Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56results about How to "Different effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
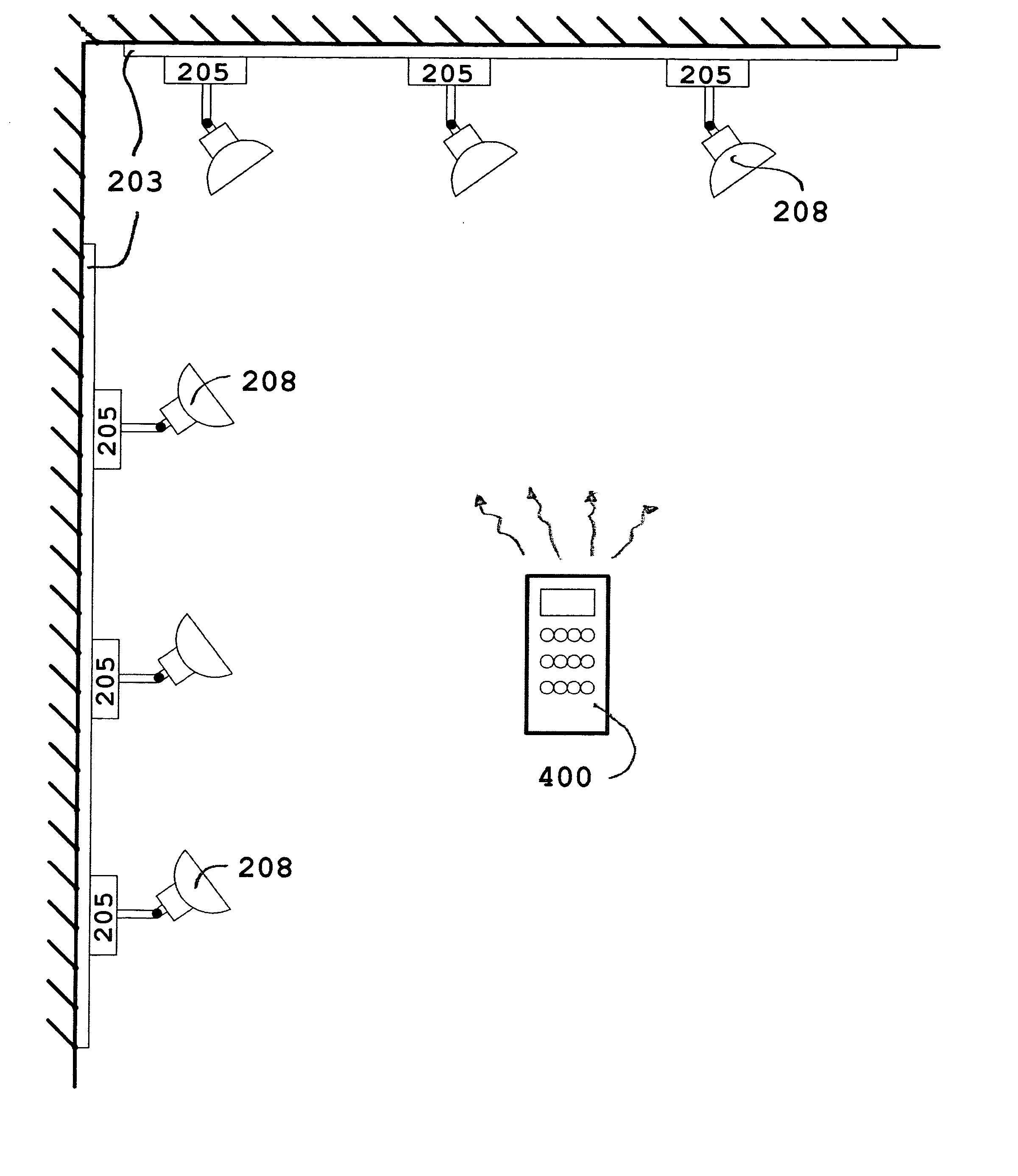
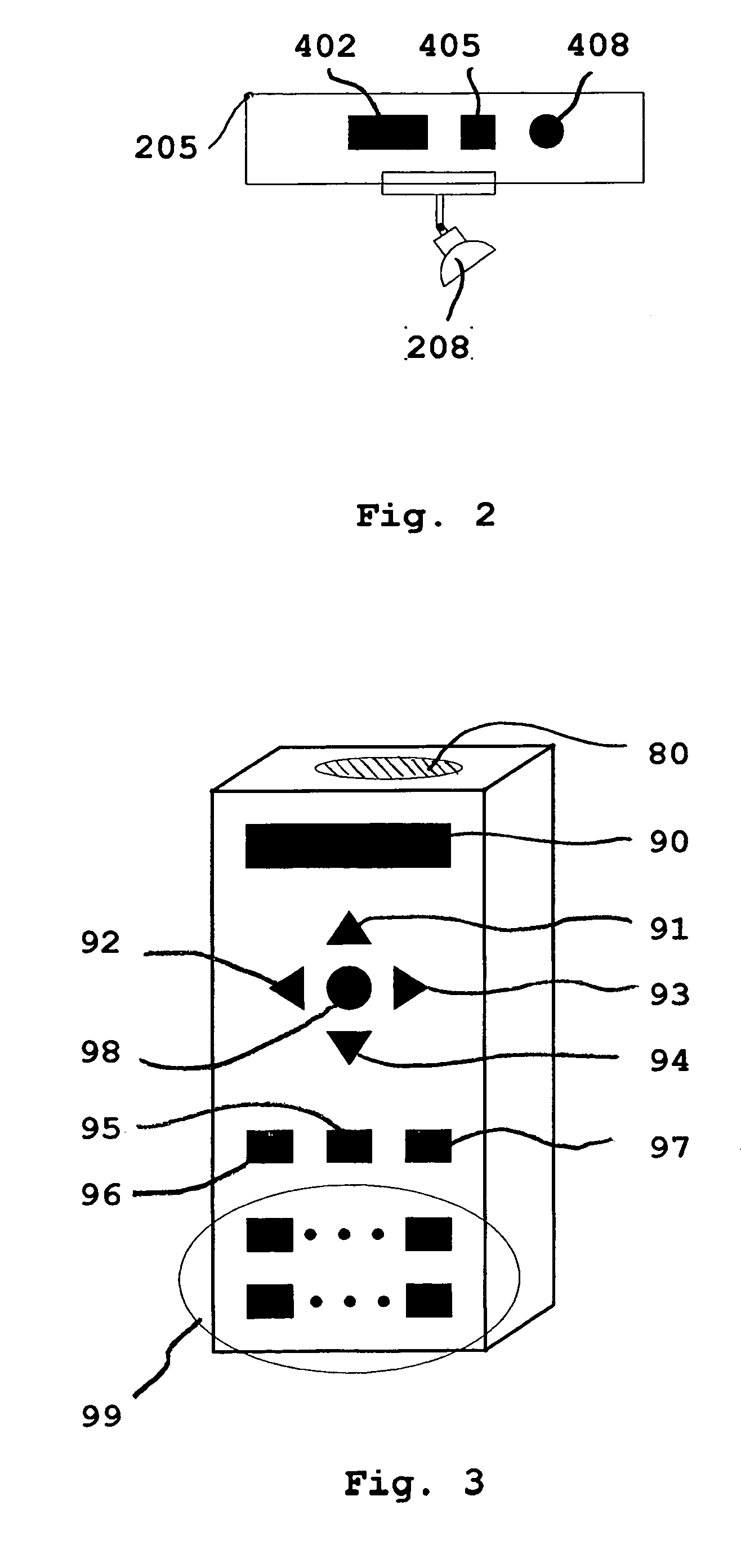
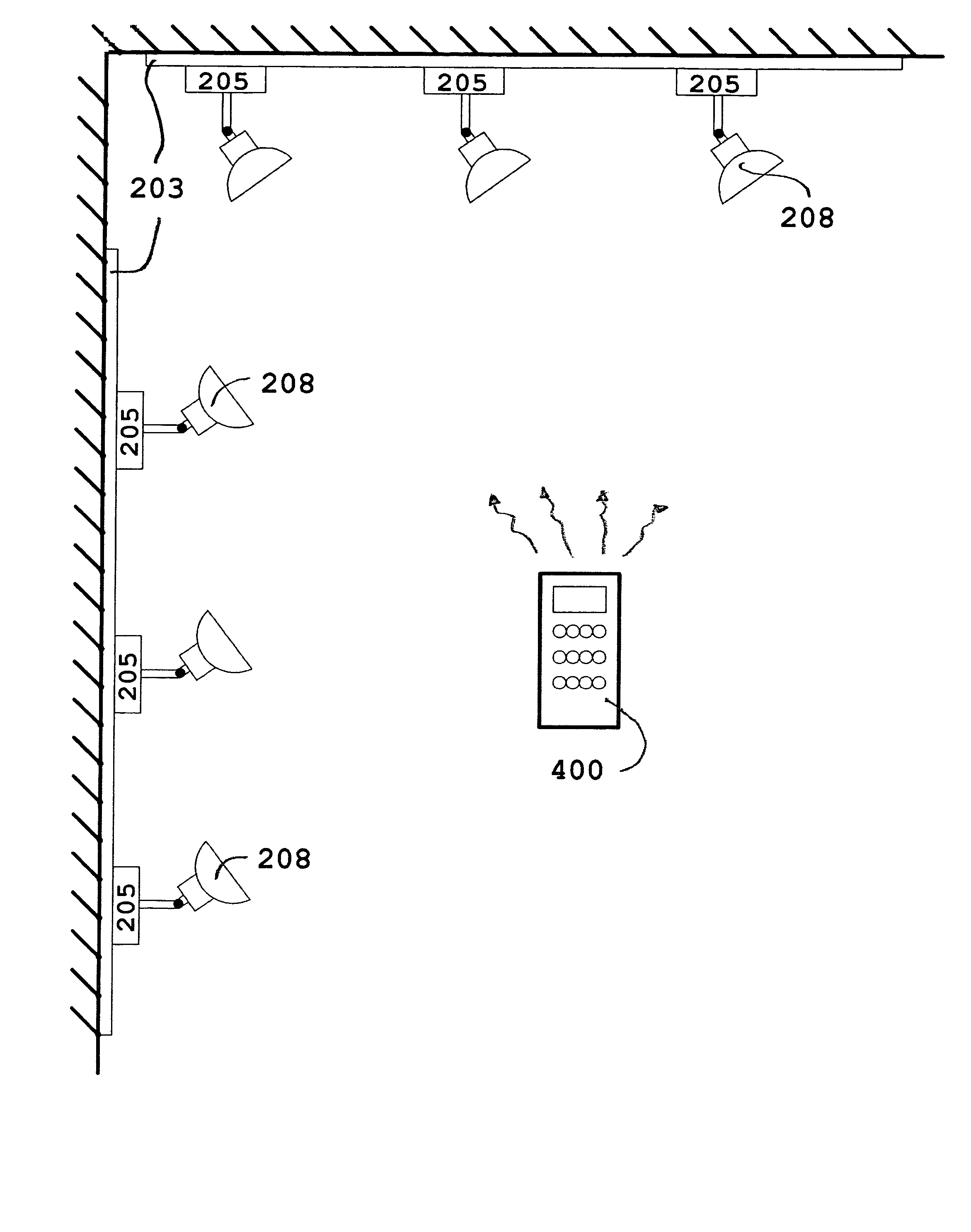
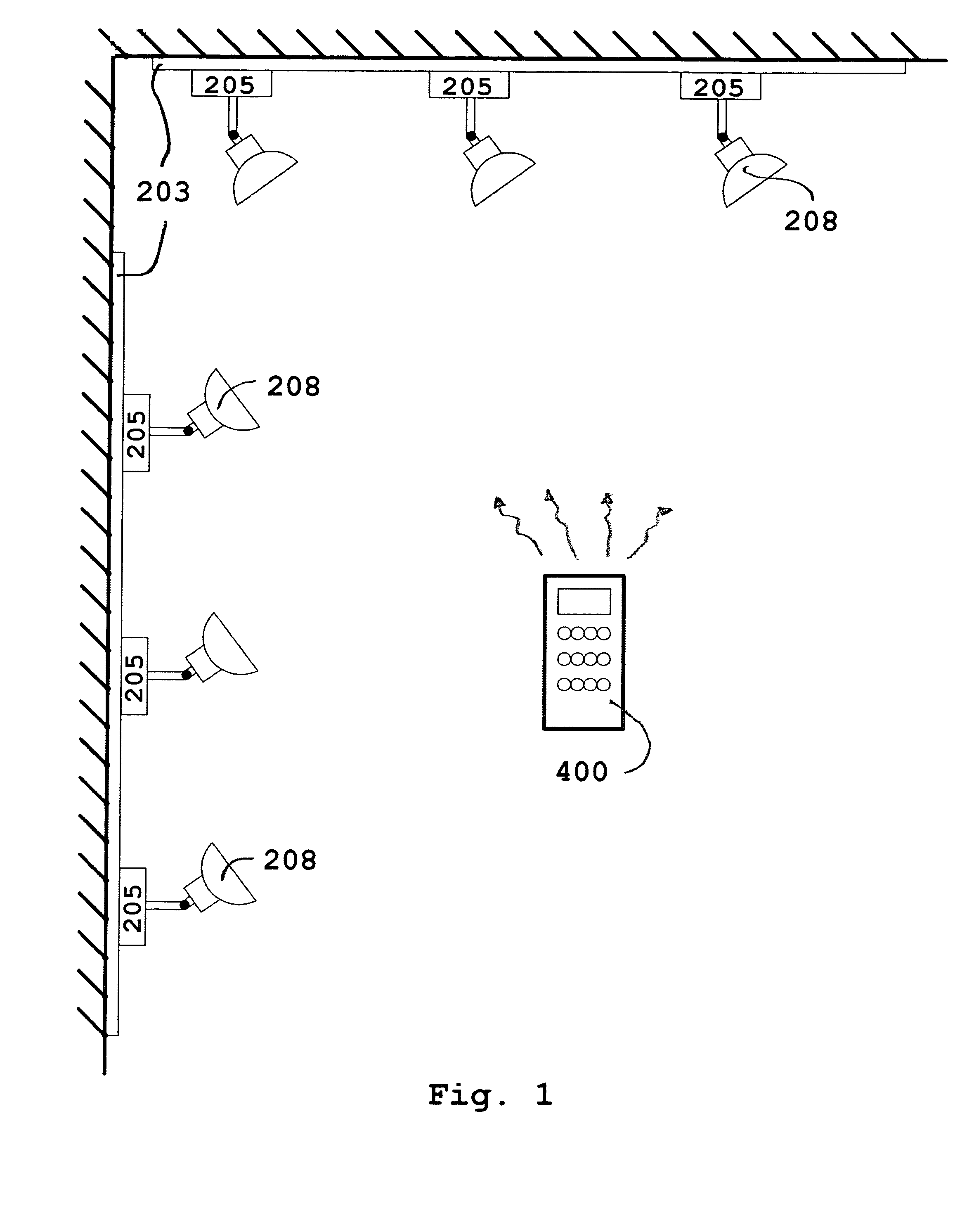
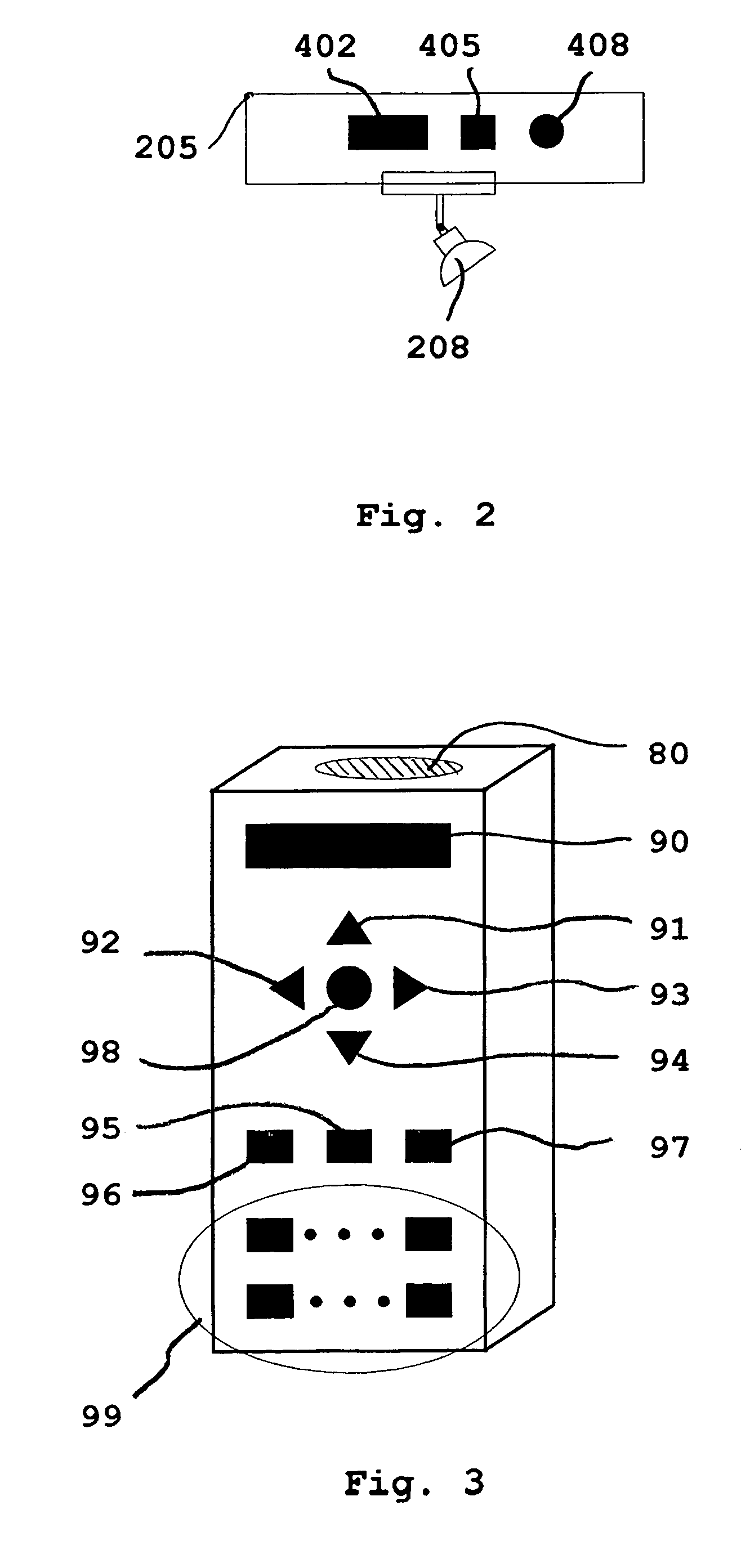
Remote controlled intelligent lighting system
InactiveUS20050231134A1Reduce usageDifferent effectElectric signal transmission systemsPoint-like light sourceRadio frequencyRotary switch
An addressable lighting device and control system uses a user-actuable infrared or radio frequency operated remote control(s) to selectively or collectively generate an electronic address for the addressable lighting device on which the device will respond to all future signals from the remote control corresponding to that electronic address. The addressable lighting device has a programming mode for setting the address and a working mode for receiving control signals on the set address and correspondingly setting the desired intensity level of light. The addressable device may have the address set and changed locally (manually) or remotely using the remote control to switch modes, thereby avoiding the problems, expenses and mistakes associated with using dual in-line package (DIP) switches, binary, hex rotary switches, or thumbwheel switches normally used to set each one of the system's unit's unique address.
