Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68results about "Metals or alloys" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
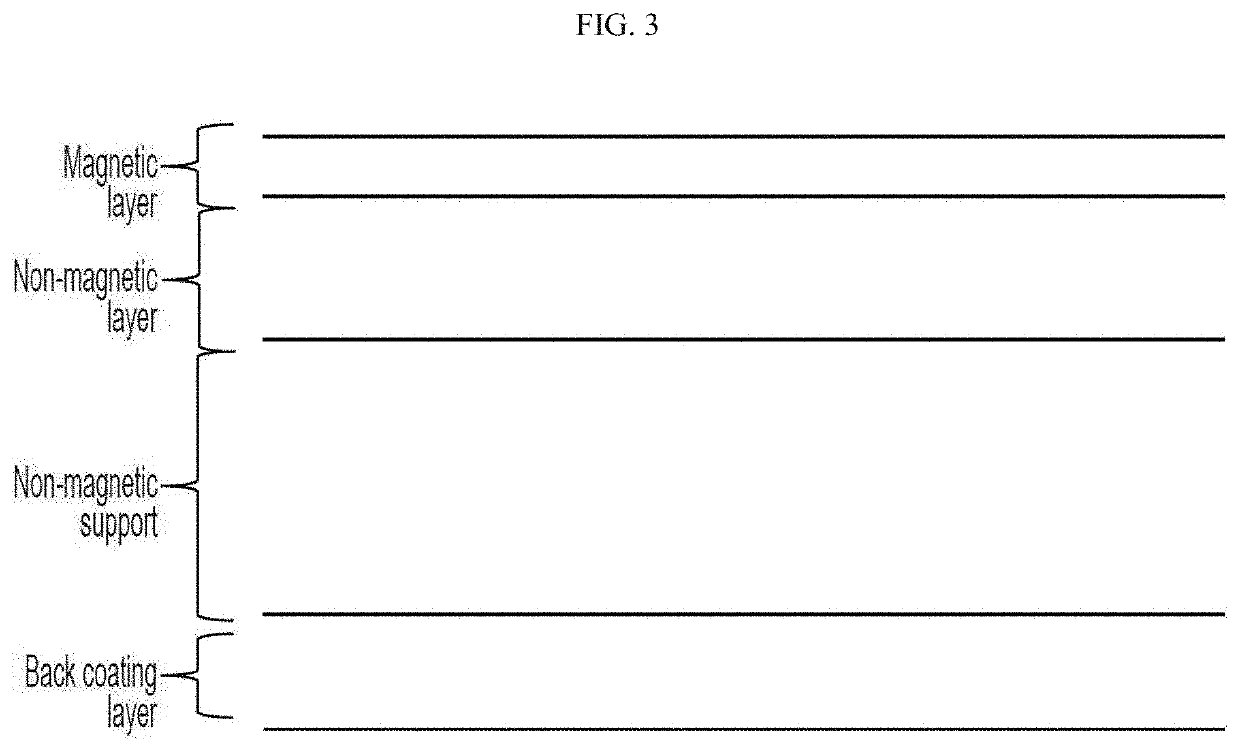
Magnetic tape
Provided is a magnetic tape in which ferromagnetic powder included in a magnetic layer is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder having an activation volume equal to or smaller than 1,600 nm3, the magnetic layer includes one or more components selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide, and an abrasive, a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is equal to or greater than 45 atom %, and a tilt cos θ of the ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder with respect to the surface of the magnetic layer acquired by cross section observation performed by using a scanning transmission electron microscope is 0.85 to 1.00.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20070020490A1Excellent electromagnetic characteristic and error rate and durabilityImproved electromagnetic characteristic and error rate and durabilityBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageHigh densityMicrometer
Provided is a magnetic recording medium for high-density recording, that has excellent electromagnetic characteristics, error rates, and durability. The magnetic recording medium comprises a magnetic layer comprising a ferromagnetic powder, a binder and an abrasive on a nonmagnetic support and is employed for recording a magnetic signal on the medium and reproducing the recorded signal with a reproduction head. The abrasive has a Vickers hardness ranging from 18 to 80 GPa and a mean particle diameter ranging from 10 to 100 nm. The magnetic layer comprises the abrasive in a quantity of 5 to 60 weight parts per 100 weight parts of the ferromagnetic powder and has a thickness ranging from 10 to 100 nm. The number of abrasive present on the surface of the magnetic layer ranges from 0.01 to 1 per {(minimum bit length of the recorded signal)×(read track width of the reproduction head)} micrometer2.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Magnetic tape and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9704527B2Increase coefficient of frictionReduced stabilityRecord information storageMetals or alloysMagnetic tapeNon magnetic
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20160247530A1Improve running stabilityReduce coefficient of frictionRecord information storageMetals or alloysMagnetic tapeTotal thickness
