Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
112results about "Occlusion effect electronic compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
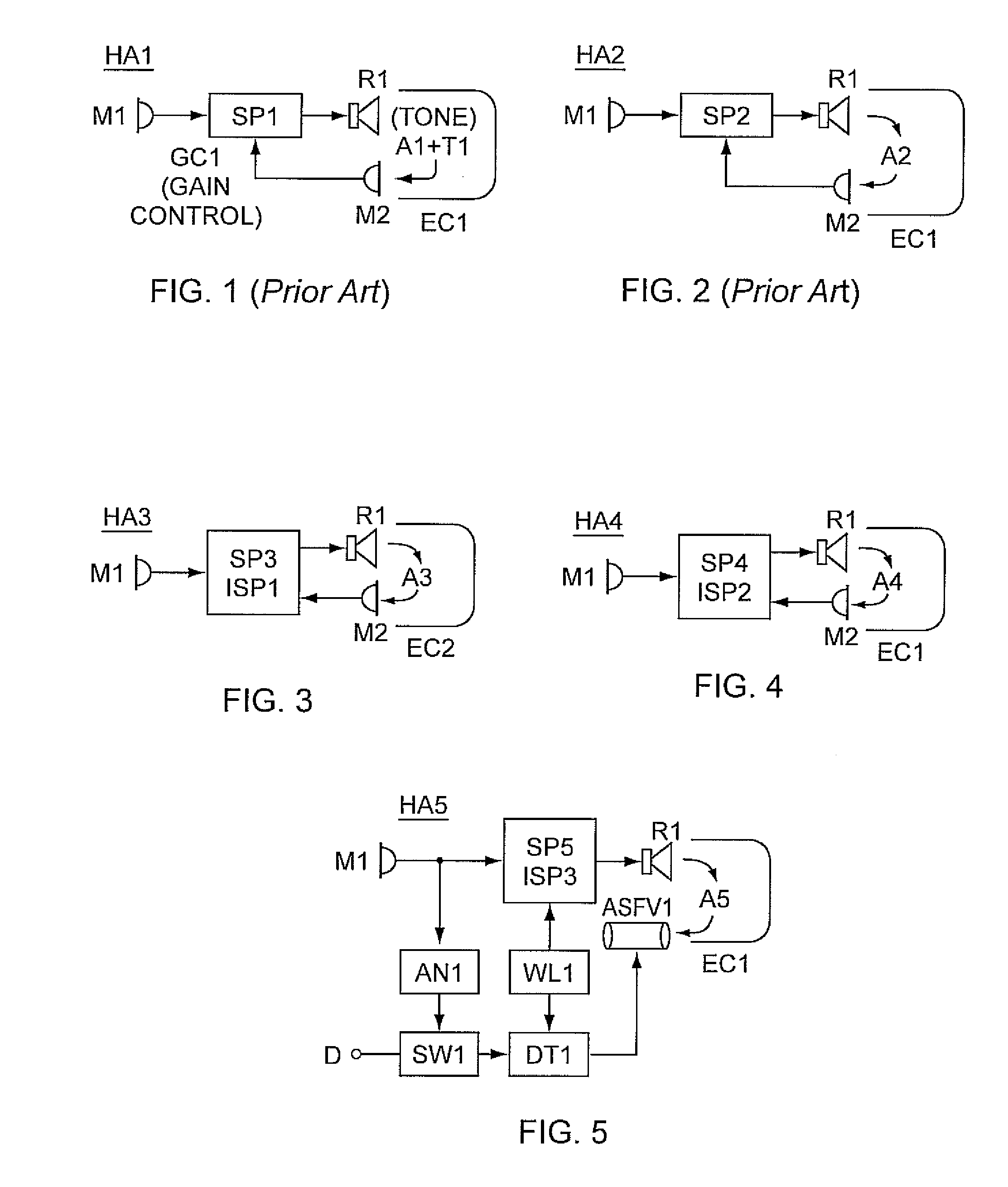
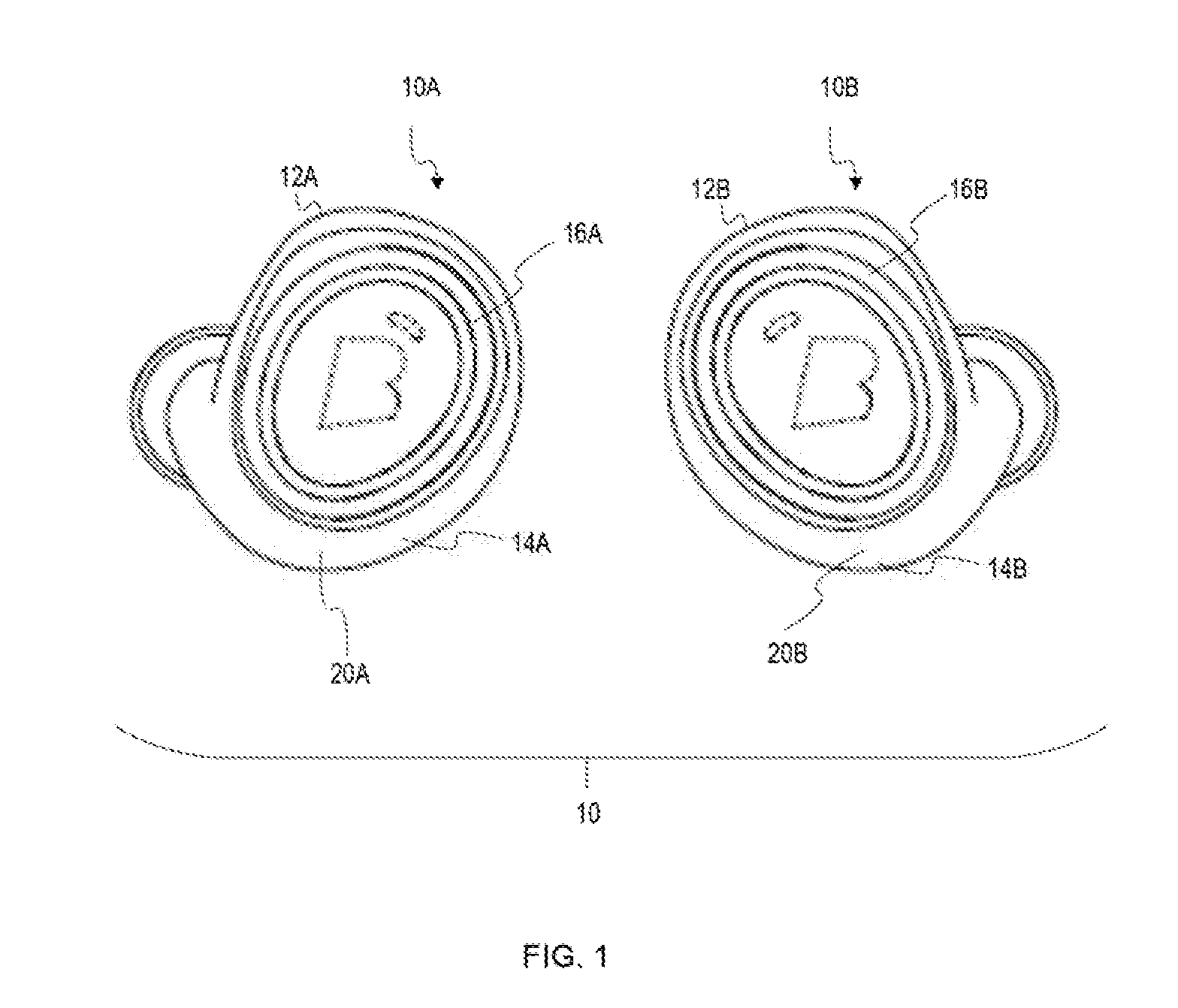
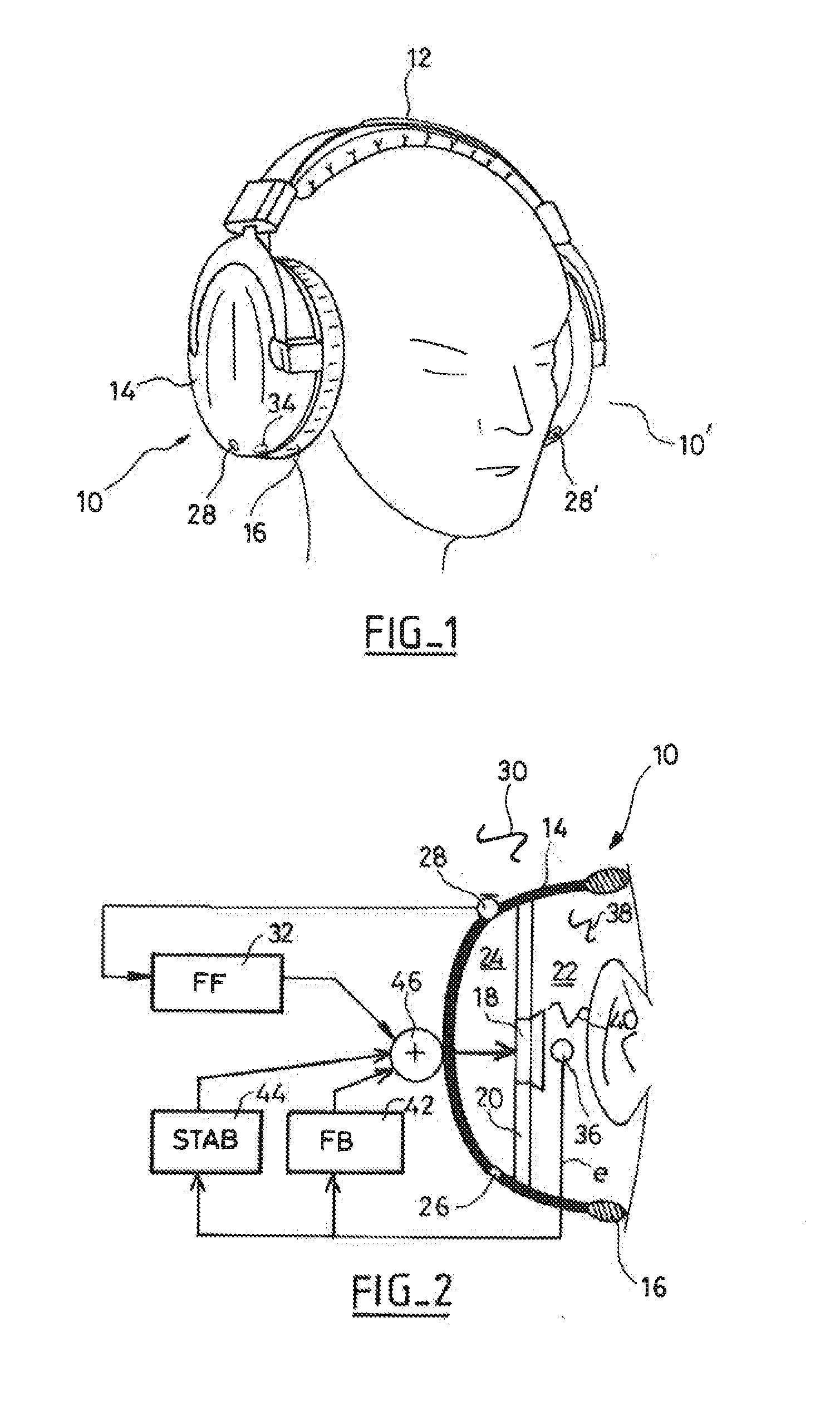
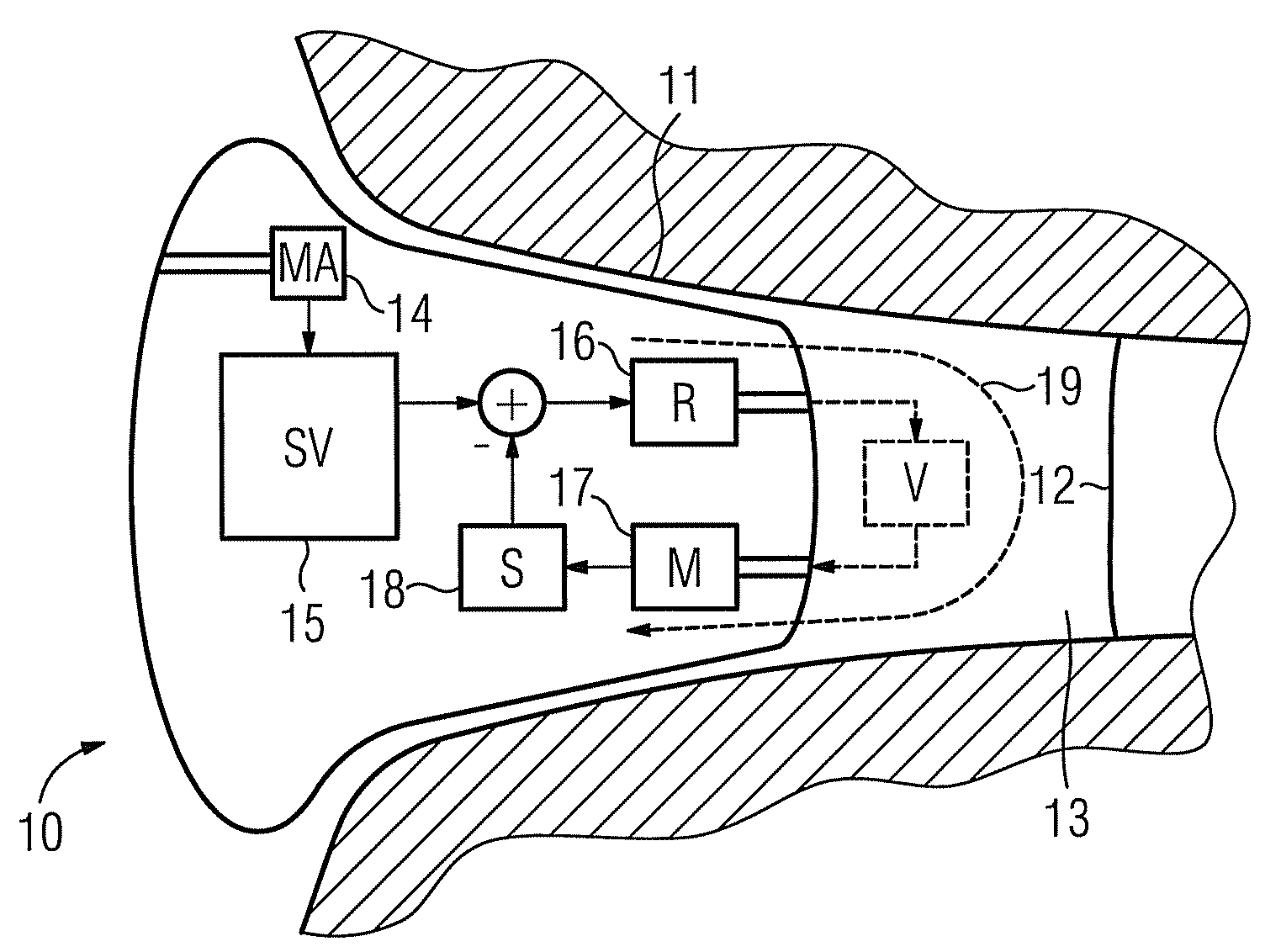
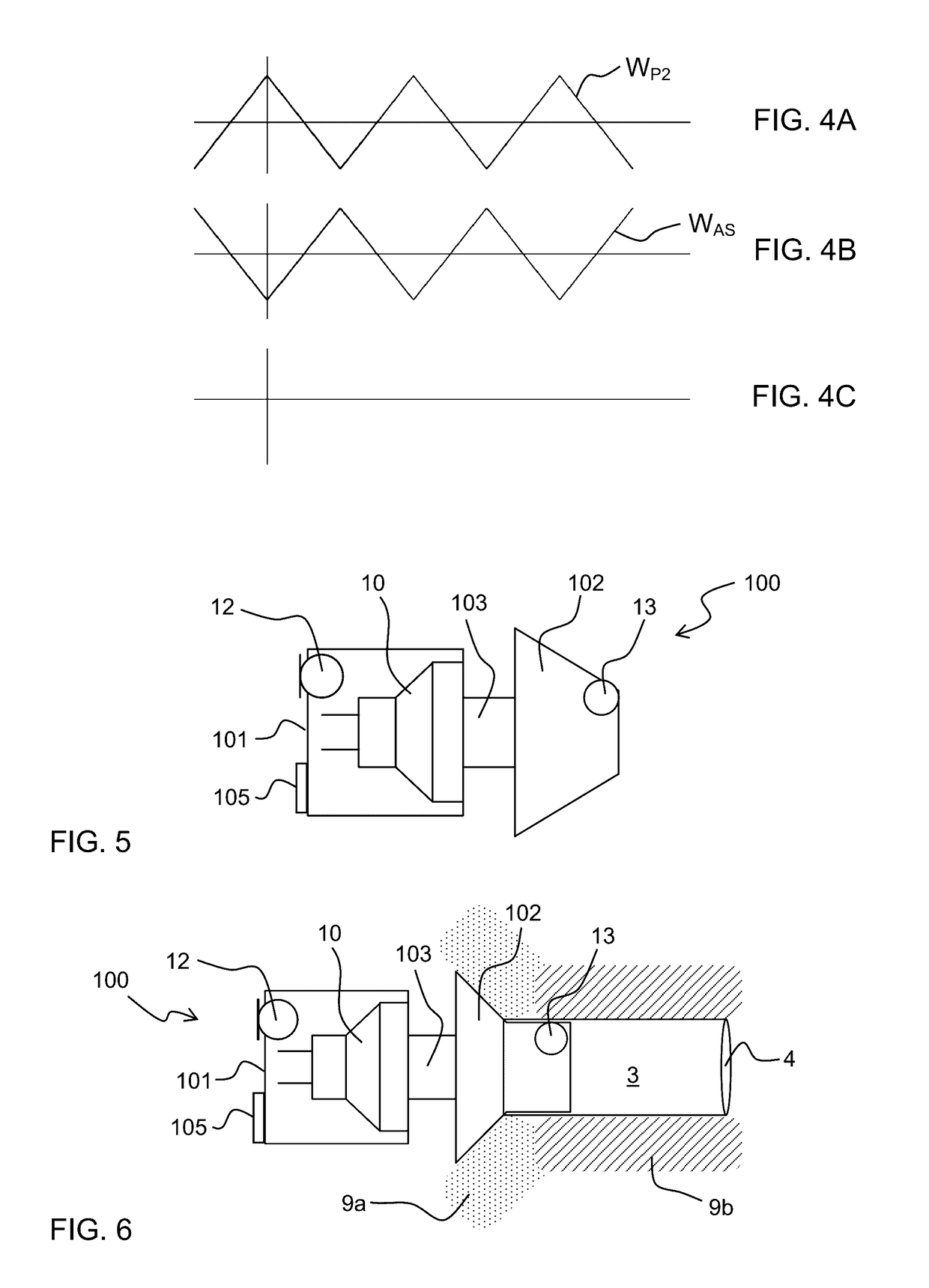
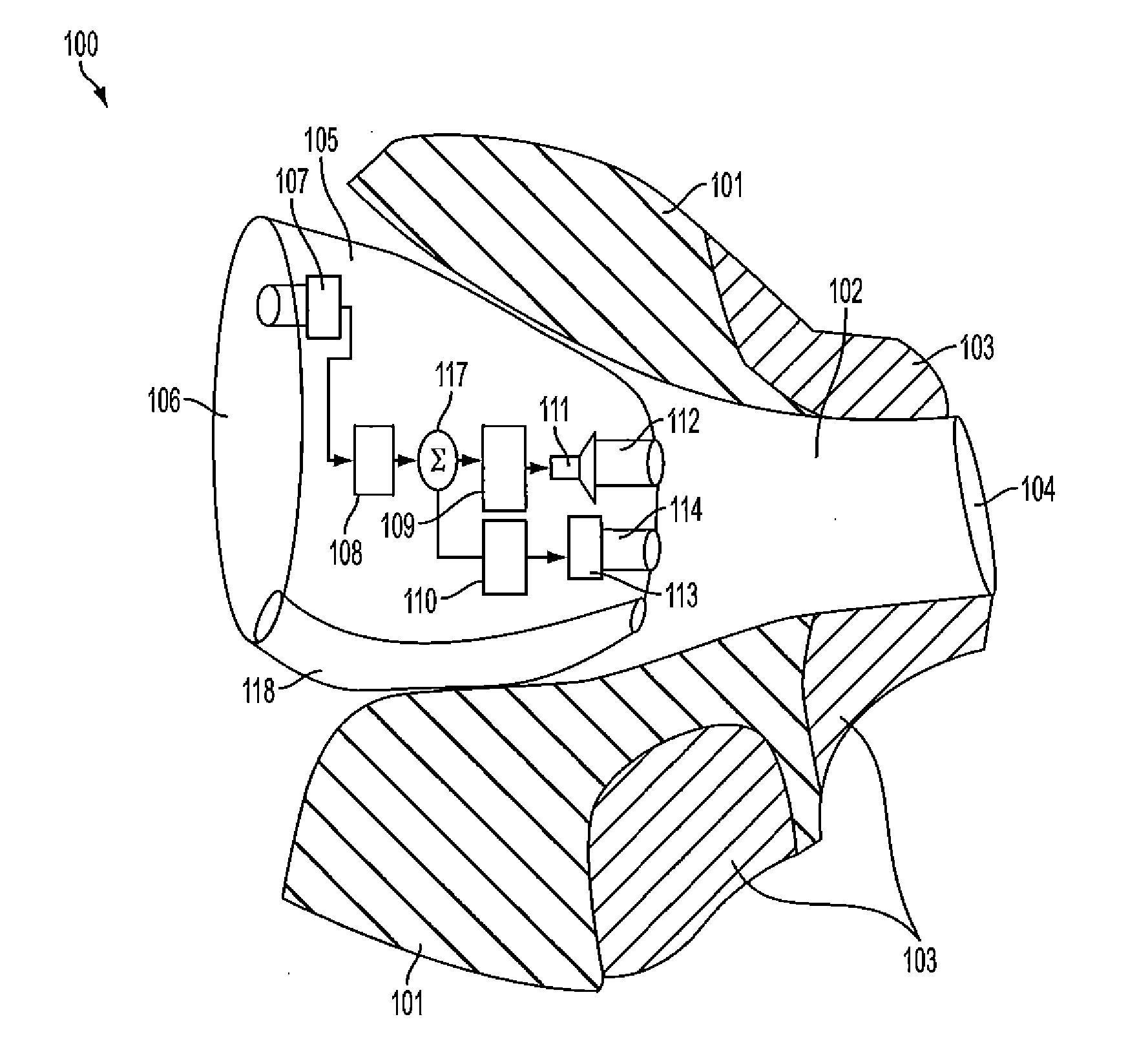
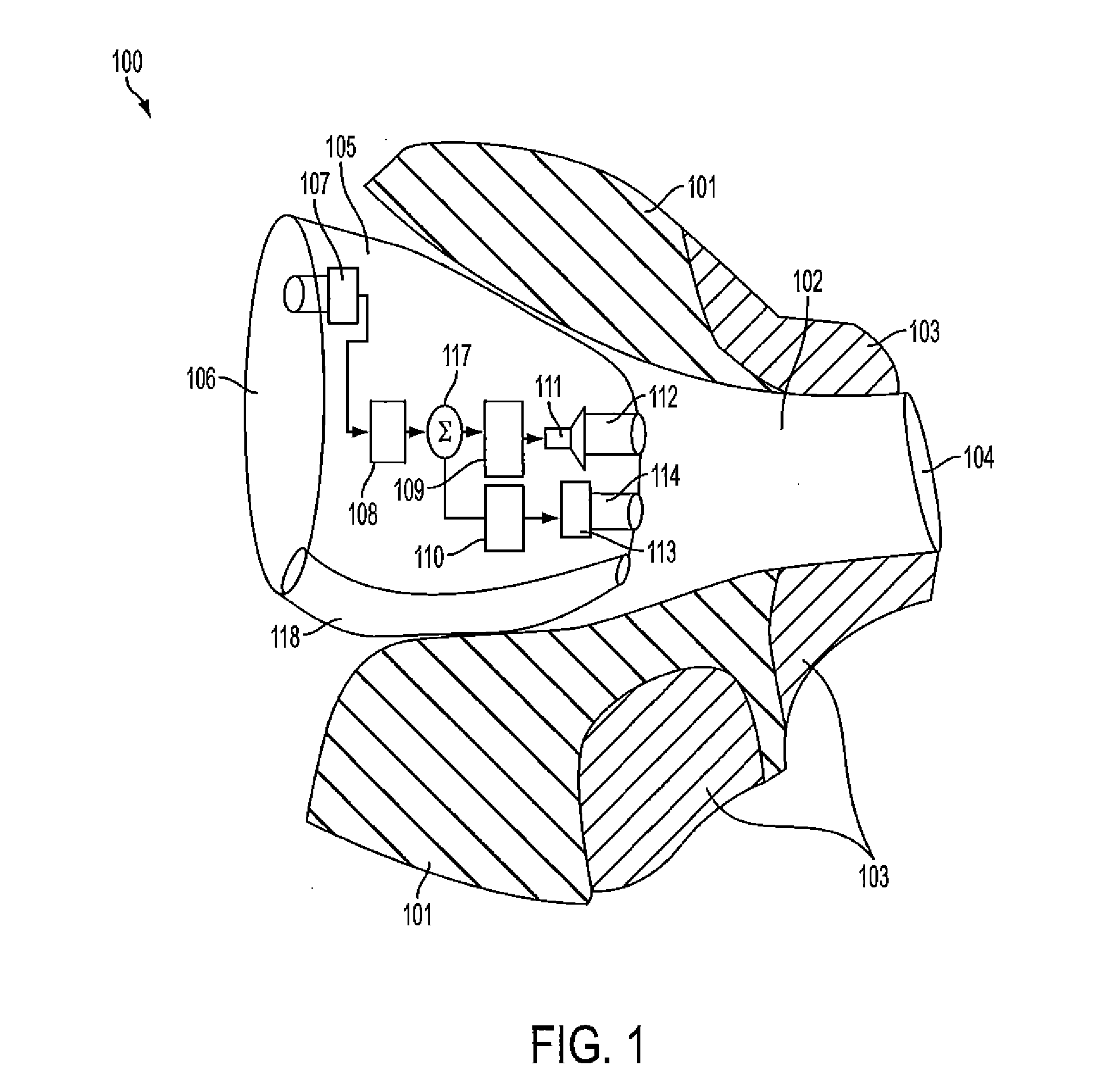
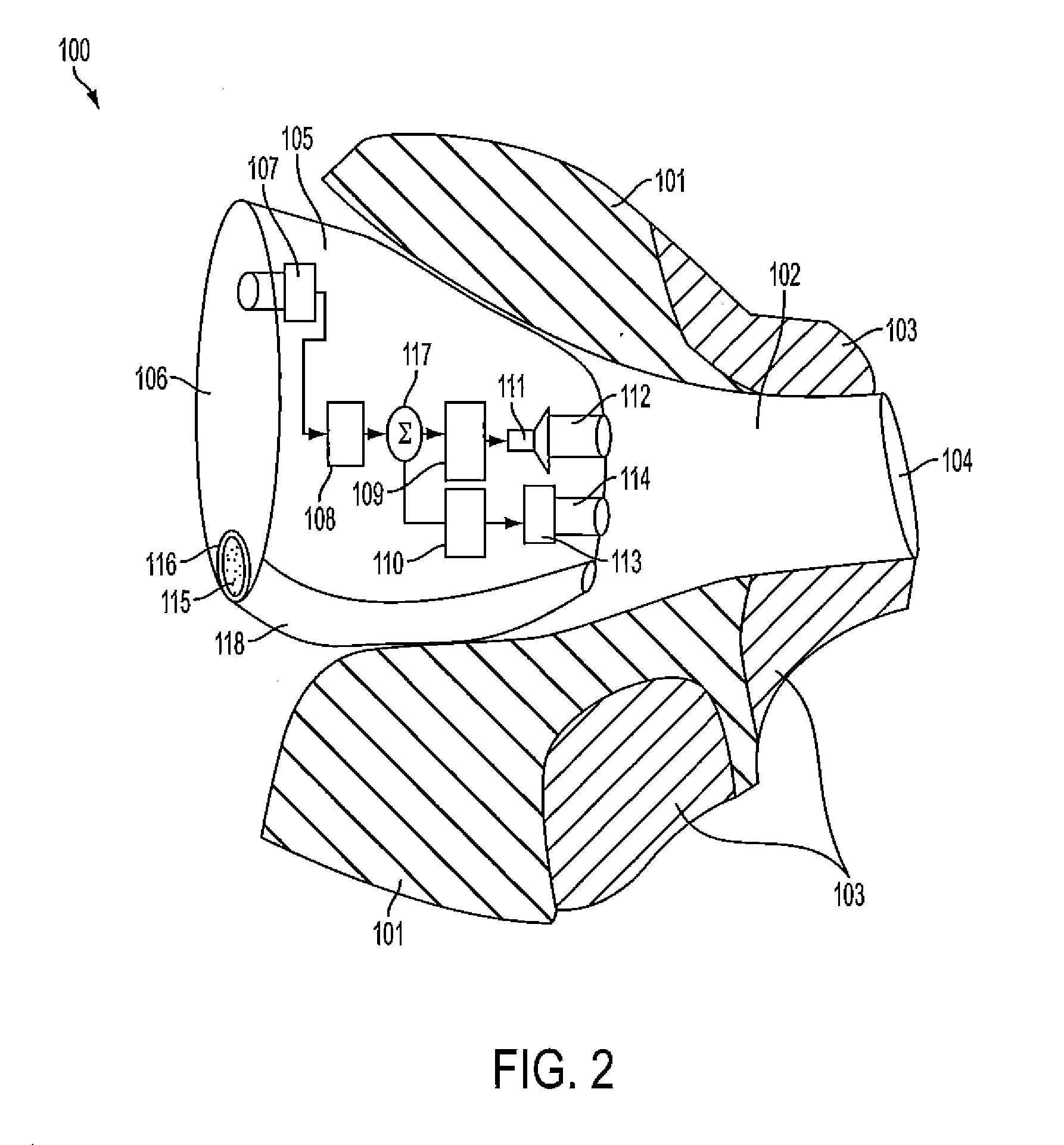
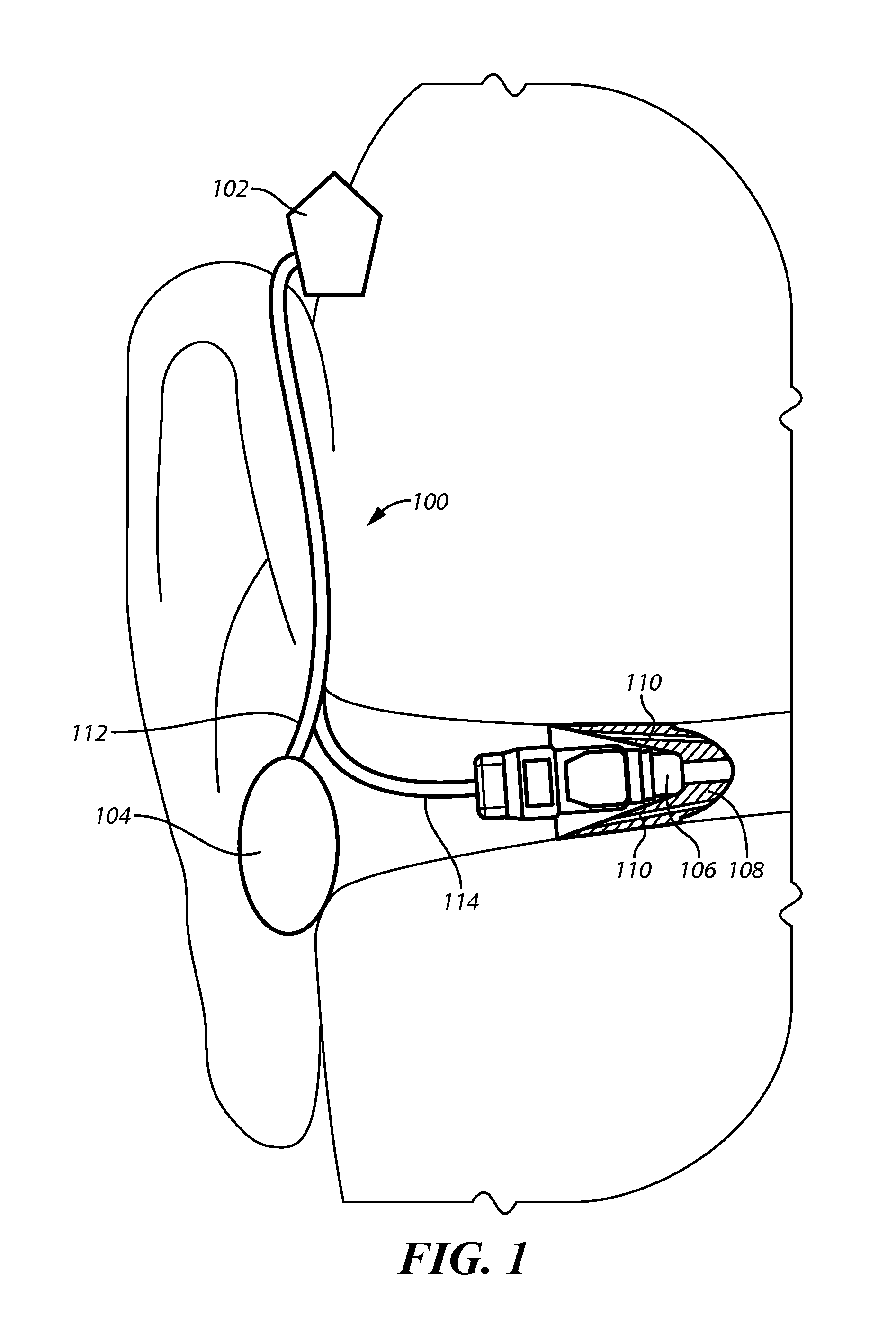
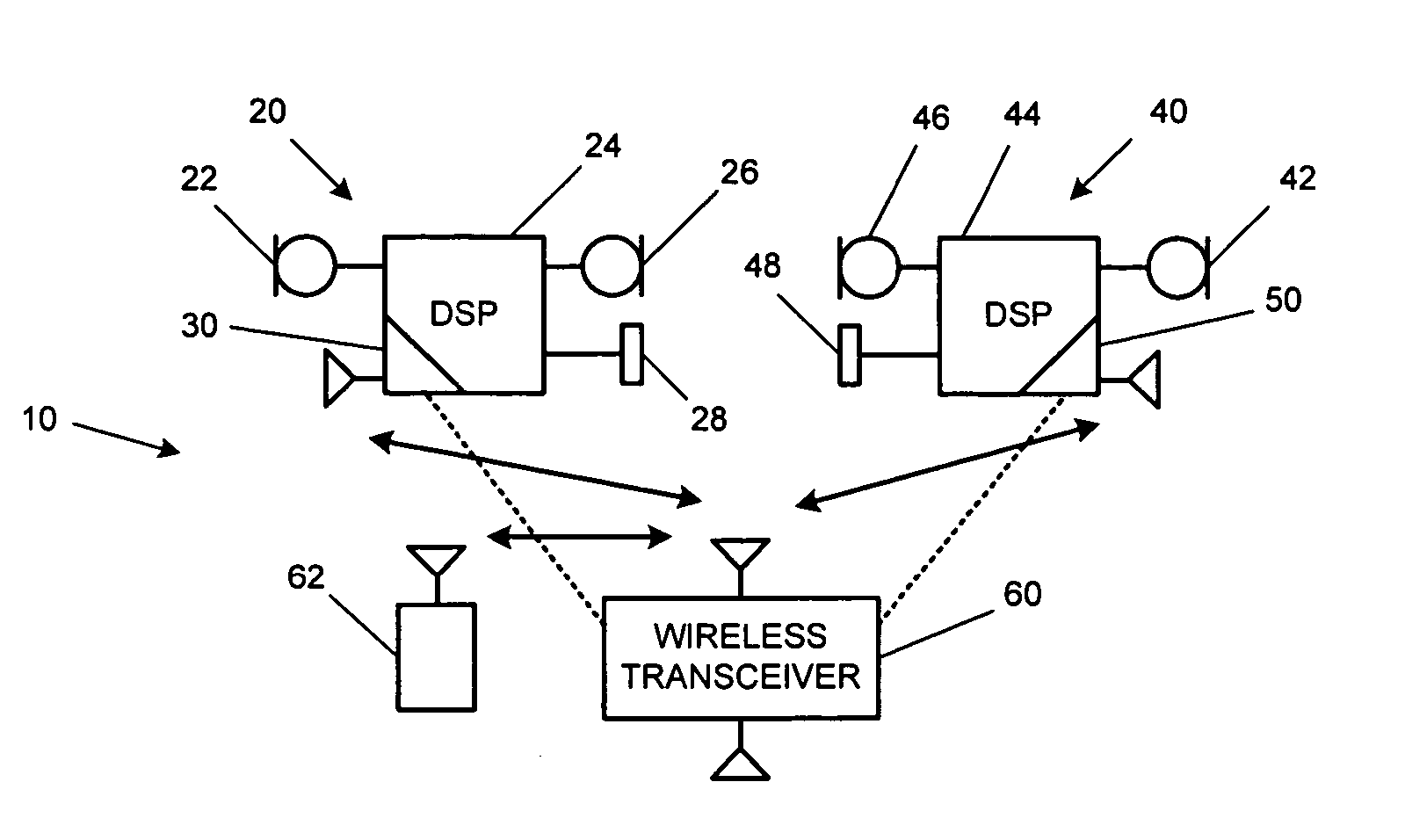
Accoustically Transparent Occlusion Reduction System and Method
ActiveUS20080063228A1Reduce occlusionImprove biteOcclusion effect electronic compensationTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEngineeringHeadphones
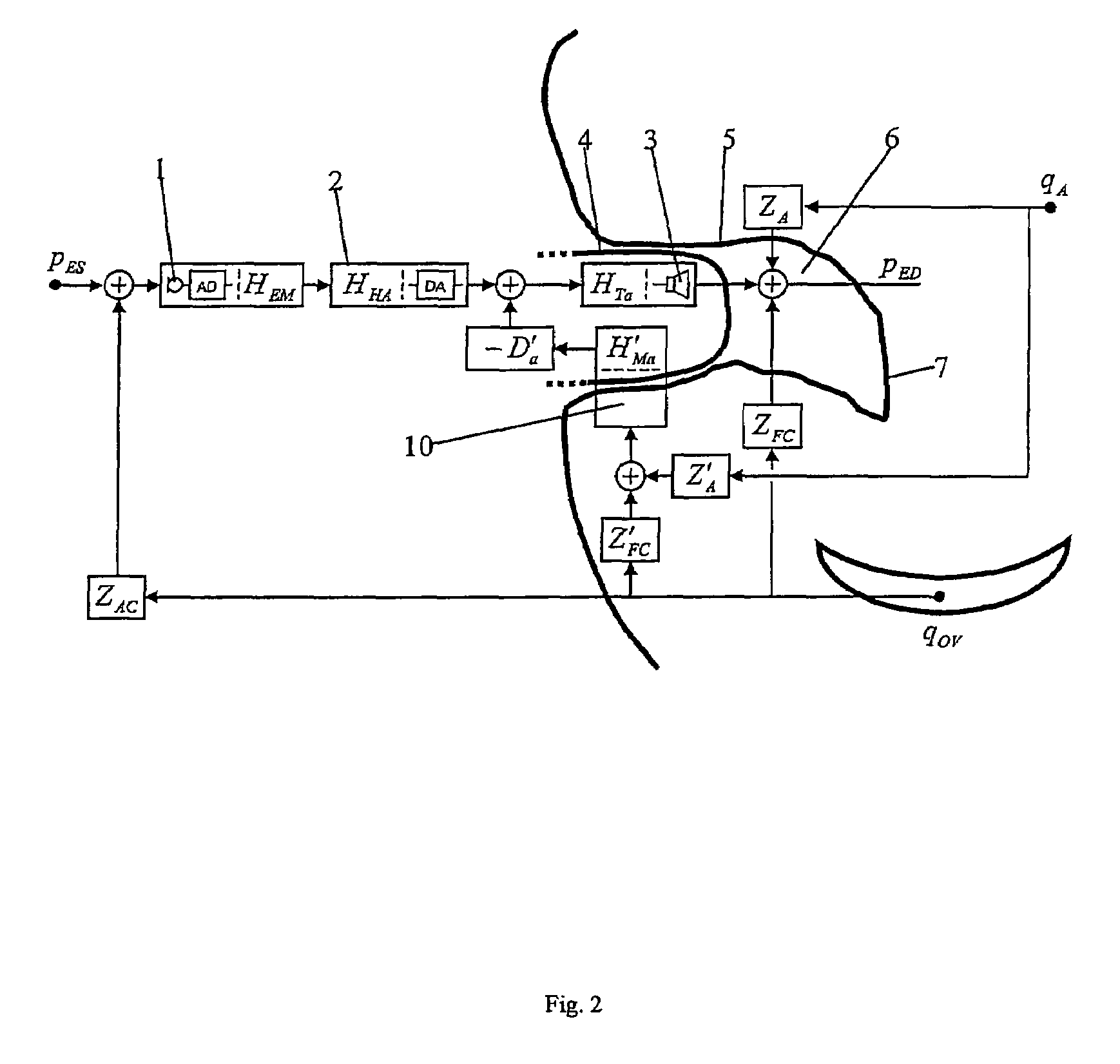
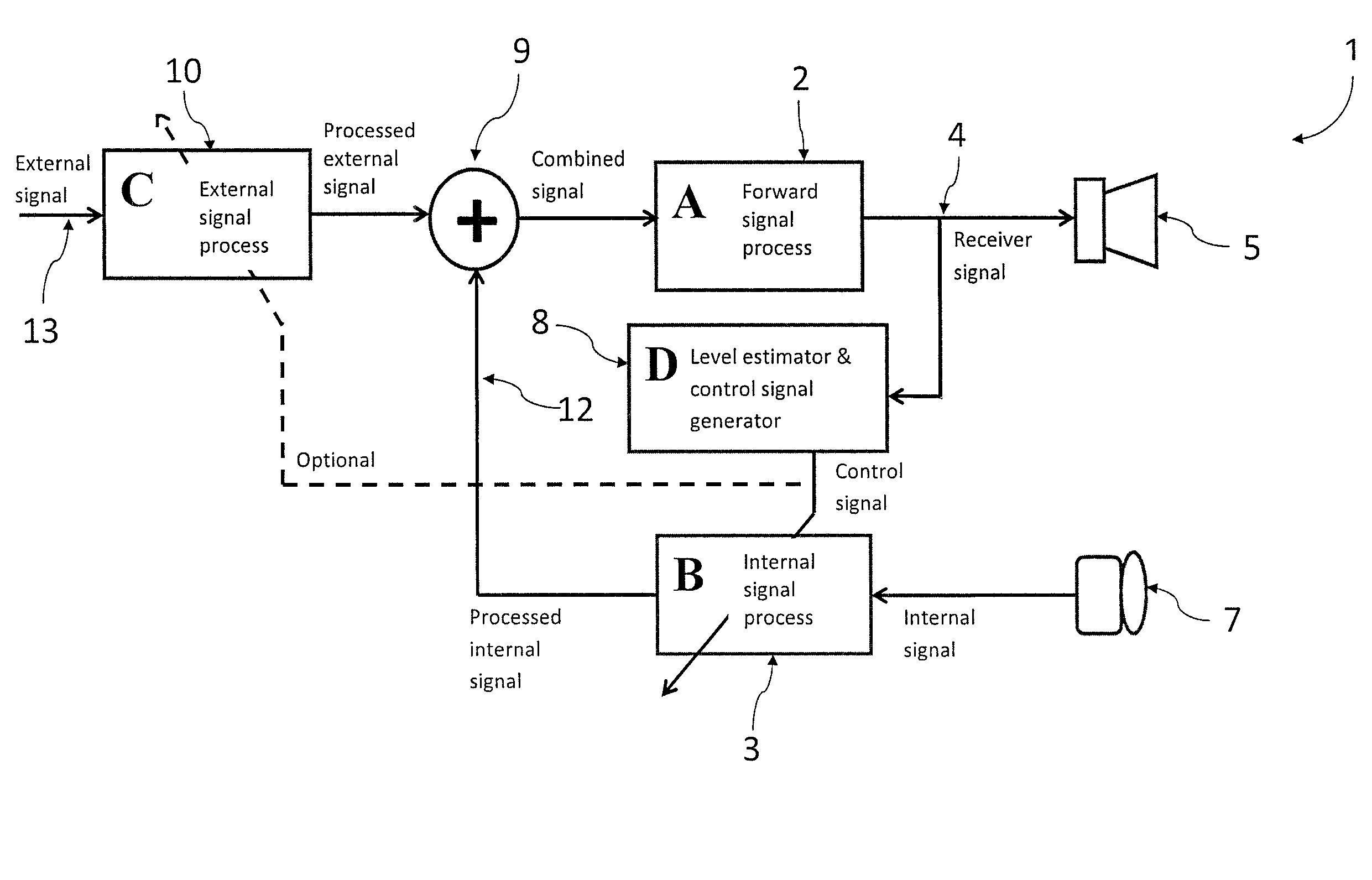
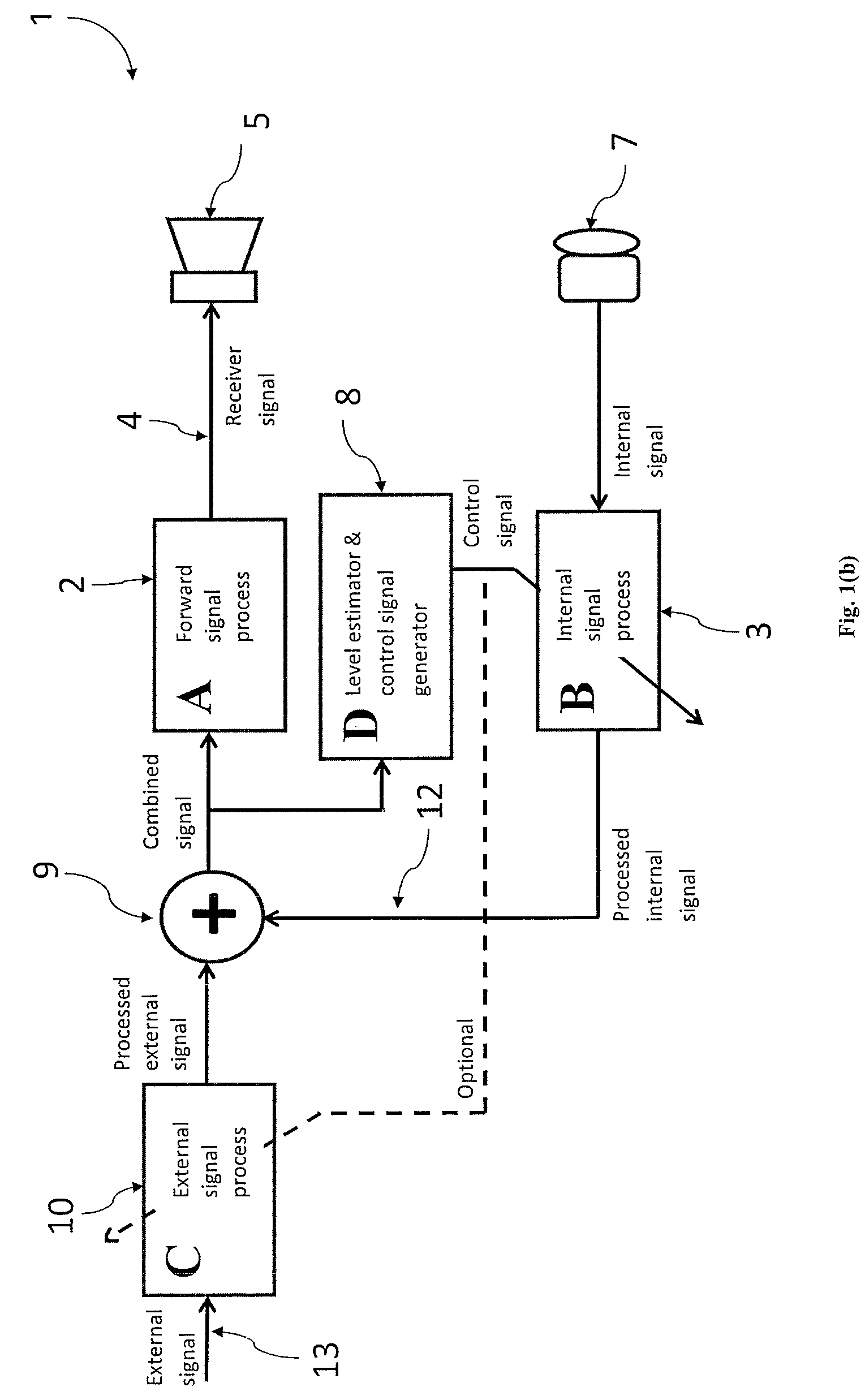
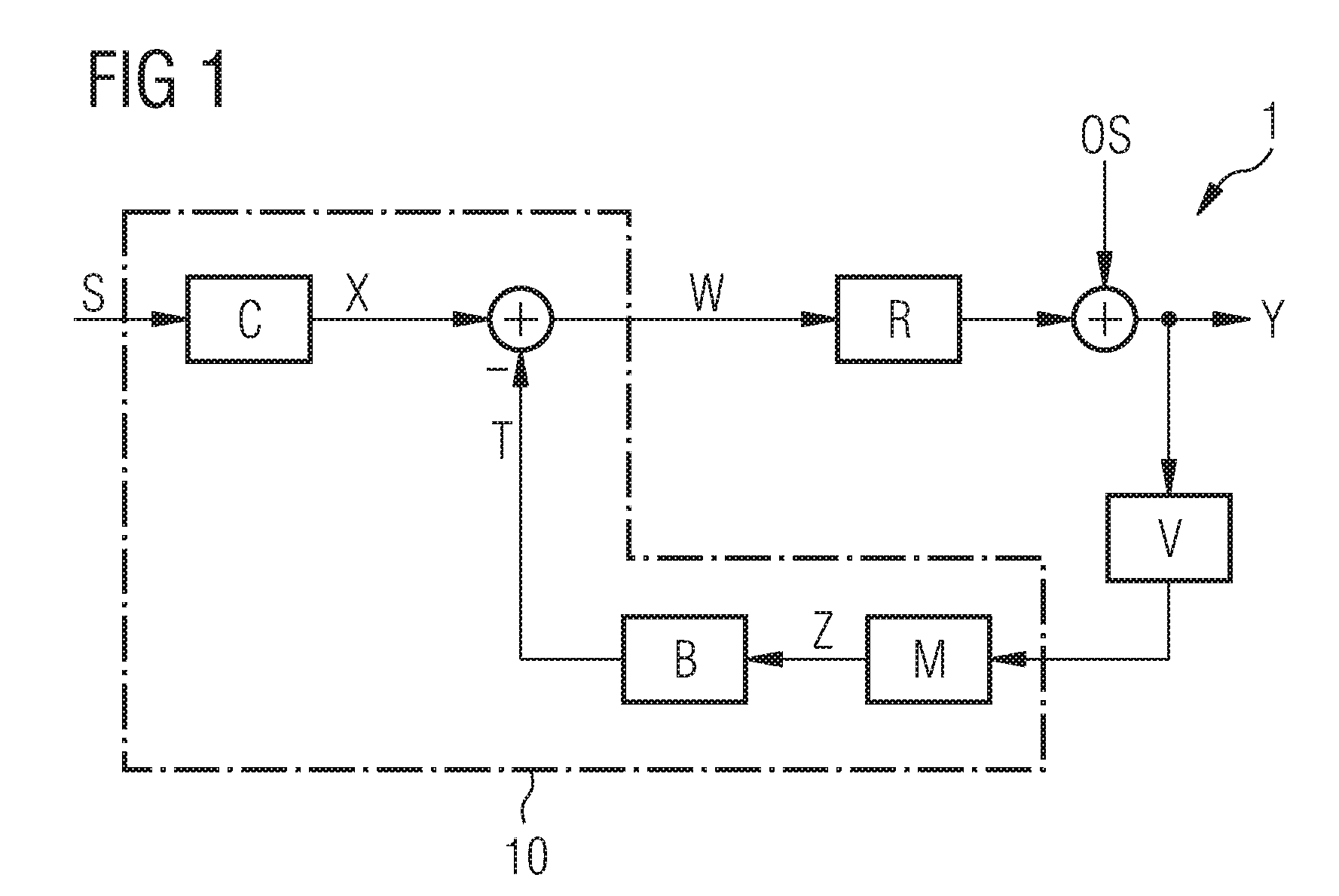
A system and method that reduces the perceptual effect resulting from ear occlusion is disclosed. It comprises of an electro-acoustic feedback network that produces phase cancelling sounds in the ear, where a receiver and a microphone are located. A novel control mechanism is disclosed that controls the response of the feedback network to minimise distortion in the ear while maintaining a desired frequency response for external signals. Devices producing the external signal include hearing aids, personal sound devices, in ear monitors, communications headsets and hearing protectors. The integration of the present invention with these devices improves the user's perception of their own voice.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Personal hearing control system and method