Owner:SID ALBERTO
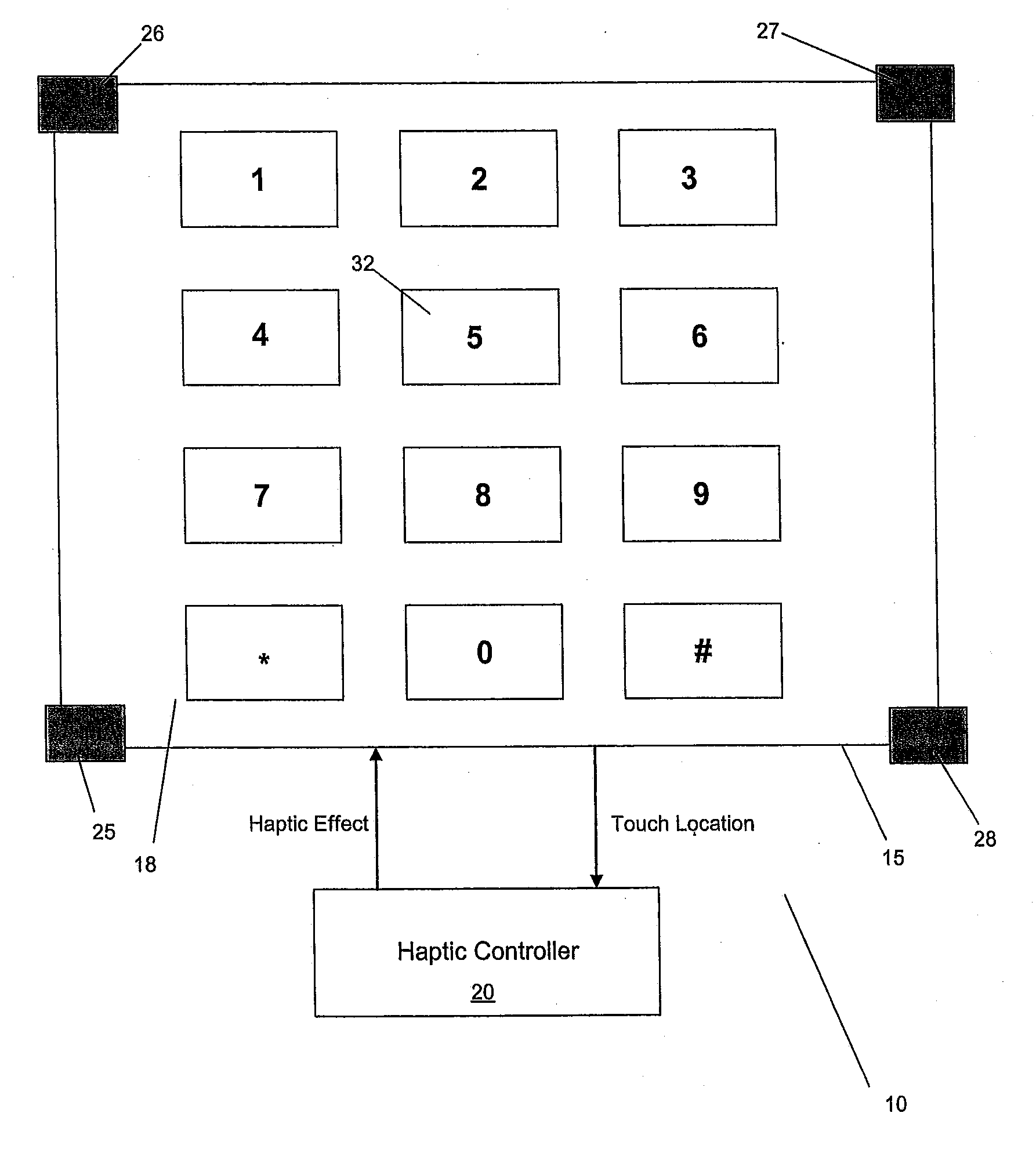
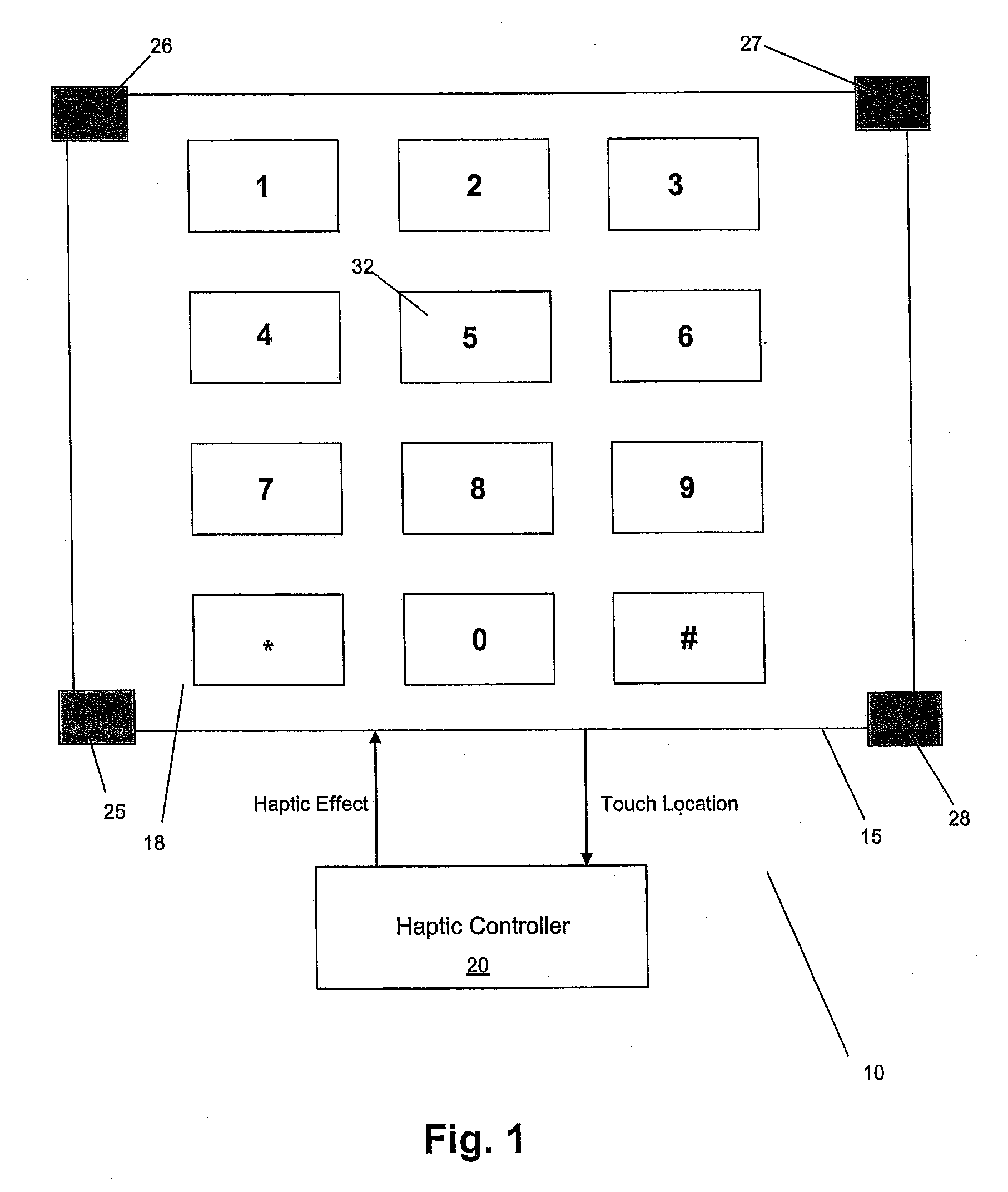
Touch Panel with a Haptically Generated Reference Key
InactiveUS20070236474A1Different effectInput/output processes for data processingTouch SensesTouchpad
A touch panel provides an indication of a reference key and non-reference keys to a user. The touch panel senses a touch and determines the location of the touch. The touch panel then generates a haptic effect if the location is the reference key, and generates a different haptic effect if the location is a non-reference key.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
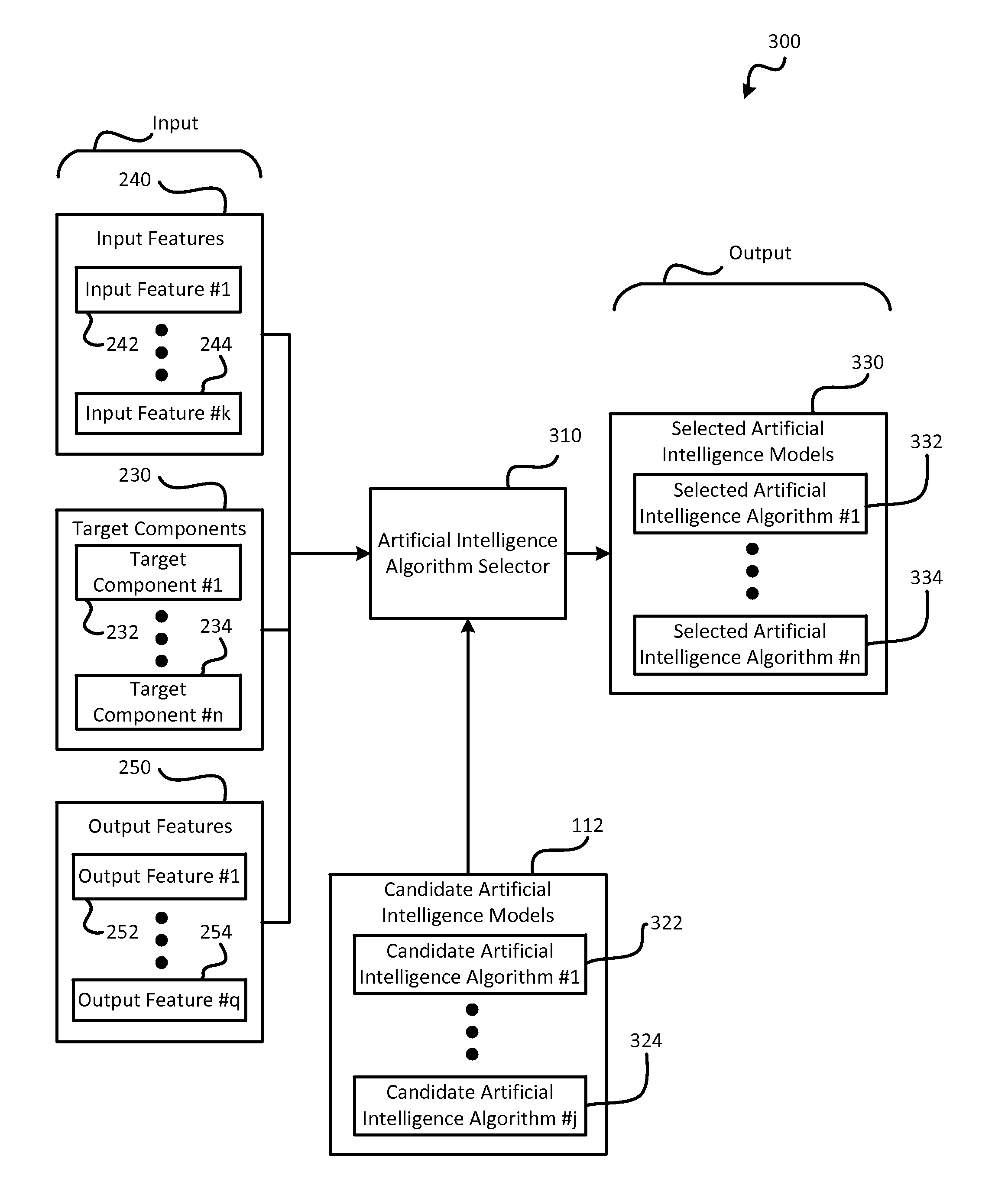
Adaptive user interfaces
ActiveUS8775332B1Different effectMaximize motivation and performanceMathematical modelsNatural language data processingAdaptive user interfaceData mining
According to various embodiments of the present invention, user performance and / or motivation for a computing system may be maximized by optimizing one or more target components of a user interface of the computing system. The target components may be aspects of the user interface that is perceived by the user. One or more input features and one or more output features may be identified, and data regarding these input and output features may be gathered. This data may be compared with the results generated by a set of candidate artificial intelligence algorithms to determine which of them provides the best fit with the data collected. Then, the selected artificial intelligence algorithm may be applied to the user interface to iteratively change the target components over time until the optimal settings for each user are discovered.
Owner:XANT INC
System for enhancing a video presentation of a live event
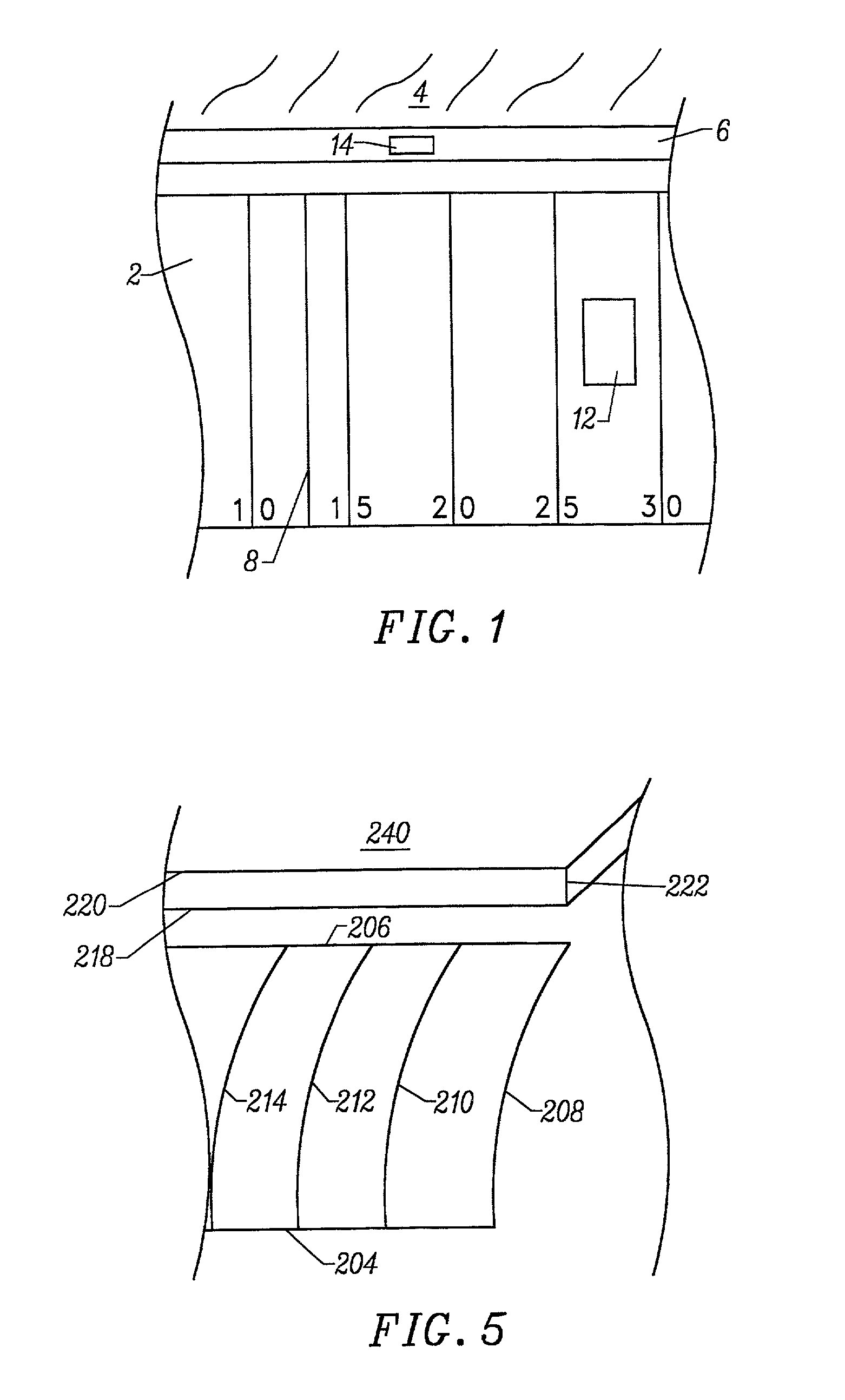
InactiveUS6266100B1Eliminate needDifferent effectTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsGraphicsThree dimensional model
A three-dimensional model is created to represent an environment to be captured on video. A camera is fitted with pan, tilt and / or zoom sensors. An operator selects a location in the environment. The three-dimensional model is used to determine the three-dimensional coordinates of the location selected by the operator. Information from the pan, tilt and / or zoom sensors is used to transform the three-dimensional coordinates to a two-dimensional position in the video from the camera. Using the two-dimensional position of the video, a graphic is properly added to the video such that the graphic appears to be at the selected location in the environment.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
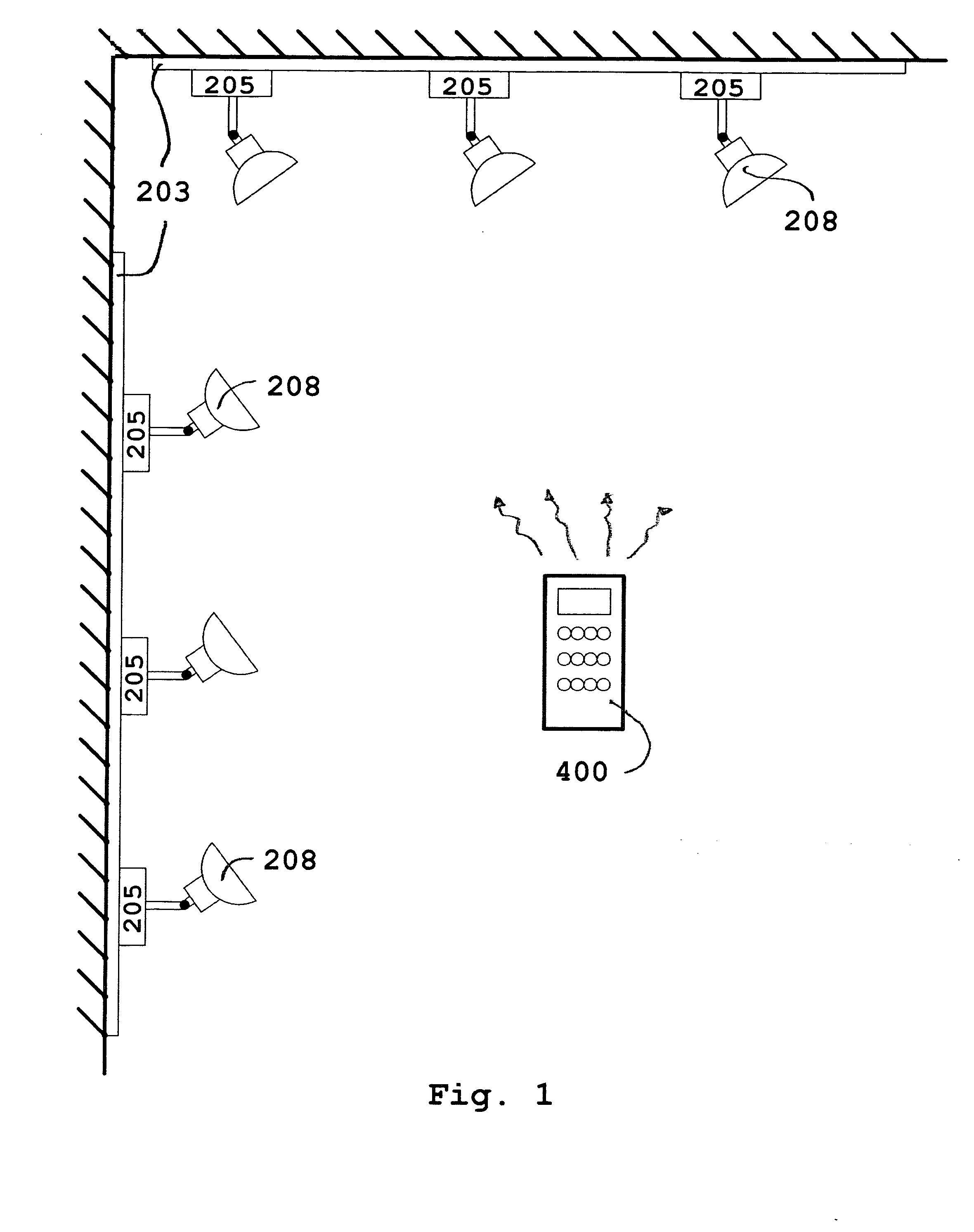
Remote controlled intelligent lighting system
InactiveUS7355523B2Reduce usageDifferent effectElectric signal transmission systemsPoint-like light sourceIntelligent lightingLight equipment
An addressable lighting device and control system uses a user-actuable infrared or radio frequency operated remote control(s) to selectively or collectively generate an electronic address for the addressable lighting device on which the device will respond to all future signals from the remote control corresponding to that electronic address. The addressable lighting device has a programming mode for setting the address and a working mode for receiving control signals on the set address and correspondingly setting the desired intensity level of light. The addressable device may have the address set and changed locally (manually) or remotely using the remote control to switch modes, thereby avoiding the problems, expenses and mistakes associated with using dual in-line package (DIP) switches, binary, hex rotary switches, or thumbwheel switches normally used to set each one of the system's unit's unique address.
