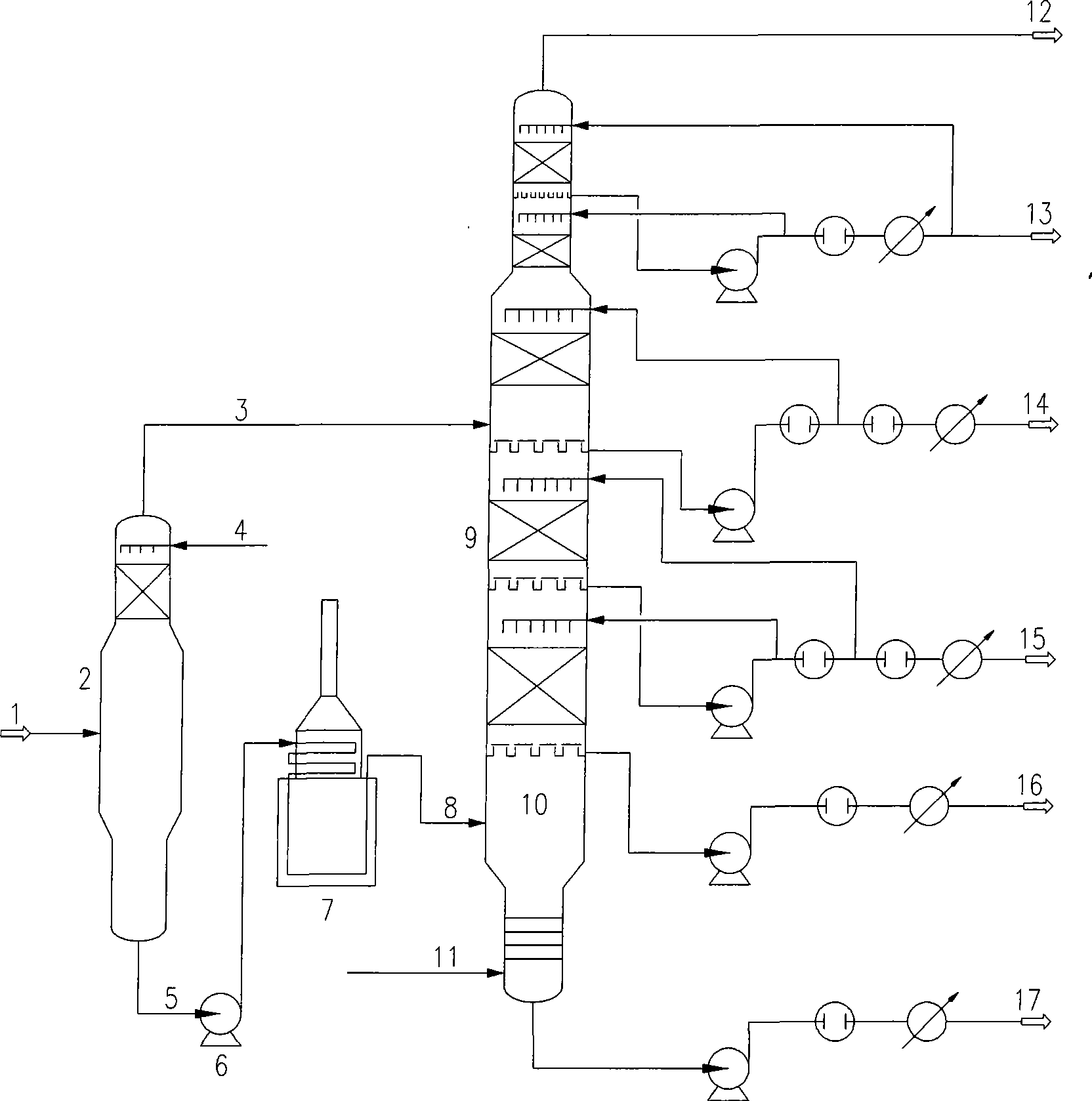Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
319results about "Vacuum distillation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Atmospheric vacuum distillation method and apparatus with vacuum flash vaporizer
InactiveCN101376068AReduce the amount of feedEasy to handleVacuum distillation separationVacuum distillationVaporizationPulp and paper industry
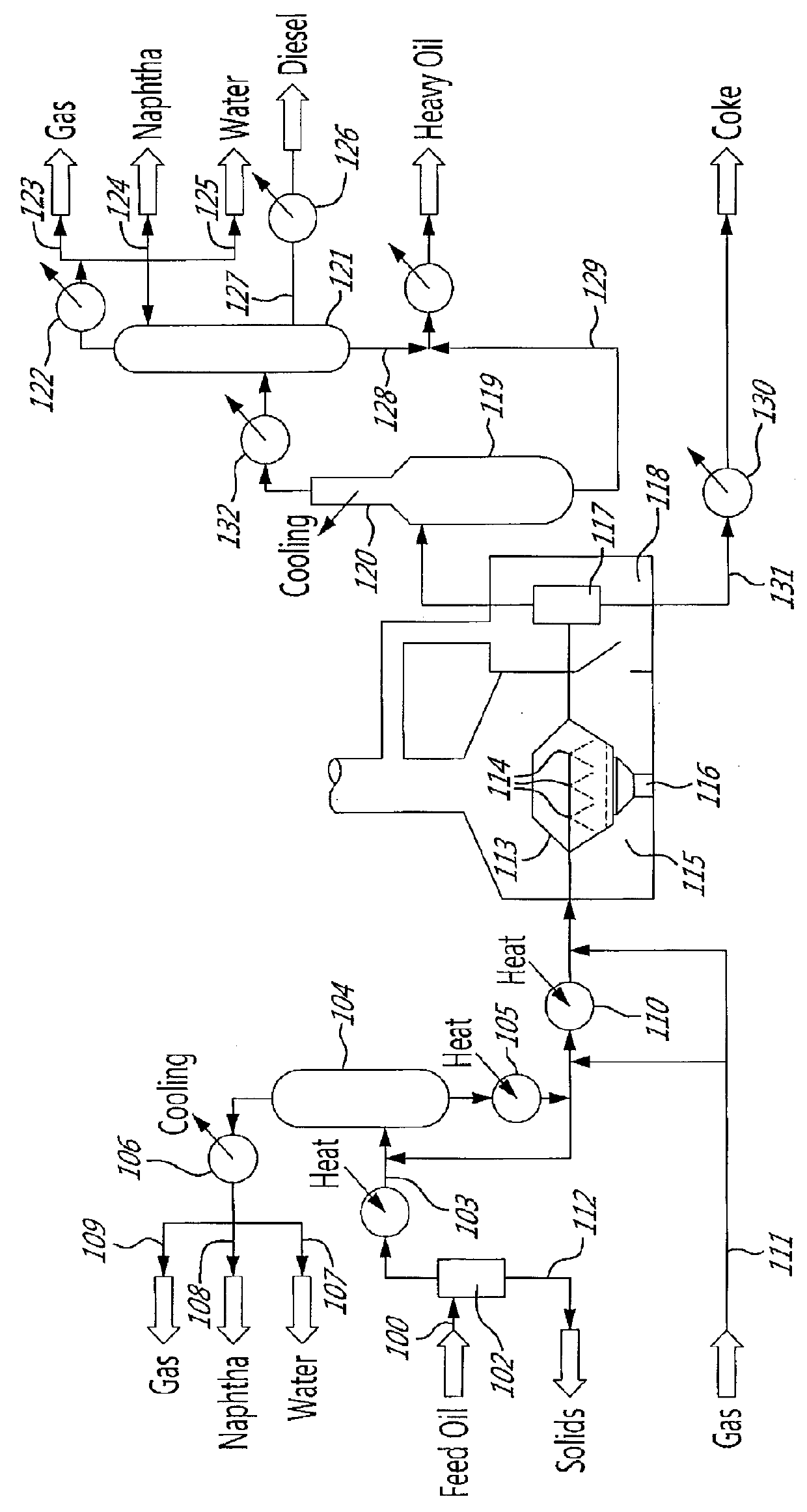
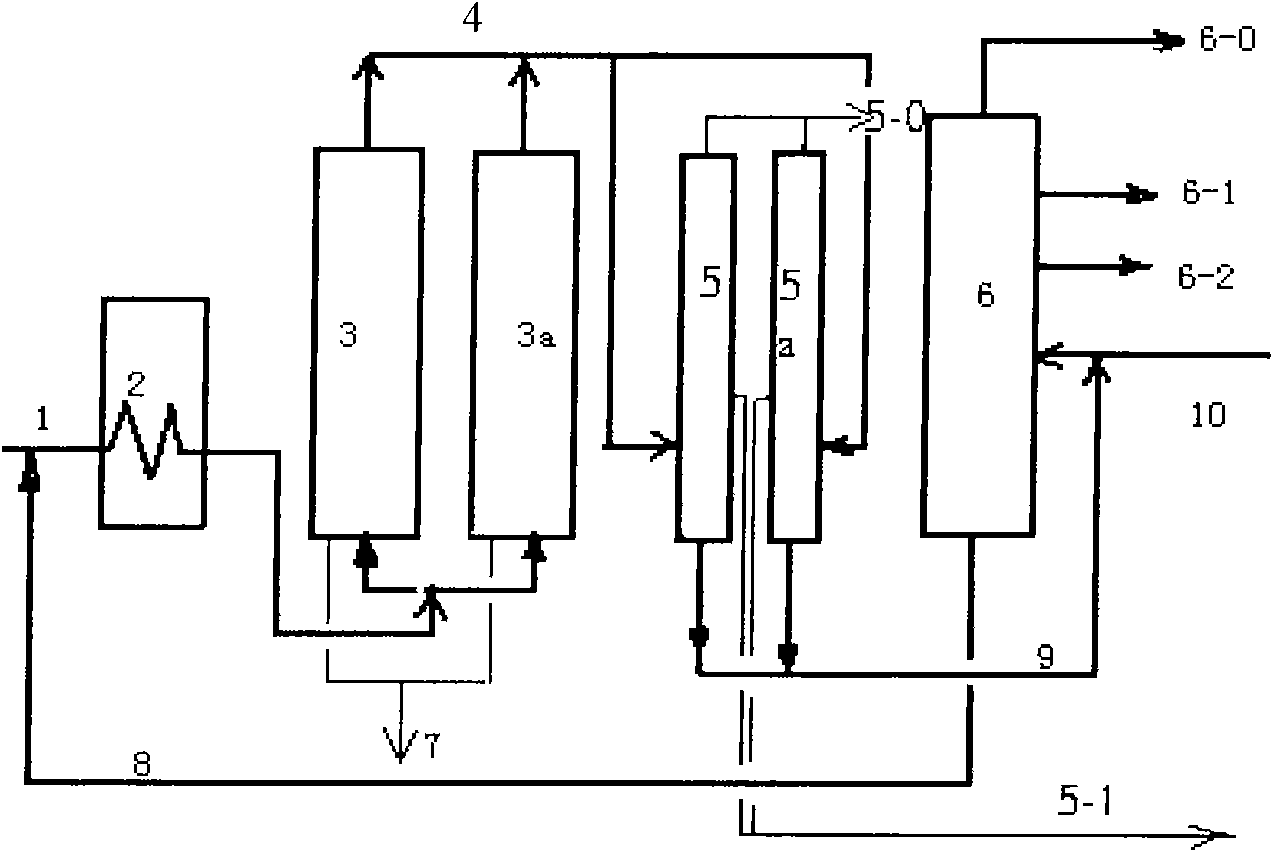
The invention relates to an atmospheric and vacuum distillation device with a vacuum flash tower and a method thereof. The atmospheric and vacuum distillation device with a vacuum flash tower is characterized in that the vacuum flash tower arranged in front of a vacuum furnace is connected with the vacuum furnace and a vacuum tower through a pump and a pipeline. Constant bottom oil (1) is introduced into the vacuum flash tower (2)at first, and the operation pressure at the top part of the vacuum flash tower is higher than the operation pressure at the top part of the vacuum tower (9) by10 to 200mmHg; Flash cap gas (3) is introduced into the upper part or the lower part of an outlet for a side product which is similar to Flash cap gas fraction; flash bottom oil (5) is introduced into the vacuum furnace (7) through a flash bottom oil pump (6); when the flash bottom oil is heated to 350 to 430 degrees, air-liquid mixing vacuum tower feed material is obtained through partial vaporization and is introduced into a flash evaporation segment (10) of the vacuum tower through a transfer line (8); and products with different fractions are drawn from the side of the vacuum tower and vacuum residue is drawn from the bottom of the vacuum tower. Through adding the vacuum flash tower to improve the working process of the atmospheric and vacuum distillation device, the invention achieves the advantages of increasing treatment capacity, increasing vacuum distillation yield, and reducing energy consumption.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +2
