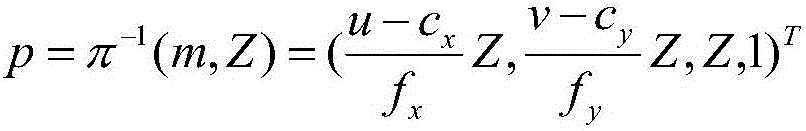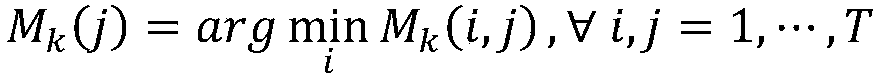Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
113 results about "Visual odometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
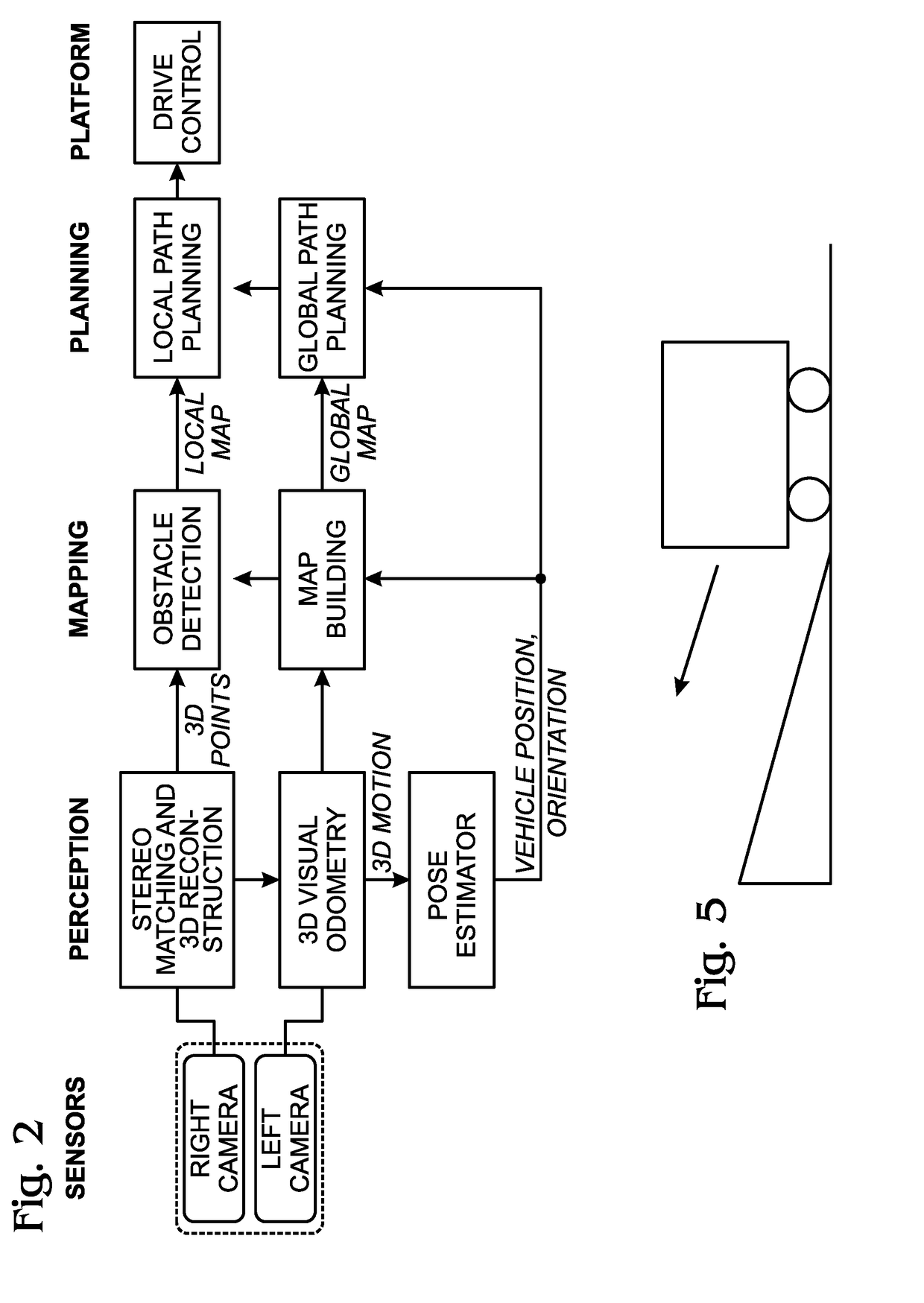
In robotics and computer vision, visual odometry is the process of determining the position and orientation of a robot by analyzing the associated camera images. It has been used in a wide variety of robotic applications, such as on the Mars Exploration Rovers.
Unified framework for precise vision-aided navigation
ActiveUS20080167814A1Improves visual odometry performanceReduce and eliminate accumulated navigation driftImage analysisPosition fixationMulti cameraPostural orientation
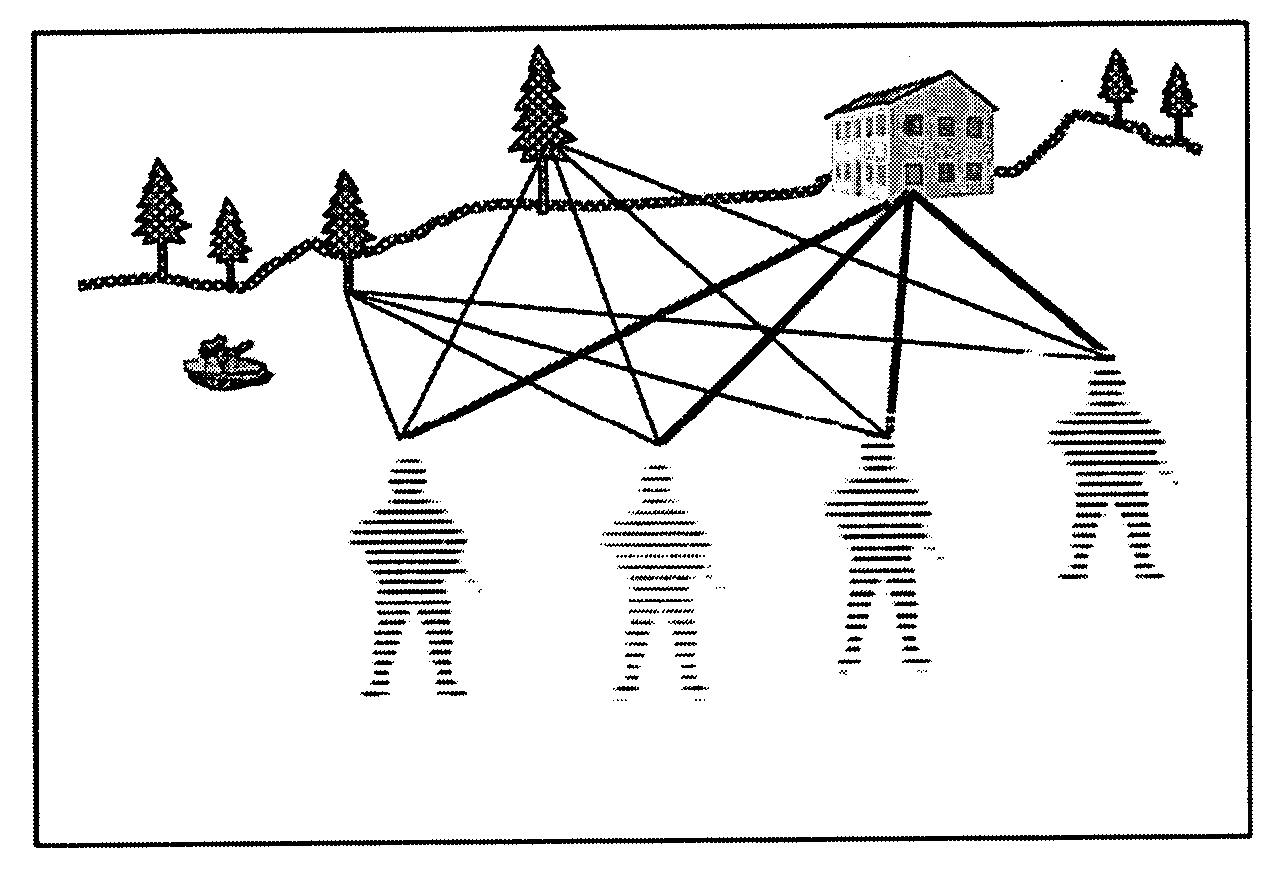
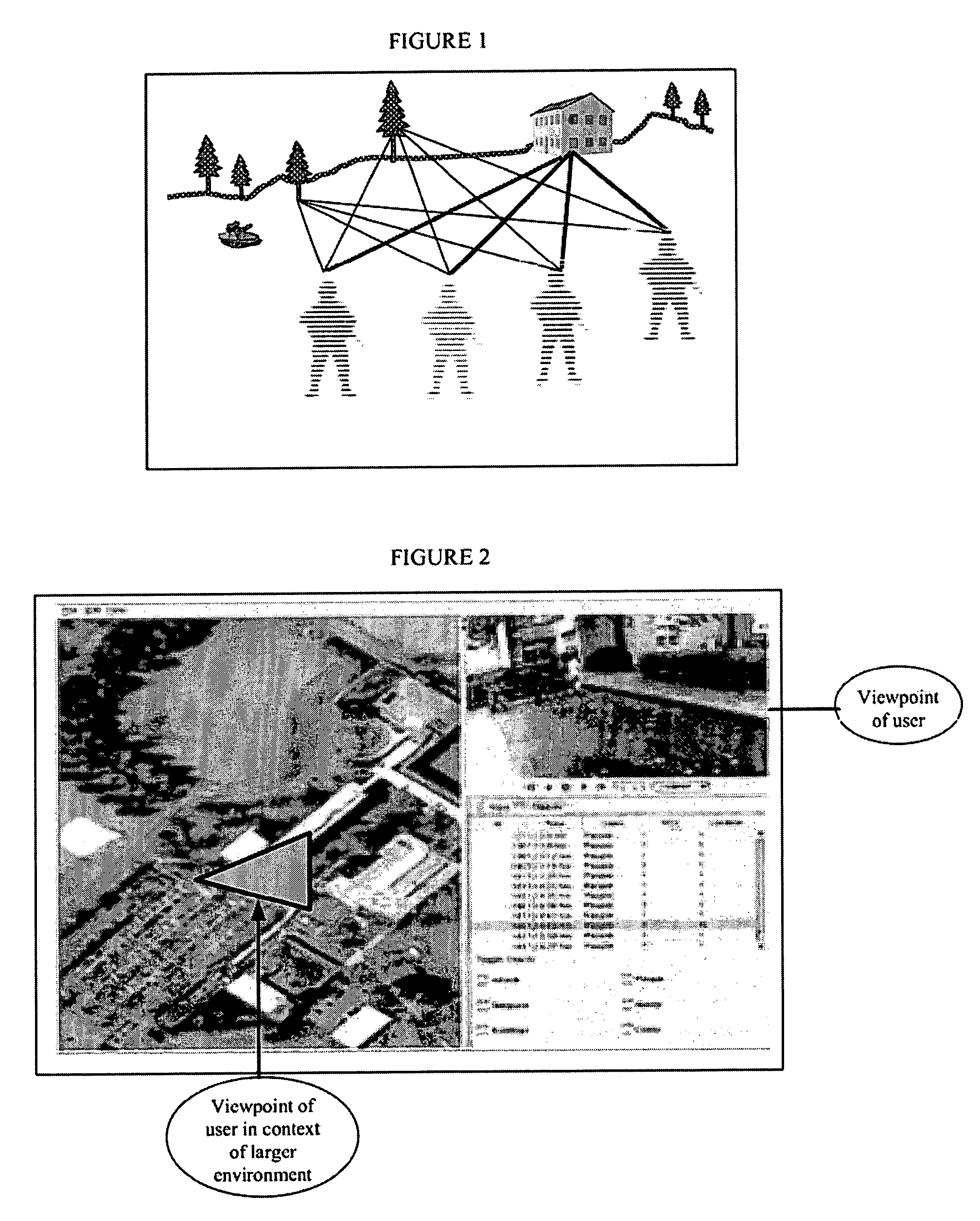
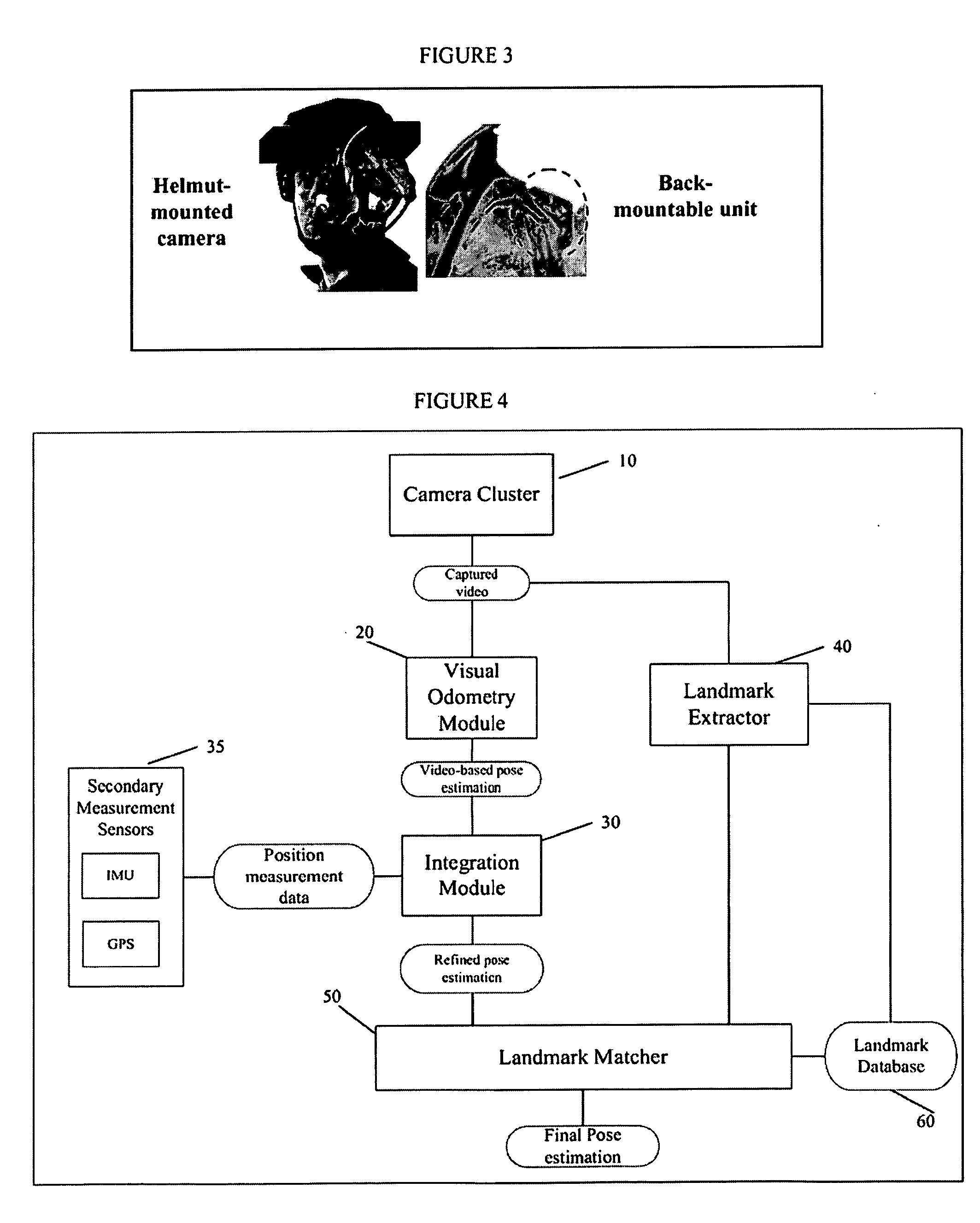
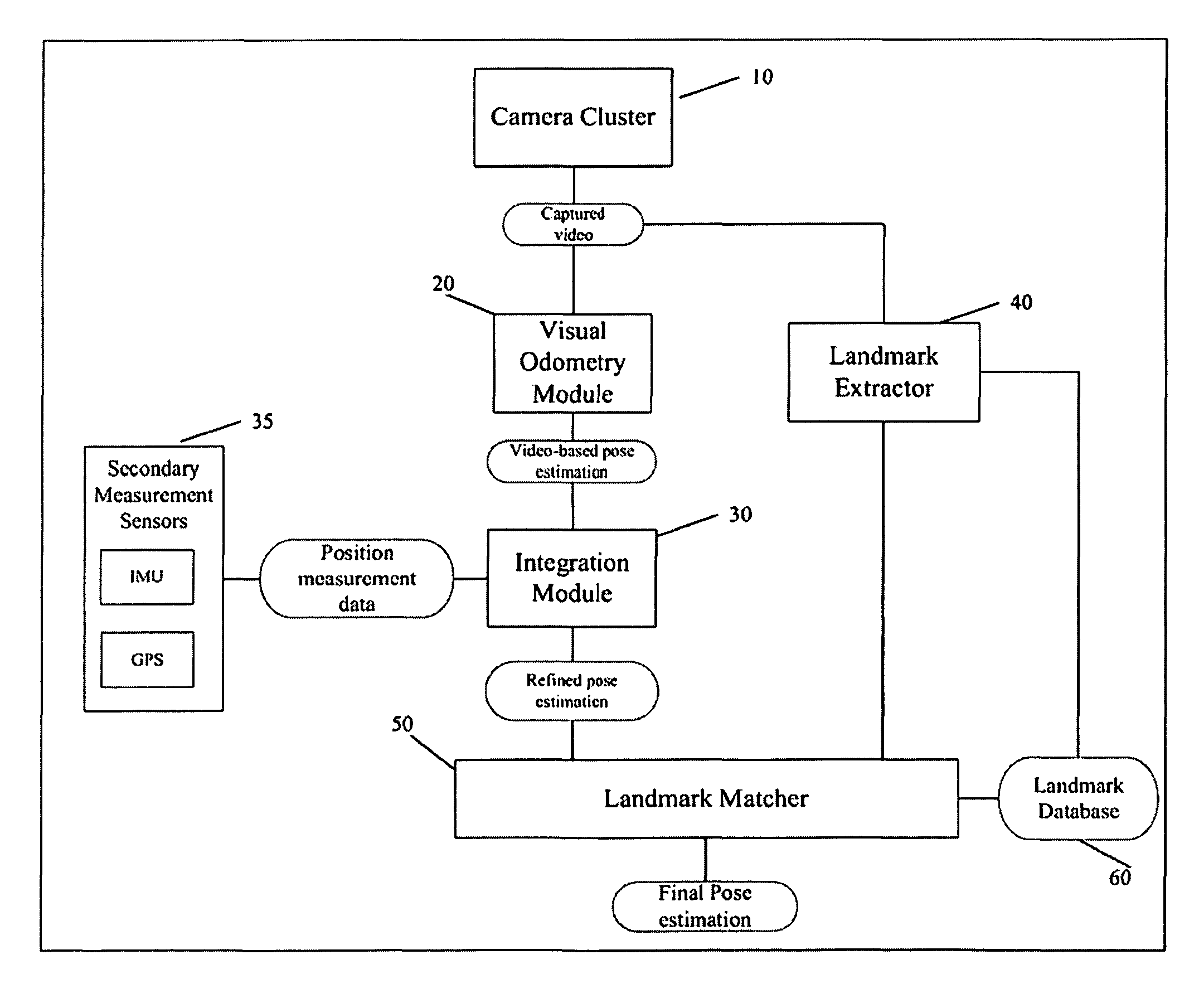
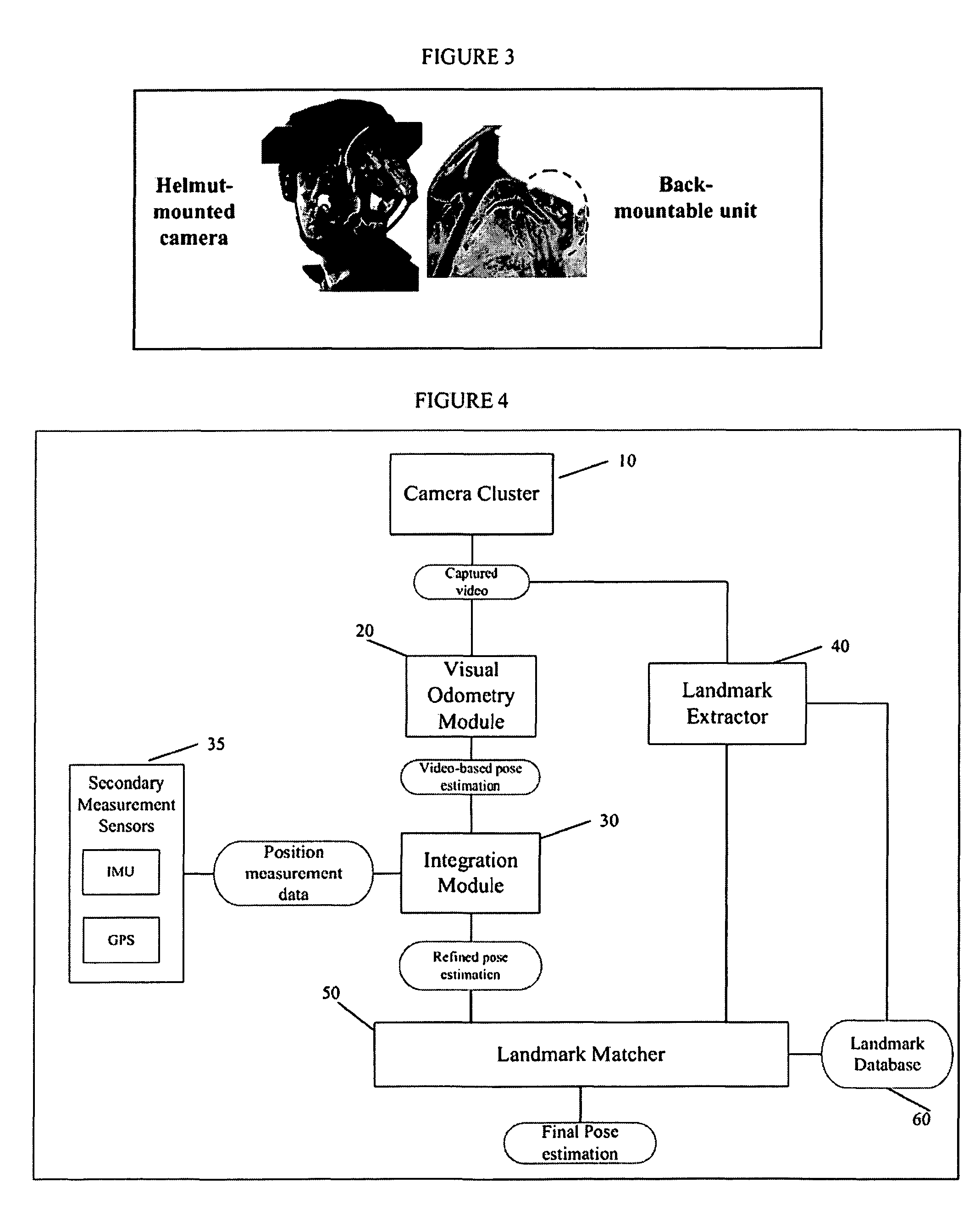
A system and method for efficiently locating in 3D an object of interest in a target scene using video information captured by a plurality of cameras. The system and method provide for multi-camera visual odometry wherein pose estimates are generated for each camera by all of the cameras in the multi-camera configuration. Furthermore, the system and method can locate and identify salient landmarks in the target scene using any of the cameras in the multi-camera configuration and compare the identified landmark against a database of previously identified