Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37results about How to "Minimum separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
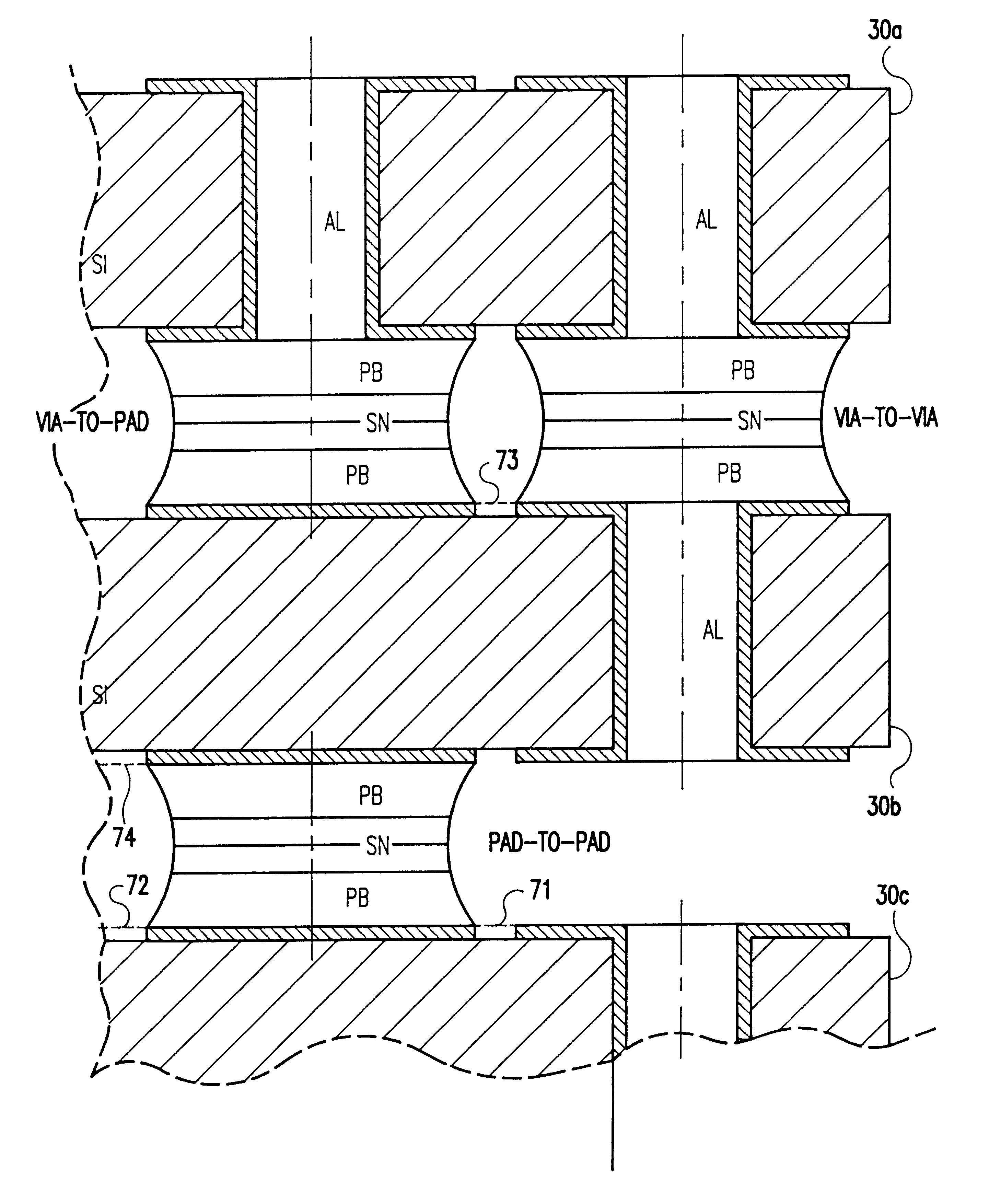
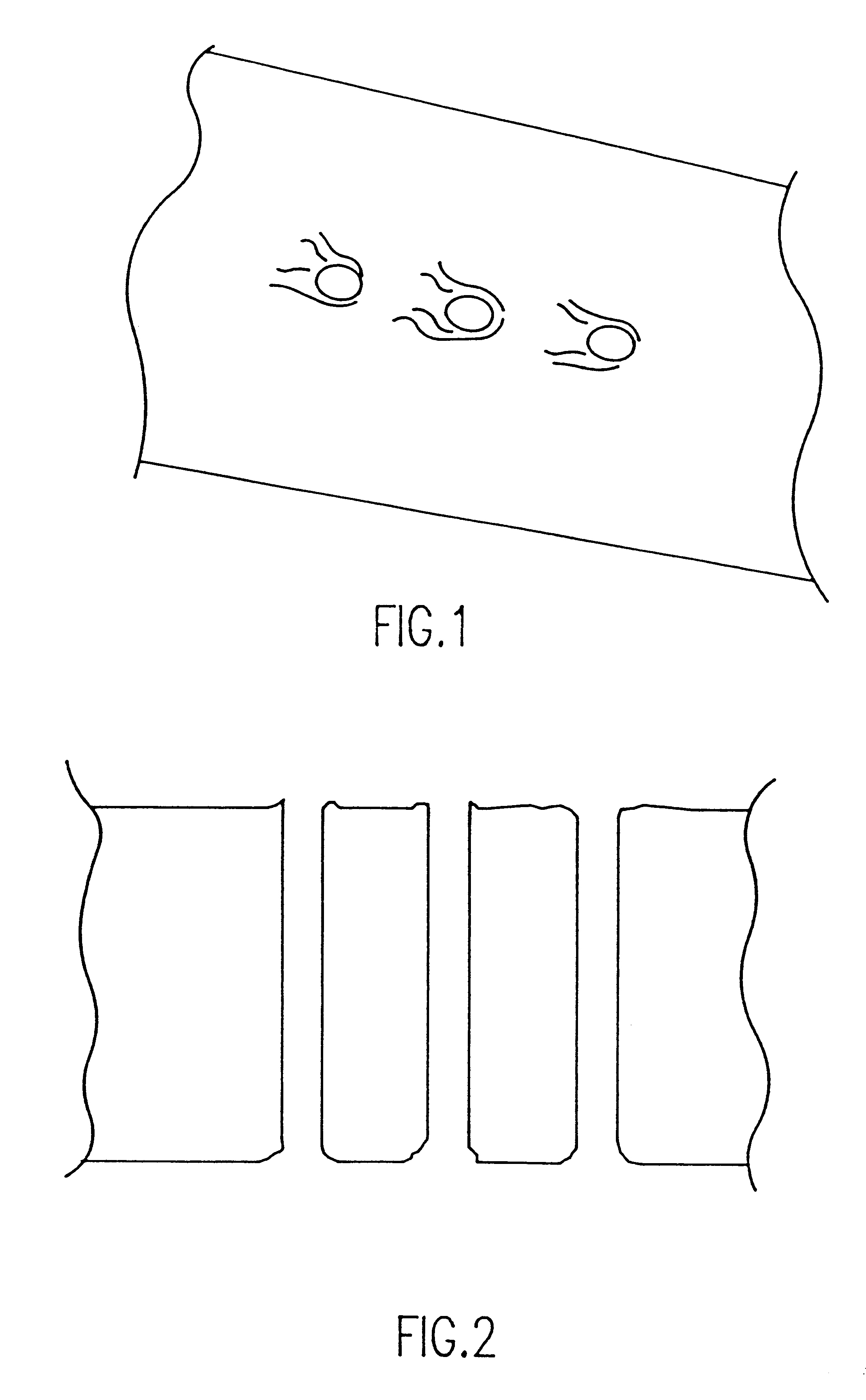
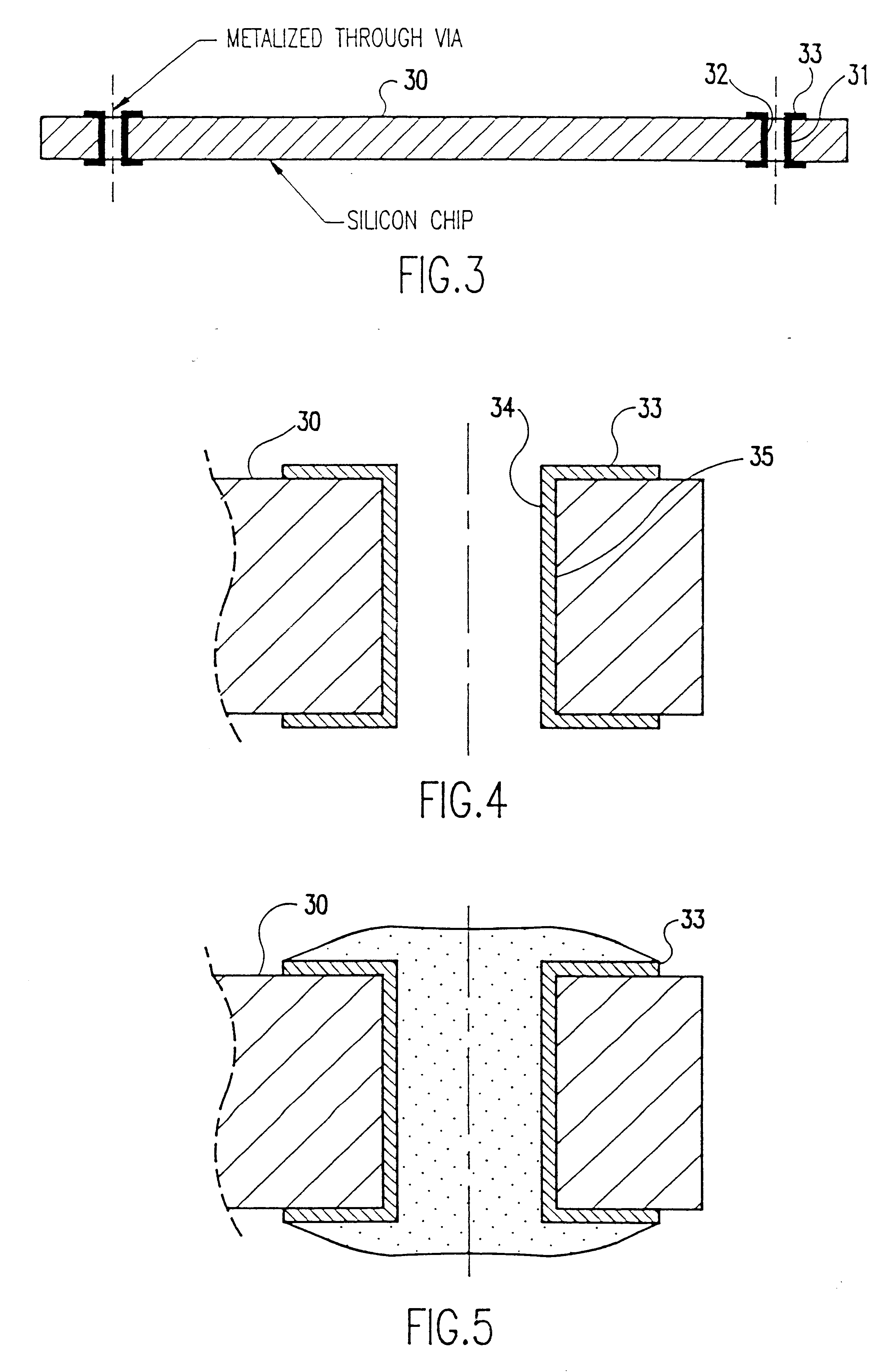
High density integrated circuit packaging with chip stacking and via interconnections
InactiveUS6236115B1Reduced connection exposureLarge capacitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringThermal expansion
Chip stacks with decreased conductor length and improved noise immunity are formed by laser drilling of individual chips, such as memory chips, preferably near but within the periphery thereof, and forming conductors therethrough, preferably by metallization or filling with conductive paste which may be stabilized by transient liquid phase (TLP) processes and preferably with or during metallization of conductive pads, possibly including connector patterns on both sides of at least some of the chips in the stack. At least some of the chips in the stack then have electrical and mechanical connections made therebetween, preferably with electroplated solder preforms consistent with TLP processes. The connections may be contained by a layer of resilient material surrounding the connections and which may be formed in-situ. High density circuit packages thus obtained may be mounted on a carrier by surface mount techniques or separable connectors such as a plug and socket arrangement. The carrier may be of the same material as the chip stacks to match coefficients of thermal expansion. High-density circuit packages may also be in the form of removable memory modules in generally planar or prism shaped form similar to a pen or as a thermal conduction module.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
High density integrated circuit packaging with chip stacking and via interconnections
InactiveUS6187678B1Reduced connection exposureLarge capacitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal expansionPrism
