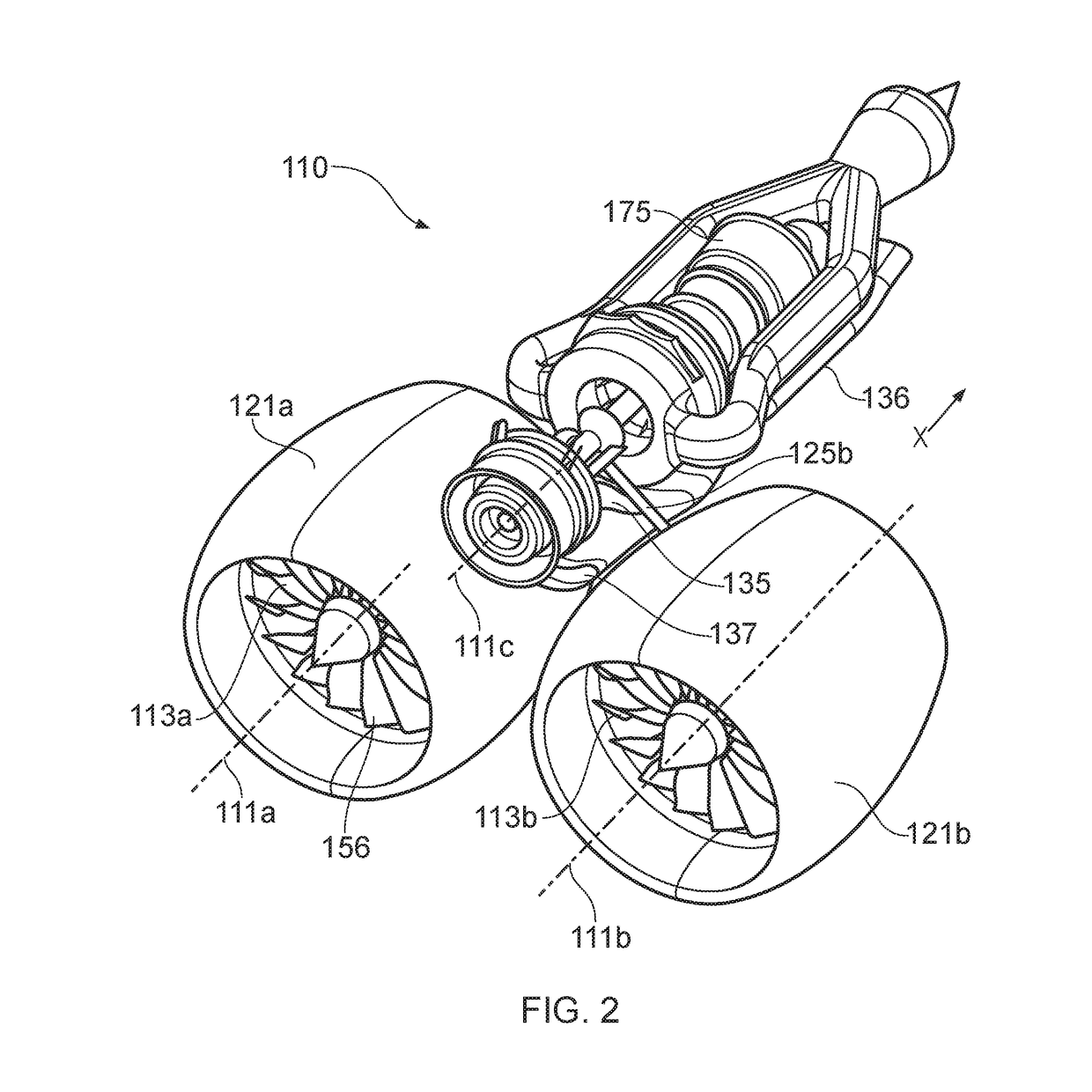
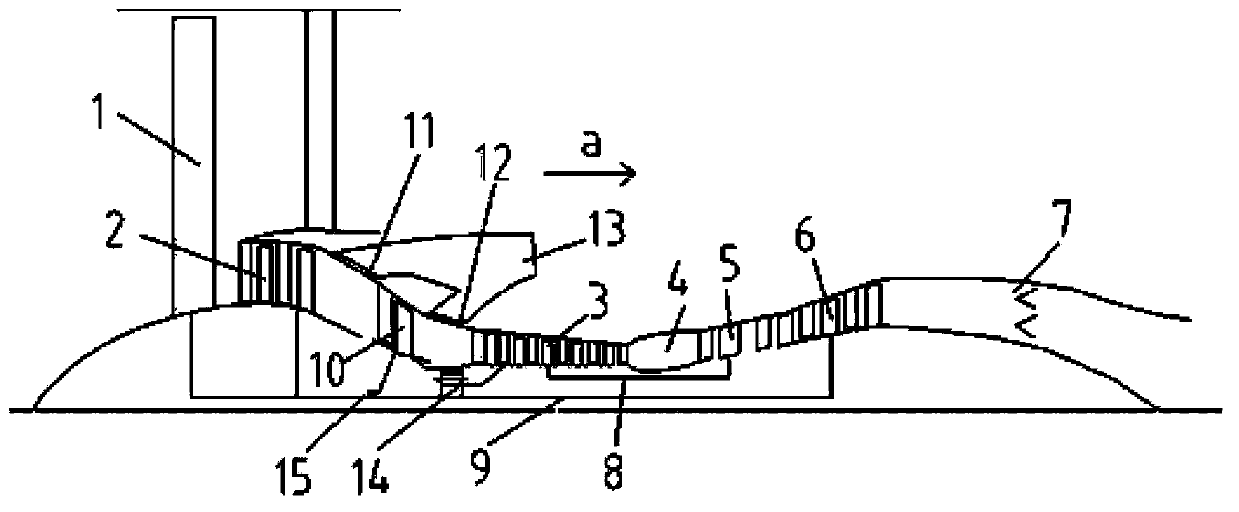
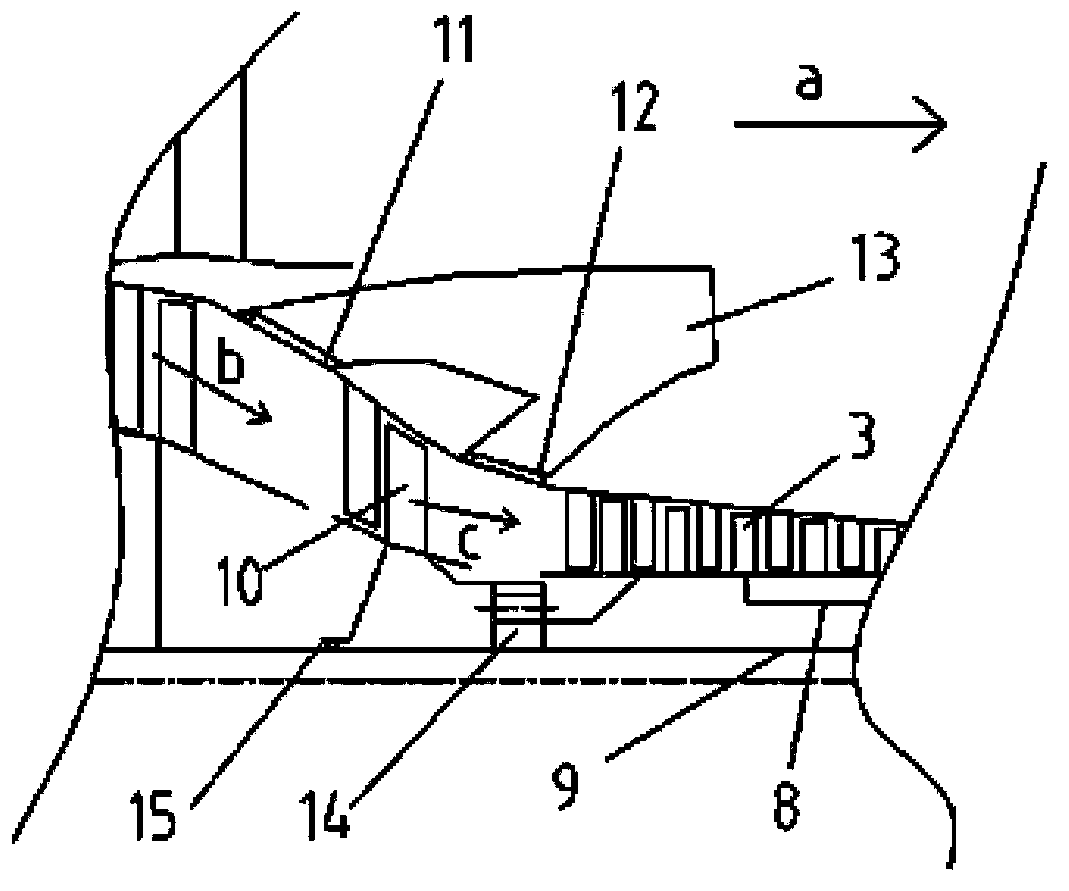
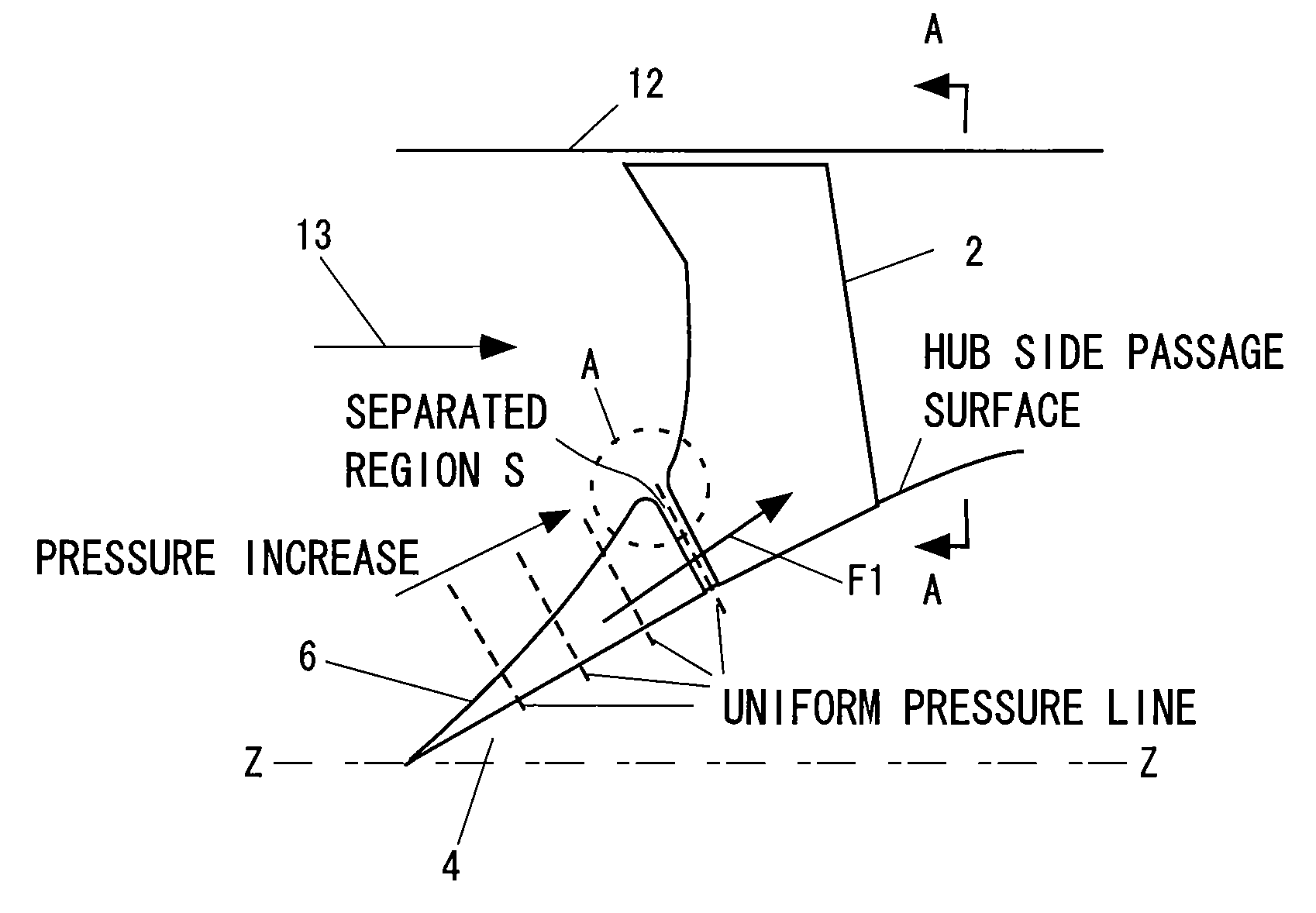
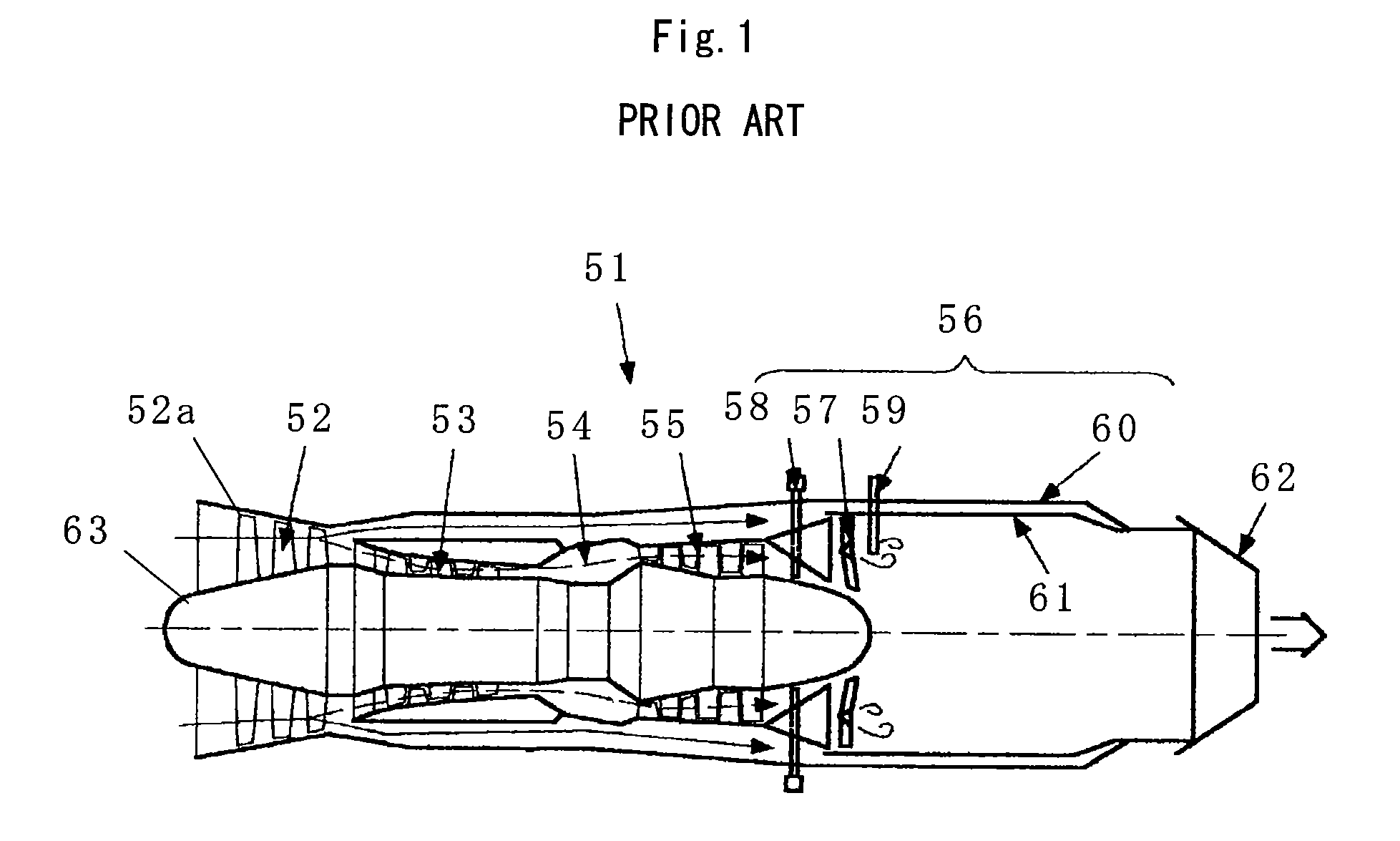
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "Increase bypass ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
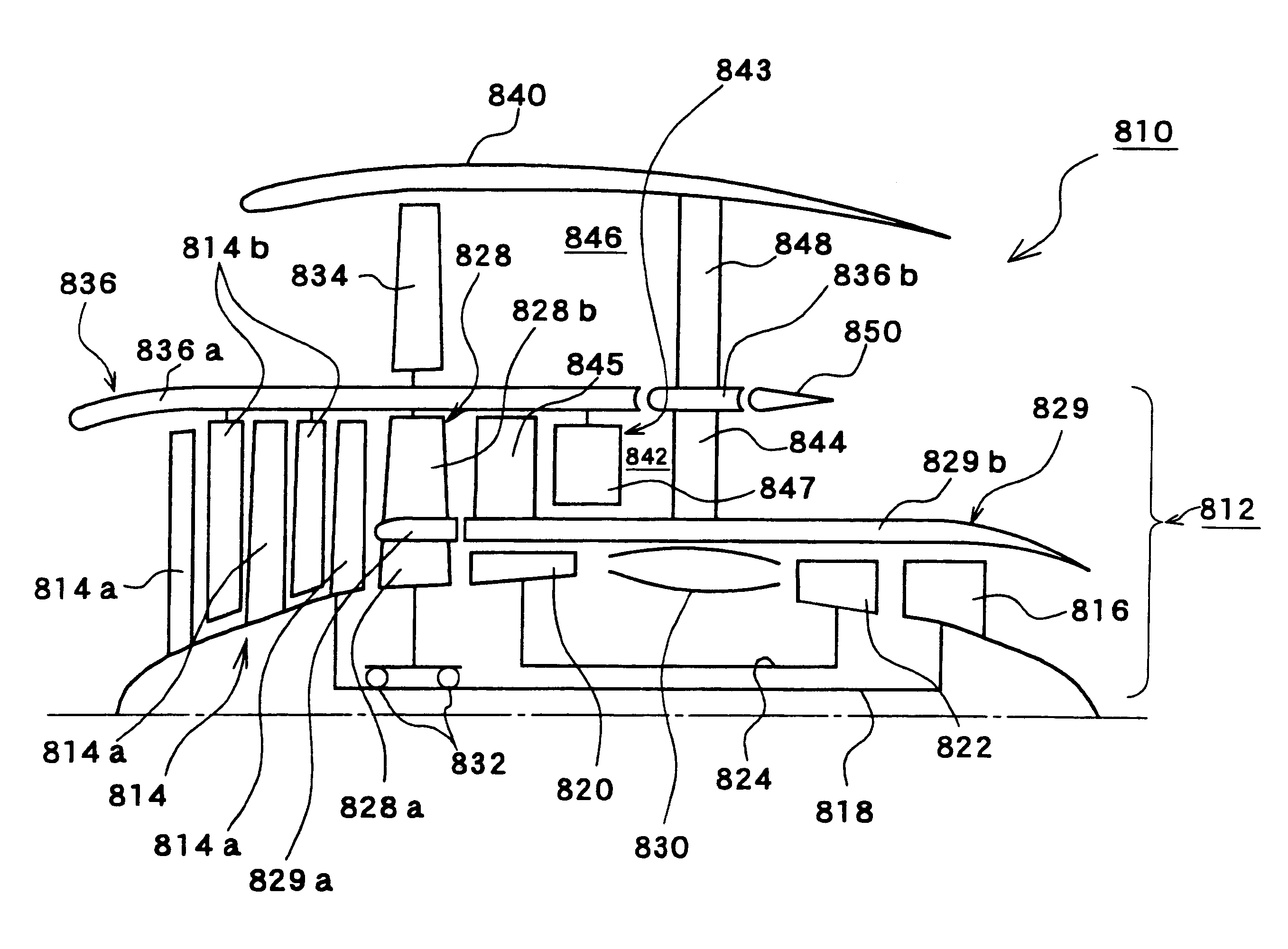
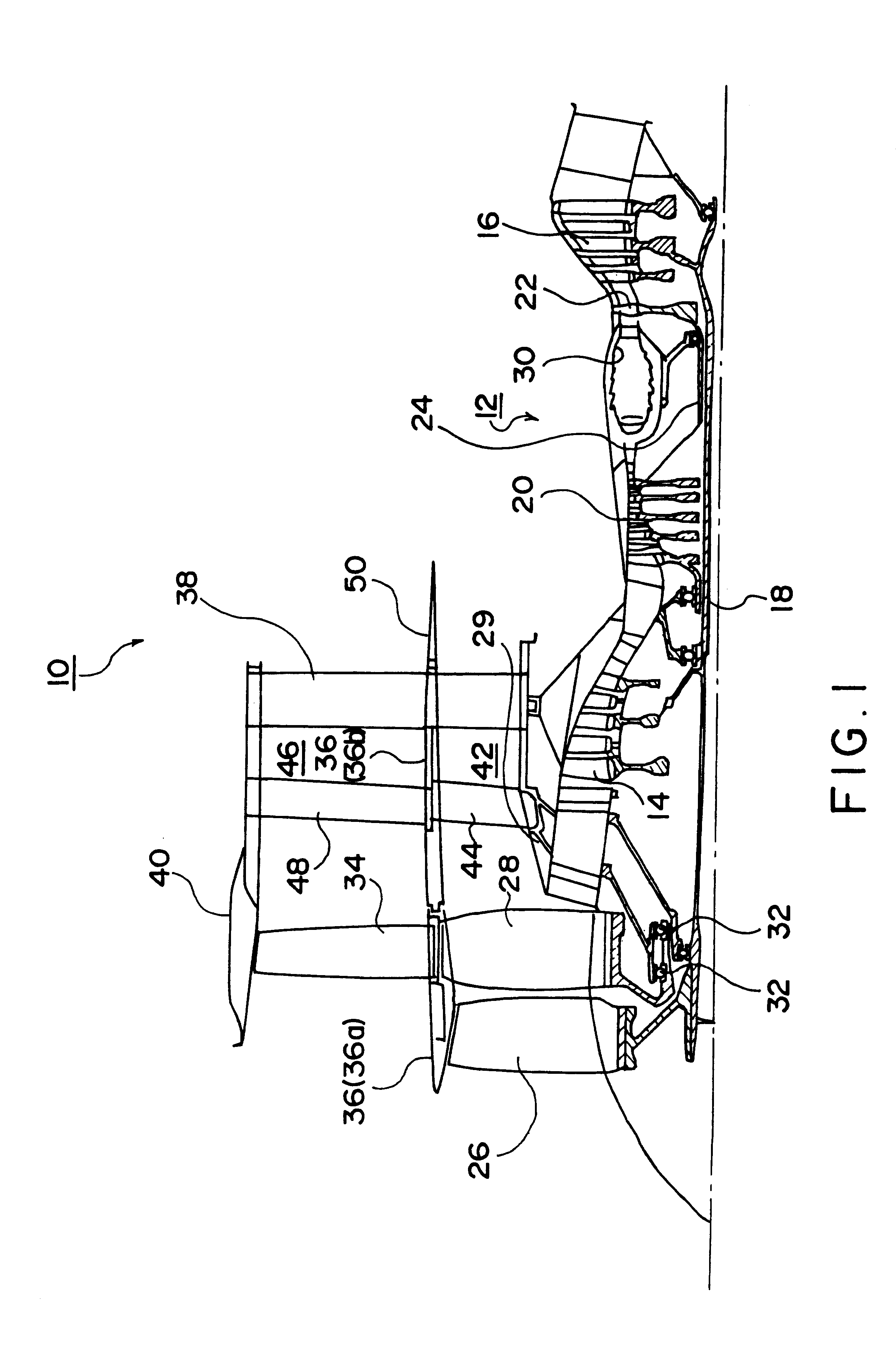
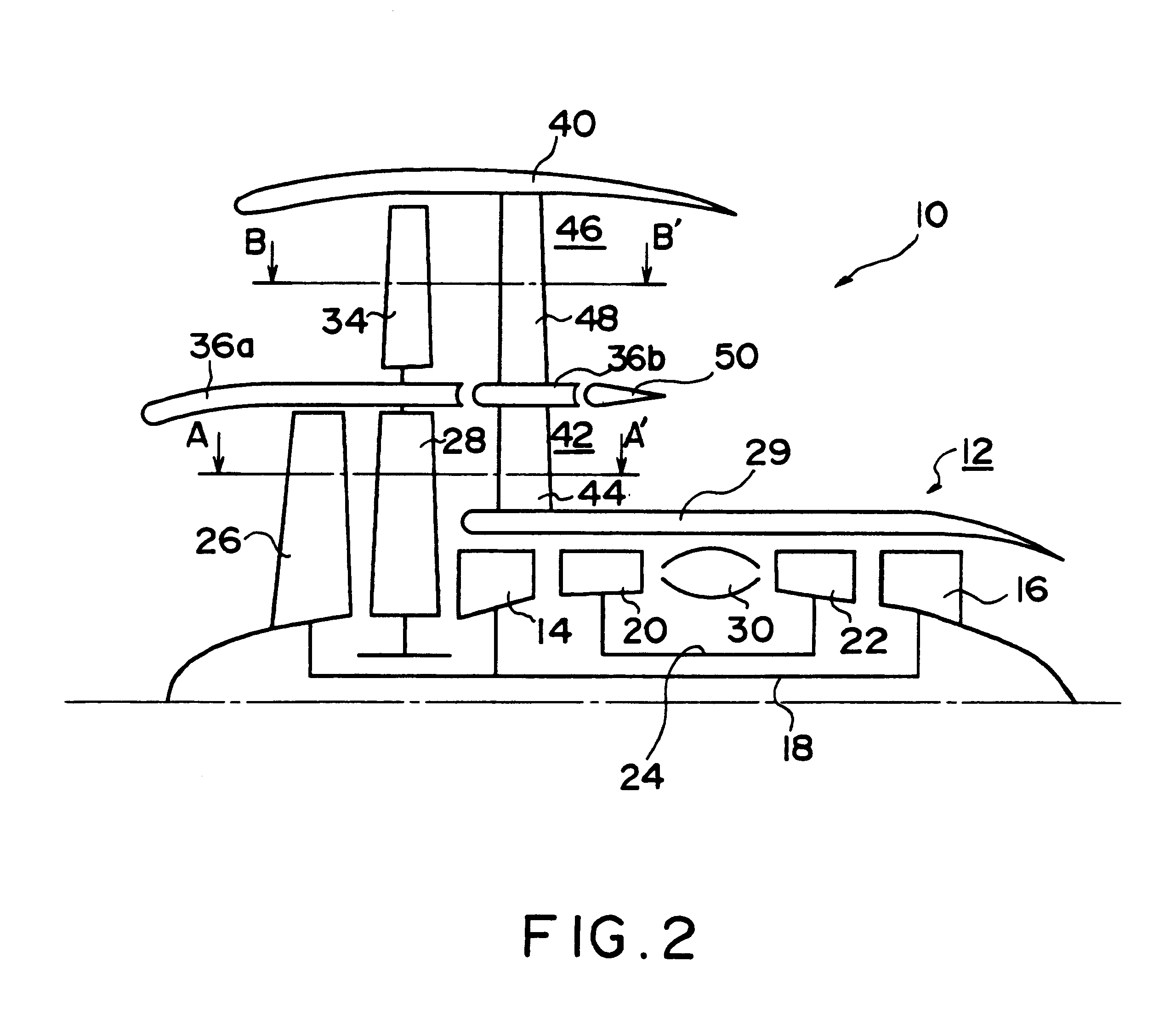
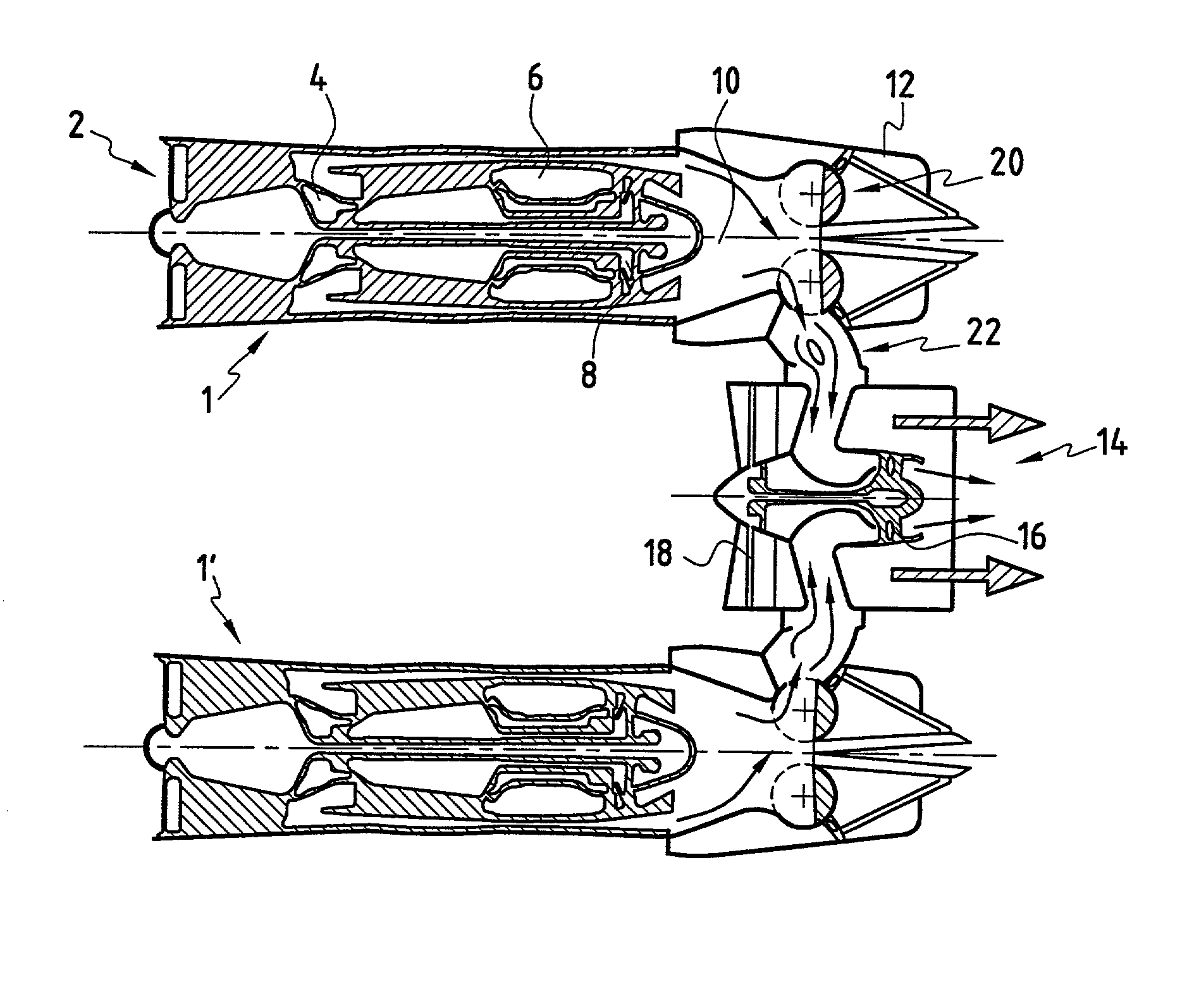
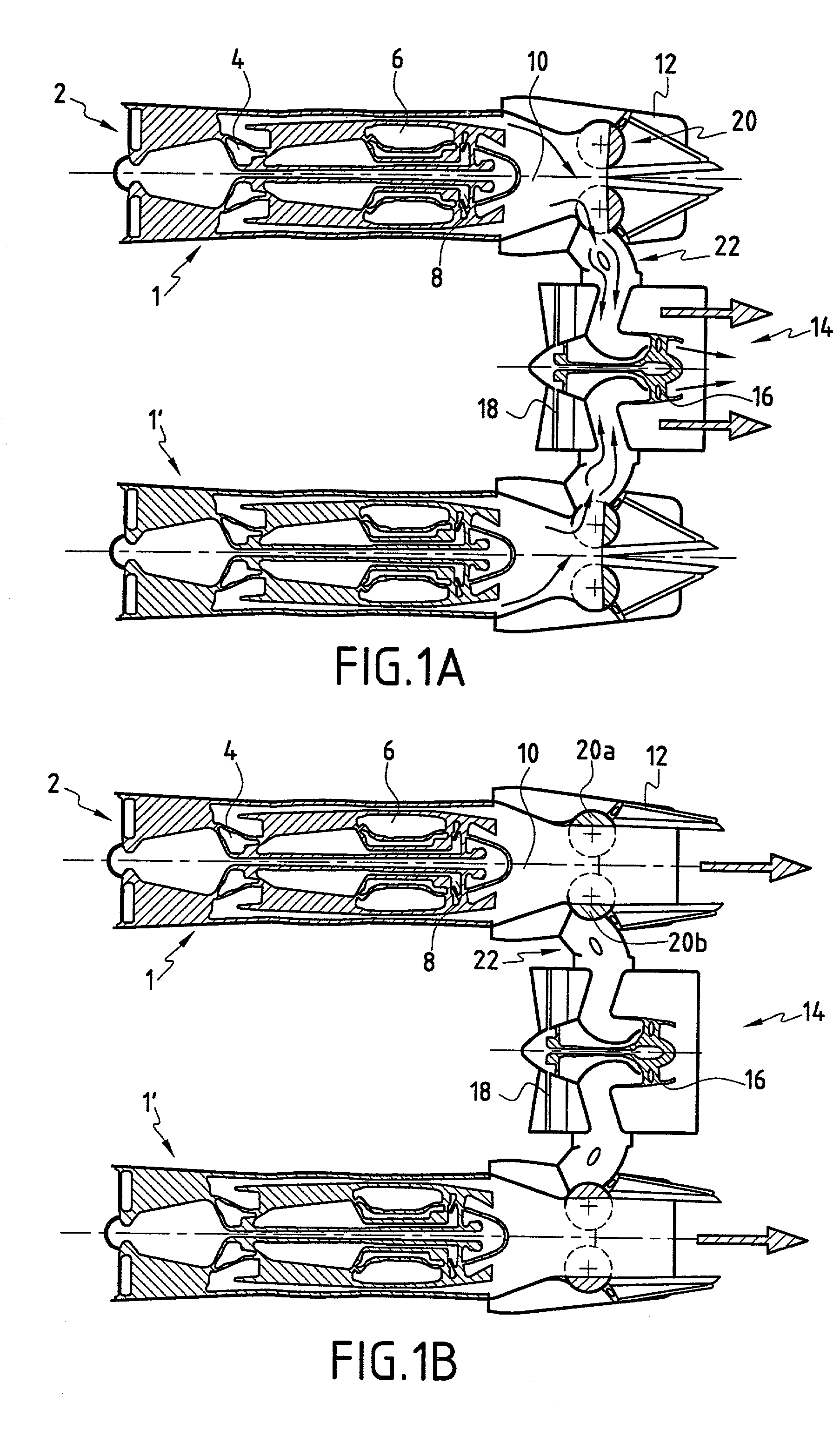
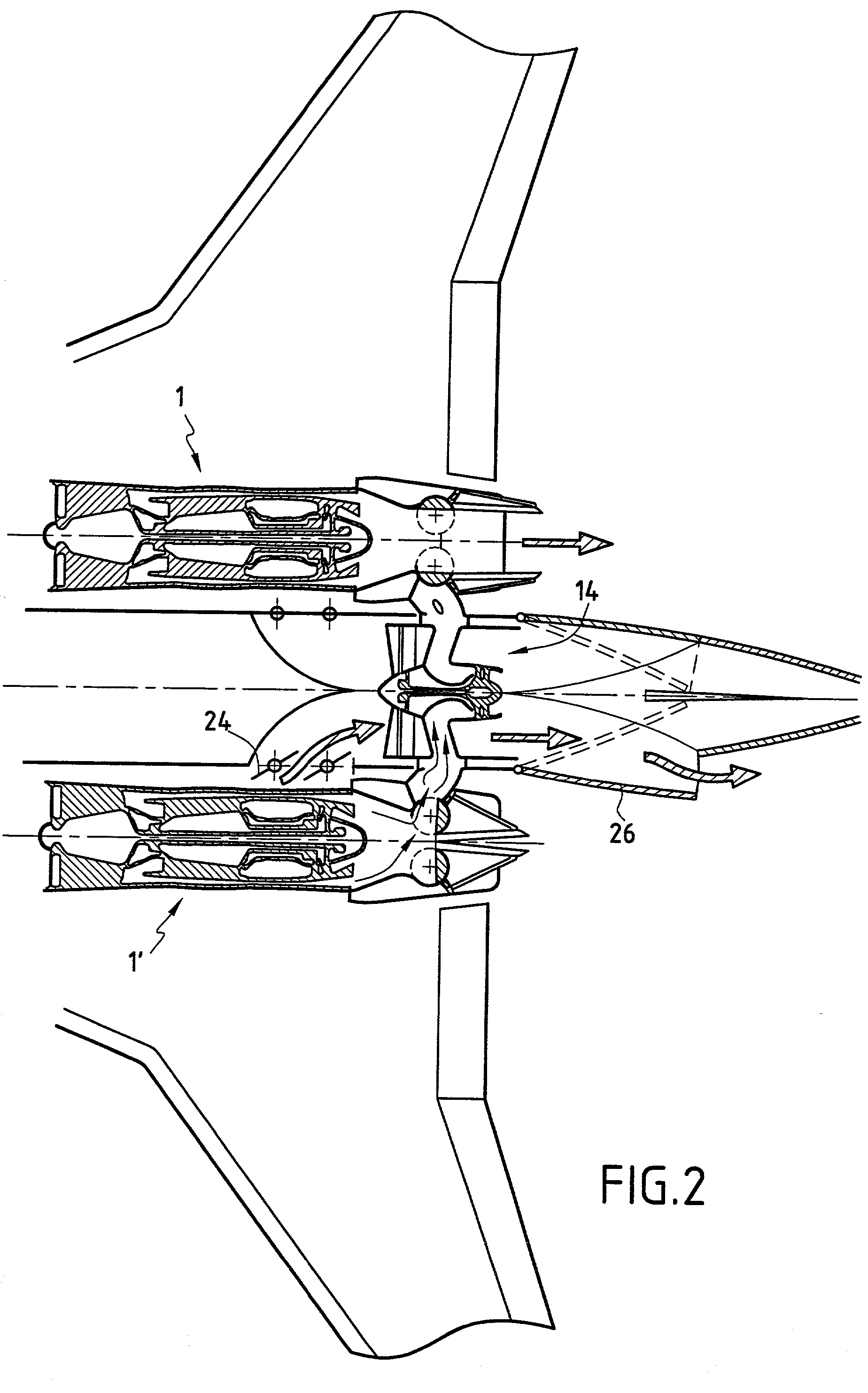
Turbofan engine including fans with reduced speed
InactiveUS6209311B1Shorten speedIncrease the outer diameterGas turbine plantsEfficient propulsion technologiesImpellerFluid coupling
An impeller is directly driven by an output shaft of a core engine. The airflow produced by the impeller rotates an air turbine and a fan disposed integrally with the air turbine. The impeller and the air turbine form a fluid coupling which serves also as a speed reducing mechanism. The rotational speed of the fan can be reduced to be lower than that of the output shaft while retaining efficiency of the core engine. The outer diameter of the fan can be increased, raising a bypass ratio.
