Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
102results about How to "Increase fuel pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
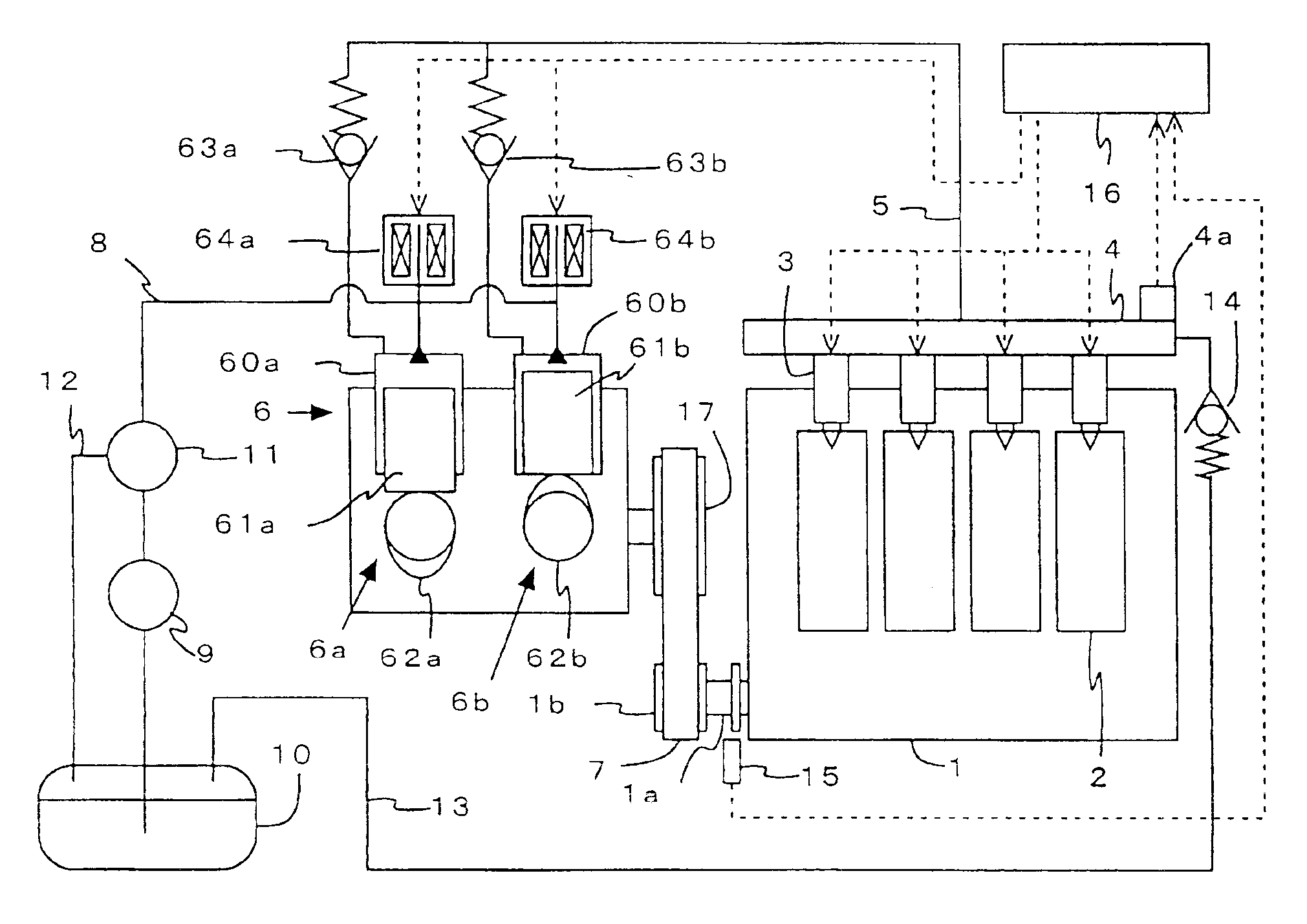
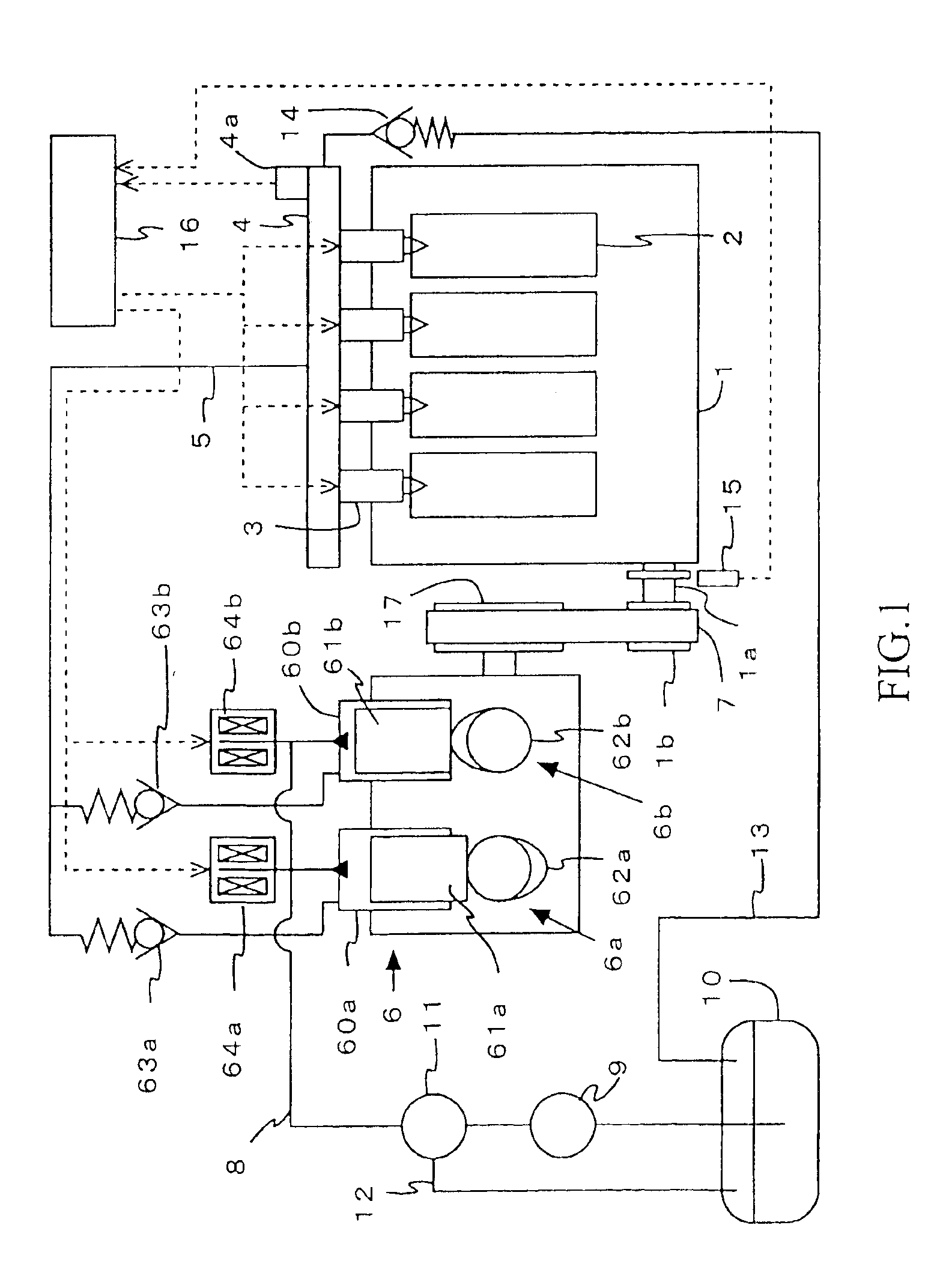
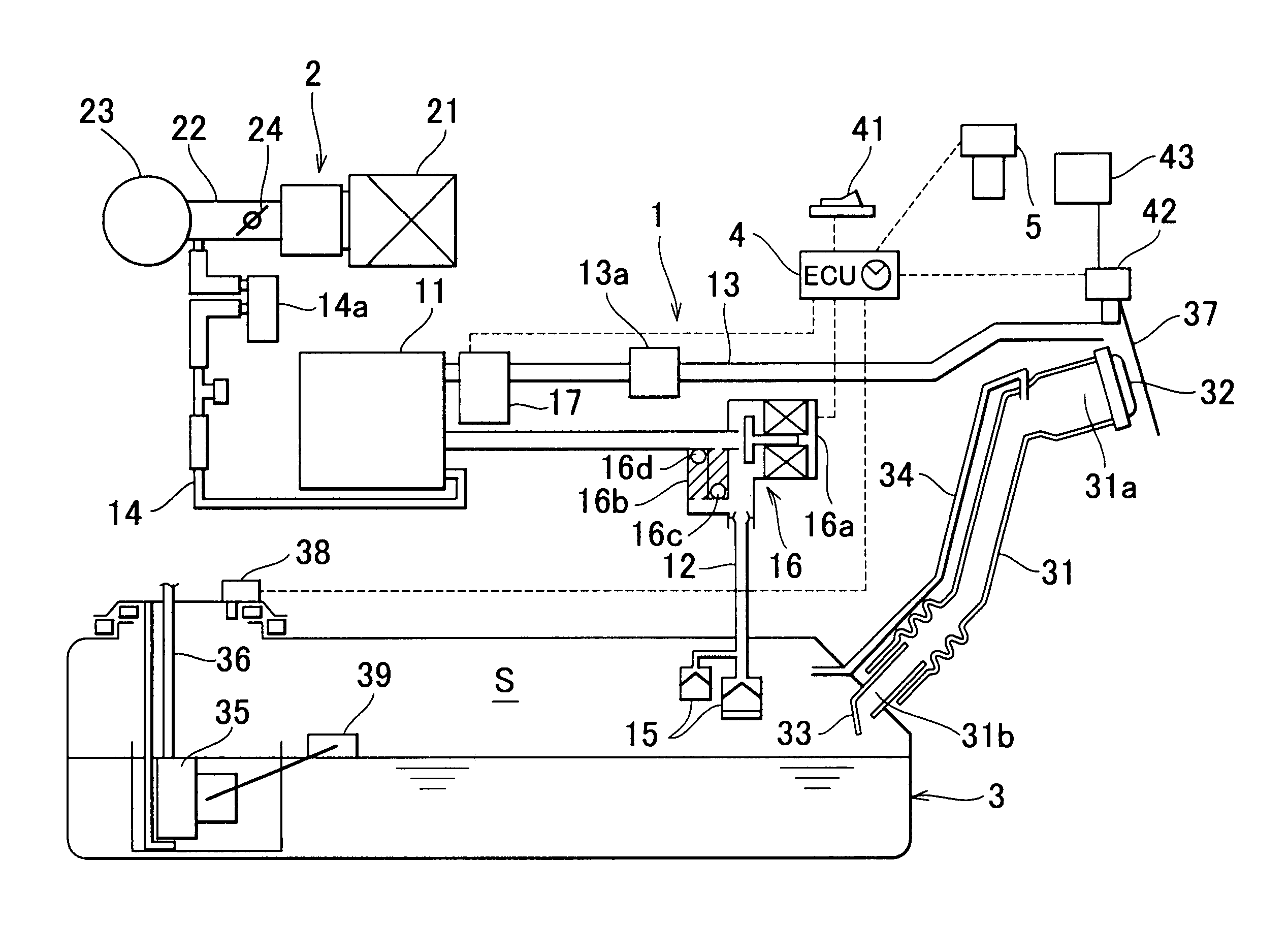
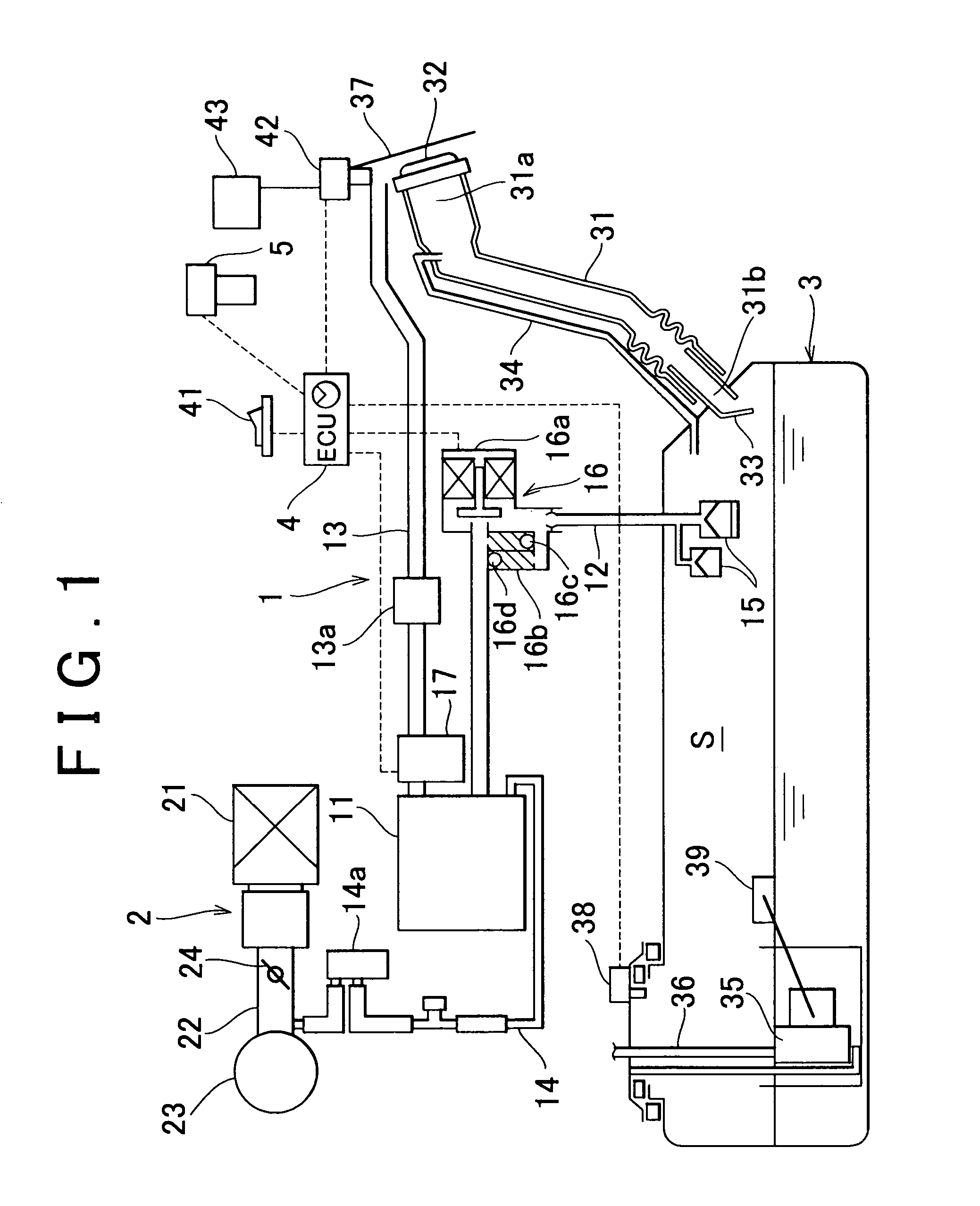
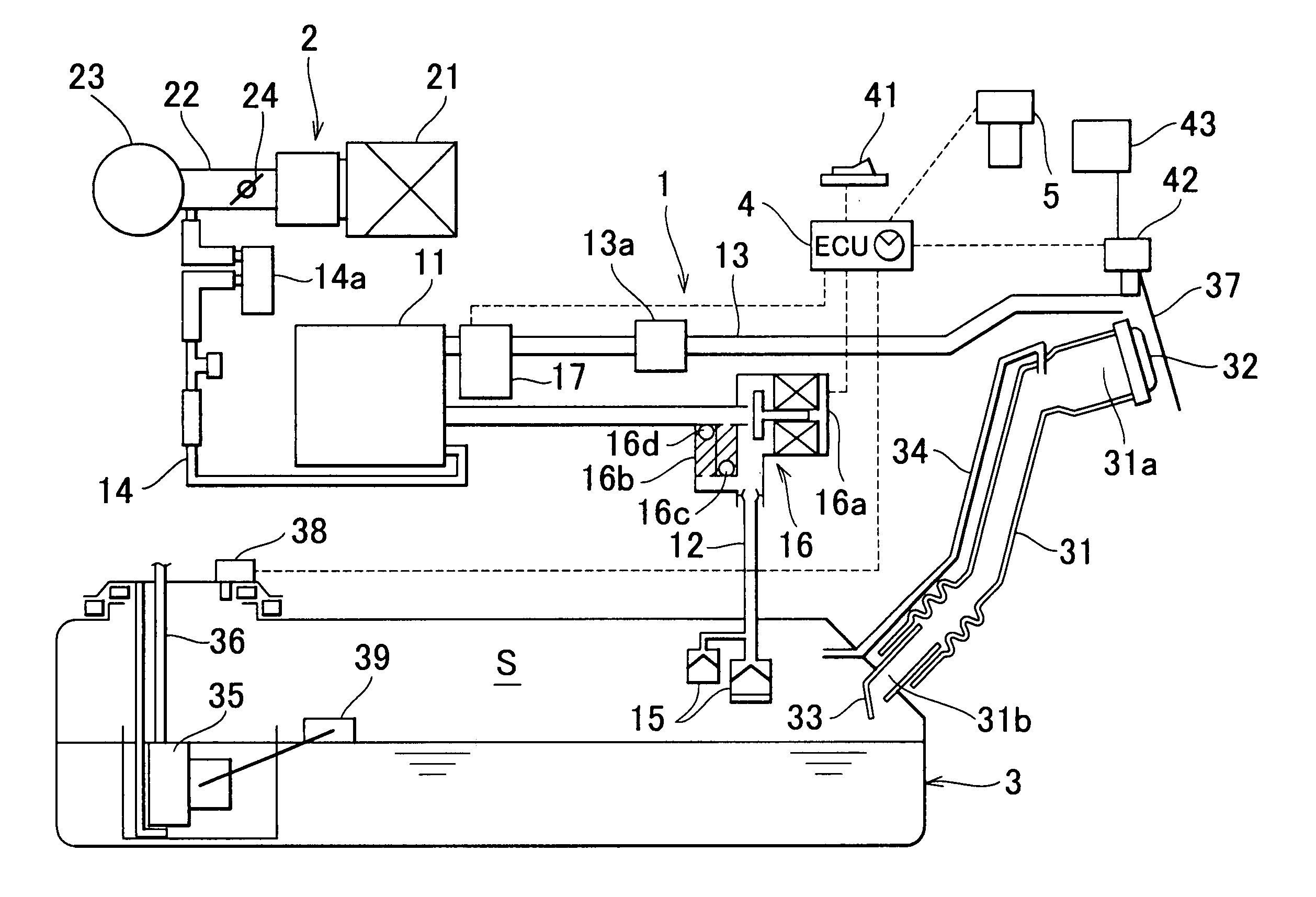
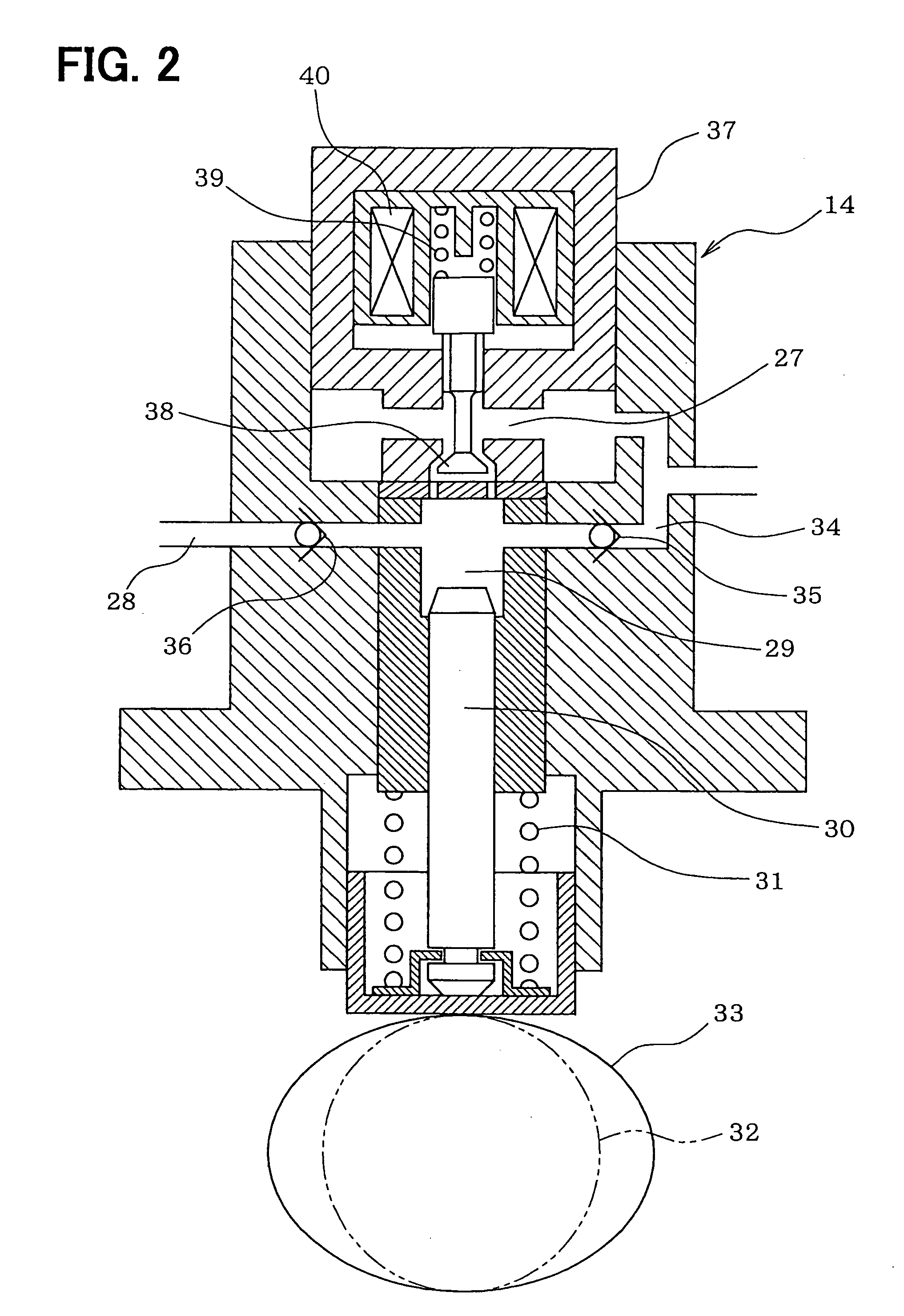
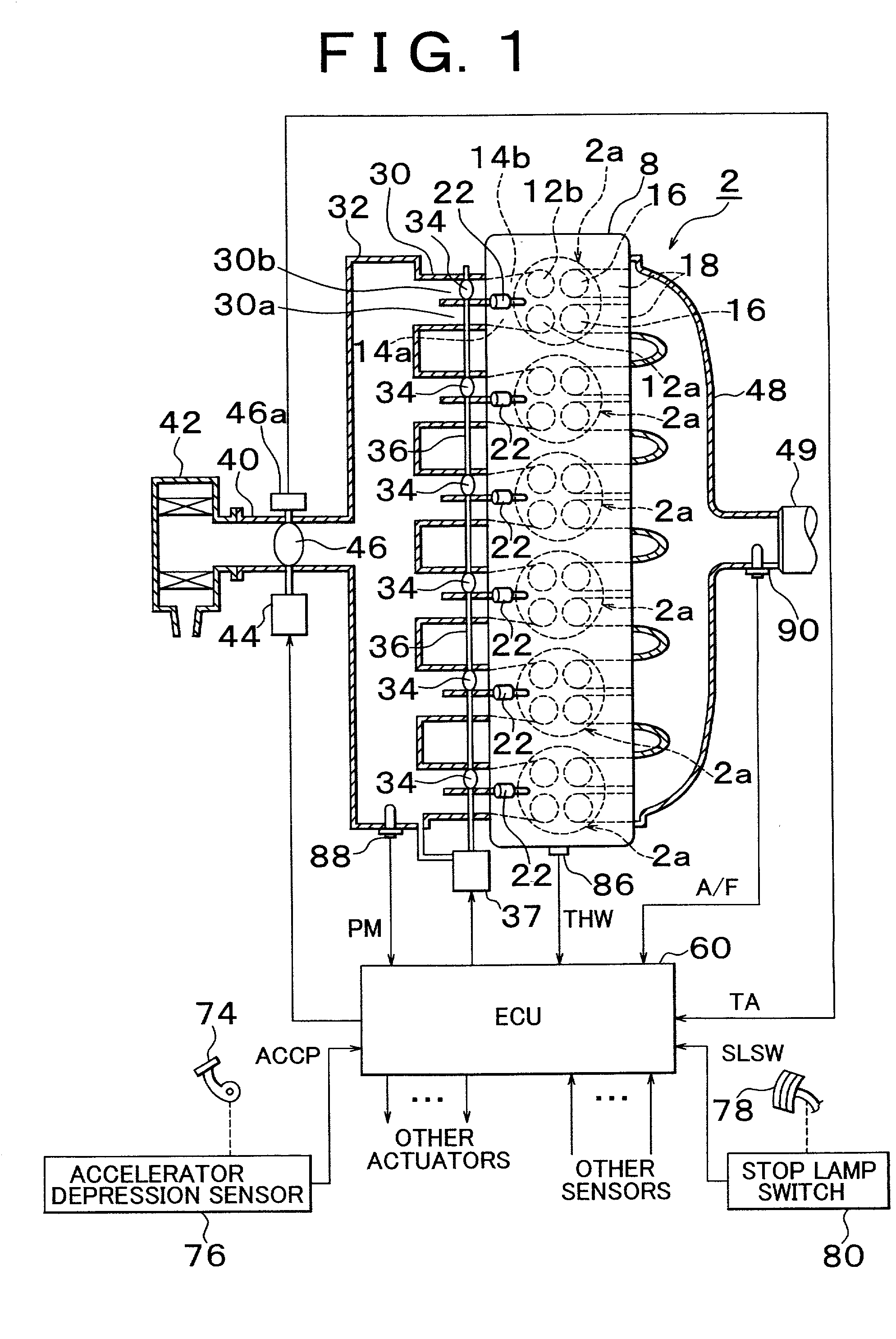
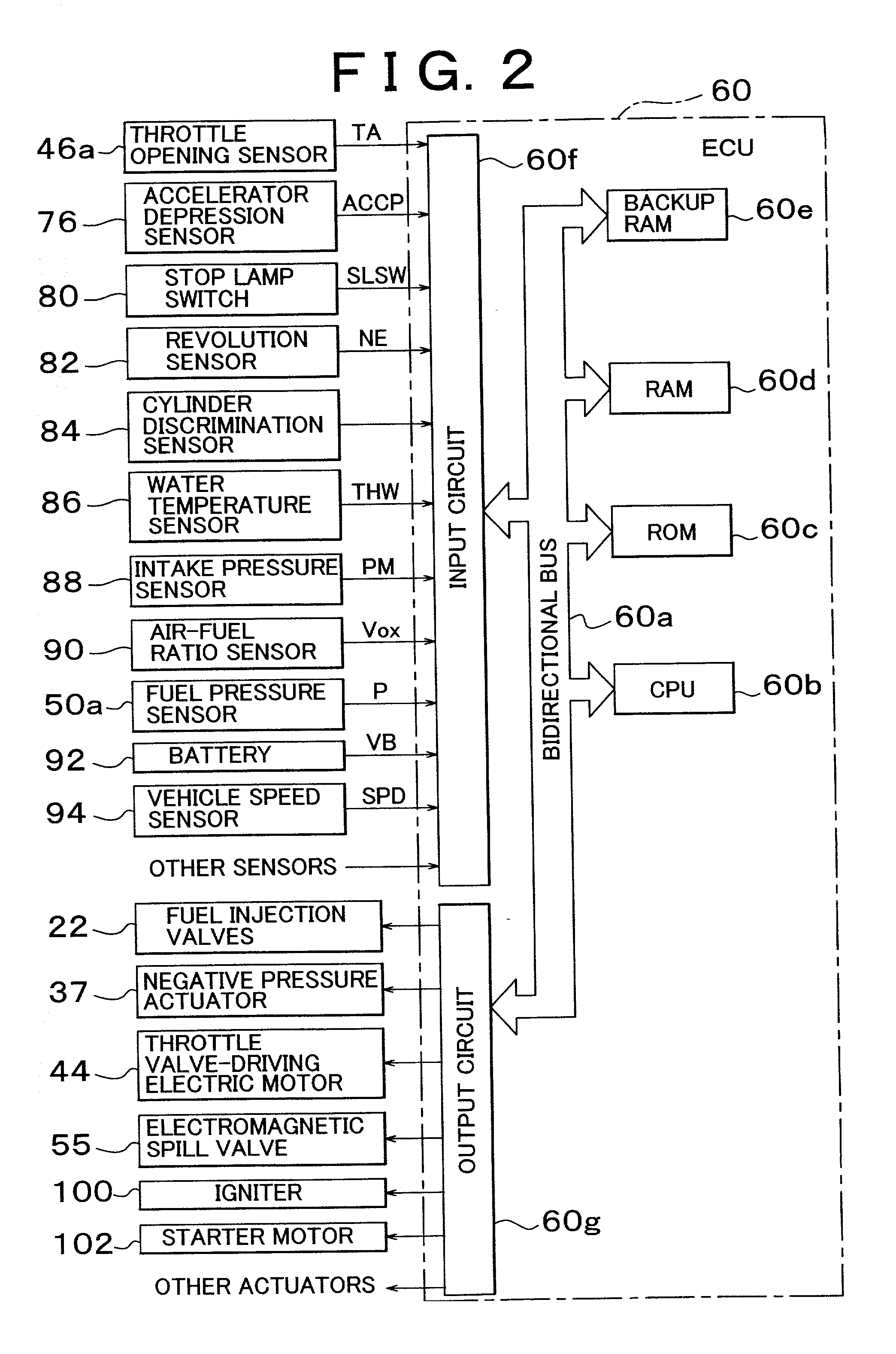
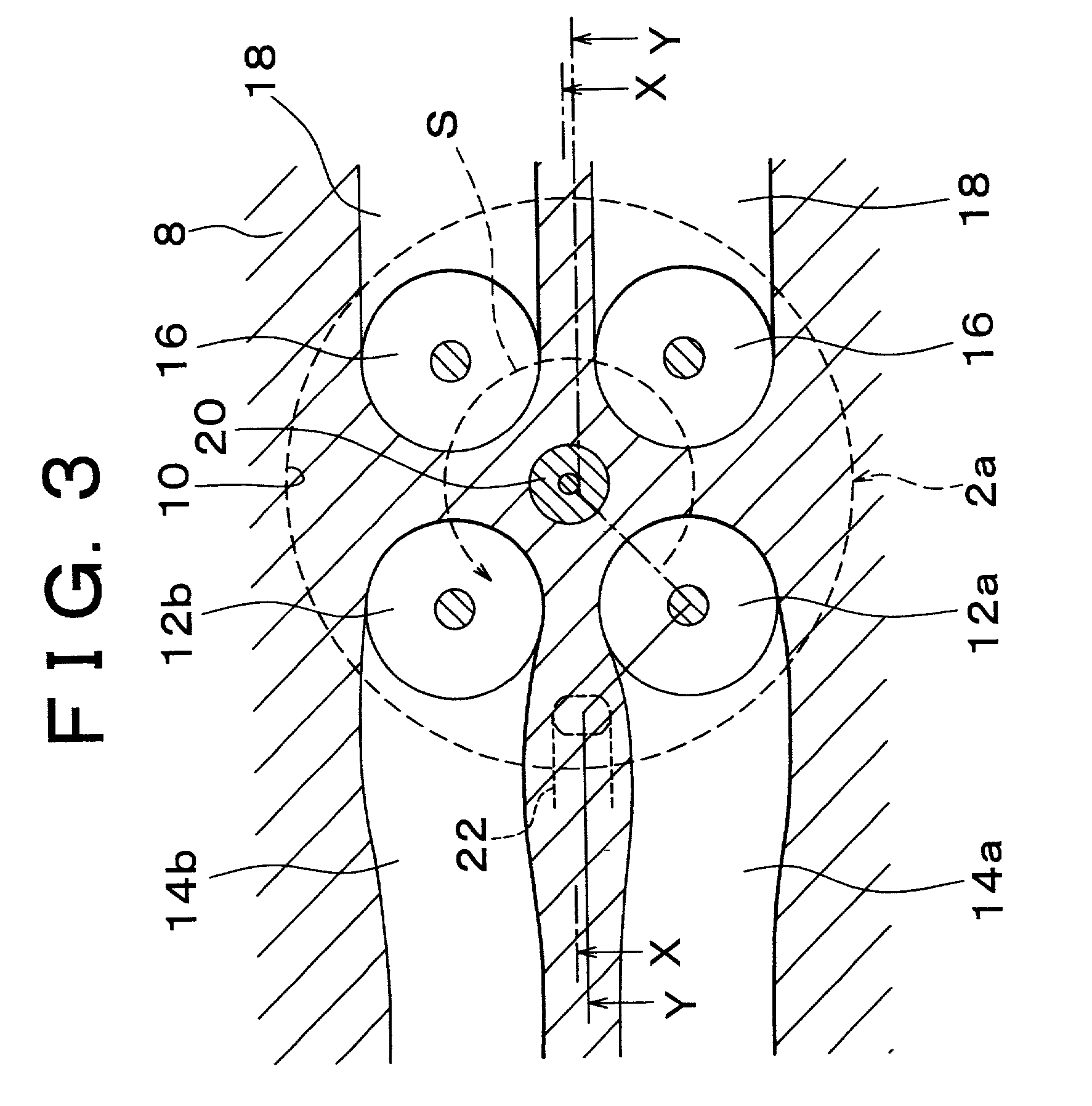
High pressure fuel pump control apparatus for an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20080216797A1Inhibit deteriorationIncrease fuel pressureElectrical controlMachines/enginesStart timeHigh pressure
In a high pressure fuel pump control apparatus for an internal combustion engine which has a high pressure fuel pump of an engine driven type capable of pressure feeding a controlled amount of fuel by driving a fuel suction valve to close at predetermined timing in a fuel delivery stroke, fuel pressure in an accumulator is swiftly raised by reliably pressure feeding a maximum amount of fuel from a fuel delivery stroke immediately after engine starting while avoiding heat generation by a solenoid for controlling the fuel suction valve, whereby deterioration of a combustion state and exhaust emissions at engine starting can be prevented. A starting time control section continuously energizes the solenoid over a period from the beginning of engine starting until when it becomes possible to perform valve closing timing control on the fuel suction valve based on the rotational position of the engine after completion of cylinder identification.