Chip stacks with decreased conductor length and improved noise immunity are formed by laser drilling of individual chips, such as memory chips, preferably near but within the periphery thereof, and forming conductors therethrough, preferably by metallization or filling with conductive paste which may be stabilized by transient liquid phase (TLP) processes and preferably with or during metallization of conductive pads, possibly including connector patterns on both sides of at least some of the chips in the stack. At least some of the chips in the stack then have electrical and mechanical connections made therebetween, preferably with electroplated solder preforms consistent with TLP processes. The connections may be contained by a layer of resilient material surrounding the connections and which may be formed in-situ. High density circuit packages thus obtained may be mounted on a carrier by surface mount techniques or separable connectors such as a plug and socket arrangement. The carrier may be of the same material as the chip stacks to match coefficients of thermal expansion. High-density circuit packages may also be in the form of removable memory modules in generally planar or prism shaped form similar to a pen or as a thermal conduction module.
Owner:IBM CORP
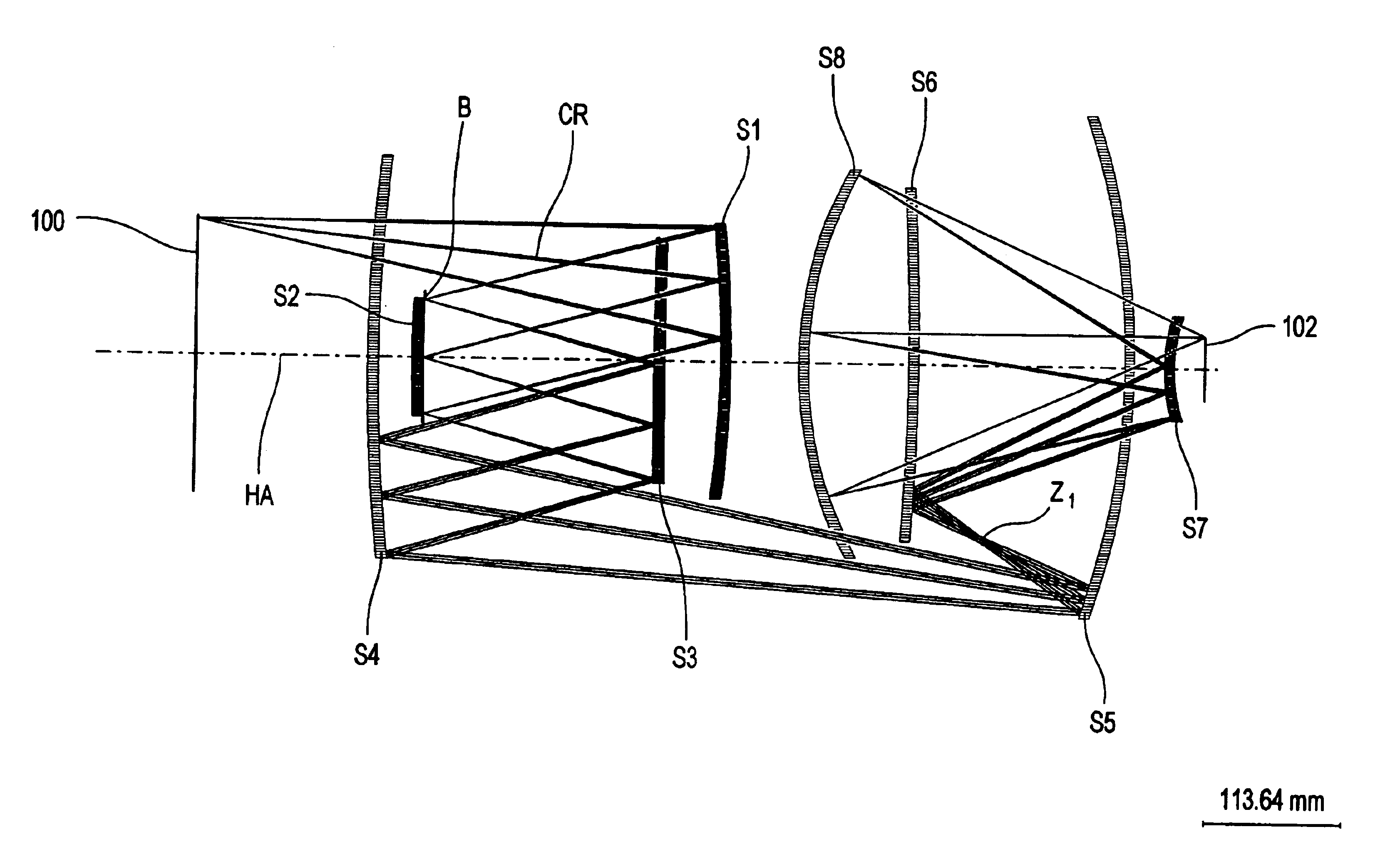
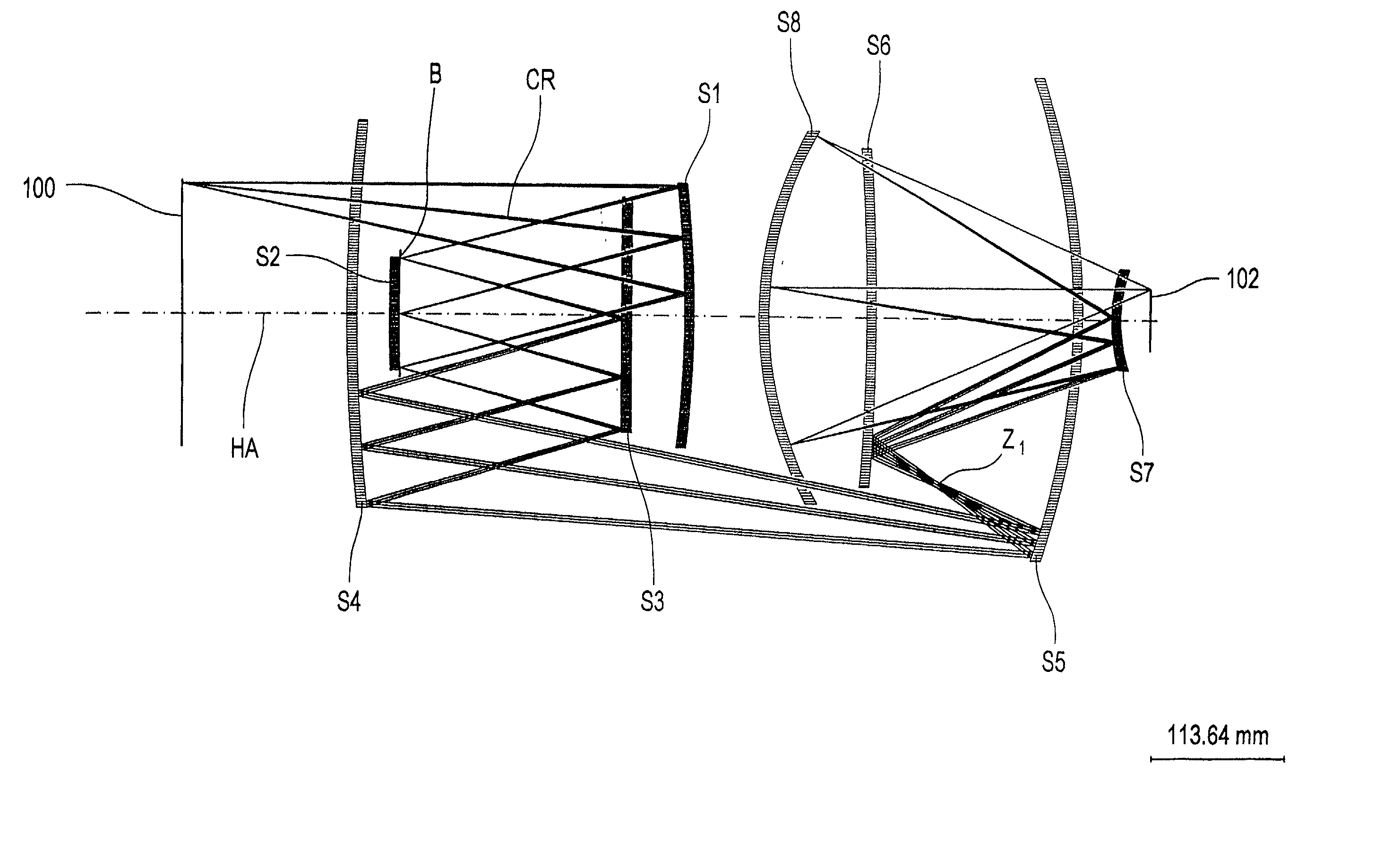
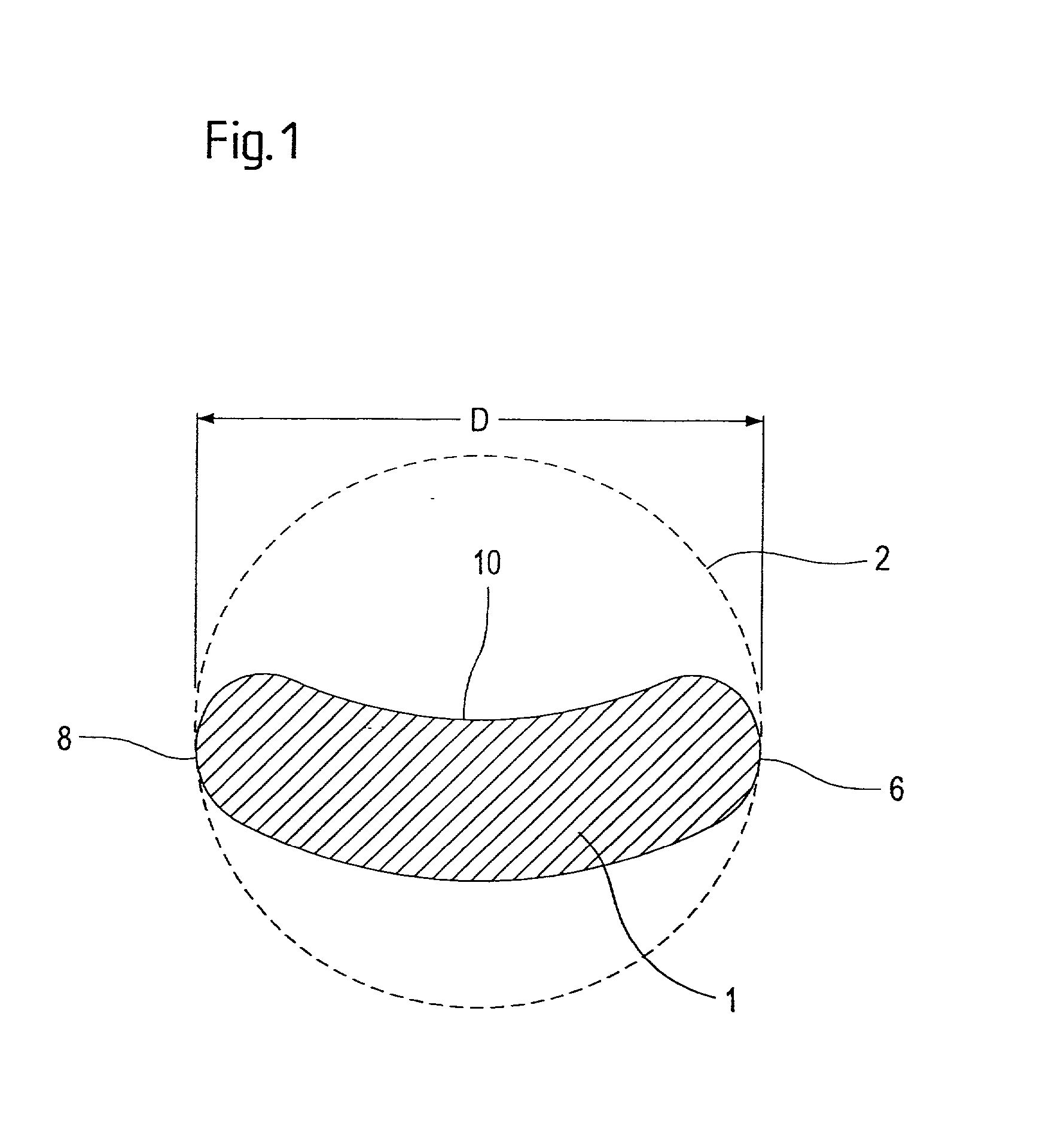
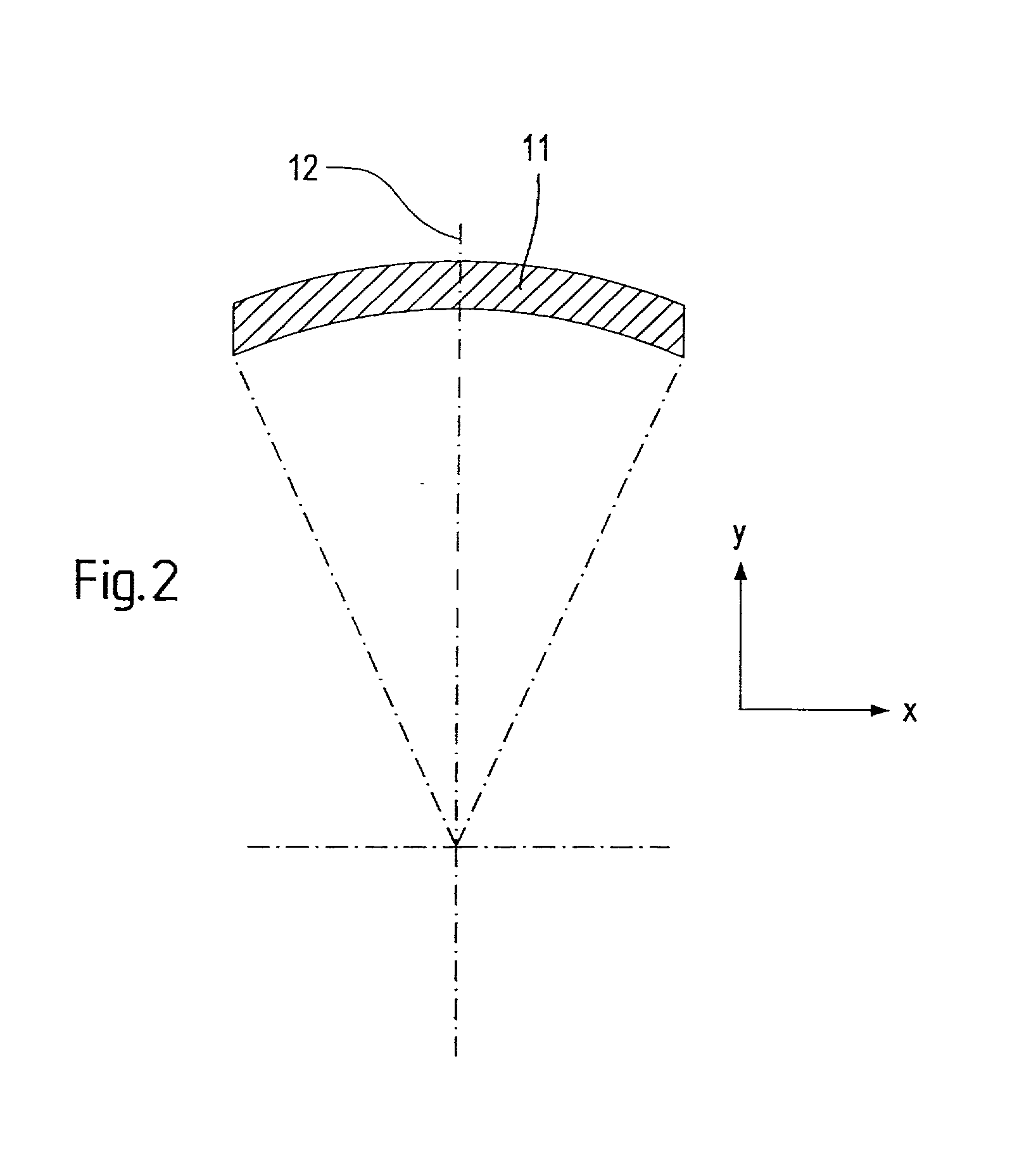
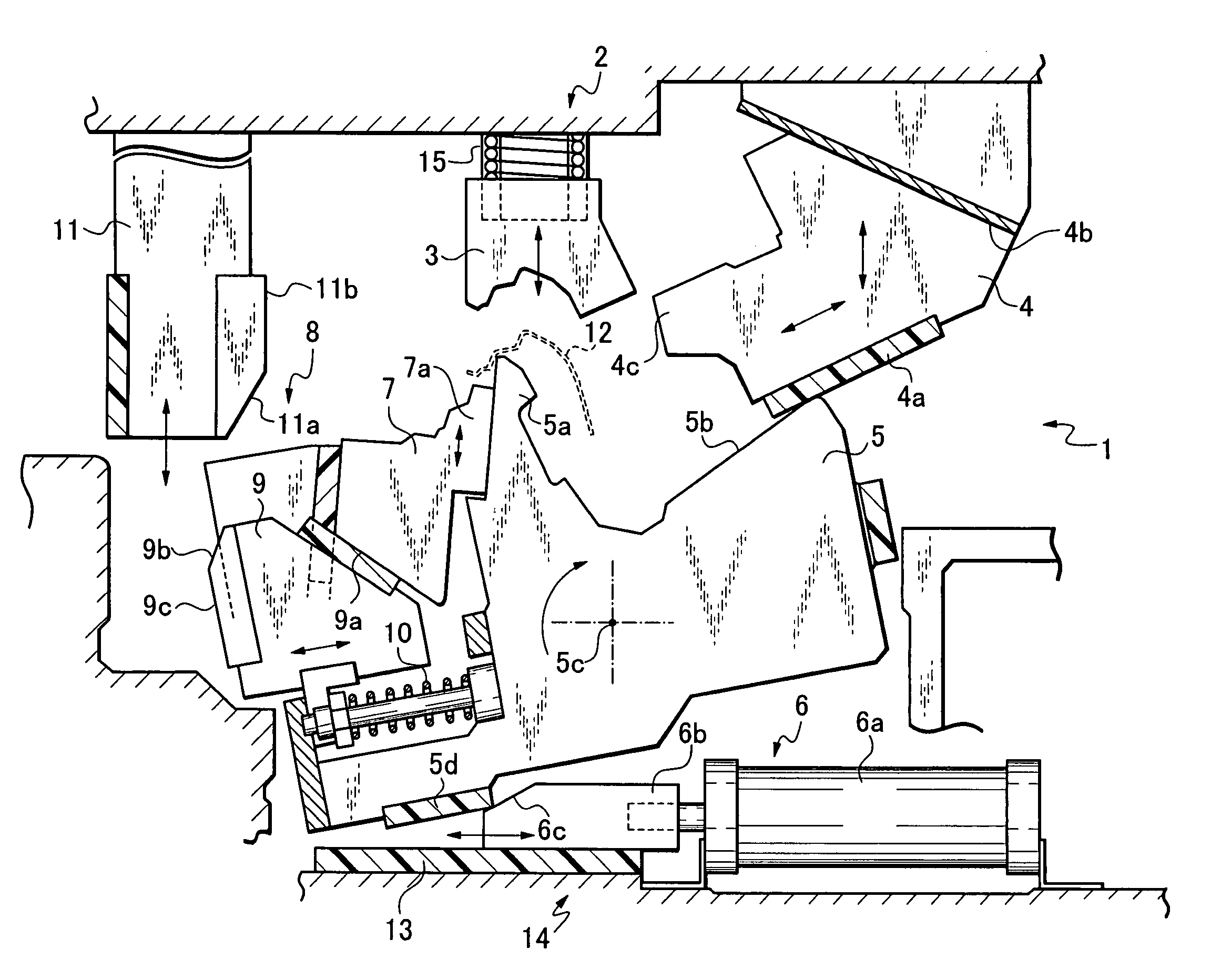
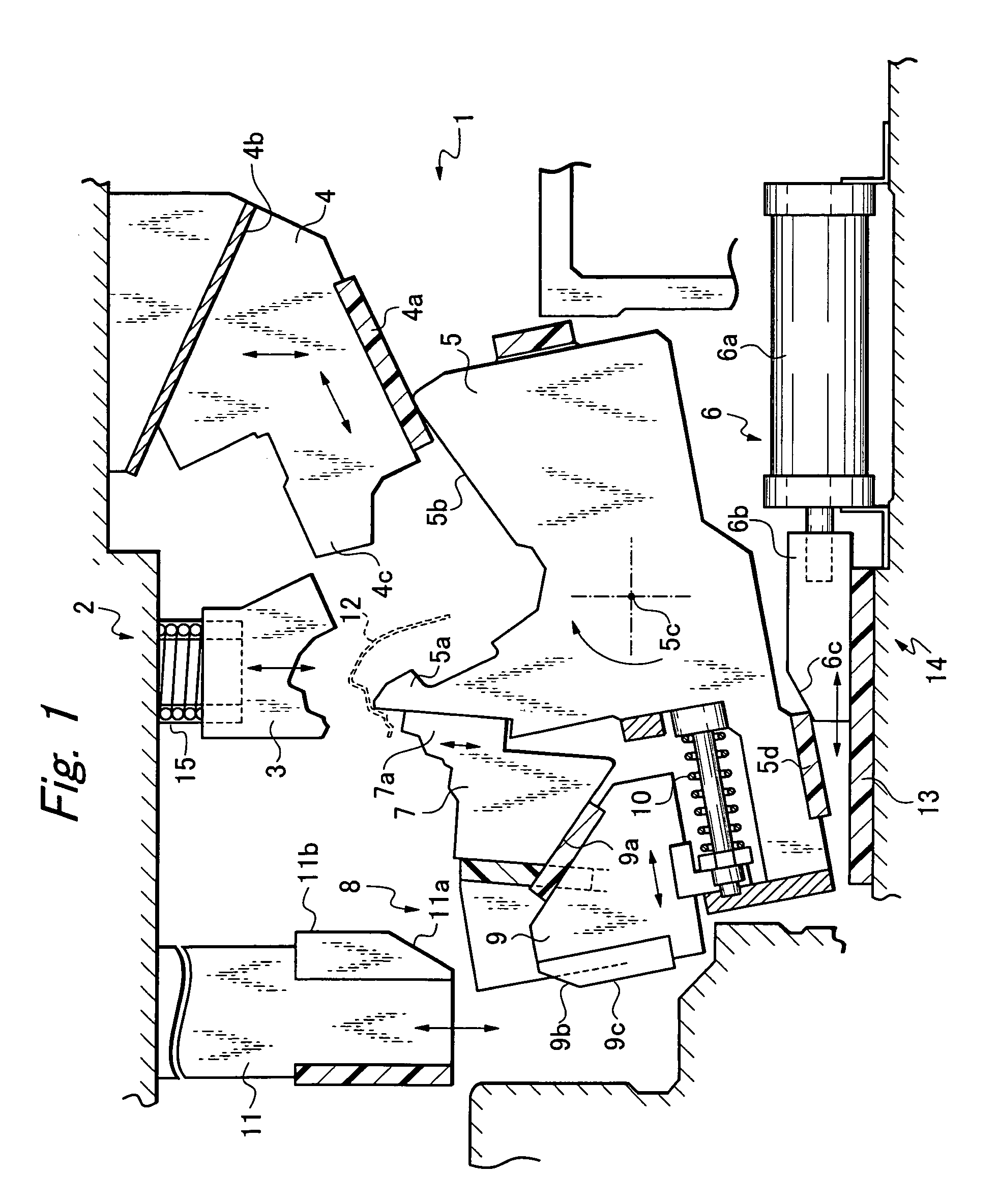
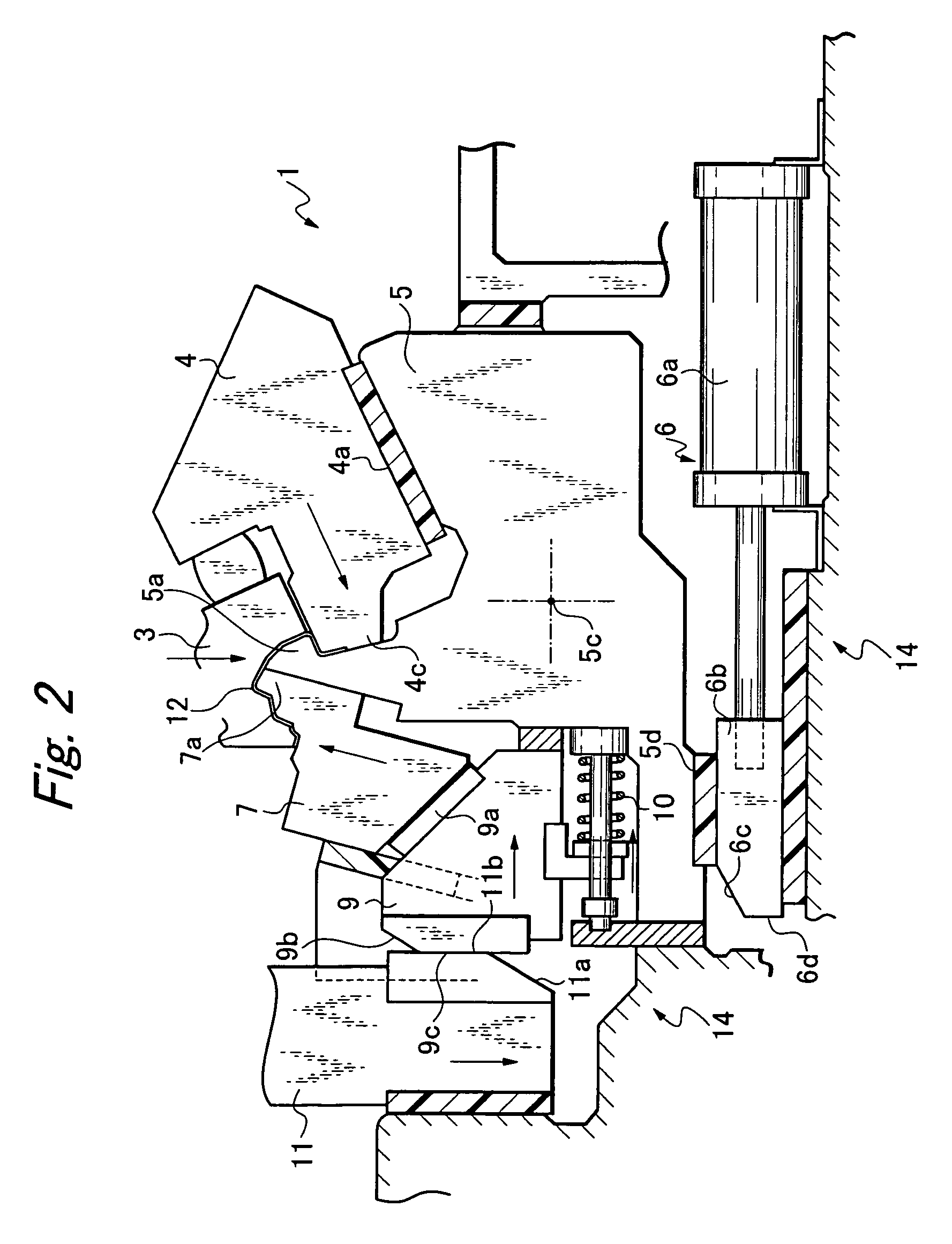
8-mirror microlithography projection objective
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
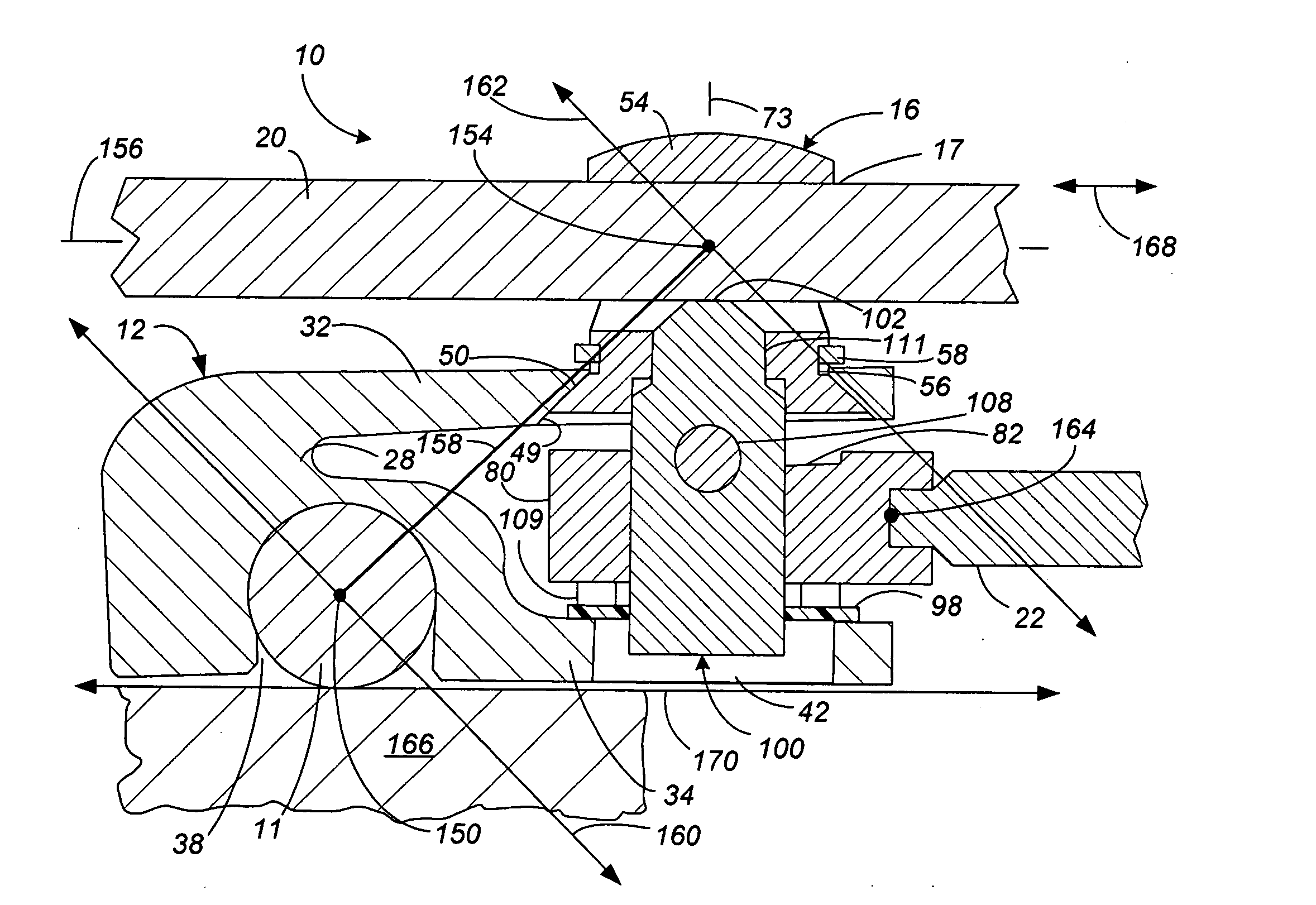
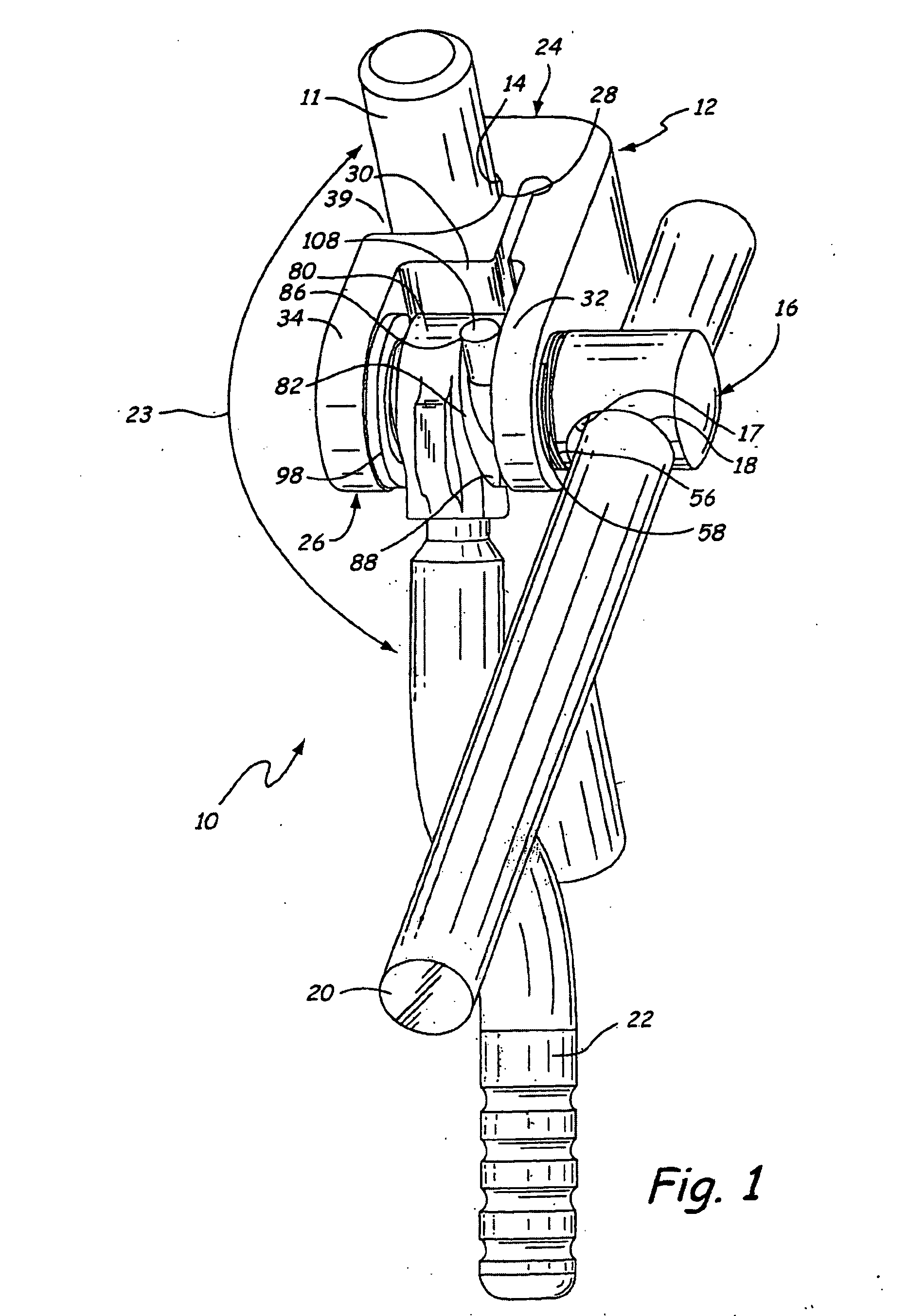
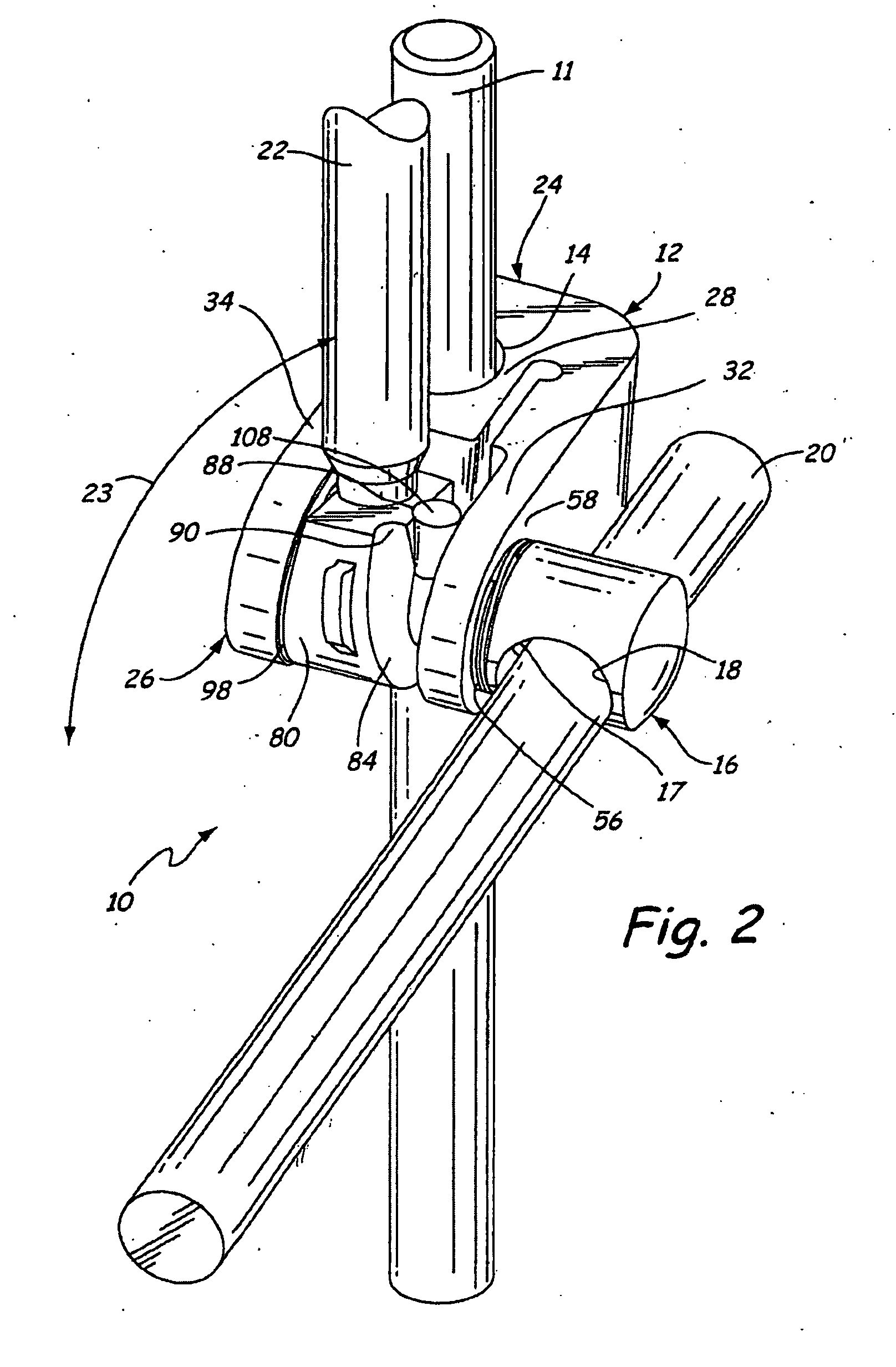
Low profile, handle-in-between surgical scissors clamp
InactiveUS20060200005A1Low profileMinimal underclearanceEndoscopesSurgical instrument supportSurgical ClampsBiomedical engineering
Owner:MINNESOTA SCI
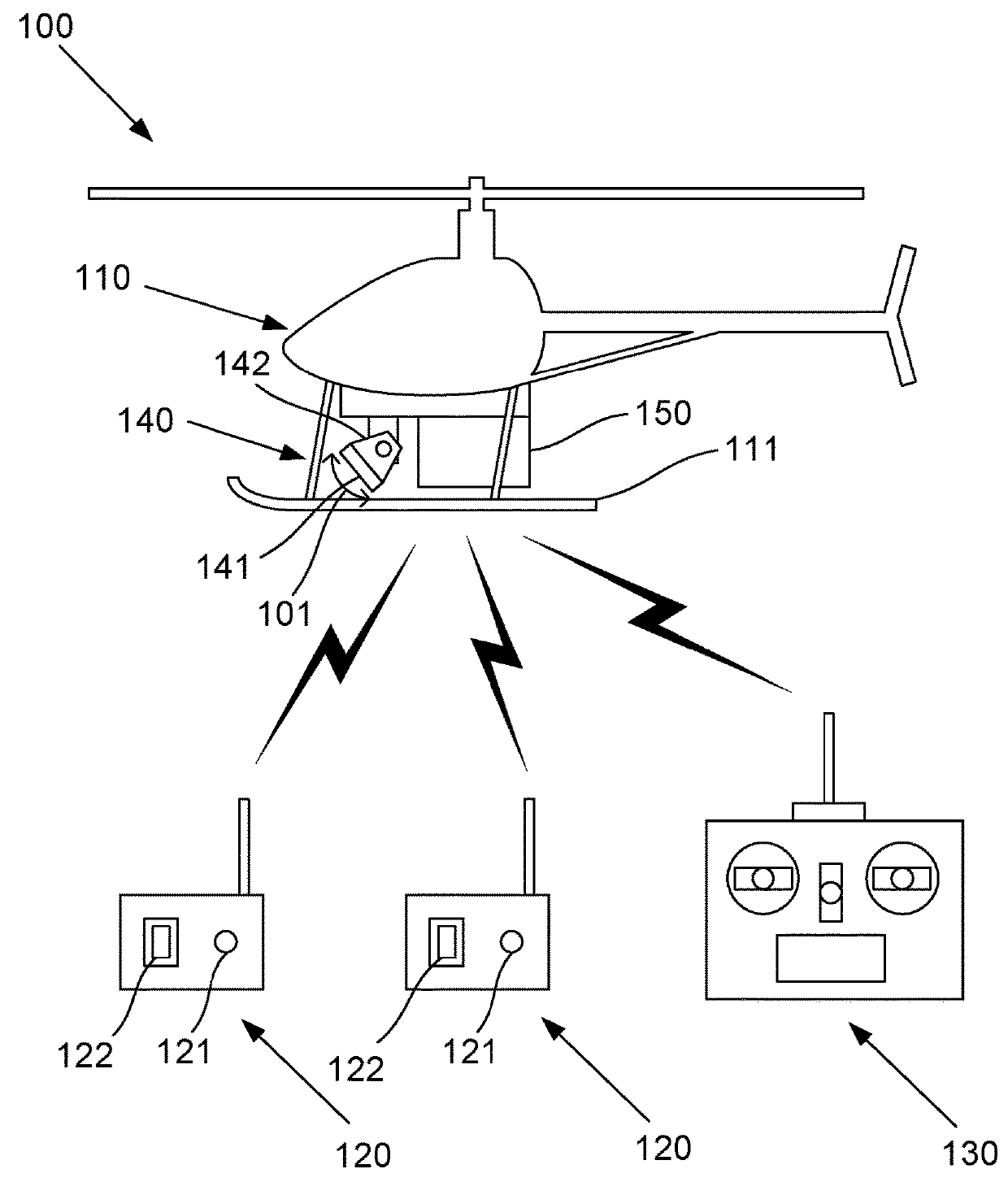
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Control Techniques
InactiveUS20180275654A1Minimum separationUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftRadarEngineering
A method of controlling an unmanned aerial vehicle executing a mission in a defined mission area including a first observation area within a Visual Line of Sight (VLOS) of a First Observer (FO), a second observation area within a VLOS of a second observer (SO), and a transition area within the VLOS of both the FO and the SO, the method including: the vehicle moving into the transition area after completing part of the mission within the first observation area, in sight of the FO; and in response to the vehicle moving into the transition area, determining whether the vehicle is in sight of the SO. The vehicle is including multiple processing systems in wireless communication with multiple remote user interfaces and a radar sensor mounted on the vehicle using a moveable mount for moving the radar sensor between different radar orientations, the radar sensor generating a range signal.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
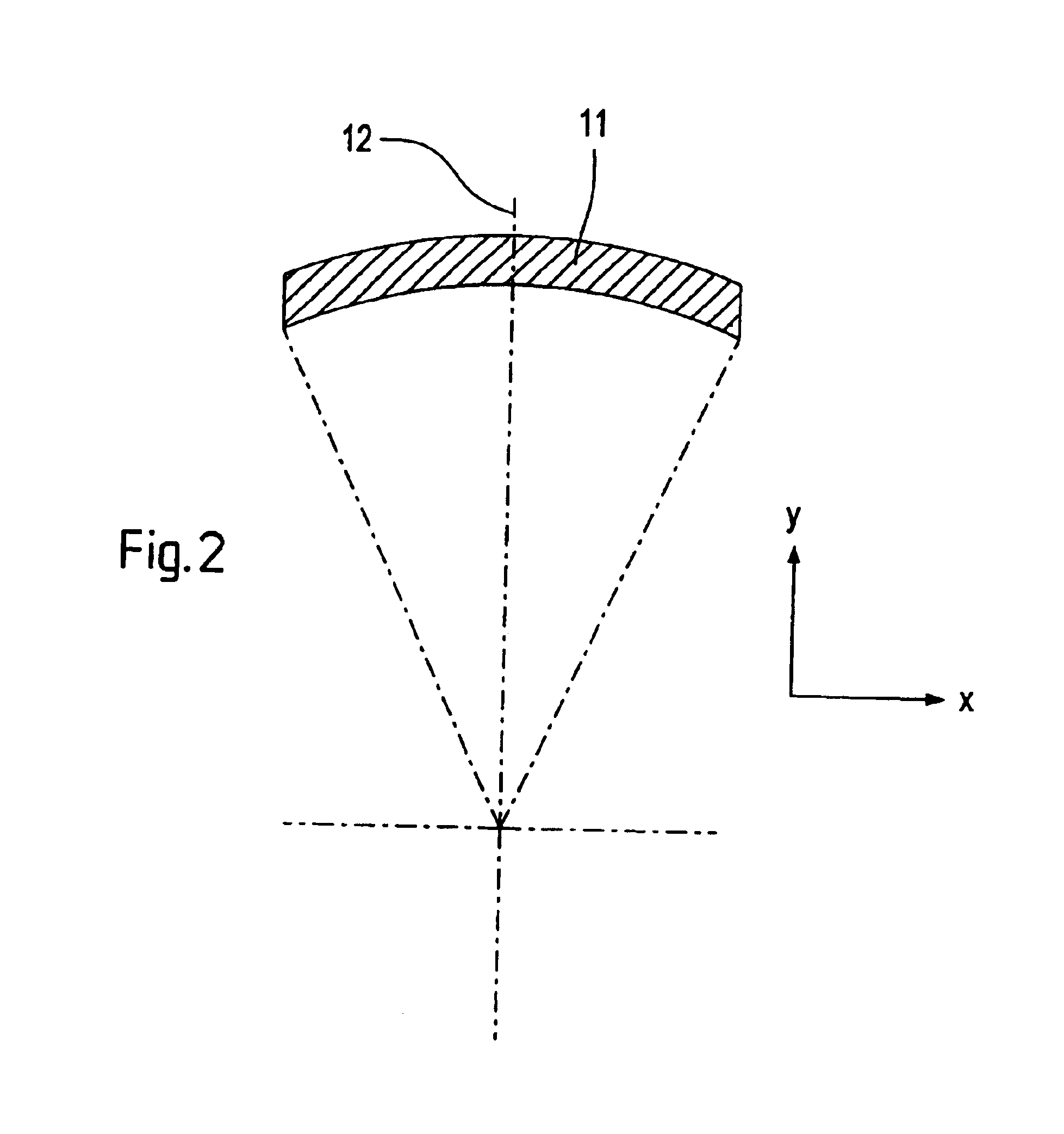
8-Mirror microlithography projection objective
A projection objective provides a light path for a light bundle from an object field in an object plane to an image field in an image plane. The projection objective comprises a first mirror (S1), a second mirror (S2), a third mirror (S3), a fourth mirror (S4), a fifth mirror (S5), a sixth mirror (S6), a seventh mirror (S7), and an eighth mirror (S8). The light path is provided via the eight mirrors, the light bundle includes light with a wavelength in the range of 10-30 nm, and the light path is free of shading.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
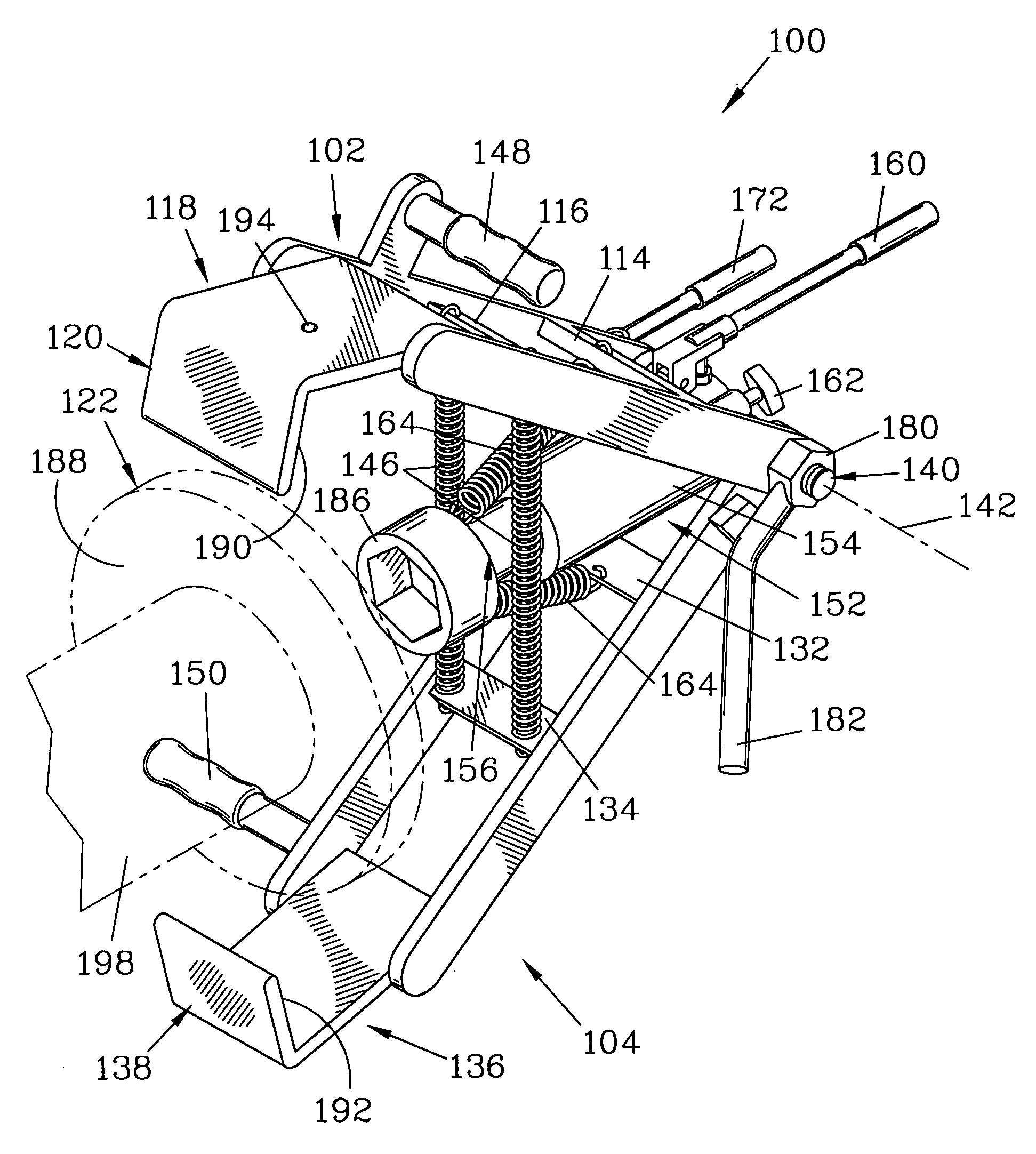
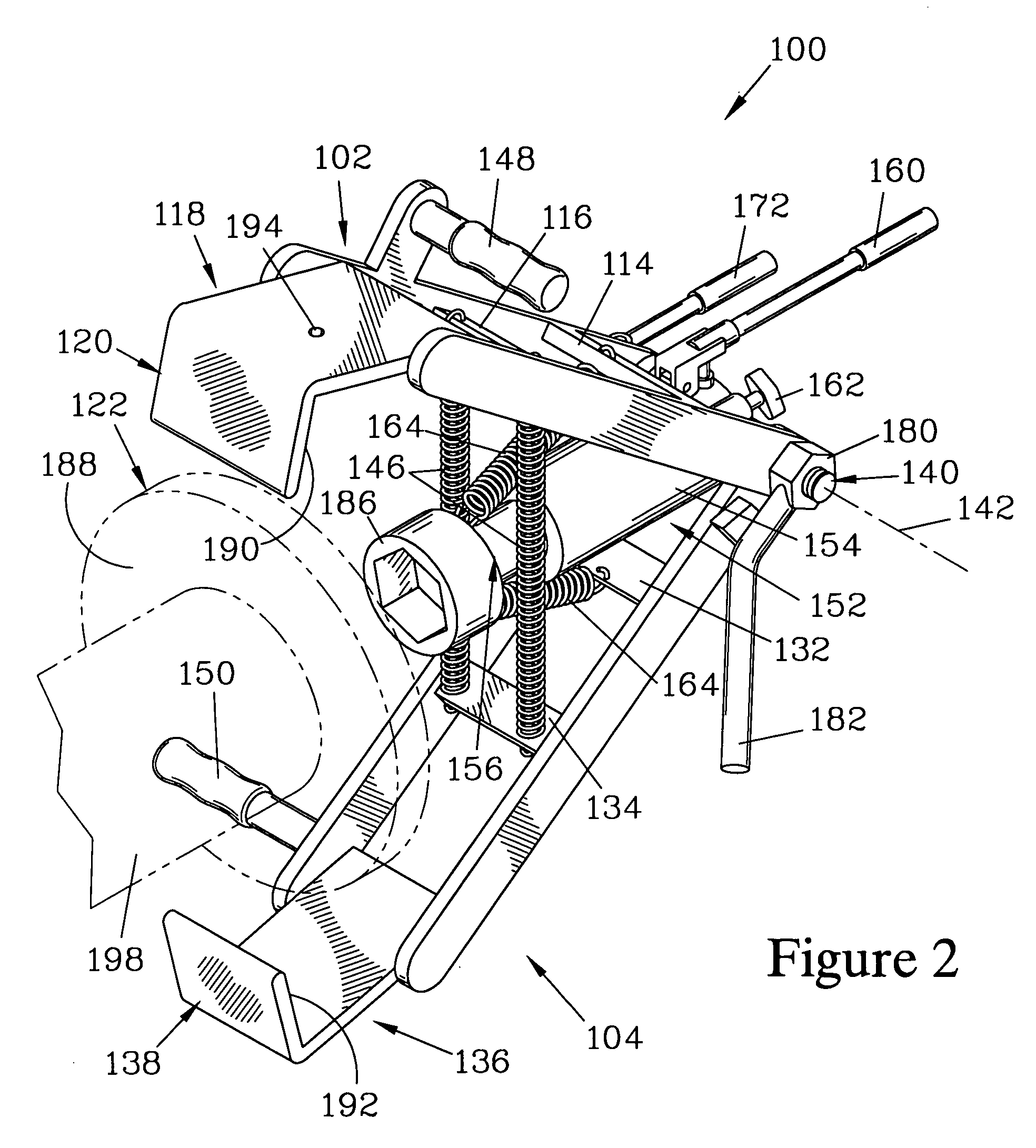
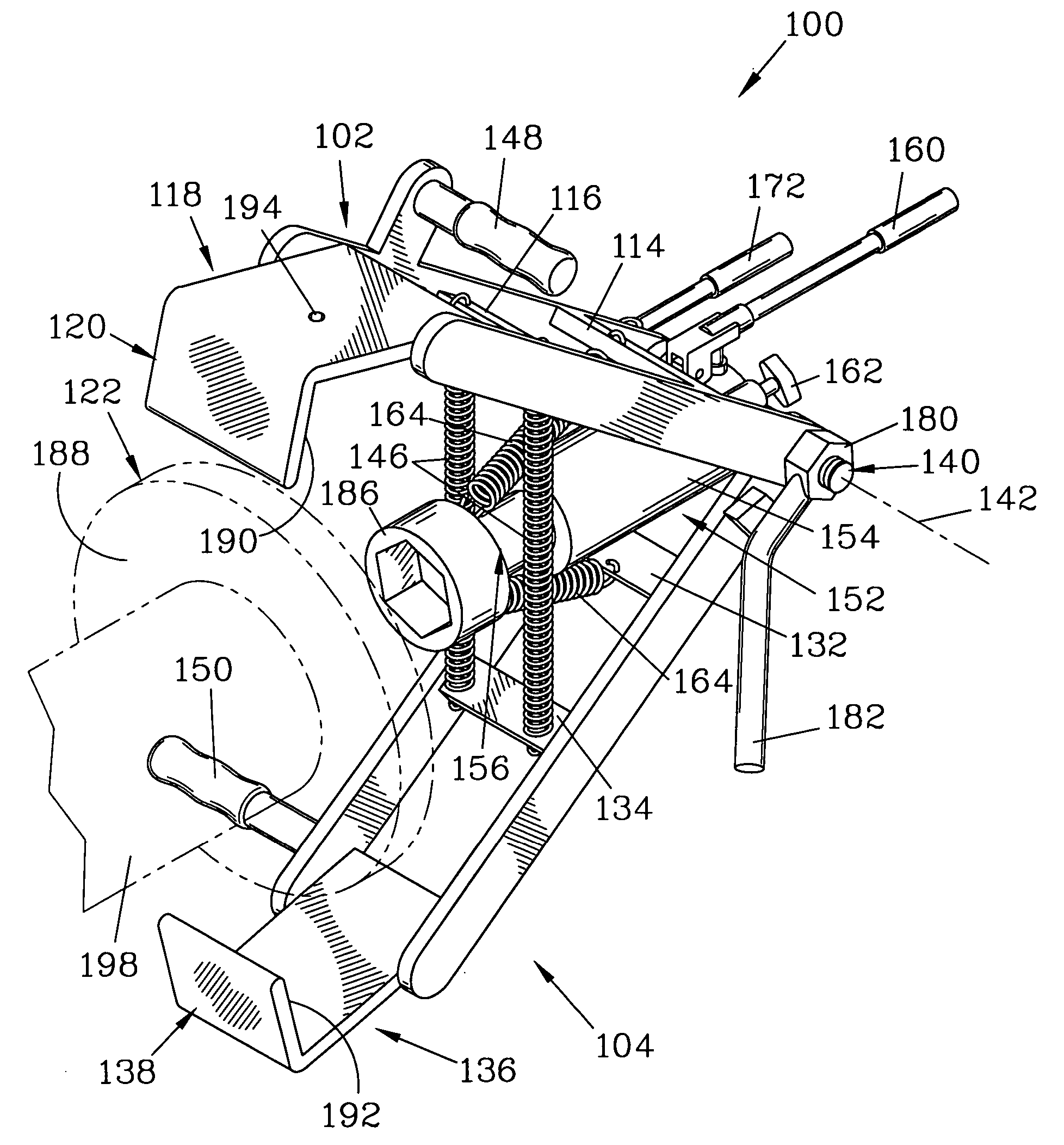
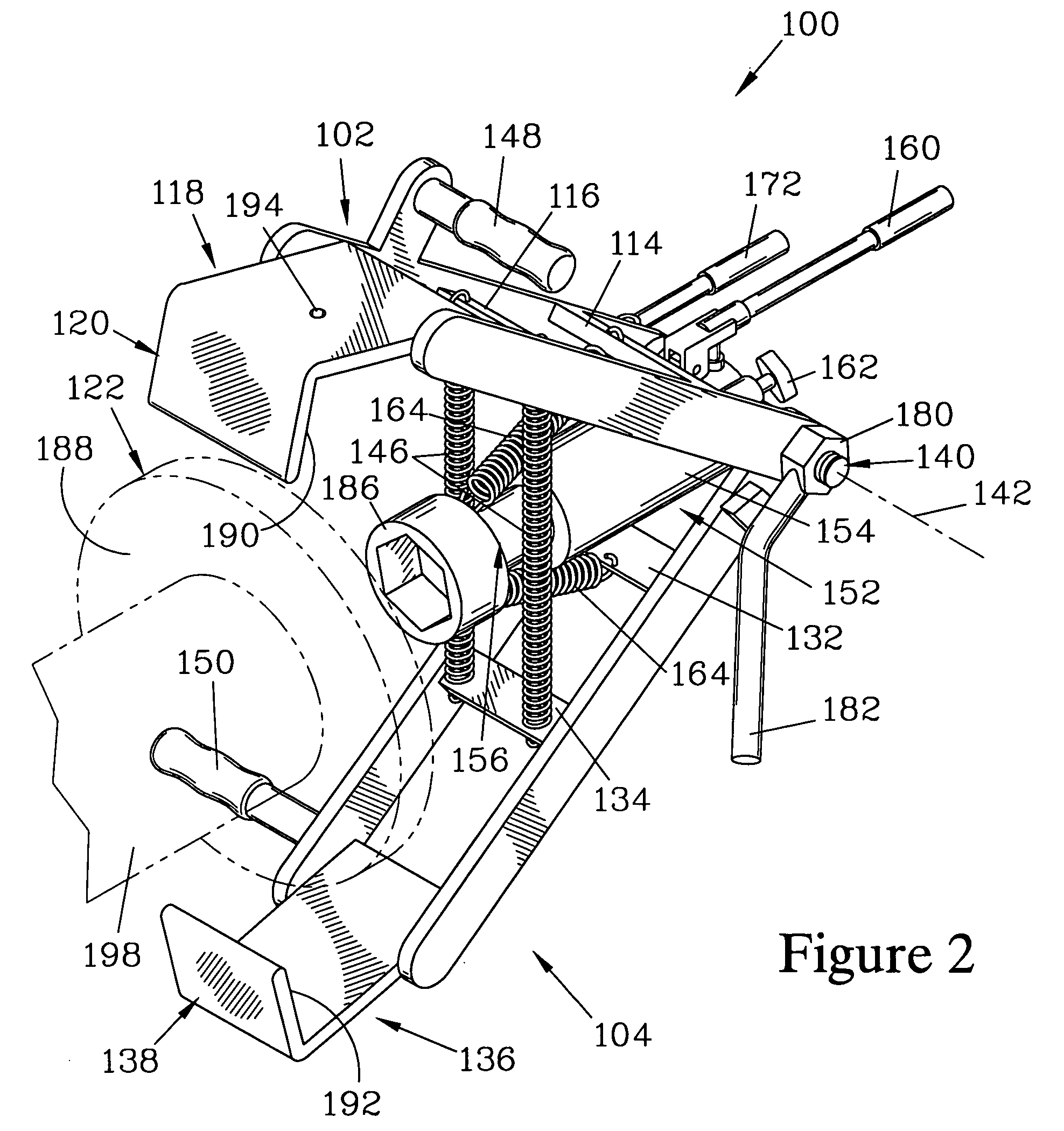
Brake rotor puller
InactiveUS6925696B1Easy to disassembleEasy to adjustMetal working apparatusMetal-working hand toolsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A rotor puller has two arm members, ending at claws, and a jack with an extendible piston. The arm members and the jack are pivotably attached together about a pivot axis. Springs bias the arm members toward each other. The claws are placed over a brake rotor and retained thereon by a pin. After the claws have been placed, the jack is centered and activated to extend the piston towards the claws. The piston forcibly engages a wheel hub while the claws forcibly engage the rotor, pulling it from the wheel hub. Handles on the arm members facilitate placement of the claws over the rotor.