Owner:SID ALBERTO
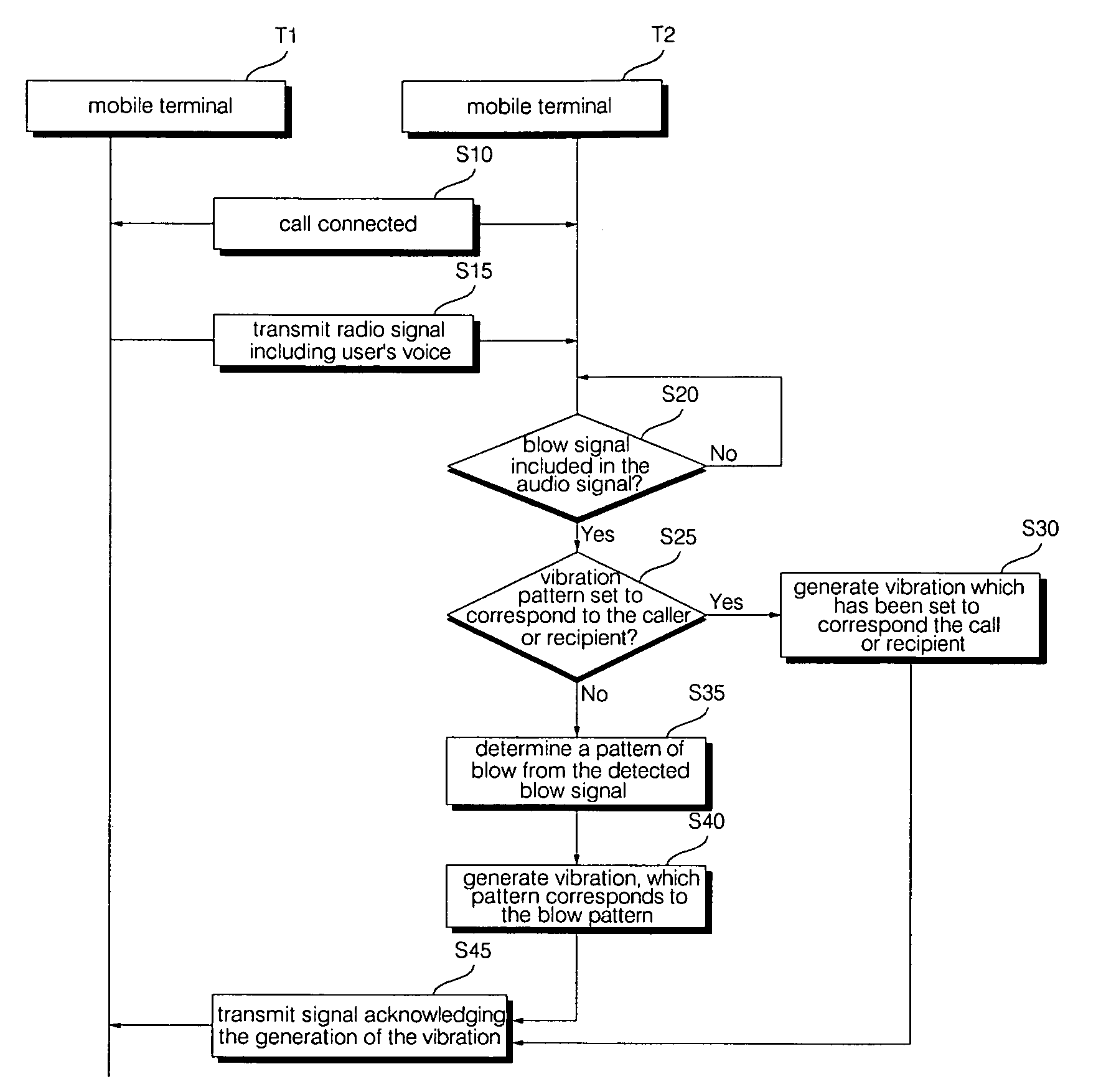
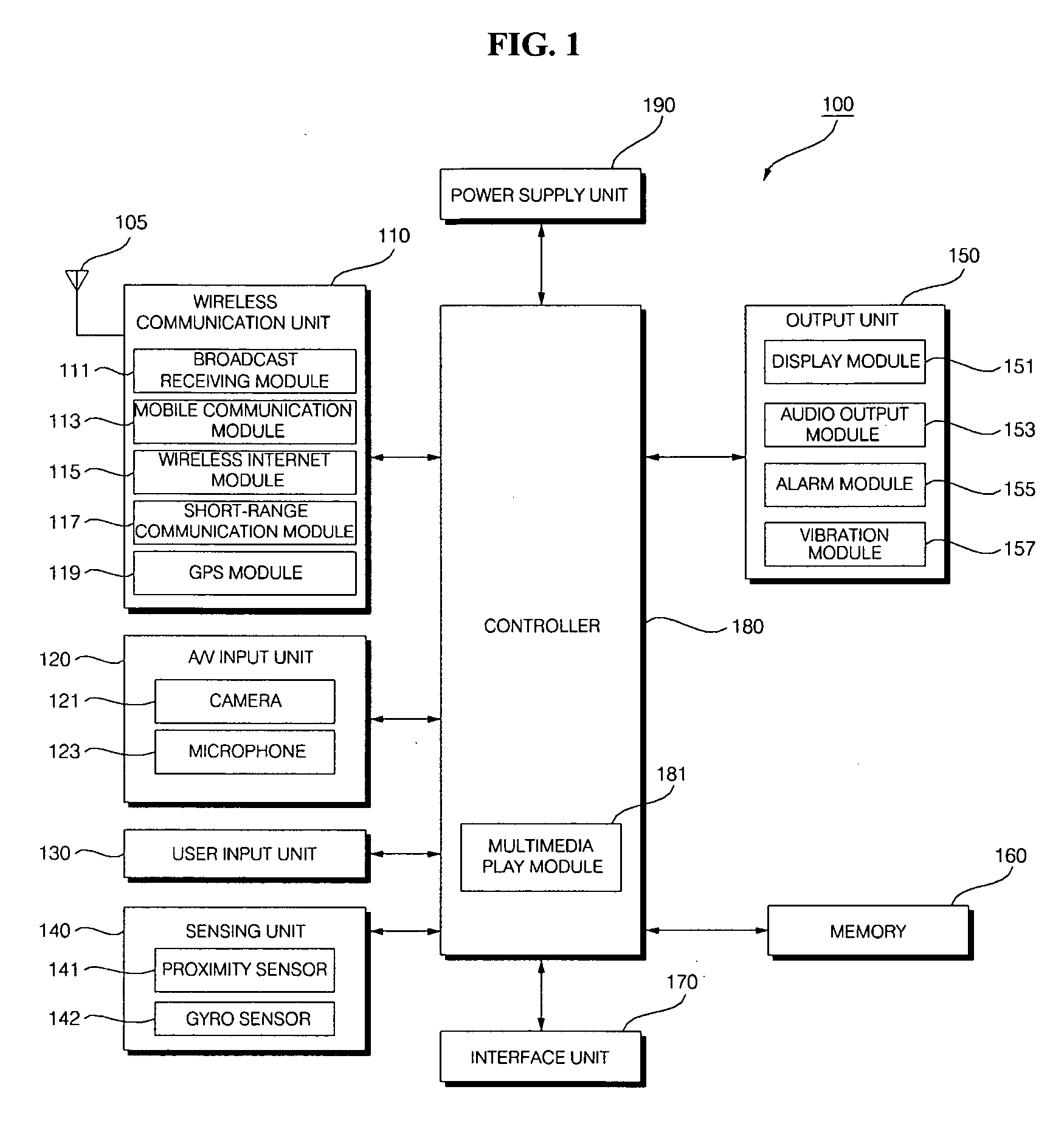
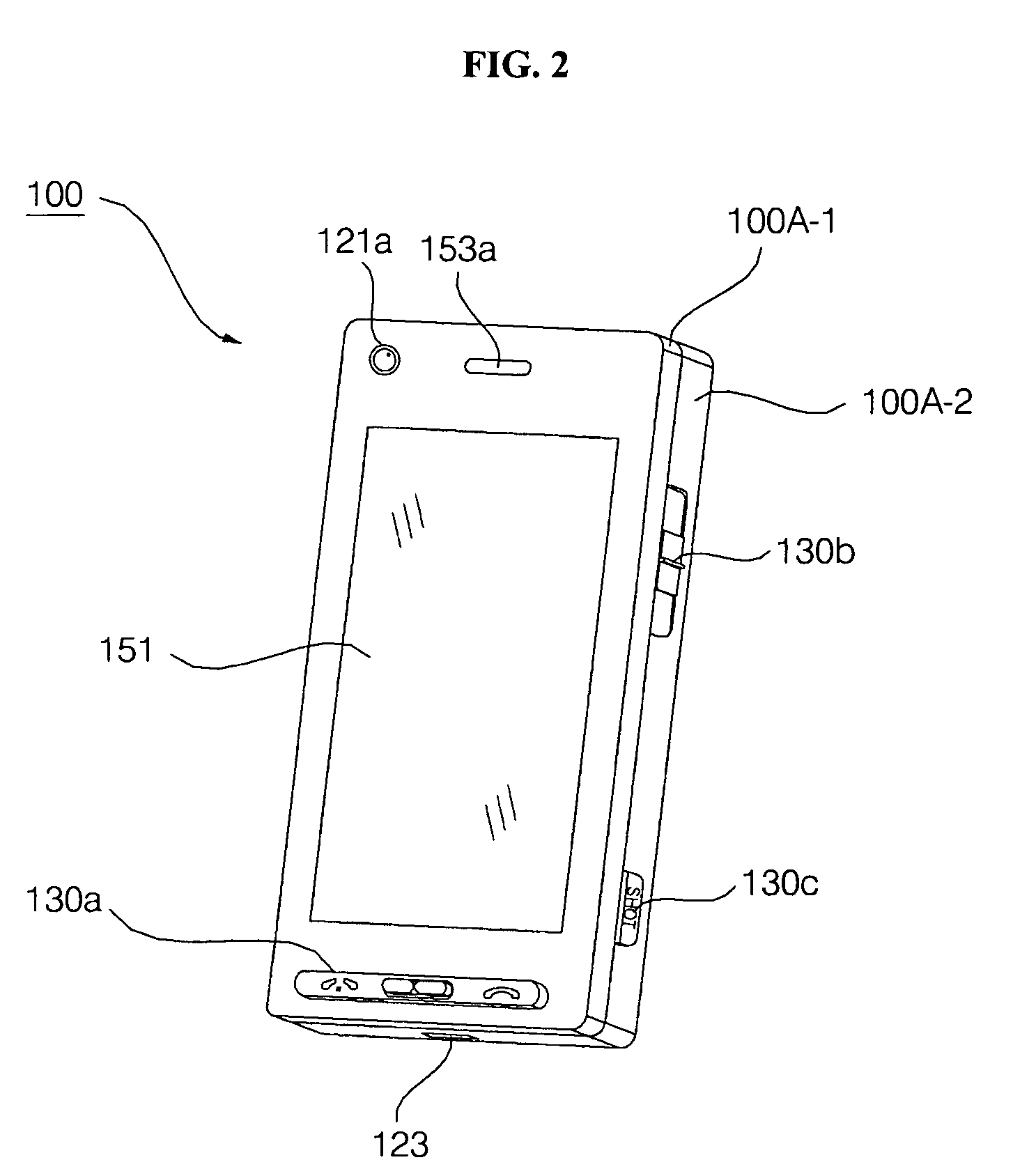
Mobile terminal and operation control method thereof
InactiveUS20100227640A1Different effectRepeater circuitsCurrent supply arrangementsEngineeringVisual perception
A method of controlling a mobile terminal, and which includes receiving an blow signal corresponding to a blowing action into a microphone of the mobile terminal, and generating at least one of a visual effect and a vibration effect based on characteristics of the blow signal.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
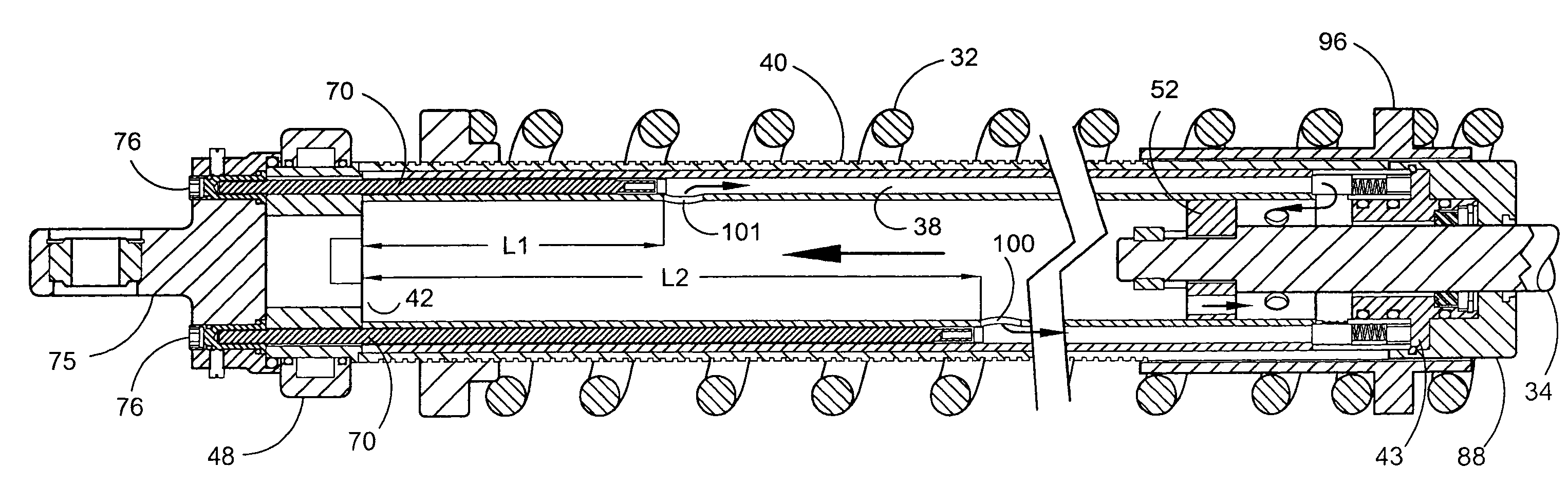
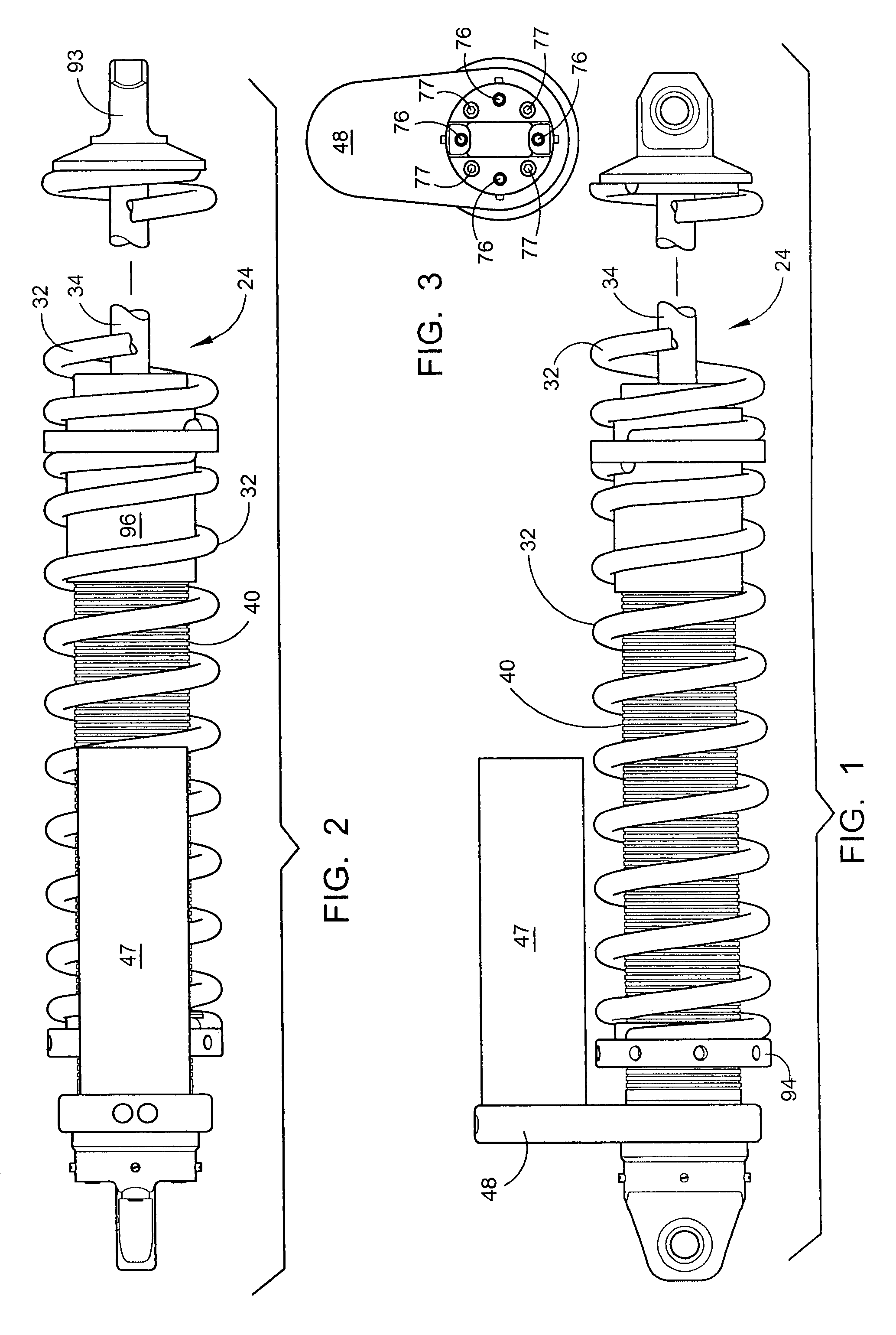
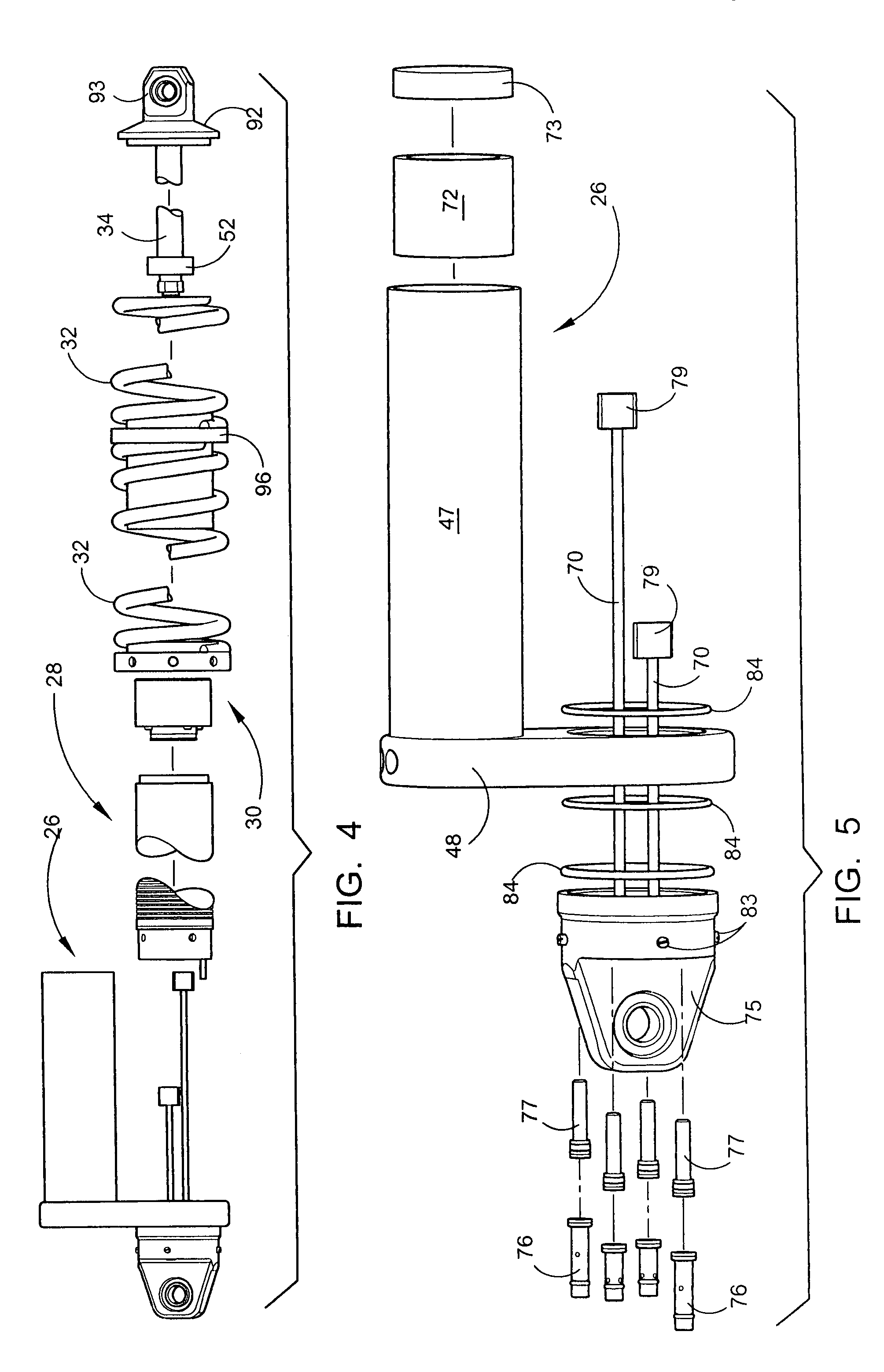
Externally adjustable internal bypass shock absorber
ActiveUS7270222B1Characteristic variesReduce the overall diameterSpringsShock absorbersReciprocating motionCoil spring
A shock absorber that combines both the suspension function and the shock absorbing function in one unit. It has an elongated shock body filled with hydraulic fluid and a piston mounted on a piston rod that reciprocally travels within the shock body. The shock body is telescopically received in a bypass cylinder body having a greater diameter that produces an annular chamber between the outer surface of the shock body and the inner surface of the bypass cylinder body. A coil spring is mounted on the outside surface of the bypass cylinder body to provide a suspension function by the shock absorber. A plurality of bypass tubes are associated with longitudinally spaced ports in the shock body. Adjuster rods are telescopically received inside the respective bypass tubes for controlling whether the individual ports are closed, partially open, or fully open. These adjuster rods would be manipulated externally of the shock absorber assembly.