Owner:NIKKISO COMPANY
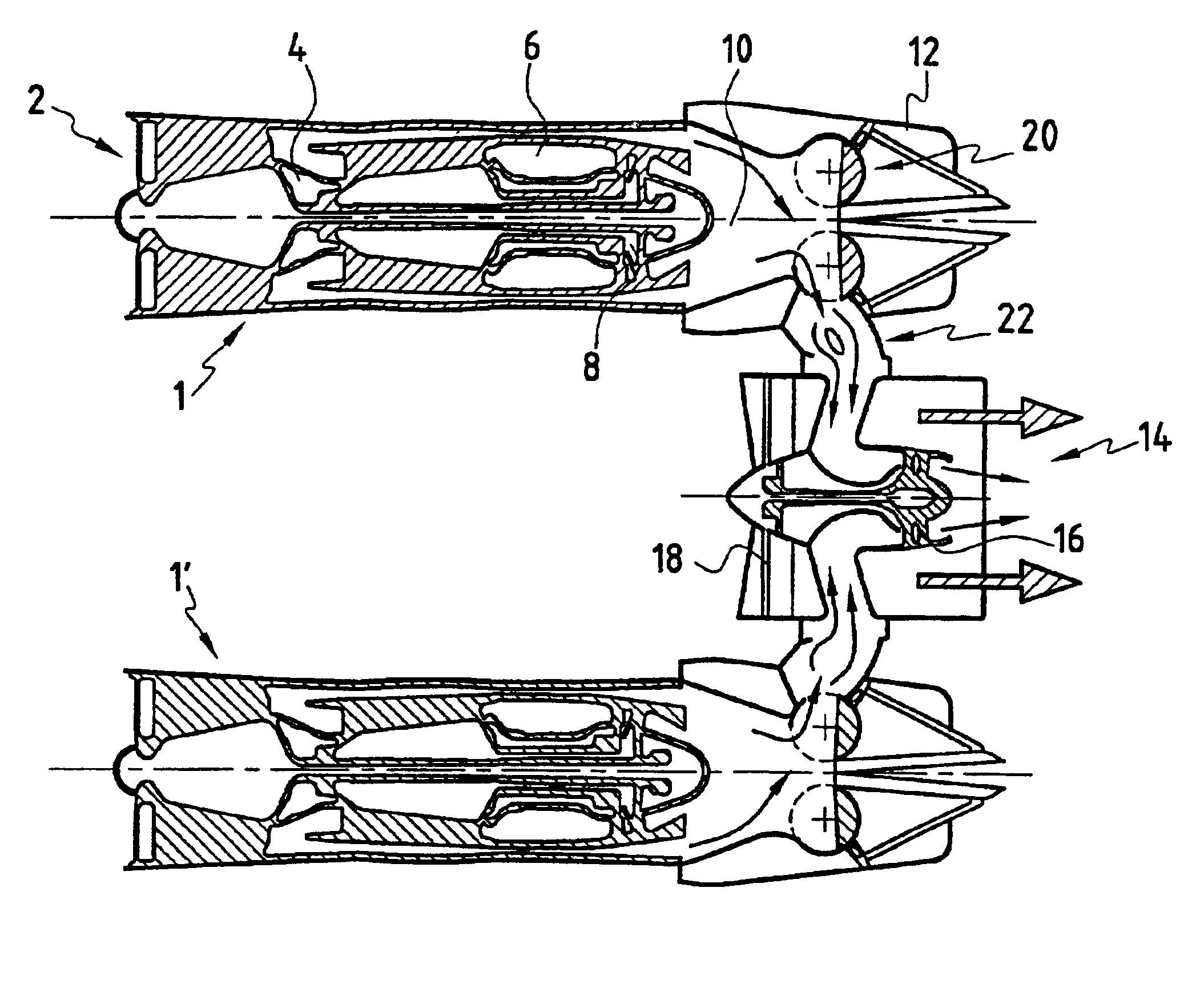
Variable cycle propulsion system with gas tapping for a supersonic airplane, and a method of operation
InactiveUS6845606B2Increase bypass ratioReduce resistanceCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusJet aeroplaneEngineering
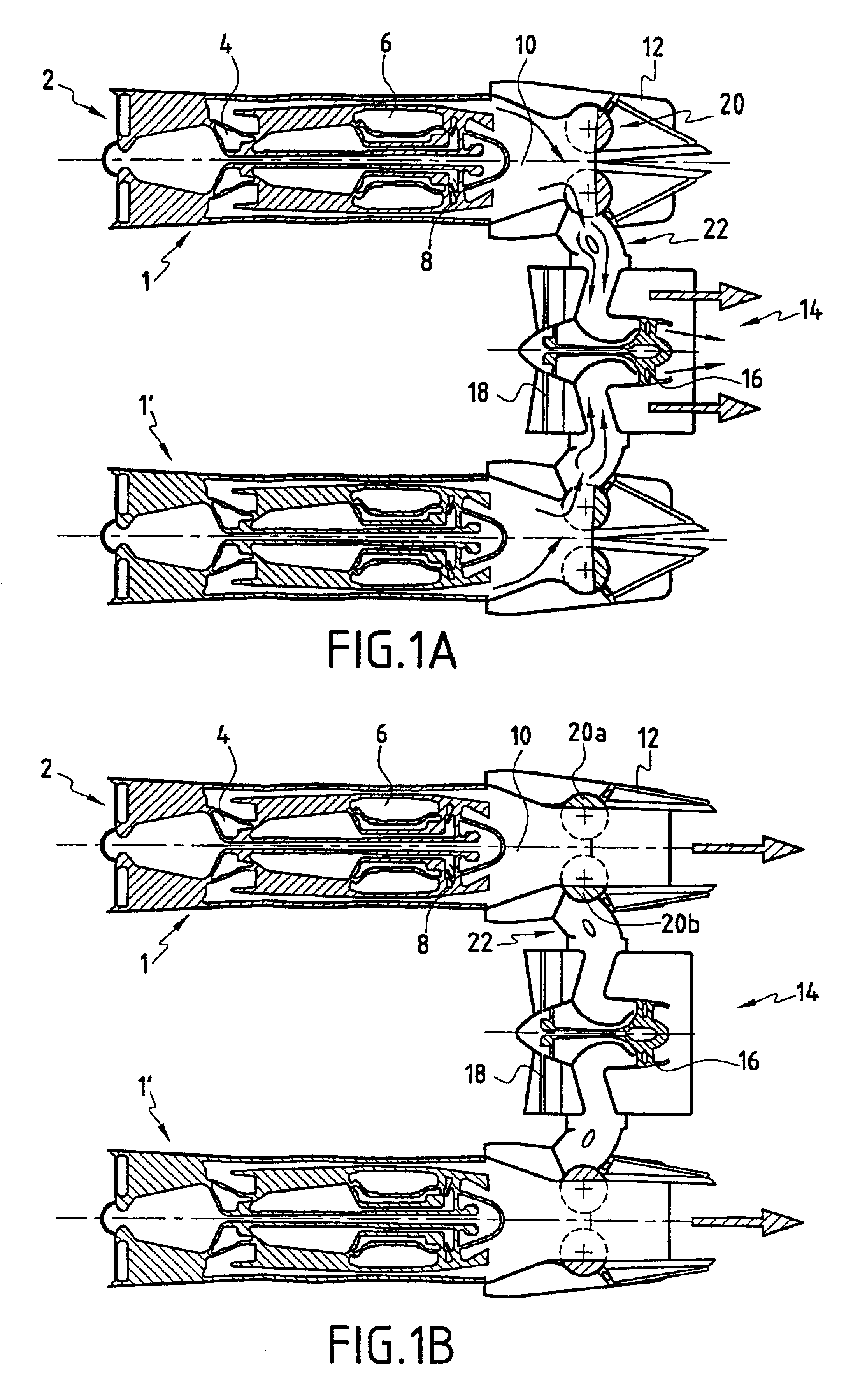
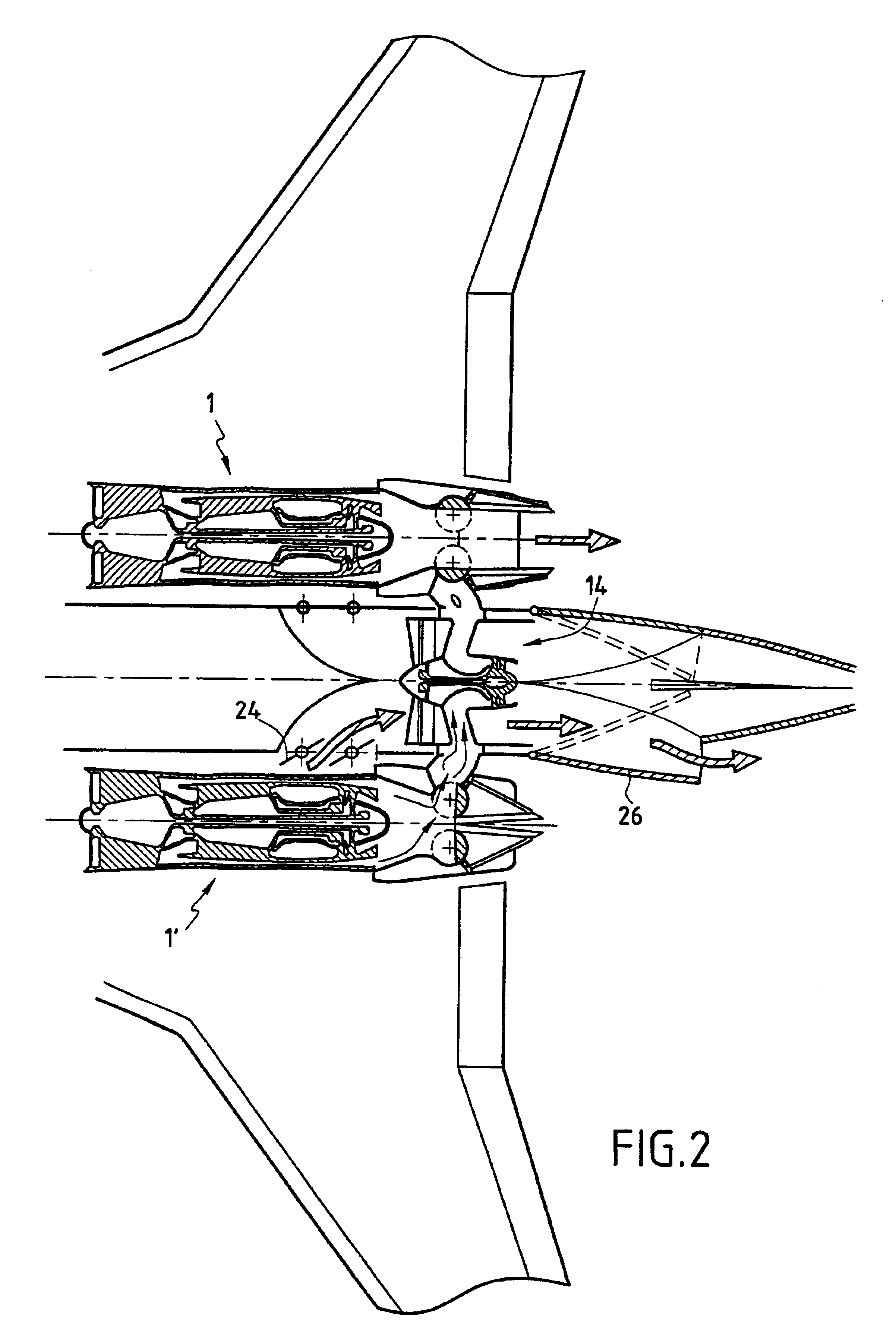
A variable cycle propulsion system for a supersonic airplane, the system comprising at least one engine having means for producing exhaust gas and a gas exhaust nozzle for generating thrust for supersonic flight speeds, and at least one separate auxiliary propulsion assembly dissociated from said engine, having no gas generator, and capable of generating thrust for takeoff, landing, and subsonic flight speeds. The system further comprises gas flow tapping means movable between a position in which they tap off at least a fraction of the exhaust gas produced by said engine and feed it to said propulsion assembly to enable it to generate thrust for takeoff, landing, and subsonic cruising flight, and a position in which the gas produced by the engine is directed solely to the engine nozzle for supersonic cruising flight.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
High bypass-ratio turbofan jet engine
InactiveUS20090226297A1Reduce air resistanceReduce the overall diameterEngine manufactureWind motor controlAerodynamic dragJet engine
To provide a turbofan jet engine which is capable of increasing the bypass ratio without increasing the fan diameter, and of reducing air resistance acting on the engine, a front fan duct that discharges air compressed by a front fan to the atmosphere and an aft fan duct that introduces air into an aft fan are disposed such as to change cross-sectional shapes thereof by rotating around a core engine in a counterclockwise direction, so that the cross-sectional geometric relationship between the front fan duct and the aft fan duct at a position immediately posterior to the front fan and a cross-sectional geometric relationship between the front fan duct and the aft fan duct at a position immediately anterior to the aft fan are inverted.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20170369179A1Improve turbine efficiencyReduce in quantityElectric power distributionGas turbine type power plantsTurbineGas turbines
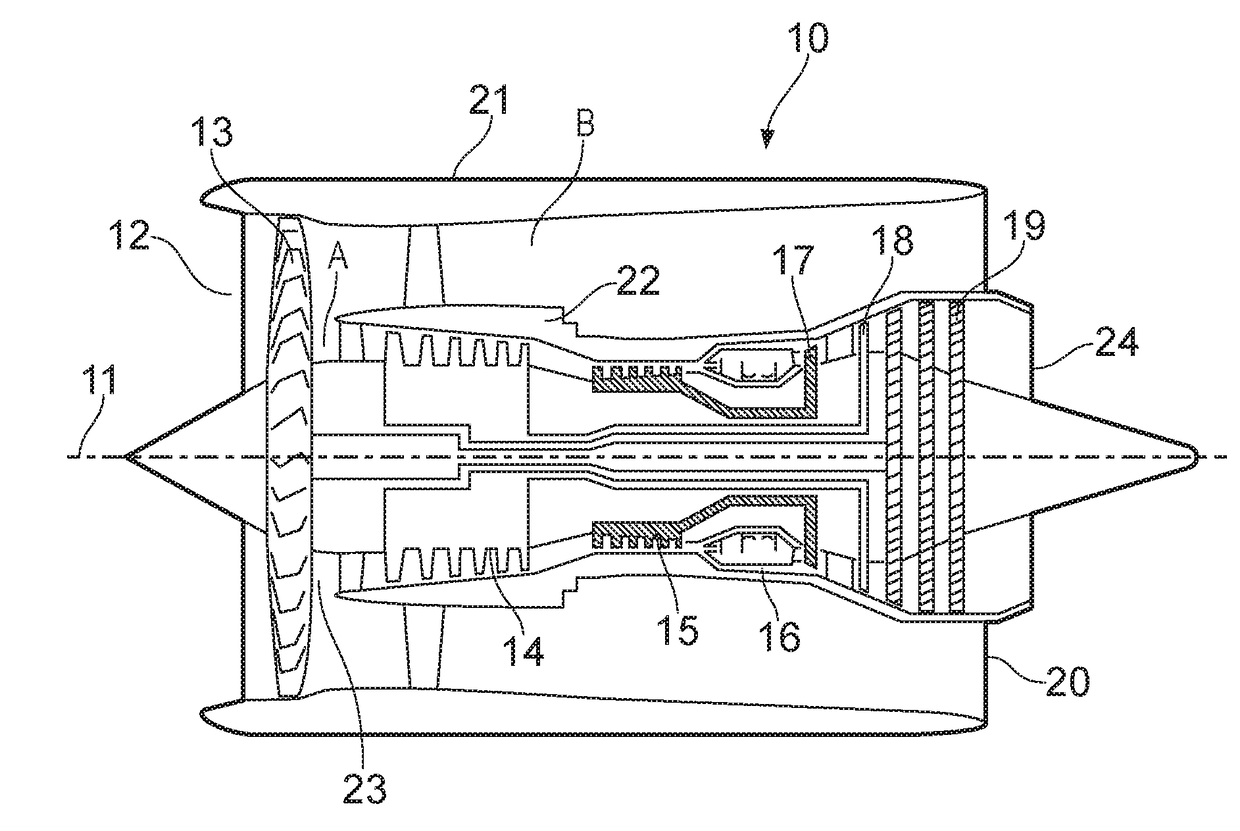
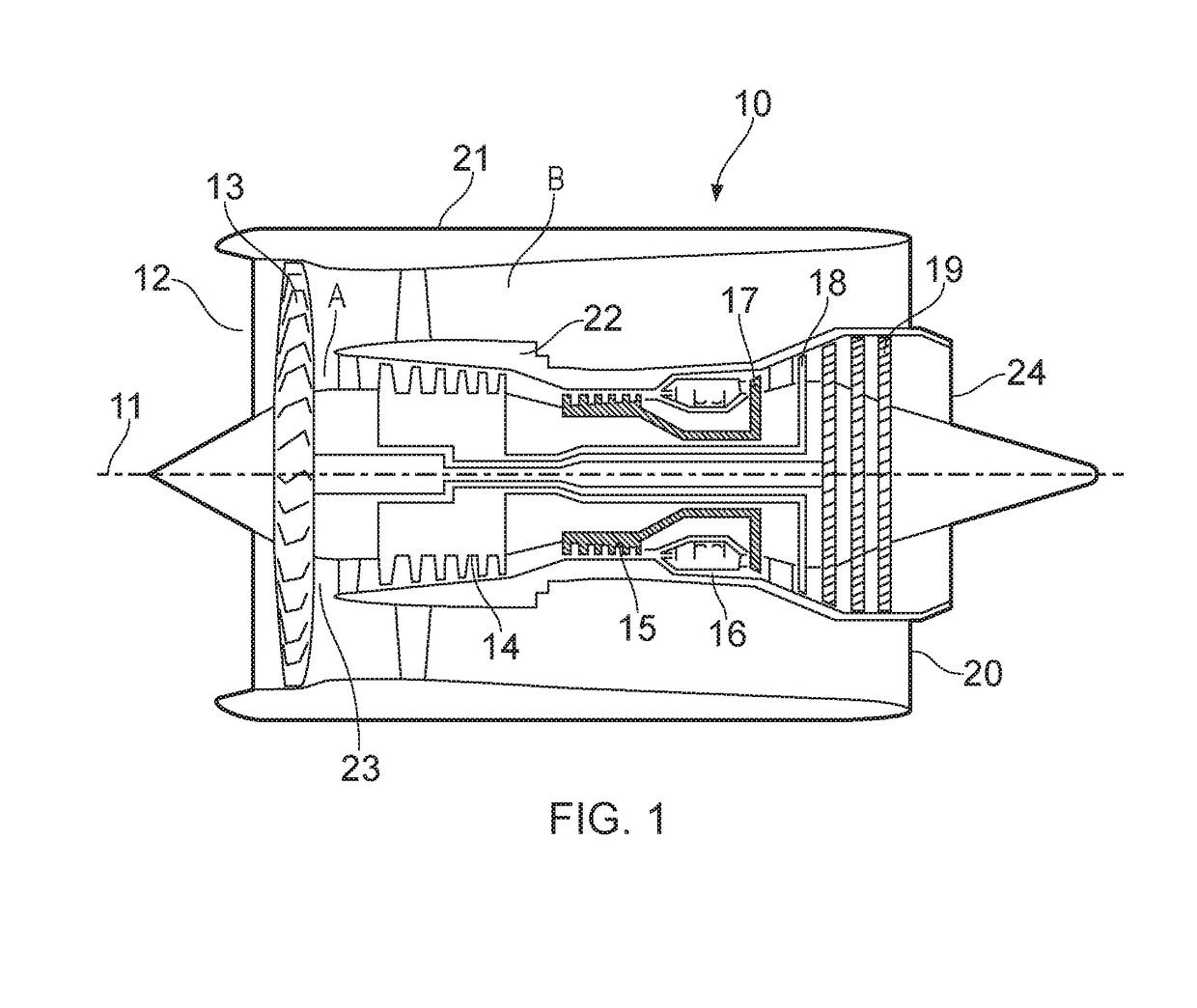
An aircraft gas turbine engine (110) comprises first and second non-coaxial propulsors (113a, 113b), each propulsor (113a, 113b) being driven by a common gas turbine engine core (176) comprising a propulsor drive turbine (143) arranged to drive the first and second propulsors (113a, 113b) via a propulsor drive coupling (127). The core (176) further comprises a first core module (190) comprising a first compressor (129) and a first turbine (131) interconnected by a first shaft (177), and a second core module (191) comprising a second compressor (128) and the propulsor drive turbine (143) interconnected by a second shaft (127), the first and second core modules (190, 191) being axially spaced.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Variable cycle propulsion system with gas tapping for a supersonic airplane, and a method of operation
InactiveUS20020189230A1Mitigate such drawbackIncrease bypass ratioCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusJet aeroplaneGas generator
A variable cycle propulsion system for a supersonic airplane, the system comprising at least one engine having means for producing exhaust gas and a gas exhaust nozzle for generating thrust for supersonic flight speeds, and at least one separate auxiliary propulsion assembly dissociated from said engine, having no gas generator, and capable of generating thrust for takeoff, landing, and subsonic flight speeds. The system further comprises gas flow tapping means movable between a position in which they tap off at least a fraction of the exhaust gas produced by said engine and feed it to said propulsion assembly to enable it to generate thrust for takeoff, landing, and subsonic cruising flight, and a position in which the gas produced by the engine is directed solely to the engine nozzle for supersonic cruising flight.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Variable cycle engine with high bypass ratio
ActiveCN103867337AImproved airflow matchingImprove surge marginJet propulsion plantsCombustorBypass ratio
