Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34results about How to "Rapid fluctuation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
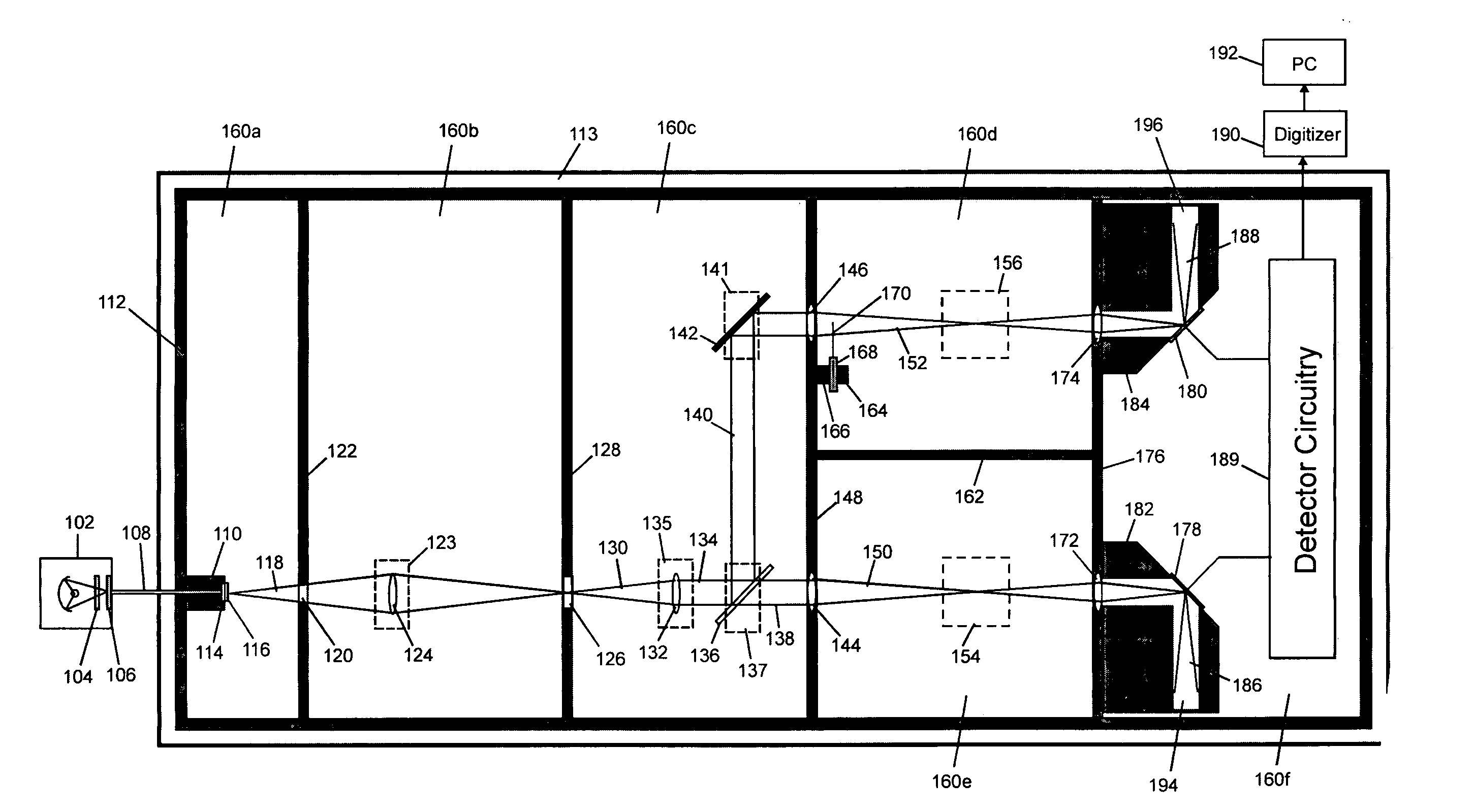
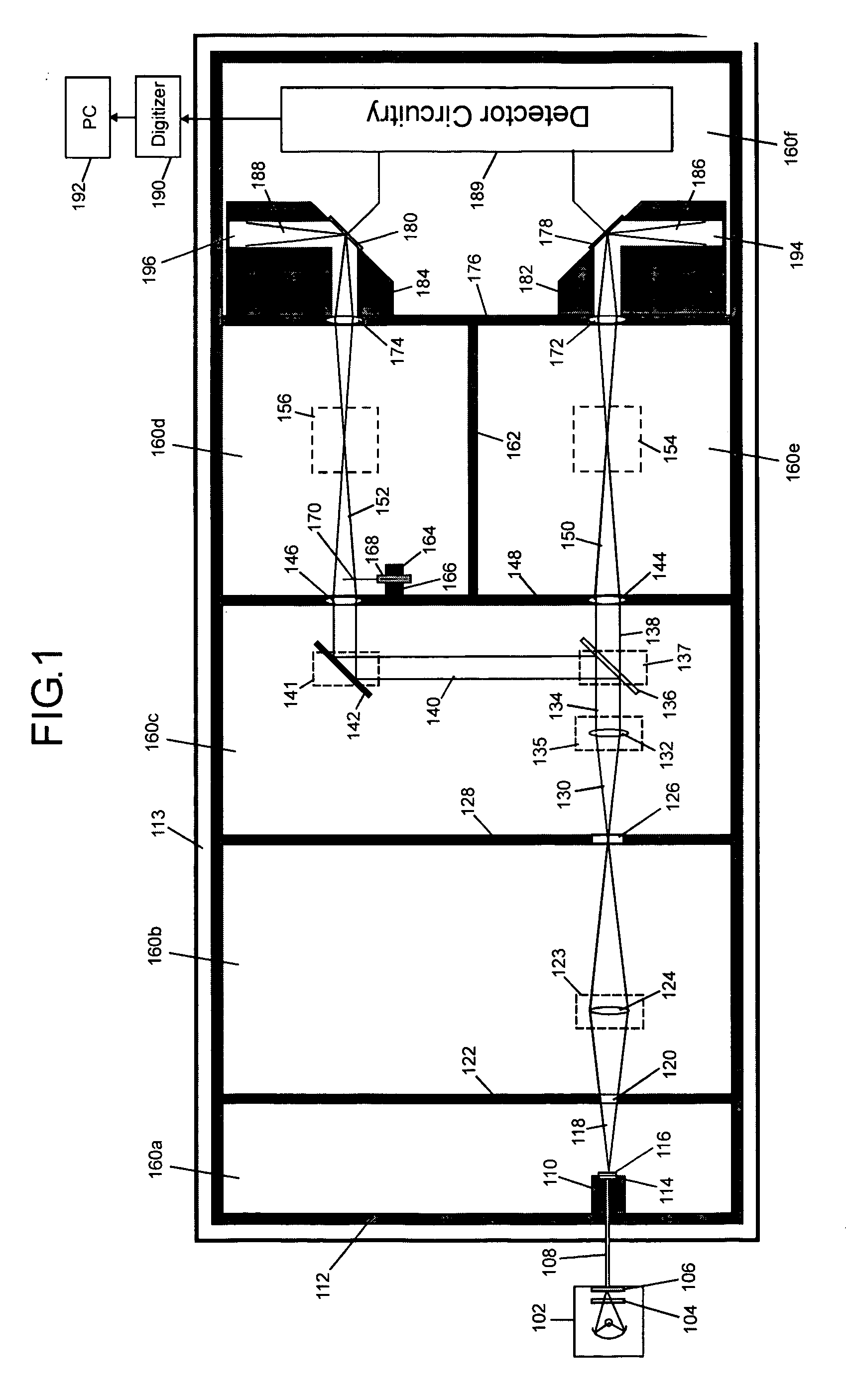
Ultrasensitive spectrophotometer
InactiveUS20060152726A1Lower Level RequirementsRapid fluctuationRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyNoise levelDiffuse reflection
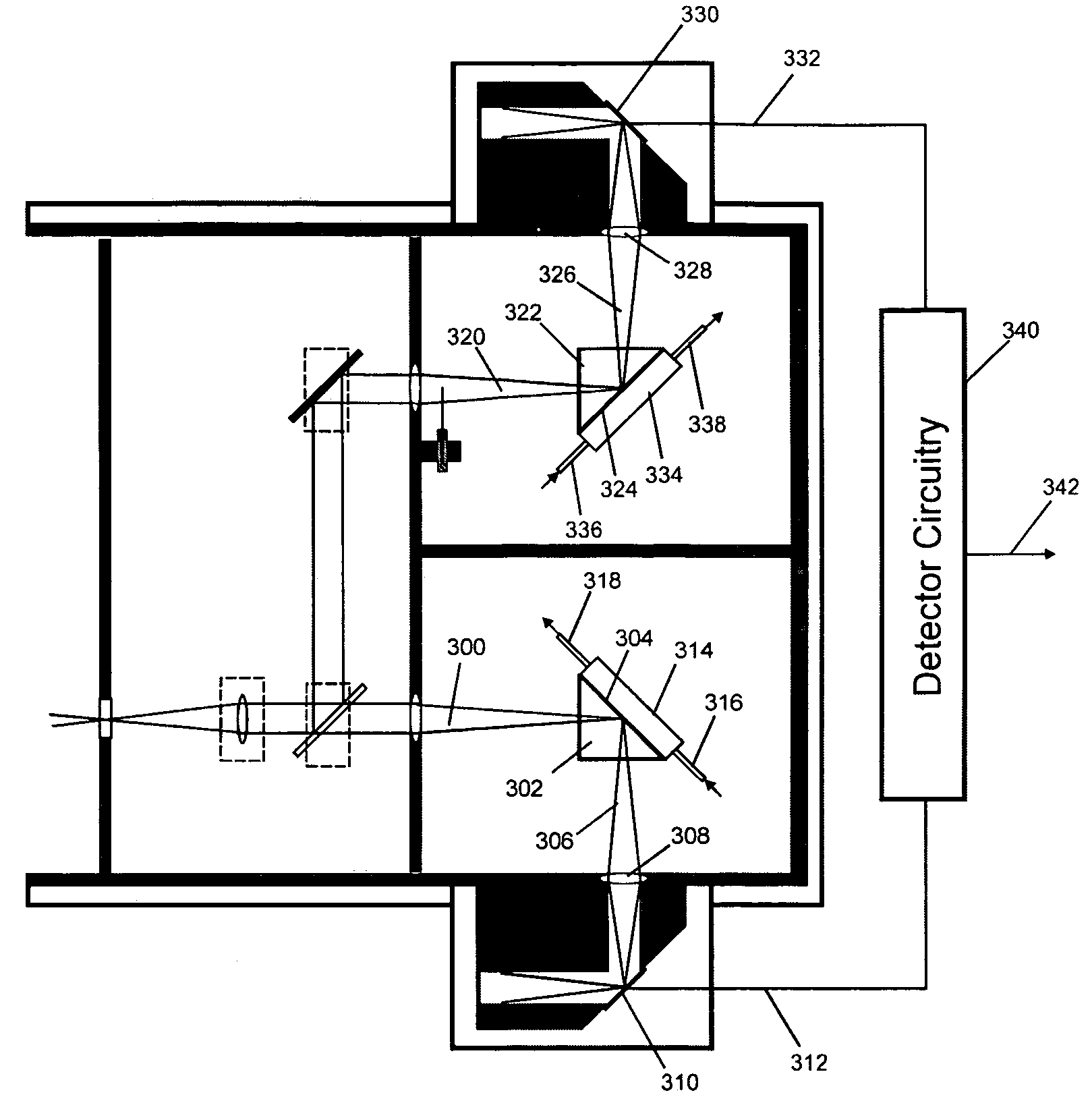
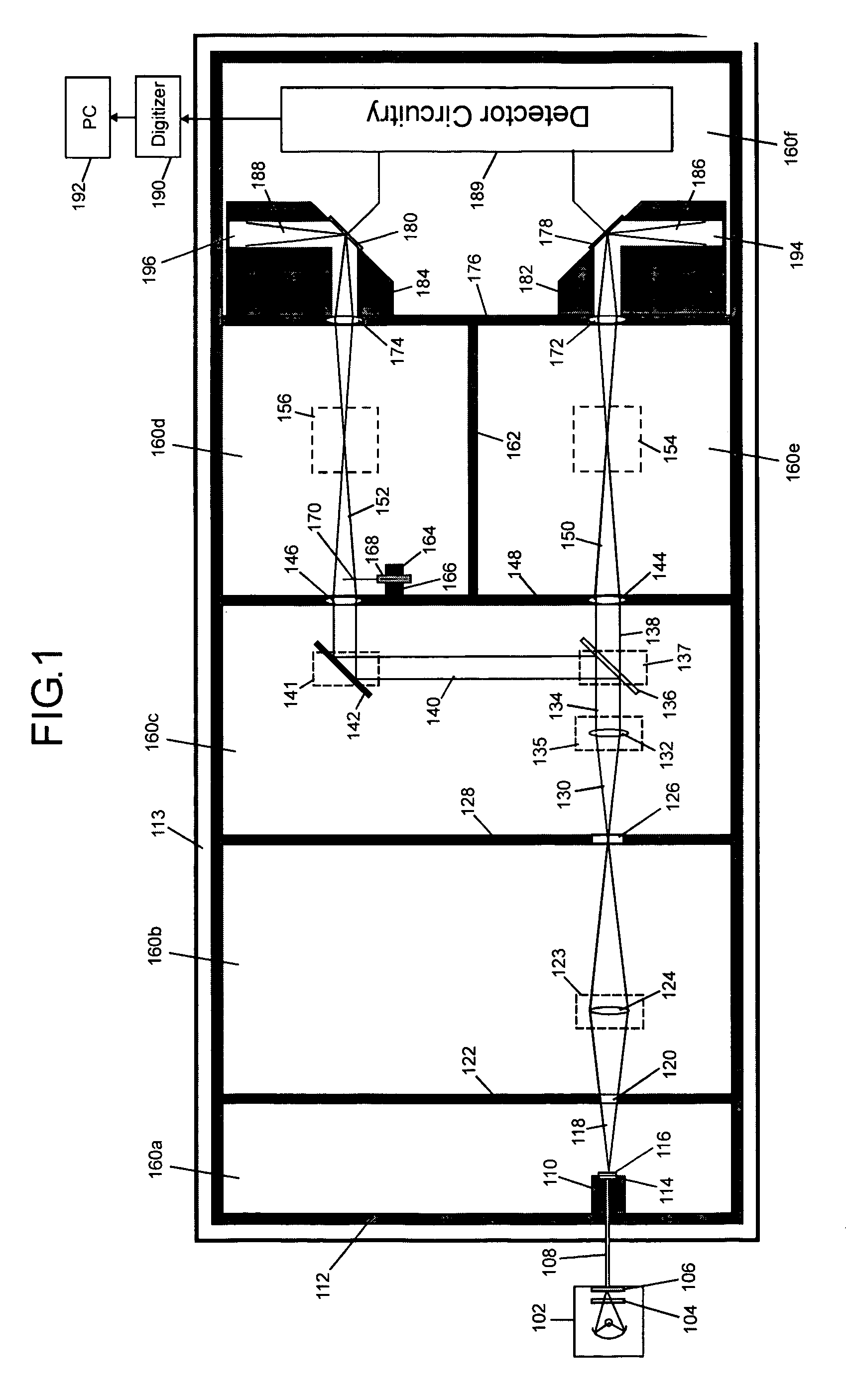
The invention concerns measurements in which light interacts with matter giving rise to changes in light intensity, and preferred embodiment spectrophotometer devices of the invention provide for ultrasensitive measurements through a reflection interaction with matter. The level of light source noise in these measurements can be reduced in accordance with the invention. Preferred embodiments of the invention use sealed housings lacking an internal light source, and reflection based sample and reference cells. In some embodiments a substantially solid thermally conductive housing is used. Other features of preferred embodiments include particular reflection based sample and reference cells. A total internal reflection embodiment includes, for example, a prism including an interaction surface, a detector, a lens that focuses a beam output from the prism onto the detector, and a closed interaction volume having an inlet and an outlet for delivering gas or liquid to the interaction surface. In a specular reflection embodiment, a reflective surface is used instead of a prism. In a diffuse reflection embodiment a matte surface is used instead of a prism and the matte surface produces scattering. Aspects of the invention include identification of noise-contributing components in spectrophotometry and the select set of preferred features in a given embodiment, and noise levels very near the shot noise limit may be realized with application of preferred embodiment devices.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
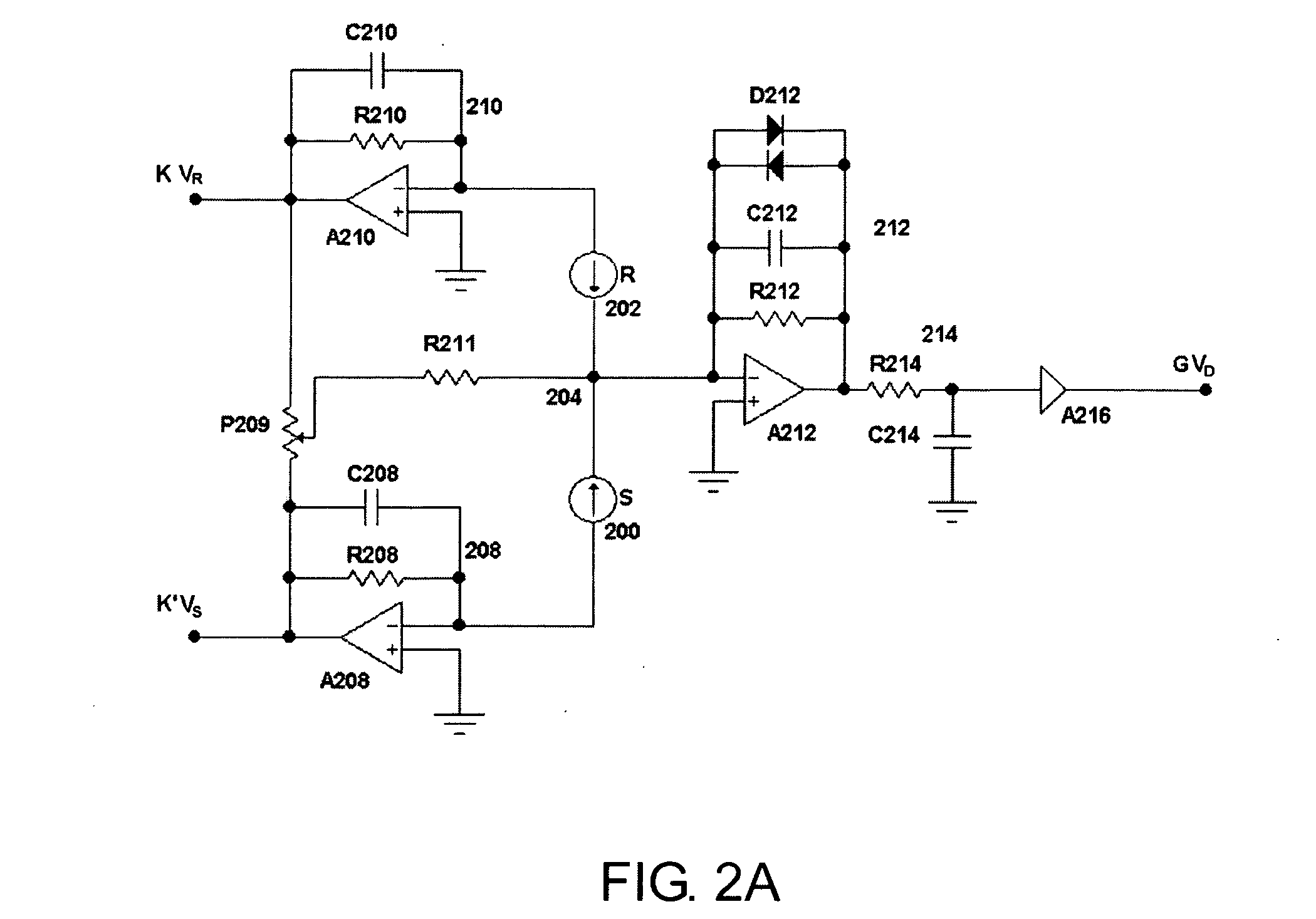
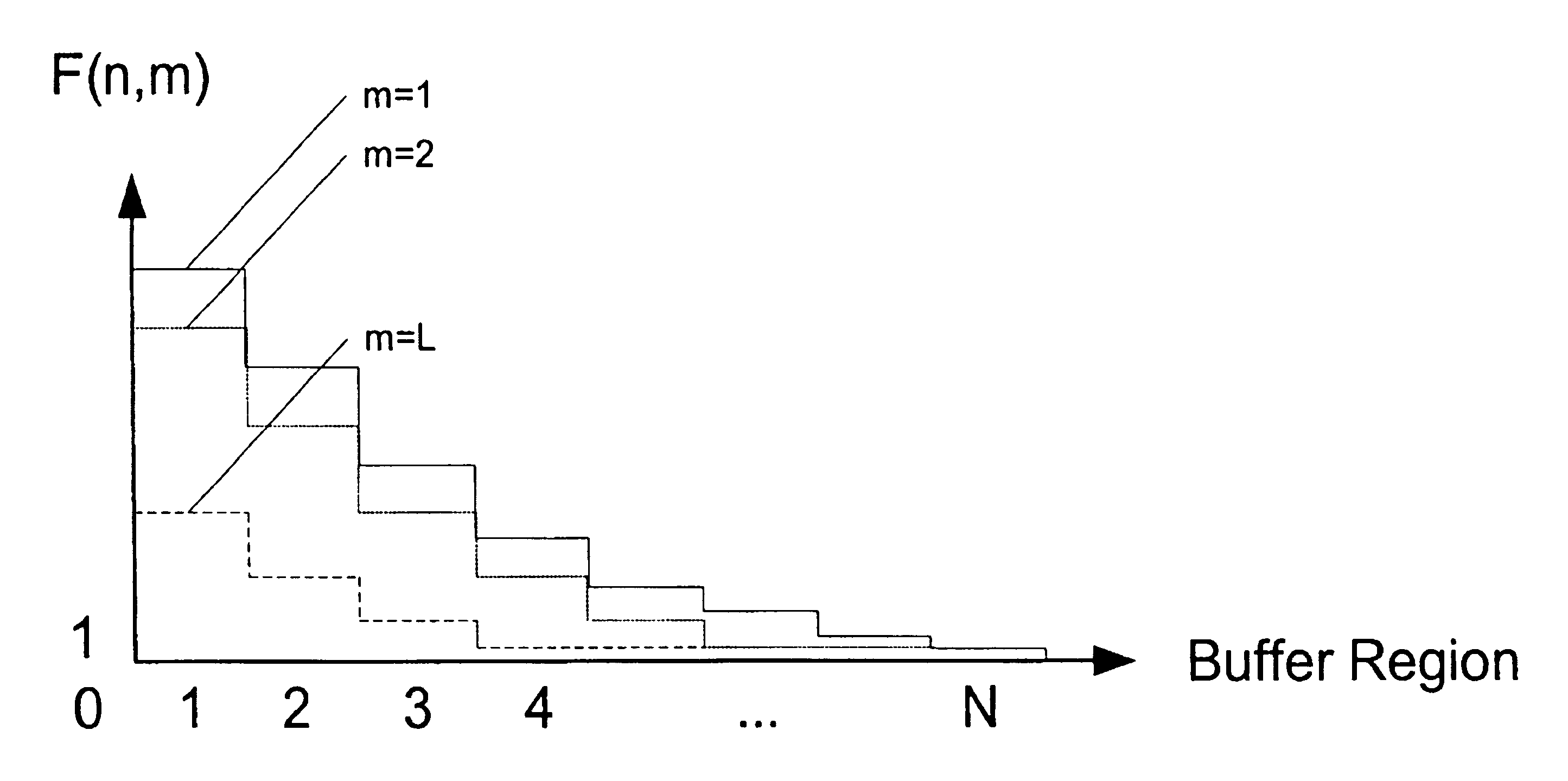
Soft, prioritized early packet discard system
InactiveUS6980516B1Simple hardware implementationRiskMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionSatelliteReal-time computing
A Soft, Prioritised Early Packet Discard System is provided, which is suitable for satellite onboard switching and very-high-speed terrestrial switching applications. The system counts the number of newly arriving packets, calculates and regularly updates an average queue size, which is used in setting a packet-count threshold via a descending staircase function. When the number of newly arriving packets reaches the packet-count threshold and when the average queue size reaches or exceeds the congestion threshold; a packet is discarded and the packet-counter is reset to zero. The counting of packets is halted while the average queue size remains below the congestion threshold. The regular dropping of packets allows simplified hardware implementations. In calculating the average queue size, a progressively higher exponential queue-length averaging parameter is used for higher instantaneous queue length, to provide faster reaction to congestion situations. The averaging parameters and packet-count thresholds are implemented using lookup tables. A priority-based method is incorporated to better match the Quality of Service requirements associated with a service class.