Owner:PRO CUT INT
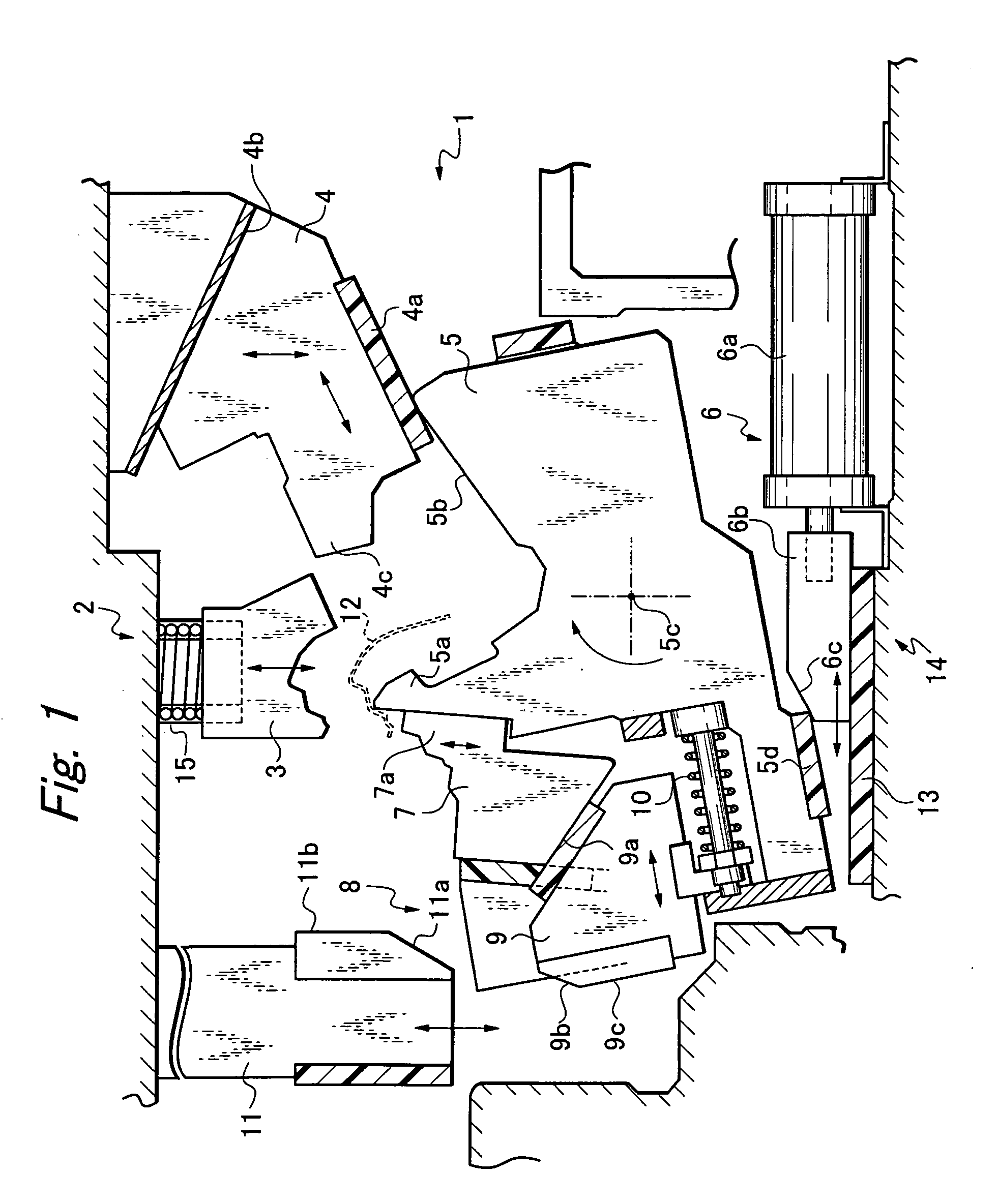
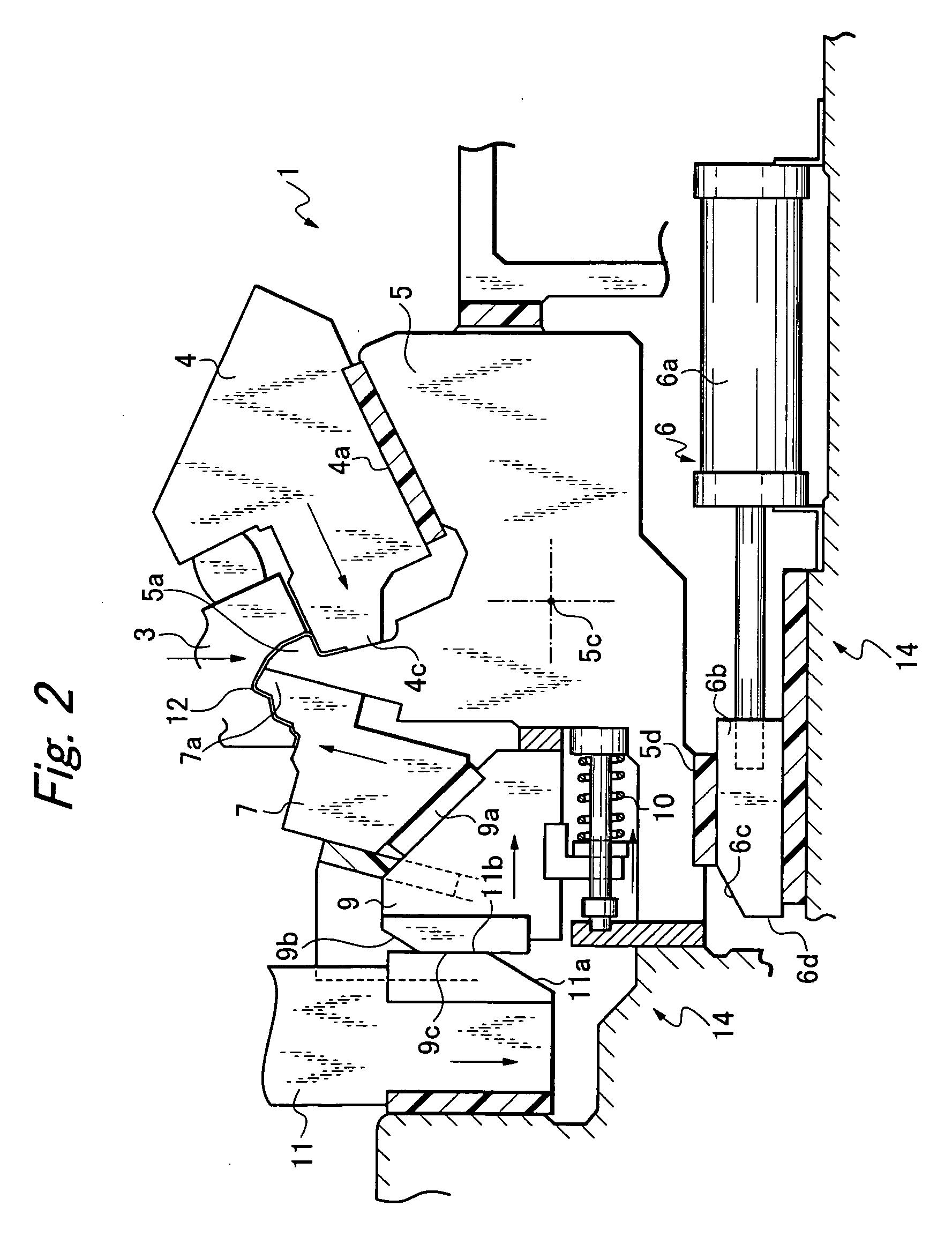
Separation process and apparatus
InactiveUS6841133B2Easy to separateMinimum separationCatalytic crackingDispersed particle separationCycloneEngineering
An apparatus and process is disclosed for the separation of solids from gases in a mixture which is most particularly applicable to an FCC apparatus. The mixture of solids and gases are passed through a conduit and exit through a swirl arm that imparts a swirl motion having a first annular direction to centripetally separate the heavier solids from the lighter gases. The mixture then enters a cyclone which has a curved outer wall and imparts a second swirling angular direction to the mixture. The second angular direction is counter to the first angular direction. The apparatus and method assures that a greater proportion of the mixture entering the cyclone is incorporated into the vortex to further enhance separation between the solids and gases.
Owner:UOP LLC
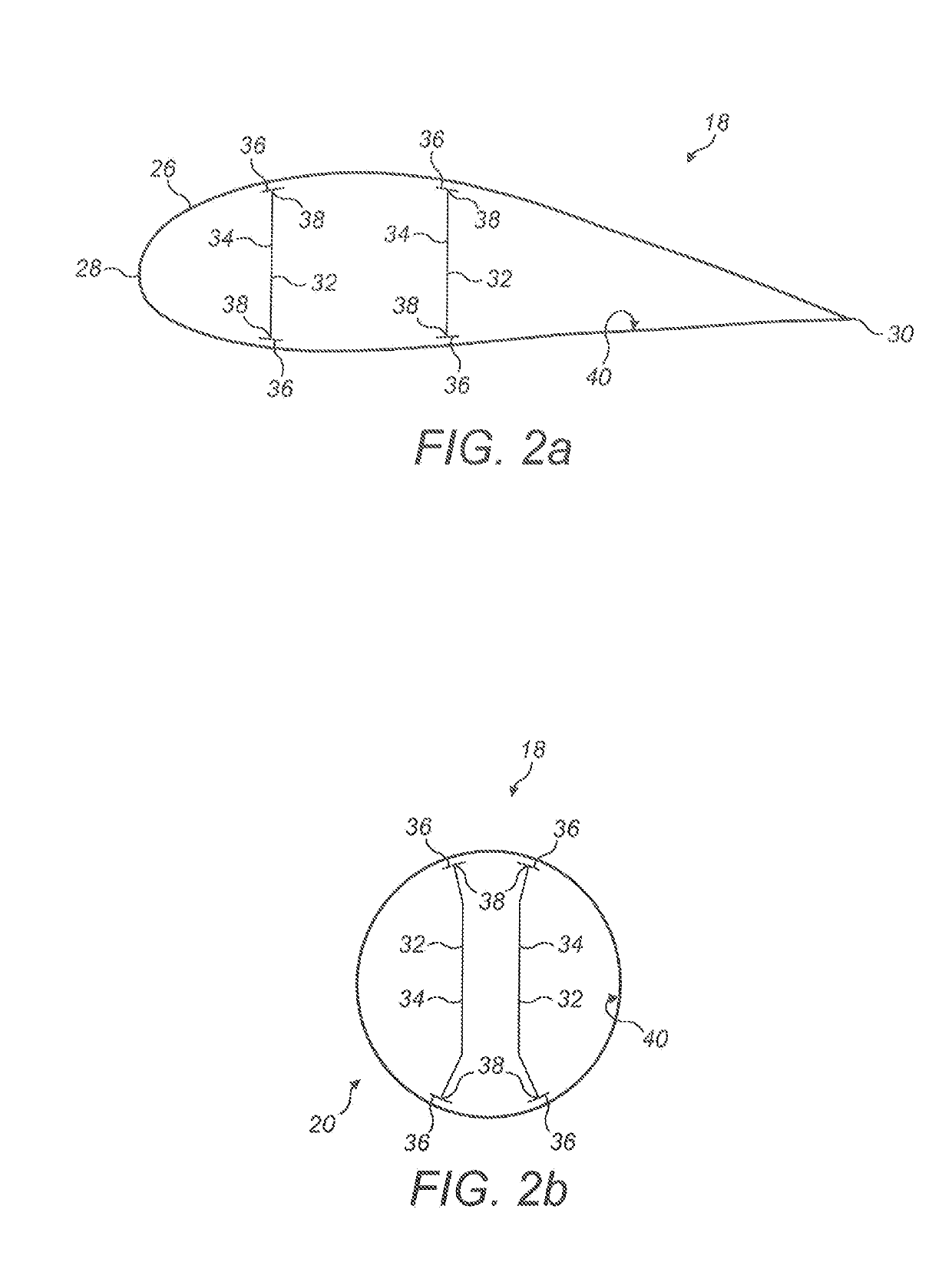
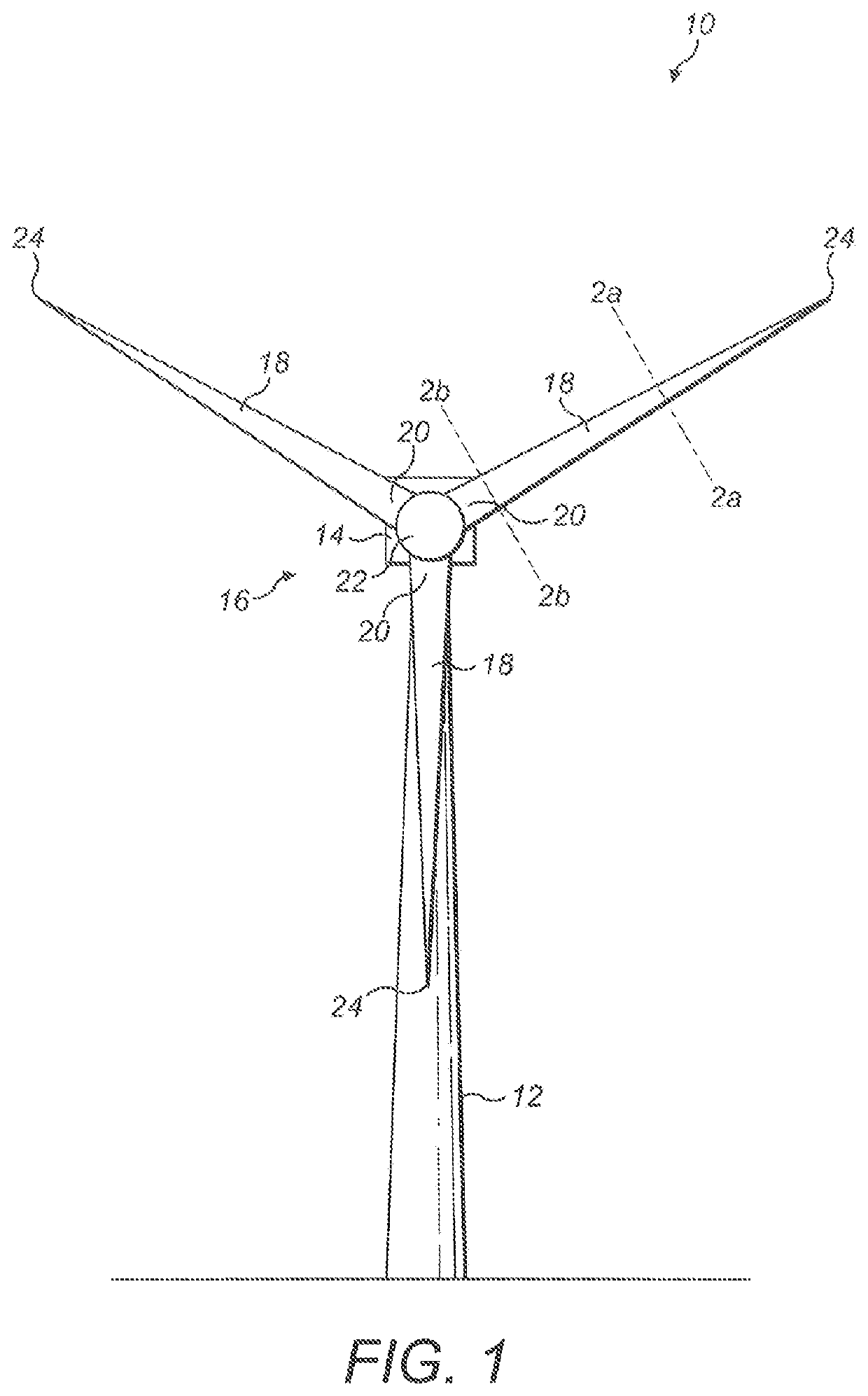
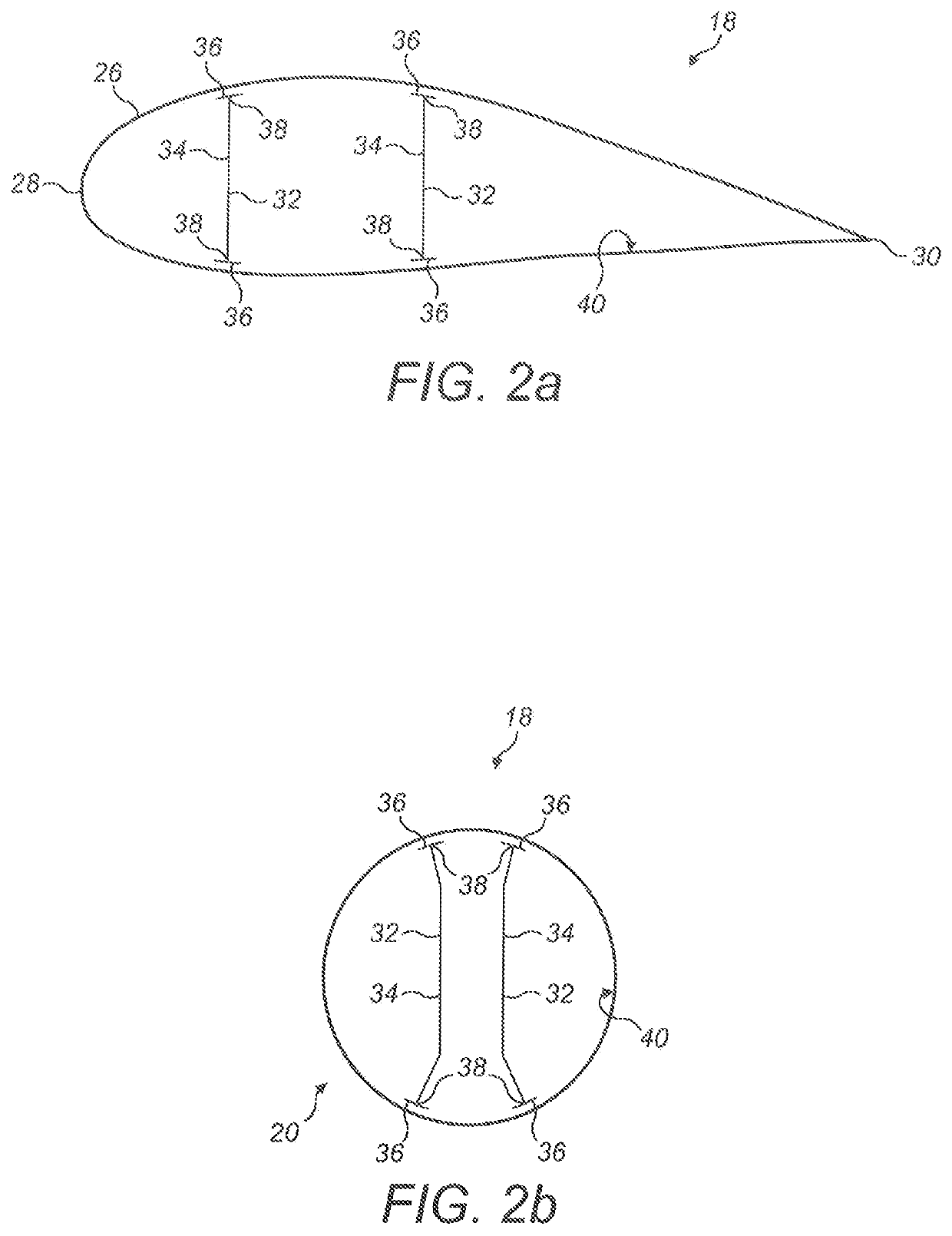
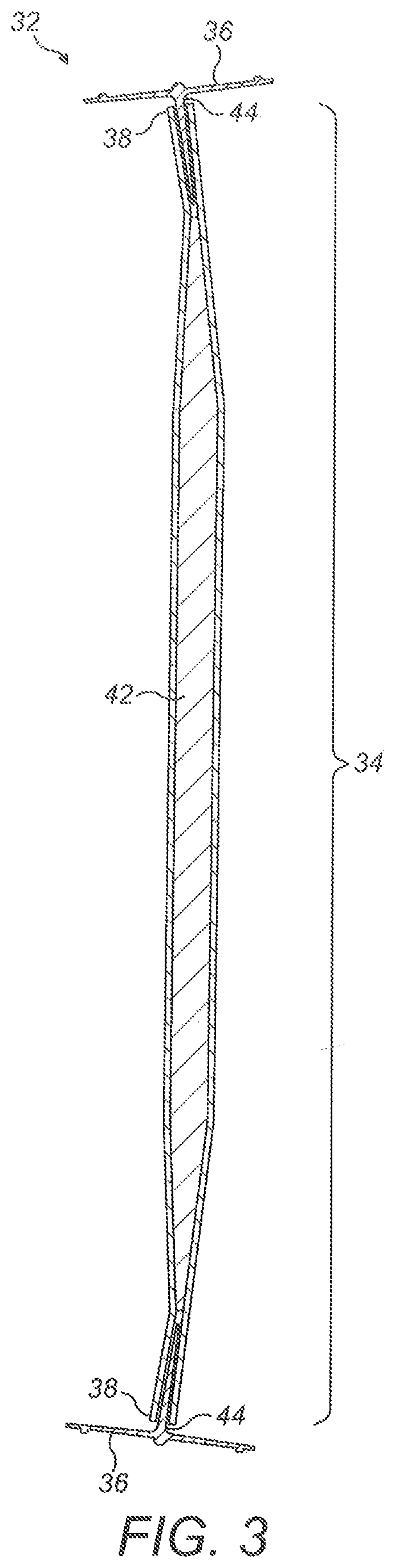
Manufacture of a wind turbine blade
ActiveUS20190178227A1Constant cross-sectionMinimal thicknessEngine manufactureFinal product manufactureTurbine bladeFlange
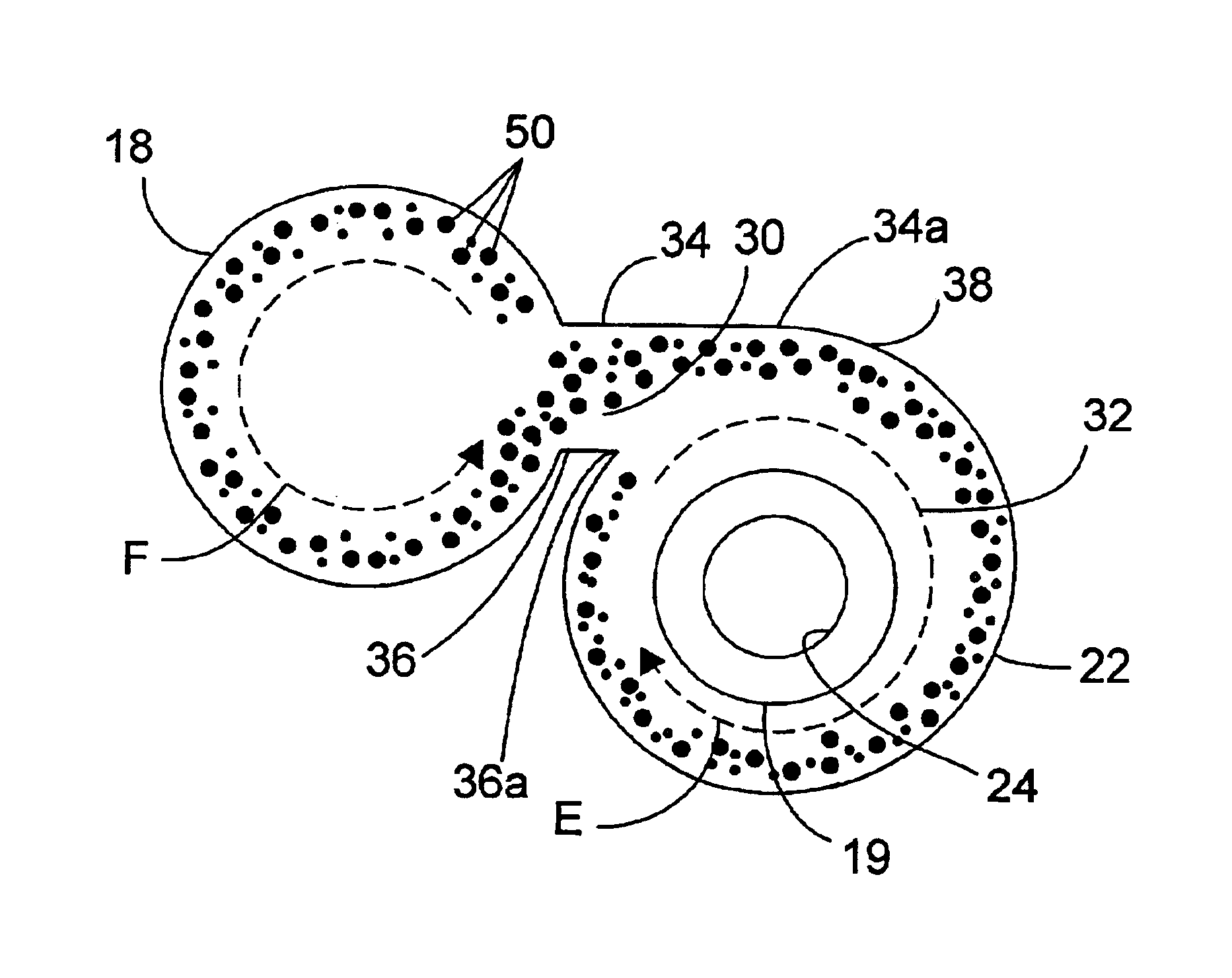
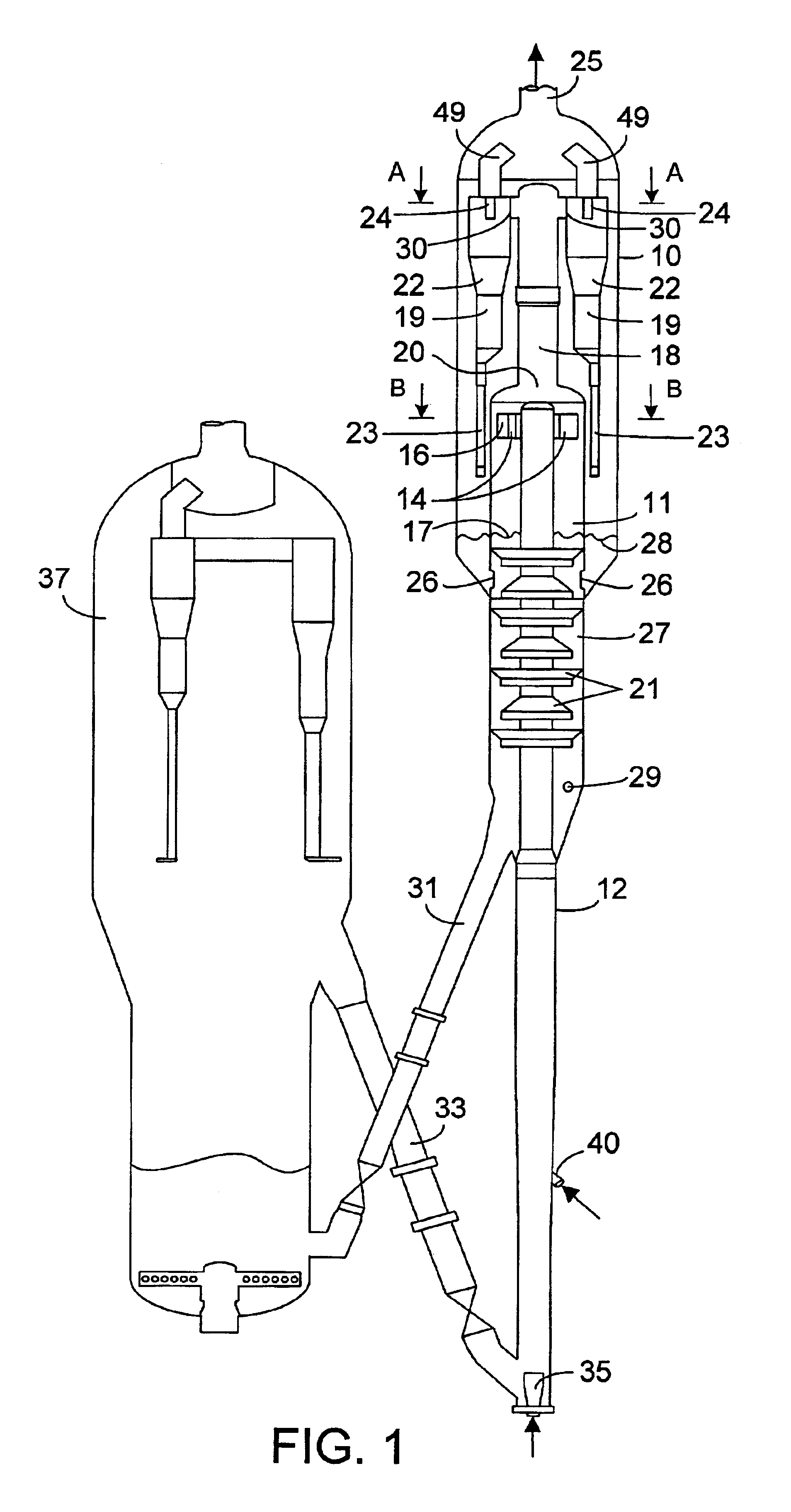
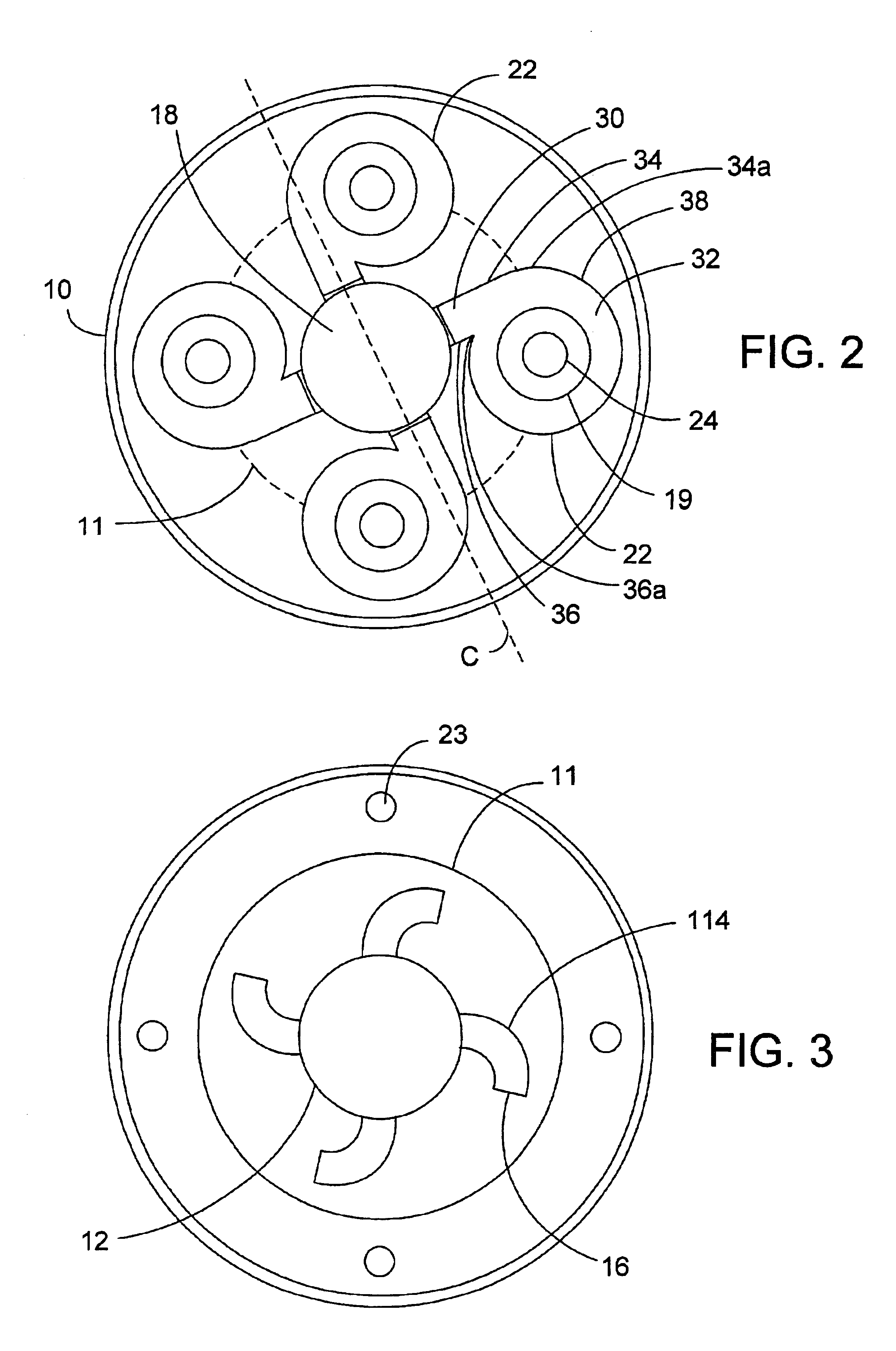
A shear web flange (36) for a shear web (32) of a wind turbine blade (18) is described. The flange (36) extends longitudinally and comprises a bonding surface (50) for bonding to an inner surface of a wind turbine blade (18). One or more protruding features (52a, 52b) protrude from the bonding surface (50). A method of making such a shear web flange (36) is also described as are a shear web (32) for a wind turbine blade (18), a wind turbine blade (18) and a method of making a wind turbine blade (18).
