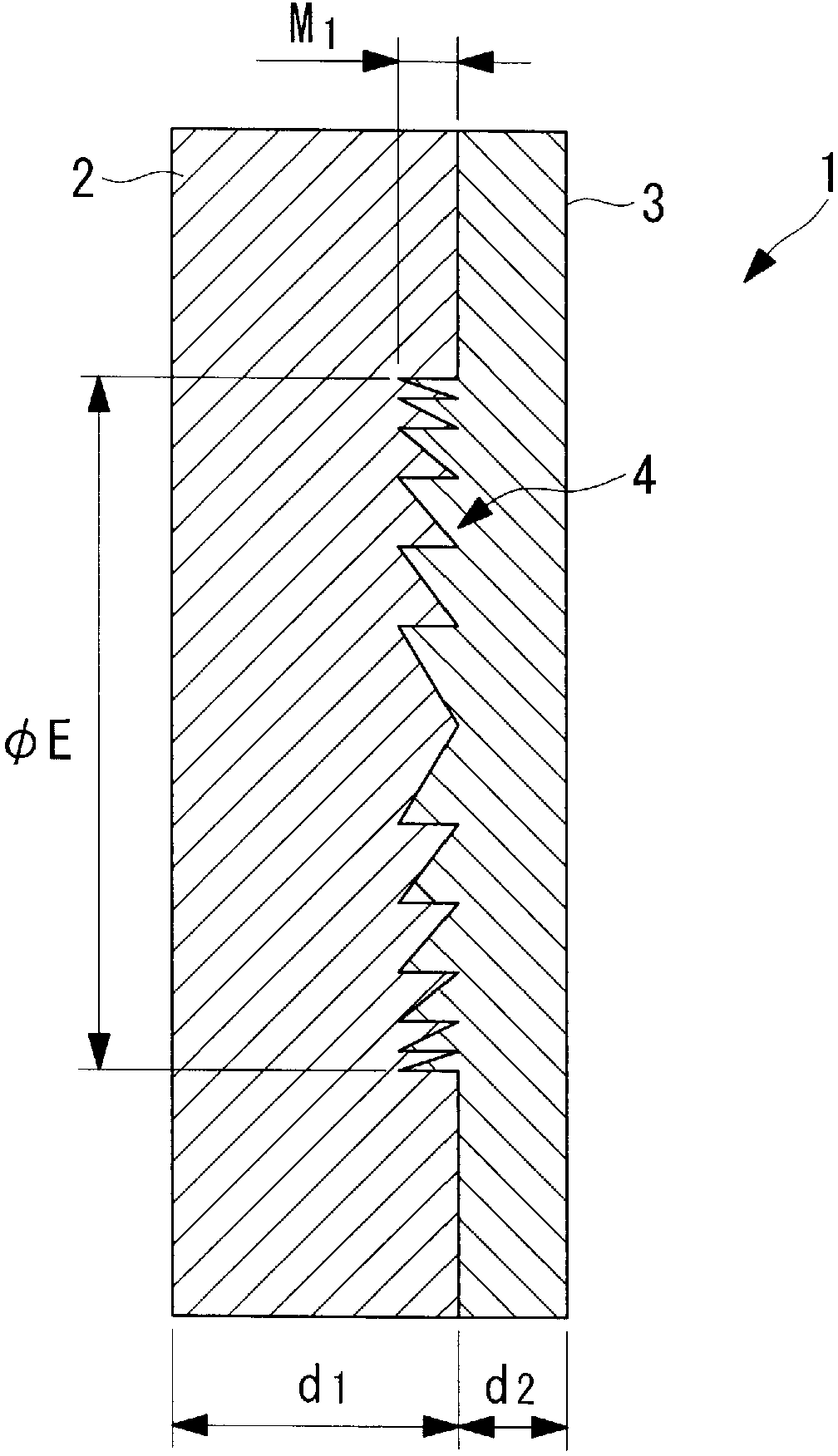
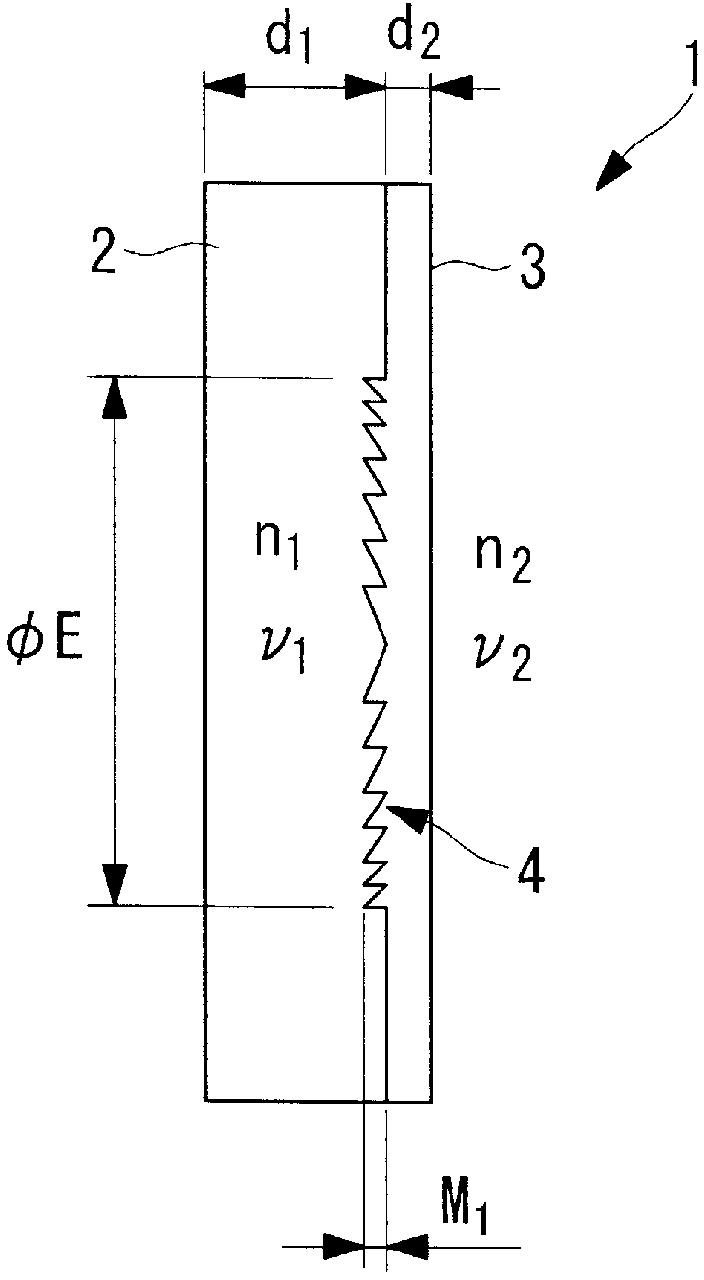
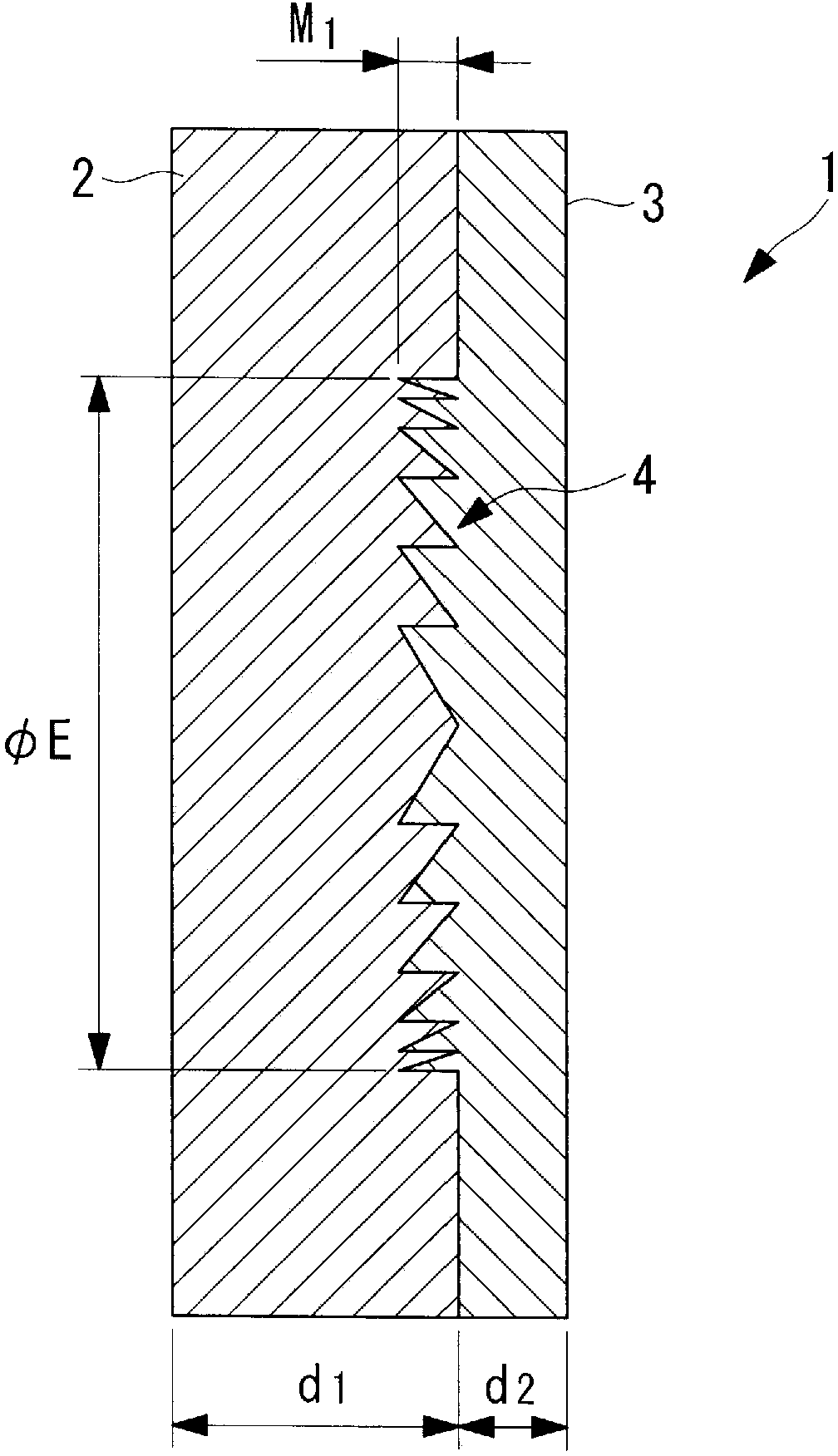
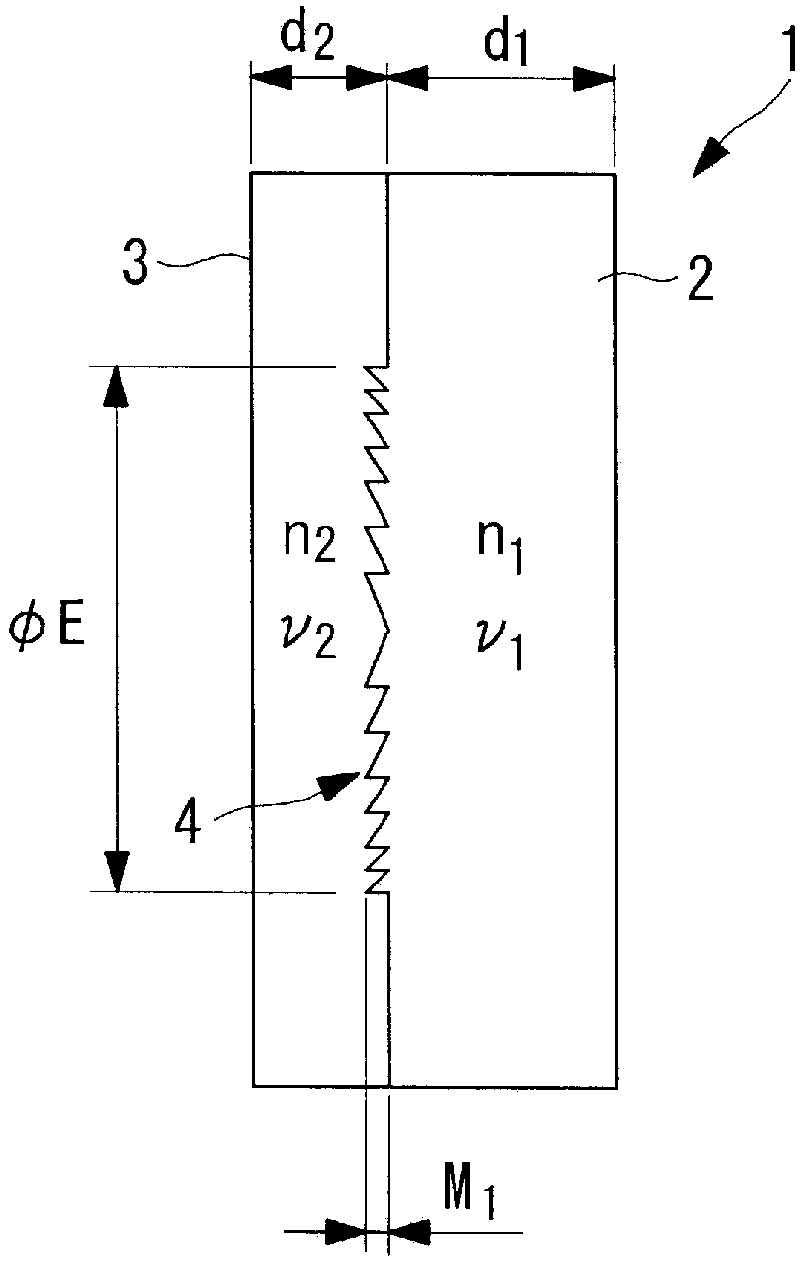
InactiveCN103080786ASmall wavelength dependenceAvoid it happening againSurgeryEndoscopesOptical diffractionConditional expression
Provided is an optical diffraction element (1) in which two optical material layers (2, 3) comprising cured resin having different energies are laminated, and a relief pattern (4) is formed at the interface of the two optical material layers (2, 3), the optical diffraction element (1) satisfying the following conditional expressions: 0.01<d2 / d1<0.2 (1); 0.05<d1 / [phi]E<1.0 (2); 0.0005<d2 / [phi]E<0.1 (3); d1 is the central thickness (mm) of the one optical material layer (2) that is cured first, d2 is the central thickness (mm) of the other optical material layer (3) that is subsequently cured, and [phi]E is the effective diameter (mm) of the relief pattern (4).