landmarks. In addition, the system and method provide for the integration of video-based pose estimations with position measurement data captured by one or more secondary measurement sensors, such as, for example, Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) and Global Positioning System (GPS) units.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
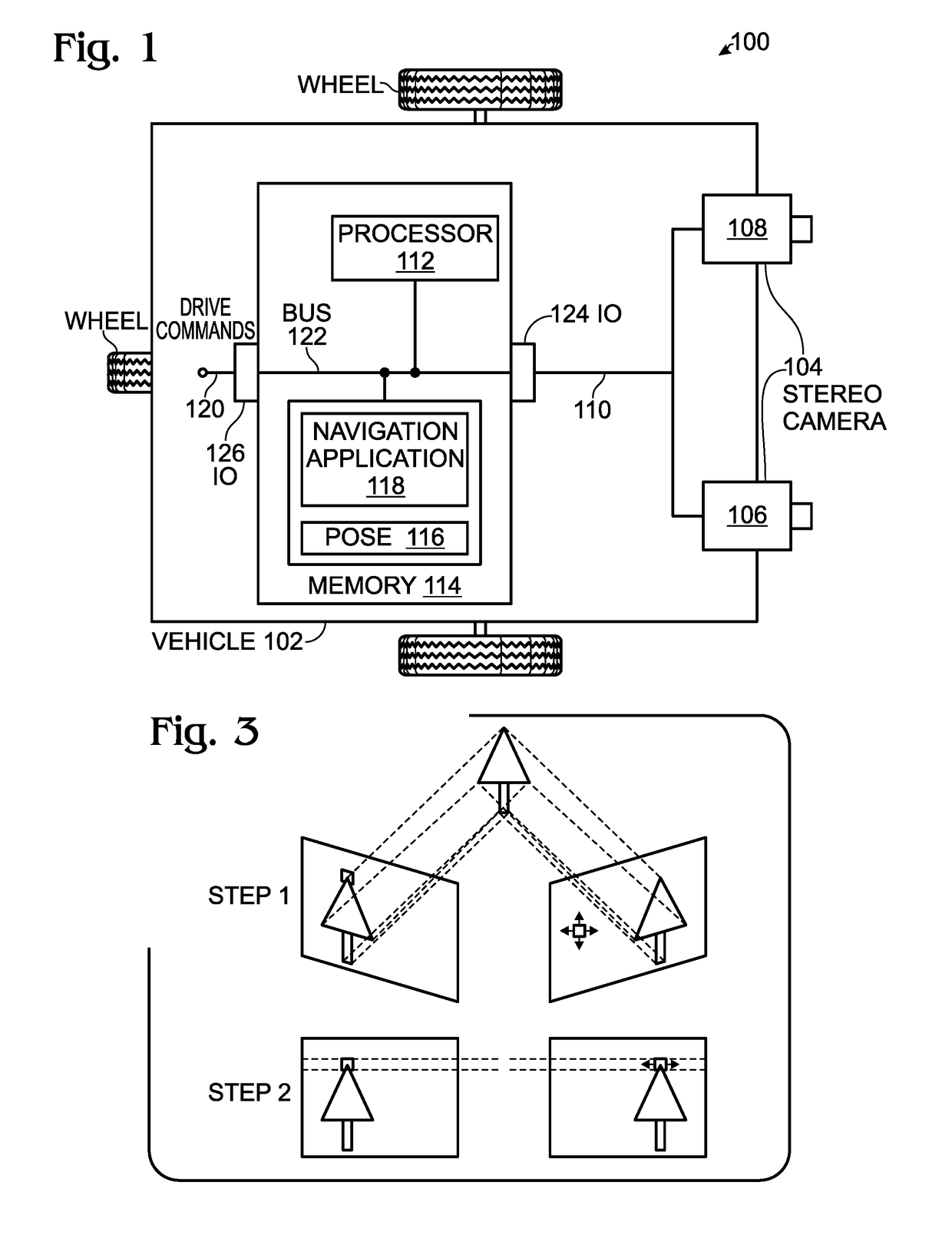
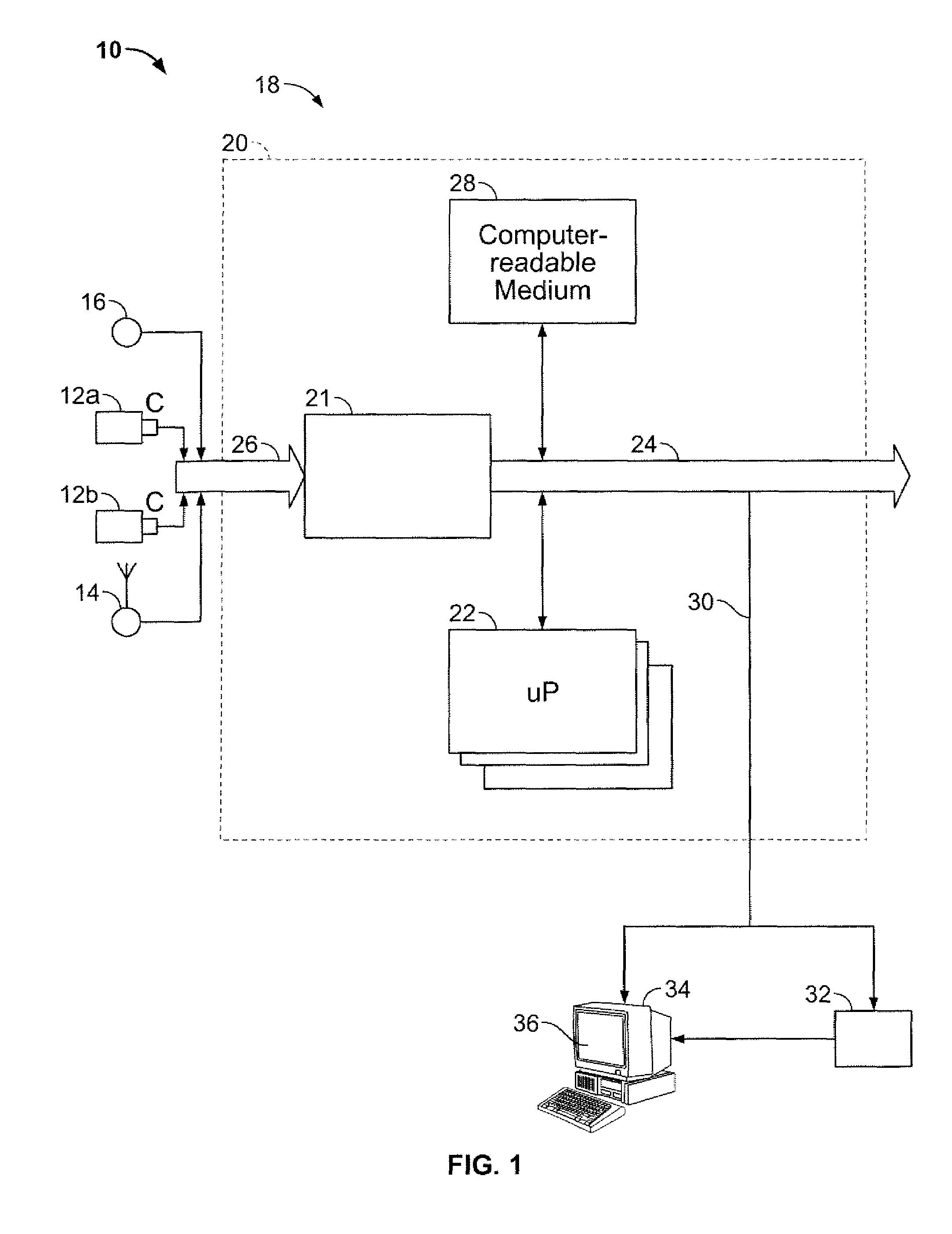
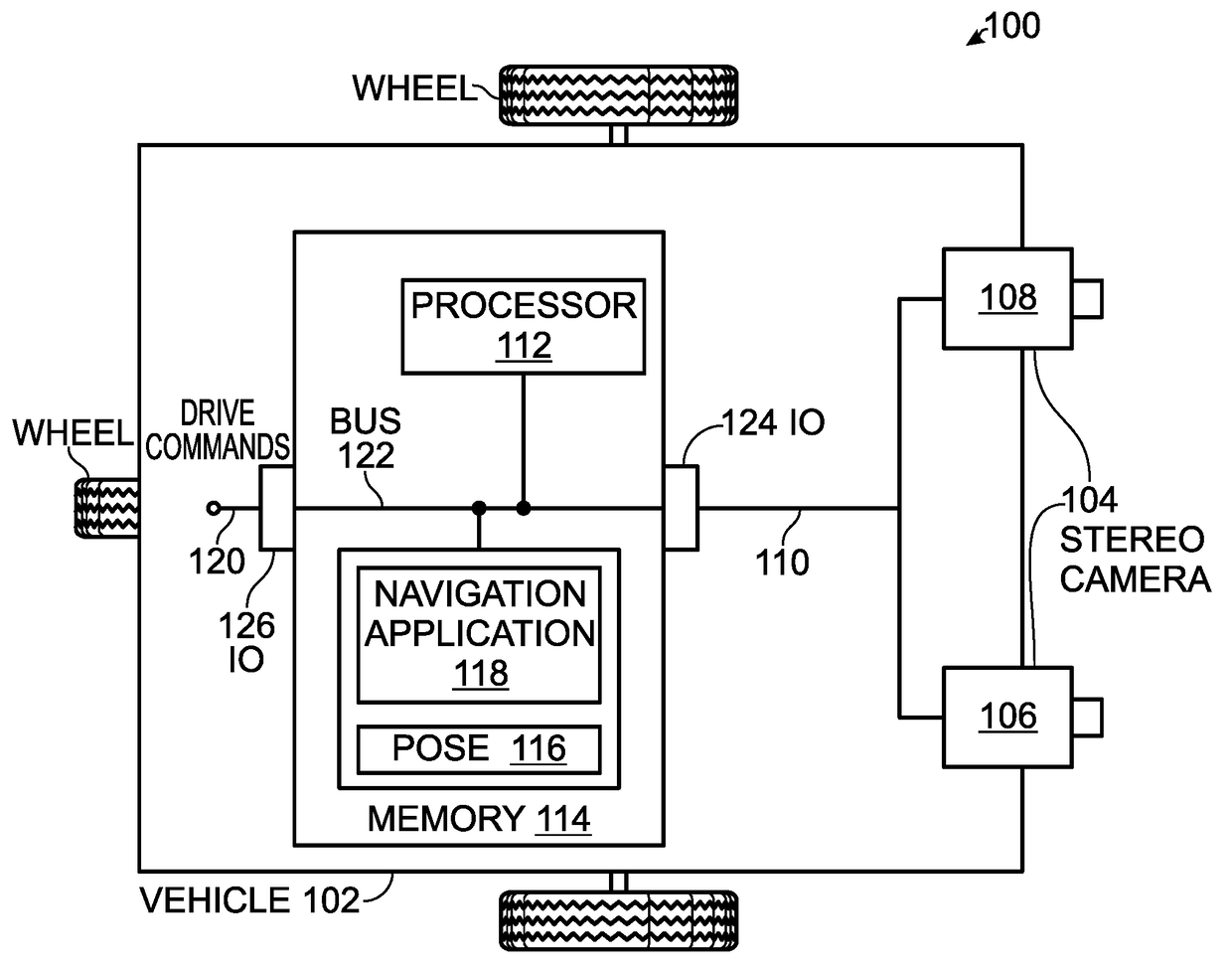
Autonomous Navigation using Visual Odometry
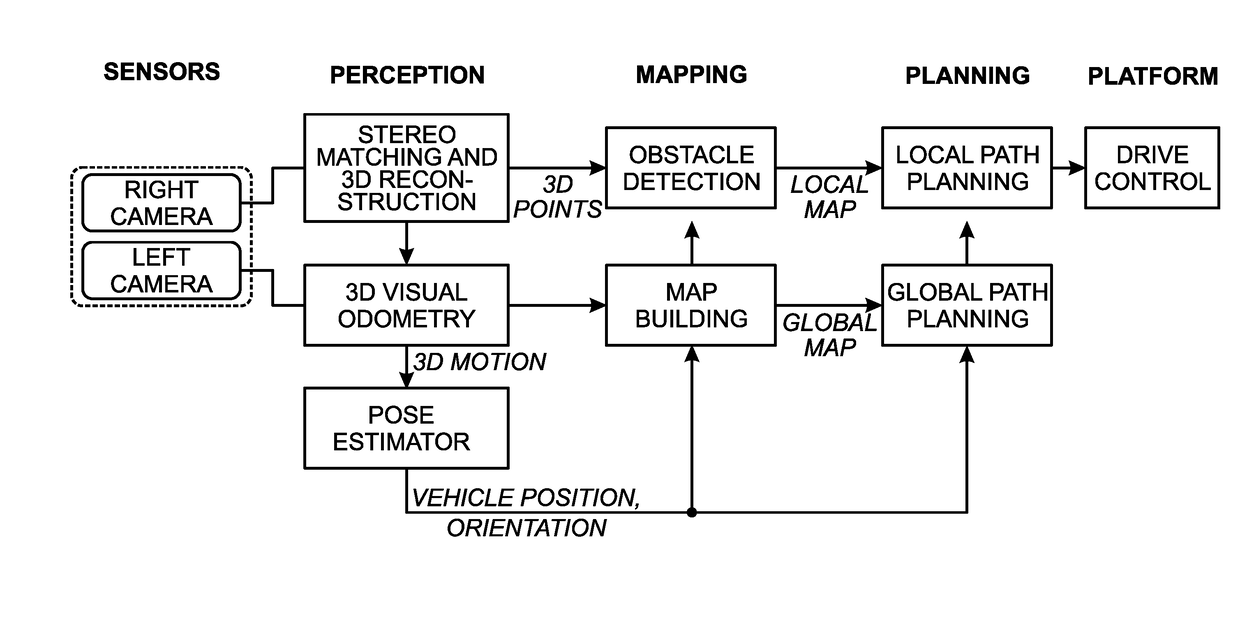
A system and method are provided for autonomously navigating a vehicle. The method captures a sequence of image pairs using a stereo camera. A navigation application stores a vehicle pose (history of vehicle position). The application detects a plurality of matching feature points in a first matching image pair, and determines a plurality of corresponding object points in three-dimensional (3D) space from the first image pair. A plurality of feature points are tracked from the first image pair to a second image pair, and the plurality of corresponding object points in 3D space are determined from the second image pair. From this, a vehicle pose transformation is calculated using the object points from the first and second image pairs. The rotation angle and translation are determined from the vehicle pose transformation. If the rotation angle or translation exceed a minimum threshold, the stored vehicle pose is updated.