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Brake rotor puller
InactiveUS20050177988A1Easy to disassembleEasy to adjustMetal working apparatusMetal-working hand toolsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A rotor puller has two arm members, ending at claws, and a jack with an extendible piston. The arm members and the jack are pivotably attached together about a pivot axis. Springs bias the arm members toward each other. The claws are placed over a brake rotor and retained thereon by a pin. After the claws have been placed, the jack is centered and activated to extend the piston towards the claws. The piston forcibly engages a wheel hub while the claws forcibly engage the rotor, pulling it from the wheel hub. Handles on the arm members facilitate placement of the claws over the rotor.
Owner:PRO CUT INT
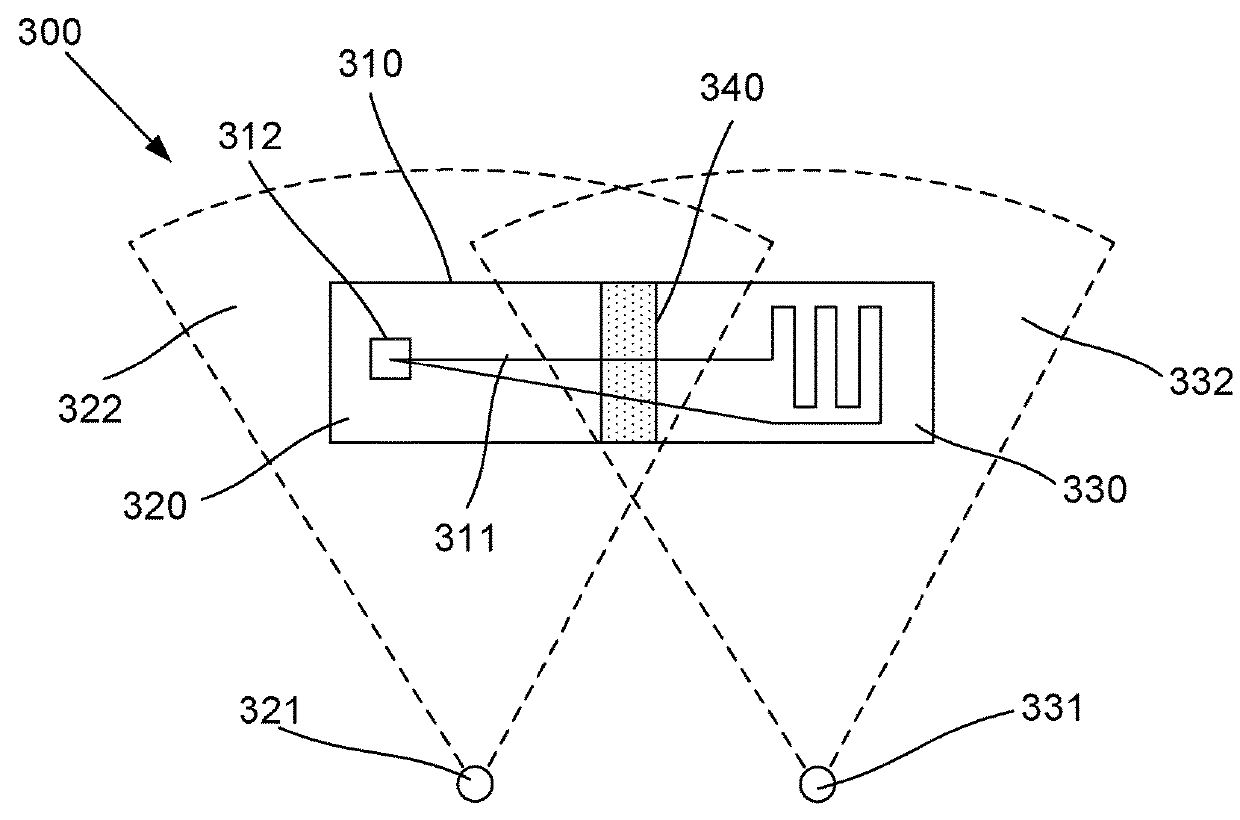
Intrinsically safe compliant circuit element spacing
ActiveUS20090180263A1Minimum separationPrinted electric component incorporationPrinted circuit aspectsFlexible circuitsActive component
A compliant circuit element spacing system comprises a circuit board, a dummy spacer component, and a compliant circuit element. One or more active components are mounted to the circuit board. The dummy spacer component is also mounted to the circuit board, such that the dummy spacer component is electrically isolated from each active component mounted to the circuit board. The compliant circuit element is positionable proximate the circuit board, and spaced from the circuit board by the dummy spacer component. The spacing component isolates the compliant circuit element from each active component mounted to the circuit board.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
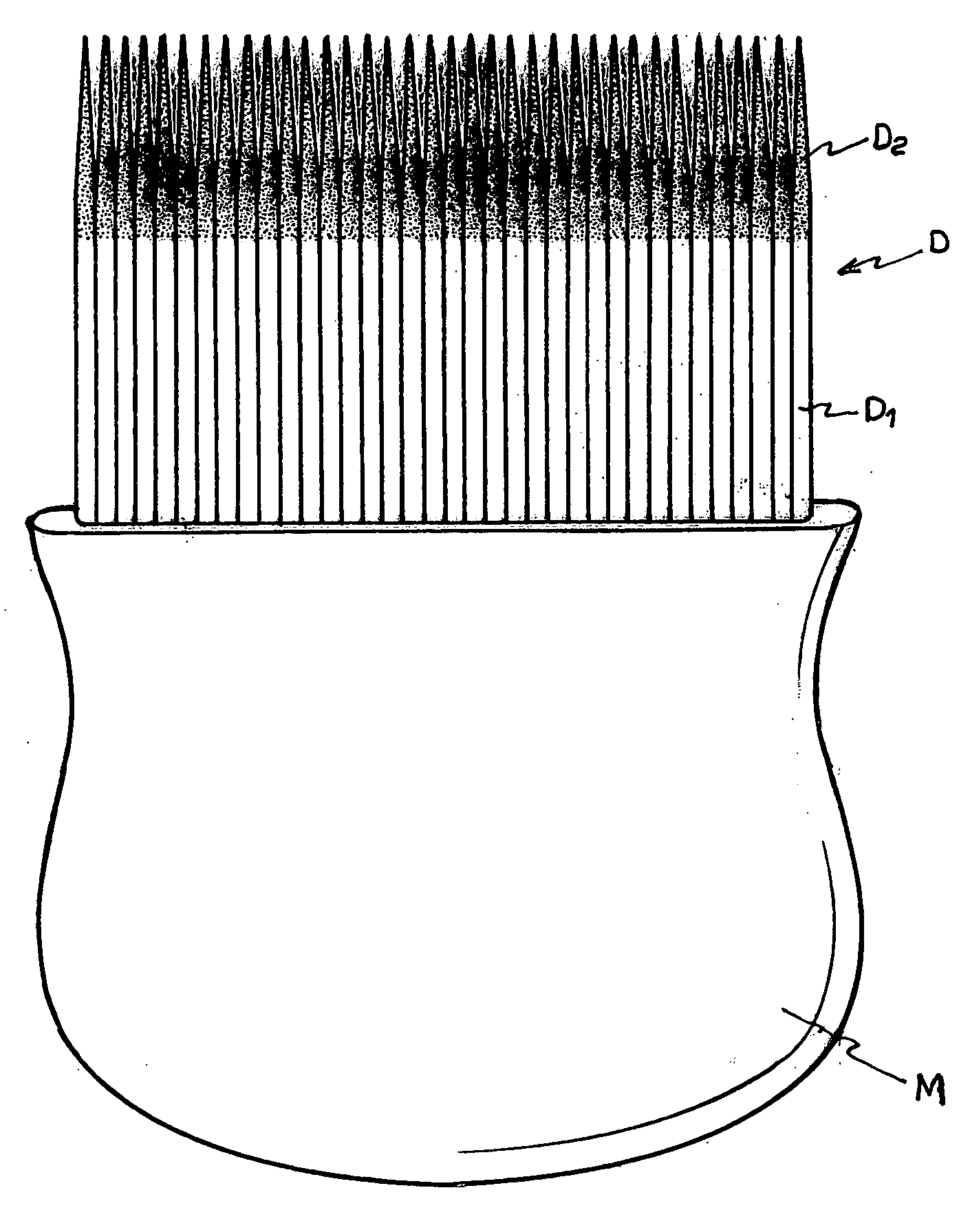
Rigid comb having microtexturized-tip teeth for hair cleaning
InactiveUS20060243293A1Preventing electrostatic chargeAvoid tanglesHair combsSurface roughnessEngineering
A comb made up of a handle wherefrom a number of sweeping teeth are projected, thus forming a rigid set of high mechanical strength, where the teeth are aligned one after the other with a minimal separation in between to define the comb front, keeping the anchorage section of each tooth within the handle body, and projecting out of the handle in a length considerably greater than the anchorage length. The teeth have a proximal section starting from their anchorage inside the handle to a point of their total length outside the handle, where a distal section begins and extends up to the free end, and where the surface roughness of the former section is different from that of the distal section, which is microtexturized.
Owner:LANNE CARLOS ERNESTO
Negative-angle press-working die
InactiveUS7665341B2Quality improvementMinimum separationShaping toolsForging press detailsCentre of rotationEngineering
Owner:YOURBUSINESS
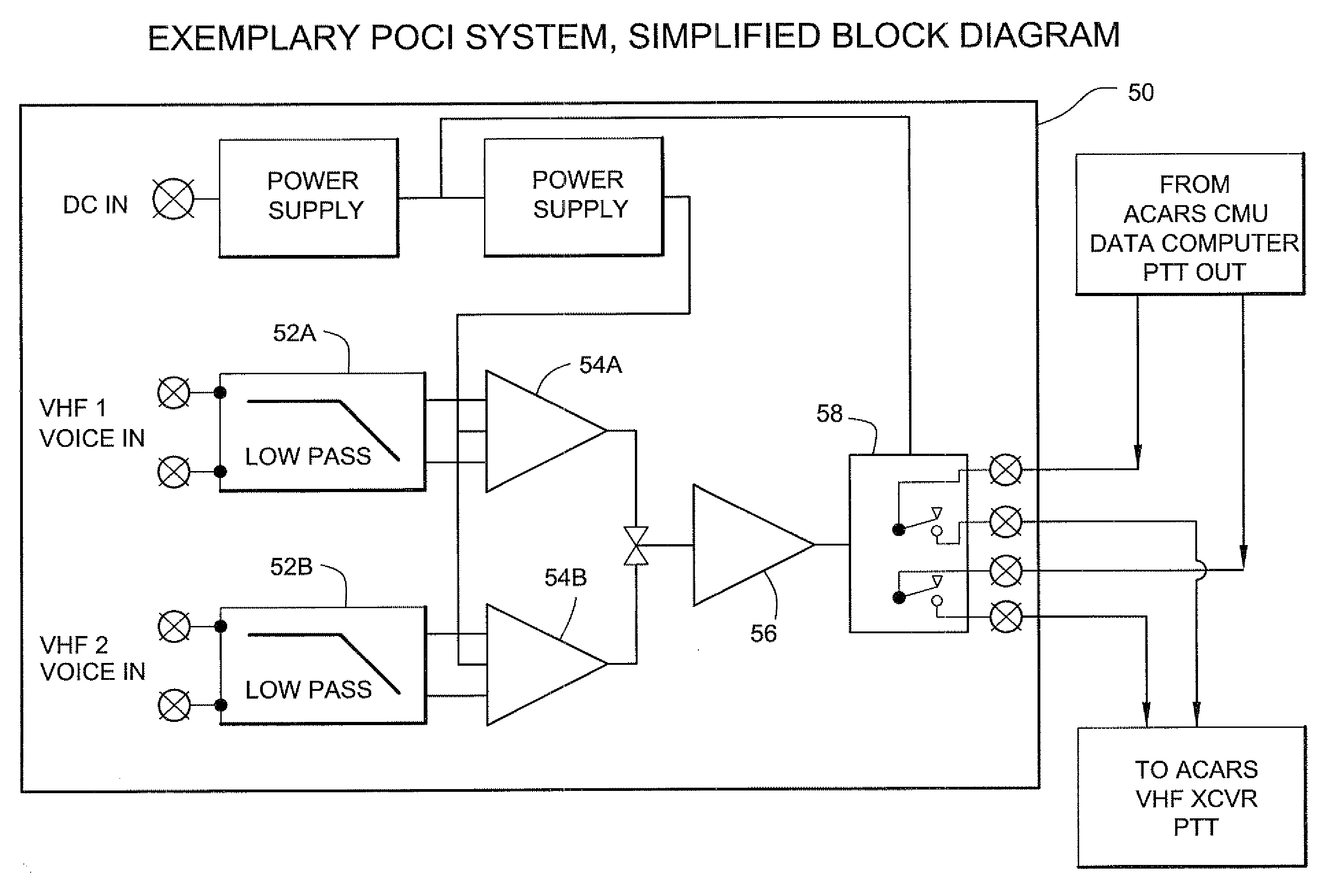
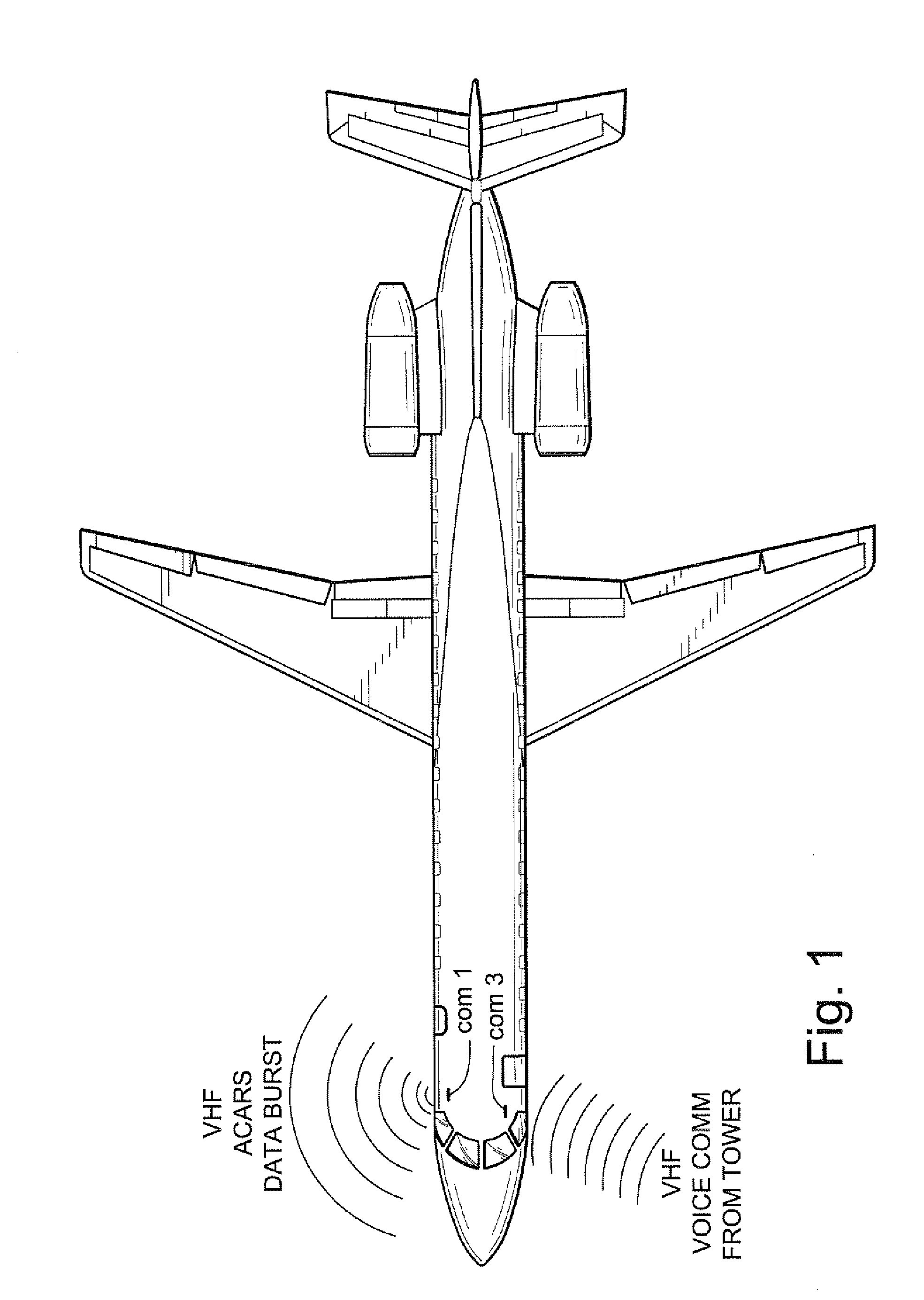
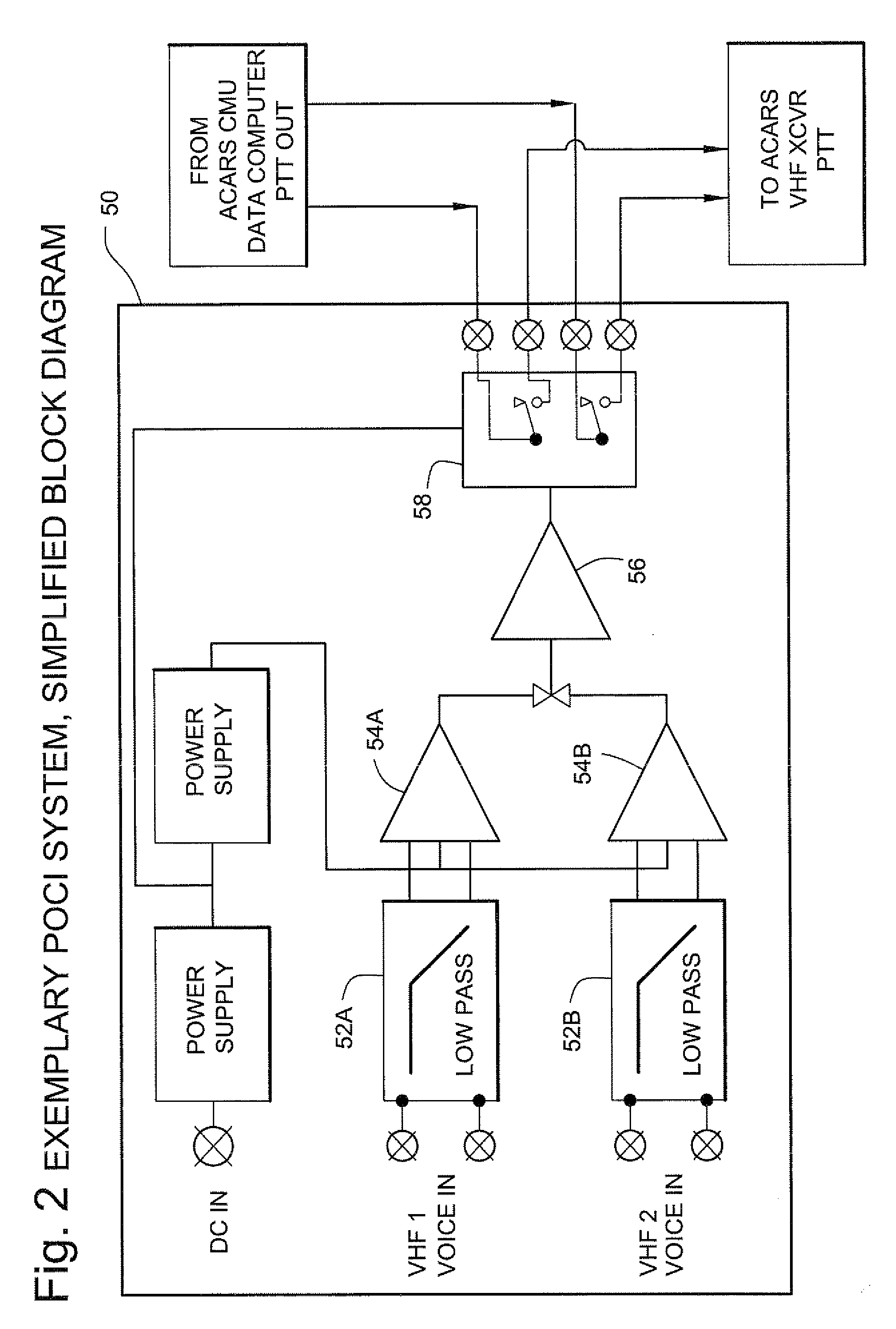
Presence of communication interlock method and apparatus for reducing or eliminating aircraft communications radio interference
InactiveUS20080254750A1Interference minimizationReduce distractionsRadio transmissionAlarmsTransceiverInterference (communication)
In one exemplary illustrative non-limiting aircraft radio communications system, a “POCI” (“Presence Of Communication Interlock”) is comprised of a double balanced low pass LC filter covering the voice range. The voice signals coming from the two VHF's are filtered and processed by an amplifier at an adequate level to be peak detected. The resulting signal is applied to an amplifier with a defined hysteresis and time constant and finally drives the relay interlock circuit that inhibits an ACARS VHF radio from transmitting whenever other on-board comm. VHF transceivers are receiving voice signals. Visual indicators provide information on system operation and system power failure.