Owner:AYMAR BRANDON
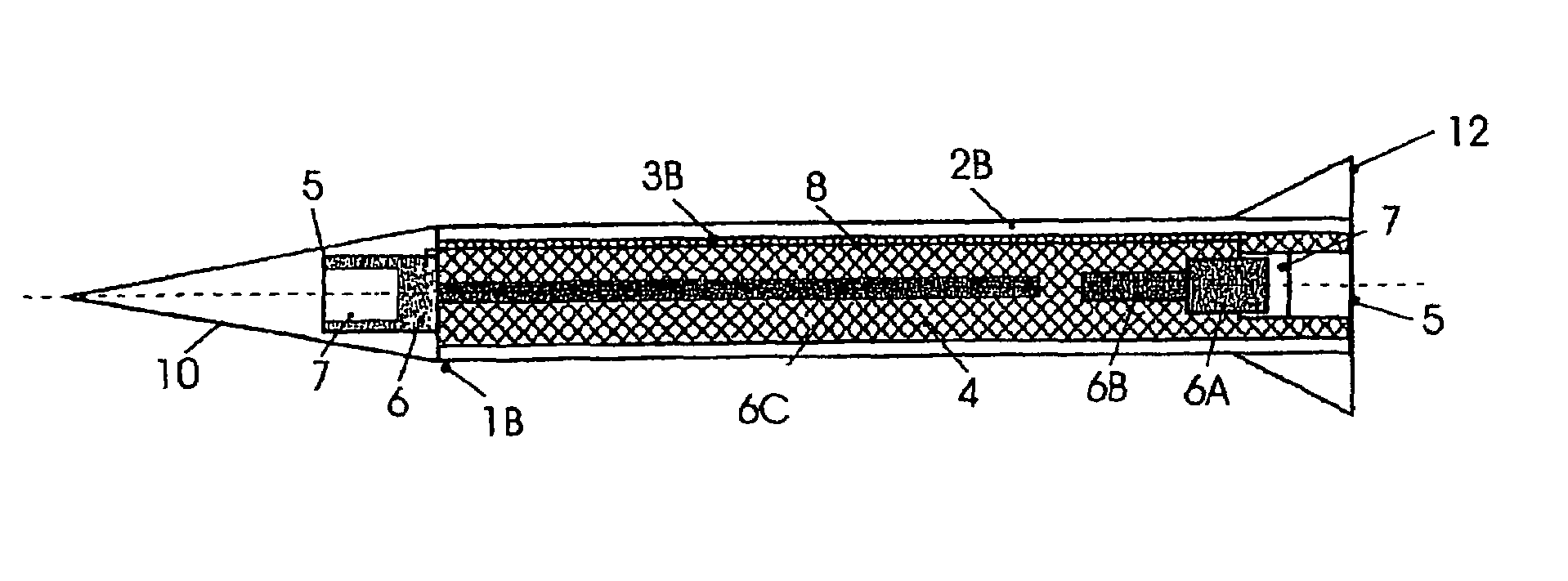
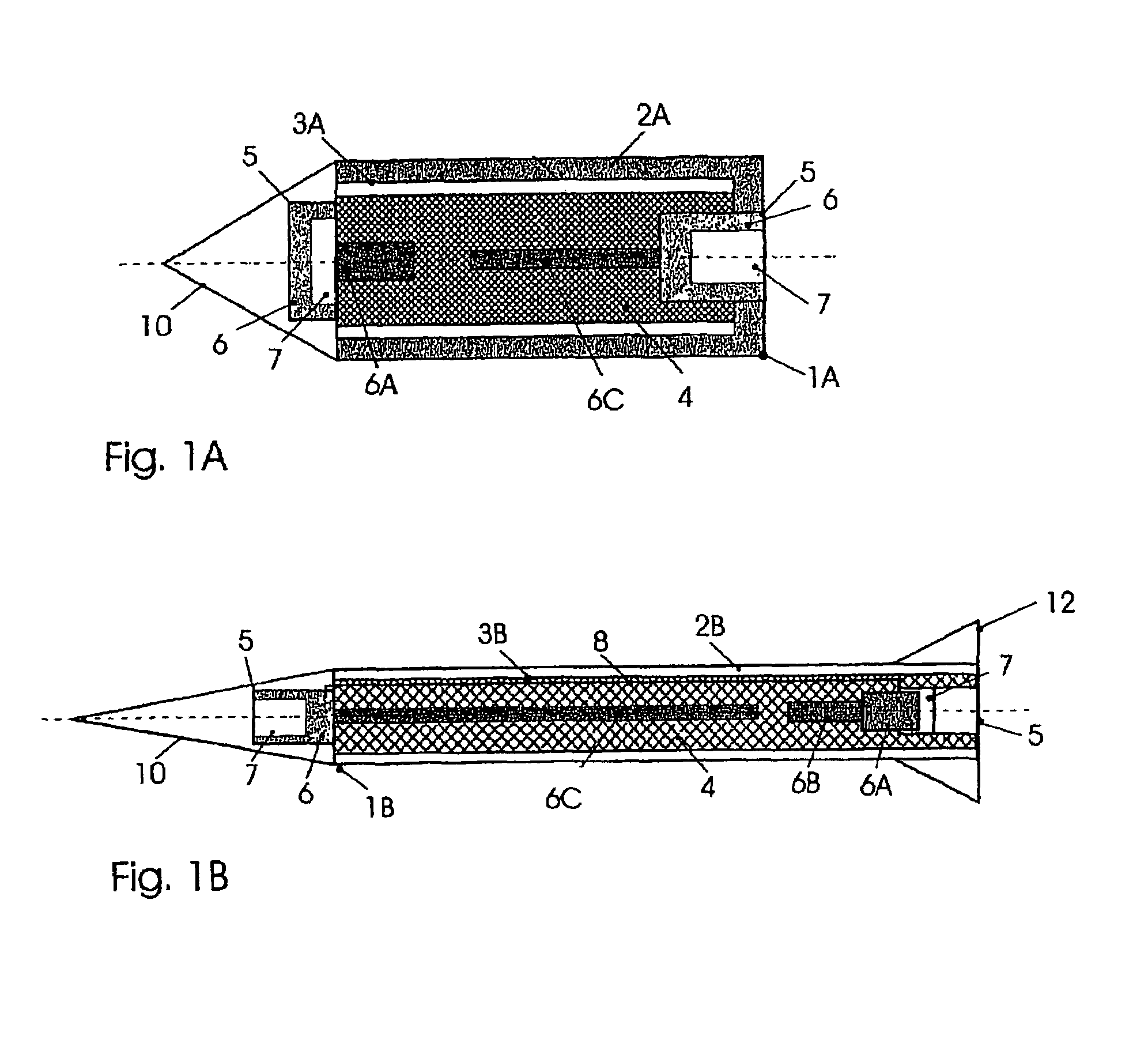
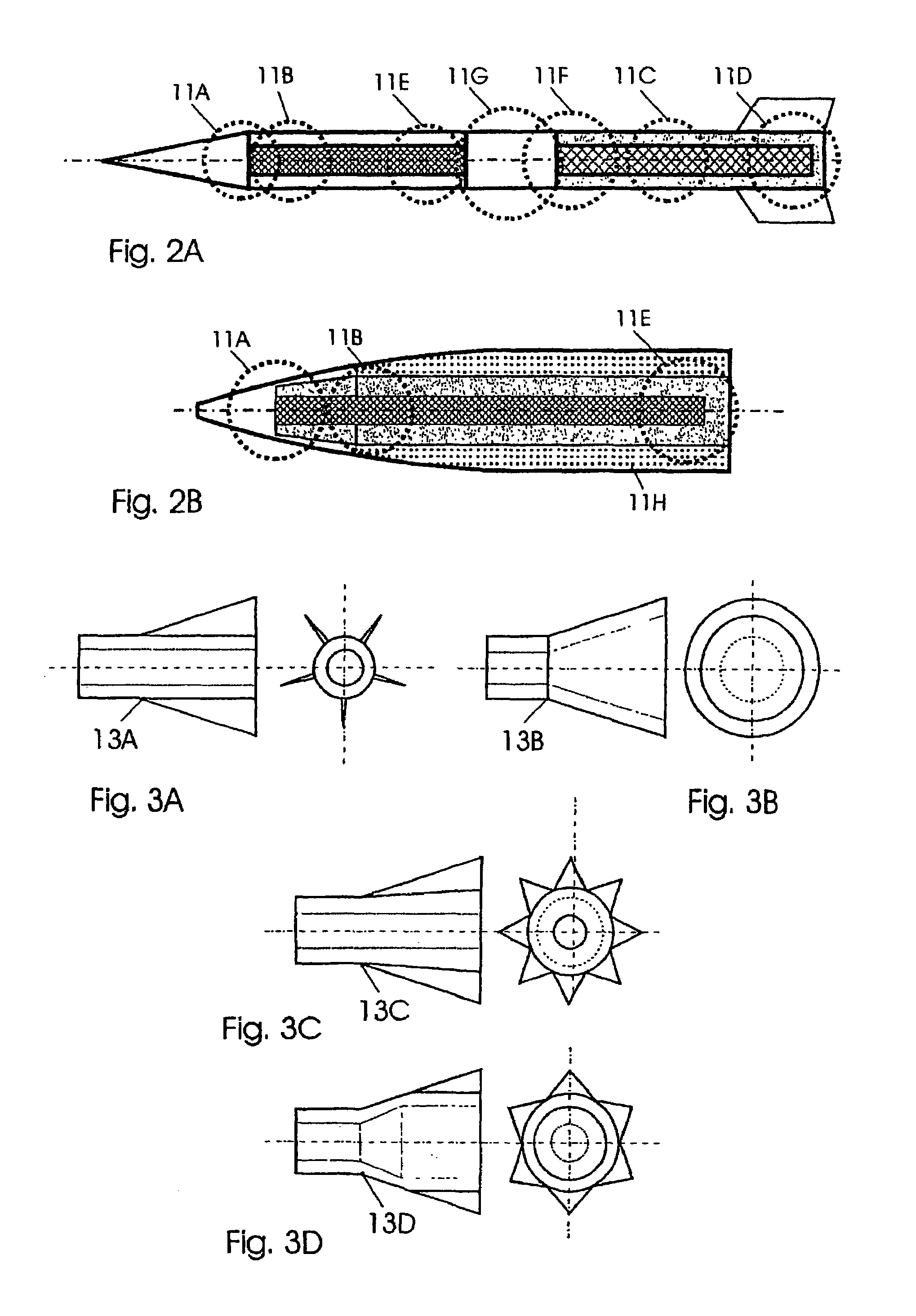
Projectiles possessing high penetration and lateral effect with integrated disintegration arrangement
InactiveUS7231876B2Increase in significanceFacilitate transmissionAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionSurface stressEngineering
A highly effective and also inert active penetrator, an active projectile, an active airborne body or an active multipurpose projectile with a constructively adjustable or settable relationship between penetrating power and lateral effect. The end ballistic total effect which is obtained from the penetrating depth and covering the surface or stressing of the surface is initiated in an active case by means of a releasable arrangement or installation which is independent of the position of the active body.
Owner:RHEINMETALL WAFFE MUNITION GMBH
System for enhancing a video presentation of a live event
InactiveUS20010005218A1Eliminate needDifferent effectTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsGraphicsThree dimensional model
A three-dimensional model is created to represent an environment to be captured on video. A camera is fitted with pan, tilt and / or zoom sensors. An operator selects a location in the environment. The three-dimensional model is used to determine the three-dimensional coordinates of the location selected by the operator. Information from the pan, tilt and / or zoom sensors is used to transform the three-dimensional coordinates to a two-dimensional position in the video from the camera. Using the two-dimensional position of the video, a graphic is properly added to the video such that the graphic appears to be at the selected location in the environment.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
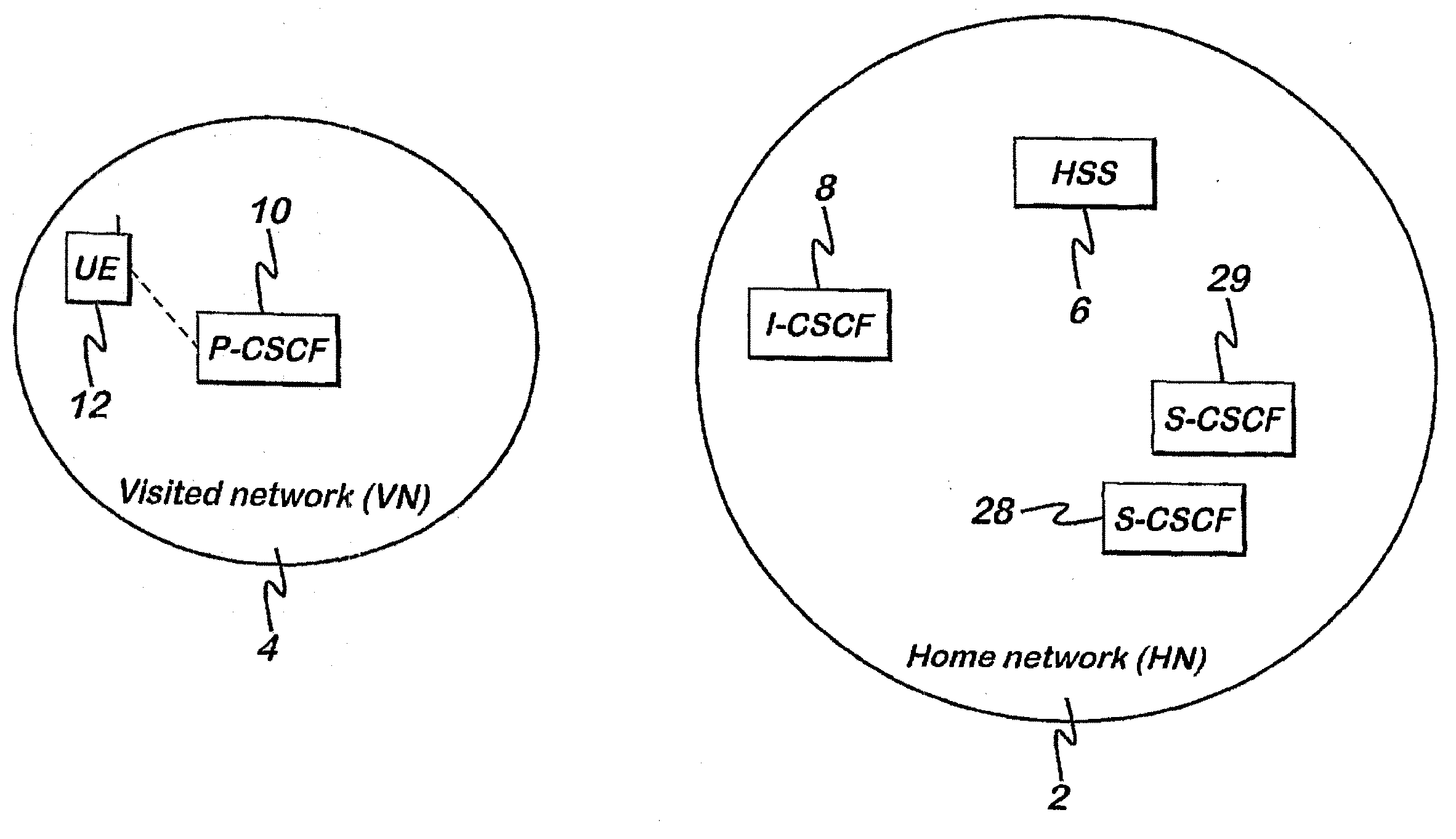
Allocation of a call state control function to a subscriber
InactiveUS20070283022A1Different effectControl complexityMultiple digital computer combinationsWireless network protocolsTelecommunicationsState control
A method of allocating one of a plurality of call state control functions to a subscriber, the method comprising: sending registration requests to the plurality of call state control functions; storing information regarding the availability of the call state control functions in response to unsuccessful registration requests; and determining a call state control function for the subscriber in dependence on said stored information.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
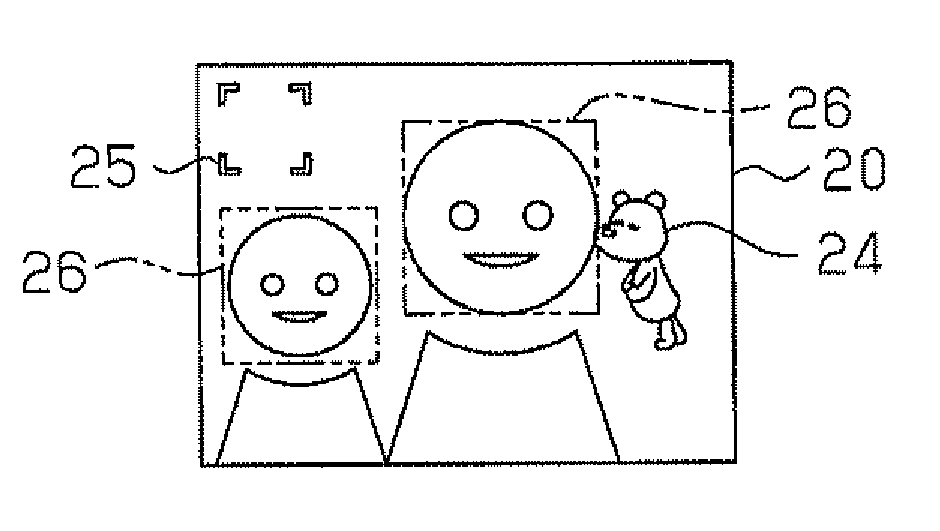
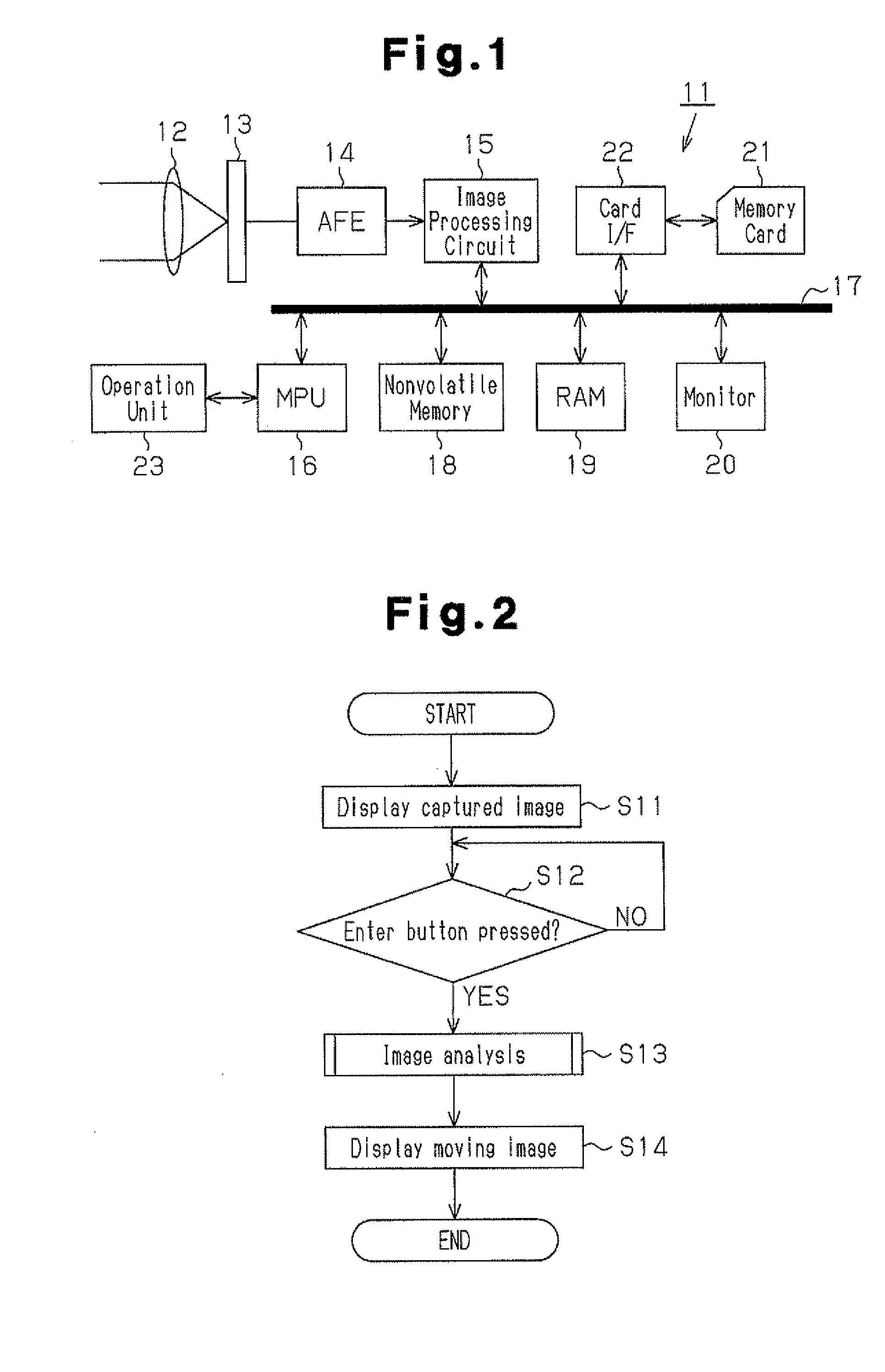
Image processor, electronic camera, and image processing program
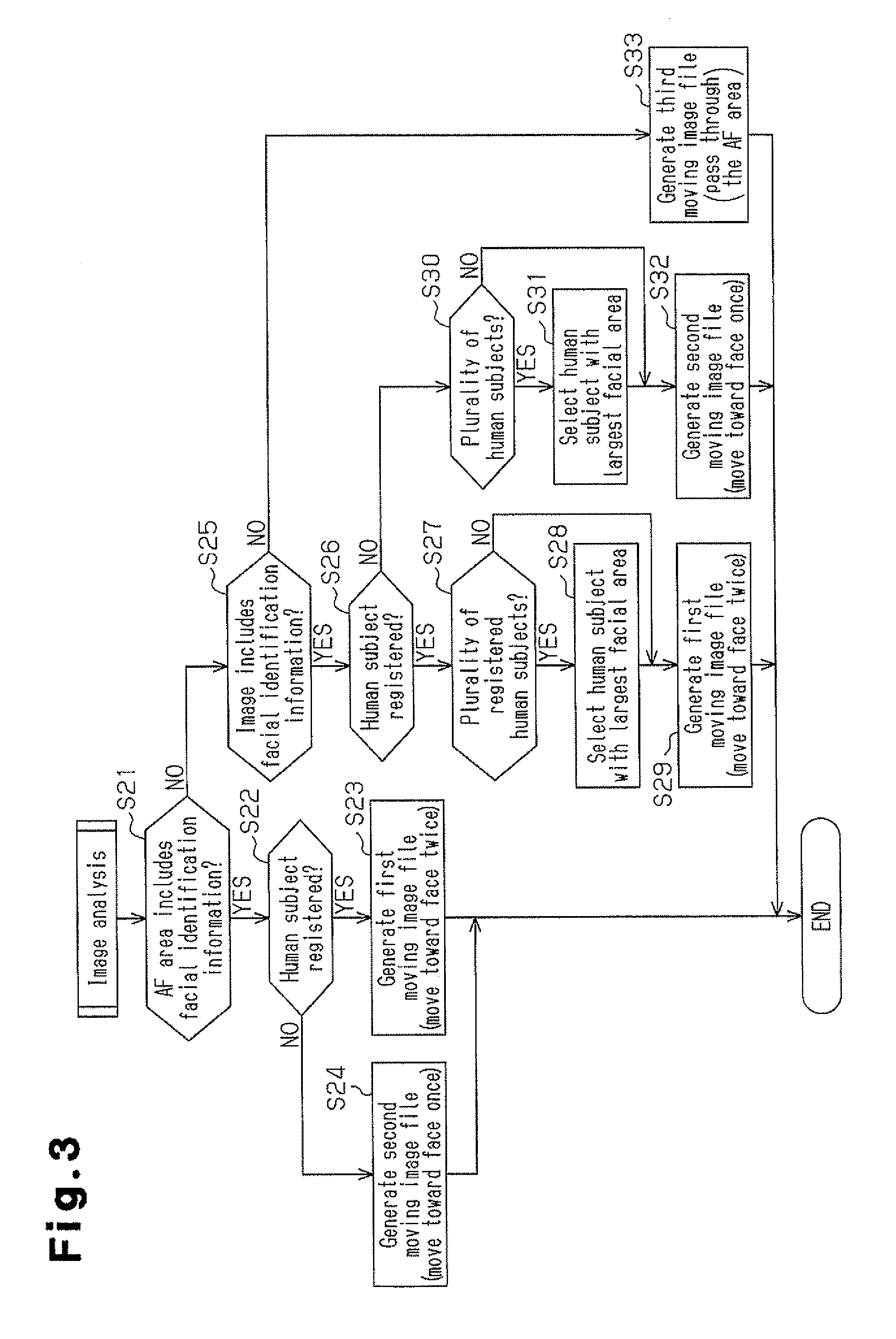
InactiveUS20110234838A1Different effectTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage analysisImaging analysis
An image processor including an acquisition unit and a moving image generation unit. The acquisition unit acquires image analysis information of a feature in an image. The moving image generation unit generates a moving image superimposed and displayed on the image so that the moving image is displayed in a pattern that changes in accordance with the image analysis information acquired by the acquisition unit.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Method for providing a vehicle tyre with studs, and a studded tyre for a vehicle
ActiveUS20170368889A1Improve propertiesDifferent effectTyresTyre tread bands/patternsMechanical engineering
Owner:NOKIAN TYRES
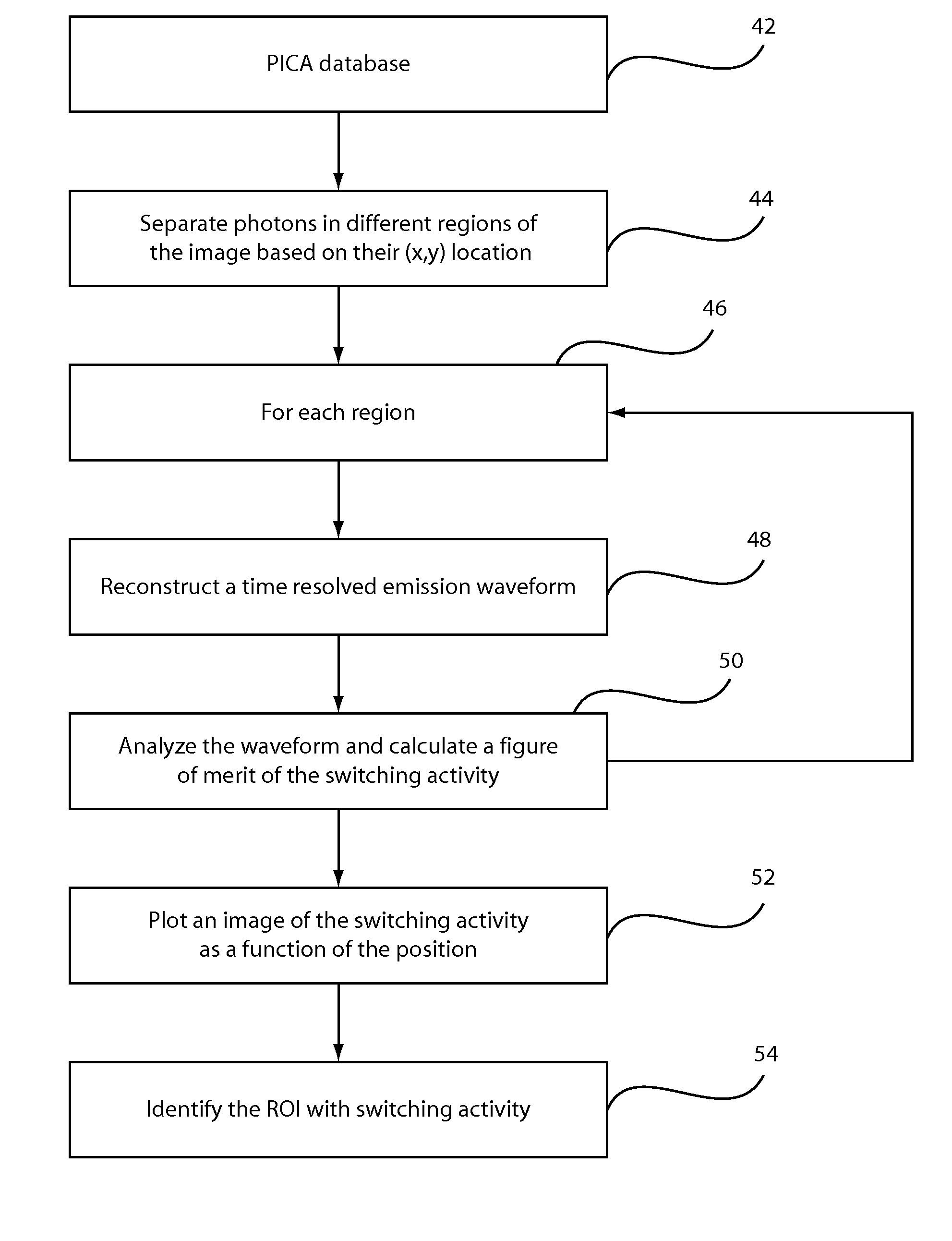
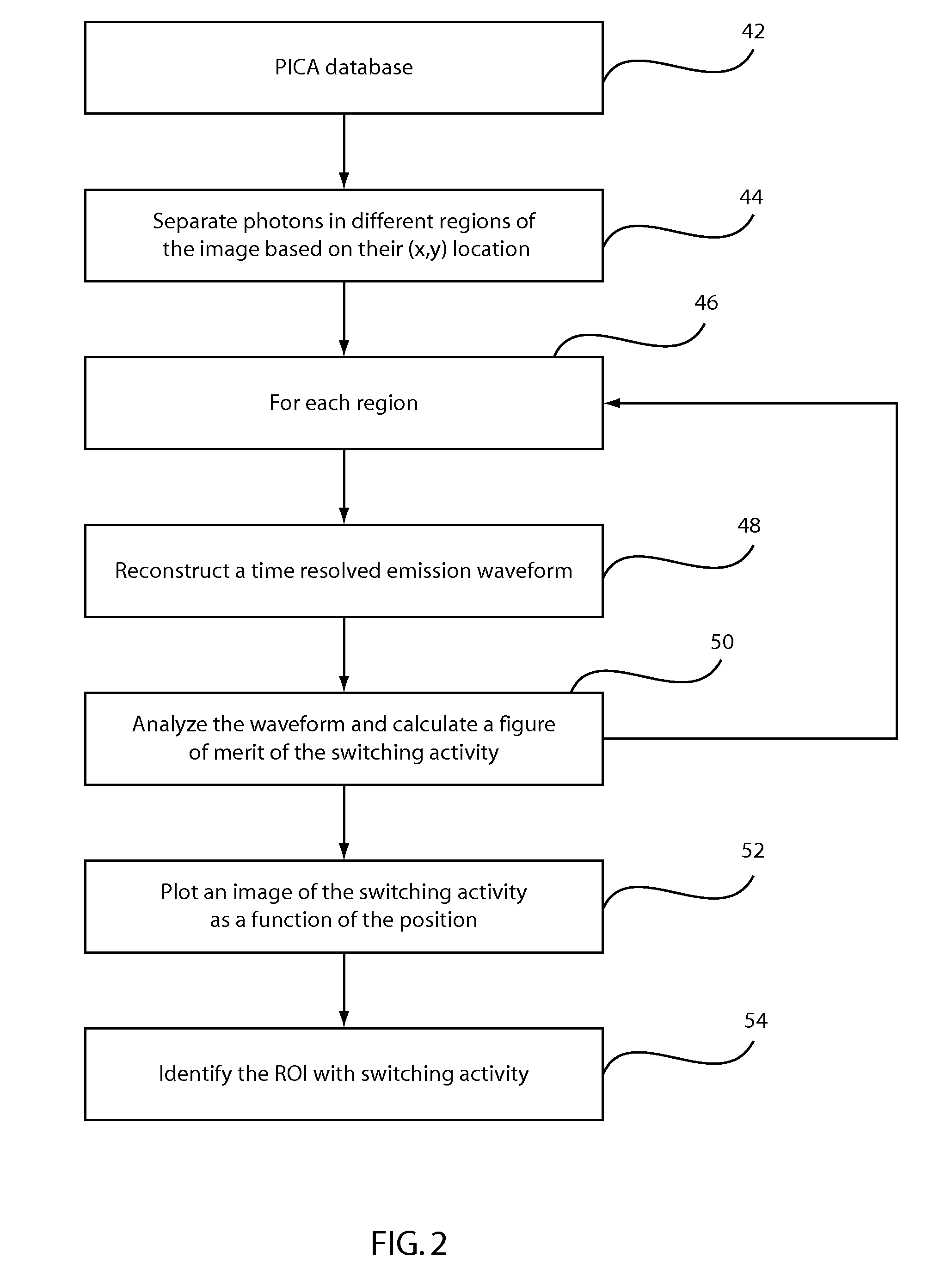
Method and system for quickly identifying circuit components in an emission image
A system and method for localization and resolvability of an integrated circuit includes selecting one or more electrical stimuli to be applied to a device under test such that the electrical stimuli are chosen to provide a baseline image and a distinguishing image effect as a result of the chosen stimuli when applied to the device under test. The one or more electrical stimuli are applied to the device under test. Emissions from the device under test are measured to provide a measurement data set from the one or more electrical stimuli using one or more measurement tools for collecting the baseline image and the distinguishing image effect. The measurement data set is analyzed to localize and evaluate circuit structures by comparing the baseline image and the distinguishing image effect.