Owner:SHARP KK
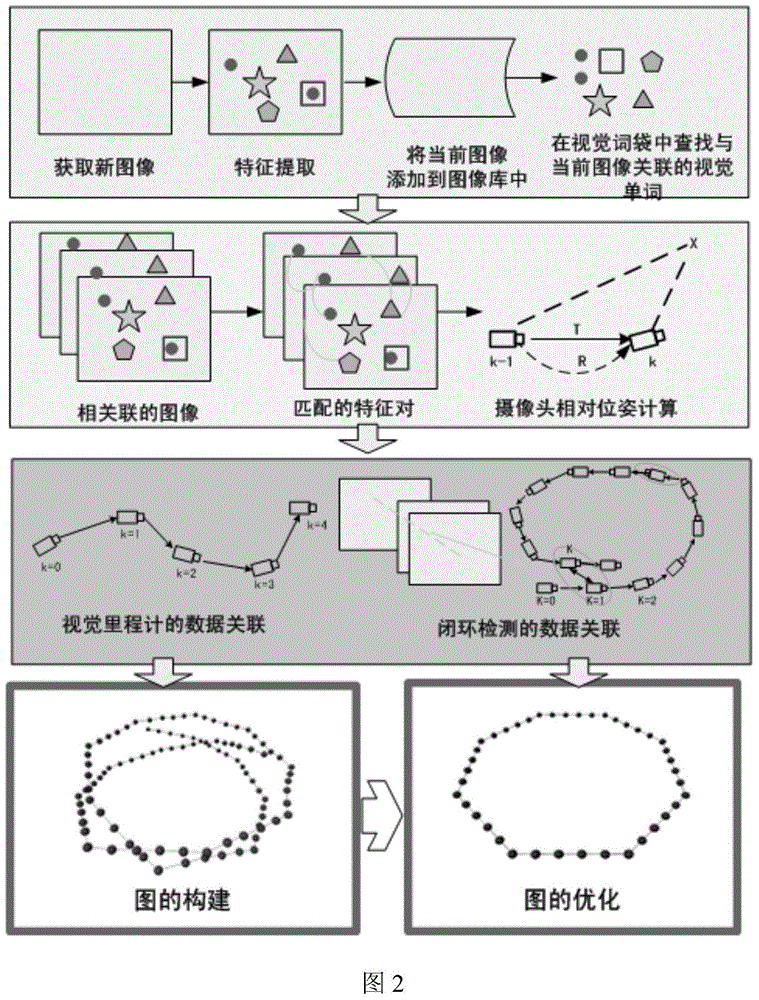
Graph-based vision SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) method
InactiveCN104374395AProof of validityInstruments for road network navigationSimultaneous localization and mappingStochastic gradient descent
The invention discloses a graph-based vision SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) method. According to the method, the matching relation between an image and visual feature can be obtained based on the natural feature probability vector representation of the image, and the relative pose between two interframes can be calculated by utilizing the space geometry relation of images. Data association of visual odometry is obtained by utilizing the corresponding relation of continuous images, so that all constraints in an image sequence can be obtained. The camera relative pose is taken as a node in a map, the space constrained relation of image interframes is taken as an edge, so that an estimated track map based on the camera relative pose is constructed. Finally, a maximum likelihood method is employed for optimizing the map, and optimized pose estimation is obtained through a random gradient descent method. Related experiments are performed in the laboratory environment based on the provided method, also the moving track of a robot is displayed, and the validity of the algorithm is confirmed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
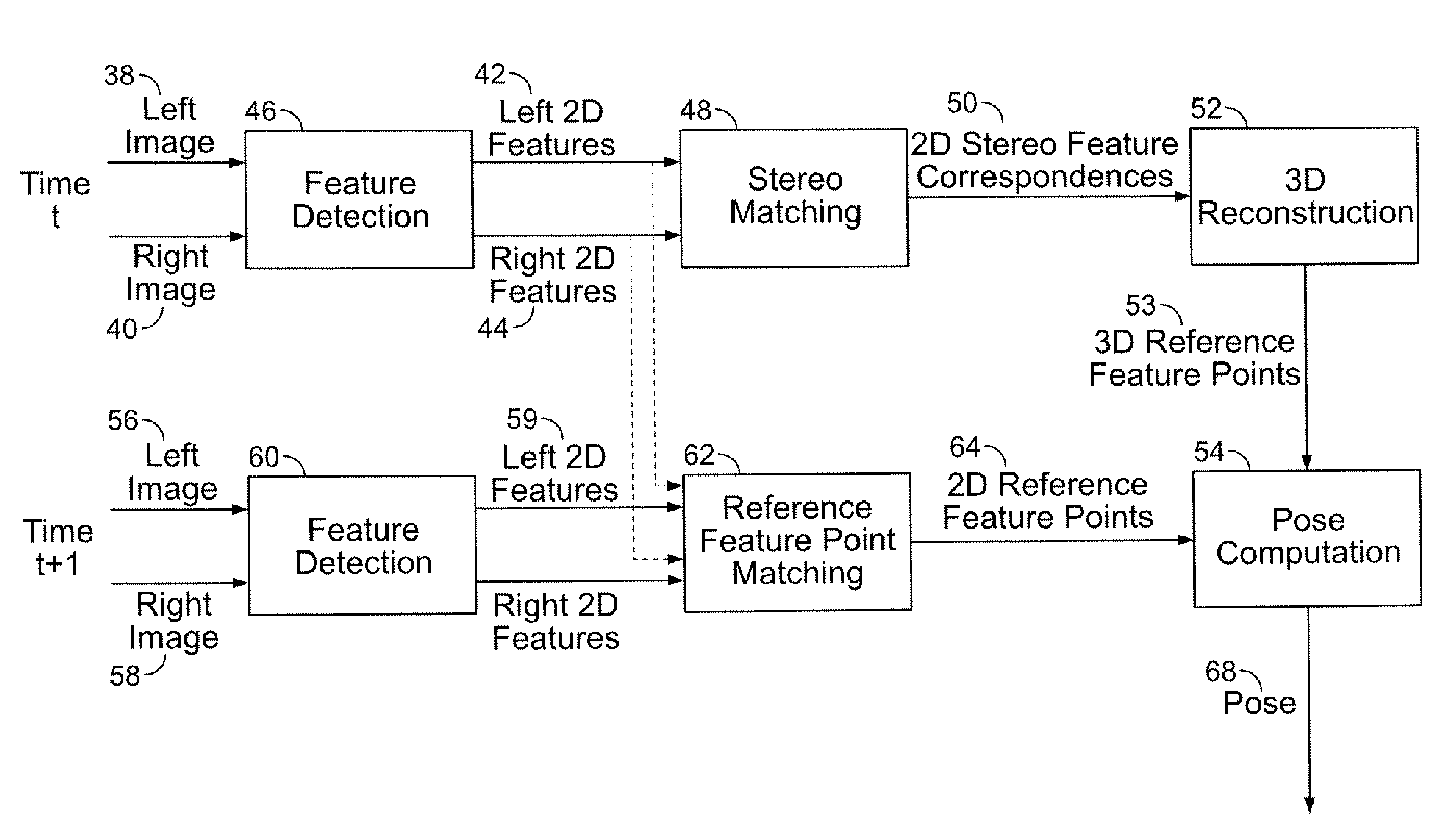
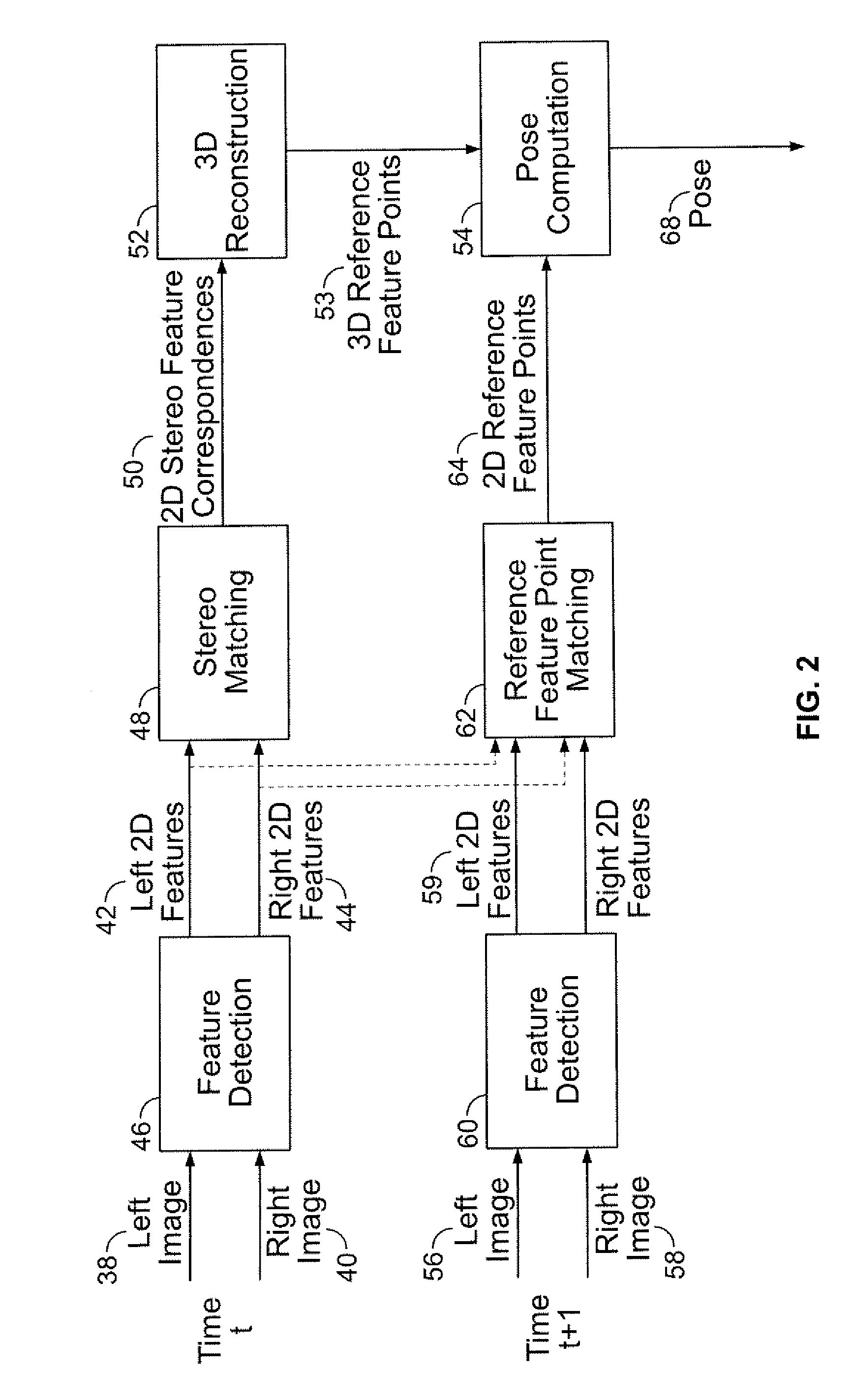
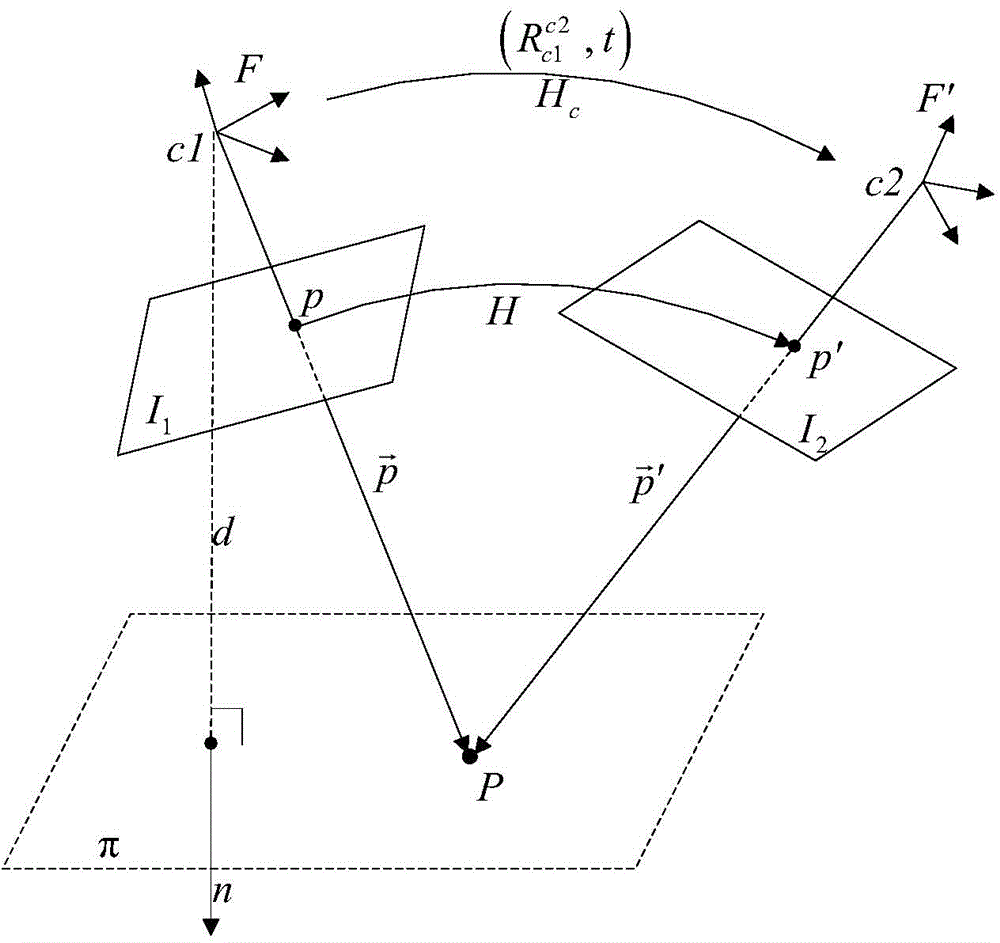
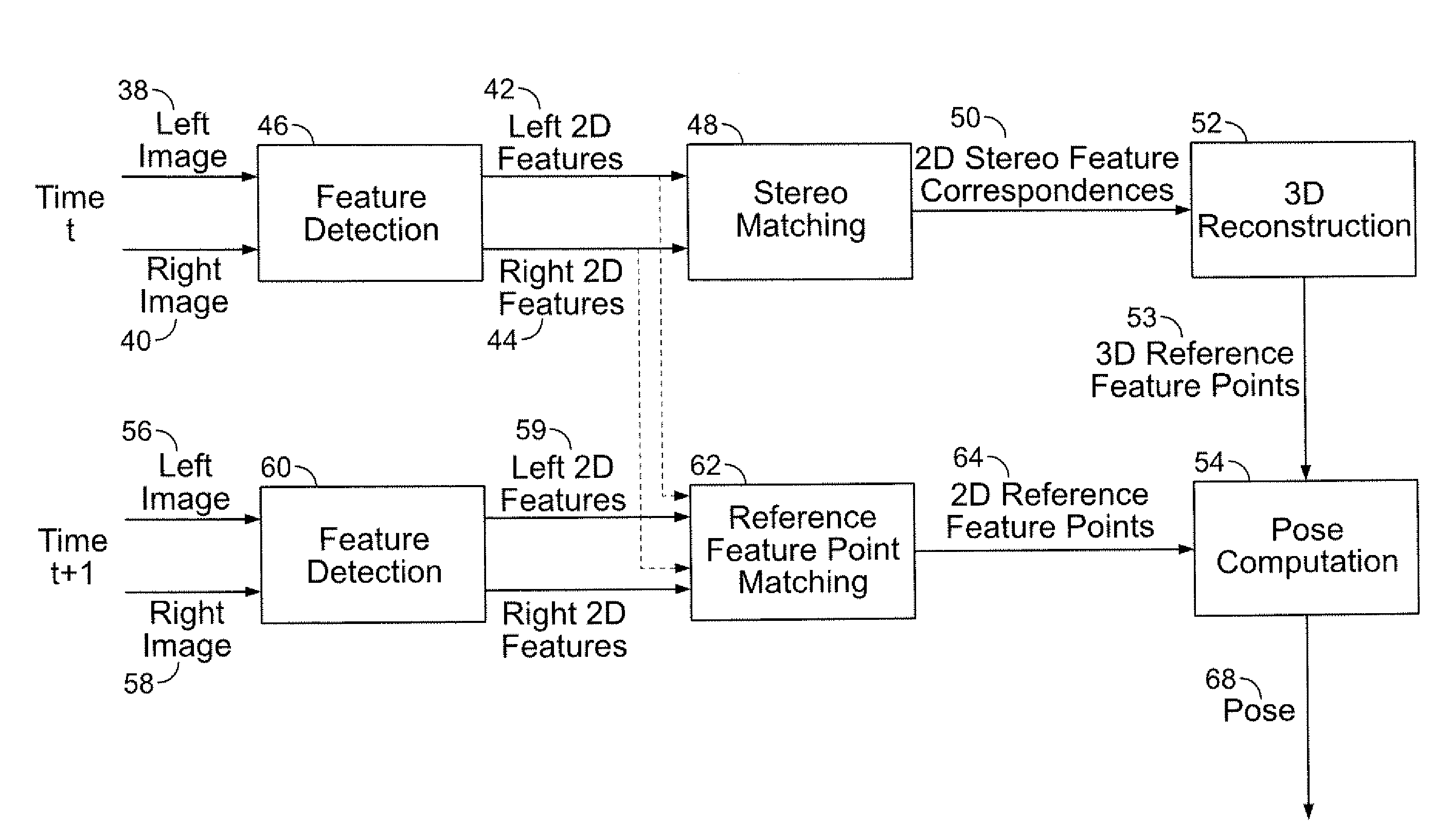
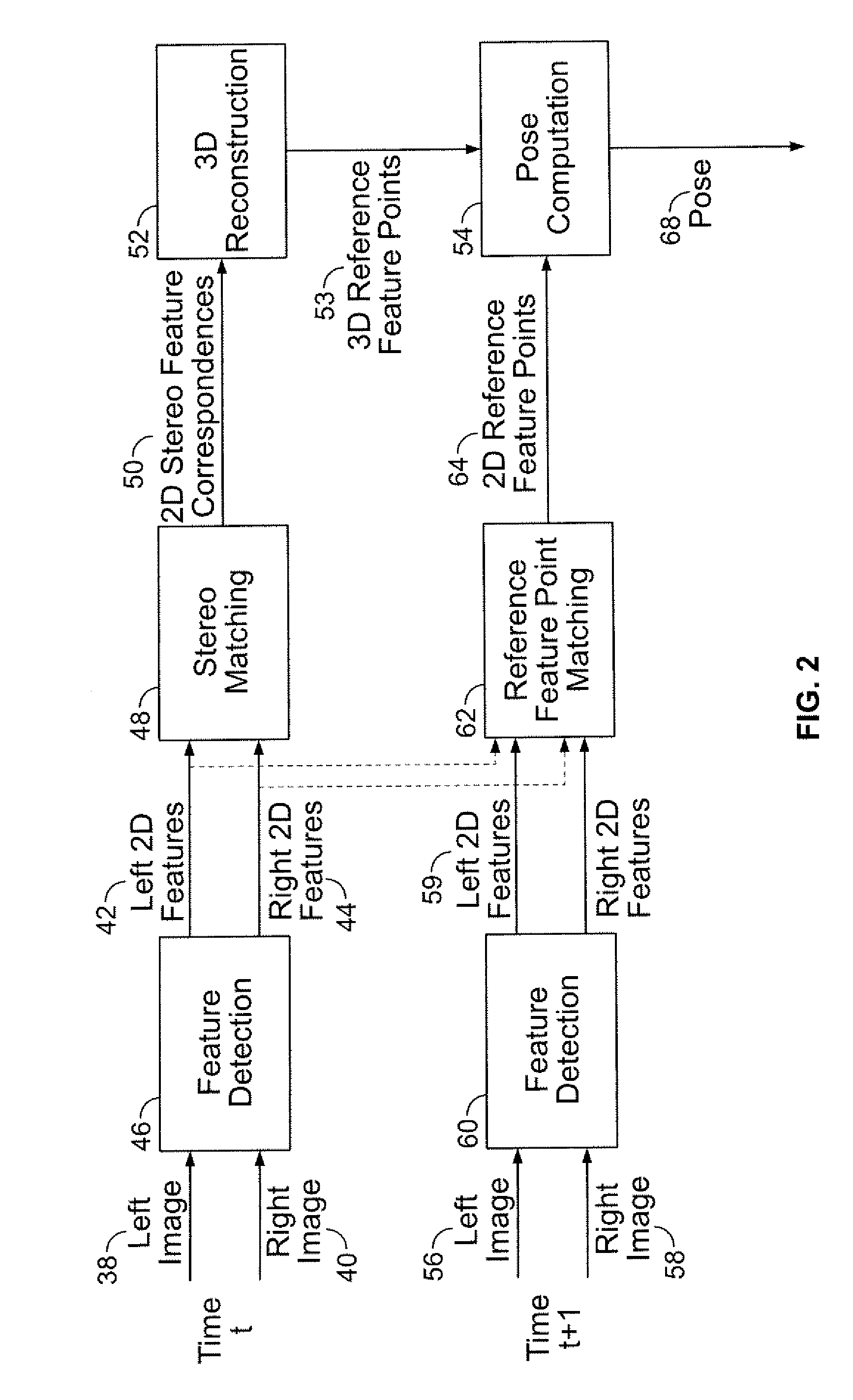
Stereo-Based Visual Odometry Method and System
ActiveUS20080144925A1Minimizes projectionImage enhancementImage analysisStereo imageVisual perception
A method for estimating pose from a sequence of images, which includes the steps of detecting at least three feature points in both the left image and right image of a first pair of stereo images at a first point in time; matching the at least three feature points in the left image to the at least three feature points in the right image to obtain at least three two-dimensional feature correspondences; calculating the three-dimensional coordinates of the at least three two-dimensional feature correspondences to obtain at least three three-dimensional reference feature points; tracking the at least three feature points in one of the left image and right image of a second pair of stereo images at a second point in time different from the first point in time to obtain at least three two-dimensional reference feature points; and calculating a pose based on the at least three three-dimensional reference feature points and its corresponding two-dimensional reference feature points in the stereo images. The pose is found by minimizing projection residuals of a set of three-dimensional reference feature points in an image plane.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Unified framework for precise vision-aided navigation
ActiveUS8174568B2Robustly determineHigh positioning accuracyInstruments for road network navigationImage analysisMulti cameraPostural orientation
A system and method for efficiently locating in 3D an object of interest in a target scene using video information captured by a plurality of cameras. The system and method provide for multi-camera visual odometry wherein pose estimates are generated for each camera by all of the cameras in the multi-camera configuration. Furthermore, the system and method can locate and identify salient landmarks in the target scene using any of the cameras in the multi-camera configuration and compare the identified landmark against a database of previously identified landmarks. In addition, the system and method provide for the integration of video-based pose estimations with position measurement data captured by one or more secondary measurement sensors, such as, for example, Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) and Global Positioning System (GPS) units.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Indoor simultaneous locating and environment modeling method for unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN103926933AIncrease flexibilityImprove controllabilityAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsData transmissionEnvironmental model