The magnetic tape has on one surface of a nonmagnetic support a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder, and on the other surface of the nonmagnetic support, a backcoat layer containing nonmagnetic powder and binder, wherein the total thickness of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 4.80 μm, the backcoat layer contains one or more components selected from the group consisting of a fatty acid and a fatty acid amide, and a C—H derived carbon, C, concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio in a C1s spectrum obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy conducted at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees on a surface on the backcoat layer side of the magnetic tape ranges from 35 to 60 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20170178677A1Reduce thicknessIncrease recording capacityBase layers for recording layersTape carriersMagnetic tapeNon magnetic
The magnetic tape includes a nonmagnetic layer containing nonmagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, and a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder, abrasive, and binder on the nonmagnetic layer, wherein a thickness of the nonmagnetic layer is less than or equal to 0.50 μm, a coefficient of friction as measured on a base portion of a surface of the magnetic layer is less than or equal to 0.35, and ΔSFD in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape as calculated with Equation 1, ΔSFD=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C., is greater than or equal to 0.50, wherein, in Equation 1, SFD25° C. denotes a SFD as measured in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape in an environment with a temperature of 25° C., and SFD−190° C. denotes a SFD as measured in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape in an environment with a temperature of −190° C.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Nanoparticle coated material and production method of same
The invention provides a method of producing a nanoparticle coated material, comprising a support and a nanoparticle layer formed on the support, wherein the nanoparticle layer contains nanoparticles comprising a CuAu type or Cu3Au type hard magnetic ordered alloy, and wherein the method satisfies at least one of the following conditions (i) and (ii): (i) the method comprises the steps of forming a shielding layer on the support before forming the nanoparticle layer; and (ii) a step of forming the nanoparticle layer comprises: the steps of applying a coating liquid containing nanoparticles capable of forming a CuAu type or Cu3Au type hard magnetic ordered alloy phase on the support to form a coating film; and irradiating laser light on the coating film.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
