Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
387results about How to "Save interior space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lightweight acoustical paint and preparation method thereof
The present invention discloses one kind of light sound absorbing paint and its preparation process. The paint consists of acrylate emulsion of average grain size of 0.15-0.5 micron as the adhesive, open-pored expanded perlite as light aggregate, pigment, stuffing and assistants combined together. It is prepared through pre-mixing, dispersing grinding and blending via fast stirring. It has low density, non-toxicity, no smell, environment friendship, simple production, simple application, coating of 1-5 mm thickness, average sound absorbing coefficient higher than 0.4 and other advantages, and is suitable for use in household, meeting room, concert hall, theater, etc.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SUPER CHEM COATING CO LTDGUANGZHOU SUPER CHEM COATING CO LTD
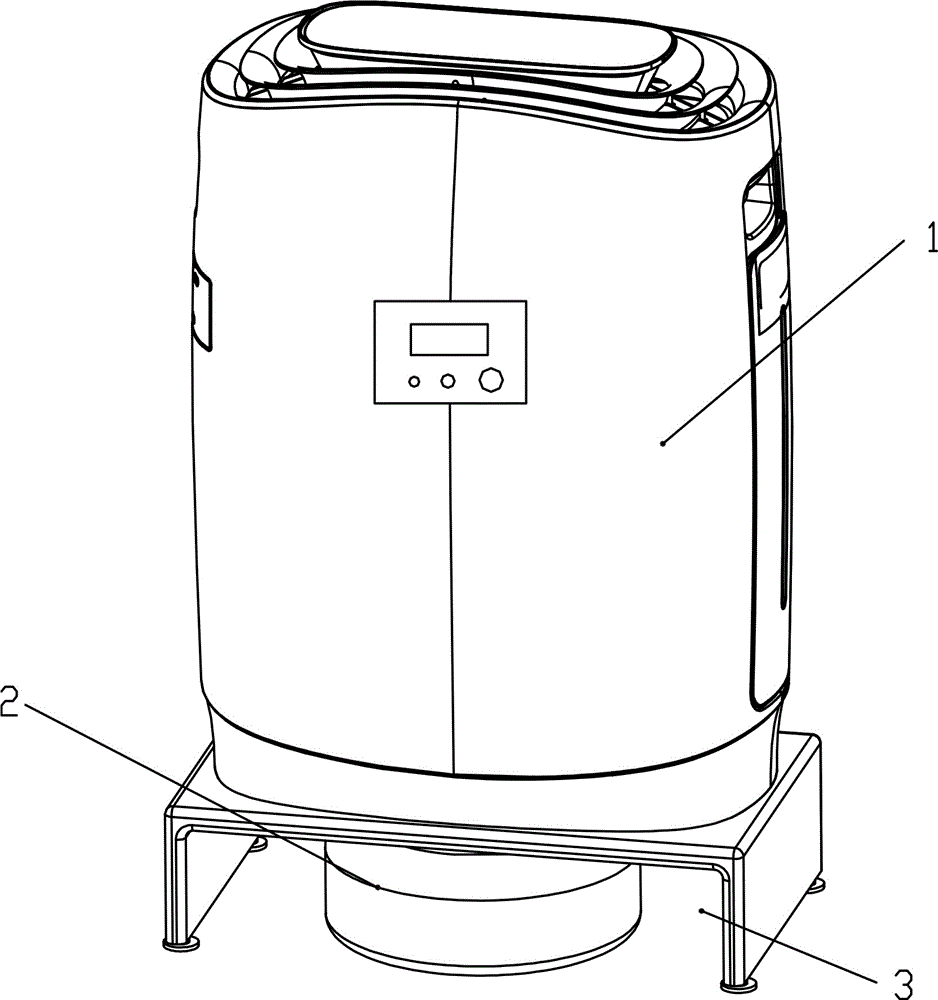
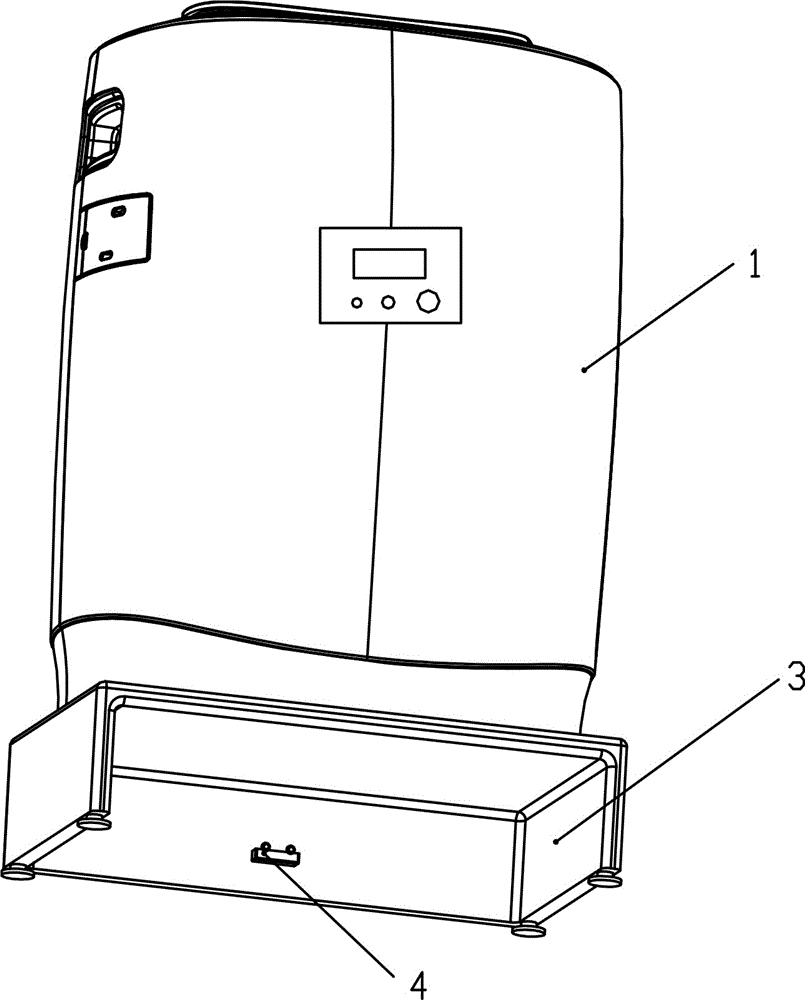
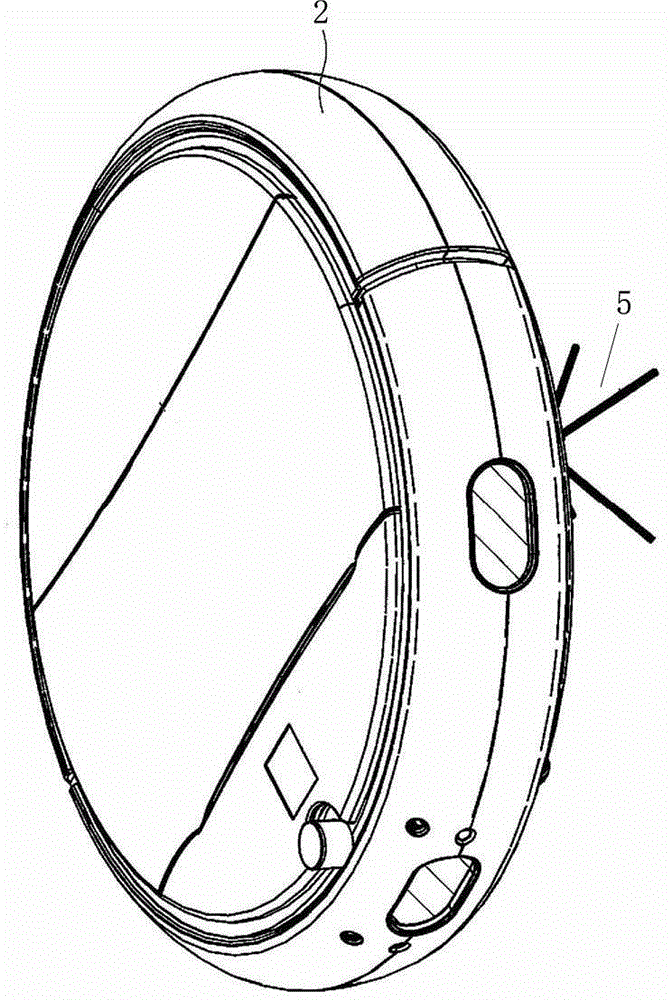
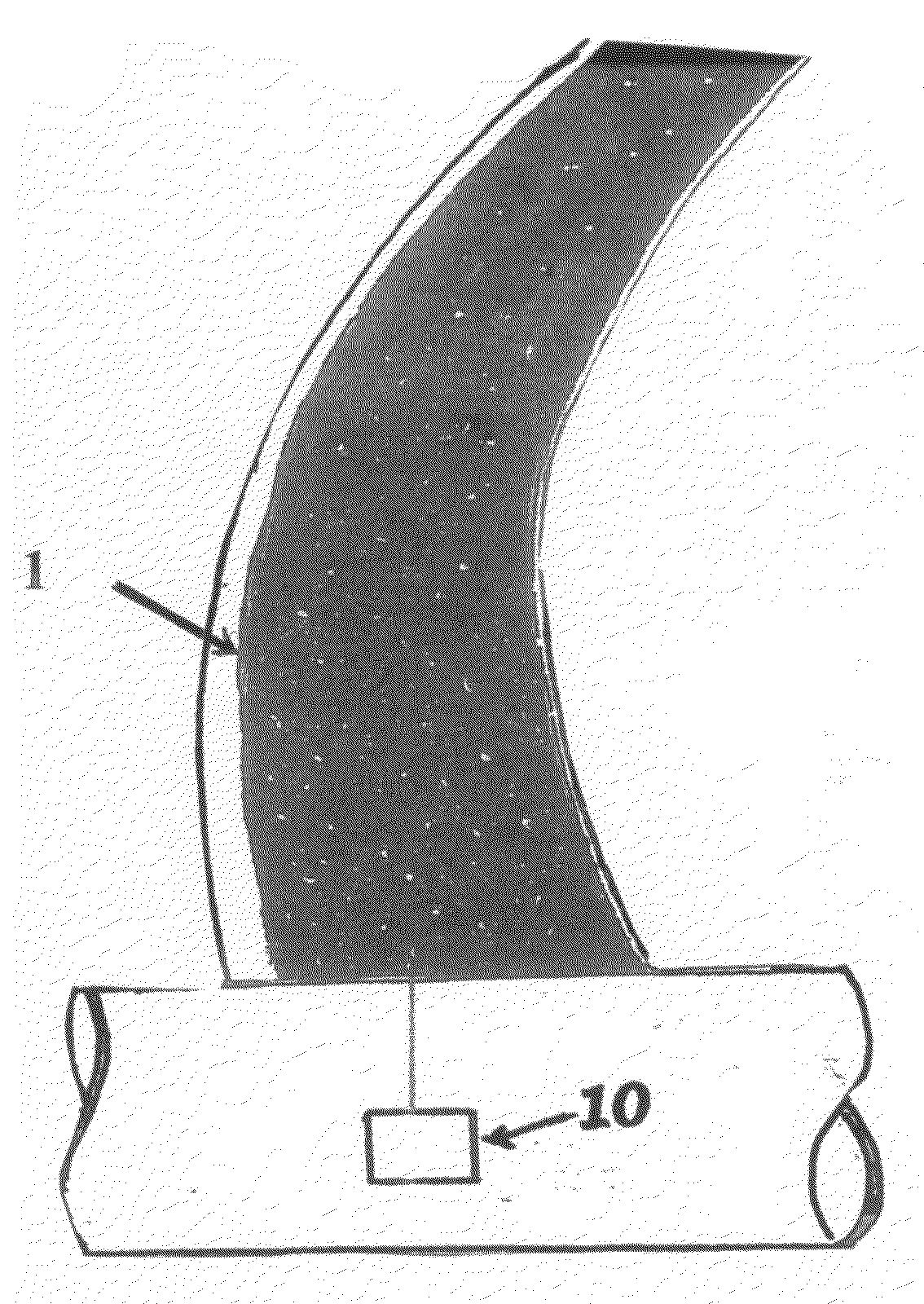
Novel air purification and automatic sweeping integrated machine
ActiveCN104132412ASo neatSave interior spaceCarpet cleanersLighting and heating apparatusEmbedded systemElectricity
The invention relates to a novel air purification and automatic sweeping integrated machine. The integrated machine comprises an air purifier. The air purifier comprises a shell and an electric control device. The integrated machine further comprises an automatic walking sweeping robot used in combination with the air purifier. A containing chamber for containing the automatic walking sweeping robot is formed in the bottom of the shell. A storage battery is arranged on the sweeping robot. A charging socket allowing the sweeping robot to be charged is arranged on the shell. The sweeping robot and the charging socket are connected through a separable electric connector. The electric control device comprises a controlled module arranged on the sweeping robot and a master control module arranged on the air purifier. The master control module and the controlled module are in wireless communication. The novel air purification and automatic sweeping integrated machine has the advantages of being convenient to use and capable of saving energy.
Owner:XIAMEN BRI ENVIRONMENTAL IND CO LTD
Controlling aircraft aerial movements, defeating icing on aircraft surfaces, aiding decontamination, and damping turbulence effects on aircraft by the method of micro-perforated airfoil coordinated precision flow management
InactiveUS20090210103A1Efficient fillingAccurate supervisionDigital data processing detailsBoundary layer controlsJet aeroplaneFlight computer