The invention discloses an indoor simultaneous locating and environment modeling method for an unmanned aerial vehicle. According to the method, flying tracks of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be located, and an indoor three-dimensional environmental model can be drawn fast. An operation platform and an operation method of the unmanned aerial vehicle are constructed, an RGB-D sensor carried by the unmanned aerial vehicle is utilized for collecting data, a visual odometry is adopted for estimating the indoor flying tracks and positions of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and an extended kalman filtering algorithm is adopted for obtaining the more accurate flying tracks and the positions of the aerial vehicle. Furthermore, the data transmission functions of the unmanned aerial vehicle and a ground communication device are utilized for feeding information collected by the sensor on the aerial vehicle back to ground operating personnel in real time, and a three-dimensional data display method of a computer is utilized for calculating and processing the collected data and carrying out indoor three-dimensional environment modeling and displaying.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Scene matching/visual odometry-based inertial integrated navigation method
ActiveCN103954283AHigh positioning accuracyStrong autonomyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsVisual perceptionHomography
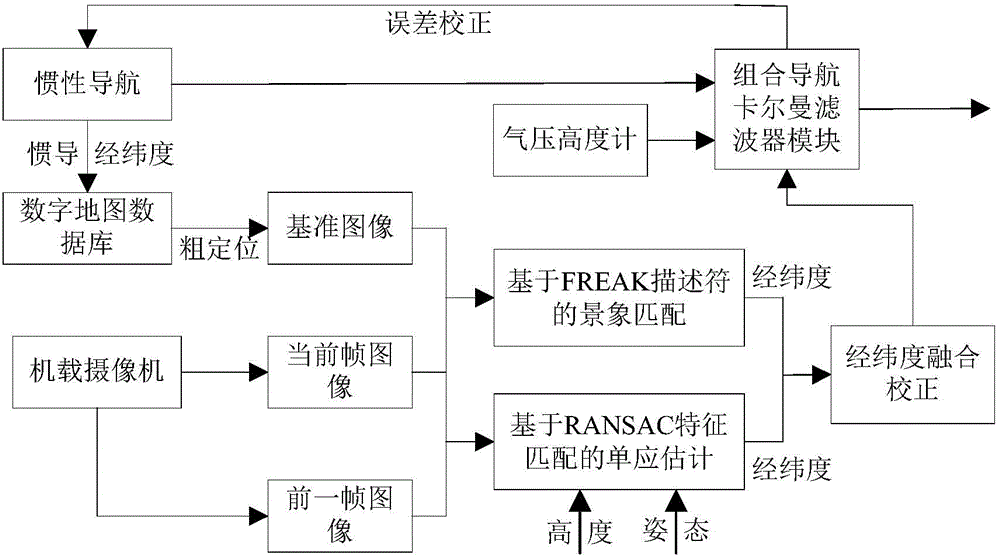
The invention relates to a scene matching / visual odometry-based inertial integrated navigation method. The method comprises the following steps: calculating the homography matrix of an unmanned plane aerial photography real time image sequence according to a visual odometry principle, and carrying out recursive calculation by accumulating a relative displacement between two continuous frames of real time graph to obtain the present position of the unmanned plane; introducing an FREAK characteristic-based scene matching algorithm because of the accumulative error generation caused by the increase of the visual odometry navigation with the time in order to carry out aided correction, and carrying out high precision positioning in an adaption zone to effectively compensate the accumulative error generated by the long-time work of the visual odometry navigation, wherein the scene matching has the advantages of high positioning precision, strong automaticity, anti-electromagnetic interference and the like; and establishing the error model of the inertial navigation system and a visual data measuring model, carrying out Kalman filtering to obtain an optimal estimation result, and correcting the inertial navigation system. The method effectively improves the navigation precision, and is helpful for improving the autonomous flight capability of the unmanned plane.
Owner:深圳市欧诺安科技有限公司
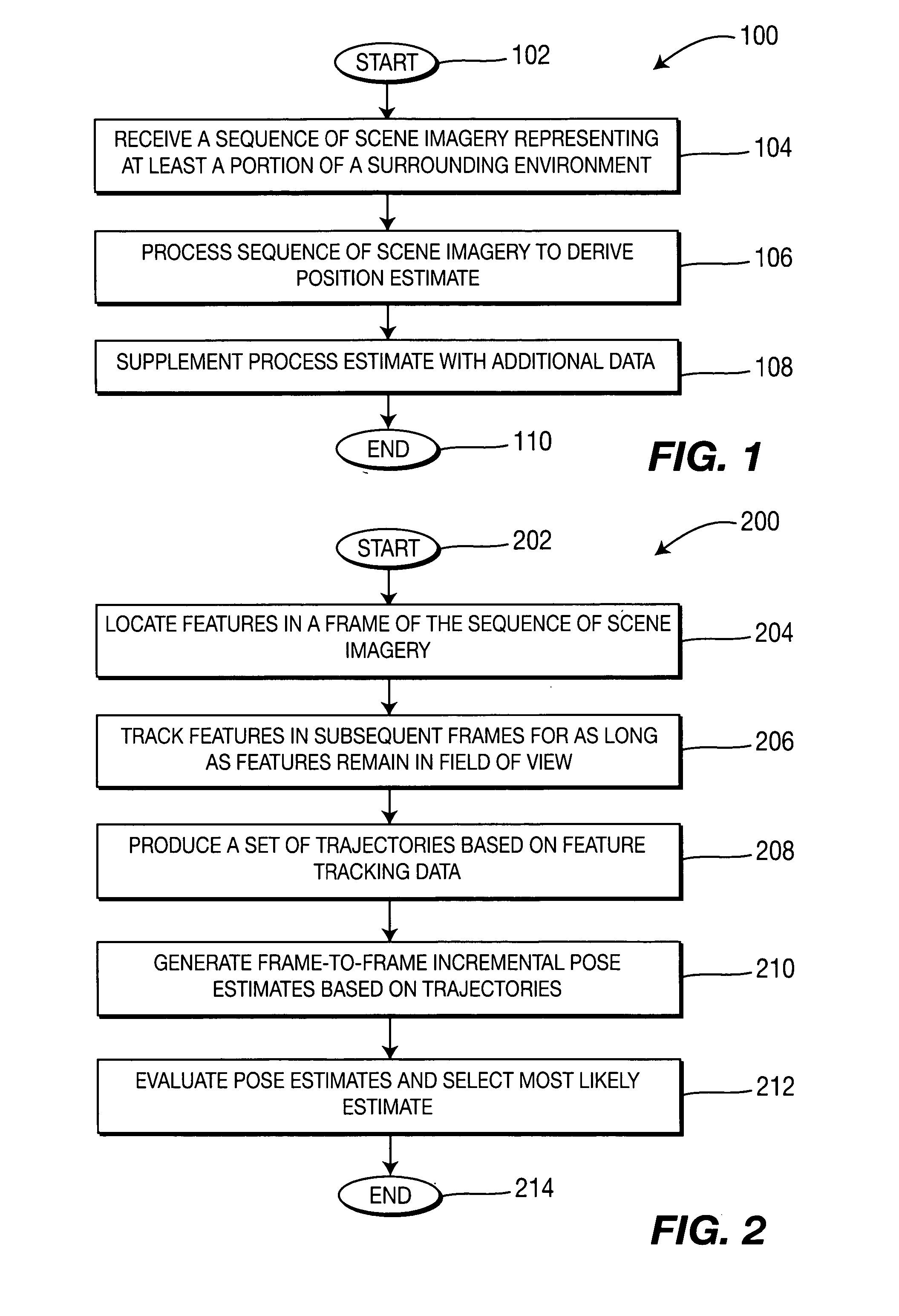
Method and apparatus for visual odometry
InactiveUS20070288141A1Image analysisDigital data processing detailsVideo processingGlobal Positioning System
A method and apparatus for visual odometry (e.g., for navigating a surrounding environment) is disclosed. In one embodiment a sequence of scene imagery is received (e.g., from a video camera or a stereo head) that represents at least a portion of the surrounding environment. The sequence of scene imagery is processed (e.g., in accordance with video processing techniques) to derive an estimate of a pose relative to the surrounding environment. This estimate may be further supplemented with data from other sensors, such as a global positioning system or inertial or mechanical sensors.