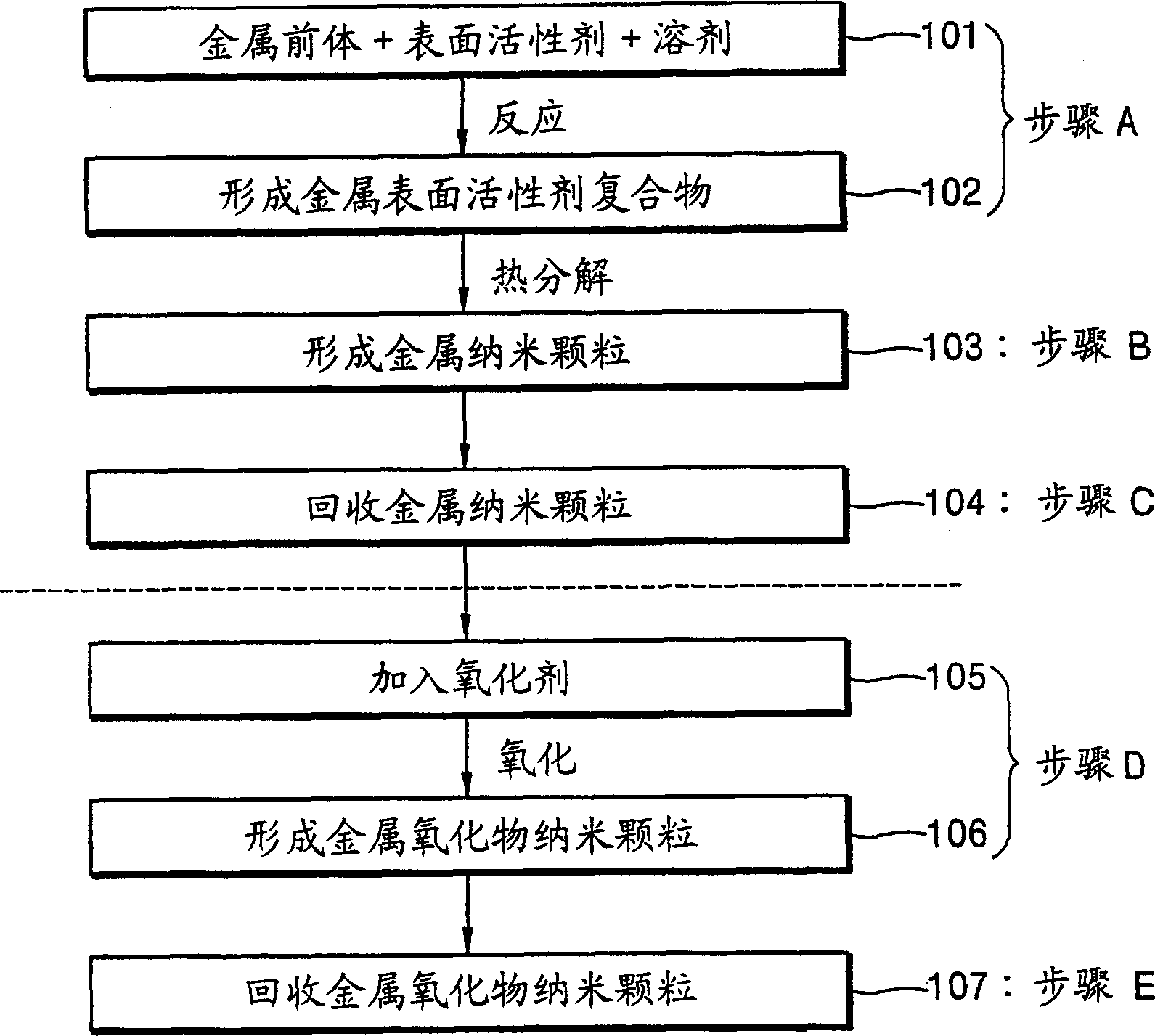
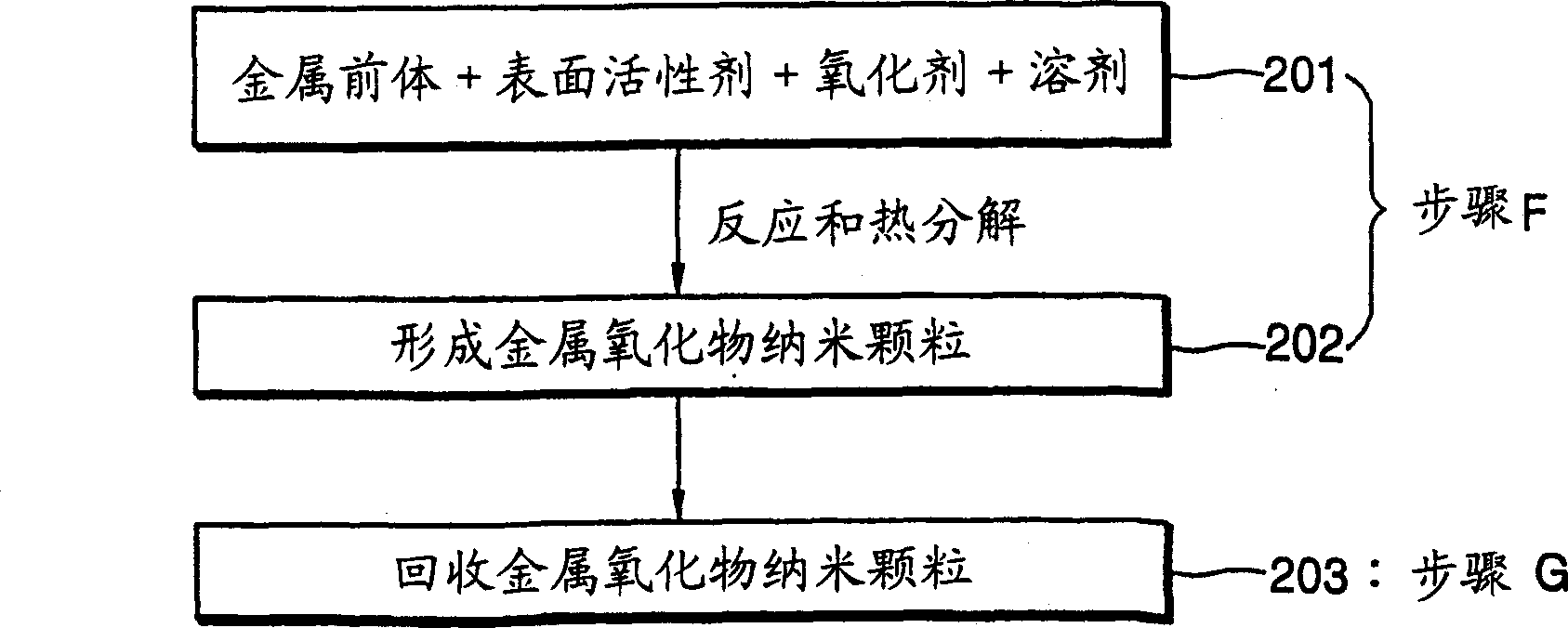
Synthesis of mono-disperse and highly crystalline nano-particles of metals, alloys, metal-oxides, and multi-metallic oxides without a size-selection process
InactiveUS7407527B2Sufficient reaction timeInduce precipitationMaterial nanotechnologyOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideMetal oxide nanoparticlesSynthesis methods
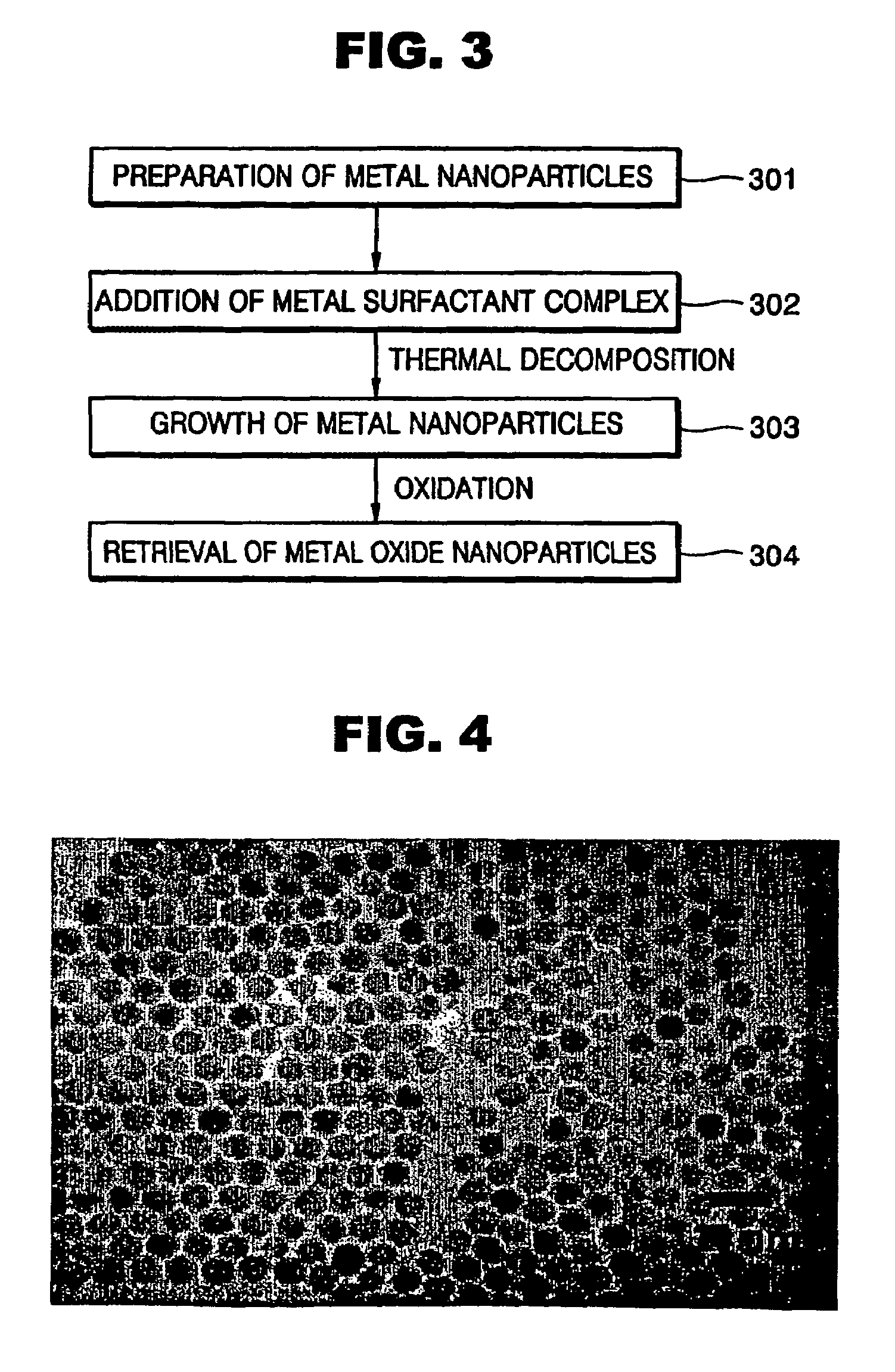
A synthetic method of fabricating highly crystalline and monodisperse nanoparticles of metals, multi-metallic alloys, monometallic oxides and multi-metallic oxides without a size selection process are disclosed. A typical synthetic method comprises the steps of, synthesis of a metal surfactant complex from the reaction of a metal precursor and a surfactant, high temperature thermal decomposition of the metal surfactant complex to produce monodisperse metal nanoparticles, and completing the formation of synthesized metal, metal alloy or metal oxide nanoparticles by adding a poor solvent followed by centrifuging. For obtaining highly crystalline monodisperse nanoparticles, additional steps are necessary as described in the invention. The resulting nanoparticles have excellent magnetic property for many applications.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Magnetic tape having characterized magnetic layer and hexagonal ferrite powder
A magnetic tape is provided in which ferromagnetic powder included in a magnetic layer is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder having an activation volume less than or equal to 1,600 nm3. The magnetic layer includes one or more components selected from a fatty acid and a fatty acid amide, and an abrasive. The C—H derived C concentration calculated from the C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is greater than or equal to 45 atom %. Also, the tilt cos θ of the ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder with respect to the surface of the magnetic layer acquired by cross section observation performed by using a scanning transmission electron microscope is 0.85 to 1.00.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Acid stable aqueous dispersion of metal particles and applications
InactiveUS6811885B1Improve colloidal stabilityProtective coatings for layersMagnetic liquidsMetal particleRecording layer
Aqueous coating compositions containing acid stable metal dispersions, prepared by chemical reduction in aqueous medium, are obtained by using a N-quaternized cellulose derivative as binder. They can be used for the preparation of heat mode recording layers, magnetic layers and conductive layers.