InactiveUS20080107287A1High audio fidelityImprove fidelityOcclusion effect electronic compensationEar moulds/tips acoustic sealsControl systemEngineering
A personal hearing control system includes a microphone located within a user's sealed ear canal, a speaker having a diaphragm which directs sound into the ear canal, and a controller which drives the speaker such that the system emulates the acoustics of the user's open ear canal. Also provided are a microphone located on the outer ear side of the sealed ear canal, which is coupled to a handheld interface unit having multiple inputs and operating modes. A user-selected input is processed by the interface unit, and the processed signal is coupled to the speaker. In one operating mode, the output of the outer ear mic is processed so as to cancel sound that leaks from the outer ear to the inner ear side of the seal.
Owner:BEARD TERRY
Hearing aid with Anti-occlusion effect techniques and ultra-low frequency response
InactiveUS20090310805A1Improve sound outputAvoid performance degradationOcclusion effect electronic compensationBone conduction transducer hearing devicesControl signalEngineering
An occluding hearing aid having anti-occlusion effect techniques combined with at least one improvement which, in the preferred embodiment, includes enhancement of acoustic output in the lower-midrange and bass frequency regions, typically between substantially 40 and 500 Hz, which regions are crucial for natural reproduction of multimedia sound and music but are not optimally processed, and generally not provided at all, in prior art hearing aids in order to avoid exacerbation of the occlusion effect. In specific embodiments, the hearing aid of the present invention includes primary or first microphone exposed to external sound plus a secondary