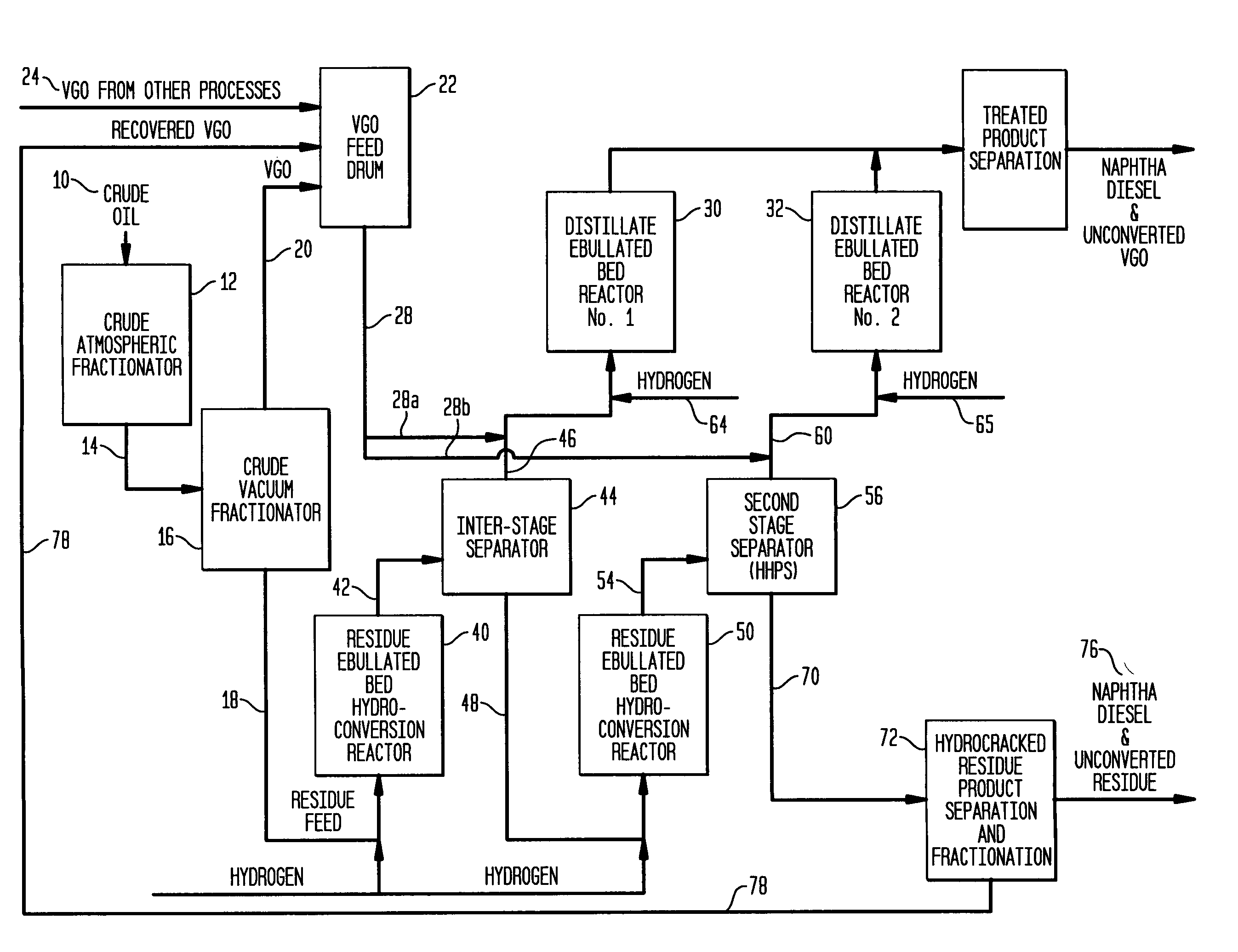
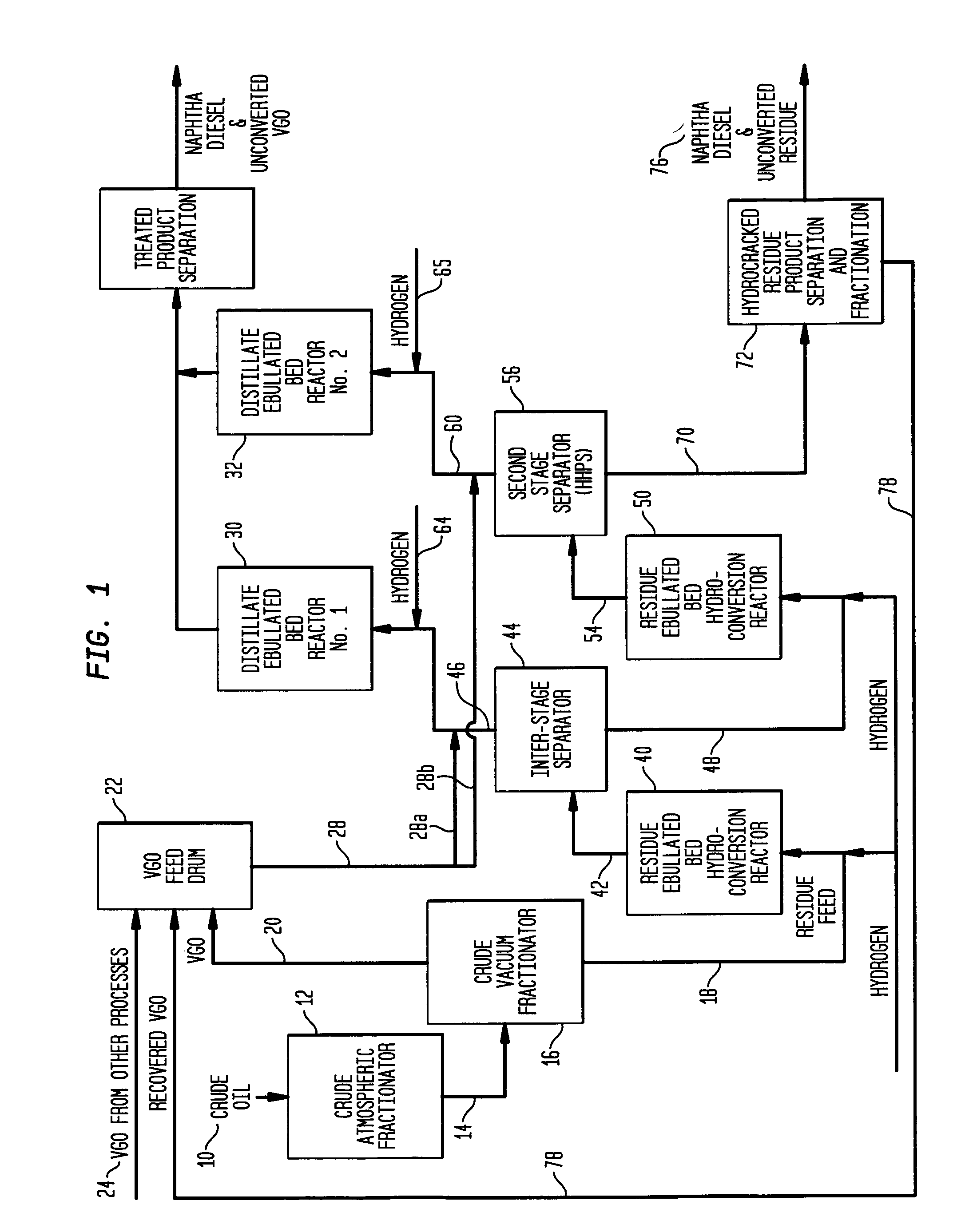
Process for multistage residue hydroconversion integrated with straight-run and conversion gasoils hydroconversion steps
InactiveUS7938952B2Improve throughputMitigate issueTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyMolecular sieve catalystsVapor liquidLiquid product
This invention relates to a novel integrated hydroconversion process for converting heavy atmospheric or vacuum residue feeds and also converting and reducing impurities in the vacuum gas oil liquid product. This is accomplished by utilizing two residue hydroconversion reaction stages, two vapor-liquid separators, and at least two additional distillate ebullated-bed hydrocracking / hydrotreating reaction stages to provide a high conversion rate of the residue feedstocks.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Crude oil desulfurization
InactiveUS6841062B2Reduce operating costsLow costHydrocarbon oil crackingTreatment with hydrotreatment processesSulfurHydrodesulfurization
This invention relates to a crude oil desulfurization process which comprises hydrodesulfurizing a crude oil feed in a crude desulfurization unit. The desulfurized crude oil is then separated into a light gas oil fraction, a vacuum gas oil fraction and a vacuum residuum fraction. The vacuum gas oil is hydrocracked to form at least one low sulfur fuel product. The light gas oil fraction is hydrotreated. The vacuum gas oil may be hydrocracked in one or more stages. Hydrocracking in the second stage, if present, will convert of at least 20% of the first zone effluent, to create a low sulfur light gas oil fraction. The light gas oil fraction may then be hydrotreated.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Method of increasing distillates yield in crude oil distillation