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Control device of high-pressure fuel pump of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7299790B2Conducive to stable combustionAccelerate emissionsElectrical controlFuel injecting pumpsExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
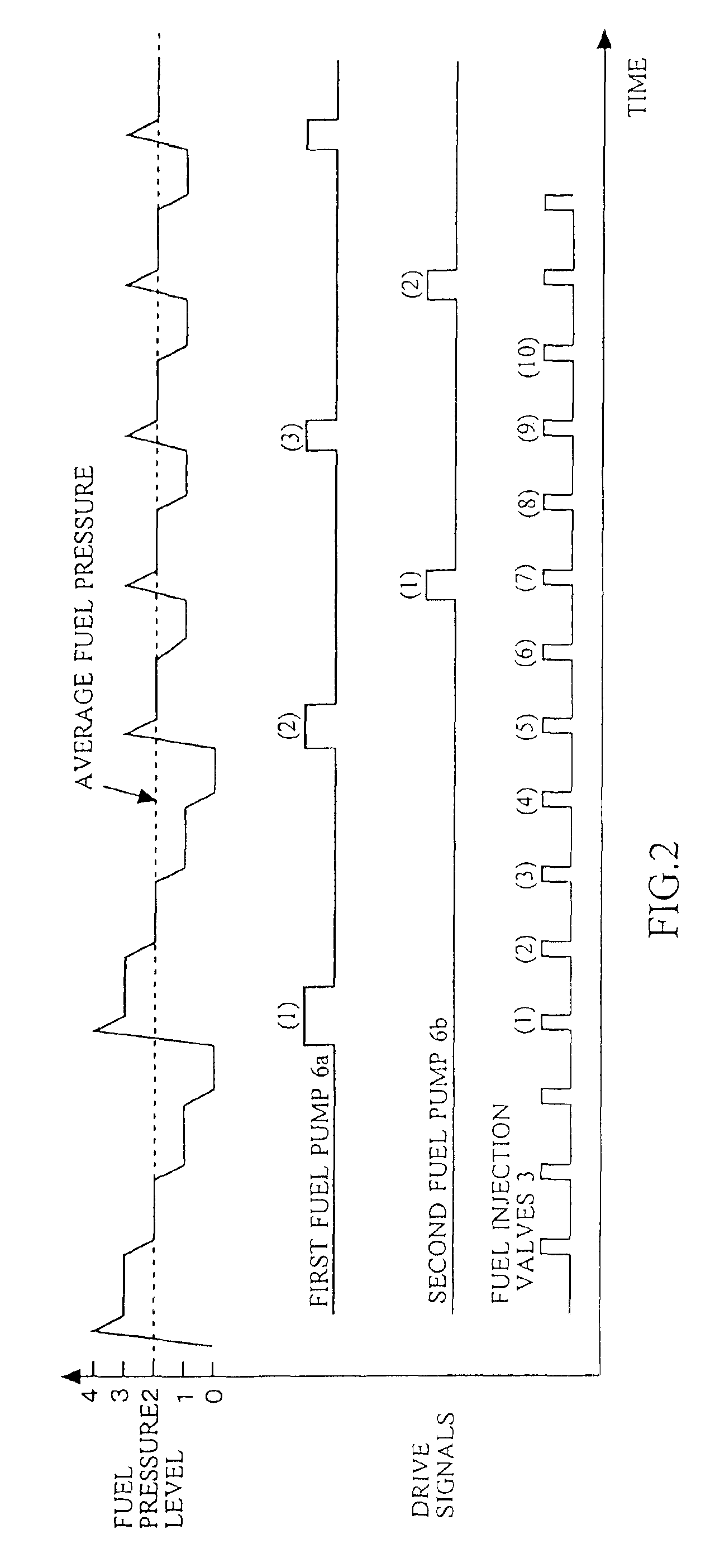
A control device of a high-pressure fuel pump of an internal combustion engine capable of improving stability in controlling the drive of the high-pressure fuel pump by limiting the end timing of a drive signal of the high-pressure fuel pump and driving an actuator in a control effective range of the high-pressure fuel pump. The control device of the high-pressure fuel pump of the internal combustion engine has a fuel injection valve provided on a cylinder and the high-pressure fuel pump for pumping fuel to the fuel injection valve, wherein the high-pressure fuel pump comprises a pressure chamber, a plunger for pressurizing the fuel in the pressure chamber, a fuel valve provided in the pressure chamber, and the actuator for operating the fuel valve. The control device has means for calculating the drive signal of the actuator so as to realize the variable discharge of the high-pressure fuel pump. The means for calculating the drive signal has means for limiting the end timing of the drive signal of the actuator to a predetermined phase and / or means for limiting the output timing of the drive signal of the actuator to be within a predetermined phase range.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
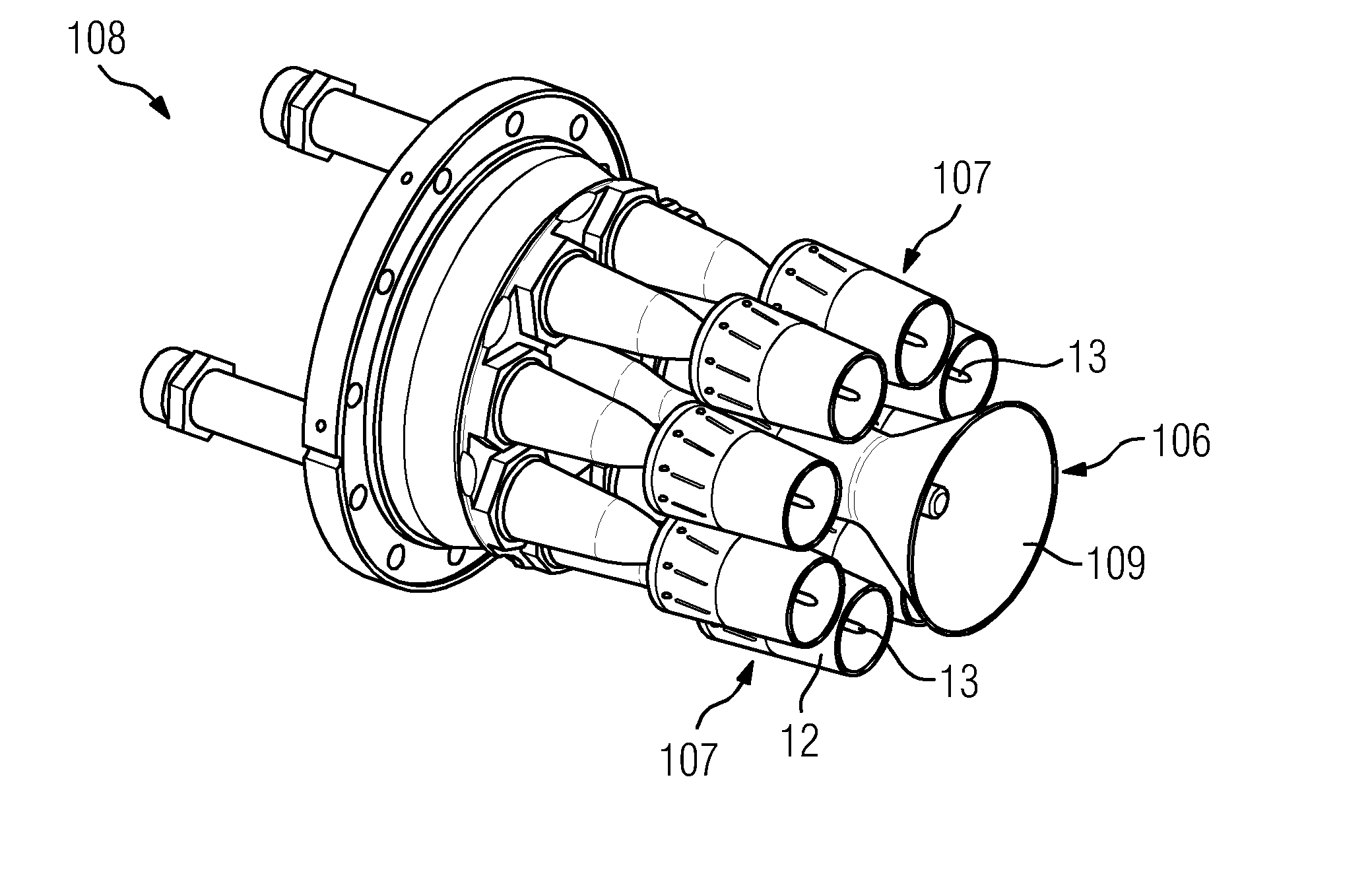