Owner:EMBRAER SA
Separation process and apparatus
InactiveUS20030029774A1Easy to separateMinimum separationCatalytic crackingLayered productsCycloneEngineering
An apparatus and process is disclosed for the separation of solids from gases in a mixture which is most particularly applicable to an FCC apparatus. The mixture of solids and gases are passed through a conduit and exit through a swirl arm that imparts a swirl motion having a first annular direction to centripetally separate the heavier solids from the lighter gases. The mixture then enters a cyclone which has a curved outer wall and imparts a second swirling angular direction to the mixture. The second angular direction is counter to the first angular direction. The apparatus and method assures that a greater proportion of the mixture entering the cyclone is incorporated into the vortex to further enhance separation between the solids and gases.
Owner:UOP LLC
Negative-angle press-working die
InactiveUS20090113978A1Quality improvementReduce work costsShaping toolsForging press detailsCentre of rotationEngineering
To enable forming a negative angle with deep bending and forming a high-quality panel, a negative-angle press-working die includes an elevatable pad fixed to an upper die, a slide cam supported slidable laterally on the upper die or a lower die and having a bending blade, a rotary cam rotatable about a rotational center having a bending part which forms a negative-angle portion on a workpiece and a cam surface abutting on the slide cam, an elevatable slide body disposed under the pad rotatably together with the rotary cam and having a hold part provided at an upper portion on a bending part side of the rotary cam and constituting a part of a male die for workpiece forming, a drive unit that rotates the rotary cam to a workpiece working position, and a slide drive unit that slides the slide body in an up and down direction.
Owner:YOURBUSINESS
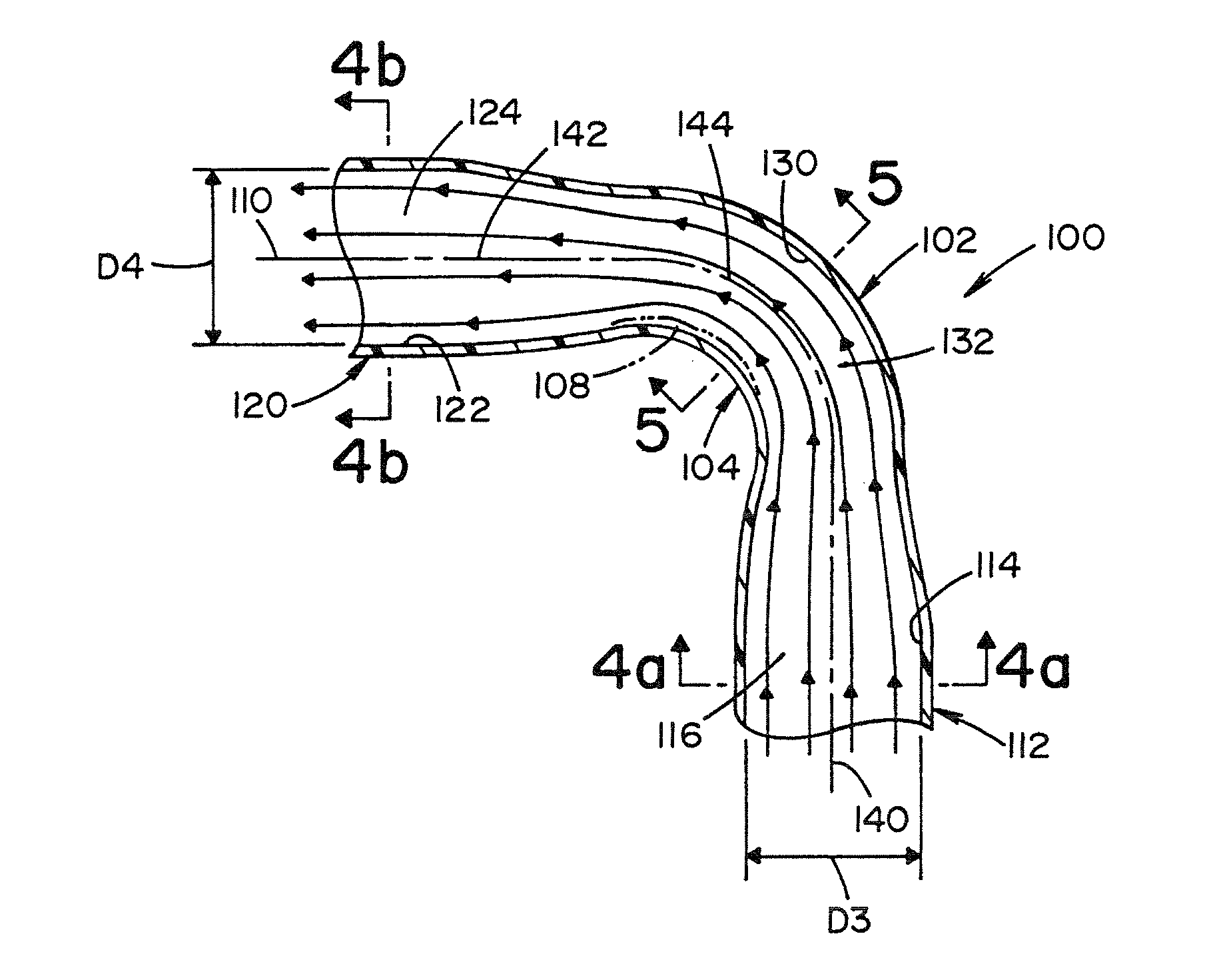
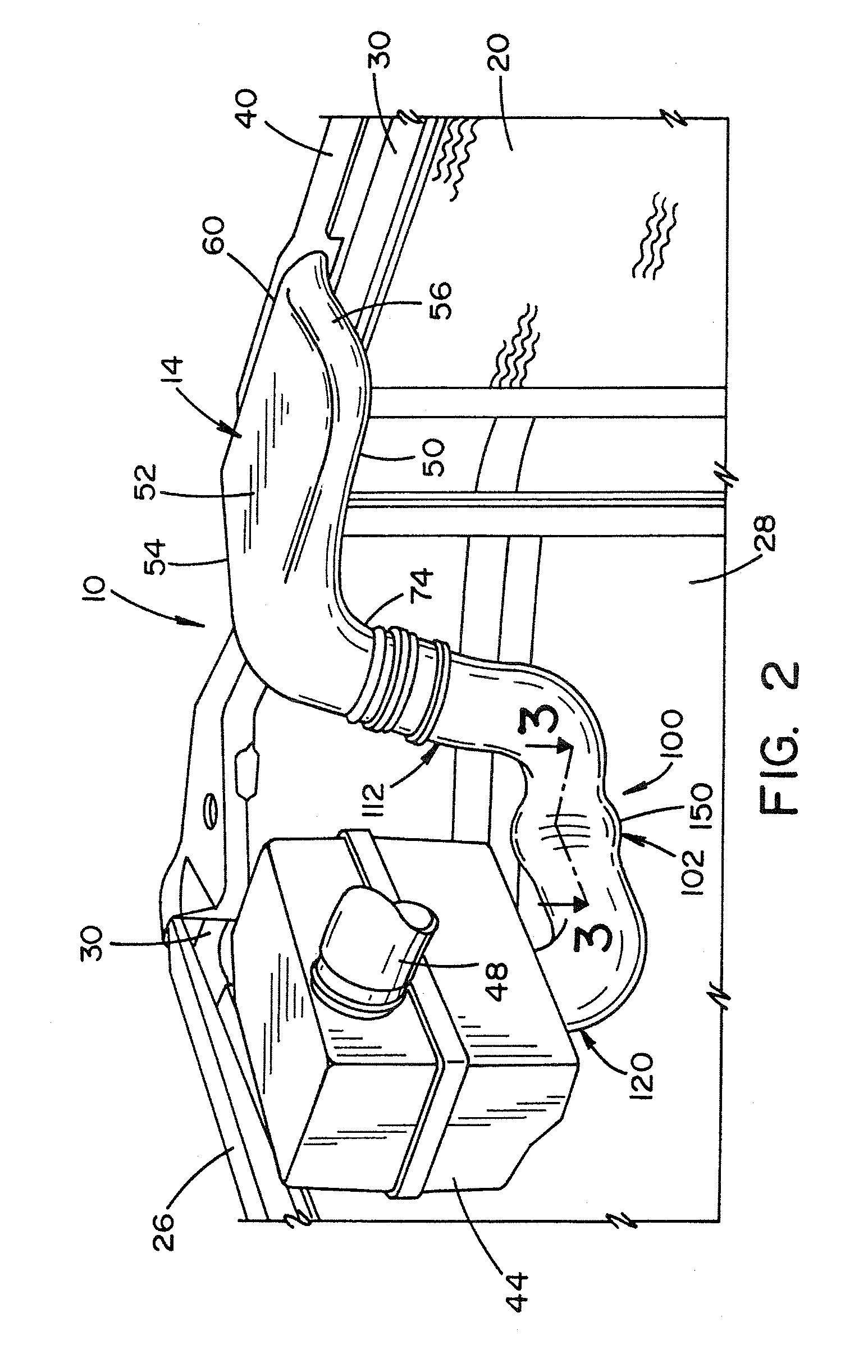
Intake system for a vehicle
InactiveUS8516986B2Minimum separationIncrease flow rateDispersed particle filtrationMachines/enginesEngineeringInlet manifold
An intake tube for an air intake system of a vehicle is provided. The air intake system is located upstream of an intake manifold and includes an intake enclosure and an air precleaner. The intake tube directs a flow of air from the intake enclosure to the air precleaner. The intake tube comprises a first end section, a second end section and a curved section. The first end section is connected to the intake enclosure and has a first longitudinal axis. An inner surface of the first end section defines a first section air passage. The second end section is connected to the air precleaner and has a second longitudinal axis. The inner surface of the second end section defines a second section air passage. The curved section is located between the first and second end sections. The curved section has a third longitudinal axis. An inner surface of the curved section defines a curved air passage. The curved section includes a compressed portion having a minor dimension and a major dimension. The major dimension is greater than the minor dimension so that the flow of air through the curved air passage has minimal separation which increases flow rate into the air precleaner.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method of controlling platooning in autonomous driving system
InactiveUS20200005650A1Minimum separationIncrease distanceAutonomous decision making processRemote controlled aircraftAutomotive engineeringReal-time computing
The present invention provides a method of controlling platooning in an autonomous driving system that can cope with occurrence of a communication blind spot in platooning. In an aspect, a method of controlling platooning in which following vehicles receiving and driving a control signal from a leader vehicle and a communicator of the leader vehicle drive in a group includes monitoring and digitizing a communication status of the platooning; checking, if the digitized communication status is less than a predetermined threshold value, a communication blind spot between the leader vehicle and the following vehicle; determining, when the following vehicle is positioned at the communication blind spot, whether a relative position change of the following vehicle is available within the platooning; and changing, if a relative position change of the following vehicle is available, a relative position of the following vehicle within the platooning.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and device for examining the faculty of hearing
Owner:UNIV TUBINGEN
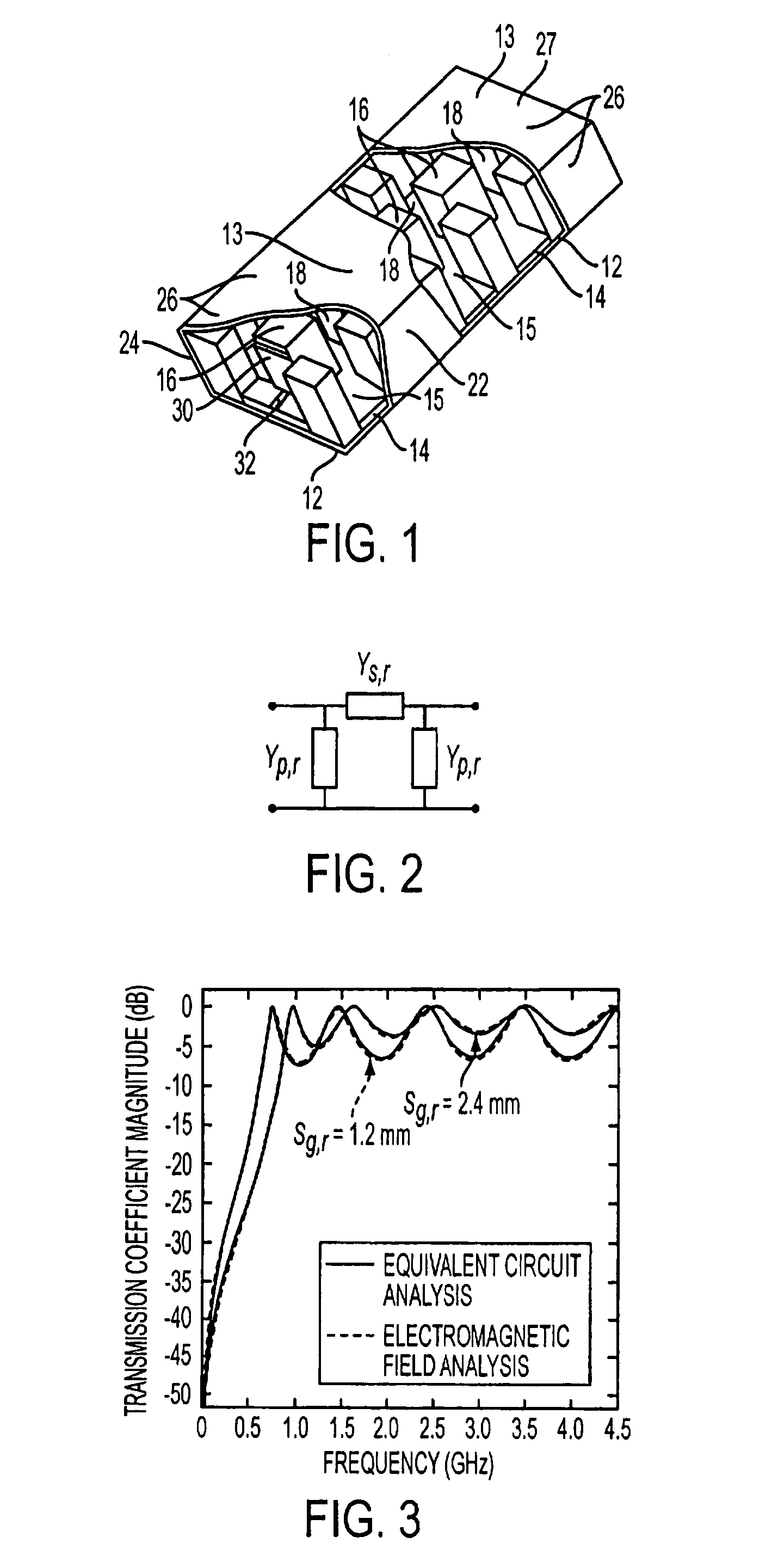
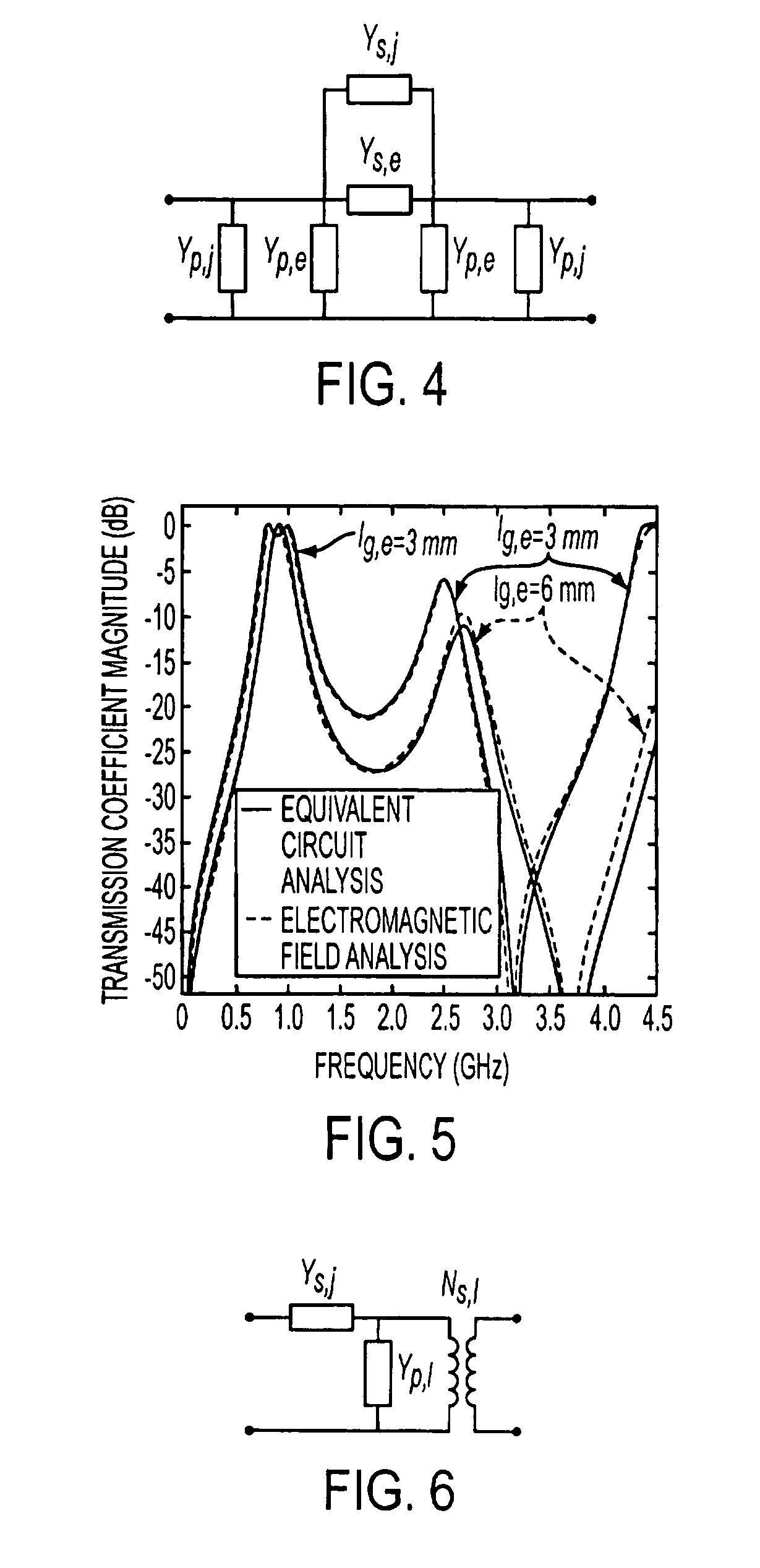
Ridge-waveguide filter and filter bank
InactiveUS20070290768A1Reduce physical sizeMaximum compactnessWaveguidesCoupling devicesEngineeringRidge
A ridge-waveguide filter with a signal input port at a first end and a signal output port at a second end contains a cascade assembly of metal-bounded ridge-waveguide sections with interspersed metal-bounded evanescent-mode coupling regions, and also contains low-loss ridge-waveguide port coupling networks to impedance-match the ends of the assembly to respective signal-port reference impedances. A frequency multiplexer with a composite-signal port and a plurality of channeled-signal ports is composed of a plurality of ridge-waveguide filters that are series-connected through a ridge-waveguide manifold containing a multiplicity of three-way waveguide junctions and quasi-lumped waveguide elements.
Owner:NAVY U S A THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF
Unmanned aerial vehicle fuselage
InactiveUS20190276128A1Minimizing transferProtect environmentFuselage framesCasings with connectors and PCBUncrewed vehiclePrinted circuit board
Owner:VORTEX LABS INC
Ridge-waveguide filter and filter bank
InactiveUS7663452B2Maximum compactnessMinimum separationWaveguidesCoupling devicesRidge waveguidesCoupling
A ridge-waveguide filter with a signal input port at a first end and a signal output port at a second end contains a cascade assembly of metal-bounded ridge-waveguide sections with interspersed metal-bounded evanescent-mode coupling regions, and also contains low-loss ridge-waveguide port coupling networks to impedance-match the ends of the assembly to respective signal-port reference impedances. A frequency multiplexer with a composite-signal port and a plurality of channeled-signal ports is composed of a plurality of ridge-waveguide filters that are series-connected through a ridge-waveguide manifold containing a multiplicity of three-way waveguide junctions and quasi-lumped waveguide elements.