Methods of separating components of a mixture, such as crude oil, are disclosed which increase the yield of individual components while decreasing the yield of residue. In one method, a heated mixture is fed to a column, a vapor stream is withdrawn from the column and separated, and a portion of the vapor stream is recycled back to the column. In another method, a mixture is separated into streams composed substantially of components having light, intermediate or heavy molecular weight and / or low, intermediate or high boiling point, respectively, and the streams are fed into the column at different positions. In both methods, individual light, intermediate and / or heavy molecular weight and / or low, intermediate and / or high boiling point component streams are then selectively withdrawn from the column.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
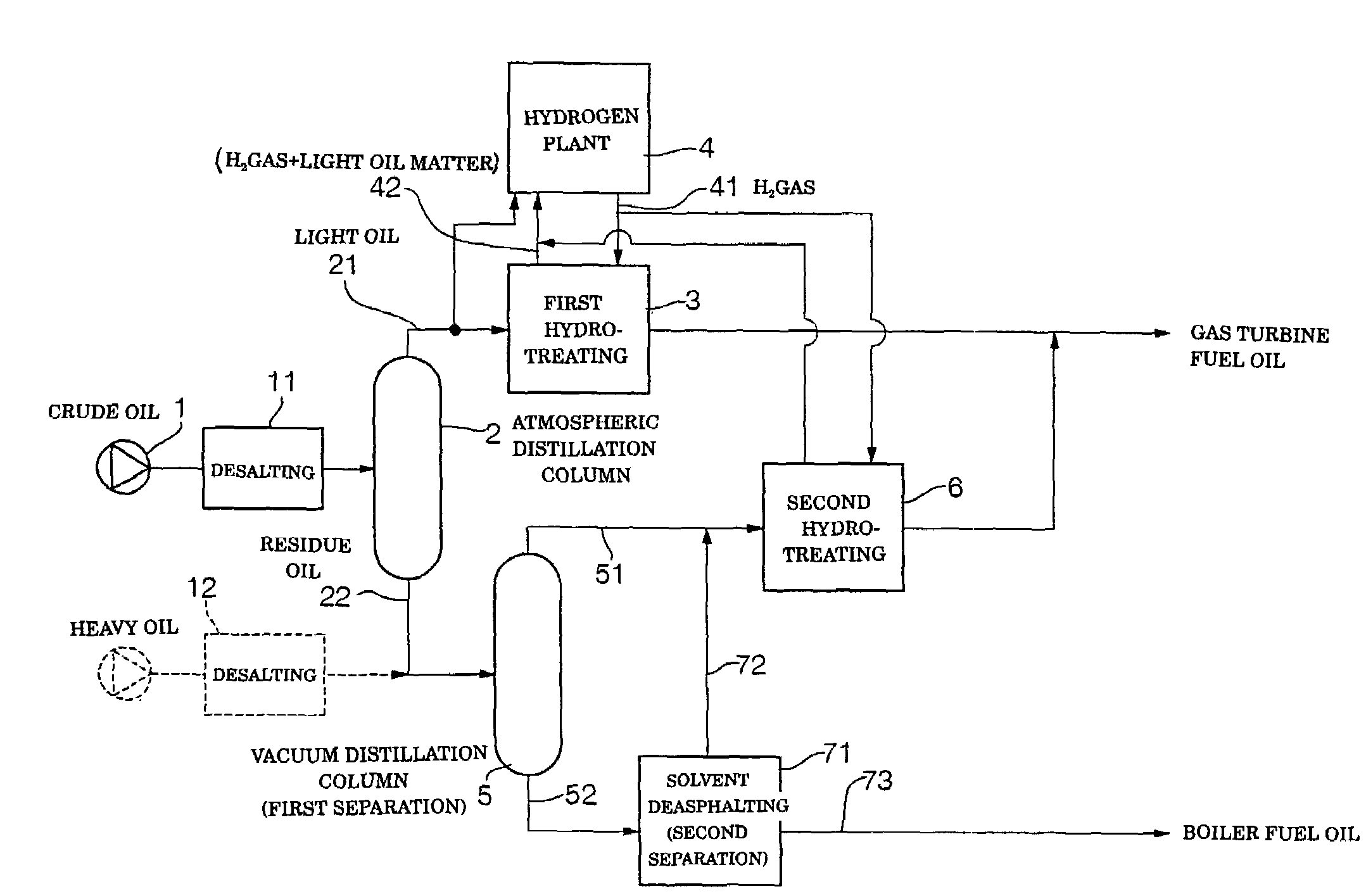
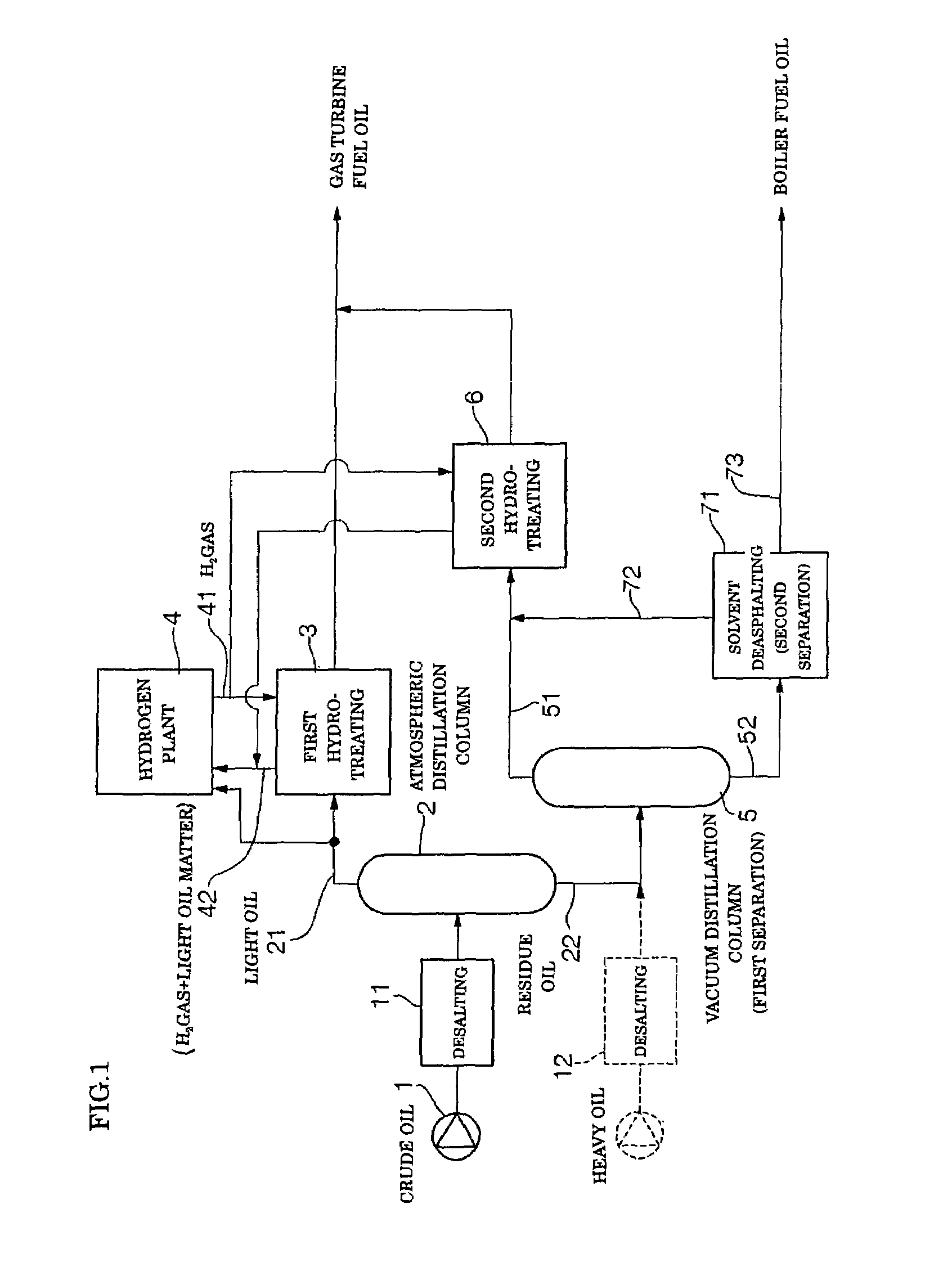
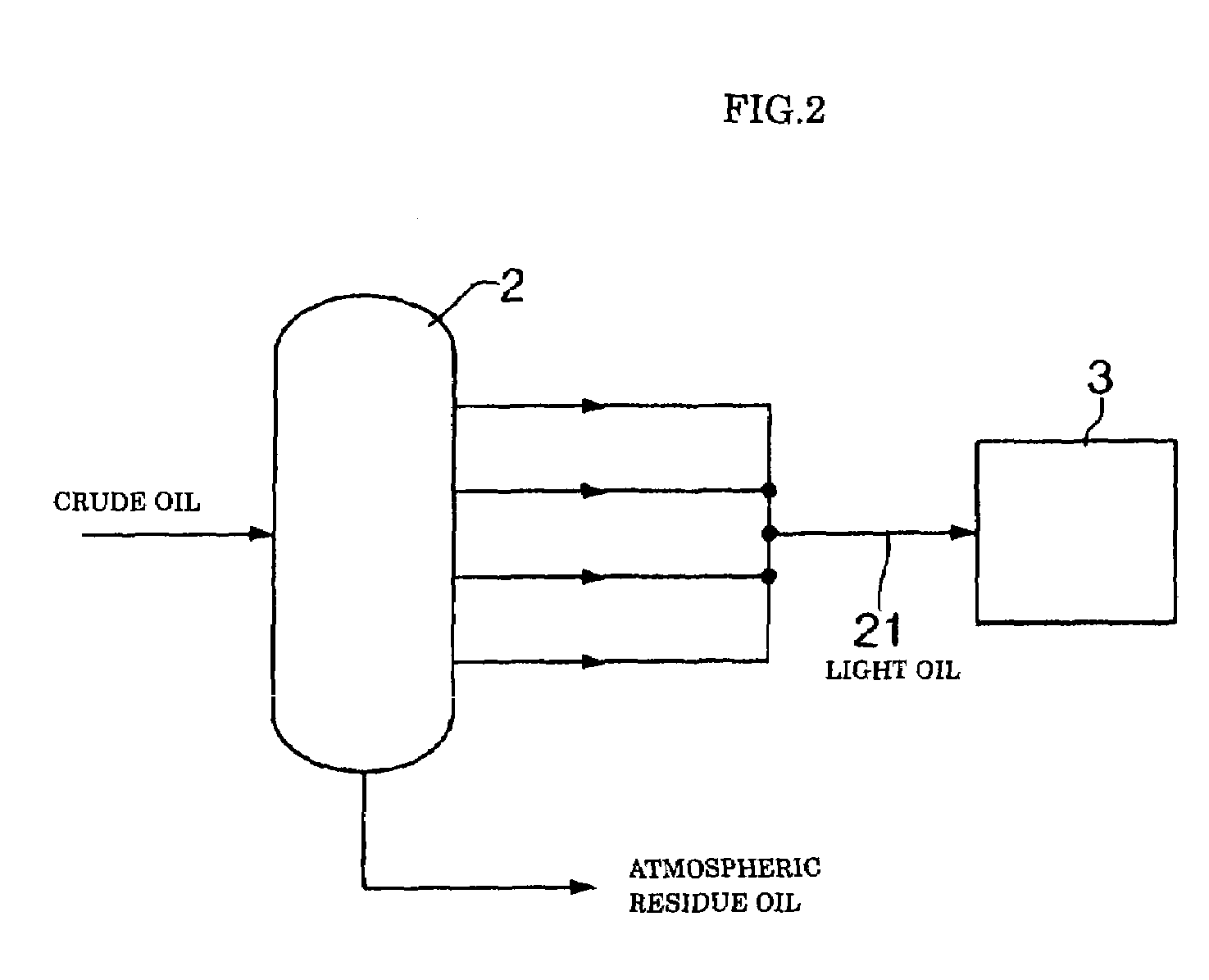
Gas turbine fuel oil and production method thereof and power generation method
InactiveUS7276151B1Carry outImprove efficiencyWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumenLiquid carbonaceous fuelsHydrogenFuel oil
Feed oil is subject to atmospheric distillation, to thereby be separated into light oil or light distillate and atmospheric residue oil. The light distillate is catalytically contacted with pressurized hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst, resulting in a first hydrotreating step being executed. In this instance, various fractions of the light distillate produced in the atmospheric distillation are subject to hydrotreating in a lump. The atmospheric residue oil is then separated into a light matter and a heavy matter. The light matter is subject to second hydrotreating in the presence of a catalyst to produce refined oil (light matter), which is mixed with refined oil produced in the first hydrotreating to prepare a mixture. The mixture is used as gas turbine fuel oil.
