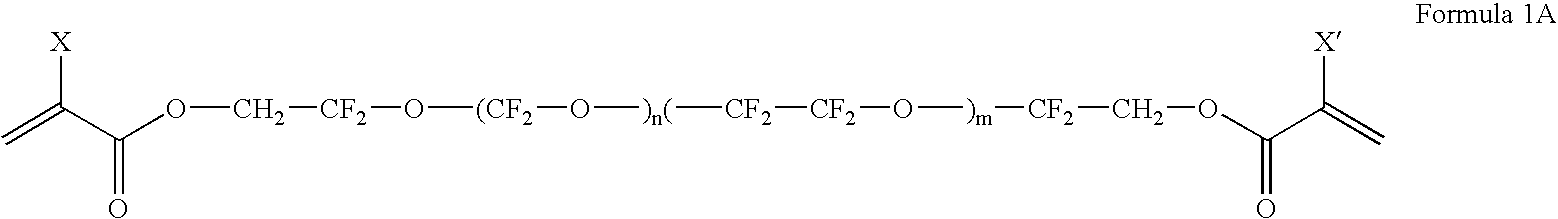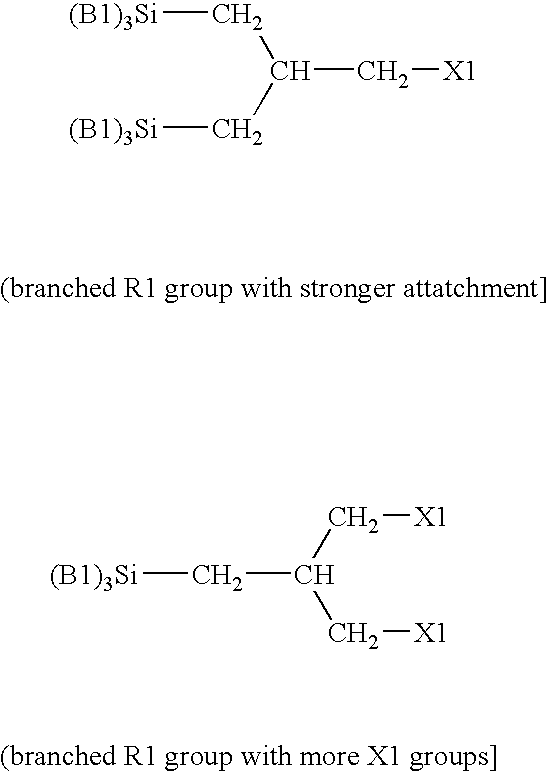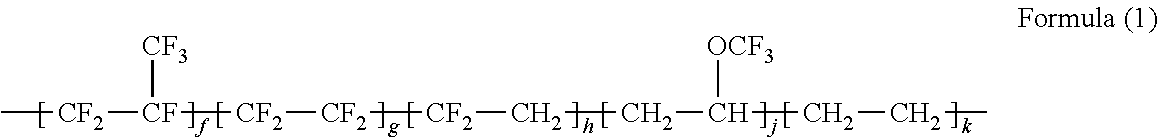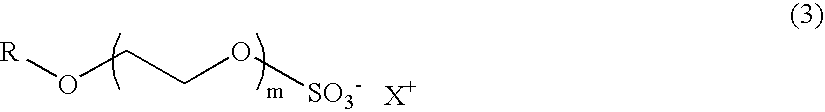Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
356results about "Printing formes reproduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
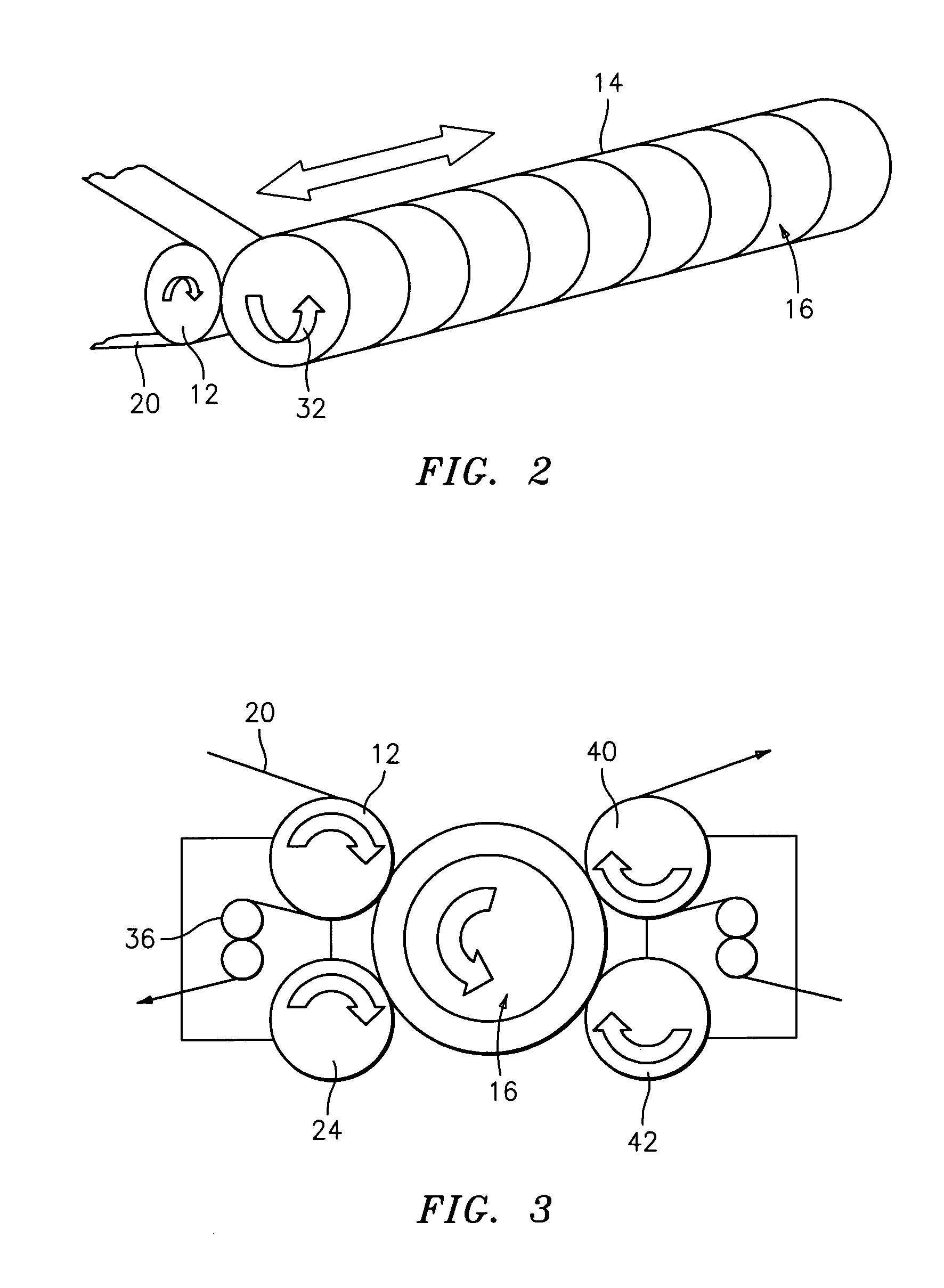
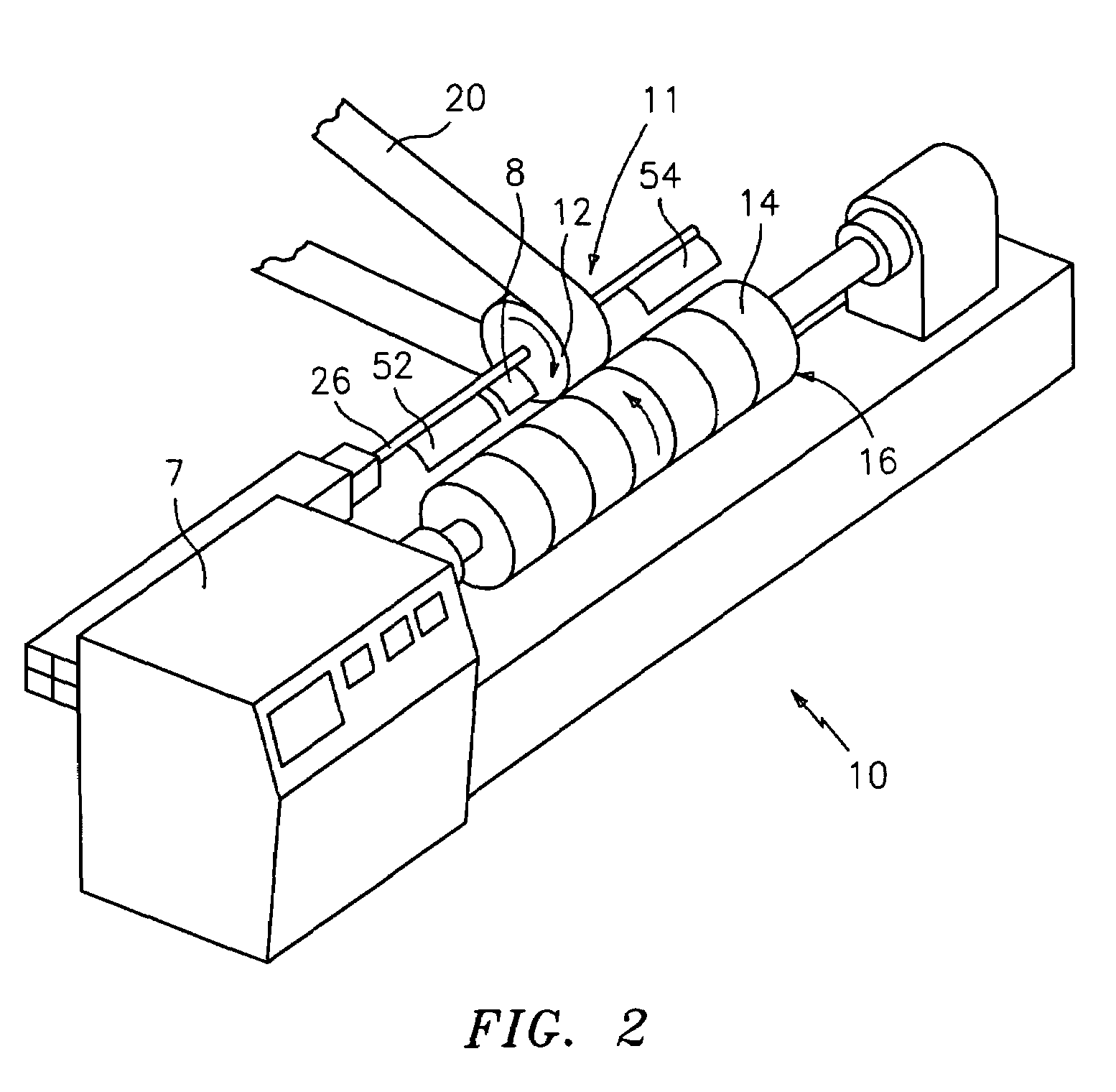
Printing form precursor and process for preparing a stamp from the precursor
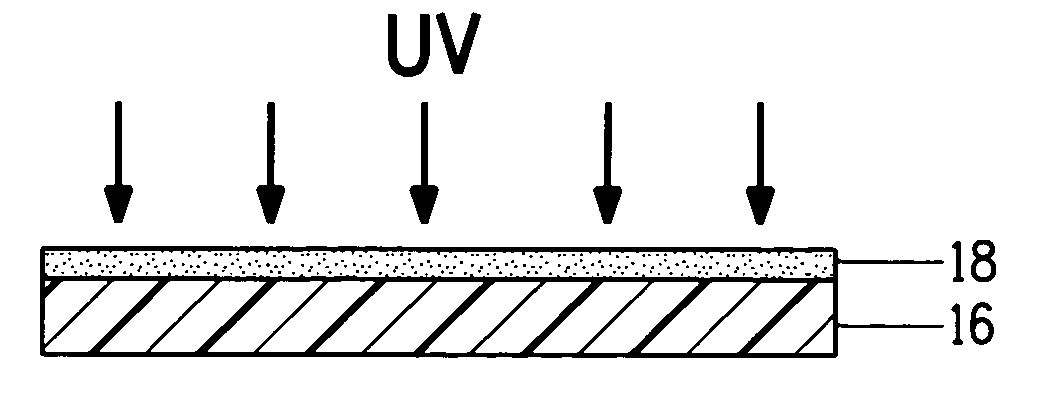
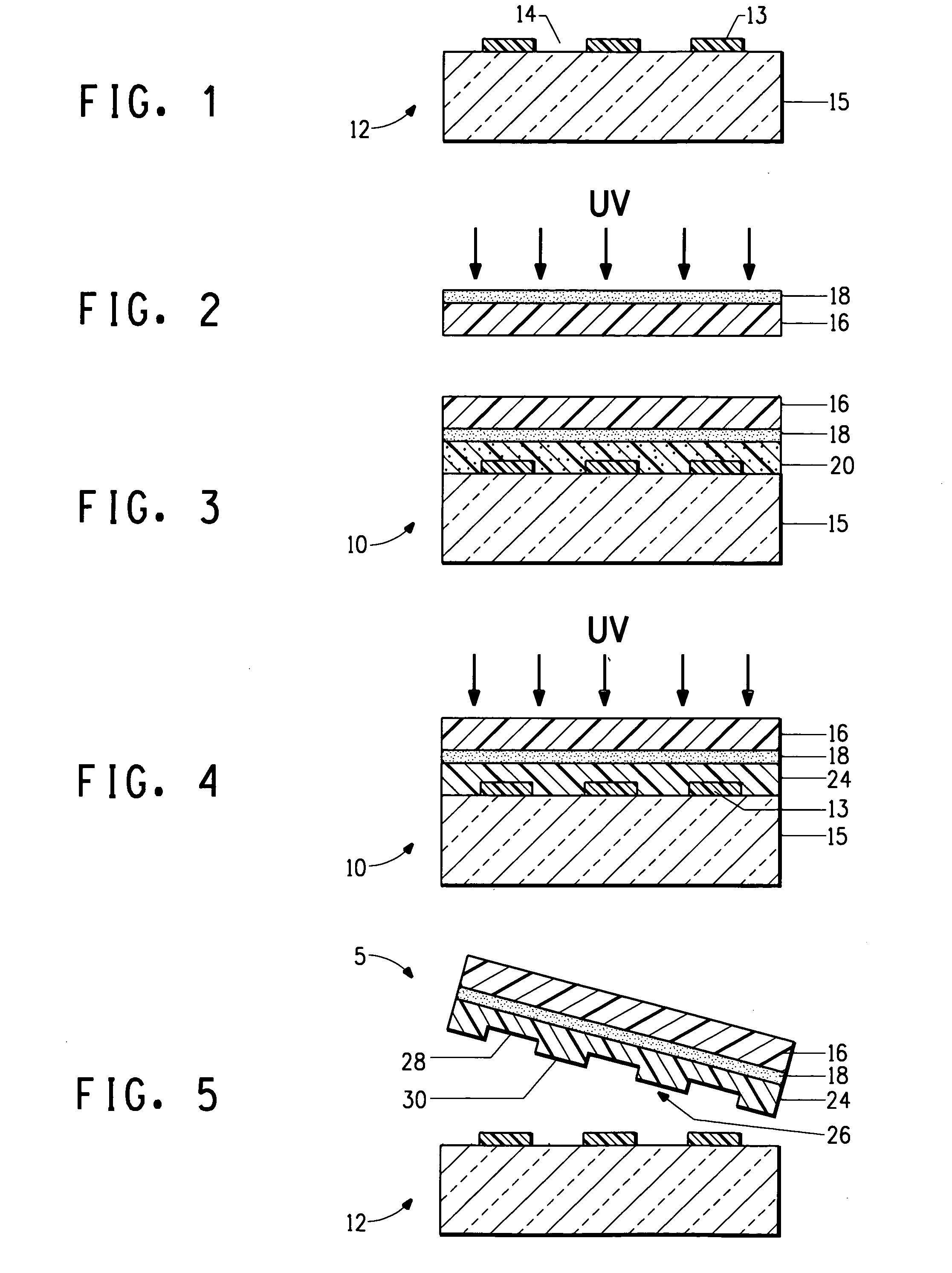
The invention pertains to a printing form precursor and a method for preparing a stamp from the precursor for use in soft lithographic applications. The printing form precursor includes a composition layer of a fluorinated compound capable of polymerization upon exposure to actinic radiation and a flexible support transparent to the actinic radiation adjacent the composition layer.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Edge transfer lithography
InactiveUS20050120902A1Wide applicabilitySmall feature sizeMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsImage resolutionEngineering
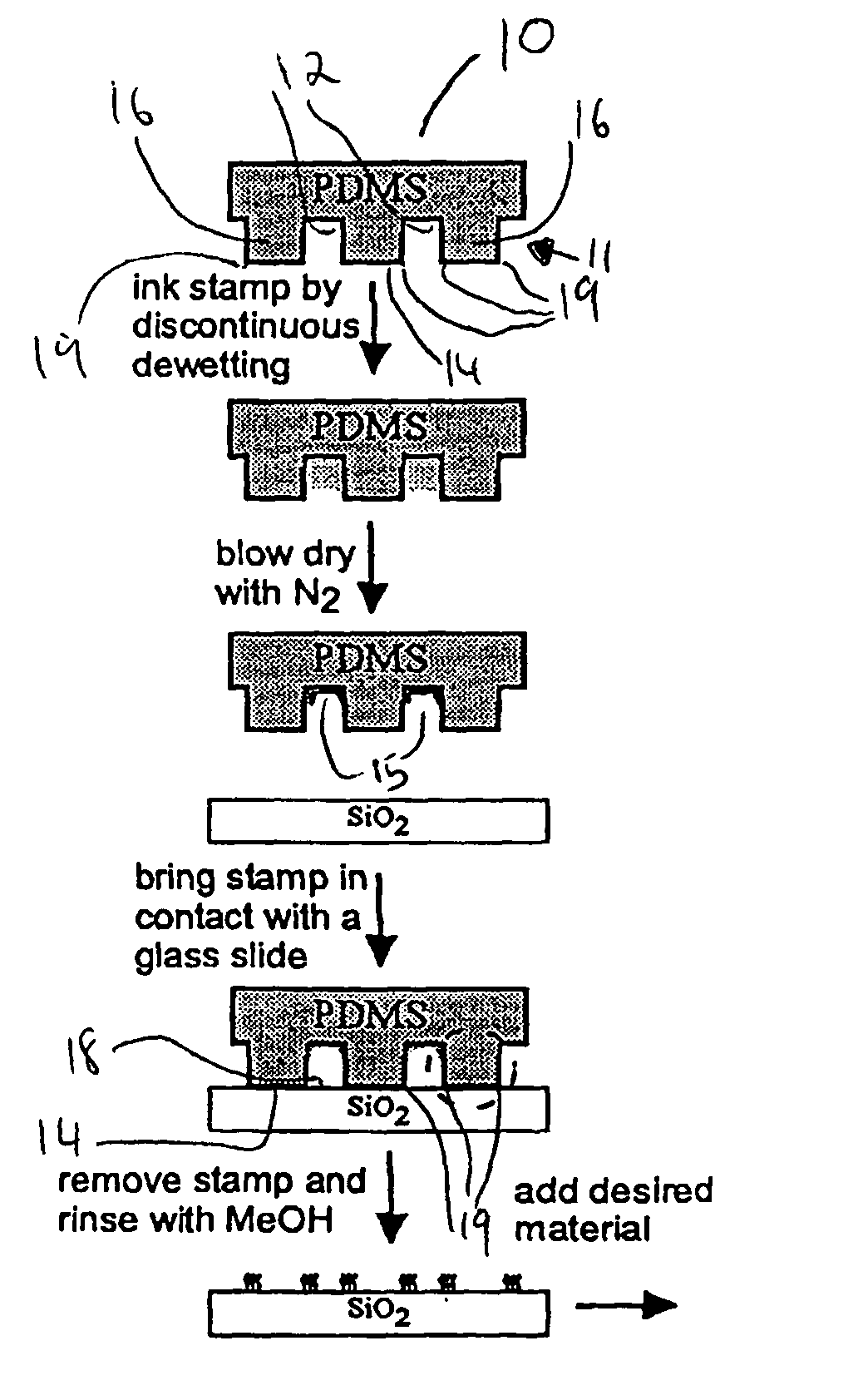
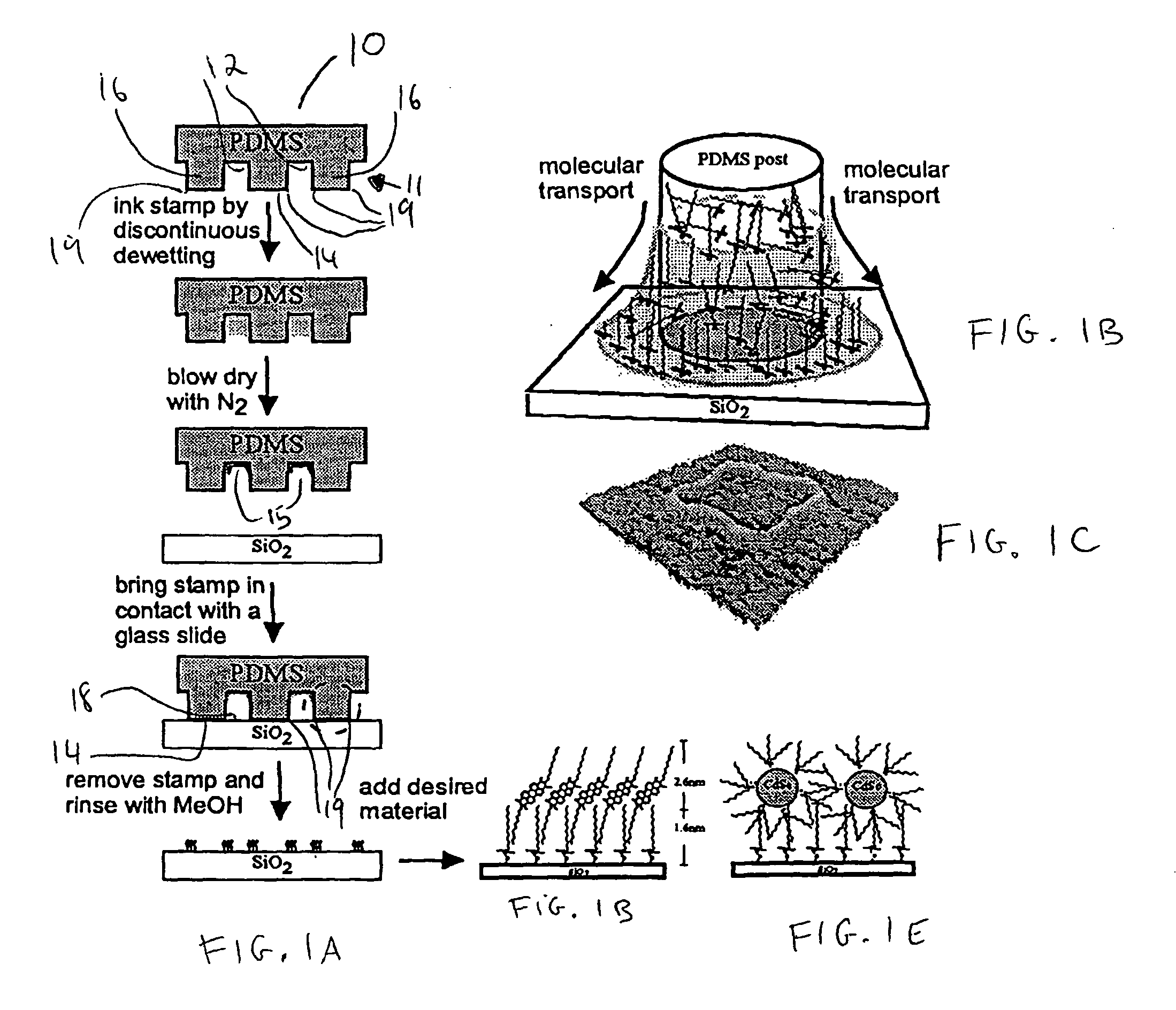
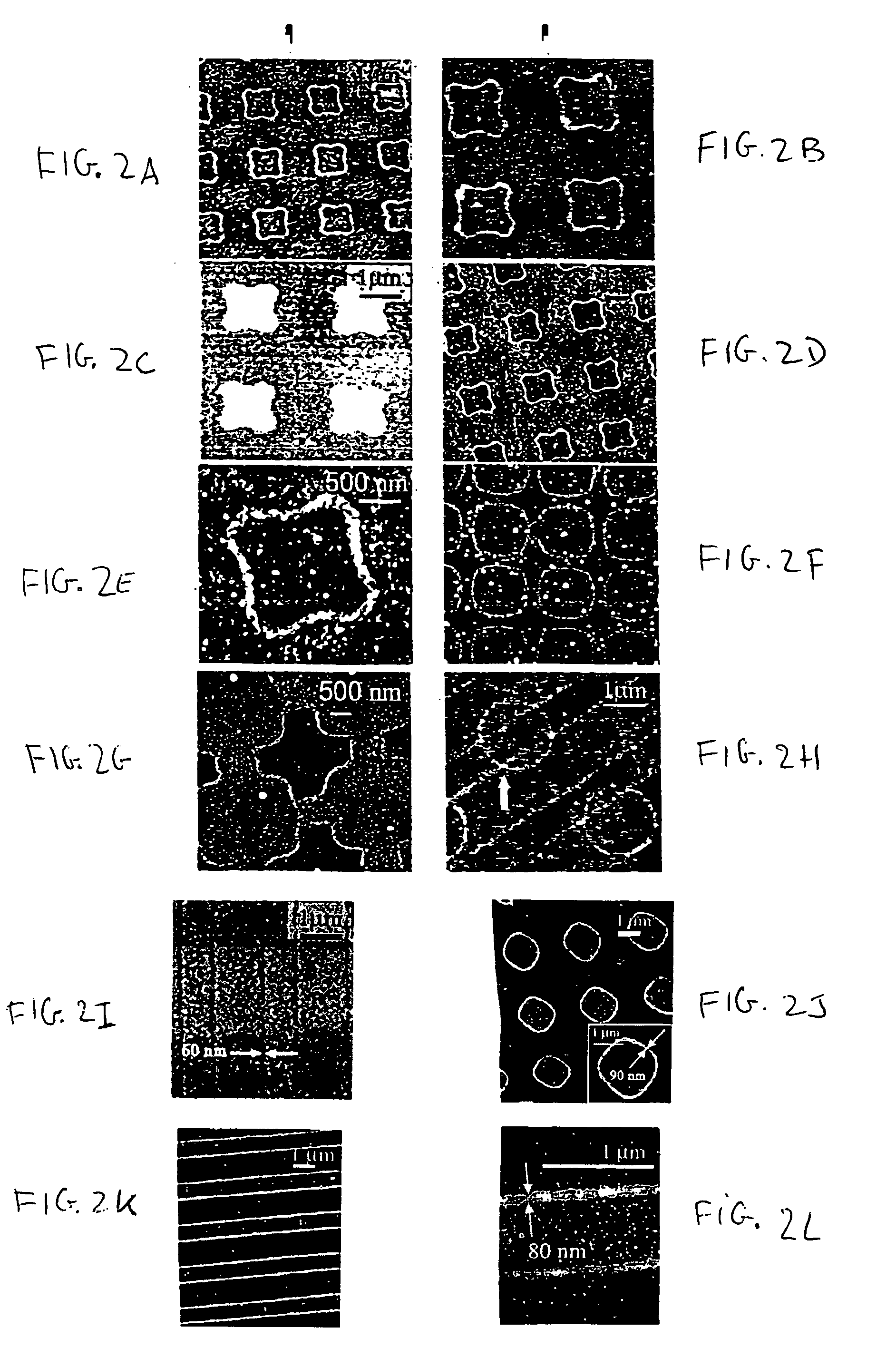
A method for applying a nanoscale resolution pattern of a molecular link onto a surface of a substrate is disclosed. The method referred to as edge transfer lithography, comprises providing a stamp structure (10) having a surface (11) with at least one protruding feature (16). Each protruding feature (16) has a stamp surface of a respective predefined shape at a protruding end thereof. Each protruding feature and its stamp surface are bounded by at least one edge (19), which edge intersects the surface of the stamp structure to form a recess. A solution of the molecular ink and a solvent is applied of the surface of the stamp structure (10) are such that the solution dewets from the surface of the stamp structure (10) is then dried to evaporate the solvent.
Owner:ADAMS DAVID +1