Owner:SARNOFF CORP
Mobile robot and simultaneous localization and map building method thereof
A simultaneous localization and map building method of a mobile robot including an omni-directional camera. The method includes acquiring an omni-directional image from the omni-directional camera, dividing the obtained omni-directional image into upper and lower images according to a preset reference to generate a first image, which is the lower image, and a second image, which is the upper image, extracting feature points from the first image and calculating visual odometry information calculating visual odometry information to track locations of the extracted feature points based on a location of the omni-directional camera, and performing localization and map building of the mobile robot using the calculated visual odometry information and the second image as an input of an extended Kalman filter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Stereo-based visual odometry method and system
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
RGB-D visual odometry taking ground constraint into consideration in indoor environment
InactiveCN106556412AImprove estimation accuracyIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisColor imagePoint cloud
The invention belongs to the field self-localization of a mobile robot, and particularly relates to RGB-D visual odometry taking ground constraint into consideration in an indoor environment. The method comprises: (1) in an indoor environment, collecting color image information and depth image information in the environment during a motion process of an RGB-D camera loaded on a mobile platform and marking adjacent frame images as Is and It; (2) performing solution through a reverse projection function [pi]-1 according to the depth image information to obtain three dimensional point cloud data Vs and Vt of the environment; and (3) extracting and matching ORB characteristics including extracting and matching characteristic points of RGB-D images through an ORB algorithm. Image pre-treatment including characteristic extraction and matching is completed through an ORB algorithm. Compared with SIFT and SURF algorithms, the ORB algorithm is accelerated by one order of magnitude. The point cloud ground is obtained through use of depth image detection and point set alignment is improved through use of ground information, thereby improving the estimation precision of motion transformation.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
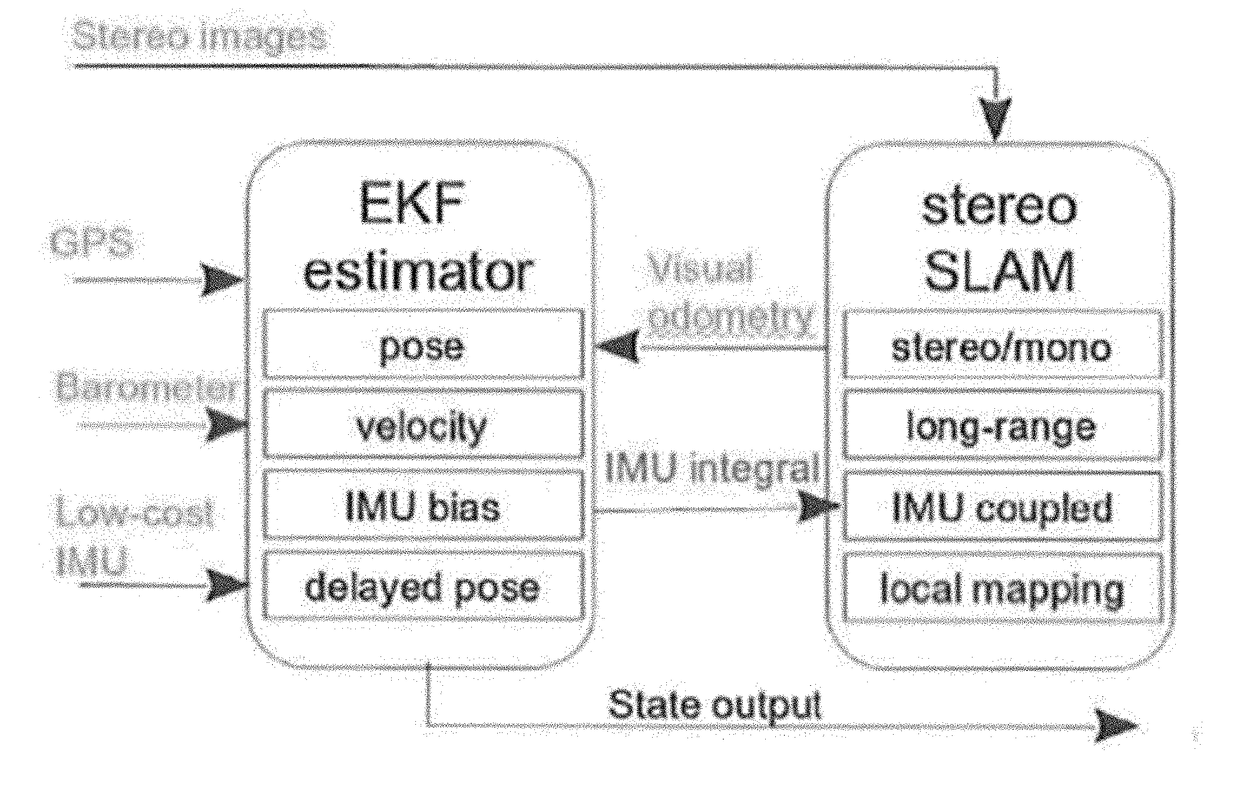
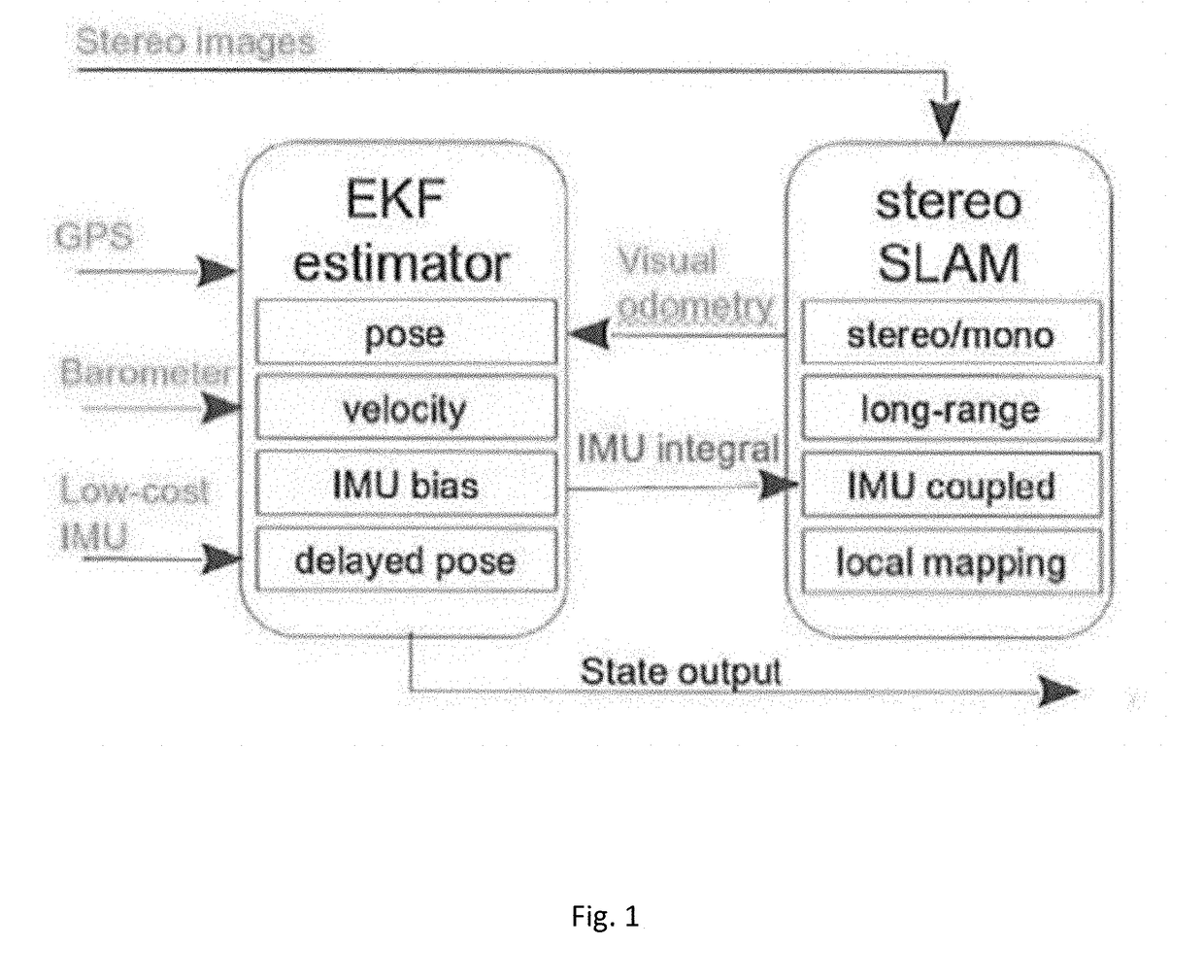
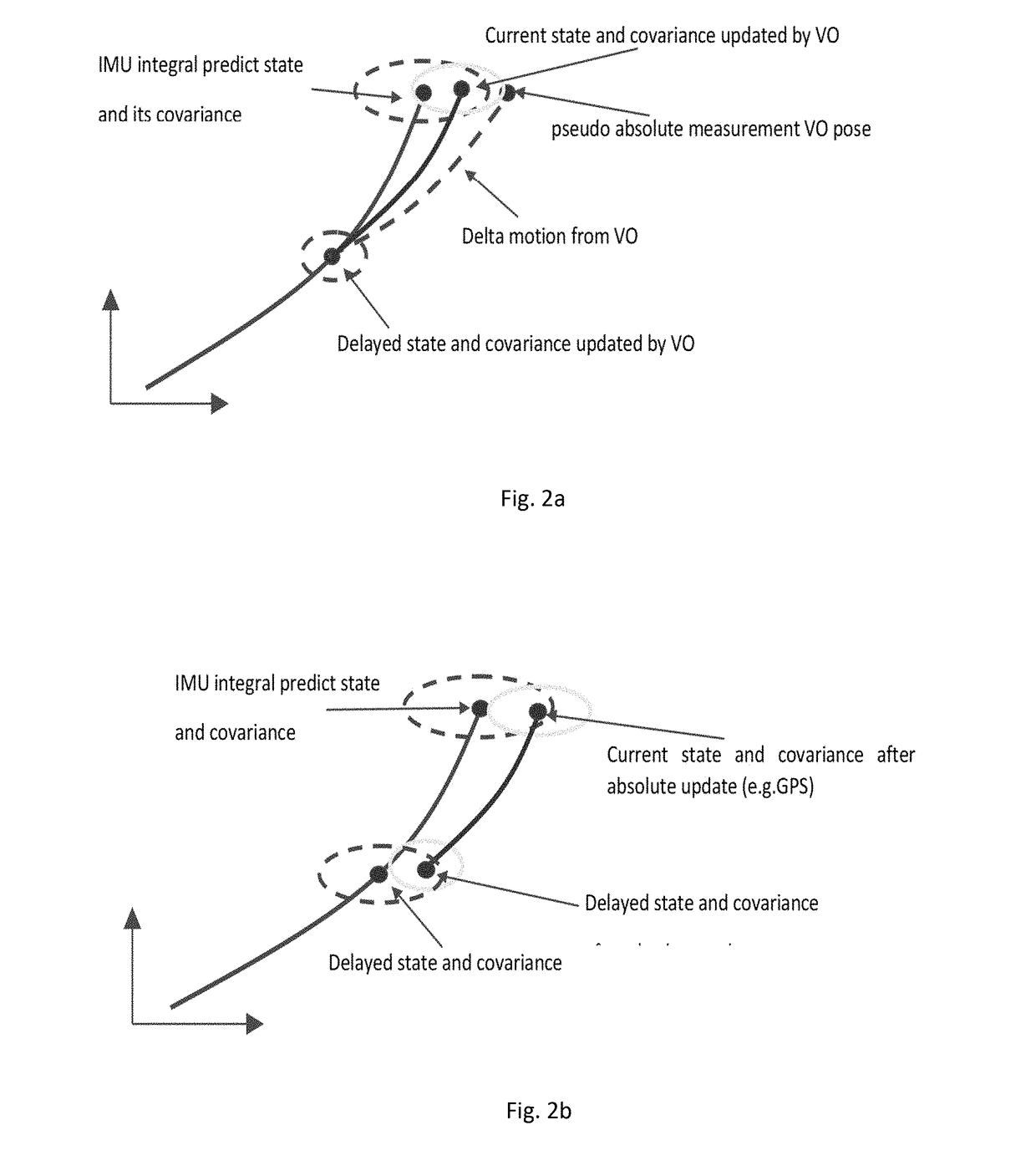
State estimation for aerial vehicles using multi-sensor fusion
ActiveUS20180031387A1Improve robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisSensor fusionVisual perception
A state estimation system that utilizes long-range stereo visual odometry that can degrade to a monocular system at high-altitude, and integrates GPS, Barometer and IMU measurements. The system has two main parts: An EKF that is loosely fused and a long-range visual odometry part. For visual odometry, the system takes the EKF information for robust camera pose tracking, and the visual odometry outputs will be the measurement for EKF state update.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
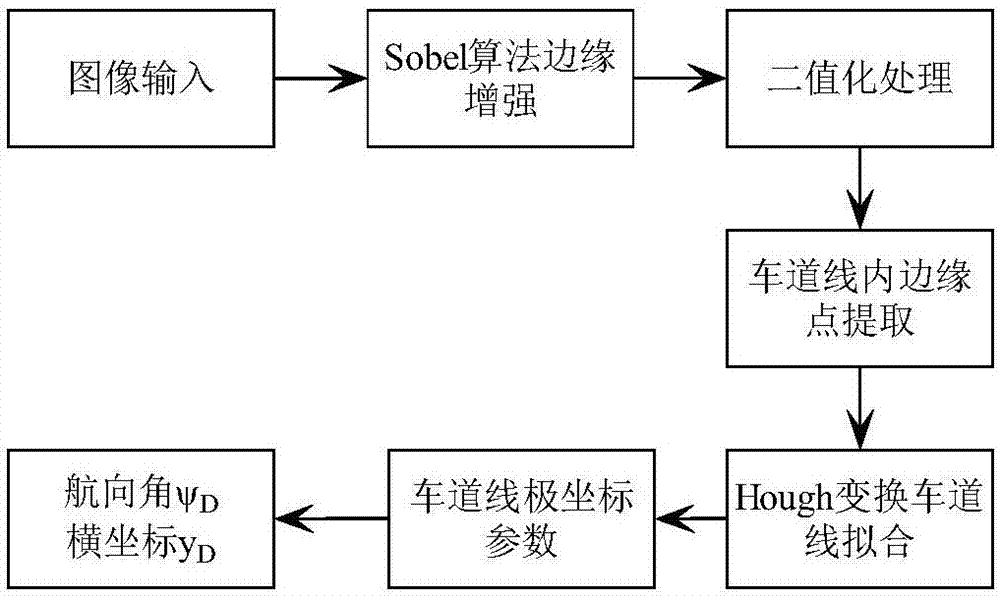
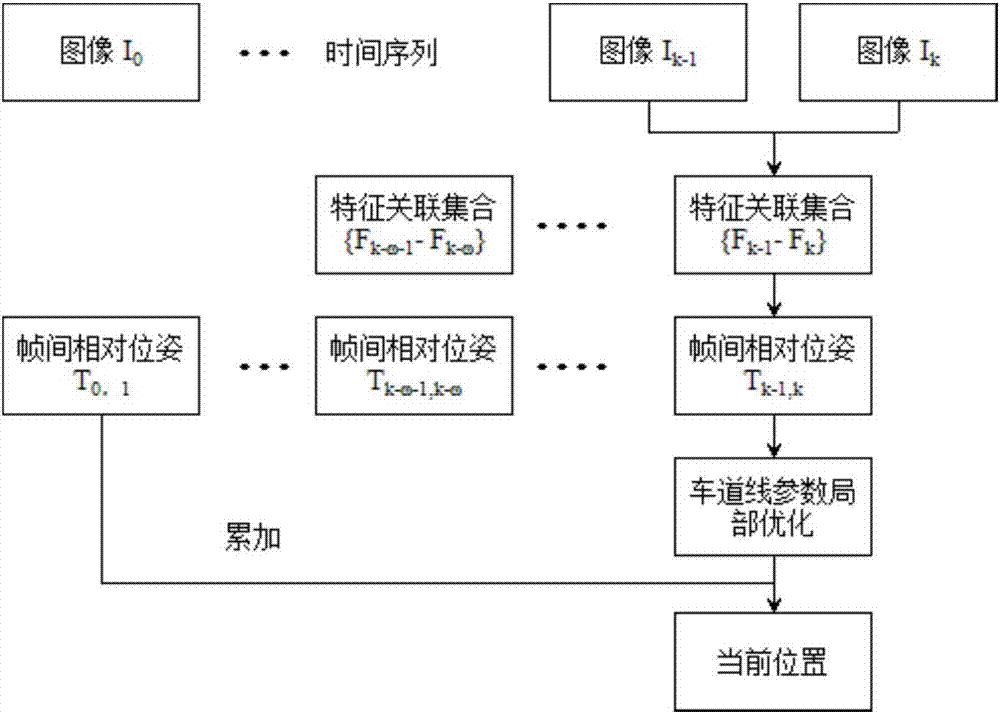
Unmanned vehicle navigation and positioning precision correction method based on GNSS and visual odometry fusion
InactiveCN107229063AHigh positioning accuracySuppression of drift errorsNavigational calculation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingNavigation systemShort terms
The invention relates to an unmanned vehicle navigation and positioning precision correction method based on GNSS and visual odometer fusion. The unmanned vehicle navigation and positioning precision correction method comprises the steps of: (1) detecting lane lines based on monocular vision; (2) optimizing positioning precision of a monocular visual odometer; (3) and correcting positioning precision of a GNSS / VO integrated navigation system. The unmanned vehicle navigation and positioning precision correction method utilizes the lane lines for assisting the visual odometer, then fusing the visual odometer with GNSS positioning to improve the reliability of a vehicle positioning system; the GNSS / VO has a high complementary feature, the GNSS can obtain a long-term stable positioning result, and VO can obtain short-term high-precision positioning data, two sensors are used for filtering a difference value of position measured values, and estimated value of VO system errors is used for correcting errors of the VO system, thereby realizing the purpose of restricting long-term drift of the VO data by utilizing the GNSS data.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Flow Separation for Stereo Visual Odometry