Owner:JGC CORP
Solvent extraction of hydrocarbons from inorganic materials and solvent recovery from extracted hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6207044B1No pollution to the environmentIncrease surface areaLiquid organic insulatorsWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by chemical meansHydrocarbon solventsSolvent vapor
A process for the solvent separation of hydrocarbons from tar sand or contaminated soils comprises extracting the hydrocarbons from the sand or soil in a solvent extraction means to form a hydrocarbon rich solvent solution. The rich solvent is separated from the hydrocarbon in a process that utilizes flashing of the solvent in a heated flashing column at ambient pressure. The hydrocarbon is withdrawn from the bottom of the column and the flashed solvent vapors are strategicly withdrawn and passed into a condensation column from which the condensed solvent may be recycled. The flashing column is divided by a series of horizontal, vertically aligned apertured trays. The solution is introduced into the top of the column and the flashing operation is facilitated by the increase in the surface area of the solution as it flows by gravity from tray to tray. The column is maintained at a temperature, preferably above the boiling temperature of the solvent. The process is particularly adapted to the use of chlorinated hydrocarbon solvents and most particularly to the use of methylene chloride.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
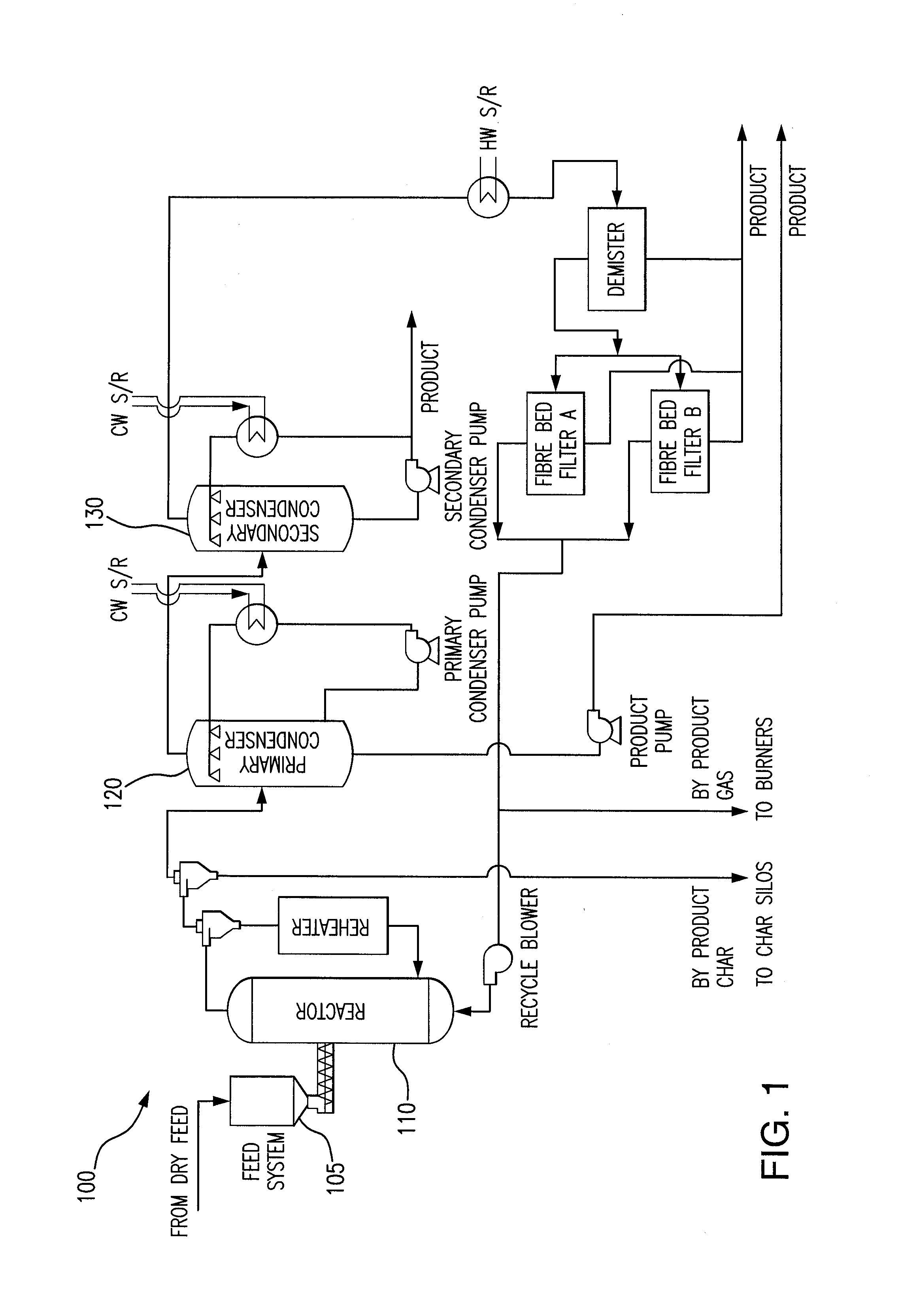
Hybrid thermal process to separate and transform contaminated or uncontaminated hydrocarbon materials into useful products, uses of the process, manufacturing of the corresponding system and plant
ActiveUS20160053184A1Increase volumeReduce contentThermal non-catalytic crackingChemical/physical/physico-chemical reactor detailsChemical compoundWaste oil
Process for reclaiming useful products from a waste oil, comprising a thermal separation step performed in a vessel at conditions, of temperature and pressure, allowing to substantially avoid cracking of the waste oil and to assure the separation of said heated waste oil into a first heavy oil fraction and into a second light oil fraction having, in comparison with the waste oil, a low content in solids and / or in other contaminants that are different from water and from inert gas. The process is further characterized in that while, during the thermal separation treatment, the waste oil is heated to a temperature about the boiling temperature of the heavy oil fraction, and below the cracking temperature of the waste oil, and at a pressure that is preferably below the atmospheric pressure, the heavy oil fraction of the vapours existing the vessel, in contact with a cooler surface, condenses and falls back into the vessel, while the second fraction, in a gaseous state, is eventually submitted to at least one further separation treatment. When water is present in the waste oil, said water is used to improve the amount of recovered light oils; and / or when no water is present in the waste oil, water or at least one inert gas or at least one component that may become an inert gas by heating may be added to the waste oil or to the thermal separation unit. Uses of the process for environmental applications and for treating used oils and to prepare oil products. Systems for reclaiming useful products from waste oils comprising at least one rotating kiln and at least one self-refluxing condenser and / or at least one dephlegmator.
Owner:ENVIROLLEA