Stamp having an antisticking layer and a method of forming of repairing such a stamp
InactiveUS20050039618A1Good effectStable antisticking layerNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusCouplingNanoscopic scale
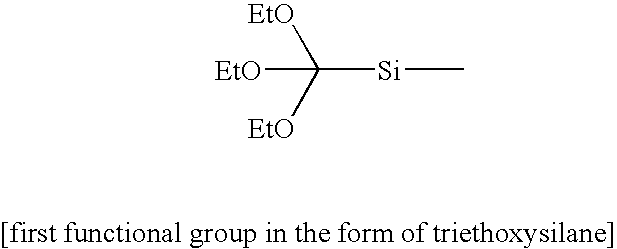
A stamp for use in transferring a pattern in nano-scale has a monomolecular antisticking layer. The anti-sticking layer comprises molecular chains, which are covalently bound to the surface of the stamp and which each comprise at least one fluorine-containing group. Each molecular chain contains a group Q, which comprises a bond which is weaker than the other bonds in the molecular chain as well as the covalent bond that binds the molecular chain to the surface of the stamp. Splitting of said bond in the group Q creates a group Q1, which is attached to the part of the molecular chain being left on the surface of the stamp and which is capable of reacting with a fluorine-containing compound to restore the antisticking layer. In a method of manufacturing a stamp for use in transferring a pattern in nanoscale, the stamp is provided with the above-mentioned molecular chain. In a method of repairing a damaged antisticking layer of the above-mentioned stamp, the stamp is treated with a repairing reagent, which has a coupling end, which is capable of reacting with the group Q1, and a fluorine-containing group located at the other end of the repairing reagent.
Owner:OBDUCAT AB SE
Printing plates comprising modified pigment products
The present invention discloses printing plates comprising a substrate and a radiation-absorptive layer, wherein the radiation-absorptive layer comprises at least one modified pigment product. The modified pigment product comprises a pigment having attached at least one organic group and at least one amphiphilic counterion. Methods of imaging printing plates are also disclosed.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Microcontact printing
InactiveUS7117790B2Generate undesired patterning resultsControl distortionMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsMicrocontact printingEngineering