Owner:SPACEBRIDGE SEMICON CORP
Method for operating a hearing device and a hearing device
ActiveUS20160105751A1Reliable and simple mannerEnhanced signalOcclusion effect electronic compensationHearing device energy consumption reductionHearing apparatusAudio frequency
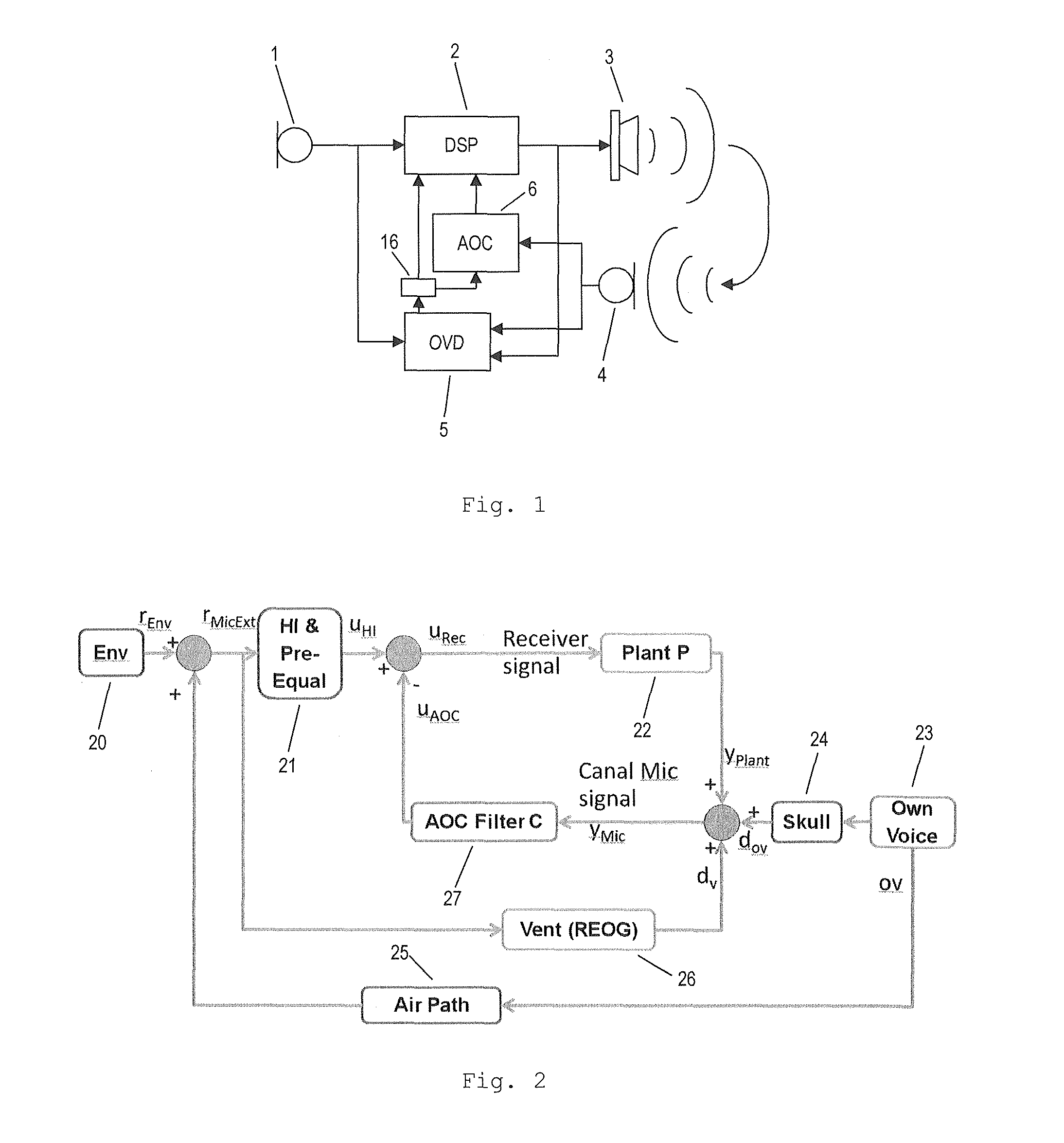
A method for operating a hearing device including an ambient microphone, a signal processing unit, a receiver and an ear canal microphone. The method includes steps of filtering the audio signal processed by the signal processing unit with a filter having a transfer function including a transfer function from an output of the receiver to an input of the ear canal microphone when the hearing device is turned on and being worn in an ear canal of the user, computing a difference between the audio signal picked up by the ear canal microphone and the filtered signal, and detecting a presence of own-voice of the user based on the difference. Furthermore, a hearing device including an own-voice detection unit is provided, which is adapted to perform the proposed method.
Owner:SONOVA AG
Vehicle drive control apparatus and method
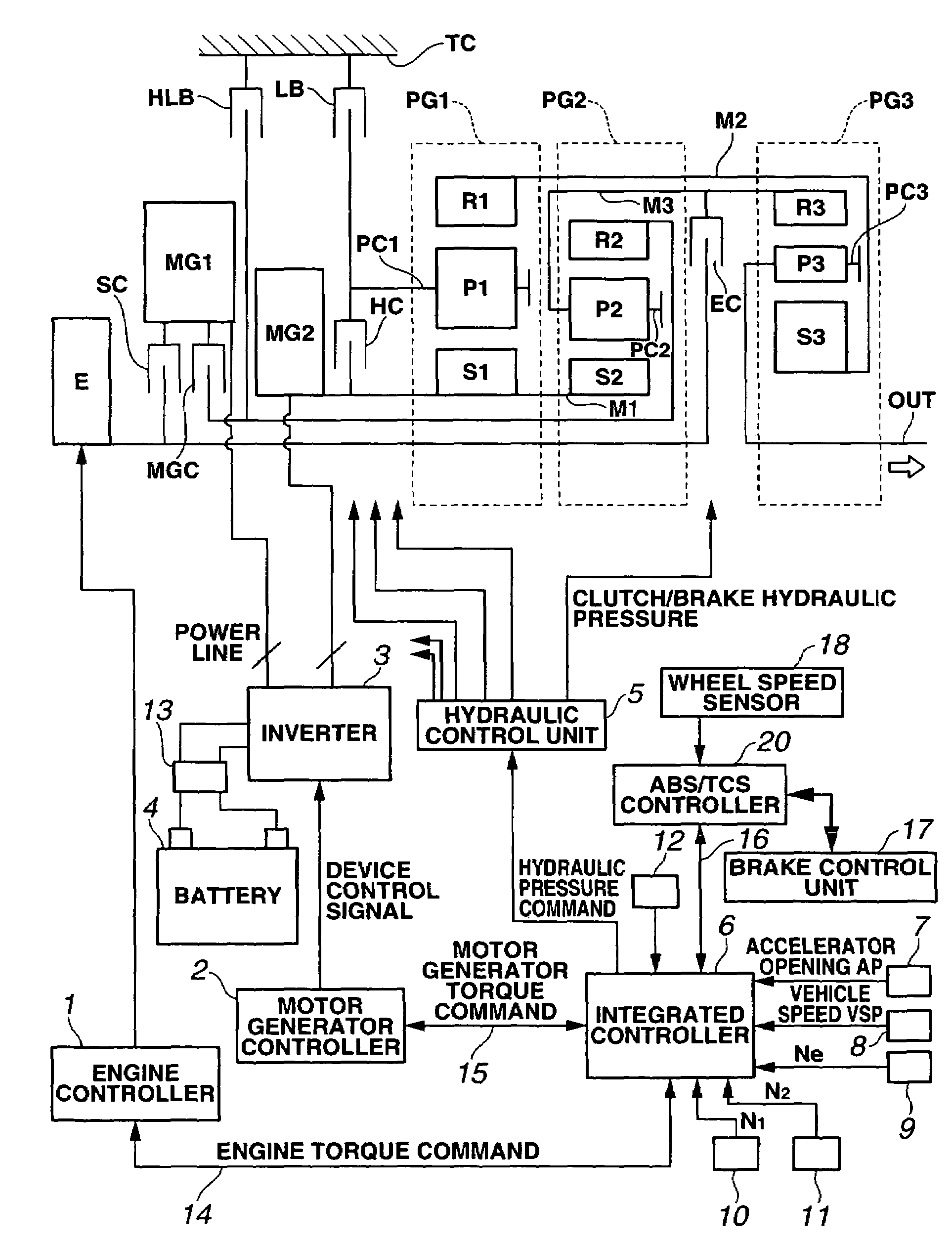
InactiveUS7650956B2Rapid fluctuationDurability of also fallsHybrid vehiclesGearing controlDrive wheelControl theory
A vehicle drive control for a wheeled vehicle including a first motor generator, and a second motor generator. A planetary gear set includes a first rotating element connected to the first motor generator, a second rotating element connected to the second motor generator, and a third rotating element connected to a drive wheel. A rotation control mechanism selectively restricts rotation of one of the first and second rotating elements of the planetary gear set to establish a fixed speed ratio mode, and releases the one of the first and second rotating elements to establish a variable speed ratio mode. A control unit is configured to control each operating state of the rotation control mechanism, the first motor generator, and the second motor generator, and configured to establish the variable speed ratio mode when a slip state of the drive wheel is detected in the fixed speed ratio mode.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Cellular network handoff decision mechanism
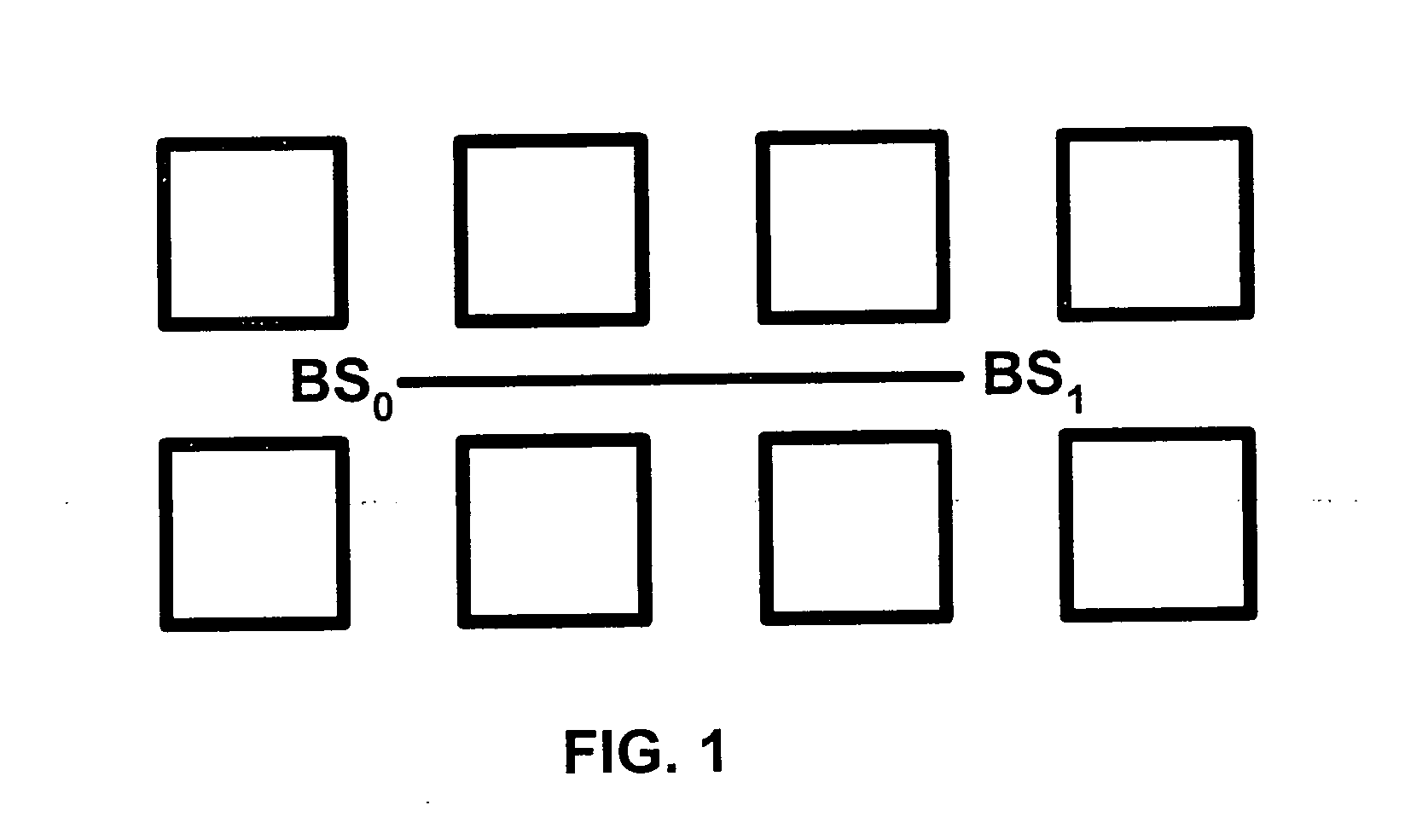
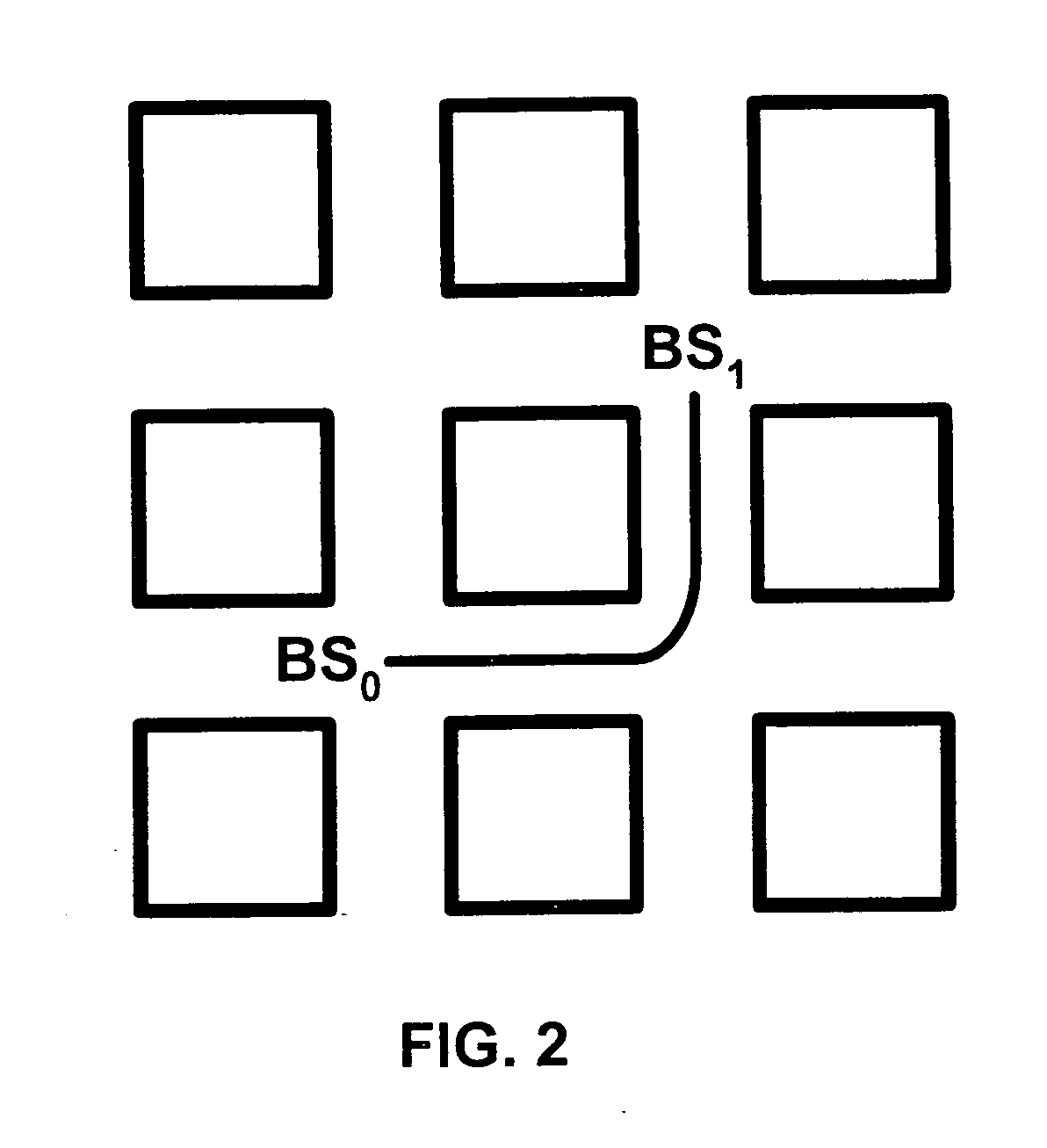
InactiveUS20050181795A1React quicklyEfficiently perform analysisRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesCarrier signalCellular network
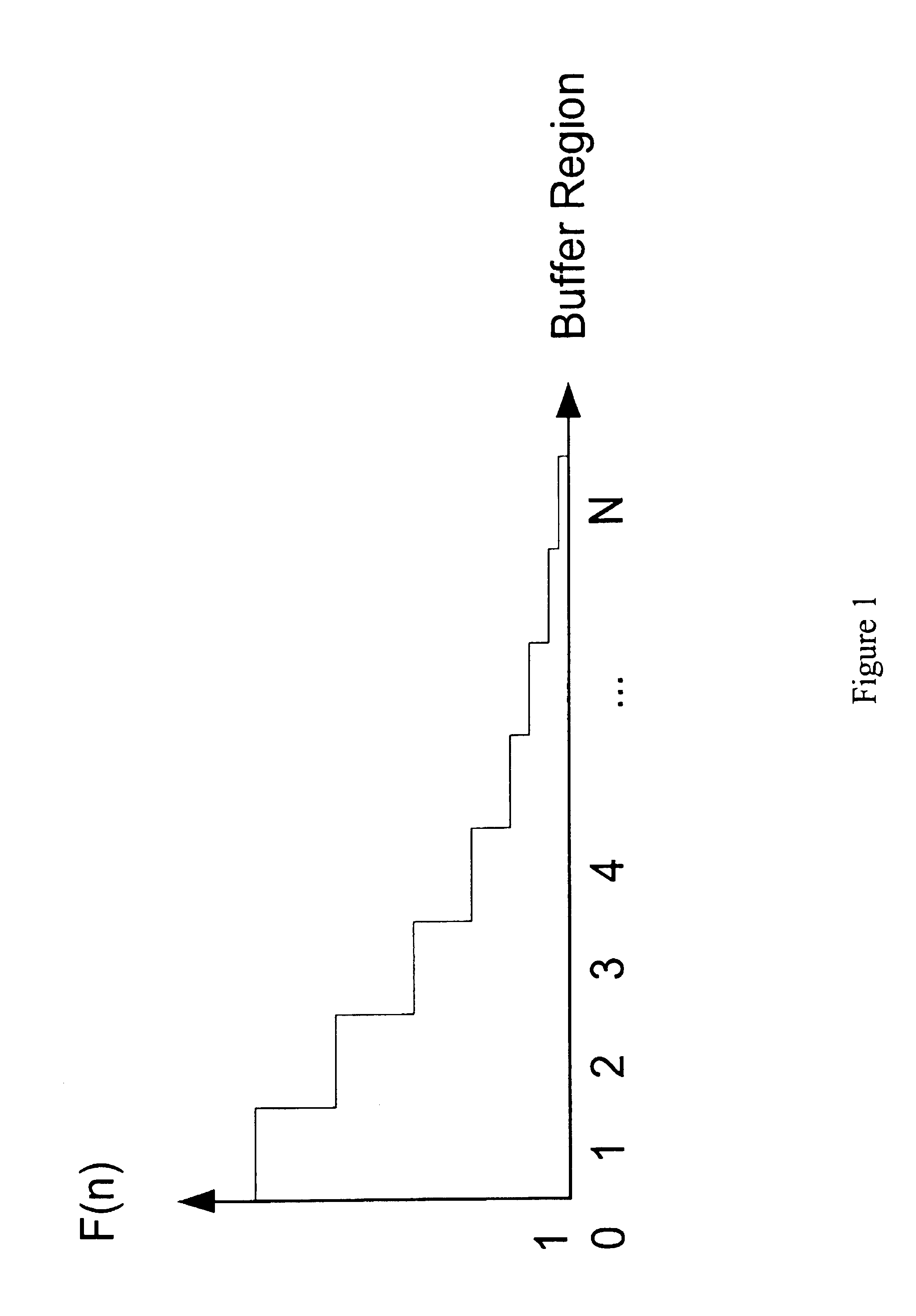
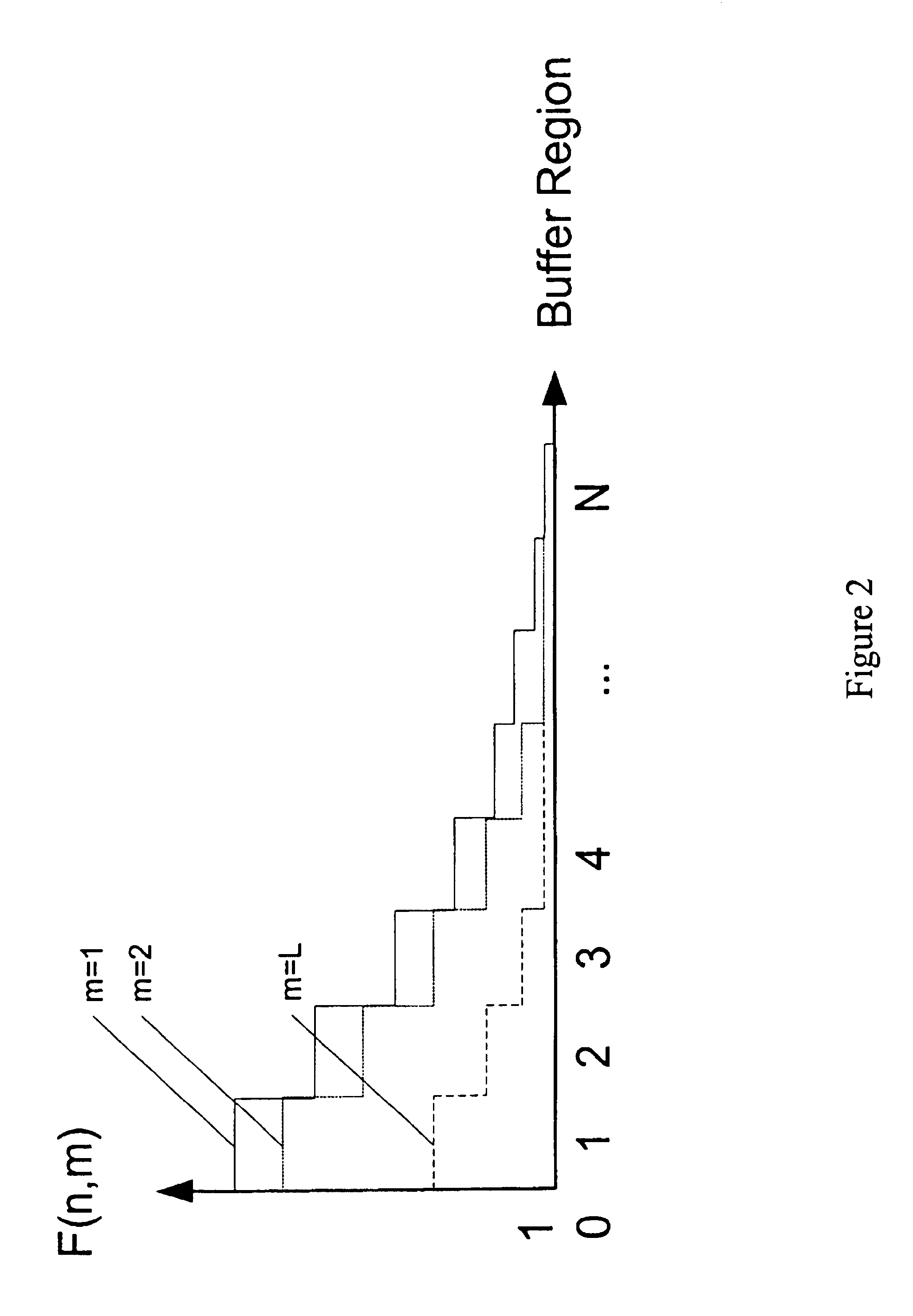
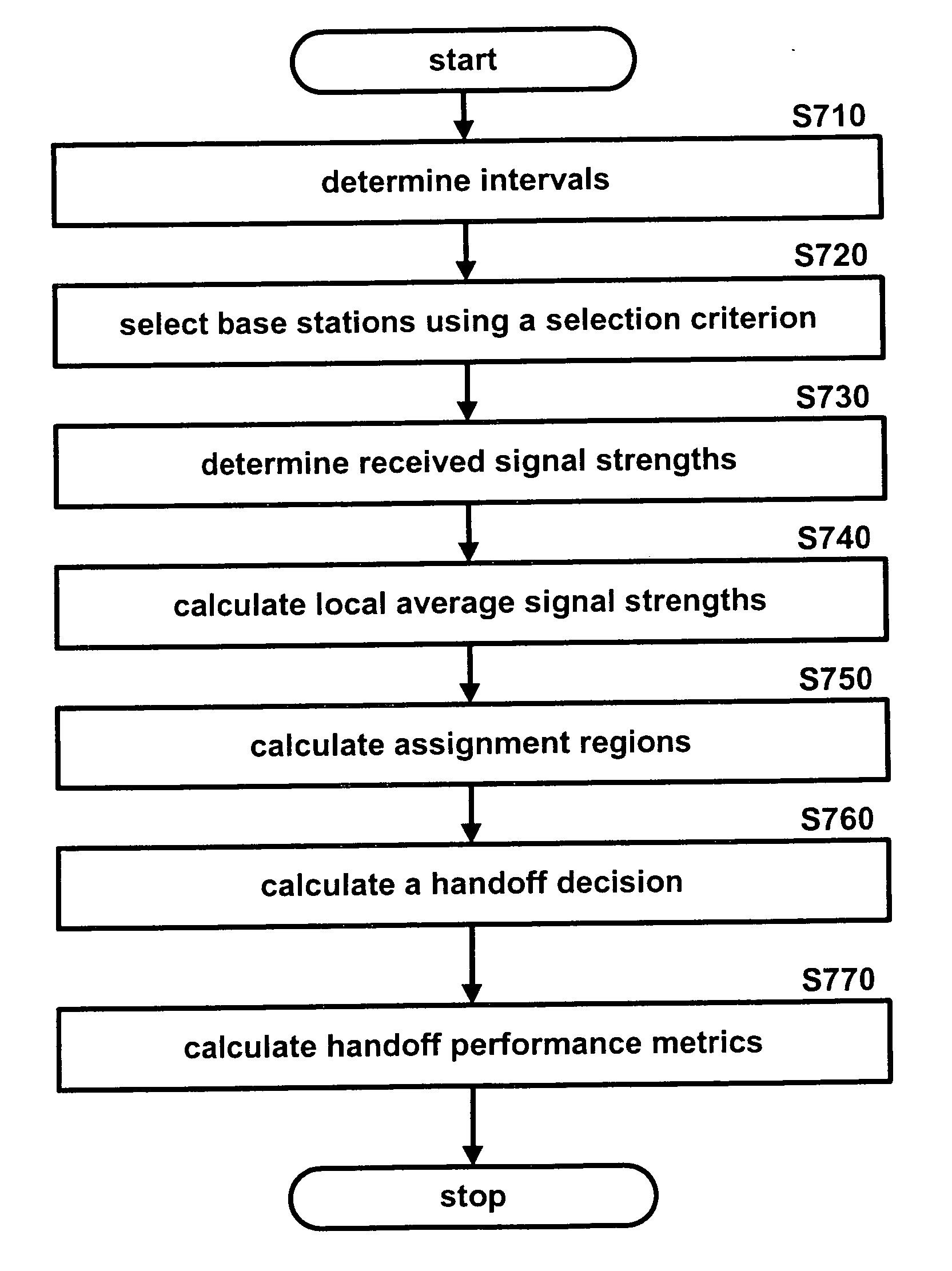