Owner:IBM CORP
Optically polarizing retardation arrangement, and microlithography projection exposure machine
InactiveUS7053988B2Different effectPolarising elementsDiffraction gratingsOptoelectronicsOptical polarization
A retardation arrangement for converting an input radiation beam, incident from an input side of the retardation arrangement, into an output radiation beam which has over its cross section a spatial distribution of polarization states which can be influenced by the retardation arrangement and differs from the spatial distribution of polarization states of the input radiation, is designed as a reflective retardation arrangement. A useful cross section of the retardation arrangement has a multiplicity of retardation zones of different retardation effect. Such a mirror arrangement having a retardation effect varying as a function of location can be used to compensate undesired fluctuations in the polarization state over the cross section of an input radiation beam and / or to set specific output polarization states, for example in order to set radial or tangential polarization.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Electronic lock
InactiveUS20070046040A1Different effectNon-mechanical controlsFastening meansStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:CHANG CHEN FEI
Cage type jewelry links
Owner:ROZENVASSER AVRAHAM
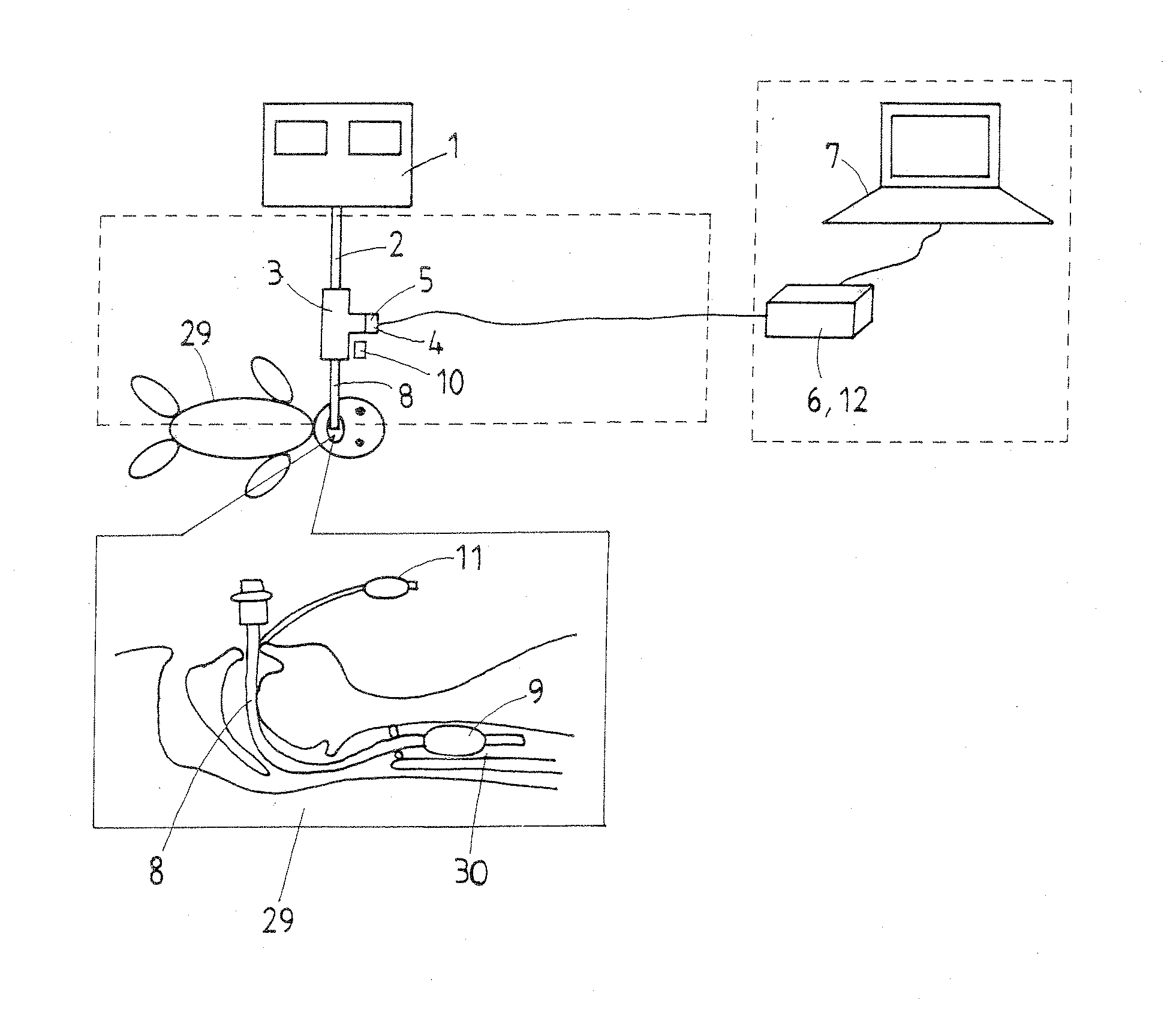
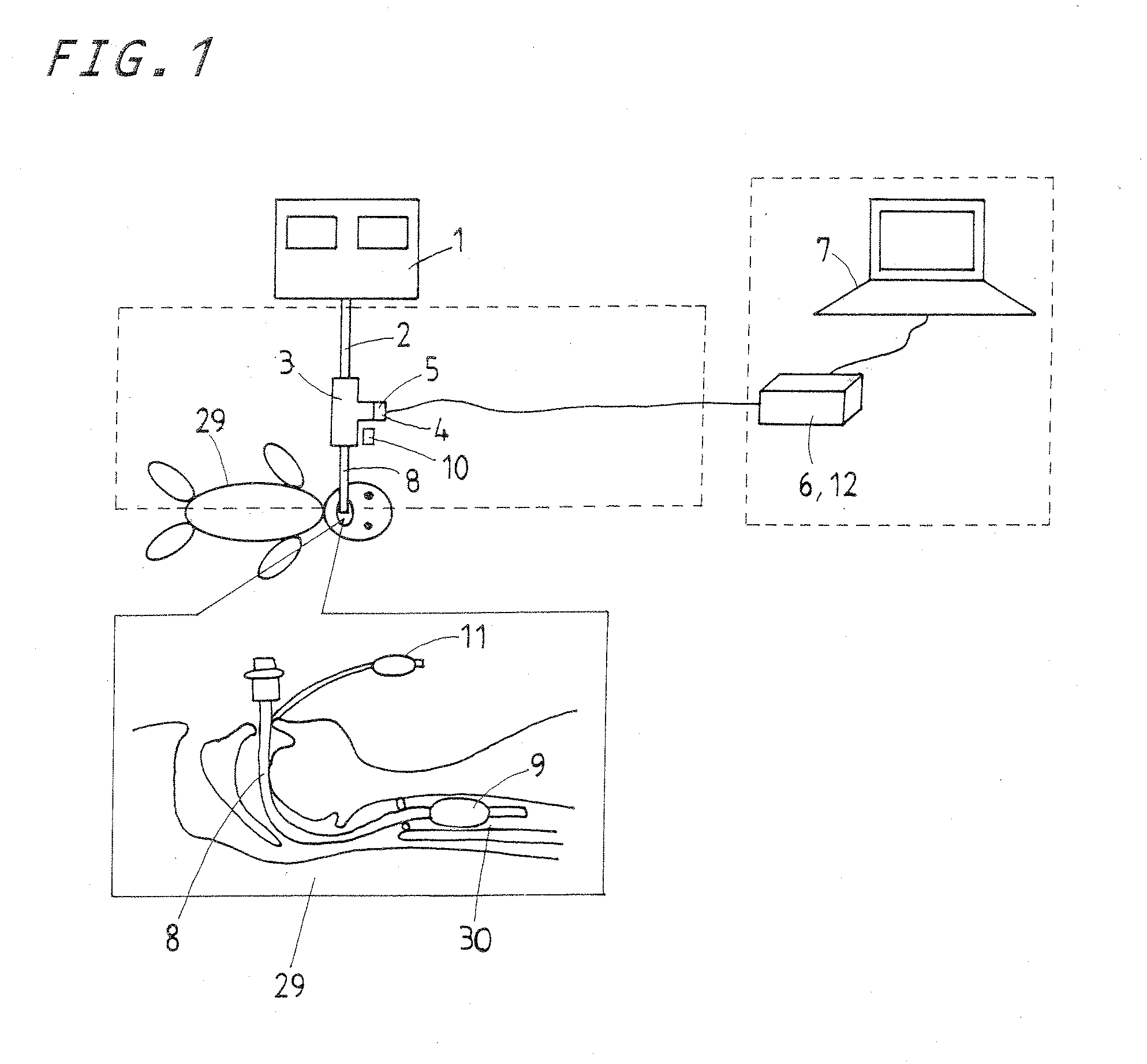
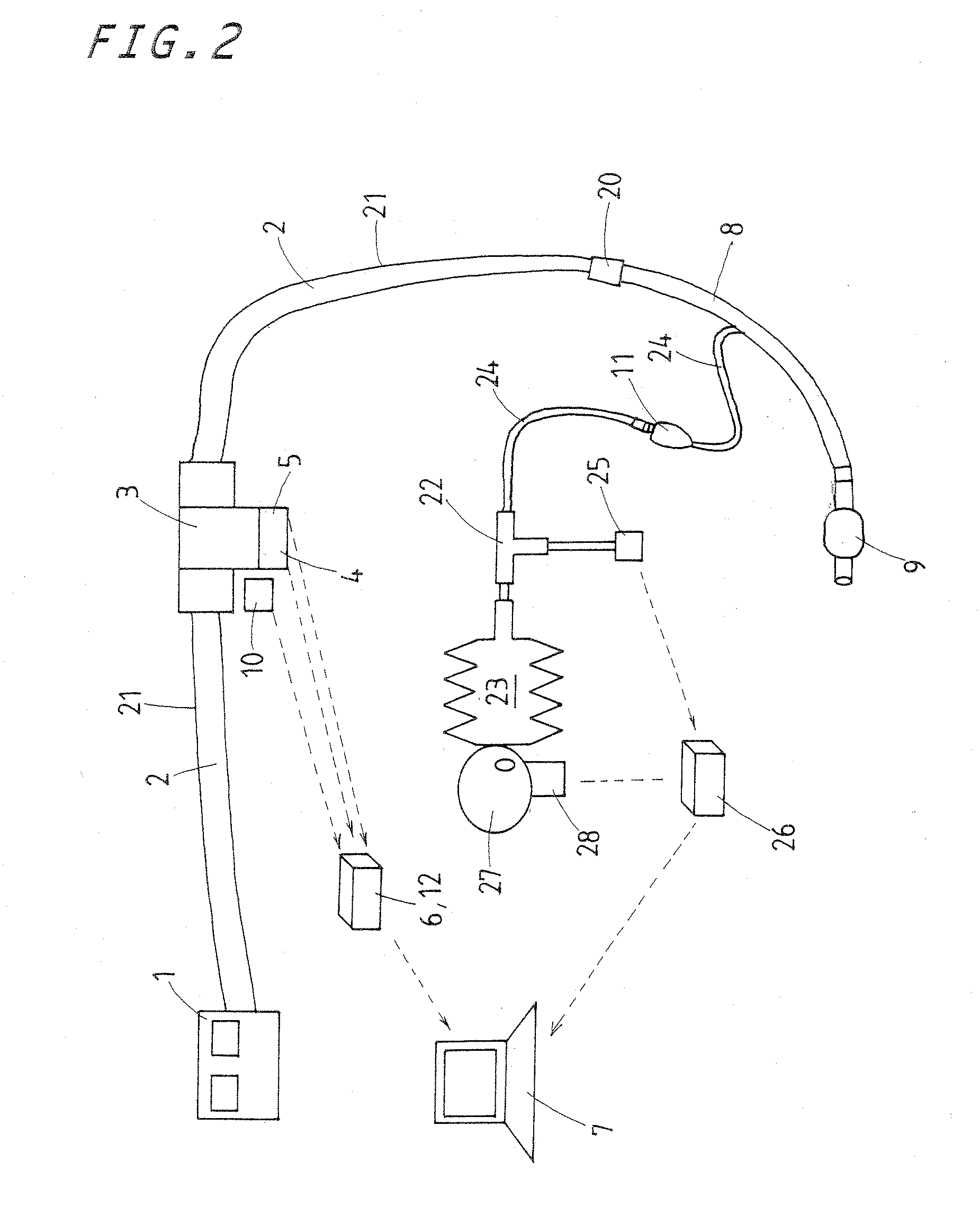
Maintenance and management system for endotracheal tube in intubation
A maintenance and management system for tracheal tube in tracheal intubation makes it easier or steadier to identify endotracheal tube placement in the airway, check a tracheal stenosis due to sputum clogging, confirm a breakaway of the tube out of the airway, store and monitor measured data, diagnose automatically the complications, and obtain data for reproducing function of sound in a breath circuit. A ventilator tube is connected to the endotracheal tube and provided therein with a microphone to sense a breath sound transmitted via the endotracheal tube and a pressure sensing element to measure a circuit pressure in the ventilator circuit for the endotracheal tube. The data derived from the sensing elements is processed in a personal computer to be used to measure whether the breath sound and the circuit pressure are within a range of a prescribed value.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP KYUSHU INST OF TECH (JP)
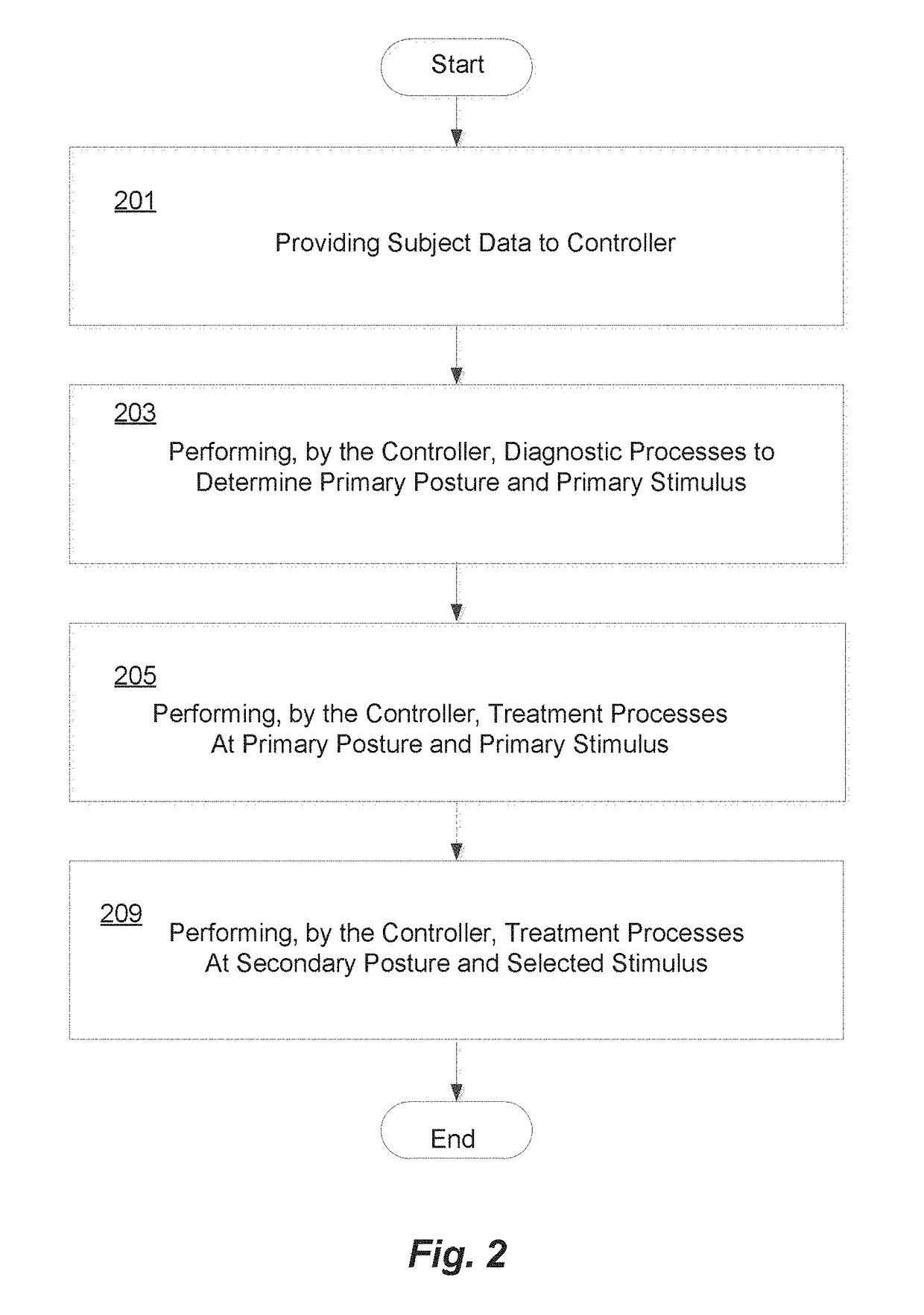
Method For Diagnosis Of And Therapy For A Subject Having A Central Nervous System Disorder
ActiveUS20140135590A1Different therapeutic efficacyDifferent effectElectrotherapyPerson identificationDiseaseMedicine
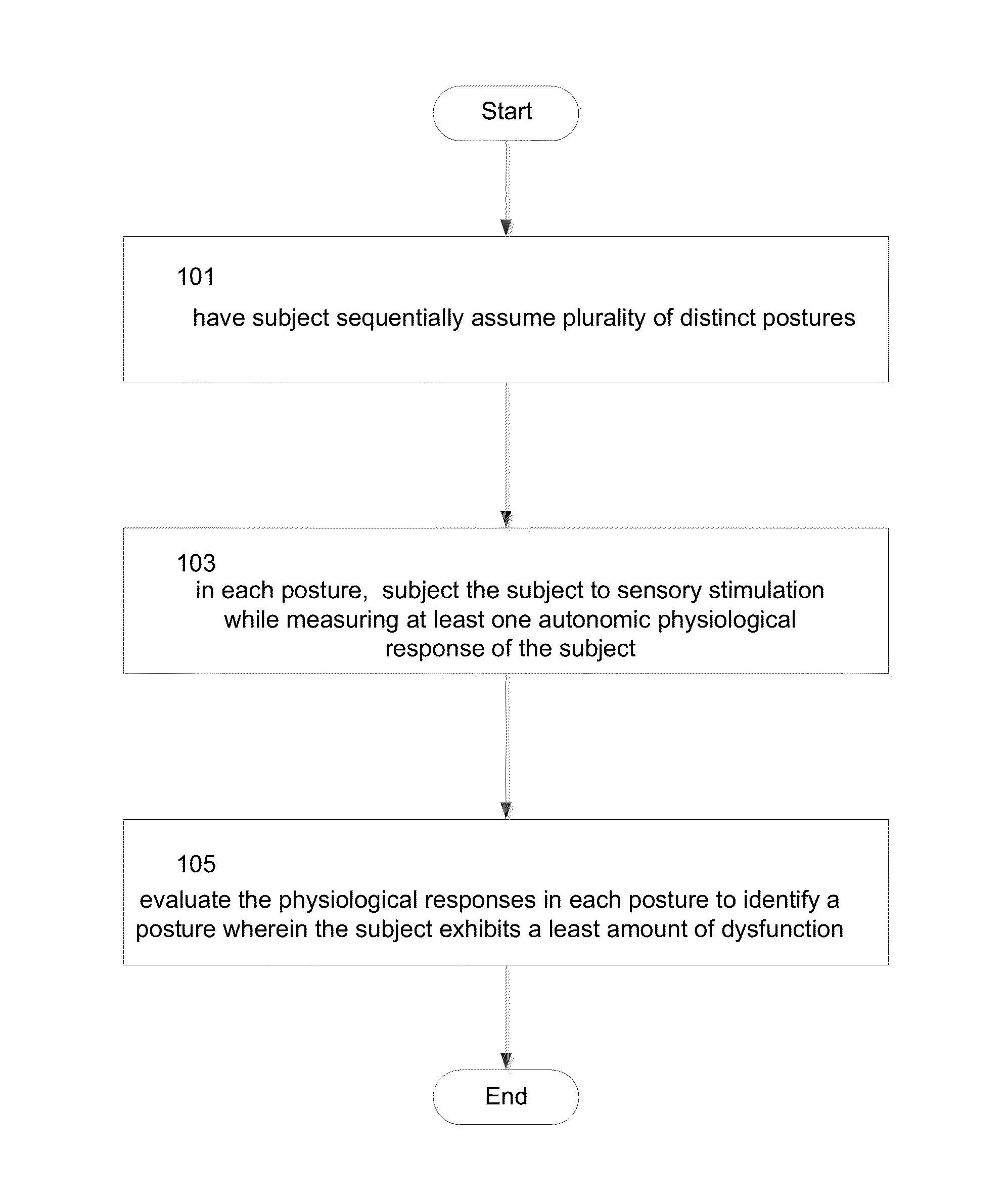
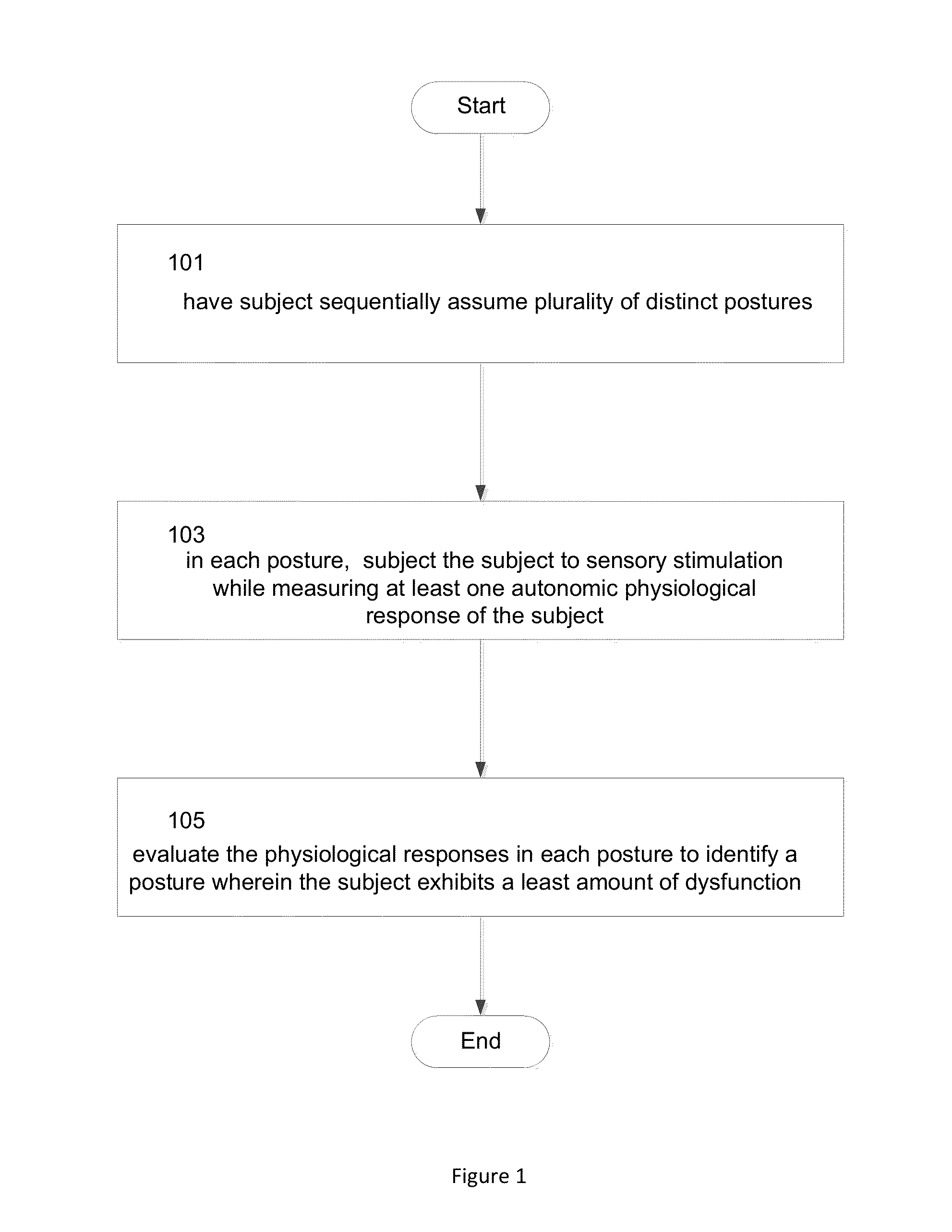
A method is provided of systematically evaluating and treating dynamic autonomic dysregulation in a subject. The method includes having the subject sequentially assume a plurality of distinct postures that may include, for example, walking, standing, sitting or supine. In each posture of the subject, the subject is subjected to sensory stimulation while measuring at least one autonomic physiological response of the subject. The autonomic physiological response may include, for example, oxygen saturation, heart rate, pupillary response, blood pressure, sweat production, pseudomotor activity or respiration. The physiological responses in each of the distinct postures are evaluated to identify a posture wherein the subject exhibits a least amount of dysfunction.
Owner:PEDRO VICTOR M
Disposable piping bags and nozzles therefor