or second microphone exposed to sound within an ear canal, in which a signal produced by the secondary microphone is applied as negative feedback to an input of a non-gain controlling signal process and amplifier driving a hearing aid receiver (transducer), whereby, it has been determined by the present inventor, the occlusion effect may be substantially canceled. The hearing aid further comprises at least one of ten combinational improvements each providing substantial performance benefits over known techniques and devices.
Owner:PETROFF MICHAEL
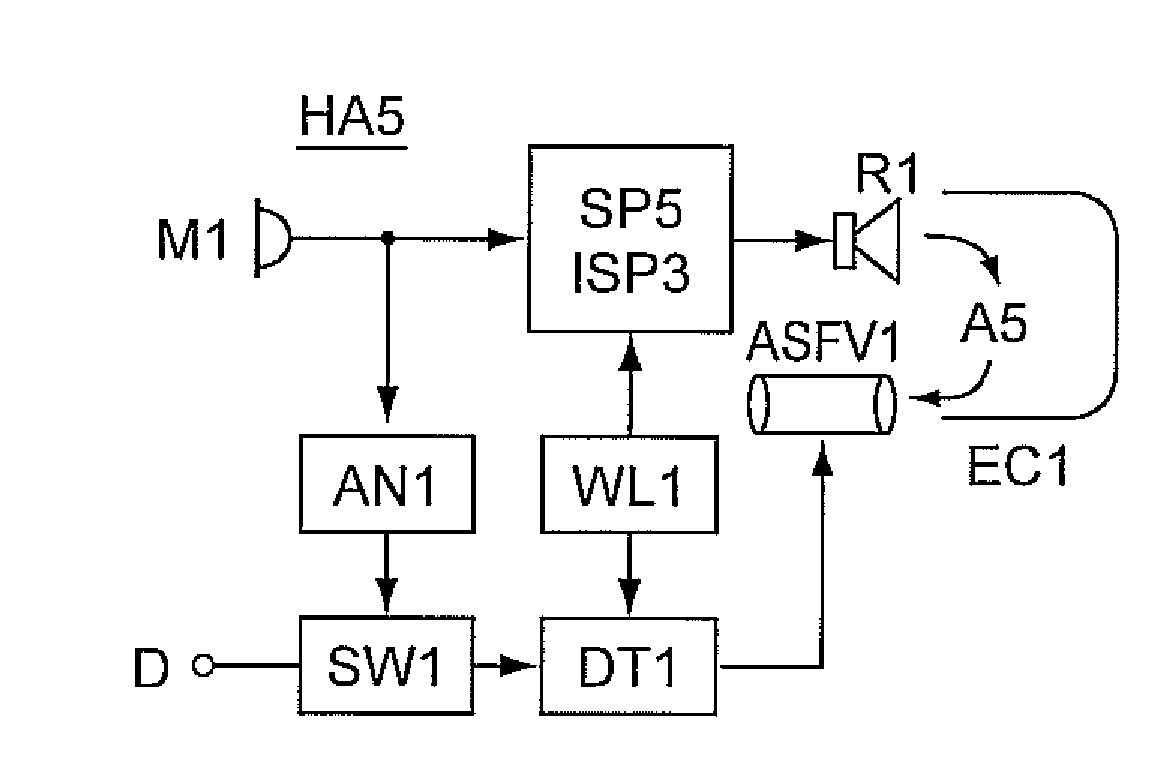
Reproduction of Ambient Environmental Sound for Acoustic Transparency of Ear Canal Device System and Method
ActiveUS20170064426A1Avoid the needOcclusion effect electronic compensationIntra aural earpiecesEnvironmental soundsExternal Acoustic Meatus
An ear piece for use by an individual having an external auditory canal includes an earpiece housing configured for placement within the external auditory canal of the individual, a processor disposed within the ear piece housing, at least one microphone disposed within the earpiece housing wherein the at least one earpiece is positioned to detect ambient environmental sound, and at least one speaker disposed within the earpiece housing. The ear piece is configured to detect ambient environmental sound proximate the external auditory canal of the individual using the at least one microphone and reproduce the ambient environmental sound at the at least one speaker within the earpiece housing. The processor is further configured to modify the ambient environmental sound based on shape of the external auditory canal such that audio perception of the ambient environmental sound is as if the ear piece was not present.
Owner:BRAGI