Process for production of hydrocarbon chemicals from crude oil
ActiveUS20130267745A1Efficient processMaximize efficient conversionThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyBoiling pointPhysical chemistry
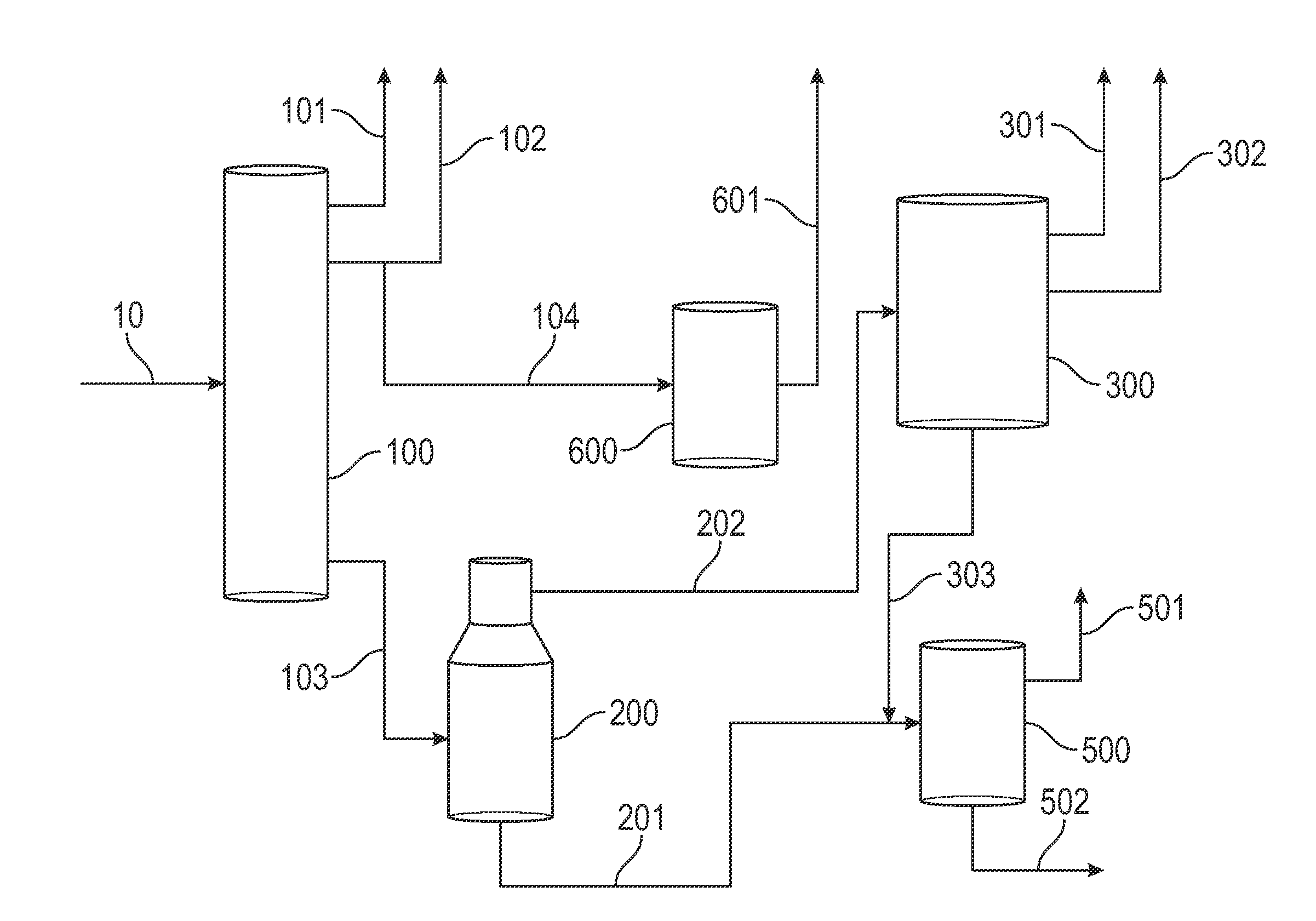
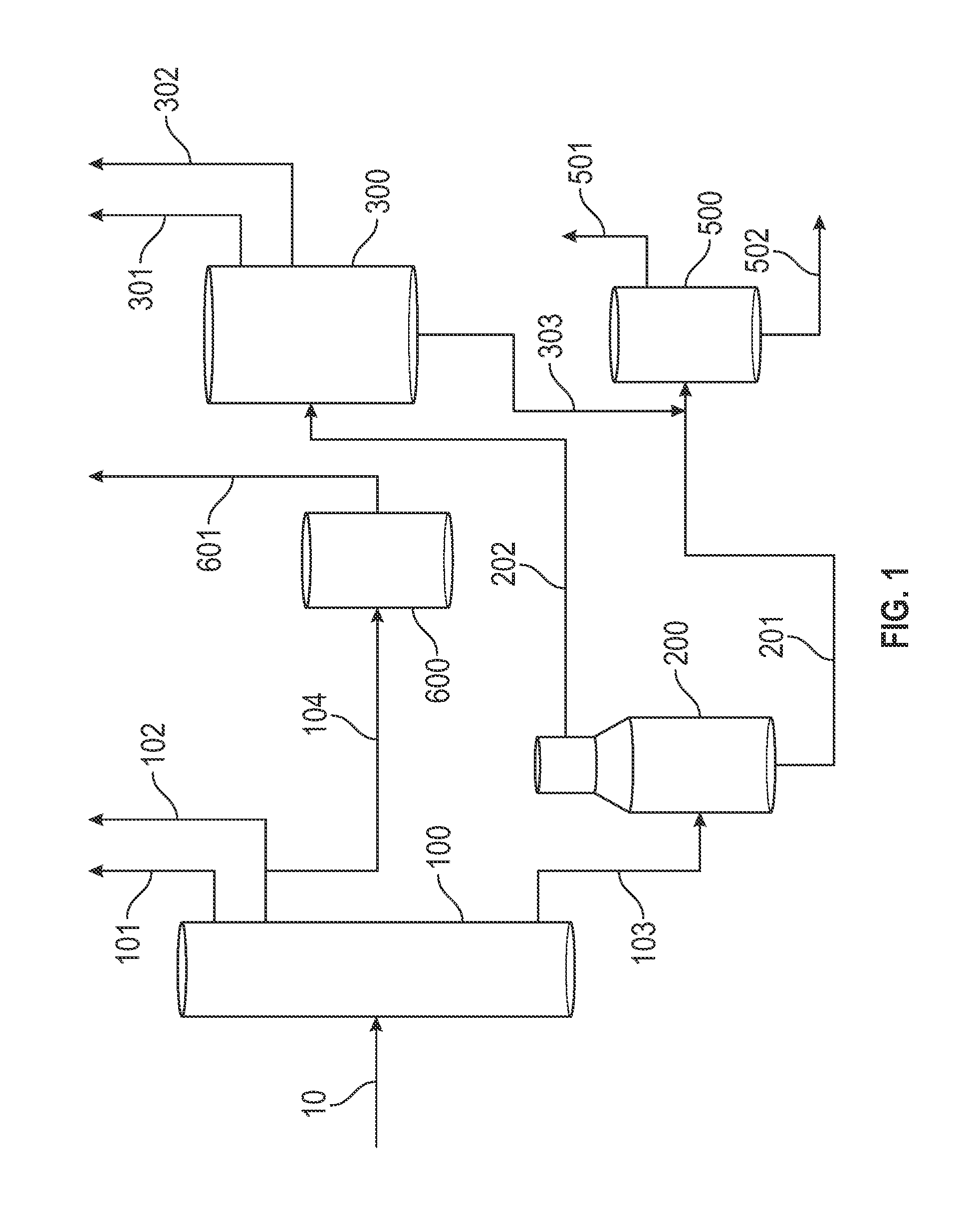
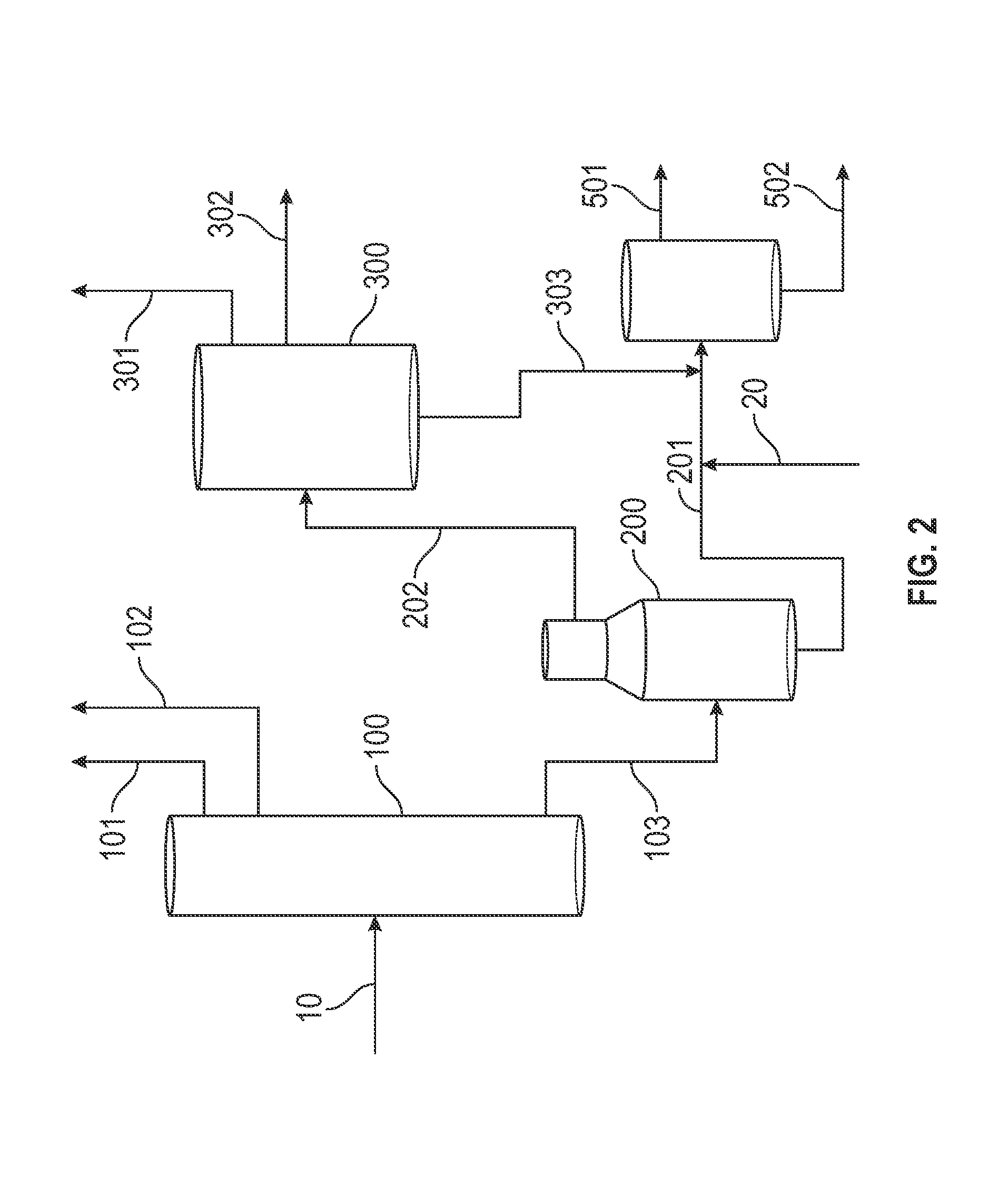
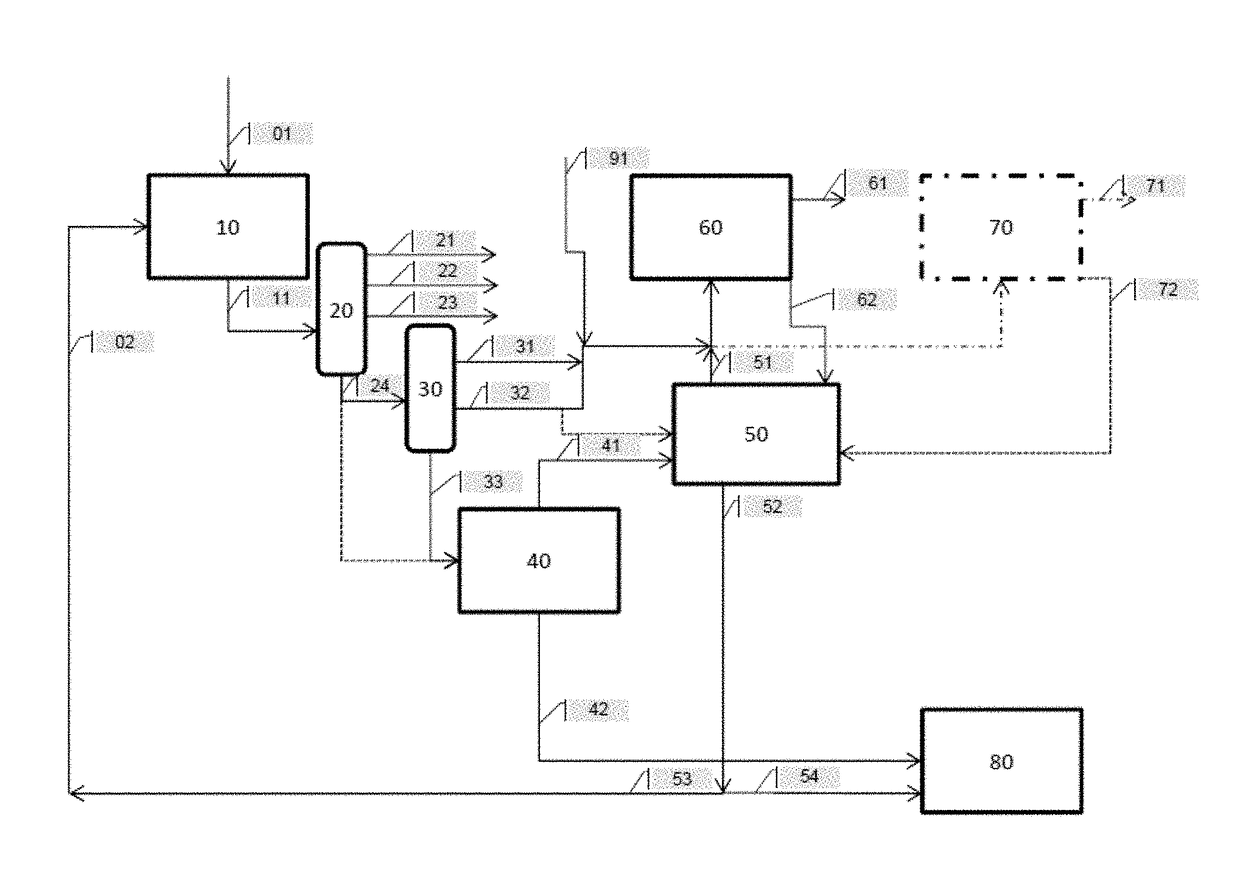
An integrated process comprising to convert crude oil, comprising: converting crude oil (10) in a feed preparation facility (800) by separating the crude oil to a gas fraction (101), liquid fraction (102), and first residuum fraction in an atmospheric distillation unit (100); separating the 1st residuum to a vacuum gas oil fraction (202) and a second residuum (201) in a vacuum distillation unit (200); converting the vacuum gas oil fraction to a CU gas fraction (301,401), a CU liquid fraction (302), and an CU higher boiling fraction (303,402) in a cracking unit (300,400); and processing the second residuum fraction to DCU gas oil / lighter fraction (501) in a coking unit (500); and steam cracking at least one of the gas fraction (101), liquid fraction (102), CU gas fraction (301,401), and DCU gas oil / lighter fraction (501) to the hydrocarbon products (920).
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
Combined processing method capable of improving coking liquid-phase product yield
ActiveCN101619237ALow costReduce operating costsThermal non-catalytic crackingVacuum distillationWaxEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a combined processing method capable of improving coking liquid-phase product yield. In the method, coke powder is removed from high-temperature oil gases produced by a delayed coking device in a coke powder-removing tank, light components are extracted at the same time, heavy components enter a reduced pressure distillation device to separate a wax oil fraction, and obtained vacuum residues are used as delayed coking feed. The method avoids product fractionation in the prior coking fractional distillation column, thereby greatly reducing investment and operation cost.The method improves the yield of coking waxy oil and ensures the quality of the coking waxy oil. With the increase of the extraction amount of the coking waxy oil, the amount of coking circulation oil is greatly reduced and the processing capacity of the coking device is improved, so the economic benefits are increased.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Regeneration process for waste lubrication oil
ActiveCN101307272AImprove protectionKeep Lubricant ComponentsVacuum distillationLubricant compositionEvaporationEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a regeneration process for waste lubricating oil, which belongs to the waste oil regeneration and recovery field. The waste lubricating oil is settled and precipitated, and is firstly subject to the reduced pressure topping distillation at a temperature of 260 DEG C and a vacuum degree of 20mmHg; then the topped waste lubricating oil is increased to between 380 and 400 DEG C, enters an evaporation tower for secondary reduced pressure distillation under the condition of a vacuum degree between 1 and 5mmHg, and enters a continuous catalytic distillation device, and a distillate is cooled to generate lubricant regenerated base oil with the yield more than 80 percent. Compared with the prior art, the process avoids using backward processes with heavier pollution such as acid cleaning, alkali neutralization and so on, and has high yield and better application prospect.