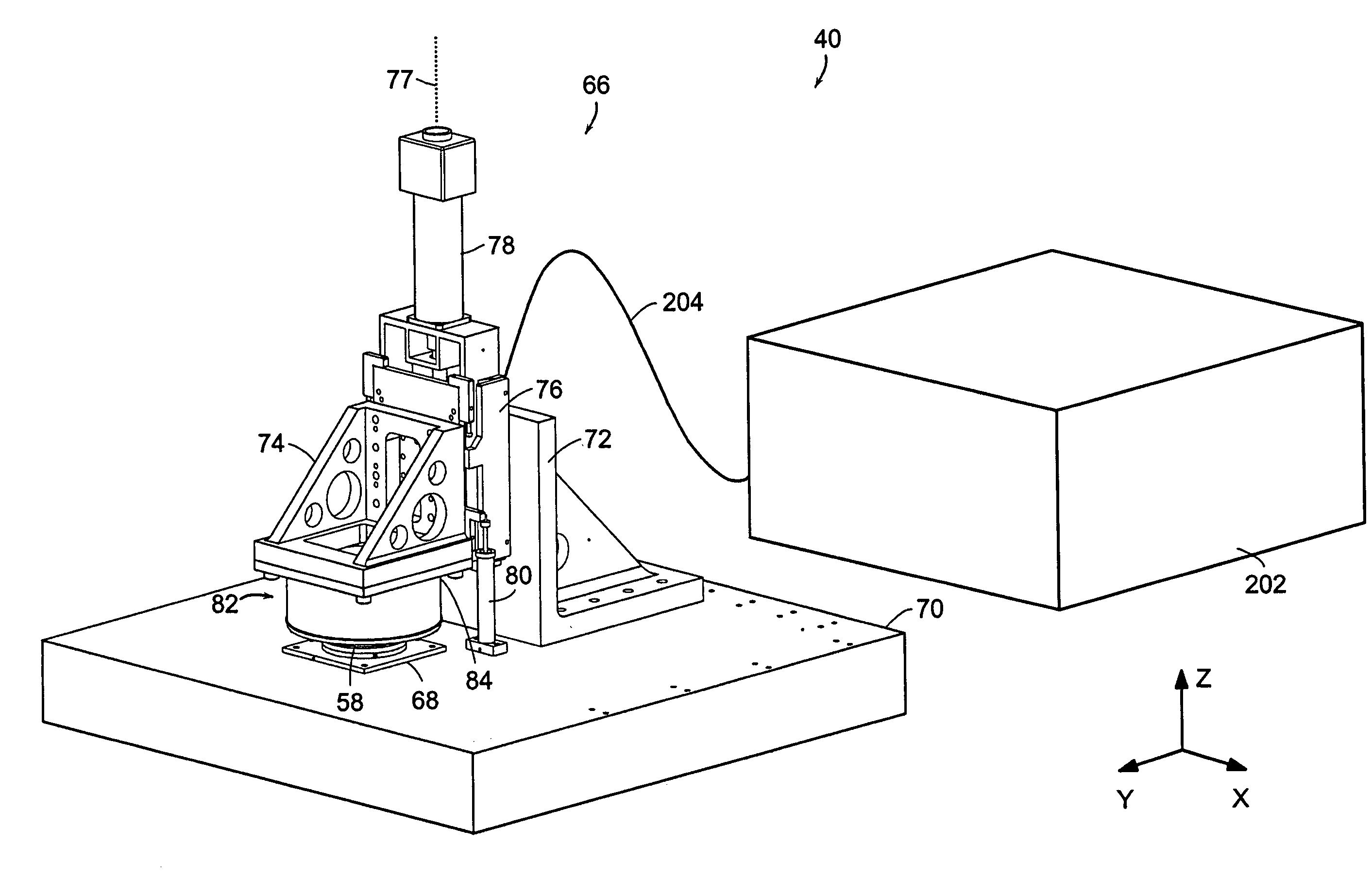
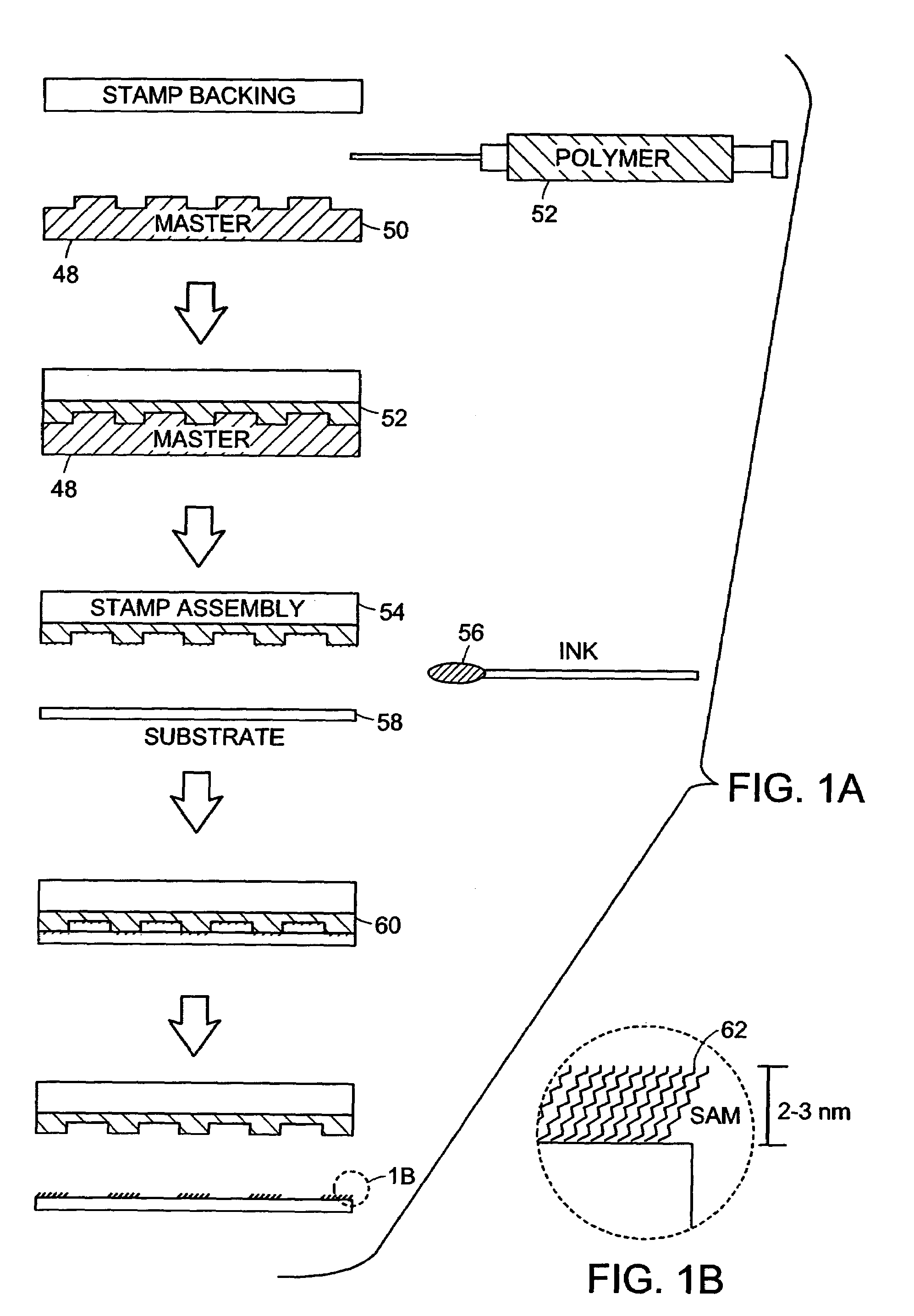
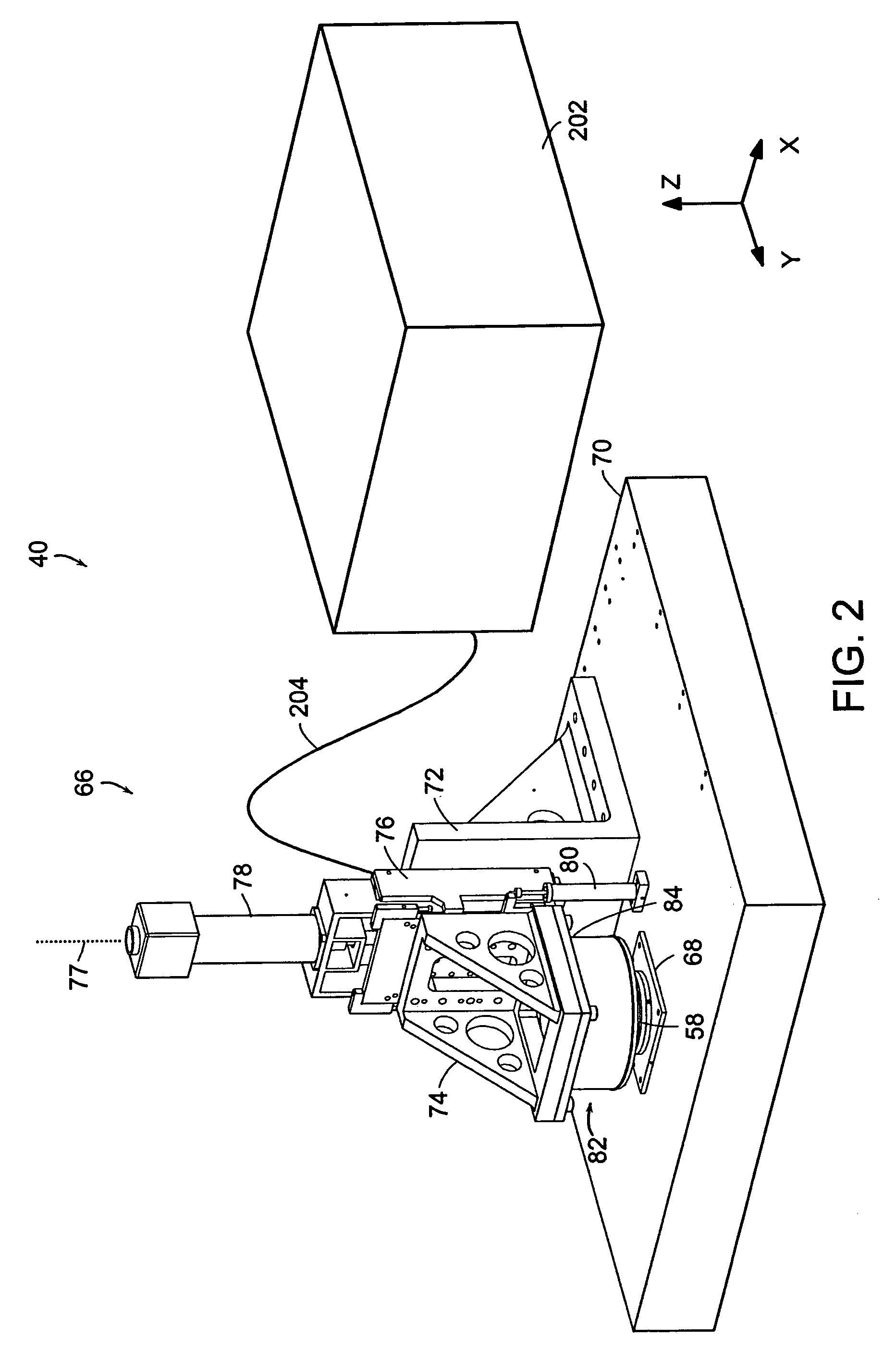
A microcontact printing tool having a print unit including a stamp head with a stamp and a wafer chuck for retaining a substrate. The stamp contained by the stamped head movable relative to the substrate by an actuator and a stage. A plurality of sensors detect the position of the stamp relative to substrate. A method of using the printing tool that includes a real-time feedback for consistent and accurate application of force during the printing of the substrate. The stamp head includes a pressure chamber carrying the stamp. The stamp backing is deflected prior to contact of the stamp with the substrate to form a minimum point and the stamp backing and the stamp is returned to a plane to create a printing propagation contact. An apparatus and method of producing the stamp on a stamp backing. The apparatus has a master backing and a stamping backing in close proximity and the stamp material drawn in through a vacuum. The stamp is separated from the master by use of a parting fluid.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
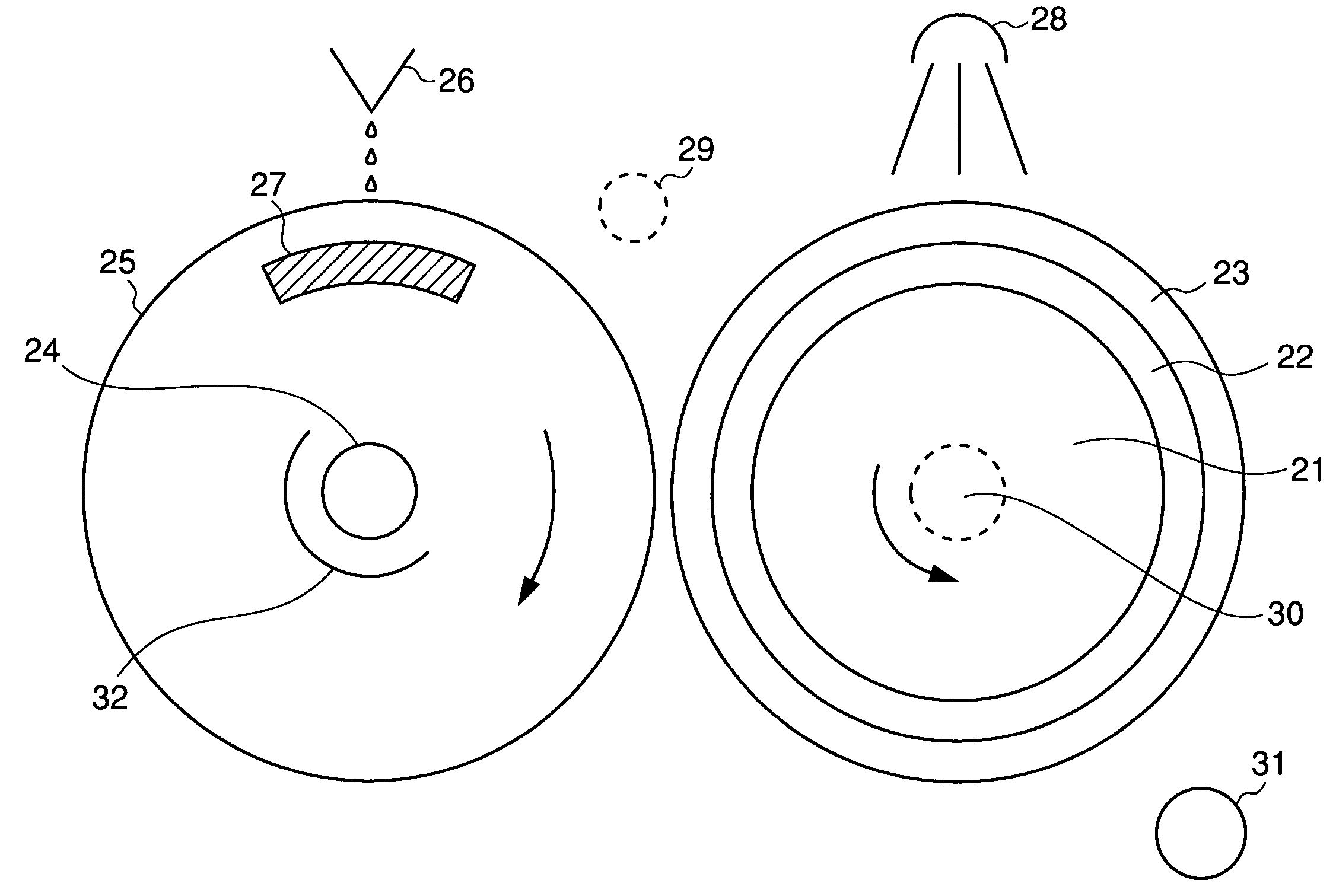
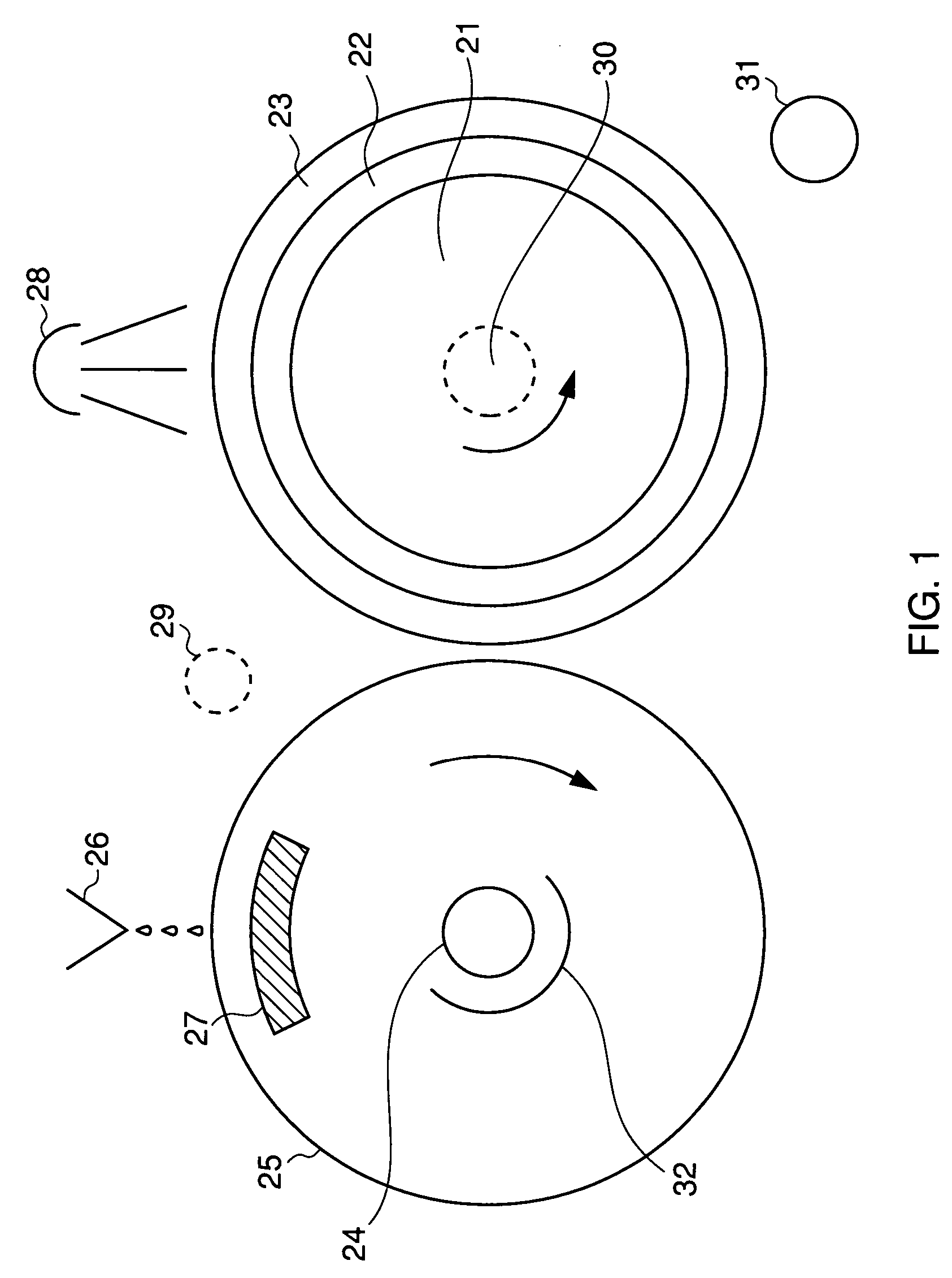
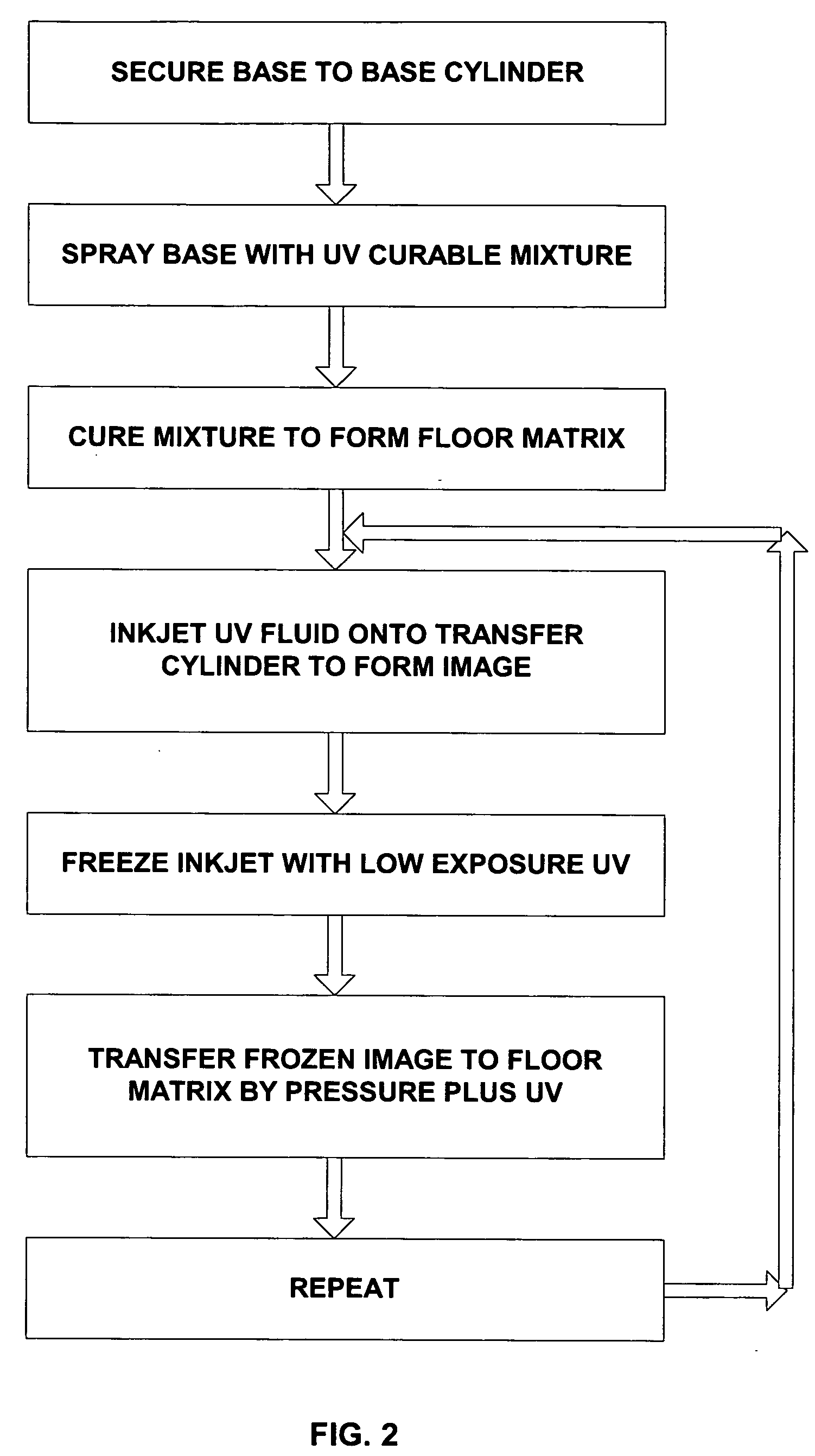
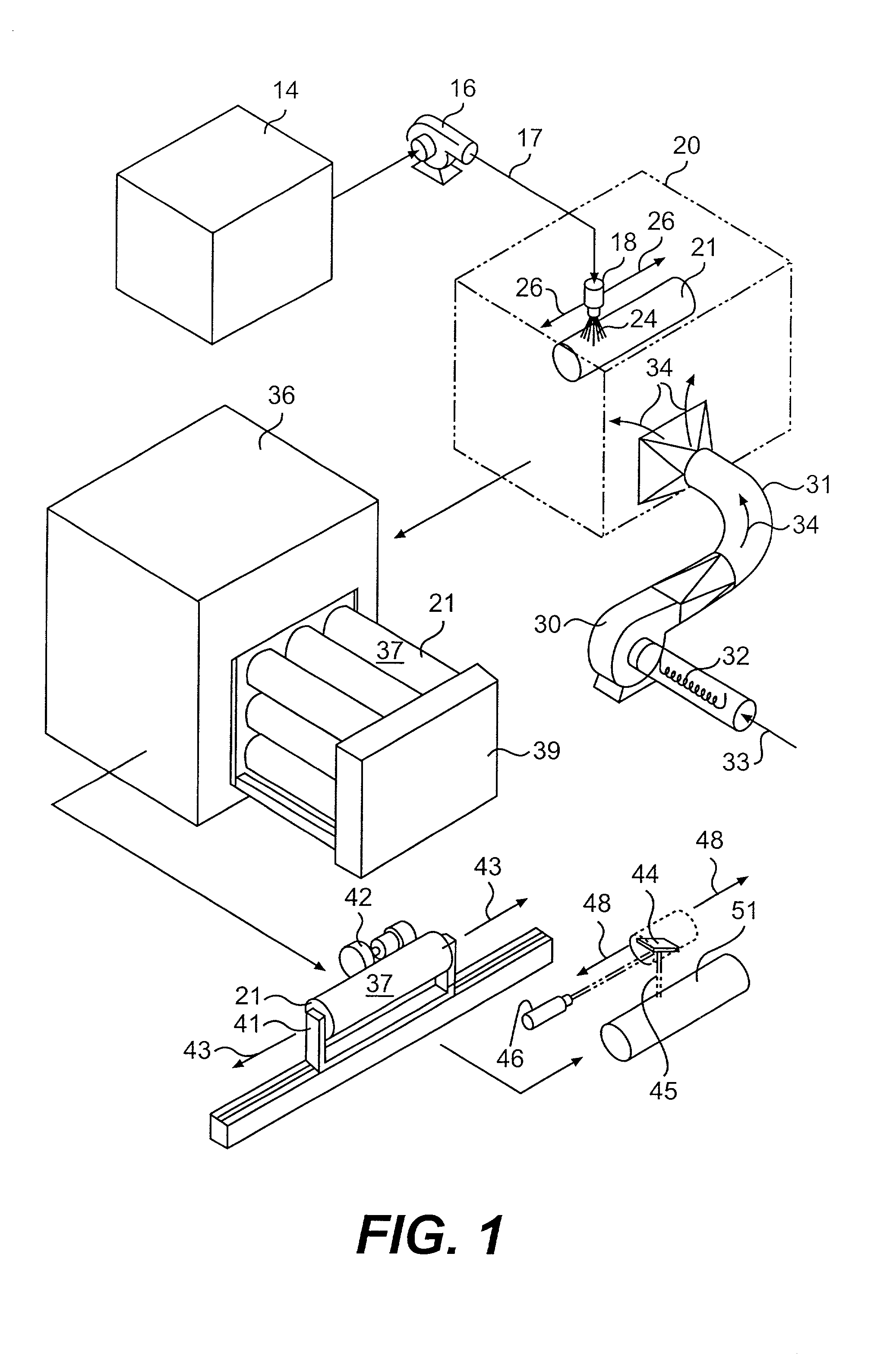
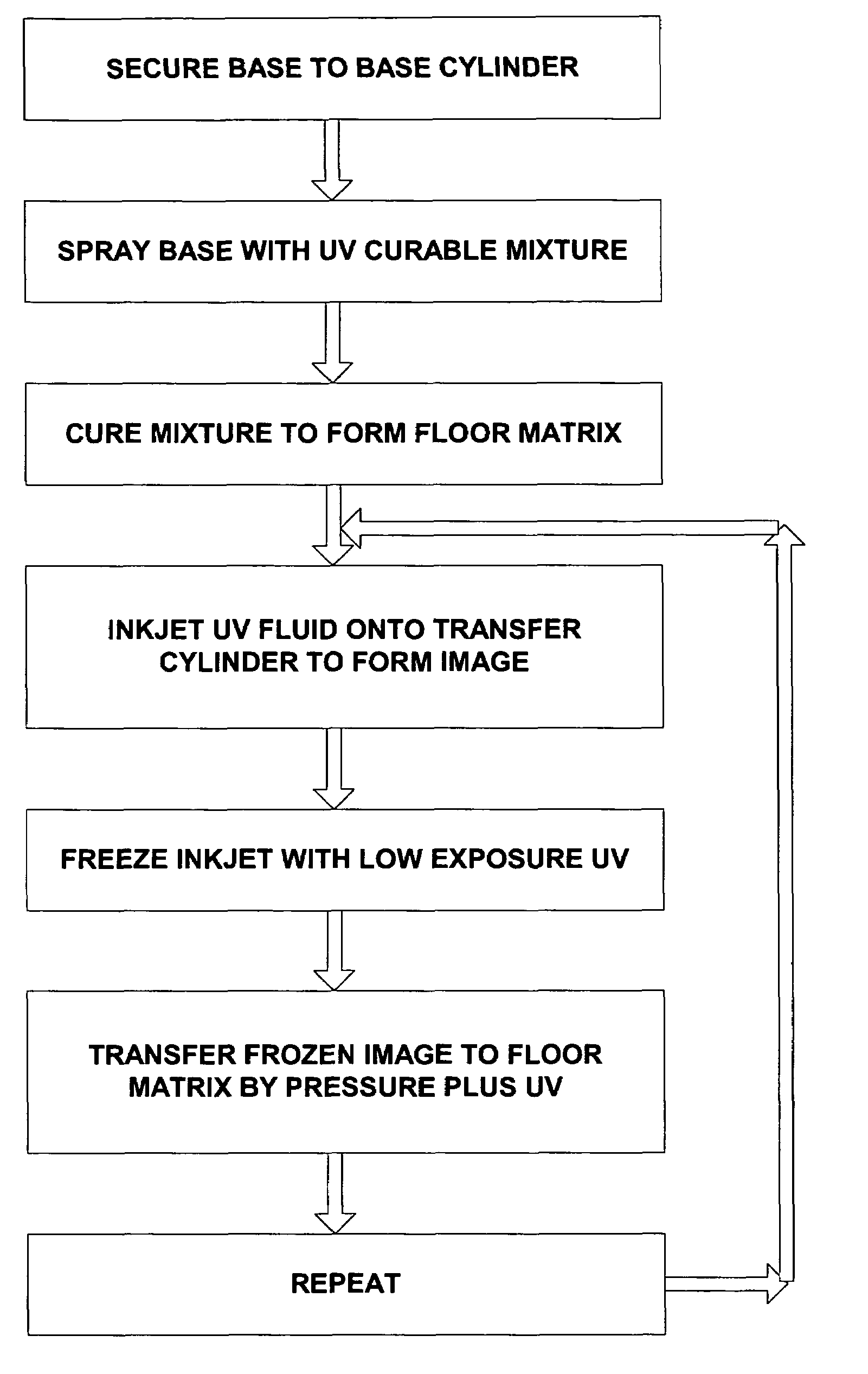
Method for producing a flexographic printing plate formed by inkjetted fluid
InactiveUS20040129158A1Rapid and inexpensive mannerDuplicating/marking methodsMounting boardsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:KODAK IL
Printing sleeves and cylinders applied with a photopolymer composition
A method of forming a photopolymer layer on a printing substrate (e.g., flexographic printing sleeves and cylinders) is provided. The method includes providing a photopolymer composition that contains a photopolymer and at least one monomer bonded to the photopolymer. The monomer can help reduce the hardness of the resulting photopolymer composition. In addition, the method also includes spraying the photopolymer composition onto a rotating generally cylindrical surface of the printing substrate. In one embodiment, the sprayed photopolymer composition is then cured. The resulting photopolymer layer is seamless and continuous and, in some embodiments, has a hardness of between about 50 to about 70 Shore A.