Disclosed is a cellular network handoff decision mechanism which comprising the steps of: determining a sampling interval using a carrier wavelength; determining a local averaging interval that is larger than the sampling interval; determining a handoff decision interval that is larger than the local averaging interval; selecting at least two base stations from a multitude of base stations having a pilot signal from a reference cellular network using a selection criterion; determining a received signal strength from the pilot signal strength for each of the selected base stations once during every sampling interval; calculating a local average signal strength value using each of the received signal strengths once during every local averaging interval; determining an assignment region in which the local average signal strength value lies using a hysteresis range; and calculating a handoff decision once during every handoff decision interval using a handoff calculation.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP INC
Ultrasensitive spectrophotometer
InactiveUS7262844B2Lower Level RequirementsRapid fluctuationRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyNoise levelLight beam
The invention concerns measurements in which light interacts with matter to generate light intensity changes, and spectrophotometer devices of the invention provide ultrasensitive measurements. Light source noise in these measurements can be reduced in accordance with the invention. Exemplary embodiments of the invention use sealed housings lacking an internal light source. In some embodiments a substantially solid thermally conductive housing is used. Other embodiments include particular reflection based sample and reference cells. One embodiment includes a prism including an interaction surface, a detector, a lens that focuses a prism beam output onto the detector, and a closed interaction volume for delivering gas or liquid to the interaction surface. Another embodiment replaces a prism with a reflective surface. Another embodiment replaces a prism with a scattering matte surface. Aspects of the invention identify noise-contributing components in spectrophotometry and realize noise levels very near the shot noise limit.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
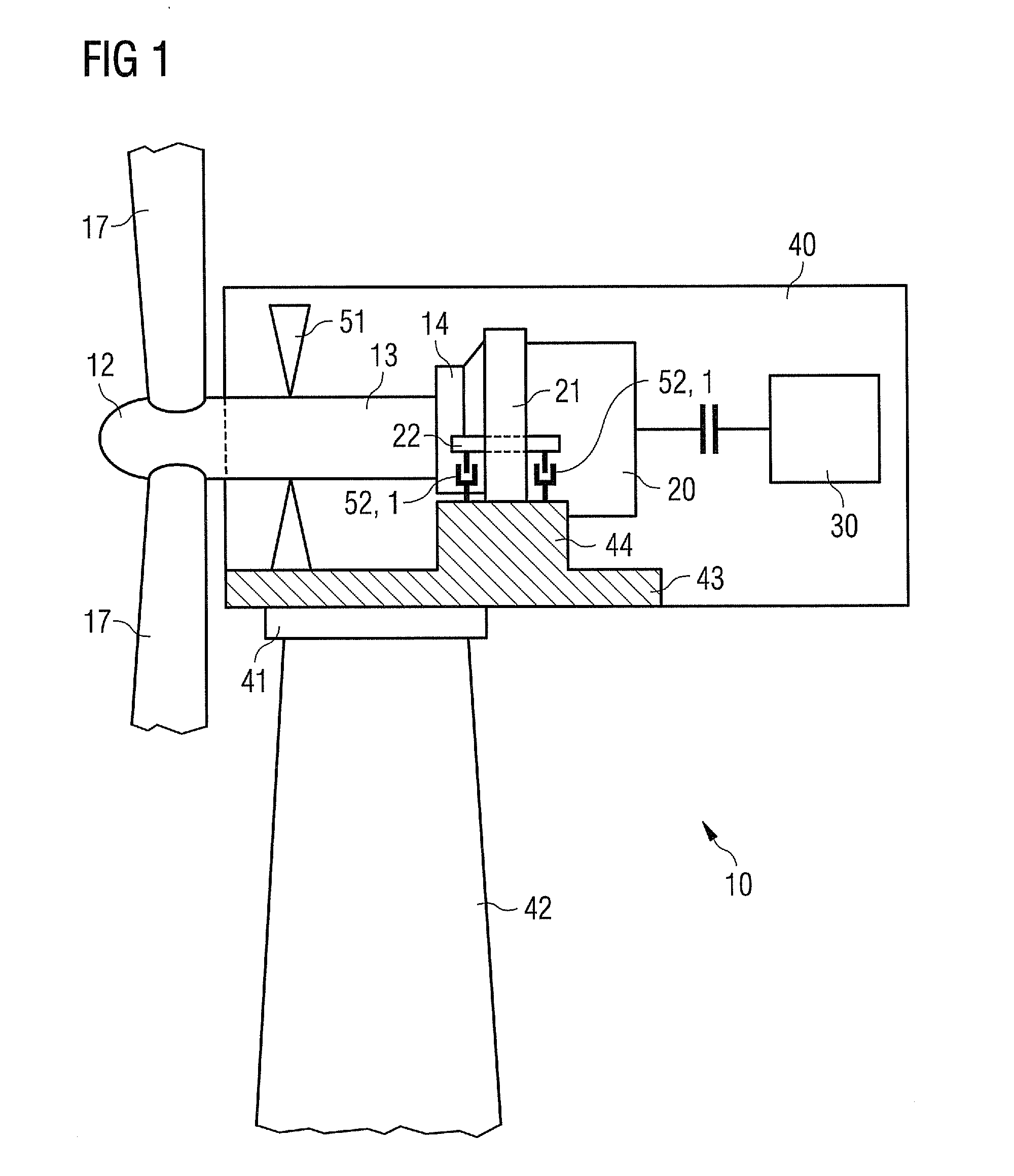
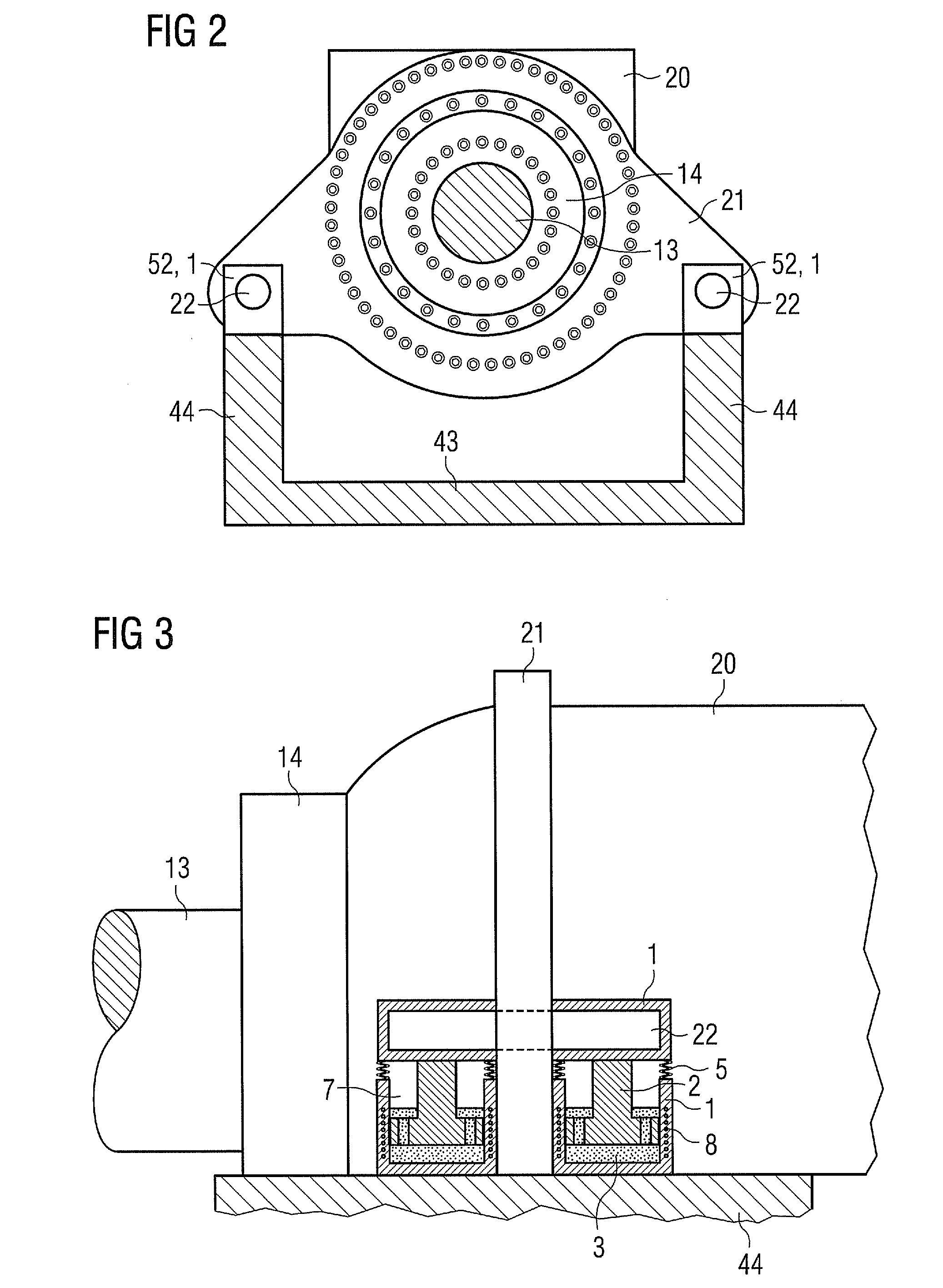
Wind turbine active damping arrangement
InactiveUS20120076652A1Improved damperPromote absorptionPropellersWind motor controlControl signalClosed chamber
A wind turbine active damping arrangement for damping forces exerted on a component connected to a main shaft of a wind turbine is proposed. The damping arrangement comprises a smart fluid damper and a control device for controlling a field generator of the smart fluid damper to control the extent of damping according to a performance parameter of the wind turbine. The smart fluid damper comprises a closed chamber containing a smart fluid and a piston. The piston travels along a direction in the chamber and comprises a channel through which the smart fluid can flow. The smart fluid damper comprises a field generator for generating a field across the smart fluid and an input for a field generator control signal for controlling the field generator to alter the field according to the performance parameter of the wind turbine.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
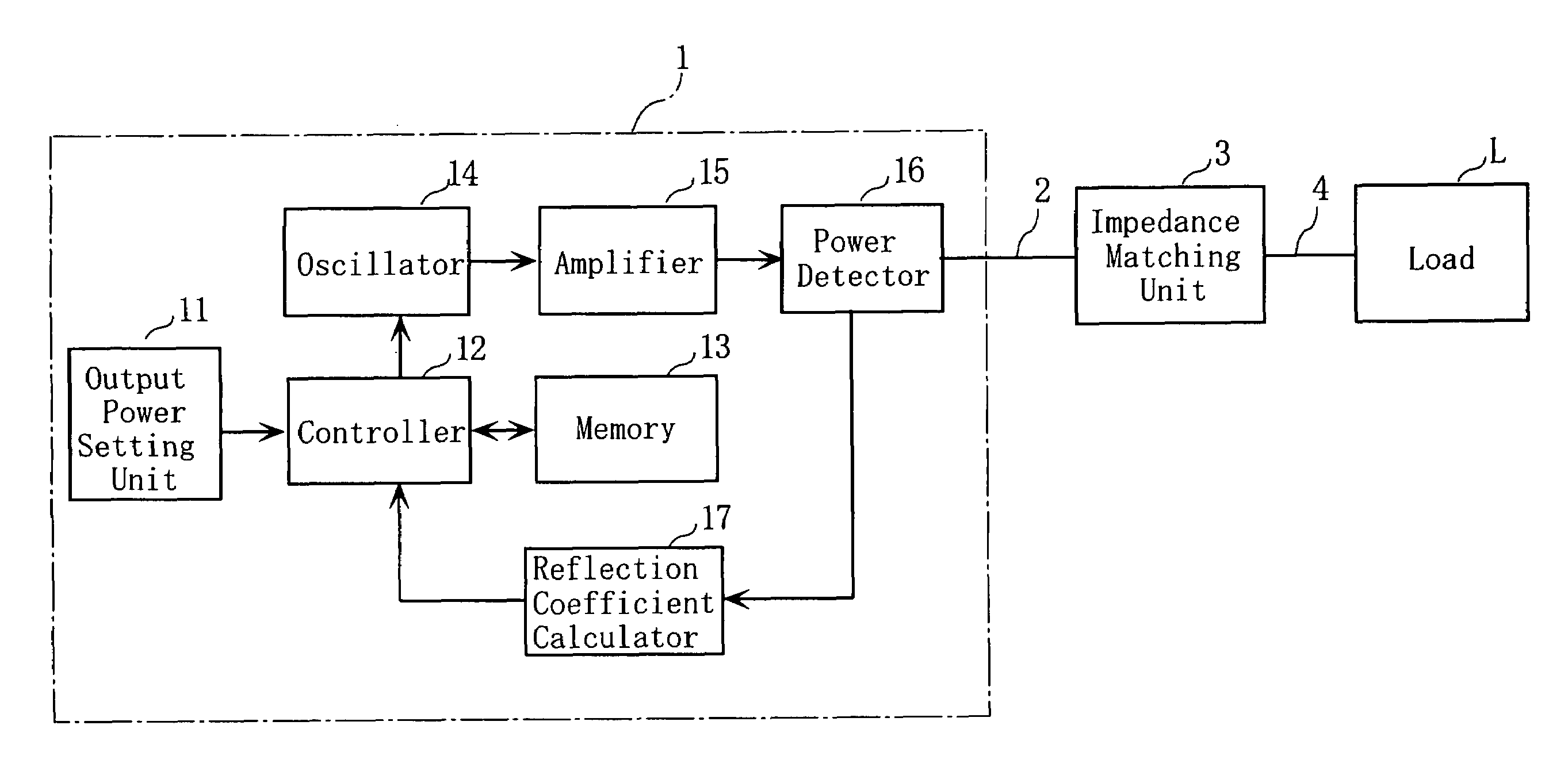
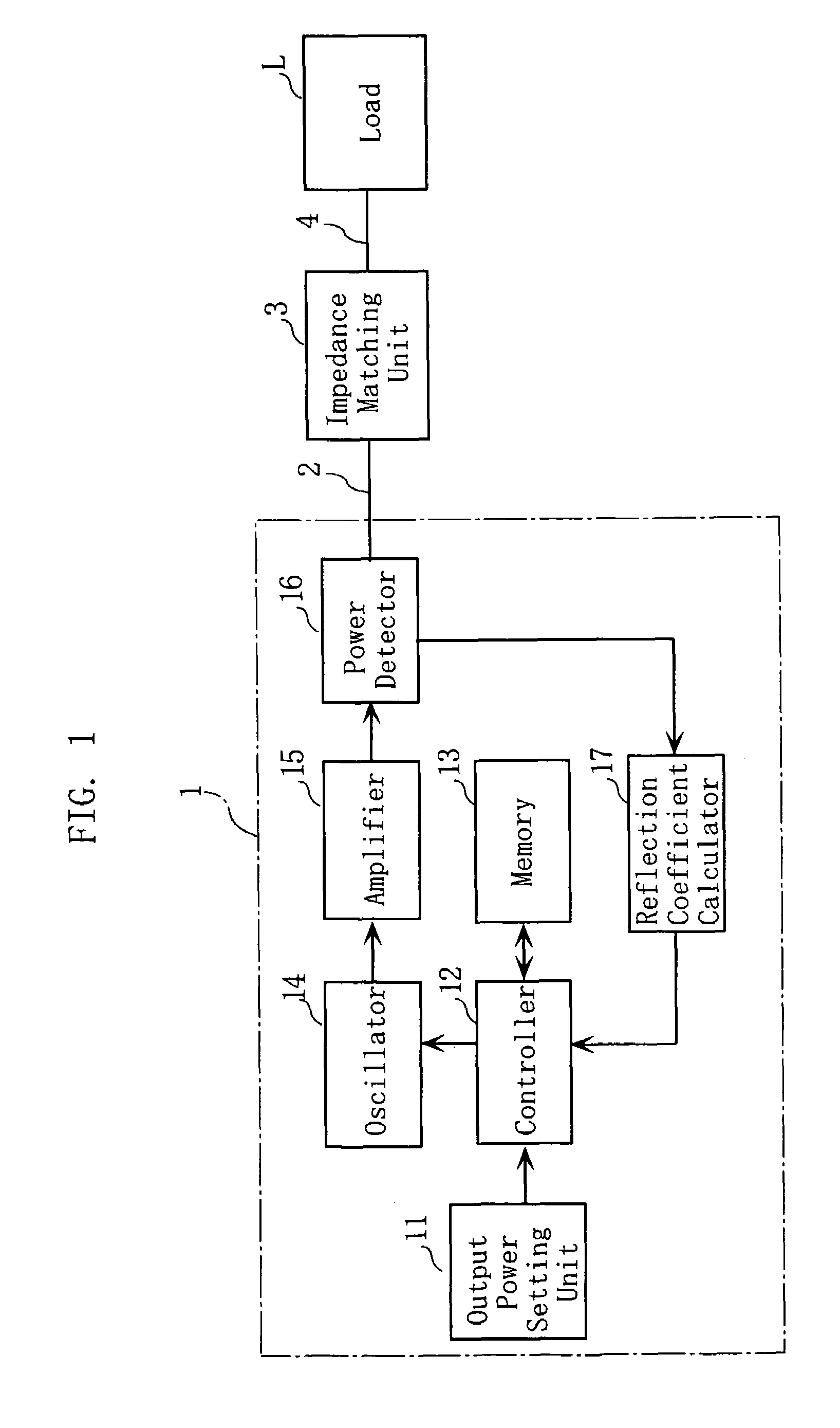
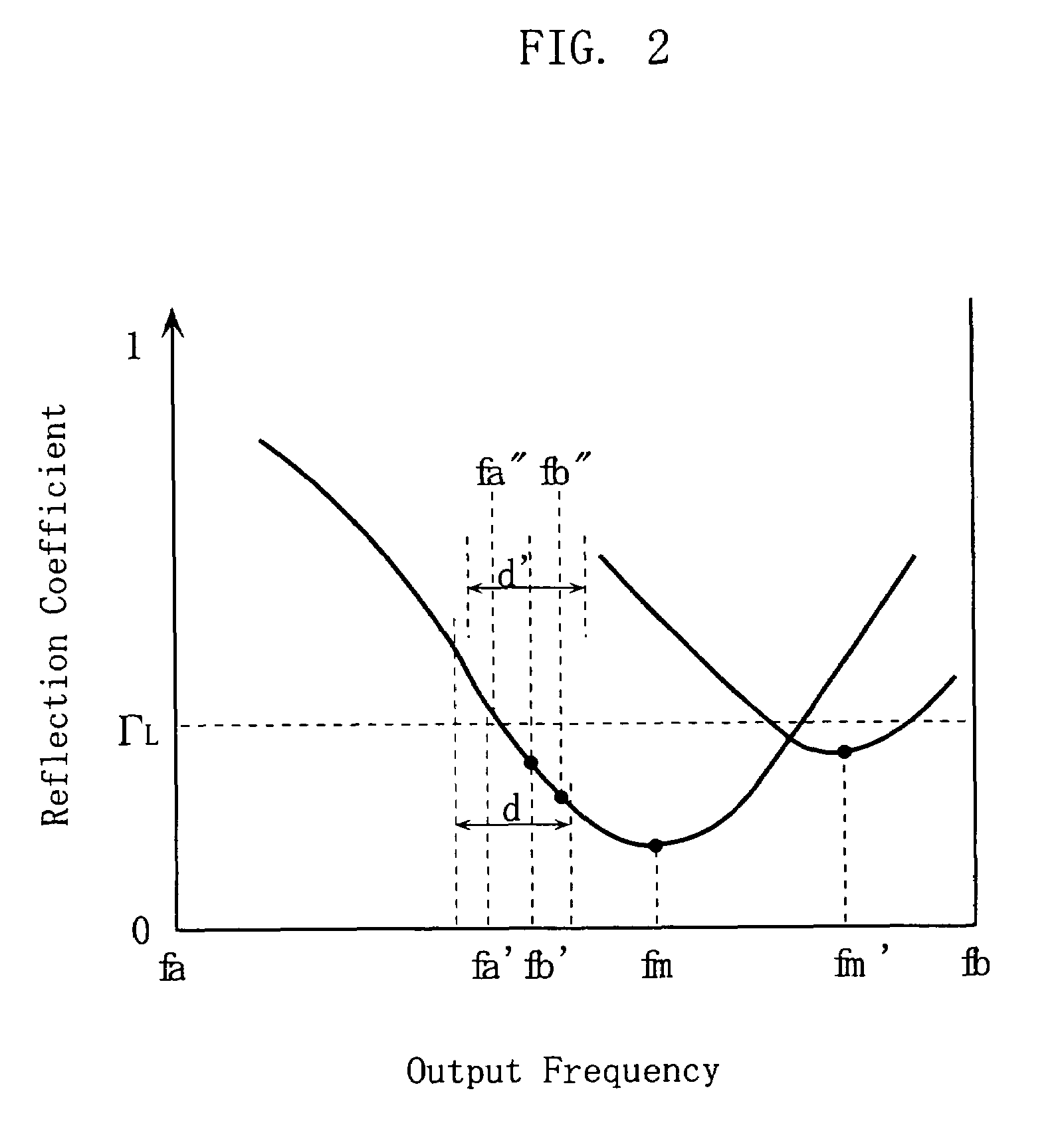
High-frequency power source
InactiveUS7292047B2Minimum value quicklyRapid fluctuationMultiple-port networksResistance/reactance/impedencePower controllerHigh frequency power