Burner assembly
InactiveUS20130104554A1Increase the diameterNarrow profileBurnersContinuous combustion chamberCombustorLiquid fuel
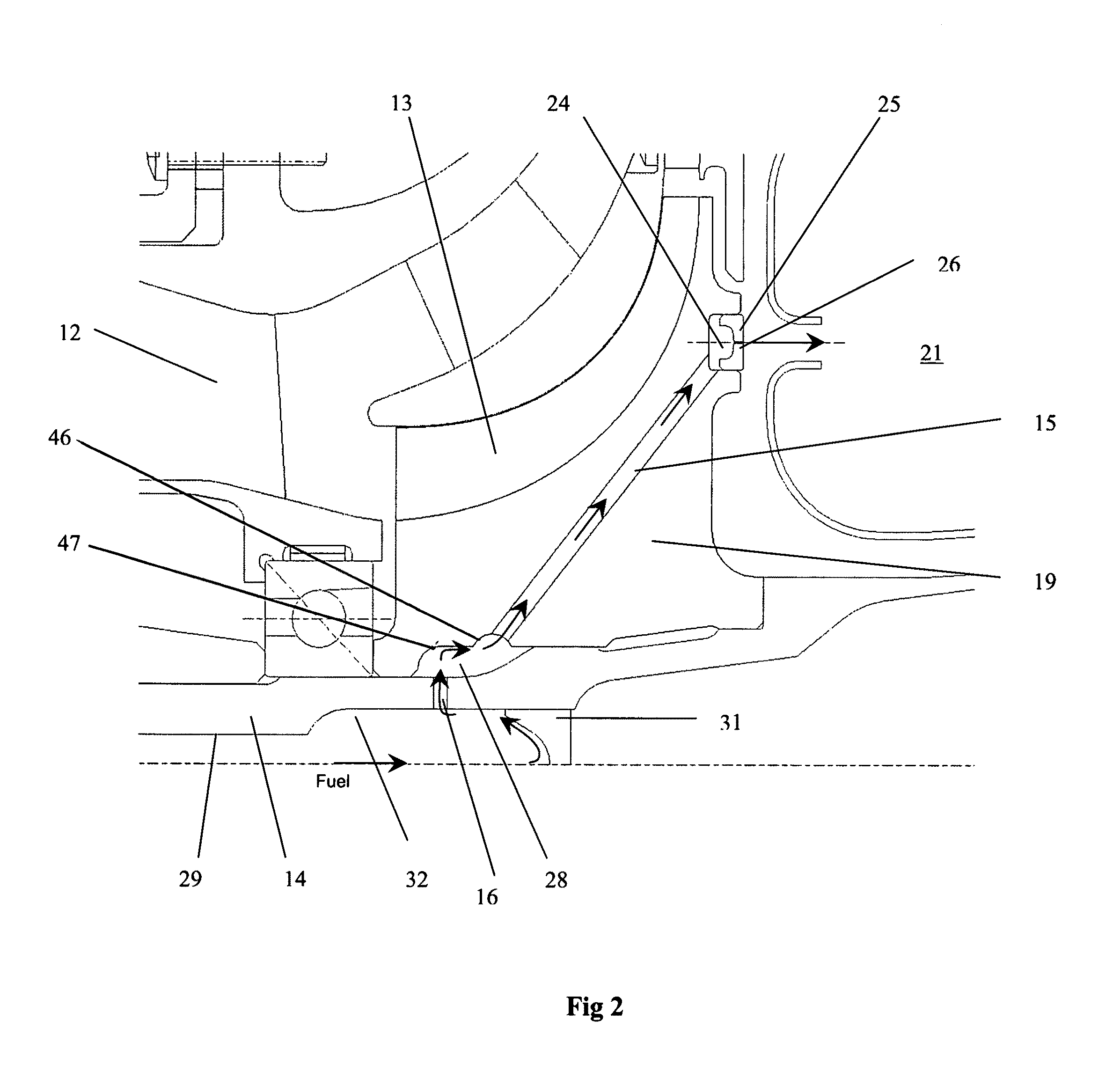
A burner assembly for a gas turbine is provided. The burner assembly has a combustor, a centrally arranged pilot burner and plurality of main burners surrounding the pilot burner. Each main burner has a cylindrical housing having a lance which is centrally arranged therein and has a fuel channel for liquid fuel. The lance is supported on the housing by swirl blades and an attachment is arranged on the lance in the direction of the combustor. The liquid fuel nozzle is arranged in the attachment downstream of the swirl blades and connected to the fuel channel. For the improved mixing of the fuel with the air, the liquid fuel nozzle is designed as a full jet nozzle and the full jet nozzle has a length and a diameter, the ratio of the length to the diameter is at least 1.5.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Fuel supply system for internal combustion engine
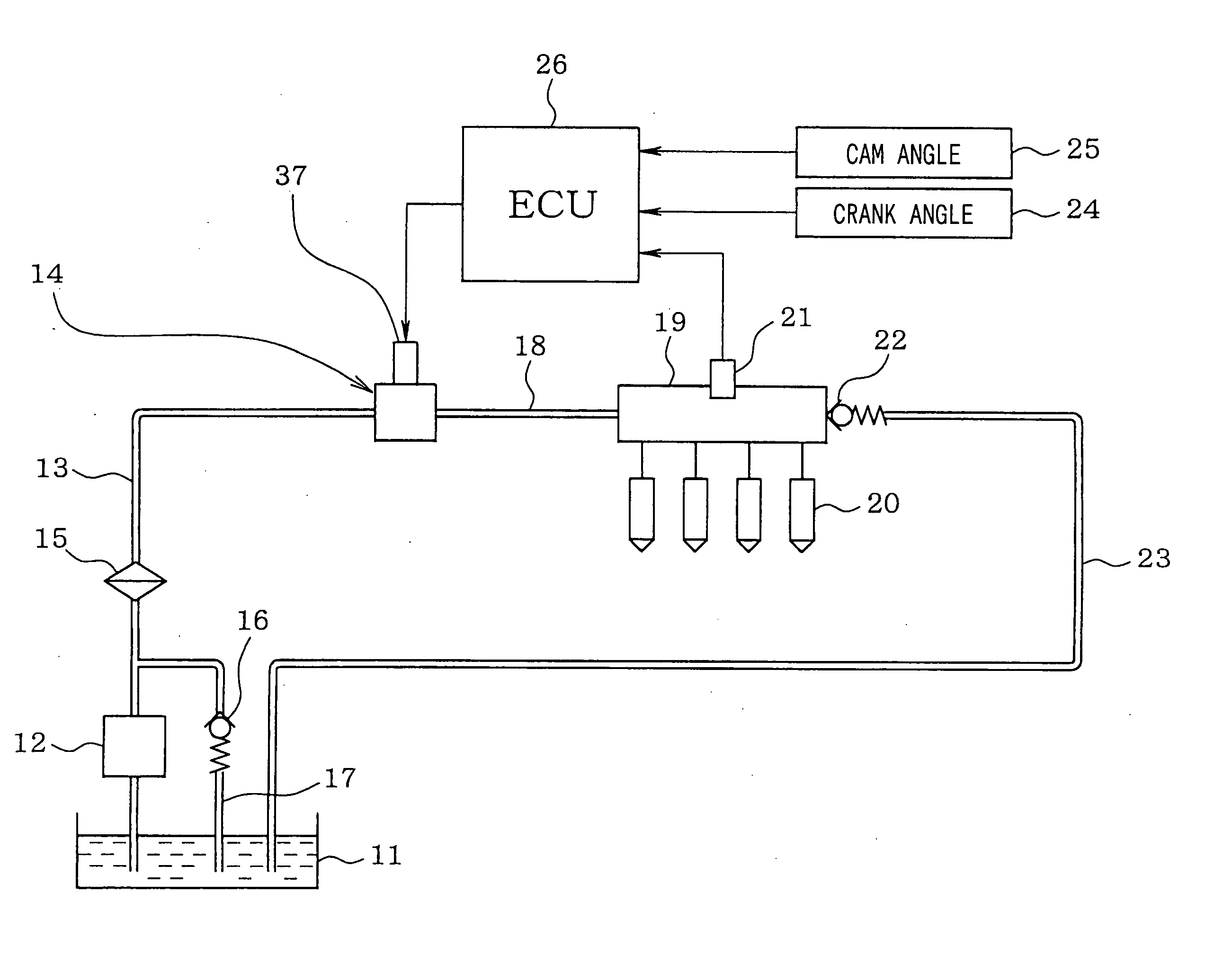
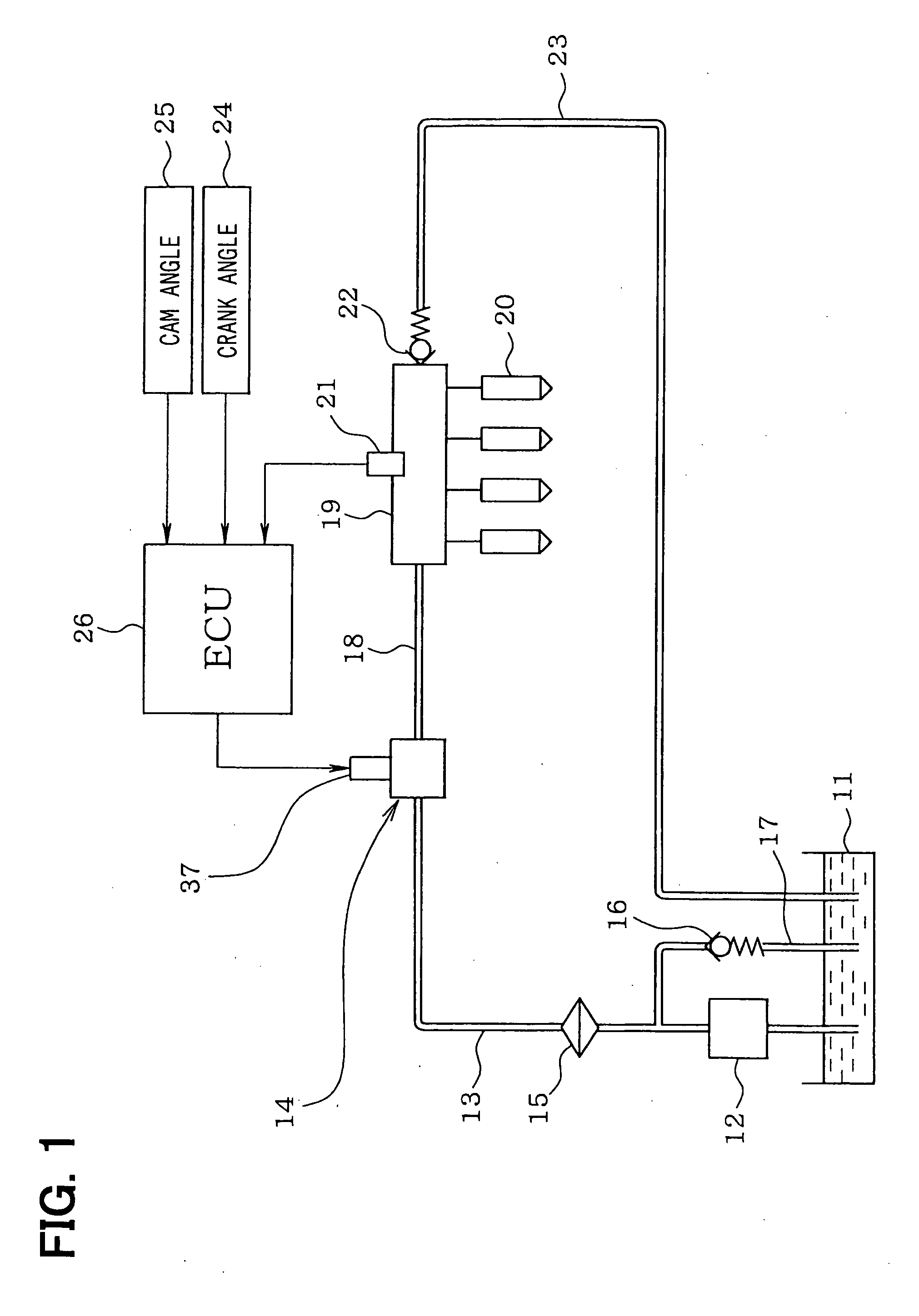
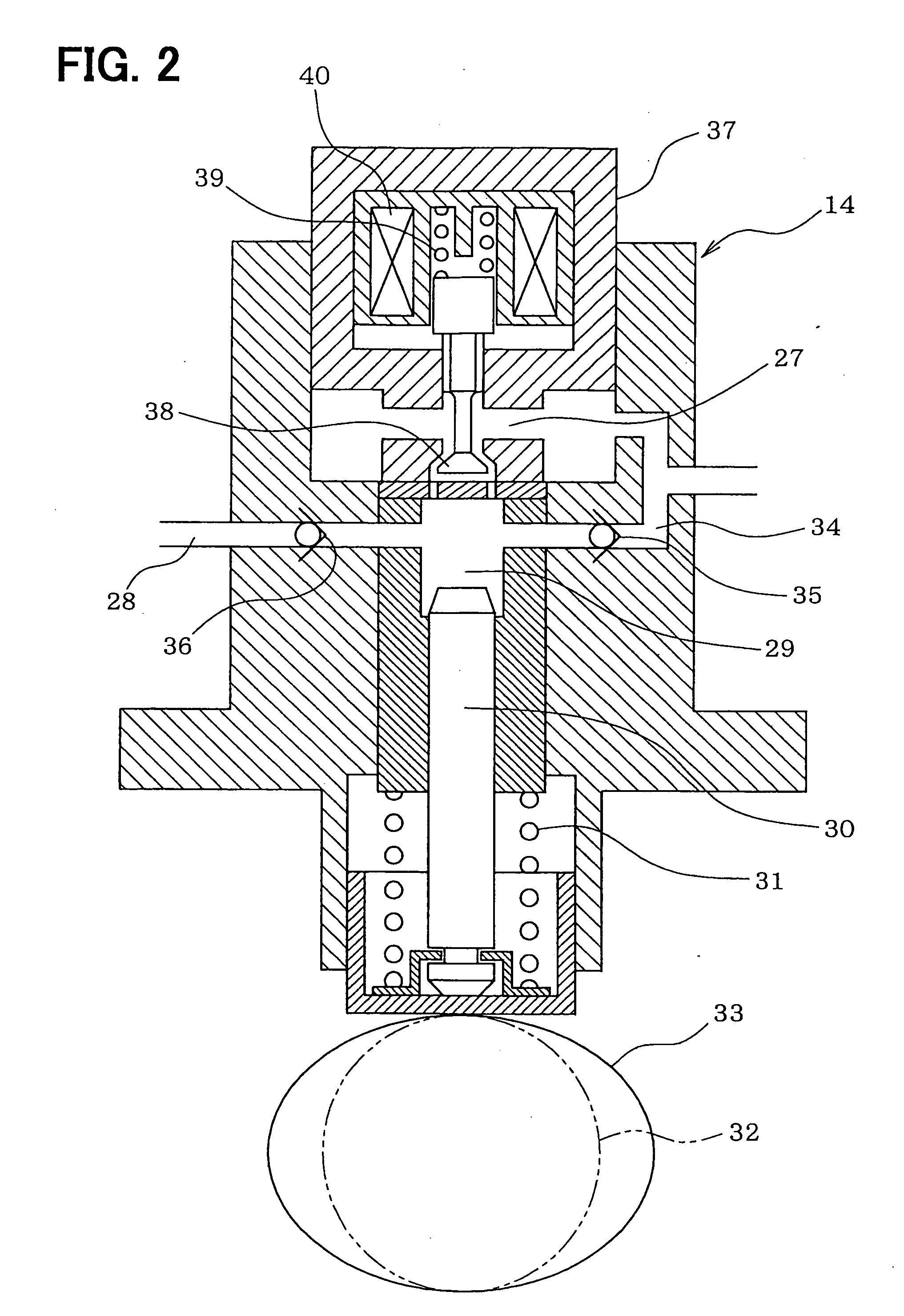
InactiveUS6899084B2Raise promptly fuel pressureIncrease fuel pressureElectrical controlLow pressure fuel injectionFuel supplyInternal combustion engine
In a fuel supply system for an internal combustion engine, there is provided a technology capable of keeping the pressure of fuel constant. Fuel pumps are provided in which the pressure of fuel to be discharged therefrom can be adjusted due to an increase and a decrease in the amount of the fuel discharged, and the discharge of fuel therefrom can be stopped. Fuel injection valves serve as a fuel pressure reducing device that reduces the fuel pressure raised by the fuel pumps. A fuel pressure adjusting section changes the number of operations of the fuel pumps and the amounts of fuel discharged from the fuel pumps in such a manner that an average value of the fuel pressure from after the fuel pressure has once been raised until the fuel pressure is again raised becomes substantially constant before and after the number of operations of said fuel pumps is changed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel supply system of internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20050211224A1Promote atomizationImprove flammabilityElectrical controlNoise reducing fuel injectionFuel supplyCheck valve
A high-pressure pump is formed with a secondary suction passage, which branches from a fuel suction passage and communicates with a pump chamber. Check valves for preventing a backflow of fuel are disposed respectively in the secondary suction passage and a discharge passage. An electromagnetic valve for regulating a fuel discharge quantity is disposed in the fuel suction passage. Normal control for controlling the fuel discharge quantity by controlling opening timing and closing timing of the electromagnetic valve with respect to reciprocating movement of a plunger is performed when an engine rotation speed is higher than a predetermined value during operation of an engine. Valve closing control for holding the electromagnetic valve at a closed state is performed when the engine rotation speed is equal to or lower than the predetermined value.
