Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
125 results about "Tubular solid oxide fuel cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
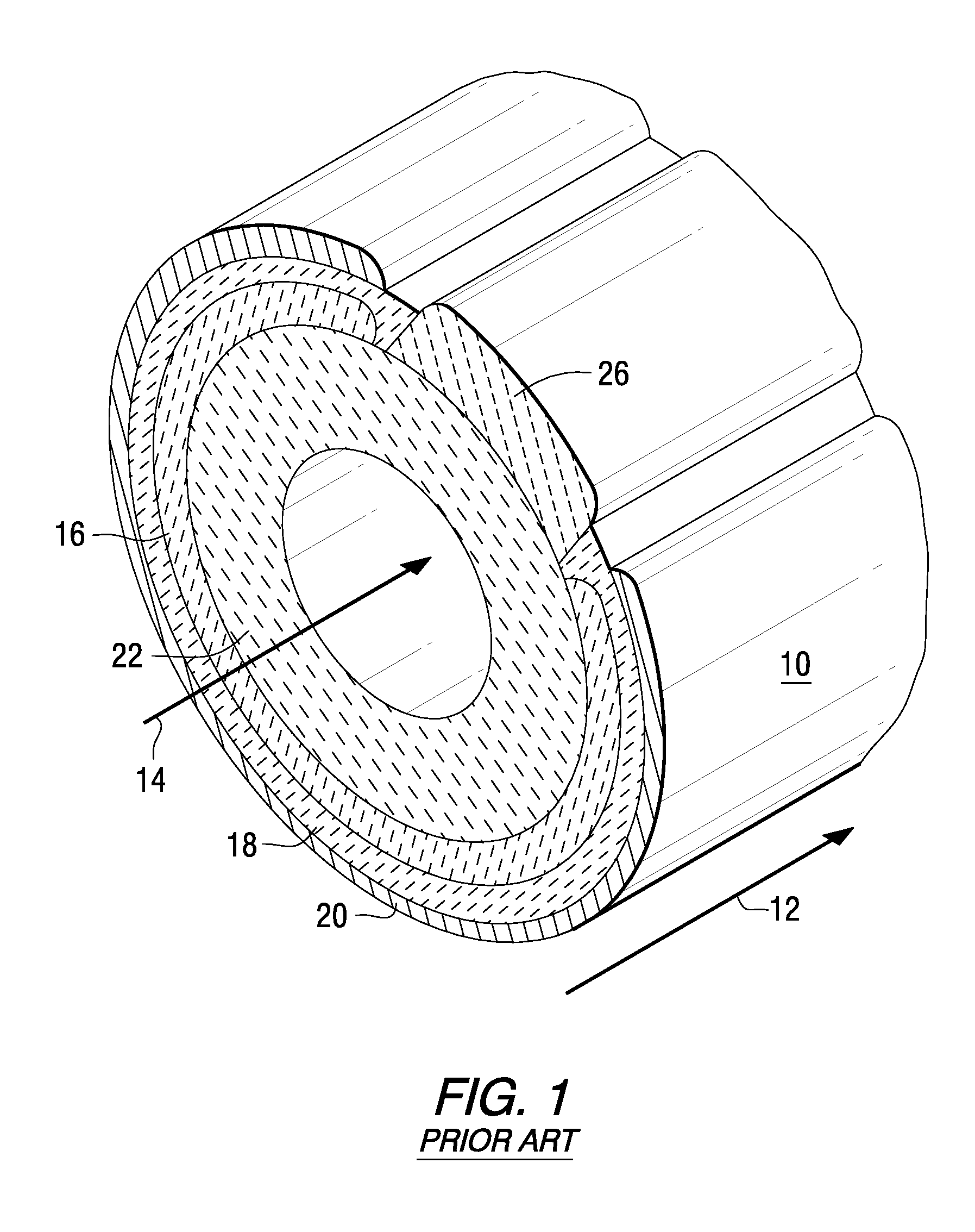
Integrated solid oxide fuel cell and reformer
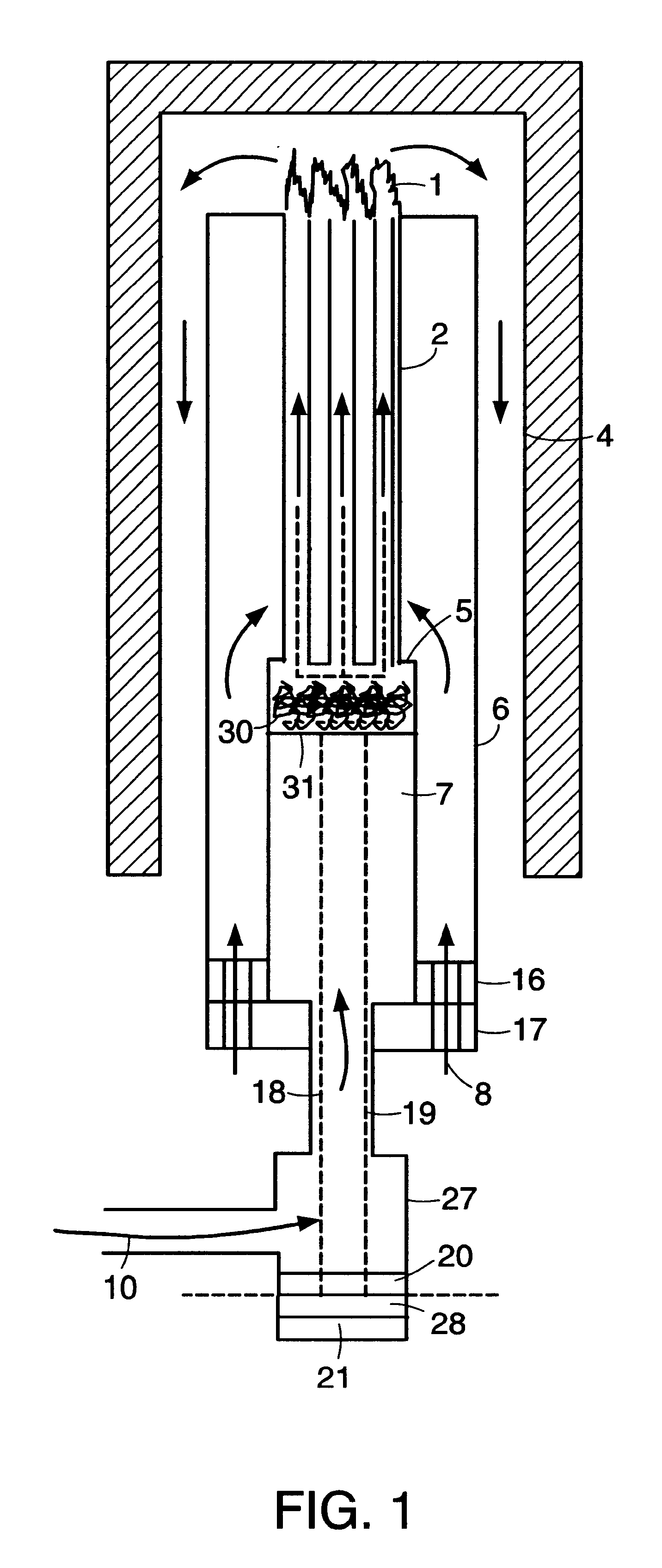
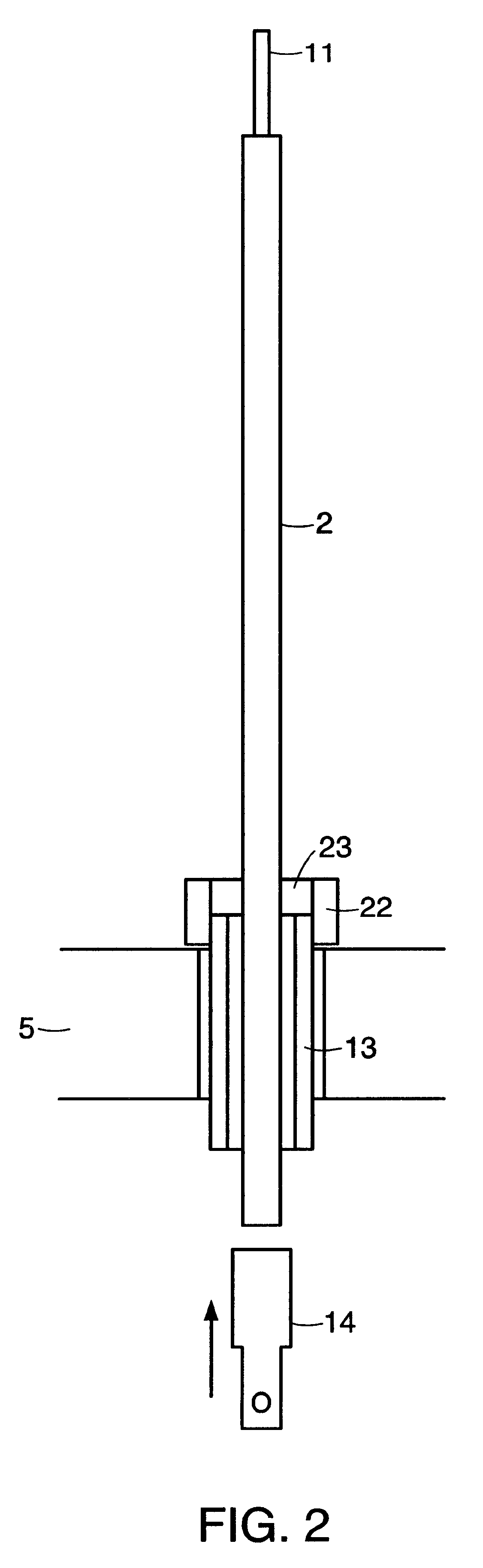
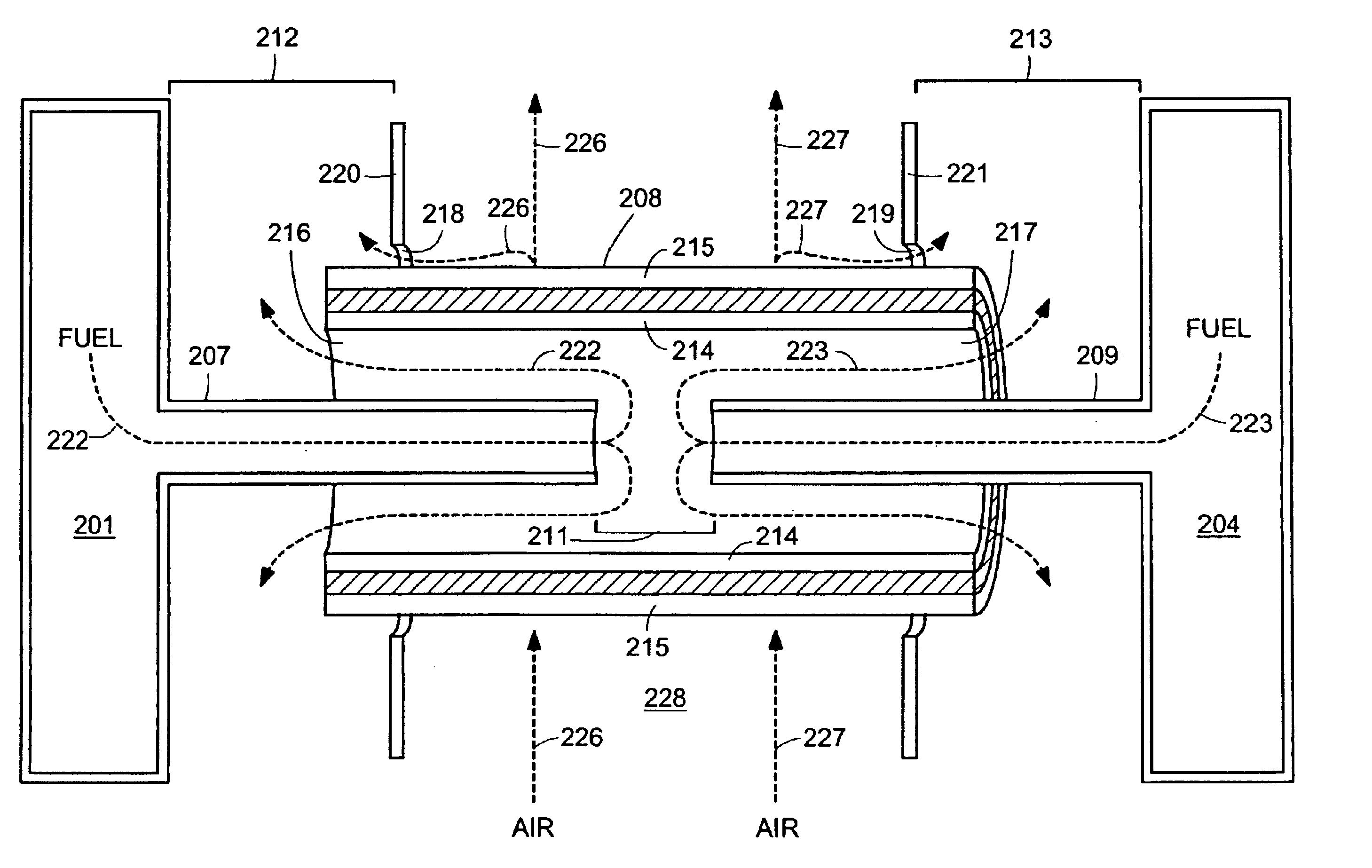
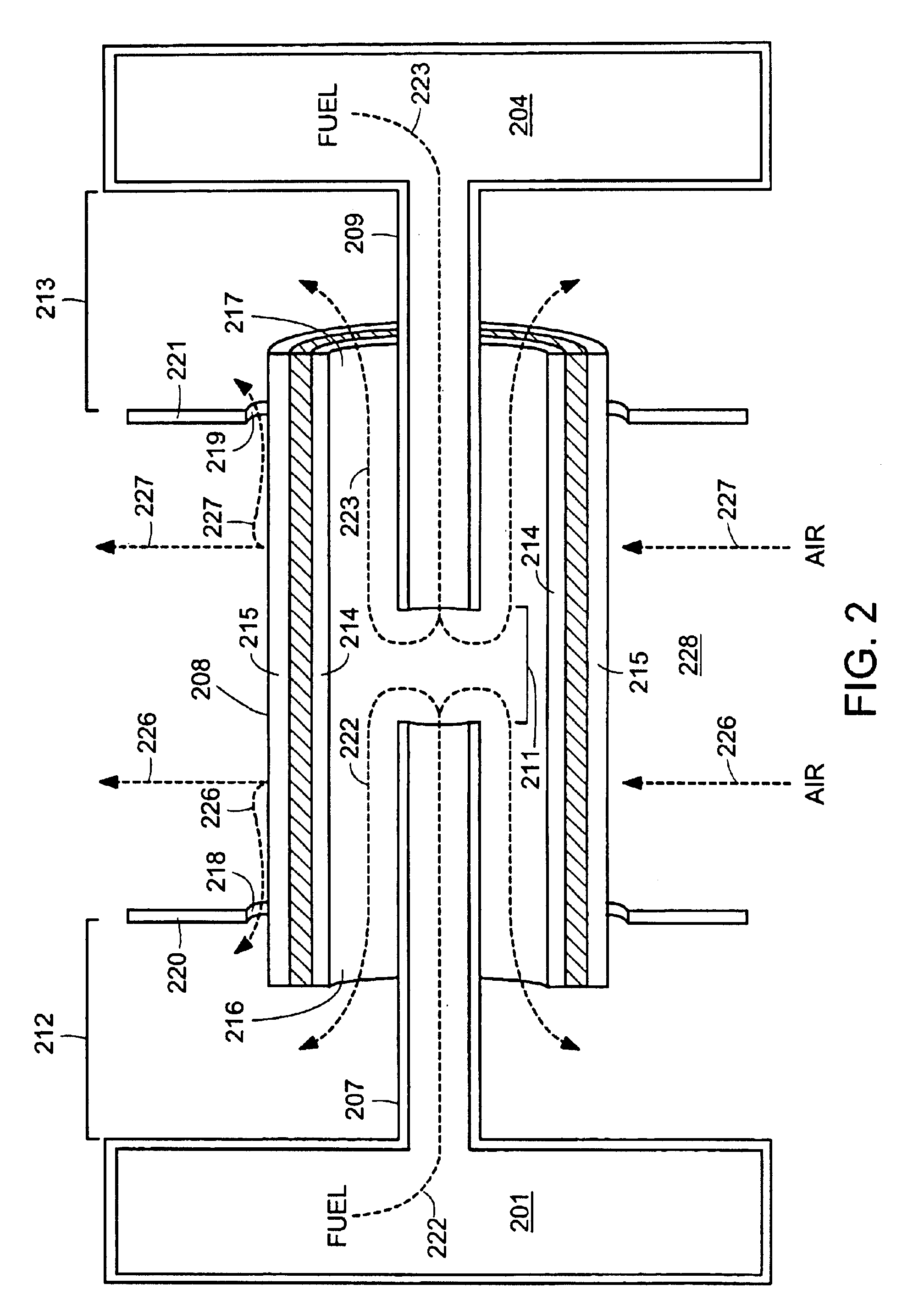
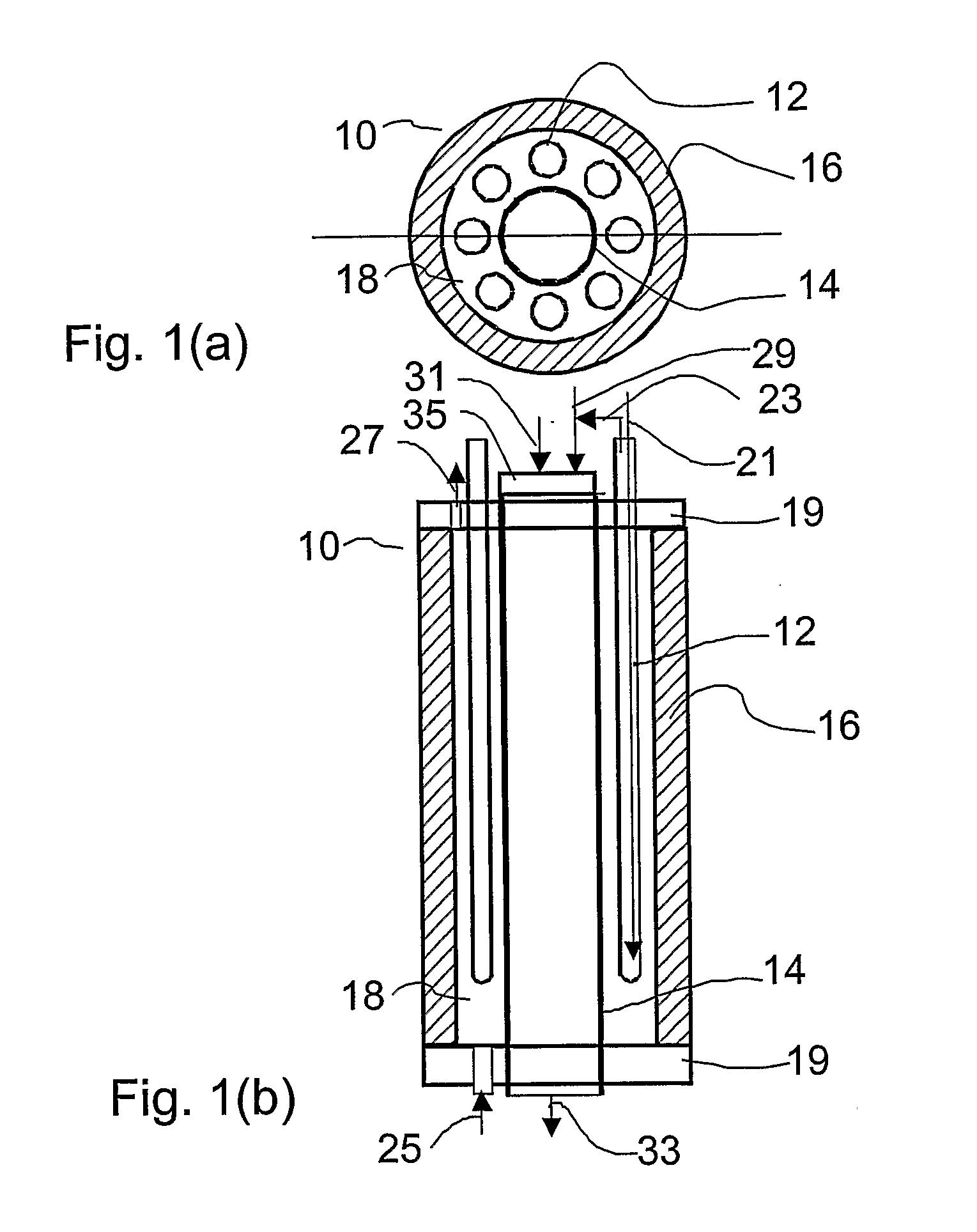
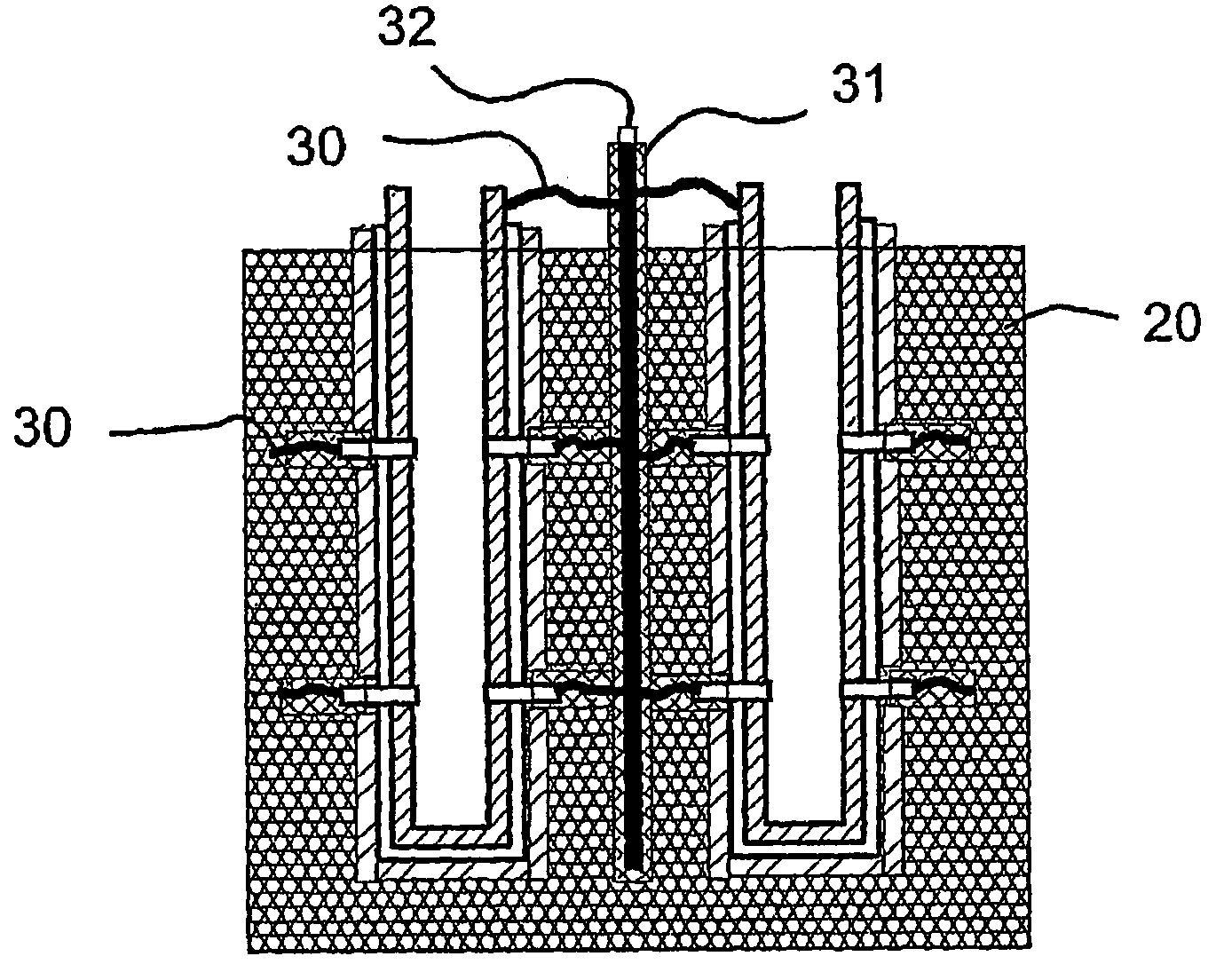
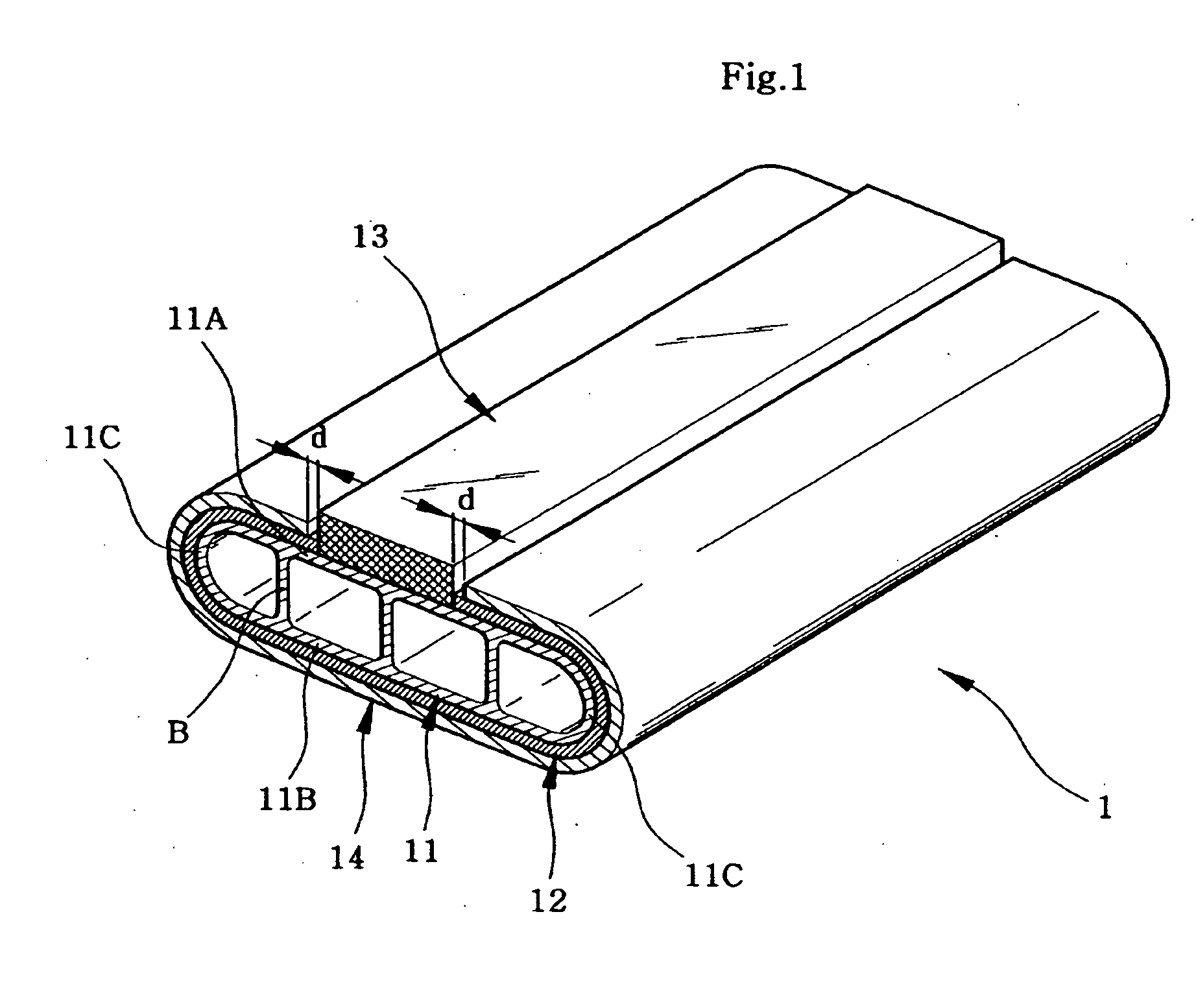
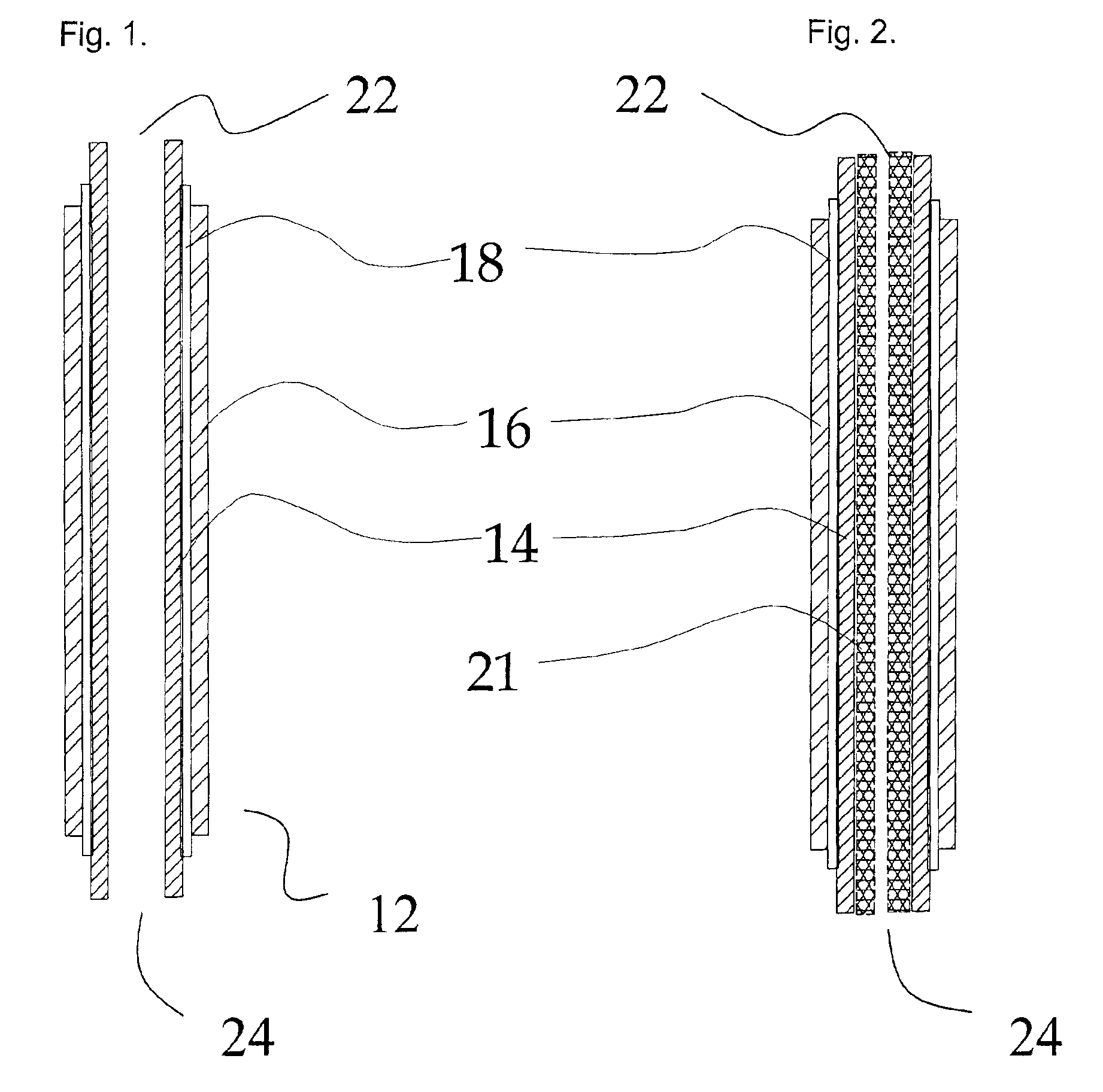
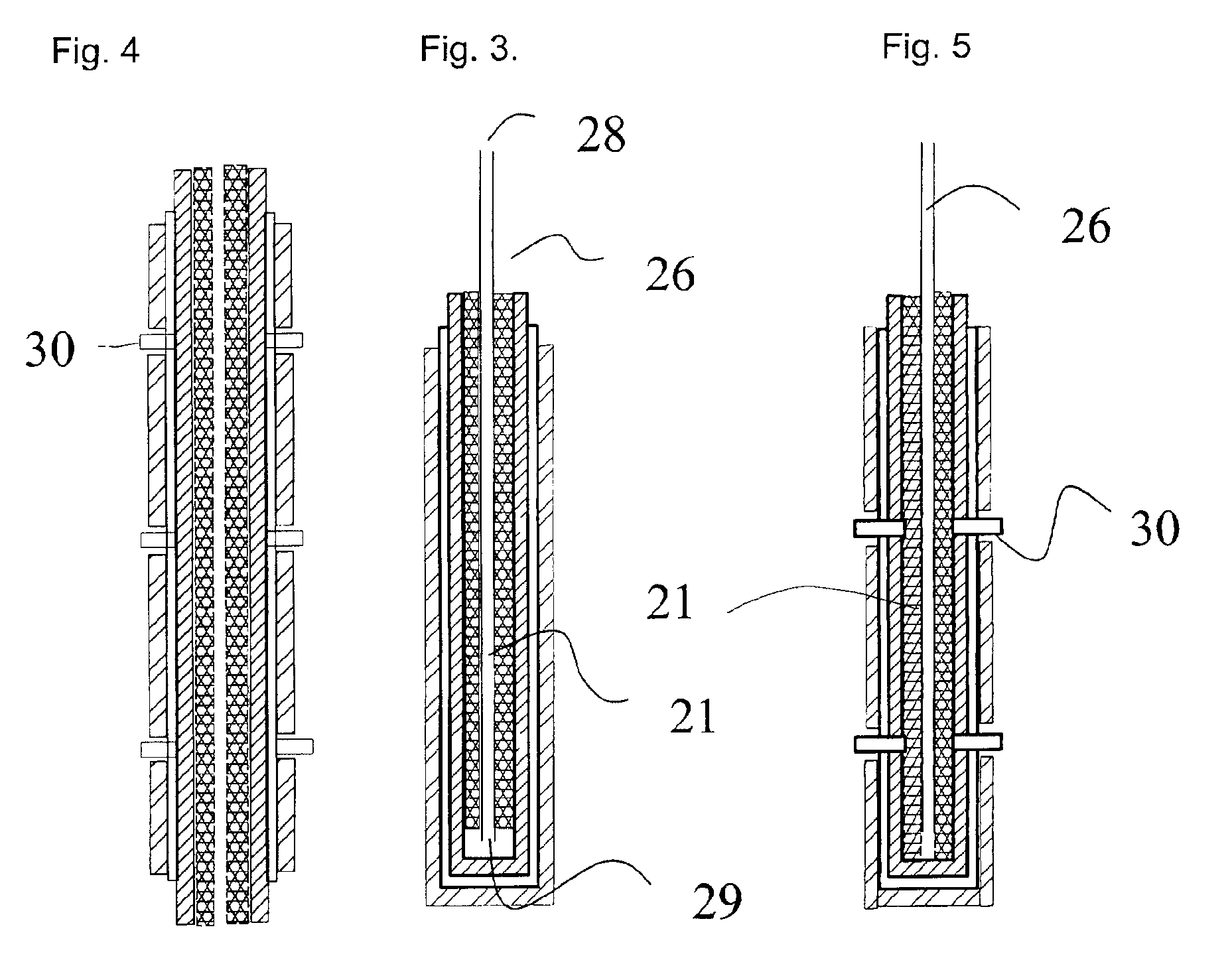
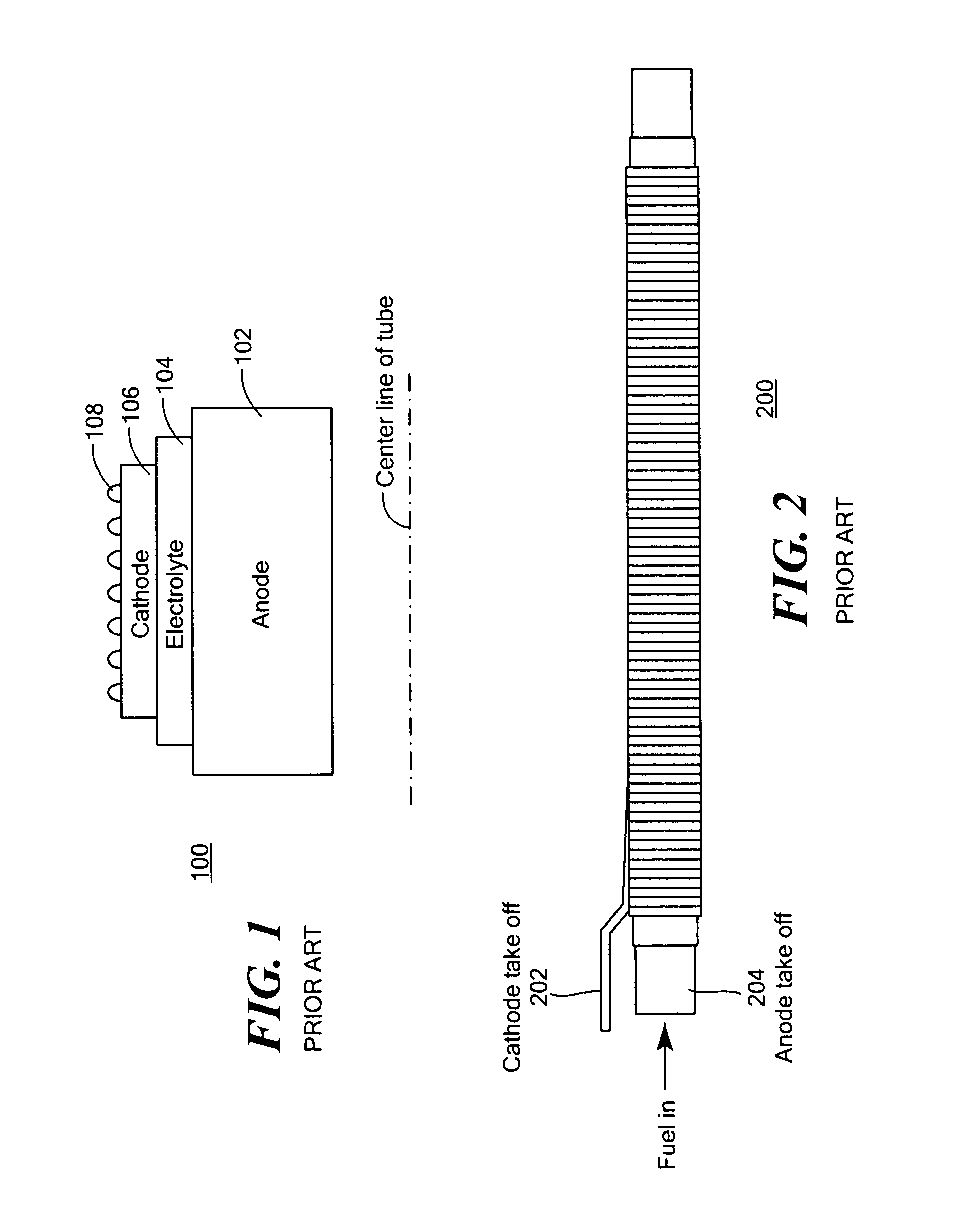
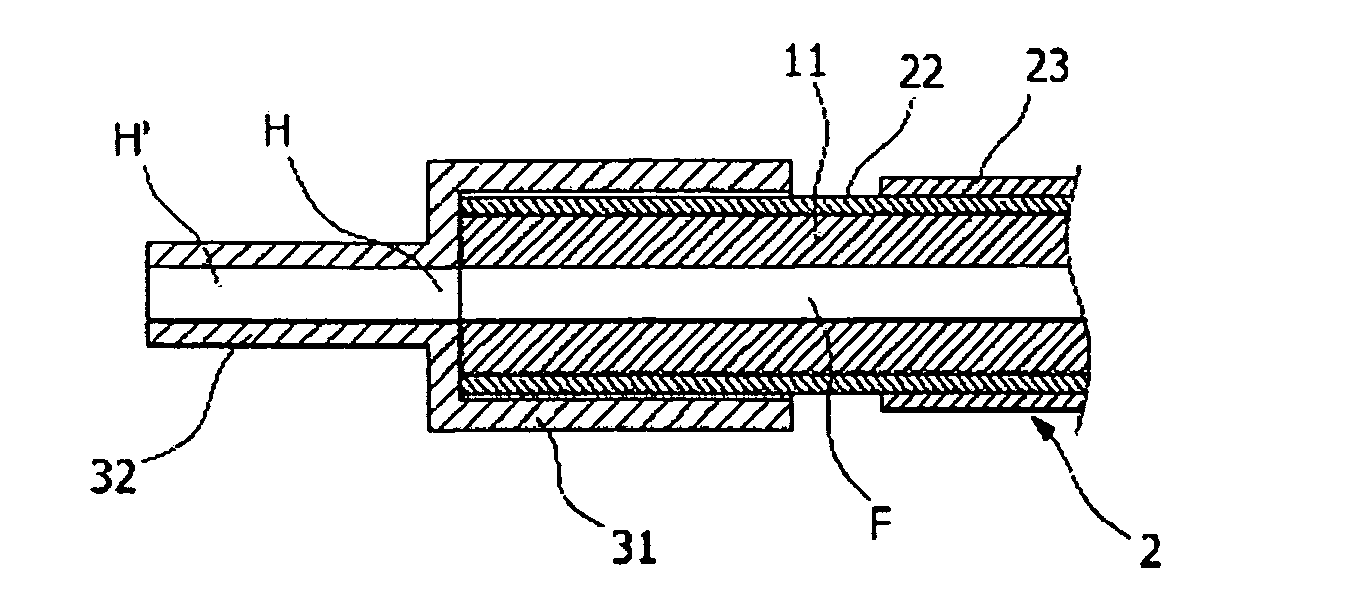
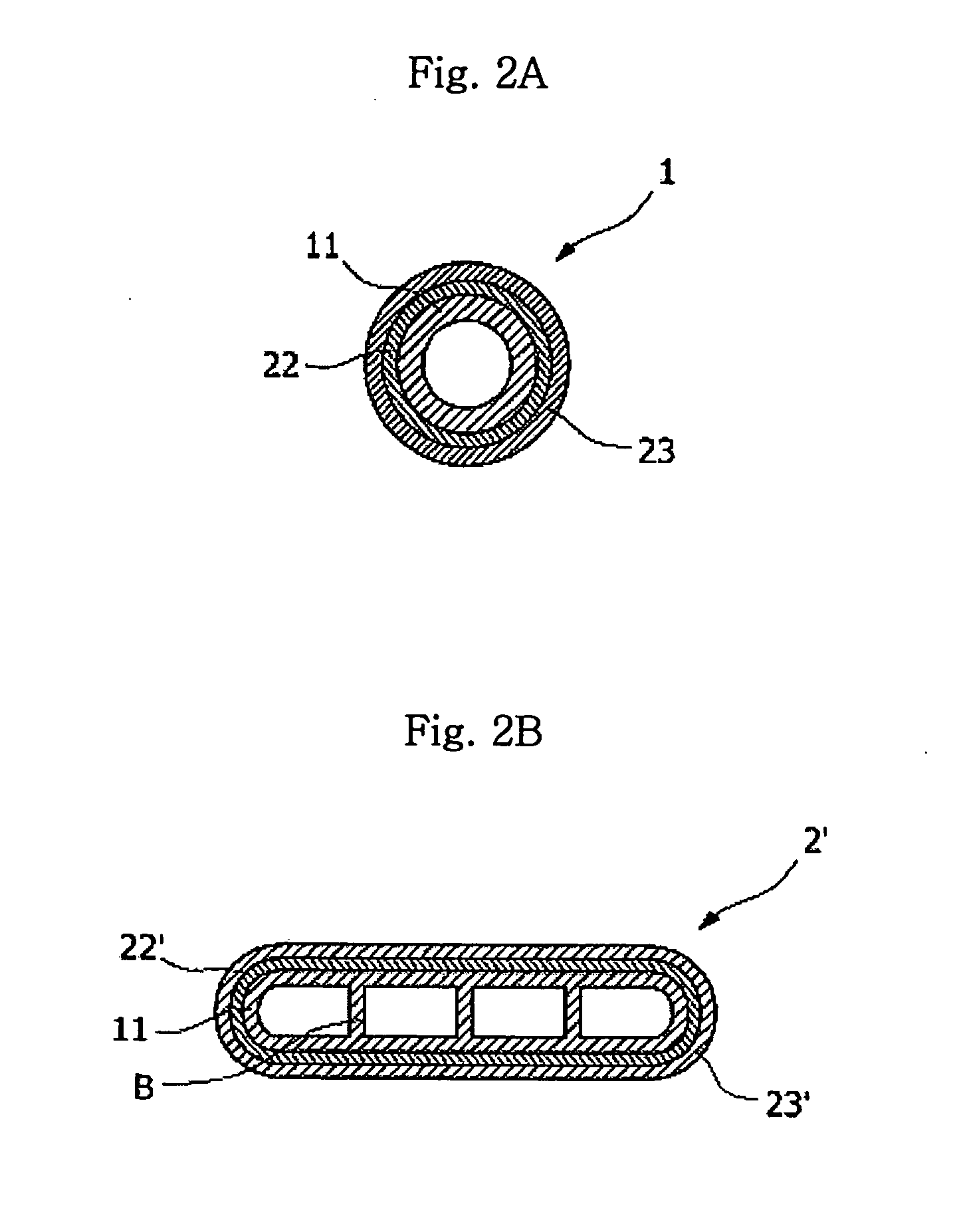
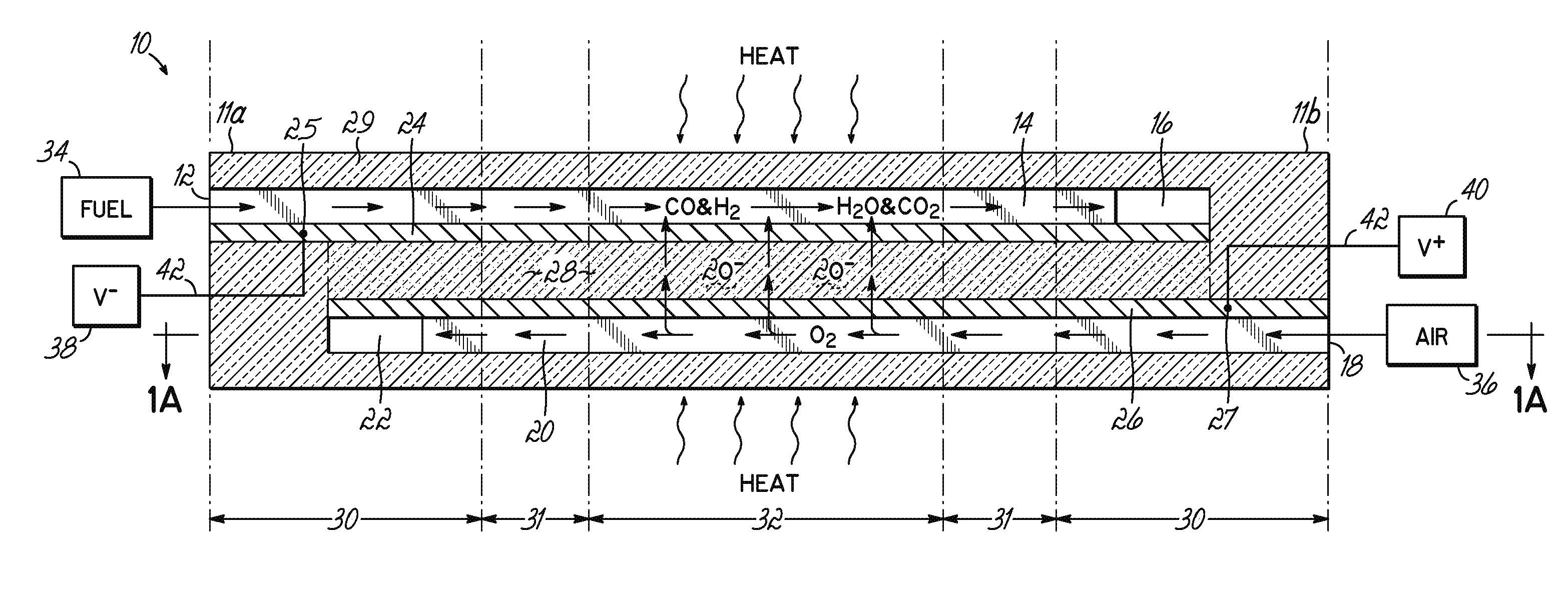
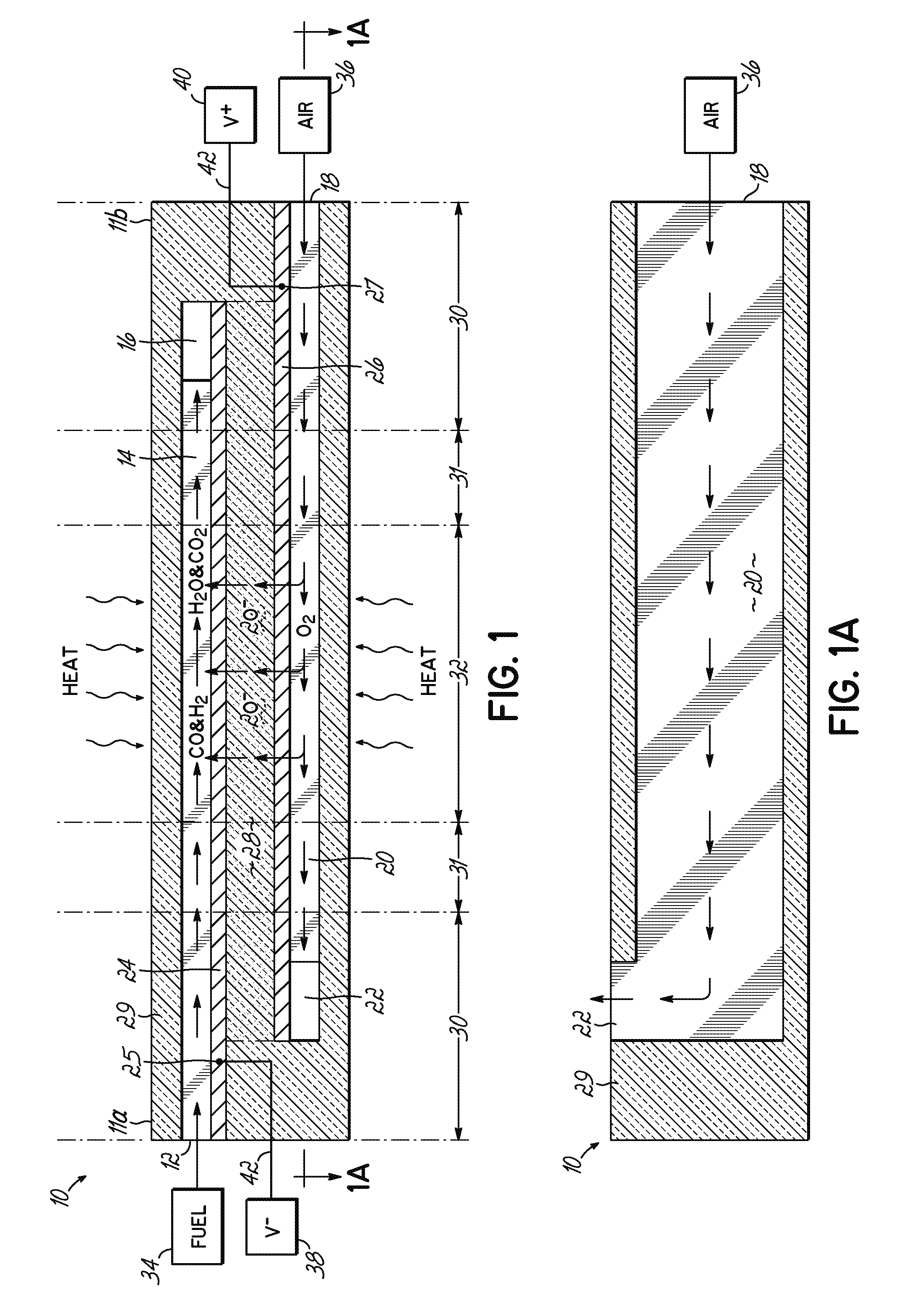
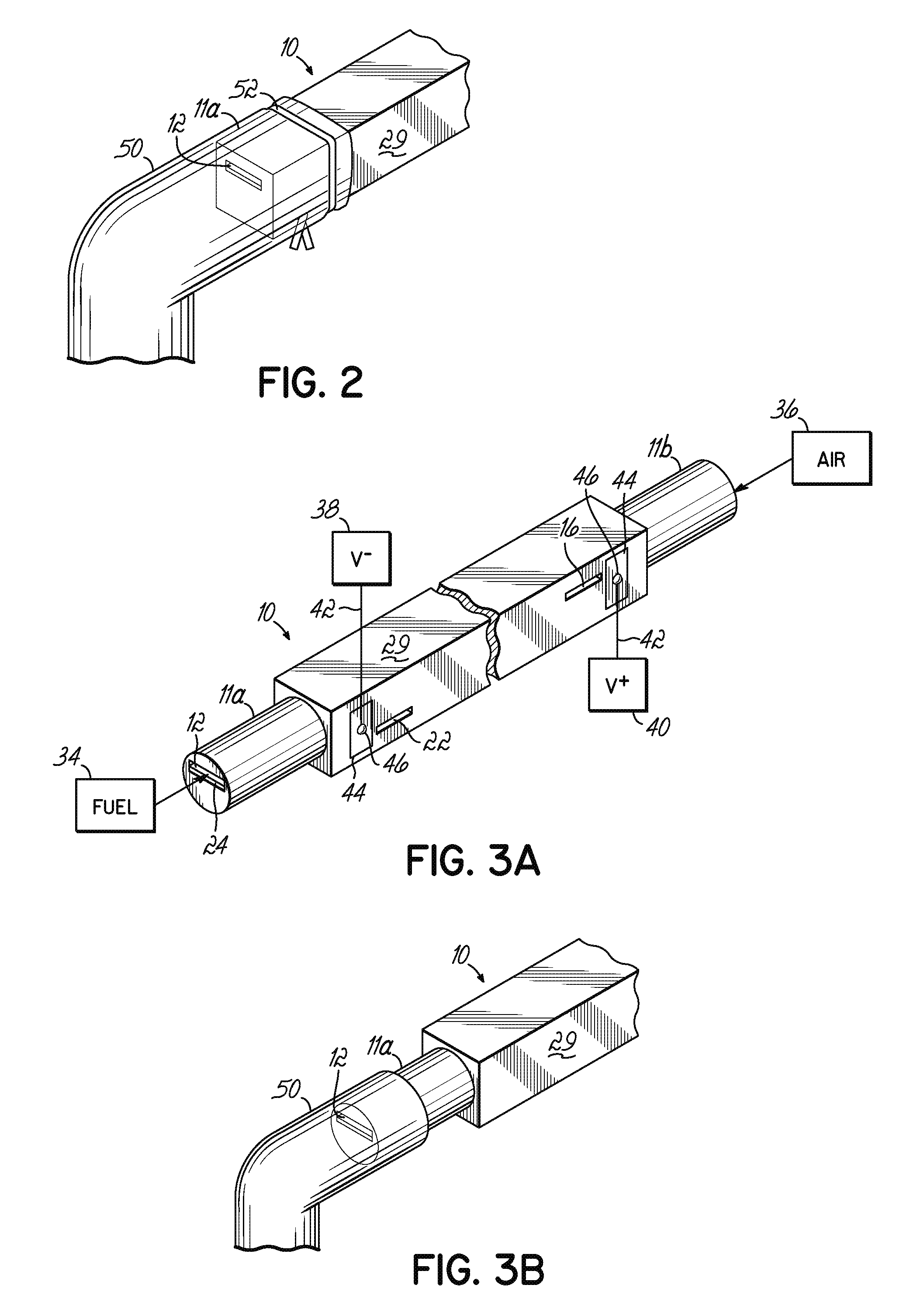
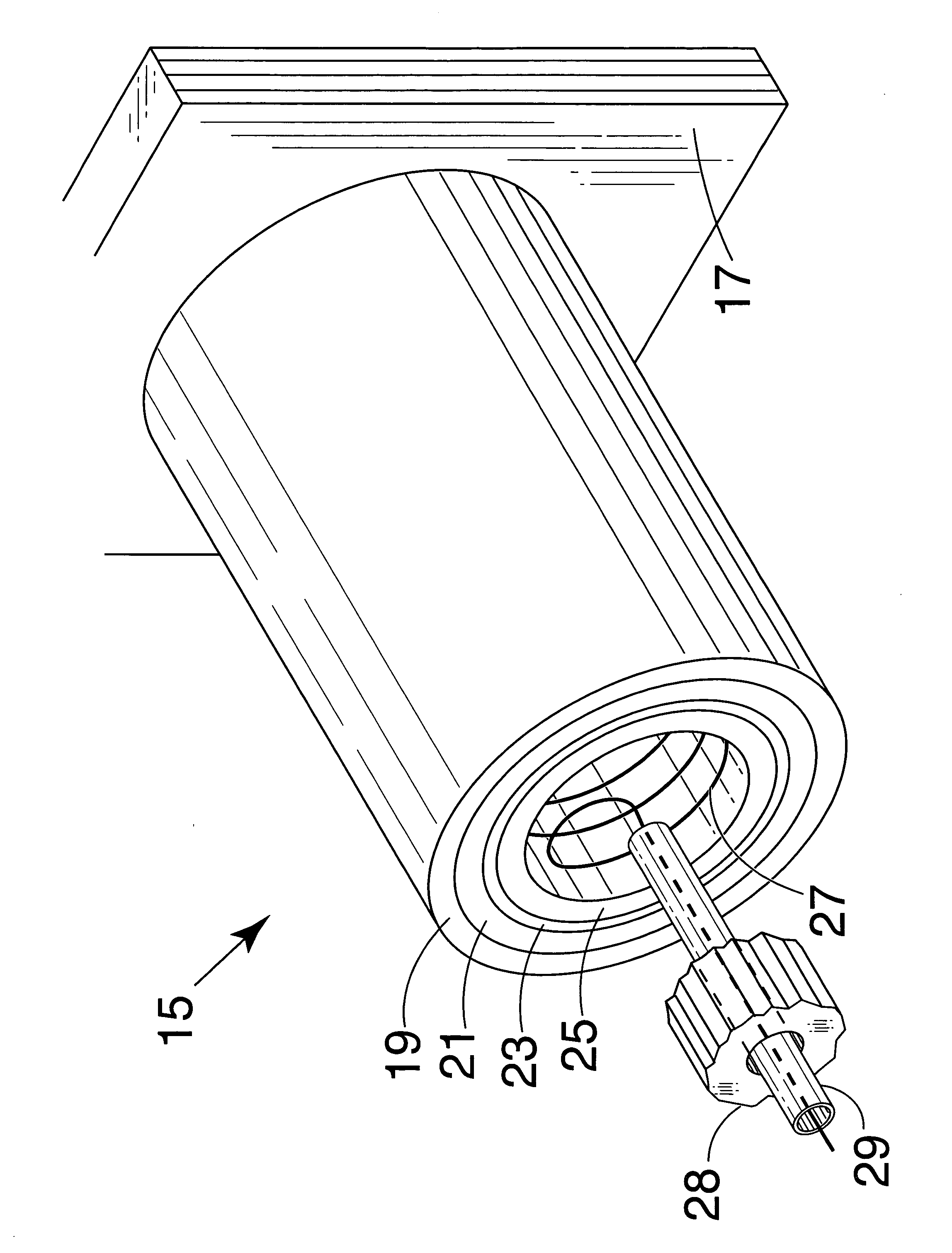
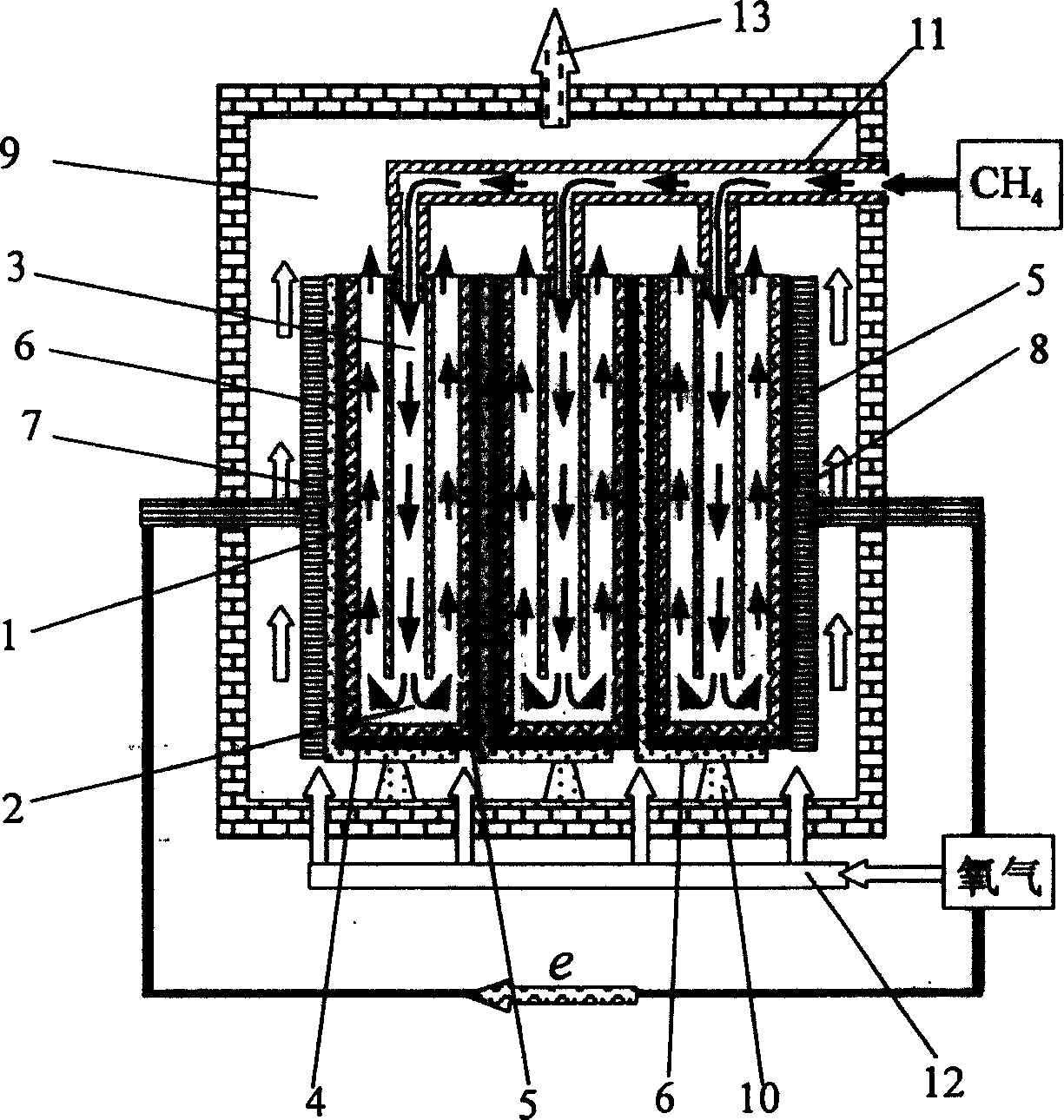
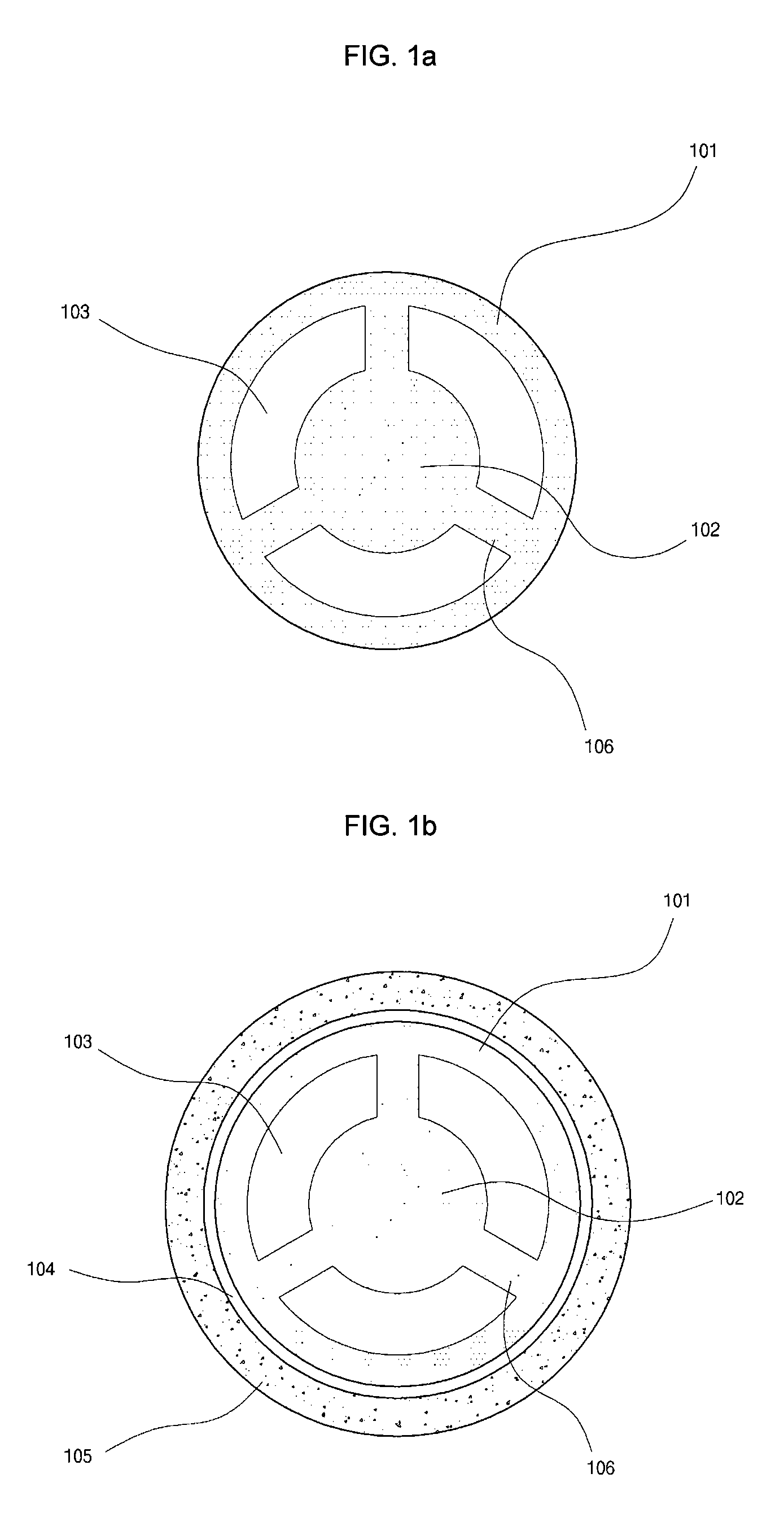
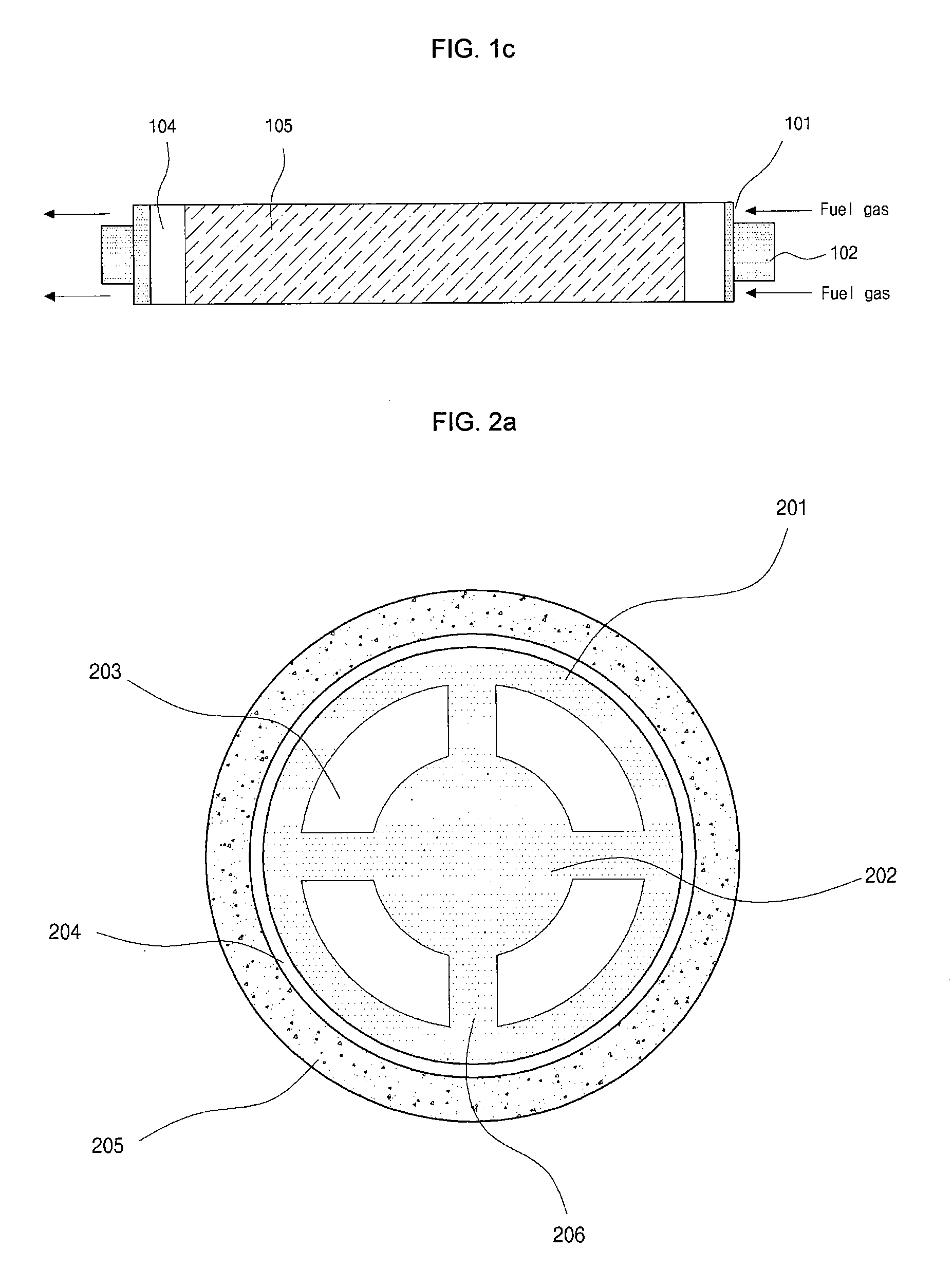
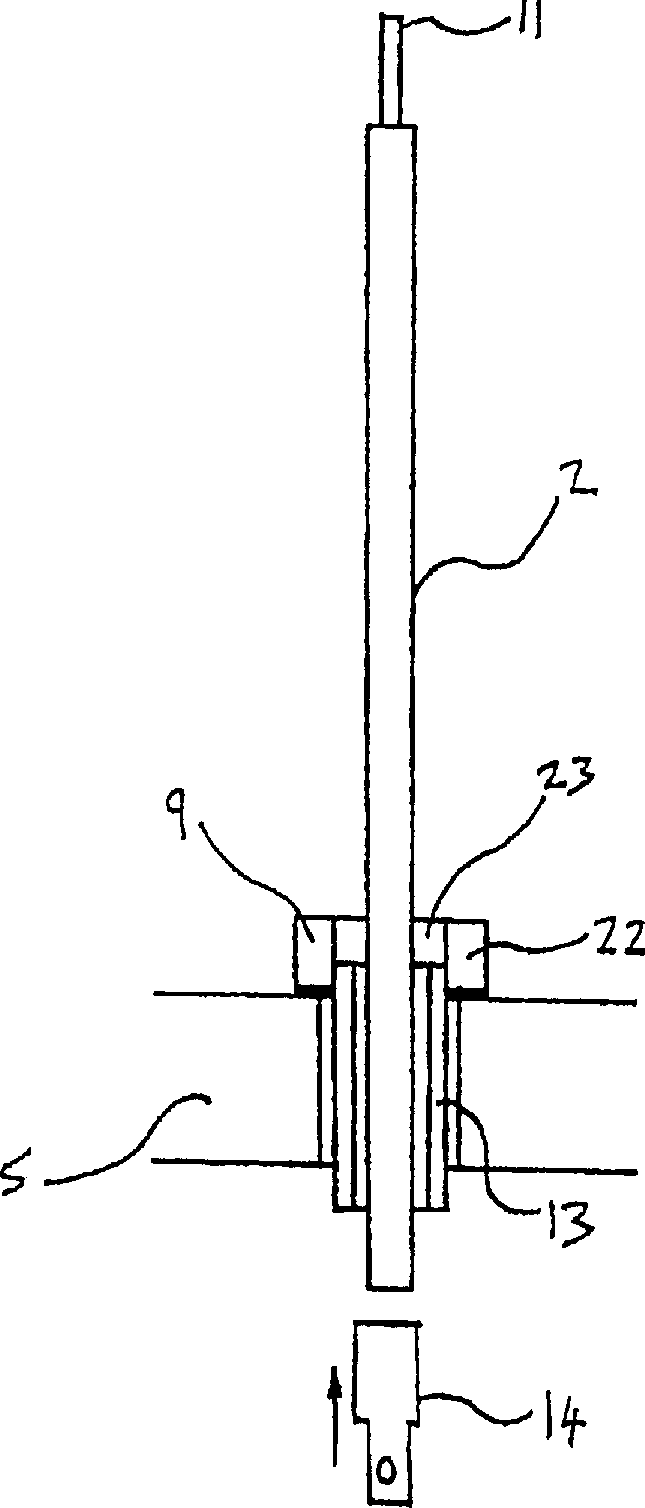
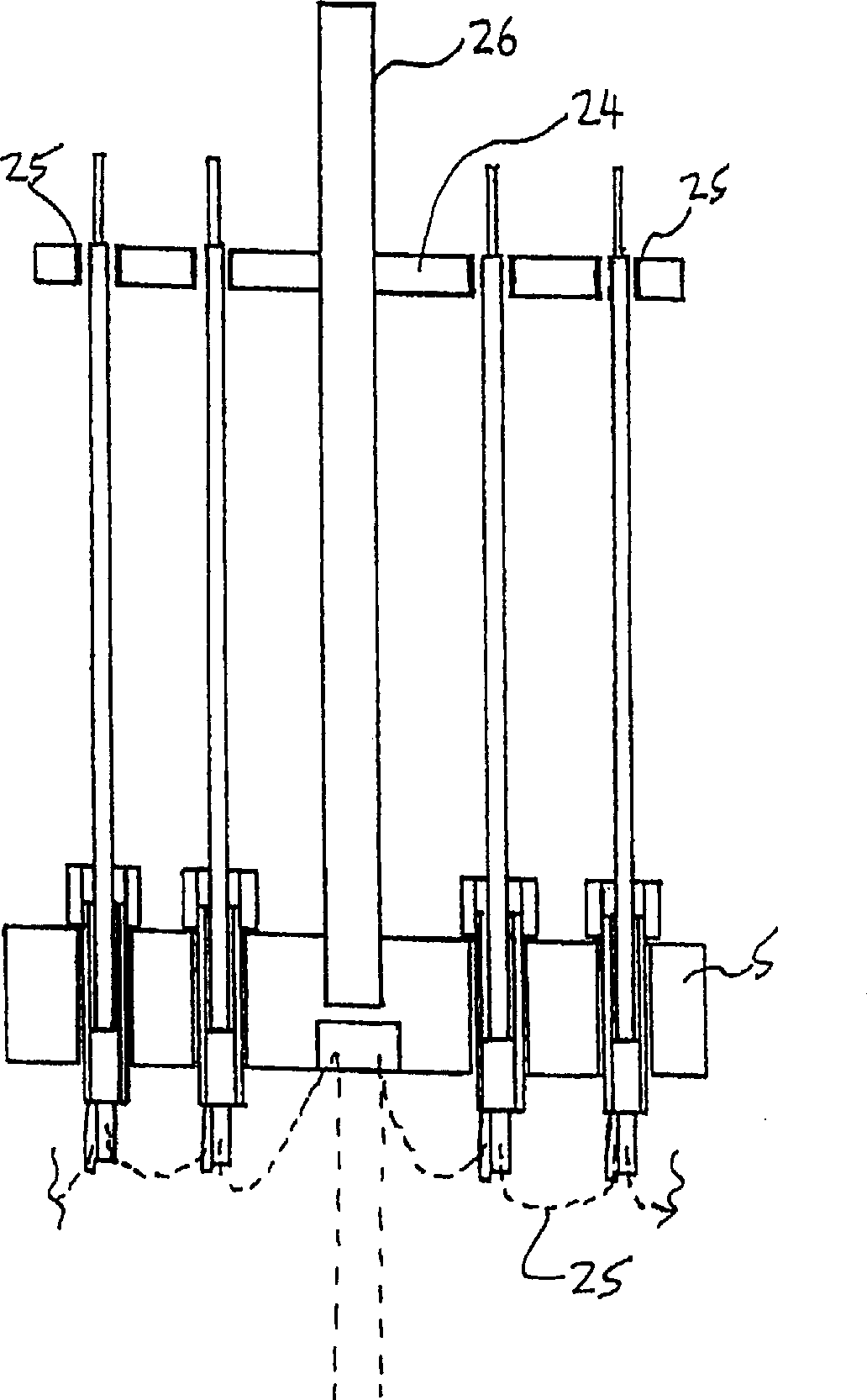