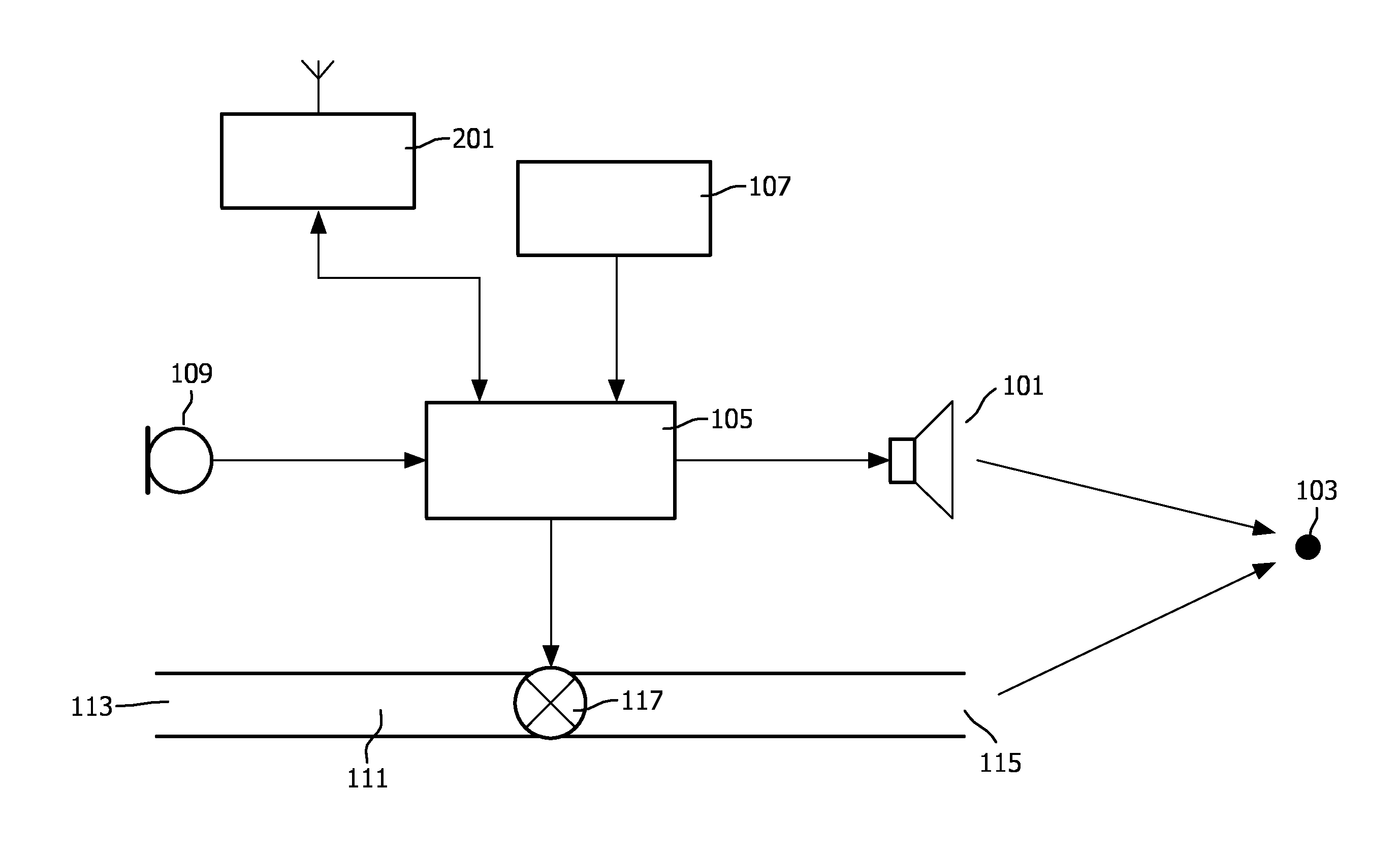
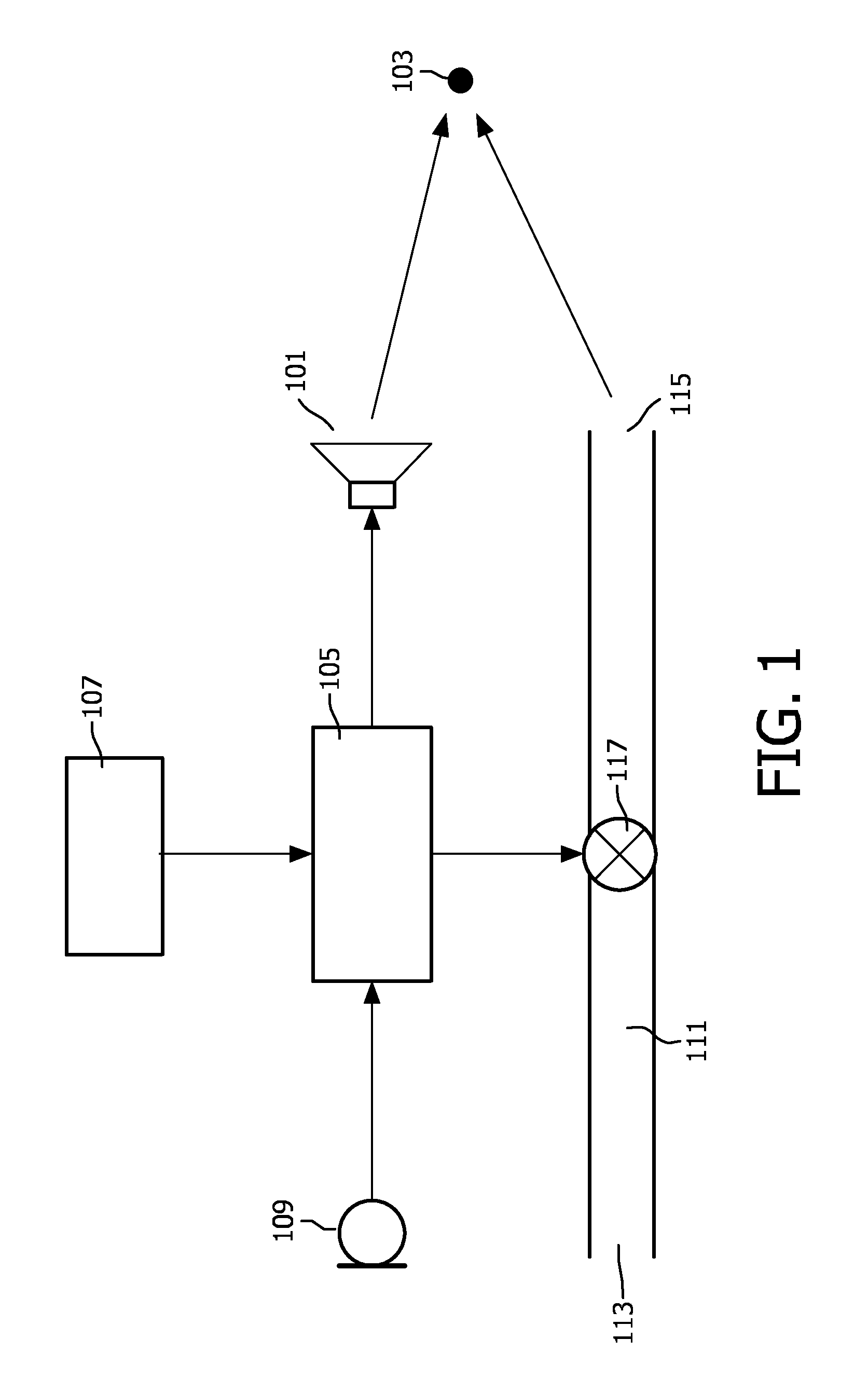
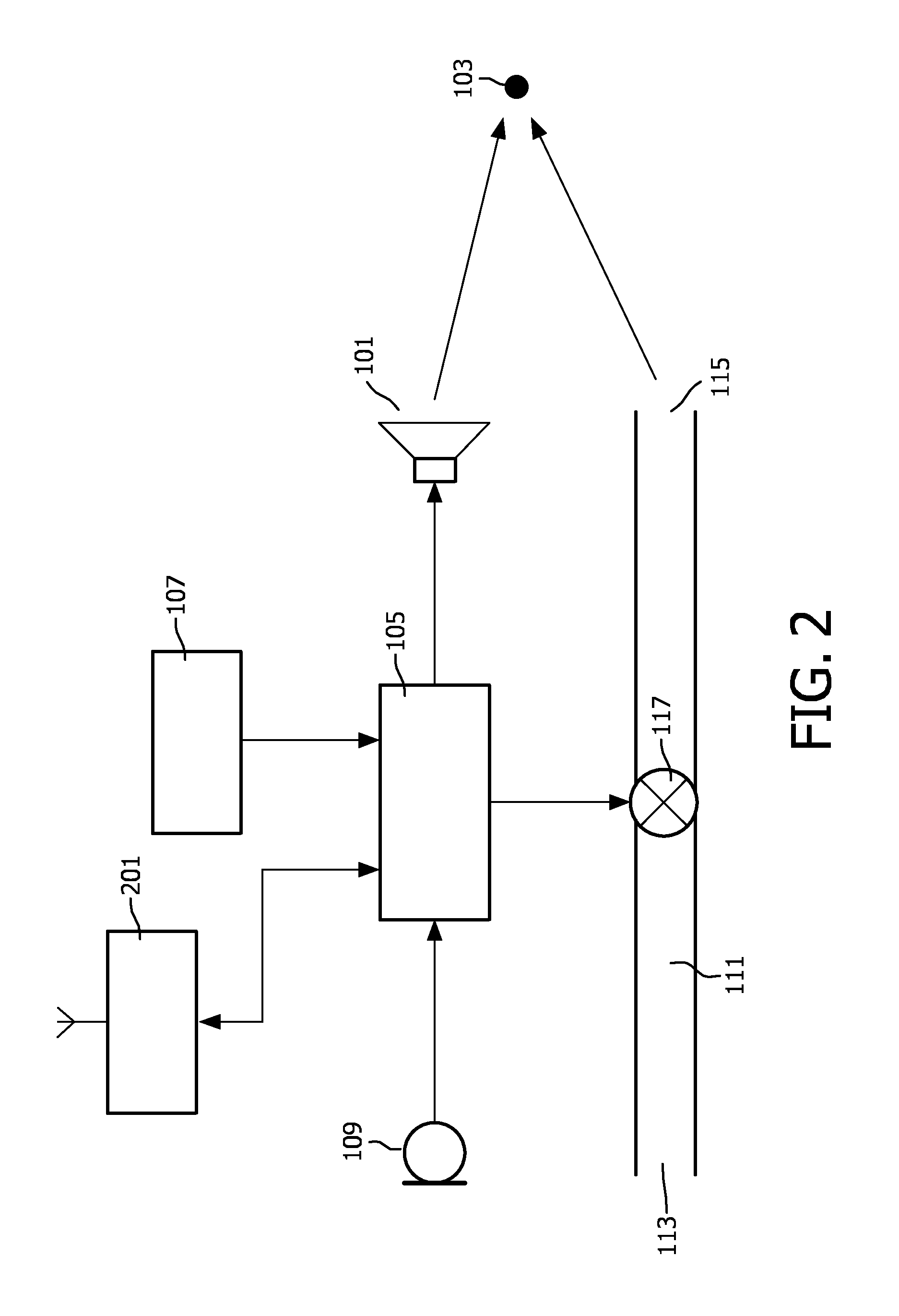
Earphone arrangement and method of operation therefor
InactiveUS20120082335A1Improve performanceConvenient ArrangementOcclusion effect electronic compensationHearing device active noise cancellationControl signalEngineering
An earphone arrangement comprises a microphone (109) which generates a microphone signal and a sound transducer (101) which radiates a first sound component to a user's ear (103) in response to a drive signal. An acoustic channel (111) is further provided for channeling external sound so as to provide a second sound component to the user's ear (103). An acoustic valve (117) allows the attenuation of the acoustic channel (111) to be controlled in response to a valve control signal. A control circuit (105) generates the valve control signal in response to the microphone signal to provide a variable attenuation resulting in a mixed sound of the first sound component and the second sound component reaching the user's ear (103). The combined use of acoustic and e.g. electric signal paths allows improved performance and in particular allows a dynamic trade-off between open and closed earphone design characteristics with respect to external sounds.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
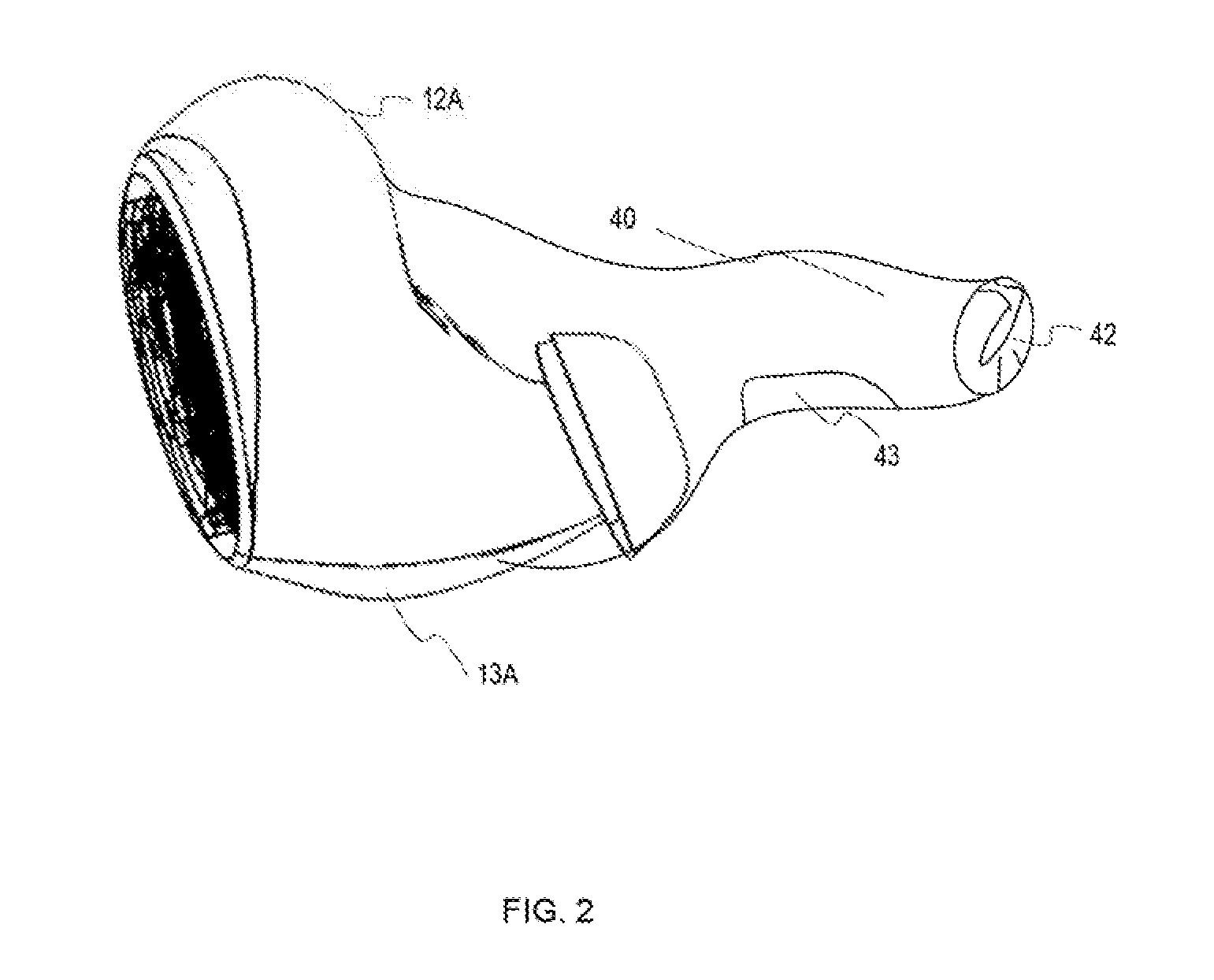
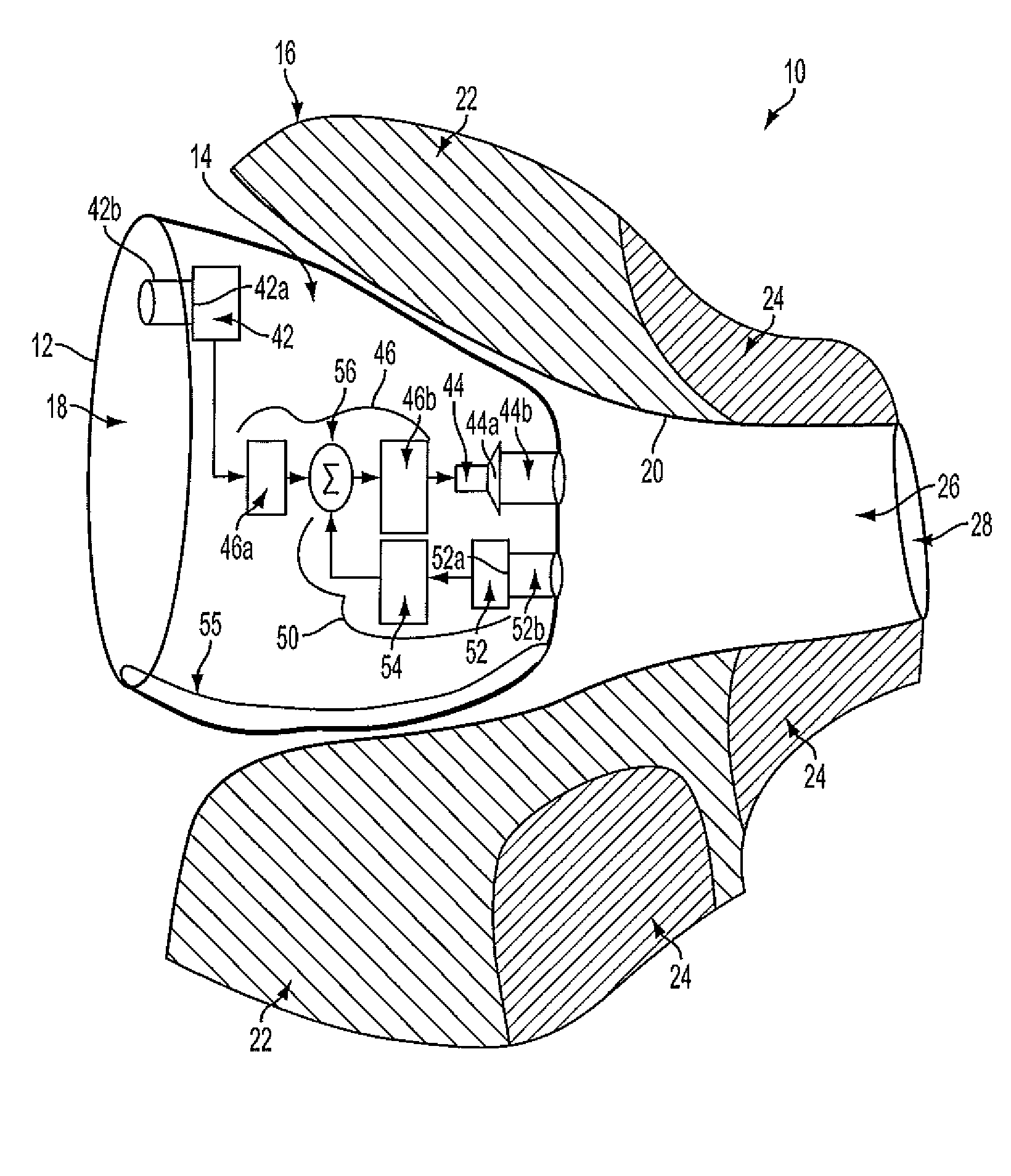
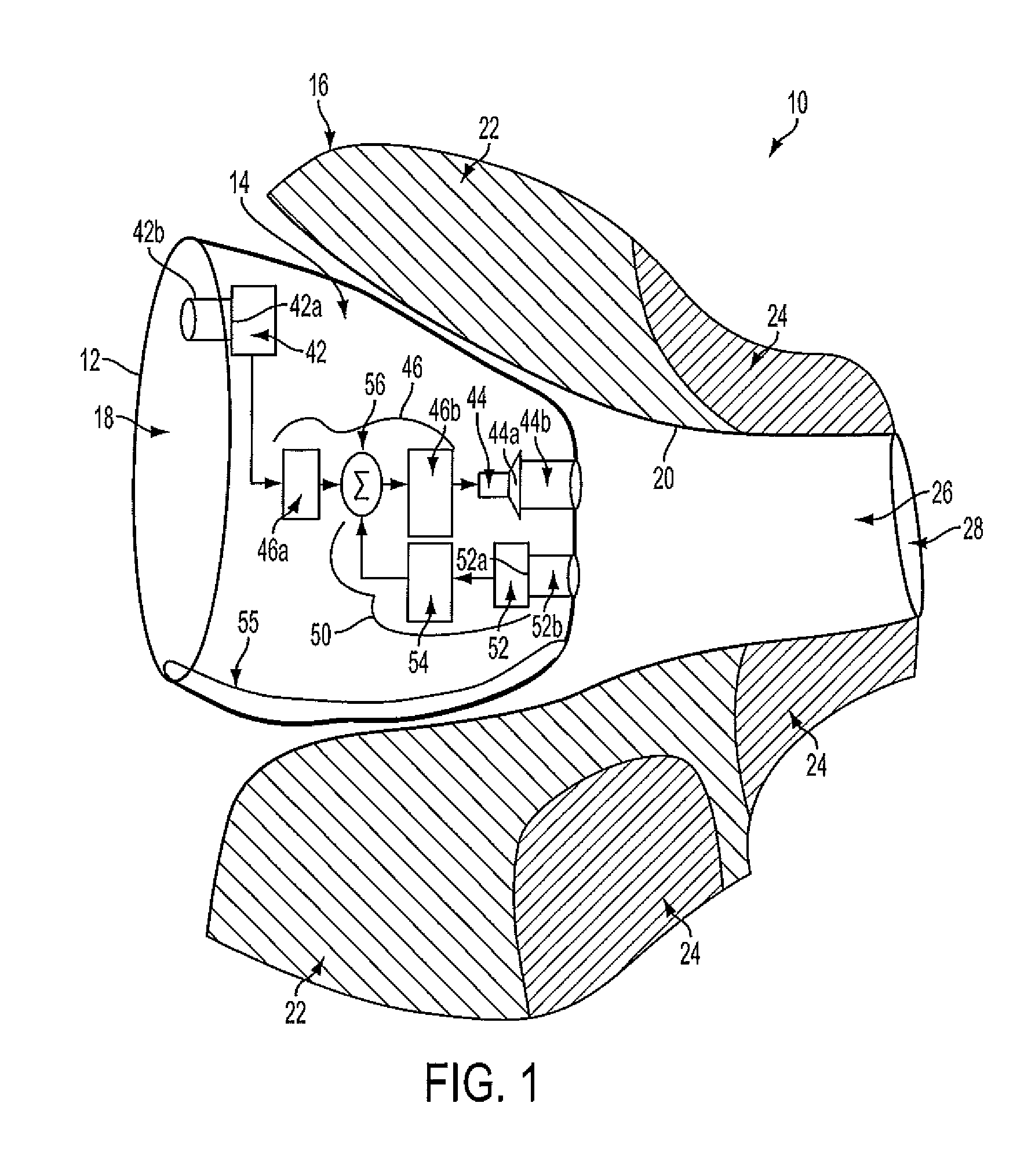
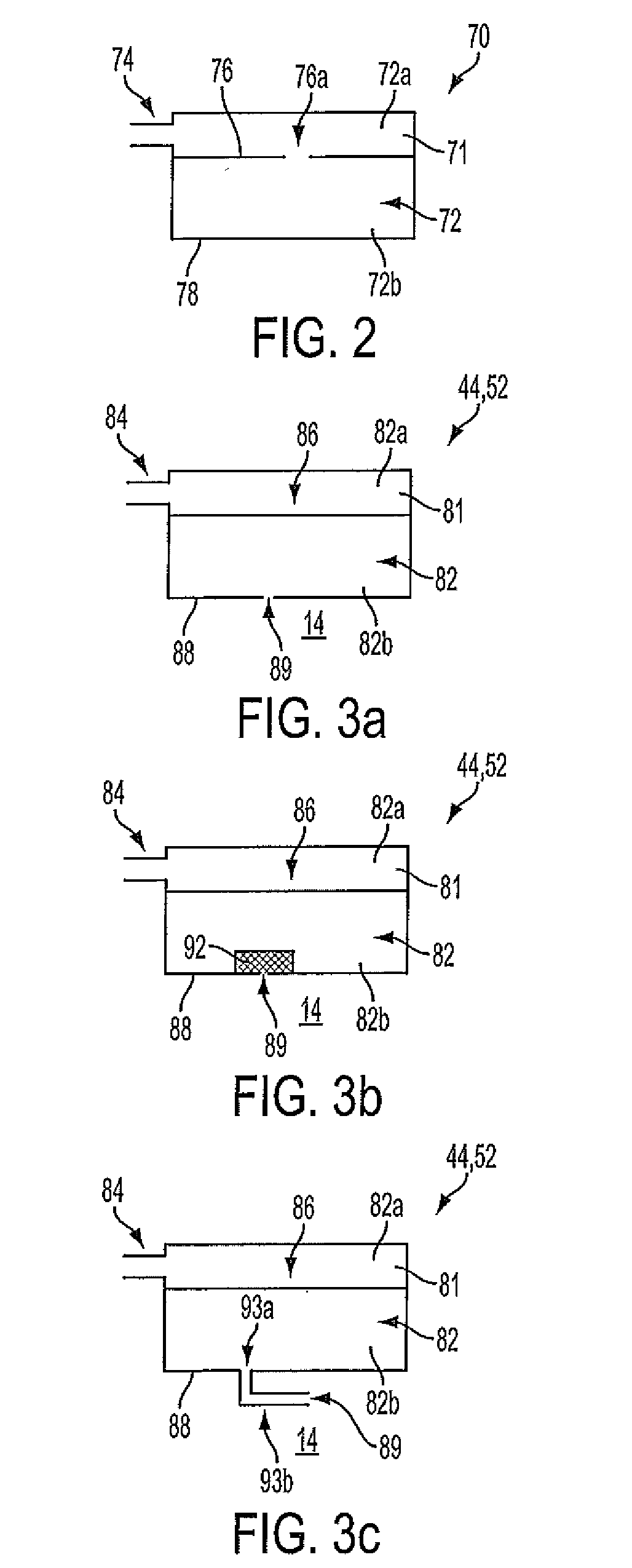
Hearing Aid
InactiveUS20110069852A1Wide rangeReduce decreaseOcclusion effect electronic compensationEar supported setsTransducerHeadphones
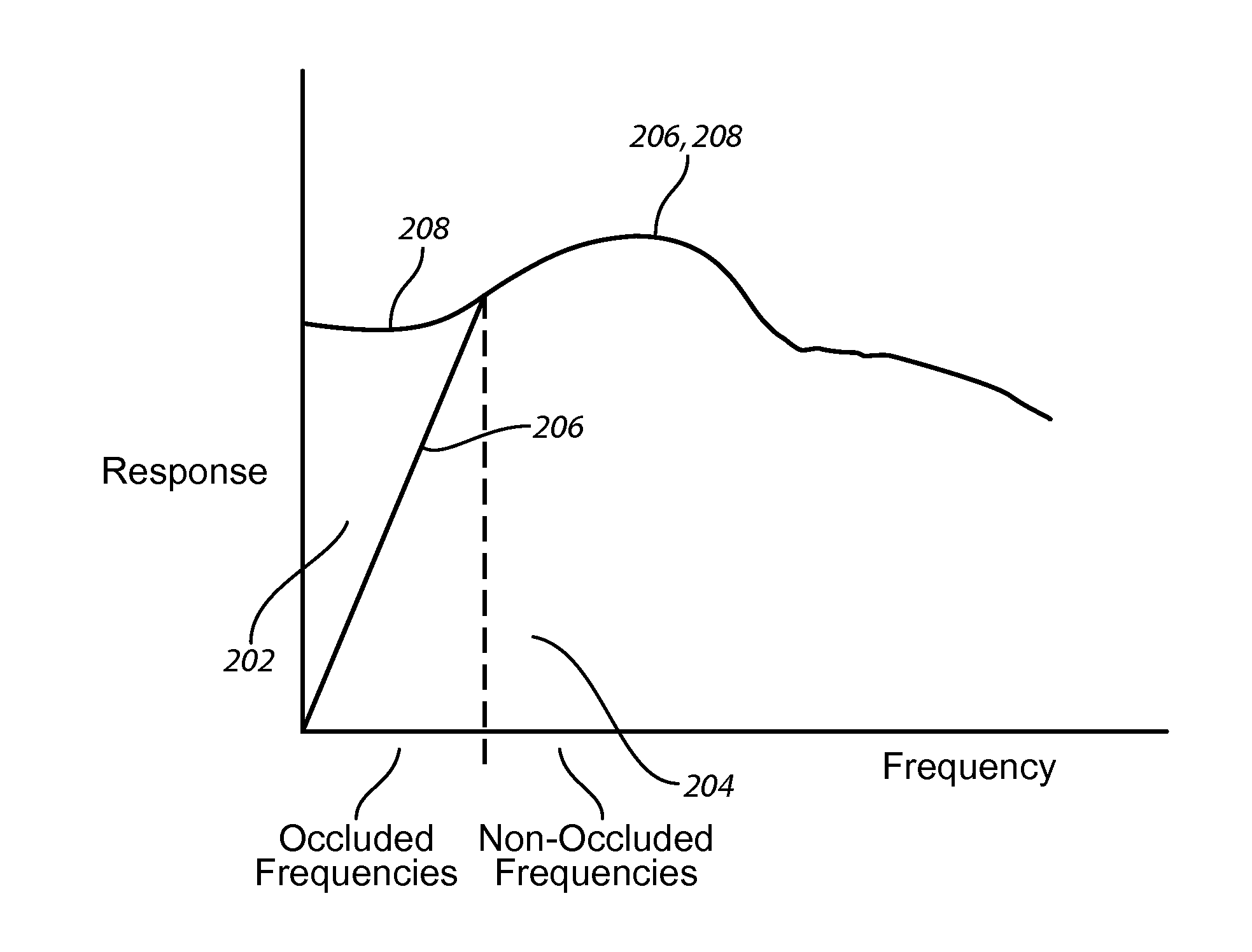
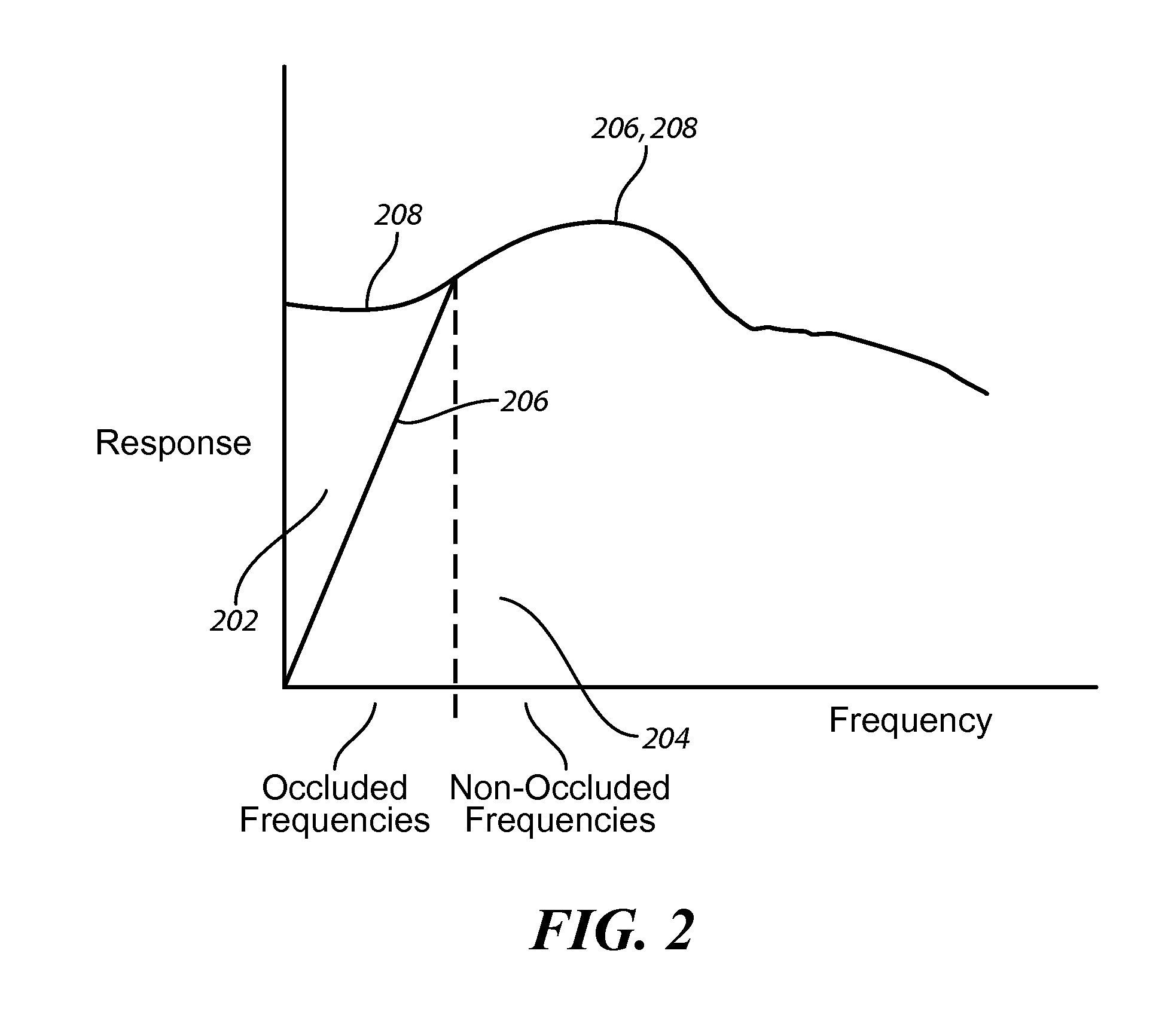