A high-frequency power source supplies high-frequency power to a load whose reflection characteristic for the power varies with time. The power source includes a frequency-variable power generator, a power detector for detecting the power into the load and the power from the load, a reflection coefficient calculator for calculating a reflection coefficient based on the detection of the power into and from the load, a frequency detector causing the power generator to generate high-frequency powers at various frequencies within a predetermined frequency range for obtaining the frequency that gives a minimum value to the calculated reflection coefficient, and a power supply controller for causing the power generator to generate a high-frequency power of the frequency obtained by the frequency detector and for supplying the high-frequency power to the load.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
Inkjet head
ActiveUS20050140754A1Effect of absorbing the fluctuation of pressure due to the flexible film is enhancedRapid fluctuationInking apparatusEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
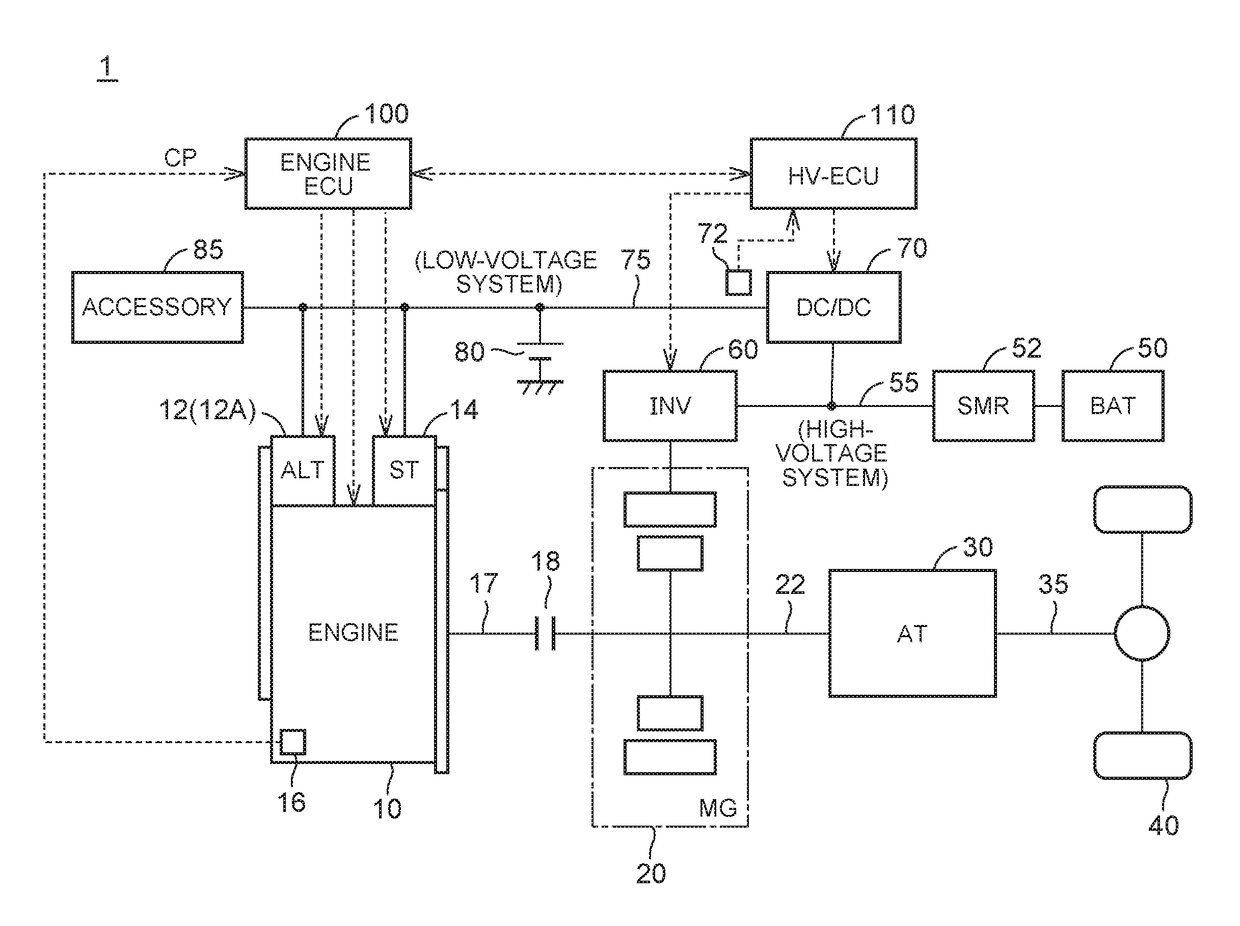
Vehicle and control method therefor
ActiveUS20180009431A1Suppress rapid fluctuationSuppress fluctuationsHybrid vehiclesVehicle sub-unit featuresBrake torqueElectric machine
A first electric power generation device configured to produce an accessory voltage according to a first instruction voltage. A second electric power generation device configured to produce the accessory voltage according to a second instruction. An electric control unit is configured to execute crank position stop control for stopping a crank of the engine at a target position when the engine is stopped by controlling the first electric power generation device such that a current is circulated in the first electric power generation device and the rotating electric machine generates braking torque. The electric control unit is configured to execute the crank position stop control in a state in which the second instruction voltage is equal to or higher than the first instruction voltage.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
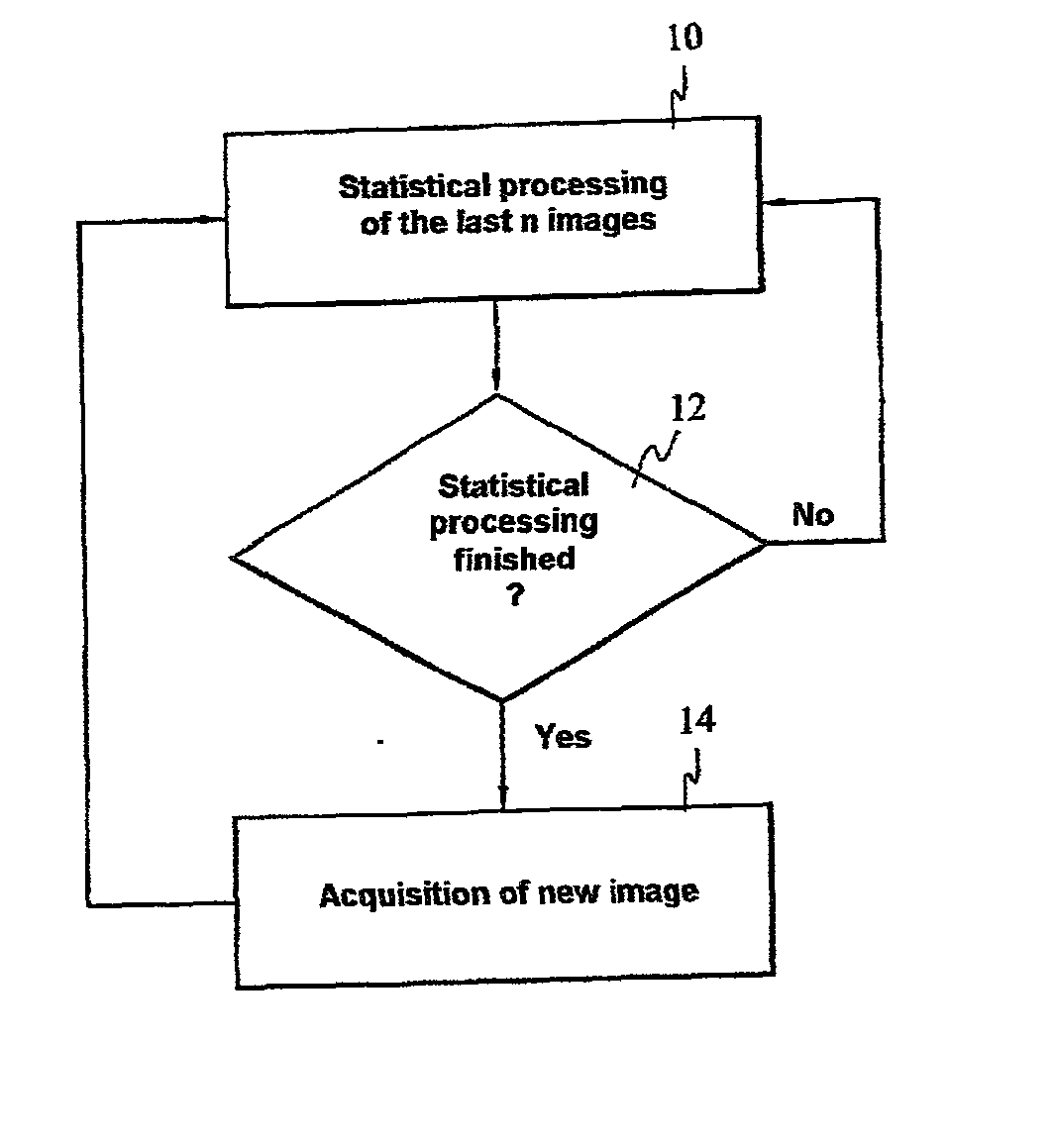
Method and device for characterizing or controlling zones of temporal fluctuations of a scene
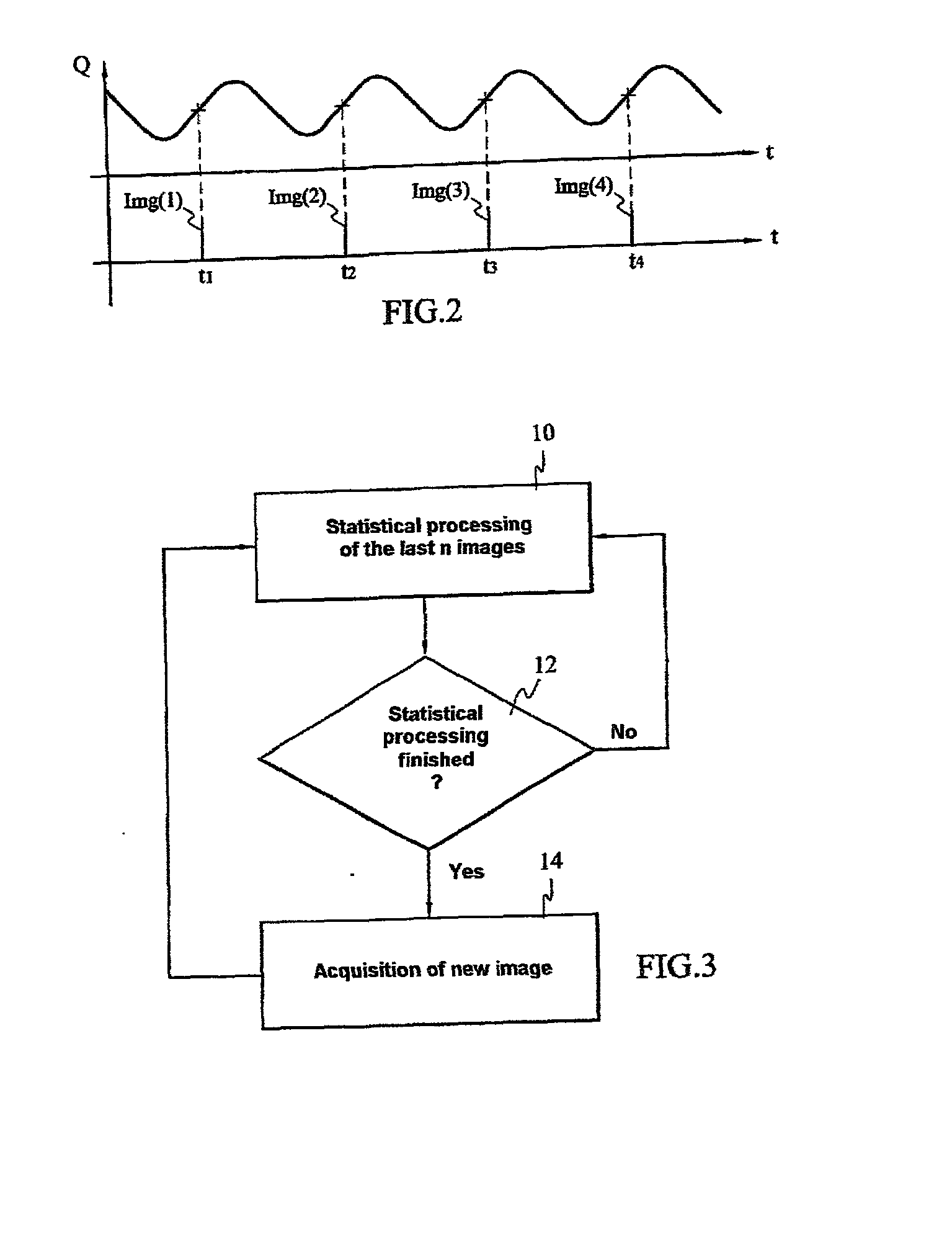
InactiveUS20020051579A1Eliminating fast fluctuation of content of imageRapid fluctuationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionThermodynamicsMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a method of processing images of at least one flame or of a scene in a furnace, characterized in that it comprises at least one sliding statistical processing of the images of the flame which are captured in the course of a sliding time interval, so as to eliminate the fast fluctuations therefrom.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Engine system having coolant control valve
InactiveUS20160160737A1High temperature control accuracyOptimize layoutLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlImpellerLine tubing