Owner:LUOYANG HAOHAI IND & TRADE
Process of hydrocracking heavy oil
InactiveUS20080156693A1High yieldMild reaction conditionsHydrocarbon oil crackingTreatment with hydrotreatment processesReaction temperatureFuel oil
To provide a process of hydrocracking heavy oil capable of obtaining cracked light oil with higher yields and / or milder reaction conditions than the conventionally proposed hydrocracking process in a suspended bed method using an iron-based catalyst when hydrocracking heavy oil containing heavy metal components produced in a refining process of crude oil into lighter oil.There are provided (1) a process of hydrocracking heavy oil containing heavy metal components produced in a refining process of crude oil, comprising a vacuum distillation step to obtain the heavy oil as distillation residue by vacuum distillation; and a reaction step to hydrocrack the heavy oil in the presence of an iron-based catalyst in a suspended bed reactor, wherein the distillation is conducted at 350° C. or less in the vacuum distillation step, (2) in the preceding process, reaction conditions in the reaction step are a reaction pressure of 60-160 kg / cm2; a reaction temperature of 430-455° C.; and a reaction time of 30-180 minutes.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD +1
Viscosity breaking method
ActiveCN101463267ALow viscosityLow costThermal non-catalytic crackingVacuum distillationNaphthaDistillation
The invention discloses a visbreaking method, comprising the steps of: under the condition of reduced pressure distillation, distilling the visbreaking raw materials under the reduced pressure to acquire a reduced distillate oil and vacuum residue having cutting temperature not less than 540 DEG C; subjecting visbreaking the reduced distillate oil under the condition of the visbreaking, mixing the product of the reduced distillate oil experiencing the visbreaking with the vacuum residue to acquire a mixed oil; visbreaking the mixed oil at the bottom of a visbreaking fractionating tower and acquiring gas, naphtha and visbreaking residue by means of fractionation; and causing the temperature of the reduced distillate oil for the visbreaking to be higher than that of the mixed oil for the visbreaking. By applying the visbreaking method provided by the invention, visbreaking conversion rate can be enhanced; meanwhile the visbreaking residue can be reduced in viscosity and is excellent in stability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Conversion process comprising at least one step for fixed bed hydrotreatment and a step for hydrocracking in by-passable reactors
ActiveUS20170355914A1Lower overall pressure dropModerate temperatureHydrocarbon oil crackingTreatment with hydrotreatment processesFixed bedMetal
The invention concerns a process for the treatment of a hydrocarbon feed in order to obtain a heavy hydrocarbon fraction with a low sulphur content, said process comprising the following steps: a) an optional step for hydrodemetallization carried out in permutable reactors, b) a step for fixed bed hydrotreatment of the effluent obtained from step a), c) a step for hydrocracking of the effluent obtained in step b) in by-passable reactors, d) a step for separation of the effluent obtained from step c).
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Systems and Methods for Refining Corrosive Crudes
ActiveUS20120261308A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by distillationMaterials scienceCrude oil
Owner:BECHTEL ENERGY TECH & SOLUTIONS INC
Process for production of hydrocarbon chemicals from crude oil
ActiveUS9550707B2Maximize efficient conversionThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyBoiling pointHydrocarbon
An integrated process comprising to convert crude oil, comprising: converting crude oil (10) in a feed preparation facility (800) by separating the crude oil to a gas fraction (101), liquid fraction (102), and first residuum fraction in an atmospheric distillation unit (100); separating the 1st residuum to a vacuum gas oil fraction (202) and a second residuum (201) in a vacuum distillation unit (200); converting the vacuum gas oil fraction to a CU gas fraction (301,401), a CU liquid fraction (302), and an CU higher boiling fraction (303,402) in a cracking unit (300,400); and processing the second residuum fraction to DCU gas oil / lighter fraction (501) in a coking unit (500); and steam cracking at least one of the gas fraction (101), liquid fraction (102), CU gas fraction (301,401), and DCU gas oil / lighter fraction (501) to the hydrocarbon products (920).
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
Process for re-refining used oils by solvent extraction
InactiveUS7226533B2No corrosionExpedited distillationWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumenTreatment with plural serial refining stagesWaste oilFuel oil
A process to re-refine used petroleum oils by extraction with aliphatic solvents, wherein after eliminating the extract solvent, the process consists of the following treatments, (a) flash, continuous vaporization, at atmospheric pressure or near atmospheric pressure, to separate the light fractions, in the presence of small amounts of a basic compound or a reducing agent or a combination of both and (b) continuous distillation, in a fractionating column, of the bottom liquid obtained in stage (a), under vacuum and moderate temperatures, in the presence of a basic compound or a reducing compound or a combination of both, with recirculation from the bottom of the column to its feed; separating, as lateral extractions, the vacuum gas-oil or spindle oil and the lubricant bases and, as bottom product, a fuel-oil or asphaltic component.
Owner:SENER GRUPO DE ING SA
Refining used motor oil through successive hydrotreating processes
ActiveUS20150361356A1Economical efficiency can be improvedAvoid accumulationTreatment with hydrotreatment processesLubricating oils distillationHydrogenGasoline
A method for refining used motor oil using two or more hydrotreating reactors arranged in series. The used motor oil may be vacuum distilled to produce an unrefined gasoil. The unrefined gasoil may then be hydrotreated in a first hydrotreating reactor with hydrogen operated at a temperature ranging from approximately 245° C. to approximately 260° C. to produce a hydrotreated gasoil. The hydrogen may comprise a mixture of fresh hydrogen and recycled hydrogen recovered from the last of the two or more hydrotreating reactors. The hydrotreated gasoil may then be hydrotreated in one or more additional hydrotreating reactors operated at temperatures ranging from approximately 260° C. to approximately 330° C. to produce a refined gasoil. The first hydrotreating reactor may remove a substantial portion of metallic impurities from the unrefined impurities, while the one or more additional hydrotreating reactors remove a substantial portion of heteroatom impurities from the unrefined gasoil.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Methods of separation of pyrolysis oils
ActiveUS9920262B1Efficient methodImprove marketabilityThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingSulfurDistillation
Methods for processing pyrolysis oil employs two or more of the following steps: A first separation creates (a) a lighter fraction and heavier fraction, (b) subjecting the lighter fraction to distillation and (c) subjecting the heavy fraction to removal of at least one of sulfur and nitrogen.
Owner:RJ LEE GRP INC
Catalytic conversion method for converting low-quality heavy oil into light clean fuel oil
ActiveCN101899323AImprove separation efficiencyEasy to separateTreatment with plural serial stages onlyVacuum distillationDistillationSolid particle