Owner:AGFA GEVAERT AG
Method of producing magnetic particles and reaction method using microreactor and microreactor
ActiveUS20050223847A1Good monodispersityReduce noiseAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingMicroreactorAlloy
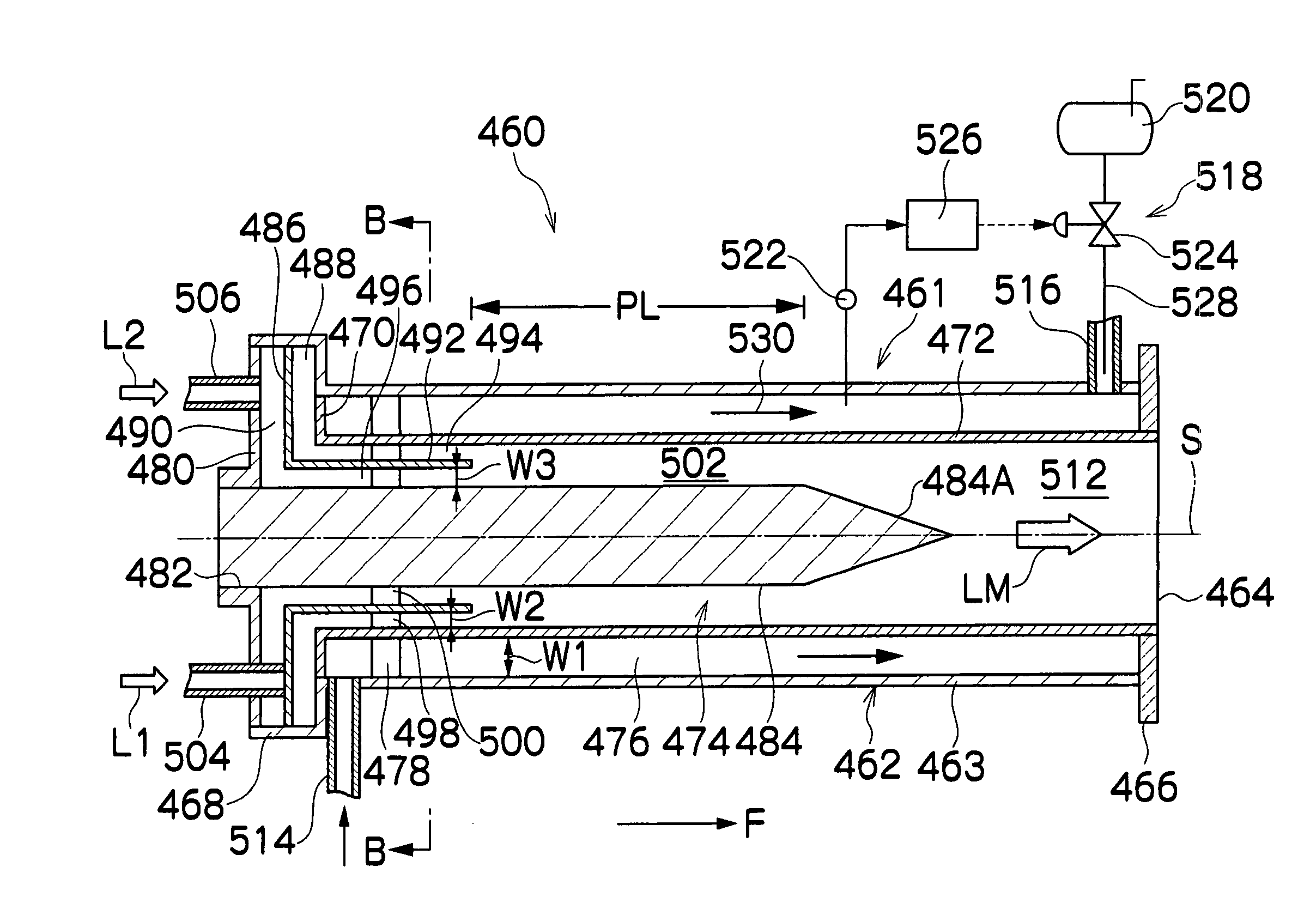
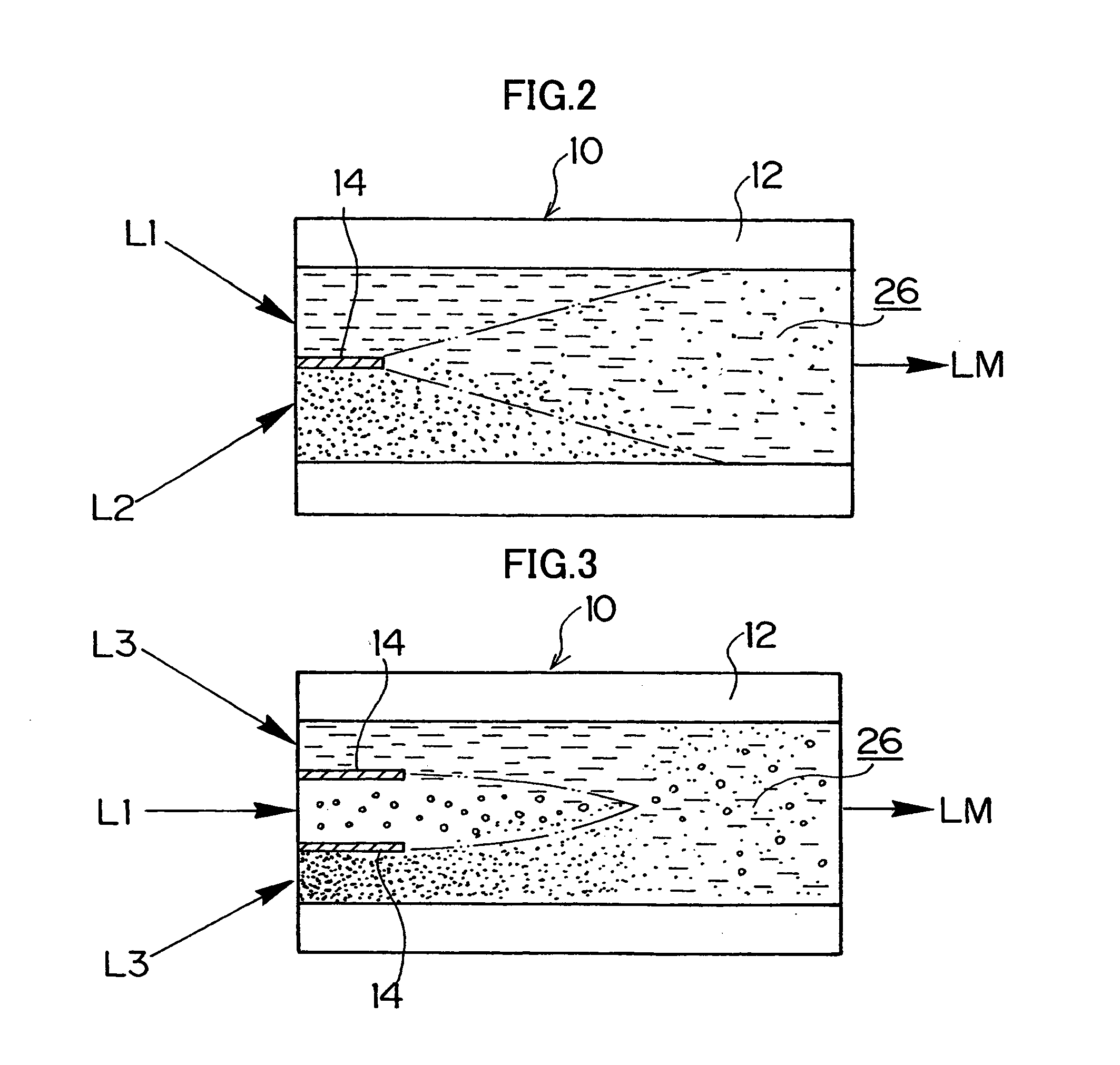
In a method of producing magnetic particles which includes the steps of preparing alloy particles capable of forming a CuAu or Cu3Au hard magnetic ordered alloy phase and of forming magnetic particles for forming CuAu or Cu3Au magnetic particles, a plurality of solutions L1 and L2 for preparing the alloy particles are passed in a thin-plate laminar flow and diffused in the direction perpendicular to the flow direction at the contact interface of the solutions L1 and L2 in a mixing channel by using a microreactor, whereby a uniform mixing reaction is conducted in a short time.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Metal oxide particle dispersion for manufacturing particulate magnetic recording medium, method of manufacturing magnetic layer-forming composition of particulate magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing particulate magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20170092316A1Avoid changeNovel featuresMagnetic liquidsRecord information storagePolyesterParticulates
The metal oxide particle dispersion for manufacturing a particulate magnetic recording medium contains metal oxide particles, solvent, and a polyester compound having one or more groups selected from the group consisting of a carboxyl group and a salt thereof, a phosphoric acid group and a salt thereof, a hydroxyl group and a nitrogen-substituted alkylene group, but substantially not containing ferromagnetic powder.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS20200035267A1Inorganic material magnetismRecord information storageZeta potentialMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on one surface side of the non-magnetic support; and a back coating layer including non-magnetic powder and a binding agent on the other surface side of the non-magnetic support, in which an isoelectric point of a surface zeta potential