Owner:NAVY U S A THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF
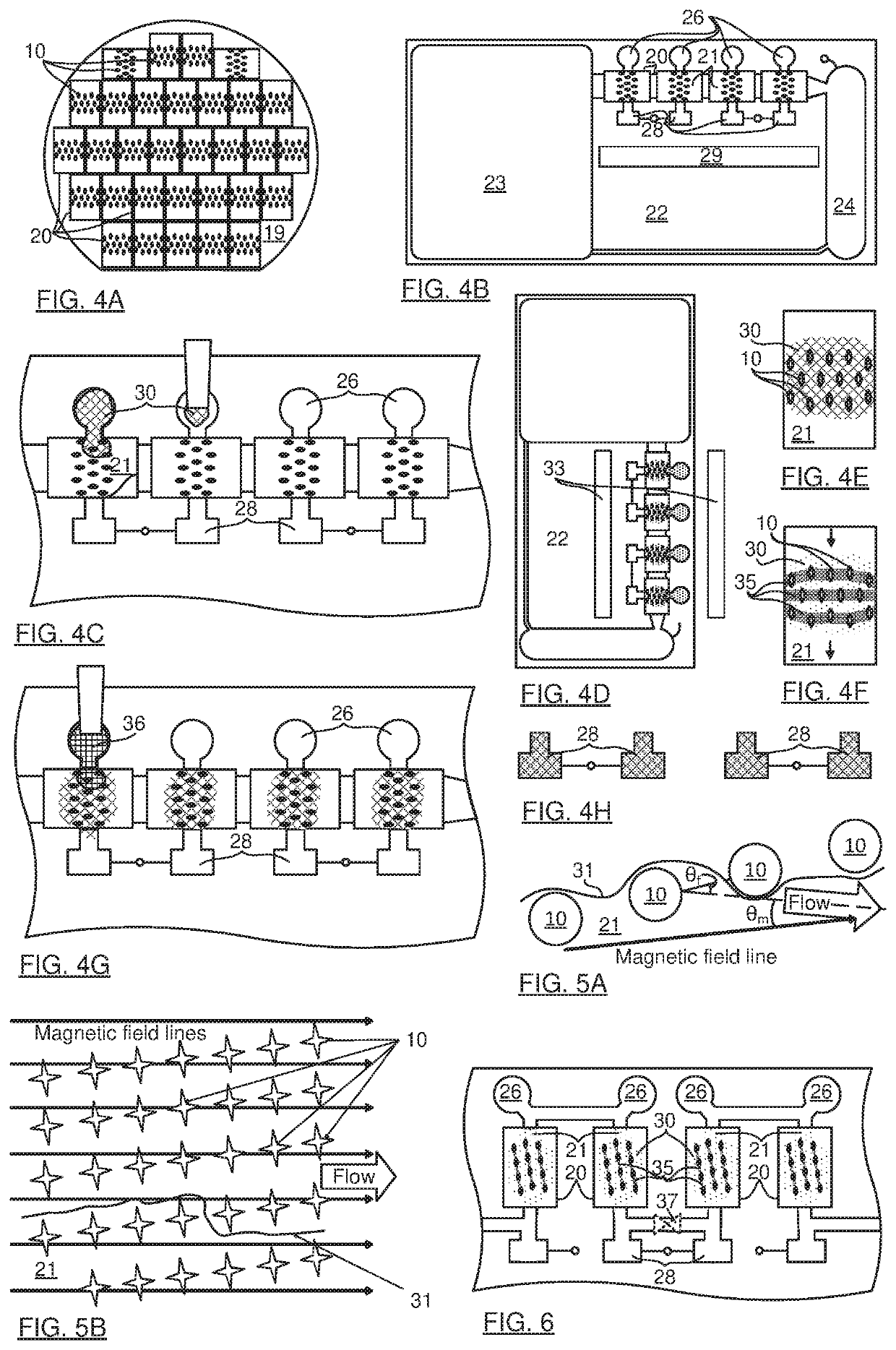
Magnetic Nanoparticle Distribution in Microfluidic Chip
PendingUS20210299656A1High strengthSolve the lack of densityMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure assemblyMagnetite NanoparticlesEngineering
The present invention relates into a device and method for controlling distribution of superparamagnetic nanoparticles (NPs) in a microfluidic chamber. By applying a strong magnetic field, localization of the NPs to inter-pillar spaces between soft magnetic coated micropillars is demonstrated, even with a modest fluid flow across the inter-pillar space. Flow splitting techniques are also provided to force particles to reliably interact with the NPs, specifically by using a Brevais lattice with a primative vector of 1°-15° with respect to flow direction. The pillars may have non-circular cross-sectional shape and be arranged to direct NP clouds more effectively. An array of the pillars has multiple axes for rotating NP cloud distributions in multiple orientations, allowing for a rotating magnetic field to move the NP cloud for mixing a fluid that is otherwise stationary.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
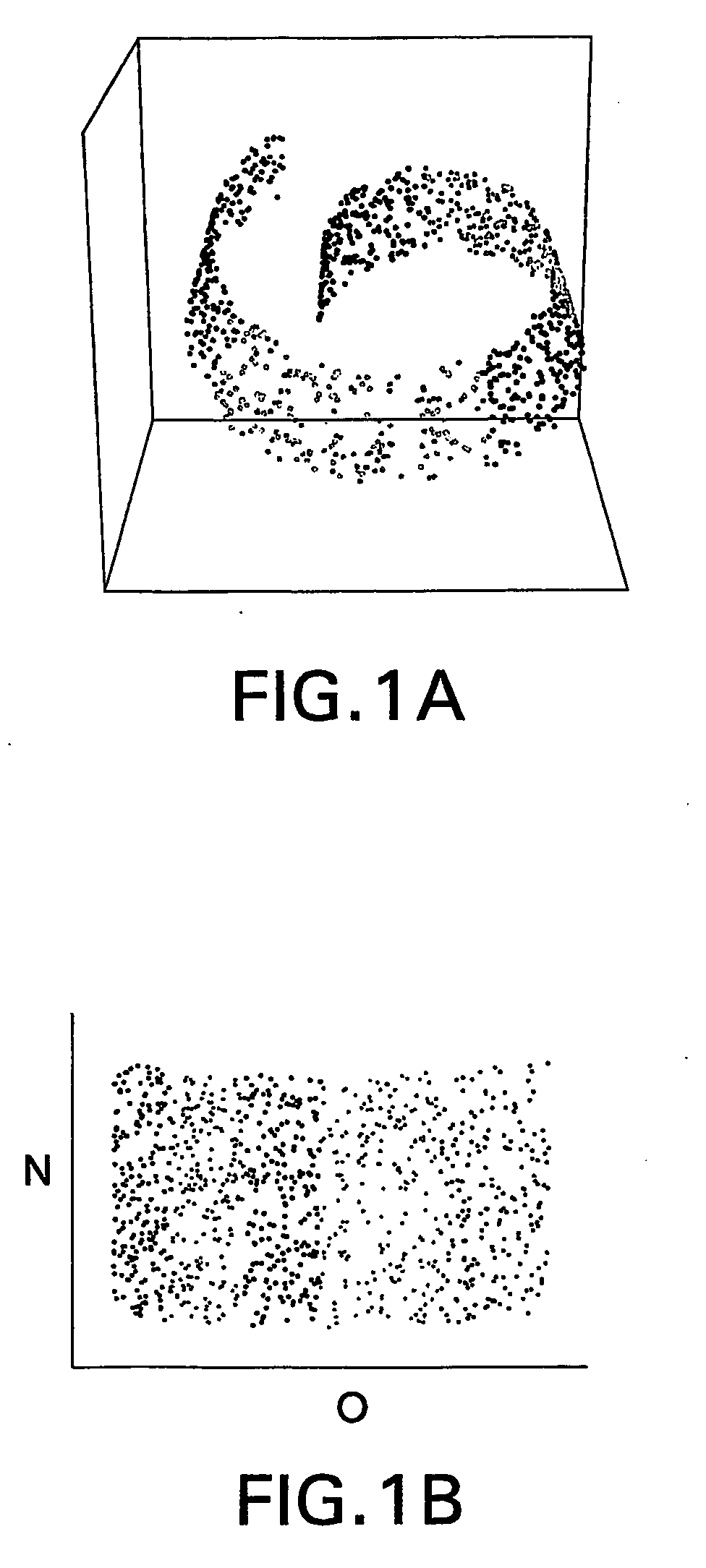
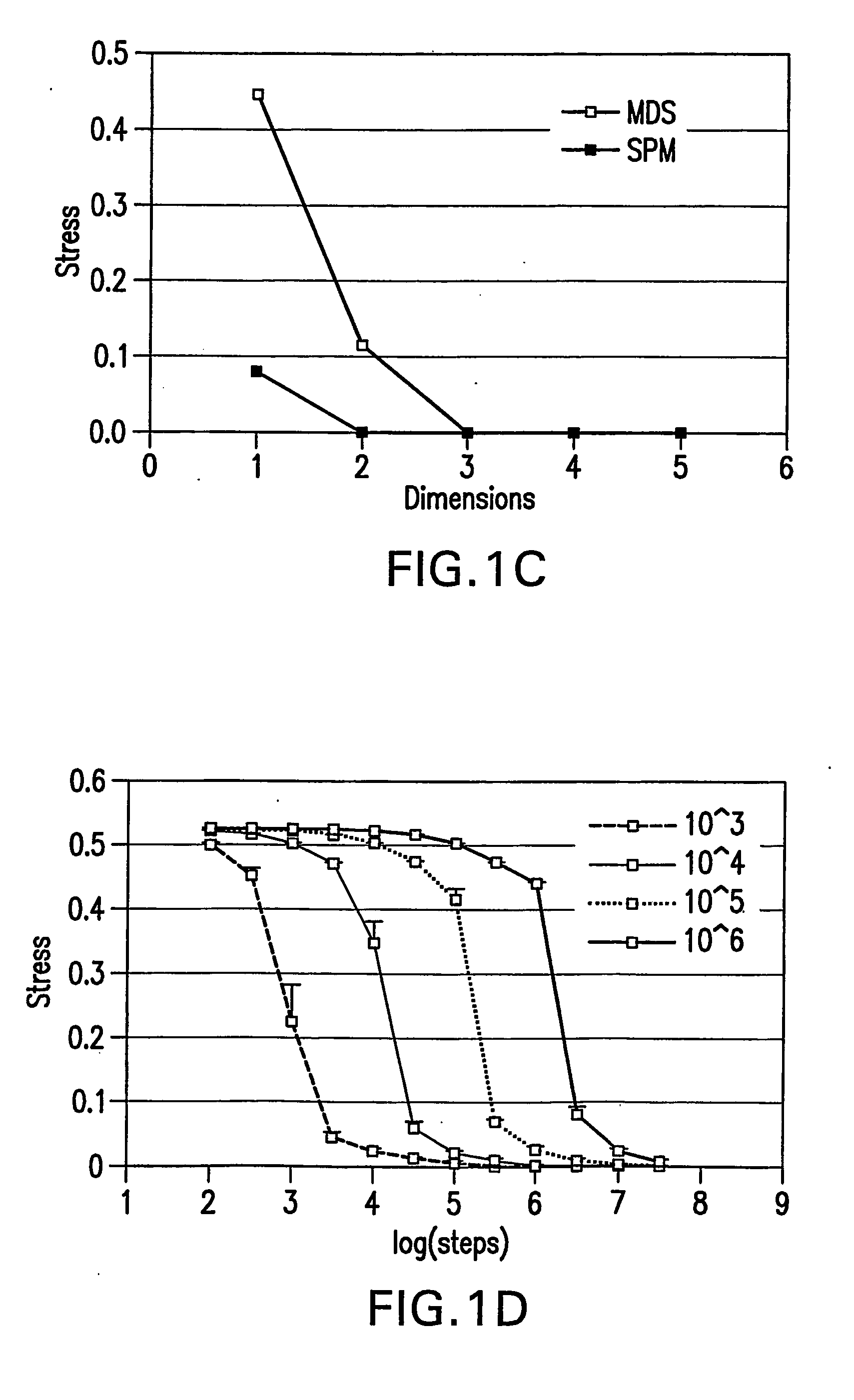
Methods, systems, and computer program products for representing object realtionships in a multidimensional space
InactiveUS20060178831A1Minimum separationBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionObject RelationshipData mining
Methods, systems and computer program products for mapping is a set of related objects into a multidimensional space. The mapping is carried out using an iterative (e.g., pairwise) refinement strategy that attempts to ensure that the distances of the objects on the map satisfy a supplied set of upper and lower bounds. In a preferred embodiment, these upper and lower bounds are derived from a supplied set of relationships (similarities, dissimilarities, or proximities) between the objects. In another preferred embodiment, these distance bounds are chosen to preserve local relationships between neighboring objects while maintaining minimum separation between remote objects.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON PHARMA RES & DEV LLC
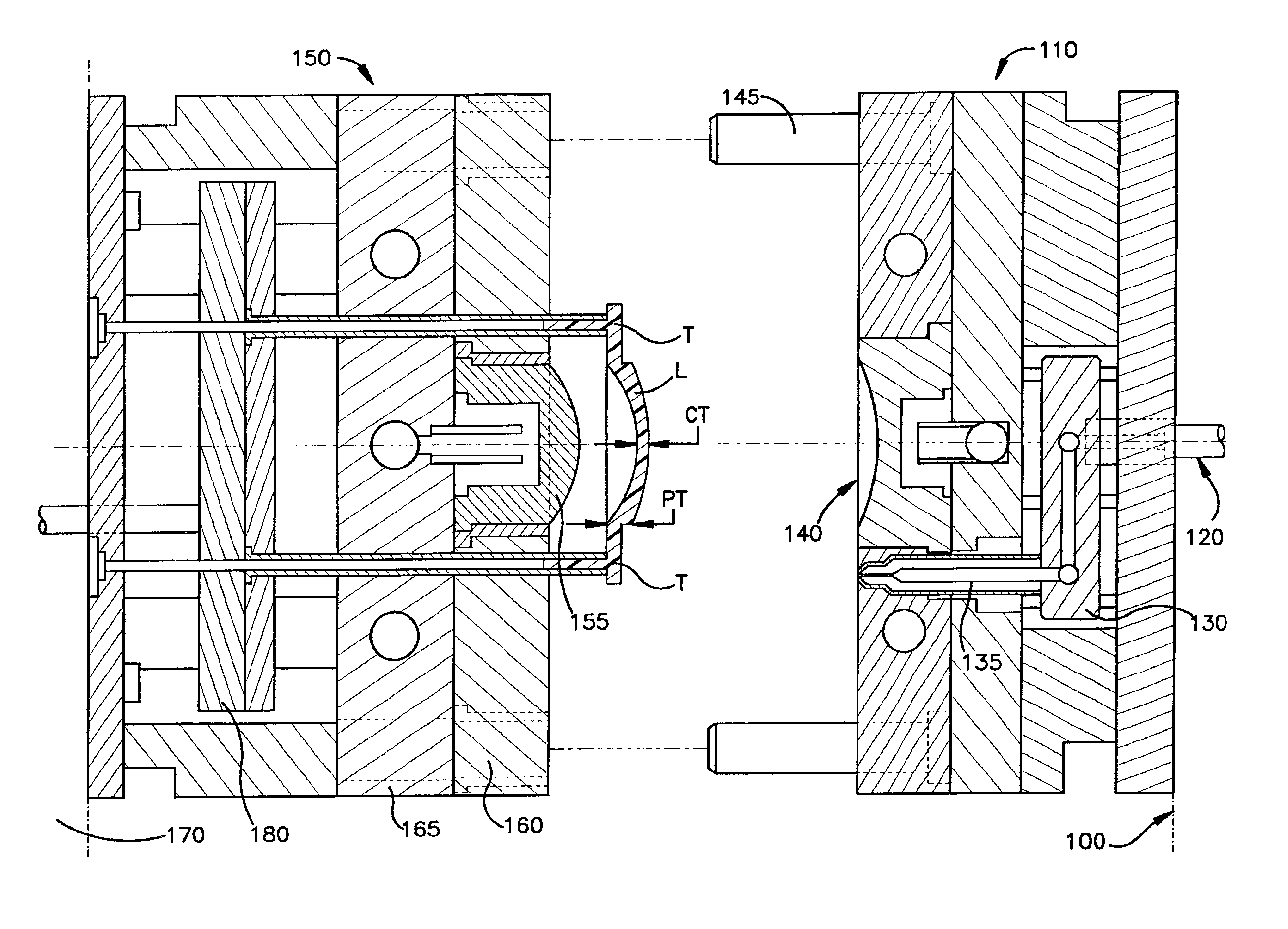
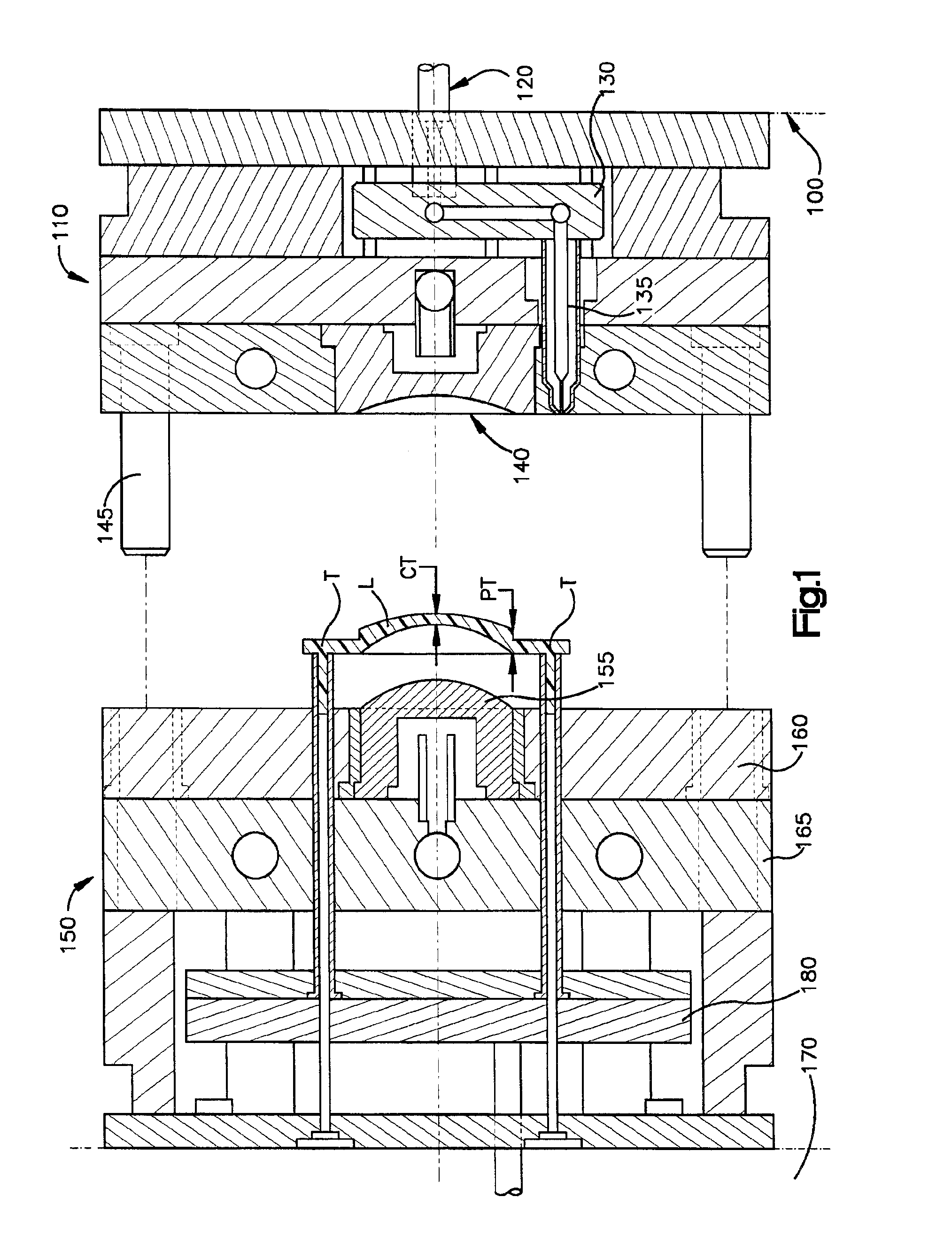
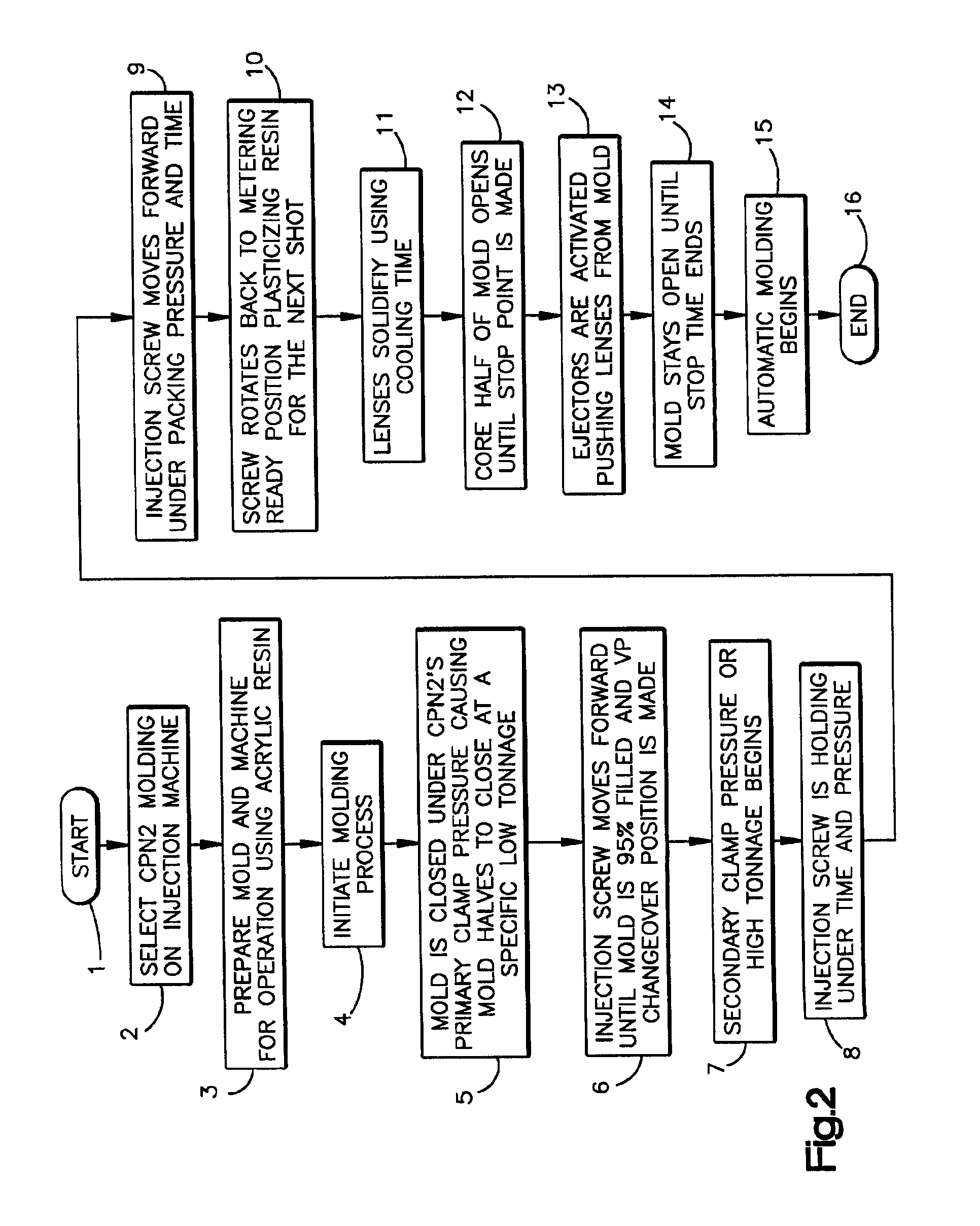
Stress-relieved acrylic optical lenses and methods of manufacture by injection coining molding
Stress-relieved molded acrylic opthalmic lenses, and injection-coining mold processes for molding stress-relieved plus and minus to high-minus diopter ophthalmic lenses of optically superior acrylic resin, able to pass standardized impact drop tests for use as eyeglass lenses, are described. The injection-coining processes use two-plate and three-plate mold assemblies. The cavity of a two plate runnerless mold is partially filled under partial tonnage, and the movable half of the mold controlled to coin and densify the acrylic resin under secondary or full tonnage, when a velocity-pressure changeover point is reached. In a process which employs a three-plate mold assembly, the lens mold cavities are partially filled under less than total clamp tonnage, with a cavity plate held by hydraulic pressure against a movable half of the mold. The mold assembly is then closed under full tonnage when a velocity-pressure changeover point is reached, collapsing the cavity plate a stationary platen, bringing the mold assembly to a total stack height. The processes produce impact resistant acrylic ophthalmic lenses which are stress-relieved and without weld lines, even in the high minus diopter range, with center thickness' as low as one millimeter, and edge thickness' up to ten millimeters.
Owner:FGX INT
Name bubble handling
ActiveUS9251404B2Minimum separationImage enhancementDigital data information retrievalComputational scienceComputer hardware
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Method and device for planning flight trajectories
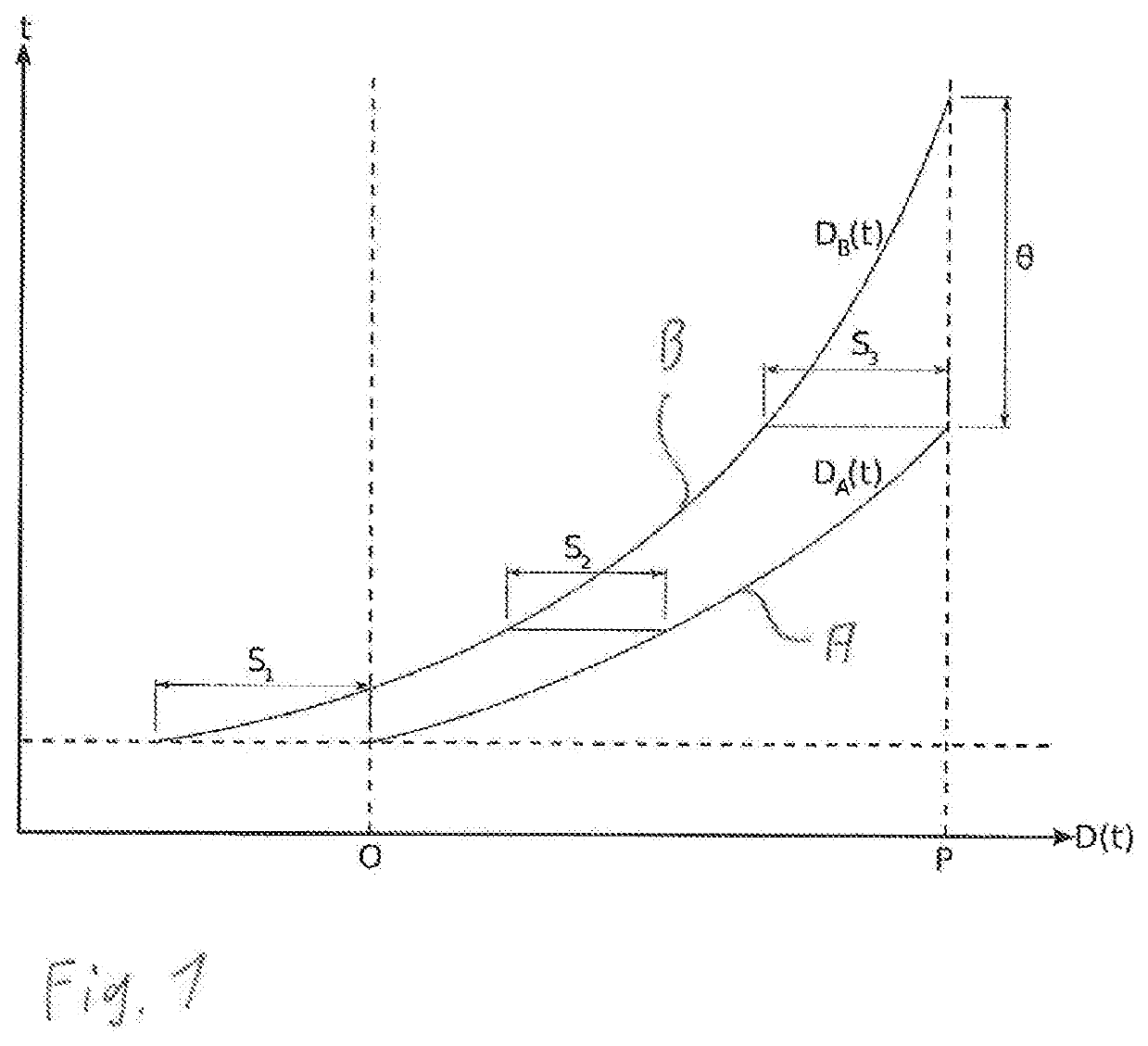
ActiveUS20200202724A1Minimum separationEasy to adjustAircraft traffic controlFlight vehicleClassical mechanics
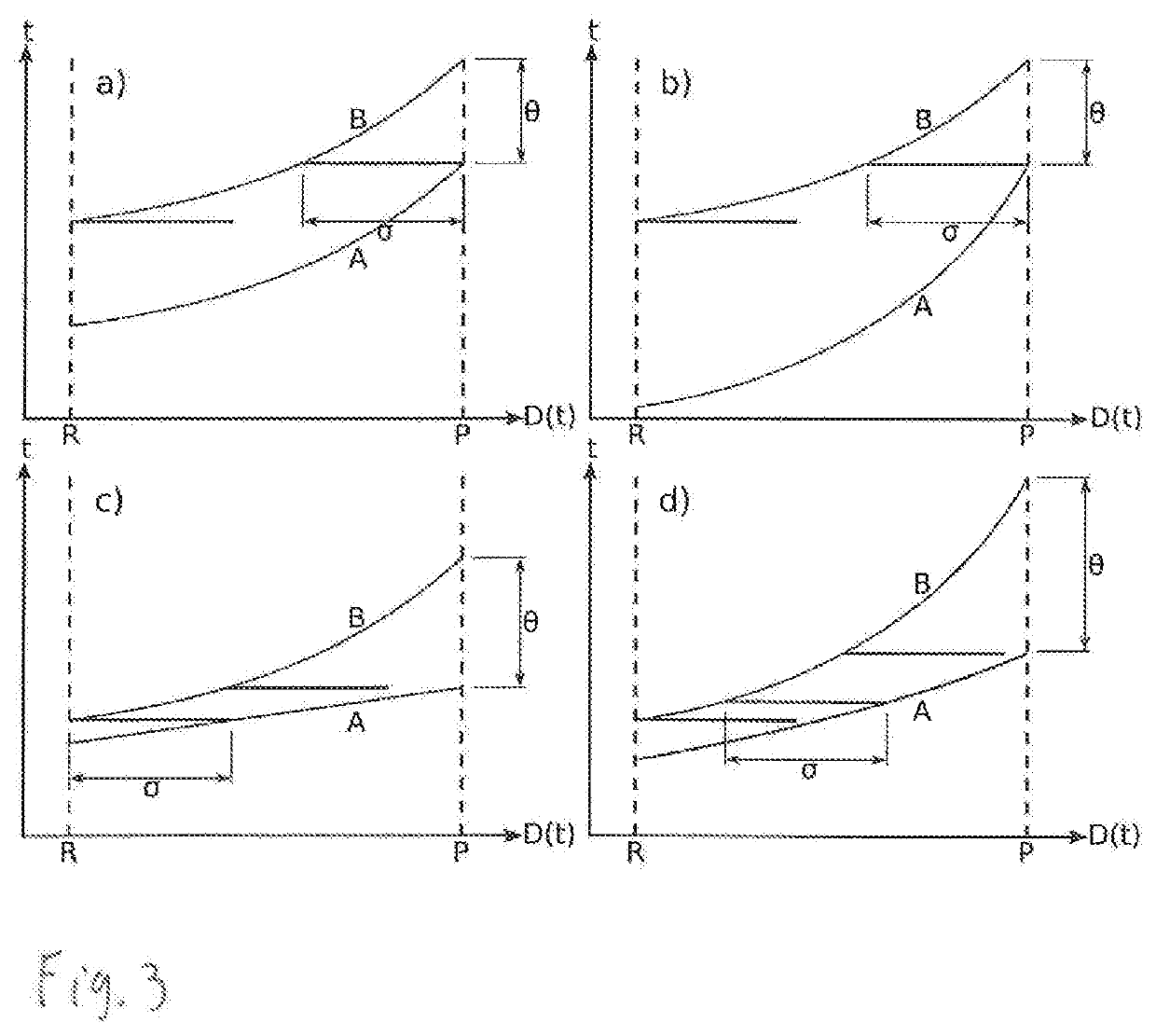
A method for planning flight trajectories for at least two aircraft aiming to subsequently approach a predefined reference point, in particular a predefined destination, wherein each aircraft travels along a flight route according to an individual flight trajectory, such that a first aircraft travels along a first flight route according to a first flight trajectory and a second aircraft travels along a second flight route according to a second flight trajectory, wherein at least the second flight trajectory is set or adjusted such that at least one predetermined minimum separation between the two aircraft approaching the predefined destination according to their respective flight trajectories is ensured and the predetermined minimum separation is ensured throughout the whole flight trajectories by setting or adjusting an adjustable trajectory parameter (θ) of the first or second flight trajectory.