The invention discloses a catalytic conversion method for converting low-quality heavy oil into light clean fuel oil, which comprises: (1), introducing low-quality raw material oil into a catalytic cracking reactor having two reaction areas for performing a cracking reaction, wherein the reaction conditions in the catalytic cracking reactor ensure the catalytic wax oil obtained by the reaction is12 to 60 weight percent based on the weight of the low-quality raw material oil; (2) introducing the catalytic wax oil carrying catalyst particles into a reduced-pressure distillation tower, and separating a catalytic wax oil light fraction from the top of the tower; (3) hydrogenating the catalytic wax oil light fraction to obtain hydrogenated catalytic wax oil; and (4) circulating the hydrogenated catalytic wax oil to a catalytic conversion device for further reaction to obtain a light fuel oil target product. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that: due to the catalyticcracking of the low-quality heavy oil raw material, the catalytic wax oil yield is high, and the dry gas yield and cock yield are low; after solid particle removal and hydrogenation, the obtained catalytic wax oil can be introduced back to the catalytic cracking device for recycling, so the light oil yield of the whole process is increased by 5 to 15 percent and oil slurry yield is reduced; and thus, the high-efficiency use of oil resources is realized.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Distillation apparatus and method of use
ActiveUS20080173531A1Improve efficiencySuccessfully and easily distillVacuum distillation separationLubricating oils distillationQuality levelDistillation
A method and apparatus is provided for distilling and processing chemicals. The apparatus is particularly suited for processing and distilling difficult to distill compounds, and is capable of producing diesel fuel and other products from used oil at a quality level similar to that of products produced from virgin crude oil.
Owner:BARKER COURT R
Delayed coking and reduced pressure distillation combined processing method
ActiveCN101619238AGood for deep pullingReduce the ratioTreatment with plural serial stages onlyVacuum distillationWaxEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a delayed coking and reduced pressure distillation combined processing method. The method comprises the following steps that: high-temperature gases produced by the delayed coking device are delivered into a coking fractional distillation column for distillation and a dry point of the wax oil is controlled to ensure the quality of the wax oil; and coking tail oil and normal-pressure residual oil are delivered into a reduced pressure distillation device together to further and deep extract residual coking wax, the residual coking wax and straight run wax oil are discharged out from the device at the same time, and reduced pressure residual oil containing a small amount of coke powder is used as delayed coking feed. The method improves the yield of coking wax oil and ensures the quality of the coking wax oil. With the increase of the extraction amount of the coking waxy oil, the amount of coking circulation oil is greatly reduced and the processing capacity of the coking device is improved, so the economic benefits are increased.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Low sulfur fuel oil bunker composition and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20200277533A1Value productAvoid the needLiquid carbonaceous fuelsHydrocarbon oil crackingEnvironmental engineeringMarine fuel
The present disclosure relates to marine fuel compositions having low sulfur content and processes for making such compositions.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Simultaneous crude oil dehydration, desalting, sweetening, and stabilization
ActiveUS10260010B2Separate and stabilizeIncreased water cutsLiquid degasification with auxillary substancesLiquid separation by electricityWash waterWater flow
Integrated gas oil separation plant systems and methods are disclosed. Systems and methods include treating a crude oil inlet feed stream with a high pressure production trap (HPPT), a low pressure production trap (LPPT), a low pressure degassing tank (LPDT), a first heat exchanger, a second heat exchanger, a LPPT recycle water stream, a fresh wash water supply stream, and a LPDT recycle water stream, where the LPDT recycle water stream is operable to supply recycle water from the LPDT to an output stream from the HPPT to form the LPPT inlet feed stream.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
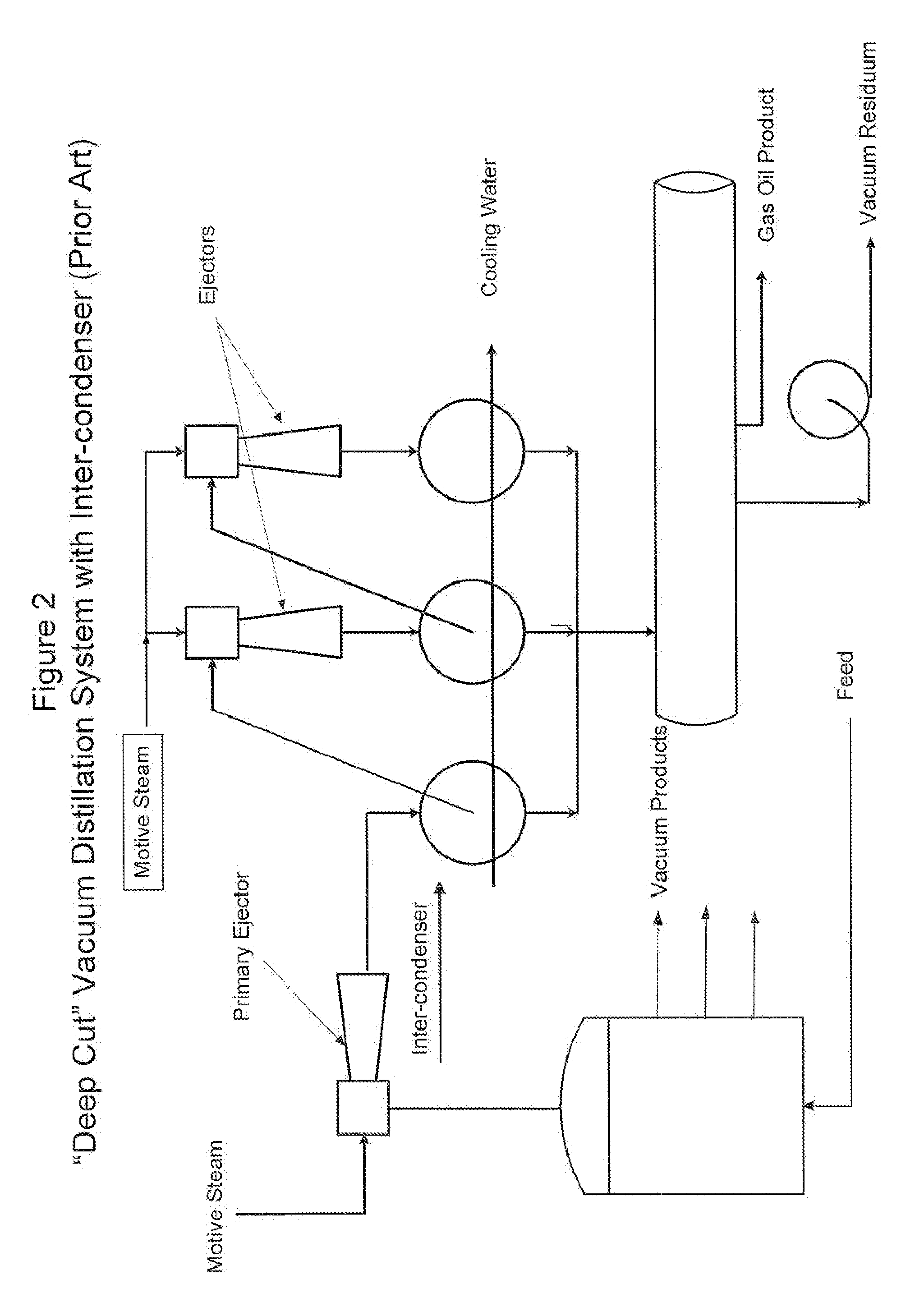
Plant and method for vacuum distillation of hydrocarbon liquids
InactiveUS20070278088A1Reduce pressureImprove operational flexibilityVacuum distillation separationDistillationTowerHydrocarbon
A vacuum distillation system and method utilizing an auxiliary, low capacity vacuum producing ejector operated in parallel with a primary ejector during the winter months enables significant reduction in the absolute pressure of a vacuum distillation column. Operation of a vacuum distillation tower at lower absolute pressures results in increased yield of desirable vacuum distillation products.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Distillate yield improving vacuum distillation method and device
ActiveCN102311772AAvoid lateral thermal displacementEasy to separateVacuum distillationHydrocarbon oils treatmentLow speedVaporization
The invention discloses a distillate yield improving vacuum distillation method and device. A flash vaporization vessel is arranged on an oil transfer line between a vacuum furnace and a vacuum distillation tower. Vacuum distillation raw materials enter the oil transfer line and the flash vaporization vessel after being heated by the vacuum furnace. Gas liquid separation is carried out in the flash vaporization vessel: liquid discharged from the bottom of the flash vaporization vessel, namely flash bottom oil, is introduced into the vacuum distillation tower; and gas discharged from the top of the flash vaporization vessel, namely flash top gas, is led out of the device after being condensed into liquid. According to the vacuum distillation method and device with the flash vaporization vessel arranged behind the vacuum furnace, on one hand, the yield of vacuum distillate is increased, on the other hand, a conventional decompression oil transfer line low-speed section is omitted, the operation load of the vacuum tower is reduced, and the diameter of the vacuum tower can be appropriately reduced, so equipment investment is saved, and the operating cost is reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Systems and Methods for the Devolatilization of Thermally Produced Liquids
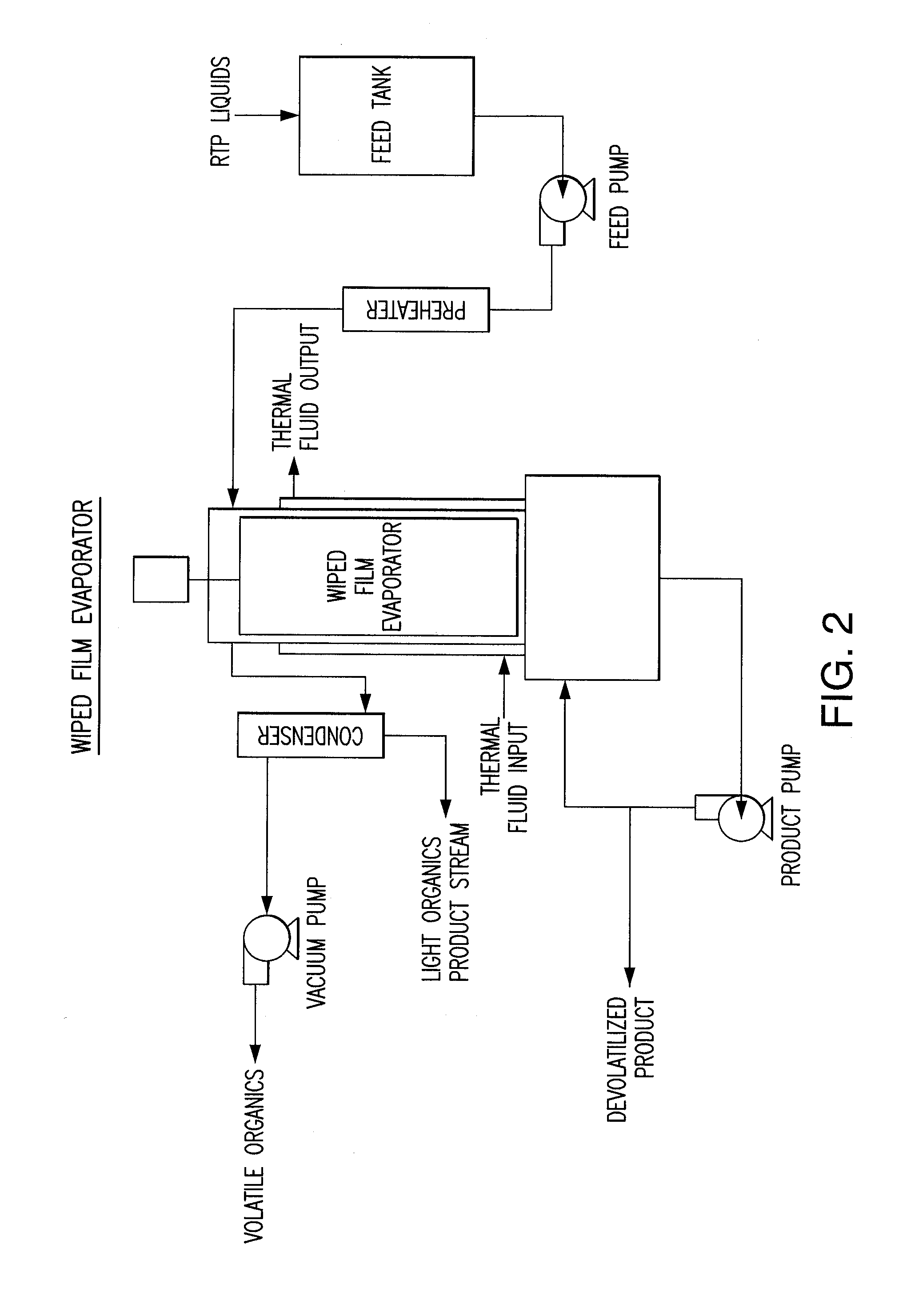
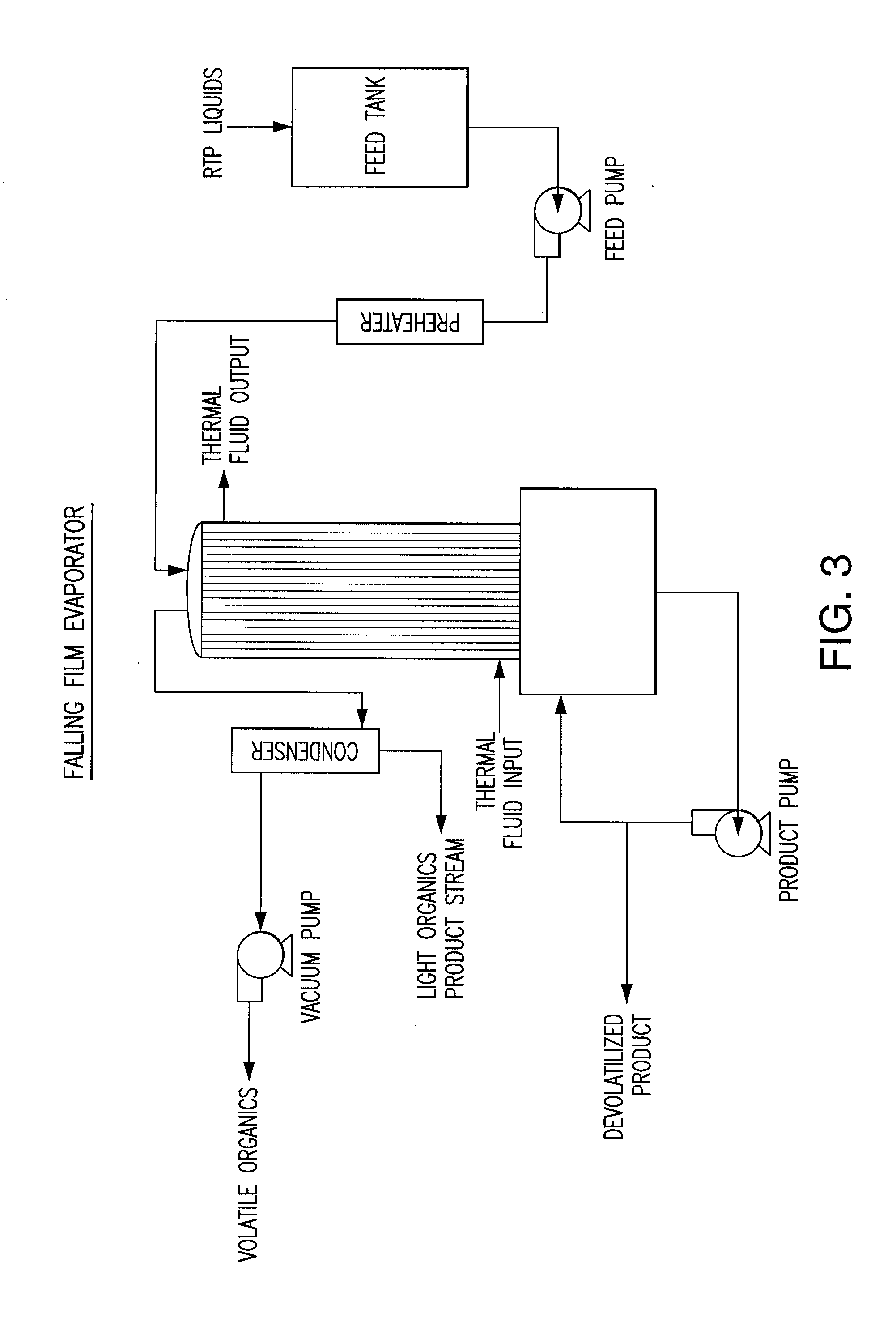
InactiveUS20140053456A1Increase pointsHigh flash pointThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingEngineeringFalling film evaporator
Methods and systems for the devolatilization of thermally produced liquids to raise the flash point are disclosed. Various methods and apparatus can be used to effectively reduce the volatile components, such as wiped film evaporator, falling film evaporator, flash column, packed column, devolatilization vessel or tank.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
Method for realizing selective reprocessing of catalytic cracking reprocessed oil slurry
InactiveCN101586037AAvoid burnsImplement selective refinementCatalytic crackingVacuum distillationHigh carbonBoiling point
The invention discloses a method for realizing selective reprocessing of catalytic cracking reprocessed oil slurry. The method comprises the steps of conveying reprocessed oil slurry produced by a catalytic cracking device into a reduced-pressure rectification column for rectification under reduced pressure, separating out low-carbon-residue fractions of which the boiling point is lower than 500 to 550 DEG C and sending the low-carbon-residue fractions to a reprocessing device. The method first performs reduced-pressure rectification on the reprocessed oil slurry produced by the catalytic cracking device through the reduced-pressure rectification column, then separates the low-carbon-residue fractions out from the reprocessed oil slurry, and sends the low-carbon-residue fractions to the reprocessing device. Because high-carbon-residue fractions do not enter the reprocessing device, the occurrence of coke generation of the reprocessing device is fundamentally avoided; the processing capacity of the device is improved; the energy consumption and maintenance cost of the device are reduced; and the energy consumption of the device can be reduced by more than 10 percent. In addition, the method also greatly reduces processing loss and increases the yield of lightweight oil by about 1 to 3 percent, thereby having significant economic benefit.