A hearing aid (10) having an active occlusion reduction system (50) that counteracts occluded sounds generated within the volume (24) of the ear canal (20) that is not blocked when the hearing aid (10), or an ear piece thereof, is inserted into the ear canal (20) and an AOR transducer (44, 52) that has a flattened frequency response for low frequency portions of the occlusion sounds to enable a wide range of frequency response by the active occlusion reduction system (50). The low frequency portions of the occlusion sounds may be in the range of 10-100 Hz.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
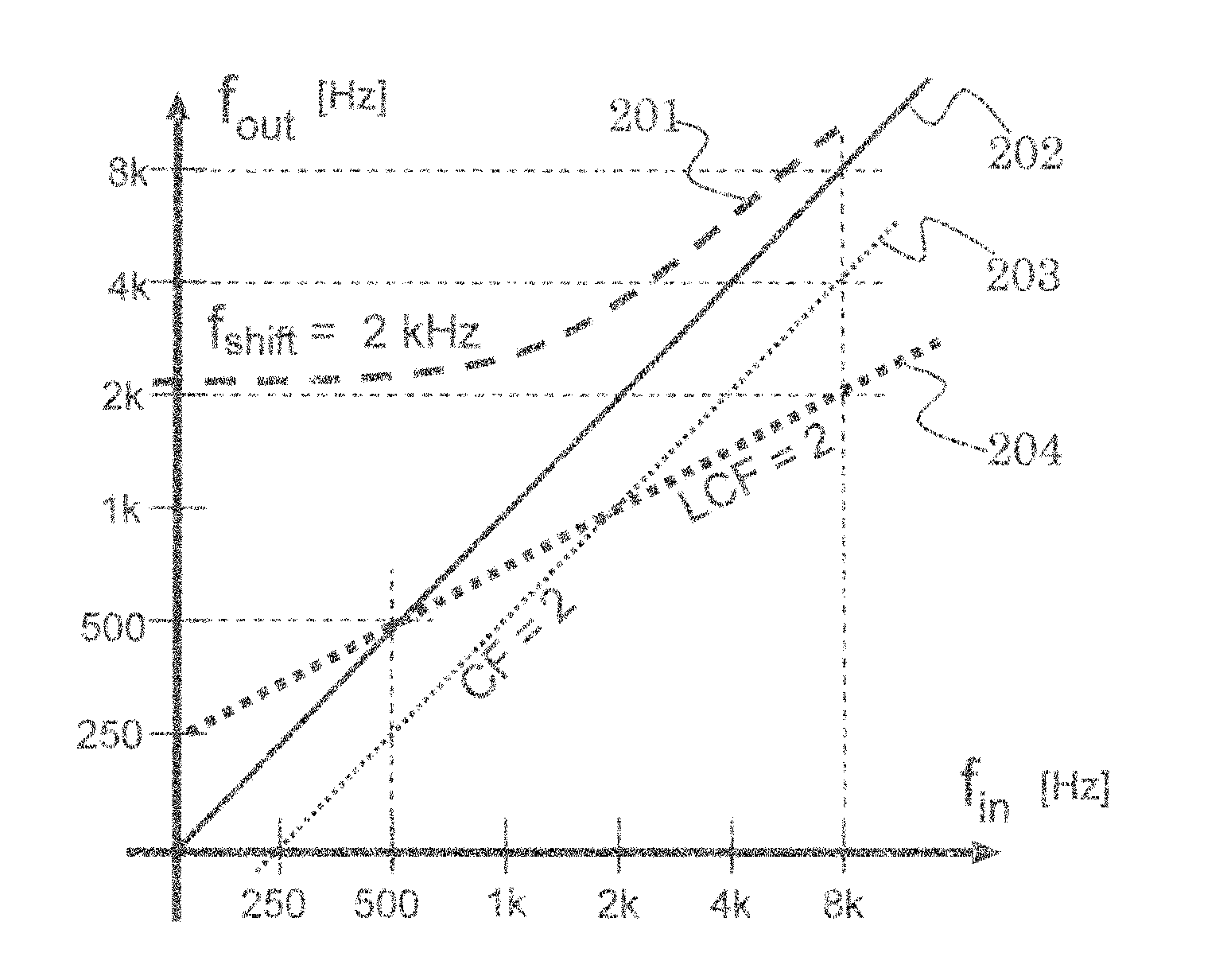
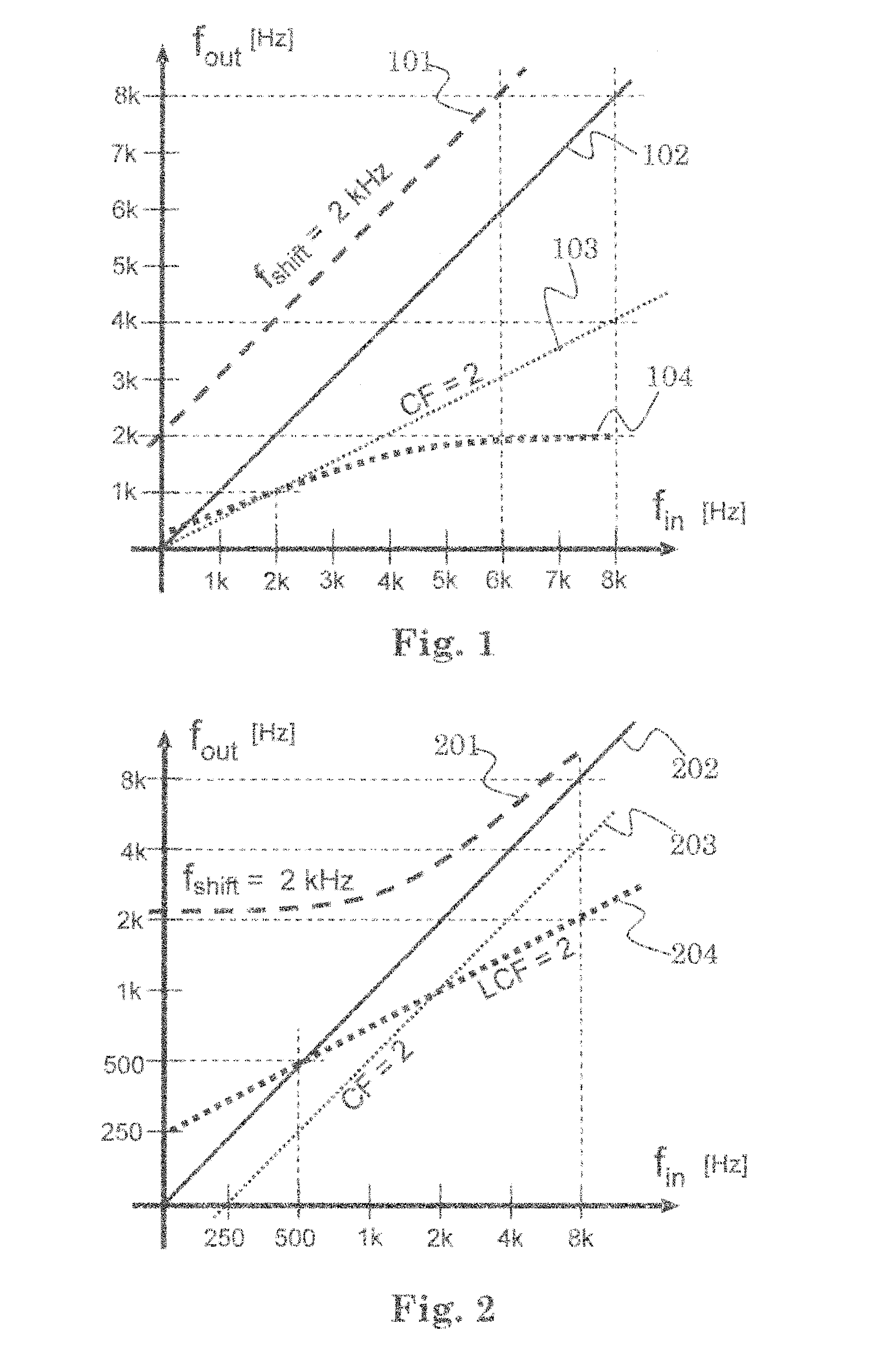
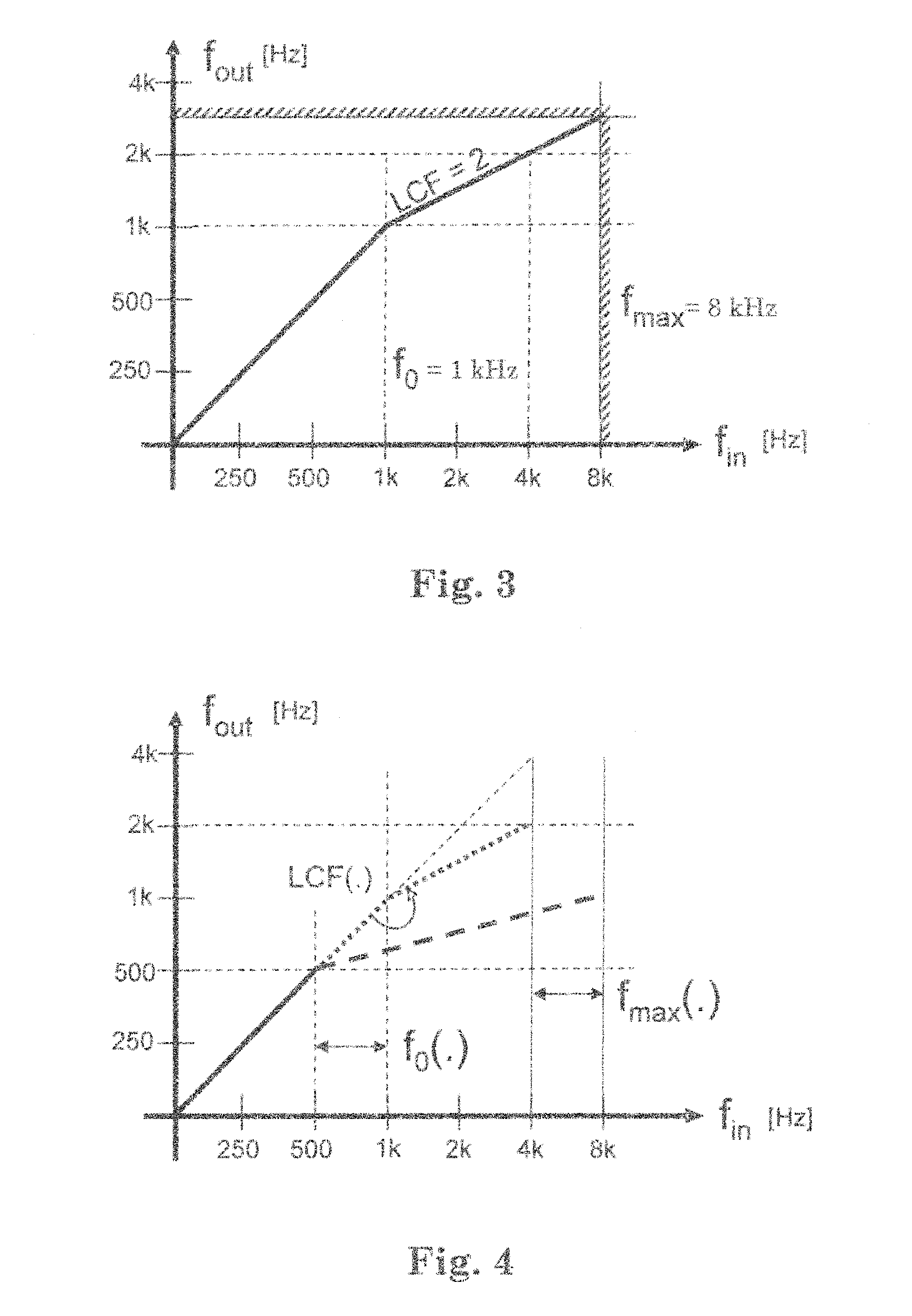
Method for adapting sound in a hearing aid device by frequency modification and such a device
InactiveUS20110150256A1Reduce presenceLess distortionOcclusion effect electronic compensationHearing device energy consumption reductionDistortionDigital hearing aid
In a digital hearing aid device (1) frequency modification is employed above a lower spectral bound and in accordance with a compression factor. The frequency modification is dynamically adjusted in dependence on a sound environment analysis (10) or an end-user input (30), by modifying the frequency modification parameters such as a lower spectral bound and a compression factor. The adjustment can be based on an interpolation between predefined parameters. In certain sound environments, such as loud noise, own-voice and telephone conversations, frequency modification is reduced or switched off. The proposed solutions have the advantage that the occurrence of disturbing noise and of distortions of harmonic relationships at the end-user's ear is reduced and signal processing resources as well as battery resources are saved.