Owner:FREQUENTIS ORTHOGON GMBH
Manufacture of a wind turbine blade
ActiveUS11131289B2Minimum separationHigh-quality bondingEngine manufactureFinal product manufactureTurbine bladeClassical mechanics
A shear web flange (36) for a shear web (32) of a wind turbine blade (18) is described. The flange (36) extends longitudinally and comprises a bonding surface (50) for bonding to an inner surface of a wind turbine blade (18). One or more protruding features (52a, 52b) protrude from the bonding surface (50). A method of making such a shear web flange (36) is also described as are a shear web (32) for a wind turbine blade (18), a wind turbine blade (18) and a method of making a wind turbine blade (18).
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Arrangement for determining a revolution rate and direction of rotation of a rotating component
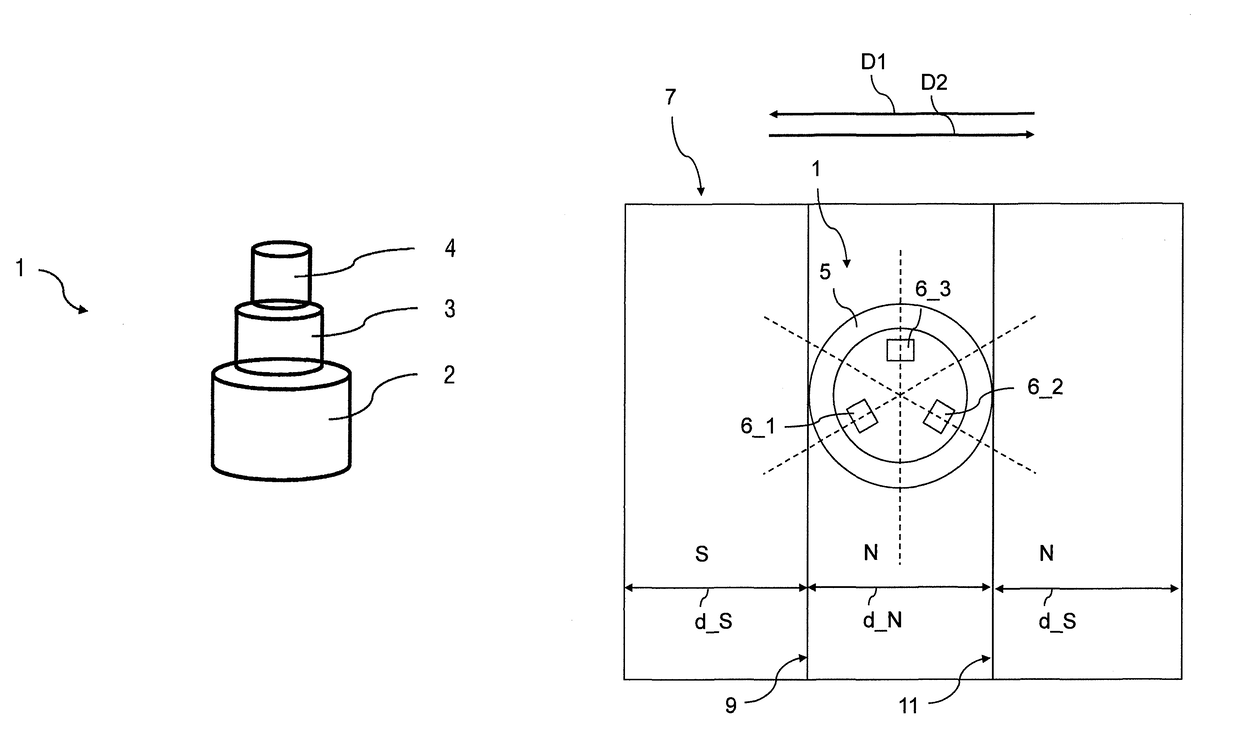
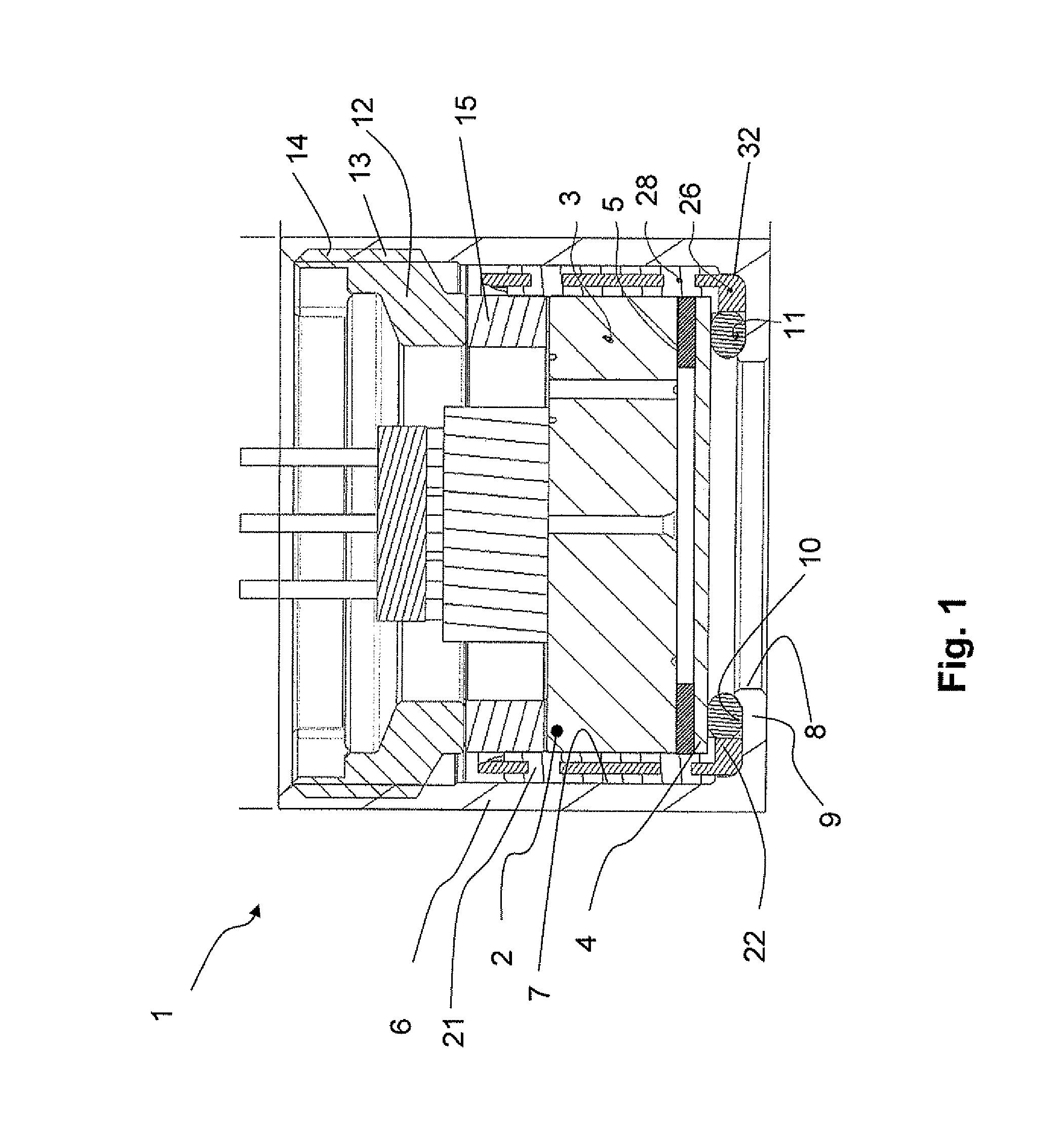
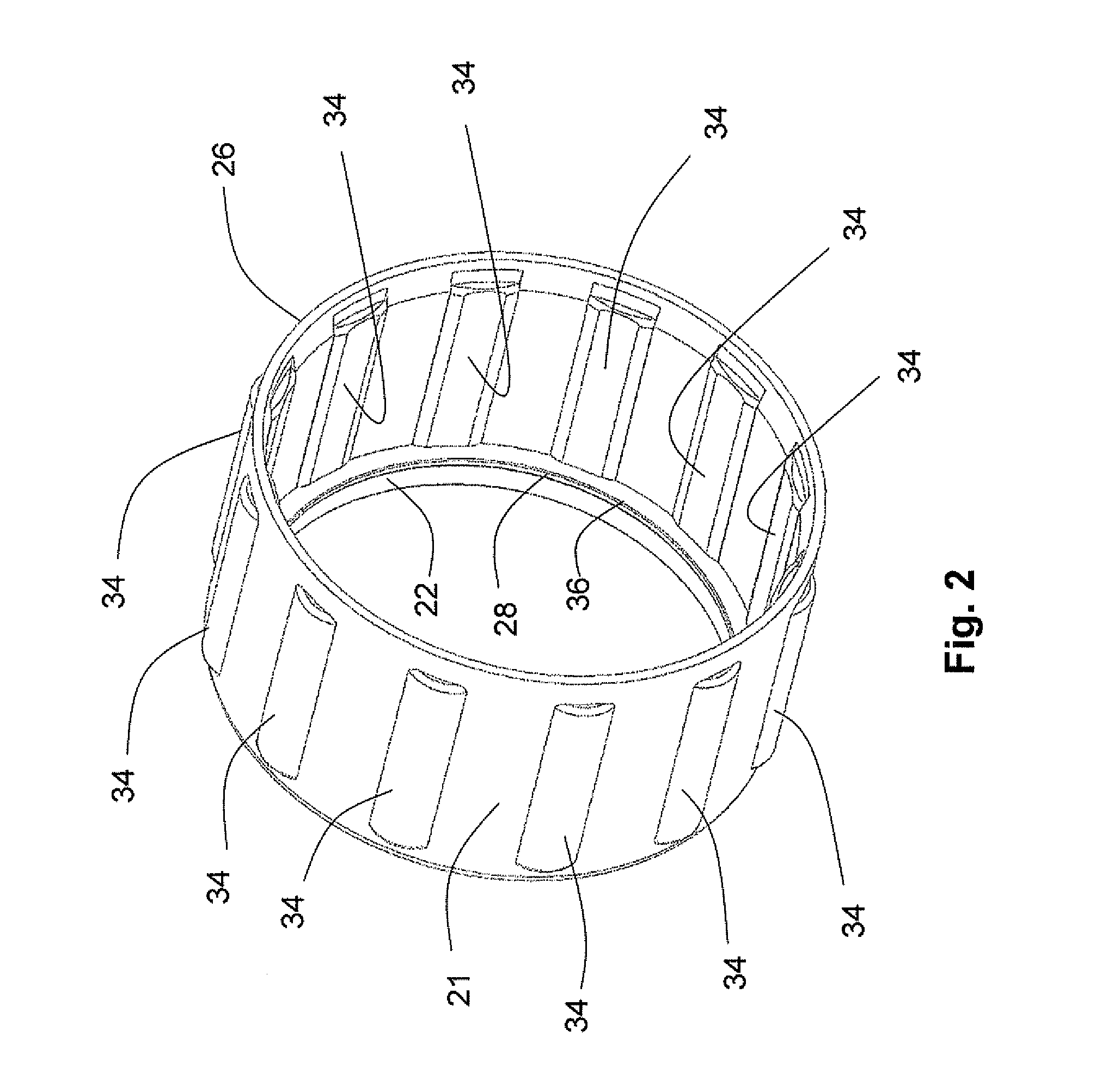
ActiveUS9766260B2Avoid disadvantagesQuick installationMagnetic measurementsUsing electrical meansRotation velocityEngineering
A sensor device for contactlessly determining a revolution rate and a direction of rotation of a component that rotates during operation of the component, the component having, on at least one peripheral region, a circumferential structure of web-shaped or tooth-shaped radial protrusions and interposed grooves or tooth gaps includes: a threaded segment configured to positionally fix an arrangement of the sensor device so that the circumferential structure of the component is movable past the sensor device; a magnetic field generating device; and a magnetic field detecting device having at least three magnetic field sensors that are not arranged in alignment along a line. A distance between the magnetic field sensors that are the farthest apart from each other is less than or equal to a width of the grooves or tooth gaps of the component.
Owner:MAN TRUCK & BUS AG
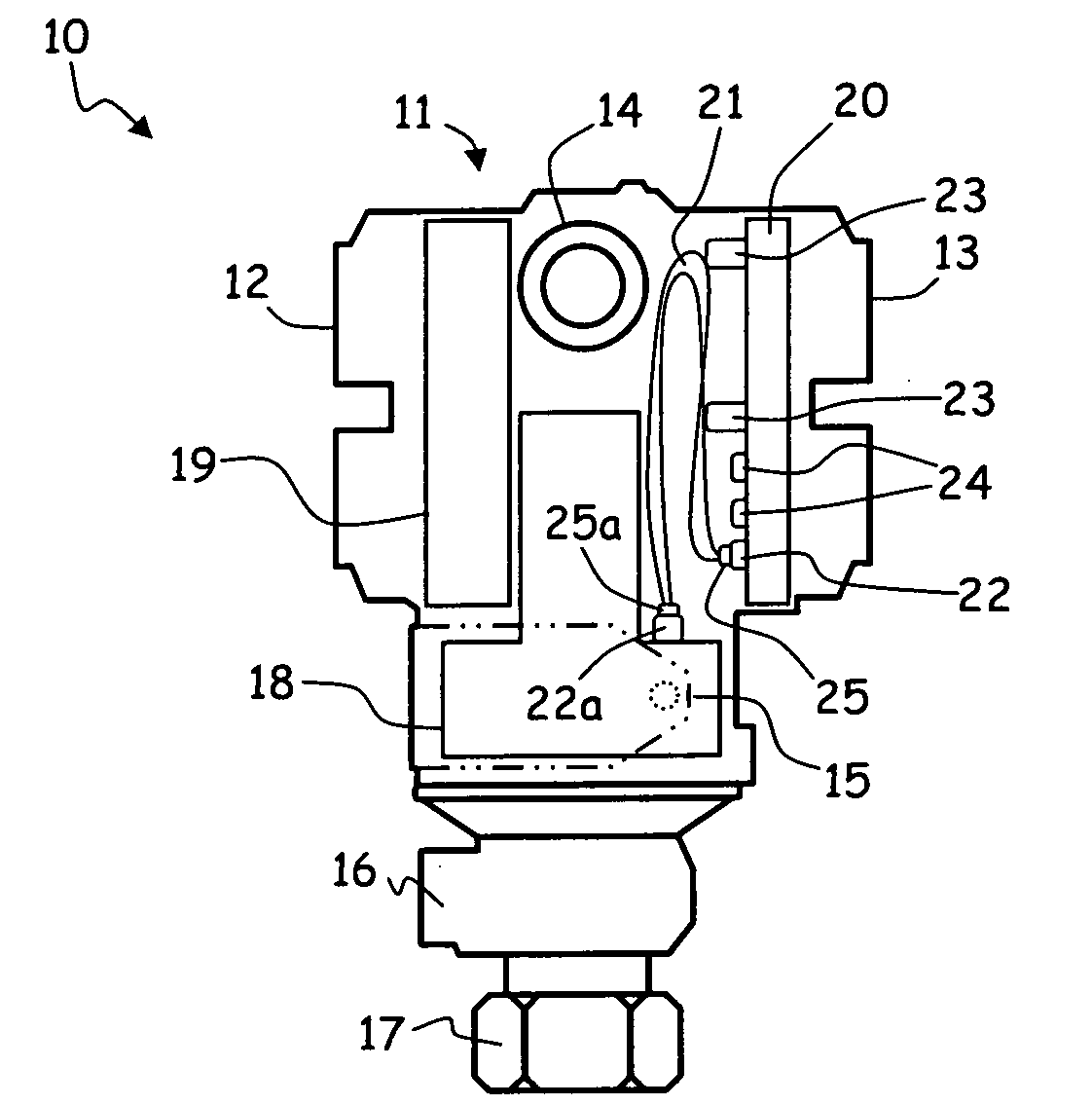
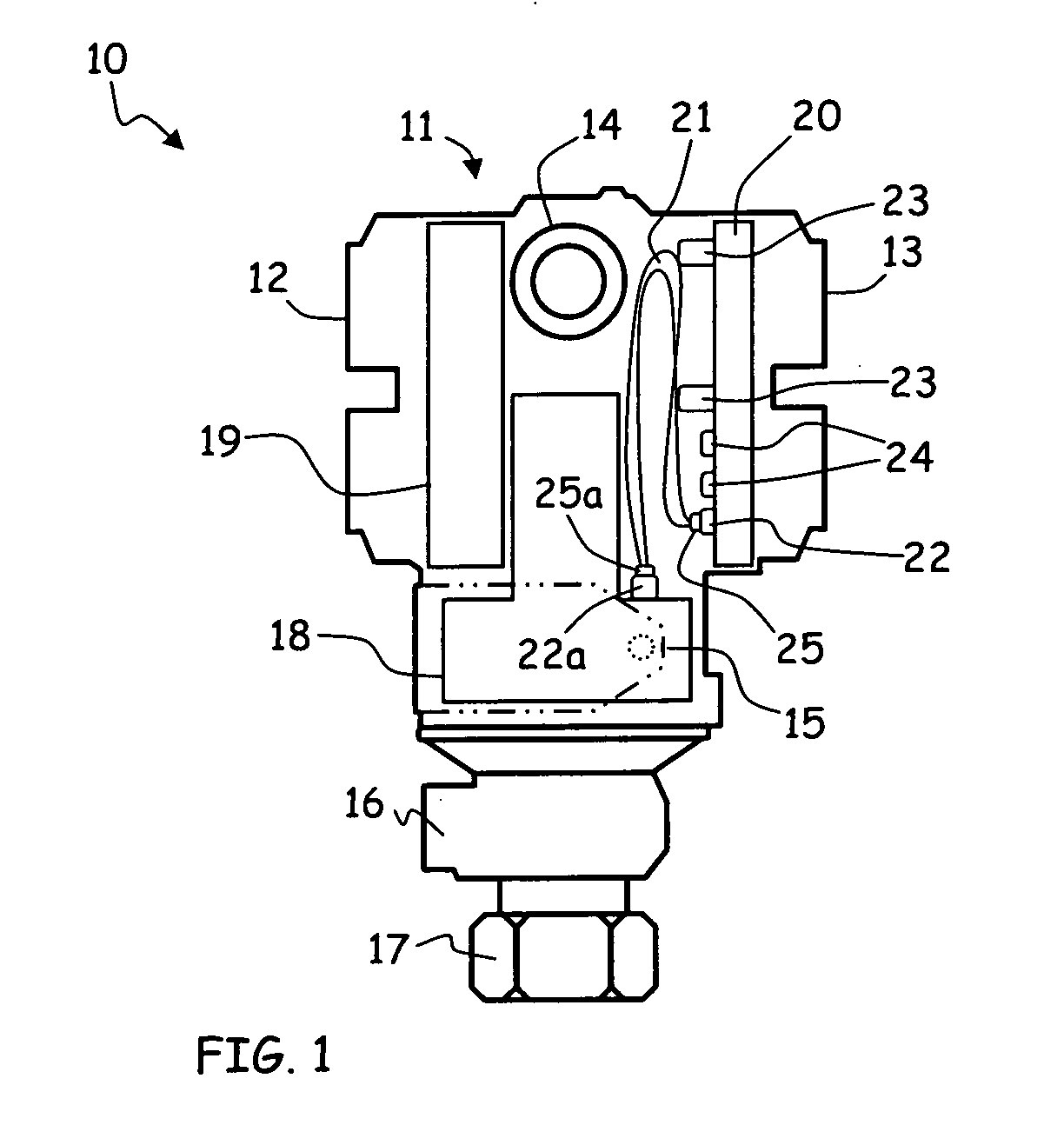
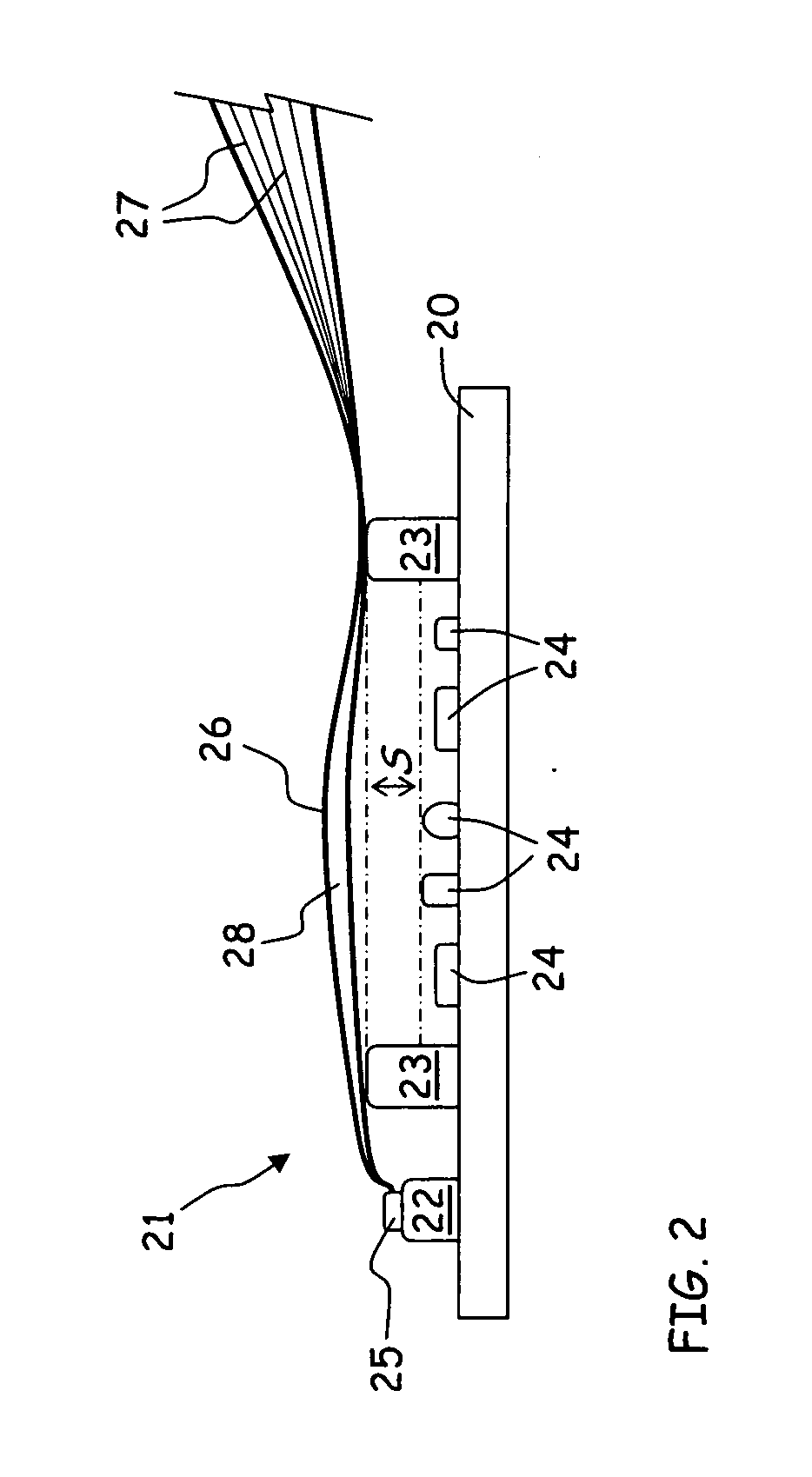
Pressure sensor having a cylindrical pressure measuring cell
ActiveUS8925388B2Minimum separationFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansPhysicsTransducer
Owner:EHNDRESS KHAUZER GMBKH KO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com