of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 3.8, and an isoelectric point of a surface zeta potential of the back coating layer is equal to or smaller than 3.0, a magnetic tape cartridge, and a magnetic tape apparatus including this magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS20200211592A1Improve surface smoothnessReduce frequencyRecord information storageMetals or alloysMagnetic tapeMaterials science
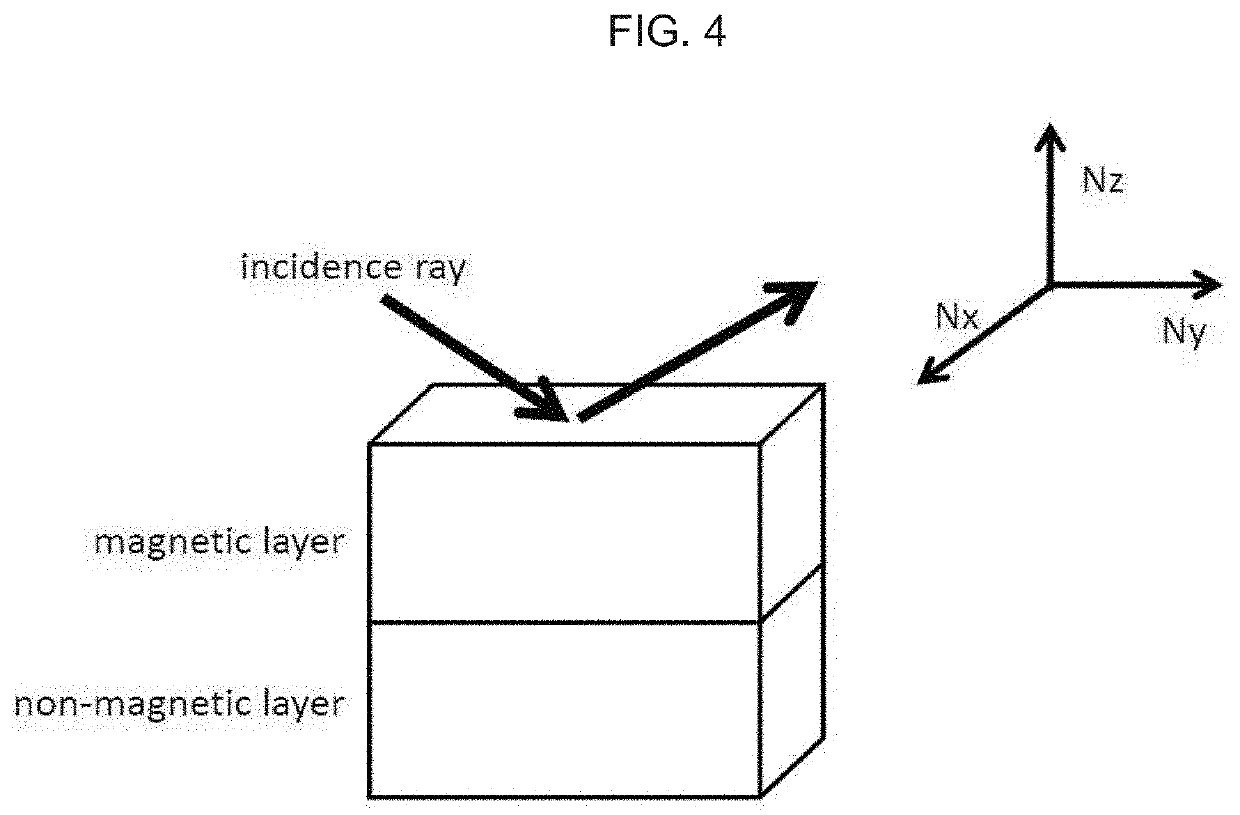
Provided are a magnetic tape including: a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, in which a total thickness of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 5.30 μm, the magnetic layer has a servo pattern, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured on a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, and an absolute value ΔN of a difference between a refractive index Nxy of the magnetic layer, measured in an in-plane direction and a refractive index Nz of the magnetic layer, measured in a thickness direction is 0.25 to 0.40, a magnetic tape cartridge and a magnetic tape apparatus including this magnetic tape, a magnetic tape cartridge and a magnetic tape apparatus including this magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic layer with high-permeability backing
InactiveUS20020160231A1Increase the magnetic field strengthImprove magnetic strengthCoating by extrusionRecord information storageHigh concentrationPolymer science
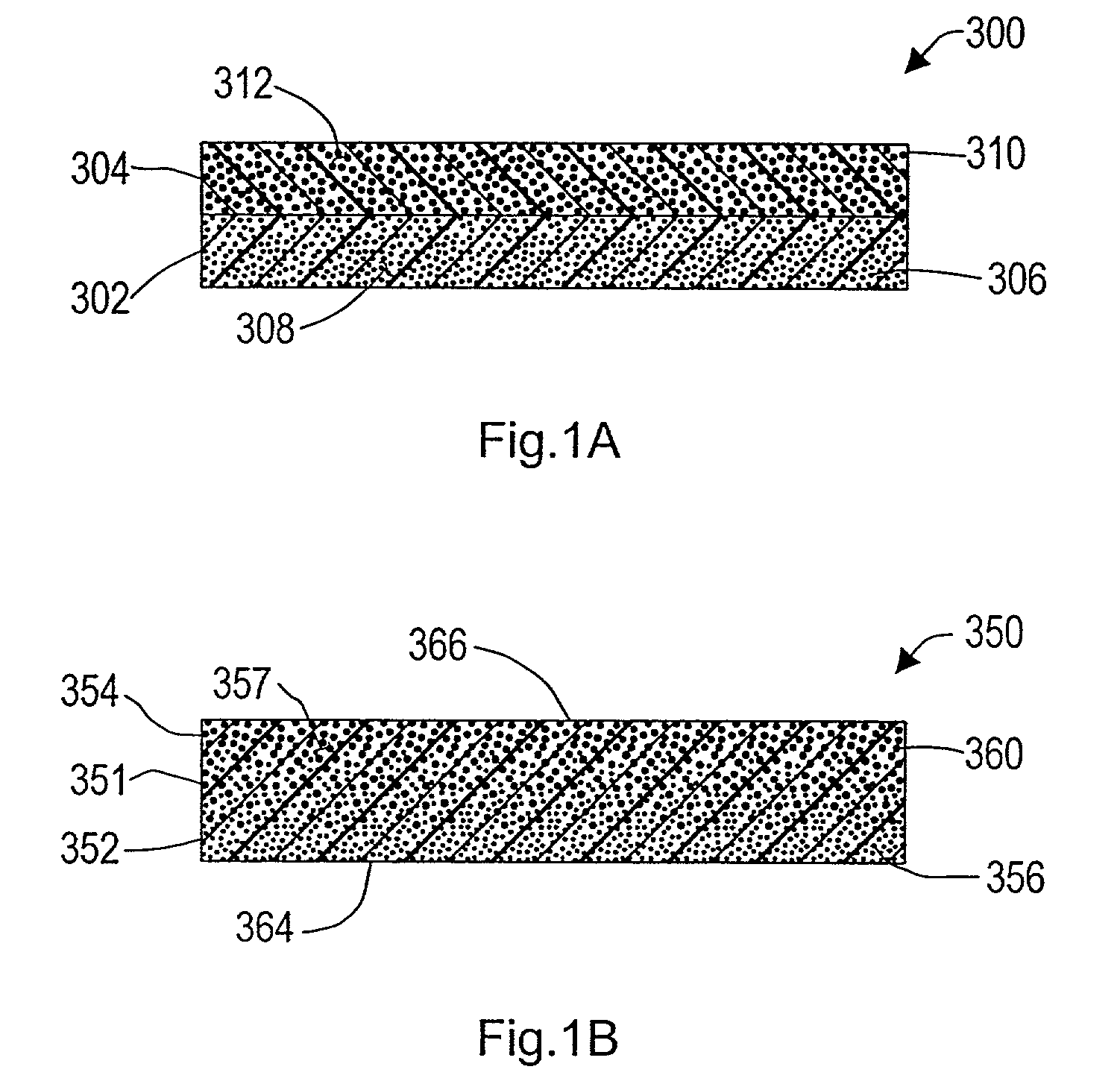
A magnetic article has a magnetic layer having magnetized particles dispersed in a natural or synthetic resin binder and an adjacent high-permeability layer having high-permeability particles dispersed in a natural or synthetic resin binder. The magnetic article may be prepared by co-extruding a mixture of magnetizable particles in a binder and high-permeability particles in a binder through a single die to produce an integral gradient function article having a region of high concentration of magnetizable particles adjacent to one surface of the article and a region of high concentration of the high-permeability particles adjacent to another surface of the article, and magnetizing at least a portion of the magnetizable particles.