A method is provided whereby airplanes or any device with the functionality and usefulness of an airplane may be controlled without the use of any traditional effectors, such as flaps, rudders, ailerons, spoilers, and all like hinged, moveable airfoils attached to a wing or a fuselage. The means of controlling such airplanes while in flight will be by controlling the laminar air flow over all lifting surfaces so as to vary the amount and quality of the lift provided. All lifting surfaces on the airplane will be divided into dozens, hundreds, or thousands of small zones, each of which can be readily controlled by a central flight computer and each of which is capable of modifying its immediate airflow condition, whether that be laminar flow or some particular degree and variety of local eddy current. Summing over all the inputs of conditions above the multitude of zones, the central flight computer will possess algorithms and programs suitable to effect any desired change in attitude, altitude, orientation, and course of the airplane that is desired.
Owner:COOK MR MICHAEL
Sound-absorbing radiation protective paint and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101831211AImprove sound absorptionGood radiation protectionRadiation-absorbing paintsLow speedHydroxyethyl cellulose
The invention relates to a sound-absorbing radiation protective paint, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 30 to 38 percent of porous modified starch, 5.0 to 9.5 percent of styrene-acrylic latex emulsion, 33 to 41 percent of barite, 0.5 to 1 percent of iron oxide, 0.25 to 1 percent of sodium polycarboxylate dispersant, 0.01 to 1 percent of brightening agent, 1.0 to 6 percent of titanium white, 0.5 to 1 percent of defoamer, 0.01 to 1 percent of mildew preventive, 13 to 18 percent of water, 0.4 to 1 percent of ethylene glycol, 0.3 to 1 percent of film-forming auxiliary agent, 0.005 to 1 percent of anti-freeze agent, 0.5 to 1 percent of graphite, 1 to 3 percent of hydroxyethyl cellulose and 0.20 to 1 percent of thickening agent. A preparation method of the sound-absorbing radiation protective paint comprises the steps of: (a) premixing, namely stirring 1 / 2 water, the sodium polycarboxylate dispersant, 1 / 2 defoamer, the mildew preventive, the thickening agent, the hydroxyethyl cellulose and the brightening agent at low speed to form colloidal solution; (b) dispersing and grinding, namely adding the titanium white, the barite, the graphite and the iron oxide into the colloidal solution and stirring the solution at high speed to prepare uniform sizing agent; (c) paint mixing, namely adding crylic acid emulsion, the film-forming auxiliary agent and the anti-freeze agent into the sizing agent, uniformly stirring the sizing agent, then dividing the porous modified starch into 1 to 5 parts, and adding the porous modified starch by 1 to 5 times into the mixture for low-speed and uniformly stirring the mixture; and (d) packaging the resulting product.