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Sparse direct method-based monocular visual odometry (VO) method of quadrotor unmanned-aerial-vehicle
ActiveCN107341814AImprove battery lifeReduce weightImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionTriangulation
The invention discloses a sparse direct method-based monocular visual odometry (VO) method of a quadrotor unmanned-aerial-vehicle. The method is characterized by: carrying out depth estimation on a key frame, wherein feature points of the key frame are determined by a feature point method, an eigenmatrix between two adjacent frames is calculated, the eigenmatrix is decomposed and a rotation matrix and a translation matrix between the two adjacent frames are calculated to obtain an external parameter matrix, and then depths of the feature points are calculated according to a triangulation method; and after obtaining depth values of the feature points, obtaining the pose of the quadrotor unmanned-aerial-vehicle by solving through a sparse-matrix direct method, and carrying out motion estimation on all frames, wherein sparse feature points are extracted, the direct method is used to calculate a position of each feature point in the next frame, and grayscale information of each pixel point in pixel blocks which have a fixed size and are around the feature points is utilized to optimize grayscale differences between the two adjacent frames to obtain the motion pose of a camera. The method has the advantages that cumulative errors are avoided, higher accuracy is maintained for a long period, and the calculation amount can also be reduced.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
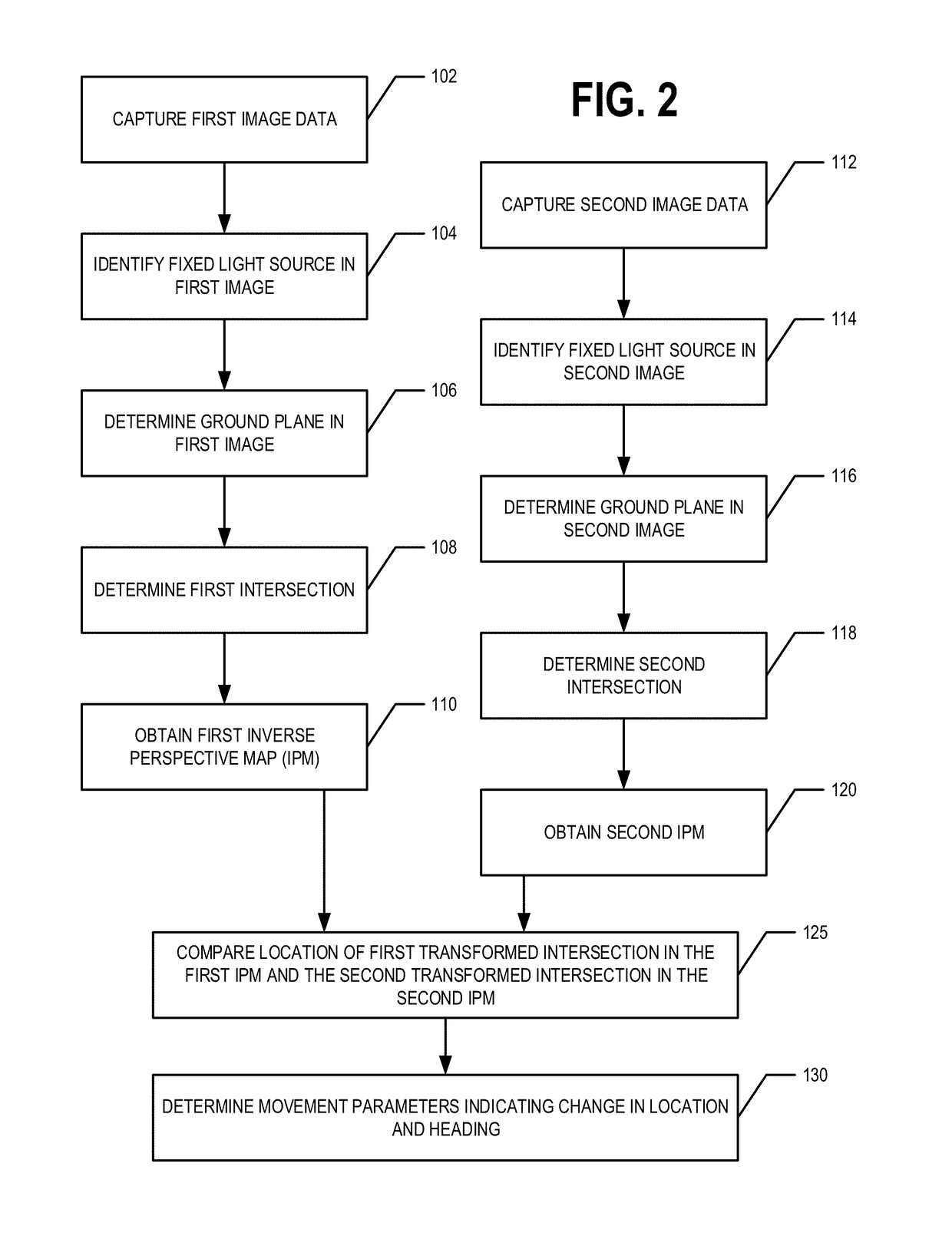
Visual odometry for low illumination conditions using fixed light sources
ActiveUS20180047147A1Sufficient overlapTelevision system detailsImage enhancementIlluminanceMotion parameter
First and second image data is captured comprising a first and second image, respectively. A fixed light source is identified in each of the first and second images. A first ground plane is determined in the first image data. A first (second) intersection is determined, wherein the first (second) intersection is a point in the first image where a virtual lamp post corresponding to the fixed light source in the first (second) image intersects with the first (second) ground plane. The first image data and the second image data are transformed to provide a first and second inverse perspective map (IPM) comprising a first transformed intersection and a second transformed intersection, respectively. Movement parameters are determined based on the location of the first transformed intersection in the first IPM and the location of the second transformed intersection in the second IPM.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
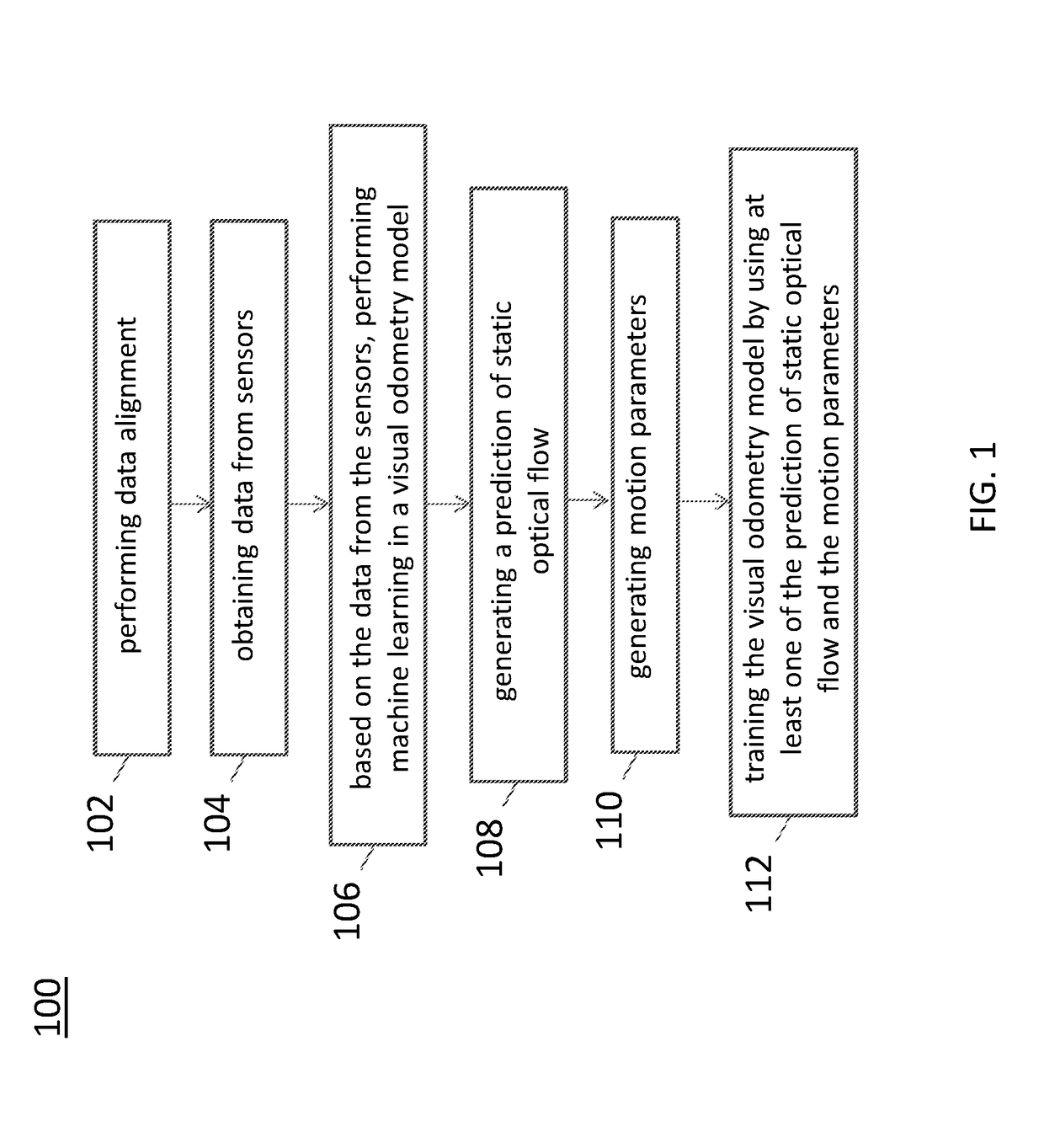
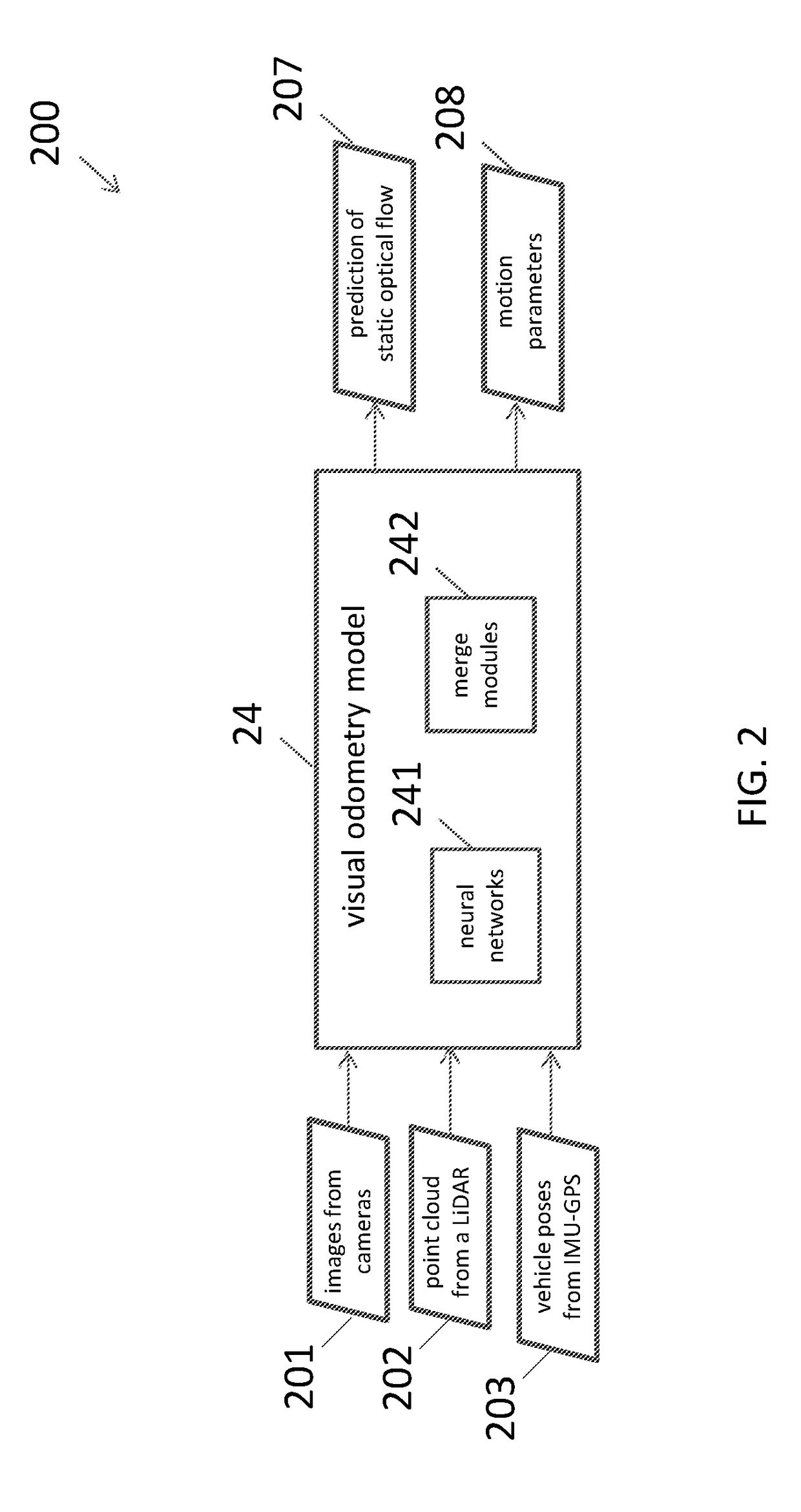
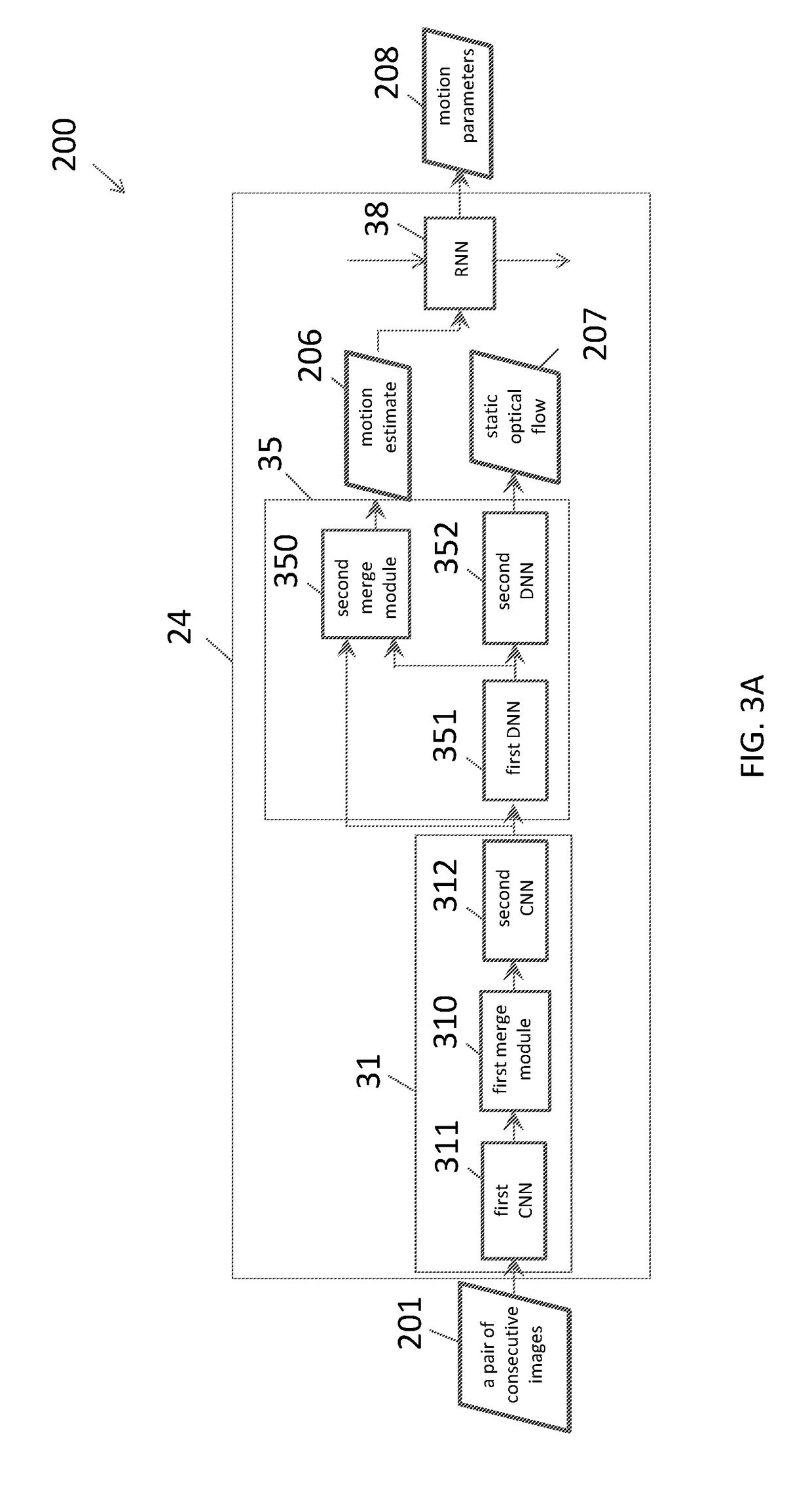
Neural network architecture system for deep odometry assisted by static scene optical flow
ActiveUS20190079534A1Reduce accumulated errorsImage enhancementInstruments for road network navigationStructure of Management InformationNetwork architecture
A system for visual odometry is disclosed. The system includes: an internet server, comprising: an I / O port, configured to transmit and receive electrical signals to and from a client device; a memory; one or more processing units; and one or more programs stored in the memory and configured for execution by the one or more processing units, the one or more programs including instructions for: extracting representative features from a pair input images in a first convolution neural network (CNN) in a visual odometry model; merging, in a first merge module, outputs from the first CNN; decreasing feature map size in a second CNN; generating a first flow output for each layer in a first deconvolution neural network (DNN); merging, in a second merge module, outputs from the second CNN and the first DNN; generating a second flow output for each layer in a second DNN; and reducing accumulated errors in a recurrent neural network (RNN).