InactiveUS20050170051A1Different effectPrevent tamperingReady-for-oven doughsMeat/fish preservationEngineeringDislocation
Piping bags including a nozzle base portion that is inserted into a disposable pouch through the fill opening and pulled into wedged, sealed position within the pouch. The nozzle base portion is provided with surface dislocations which resist the dislodgement of the nozzle base under the influence of various forces to which it is or may be subjected, without resorting to welding or the like. Accordingly, the nozzle may be easily engaged with and removed from the pouch of the piping bag in a domestic or small-scale commercial environment without marring, and re-used with a fresh pouch. The nozzle may also include a cap portion which is selectively matable with the base portion, and which serves inter alia to trap portions of the pouch to resist the dislodgement of the nozzle. The pouch itself may suitably form a security seal where the bag is distributed in a filled condition.
Owner:FOLKMAR JAN
Adjustable Traction System and Method for Footwear
InactiveUS20090293317A1Adjustability is providedDifferent effectFasteningsTraction systemElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:PRIDE MFG CO LLC
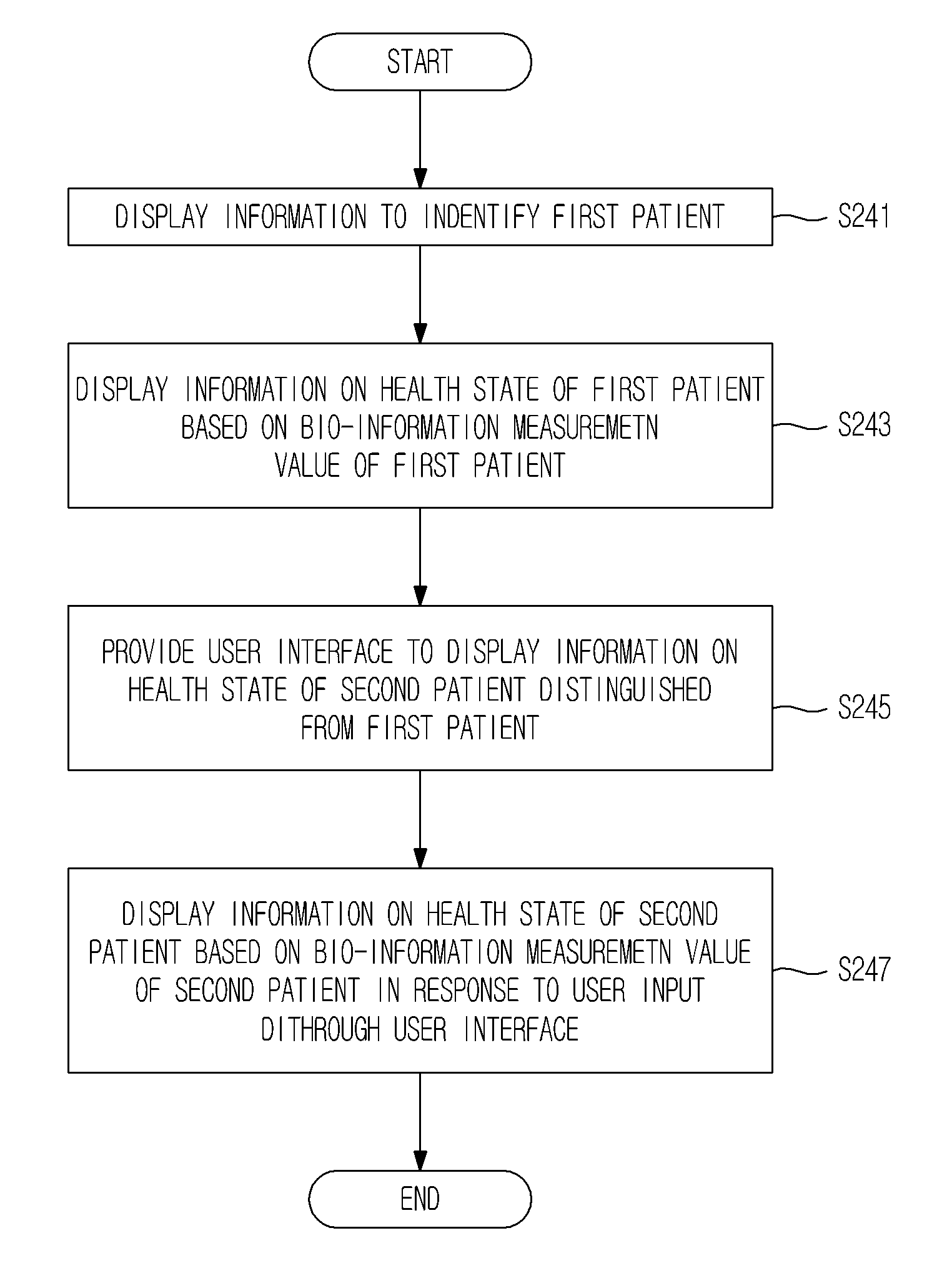
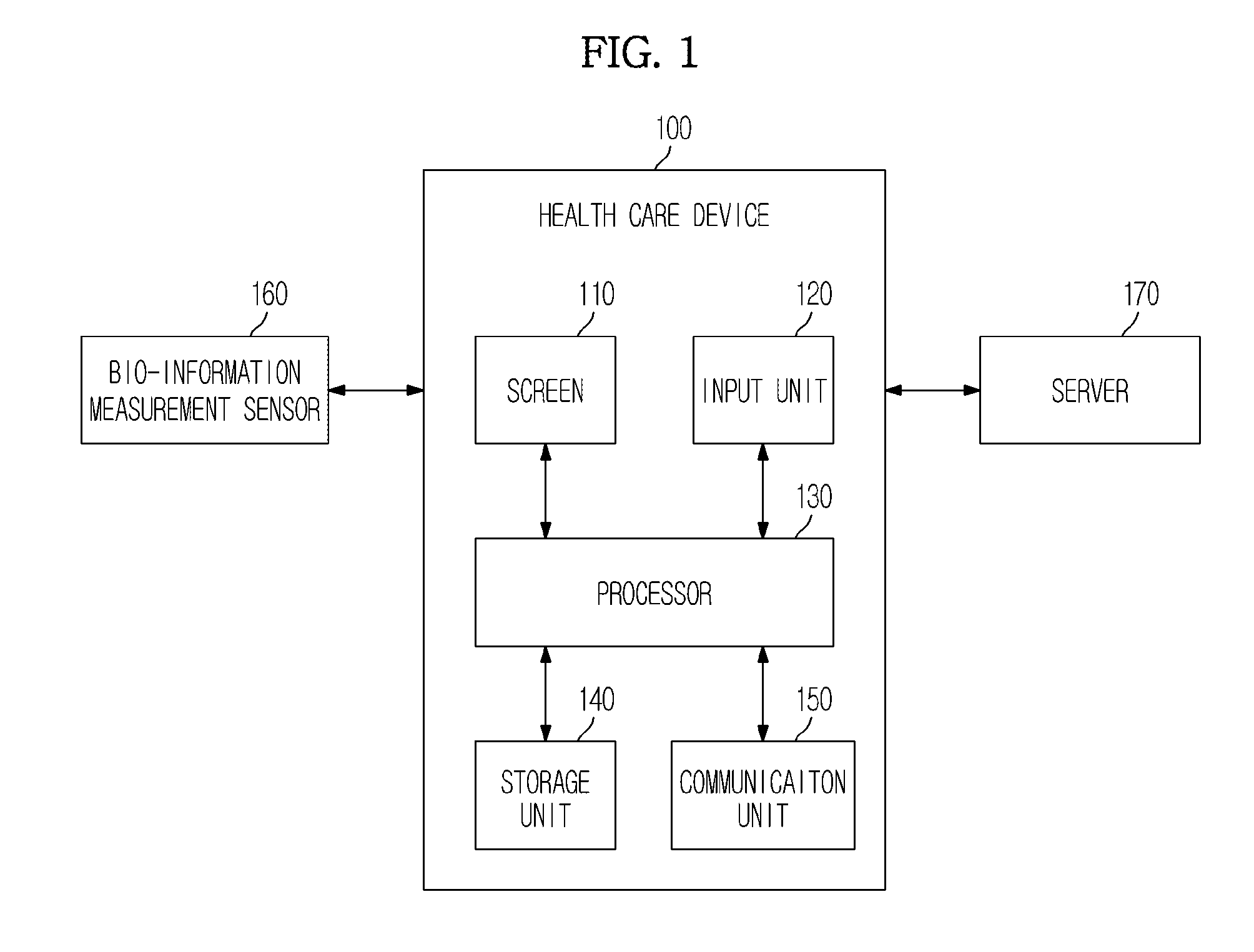
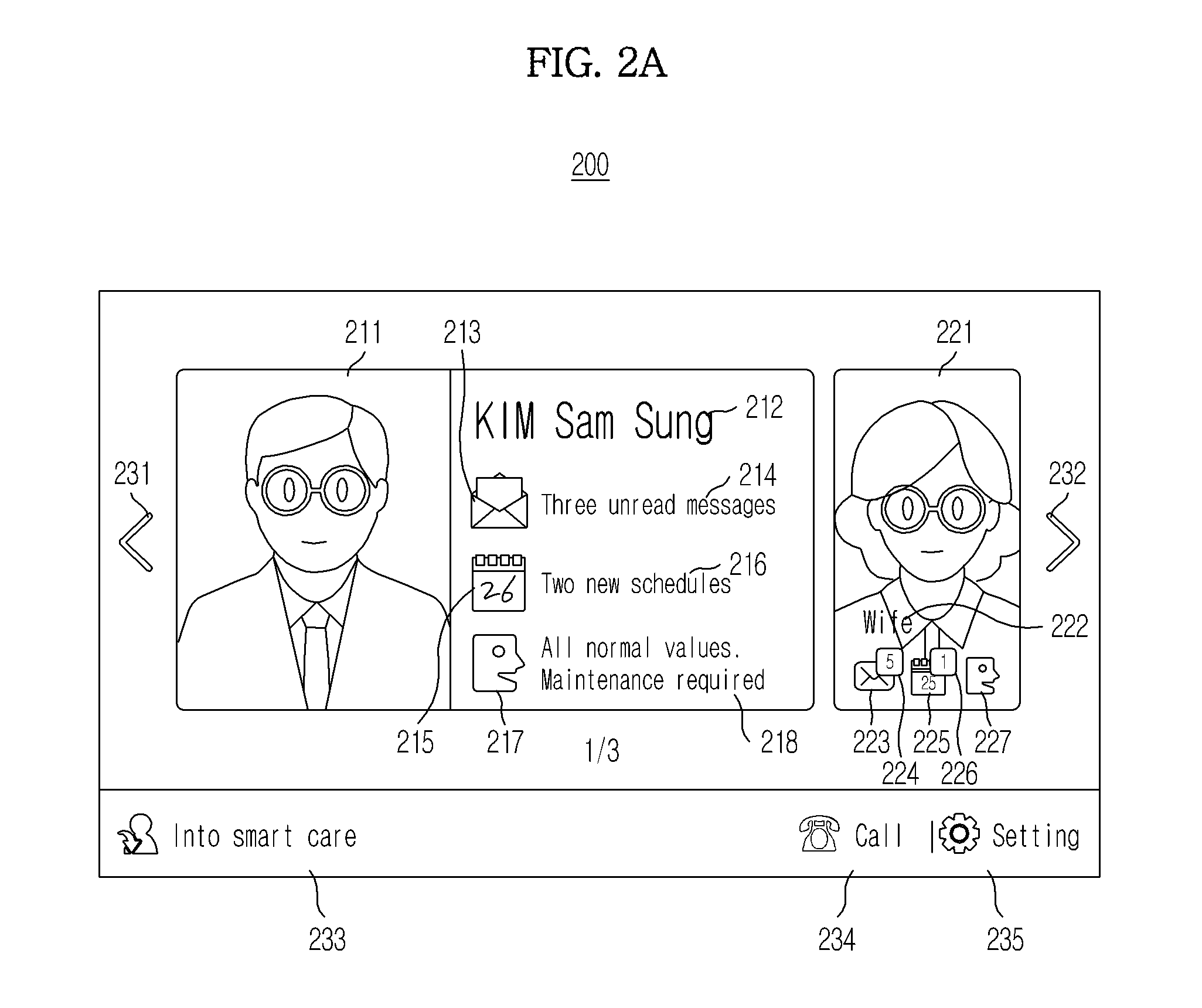
Health care device, method and graphical user interface for health care
InactiveUS20120143621A1Different effectPhysical therapies and activitiesData processing applicationsGraphical user interfaceHealth condition
A health care management method and device which display information to identify a first patient, display information on a health state of the first patient based on a bio-information measurement value of the first patient, display a user interface to display information on a health state of a second patient, and display information on a health state of the second patient based on a bio-information measurement value of the second patient.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus for producing active water
InactiveUS20060131223A1Improve permeabilityImprove solubilityWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsLiquid dispensingEngineeringBio engineering
This practical new type of device deals with the domain of water treatment technology. It is a device that prepares water of small molecular groups in various polymerization forms under varied operation conditions. It is applicable to various fields including planting, human health care, bio-engineering, descaling of thermal systems and printing and dyeing in textile industry. The new type has these features: The magnetizer is installed in the inner core, and the permanent magnet is installed in the magnetizer; Its advantages are: The structure is fresh, the adaptability is wide, the function is multiple, and the effect is stable and evident (for example, in vegetable growing, the yield of the various vegetables irrigated by the active water increased by 30%-103%).
Owner:HOU ZHIWEI +2
Casing, method for manufacturing the same, and electronic device having the same
InactiveUS20100046162A1Different effectWave amplification devicesFurniture partsTransmittanceEngineering
A casing includes a main body and a covering layer. The main body has a first transparent area and a second transparent area disposed as mirror images. Light passes through the first transparent area and the second transparent area. The covering layer covers the second transparent area and has a transmittance gradient. A method for manufacturing the casing and an electronic device having the casing are also disclosed.