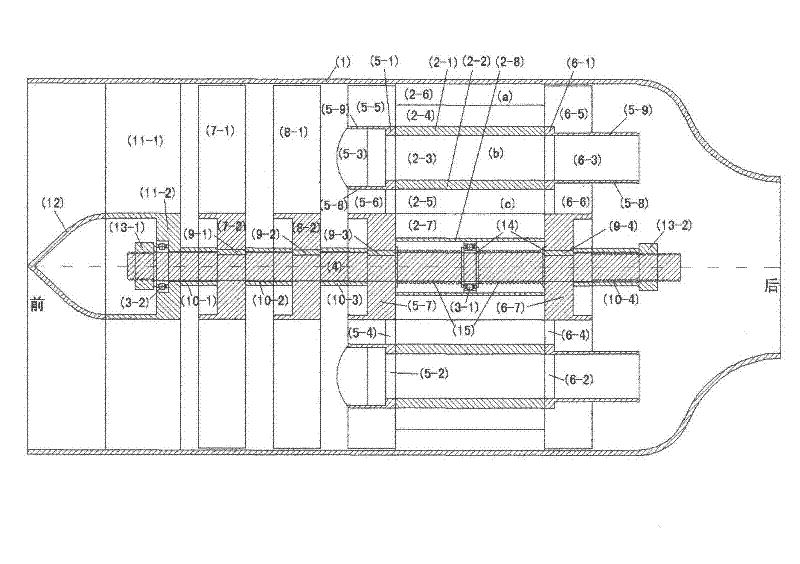
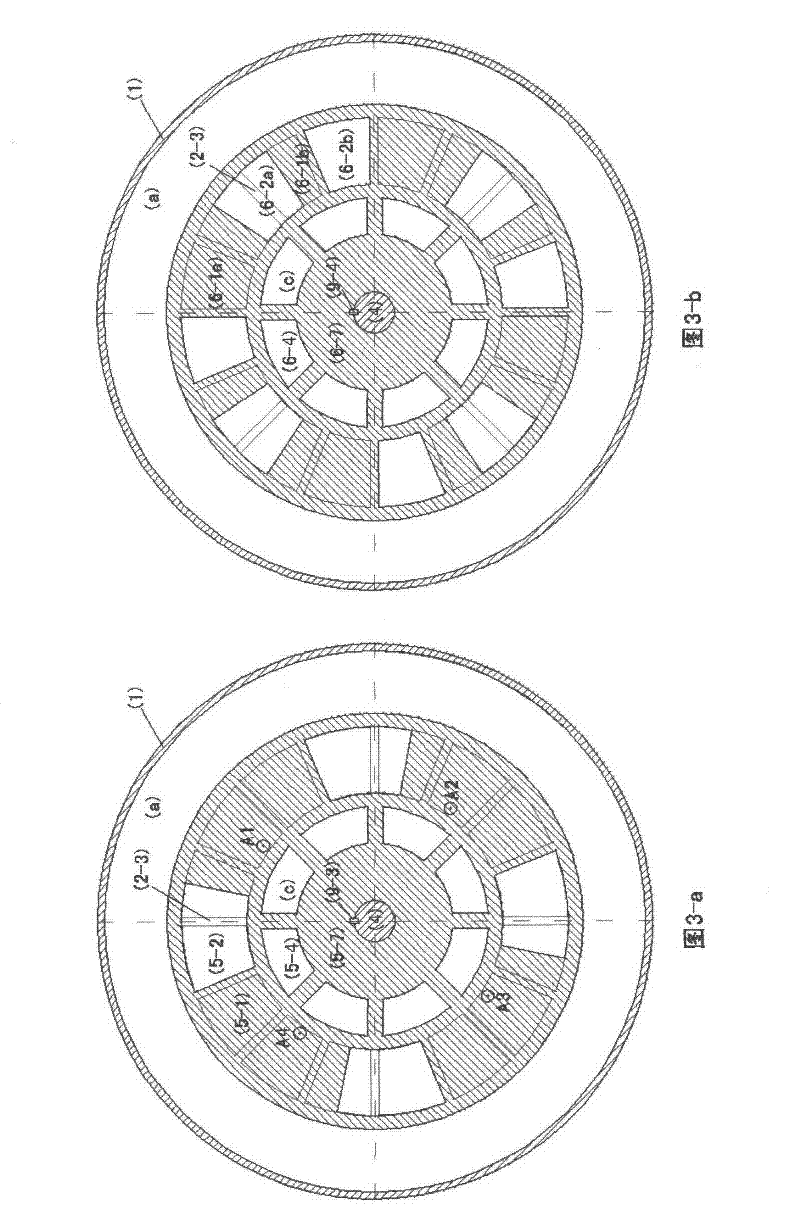
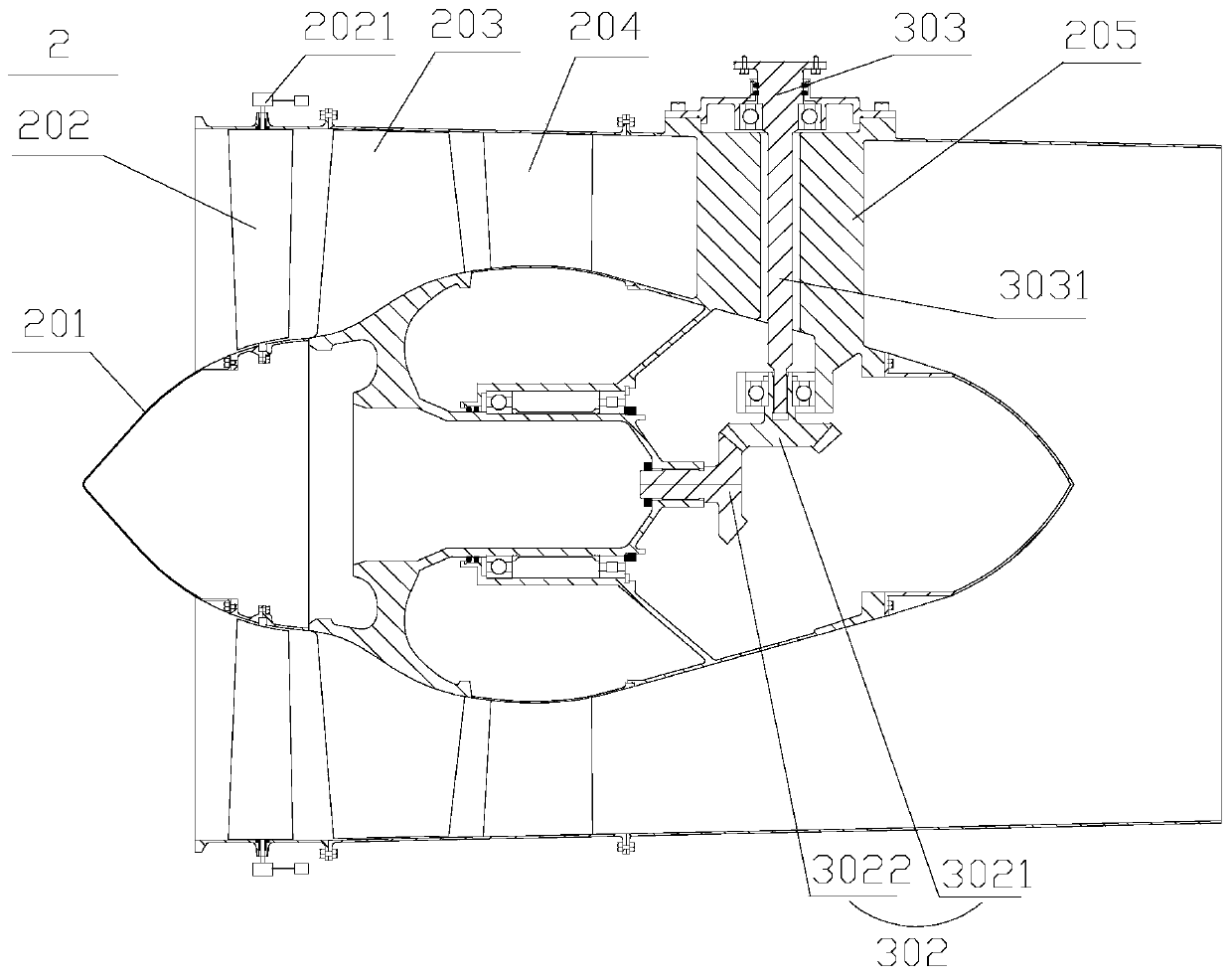
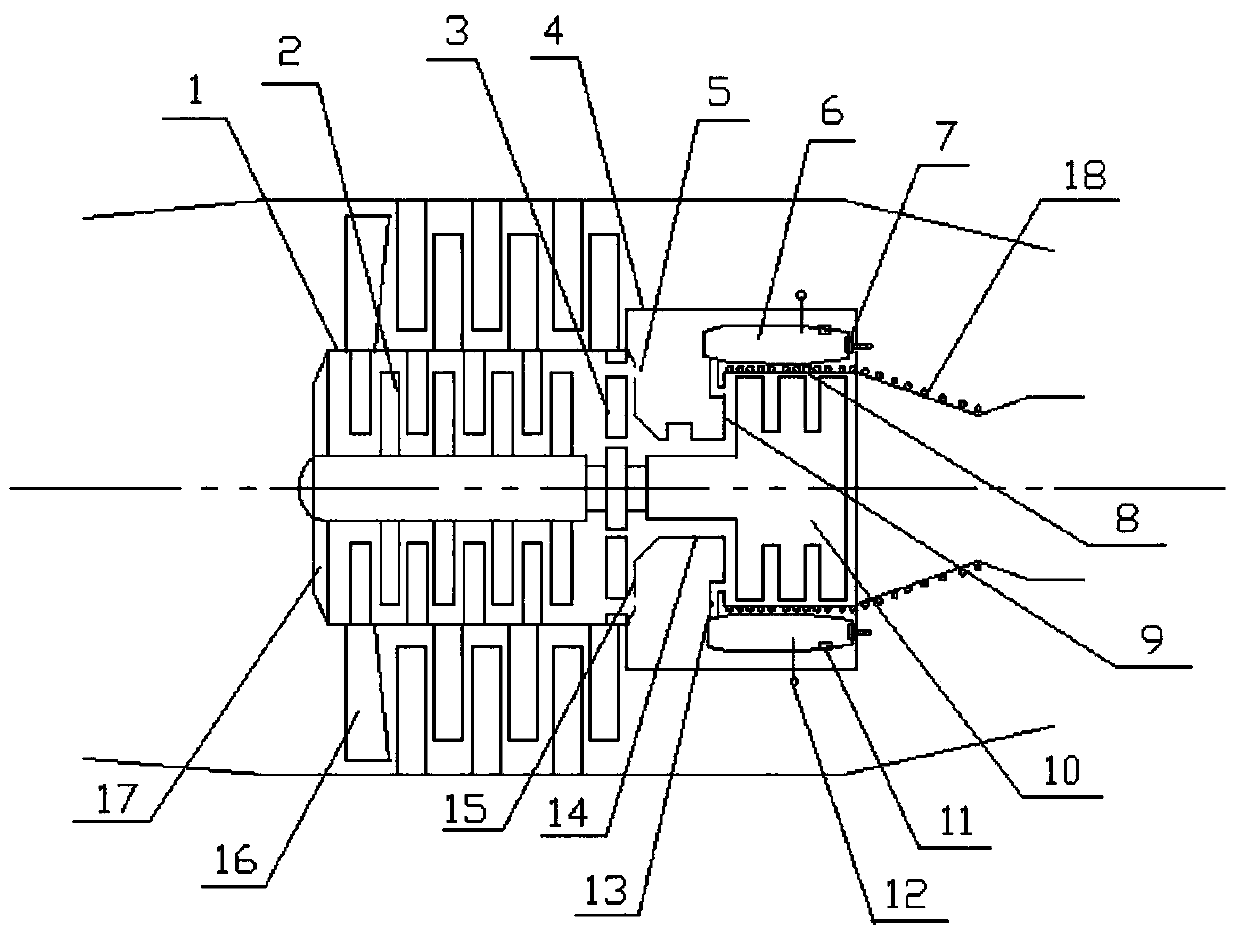
The invention relates to a variable cycle engine with a high bypass ratio. The variable cycle engine comprises a front fan (1), a booster stage (2), a high-pressure compressor (3), a combustor (4), a high pressure turbine (5), a low-pressure turbine (6) and a tail pipe nozzle (9), wherein the high-pressure compressor (3) and the booster stage (2) are respectively driven by the high pressure turbine (5), the low-pressure turbine (6) and the exhaust nozzle (9) through a high pressure shaft (8) and a low pressure shaft (9); a rear fan (10) is arranged between the booster stage (2) and the high-pressure compressor (3), the revolving speed of the rear fan (10) is between the revolving speed of the booster stage (2) and the revolving speed of the high-pressure compressor (3), and a plurality of first bypass valves (12) and corresponding bypass channels are arranged on the outlet of the rear fan (10). The air current matching of engine parts can be improved by additionally setting the rear fan between the booster stage and the high-pressure compressor, and bypass valves capable of being opened or closed are arranged on the outlet of the rear fan, so that the bypass ratio of the engine can be changed so as to be applied to the requirements of different power states.
Owner:AECC COMML AIRCRAFT ENGINE CO LTD
Turbofan engine
ActiveUS7748950B2Increase bypass ratioReduce weightPropellersReaction enginesSpiral bladeEngineering
A turbofan engine of the invention is provided with a fan first-stage moving blade for taking an air therein, and a spinner rotationally driving the fan first-stage moving blade, the spinner has a spiral blade extending spirally to an outer side in a radial direction, sucking the air from a front face of the spinner and supplying the air to the fan first-stage moving blade. Further, the fan first-stage moving blade and the spinner are integrally coupled, and the spiral blade and the fan first-stage moving blade are formed such that blade surfaces are smoothly connected.
Owner:IHI CORP
Self-driven fan large-bypass-ratio turbofan engine with inner loop air turbine
ActiveCN104500269AAvoid RPM Mismatch ProblemsAvoid integrated manufacturingJet propulsion plantsLow voltageInner loop
The invention relates to a self-driven fan large-bypass-ratio turbofan engine with an inner loop air turbine and a design method. The self-driven fan large-bypass-ratio turbofan engine is characterized in that an outer bypass part is provided with a self-driven fan rotor with a larger bypass ratio and with an inner loop air turbine, the rotor comprises an auxiliary bypass fan rotor (1), an air-driving turbine rotor (3) and a rotating medium casing (5); an auxiliary bypass fan stator (2) is arranged on the downstream of the auxiliary bypass fan rotor (1); an air-driving turbine stator (4) is arranged on the downstream of the air-driving turbine rotor (3). The self-driven fan large-bypass-ratio turbofan engine has advantages: (1) while the bypass ratio is increased, the problem of the large-bypass-ratio turbofan that the rotation speed of the fan is not matched with that of the low voltage rotor can be avoided; (2) compared with the scheme of a gear turbofan engine (GTF) and a three-rotor turbofan engine for solving the mismatch problem of the rotation speed, the structure is simplified; (3) the self-driven fan large-bypass-ratio turbofan engine can be improved on the basis of the existing two-rotor turbofan engine, so that the technical risk and research cost can be reduced, and the research period can be shortened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Turbofan engine
ActiveUS8579592B2Increase intake flowImproves the turbofan enginePropellersEngine manufactureLeading edgeEngineering
A hub-side leading edge part of a fan first-stage rotating blade 10 for taking an air thereinto more extends in a forward direction of an engine than a tip-side leading edge part and a mid-span leading edge part. The hub side of the fan first-stage rotating blade 10 is integrally connected as one with the tip side and the mid span while having a longer chord length than those of the tip side and the mid span. A radius at a root of the hub-side leading edge part is set in a boss ratio of 0 to 0.4.