A disclosed apparatus for generating electrical power has, according to one embodiment of the invention, a plurality of tubular solid oxide fuel cells contained in a reaction chamber. The fuel cells are secured at one end thereof in a manifold block, the other ends thereof passing freely through apertures in a baffle plate to reside in a combustion chamber. Reaction gases are supplied to the insides of the tubular fuel cells from a plenum chamber below the manifold block and to the reaction chamber surrounding the outsides of the fuel cells through an annular inlet path, which may include a reformation catalyst. The gases inlet path to the plenum chamber, and the annular inlet path surround the reaction chamber, are both in heat conductive relation with the reaction chamber and the combustion chamber, and raise the gases to formation and reaction temperatures as appropriate.
Owner:ACUMENTRICS
Tubular solid oxide fuel cells
InactiveUS20050037252A1Strong electrical contactImprove power densityFuel cells groupingCell electrodesFuel cellsThermal expansion
An anode-supported tubular fuel cell stack includes interconnect structures that are oxidation resistant at high temperature, flexible to accommodate thermal expansion stress and to provide strong electrical contact, have low electrical resistance, and are inexpensive and light weight. The interconnect structures may be formed out of metal sheet, which provide improved heat homogeneity throughout the fuel cell stack because of the high thermal conductivity of the metal. The interconnect structures are further shaped to provide resilience or spring-like features to allow movement between the tubular cells. Thus good electrical contact, thermal stress release, and shock absorption are simultaneously achieved.
Owner:EVOGY
Horizontal fuel cell tube system and methods
In one disclosed embodiment according to the invention, a fuel cell system for generating electrical power comprises: an open-ended tubular solid oxide fuel cell; a first fuel injector tube extending from a first fuel plenum chamber through one open end of the fuel cell; and a second fuel injector tube extending from a second fuel plenum chamber through another open end of the fuel cell; wherein the first and second fuel injector tubes form a gap within the fuel cell from which a hydrogen-containing fuel gas may flow towards the open ends of the fuel cell. Further related systems and method are also disclosed.
