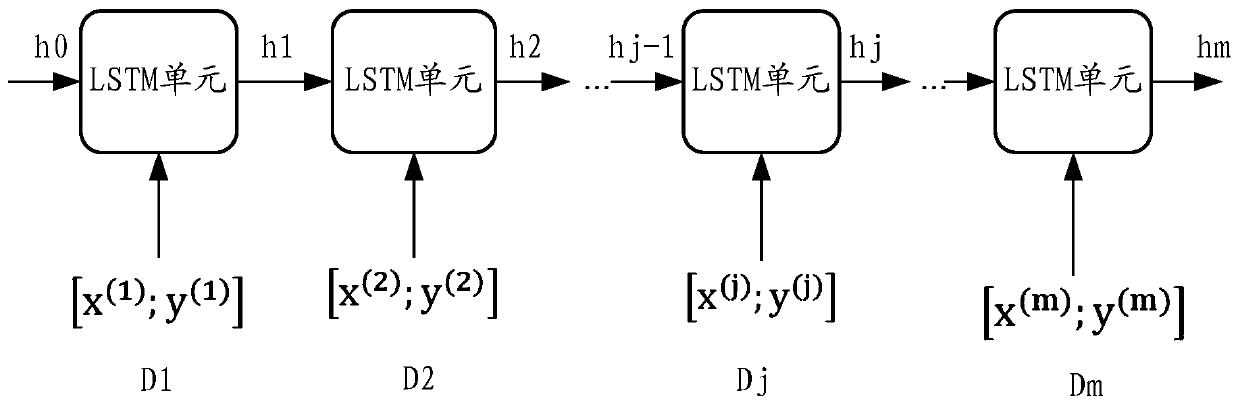
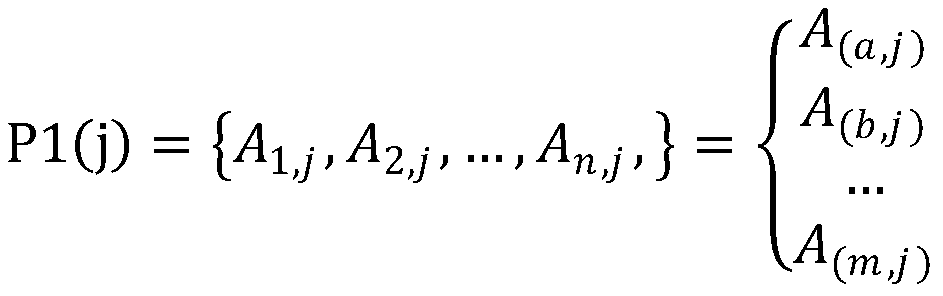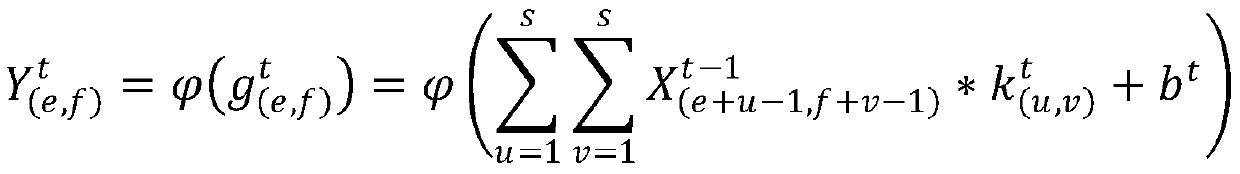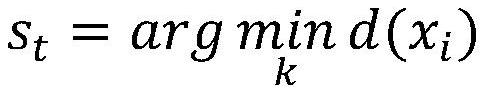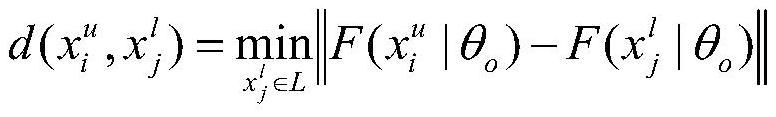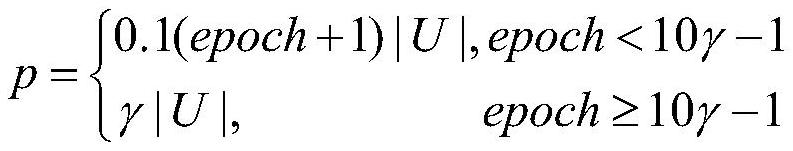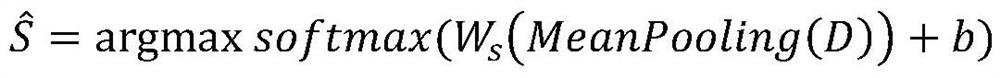Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "Enrich training data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
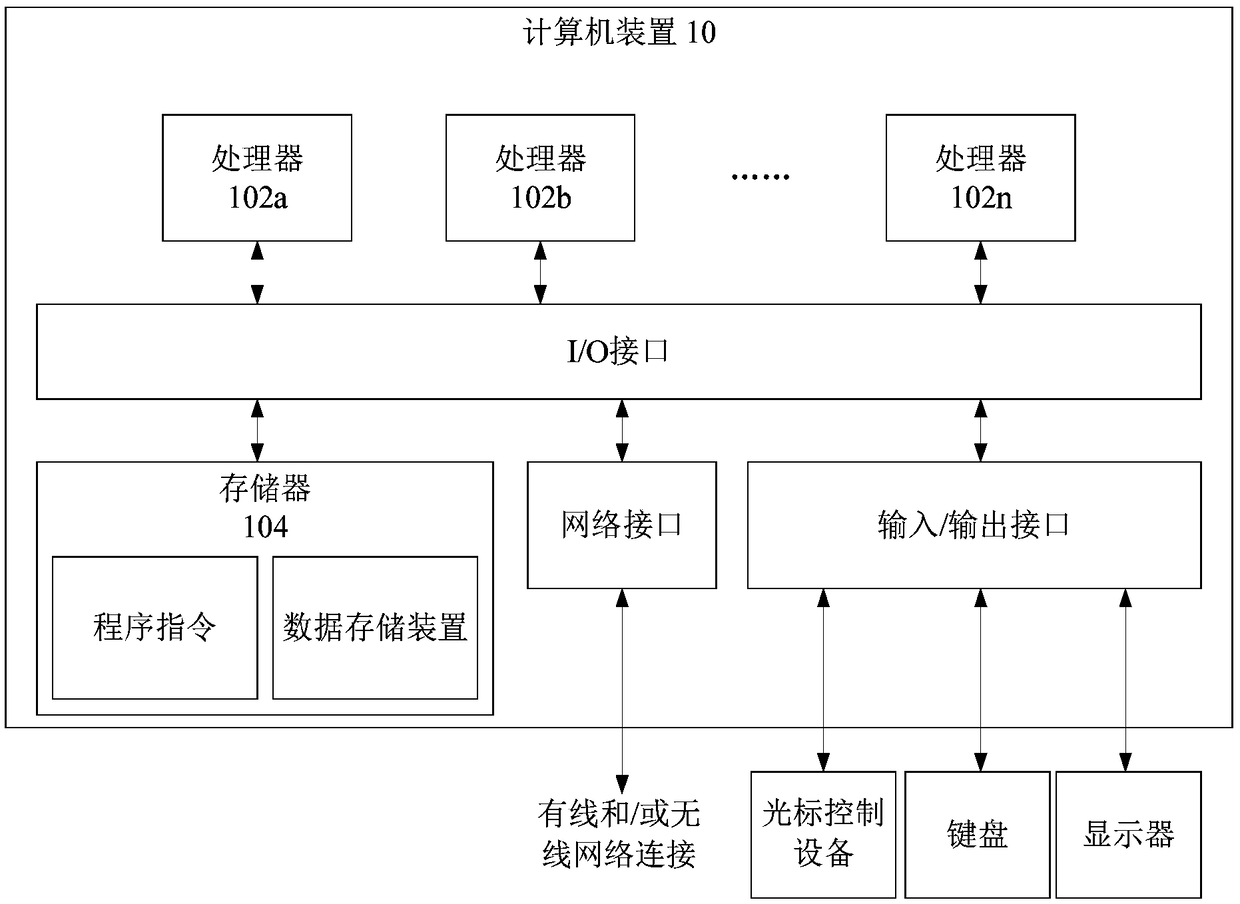
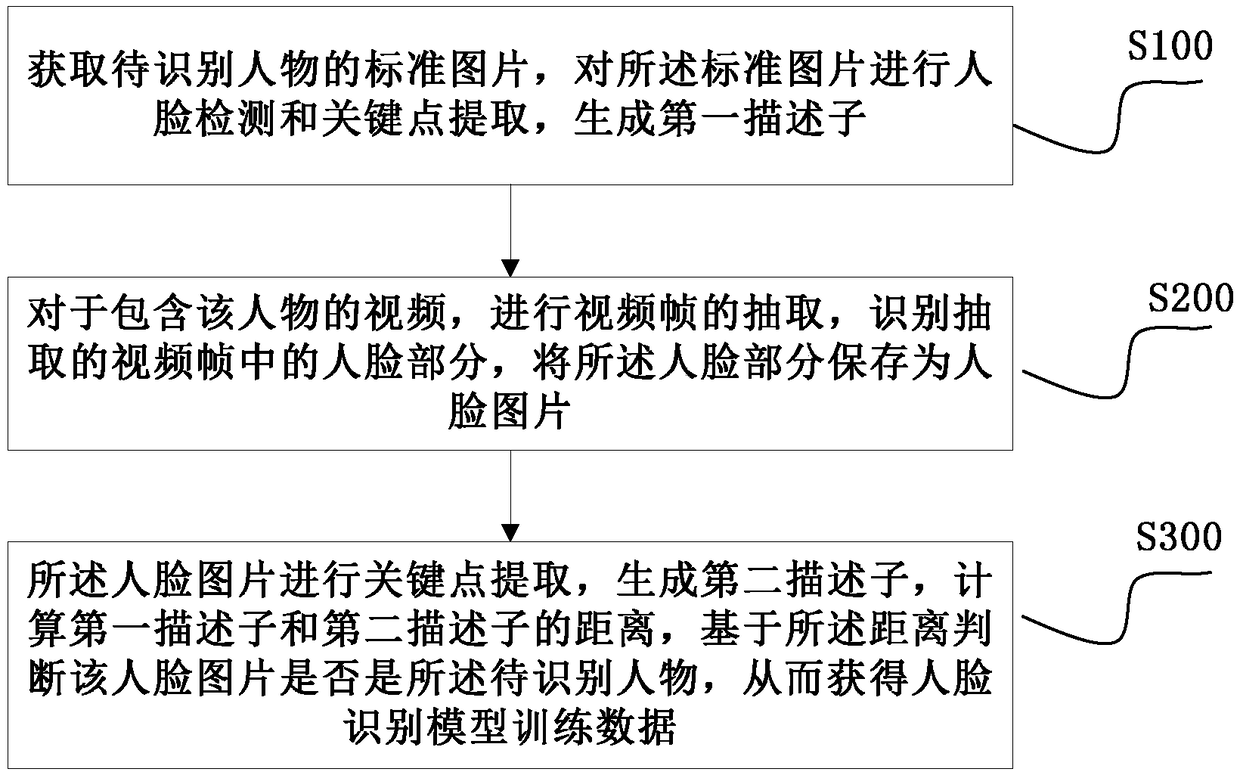
Method, device and medium for acquiring face recognition model training data based on video
ActiveCN109284729AEnrich training dataReduce workloadCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionPattern recognition
The present application discloses a method, apparatus and medium for acquiring face recognition model training data based on video. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a standard picture of a person to be recognized; performing face detection and key point extraction on the standard picture to generate a first descriptor; for the video including the person, the video frame is extracted, the face part in the extracted video frame is recognized, and the face part is saved as a face picture; the key points of the face picture are extracted, a second descriptor is generated, thedistance between the first descriptor and the second descriptor is calculated, and whether the face picture is the person to be recognized is judged based on the distance, so as to obtain the face recognition model training data. This method can enrich the training data of face recognition model, reduce the workload of manual screening, and thus solve the problems of incomplete preparation of training data, single type, and great difficulty in cleaning.
Owner:BEIJING YINGPU TECH CO LTD
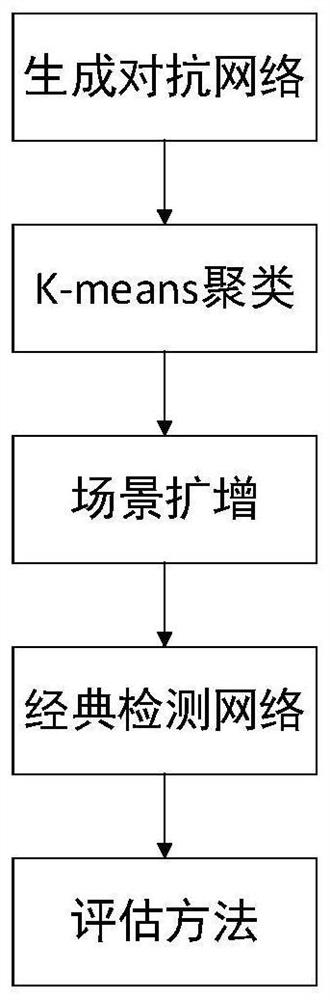
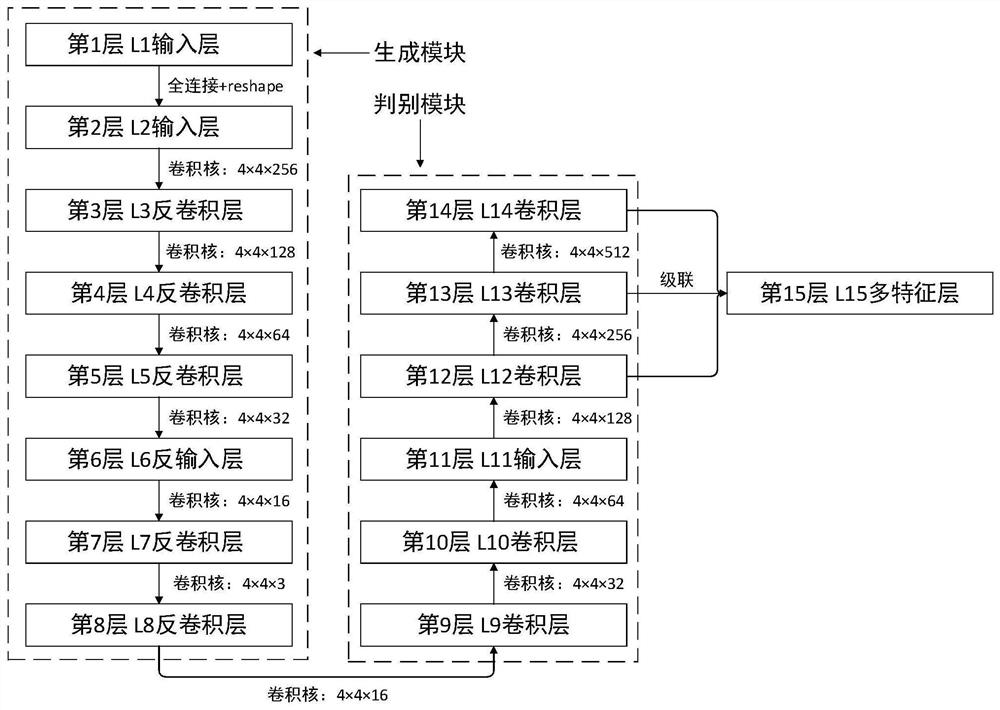
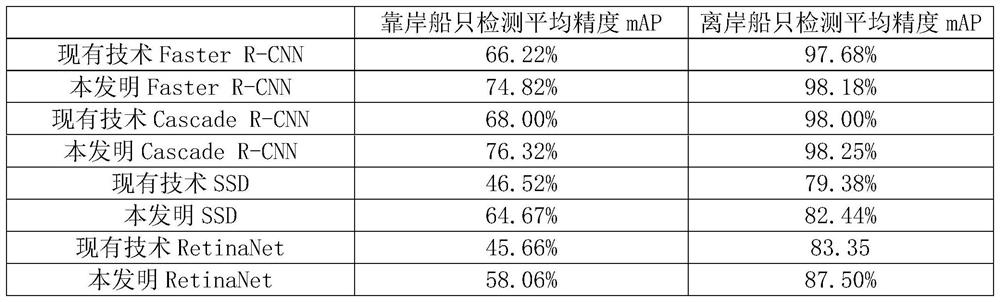
Method for improving detection precision of ships approaching shore in SAR image
PendingCN112285712AImprove detection accuracyEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setFeature extraction
The invention discloses a method for improving the detection precision of ships approaching a shore in an SAR image. The method is based on a deep learning theory, and mainly comprises four parts: a generative adversarial network, K-means clustering, scene amplification, and a classic detection network (Faster R-CNN, Cascade R-CNN, SSD, and RetinaNet). The generative adversarial network realizes image feature extraction, the K-means clustering method realizes image dichotomy by using extracted features to obtain a classification result of each image, scene amplification is performed to obtaina more balanced data set, and the classical detection network performs training by using the processed data set and executes a detection task. While the detection precision of the offshore ship is slightly improved, the detection precision of the ship approaching the shore on the Faster R-CNN, the Cascade R-CNN, the SSD and the RetinaNet network is improved by 8.60%, 8.32%, 18.15% and 12.40% respectively, and the detection precision of the ship approaching the shore is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
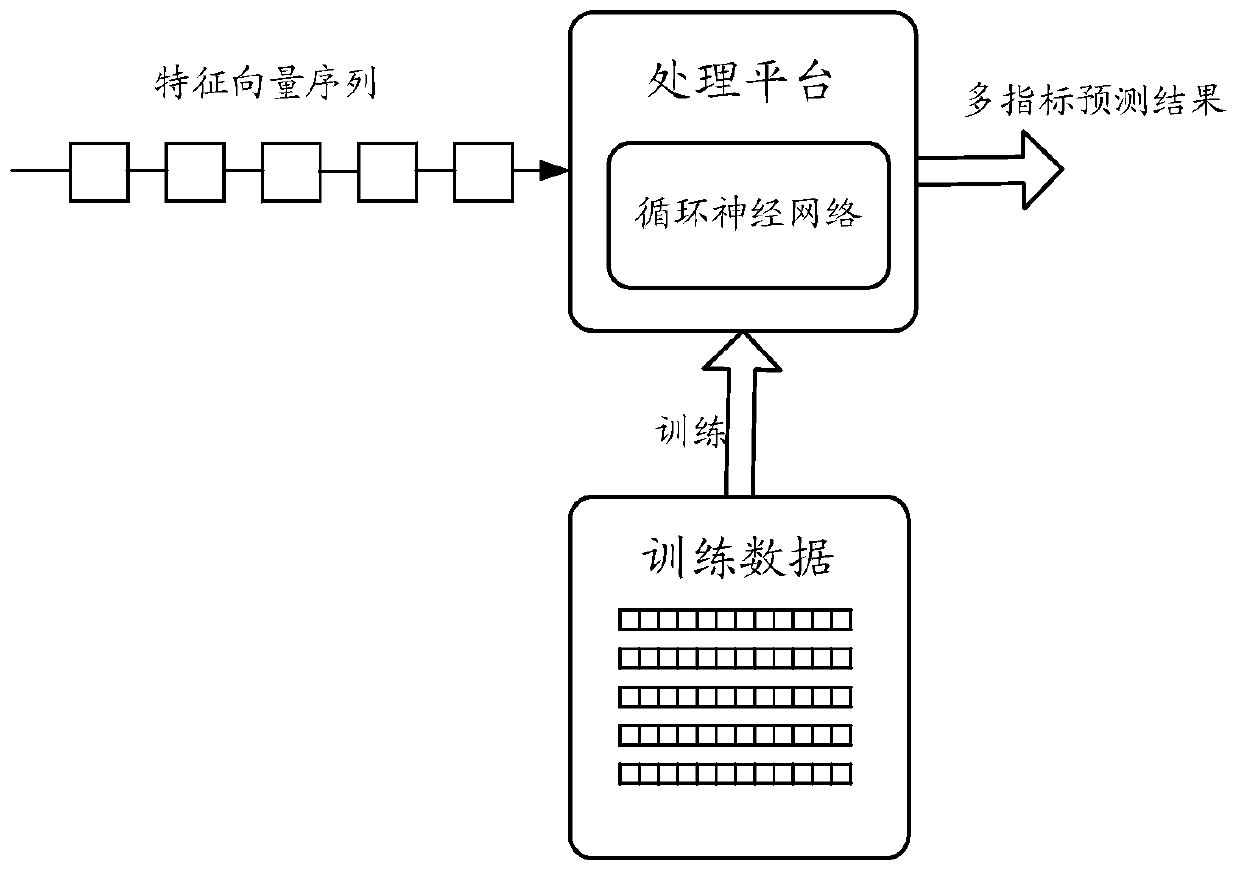
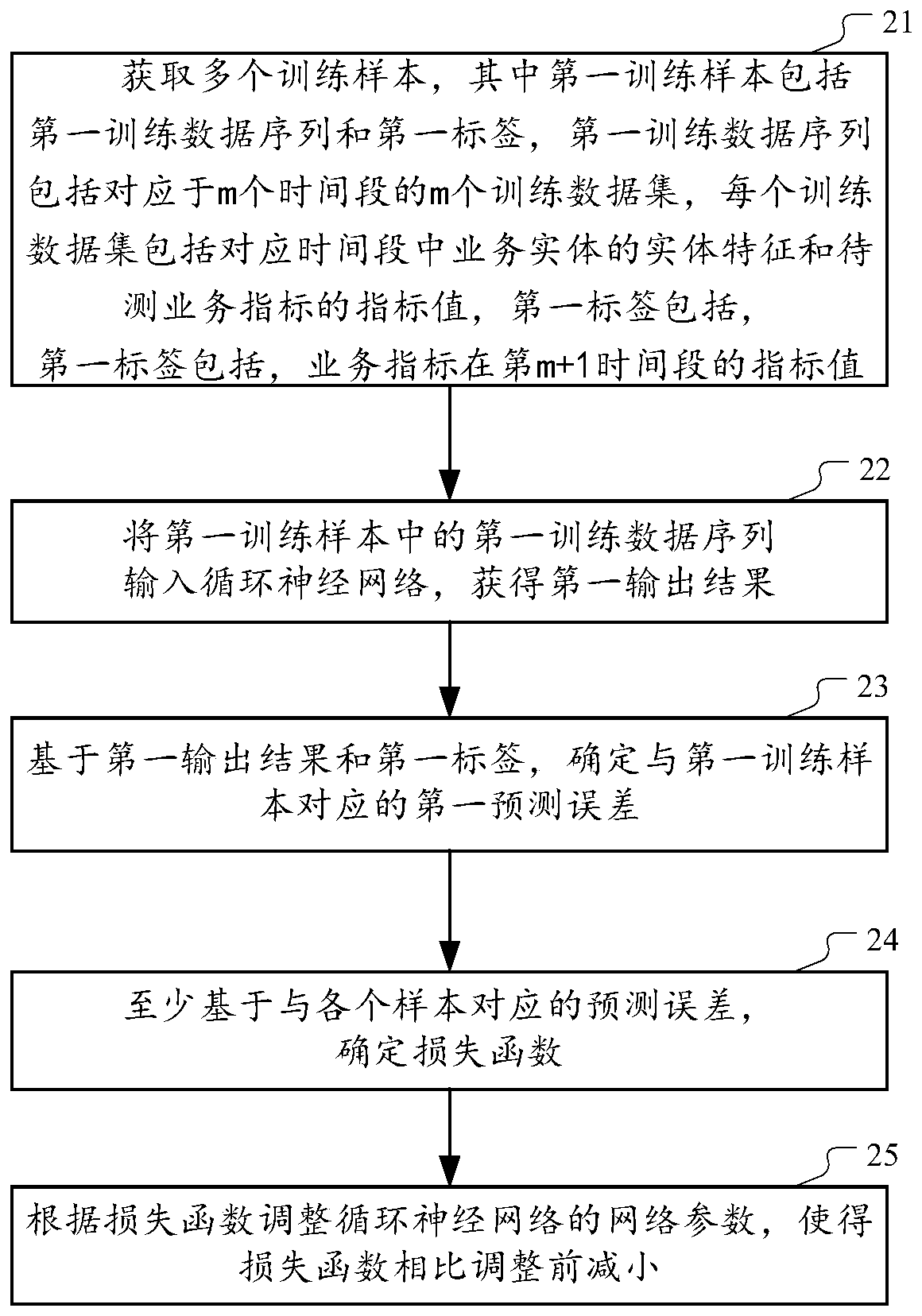
Method and device for predicting service index
PendingCN110009384AEnrich training dataImprove accuracyNeural architecturesMarketingTime sequenceData mining