Owner:PEGATRON
Enhanced safety bobbing head sculptural sculptures
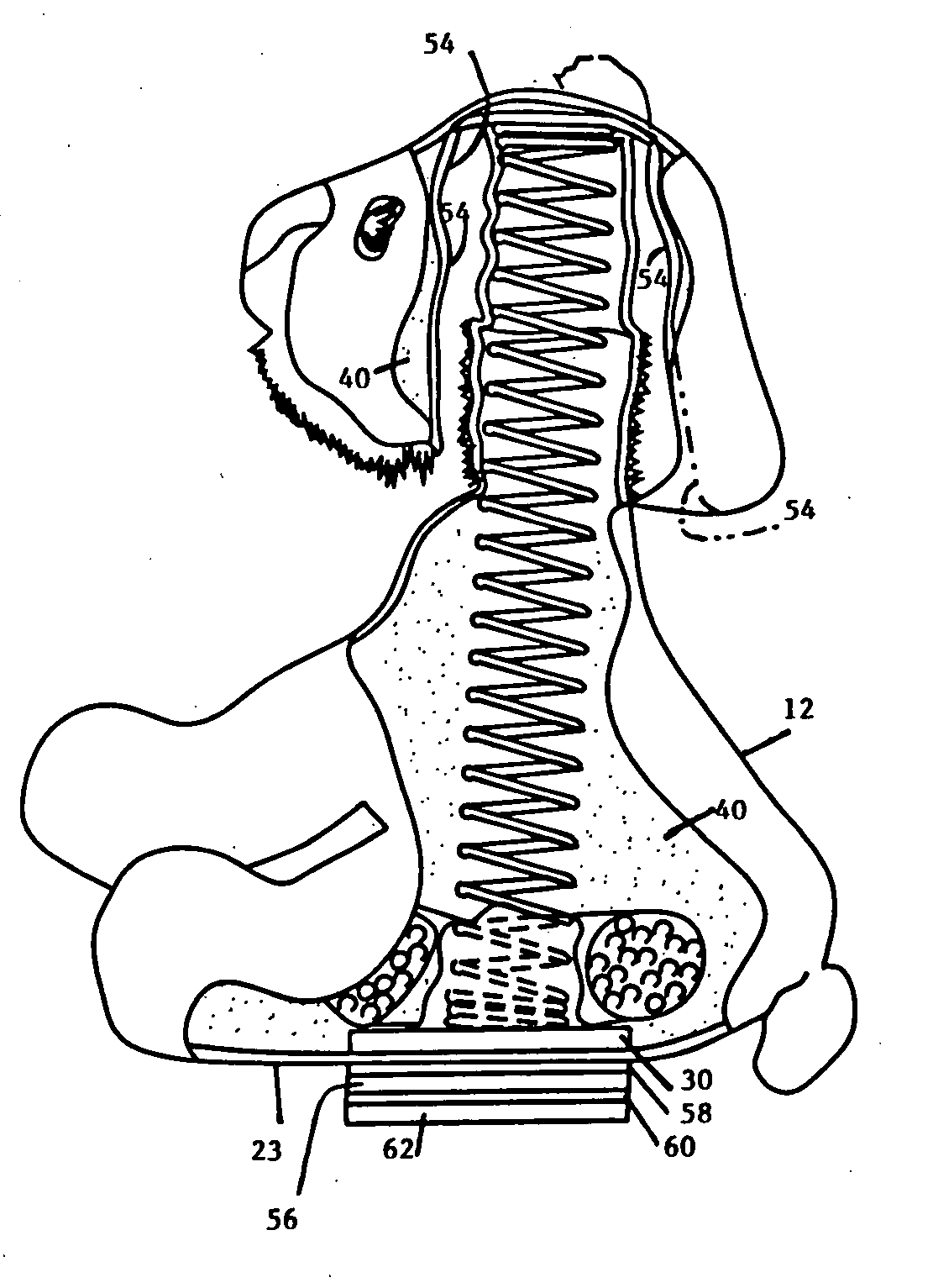
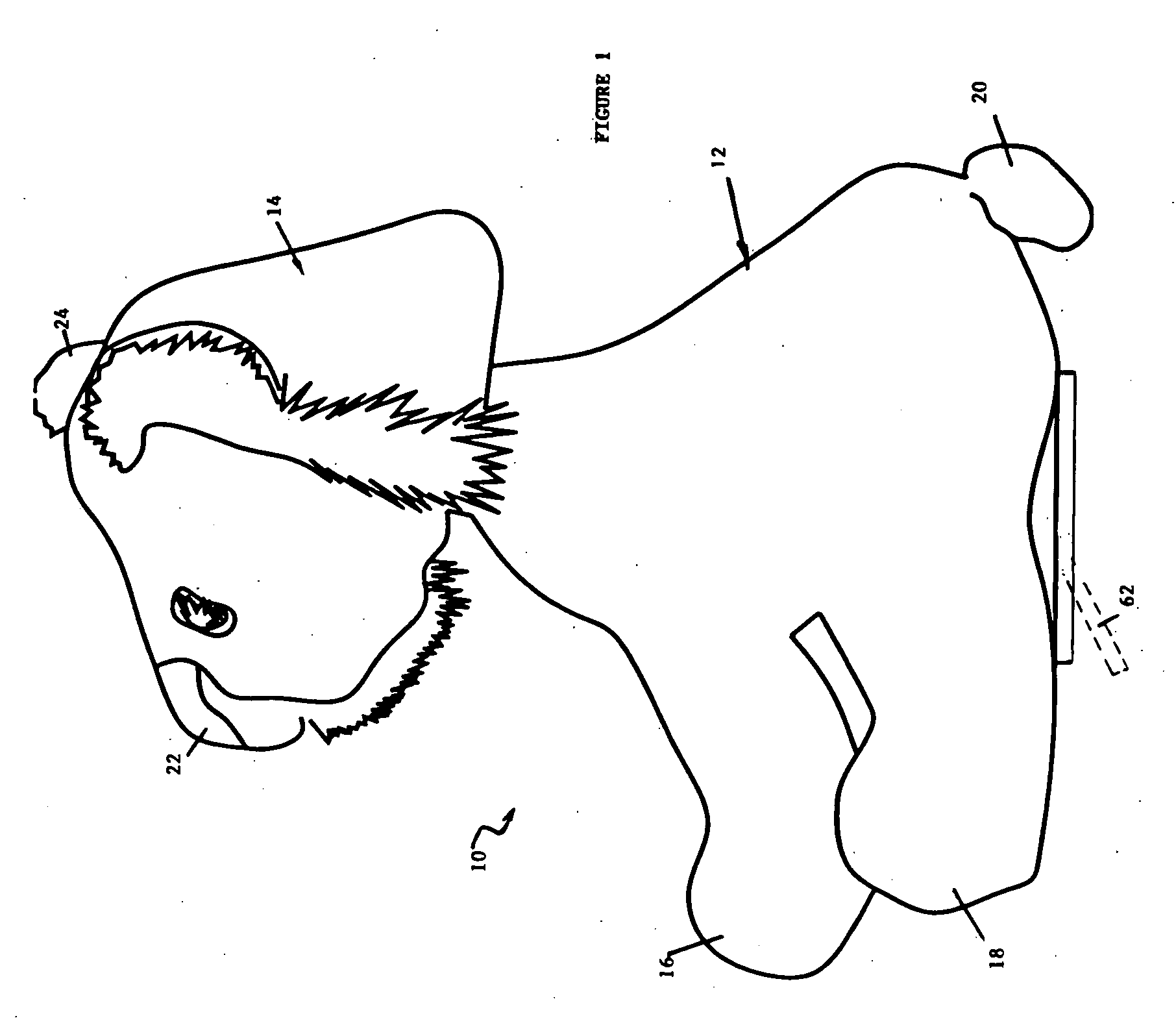
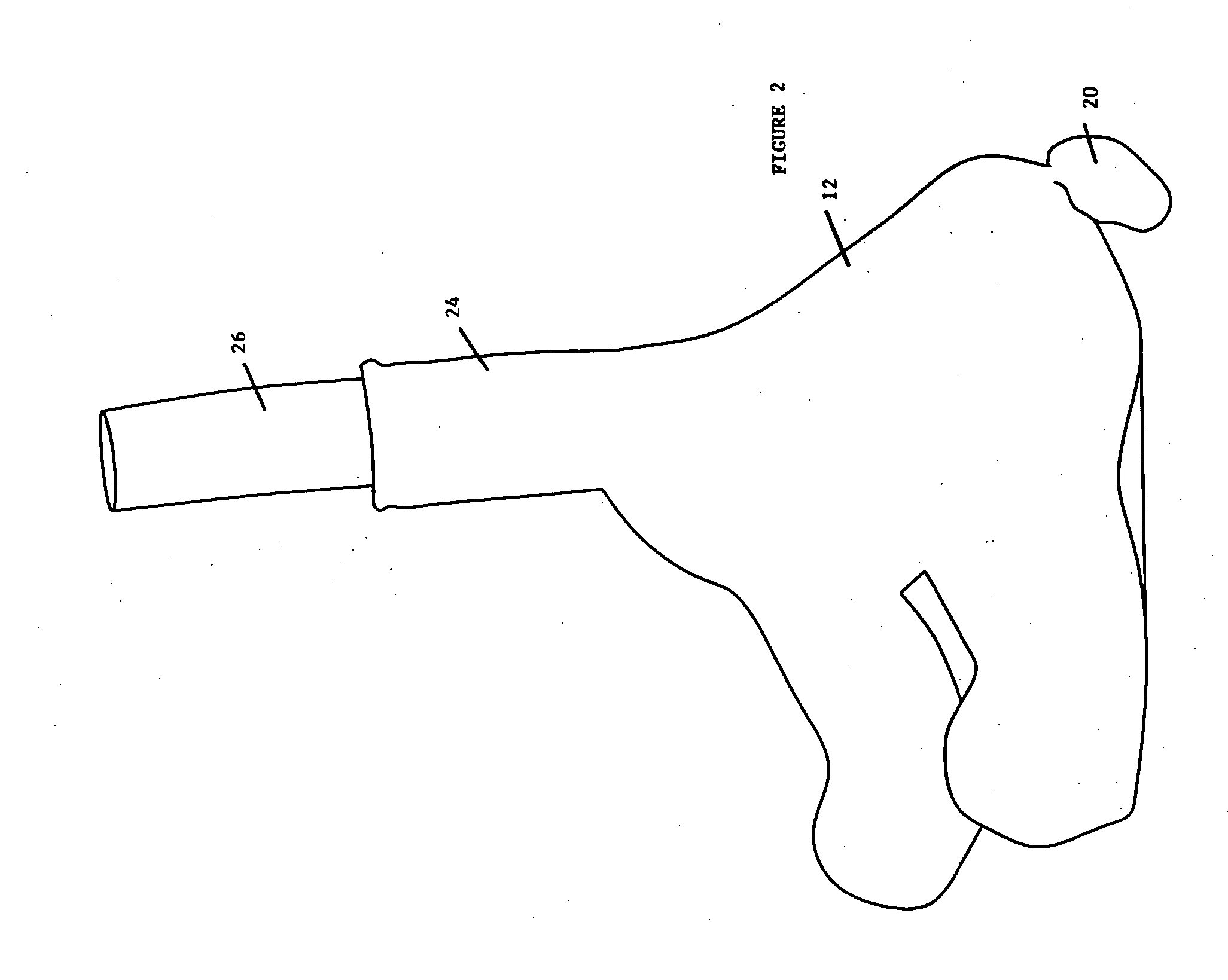
A bobble head sculpture comprising a base portion which is defined by an outer surface member defining an internal volume is disclosed. A spring has first and second ends. A bobbing member is mounted on the first end of the spring. A support base member is secured to the second end of the spring. The support base member is contained within the internal volume. Stuffing is contained within the internal volume. The stuffing bears against the support base member. The support base member extends to the edges of the volume at a plurality of points on the outer surface member whereby the support base member is held in a relatively stationary position by those points on the outer surface member and the stuffing. In accordance with the invention, the base portion may be the body portion of a figure and the bobbing member the head of the figure. The stuffing may comprise a mixture of plastic beads and a fibrous material. Optionally, the spring is covered by a crimped or gathered fabric sleeve. A measure of safety is provided by the inventive system by making the sculpture soft account of the nature of the stuffing disposed in the internal body.
Owner:CHOSUN INT
LED projection lamp
InactiveUS20140016310A1Different effectHigh color rendering indexNon-electric lightingLight source combinationsIlluminanceColor rendering index
The present invention disclosed an LED projection lamp, including a lamp bracket, where the LED projection lamp further includes a plurality of light mixing units; the light mixing units each include a lens assembly and a plurality of LEDs, and are fixed on a surface of the lamp bracket in a disperse manner; and each position on the surface of the bracket has a different spatial angle. In the present invention, the light mixing units are fixed at fixation surfaces with different inclined angles on the lamp bracket, so that the light mixing units are arranged in a disperse manner, hence realizing different pixel effects. The white light LEDs and colored-light LEDs are used in coordination, so that the full-color adjustment function is implemented on each pixel while sufficient illuminance is provided; in addition, through a light mixing function between the single color LED and white-light LED, the color rendering index is improved to 90% or higher.
Owner:SHANGHAI GRANDAR LIGHT ART & TECH
Flexible toy
InactiveUS20060217032A1Different visual organoleptic effectDifferent effectDollsColor differenceEngineering
A flexible toys comprises mainly a flexible main body provided with a holding portion extending from the top of the flexible main body, and engaged with at least one swing part on the middle section thereof; wherein said flexible swing part is provided with several flexible bars; the flexible main body and the flexible swing part can be designed to have different colors. As the operator holds the holding portion on the top of the flexible main body, said flexible main body is in a stretched state, whereby as the operator rotates the flexible main body to the right, the flexible main body becomes twisted. Upon releasing the flexible main body, the flexible main body will turn quickly to the left, thereby cause the fling of the flexible bars of the flexible swing part. As the flexible main body rotates left to a certain extent, the flexible main body becomes twisted and then turns to the right again. Under such constant rotation to right and left, the fling of the main body and swing part can persist. During the course of the fling, a lurid color could be presented due to the color difference between the flexible main body and the flexible and the purpose of amusement can be achieved.
Owner:KUO WEN CHUAN
Adjustable and replaceable lens structure for portable electronic devices
A movable and replaceable lens structure for electronic devices has a lens-mounting body mounted on and electrically connected with a electronic device, and a movable lens module mounted on the lens-mounting body and having a movable mechanism mounted on the lens-mounting body or a housing of the electronic device. The movable lens module has a movable mechanism mounted on the lens-mounting body or the housing of the electronic device. A lens is connected with the movable mechanism. An operation part is connected with the movable mechanism. The movable mechanism can be operated to move along a straight line, rotate or pivot, thereby moving the lens to align with an optical axis of the movable lens module and varying the focus of field of view of the movable lens module. Accordingly, the lens with different picture-taking effect can be provided, such as a wide-angle, microscopic or telescopic lens.
Owner:DIGILENS
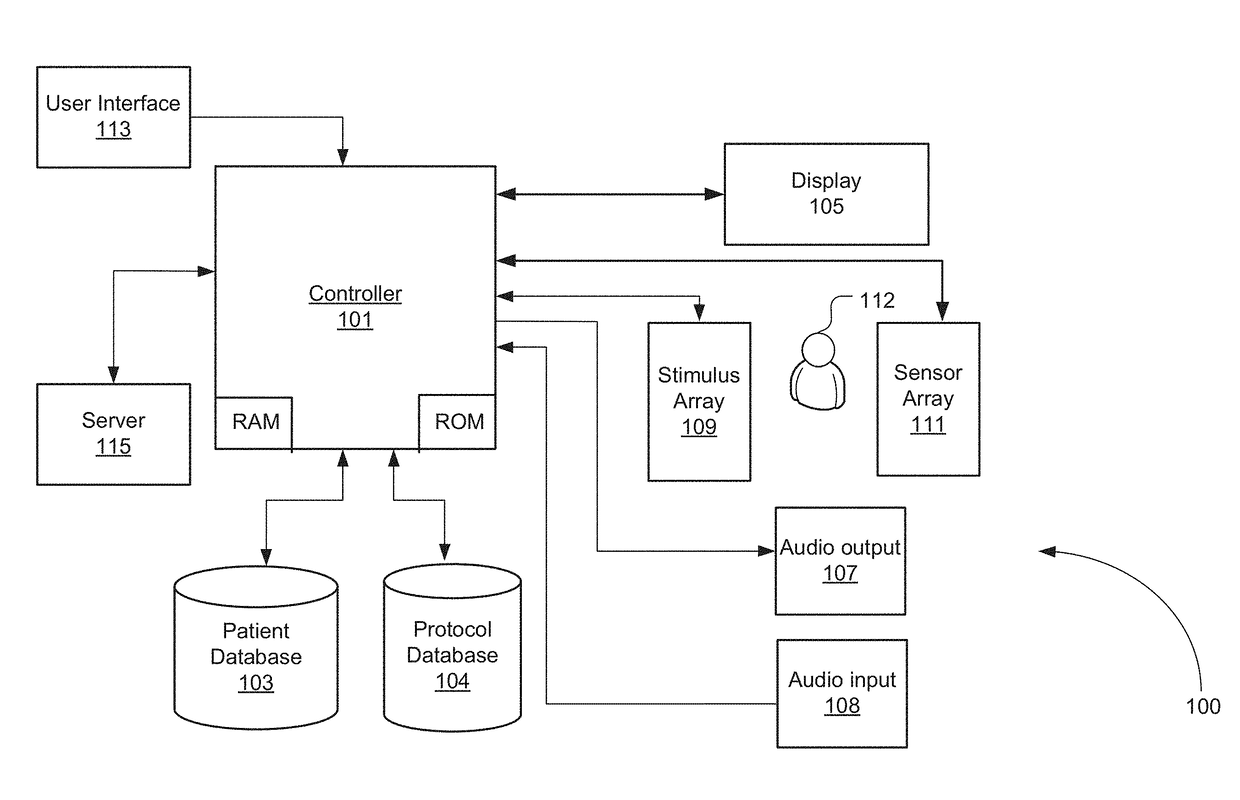
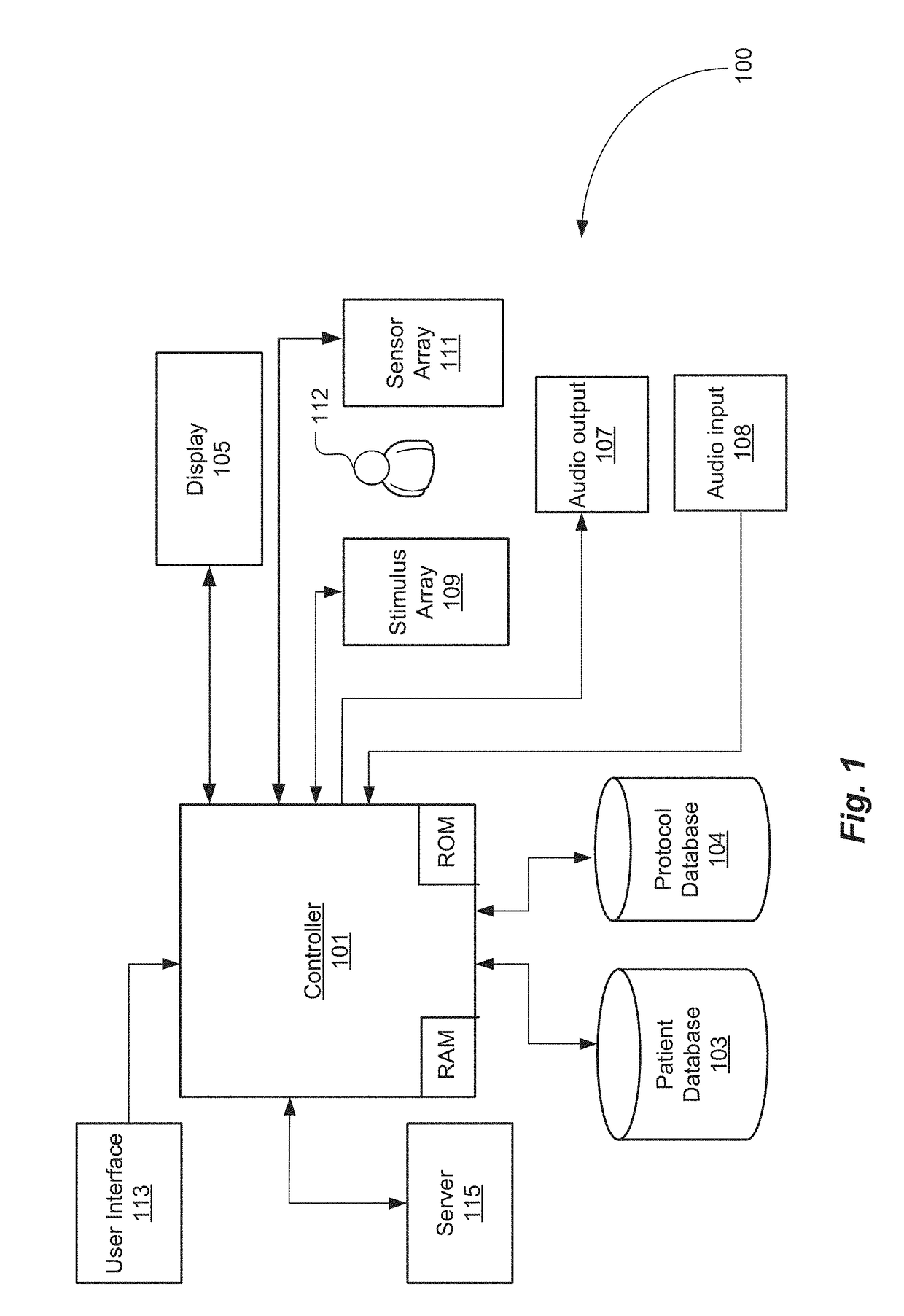
Controller-Based Apparatus and Method for Diagnosis and Treatment of Acquired Brain Injury and Dysfunction
ActiveUS20170231515A1Good treatment effectMinimizing health practitioner involvementMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesTelemedicineNervous systemPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
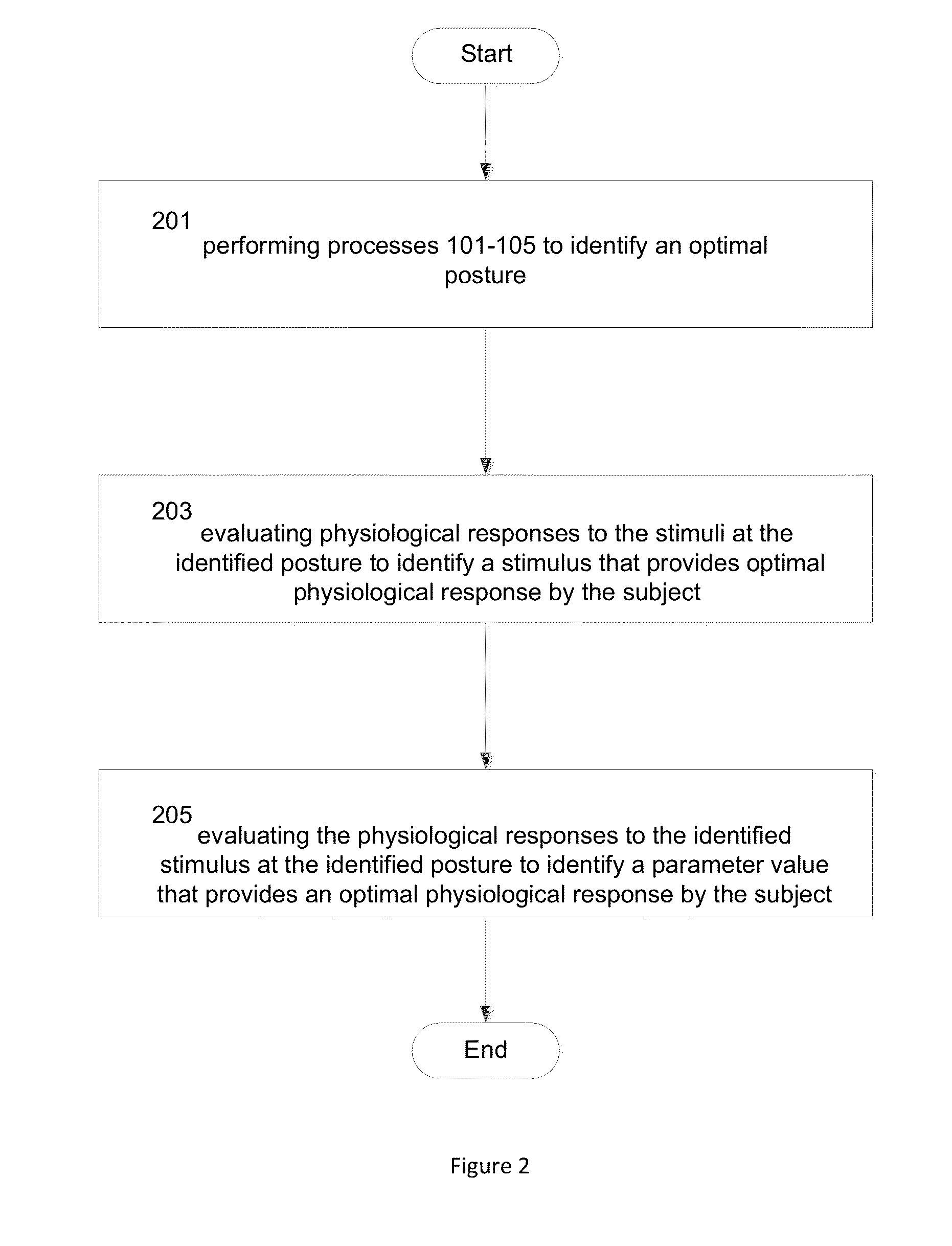
A controller-based apparatus for diagnosis and treatment of a subject with acquired brain injury and dysfunction. Various embodiments of the invention described herein recognize that different body postures affect the autonomic nervous system differently, and therefore various external stimuli may have different therapeutic efficacies when a patient or subject is in each body posture. Postures, such as walking, sitting, standing, prone and supine, have different effects on the autonomic nervous system, and therefore some stimuli have different physiological efficacies while a patient or subject is in a given body posture. Disclosed embodiments of the present invention leverage this relationship to provide a controller-based apparatus that determines a combination of posture and stimulus that has optimal therapeutic effect, while minimizing health practitioner involvement. The controller based apparatus provides a treatment that stimulates the nervous system through a combination of noninvasive therapies that stimulate brain cells to increase their efficiency—this promotes the formation of pathways that help transfer information throughout the brain in such a way that in the end, the affected area of the brain and overall brain function are improved without medication or surgery.