An engine system having a coolant control valve may include a cylindrical valve having a pipe structure with one side opened and including coolant passages formed in preset positions from one inner circumferential surface to an outer circumferential surface of the cylindrical valve to allow a coolant to pass therethrough, a valve housing configured for the cylindrical valve to be rotatably disposed therein and having connection pipes connected thereto to correspond to the coolant passages, a valve driving device, a pump housing disposed in one end portion of the cylindrical valve to correspond to the opened side of the cylindrical valve, having a pump impeller disposed therein, and coupled to the valve housing, a pump driving device disposed to rotate the pump impeller, and a pump discharge line connected to the pump housing to transmit a coolant pumped by the pump impeller to a cylinder block.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Inkjet head
ActiveUS7278710B2Effect of absorbing the fluctuation of pressure due to the flexible film is enhancedRapid fluctuationInking apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
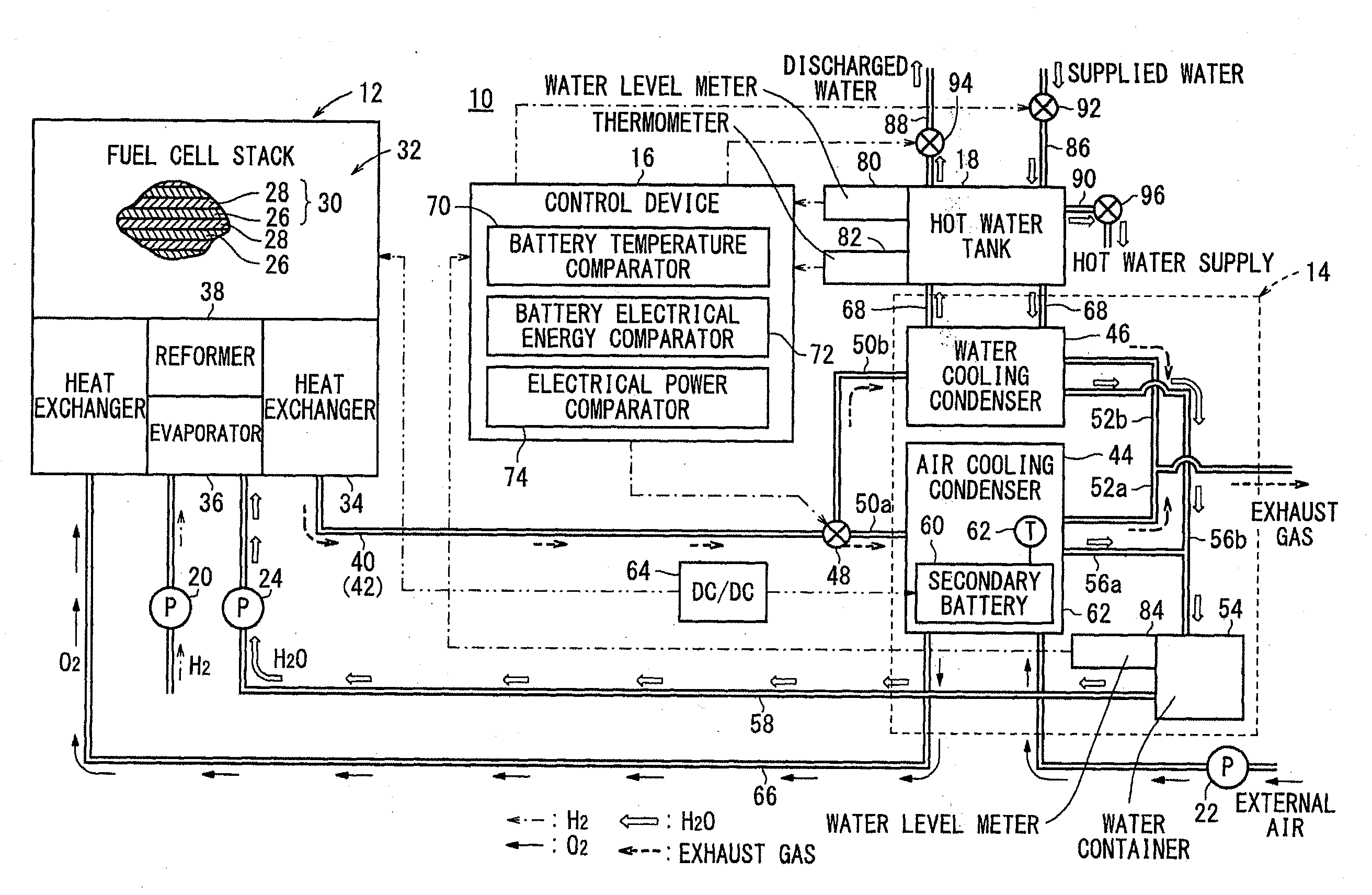
Fuel cell system
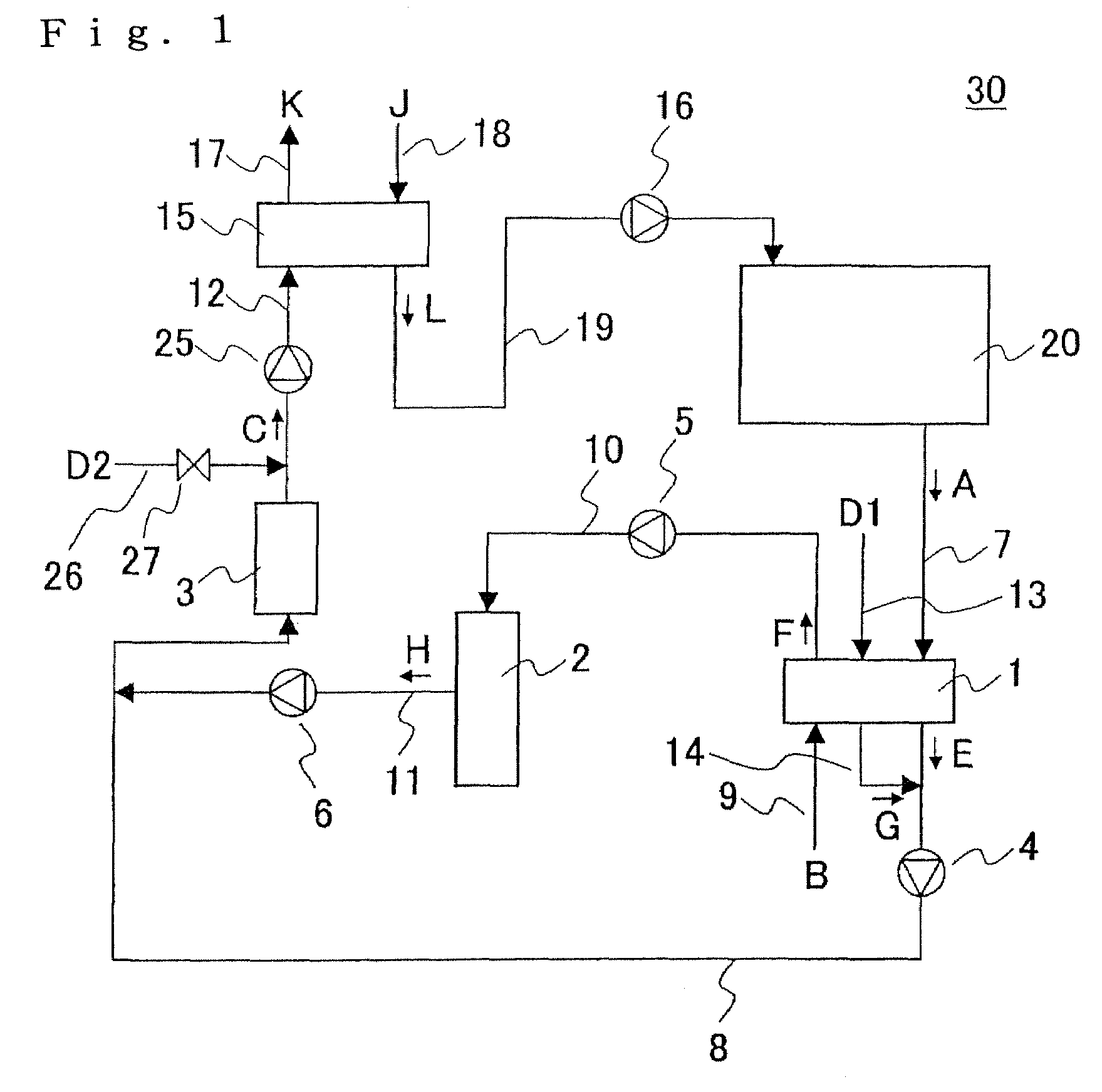
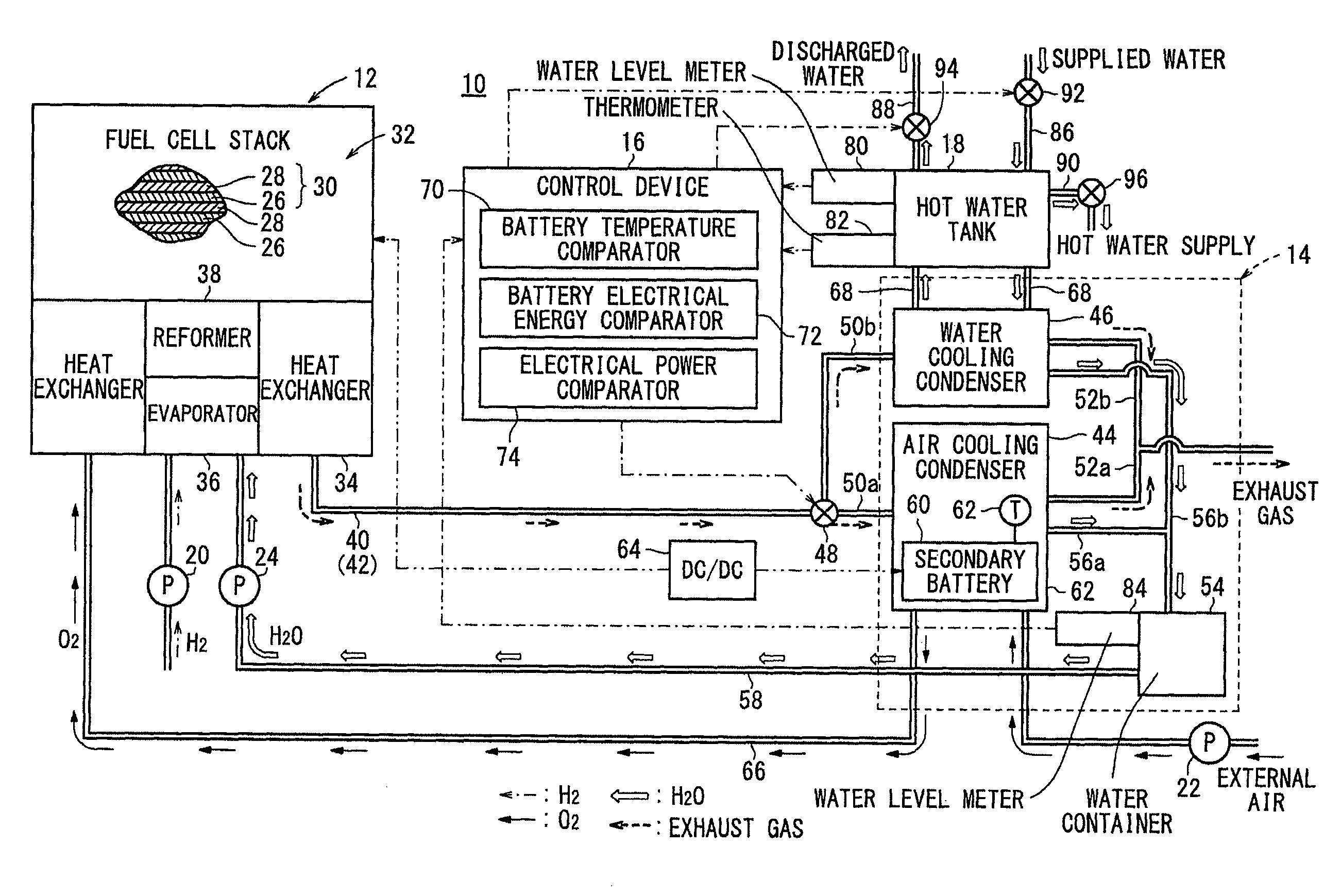
ActiveUS20150010785A1Fluctuation of electrical powerRapid fluctuationFuel cell heat exchangeCell temperature controlElectrochemical responseWater vapor
A fuel cell system includes a fuel cell module for generating electrical energy by electrochemical reactions of a fuel gas and an oxygen-containing gas, a condenser for condensing water vapor in an exhaust gas discharged from the fuel cell module by heat exchange between the exhaust gas and a coolant to collect the condensed water and supplying the collected condensed water to the fuel cell module. The condenser includes an air cooling condensing mechanism using the oxygen-containing gas as the coolant. The air cooling condensing mechanism includes a secondary battery for inducing endothermic reaction during charging and inducing exothermic reaction during discharging.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Vehicle and control method therefor
ActiveUS10124794B2Suppressing rapid fluctuationSuppress fluctuationsHybrid vehiclesVehicle sub-unit featuresBrake torqueElectric machine
A first electric power generation device configured to produce an accessory voltage according to a first instruction voltage. A second electric power generation device configured to produce the accessory voltage according to a second instruction. An electric control unit is configured to execute crank position stop control for stopping a crank of the engine at a target position when the engine is stopped by controlling the first electric power generation device such that a current is circulated in the first electric power generation device and the rotating electric machine generates braking torque. The electric control unit is configured to execute the crank position stop control in a state in which the second instruction voltage is equal to or higher than the first instruction voltage.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
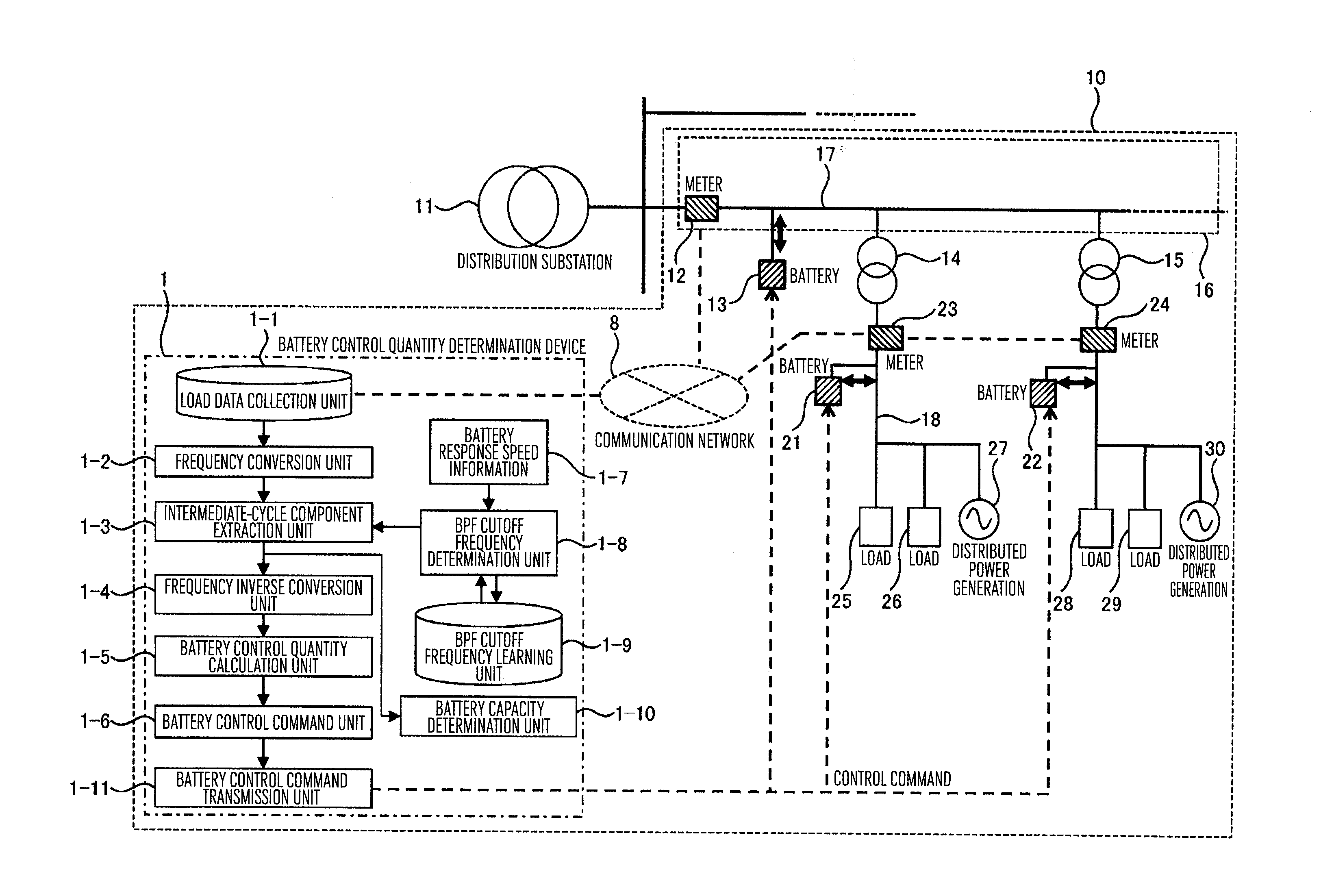
Method and apparatus for control battery and specification determining method of battery
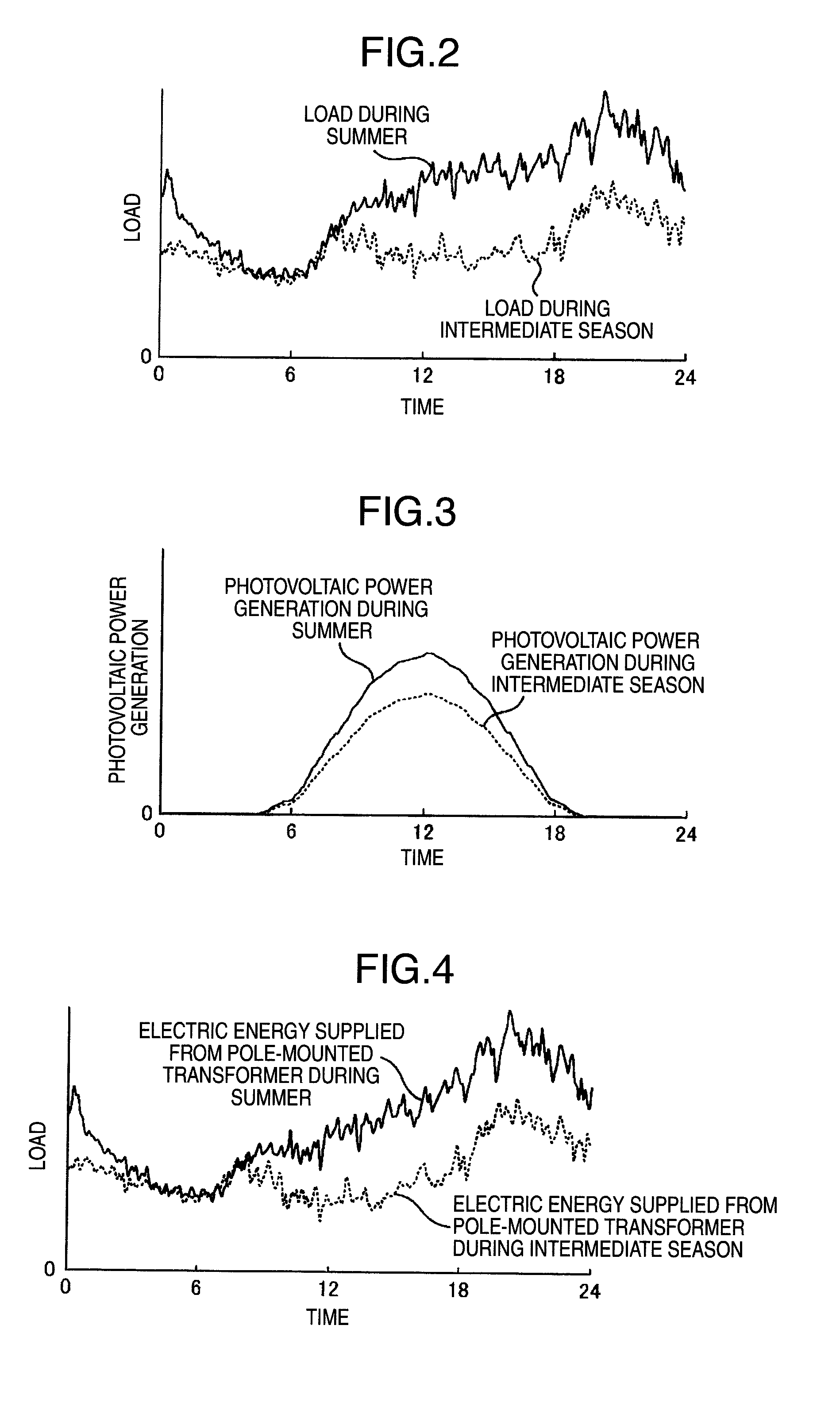
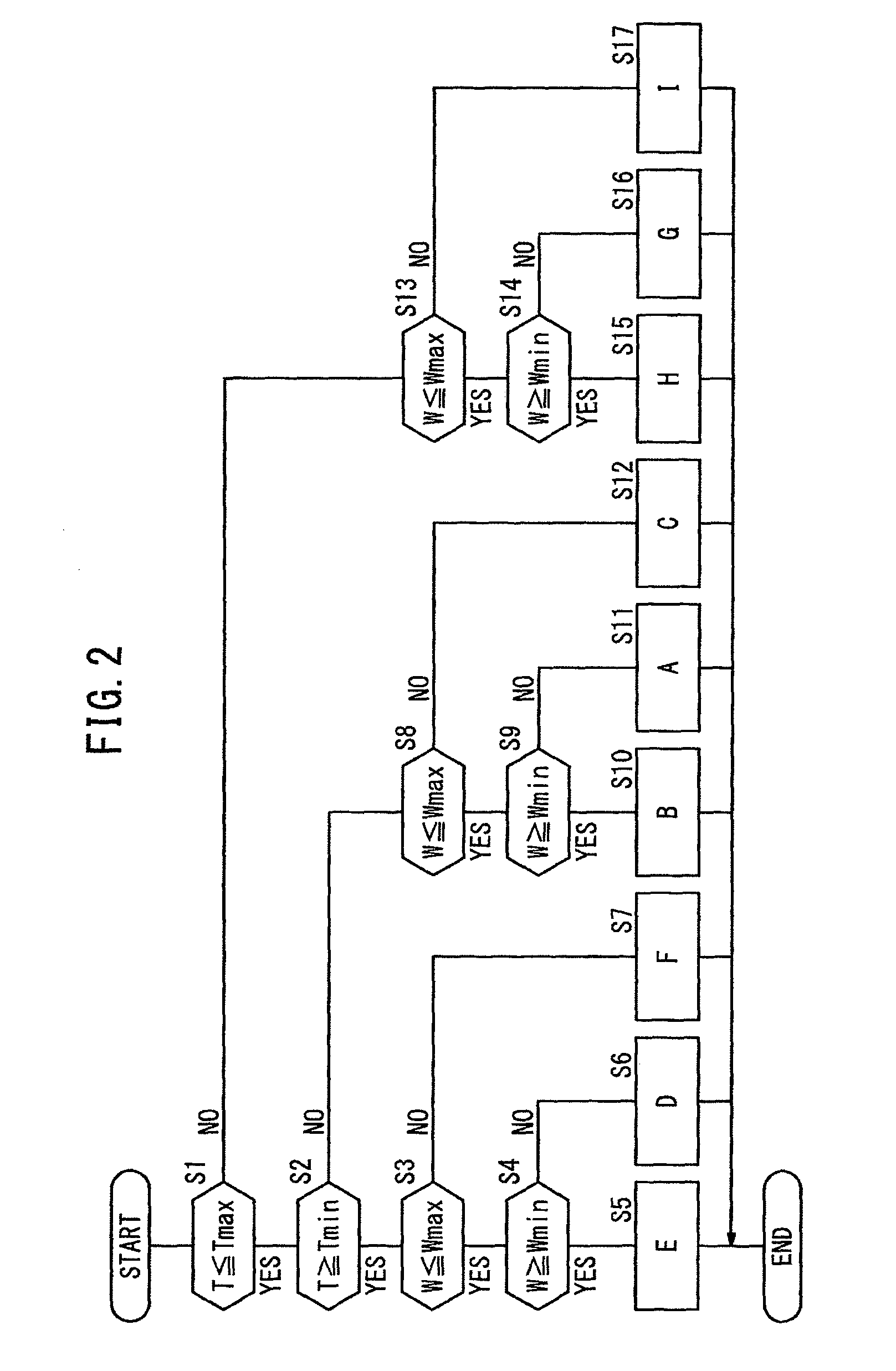