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for predicting a service index executed by a computer. The method comprises: first, obtaining dataset sequences, wherein the data set sequence comprises m data sets which correspond to m continuous time periods and are arranged according to a time sequence, and the ith data set in the m data sets comprises entity characteristics of a to-be-tested service entity in the ith time period and respective index values of a plurality of to-be-tested service indexes of the to-be-tested service entity; inputting the data set sequence into apre-trained recurrent neural network to obtain an output result. Therefore, according to the output result, the index values of the plurality of to-be-tested service indexes of the to-be-tested service entity in the next time period of the mth time period can be determined.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
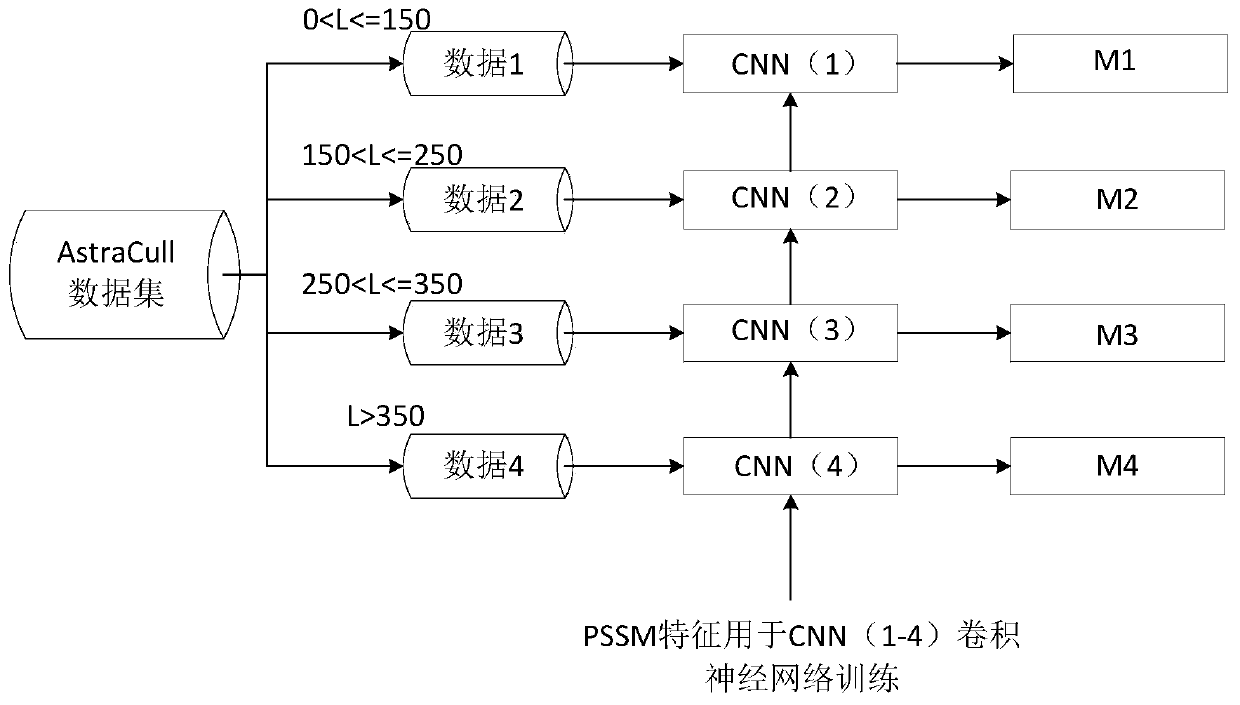
Method and system for classification modeling based on protein length and DCNN
PendingCN110310698AHigh precisionEnrich training dataInstrumentsMolecular structuresProtein lengthSlide window
The invention discloses a method and system for classification modeling based on protein length and DCNN, and belongs to the field of protein prediction and analysis. The technical problem to be solved is how to use deep learning to predict and analyze the secondary structure of the protein and improve the accuracy. The method comprises the following steps: taking a plurality of big data sets as atraining set, extracting PSSM features generated by PSI-Blast in the data sets, and performing format conversion on the PSSM features through a sliding window; grouping proteins in the training set based on the protein length to obtain a plurality of model groups; and constructing a predication model corresponding to every model group based on a deep convolutional network, and training the prediction models by the model groups to obtain trained prediction models. The system includes an input module, a format conversion module, a grouping module and a model training module.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
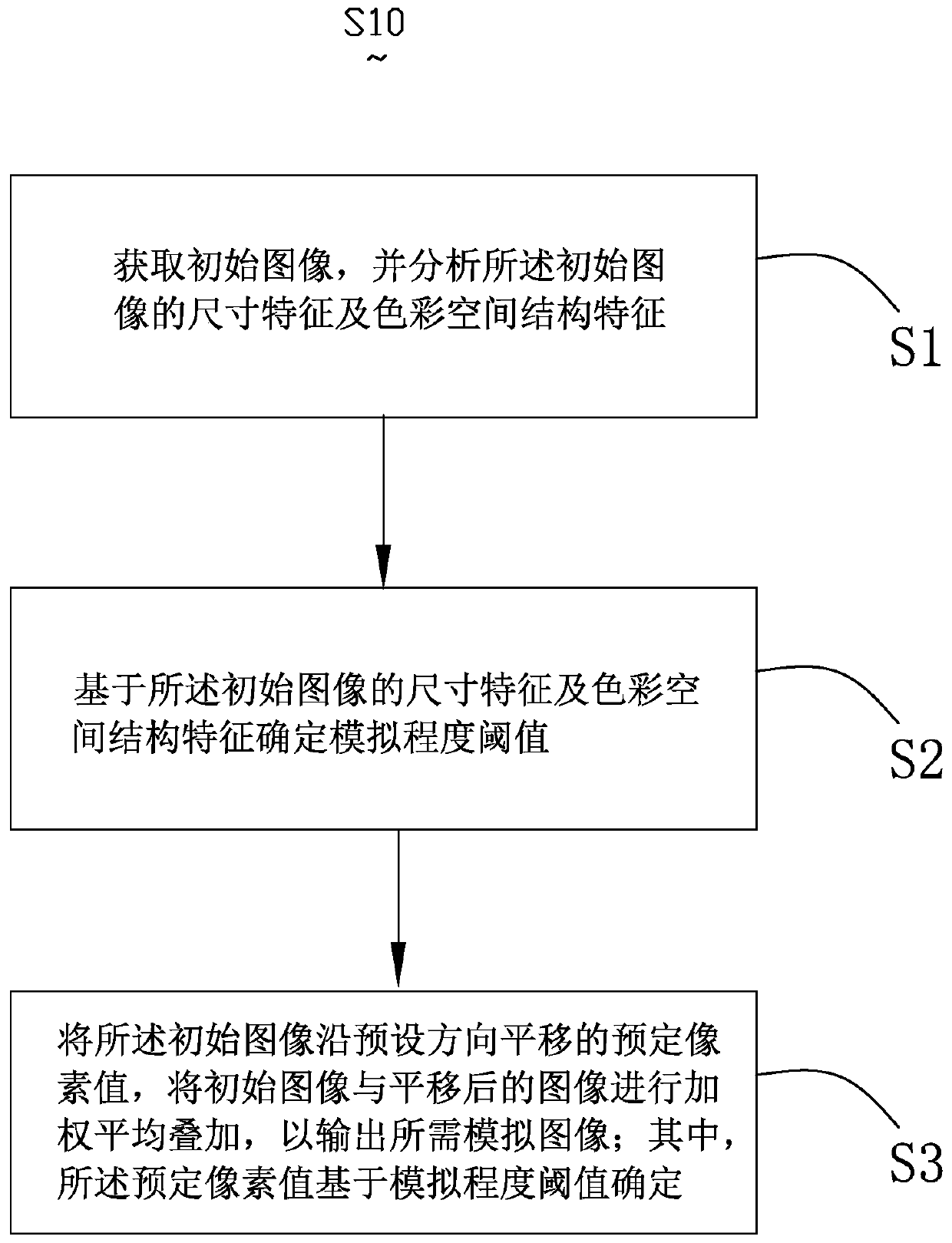
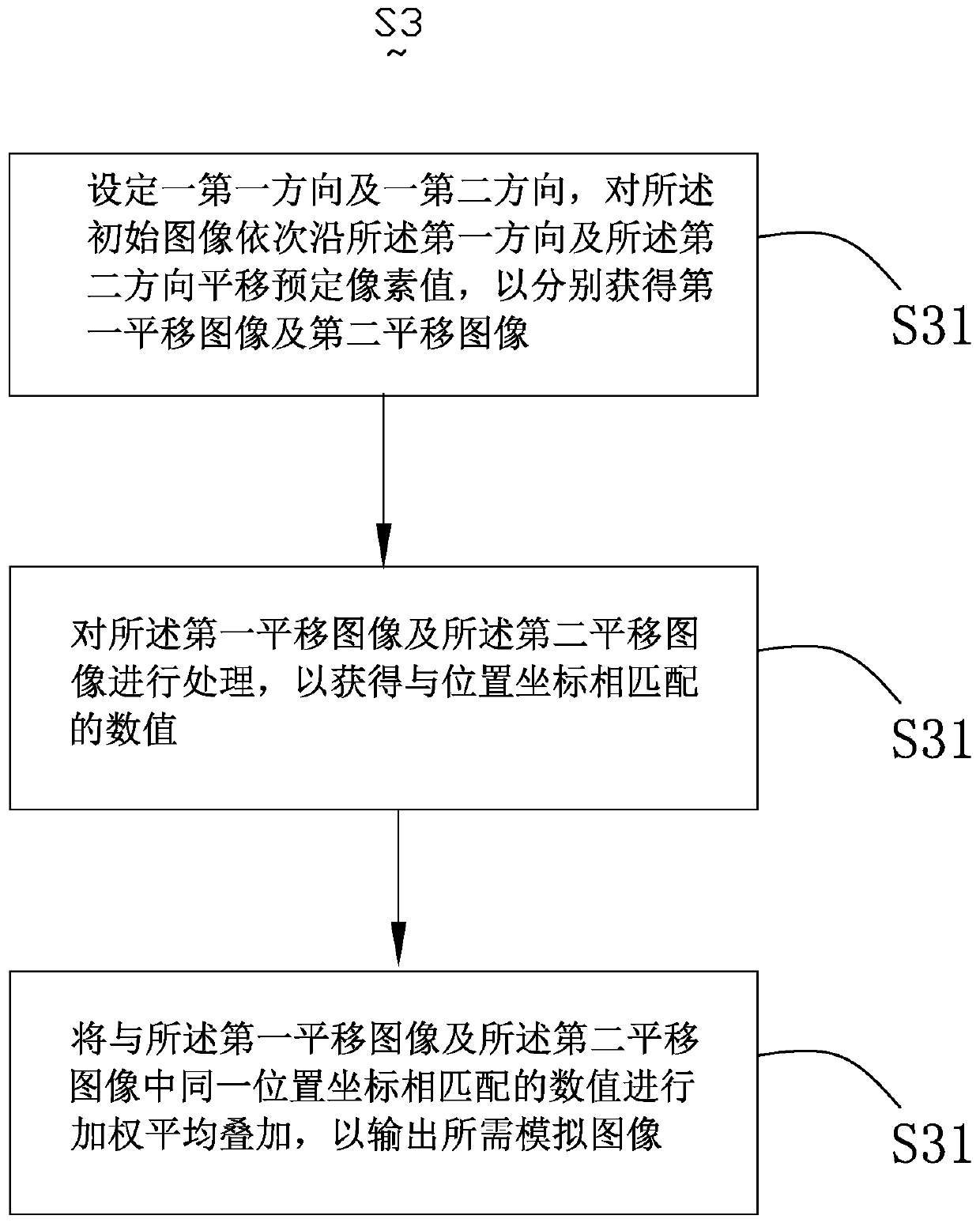
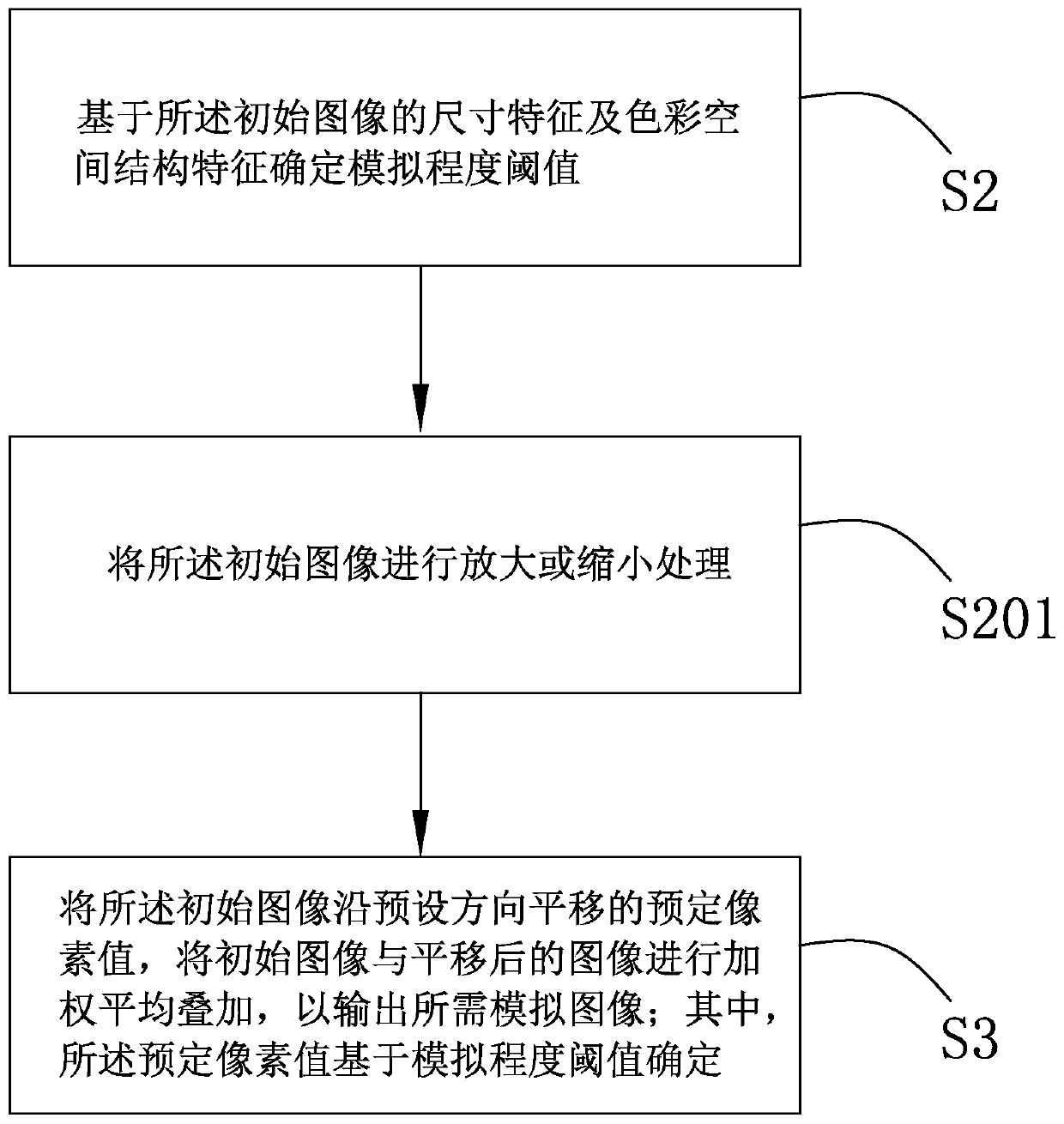
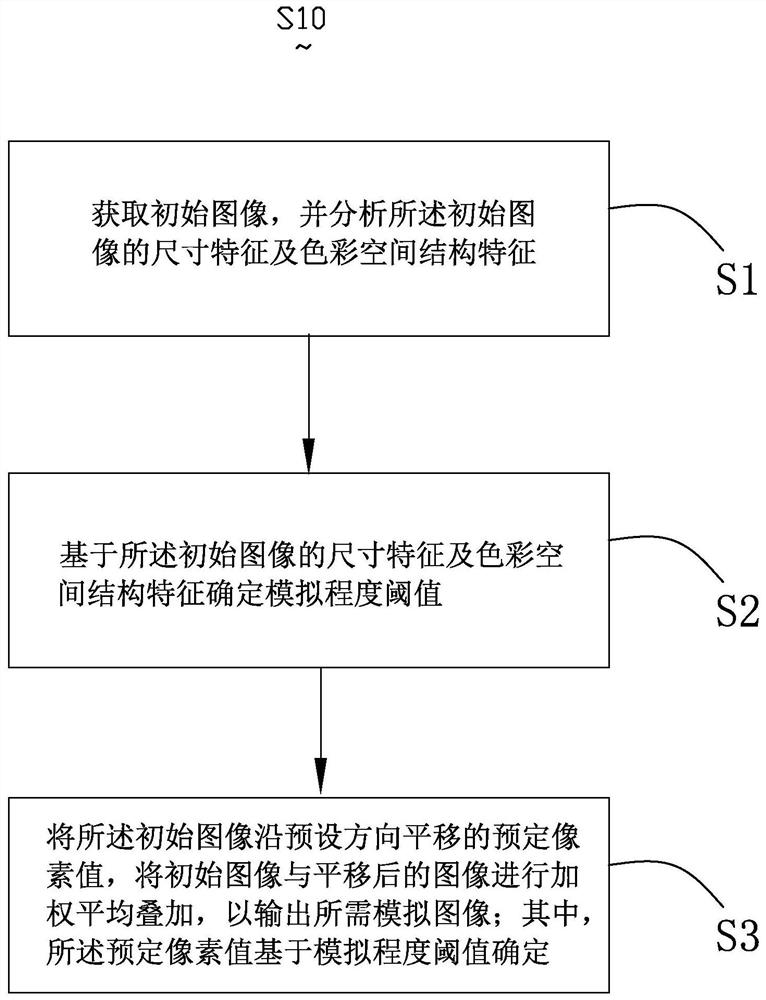
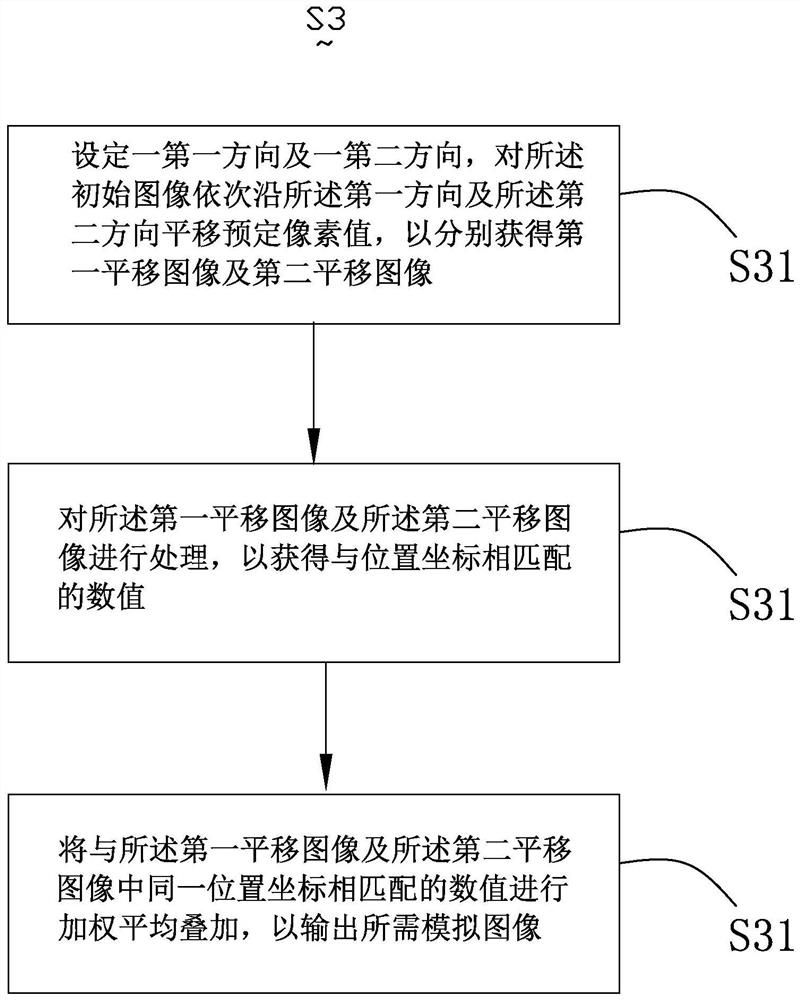
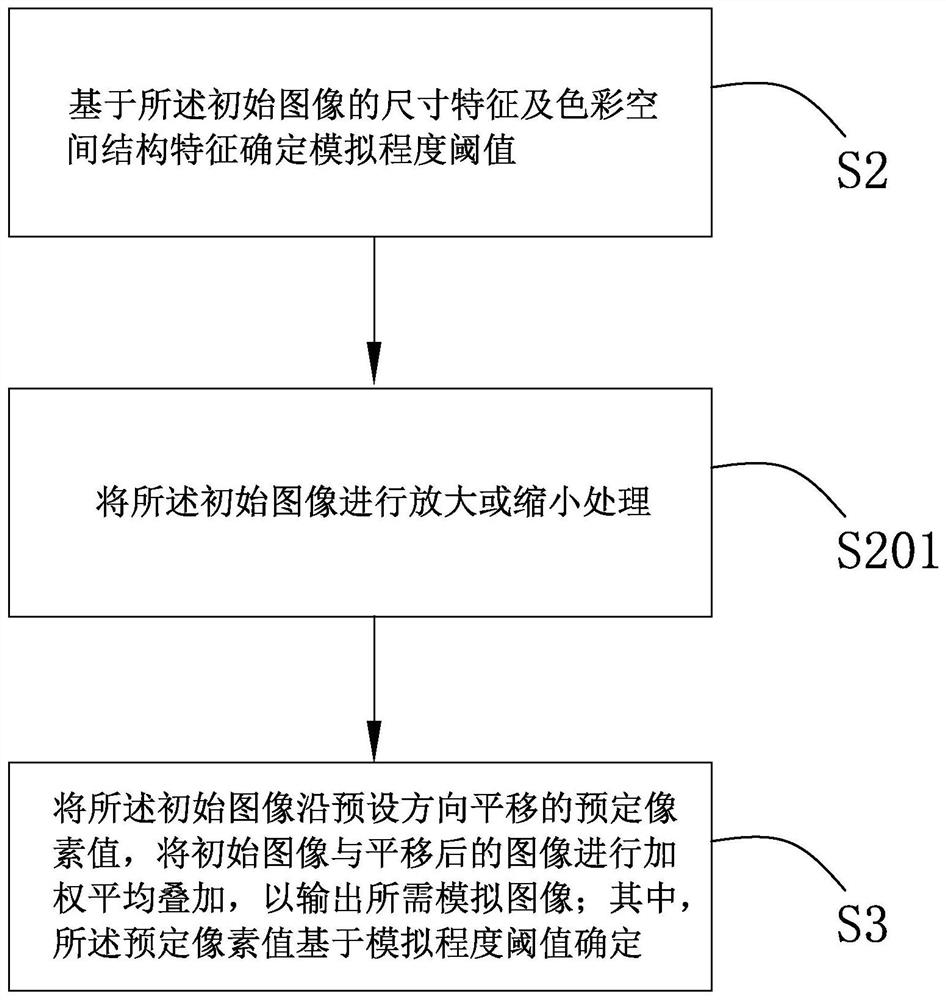
Image simulation generation method and system, deep learning algorithm training method and electronic equipment
ActiveCN110335330AImprove performanceGood Physical Simulation ResultsGeometric image transformationFilling planer surface with attributesPattern recognitionElectron
The invention provides an image simulation generation method. According to the method, a simulation degree threshold value is determined based on preliminary analysis of an initial image. The translation predetermined pixel values of the initial image in at least two directions are determined based on the simulation degree threshold value. The weighted average superposition is performed on the translated images so as to output the required simulation image. By utilizing the method, the technical problem that image aberration and the like caused by lenses, optics, photosensitive elements and the like cannot be effectively simulated by the existing image simulation technology can be solved. The image simulation generation system and the electronic equipment thereof have the same technical effects as the method. Based on the deep learning algorithm training method provided by the invention, the problem that the existing data amplification technology cannot well simulate the generated image into a real sampling image can be solved, and a better training effect can be obtained.