Owner:DENSO CORP
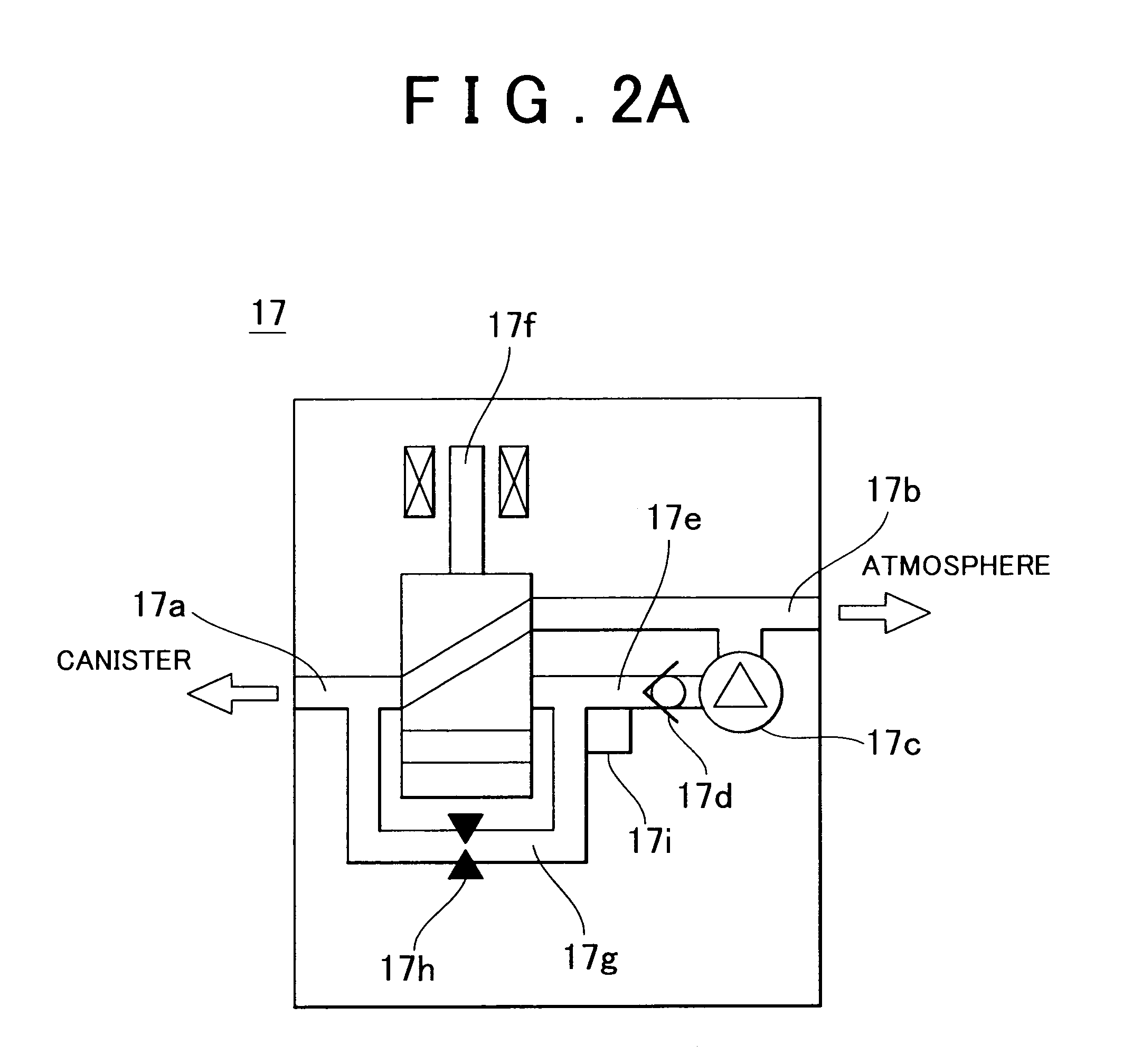
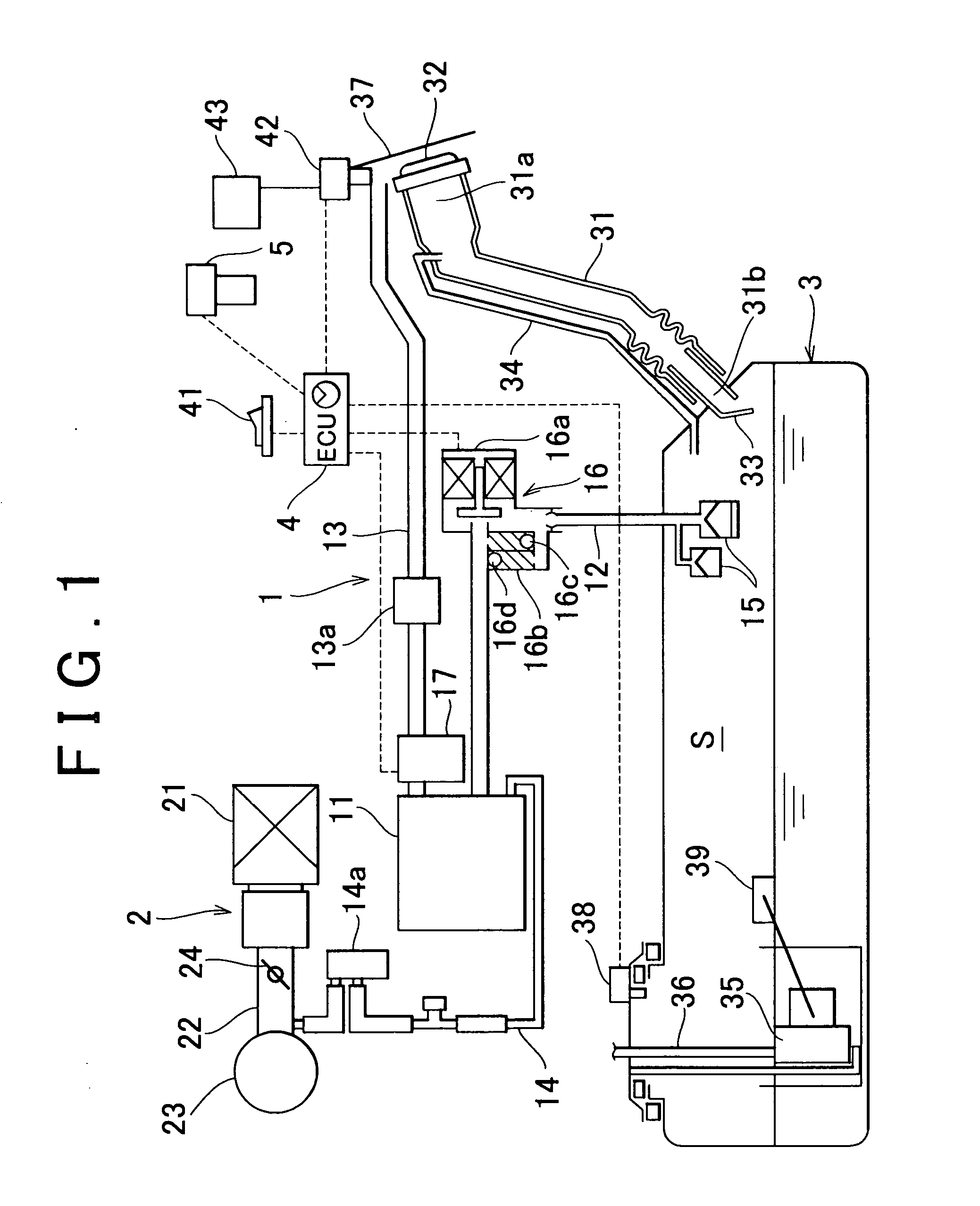
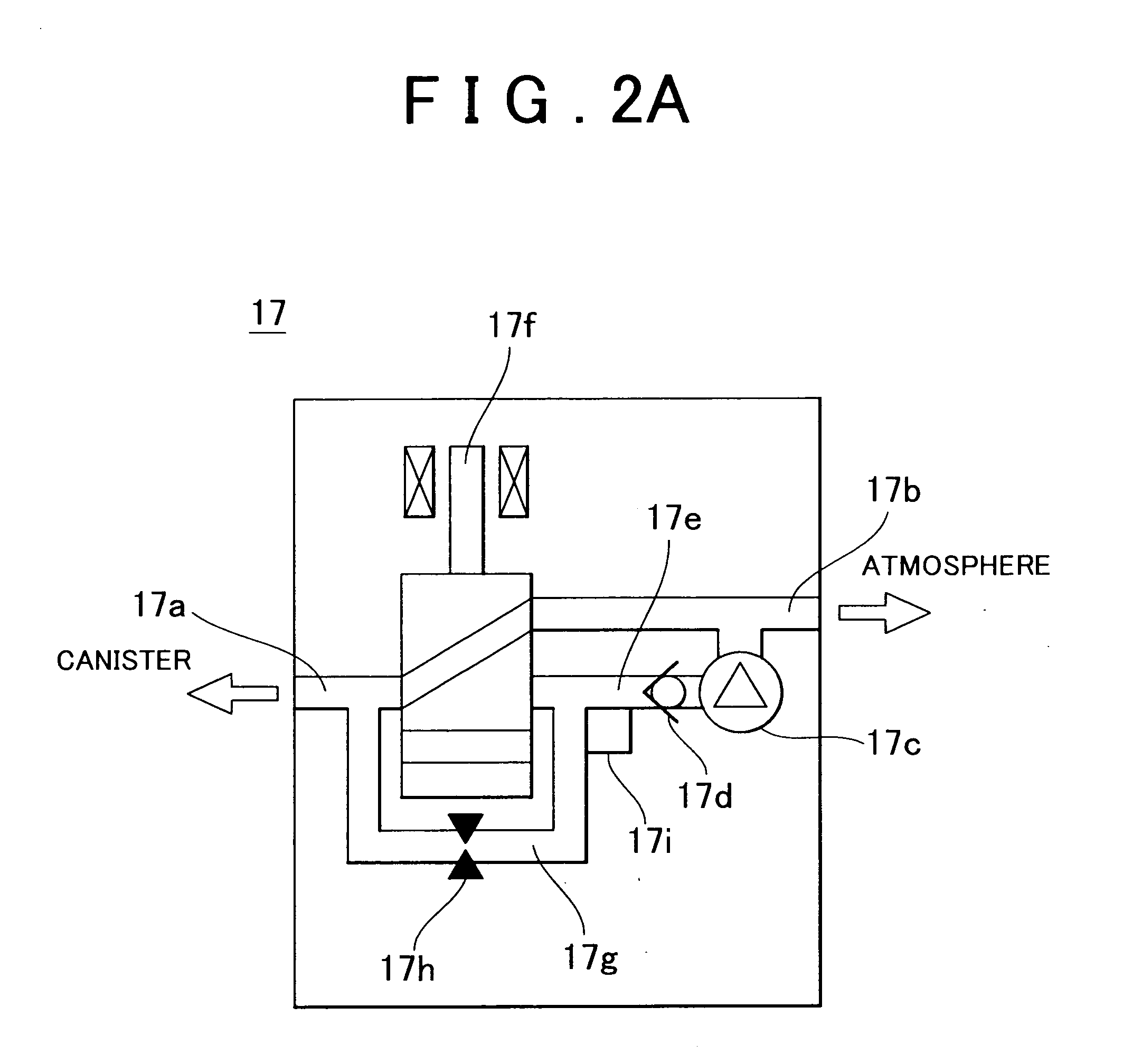
Evaporated fuel treatment device of internal combustion engine and evaporated fuel treatment method
InactiveUS7152587B2Case blockedAvoid dischargeNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngine testingExternal combustion engineFuel treatment
In a canister system of seal type, a purge VSV is closed even if a predetermined purge condition is established so as to prevent direct purging of an evaporated fuel within a fuel tank into an intake system of an engine when one of the following conditions is established, that is, (1) a motor pump of an OBD pump module is driven; (2) a switching valve of the OBD pump module is set to ON; and (3) a closing valve is opened.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
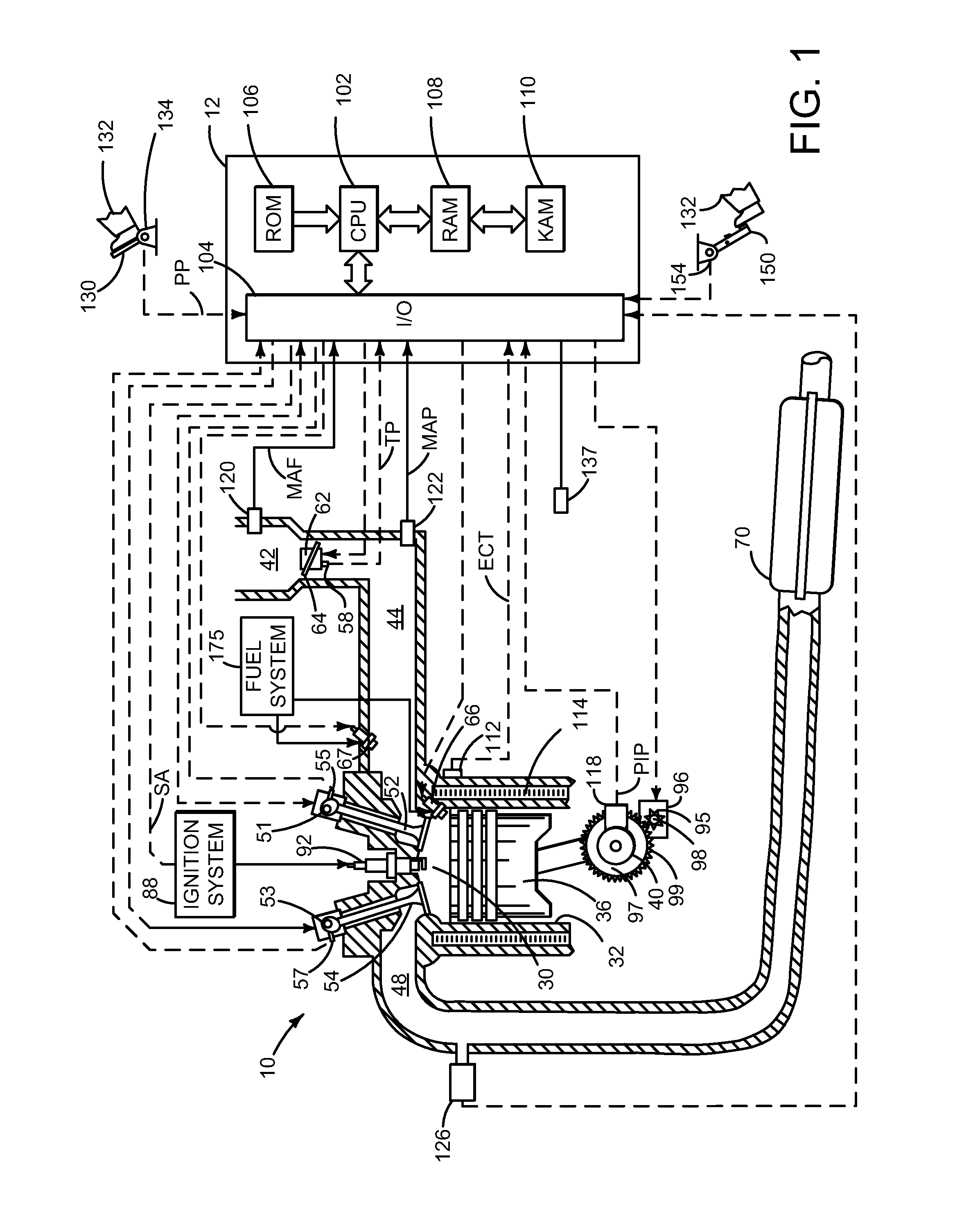
Addressing fuel pressure uncertainty during startup of a direct injection engine
ActiveUS7832375B2Improve the level ofLow efficiencyElectrical controlLow-pressure fuel injectionInternal combustion enginePressure sensor
An engine system and a method of starting an internal combustion engine of the engine system are described. In one embodiment, the method includes adjusting a fuel pressure within a fuel rail to exceed a pressure of a pressure relief valve. The method may be particularly useful during degradation of a fuel pressure sensor.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Evaporated fuel treatment device of internal combustion engine and evaporated fuel treatment method
InactiveUS20060086343A1Case blockedAvoid dischargeNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngine testingFuel tankFuel treatment
In a canister system of seal type, a purge VSV is closed even if a predetermined purge condition is established so as to prevent direct purging of an evaporated fuel within a fuel tank into an intake system of an engine when one of the following conditions is established, that is, (1) a motor pump of an OBD pump module is driven; (2) a switching valve of the OBD pump module is set to ON; and (3) a closing valve is opened.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel filter device
InactiveUS20090120858A1Reduce loadIncrease pressureMachines/enginesPressure lubricationEngineeringFuel filter
A fuel filter device includes a bag-shape filter body and a space forming member disposed in the filter body. The filter body includes an upper surface part, and a lower surface part welded with the upper surface part at edges to form a bag shape. At least the lower surface part has a woven mesh outer layer part, a first inner layer part situated adjacent to the outer layer part and formed of a melt blown non-woven cloth, and a second inner layer part situated adjacent to the first inner layer part at a side opposite to the outer layer part. The second inner layer part is formed of a spun-bonded non-woven cloth. The upper surface part and the lower surface part are all made of polypropylene that is not soaked and swollen with fuel to thereby maintain a mesh size of the filter body without change.