Owner:IHI CORP
Bypass ratio ultra-wide adjustable turbofan engine structure based on variable booster stage
ActiveCN113279859AIncrease speedIncrease bypass ratioGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsLow speedCharacteristic velocity
The invention provides a bypass ratio ultra-wide adjustable double-shaft turbofan engine structure based on a variable booster stage. The defects and shortage that the booster stage and a fan in an existing double-shaft turbofan engine are coaxial and have the same rotating speed, as the cruising height of a platform is higher and higher, the characteristic Reynolds number of the booster stage is continuously reduced due to the fact that the characteristic speed of the booster stage is low and the size of the booster stage is small, thus a boundary layer of the booster stage is separated, and the performance is sharply decayed are overcome; the booster stage is in driving connection with a high-pressure shaft through a variable reduction ratio gearbox, when an engine cruises at a low speed, the variable reduction ratio gearbox is set to be in a high speed reduction ratio, so that the rotating speed of the booster stage is relatively low, the total temperature and the total pressure of inlet airflow of a high-pressure compressor are relatively low, and the bypass ratio of the engine is relatively large; and when the engine cruises at a high speed, the variable reduction ratio gearbox is set to be at a low reduction ratio, so that the rotating speed of the booster stage is relatively high, the mass flow sucked by the high-pressure compressor is large, and the bypass ratio of the engine is relatively small.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
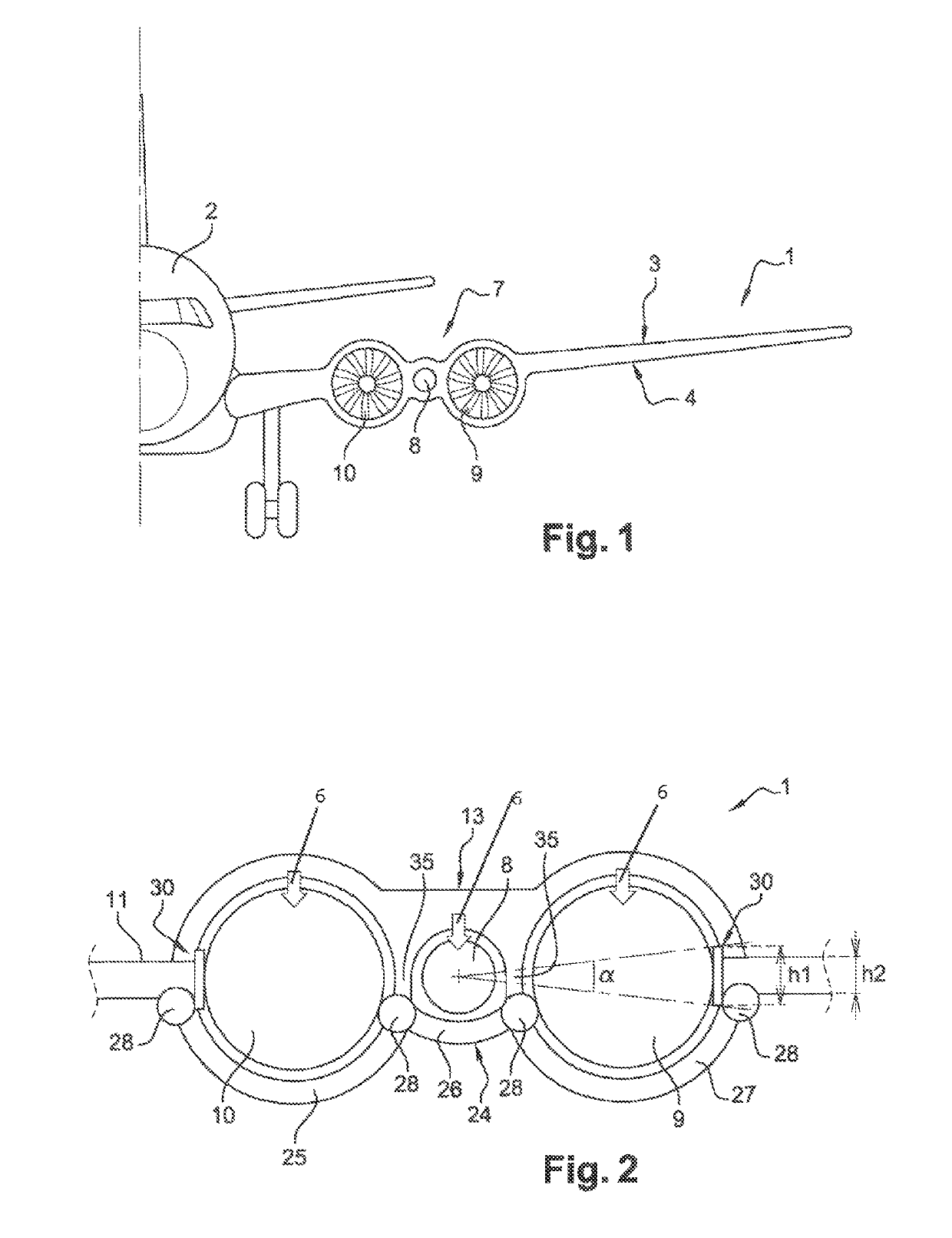
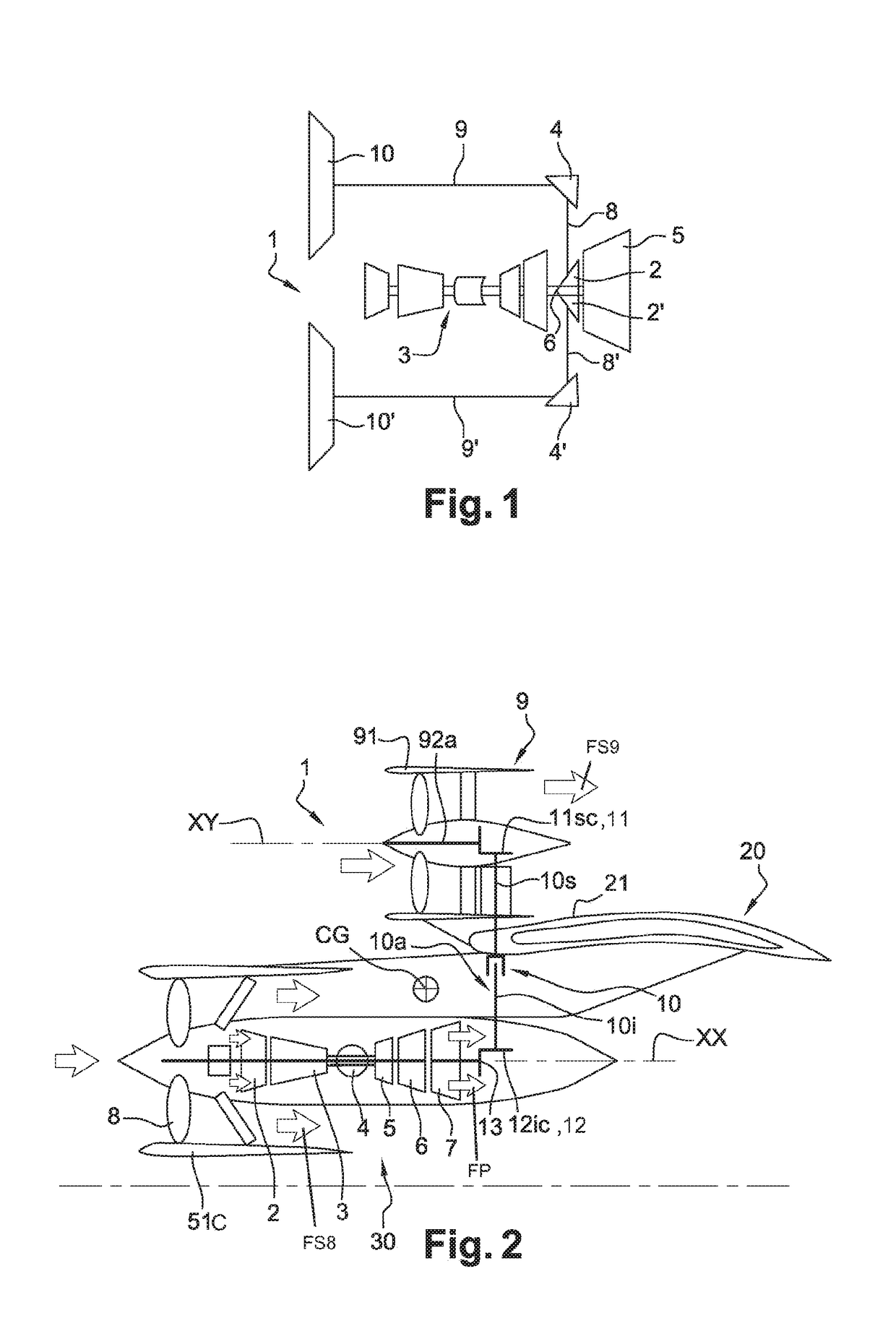
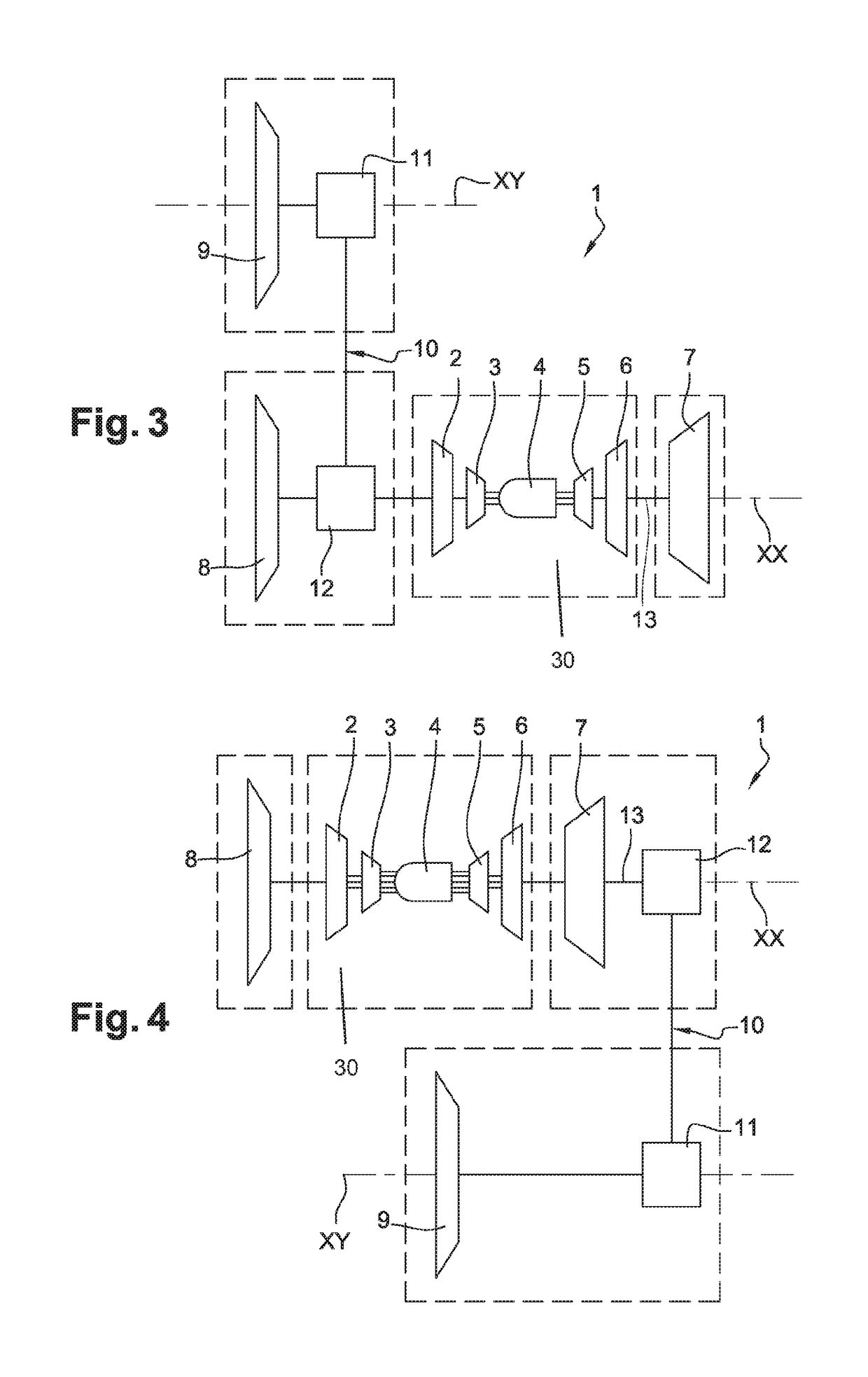
Propulsive wing of an aircraft
ActiveUS10450079B2Increase bypass ratioReduce weightJet type power plantsWingsRigid structureGas generator
A propulsive wing of an aircraft including at least two structural spars, upstream and downstream that extend in a wing span direction of the wing. A propulsion assembly includes at least two fans that are each driven by at least one gas generator. The at least one gas generator extends along an axis that is remote from the axis of rotation of at least one fan. At least one of the spars includes a first part and a second part between which the propulsion assembly is arranged. The first and second parts are interconnected by a rigid structure that is shaped to extend at least in part around the fans. The propulsion assembly is supported by the rigid structure.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
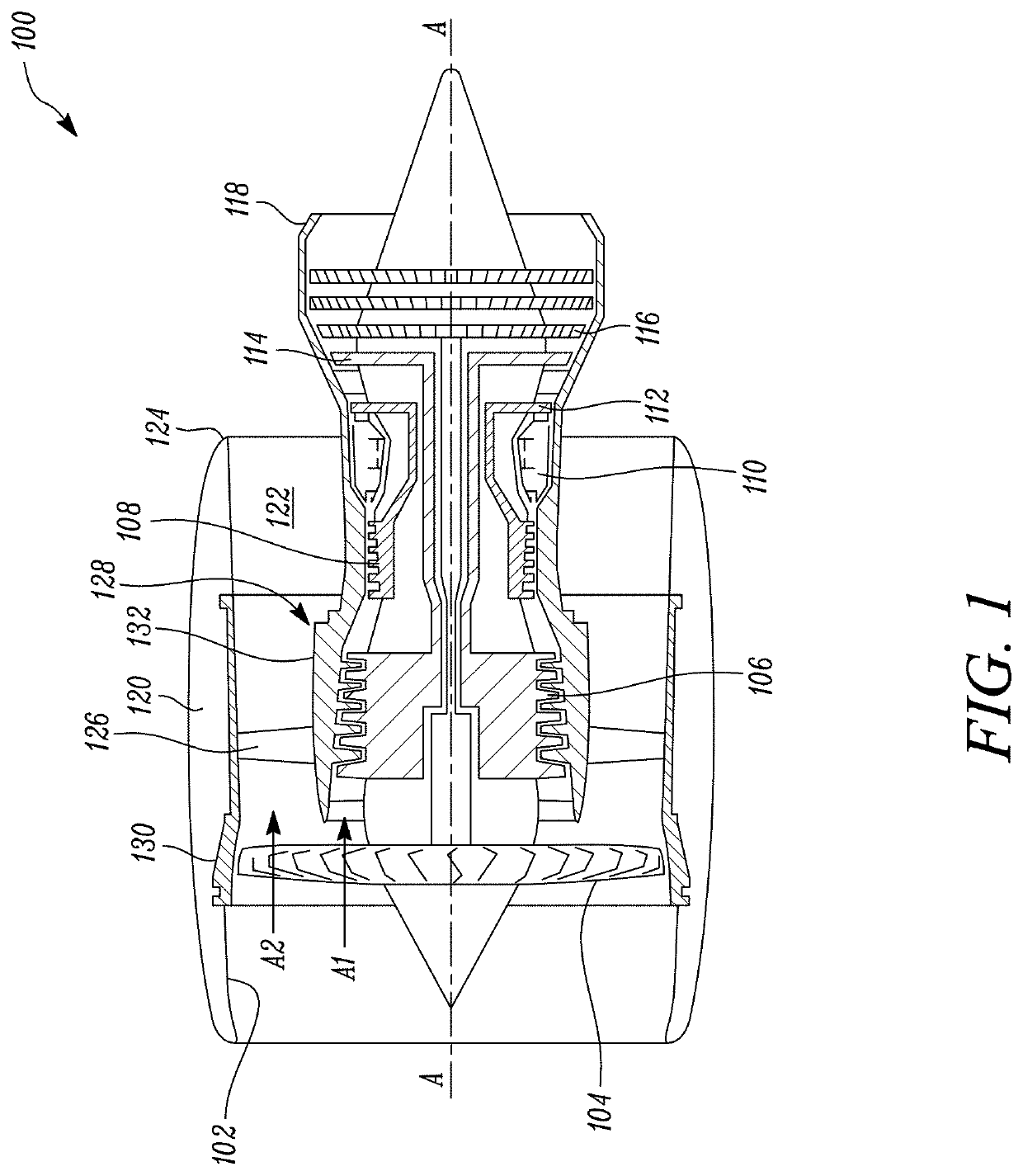
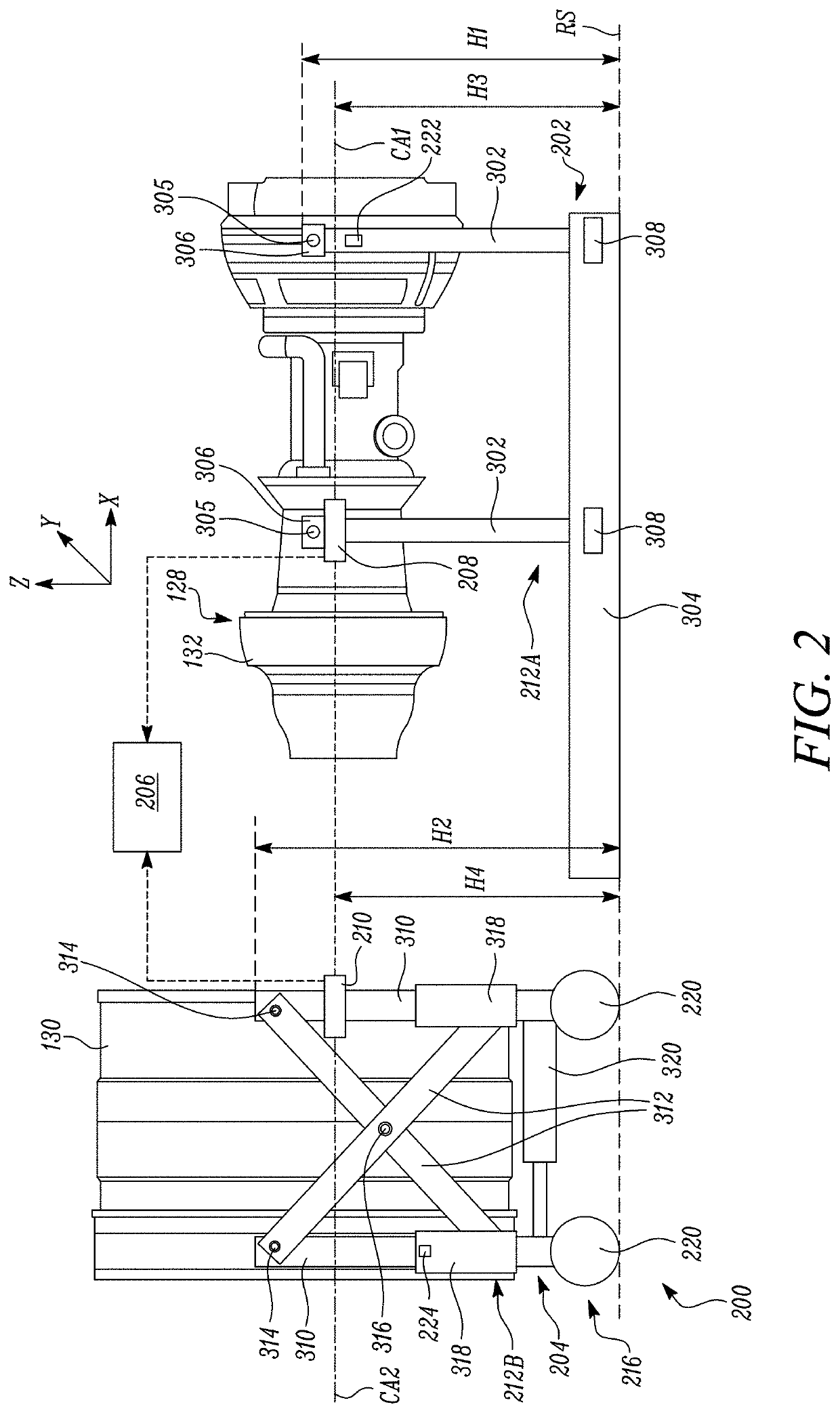
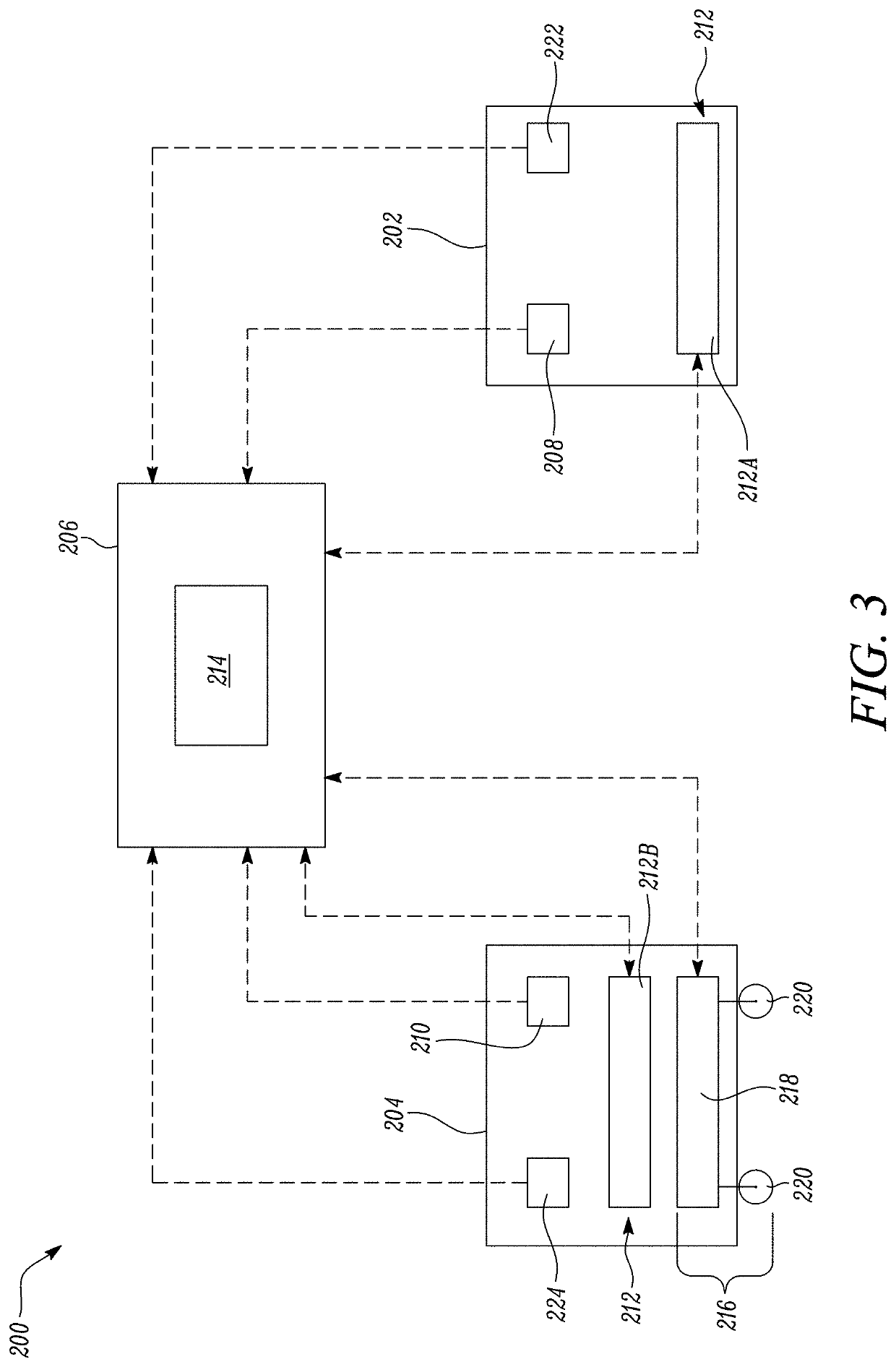
System and method for assembling components of a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20200248591A1Minimal manpower requirementMisalignment and damage assemblyProgramme controlComputer controlAutomotive engineeringEngineering