Owner:ACUMENTRICS
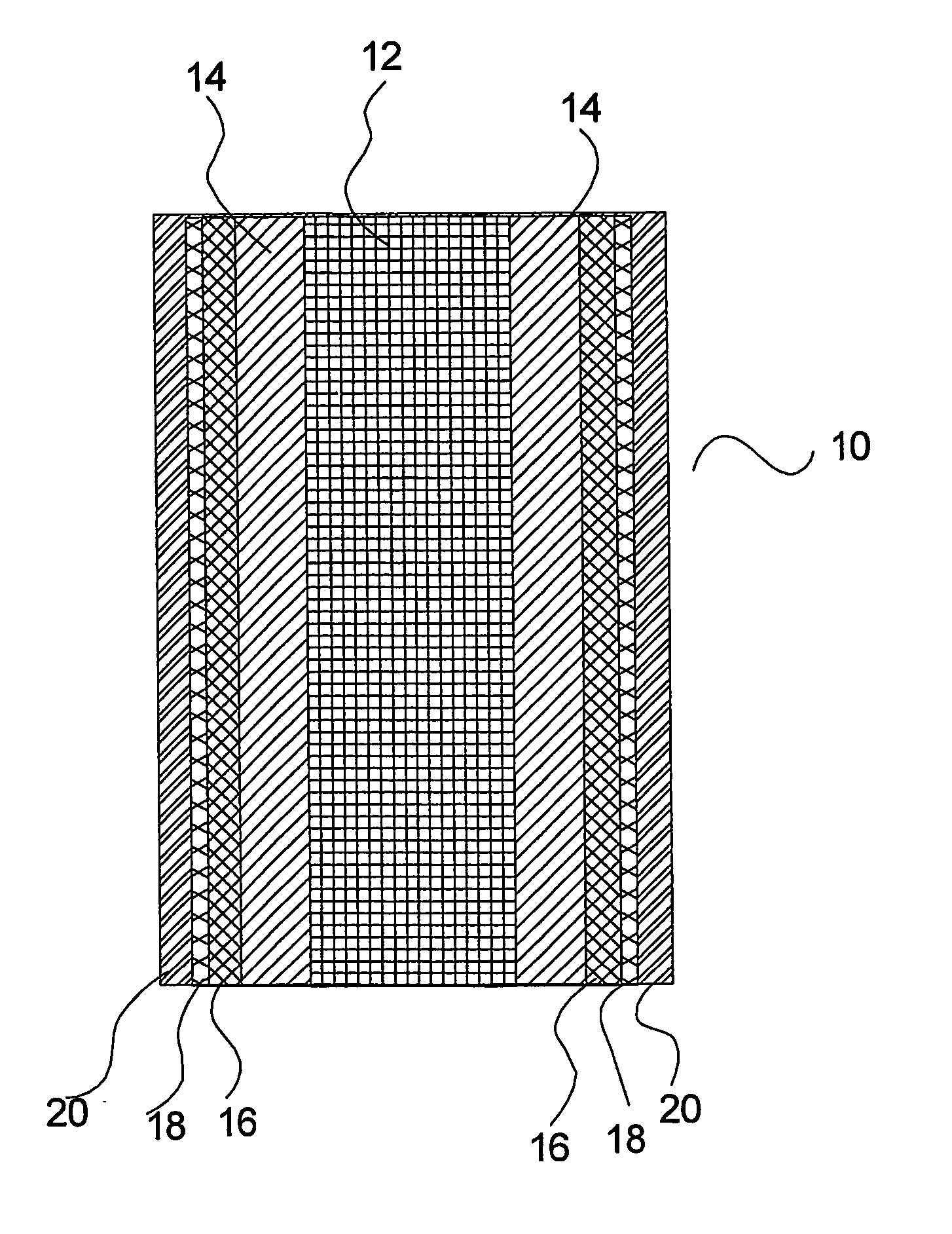
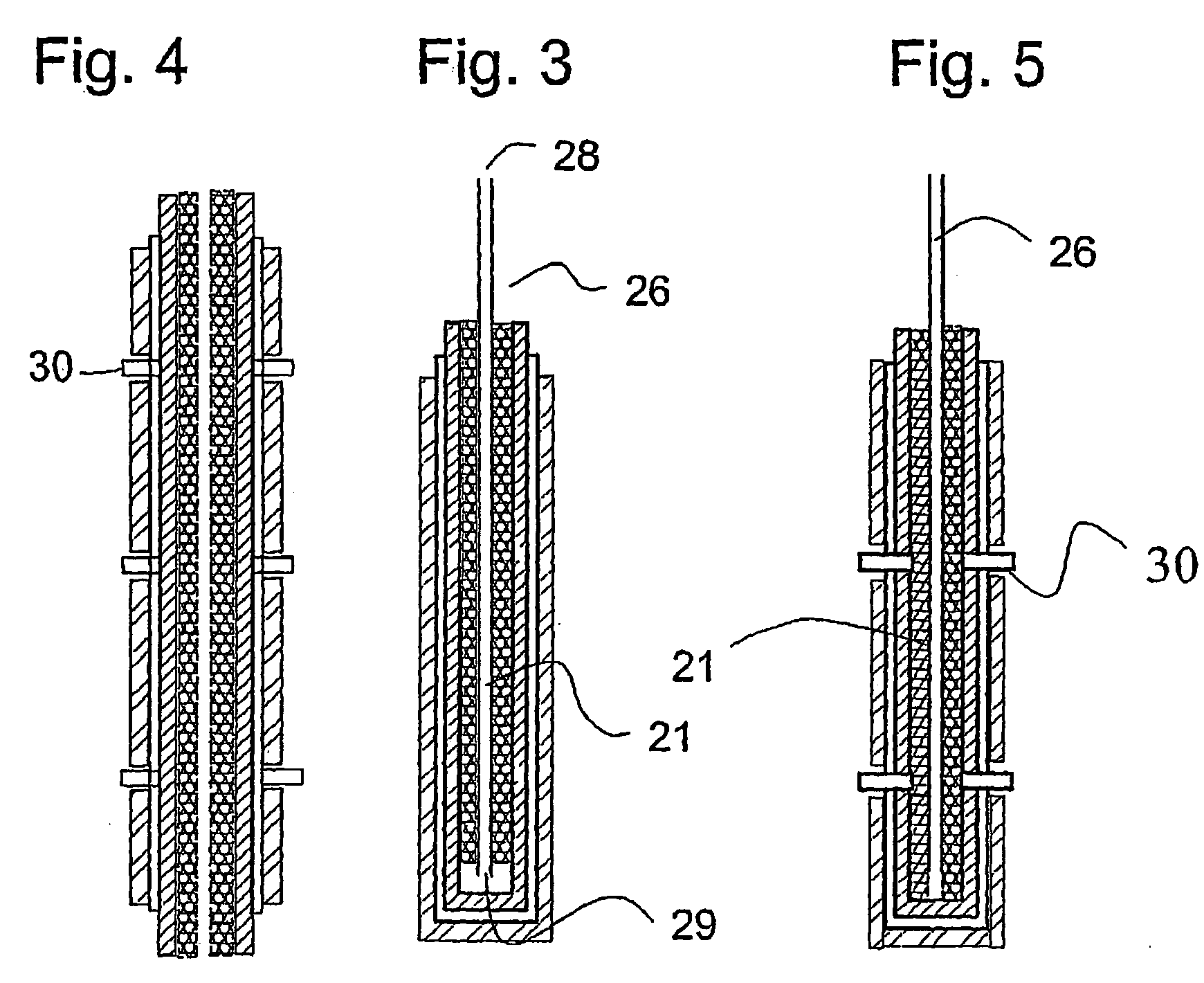
Tubular solid oxide fuel cell stack
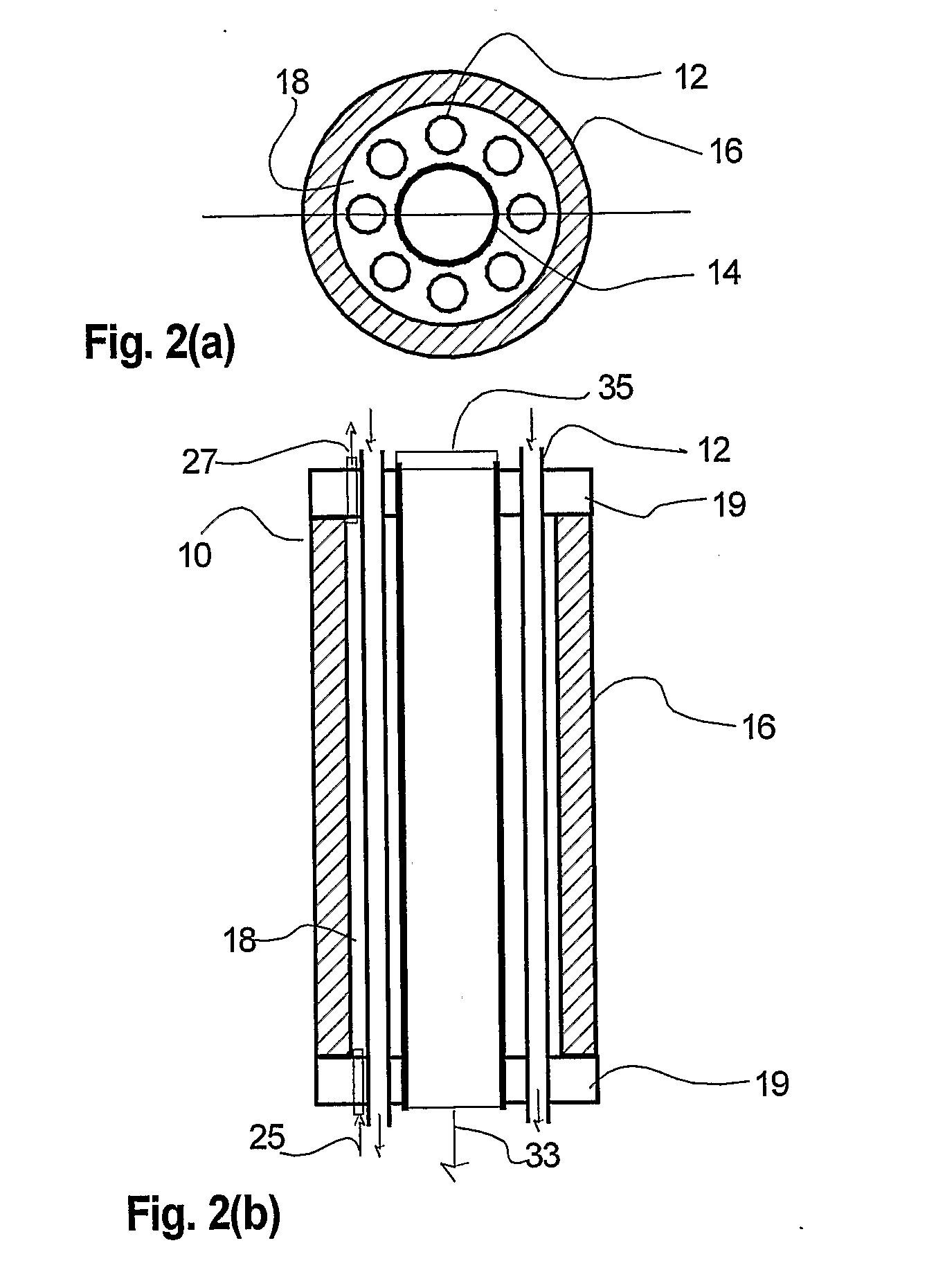
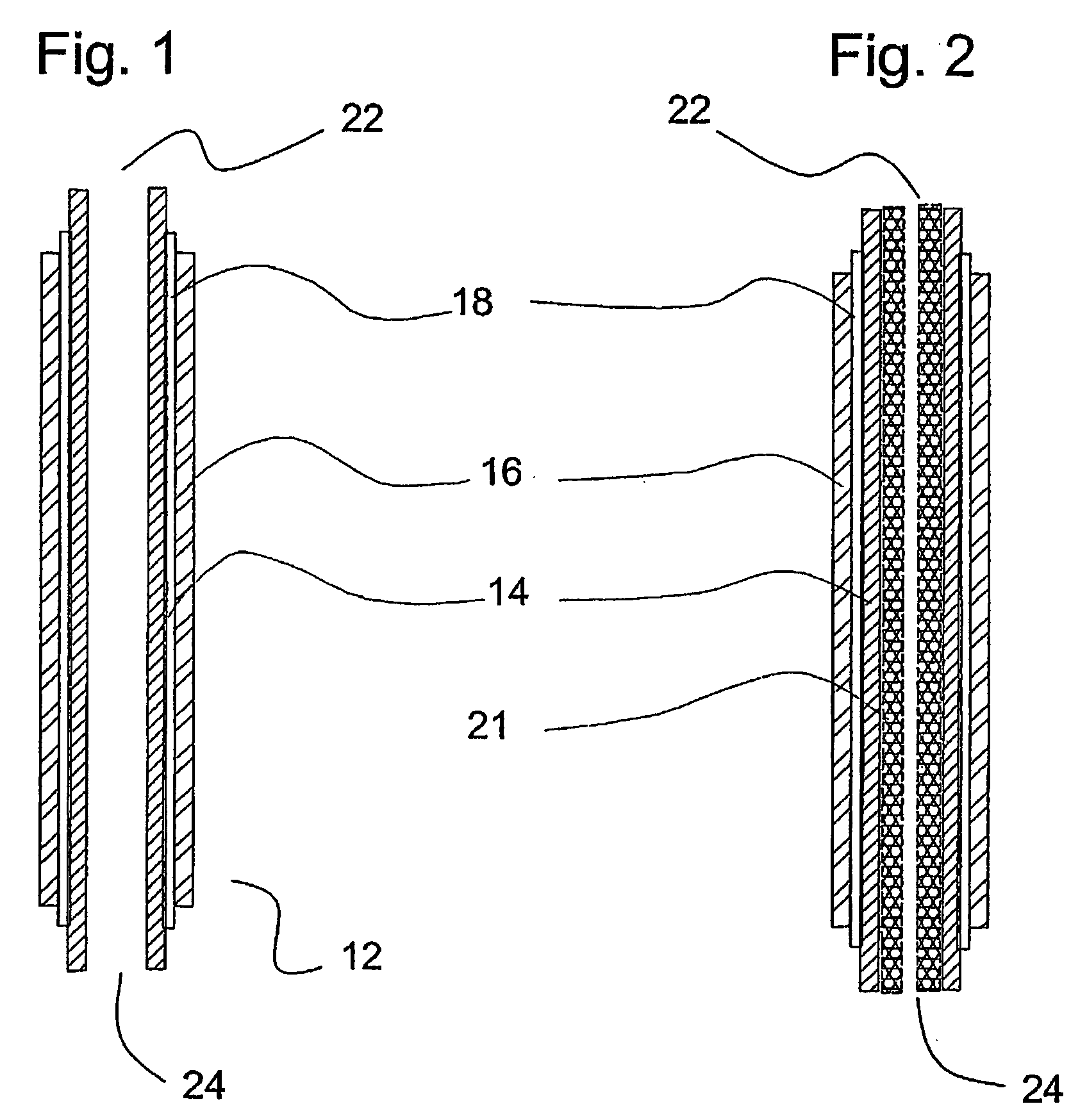
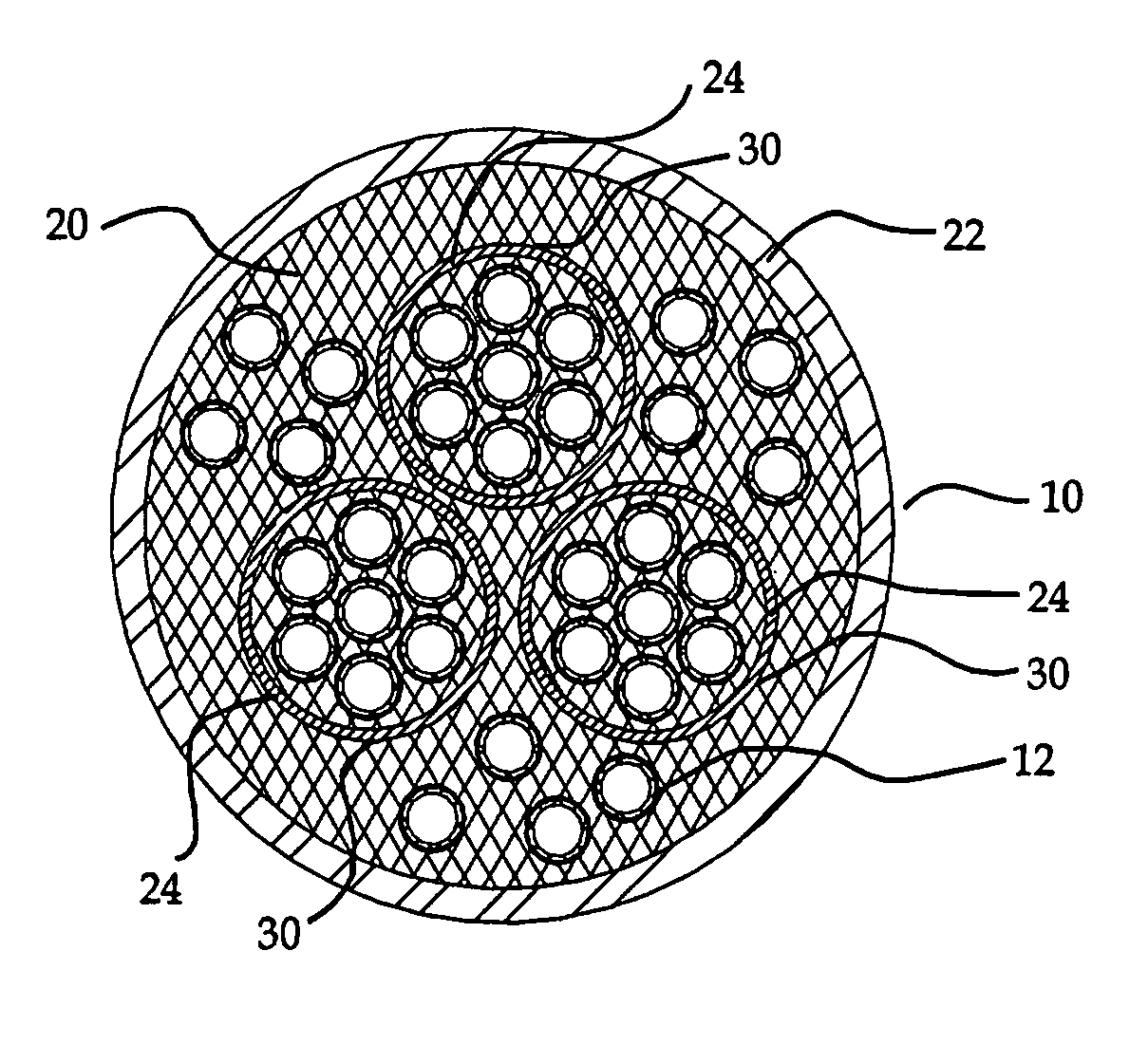
This invention relates to a stack comprising a continuous solid-phase matrix and tubular fuel cells embedded in the matrix. Each fuel cell comprises an inner electrode layer, an outer electrode layer, and an electrolyte layer sandwiched between the inner and outer electrode layers. The matrix is sufficiently porous to allow a first reactant to flow through the matrix and to the outer electrode of each fuel cell, and have sufficient mechanical strength to support the fuel cells in the stack. The fuel cells are embedded such that a second reactant may be flowed through the inside of each tubular fuel cell and to the inner electrode thereof. Alternatively, a stack of tubular separation membranes or a stack of tubular membrane reactors may be embedded in the matrix. The matrix material may comprise solid state foam, metal filament, or metal, cermet, or ceramic wool.
Owner:INNOTECH ALBERTA INC
Metal-supported tubular fuel cell
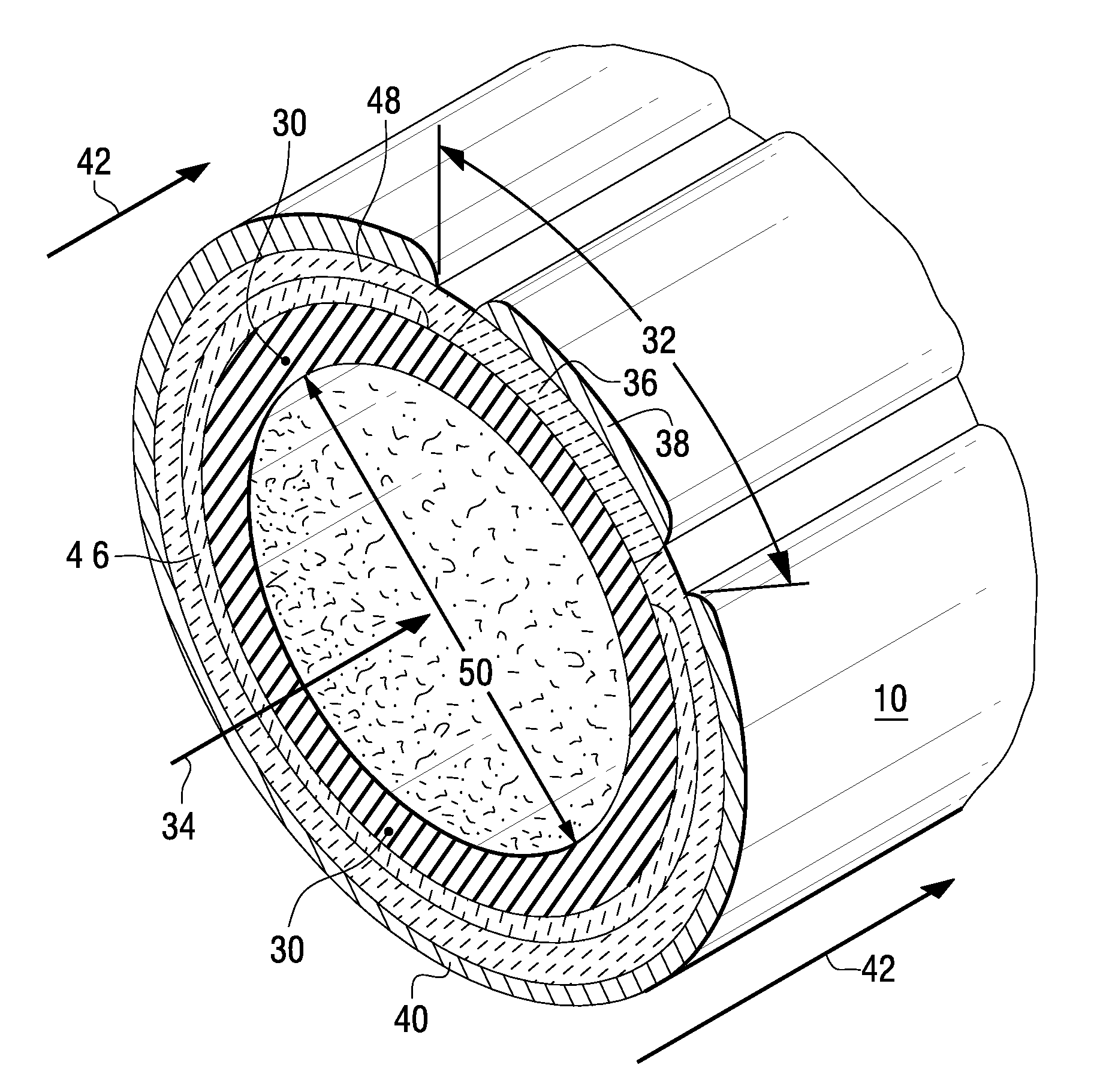
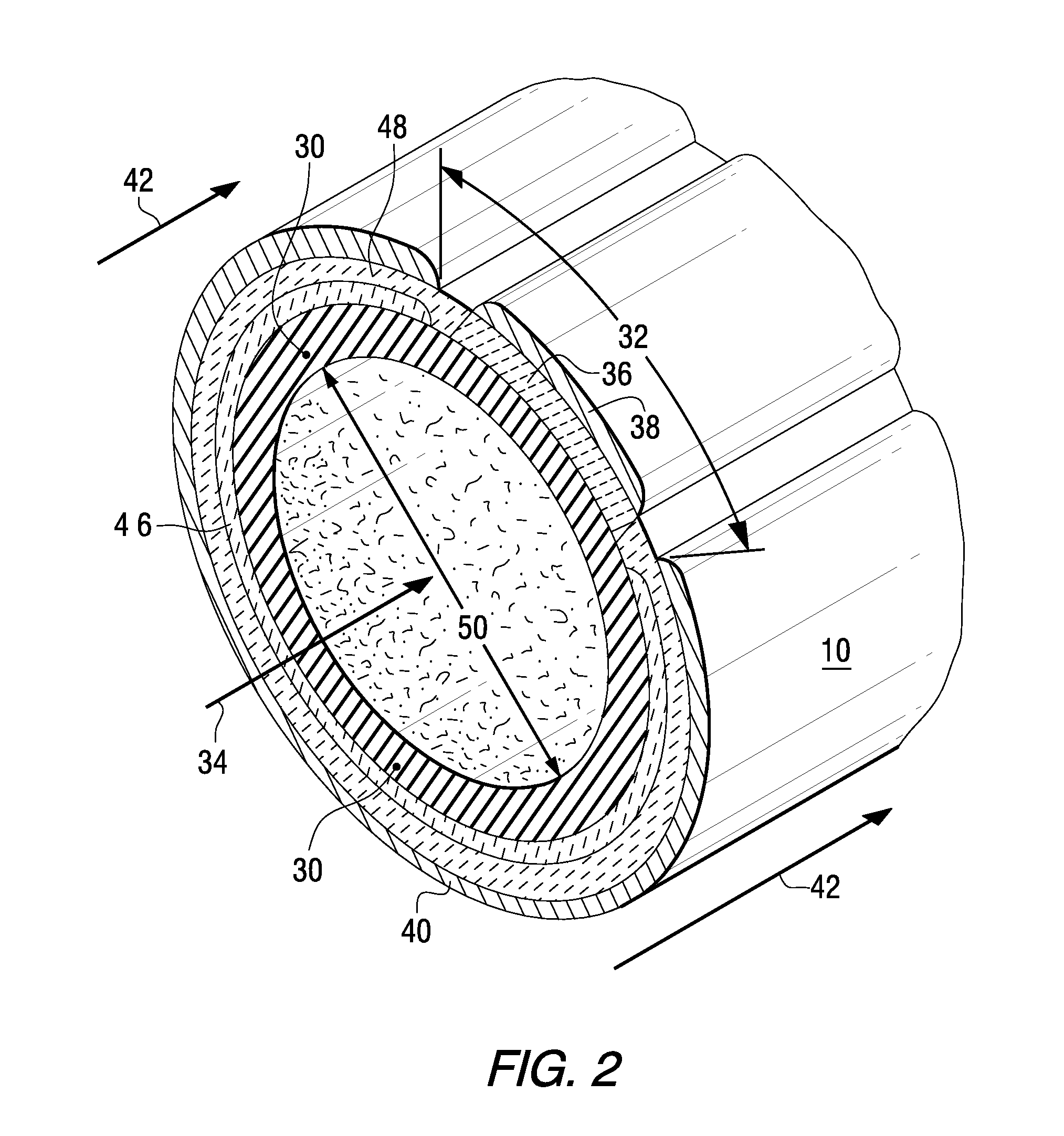
InactiveUS20060051643A1High mechanical strengthSolve Porosity InsufficiencyElectrolyte holding meansFuel cells groupingPorosityFuel cells
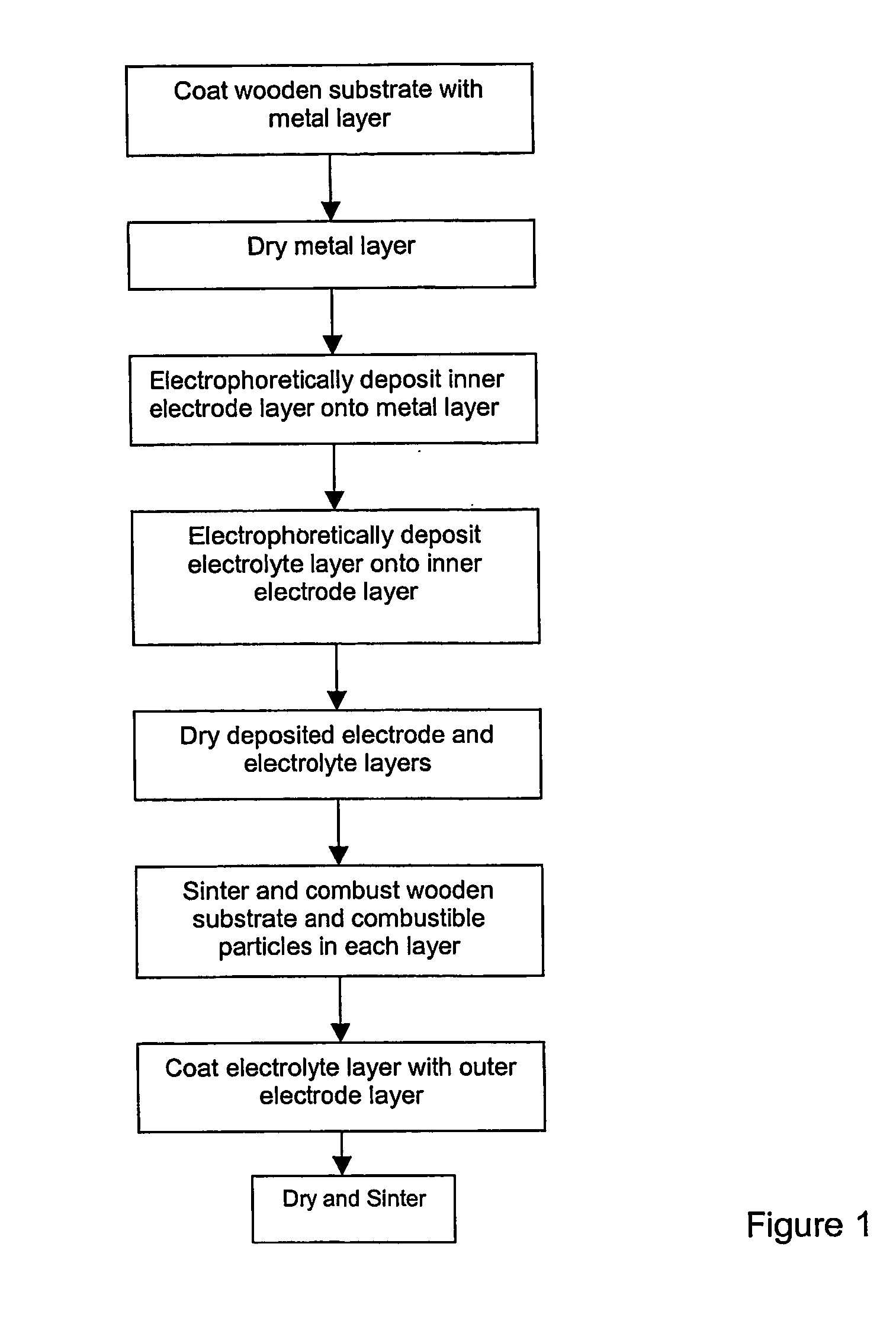
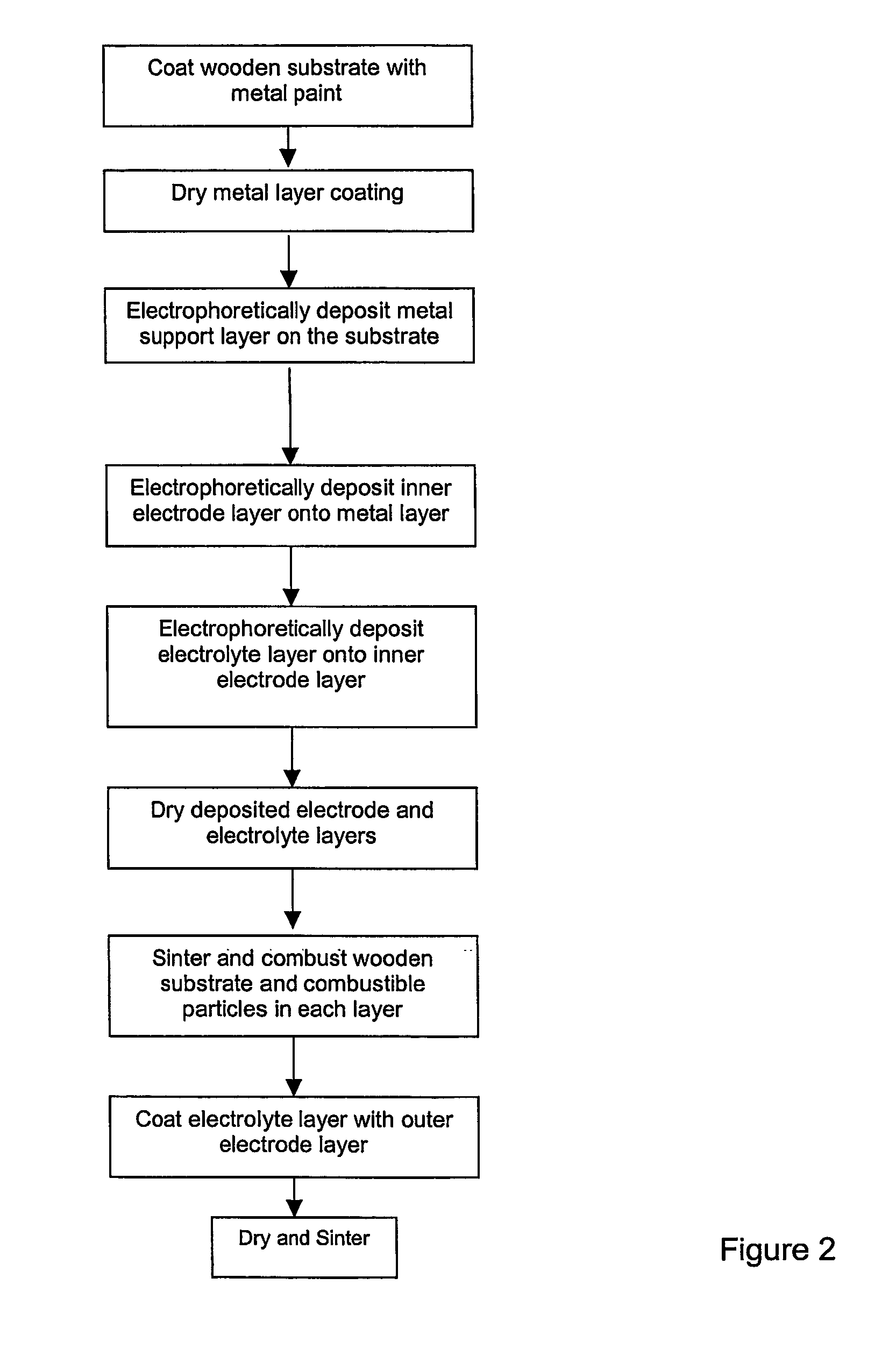
This invention relates to a method of manufacturing a metal-supported tubular micro-solid oxide fuel cell, and a fuel cell made from such method. The method comprises the steps of coating a wooden substrate member with a conductive substrate layer, coating the substrate layer with an inner electrode layer, coating the inner electrode layer with an electrolyte layer, drying and sintering the coated substrate member such that the substrate member combusts, coating the electrolyte layer with an outer electrode layer, and then drying and sintering the layers. The invention further relates to a method of manufacturing a tubular solid oxide fuel cell assembly comprising: a) coating a tubular substantially metallic support layer with a ceramic or cermet inner electrode layer, b) coating the inner electrode layer with a ceramic electrolyte layer; c) coating the electrolyte layer with a ceramic or cermet outer electrode layer, then d) sintering the layers to produce a hollow tubular metal-supported fuel cell; the electrode and electrolyte layers having a collective wall thickness of 80 μm or less, the support layer having sufficient mechanical strength to support the electrode and electrolyte layers and sufficient porosity to flow a reactant therethrough.