Owner:李焕然
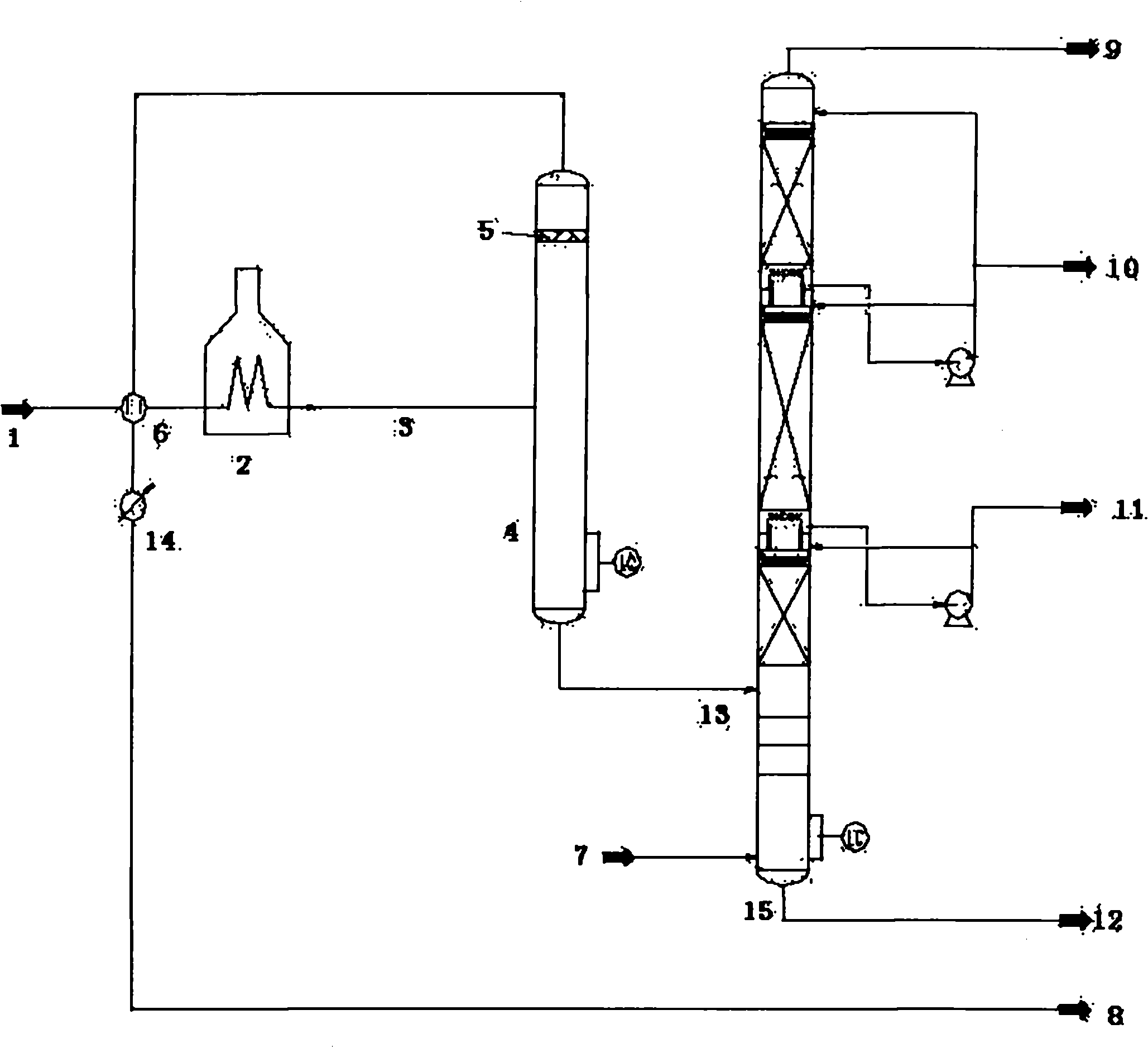
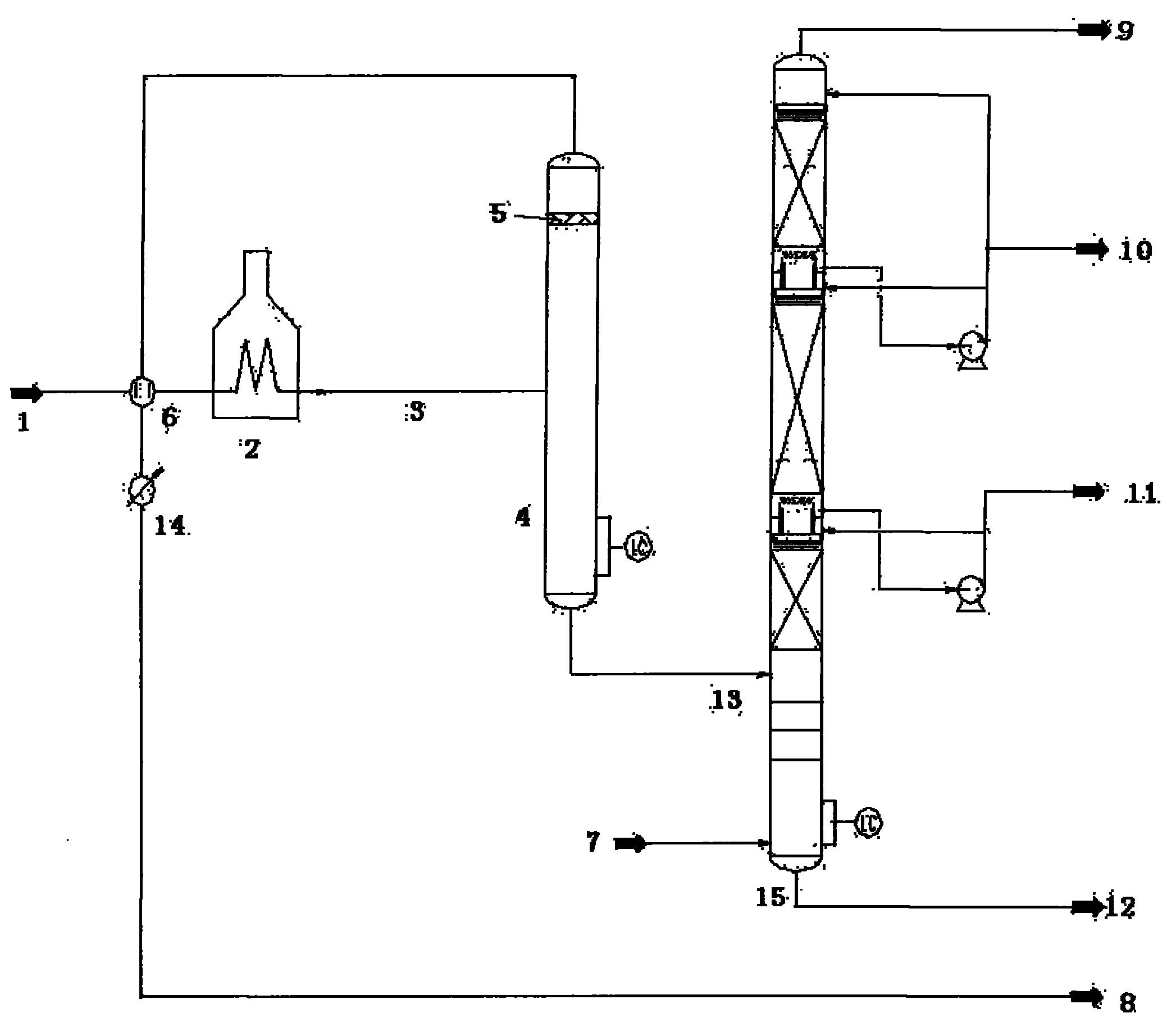
Reduced pressure distillation method and device
ActiveCN102309863AIncrease gasification rateShort processVacuum distillation separationVacuum distillationChemistryLiquid phase
The invention discloses a reduced pressure distillation method and a reduced pressure distillation device. A flash tower is arranged between a reduced pressure furnace and a reduced pressure distillation tower, an oil transfer line is canceled, a reduced pressure distillation raw material is heated in the reduced pressure furnace and then directly enters the flash tower, and gas-liquid separation is performed in the flash tower; the liquid phase, namely flash bottom oil, discharged from the bottom of the flash tower is introduced into the reduced pressure distillation tower; and the gas phase, namely flash top gas, discharged from the top of the flash tower is condensed into liquid phase, and the liquid phase is led out of the device. According to the reduced pressure distillation method and the reduced pressure distillation device using the flash tower in back of the reduced pressure furnace, on the one hand, the yield of reduced pressure distillate is improved; and on the other hand, the conventional reduced pressure oil transfer line is canceled, the operation load of the reduced pressure tower is reduced, and the diameter of the reduced pressure tower can be properly reduced so that the equipment investment is saved and the operation cost is lowered.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
VPS tar separation
ActiveUS20080053869A1Decrease and minimizes entrainmentEfficient use ofThermal non-catalytic crackingRetortsTarEngineering
A process is described for producing deasphalted steam cracker tar comprising feeding steam cracker tar to a vacuum pipestill (VPS) including a flash zone separated from a zone comprising trays by at least one annular entrainment ring and obtaining as an overheads a deasphalted tar product and as a bottoms an asphaltenic heavy tar product. Also according to the invention, there is a system for the upgrading of tar comprising said VPS with at least one annular entrainment ring.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Deep hydroconversion process using an extraction of aromatics and resins, with upgrading of the hydroconversion extract and raffinate in downstream units
InactiveUS20170369796A1Low impurity contentTreatment with hydrotreatment processesVacuum distillationOrganic solventFractionation
Process for deep conversion of heavy hydrocarbon feed, which includes:a) ebullated bed hydroconverting the feed in at least one three-phase reactor containing at least one supported hydroconversion catalyst;b) atmospheric fractionating effluent from a) producing gasoline fraction, gas oil cut, and atmospheric residue;c) vacuum fractionation of at least a portion of the atmospheric residue to obtain a vacuum gas oil fraction and an unconverted vacuum residue fraction;d) deasphalting at least a portion of the unconverted vacuum residue fraction with an organic solvent obtaining a hydrocarbon cut depleted in asphaltenes, termed deasphalted oil, and residual asphalt; ande) liquid / liquid extraction on the hydrocarbon cut depleted in asphaltenes extracting aromatics by a polar solvent producing an extract enriched in aromatics and resins and a raffinate depleted in aromatics and resins, at least a portion of the extract sent to the inlet of the hydroconversion as an aromatic diluent.
Owner:AXENS SA
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com