A system and a method for assembling a core engine and a fan case of a gas turbine engine. The system includes a core engine support that detachably supports the core engine. The core engine support includes at least one core engine alignment sensor. The system further includes a fan case support that detachably supports the fan case. The fan case support includes at least one fan case alignment sensor. The system further includes a computer-controllable unit configured to align the core engine support and the fan case support based on signals from the at least one core engine alignment sensor and the at least one fan case alignment sensor. The computer-controllable unit is further configured to guide a movement of at least one of the core engine support and the fan case support to couple the core engine with the fan case.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Aircraft propulsion assembly equipped with a main fan and with at least one offset fan
ActiveUS20180283272A1Increase bypass ratioPossible to maintainEngine manufacturePower plant constructionTurbineAirplane
An aircraft propulsion assembly comprising at least a main turbine mounted along a longitudinal axis, at least one main fan arranged upstream of the main turbine along the longitudinal axis and driven in rotation by the said main turbine, the said main fan being ducted by a main fan casing, an auxiliary turbine mounted along the longitudinal axis, the auxiliary turbine being independent of the main turbine, an auxiliary fan of axis offset with respect to the longitudinal axis and driven by the auxiliary turbine, the auxiliary fan being ducted by an auxiliary fan casing, the main casing being separate and distinct from the auxiliary casing so as respectively to generate a main secondary flow and an auxiliary secondary flow which remain independent of one another until they are discharged into the atmosphere.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
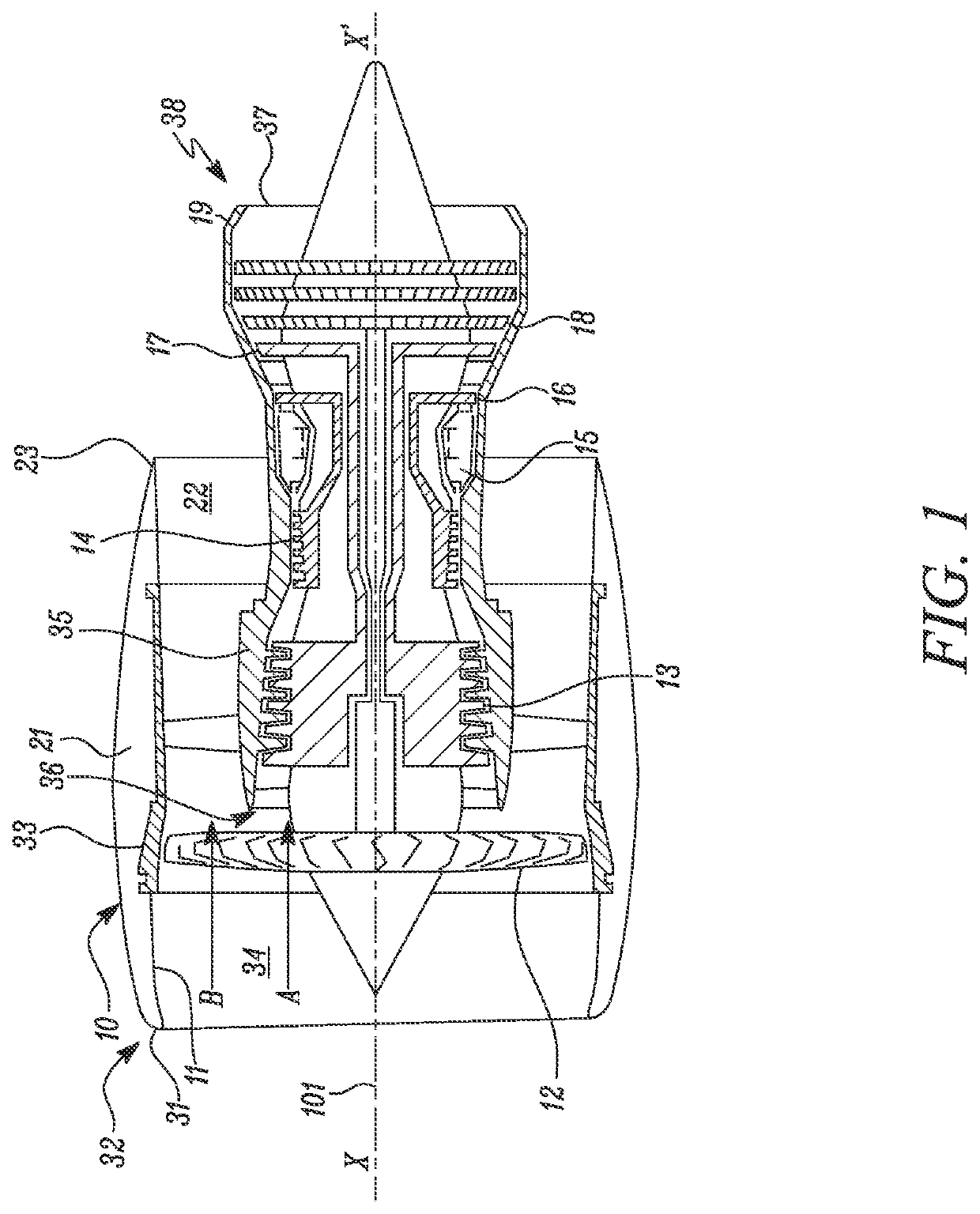
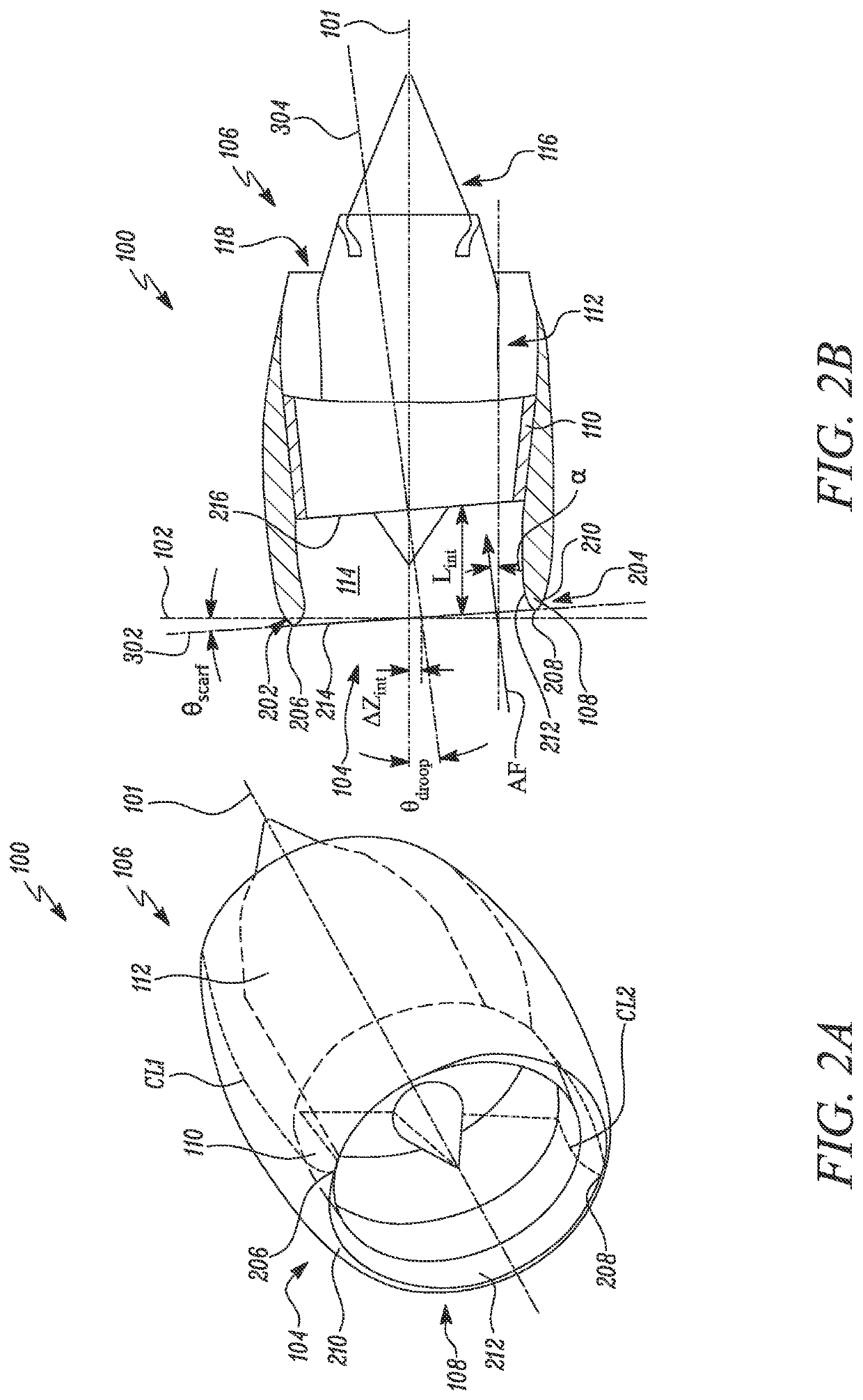
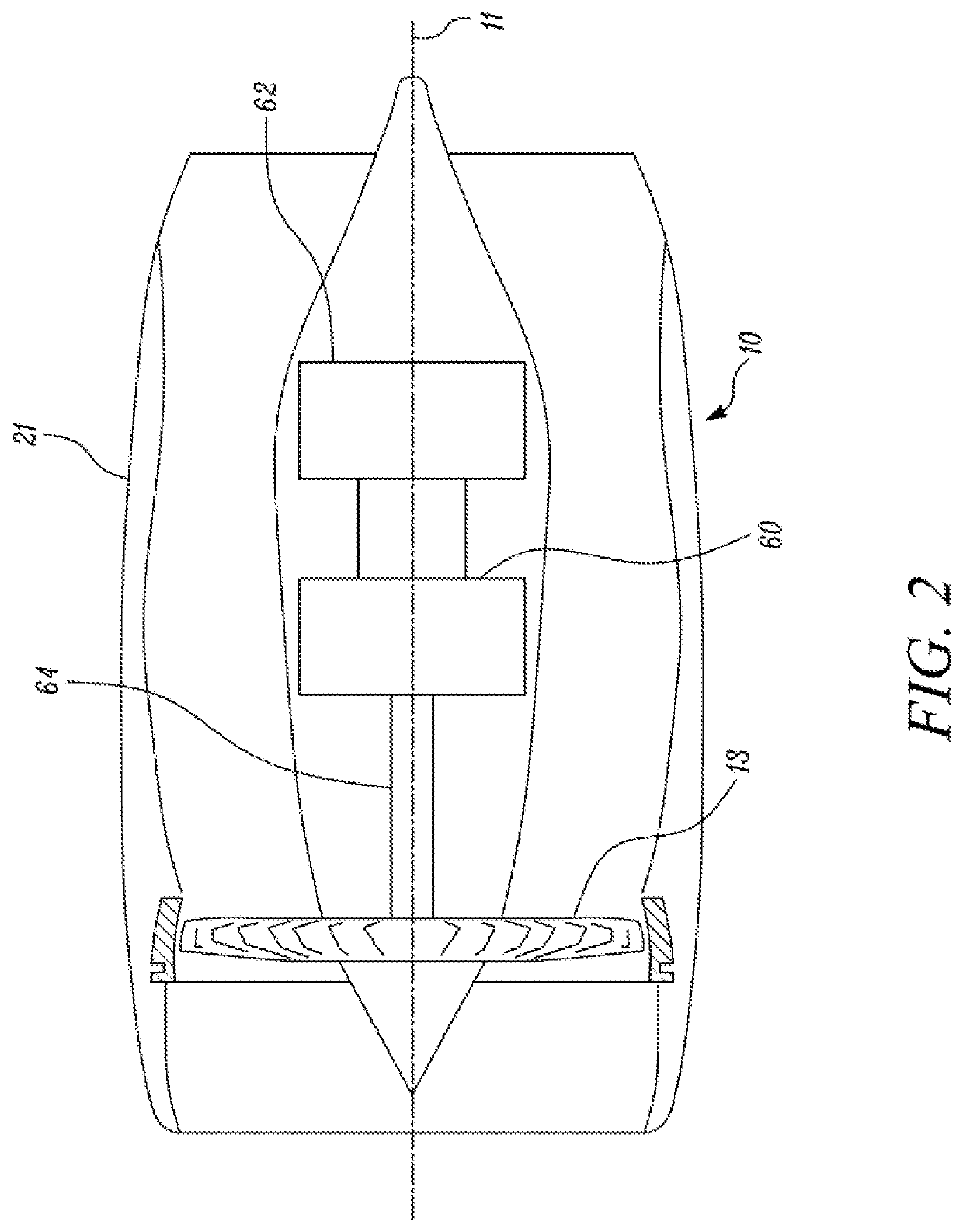
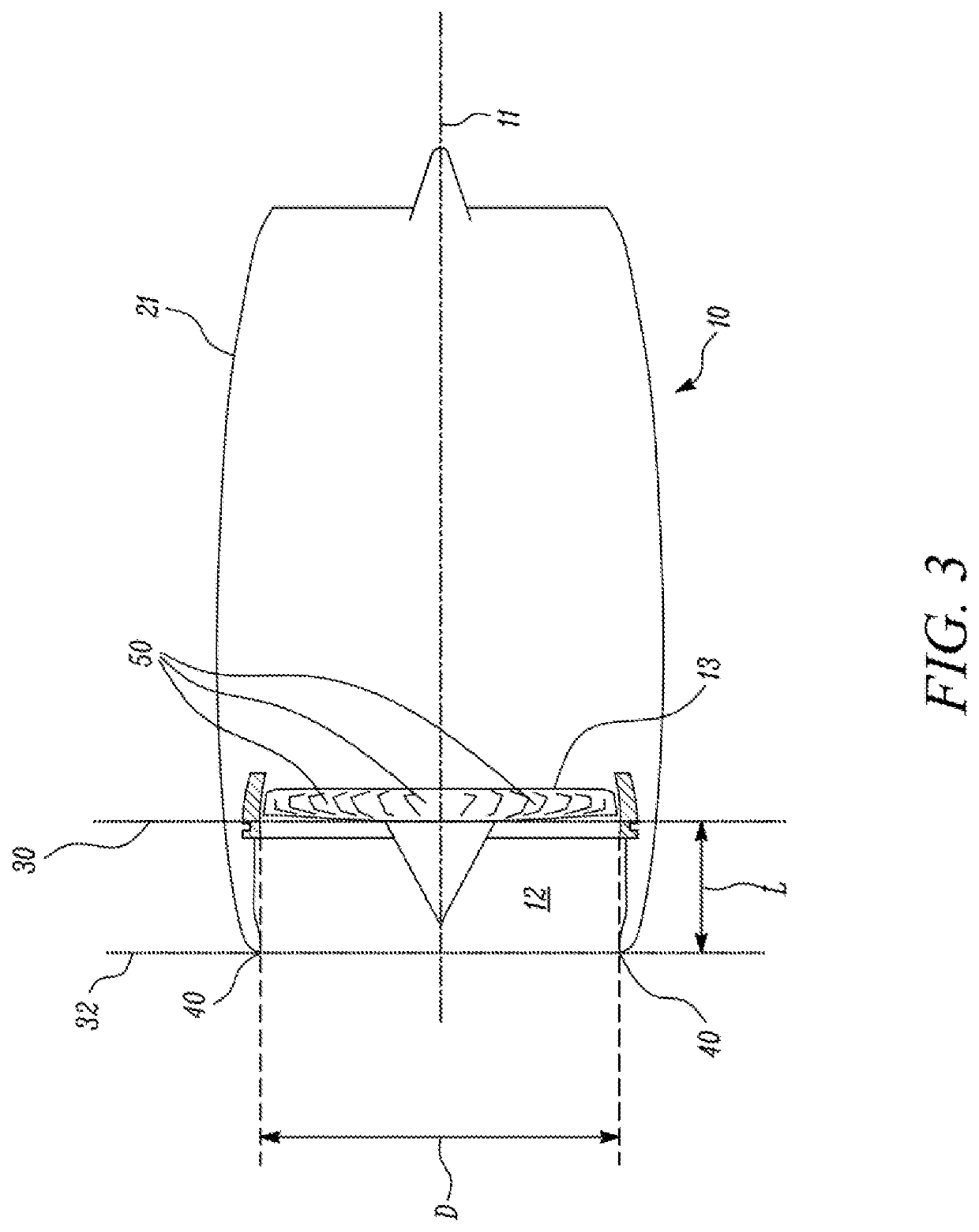
Nacelle for a gas turbine engine
ActiveUS11313241B2Drag minimizationReduce resistanceEngine manufactureEngine fuctionsNacelleClassical mechanics
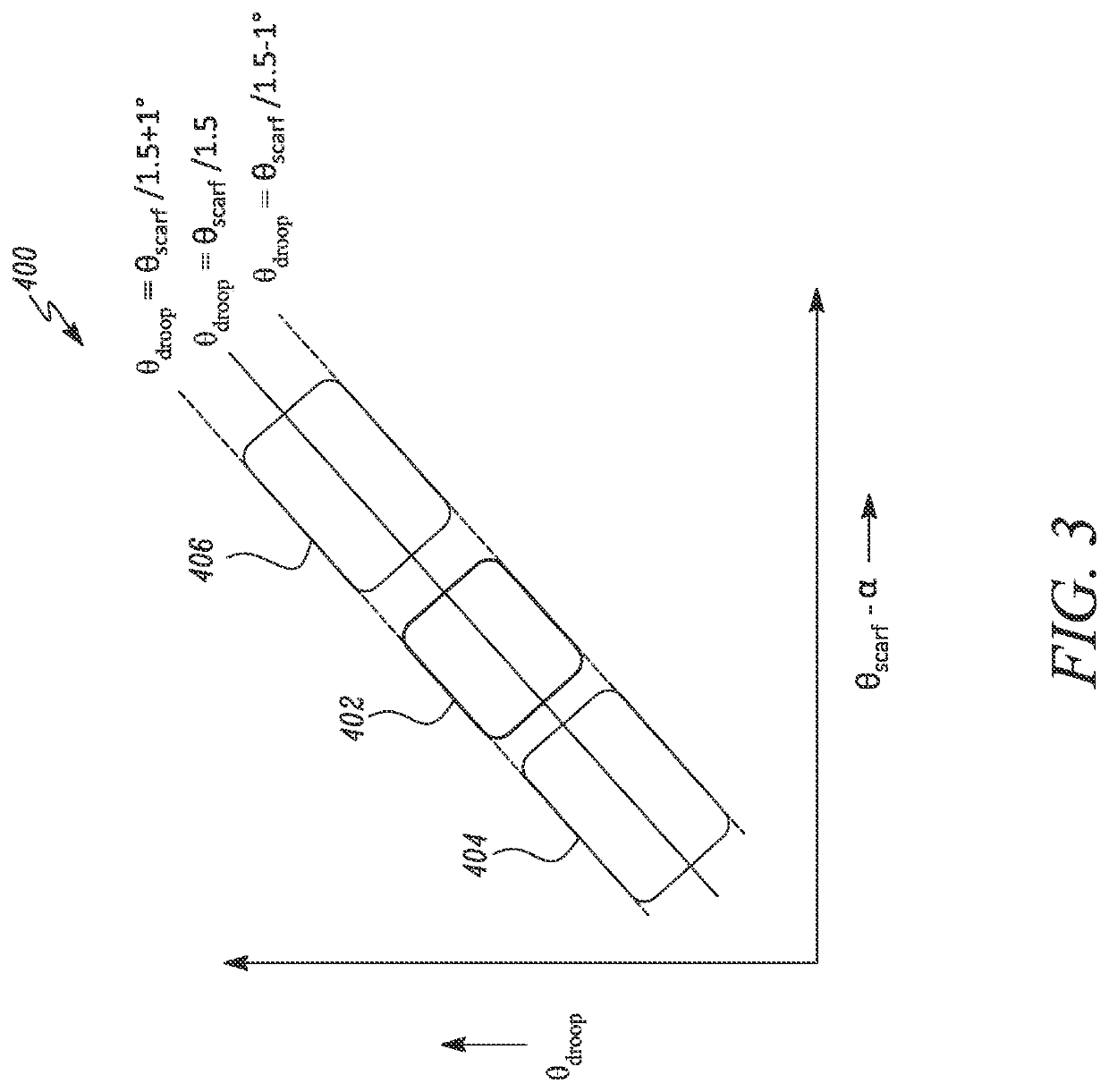
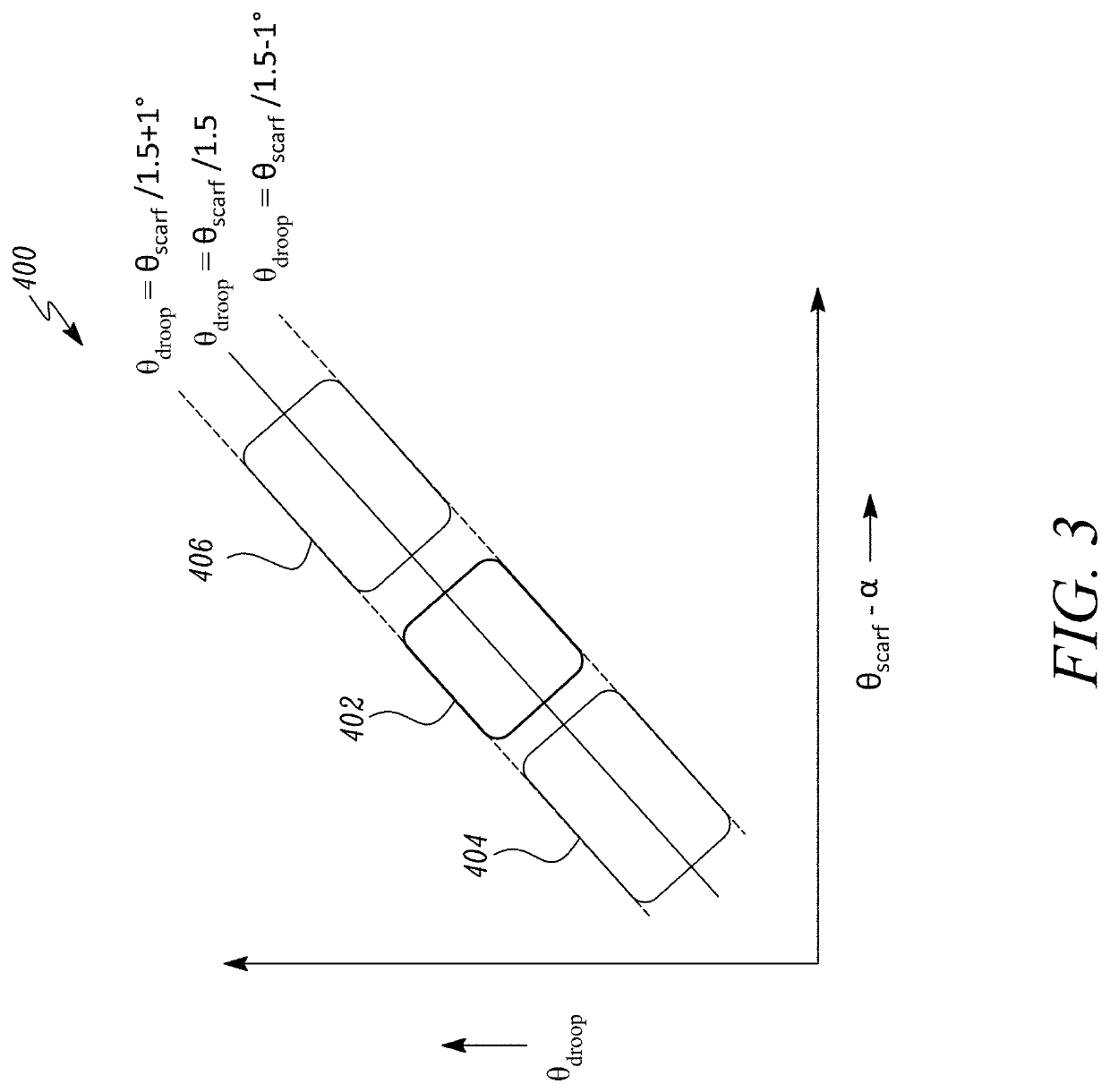
A nacelle for a gas turbine engine having a longitudinal centre line includes an intake lip disposed at an upstream end of the nacelle. The intake lip includes a crown and a keel. The crown includes a crown leading edge and the keel includes a keel leading edge. The crown leading edge and the keel leading edge define a scarf line therebetween. The scarf line forms a scarf angle (θscarf) relative to a reference line perpendicular to the longitudinal centre line. A fan casing is disposed downstream of the intake lip and includes a casing leading edge. The casing leading edge defines a droop line normal to the casing leading edge. The droop line forms a droop angle (θdroop) relative to the longitudinal centre line. A relationship between the droop angle (θdroop) and the scarf angle (θscarf) is given by: θdroop=θscarf / 1.5±1 degree.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