Owner:ROSSINI SPA
Digitally printed products and process
InactiveUS20070289705A1Speed color-matching processingExcellent abrasion resistanceLamination ancillary operationsDuplicating/marking methodsColor printingComputer printing
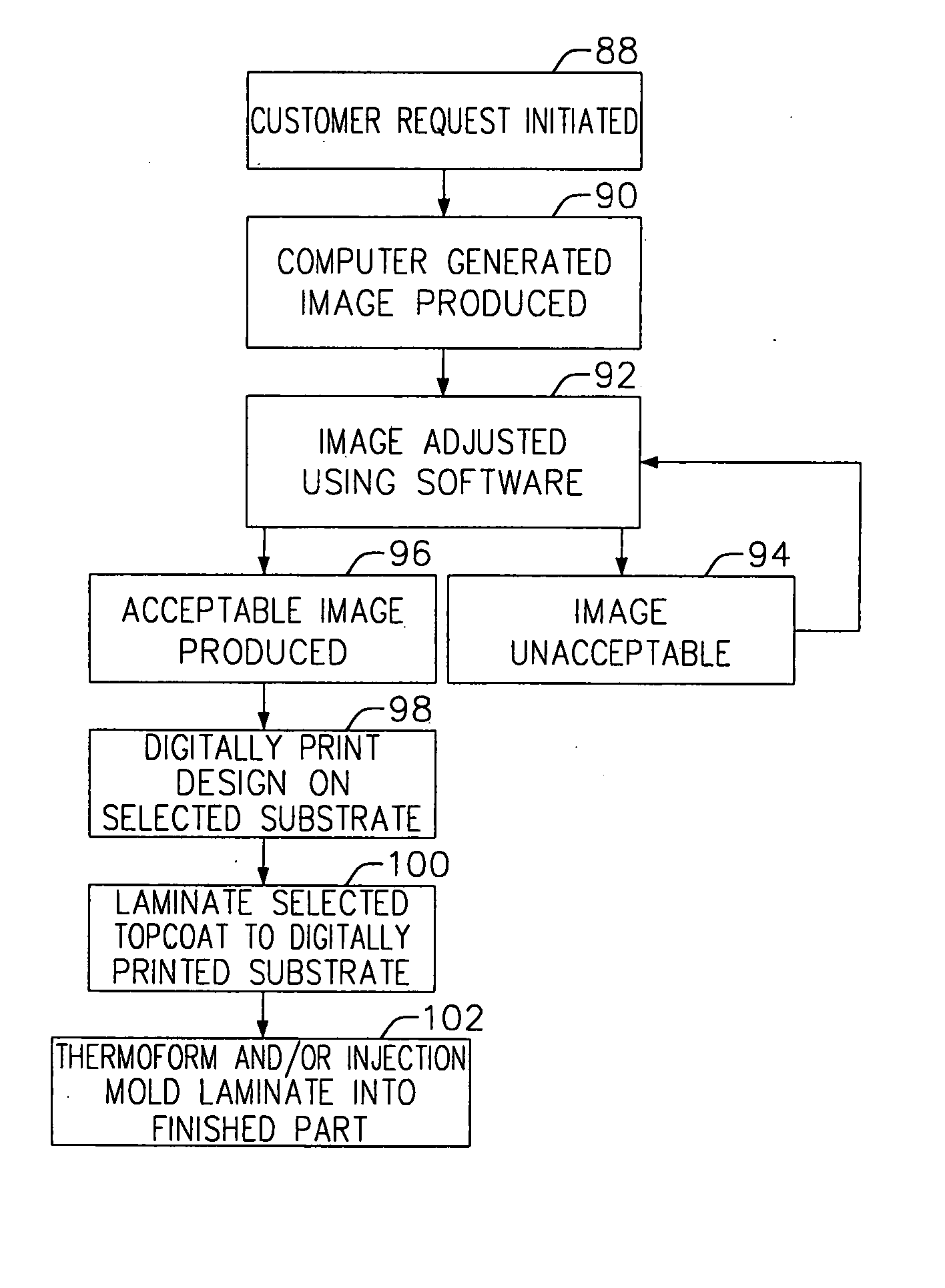
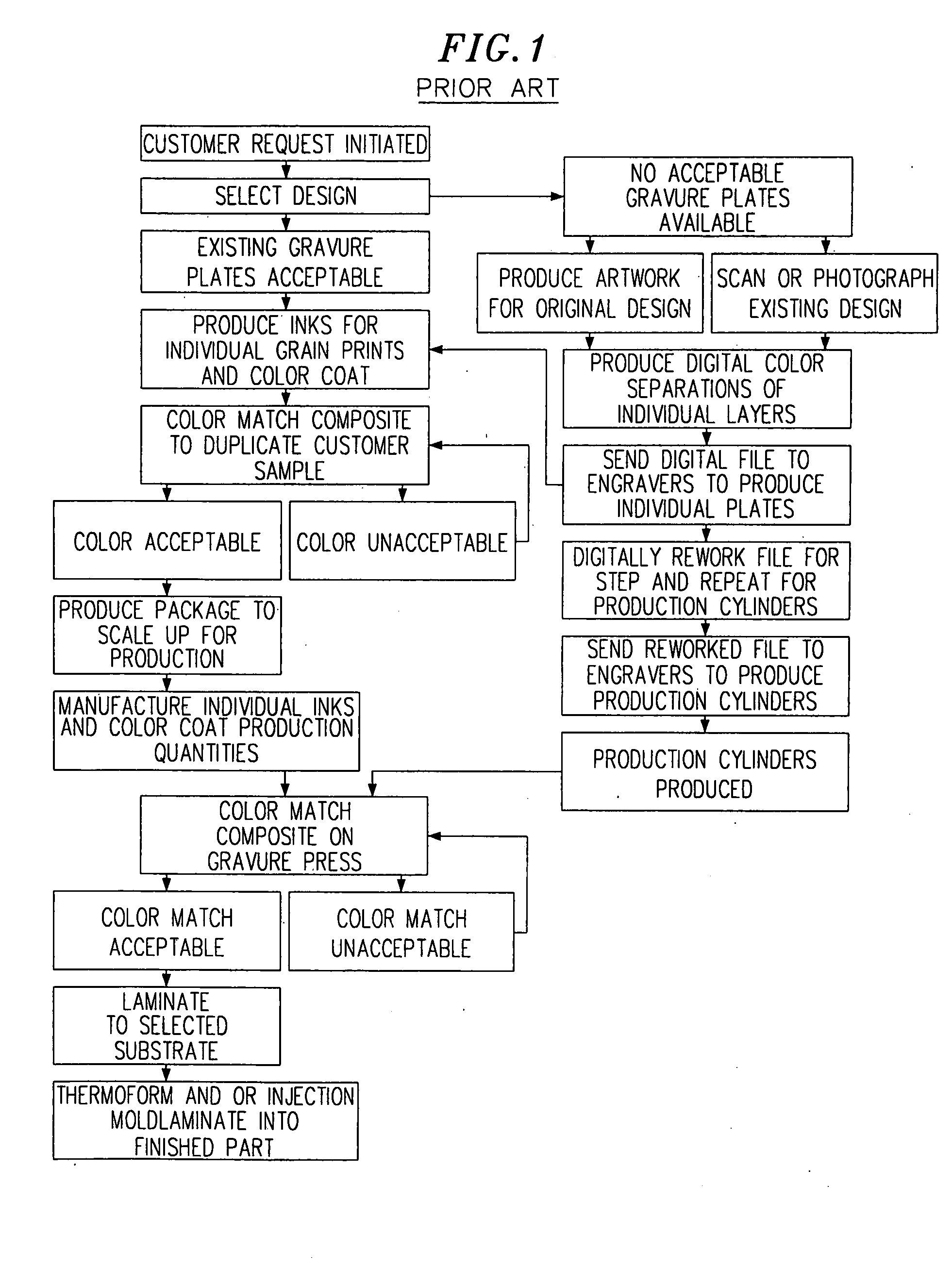
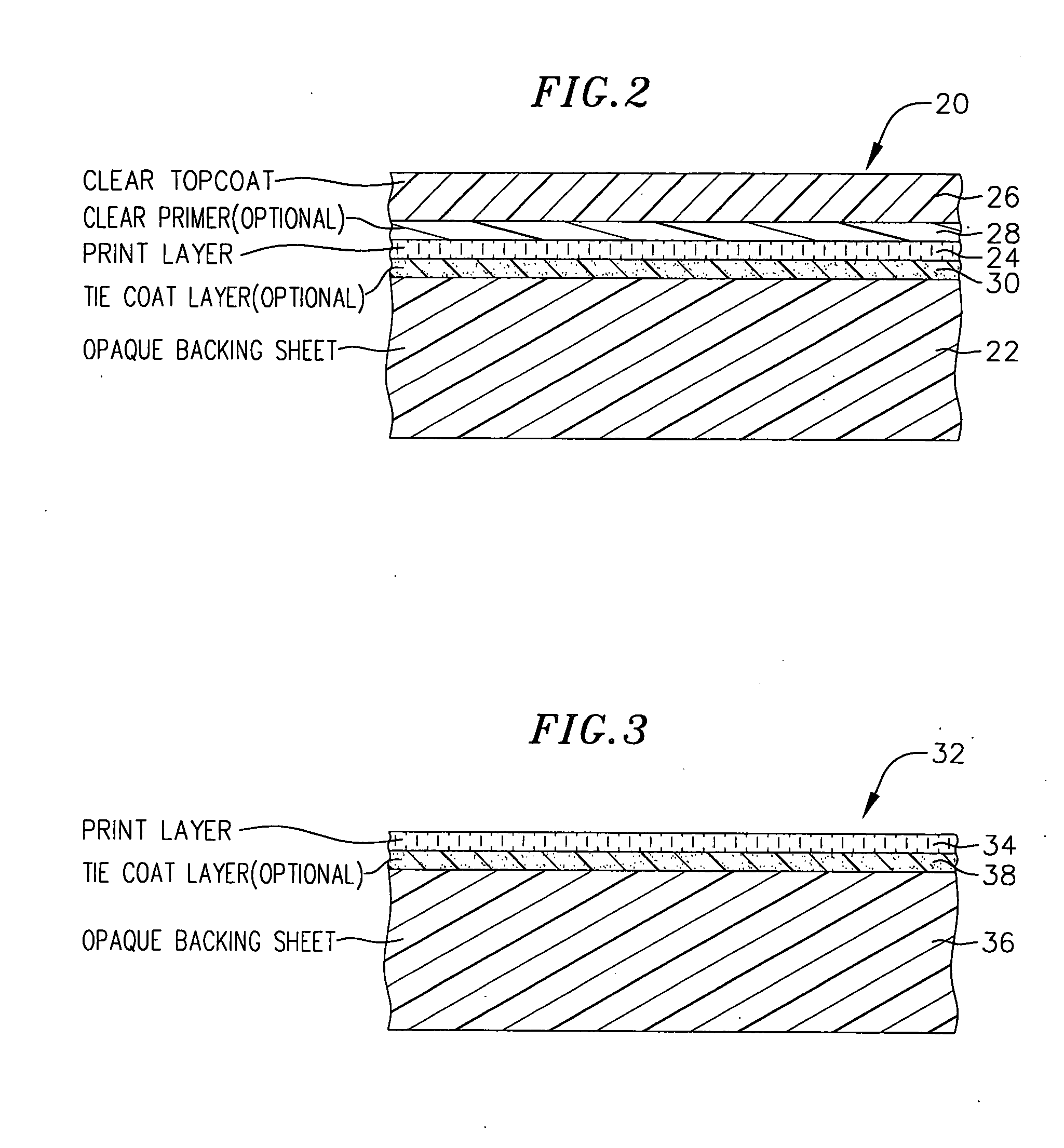
A process for manufacturing three-dimensionally shaped polymeric sheets and laminates with color-matched digitally printed full color ink jet images. A flexible thermoformable polymeric baseweb is placed in an ink jet printer and a solvent-based (non-aqueous) digital printing ink is applied directly to the baseweb, in the absence of an ink receptive layer on the baseweb, to form a decorative pattern in multiple colors in a single pass through the printer. The finished product can be thermoformed or injection molded to a three-dimensional shape. A protective topcoat can be laminated to the digitally printed sheet prior to the thermoforming and / or injection molding step. A process for making color-matched products comprises producing a software-driven image of a pattern on a screen representing a standard color print pattern; evaluating and adjusting the standard displayed on the screen using software-driven image related adjustments for hue, contrast, lightness / darkness, etc.; producing a test print by applying a decorative pattern to the baseweb by a digital ink jet printer and making an optional software-driven image-related adjustment in the standard to color match the standard to the test print image; and when the adjusted standard image displayed on the screen is acceptable, passing an image-related output to the digital ink jet printer for printing a decorative print color-matched to the accepted onscreen standard.