Owner:SONOVA AG
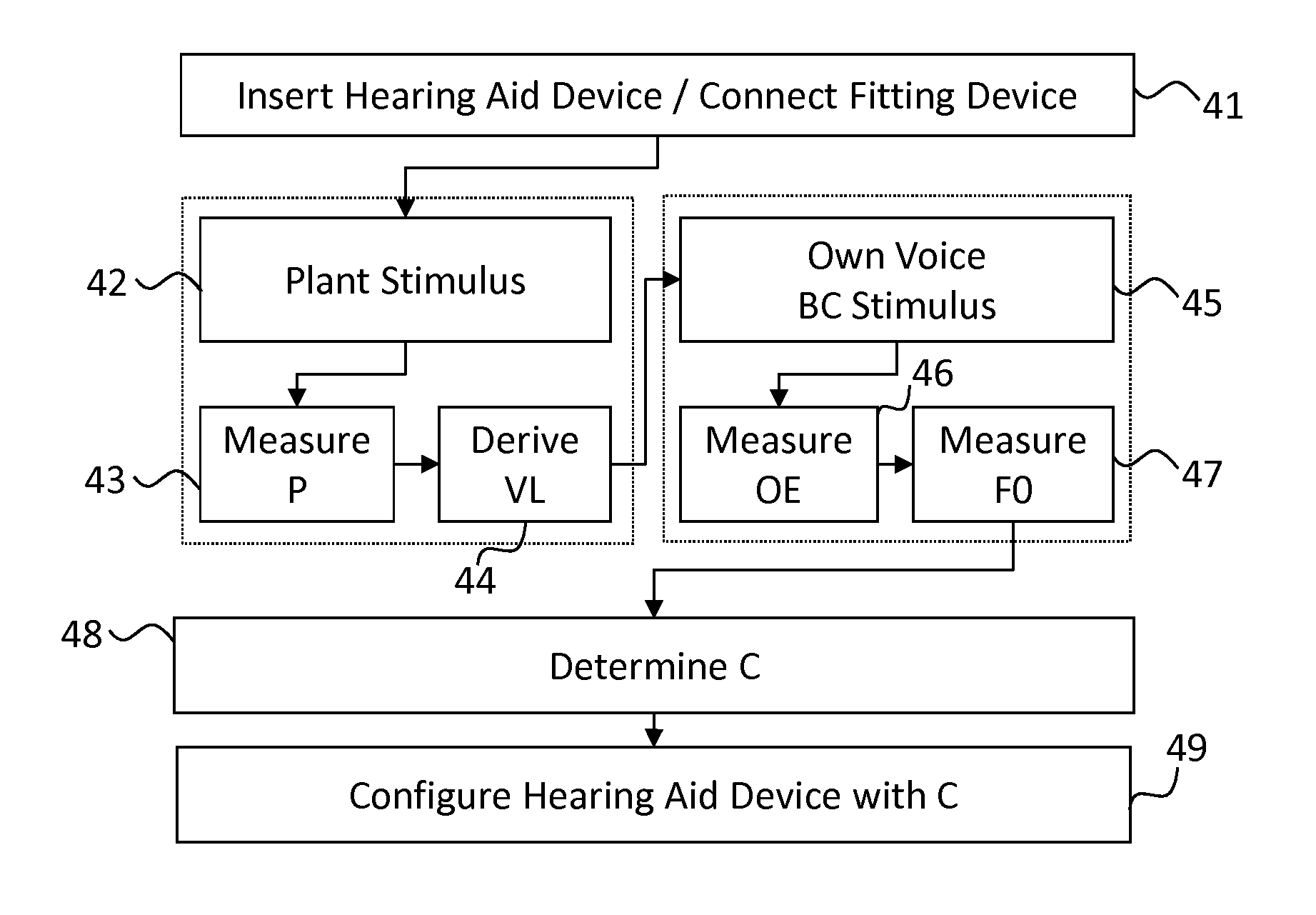
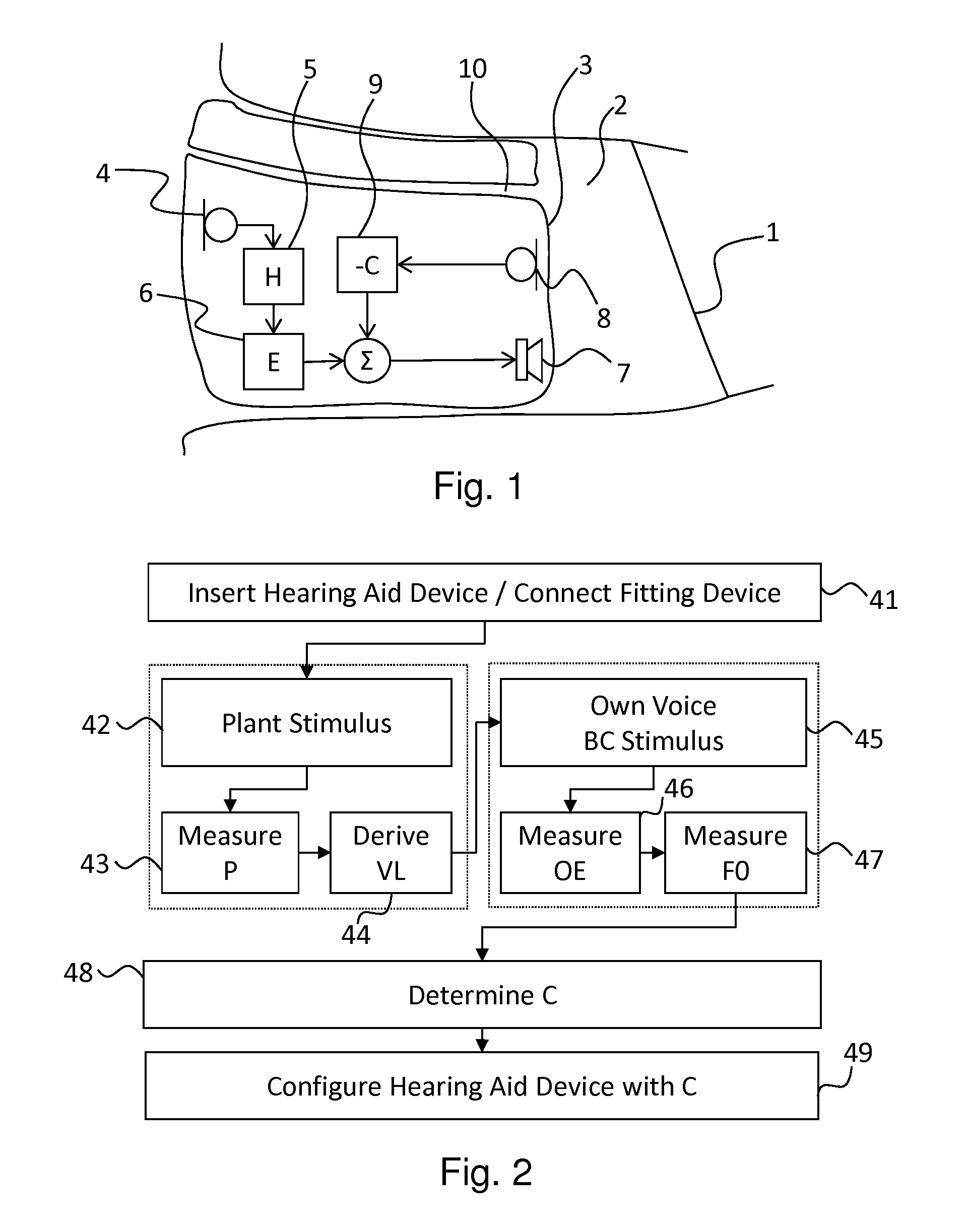
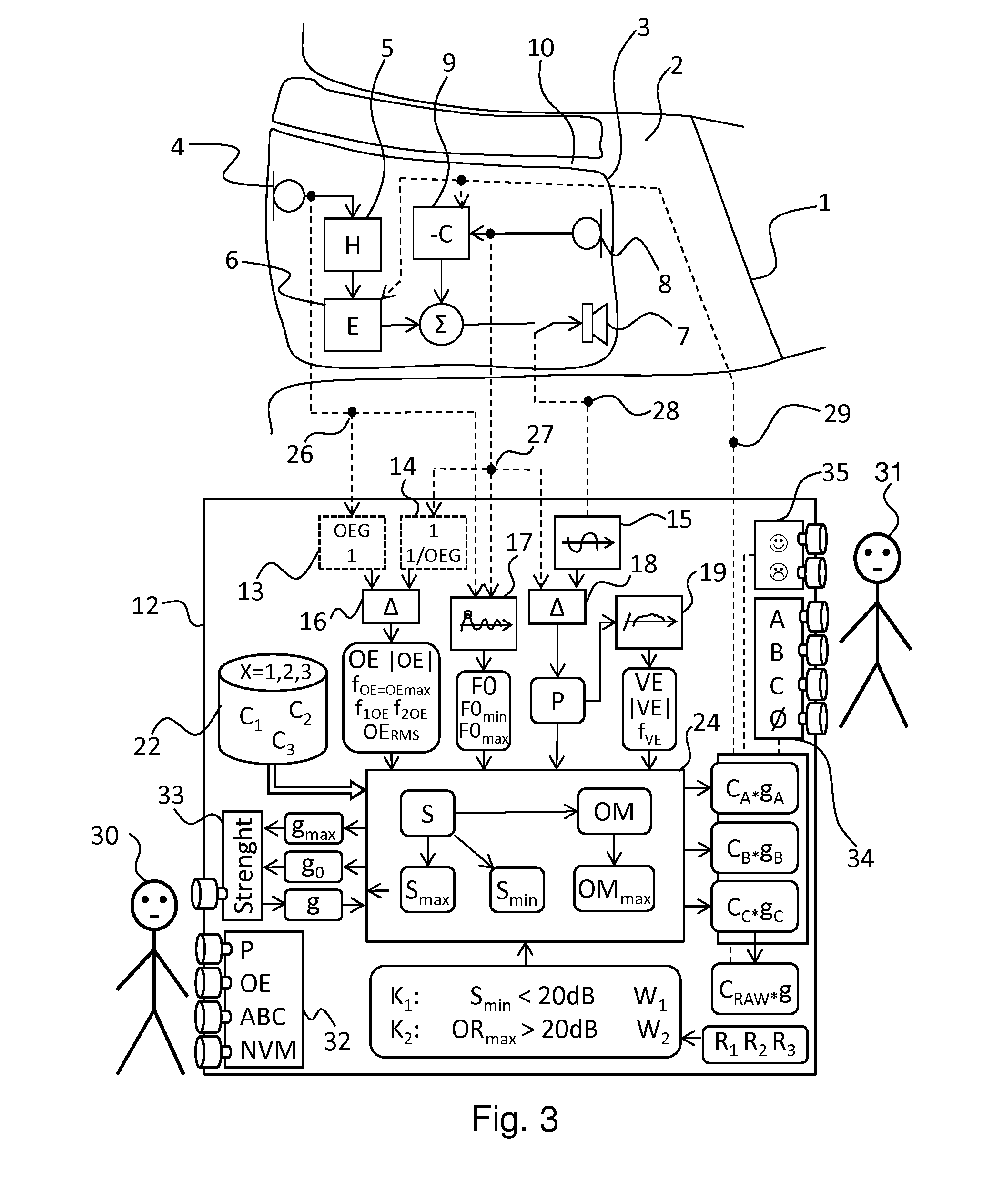
Method for Fitting a Hearing Aid Device With Active Occlusion Control to a User
ActiveUS20130243209A1Reduce occlusionLess demandingOcclusion effect electronic compensationHearing device active noise cancellationMedicineHearing aid
Methods and apparatus for fitting a hearing aid device (3) that includes a part which is arranged in the ear canal (2) of a user (31).
Owner:SONOVA AG
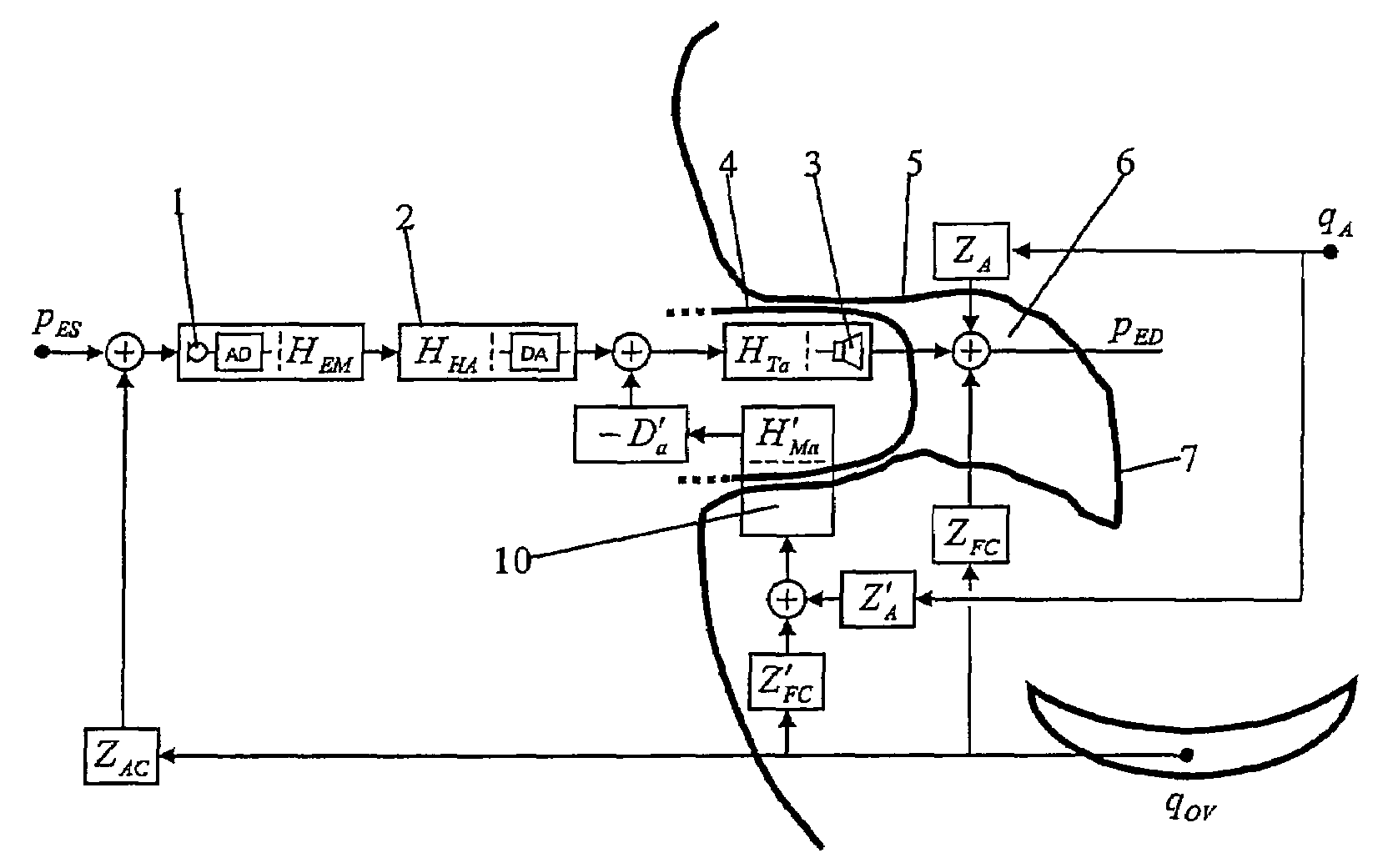
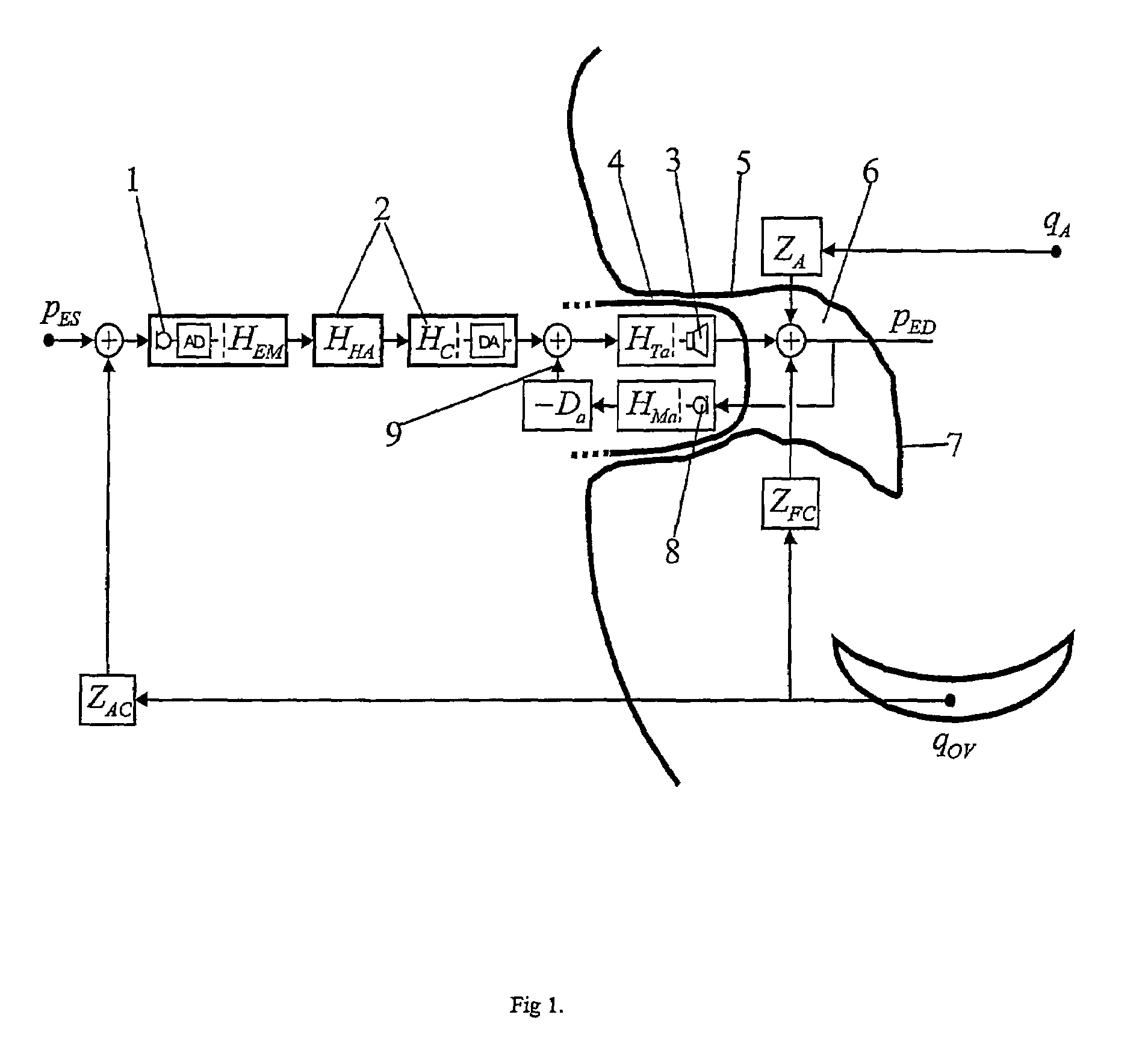
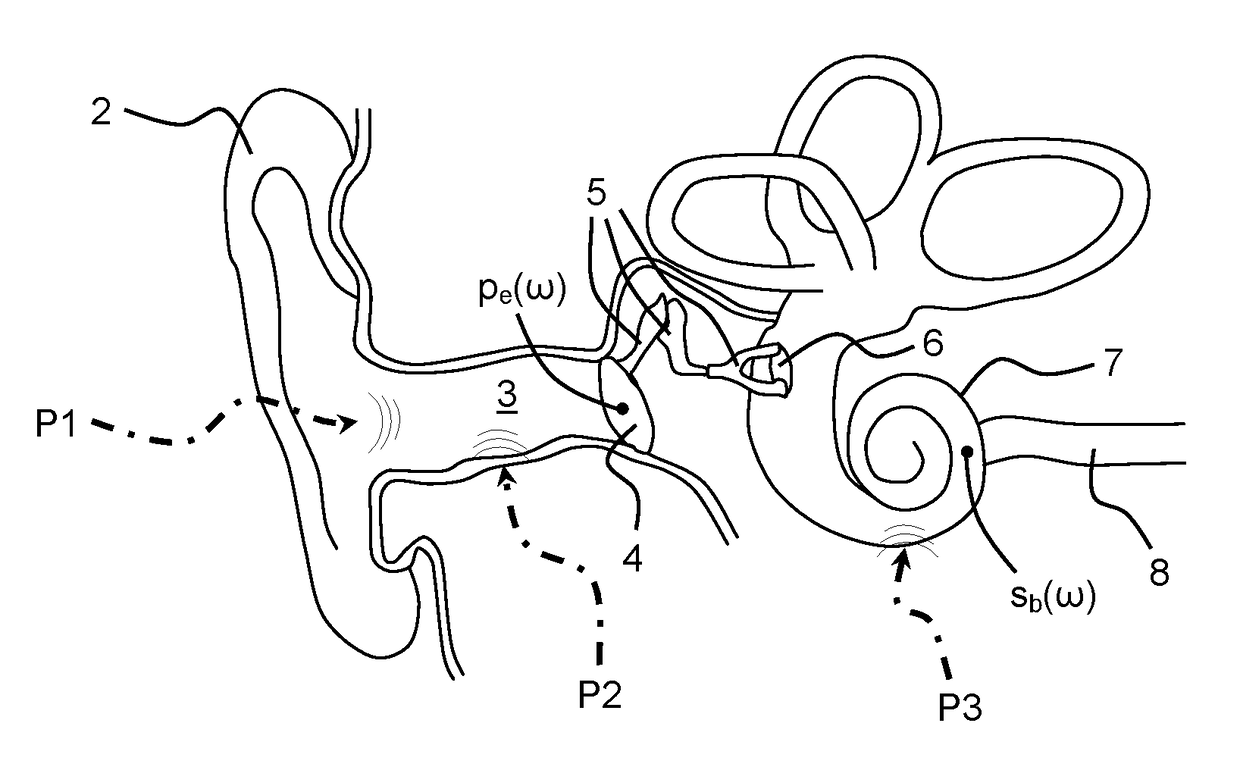
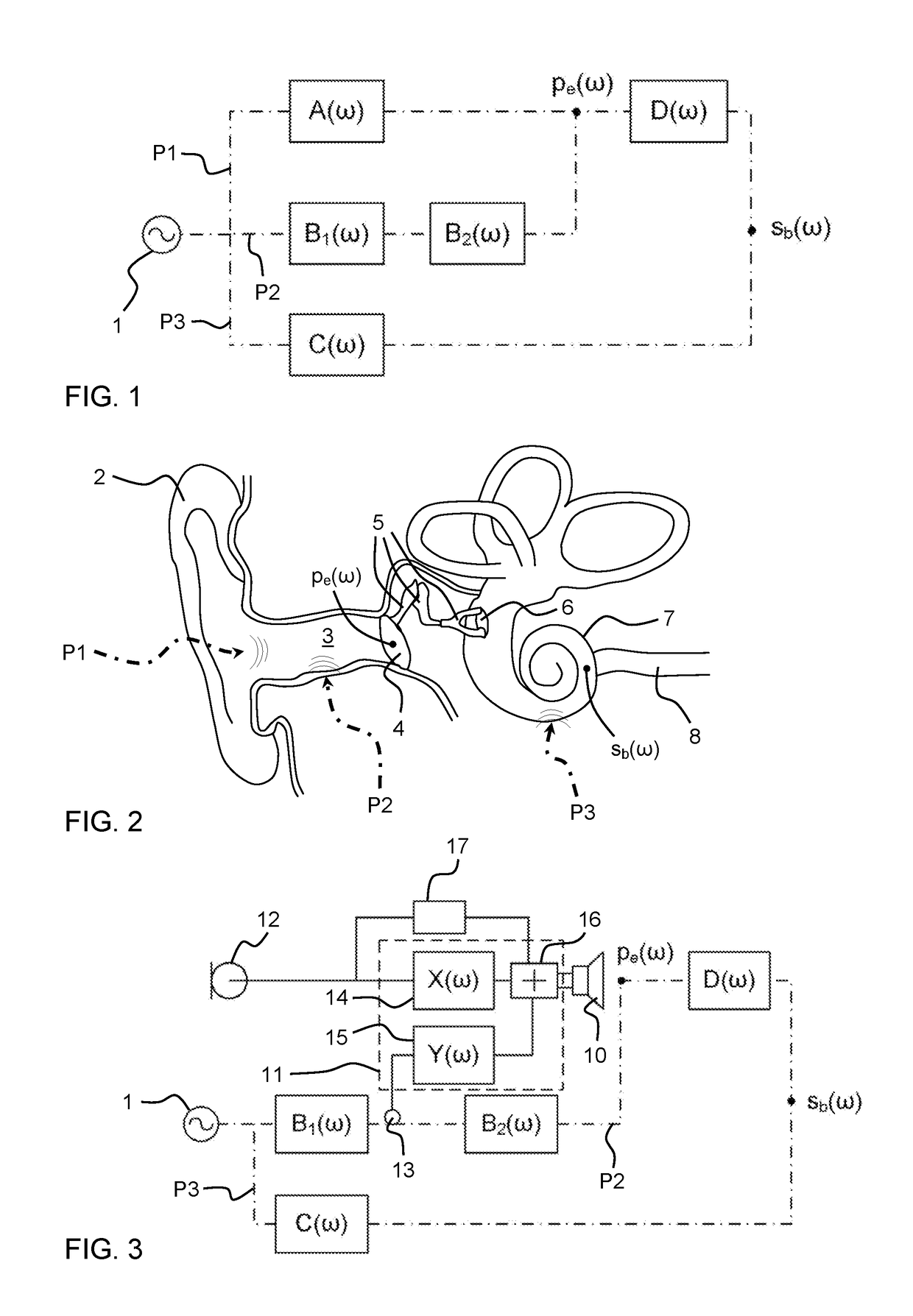
Method for counteracting the occlusion effects
ActiveUS7477754B2Enhanced signalReduced amplificationOcclusion effect electronic compensationNoise generationOcclusion effectTympanic Membranes
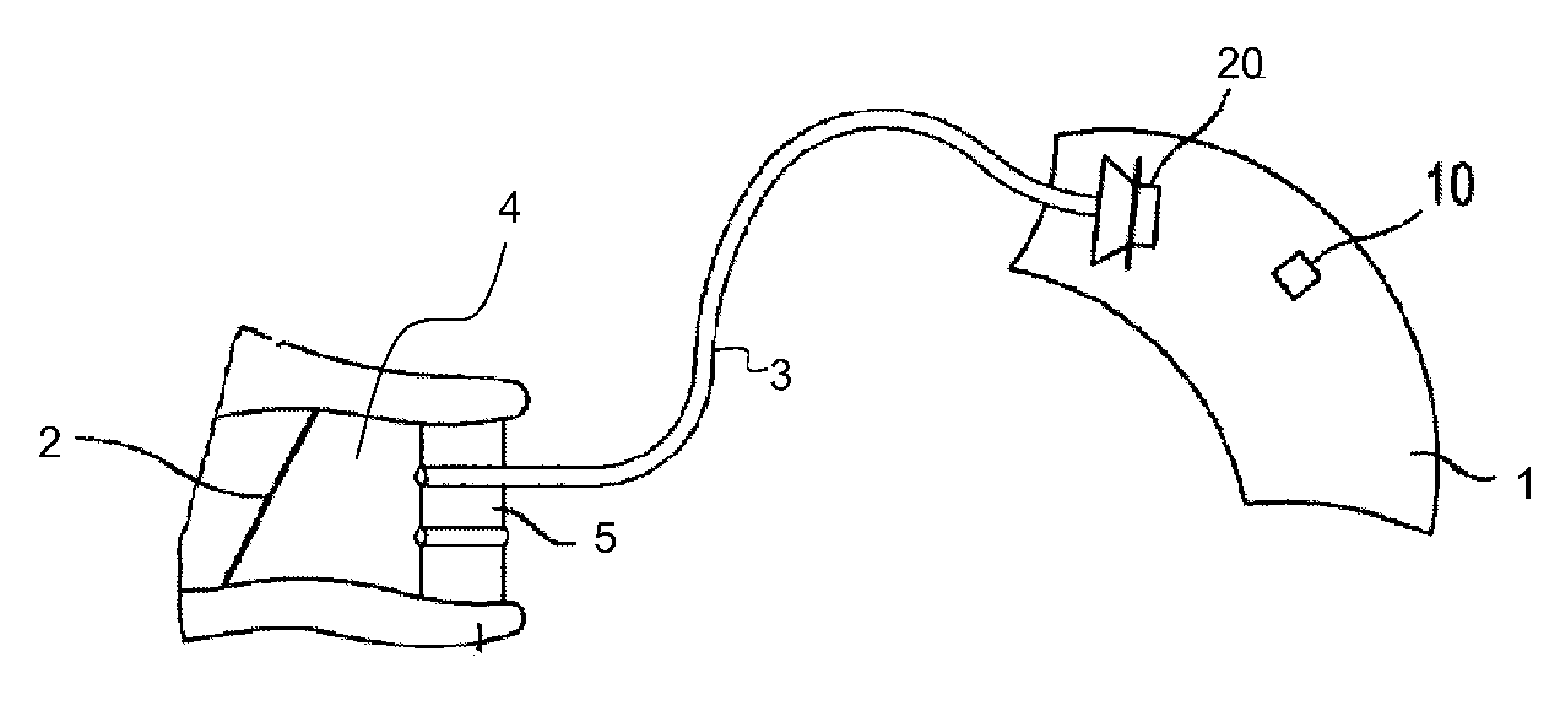
A method for counteracting the occlusion effect of an electronic device delivering an audio signal to the ear, like a hearing aid or an active ear protector, where the electronic device includes a transmission path with an external microphone or input line which receives a signal from the environment and an signal processor and a receiver which receives processes signal from the signal from the signal processor and delivers sound signals to the ear, whereby an ear piece is inserted into the ear canal and totally or partially blocks the canal. The sound conditions in the cavity between the ear piece and the tympanic membrane are directly or indirectly determined, and whenever condition leading to occlusion problems are determined, the transmission characteristics of the transmission path or the receiver changes in order to counteract the occlusion effect.