Owner:MAGNUM MAGNETICS
Nanoparticle, method of producing nanoparticle and magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS7066978B2Not easily coagulated with each otherImprove coatabilityNanostructure applicationMaterial nanotechnologySaline waterOrganic solvent
A method of producing a nanoparticle, the method comprising: a reducing step of adding an reverse micelle solution (II) obtained by mixing a water-insoluble organic solvent containing a surfactant with an aqueous metal salt solution to an reverse micelle solution (I) obtained by mixing a water-insoluble organic solvent containing a surfactant with an aqueous reducing agent solution, to carry out a reducing reaction; and a maturing step of raising the temperature of the reduced mixture to mature the reduced mixture is provided. A method of producing a plural type alloy nanoparticle, the method comprising producing a nanoparticle made of a plural type alloy through a reducing step of mixing one or more reverse micelle solutions (I) containing a metal salt with an reverse micelle solution (II) containing a reducing agent to carry out reducing treatment and a maturing step of carrying out maturing treatment is also provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Magnetic particle of CuAu(1) or CuAu(III) type its production method, magnetic recording medium and its production method
The present invention relates to a method of producing a magnetic particle including forming a layer containing an alloy particle that can form a CuAu-type or Cu3Au-type hard magnetic ordered alloy phase on a support, oxidizing the layer, and annealing the layer in a non-oxidizing atmosphere. The invention also relates to a method of producing a magnetic particle including producing an alloy particle that can form a hard magnetic ordered alloy phase, oxidizing the alloy particle, and annealing the particle in a non-oxidizing atmosphere, and a magnetic particle produced by the foregoing production method. Further, the invention relates to a magnetic recording medium comprising a magnetic layer containing a magnetic particle and a method of producing a magnetic recording medium including forming a layer containing an alloy that can form the foregoing hard magnetic ordered alloy phase, oxidizing the layer, and annealing the layer in a non-oxidizing atmosphere.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape with particular refractive index characteristics, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS20210280212A1Improve accuracyExact reproductionRecord information storageMetals or alloysMagnetic tapeRefractive index
Provided are a magnetic tape including: a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, in which a total thickness of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 5.30 μm, the magnetic layer has a servo pattern, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured on a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, and an absolute value ΔN of a difference between a refractive index Nxy of the magnetic layer, measured in an in-plane direction and a refractive index Nz of the magnetic layer, measured in a thickness direction is 0.25 to 0.40, a magnetic tape cartridge and a magnetic tape apparatus including this magnetic tape, a magnetic tape cartridge and a magnetic tape apparatus including this magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Synthesis of mono-disperse and highly crystalline nano-particles of metals, alloys, metal-oxides, and multi-metallic oxides without a size-selection process
A synthetic method of fabricating highly crystalline and monodisperse nanoparticles of metals, multi-metallic alloys, monometallic oxides and multi-metallic oxides without a size selection process are disclosed. A typical synthetic method comprises the steps of, synthesis of a metal surfactant complex from the reaction of a metal precursor and a surfactant, high temperature thermal decomposition of the metal surfactant complex to produce monodisperse metal nanoparticles, and completing the formation of synthesized metal, metal alloy or metal oxide nanoparticles by adding a poor solvent followed by centrifuging. For obtaining highly crystalline monodisperse nanoparticles, additional steps are necessary as described in the invention. The resulting nanoparticles have excellent magnetic property for many applications.