Owner:INNOTECH ALBERTA INC
Heating Solid Oxide for Fuel Cell Stack
This invention relates to a solid oxide fuel cell system comprising at least one longitudinally extending tubular solid oxide fuel cell and a longitudinally extending heater mounted in thermal proximity to the fuel cell to provide heat to the fuel cell during start up and during operation as needed. The heater and fuel cell can be encased within a tubular thermal casing; the inside of the casing defines a first reactant chamber for containing a first reactant, such as oxidant. The fuel cell comprises a ceramic solid state electrolyte layer and inner and outer electrode layers concentrically arranged around and sandwiching the electrolyte layer. The outer electrode layer is fluidly communicable with the first reactant, and the inner electrode layer is fluidly isolated from the first reactant and fluidly communicable with a second reactant, such as fuel.
Owner:INNOTECH ALBERTA INC
Solid oxide fuel cell system
InactiveUS20050196657A1Solve Porosity InsufficiencyReduce deliveryFuel cells groupingFuel cell shape/formPorosityFuel cells
Owner:INNOTECH ALBERTA INC
Tubular solid oxide fuel cell assembly and fuel cell device incorporating same
ActiveUS20130230787A1Improvement factorEliminating and mitigating ohmic lossFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingFuel cellsCurrent collector
A tubular solid oxide fuel cell assembly includes at least two tubular solid oxide fuel cell units, at least one shared current collector and a retainer for retaining a section of the fuel cell units and shared current collector in close fitting relationship therewith.
Owner:WATT FUEL CELL CORP
Anode-supported flat-tubular solid oxide fuel cell stack and fabrication method of the same
InactiveUS20050095483A1Low powerSecure advantageFuel cells groupingFinal product manufactureFuel cellsTubing types
Disclosed is an anode-supported flat-tubular solid oxide fuel cell stack, which includes an anode-supported tube having semi-cylinder parts and plate parts, thereby securing a combined structure of a tube-type and a plate-type anode-supported body, and a method of fabricating the same. The anode-supported flat-tubular solid oxide fuel cell stack includes a plurality of fuel cells and a plurality of connector plates. Each of the fuel cells includes a supported tube having the semi-cylinder parts and plate parts, a connector coated on an upper plate of the supported tube as a way to be positioned at the center of the upper plate, an electrolyte layer partly coated on an external surface of the supported tube except for a portion of the supported tube coming into contact with the connector, and an air electrode coated on an external surface of the electrolyte layer. Additionally, each of the connector plates includes a lower connector plate, one or more middle connector plates, and an upper connector plate. In this regard, a plurality of gas channels are formed on the middle and lower connector plates. Therefore, the anode-supported flat-tubular solid oxide fuel cell stack has advantages of a large capacity, an improved power density, mass production, and reduced production costs.
Owner:TRUE DIGITAL LEADER CO LTD
Solid oxide fuel cell system
This invention relates to a fuel cell system comprising a fuel cell stack, external circuit electrical leads coupled to the fuel cell electrodes, and a thermal enclosure assembly enclosing the stack. The stack includes a plurality of inner tubular solid oxide fuel cells, the inside of the inner fuel cells being fluidly couplable to a first reactant source, and a porous support matrix embedding the inner fuel cells and being fluidly couplable to a second reactant source such that a second reactant is flowable through the matrix and to the outer surface of the embedded fuel cells. The stack may also include an outer tubular solid oxide fuel cell surrounding the matrix and the inner fuel cells such that the second reactant is flowable through the matrix and to an inside surface of the outer fuel cell and wherein the outer surface of the outer fuel cell is fluidly couplable to a first reactant source.
Owner:INNOTECH ALBERTA INC
Large size tubular solid oxide fuel cell and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101359746AEasy to operateGood repeatabilityFinal product manufactureSolid electrolyte fuel cellsAdhesiveSlurry
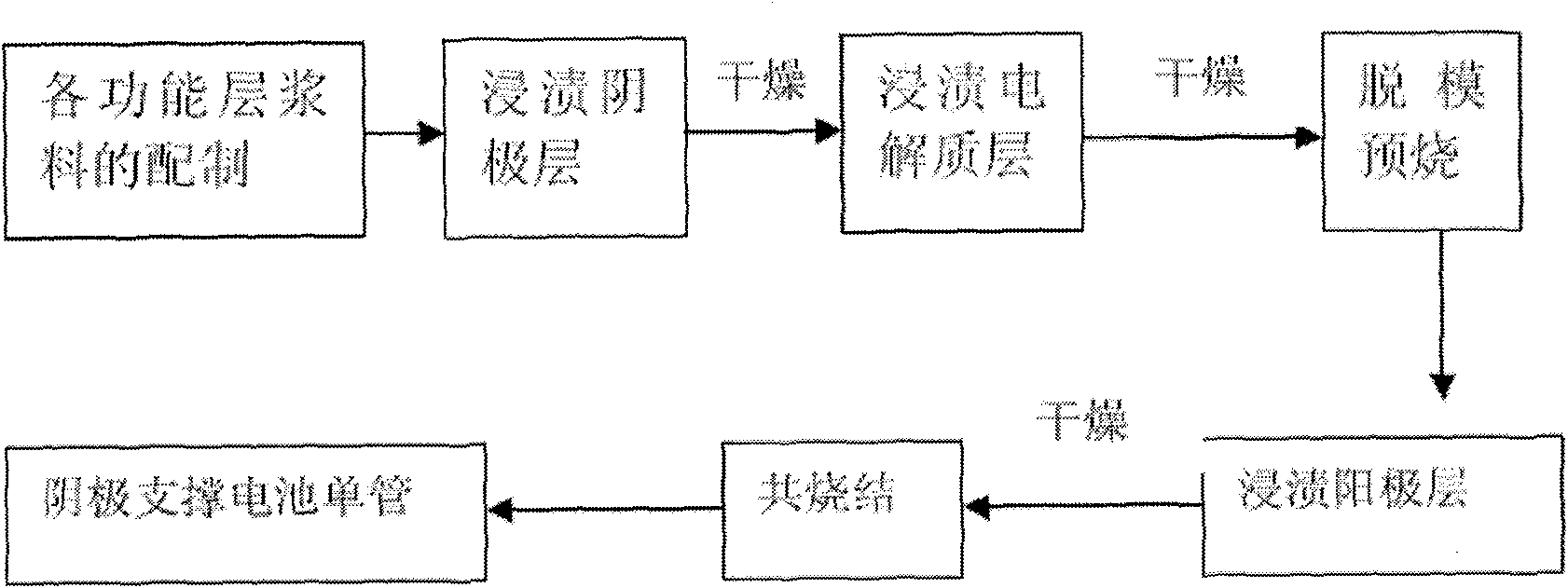
The invention discloses a large-size tubular solid oxide fuel cell and a preparation method thereof, and the method comprises: powder material of each functional layer of a solid oxide fuel cell is respectively added with an organic solvent, a dispersant, an adhesive and a plasticizer, and fully ground to obtain a uniform support anode slurry, an active anode slurry, an electrolyte slurry, an active cathode slurry and an electricity-receiving cathode slurry. The outer surface of a mold is impregnated with the support anode layer by layer after the vacuum treatment; the support anode tube is filled with combustible organic matter after demoulding; the active anode and the electrolyte are impregnated to form a support anode / active anode / electrolyte composite membrane; then the external side of the electrolyte is impregnated with the active cathode and the electricity-receiving cathode after sub-temperature sintering, that is, after pre-burning and high-temperature sintering; and the large-size tubular solid oxide fuel cell is obtained after sintering. The invention has advantages of simple process, low manufacturing cost, achieving good-performance large-size tubular solid oxide fuel cell and good prospect of industrialization.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fuel cell support structure
InactiveUS20060246337A1Add support structureShock and vibrationFuel cells groupingCell electrodesPorosityFuel cells
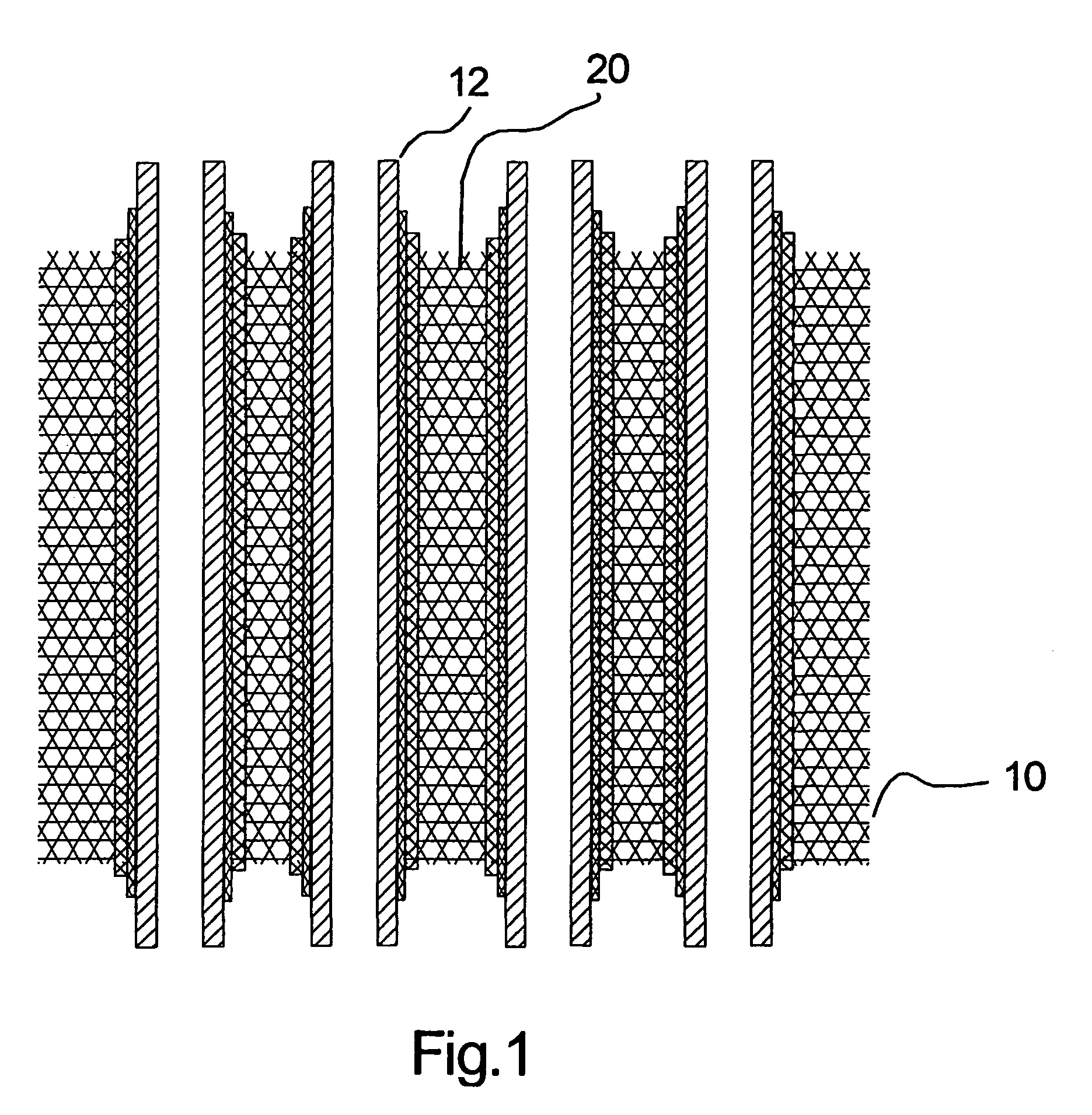
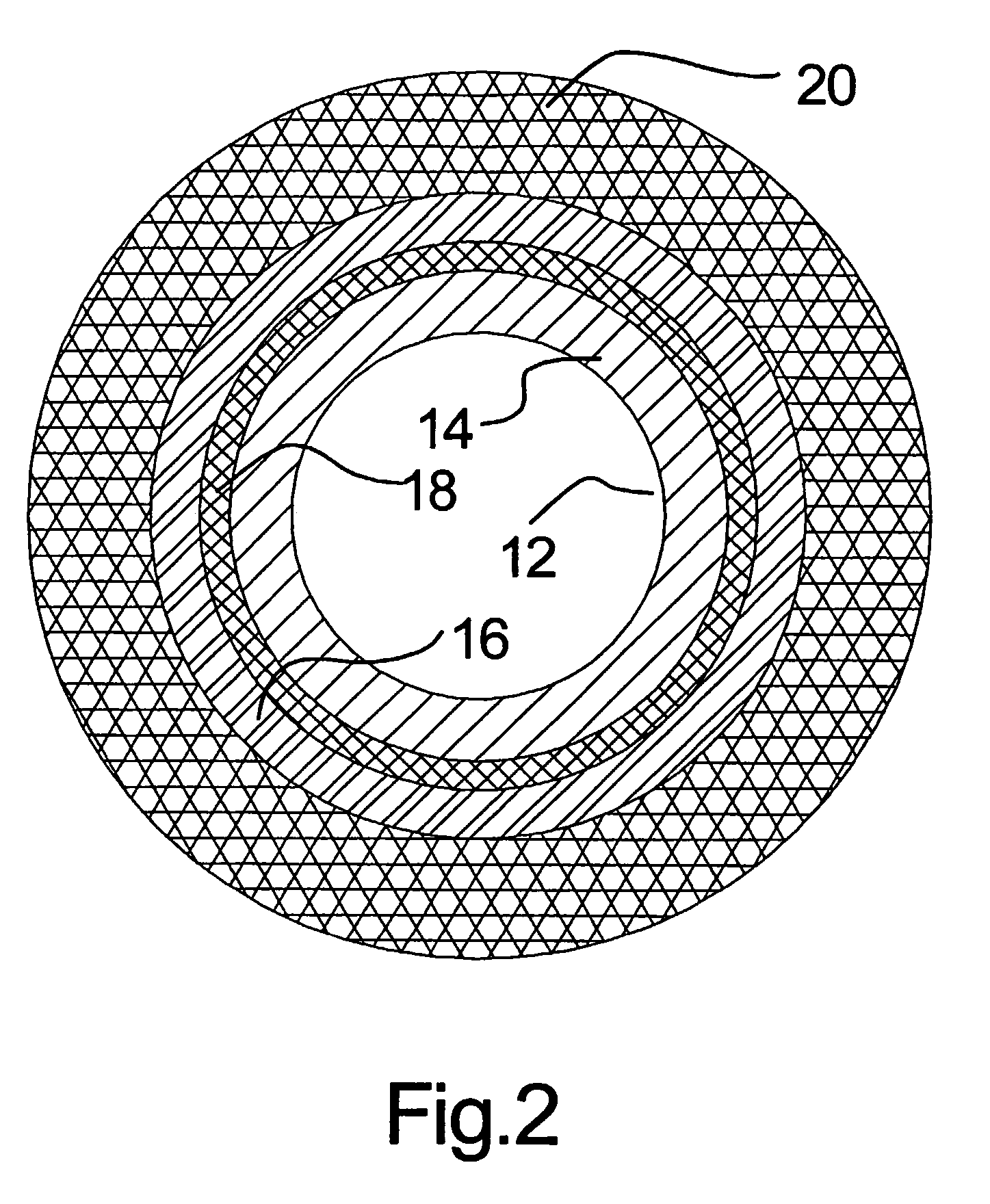
A plurality of tubular solid oxide fuel cells are embedded in a solid phase porous foam matrix that serves as a support structure for the fuel cells. The foam matrix has multiple regions with at least one property differing between at least two regions. The properties include porosity, electrical conductivity, and catalyst loading.
Owner:INNOTECH ALBERTA INC
Method for preparing cathode-supported tubular solid oxide fuel cells
ActiveCN101577340ALow costEasy to operateFinal product manufactureSolid electrolyte fuel cellsOrganic solventFuel cells
The invention relates to a method for preparing cathode-supported tubular solid oxide fuel cells (CTS OFCs), which is characterized in that: adding an organic solvent, a dispersant, an adhesive, a pore-forming material and a plasticizer into powder of various functional layers (cathodes, anodes and electrolyte) to prepare slurry of the various functional layers; soaking a cathode supporting body, the electrolyte and an anode layer on a tubular substrate in turn, and obtaining the CTS OFCs after demolding and primary sintering; or soaking the cathode and the electrolyte, performing demolding and preburning, soaking the anode layer on the outside of the electrolyte, and obtaining the CTS OFCs through co-sintering. The method has simple technological process and low manufacturing cost, and can realize the densification of the electrolyte at a low temperature of between 1,200 and 1,300 DEG C, and the obtained cells have superior performance and good industrialization prospect.
Owner:江苏先进无机材料研究院
Stack configurations for tubular solid oxide fuel cells
InactiveUS20060228615A1Use minimizedReduce manufacturing costFuel cells groupingCell electrodesFuel cellsReactive gas
A fuel cell unit includes an array of solid oxide fuel cell tubes having porous metallic exterior surfaces, interior fuel cell layers, and interior surfaces, each of the tubes having at least one open end; and, at least one header in operable communication with the array of solid oxide fuel cell tubes for directing a first reactive gas into contact with the porous metallic exterior surfaces and for directing a second reactive gas into contact with the interior surfaces, the header further including at least one busbar disposed in electrical contact with at least one surface selected from the group consisting of the porous metallic exterior surfaces and the interior surfaces.
Owner:WORLDWIDE ENERGY INC OF DELAWARE
Current collection in anode supported tubular fuel cells
InactiveUS20070099065A1Reduce effective operational lengthFuel cells groupingElectrode carriers/collectorsFuel cellsEngineering
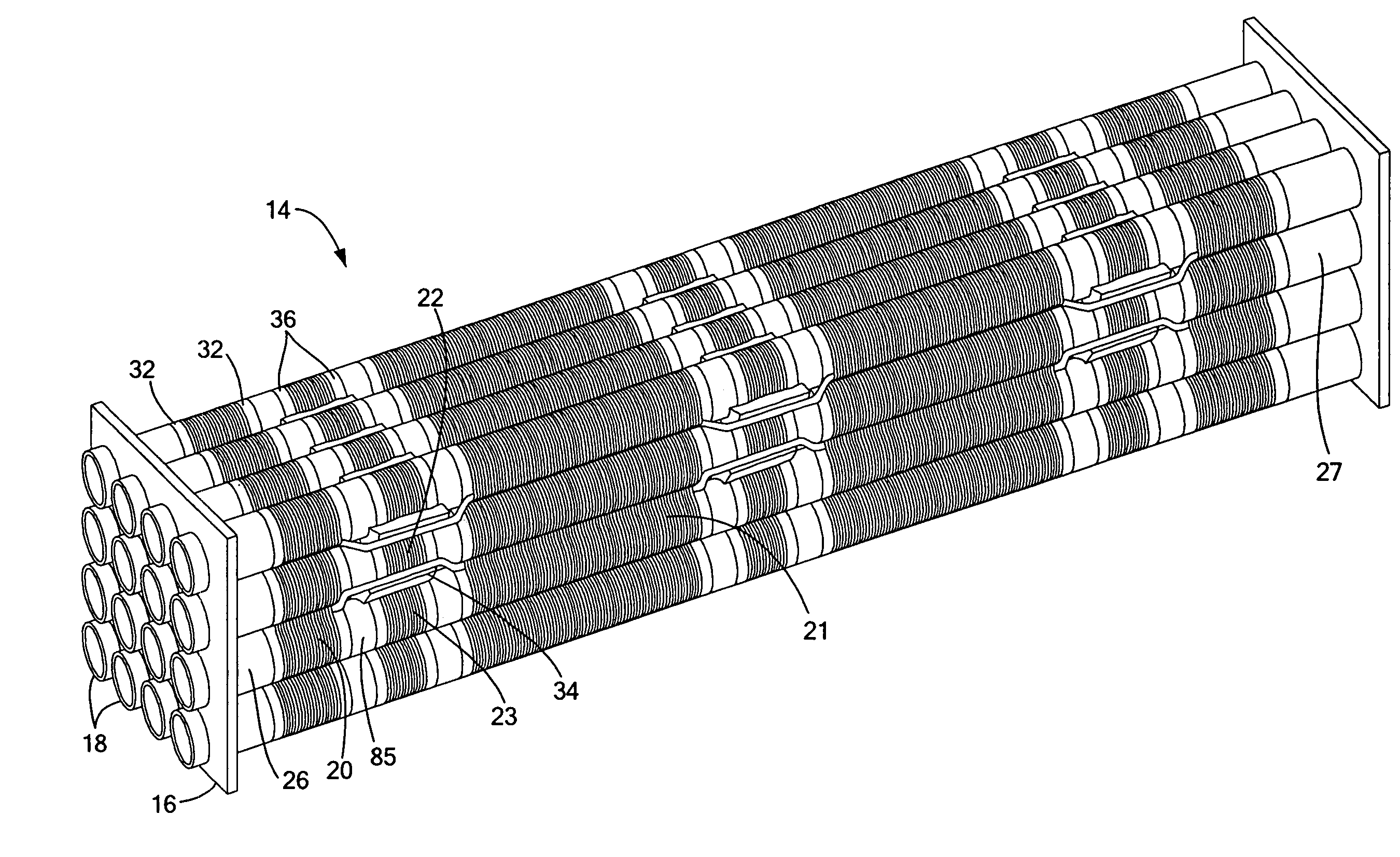
In a tubular solid-oxide fuel cell, current is collected from an inner anode layer at one or more discrete points along the length of the fuel cell that are accessible from the outside of the fuel cell. Current can be collected from the anode layer at both ends of the fuel cell, once in the center of the fuel cell, or at any of a multitude of axial points along the length of the fuel cell.
Owner:ACUMENTRICS
Anode-supported solid oxide fuel cell, cell stack and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102651480ARaise the sintering temperatureHigh strengthFuel cells groupingSolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cellsHigh power density
The invention relates to an anode-supported solid oxide fuel cell, a cell stack and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the field of fuel cell materials. The anode-supported tubular solid oxide fuel cell comprises an anode support tube with one end sealed, wherein a bar-shaped ceramic connector layer is arranged on the outer side surface of the anode support tube; a compact electrolyte layer is arranged at the part of the outer surface of the anode support tube without the ceramic connector layer, and the compact electrolyte layer and the bar-shaped ceramic connector layer are adjacent to each other and completely cover the outer surface of the anode outer surface; the anode support tube, the compact electrolyte layer and the ceramic connector layer are integrated through cofiring; and a cathode layer is further arranged outside the compact electrolyte layer and disconnected with the ceramic connector layer. The anode-supported solid oxide fuel cell is easy for stacking and has high operating temperature and generating efficiency; a connector is stable and reliable and has a long service life; as the connector and the anode support tube biscuit are prepared through cofiring, convenience and low cost are realized; and meanwhile, the cell structure with one end sealed achieves internal reforming of fuel, compact structure and high power density are also realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sealing element for anode-supported tubular solid oxide fuel cell and sealing method using the same
InactiveUS20070231660A1Improve sealingShorten heating timeFinal product manufactureFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsEngineering
Disclosed are a sealing element and a sealing method for sealing both ends of an anode-supported tubular solid oxide fuel cell. The sealing element includes a coupling tube having a first end portion opened to an exterior and a second end portion having a perforation hole, in which the coupling tube is formed with an internal cavity having a shape corresponding to an external appearance of an end portion of the fuel cell; and a flow tube extending outward from the center of the second end portion of the coupling tube and being formed with a hollow section, which axially extends while communicating with the perforation hole of the coupling tube. The sealing method includes the steps of cleaning the sealing element and the fuel cell; surrounding an outer peripheral surface of an electrolyte layer formed on both ends of the fuel cell with a metallic filler material such that the electrolyte layer does not make contact with a cathode, inserting the fuel cell into a connection tube of the sealing element, heating and melting the metallic filler material, and solidifying the melted metallic filler material. The sealing element improves the endurance and performance of the fuel cell. Since it is possible to use the sealing element as an anode collector, a fuel cell stack having a simple structure is realized.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ENERGY RES
Compact solid oxide fuel cell stack
InactiveUS20060134489A1High maximum operating temperatureFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingTubular solid oxide fuel cellOperating temperature
This invention relates to a solid oxide fuel cell stack comprising a plurality of tubular solid oxide fuel cells each comprising concentric inner and outer electrode layers sandwiching a concentric electrolyte layer. The fuel cells extend in the same direction and are arranged in a cluster with at least one fuel cell having an electrolyte layer with a different composition and different maximum operating temperature than another fuel cell in the cluster. The fuel cell having the electrolyte layer with a higher maximum operating temperature is located closer to the core of the cluster than the fuel cell having the electrolyte layer with a lower maximum operating temperature.