Owner:OTICON
Accoustically transparent occlusion reduction system and method
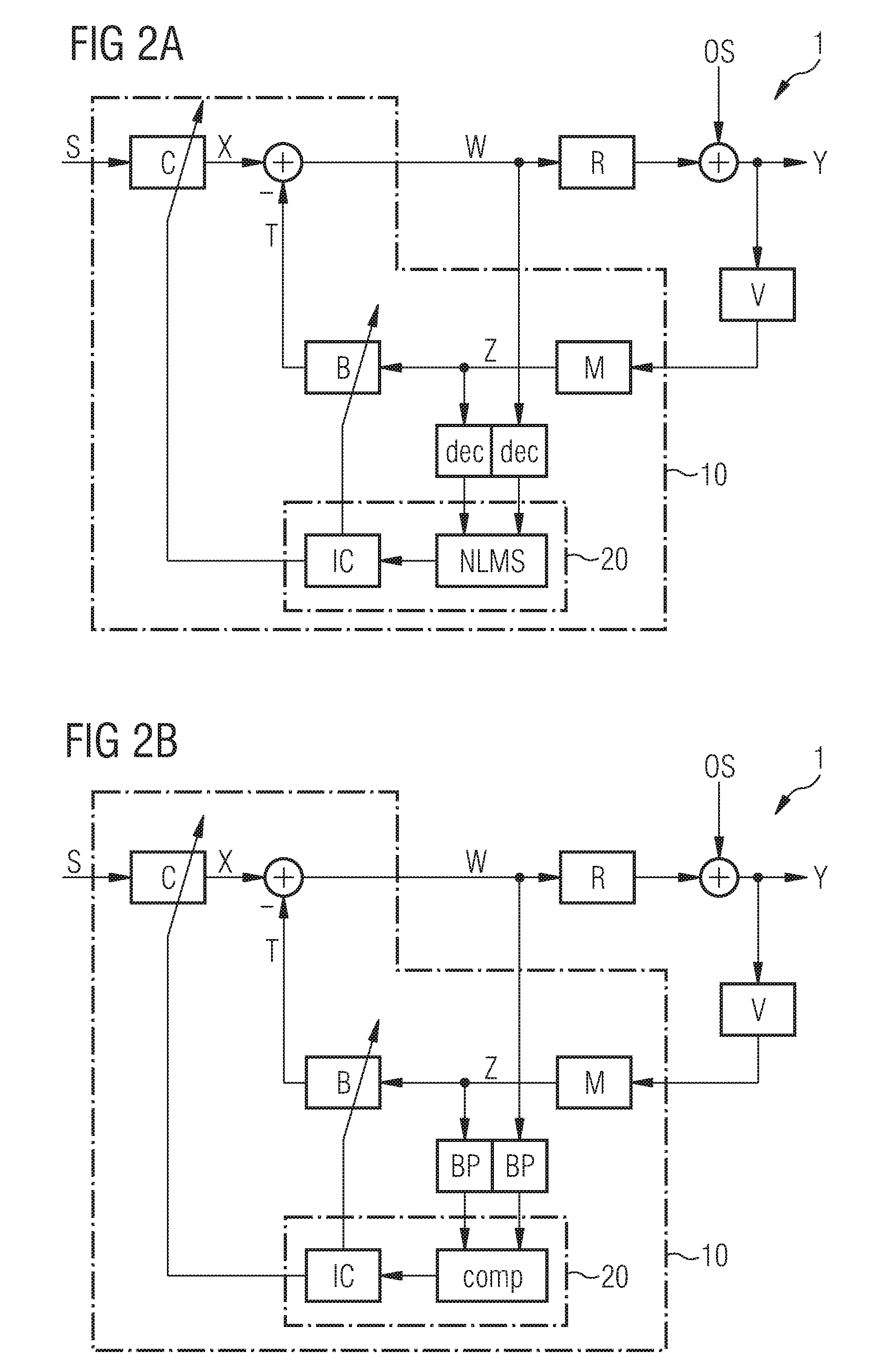
ActiveUS8116489B2Improve biteOcclusion effect electronic compensationTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEngineeringHeadphones
A system and method that reduces the perceptual effect resulting from ear occlusion include an electro-acoustic feedback network that produces phase canceling sounds in the ear, where a receiver and a microphone are located. A control mechanism controls the response of the feedback network to minimize distortion in the ear while maintaining a desired frequency response for external signals. Devices producing the external signal include hearing aids, personal sound devices, in ear monitors, communications headsets and hearing protectors. The integration of the above with these devices improves a user's perception of their own voice.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
System, method and hearing aids for in situ occlusion effect measurement
ActiveUS20110299692A1Increased sound levelSpeed up the flowOcclusion effect electronic compensationSignal processingOcclusion effectElectricity
A hearing aid (1) adapted for operation in a sound amplification mode and for operation in an occlusion measurement mode, has a microphone (10) adapted for transforming an acoustic sound level external to a hearing aid users ear canal (4) into a first electrical signal which is guided to an ND converter forming a first digitized electrical signal. The hearing aid has signal processing means with a filter bank (41, 42) with means for splitting an electrical signal into frequency bands, and a receiver (20) adapted for generating acoustic sounds in the ear canal of a user when in said amplification mode, and for transforming the acoustic sound level in the ear canal into a second electrical signal, when in occlusion measurement mode. The invention also provides a system and a method for measuring the occlusion effect
Owner:WIDEX AS
Advanced communication earpiece device and method
InactiveUS20140010378A1Accurate calculationImprove biteGain controlTransducer protection circuitsHeadphonesComputer science
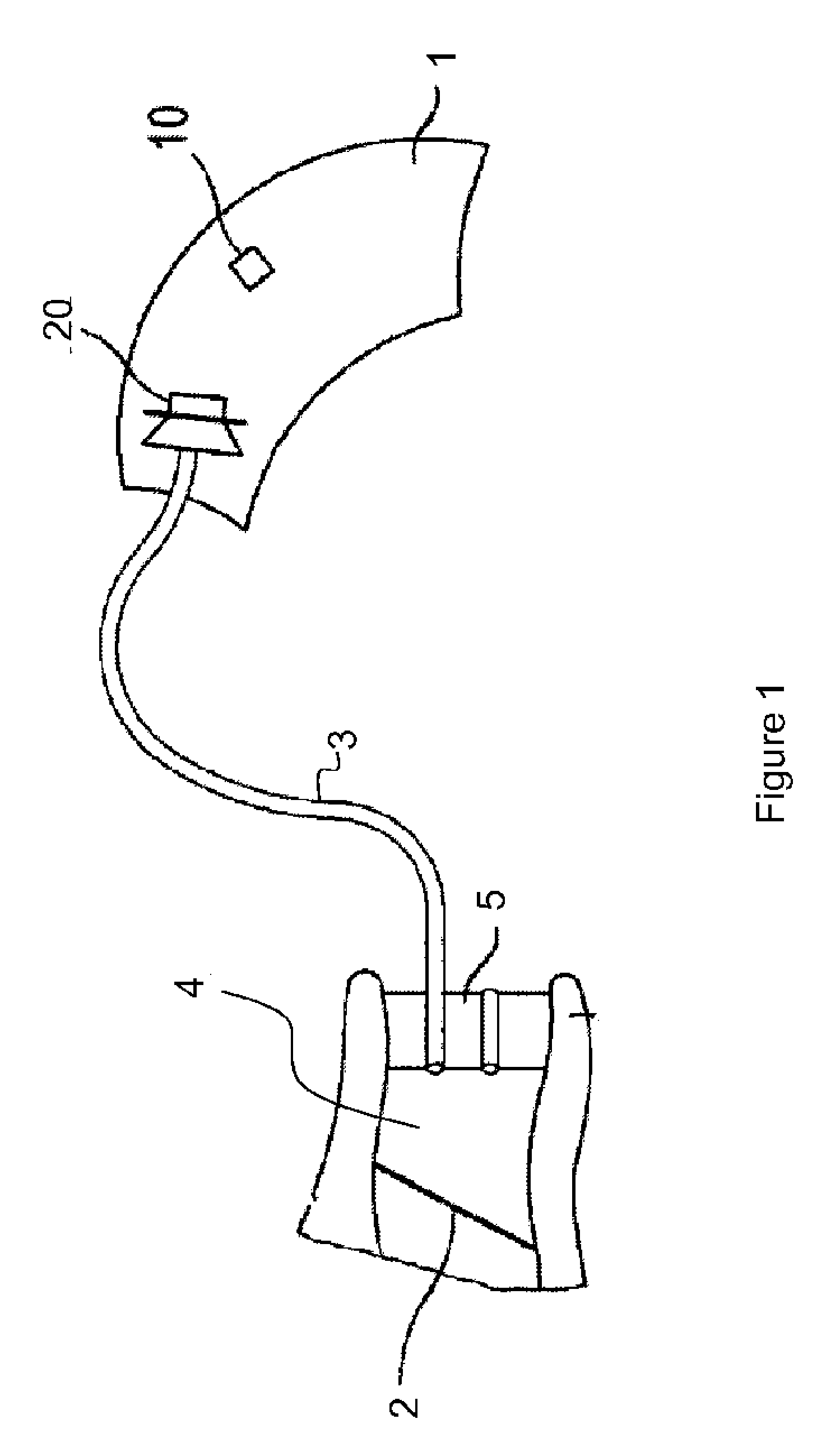
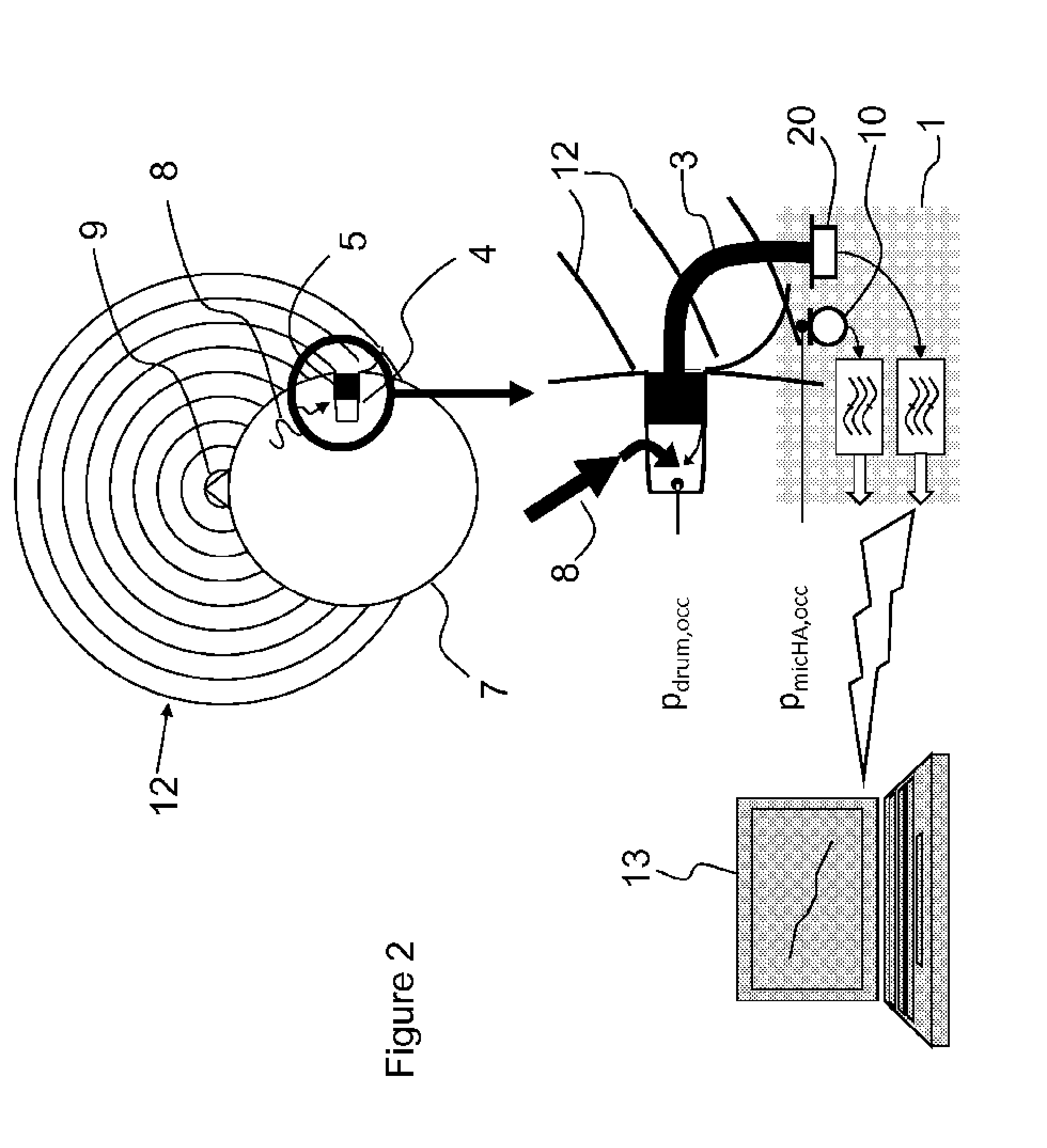
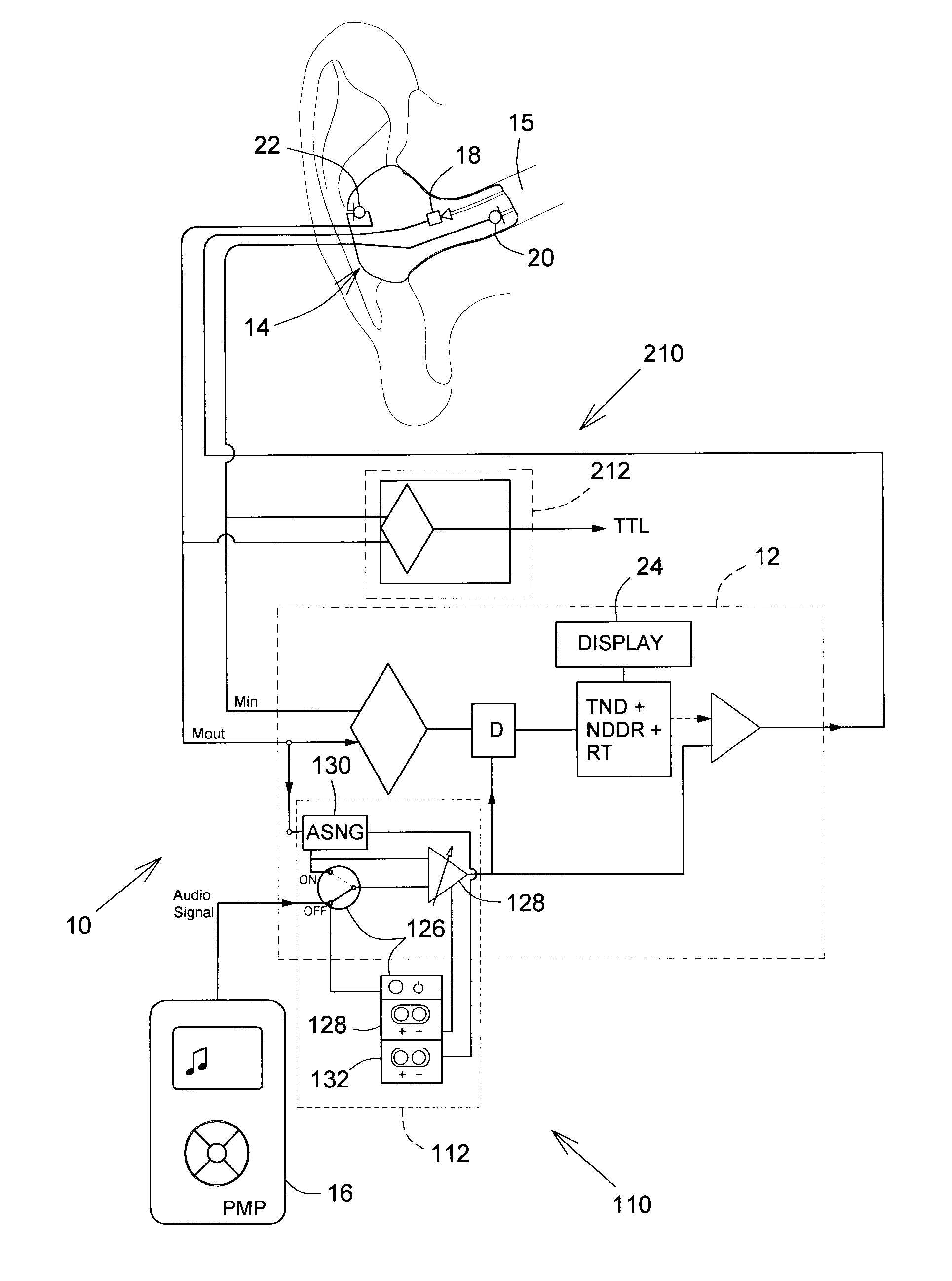
An earpiece device (10, 110, 210, 210′) provides advanced communication to the user thereof, for controlling a total sound dose (TND), including an audio output from an audio source (16) reaching an ear of the user occluded at the outer ear canal (15) by an in-ear device (14), for allowing an external ambient sound to be heard by the ear of the user, and for allowing a voice (NSV) of the user to be transmitted to a telecommunication transmission link (TTL). The present invention also contemplates a method of operation of the earpiece device (10, 110, 210, 210′).
Owner:VOIX JEREMIE +3
Method and apparatus for adjusting air pressure inside the ear of a person wearing an ear-wearable device
ActiveUS20150092971A1Occlusion effect electronic compensationIn the ear hearing aidsEngineeringVALVE PORT
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Personal hearing control system and method
InactiveUS8027481B2Improve fidelityReduce occlusionOcclusion effect electronic compensationEar moulds/tips acoustic sealsControl systemEngineering
A personal hearing control system includes a microphone located within a user's sealed ear canal, a speaker having a diaphragm which directs sound into the ear canal, and a controller which drives the speaker such that the system emulates the acoustics of the user's open ear canal. Also provided are a microphone located on the outer ear side of the sealed ear canal, which is coupled to a handheld interface unit having multiple inputs and operating modes. A user-selected input is processed by the interface unit, and the processed signal is coupled to the speaker. In one operating mode, the output of the outer ear mic is processed so as to cancel sound that leaks from the outer ear to the inner ear side of the seal.
Owner:BEARD TERRY
In-ear monitoring system and method
InactiveUS20050281423A1Minimizing outside interferenceInterference minimizationOcclusion effect electronic compensationHeadphones for stereophonic communicationOcclusion effectDigital signal processing
An in-ear monitor system facilitates stereo depth perception using microphones at each ear, minimizes occlusion effects, and provides a digital platform for both audio digital signal processing and wireless transmission.