Owner:CCL LABEL INC
Screened film intermediate for use with flexographic printing plate having improved solids rendition
InactiveUS6492095B2Digitally marking record carriersInking apparatusColor saturationMechanical engineering
flexographic printing plate having solid image areas which are covered by a plurality of very small and shallow cells similar to the ink carrying cells found in anilox ink metering rolls. These cells fill with ink during the plate inking step and reproduce solid image areas with better color saturation while at the same time reducing the halo typical of flexographic printing of solids. Associated with this plate is a method for producing the cells, including the use of an intermediate screened film and of a computer program for generating the film intermediate.
Owner:ESKO SOFTWARE
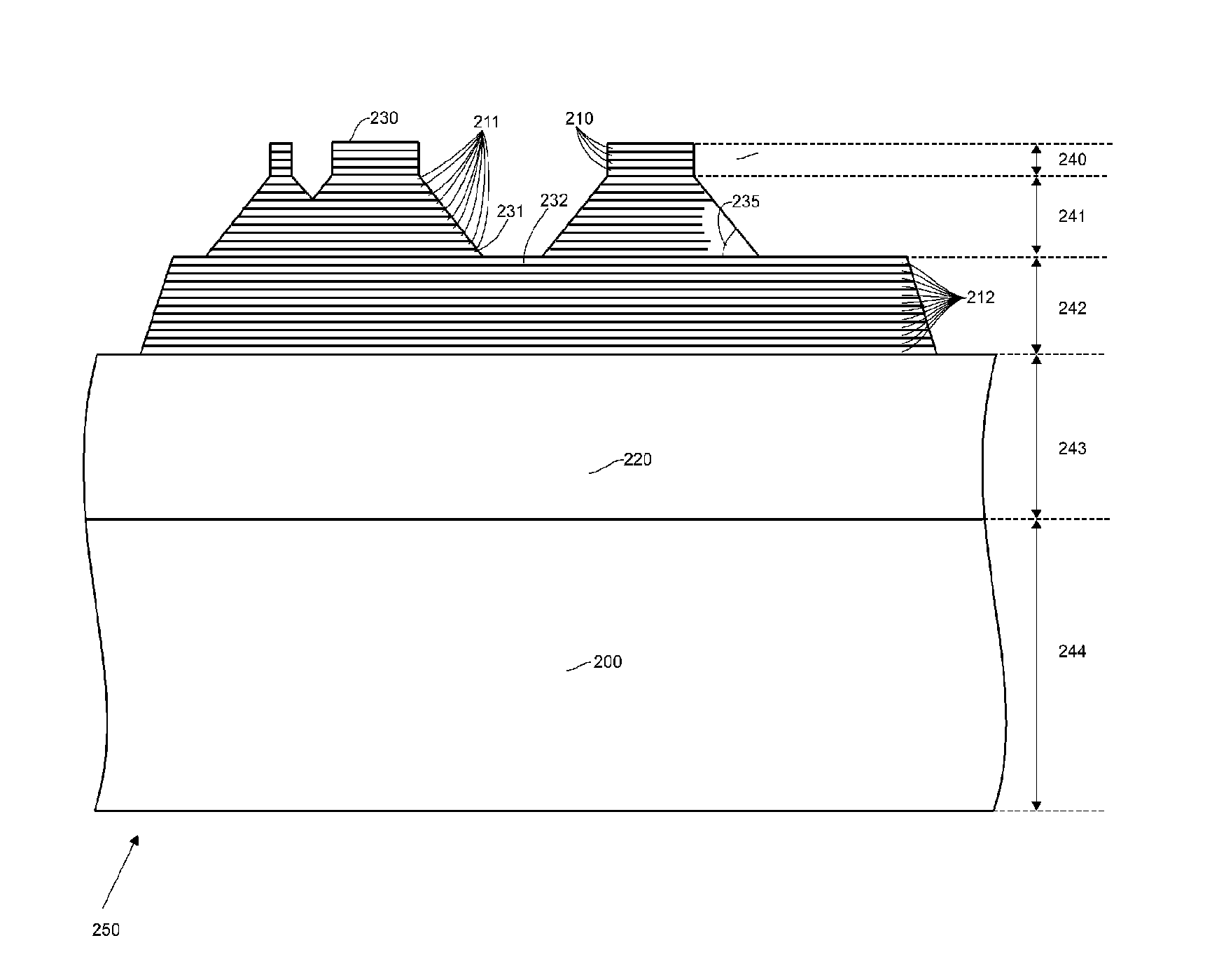
Hybrid optical head for direct engraving of flexographic printing plates
An optical imaging head for direct engraving of flexographic printing plates, comprising: at least two groups of radiation sources, each group comprising at least one radiation source, wherein the radiation sources within each group emit radiation having the same intensity and spot size, different from the intensity and spot size of radiation sources in the other groups, said groups of radiation sources operating simultaneously.
Owner:MIRACLON CORP
Method for producing flexographic printing plates by means of laser engraving
InactiveUS6935236B2High resolutionAvoid it happening againDuplicating/marking methodsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCross-linkLaser engraving
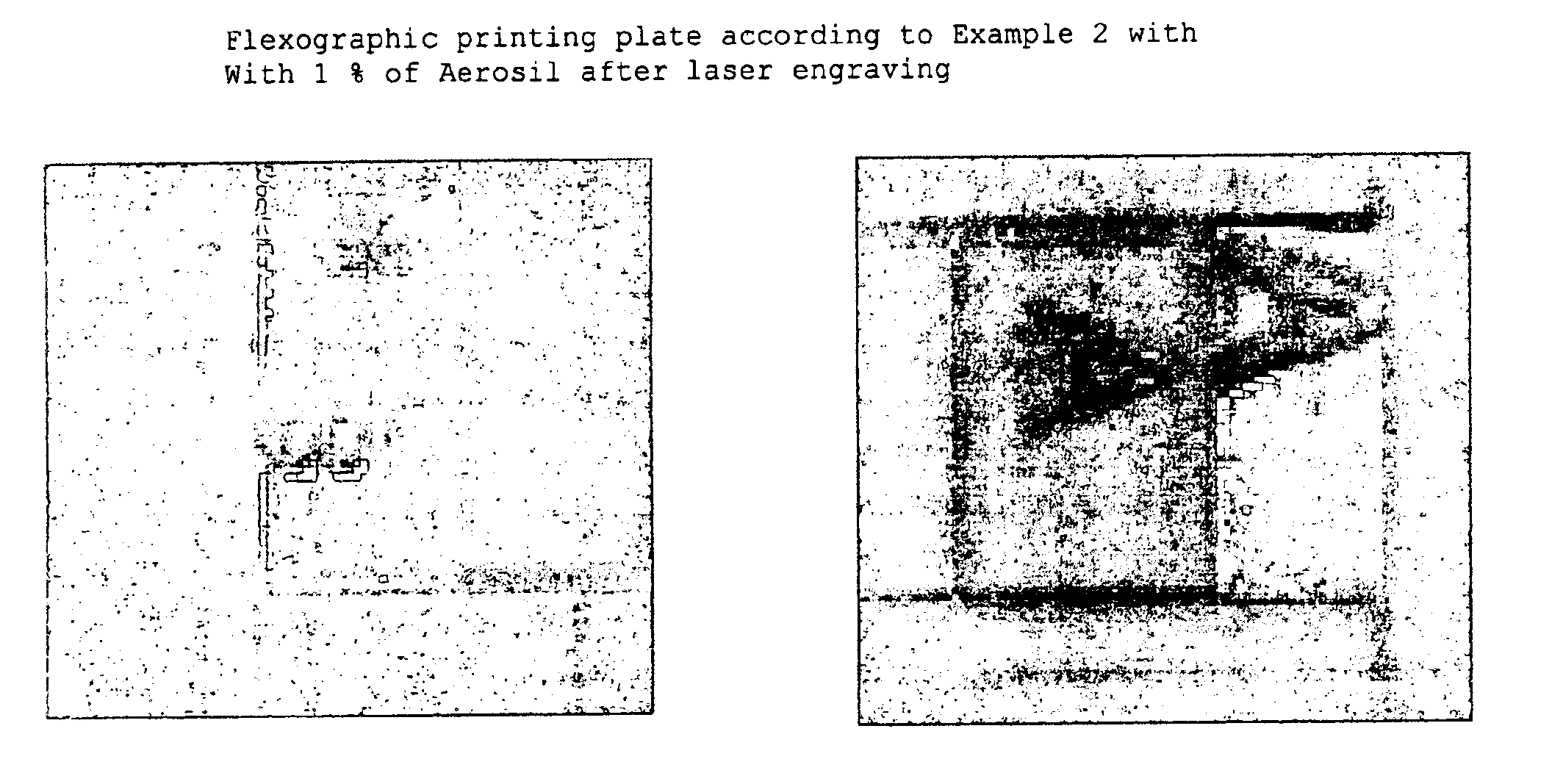
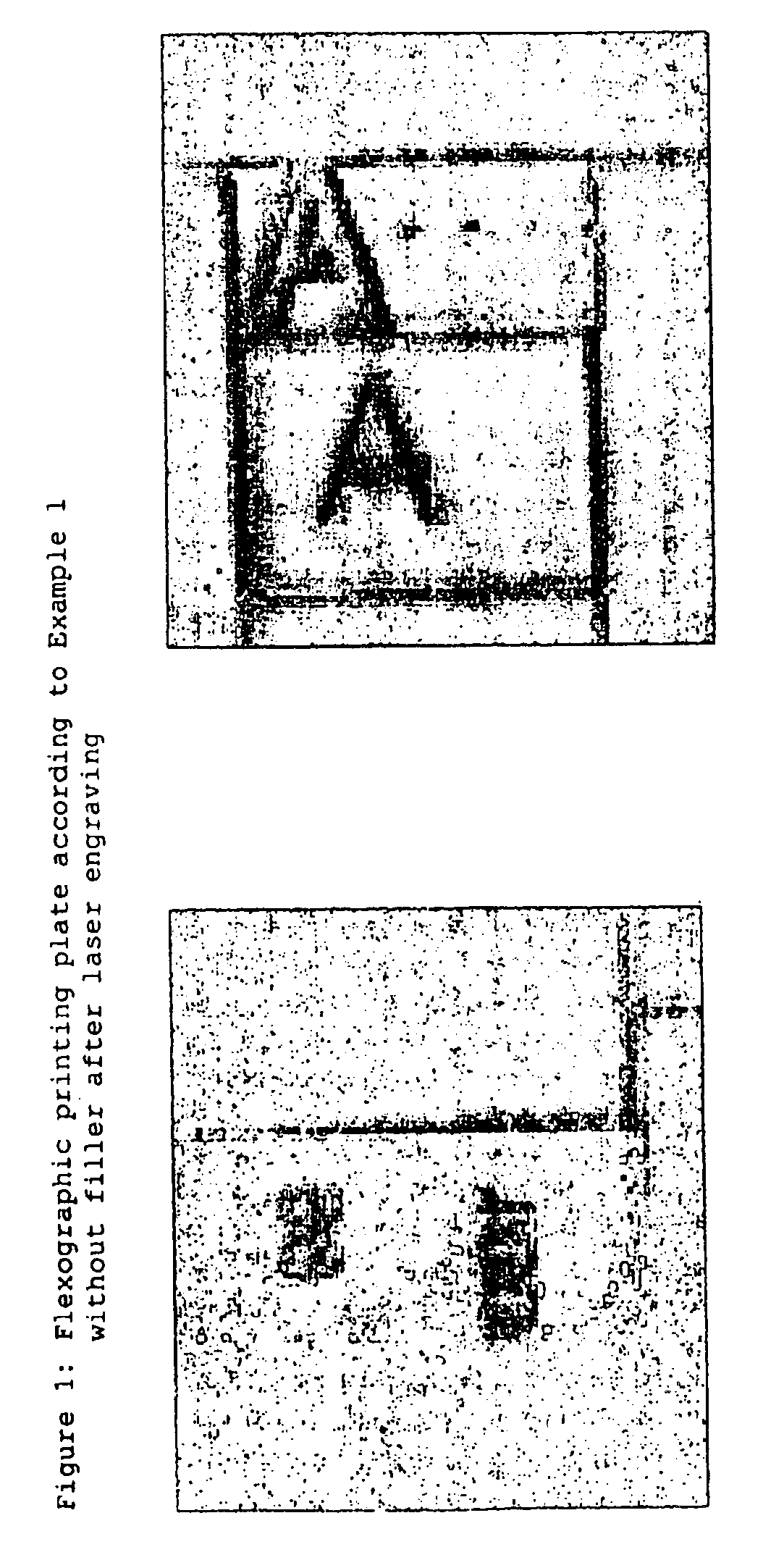
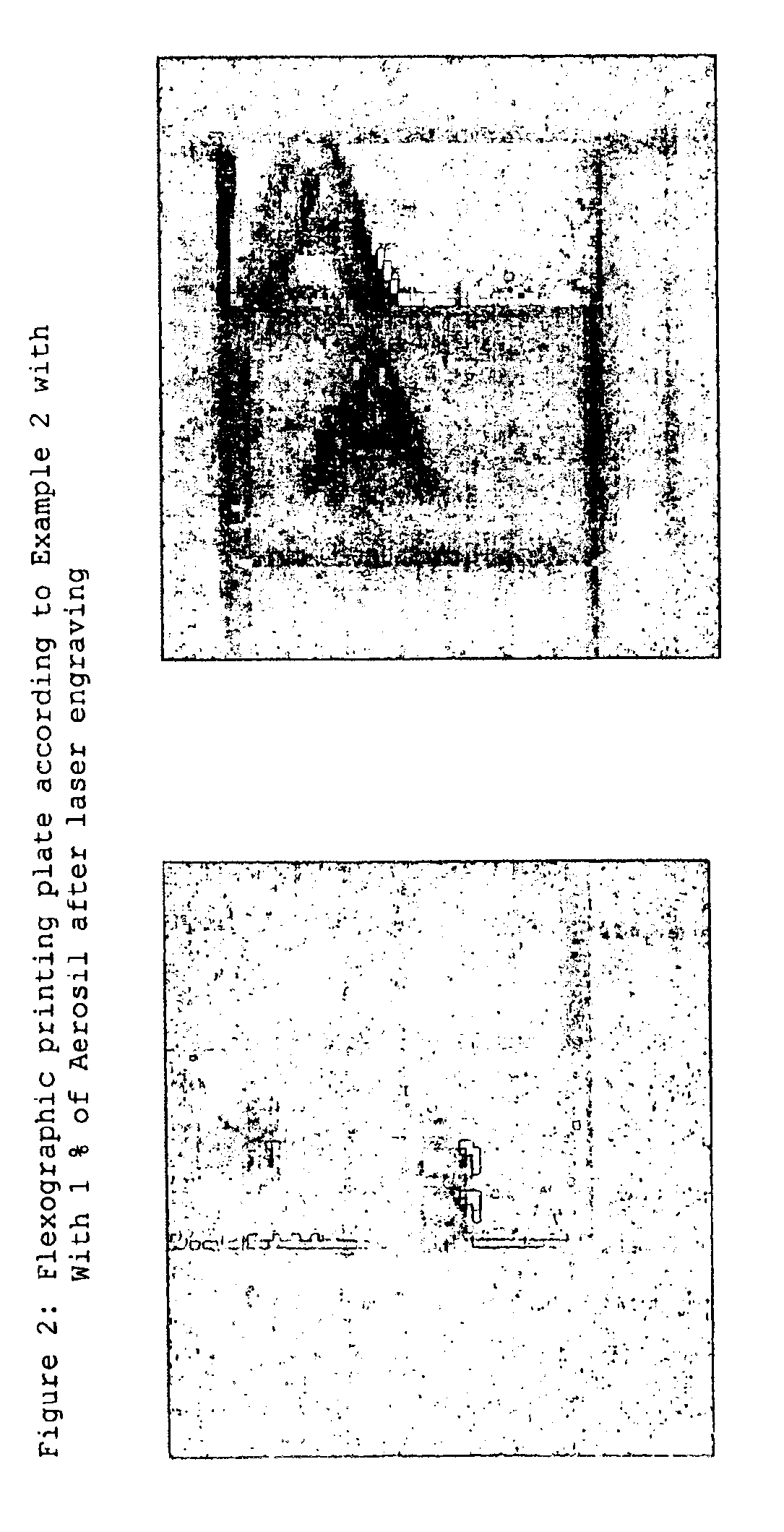
The invention relates to a method for producing flexographic printing forms by engraving a printing relief on a flexographic printing element that can be laser engraved, said element having a photochemically cross-linked relief layer. The relief layer is transparent and comprises oxidic, siliceous or zeolitic solid matter with a particle size between 1 and 400 nm in a quantity of between 0.1 and 8 wt. % in relation to the quantity of all components in the relief layer.