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
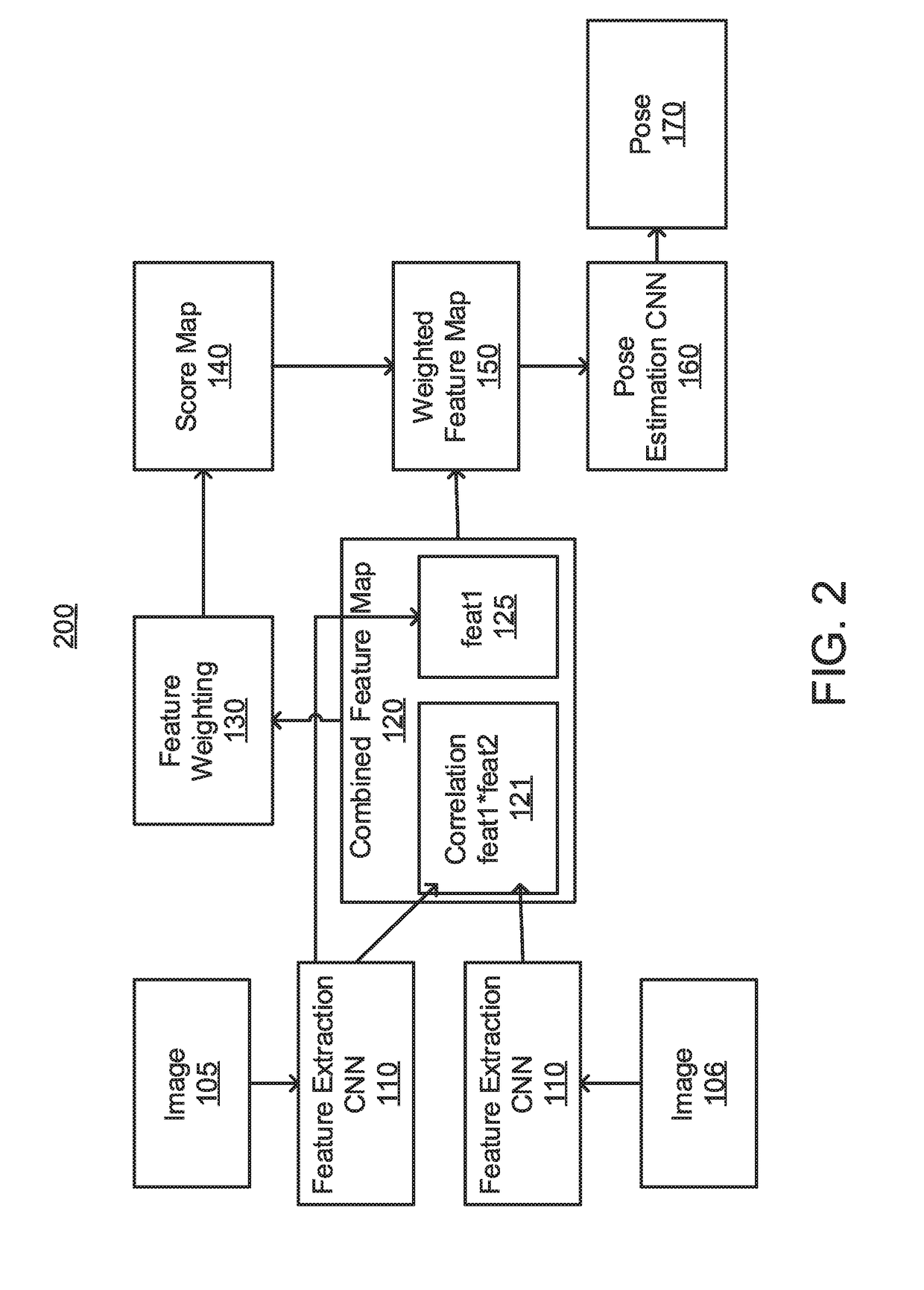
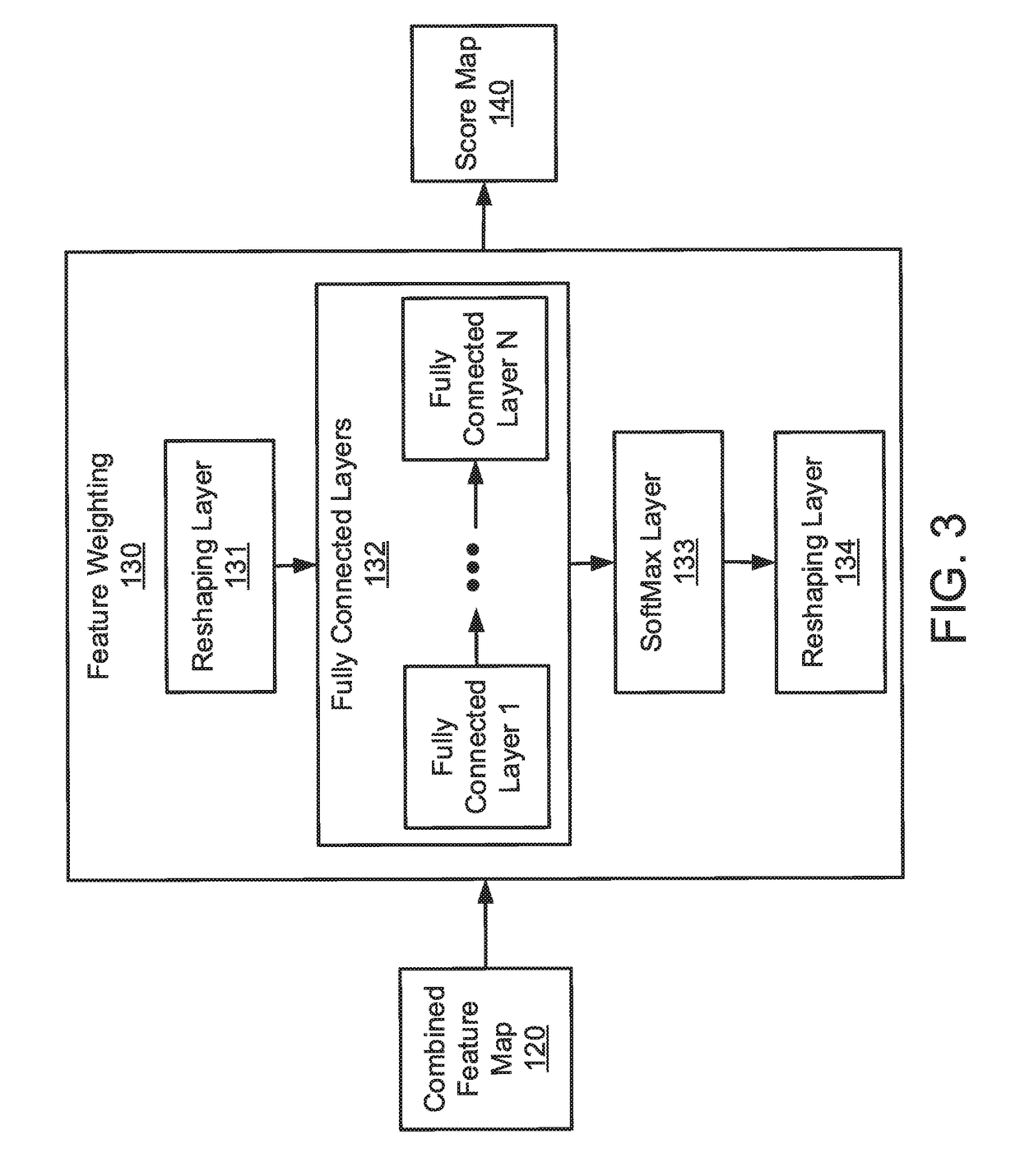
Learning good features for visual odometry
ActiveUS20190066326A1Image enhancementAutonomous decision making processFeature extractionPostural orientation
A computer-implemented method, system, and computer program product are provided for pose estimation. The method includes receiving, by a processor, a plurality of images from one or more cameras. The method also includes generating, by the processor with a feature extraction convolutional neural network (CNN), a feature map for each of the plurality of images. The method additionally includes estimating, by the processor with a feature weighting network, a score map from a pair of the feature maps. The method further includes predicting, by the processor with a pose estimation CNN, a pose from the score map and a combined feature map. The method also includes controlling an operation of a processor-based machine to change a state of the processor-based machine, responsive to the pose.
Owner:NEC CORP
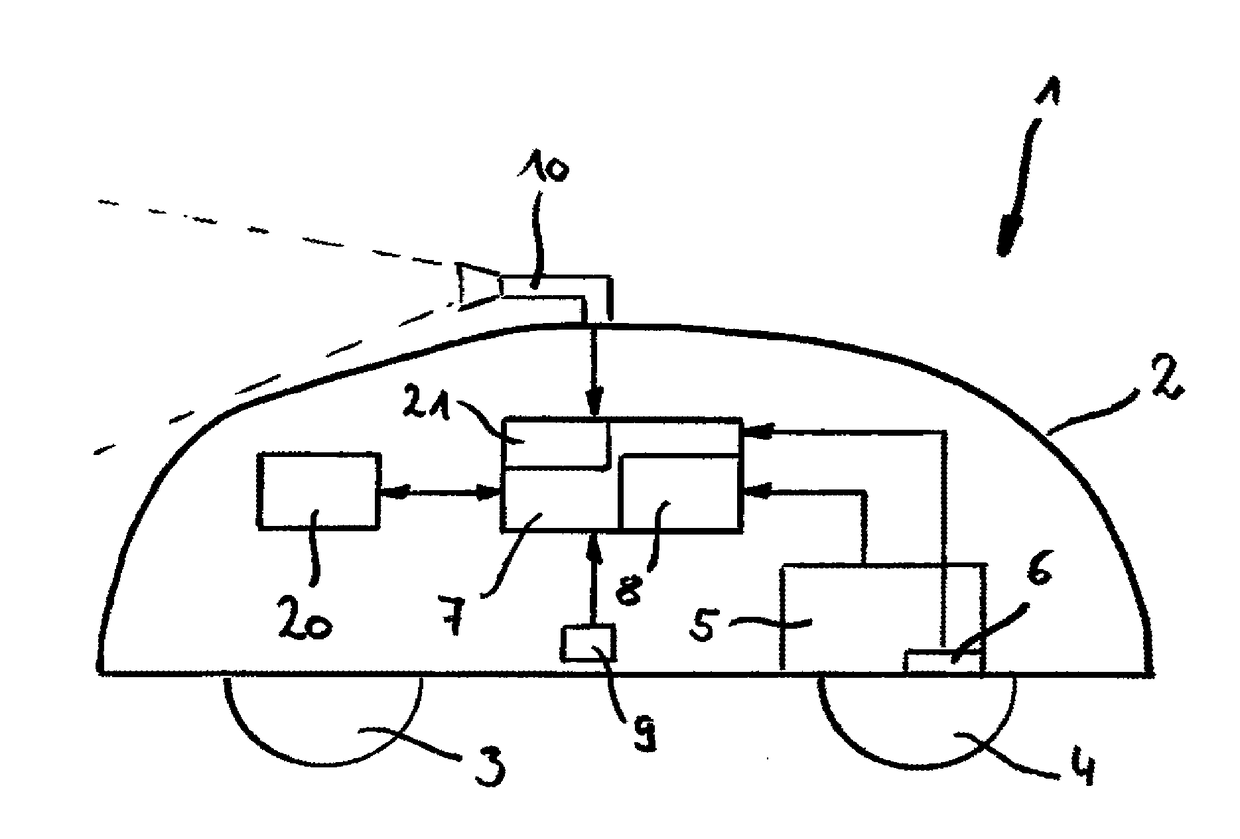
Autonomous working machine such as autonomous lawn mower
ActiveUS20170188510A1Improve performanceSolve the lack of precisionImage enhancementImage analysisEngineeringRobotic lawn mower
The invention regards an autonomous working machine comprising drive means, current position estimation means, control means including a driving control unit and a camera. With aid of the current position estimation means the current position of the autonomous working machine is estimated. Furthermore, the driving control unit generates driving commands for the driving means on the basis of an intended movement of the autonomous working machine and the estimated current position. The camera is configured to capture images of the environment of the working machine. For estimating the current position, the current position estimation means is formed by the control means, which is configured to apply visual odometry on the captured images for estimating the current position of the working machine.