Owner:ALBERTA INNOVATES TECH FUTURES
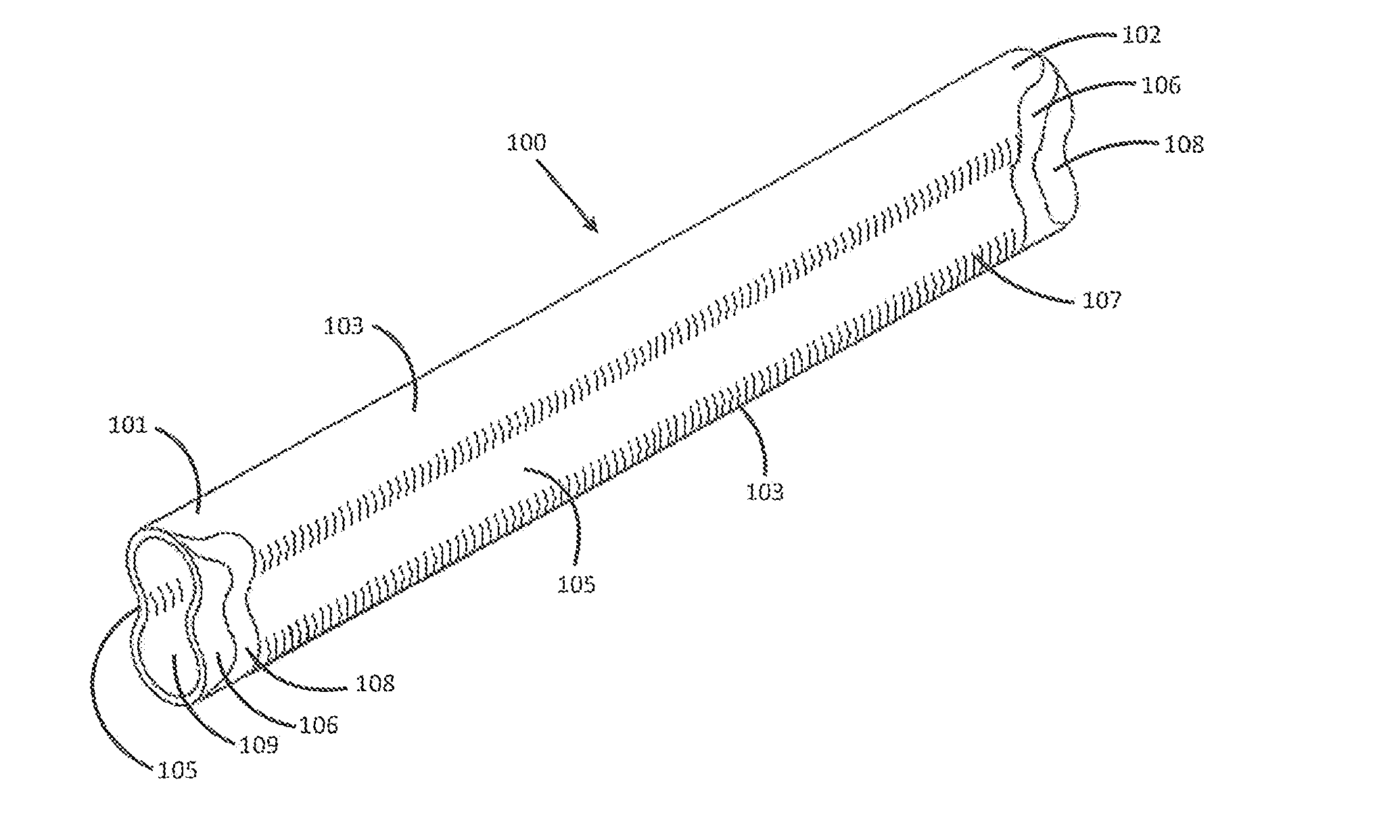
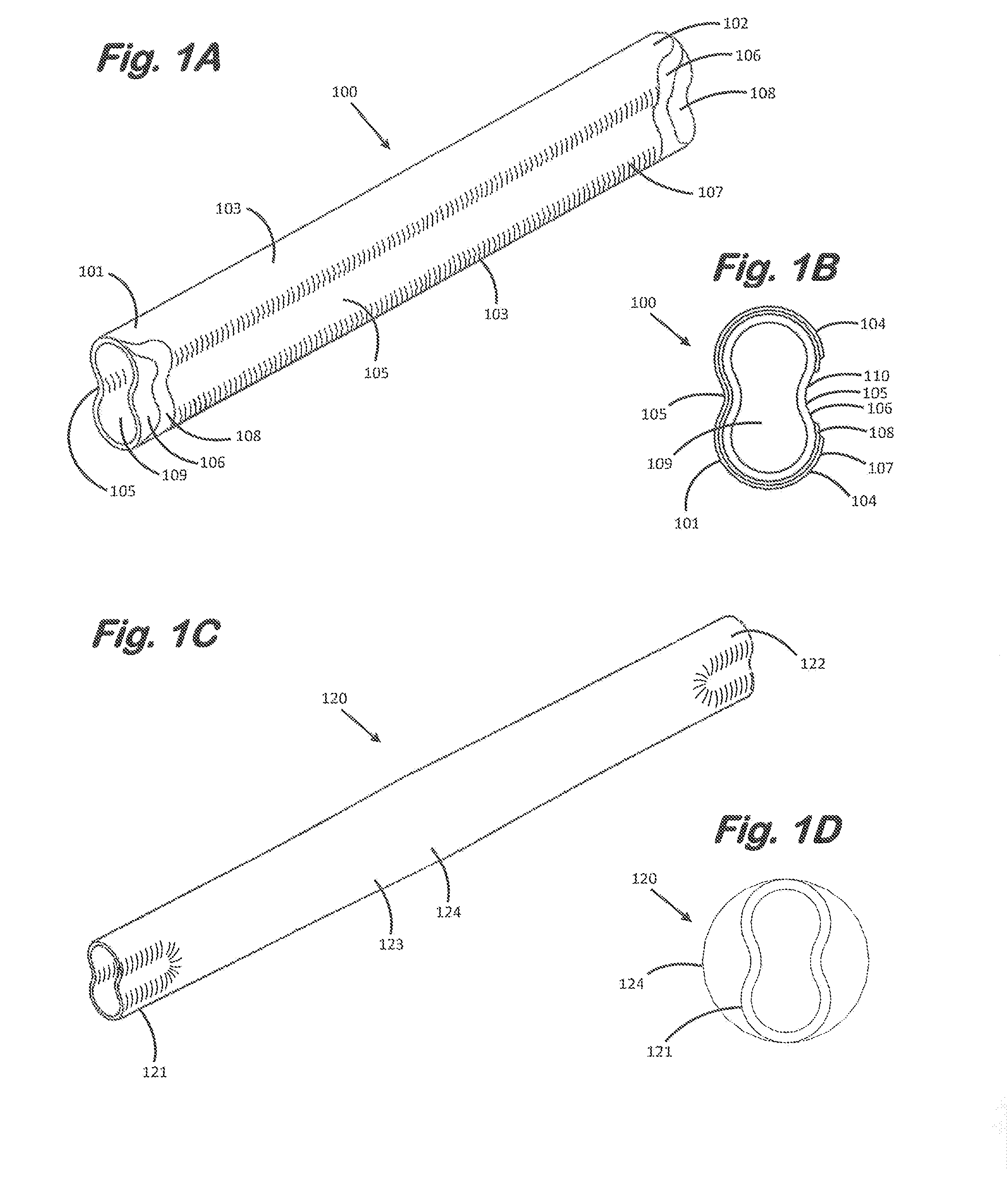
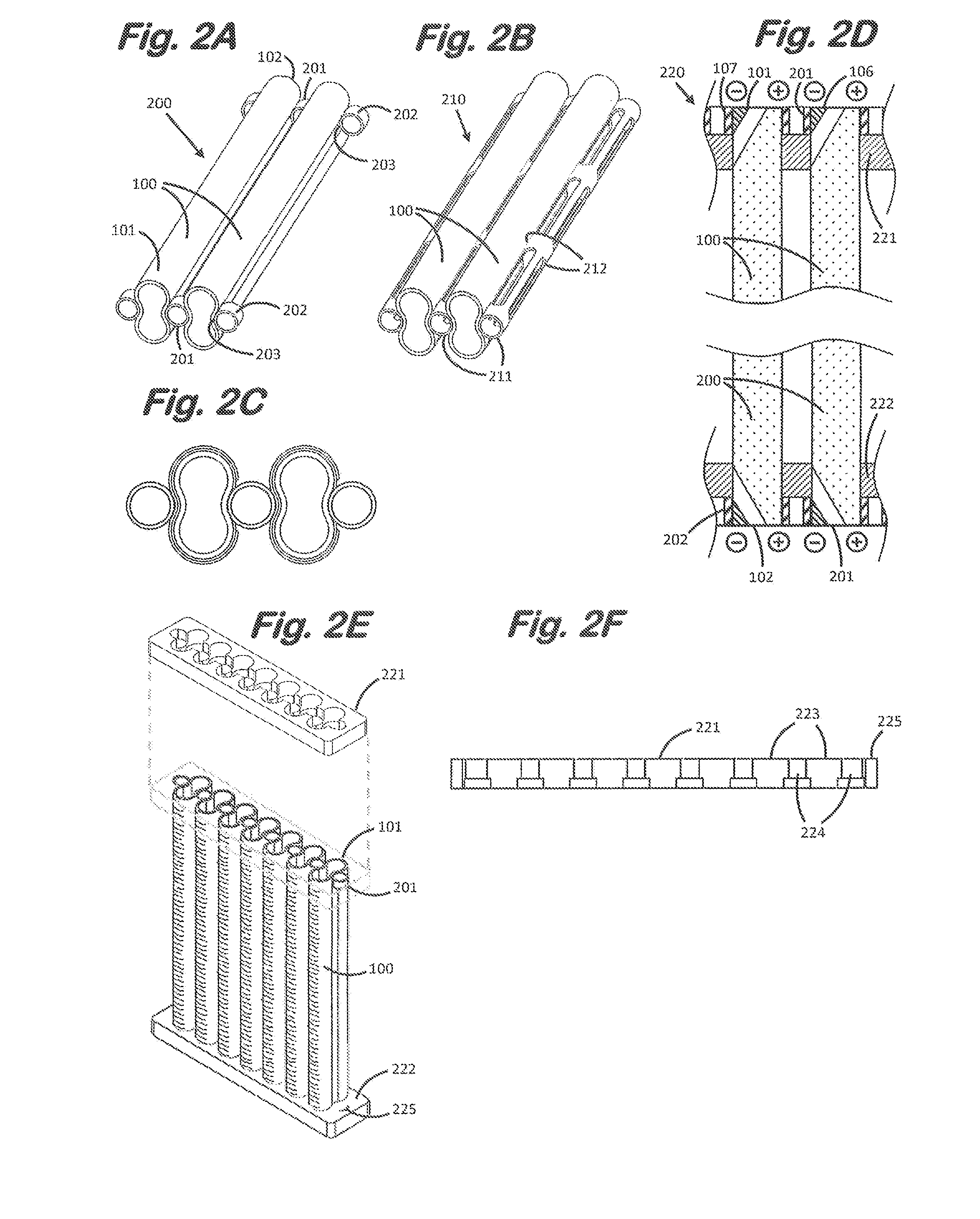
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Device and System
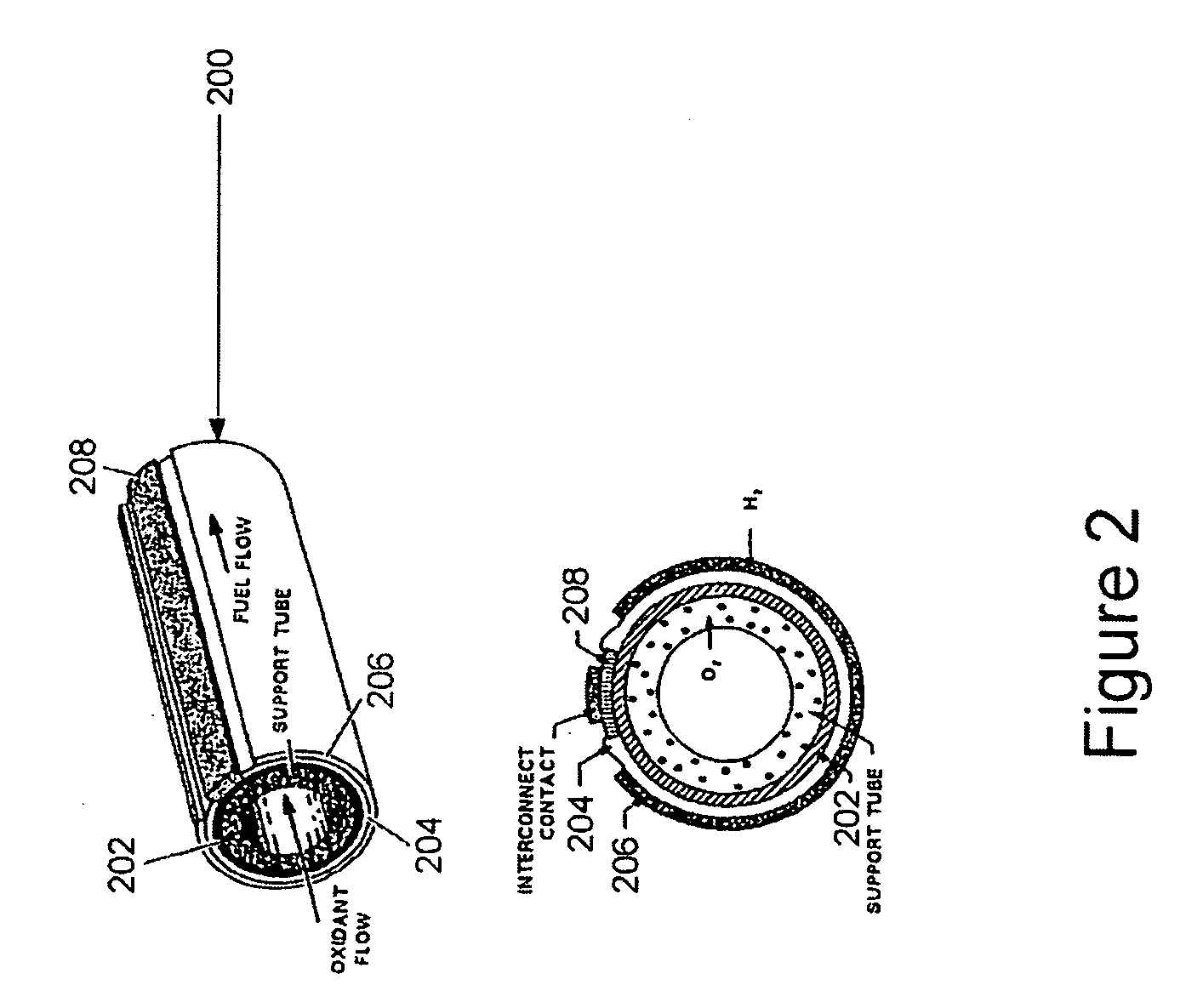
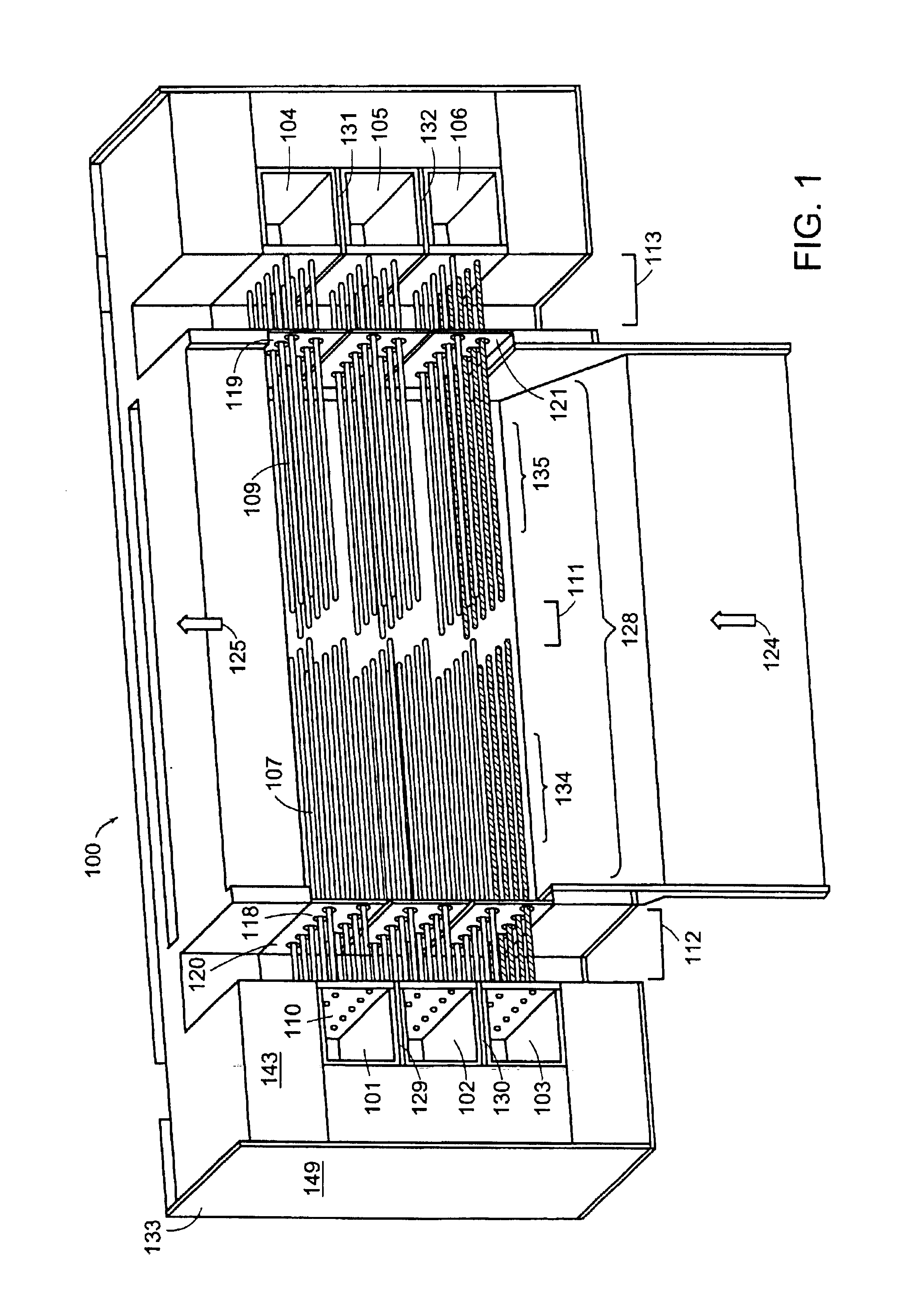
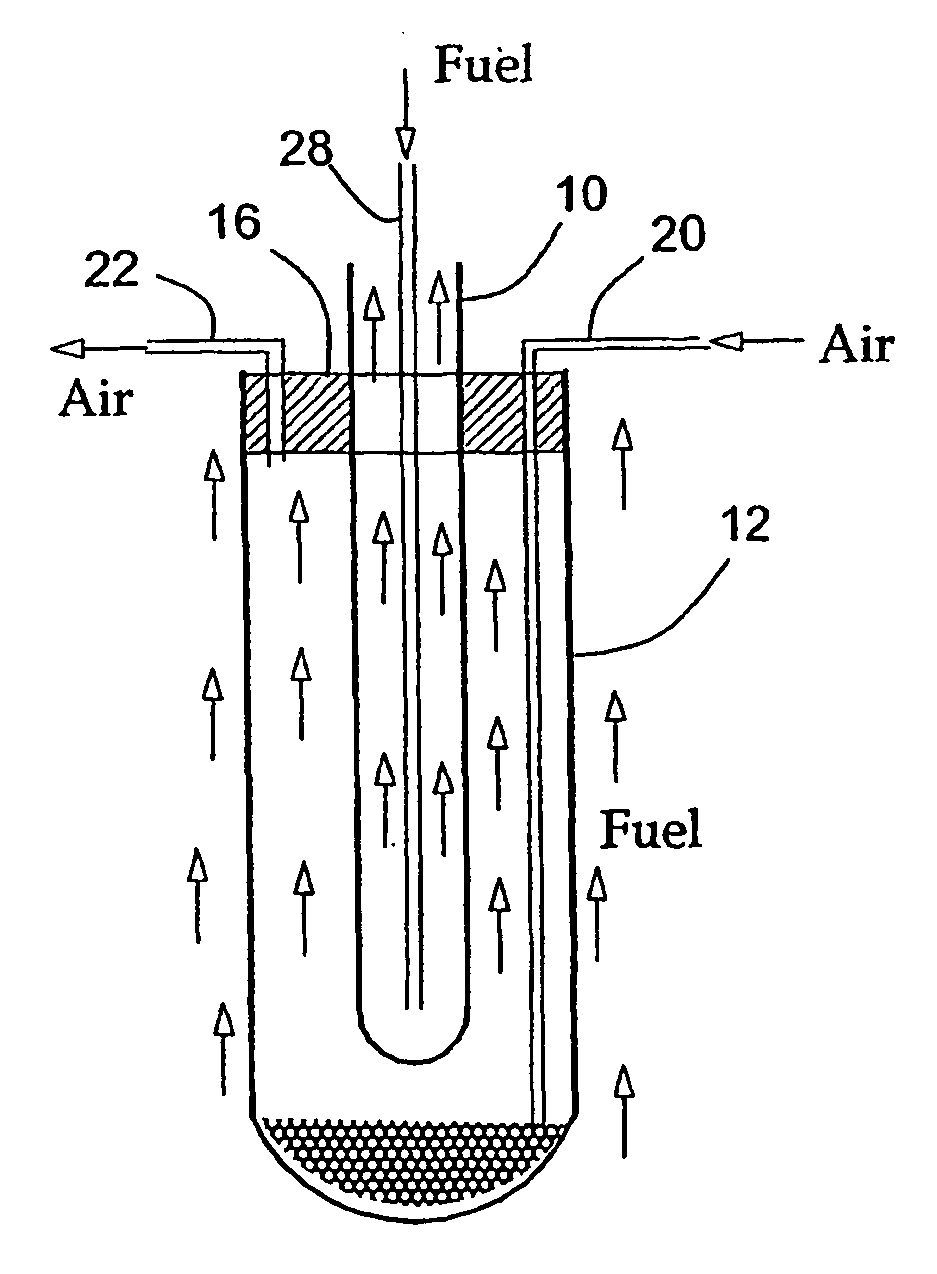
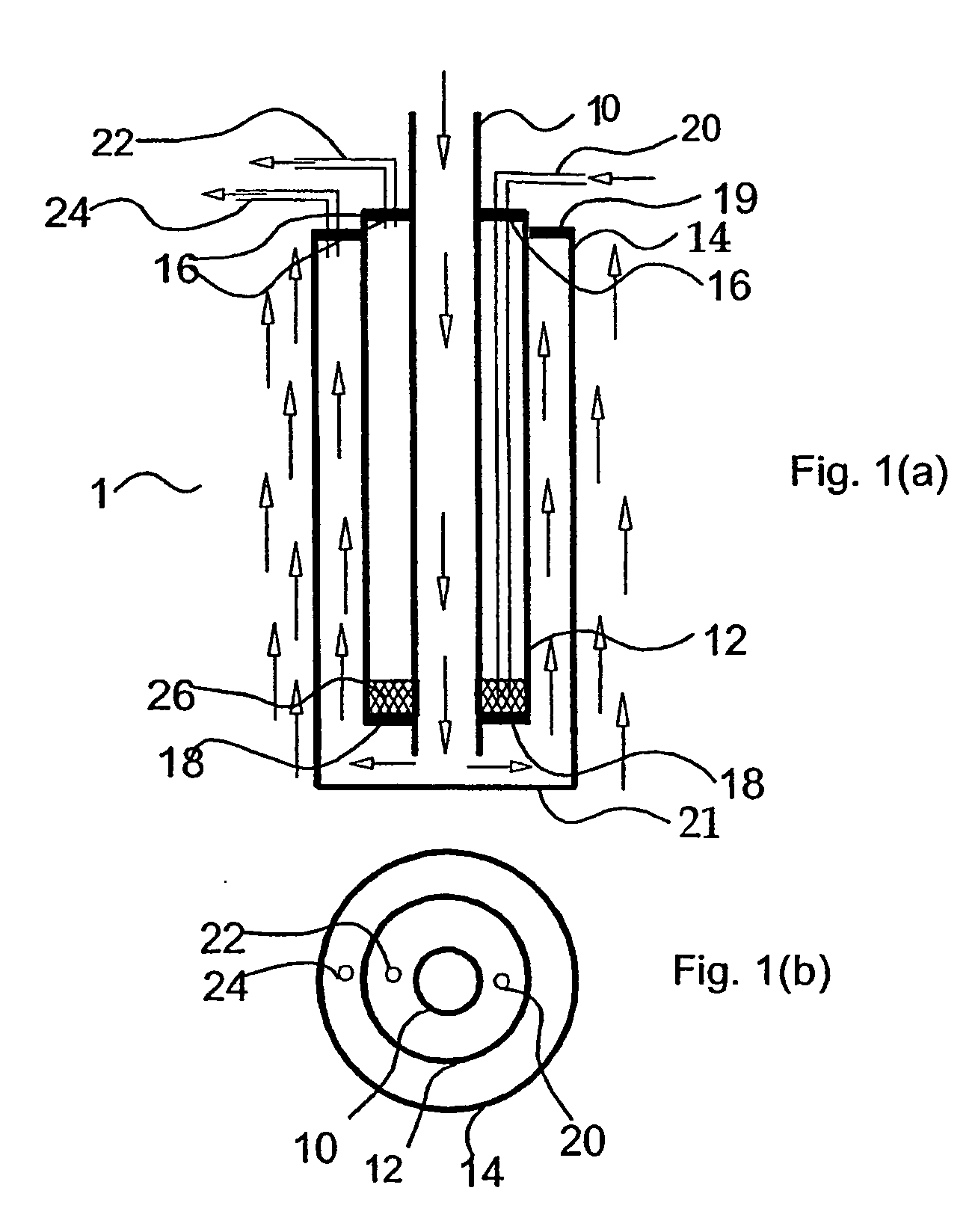
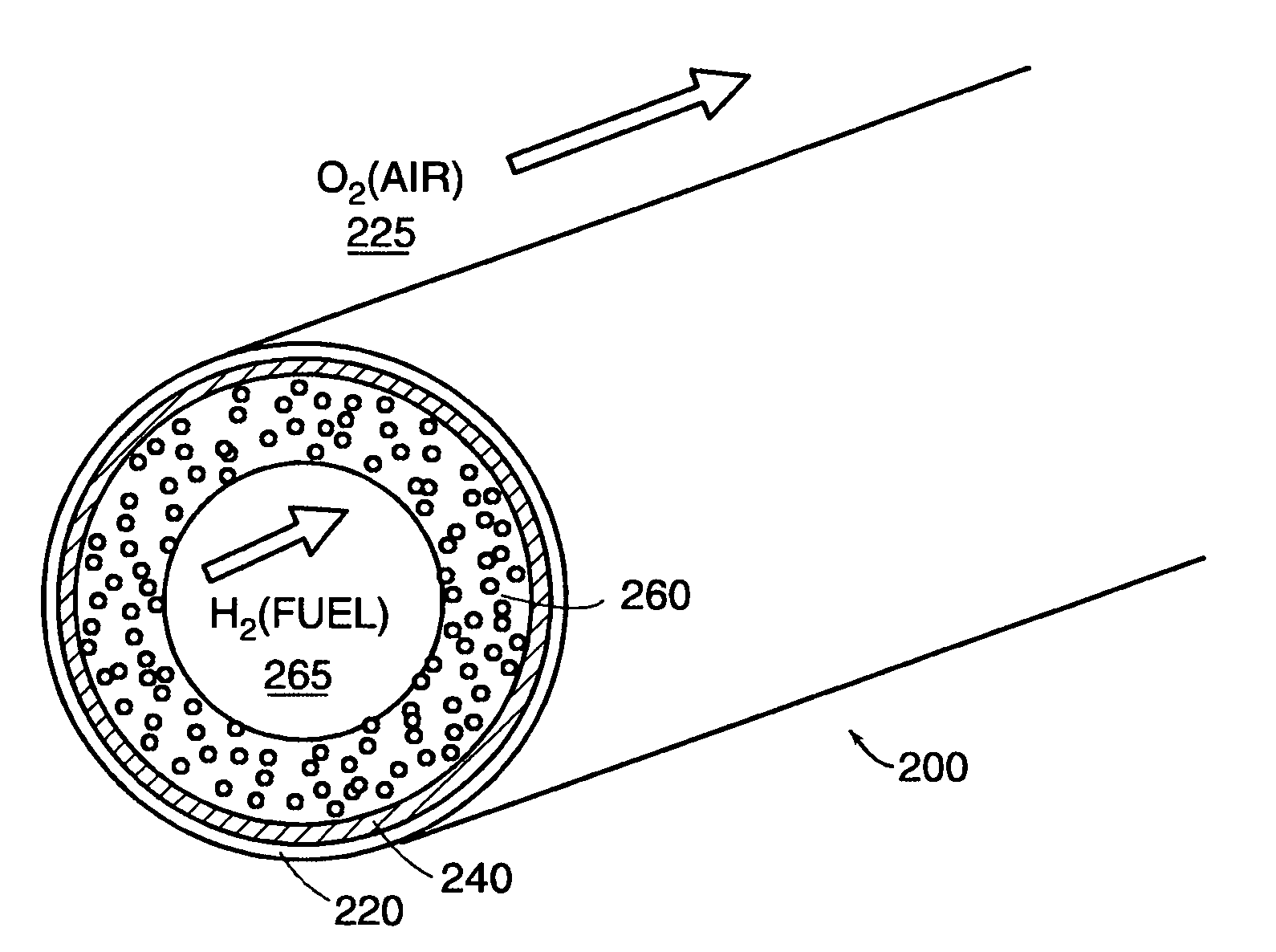
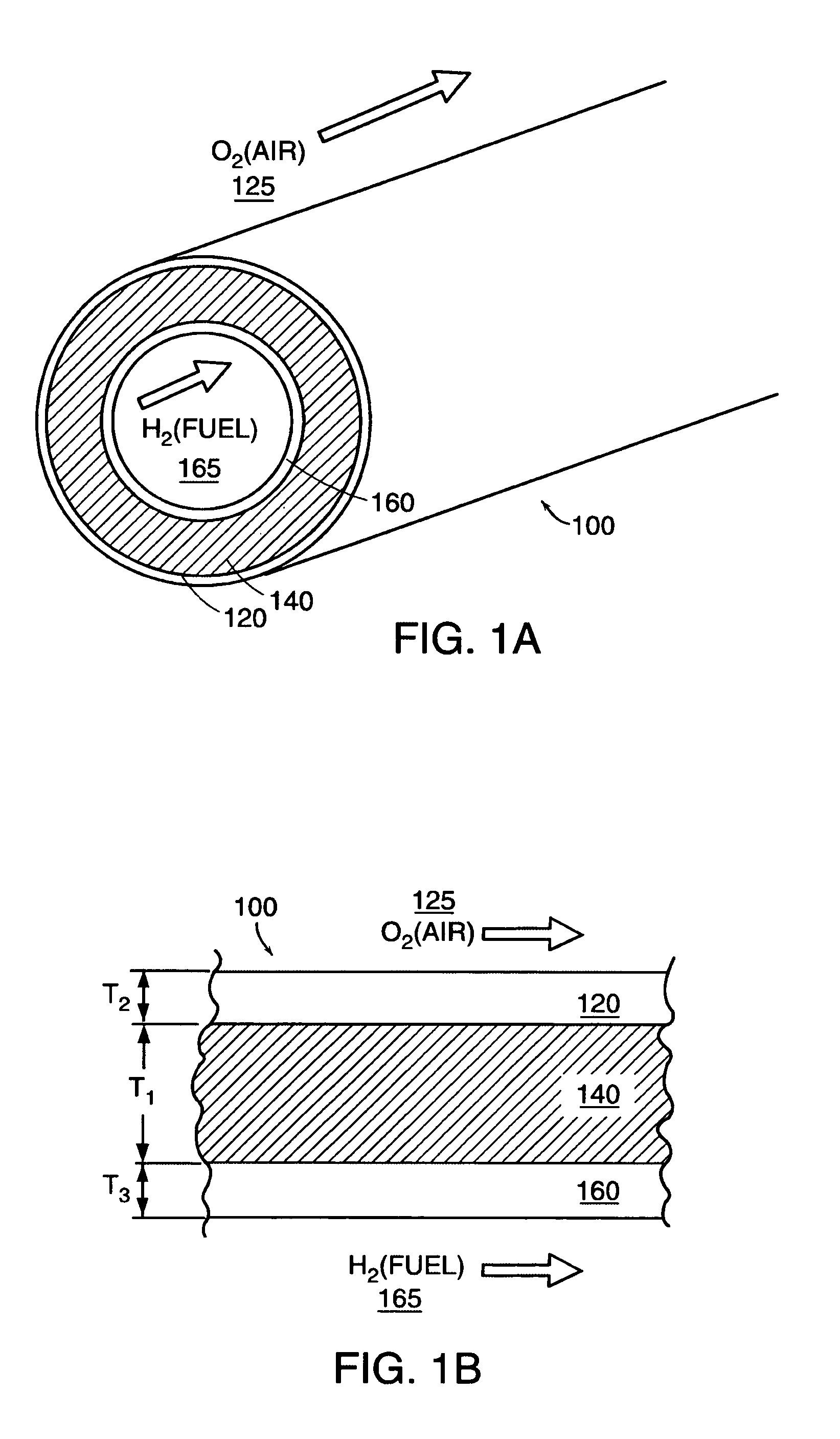
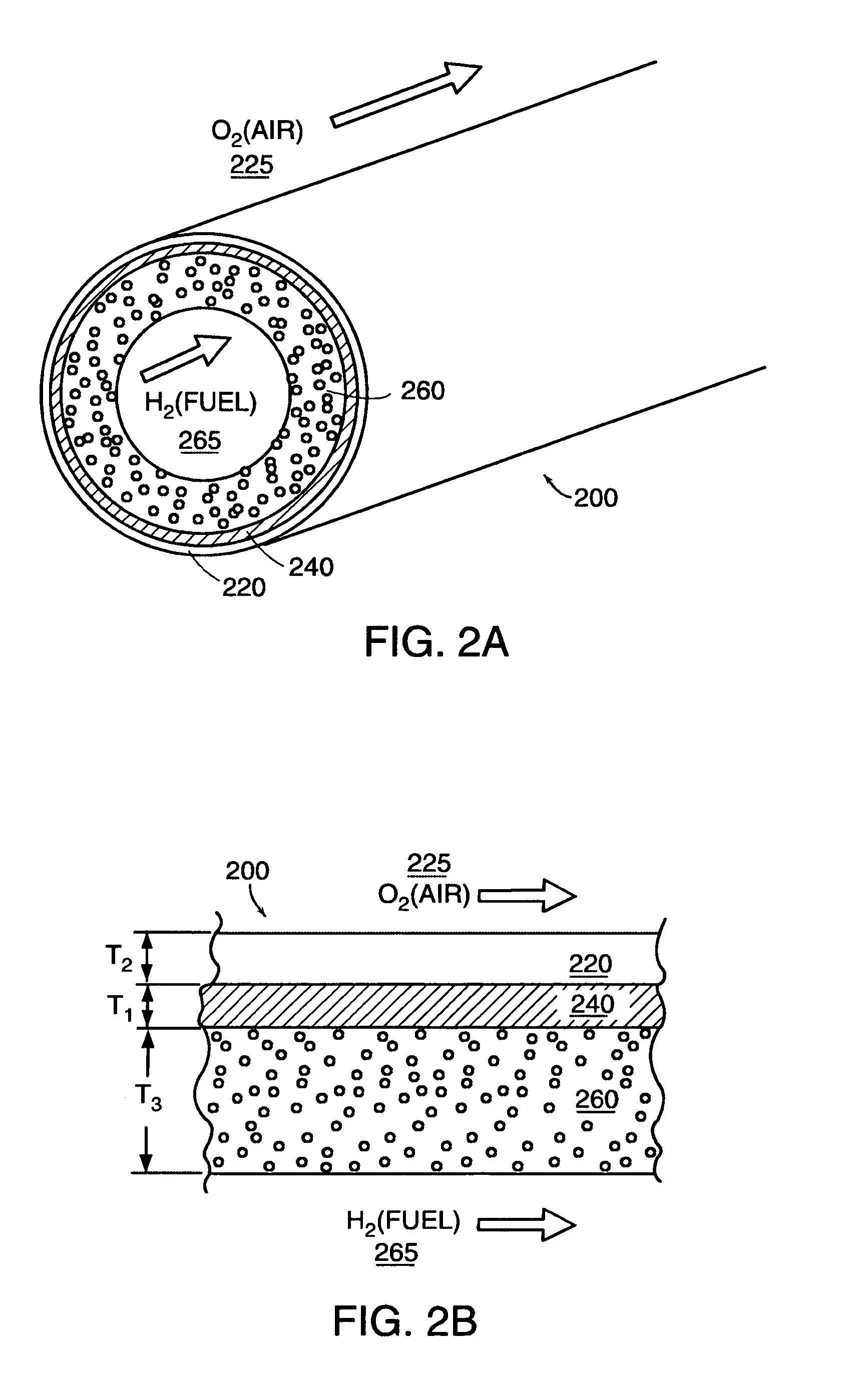
The invention provides tubular solid oxide fuel cell devices and a fuel cell system incorporating a plurality of the fuel devices, each device including an elongate tube having a reaction zone for heating to an operating reaction temperature, and at least one cold zone that remains at a low temperature below the operating reaction temperature when the reaction zone is heated. An electrolyte is disposed between anodes and cathodes in the reaction zone, and the anode and cathode each have an electrical pathway extending to an exterior surface in a cold zone for electrical connection at low temperature. In one embodiment, the tubular device is a spiral rolled structure, and in another embodiment, the tubular device is a concentrically arranged device. The system further includes the devices positioned with their reaction zones in a hot zone chamber and their cold zones extending outside the hot zone chamber. A heat source is coupled to the hot zone chamber to heat the reaction zones to the operating reaction temperature, and fuel and air supplies are coupled to the tubes in the cold zones.