Owner:创新奇智(北京)科技有限公司
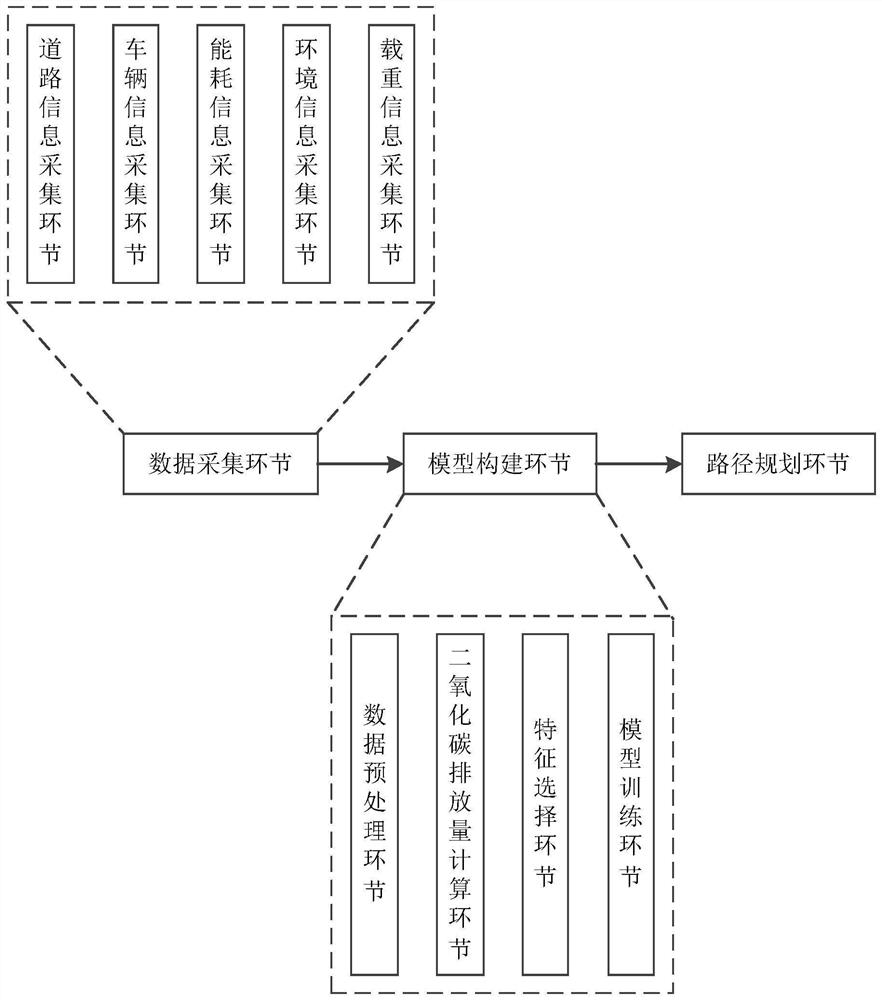
Path planning method based on carbon emission measurement scale
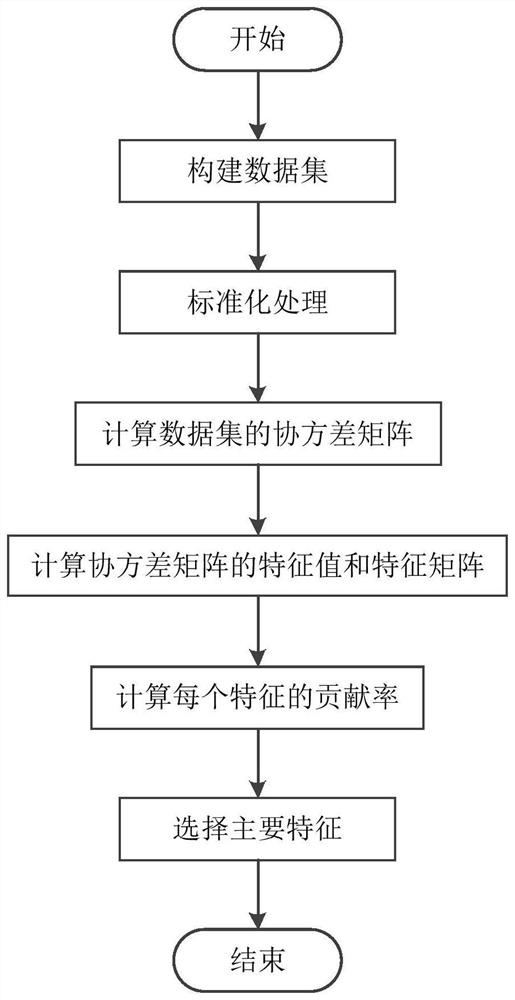
ActiveCN114819305ARealize quantitative evaluationEnrich training dataEnsemble learningForecastingData setPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a path planning method based on a carbon emission measurement scale, and belongs to the technical field of road traffic path planning. According to the method, firstly, multi-dimensional information such as roads, vehicles, energy consumption, environments and loads is collected to construct a data set; according to the IPCC standard, the carbon dioxide emission amount is calculated in combination with the energy consumption information; secondly, calculating the contribution rate of each feature by using a principal component analysis method, and further screening out main features; according to different numbers of the main features, performing multi-model training on the main features by using linear regression, and performing bagging ensemble learning method fusion on a plurality of models; and finally, generating a plurality of driving paths in combination with a map open API, respectively calculating carbon dioxide emissions of different driving paths, and selecting the driving path with the minimum carbon emission to be recommended to the user. The method focuses on realizing the minimization of the carbon emission of the vehicle in the path planning, and finally assists in promoting China to realize the goals of carbon peak reaching and carbon neutralization.
Owner:山东高速云南发展有限公司
Semi-supervised learning pseudo label assignment method based on clustering fusion
PendingCN112418331AFully excavatedEasy to implementCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setData information
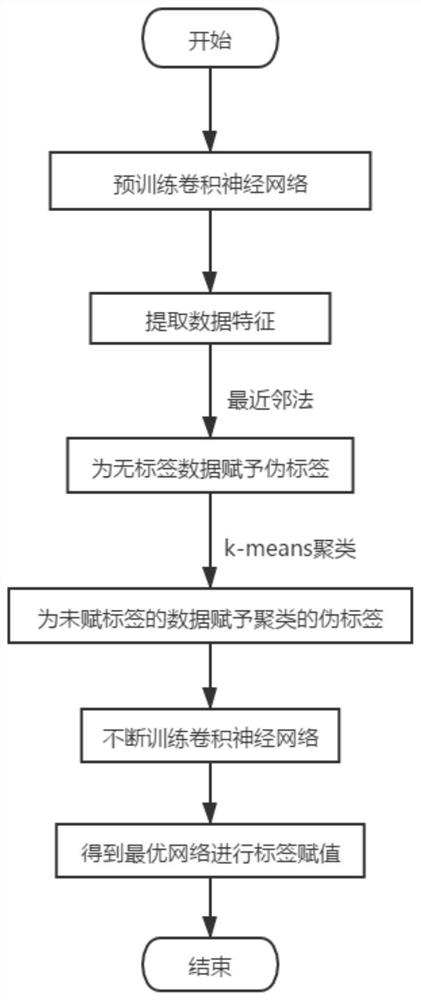
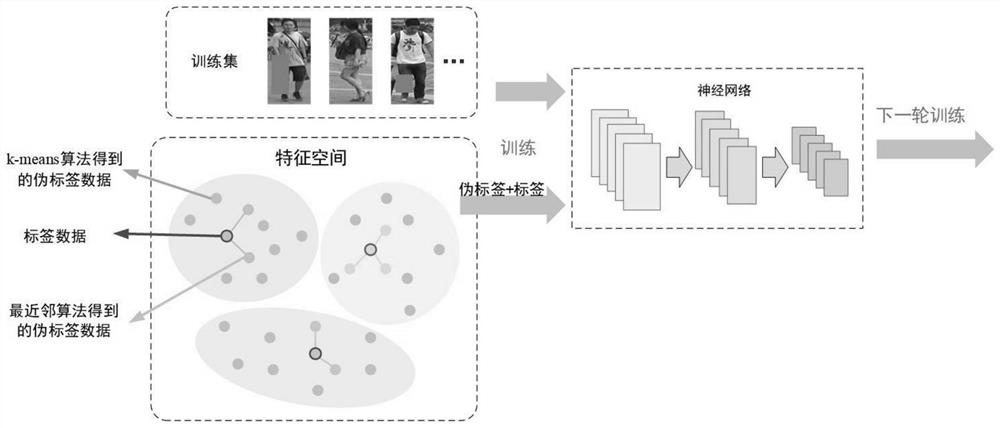
The invention discloses a semi-supervised learning pseudo label assignment method based on clustering fusion, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the semi-supervised learning of a convolutional neural network with a label-free data set, carrying out the pre-training of the neural network through employing labeled data and label-free data, and extracting data features through employinga trained network; assigning pseudo tags to N pieces of untagged data closest to the tagged data by using a nearest neighbor method; analyzing all the data information by using k-means clustering, and endowing clustered pseudo tags to the data which is not tagged; and continuously training the convolutional neural network by using the obtained label data and pseudo label data to obtain an optimalnetwork for label assignment. The method can be suitable for semi-supervised learning under deep learning in various fields; information of label-free data can be fully mined, and training data withricher content are provided for a network; the principle is clear and easy to understand, and codes are easy to implement.