Owner:谢绍何
Coiled tube type wall body strengthening ventilation air-conditioner energy-saving system
InactiveCN103256674AReduce power consumptionEliminate sanitary cornersWallsLighting and heating apparatusElectric consumptionRefrigeration
The invention relates to the technology of building ventilation and the field of natural energy application, in particular to a strengthening ventilation air-conditioner system which uses underground water natural cold-heat sources and a solar heating air strengthening hot-pressing effect for supplying natural energy of airflow power and the like, and particularly relates to a coiled tube type wall body strengthening ventilation air-conditioner energy-saving system with wall body heat exchange and ventilation. Underground constant-temperature water and solar heating air are used for improving hot-pressing difference to achieve building refrigeration (heating supply) and ventilation effects, electricity consumption of ventilation of a building air conditioner is greatly reduced, the space size of a ventilation heat-exchange interlayer is effectively reduced especially when a heat-exchange coiled tube is used in a ventilation wall body, the effective utilization of wall body space is achieved, and compared with a traditional air conditioner, the system saves indoor space, eliminates hygiene dead angles of the air conditioner, and is more attractive in appearance and suitable for popularization and promotion in an area with rich underground water sources.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Air cleaning door
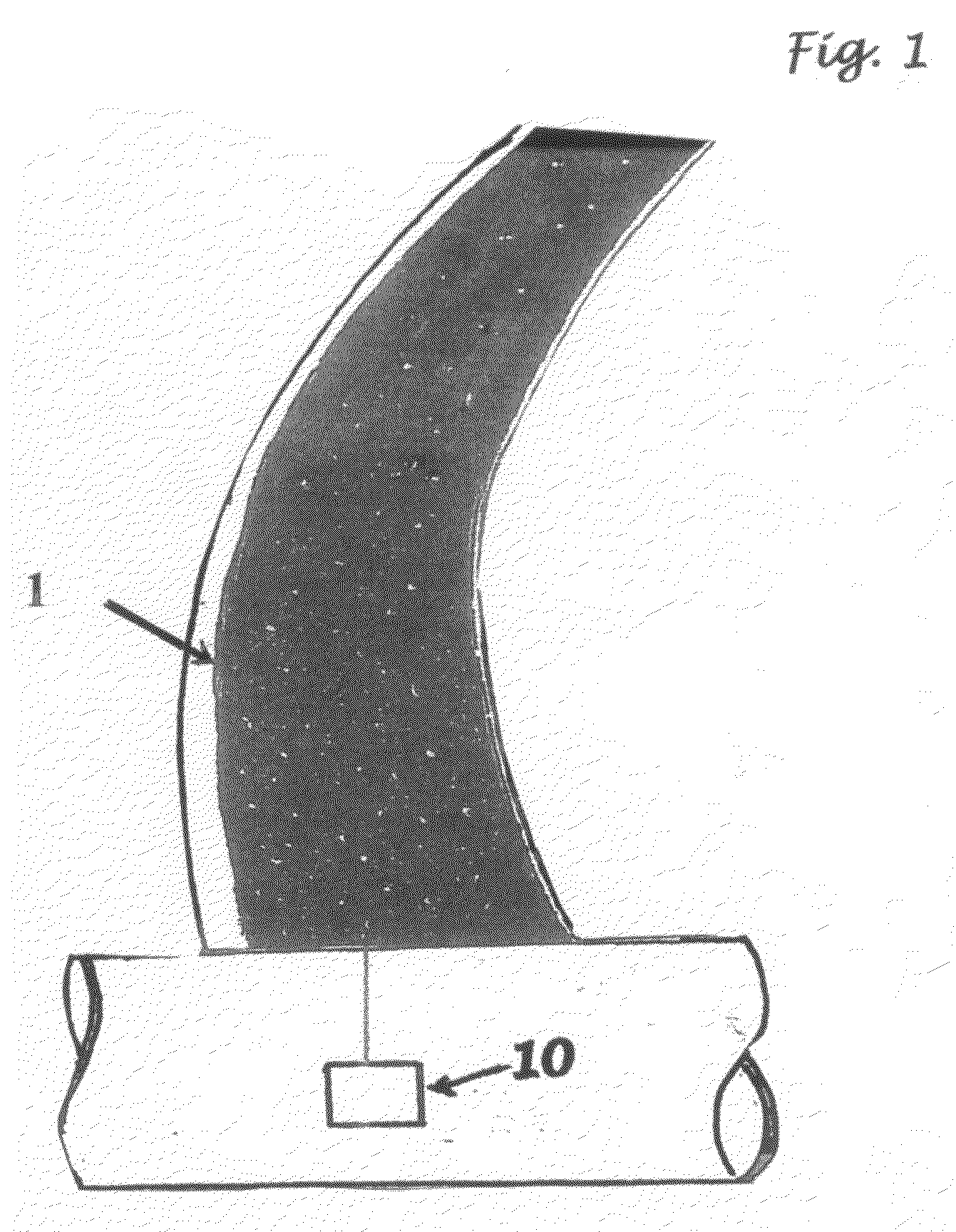
ActiveCN104912464ATo achieve the purpose of clean airPrevent oxidationNoise insulation doors/windowsSpecial door/window arrangementsActivated carbonParticulates
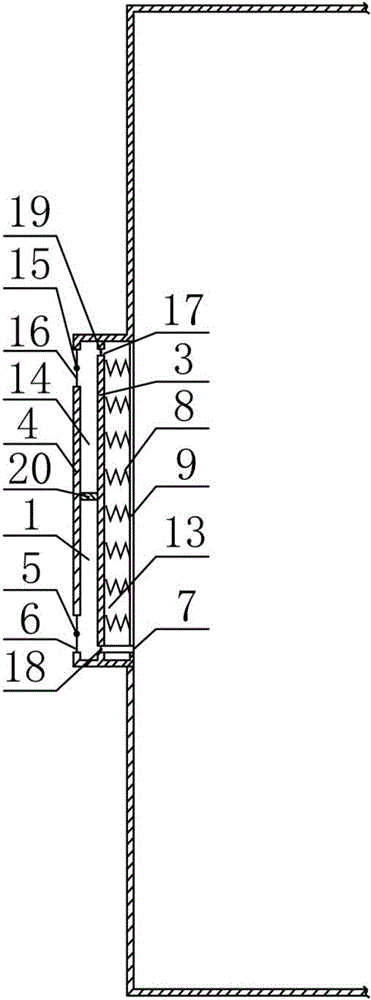
The invention discloses an air cleaning door which comprises a door body 1, a door frame, hinges, an air cleaning device and a fan 8, wherein one side of the door body 1 is connected with the door frame through the hinges; a cavity 2 is formed inside the door body 1; the air cleaning device and the fan 8 are installed in the cavity 2; at least one air inlet 3 is formed in the front face of the door body 1; at least one air outlet 4 is formed in the back face of the door body 1; the air inlet 3 and the air outlet 4 are communicated with the cavity 2; the air cleaning device comprises a rough filtration layer 5, an activated carbon layer 6 and a high-density air filtering material layer 7; the rough filtration layer 5, the activated carbon layer 6 and the high-density air filtering material layer 7 are sequentially arranged between the air inlet 3 and the air outlet 4; the rough filtration layer is made of rough filtration paper; and the high-density air filtering material layer is formed by adopting an HEPA (high efficiency particulate air) filtrating screen. The air cleaning door can effectively solve the problems that existing air cleaning doors are poor in cleaning effect and cause loud noise.
Owner:南通兰天空气洁净门有限公司
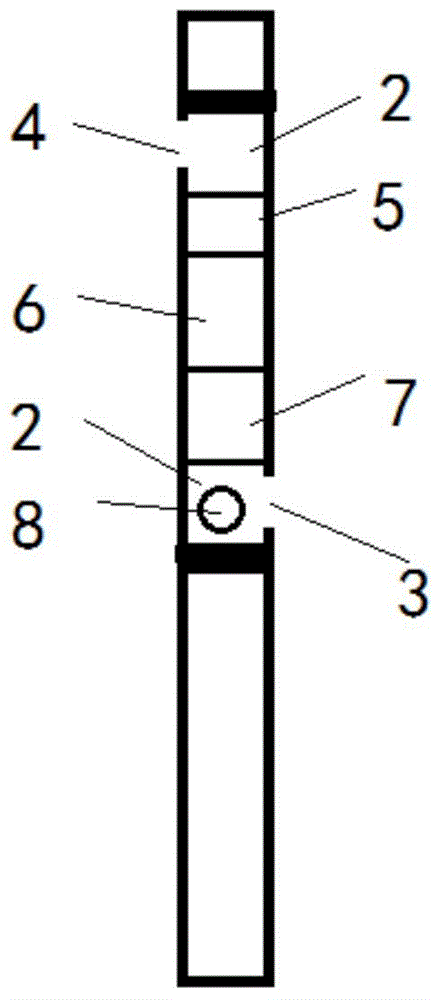
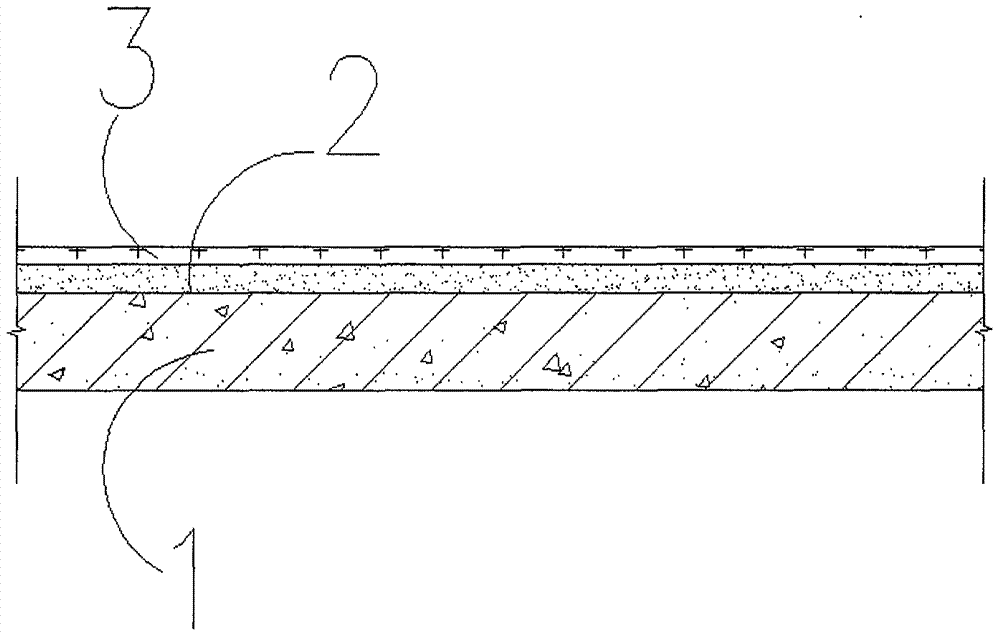
Heat-insulating soundproof construction method for building floor slab
InactiveCN106957162AImprove sound insulationWith insulation requirementsSolid waste managementFloorsSurface layerFloor slab
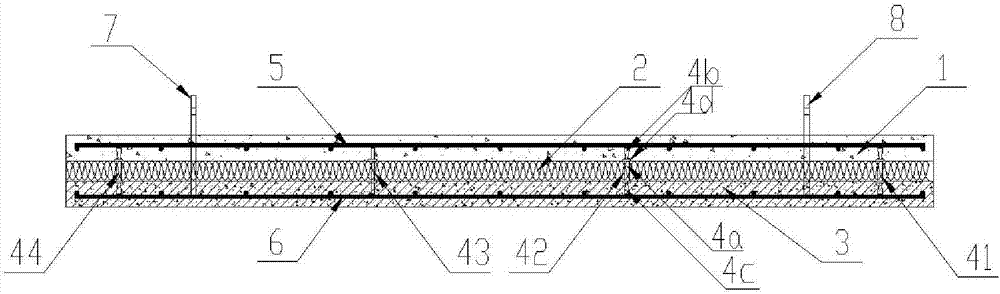
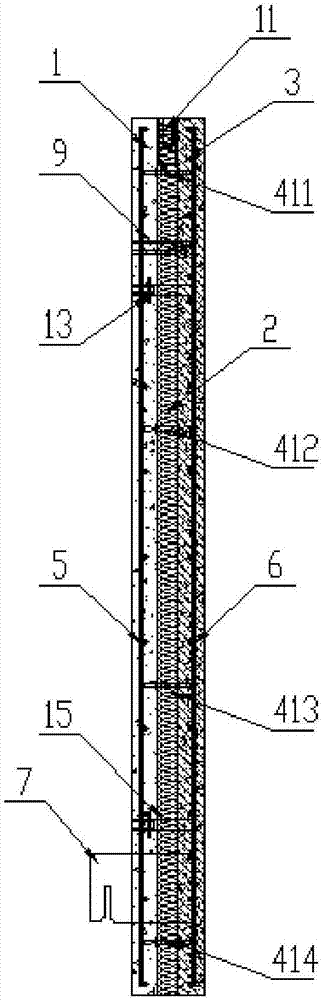
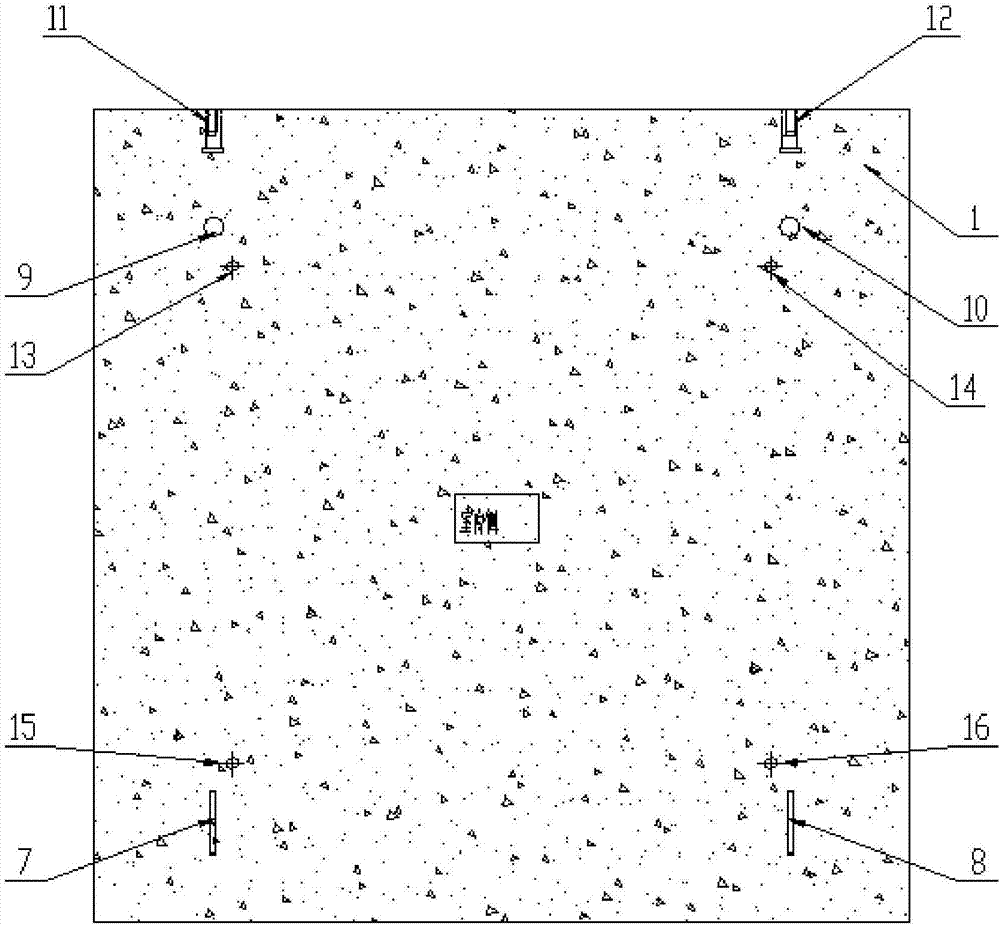
The invention relates to a heat-insulating soundproof construction method for a building floor slab. The construction method comprises the following steps: paving 10-50mm thick soundproof mortar (2) on the top of a reinforced concrete floor (1) and paving 5-10mm thick high-strength soundproof mortar (3) on the surface layer of the soundproof mortar.
Owner:杜飞月
Hidden projector hanger
InactiveCN102298254AAvoid damageGuaranteed aestheticsMachine supportsLighting support devicesEngineeringProjector
The invention discloses a concealed projector hanger, which comprises a fixed top frame. A lifting hanger device is installed below the fixed top frame. An illuminating lamp holder is connected below the lifting hanger device. Illuminating lamps are installed below the illuminating lamp holder. A projector support is installed below the fixed top frame or above the illuminating lamp holder. A shading skirt is fixed on the outer periphery of the illuminating lamp holder. When the lifting hanger device reaches an upper lifting limit, parts above the illuminating lamp holder are in the shading skirt. By installing a projector between the fixed top frame and the illuminating lamp holder and by using the lifting hanger device to control the illuminating lamp holder and the skirt to be lifted up or lowered down to expose or conceal the projector and to be matched with the projector in use, the concealed installation of the projector can be realized and the situation that too many installation holes are drilled on a ceiling can be avoided; and by installing a plurality of equipment together, the overall attractiveness of the ceiling can be ensured and the indoor space can be effectively saved.
Owner:刘坎坎
Multi-story building radiation heat exchanging air conditioner wall body
ActiveCN105780943ARealize cascade utilizationAvoid lostWallsLighting and heating apparatusFloor slabAir volume