ActiveUS20120004787A1Effective controlReduce capacityLevel controlWind energy generationTransformerFrequency conversion
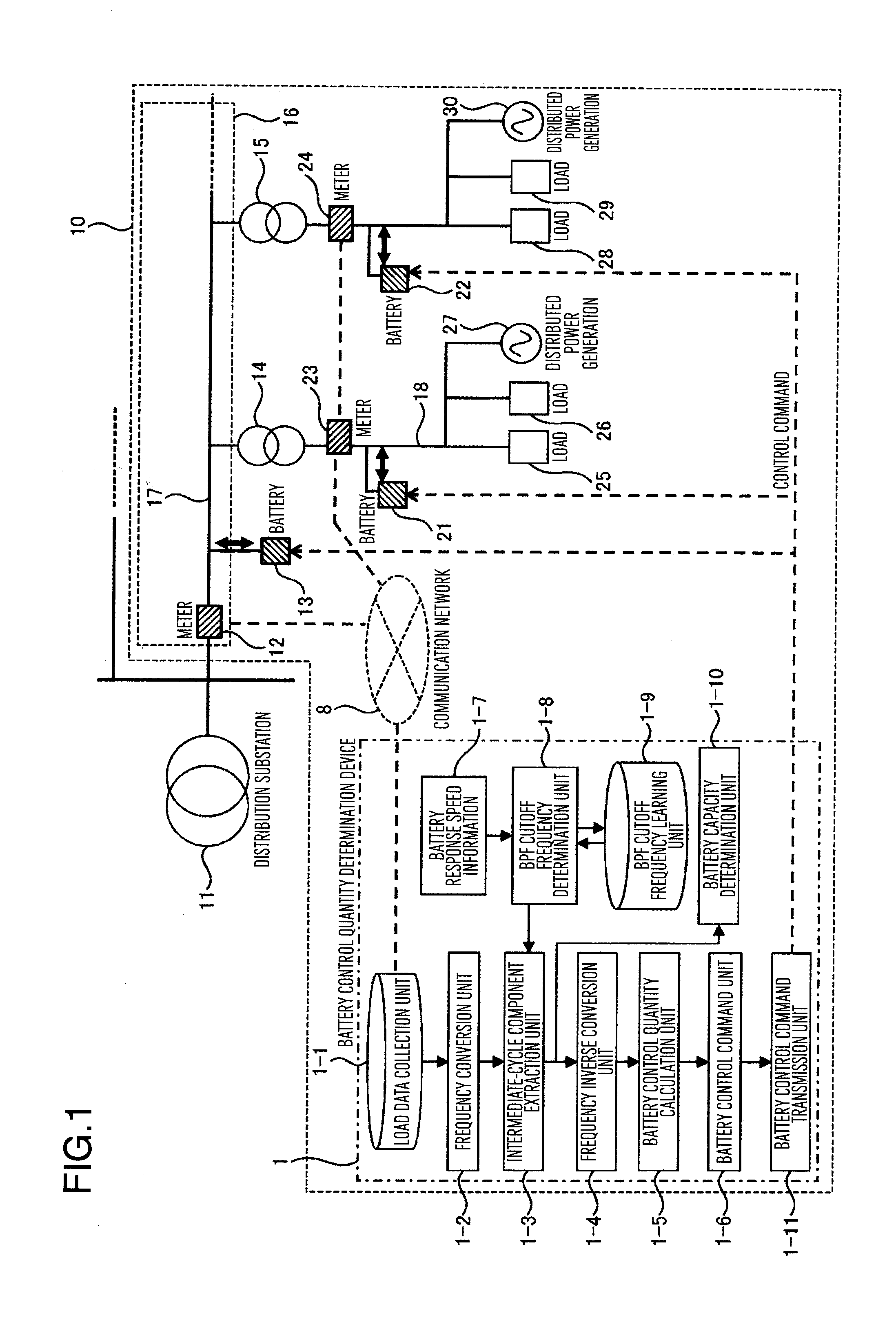
A battery control apparatus of this invention is provided which comprises: a battery installed on a feeder of a utility distribution system; batteries installed between pole-mounted transformers and branch points of the distribution lines; a communication network to transmit measurement data measured by meters; a battery control quantity calculation unit to determine battery control quantities from the measurement data acquired from the communication network; a load data collection unit to collect load data representing a combination of power consumption by a plurality of loads and generated power of distributed power generations; a frequency conversion unit to perform a frequency analysis on the load data; an intermediate-cycle component extraction unit to extract intermediate-cycle components; a battery control quantity calculation unit to determine battery control quantities from the extracted intermediate-cycle components; and a battery control command transmission unit to transmit the calculated control quantities to the batteries.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for operating a hearing device and a hearing device
ActiveUS9584932B2Reliable and simple mannerEnhanced signalOcclusion effect electronic compensationHearing device energy consumption reductionFilter (signal processing)Hearing apparatus
A method for operating a hearing device including an ambient microphone, a signal processing unit, a receiver and an ear canal microphone. The method includes steps of filtering the audio signal processed by the signal processing unit with a filter having a transfer function including a transfer function from an output of the receiver to an input of the ear canal microphone when the hearing device is turned on and being worn in an ear canal of the user, computing a difference between the audio signal picked up by the ear canal microphone and the filtered signal, and detecting a presence of own-voice of the user based on the difference. Furthermore, a hearing device including an own-voice detection unit is provided, which is adapted to perform the proposed method.
Owner:SONOVA AG
Method for processing organic solvent-containing air
InactiveUS20070209510A1High thermal efficiencyRapid fluctuationGas treatmentOrganic chemistryCombustionOrganic solvent
A method for processing an organic solvent-containing air capable of being operated in spite of a rapid fluctuation of the concentration of organic solvents in the air to be processed and capable of using a combustion furnace exhaust gas as an air for regenerating dehumidifying member is provided. The method comprises carrying out simultaneously and continuously a dehumidification step (a), an adsorption-removing step (b), an adsorbing member-regeneration step (c), a combustion step (d), and a dehumidifying member-regeneration step (e) comprising mixing the adsorption-treated air produced in the adsorbing-removing step (b) with a combustion furnace exhaust gas produced in the combustion step (d) to obtain a mixed gas, decomposing the organic solvents in the mixed gas by oxidation, and causing the resulting purified gas to flow through the dehumidifying member which has adsorbed moisture, thereby regenerating the dehumidifying member.