Owner:DEVOE ALAN +1
Tubular Solid Oxide Fuel Cells With Porous Metal Supports and Ceramic Interconnections
InactiveUS20100330450A1CostLow costFuel cells groupingFuel cell shape/formInterconnectionUltimate tensile strength
An intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell structure capable of operating at from 600° C. to 800° C. having a very thin porous hollow elongated metallic support tube having a thickness from 0.10 mm to 1.0 mm, preferably 0.10 mm to 0.35 mm, a porosity of from 25 vol. % to 50 vol. % and a tensile strength from 700 GPa to 900 GPa, which metallic tube supports a reduced thickness air electrode having a thickness from 0.010 mm to 0.2 mm, a solid oxide electrolyte, a cermet fuel electrode, a ceramic interconnection and an electrically conductive cell to cell contact layer.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Tubular solid oxide fuel cell current collector
An internal current collector for use inside a tubular solid oxide fuel cell (TSOFC) electrode comprises a tubular coil spring disposed concentrically within a TSOFC electrode and in firm uniform tangential electrical contact with the electrode inner surface. The current collector maximizes the contact area between the current collector and the electrode. The current collector is made of a metal that is electrically conductive and able to survive under the operational conditions of the fuel cell, i.e., the cathode in air, and the anode in fuel such as hydrogen, CO, CO2, H2O or H2S.
Owner:WORLDWIDE ENERGY INC OF DELAWARE
Interconnection of bundled solid oxide fuel cells
ActiveUS20070148523A1Improve fuel cell densityDensely packedFuel cells groupingFuel cell shape/formFuel cellsElectrical connection
Owner:ACUMENTRICS
Method for preparing tubular solid oxide fuel cell
ActiveCN106207221AImprove mechanical propertiesMany poresFinal product manufactureSolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cellsSolid fuel
The invention belongs to the technical field of a solid fuel cell, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a tubular solid oxide fuel cell. The method for preparing the tubular solid oxide fuel cell comprises the following steps of (1) preparing a tubular porous positive electrode support body die; (2) preparing a tubular porous positive electrode support body; (3) uniformly spraying or immersing electrolyte paste on a surface of the tubular porous positive electrode support body; (4) uniformly spraying or immersing functional layer paste on a surface of an electrolyte layer of the tubular porous positive electrode support body; and (5) uniformly spraying or immersing a negative electrode paste on a surface of a functional layer of the tubular porous positive electrode support body. The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity, environmental friendliness and high repeatability, the production cost is reduced, and industrial application is facilitated.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Anode support tube type solid oxide fuel battery
InactiveCN1464582AIncrease profitSimplified assistance systemSolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cellsEngineering
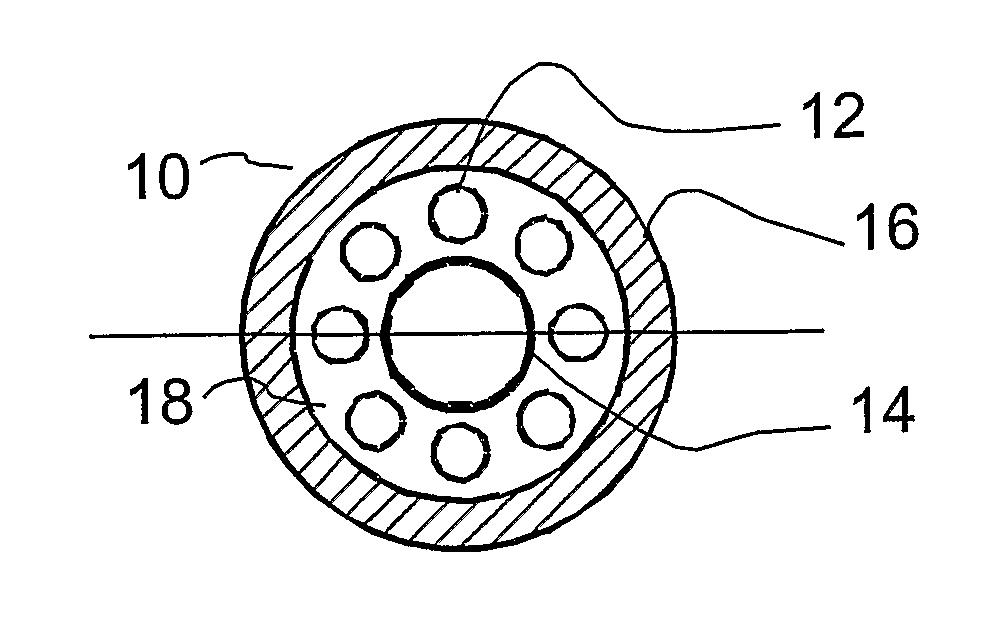
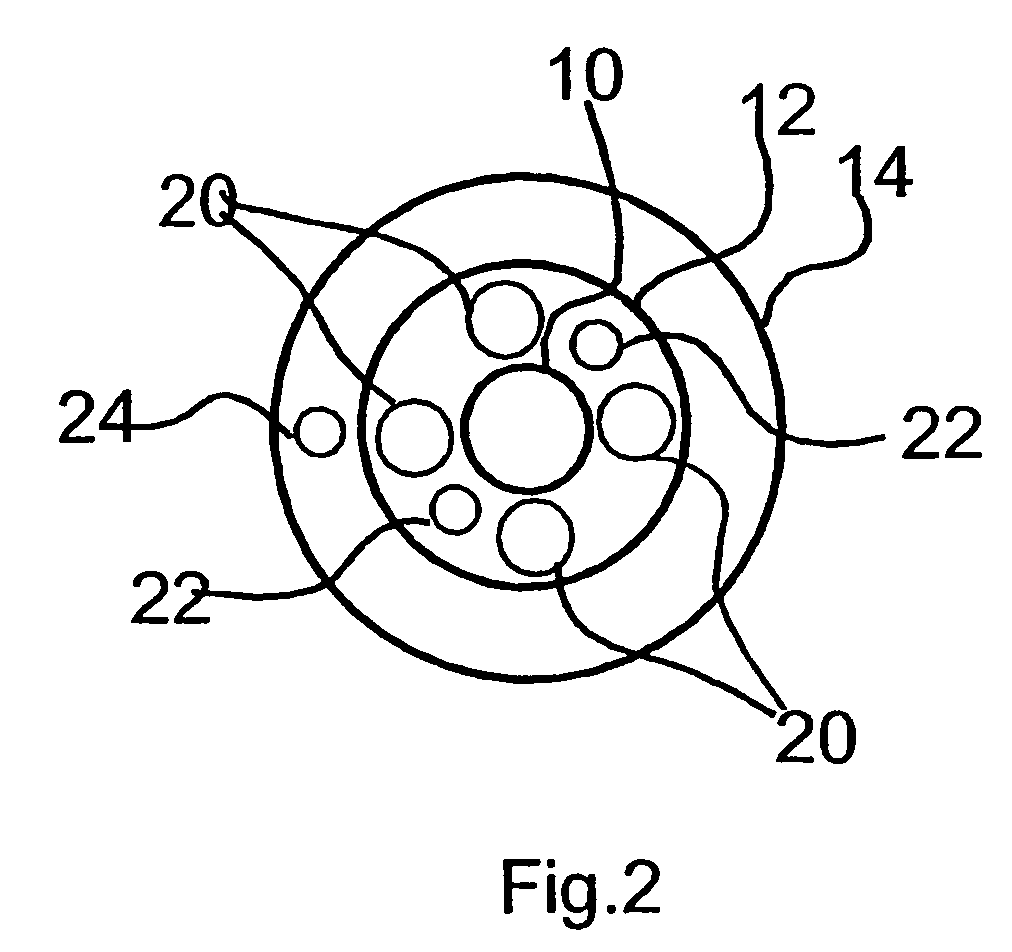
The present invention provides a tubular solid oxide fuel cell supported with anode,characterized by, multihole anode is used as strut body, layer tube in the strut body is divided into a plurality of branch pipes connected each other at bottom, the upper end of center branch pipe is connected with fuel tube, the cross-sectional shape for the outer wall of the inner layer tube is triangle or arched portrait grooves adjoining each other, in which, part of the outer surface for the abutting grooves is consecutive densify ionogen layer, and the other is consecutive densify electric interlock material layer, the consecutive densify ionogen layer and consecutive densify electric interlock material layer are interconnected so that the outer surface is completely covered, and thus forms airproof interlayer, the outside of the densify ionogen layer is multihole catodic layer, the convexconcave grooves increase effective response area, and improve power density of the body. The center branch pipe is used as fuel gas input pipe as well as fuel reforming reactor, so that separate reformer is omitted, and utilization efficiency of space in the strut body pipe is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Tubular solid oxide fuel cells
InactiveUS20090155660A1Reduce wall thicknessHigh mechanical strengthSolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cell detailsFuel cellsDouble wall
Tubular solid oxide fuel cells are provided. In one embodiment, fluid flow channels are defined by a plurality of bridges between a core and an outer wall of an electrode support. In another embodiment, a fluid supply channel and fluid discharge channels of an electrode support are formed in a double-wall structure. Electric current distribution and gas distribution are facilitated in the solid oxide fuel cells.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ENERGY RES
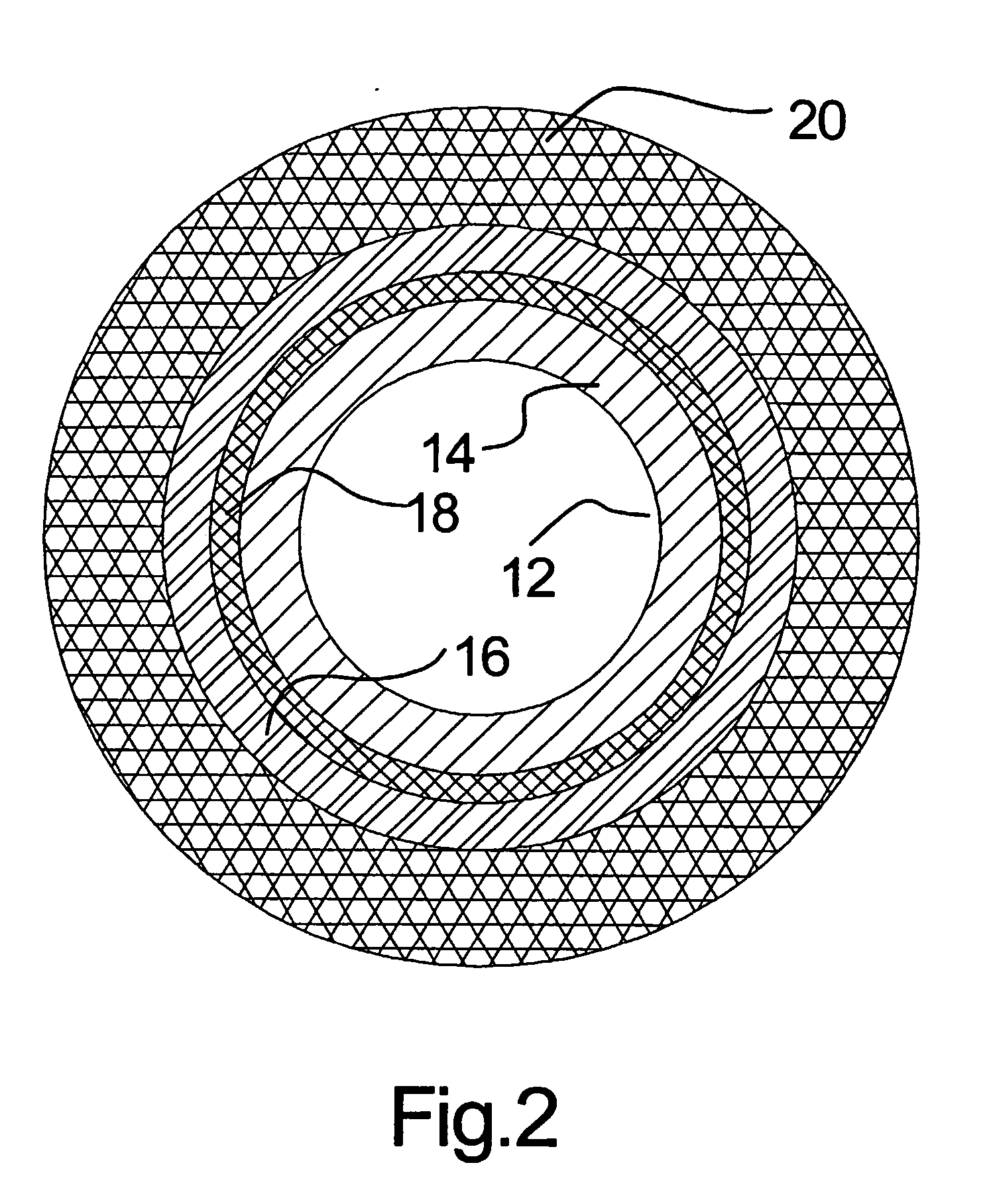
Electrode-supported solid state electrochemical cell
A process for manufacturing a solid oxide fuel cell comprises, in one embodiment according to the invention: forming a plastic mass comprising a mixture of an electrolyte substance and an electrochemically active substance; extruding the plastic mass through a die to form an extruded tube; and sintering the extruded tube to form a tubular anode capable of supporting the solid oxide fuel cell. The process may further comprise, after sintering the extruded tube, layering an electrolyte onto the tubular anode; and, after layering the electrolyte, layering a cathode onto the electrolyte.In a further related embodiment, the process further comprises co-extruding more than one anode layer to form the tubular anode. Each of the anode layers may comprise a ratio of electrochemically active substance to electrolyte substance, with such ratios being higher for layers that are layered further from a surface of the anode that contacts a fuel gas than for layers that are layered closer to the fuel gas.Anode-supported tubular solid oxide fuel cells, which may be formed by such processes, are also disclosed. Additionally, electrode-supported oxygen pumps and oxygen sensors, and methods of manufacturing them, are disclosed.
Owner:ACUMENTRICS
Tubular solid oxide fuel cell stack
This invention relates to a stack comprising a continuous solid-phase matrix and tubular fuel cells embedded in the matrix. Each fuel cell comprises an inner electrode layer, an outer electrode layer, and an electrolyte layer sandwiched between the inner and outer electrode layers. The matrix is sufficiently porous to allow a first reactant to flow through the matrix and to the outer electrode of each fuel cell, and have sufficient mechanical strength to support the fuel cells in the stack. The fuel cells are embedded such that a second reactant may be flowed through the inside of each tubular fuel cell and to the inner electrode thereof. Alternatively, a stack of tubular separation membranes or a stack of tubular membrane reactors may be embedded in the matrix. The matrix material may comprise solid state foam, metal filament, or metal, cermet, or ceramic wool.