Owner:NIFCO INC
Fuel supply system of internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7198033B2Improve quietnessAccelerate emissionsElectrical controlNoise reducing fuel injectionSolenoid valveExternal combustion engine
A high-pressure pump is formed with a secondary suction passage, which branches from a fuel suction passage and communicates with a pump chamber. Check valves for preventing a backflow of fuel are disposed respectively in the secondary suction passage and a discharge passage. An electromagnetic valve for regulating a fuel discharge quantity is disposed in the fuel suction passage. Normal control for controlling the fuel discharge quantity by controlling opening timing and closing timing of the electromagnetic valve with respect to reciprocating movement of a plunger is performed when an engine rotation speed is higher than a predetermined value during operation of an engine. Valve closing control for holding the electromagnetic valve at a closed state is performed when the engine rotation speed is equal to or lower than the predetermined value.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Direct injection type internal combustion engine control apparatus and control method of the same
InactiveUS20010042535A1Sufficient improvements in fuel economy and the likeHigh frequencyElectrical controlCombustion enginesPressure decreaseCombustion chamber
A direct injection type internal combustion engine control apparatus is capable of increasing the frequency of performing the compression-stroke fuel injection following an automatic start of the engine by maintaining a sufficient fuel pressure for the compression-stroke injection even after the engine has been stopped by an automatic stop function. When an immediately-before-automatic-stop flag is "ON", the control apparatus sets the control duty of an electromagnetic spill valve to 100(%) to raise the fuel pressure immediately before the automatic stop. As a result, after the engine stops, the fuel pressure starts to decrease from a high pressure, so that there will be a long time before the fuel pressure decreases to a level that makes it impossible to perform appropriate fuel injection into the combustion chamber during the compression stroke. Therefore, the possibility of performance of the compression-stroke injection immediately following an automatic start is increased, and the frequency of performing the compression-stroke injection is increased. Thus, sufficient improvements in fuel economy and the like can be achieved.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel pump, fuel supply equipment using fuel pump and method for manufacturing fuel pump
InactiveUS20050220641A1Lower average currentSmall sizeCircumferential flow pumpsTransverse flow pumpsBrushless motorsMagnetic poles
A fuel pump mounted in the fuel tank for the motor cycle comprises a motor and a pump driven by the motor for increasing a pressure of the sucked fuel. The motor is a brushless motor and has a stator core, coils and a rotor. An electrical energization for the coils wound around the stator core is controlled in response to a rotating position of the rotor, thereby the rotor is rotated. The rotor has a shaft, a rotating core and a permanent magnet, and the rotor is rotatably mounted at the inner circumference of the stator core. The permanent magnet is mounted at the outer circumference of the rotating core and magnetically energized so as to form magnetic poles different alternatively in a rotating direction at the outer circumferential surface facing the stator core.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Energy-storing-type high-pressure electric fuel pump, fuel-supplying apparatus, and application method therefor
ActiveUS20160186732A1Increase capacitySuppress pressure fluctuationsFuel injecting pumpsPiston pumpsEngineeringHigh pressure
An energy-storing-type high-pressure electric fuel pump includes an electromagnetic driving apparatus and a plunger sleeve cylinder component. The plunger sleeve cylinder component includes a high-pressure volume, a plunger sleeve having a plunger hole, and a plunger capable of sliding within the plunger hole. A clearance volume of the plunger in the plunger hole is a high-pressure fuel chamber. A clearance volume between the electromagnetic driving apparatus and the plunger sleeve cylinder component forms a low-pressure fuel chamber. Under the action of the electromagnetic driving apparatus, the plunger sleeve cylinder component sucks a fuel in the low-pressure fuel chamber into the high-pressure fuel chamber and pressure-feeds the fuel into the high-pressure volume. The electromagnetic driving apparatus includes an energy storage apparatus, a movable part, and a still part.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FAI ELECTRONICS
Engine fuel delivery system
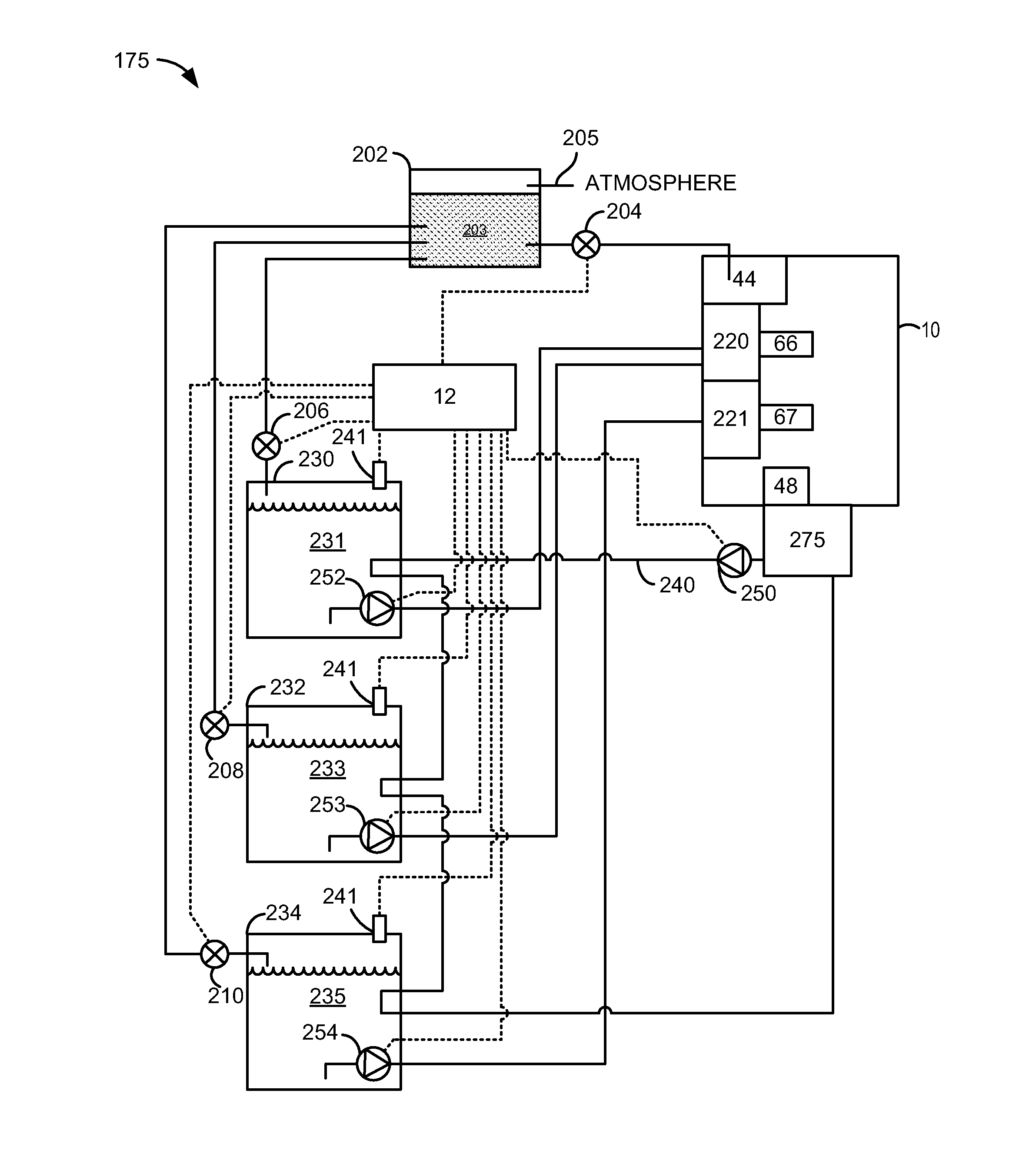
InactiveUS6913000B2Increase fuel pressureImprove fuel efficiencyPower operated startersElectrical controlFuel efficiencyHigh pressure
An engine fuel delivery system is provided to raise the fuel pressure rapidly in the initial stage of engine starting without increasing the cranking load, thereby making it possible to achieve an atomized fuel spray through high-pressure fuel injection, improve the fuel efficiency, and reduce emissions. The engine fuel delivery system uses a variable transmission mechanism that is configured to change the drive rotational ratio of a power transmission path between a crankshaft of an engine and a high-pressure fuel pump. The variable transmission mechanism controls the rotational speed of the high-pressure fuel pump to a rotational speed that is higher than the normal pump rotational speed in the initial stage of engine starting after the engine has been cranked to complete explosion.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Fuel separation system for reducing parasitic losses
ActiveUS20150114359A1Improve engine performanceImprove fuel economyElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFuel tankEngineering
Systems and methods for separating higher octane fuel from a fuel mixture are presented. In one example, higher octane fuel is separated from lower octane fuel and allowed to condense in a fuel tank holding higher octane fuel so that parasitic engine losses are not increased by having to separate higher octane fuel from lower octane fuel a second time. The approach may be applied to fuel systems that include multiple fuel tanks storing different types of fuel.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
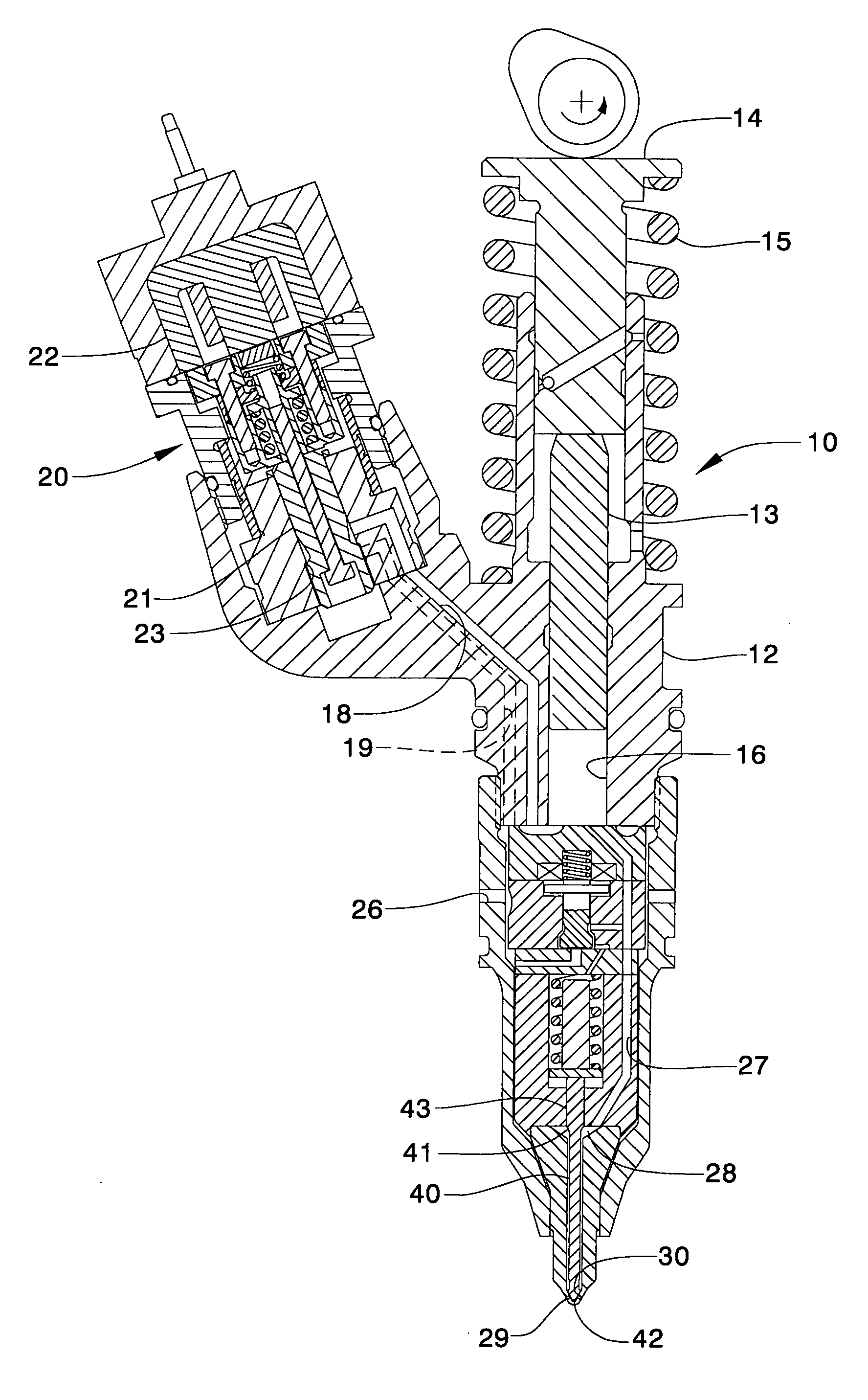
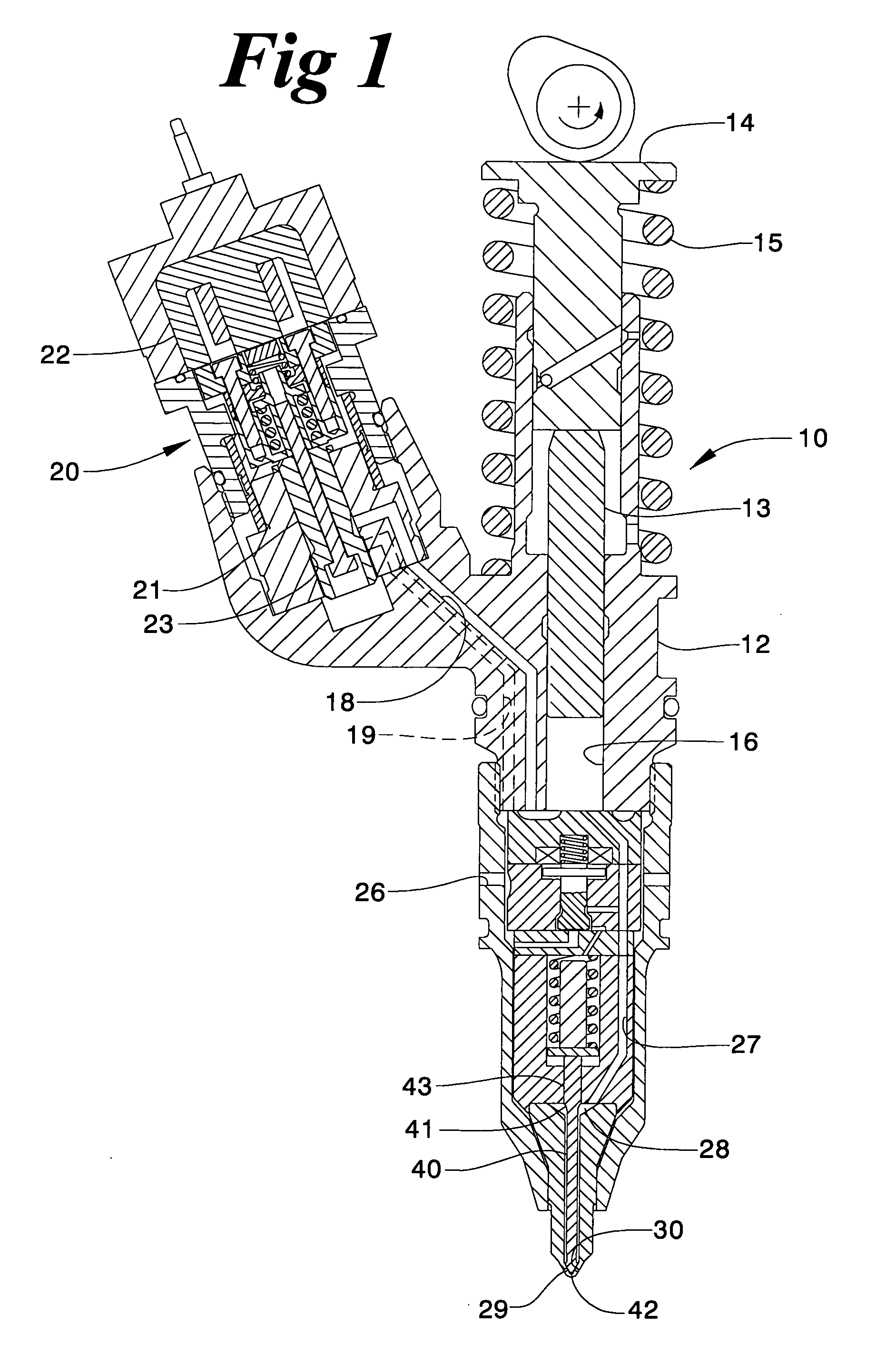
Electronic unit injector with pressure assisted needle control
ActiveUS20050194462A1Increase fuel pressureFuel-injection pumpsFluid pressure injection controlEngineeringHigh pressure
An electronically controlled fuel injector includes a reduced part count and complexity over similar fuel injectors without a substantial reduction in performance capabilities. This is accomplished by using a one-piece needle that is hydraulically balanced and biased toward a closed position with a spring positioned in the needle control chamber. Although subtle, this injector has some ability to control the fuel pressure when the needle valve is opening and closing by adjusting a relative timing of a pressure control valve opening relative to a needle control chamber, using separate electrical actuators. The invention is particularly applicable to fuel injectors that cycle through high and low pressure states during and between injection events, respectively. Cam actuated fuel injectors being particularly well suited.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Lever float valve
InactiveUS20180003315A1Increase fuel pressureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesUnderstructuresMarine engineeringVertical axis
A lever float valve comprising a float stem with a central vertical axis; a float body coupled to the float stem and rotatable relative to the central vertical axis of the float stem; a valve segment positioned within the float body and configured to pivot around a first axis perpendicular to the vertical axis; and a lever comprising a float arm and a float coupled to the valve segment and configured to pivot around a second axis perpendicular to the vertical axis.
