Gas turbine fuel oil and production method thereof and power generation method
a technology of gas turbines and fuel oil, which is applied in the direction of hydrocarbon distillation, liquid carbonaceous fuels, fuels, etc., can solve the problems of large amount of energy outwardly discharged in the form of greenhouse gas without being recovered, certain amount of sox to be present in exhaust gas or flue gas discharged therefrom, and the system is deteriorating in power generation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
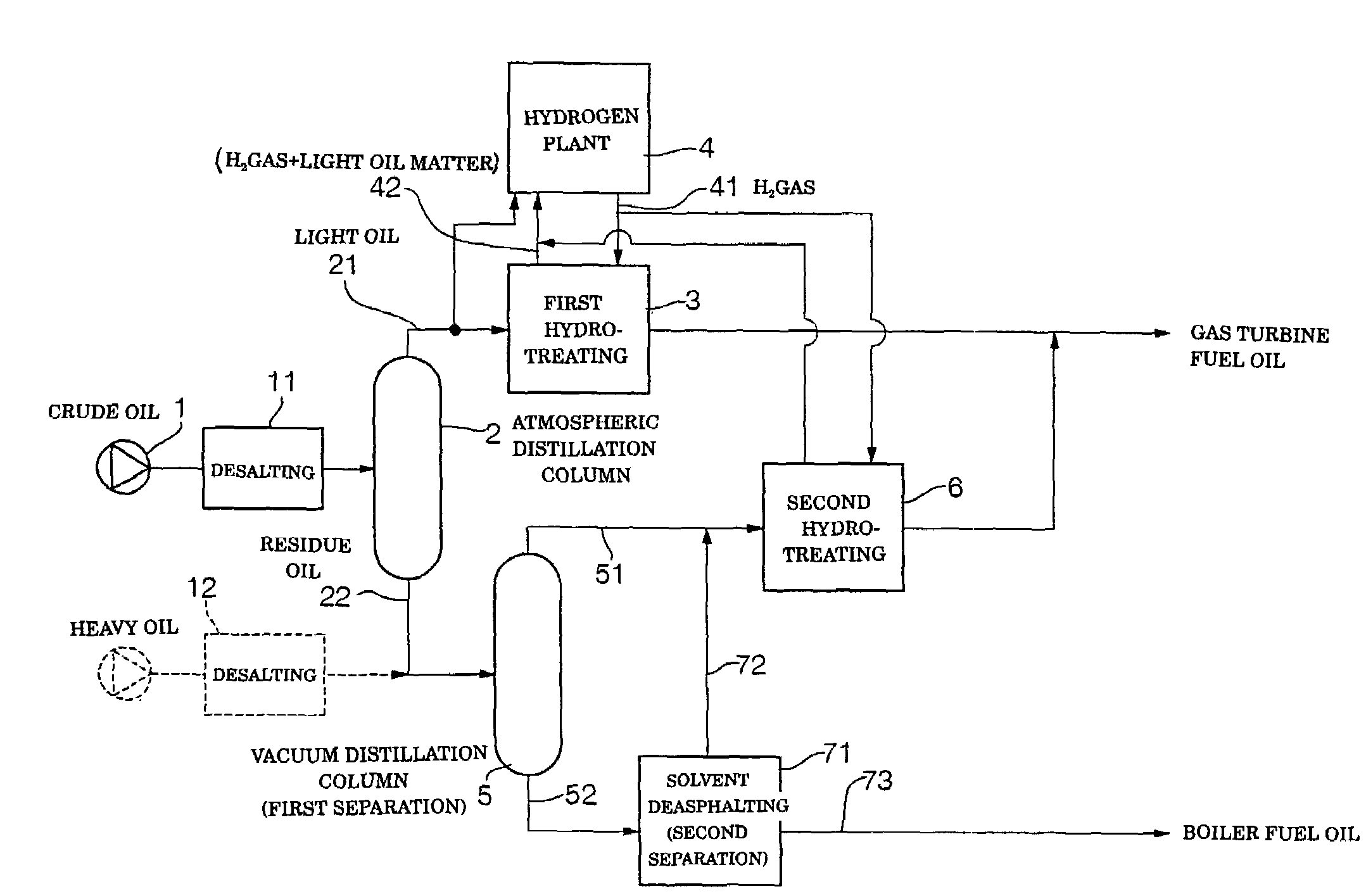
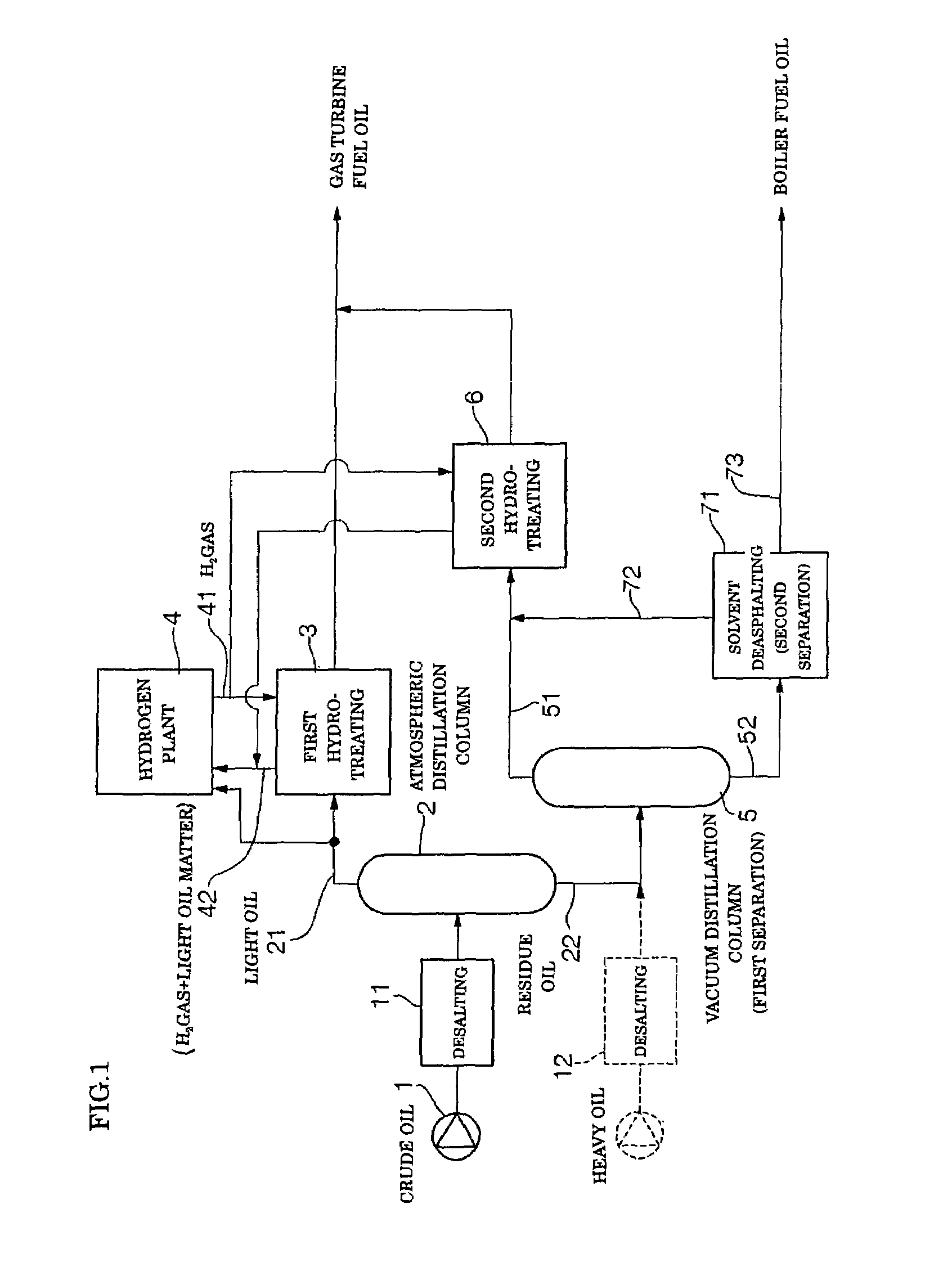
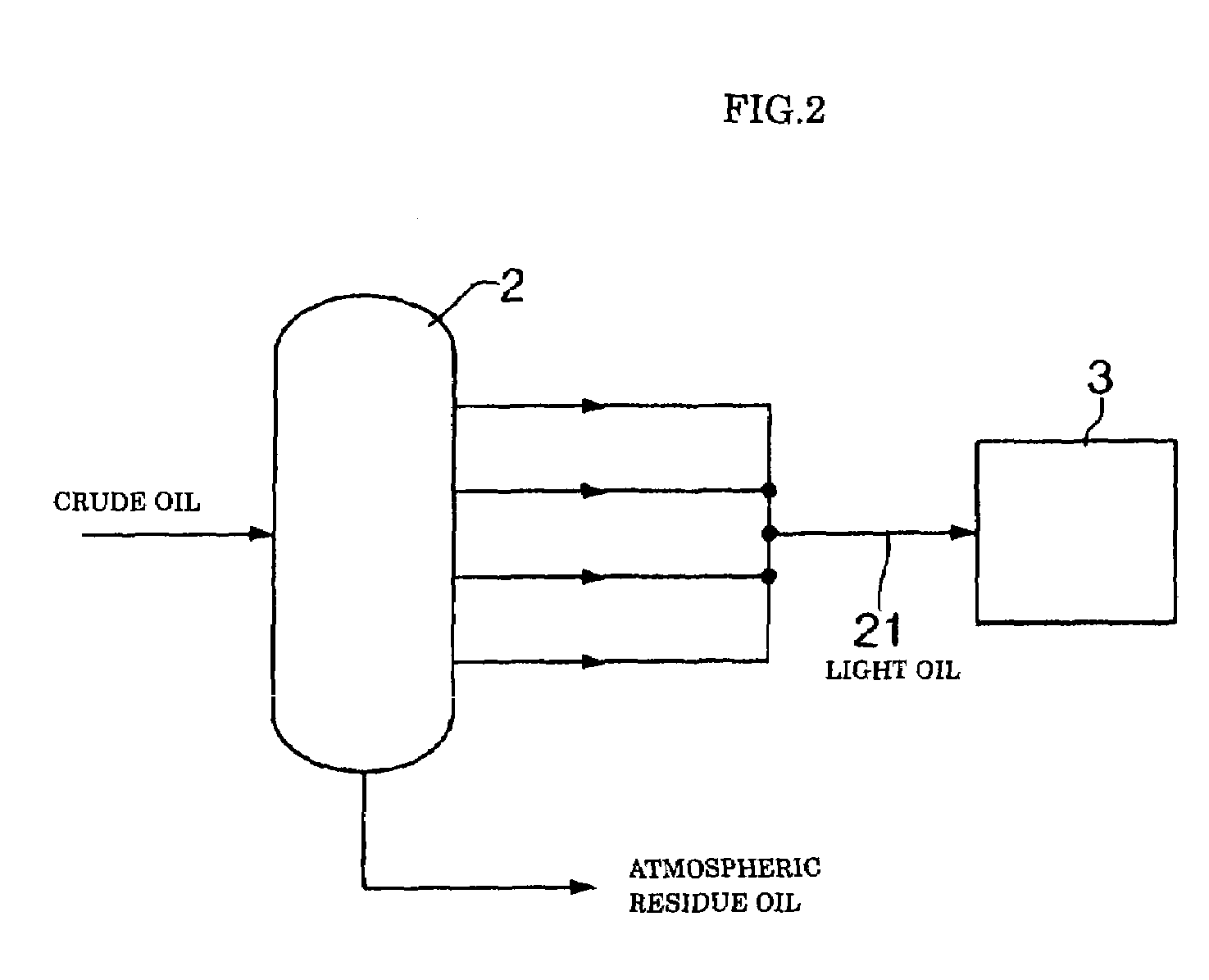
[0079]Arabian light crude oil (S content: 1.77% by weight) which is most readily available in the art was used as feed oil, to thereby produce gas turbine fuel oil by means of the system shown in FIG. 1. More particularly, the crude oil was separated into