Owner:INNOTECH ALBERTA INC
Powder mixture for layer in a solid oxide fuel cell
InactiveUS20140170531A1Final product manufactureActive material electrodesElectrical conductorPowder mixture
The present disclosure relates to solid oxide fuel cells, and particularly raw powder materials which form a layer in a solid oxide fuel. The raw powder materials include an ionic conductor powder material; and an electronic conductor powder material. The ratio of an average particle diameter of the ionic conductor powder material to an average particle diameter of the electronic conductor powder material is greater than about 1:1, and an average particle diameter of at least one of the electronic conductor powder material or the ionic conductor powder material is coarse.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN CERAMICS & PLASTICS INC
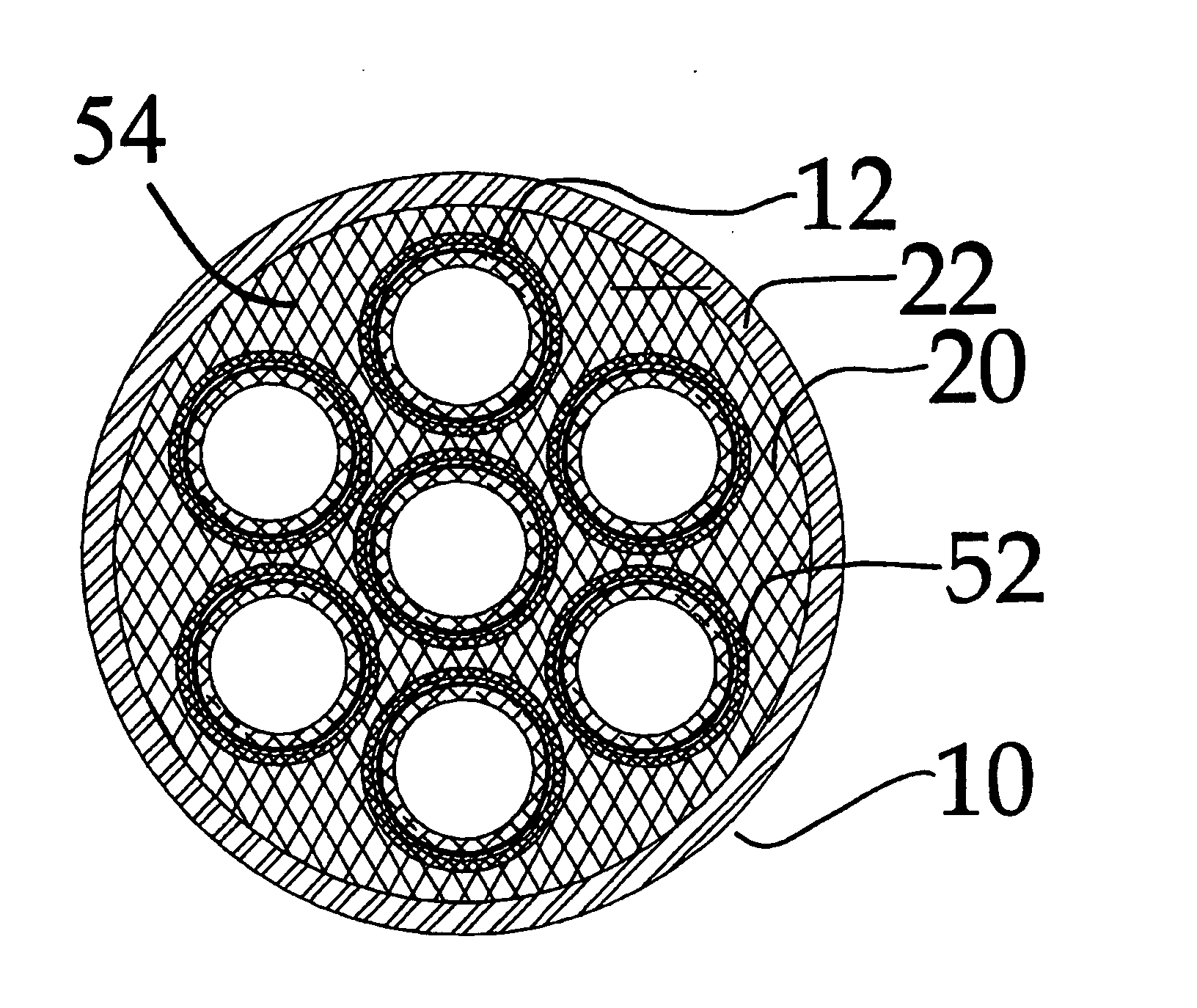
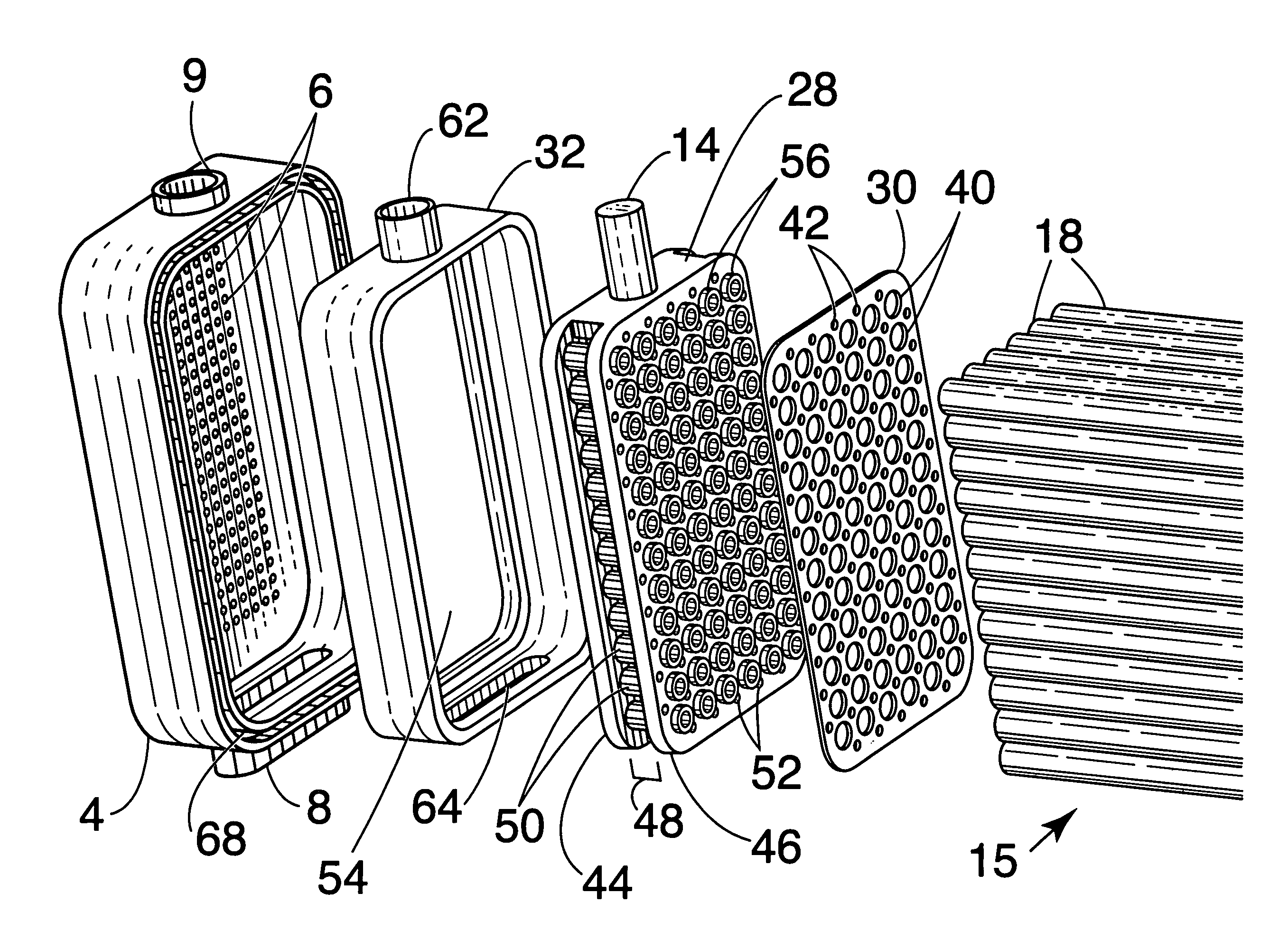
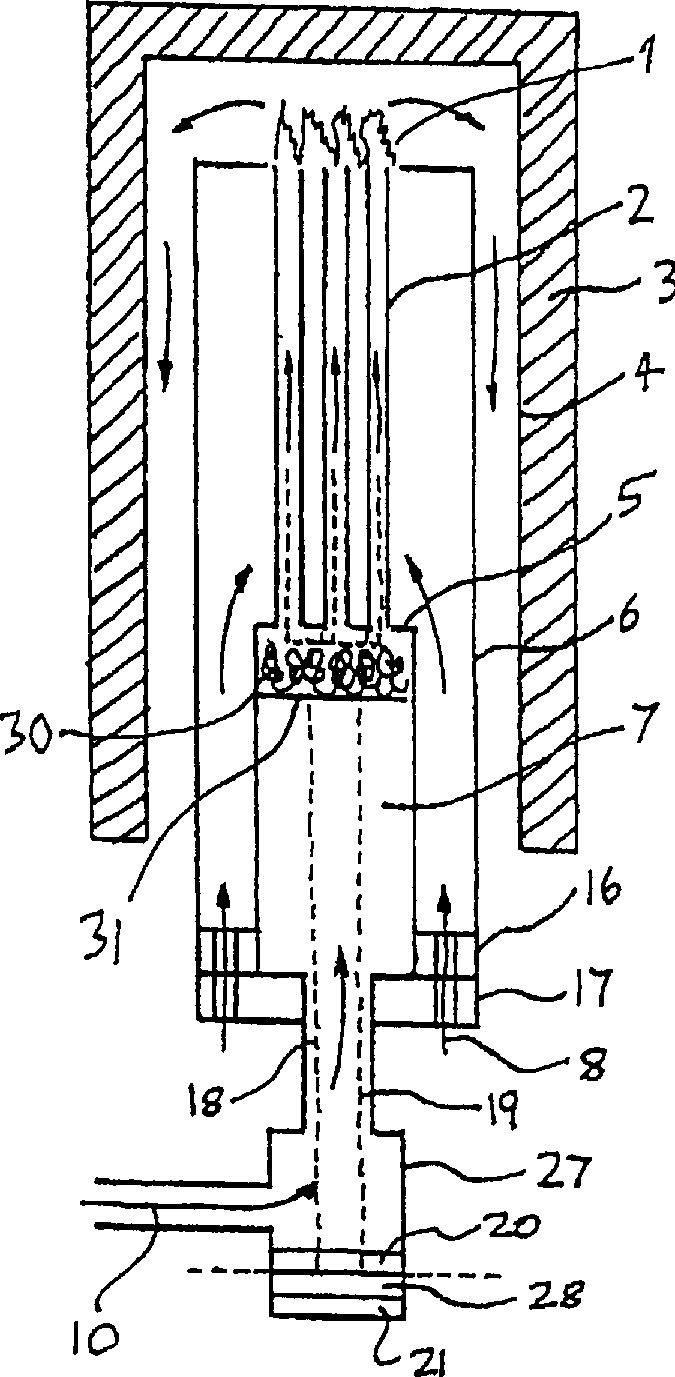
Integrated solid oxide fuel cell and reformer
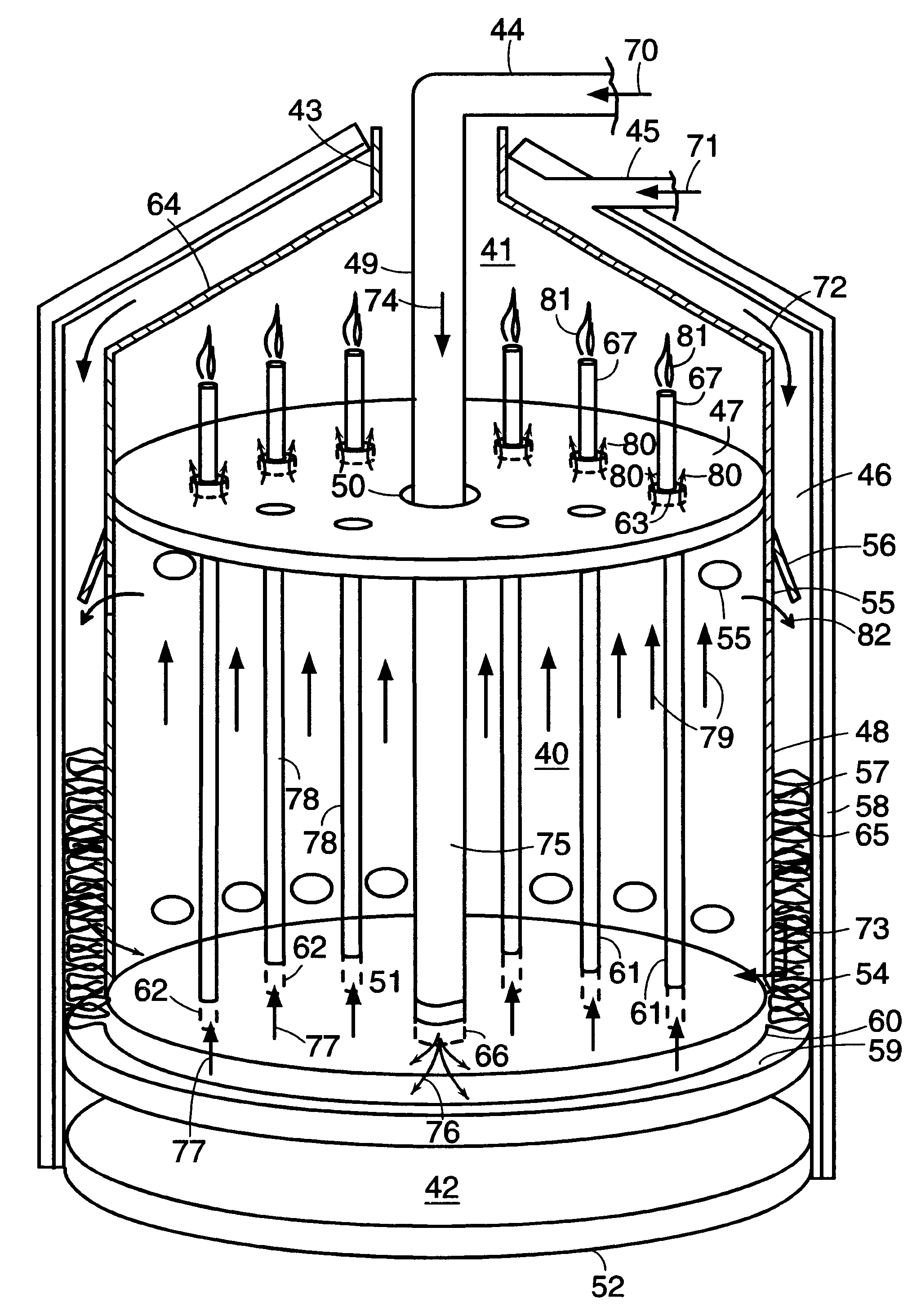
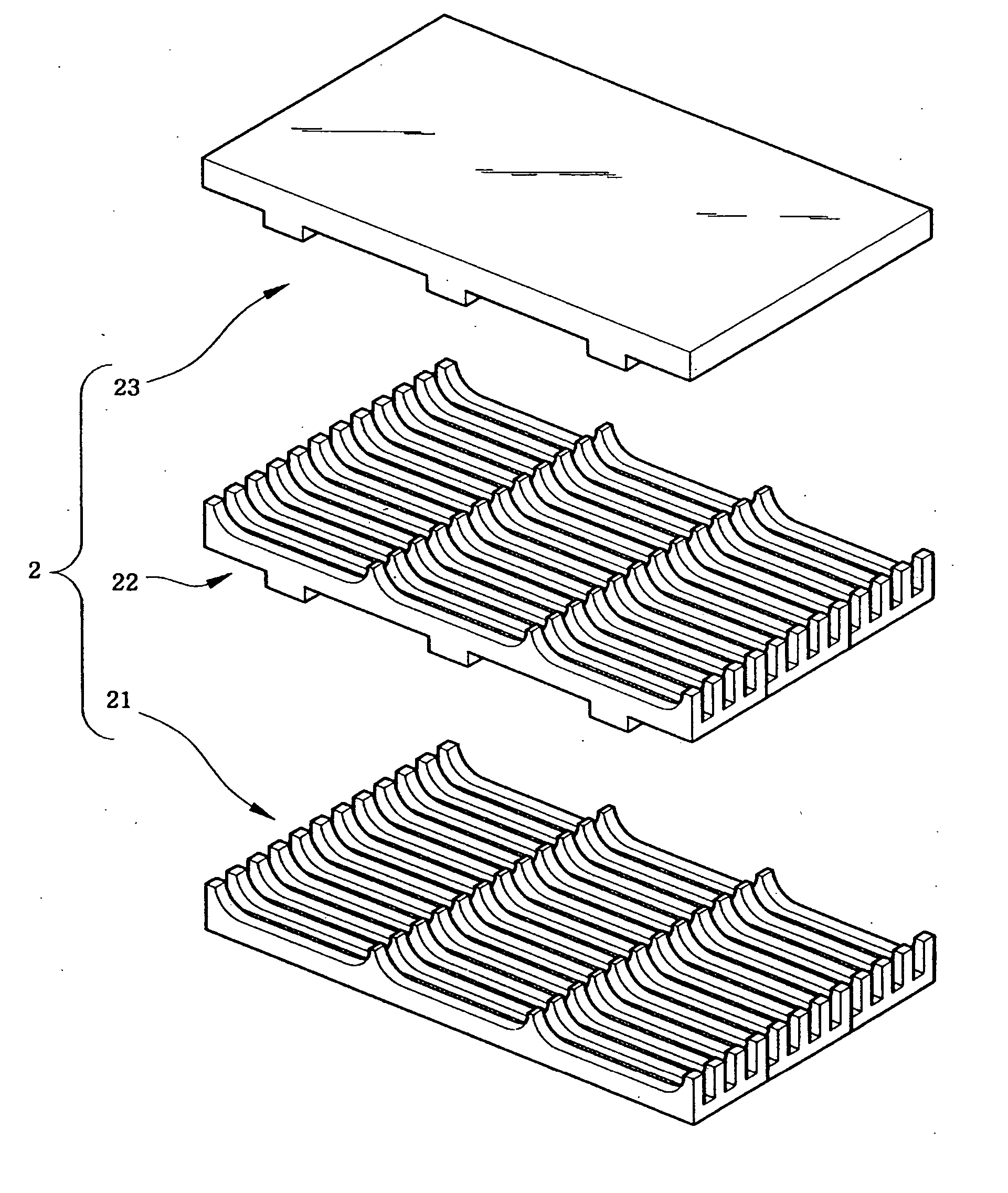
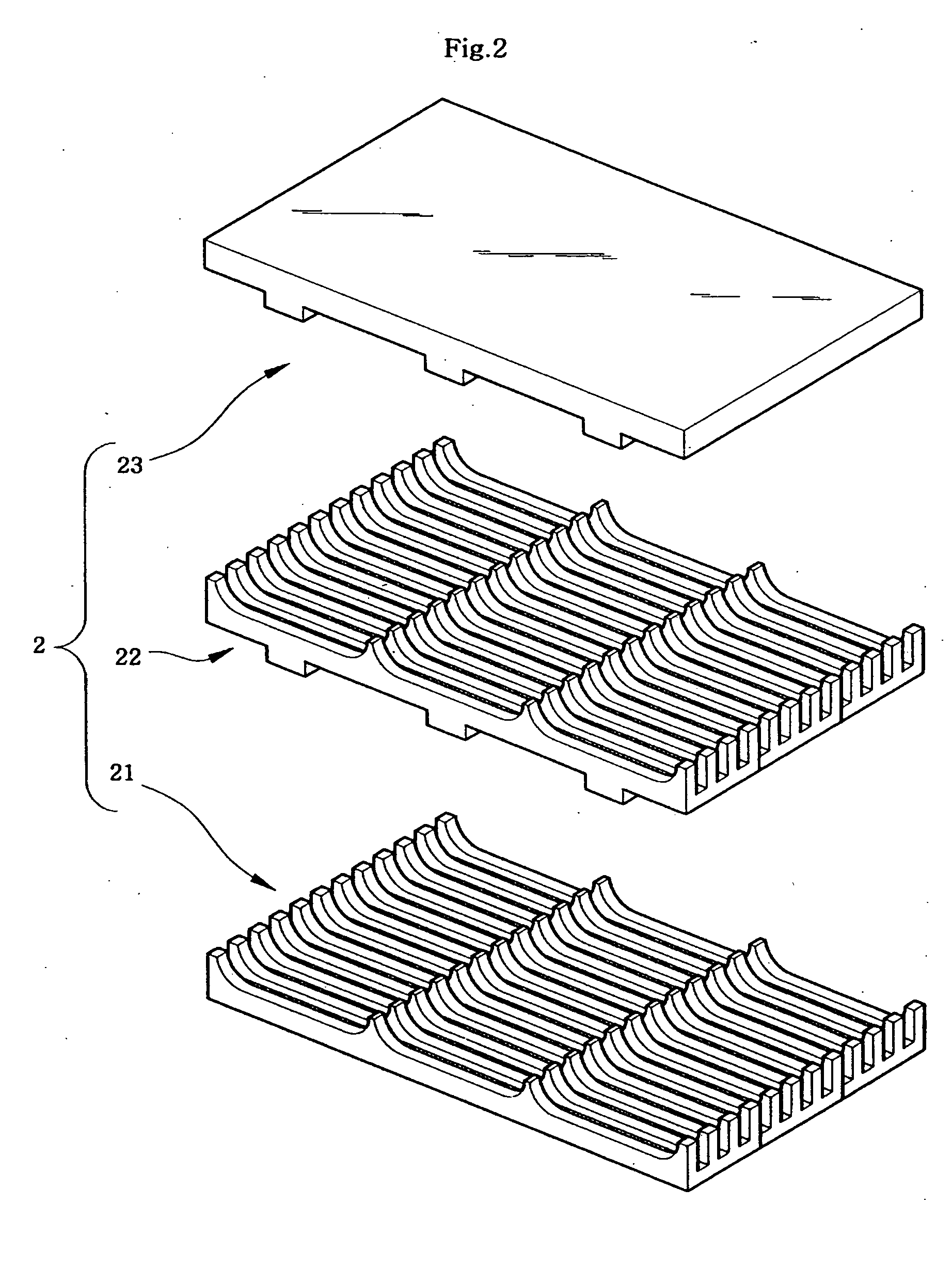
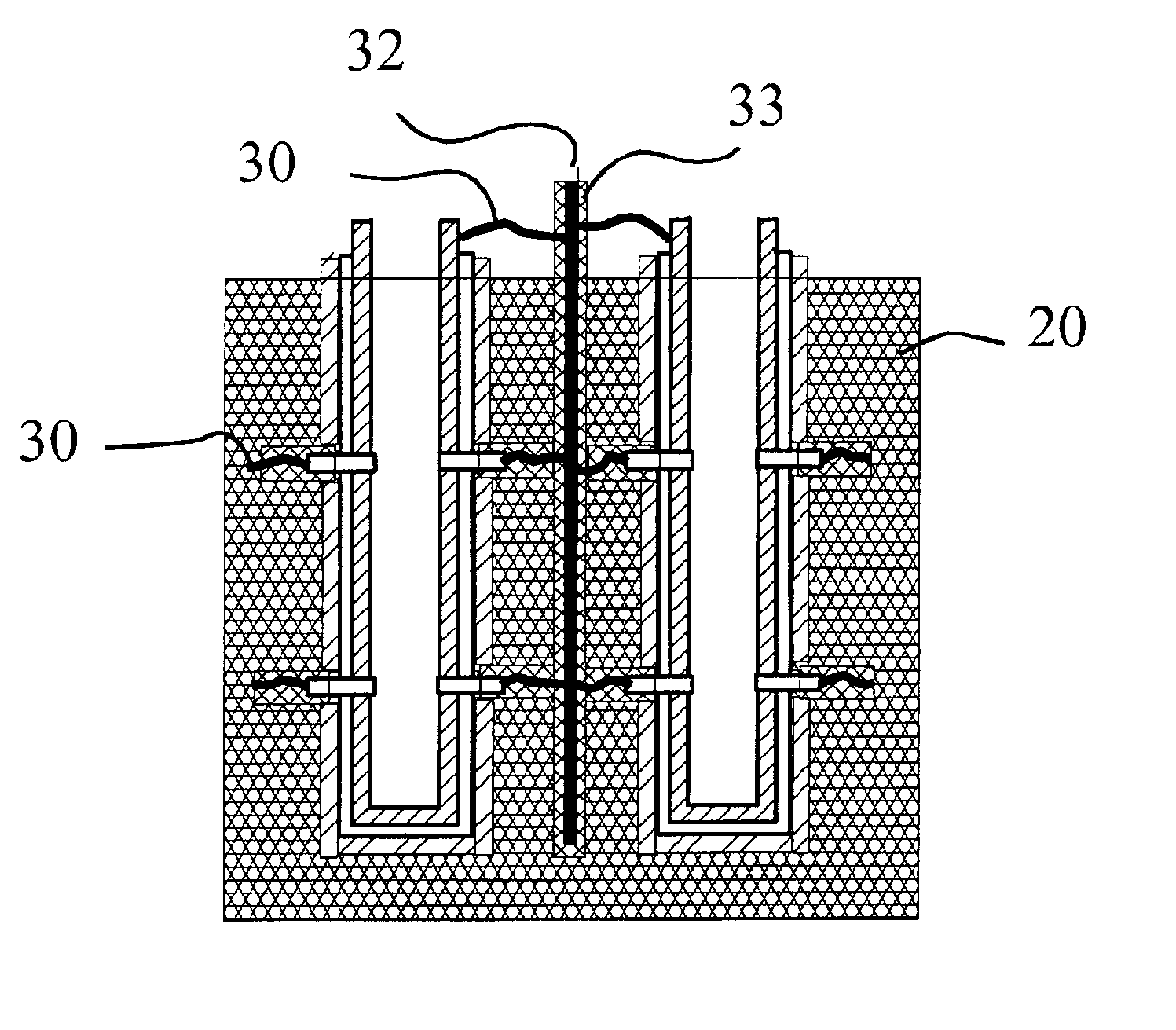
Described is an apparatus for generating electrical power. The apparatus has a plurality of tubular solid oxide fuel cells (2) contained in a reaction chamber (40). Fuel cells (2) are secured at one end thereof in a manifold block (51), the other ends thereof passing freely through apertures (63) in a baffle plate (47) to reside in a combustion chamber (41). Reaction gases are supplied to the insides of the tubular fuel cells (2) from a plenum chamber (42) below the manifold block (51) and to the reaction chamber (41) surrounding the outsides of the fuel cells through an annular inlet path, which may include a reformation catalyst. The gases inlet path to the plenum chamber (42), and the annular inlet path surrounding the reaction chamber, are both in heat conductive relation with the reaction chamber and the combustion chamber, and raise the gases to formation and reaction temperatures as appropriate.
Owner:ACUMENTRICS
Tubular solid oxide fuel cell structure
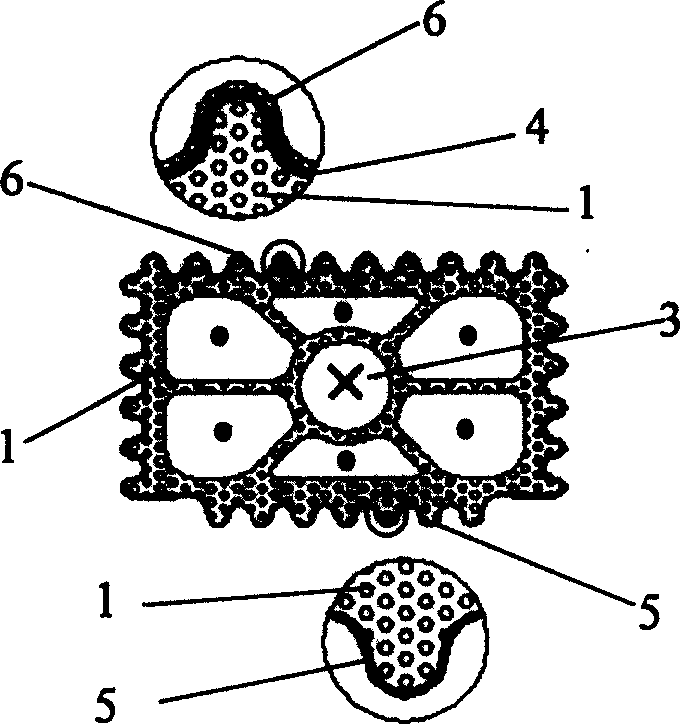
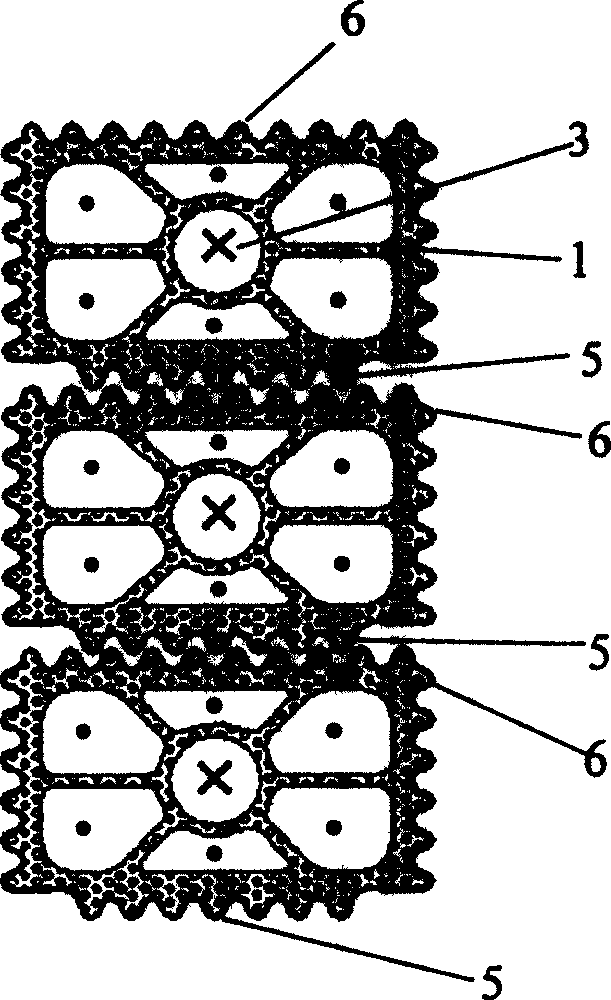
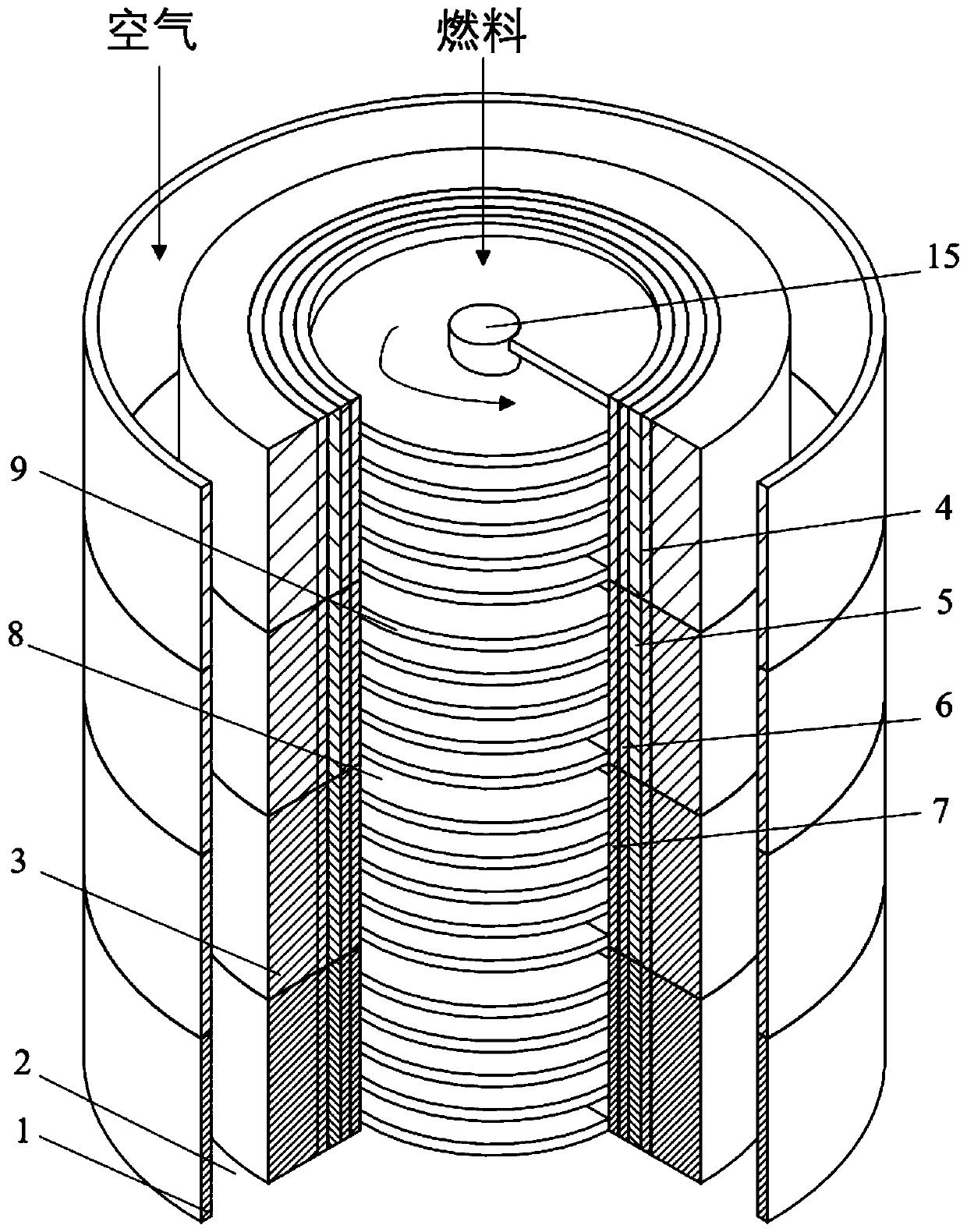
The invention discloses a tubular solid oxide fuel cell structure. The structure is divided into a plurality of layers along the axial direction; each layer comprises a complete tubular fuel cell small unit, each fuel cell small unit sequentially comprises an outer shell layer, an anode electrode, an electrolyte layer, a cathode electrode and a spiral flow guide fin from outside to inside, the anode electrode comprises an anode electrode supporting layer and an anode reaction layer, and the cathode electrode comprises a cathode reaction layer and a cathode supporting layer; an anode gas channel is formed between the outer shell and the anode electrode supporting layer at an interval, and an axis channel in the cathode supporting layer is a cathode gas channel; and electrode layers corresponding to small fuel cell units are the same in thickness, but different in axial width, composition particles and distribution of the composition particles, and the diameters of the particles of different layers are regularly distributed along the axial direction. The mass transfer characteristic of the battery can be effectively enhanced, the battery efficiency is improved, the battery temperature and other axial distribution can be adjusted, and the supercooling effect of a fuel inlet section is controlled.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com