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
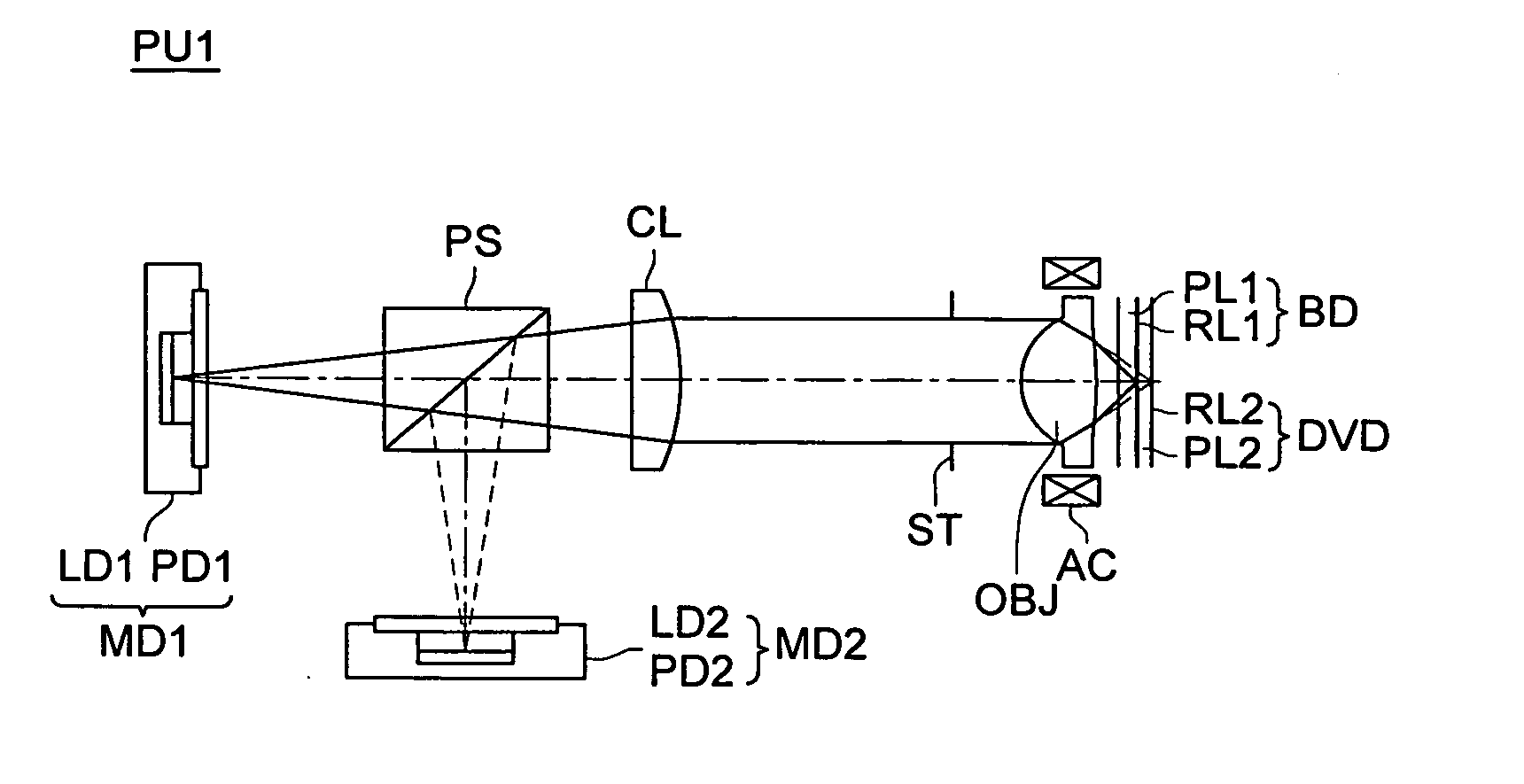
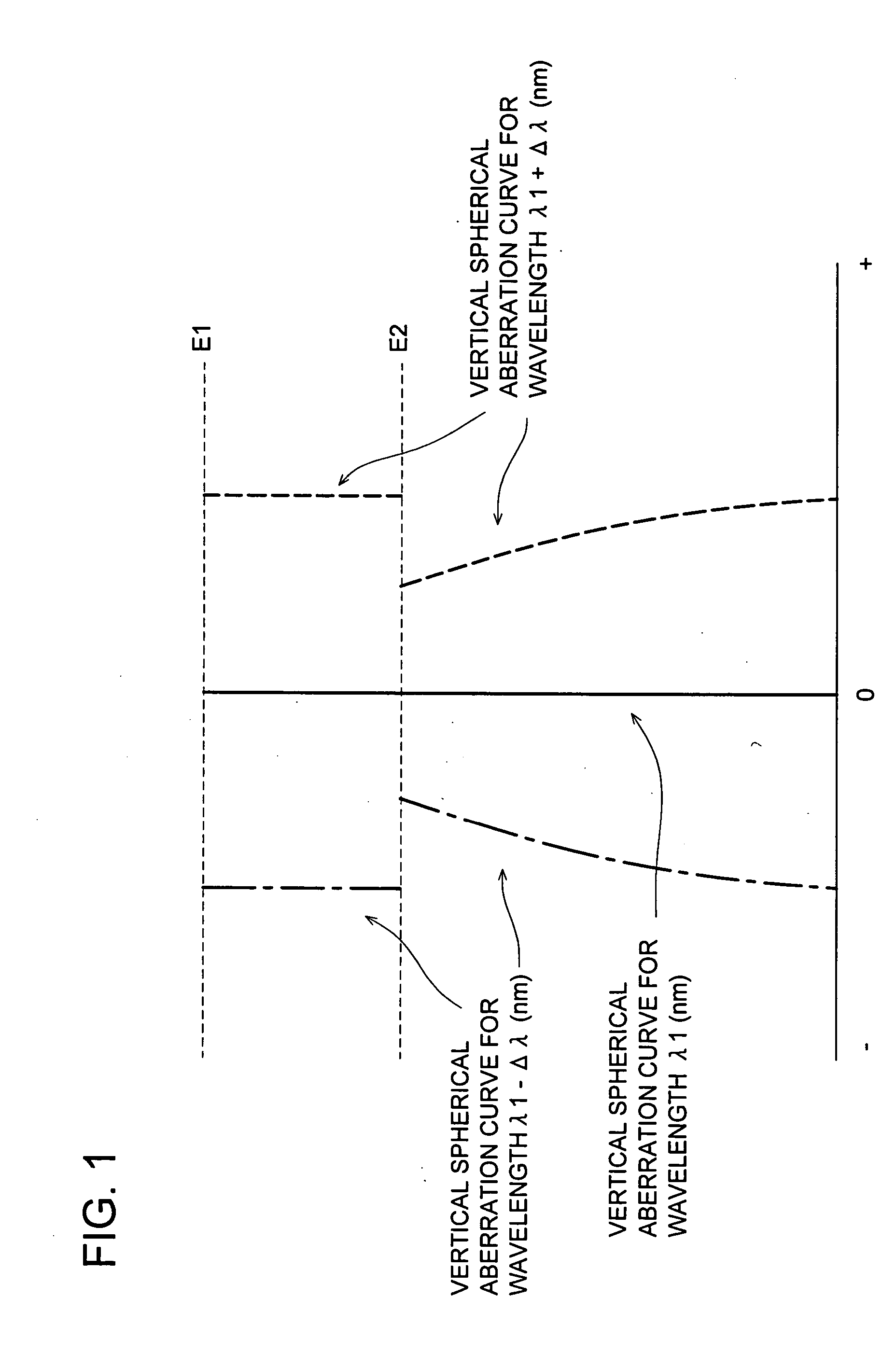
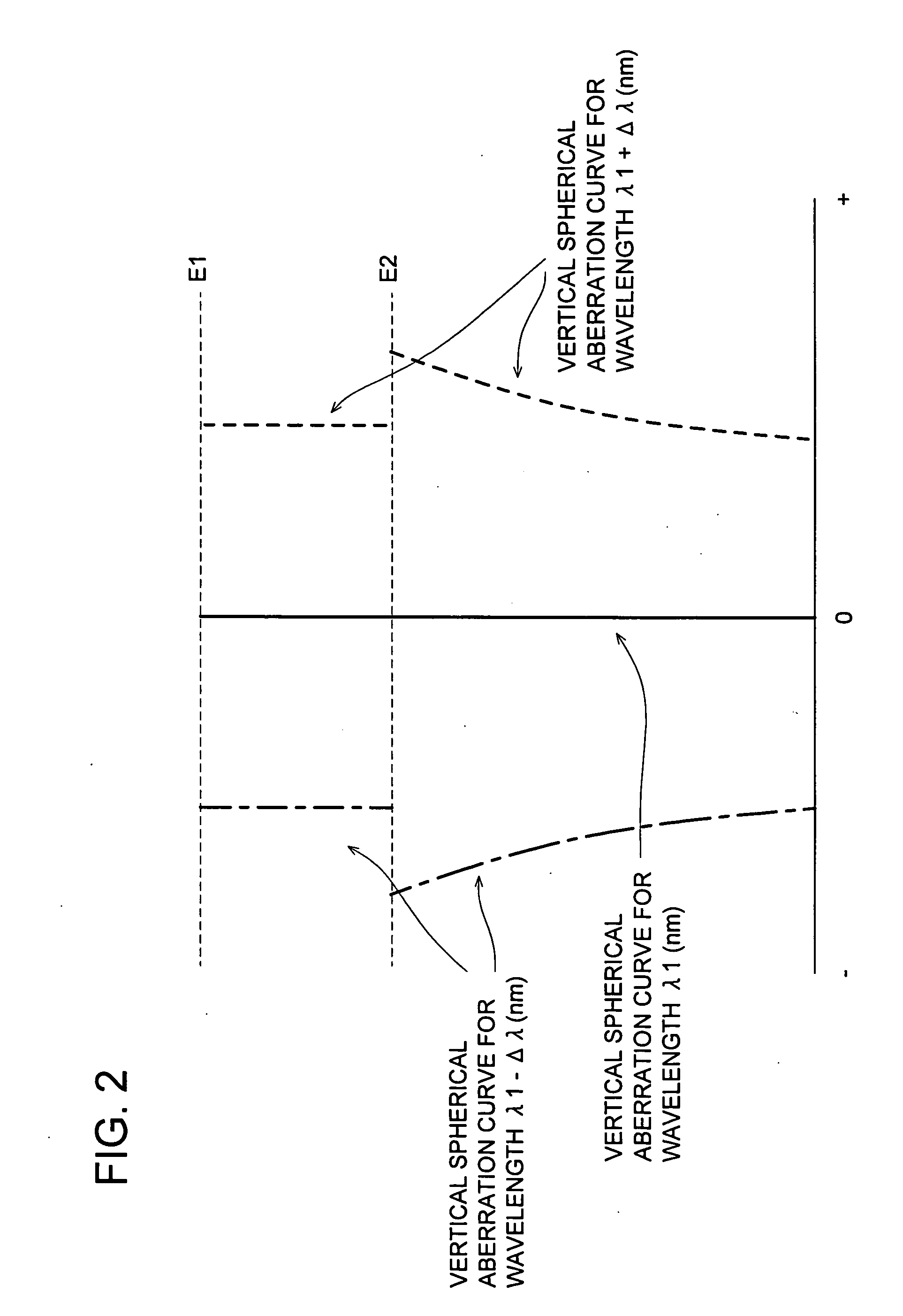
Objective lens, optical pickup apparatus and optical information recording and/ or reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20060209644A1Small wavelength dependenceHigh light transmittanceRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupLight flux
An objective lens according to the present invention is an objective lens used for an optical pickup apparatus, and the objective lens includes a superimposed structure on a surface of a lens with a power in which a first optical path difference providing structure changing spherical aberration in under-corrected direction when a wavelength of an incident light flux becomes longer, and a second optical path difference providing structure changing spherical aberration in over-corrected direction when a wavelength of an incident light flux becomes longer are superimposed.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Resin compositions for light-scattering layer, light-scattering layer and organic electro luminescence device
ActiveCN103207523BImprove light extraction efficiencySmall wavelength dependenceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefractive indexDouble bond
The invention relates to a light-scattering layer used for forming an organic EL device. The light-scattering layer comprises an adhesive composition containing at least one resin (A) and resin compositions for a light-scattering layer of light-scattering particles (B). In a first resin composition for the light-scattering layer, an average particle diameter of the light-scattering particles (B) is above 200nm and below 500nm, and particles having a particle diameter above 600nm accounts for 20 volume% of the total amount of the light-scattering particles (B), and a refraction difference between the adhesive composition and the light-scattering particles (B) is above 0.1. In a second resin composition for the light-scattering layer, the resin (A) has double bonds and / or a cross-linking group, and has a mass average molecular weight (Mw) above 5,000 and less than 20,000; the light-scattering particles (B) has an average particle diameter above 200nm and below 1.0[miu]m in the resin compositions for the light-scattering layer; and a refraction difference between the adhesive composition and the light-scattering particles (B) is above 0.1.