Owner:STATE GRID GASU ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
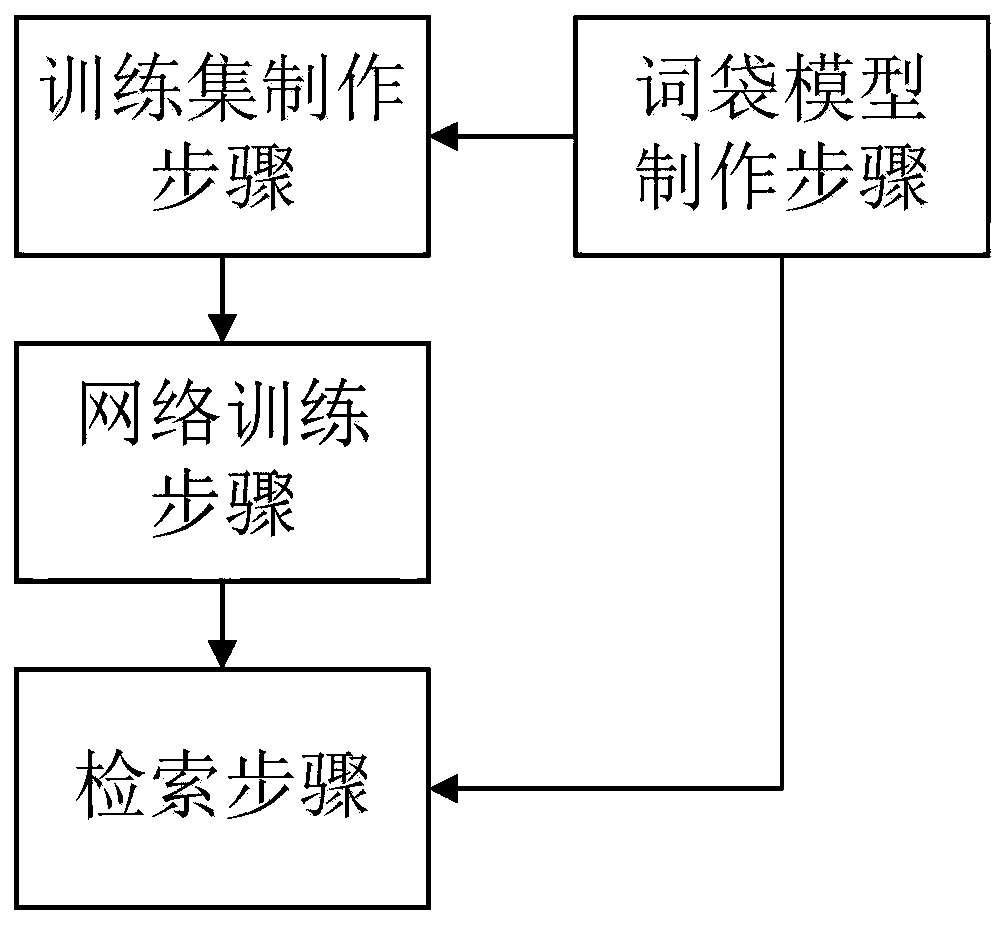
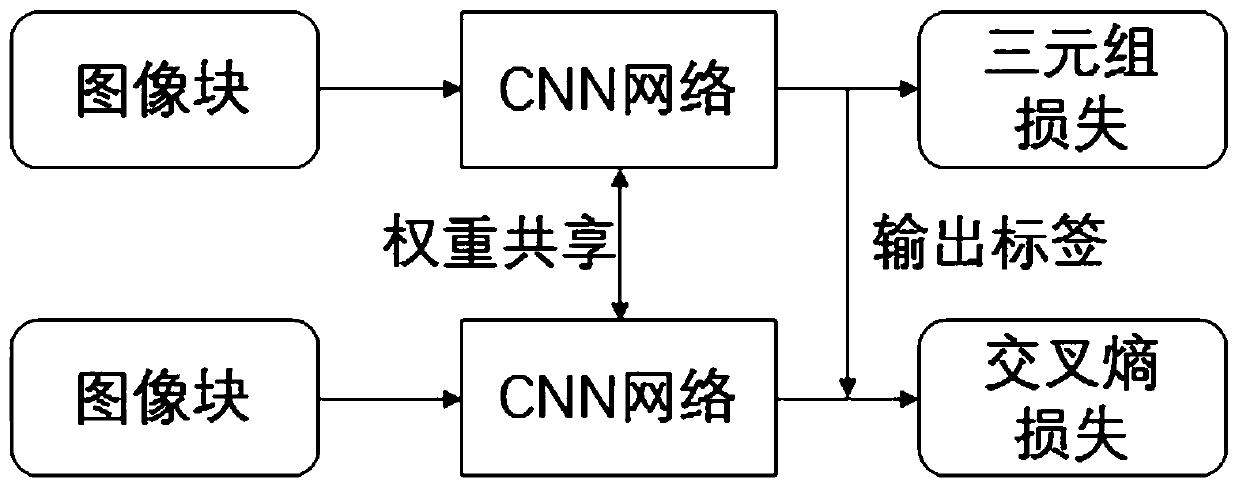
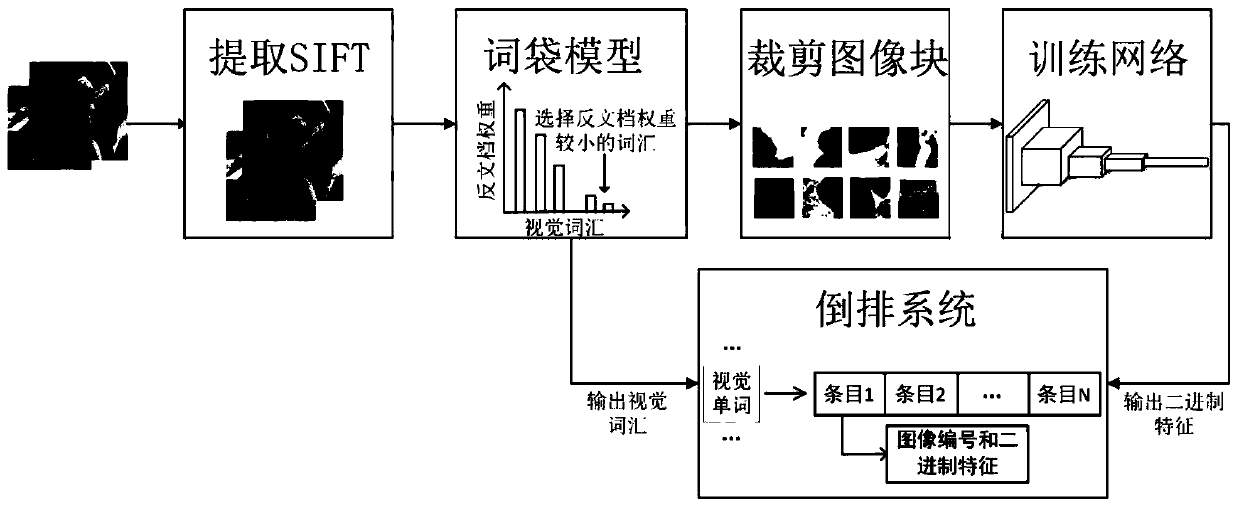
Mass image infringement retrieval method and system and computer readable storage medium thereof
PendingCN110968721AEasy to manufactureEnrich training dataCharacter and pattern recognitionStill image data indexingBag-of-words modelEngineering
The invention provides a massive image infringement retrieval method and system and a computer readable storage medium thereof. The method comprises the steps: S1, generating a bag-of-words model, extracting SIFT feature points of a template image, obtaining visual vocabularies through clustering processing, and establishing the bag-of-words model; s2, making a training set: calculating an inversedocument weight of each visual vocabulary, and positioning SIFT feature points conforming to a preset threshold value to obtain original training data bying correspondingly cutting the template image; s3, training a neural network: training a CNN network by adopting the original training data in the step S2 according to a comprehensive metric learning and hash learning method to generate binary features; and S4, retrieval judgment: constructing an inverted index system by using the bag-of-words model in the step S1, traversing entries corresponding to the visual vocabularies in the to-be-retrieved image, calculating a Hamming distance between binary features, judging whether the binary features are matched or not according to a preset threshold, and giving an infringement coefficient according to accumulated matching. The infringement image retrieval speed is increased, and meanwhile, relatively high accuracy is ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRSTBRAVE INFORMATION TECH
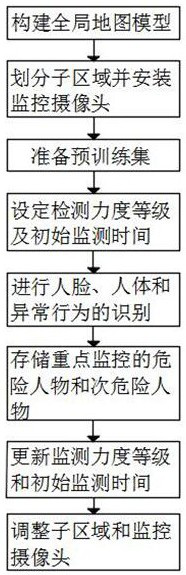
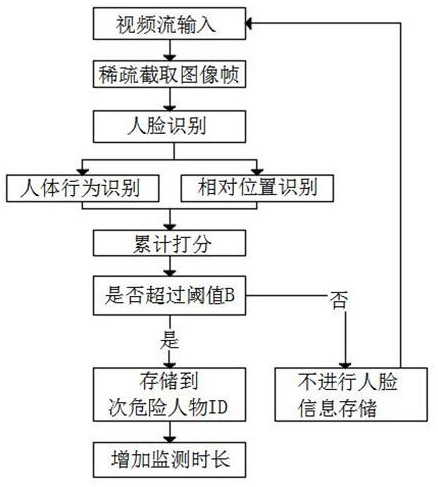
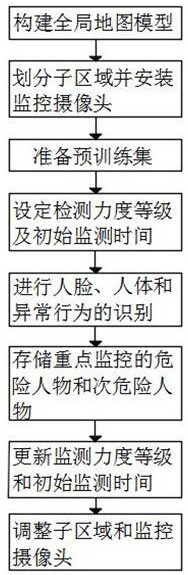
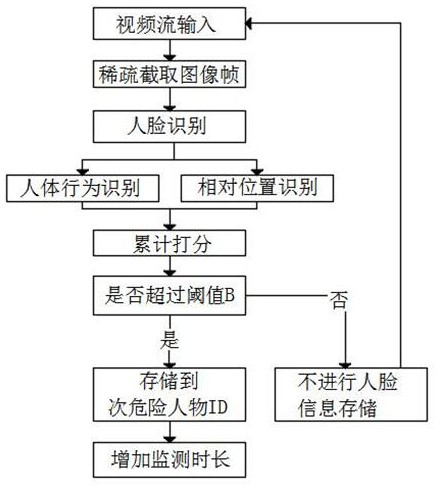
Multi-mode security monitoring method based on deep learning image processing
ActiveCN112733819ASupervision is outstandingReduce overheadCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesReal-time computingDeep learning
The invention provides a multi-mode security monitoring method based on deep learning image processing, and the method comprises the steps: dividing a to-be-monitored scene according to the importance degree, carrying out periodic adjustment according to a subsequent machine learning result, and achieving the application of limited monitoring resources to a place where monitoring is most needed; focusing on content needing to be monitored, screening out people who most possibly appear and need to be monitored by setting the danger ID and the sub-danger ID, performing focusing monitoring on people who most possibly appear and need to be monitored in a place where monitoring is most needed by combining the two operations, and meanwhile, collecting an actual scene needing to be monitored, so as to realize real-time monitoring. And a large amount of external training data is pasted, so that the pre-training set data conforming to the to-be-monitored scene is enriched, and the final recognition precision is improved. Meanwhile, through the result after training, the area where the abnormal behavior is most likely to be sent can be adjusted and supervised. The video online monitoring with the maximum efficiency is achieved with low equipment cost and expenditure.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV
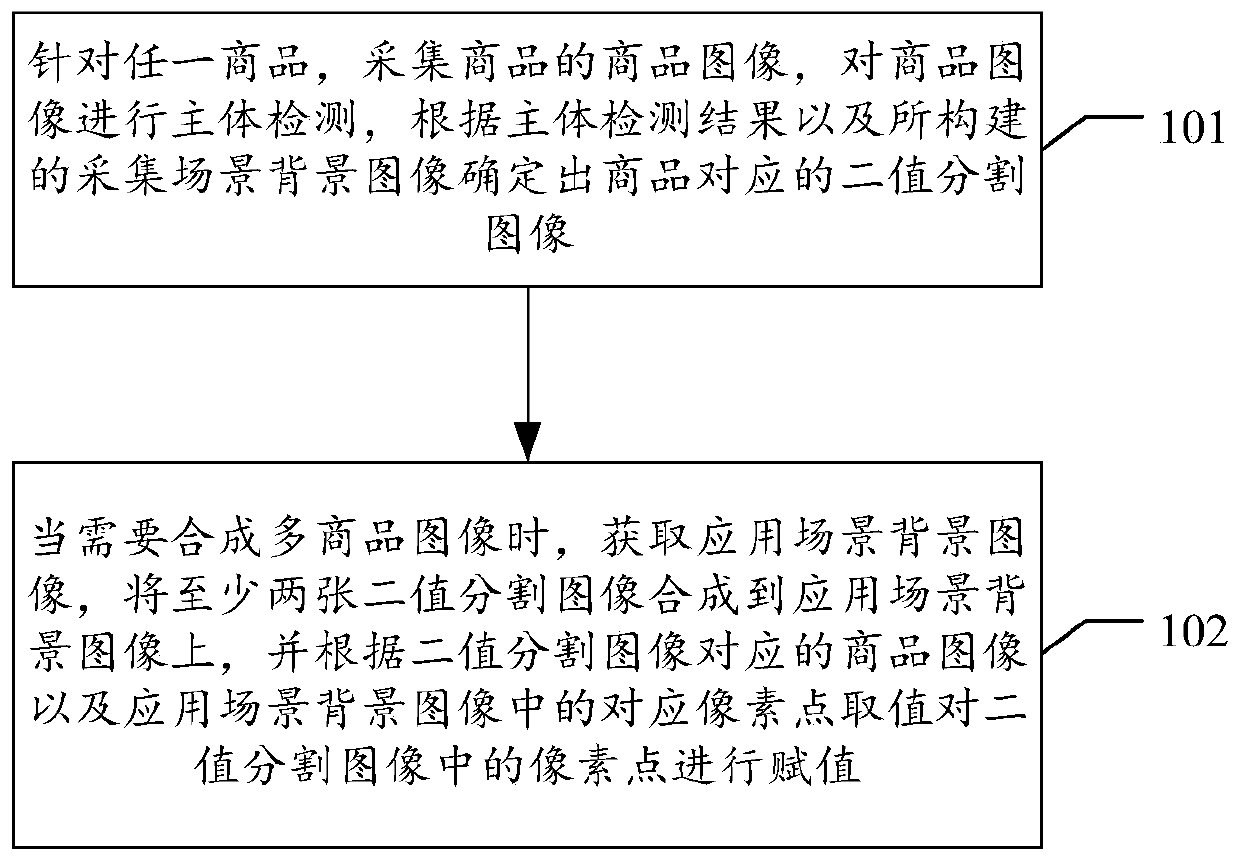
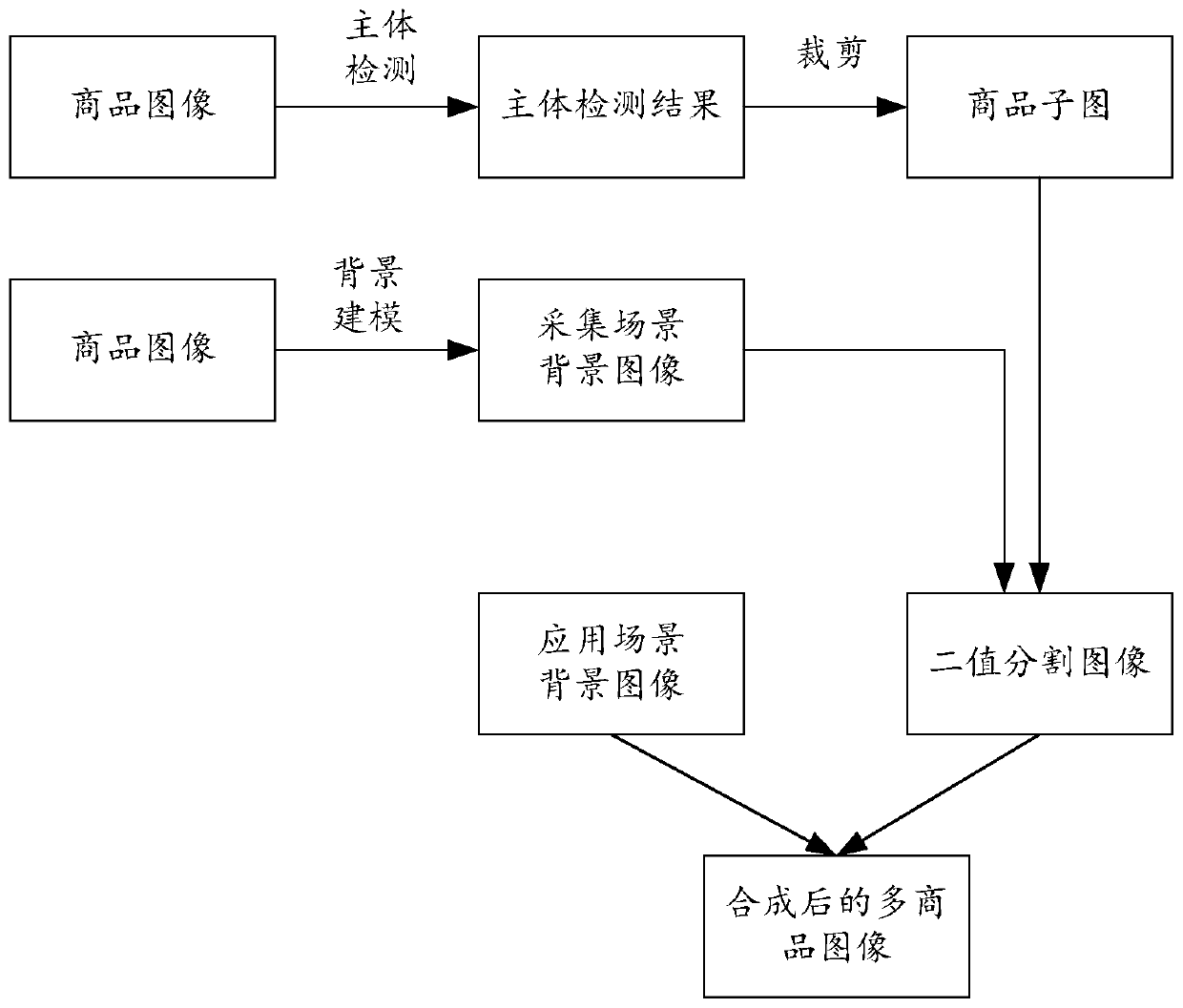
Multi-commodity image synthesis method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN110992297AReduce labor costsImprove processing efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Engineering
The invention discloses a multi-commodity image synthesis method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method relates to the field of deep learning, and can comprise the steps: collecting a commodity image of a commodity for any commodity, carrying out the main body detection of the commodity image, and determining a binary segmentation image corresponding to the commodity according to a main body detection result and a constructed collection scene background image; and when a multi-commodity image needs to be synthesized, obtaining an application scene background image, synthesizing the at least two binary segmentation images to the application scene background image, and performing assignment on pixel points in the binary segmentation images according to the commodity images corresponding to the binary segmentation images and corresponding pixel point values in the application scene background image. By applying the scheme of the invention, the labor cost can besaved, and the processing efficiency can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
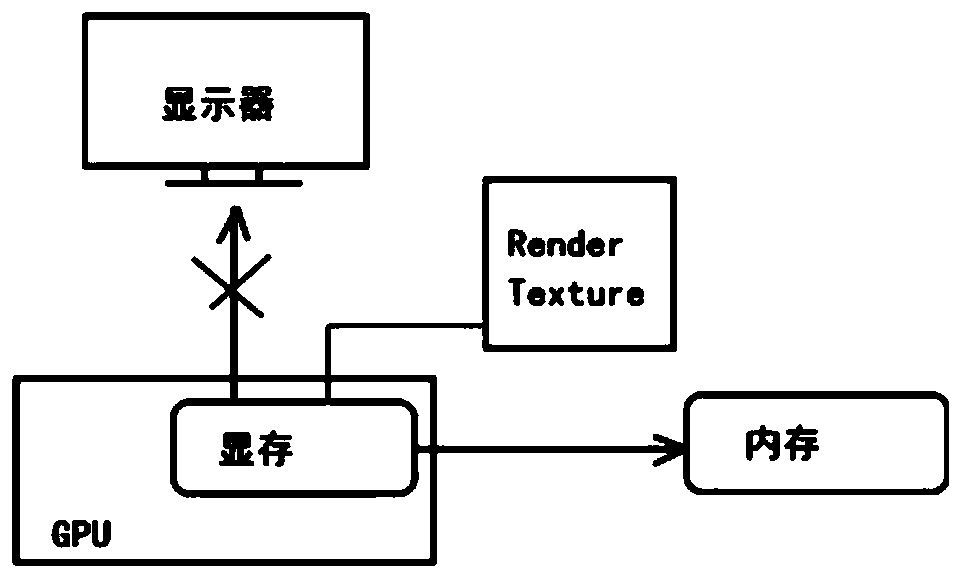
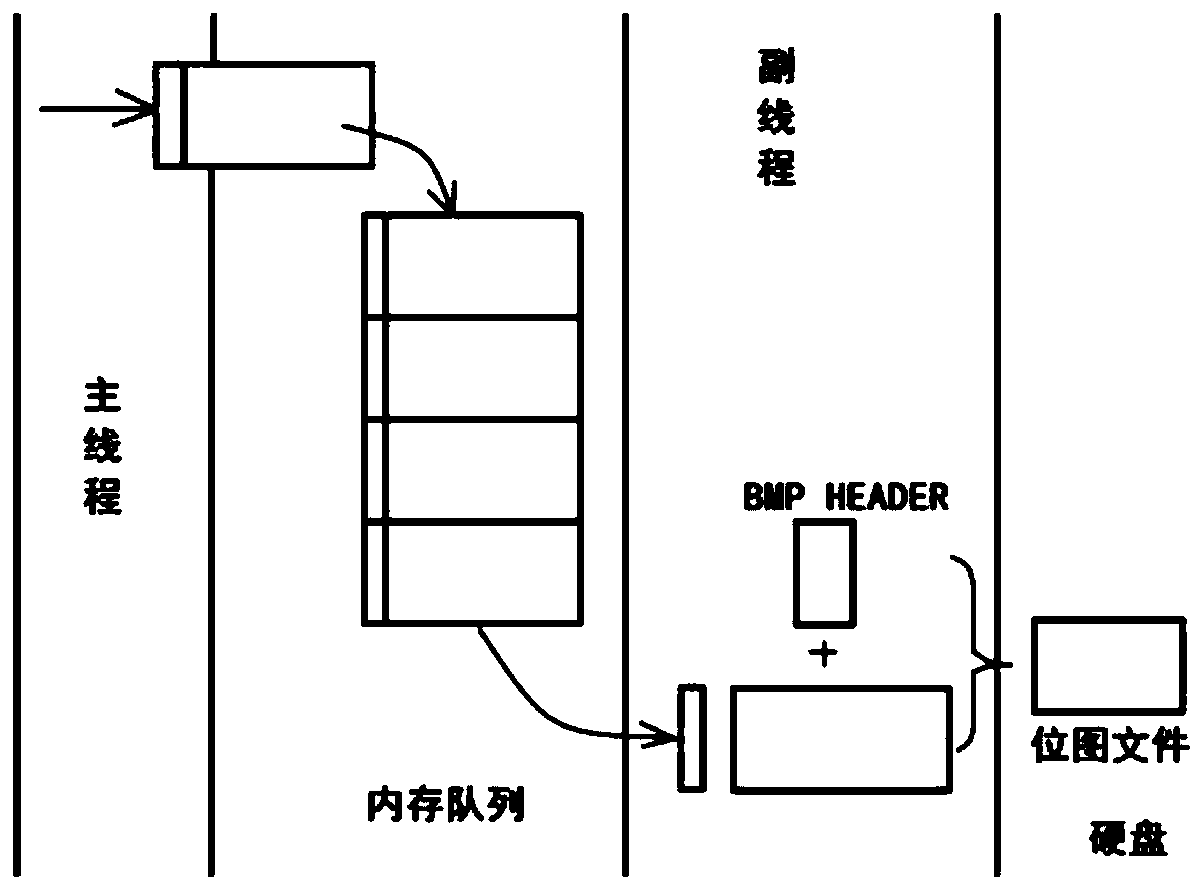
Rapid image storage method and system suitable for autonomous driving simulation platform
PendingCN110012252AImprove versatilityEnrich training dataStill image data retrievalTelevision system detailsVideo memoryComputer memory