The invention relates to a multi-story building wall body, in particular to a multi-story building radiation heat exchanging air conditioner wall body. To solve the technical problems, the multi-story building radiation heat exchanging air conditioner wall body is provided. The provided multi-story building radiation heat exchanging air conditioner wall body comprises a first ventilation interlayer, a second ventilation interlayer, a radiation heat exchanging interlayer and floor slabs. The first ventilation interlayer comprises a heat preservation outer wall and a first humidity adjusting valve. The second ventilation interlayer is arranged behind the first ventilation interlayer and comprises the heat preservation outer wall, a first air volume adjusting valve and a second air volume adjusting valve. The radiation heat exchanging interlayer is arranged on the right side of the first ventilation interlayer and on the right side of the second ventilation interlayer and comprises a heat preservation inner wall, a radiation plate and heat exchanging fins. The floor slabs are arranged on the right side of the heat preservation inner wall and provided with ventilation openings. The provided multi-story building radiation heat exchanging air conditioner wall body has the advantages of being comfortable, healthful, capable of protecting environment and saving energy and the indoor space, low in operating cost and the like and is applied and popularized beneficially.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
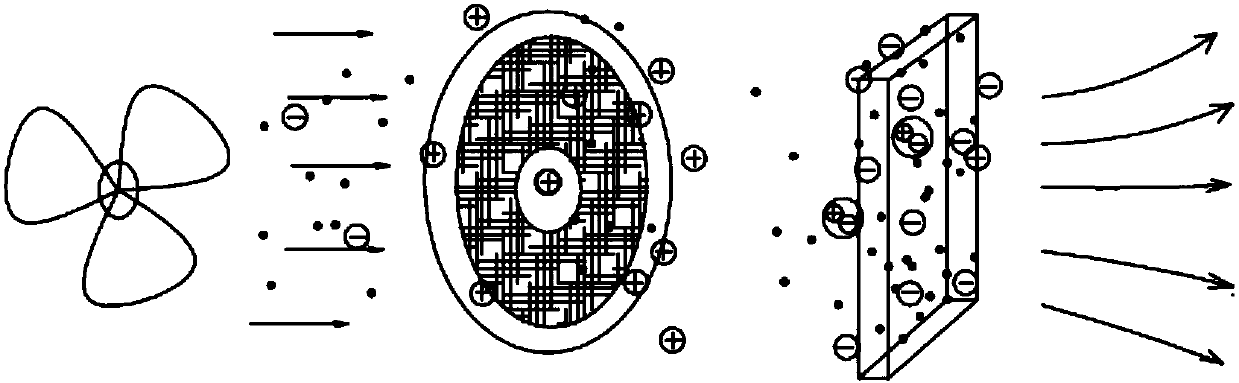
High-efficiency static electricity dust removal device based on electrification-by-friction principle of differential hairbrushs
ActiveCN107842933AReduce lossImprove charge durabilityHuman health protectionMechanical apparatusFiberFiltration
The invention relates to a high-efficiency static electricity dust removal device based on the electrification-by-friction principle of differential hairbrushes. The high-efficiency static electricitydust removal device based on the electrification-by-friction principle of the differential hairbrushes mainly comprises a box, a grid plate, a motor, a center shaft, a draught fan shell, a draught fan, an electromagnetic clutch, a push-pull type dust collection tank, an annular metal net, a flat key, a fibrous membrane, the hairbrushes and a filtration component, wherein the fibrous membrane withthe bulged soft hairbrushes is arranged on the annular metal net; the hairbrushes are in contact with the surface of the first layer of electrospinning fibrous membrane of the filtration component tocause mutual friction, thereby enabling the contact surface to generate charge transfer and generating static electricity; the electromagnetic clutch is arranged between the draught fan and the annular metal net, so that the intermittent friction is generated between the hairbrushes and the filtration component, and the charge neutralization time of the fibrous membrane with the bulged soft hairbrushes and the filtration component is delayed; the membrane loss is reduced; and the electrified durability is improved. The high-efficiency static electricity dust removal device based on the electrification-by-friction principle of the differential hairbrushes has the beneficial effects that the filtration component has a good charge performance and a filtration performance on the whole; the fibers can be degraded and are green and environmentally-friendly; the static electricity dust removal is carried out by autoexcitation friction; the energy consumption and equipment cost can be obviously reduced; and the device is simple and convenient, has extra small volume and can save indoor space.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
All-weather photo-thermal photovoltaic integrated automatic control heat pipe water heater
ActiveCN106766237ANo guarantee rate zeroHigh initial investmentSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersAutomatic controlEvaporation
The invention provides an all-weather photo-thermal photovoltaic integrated automatic control heat pipe water heater. The water heater comprises a solar water tank, a support, heat pipes, a thermoelectric generation module, a storage battery, a cold water circulation system and a controller which are mutually connected. The all-weather photo-thermal photovoltaic integrated automatic control heat pipe water heater has the effect that the problem of energy waste caused by hot water boiling and evaporation in an existing hot water tank is effectively solved through the water heater. Heat exchange between a water storing tank and the cold end for cooling the thermoelectric generation module is conducted through a cold water inlet pipe and a cold water outlet pipe, so that the temperature in the water storing tank can be increased by 10-20 DEG C, correspondingly, water supplied to the solar water tank from the water storing tank is preheated once, and heat is fully utilized. The all-weather photo-thermal photovoltaic integrated automatic control heat pipe water heater can not only provide hot water for a user, but also fully utilize the temperature difference between cold water and the hot water to generate electricity, thereby saving energy and being environmentally friendly, safe and efficient.