Owner:WEIR MINERALS AUSTRALIA LTD
Fuel system with electrically-controllable mechanical pressure regulator
InactiveUS8210156B2Improve efficiencyIncrease rangeElectrical controlExhaust apparatusEngineeringMechanical pressure
A method for operating an engine direct injection fuel system is provided. The direct injection fuel system includes a mechanical fuel pressure regulator that has a spring actuatable by an electric motor. The method includes adjusting a preload of the spring by operating the electric motor to adjust a set-point fuel pressure from a first set-point fuel pressure to a second set-point fuel pressure in response to an operating condition, and maintaining the preload of the spring mechanically when the electric motor is not operating.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Integral gas turbine compressor and rotary fuel injector
InactiveUS7896620B1Rapid and effective fuel atomizationPromote combustionPropellersEngine manufactureCombustion chamberCombustor
An integral impeller and fuel pump for a small gas turbine engine, the impeller being a centrifugal impeller to supply compressed air to the combustor, the rotor disk of the centrifugal compressor having at least one radial fuel passage connecting a central bore of the rotor disk to a fuel nozzle located on the rear face of the rotor disk. A low pressure fuel supplied by a small pump delivers the fuel to the central bore where the fuel is collected within helical grooves and channeled into the radial fuel passages where the fuel is pressurized to a relatively high pressure due to the high rotational speed of the centrifugal compressor. Highly compressed fuel is injected into the combustor through fuel nozzles in an axial direction as the rotor disk rotates. Helical grooves in the central bore each connected to a radial fuel passage move the fuel to an opposite side of the central bore to counteract rotor imbalance. In another embodiment, a primary annular groove collects fuel and, at a low speed, passes all of the fuel to a first radial fuel passage into a first fuel nozzle such that only some of the fuel nozzles inject fuel into the combustor. At a higher speed, some of the fuel collected in the primary annular groove is spilled over into a secondary annular groove that passes the spilled-over fuel into a second radial passage and second fuel nozzle such that all of the fuel nozzles inject fuel into the combustor.
Owner:FLORIDA TURBINE TECH
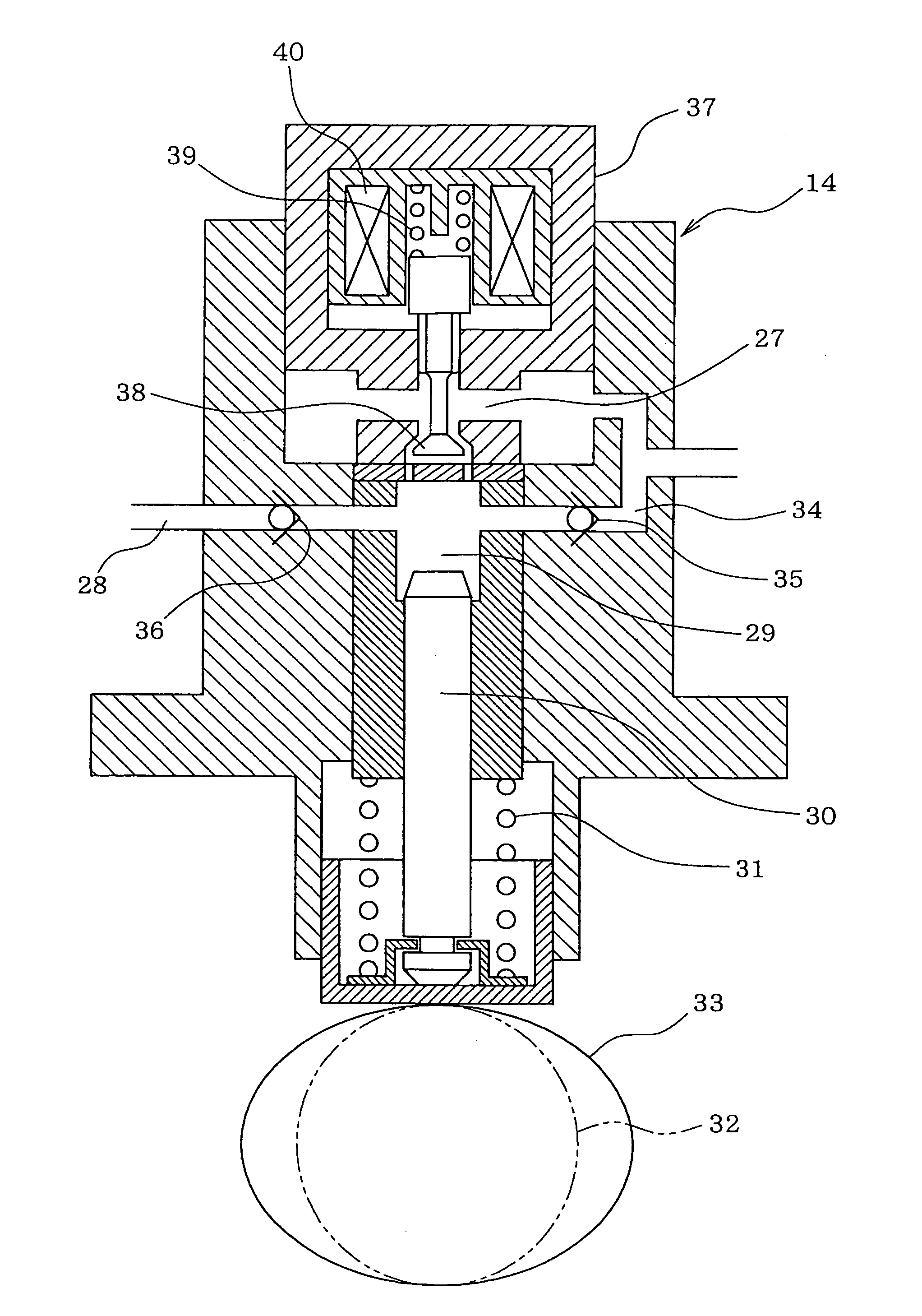
Control Apparatus for Cylinder Injection Internal Combustion Engine with High-Pressure Fuel Pump
InactiveUS20090082939A1Decreased fuel pressure pulsationMinimize the differenceValve arrangementsElectrical controlFuel oilCylinder block
There is provided a control apparatus for a cylinder injection internal combustion engine which suppresses fuel pulsation caused by cam phase deviation and thereby prevents internal combustion engine exhaust deterioration, so that the reliability of a high-pressure fuel system using a high-pressure fuel pump is improved. The control apparatus for a cylinder injection internal combustion engine includes a high-pressure fuel pump that raises the pressure of fuel and discharges the fuel to a fuel rail, and a fuel pressure sensor that detects a pressure of fuel stored in the fuel rail. The control apparatus controls the high-pressure fuel pump based on the fuel pressure detected by the fuel pressure sensor. The control apparatus further includes a cam phase estimation means for estimating a phase of a cam shaft of the internal combustion engine which drives the high-pressure fuel pump, and based on the phase estimation value calculated by the cam phase estimation means, corrects the amount of controlling the high-pressure fuel pump.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Fuel pump and a method for controlling a fuel pump
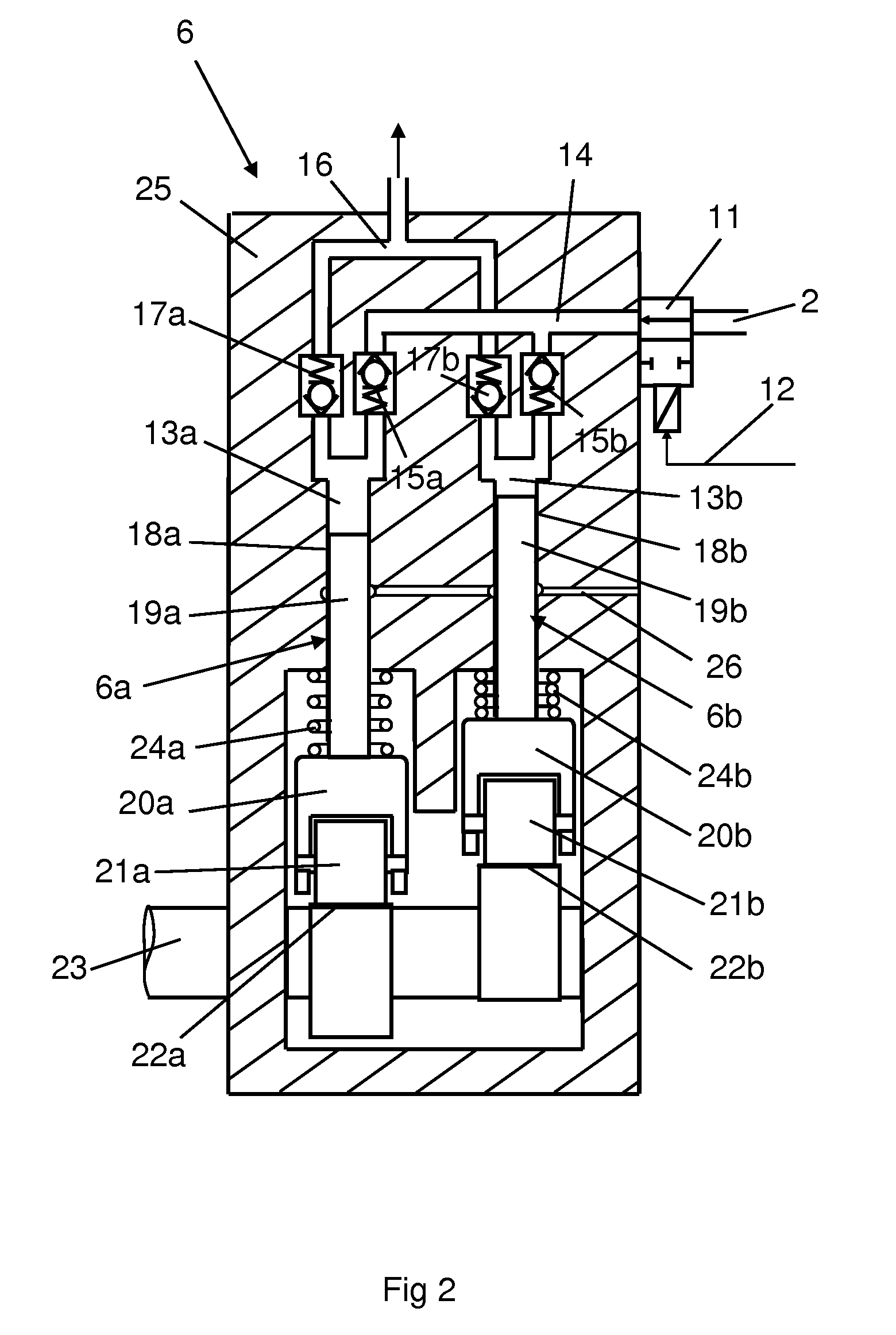
InactiveUS20100043759A1Improve efficiencyImprove accuracyElectrical controlMachines/enginesLow noiseEngineering
A fuel pump and a method for controlling a fuel pump. At least two pumps run at a mutual phase displacement such that they are able to receive fuel during different periods of time. A control unit causes a valve, which is only settable in an open position and a closed position, to lead a desired amount of fuel to the respective pump. The control unit places the valve in the open position for a variable portion of the periods so that an individually controlled amount of fuel is led to the respective pump during those periods. Maintenance of good efficiency of the fuel pump and low noise emissions is thus made possible in operating situations where the fuel pump delivers a reduced amount of fuel.
Owner:SCANIA CV AB
Fuel supply apparatus
ActiveUS7827966B2Reduces clogged filtersIncrease the number ofDigital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:DENSO CORP
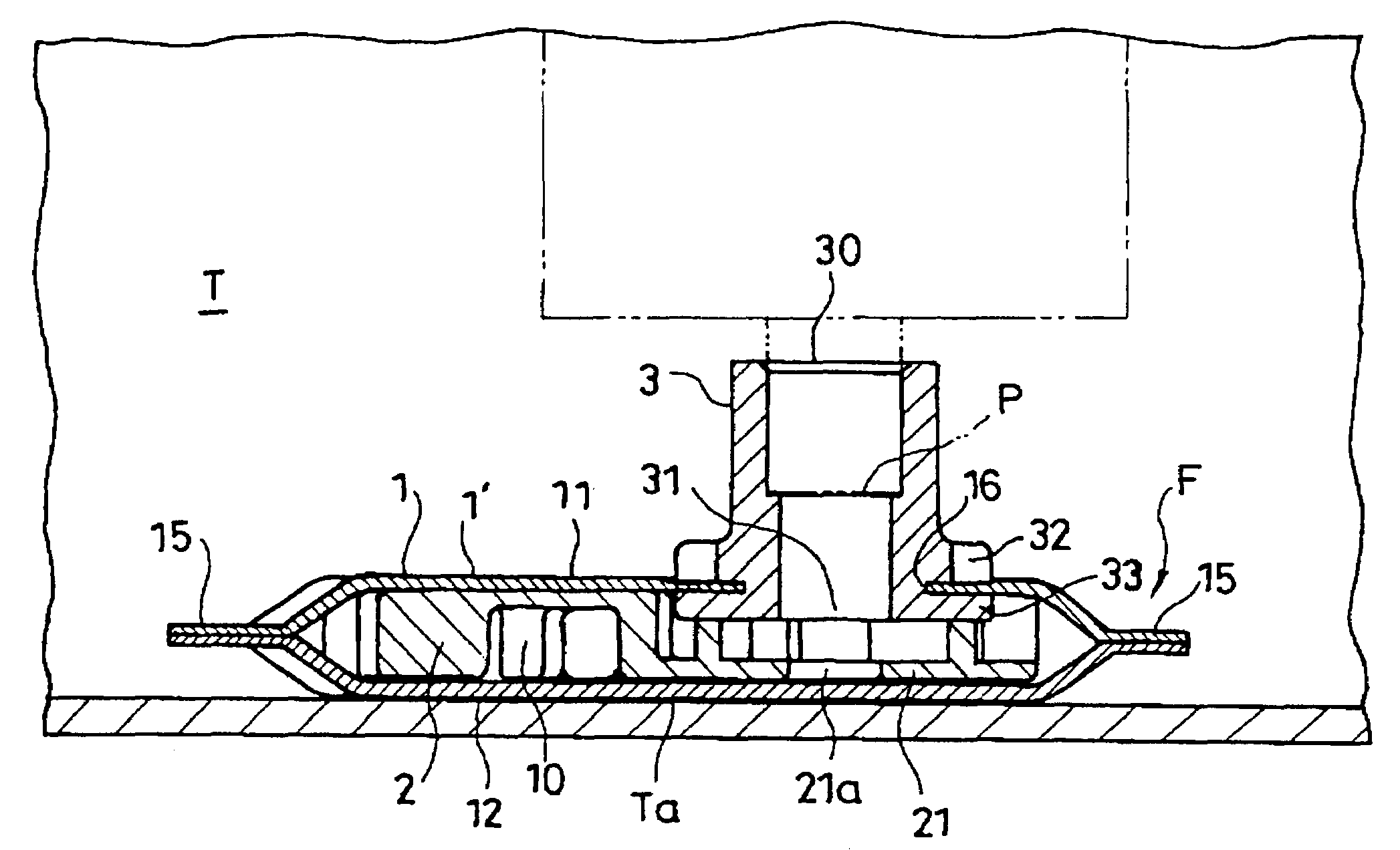
Fuel evaporation gas leakage detecting system and method of detecting fuel evaporation gas leakage
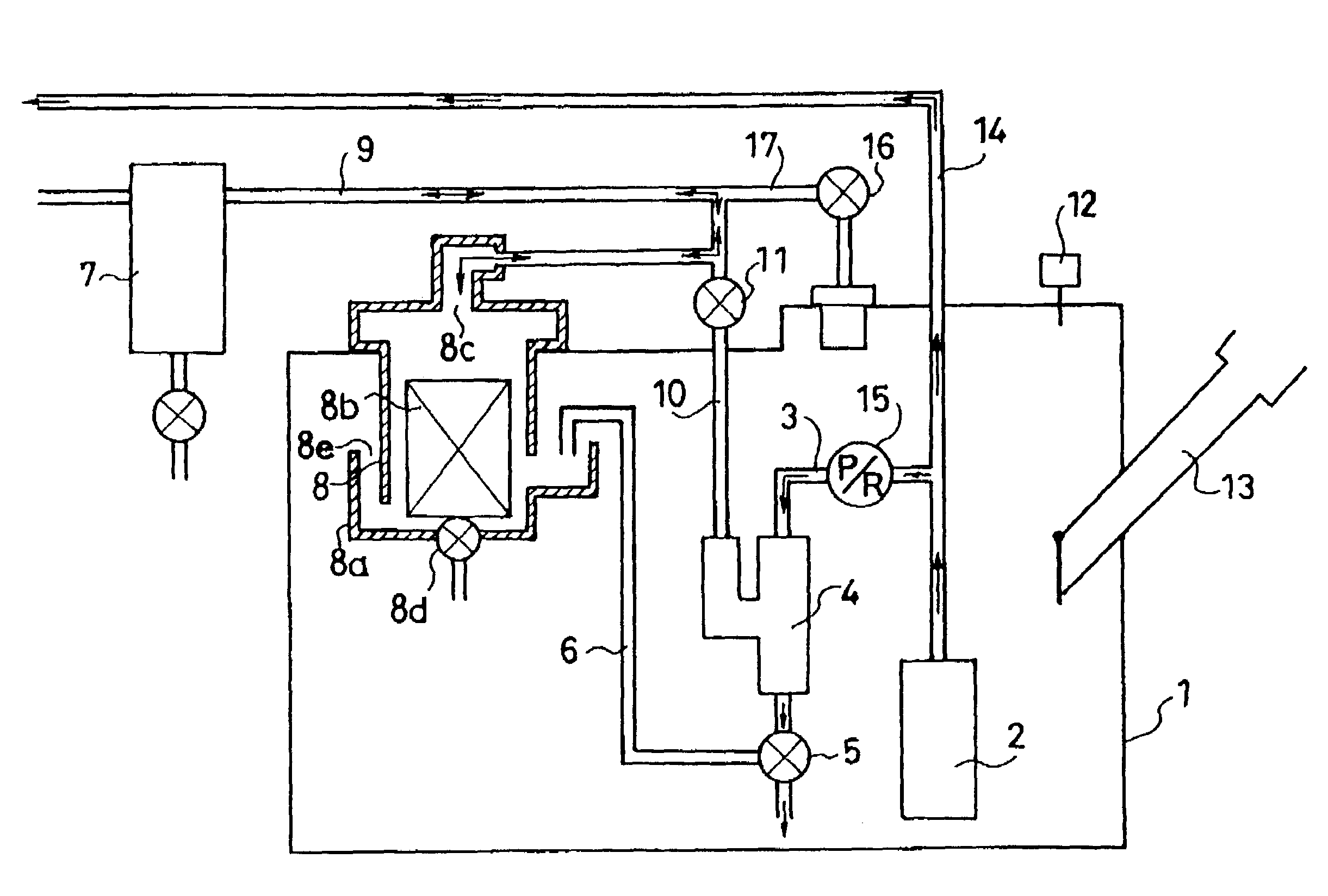
InactiveUS20050133097A1Reduce decreaseAccurate detectionDetection of fluid at leakage pointNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal pressureEvaporation
A leak detecting system detects fuel gas leakage of a fuel tank. The detecting system includes a fuel pump, a jet pump, and a bent valve, which are disposed in the fuel tank. A fuel flow path system includes a relief line connected to the fuel pump for relieving an excess fuel, a relief flow path switching valve disposed in the relief line, and a sub-line for connecting the switching valve and the vent valve. An air flow path system includes a first air flow line to connect the vent valve to a canister, a second air flow line for connecting the first air flow line to the jet pump, and an air flow switching valve for switching communication between the first and second air flow lines. An inner pressure sensor is provided to the fuel tank for detecting an inner pressure of the fuel tank.