The invention discloses a rapid image storage method and system suitable for an autonomous driving simulation platform. The rapid image storage method comprises the steps that an image stored in a video memory is directly sent into a computer memory; according to the invention, high-speed lossless screenshot can be realized on the autonomous driving simulation platform, the universality of the autonomous driving simulation platform is improved, and more and more accurate training data can be provided for deep learning algorithm development.
Owner:北京奥特贝睿科技有限公司
Pedestrian re-identification network training method based on branch learning and layered pseudo label
ActiveCN113609927AFully excavatedEnrich training dataCharacter and pattern recognitionData setEngineering
The invention relates to a pedestrian re-identification network training method based on branch learning and layered pseudo labels, wherein a pedestrian re-identification network is a mutual average teaching network. The training method comprises the following steps: obtaining a label data set and a label-free data set, taking the label data set as one layer, dividing the label-free data set into N layers, and assigning the pseudo label to the label-free data of each layer to form N layers of pseudo label data, wherein N is a constant; constructing a branch learning framework comprising N+1 mutual mean-teaching network branches sharing weights, wherein one branch is used for inputting label data for training, and the N layers of pseudo label data are correspondingly input into the other N branches for training; and constructing a loss function of each branch, determining a total loss function of the branch learning framework, performing multiple rounds of training based on the total loss function, and re-layering the label-free data set in each round of training process. Compared with the prior art, the network trained by the invention is more accurate, and the convergence speed of the network during training is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
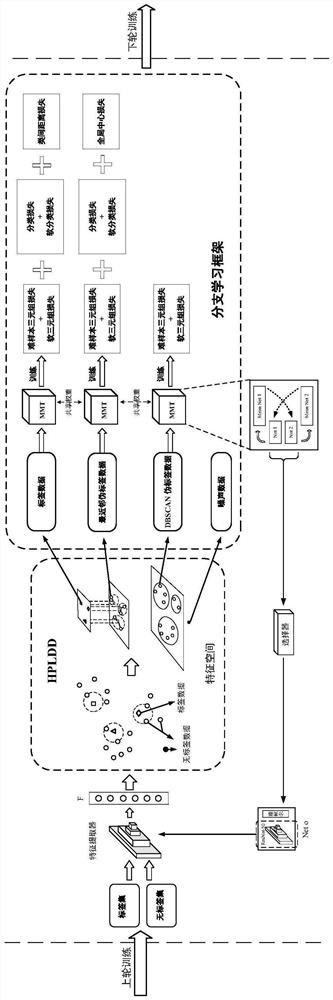
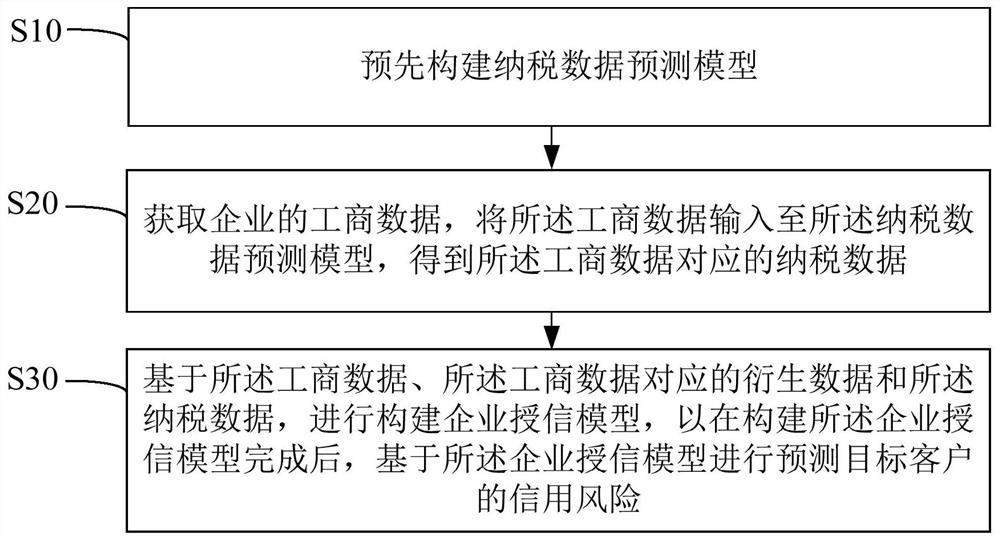
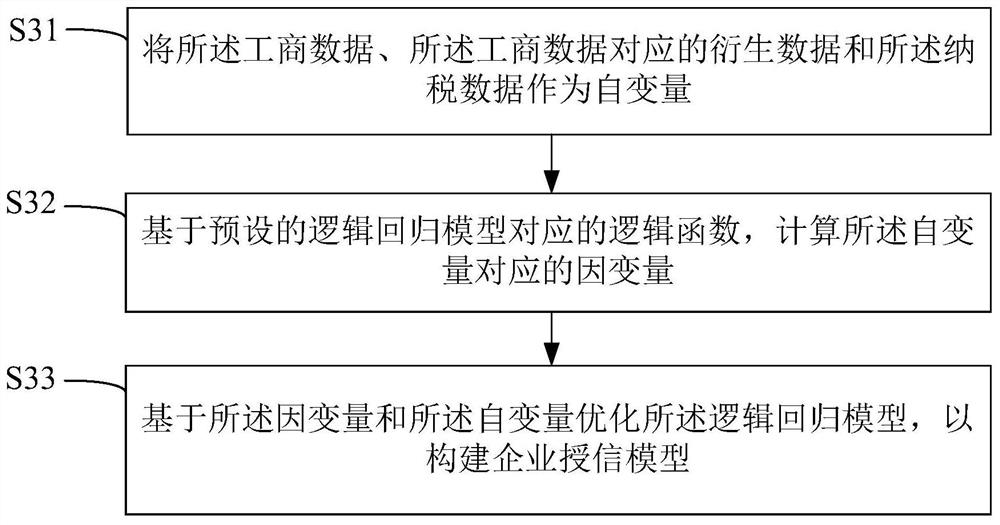
Enterprise credit extension model construction method, apparatus and device, and readable storage medium
PendingCN112529679AEnrich training dataComprehensive assessmentFinanceForecastingData predictionData input
The invention discloses a enterprise credit extension model construction method, device and equipment and a readable storage medium. The construction method comprises the following steps: constructinga tax payment data prediction model in advance; obtaining industrial and commercial data of an enterprise, and inputting the industrial and commercial data into the tax payment data prediction modelto obtain tax payment data corresponding to the industrial and commercial data; and based on the industrial and commercial data, the derivative data corresponding to the industrial and commercial dataand the tax payment data, constructing an enterprise credit extension model, so as to predict the credit risk of the target customer based on the enterprise credit extension model after the enterprise credit extension model is constructed. According to the invention, the credit risk of the enterprise can be assessed more comprehensively, so that the result of predicting the credit risk of the target customer is more reliable, and the technical problem that the risk level of the enterprise cannot be assessed comprehensively and multi-dimensionally by the existing enterprise credit scoring technology is solved.
Owner:WEBANK (CHINA)
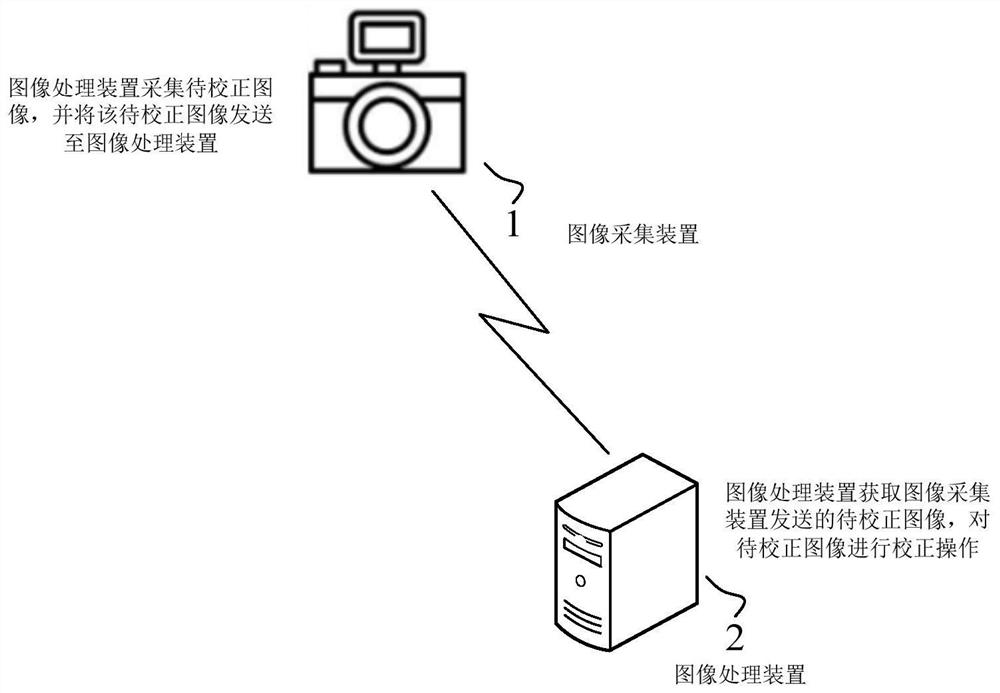
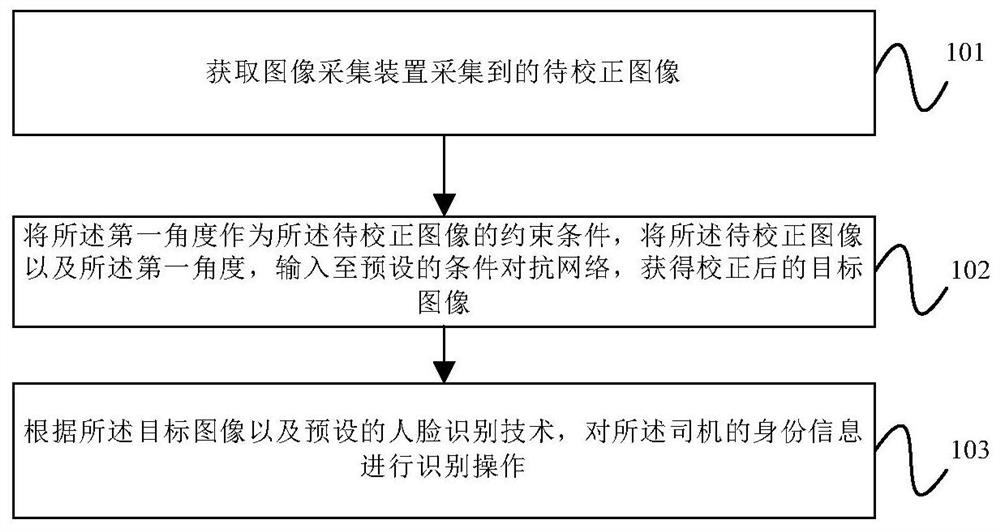
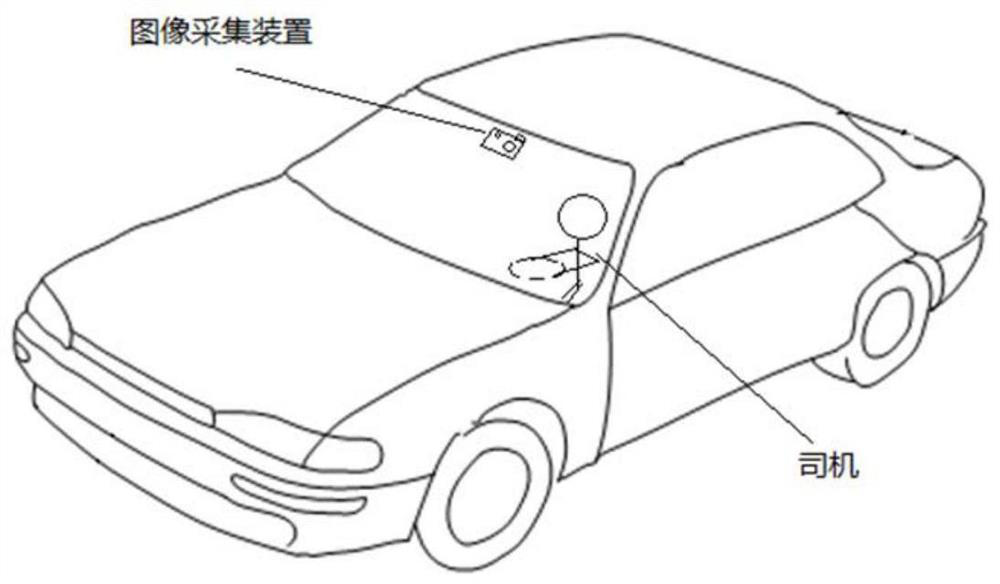
Image processing method, device and equipment and computer readable storage medium
PendingCN111860093AEnrich training dataCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesEngineeringComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides an image processing method, device and equipment and a computer readable storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a to-be-corrected image collected by an image collection device, wherein the to-be-corrected image is a driver face image with a face rotating by a preset first angle, and the first angle is determined according to an included angle between the image collection device and a driver; taking the first angle as a constraint condition of the to-be-corrected image, and inputting the to-be-corrected image and the first angle into a preset conditional adversarial network to obtain a corrected target image, the target image being a front face image of the driver; and according to the target image and a preset face recognition technology, carrying out recognition operation on the identity information of the driver. Different from the existing technical scheme of labeling the face feature information in the image, the first angle is used asthe constraint condition, and the training data is relatively rich. In the process of face recognition based on a target image, the target image is the front face image of a driver, so that the recognition precision is improved.