Owner:(财)国立首尔大学校产学协力财团
Method and system for magnetic recording using self-organized magnetic nanoparticles
A method and system for magnetic recording using self-organized magnetic nanoparticles is disclosed. The method may include depositing surfactant coated nanoparticles on a substrate, wherein the surfactant coated nanoparticles represent first bits of recorded information. The surfactant coating is then removed from selected of the surfactant coated nanoparticles. The selected nanoparticles with their surfactant coating removed may then be designated to represent second bits of recorded information. The surfactant coated nanoparticles have a first saturation magnetic moment and the selected nanoparticles with the surfactant coating removed have a second saturation magnetic moment. Therefore, by selectively removing the surfactant coating from certain nanoparticles, a write operation for recording the first and second bits of information may be performed. A read operation may be carried out by detecting the different magnetic moments of the surfactant coated nanoparticles and the non-surfactant coated nanoparticles.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Process for manufacturing magnetic material, magnetic material and high density magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20060204793A1High densityEfficiently obtainedNanomagnetismInorganic material magnetismHigh densityFerromagnetic order
A process for manufacturing a magnetic material, comprising: coating a nanoparticle dispersion containing alloy nanoparticles capable of forming a ferromagnetic ordered alloy phase, and a fusion inhibitor on a support to form a coated film of a nanoparticle magnetic layer, and heat-treating the coated film to ferromagnetize the alloy nanoparticles. Further, a magnetic material comprising a support and a nanoparticle magnetic layer of a nanoparticle dispersion coated thereon, wherein the nanoparticle dispersion comprises alloy nanoparticles capable of forming a ferromagnetic ordered alloy phase and a fusion inhibitor, is provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveCN109478410AImprove C/N valueRecord information storageMetals or alloysLength waveRecording layer
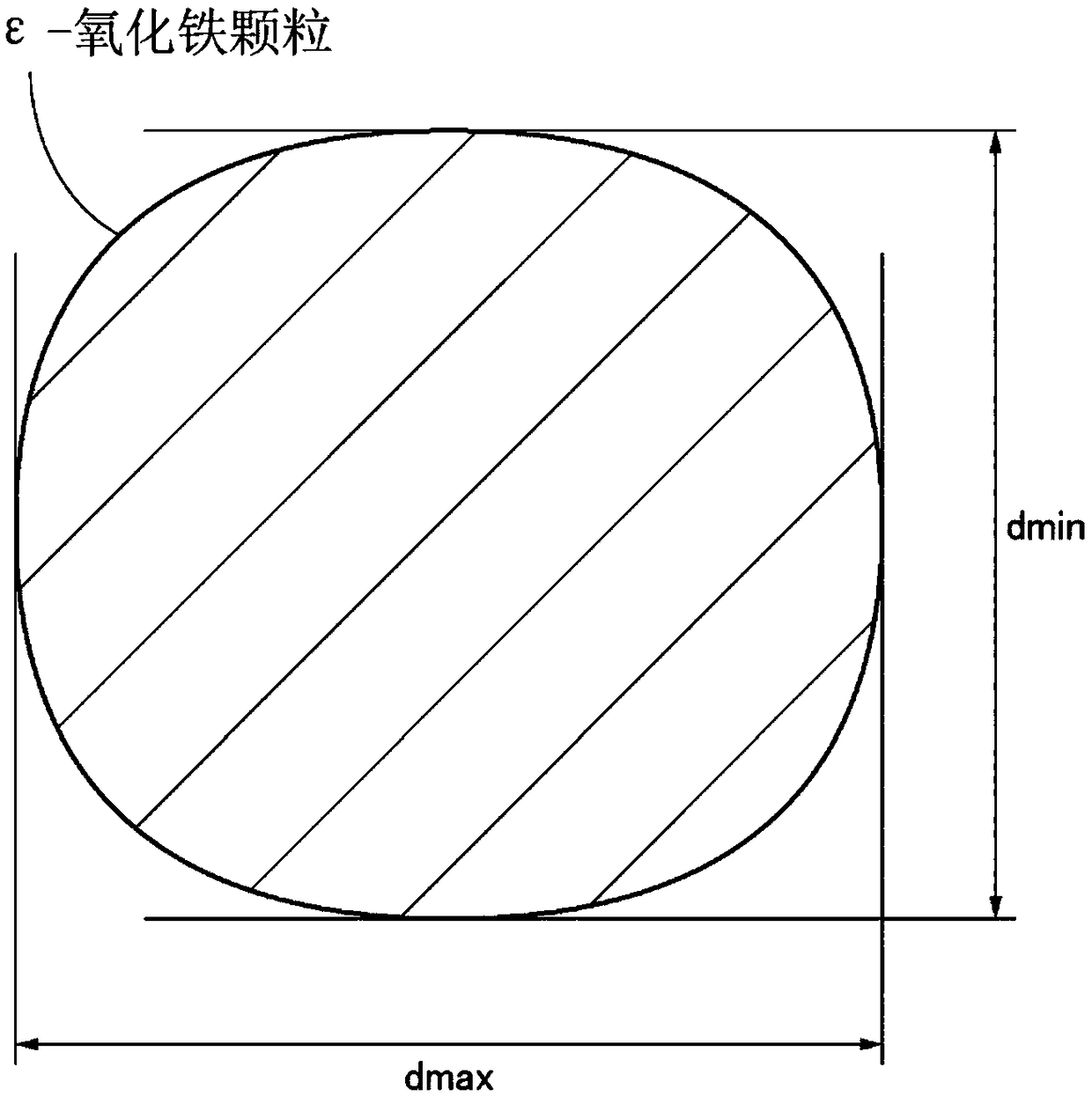
A magnetic recording medium is adopted in a recording and reproduction device that has the shortest recorded wavelength of 75 nm or less, the magnetic recording medium including a recording layer thatcontains a particle powder containing epsilon-iron oxide. A squareness ratio measured along the travel direction of the magnetic recording medium is 30% or less; a ratio (Dmax / Dmin) of the averagelongest diameter Dmax of particles to the average shortest diameter Dmin satisfies a relationship of 1.0 <= (Dmax / Dmin) <= 1.1; the average thickness [delta]mag of the recording layer is 100 nm or less; and a ratio ([delta]mag / Dmin) of the average thickness [delta]mag of the recording layer to the average shortest diameter Dmin of particles satisfies a relationship of [delta]mag / Dmin <= 5.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnetic layer with high permeability backing
InactiveUS20050064242A1Enhanced magnetic gauss levelIncrease the magnetic field strengthManufacture head surfaceCoating by extrusionHigh concentrationPolymer science
A magnetic article has a magnetic layer having magnetized particles dispersed in a natural or synthetic resin binder and an adjacent high-permeability layer having high-permeability particles dispersed in a natural or synthetic resin binder. The magnetic article may be prepared by co-extruding a mixture of magnetizable particles in a binder and high-permeability particles in a binder through a single die to produce an integral gradient function article having a region of high concentration of magnetizable particles adjacent to one surface of the article and a region of high concentration of the high-permeability particles adjacent to another surface of the article, and magnetizing at least a portion of the magnetizable particles.
Owner:DANA AUTOMOTIVE SYST GRP LLC
Alloy nano-particles
InactiveUS20050022628A1Material nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingMaterials scienceMagnetic films
Disclosed are alloy nano-particles having a fluctuation coefficient of particle size of 20% or less and a fluctuation coefficient of composition of 20% or less. The alloy nano-particles have a low transformation point and hardly aggregate and which can form a flat magnetic film having high coercive force.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20190295584A1Improve C/N valueIncrease valueRecord information storageMetals or alloysLength waveMaterials science
A magnetic recording medium is used in a recording / reproduction apparatus having a shortest recording wavelength of not more than 75 nm, the magnetic recording medium including a recording layer that contains a powder of particles containing ε-iron oxide, in which a squareness ratio measured in a traveling direction of the magnetic recording medium is not more than 30%, a ratio (Dmax / Dmin) of an average longest diameter Dmax of the particles to an average shortest diameter Dmin of the particles satisfies a relationship of 1.0≤(Dmax / Dmin)≤1.1, an average thickness δmag of the recording layer is not more than 100 nm, and a ratio (δmag / Dmin) of the average thickness δmag of the recording layer to the average shortest diameter Dmin of the particles satisfies a relationship of δmag / Dmin≤5.