Owner:NIFCO INC +1
Fuel supply apparatus
ActiveUS20160272063A1Speed up the flowSuppress turbulenceMachines/enginesLiquid fuel feedersVaporizationFuel supply
An object is to provide a fuel supply apparatus that is configured to cause fuel vapor generated by vaporization of a fuel circulated in a fuel tank to be smoothly joined with the supplied fuel. The fuel supply apparatus comprises a filler neck body that is configured to include a hollow fuel passage-forming portion arranged to define a fuel passage and a breather port; a nozzle guide that is placed inside of the fuel passage-forming portion and is configured to introduce a fueling nozzle; a guide portion that is configured to introduce an inflow gas flowing in from the breather port, to the fuel passage via an outer circumferential space; and a rib that is provided between the guide portion and a lower end in the first direction of the nozzle guide and is configured to divide the inflow gas introduced through the fuel passage.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD +1
Fluid reforming apparatus for maintaining thermal conductivity of a fluid in a flow channel
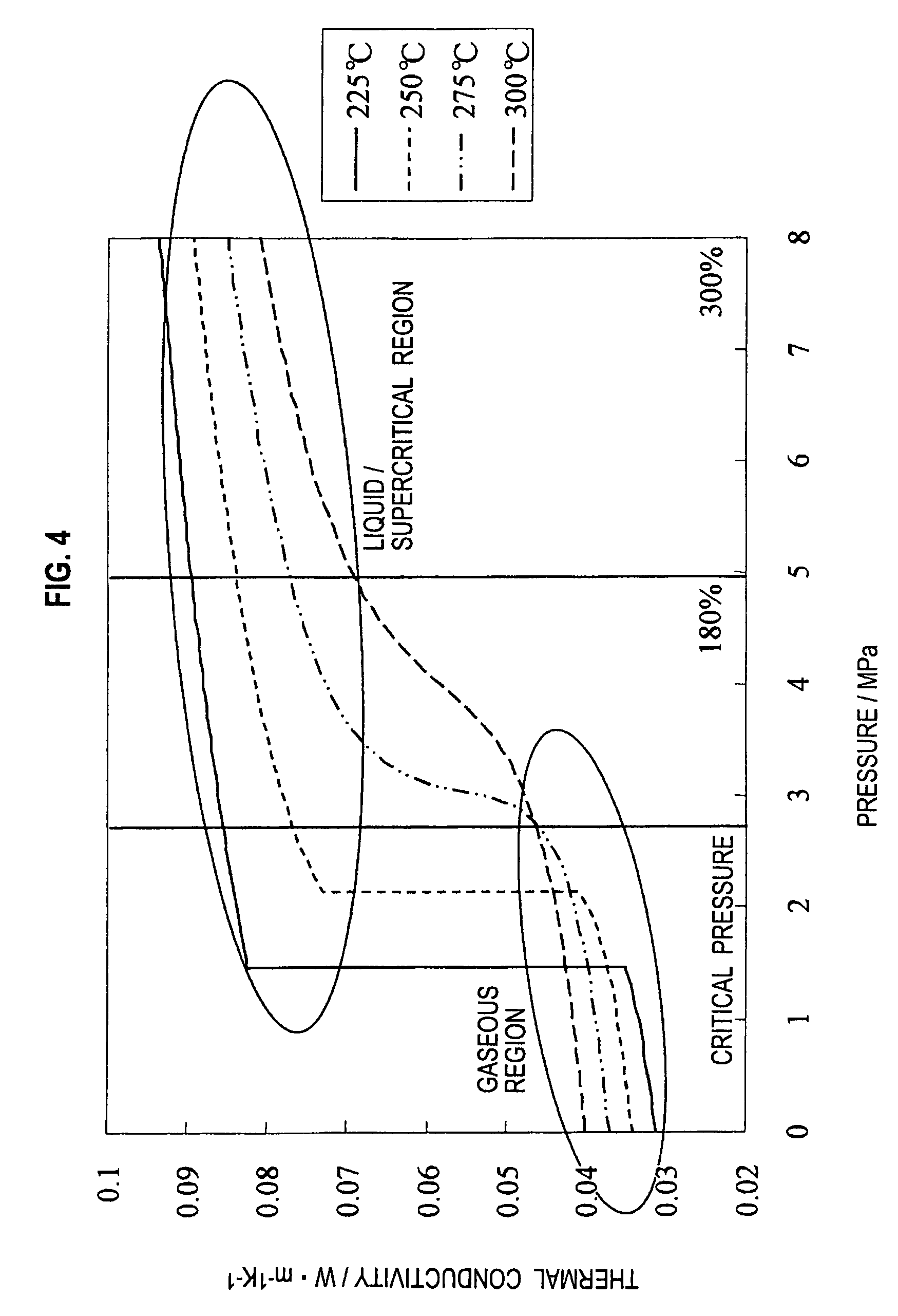
InactiveUS8623106B2High thermal conductivityIncrease fuel pressureInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusThermodynamicsPtru catalyst
A fluid reforming apparatus of the present invention includes: a flow channel (30) in which a catalyst (1) is fixed to an inner wall; a fluid heating device (40) which heats a fluid to be reformed by the catalyst (1) and / or heats the catalyst (1) in the flow channel (30); catalyst temperature measuring devices (51, 52, 53, 54) which measure temperatures of the catalyst (1); and a pressure control device (10, 20, 60) which controls a pressure of the fluid in the flow channel so that the fluid can have a target pressure. The pressure control device (10, 20, 60) increases the target pressure when a difference between the temperatures of the catalyst (1) in a flow direction of the fluid exceeds a predetermined value during a period while the fluid in the flow channel (30) is being heated up to a target temperature.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Fuel injection valve device
InactiveUS7798433B2High strengthImprove featuresSpray nozzlesMachines/enginesStress concentrationEngineering
A fuel injection valve device is capable of thinning a nozzle hole plate and improving fuel spray characteristics by a construction for reducing stress concentration that occurs at the weld part of the nozzle hole plate. The fuel injection valve device includes: a nozzle having a fuel passage inside and in which a valve seat is formed at an end; a needle valve for opening and closing the fuel passage by coming in contact with and separating from the valve seat; and an nozzle hole plate that is disposed at the tip of the nozzle and injects a fuel in the fuel passage at the time of opening the needle valve. The nozzle hole plate and the nozzle are fixed by welding in a state of forming an even gap between them.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Fuel injection valve for internal combustion engines
InactiveUS20040050972A1High tensile strengthIncrease elasticityMachines/enginesFuel injecting pumpsCombustion chamberEngineering
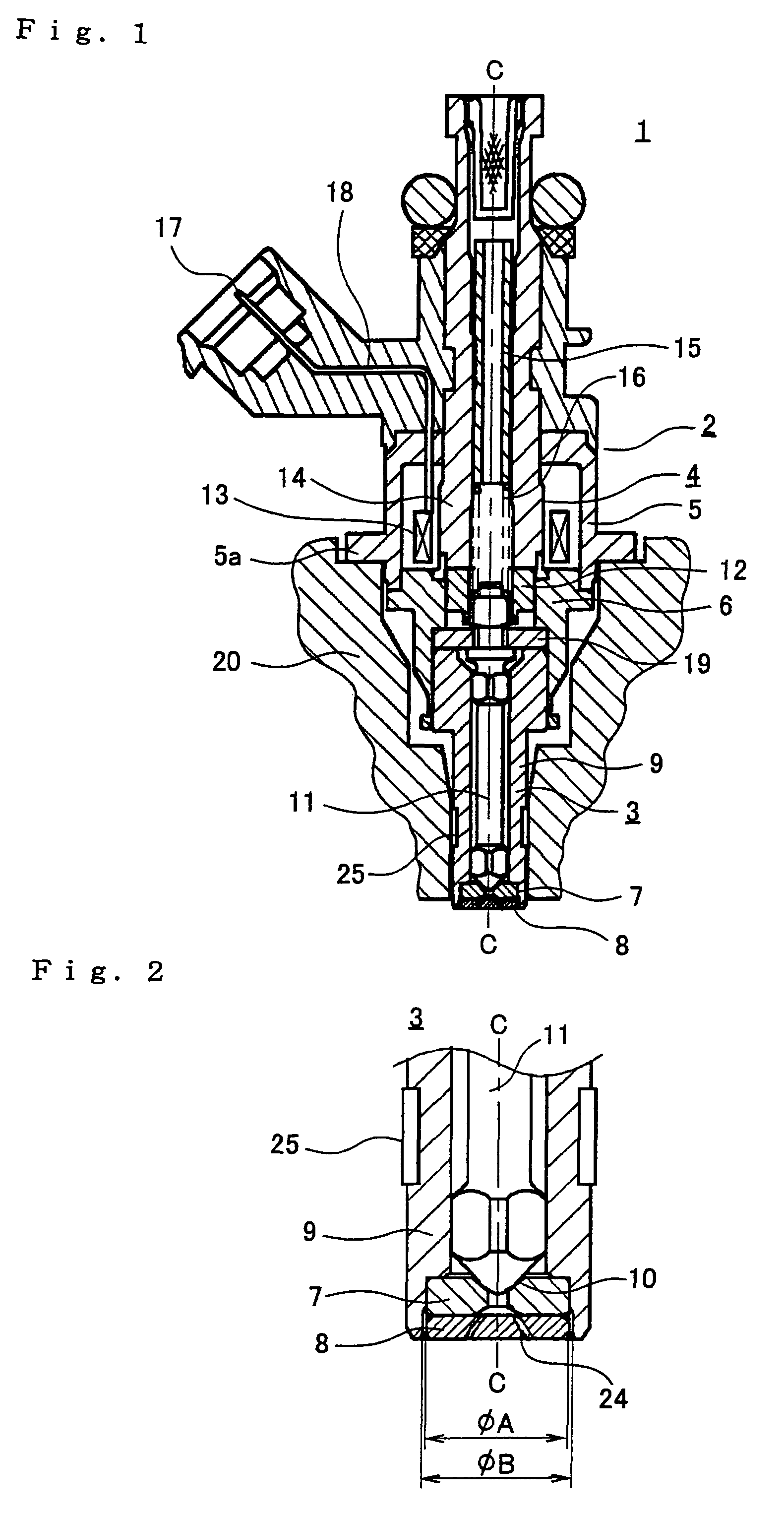
A fuel injection valve for internal combustion engines, having a valve body (1) in which a bore (3) is embodied that has a longitudinal axis (14), and on the end toward the combustion chamber of which bore a valve seat (17) is embodied. In the region of the valve seat (17), at least one injection opening (20) is disposed that connects the bore (3) with the combustion chamber of the engine. A valve member (5) is disposed longitudinally displaceably in the bore (3) and with a sealing face (15) cooperates with the valve seat (17) for controlling the at least one injection opening (20). Between the wall of the bore (3) and the valve member (5), a pressure chamber (10) is embodied that can be filled with fuel at high pressure. The valve body (1) is surrounded, in the region of the pressure chamber (10), by a sleeve (22) that has anisotropic strength properties, so that the valve body (1) exhibits less deformation from the pressure in the pressure chamber (FIG. 1).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method and control unit for starting an otto engine
ActiveUS20130275029A1Increase costReliable startElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsOperating pointGasoline
A method and control unit for a start of an Otto engine operated at low temperatures, using ethanol and / or gasoline, having direct injection. The method includes generating by a high pressure pump a fuel pressure in a high pressure system connected to a high pressure reservoir; a sensor monitoring the fuel pressure in the reservoir and the system; injecting the fuel, by an injector, from the reservoir into a cylinder of the engine, the fuel pressure, an injection quantity and a fuel quantity being specified by a control unit based on, sensor the fuel pressure being specified based on the operating point of the engine up to an upper pressure which is below a starting pressure to which the fuel is increased before the fuel injection, and the fuel pressure in the reservoir and the system being limited to a maximum by an opening pressure of a limiting valve.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fuel supply system for internal combustion engine with direct fuel injection
InactiveUS20050235962A1High peak pressureIncrease pressureElectrical controlLow-pressure fuel injectionInternal combustion engineHigh pressure
In a fuel supply system for an internal combustion engine with direct fuel injection including a fuel supply pump and, downstream thereof, a high pressure pump for supplying high pressure fuel to a plurality of injectors and, parallel to the high pressure fuel pump, a hydraulic transmission operated by the low pressure fuel of the fuel supply pump for generating initially high pressure fuel to the fuel injectors so as to permit instant engine startup upon actuation of a valve disposed in the fuel supply line from the fuel supply pump to the hydraulic transmission.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Fuel evaporation gas leakage detecting system and method of detecting fuel evaporation gas leakage
InactiveUS7207209B2Increase fuel pressureShort timeDetection of fluid at leakage pointNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal pressureExhaust valve
A leak detecting system detects fuel gas leakage of a fuel tank. The detecting system includes a fuel pump, a jet pump, and a bent valve, which are disposed in the fuel tank. A fuel flow path system includes a relief line connected to the fuel pump for relieving an excess fuel, a relief flow path switching valve disposed in the relief line, and a sub-line for connecting the switching valve and the vent valve. An air flow path system includes a first air flow line to connect the vent valve to a canister, a second air flow line for connecting the first air flow line to the jet pump, and an air flow switching valve for switching communication between the first and second air flow lines. An inner pressure sensor is provided to the fuel tank for detecting an inner pressure of the fuel tank.
Owner:NIFCO INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com