Owner:BEIJING DIDI INFINITY TECH & DEV
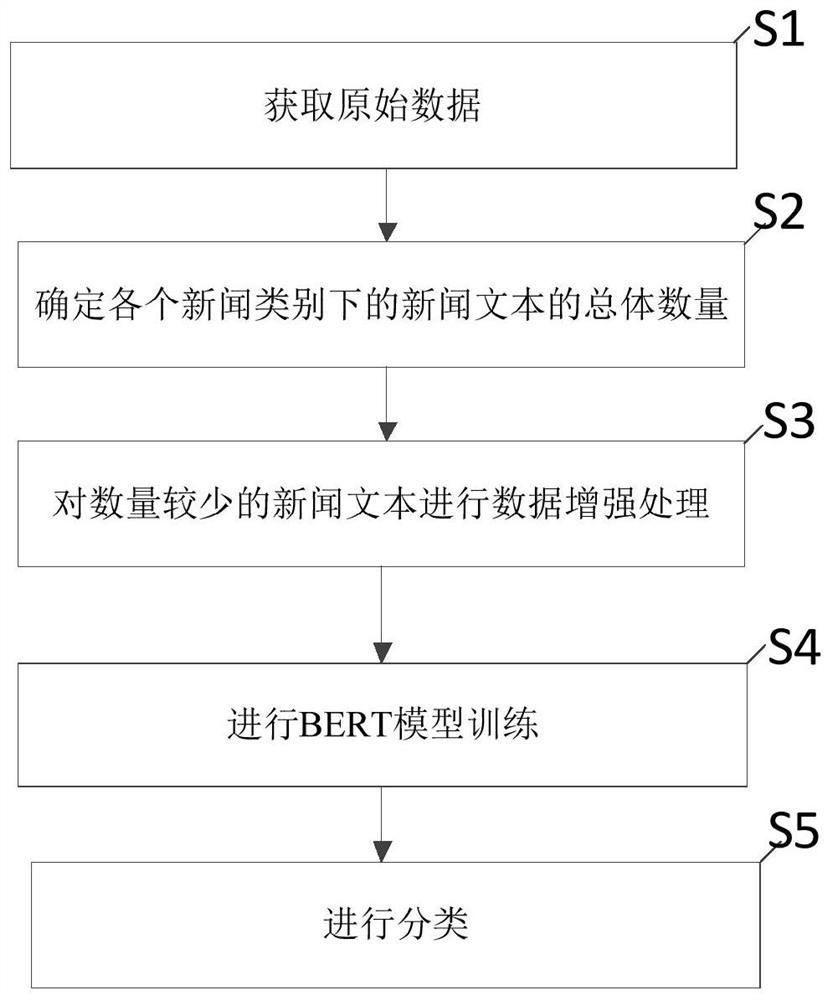
News classification method and computer readable storage medium
PendingCN112131384AHigh precisionEnrich training dataNeural learning methodsSpecial data processing applicationsOriginal dataClassification methods
The invention discloses a news classification method and a computer readable storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining original data which comprises a news text and a news category; determining the total number of news texts under each news category; when the total number of the news texts under a certain news category is smaller than a preset threshold value, carrying out dataenhancement processing on the news texts under the news category, so that the total number of the processed news texts under the news category is not smaller than the preset threshold value; and respectively screening out news texts with the same number as the preset threshold from all news texts under each news category as training data, and inputting the news texts into a BERT model for training. According to the news classification method and the computer readable storage medium, the classification accuracy can be improved.
Owner:科航(苏州)信息科技有限公司
A multi-modal security monitoring method based on deep learning image processing
ActiveCN112733819BSupervision is outstandingReduce overheadCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesImaging processingImage manipulation
The present invention proposes a multi-mode security monitoring method based on deep learning image processing, which divides the scenes that need to be monitored according to the degree of importance, and regularly adjusts them according to the follow-up machine learning results, so as to realize the application of limited monitoring resources in the most needed monitoring At the same time, focus on the content that needs to be monitored. By setting the dangerous ID and the sub-dangerous ID, the people who are most likely to be monitored will be screened out. Focus on the people who need to be monitored the most. At the same time, by collecting the actual scenes that need to be monitored and pasting a large amount of external training data, the data of the pre-training set that meets the scenes to be monitored is enriched, thereby improving the accuracy of the final recognition. At the same time, through the training results, it is also possible to adjust and supervise the areas most likely to send abnormal behavior. Realize video online monitoring with lower equipment cost and overhead to achieve maximum efficiency.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV
Power transmission line image augmentation method and system based on improved DCGAN
InactiveCN113673670ARich image informationHelp generateCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setAlgorithm
The invention provides a power transmission line image augmentation method and system based on an improved DCGAN. The method comprises the steps of collecting original defect image sample data of a power transmission line; improving the structure of the DCGAN network model, and obtaining the DCGAN network model with the improved structure; preprocessing the original defect image sample data by using a DCGAN network model with an improved structure to obtain a training set; training the DCGAN network model with the improved structure until a generator G and a discriminator D reach Nash equilibrium; and generating the augmented data by using the generator G. According to the invention, the original data is preprocessed by using the augmentation function, so that more training data can be provided for DCGAN training, a network can learn more comprehensive data set features, and a more effective data set is generated.
Owner:广西电网有限责任公司河池供电局
Image simulation generation method and system thereof, deep learning algorithm training method and electronic equipment
ActiveCN110335330BImprove performanceGood Physical Simulation ResultsGeometric image transformationFilling planer surface with attributesAlgorithmEngineering
Owner:创新奇智(北京)科技有限公司
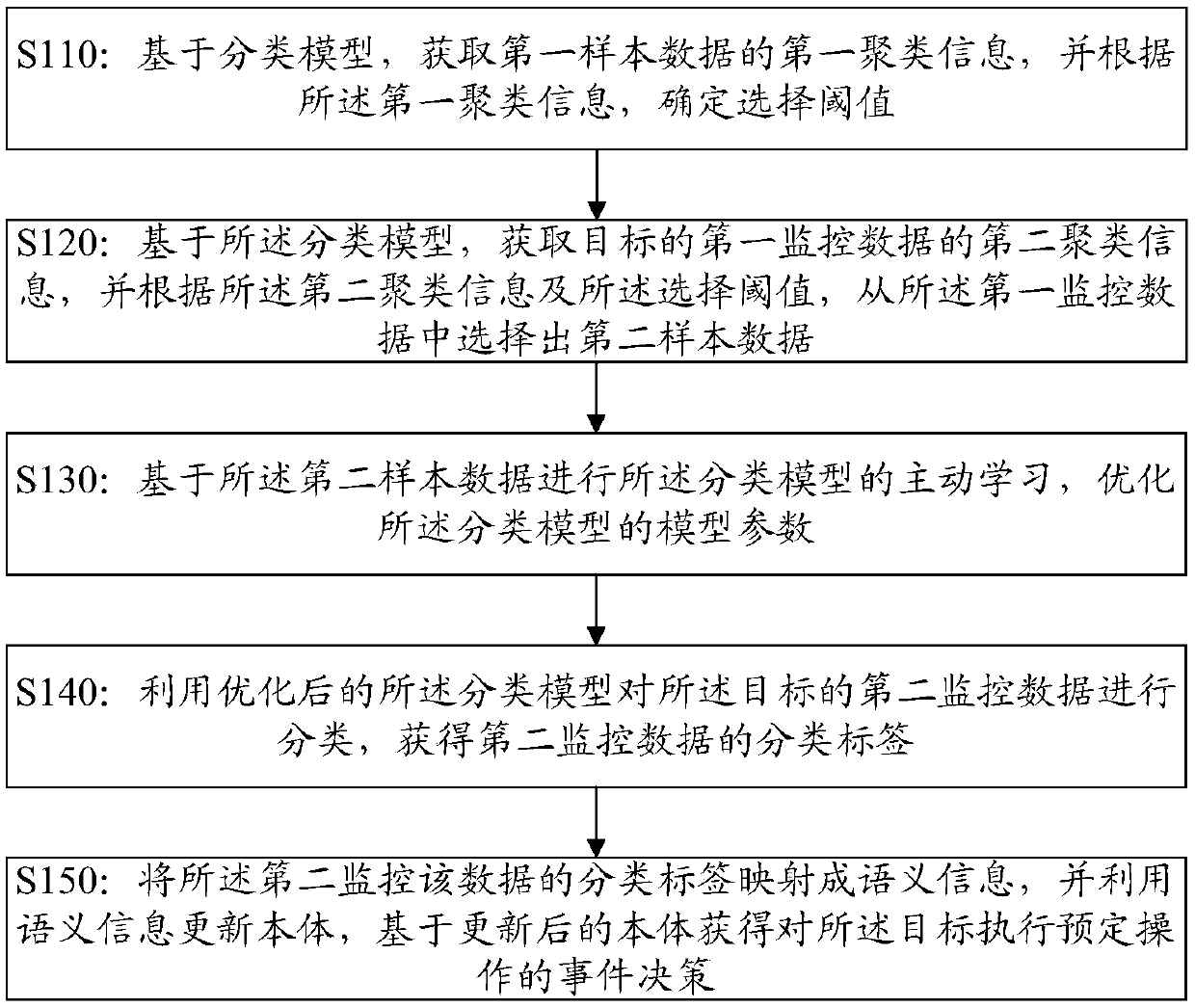
Data processing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
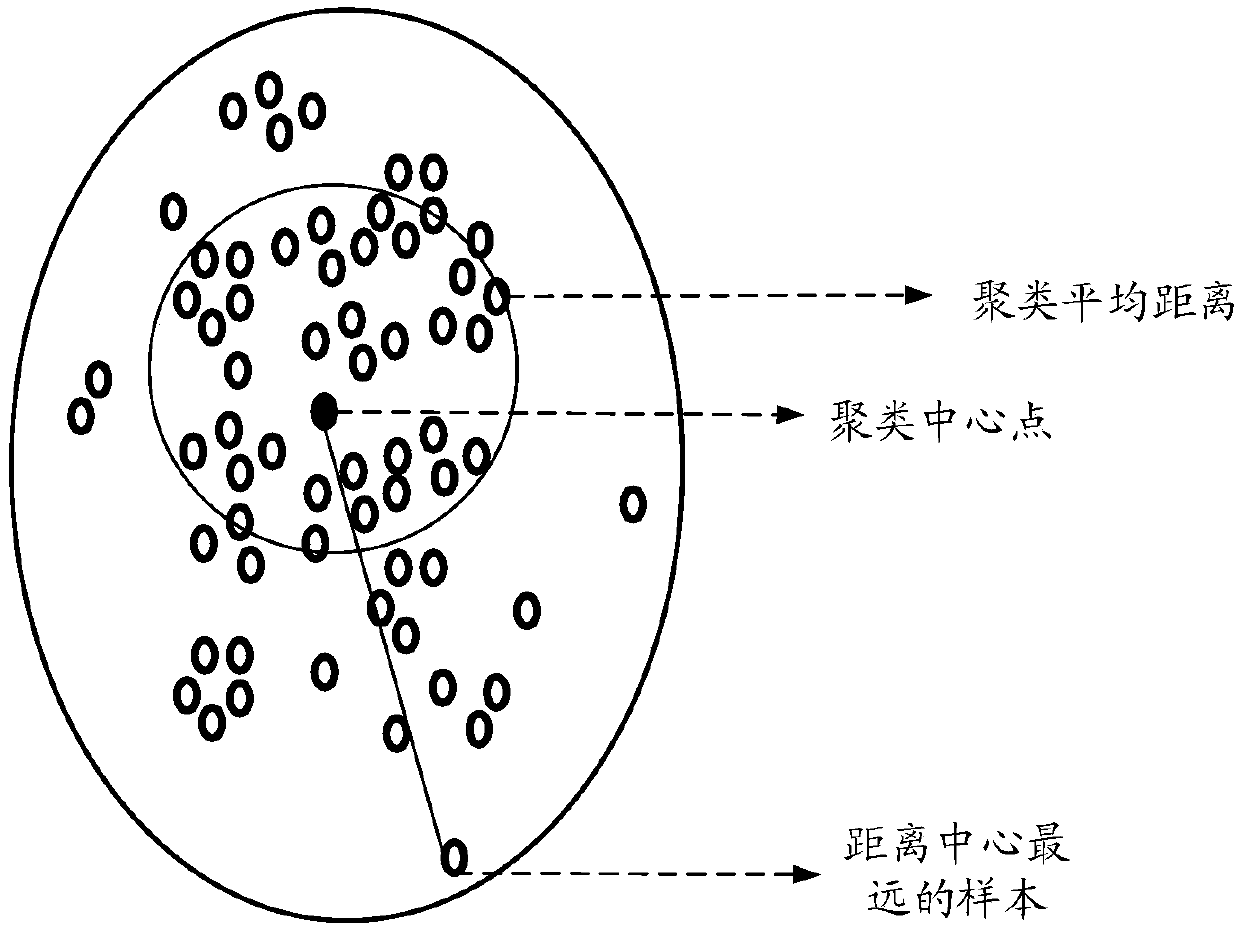
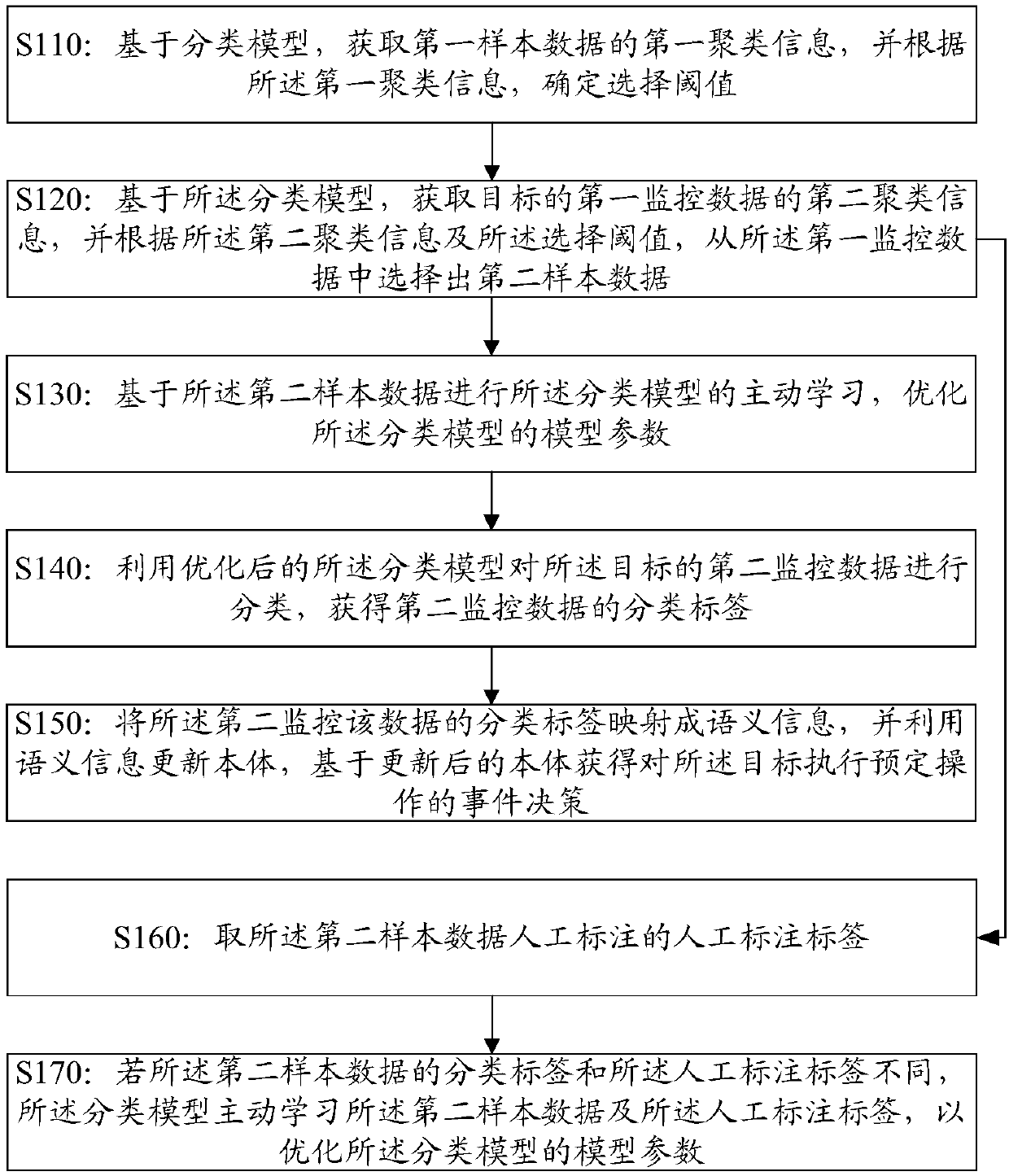
ActiveCN111090707AEnrich training dataReduce the phenomenon of inaccurate classificationDatabase modelsEngineeringData mining
The invention discloses a data processing method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method further comprises the steps of obtaining first clustering information of first sampledata based on a classification model, and determining a selection threshold value according to the first clustering information; acquiring second clustering information of first monitoring data of atarget based on the classification model, and selecting second sample data from the first monitoring data according to the second clustering information and the selection threshold; performing activelearning of the classification model based on the second sample data, and optimizing model parameters of the classification model; classifying the second monitoring data of the target by using the optimized classification model to obtain a classification label of the second monitoring data; and mapping the classification label of the second monitoring data into semantic information, updating the ontology by utilizing the semantic information, and obtaining an event decision for executing a predetermined operation on the target based on the updated ontology.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM LTD RES INST +1
Training method of recommendation model, recommendation method and computer-readable storage medium
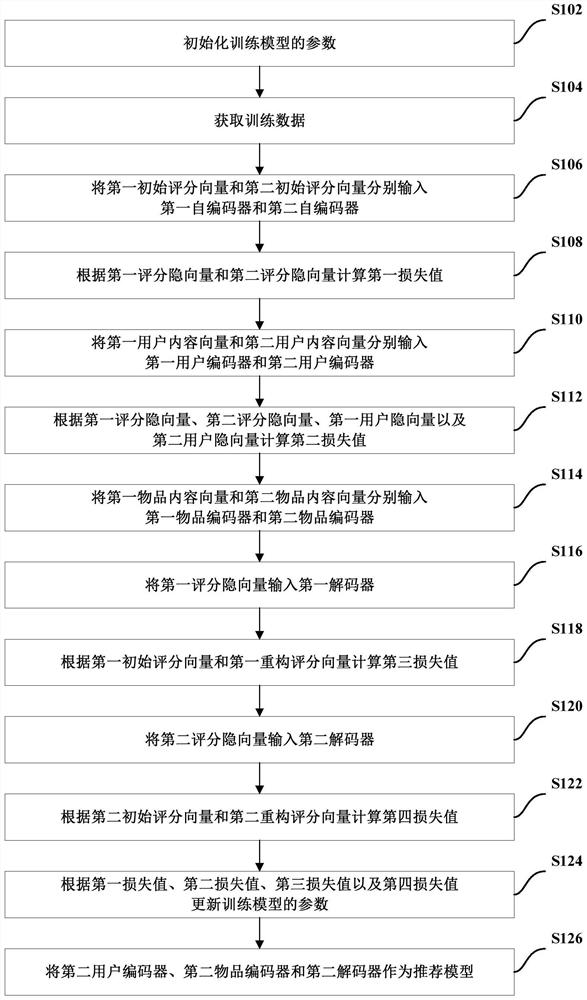
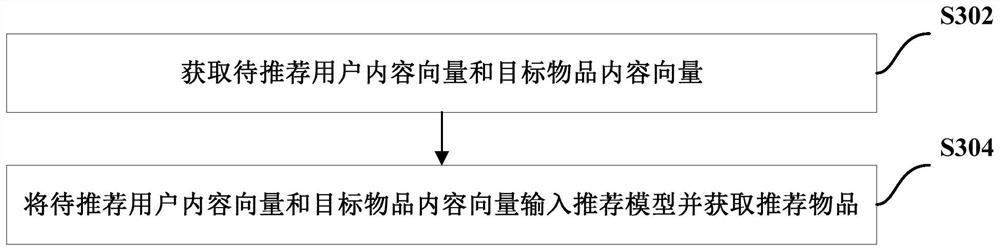
ActiveCN113935477BImprove recommendation effectAlleviate the sparsity problemNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsData packRecommendation model
The present invention provides a training method for a recommendation model, comprising: initializing parameters of the training model, wherein the training model includes a first self-encoder, a first item encoder, a first user encoder, a first decoder, a second The self-encoder, the second item encoder, the second user encoder and the second decoder; obtain training data, wherein the training data includes the first initial score vector of the source domain, the first user content vector, and the first item content vector and the second initial scoring vector, the second user content vector, and the second item content vector of the target domain; the training model is trained according to the training data, and the second user encoder, the second item encoder and the second decoder are used as recommendation Model. The technical scheme of the present invention effectively solves the data sparse problem and the cold start problem.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINIEYE INNOVATION TECH CO LTD
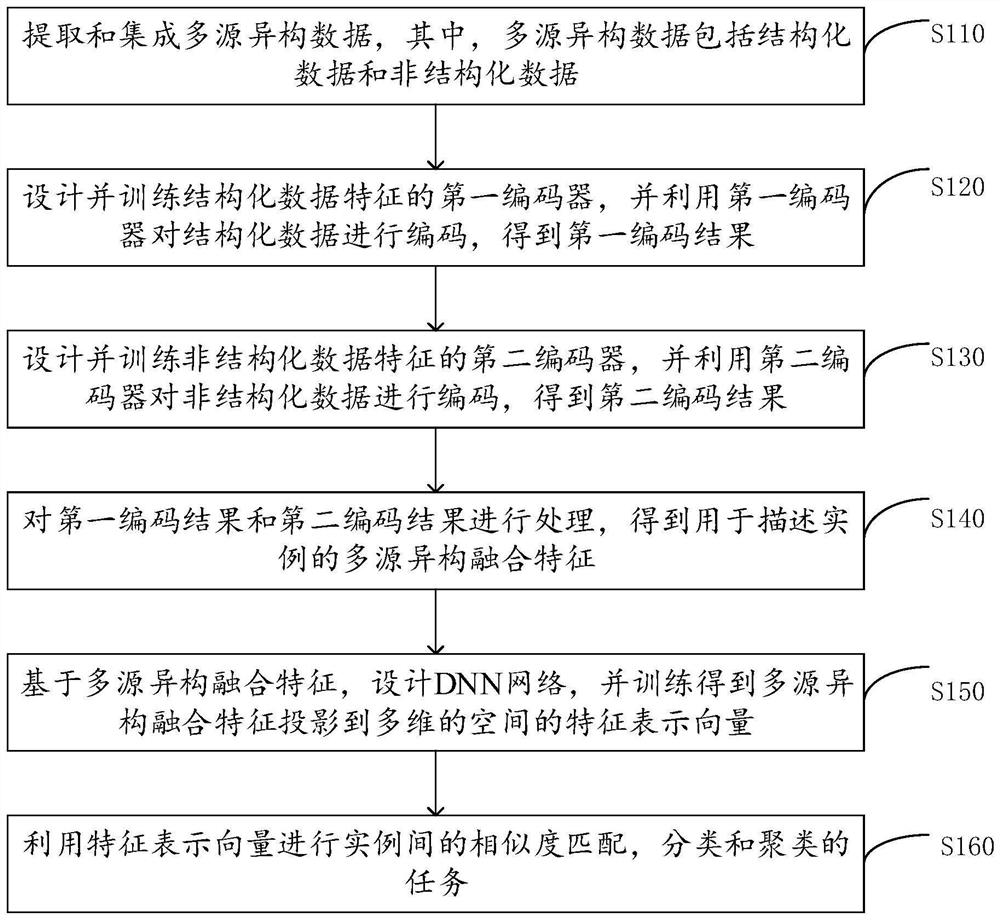
Unsupervised representation learning method and device based on multi-source heterogeneous features
ActiveCN114219084AImprove performanceExcellent effectCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesNetwork structureUnstructured data
The invention discloses an unsupervised representation learning method and device based on multi-source heterogeneous features, and the method comprises the steps: extracting and integrating multi-source heterogeneous data, designing and training a first encoder of structured data features, and carrying out the coding of the structured data through the first encoder, and obtaining a first coding result; designing and training a second encoder with unstructured data features, and encoding the unstructured data by using the second encoder to obtain a second encoding result; processing the first coding result and the second coding result to obtain a multi-source heterogeneous fusion feature for describing the instance; designing a DNN network based on the multi-source heterogeneous fusion features, and training to obtain feature representation vectors of the multi-source heterogeneous fusion features projected to a multi-dimensional space; and performing the tasks of similarity matching, classification and clustering among the instances by using the feature representation vectors. On the basis of an unsupervised condition, discriminative representation learning of an instance level is realized; and more training data and a better network structure are provided.