Owner:PEDRO VICTOR M
Head light
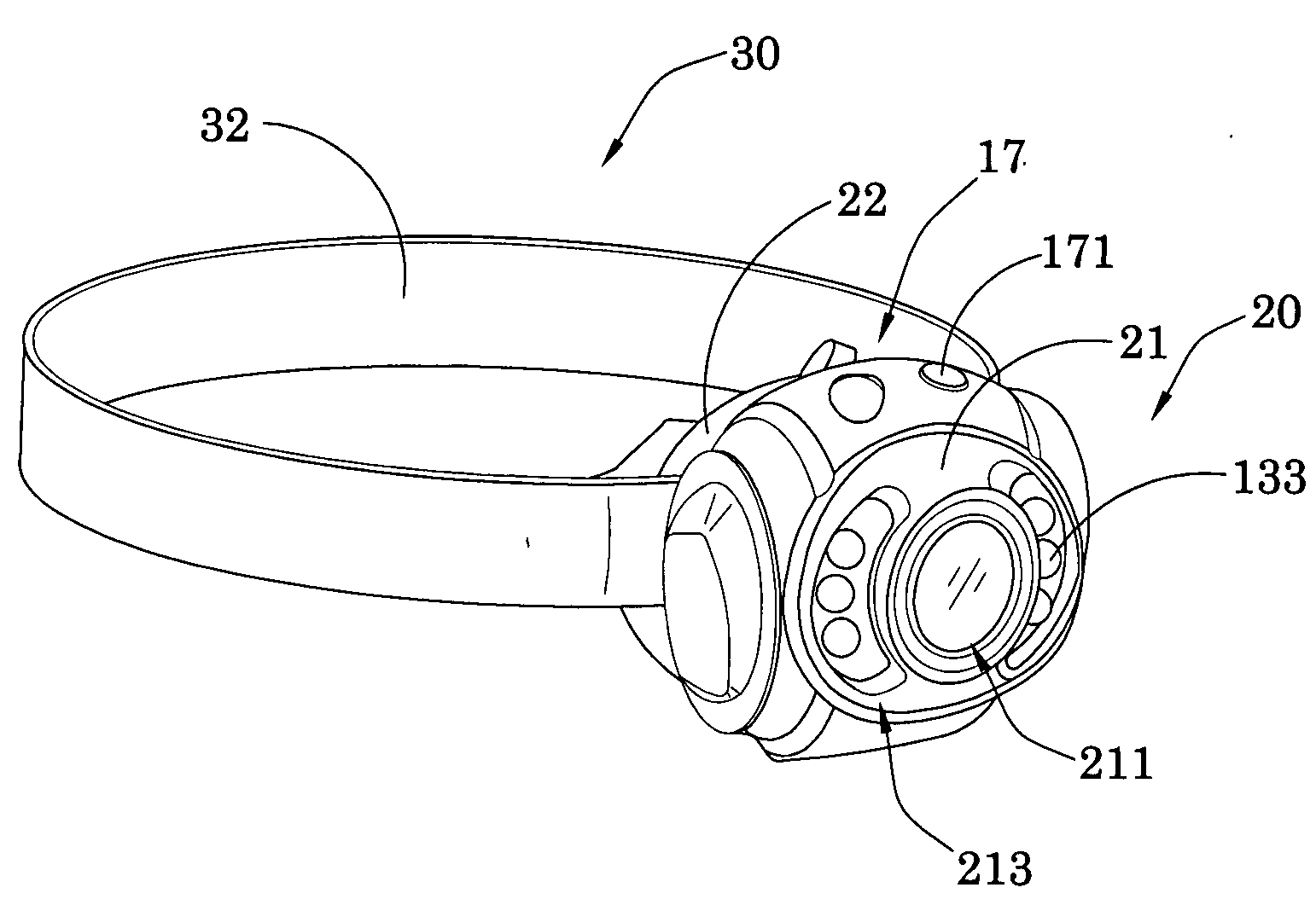
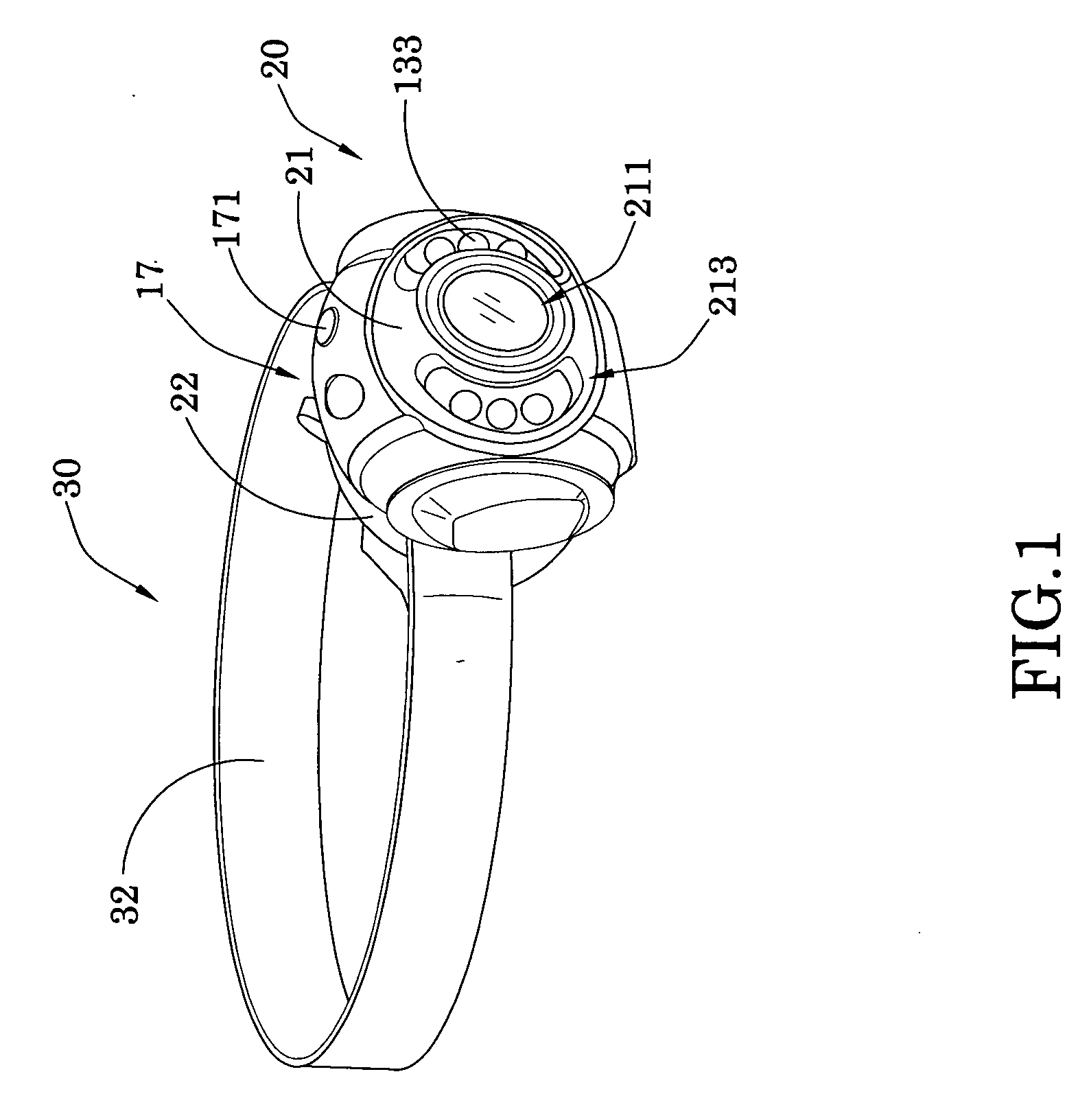
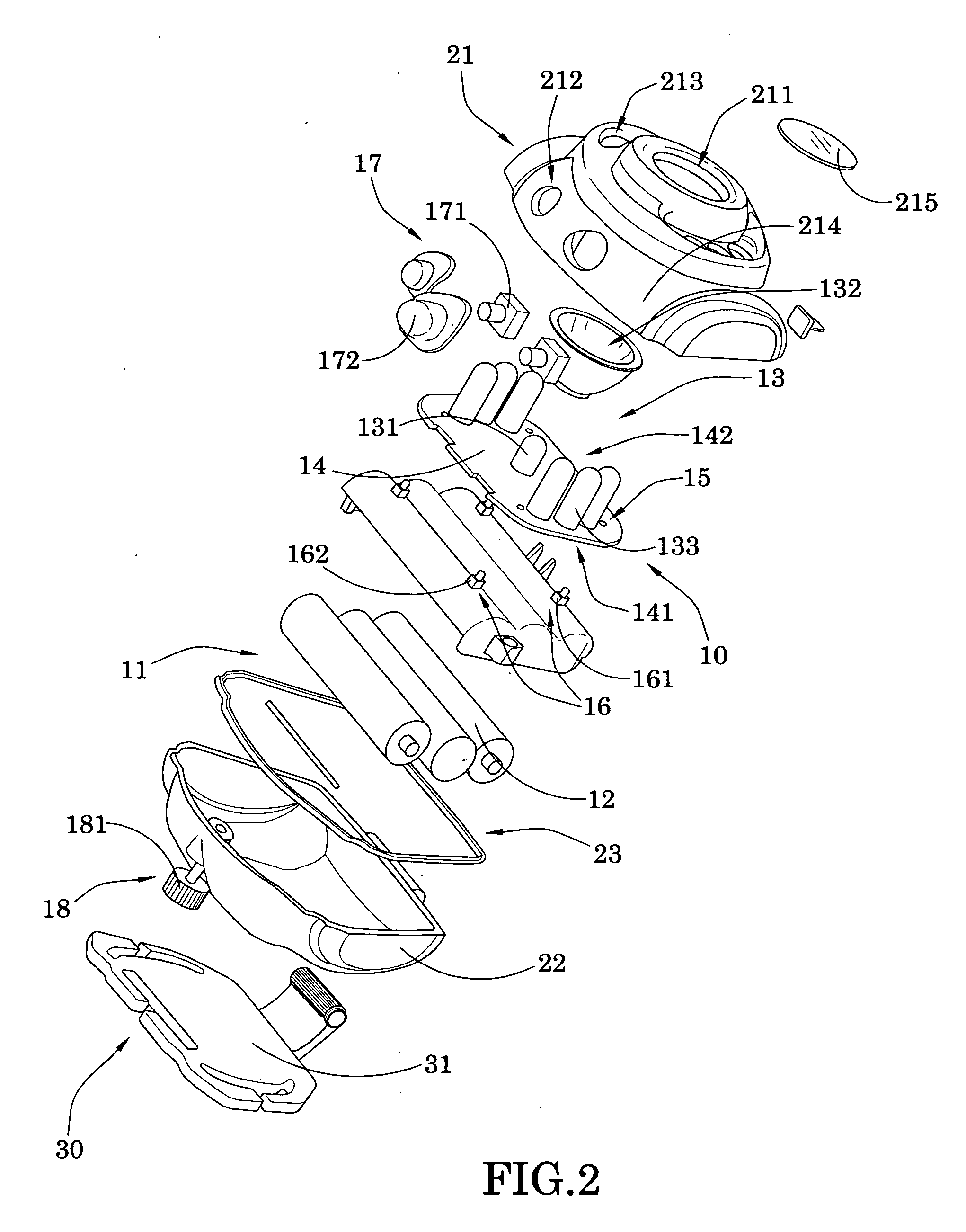
InactiveUS20100271810A1Different effectGood choiceLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceLight sourceHeaded light
A head light includes a light core, an assembling accessory and a hear gear. The light core includes a light source for generating light. The assembling accessory includes a front casing and a back casing and defines a core cavity within the front and back casings to receive the light core, wherein the front casing has a light window aligning with the light source such that when the light core is supported within the core cavity, the light source is controllably activated to generate the light through the light window, wherein the assembling accessory is a building part that the assembling accessory is adapted for not only being pieced together with the light core for creating a particular ornamental design and light effect of the head light, but also being disassembled to mix and match with an alternated light core for producing different light effects.
Owner:LAU FERMI CHI HUNG
Curved surface adjustment structure for LED display screen and LED display screen
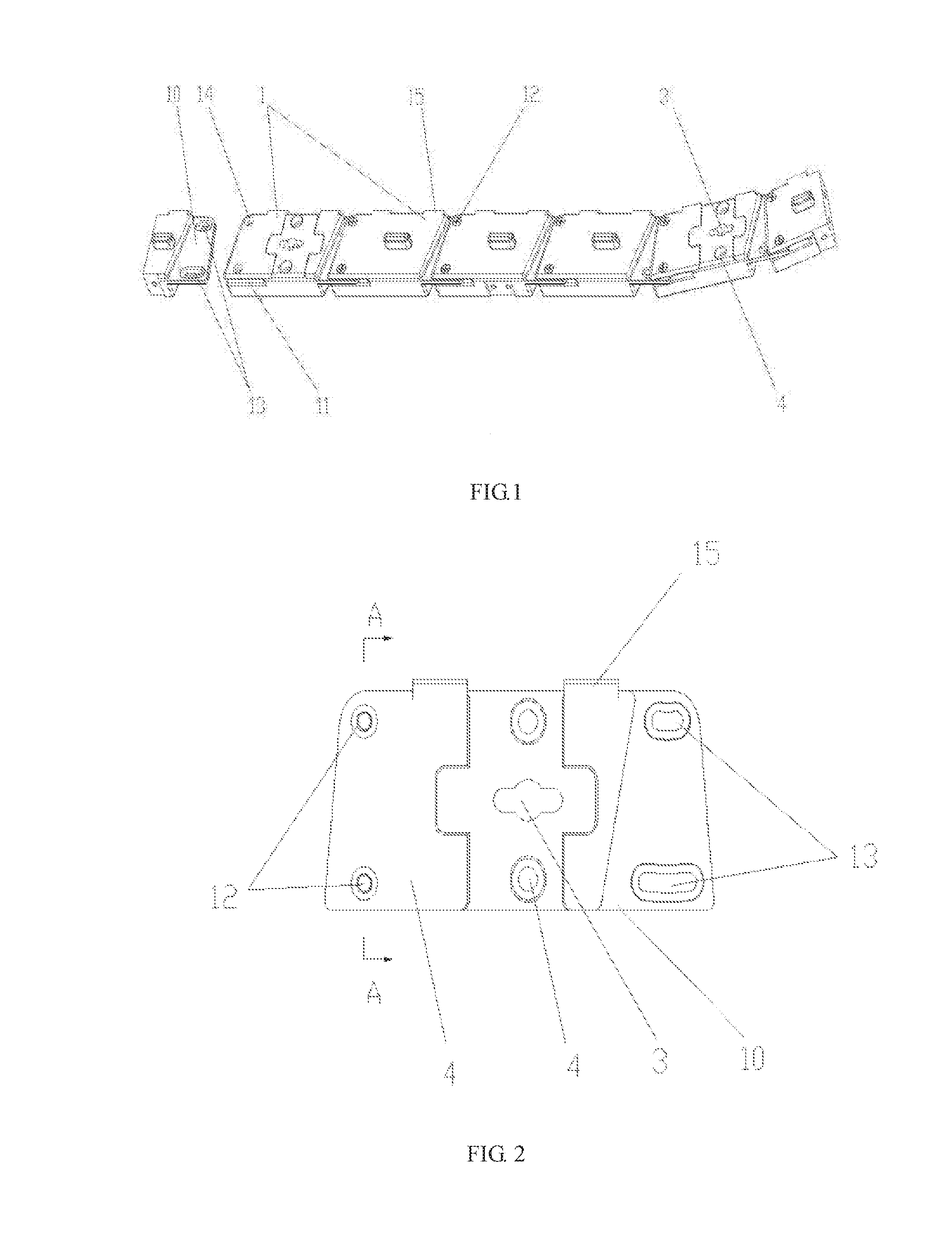
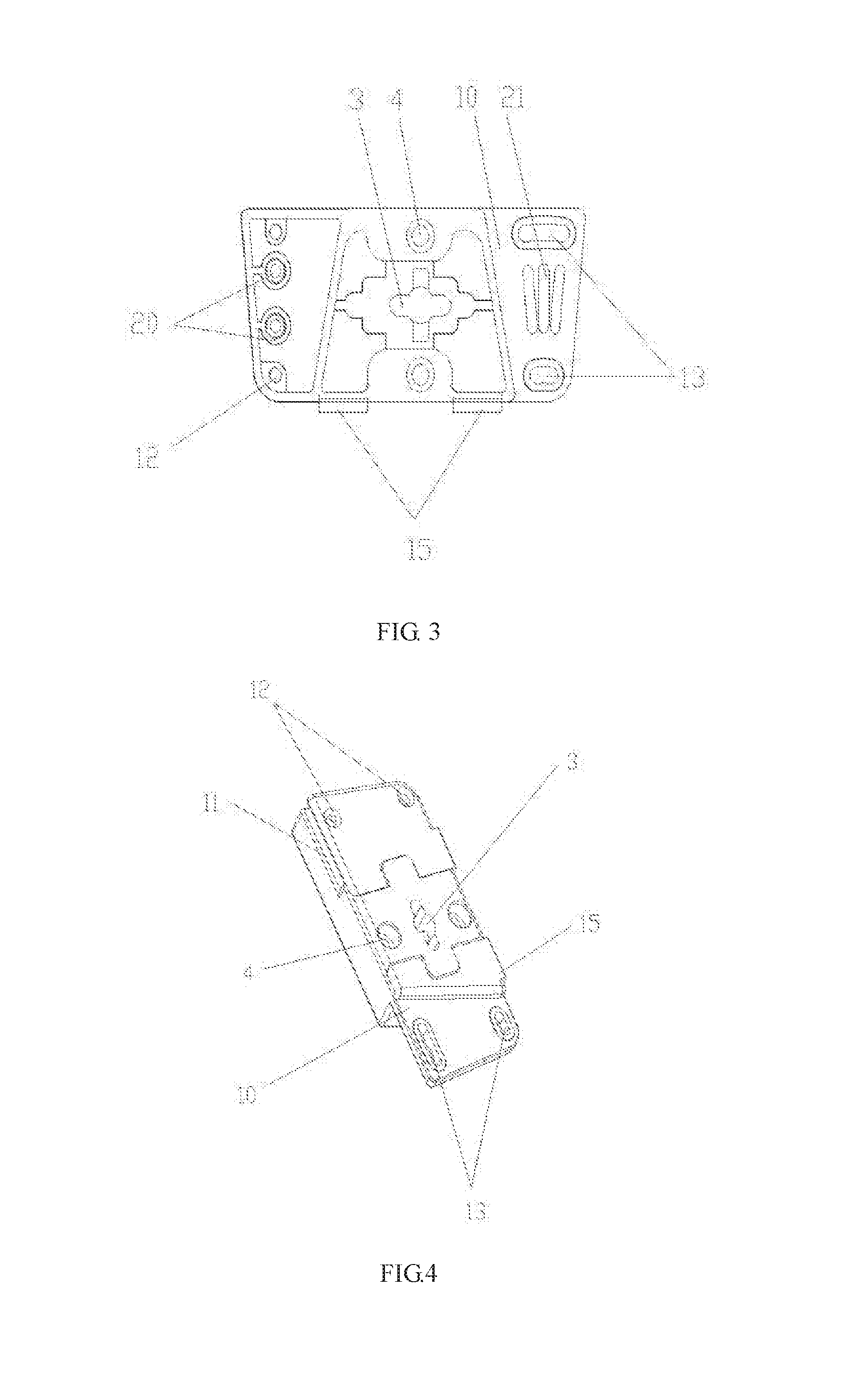
ActiveUS20160224056A1Different effectStable structureDigital data processing detailsIdentification meansLED displayEngineering
A curved surface adjustment structure for an LED display screen, and an LED display screen. An upper frame and a lower frame of a box body of the LED display screen are both formed by rotatably connecting hinge blocks. Each of the hinge blocks comprises a hinge block body, on which a rotating connecting structure and a locating structure are provided. The rotating connecting structure comprises a lug and a groove body which are respectively arranged on two side edges of each hinge block, and a lateral groove is provided in the groove body; the lug on one hinge block is inserted into the groove of another hinge block which is adjacent thereto, and is movably connected together through a limiting shaft; and an arc-shaped groove hole, which is used as a motion track of the limiting shaft, is provided on the lug.
Owner:CREATELED ELECTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com