light oil or light distillate 21 of 350° C. or less in boiling point and heavy oil or residue 22 above 350° C. in boiling point and a hydrogen gas pressure in the first hydrotreating step was set to be 45 kg / cm2, resulting in gas turbine fuel oil being produced. Also, the vacuum distillation step provided a light oil matter 51 of 565° C. or less in boiling point (boiling point under an atmospheric pressure) and a heavy oil matter 52 having a boiling point above 565° C. by separation. In addition, a hydrogen gas pressure in the second hydrotreating step was set to be 55 kg / cm2, to thereby obtain gas turbine fuel oil, which was then mixed with the gas turbine fuel oil produced in the first hydrotreating step. Any alkaline metal, alka...
example 2
[0083]Of Middle East crude oil, Oman crude oil is known to have a relatively low sulfur content. Such Oman crude oil was used for producing gas turbine fuel oil by means of the system shown in FIG. 1. Oman crude oil has a sulfur concentration of 0.94% by weight, thus, it corresponds to low-sulfur crude oil described in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open Publication No. 207179 / 1994. In Example 2, the crude oil was subject to atmospheric distillation, to thereby be separated into light oil or light distillate 21 of 350° C. or less in boiling point and heavy oil or residue 22 having a boiling point above 350° C. Also, a hydrogen gas pressure in the first hydrotreating step was set to be 40 kg / cm2, resulting in gas turbine fuel oil being produced. Also, the vacuum distillation step provided a light oil matter 51 of 565° C. or less in boiling point (boiling point under an atmospheric pressure) and a heavy oil matter 52 having a boiling point above 565° C. by separation. In addition, a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com