Owner:SOUND DESIGN TECH
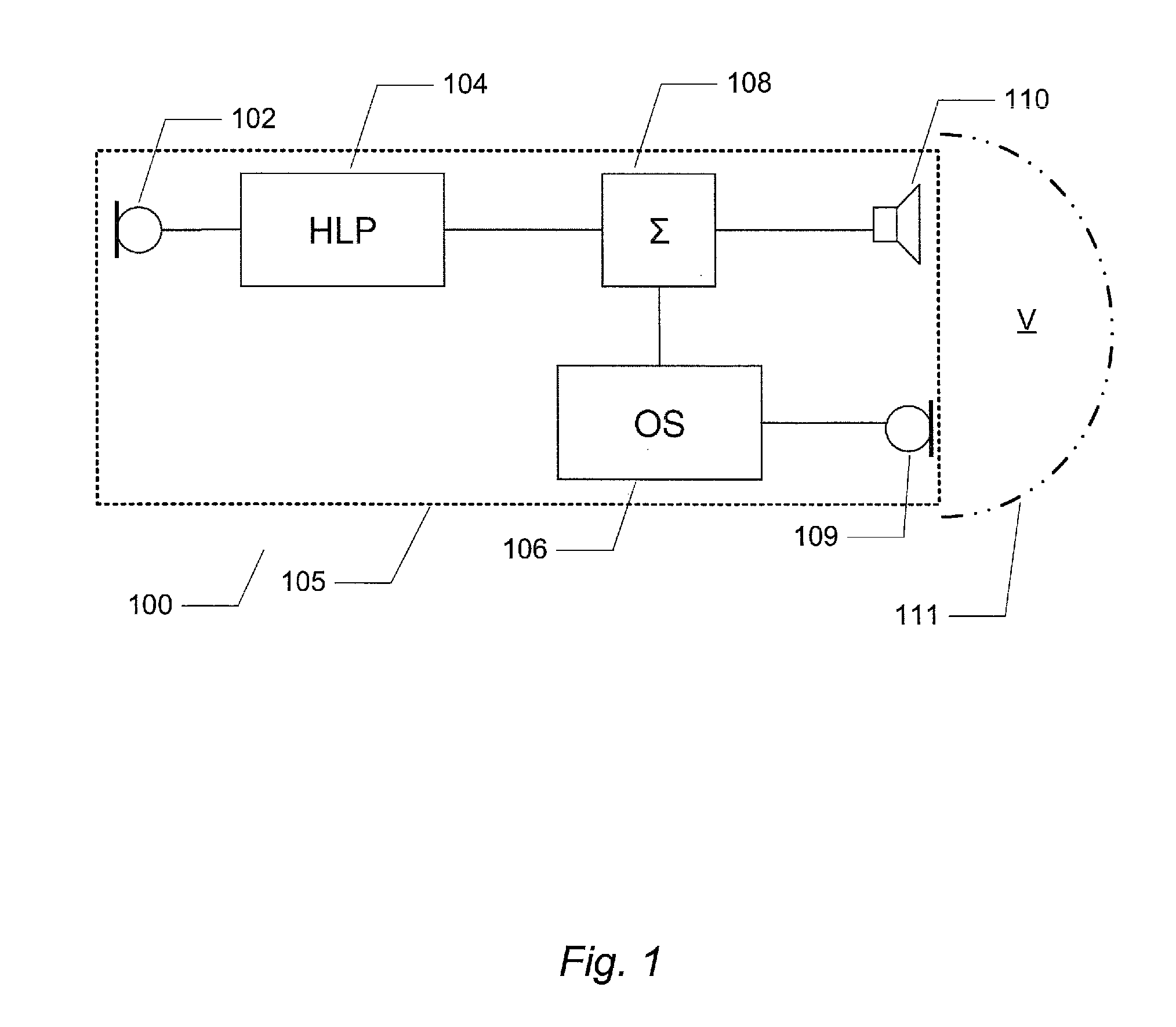
Audio headset with active noise control of the non-adaptive type for listening to an audio music source and/or for "hands-free" telephony functions
InactiveUS20130129105A1High gainIncreased phase marginOcclusion effect electronic compensationMicrophonesBandpass filteringNoise control
The headset comprises two earpieces each having a transducer for playing back the sound of an audio signal and received in an acoustic cavity defined by a shell having an ear-surrounding cushion. The active noise control comprises, in parallel, a feedforward bandpass filter receiving the signal from an external microphone, a feedback bandpass filter receiving as input an error signal delivered by an internal microphone, and a stabilizer bandpass filter locally increasing the phase of the transfer function of the feedback filter in an instability zone, in particular a waterbed effect zone around 1 kHz. A summing circuit delivers a weighting linear combination of the signal delivered by these filters together with the audio signal to be played back. Control is non-adaptive, with the parameters of the filters being static.
Owner:PARROT
Sound reproducing apparatus using in-ear earphone
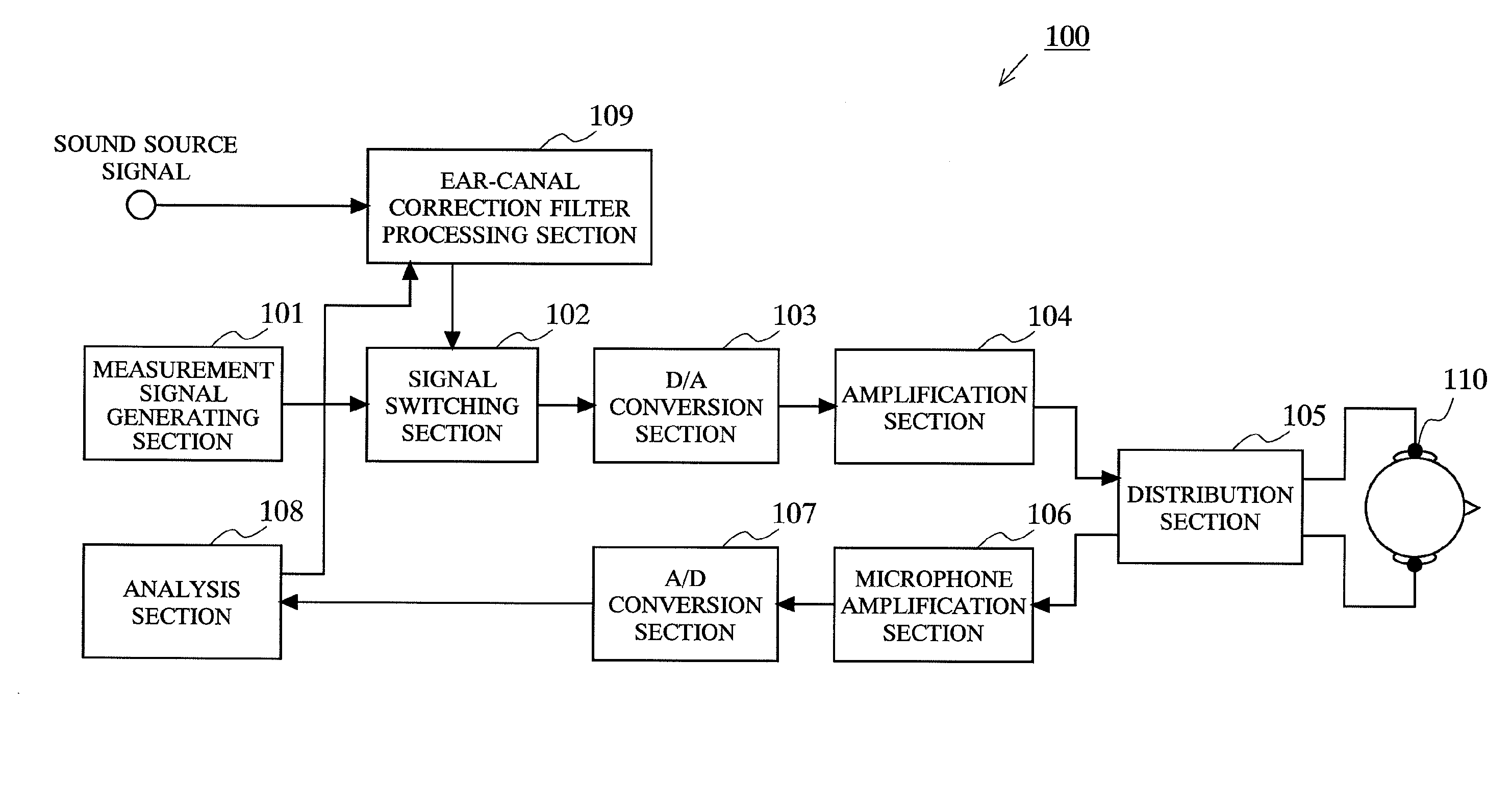
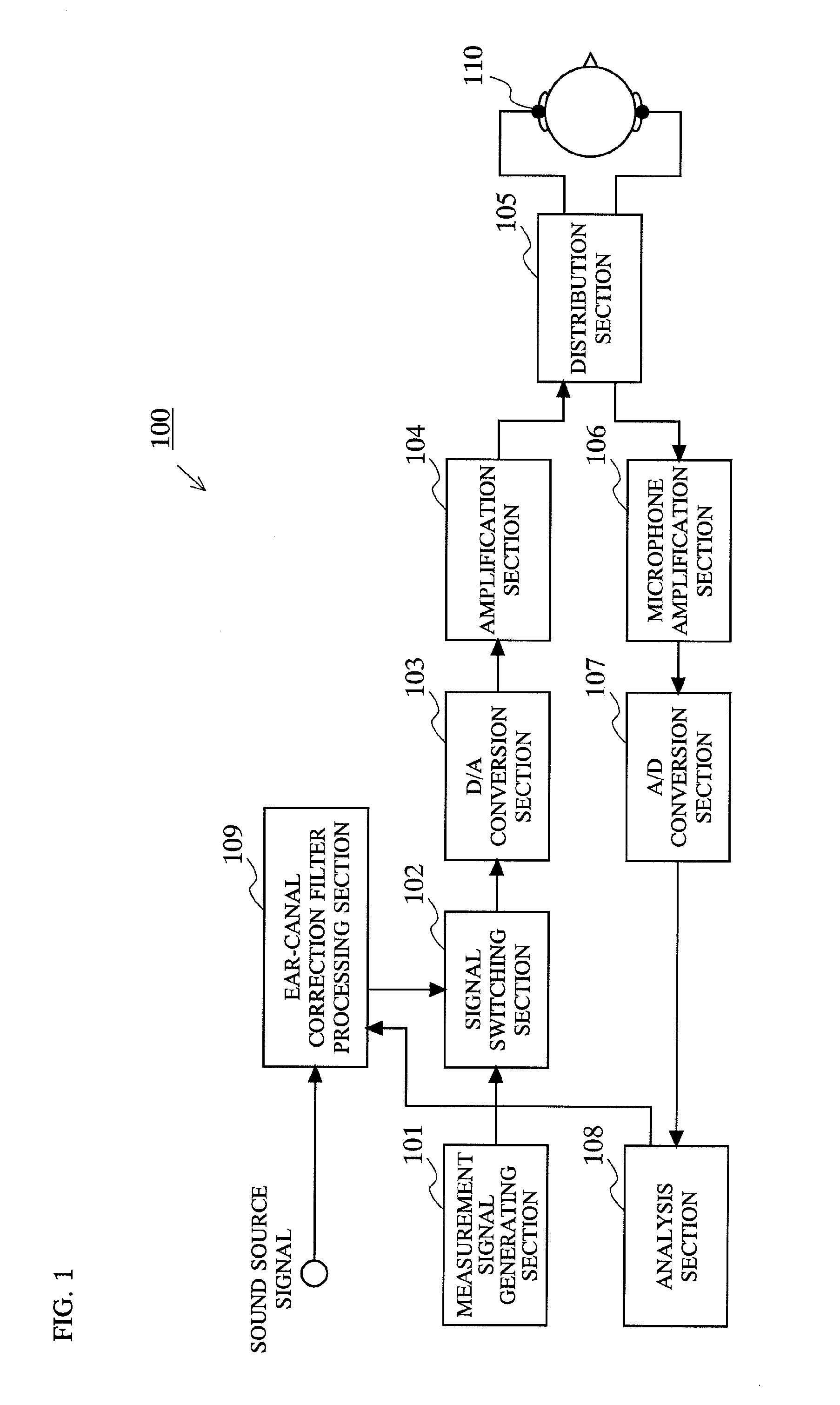
ActiveUS20100177910A1Optimum ear-canal correction filterOcclusion effect electronic compensationHeadphones for stereophonic communicationEar canalEngineering
First, in a state where a pair of earphones 110 are worn in both ears of a listening person, a measurement signal generated by a measurement signal generating section 101 is outputted from the earphone 110. The signal (wearing-state signal) which is reflected by an eardrum and returns to the earphone 110 is measured, and stored in an analysis section 108. Next, in a state where the pair of earphones 110 are not worn in both ears of the listening person, a signal measured (unwearing-state signal) in the same manner as described above is stored in the analysis section 108. The analysis section 108 calculates an ear-canal correction filter based on a difference between the wearing-state signal and the unwearing-state signal. An ear-canal correction filter processing section 109 convolves a sound source signal with the calculated ear-canal correction filter.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Method for operating a hearing device and a hearing device
ActiveUS20160105751A1Reliable and simple mannerEnhanced signalOcclusion effect electronic compensationHearing device energy consumption reductionHearing apparatusAudio frequency
A method for operating a hearing device including an ambient microphone, a signal processing unit, a receiver and an ear canal microphone. The method includes steps of filtering the audio signal processed by the signal processing unit with a filter having a transfer function including a transfer function from an output of the receiver to an input of the ear canal microphone when the hearing device is turned on and being worn in an ear canal of the user, computing a difference between the audio signal picked up by the ear canal microphone and the filtered signal, and detecting a presence of own-voice of the user based on the difference. Furthermore, a hearing device including an own-voice detection unit is provided, which is adapted to perform the proposed method.
Owner:SONOVA AG
Hearing aid with occlusion suppression
ActiveUS20120070024A1Lowered cut-off frequencyOcclusion effect electronic compensationDeaf-aid setsEnvironmental soundsSuppressor
A hearing aid includes an ambient microphone configured to receive and convert environmental sound into an electronic input signal, a hearing loss processor configured to process the electronic input signal in accordance with a hearing loss of a user, and generate an electronic output signal, a receiver, an ear canal microphone configured for converting ear canal sound pressure into an ear canal signal, an occlusion suppressor for reception and processing of the ear canal signal and for transmitting an occlusion suppression signal, and a signal combiner configured for combining the occlusion suppression signal and the electronic output signal to form a combined signal, and for transmitting the combined signal to the receiver, wherein the receiver is configured to receive the combined signal, and convert the combined signal into an acoustic output signal, and wherein the receiver has a frequency response with a lower cut-off frequency that is less than 40 Hz.
Owner:GN HEARING AS
Earphone arrangement and method of operation therefor
InactiveUS8655003B2Convenient ArrangementWell mixedOcclusion effect electronic compensationEar treatmentUltrasound attenuationControl signal
An earphone arrangement comprises a microphone (109) which generates a microphone signal and a sound transducer (101) which radiates a first sound component to a user's ear (103) in response to a drive signal. An acoustic channel (111) is further provided for channeling external sound so as to provide a second sound component to the user's ear (103). An acoustic valve (117) allows the attenuation of the acoustic channel (111) to be controlled in response to a valve control signal. A control circuit (105) generates the valve control signal in response to the microphone signal to provide a variable attenuation resulting in a mixed sound of the first sound component and the second sound component reaching the user's ear (103). The combined use of acoustic and e.g. electric signal paths allows improved performance and in particular allows a dynamic trade-off between open and closed earphone design characteristics with respect to external sounds.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for actively reducing occlusion comprising plausibility check and corresponding hearing apparatus
ActiveUS20090238387A1Long calculation timeGuaranteed to workOcclusion effect electronic compensationEar treatmentTransducerEngineering
Adaption of signal processing for actively reducing occlusion in hearing apparatuses, and in particular in hearing aids, is to be automated further. For this purpose, a transducer transmission function, which is defined for the transmission path from the input of a receiver via the auditory canal to the output of a microphone, be subjected to an automatic plausibility check. An adjustable filter via which the microphone signal is fed back is only altered if the transducer transmission function is plausible according to a predefined criterion. Disadvantageous convergences of the adaptation algorithm can be avoided hereby and unnecessarily high computing times can be prevented.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Controlling own-voice experience of talker with occluded ear
ActiveUS20170171679A1Simple and inexpensive implementationOcclusion effect electronic compensationMicrophonesOcclusion effectEngineering
A system and method are provided for controlling the own-voice experience of a user who talks while an earpiece is mounted to occlude an ear of the user. A vibration sensor is engaged with the user's head to sense vibrations formed by the user speaking and conducted by the user's head to the vibration sensor. A signal generator operates a speaker element, which is integrated with the earpiece, to generate sound waves in the ear canal of the user, based on the output signal of the vibration sensor. The signal generator generates the sound waves to at least partially cancel other sound waves that are generated by at least part of said vibrations entering the ear canal from surrounding bone and / or tissue. The system and method counteracts the occlusion effect and are applicable in connection with in-ear headsets, earphones, in-ear headphones, in-ear monitors, circumaural headphones, hearing aids, earplugs and earmuffs.
Owner:SONY CORP
Hearing aid with occlusion reduction
ActiveUS20120008808A1Minimize distortionOcclusion effect electronic compensationIn the ear hearing aidsEngineeringHearing aid
A hearing aid having hearing loss-compensating components, active occlusion reduction components, a vent, a tuned piston, and a flexible surround. The piston and the surround combination are assembled on the faceplate and cover the outside end of the vent that is situated on the faceplate. The piston and the surround combination minimize the adverse effects of walk-induced head vibrations.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Dynamic Driver In Hearing Instrument
ActiveUS20150049893A1Occlusion effect electronic compensationSets with customised acoustic characteristicsOcclusion effectEngineering
A hearing instrument includes a first speaker having a first frequency range. The hearing instrument also includes a second speaker that is disposed in the ear of a listener. The second speaker has a second frequency range that is wider than the first frequency range. A microphone unit is coupled to the first speaker and the second speaker. The first speaker creates replacement sounds within the first frequency range that replicate sounds that are lost to the listener as a result of an occlusion effect at the second speaker. The replacement sounds are presented to the listener.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
Hearing Aid Having an Occlusion Reduction Unit and Method for Occlusion Reduction
ActiveUS20100002896A1Avoid matching problemsReduce computational complexityOcclusion effect electronic compensationEar treatmentLoop filterOcclusion effect
A method is described for reduction of occlusion effects in an acoustic appliance which closes an auditory channel, wherein an audio signal in the transmission path of the acoustic appliance is processed by a signal processing unit and is emitted via an output transducer, which is arranged in the auditory channel, as an acoustic signal. A resultant sound signal is then detected by an auditory channel microphone and is supplied to a variable loop filter, which is arranged in a feedback loop of an occlusion reduction unit for the acoustic appliance. The output signal from the loop filter is injected into the transmission path of the audio signal. The occlusion reduction unit is in this case controlled adaptively, with at least one signal from the transmission path of the audio signal and / or from the feedback loop being used to control the loop filter for the occlusion reduction unit.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Suppression of perceived occlusion
InactiveUS7031484B2Suppression problemImprove sound qualityOcclusion effect electronic compensationDeaf aid adaptationAudio power amplifierLow frequency band
A fitting method is provided for a multichannel hearing aid with at least one low frequency channel having an individually adjustable compressor. The method comprises the steps of first adjusting the characteristic of the compressor according to the hearing loss to be compensated by the hearing aid, followed by the step of increasing the compression ratio of the characteristic of the compressor in the at least one low frequency band. The at least one low frequency channel may further comprise an offset amplifier adding an offset gain to the compressor characteristic, and the method may further comprise the step of adjusting the offset gain in the range from −20 dB to 20 dB. After adjustment according to the method, compressors operating at low frequencies enhance low level signals and attenuate high level signals whereby perception of occlusion is suppressed.
Owner:WIDEX AS
First person acoustic environment system and method
InactiveUS20050281421A1Minimizing outside interferenceInterference minimizationOcclusion effect electronic compensationHeadphones for stereophonic communicationMonitoring systemVocal tract
An in-ear monitoring system transmits right- and left-channel audio data for one or more in-ear playback devices to create a first person acoustic environment for one or more third persons.
Owner:SOUND DESIGN TECH
Method for operating a hearing device capable of active occlusion control and a hearing device with user adjustable active occlusion control
ActiveUS20160150330A1Simple processOcclusion effect electronic compensationCompletely in canal hearing aidsControl signalHearing apparatus
A method for operating a hearing device for being worn at least partially within an ear canal of a user, including an ear canal microphone, a filtering unit and an electrical-to-acoustical converter, capable of active occlusion control (AOC) and allowing the user to adjust the AOC functionality according to his or her preferences. The method includes picking up an ear canal internal sound at the microphone which provides a signal representative of the internal sound, filtering the signal with the filtering unit to reduce a perceived level of body sounds produced by the user, providing the filtered signal to the converter which outputs sound into the ear canal, and changing at least one setting or parameter of the filtering unit in dependence of a control signal, wherein the control signal is initiated by the user. Moreover, a hearing device adapted to perform the method is provided.
Owner:SONOVA AG
In-ear monitoring system and method with bidirectional channel
InactiveUS20050281422A1Minimizing outside interferenceInterference minimizationOcclusion effect electronic compensationHeadphones for stereophonic communicationVoice communicationMonitoring system
An in-ear monitor assembly includes an internal microphone to facilitate a bidirectional voice communication channel.
Owner:SOUND DESIGN TECH
Method for adapting sound in a hearing aid device by frequency modification and such a device
InactiveUS8571242B2Efficient and accurate and easily configurableAdjustable frequencyOcclusion effect electronic compensationHearing device energy consumption reductionFrequency spectrumHarmonic
Owner:SONOVA AG
Popular searches
Transducer circuits Stereophonic systems Hearing aid vents Details for specific frequency response Earpiece/earphone manufacture/assembly Earpiece/earphone mechanical/electrical switches Circuit lead arrangements/relief Earpiece/earphone noise reduction Dc-dc conversion Hearing aids signal processing
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com