Owner:TIANJIN CHENGJIAN UNIV +1
Automatic control lifting table
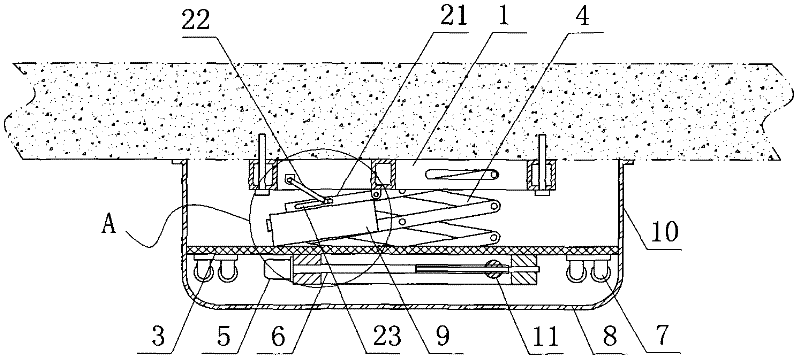
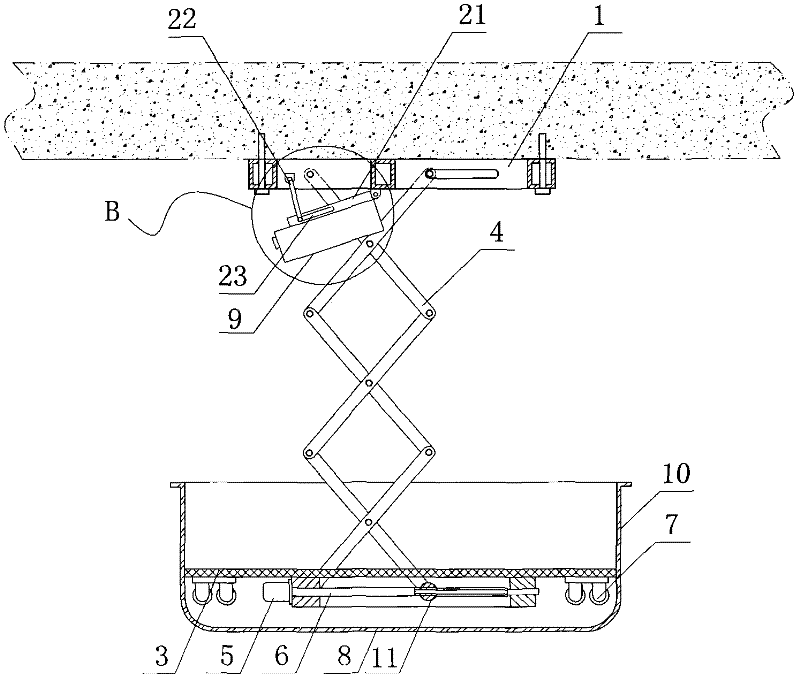
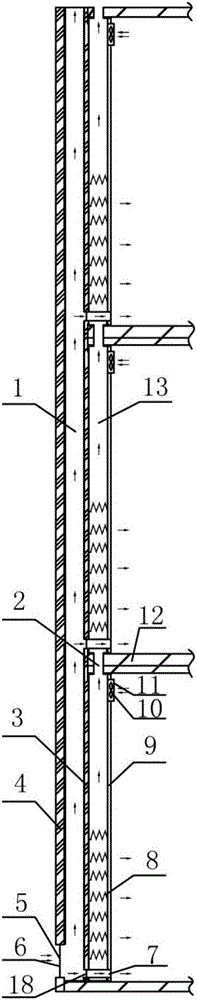
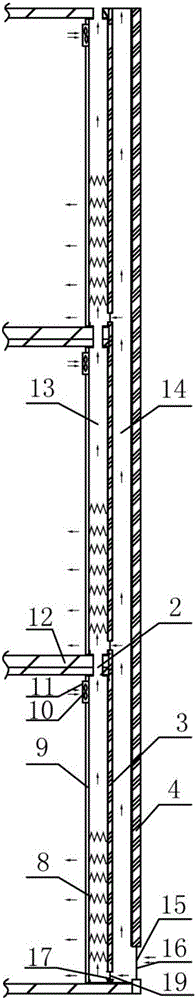
InactiveCN102389203ASave interior spaceSoft stateServing tablesVariable height tablesAutomatic controlIndustrial engineering
The invention relates to an automatic control lifting table. In the invention, by adopting a counterweight support device relative to the sum of the weight of a tabletop, and upper slideway and a horizontal hook trough plate, the table can be stably and softly changed into the shape of a tea table and a dining table only by equal and small force of one hand when the tabletop raises and falls. The automatic control lifting table has the beneficial effects that indoor space is saved, and the peripheral range of the occupied area of the tea table can meet the conditions of dining or work for a plurality of persons; a locating clip and a plate-type hook can respectively keep the status of the automatic control lifting table unchanged under dining table and tea table statuses in the case of lifting and moving the automatic control lifting table; and under the dining table status, legs and feet of diners can be placed in comfortable space just like the common dining table, and four legs and storage drawers can be disassembled and assembled conveniently so as to facilitate package and transportation. Therefore, the automatic control lifting table can meet the demand for one table as a plurality of life appliances in a small-sized apartment.
Owner:钟延波
PC light composite sandwich thermal-insulated integrated wallboard
The invention relates to a PC light composite sandwich thermal-insulated integrated wallboard, and belongs to the technical field of building structure construction. The light composite sandwich thermal-insulated integrated wallboard sequentially comprises an inner vane plate, a thermal insulating layer and an outer vane plate, an inner mesh is arranged in the inner vane plate, and an outer mesh is arranged in the outer vane plate; a plurality of connecting pieces are connected between the outer mesh and the inner mesh, a pre-embedded piece is arranged on the outer mesh, the pre-embedded piece penetrates through the thermal insulating layer and the inner vane plate, the outer end of the pre-embedded piece extrudes above the inner surface of the inner vane plate. The PC light composite sandwich thermal-insulated integrated wallboard is applied to steel building construction, and has the advantages of being small in weight, high in thermal insulation, convenient and efficient.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GREEN BUILDING INTEGRATION TECH CO LTD
Technology timely oxytocin and incubation for oviparous snakes
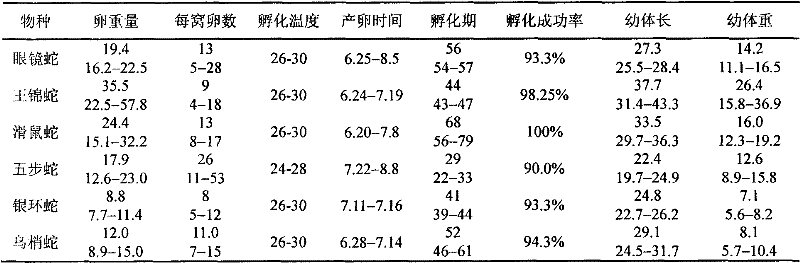
In the process of breeding snakes, individual households frequently meet the problems that the snake is difficulty to delivery and lays few eggs. The invention discloses a method for improving the survival rate of the snakes and hatching success rate of the snake eggs by timely oxytocin for the female snake with eggs and scientific management. The method is good for the growth and maintenance of the snakes in pregnancy, improves the success rate of the propagation of the female snakes and the snake egg incubation, improves the artificial breeding technology of the snakes, and realizes the industrial aquaculture of the snakes.