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE
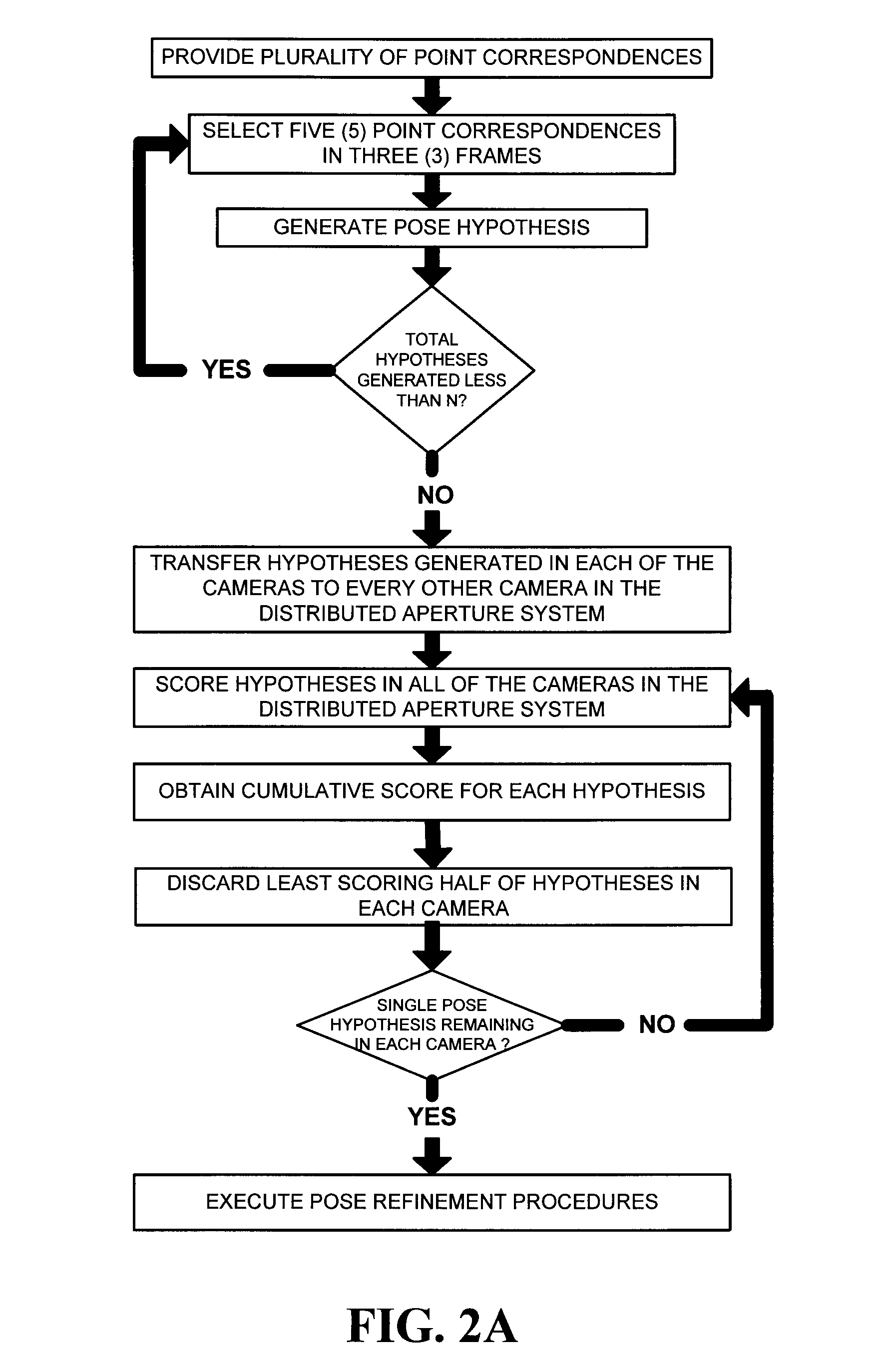
System and method for multi-camera visual odometry
ActiveUS8305430B2High degreeHigh precisionTelevision system detailsSteroscopic systemsMulti cameraPostural orientation
A visual odometry system and method for a fixed or known calibration of an arbitrary number of cameras in monocular configuration is provided. Images collected from each of the cameras in this distributed aperture system have negligible or absolutely no overlap. The relative pose and configuration of the cameras with respect to each other are assumed to be known and provide a means for determining the three-dimensional poses of all the cameras constrained in any given single camera pose. The cameras may be arranged in different configurations for different applications and are made suitable for mounting on a vehicle or person undergoing general motion. A complete parallel architecture is provided in conjunction with the implementation of the visual odometry method, so that real-time processing can be achieved on a multi-CPU system.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Output of a neural network method for deep odometry assisted by static scene optical flow
A method of visual odometry for a non-transitory computer readable storage medium storing one or more programs is disclosed. The one or more programs includes instructions, which when executed by a computing device, causes the computing device to perform the following steps comprising: performing data alignment among sensors including a LiDAR, cameras and an IMU-GPS module; collecting image data and generating point clouds; processing, in the IMU-GPS module, a pair of consecutive images in the image data to recognize pixels corresponding to a same point in the point clouds; and establishing an optical flow for visual odometry.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
Intelligent cleaning robot
An intelligent, autonomous interior cleaning robot capable of autonomously mapping and cleaning multiple rooms in a house in an intelligent manner is described. Various combinations of passive and active sensors may be used to perform mapping, localization, and obstacle avoidance. In particular, the robot uses stereo cameras with a static projected light pattern to generate 3D data. In addition, the robot may use optical sensors in various locations, laser ToF sensors, inertial measurement units and visual odometry to enhance the localization and mapping capabilities.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Full cycle visual SLAM algorithm using CNNs feature detection
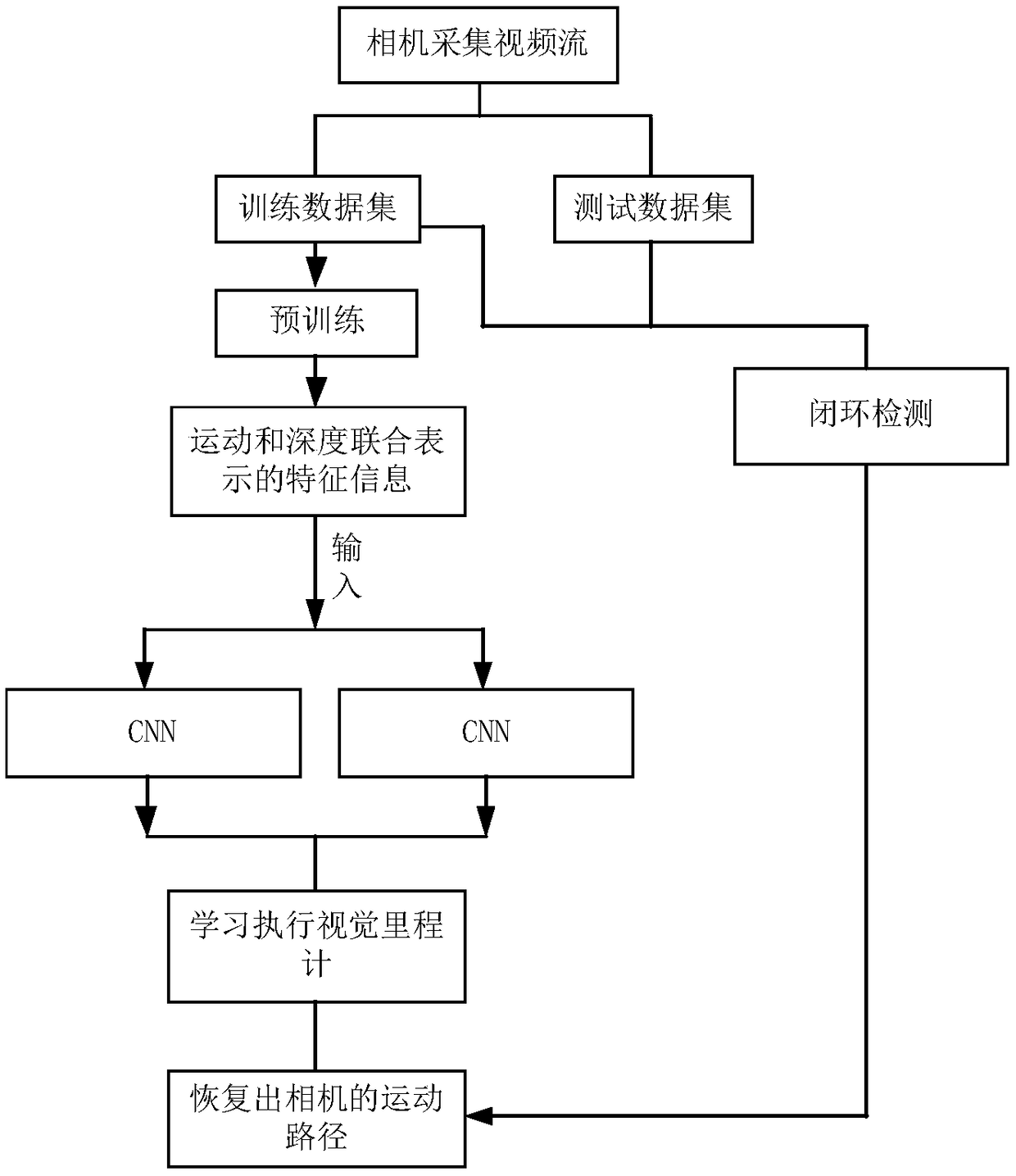
ActiveCN109341703AFast online computingGood location recognitionInstruments for road network navigationCharacter and pattern recognitionFull cycleNetwork architecture
The invention discloses a full-cycle visual SLAM algorithm using CNNs feature detection. First, in the front end, the original image data is pre-trained by an unsupervised model, and then the pre-trained data is used through CNN network architecture to correlate the joint representation of motion and depth with the changes in local velocity and direction, thus executing the visual odometry. Finally, the path prediction is performed. The invention also uses the OverFeat neural network model for loop detection to eliminate the accumulated errors caused by the front end and constructs a visual SLAM architecture based on deep learning. At the same time, a time and space continuity filter is constructed to verify the matching results, improve the matching accuracy and eliminate mismatching. Theinvention has tremendous advantages and potentials in improving the accuracy of visual odometry and the correct rate of closed-loop detection.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
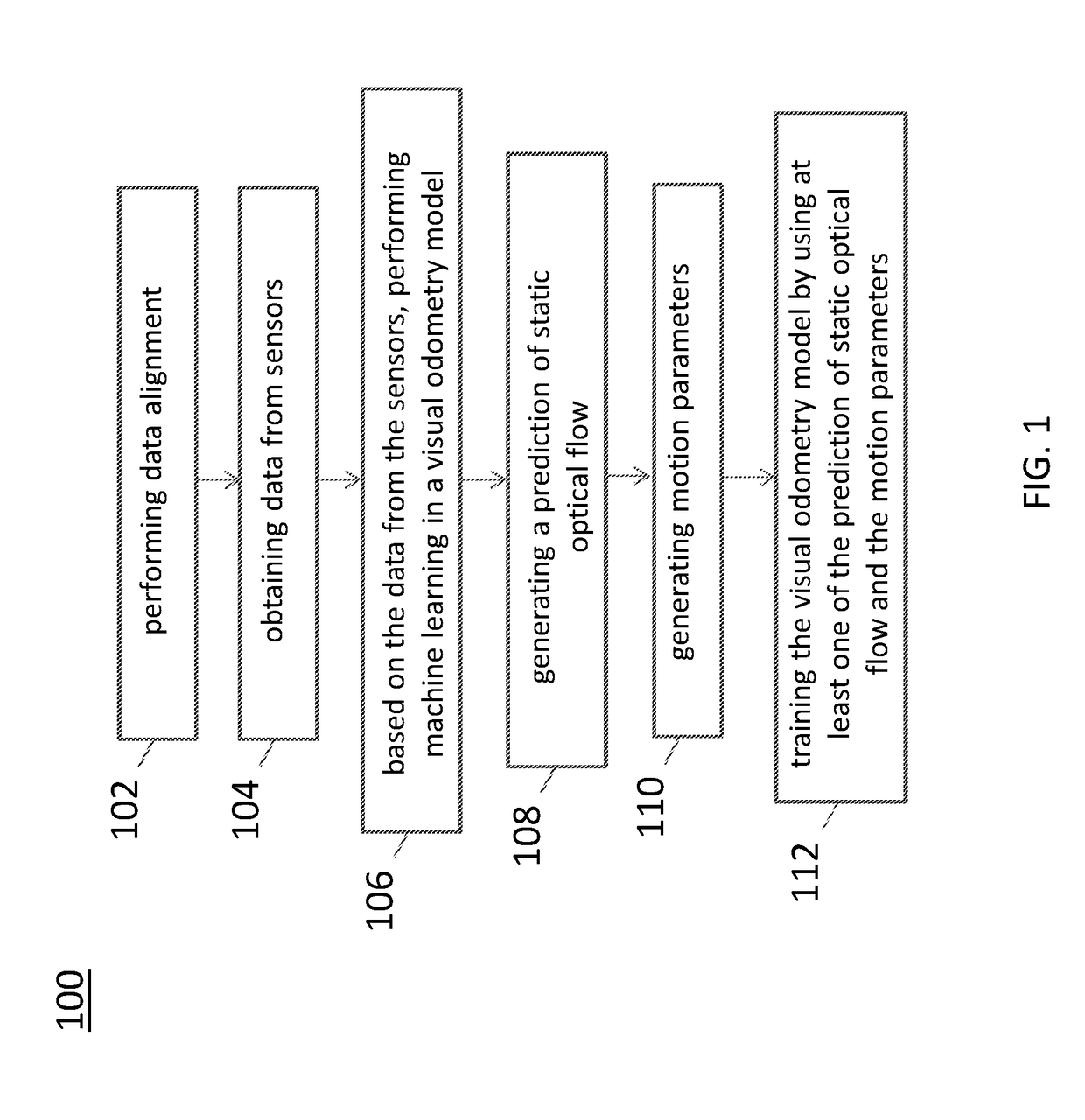
Training and testing of a neural network system for deep odometry assisted by static scene optical flow
A system for visual odometry is provided. The system includes: an internet server, comprising: an I / O port, configured to transmit and receive electrical signals to and from a client device; a memory; one or more processing units; and one or more programs stored in the memory and configured for execution by the one or more processing units, the one or more programs including instructions for: in response to images in pairs, generating a prediction of static scene optical flow for each pair of the images in a visual odometry model; generating a set of motion parameters for each pair of the images in the visual odometry model; training the visual odometry model by using the prediction of static scene optical flow and the motion parameters; and predicting motion between a pair of consecutive image frames by the trained visual odometry model.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
Method and system for scanning an object using an rgb-d sensor
ActiveUS20170287162A1Precise alignmentAccurate distinctionImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionVisual perception
A method and system for scanning an object using an RGB-D sensor, the method includes: a plurality of elementary scans of the object using an RGB-D sensor and visual odometry, each elementary scan delivering a plurality of key frames associated with a pose of the sensor with respect to the object, and each elementary scan being associated with a position of the object; for each elementary scan, elaborating a three-dimensional model of the object using the plurality of key frames and poses of the scan; merging each three-dimensional model into a merged three-dimensional model of the object.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
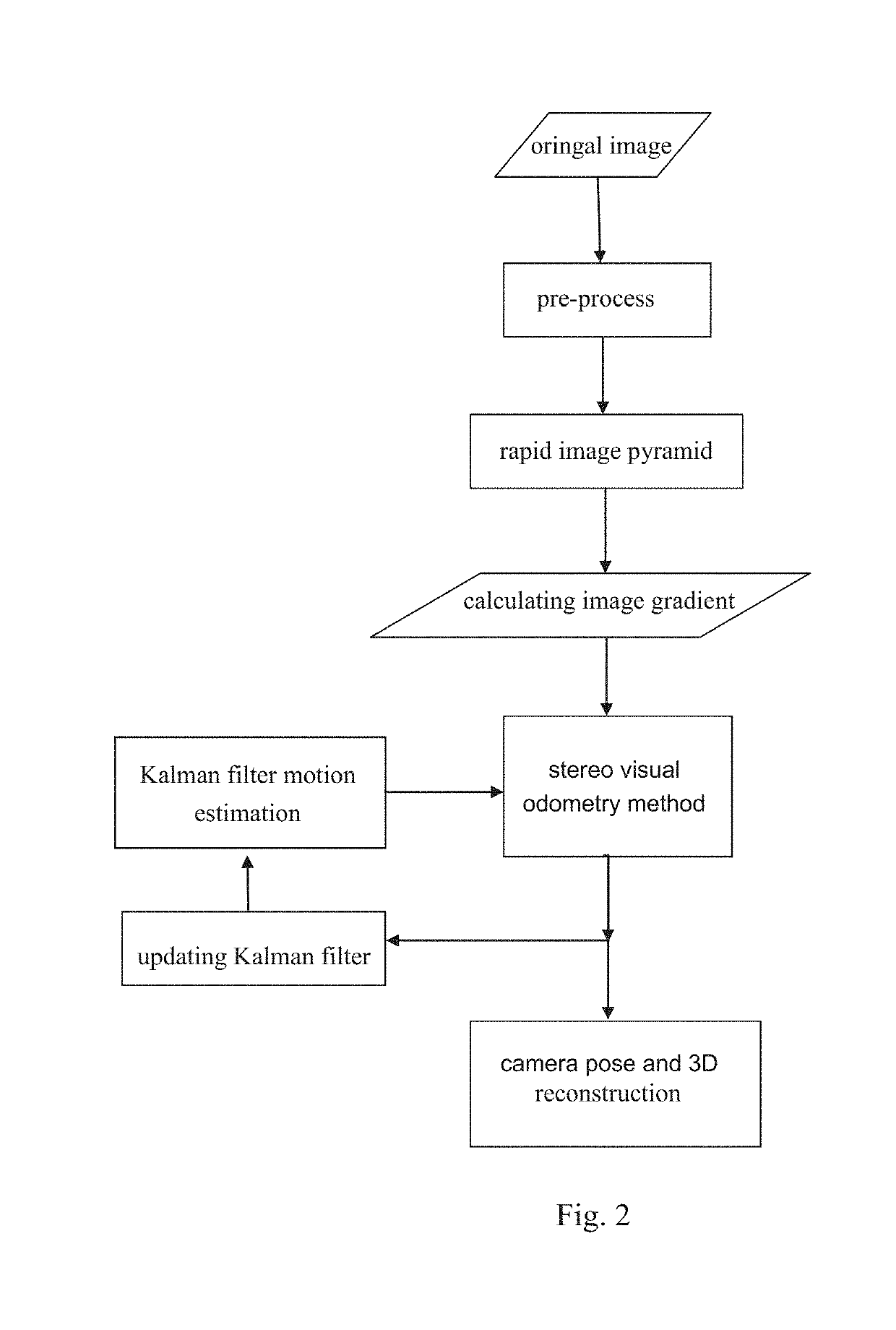
Stereo visual odometry method based on image gradient joint optimization
ActiveUS20190333231A1Reduce computing costImprove system performanceImage enhancementImage analysisKaiman filterImage gradient
A stereo visual odometry method based on image gradient joint optimization includes steps of: pre-processing each frame of images of a stereo video input; calculating a stereo image disparity map of a stereo video frame, and obtaining a metric distance; scaling to form scale images with different scales for forming a pyramid model, and calculating features to obtain a series of feature images; processing the images with a Kalman filter according to the metric distance, so to predict and estimate a motion process of a camera pose, wherein camera motion models is built in the Kalman filter; accurately calculating a camera pose of a current frame by using a gradient-based stereo visual navigation method; and updating the camera motion models in the Kalman filter with the camera pose of the current frame.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Visual odometry for low illumination conditions using fixed light sources
First and second image data is captured comprising a first and second image, respectively. A fixed light source is identified in each of the first and second images. A first ground plane is determined in the first image data. A first (second) intersection is determined, wherein the first (second) intersection is a point in the first image where a virtual lamp post corresponding to the fixed light source in the first (second) image intersects with the first (second) ground plane. The first image data and the second image data are transformed to provide a first and second inverse perspective map (IPM) comprising a first transformed intersection and a second transformed intersection, respectively. Movement parameters are determined based on the location of the first transformed intersection in the first IPM and the location of the second transformed intersection in the second IPM.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
Method for stereo visual odometry using points, lines and planes
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
System and method for vehicle convoys
ActiveUS20190088142A1Use of such equipmentReduce inaccuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSteering partsComputer moduleVisual perception
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for use in a non-lead vehicle in a convoy, particularly an off-road convoy. The system comprises an image handling module adapted to obtain non-lead image data of the scene in the vicinity of the non-lead vehicle; a communications module adapted to receive data from a preceding vehicle in the convoy, the data comprising at least lead image data of the scene in the vicinity of the preceding vehicle; a processing module adapted to: obtain pose data of the preceding vehicle and a sparse map, both derived from the lead image data, wherein the sparse map comprises coordinates of a set of identifying features in the scene, and derive pose data of the non-lead vehicle relative to the preceding vehicle from the non-lead image data and the sparse map via visual odometry.
Owner:JAGUAR LAND ROVER LTD
Autonomous navigation using visual odometry
A system and method are provided for autonomously navigating a vehicle. The method captures a sequence of image pairs using a stereo camera. A navigation application stores a vehicle pose (history of vehicle position). The application detects a plurality of matching feature points in a first matching image pair, and determines a plurality of corresponding object points in three-dimensional (3D) space from the first image pair. A plurality of feature points are tracked from the first image pair to a second image pair, and the plurality of corresponding object points in 3D space are determined from the second image pair. From this, a vehicle pose transformation is calculated using the object points from the first and second image pairs. The rotation angle and translation are determined from the vehicle pose transformation. If the rotation angle or translation exceed a minimum threshold, the stored vehicle pose is updated.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com