Owner:XSYS PRINT SOLUTIONS DEUT GMBH
Imaging apparatus and method for making flexographic printing masters
InactiveUS20110219973A1Short manufacturing timeMounting boardsPlate printingEngineeringInkjet printing
A method for making a flexographic printing master includes the steps of providing a flexographic printing support; providing an inkjet printing device; applying a mesa relief on the flexographic printing support with the inkjet printing device; and applying an image relief with the inkjet printing device on the mesa relief. A method for making a flexographic printing master includes the imaging apparatus.
Owner:AGFA NV
Method and system for forming a semiconductor device
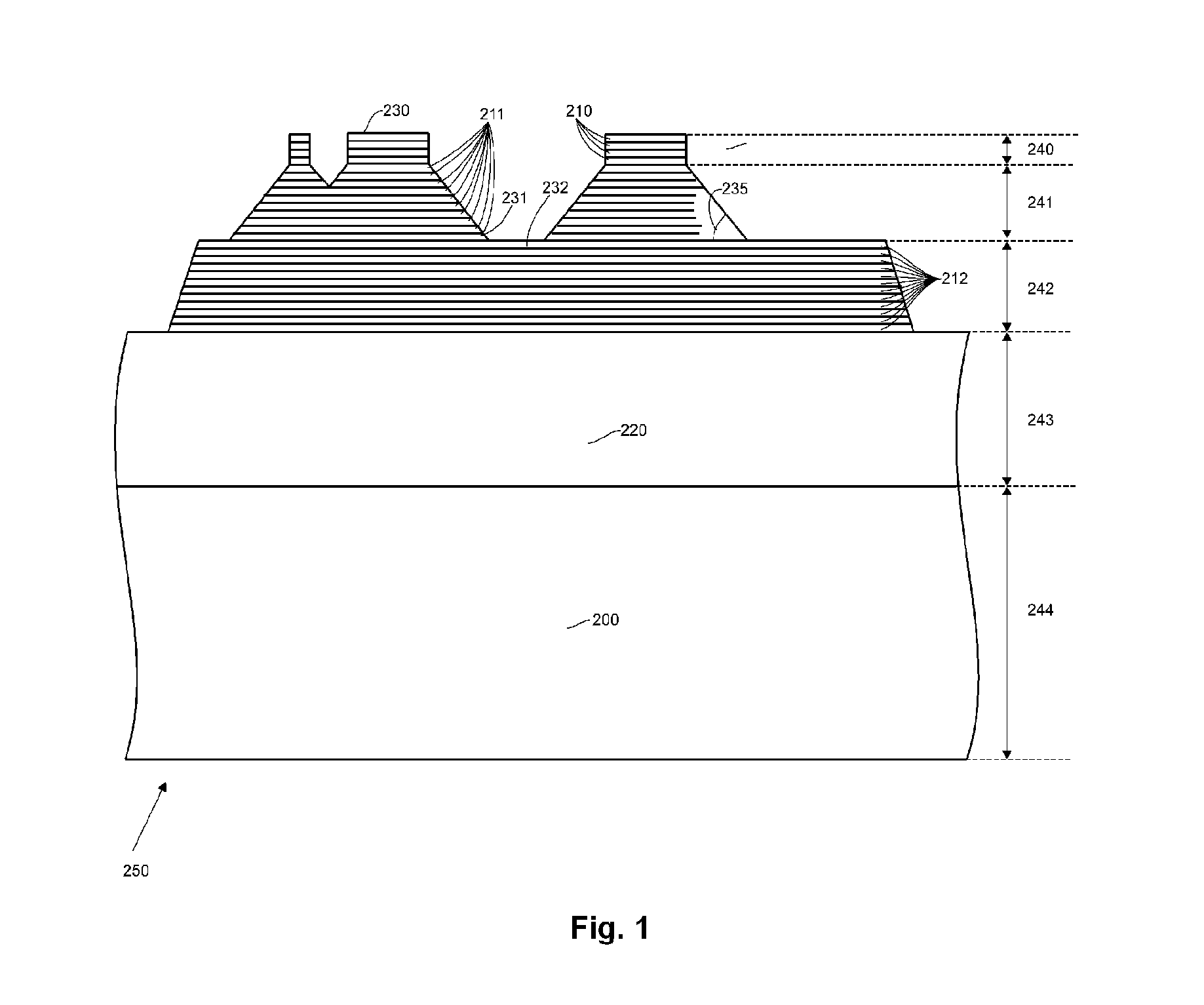
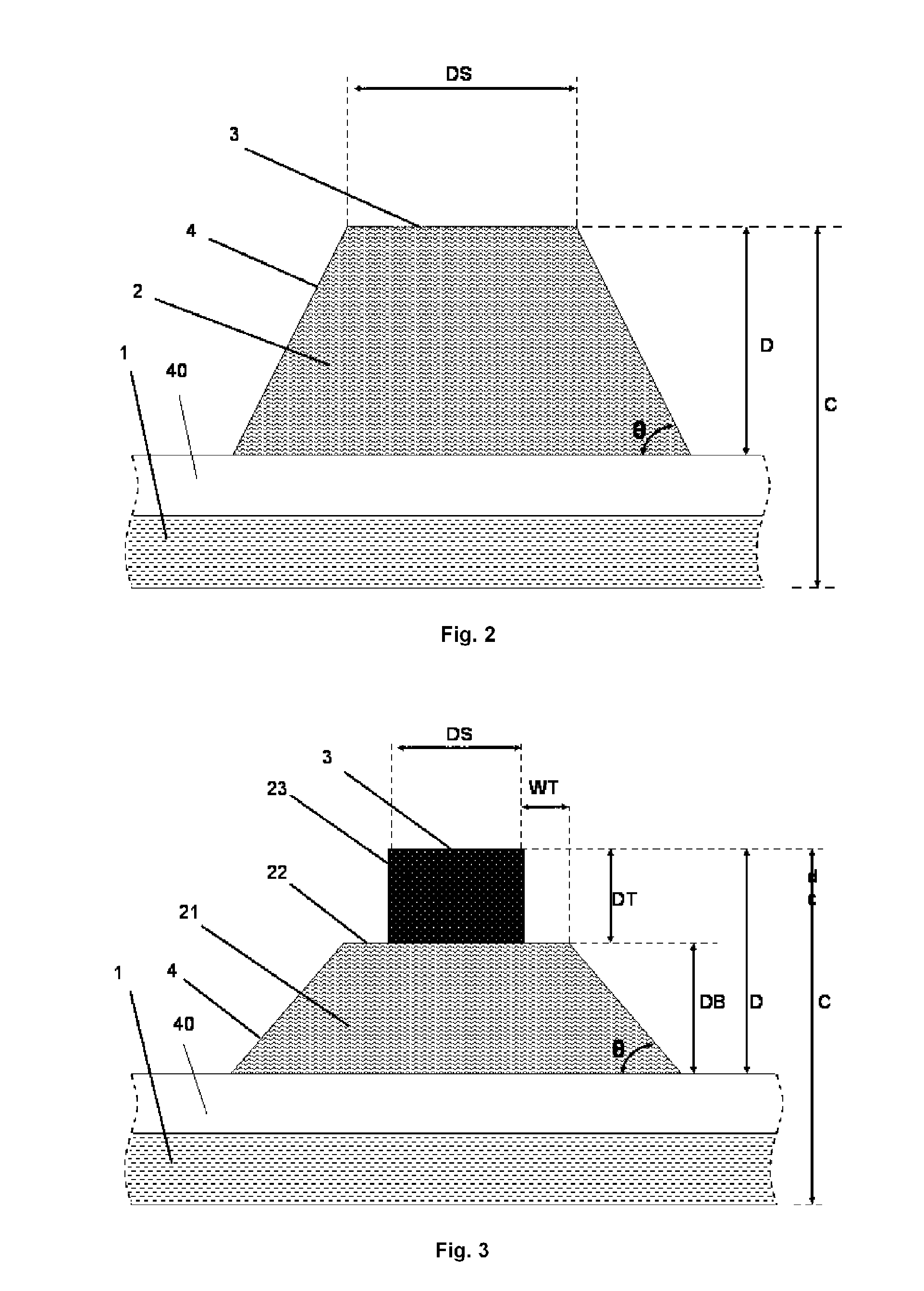
A method and system for forming a semiconductor device is provided. The method and system involves the utilization of a stamping tool to generate three-dimensional resist structures whereby thin film patterning steps can be transferred to the resist in a single molding step and subsequently revealed in later processing steps. Accordingly, the alignments between successive patterning steps can be determined by the accuracy with which the stamping tool has been fabricated, regardless of the dilations or contractions that can take place during the fabrication process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
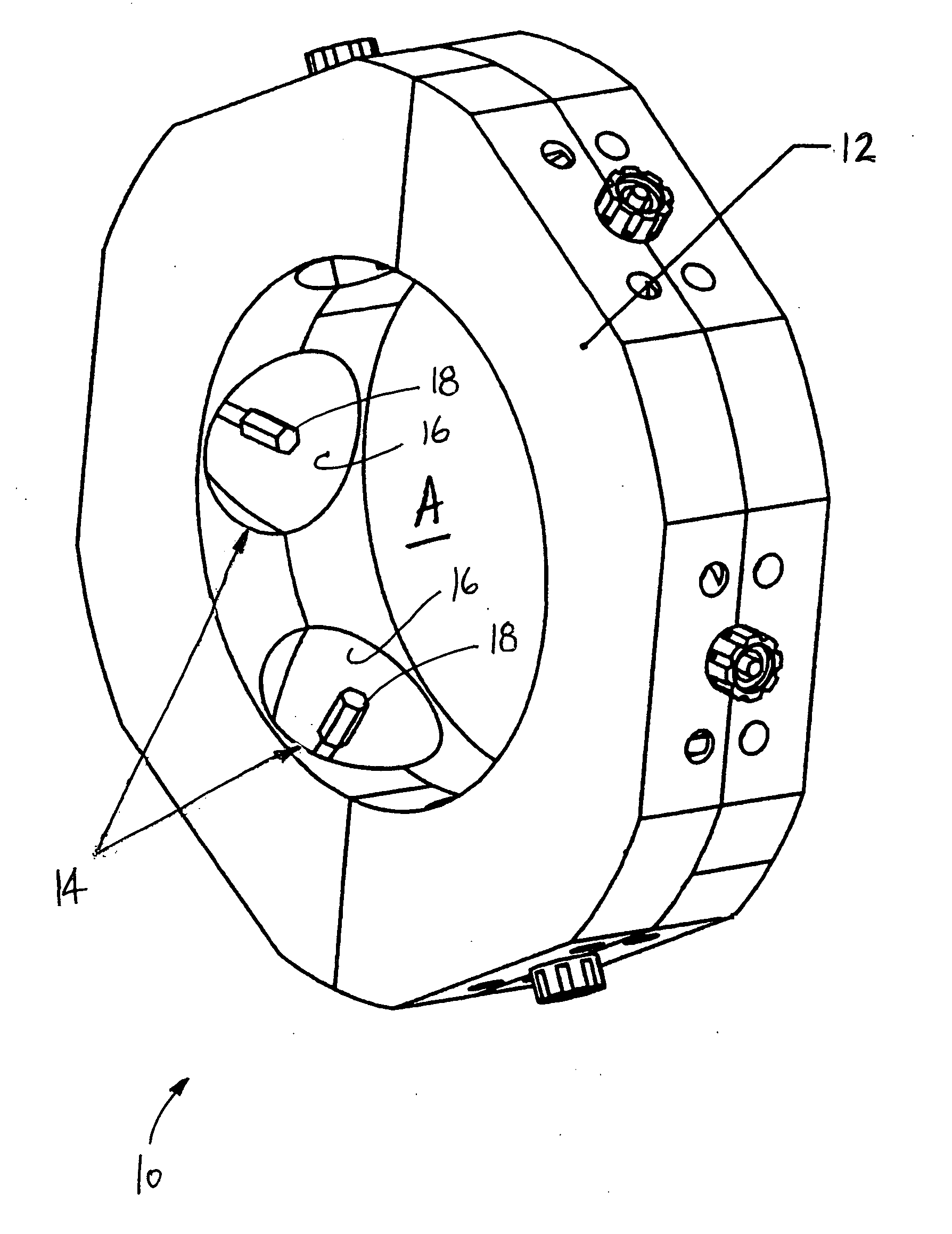
Integrated, in-line bumping and exposure system
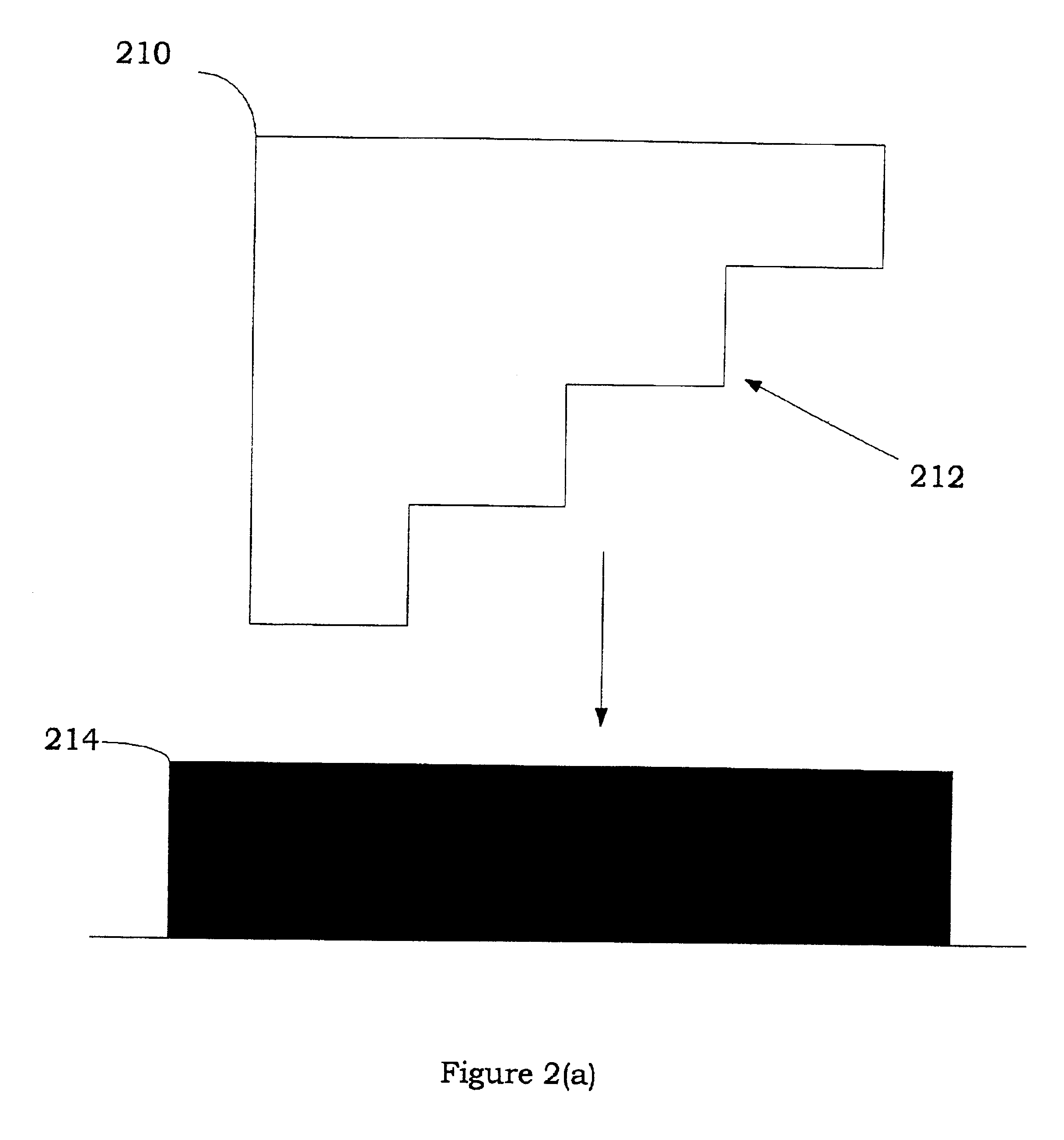
ActiveUS20050011382A1Improve image qualityLow costMounting boardsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusGratingSpatial light modulator
An integrated, in-line bumping and exposure system for printing plates or other substrates having a photosensitive layer. A linear illumination source or sources are for bumping the photosensitive material with a band of illumination to consume dissolved oxygen within the photosensitive layer. A raster scan optical assembly or an illuminated and re-imaged spatial light modulator array exposes the photosensitive material with a rasterized beam or beams or an array of modulated electromagnetic radiation located downstream of the bumping illumination. A conveyance mechanism is configured to provide relative continuous motion between one or more substrates and the bands of illumination to continuously bump and pattern one portion of the plate or plates while the other portion of the plate or plates is bumped in anticipation of patterning.