Owner:屈彦福 +4
Cup holder with adjustable depth
ActiveUS20160000248A1Small heightSuitable for installationVehicle arrangementsContainer/bottle contructionHandrailEngineering
A cup holder with an adjustable depth includes: a cup-holder base, having at least one accommodation hole; a fixed cup holder, fixed in the accommodation hole of the cup-holder base; and a moveable cup holder, moveably sleeved over the fixed cup holder and capable of rotating around the fixed cup holder to ascend and descend, where during ascending and descending of the moveable cup holder, an inner cavity of the moveable cup holder and an inner cavity of the fixed cup holder jointly define a container placement hole for placement of containers of different heights. The present invention solves the problem that containers of different heights placed in the cup holder easily fall out when the automobile is accelerating, hard braking or travelling over uneven road surfaces. In addition, after the moveable cup holder descends to the lowest position, the moveable cup holder can completely overlap the fixed cup holder, so that the entire cup holder has a small height and is therefore suitable for installation in a thin interior trim part of the automobile, for example, in the armrest at the rear seat, thereby saving interior trim space in the automobile.
Owner:YANFENG ADIENT SEATING CO LTD
Intelligent laundry rack based on open balcony
InactiveCN104631068ASave interior spaceLow costOther drying apparatusTextiles and paperControl systemLaundry
An automatic telescopic rain sheltering laundry rack based on an open balcony is characterized by comprising a control system, a motor and lead screw drive system and a laundry rack body, wherein the laundry rack body comprises a laundry rack frame, laundry poles and rolling wheels, the laundry rack frame is fixed to the upper portion of the balcony through expansion screws, the laundry poles are connected with the laundry rack frame through the rolling wheels fixed to the laundry poles, the motor and lead screw drive system comprises a single-phase alternating current motor and a lead screw, the single-phase alternating current motor is connected with the lead screw through a coupler, the lead screw is installed on the laundry rack frame through sliding bearing pedestals, the control system comprises a controller, a raindrop sensor, a photosensitive sensor and a limit switch, and the raindrop sensor, the photosensitive sensor and the limit switch are connected to the controller through wires. The laundry rack is simple in structure and can achieve the functions that clothes are aired on sunny days and are automatically put away on rainy days.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
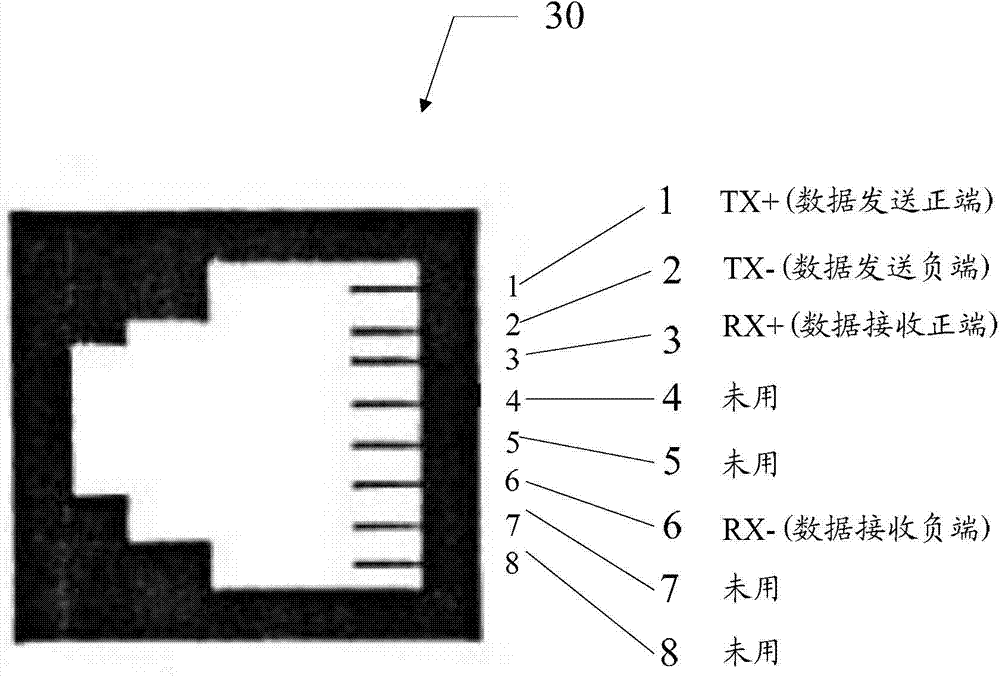
POE (Power Over Ethernet) multimedia terminal
InactiveCN104125076AFlexible use of electricityElectrical SafetyData switching current supplyData connectionComputer module
The invention provides a POE (Power Over Ethernet) multimedia terminal that supplies power voltage and Ethernet data connection to an electronic device. The Ethernet power supply multimedia terminal comprises a power module, a power supply module and a plurality of interfaces; one end of the power supply module is electrically connected with the power module, and while the other end of the power supply module is electrically connected with the interfaces; the power module supplies voltage to the power supply module; the power supply module receives and processes the voltage supplied by the power module and provides Ethernet data and electric energy to the electronic device through the interfaces at the same time. The Ethernet power supply multimedia terminal has the advantages that the indoor space and line cost are saved, the power is flexibly and safely supplied, and the compatibility is high.
Owner:SHENZHEN SKYWORTH DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
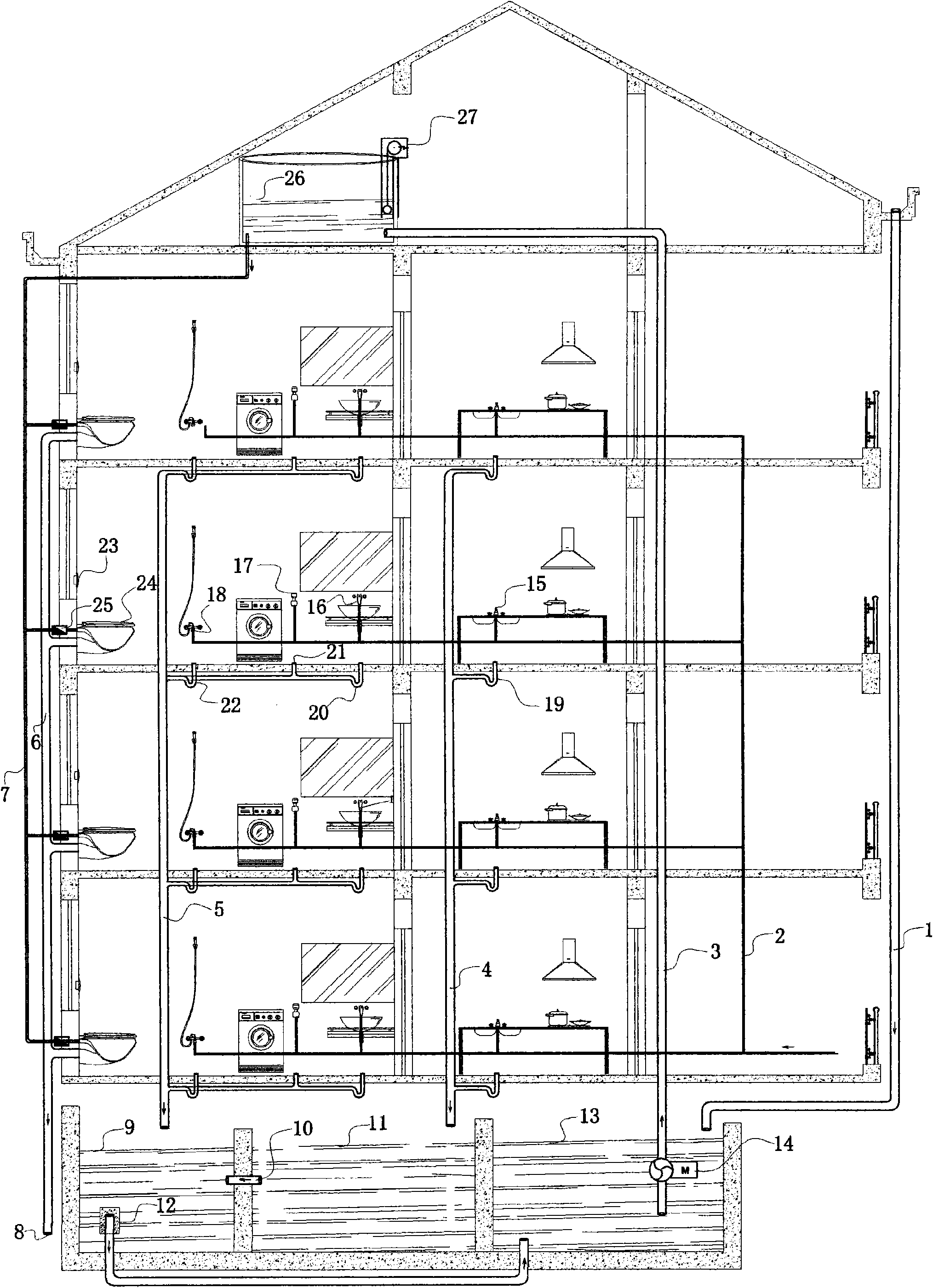
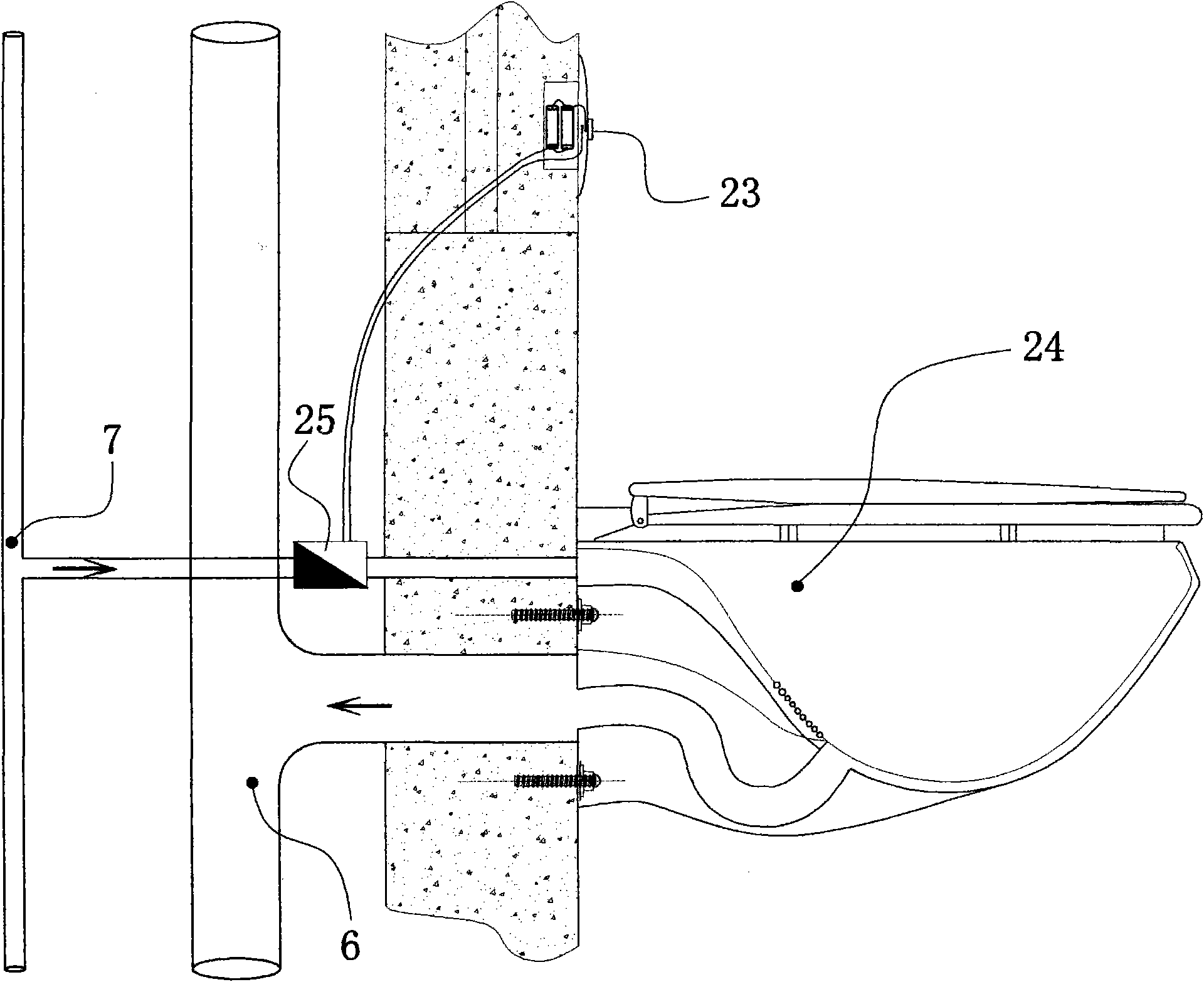
Residential building water-saving piping system
InactiveCN101550715AImprove the indoor environmentEmission reductionWater closetsFlushing devicesWash waterEngineering
The invention relates to a residential building water-saving piping system, which can effectively collect and perform centralized classification processing to wash water, bathing water, kitchen vegetable washing water, laundry water and rain water, and then can be used for flushing toilets by pumping the water to a water tower at the building roof by a water pump. The invention has features that a water tank is no longer needed to load in the wall hanging toilets in the bathroom, a flushing electromagnetic valve [25] is controlled by flicking a flushing switch [23] of the wall hanging toilet [24] to use reclaimed water after recovery processing to flush the toilet. The design proposal has reasonable structure, which can not only saves water and reduces the discharge, but also can effectively improve the bathroom indoor environment, save interior space so that the indoor appears to be more clean, beautiful and modern. The invention has very strong feasibility, and larger enormous social and economic benefits.
Owner:熊志诚