Owner:NICHIAS CORP
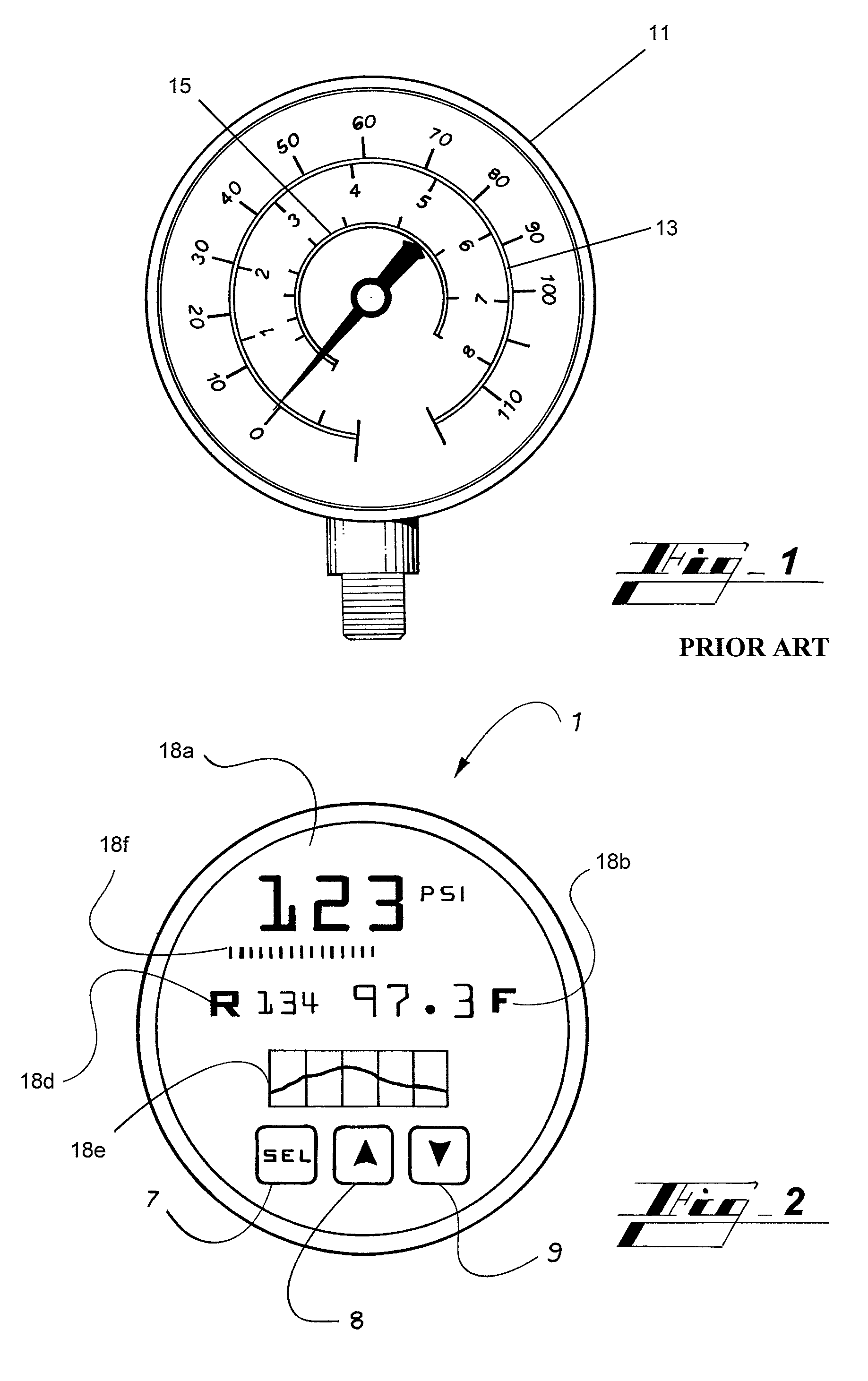
Heating and air conditioning service gauge
ActiveUS8069731B2Understand clearlyRapid fluctuationMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsEngineeringRefrigerant
A service gauge for determining refrigerant pressure and the saturated vapor equivalent temperature, or other parameters, for a refrigerant in an HVAC system. In one embodiment, the service gauge employs a bourdon tube with at least one attached strain gauge to sense the refrigerant pressure and produce an electronic pressure signal. In another embodiment, a magnet and rotary position sensor produces an electronic signal proportional to the refrigerant pressure. The electronic pressure signal from the output of the strain gauge or the rotary position sensor is connected to a microprocessor, which calculates and displays the refrigerant pressure, the saturated vapor equivalent temperature for a variety of refrigerants, produces instantaneous and time lapsed representations of those parameters, and other parameters of the refrigerant.
Owner:DIVERSITECH
Cellular network handoff decision mechanism
InactiveUS7218933B2Rapid responseRapid fluctuationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesHysteresisCarrier signal
Disclosed is a cellular network handoff decision mechanism which comprising the steps of: determining a sampling interval using a carrier wavelength; determining a local averaging interval that is larger than the sampling interval; determining a handoff decision interval that is larger than the local averaging interval; selecting at least two base stations from a multitude of base stations having a pilot signal from a reference cellular network using a selection criterion; determining a received signal strength from the pilot signal strength for each of the selected base stations once during every sampling interval; calculating a local average signal strength value using each of the received signal strengths once during every local averaging interval; determining an assignment region in which the local average signal strength value lies using a hysteresis range; and calculating a handoff decision once during every handoff decision interval using a handoff calculation.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP INC
Interest calculation tool
ActiveUS20050071398A1Good precisionRapid in account balanceFinanceInput/output processes for data processingSimulationTime parameter
Embodiments of the present invention relate to a computer-implemented method and system for performing interest calculations on account balances. The calculations may be based on time intervals of less than a day, and using time parameters defined in terms of seconds.
Owner:SAP AG
Interest calculation tool
ActiveUS7499884B2Fast balanceAccurate calculationFinanceInput/output processes for data processingSimulationTime parameter
Embodiments of the present invention relate to a computer-implemented method and system for performing interest calculations on account balances. The calculations may be based on time intervals of less than a day, and using time parameters defined in terms of seconds.