Owner:THE PERKIN ELMER CORP
Apparatus and method for thermally developing flexographic printing elements
ActiveUS20050211120A1Improve developmentGood removal effectX-ray/infra-red processesDuplicating/marking methodsPhotopolymerElectrical and Electronics engineering
An improved apparatus for thermally developing a flexographic printing element to reveal a relief image on the surface and a method of using the apparatus to expose and develop a flexographic printing element. The apparatus typically comprises means for softening or melting non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element; at least one roll that is contactable with the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element and capable of moving over at least a portion of the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element to remove the softened or melted non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element; and means for maintaining contact between the at least one roll and the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element. The means for softening or melting non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element comprise a heater positioned adjacent to the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element and / or heating the at least one roll that contactable with the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element. The apparatus may also contain an exposure device to crosslink and cure the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element prior to thermal development.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
Apparatus and method for thermally developing flexographic printing sleeves
ActiveUS6998218B2Good removal effectIncrease speedMulticolor photographic processingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotopolymerCrosslinked polymers
An improved thermal development apparatus is used to remove uncured photopolymer from the imaged surface of a flexographic printing element. The apparatus typically comprises one or more heatable rolls that are contactable with an imaged surface of a flexographic printing element; and means for maintaining contact between the one or more heatable rolls and the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element. The one or more heatable rolls are heated and is moved over at least a portion of the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element, and non-crosslinked polymer on the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element is melted and removed by the one or more heatable rolls.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
Anti-reflective film and production method thereof, and stamper for producing anti-reflective film and production method thereof
ActiveUS20070289874A1Reduce reflectionWell formedAnodisationConfectioneryShell moldingRefractive index
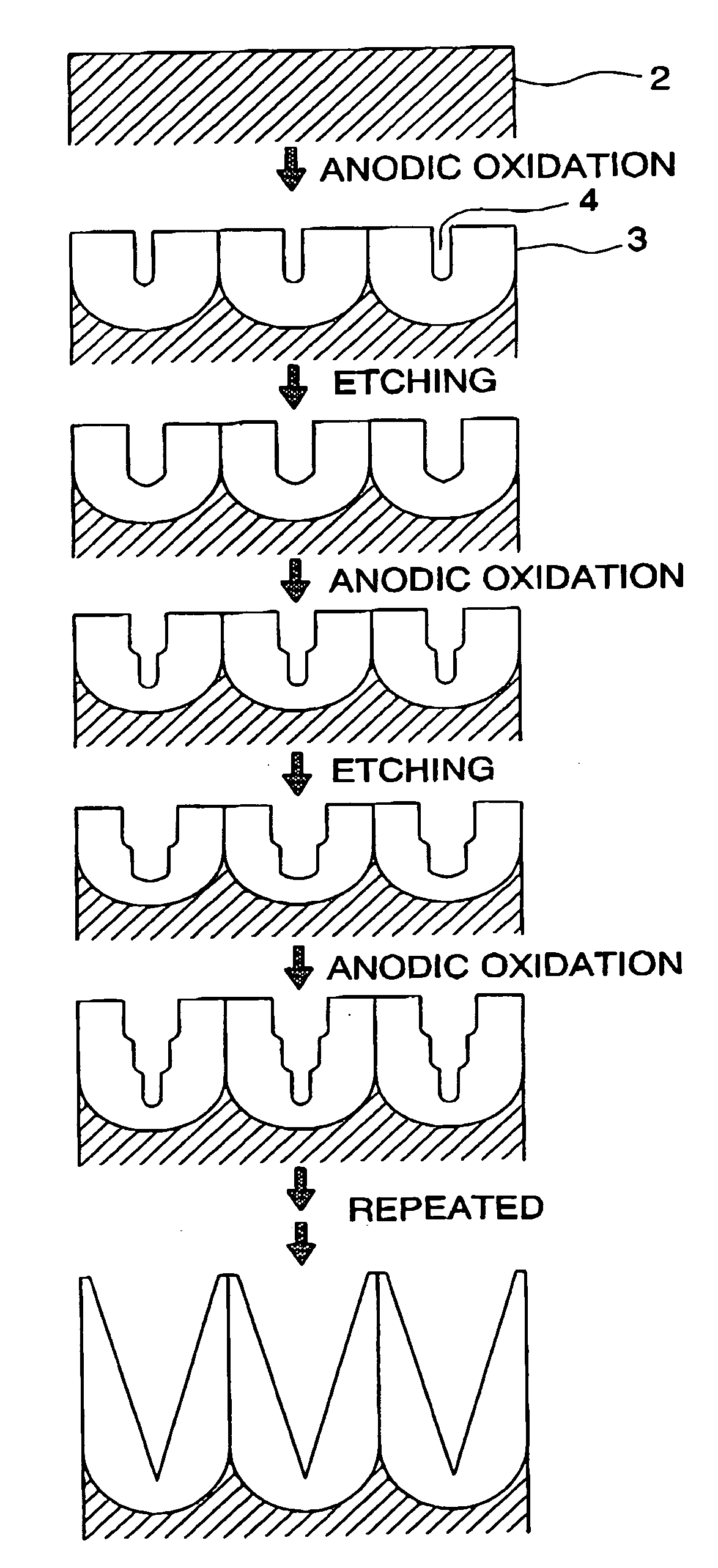
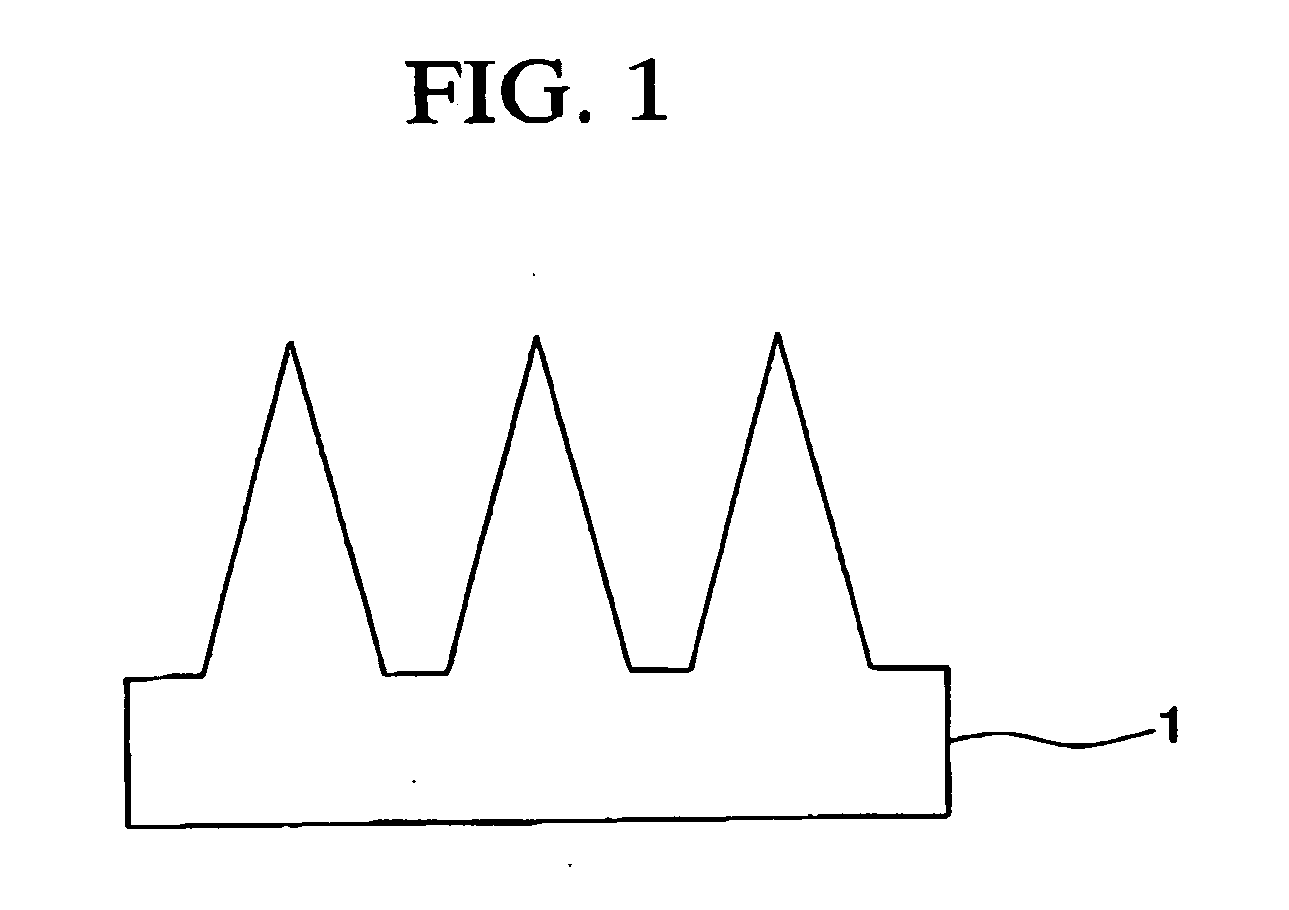
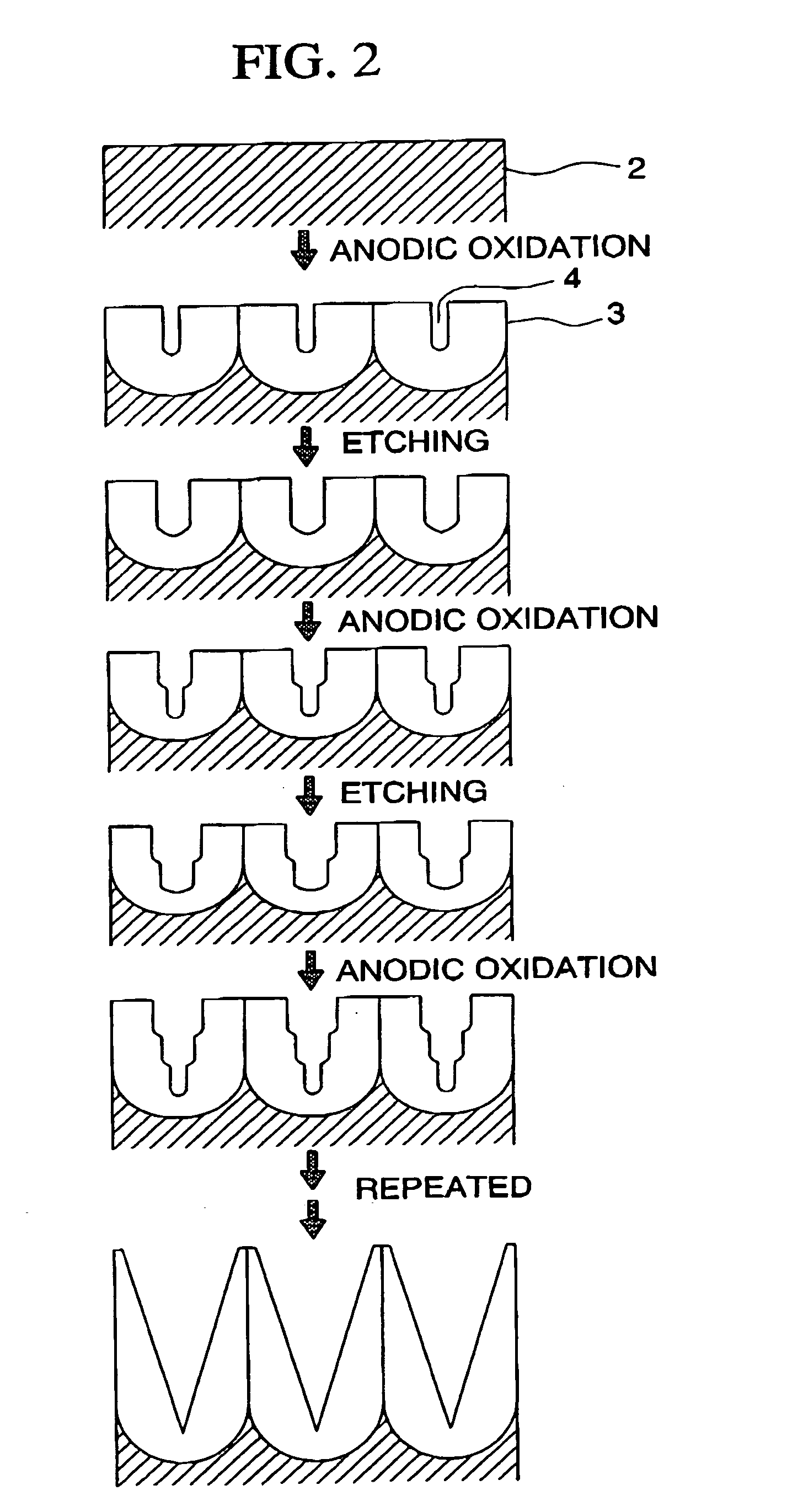
In this method for producing an anti-reflective film, pores are formed on a surface of a polymer molding material to continuously change a refractive index and then reduce reflectance, in which anodic oxidized porous alumina, in which pores having a tapered shape and whose pore diameter continuously changes, are formed by repeating anodic oxidation at about the same formation voltage and pore diameter enlargement treatment, is used as a mold, or a stamper, which is produced by using the anodic oxidized porous aluminum as a mold, is used as a mold.
Owner:KANAGAWA INST OF IND SCI & TECH
Imaging member for offset printing applications
ActiveUS20140060352A1Uniform layersFree from defectPlaten pressesPlate printingSurface layerPerfluoropolyether
An imaging member includes a surface layer comprising a fluoroelastomer-perfluoropolyether composite formed from a reaction mixture comprising a fluoroelastomer and a perfluoropolyether compound. Methods of manufacturing the imaging member and processes for variable lithographic printing using the imaging member are also disclosed.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Methods of and apparatus for molding structures using sacrificial metal patterns
InactiveUS7229542B2Improve abilitiesBroaden applicationAcceleration measurement using interia forcesMouldsImage resolutionShell molding
Molded structures, methods of and apparatus for producing the molded structures are provided. At least a portion of the surface features for the molds are formed from multilayer electrochemically fabricated structures (e.g. fabricated by the EFAB™ formation process), and typically contain features having resolutions within the 1 to 100 μm range. The layered structure is combined with other mold components, as necessary, and a molding material is injected into the mold and hardened. The layered structure is removed (e.g. by etching) along with any other mold components to yield the molded article. In some embodiments portions of the layered structure remain in the molded article and in other embodiments an additional molding material is added after a partial or complete removal of the layered structure.
Owner:MEMGEN
Screened film intermediate for use with flexographic printing plate having improved solids rendition
A flexographic printing plate having solid image areas which are covered by a plurality of very small and shallow cells similar to the ink carrying cells found in anilox ink metering rolls. These cells fill with ink during the plate inking step and reproduce solid image areas with better color saturation while at the same time reducing the halo typical of flexographic printing of solids. Associated with this plate is a method for producing the cells, including the use of an intermediate screened film and of a computer program for generating the film intermediate.