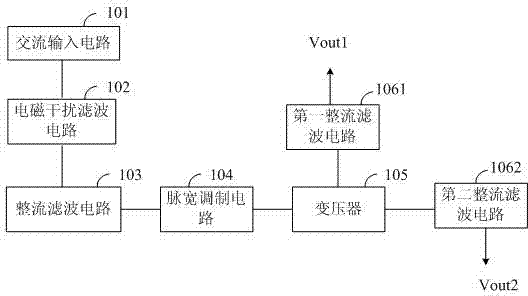
Power adapter
InactiveCN103051211AReduce procurement costsMeet normal work needsAc-dc conversion without reversalTransformerElectromagnetic interference
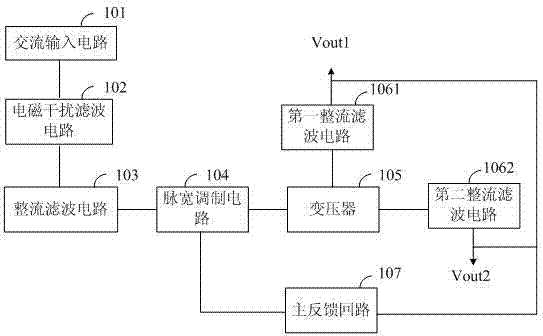
The invention discloses a power adapter comprising an alternating current input circuit, an electromagnetic interference filter circuit, a rectifier filter circuit, a pulse width modulation circuit, a transformer, a first rectifier filter circuit and a second rectifier filter circuit; the alternating current input circuit is connected with an external alternating current power supply; the electromagnetic interference filter circuit is connected with an alternating current input circuit; the rectifier filter circuit is connected with the electromagnetic interference filter circuit; the pulse width modulation circuit is connected with the rectifier filter circuit; the transformer is connected with the pulse width modulation circuit; the first rectifier filter circuit is respectively connected with the transformer and a first voltage output end Vout1; the first voltage output end Vout1 is connected with first electric appliance equipment; the second rectifier filter circuit is respectively connected with the transformer and second voltage output end Vout2; and the second voltage output end Vout2 is connected with second electric appliance equipment. According to the power adapter disclosed by the invention, double-circuit voltage independent output can be realized, so that the normal working requirements of two pieces of electric appliance equipment are met, the adapter purchasing cost of a user and the valuable indoor space of a user are saved.
Owner:TIANJIN SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Casement and sliding integrated window
ActiveCN104405236AEasy to useEnsure indoor safetyFixed grillesInsect protectionPush and pullSash window
The invention discloses a casement and sliding integrated window. The casement and sliding integrated window comprises a window frame, a column, a first casement and a second casement, wherein the window frame comprises an inner frame and an outer frame; the column is vertically arranged on the outer frame, and the two ends of the column are fixed on the upper and lower sides of the outer frame, respectively, so that the space of the outer frame can be divided into a first space and a second space; one side edge of the first casement is pivoted to the column or one side edge of the window frame, the first casement is located within the first space and a first piece of glass is mounted in the first casement; a screen is mounted in the second casement; a sliding rail is arranged in at least one transverse rim of the inner frame or inside the window frame at a position parallel to the transverse rim of the inner frame; a sliding device is arranged on the lower part of the cross edge of the second casement, and arranged to slide along the sliding rail so that the second casement is capable of moving along the inner frame. The casement and sliding integrated window breaks through the traditional combination form of the sliding or push-and pull casement and the screen, is convenient to open without occupying indoor space, and good in airtightness, and has a plurality of functions of prevention of burglary, thermal insulation, sound insulation, and dust and water prevention.
Owner:GUANGXI FUMEIYAO ENERGY SAVING WINDOWS & DOORS
Pipe inner combustion type nodular casting iron pipe conformal furnace shell annealing furnace
InactiveCN102021303ASave interior spaceShorten heating timeFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesProduction rateHeating time
The invention provides a pipe inner combustion type nodular casting iron pipe conformal furnace shell annealing furnace, comprising a conformal furnace shell, a riding wheel mechanism and a heating mechanism, wherein the riding wheel is mounted at the lower part of the conformal furnace shell; the conformal furnace shell is composed of an upper retractable cover and a lower fixed casing which are hinged together, and the upper retractable cover is connected with a retractable mechanism capable of opening or closing the upper retractable cover; and the heating mechanism comprises thermal storage burners, blast pipes and fuel inlet pipes, both ends of the conformal furnace shell are respectively provided with the thermal storage burner, the thermal storage burner at each end is provided with the blast pipe and the fuel inlet pipe, the fuel inlet pipe is connected with a fuel pipeline via a fuel switch valve, and the blast pipe is connected with a combustion fan and a smoke exhaust fan via a reversing valve. The pipe inner combustion type nodular casting iron pipe conformal furnace shell annealing furnace provided by the invention enables burner flames to be directly sprayed in the pipe inner cavity of a nodular casting iron pipe so as to heat from the pipe inner wall to the outside, thus facilitating cast pipe charging, reducing the inner space of a furnace shell chamber, having small heat loss, effectively improving heat efficiency, shortening the pipe temperature heating time and enhancing productivity.