Owner:GUANGZHOU XUANWU WIRELESS TECH CO LTD
Image processing method and device and storage medium
PendingCN112750427ADoes not cause missingNo change in quantitySpeech recognitionPattern recognitionTime domain
The embodiment of the invention provides an image processing method and device and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a first image which comprises at least one time domain feature and at least one frequency domain feature and is obtained according to first voice data to be processed, and updating the first image according to a preset strategy to obtain a second image, wherein the preset strategy at least comprises one of the following items: transforming a time domain position of at least one time domain feature on a time domain, or transforming the frequency domain position of at least one frequency domain feature on the frequency domain. According to the scheme, rich and diversified training data can be provided for the training model, so that the training effect is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV +1
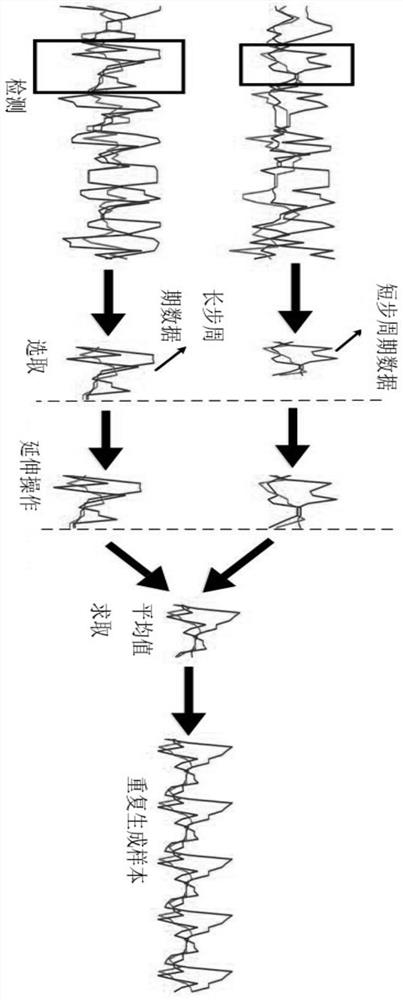
A Physical Layer Authentication Method Based on Exponential Average Data Augmentation
ActiveCN110944002BEnrich training dataImprove accuracyBiological neural network modelsData switching networksData setPhysical layer
The invention discloses a physical layer authentication method based on exponential average data enhancement. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a channel information data set of akth known node; constructing a new pseudo-channel information sample by adopting an exponential average data enhancement method; repeating the previous step to obtain a plurality of new pseudo-channel information samples; adding the plurality of obtained pseudo-channel information samples into an input sample set; constructing a label matrix as an output sample set for the input sample set afteraverage data enhancement, and then constructing a new channel information data set; repeating all the steps to obtain a training data set of Q known nodes, and adding the training data set into a total training data set; and training a classifier model by using the total training data set to complete physical layer authentication of the unknown node. According to the method, the new channel information sample is constructed from the directly extracted channel information by using an exponential weighted average method, so that more training data is obtained, enough channel information samplescan be obtained, and the authentication accuracy is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU +1
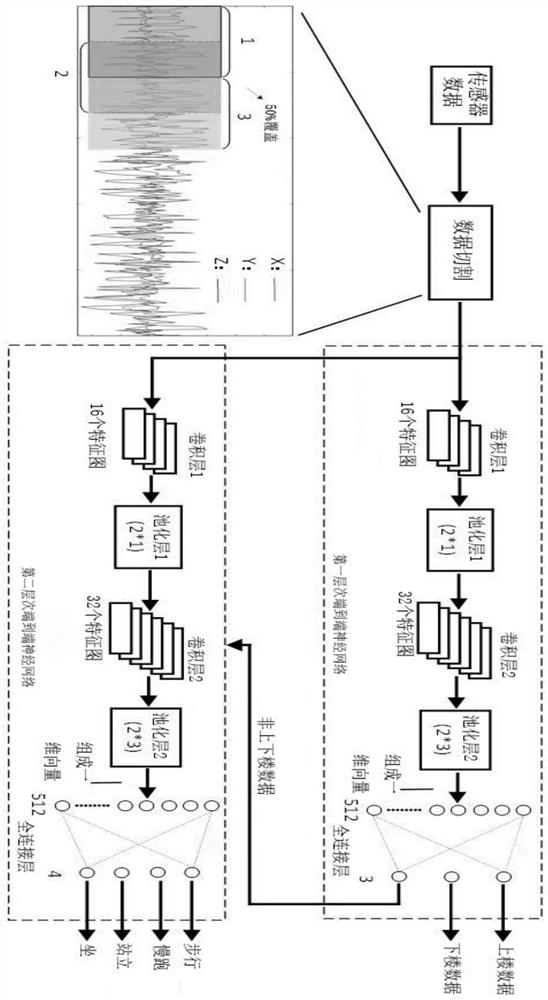
Human activity gesture recognition method based on multi-level end-to-end neural network
ActiveCN109325428BImprove recognition accuracyEnrich training dataCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesComputation complexityEngineering
Owner:周军
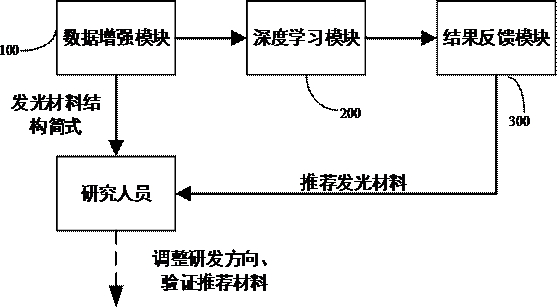
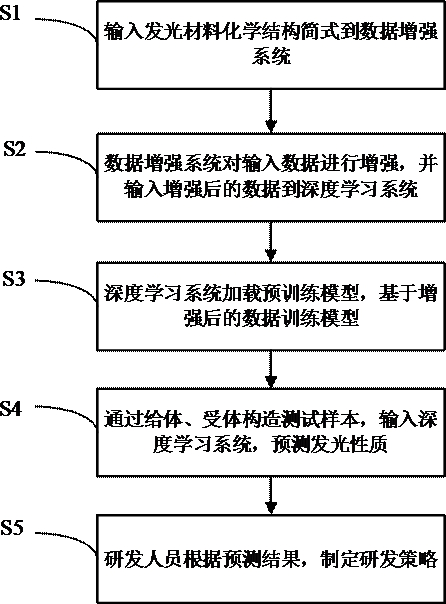
Method, system, electronic device and storage medium for predicting properties of luminescent materials
ActiveCN112396134BAccelerate the development processReduce dependenceChemical property predictionMolecular designImaging dataLuminescent material
Owner:JIHUA LAB
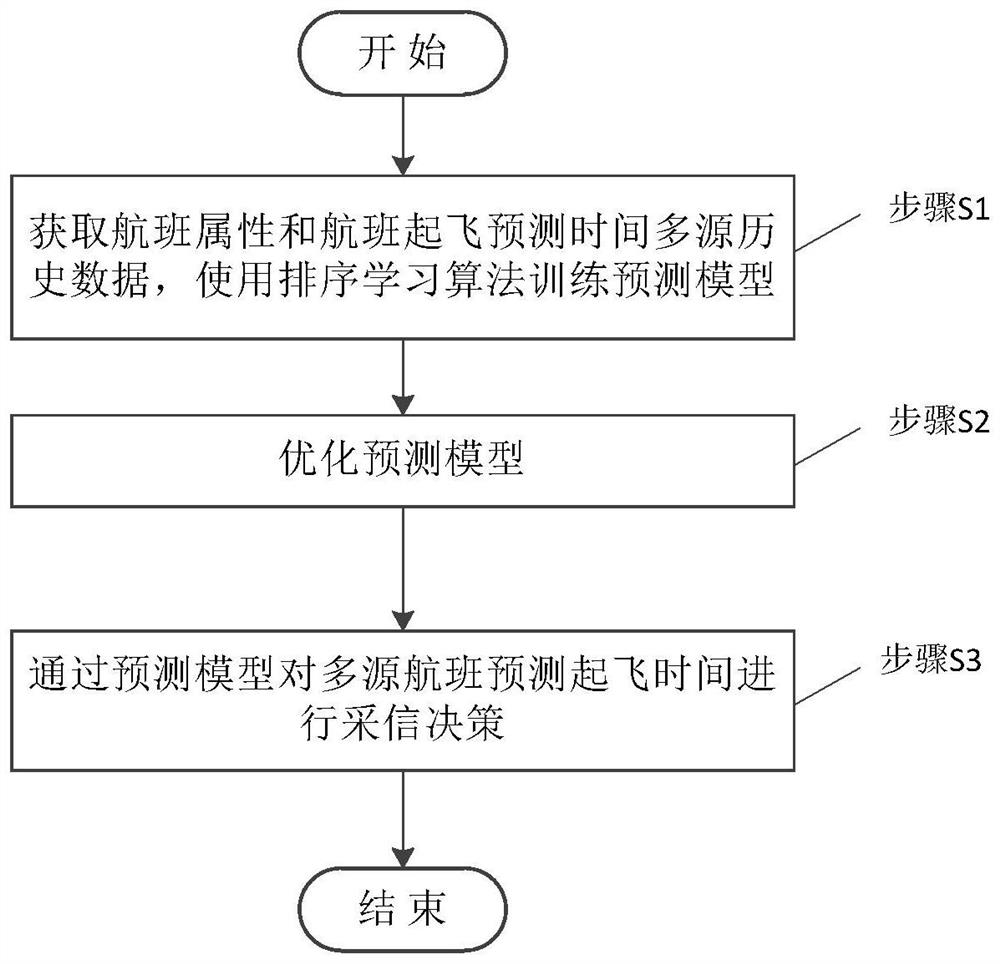
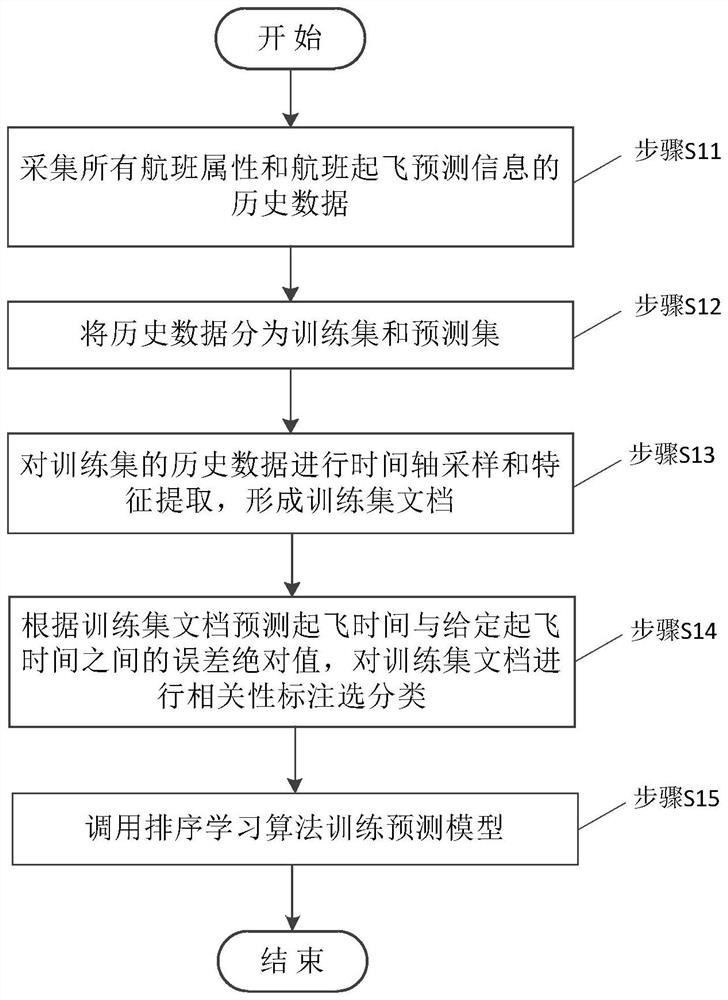
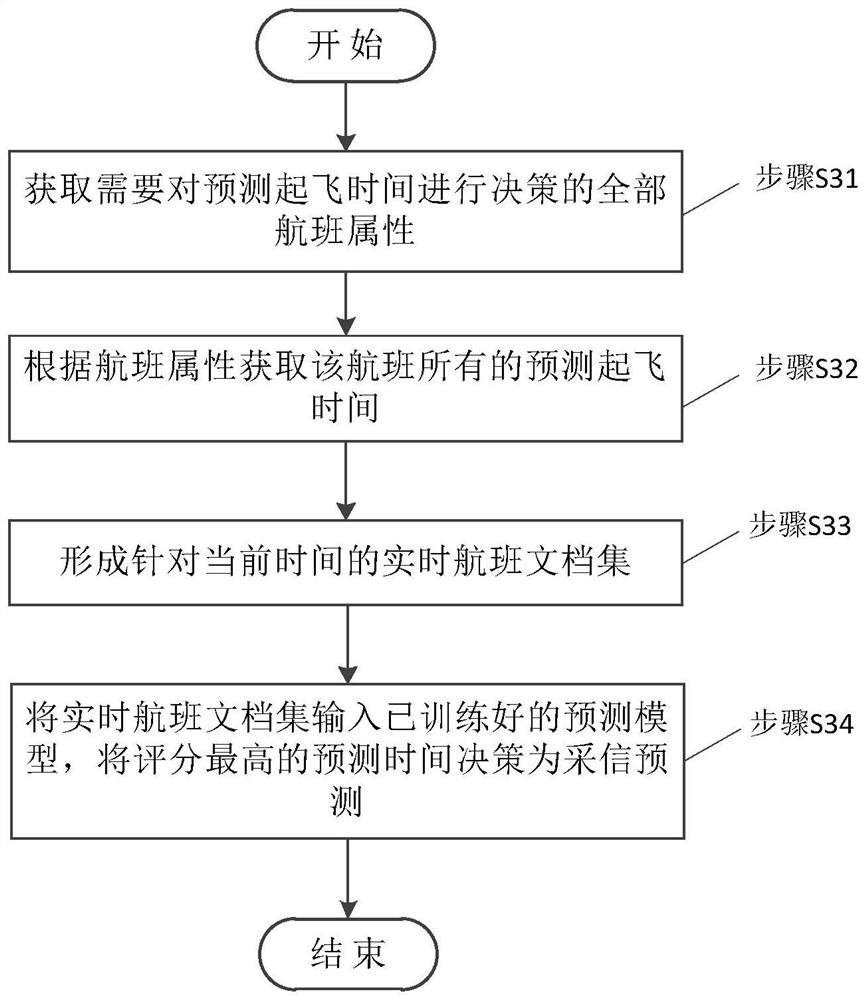
A Multi-data Source Flight Departure Time Prediction Method Based on Sorting Learning
The invention discloses a multi-data source flight departure time prediction method based on ranking learning, which comprises the following steps: using flight attributes and historical data of flight departure prediction time to perform prediction model training; optimizing the prediction model; The real-time data of the flight departure time of the data source is accepted. This method applies the ranking learning algorithm to the multi-data source decision-making of flight estimated departure time prediction, time-samples the historical data of flight prediction departure time based on multiple data sources, forms a flight document set by combining flight attributes, and based on the prediction error The flight departure time prediction is marked with relevance, and the ranking learning algorithm is called to obtain the predicted departure time with the highest score as the decision acceptance. The scheme of the present invention combines the historical prediction data of all data sources of the flight, reasonably utilizes the amount of prediction information, enriches the training data, and unifies the model to solve the comprehensive decision-making of the prediction and acceptance problem at any time in the entire life cycle of the flight.