Owner:SONY CORP
Nanoparticle, method of producing nanoparticle and magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20050158506A1Not easily coagulated with each otherImprove coatabilityNanostructure applicationPowder deliverySaline waterOrganic solvent
A method of producing a nanoparticle, the method comprising: a reducing step of adding an reverse micelle solution (II) obtained by mixing a water-insoluble organic solvent containing a surfactant with an aqueous metal salt solution to an reverse micelle solution (I) obtained by mixing a water-insoluble organic solvent containing a surfactant with an aqueous reducing agent solution, to carry out a reducing reaction; and a maturing step of raising the temperature of the reduced mixture to mature the reduced mixture is provided. A method of producing a plural type alloy nanoparticle, the method comprising producing a nanoparticle made of a plural type alloy through a reducing step of mixing one or more reverse micelle solutions (I) containing a metal salt with an reverse micelle solution (II) containing a reducing agent to carry out reducing treatment and a maturing step of carrying out maturing treatment is also provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for extracting magnetically hard alloy nanoparticles and magnetic recording material
InactiveUS20050204865A1Reduce drying loadShort timeNanomagnetismMagnetic liquidsOrganic solventBoiling point
Disclosed is a method for extracting magnetically hard alloy nanoparticles, which comprises preparing a magnetic alloy nanoparticle dispersion by heating an organometallic compound containing a metal constituting a magnetically hard ordered alloy with a polyol compound having a boiling point of 150 to 350° C. and extracting magnetically hard alloy nanoparticles from the dispersion into a hydrophobic organic solvent in the presence of a hydrophobic surface modifying agent. The method can provide magnetically hard alloy nanoparticles showing almost no particle aggregation and markedly reduced load for drying.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic particles and method of producing the same and magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20050089683A1Improve productivityMaterial nanotechnologyMetal-working apparatusFerromagnetic orderAlloy
Magnetic particles including a ferromagnetic ordered alloy phase, wherein the surface of the magnetic particles is in contact with an organic substance. The invention also provides a method of producing magnetic particles having a ferromagnetic ordered alloy phase, including preparing alloy particles capable of forming the ferromagnetic ordered alloy phase, subjecting the alloy particles to an oxidation treatment, and then annealing the alloy particles in a solvent. A magnetic recording medium including a magnetic layer which contains the magnetic particles described above is also provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Magnetic particle-coated material, magnetic recording medium, electromagnetic shield material, and methods of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20060029741A1High densityMagnetic/electric field screeningBase layers for recording layersFerromagnetic orderElectromagnetic shielding
The present invention provides a magnetic particle-coated material having a layer including a CuAu type or Cu3Au type ferromagnetic ordered alloy phase on an organic support. Further, the present invention provides a method of manufacturing a magnetic particle-coated material that sequentially includes a step of manufacturing alloy particles capable of forming a ferromagnetic ordered alloy phase, a step of coating an organic support with the alloy particles to form a coating film, and a step of annealing the coating film in a reducing atmosphere to make the alloy particles into magnetic particles, and further includes a step of oxidizing the alloy particles, the oxidizing step being performed between the alloy particle manufacturing step and the annealing step.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing method using the same
ActiveUS20050214593A1Good magnetoelectric transform characteristicExcellent in high-density recordingLayered productsRecord information storageAxial ratioLong axis
A magnetic recording medium comprising a non-magnetic support and a magnetic layer containing a ferromagnetic metal powder and a binder, wherein the ferromagnetic metal powder comprises an oxide layer and a metal portion surrounded by the oxide layer, and the ferromagnetic metal powder has an average long axis length of from 30 nm to 55 nm, a coefficient of variation of long axis length of not more than 25%, a coefficient of variation of axial ratio of not more than 20%, and a coefficient of variation of a thickness of the oxide layer of not more than 15%.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Magnetic recording medium
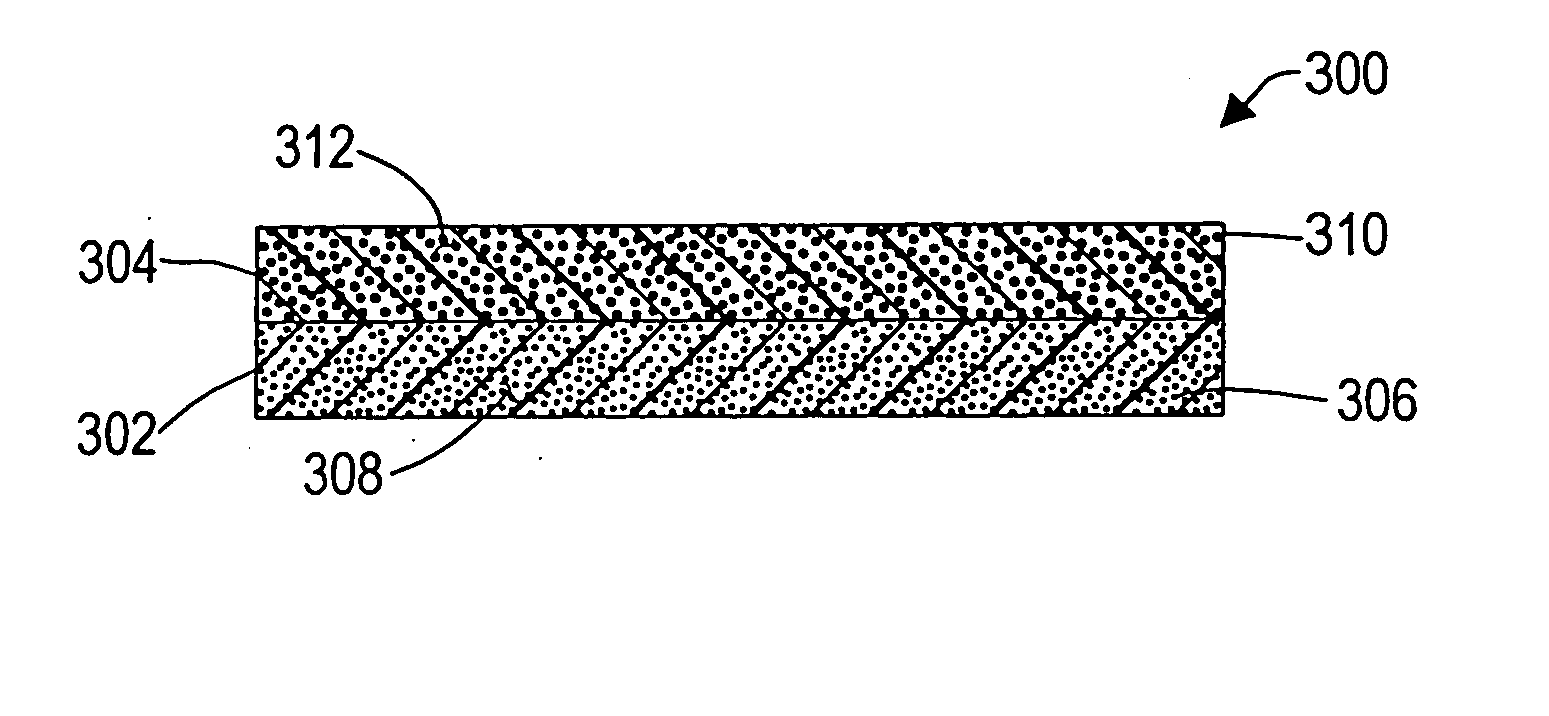
InactiveUS20050238925A1Excellent long-term storage stability and electromagnetic conversion characteristicBase layers for recording layersSynthetic resin layered productsNon magneticPhotochemistry
A magnetic recording medium is provided that includes a non-magnetic support, a radiation-cured layer cured by exposing a layer containing a radiation curing compound to radiation, and a magnetic layer comprising a ferromagnetic powder dispersed in a binder. The radiation-cured layer and the magnetic layer are provided in that order above the non-magnetic support. The radiation curing compound has a C2 to C18 alkyl group, a C6 to C10 cyclic structure, and two or more radiation curing functional groups per molecule.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com