Owner:TOYO INK SC HOLD CO LTD +1
Optical information recording medium
InactiveUS20050282085A1Good recording characteristicSmall wavelength dependenceInformation arrangementRadiation applicationsLuminosityLength wave
An optical information recording medium including a substrate in which at least one of a groove and a pit is formed; a recording layer located overlying the substrate and including a dye; and a reflection layer located overlying the recording layer, wherein the optical information recording medium has an absorbance curve with an absorbance L of from 10 to 40% against light having a wavelength λ of from 645 nm to 670 nm, a ratio (Lmax / Lmin) of a maximum absorbance Lmax of the absorbance curve to a minimum absorbance Lmin of from 1.0 to 2.0 at the wavelength range of from 645 nm to 670 nm, and a reflectance of from 45 to 85% against the light having a wavelength λ of from 645 nm to 670 nm.
Owner:RICOH KK
Metal heating apparatus, metal heating method, and light source apparatus
InactiveUS8303738B2Efficient heatingIncrease output powerSoldering apparatusOhmic-resistance heatingLength waveWavelength range
A metal heating apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises a light output portion for outputting light having a center wavelength in a wavelength range of 200 nm to 600 nm.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
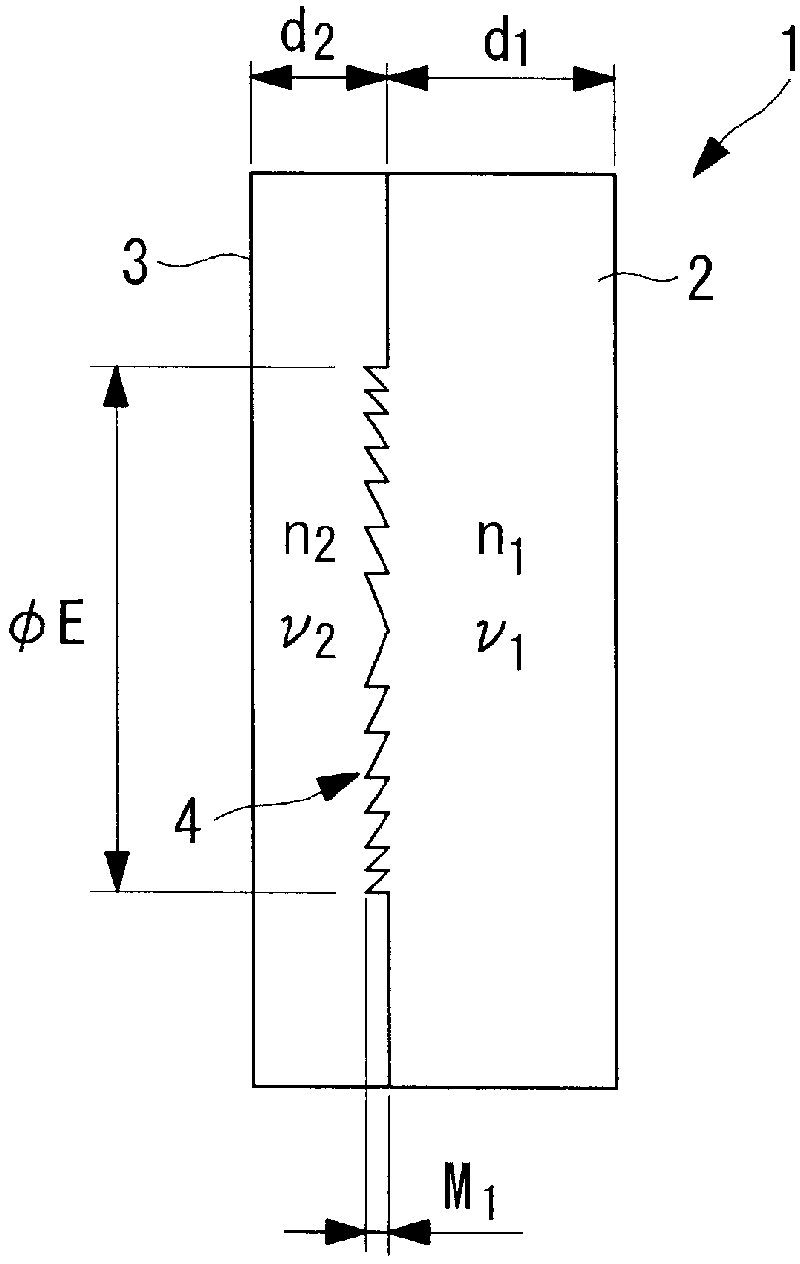
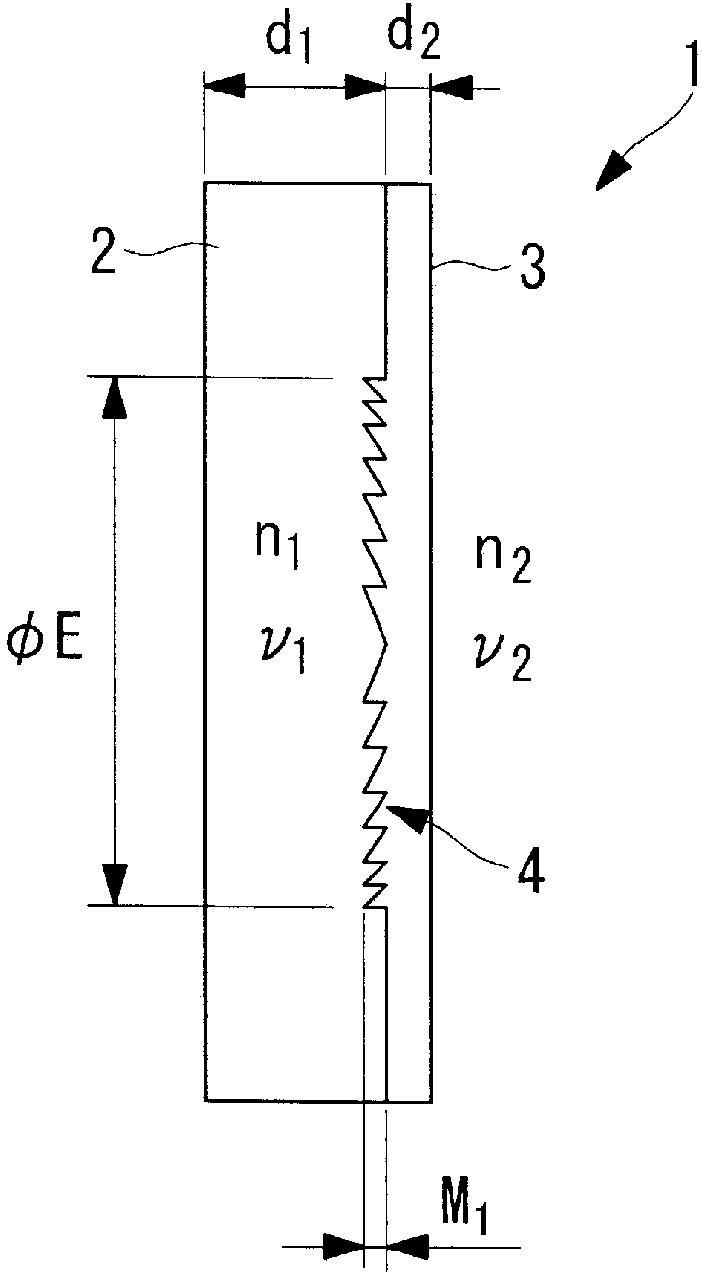
Optical diffraction element and endoscope
InactiveCN103080786BSmall wavelength dependenceAvoid it happening againSurgeryEndoscopesOptical diffractionConditional expression
Provided is a diffractive optical element (1) that is formed by laminating two optical material layers (2 and 3) formed of different energy-cured resins; in which a relief pattern (4) is formed at the interface between the two optical material layers (2 and 3); and that satisfies the following conditional expressions: wherein d 1 is the center plate thickness (mm) of one optical material layer 2 that is cured first, d 2 is the center plate thickness (mm) of the other optical material layer 3 that is cured later, and ÆE is the effective diameter (mm) of the relief pattern 4.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
A Waveguide Adjustable Analyzer
InactiveCN105606221BSimple structureSimple designLight polarisation measurementRefractive indexEngineering
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com