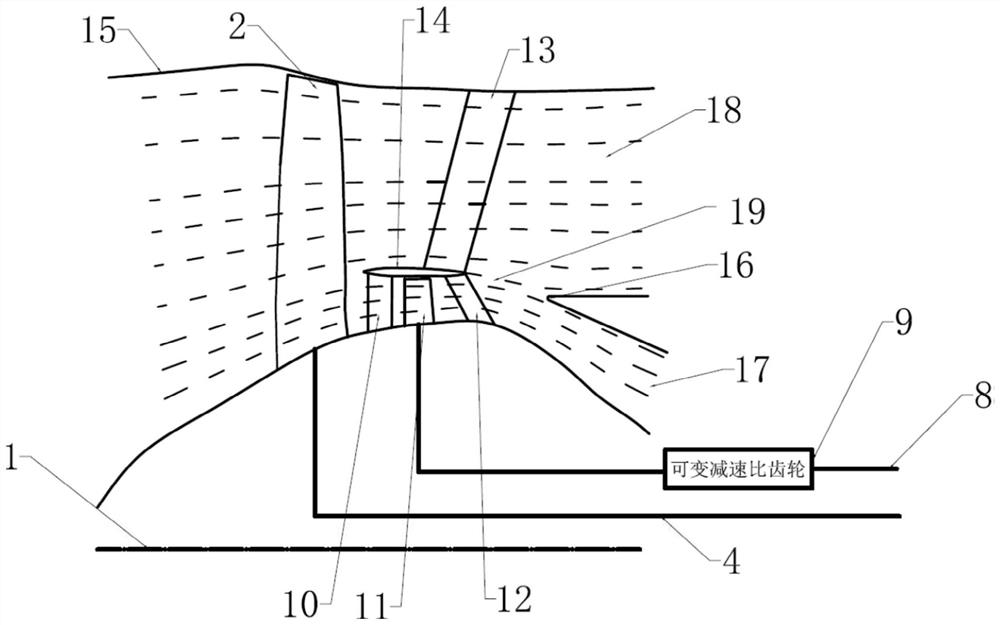
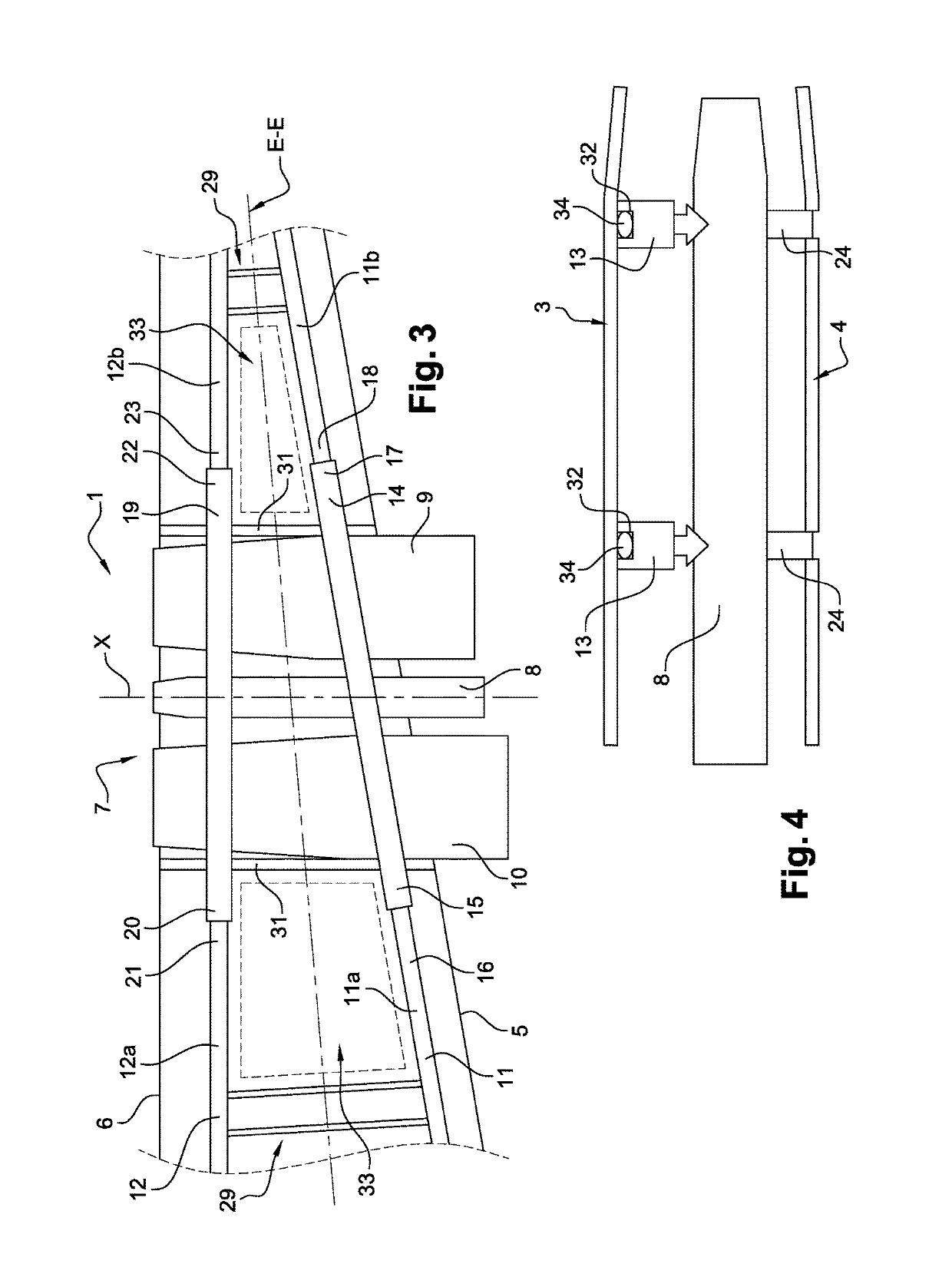
Propulsive wing of an aircraft
ActiveUS20170137136A1Reduce weightReduction in in aerodynamic dragJet type power plantsWingsRigid structureGas generator
The invention relates to a propulsive wing (1, 7) of an aircraft (10), comprising at least two structural spars, upstream and downstream (11, 12), that extend in a wing span direction of the wing (E-E), and a propulsion assembly (7) comprising at least two fans (9, 10) that are each driven by at least one gas generator (8).According to the invention, at least one gas generator (8) extends along an axis that is remote from the axis of rotation of at least one fan (9, 10), and at least one of the spars (11, 12) comprises a first part and a second part (11a, 11b, 12a, 12b) between which the propulsion assembly (7) is arranged, the first and second parts being interconnected by a rigid structure (13) that is shaped so as to extend at least in part around said fans, the propulsion assembly (7) being supported by the rigid structure.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Technical scheme of intermittent inflating turbine engine
InactiveCN102654079ASimple structureNot easy to block by carbon depositsContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsOperating temperatureAutomotive engineering
The invention provides a technical scheme of an intermittent inflating turbine engine. The type of engine mainly comprises a ring-body-shaped combustion chamber stator, a front functional end cover (rotor) and a rear functional end cover (rotor), wherein the ring-body-shaped combustion chamber stator is formed by a plurality of integral combustion chambers which are arranged into a ring and are same in shape and dimension, and the two functional end covers (rotors) rotate synchronously. During the operation process, when the front and rear parts of the combustion chamber are open, the combustion chamber is pressurized and ventilated, when oil mixing and ignition are carried out in the combustion chambers, the front end of the combustion chamber is sealed by the front end cover, thus a turbine blade behind the combustion chamber is pushed to rotate and do wok by utilizing high-pressure fuel gas efficiently; from the point of view of the whole engine, the engine pushes the turbine blade to rotate and do work by utilizing the high-pressure fuel gas continuously; from the point of view of certain combustion chamber, the combustion chamber has the characteristic of intermittent and cycle operation; the technical scheme of the intermittent inflating turbine engine is suitable for all occasions with easy flowing fuel materials which are combusted by virtue of air, and is widely applied to all mechanical motive power devices, is simple in structure, is low in operating temperature of the engine body, is short in engine body, is light in weight, is high in fuel oil power efficiency, and obtains high bypass ratio and thrust-weight ratio.