Owner:冯新林
Bonsai-type warmer
InactiveCN102072521ASave interior spaceImprove the indoor environmentLighting and heating apparatusSpecial ornamental structuresEngineeringBaseboard
The invention relates to a bonsai-type warmer, which is provided with a hollow rectangular metal flowerpot; wherein the metal flowerpot is communicated with a hollow metal bonsai; a concave space is arranged on the side face of the bonsai; a water inlet, a water outlet and a ventilation door are arranged in the concave space; and the surface of the concave space is a cover with the shape in accordance with the bonsai. A communicating pipe leading downwards to the bottom surface of the bonsai is arranged on the baseboard in the concave space; and the communicating pipe is hermetically isolated from the inside of the hollow rectangular metal flowerpot and the hollow bonsai. In the bonsai-type warmer, the indoor displayed bonsai is combined with a warming device, so that the indoor space is saved, the indoor environment is beautified and the purpose of warming is achieved. The bonsai-type warmer can be moved at random based on the warming requirementd just by connecting the water inlet pipe and the water outlet pipe of a heater with a hose. The bonsai-type warmer is convenient to use and is only arranged in the room needing warming, thereby unnecessary warming is omitted and the purpose of saving energy is achieved.
Owner:天津吉鑫达商贸营销有限公司
Novel liquid crystal display fixing device
InactiveCN105402574ASave interior spaceConvenient Height and AngleStands/trestlesLiquid-crystal displayElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention provides a novel liquid crystal display fixing device. The novel liquid crystal display fixing device comprises an installation frame, a first movable frame, a front display fixing frame, a rear display fixing frame, a liquid crystal display and a turning device. The first movable frame is movably installed on the installation frame. The lower portion of the rear display fixing frame is rotatably connected with the lower portion of the first movable frame. The turning device comprises a driving gear, a driven gear set, a positioning frame, a wire winding rod, a second movable frame, a telescopic rod, a connecting rod and a connecting rope. A first bevel gear is installed on the wire winding rod. Second bevel gears are installed at the two ends of the telescopic rod respectively. Third bevel gears are installed at the two ends of the connecting rod respectively. The driven gear set is composed of a plurality of fourth bevel gears with unequal outer diameters. According to the novel liquid crystal display fixing device, indoor space is effectively saved, and the height and angle of the liquid crystal display can be adjusted by a looker easily when the looker watches the liquid crystal display.
Owner:合肥愿与网络技术有限公司
Thin-walled fan coil
InactiveCN102538073AReduce noiseGuaranteed cooling effectLighting and heating apparatusAir conditioning systemsControl systemEngineering
A thin-walled fan coil comprises a rear cover and a front cover which are fittingly connected. An air deflector, a filter screen and a control system are arranged on the front cover, a fan device is connected between the rear cover and the front cover and is a cross-flow fan set connected with a motor, and the fan device is fittingly connected with a surface air cooler and a water receiving groove. The thin-walled fan coil has the advantages that firstly, energy is saved; secondly, an indoor space is saved; thirdly, resources are saved; fourthly, noise of products is greatly reduced; and fifthly, comfort of an air conditioner is improved.
Owner:刘刚 +3
Method for rapid replacement of large coal mine skip
The invention relates to the field of skip devices, and in particular to a method for rapid replacement of a large coal mine skip. The method comprises the steps that an upper body and a lower body ofthe skid are separately conveyed in and out by disassembling a skid middle flange; the height of a first layer heapstead and the height of a sleeve frame in and out of the skip are lowered; an open-close type movable sleeve frame is arranged, and the sleeve frame and a cage guide are opened and closed integrally; the difficulty and workload of dismantling and installing and restoring the sleeve frame are reduced; a spare skid is stored in a warehouse, and the storage in the heapstead or a headframe is canceled; the floor area and load of the heapstead or the headframe and lifting equipment isreduced; a temporary rail mounting beam is reserved during the design of the sleeve frame and is connected with an outer fixing track of the sleeve frame; and a temporary track is installed quickly when the skip is replaced. An outlet headframe is paved on the track, the transfer of the skid in the headframe is avoided, the movement is smooth, and the process is less. The technical defects of high cost, large occupied area and long time consuming in the existing technical problems are solved. The method for rapid replacement of the large coal mine skip is simple, quick, low in cost and practical.
Owner:CHINA COAL SCI & TECH GRP NANJING DESIGN & RES INST CO LTD
Environment-friendly and sound-insulation building paint and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106752582AAchieve removalAchieve long-term effectFireproof paintsAntifouling/underwater paintsFiberEpoxy
The invention discloses environment-friendly and sound-insulation building paint and a preparation method thereof. The environment-friendly and sound-insulation building paint is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 25 to 35 parts of quartz sand, 20 to 30 parts of aqueous silicone acrylic emulsion, 18 to 25 parts of lightweight calcium carbonate, 10 to 15 parts of lignosulfonates, 15 to 20 parts of diatomite, 10 to 15 parts of sodium polycarboxylate, 15 to 25 parts of montmorillonite clay, 2 to 4 parts of organic silicon modified epoxy resin, 5 to 8 parts of nanometer aluminum silicate and 6 to 9 parts of talcum powder. The environment-friendly and sound-insulation building paint has a good sound-adsorption effect and is safe and environmentally friendly; the indoor space is saved; a coating has a good sound-adsorption effect and the coating has no seams and is stuck with a wall body to form a whole body, so that an indoor space is hardly occupied; meanwhile, the environment-friendly and sound-insulation building paint disclosed by the invention also has the effects of purifying air and adjusting the humidity; a coating film contains a plurality of pores and the inner area is large; toxic and harmful gas in the air can be adsorbed; and meanwhile, the humidity of the indoor air can be adjusted, and a pore wall, especially wood fibers, can adsorb certain moisture when the air humidity is relatively great.
Owner:芜湖浩权建筑工程有限公司
PM2.5-class purification air conditioning terminal with special-shaped filter screen and heat exchanger
ActiveCN103062882AAvoid wastingIncrease the purification areaLighting and heating apparatusSpace heating and ventilation detailsInlet channelAir filter
The invention discloses a PM2.5-class purification air conditioning terminal with a special-shaped filter screen and a heat exchanger. The PM2.5-class purification air conditioning terminal with the special-shaped filter screen and the heat exchanger comprises an irregular efficient filter screen module. The irregular efficient filter screen module comprises an air inlet channel (9) and an air outlet channel. The air inlet channel (9) and the air outlet channel are provided with frame-shaped high-efficiency filters (99). The frame-shaped high-efficiency filter is an air-filtered structure (9) encircled by a plurality of plate-type high-efficiency filters with one end closed and the other end opened to face the air inlet channel. The PM2.5-class purification air conditioning terminal further comprises a heat-exchanged cooling and heating zone, a fresh air delivering, preheating and energy saving zone, an air purifying zone and an automatically water-adding and cleaning zone which respectively have functions of heat-exchange cooling and heating, fresh-air delivering, preheating and energy saving, air purifying and water filling and automatic cleaning.
Owner:广东凯华建设工程有限公司
Net brick
InactiveCN101260717APresent aestheticsConvenient lightingSingle unit pavingsProtective constructionThin shellsCarrying capacity
The invention relates to a net brick, which is mainly characterized in that: netty multidirectional channels which are vertically, horizontally and uprightly intercrossed spatially, run through each other and are communicated with the surface of a brick body are arranged inside the brick body, and a thin-shell arched net structure is formed in the brick body. The brick body can meet mechanical bearing requirements, and simultaneously the surface area of the brick body, the internal volume and the internal carrying capacity of the brick body are increased. Under the condition of combined use of net bricks, multidirectional channels in the brick body can be intercrossed, thereby the shape of a layered net can be formed; moreover, opposite directions of the channels are abundant, thereby brick net structures with different shapes and types can be formed; the net brick also is characterized by ventilation, aeration and water permeability. Furthermore, the net brick has multiple functions and wide application range and can have multiple uses with one brick, be effectively applied in different fields and play different roles.
Owner:宋金楠
Multifunctional furniture and functional module thereof
ActiveCN102885499AIncrease the use of functionsSave raw materialsLighting and heating apparatusFurniture partsIndoor air qualityQuality optimization
The invention discloses multifunctional furniture and a functional module of the multifunctional furniture. The functional module which has air quality optimization capability is used as a constitutional component for a furniture structure to be integrated or embedded into the furniture structure so as to form the multifunctional furniture. The functional module is a hollow box body of which furniture sheets are manufactured into a rectangular hexahedron in appearance or a deformation design according to the molding of the furniture; an air outlet, a fresh air port, an air damper port and an air filter installation port which are circular or rectangular are formed in proper positions on the walls of the sheets of the box body respectively; and a plurality of structural components and a plurality of functional components are arranged on an internal air duct of the box body which is arranged between the air outlet and the fresh air port, so that a series of pieces of furniture which not only can meet using function requirement of the furniture but also can optimize indoor air quality are manufactured.
Owner:QUANYOU FURNITURE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com