Owner:ESKO SOFTWARE
Clean Flexographic Printing Plate and Method of Making the Same
ActiveUS20130228086A1Printing cleanly during a print runEasy constructionMounting boardsPlate printingPhotopolymerEngineering
A clean running flexographic relief image printing element and a method of making the same is described. The relief image printing element comprises (a) a backing layer; (b) a floor layer disposed on the backing layer and comprising a photopolymer containing a silicone monomer or silicone oil, wherein the cured floor layer has a surface energy of between about 18 to about 25 dynes / cm; (c) a cap layer disposed on the floor layer and comprising a photocurable composition that is capable of being imagewise exposed to actinic radiation to create a relief image therein, wherein the cap layer has a surface energy of between about 30 and about 40 dynes / cm; and (d) a removable cover sheet. The differential of surface energies between the floor layer and the cap layer increases how clean the plate will print over time.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
Apparatus and method for thermally developing flexographic printing elements
ActiveUS7041432B2Good removal effectIncrease speedX-ray/infra-red processesDuplicating/marking methodsPhotopolymerElectrical and Electronics engineering
An improved apparatus for thermally developing a flexographic printing element to reveal a relief image on the surface and a method of using the apparatus to expose and develop a flexographic printing element. The apparatus typically comprises means for softening or melting non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element; at least one roll that is contactable with the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element and capable of moving over at least a portion of the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element to remove the softened or melted non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element; and means for maintaining contact between the at least one roll and the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element. The means for softening or melting non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element comprise a heater positioned adjacent to the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element and / or heating the at least one roll that contactable with the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element. The apparatus may also contain an exposure device to crosslink and cure the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element prior to thermal development.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
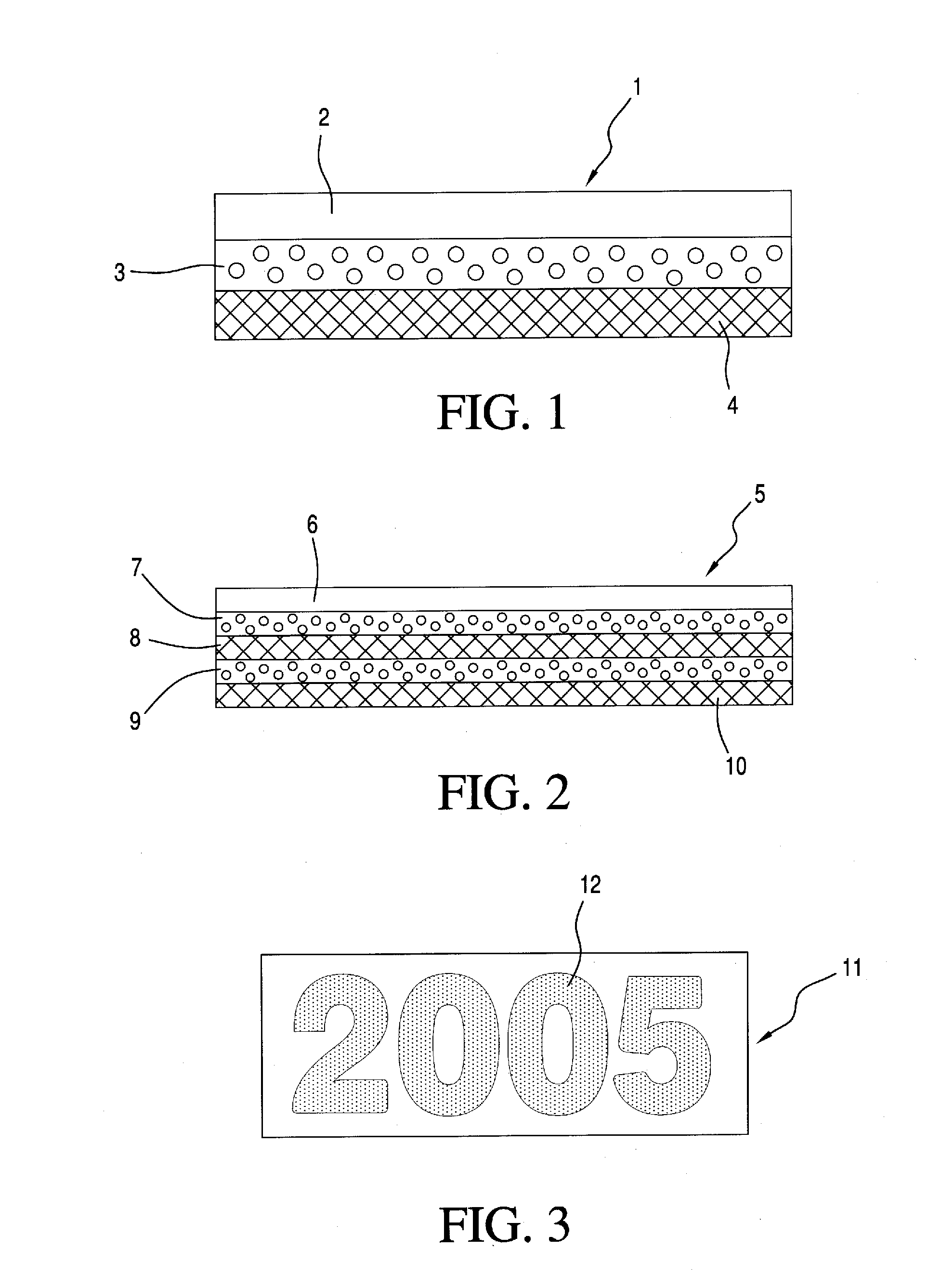
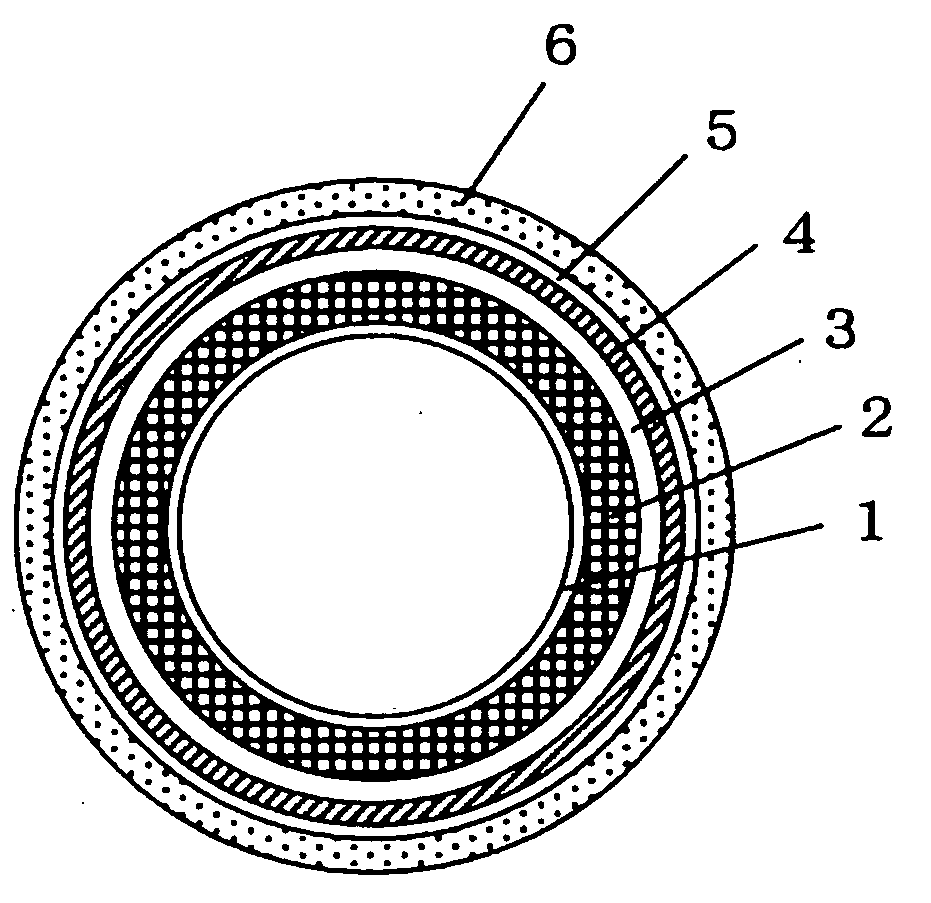
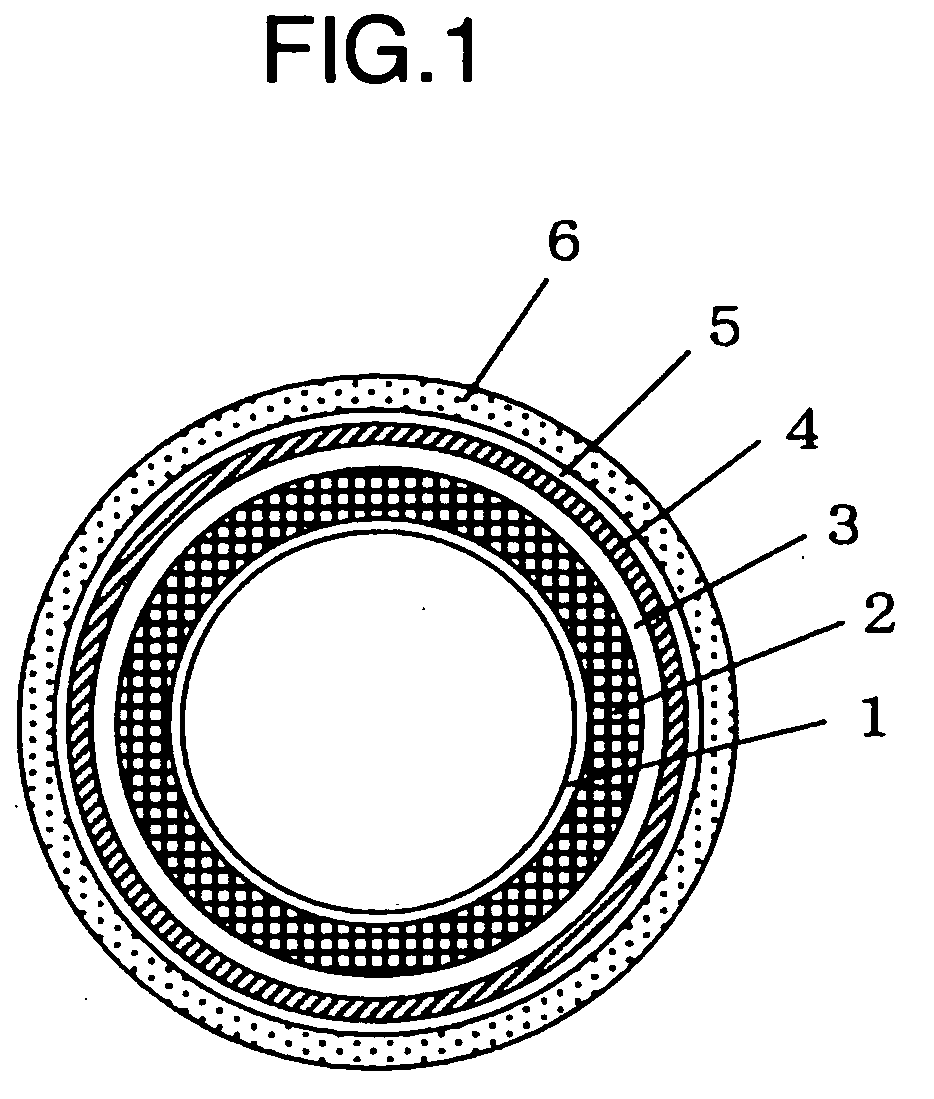
Multiple-layer flat structure in the form of a printing blanket or a printing plate for flexographic and letterpress printing with laser engraving
InactiveUS20120103216A1Quick clean upFast formingMounting boardsPlate printingLetterpress printingLaser engraving
The invention is directed to a multiple-layer flat structure (1) in the form of a printing blanket or a printing plate for flexographic and letterpress printing with: a printing layer (2) which is made from a polymeric material and is provided with laser engraving; at least one compressible layer (3); and, at least one strength-support layer (4); wherein the individual layers form an adhesive connection among one another. The multiple-layer flat structure (1) according to the invention is distinguished by the fact that the polymeric material of the printing layer (2) is a vulcanizate. Advantageous materials are proposed in this regard. The printing layer (2) expediently lies directly on a compressible layer (3). The compressible layer (3) is in turn in direct contact with a strength-support layer (4).
Owner:CONTITECH ELASTOMER BESCHICHTUNGEN
Flexo processor
ActiveUS7237482B2The process is convenient and fastGood flexibilityPlaten pressesMulticolor photographic processingHeat sensitivePost exposure
An improved flexo processor and a method of using the improved flexo processor to increase the flexibility of both the type and the size of the flexographic printing element that may be processed. The novel thermal plate processor system is capable of processing both flat and round photosensitive printing elements with only minimal changes to the system. The thermal plate processor system may also include means for exposure and post-exposure / detack in the same system.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
Hollow Cylindrical Printing Element
InactiveUS20080156212A1Good plate thickness accuracy accuracyHigh dimensional accuracyPipe couplingsSynthetic resin layered productsFiberHardness
A hollow cylindrical printing element, comprising a hollow cylindrical core material (A) and a resin layer (B) or a resin layer (C). The hollow cylindrical core material (A) further comprises a photosensitive resin hardened layer (1) of 0.05 to 50 mm in thickness having a fiber-like, cloth-like, or film-like reinforcement material and the shore hardness D of 30 to 100°. The resin layer (B) is laminated on the hollow cylindrical core material (A), has a thickness of 0.1 to 100 mm, and allows a pattern to be formed on the surface thereof. The resin layer (C) has a pattern formed on the surface thereof.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Lithographic printing plate precursor
ActiveUS20070214987A1Good on-press development propertySufficient printing durabilityPlaten pressesPhotosensitive materialsImage recordingPrinting ink
A lithographic printing plate precursor which is capable of undergoing on-press development by supplying at least one of printing ink and dampening water and includes a support and an image-recording layer, wherein the image-recording layer contains at least one of compounds represented by the formulae (1) to (3) as defined herein.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Curable jettable fluid for making a flexographic printing master
The present invention relates to a curable jettable fluid for making a flexographic printing master characterized in that the jettable fluid comprises a monofunctional (meth)acrylate monomer, a polyalkylene glycol di(meth)acrylate monomer of which the polyalkylene glycol chain has a MW of at least 300 and at least 1 wt. % of a difunctional (meth)acrylate monomer according to Formula I) or (II), wherein k and m in Formula (I) is an integer ranging from 0 to 5, l in Formula (I) is an integer ranging from 1 to 20, n in Formula (II) is 1, 2, 3 or 4, R in Formula (I) and (II) is H or CH3, and R′ in Formula (II) is H or an alkyl group.
Owner:AGFA NV
Polymeric Fluid Transfer and Printing Devices
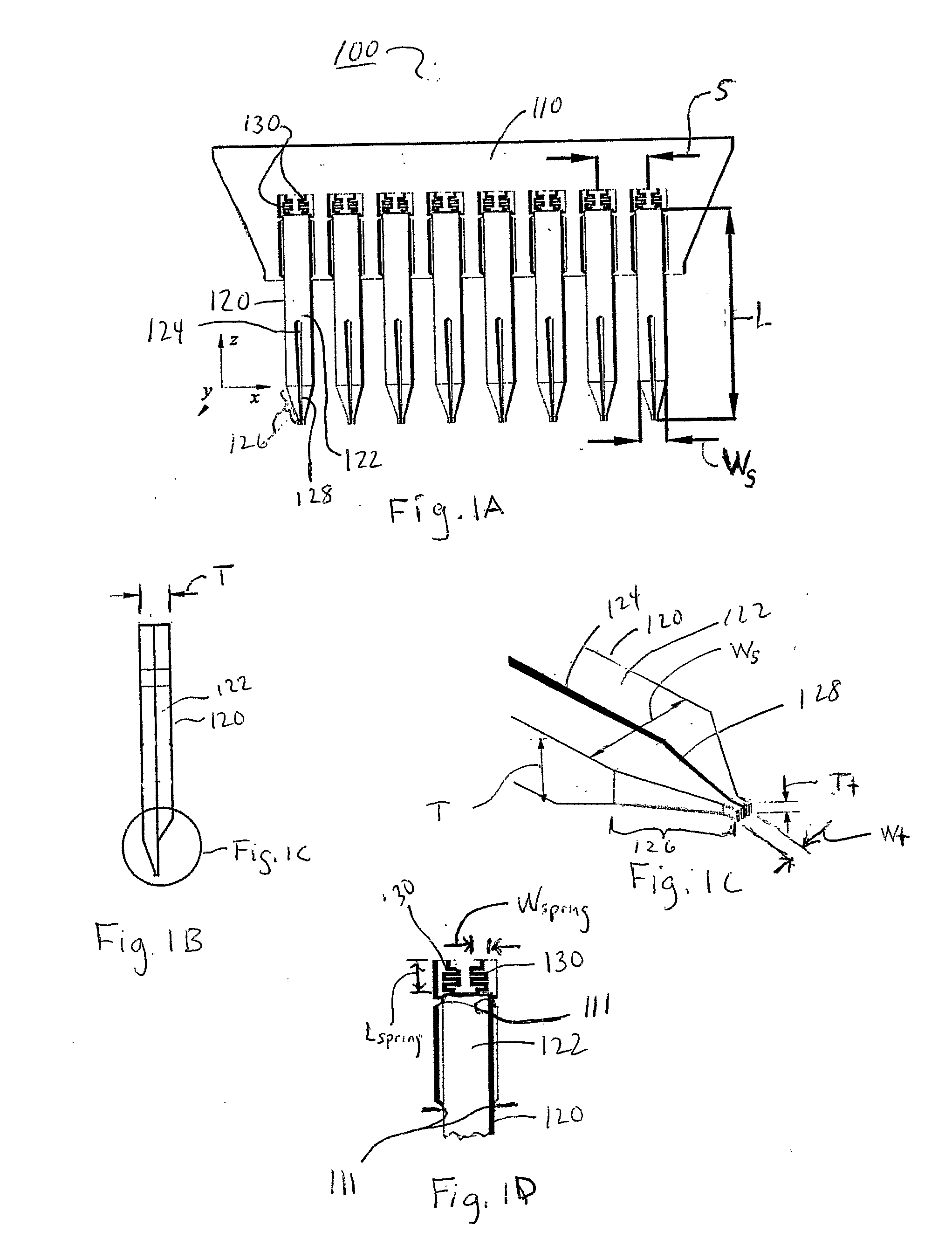
InactiveUS20080279727A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsSequential/parallel process reactionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A method and apparatus for making a polymeric printhead having one or more pins for fluid transfer and printing, including the steps of forming a positive mold of the printhead using a bulk micromachining process, forming a negative mold of the printhead from the positive mold using an electroforming process, and forming the printhead from a polymeric material in the negative mold, the polymeric printhead being operative for fluid transfer and / or printing. Also, printheads and pins, holders and dispensing trays microfabricated from a polymeric materials for fluid transfer and printing.
Owner:HAUSHALTER ROBERT C
Method for producing a flexographic printing plate formed by inkjetted fluid
InactiveUS7036430B2Rapid and inexpensive mannerDuplicating/marking methodsMulticolor photographic processingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:KODAK IL
Combined ablation and exposure system and method
Owner:ESKO GRAPHICS IMAGING +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com