Owner:周耀瑜
Blade in fan, and fan
ActiveUS9976430B2Increase fuel consumptionImprove rigidityPump componentsBlade accessoriesEngineeringFlange
A platform of a fan outlet guide blade has a first rib and a second rib in an opposite surface of a flow passage surface thereof. The first rib and the second rib are formed in portions excluding a predetermined area separated to an upstream side and a downstream side by 8 to 30% of an inter-flange distance between a first flange and a second flange with respect to an axial center of the platform, the portions being located on a pressure surface side in the opposite surface.
Owner:IHI CORP
Fan aerodynamic layout structure and method of a turbofan engine
ActiveCN103573469BReduce fuel consumptionImprove liquidityPump componentsBlade accessoriesAviationNoise level
The invention discloses a fan aerodynamic layout structure and method of an inlet turbofan engine with a non-full-blade high-pressure rotor, which belongs to the technical field of aero-engine fans. The blades of the rotor are pressed to pressurize the airflow near the fan inlet disc. By rationally designing the non-full-blade high-pressure rotor at the fan inlet, the circulation capacity of the fan can be effectively improved, and the internal pressure ratio of the fan can be effectively improved at the same time. The invention can be directly applied to a high-performance turbofan engine, and can reduce the weight, fuel consumption rate and noise level of the turbofan engine without increasing the external dimension of the engine.
Owner:中科航星科技股份有限公司
Turbofan engine and spacecraft
ActiveCN107246330BShorten the axial lengthLarge thrustGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsCombustion chamberBypass ratio
The invention discloses a turbine turbofan engine and a spacecraft. The turbine turbofan engine comprises an inner supporting structure arranged at the periphery of a main shaft and an outer supporting structure arranged at the periphery of the inner supporting structure, wherein an outer bypass airflow channel is formed between the inner supporting structure and the outer supporting structure; a combustion chamber is arranged in the outer supporting structure positioned outside the outer bypass airflow channel; an inner bypass airflow channel enables air to flow from an air inlet of the inner supporting structure and communicates to the inside of the combustion chamber along a radially-penetrating outer bypass airflow channel. The whole structure of the turbine turbofan engine is simple, large bypass ratio can be realized at a temperature before a low turbine, the propulsive force of the engine is increased, and the oil consumption rate is reduced.
Owner:AECC HUNAN AVIATION POWERPLANT RES INST
Self-propelled fan high bypass ratio turbofan engine with inner ring air turbine
ActiveCN104500269BAvoid RPM Mismatch ProblemsAvoid integrated manufacturingJet propulsion plantsLow voltageBypass ratio
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Low-pitch variable-setting fan of a turbine engine
ActiveUS10830066B2Low axialIncrease bypass ratioPump componentsEngine fuctionsCircular discClassical mechanics
A fan of a turbine engine includes a disc provided with blades at the periphery thereof, the blades being mounted so as to pivot on the disc about a pivot axis, and a mechanism for changing the pitch of the blades. The mechanism is configured to adjust an angular position of each blade around the pivot axis. The angular position is in an angular setting range no greater than 20°.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Aeroengine core machine, control method and aeroengine
ActiveCN112392628BReduce design costImpact sizeGas turbine plantsEfficient propulsion technologiesBypass ratioControl theory
The invention relates to an aero-engine core machine, a control method and an aero-engine, wherein the aero-engine core machine comprises a fan, a low-pressure compressor, a high-pressure compressor, a nozzle, a first movable part and a second movable part, and the low-pressure compressor It is arranged downstream of the fan; the first movable part is arranged between the fan and the low-pressure compressor, and is used to adjust the bypass ratio of the core engine of the aero-engine through its own motion; the high-pressure compressor is arranged downstream of the low-pressure compressor; the nozzle pipe It is arranged between the low-pressure compressor and the high-pressure compressor, and is used for exporting the outlet air flow of the low-pressure compressor; the second movable part is arranged at the inlet of the nozzle, and is used to open or close the inlet of the nozzle. The aero-engine includes the above-mentioned core engine. The present invention can realize the adaptability to different operating conditions of the engine through the cooperation of the first movable element and the second movable element.
Owner:AECC COMML AIRCRAFT ENGINE CO LTD
External parallel fan turbine engine and application thereof in field of flying wing aircrafts
InactiveCN110056451AIncrease bypass ratioLarge thrustGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsBypass ratioBevel gear
The invention discloses an external parallel fan turbine engine and application thereof in the field of flying wing aircrafts. The external parallel fan turbine engine comprises a main engine assembly, bypass fan assemblies and a bevel gear transmission assembly; the main engine assembly is a turboshaft engine / turboprop engine; the two or more sets of bypass fan assemblies are symmetrically and externally arranged on the two sides of the main engine assembly; a power turbine shaft of the main engine assembly and fan rotary shafts of the bypass fan assemblies are arranged in parallel; the transmission assembly comprises a main engine built-in transmission assembly and bypass fan built-in transmission assemblies; and the main engine assembly is connected with the bypass fan assemblies through the transmission assembly. Compared with conventional turbofan engines, the high bypass ratio design of the external parallel fan turbine engine can be achieved under a small engine height dimension, fuel consumption can be reduced, and the external parallel fan turbine engine is suitable for providing propulsion power for the flying wing aircrafts as blended wing bodies and is a power device with great potential for the new generation of passenger aircrafts with blended wing bodies.
Owner:AECC HUNAN AVIATION POWERPLANT RES INST
Air-driven ducted fan jet propulsion power system
ActiveCN112443423BIncrease bypass ratioReduce restrictionsPump componentsPump controlJet propulsionFlight vehicle
The invention discloses an air-driven ducted fan jet propulsion power system, comprising a core turbine, a ducted fan connected to the core turbine through an air induction pipe, and a blade tip turbine coaxially installed with the ducted fan, the core turbine exhausts gas It is transmitted to the blade tip turbine, and the blade tip turbine works on the expansion of the gas, driving the bypass fan to rotate and inhale the air to generate thrust, which breaks through the design limitation of conventional turbofan engines with large bypass ratio, greatly increases the bypass ratio of the engine, and further exerts its large capacity. The basic principle of bypass ratio turbofan engine to improve propulsion efficiency, lower fuel consumption and higher power output, and the function of the induction pipe connected between the energy source core turbine and the bypass fan is only the airflow channel without complicated machinery The connection can be arranged inside the fuselage and wings according to the design needs of the aircraft, giving the aircraft a more flexible layout.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
small turbofan engine
ActiveCN106837602BAffect air intakeIncrease bypass ratioTurbine/propulsion air intakesJet propulsion plantsAir compressionImpeller
Owner:刘展文
High Bypass Ratio Turbofan Engine with Tip Jet Driven Fan
ActiveCN104675556BIncrease bypass ratioRealize boost boost and reduce consumptionJet propulsion plantsTorque transmissionBypass ratio
The invention provides a large-bypass-ratio turbofan engine of a vane tip jet driven fan and a designing method. A large-bypass-ratio fan rotor driven by vane tip jet is arranged on an external duct portion and comprises an additional ducted fan rotor, a vane tip driving portion and a rotary additional duct rotor hub; an additional duct stator is arranged on a downstream portion of the additional ducted fan rotor and a downstream portion of a vane tip driving portion; and air is led to vane tips of the additional ducted fan rotor from an external duct of the original double-rotor turbofan engine by an air leading channel. The large-bypass-ratio turbofan engine of the vane tip jet driven fan has the advantages that the bypass ratio is increased, torque transmission is implemented by an aerodynamic force, and the problem that the rotation speed of the fan is not matched with that of the driving component; the peripheral speed is greatly improved, and the improvement potential of the bypass ratio is high; compared with the prior art, the large-bypass-ratio turbofan engine is simple in structure; and the large-bypass-ratio turbofan engine is improved on the basis of the existing double-rotor turbofan engine, development risk and the development cost of the large-bypass-ratio turbofan engine of the vane tip jet driven fan are reduced, and the development cycle is shortened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
A multi-fan super bypass ratio turbine thrust system
InactiveCN104595032BReduce consumption rateReduce fuel consumptionGas turbine plantsWeight reductionFlue gasLiquid fuel
The invention relates to a multi-fan turbine thrust system with an ultra-large bypass ratio, wherein the system includes frequency converters (1), flue gas turbine-electric generator units (2), motor-fan propulsion units (3), an electric conductive cable (4), a flue transmission pipeline (5) and a liquid fuel storage tank (6); the flue gas turbine-electric generator units (2), the frequency converters (1) and the motor-fan propulsion units (3) are connected successively by the electric conductive cable (4); the liquid fuel storage tank (6) is connected with the flue gas turbine-electric generator units (2) through the fuel transmission pipeline (5); a gasification partial pipeline of the fuel transmission pipeline (5) is arranged on the motor-fan propulsion units (3). Compared with the prior art, the system has the advantages that the ultra-high bypass ratio of an engine is achieved in a large civil passenger plane, and at the same time, has the advantage that the weight and the gas intake area are effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Aircraft engine
ActiveUS20220074308A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove fuel efficiencyGas turbine type power plantsBlade accessoriesLeading edgeNacelle
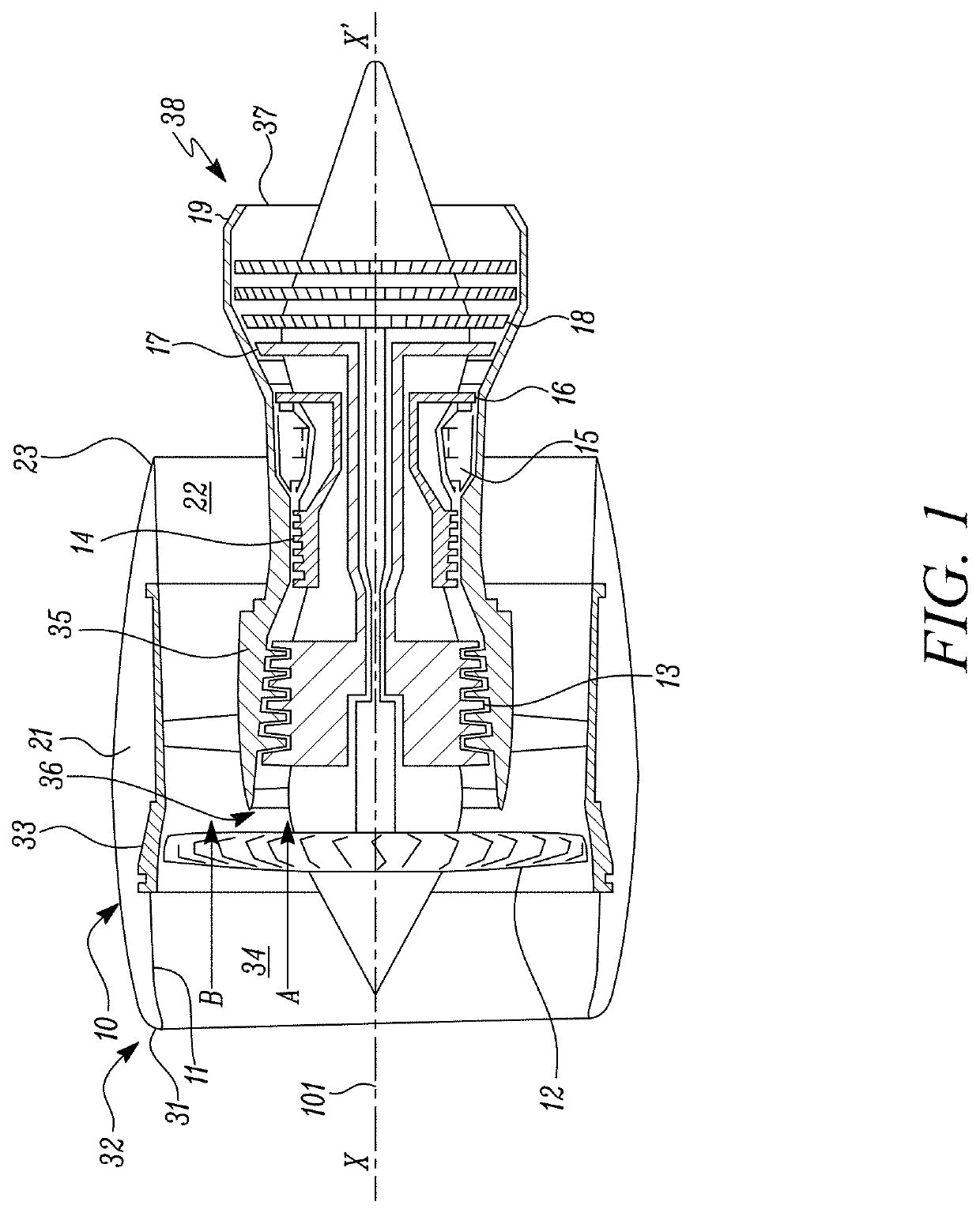
An aircraft engine comprising a fan, the fan having a diameter D and including a plurality of fan blades, the fan blades having a sweep metric S, each fan blade having a leading edge, and a forward-most portion on the leading edge of each fan blade being in a first reference plane. The aircraft engine further comprises a nacelle, comprising an intake portion forward of the fan, a forward edge on the intake portion being in a second reference plane, wherein the intake portion has a length L measured along an axis of the aircraft engine between the first reference plane and the second reference plane, the aircraft engine having a cruise design point condition Mrel, wherein Mrel is between 0.4 and 0.93, and L / D is between 0.2 and 0.45.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
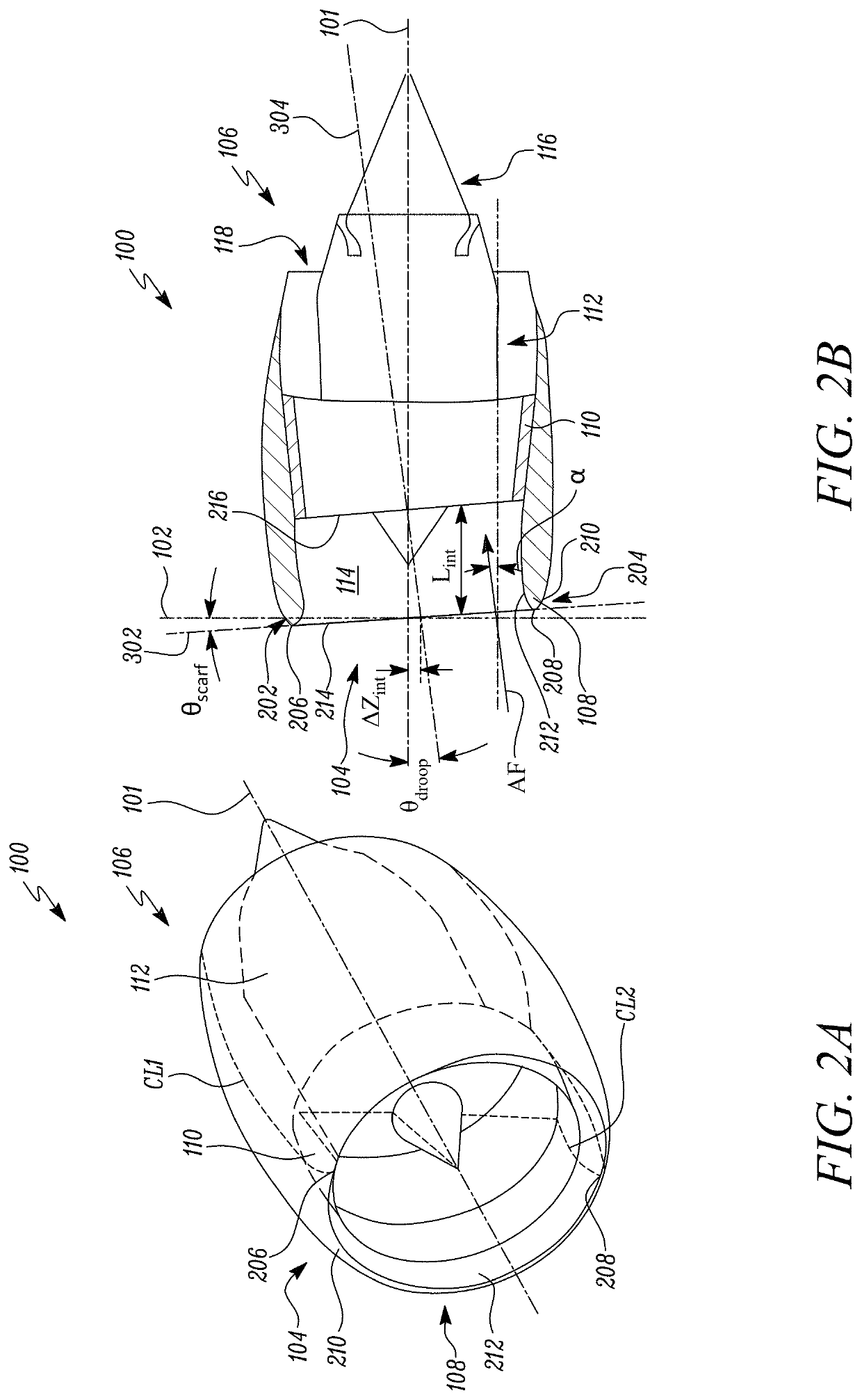
Nacelle for a gas turbine engine
ActiveUS20210164356A1Reduce resistanceDrag minimizationEngine manufactureEngine fuctionsNacelleClassical mechanics
A nacelle for a gas turbine engine having a longitudinal centre line includes an intake lip disposed at an upstream end of the nacelle. The intake lip includes a crown and a keel. The crown includes a crown leading edge and the keel includes a keel leading edge. The crown leading edge and the keel leading edge define a scarf line therebetween. The scarf line forms a scarf angle (θscarf) relative to a reference line perpendicular to the longitudinal centre line. A fan casing is disposed downstream of the intake lip and includes a casing leading edge. The casing leading edge defines a droop line normal to the casing leading edge. The droop line forms a droop angle (θdroop) relative to the longitudinal centre line. A relationship between the droop angle (θdroop) and the scarf angle (θscarf) is given by: θdroop=θscarf / 1.5±1 degree.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Feed additive composition for ruminants, and feed containing the same, and method of fabricating such feed additive composition for ruminants
ActiveUS8642070B2Maintain good propertiesLow costBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDehydroacetic acidBenzoic acid
The coating composition which coats the biologically active substance includes at least one protective material selected from the group consisting of a hardened animal fat, a hardened vegetable oil, a linear or branched, saturated or unsaturated aliphatic monocarboxylic acid having 12 to 22 carbon atoms, a fatty acid ester, and a wax group; lecithin; and at least one preservative selected from a propionic acid or its salt, a sorbic acid or its salt, a benzoic acid or its salt, a dehydroacetic acid or its salt, parahydroxybenzoic acid esters, an imazalil, a thiabendazole, an orthophenyl phenol, an orthophenyl phenol natrium, and a diphenyl.
Owner:BIO SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com