Owner:MOBILE TECH COMPANY CHINA TRAVELSKY HLDG
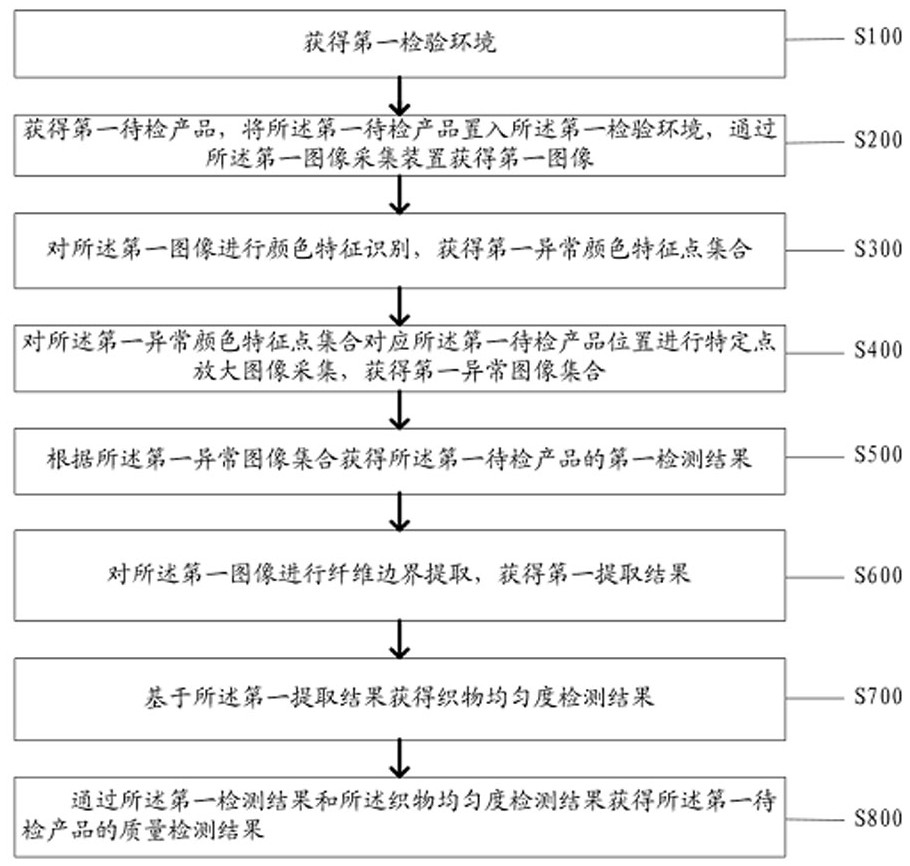
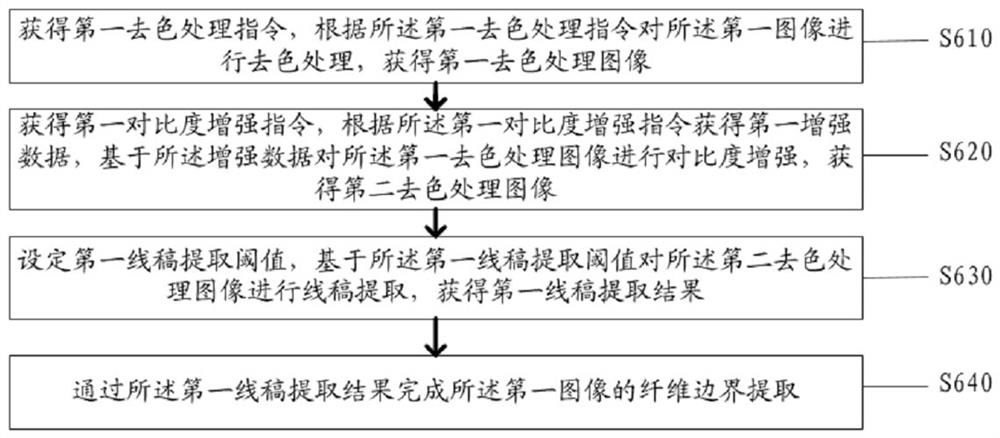
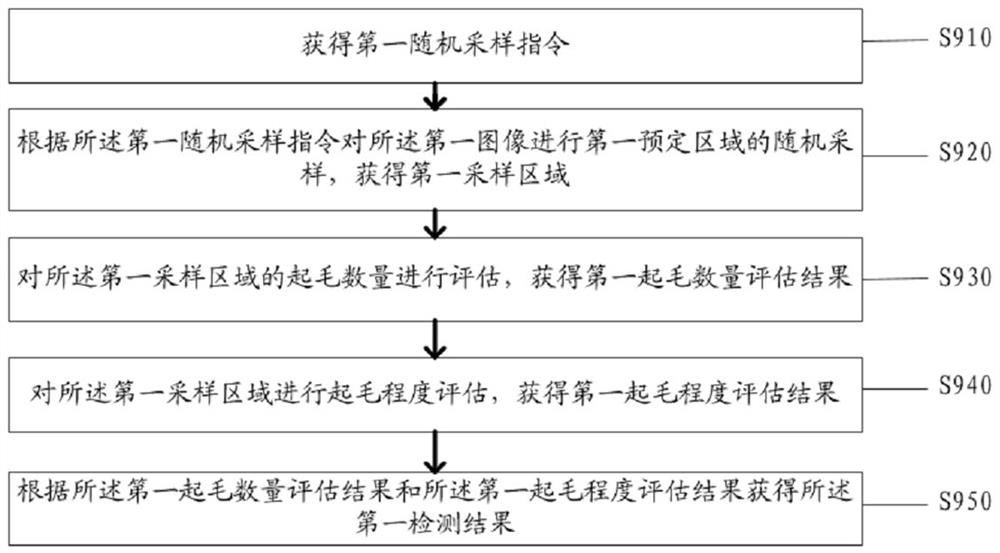
A textile quality inspection method and system based on image recognition
ActiveCN113706528BImprove detection applicabilityEnrich training dataImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionEngineering
Owner:南通祥元纺织有限公司
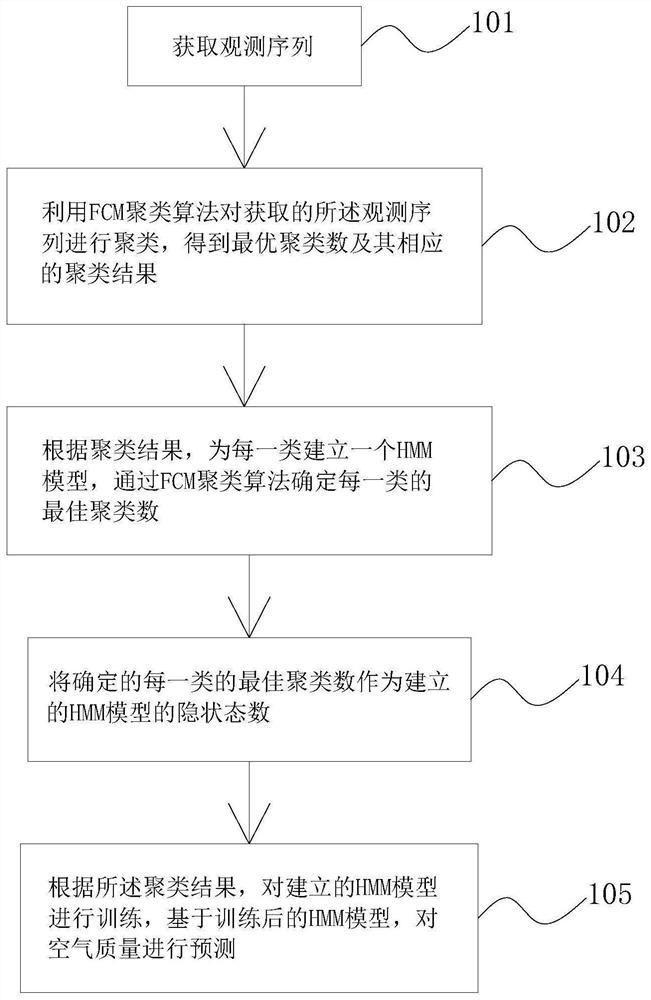
A Neural Network Prediction Method of Air Quality Based on Decision Tree Index
ActiveCN110363347BEasy to identifyImprove the forecast effectAnalysing gaseous mixturesForecastingData setTime series dataset
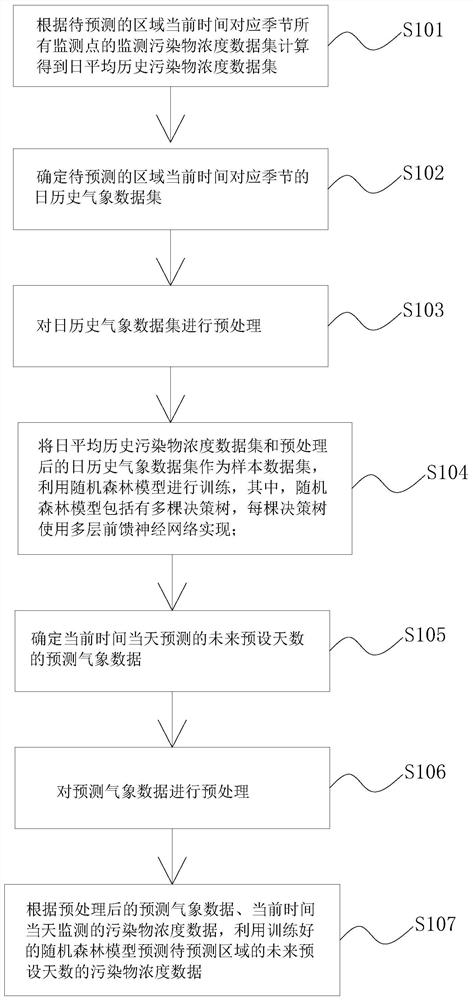
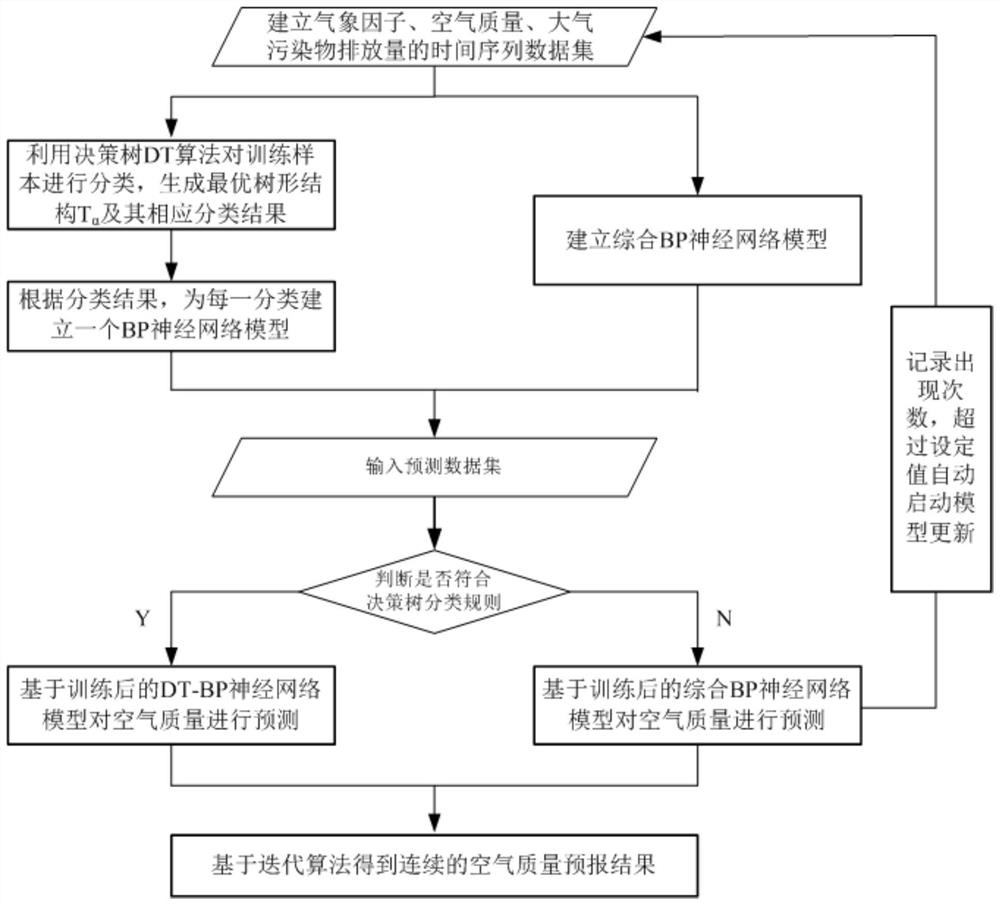
The invention relates to a method for predicting air quality based on a neural network index of a decision tree, comprising the following steps: establishing a time series data set of relevant meteorological factors, air quality and air pollutant emissions; using a decision tree DT algorithm to train the obtained training The samples are classified to generate the optimal tree structure T oriented by air quality characteristics α and the corresponding classification results; according to the classification results, establish a BP neural network model for each classification, and carry out model training; input the prediction data set, carry out classification index based on the decision tree, and select the DT-BP neural network model after training Or integrated BP neural network to predict air quality; obtain continuous air quality prediction results based on iterative algorithm; record the number of data sets that do not meet the classification and matching rules of decision tree, and automatically start model update if the set value is exceeded. The invention is suitable for air quality prediction and forecast of normal weather, sudden change weather and heavy pollution weather.
Owner:江苏天长环保科技有限公司
Intelligent customer service construction method driven by business document
PendingCN114116999AIncrease training timeEnrich training dataNeural architecturesSpecial data processing applicationsBusiness documentsEngineering
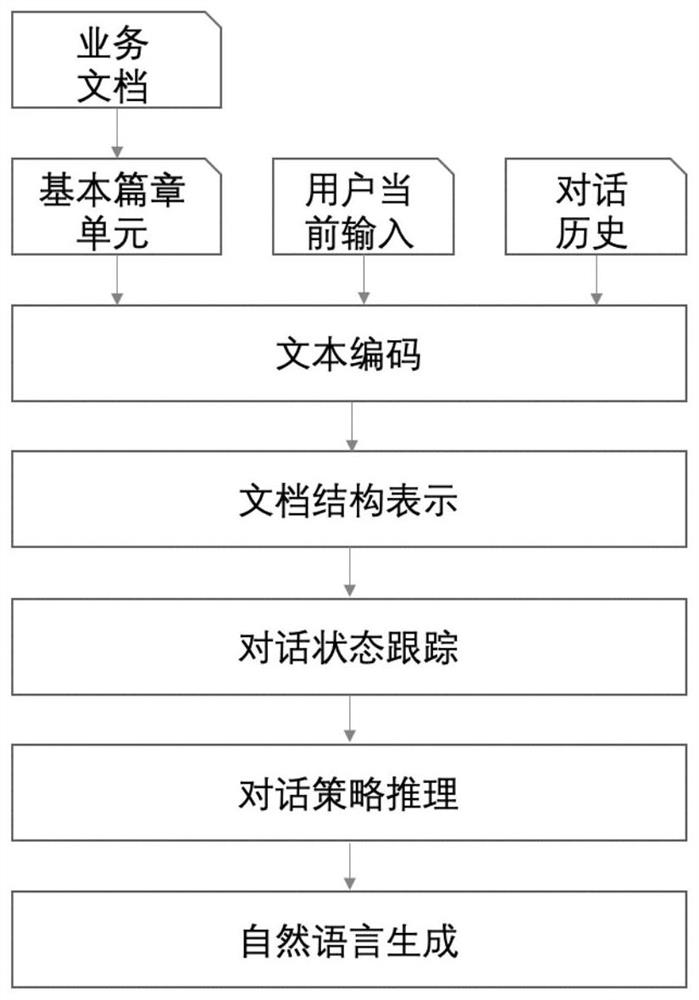
A business document-driven intelligent customer service construction method is characterized by comprising the following steps: step 1, collecting a current input q of a user, a business document D and a dialogue history, and encoding and pooling the current input q, the business document D and the dialogue history to obtain a sentence level representation of the current input q, the business document D and the dialogue history; 2, taking each item in the sentence level representation Ds of the business document as a discourse unit, and sequentially establishing a correlation between the sentence level representation q currently input by the user and each discourse unit and a correlation between each discourse unit and the sentence level representation Hs of the dialogue history, therefore, document structure analysis and dialogue state tracking are realized in sequence; and step 3, classifying the business document and the dialogue history based on the association relationship obtained in the step 2, and reasoning the current answer to generate an optimal strategy. Corpus association and accurate reasoning are realized by referring to a rhetorical structure theory, the problem of an information slot is overcome, system dialogue is represented by an interaction state of a discourse unit, and the system dialogue efficiency is improved. And the conversation is smoothly driven.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD MARKETING SERVICE CENT
Method, device and medium for acquiring face recognition model training data based on video
ActiveCN109284729BEnrich training dataReduce workloadCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionFace detection
The present application discloses a method, device and medium for acquiring face recognition model training data based on video. Wherein, the method includes: obtaining a standard picture of the person to be identified, performing face detection and key point extraction on the standard picture, and generating a first descriptor; for a video containing the person, performing video frame extraction, and identifying the extracted video The face part in the frame, save the face part as a face picture; carry out key point extraction to the face picture, generate the second descriptor, calculate the distance between the first descriptor and the second descriptor, based on the The distance is used to judge whether the face picture is the person to be recognized, so as to obtain the face recognition model training data. This method can enrich the training data of the face recognition model, reduce the workload of manual screening, and thus solve the problems of incomplete training data preparation, single type, and difficult cleaning.
Owner:BEIJING YINGPU TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com