Owner:SAP AG
Method for processing organic solvent-containing air
InactiveUS7582139B2Increase contentGuaranteed uptimeGas treatmentOrganic chemistryOrganic solventPhysical chemistry
Owner:NICHIAS CORP
Method and apparatus for control battery and specification determining method of battery
ActiveUS8831790B2Minimize fluctuationEffective controlMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlTransformerFrequency conversion
A battery control apparatus of this invention is provided which comprises: a battery installed on a feeder of a utility distribution system; batteries installed between pole-mounted transformers and branch points of the distribution lines; a communication network to transmit measurement data measured by meters; a battery control quantity calculation unit to determine battery control quantities from the measurement data acquired from the communication network; a load data collection unit to collect load data representing a combination of power consumption by a plurality of loads and generated power of distributed power generations; a frequency conversion unit to perform a frequency analysis on the load data; an intermediate-cycle component extraction unit to extract intermediate-cycle components; a battery control quantity calculation unit to determine battery control quantities from the extracted intermediate-cycle components; and a battery control command transmission unit to transmit the calculated control quantities to the batteries.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
High efficiency plastic light conversion components by incorporation of phosphor in a polymer by adding to monomers before polymerisation
InactiveUS20140217445A1Solve the real problemEasy to manufactureLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devicesPolymer sciencePhosphor
The invention relates to a method for producing a polymer product having integrated luminescent material particles, the polymer product being produced from at least one monomer in liquid phase and at least one kind of powder of luminescent material particles. The method is characterized by adding the luminescent material to the liquid monomer before polymerisation. The invention further relates to a plastic component for light conversion made of the polymer produced according to said method; a Light-emitting device comprising said plastic component; and the use of a polymer produced according to said method.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV +1
Fuel cell system
ActiveUS9537193B2Easy to operateImprove efficiencyElectricity cogenerationFuel cell heat exchangeElectrochemical responseFuel cells
A fuel cell system includes a fuel cell module for generating electrical energy by electrochemical reactions of a fuel gas and an oxygen-containing gas, a condenser for condensing water vapor in an exhaust gas discharged from the fuel cell module by heat exchange between the exhaust gas and a coolant to collect the condensed water and supplying the collected condensed water to the fuel cell module. The condenser includes an air cooling condensing mechanism using the oxygen-containing gas as the coolant. The air cooling condensing mechanism includes a secondary battery for inducing endothermic reaction during charging and inducing exothermic reaction during discharging.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
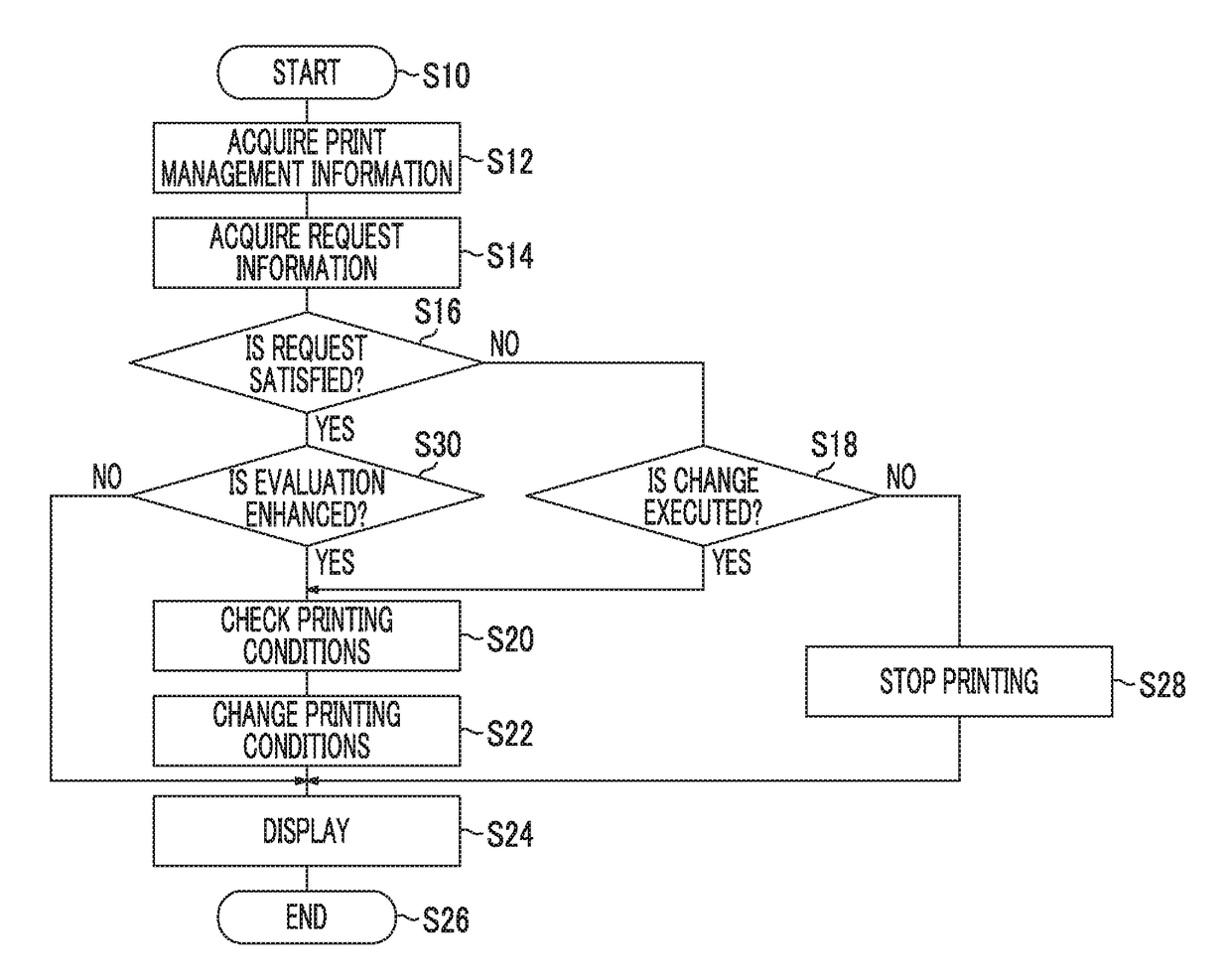
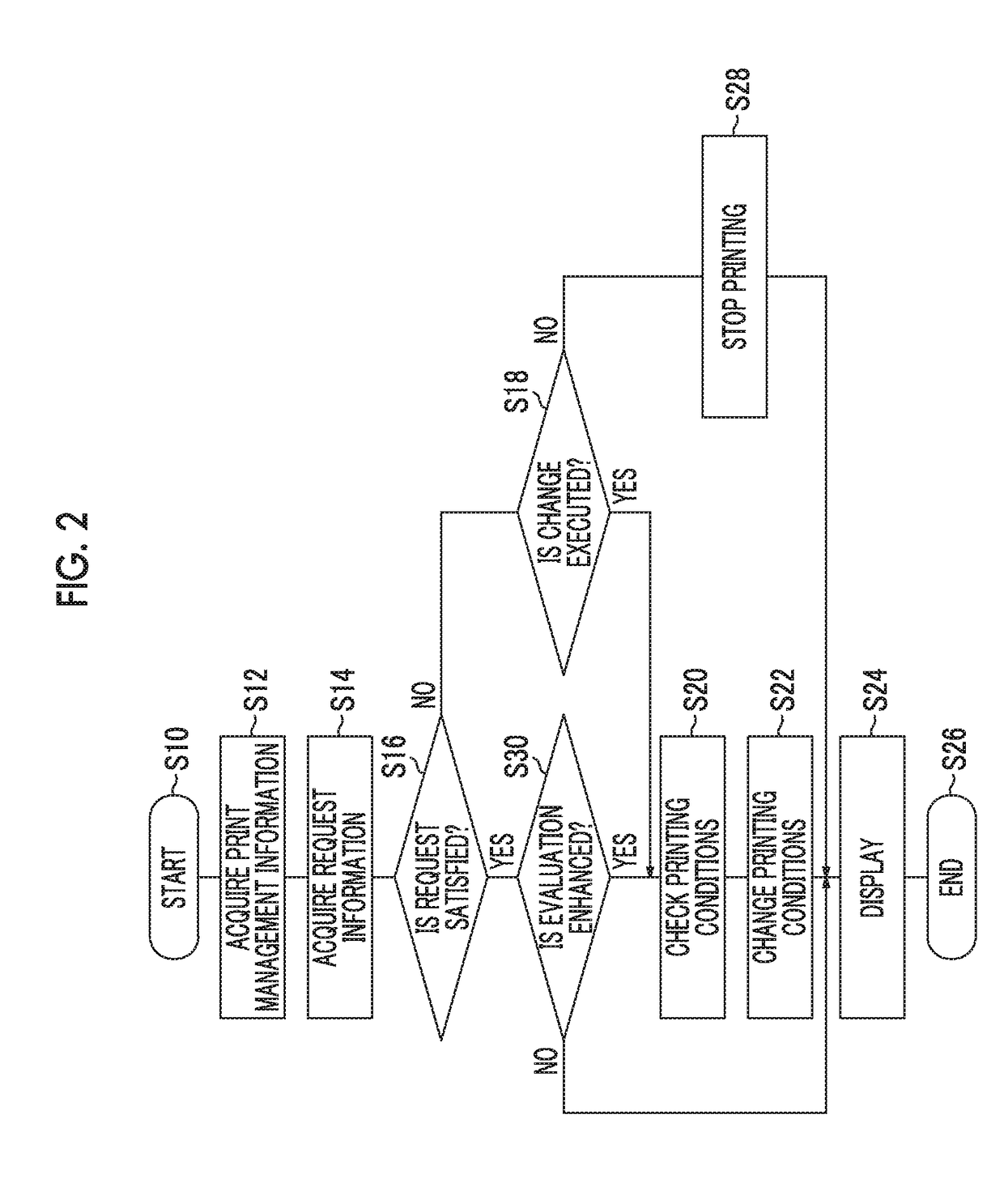
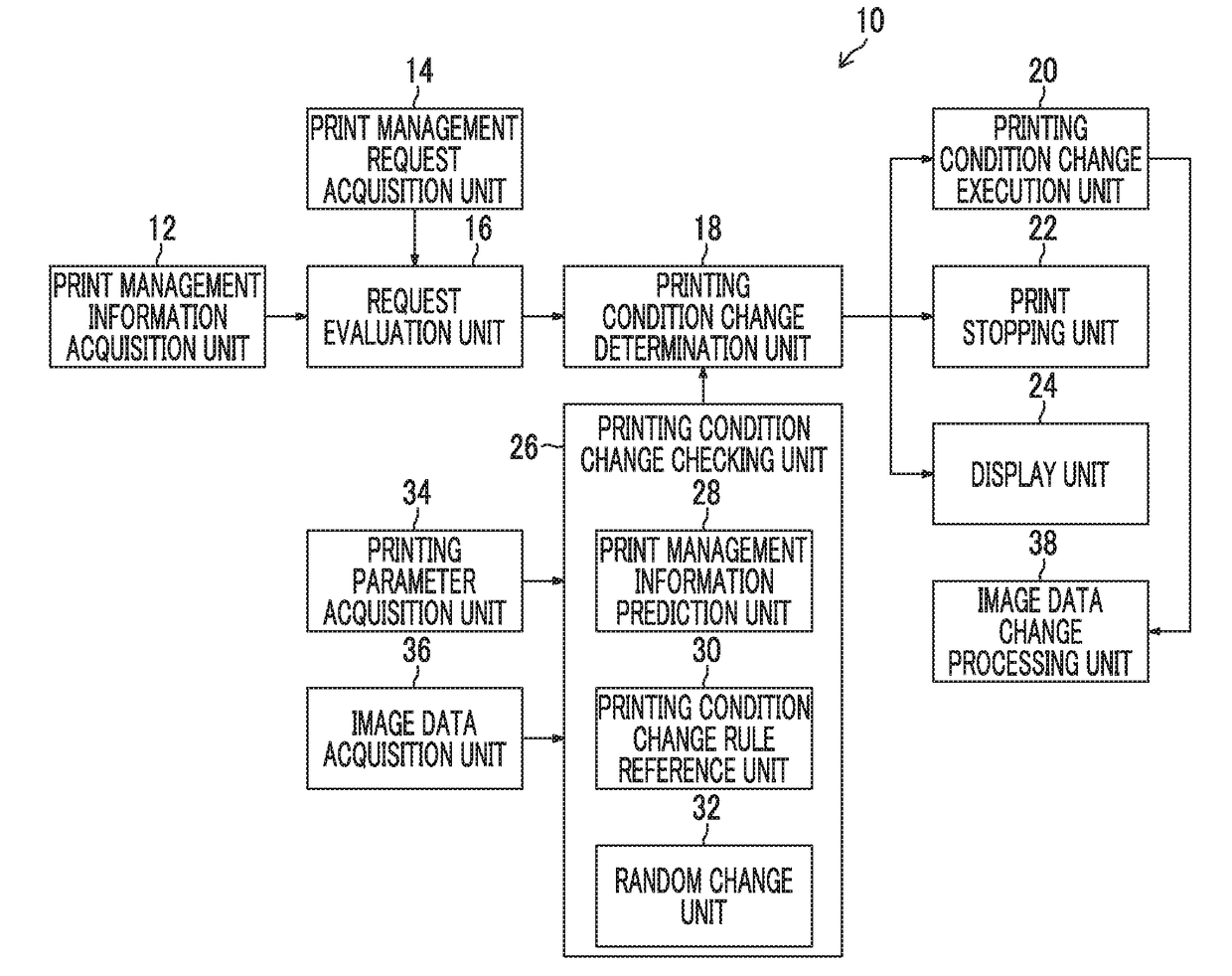
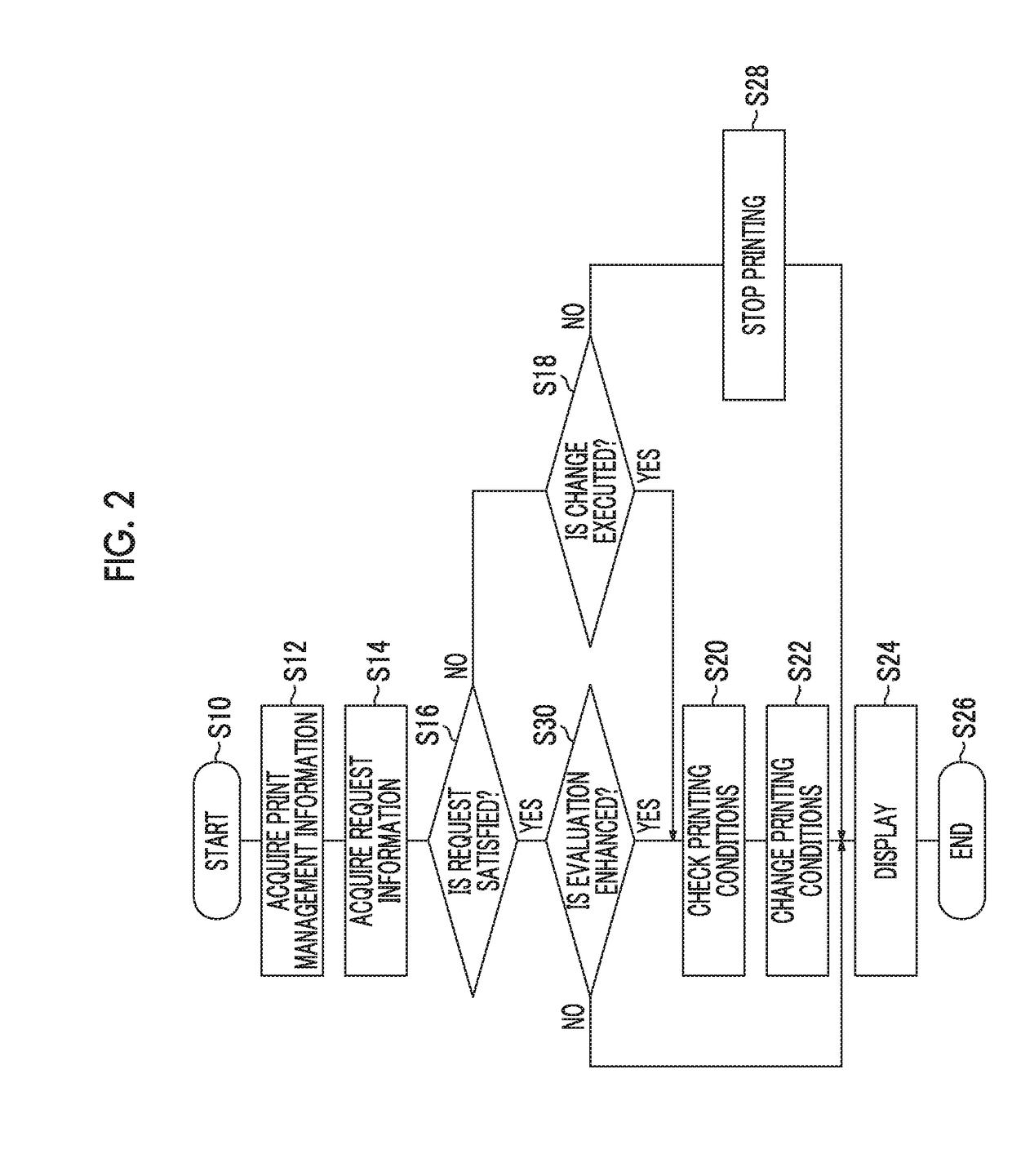
Print management device, print management method, and print management program
ActiveUS9950548B2Rapid fluctuationImprove satisfactionOther printing apparatusDigital output to print unitsEvaluation resultApproaches of management
The print management device includes a print management information acquisition unit that acquires print management information including first information indicating quality of a printed material printed in a print job during execution and second information indicating an evaluation index of the printed material, different from the first information, in the print job during execution, a print management request acquisition unit that acquires request information indicating a request relating to print management of the printed material in the print job, a request evaluation unit that evaluates the degree of satisfaction of the printed material printed in the print job for the request relating to the print management indicated by the request information, based on the print management information, using one or more evaluation references, and a printing condition change determination unit that determines whether change in printing conditions in the print job during execution is necessary, based on an evaluation result.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Print management device, print management method, and print management program
ActiveUS20170182822A1Rapid fluctuationImprove satisfactionOther printing apparatusDigital output to print unitsEvaluation resultApproaches of management
The print management device includes a print management information acquisition unit that acquires print management information including first information indicating quality of a printed material printed in a print job during execution and second information indicating an evaluation index of the printed material, different from the first information, in the print job during execution, a print management request acquisition unit that acquires request information indicating a request relating to print management of the printed material in the print job, a request evaluation unit that evaluates the degree of satisfaction of the printed material printed in the print job for the request relating to the print management indicated by the request information, based on the print management information, using one or more evaluation references, and a printing condition change determination unit that determines whether change in printing conditions in the print job during execution is necessary, based on an evaluation result.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Semiconductor device, method of measuring light intensity distribution of laser light, laser annealing apparatus, and crystallization method
InactiveUS20060065644A1Accurate measurementRapid fluctuationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotometry for measuring UV lightAmorphous siliconLaser light
An amorphous silicon layer is deposited on a glass substrate via an underlayer insulating film, and further a light-emitting layer is inserted between the glass substrate and the underlayer insulating film in a partial region on the glass substrate. To measure light intensity distribution of laser light applied to the amorphous silicon layer, the laser light is applied to the light-emitting layer from the surface of a substrate to be treated. The light intensity distribution of the light emitted from the light-emitting layer is two-dimensionally imaged using an optical image pickup system from the back surface of the substrate to be treated, and measured using an image pickup device. The light intensity distribution of the laser light in the face to be treated is obtained from the light intensity distribution of the emission measured in this manner.
Owner:ADVANCED LCD TECH DEVMENT CENT
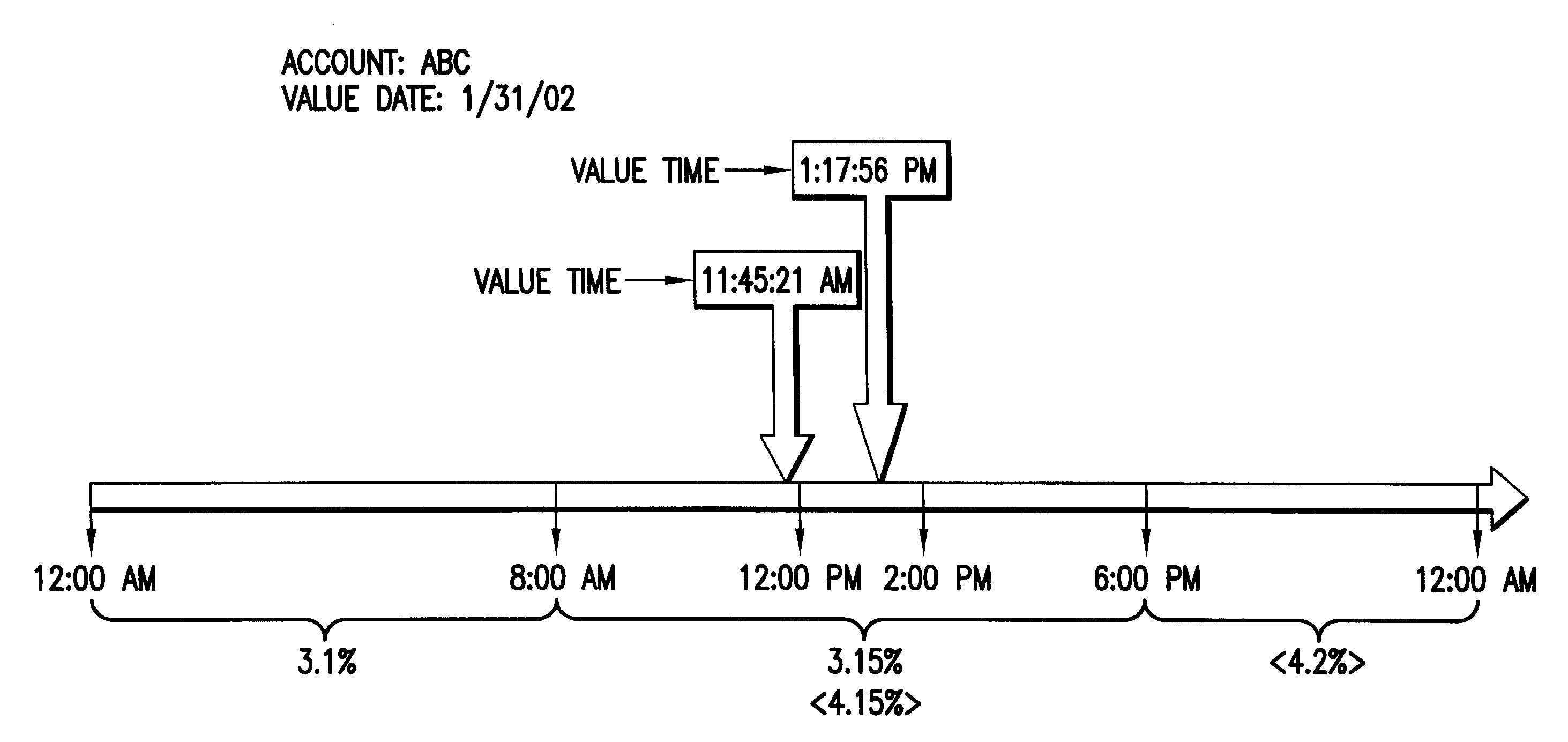
Management of intra-day interest calculations for bank accounts
Embodiments of the present invention relate to a computer-implemented method and system for managing intra-day interest calculation on a bank account. The embodiments provide for control of and support for interest calculations that, instead of being based on daily end-of-day account balances, are based on a plurality of net account balances as determined for a plurality of points in time within a day.
Owner:SAP AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com